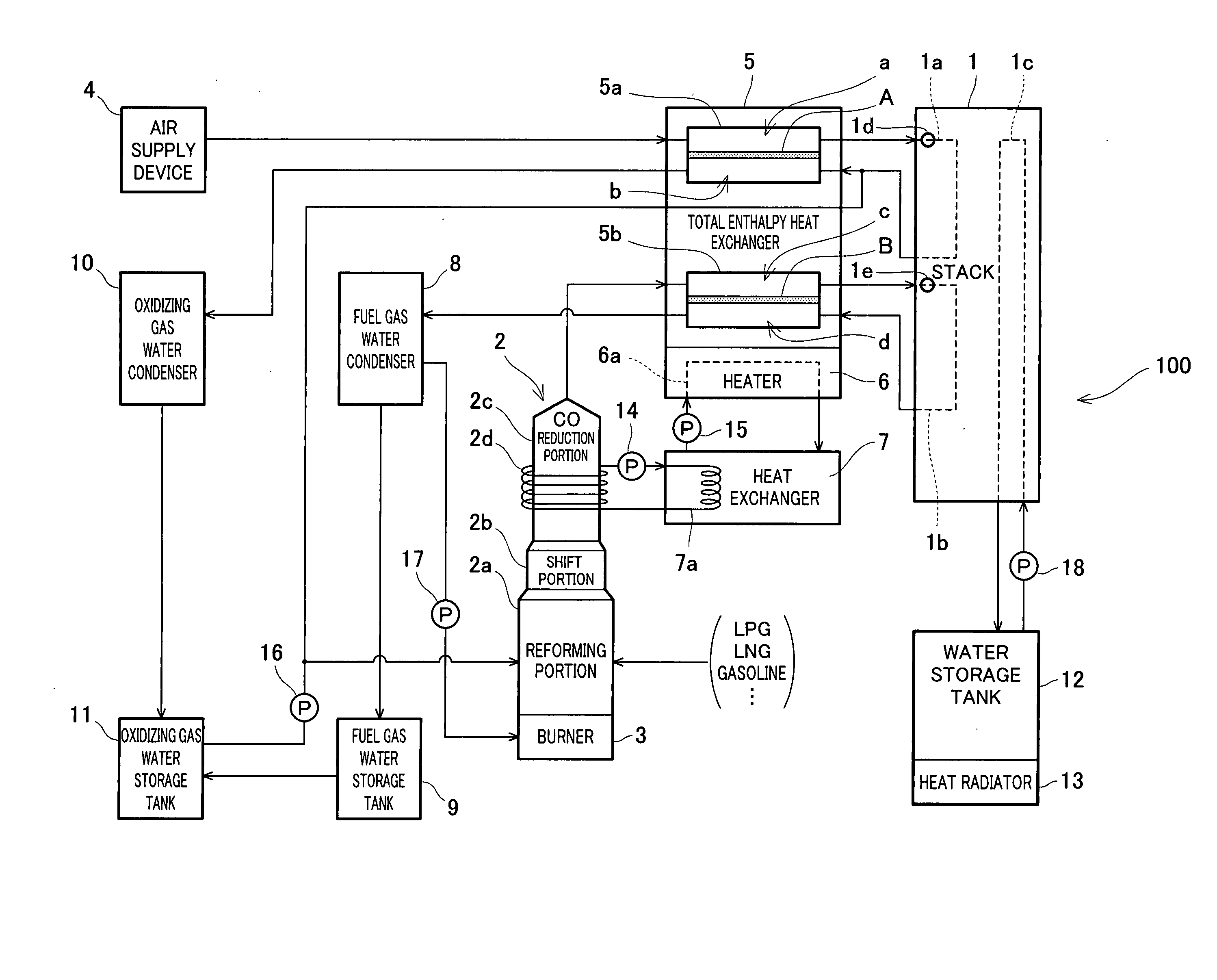
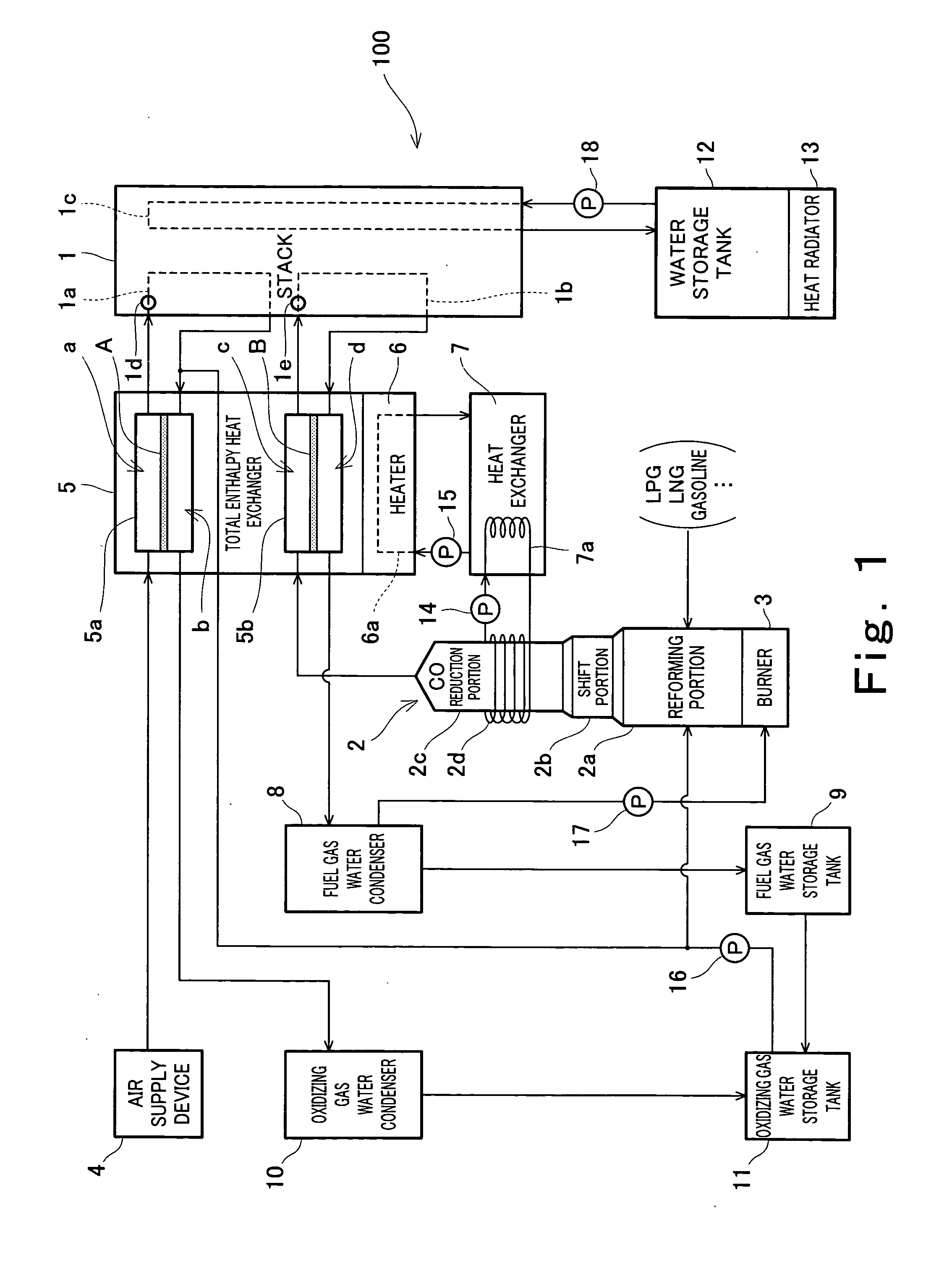
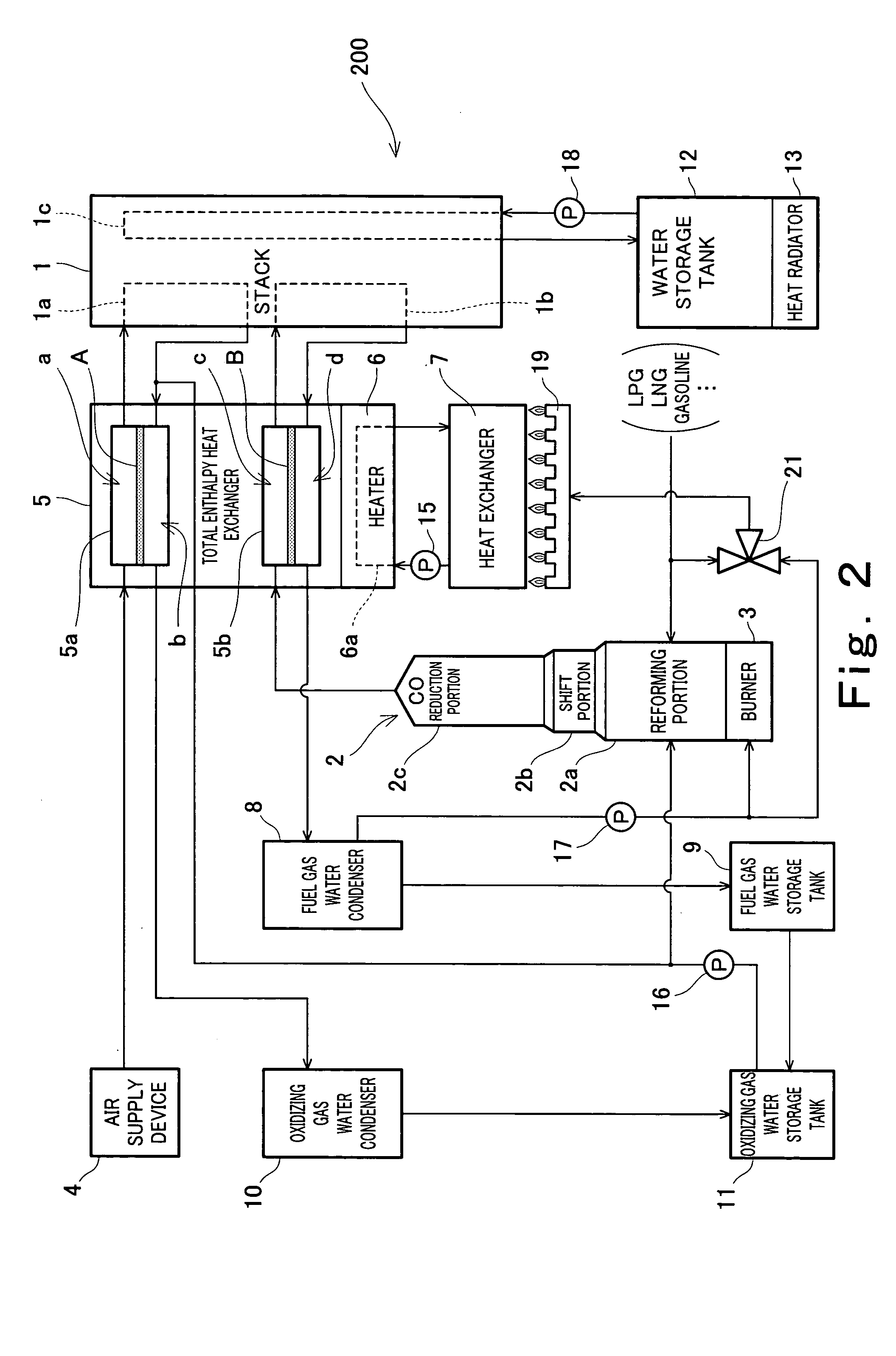
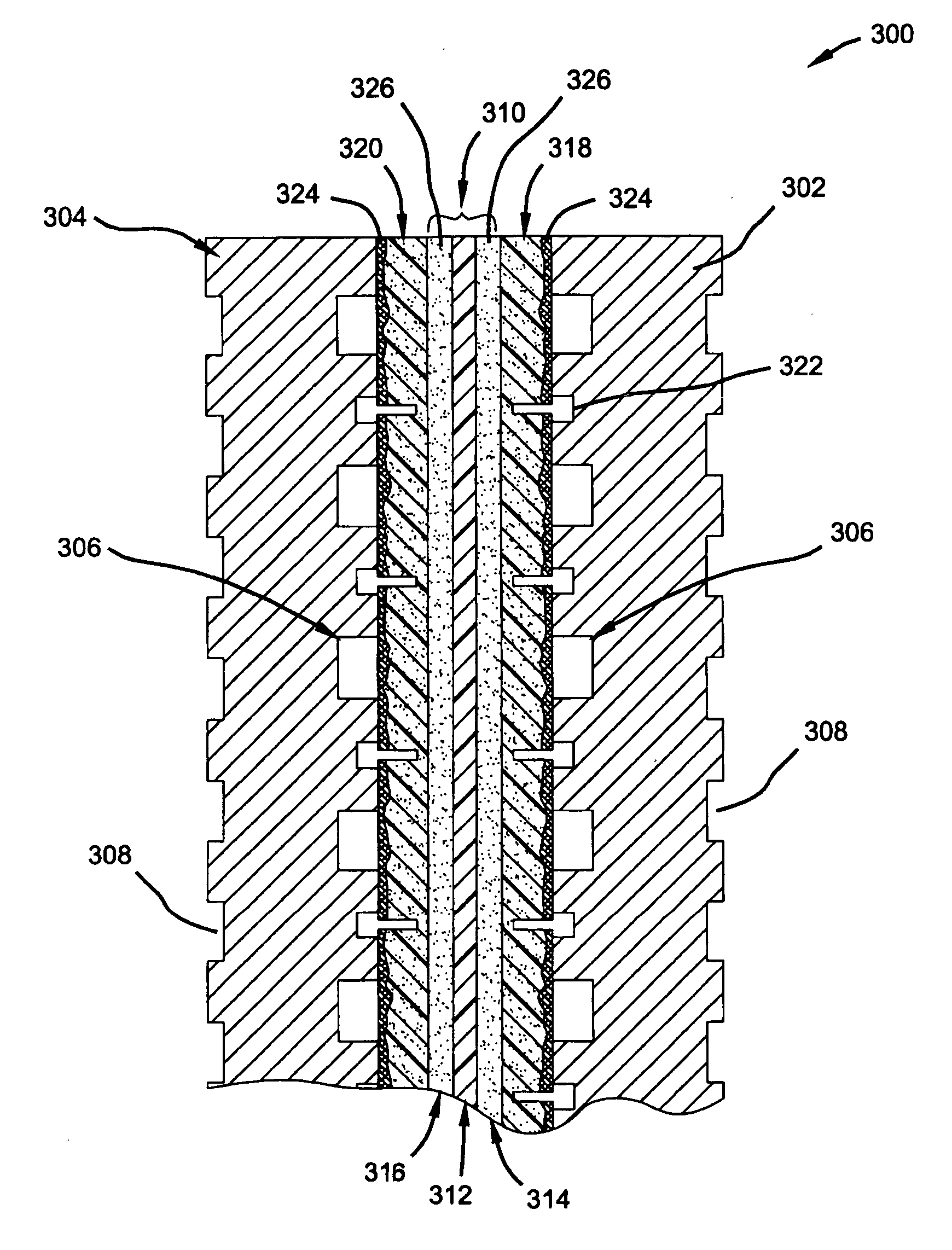
Patents
Literature
1311results about "Water management in fuel cells" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
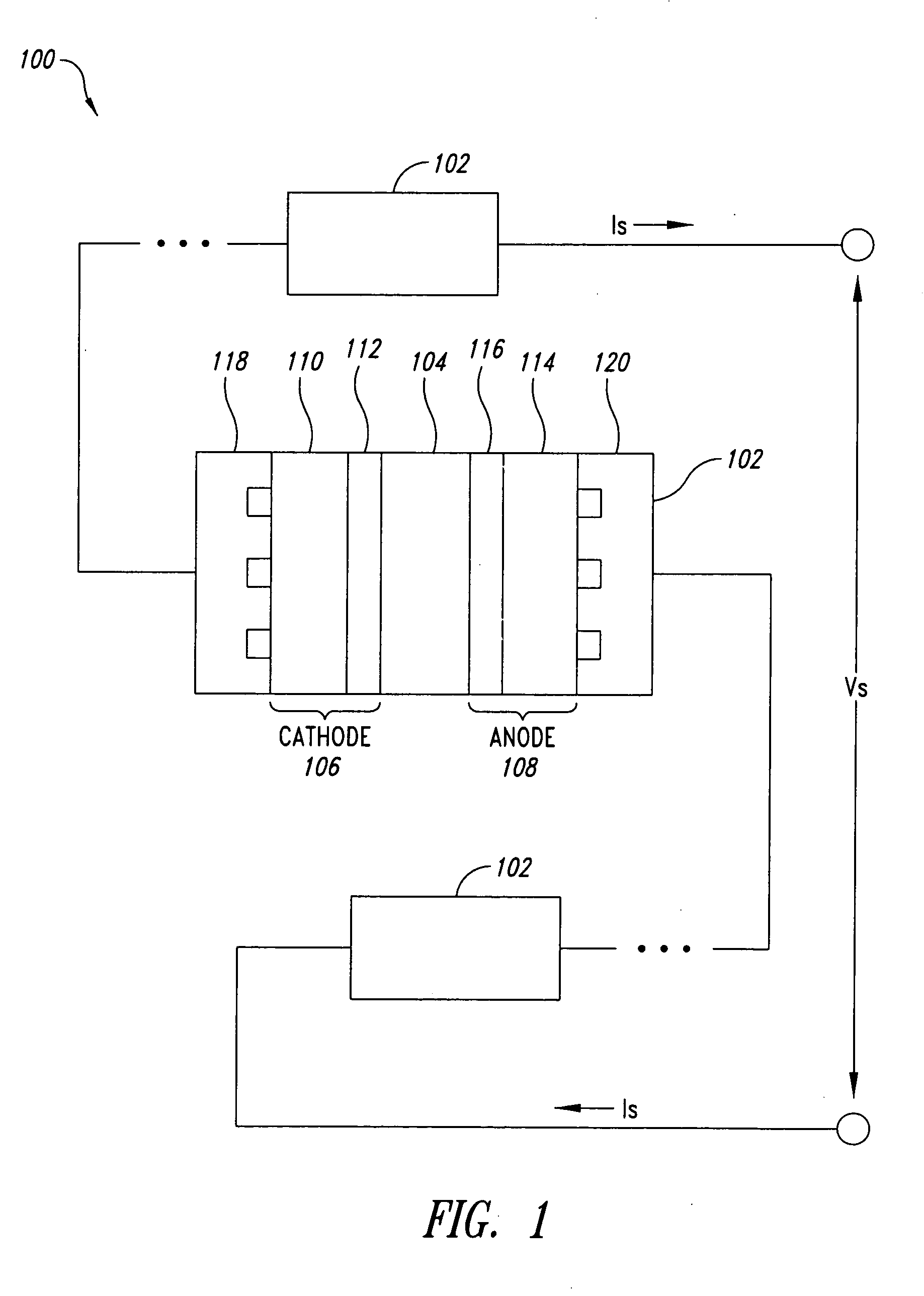
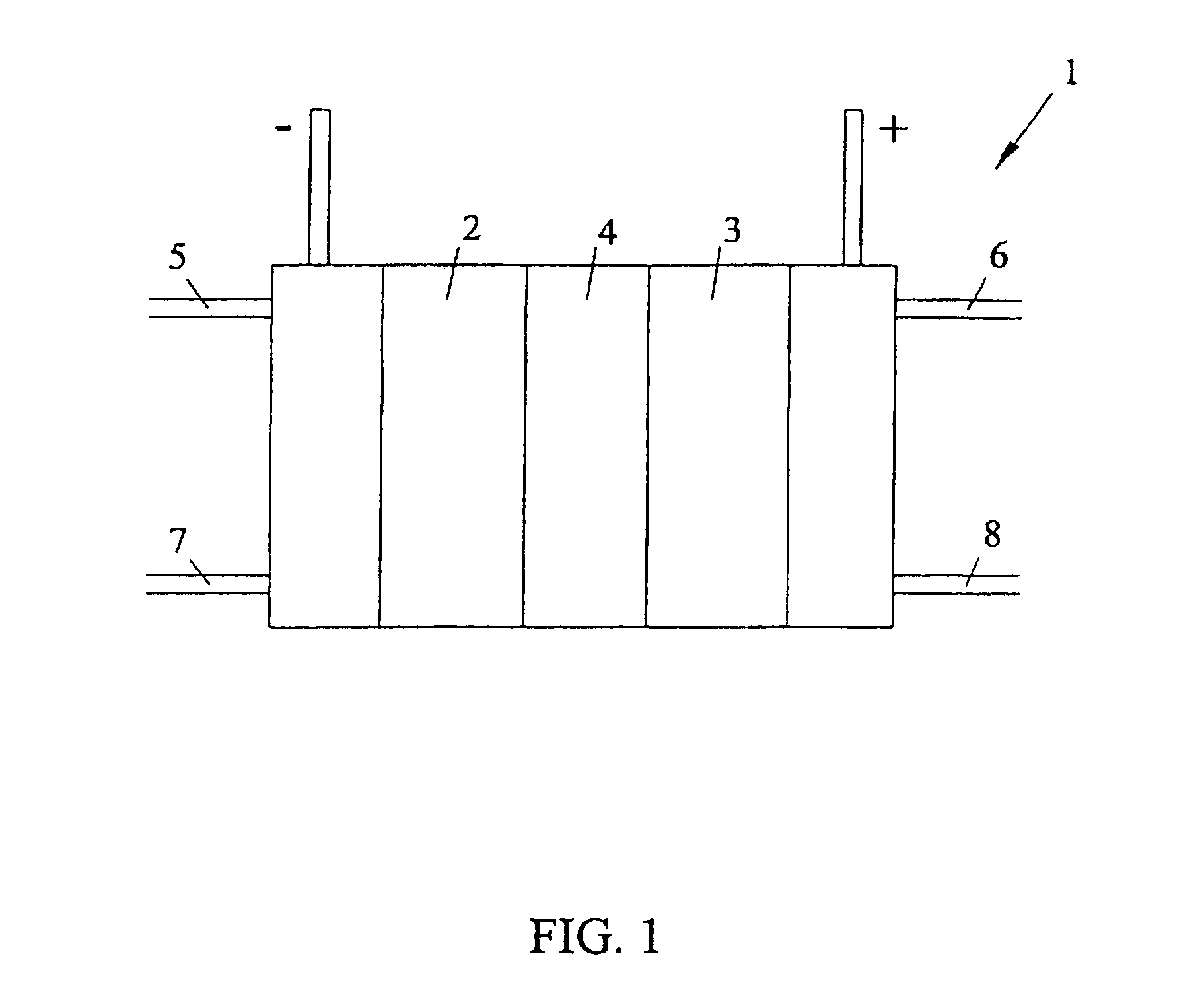
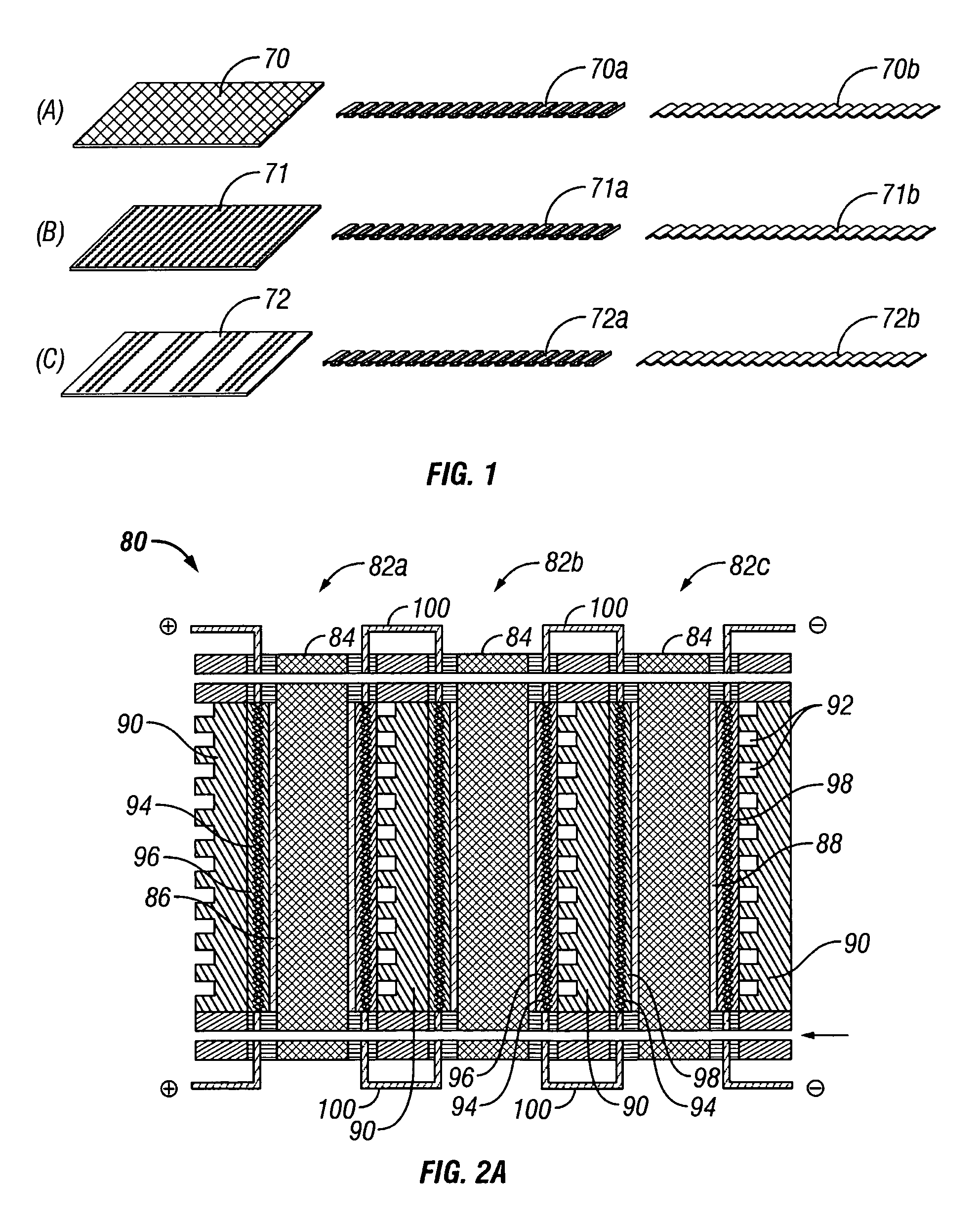
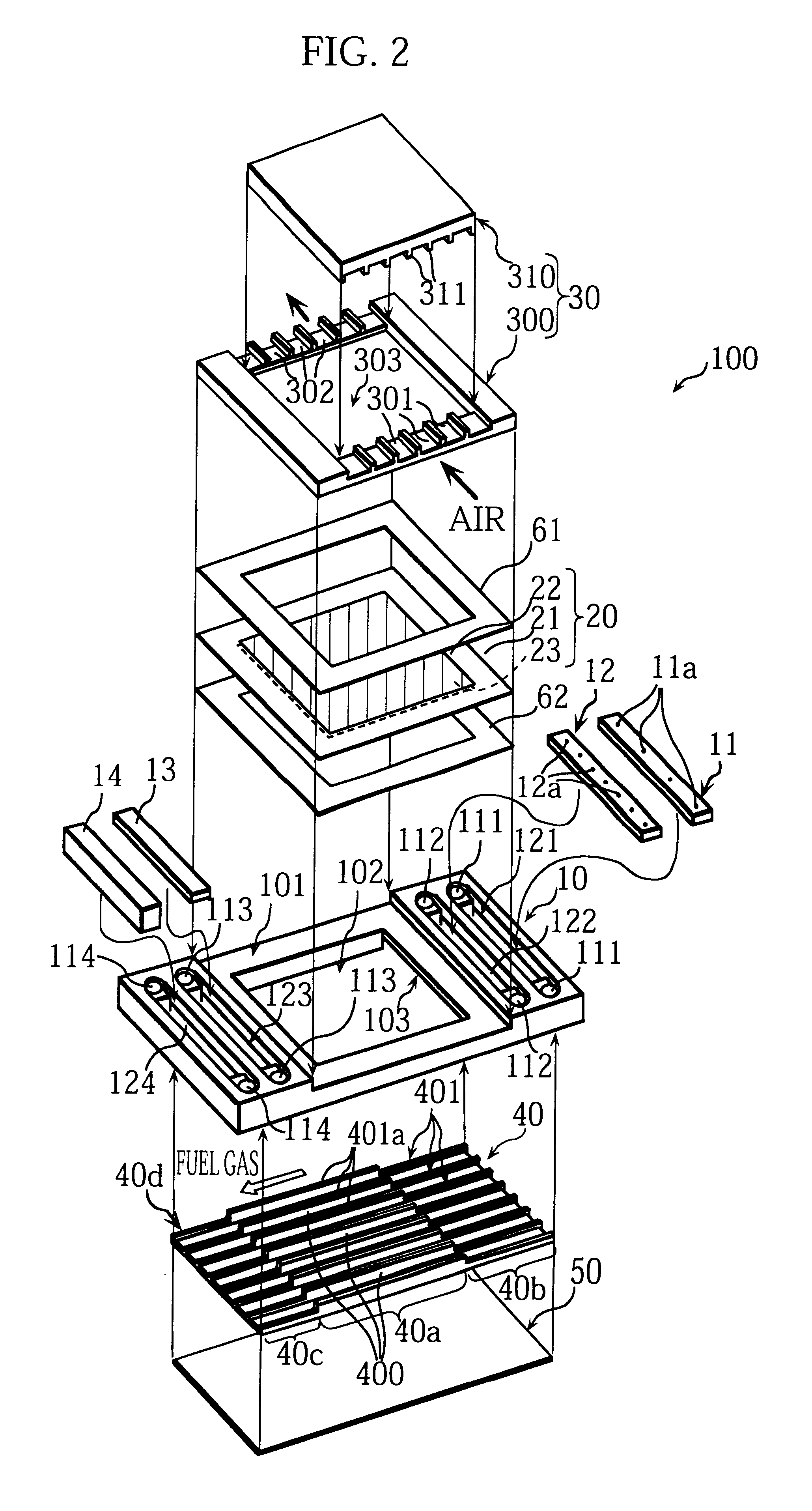
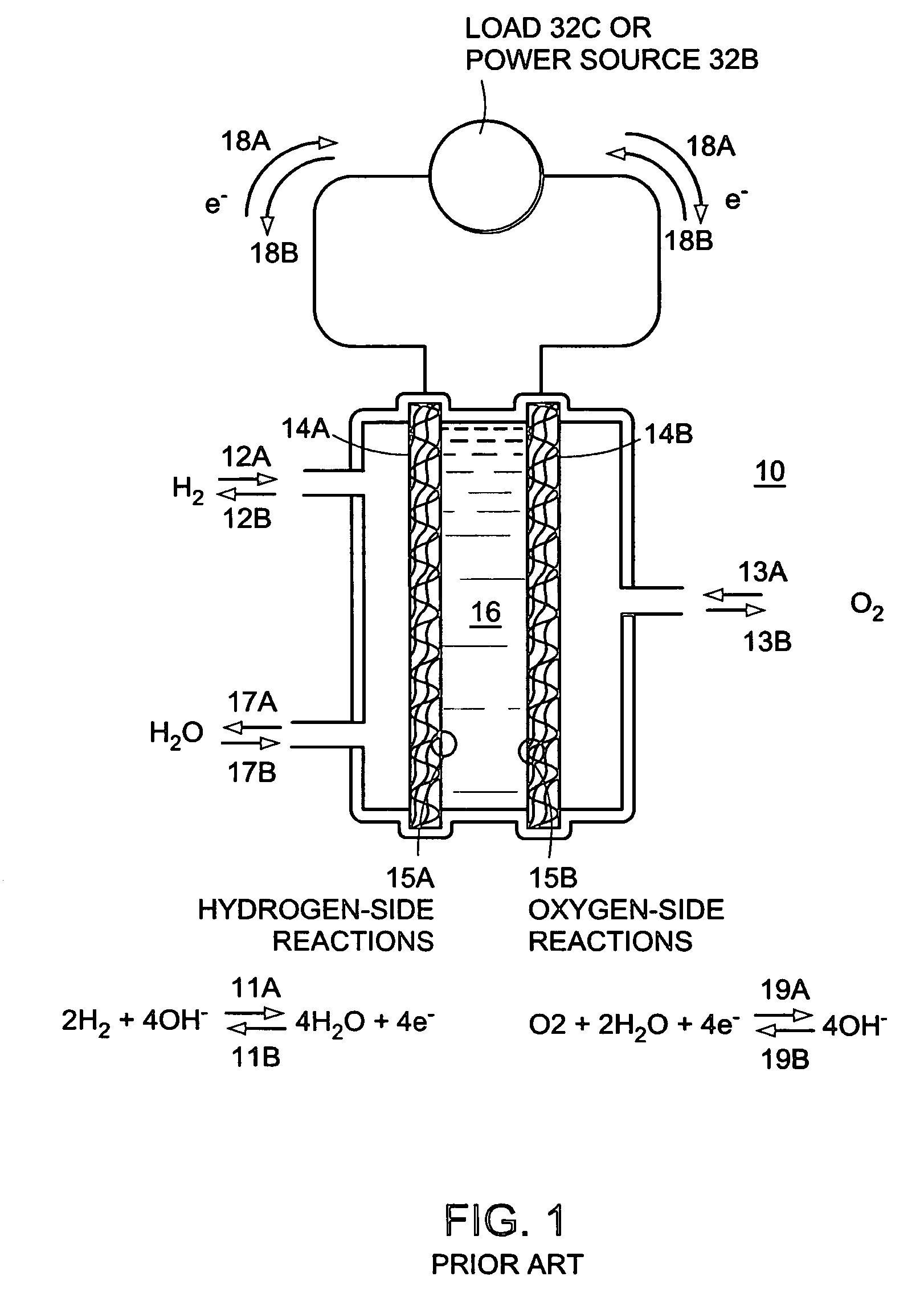
Solid polymer fuel cell with improved voltage reversal tolerance
In a solid polymer fuel cell series, various circumstances can result in the fuel cell being driven into voltage reversal. For instance, cell voltage reversal can occur if that cell receives an inadequate supply of fuel (for example, fuel starvation). In order to pass current during fuel starvation, reactions other than fuel oxidation may take place at the fuel cell anode, including water electrolysis and oxidation of anode components. The latter may result in significant degradation of the anode. Such fuel cells can be made more tolerant to cell reversal by promoting water electrolysis over anode component oxidation at the anode. This can be accomplished by incorporating a catalyst composition at the anode to promote the water electrolysis reaction, in addition to the typical anode electrocatalyst for promoting fuel oxidation.
Owner:BALLARD POWER SYSTEMS +1
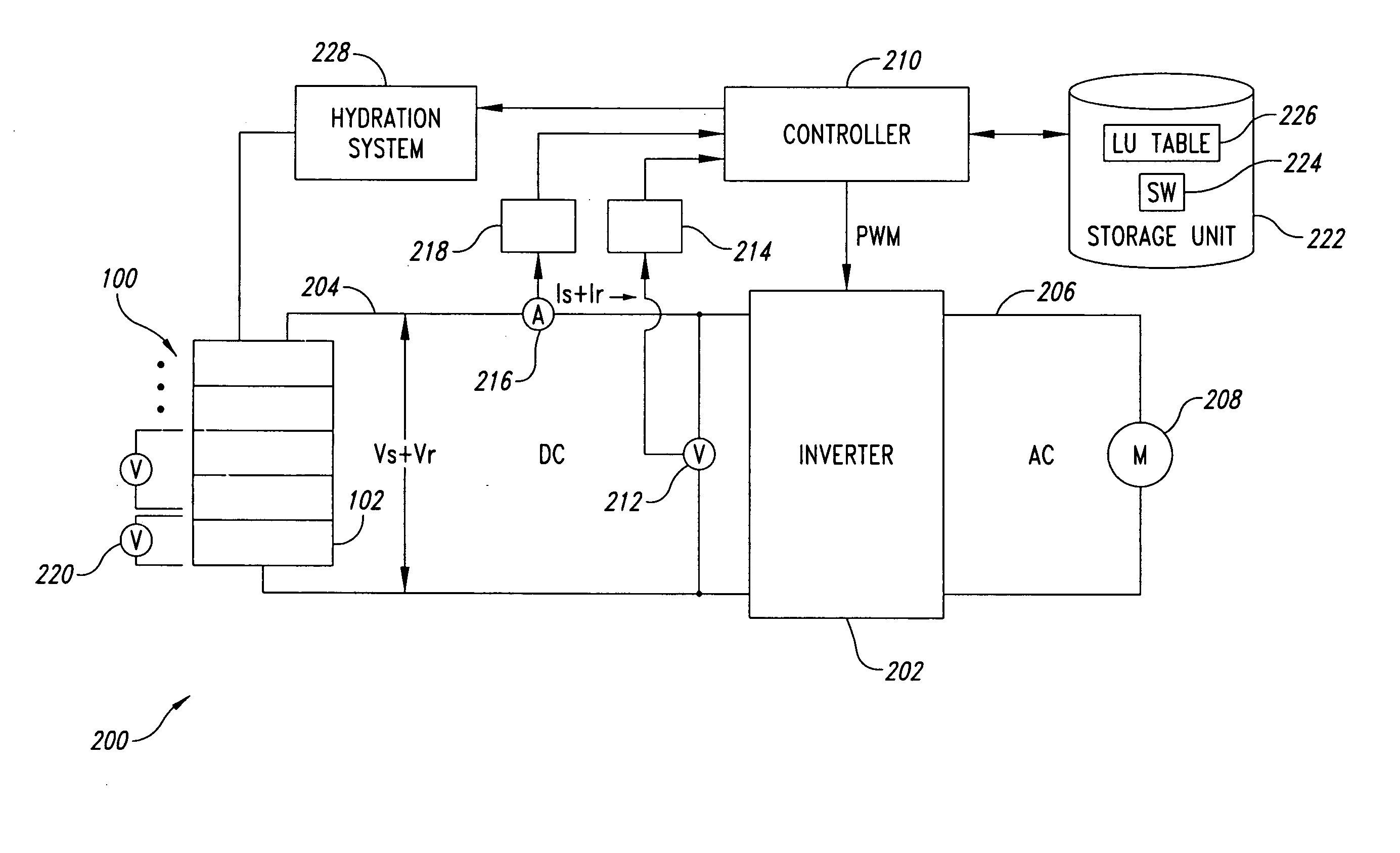
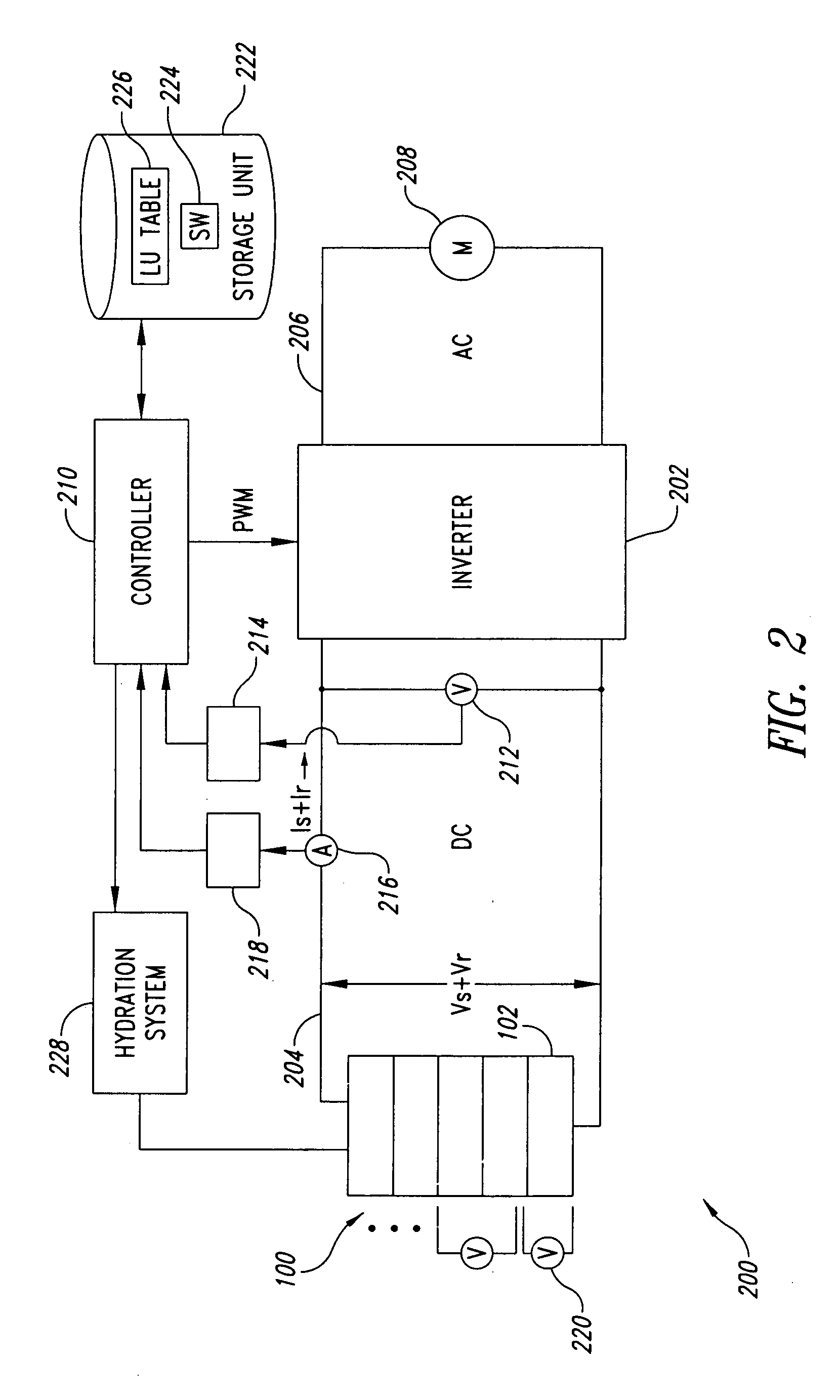
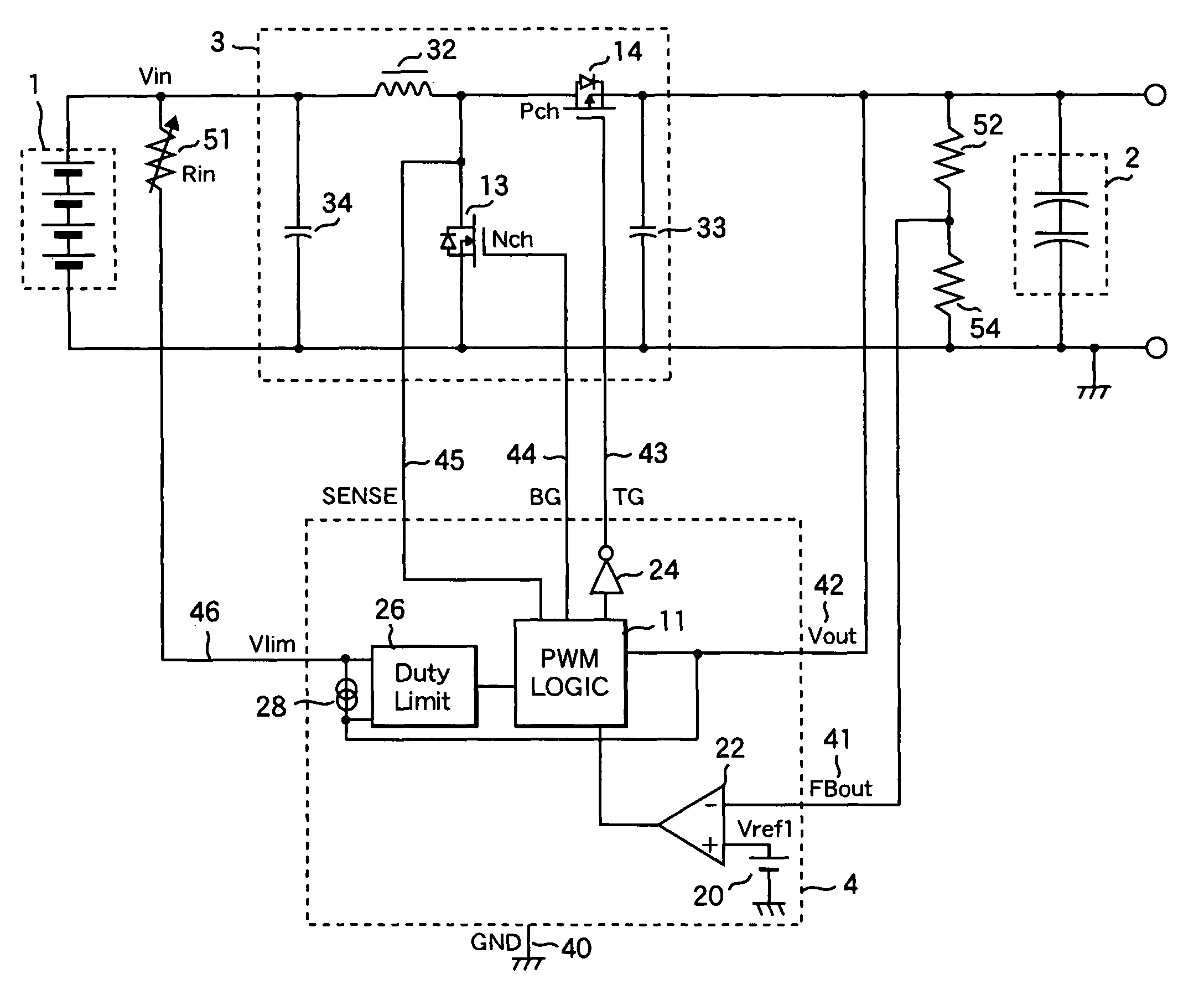
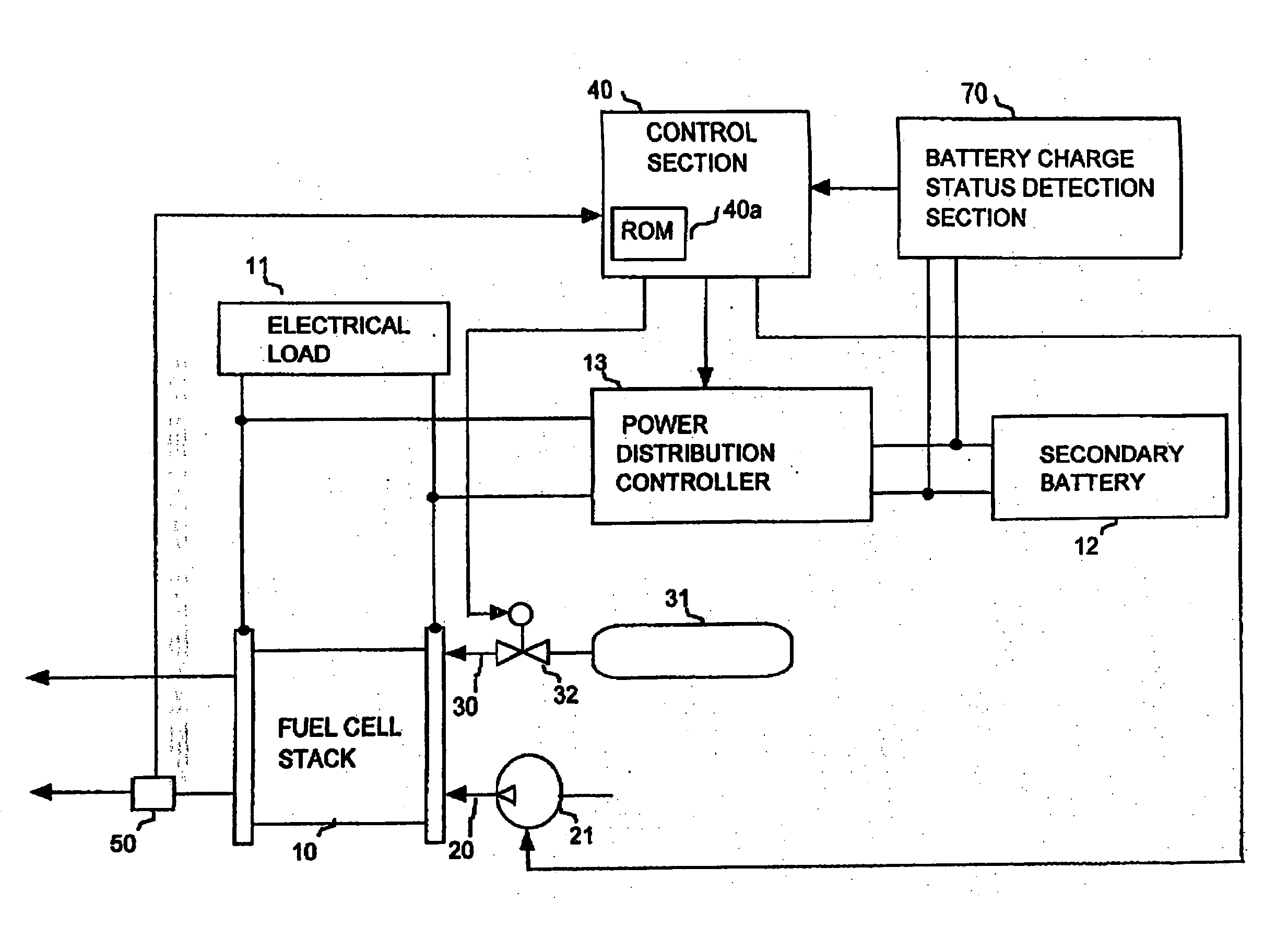
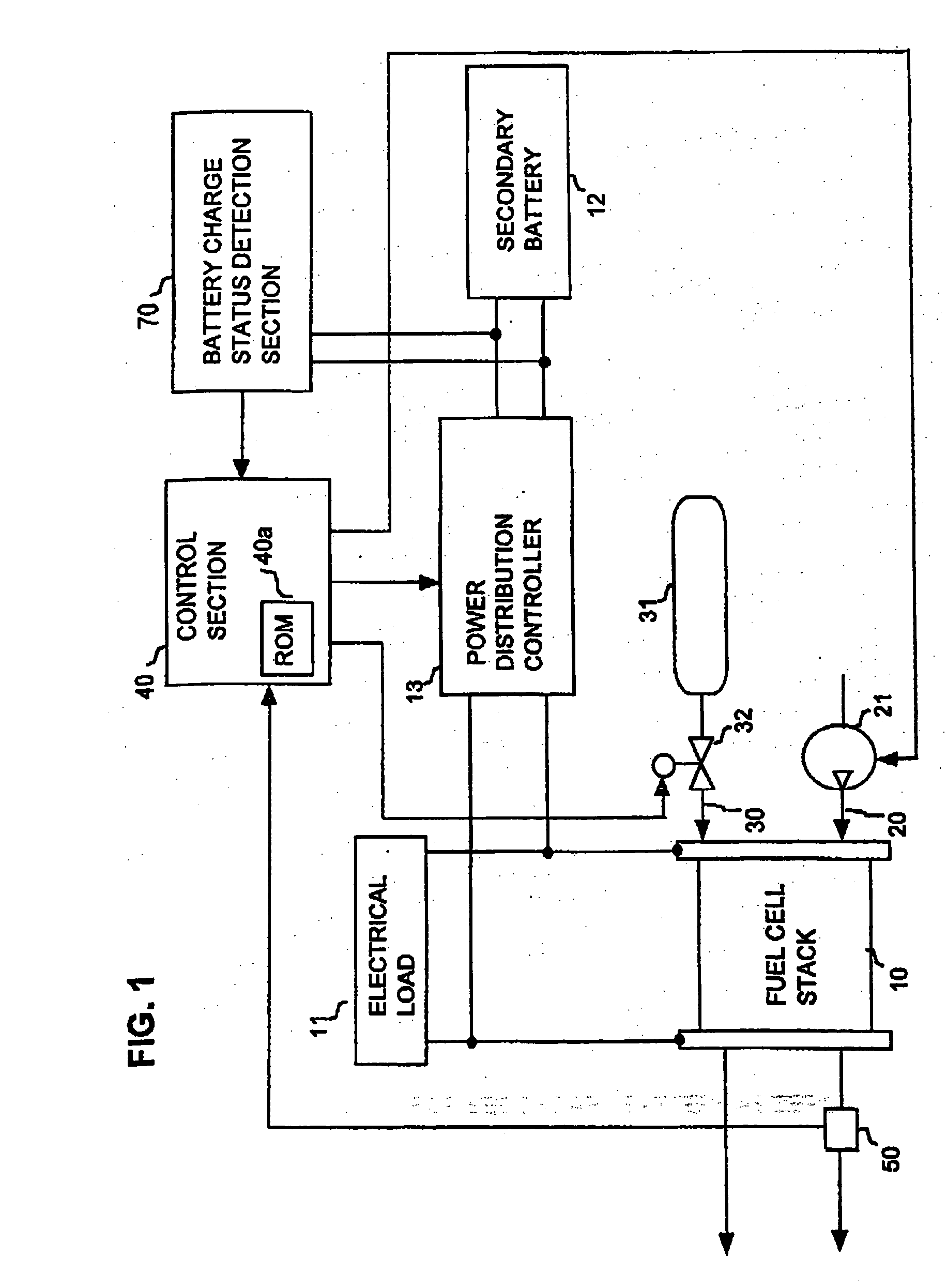
Power supply apparatus with fuel cell and method of controlling the same
InactiveUS7883808B2Stable power supply to equipmentGuaranteed uptimeDc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsFuel cellsEngineering
A power supply apparatus has a fuel cell unit as a source of input power. A control device limits the output of the fuel cell unit within an operating range of up to a maximum power point, even if a load power is not lower than the maximum power of said fuel cell unit. In addition to the fuel cell, a charge storing device is provided at the output side of the power supply apparatus. The charge storing device is capable of making up a shortage of power of the fuel cell.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Water vapor transport power generator
An improved system for generating electrical power using a fuel cell. More particularly, a system for generating hydrogen gas by reacting water vapor with a substantially non-fluid substance and transporting the generated hydrogen gas to the fuel cell which generates electrical power. Reacting water vapor with the non-fluid hydrogen generating substance rather than liquid water prevents caking of the non-fluid substance and deposition of byproducts onto the non-fluid substance that interfere with continued generation of hydrogen gas.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
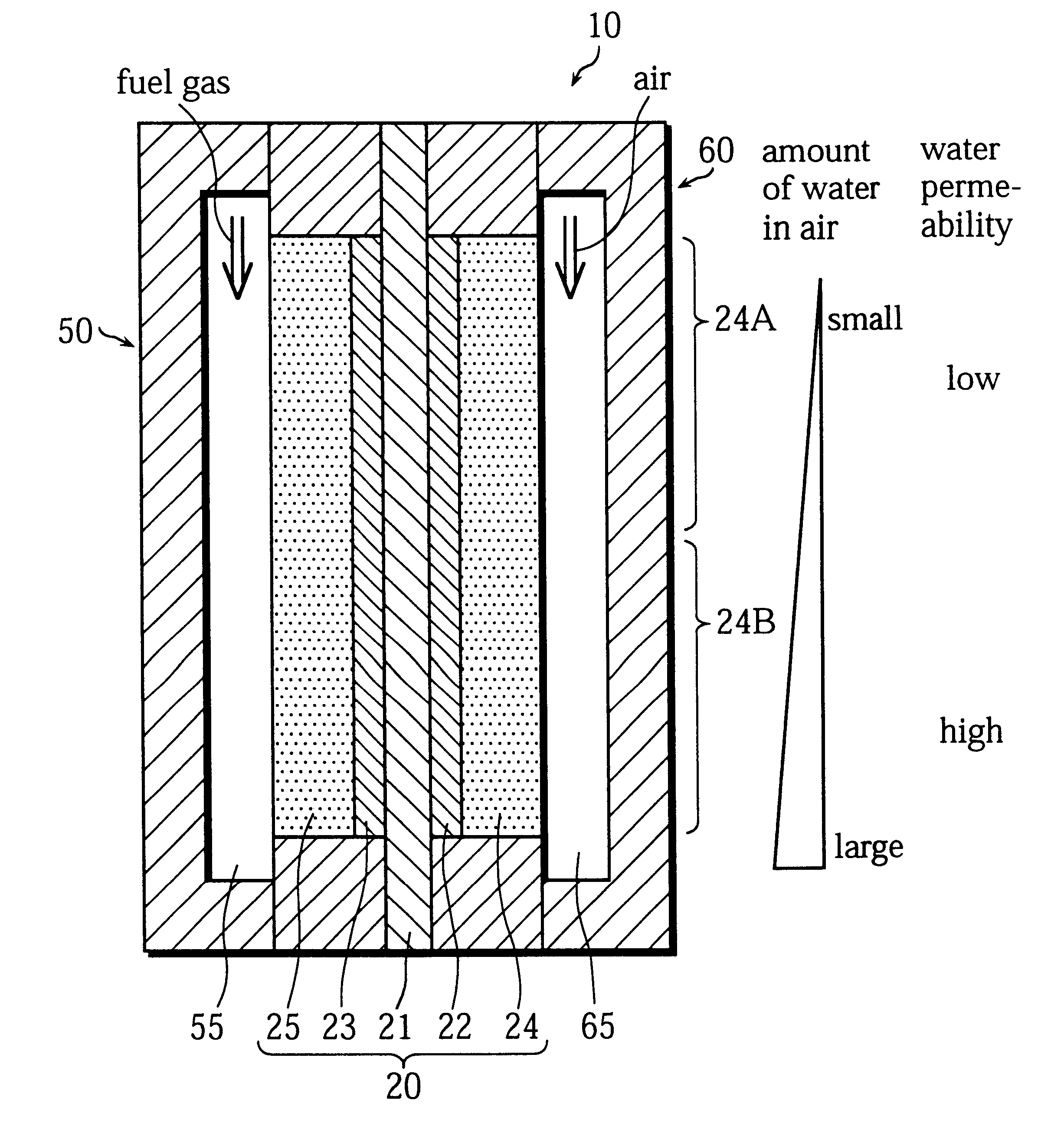
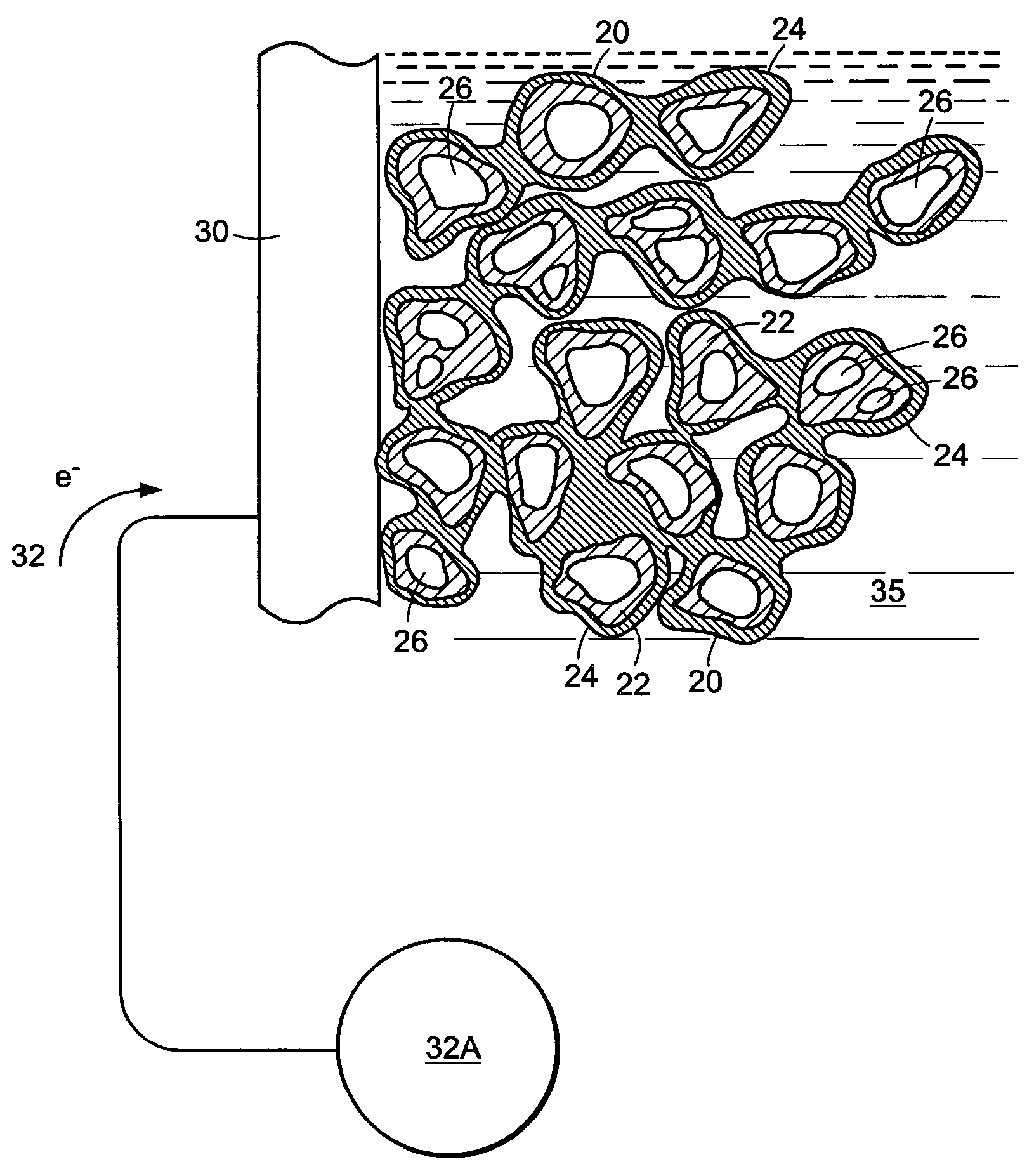
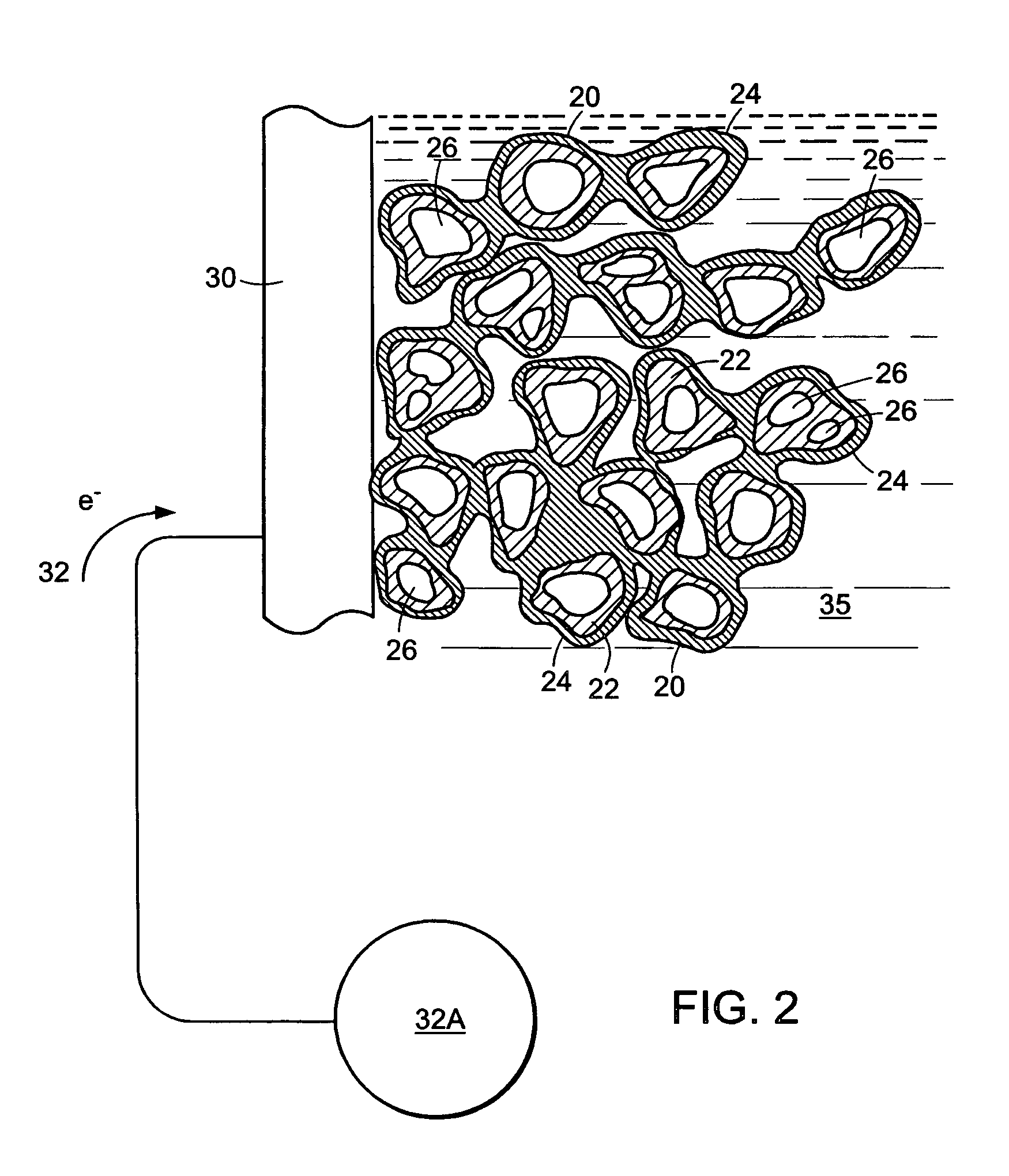
Fuel cell having water permeability adjustment capability
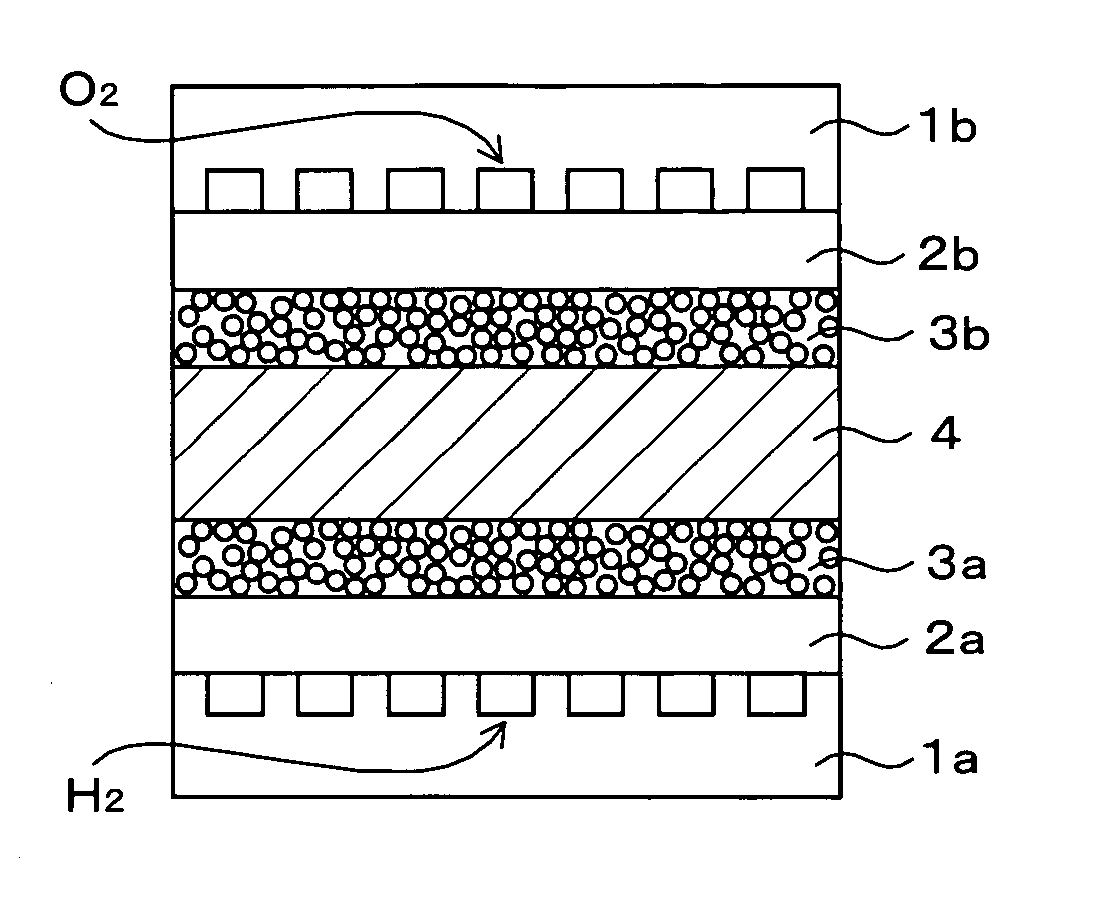
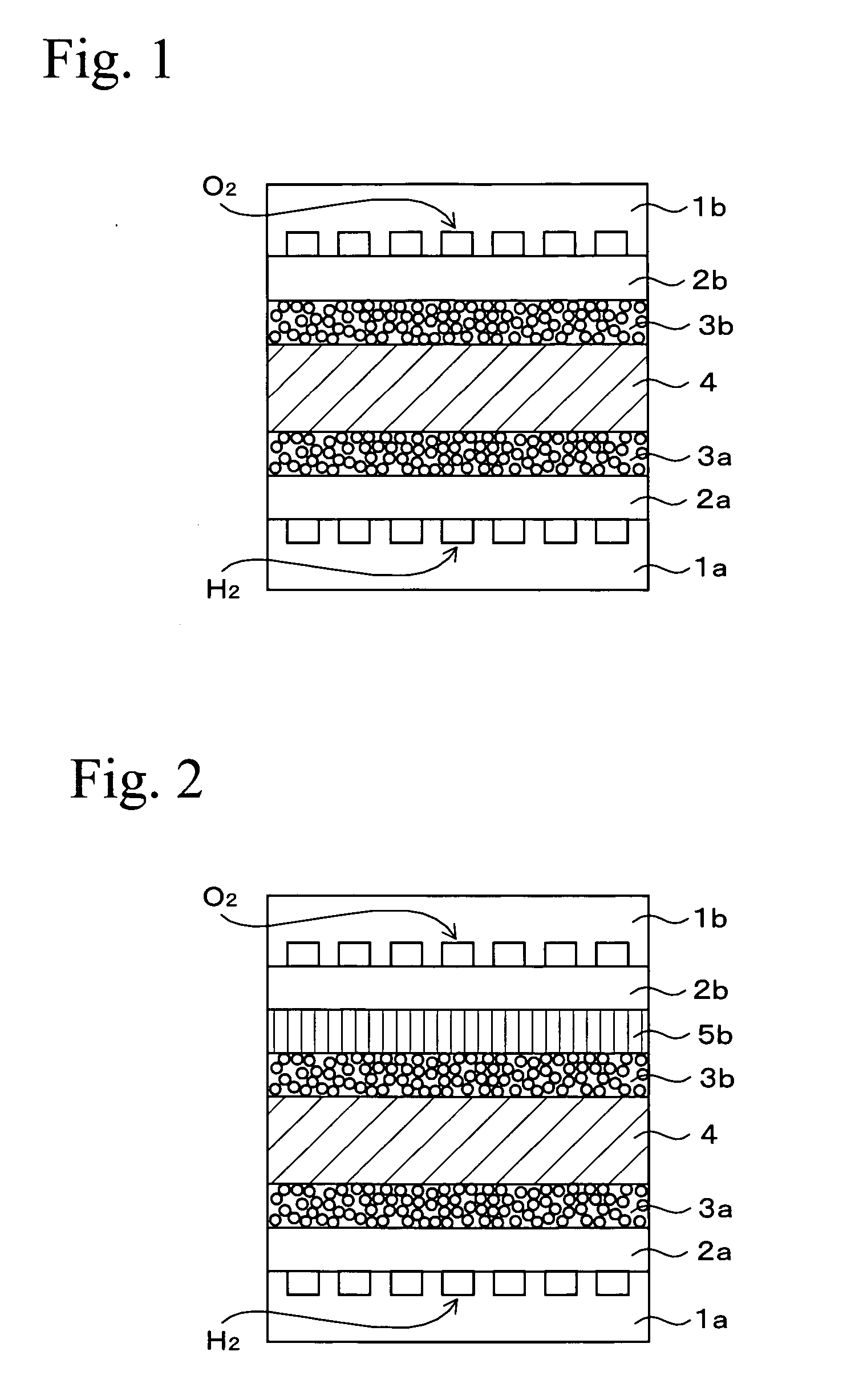
The object of the present invention is to provide fuel cell including a cell that is formed by sandwiching solid polymer membrane between an anode and a cathode that generates electricity with stability and high performance by evenly moistening the solid polymer membrane. For this purpose, in a gas diffusion layer 24, which is positioned adjacent to a cathode catalyst layer 22, the content of fluororesin in an area on the side of the entrance for the oxidizer is set to be higher than in another area on the side of the exit so that the water repellency in the entrance side area is higher than in the exit side area. As a result, a water permeation suppressing part 24A, where the water permeability is relatively low, is formed in the area on the entrance side, while a water permeable part 24B, where the water permeability is relatively high, is formed in the area on the exit side.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
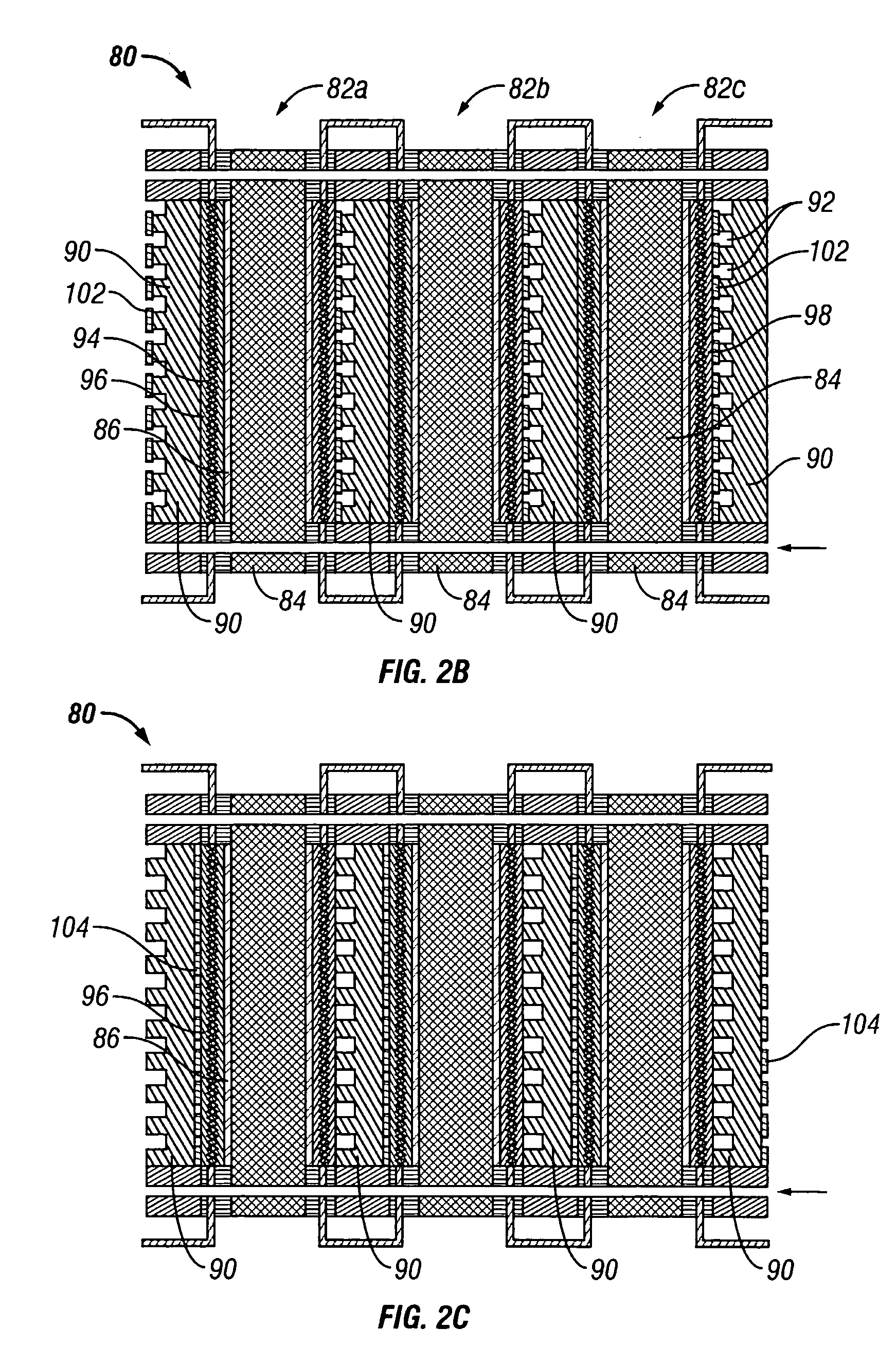
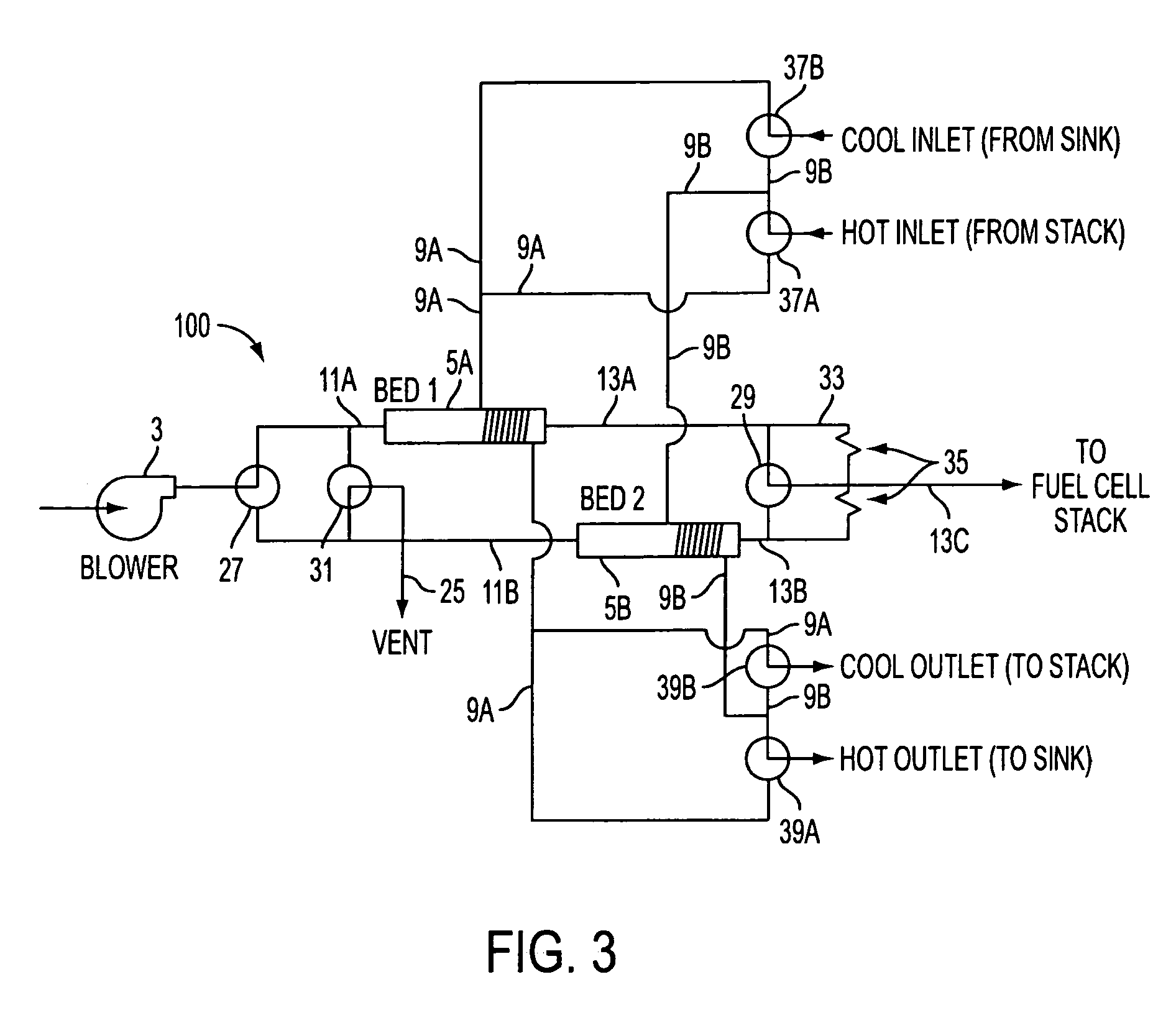
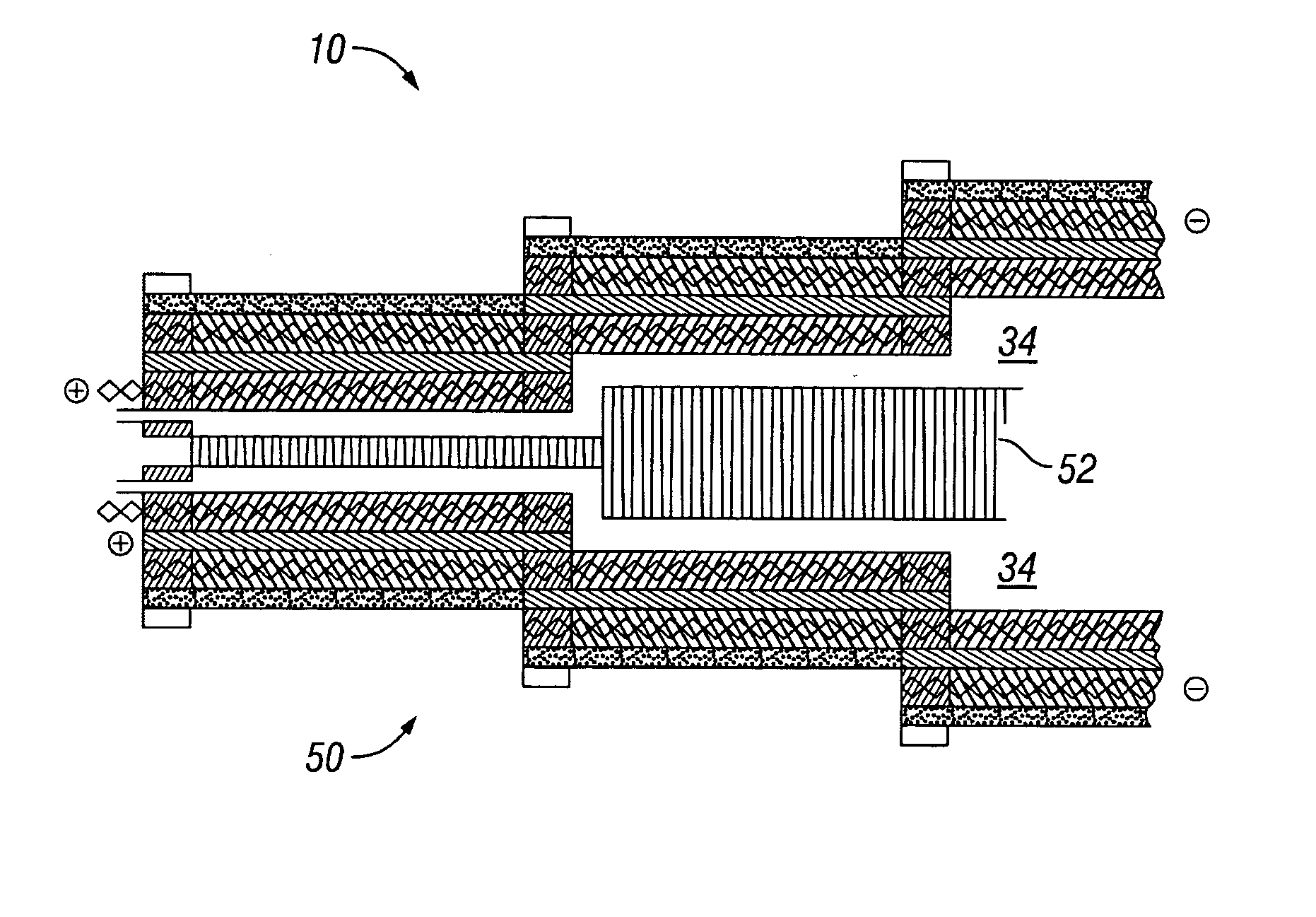
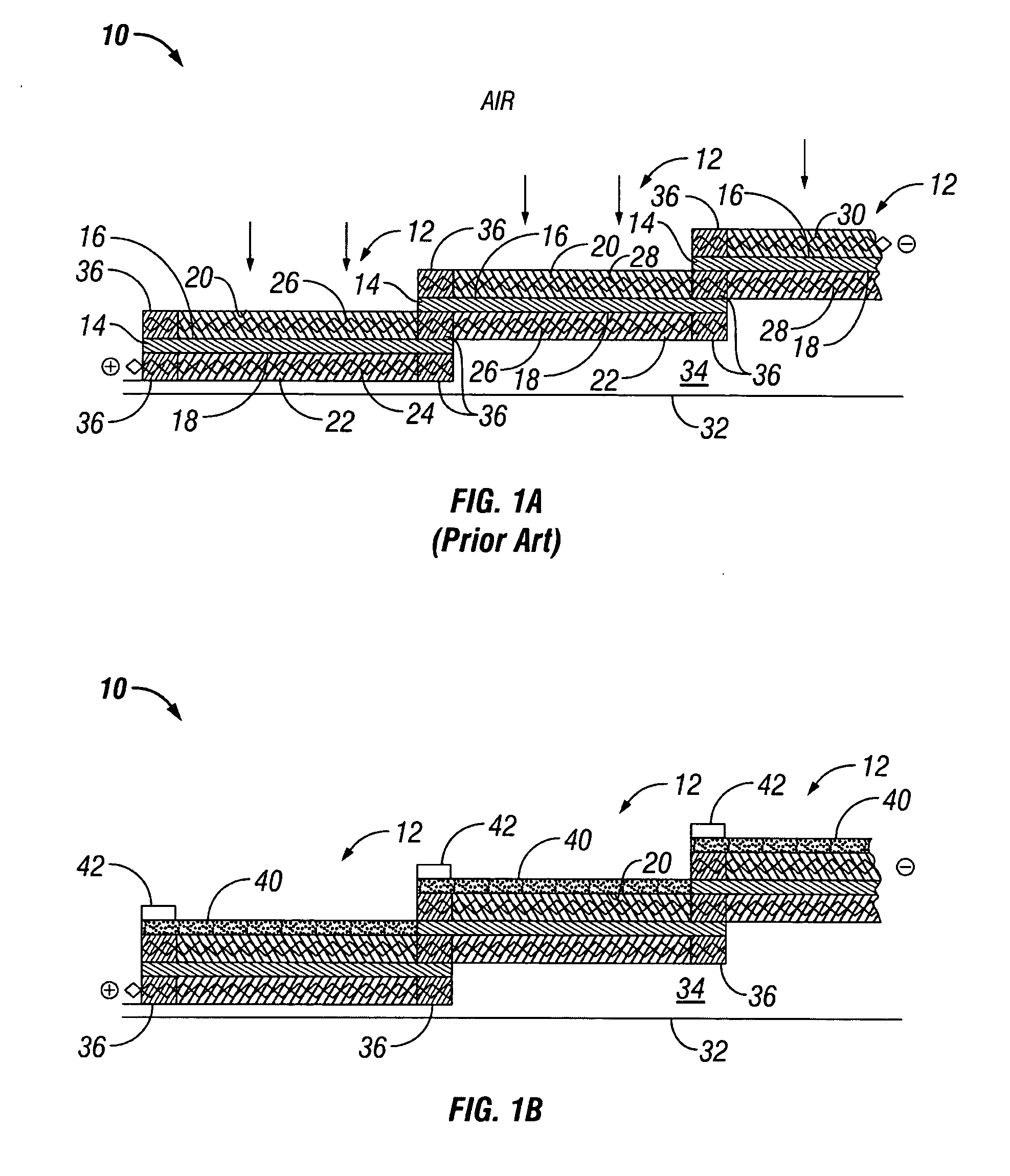
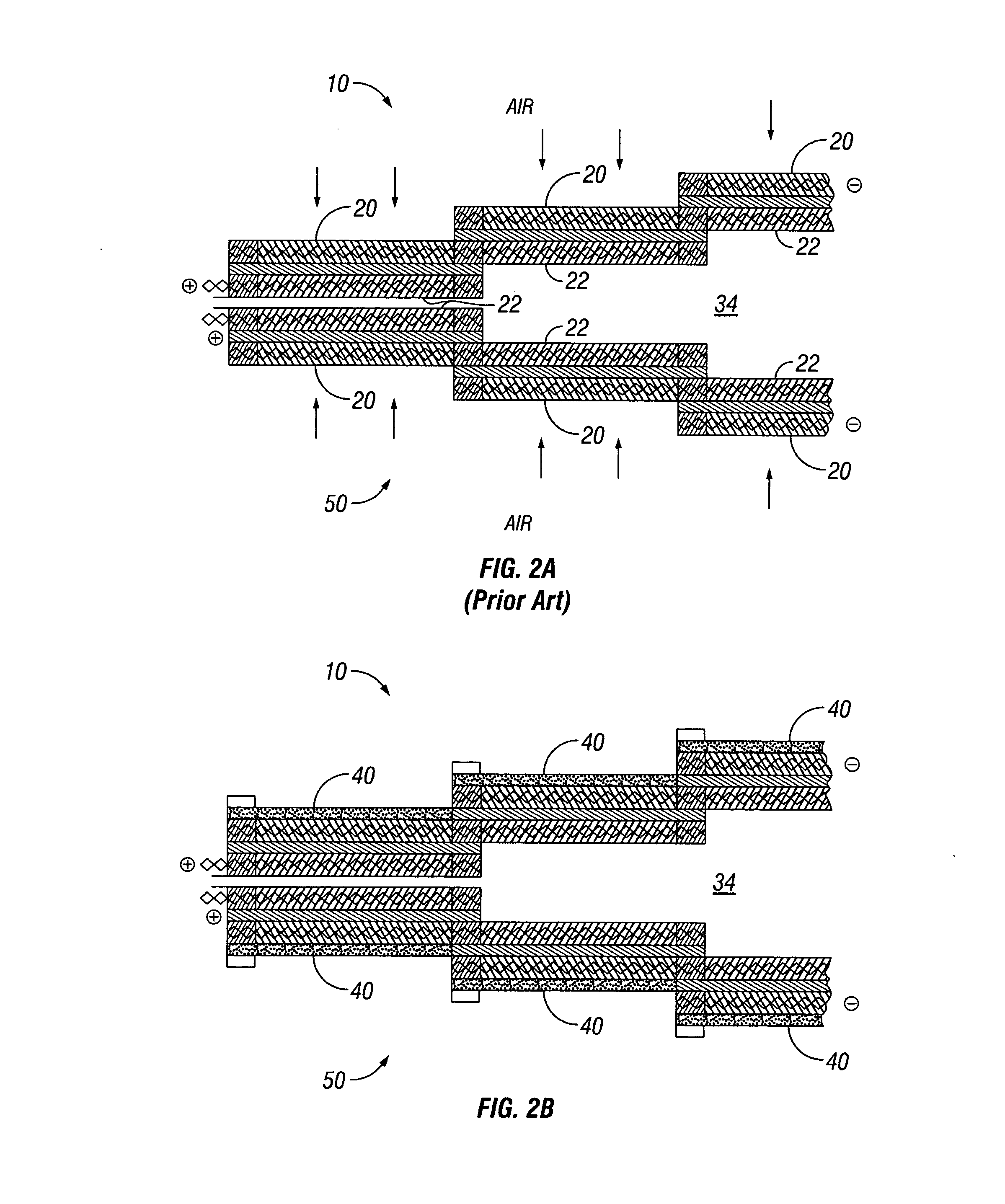
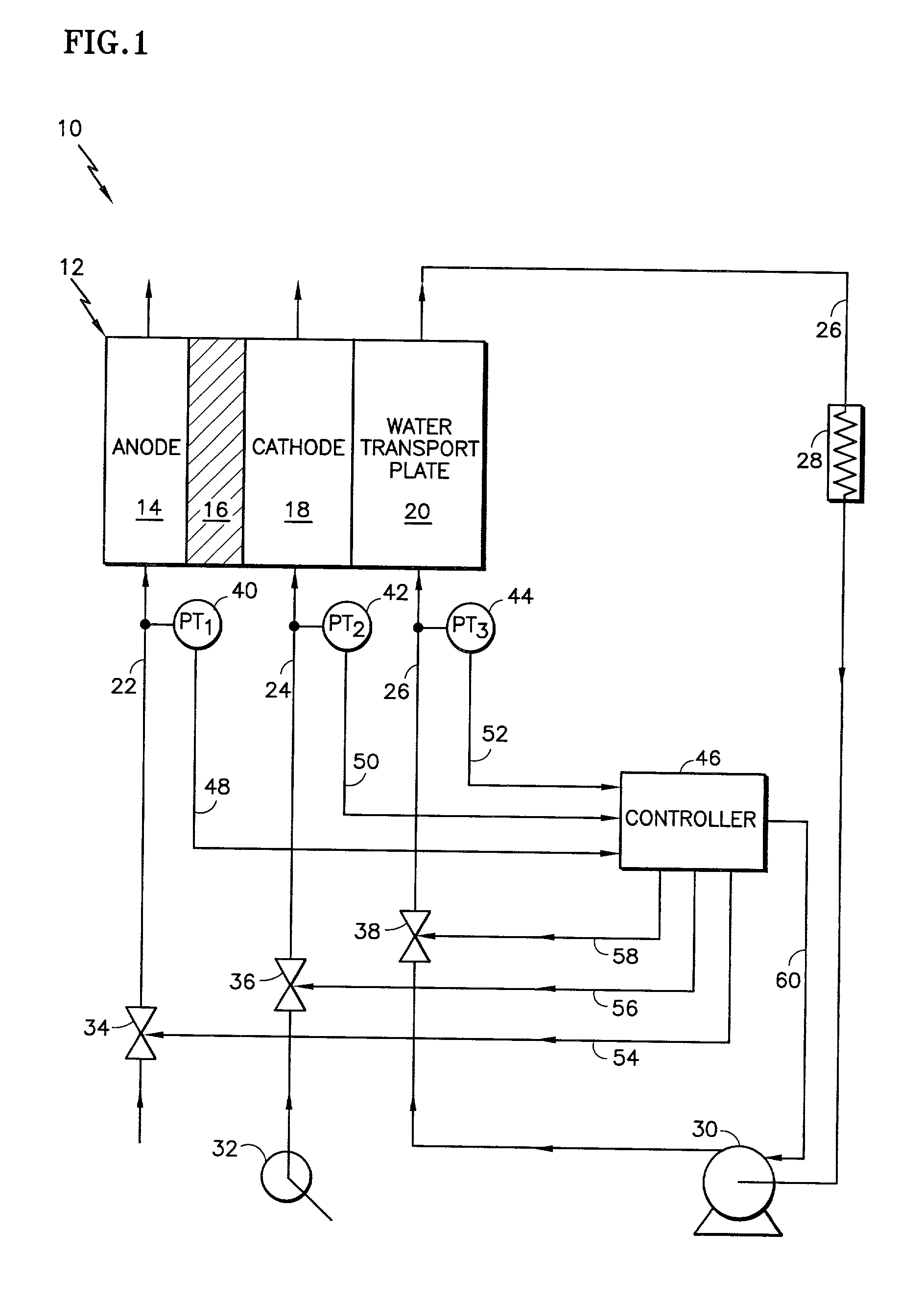
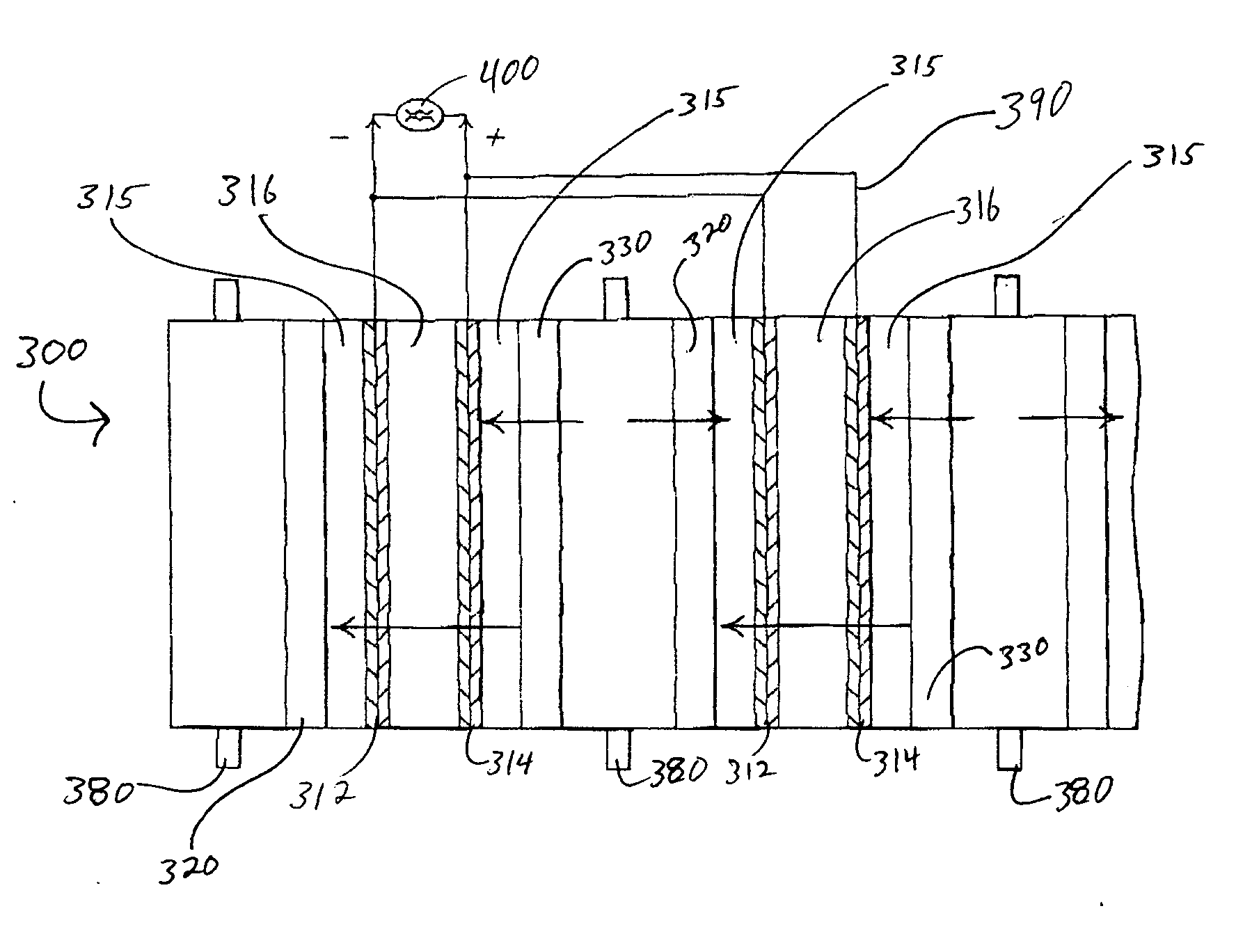
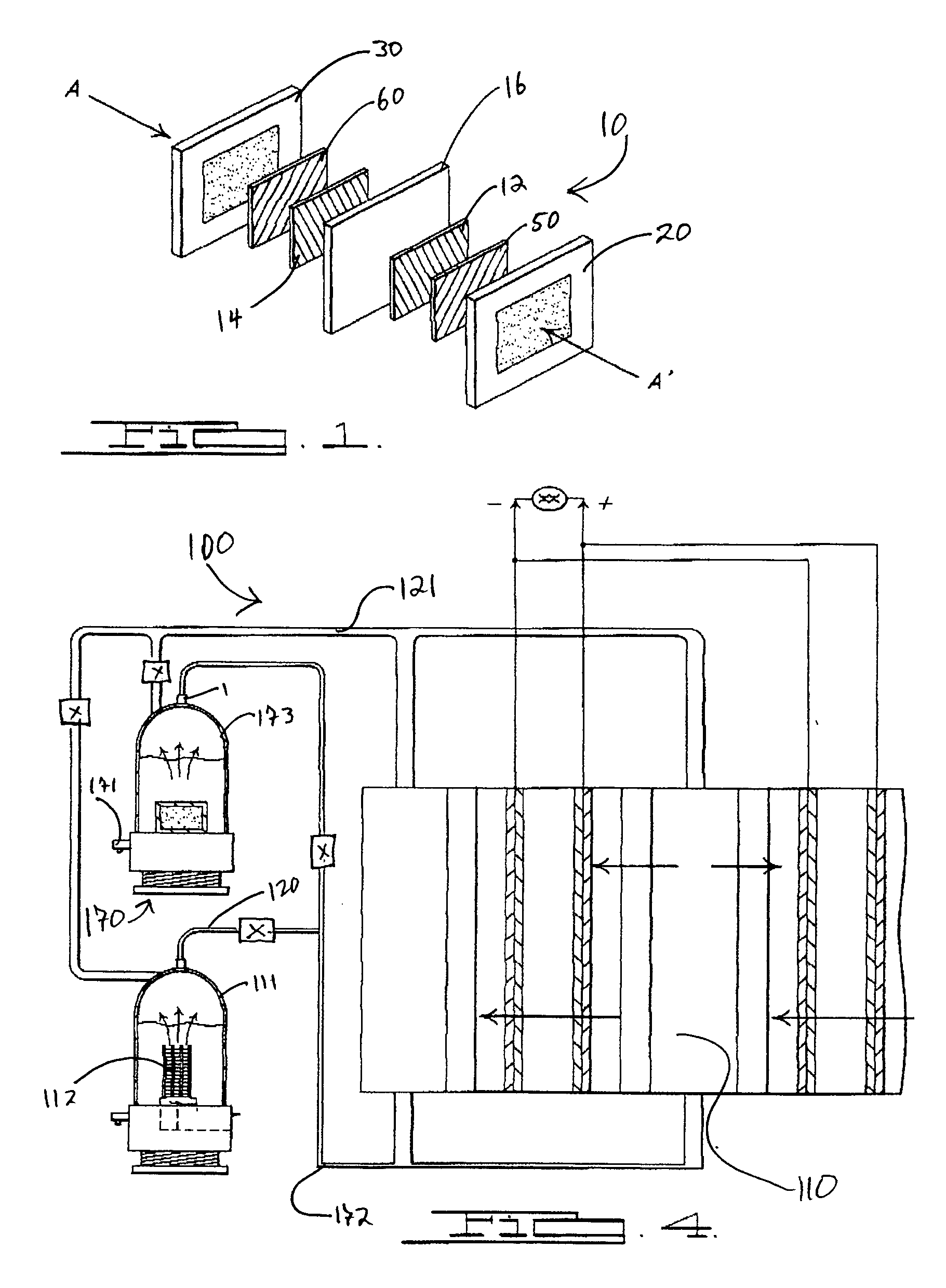
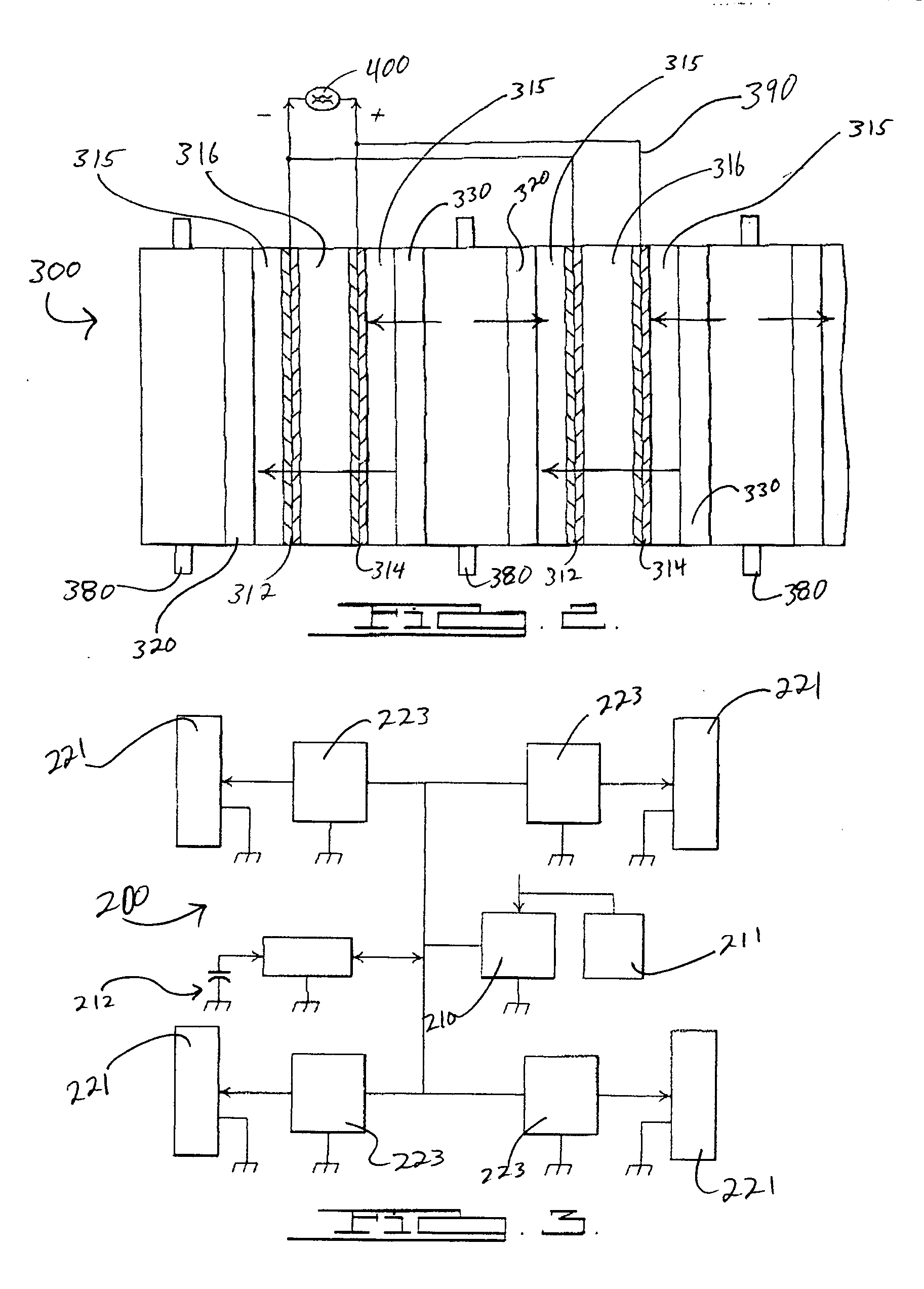
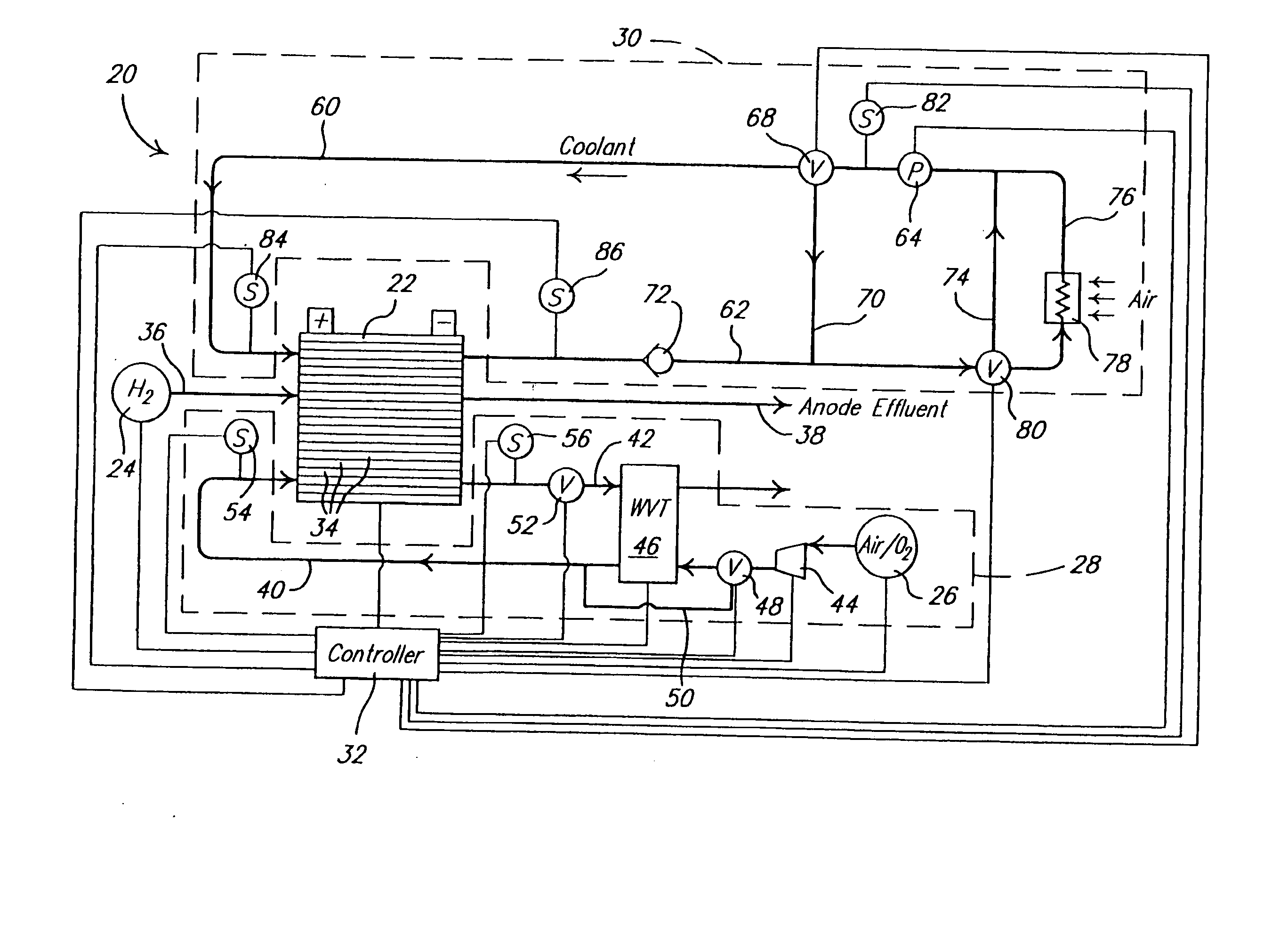
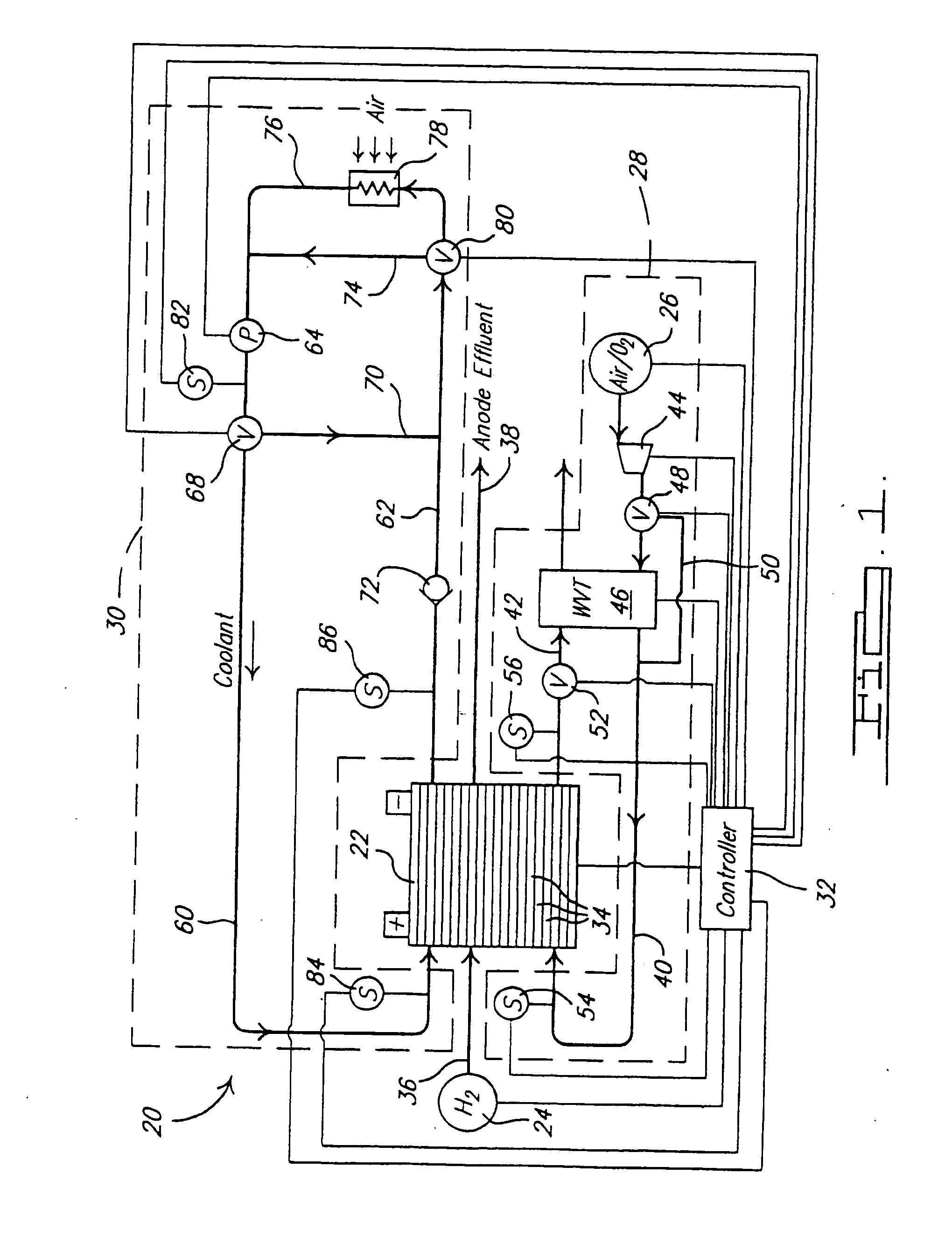
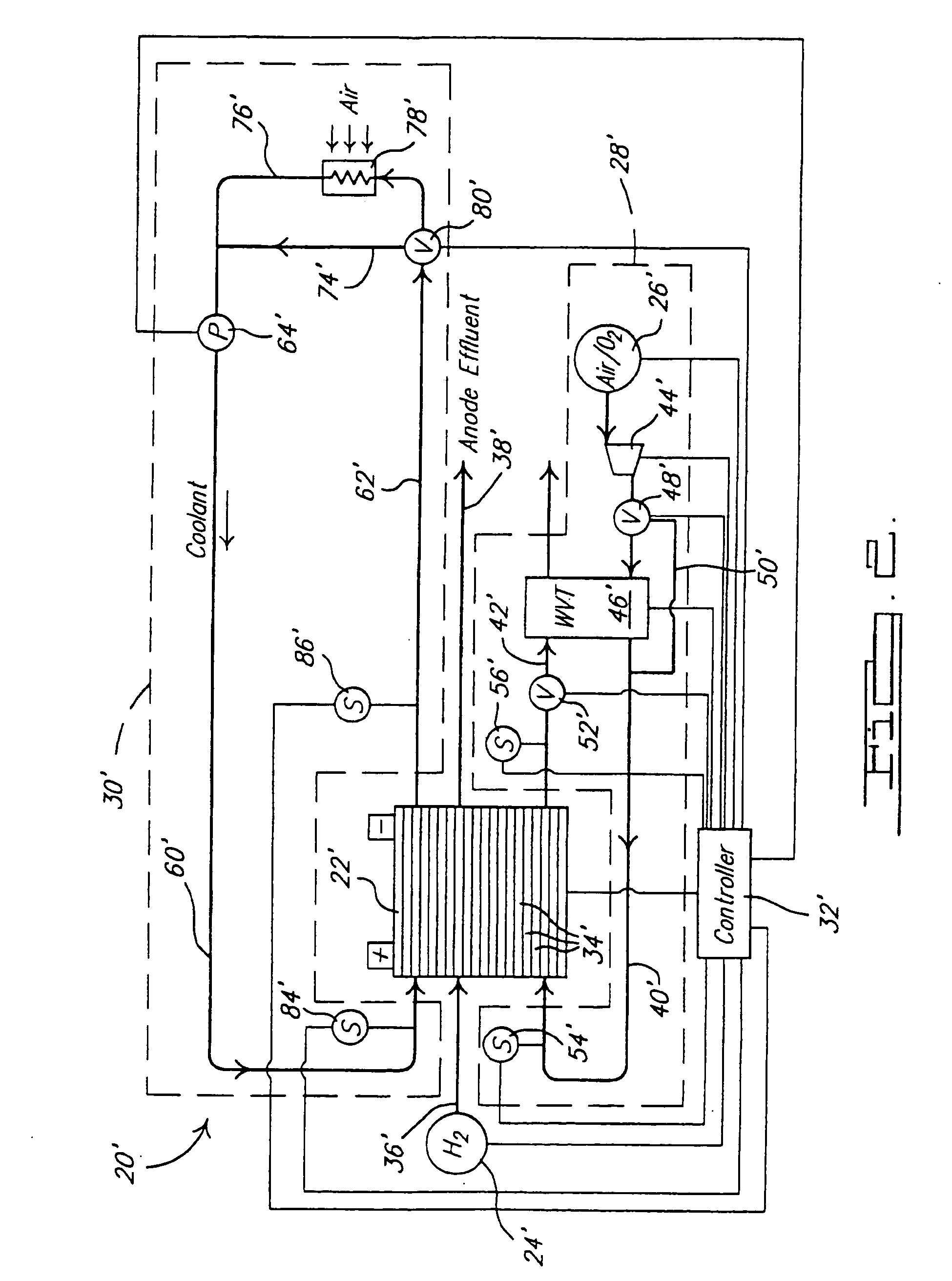
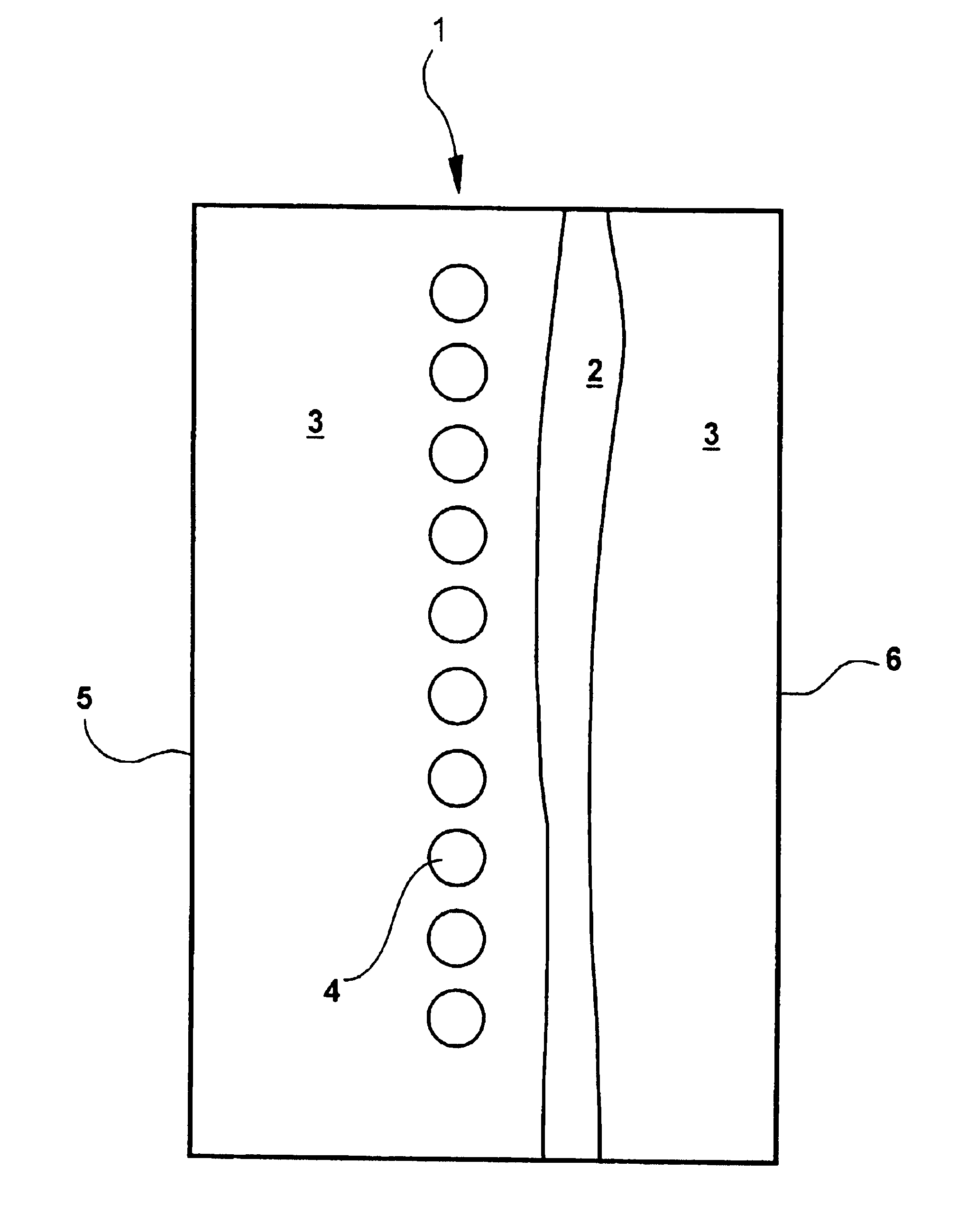
Water management in bipolar electrochemical cell stacks
InactiveUS20060199061A1Reduce probabilityPromote loss of waterFuel cells groupingWater management in fuel cellsPolymer electrolytesLiquid water
A bipolar, filter press-like electrochemical cell stack comprising a plurality of electrochemical cells, where each electrochemical cell is supplied with a gaseous anodic reactant and either supplied with a gaseous cathodic reactant or produces a gaseous cathodic product, and where each electrochemical cell avoids drying out the ion exchange membrane polymer electrolyte, avoids flooding at the cathode, facilitates recovery of liquid water at the anode, and reduces water losses from at least one of the electrodes. A water retention barrier is variously positioned, such as between a gas diffusion electrode and a fluid flow field. The barrier may be either: (i) a thin, gas permeable, liquid water impermeable membrane; (ii) a thin, porous sheet of material; or (iii) a thin, substantially solid sheet of material except for a plurality of small through-holes that penetrate from one side of the sheet to an opposing side of the same sheet. The barrier is advantageously used at the cathode and facilitates air cooling of the cell.
Owner:LYNNTECH
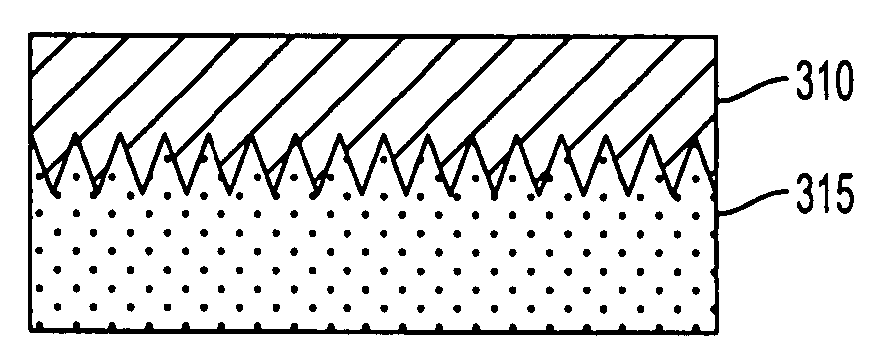
Textured electrolyte for a solid oxide fuel cell
ActiveUS7045237B2Decreases cost per wattImprove adhesionFuel cell heat exchangeFuel cells groupingFuel cellsMaterials science
A ceramic electrolyte for a solid oxide fuel cell includes at least one non-uniform surface portion. Preferably, the electrolyte surface is textured.
Owner:BLOOM ENERGY CORP
Water reclamation in a micropower generator
A waterless power generator, particularly a waterless electrical power generator and a passively controlled process for producing electricity with a fuel cell using stoichiometric amounts of a solid hydrogen fuel and byproduct water vapor produced by the fuel cell to generate hydrogen gas. A fuel cell reaction of hydrogen and oxygen produces electrical energy as well as by-product water which diffuses back into the power generator as water vapor to react with the hydrogen fuel, producing more hydrogen gas. This generated hydrogen gas is then used as a fuel which allows the fuel cell to generate additional electrical power and additional water. The process runs without any attached water source or water supply other than the water which is produced by the fuel cells themselves.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Water management in monopolar fuel cells
A monopolar fuel cell stack comprising proton exchange membrane fuel cells supplied with a gaseous anodic reactant, preferably hydrogen, and a gaseous cathodic reactant, preferably air. The monopolar fuel cell stack, forming at least one substantially planar array, includes a liquid water retention barrier disposed over an electrode to retain liquid water within the fuel cells. The barrier is preferably used over the cathode side of each fuel cell and allows excess air flow to cool the fuel cell stack without drying the membrane in each fuel cell. The liquid water retention barrier may be either: (i) a thin, gas permeable, liquid water impermeable membrane; (ii) a thin, porous sheet of material; or (iii) a thin, substantially solid sheet of material except for a plurality of small through-holes that penetrate from one side of the sheet to an opposing side of the same sheet.
Owner:LYNNTECH
Polymer electrolyte fuel cell and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20040197633A1Improves product water-removal efficiencyEvenly distributedFuel cell heat exchangeFinal product manufacturePolymer electrolytesFuel cells
The present invention relates to a polymer electrolyte fuel cell comprising: an electrolyte membrane-electrode assembly including an anode, a cathode and a polymer electrolyte membrane interposed therebetween; an anode-side conductive separator plate having a gas flow channel for supplying a fuel gas to the anode; and a cathode-side conductive separator plate having a gas flow channel for supplying an oxidant gas to the cathode. A conductive separator plate made of carbon has poor wettability with water. This has posed the disadvantage that variations in performance are induced by nonuniform gas distribution among cells due to the accumulation of product water or humidifying water in the gas flow channel on the surface of the separator plate. The present invention employs a conductive separator plate comprising a conductive carbon having a hydrophilic functional group, at least in a portion of the gas flow channels, thereby preventing water from accumulating in the gas flow channels.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Textured electrolyte for a solid oxide fuel cell
ActiveUS20050074650A1Decreases cost per wattImprove adhesionFuel cell heat exchangeFuel cells groupingFuel cellsMaterials science
A ceramic electrolyte for a solid oxide fuel cell includes at least one non-uniform surface portion. Preferably, the electrolyte surface is textured.
Owner:BLOOM ENERGY CORP
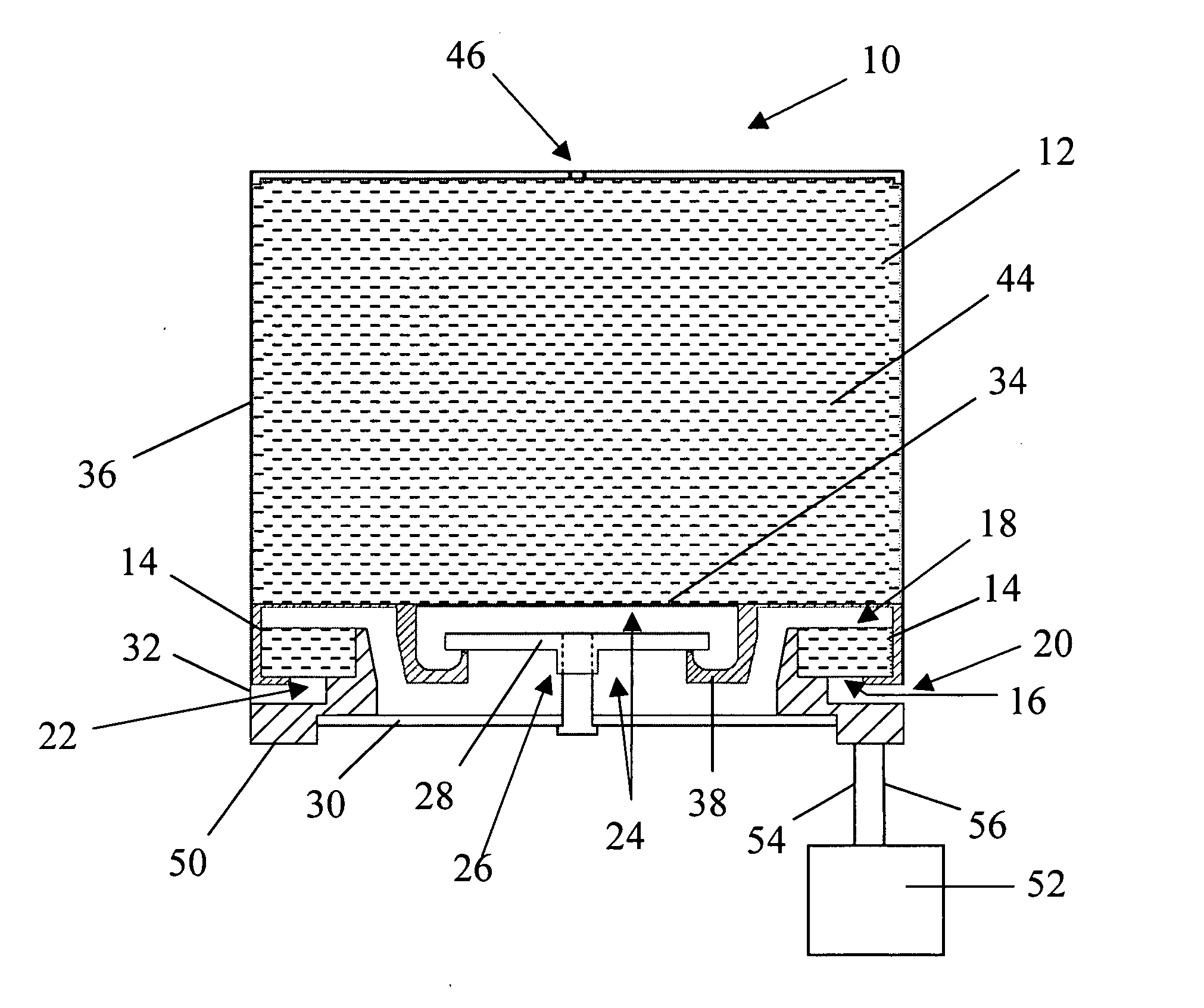
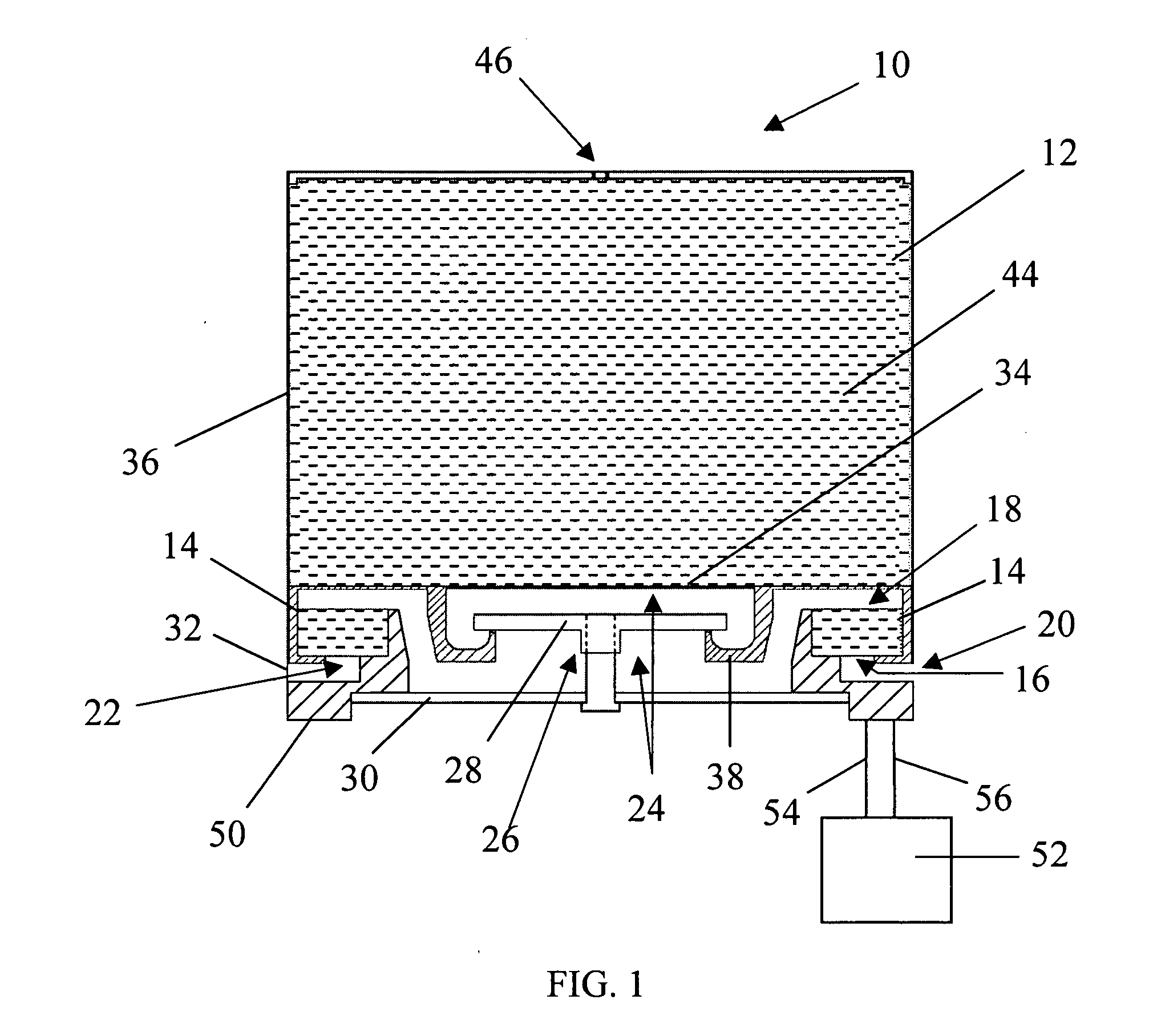
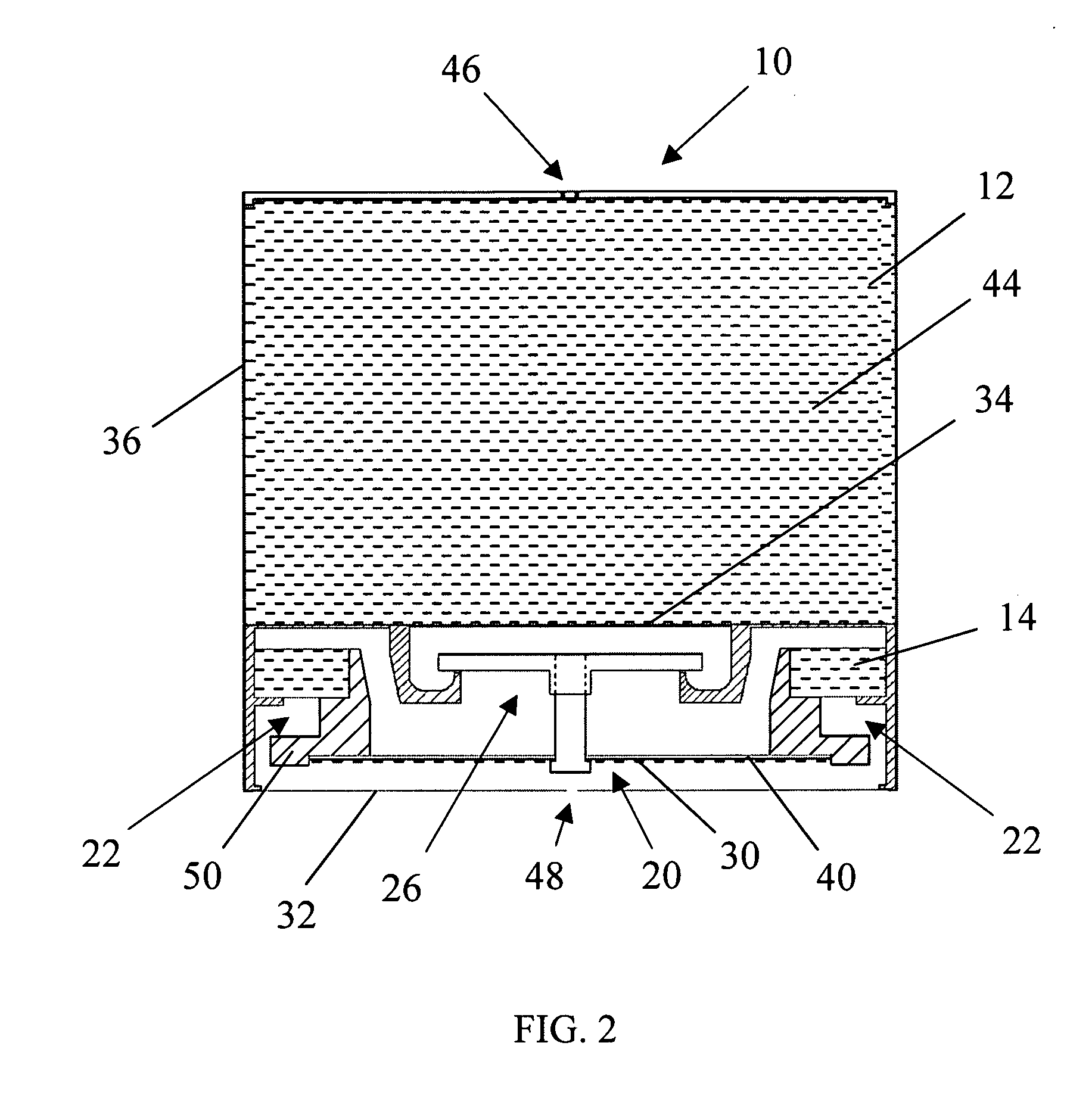
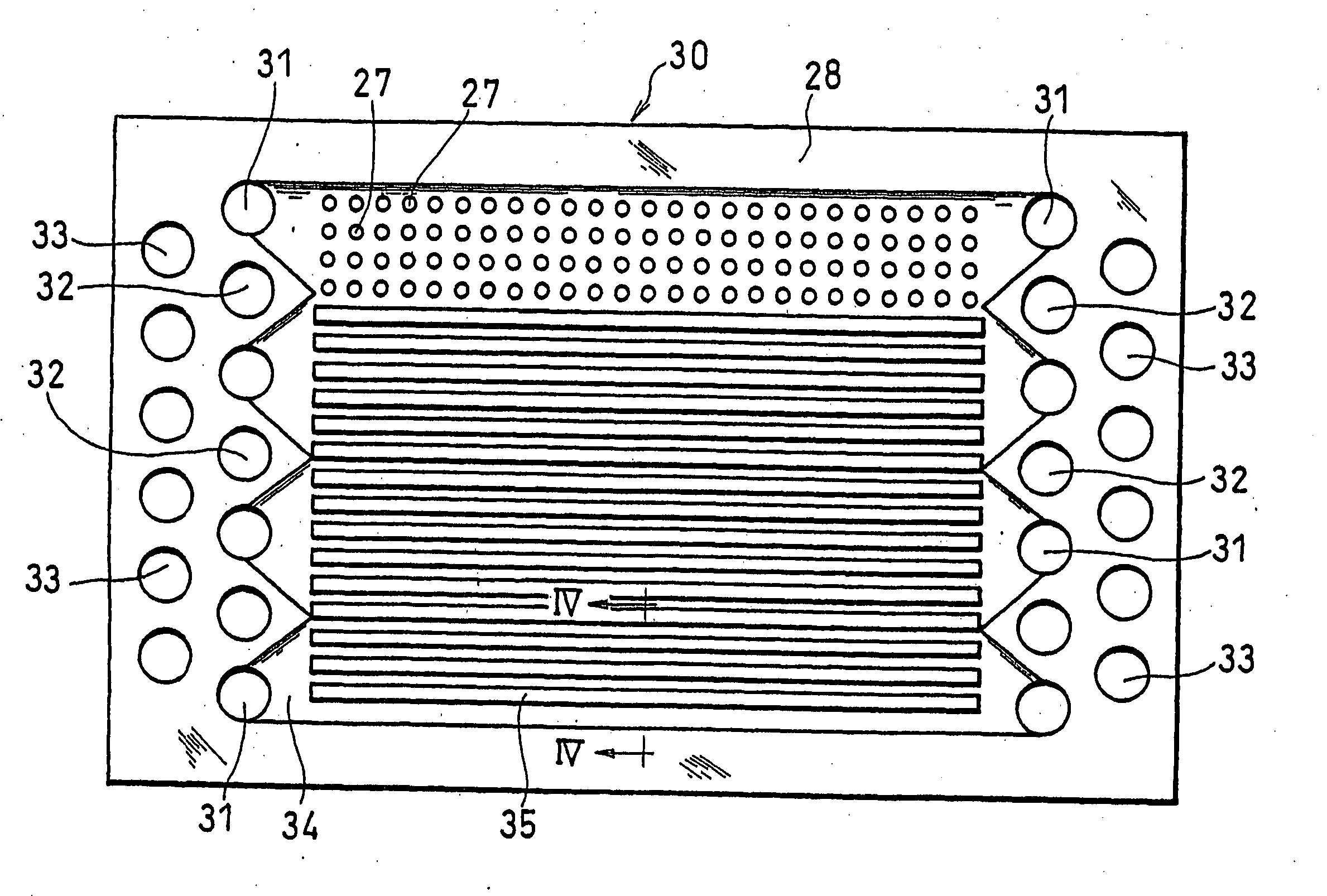
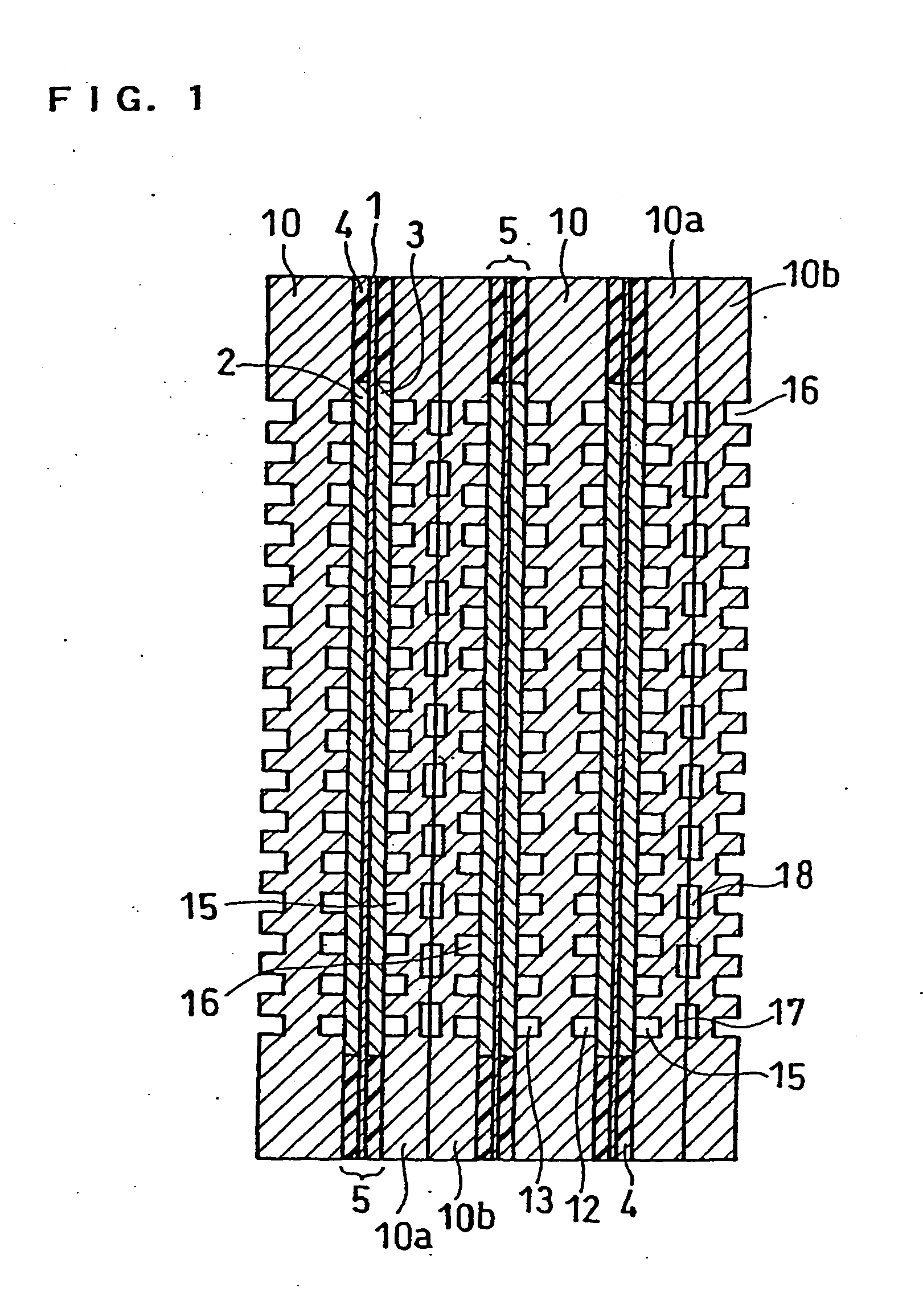
Solid high polymer type cell assembly
InactiveUS20050233181A1Increase flow rateReduce concentrationFuel cells groupingWater management in fuel cellsCell assemblyOxygen
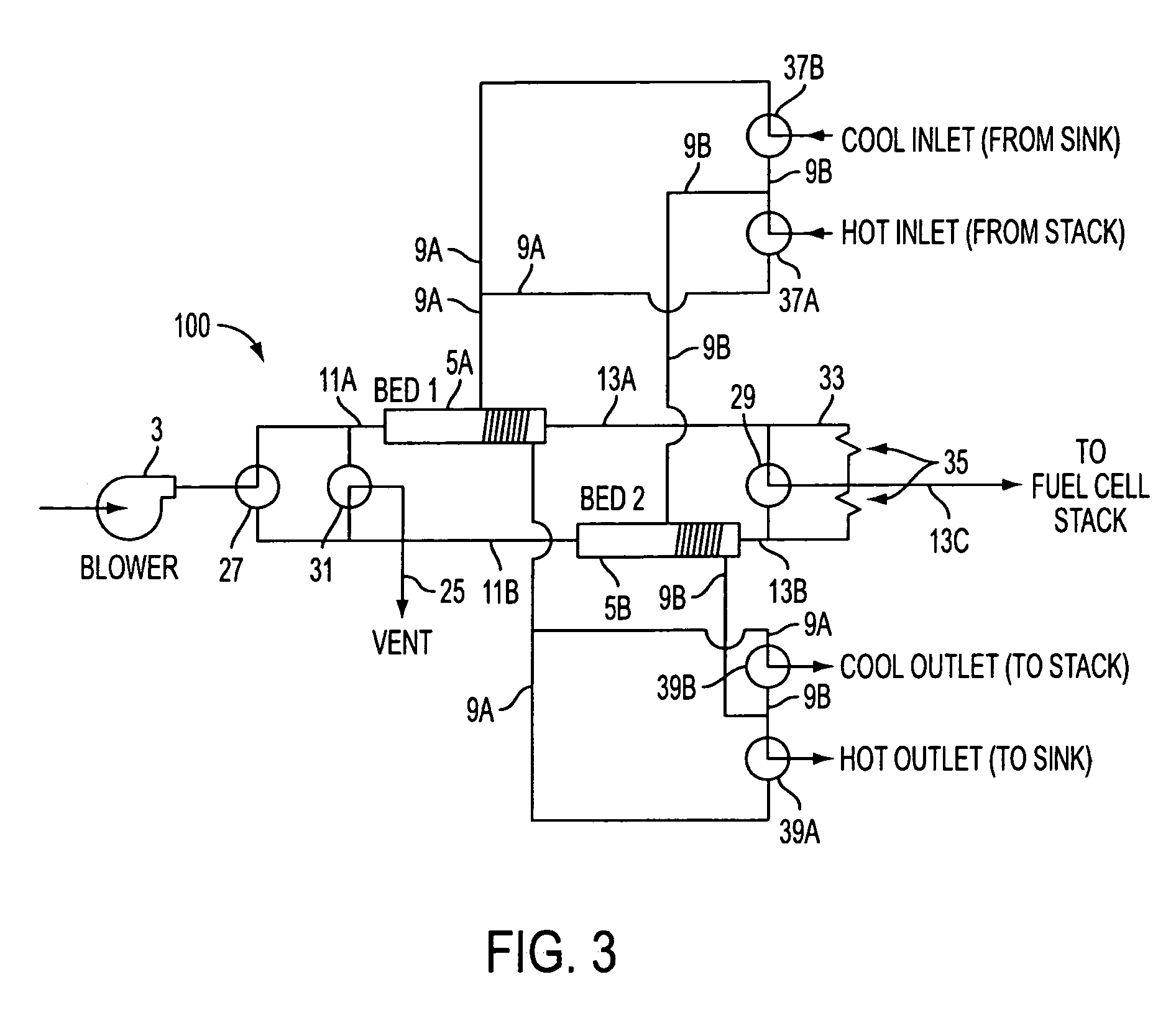
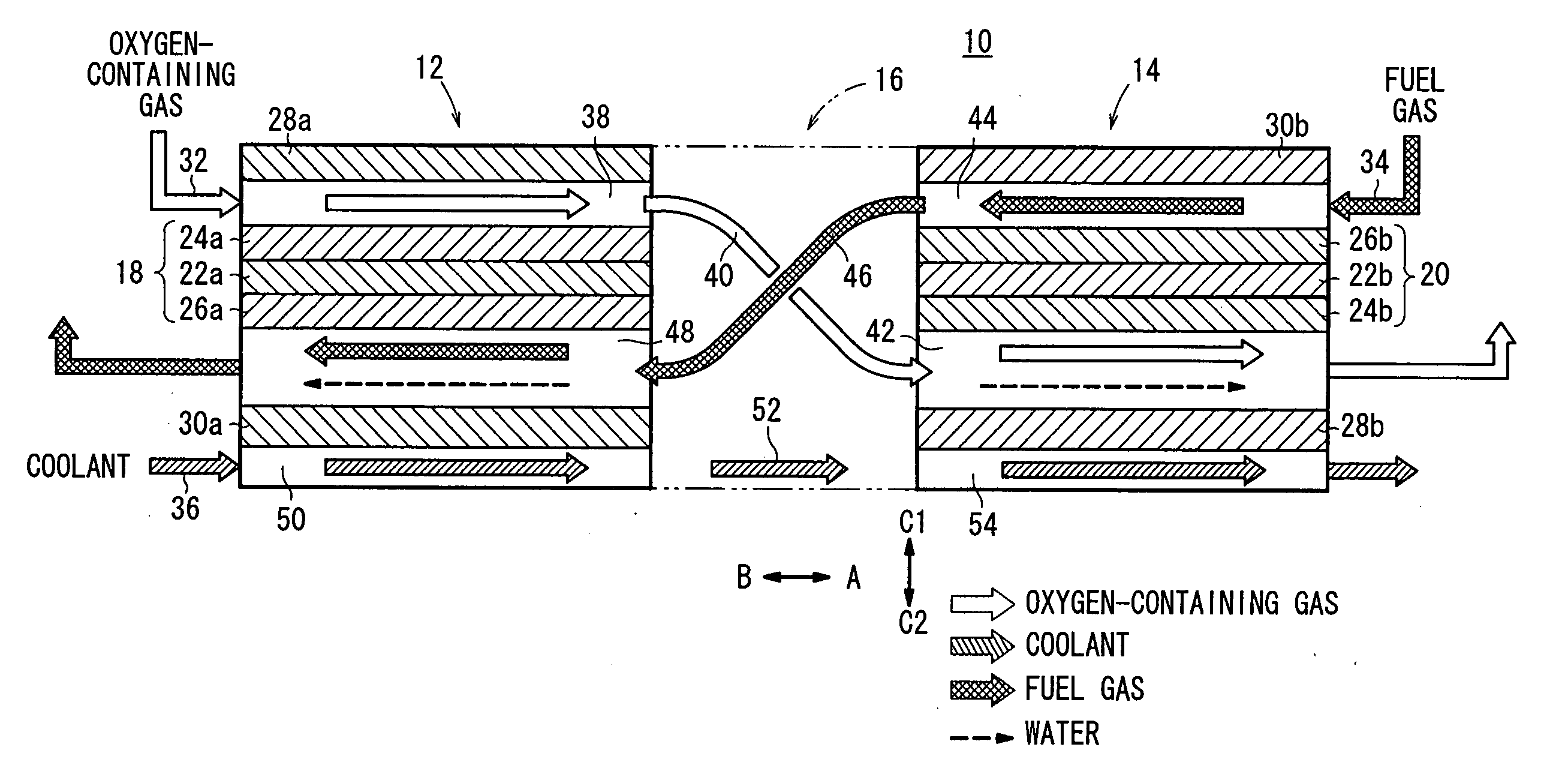
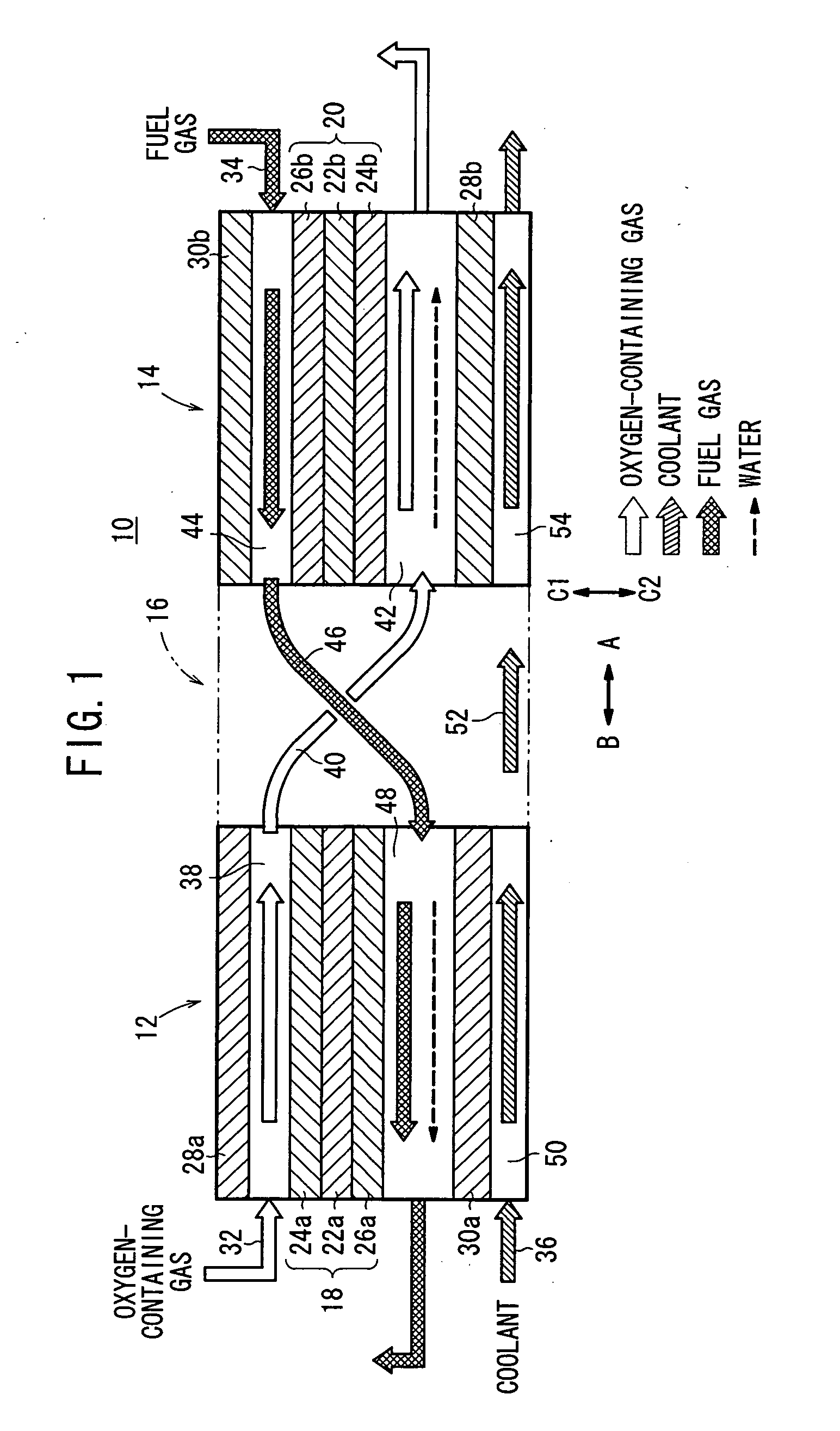
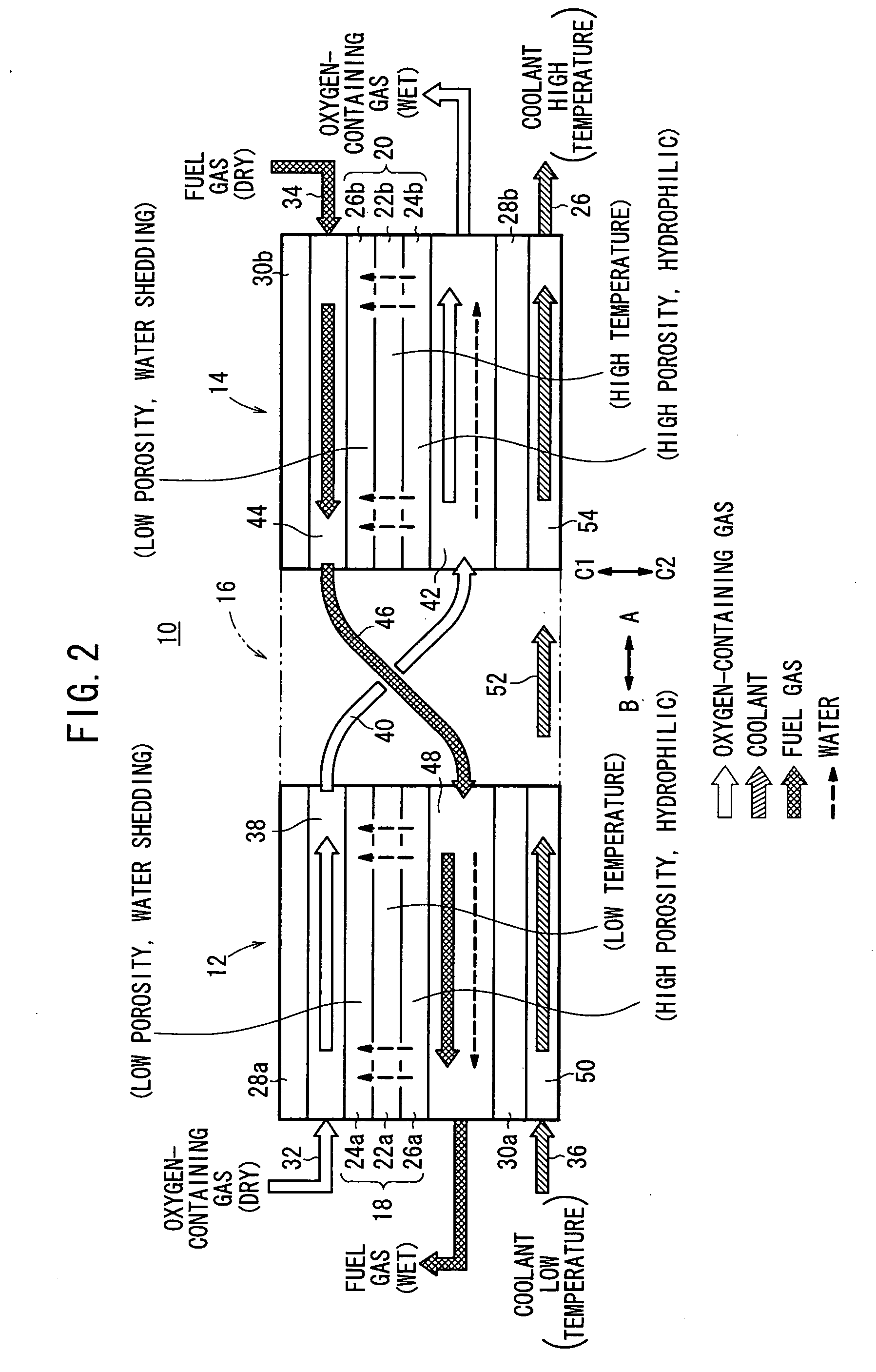
A cell assembly (10) includes a first unit cell (12) and a second unit cell (14). The first unit cell (12) and the second unit cell (14) are juxtaposed such that electrode surfaces of the first unit cell (12) and electrode surfaces of the second unit cell (14) are aligned in parallel with each other. An oxygen-containing gas flow passage (32) includes a first oxygen-containing gas passage (38) in the first unit cell (12), an oxygen-containing gas connection passage (40) in a connection passage member (16), and a second oxygen-containing gas passage (42) in the second unit cell (14). The first oxygen-containing gas passage (38), the oxygen-containing gas connection passage (40), and the second oxygen-containing gas passage (42) are connected serially from the first unit cell (12) to the second unit cell (14).
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Polymer electrolyte fuel cell system and operation method thereof
InactiveUS20050048338A1Stable supplyReduce heat lossFuel cell heat exchangeWater management in fuel cellsFuel cellsDew
A polymer electrolyte fuel cell system is disclosed, comprising a fuel cell having a predetermined power generation portion configured to operate at a predetermined temperature to generate an electric power using a fuel gas and an oxidizing gas supplied to said fuel cell, and a humidifier configured to humidify the fuel gas and the oxidizing gas, wherein the humidifier is configured to humidify the fuel gas and the oxidizing gas to allow the fuel gas and the oxidizing gas to have dew points higher than the predetermined temperature, the humidified fuel gas and oxidizing gas having the dew points higher than the operating temperature being supplied to the fuel cell.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
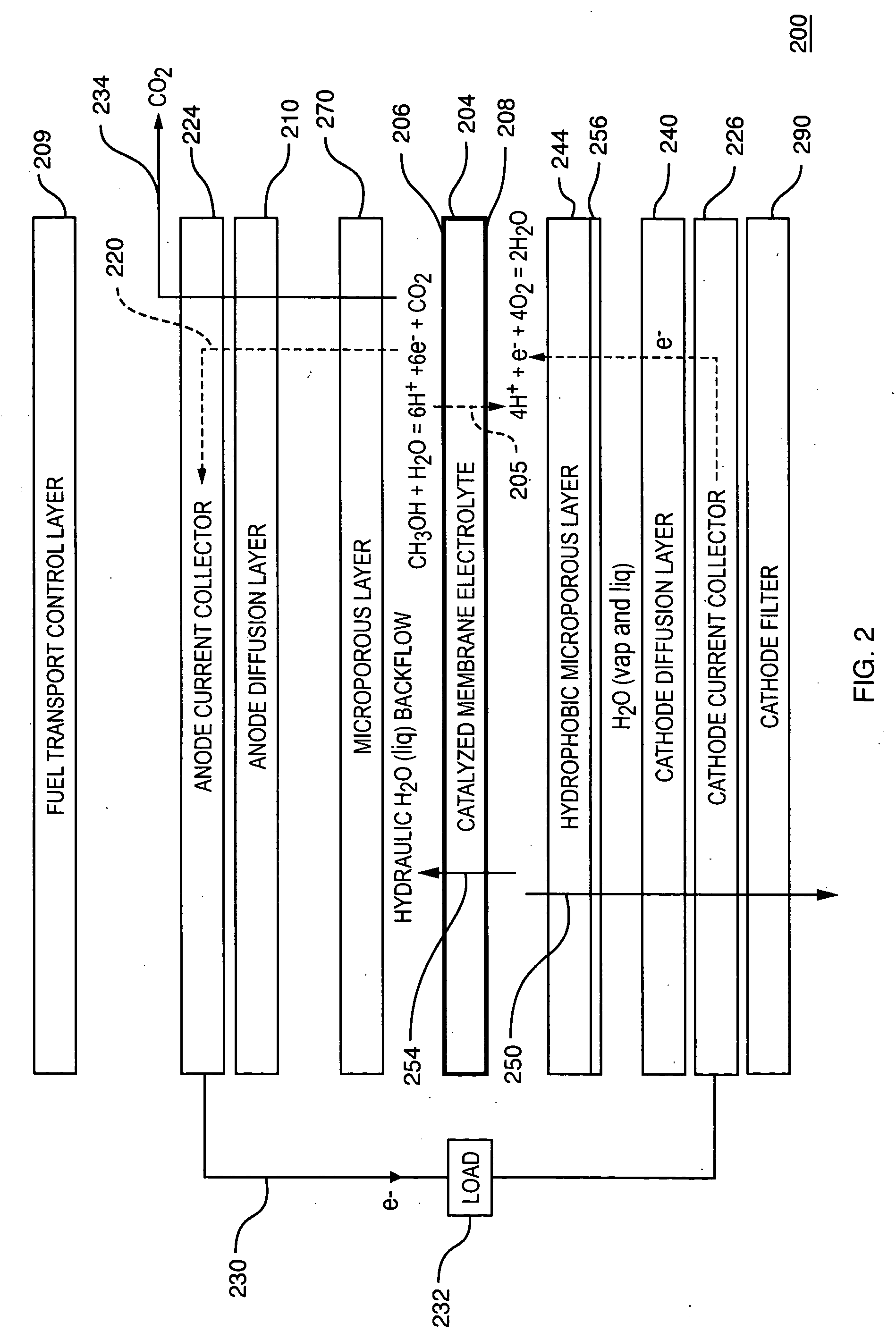
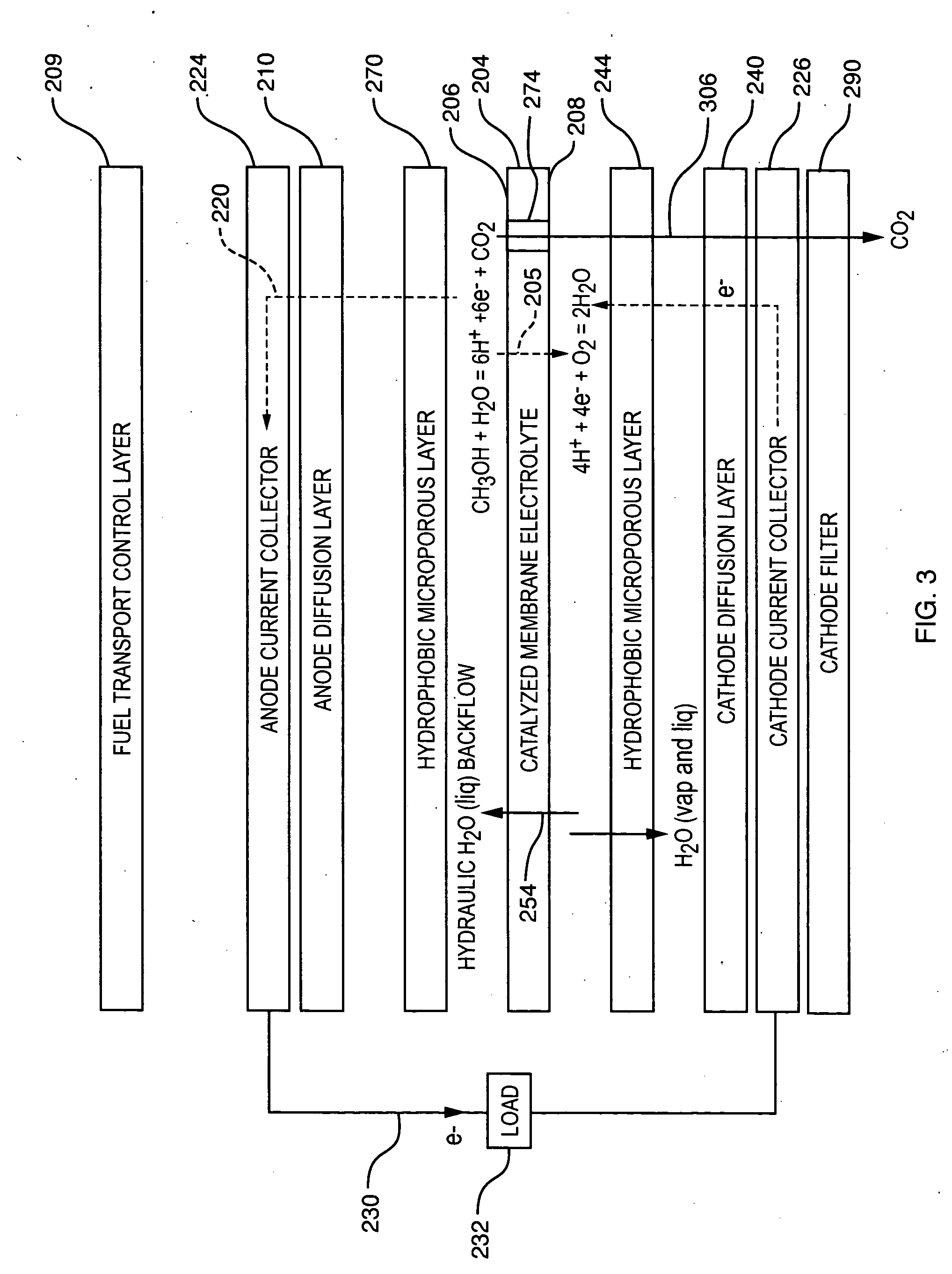
Balanced humidification in fuel cell proton exchange membranes
ActiveUS20050208366A1Improve moisture distributionEqually distributedCell electrodesWater management in fuel cellsFuel cellsGaseous diffusion
A fuel cell with a gas diffusion media having a hydrophobic layer adjacent a flow field plate and a hydrophilic layer adjacent the membrane electrode assembly of the fuel cell. The two layers enable balanced humidification of reactant gas along with a basis for managing capillary water addition into the gas diffusion media. The combination of balanced moisture flux (via the hydrophobic layer) and the retention of water (via the hydrophilic layer) for humidifying reactant gas sustains hydration of the proton exchange membrane while preserving the catalyst at full activity.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Polymer electrolyte fuel cell showing stable and outstanding electric-power generating characteristics
InactiveUS6329094B1Stable power generationAvoid cloggingSolid electrolytesFuel cells groupingFuel cellsWater source
A solid polymer fuel cell which can stably generate electric power for long, because the cell is enabled to uniformly supply a fuel gas to all anodes by means of extended flow passages which are extended from anode-side flow passages and formed on a anode-side plate on the downstream side of the ends of the anodes in the direction of fuel gas flow, a water absorbing means for nearly uniformly performing water absorption, water retention, and drainage on all channels provided at the ends of the extended flow passages, and a selective gas discharging means for discharging a gas more selectively than water on the upstream side of the water absorbing means. In addition, the power generation characteristics and service life of the fuel cell can be improved further, because the cell can maintain a solid polymer film in a moist state as a whole and can efficiently supply the fuel gas to all anodes by a means for distributing the fuel gas to the inlet sections of the anode-side flow passages and a means for distributing water from a water source to the inlet sections of the anode-side flow passages through holes having a prescribed form and leading to the inlet sections of the anode-side flow passages.
Owner:JX NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP
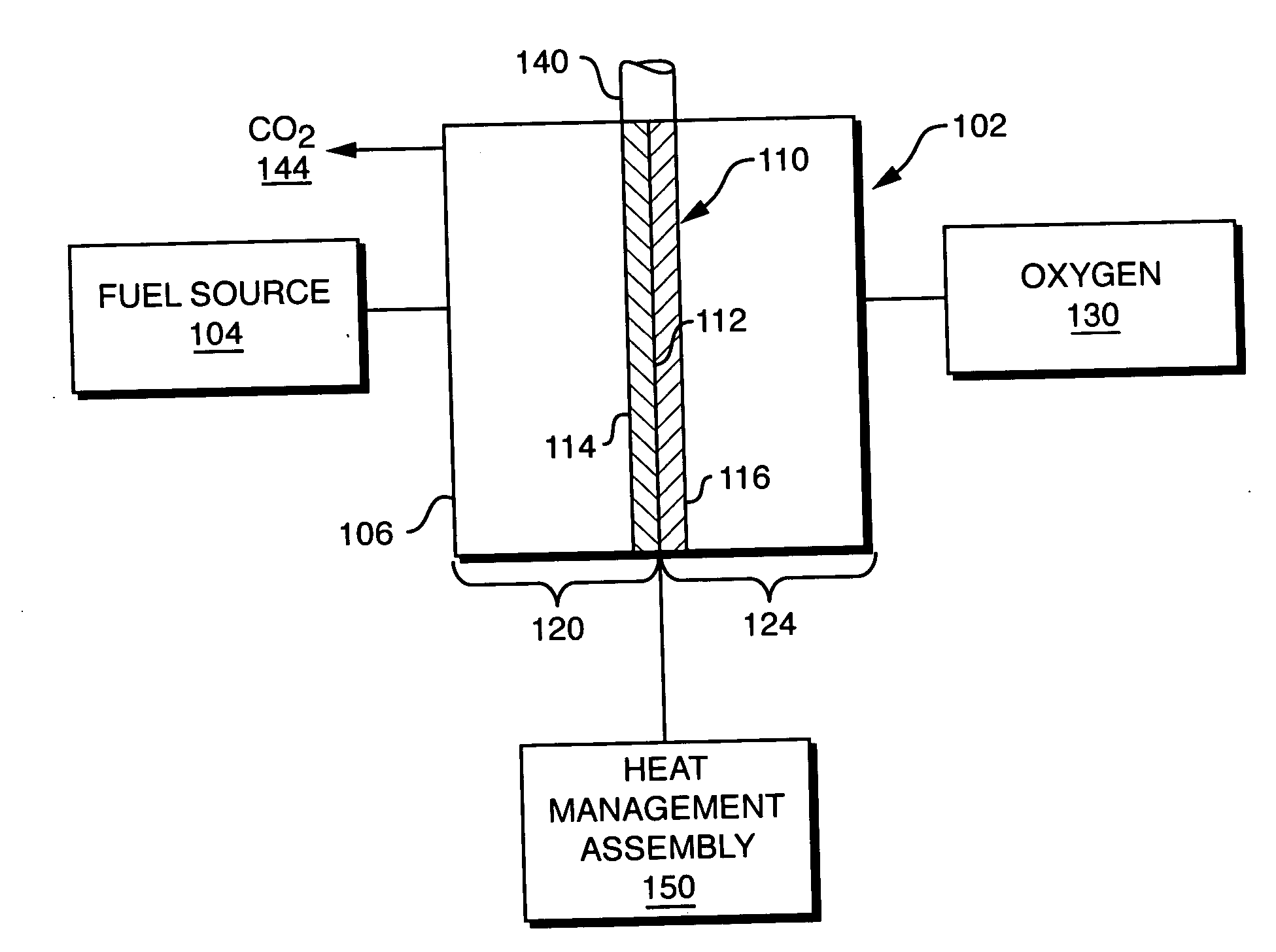
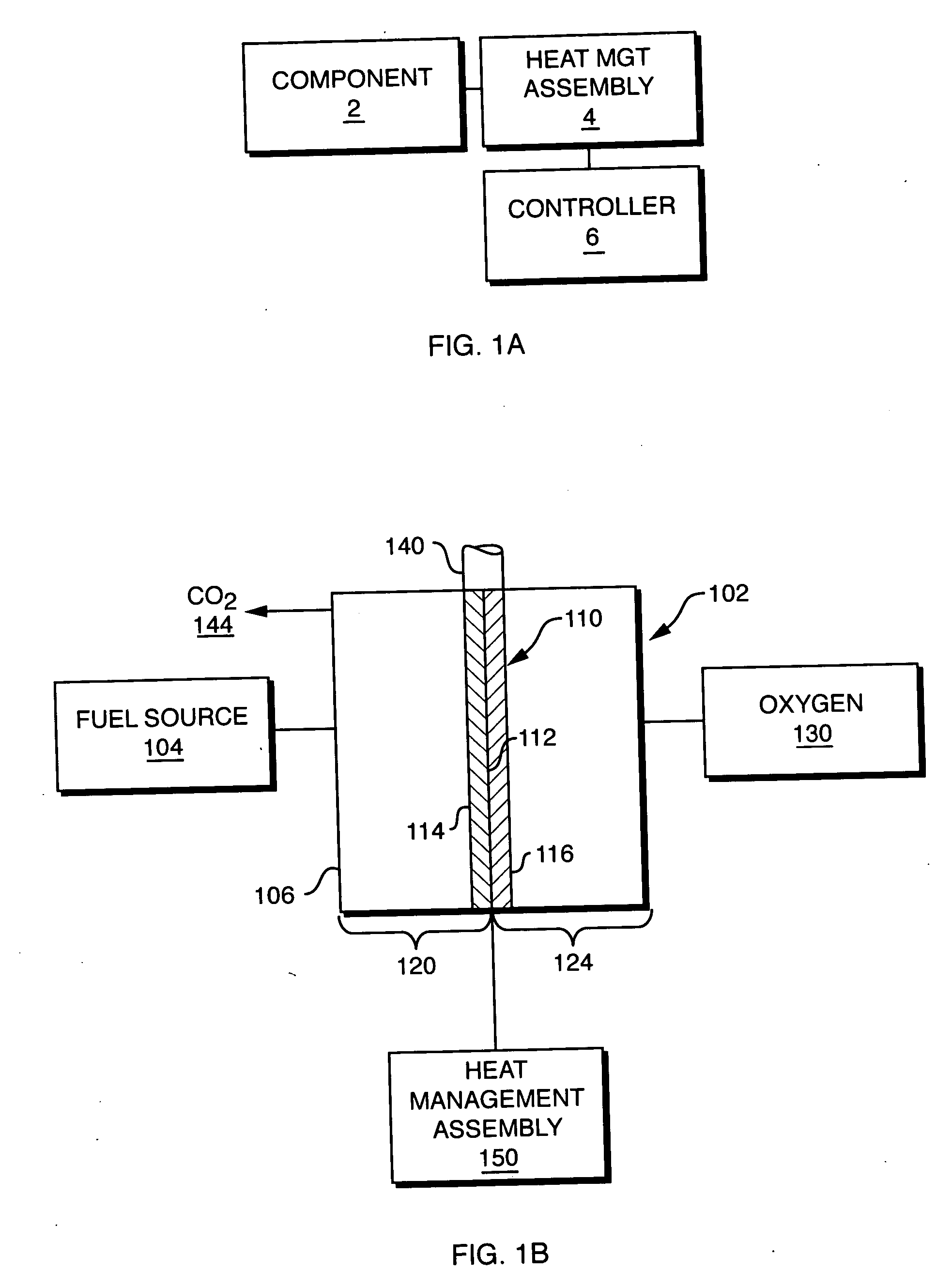
Apparatus and method for variable conductance temperature control
An integrated heat management assembly that is thermally coupled to a component requiring temperature control is provided. The integrated heat management assembly in one embodiment of the invention is a heat switch which includes two opposed surfaces, a first surface being a hot contact which is coupled to the component, and the second surface being a cold contact which is coupled to a heat sink. An actuator which may be a phase changing material, is mechanically coupled to one of the two surfaces such that when the component reaches a threshold temperature, the actuator is triggered to bring the two surfaces into contact. In this manner, the hot surface conducts heat to the cold surface which then delivers heat to the heat sink to thereby lower the temperature of the component. Other embodiments include heat pipes associated with the heat switch in order to further dissipate heat or to divert it to other areas of the component requiring temperature control. Corresponding techniques are provided in accordance with the method of the invention.
Owner:MTI MICROFUEL CELLS
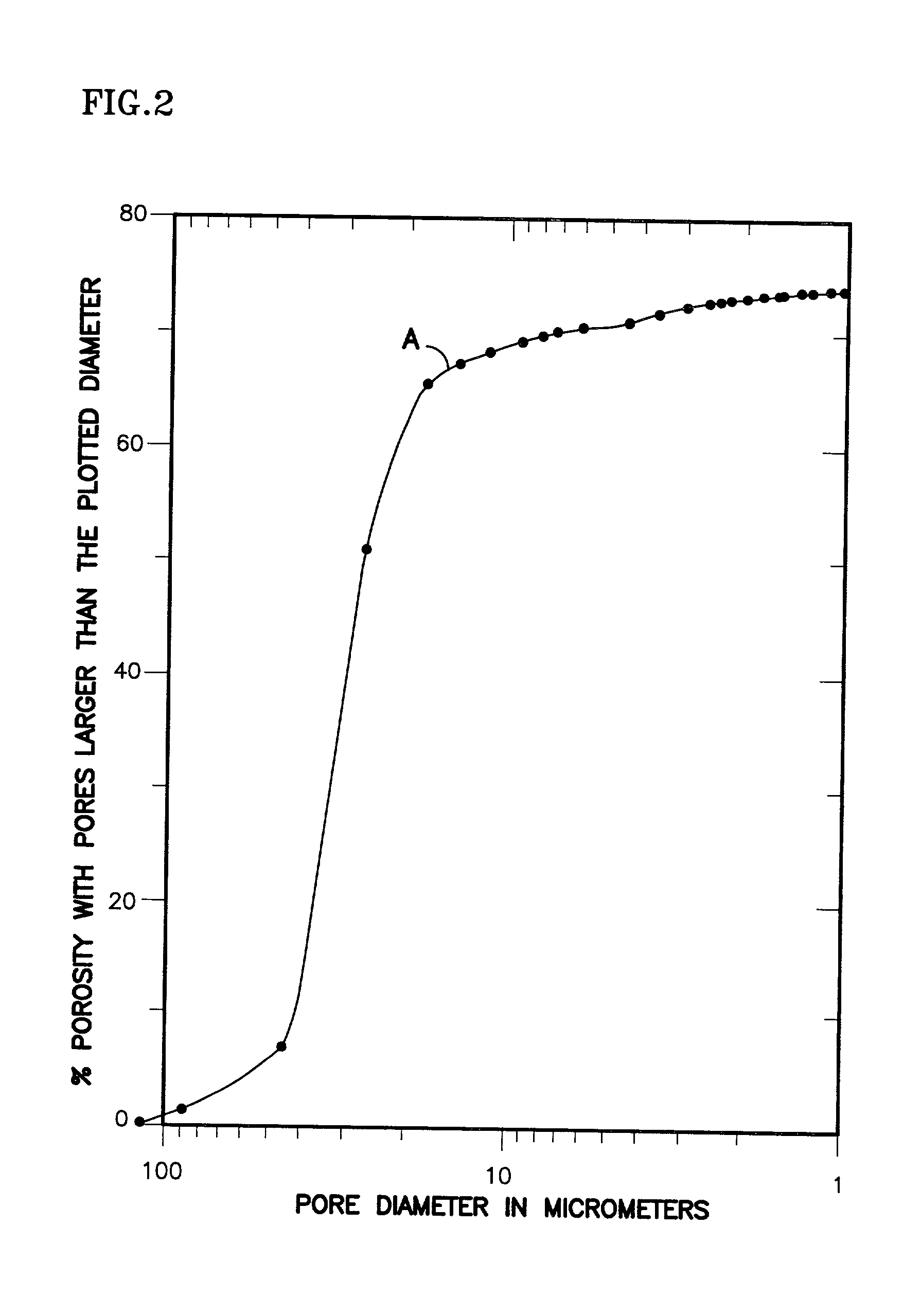
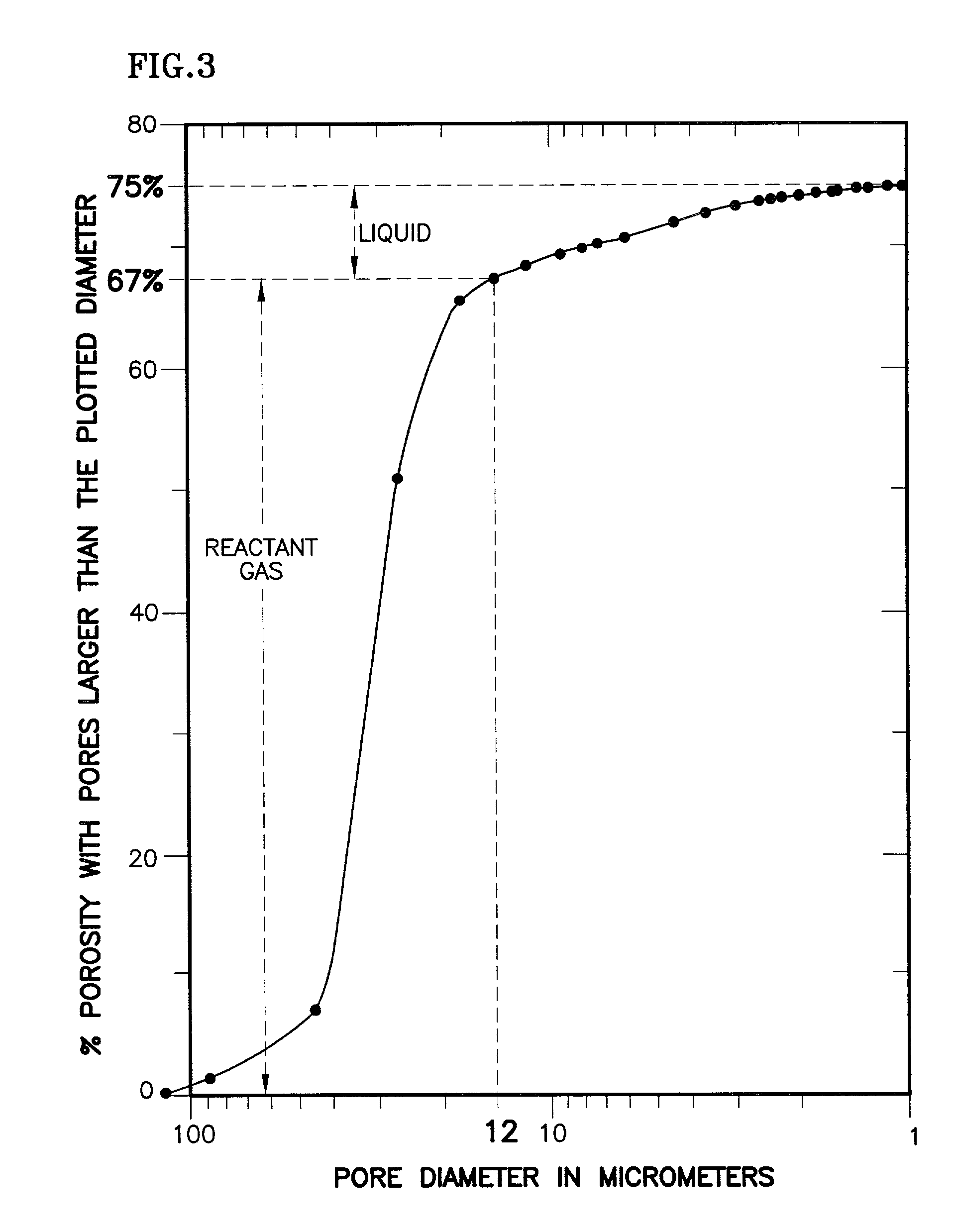
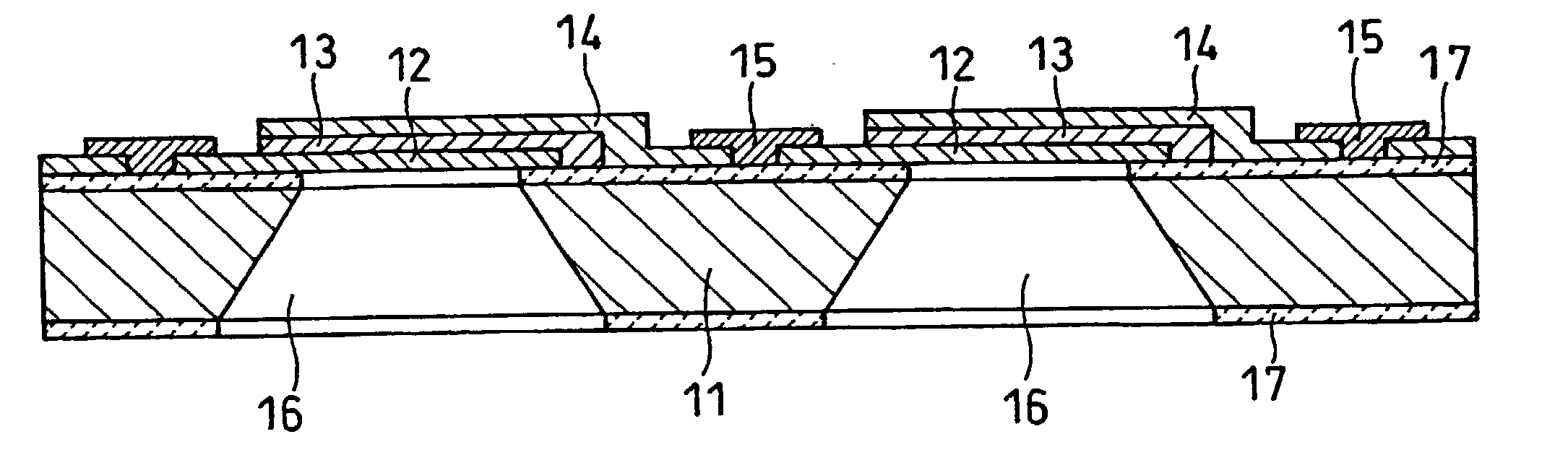
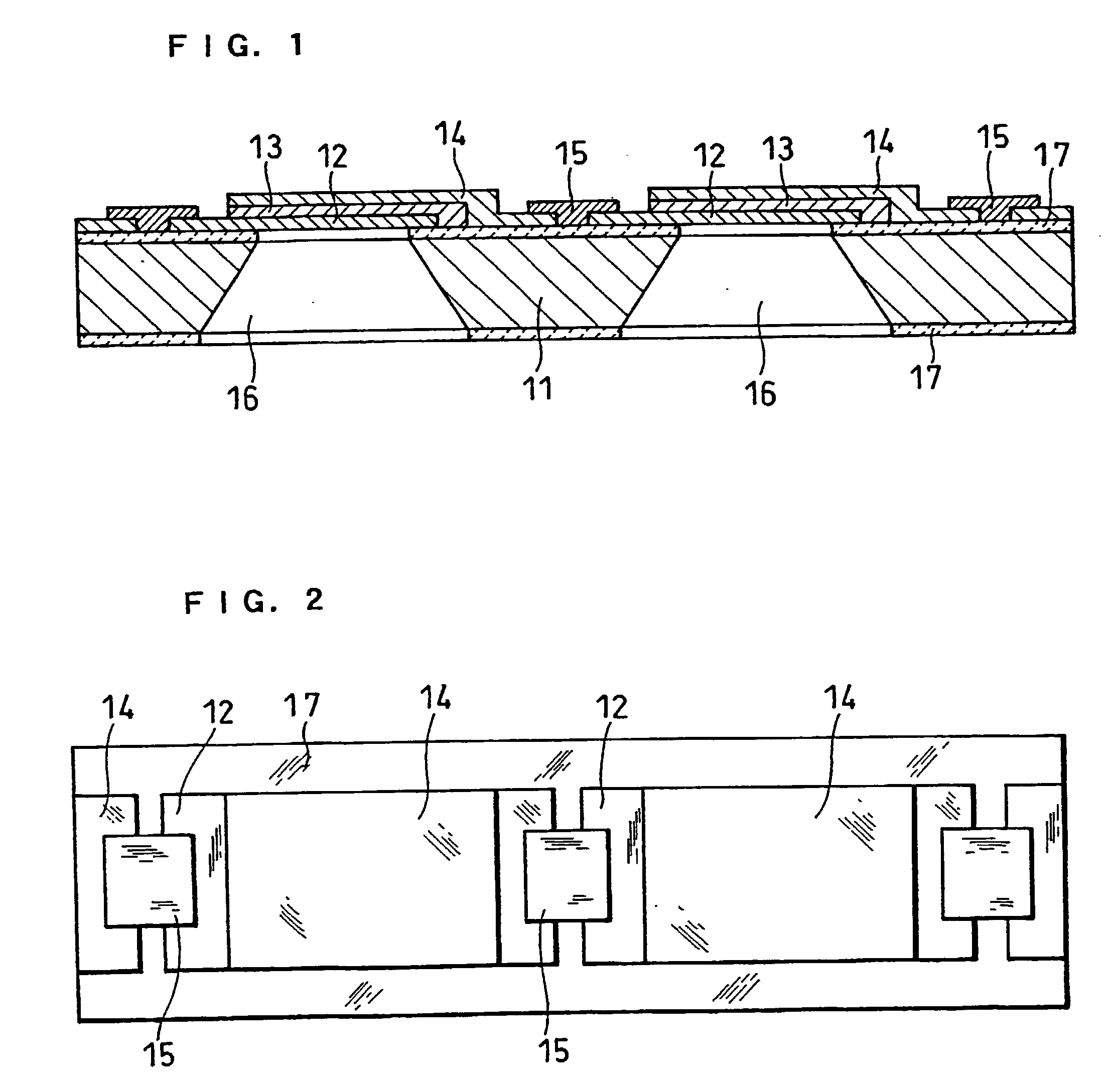
Fuel cell having interdigitated flow channels and water transport plates
InactiveUS20010004501A1Increasing migrationHigh water removal rateCell electrodesWater management in fuel cellsEngineeringWater transport
The present invention is a fuel cell power plant that includes a fuel cell having a membrane electrode assembly (MEA), which is disposed between an anode support plate and a cathode support plate, and porous water transport plates adjacent the anode and cathode support plates. The porous water transport plates have interdigitated flow channels for the reactant gas streams to pass therethrough and conventional flow channels for a coolant stream to pass therethrough. The fuel cell power plant also has means for creating a pressure differential between the reactant gas streams and the coolant stream such that the pressure of the reactant gas streams is greater than the coolant stream. Incorporating the interdigitated flow channels into the porous water transport plates and operating the fuel cell at a pressure differential allows the coolant water to saturate the water transport plates thereby forcing the reactant gases into the anode and cathode support plate. This, in turn, increases the mass transfer of such gases into the support plates, thereby increasing the electrical performance of the fuel cell. Current densities of about 1.6 amps per square meter are achieved with air stochiometries of not over 2.50.
Owner:AUDI AG
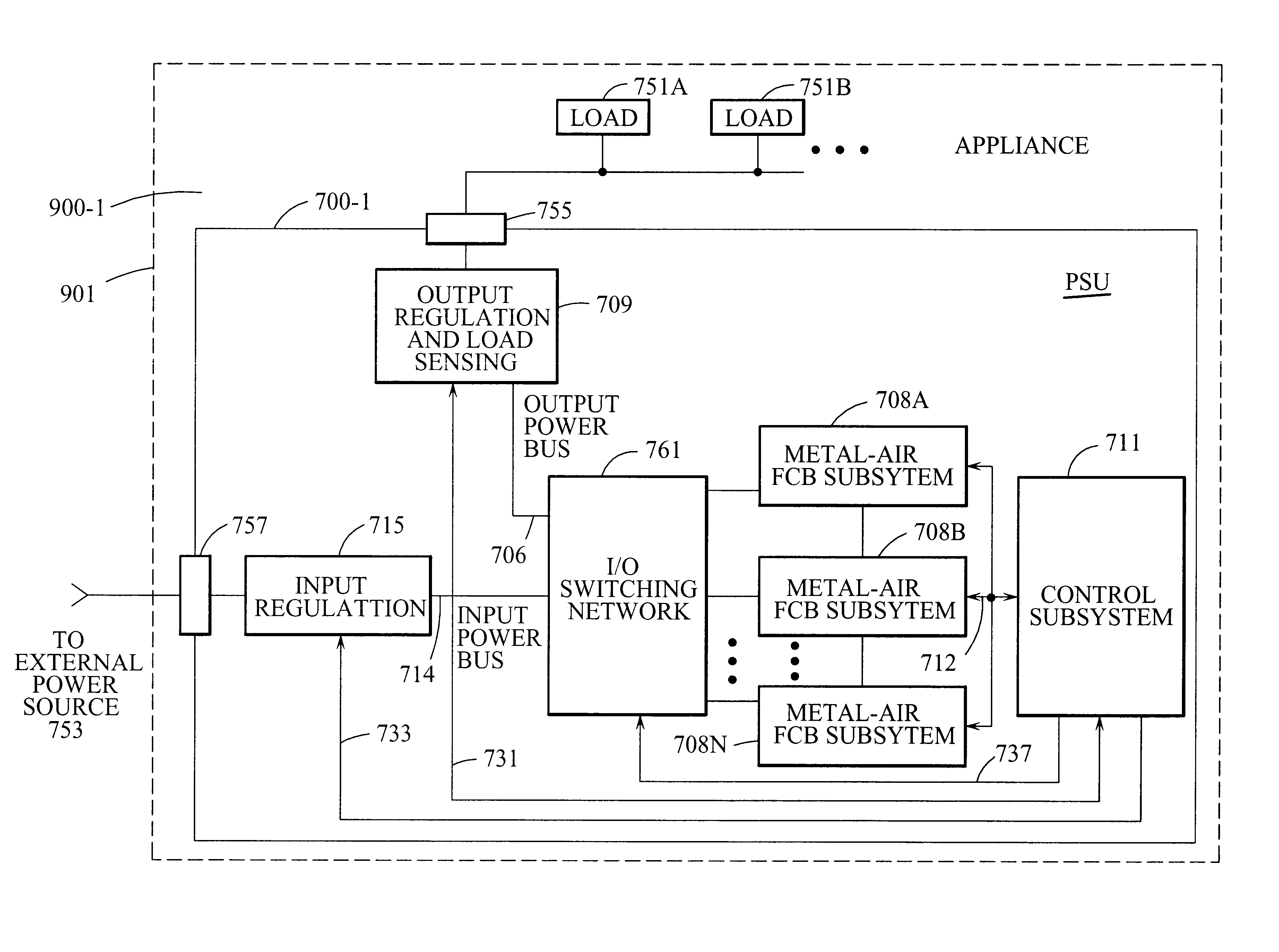
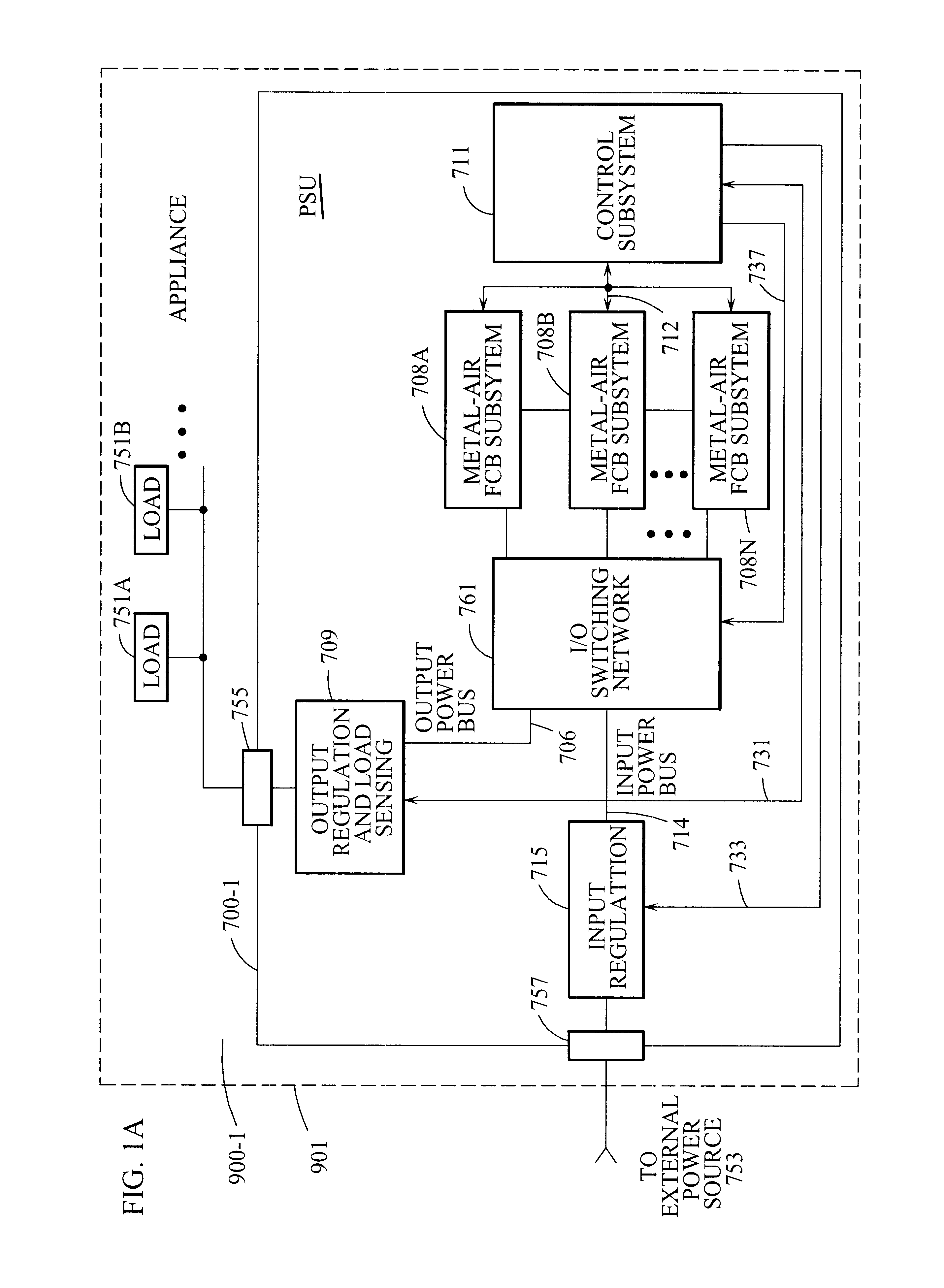
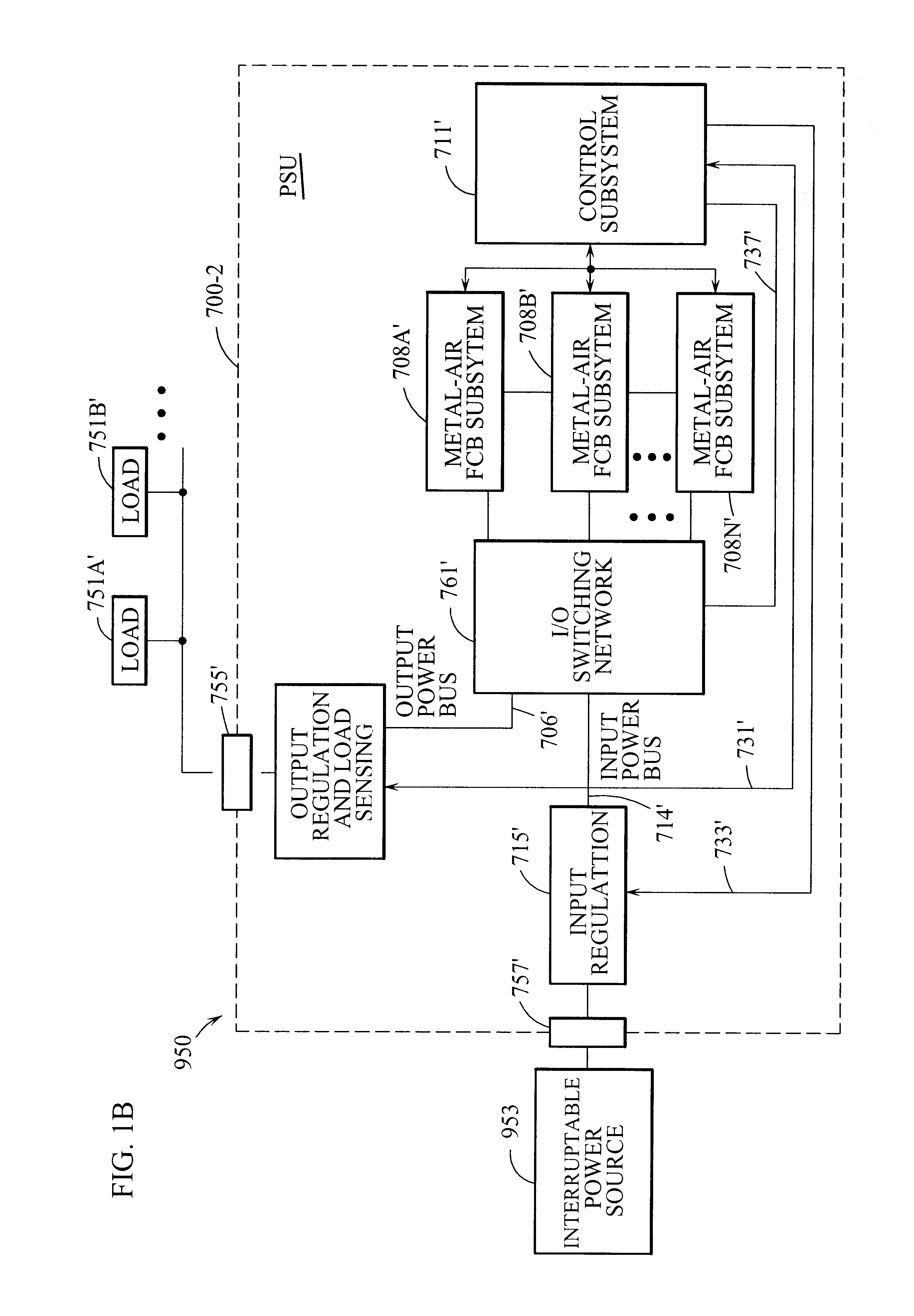
Refuelable and rechargeable metal-air fuel cell battery power supply unit for integration into an appliance
InactiveUS6569555B1Without riskWithout limitationSeveral cell simultaneous arrangementsFuel and primary cellsElectricityFuel cells
A refuelable and rechargable metal-air FCB based power supply unit for integration into a device / system for generating and providing electrical power to at least one electrical-energy-consuming load device disposed therein. An external power source is used to recharge the metal-air FCB subsystems embodied therein. A control subsystem automatically transitions between discharging mode (wherein at least one metal-air FCB subsystem supplies electrical power to the electrical power-consuming load device) and a recharging mode (wherein the external power source is electrically coupled to at least one metal-air FCB subsystem to thereby recharge the metal-air FCB subsystem(s). The metal-air FCB subsystem(s) are refueled by manually loading and unloading metal-fuel from the metal-air FCB subsystem(s). Preferably, electrical power provided to the at least one electrical power-consuming load device is supplied solely by electrical power generated by discharging metal-fuel in the metal-air fuel cell battery subsystem(s). In addition, the metal-air FCB subsystem(s) preferably has a modular architecture that enable flexible and user-friendly operations in loading of metal-fuel, unloading of consumed metal-fuel, replacement of the ionic-conducting medium, and replacement of the cathode.
Owner:REVEO
Polymer electrolyte fuel cell
InactiveUS20050227138A1High voltageImprove power generation efficiencySolid electrolytesSemi-permeable membranesFiberCarbon fibers
A polymer electrolyte fuel cell consists of plural units, and the unit has an anode side separator, an anode diffusion layer, an anode catalytic layer, polymer electrolyte membrane, a cathode catalytic layer, a cathode diffusion layer, and a cathode side separator. The cathode catalytic layer further includes a catalyst in which platinum or platinum alloy is supported on a carbon supporting body having an average lattice space d002 of [002] surface of 0.338 to 0.355 nm and specific surface area of the supporting body of 80 to 250 m2 / g, electrolyte containing ion exchange resin, and vapor grown carbon fiber. Furthermore, a water holding layer containing ion exchange resin, carbon particles, and vapor grown carbon fiber is arranged at an interface of the cathode diffusion layer and the cathode catalytic layer.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD +1
Proton conductive composition and proton conductive membrane
InactiveUS20050116206A1Good effectImprove proton conductivitySolid electrolytesCell electrodesIridiumFiber
The present invention provides a proton conductive membrane having capabilities of self-generating water and maintaining water, excellent ion conductivity and excellent effect of inhibiting crossover and usable for solid polymer electrolyte type fuel cells and also provides a proton conductive composition used for preparing the proton conductive membrane. The proton conductive composition comprises 100 parts by weight of a polyarylene having a sulfonic group and 0.01 to 80 parts by weight of at least one metal catalyst selected from the group consisting of platinum, gold, palladium, rhodium, iridium and ruthenium, or comprises 100 parts by weight of a polyarylene having a sulfonic group, 0.01 to 80 parts by weight of the metal catalyst, and 0.01 to 50 parts by weight of metal oxide fine particles and / or fibers in total.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON +1
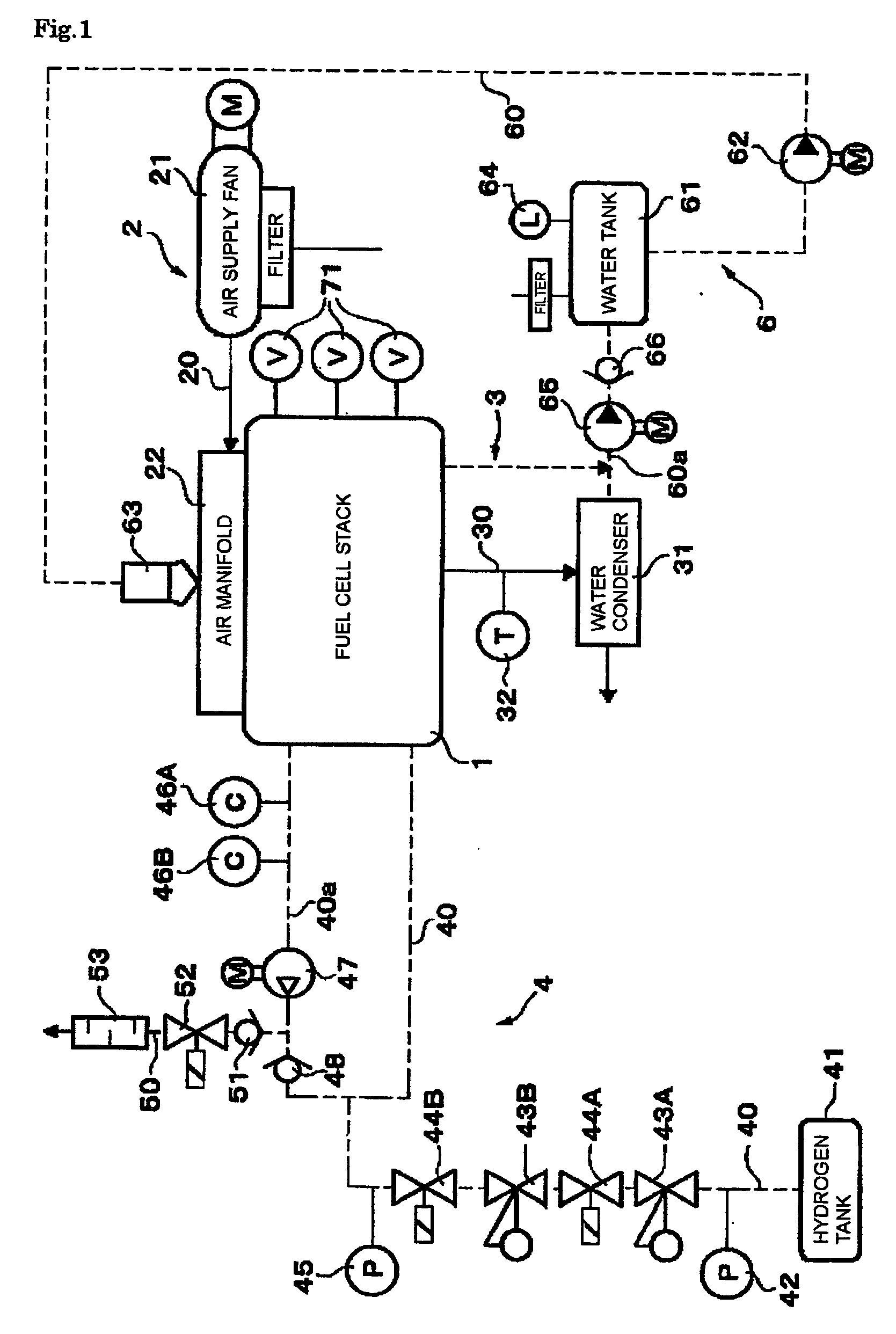
Fuel cell system utilizing control of operating current to adjust moisture content within fuel cell
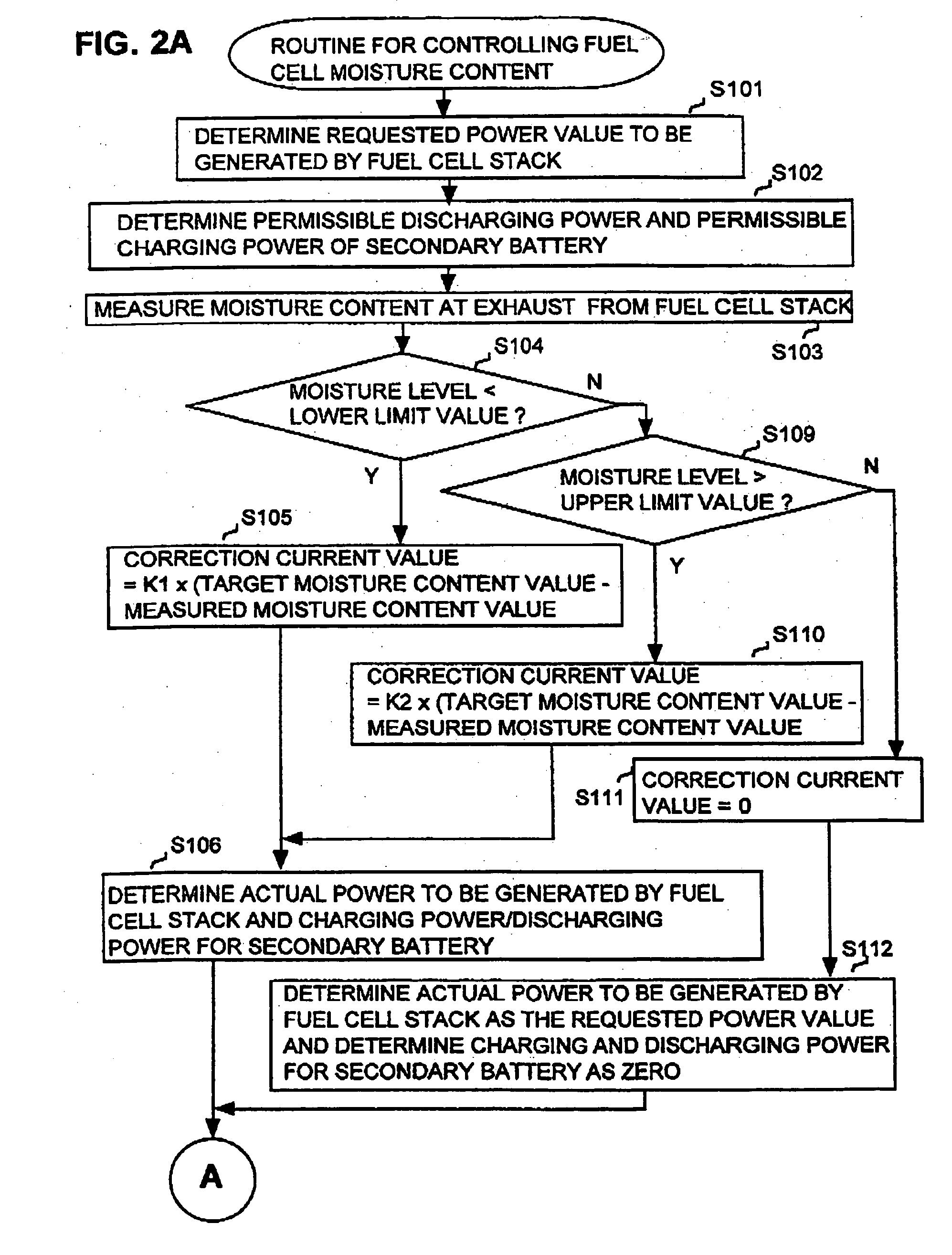
InactiveUS20040166387A1Keep dryIncrease spawn rateDc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsFuel cellsHydrogen
In a fuel cell system utilizing fuel cells which generate electric power by a reaction between oxygen and hydrogen, the moisture content within a fuel cell is adjusted to be brought within an appropriate range by adjusting the operating current of the fuel cell. The total amount of electric power generated by the system is maintained at a required value by supplying / obtaining electric power to / from a secondary battery as required, or by utilizing a plurality of separately controlled fuel cells (or fuel cell stacks) and increasing or decreasing the electric power generated by another fuel cell or stack that is currently operating with an appropriate moisture content.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Mixed reactant molecular screen fuel cell
InactiveUS20050058875A1Eliminate the problemReduce decreaseSolid electrolytesFuel cells groupingFuel cellsElectrolyte
In one aspect, the present invention provides a fuel cell having a first membrane selective to a fuel, a second membrane selective to an oxidant, and a mixed reactant flow provided to the screens. The invention further includes an anode, a cathode and a semi-permeable electrolyte fluidly separating the same.
Owner:JEROME ALLAN
High-polymer eletrolyte type thin film fuel cell and its driving method
InactiveUS20030170520A1Improve power generation efficiencySmall thicknessFuel cells groupingCell electrodesPolymer electrolytesFuel cells
It is difficult to realize a small fuel cell capable of being installed in mobile device by merely downsizing a conventional fuel cell without changing the configuration. The present invention provides a small fuel cell employing a polymer electrolyte thin film, by using a semiconductor process. A polymer electrolyte thin film fuel cell in accordance with the present invention comprises: a substrate having a plurality of openings; an electrolyte membrane-electrode assembly formed on the substrate so as to cover each of the openings, the assembly comprising a first catalyst electrode layer, a hydrogen ion conductive polymer electrolyte membrane and a second catalyst electrode layer which are formed successively; and fuel and oxidant supply means for supplying a fuel or an oxidant gas to the first catalyst electrode layer through the openings, and an oxidant gas or a fuel to the second catalyst electrode layer.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
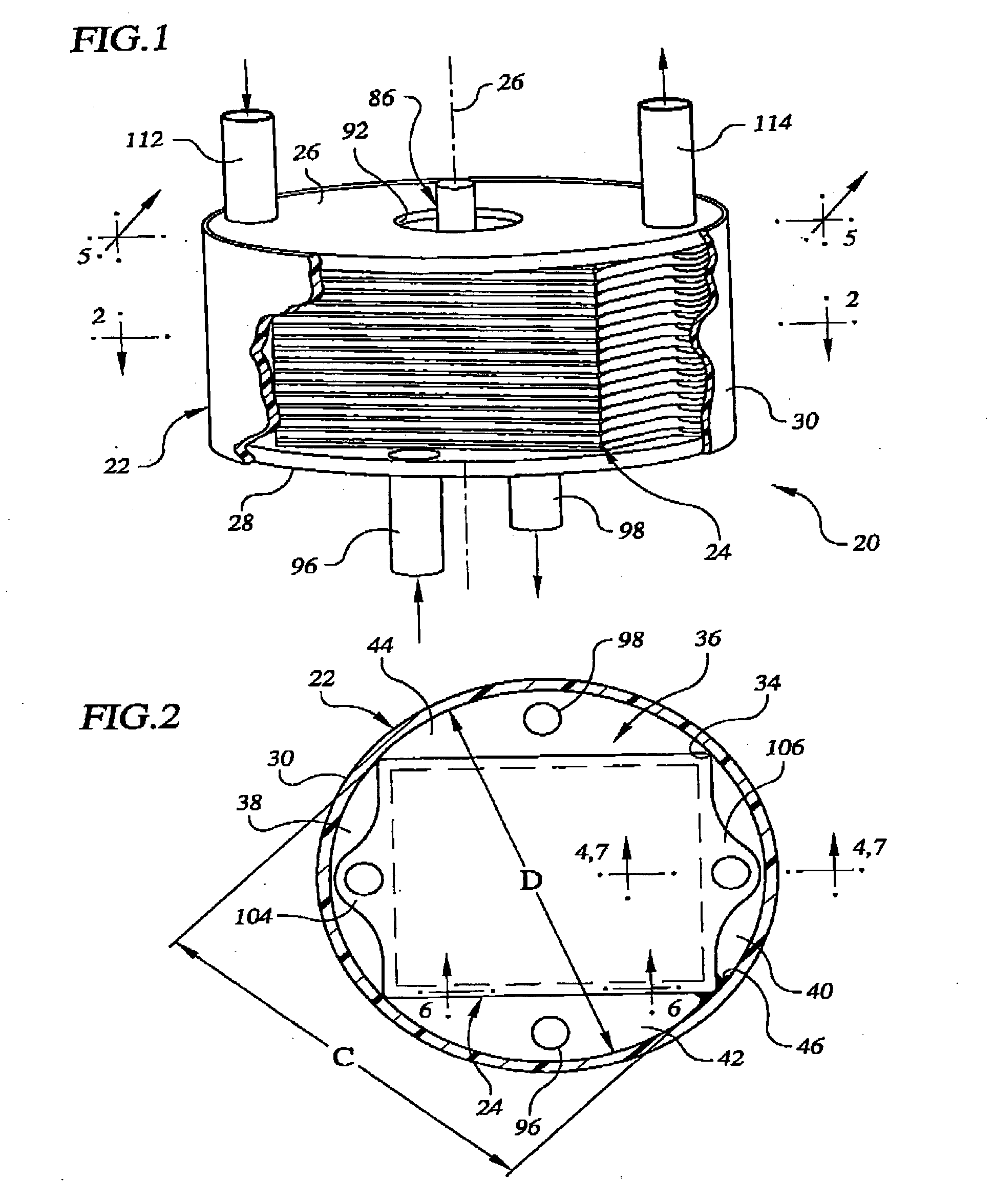
Fuel cell stack
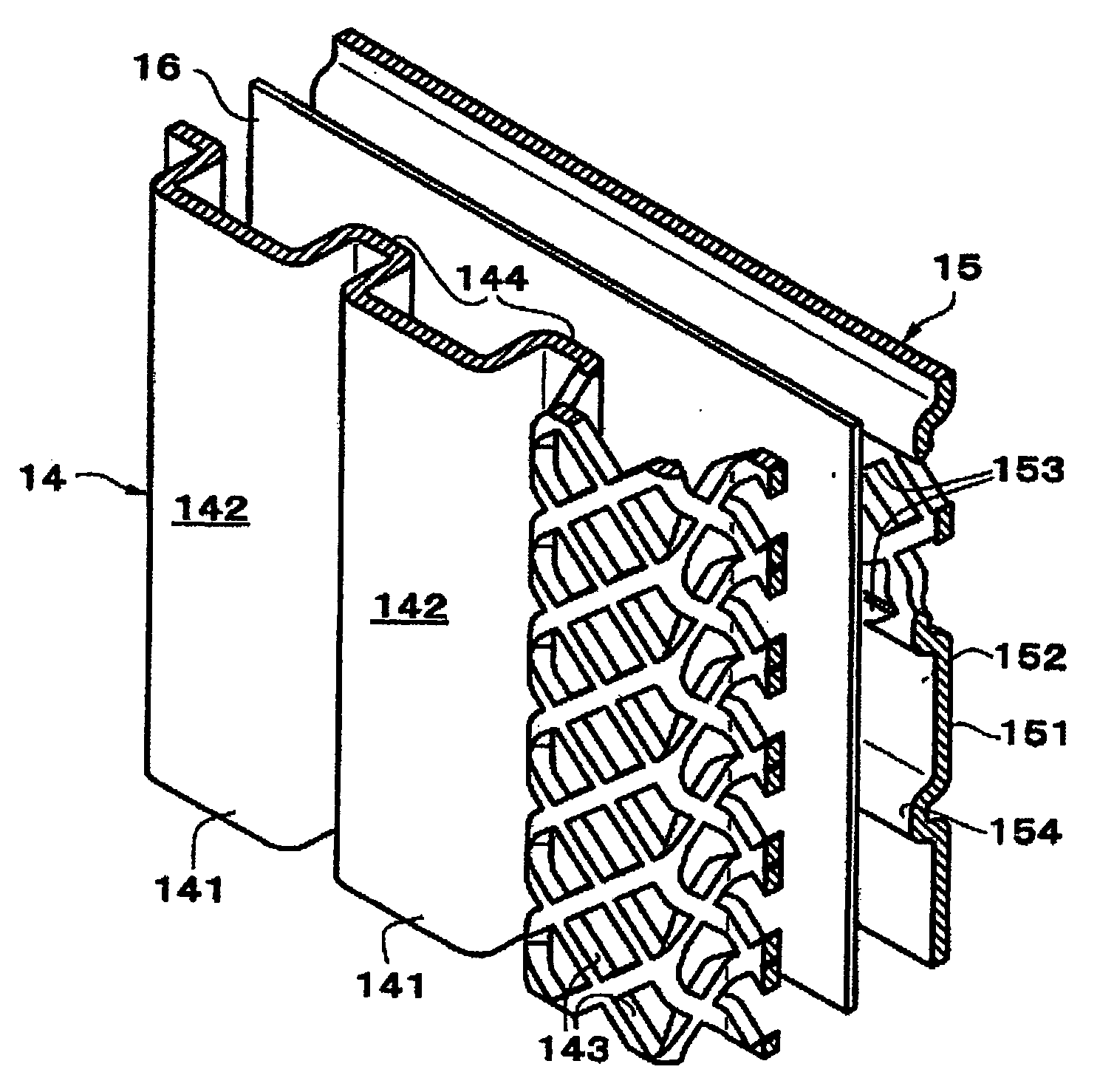
InactiveUS20060110650A1Simple and economical structureMaintain power generation performanceFuel cells groupingWater management in fuel cellsFuel cellsFuel gas
A fuel cell stack includes a stack body, an end separator, a terminal plate, an insulating plate, and an end plate provided at one end of the stack body in a stacking direction. The insulating plate has a recess for accommodating the terminal plate. Further, the insulating plate has a bypass passage connected between a fuel gas supply passage and a fuel gas discharge passage outside the recess for discharging condensed water. An insulating seal member is provided on the end separator to cover the bypass passage. The condensed water flows through an insulated passage formed by the insulating seal member and the bypass passage.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Fuel cell
InactiveUS20050164071A1Adequate opening ratioImprove reliabilityCircuit monitoring/indicationFuel cells groupingFuel cellsElectrical conductor
A fuel cell includes a separator (10B) interposed between adjacent unit cells (10A). A mixed fluid of air and water is supplied to an air electrode (12) of each unit cell. The separator includes a mesh conductor (14) on at least a surface facing the air electrode of the unit cells, and the mixed fluid passes through the mesh conductor. Water is retained on the mesh portion of the conductor. With this configuration, it is possible for the unit cell to be cooled by the release of latent heat when the water is evaporated by the heat of unit cell, without any clogging which inhibits contact between the electrode and the air.
Owner:EQUOS RES
Controlled direct liquid injection vapor feed for a DMFC
InactiveUS20050170224A1Simple and effective carbon dioxide releaseEvenly distributedCell electrodesWater management in fuel cellsFuel cellsInjection port
A fuel cell system having a methanol vapor delivery component or film is provided. The component includes an evaporation pad. The evaporation pad is disposed within the fuel cell generally parallel to the anode diffusion layer, but with a vapor gap provided between the evaporation pad and the anode diffusion layer. A fuel delivery conduit having at least one injection port is provided through which liquid fuel is delivered from an associated source of highly concentrated fuel into the evaporation pad, at a controlled, adjustable rate. Multiple parallel liquid delivery points can also be provided. In order to ensure uniform delivery of fuel across the across the active area of the anode, one or more dispersion members are placed on the evaporation pad to effectively disperse the fuel laterally around each injection port.
Owner:MTI MICROFUEL CELLS
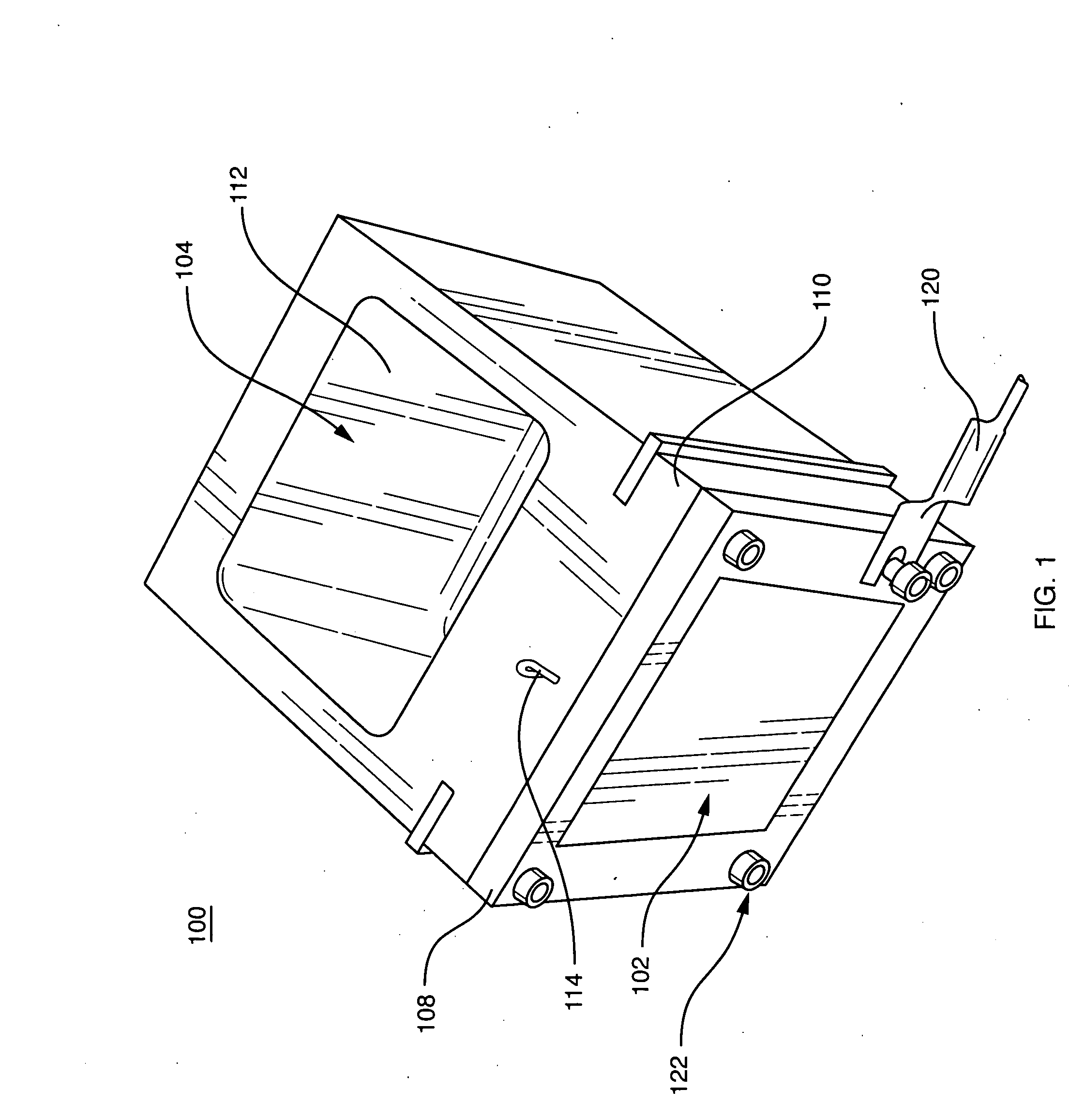
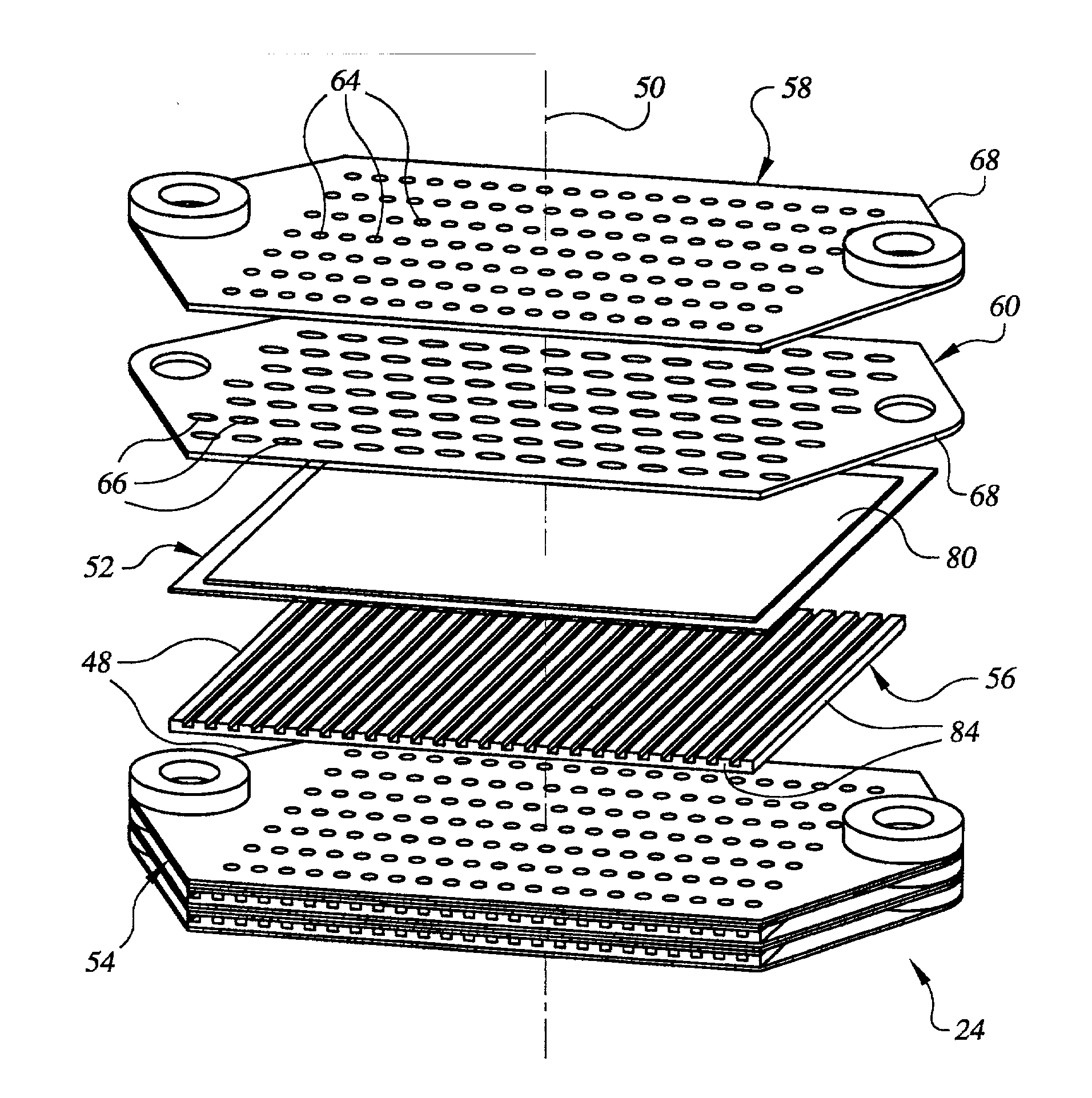
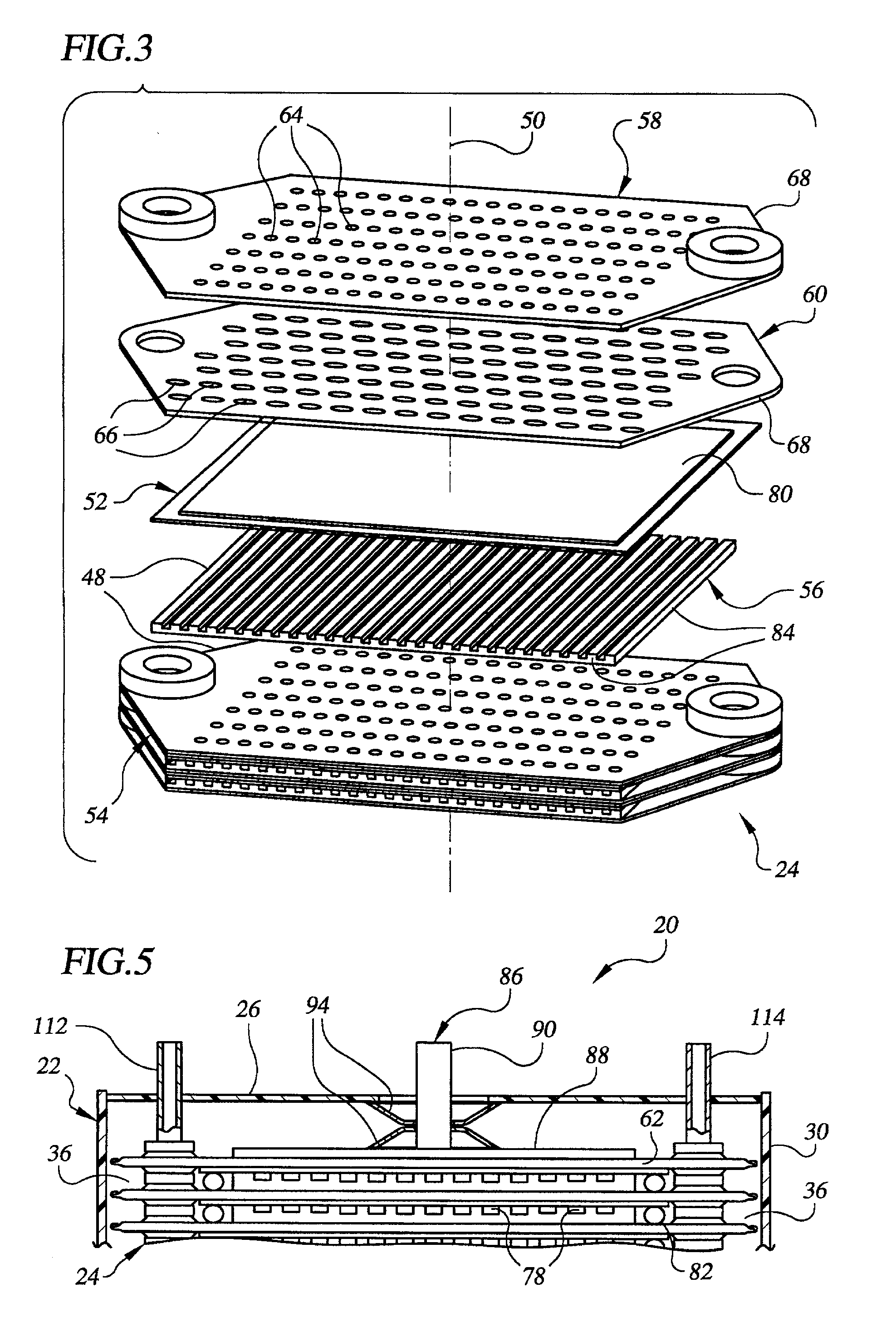
Lightweight direct methanol fuel cell and supporting systems
InactiveUS20070015035A1Fuel cell heat exchangeReactant parameters controlHandling systemCompression member
A lightweight direct methanol fuel cell unit (20) comprising a fuel cell stack (24) enclosed within a housing (22). In one embodiment the fuel cell stack includes a plurality of polymer electrolyte membrane electrode assemblies (52) stacked alternatingly with a plurality of bipolar plates (48). Each bipolar plate includes a cathode flow field (78) defined by a porous cathode flow field structure (56) and an anode flow field (62) defined by an upper plate (58) and a lower plate (60) separated from one another by a plurality of spacers (64). The anode flow fields are manifolded with one another via manifold embossments (118, 120) that are hermetically sealed with one another with a gasket (126). The fuel cell stack and housing are shaped so as to form four manifold regions (36) in the spaces between the fuel cell stack and housing. The fuel cell stack is compressed within the housing by compression members (94) located between the fuel cell stack and housing so as to place the sidewall (30) of the housing into tension. Supporting systems for the fuel cell unit include a fuel handling system (502), an oxidant handling system (600), and a liquid inventory control system (700).
Owner:CREARE INC
Electrochemical generation, storage and reaction of hydrogen and oxygen
ActiveUS7198867B2Increase ratingsEasy transferSilver accumulatorsElectrolysis componentsChemical reactionMicrosphere
An electrolytic apparatus for using catalyst-coated hollow microspheres to produce gases, store them, and to make them available for later use. The apparatus uses catalyst-coated hollow microspheres in reversible electrochemical processes and reactions, such as those used in conjunction with water dissociation, fuel cells, and rechargeable batteries. The apparatus can be used to manufacture and store hydrogen and or oxygen and to make them available for subsequent use as raw materials for use in electrochemical and chemical reactions or as a fuel and or oxidizer for a combustion engine. The apparatus can be used as a hydrogen-oxygen hermetically seal secondary battery. The apparatus can be used as a hydrogen storage portion of certain types of secondary batteries. Hydrogen and oxygen can be stored within hollow microspheres at moderate temperature and pressure, eliminating the need for expensive storage and handling equipment, and increasing the mobility of hydrogen-powered vehicles. Storage of hydrogen and or oxygen within the microspheres significantly reduces flammability and explosion concerns and resolves many fuel cell scalability issues.
Owner:DIFFUSION SCI
Relative humidity profile control strategy for high current density stack operation
ActiveUS20060263651A1High current density operationFuel cell heat exchangeWater management in fuel cellsHigh current densityFuel cells
A control strategy results in a relative humidity profile that is substantially the same or constant regardless of the operational power level of the fuel cell stack. The strategy maintains the relative humidity profile within a range that enables high current density operation of the fuel cell stack. The profile is achieved by adjusting a coolant flow rate through the fuel cell stack to maintain a temperature change across the coolant flow path from inlet to outlet substantially constant regardless of the operational power level of the fuel cell stack.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Catalytic hydrogen storage composite material and fuel cell employing same
InactiveUS6875536B2High catalytic activityImprove corrosion resistanceWater management in fuel cellsElectrode carriers/collectorsFuel cellsPhysical chemistry
A composite hydrogen storage material including 1) an active material having hydrogen storage capacity; and 2) a catalytic material having greater catalytic activity toward the dissociation of molecular hydrogen and / or oxidation of hydrogen than that of said active material having hydrogen storage capacity. Also, a fuel cell employing anodes formed from the composite hydrogen storage material. The fuel cell has the ability to start up instantly and can accept recaptured energy such as that of regenerative braking by operating in reverse as an electrolyzer.
Owner:TACTICAL FUEL CELLS
Popular searches
Resistance/reactance/impedence Voltage-current phase angle Control using feedback Solid electrolyte fuel cells Ratio control Special data processing applications Material dimension control Active material electrodes Non-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodes Secondary cells servicing/maintenance
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com