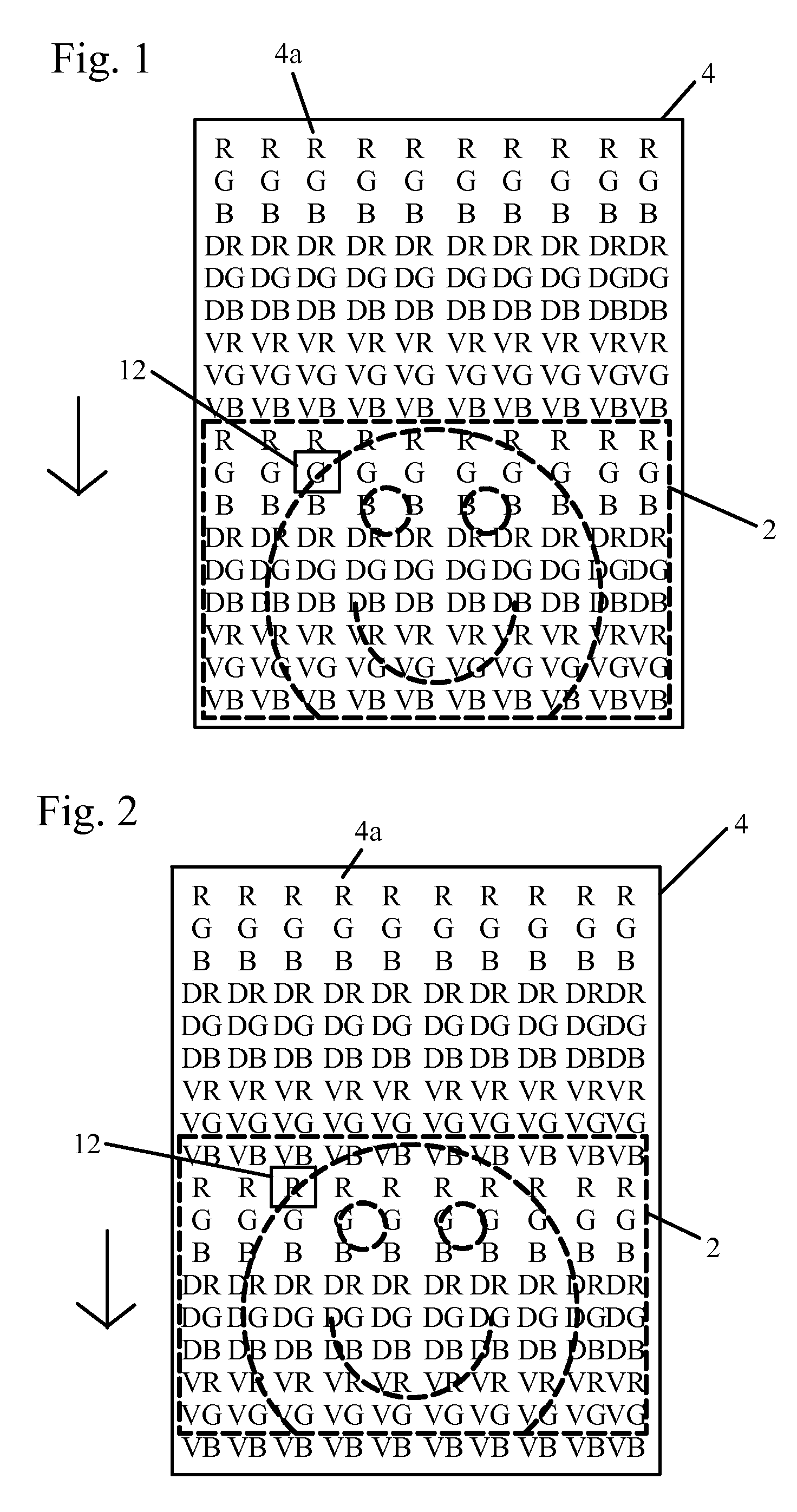
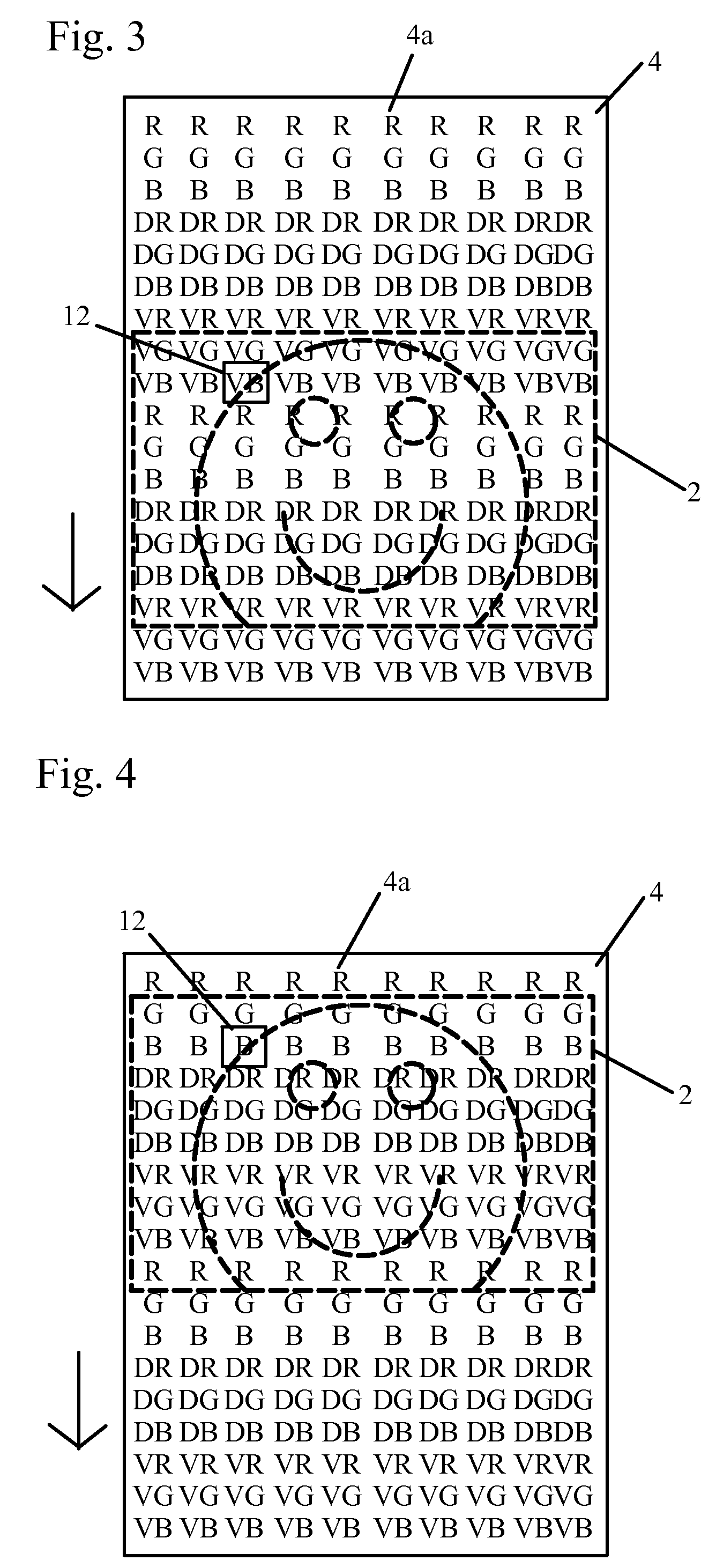
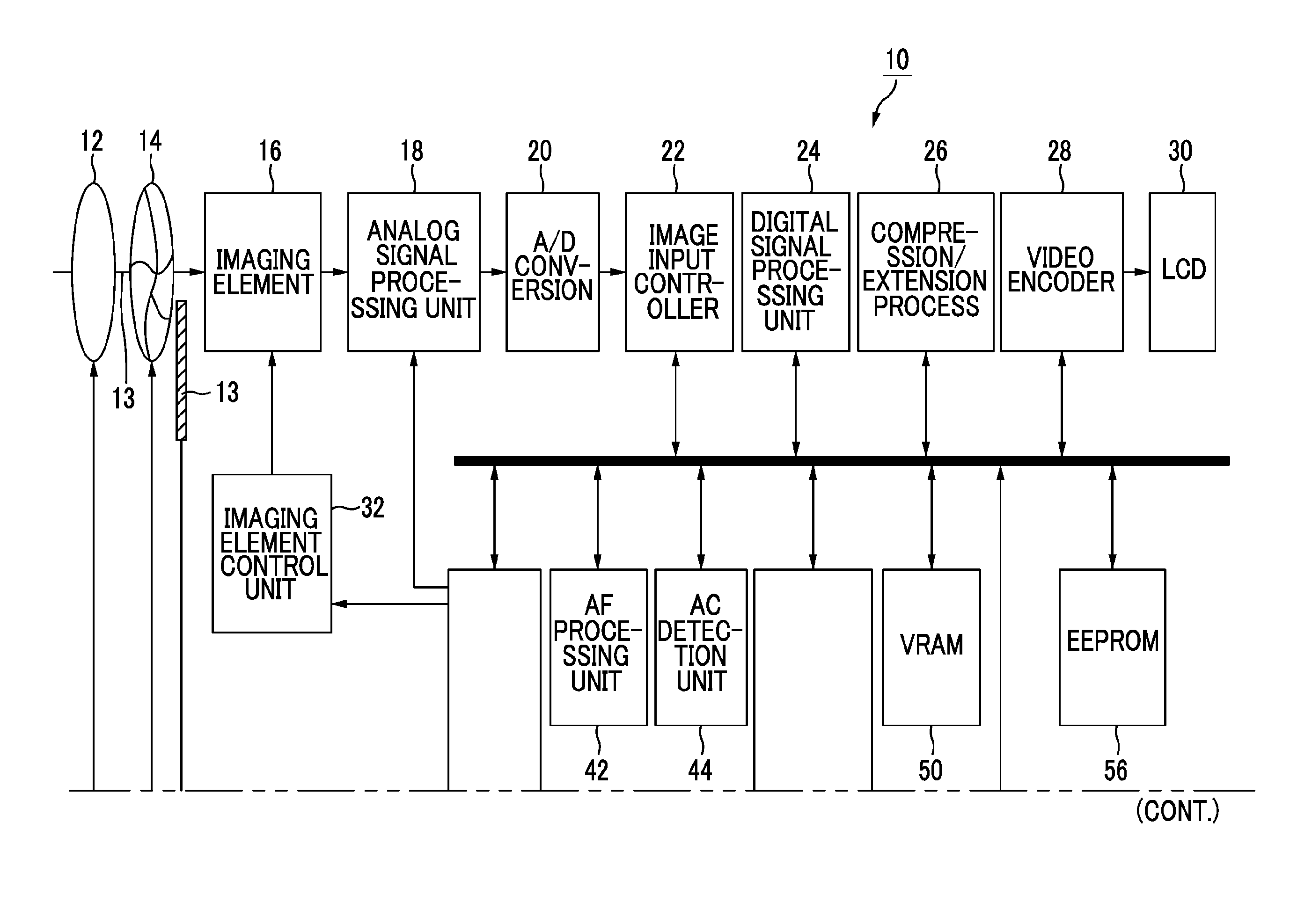
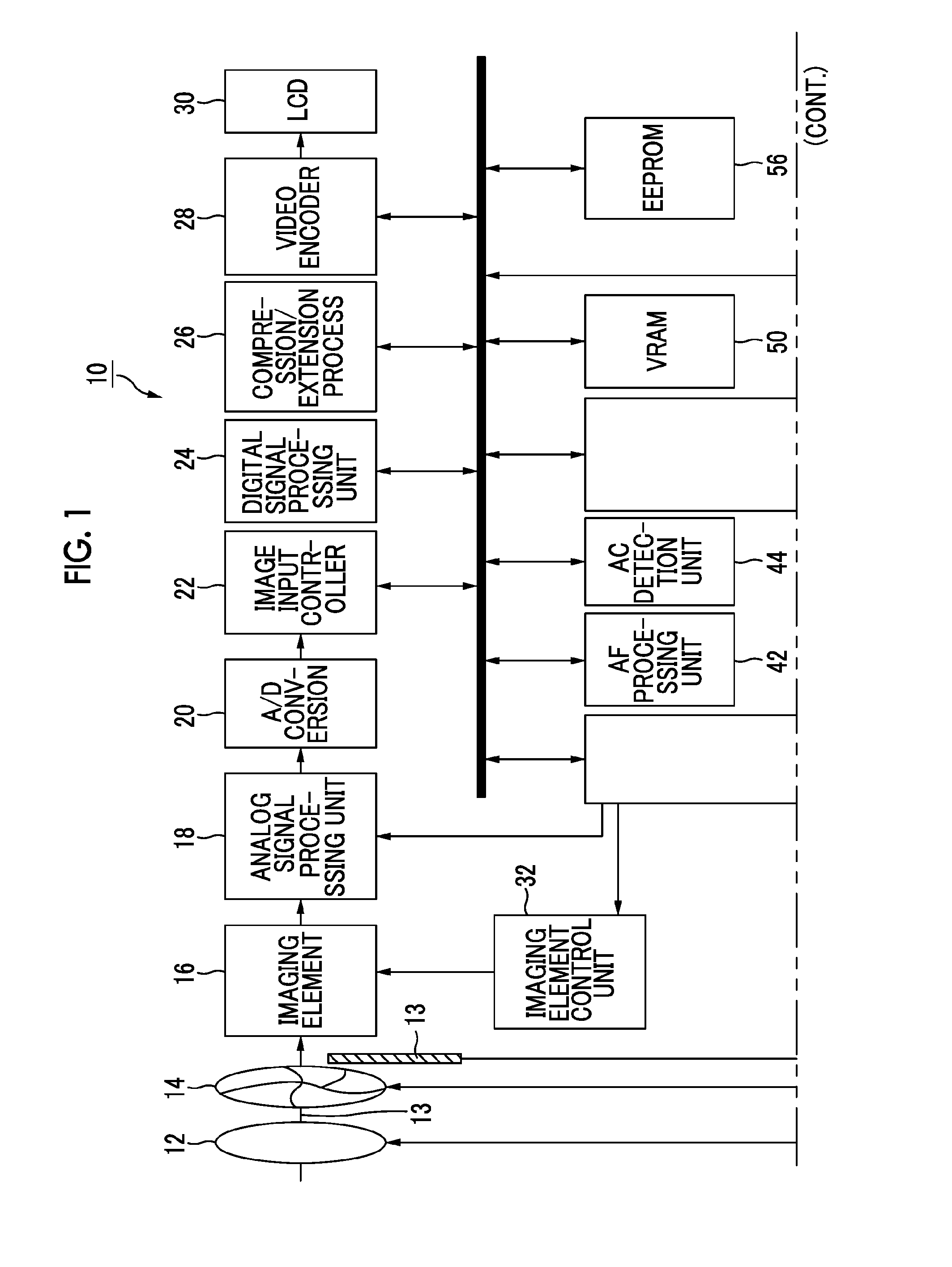
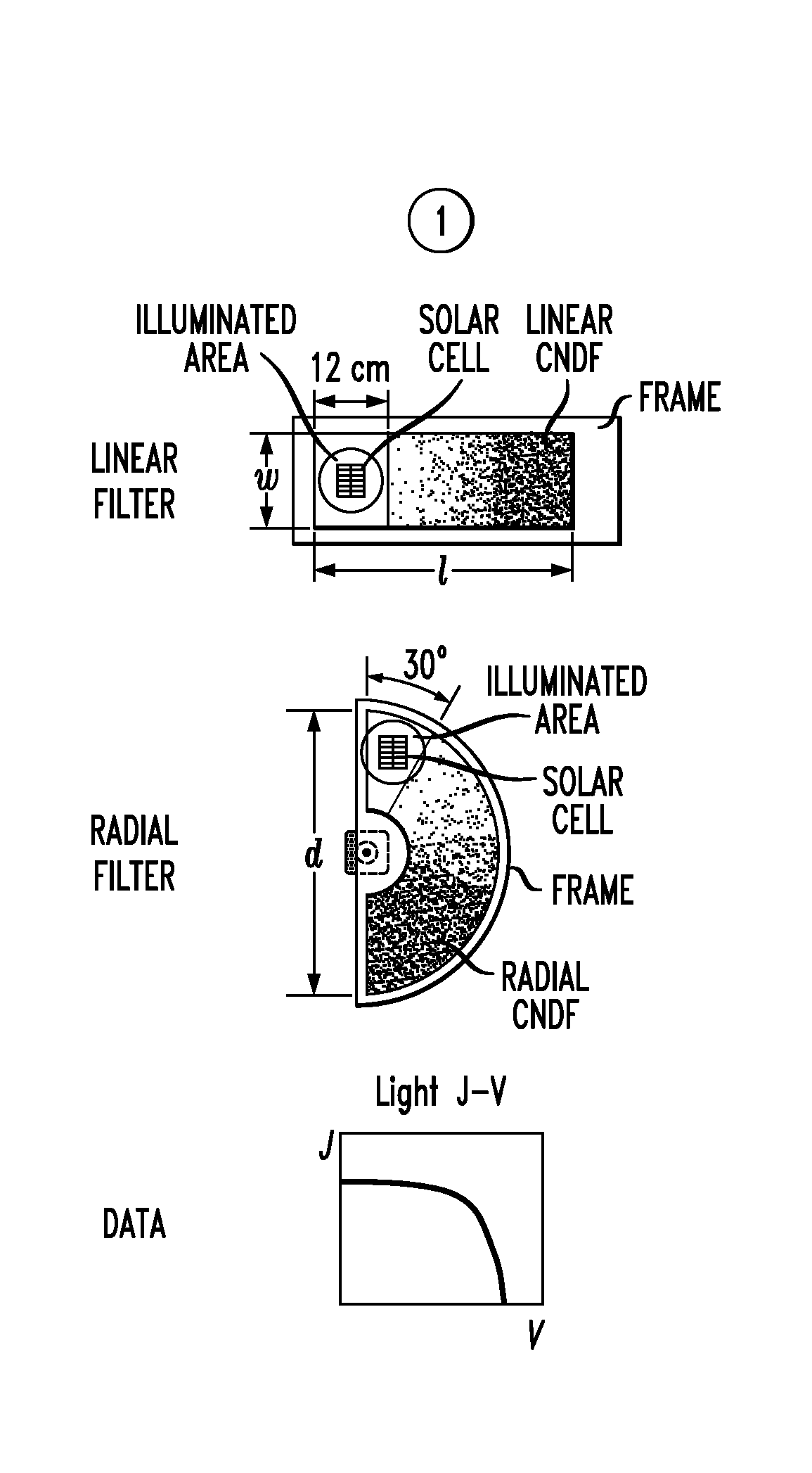
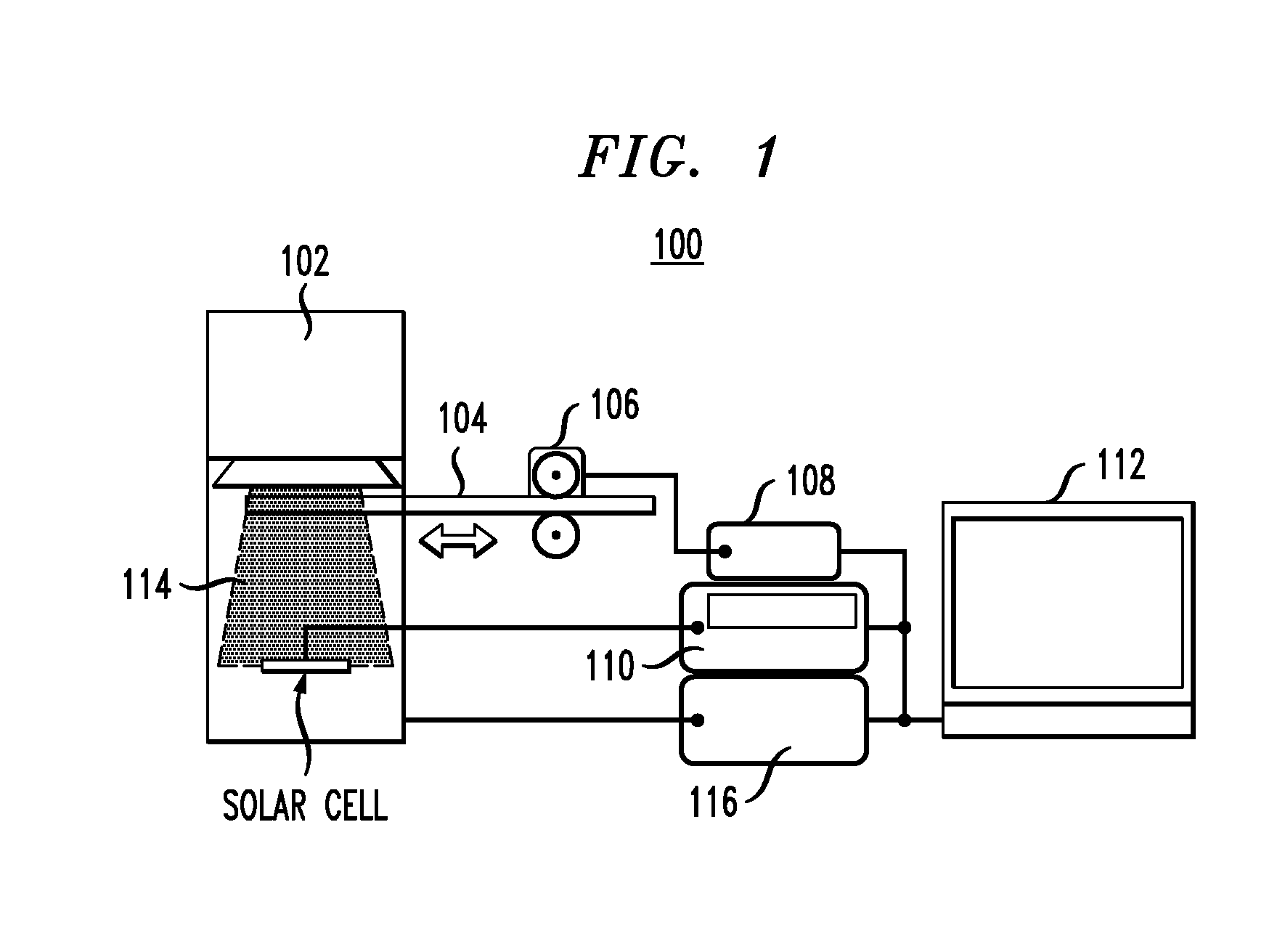
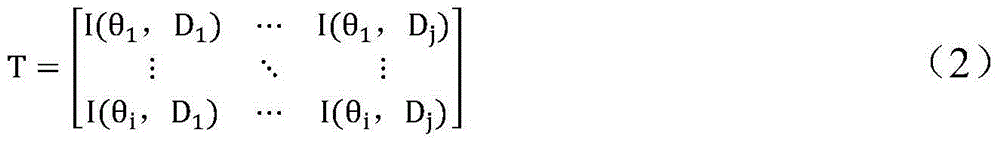Patents
Literature
158 results about "Neutral density filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
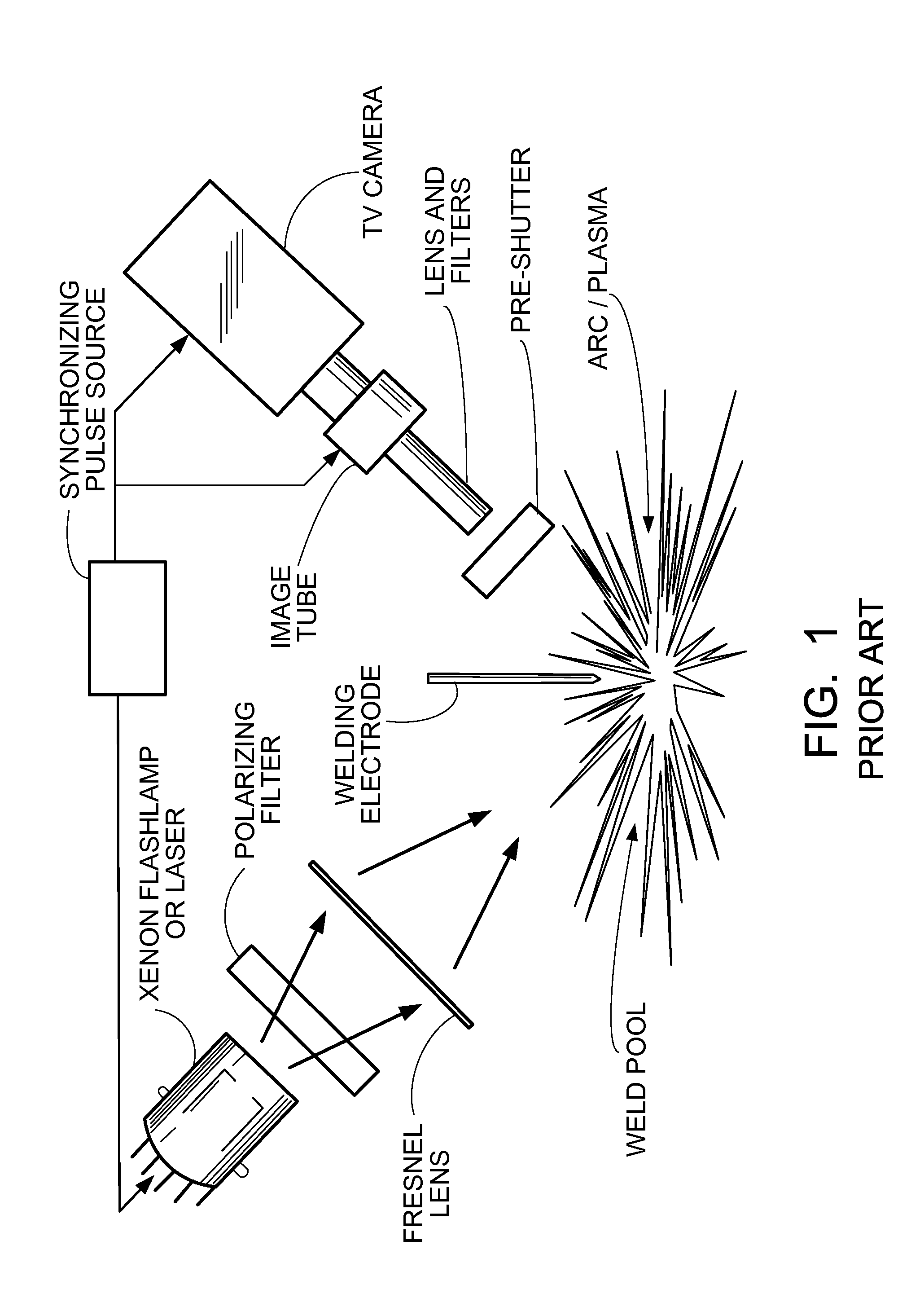
In photography and optics, a neutral-density filter, or ND filter, is a filter that reduces or modifies the intensity of all wavelengths, or colors, of light equally, giving no changes in hue of color rendition. It can be a colorless (clear) or grey filter, and is denoted by Wratten number 96. The purpose of a standard photographic neutral-density filter is to reduce the amount of light entering the lens. Doing so allows the photographer to select combinations of aperture, exposure time and sensor sensitivity that would otherwise produce overexposed pictures. This is done to achieve effects such as a shallower depth of field or motion blur of a subject in a wider range of situations and atmospheric conditions.
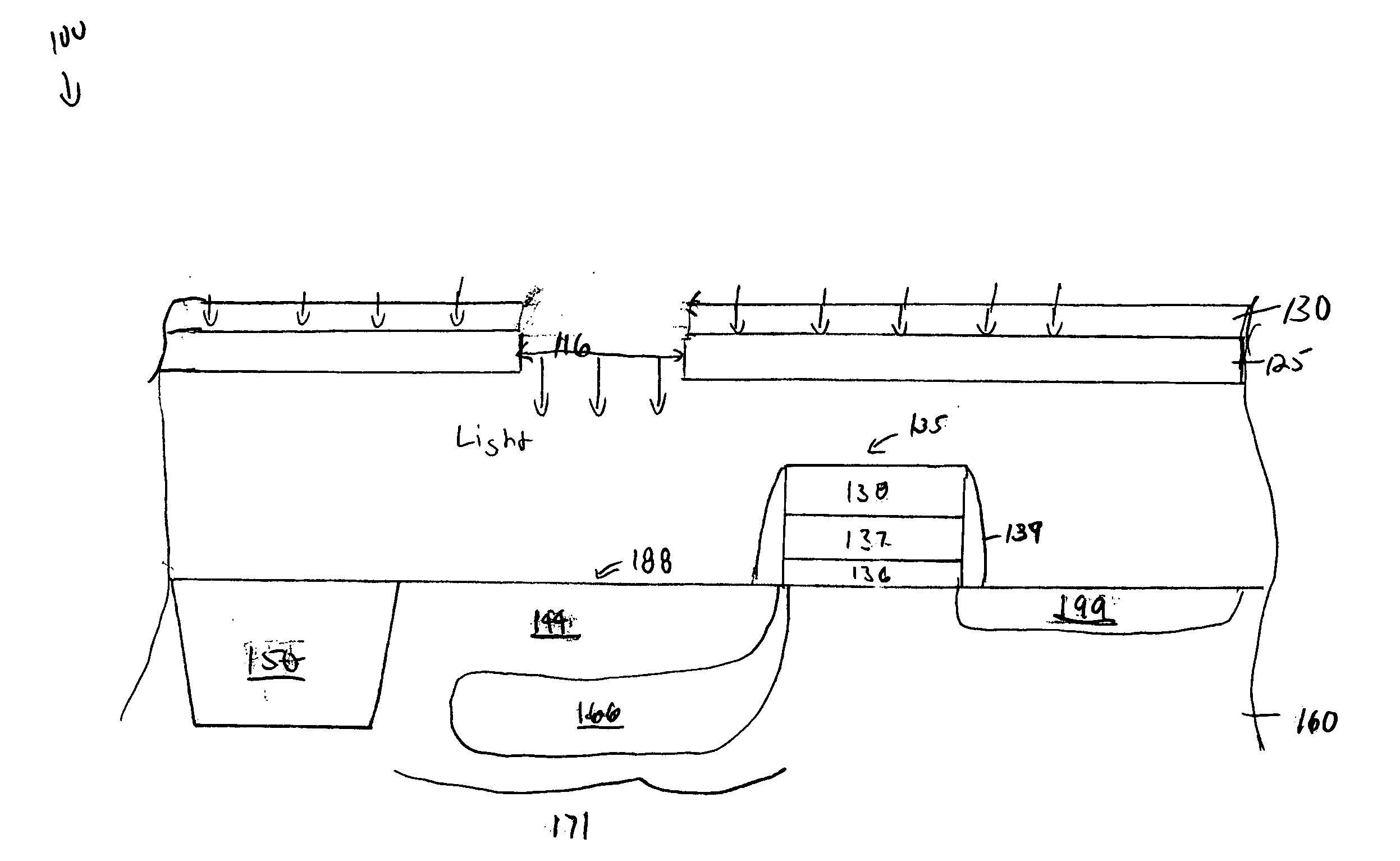
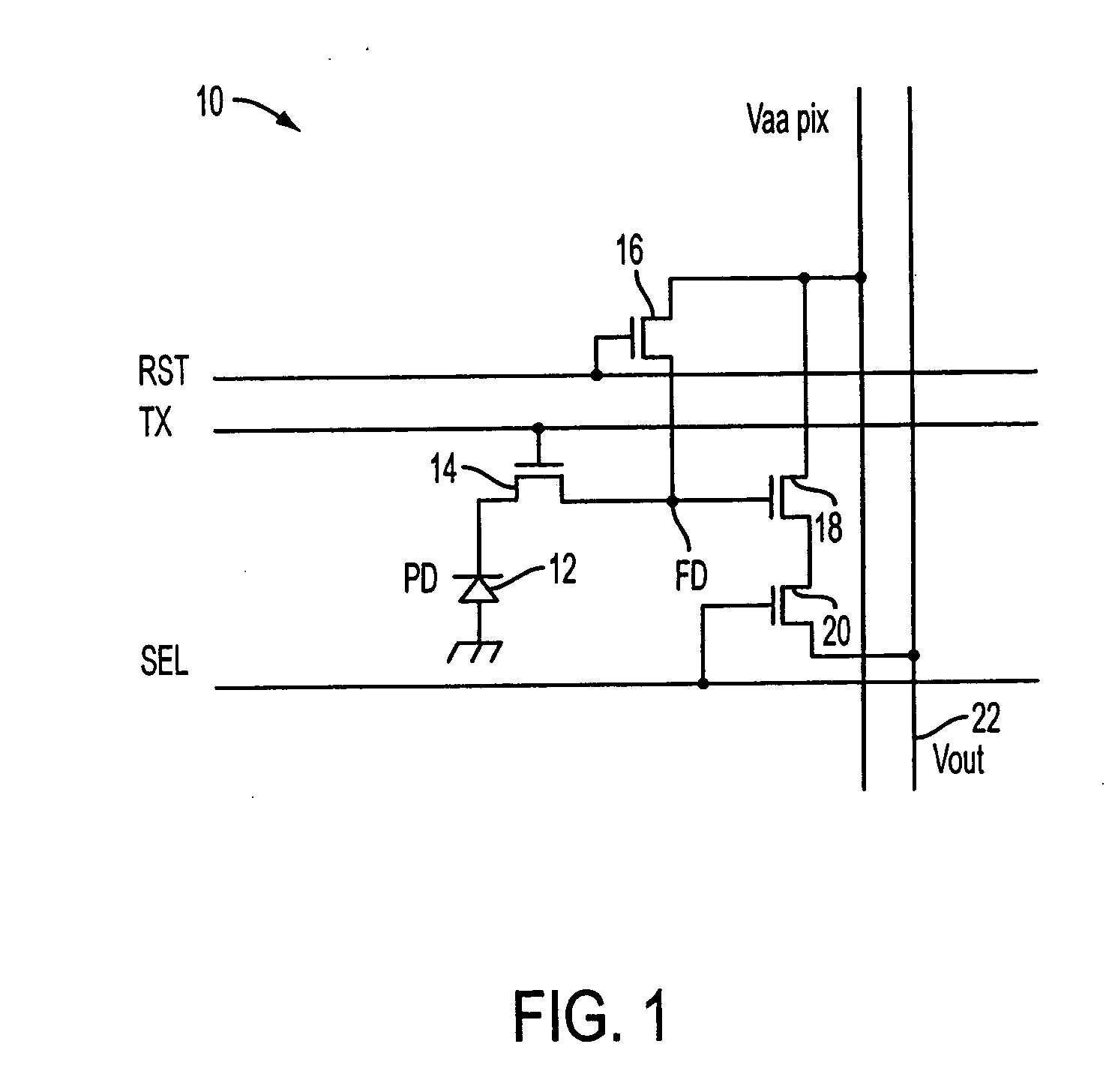
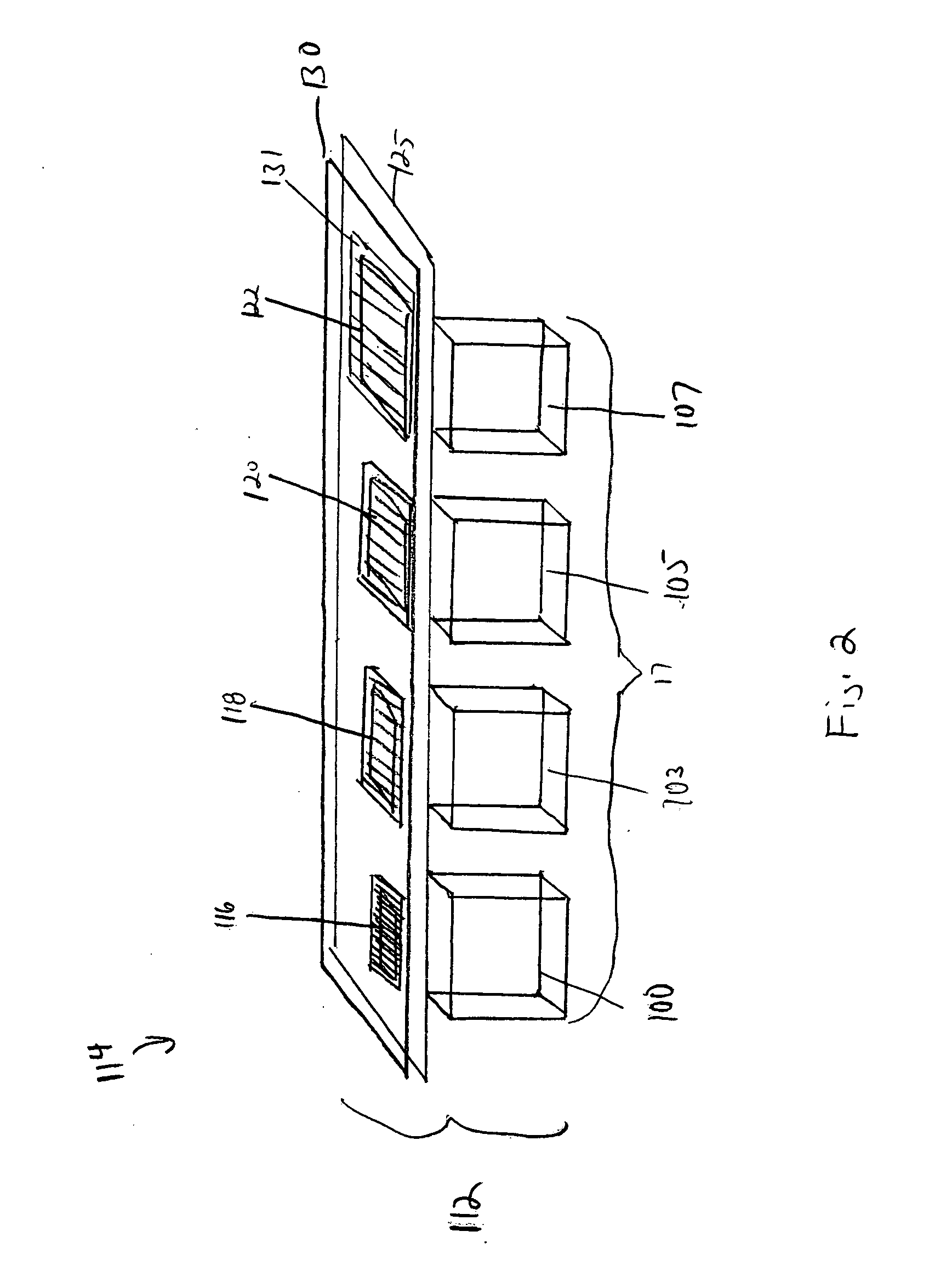
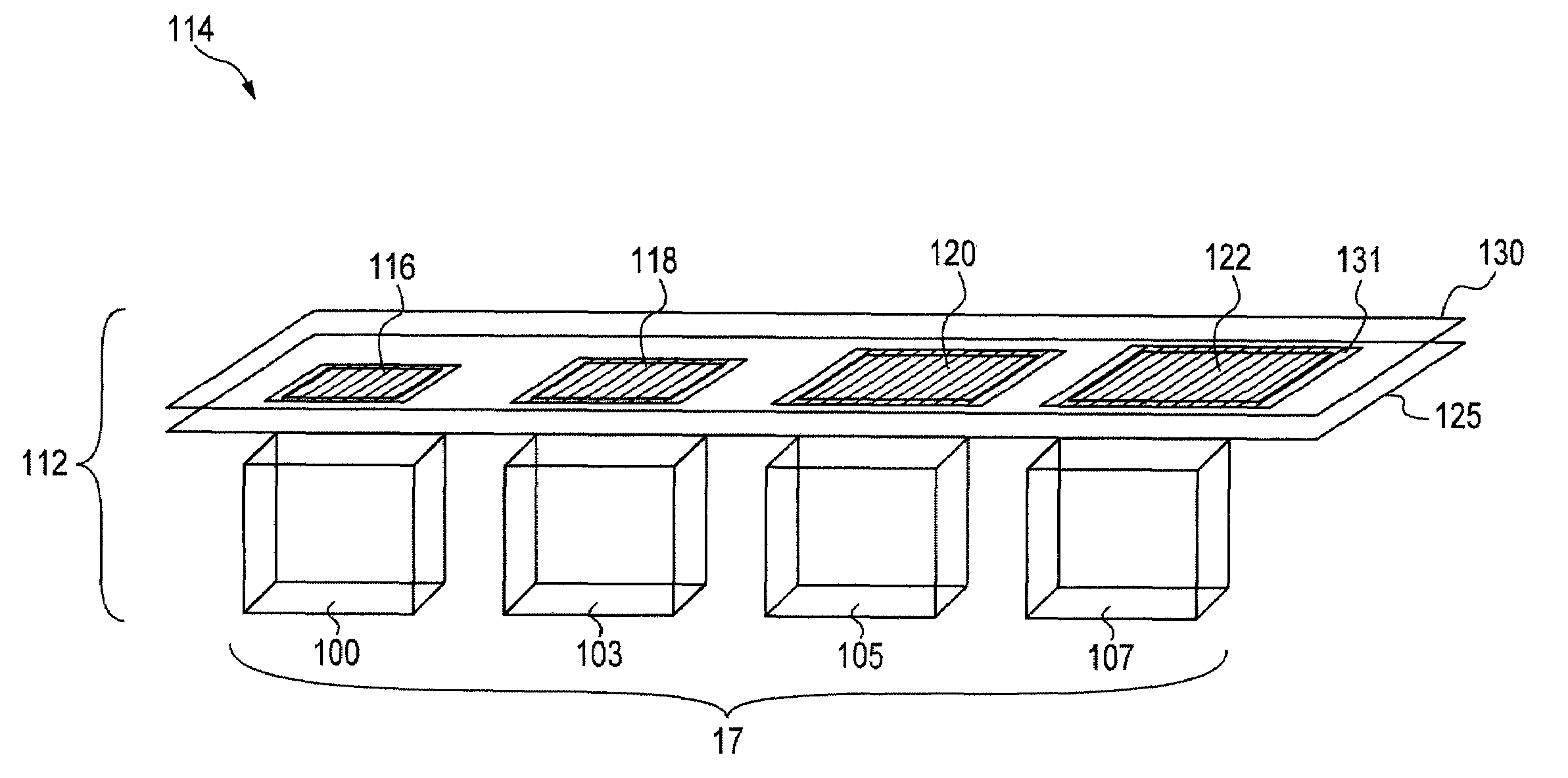
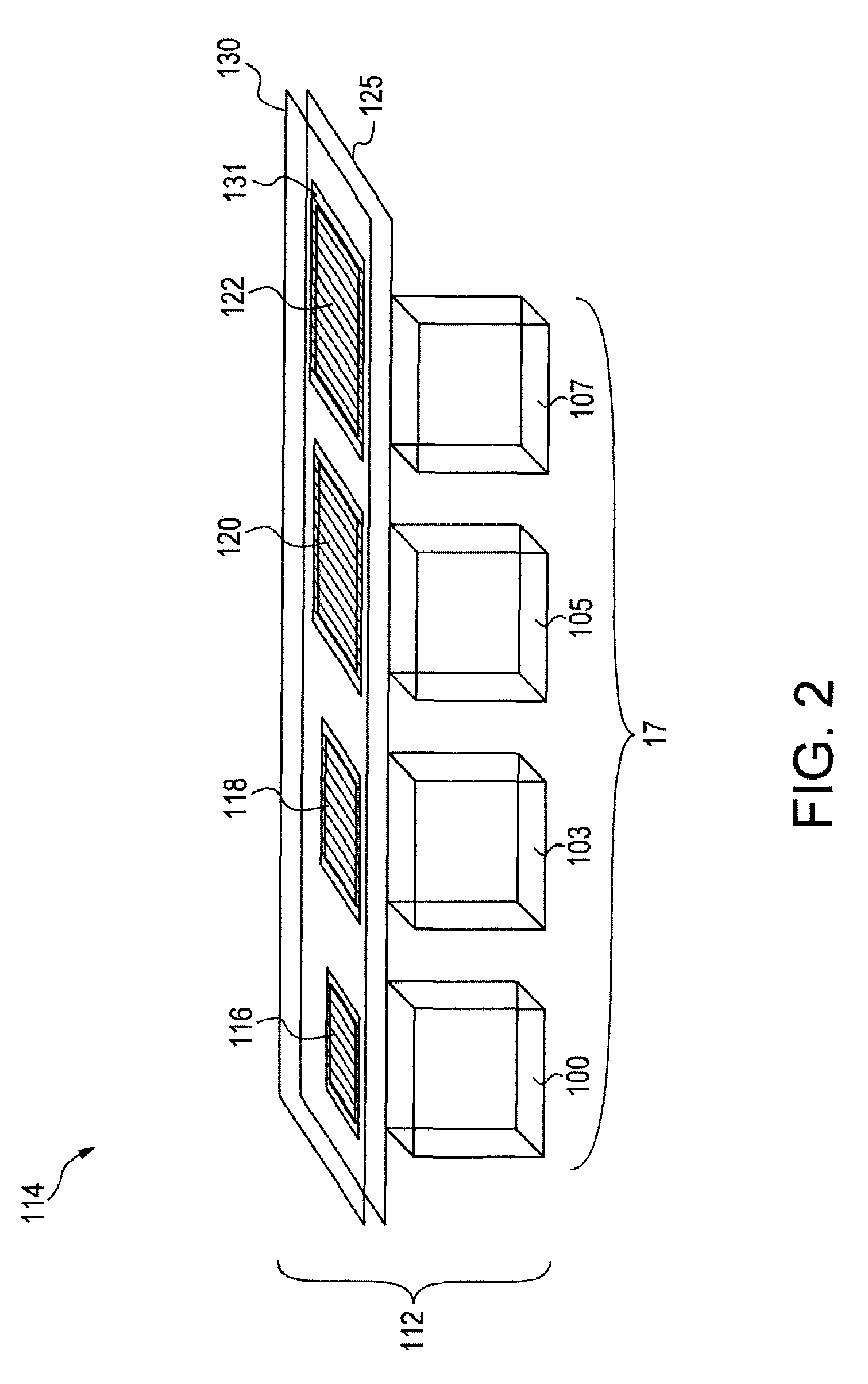
High dynamic range imaging device using multiple pixel cells
ActiveUS20070035653A1Improve dynamic rangeReduce Fixed Pattern NoiseTelevision system detailsImage enhancementHigh-dynamic-range imagingVolumetric Mass Density
A method and apparatus for achieving high-dynamic range operation with a set of spatially distributed pixel cells is provided. A pixel array with a row of pixels having apertures of varying sizes in a metal mask formed thereon controls the sensitivity of each pixel cell to light. A neutral density filter having varying light transparency values is also provided over the set of pixel cells to control the sensitivity of each pixel cell to light. The pixel cells voltage outputted is combined to obtain high-dynamic range operation.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
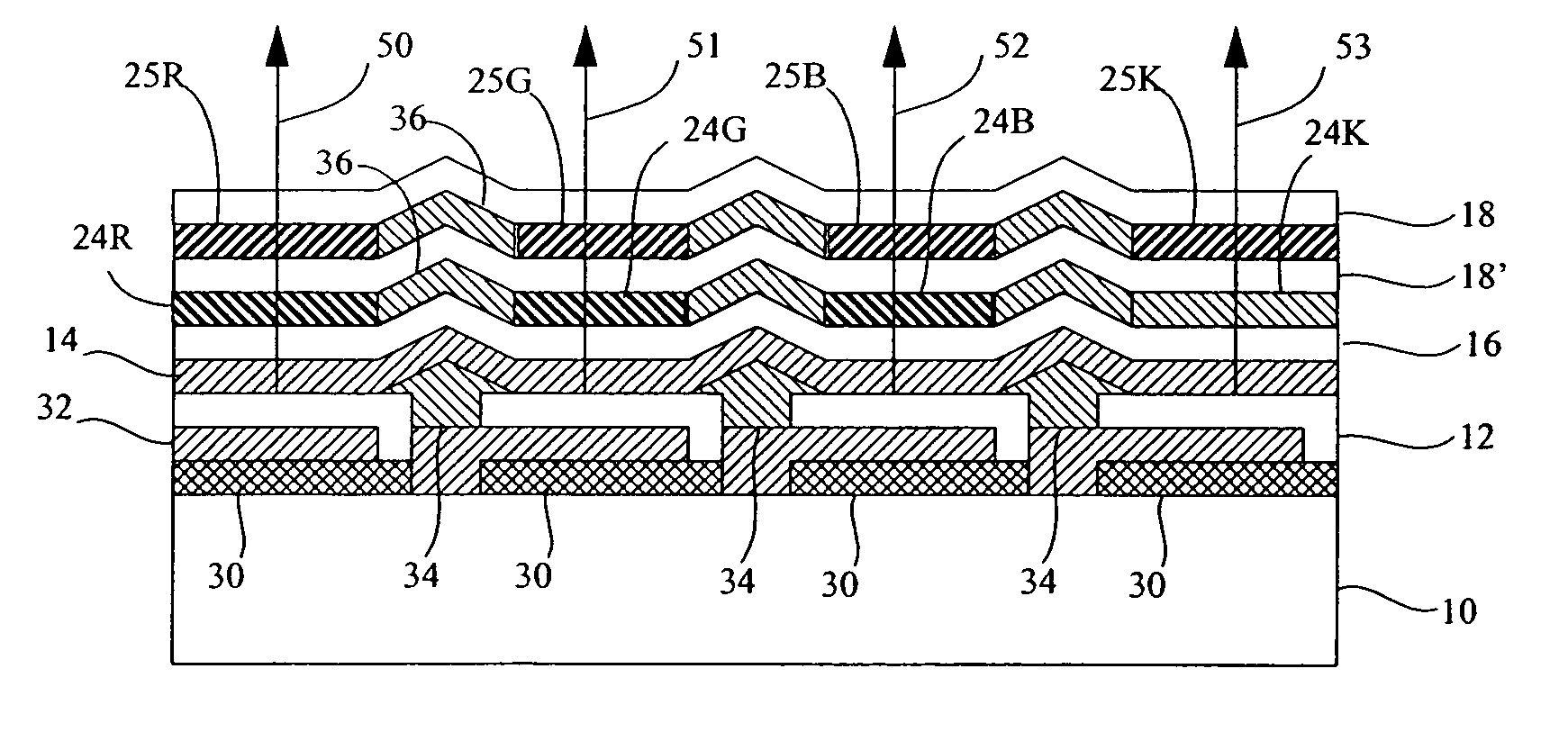
OLED device having improved contrast
ActiveUS20070090751A1Increase contrastImprove light outputDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesGamutLight-emitting diode
A full-color organic light-emitting diode (OLED) device, comprising: a) a plurality of light emitting OLED pixels, each pixel having three or more color light-emitting elements for emitting different colors of light specifying a gamut and at least one additional light-emitting element for emitting a color of light within the gamut and wherein the power efficiency of the additional element is higher than the power efficiency of at least one of the three or more gamut elements; and b) a patterned neutral density filter selectively filtering the emitted light from the additional light emitting element.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Method and apparatus to extend the effective dynamic range of an image sensing device
InactiveUS6909461B1Slow responseImprove dynamic rangeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLight spotEngineering
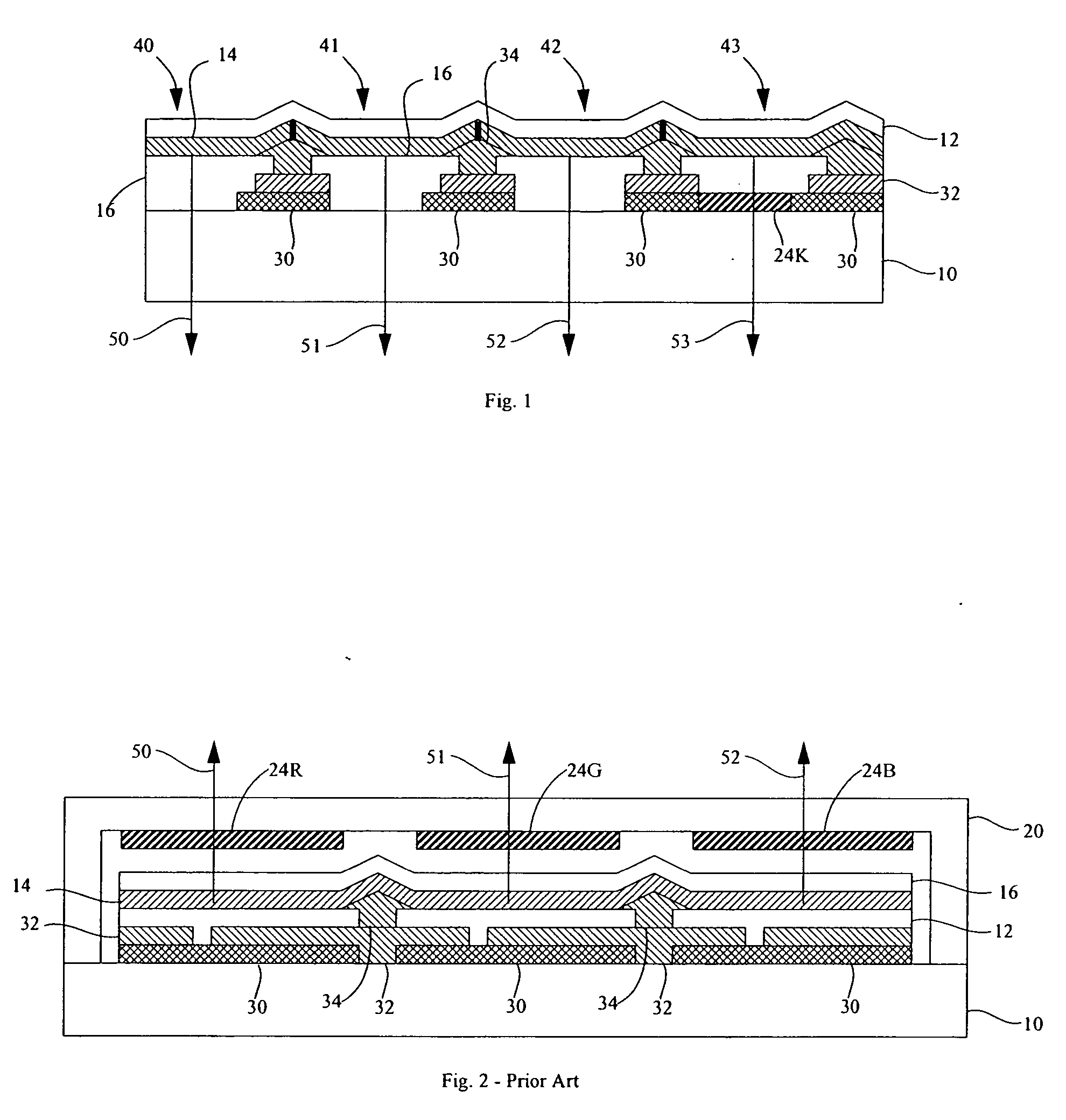
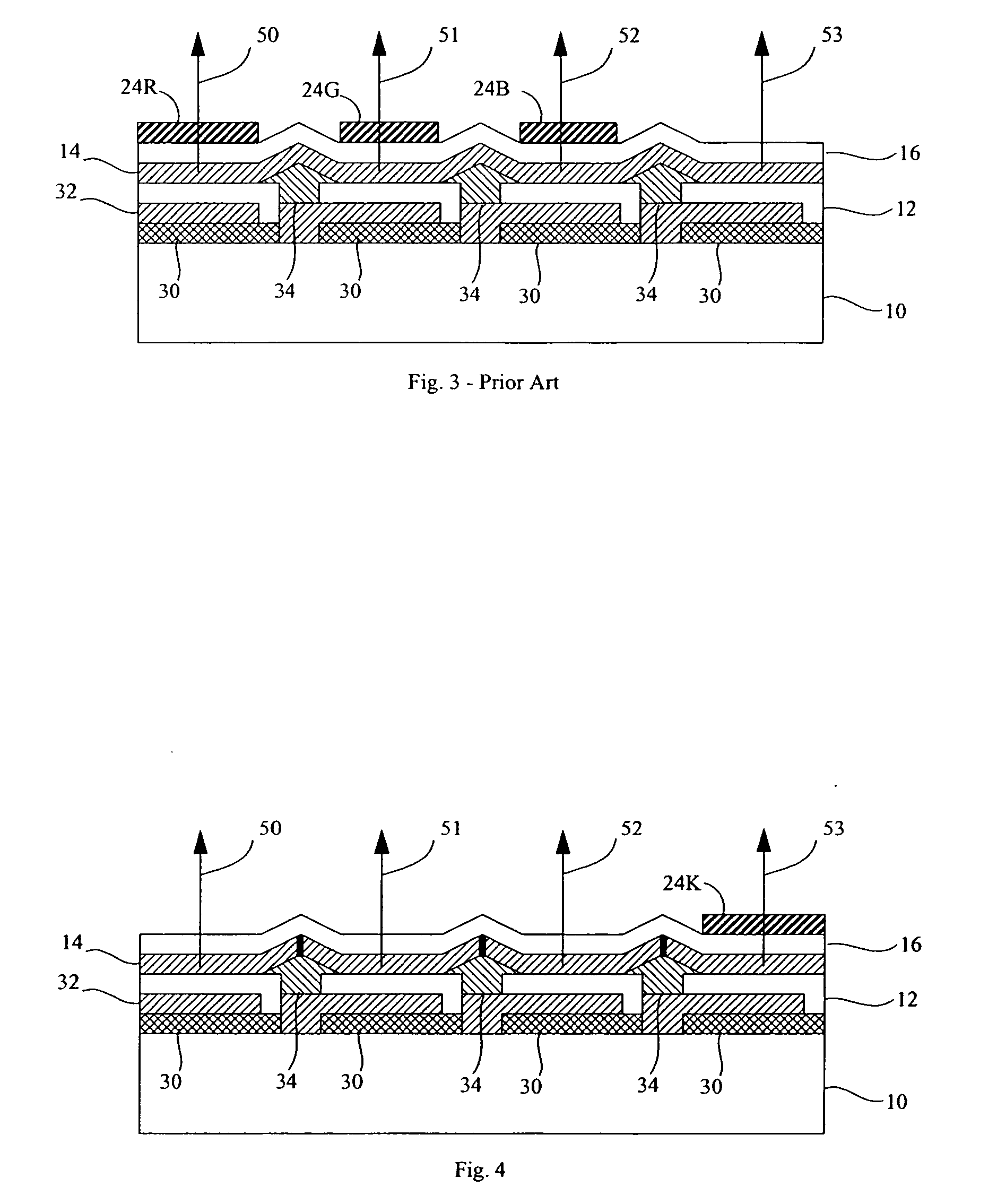
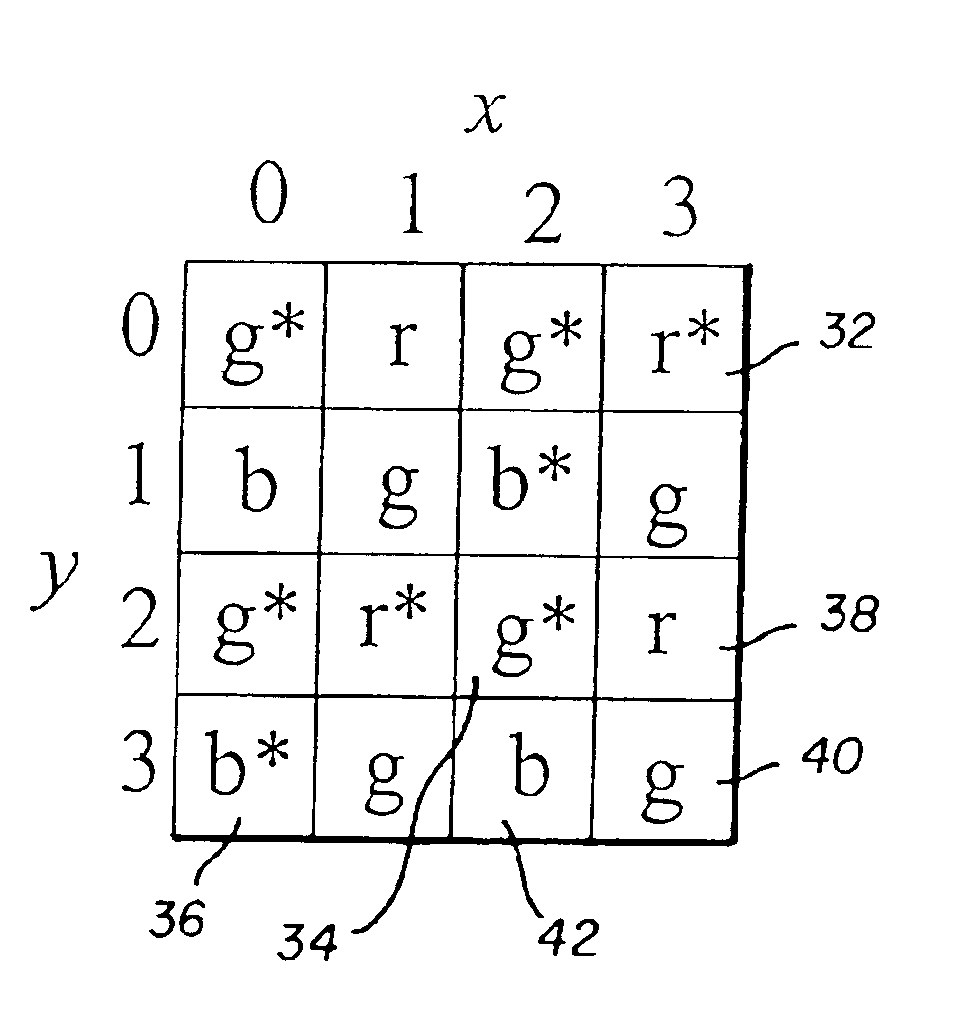
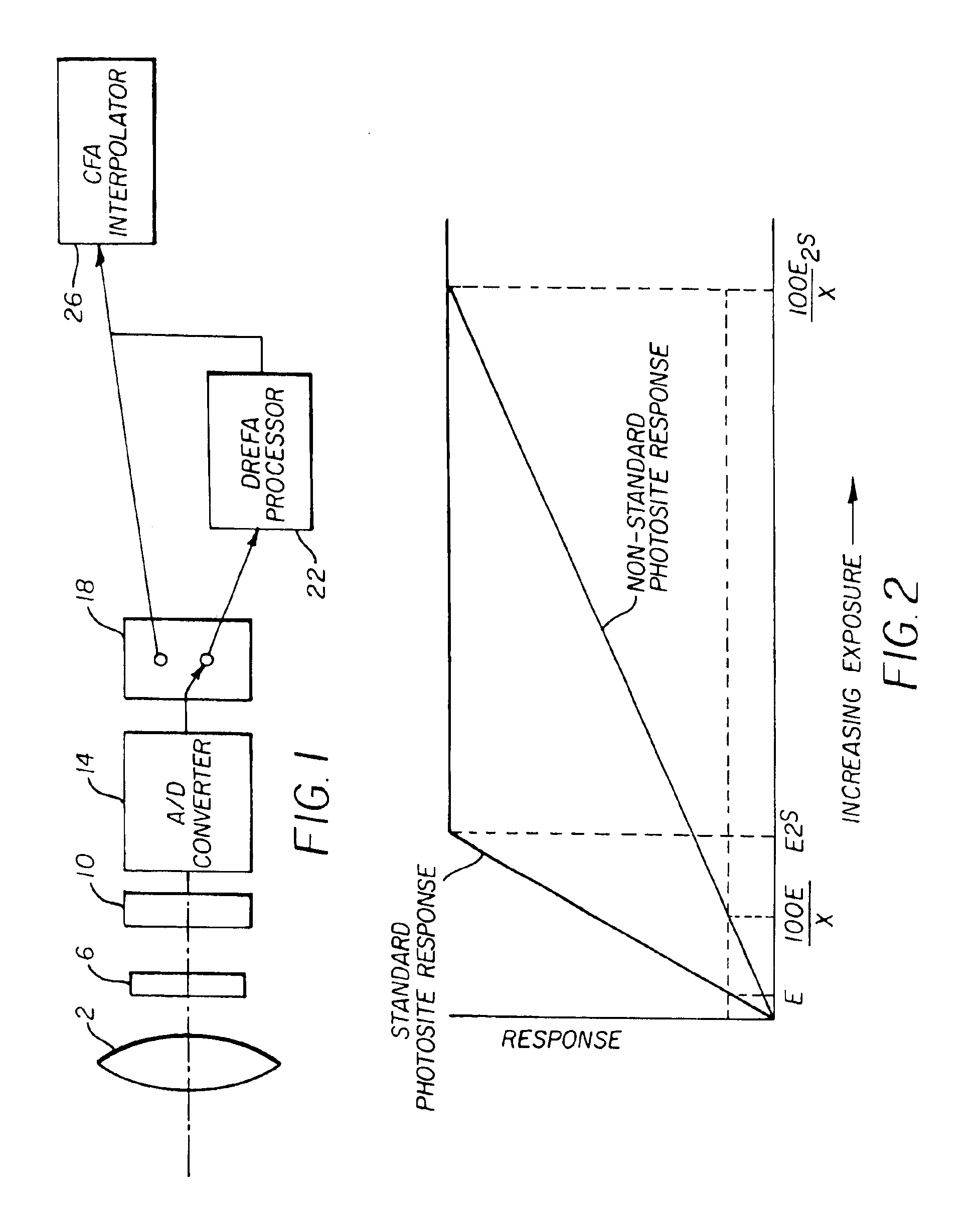
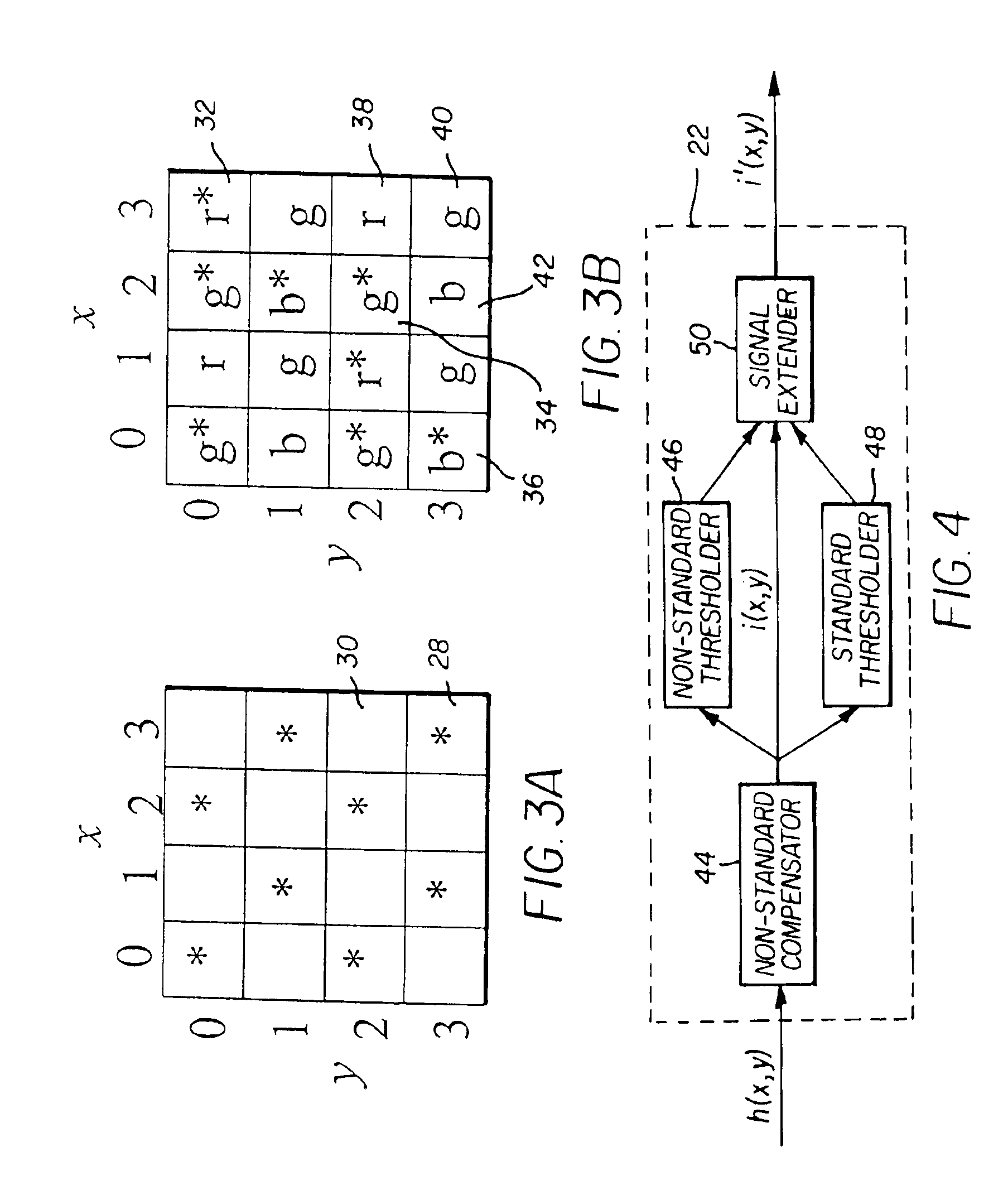
An image capture system generates an extended effective dynamic range from a signal provided by an image sensor by utilizing an image sensing device having standard photosites with a predetermined response to a light exposure and non-standard photosites with a slower response to the same light exposure. An optical section exposes the image sensing device to image light, thereby causing the image sensing device to generate an image signal and a processing section expands the response of the standard photosites to increased light exposures by utilizing the image signals from neighboring non-standard photosites. Furthermore, the processing section may expand the response of the non-standard photosites to decreased light exposures by utilizing the image signals from neighboring standard photosites. The differential response of the image sensor is provided by a structural element, such as an array of lenslets, a mask or a neutral density filter, overlying the photosites and providing the standard photosites with a predetermined standard response to a light exposure and the non-standard photosites with a slower response to the same light exposure.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Motor driven optical fiber variable attenuator
InactiveUS6144794ASmooth movementEliminate backlashCoupling light guidesUltrasound attenuationMotor drive
A variable attenuator comprises a motor which actuates a lead screw to move rotatably, and a nut associated with the lead screw to move linearly. A neutral density filter moves along with the linearly moving nut wherein the filter is positioned between two spaced collimators for providing linear attenuation changes of light transmitted therebetween.
Owner:ALLIAN FIBER OPTIC PROD INC
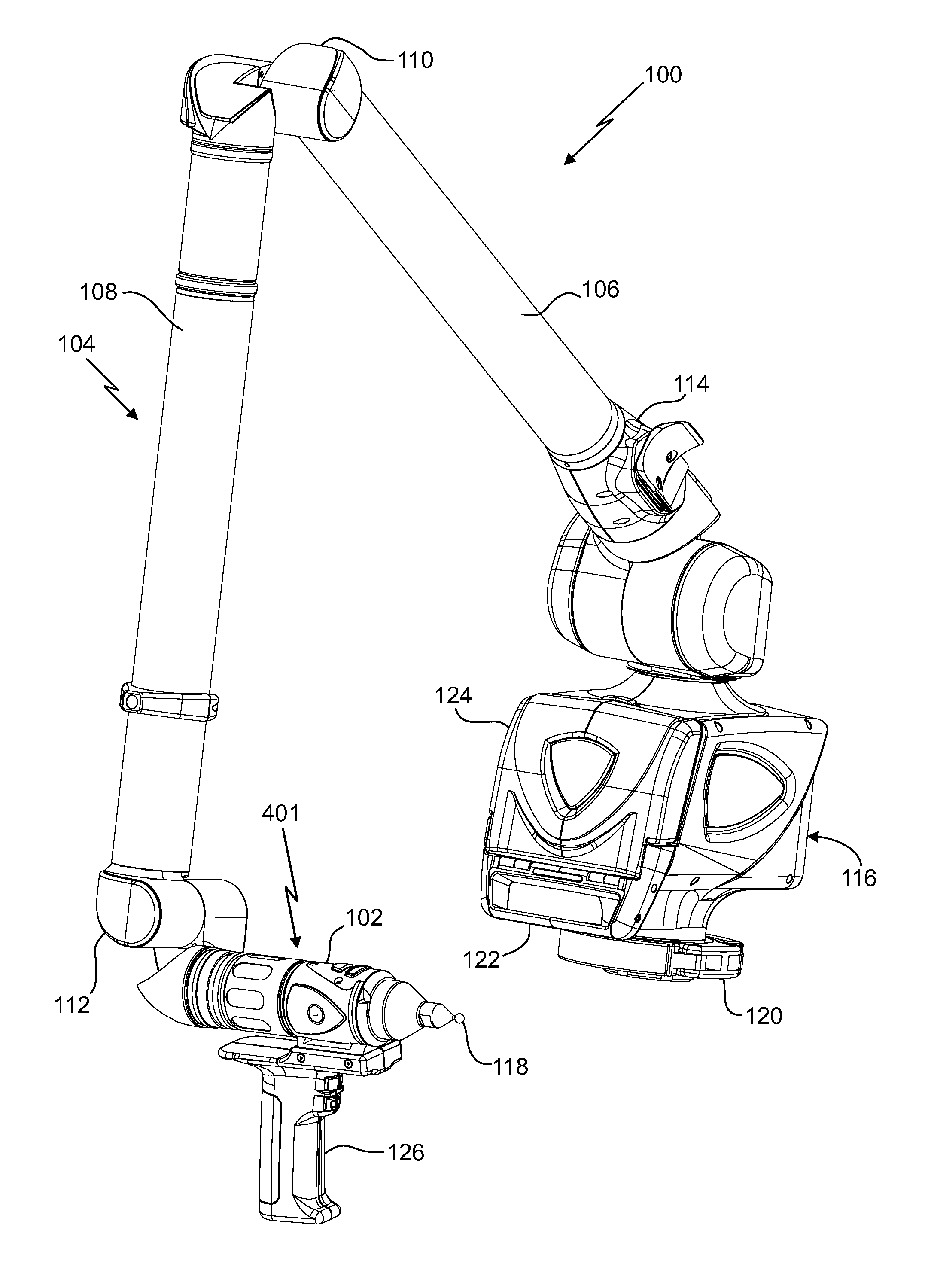
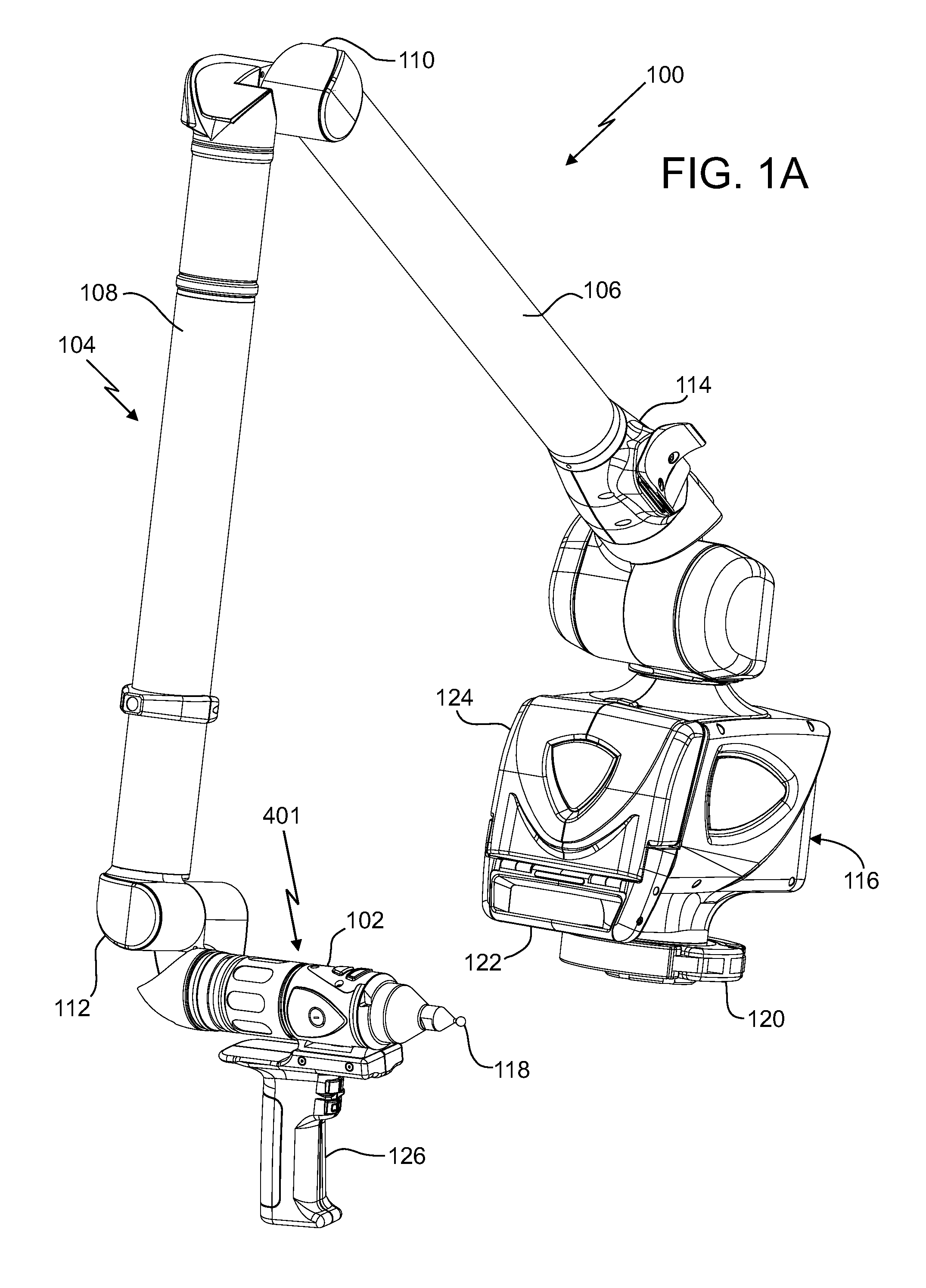
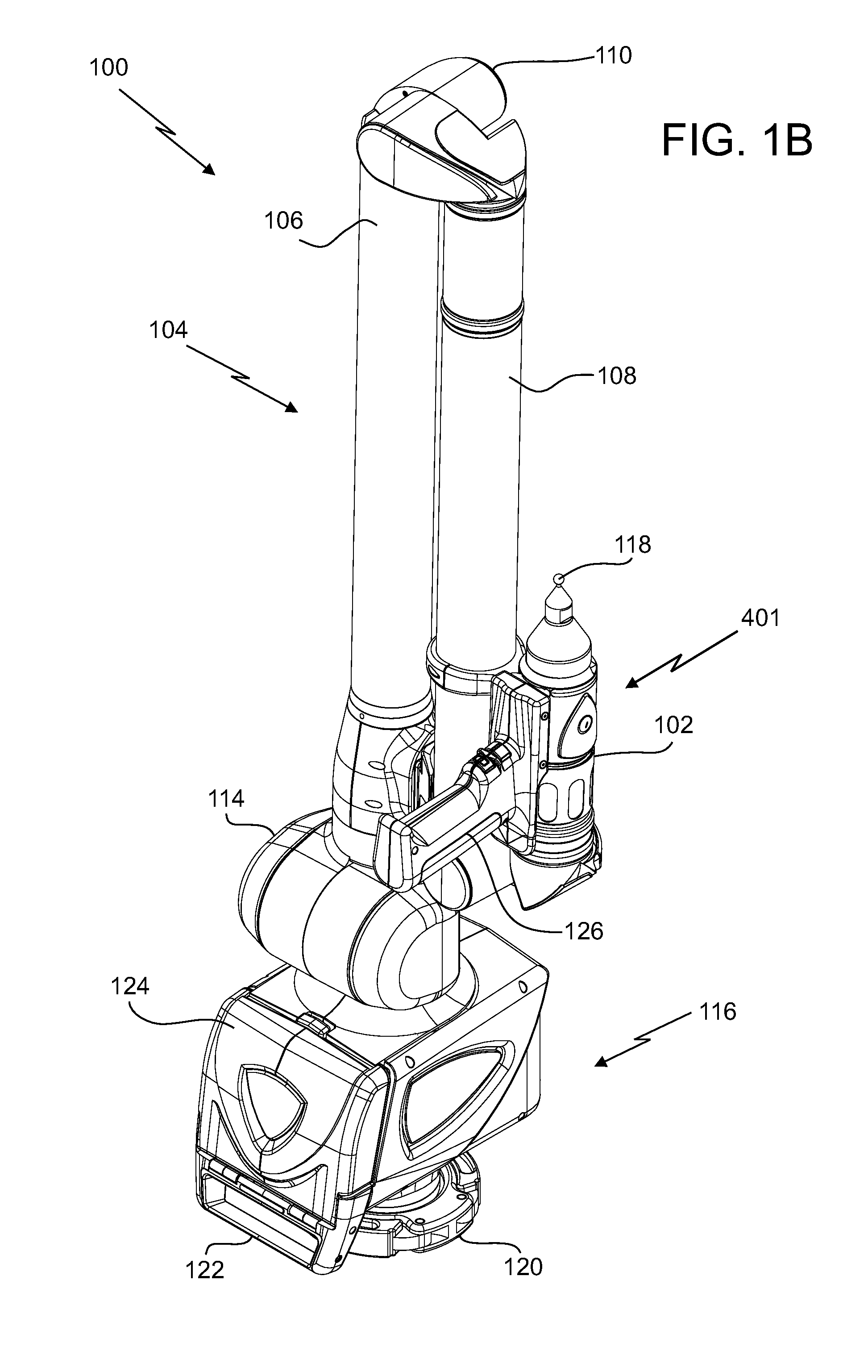
Laser line probe that produces a line of light having a substantially even intensity distribution
A laser line probe (LLP) configured to measure an object is provided. The LLP includes a projector, a camera, a bracket, and an electronic circuit. The projector includes a light source, a first lens system and a continuously varying neutral density filter. The projector is configured for generating a line of light having a substantially even intensity distribution and for projecting the line of light onto the object. The camera includes a second lens system and a photosensitive array. The second lens system is configured to collect the light reflected by or scattered off the object as a first collected light and to image the first collected light onto the photosensitive array. The electronic circuit includes a processor and is configured to determine three-dimensional coordinates of a plurality of points of light projected on the object by the projector.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
Visual monitoring, or imaging, system and method for using same
Owner:BWXT NUCLEAR OPERATIONS GRP
Stable light source device
ActiveUS20120248989A1Electroluminescent light sourcesElectric light circuit arrangementLuminous fluxLight emission
A stable light source device is provided with a light source, a pinhole constricting optical flux emitted from the light source, a first integrating element inside which optical flux from the pinhole is multiply reflected, a light detection sensor monitoring a light amount, a control section controlling the light source on the basis of the light amount monitored by the light detection sensor and making the light amount consistent, an aperture formed in the first integrating element and emitting light outside the first integrating element, a diffusion-transmission member disposed at a light emission side of the aperture, a branching section disposed at a light emission side of the diffusion-transmission member and branching incident light towards plural light emission portions, and neutral density filters provided at the light emission portions, transmitted light amounts thereof respectively differing such that light amounts at the light emission portions are respectively different.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
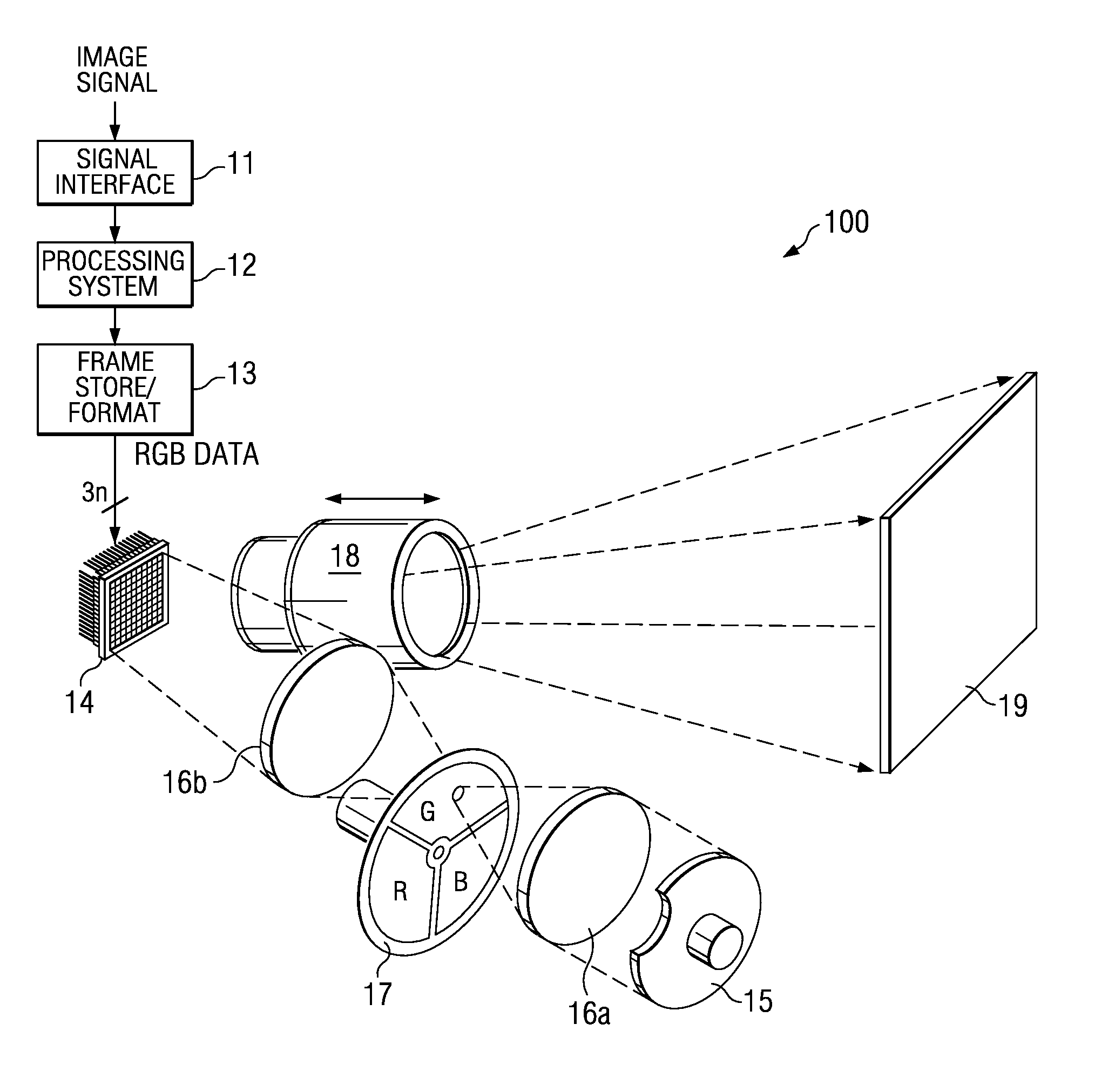
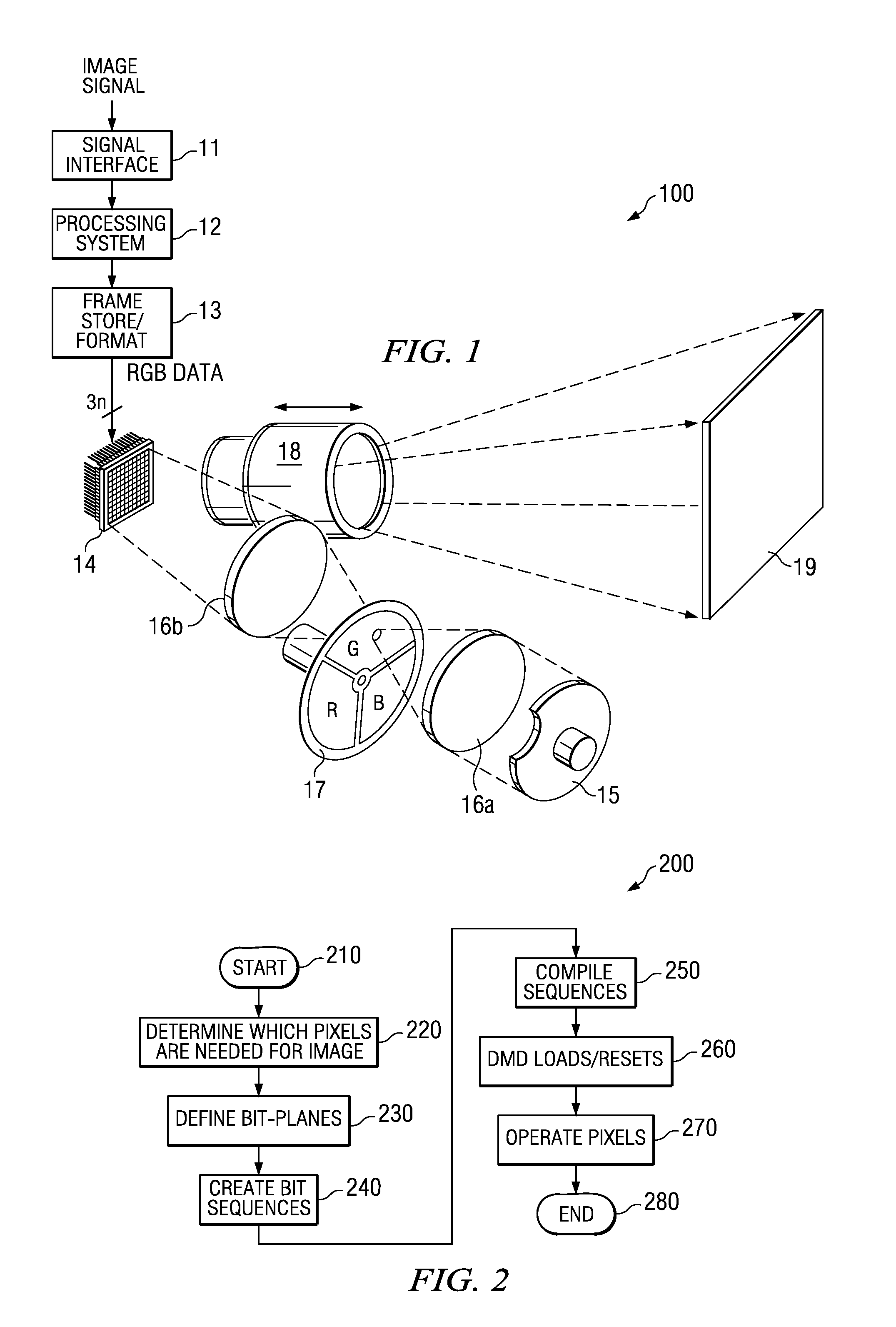
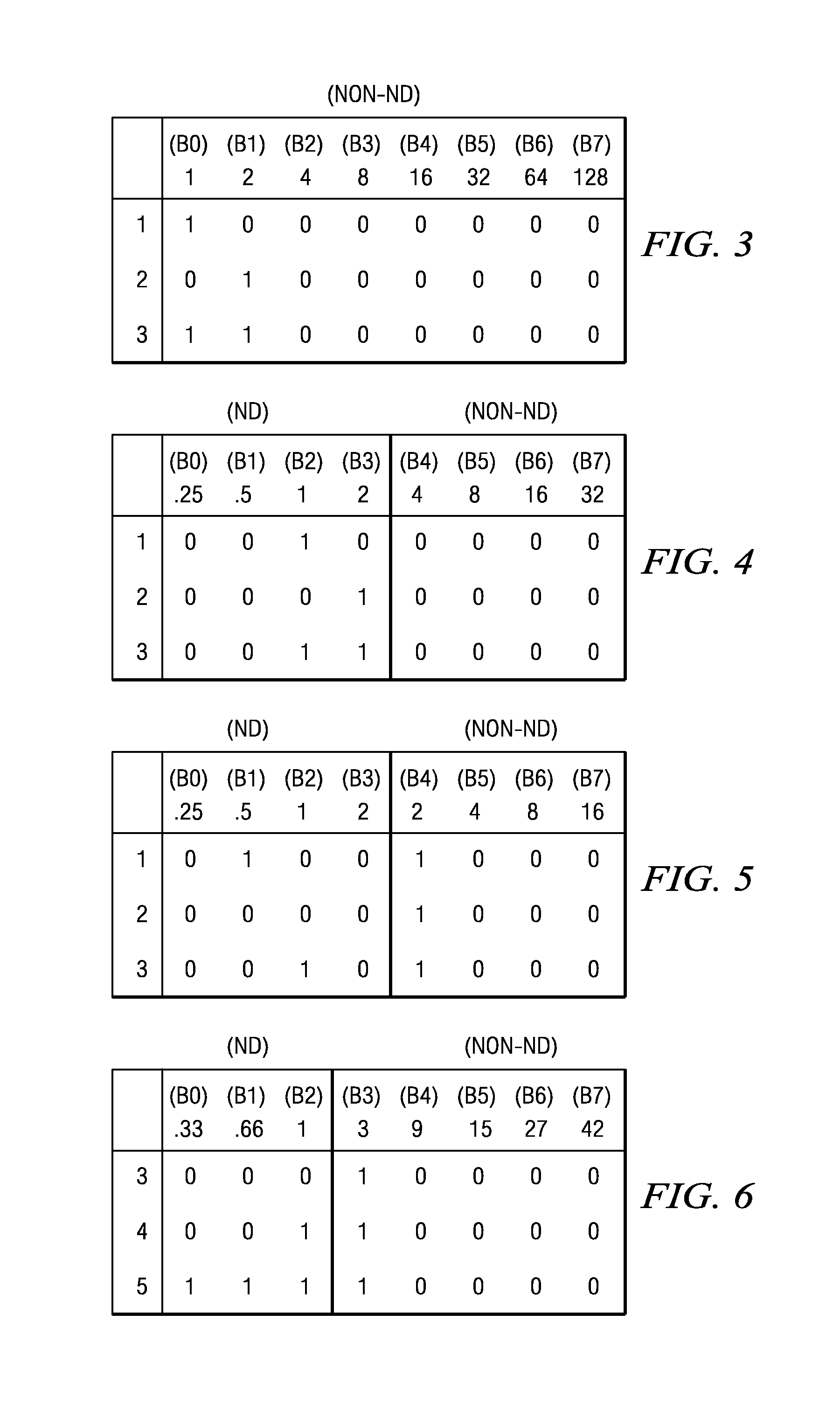
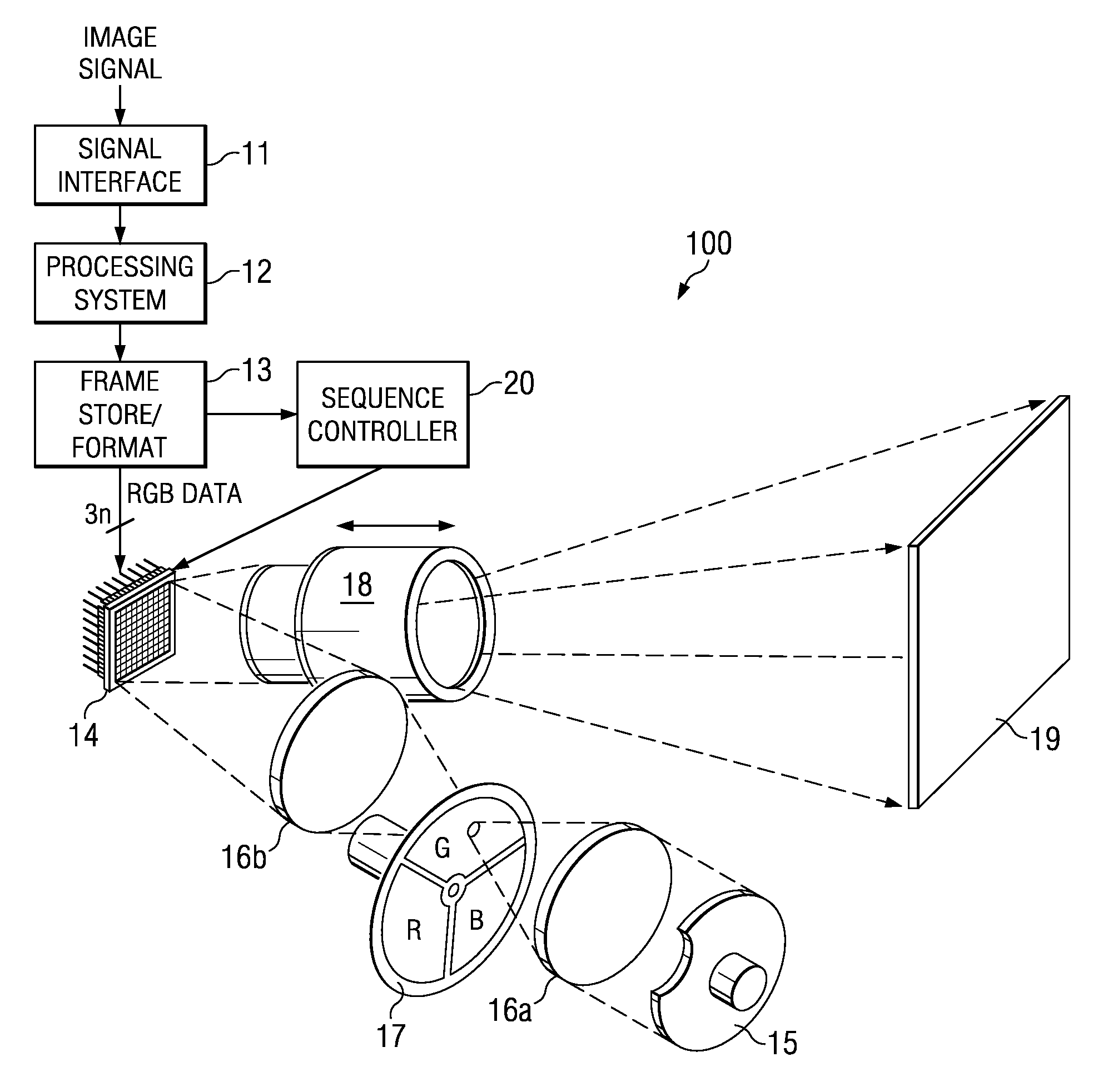
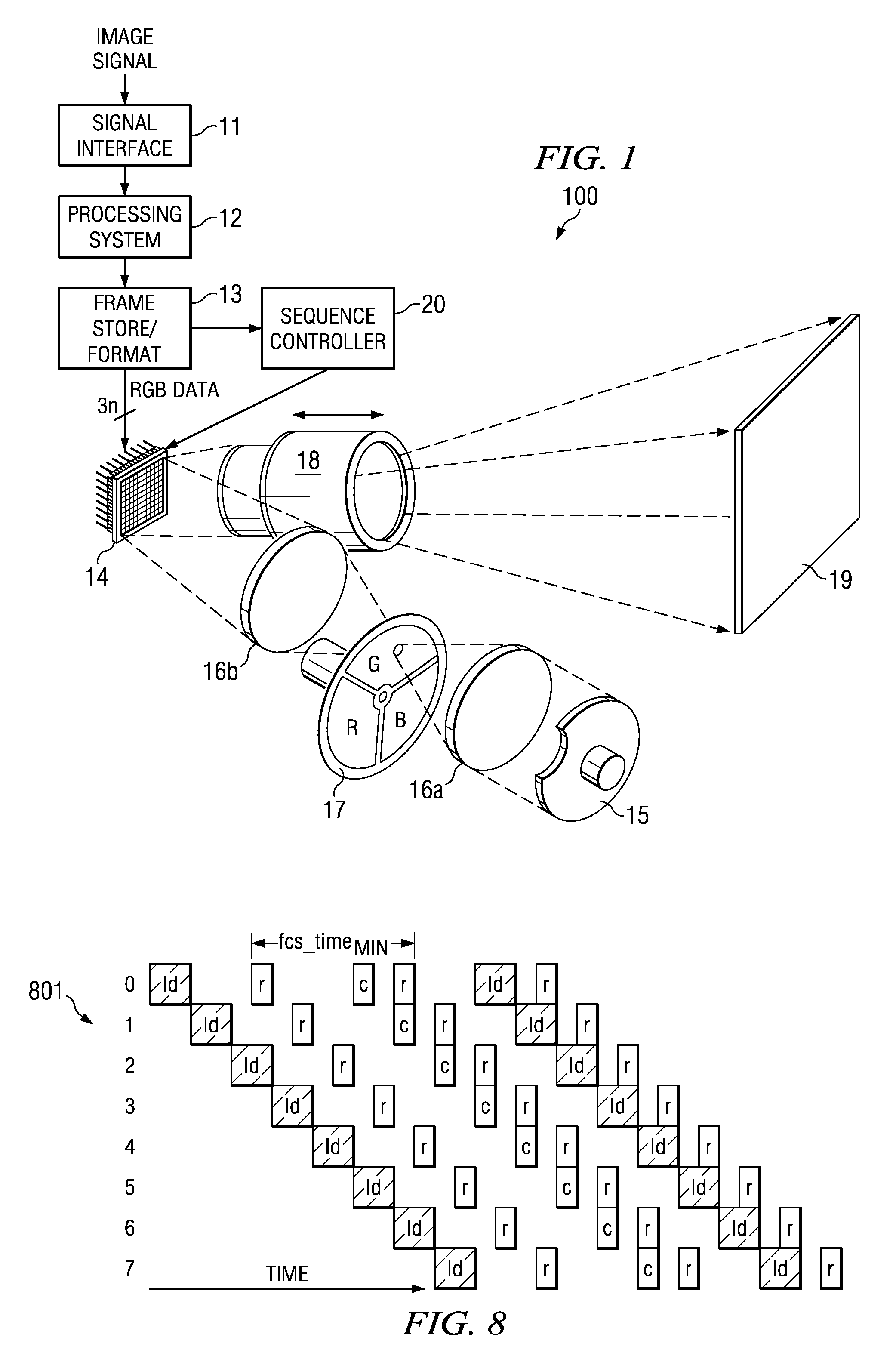
Digital system and method for displaying images using shifted bit-weights for neutral density filtering applications
Disclosed herein are visual display systems and methods capable of having shifted bit-weights in neutral density filtering (NDF) applications. In one embodiment, a method (200) of displaying an image comprises transmitting light through an optical filter (17) comprising at least one high transmissivity portion configured to output light at an initial intensity, and at least one low transmissivity portion configured to output light at a lower intensity than the initial intensity, where the initial intensity and lower intensity output light illuminates a spatial light modulator (14). The method also includes providing a plurality of data bits (non-ND) from a predetermined number of data bits (B0–B7), where each of the plurality comprises a pulse-width longer than a load-time for operating the spatial light modulator (14). In this embodiment, the method further includes providing at least one data bit (ND) from the predetermined number of data bits, where the at least one data bit comprises an initial pulse-width less than the load-time and comprises an adjusted pulse-width greater than the load-time. Then, the method further comprises operating selected portions of the spatial light modulator (14) in coordination with the initial intensity and lower intensity output light using the pulse-widths of one or more of the plurality of data bits (non-ND) and the adjusted pulse-width of the at least one data bit (ND).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Machine for binocular testing and a process of formatting rival and non-rival stimuli
A process for formatting rivalrous fusible images having similarly shaped stimuli of similar binocular luminance and having other similarly shaped stimuli of different binocular luminance, which metamorphose during perception into identifiable shapes that distinguish fusion from suppression. The preferred embodiment is an invertible stereoscope for viewing rivalrous images, non-rivalrous images, and stereograms, having adjustable eyepieces, lighting control of front and rear chambers, and lighting control of right and left sides. In a further preferred embodiment, rivalrous stimuli in a complementary color scheme are viewed on printed material or on a computer screen through lenses of complementary colors. Neutral density filter placement that asymmetrically attenuates light to the eyes for detection of sub-threshold afferent defects is disclosed.
Owner:HOFELDT ALBERT JOHN
Dichroic neutral density optical filter
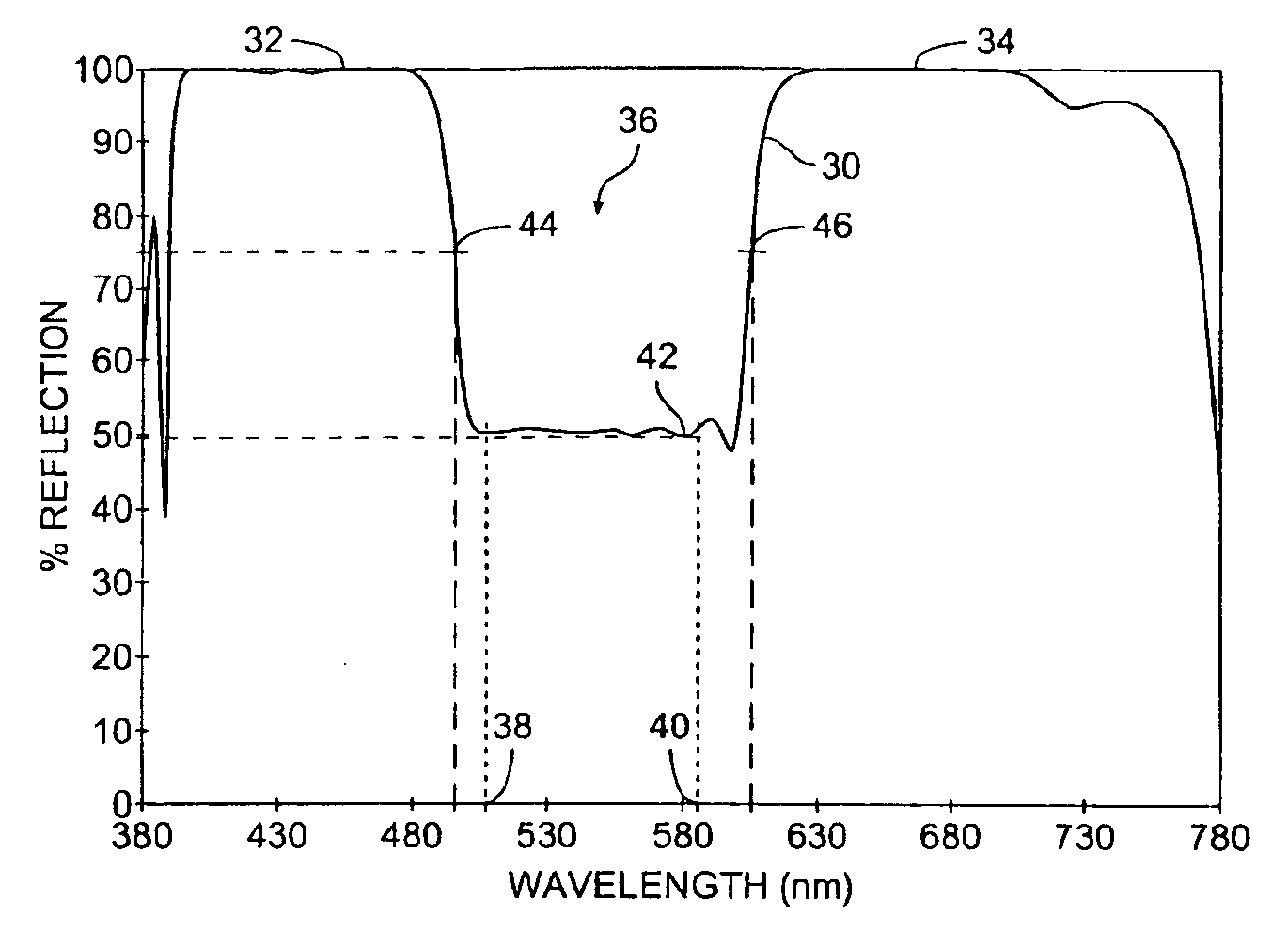
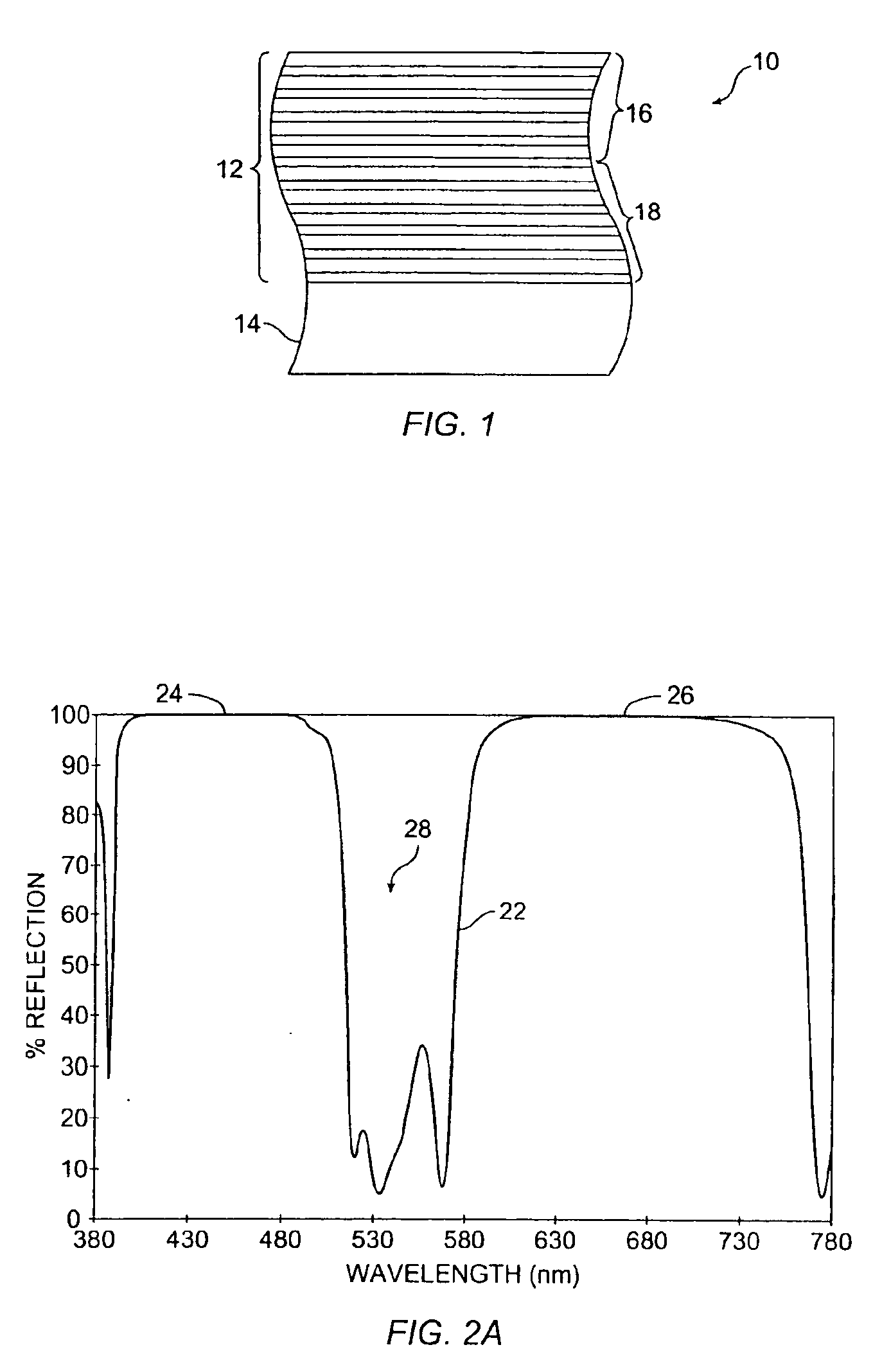
An optical thin film stack provides reflection of essentially all light except for a selected amount of transmission over a selected wavelength range. Reflecting, rather than absorbing, unwanted light avoids heating caused by light absorption and allows productive use of the non-transmitted light in some applications. In some embodiments, reflector designs are “stacked” on an optical substrate to provide serial optical reflectors. Stacking dichroic filters provides reduced sensitivity to cone angle and manufacturing advantages.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
High dynamic range imaging device using multiple pixel cells
ActiveUS7636115B2High sensitivityEasily saturatedImage enhancementTelevision system detailsHigh-dynamic-range imagingComputer science
A method and apparatus for achieving high-dynamic range operation with a set of spatially distributed pixel cells is provided. A pixel array with a row of pixels having apertures of varying sizes in a metal mask formed thereon controls the sensitivity of each pixel cell to light. A neutral density filter having varying light transparency values is also provided over the set of pixel cells to control the sensitivity of each pixel cell to light. The pixel cells voltage outputted is combined to obtain high-dynamic range operation.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Sinusoidal phase modulation type laser self-mixing interferometer and measuring method thereof
InactiveCN103528511ASimple structureCompact structureUsing optical meansElectromagnetic wave reradiationFrequency multiplierOmega
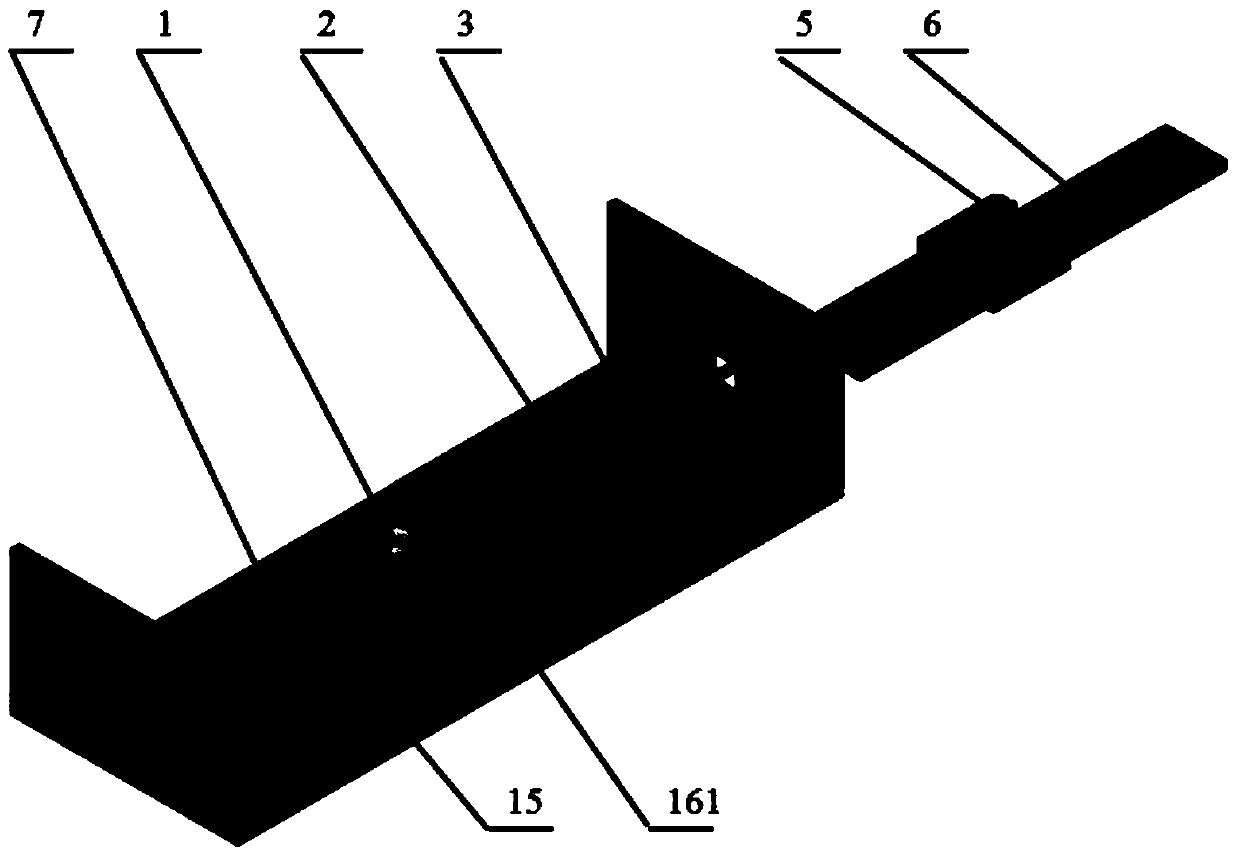
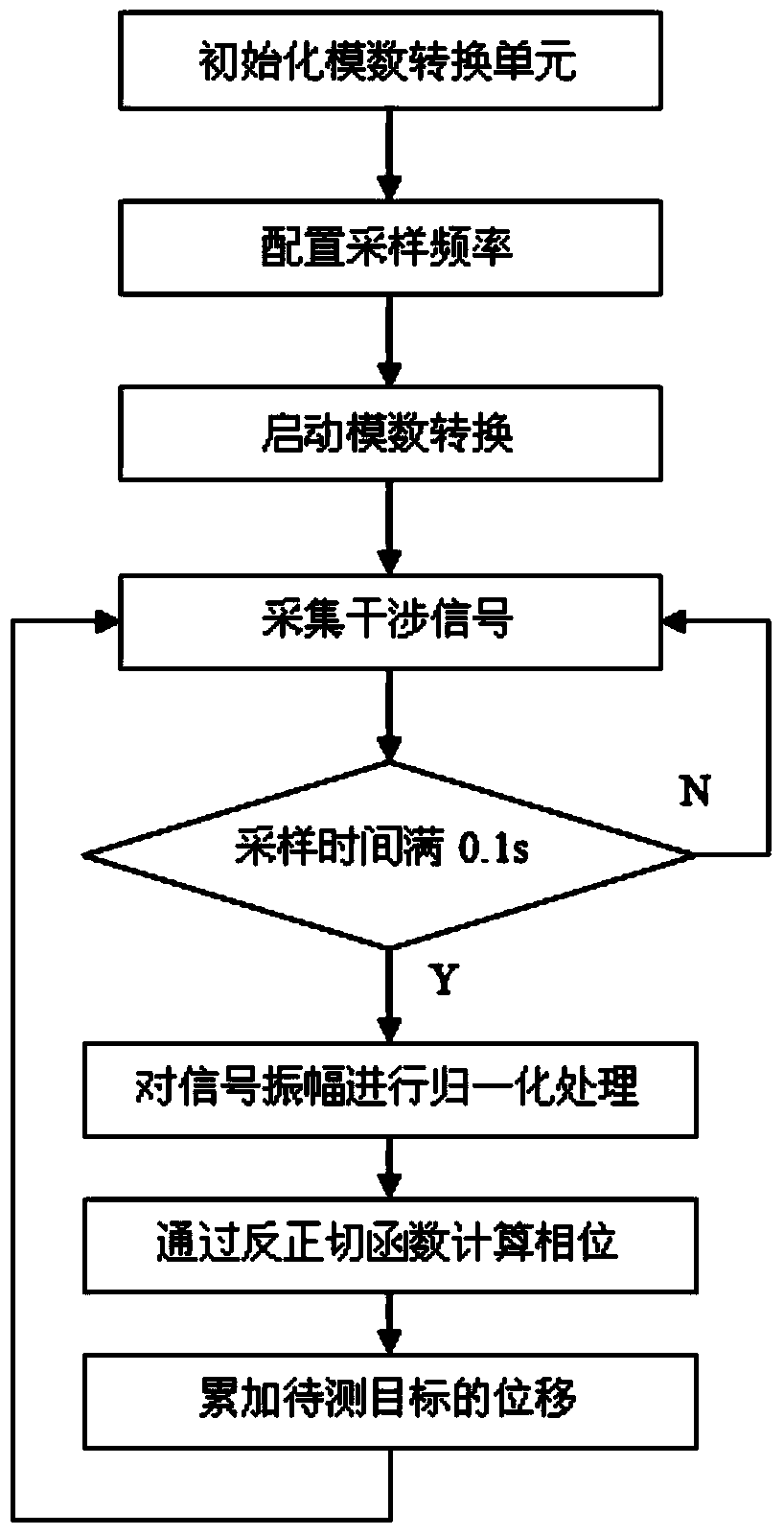
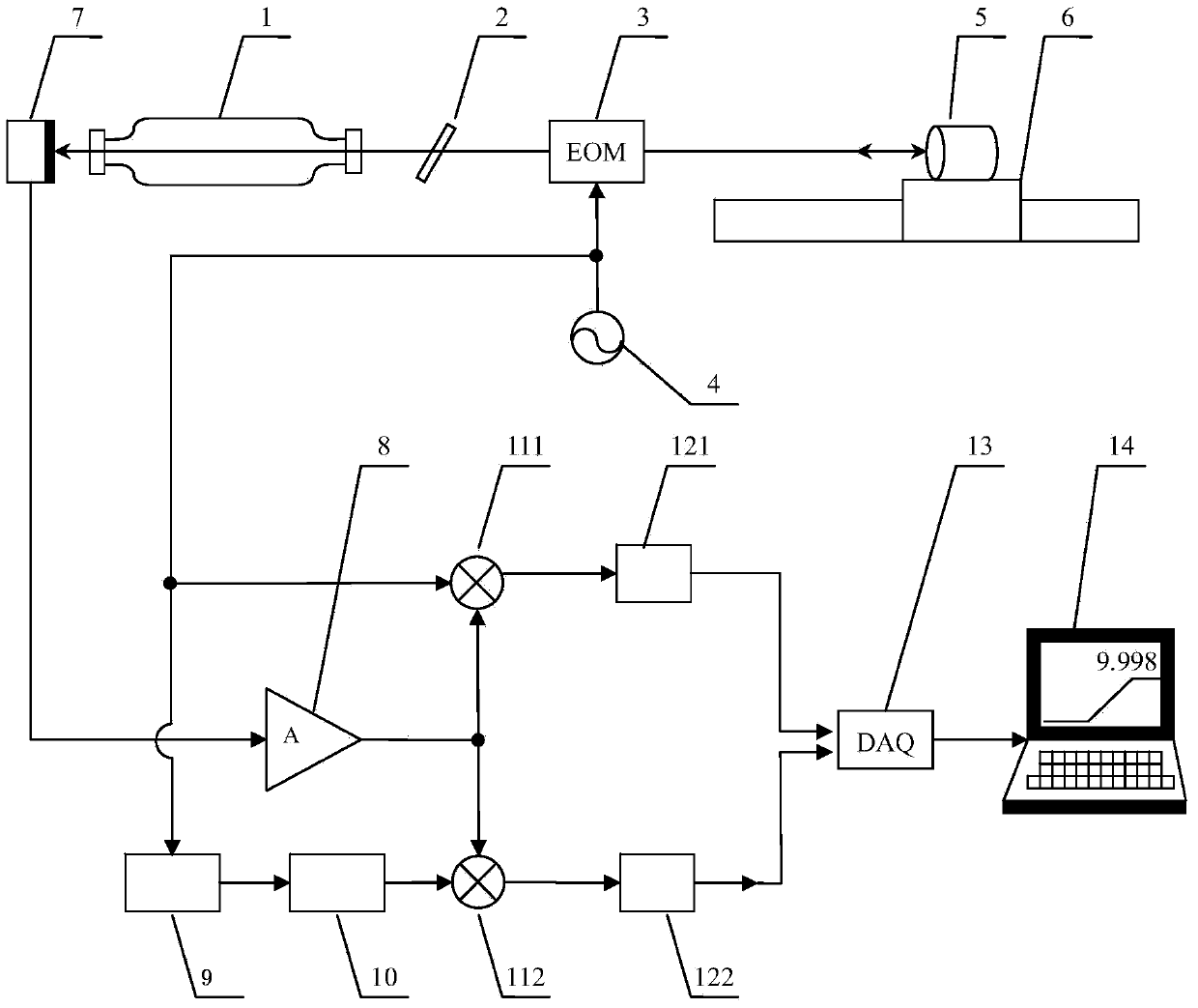
The invention discloses a sinusoidal phase modulation type laser self-mixing interferometer and a measuring method thereof. The interferometer comprises a helium-neon laser, a variable neutral density filter, an electro-optical crystal modulator, a target to be measured, a photoelectric detector and a signal generator. The signal generator is used for generating sinusoidal signals with frequency of omega<m>, wherein one loop of signals is used for driving the electro-optical crystal modulator, one loop of signals is used as base-frequency signal output and the other loop of signals passes through a frequency doubler and a phase shifter and then outputs doubled-frequency signals with frequency of 2 omega<m>. The output of the photoelectric detector is amplified by an operational amplifier and then is respectively mixed with the base-frequency signals and the doubled-frequency signals to obtain two loops of signals. The signals are subject to low-pass filtering and then a computer unit controls an analog-to-digital conversion unit to acquire and demodulate a phase, so as to obtain and display the real-time displacement of the target to be measured. After the interferometer is calibrated, relative measurement accuracy of 10<-6>*L can be obtained, the measurement uncertainties within the measurement ranges of 100mum and 300mum are respectively 10nm and 0.15mum, and the measurable speed range is 0-60mm / s.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Camera blade shutter module
The present invention is a miniature camera shutter module for use in miniature camera applications. It is an object of the present invention to provide the miniature camera shutter module with solenoid controlled blades in order to alter the amount and quality of light passing through a conduit disposed on the surface of the module. In some embodiments of the present invention, the blade comprises a shutter to completely block light. In other embodiments, the blade comprises an aperture, a neutral-density filter, a monochromatic filter, and the like. In some embodiments of the present invention, the miniature camera shutter module is positioned within a more elaborate miniature camera chassis.
Owner:NANCHANG O FILM OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Double-beam delayed laser damage testing system
ActiveCN104101486AMeet laser damage test requirementsTesting optical propertiesElectronic shutterAutomatic control
The invention discloses a double-beam delayed laser damage testing system. The system is composed of a pulse laser, a laser controller, seven reflecting mirrors, four light splitters, two annular changeable neutral-density filtering sheets, an electrically controlled translation platform, a motor driver, a main control computer, an electronic shutter, two plano-convex lenses, a three-dimensional electrically controlled sample platform, a beam quality analyzer, an energy detector, a high-resolution color CCD imaging device and a white light source. With the utilization of the computer, the double-beam delayed laser damage testing system realizes automatic control by utilizing the computer, and can perform laser damage threshold testing of lasers in different pulse widths on the surface of an optical element.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
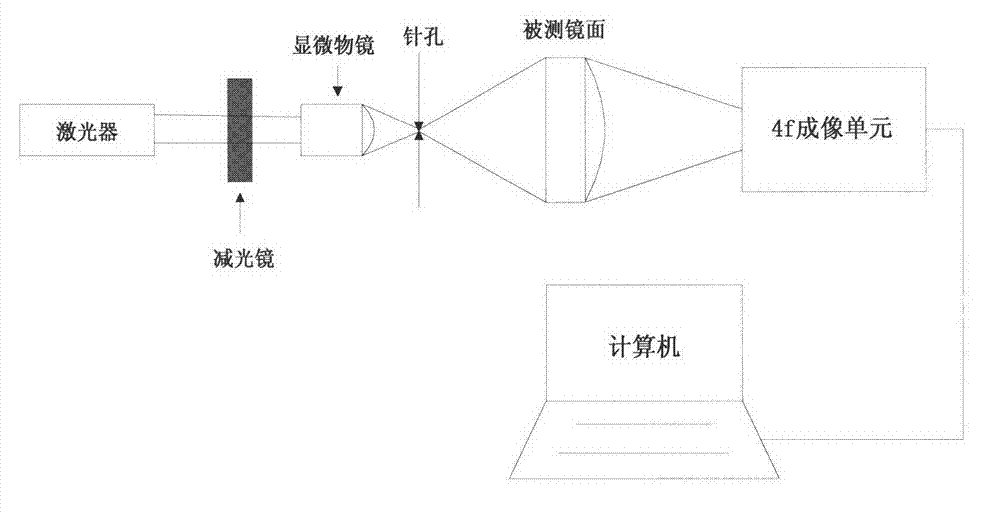
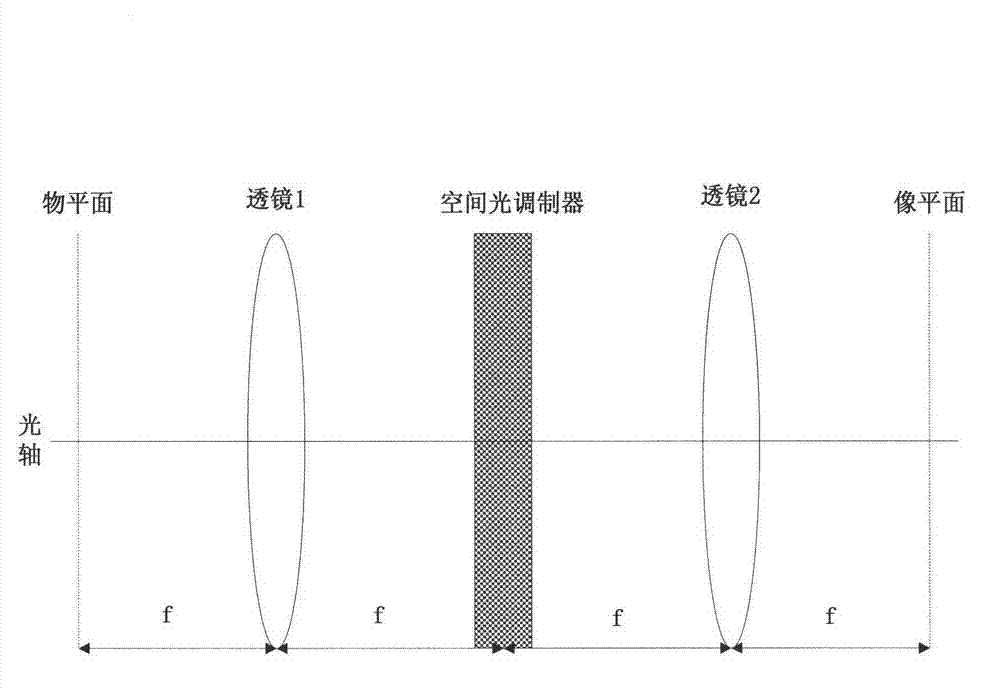
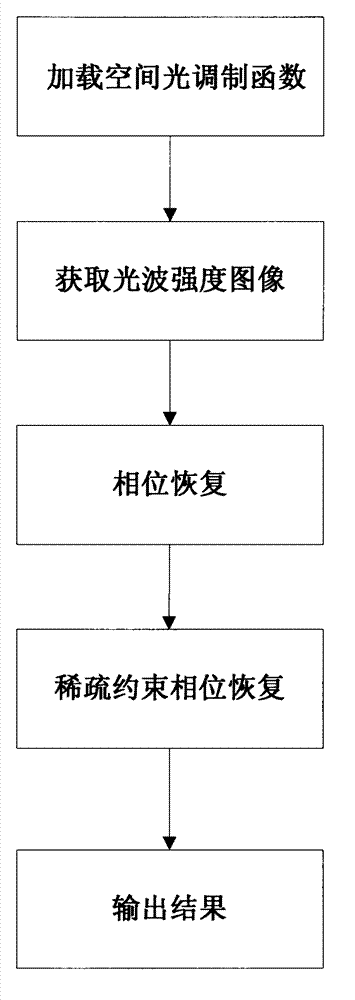
Phase retrieval based 4f mirror surface detection imaging system and phase retrieval based 4f mirror surface detection imaging method
InactiveCN102865832ARealize multiple modulation samplingOvercome the disadvantage of poor stability of strengthUsing optical meansTesting optical propertiesSpatial light modulatorSparse constraint
The invention discloses a phase retrieval based 4f mirror surface detection imaging system and a phase retrieval based 4f mirror surface detection imaging method. The system comprises a laser, a neutral density filter, a microobjective, a pinhole, a measured mirror surface, a 4f imaging unit and a computer, wherein the 4f imaging unit comprises a lens 1, a space light modulator, a lens 2 and a charge coupled device (CCD) camera. The light emitted by the laser irradiates the measured mirror surface after passing through the neutral density filter, the microobjective and the pinhole. The CCD camera arranged in the 4f imaging unit is used for acquiring a plurality of times of a light wave modulation image, and then the image is sent into the computer for sparse constraint phase recovery treatment. Based on the acquired light wave intensity image of the measured mirror surface, the method utilizes the sparse constraint phase recovery treatment to obtain the phase position of the light wave on the measured mirror surface, thus realizing the error detection for the measured mirror surface. The invention has the advantages of being high in accuracy, good in stability, simple in operation and good in noise robustness.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Photo Sensor Array Using Controlled Motion
InactiveUS20100091124A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSensor arrayExposure value
A movable sensor including a plurality of photo pixel sites arranged in an array comprising a photo sensor and a neutral density filter filtering the photo sensor. Each of the neutral density filters have a density value that are graduated over a range of densities. The sensor is linearly movable across an image. Each point in the image is exposed to at least one pixel site with the graduated density values and each of the photo pixel sites of the array is exposed to a same light input during a time span of exposure, such that the image is captured at a defined range of exposure values and can be combined into a single high dynamic range image.
Owner:IBM CORP
Image capturing device and image capturing method
InactiveUS20130107017A1Reduce the amount requiredQuality improvementTelevision system detailsCamera filtersParallaxLuminous flux
The quality of a planar image is improved while maintaining the parallax of a stereoscopic image. An image capturing device includes an imaging element that performs photoelectric conversion on respective light fluxes passing through different regions of a single pickup lens. The image capturing device includes a neutral density filter an AE control unit that acquires subject brightness, and a diaphragm control unit that, in a case of the stereoscopic pickup, controls whether or not to reduce the amount of light which reaches the imaging element using the neutral density filter based on the subject brightness, and that, in a case of the plane pickup, causes a diaphragm value of the diaphragm to be greater than a diaphragm value in the case of the stereoscopic pickup while setting the light extinction filter to a non-insertion state.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Bit segment timing organization providing flexible bit segment lengths
Disclosed are reset techniques for a spatial light modulator, and related system for displaying an image. The systems and methods have pixels that are loaded with data and reset commands to take on binary states, where the methods employ adaptable algorithms to provide flexibility in placement of the reset commands. Specifically, valid regions for such reset commands are determined, and times for consecutive bit segments are calculated; and DMD load times are adjusted for a proper sequence. An advantage of the disclosed methods is that two consecutive bit segments are no longer restricted to following a pattern of normal / short bit segments. In contrast, with the disclosed technique short segments may be consecutive, allowing the implementation of additional enhancements, including neutral density filtering (NDF) techniques that typically include adjacent short bits in the bit sequence.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Laser height measuring device and component mounting machine
ActiveCN103609209AEasy to controlGuaranteed control accuracyUsing optical meansElectrical componentsOptoelectronicsIrradiation
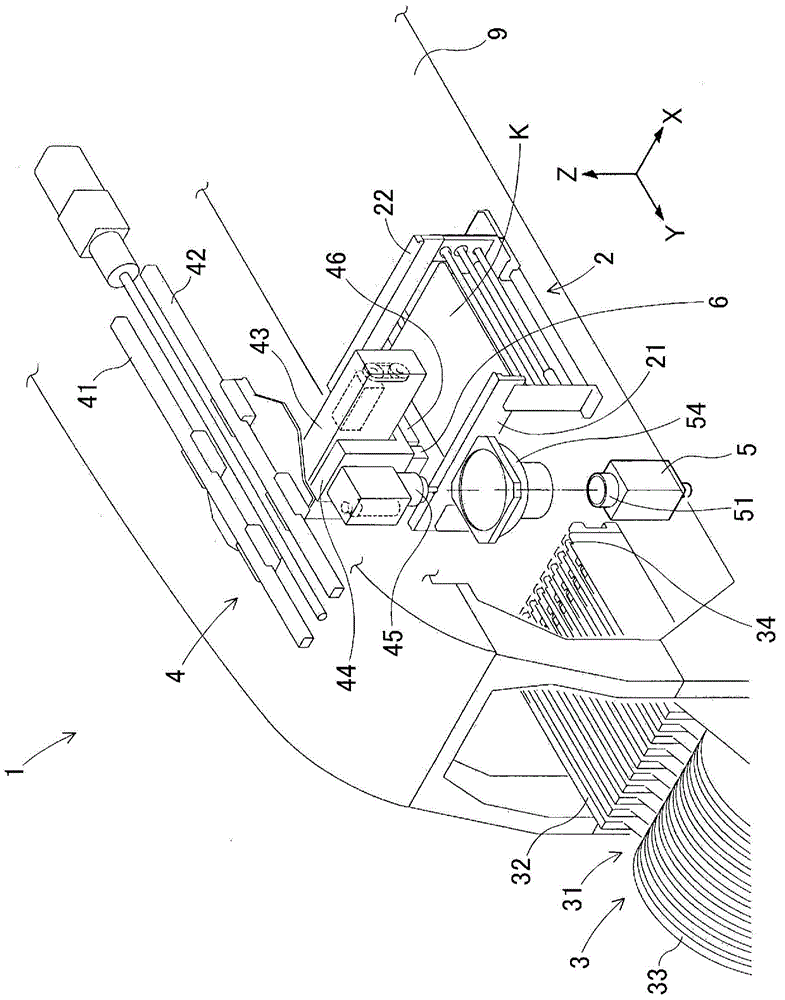
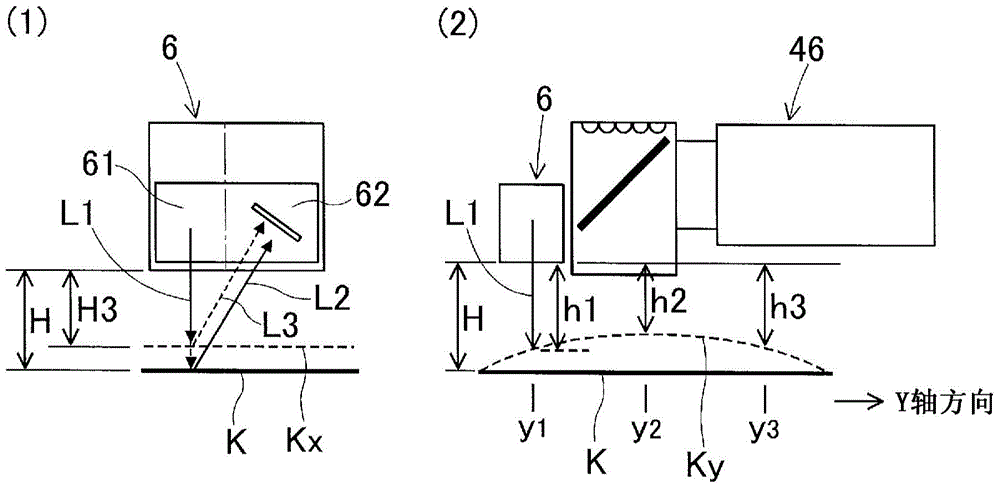
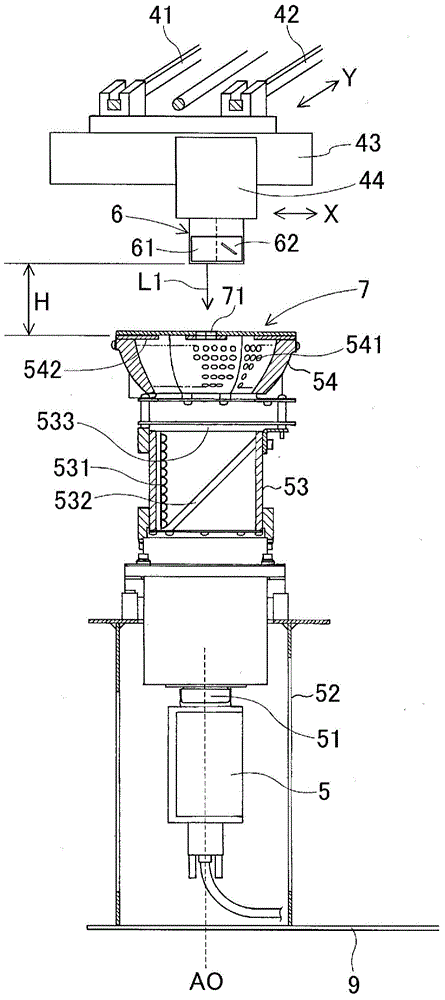
This laser height measuring device is provided with: a laser height sensor (6) comprising a laser beam irradiation section (61) for emitting a laser beam (L1) and a reflected light detection section (62) for detecting the laser beam reflected off an object to be irradiated; a sensor movement mechanism (head drive mechanism (41-43)) for moving the laser height sensor (6) within a plane; an imaging camera (component camera (5)) that is provided at a predetermined calibrating position (light incidence axis (AO); a neutral density filter (71) that allows the laser beam (L1) to pass while attenuating the laser beam; a laser beam imaging means that positions the laser height sensor (6) at the calibrating position (AO), emits the laser beam (L1), and captures an image of the laser beam which has passed the neutral density filter (71) using the imaging camera (5) in order to obtain a laser beam image; and a correction value acquisition means that obtains values for correcting the coordinates of the laser beam on the basis of the position of the laser beam in the laser beam image. Thus, the measuring position can be controlled accurately, and the accuracy of measuring position control can be maintained without requiring a sensor installation position adjustment mechanism or a positional adjustment operation.
Owner:FUJI KK
Lens barrel
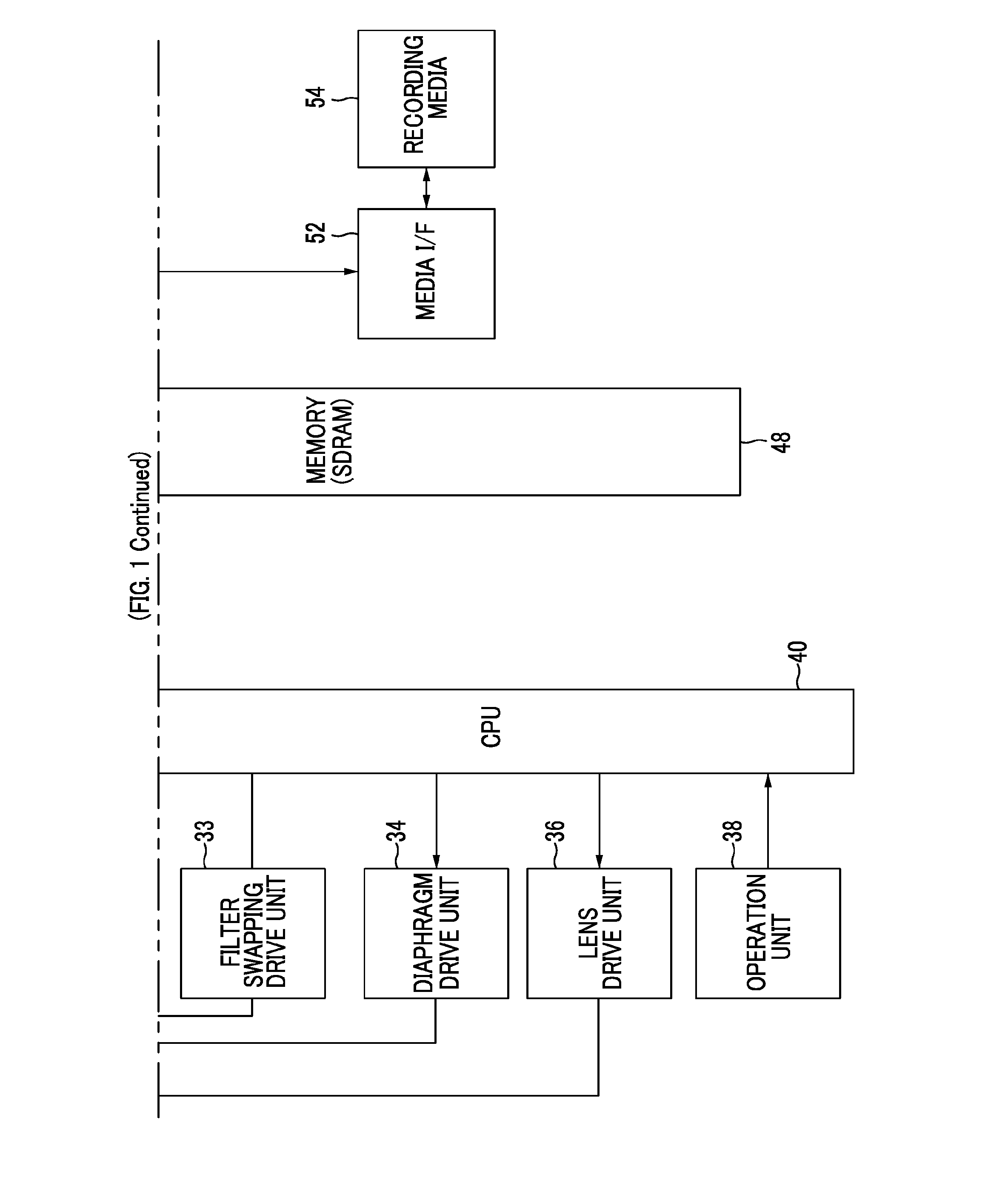
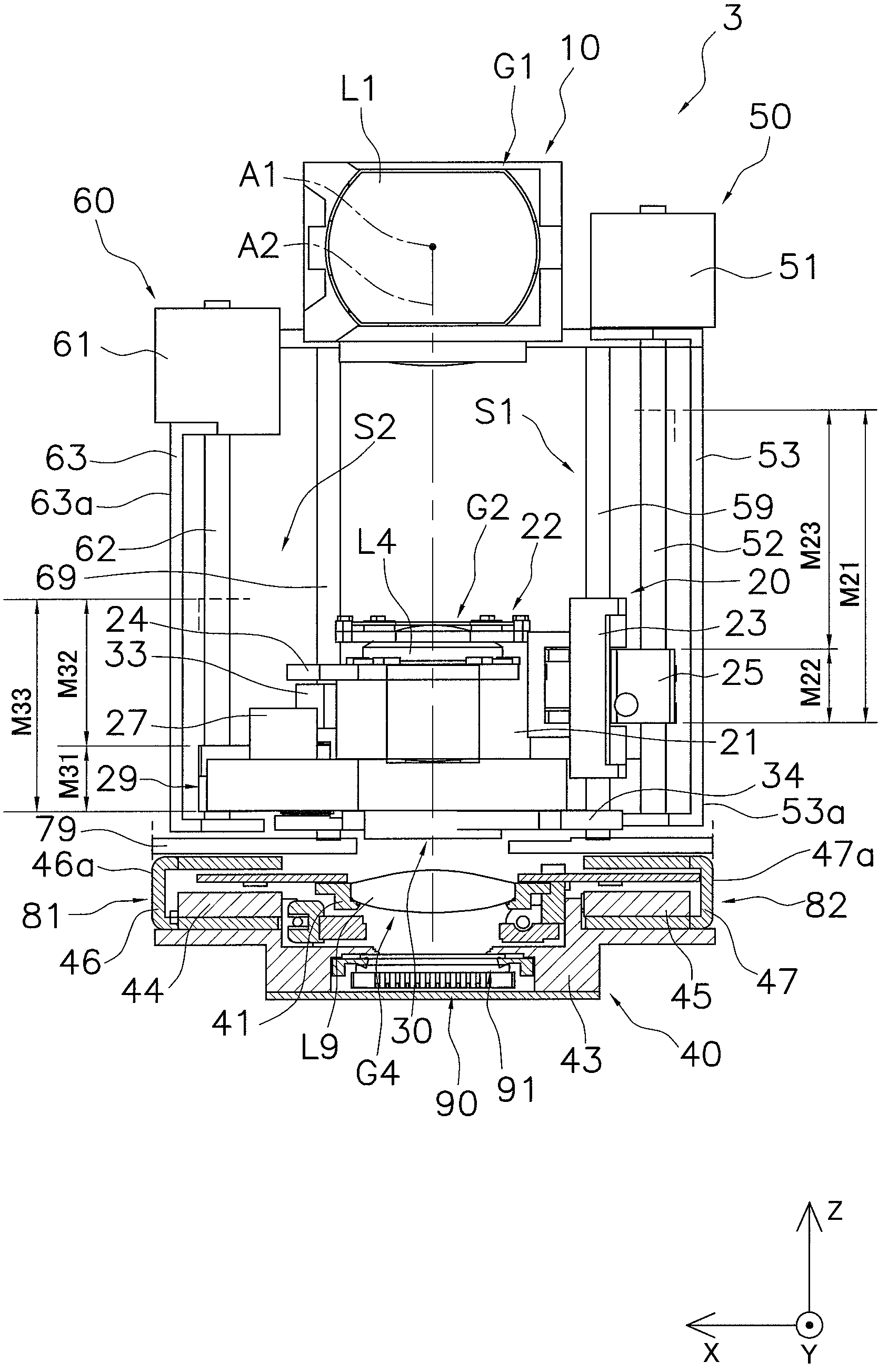
A lens barrel has a first lens group, a second lens group, a third lens group, a first support frame for supporting the first lens group, a second support frame for supporting the second lens group, a first driving unit, a shutter unit, and an aperture unit. The first lens group has an overall negative refractive power, and includes a prism. The second support frame is driven along a second optical axis by the first driving unit. The shutter unit has a shutter mechanism, a shutter drive motor configured to drive the shutter mechanism, a neutral density filter, and a filter drive motor configured to drive the neutral density filter. The shutter drive motor and the filter drive motor are disposed flanking the second optical axis when viewed in a direction along the second optical axis.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Concentration measuring device and method for dust in large diameter range
ActiveCN104374677AHigh sensitivityQuick responseParticle suspension analysisComputational physicsLight extinction
The invention discloses a concentration measuring device and method for dust in large diameter range. Aiming at the shortcoming that scattering integration method in the prior art is not applicable when the particle size is smaller than 10 microns, the measuring device uses a multistep neutral density filter to attenuate transmission light and scattered light to a same light intensity level, realizes simultaneous shooting of transmission light and scattered light in a measurement system of a single digital area-array camera, and has the advantages of high sensitivity, fast response and simple and compact optical system. According to the obtained information of scattered light and transmission light, the distribution of particle size can be acquired; with the known particle size distribution, a method combined scattered light with scattering integration can be used to measure dust concentration of micron level, and a method combined transmission light with light extinction can be used to realize the measurement of dust concentration of submicron and nanometer levels. The invention successfully realizes the measurement of dust concentration of micron, submicron and nanometer levels, covers large particle size range, and has great market advantage.
Owner:NANJING INST OF MEASUREMENT & TESTING TECH
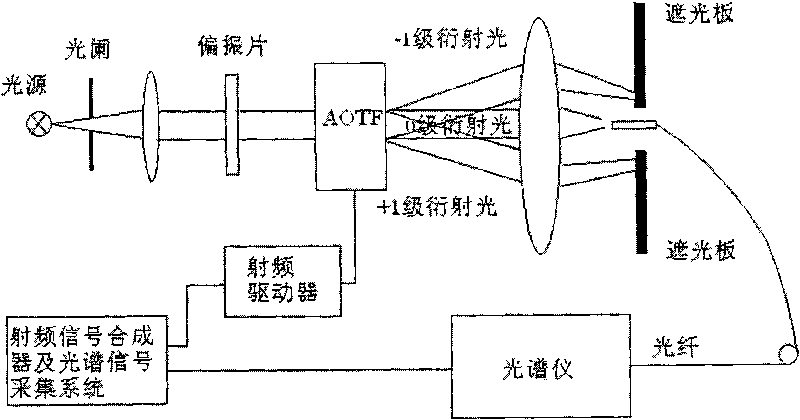
System and method for testing diffraction efficiency of acousto-optic tunable filter
InactiveCN101706361AMeet the densityMeet needsTesting optical propertiesBeam splittingAcousto-optics
The invention discloses a system for testing the diffraction efficiency of an acousto-optic tunable filter (AOTF). The system comprises a wavelength tunable laser, a neutral density filter, a diaphragm orifice, a beam splitting mirror, a two-dimensional electric turnplate and an energy meter. The wavelength tunable laser can generate laser beams with continuously adjustable wavelength, the laser beams after passing through the neutral density filter and the diaphragm orifice are split into two beams of lasers with fixed beam splitting ratio by the beam splitting mirror, and the energy of reflecting beams is used as reference energy; transmission beams enter the AOTF, the energy of diffracted light is received when radio-frequency drive is applied to the transmission beams, and energy with direct penetration is received when the drive is not applied to the transmission beams, thereby calculating the diffraction efficiency of the AOTF. Meanwhile, the measurement of an aperture angle can be realized by changing the angle of incident light through the two-dimensional electric turnplate. The device has the characteristics of simple principle and strong operability, can meet the requirement of testing the continuous wavelength of the AOTF and can also enhance the testing accuracy greatly by utilizing reference beams generated by the beam splitting mirror.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Coherent self-adaptive optical aberration correction system
InactiveCN105242397ARealize aberration correctionAchieve coherent enhancementOptical elementsSpatial light modulatorLight beam
The invention discloses a coherent self-adaptive optical aberration correction system. The system comprises a laser light source, a reflective mirror, a spatial light modulator, and a neutral density filter, a half-wave plate and a beam expanding lens that are sequentially disposed in an incident light path of the reflective mirror. The reflected light of the reflective mirror serves as incident light of the spatial light modulator, and an angle between the incident light and the reflected light of the spatial light modulator is controlled by means of the reflective mirror. The control over coherent emphasis and coherent weakening of two light beams, regulation and control on the phase position of one of the two light beams can be achieved, so aberration correction of a microscopic system is achieved. A reference light source needs not to be implanted in sample, and the aberration correction speed is fast, so the system is quite suitable for deep aberration correction imaging of an in vivo sample.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Method and device for forming PN junction on P type mercury cadmium telluride by laser process
InactiveCN101315957AReduce photolithography process stepsThe knotting process is simpleLaser beam welding apparatusSemiconductor devicesFemto second laserDisplay device
The invention relates to a laser processing method for forming a PN-junction on a P-typed Hg-Cd-Te material and a device thereof. The method comprises the following steps that: a pulse laser is focused on the surface of the P-typed Hg-Cd-Te material and the P-typed Hg-Cd-Te material is radiated in short time, thus forming a porous area melted and corroded on the material by the laser; the diameter of the pore is within a range from several micrometers to ten micrometers or so; an inversion area, namely an N-typed area is formed in the several micrometer area around the pore; the inversion area and the P-typed area at the periphery of the pore form a PN-junction area. The device of the invention consists of a femto-second laser, a deflecting mirror, a neutral density filter, a pupil, an aperture, a dichroic mirror, a lens, a CCD camera, a display and a workpiece platform. As the method of the invention has the advantages of laser direct writing, saves the lithography process step in the traditional junction-forming technique, leads the junction-forming process to be simplified and is beneficial to reducing the dead pixel caused by the process complexity. The method of the invention is completely compatible with other techniques of the prior art in the field such as read-out circuit technique and has direct and practical value.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
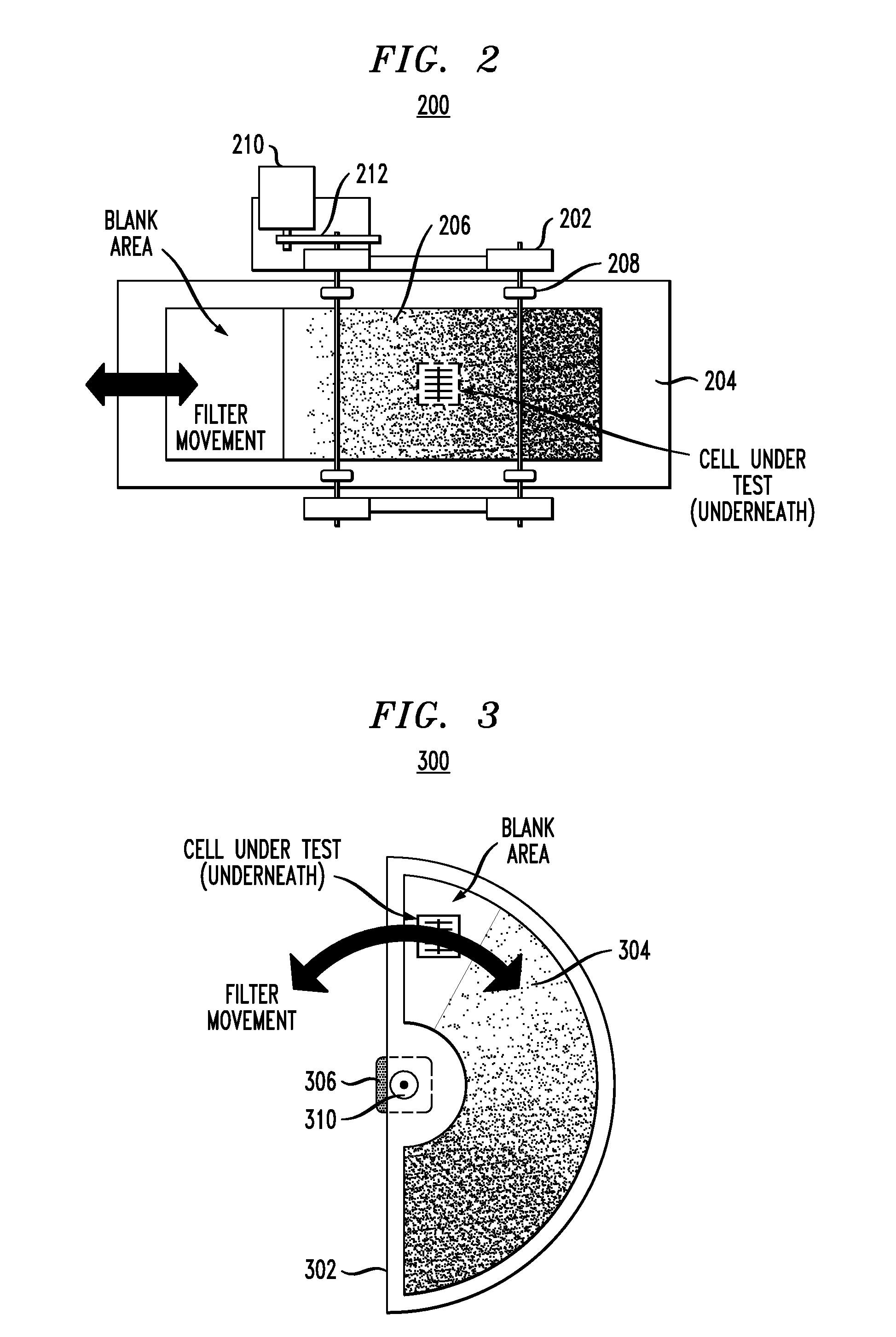
Solar cell characterization system with an automated continuous neutral density filter
Techniques for solar cell electrical characterization are provided. In one aspect, a solar testing device is provided. The device includes a solar simulator; and a continuous neutral density filter in front of the solar simulator having regions of varying light attenuation levels ranging from transparent to opaque, the continuous neutral density filter having an area sufficiently large to filter all light generated by the solar simulator, and wherein a position of the continuous neutral density filter relative to the solar simulator is variable so as to control a light intensity produced by the device. A solar cell electrical characterization system and a method for performing a solar cell electrical characterization are also provided.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Solid state light source with hybrid optical and electrical intensity control
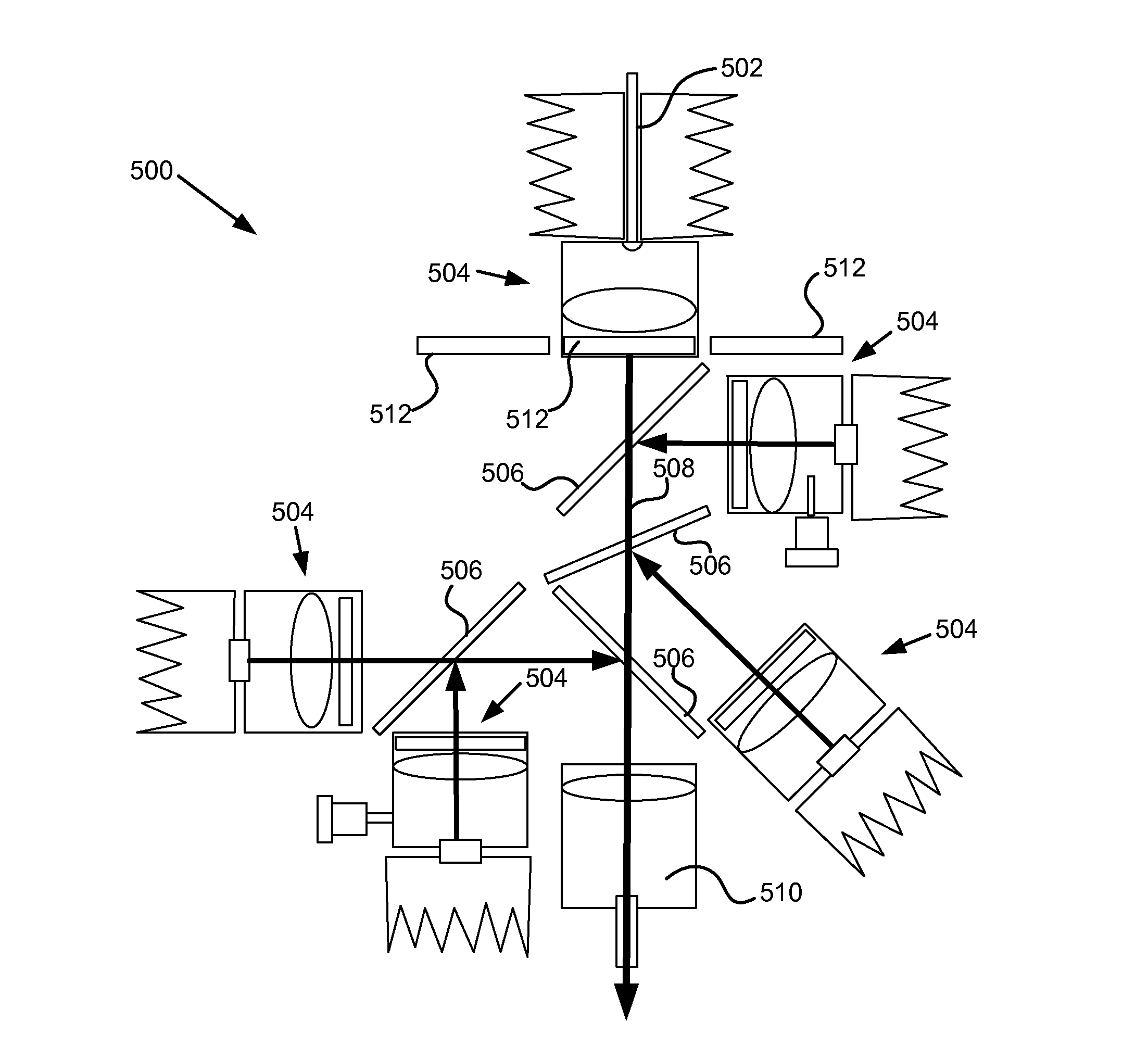
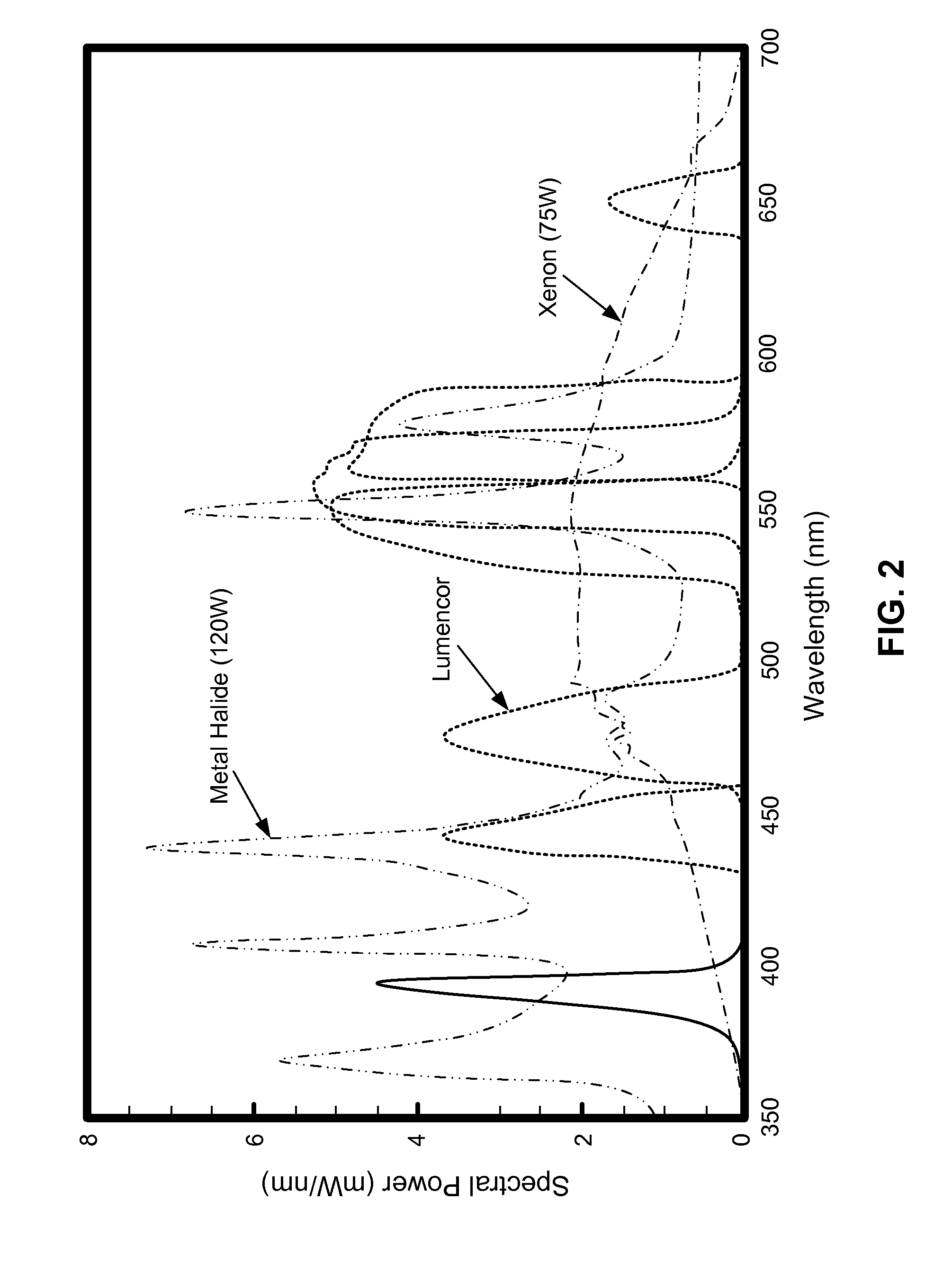
ActiveUS20130242595A1Large controllable rangeImprove reliabilitySurgeryEndoscopesFluorescenceVolumetric Mass Density
A solid state illumination system is provided as a replacement for conventional arc light, metal halide and Xenon light sources for applications in microscopy, fluorescence microscopy, and endoscopy. The illumination system includes hybrid optical and electrical control of output intensity in which the light output of one or more of the light sources is attenuated optically such that it is not necessary to reduce the electrical drive power / current of the LEDs at a level where the spectral power distribution is variable. One or more fixed, selectable, or variable neutral density filters is interposed in the output beam of one or more sources to achieve optical attenuation of the light output. The hybrid optical and electrical control of output intensity allows greater dynamic range of intensity to be achieved than could be achieved with electrical control of the LEDs alone while maintaining the desired spectral power distribution.
Owner:LUMENCOR
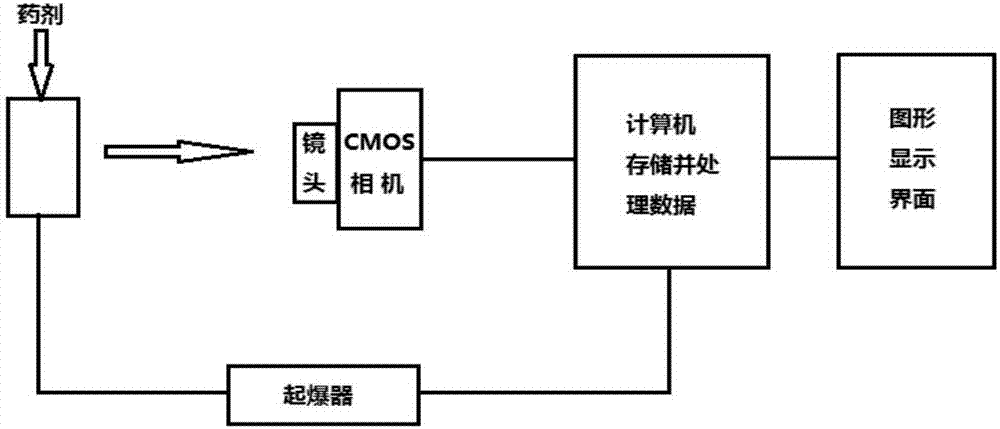
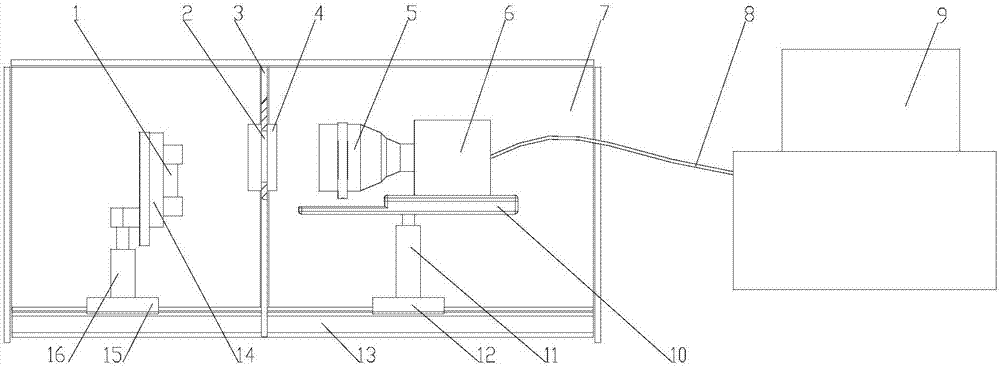
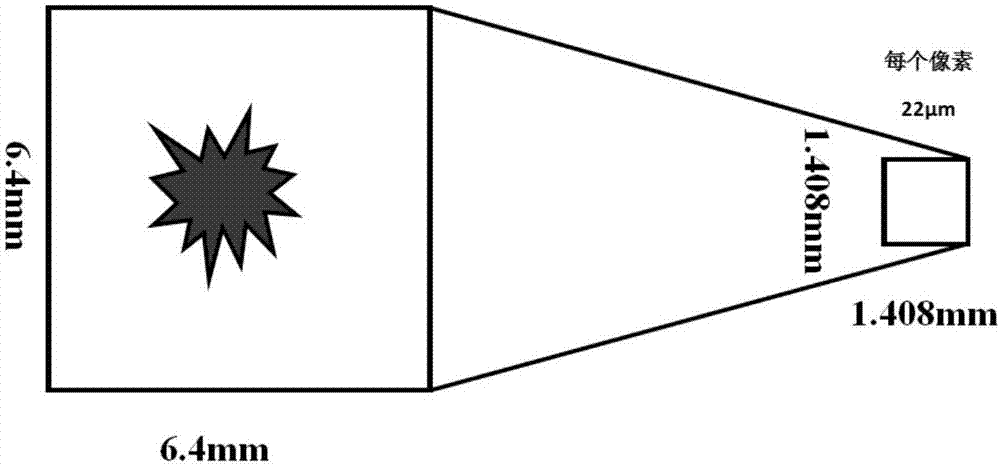
Micro-scale initiating explosive device ignition temperature field measuring device and temperature measurement method thereof
ActiveCN107202651ASimple methodImprove measurement accuracyThermometers using physical/chemical changesMeasurement deviceEngineering
The invention discloses a micro-scale initiating explosive device ignition temperature field measuring device and a temperature measurement method thereof. The micro-scale initiating explosive device ignition temperature field measuring device comprises an image capture light path system, a mechanical installation device, a computer and software. The image capture light path system comprises a neutral-density filter, an imaging lens and a high-speed camera; the mechanical installation device comprises a light-shading installation box, a window fixed ring, a guide rail, a sliding block, a supporting rod, a fixture, a camera installation platform and the like; and the computer and the software comprise the computer, a data transmission line, temperature measurement processing software and the like. The neutral-density filter is used for uniform filtering in a wave band of 400 to 700 nm, and the upper limit of temperature measurement can be improved, so that the light intensity is prevented from being too high to measure the temperature. The imaging lens and the high-speed camera are used for capturing image signals, the light-shading installation box can prevent the influence of environmental false light, and all components and parts can be fixed by the guide rail, the sliding block, the supporting rod, the fixture, the camera installation platform and the like, so that measurement alignment is guaranteed; and the computer and the software can be used for processing images during standardization and measurement.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
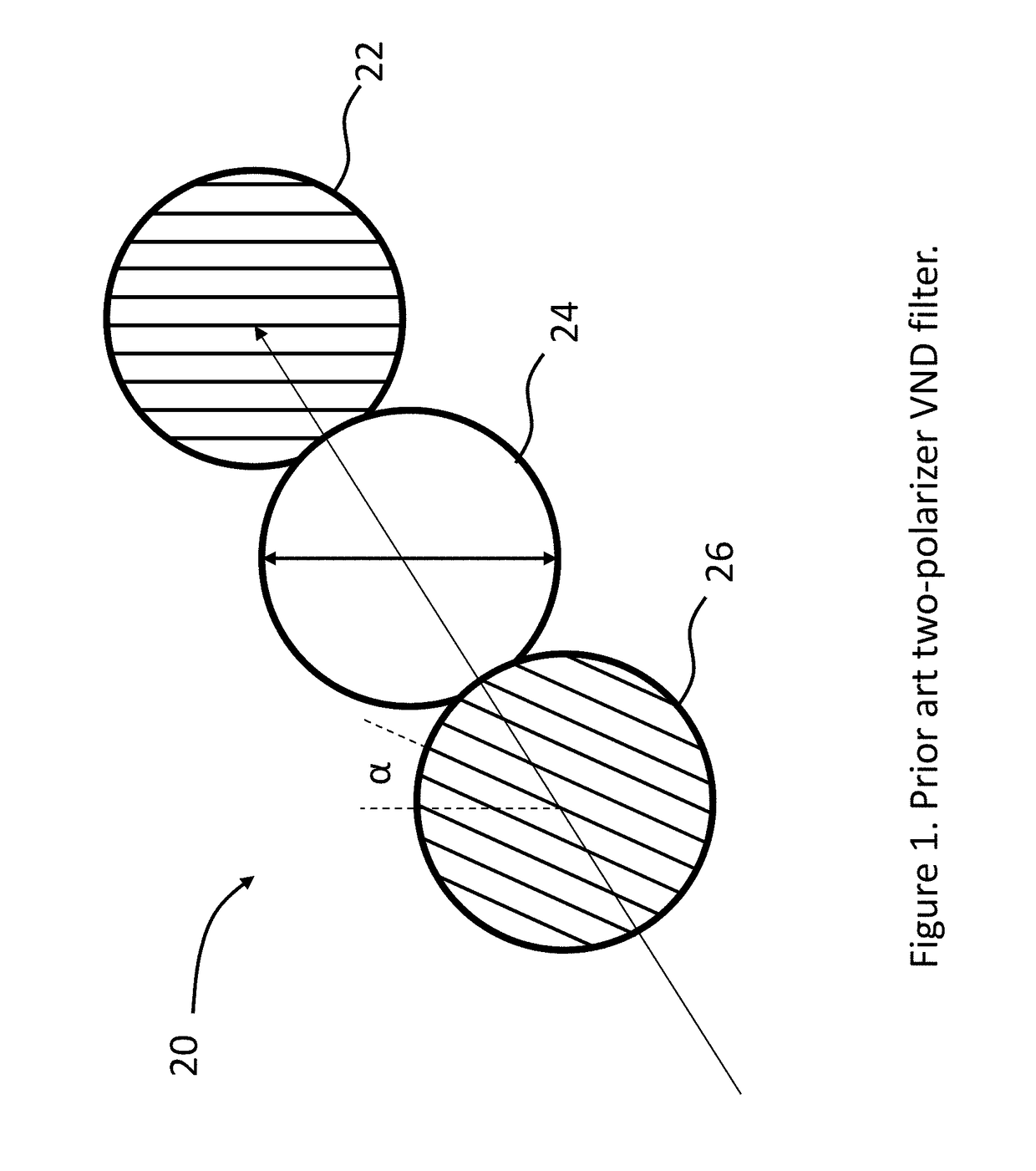
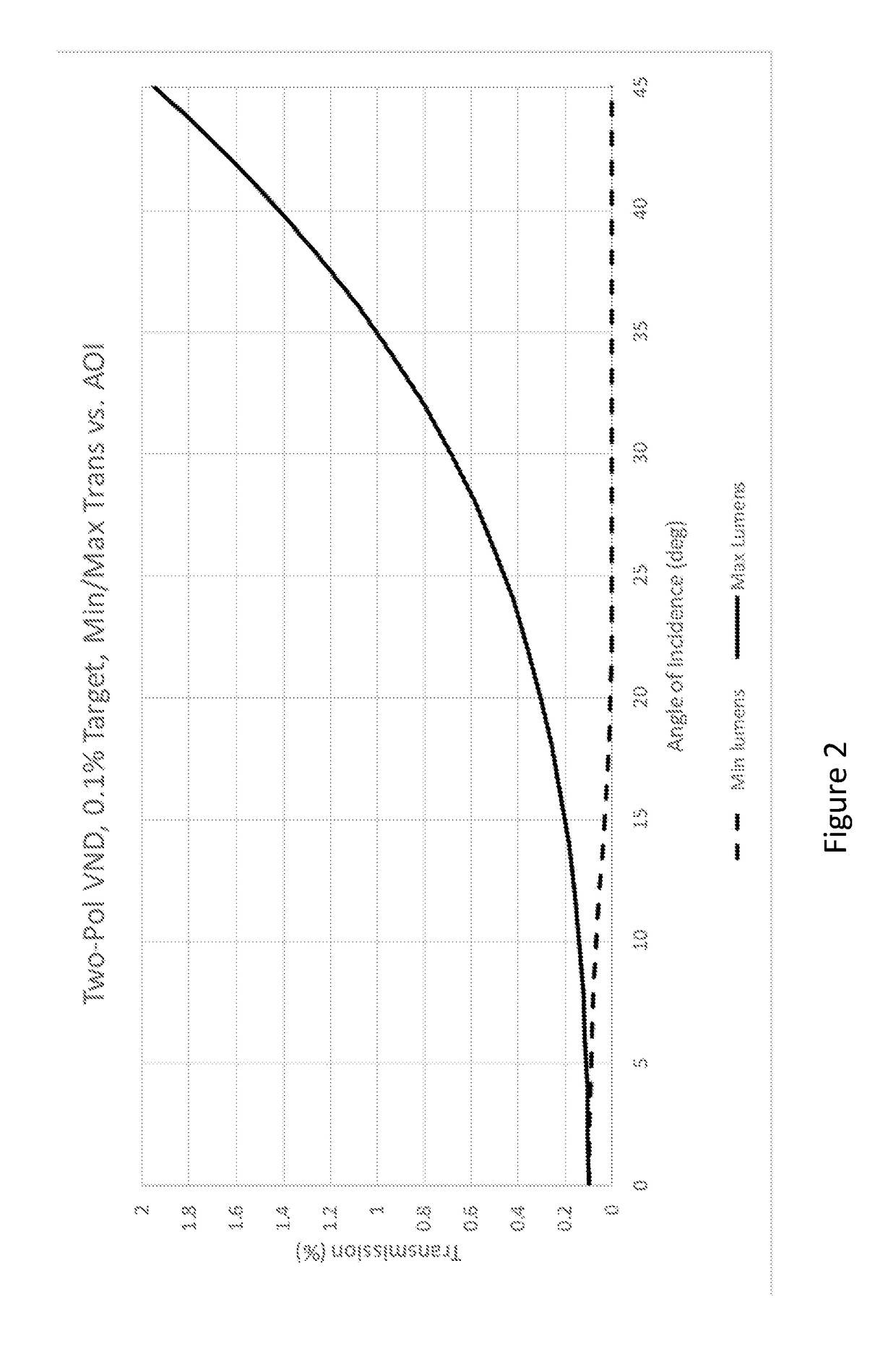
Wide angle variable neutral density filter
ActiveUS20180259692A1Reduce angle resolution requirementMinimize transmitted brightnessTelevision system detailsOptical filtersUltrasound attenuationAngular degrees
A three (or more) polarizer arrangement is used to demonstrate a wide-angle variable-neutral-density (VND) filter that has both contrast uniformity and color uniformity. According to one embodiment, the outer polarizers effectively counter-rotate with respect to a fixed center polarizer as a means of compensating for transmission non-uniformity associated with geometrical polarization distortions experienced by off-normal rays. In particular, the achromatic compensation arrangement enables angle uniformity relative to normal-incidence transmission when the number of stops of attenuation grows large (e.g. 10-stops, or OD3). The filters are useful for cameras or instrumentation allowing mechanical or electromechanical tuning.
Owner:META PLATFORMS TECH LLC
Double-wavelength differential near-infrared non-invasive glucose meter
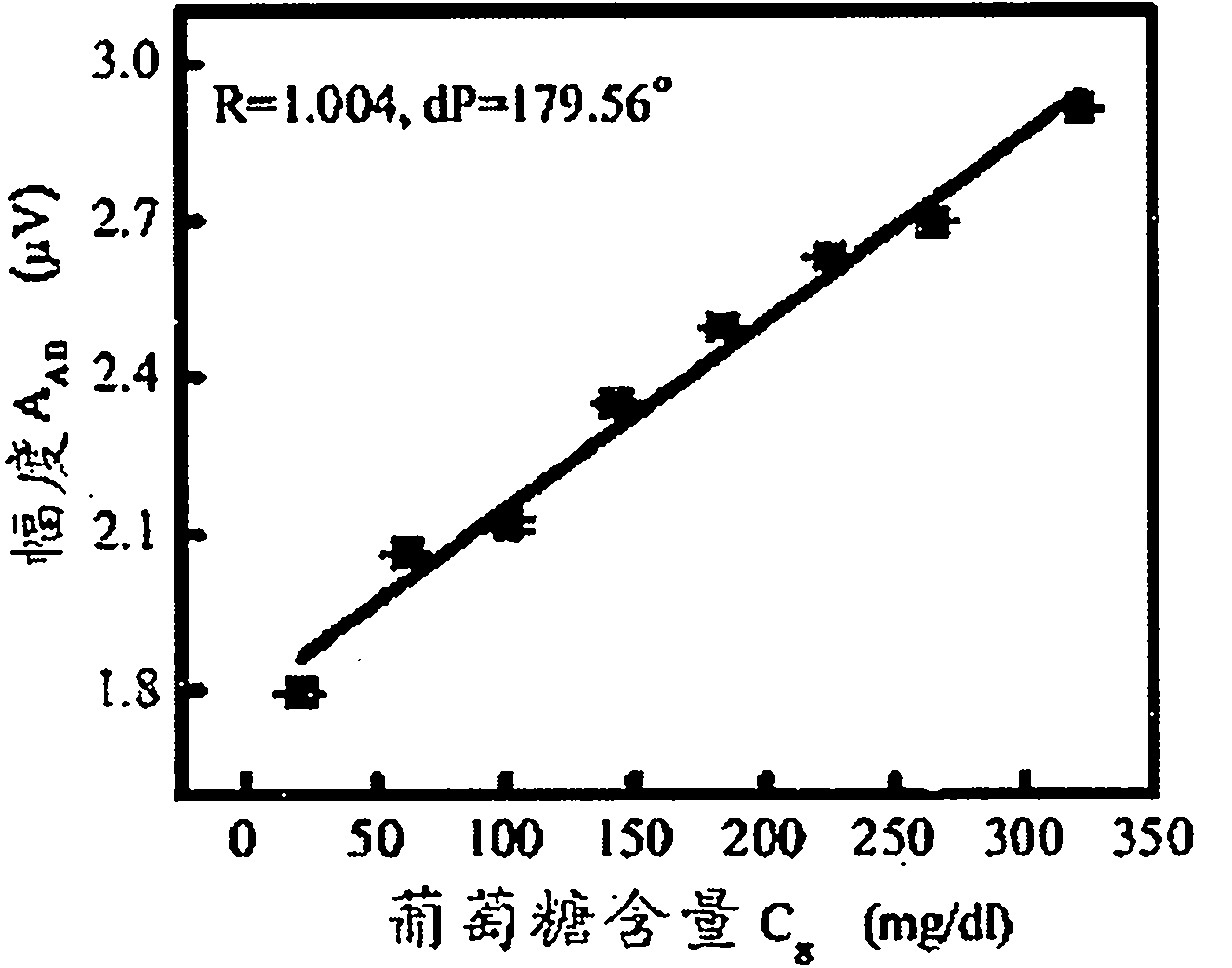
ActiveCN103349553AHigh measurement accuracyAvoid accidental injuryDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsGlucose meter devicePhase difference
The invention discloses a double-wavelength differential near-infrared non-invasive glucose meter. The double-wavelength differential near-infrared non-invasive glucose meter comprises a laser device I (11), a plane mirror I (12), a protective layer (13), a sample (14), a function generator (15), a laser device II (16), an optical neutral density light filter (17), a parabolic mirror I (18), a plane mirror II (19), a phase-locked amplifier (110), a broadband optical near-infrared detector (111), a double-channel optical filter (112) and a parabolic mirror II (113), wherein the optical neutral density light filter can be used for adjusting the power of the laser device II (16), so that the output power ratio of the laser device I (11) to the laser device II (16) is adjusted; and the phase difference is controlled by the function generator (15) and the phase-locked amplifier (110). The double-wavelength differential near-infrared non-invasive glucose meter not only has non-invasive detecting capacity, but also has high measuring precision, especially within a hypoglycemic range by combining the amplitude and the phase characteristics of the near-infrared light and utilizing the crest and trough variation difference of absorption spectrum. Meanwhile, the protective layer is provided for preventing the laser devices from accidently injuring skin tissues.
Owner:杨立峰
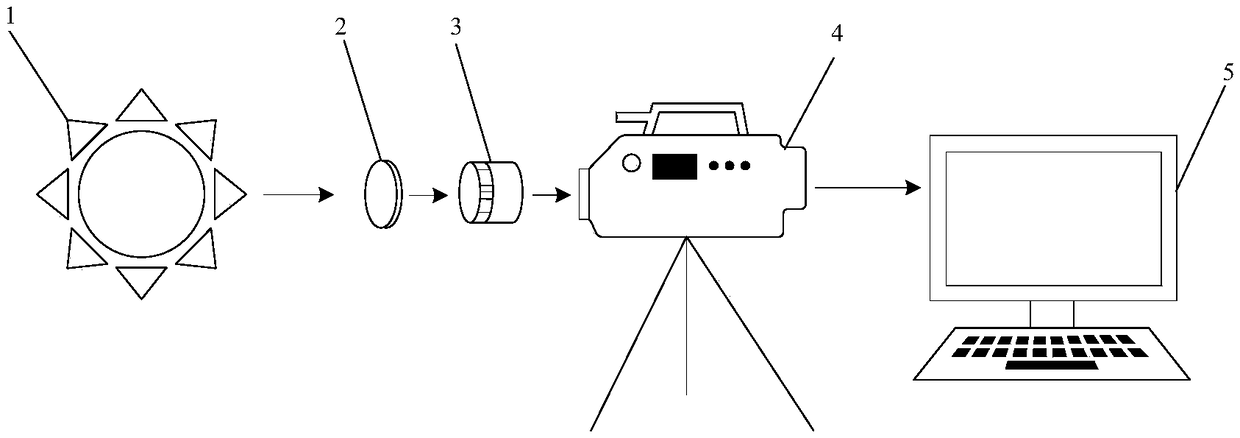
Transient temperature field test method and system based on high-speed imaging technology
InactiveCN109506782AShort response timeHigh upper limit of temperature measurementRadiation pyrometryCMOS sensorField tests
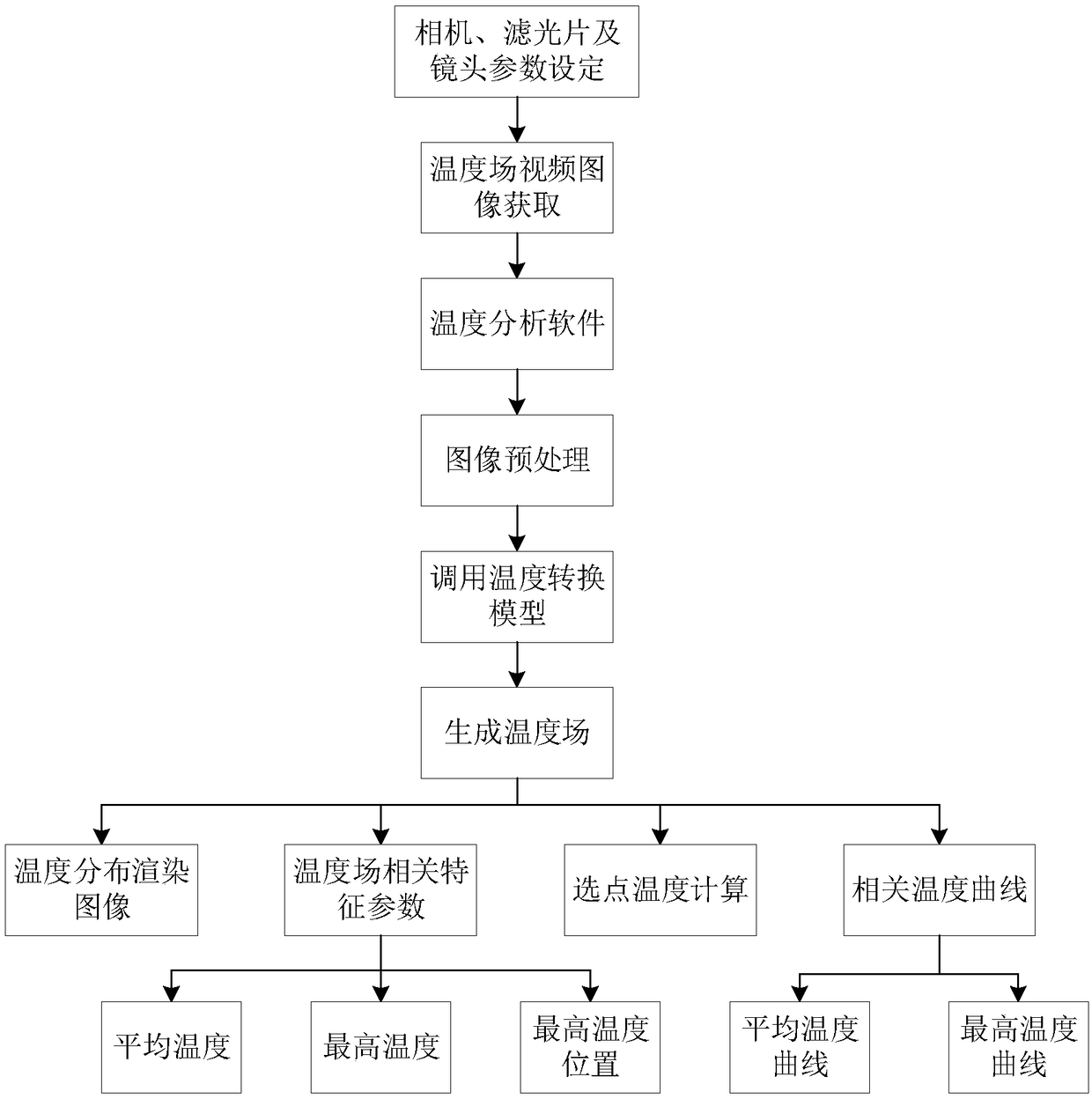
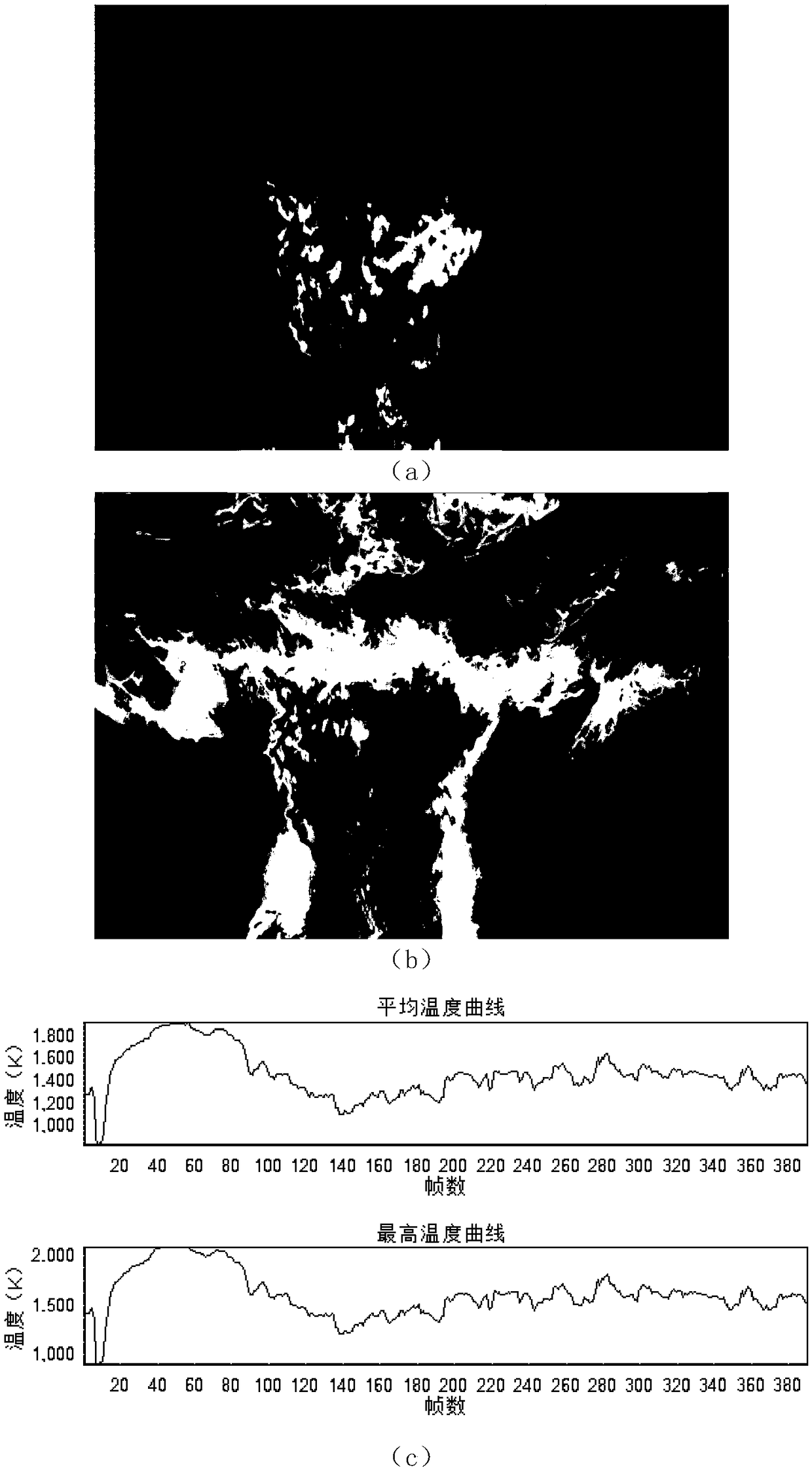
The invention discloses a transient temperature field test method and system based on a high-speed imaging technology. The transient temperature field test system comprises a color high-speed camera,a medium-density optical filter, an optical lens and a computer. The transient temperature field test method comprises the steps that the optical lens focuses lightness information generated by a transient temperature field on a CMOS image sensor of the high-speed camera; the medium-density optical filter is used for controlling the light amount so that it can be guaranteed that the camera works in an unsaturated area and the upper temperature measurement limit can be expanded at the same time; the high-speed camera converts the light information which is imaged on the CMOS sensor into digitalimage RGB information; the computer analyzes the transient temperature field image information collected by the high-speed camera, and according to a temperature conversion model which is obtained through calibration of the camera and is arranged in software, the transient temperature field and related characteristic parameters can be obtained. The transient temperature field test method and system can achieve remote distance measurement of the transient temperature field, have the advantages of high time resolution and high temperature measurement upper limit, and can visually acquire a temperature distribution render graph of every moment and the related temperature characteristic parameters.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com