Patents
Literature
174 results about "Lenslet array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
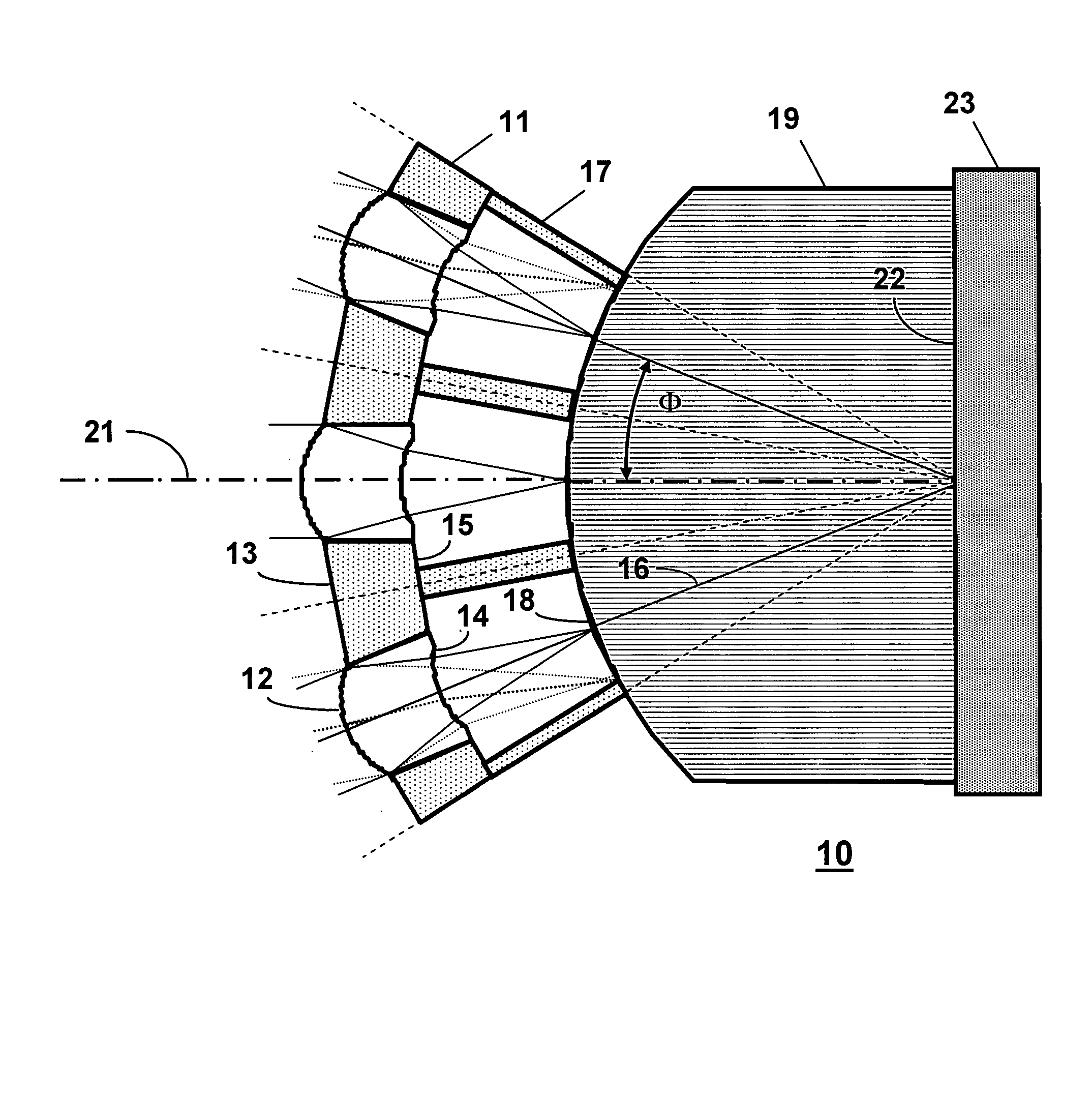
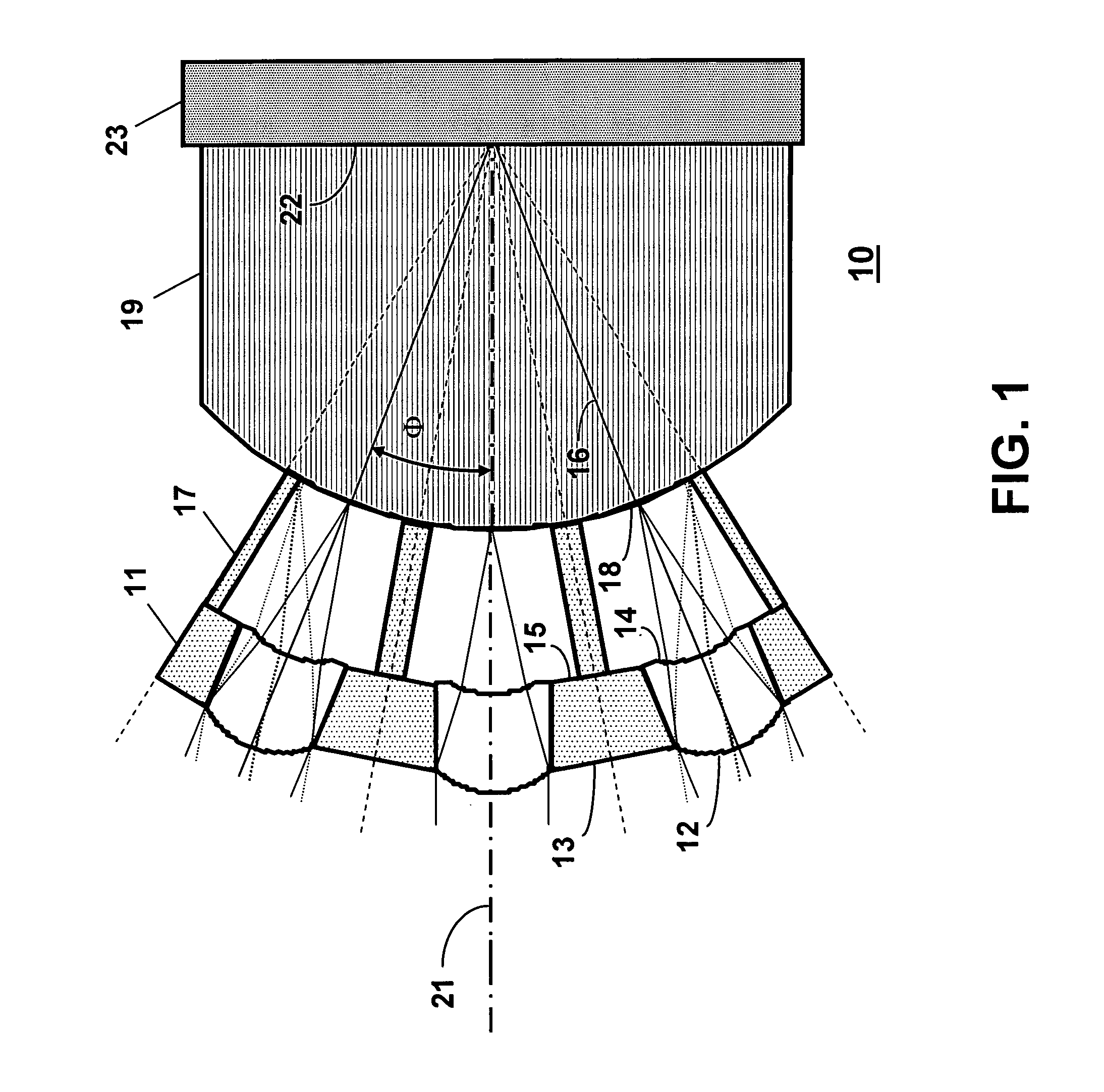
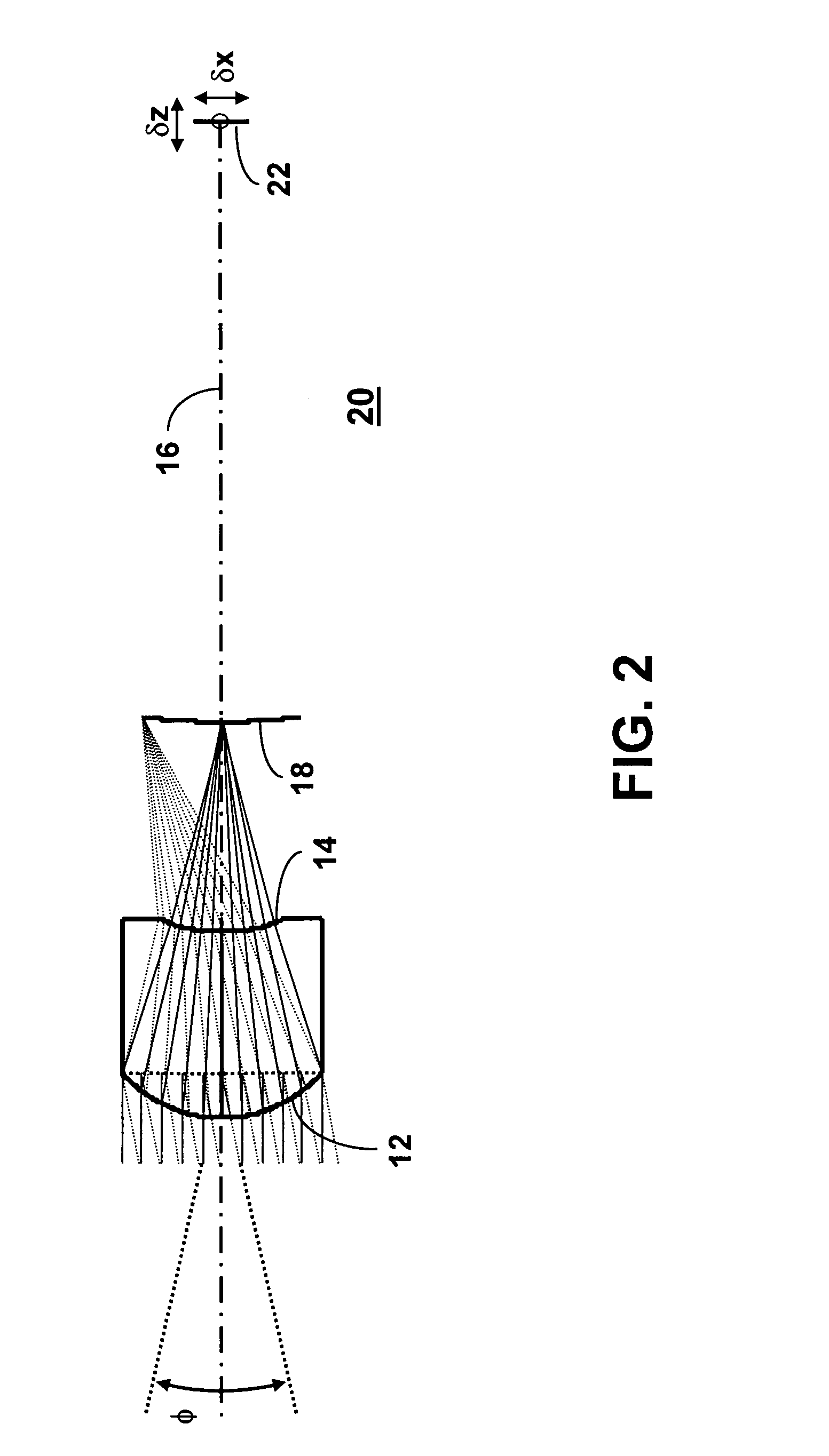
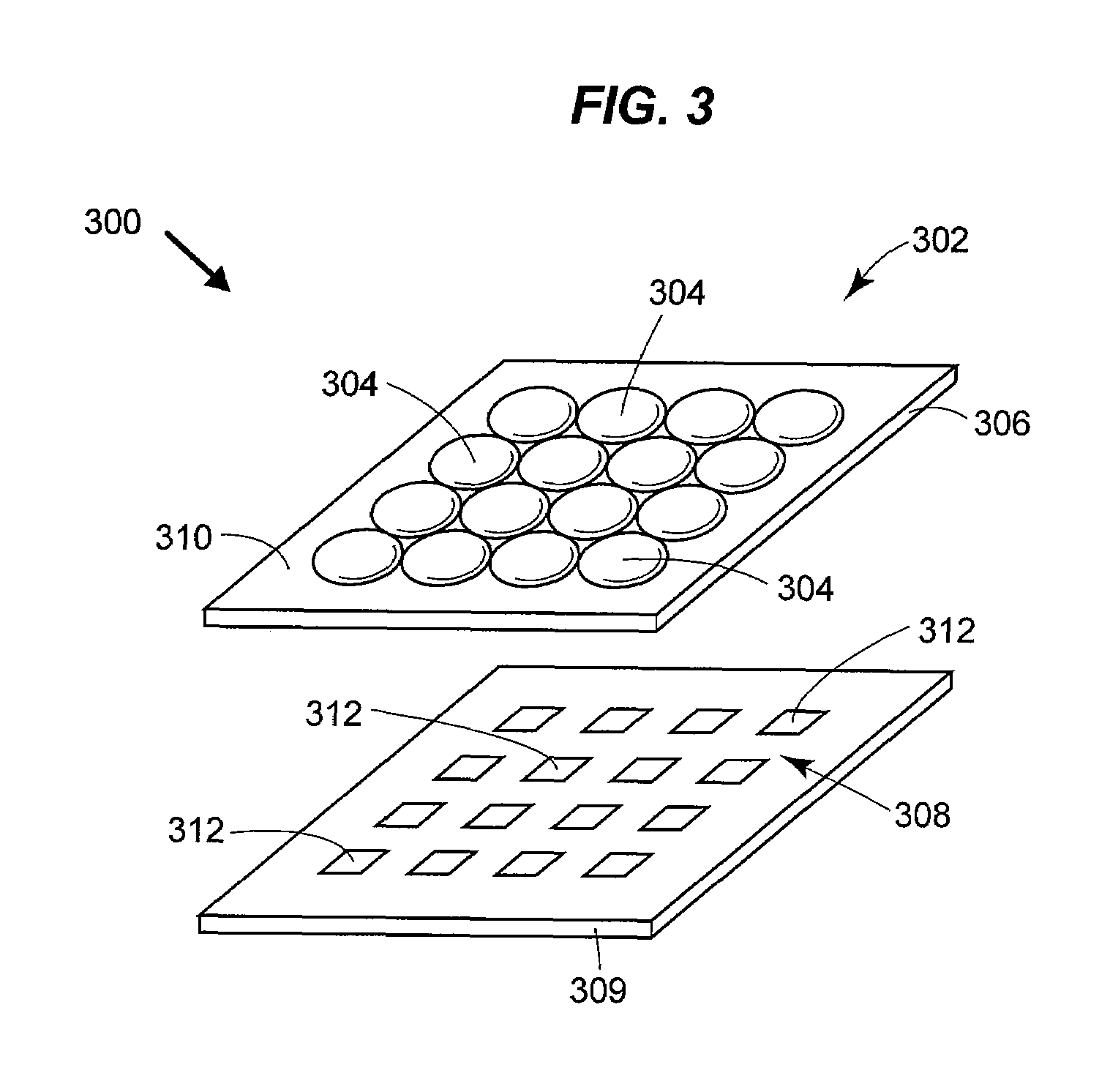
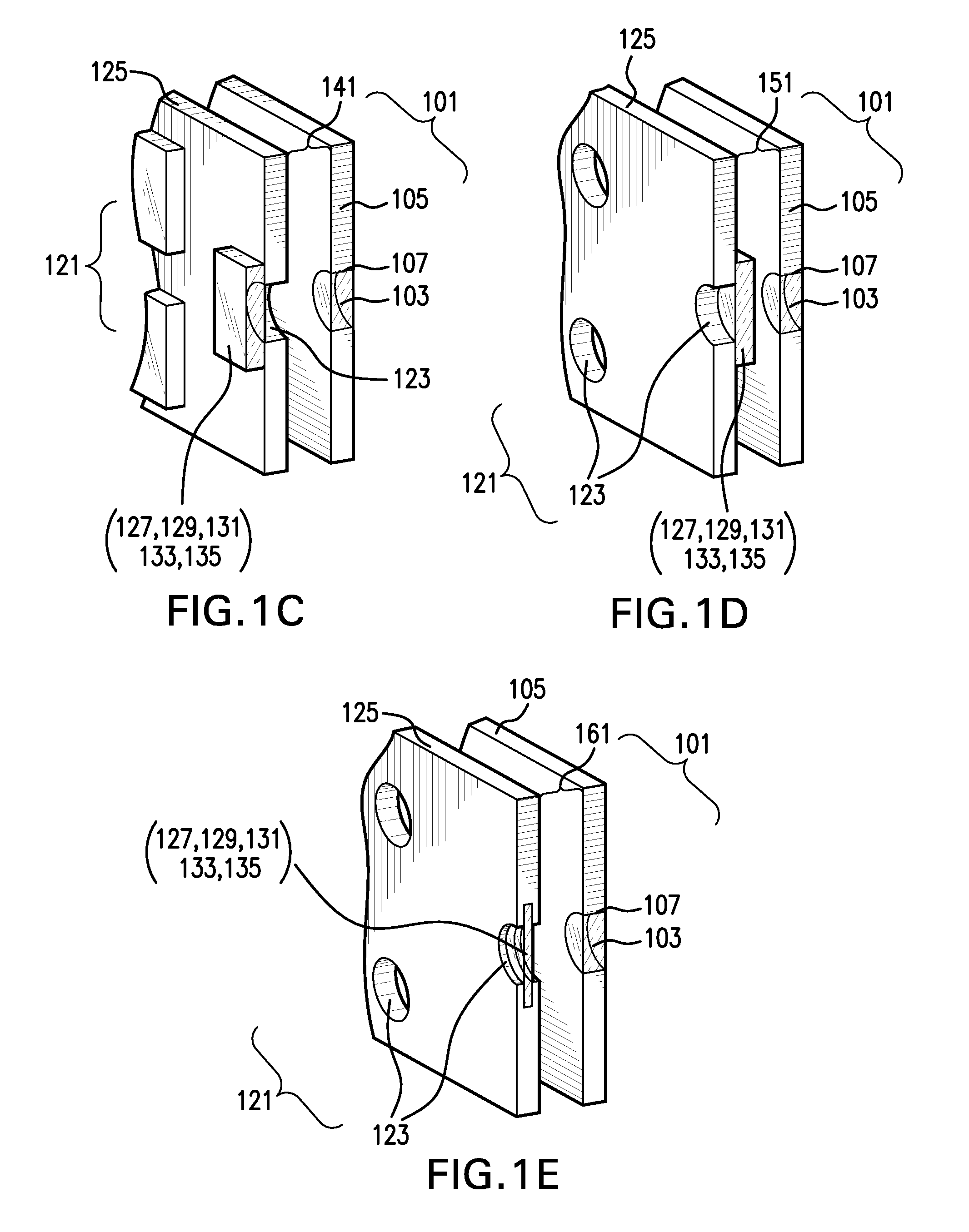
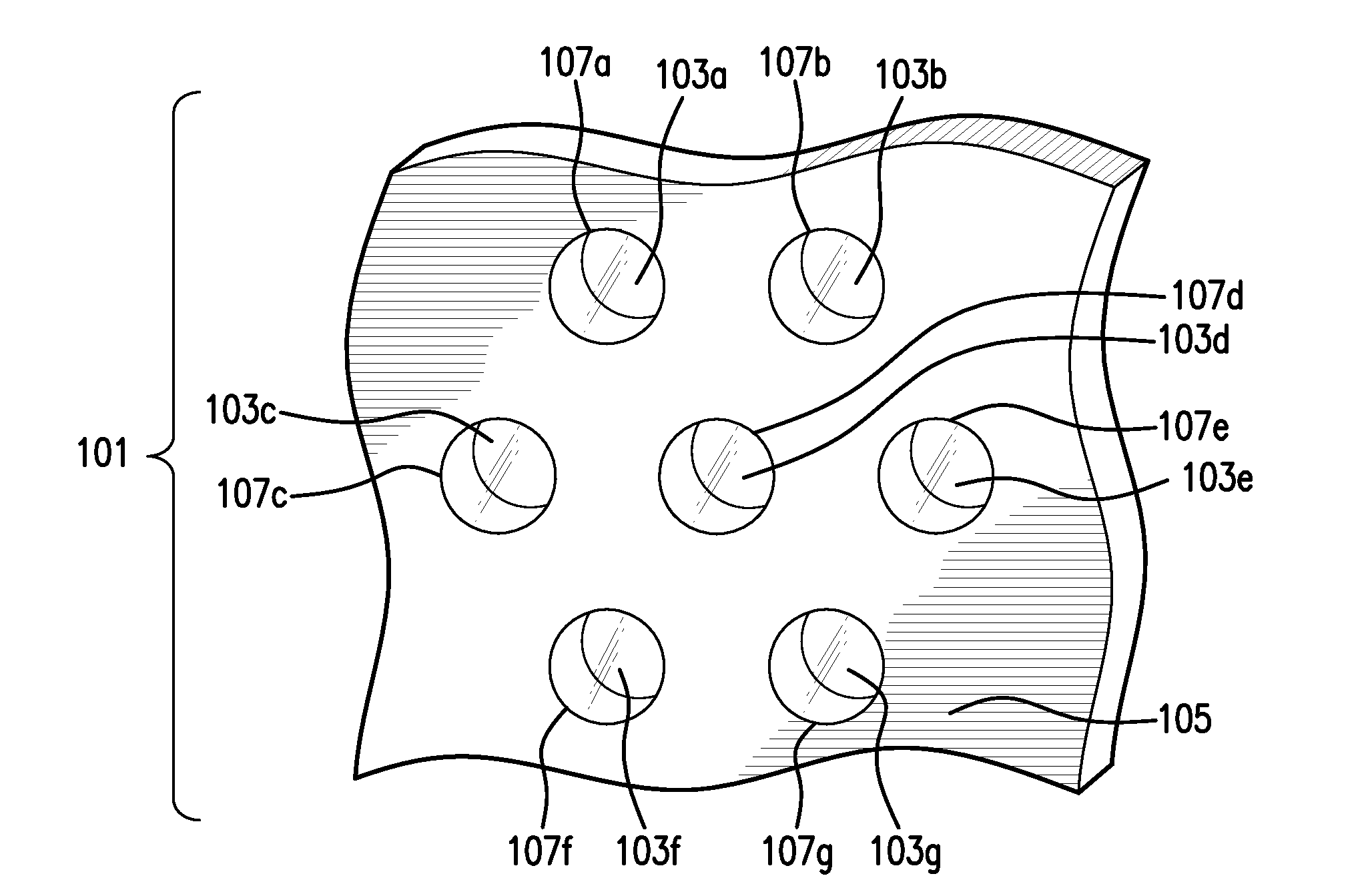
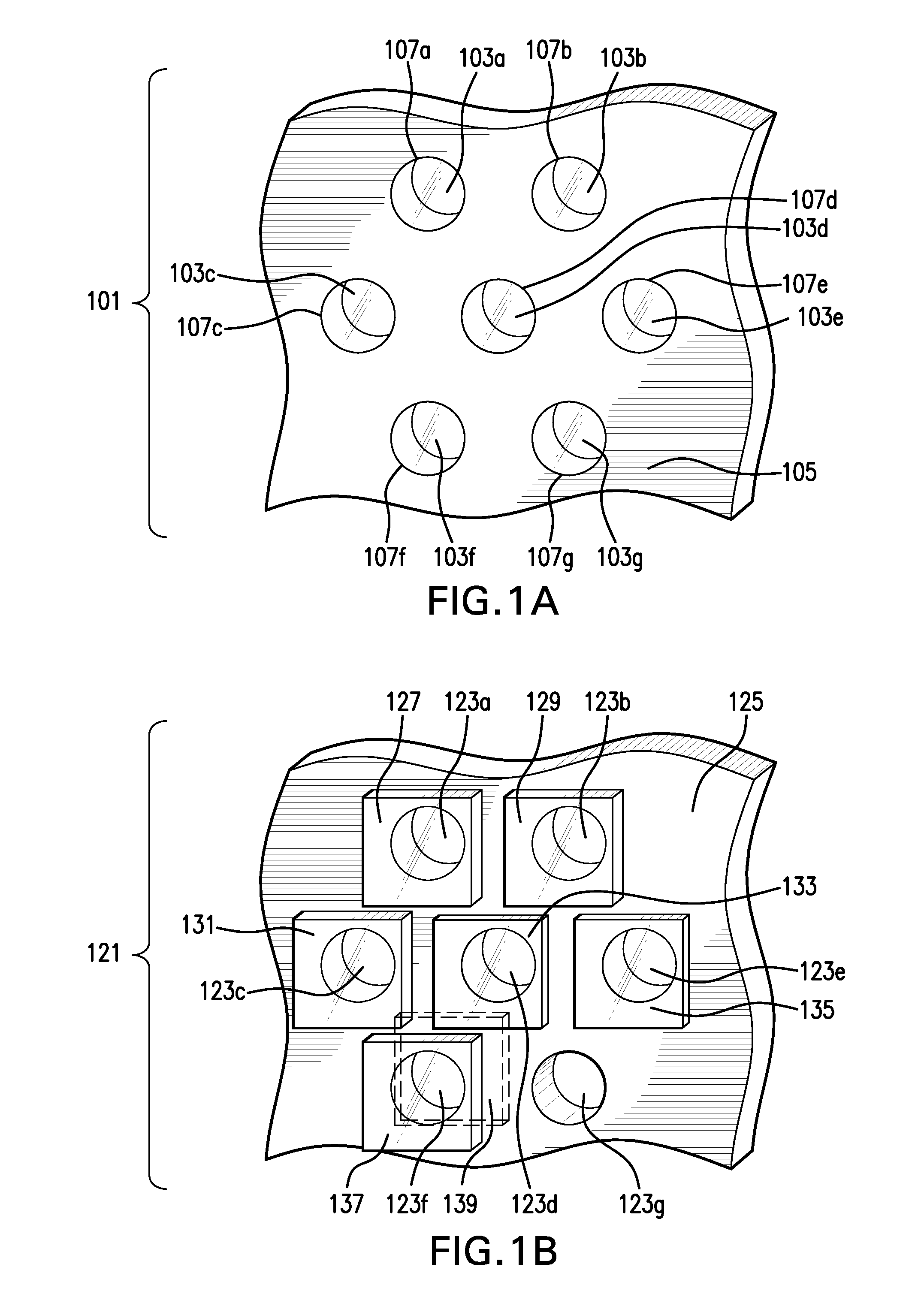
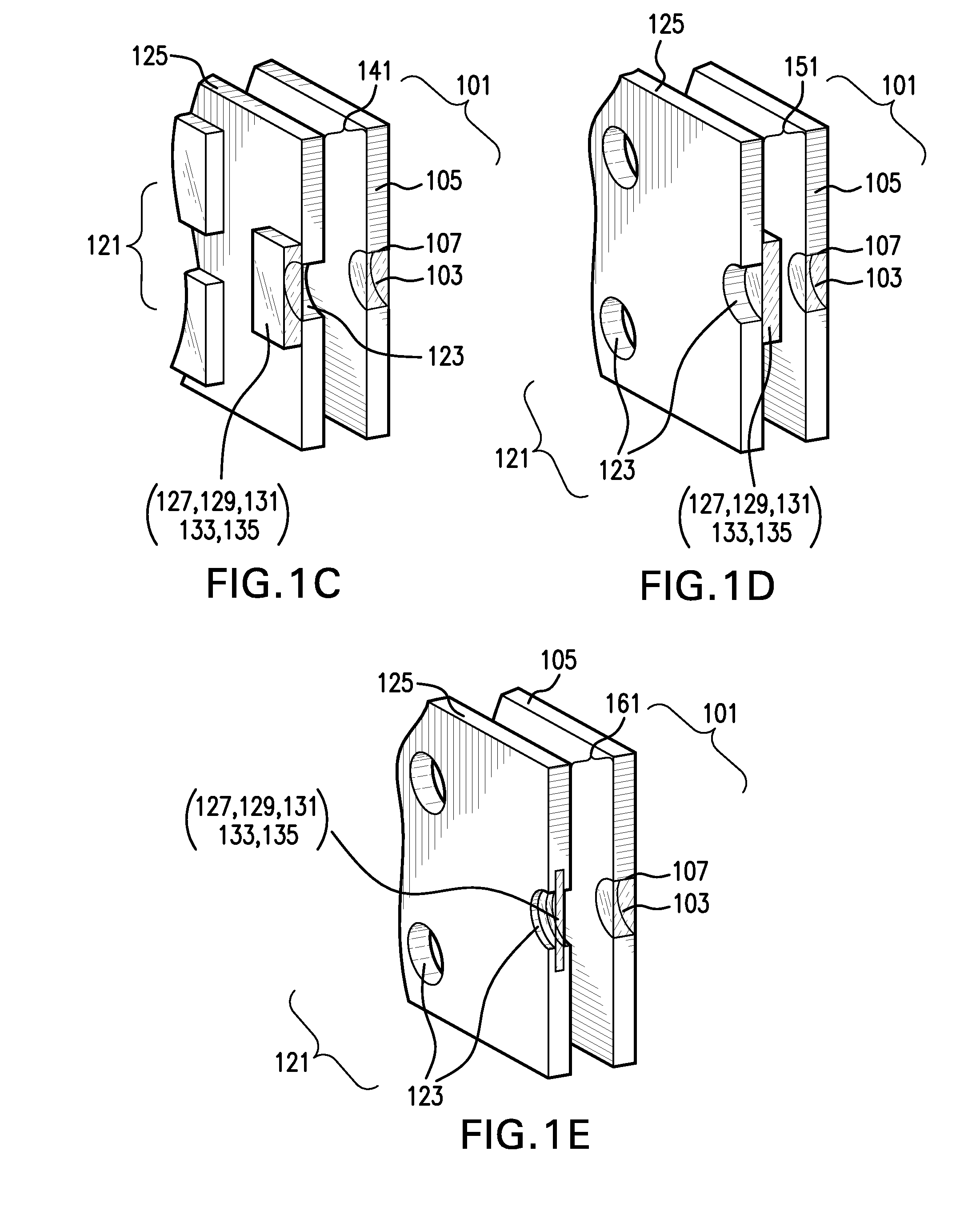
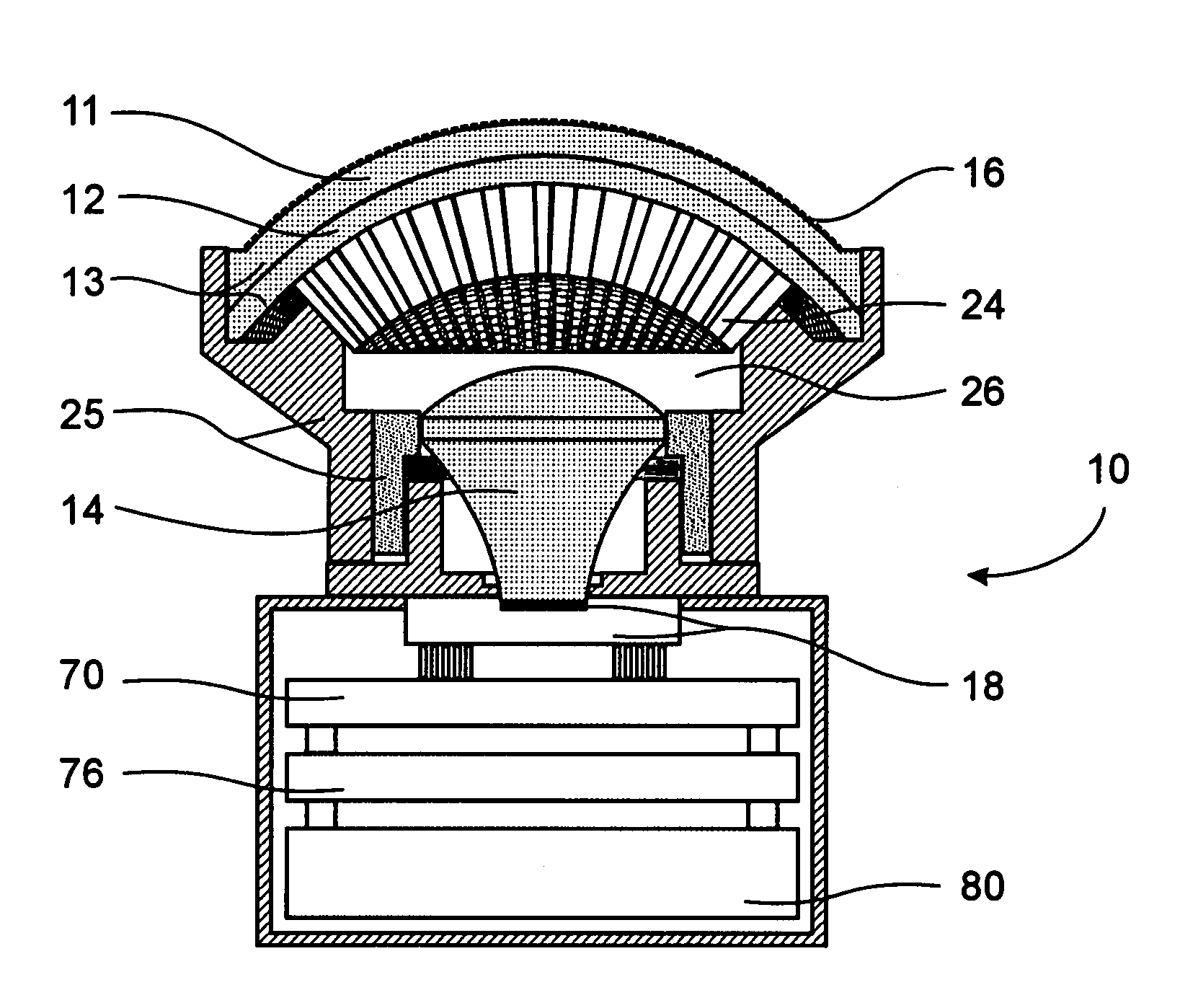
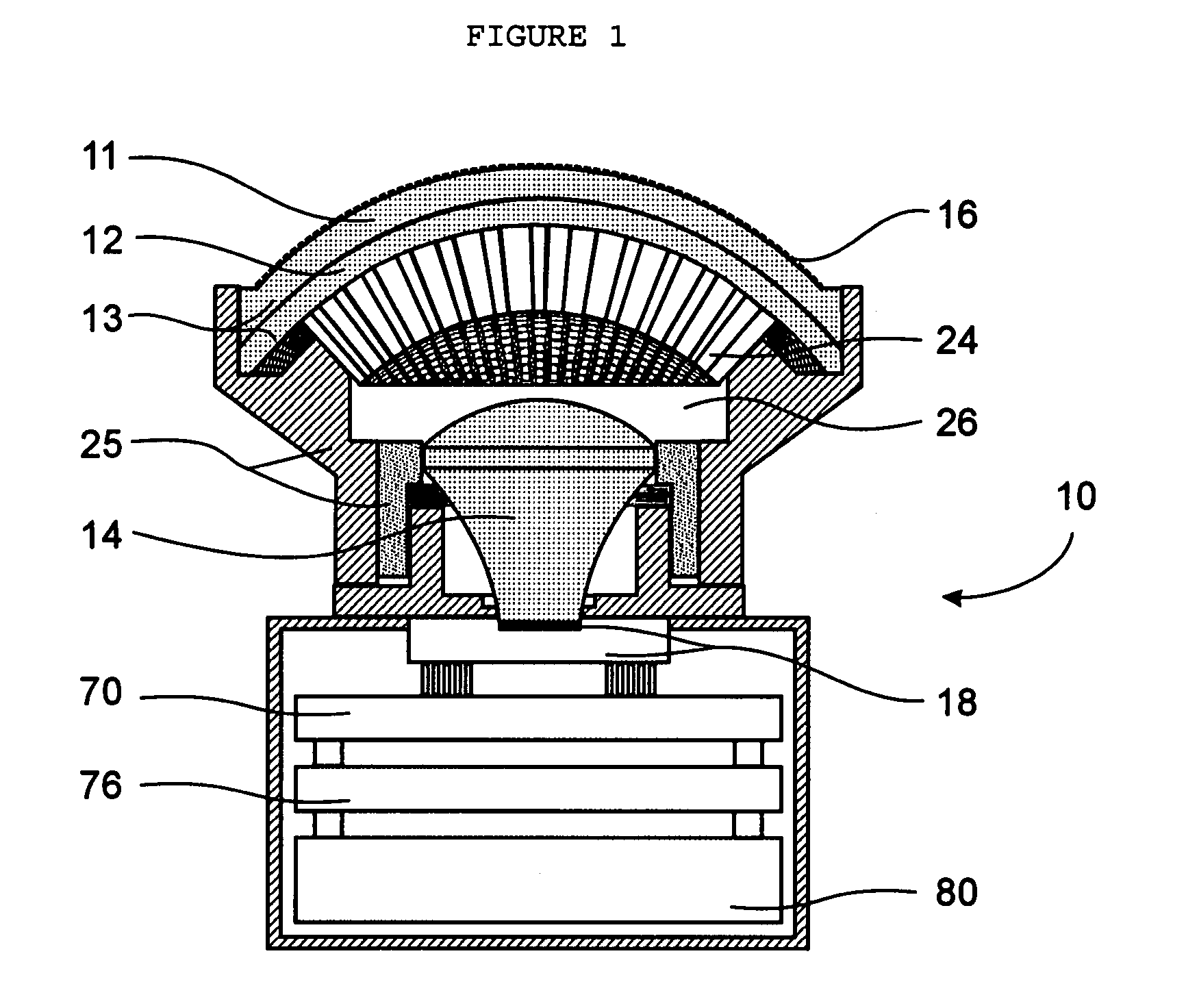
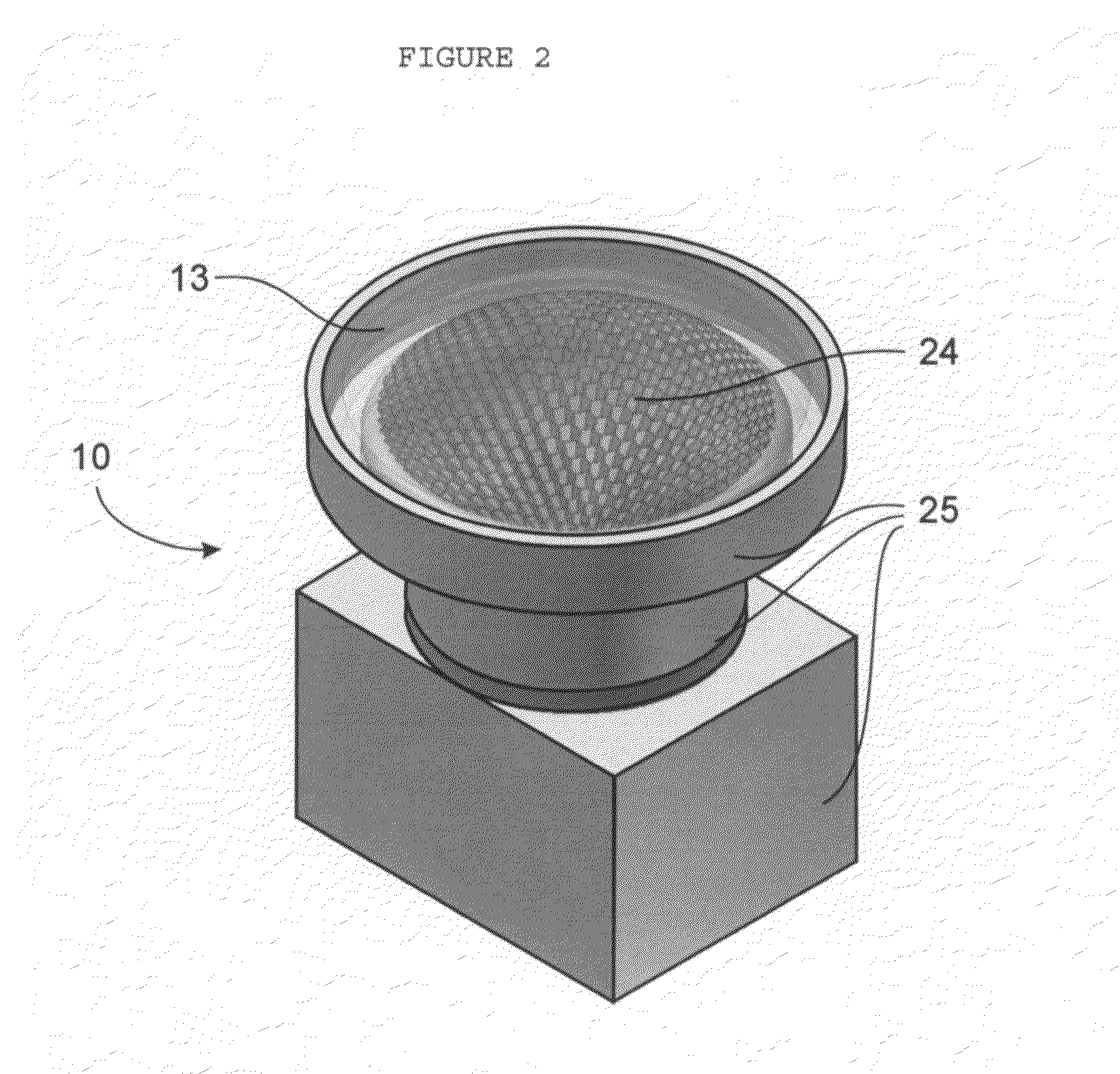
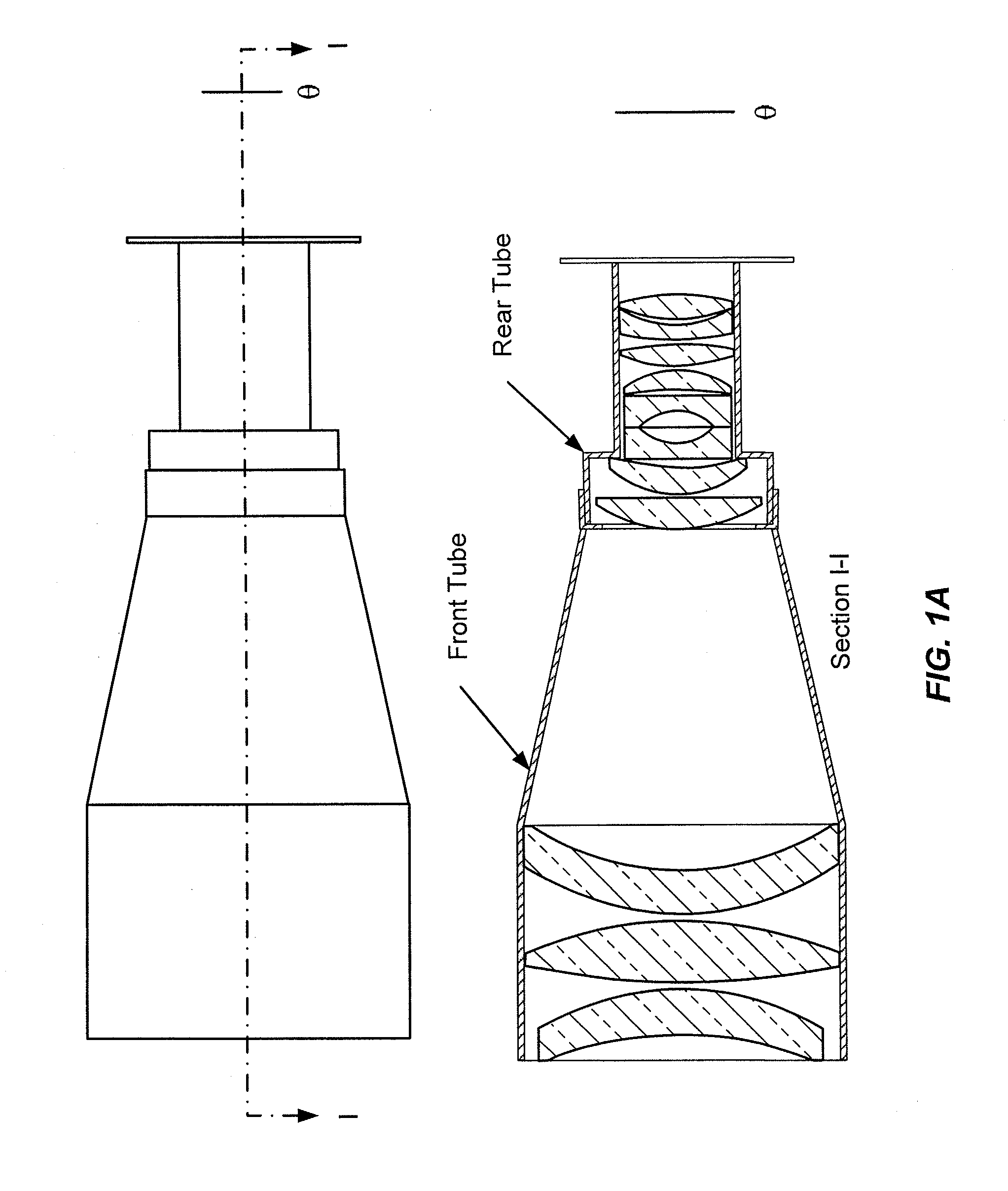
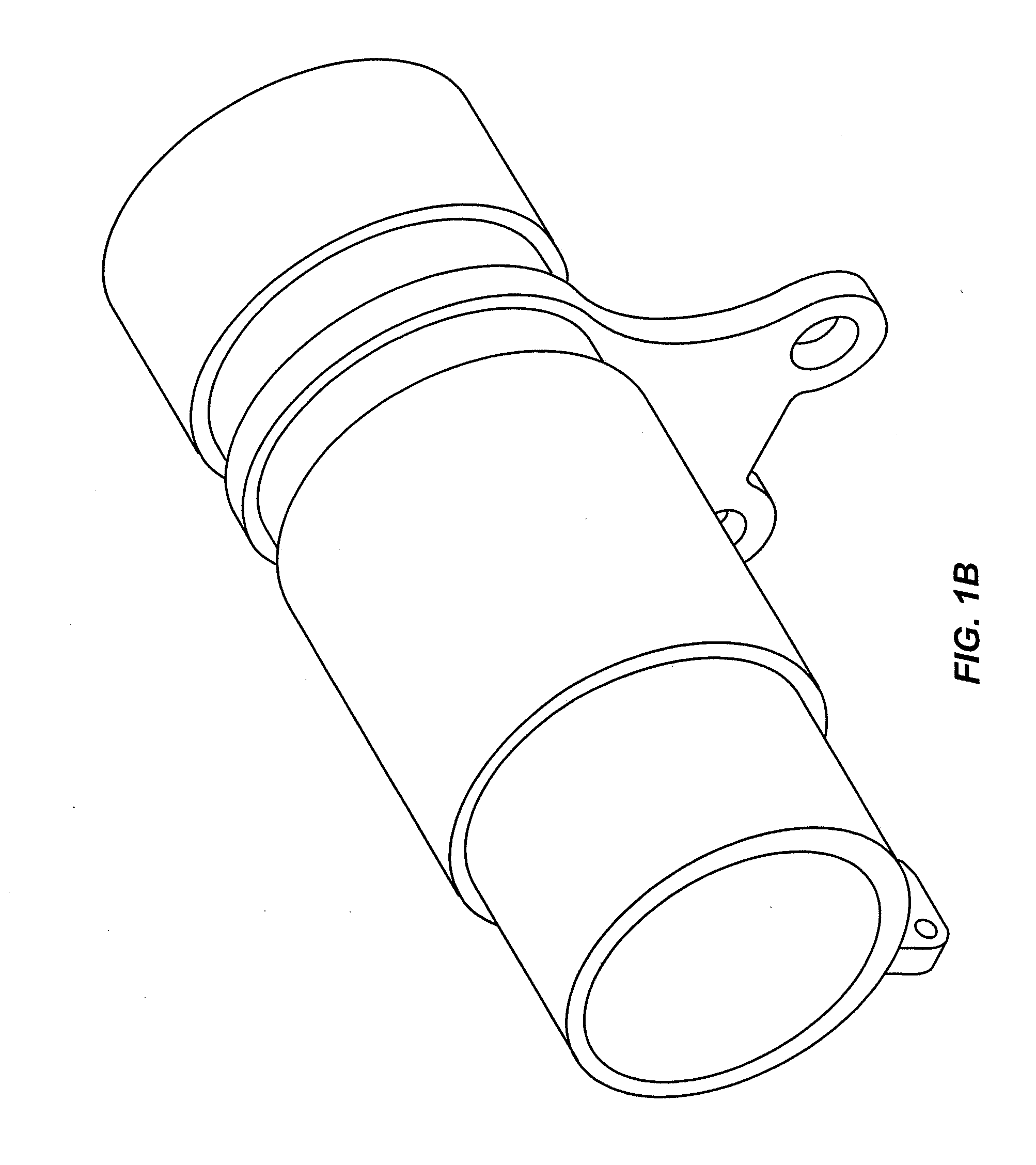
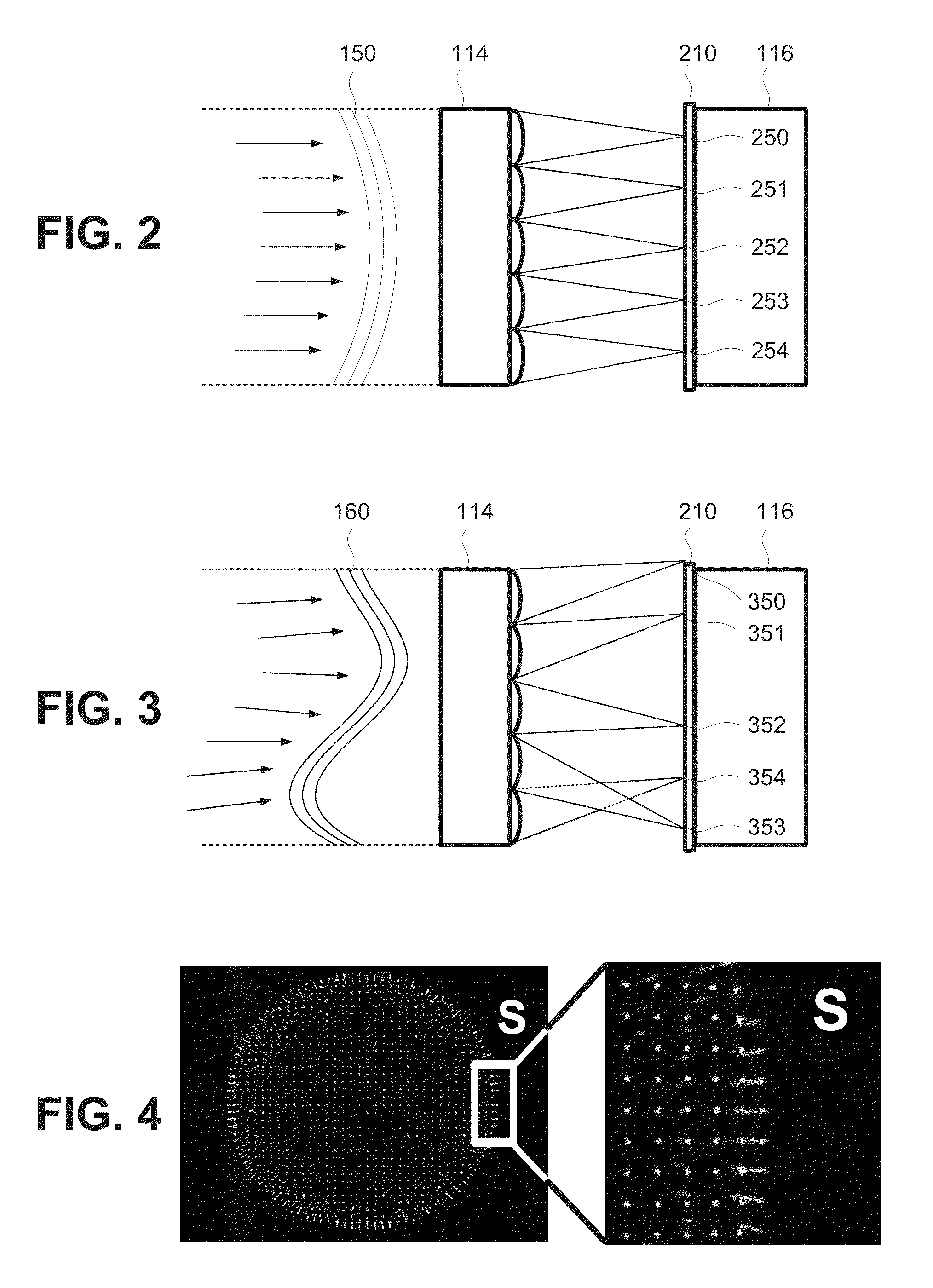
Fast Computational Camera Based On Two Arrays of Lenses
ActiveUS20090102956A1Less expenseQuality improvementTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsRadianceInformation capture
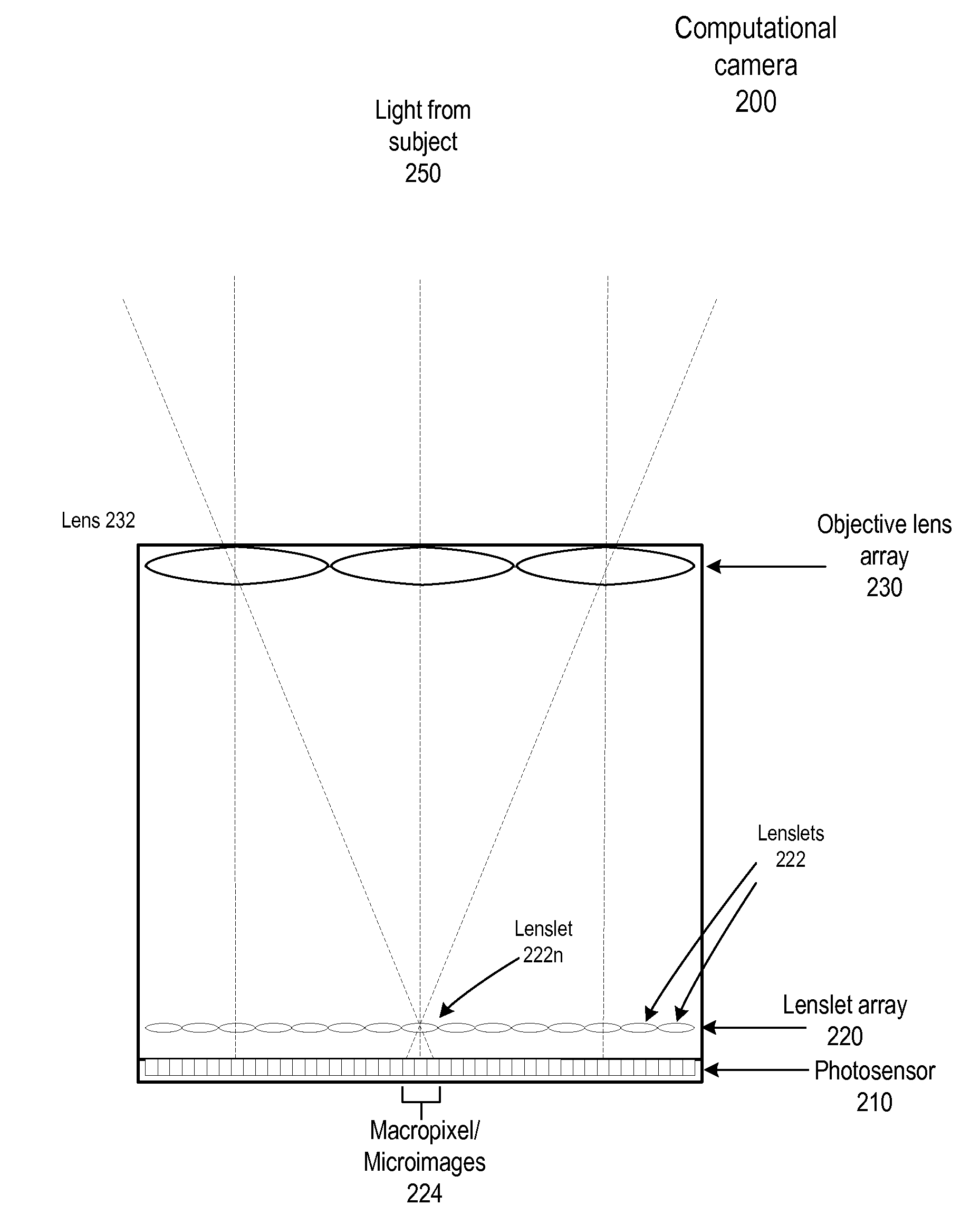
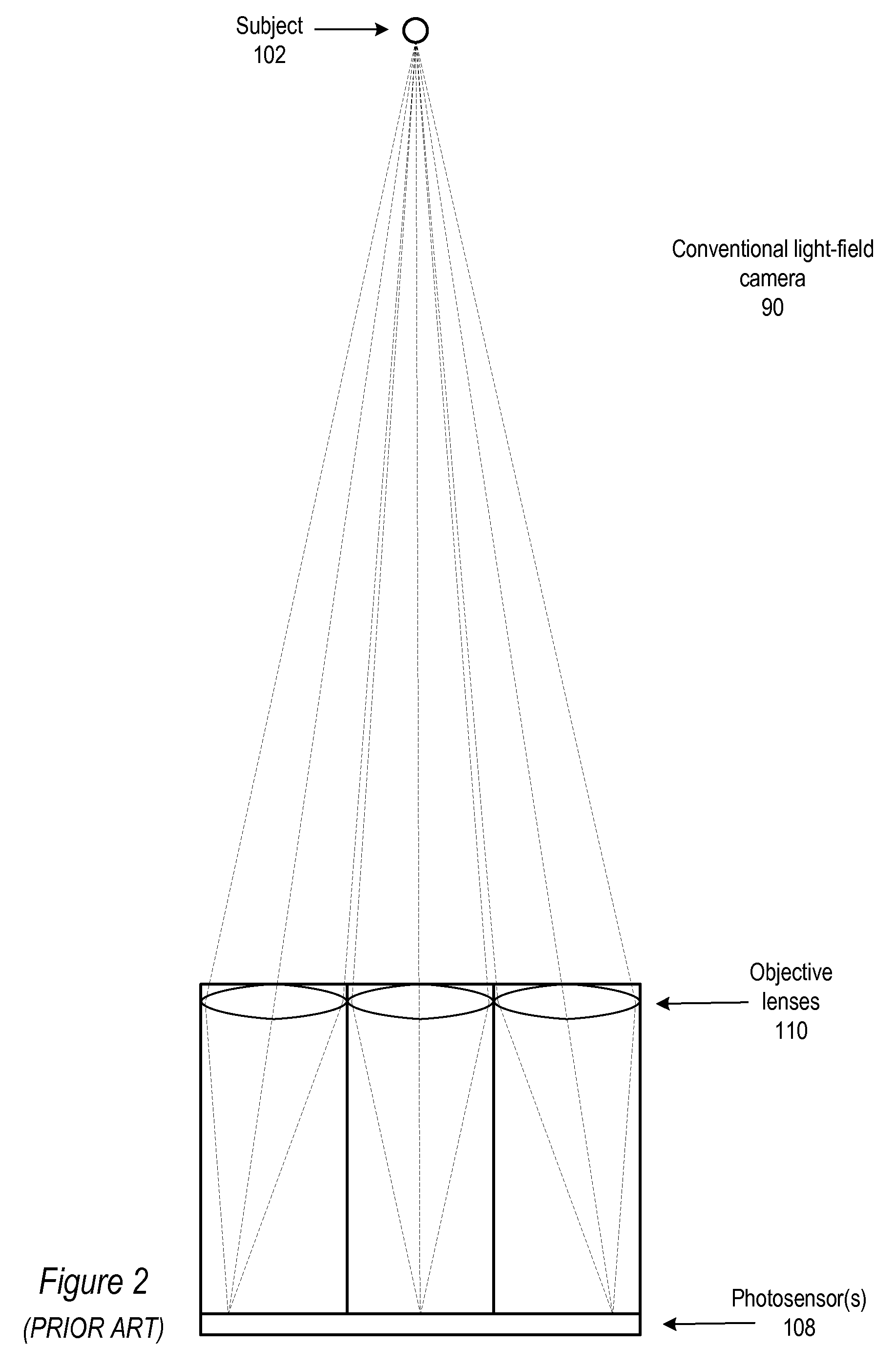
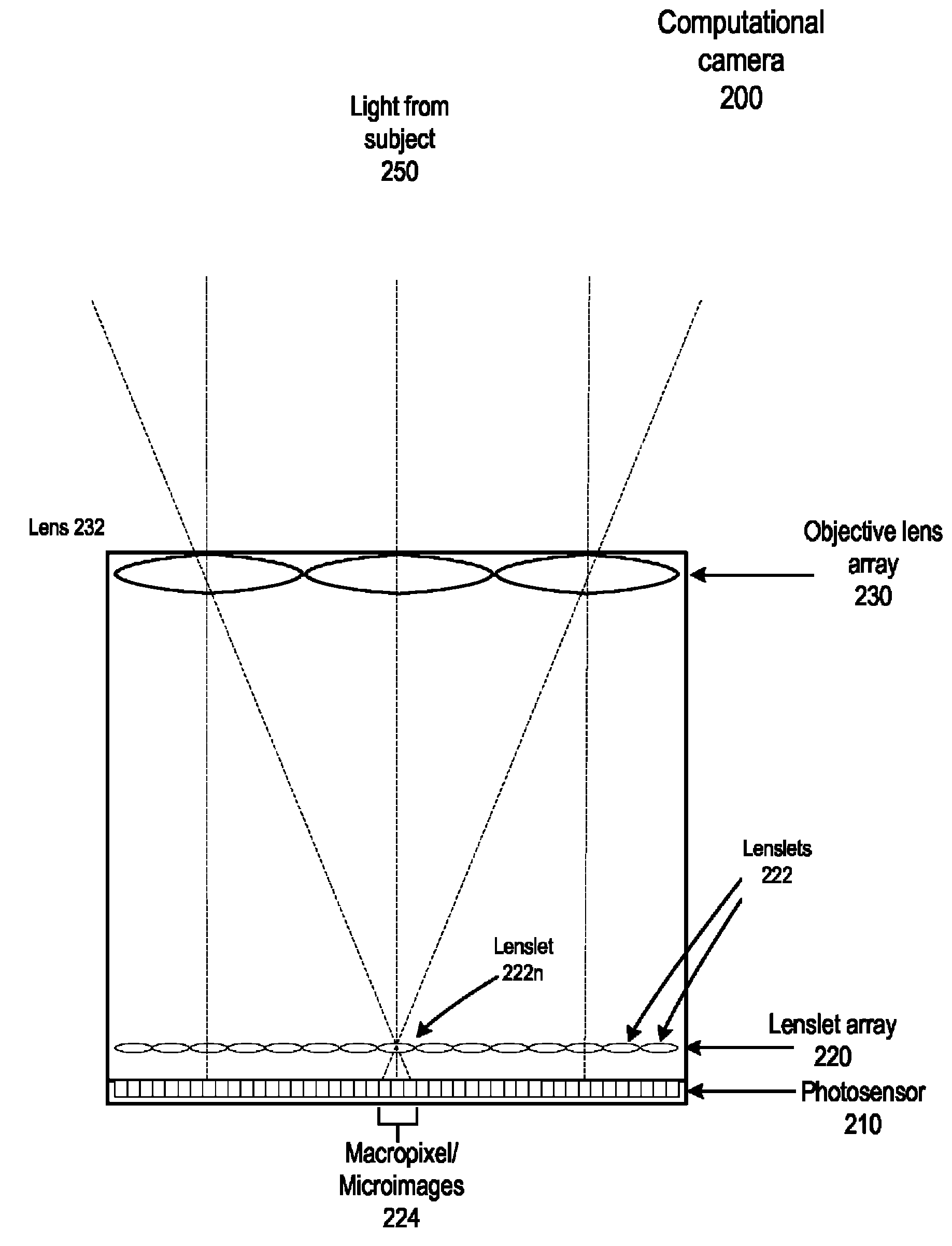
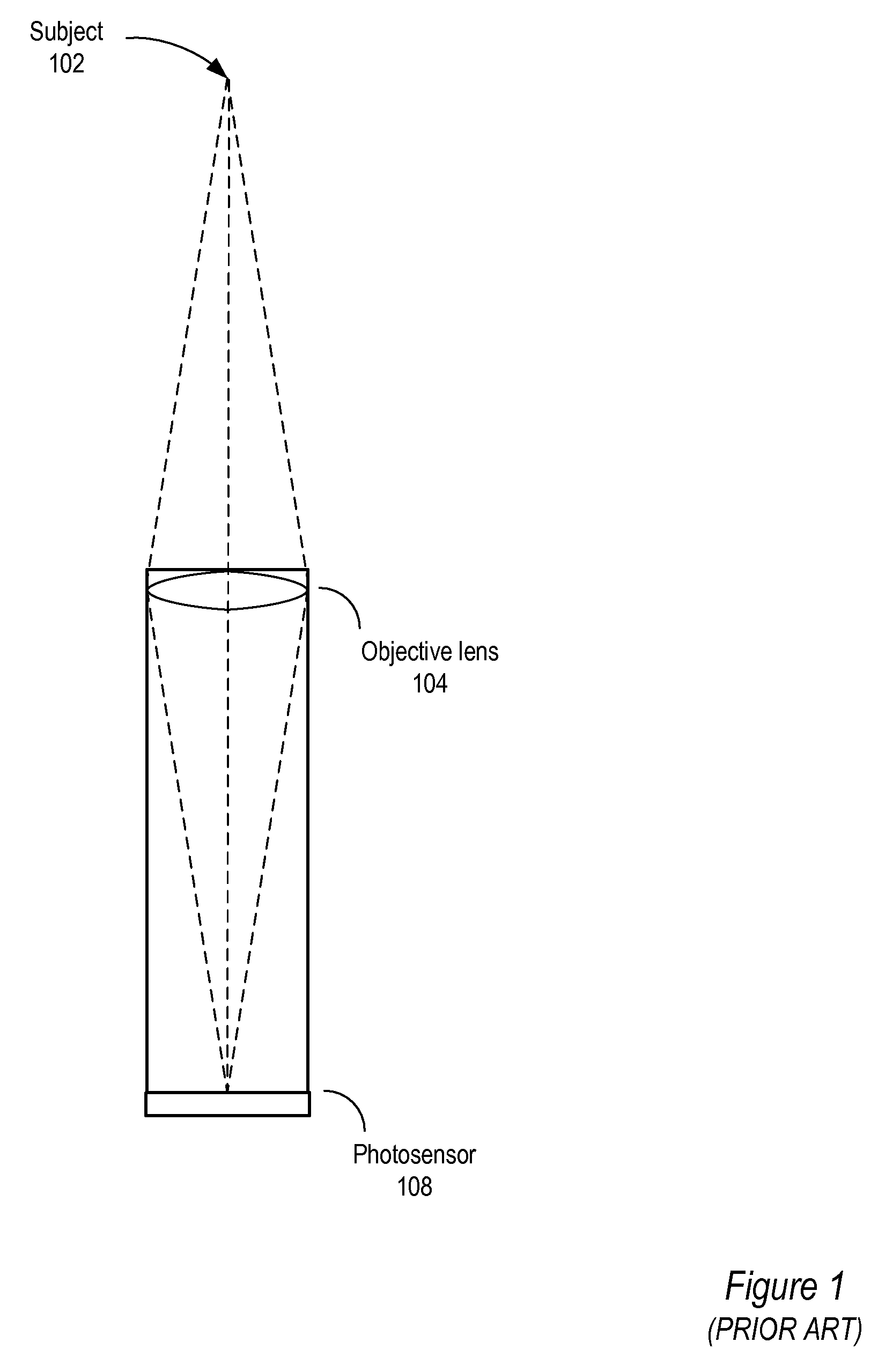
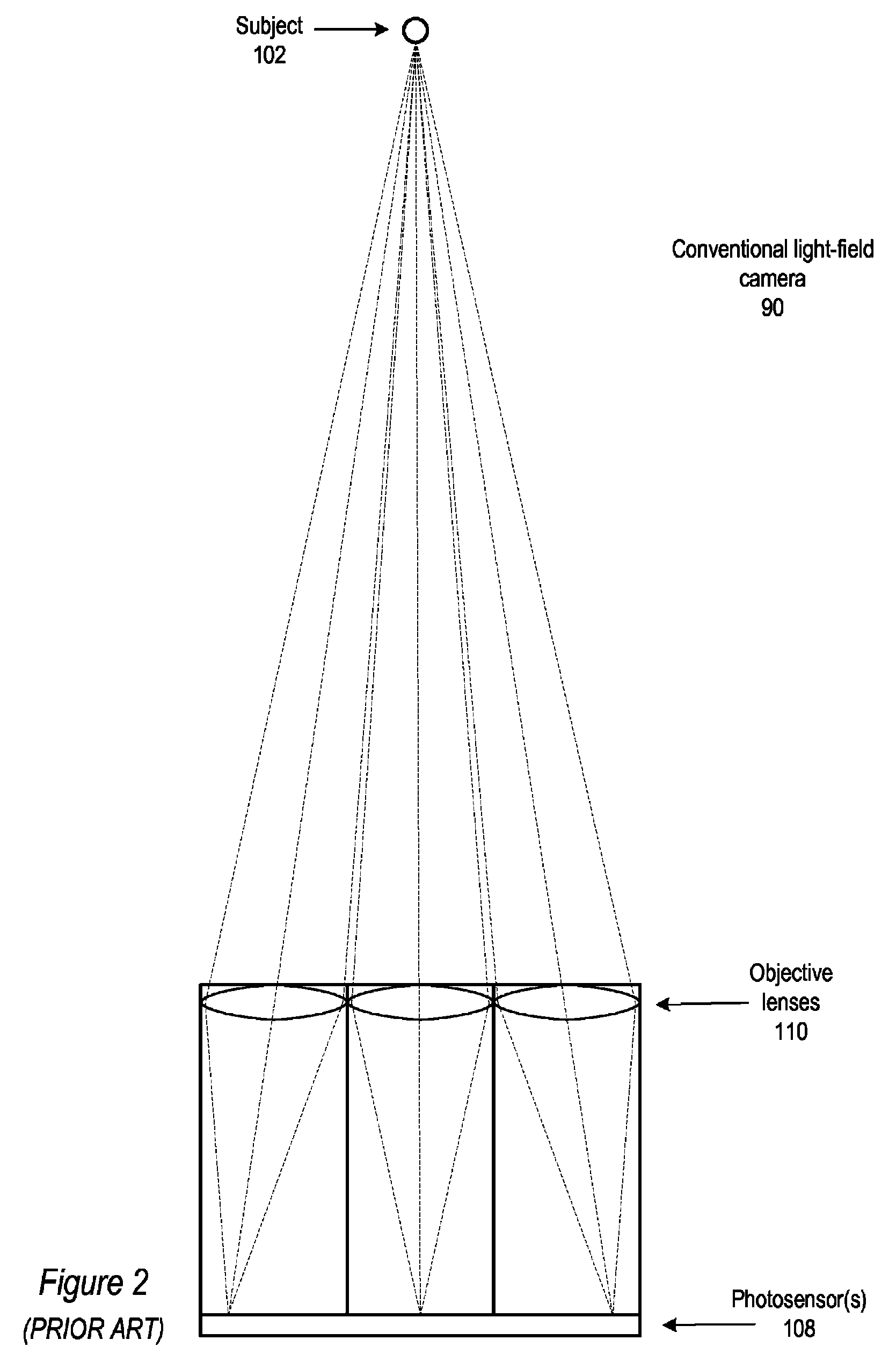
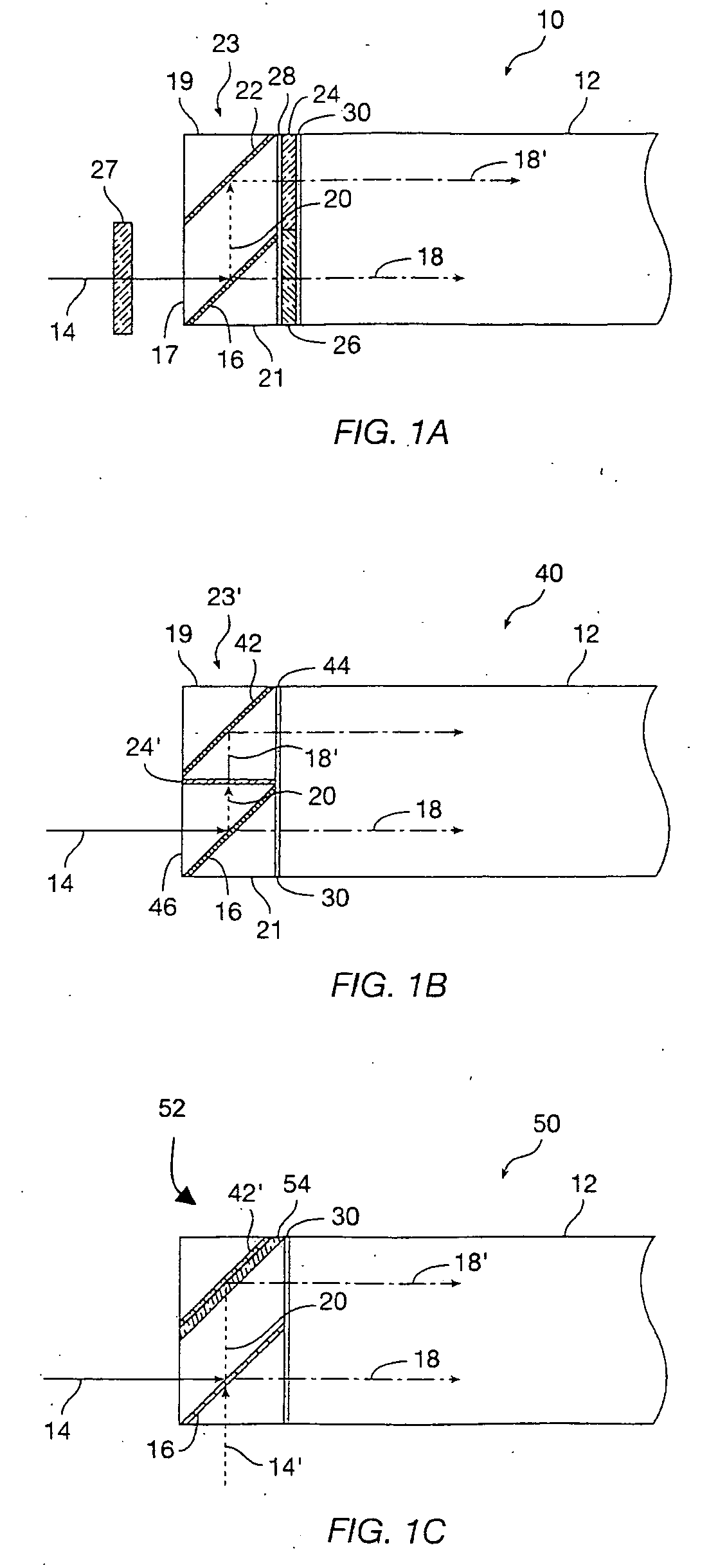
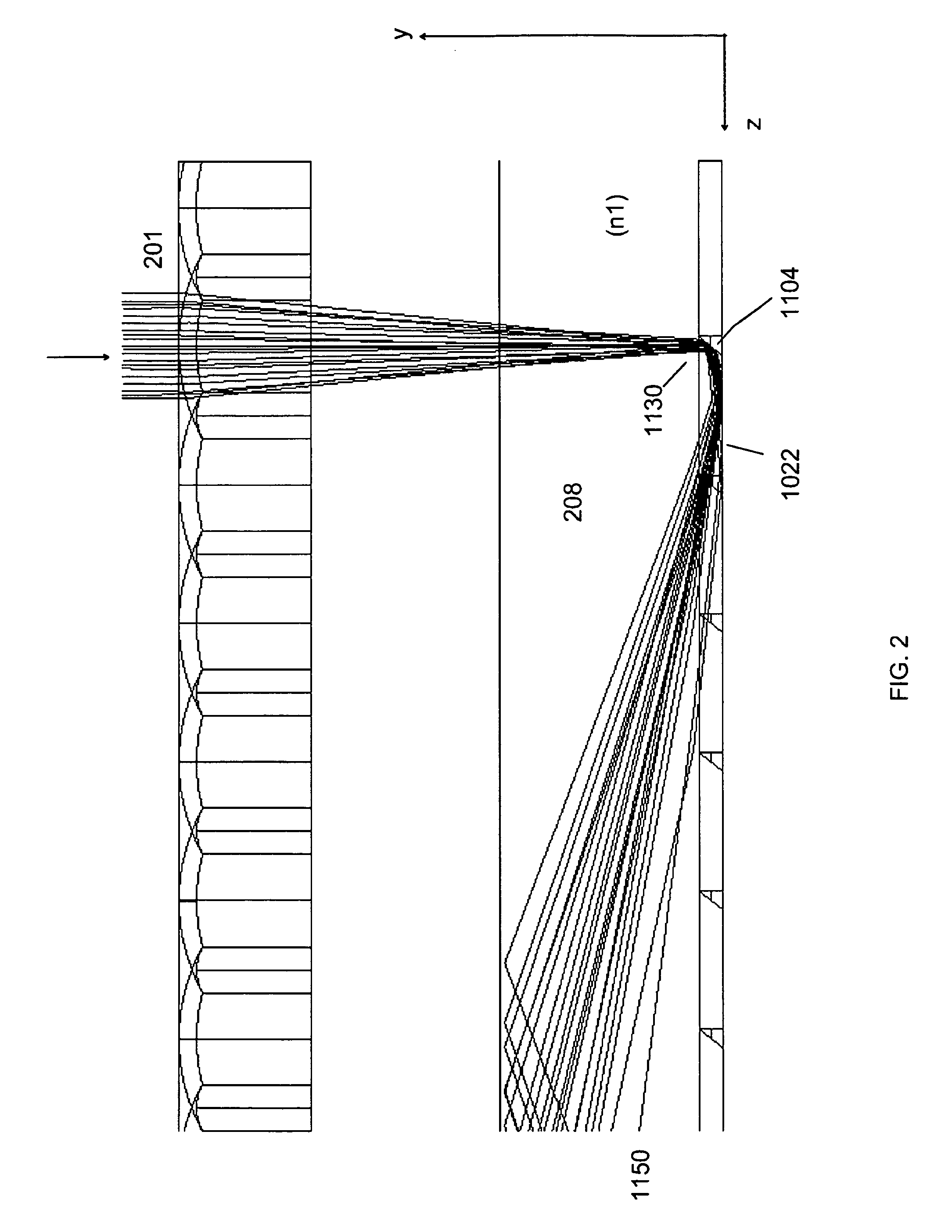
Method and apparatus for a fast (low F / number) computational camera that incorporates two arrays of lenses. The arrays include a lenslet array in front of a photosensor and an objective lens array of two or more lenses. Each lens in the objective lens array captures light from a subject. Each lenslet in the lenslet array captures light from each objective lens and separates the captured light to project microimages corresponding to the objective lenses on a region of the photosensor under the lenslet. Thus, a plurality of microimages are projected onto and captured by the photosensor. The captured microimages may be processed in accordance with the geometry of the objective lenses to align the microimages to generate a final image. One or more other algorithms may be applied to the image data in accordance with radiance information captured by the camera, such as automatic refocusing of an out-of-focus image.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Use of a lenslet array with a vertically stacked pixel array
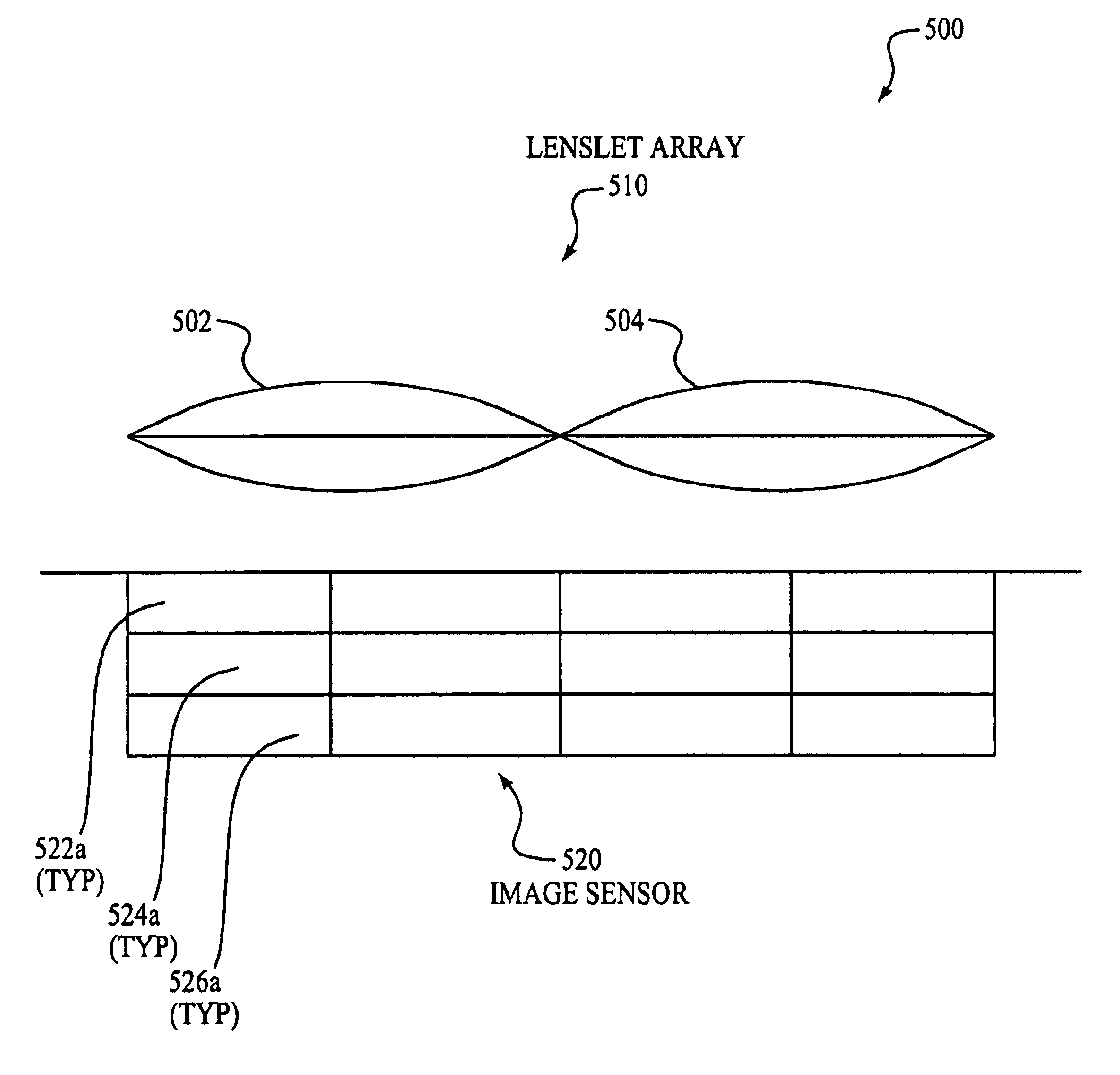
InactiveUS6958862B1Focal length minimizedColor minimizedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingComputer scienceLenslet array
An improved optical imaging system includes a vertically stacked pixel array and a lenslet array for capturing images while minimizing the focal length. The vertically stacked pixel array is configured to operate as an image sensor. The lenslet array is configure to focus the image on the image sensor. Each lens of the lenslet array focuses an image on a sub-array of the image sensor. Each sub-array is shifted from one another so that additional data obtained for each equivalent pixel in each sub-array. An image is obtained by combining the data of each sub-array.
Owner:FOVEON
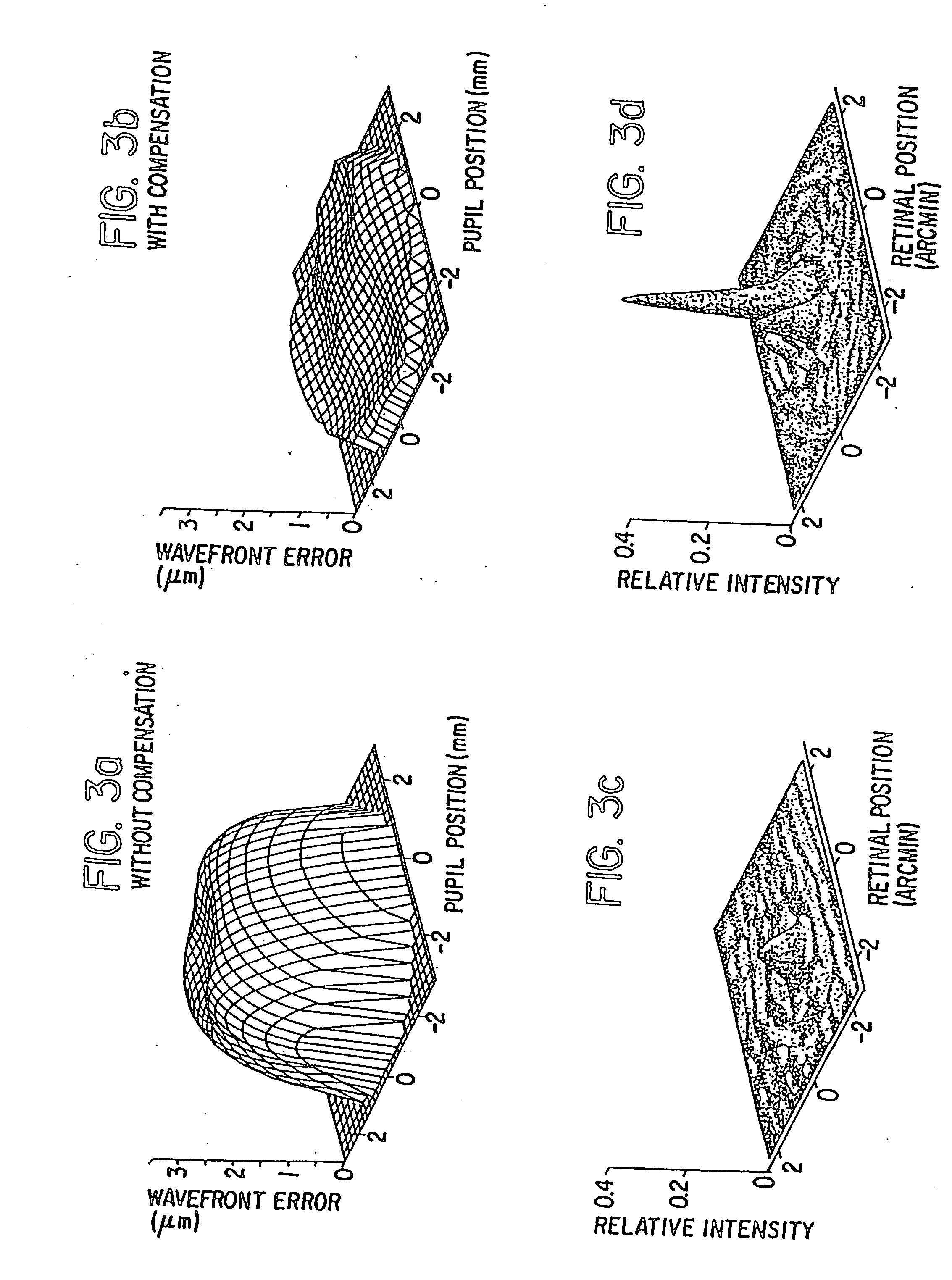
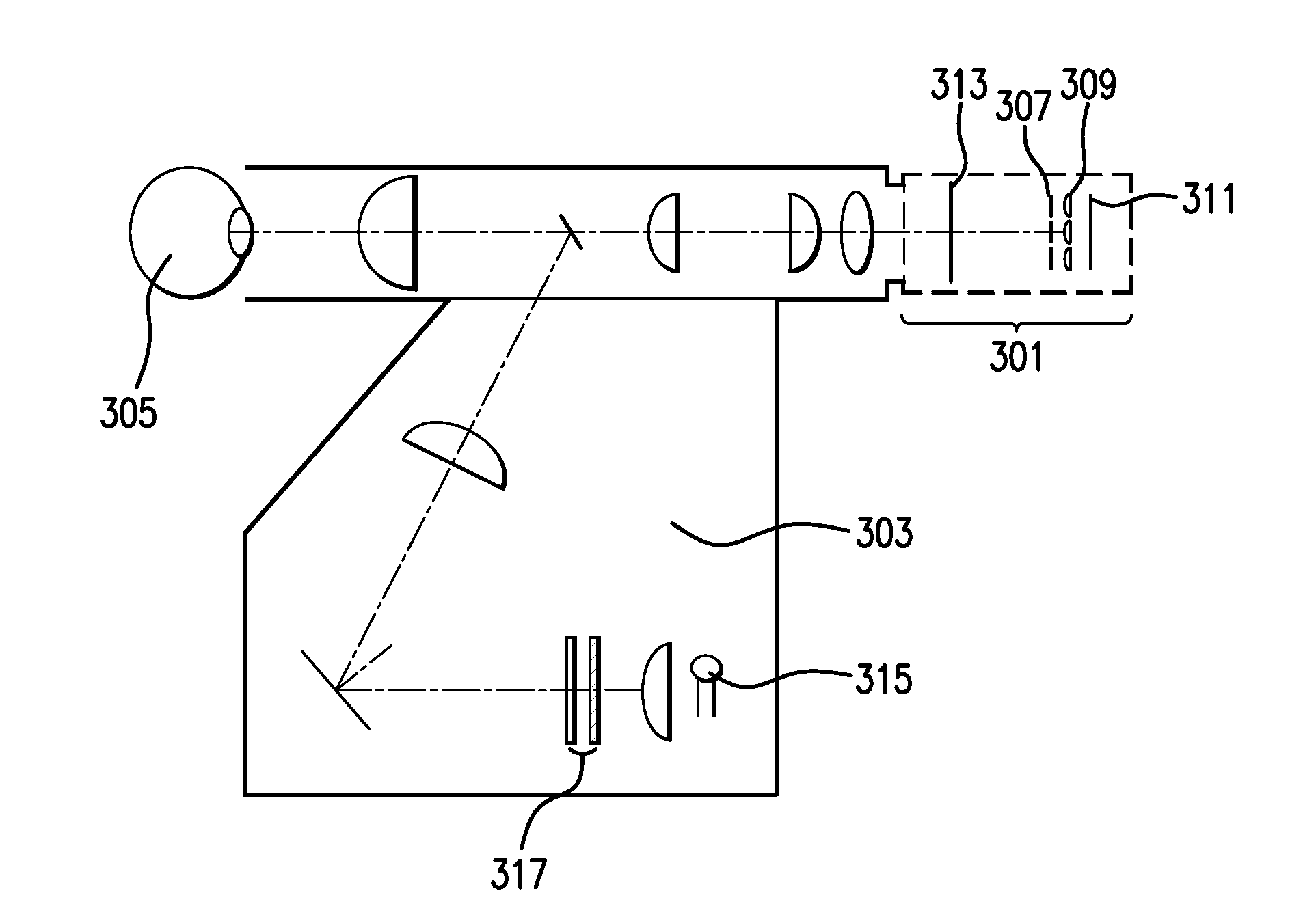
Method and apparatus for improving vision and the resolution of retinal images
InactiveUS20060044510A1Accurate measurementHigh resolutionOptical measurementsEye surgeryCcd cameraLaser beams
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Microelectrical mechanical structure (MEMS) optical modulator and optical display system
InactiveUS20050002086A1Eliminating light attenuation of lightEliminating expenseTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPlanar substrateActuator
A MEMS optical display system includes an illumination source for providing illumination light, a collimating lens for receiving the illumination light and forming from it collimated illumination light, and a converging microlens array having an array of lenslets that converge the collimated illumination light. The converging microlens array directs the illumination light to a microelectrical mechanical system (MEMS) optical modulator. The MEMS optical modulator includes, for example, a planar substrate through which multiple pixel apertures extend and multiple MEMS actuators that support and selectively position MEMS shutters over the apertures. A MEMS actuator and MEMS shutter, together with a corresponding aperture, correspond to pixel. The light from the converging microlens array is focused through the apertures and is selectively modulated according to the positioning of the MEMS shutters by the MEMS actuators, thereby to impart image information on the illumination light. The light is then passed to a diffused transmissive display screen by a projection microlens array.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
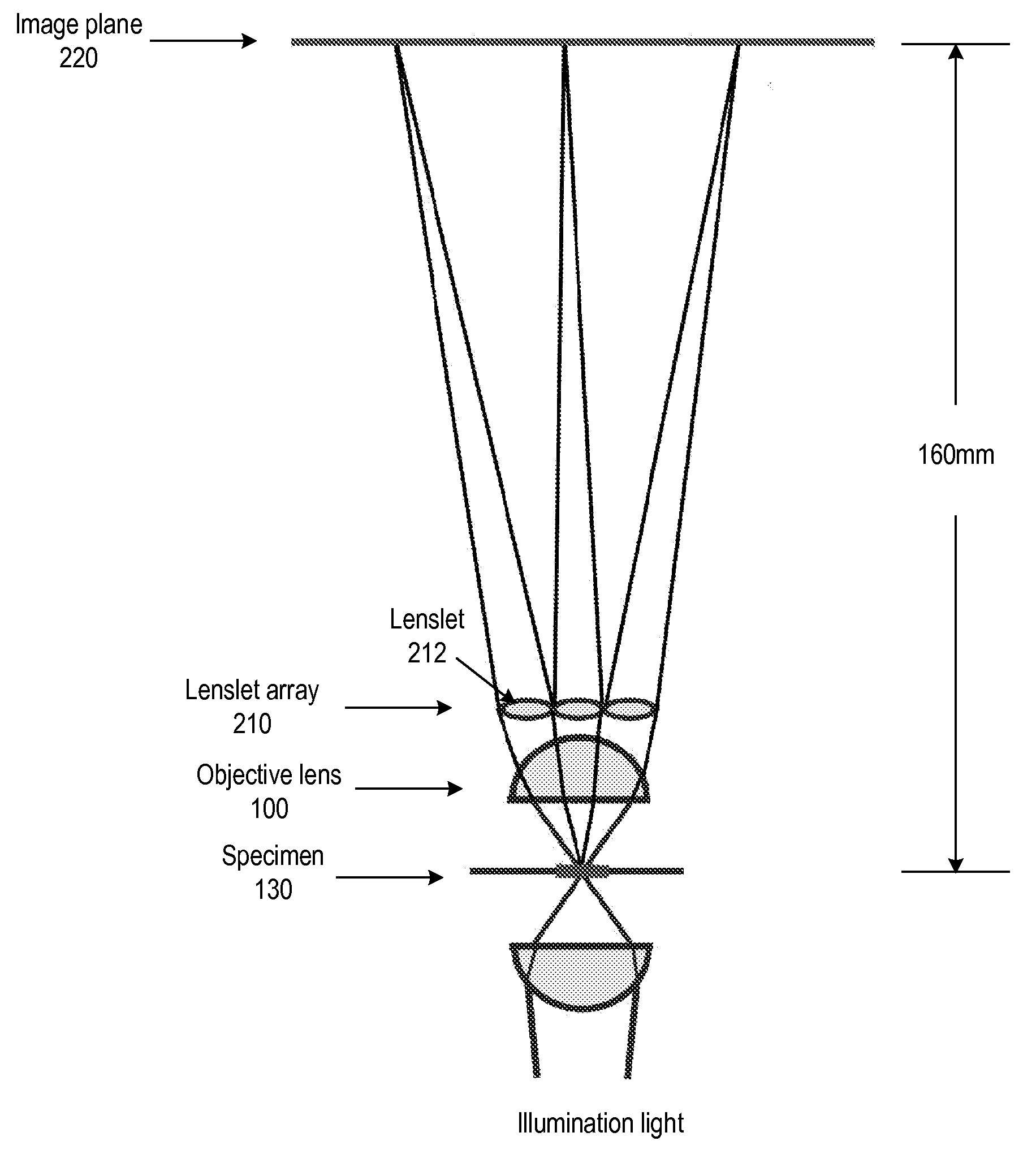
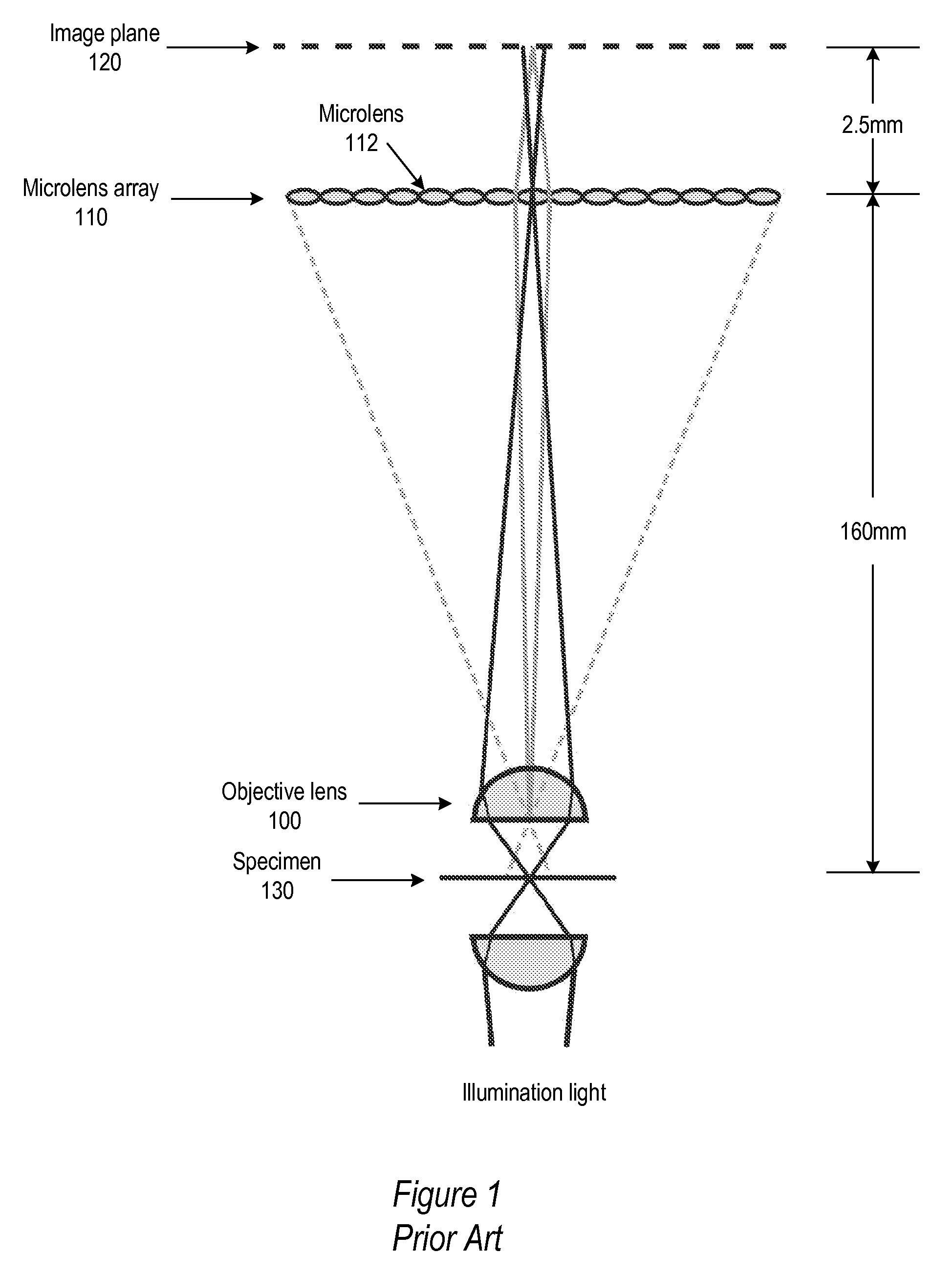
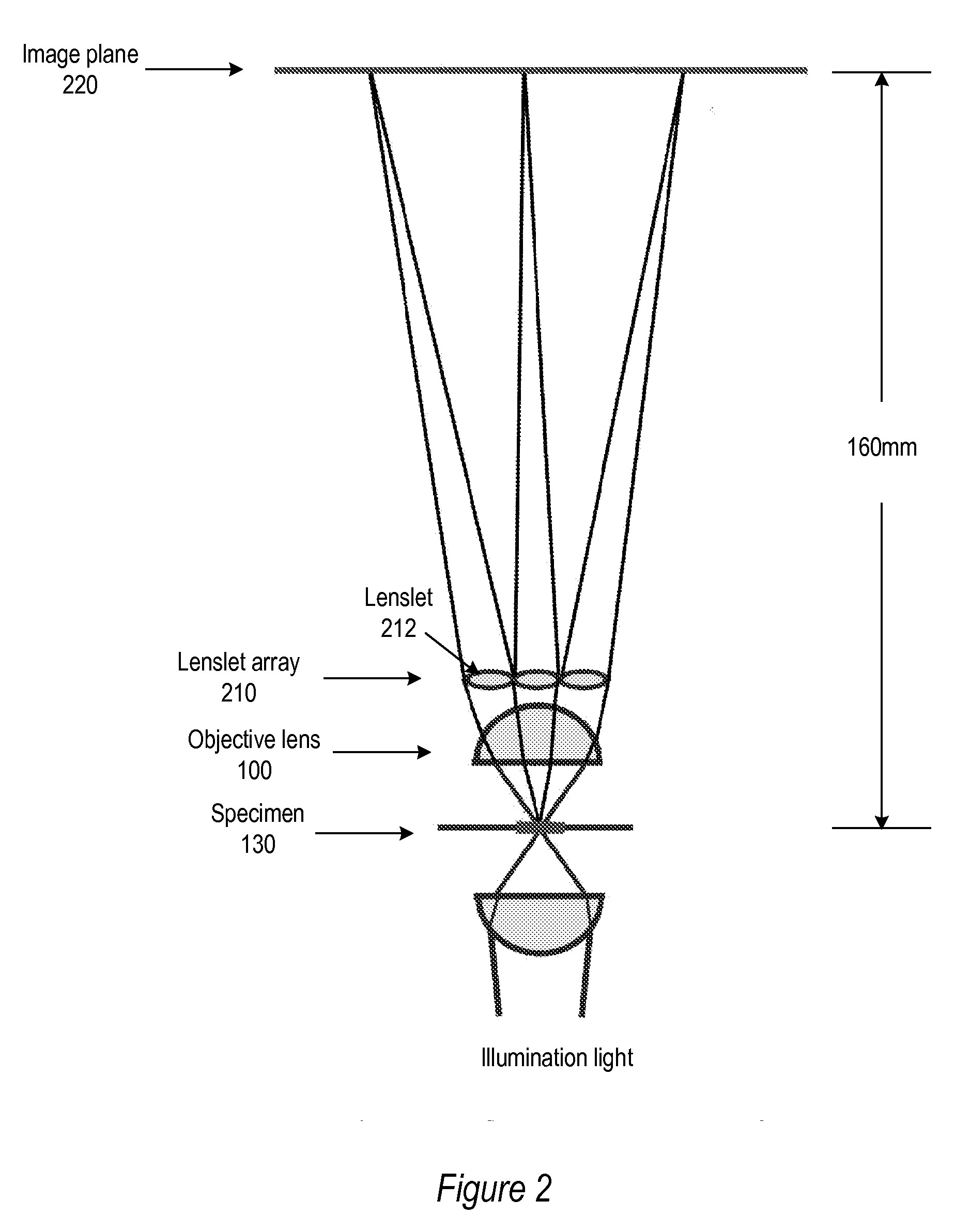
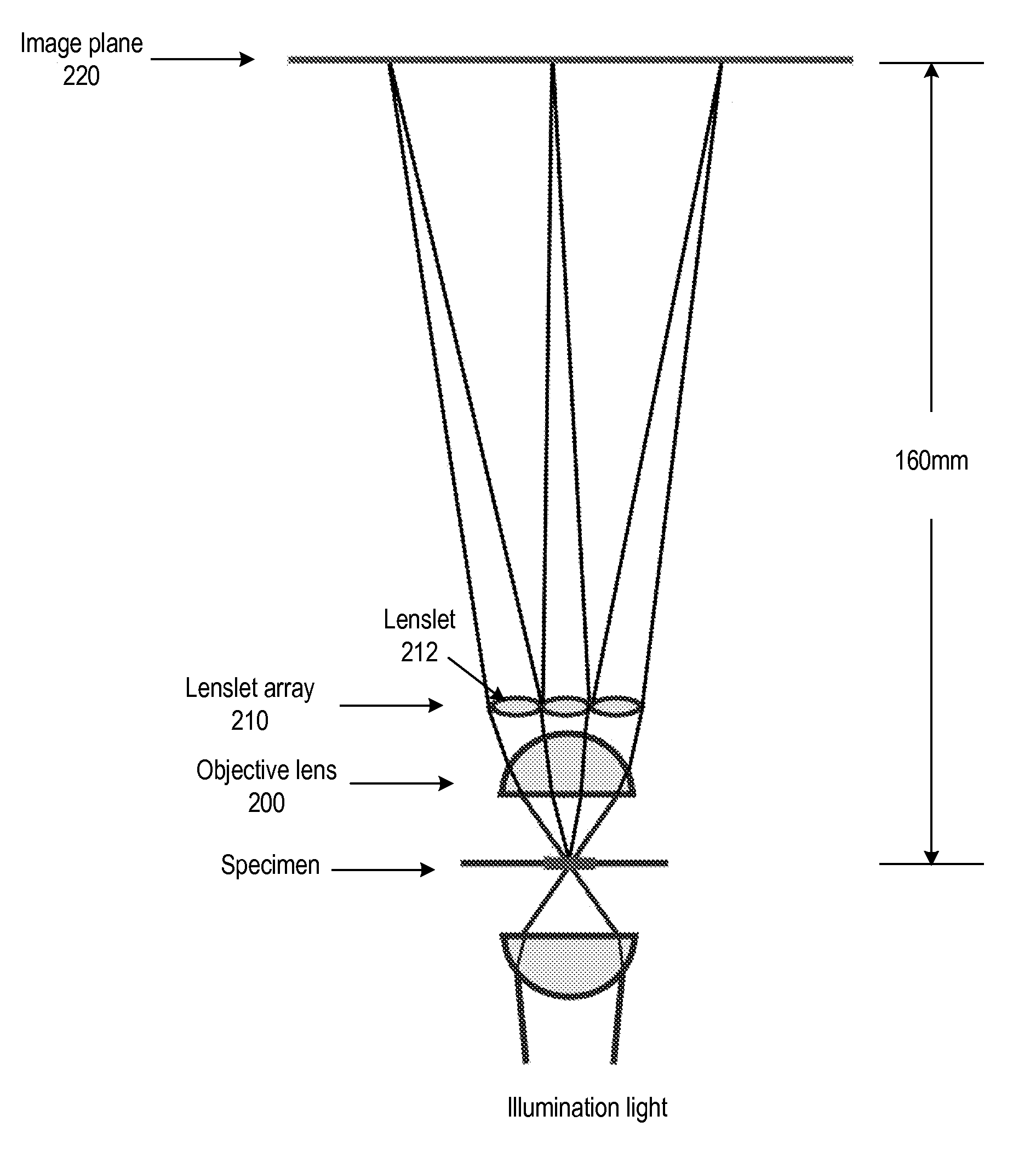
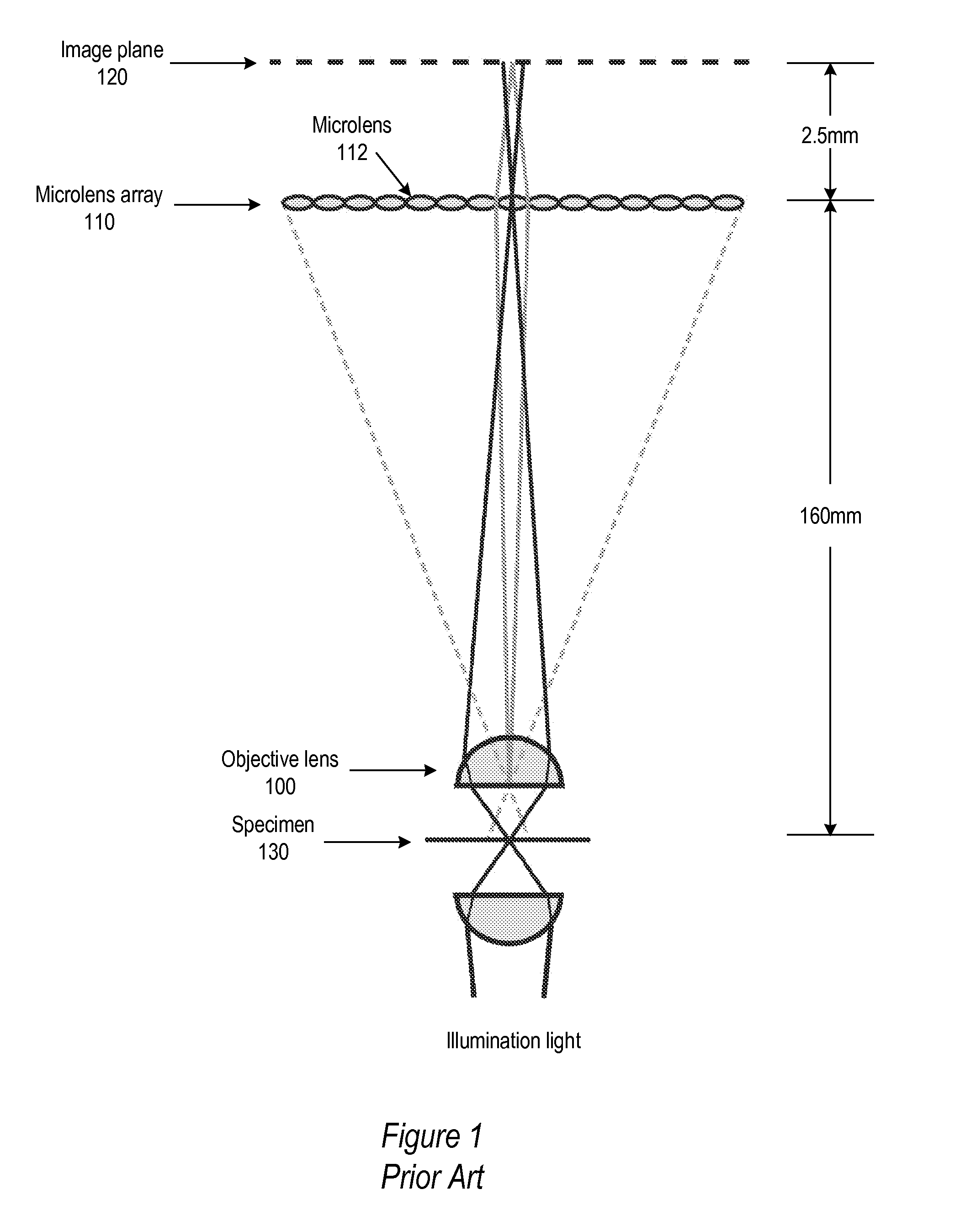
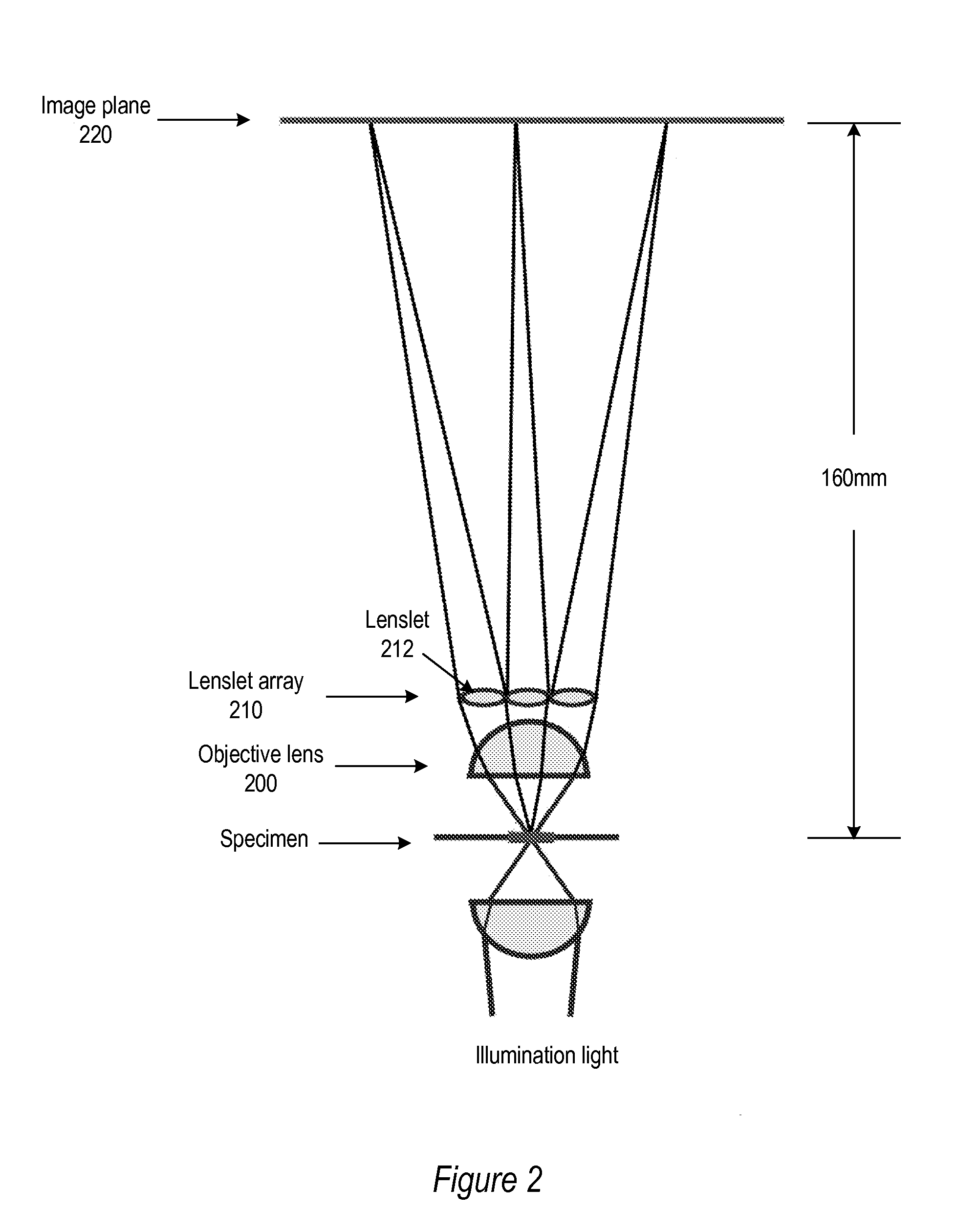
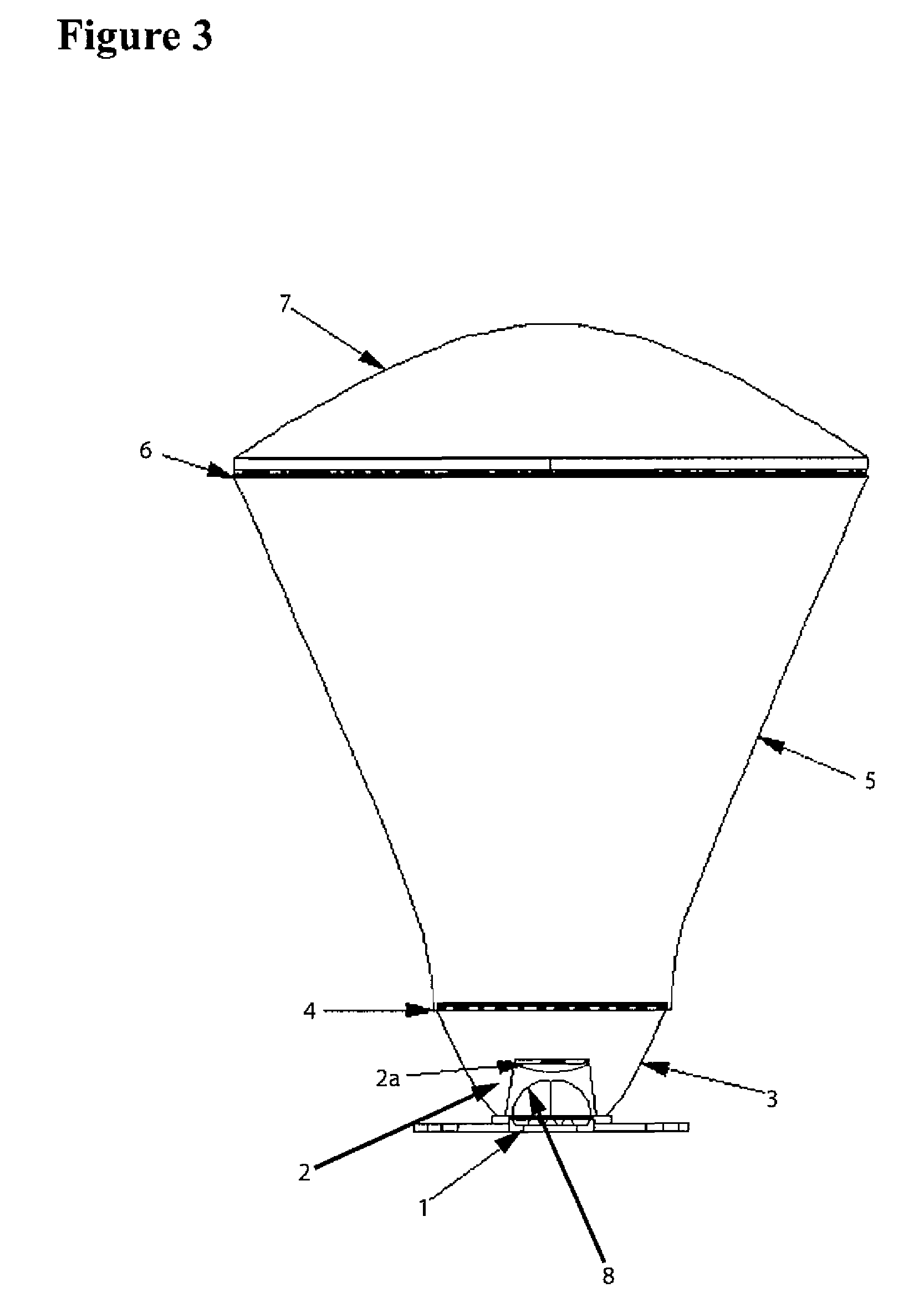
Light Field Microscope With Lenslet Array
ActiveUS20080180792A1Avoids mechanical complicationAberration correctionMicroscopesLensViewpointsImage plane
A light field microscope incorporating a lenslet array at or near the rear aperture of the objective lens. The microscope objective lens may be supplemented with an array of low power lenslets which may be located at or near the rear aperture of the objective lens, and which slightly modify the objective lens. The result is a new type of objective lens, or an addition to existing objective lenses. The lenslet array may include, for example, 9 to 100 lenslets (small, low-power lenses with long focal lengths) that generate a corresponding number of real images. Each lenslet creates a real image on the image plane, and each image corresponds to a different viewpoint or direction of the specimen. Angular information is recorded in relations or differences among the captured real images. To retrieve this angular information, one or more of various dense correspondence techniques may be used.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Retroreflection based multitouch sensor
A detection apparatus includes a multilocation sensor. The apparatus includes a sheet in communication with the sensor, which when a plurality of locations of the sheet are simultaneously activated, the sensor senses these locations, simultaneously. Alternatively, the apparatus includes a surface. The apparatus includes a sensor in communication with the surface that detects variable pressure regarding a touch on the surface. Alternatively, the apparatus includes a sensor in communication with the surface that is capable of detecting a touch on a surface and also a presence of an object near the surface but not touching the surface. Alternatively, the apparatus includes a lenslet array where the lenslets are diffractive. The apparatus includes a sensor for determining where the array is being touched. The sensor includes a first light source producing light at a first frequency, a second light source producing light at a second frequency, a camera which records images from the frequencies of light from the array, and a computer which determines where the surface is being touched from the images. Alternatively, the apparatus includes a sensor for determining where the surface is being touched, including a plurality of cameras that take images of the surface, a first array of lights positioned such that light from the first array is on a vertical line with one or more of the cameras, a second array of lights that are positioned such that light from the second array is on a horizontal line with one or more of the cameras and a computer connected to the cameras which determines where the surface is being touched from the images. Alternatively, the apparatus includes a sheet containing a plurality of elements which are at least one of refractive, diffractive, retroreflective, reflective, or focusing. The apparatus includes a sensor which determines where the sheet is touched based on light being one of refracted, diffracted, retroreflected, reflected or focused by the sheet to the sensor. Alternatively, the apparatus includes a sheet having no active components in, on, or adjoining the sheet. The apparatus includes active components separate and apart from the sheet which determine where the sheet is touched. The apparatus can include an autostereo display including a multitouch retroreflective surface and a projector. A method for detection. A software program stored on a computer 5 readable medium.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
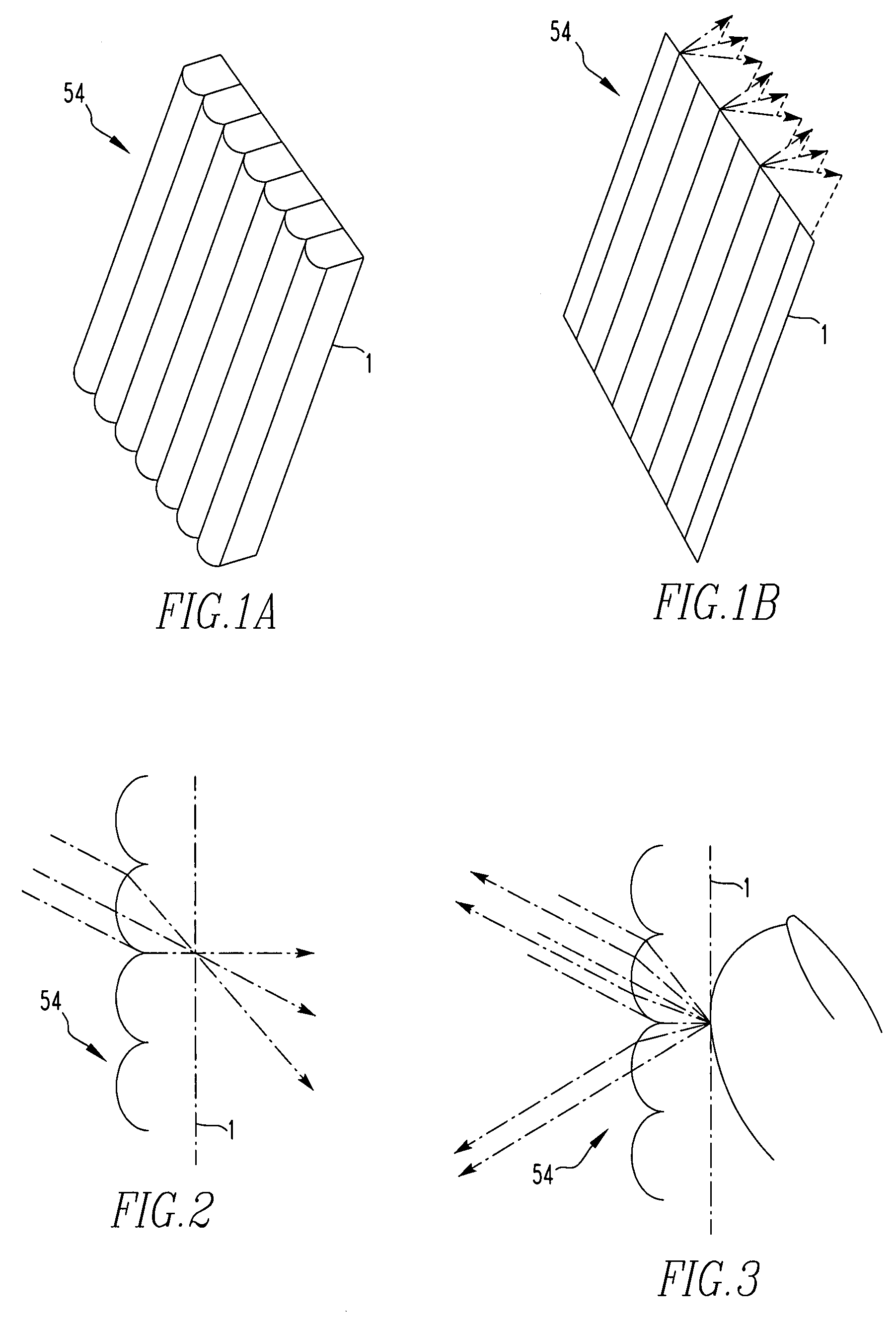
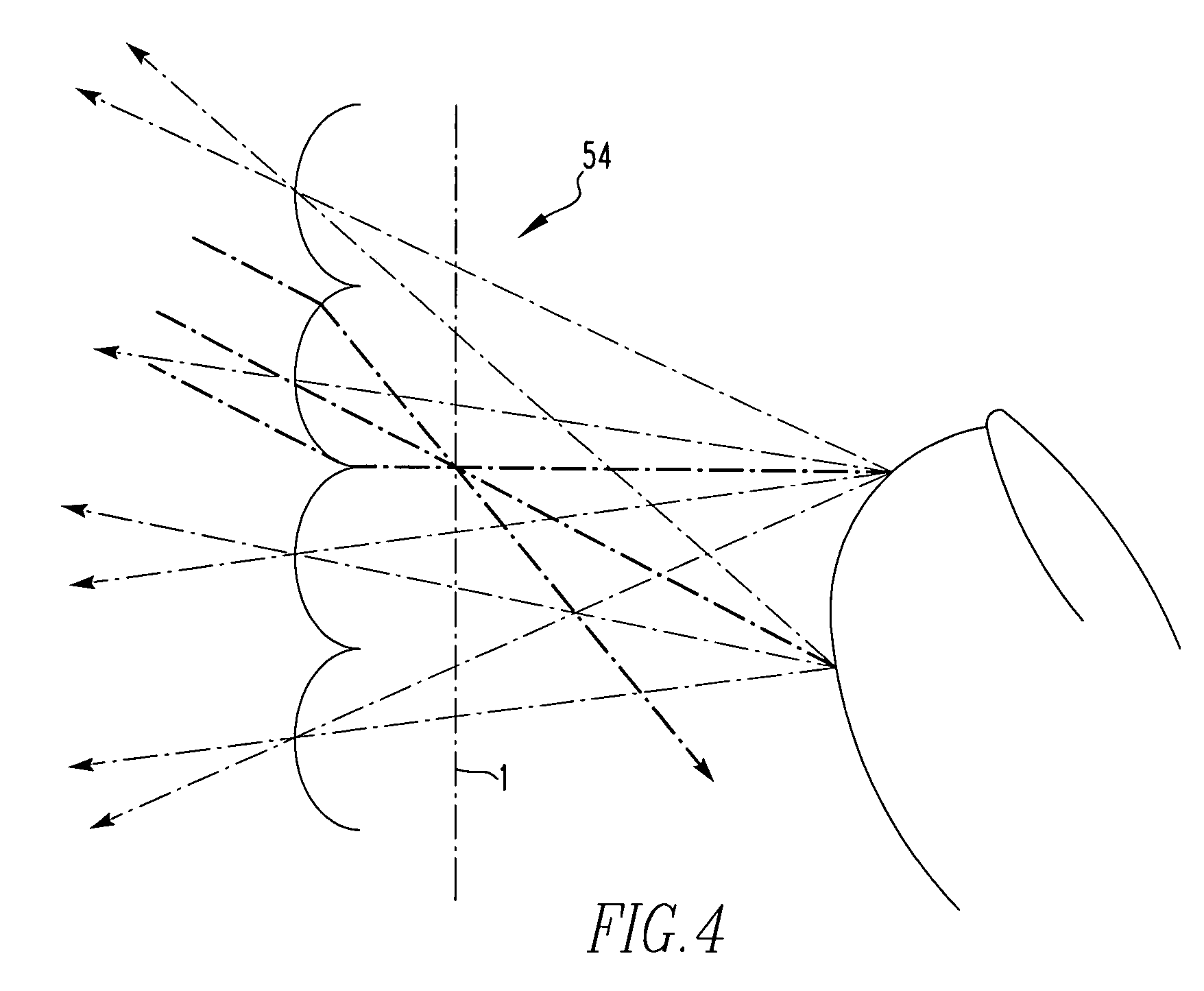
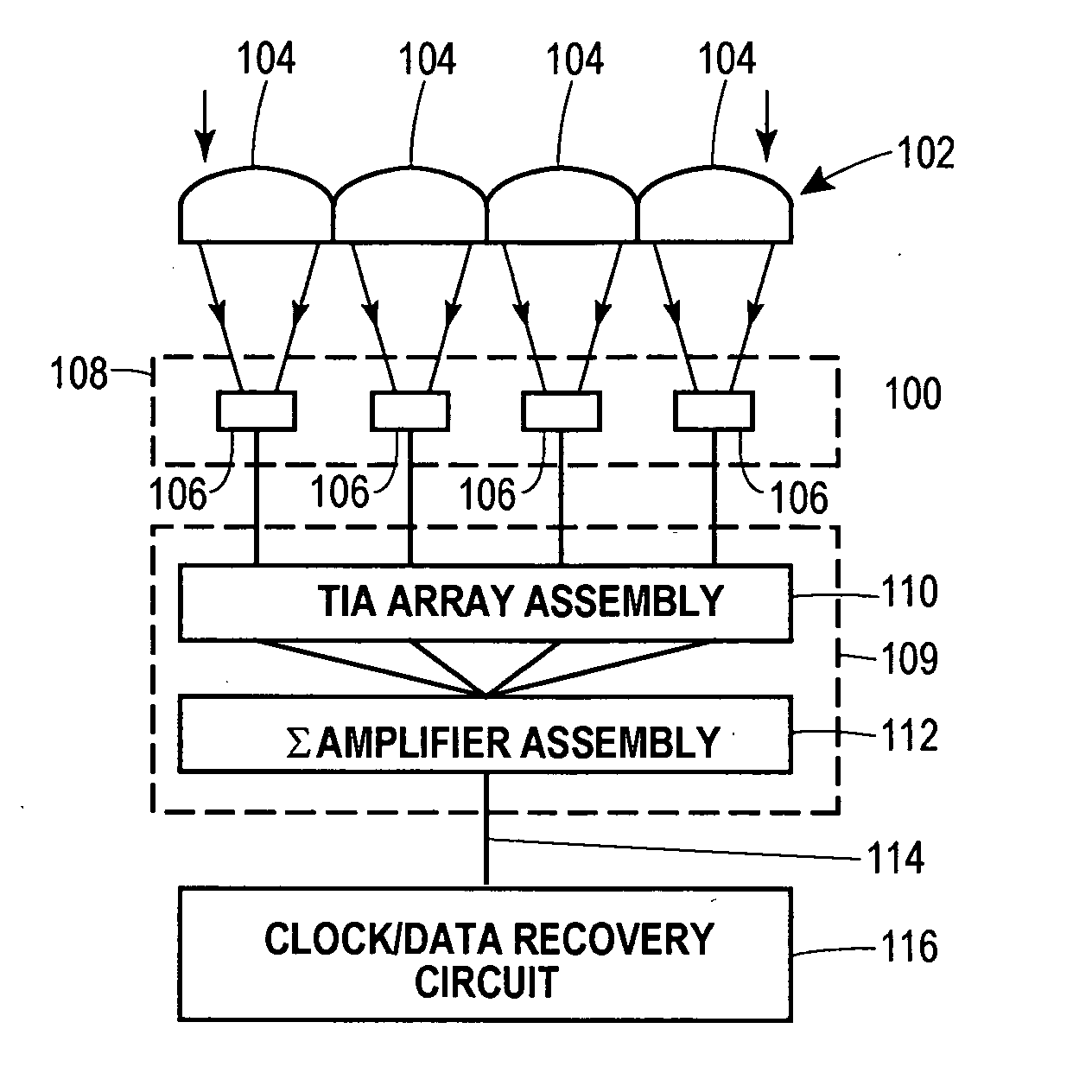
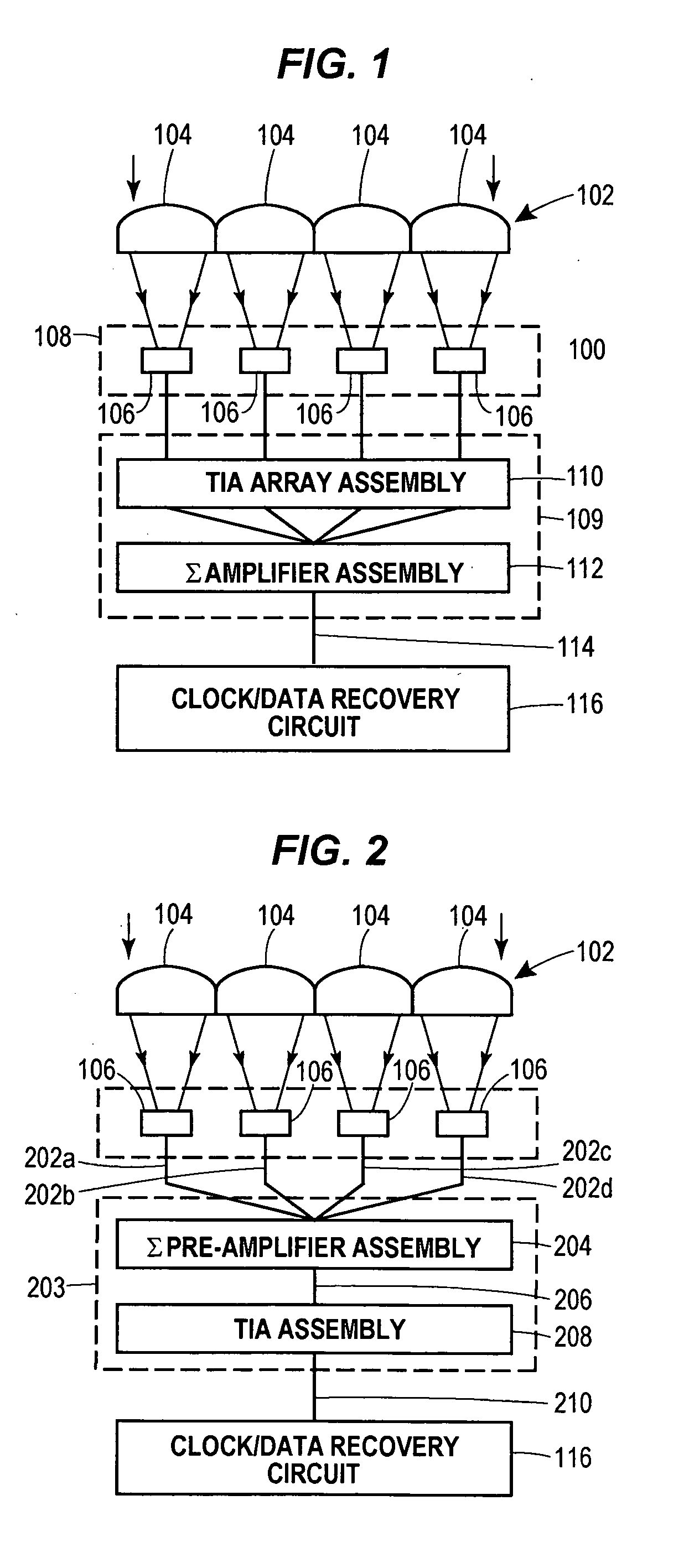
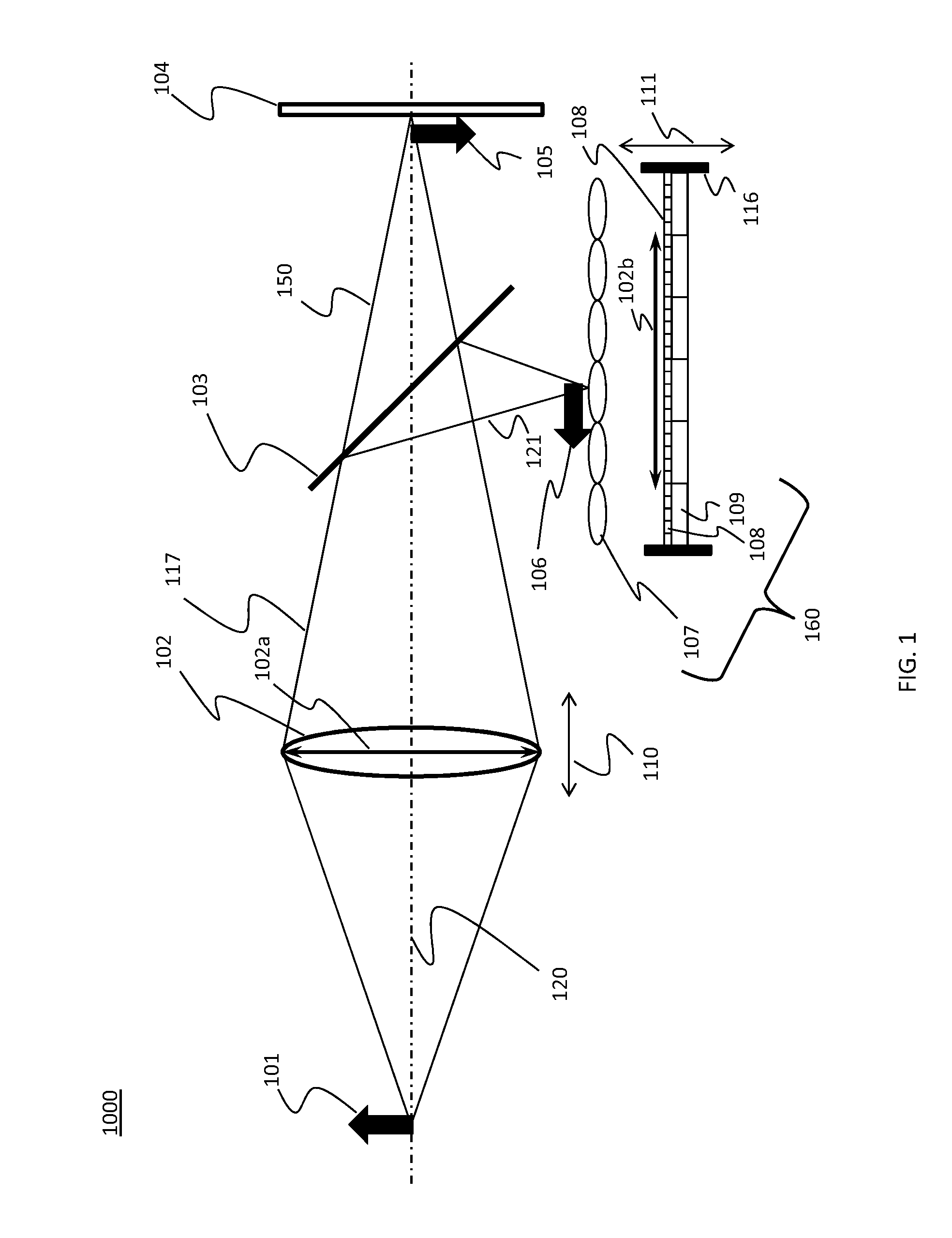
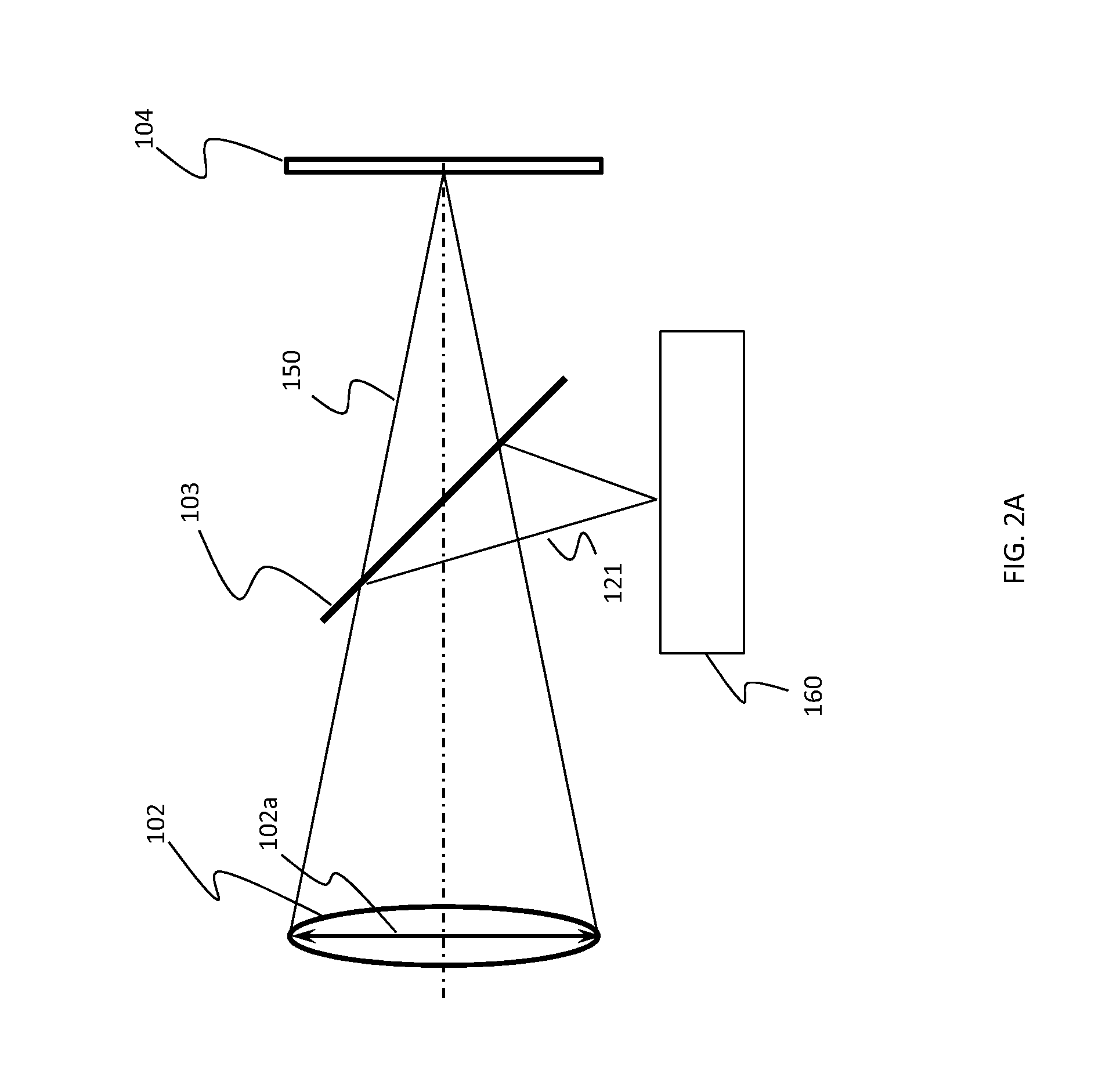
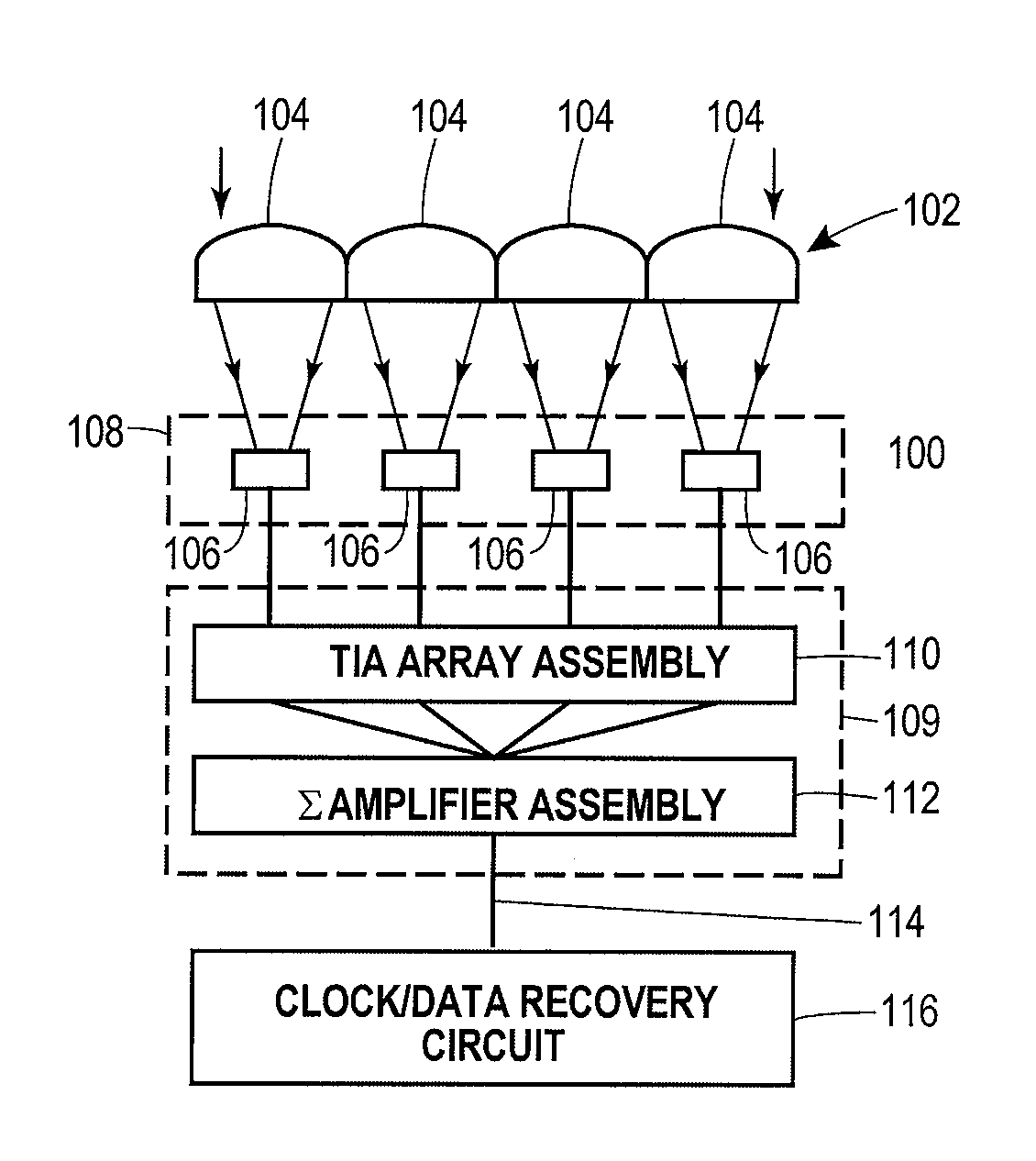
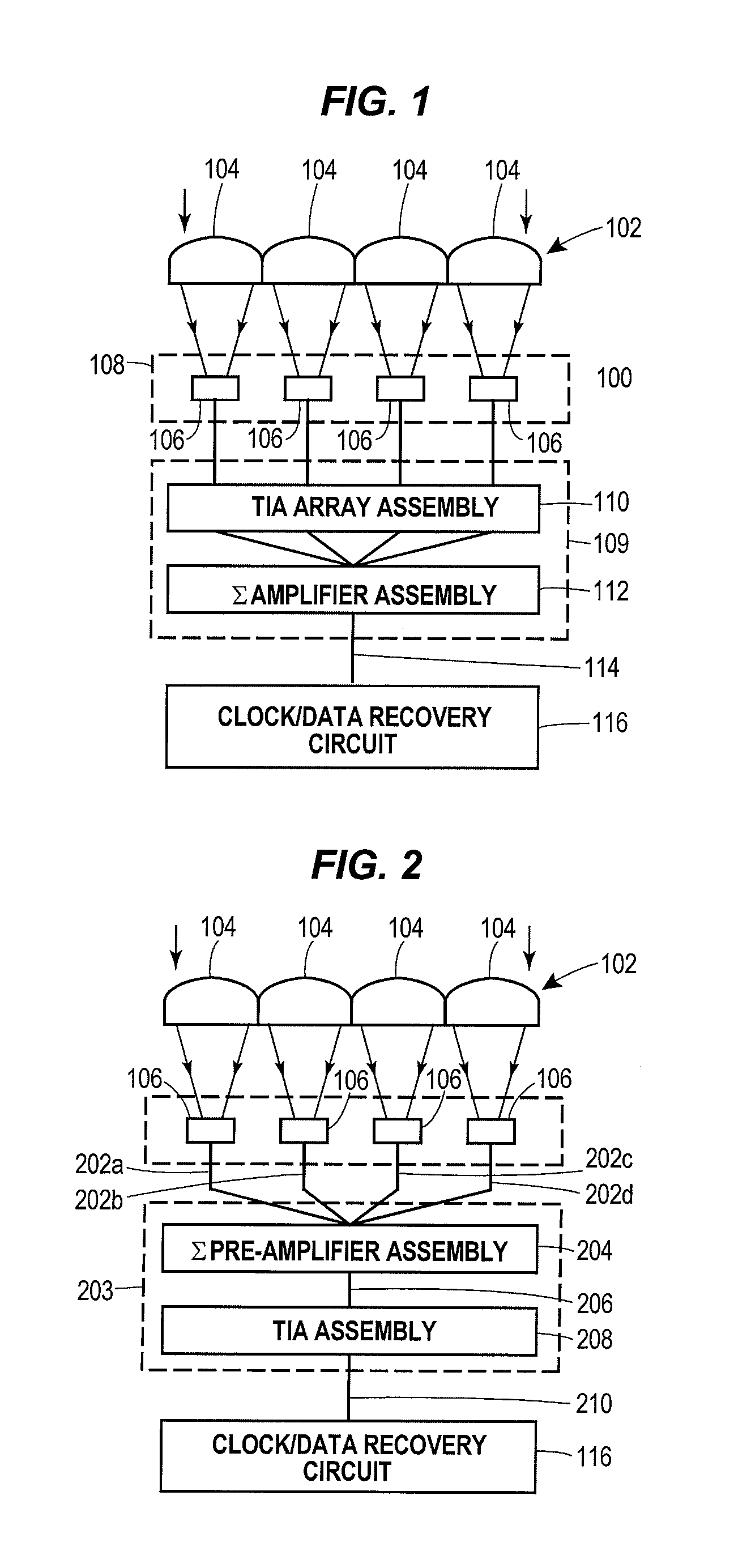
Lenslet/detector array assembly for high data rate optical communications
InactiveUS20060076473A1Reduce capacitanceHigh bandwidthSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotodetectorDetector array
An assembly is provided that may be used in high data rate optical communications, such as free-space communication systems. The assembly may include a main optical receiver element and a lenslet array or other optical element disposed near the focal plane that collects an optical signal and focuses that signal as a series of optical signal portions onto a photodetector array, formed of a series of InGaAs photodiodes, for example. The electrical signals from the photodetectors may be amplified using high bandwidth transimpedance amplifiers connected to a summing amplifier or circuit that produces a summed electrical signal. Alternatively, the electrical signals may be summed initially and then amplified via a transimpedance amplifier. The assembly may be used in remote optical communication systems, including free-space laser communication environments, to convert optical signals up to or above 1 Gbit / s or higher data rates into electrical signals at 1 Gbit / s or higher data rates.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
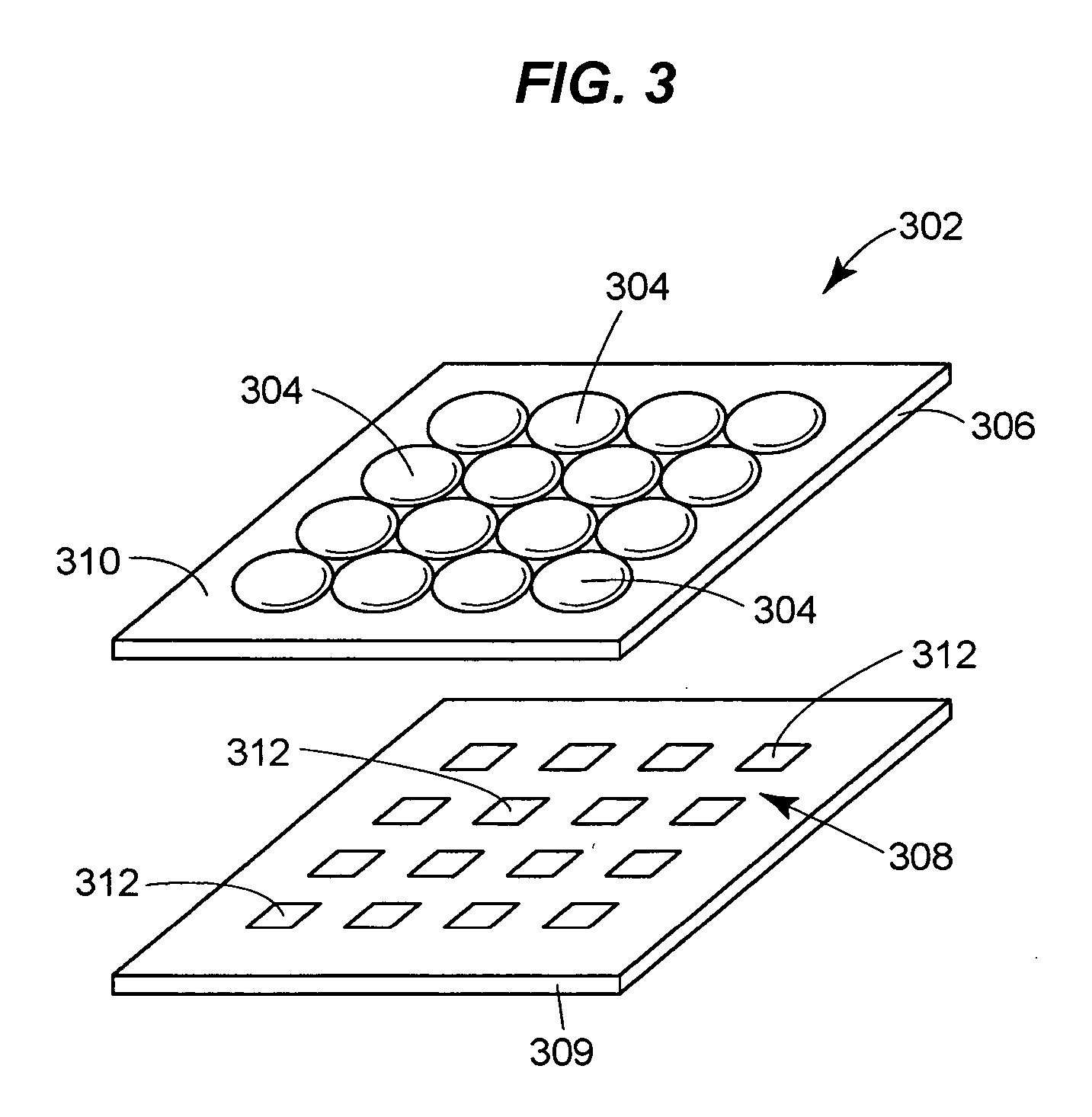
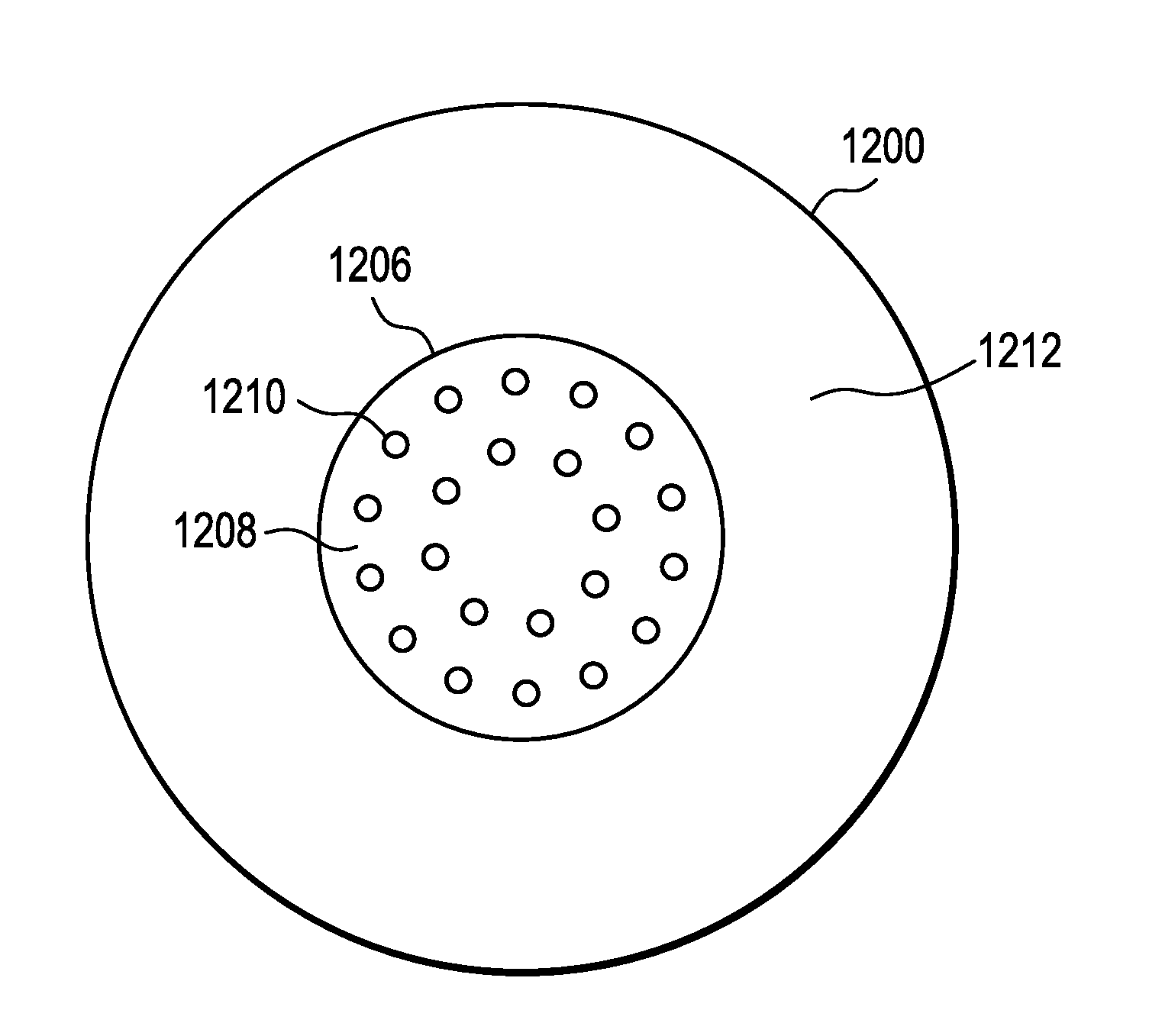
Contact lens comprising non-coaxial lenslets for preventing and/or slowing myopia progression
ActiveUS20160377884A1Good distance vision correctionCorrection acuitySpectales/gogglesOptical partsPupilRetina
Contact lenses incorporating an array of non-coaxial lenslets with add power that create non-coaxial myopic defocus within the optic zone of the lens may be utilized to prevent and / or slow myopia progression. The positive, non-coaxial lenslets cover about twenty to eighty percent of the central pupil area to deliver positive foci of light in front of the retina to slow the rate of myopia progression.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON VISION CARE INC
Microoptical compound lens
InactiveUS7286295B1Improve image qualityLarge numerical apertureTelevision system detailsColor television detailsWide fieldFiber bundle
An apposition microoptical compound lens comprises a plurality of lenslets arrayed around a segment of a hollow, three-dimensional optical shell. The lenslets collect light from an object and focus the light rays onto the concentric, curved front surface of a coherent fiber bundle. The fiber bundle transports the light rays to a planar detector, forming a plurality of sub-images that can be reconstructed as a full image. The microoptical compound lens can have a small size (millimeters), wide field of view (up to 180°), and adequate resolution for object recognition and tracking.
Owner:SANDIA
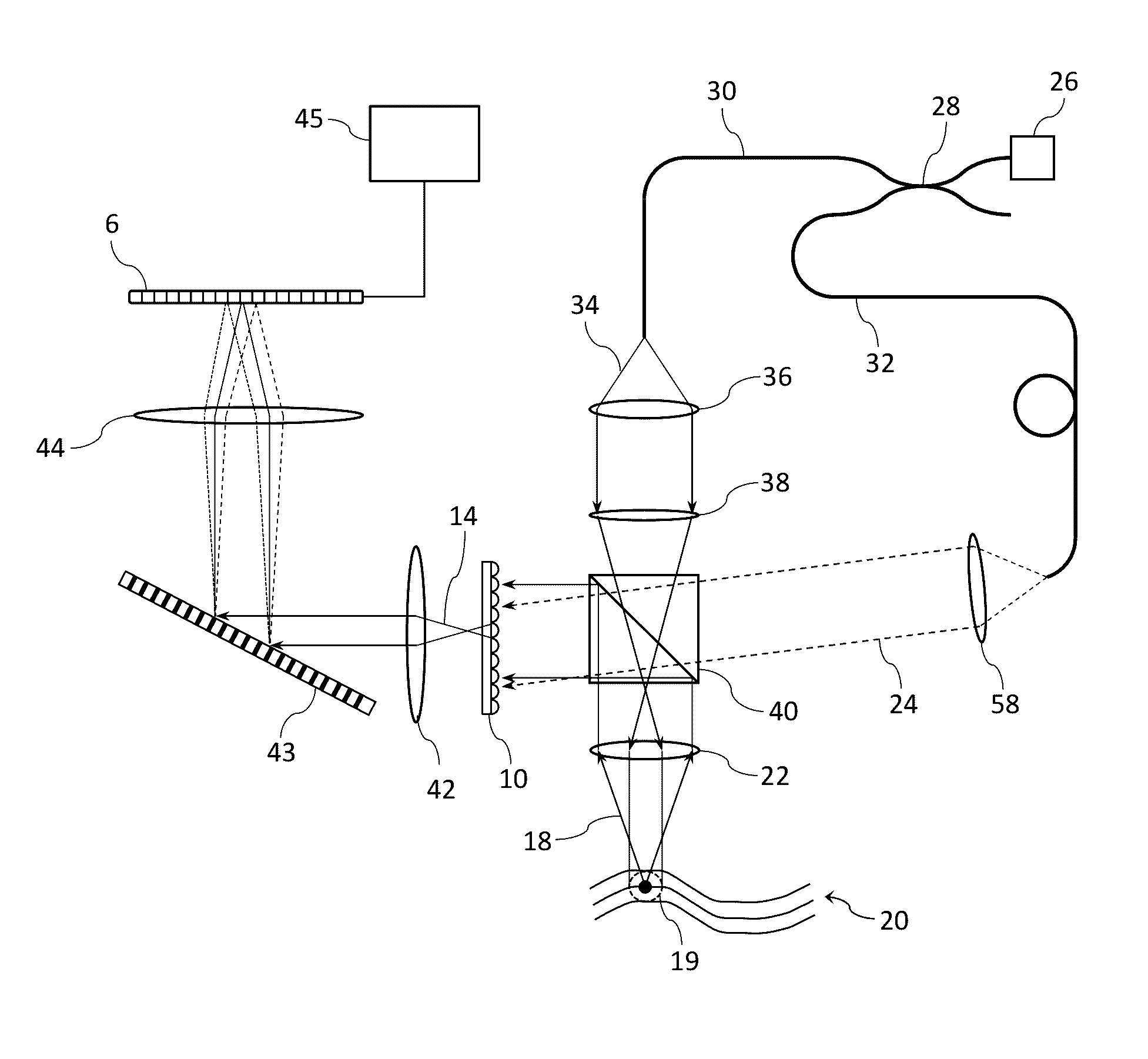
Apparatus and method for acquiring information about light-field data
An apparatus to acquire information about light-field data includes: a beam splitter configured to split light, through a lens unit which is connected to the apparatus, from an object into a first light beam and a second light beam; an image sensor configured to detect the first light beam to form an image of the object; and a light-field sensor, including a lenslet array and a detecting unit to detect the second light beam through the lenslet array, configured to acquire information about the light-field data, the lenslet array including a plurality of lenslets, wherein a first position where the detecting unit is provided is conjugate to a second position of a pupil of the lens unit.
Owner:CANON KK
Lenslet/detector array assembly for high data rate optical communications
An assembly is provided that may be used in high data rate optical communications, such as free-space communication systems. The assembly may include a main optical receiver element and a lenslet array or other optical element disposed near the focal plane that collects an optical signal and focuses that signal as a series of optical signal portions onto a photodetector array, formed of a series of InGaAs photodiodes, for example. The electrical signals from the photodetectors may be amplified using high bandwidth transimpedance amplifiers connected to a summing amplifier or circuit that produces a summed electrical signal. Alternatively, the electrical signals may be summed initially and then amplified via a transimpedance amplifier. The assembly may be used in remote optical communication systems, including free-space laser communication environments, to convert optical signals up to or above 1 Gbit / s or higher data rates into electrical signals at 1 Gbit / s or higher data rates.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Light field microscope with lenslet array
A light field microscope incorporating a lenslet array at or near the rear aperture of the objective lens. The microscope objective lens may be supplemented with an array of low power lenslets which may be located at or near the rear aperture of the objective lens, and which slightly modify the objective lens. The result is a new type of objective lens, or an addition to existing objective lenses. The lenslet array may include, for example, 9 to 100 lenslets (small, low-power lenses with long focal lengths) that generate a corresponding number of real images. Each lenslet creates a real image on the image plane, and each image corresponds to a different viewpoint or direction of the specimen. Angular information is recorded in relations or differences among the captured real images. To retrieve this angular information, one or more of various dense correspondence techniques may be used.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
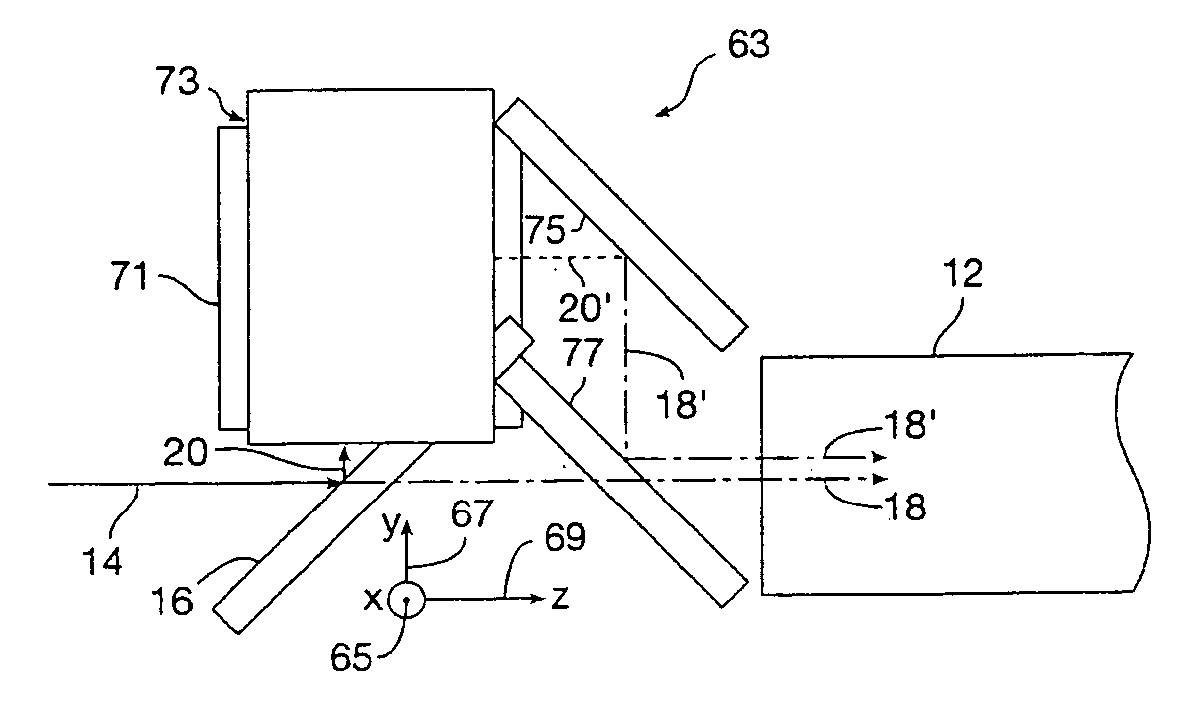
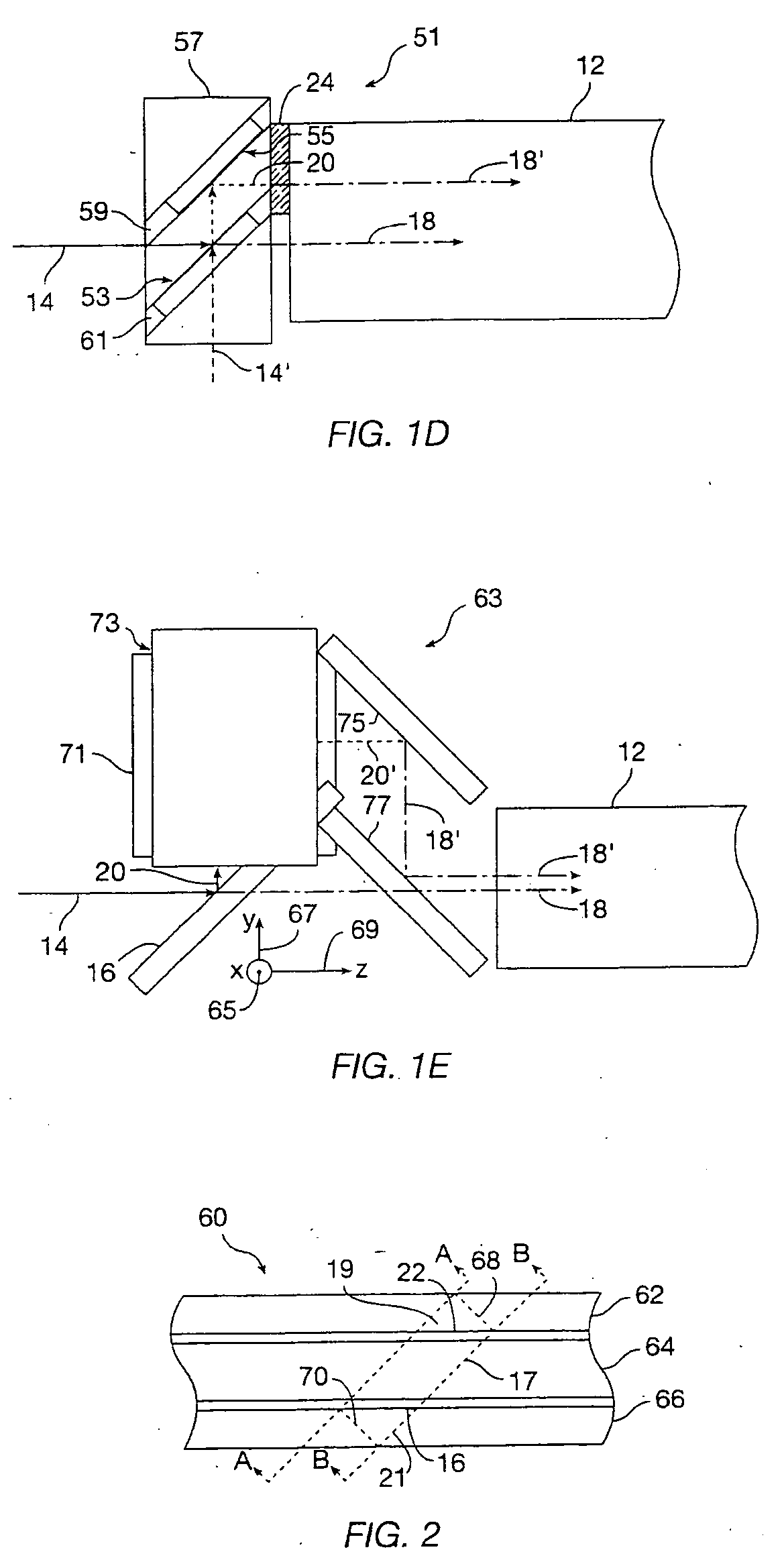
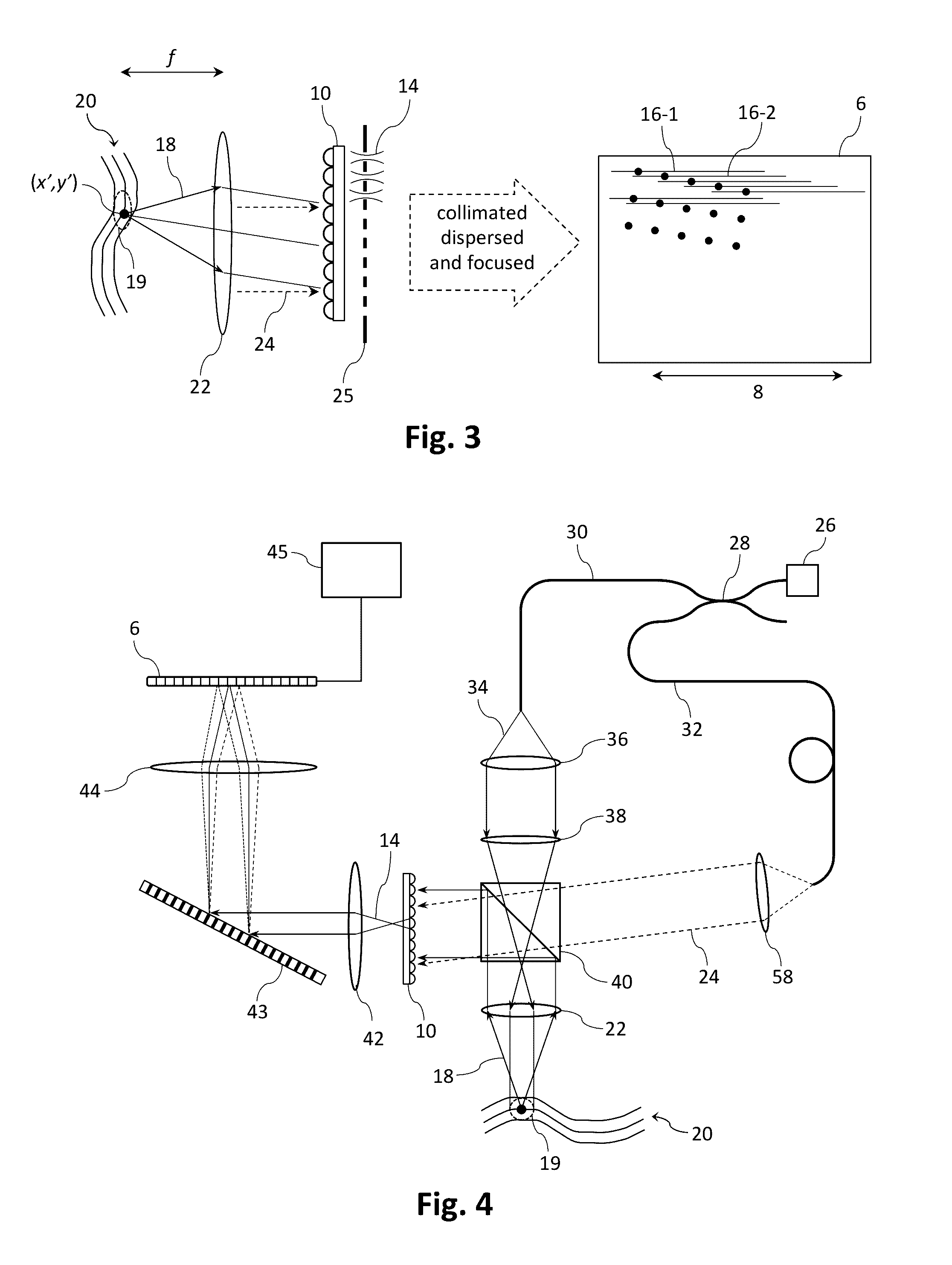
Fast computational camera based on two arrays of lenses
ActiveUS7956924B2Less expenseQuality improvementTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCamera lensRadiance
Method and apparatus for a fast (low F / number) computational camera that incorporates two arrays of lenses. The arrays include a lenslet array in front of a photosensor and an objective lens array of two or more lenses. Each lens in the objective lens array captures light from a subject. Each lenslet in the lenslet array captures light from each objective lens and separates the captured light to project microimages corresponding to the objective lenses on a region of the photosensor under the lenslet. Thus, a plurality of microimages are projected onto and captured by the photosensor. The captured microimages may be processed in accordance with the geometry of the objective lenses to align the microimages to generate a final image. One or more other algorithms may be applied to the image data in accordance with radiance information captured by the camera, such as automatic refocusing of an out-of-focus image.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
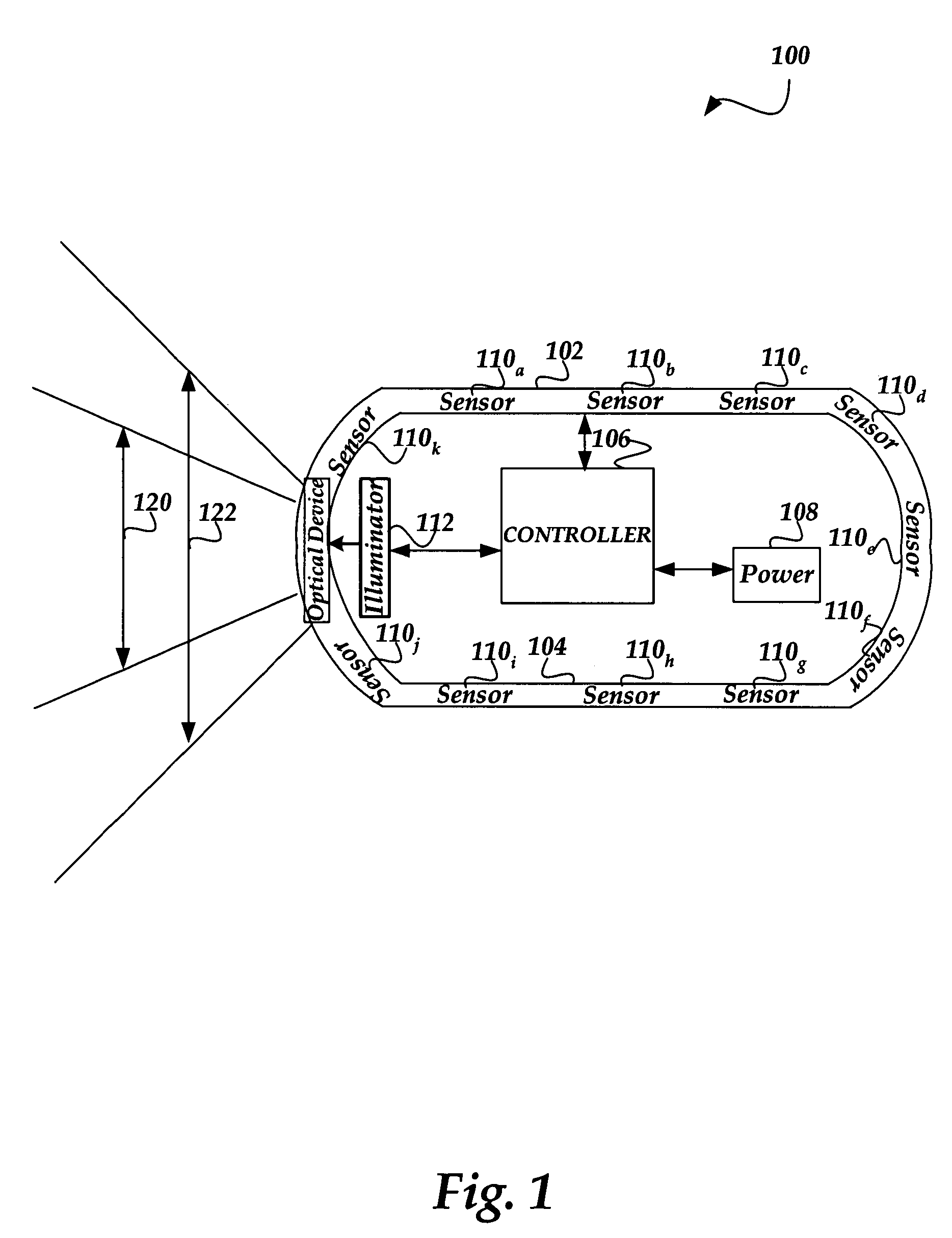
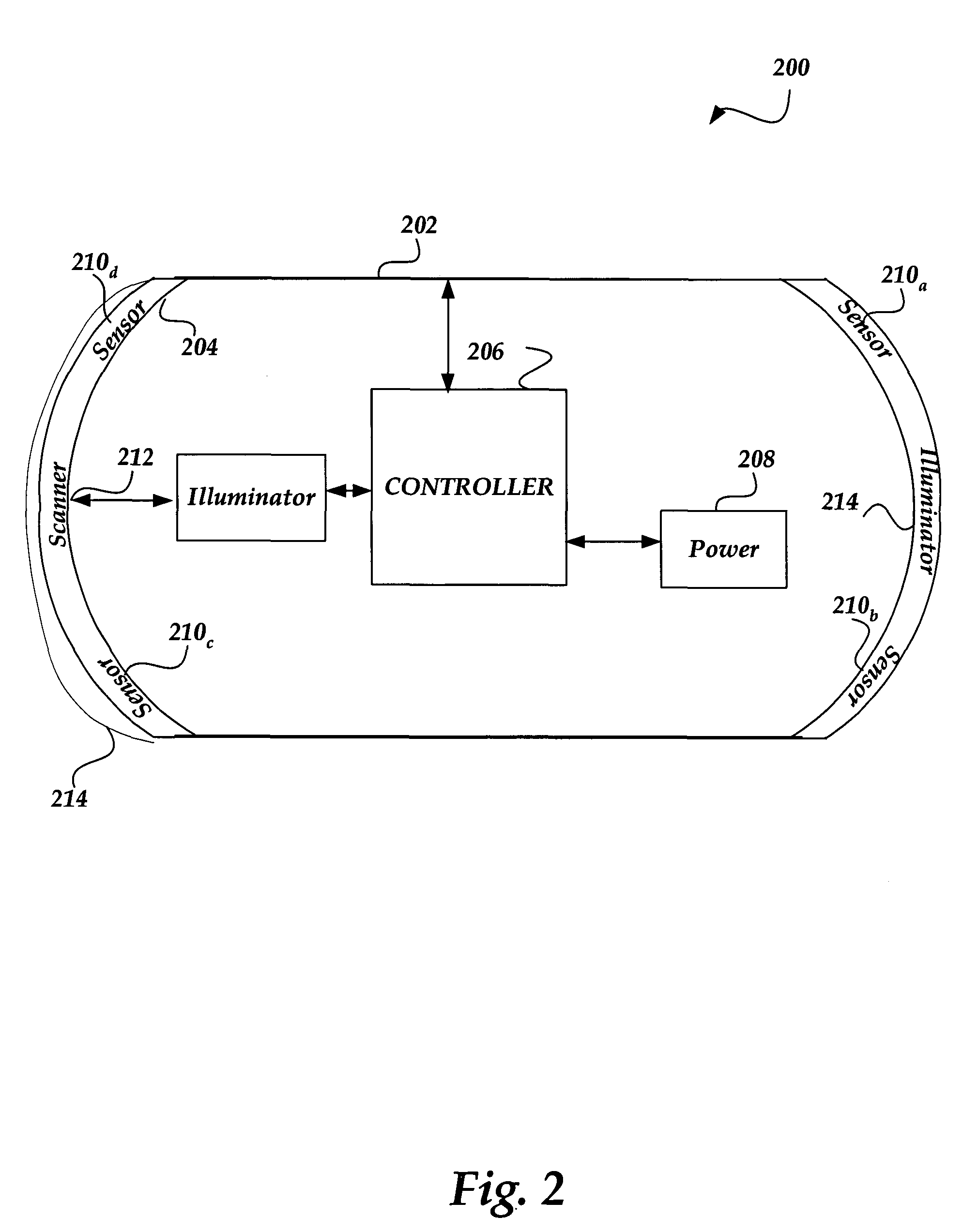
Method and system for dynamically adjusting field of view in a capsule endoscope
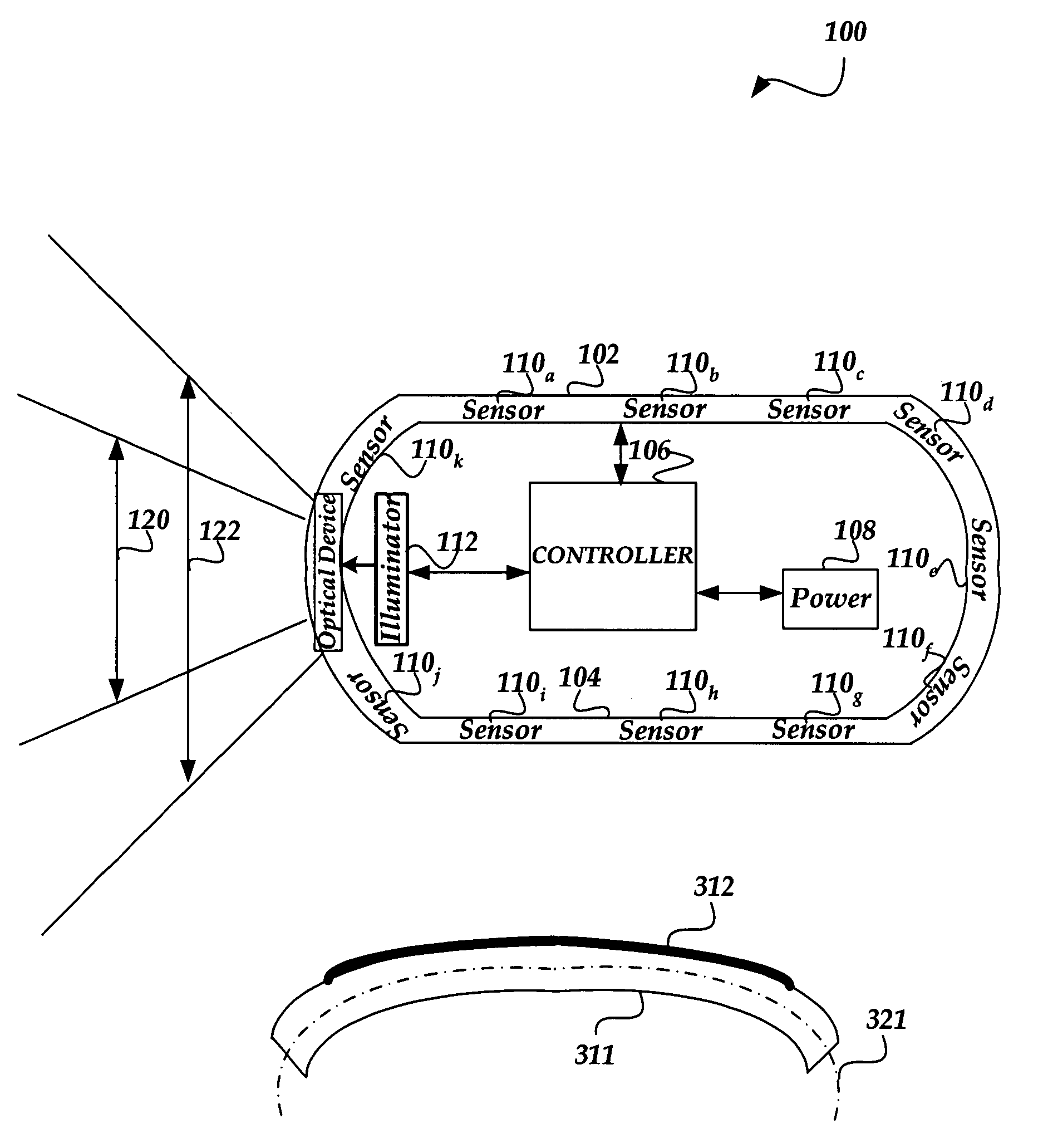
A capsule endoscope (CE) having a field of view that may be dynamically adjusted. The CE includes an illuminator that may be an optical or acoustical illuminator designed to illuminate the lining of a GI tract. A scanner, such as a MEMS scanner may be used to scan the illumination source onto the lining. The scanner may be controlled to dynamically adjust the field of view. A lenslet array may also be used to focus the illumination. The sensor is formed such that it may be curved to a contour and includes a support having sufficient flexibility such that it can be formed to the contour. The substrate includes the sensor and is formed sufficiently thin so that it can be shaped to the contour. The substrate is coupled with the support such that the combination can be formed to the contour.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
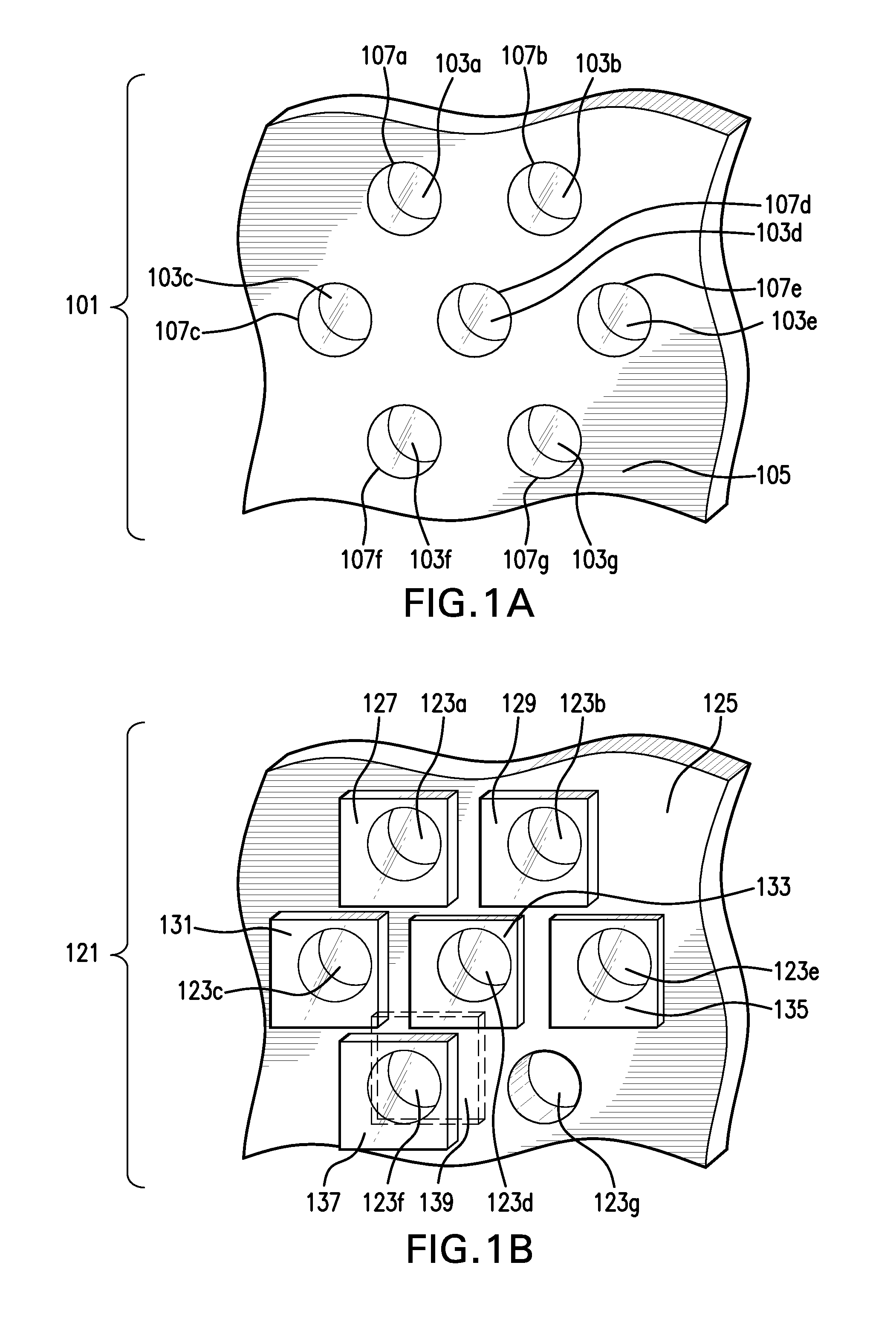
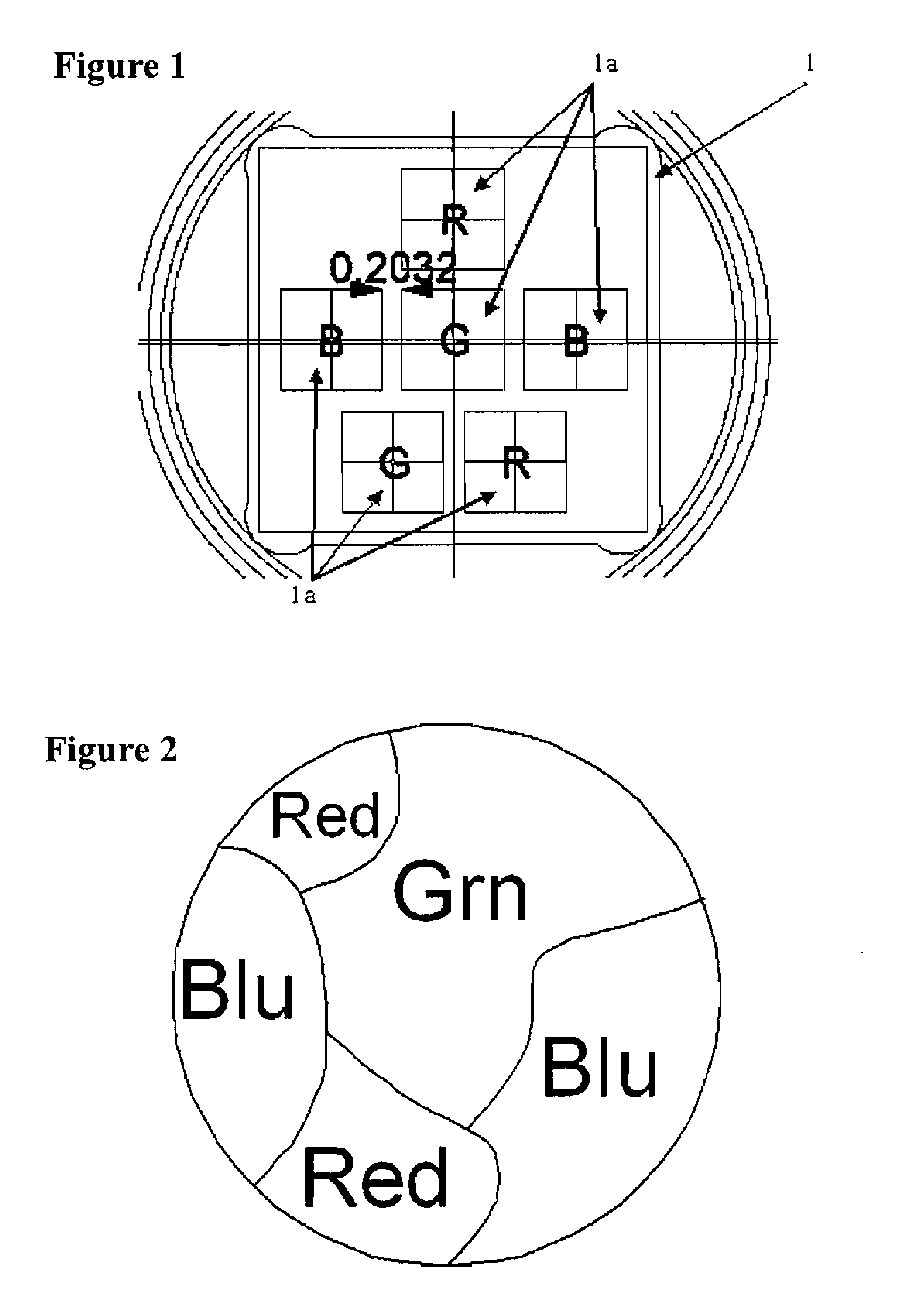
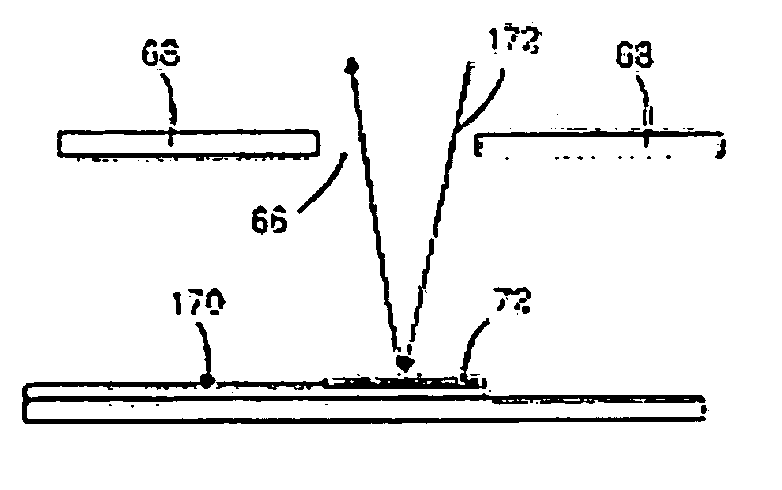
Lenslet array for retinal oximetry
The multi-aperture system of the present invention provides a retinal oximetry apparatus for determining the level of oxygen saturation in retinal vessels using a lenslet array comprising at least seven lenses for the simultaneous measurement of reflected light with at least three wavelengths and at least four polarization states. The multi-aperture system of the present invention further provides an apparatus for determining the level of oxygen saturation in retinal vessels using a lenslet array comprising at least ten lenses for the simultaneous measurement of reflected light with at least three wavelengths for oxygen measurement, at least three wavelengths for melanin content, and at least four polarization states. Methods of operating the same are also provided.
Owner:CATHOLIC UNIV OF AMERICA
Lenslet array for retinal oximetry
The multi-aperture system of the present invention provides a retinal oximetry apparatus for determining the level of oxygen saturation in retinal vessels using a lenslet array comprising at least seven lenses for the simultaneous measurement of reflected light with at least three wavelengths and at least four polarization states. The multi-aperture system of the present invention further provides an apparatus for determining the level of oxygen saturation in retinal vessels using a lenslet array comprising at least ten lenses for the simultaneous measurement of reflected light with at least three wavelengths for oxygen measurement, at least three wavelengths for melanin content, and at least four polarization states. Methods of operating the same are also provided.
Owner:CATHOLIC UNIV OF AMERICA
Polarization conversion light integrator
InactiveUS20050174641A1High acceptance angleAvoid the needPolarising elementsPicture reproducers using projection devicesBeam splitterIntegrator
A polarizing conversion system uses a polarizing beam splitter and reflector with a polarization conversion element to convert light from a lamp to a selected polarization state before providing the light to a light integrator, such as a light pipe or light tunnel. The light integrator provides homogenized polarized light to a light modulator. The polarization conversion system avoids increases efficiency compared to absorptive or simple reflective polarizers with fewer components than polarization conversion systems using patterned retarder plates and lenslet arrays. In one embodiment, the conversion elements are held to avoid adhesive or other bonds in the optical path. In other embodiments, high-temperature optical adhesive or optical contact bonding is used to assemble optical components for high-temperature operation. In a particular embodiment, a single-crystal quartz retarder plate is thermally matched to glass components in the polarization conversion system.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
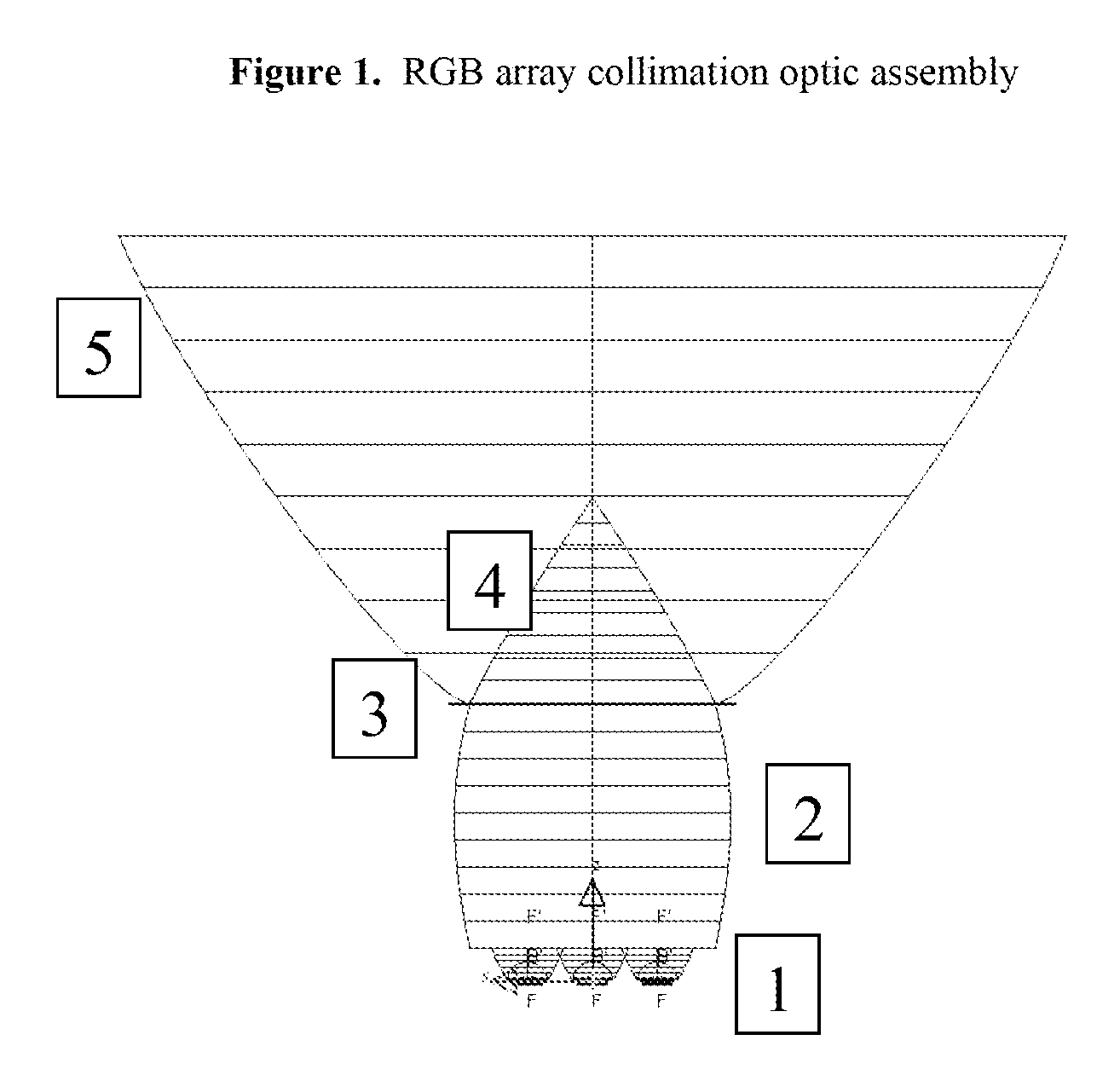
Multi-primary LED collimation optic assemblies
ActiveUS20090168414A1High strengthImprove uniformityMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourceFree formStigmatism
The present invention relates to an optical assembly which improves color uniformity and improved collimation of light produced by multiple LED light sources in a light engine. The optical assembly is specifically tailored to match the placement of the solid-state emitters making up the light engine or light producing element. Specifically, a shaped free-form spline patch inner collimation lens having an optimized cross-sectional shape and micro-ridges is used to disperse light; multi-lobe TIR collimation lens having an optimized cross-sectional shape and micro-ridges is used to disperse and redistribute phase as well as provide collimation; primary mixing lenslet array having an optimized surface is used to disperse light from the light emitter; a spline profile reflector further mixes and collimates the light; a secondary lenslet array further mixes the light; and a secondary collimation lens further collimates the light.
Owner:LIGHTING SCI GROUP
High resolution 3-d spectral domain optical imaging apparatus and method
ActiveUS20160345820A1Improved high resolution optical imageProvide usageReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis by optical meansSensor arrayDepth of field
Methods and apparatus are presented for obtaining high-resolution 3-D images of a sample over a range of wavelengths, optionally with polarisation-sensitive detection. In preferred embodiments a spectral domain OCT apparatus is used to sample the complex field of light reflected or scattered from a sample, providing full range imaging. In certain embodiments structured illumination is utilised to provide enhanced lateral resolution. In certain embodiments the resolution or depth of field of images is enhanced by digital refocusing or digital correction of aberrations in the sample. Individual sample volumes are imaged using single shot techniques, and larger volumes can be imaged by stitching together images of adjacent volumes. In preferred embodiments a 2-D lenslet array is used to sample the reflected or scattered light in the Fourier plane or the image plane, with the lenslet array suitably angled with respect to the dispersive axis of a wavelength dispersive element such that the resulting beamlets are dispersed onto unique sets of pixels of a 2-D sensor array.
Owner:CYLITE
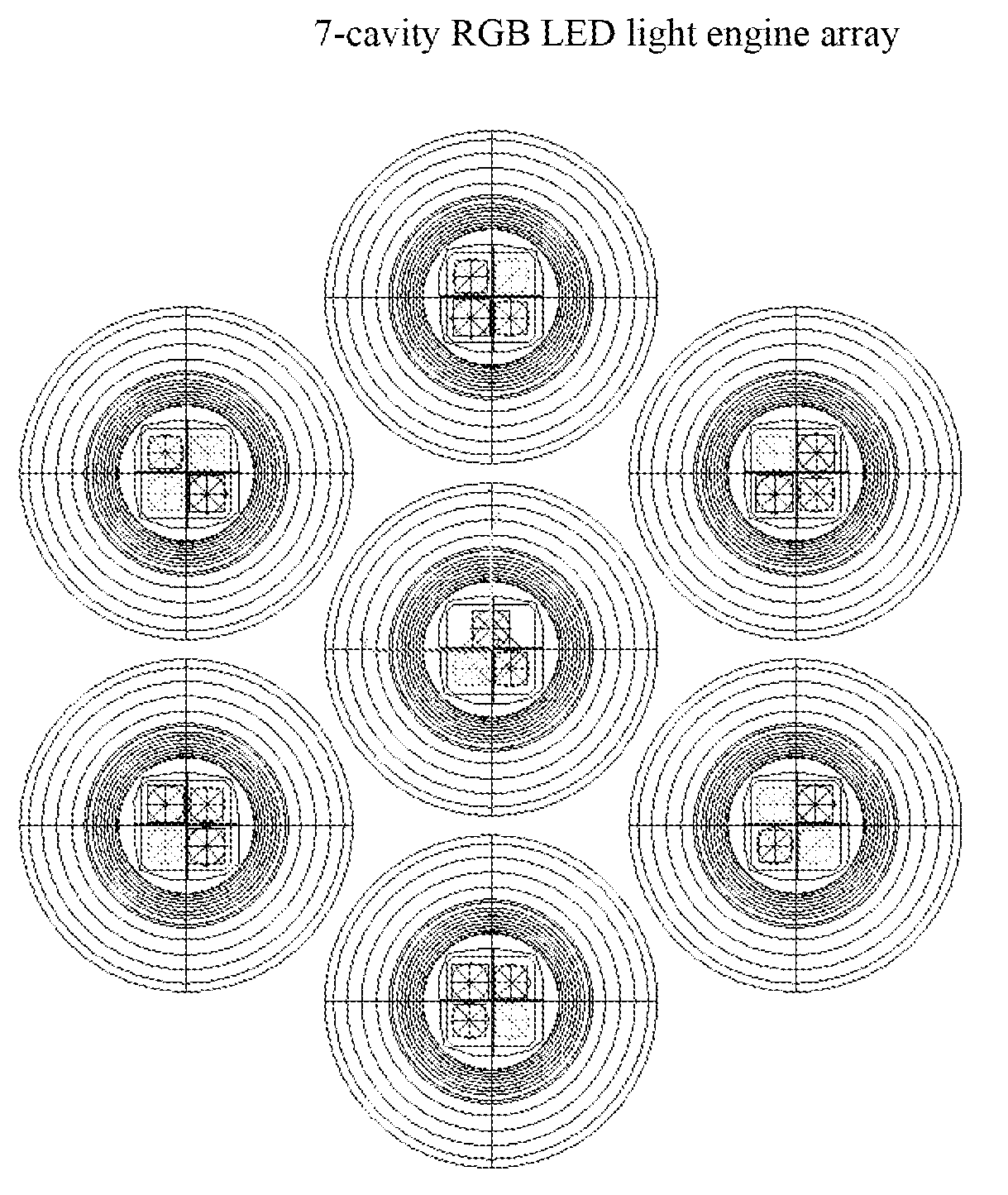
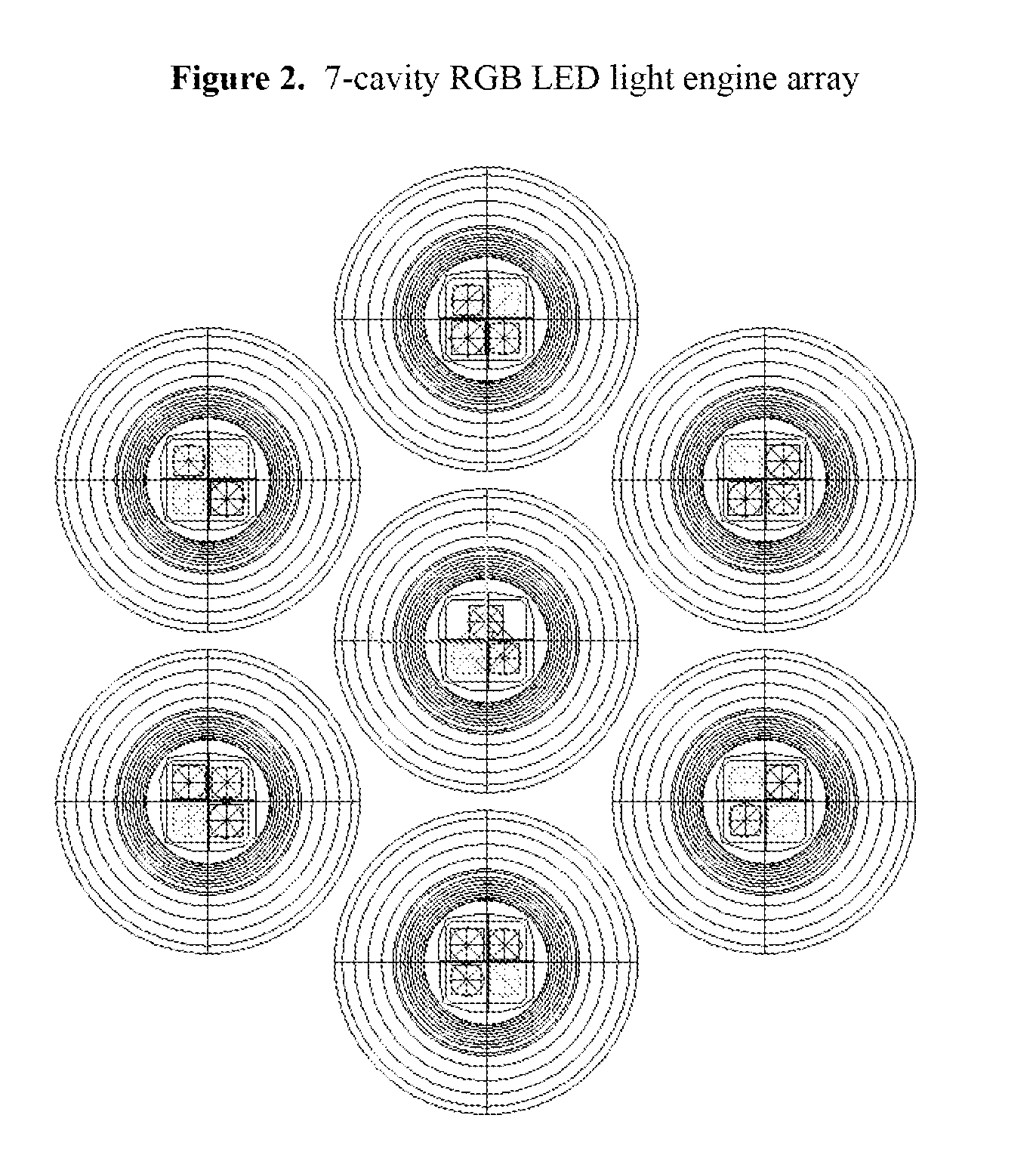
Multi-cavity LED array RGB collimation optic
ActiveUS20100238645A1Light colorImprove color uniformityNon-electric lightingPoint-like light sourceLed arrayLenslet array
This invention relates to optical devices. More specifically, the present invention relates to a collimated optical light source assembly that produces a uniform white light. Specifically, light from a multi-cavity RGB LED array is dispersed in a reflecting cavity having a Lambertian texture on the interior surface. The light is then emitted though a lenslet array and a cone lens which together further disperses the light emitted by the individual LEDs. The dispersed light is then collimated by a reflector.
Owner:LIGHTING SCI GROUP +1
Reflective microelectrical mechanical structure (MEMS) optical modulator and optical display system
InactiveUS20050248827A1Eliminating light attenuation and expense of lightIncrease contrastOptical elementsActuatorMicro lens array
A MEMS optical display system includes an illumination source for providing illumination light, a collimating lens for receiving the illumination light and forming from it collimated illumination light, and a microlens array having an array of lenslets for receiving the illumination light from the collimating lens. The converging microlens array directs the illumination light through an array of pixel apertures in an aperture plate to a microelectrical mechanical reflector array positioned opposite the aperture plate. The microelectrical mechanical reflector array includes an array of microelectrical mechanical actuators that support reflectors in alignment with the array of pixel apertures and selectively orients the reflectors to direct the illumination light back through the pixel apertures (to form part of a display image) or against the aperture plate (to be blocked). The illumination light passing back through the pixel apertures passes through the microlens array and a beamsplitter to a display screen.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
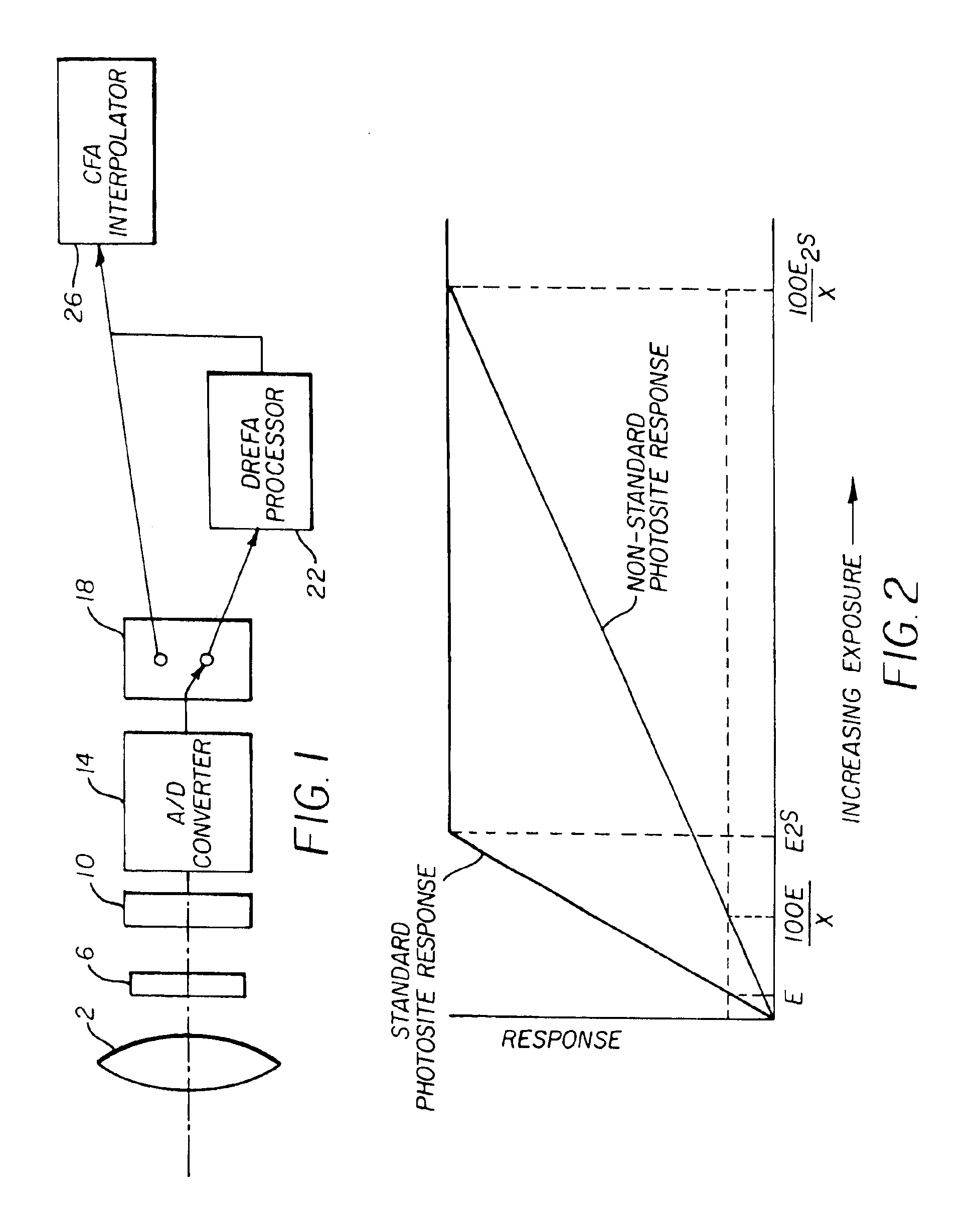
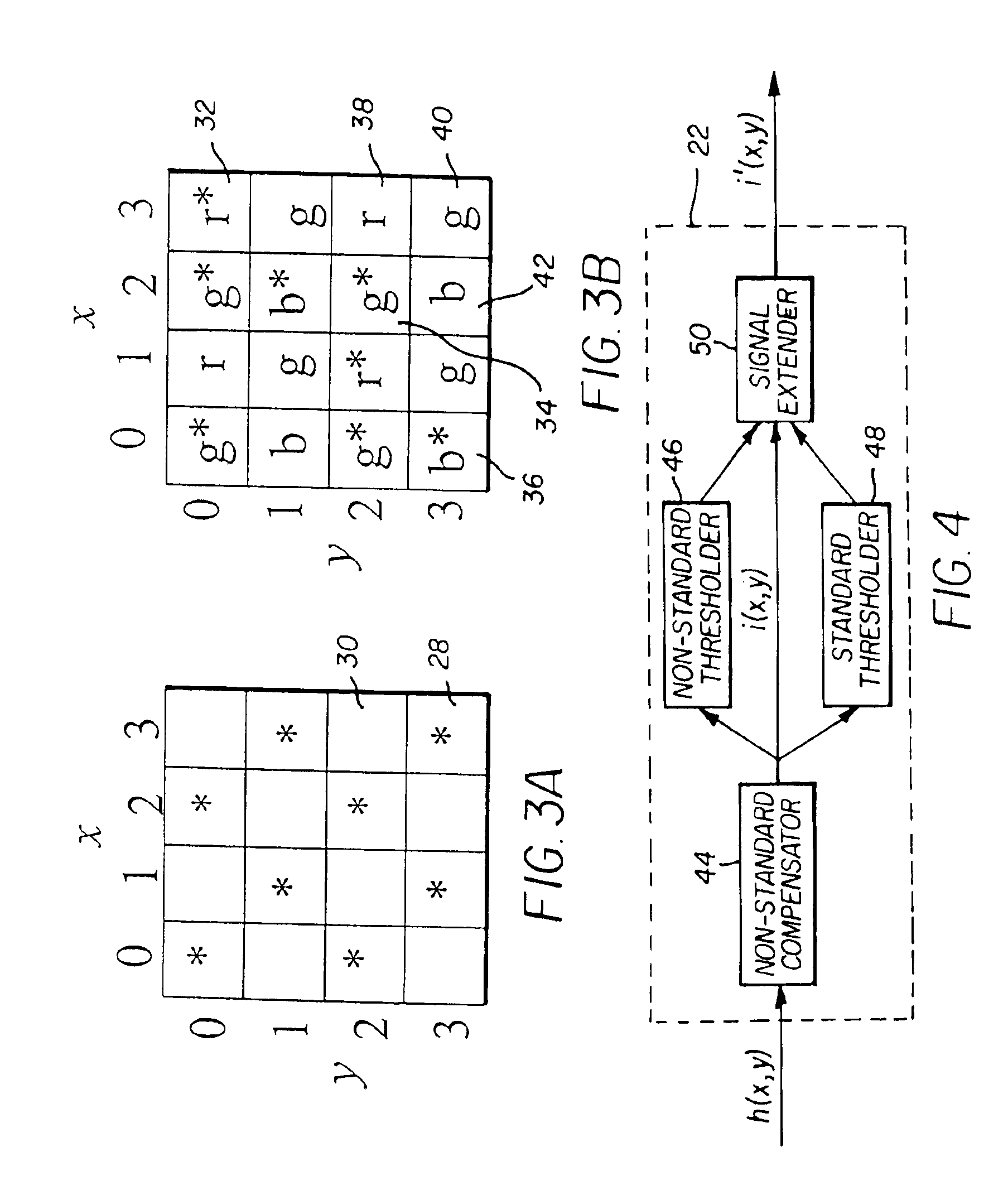
Method and apparatus to extend the effective dynamic range of an image sensing device
InactiveUS6909461B1Slow responseImprove dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLight spotEngineering
An image capture system generates an extended effective dynamic range from a signal provided by an image sensor by utilizing an image sensing device having standard photosites with a predetermined response to a light exposure and non-standard photosites with a slower response to the same light exposure. An optical section exposes the image sensing device to image light, thereby causing the image sensing device to generate an image signal and a processing section expands the response of the standard photosites to increased light exposures by utilizing the image signals from neighboring non-standard photosites. Furthermore, the processing section may expand the response of the non-standard photosites to decreased light exposures by utilizing the image signals from neighboring standard photosites. The differential response of the image sensor is provided by a structural element, such as an array of lenslets, a mask or a neutral density filter, overlying the photosites and providing the standard photosites with a predetermined standard response to a light exposure and the non-standard photosites with a slower response to the same light exposure.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Stepped light collection and concentration system, components thereof, and methods
A light guide includes a light guide layer having a transversely oriented side-end surface that forms a primary output aperture (exit) for light traveling in a forward propagation direction out of the end surface of the light guide (for, e.g., CPV applications) and, which forms a primary input aperture (entrance) for light traveling in a rearward propagation direction into the end surface of the light guide (for, e.g., illuminator applications), and a first plurality of light injection elements stepped (staggered) in a forward light propagation direction in a first plane along lines parallel to the side-end surface or clocked (tilted) about a y-axis in a z-axis-light propagation direction in a respective first plane, wherein the light injection elements are disposed along parallel lines normal to the side-end surface. The light guide component may further comprise at least a second plurality of light injection elements stepped in at least second plane. A light guide system includes a component light guide, a lenslet array disposed adjacent a top surface of the light guide, and a light-transmitting, TIR medium layer disposed immediately adjacent at least one of the top and bottom surfaces of the light guide.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER +1
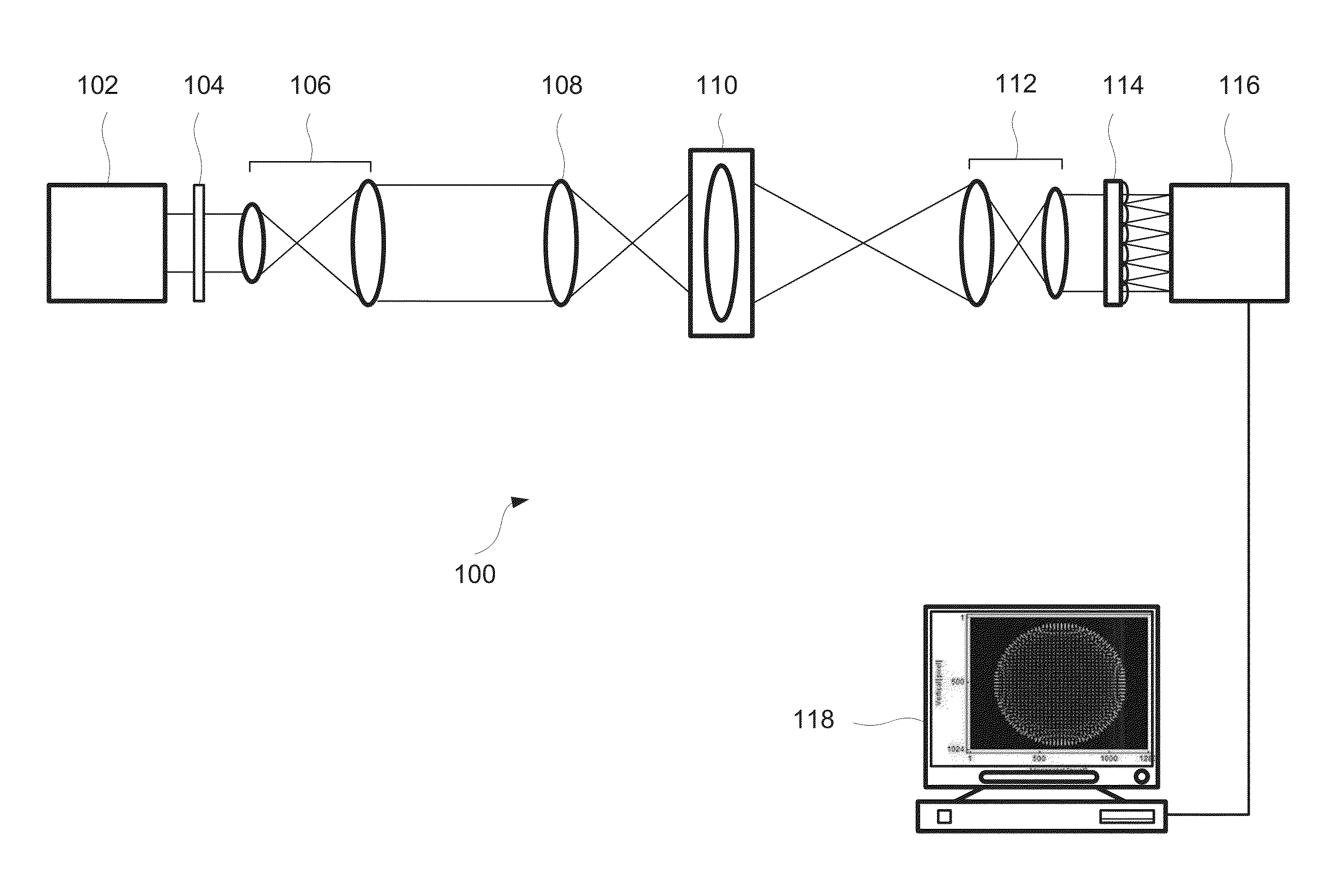
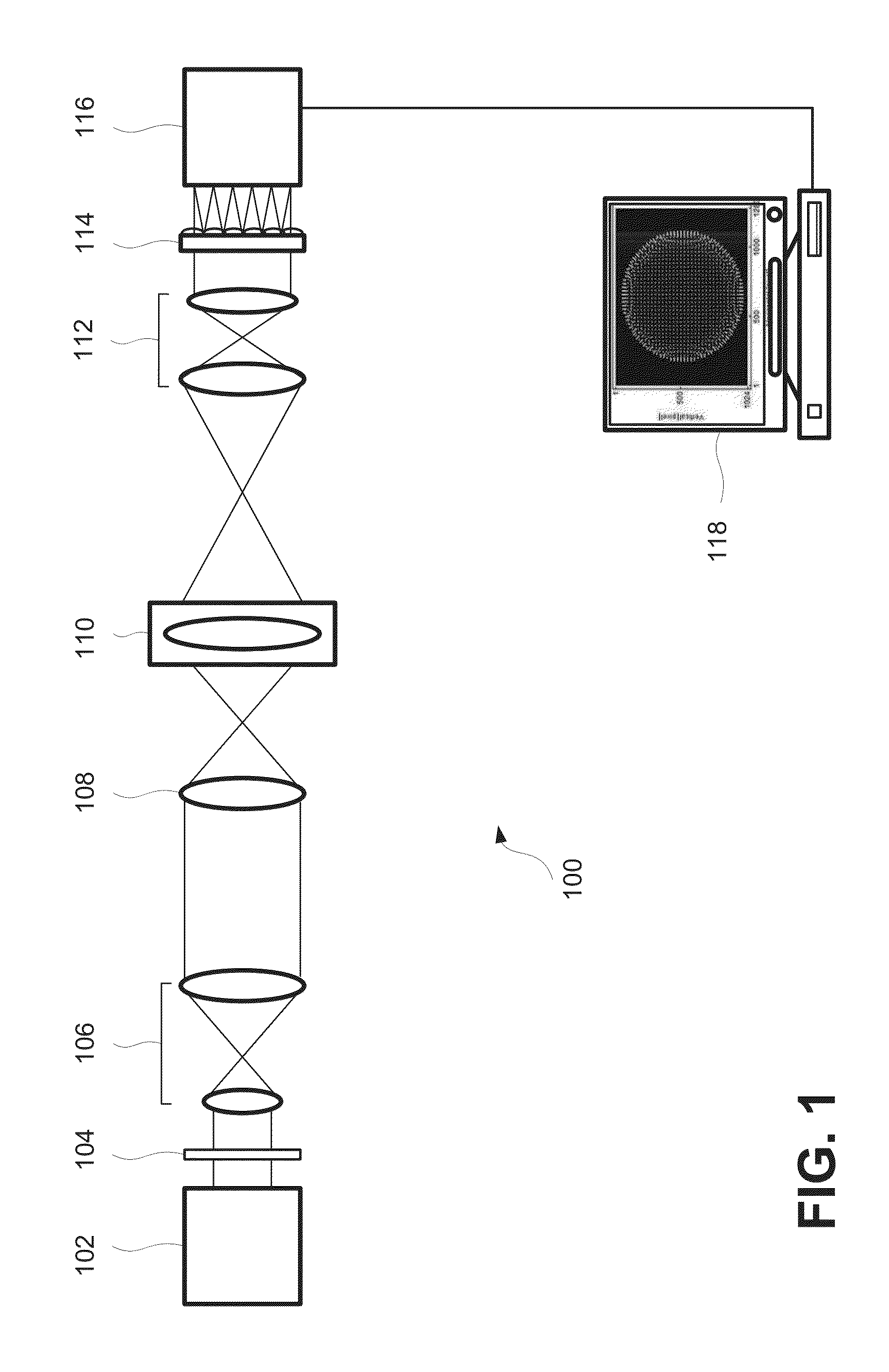
Imaging device
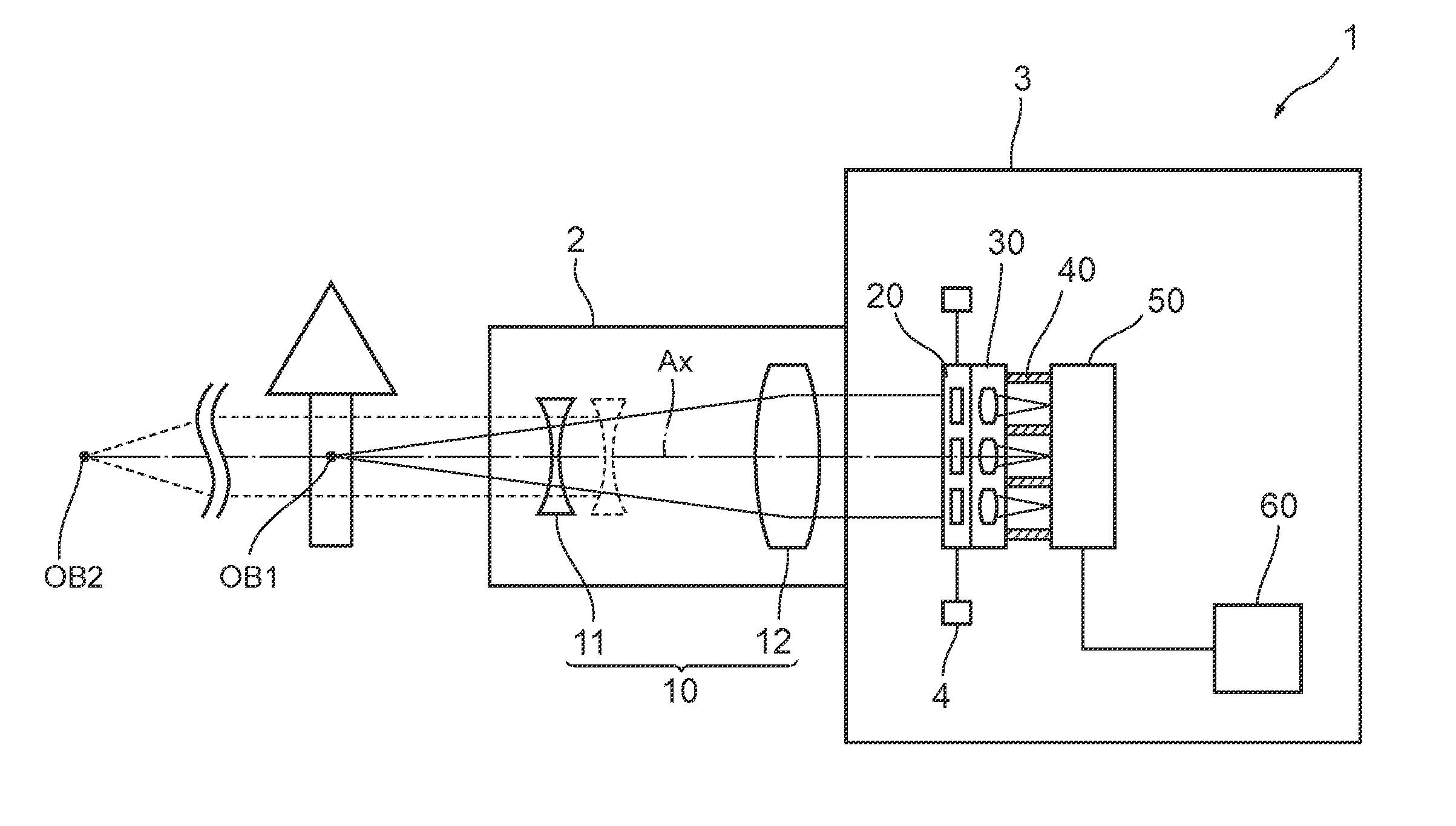
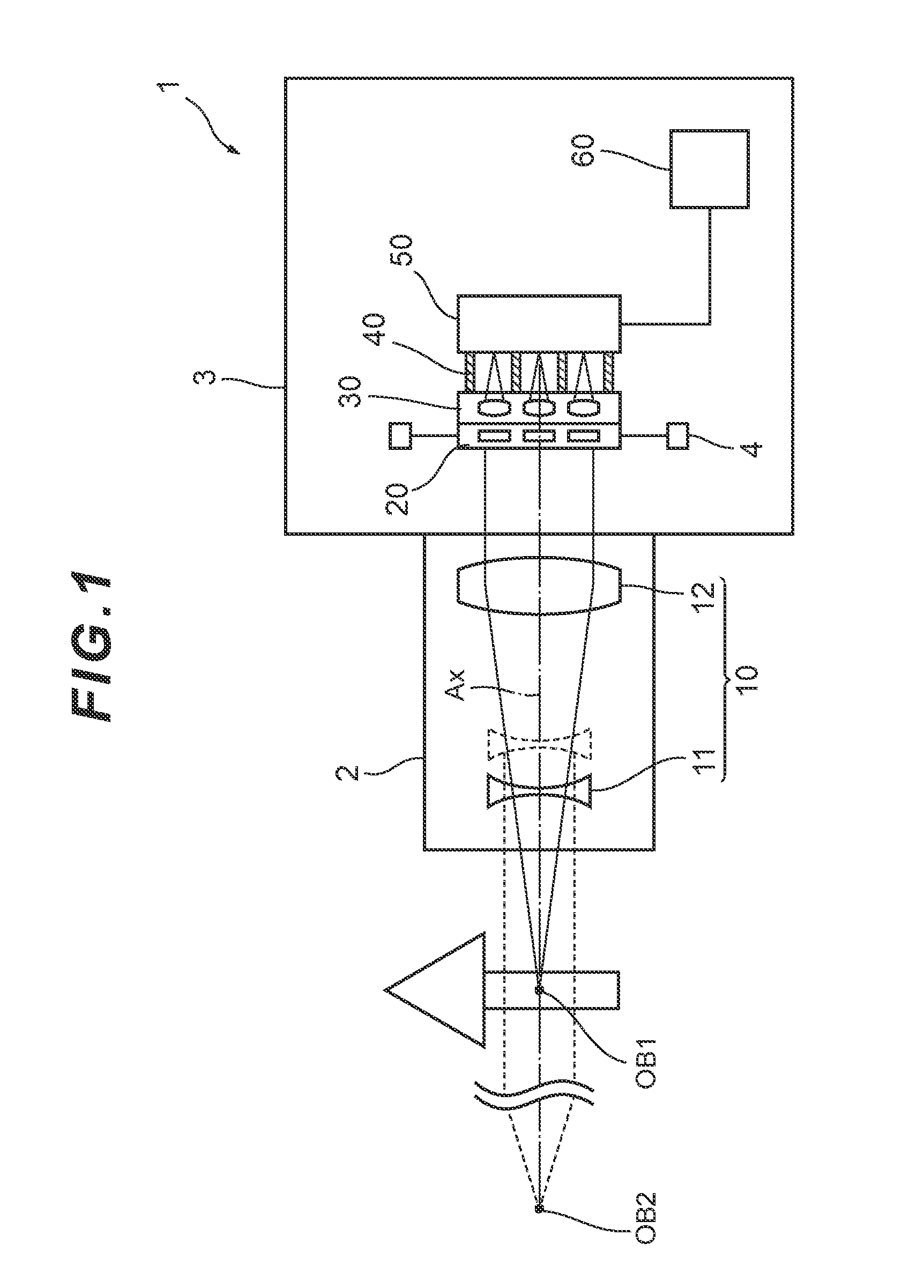
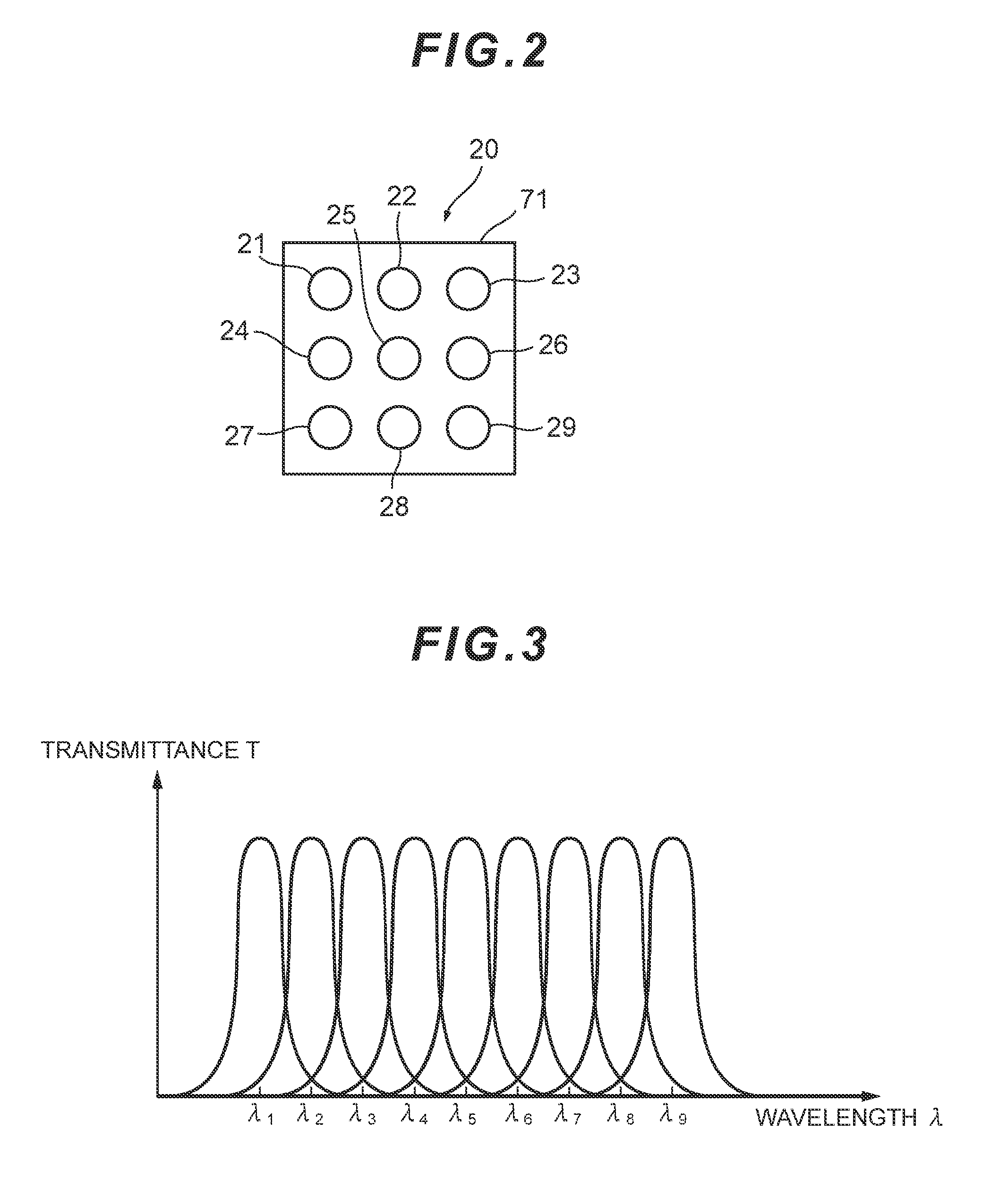
ActiveUS9395516B2Reduce processing loadTelevision system detailsSpectrum investigationSmall lensLuminous flux
Provided is an imaging device (1) having: a front optical system (10) that transmits light from an object; a spectral filter array (20) that transmits light from the front optical system (10) via a plurality of spectral filters; a small lens array (30) that transmits the light from the plurality of spectral filters via a plurality of small lenses respectively, and forms a plurality of object images; a picture element (50) that captures the plurality of object images respectively; and an image processor (60) that determines two-dimensional spectral information on the object images based on image signals output from the picture element (50). The front optical system (10) is configured to transmit the light from the focused object to collimate the light into a parallel luminous flux.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Fiber coupled artificial compound eye
InactiveUS7376314B2Sharpen imageReduce optical aberrationAdditive manufacturing apparatusCoupling light guidesDistortion freeDetector array
A multiple aperture array, wide angle imaging system incorporates compound refractive optics modeled after the eyes of insects. The system channels light through the apertures of a convex spatial filter and a pair of lenslet arrays hot press molded on a positive meniscus form. The lenslets act as afocal Keplerian telescopes to superpose light from hundreds of adjacent channels to a common point on the convex surface of a fiber optic imaging taper. The superposed light from all the channels form a curved, high intensity image that is transformed by the taper into a flat format for readout by a mosaic detector array. The image is upright and distortion free with an infinite depth of field. Ghost images are blocked by a honeycomb louver baffle positioned between the lenslets and the imaging taper. The system is conformable to the geometry of any convex mounting surface, whether spherical, aspherical, or cylindrical.
Owner:SPECTRAL IMAGING LAB
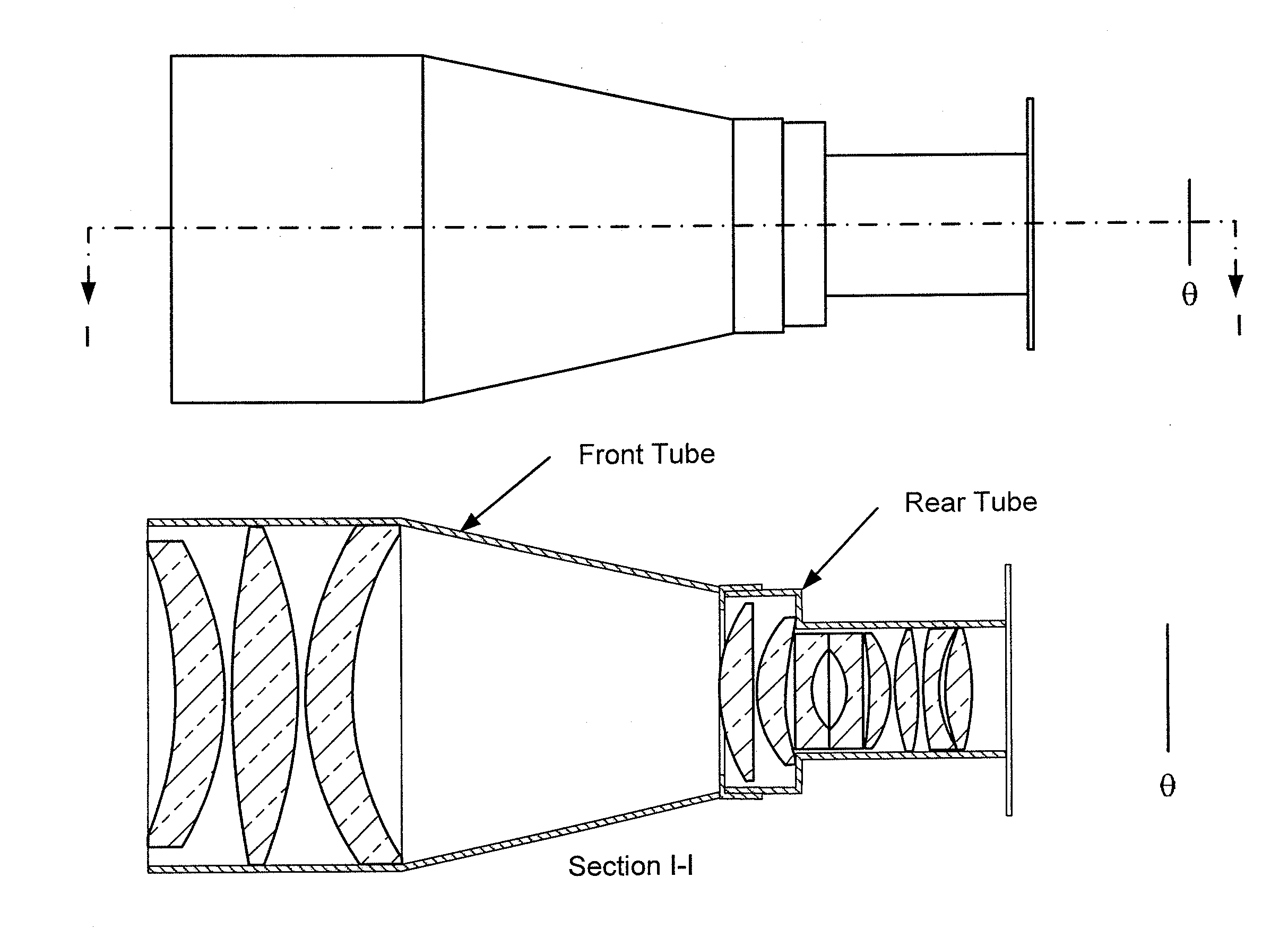
Super light-field lens with doublet lenslet array element
Light field imaging systems, and in particular light field lenses that can be mated with a variety of conventional cameras (e.g., digital or photographic / film, image and video / movie cameras) to create light field imaging systems. Light field data collected by these light field imaging systems can then be used to produce 2D images, right eye / left eye 3D images, to refocus foreground images and / or background images together or separately (depth of field adjustments), and to move the camera angle, as well as to render and manipulate images using a computer graphics rendering engine and compositing tools. A doublet lenslet array element for use in light field imaging systems includes a first lenslet array element having a first plurality of lenslet array elements, and a second lenslet array element having a first plurality of lenslet array elements, wherein the first lenslet array element is coupled in close proximity to the second lenslet array element. The first and second lenslet array elements are glued together or otherwise bonded together and the first lenslet array element is made from a first optical material different than a second material forming the second lenslet array element.
Owner:PIXAR ANIMATION
Apparatus and method for estimating wavefront parameters
ActiveUS20130092816A1Photometry using reference valueOptical measurementsSensor arrayWavefront sensor
An apparatus for estimating a wavefront parameter includes a light source, a lenslet array, a detector for detecting light generated by the light source and passed through the lenslet array, a wavefront corrective element disposed between the lenslet array and the light source; and a data analyzer configured to estimate at least one wavefront parameter at a plane located on the light source side of the corrective element. The lenslet array and the sensor array are arranged to form a wavefront sensor, and the wavefront corrective element is configured to correct an aberration of the wavefront.
Owner:CANON KK +1
Image reading and writing using a complex two-dimensional interlace scheme
ActiveUS20100127431A1Improve throughputPhotomechanical apparatusCo-operative working arrangementsDetector arrayElectron
The current invention relates to writing or reading a pattern on a surface, such as in microlithography or inspection of mircrolithographic patterns. In particular, Applicant discloses systems recording or reading images by scanning sparse 2D point arrays or grids across the surface, e.g., multiple optical, electron or particle beams modulated in parallel. The scanning and repeated reading or writing creates a dense pixel or spot grid on the workpiece. The grid may be created by various arrays: arrays of light sources, e.g., laser or LED arrays, by lenslet arrays where each lenslet has its own modulator, by aperture plates for particle beams, or arrays of near-field emitters or mechanical probes. For reading systems, the point grid may be created by a sparse point matrix illumination and / or a detector array where each detector element sees only one spot. The idea behind the use of large arrays is to improve throughput. However, the throughput does not scale with the array size, since above a certain size of arrays, previously known schemes fall into in their own tracks and start repeating the same data over and over again. This application discloses methods to scan workpieces with large arrays while preserving the scaling of throughput proportional to array size, even for very large arrays, in fact essentially without limits.
Owner:MICRONIC LASER SYST AB
Reflective microelectrical mechanical structure (MEMS) optical modulator and optical display system
InactiveUS20050057793A1Eliminating light attenuation of lightEliminating expenseStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsActuatorMicro lens array
A MEMS optical display system includes an illumination source for providing illumination light, a collimating lens for receiving the illumination light and forming from it collimated illumination light, and a microlens array having an array of lenslets for receiving the illumination light from the collimating lens. The converging microlens array directs the illumination light through an array of pixel apertures in an aperture plate to a microelectrical mechanical reflector array positioned opposite the aperture plate. The microelectrical mechanical reflector array includes an array of microelectrical mechanical actuators that support reflectors in alignment with the array of pixel apertures and selectively orients the reflectors to direct the illumination light back through the pixel apertures (to form part of a display image) or against the aperture plate (to be blocked). The illumination light passing back through the pixel apertures passes through the microlens array and a beamsplitter to a display screen.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Retromodulation-based data communication
A data communication system comprising a transceiver unit for retromodulated optical communication with at least one of a plurality of retromodulator units, the transceiver unit comprising at least one of a plurality of transceivers, the transceivers transmitting diffused radiant energy at different angles covering a predetermined three-dimensional area, wherein each transceiver is enabled to set up and execute communication with at least one retromodulator unit located within its coverage area. Furthermore, a retromodulator comprising multiple arrays of lenslets or spherically arranged lenslets is provided for achieving a wide angle of acceptance. Further more a number of novel applications based on the data communication system are provided, including a remote wireless network connection for a portable computing device, a smart card for remote wireless identification, remote data collection, and remote downloading of digital photographs.
Owner:IRALINK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com