Patents
Literature
2577 results about "Cell voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
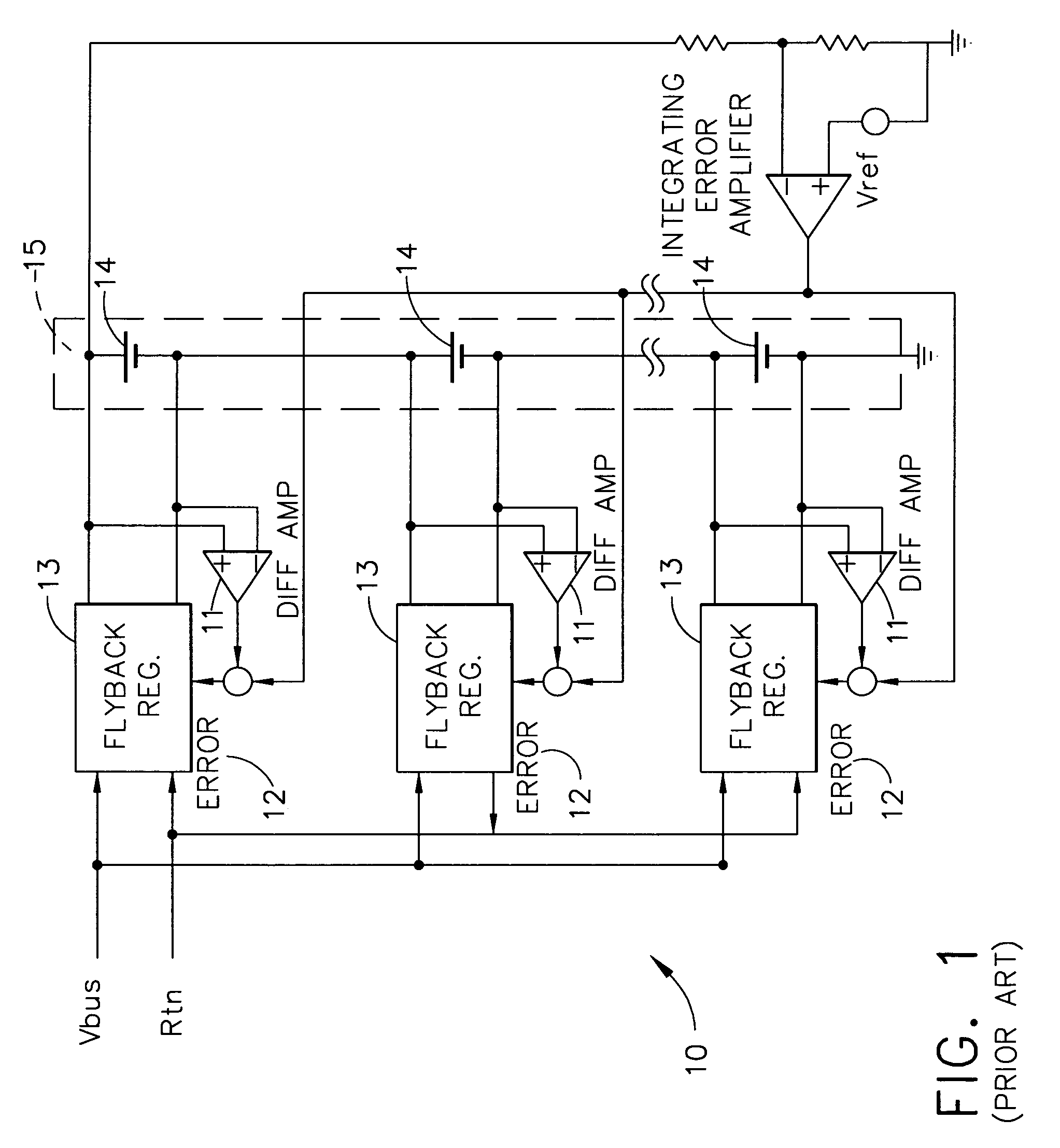
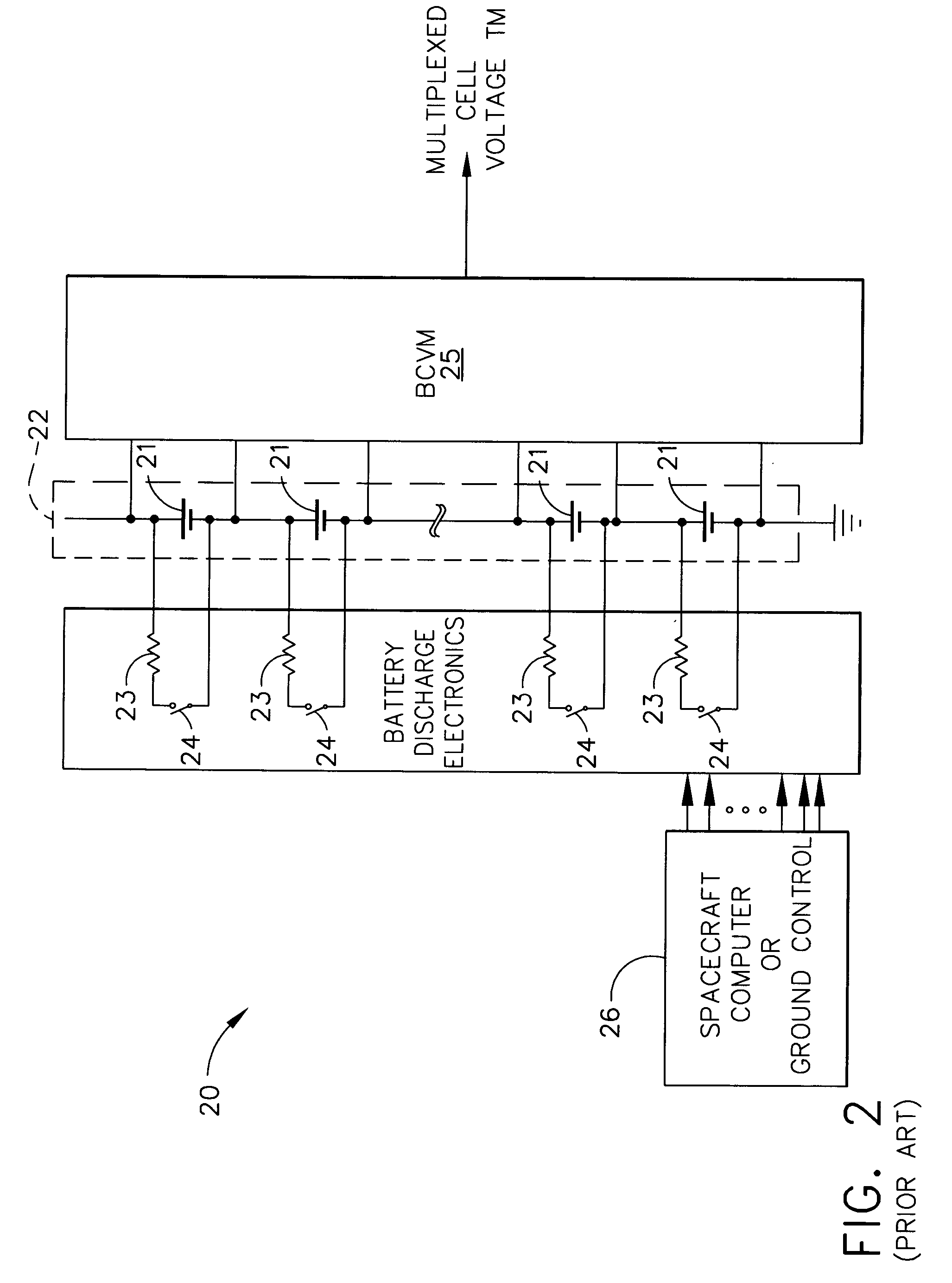
""Cell voltage"" usually refers to nonequilibrium conditions, that is when current is flowing through the cell (although this convention is not always followed). The ""cell voltage"" differs from the electromotive force (emf) (or open-circuit voltage (ocv)) of the cell by the amount of the overvoltage.
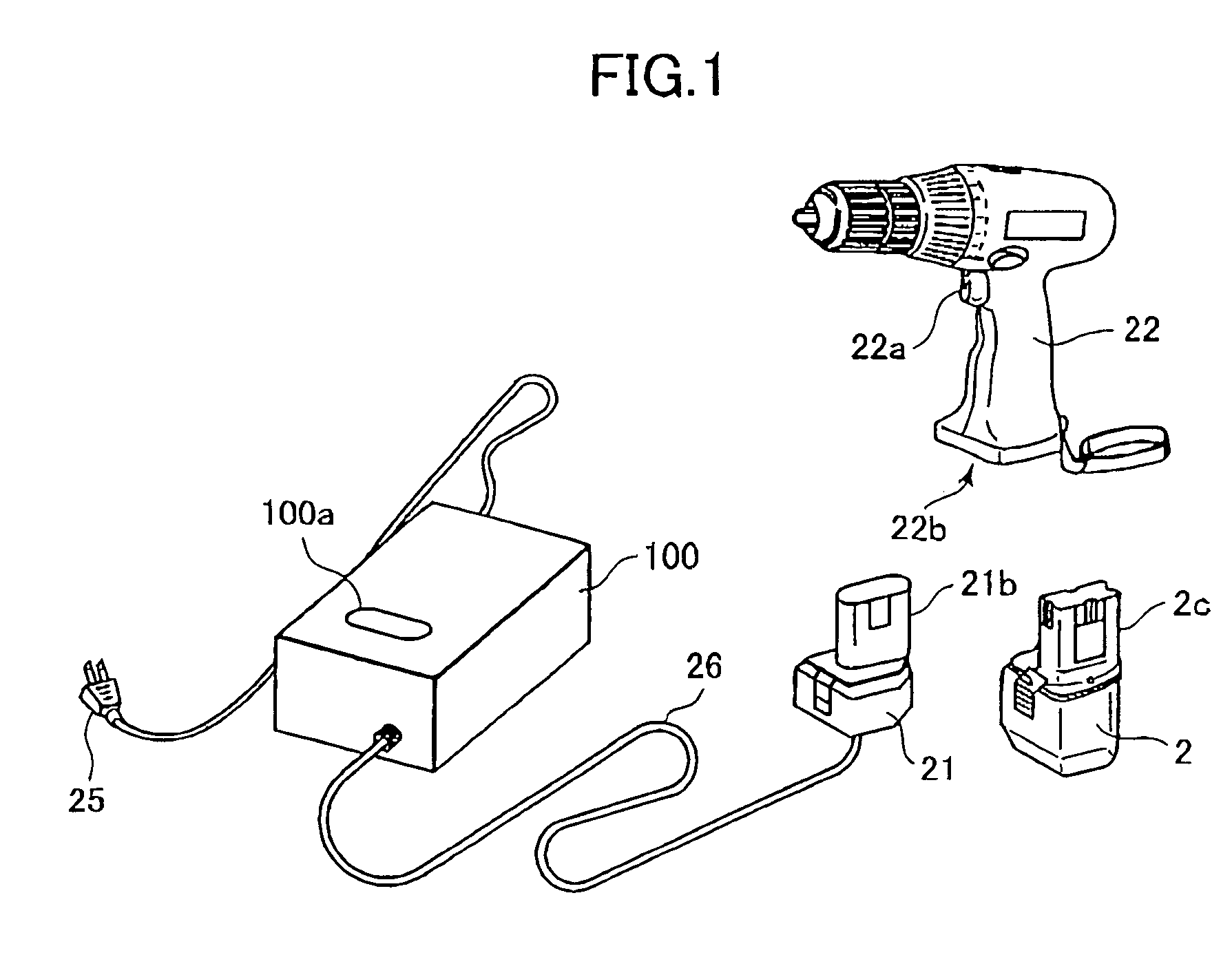
Methods of charging battery packs for cordless power tool systems
In a method of charging a battery pack, the pack is inserted in a charger and an initial set of checks of cell voltage and pack temperature is performed. Once the initial set of checks is satisfied, the cells may be charged at a first constant current level. The first constant current level is adjusted to one or more lower levels of constant current until cell voltages of all the cells are within a full charge voltage window. The voltage window is defined between a minimum full charge cell voltage level and a maximum full charge cell voltage level. The charge may be terminated once all of the cells are within the full charge voltage window.
Owner:BLACK & DECKER INC
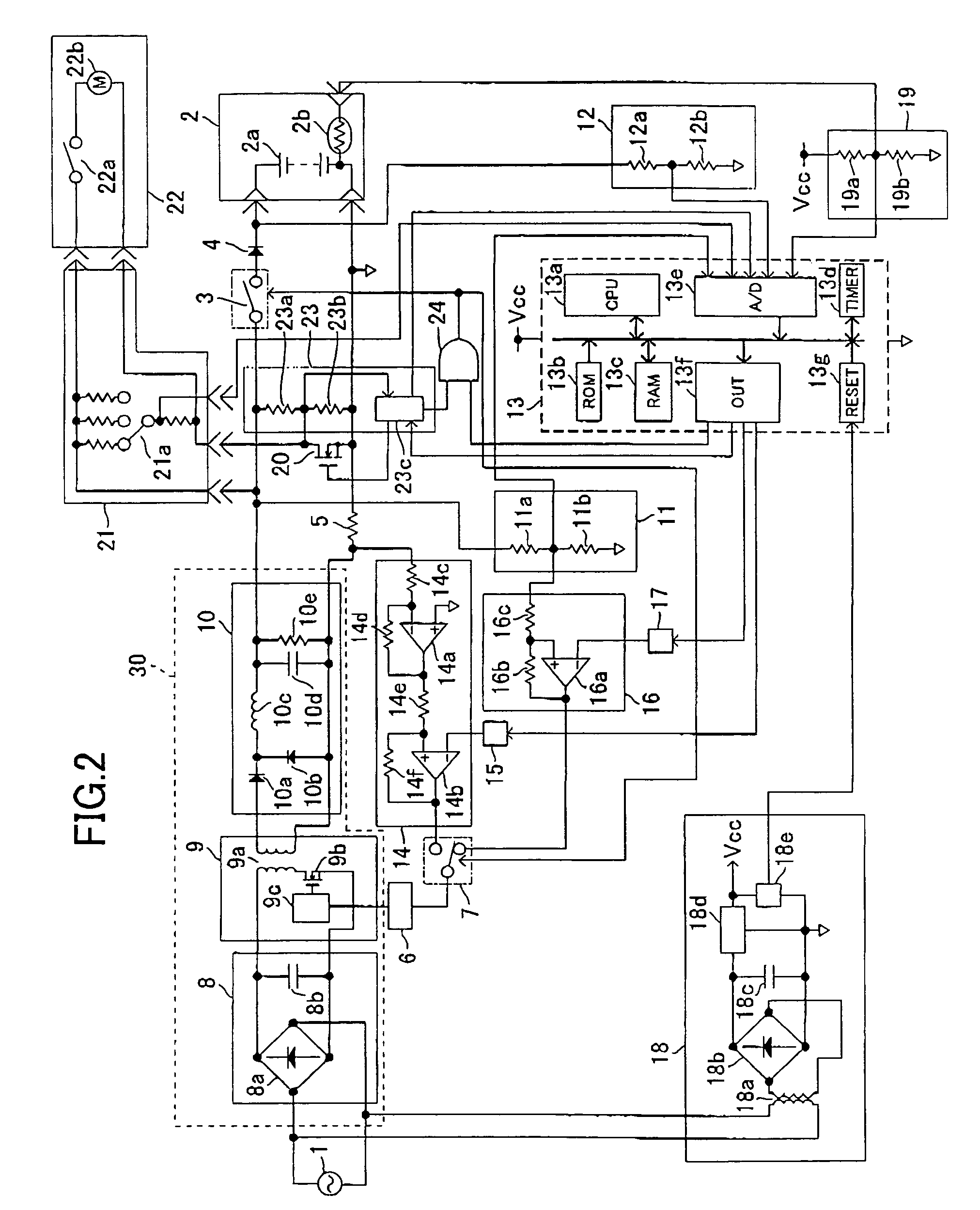
DC power source unit with battery charging function
Owner:KOKI HLDG CO LTD
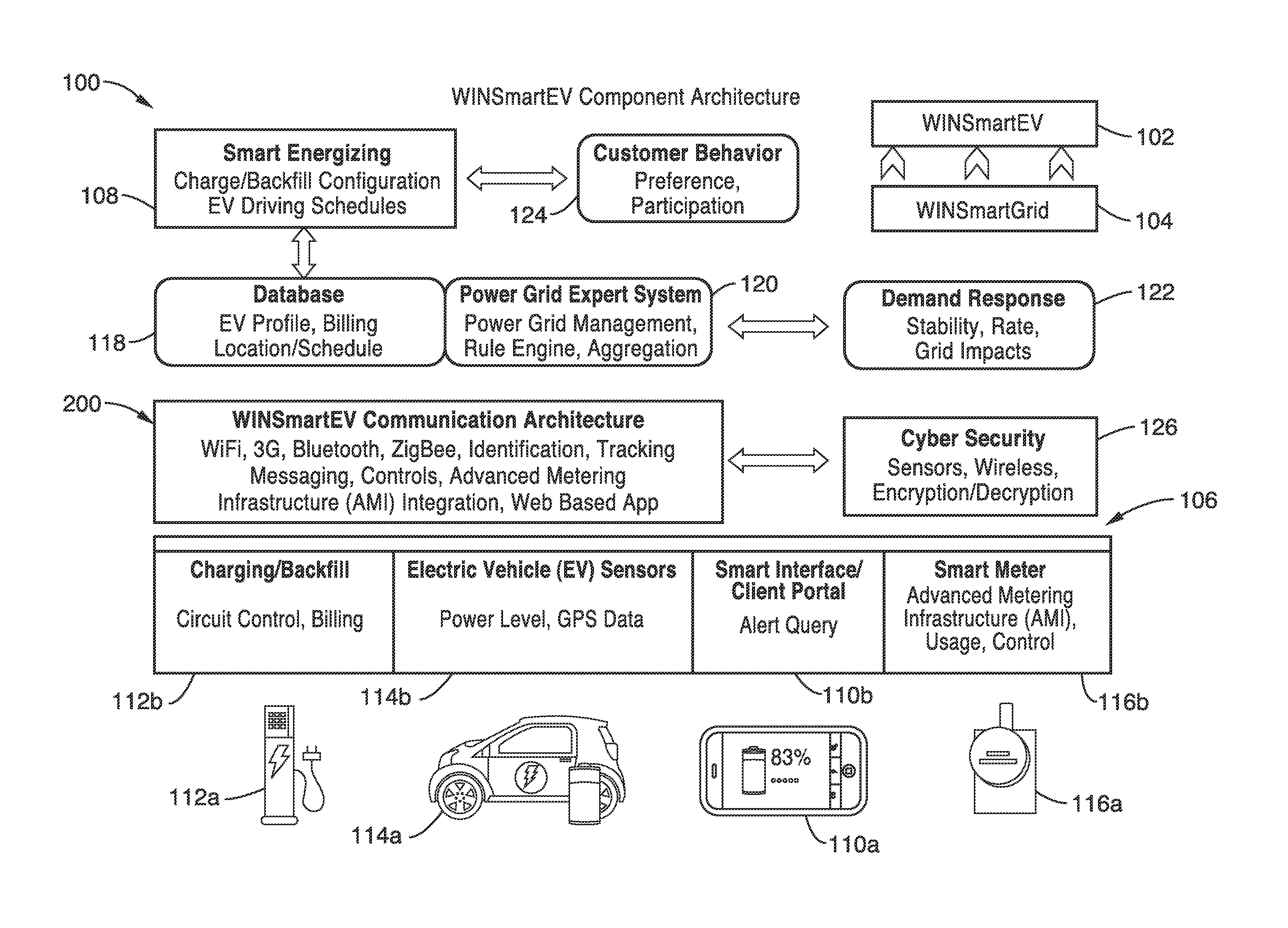
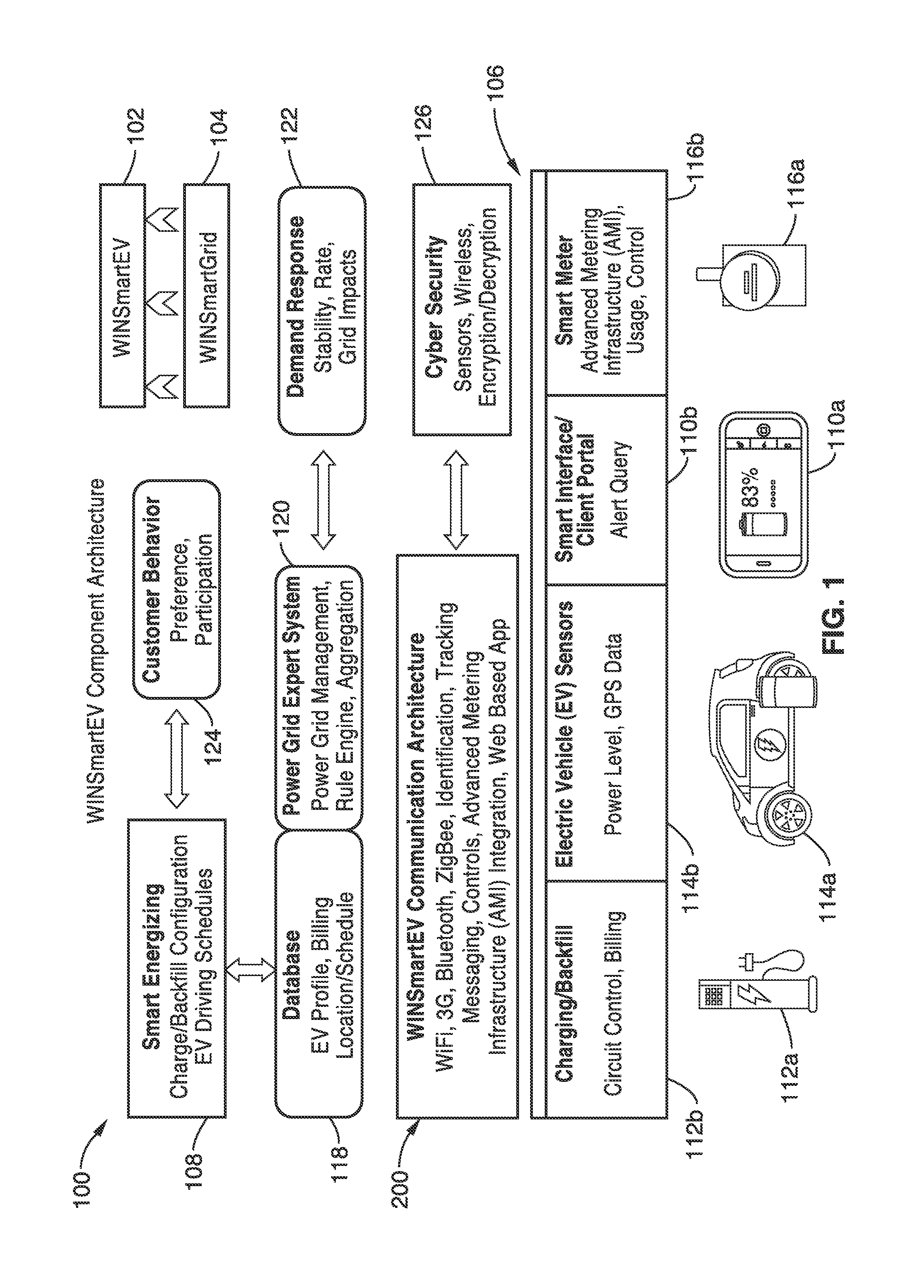
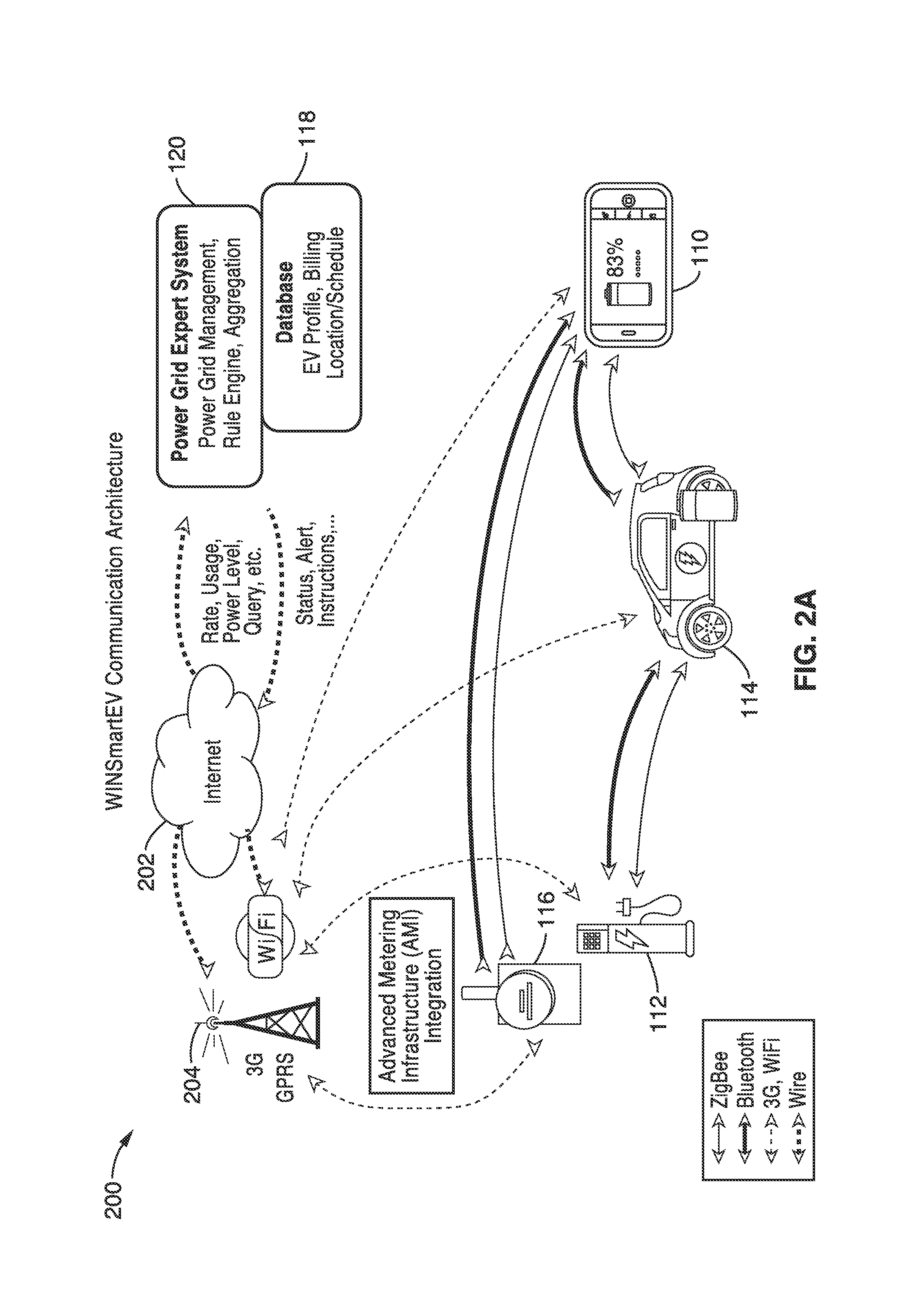
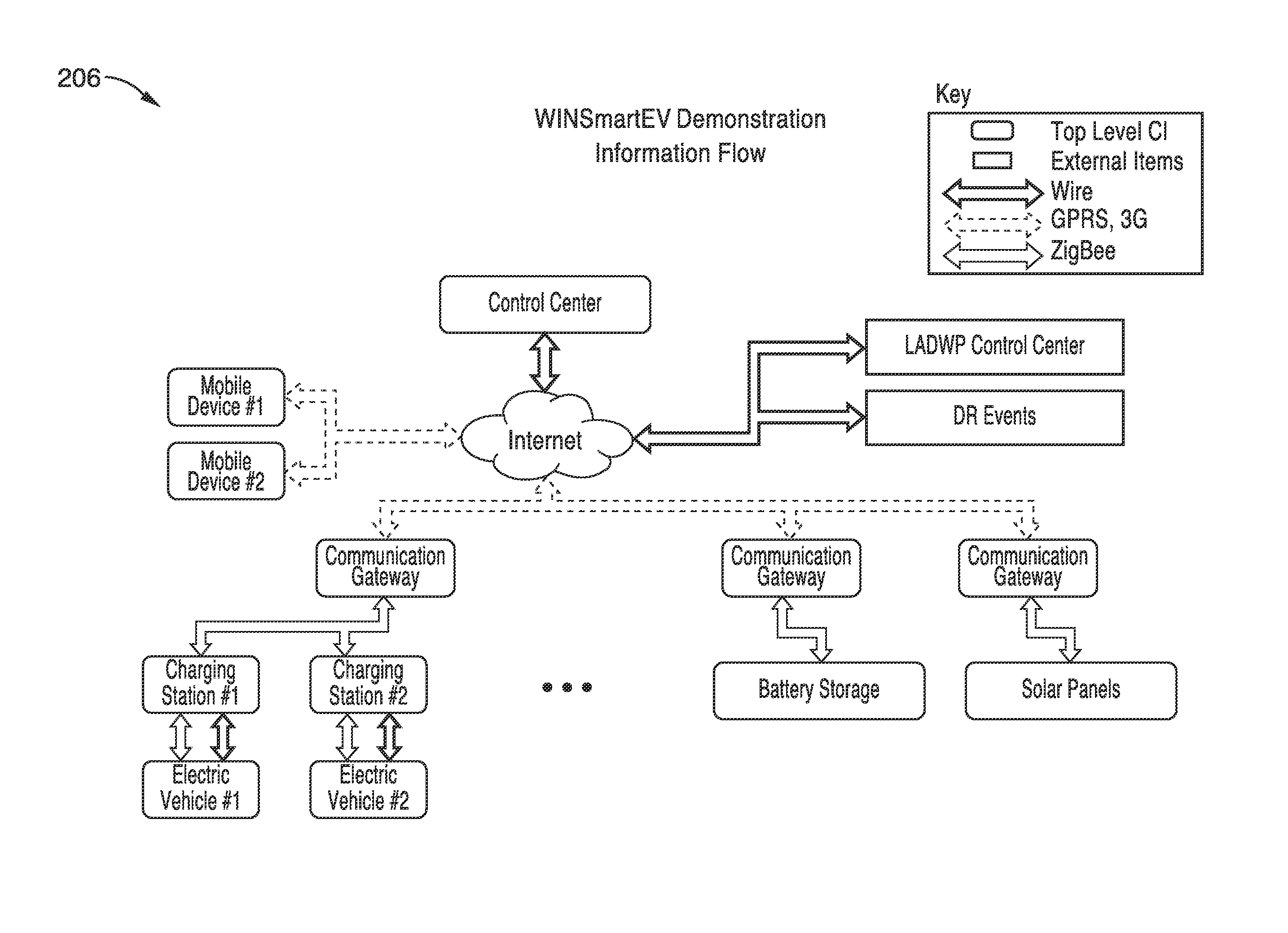
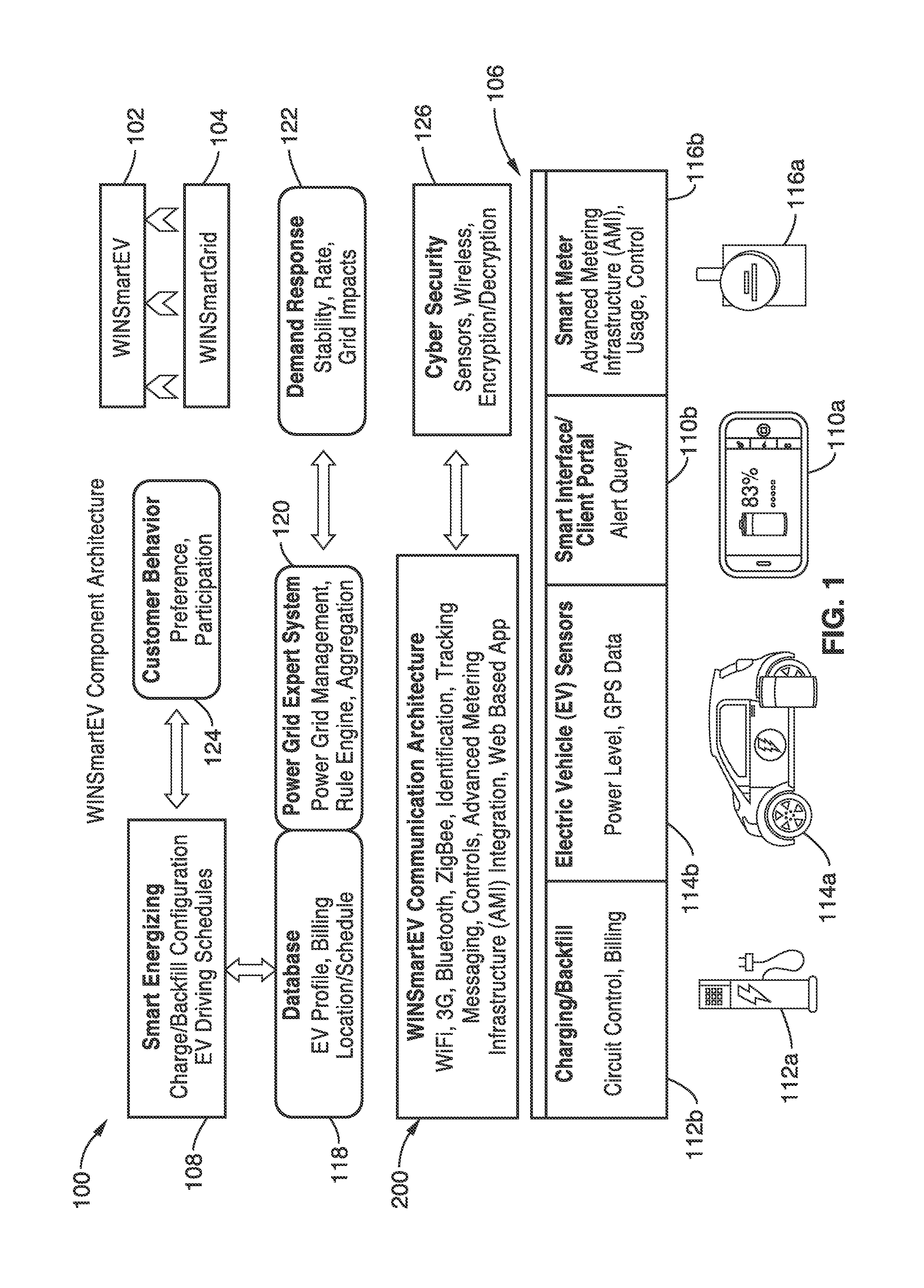
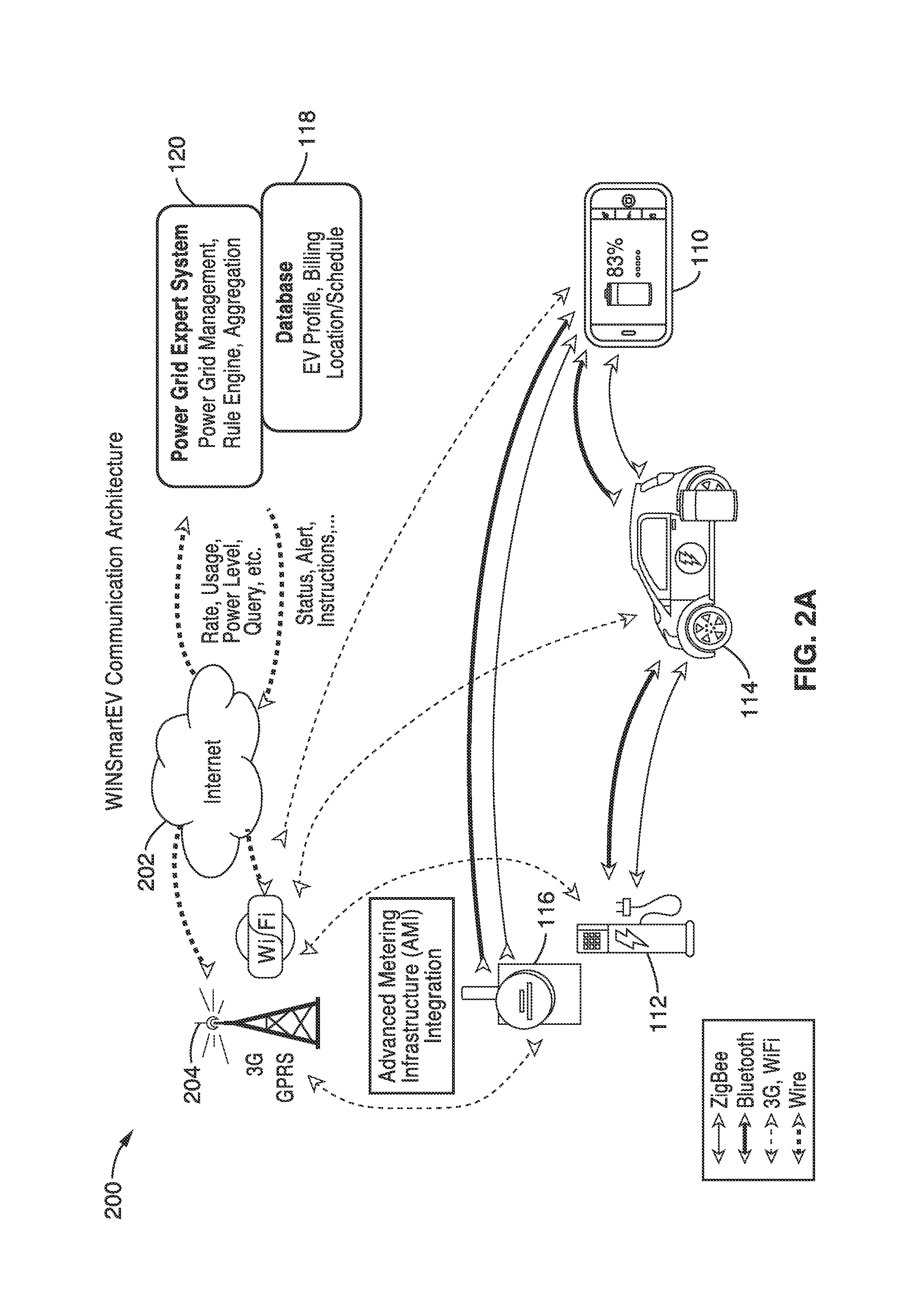
Smart electric vehicle (EV) charging and grid integration apparatus and methods
ActiveUS9026347B2Increase capacityAdding smartnessAnalogue computers for vehiclesBatteries circuit arrangementsGrid-tie inverterElectrical battery
An expert system manages a power grid wherein charging stations are connected to the power grid, with electric vehicles connected to the charging stations, whereby the expert system selectively backfills power from connected electric vehicles to the power grid through a grid tie inverter (if present) within the charging stations. In more traditional usage, the expert system allows for electric vehicle charging, coupled with user preferences as to charge time, charge cost, and charging station capabilities, without exceeding the power grid capacity at any point. A robust yet accurate state of charge (SOC) calculation method is also presented, whereby initially an open circuit voltage (OCV) based on sampled battery voltages and currents is calculated, and then the SOC is obtained based on a mapping between a previously measured reference OCV (ROCV) and SOC. The OCV-SOC calculation method accommodates likely any battery type with any current profile.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
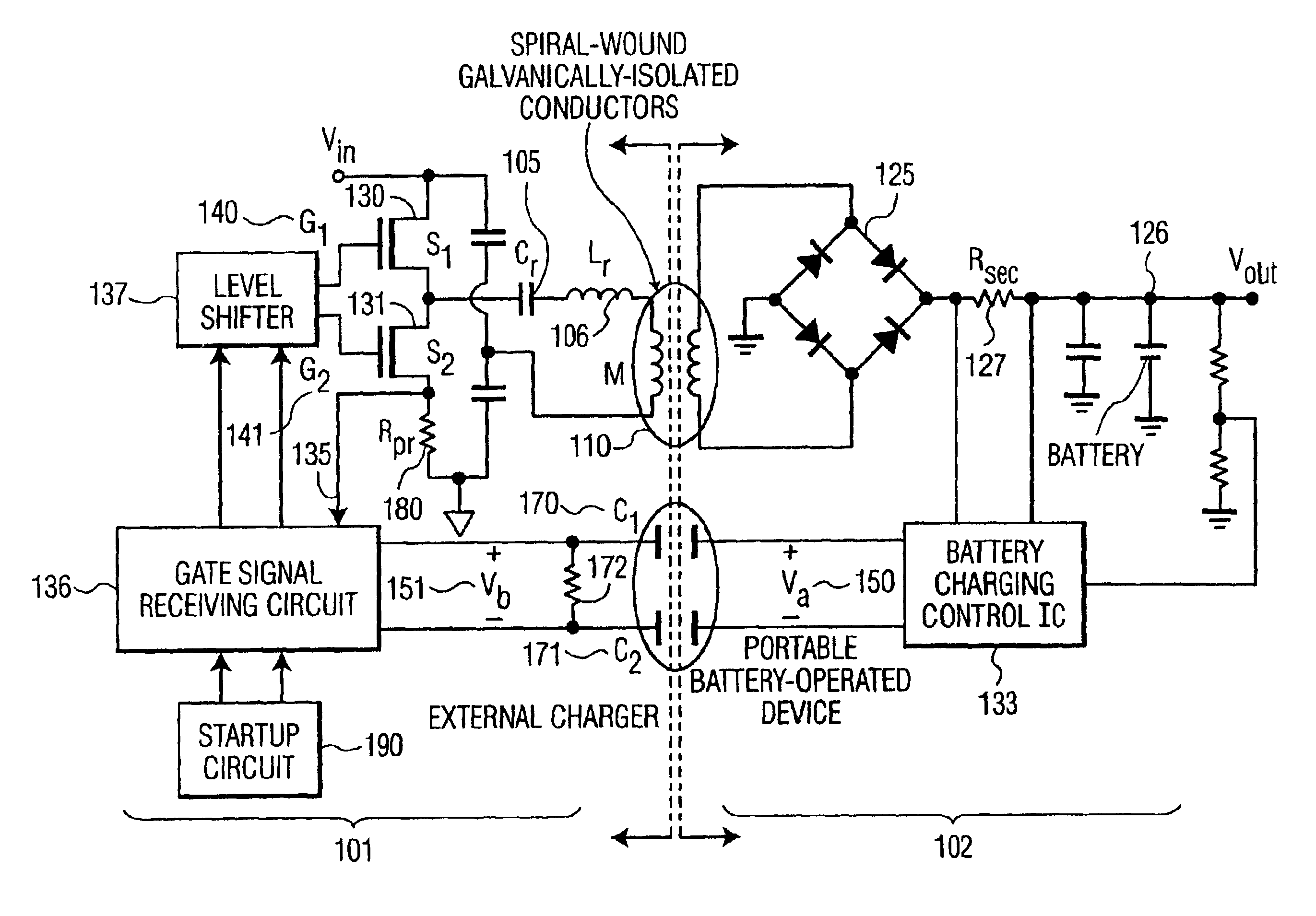
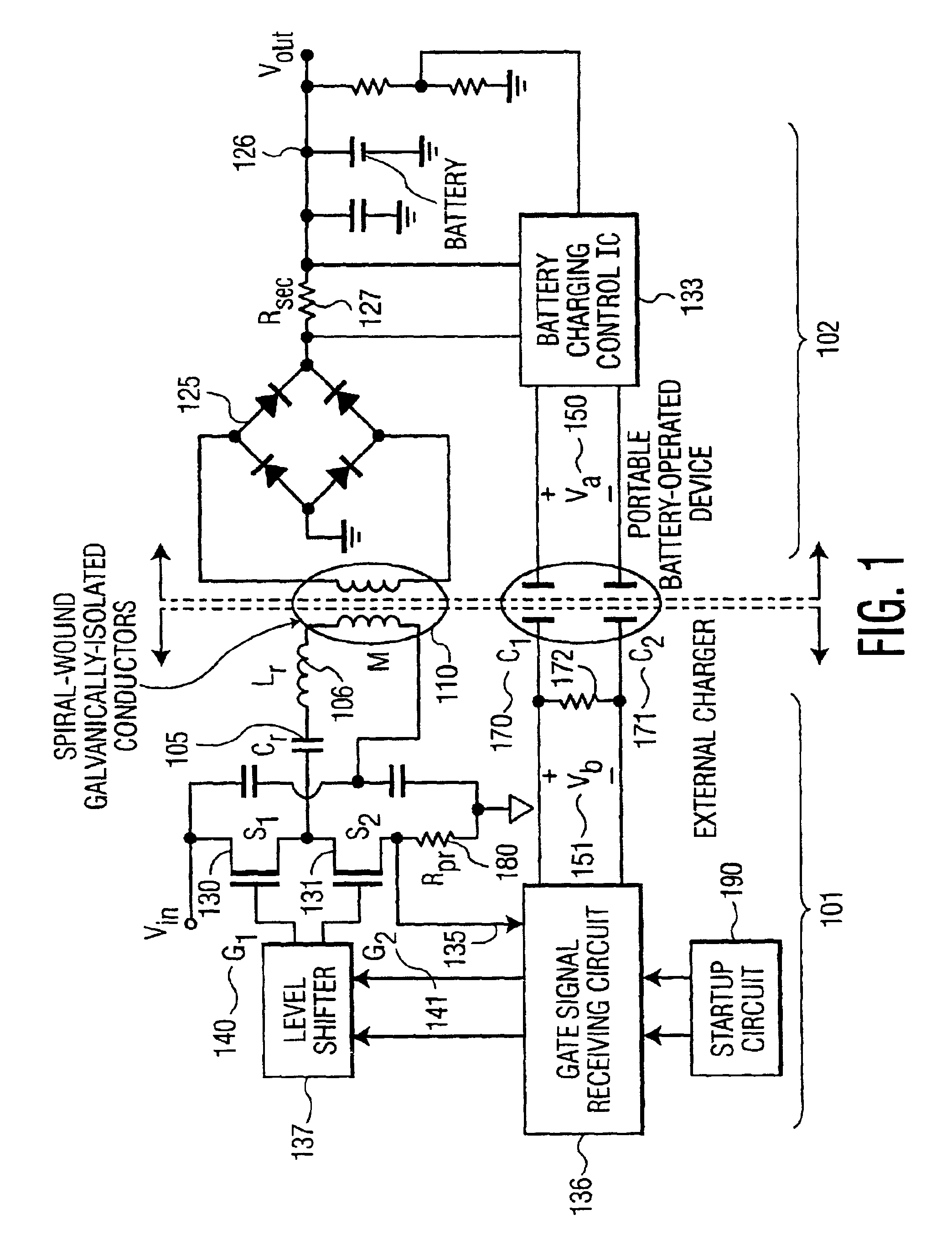
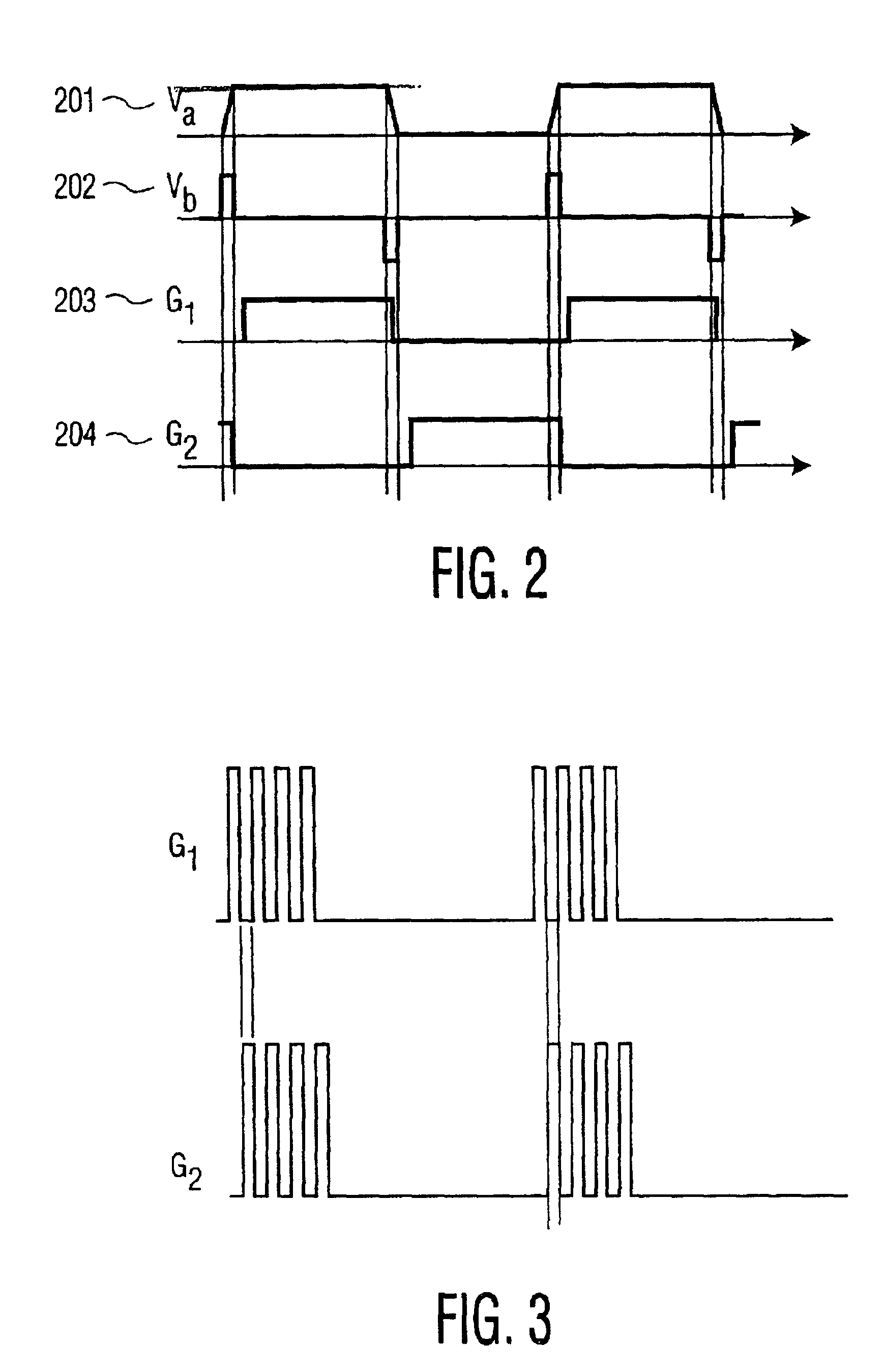
System, method and apparatus for contact-less battery charging with dynamic control
InactiveUS6844702B2Reduce complexityImprove efficiencyNear-field transmissionElectromagnetic wave systemBattery chargeEngineering
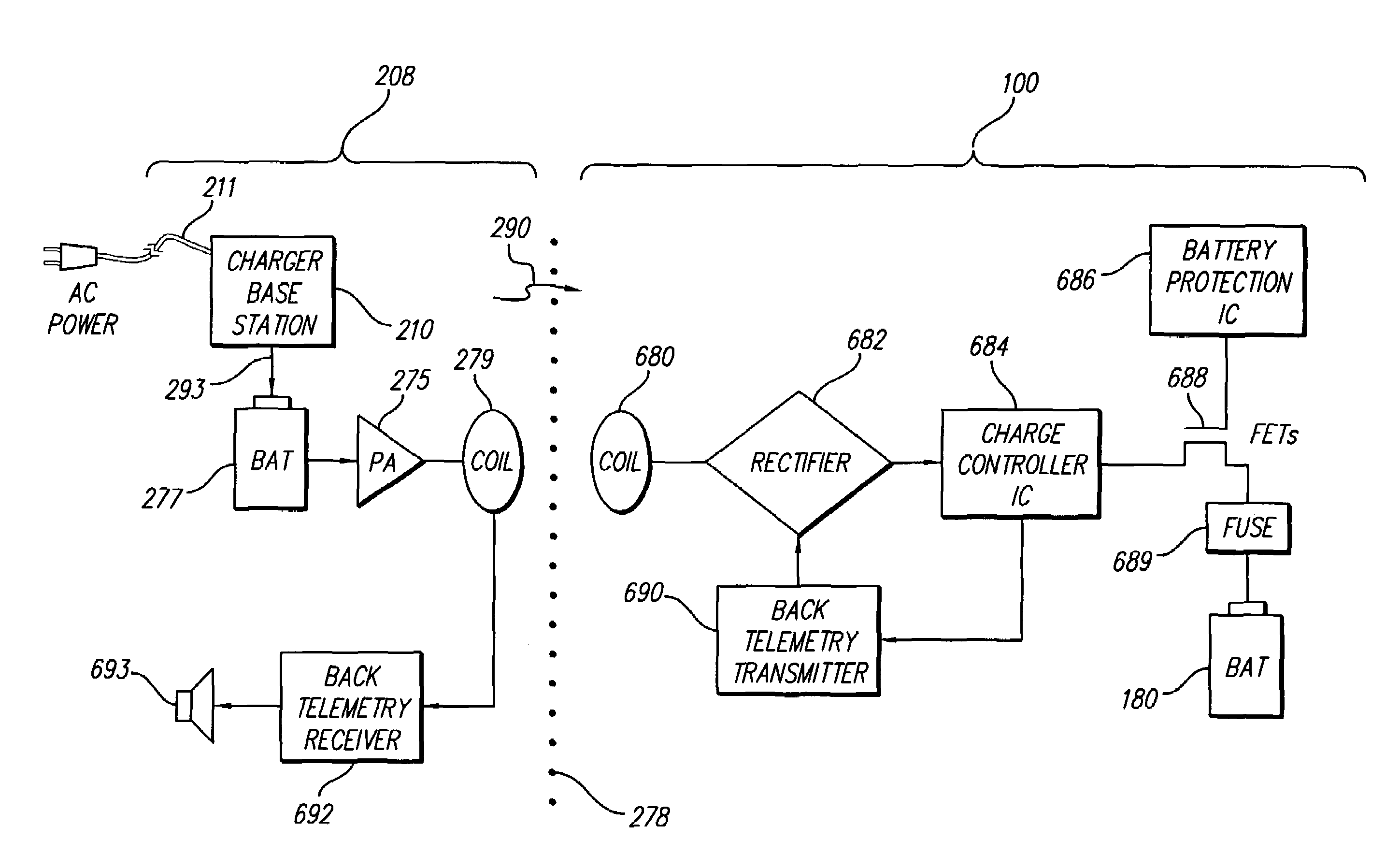
A system, method and apparatus for contact-less charging of battery operated devices, including a host charger with a power converter and resonant tank circuit and a portable device where the battery is located, with a battery charging control IC, wherein the method obviates the need for a voltage controller in each of both the host and the portable stages. The charging of the battery in the portable device is controlled by a charging controller therein, which is in continual electric communication with the host, whose output power the control IC dynamically monitors and controls. In one embodiment, component count is minimized but battery charging is not optimized when the battery voltage is very low. In the other embodiment, charging efficiency is maximized regardless of the output voltage of the battery.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Smart electric vehicle (EV) charging and grid integration apparatus and methods
ActiveUS20130179061A1Increase capacityAdding smartnessAnalogue computers for vehiclesBatteries circuit arrangementsGrid-tie inverterState of charge
An expert system manages a power grid wherein charging stations are connected to the power grid, with electric vehicles connected to the charging stations, whereby the expert system selectively backfills power from connected electric vehicles to the power grid through a grid tie inverter (if present) within the charging stations. In more traditional usage, the expert system allows for electric vehicle charging, coupled with user preferences as to charge time, charge cost, and charging station capabilities, without exceeding the power grid capacity at any point. A robust yet accurate state of charge (SOC) calculation method is also presented, whereby initially an open circuit voltage (OCV) based on sampled battery voltages and currents is calculated, and then the SOC is obtained based on a mapping between a previously measured reference OCV (ROCV) and SOC. The OCV-SOC calculation method accommodates likely any battery type with any current profile.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
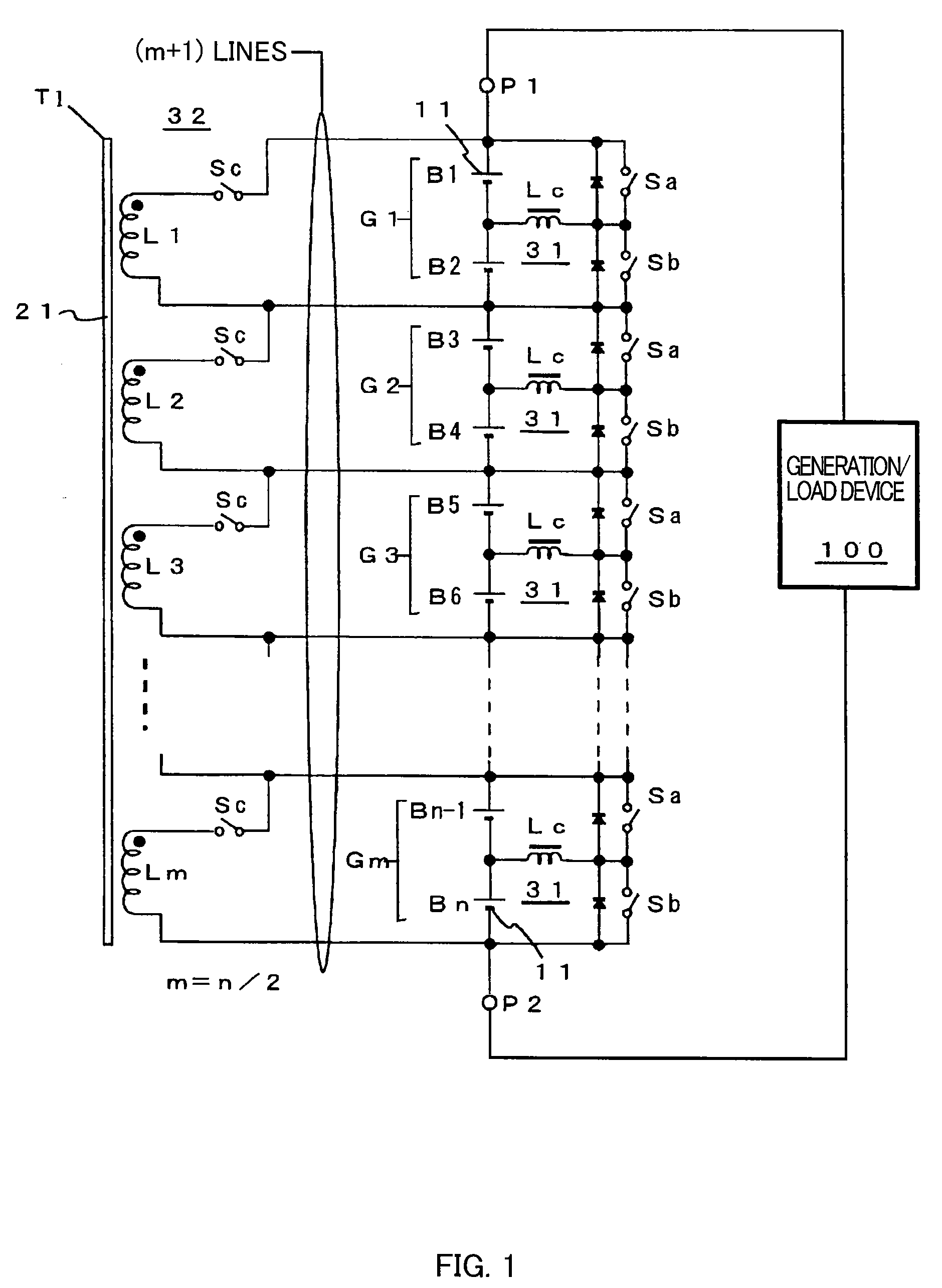
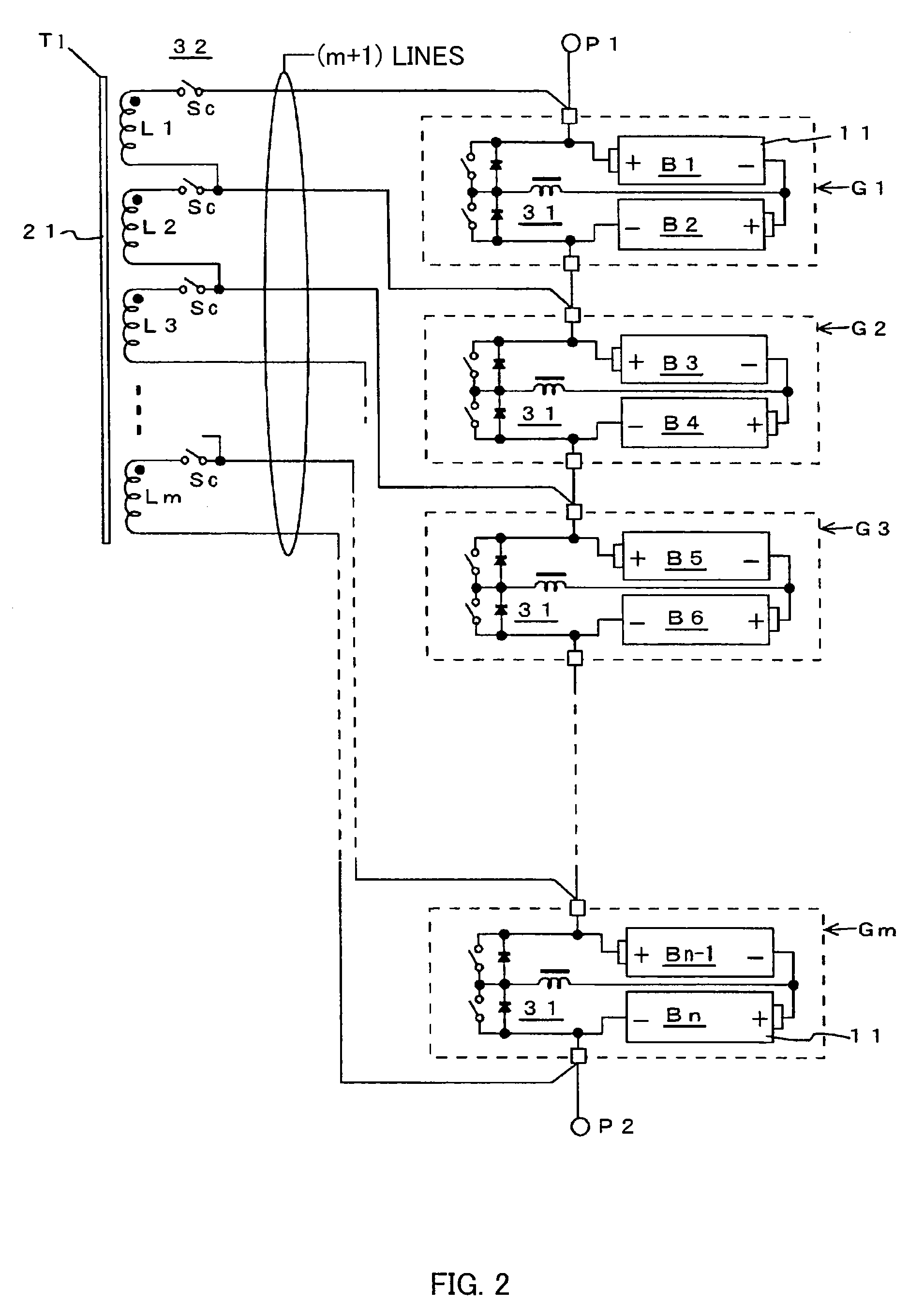
Series-connected rechargeable cells, series-connected rechargeable cell device, voltage-balance correcting circuit for series-connected cells
ActiveUS20090278496A1Inhibit deteriorationAvoid breakingCharge equalisation circuitElectric powerTransformerRechargeable cell
[Object] There is provided series-connected rechargeable cells in which a large number of cells are series-connected and that makes it possible to improve performance on operations such as assembly or exchange and to perform speedy and smooth voltage-balance correcting for all cells.[Means for Solution] Series-connected rechargeable cells includes: a large number of rechargeable cells that are series-connected, and that are divided into a plurality of series-connected cell groups placed continuously in order of connecting; and a voltage-balance correcting circuit that balances the voltages of the cells, and that is provided with an inter-cell voltage-balance correcting circuit that performs voltage-balance correcting between adjacent cells in each of the cell groups and an inter-group voltage-balance correcting circuit that performs balance correcting of series-connection voltages of the cell groups by AC-coupling formed with a transformer coil and a switching circuit.
Owner:FDK CORP
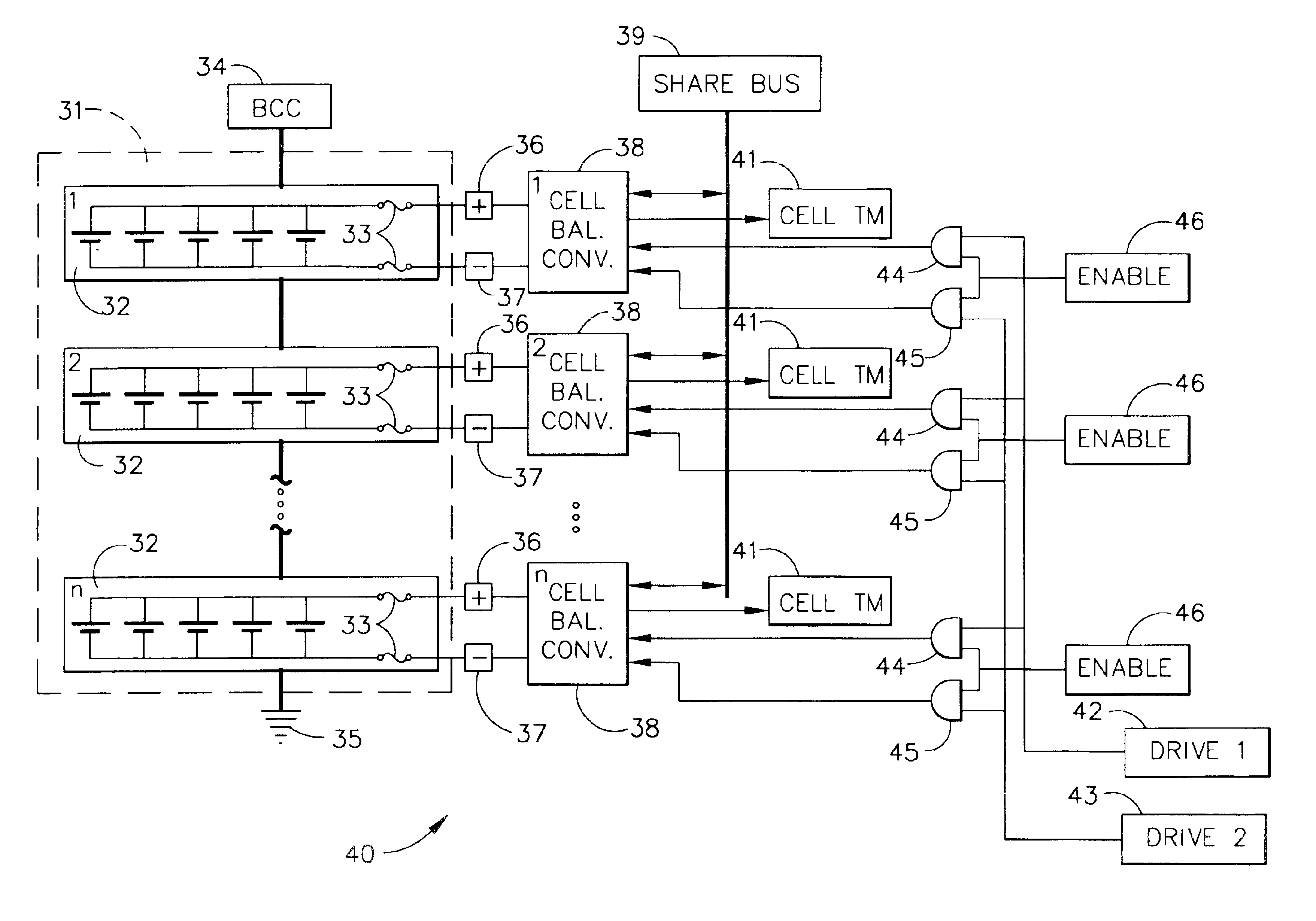
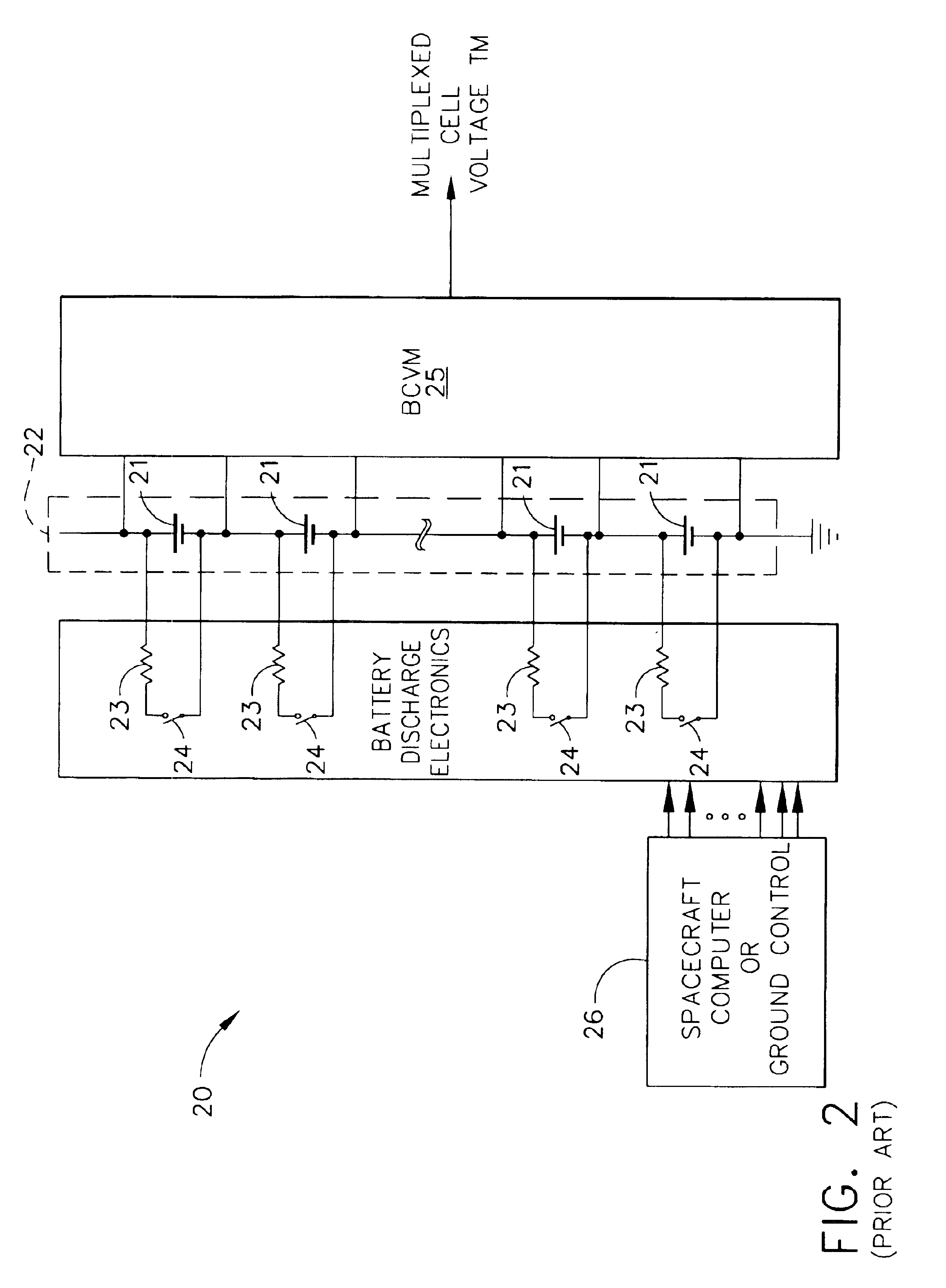
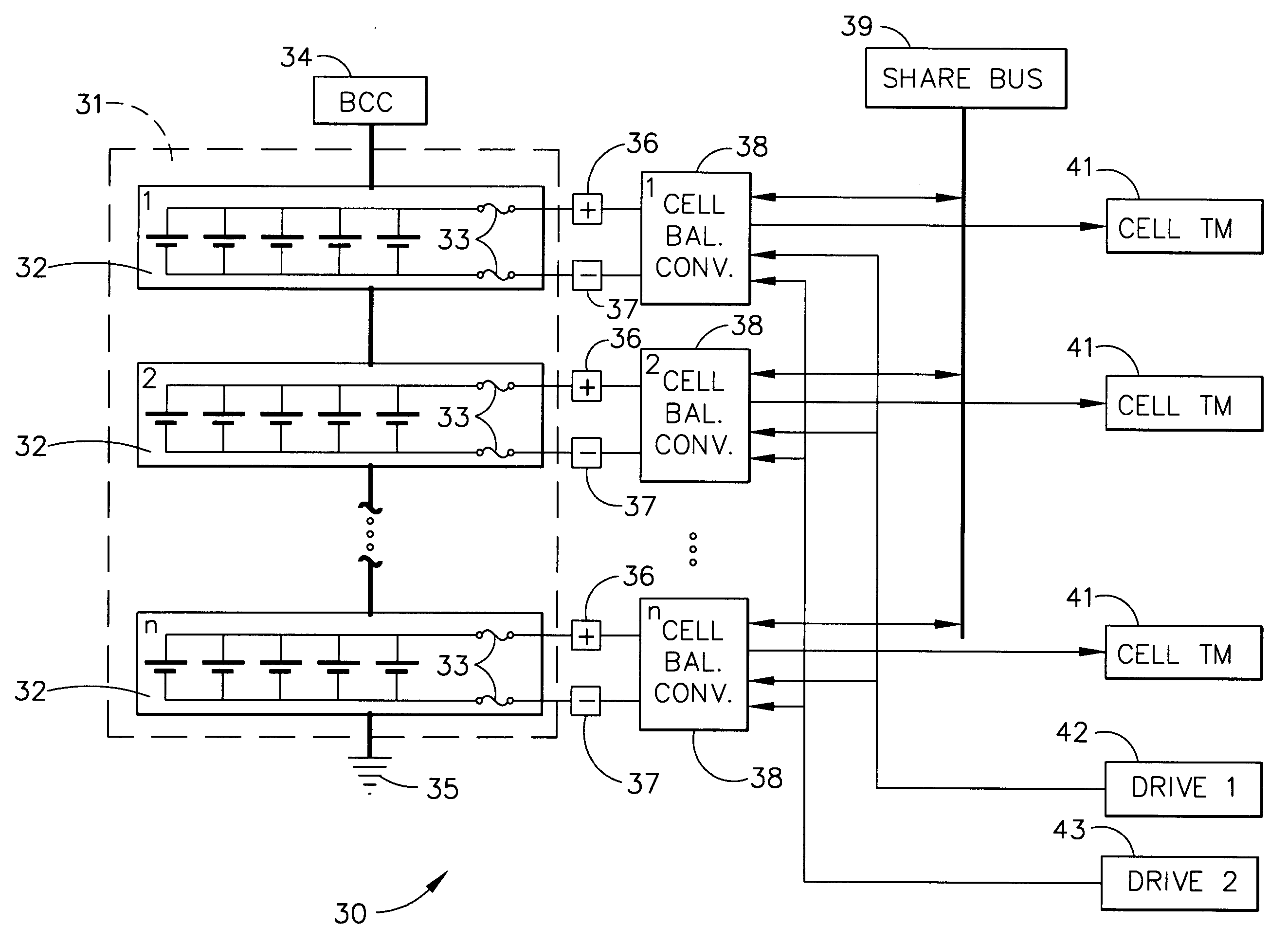
Autonomous battery cell balancing system with integrated voltage monitoring
InactiveUS6873134B2Circuit monitoring/indicationCharge equalisation circuitLithium-ion batteryControl circuit
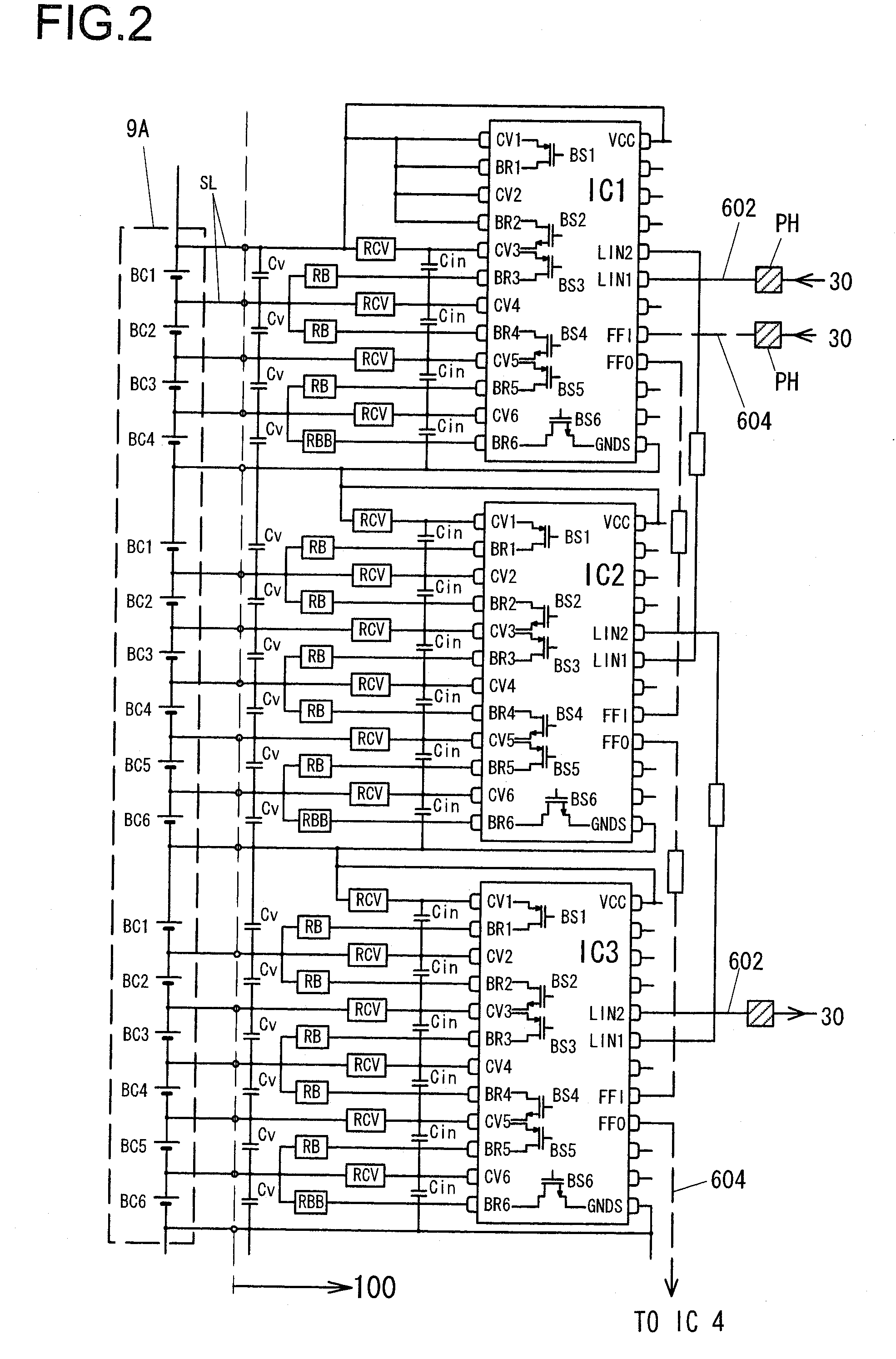
An autonomous lithium-ion cell balancing system with integrated voltage monitoring includes a lithium-ion battery having a plurality of cells, a cell balancing circuit and a cell balancing control circuit. The heart of the cell balancing circuit is a plurality of gated cell balancing converters that are connected with the battery cells and a common share bus. Each gated lithium-ion cell balancing converter receives and input drive voltage and an input sample voltage and transfers energy from highly charged lithium-ion cells to the less charged lithium-ion cells, forcing all cells to have the same energy level. Further, the gated cell balancing converter provides a telemetry output voltage analog to an input cell voltage, eliminating the need for a separate cell voltage monitor.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Autonomous battery cell balancing system with integrated voltage monitoring
InactiveUS20050017682A1Circuit monitoring/indicationCharge equalisation circuitLithium-ion batteryControl circuit
An autonomous lithium-ion cell balancing system with integrated voltage monitoring includes a lithium-ion battery having a plurality of cells, a cell balancing circuit and a cell balancing control circuit. The heart of the cell balancing circuit is a plurality of gated cell balancing converters that are connected with the battery cells and a common share bus. Each gated lithium-ion cell balancing converter receives and input drive voltage and an input sample voltage and transfers energy from highly charged lithium-ion cells to the less charged lithium-ion cells, forcing all cells to have the same energy level. Further, the gated cell balancing converter provides a telemetry output voltage analog to an input cell voltage, eliminating the need for a separate cell voltage monitor.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
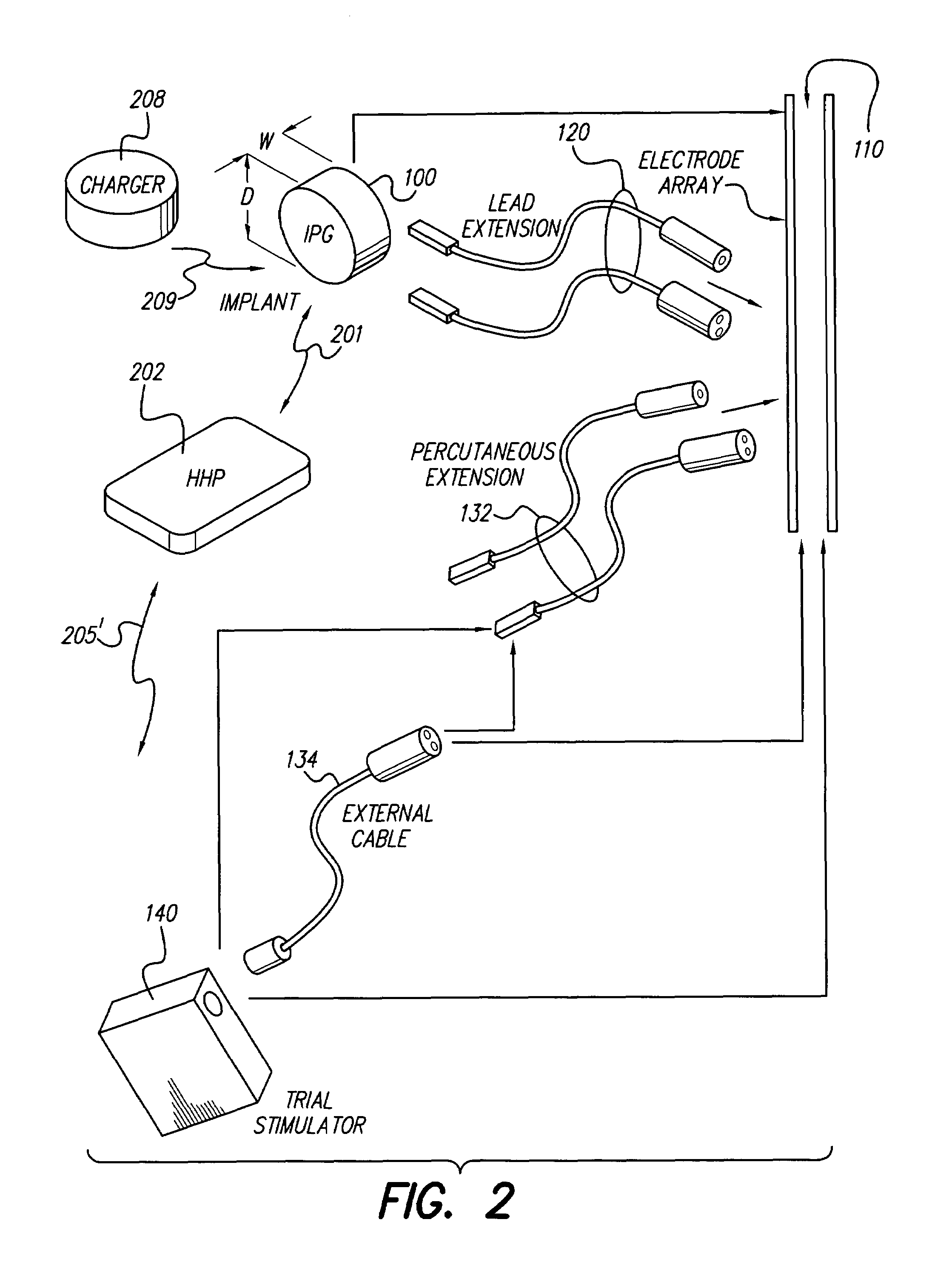
Implantable devices using rechargeable zero-volt technology lithium-ion batteries
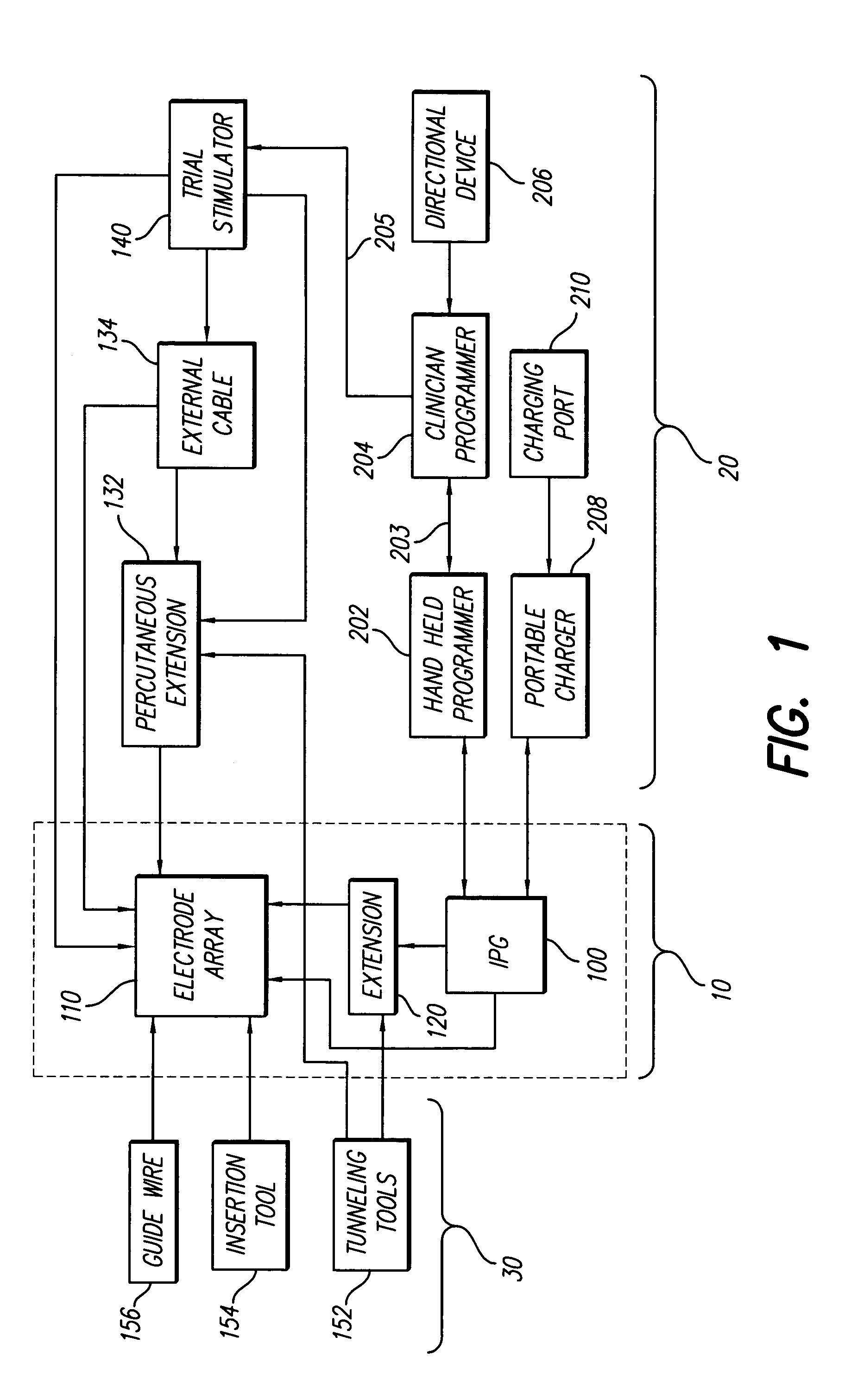
InactiveUS7184836B1Assures safe and reliable operation of systemFirmly connectedElectrotherapyLoad circuitLow voltage
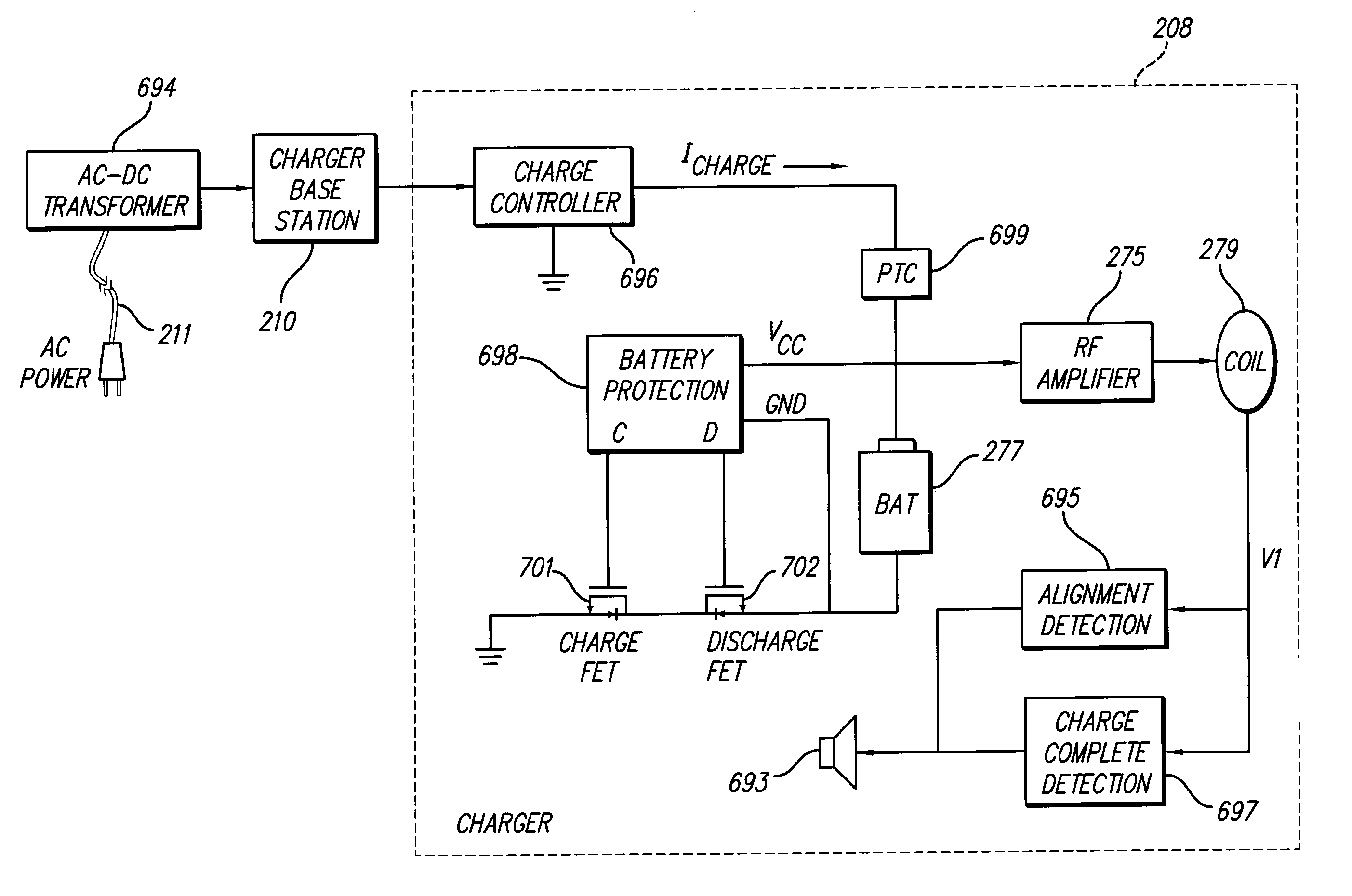
An implantable medical device, such as an implantable pulse generator (IPG) used with a spinal cord stimulation (SCS) system, includes a rechargeable lithium-ion battery having an anode electrode with a substrate made substantially from titanium. Such battery construction allows the rechargeable battery to be discharged down to zero volts without damage to the battery. The implantable medical device includes battery charging and protection circuitry that controls the charging of the battery so as to assure its reliable and safe operation. A multi-rate charge algorithm is employed that minimizes charging time while ensuring the battery cell is safely charged. Fast charging occurs at safer lower battery voltages (e.g., battery voltage above about 2.5 V), and slower charging occurs when the battery nears full charge higher battery voltages (e.g., above about 4.0 V). When potentially less-than-safe very low voltages are encountered (e.g., less than 2.5 V), then very slow (trickle) charging occurs to bring the battery voltage back up to the safer voltage levels where more rapid charging can safely occur. The battery charging and protection circuitry also continuously monitors the battery voltage and current. If the battery operates outside of a predetermined range of voltage or current, the battery protection circuitry disconnects the battery from the particular fault, i.e. charging circuitry or load circuits.
Owner:QUALLION +1
Battery optimization system and method of use
InactiveUS7489106B1Battery capacity can be maximizedMinimizing electrical componentCharge equalisation circuitElectric devicesSystem optimizationBattery capacity
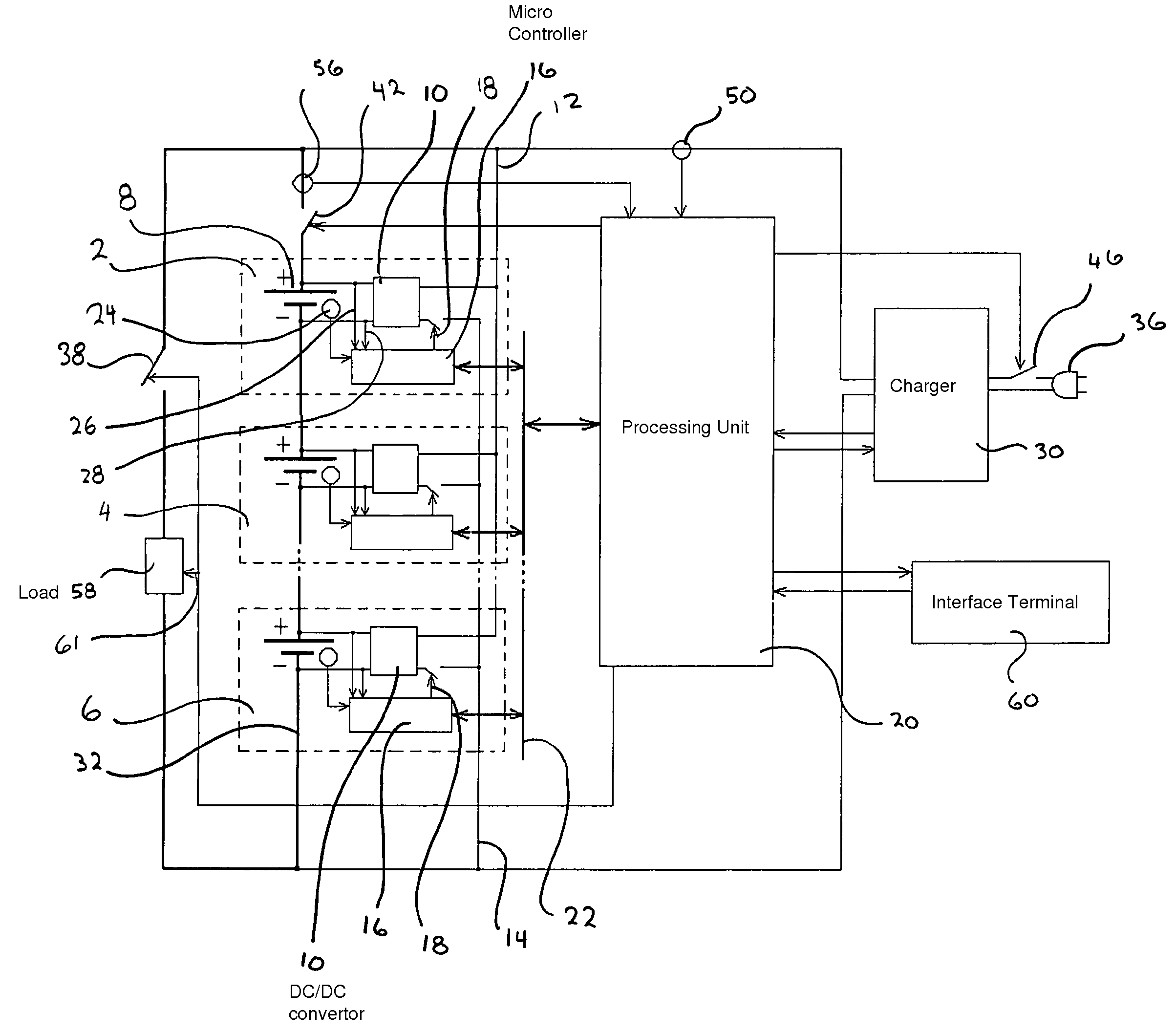
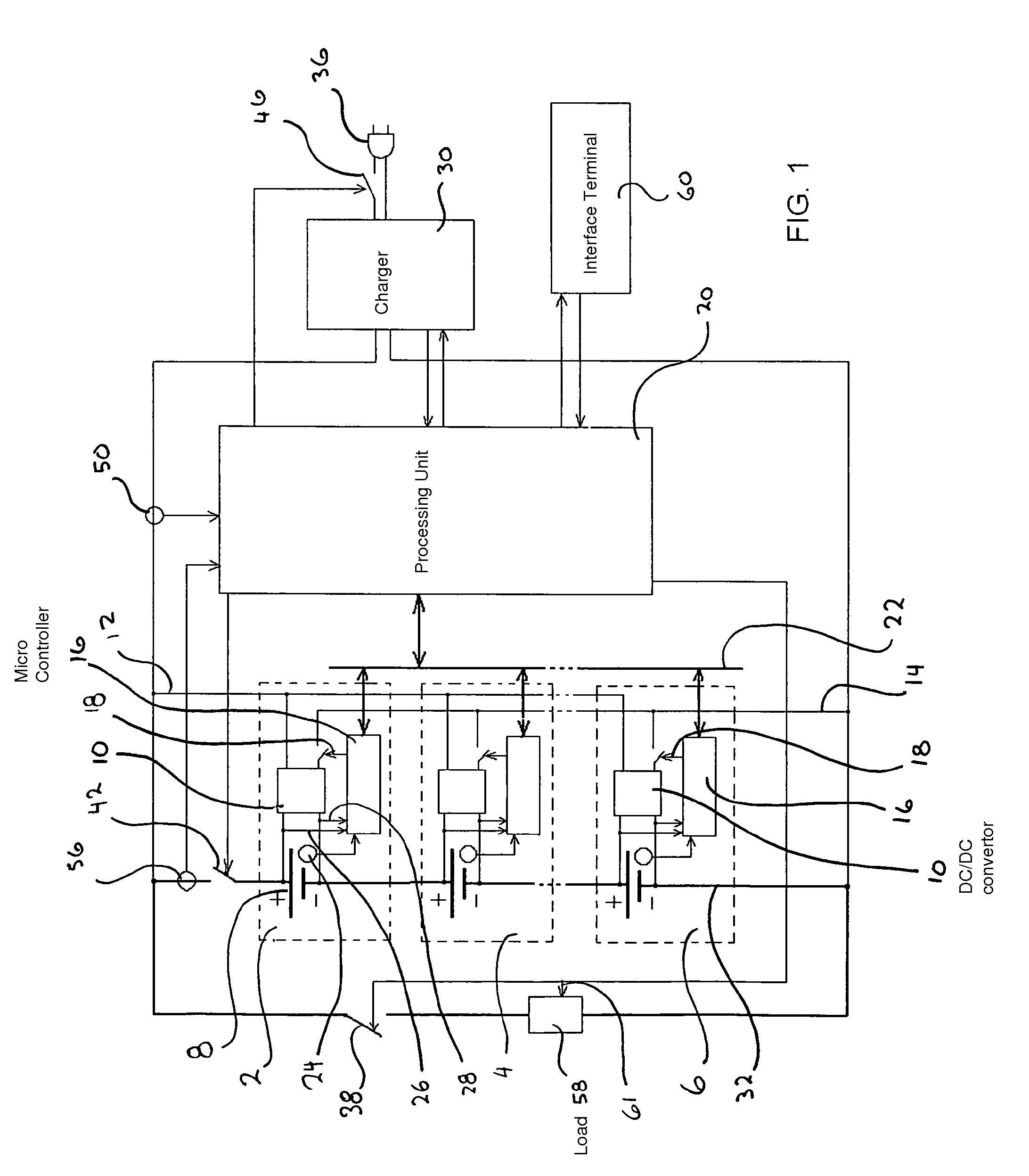
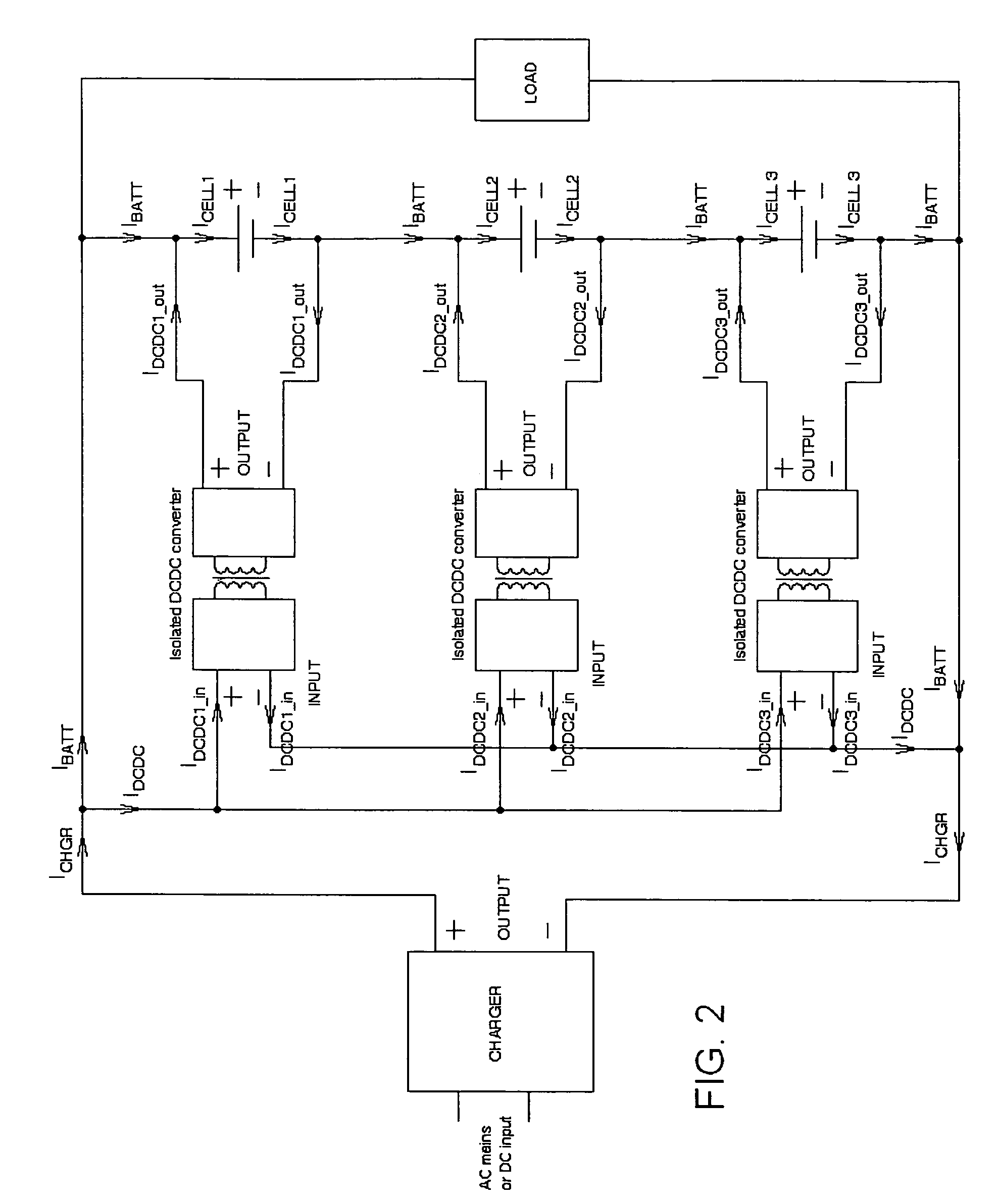
The present invention relates to a microprocessor controlled battery management system that optimizes the total electrical capacity of that battery. It uses localized cell power sources that correct the capacity of the individual connected cells to achieve the maximum capacity of the battery as it acts in a synergistic series connection of cells. The microprocessor retrieves data of battery load current, cell voltage, cell temperature, and battery charger current in timed increments. Through the application of the microprocessor's algorithms, after an initial cell profiling of individual cell capacities has been performed, individual cell DC / DC converters are enabled to correct the condition of the individual cells. In this manner the battery capacity is not affected by the capacity of the weakest cell.
Owner:TIKHONOV VICTOR
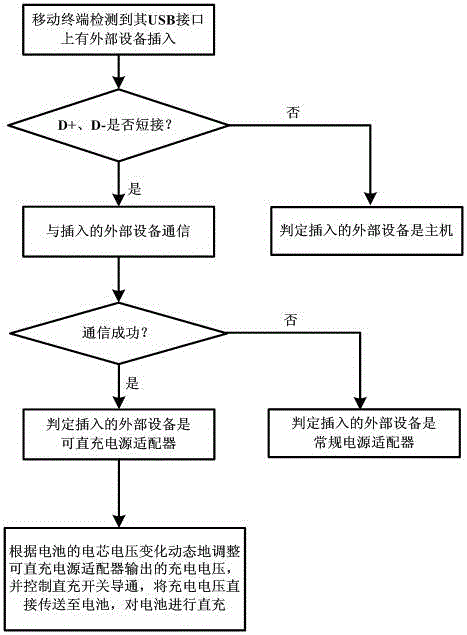
Mobile terminal, direct charging power adapter and charging method
ActiveCN105098900AFast chargingShorten the timeSecondary cells charging/dischargingElectric powerBattery chargeEngineering
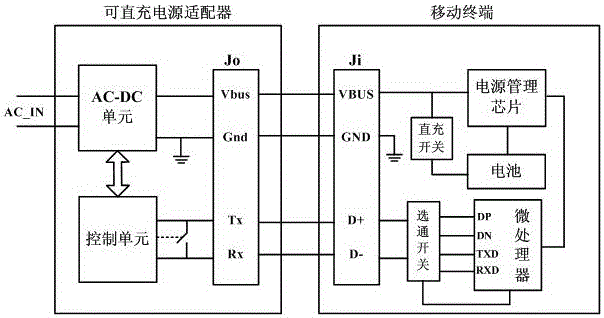
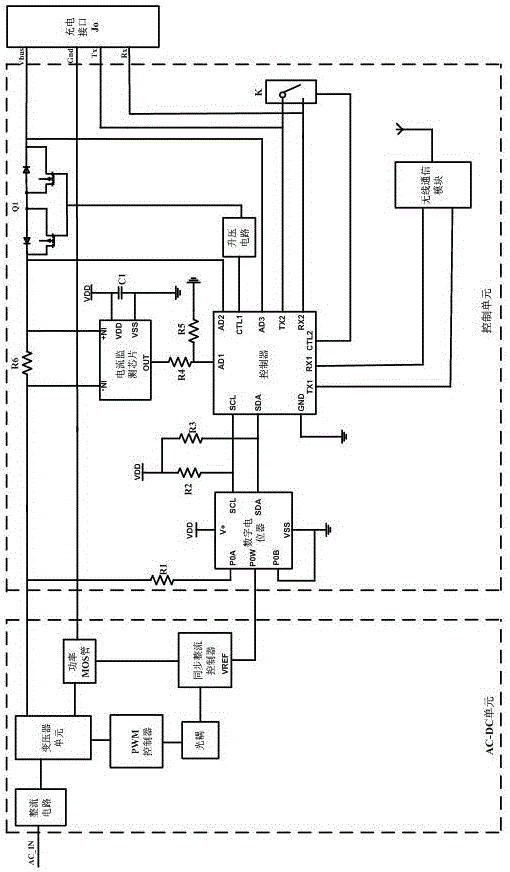
The invention discloses a mobile terminal, a direct charging power adapter and a charging method. The method comprises the steps: the mobile terminal detects the short circuit condition of two communication pins in the USB interface of the mobile terminal, when the mobile terminal is inserted by an external equipment which is the power adapter, the mobile terminal can automatically identify the type of the external connected charging equipment by adopting the power adapter communication; at the same time, a special express charge mode is designed for the direct charging power adapter, when a battery of the mobile terminal is concentratedly charged, the battery is directly charged with heavy current by using the charging voltage outputted by the direct charging power adapter, and the volt value of the charging voltage can be dynamically adjusted according to the variation of the voltage of the battery. According to the above, on the premise that the safety of the battery charge is guaranteed, the great increase of the battery charging speed is realized, the required time of single charging of the mobile terminal is shortened, the influences on daily use of user caused by the repeatedly and long time charging of the mobile terminal is reduced, and the user satisfaction is greatly improved.
Owner:QINGDAO HISENSE MOBILE COMM TECH CO LTD
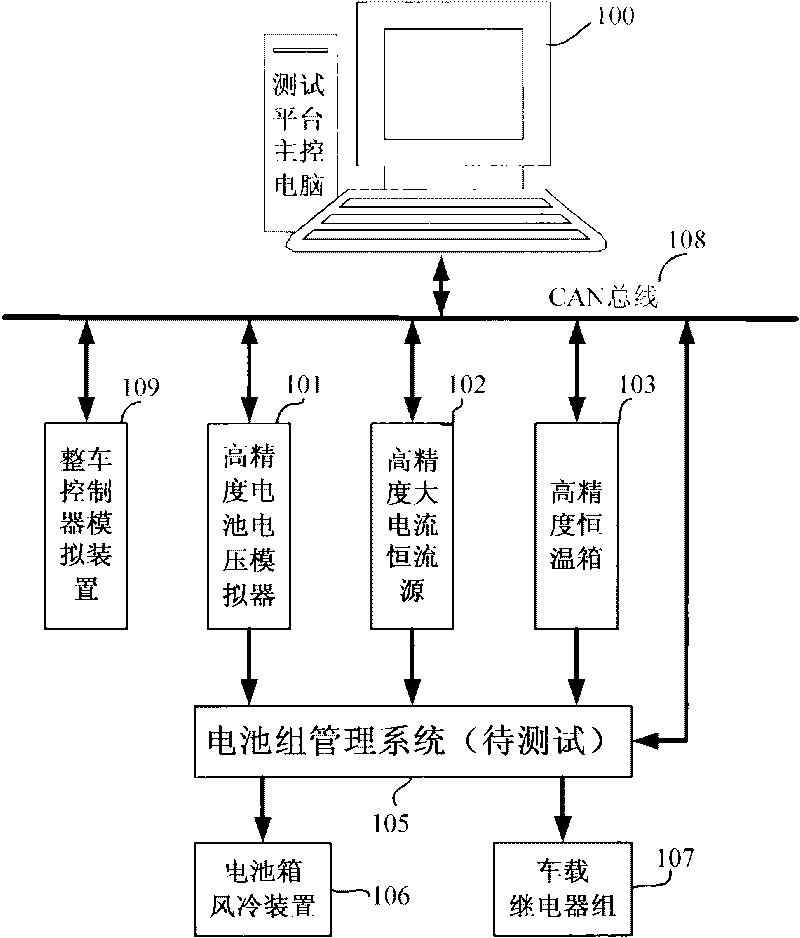
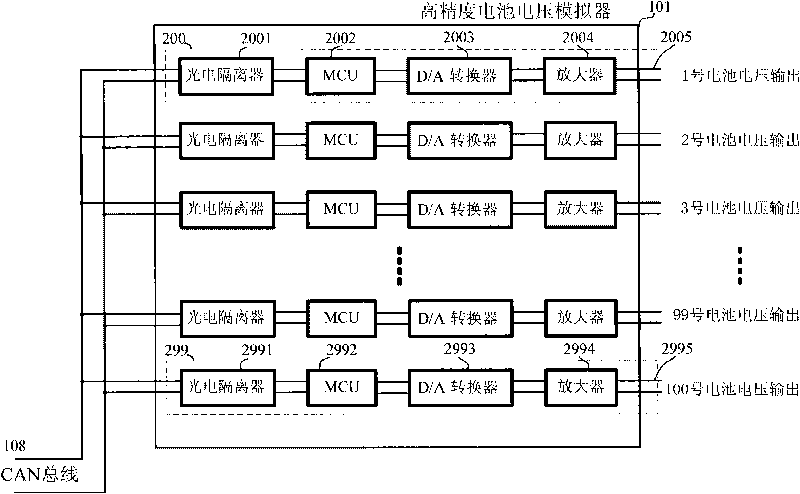
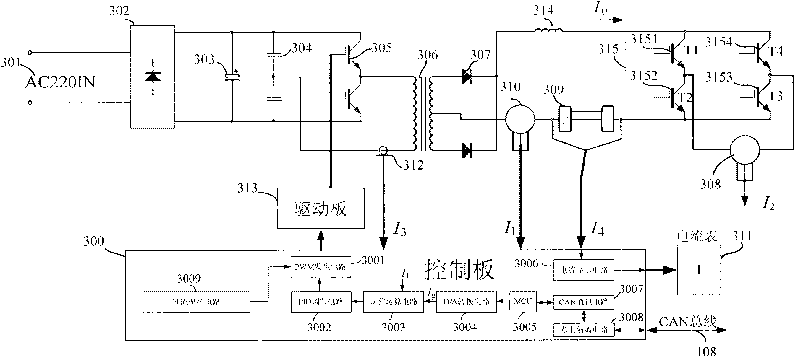
Battery managing system testing platform
InactiveCN101762800AHigh precisionSimple structureElectrical testingElectrical batteryData acquisition
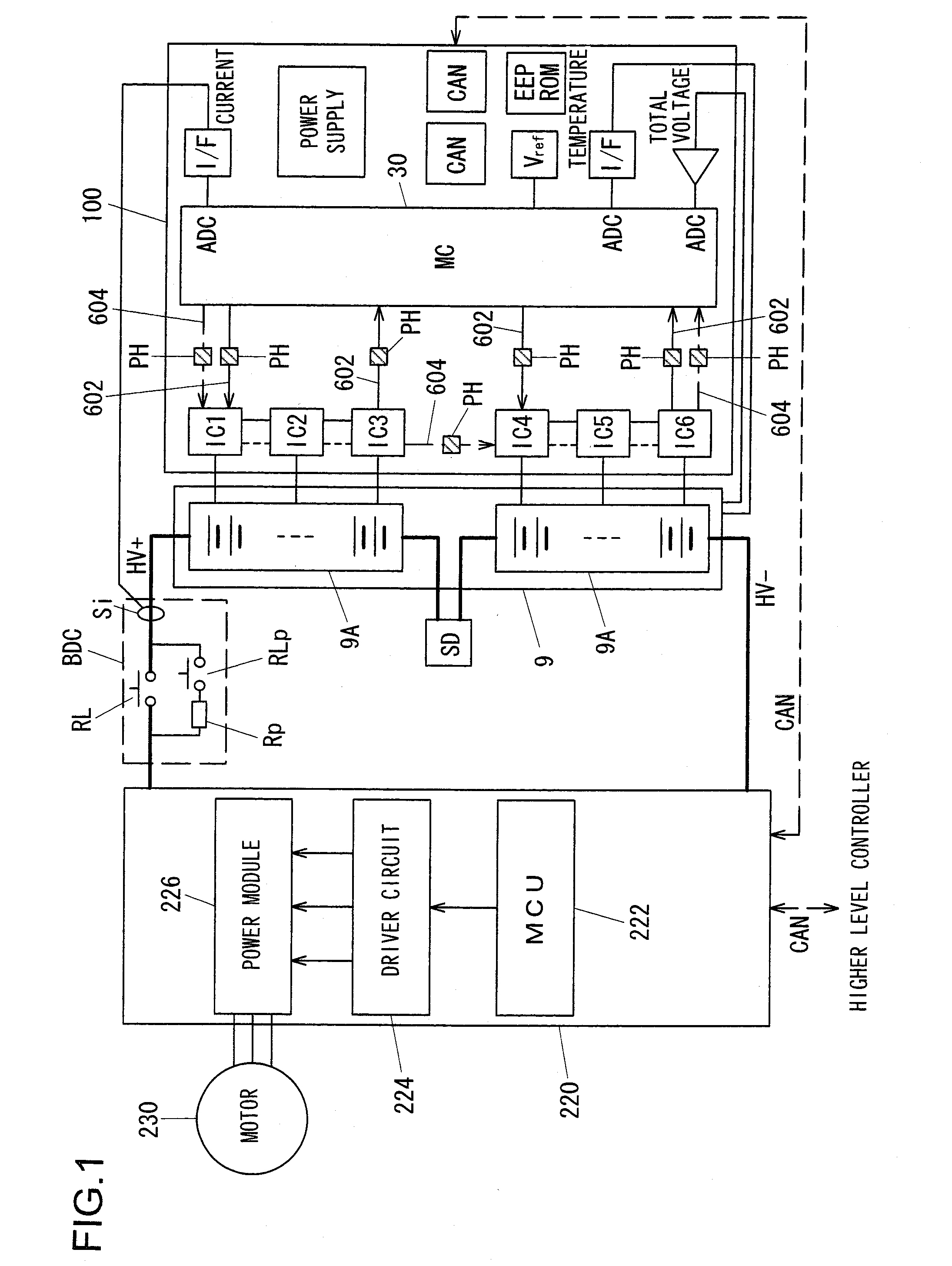
The invention discloses a battery managing system (BMS) testing platform comprising a testing platform main control computer, a high-precision cell voltage simulator, a high-precision large-current constant-current source, a high-precision thermotank, a battery managing system to be tested, a whole vehicle controller simulator and the like which are connected by CAN buses. The battery managing system is connected with a cell box air cooling device, a vehicle relay assembly and the like. The battery managing system testing platform can truly simulate the output state of a battery, comprising single cell voltage, total voltage, charging and discharging current, temperature and the like of the battery, can complete various communication and command functions, protection functions, battery heavy current applying process between the battery managing system and the whole vehicle, and the test and the verification on the functions of overhead protection and the like of the battery. The invention can carry out testing evaluation on the data collection precision of the battery managing system, the evaluation precision of the charge state of the battery and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Solid polymer fuel cell with improved voltage reversal tolerance
In a solid polymer fuel cell series, various circumstances can result in the fuel cell being driven into voltage reversal. For instance, cell voltage reversal can occur if that cell receives an inadequate supply of fuel (for example, fuel starvation). In order to pass current during fuel starvation, reactions other than fuel oxidation may take place at the fuel cell anode, including water electrolysis and oxidation of anode components. The latter may result in significant degradation of the anode. Such fuel cells can be made more tolerant to cell reversal by promoting water electrolysis over anode component oxidation at the anode. This can be accomplished by incorporating a catalyst composition at the anode to promote the water electrolysis reaction, in addition to the typical anode electrocatalyst for promoting fuel oxidation.
Owner:BALLARD POWER SYSTEMS +1
Battery Monitoring System
ActiveUS20100244847A1Great data lengthEnsure correct executionCircuit monitoring/indicationCharge equalisation circuitMonitoring systemEngineering
A battery monitoring system, comprises a battery state detection circuit that detects battery states of a plurality of battery cells that are connected in series, based on respective cell voltages of the plurality of battery cells, and a control circuit that monitors state of a battery cell, based on each cell voltage of the plurality of battery cells. The control circuit inputs pseudo voltage information to the battery state detection circuit, and thereby diagnoses whether or not the battery state detection circuit is operating normally.
Owner:HITACHI AUTOMOTIVE SYST LTD +1
Implantable devices using rechargeable zero-volt technology lithium-ion batteries
InactiveUS7295878B1Assures safe and reliable operation of systemFirmly connectedImplantable neurostimulatorsLoad circuitLow voltage
An implantable medical device, such as an implantable pulse generator (IPG) used with a spinal cord stimulation (SCS) system, includes a rechargeable lithium-ion battery having an anode electrode with a substrate made substantially from titanium. Such battery construction allows the rechargeable battery to be discharged down to zero volts without damage to the battery. The implantable medical device includes battery charging and protection circuitry that controls the charging of the battery so as to assure its reliable and safe operation. A multi-rate charge algorithm is employed that minimizes charging time while ensuring the battery cell is safely charged. Slow charging occurs at lower battery voltages (e.g., battery voltage below about 2.5 V), and fast charging occurs when the battery voltage has reached a safe level (e.g., above about 2.5 V). When potentially less-than-safe very low voltages are encountered (e.g., less than 2.5 V), then very slow (trickle) charging occurs to bring the battery voltage back up to the safer voltage levels where more rapid charging can safely occur. The battery charging and protection circuitry also continuously monitors the battery voltage and current. If the battery operates outside of a predetermined range of voltage or current, the battery protection circuitry disconnects the battery from the particular fault, i.e. charging circuitry or load circuits.
Owner:QUALLION +1
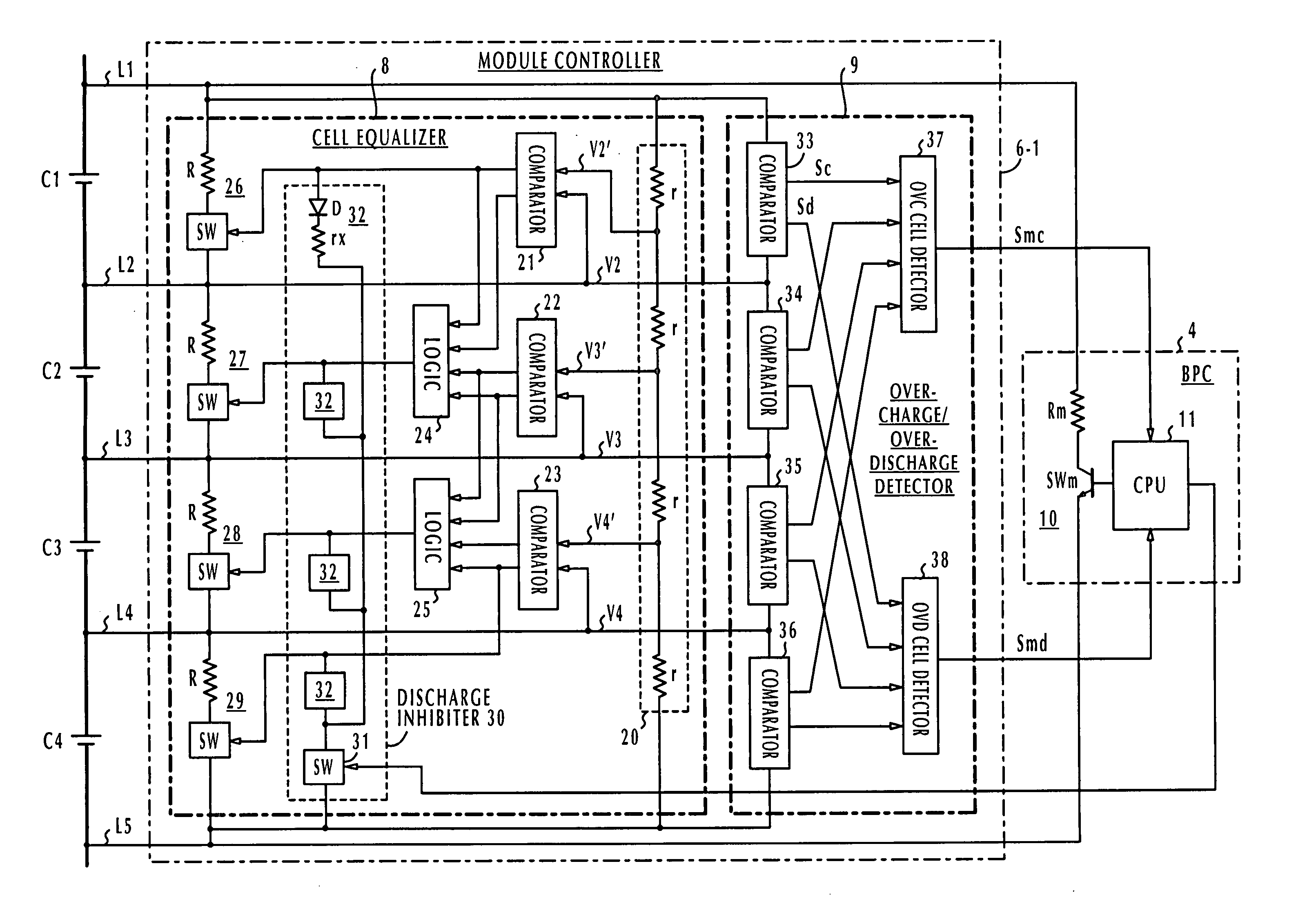
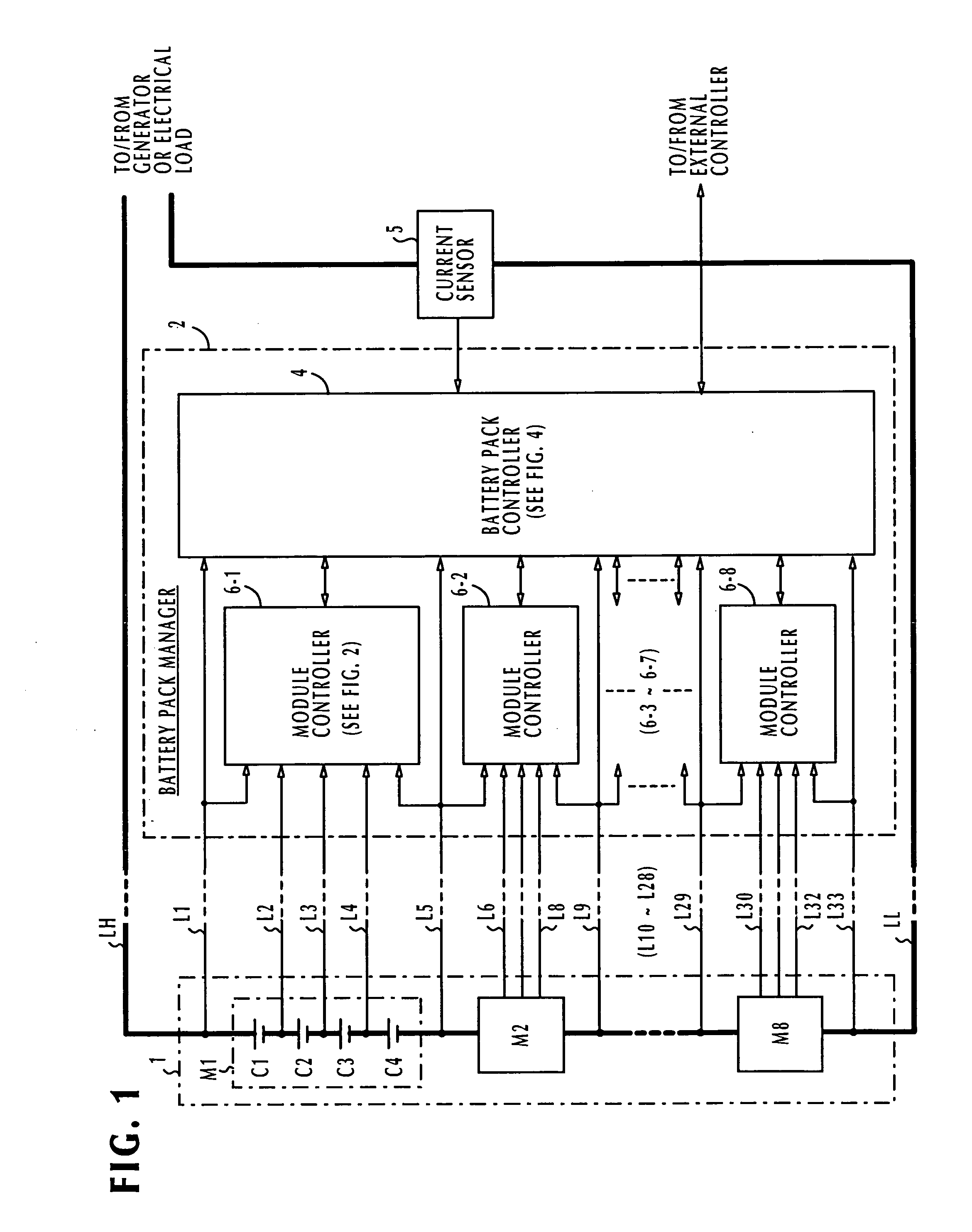
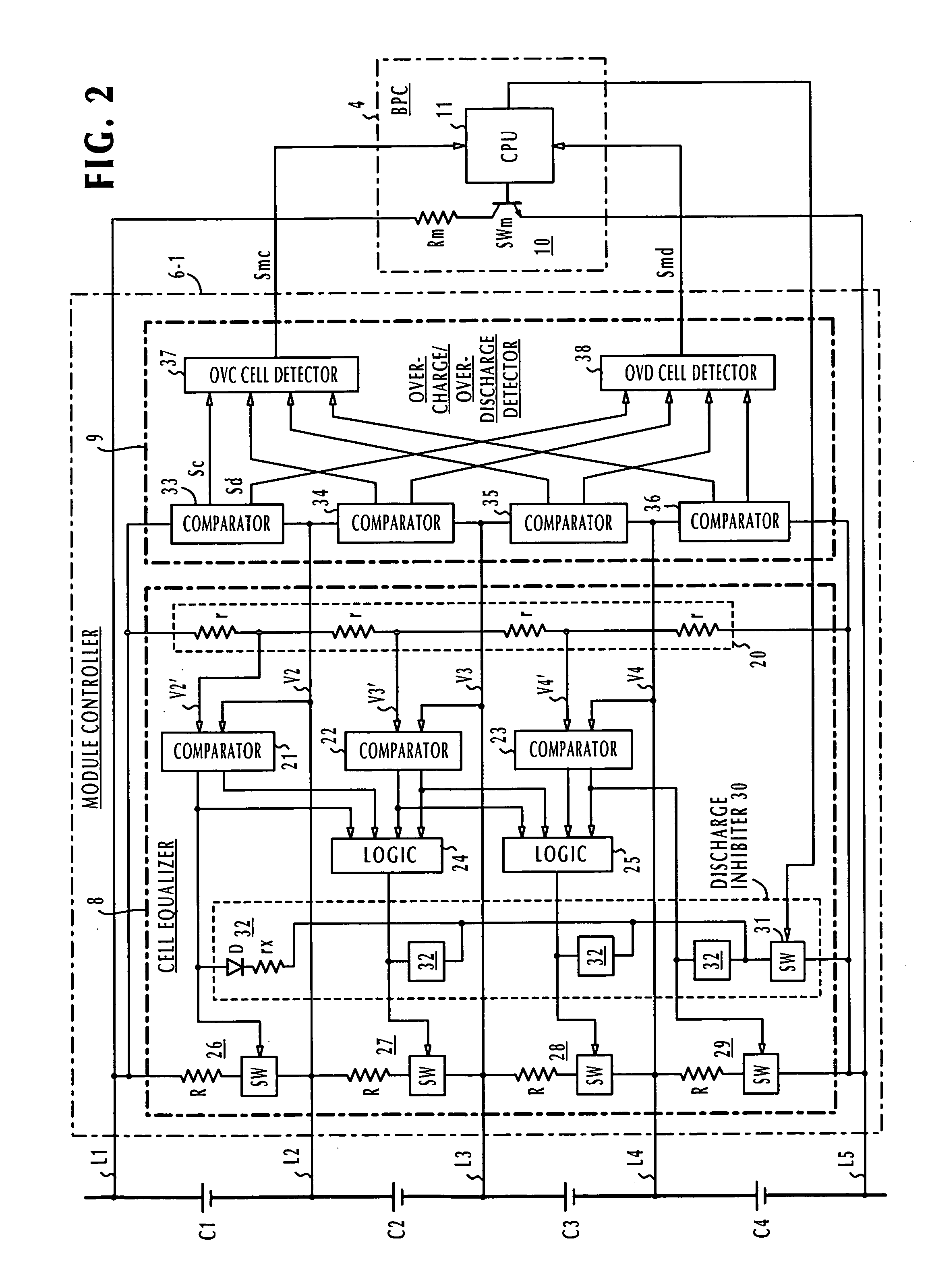
Battery pack manager
ActiveUS20060103351A1Without introducing complexityIncrease power consumptionCharge equalisation circuitMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansEngineeringVoltage reference
In a battery pack manager that manages series-connected rechargeable unit cells, a cell equalizer equalizes the cell voltages by individually discharging the unit cells according to deviations from reference voltages. An overcharge / overdischarge detector detects an overcharge and an overdischarge state of each unit cell. An inhibit circuit prevents the cell equalizer from discharging the unit cells when the overcharge / overdischarge detector is activated to reduce the cell voltage variability, which would otherwise occur as a result of interference from the overcharge / overdischarge detector, so that the overcharge / overdischarge states of all unit cells can be determined with precision. Connecting lines of the unit cells are monitored to detect a line-cut. The inhibit circuit further inhibits the cell equalizer when the connecting lines are being monitored to reduce the cell voltage variability, which would otherwise occur as a result of interference from the line-cut detection, so that false line-cut detection is avoided.
Owner:DENSO CORP
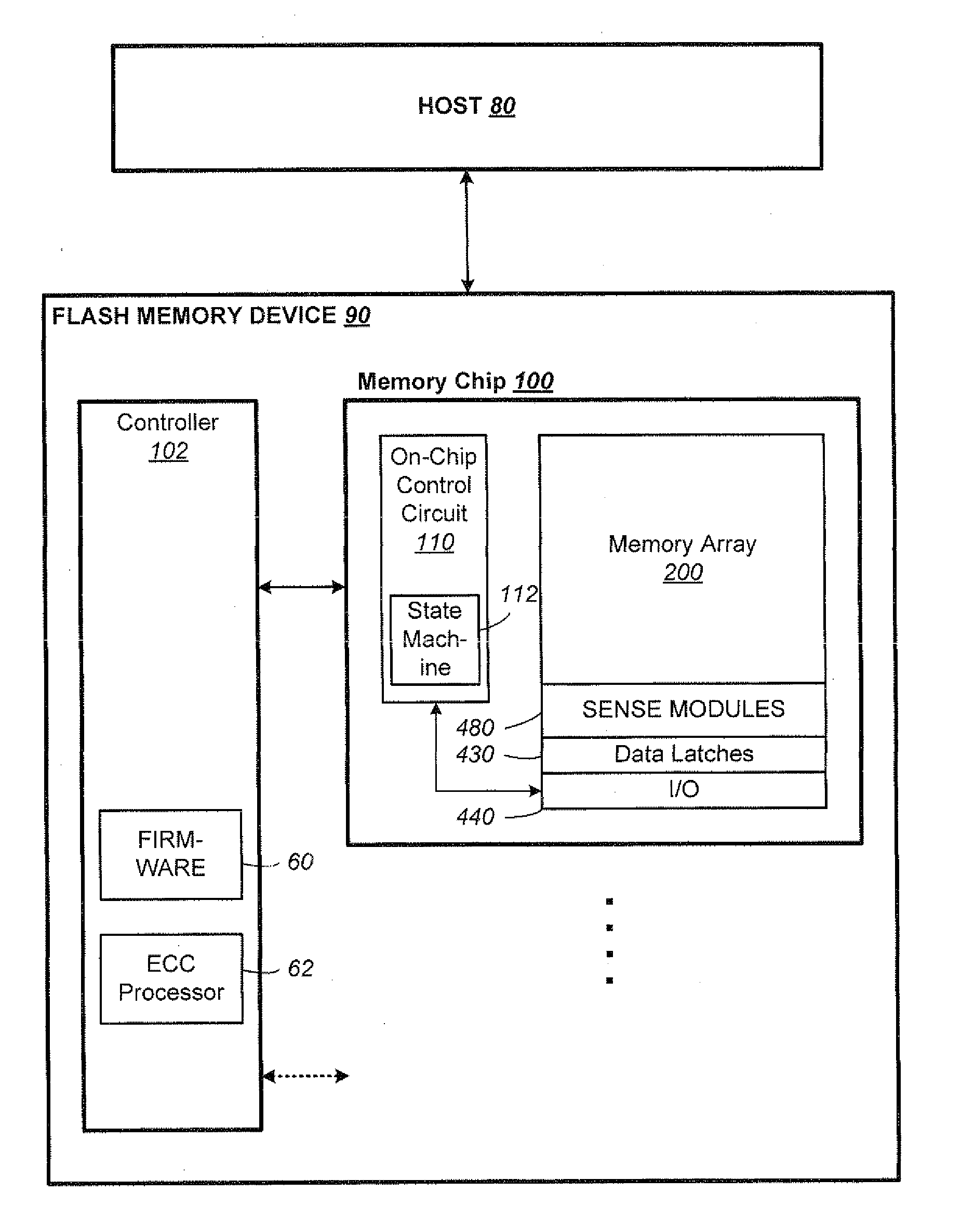
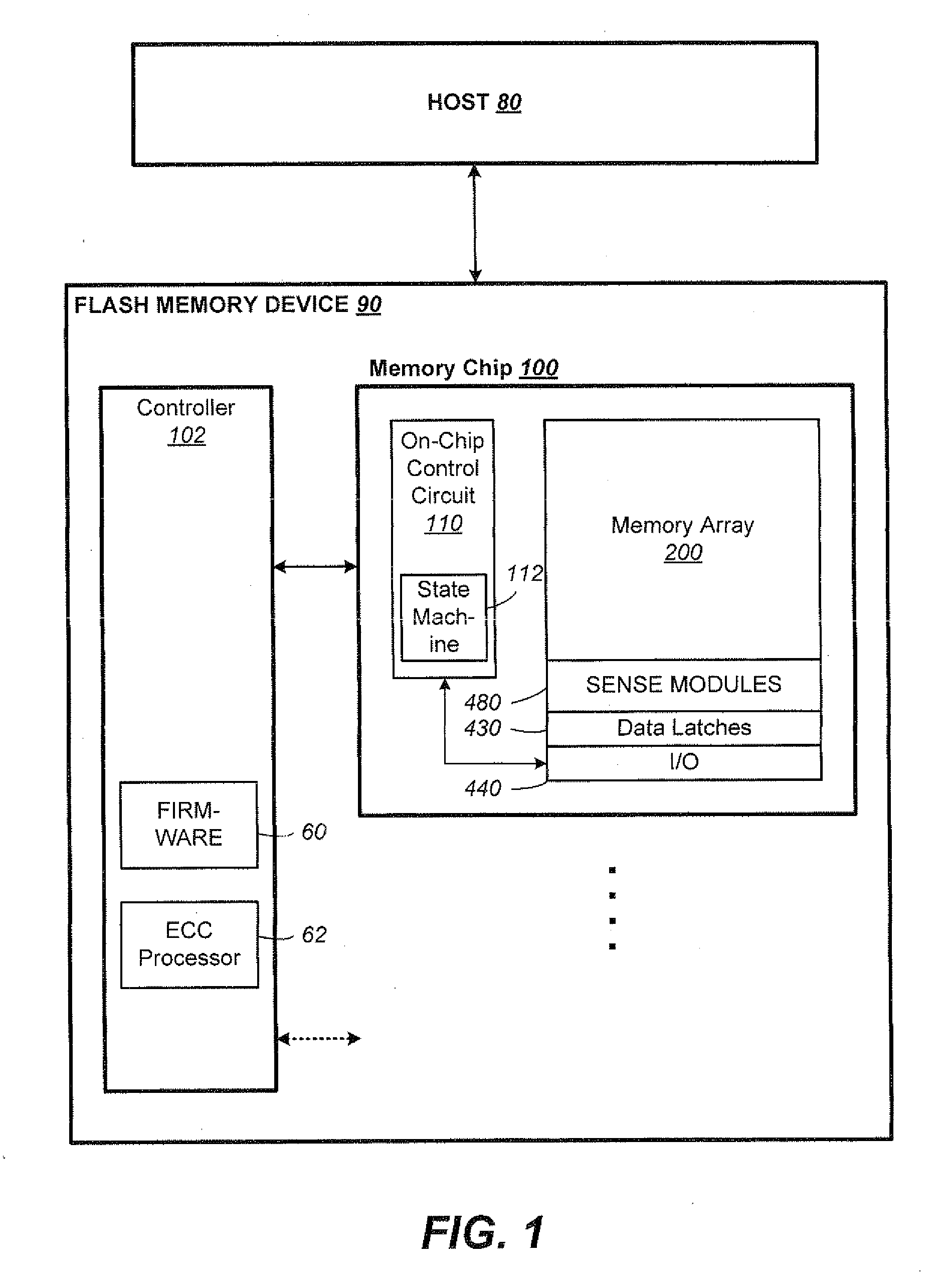
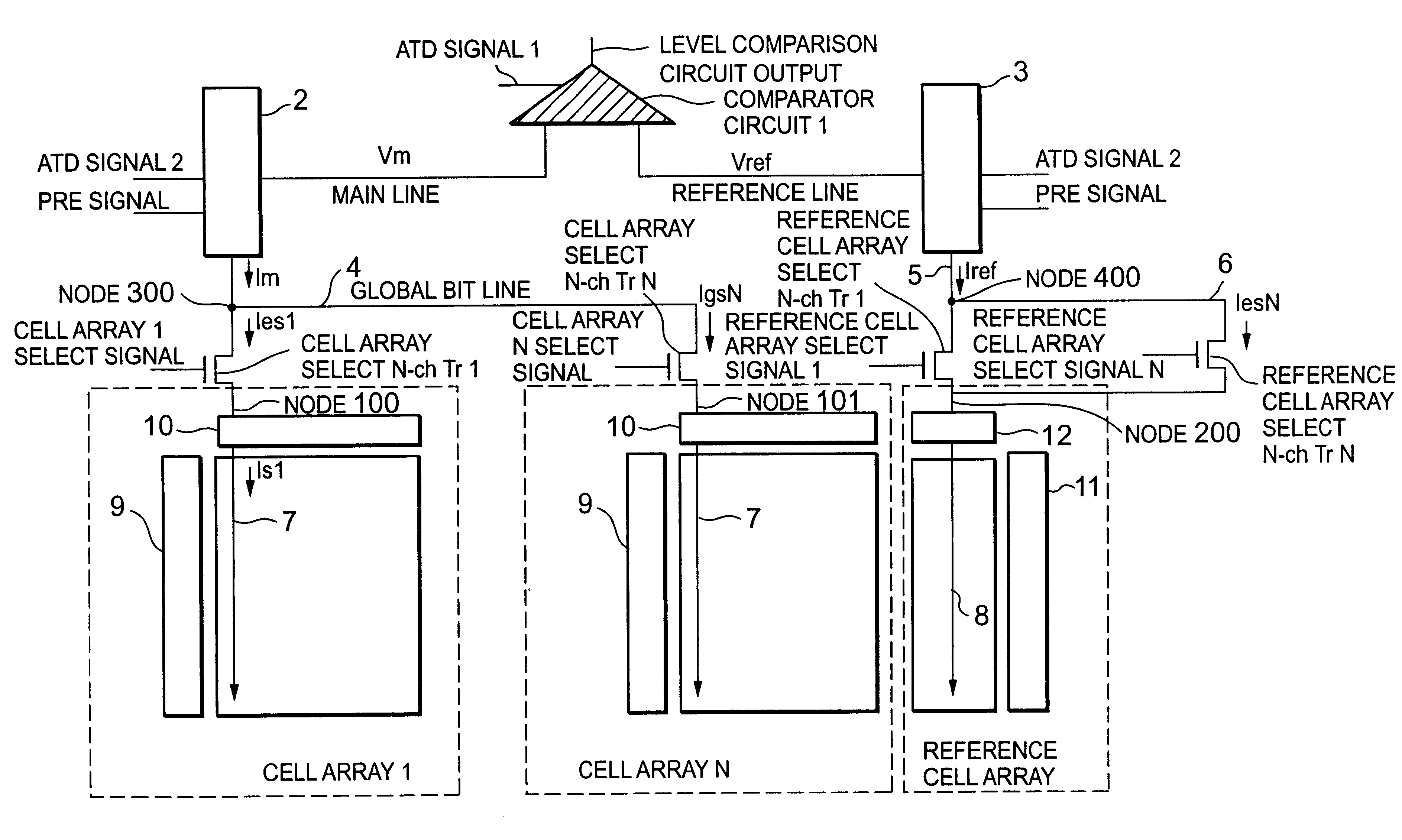
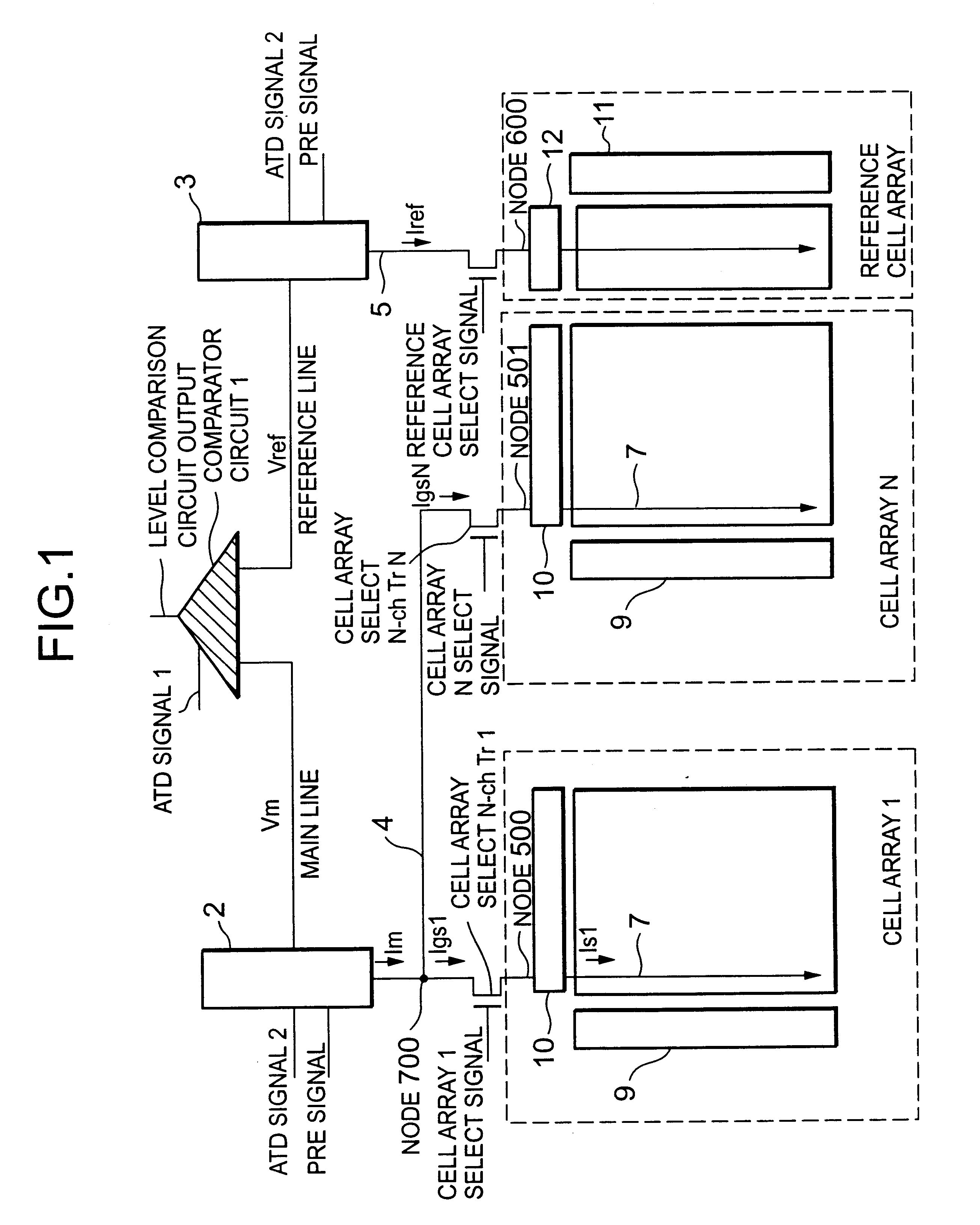
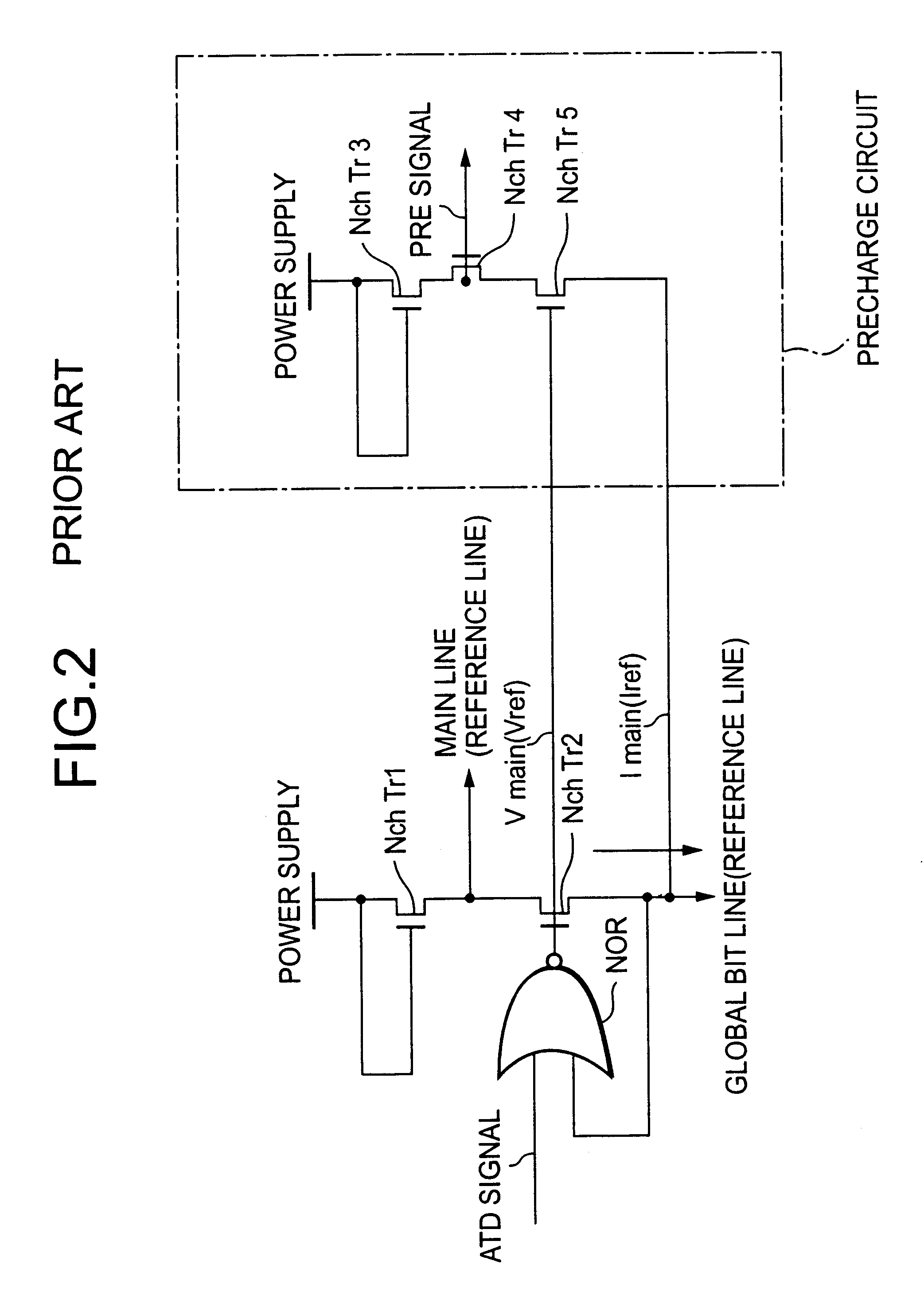
Simultaneous Sensing of Multiple Wordlines and Detection of NAND Failures
Techniques for a post-write read are presented. In an exemplary embodiment, a combined simultaneous sensing of multiple word lines is used in order to identify a problem in one or more of these word lines. That is, sensing voltages are concurrently applied to the control gates of more than one memory cell whose resultant conductance is measured on the same bit line. The combined sensing result is use for measuring certain statistics of the cell voltage distribution (CVD) of multiple word lines and comparing it to the expected value. In case the measured statistics are different than expected, this may indicate that one or more of the sensed word lines may exhibit a failure and more thorough examination of the group of word lines can be performed.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
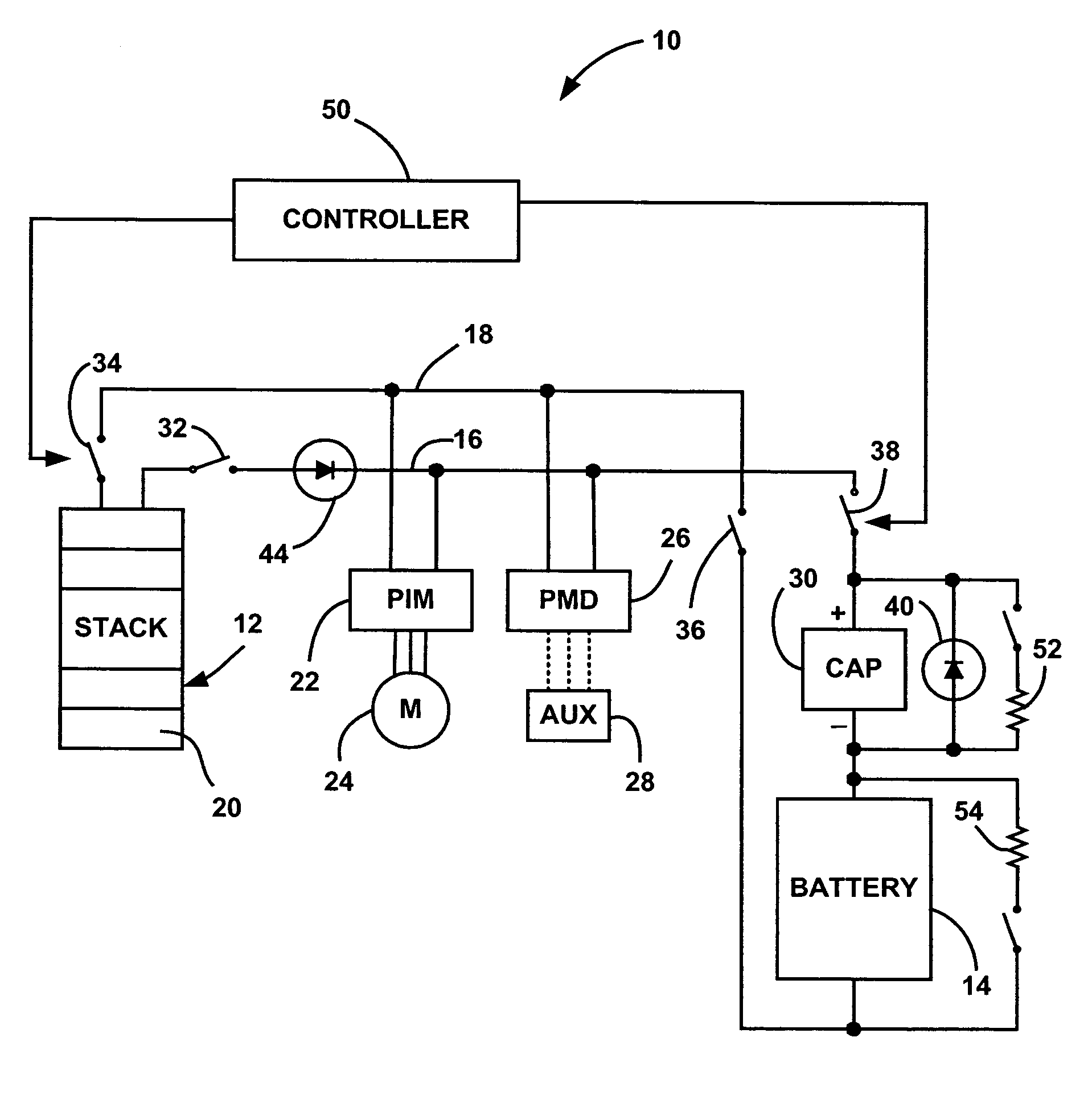
Hybrid fuel cell system with battery capacitor energy storage system
A fuel cell system that employs a super capacitor and battery electrically coupled in series with each other and in parallel with a fuel cell stack on a power bus line. As the voltage on the power bus line changes over the operating requirements of the system, the super capacitor is charged and discharged over a relatively large voltage swing, such as an 85% SOC swing. The super capacitor equalizes or voltage matches the voltage variation on the power bus line as set by the stack voltage to the voltage of the battery. Therefore, the battery, while providing the majority of the energy and power during charge and discharge, has a relatively small defined SOC swing, which acts to maintain the battery life. The system can also include a diode electrically coupled in parallel with the super capacitor that provides reverse voltage protection and electrical power by-pass.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
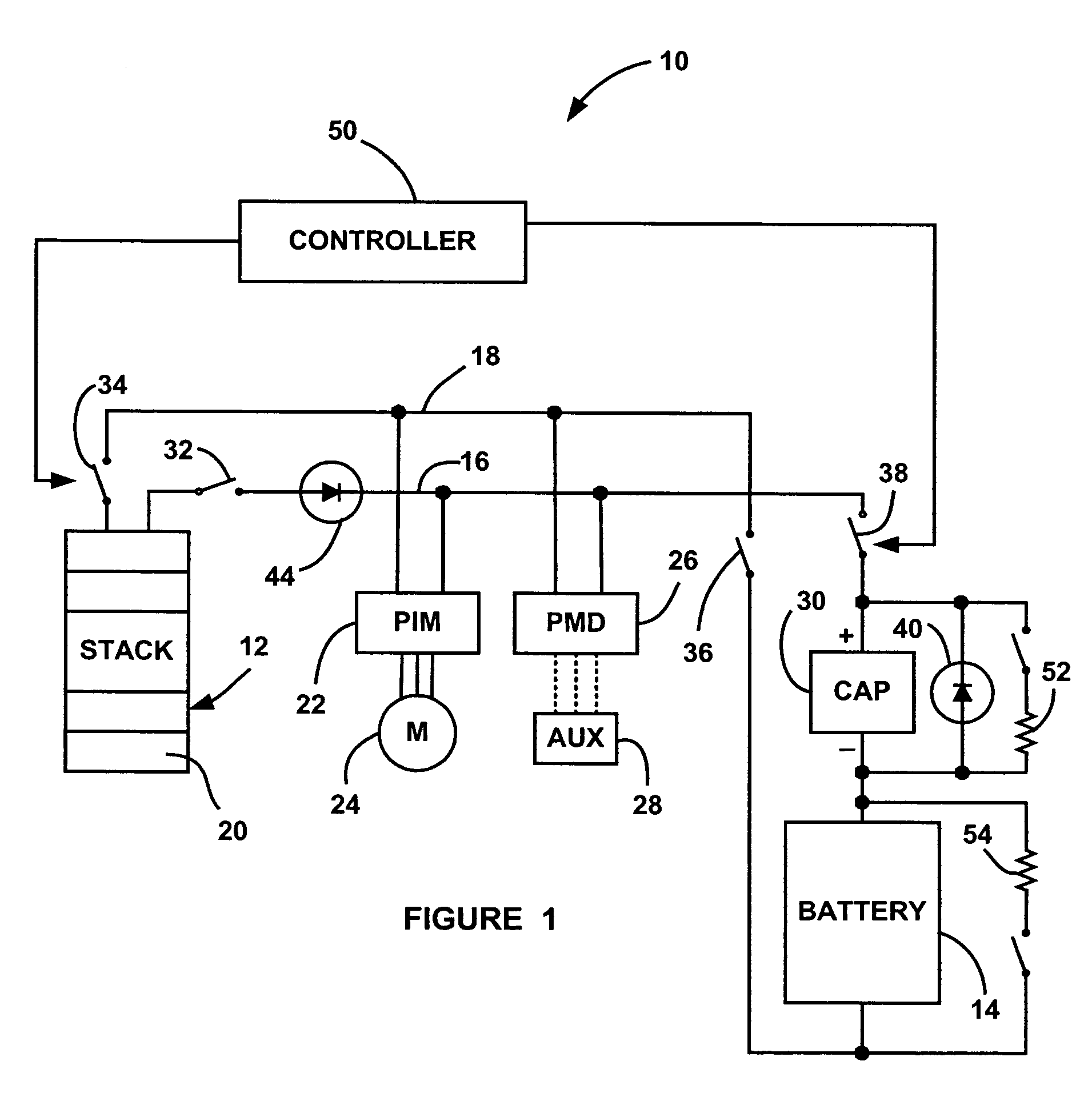
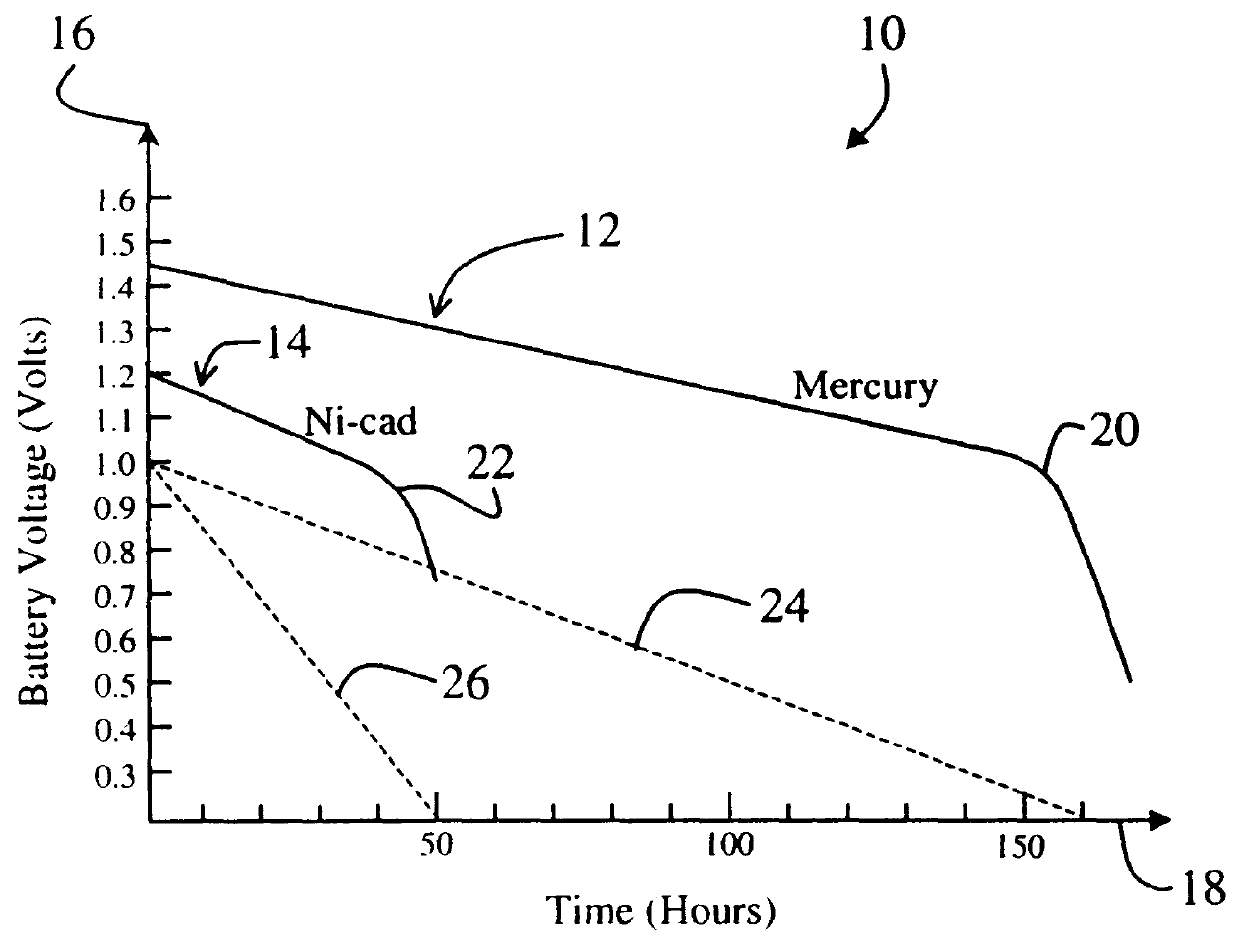
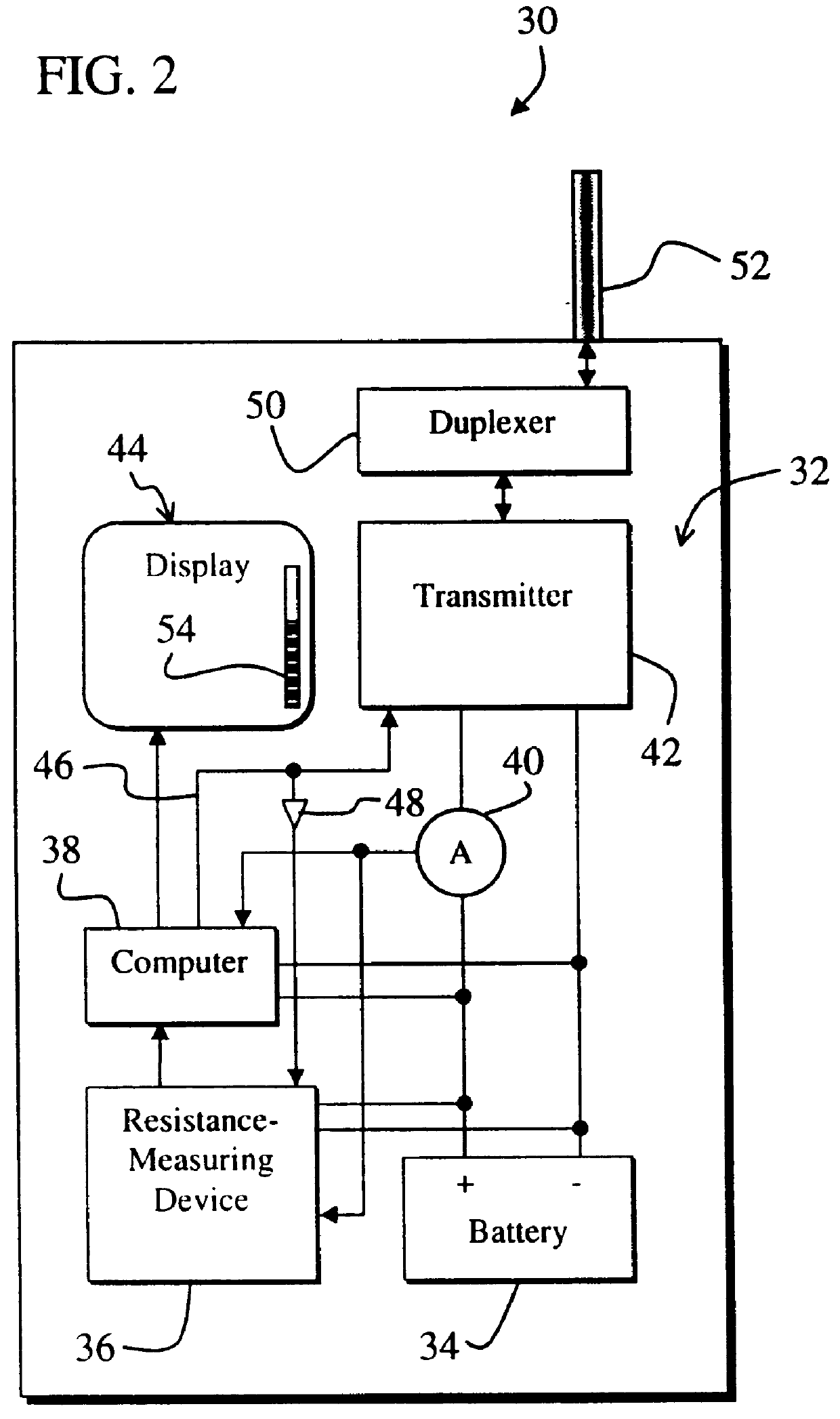
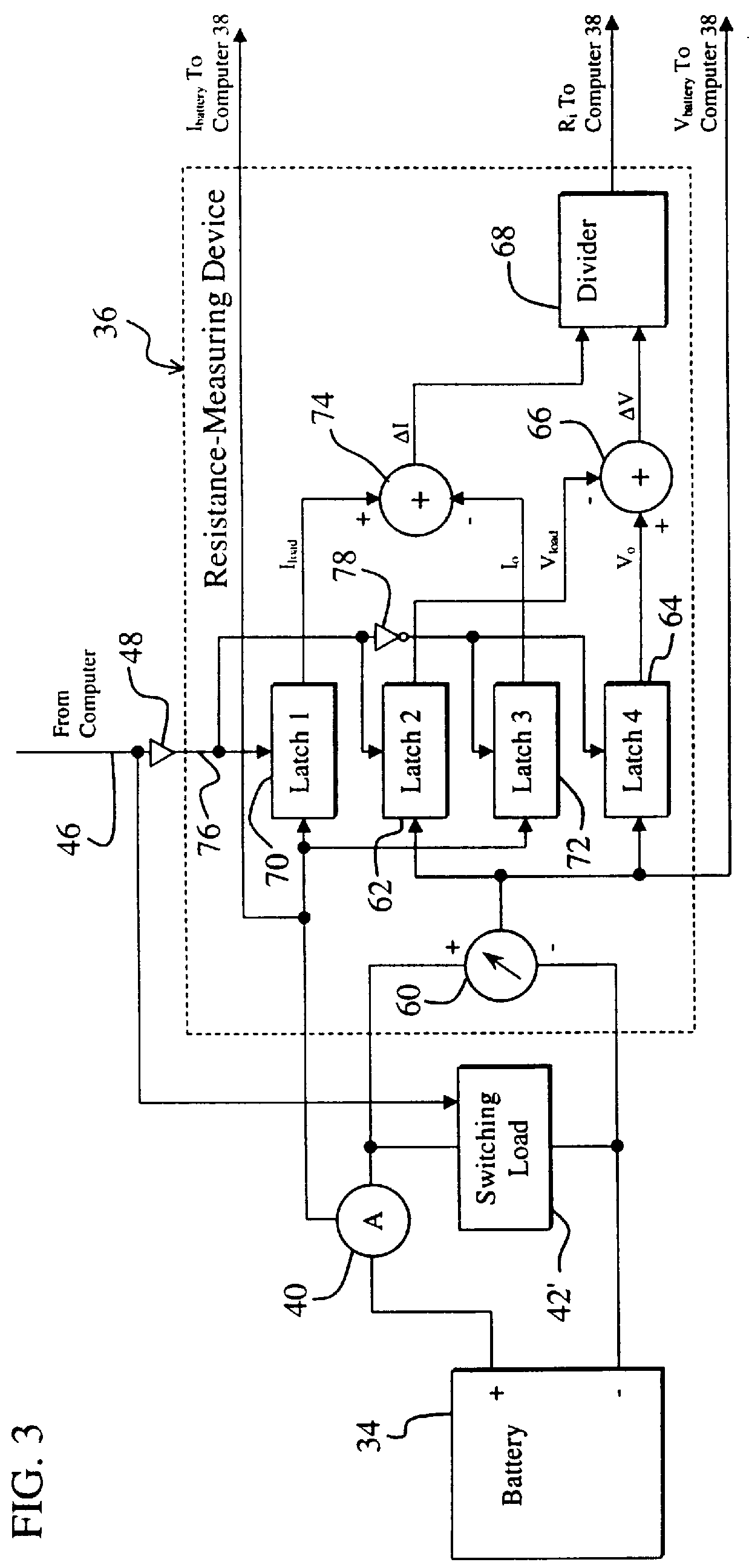
System and method for accurately determining remaining battery life
InactiveUS6087808ACircuit monitoring/indicationElectrical testingCurrent meterElectrical resistance and conductance
A system for providing an accurate indication of the remaining life of a battery. The system includes a first circuit that provides a control signal. A second circuit employs an internal resistance value of the battery and a battery voltage to provide the indication of remaining battery life in response to the control signal. In a specific embodiment, the second circuit includes a third circuit that measures the internal resistance of the battery in response to the control signal. The third circuit also includes a circuit for measuring an output current and an output voltage of the battery at varying battery loads. The circuit for measuring an output current includes an ammeter and a switching load. In a more specific embodiment, the switching load is implemented as a transmitter that is selectively activated via the control signal. A fourth circuit, included in the second circuit, provides the indication of remaining battery life in response to the internal resistance. The fourth circuit also includes a circuit for selecting a battery discharge curve in accordance with the internal resistance. Software running on the first circuit generates the estimate based on the discharge curve, which is subsequently displayed via a display.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
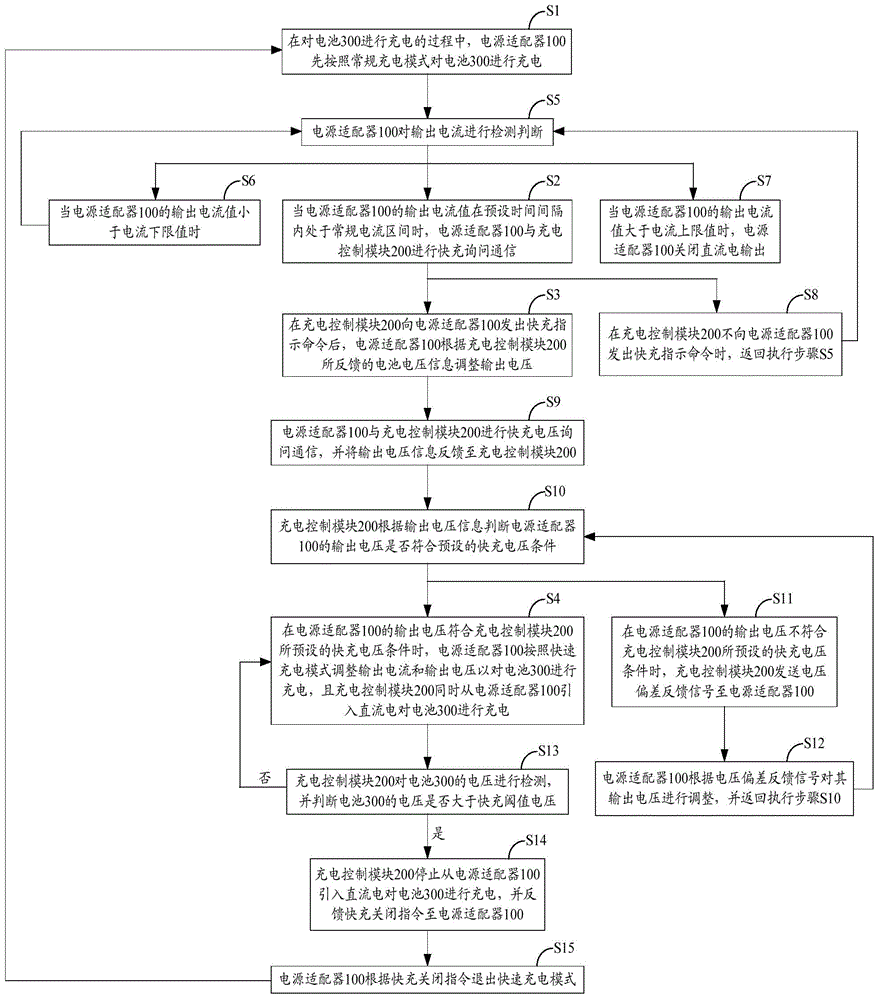
Cell charging device and method
ActiveCN104810877AShorten charging timeSecondary cells charging/dischargingElectric powerCurrent rangeCharge control
The invention belongs to the technical field of charging and provides a cell charging device and method. In the process of charging a cell by utilizing the cell charging device comprising a power adapter and a charging control module, the power adapter charges the cell in a conventional charging mode first; when the output current value of the power adapter is in a conventional current range in a preset time interval, the power adapter is in quick charge inquiry communication with the charging control module; after the charging control module sends a quick charge instruction command to the power adapter, the power adapter adjusts output voltage according to the cell voltage information fed back by the charging control module; when the output voltage accords with the preset quick charge voltage condition of the charging control module, the power adapter adjusts output current and output voltage according to the quick charge mode so as to charge the cell; and meanwhile, the charging control module introduces a direct current from the power adapter to charge the cell, and thus the purpose of reducing charging time by carrying out quick charge on the cell is realized.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Semiconductor memory device
Owner:NEC ELECTRONICS CORP
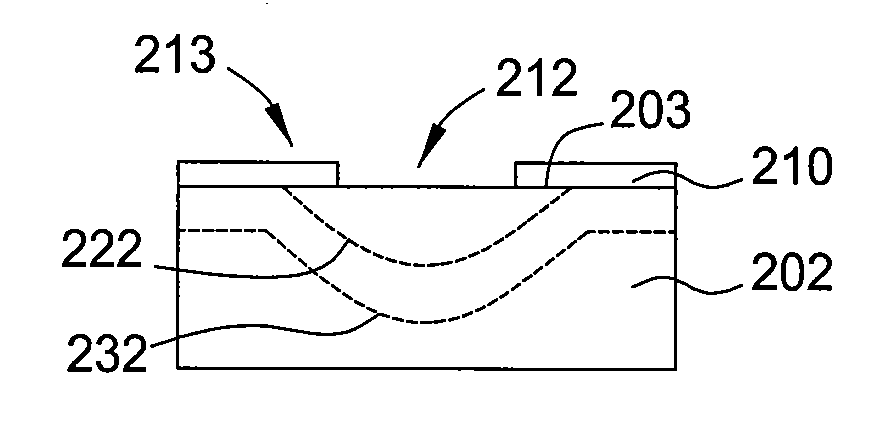
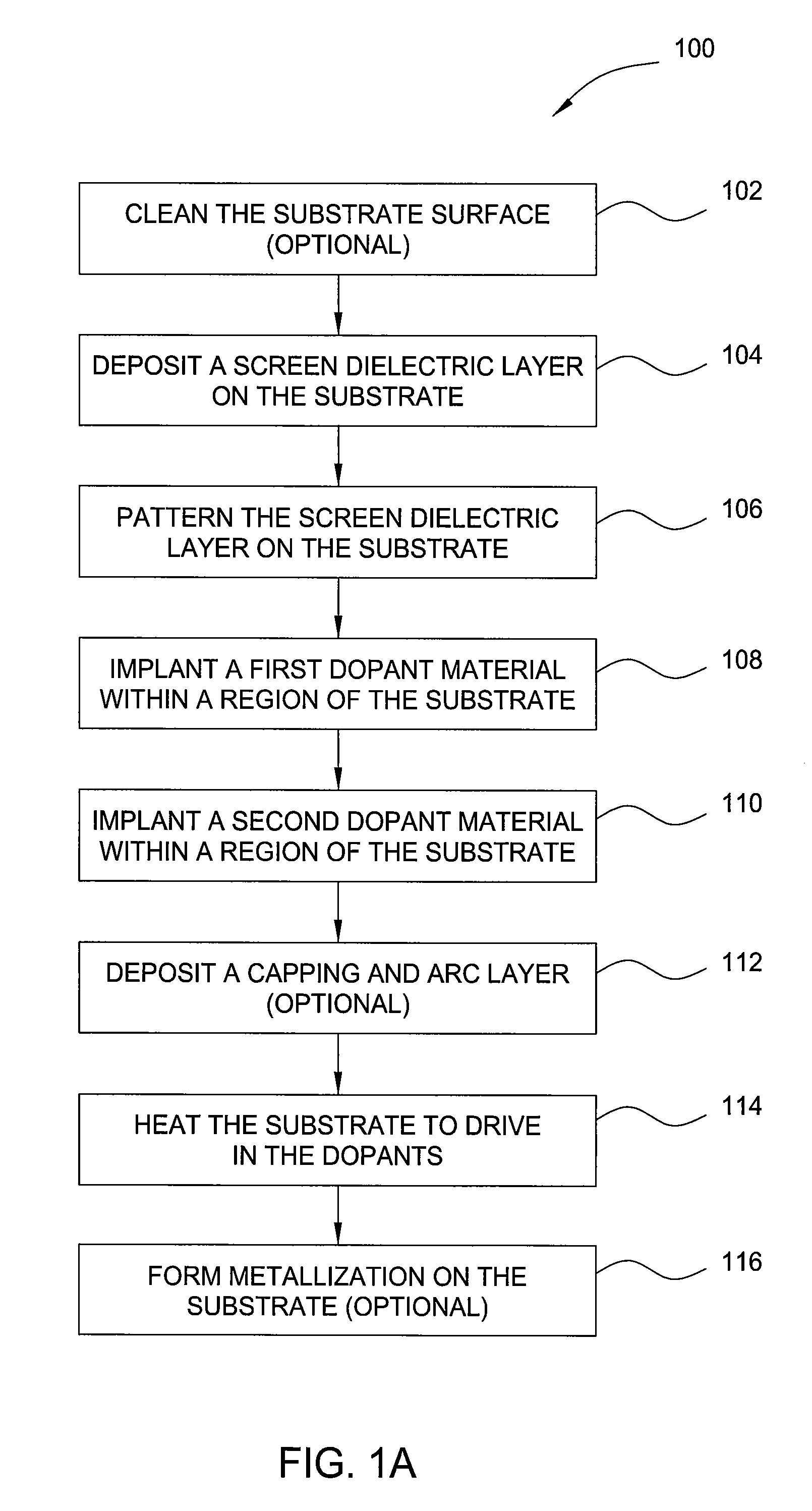
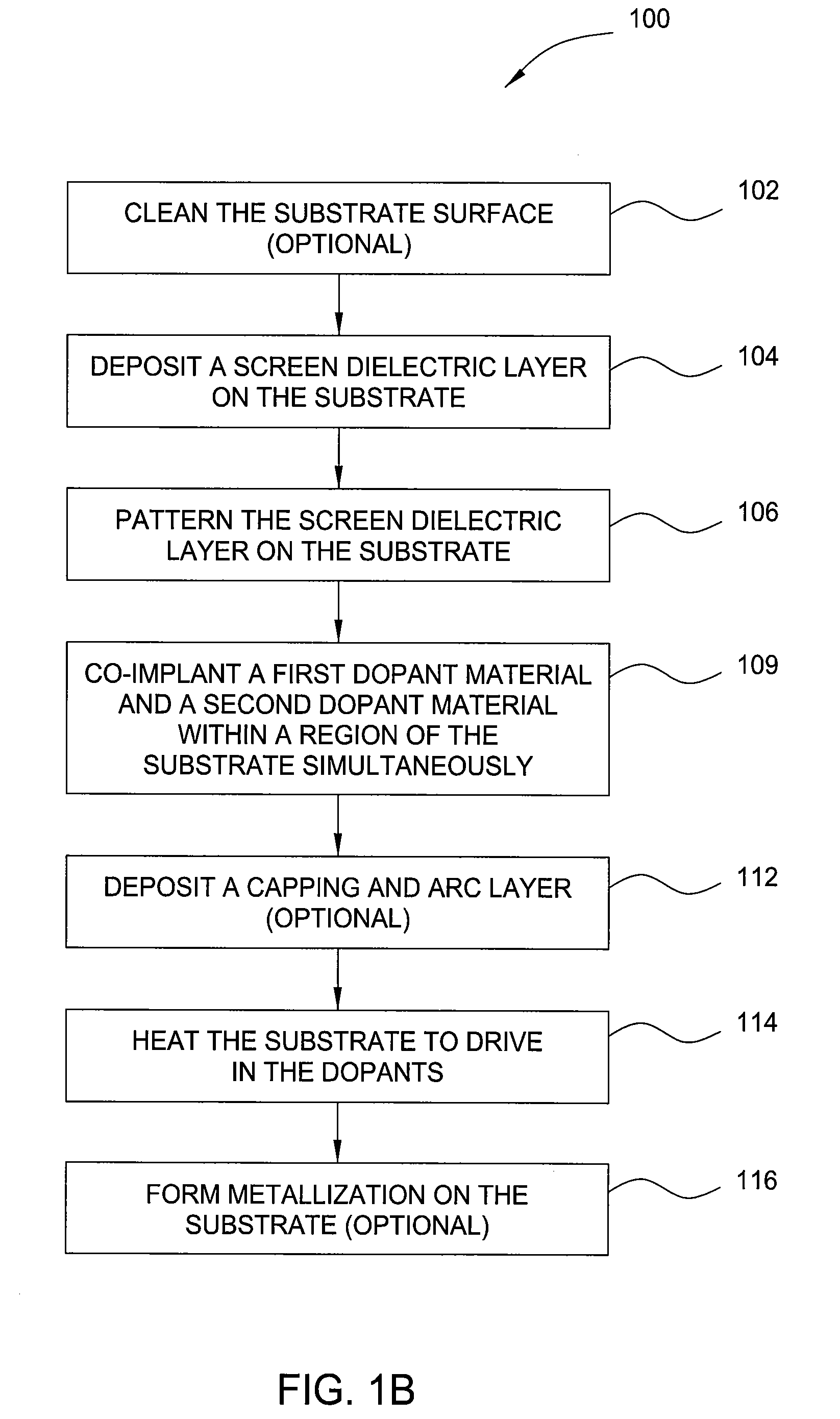
Methods of emitter formation in solar cells
InactiveUS20090068783A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantElectrical resistance and conductance
Embodiments of the invention contemplate high efficiency emitters in solar cells and novel methods for forming the same. One embodiment of the improved emitter structure, called a high-low type emitter, optimizes the solar cell performance by equally providing low contact resistance to minimize ohmic losses and isolation of the high surface recombination metal-semiconductor interface from the junction to maximize cell voltage. Another embodiment, called an alternating doping type emitter, provides regions of alternating doping type for use with point contacts in the back-contact solar cells. One embodiment of the methods includes depositing and patterning a doped or undoped dielectric layer on a surface of a substrate, implanting a fast-diffusing dopant and / or a slow-diffusing dopant into the substrate either simultaneously or sequentially, and annealing the substrate to drive in the dopants. Another embodiment of the methods includes using a physical mask to form a patterned dopant distribution in a substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Pulse generator having an efficient fractional voltage converter and method of use
InactiveUS20060170486A1Minimize the number of componentsReduce in quantityElectrotherapyApparatus without intermediate ac conversionVoltage converterVoltage multiplier
Disclosed are systems and methods which provide voltage conversion in increments less than integer multiples of a power supply (e.g., battery) voltage. A representative embodiment provides power supply voltage multipliers in a binary ladder distribution to provide a desired number of output voltage steps using a relatively uncomplicated circuit design. By using different sources in various combinations and / or by “stacking” different sources in various ways, the voltage multiplier circuit may be used to provide desired voltages. In order to minimize the number of components used in a voltage converter of an embodiment, a capacitive voltage converter circuit uses one or more storage capacitors in place of pump capacitors in a voltage generation cycle. Also, certain embodiments do not operate to generate an output voltage until the time that voltage is needed.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Battery charger
InactiveUS6191560B1Short timeIncrease the allowable valueSecondary cells charging/dischargingElectric powerSwitched currentBattery charge
A map is retrieved based on a battery temperature and a temperature rise value (in a step S40) and an allowable current value, with which a battery can be charged while battery temperature rise is being suppressed, is obtained and the battery is charged with the allowable current value (in a step S42). By doing so, it is possible to charge a nickel metal hydride battery in a short time without causing deterioration due to temperature rise. If it is determined that a battery state is not in a final charging period from the change of battery voltage ("Yes' in a step S30), a change in temperature is corrected (in a step S34) and a relatively high allowable current value is thereby obtained from the map (in a step S40). That is, before the final charging period, battery charge can be completed in a short time by applying high current without switching current values for adjustment purposes.
Owner:MAKITA CORP
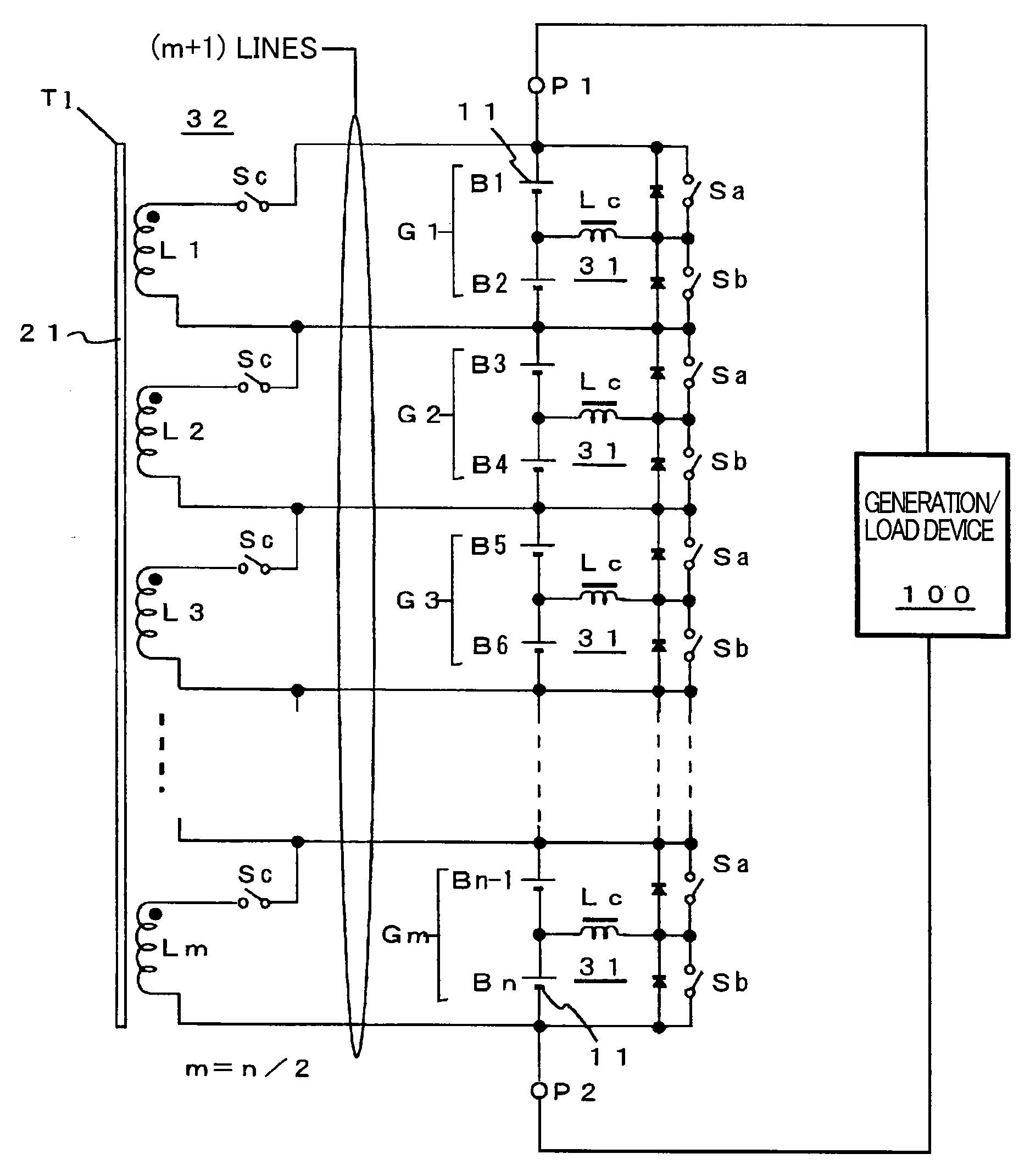
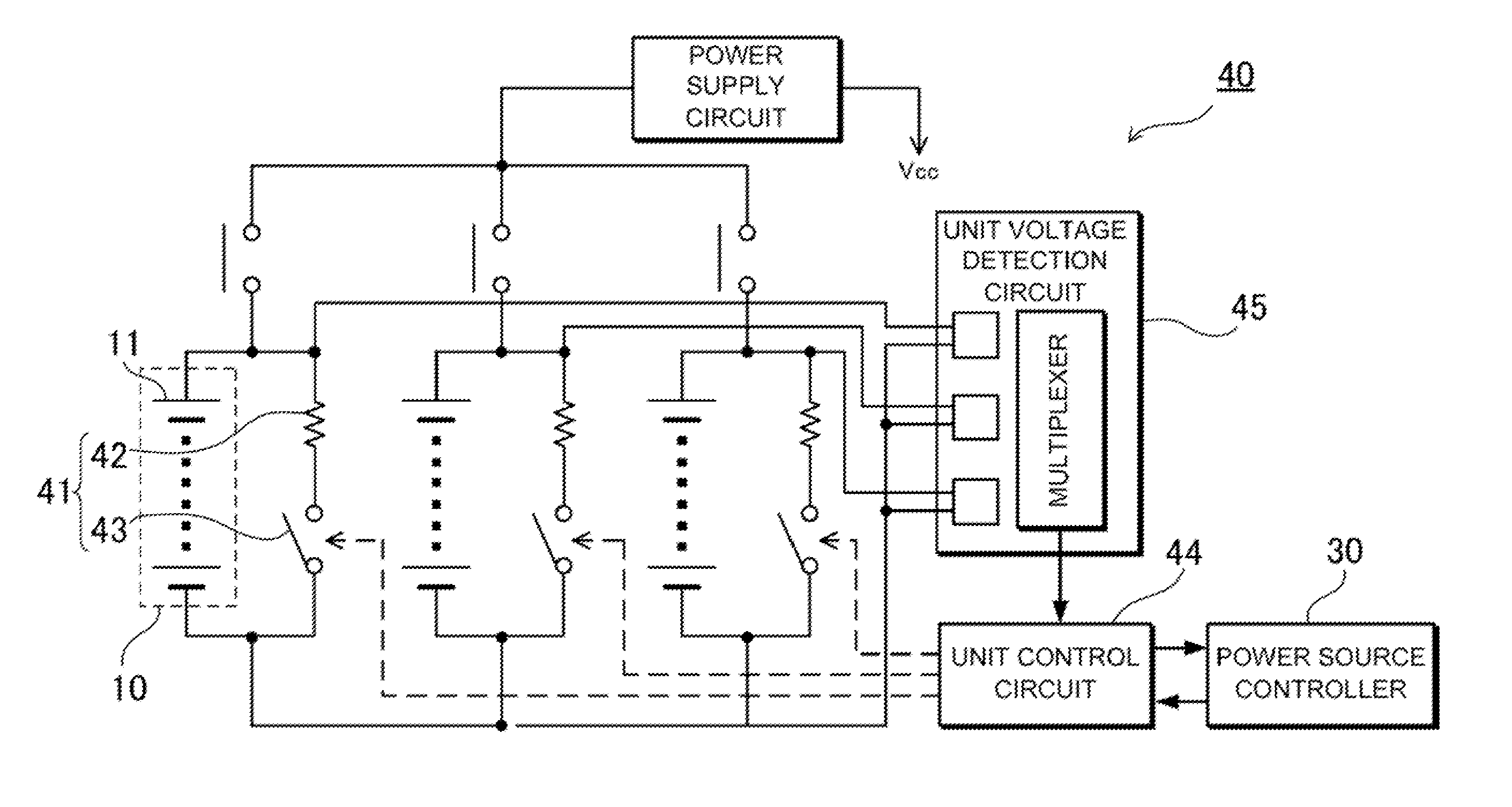
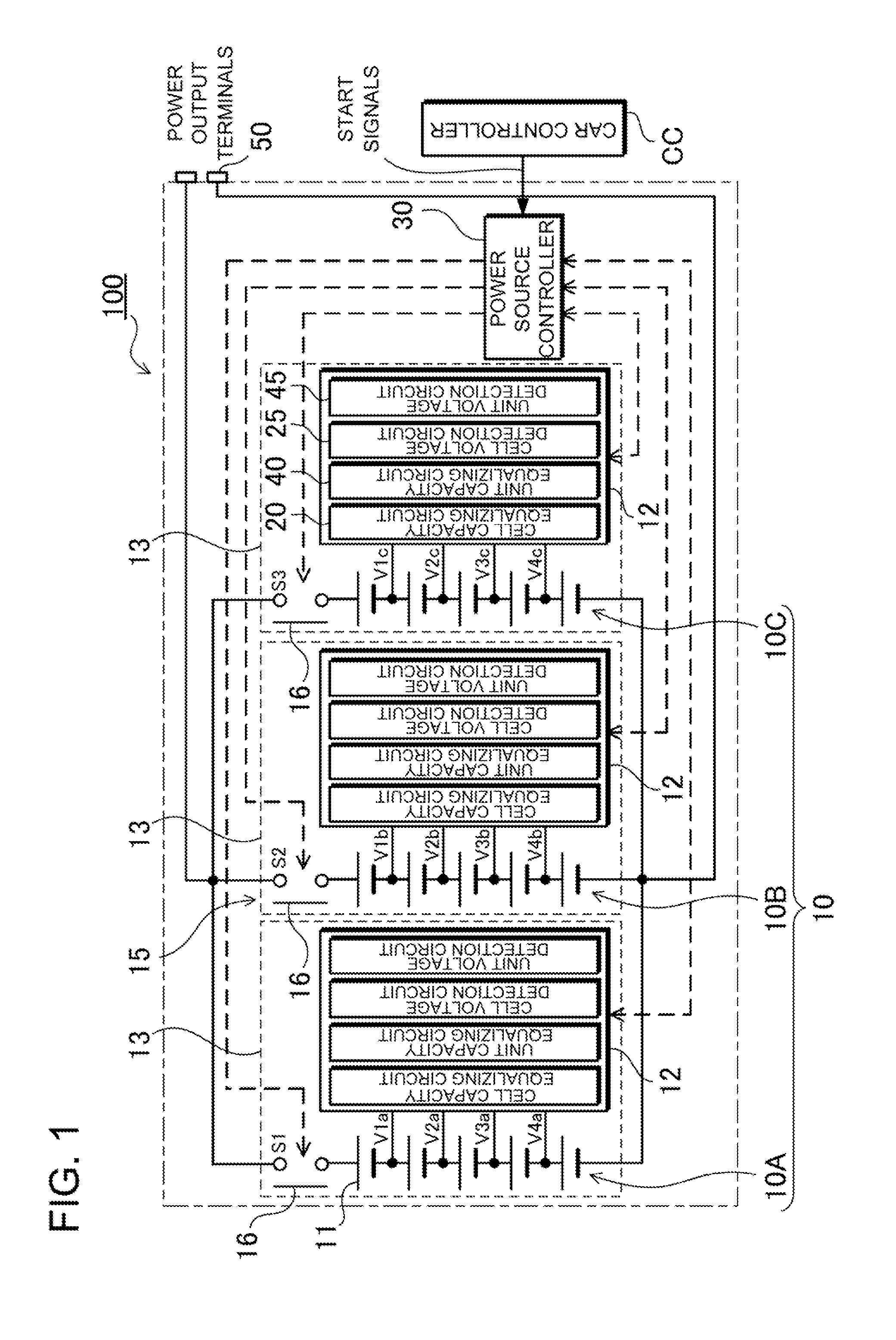
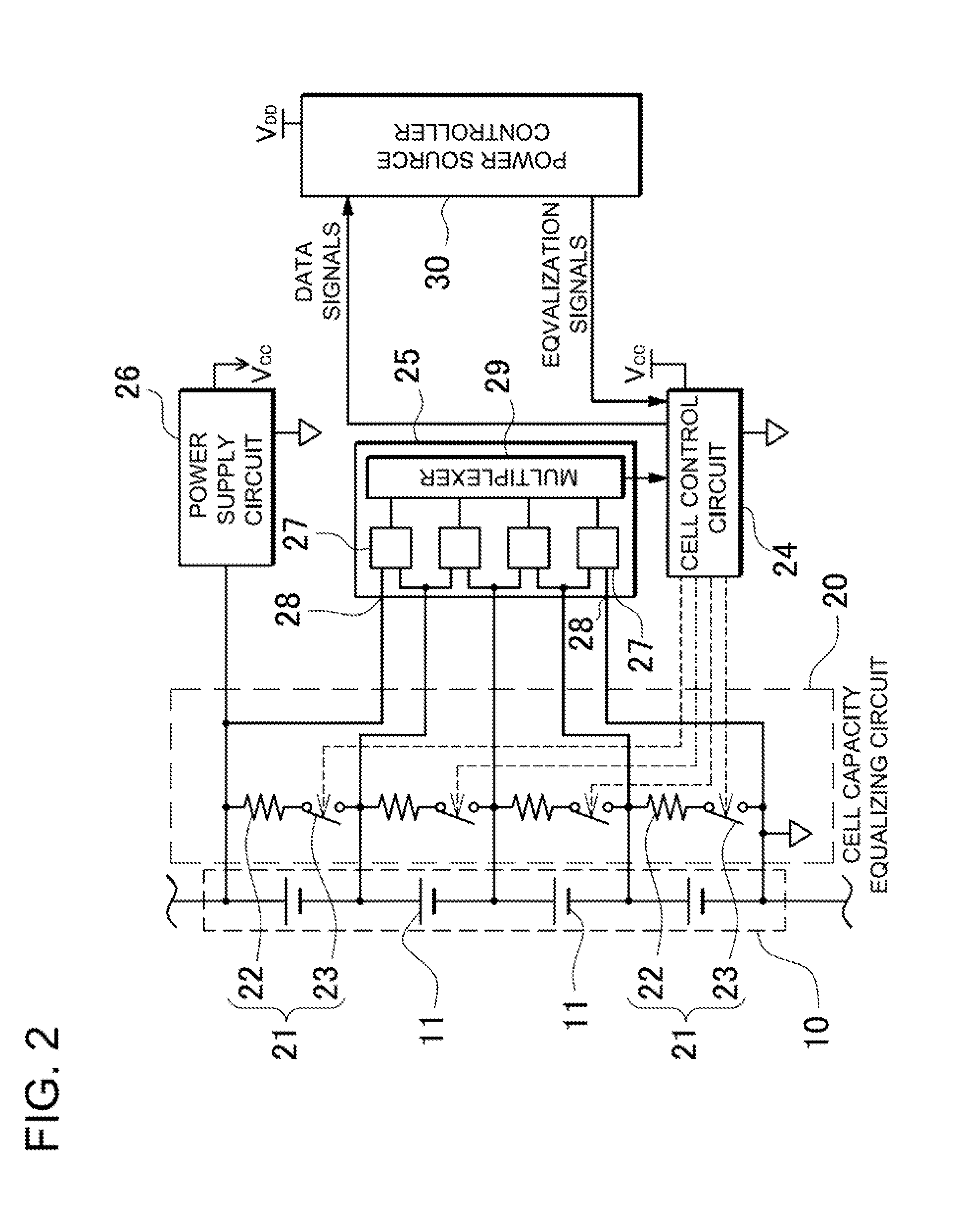
Car power source apparatus, and capacity equalizing method for the car power source apparatus
InactiveUS20110074354A1Reduce capacityCapacitors having nonuniform capacityHybrid vehiclesCharge equalisation circuitCapacitanceEngineering
The power source apparatus is provided with a unit switch 16 connected in series with each battery unit 10, cell capacity equalizing circuits 20 to suppress variation in the remaining capacities of the battery cells 11 that make up each battery unit 10 based on the cell voltages, unit voltage detection circuits 45 to detect unit voltage that is the overall voltage of a battery unit 10, unit capacity equalizing circuits 40 to suppress variation in the remaining capacities of the battery units 10 based on the unit voltages detected by the unit voltage detection circuits 45, and a power source controller 30 that controls the cell capacity equalizing circuits 20 to equalize battery cell 11 remaining capacities in each battery unit 11 and subsequently controls the unit capacity equalizing circuits 40 to equalize battery unit 10 remaining capacities over the entire battery block 15.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
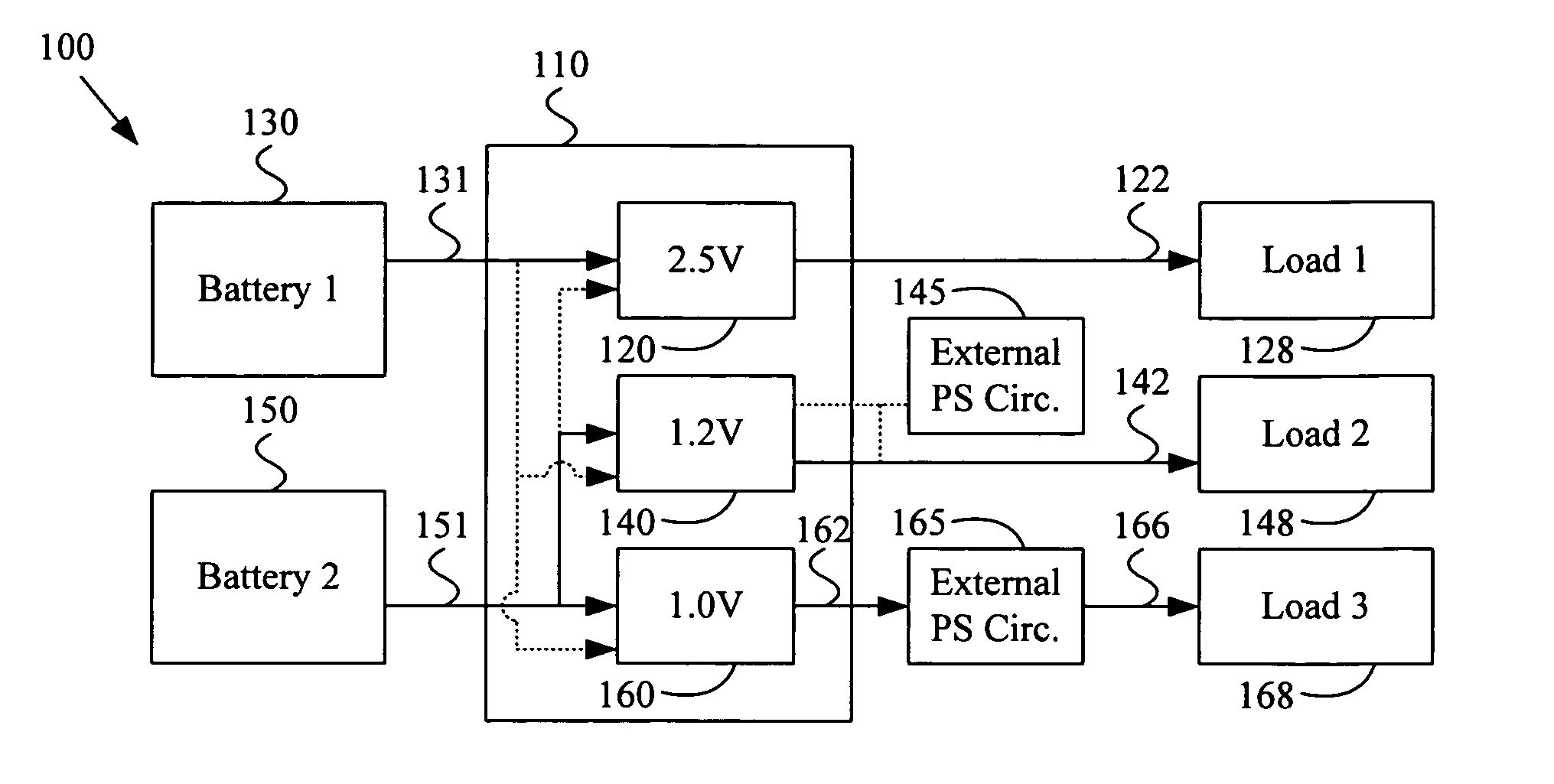
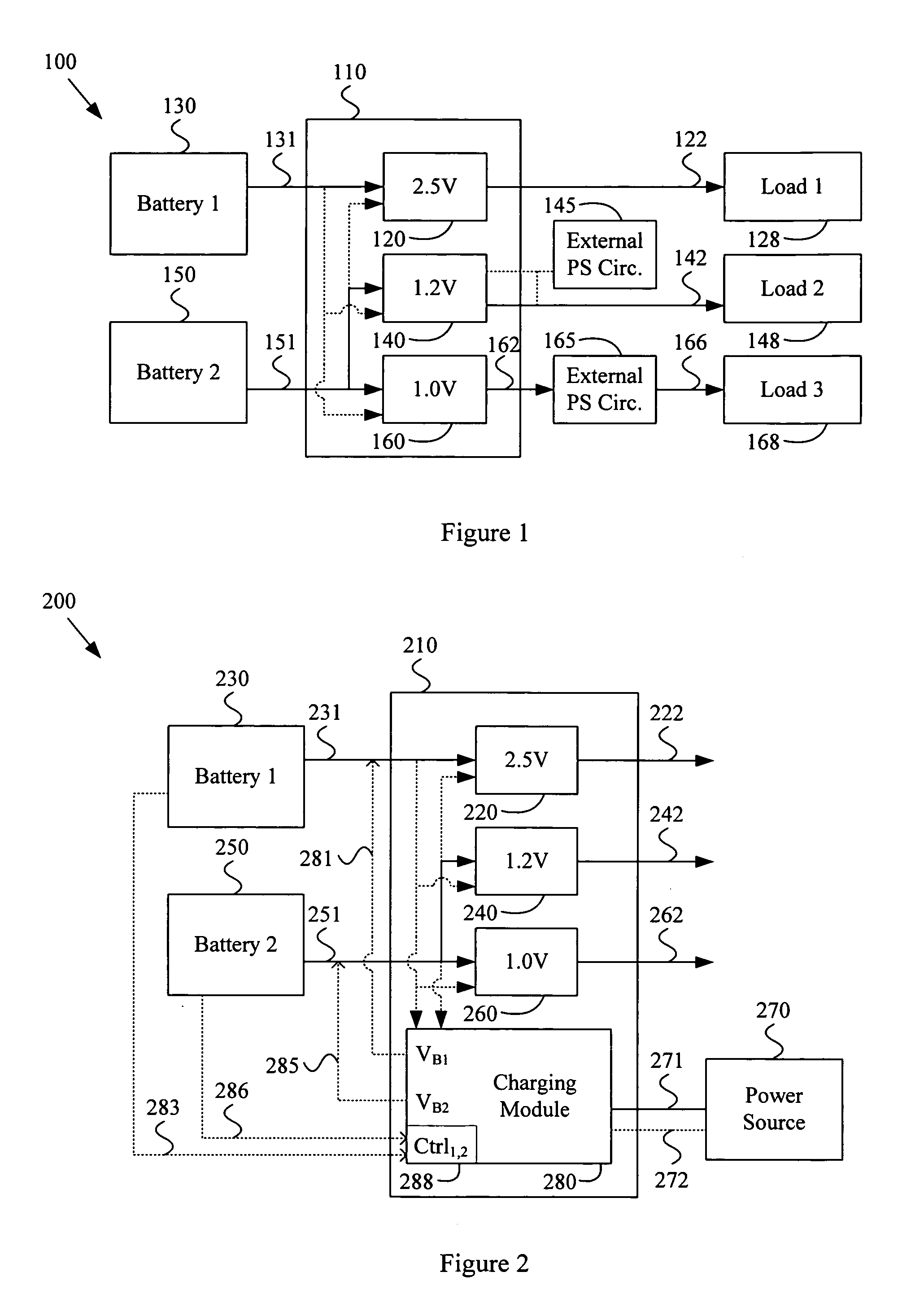
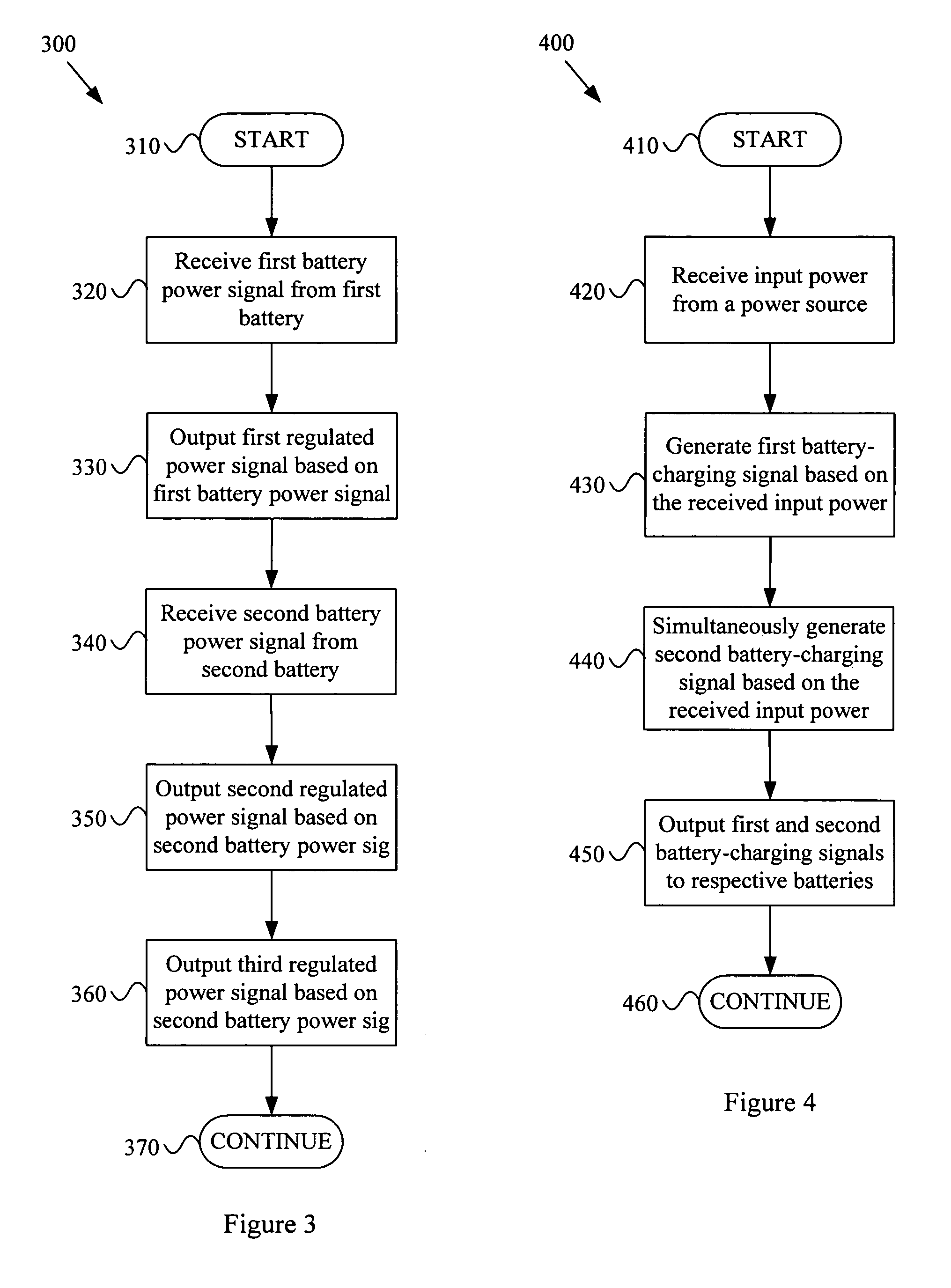
Multi-voltage multi-battery power management unit
InactiveUS20050289375A1Volume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingElectrical batteryPower Management Unit
A system and method for implementing a multi-voltage multi-battery power management integrated circuit. Various aspects of the present invention provide a power management integrated circuit. The power management IC may comprise a first regulator module that receives a first battery power signal from a first battery characterized by a first battery voltage and outputs a first regulated power signal, based at least in part on the first battery power signal. The power management IC may also comprise a second regulator module that receives a second battery power signal from a second battery characterized by a second battery voltage and outputs a second regulated power signal, based at least in part on the second battery power signal. The second battery voltage may, for example, be substantially different than the first battery voltage. The power first and second regulated power signals may, for example, correspond to substantially different power supply voltages.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
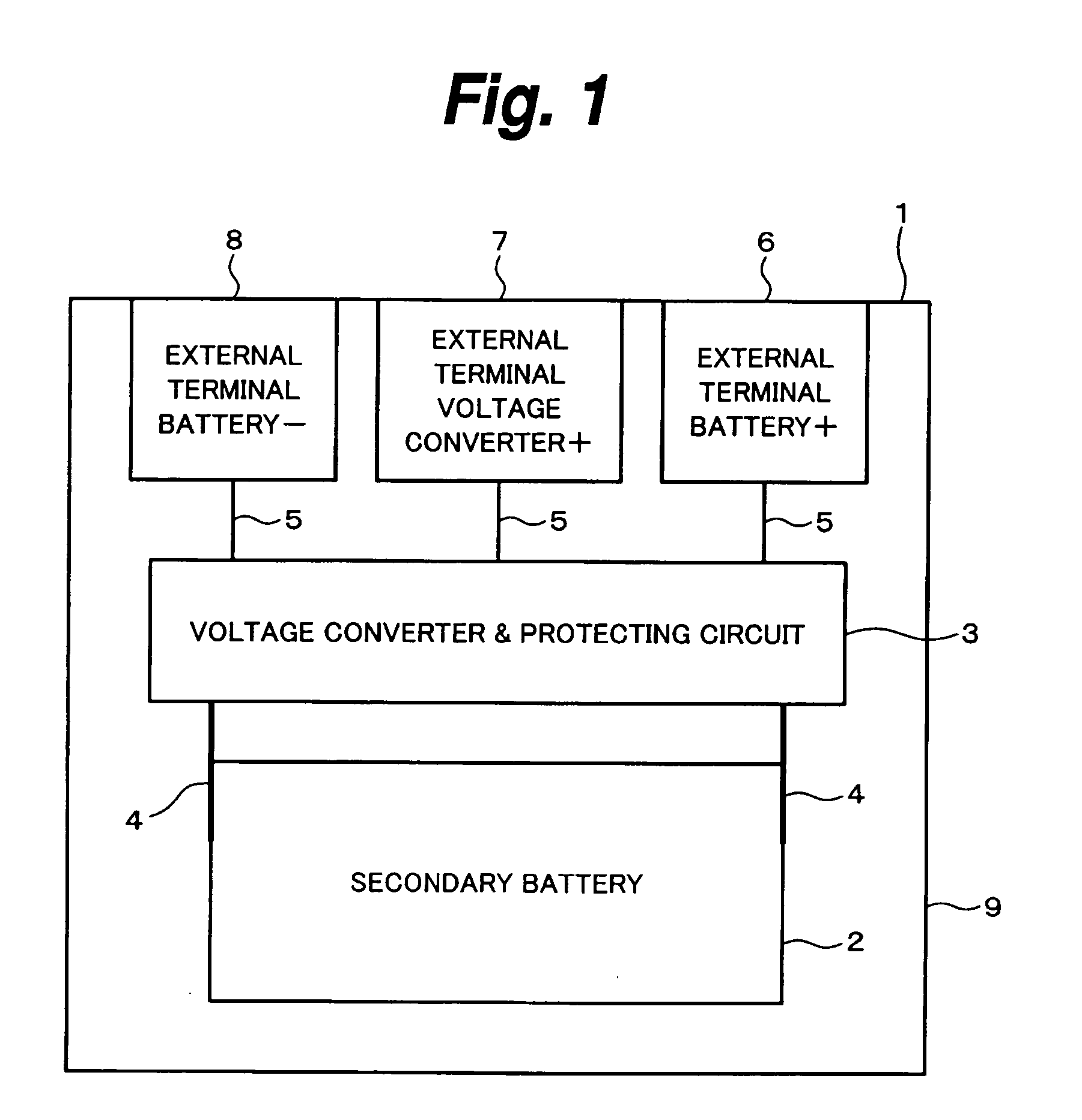
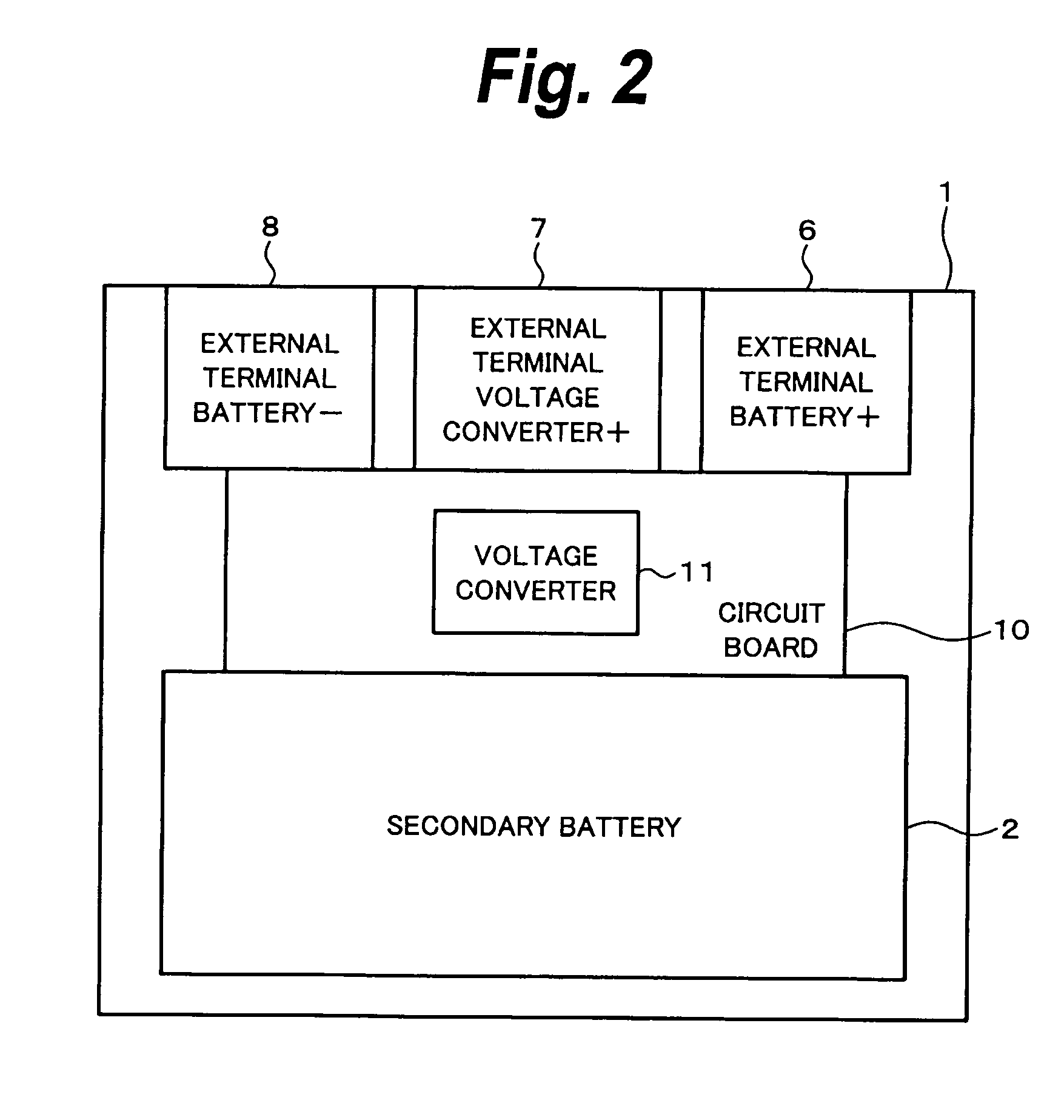
Battery pack
ActiveUS20050156574A1Suppress energy lossEmergency protective circuit arrangementsSecondary cells charging/dischargingVoltage converterLower limit
A protecting circuit monitors a voltage of a secondary battery and supplies the signal to permit a discharge to a gate terminal of a discharge control FET when the voltage is equal to or more than a lower limit value in a rated voltage range. When the discharge control FET receives this signal, it is connected and passes a discharge current. In the other cases, it shuts off the discharge current. Further, when the voltage is equal to or more than a predetermined value, a signal of a voltage of a battery voltage or more is supplied from a voltage converter to the gate terminal. When the voltage is equal to or less than an upper limit value in the rated voltage range, the protecting circuit supplies the signal to permit a charge to a gate terminal of a charge control FET. Further, when the voltage is equal to or more than a predetermined value, the voltage output from the voltage converter is supplied to the gate terminal. A battery pack in which by applying the voltage of the battery voltage or more to the gate terminal, the discharge control FET and the charge control FET are controlled and an energy loss is suppressed to the minimum is provided.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
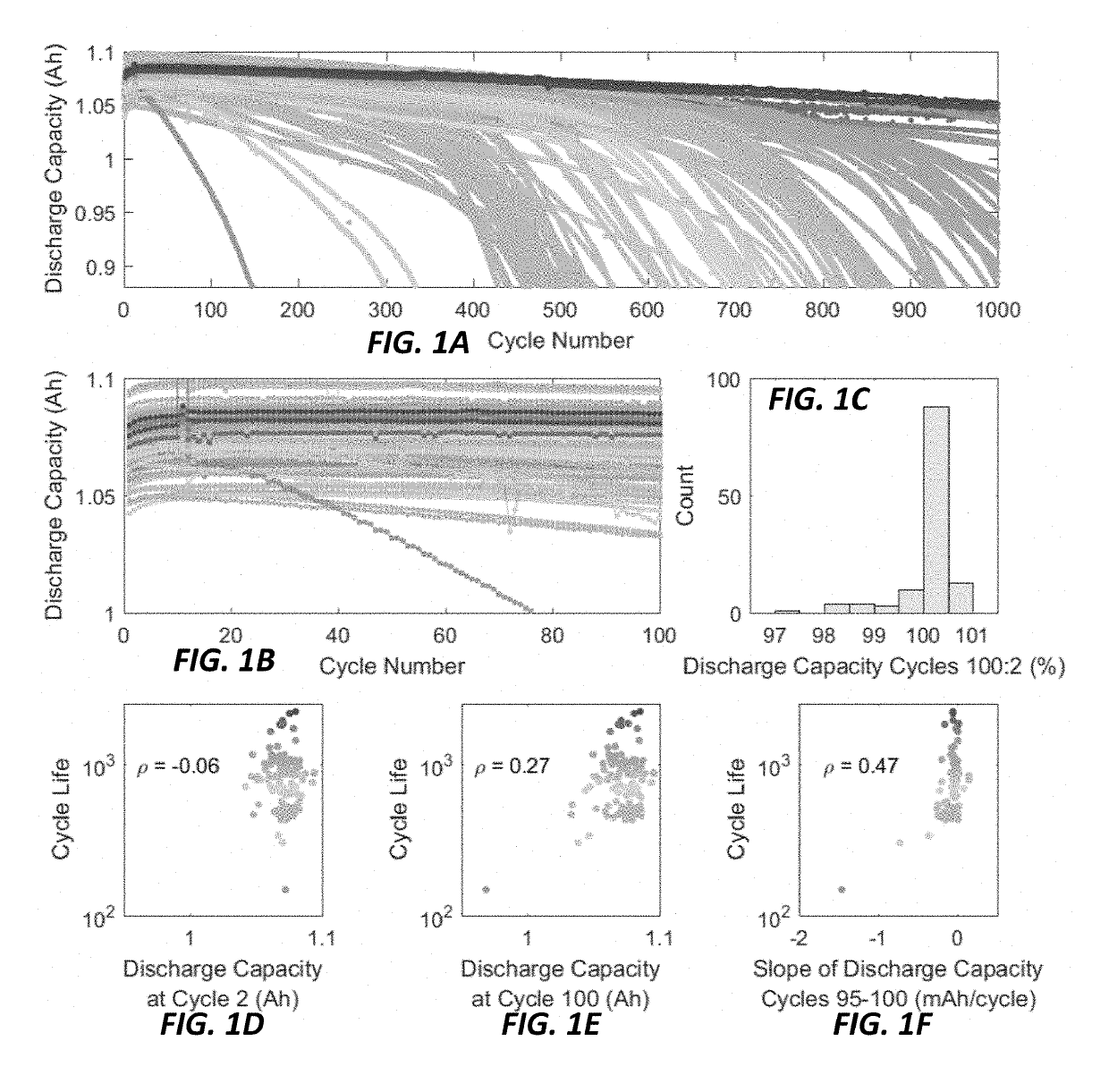
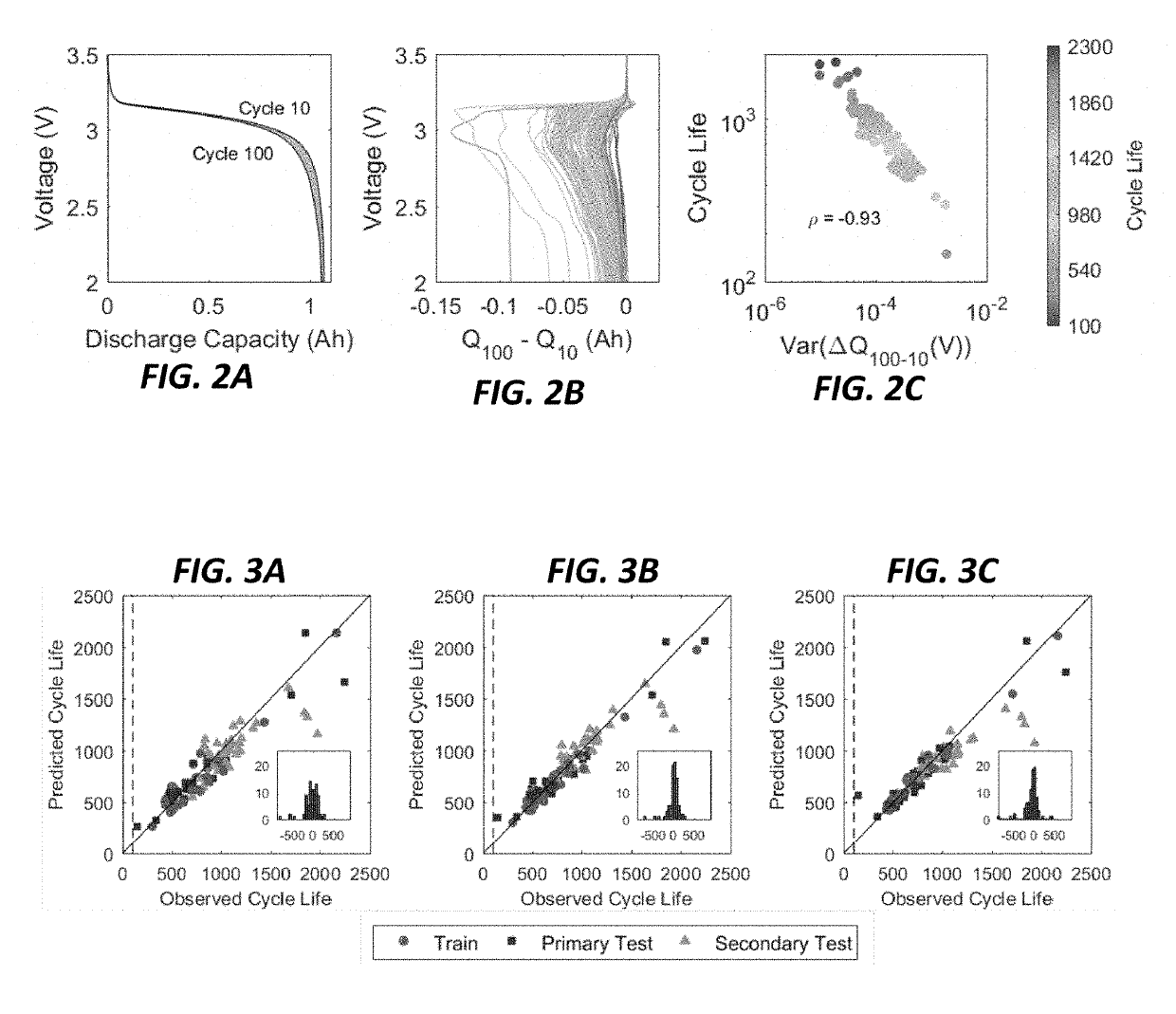
Data-driven Model for Lithium-ion Battery Capacity Fade and Lifetime Prediction
ActiveUS20190113577A1Electrical testingSecondary cells charging/dischargingData streamInternal resistance
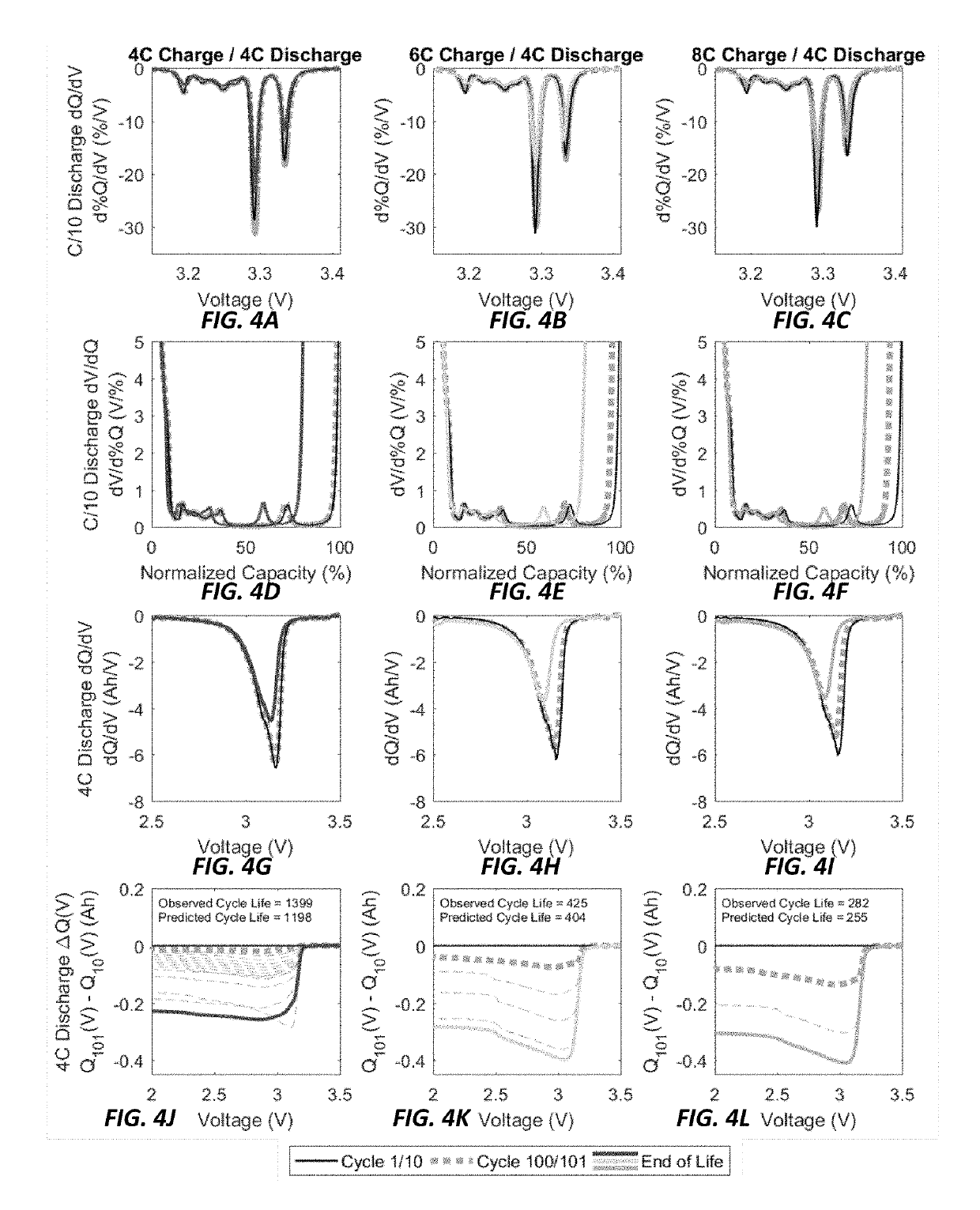
A method of using data-driven predictive modeling to predict and classify battery cells by lifetime is provided that includes collecting a training dataset by cycling battery cells between a voltage V1 and a voltage V2, continuously measuring battery cell voltage, current, can temperature, and internal resistance during cycling, generating a discharge voltage curve for each cell that is dependent on a discharge capacity for a given cycle, calculating, using data from the discharge voltage curve, a cycle-to-cycle evolution of cell charge to output a cell voltage versus charge curve Q(V), generating transformations of ΔQ(V), generating transformations of data streams that include capacity, temperature and internal resistance, applying a machine learning model to determine a combination of a subset of the transformations to predict cell operation characteristics, and applying the machine learning model to output the predicted battery operation characteristics.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Electric vehicle
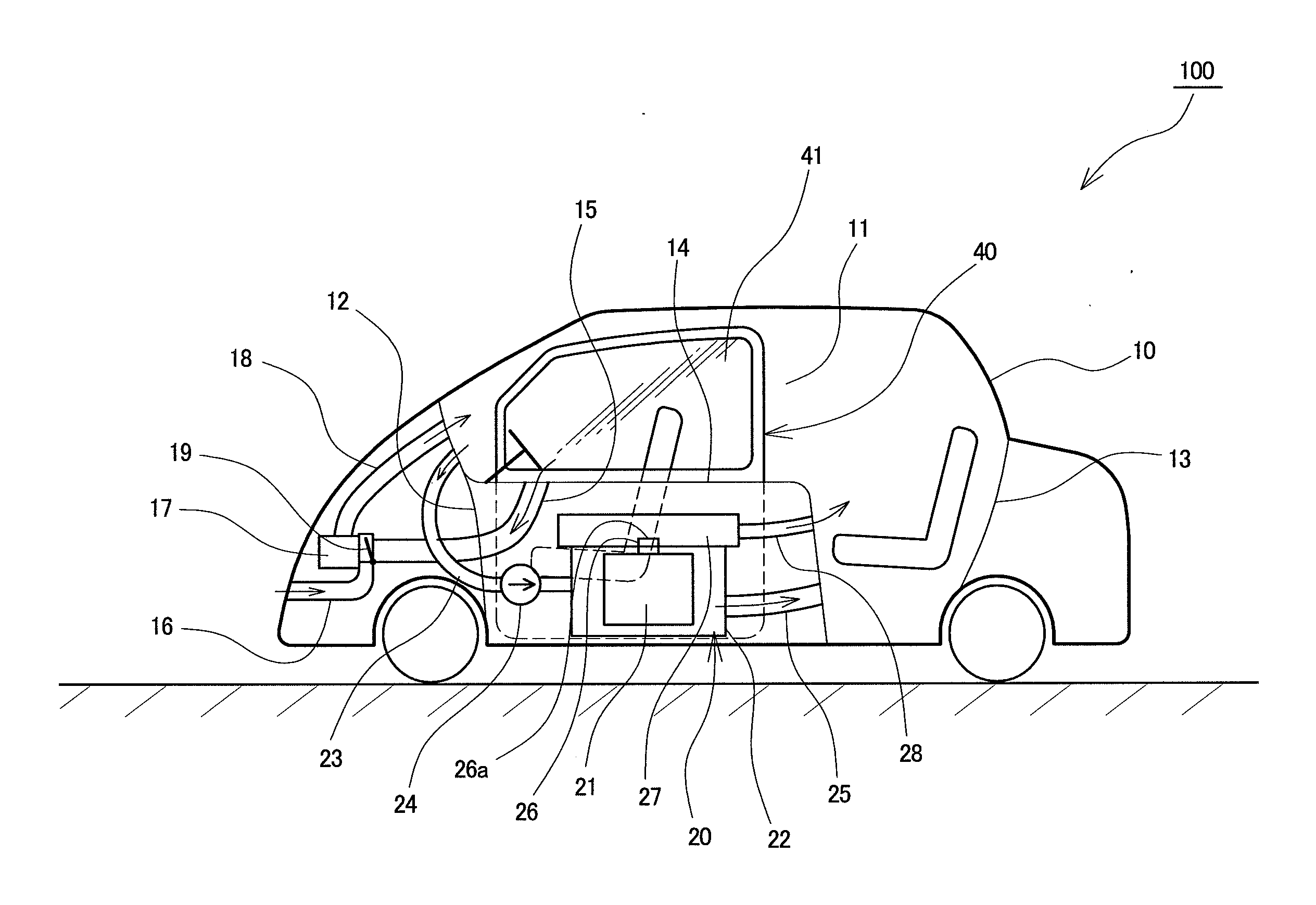
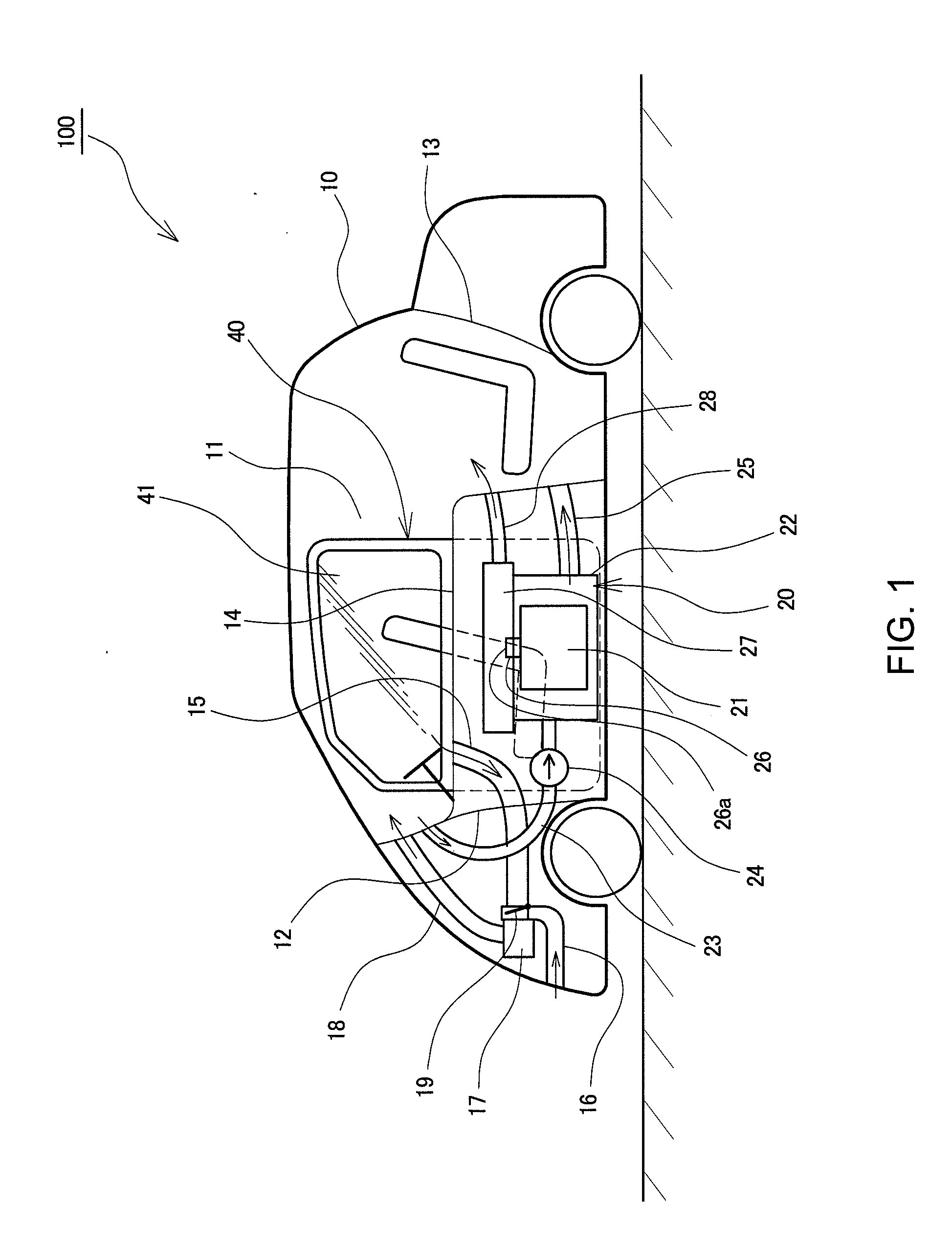
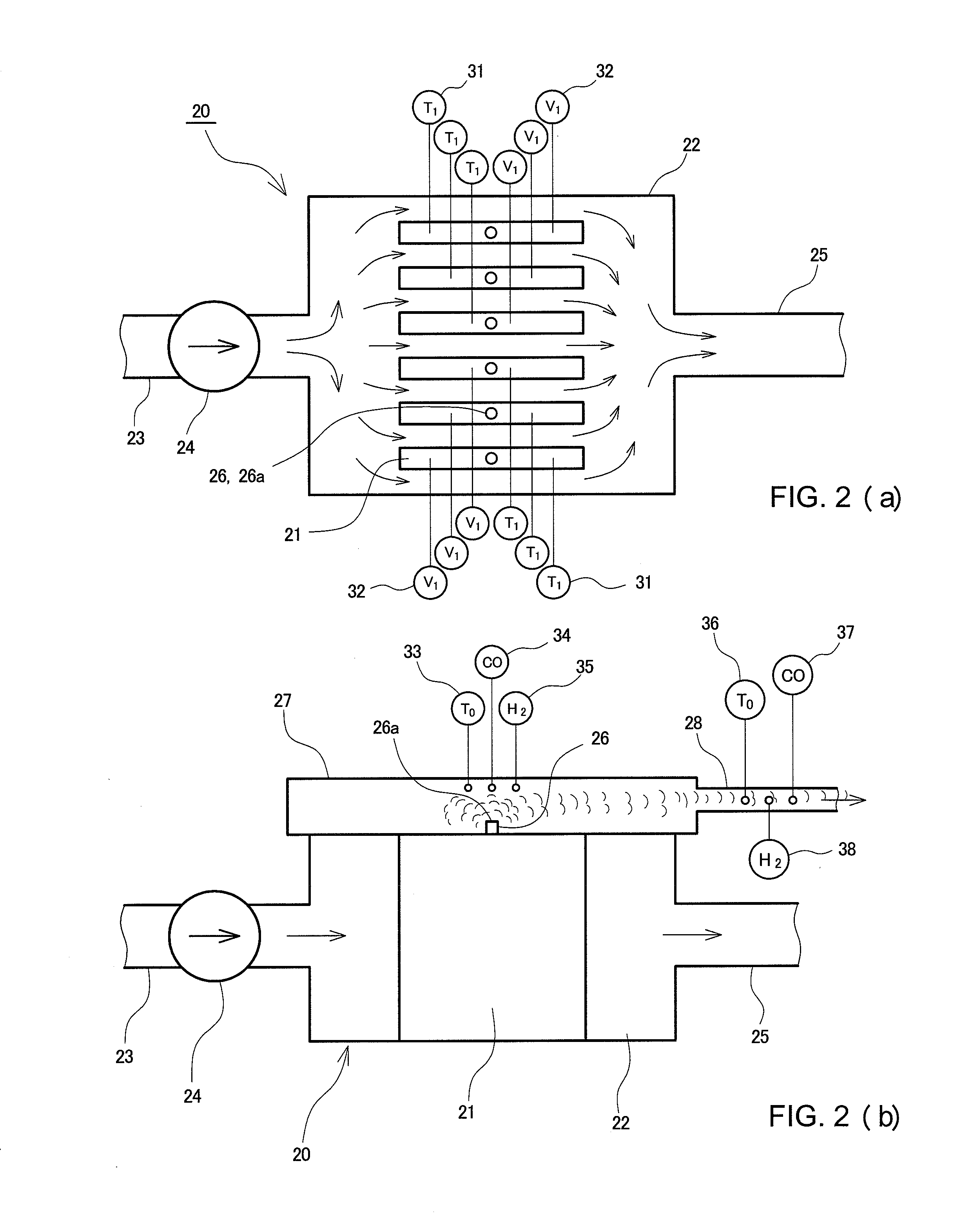
An electric vehicle is provided with a cell voltage sensor (32) and a cell temperature sensor (31) which are mounted to each of a plurality of cells (21); a gas temperature sensor (33), a carbon monoxide gas sensor (34), and a hydrogen gas sensor (35) which are mounted to a chamber (27); a gas temperature sensor (36), a carbon monoxide gas sensor (37), and a hydrogen gas sensor (38) which are mounted to a gas exhaust passage (28); and an air-conditioning fan (17), a channel-switching damper (19), and a driving motor (42) which lowers a window glass (41). When battery state values detected by the sensors (31) to (38) exceed predetermined thresholds, a battery pack (20) is judged to be abnormal. Then, the channel-switching damper (19) and the air-conditioning fan (17) are started and the window glass (41) is lowered to ventilate the vehicle interior. This speedily exhausts smoke generated from a lithium ion battery.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method and apparatus for using residual energy in a battery-powered computer
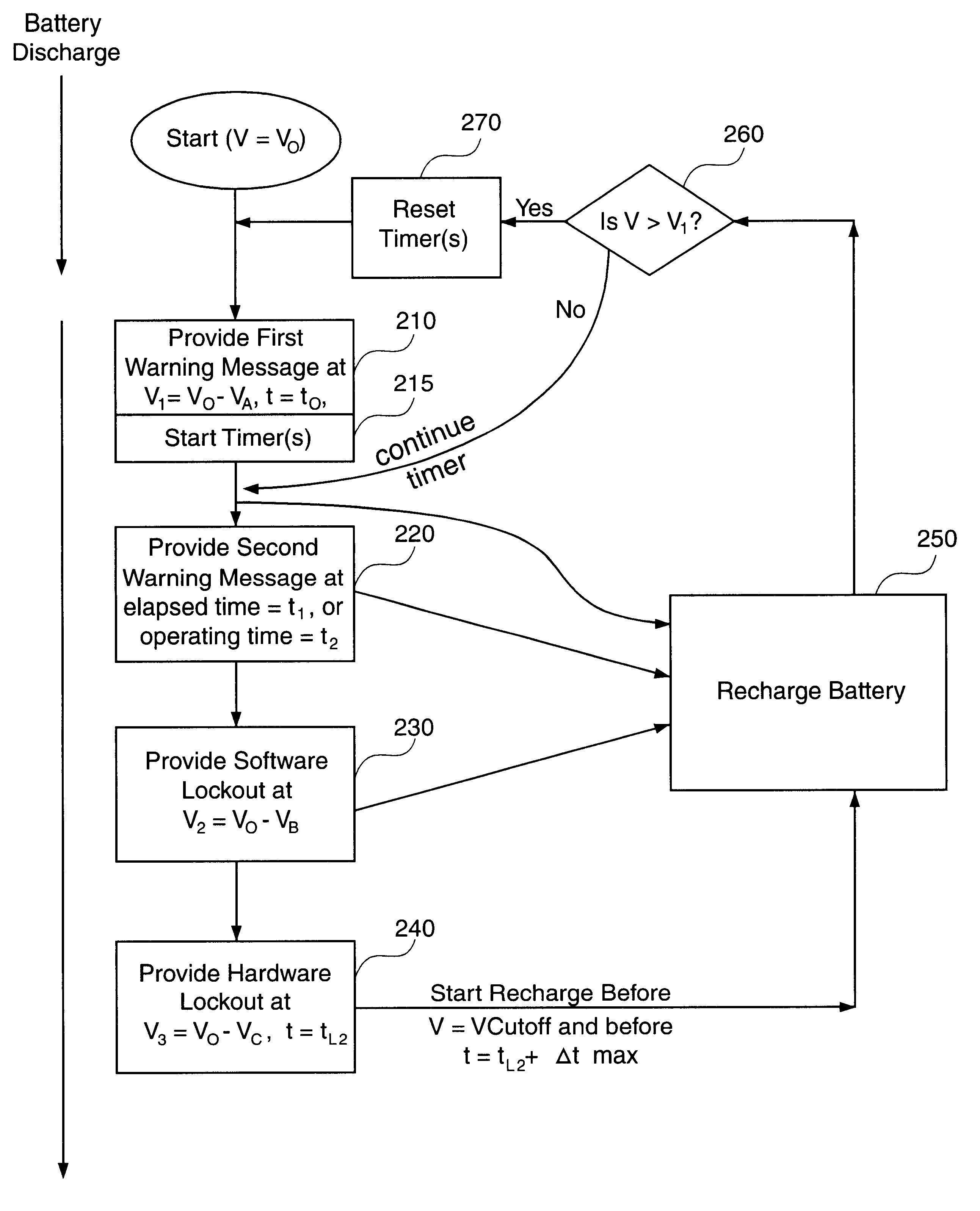
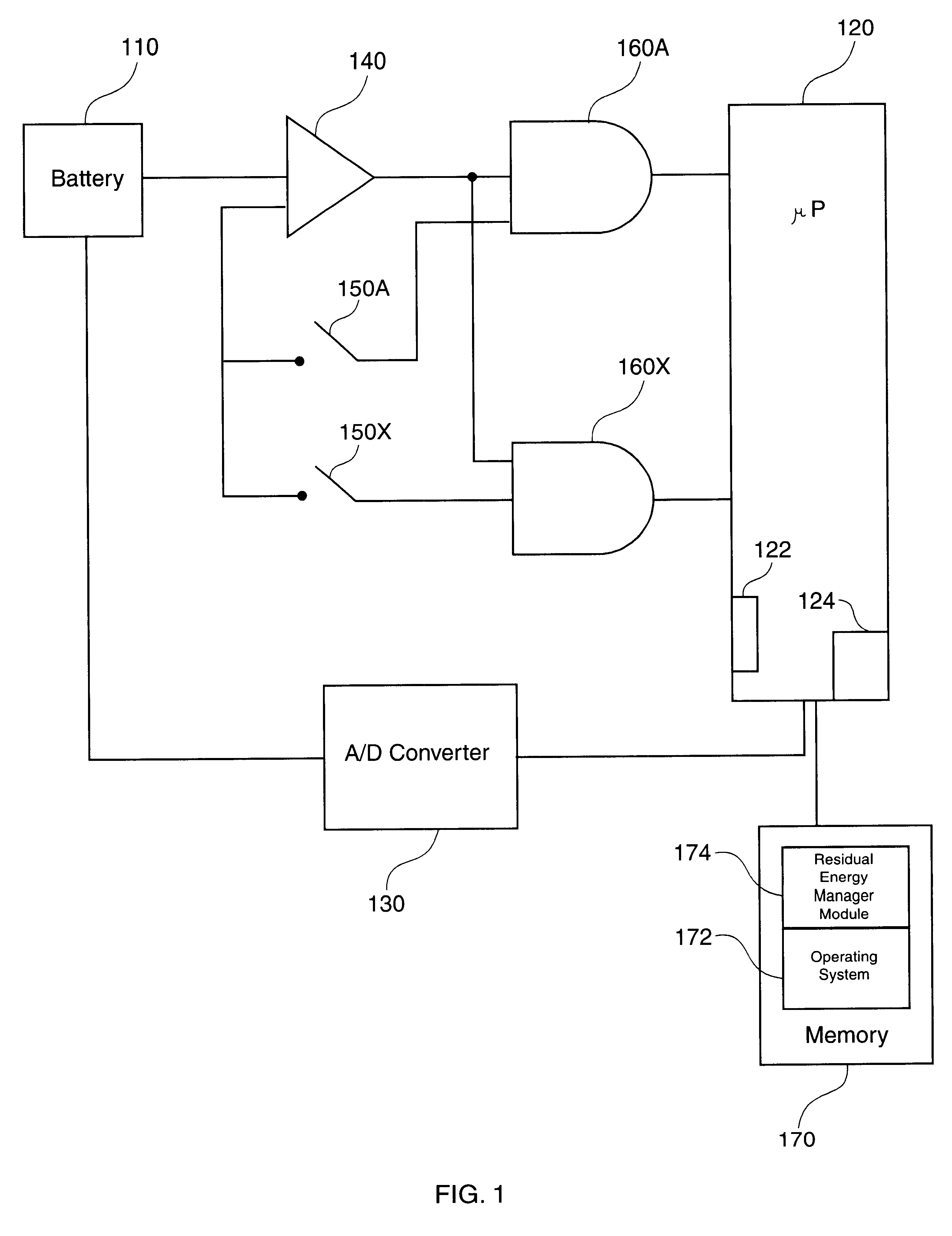
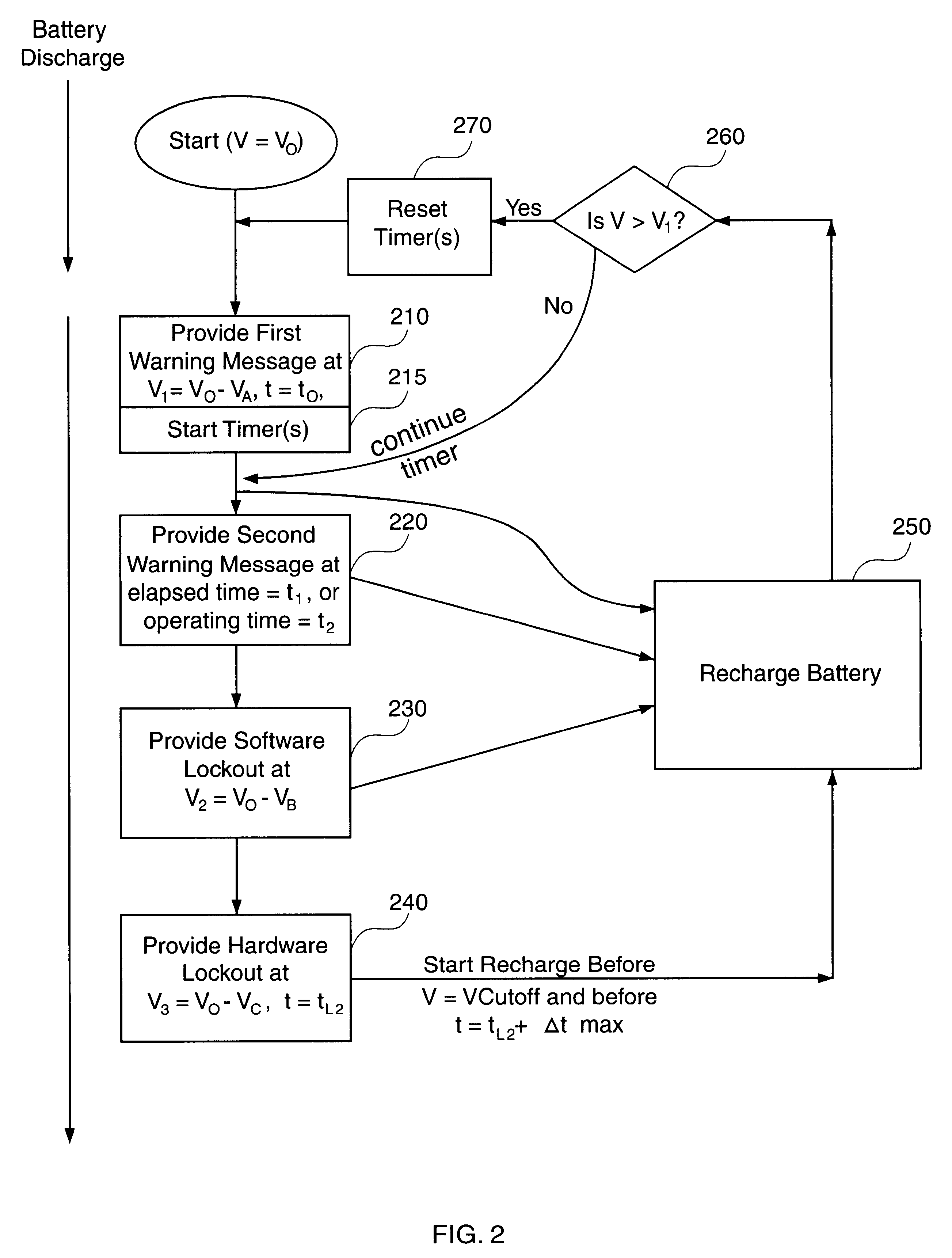
InactiveUS6425087B1Avoid lostCost effectiveHardware monitoringPower supply for data processingElectrical batteryCutoff function
Methods and apparatus are described for providing a time-based warning indicating that the energy capacity of a primary energy source of a battery-powered computer has discharged to a low level, and using residual energy of the primary energy source to perform at least one pre-cutoff function. The time-based warning ensures that the warning is provided in a timely manner by overcoming problems caused by analog to digital converter voltage measurement accuracy limitations and flat battery operating voltage versus discharge curves. The primary energy source can be a rechargeable battery, which can also be the sole energy source for the computer. The battery provides power to operate the computer until the battery voltage discharges to the cutoff voltage. The methods and apparatus provide advantages because they reserve the residual energy in the battery to perform at least one pre-cutoff function within a first duration before the battery discharges to the cutoff voltage. For example, the residual energy can be used to retain data stored in the computer between opportunities to charge the battery. Some embodiments of the invention include hardware resources coupled with the processor to lock out power and application activation when the rechargeable battery has discharged to a predetermined hardware lockout voltage. The value of the hardware lockout voltage can be based on the battery retaining a residual energy sufficient for performing the corresponding pre-cutoff function within an amount of time that is expected to enable the user to perform the function.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com