Patents
Literature
273 results about "Lenslet" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
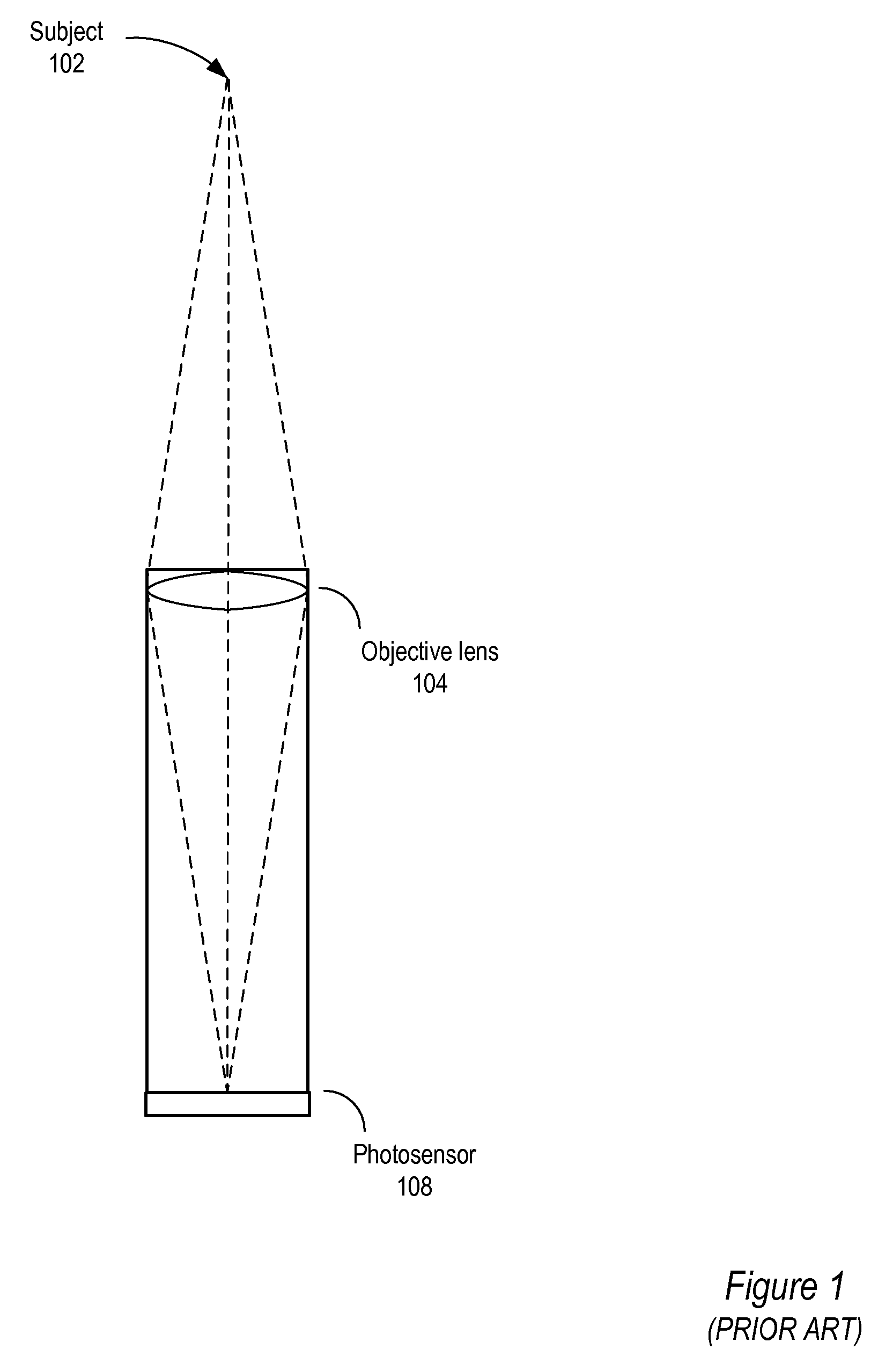
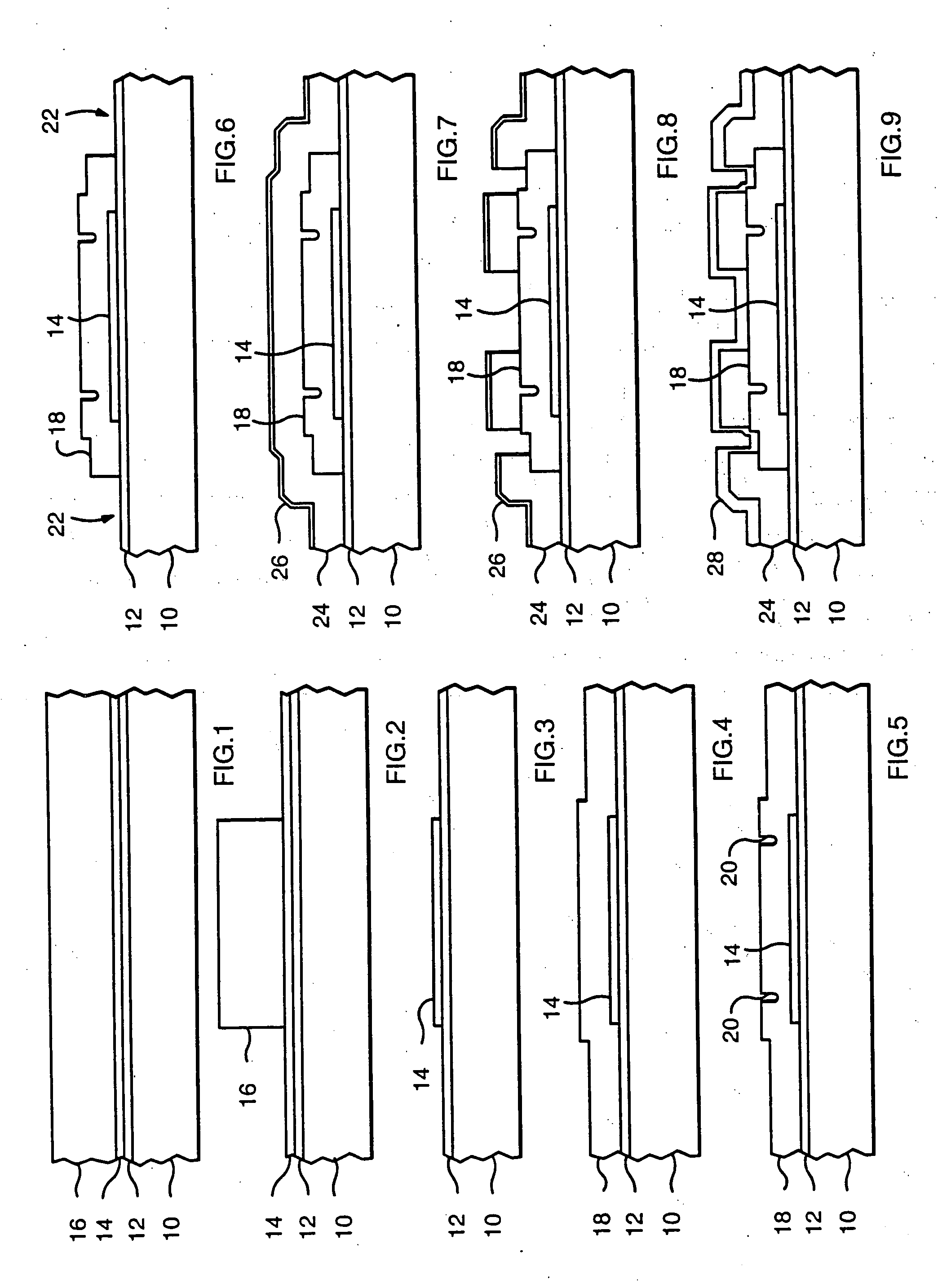
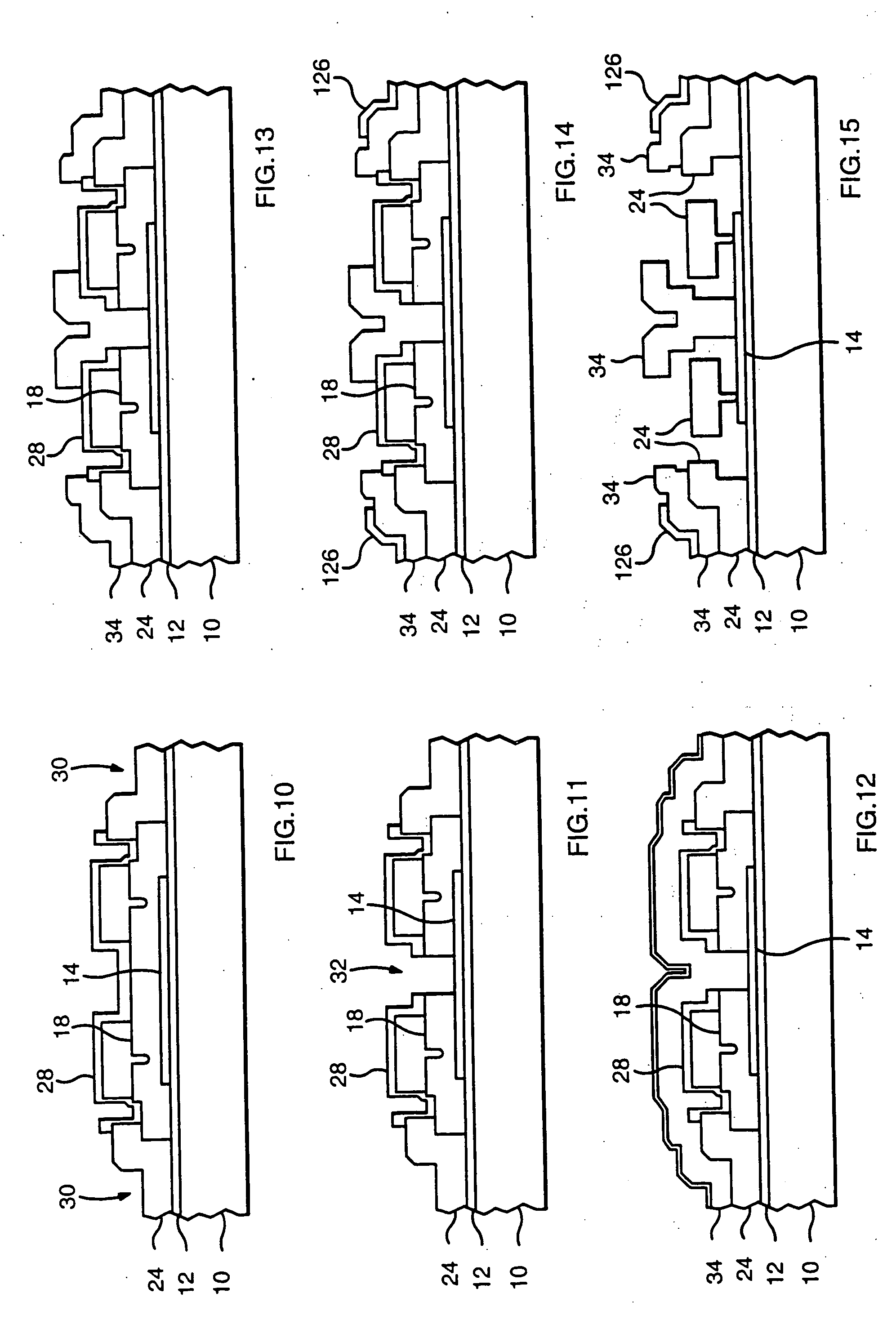
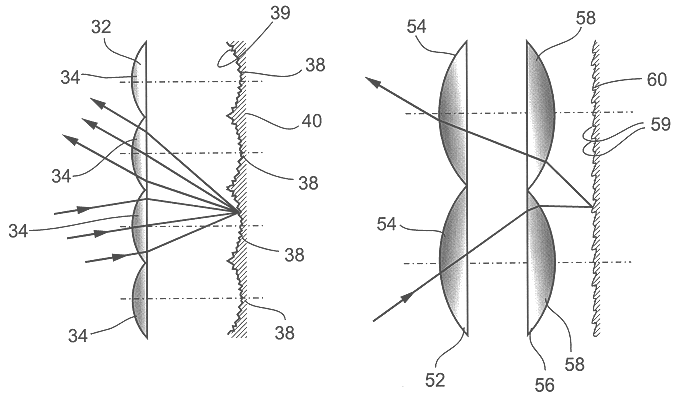
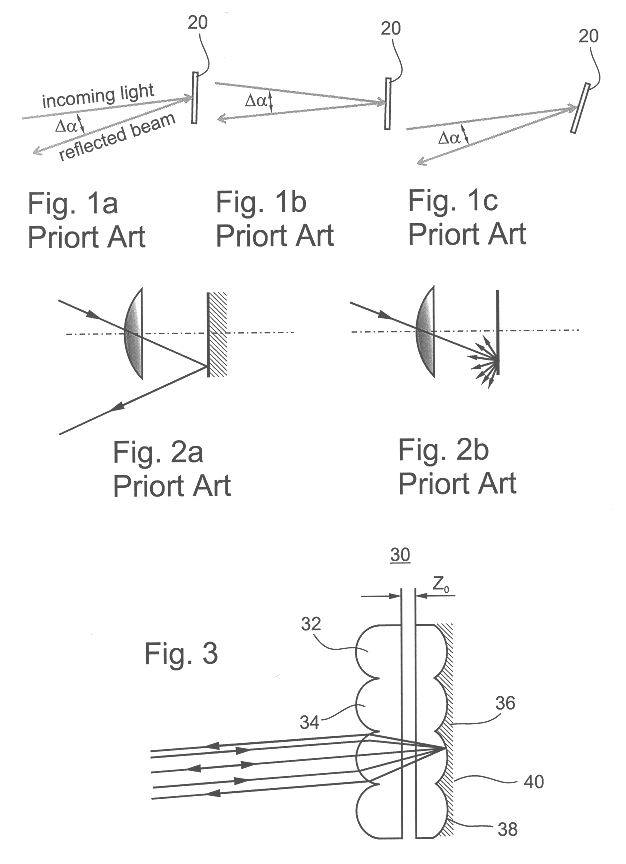
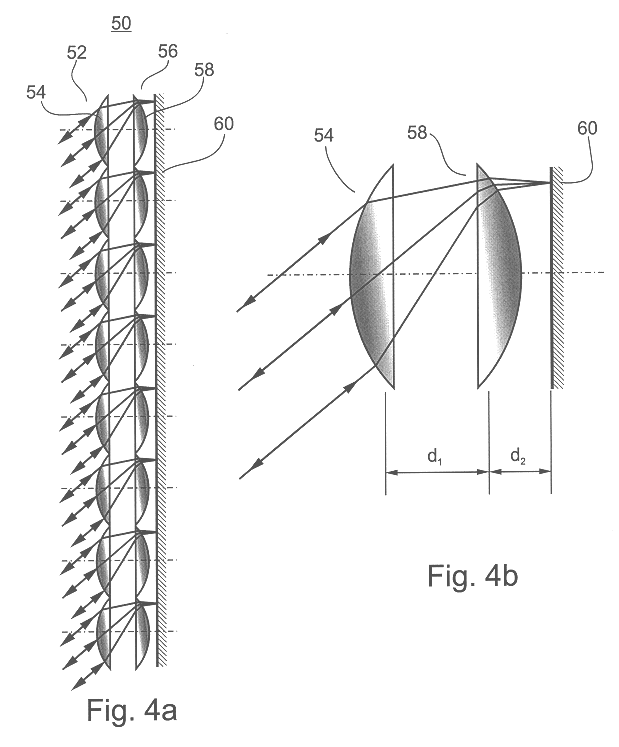
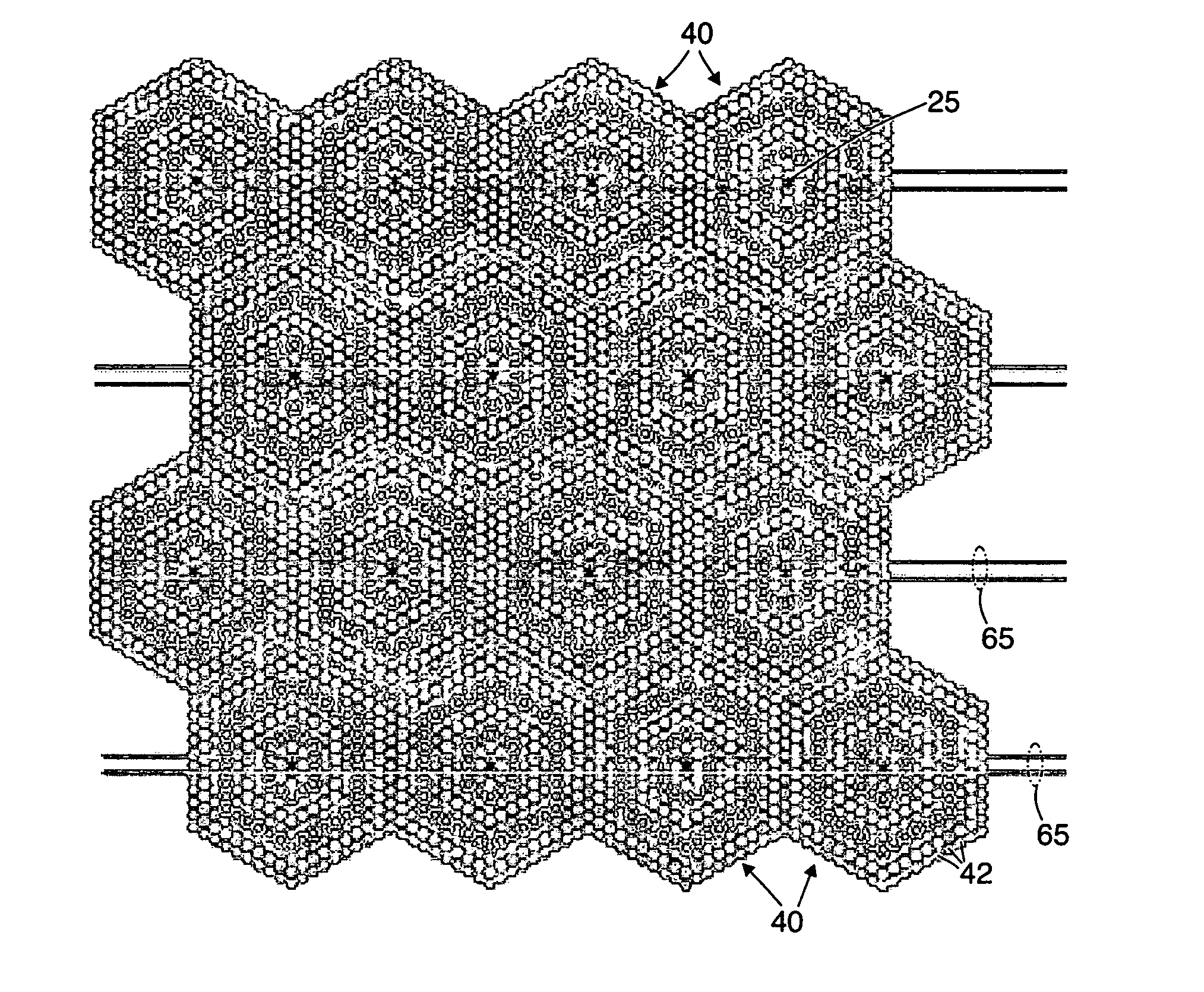
A lenslet is literally a small lens. The fact that distinguishes it from a small lens is that it is part of a lenslet array. A lenslet array consists of a set of lenslets in the same plane. Each lenslet normally has the same focal length.
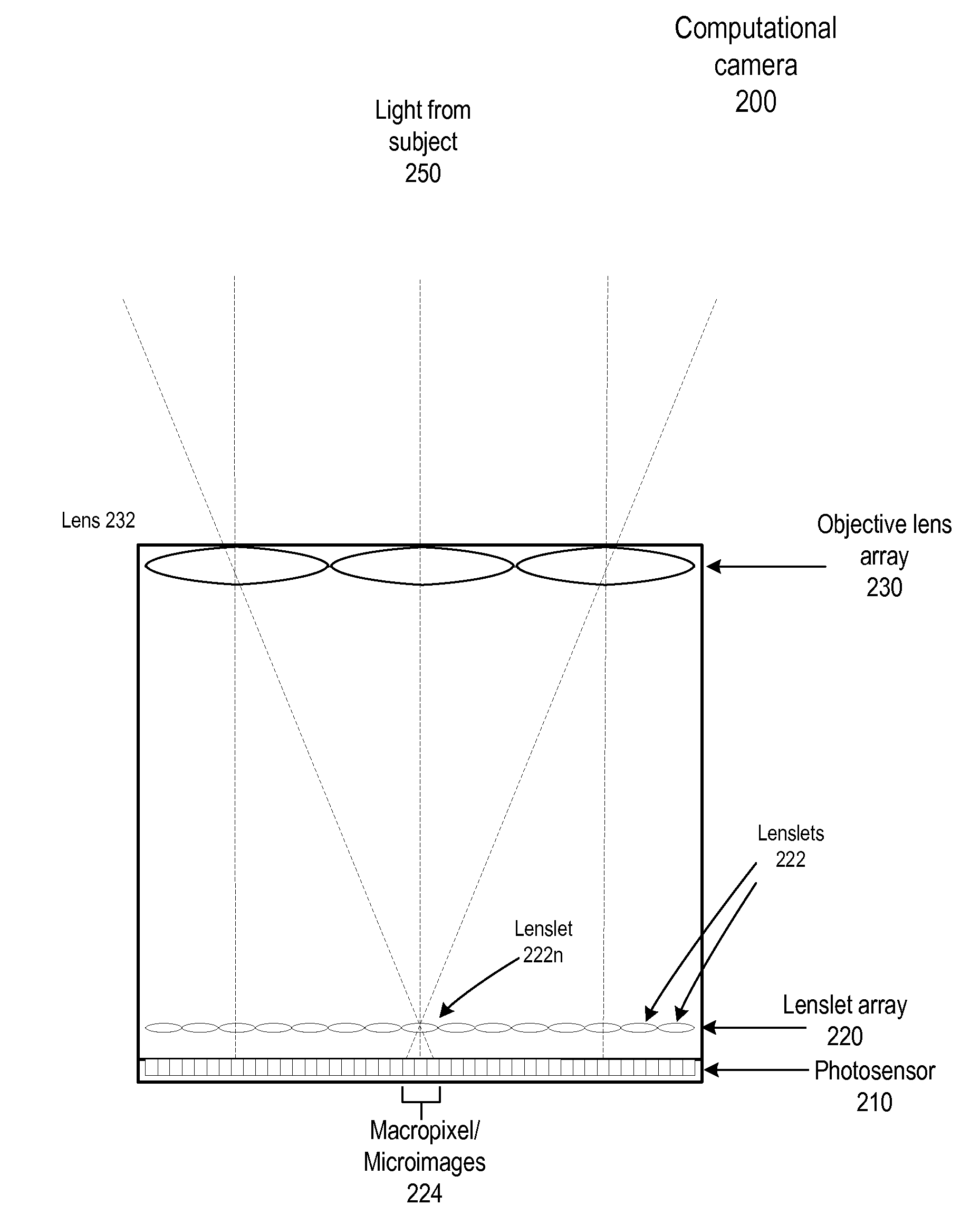
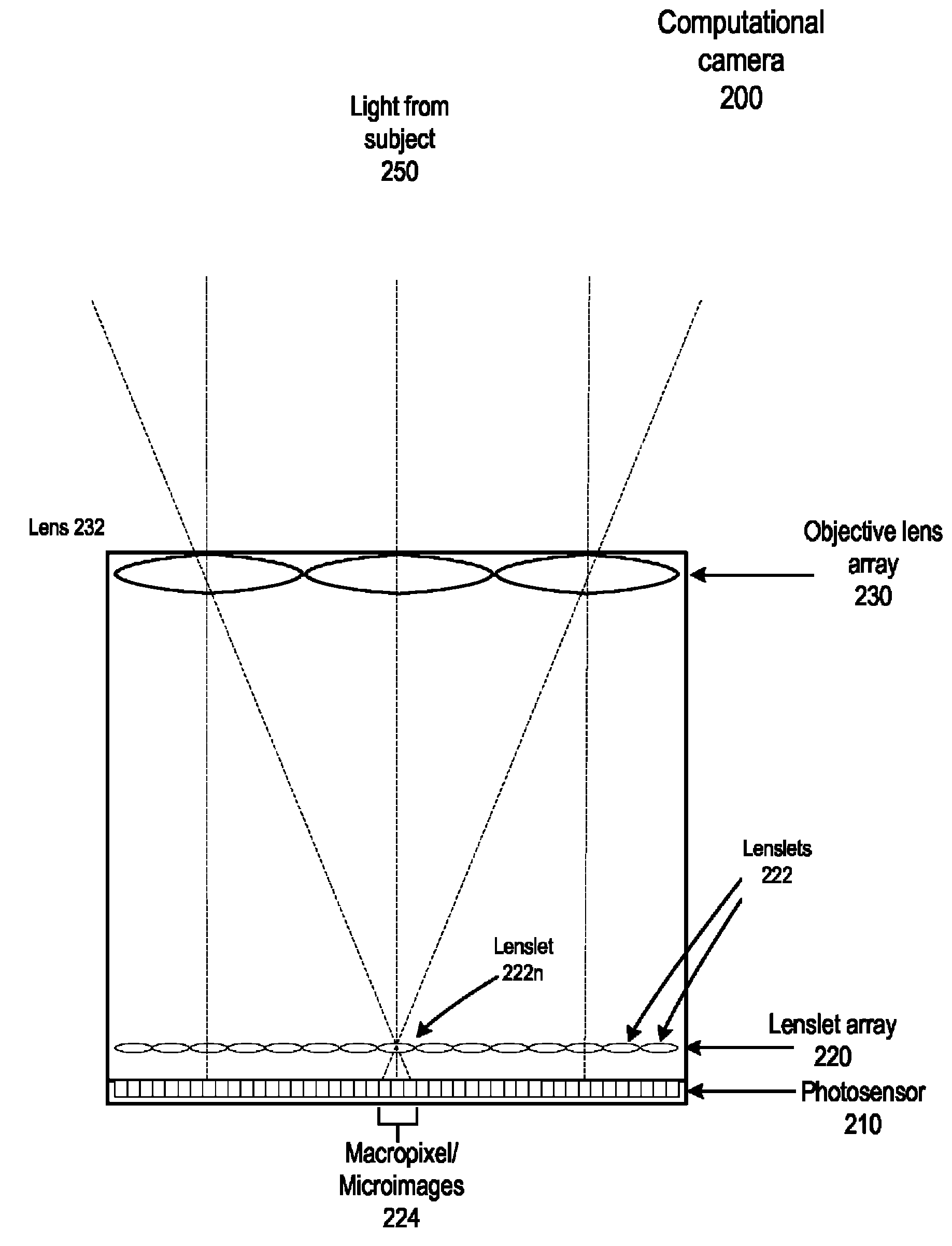
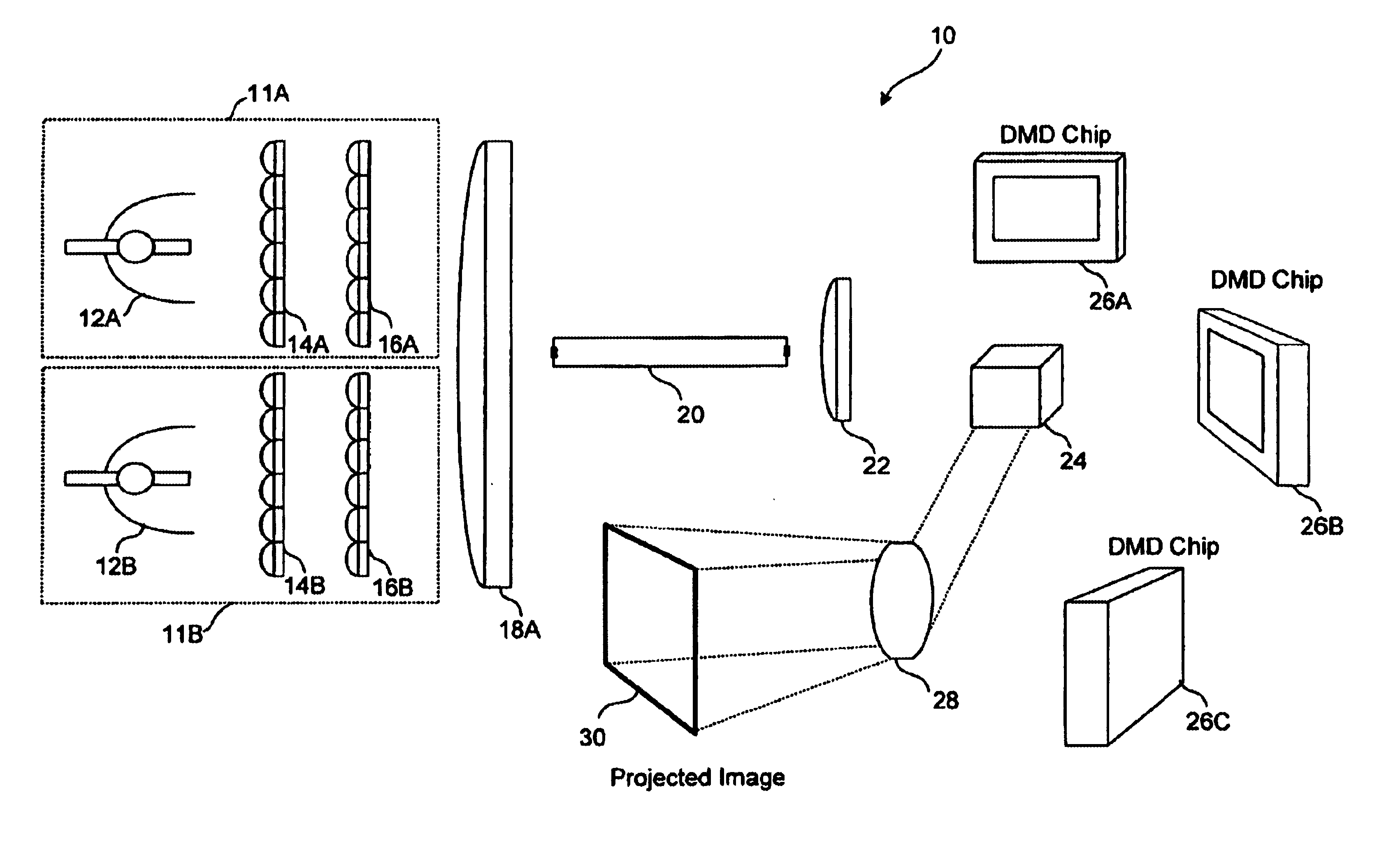
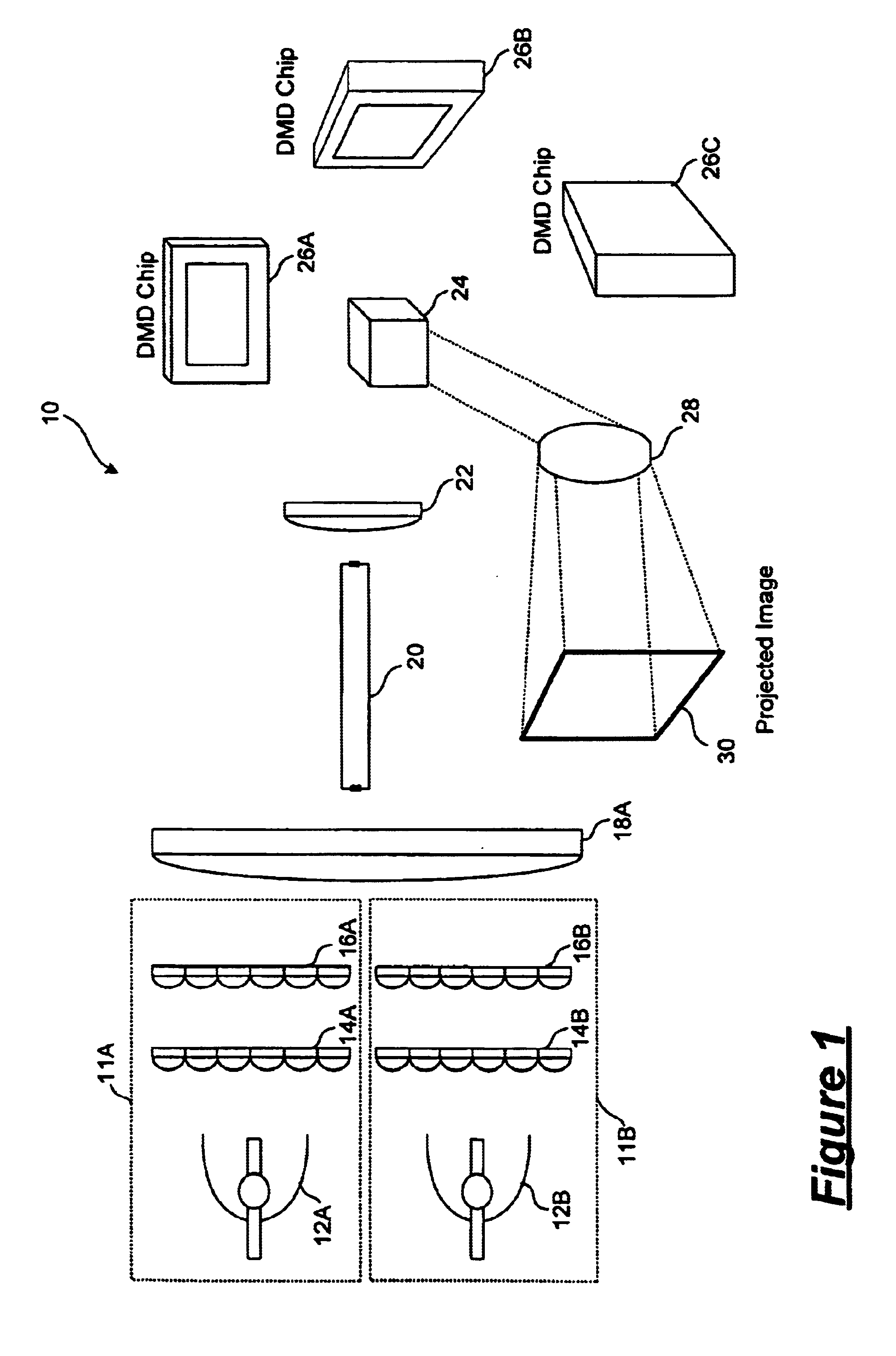
Fast Computational Camera Based On Two Arrays of Lenses
ActiveUS20090102956A1Less expenseQuality improvementTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsRadianceInformation capture
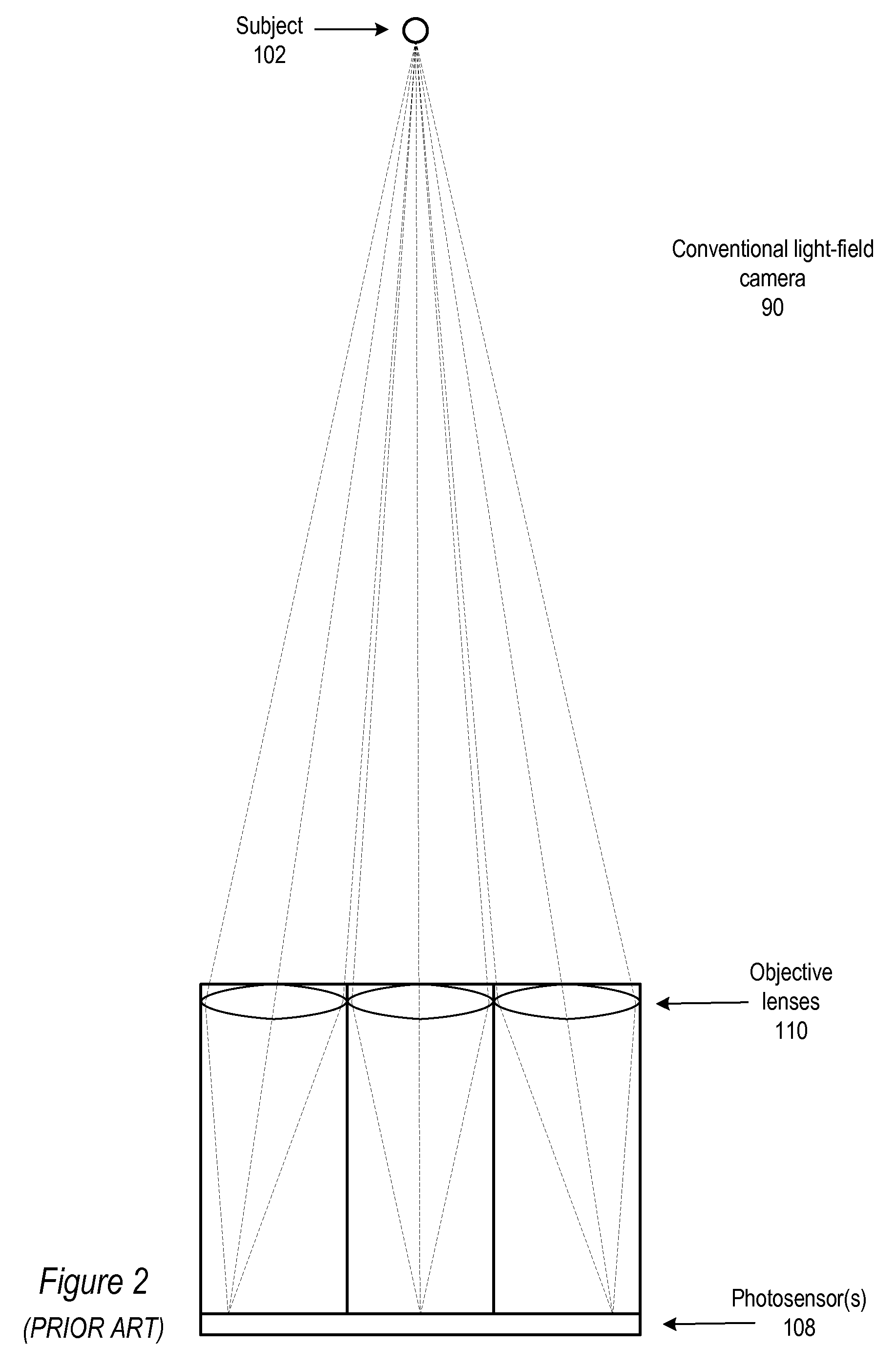
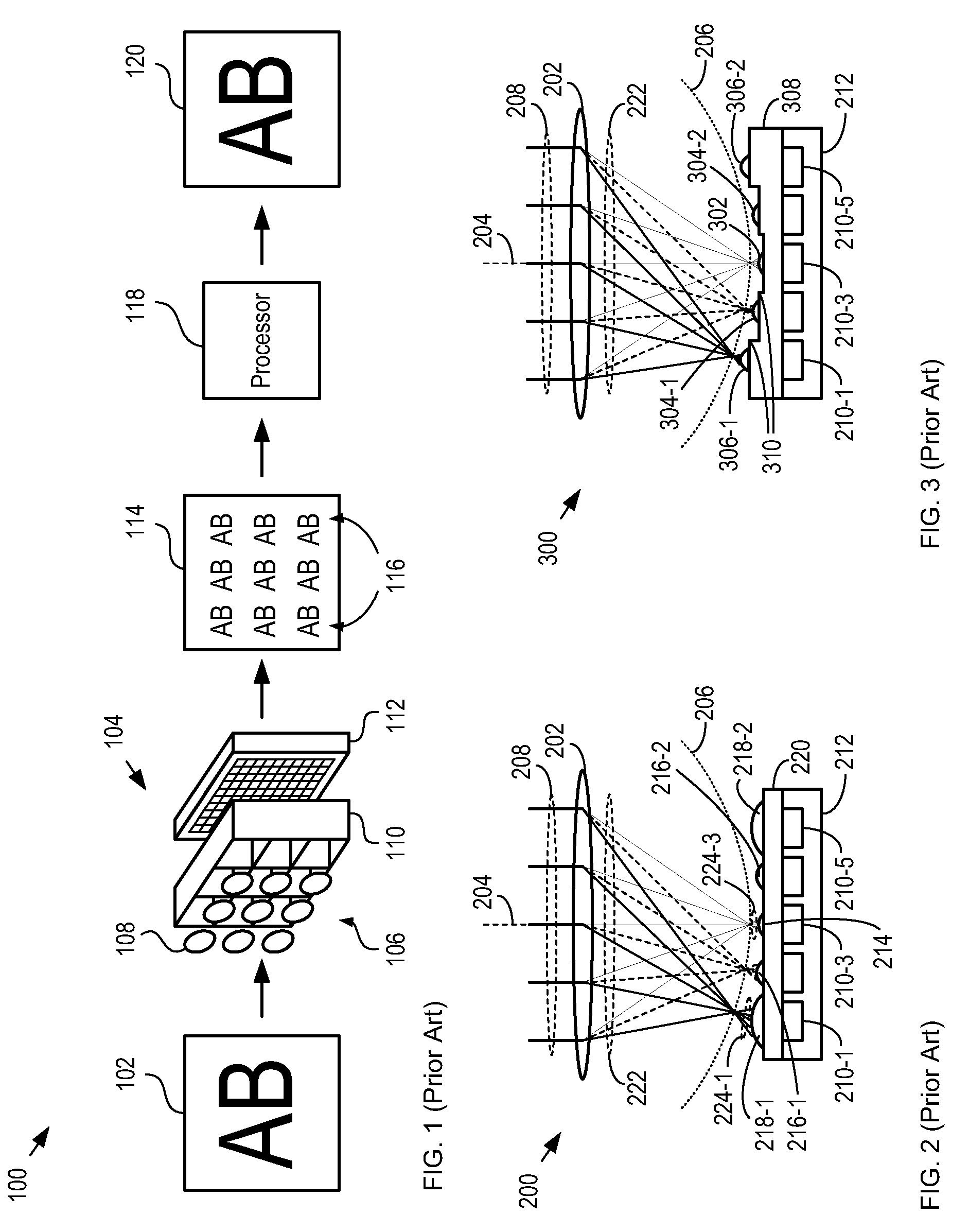
Method and apparatus for a fast (low F / number) computational camera that incorporates two arrays of lenses. The arrays include a lenslet array in front of a photosensor and an objective lens array of two or more lenses. Each lens in the objective lens array captures light from a subject. Each lenslet in the lenslet array captures light from each objective lens and separates the captured light to project microimages corresponding to the objective lenses on a region of the photosensor under the lenslet. Thus, a plurality of microimages are projected onto and captured by the photosensor. The captured microimages may be processed in accordance with the geometry of the objective lenses to align the microimages to generate a final image. One or more other algorithms may be applied to the image data in accordance with radiance information captured by the camera, such as automatic refocusing of an out-of-focus image.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Method and apparatus for constructing a contact lens with optics
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems, methods, and processes for constructing a contact lens. In one embodiment, a contact lens assembly is provided, comprising: a curved polymer polarizer with an aperture; a lenslet disposed inside the aperture, wherein the lenslet enables imaging near objects; and a filter attached to the lenslet. In further embodiments, a method for fabricating a flexible contact lens is provided, comprising: fabricating an element having an extrusion; providing a front concave mold, wherein the front mold has an intrusion to accommodate the extrusion of the optical element; affixing the extrusion of the optical element to the intrusion of the front mold; attaching a back convex mold to the front concave mold, thereby forming a mold cavity; and filling the mold cavity with a pre-polymerized liquid, whereby upon polymerization, the pre-polymerized liquid forms the flexible contact lens and the optical element is partially encapsulated within the lens.
Owner:INNOVEGA
Lens array assisted focus detection
InactiveUS20080095523A1Fast analysisQuick captureTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCamera lensComputer science
A focus detection device includes an image sensor and a plurality of lenslets. Each of the plurality of lenslets has a distinct conjugate length and is associated with a distinct portion of the image sensor.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES FUND 83 LLC
Multiscale Optical System
ActiveUS20100171866A1Low costImproved optical imagingTelevision system detailsColor television detailsSpatial correlationCamera lens
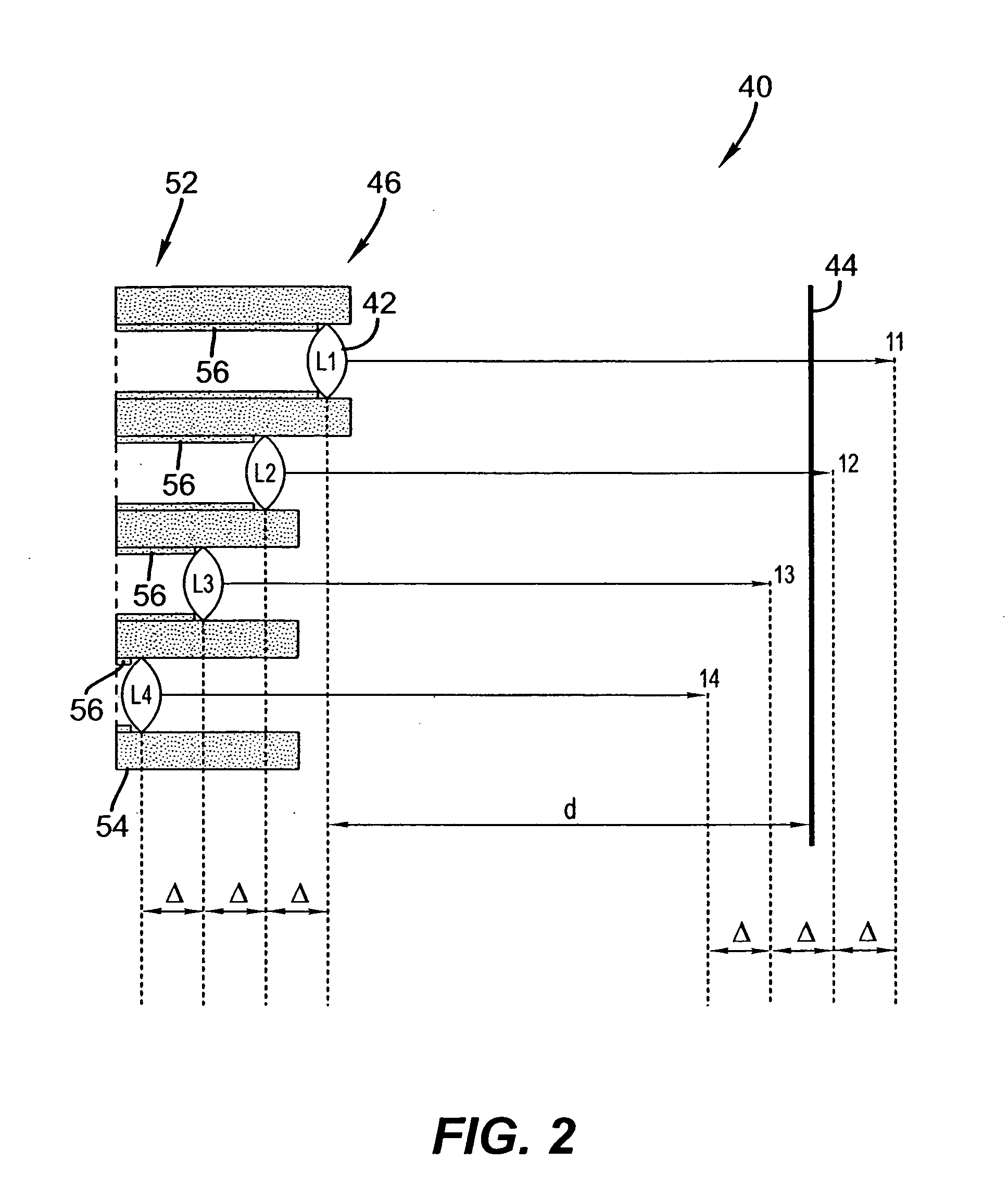
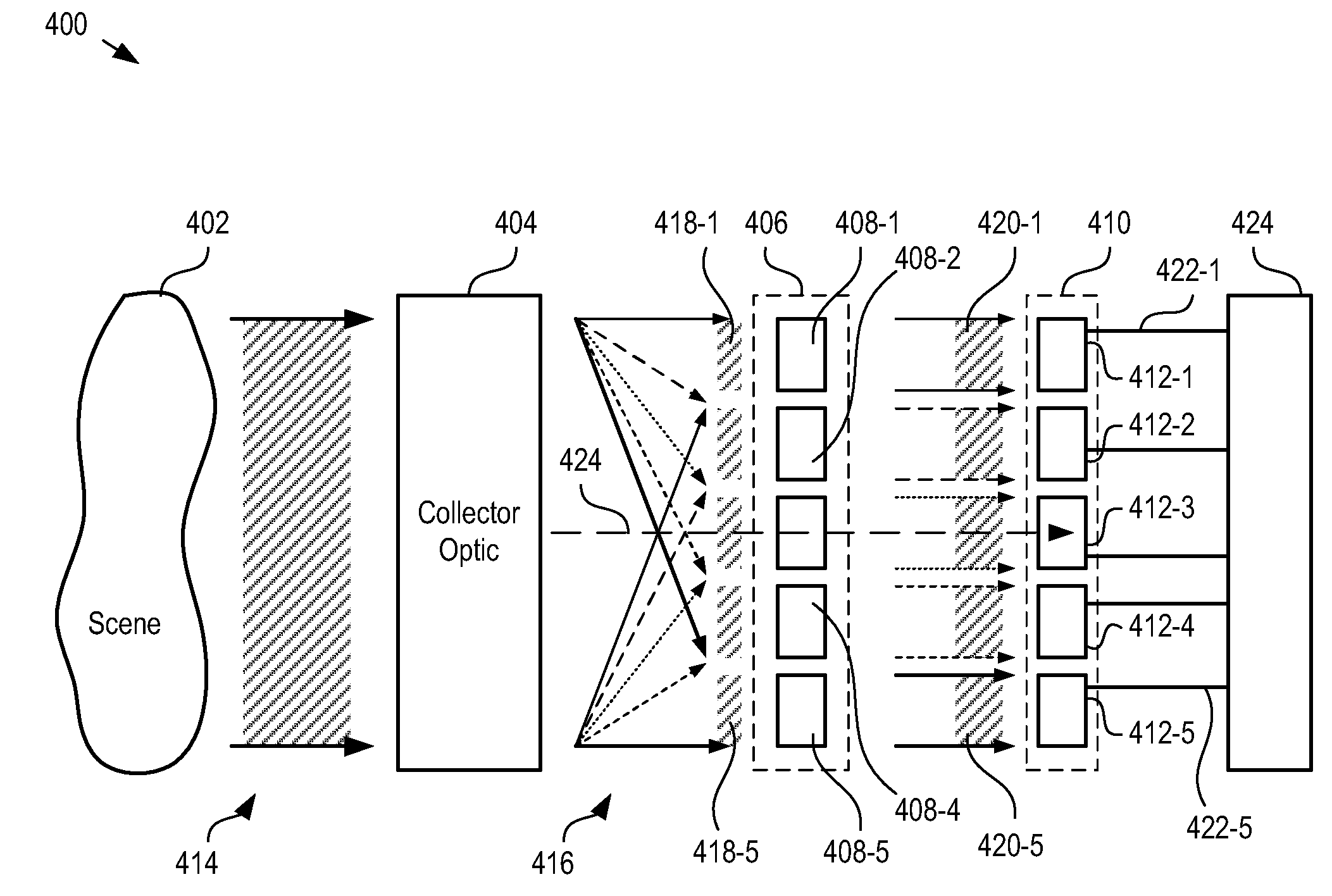
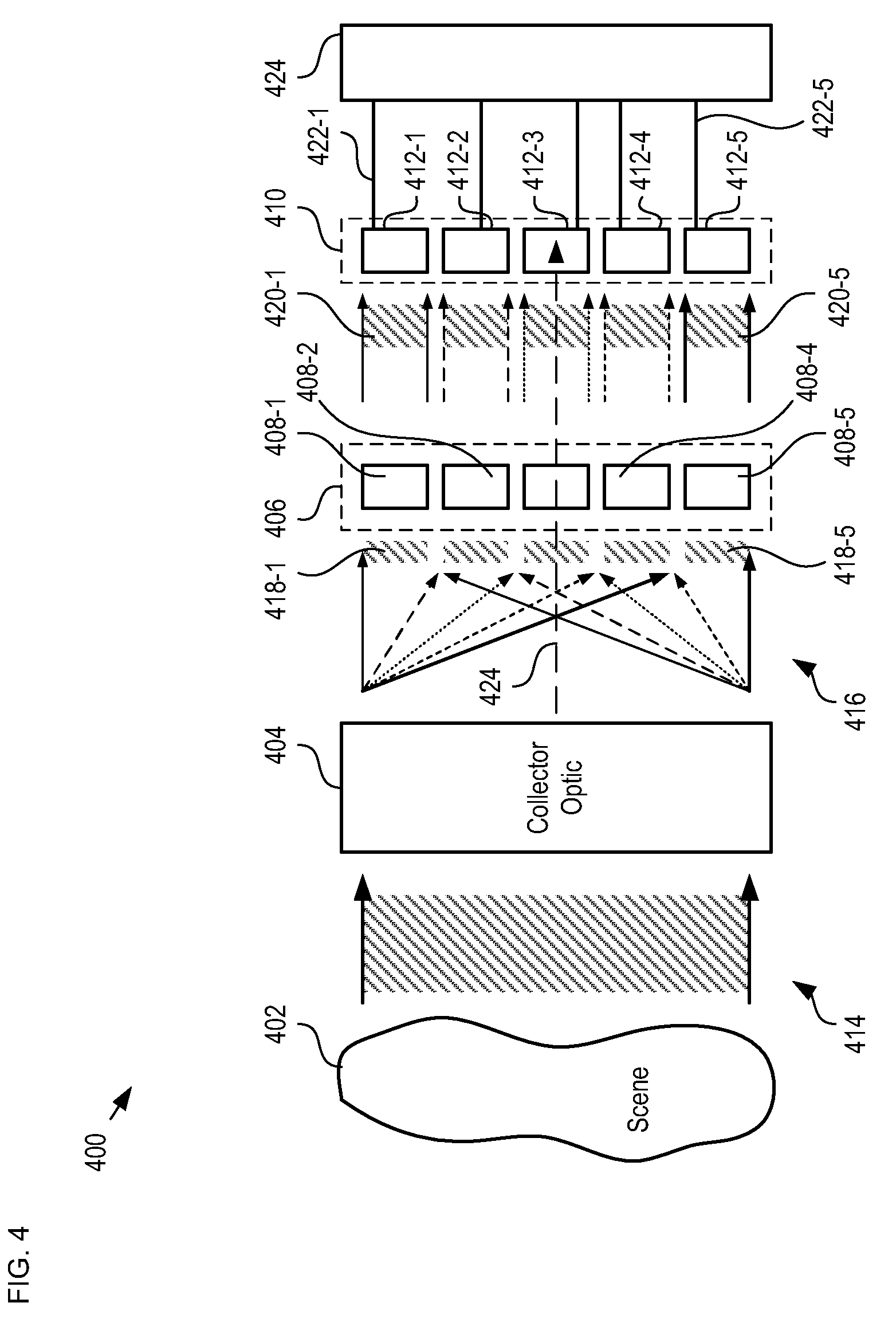
A means of enabling an imaging lens system that overcomes some of the costs and disadvantages of the prior art is disclosed. A lens system in accordance with the present invention reduces or eliminates one or more aberrations of an optical input by separating image collection functionality from image processing functionality. As a result, each function can be performed without compromising the other function. An embodiment of the present invention comprises a collection optic that provides a first optical field, based on light from a scene, to a processing optic that comprises a plurality of lenslets. The processing optic tiles the first optical field into a plurality of second optical fields. Each lenslet receives a different one of the plurality of second optical fields, reduces at least one localized aberration in its received second optical field, and provides the corrected optical field to a different one of plurality of photodetectors whose collective output is used to form a spatially correlated sub-image of that corrected optical field. The sub-images are readily combined into a spatially correlated image of the scene.
Owner:APPLIED QUANTUM TECH +1
Method and apparatus for improving vision and the resolution of retinal images
InactiveUS20060044510A1Accurate measurementHigh resolutionOptical measurementsEye surgeryCcd cameraLaser beams
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Microelectrical mechanical structure (MEMS) optical modulator and optical display system
InactiveUS20050002086A1Eliminating light attenuation of lightEliminating expenseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPlanar substrateActuator
A MEMS optical display system includes an illumination source for providing illumination light, a collimating lens for receiving the illumination light and forming from it collimated illumination light, and a converging microlens array having an array of lenslets that converge the collimated illumination light. The converging microlens array directs the illumination light to a microelectrical mechanical system (MEMS) optical modulator. The MEMS optical modulator includes, for example, a planar substrate through which multiple pixel apertures extend and multiple MEMS actuators that support and selectively position MEMS shutters over the apertures. A MEMS actuator and MEMS shutter, together with a corresponding aperture, correspond to pixel. The light from the converging microlens array is focused through the apertures and is selectively modulated according to the positioning of the MEMS shutters by the MEMS actuators, thereby to impart image information on the illumination light. The light is then passed to a diffused transmissive display screen by a projection microlens array.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
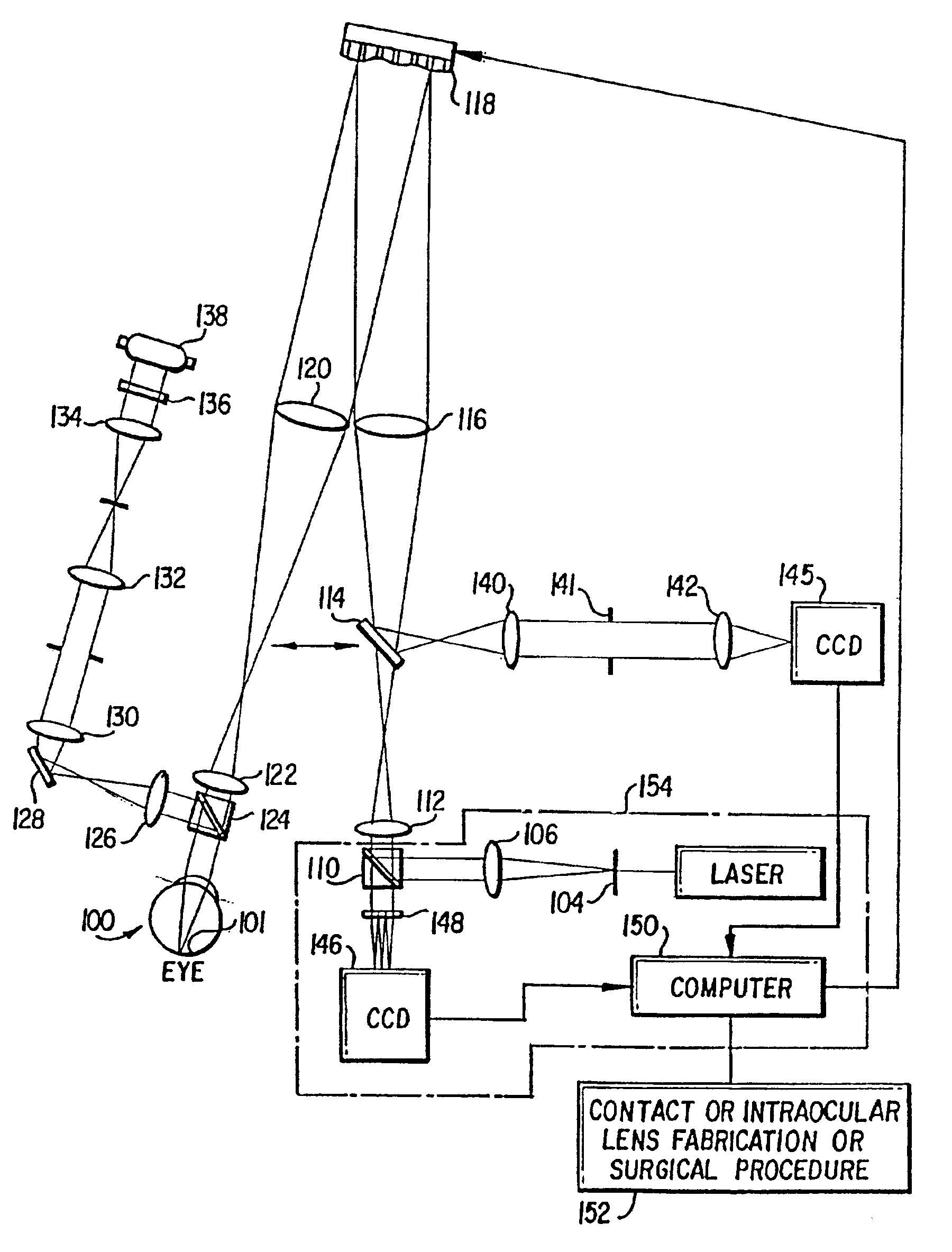
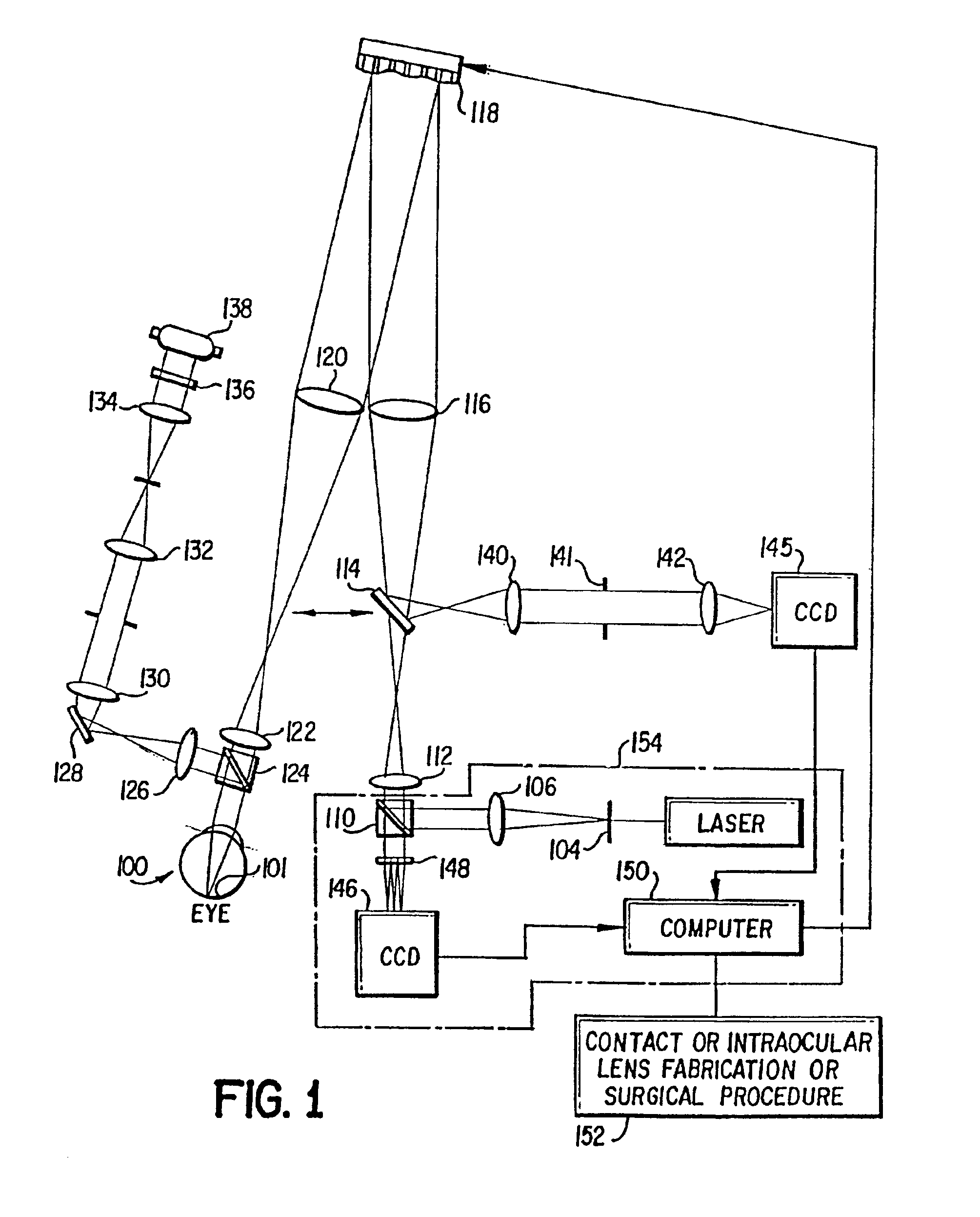
Method and apparatus for improving vision and the resolution of retinal images
InactiveUS6948818B2Accurate measurementAberration compensationOptical measurementsEye surgeryPhysicsLenslet
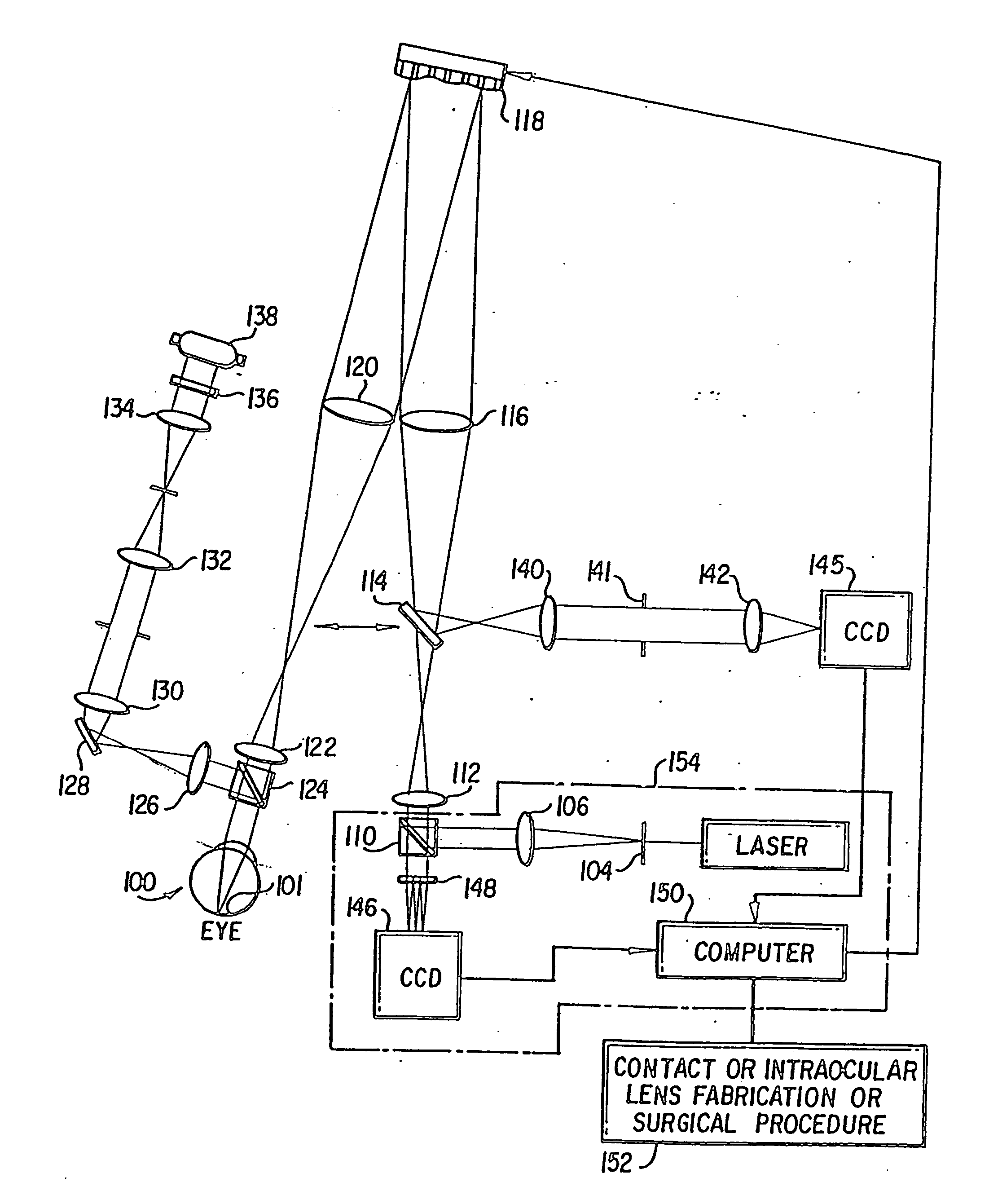
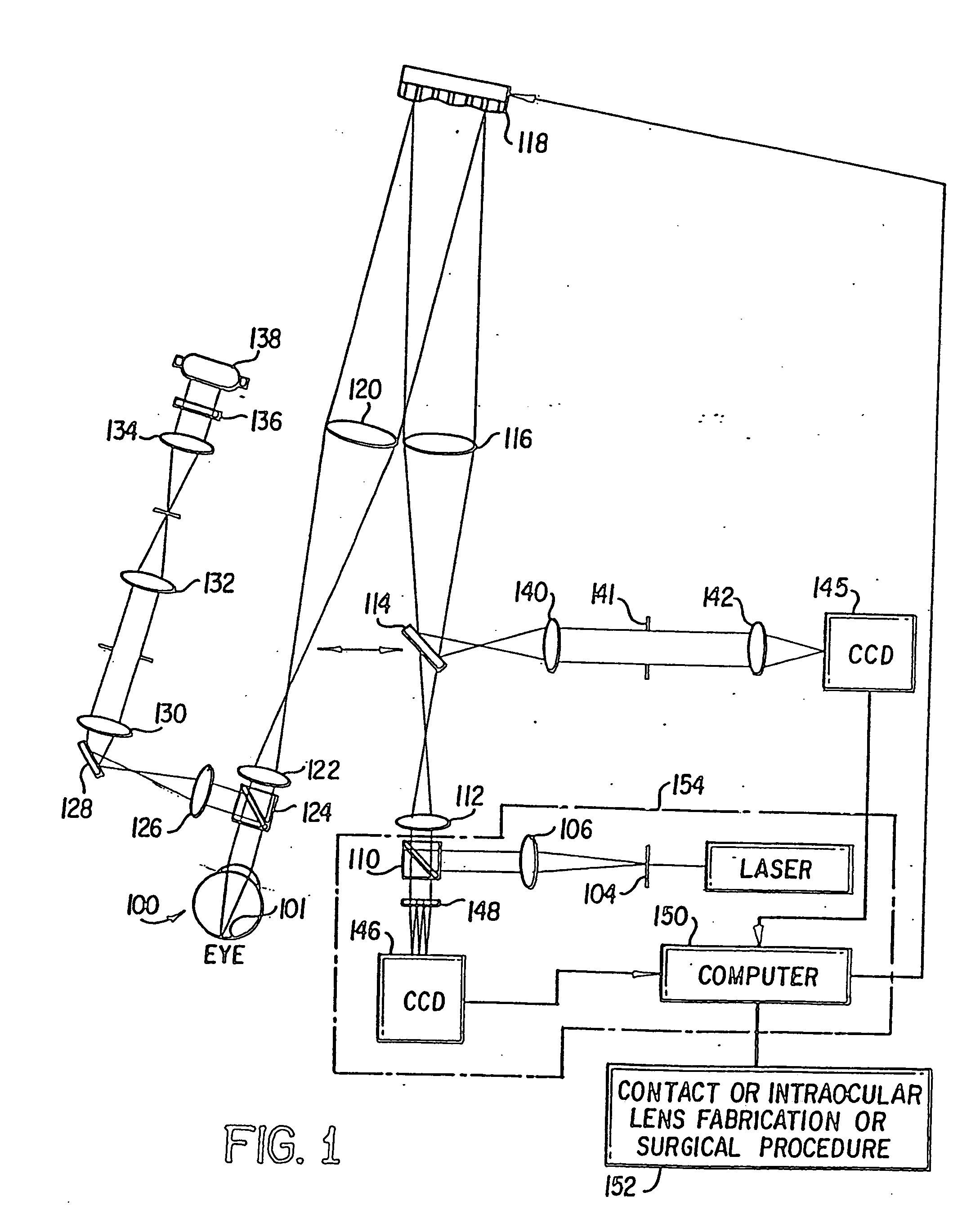
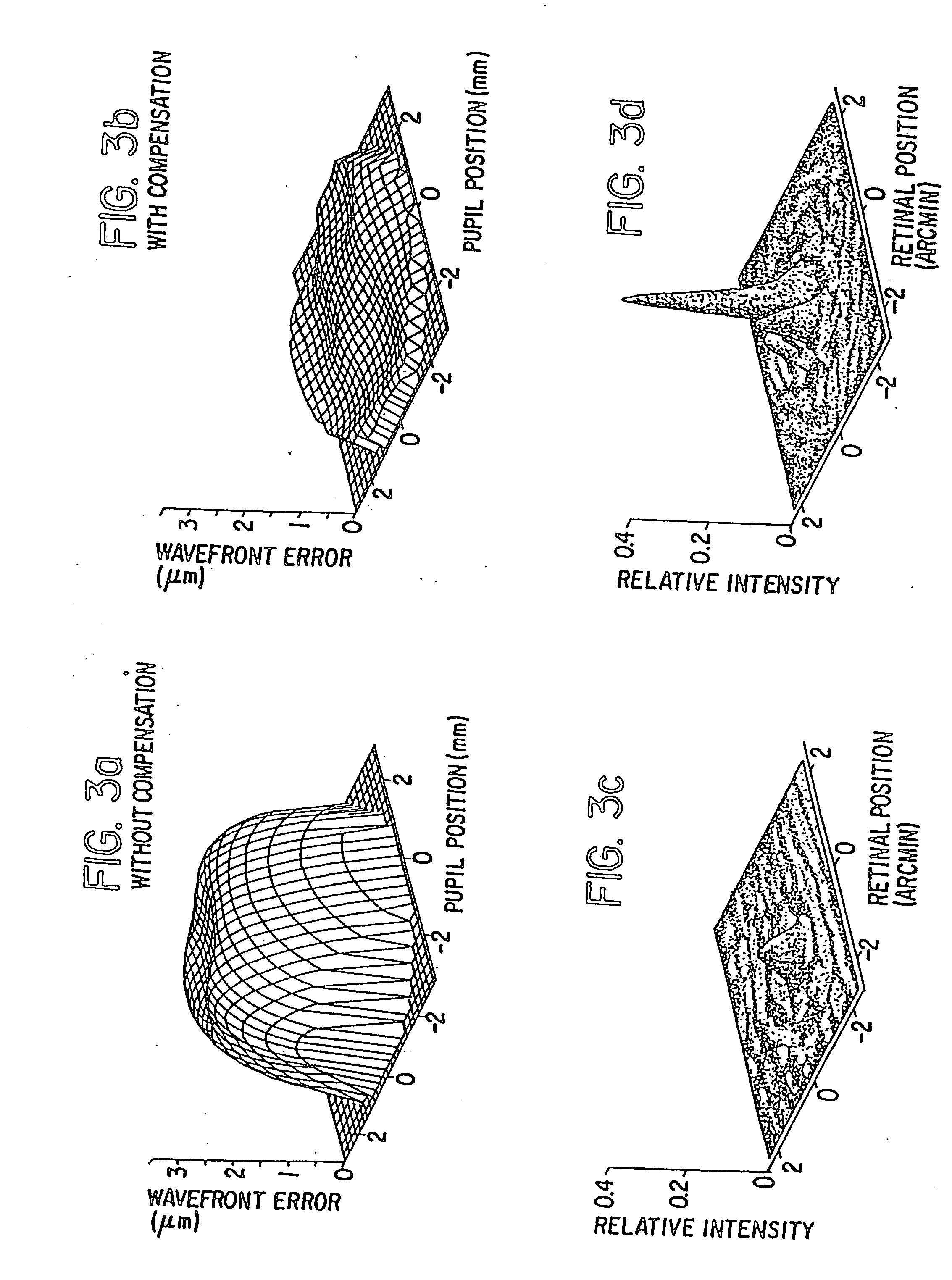
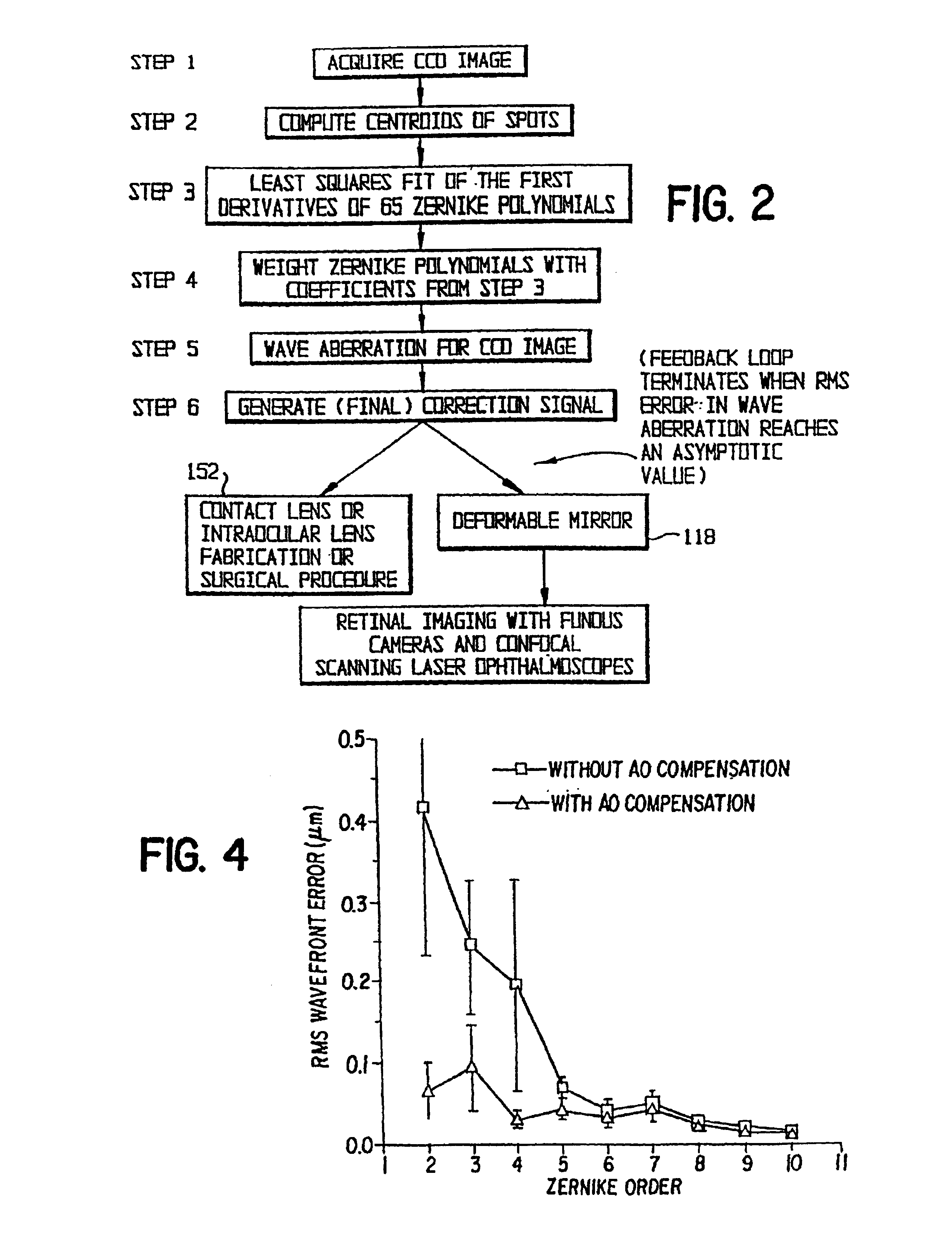
A method of and apparatus for improving vision and the resolution of retinal images is described in which a point source produced on the retina of a living eye by a laser beam is reflected from the retina and received at a lenslet array of a Hartmann-Shack wavefront sensor such that each of the lenslets in the lenslet array forms an aerial image of the retinal point source on a CCD camera located adjacent to the lenslet array. The output signal from the CCD camera is acquired by a computer which processes the signal and produces a correction signal which may be used to control a compensating optical or wavefront compensation device such as a deformable mirror. It may also be used to fabricate a contact lens or intraocular lens, or to guide a surgical procedure to correct the aberrations of the eye. Any of these methods could correct aberrations beyond defocus and astigmatism, allowing improved vision and improved imaging of the inside of the eye.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Micro-lens array with precisely aligned aperture mask and methods of producing same
A micro-lens array with a precisely aligned aperture mask, and a method of forming the same, is provided. The aperture mask is formed by projecting light onto a mask layer using each lenslet in the micro-lens array. The intensity of the light and the mask layer material are chosen so that the light forms apertures in the mask layer via a non-ablative process. The resulting apertures are automatically aligned with their respective lenslets.
Owner:BRIGHT VIEW TECHNOLOGIES CORPORATION
Directed reflectors and systems utilizing same
A wide angle directed reflector is disclosed. The directed reflector includes a lenticular layer including at least one array of lenslets, each of which having a focal length, The directed reflector further includes a reflective layer which is disposed relative to the lenticular layer. The lenticular layer and the reflective layer are constructed, designed and relatively disposed such that light incident at an angle of incidence on the lenticular layer is reflected by the reflective layer and redirected through the lenticular layer at a substantially constant angle relative to the angle of incidence.
Owner:OPTIDTECH OPTICAL IDENTIFICATION TECH
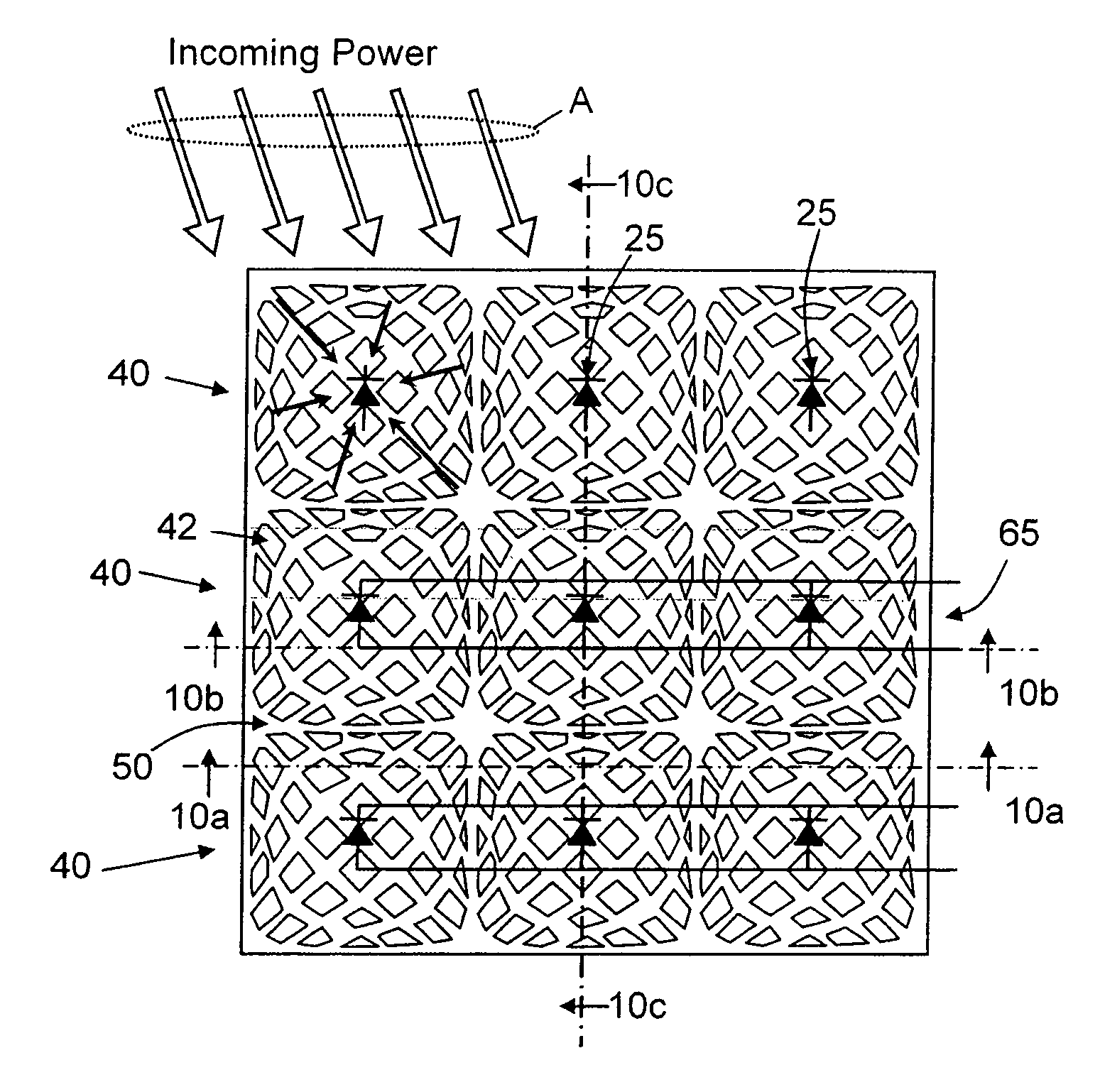
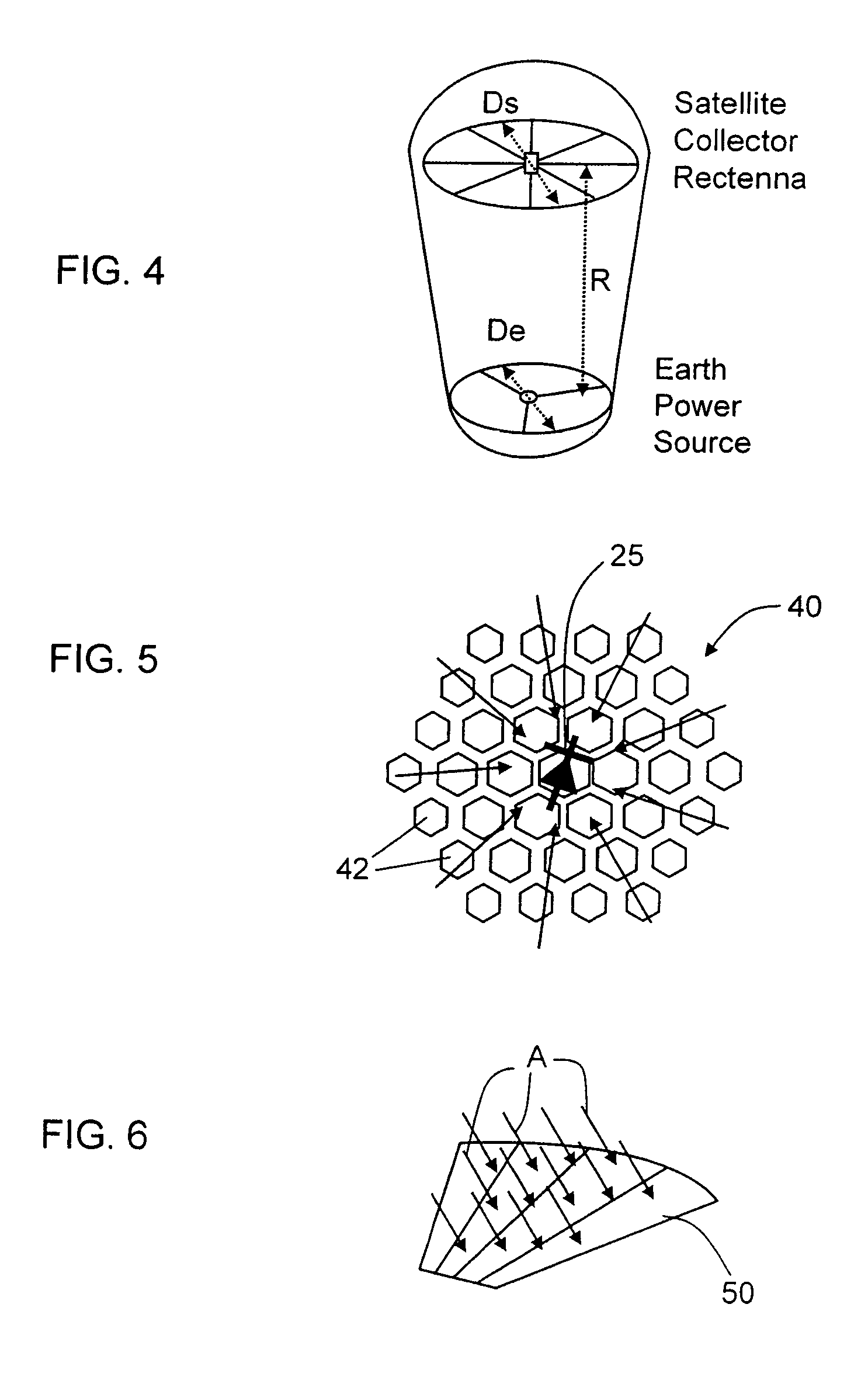
Large aperture rectenna based on planar lens structures
A rectenna structure comprising a flexible, dielectric sheet of material; a plurality of metallic lenslets disposed on the sheet of material; and a plurality of diodes disposed on the sheet of material, each diode in said plurality of diodes being arranged at a focus of a corresponding one of said plurality of metallic lenslets.
Owner:HRL LAB
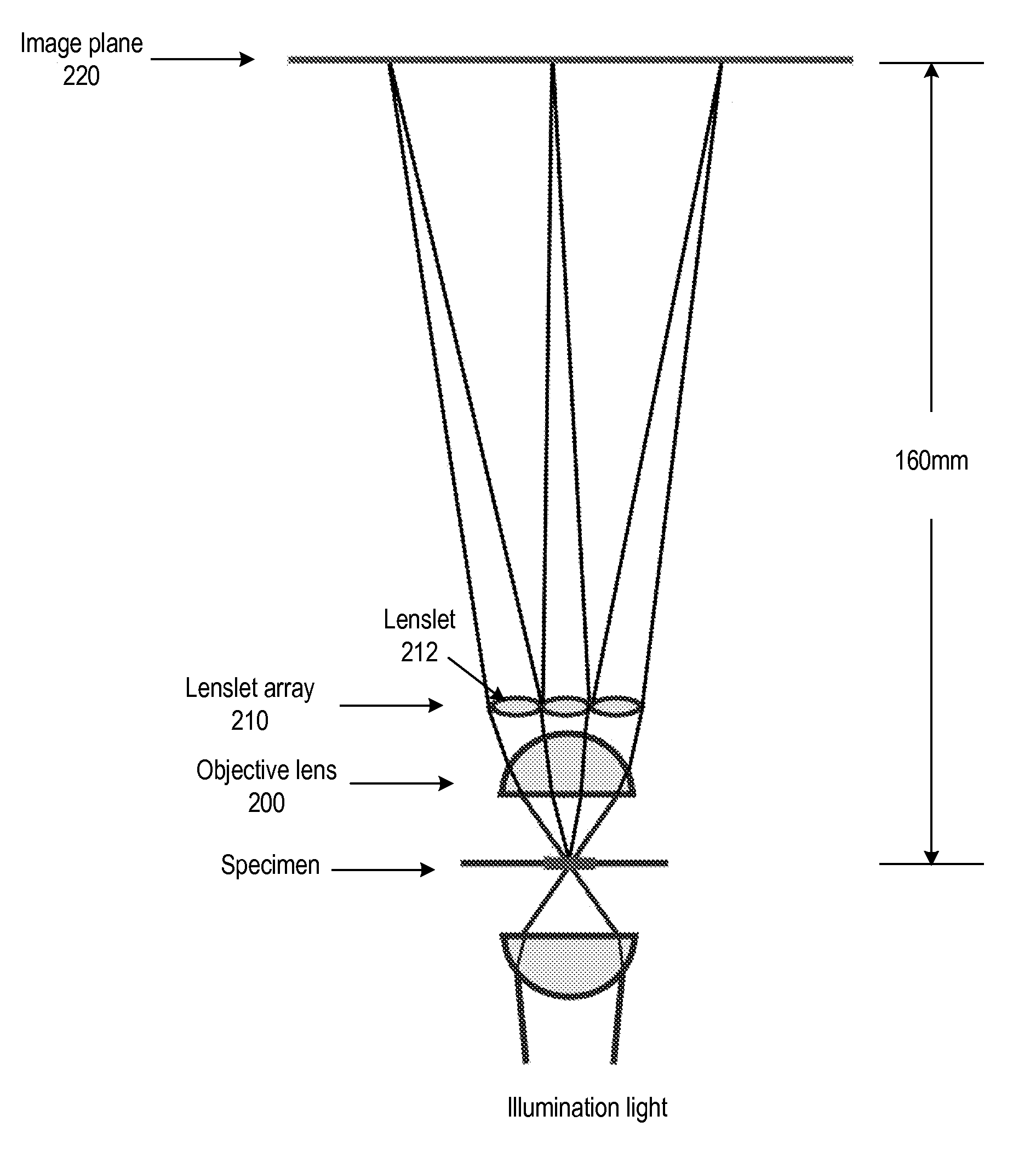
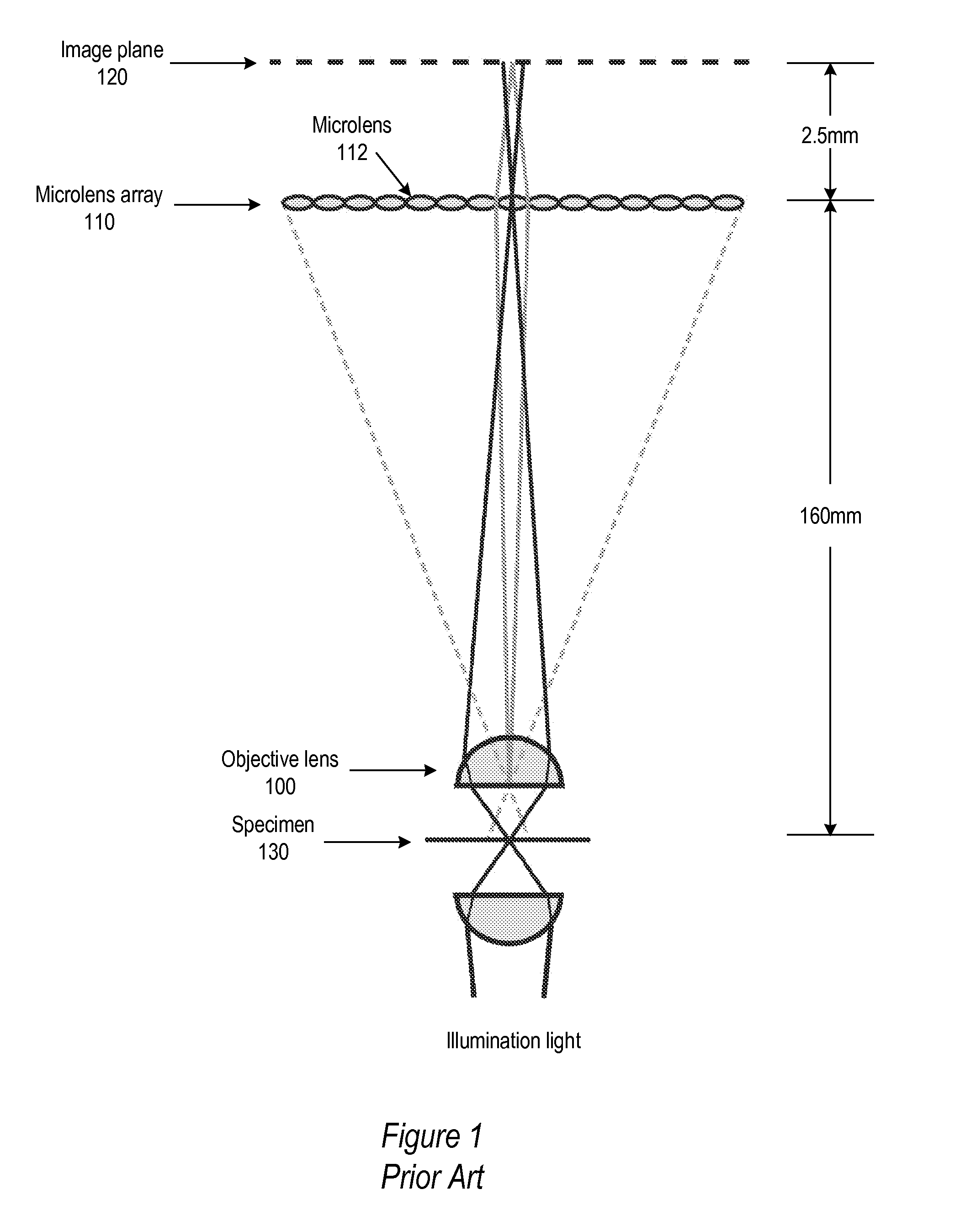
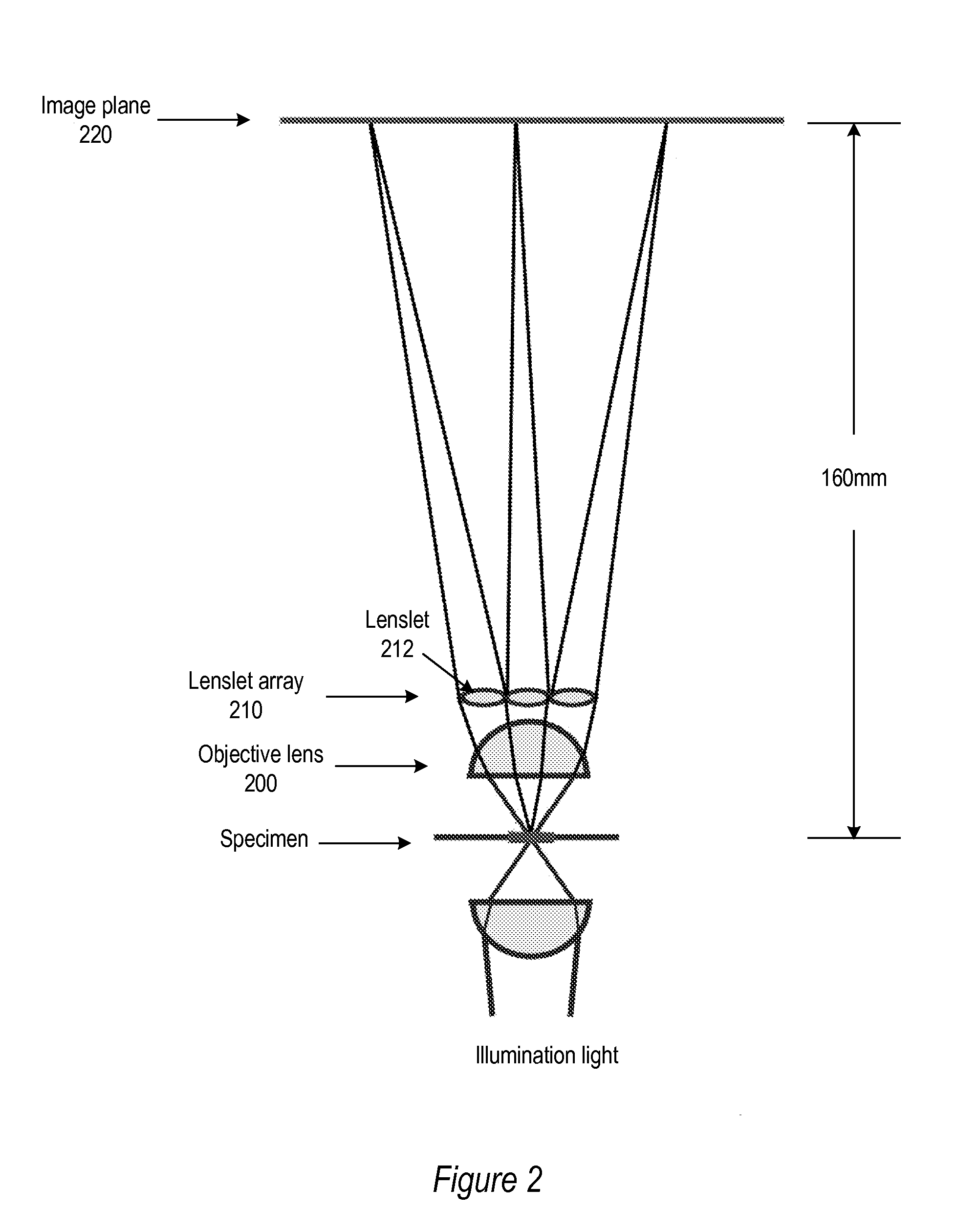
Light Field Microscope With Lenslet Array
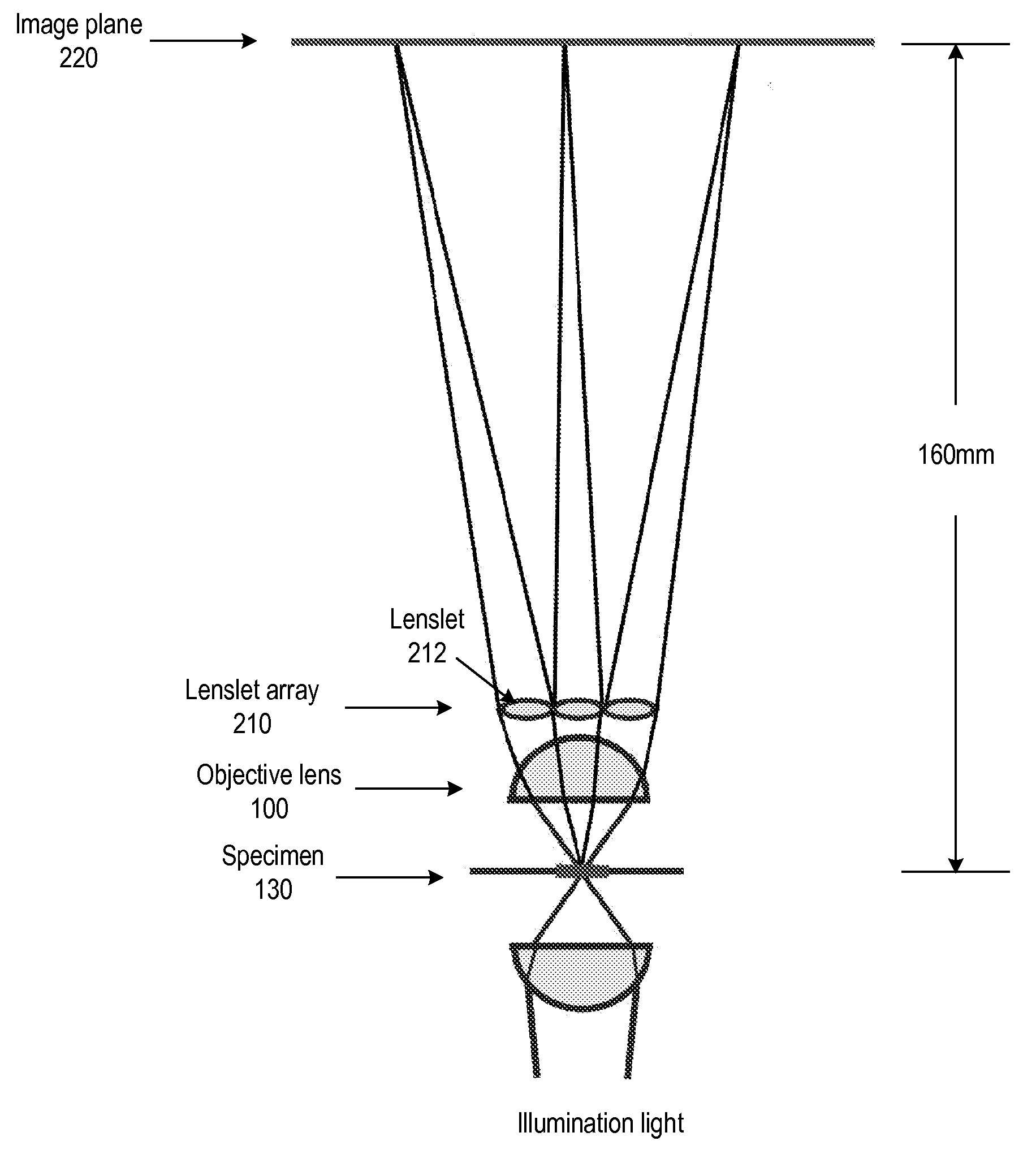
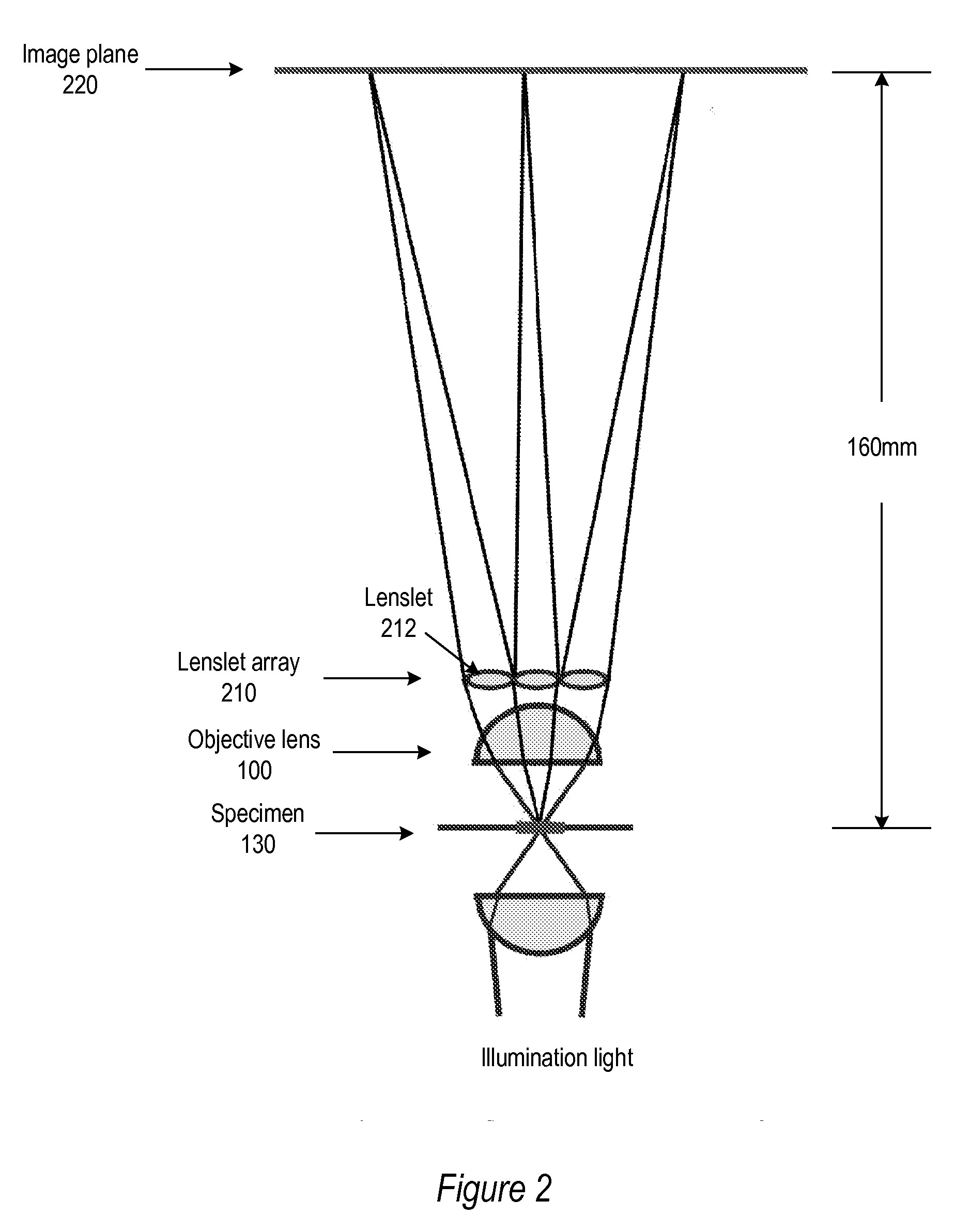
ActiveUS20080180792A1Avoids mechanical complicationAberration correctionMicroscopesLensViewpointsImage plane
A light field microscope incorporating a lenslet array at or near the rear aperture of the objective lens. The microscope objective lens may be supplemented with an array of low power lenslets which may be located at or near the rear aperture of the objective lens, and which slightly modify the objective lens. The result is a new type of objective lens, or an addition to existing objective lenses. The lenslet array may include, for example, 9 to 100 lenslets (small, low-power lenses with long focal lengths) that generate a corresponding number of real images. Each lenslet creates a real image on the image plane, and each image corresponds to a different viewpoint or direction of the specimen. Angular information is recorded in relations or differences among the captured real images. To retrieve this angular information, one or more of various dense correspondence techniques may be used.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Retroreflection based multitouch sensor
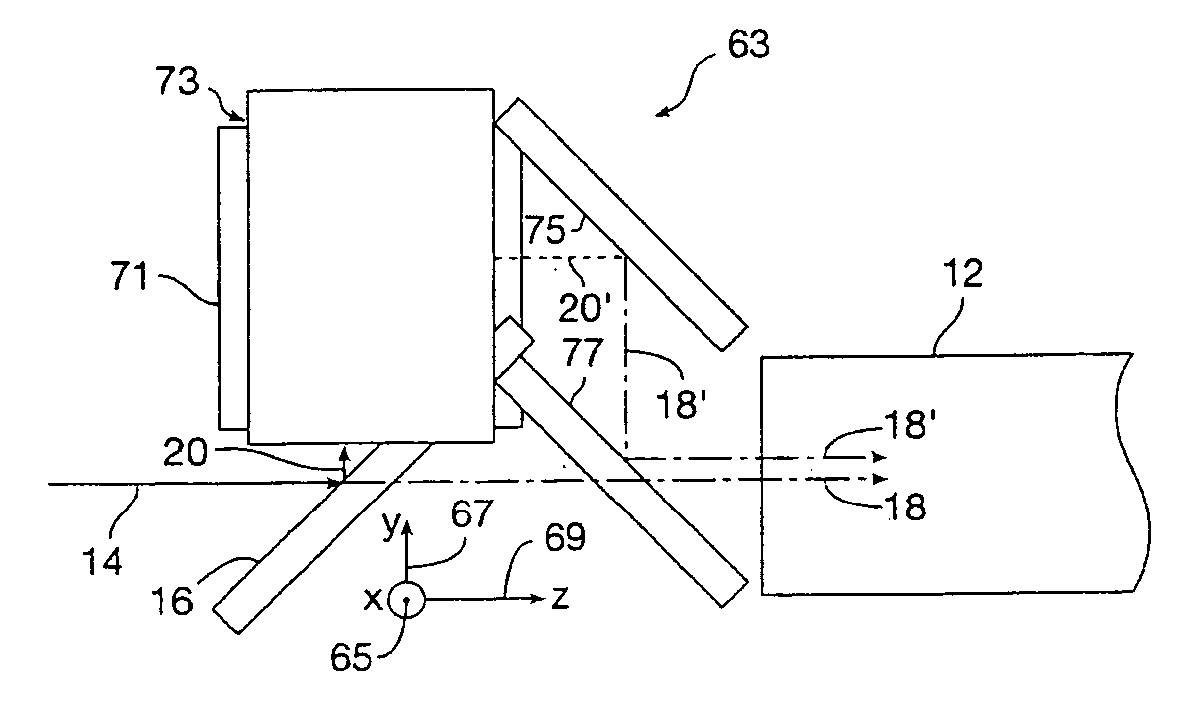
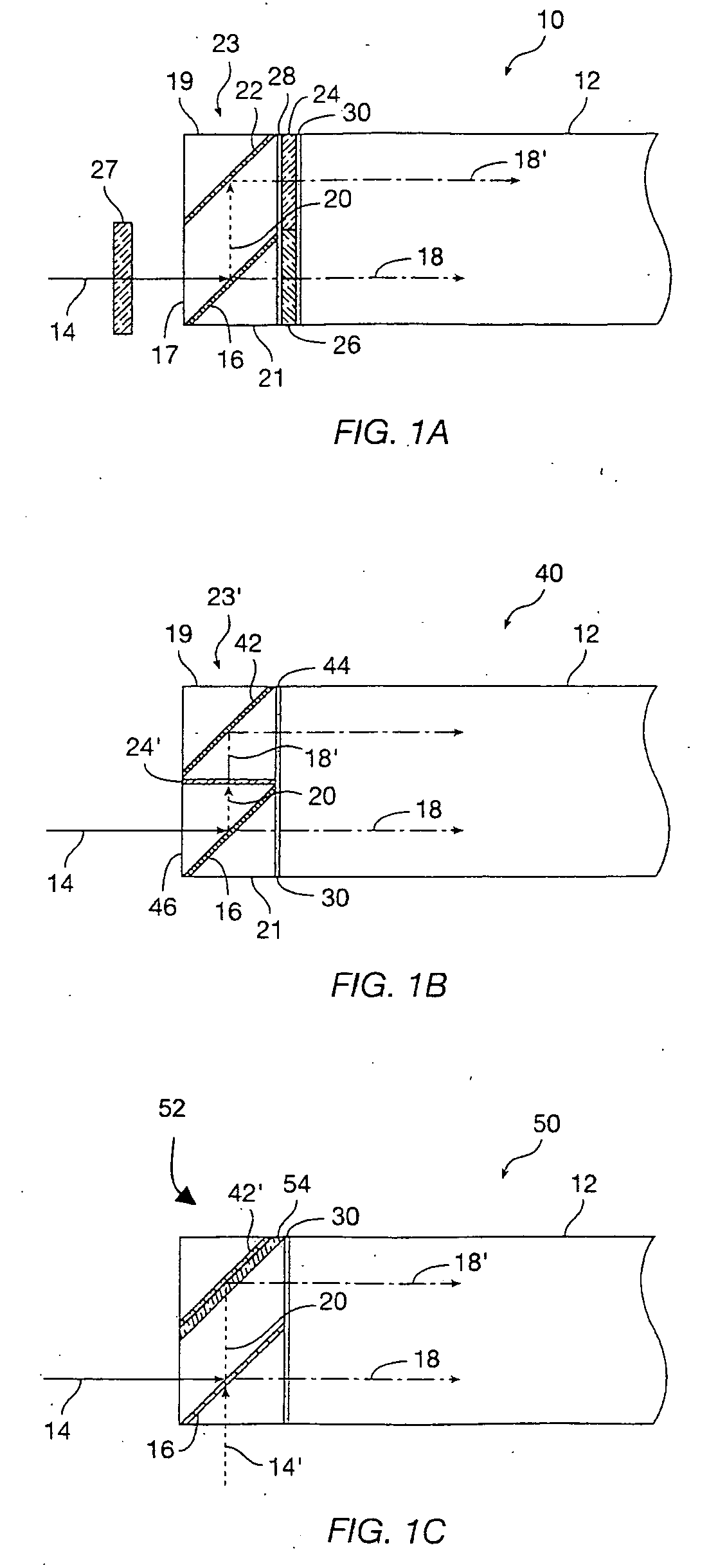
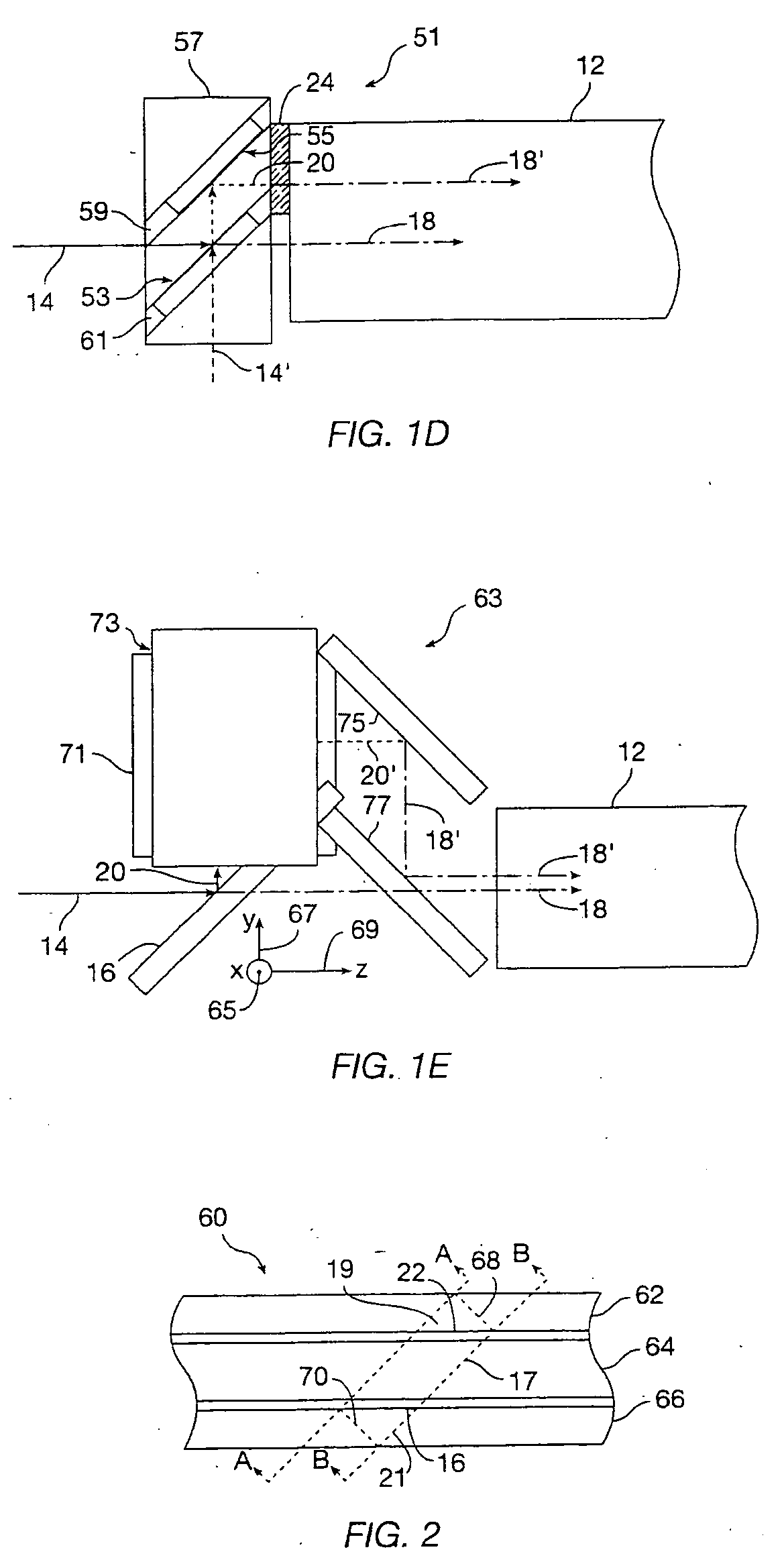
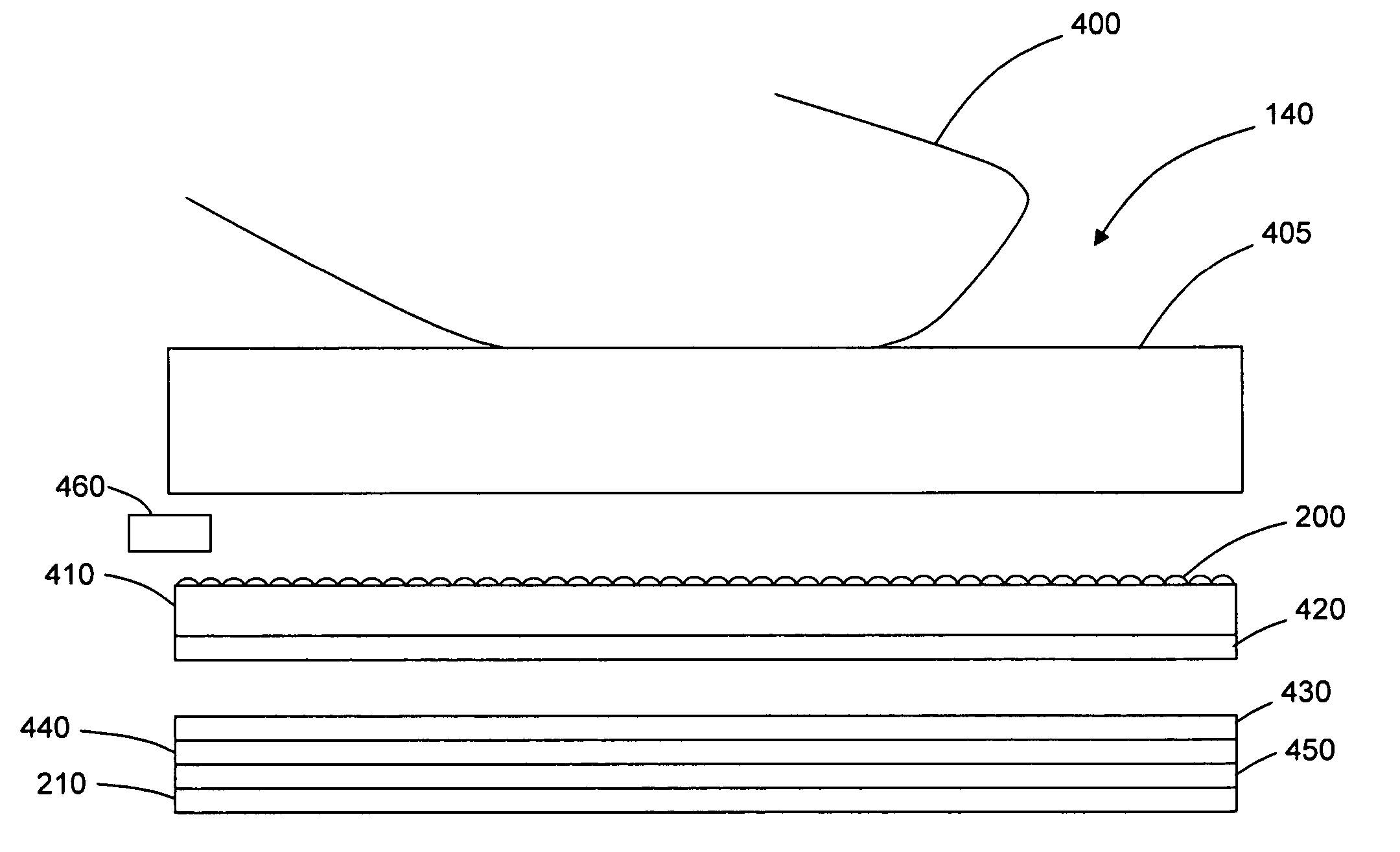
A detection apparatus includes a multilocation sensor. The apparatus includes a sheet in communication with the sensor, which when a plurality of locations of the sheet are simultaneously activated, the sensor senses these locations, simultaneously. Alternatively, the apparatus includes a surface. The apparatus includes a sensor in communication with the surface that detects variable pressure regarding a touch on the surface. Alternatively, the apparatus includes a sensor in communication with the surface that is capable of detecting a touch on a surface and also a presence of an object near the surface but not touching the surface. Alternatively, the apparatus includes a lenslet array where the lenslets are diffractive. The apparatus includes a sensor for determining where the array is being touched. The sensor includes a first light source producing light at a first frequency, a second light source producing light at a second frequency, a camera which records images from the frequencies of light from the array, and a computer which determines where the surface is being touched from the images. Alternatively, the apparatus includes a sensor for determining where the surface is being touched, including a plurality of cameras that take images of the surface, a first array of lights positioned such that light from the first array is on a vertical line with one or more of the cameras, a second array of lights that are positioned such that light from the second array is on a horizontal line with one or more of the cameras and a computer connected to the cameras which determines where the surface is being touched from the images. Alternatively, the apparatus includes a sheet containing a plurality of elements which are at least one of refractive, diffractive, retroreflective, reflective, or focusing. The apparatus includes a sensor which determines where the sheet is touched based on light being one of refracted, diffracted, retroreflected, reflected or focused by the sheet to the sensor. Alternatively, the apparatus includes a sheet having no active components in, on, or adjoining the sheet. The apparatus includes active components separate and apart from the sheet which determine where the sheet is touched. The apparatus can include an autostereo display including a multitouch retroreflective surface and a projector. A method for detection. A software program stored on a computer 5 readable medium.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
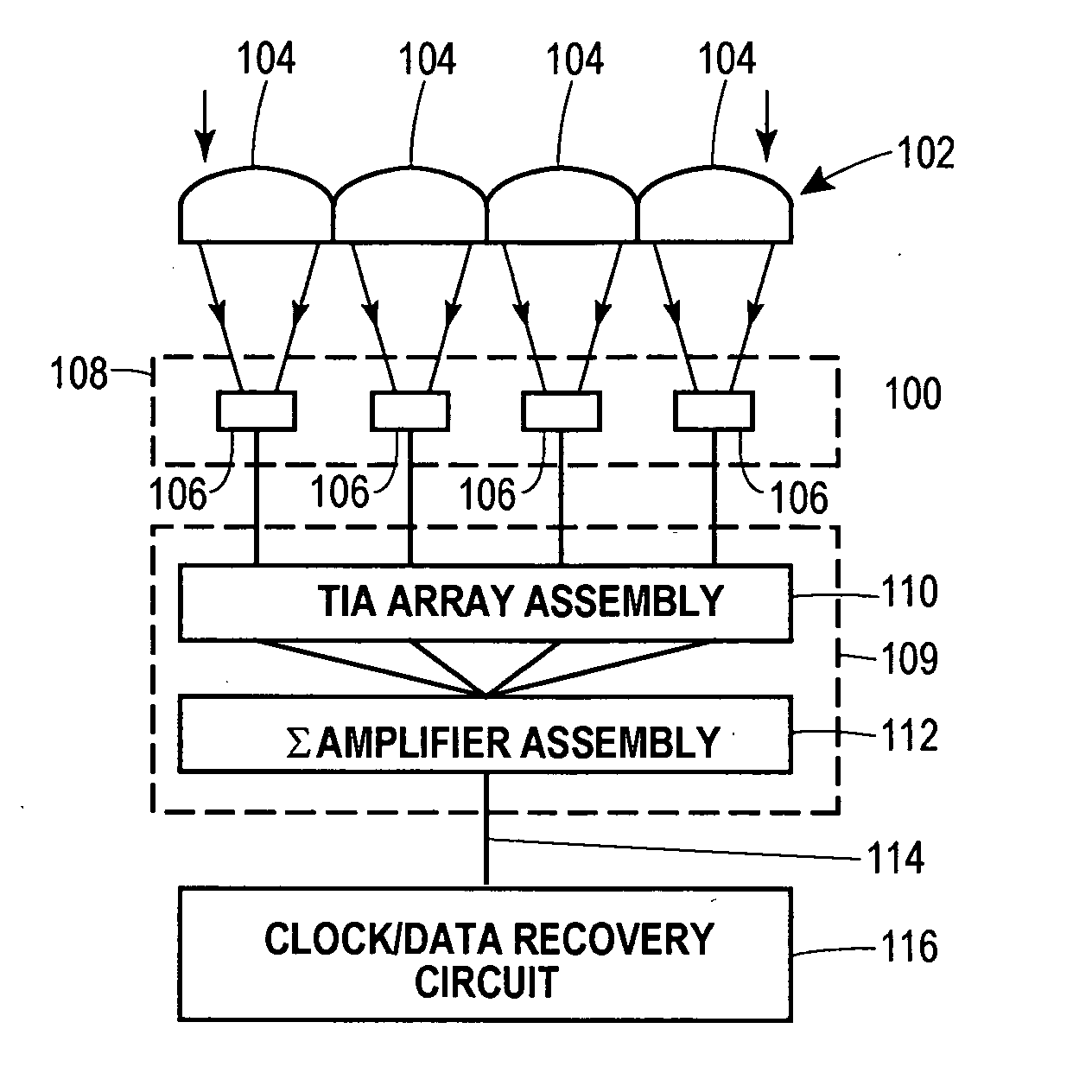
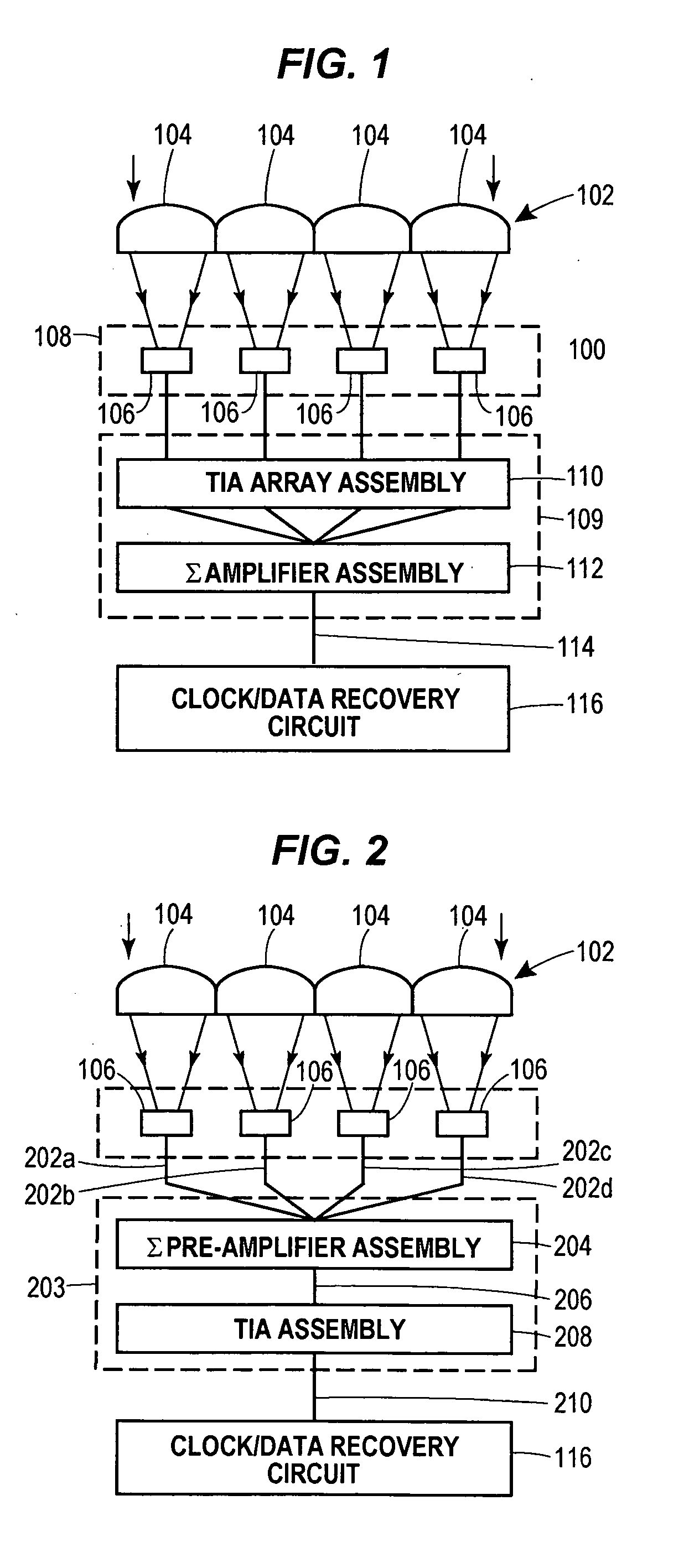
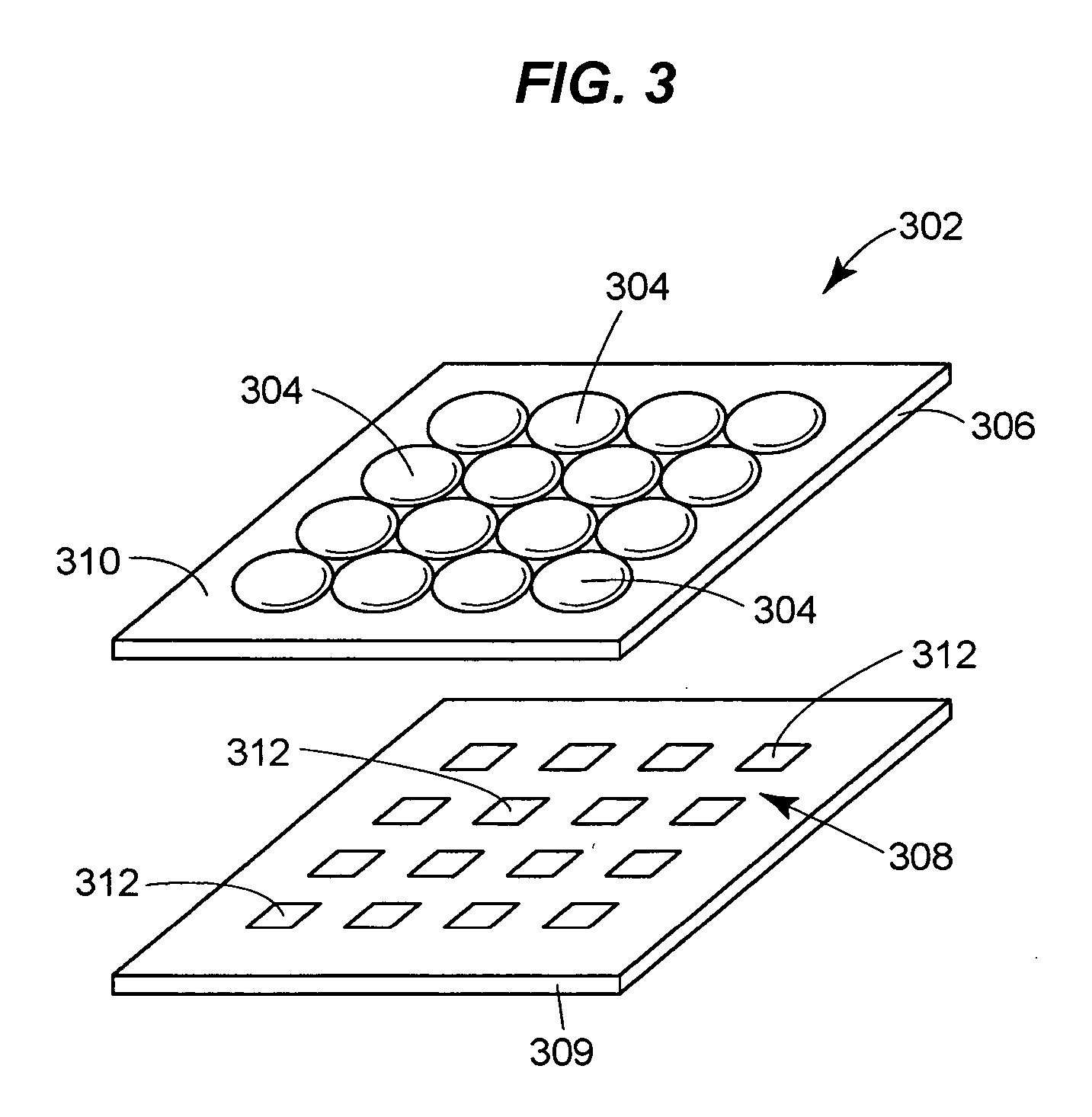
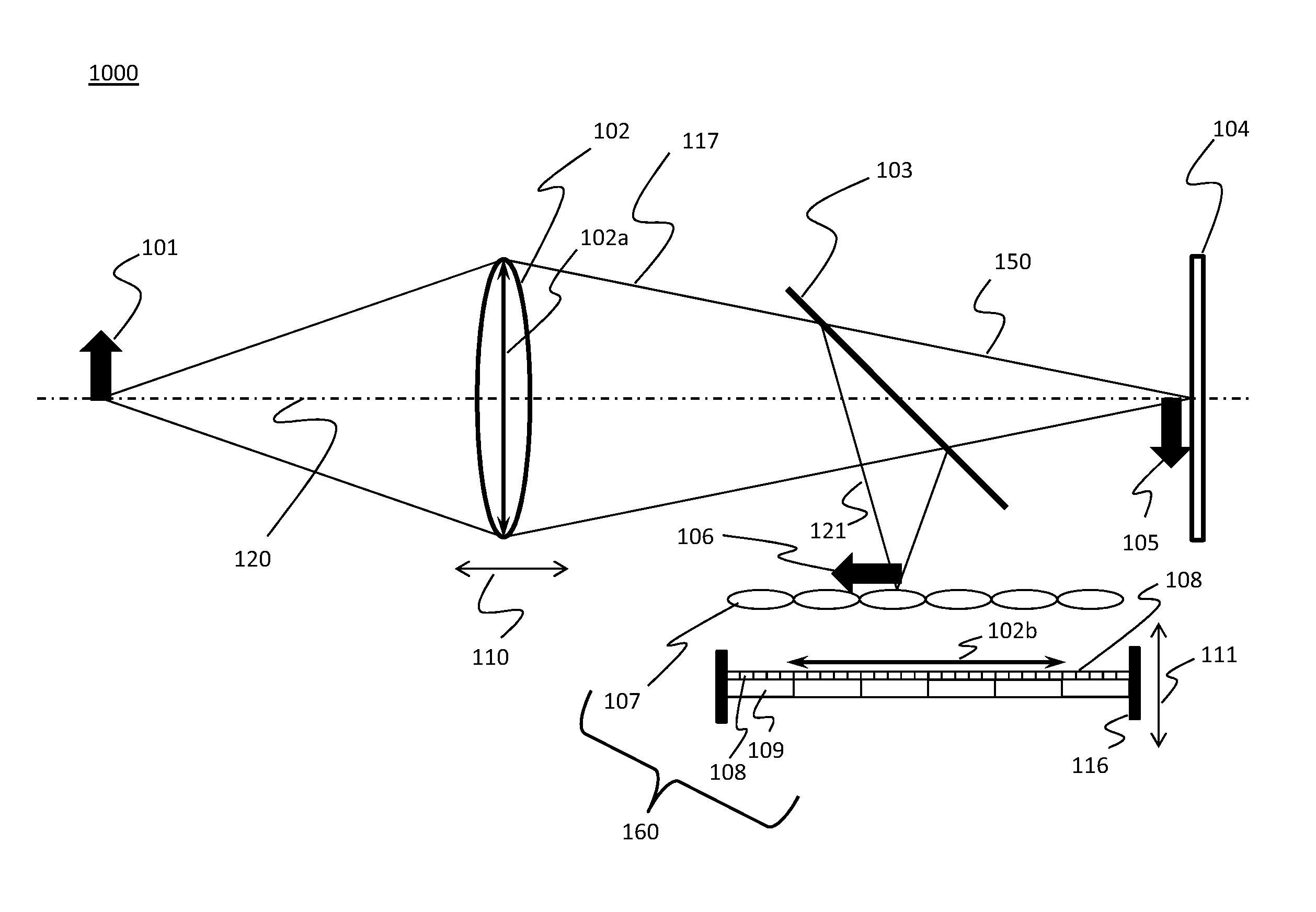
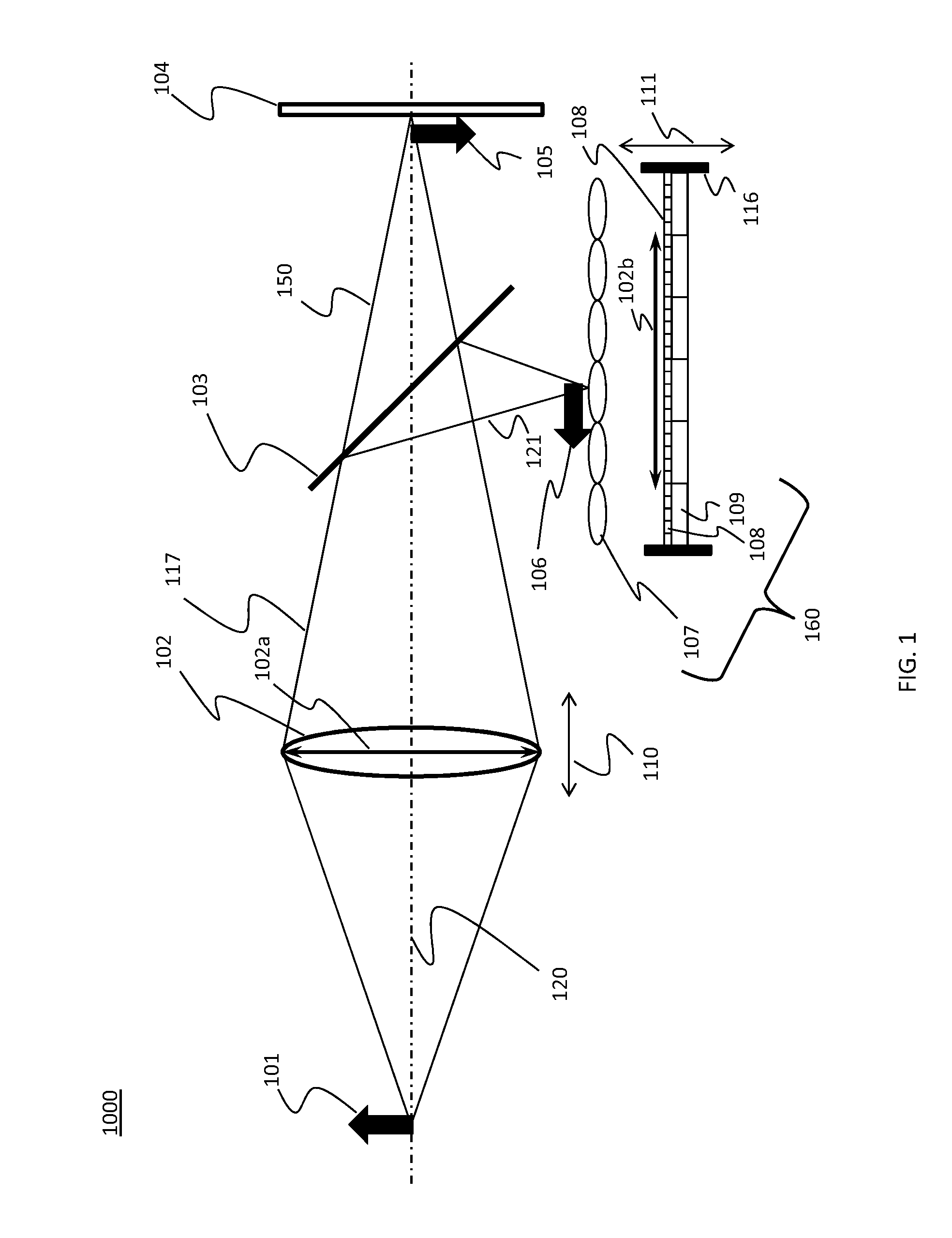
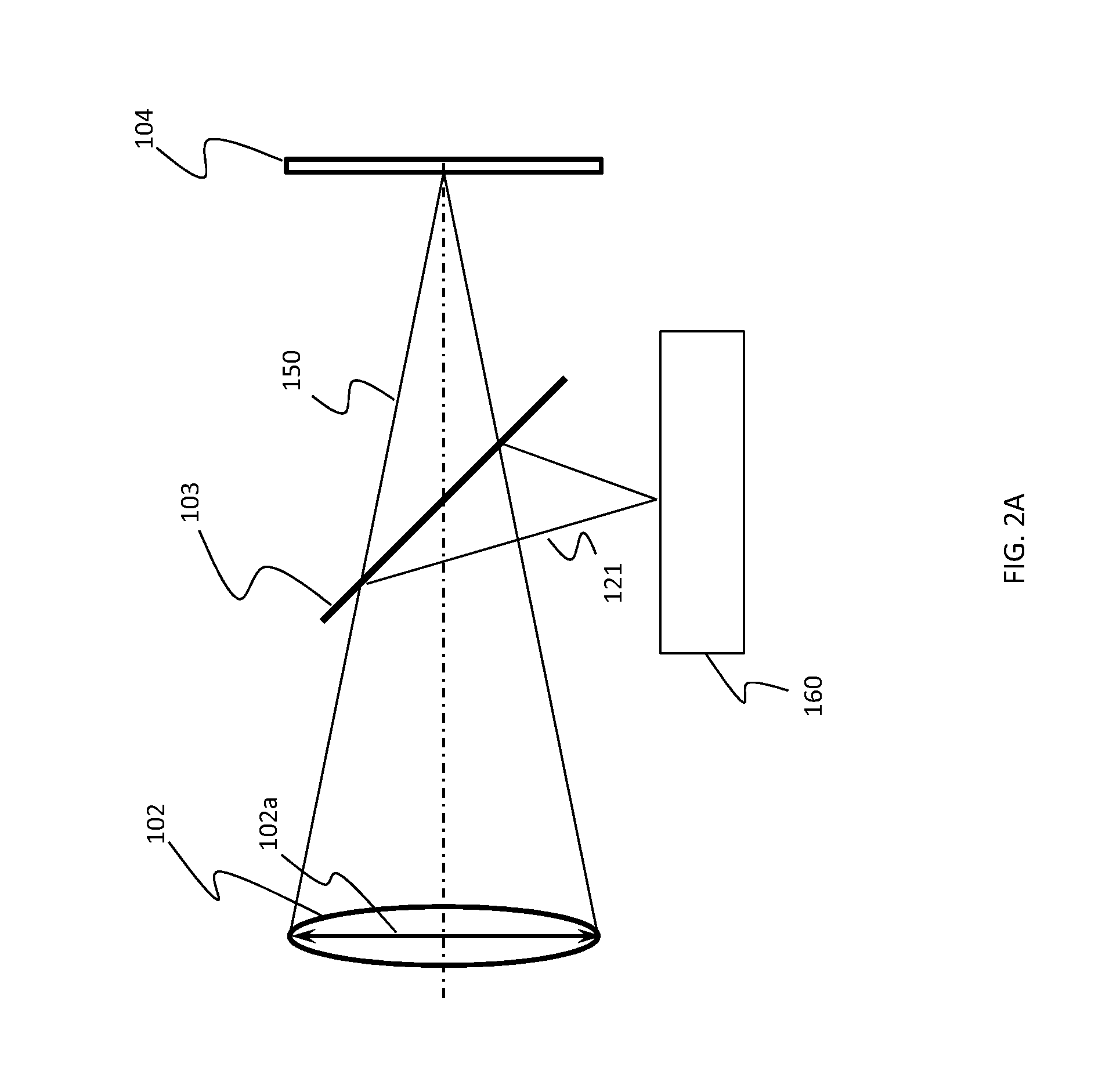
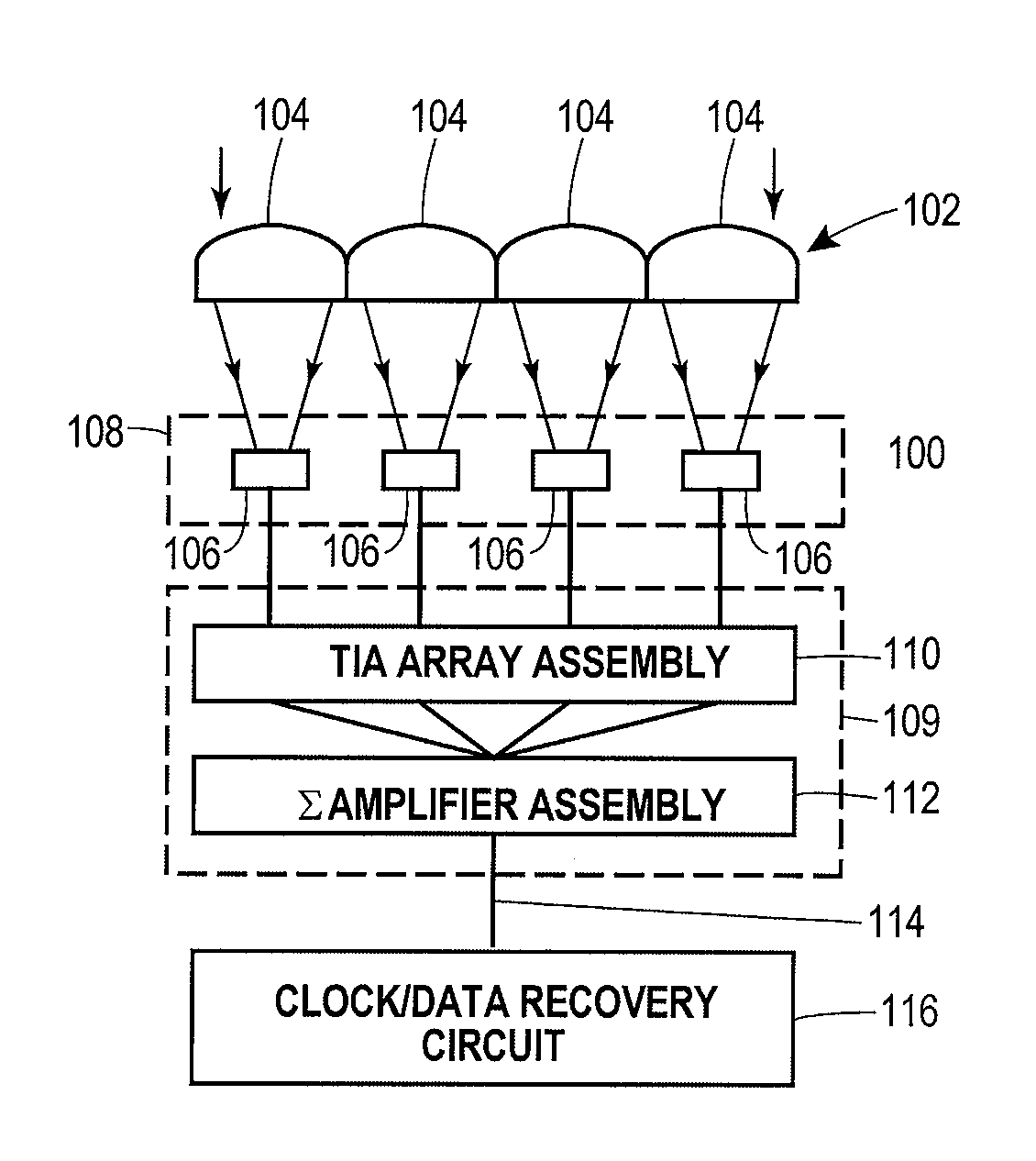
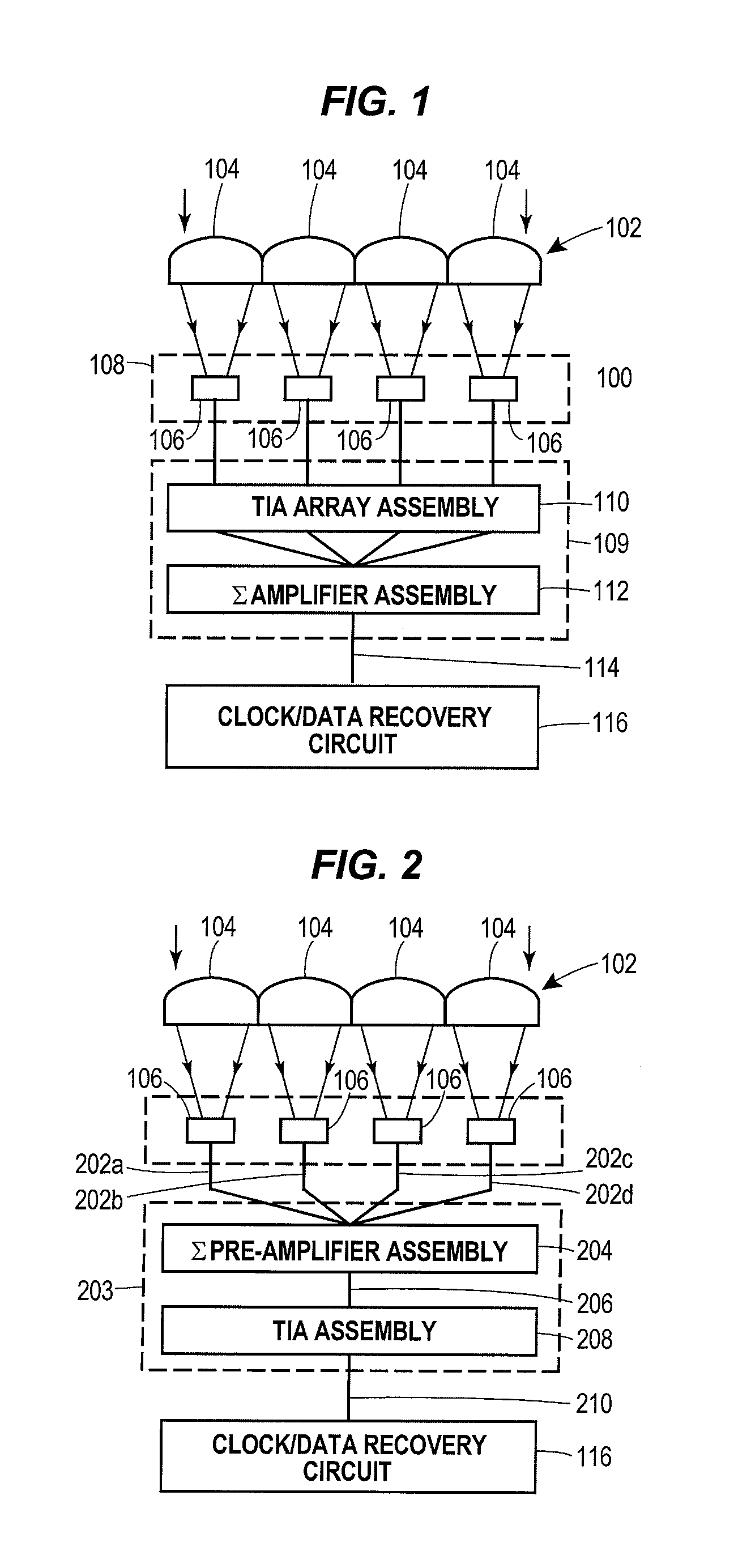
Lenslet/detector array assembly for high data rate optical communications
InactiveUS20060076473A1Reduce capacitanceHigh bandwidthSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotodetectorDetector array
An assembly is provided that may be used in high data rate optical communications, such as free-space communication systems. The assembly may include a main optical receiver element and a lenslet array or other optical element disposed near the focal plane that collects an optical signal and focuses that signal as a series of optical signal portions onto a photodetector array, formed of a series of InGaAs photodiodes, for example. The electrical signals from the photodetectors may be amplified using high bandwidth transimpedance amplifiers connected to a summing amplifier or circuit that produces a summed electrical signal. Alternatively, the electrical signals may be summed initially and then amplified via a transimpedance amplifier. The assembly may be used in remote optical communication systems, including free-space laser communication environments, to convert optical signals up to or above 1 Gbit / s or higher data rates into electrical signals at 1 Gbit / s or higher data rates.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
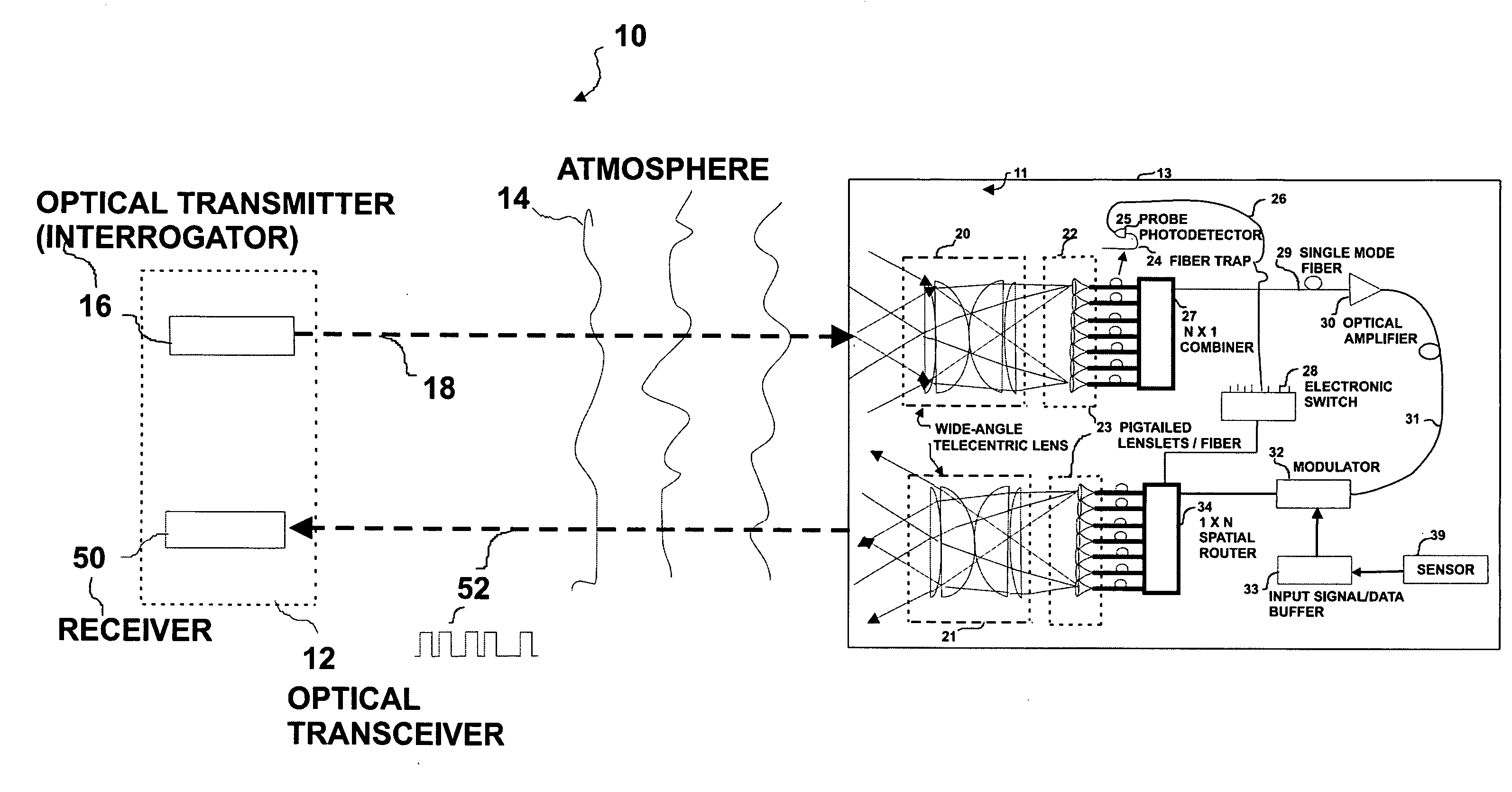
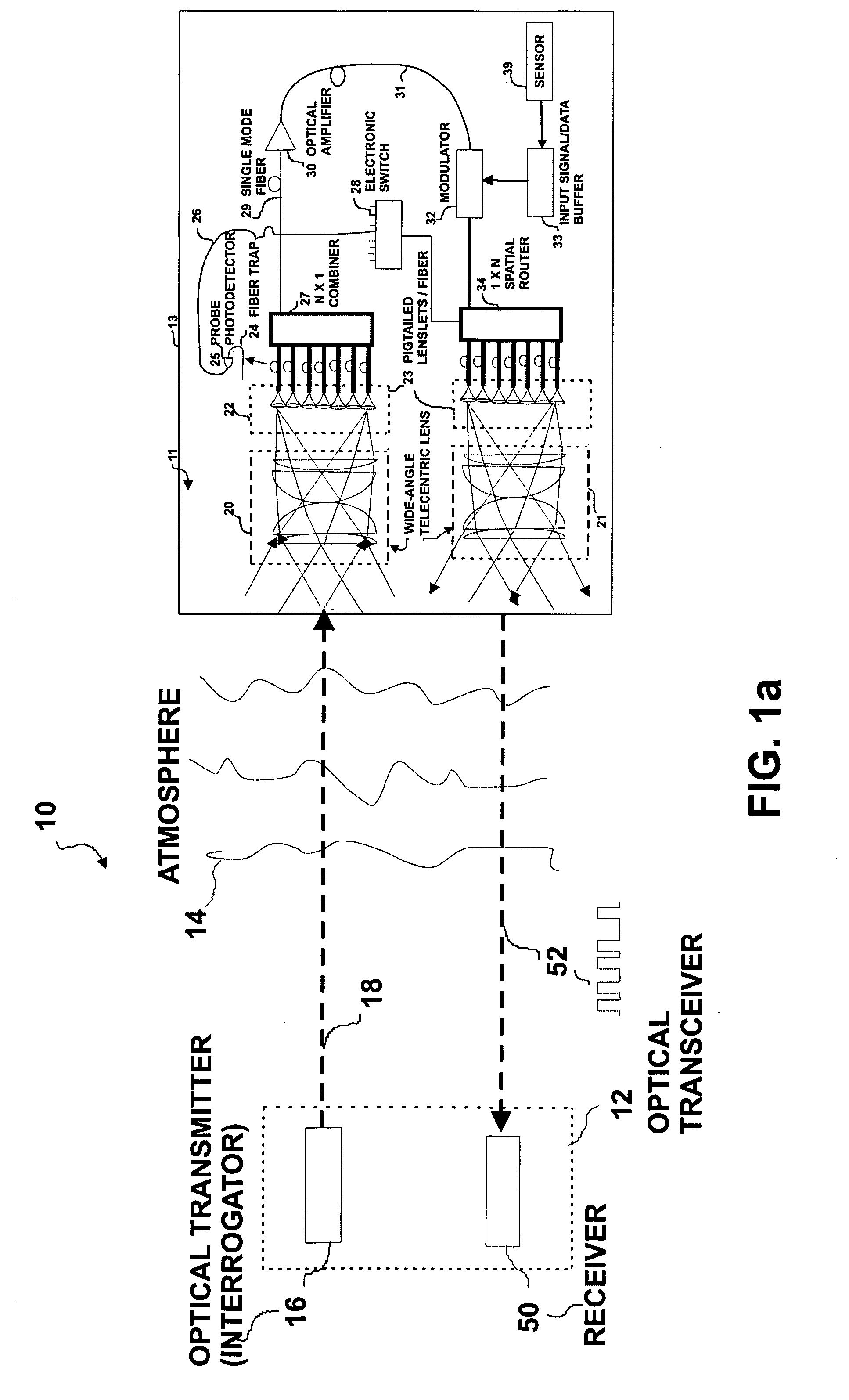
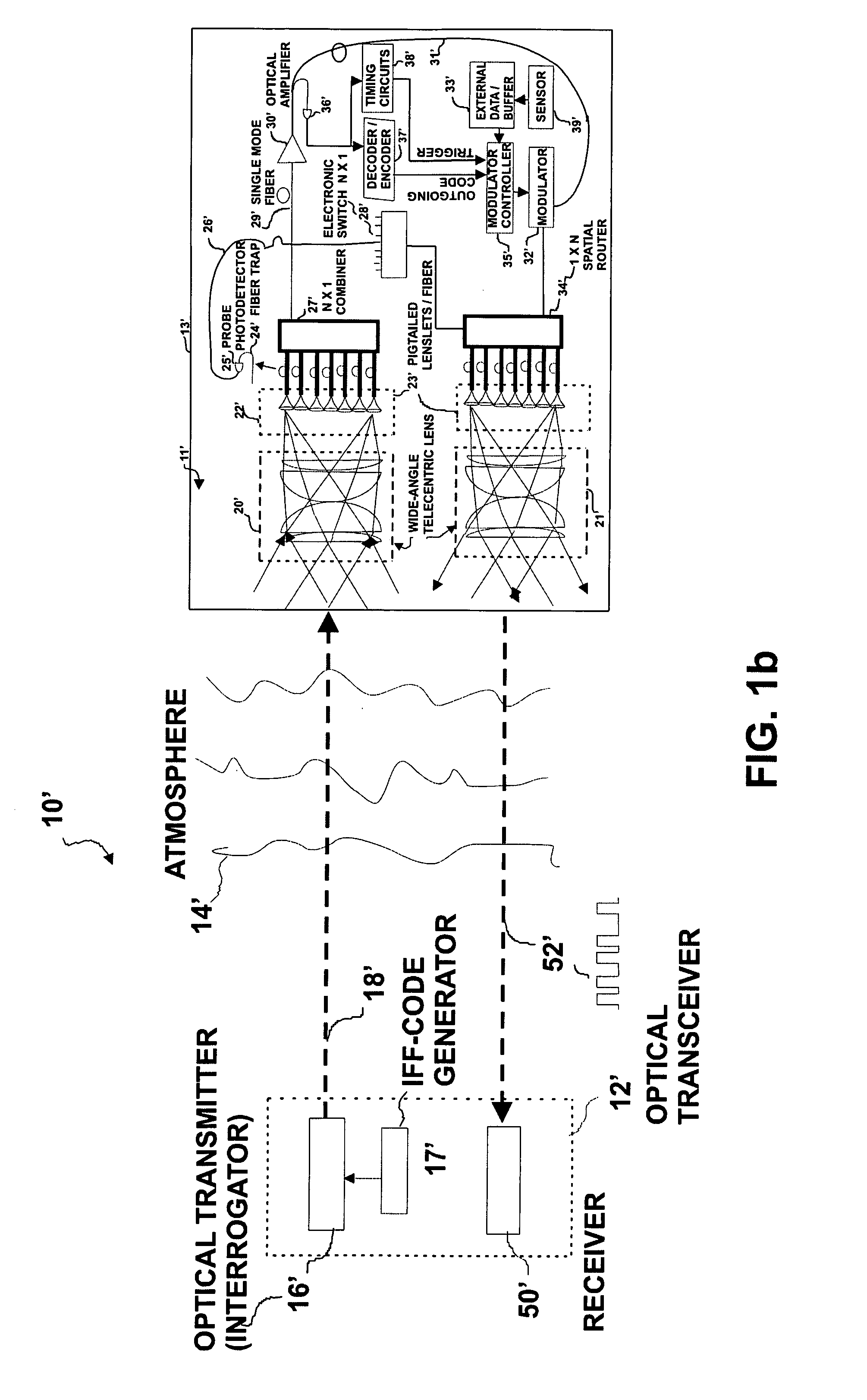
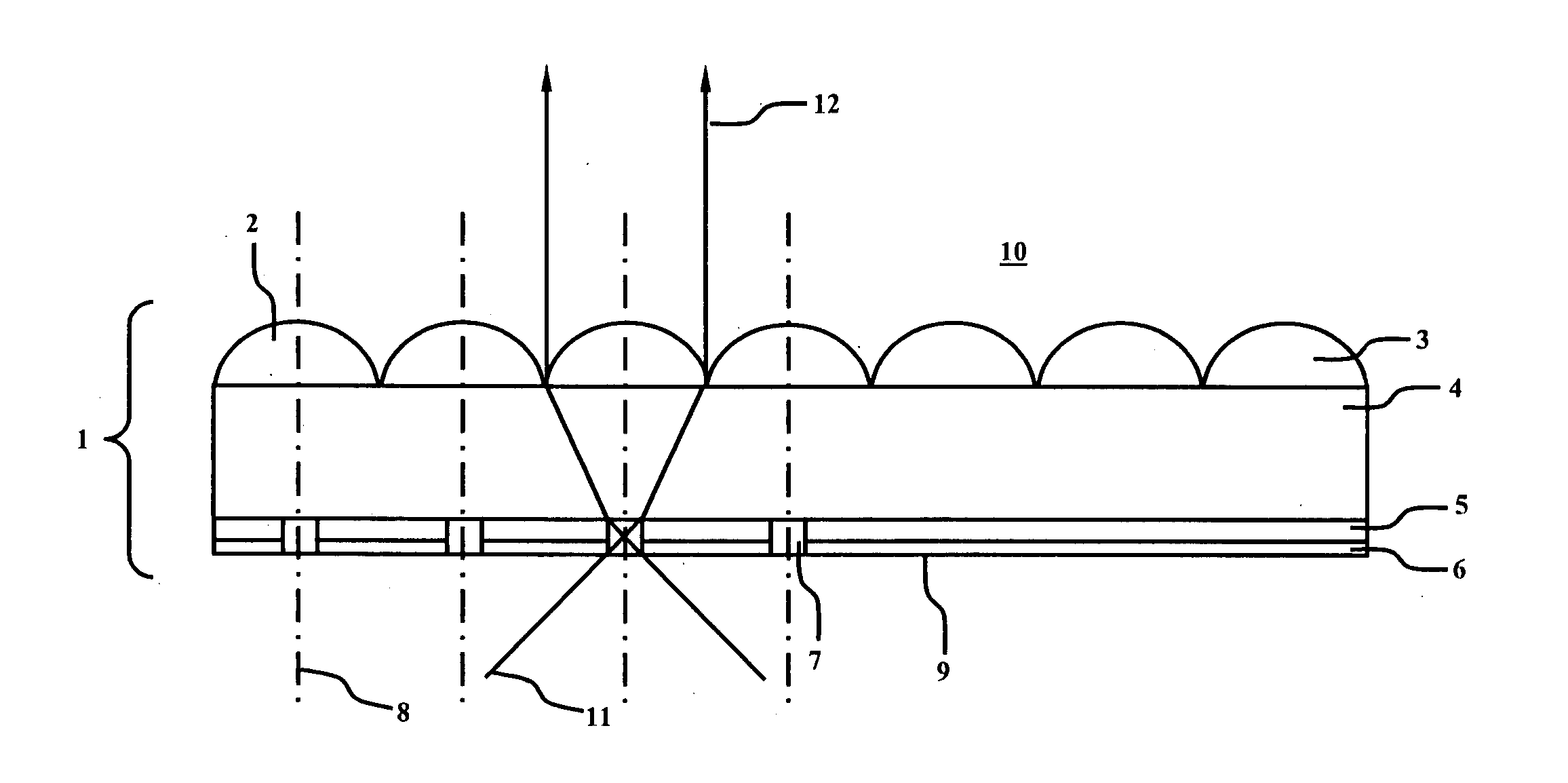
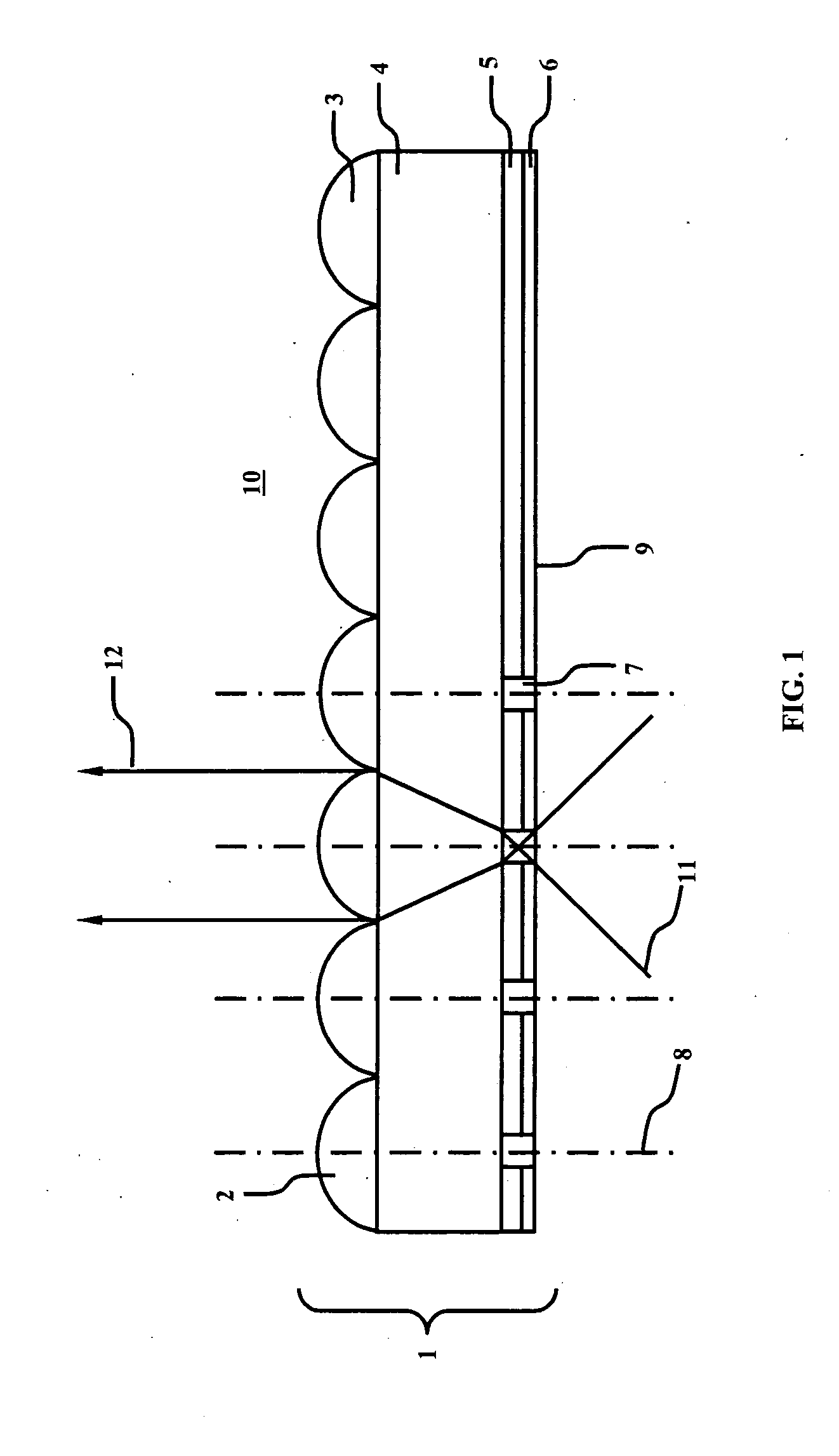
Wide field-of-view amplified fiber-retro for secure high data rate communications and remote data transfer
InactiveUS20090202254A1Increase data rateReduce power consumptionElectromagnetic transmissionSubscribers indirect connectionFiber arrayOptical communication
An optical system for remotely optical communications at a high data rate between a base station and a remote station under atmospheric turbulence conditions is disclosed. The remote station includes an entirely different type of retroreflector that does not use the conventional type of retroreflection, but instead consists of two sets of lenslets coupled with single-mode fiber array, called fiber “retro”. Amplified retromodulation is achieved requiring only one single optical amplifier and one single modulator. A transmitter located at the base station sends an interrogating optical beam to the fiber “retro” which modulates the optical beam according to the input signal / data, and redirects the modulated optical beam to the base station for detection by a receiver. The present invention includes the capabilities of providing Identification of Friend-or-Foe (IFF), secure communication, and a means of achieving a wide field-of-view (FOV) with a fiber-coupled lenselet array.
Owner:MAJUMDAR ARUN KUMAR +1
Collimating microlens array
InactiveUS20070002452A1Increase output brightnessHigh lumen efficiencyStatic indicating devicesProjectorsDielectricDisplay device
A collimating sheet, for use with a backlit display and the like, that includes a substrate, a plurality of microlenses on the output side of the substrate, a specularly reflective layer on the side of the substrate opposite the microlenses, and a plurality of apertures in the reflective layer in direct correspondence to the microlenses of the lens array. The specularly reflective layer can be relatively thinner than a diffuse reflective layer, which allows light to pass through the more readily. One or more layers of dielectric can be placed on top of one or more reflective material layers to further improves overall reflectivity. Apertures are preferably made in the light-absorptive and reflective layers with a laser ablation process wherein laser light illuminates the output side of the film. The laser light is brought to a focus by the lenslets of the lens array onto the light-absorptive layer, which then ablates a hole or aperture into the light-absorptive and reflective layer. In this way, the apertures are self-aligned with the lenslets.
Owner:ORAFOL AMERICAS
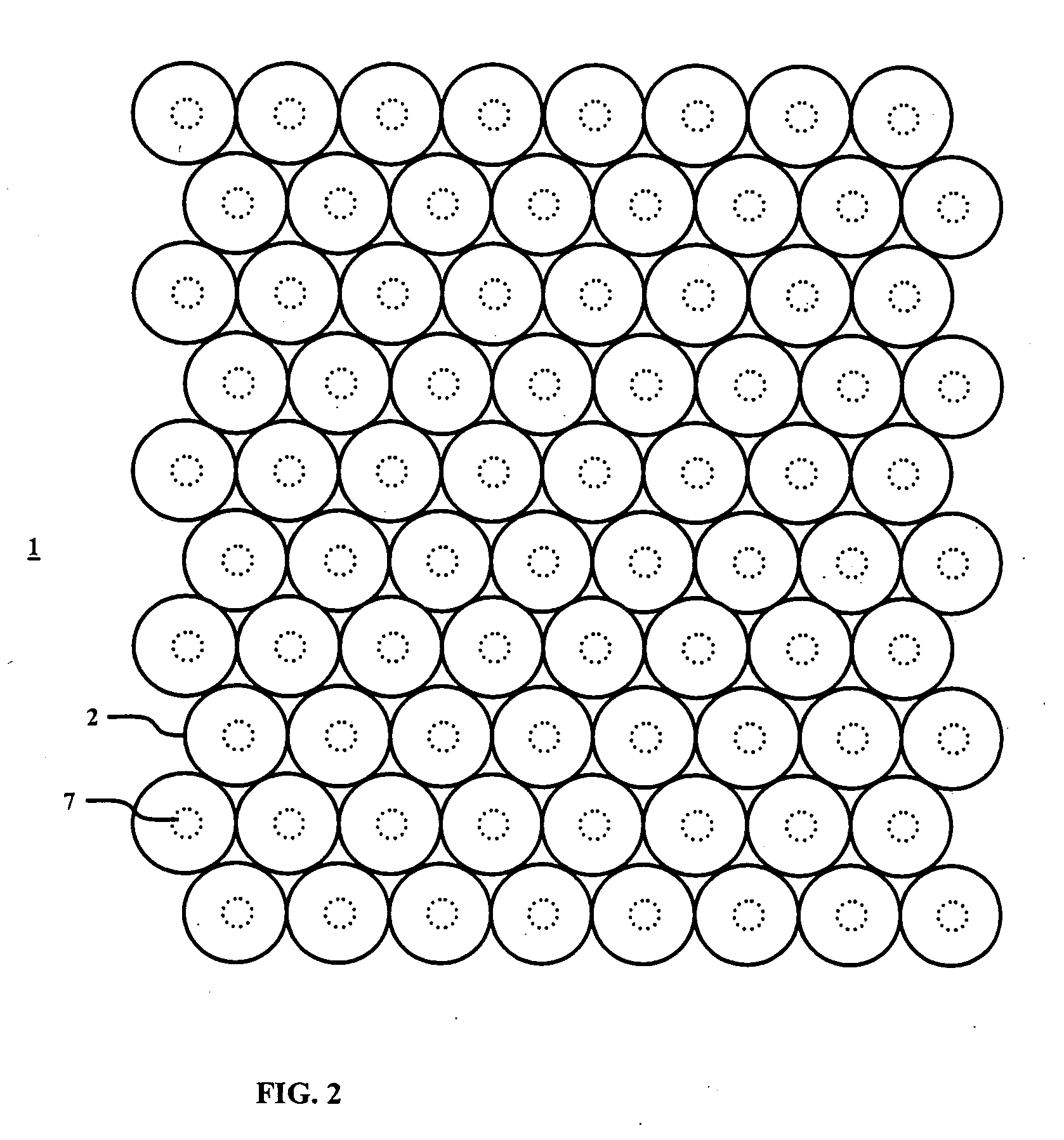
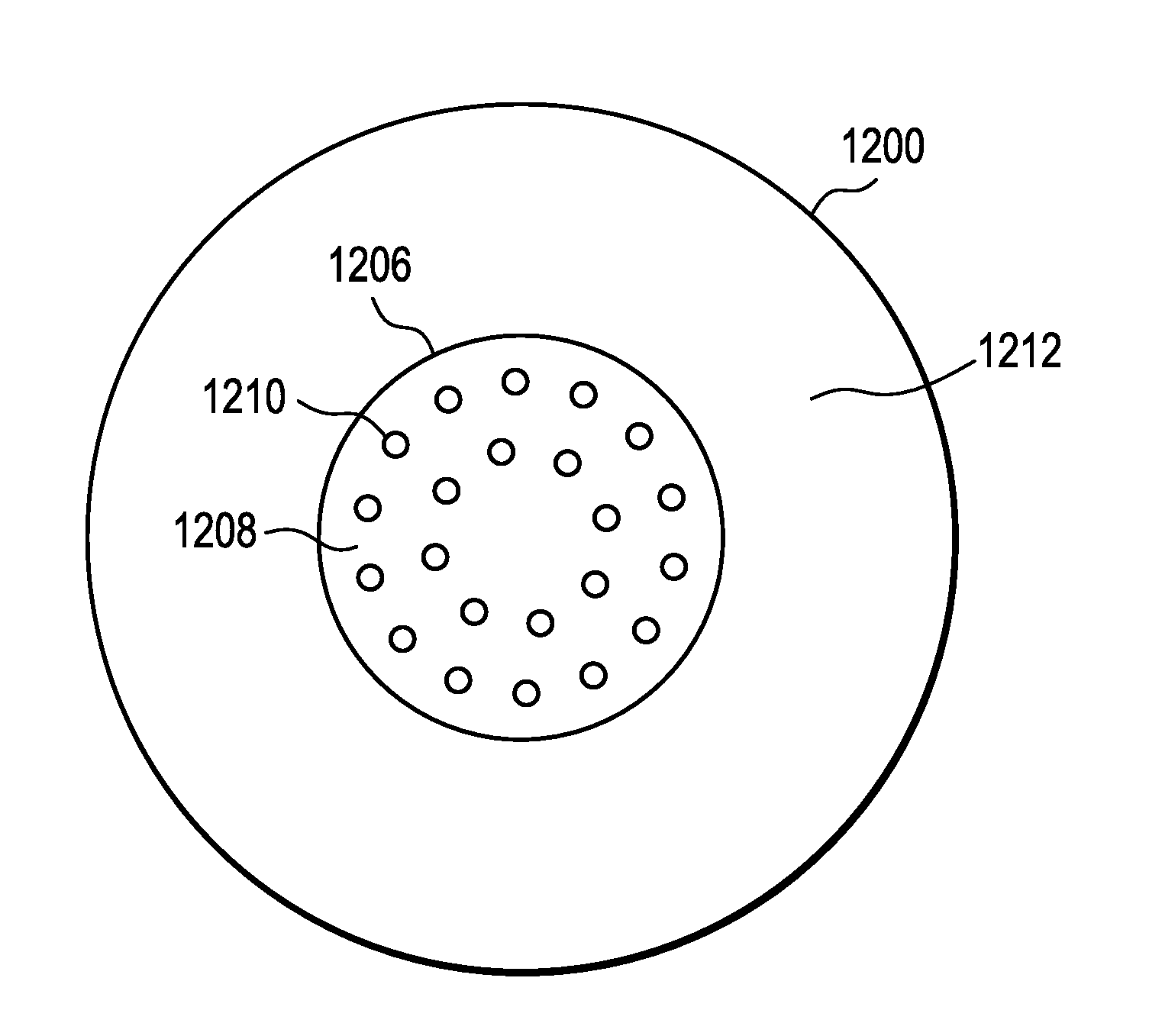
Contact lens comprising non-coaxial lenslets for preventing and/or slowing myopia progression
ActiveUS20160377884A1Good distance vision correctionCorrection acuitySpectales/gogglesOptical partsPupilRetina
Contact lenses incorporating an array of non-coaxial lenslets with add power that create non-coaxial myopic defocus within the optic zone of the lens may be utilized to prevent and / or slow myopia progression. The positive, non-coaxial lenslets cover about twenty to eighty percent of the central pupil area to deliver positive foci of light in front of the retina to slow the rate of myopia progression.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Warm white lighting device
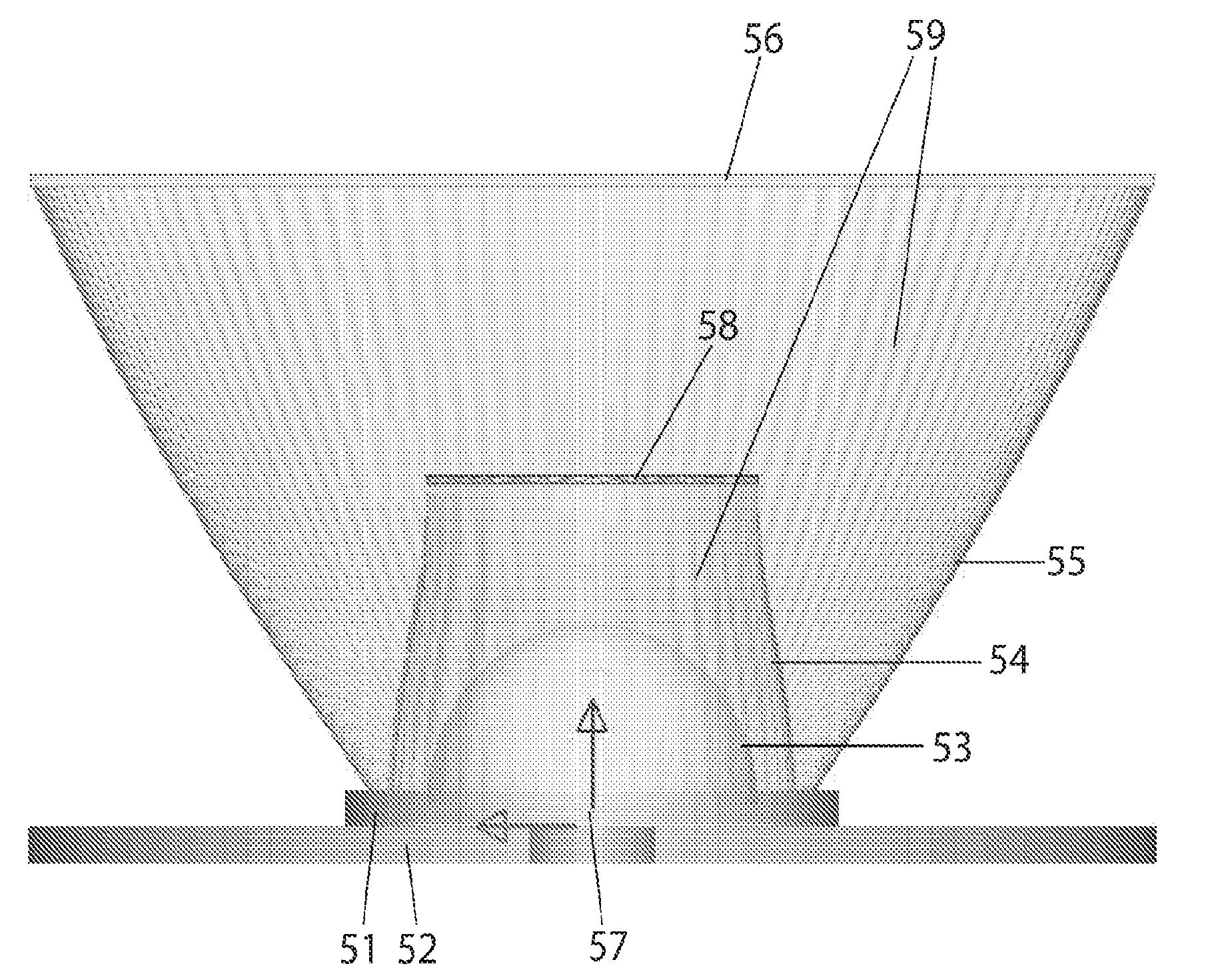
ActiveUS20110051394A1Improved light generationImprove homogenizationNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceLensletHuman eye
The present invention relates to warm white light engines including combinations of blue, cyan, and red, red-orange, or amber emitters and one or more phosphors that produce a white light pleasing to the human eye through the use of improved color uniformity and improved collimation of light. Specifically, a micro-lenslet array having an optimized surface is used to disperse light from the light emitter; an innercollimation lens having an optimized cross-sectional shape and micro-ridges is used to disperse light; a TIR reflector having an optimized cross-sectional shape and micro-ridges is used to disperse and redistribute phase as well as provide collimation; and a final micro-lenslet layer includes optimized lenslet design placement and randomization factor to homogenize light to produce a uniform warm white light.
Owner:LIGHTING SCI GROUP
Microoptical compound lens
InactiveUS7286295B1Improve image qualityLarge numerical apertureTelevision system detailsColor television detailsWide fieldFiber bundle
An apposition microoptical compound lens comprises a plurality of lenslets arrayed around a segment of a hollow, three-dimensional optical shell. The lenslets collect light from an object and focus the light rays onto the concentric, curved front surface of a coherent fiber bundle. The fiber bundle transports the light rays to a planar detector, forming a plurality of sub-images that can be reconstructed as a full image. The microoptical compound lens can have a small size (millimeters), wide field of view (up to 180°), and adequate resolution for object recognition and tracking.
Owner:SANDIA
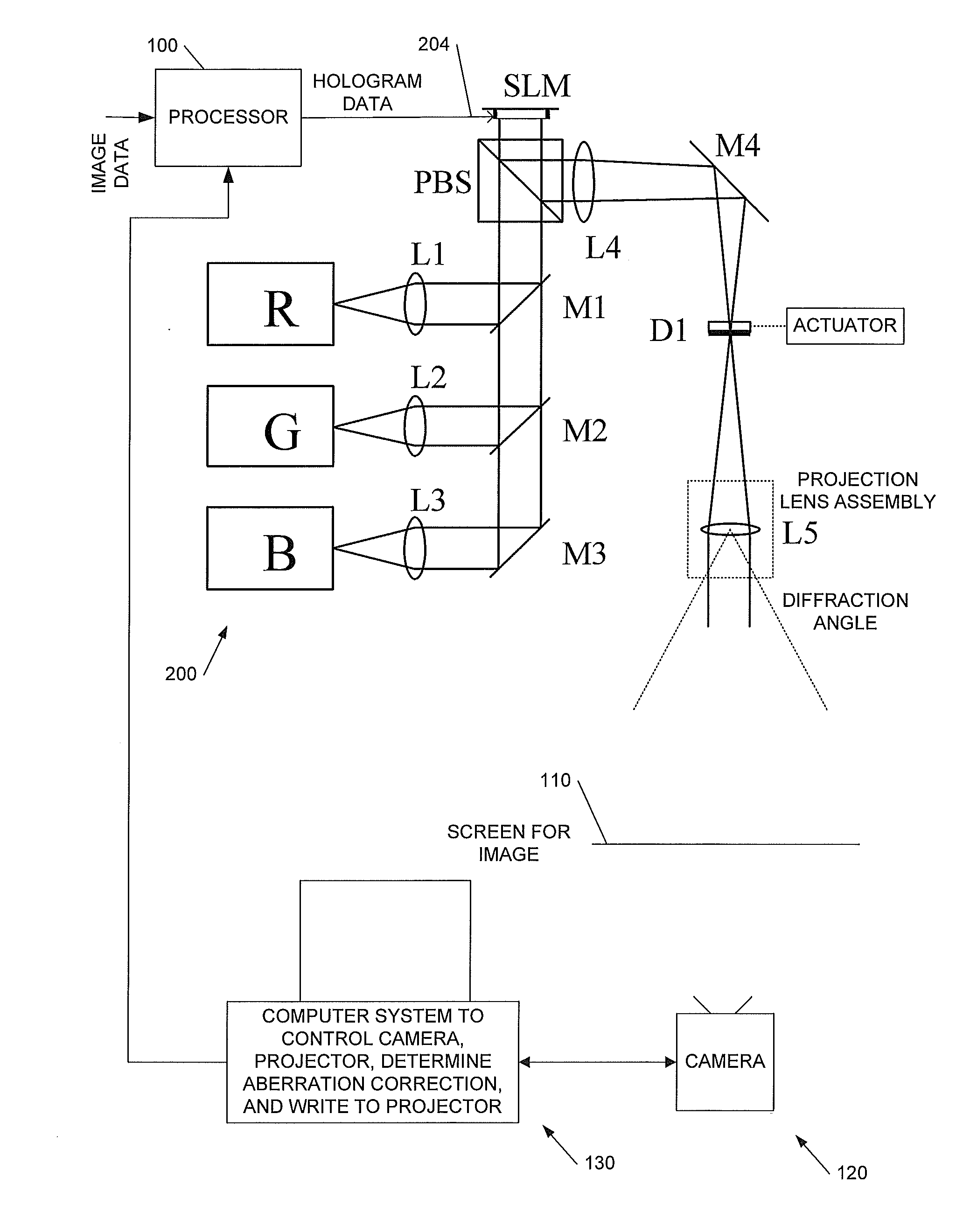
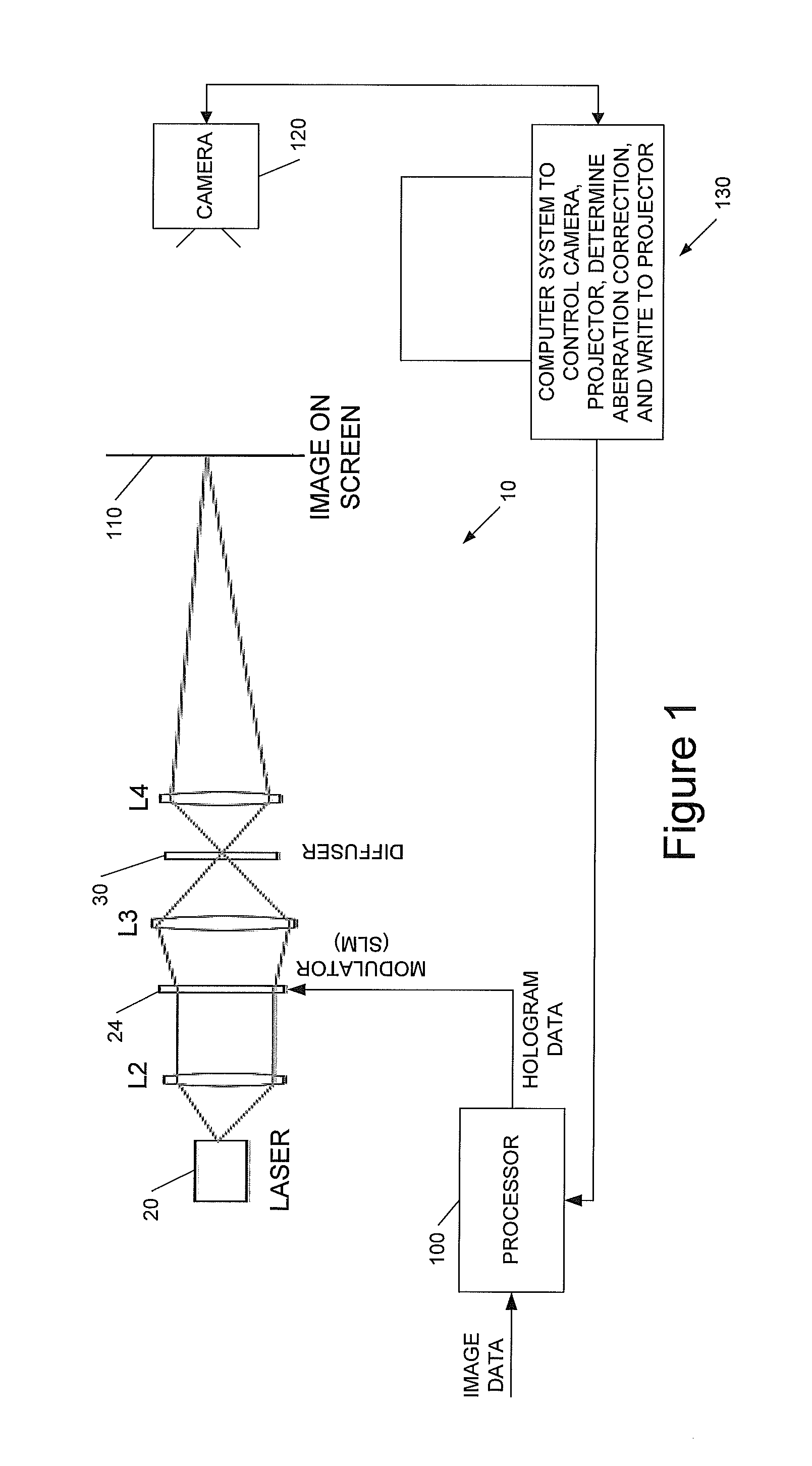
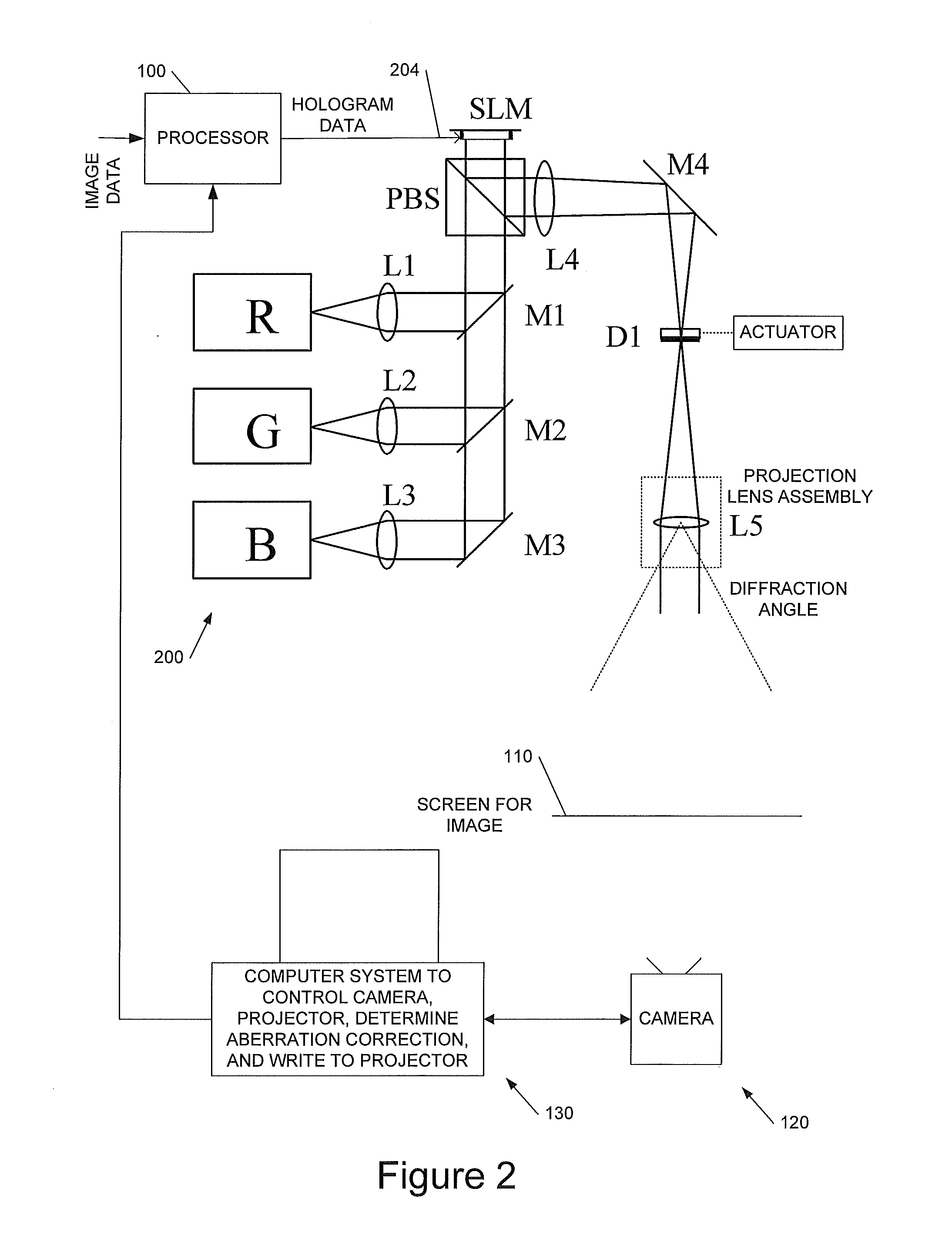
Holographic Image Display Systems
InactiveUS20120008181A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioFacilitate multiple iterationTelevision system detailsHolographic optical componentsProjection opticsSpatial light modulator
We describe a method of determining an aberration correction for a holographic image display system using a spatial light modulator (SLM) to display a hologram. Embodiments of the invention measure the corrections needed for a particular projection system, using the same system SLM as used to generate the images to provide wavefront-sensing holograms. The projector's projection optics are used to provide the wavefront sensor and there is no need for lenslets. Embodiments of the invention use a plurality of successive holograms directing light from differently-located patches on the hologram into the image.
Owner:LIGHT BLUE OPTICS
Luminaire and method of operation
A luminaire and a method of operating a luminaire is provided. The luminaire includes a light source emitting a plurality of light rays. A collimation device is arranged to receive a portion of light from the light source and transmits the portion of light through an exit aperture towards an illuminated area. The exit aperture includes a planar portion and at least one lenslet formed thereon. The lenslet is arranged having a first profile and a second profile, where the portion of light is refracted on a plurality of angles to form a twisted profile by the lenslet.
Owner:LIGHTING SCI GROUP
Apparatus and method for acquiring information about light-field data
An apparatus to acquire information about light-field data includes: a beam splitter configured to split light, through a lens unit which is connected to the apparatus, from an object into a first light beam and a second light beam; an image sensor configured to detect the first light beam to form an image of the object; and a light-field sensor, including a lenslet array and a detecting unit to detect the second light beam through the lenslet array, configured to acquire information about the light-field data, the lenslet array including a plurality of lenslets, wherein a first position where the detecting unit is provided is conjugate to a second position of a pupil of the lens unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Lenslet/detector array assembly for high data rate optical communications
An assembly is provided that may be used in high data rate optical communications, such as free-space communication systems. The assembly may include a main optical receiver element and a lenslet array or other optical element disposed near the focal plane that collects an optical signal and focuses that signal as a series of optical signal portions onto a photodetector array, formed of a series of InGaAs photodiodes, for example. The electrical signals from the photodetectors may be amplified using high bandwidth transimpedance amplifiers connected to a summing amplifier or circuit that produces a summed electrical signal. Alternatively, the electrical signals may be summed initially and then amplified via a transimpedance amplifier. The assembly may be used in remote optical communication systems, including free-space laser communication environments, to convert optical signals up to or above 1 Gbit / s or higher data rates into electrical signals at 1 Gbit / s or higher data rates.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Light field microscope with lenslet array
A light field microscope incorporating a lenslet array at or near the rear aperture of the objective lens. The microscope objective lens may be supplemented with an array of low power lenslets which may be located at or near the rear aperture of the objective lens, and which slightly modify the objective lens. The result is a new type of objective lens, or an addition to existing objective lenses. The lenslet array may include, for example, 9 to 100 lenslets (small, low-power lenses with long focal lengths) that generate a corresponding number of real images. Each lenslet creates a real image on the image plane, and each image corresponds to a different viewpoint or direction of the specimen. Angular information is recorded in relations or differences among the captured real images. To retrieve this angular information, one or more of various dense correspondence techniques may be used.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Fast computational camera based on two arrays of lenses
ActiveUS7956924B2Less expenseQuality improvementTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCamera lensRadiance
Method and apparatus for a fast (low F / number) computational camera that incorporates two arrays of lenses. The arrays include a lenslet array in front of a photosensor and an objective lens array of two or more lenses. Each lens in the objective lens array captures light from a subject. Each lenslet in the lenslet array captures light from each objective lens and separates the captured light to project microimages corresponding to the objective lenses on a region of the photosensor under the lenslet. Thus, a plurality of microimages are projected onto and captured by the photosensor. The captured microimages may be processed in accordance with the geometry of the objective lenses to align the microimages to generate a final image. One or more other algorithms may be applied to the image data in accordance with radiance information captured by the camera, such as automatic refocusing of an out-of-focus image.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
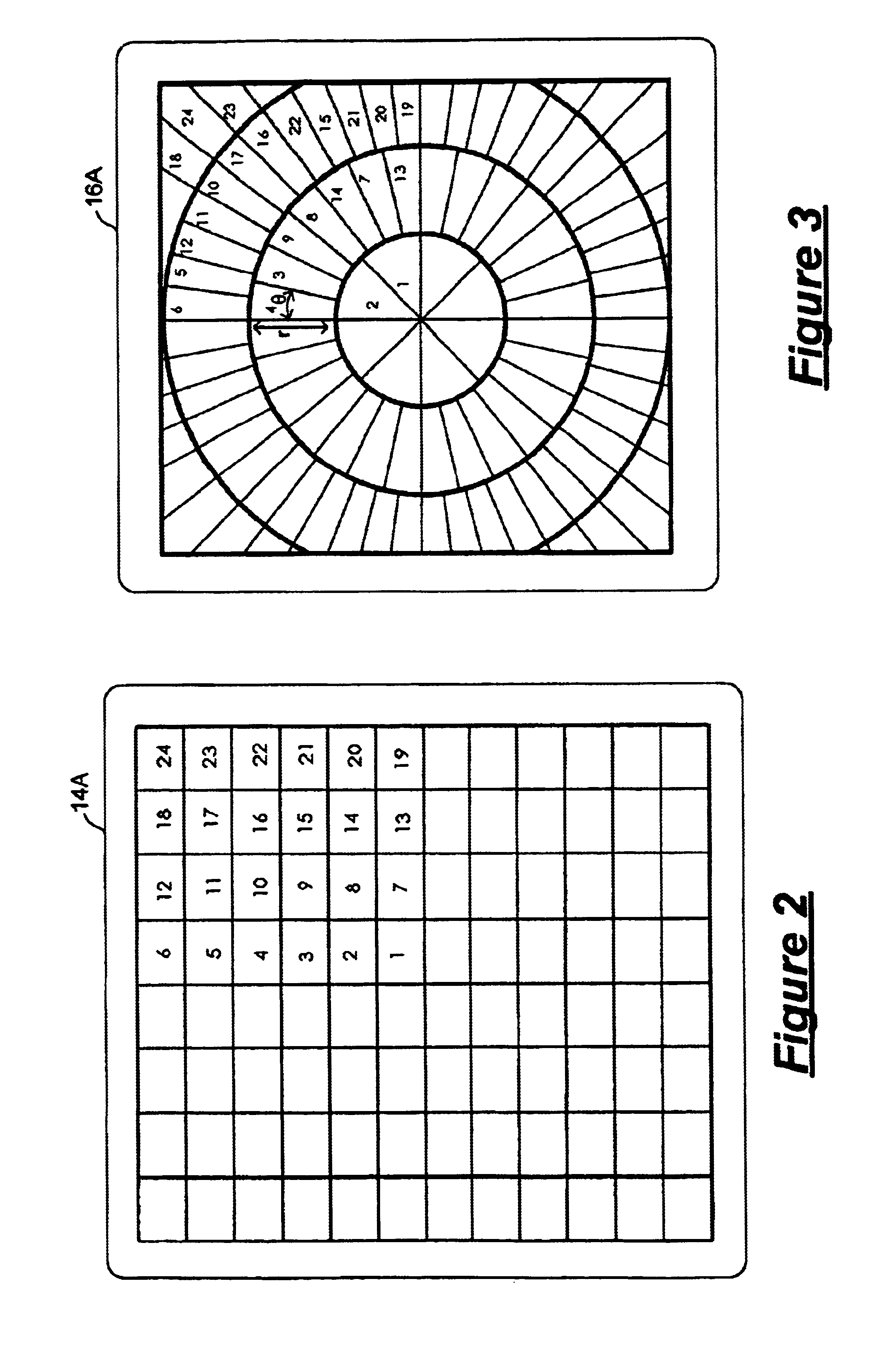
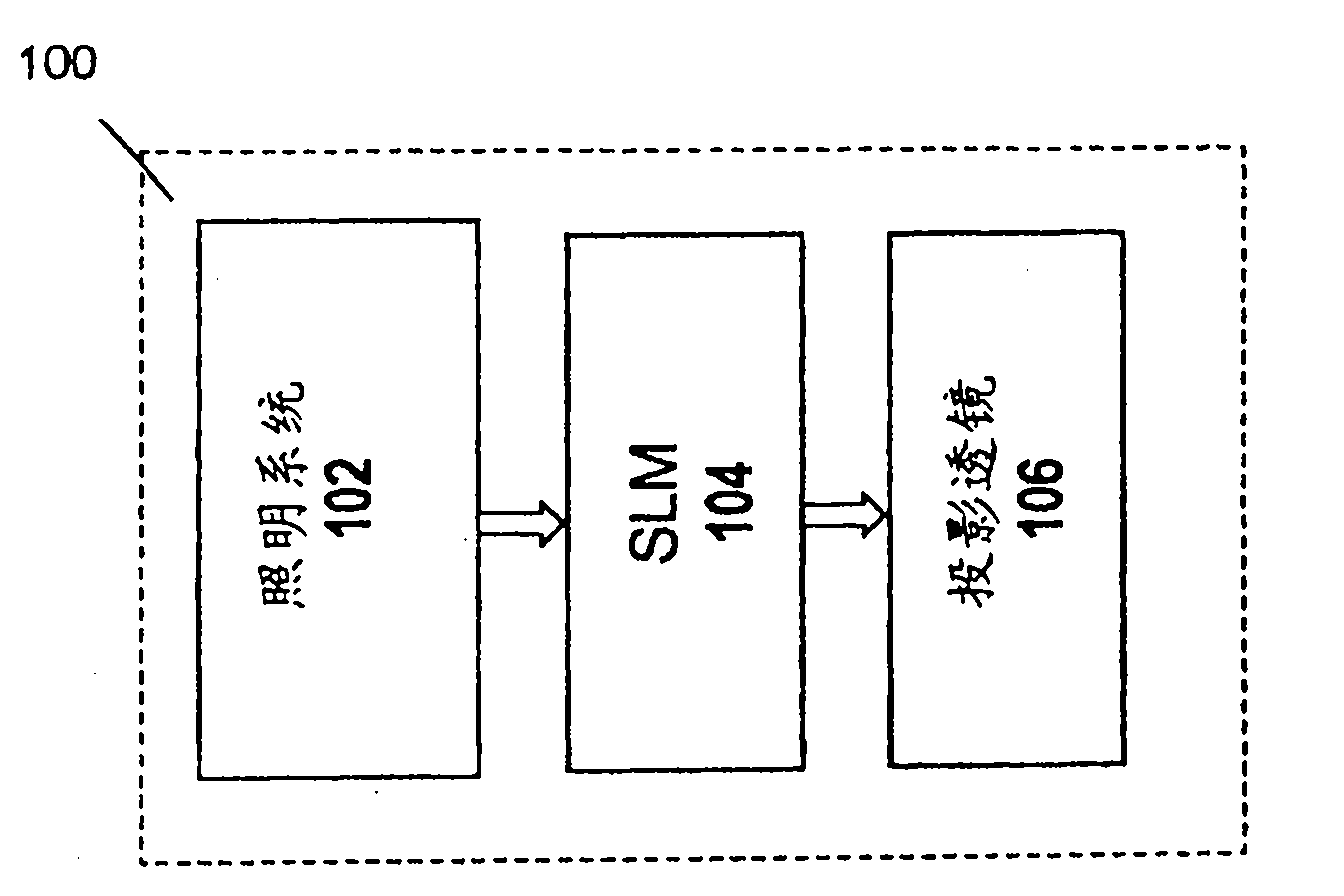
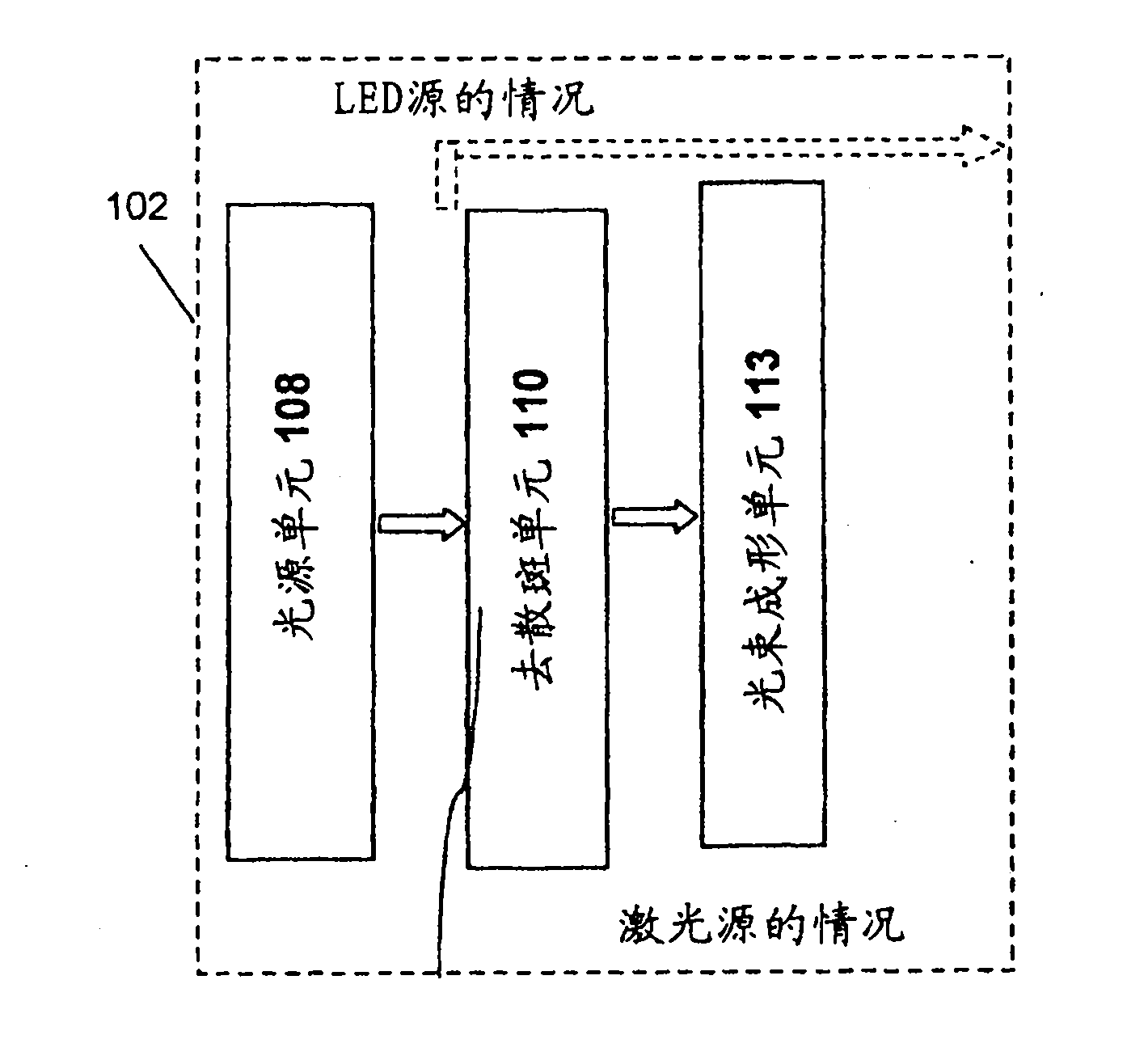
Illumination system for a projection system
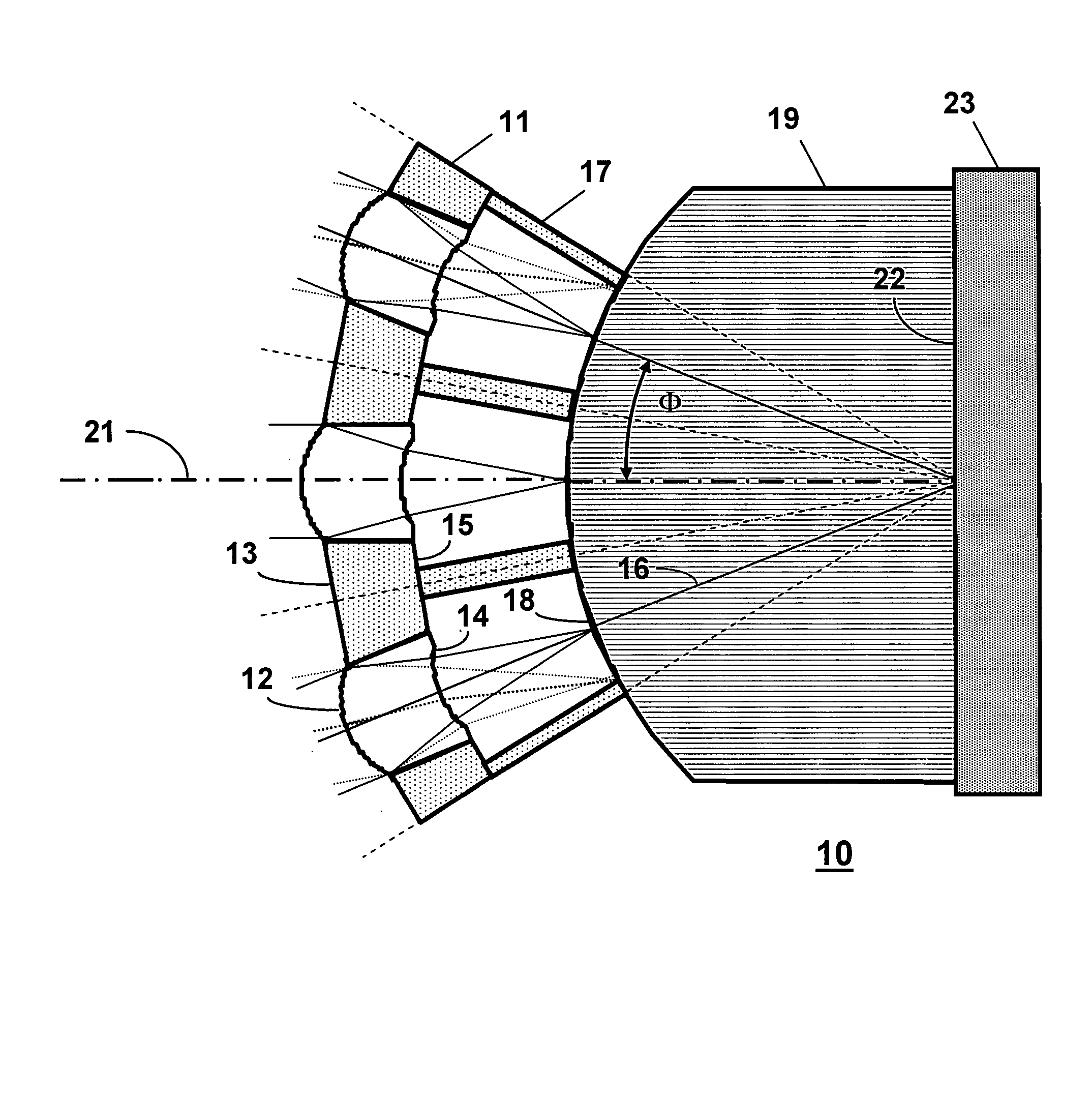
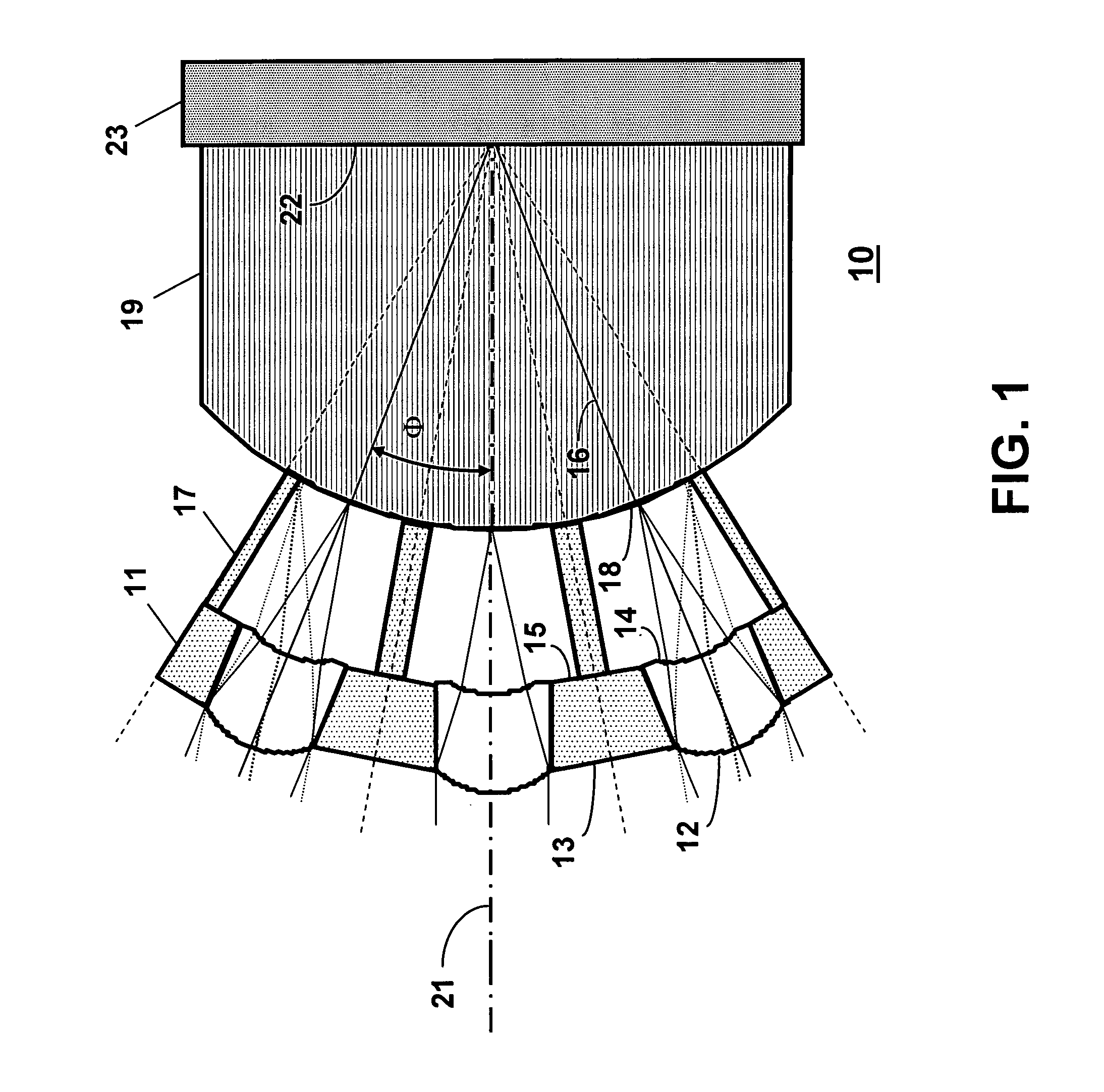
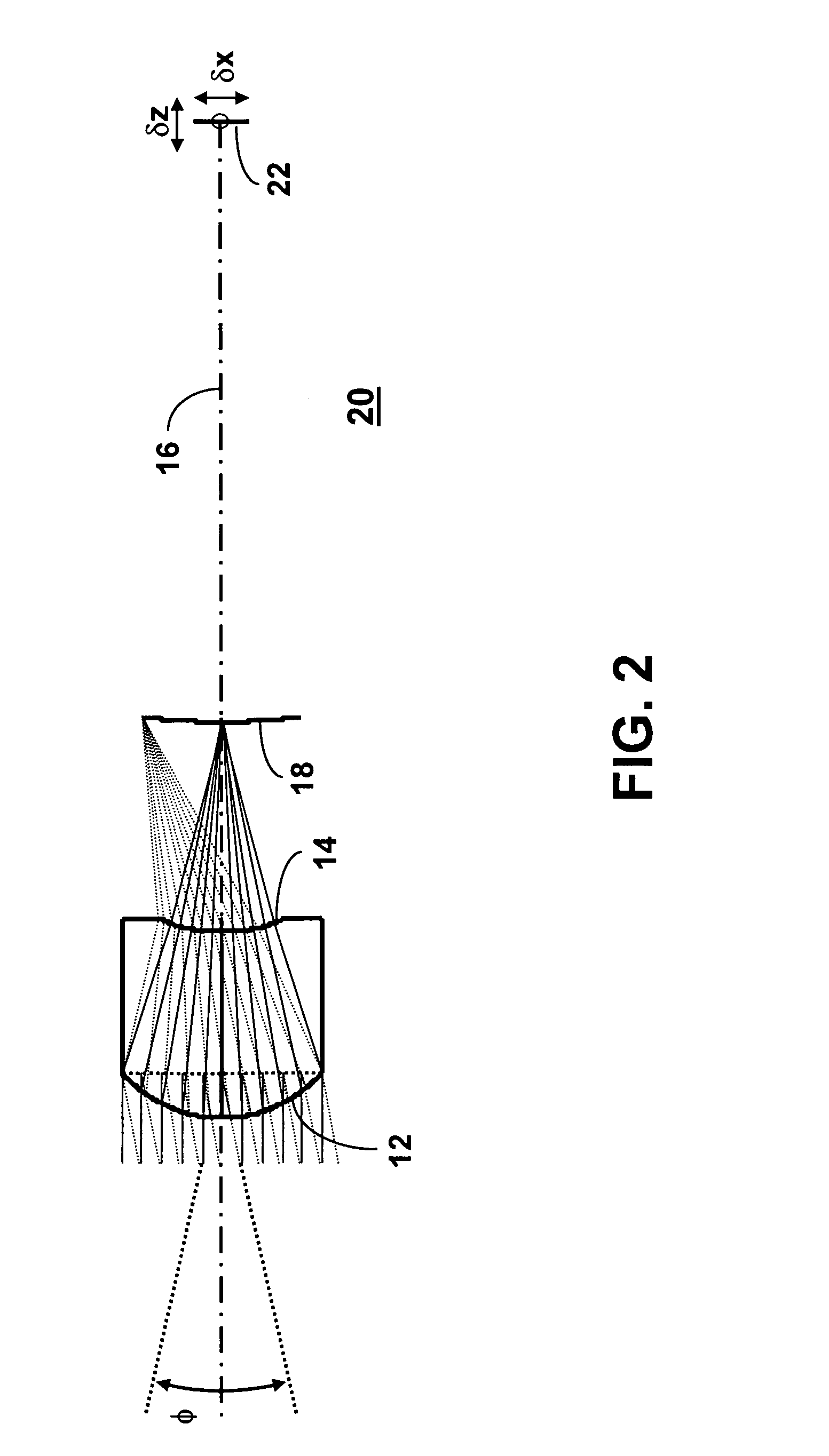
An illumination system for illuminating an object includes a light source and a lens array system. The light source includes an illumination element emitting light rays and surrounded by a parabolic reflector. The lens array system includes a first lens array plate and a second lens array plate. The first lens array plate includes a matrix of lenslets where, in one embodiment, each lenslet has a shape matching the aspect ratio of the object to be illuminated. The second lens array plate includes a radial pattern of wedge shaped lenslets each corresponding to a lenslet in the first lens array plate. Each wedge shaped lenslet in the second lens array plate has dimensions that are selected to provide a radial and theta collection angles matching the maximum divergence angle of the light source and the maximum divergence angles of the corresponding lenslet in the first lens array plate.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
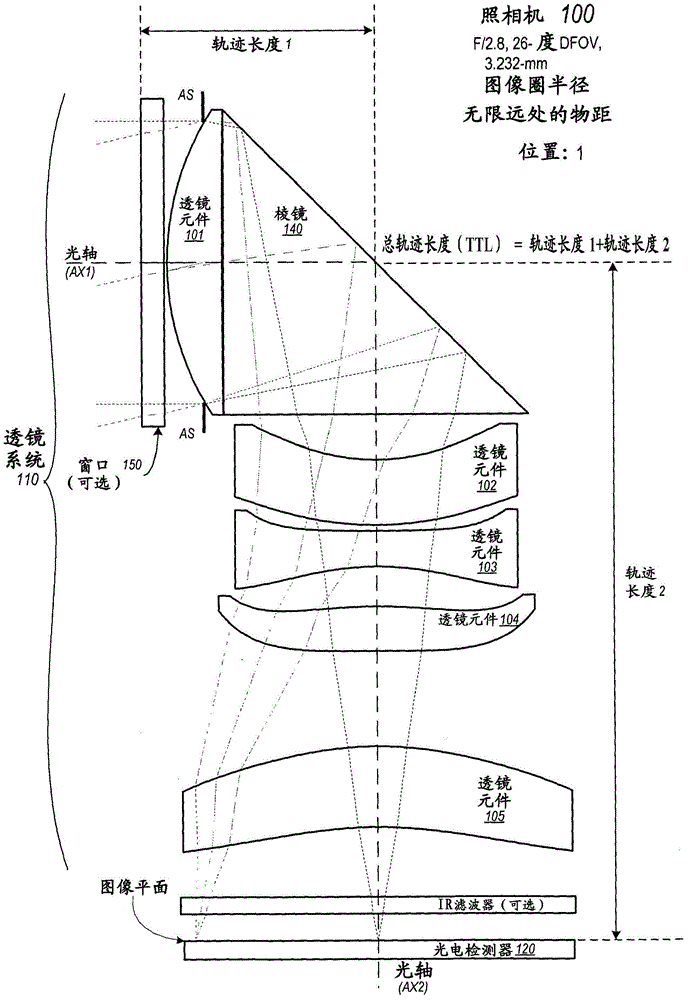
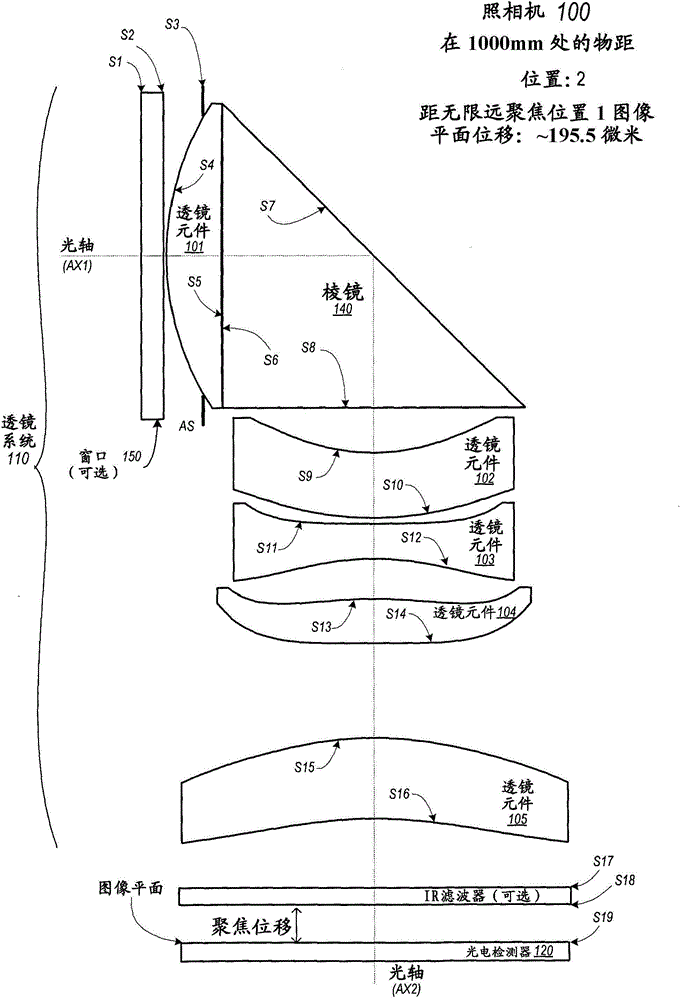
Folded camera lens systems
ActiveCN104898352AMeet the effective focal length requirementsReduced chromaticity variationTelevision system detailsCamera body detailsCamera lensOphthalmology
A folded lens system may include multiple lenses with refractive power and a light path folding element. Light entering the camera through lens(es) on a first optical path or axis is refracted to the folding element, which changes direction of the light onto a second optical path or axis with lens(es) that refract the light to form an image plane at a photosensor. At least one of the object side and image side surfaces of at least one of the lens elements may be aspheric. Total track length (TTL) of the lens system may be 16.0 mm or less. The lens system may be configured so that the telephoto ration |TTL / f| is greater than 1.0. Materials, radii of curvature, shapes, sizes, spacing, and aspheric coefficients of the optical elements may be selected to achieve quality optical performance and high image resolution in a small form factor camera.
Owner:APPLE INC
Large aperture rectenna based on planar lens structures
ActiveUS7456803B1Simultaneous aerial operationsAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesEngineeringLenslet
A rectenna structure comprising a flexible, dielectric sheet of material; a plurality of metallic lenslets disposed on the sheet of material; and a plurality of diodes disposed on the sheet of material, each diode in said plurality of diodes being arranged at a focus of a corresponding one of said plurality of metallic lenslets.
Owner:HRL LAB
Micro-projector
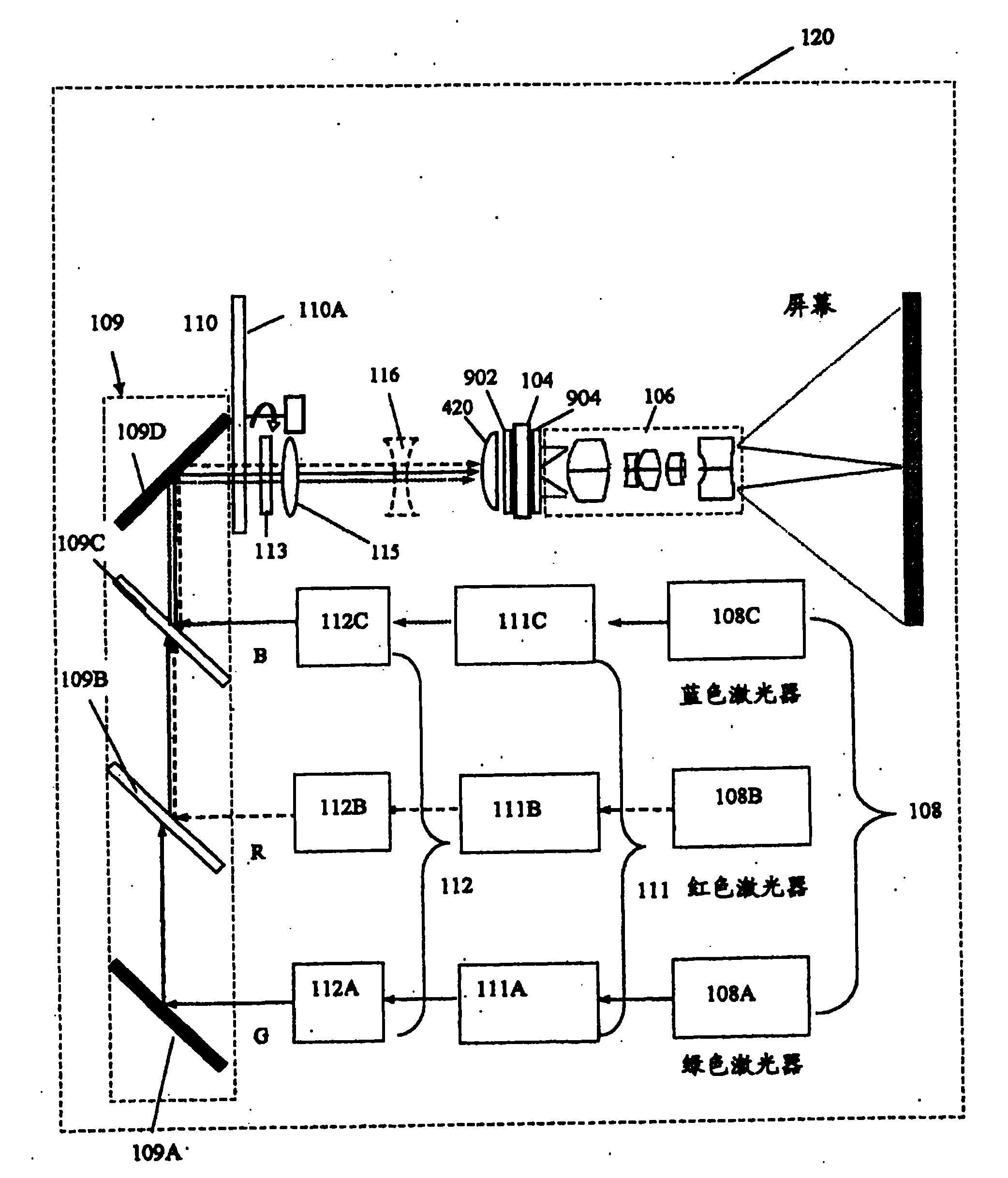
InactiveCN101855902AMonitor and correct white balanceTelevision system detailsPrismsDisplay deviceLaser source
The present invention provides a projection display comprising an illumination system comprising at least one laser source unit and configured and operable for producing one or more light beams; a spatial light modulating (SLM) system accommodated at output of the illumination system and comprising one or more SLM units for modulating light incident thereon in accordance with image data; and a light projection optics for imaging modulated light onto a projection surface. The illumination system comprises at least one beam shaping unit comprising a Dual Micro-lens Array (DMLA) arrangement formed by front and rear micro-lens arrays (MLA) located in front and rear parallel planes spaced-apart along an optical path of light propagating towards the SLM unit, the DMLA arrangement being configured such that each lenslet of the DMLA directs light incident thereon onto the entire active surface of the SLM unit, each lenslet having a geometrical aspect ratio corresponding to an aspect ratio of said active surface of the SLM unit.
Owner:EXPLAY
Polarization conversion light integrator
InactiveUS20050174641A1High acceptance angleAvoid the needPolarising elementsPicture reproducers using projection devicesBeam splitterIntegrator
A polarizing conversion system uses a polarizing beam splitter and reflector with a polarization conversion element to convert light from a lamp to a selected polarization state before providing the light to a light integrator, such as a light pipe or light tunnel. The light integrator provides homogenized polarized light to a light modulator. The polarization conversion system avoids increases efficiency compared to absorptive or simple reflective polarizers with fewer components than polarization conversion systems using patterned retarder plates and lenslet arrays. In one embodiment, the conversion elements are held to avoid adhesive or other bonds in the optical path. In other embodiments, high-temperature optical adhesive or optical contact bonding is used to assemble optical components for high-temperature operation. In a particular embodiment, a single-crystal quartz retarder plate is thermally matched to glass components in the polarization conversion system.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Electronic device with integrated optical navigation module and microlens array therefore
ActiveUS20070215793A1Material analysis by optical meansCounting objects on conveyorsLensletHand held devices
A portable device includes a transparent surface; a microlens array having lenslets, each lenslet forming a corresponding image of an object using light received through the transparent surface; a light sensor having pixels, each pixel corresponding uniquely to one of the plurality of lenslets, to detect the formed images of the object; and a controller to use the detected images to determine a motion of the object relative to the transparent surface, and to output the detected motion to a display for use in navigating a cursor and / or a menu on the display according to the determined motion. The portable device can be used in a telephone, personal digital assistant, and / or other handheld devices which control navigation on a display included in the device or external to the device.
Owner:PIXART IMAGING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com