Patents
Literature
1453results about "Camera diaphragms" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
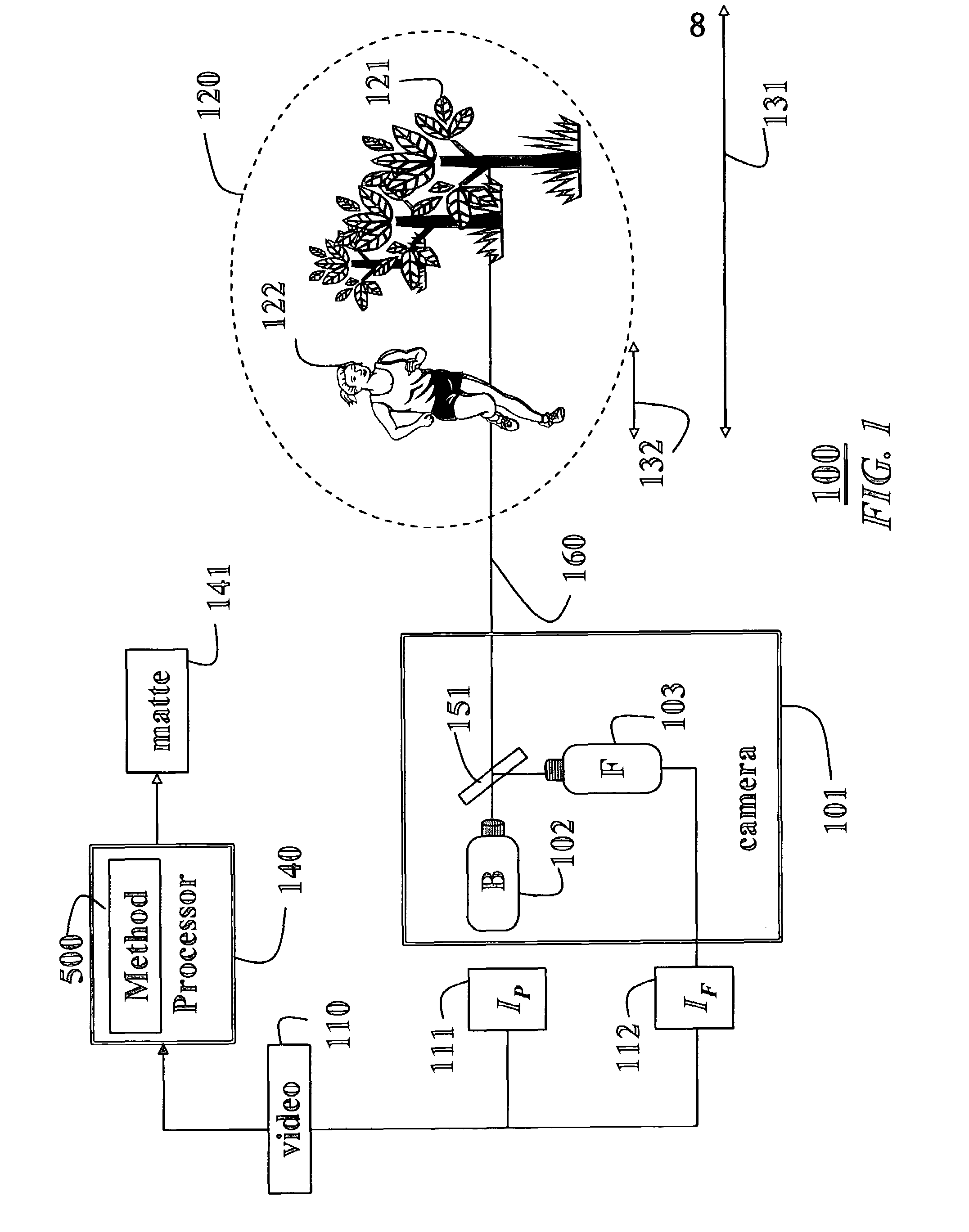
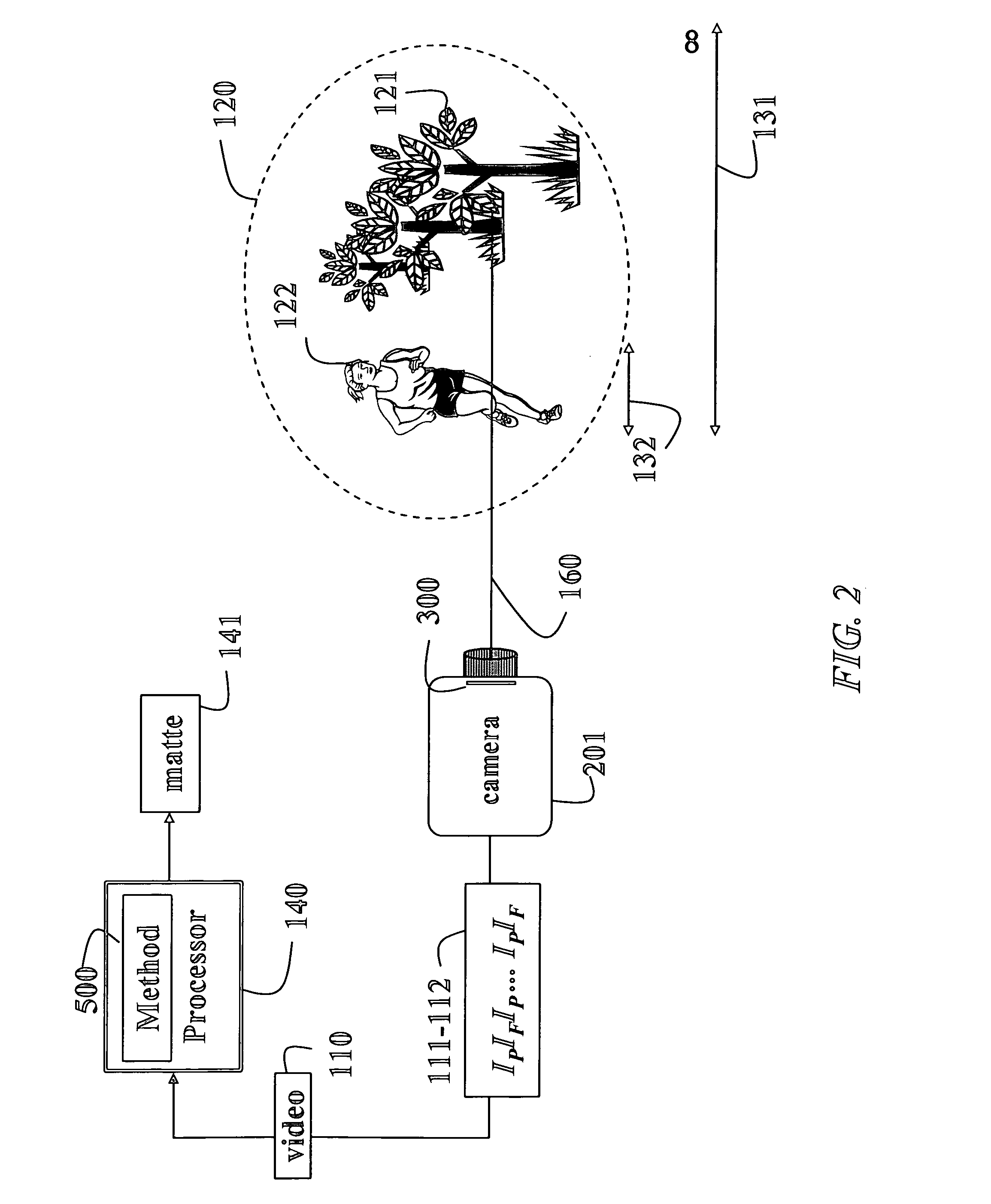
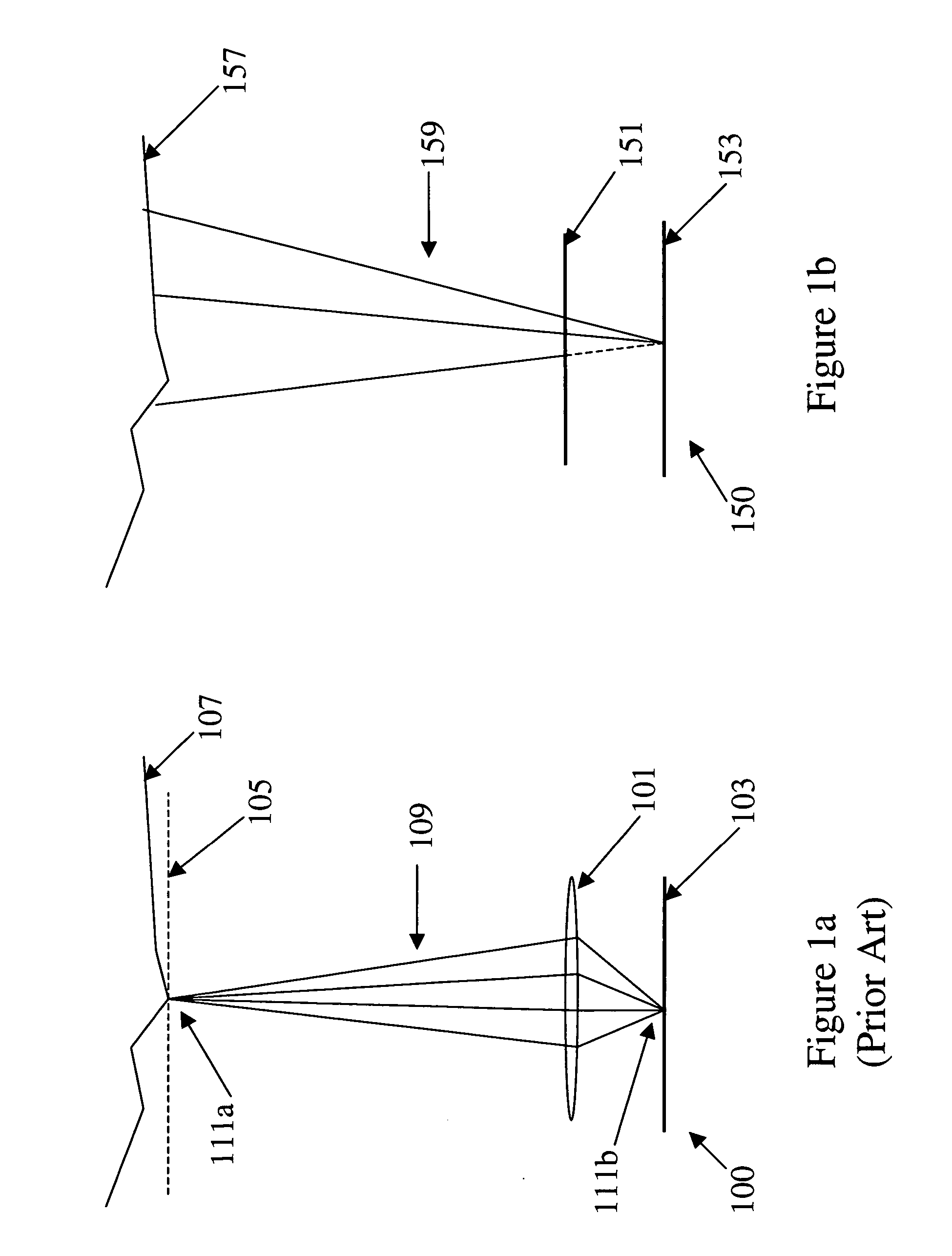
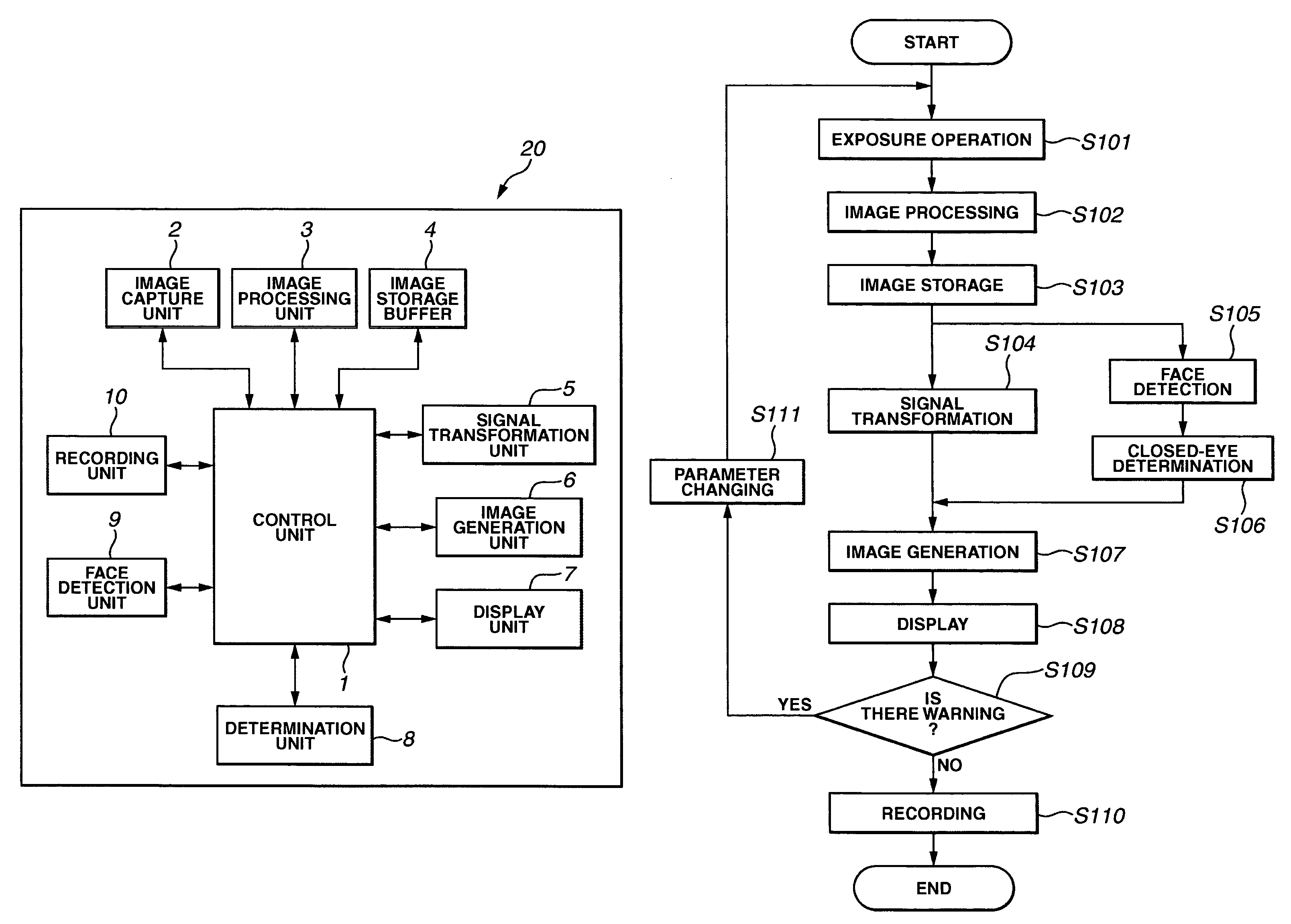
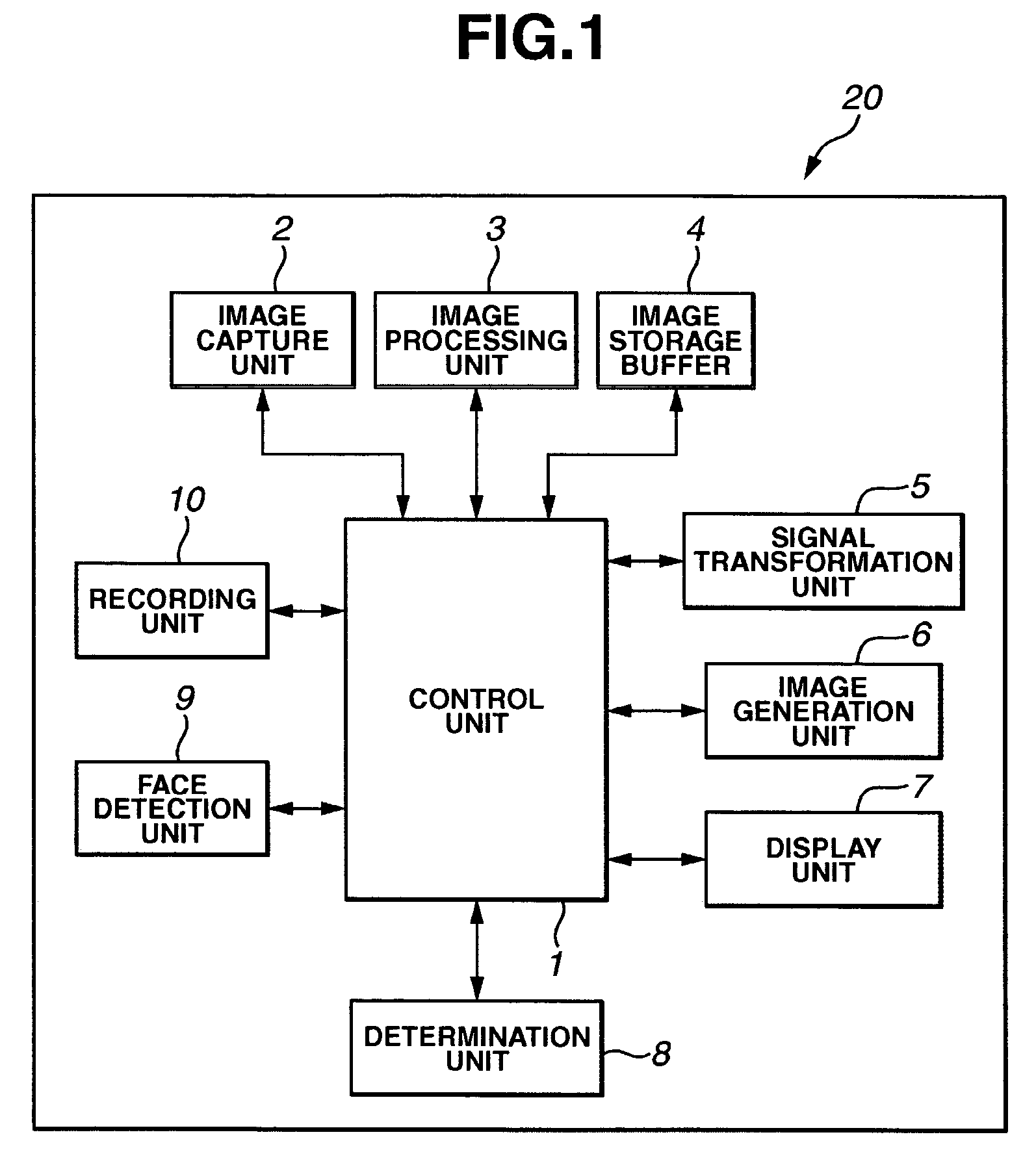
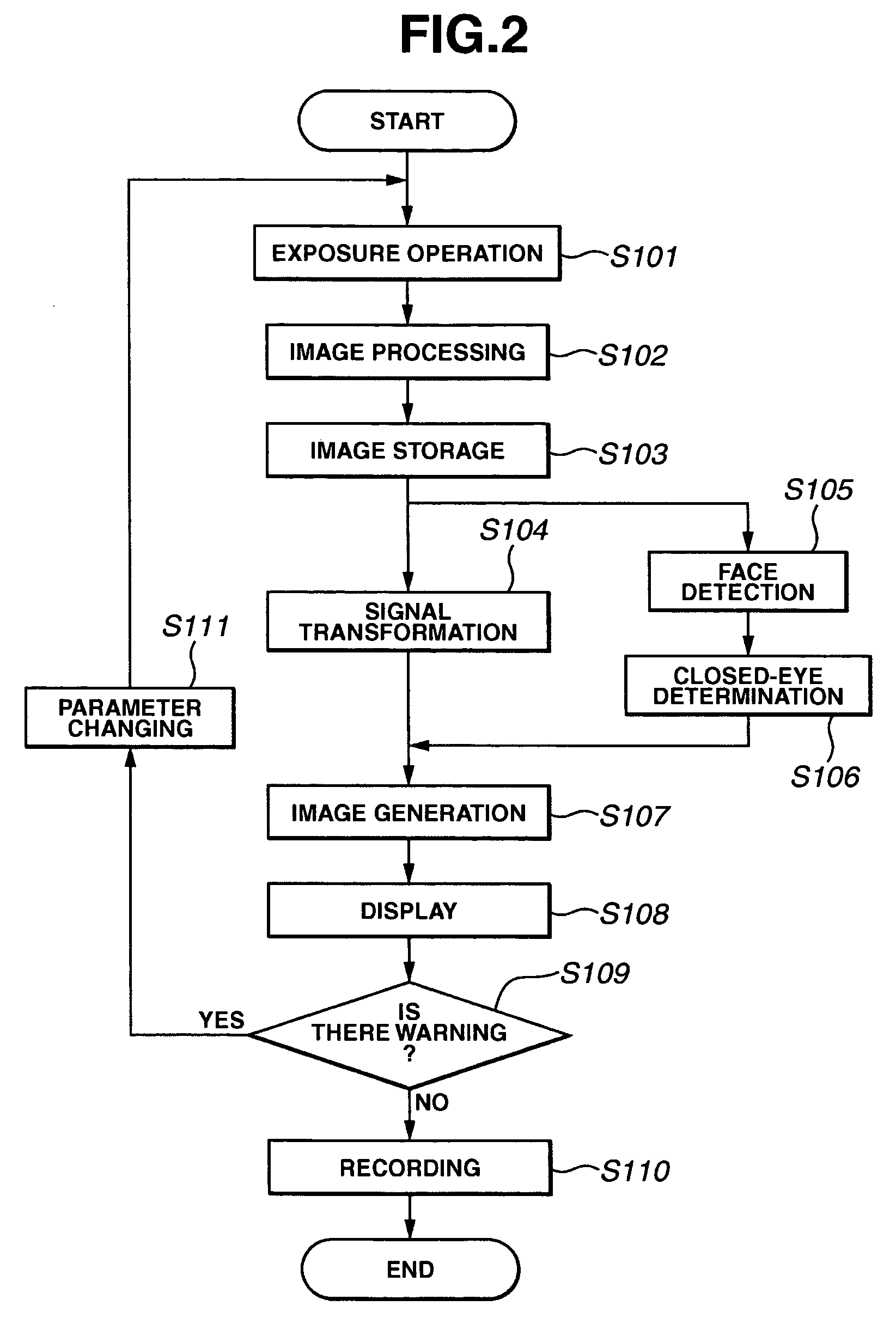
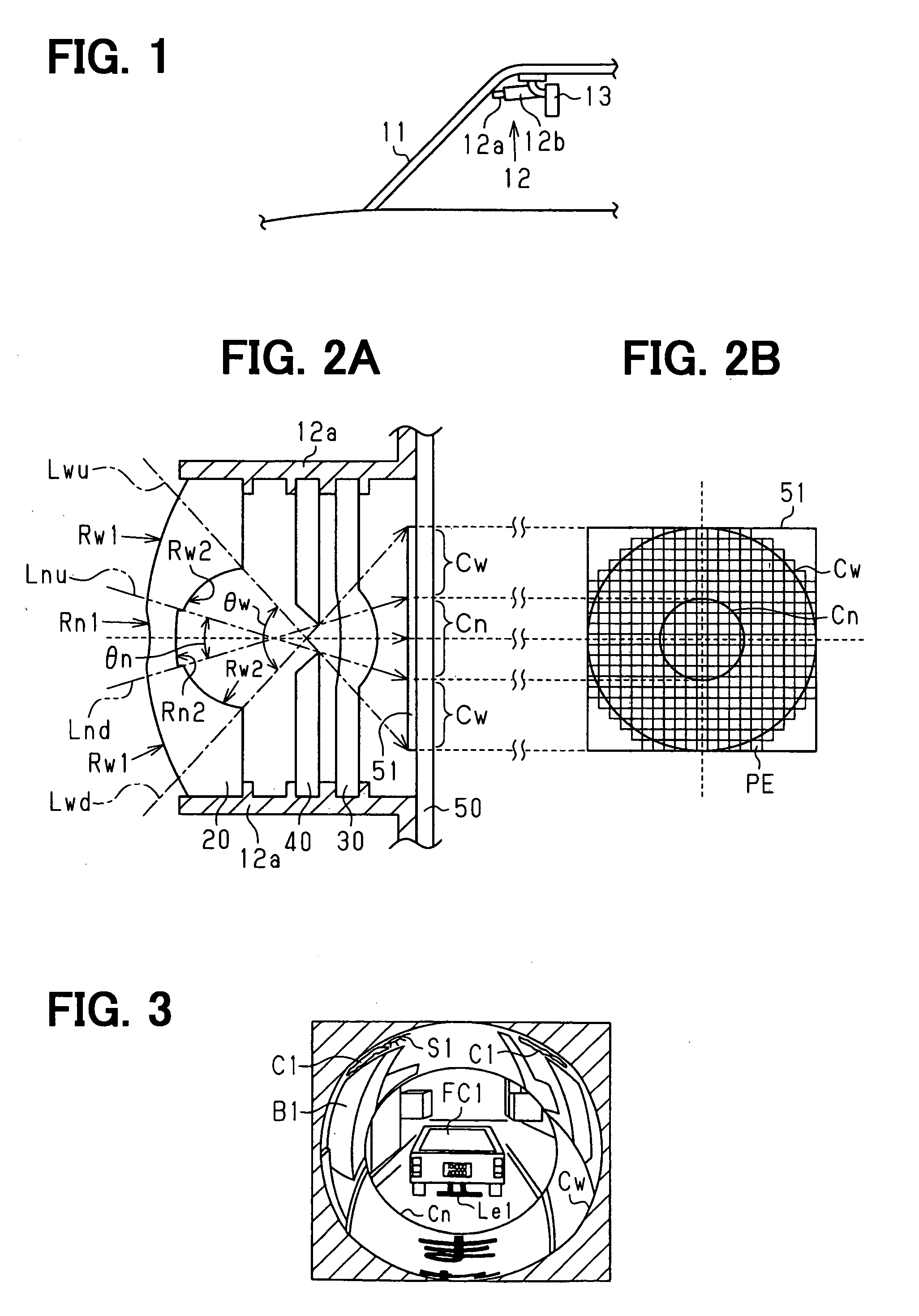
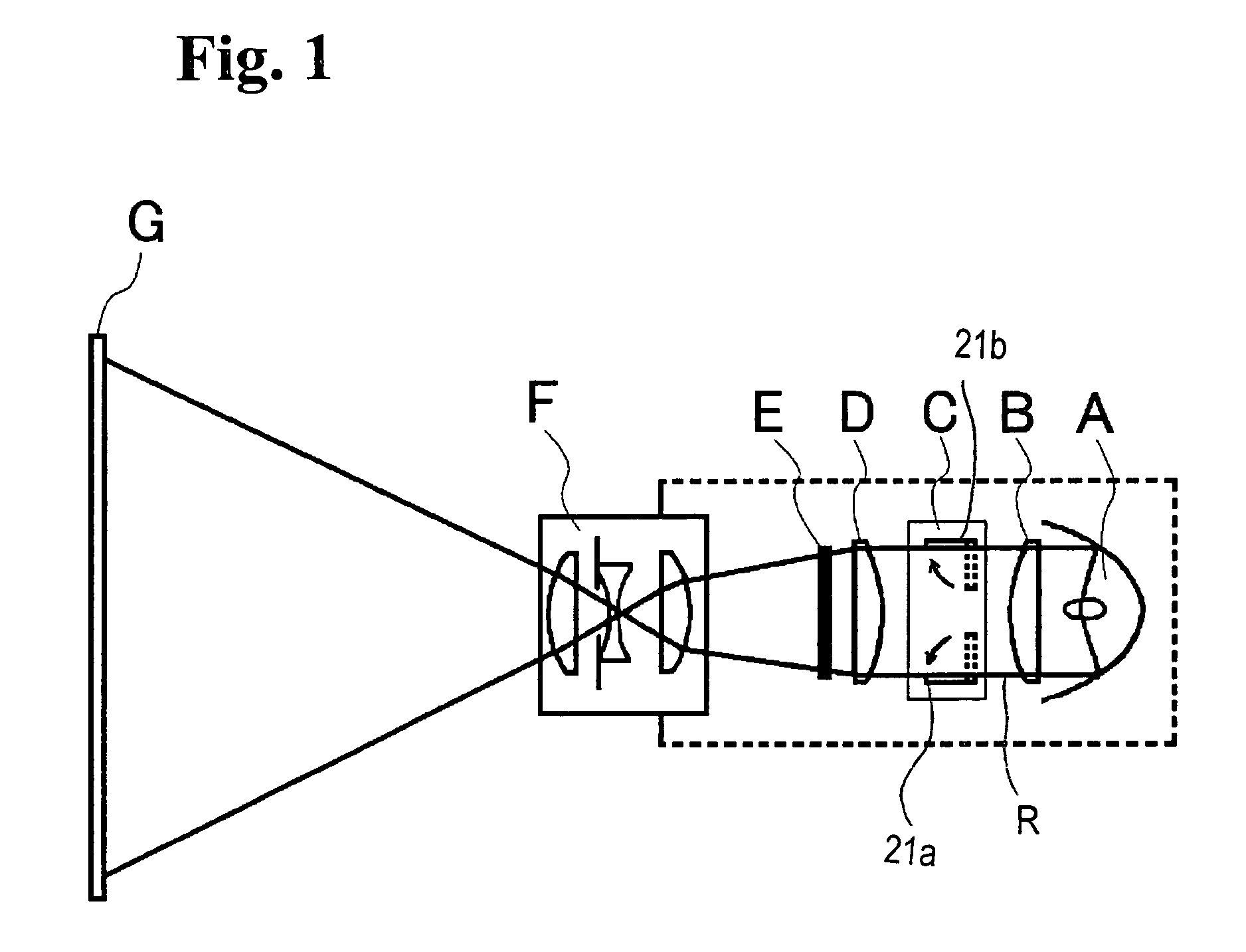
Apparatus and Method for Reducing Glare in Images
InactiveUS20090273843A1Reduce contrastReduce glareTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer visionComputer science
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Light-controlling element for a camera
InactiveUS20070133983A1Improve image qualityReduce excess spaceTelevision system detailsCamera diaphragmsTransmittanceComputer science
A light-controlling element for a camera, and a method and computer program product for admitting light to pass through such light-controlling element. The light-controlling element comprises a first zone and a second zone. The first zone is configured to admit light to pass through the light-controlling element. Furthermore, the second zone has a transmittance, which is controllable for adjusting the area of the first zone.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
Lens driving device
InactiveUS6856469B2Reduce power consumptionSimple structureProjector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementCamera lensOptical axis
A lens driving device includes a moving body equipped with a lens and a driving magnet attached to the lens, and a fixed body that is equipped with a driving coil that forms together with the driving magnet a magnetic circuit and moves the moving body in an optical axis direction of the lens between a first lens retaining position and a second lens retaining position, and at least one magnetic member disposed adjacent to at least one of two end sections in the optical axis direction of the driving magnet. The moving body is retained at the first lens retaining position by magnetic attraction caused by the driving magnet and the magnetic member when energization of the driving coil is stopped. Accordingly, the driving coil does not need to be energized while the lens is retained at the first lens retaining position.
Owner:SANKYO SEIKI MFG CO LTD
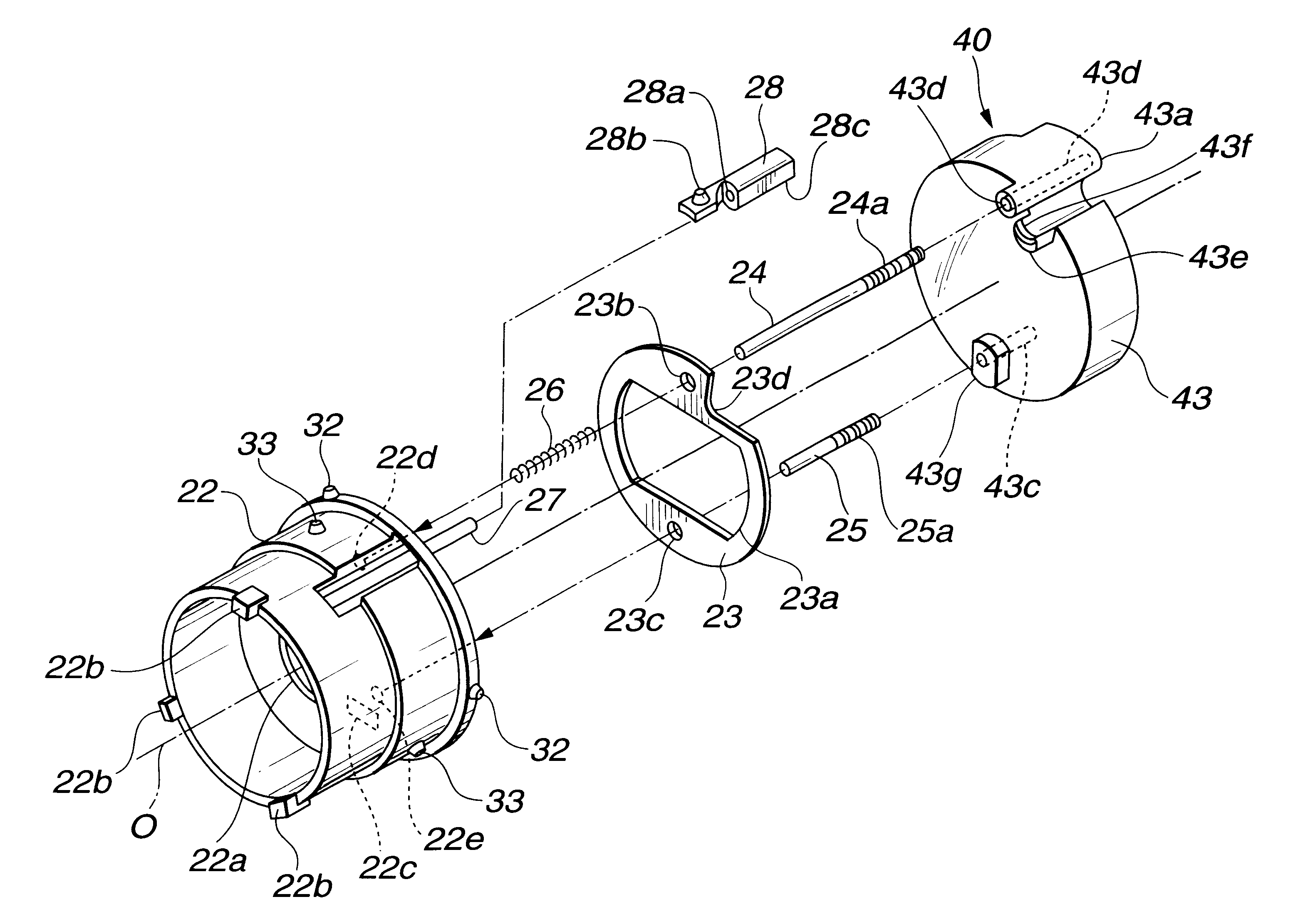
Lens housing having aperture device
A lens housing including an anti-flare aperture device in the form of a thin planar aperture member. In one embodiment, a plurality of guide pins extend from a group-3 lens element, with a compression spring on one of the guide pins to bias the group-3 lens in the direction of its optical axis. The aperture member, the position of which is defined by two guide pins, is sandwiched between the group-3 lens and the compression spring, thereby being supported. The aperture member moves backward and forward together with the group-3 lens supported by the guide pins. In a second embodiment, the aperture device is attached directly to one side of the lens elements.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
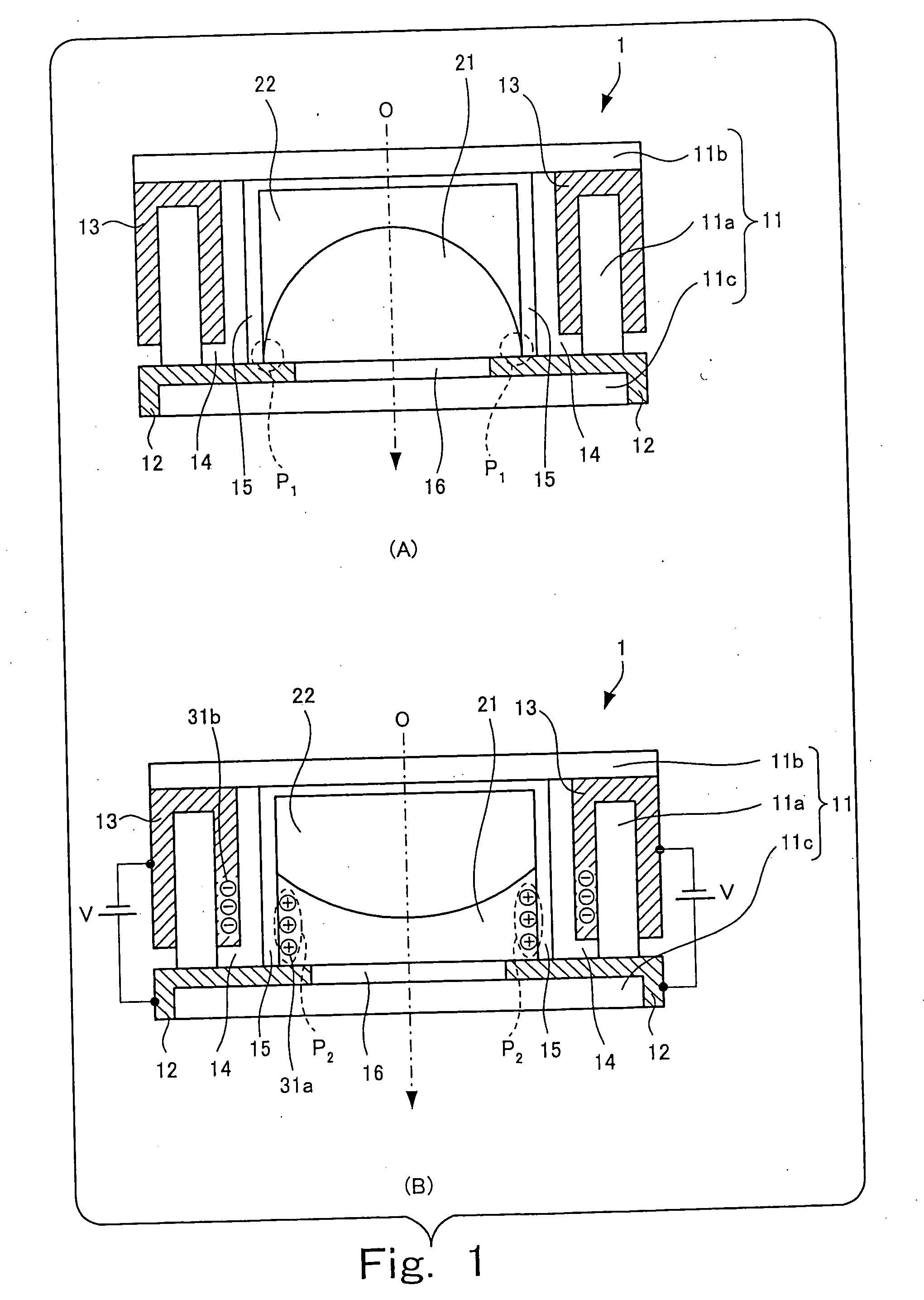
Fast switching camera aperture
A camera aperture includes a first polarizer and a second polarizer with a polarization 90° with respect to the first polarizer. The second polarizer has a through hole at a center. A polarizing rotator is disposed between the first polarizer and the second polarizer. A size of the aperture is changed when a voltage is applied selectively to the polarizing rotator.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Adapter, camera system, and adapter control program
An adapter includes: a first mount section that is detachably attached to a camera body; a second mount section that is provided separately from the first mount section and is detachably attached to any one of a plurality of types of interchangeable lenses which are different from each other in a method of controlling a diaphragm; and an accessory control section that controls the diaphragm of the interchangeable lens in response to a common control command which is received from the camera body regardless of the type of the interchangeable lens mounted on the second mount section.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Monocular three-dimensional imaging
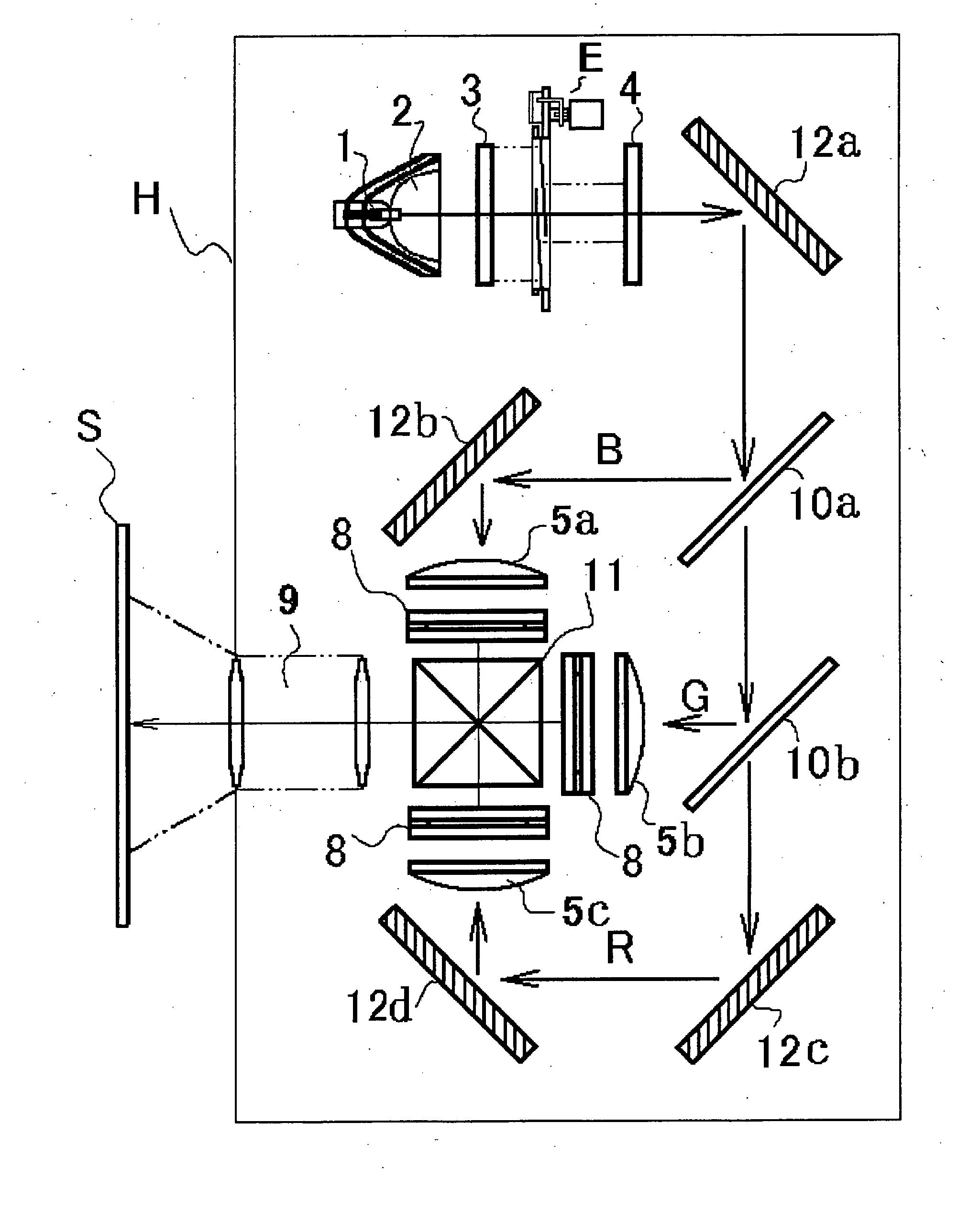
ActiveUS20080013943A1Stereoscopic photographyCamera diaphragmsOptical pickupThree dimensional imaging
A three-dimensional imaging system uses a single primary optical lens along with various configurations of apertures, refocusing facilities, and the like to obtain three offset optical channels each of which can be separately captured with an optical sensor.
Owner:MEDIT CORP
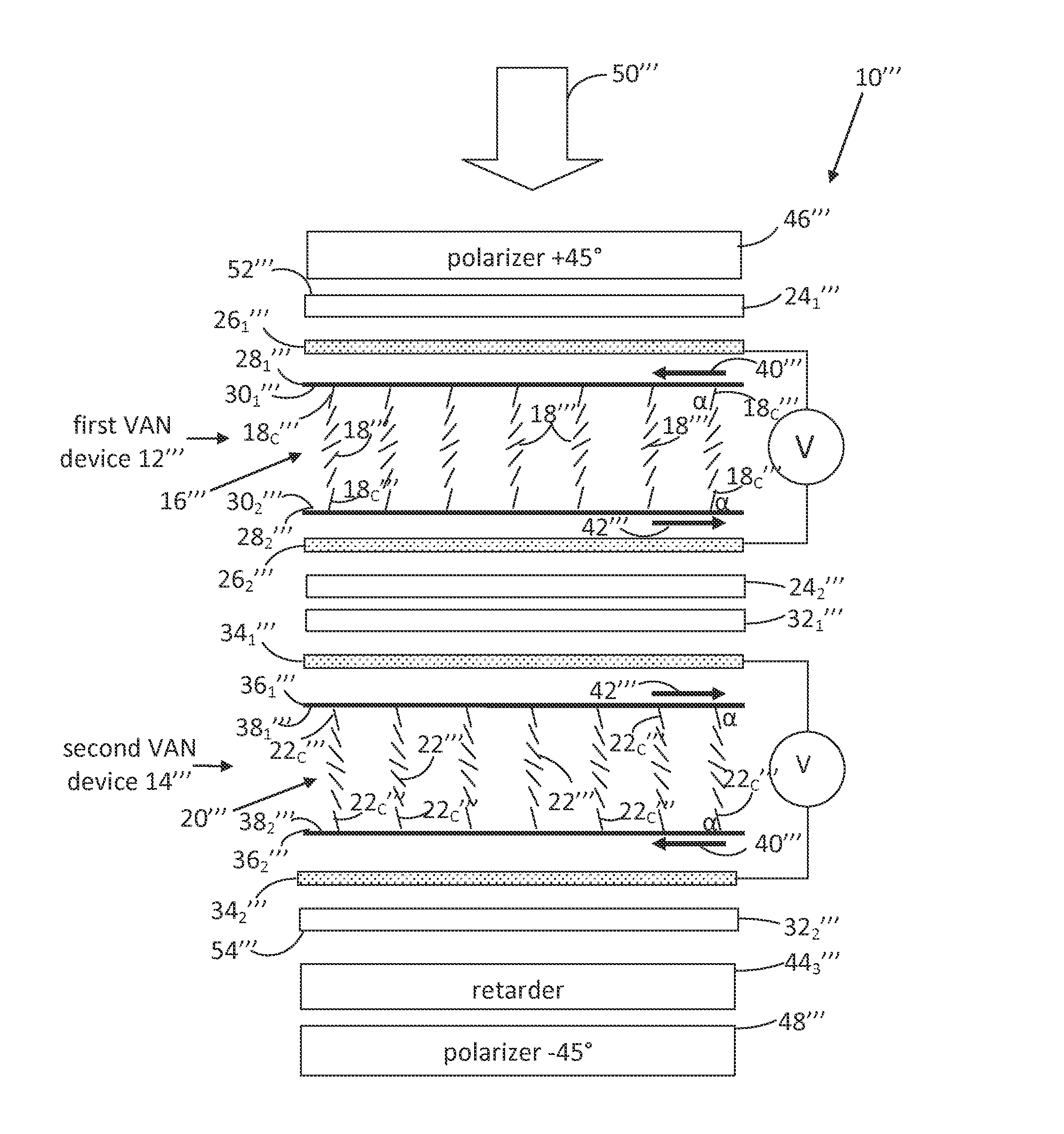
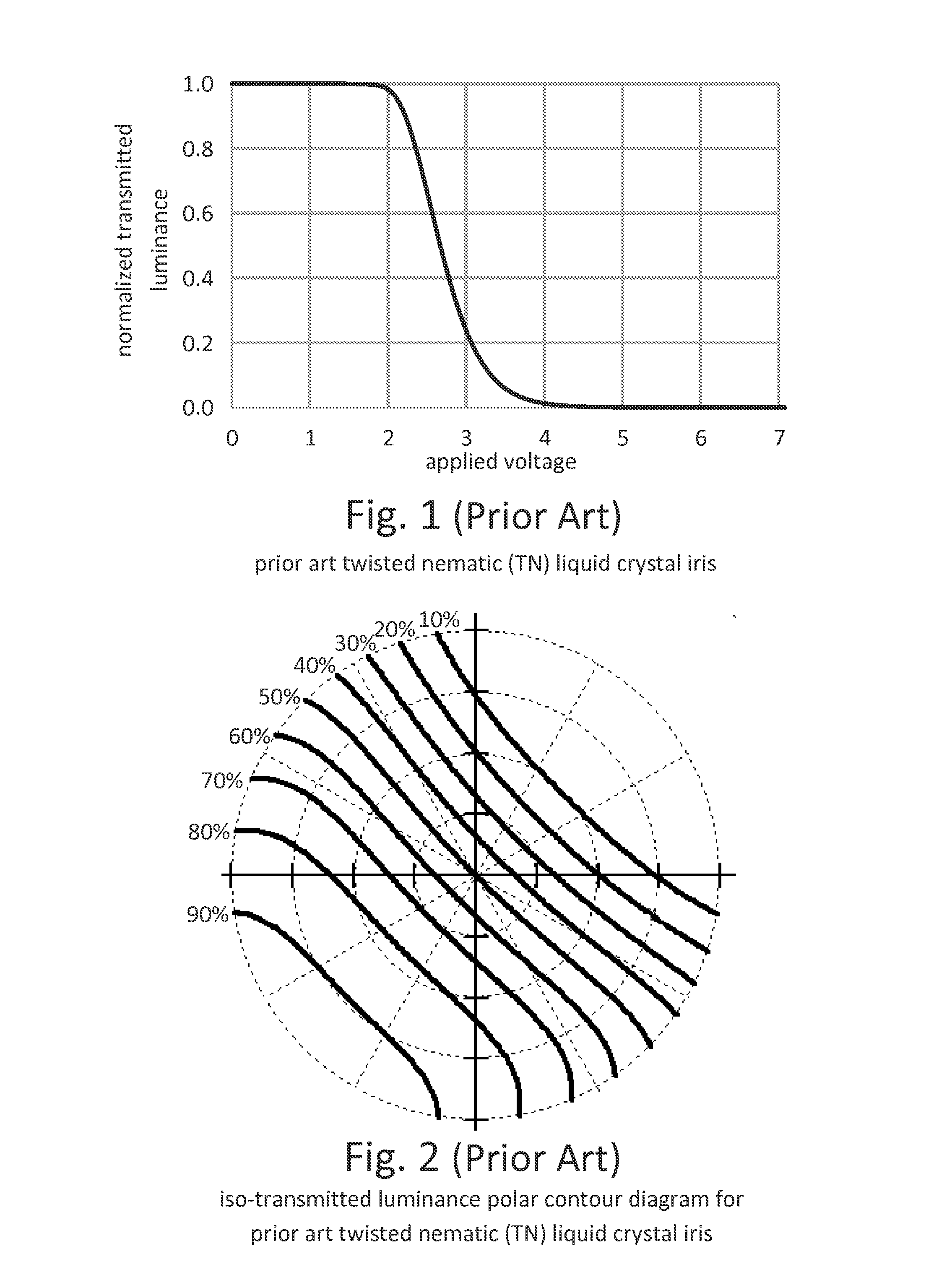
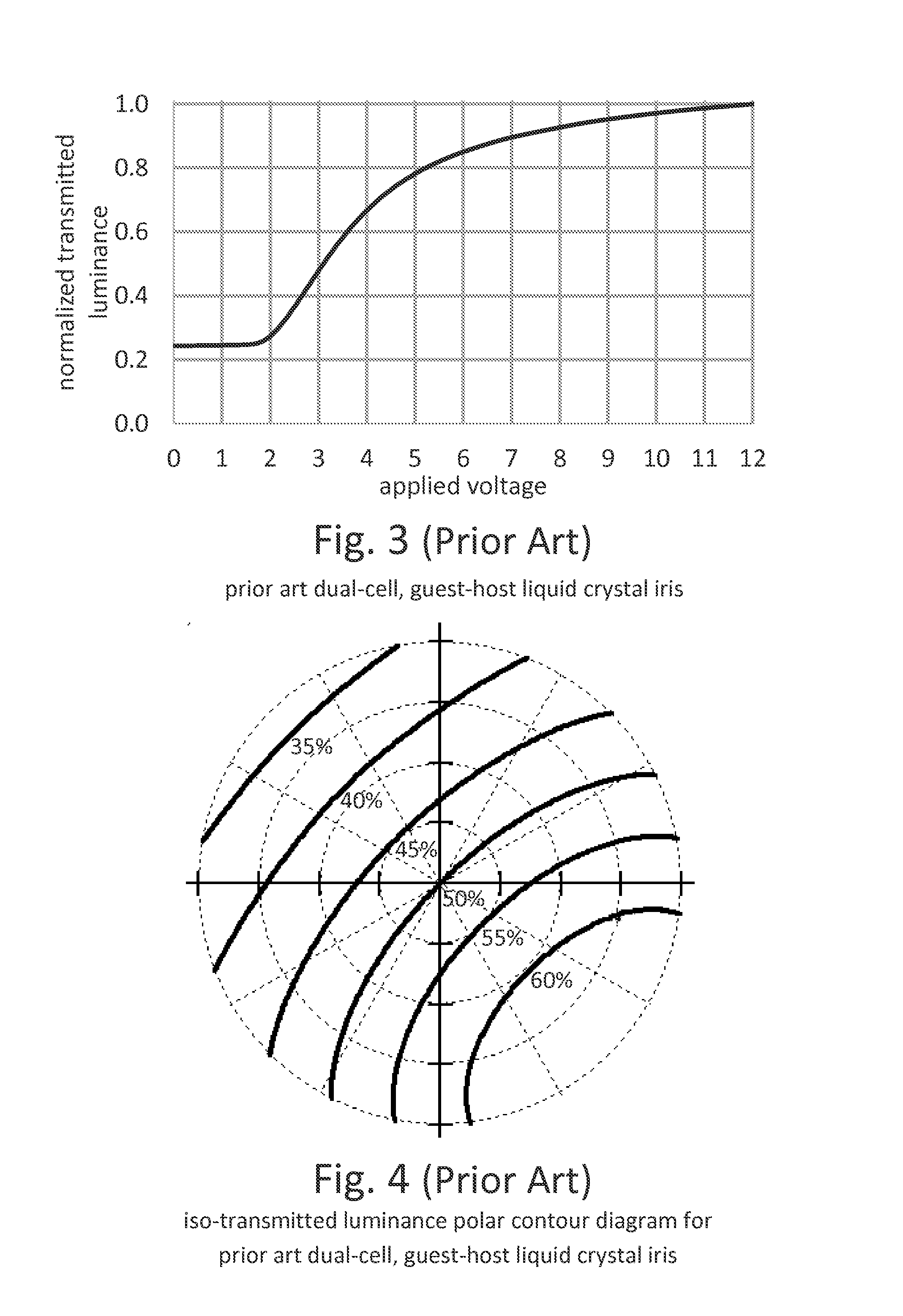
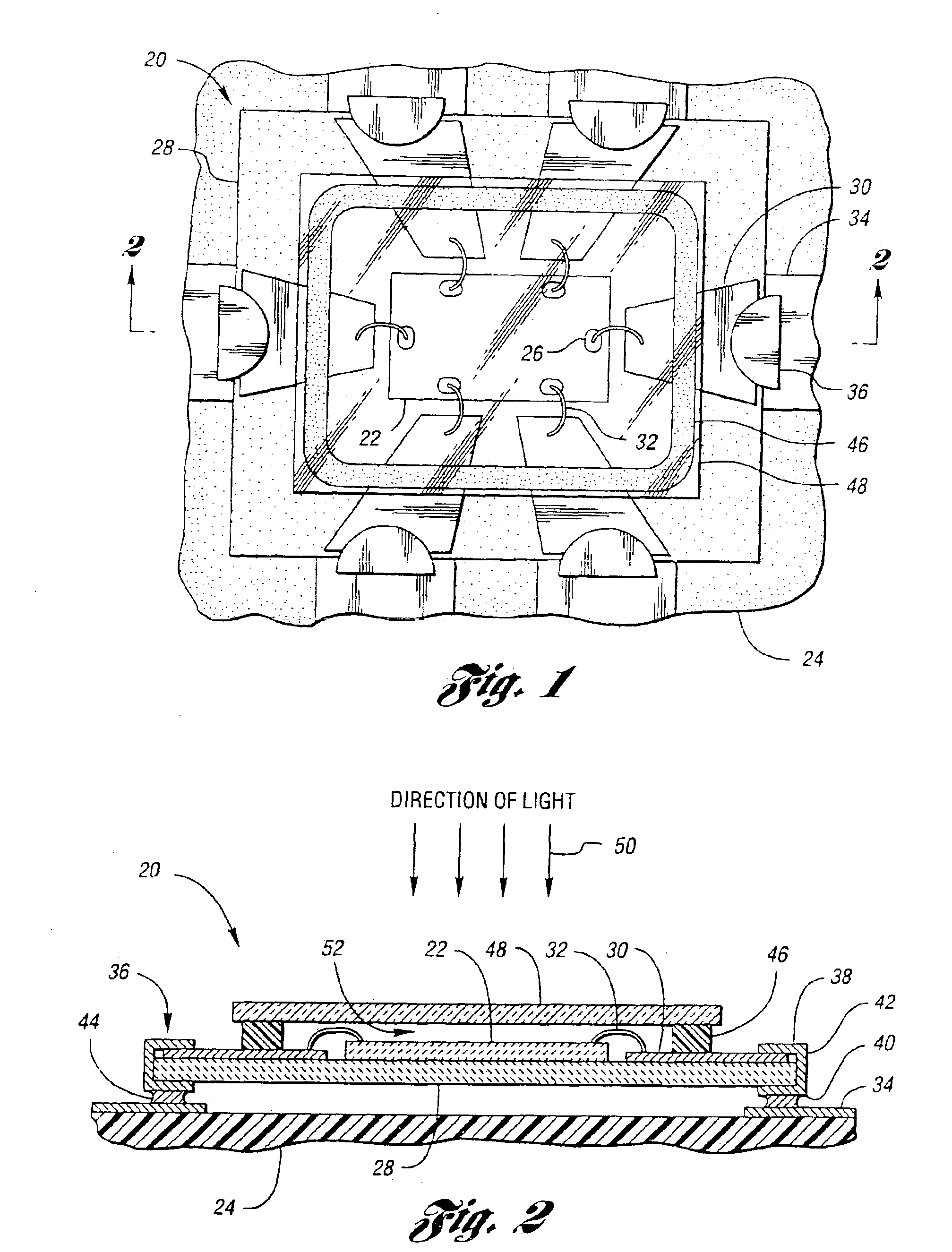
High contrast electro-optic liquid crystal camera iris providing angle independent transmission for uniform gray shades
ActiveUS20160238869A1Maximum light transmittanceLarge throughputTelevision system detailsExposure controlAzimuth directionPolarizer
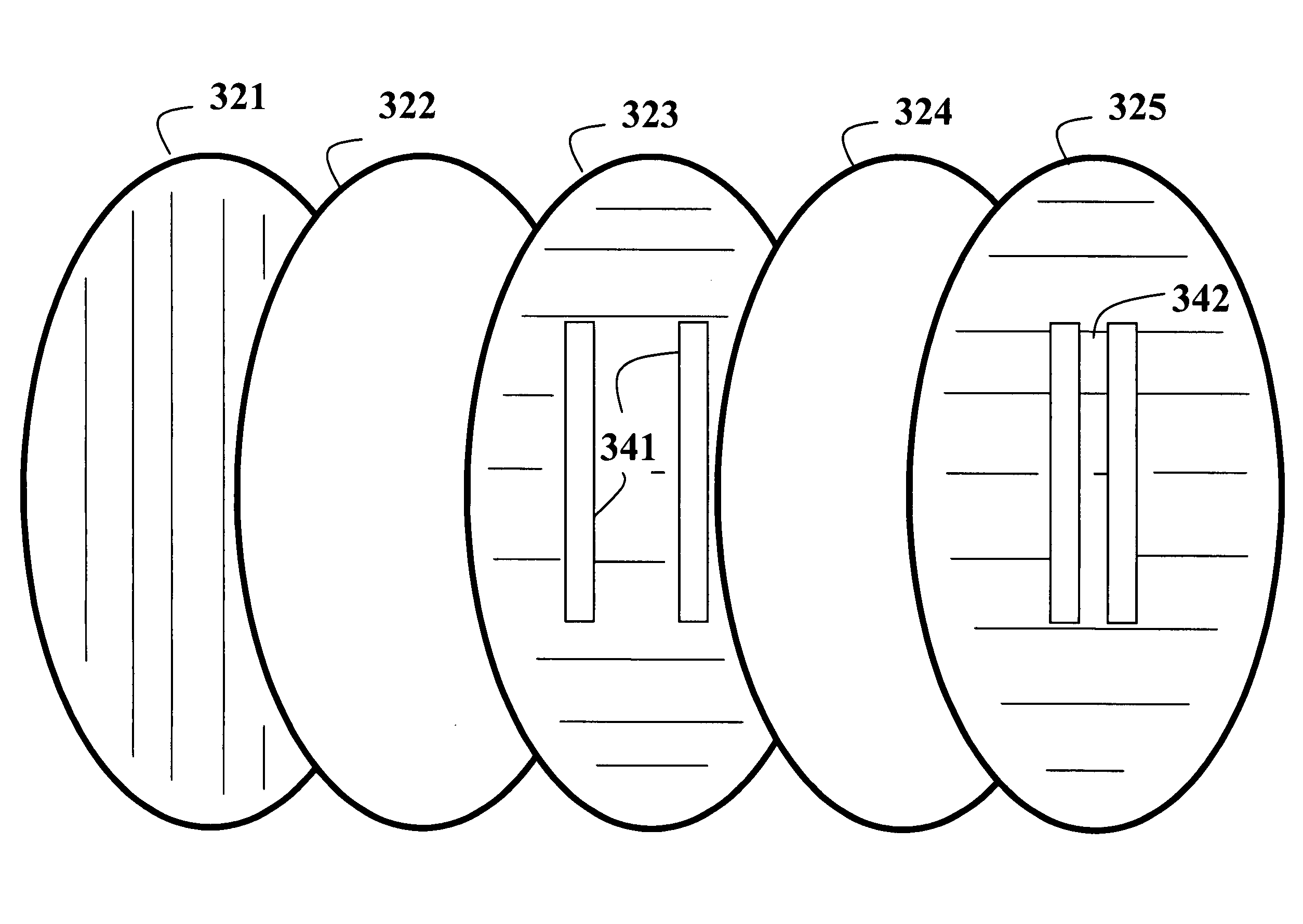
A high-contrast electro-optic liquid crystal camera iris (10) provides angle independent transmission for uniform gray shades. The liquid crystal iris comprises a combination of first and second liquid crystal devices (12, 14) arranged in optical series and positioned between optical polarizers (46, 48). The director field (18) of the second liquid crystal device is a mirror image of the director field (16) of the first liquid crystal device, and the first and second liquid crystal devices are placed together so that the azimuthal directions (42) of the surface-contacting directors (18c, 22c) are in parallel alignment at the adjoining or confronting surfaces of the substrates (242, 321) of the first and second liquid crystal devices. The liquid crystal iris provides, therefore, less angular variation of intermediate transmittances compared with that provided by prior art liquid crystal irises.
Owner:LC TEC DISPLAY
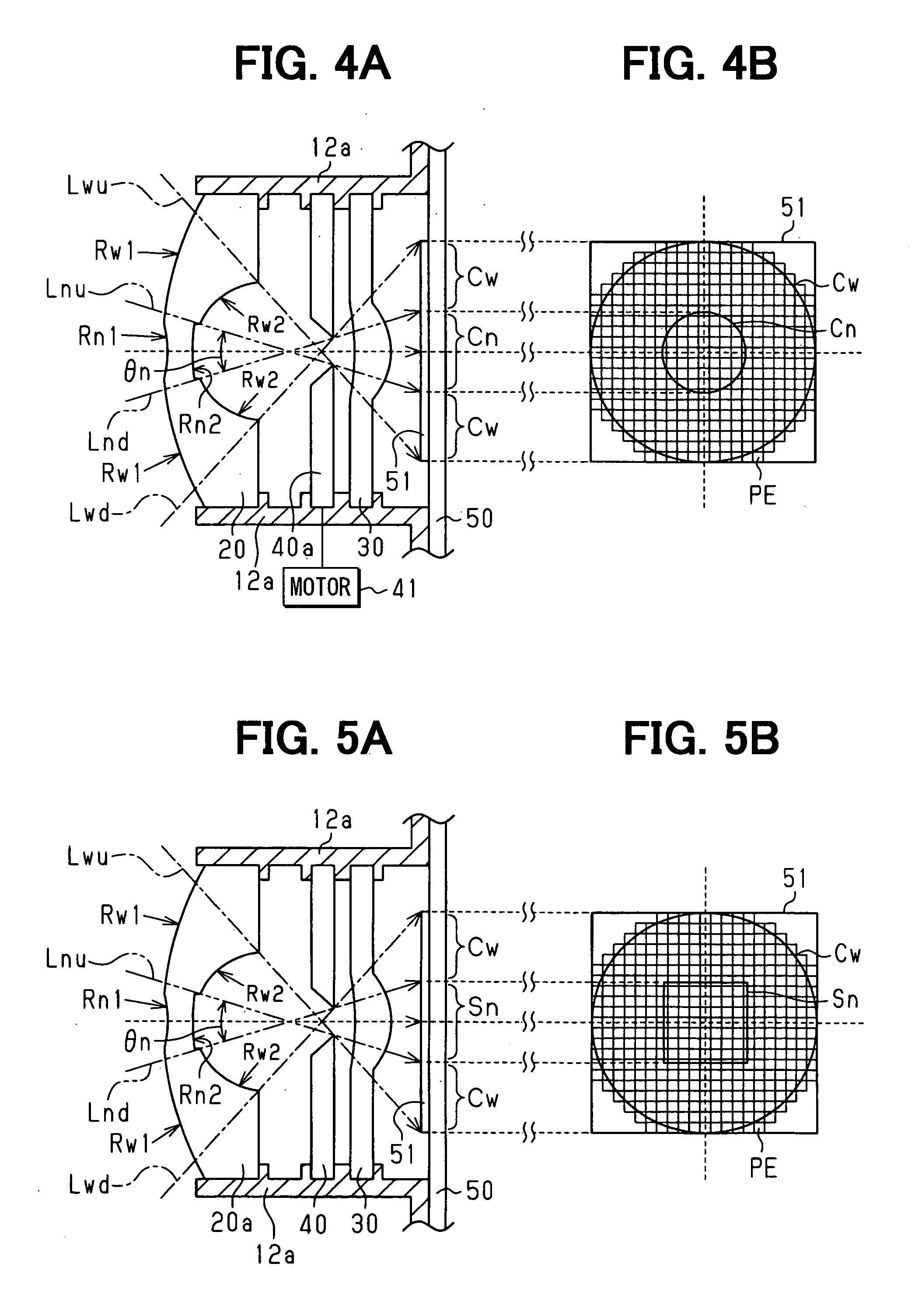
Manual focus device and autofocus camera
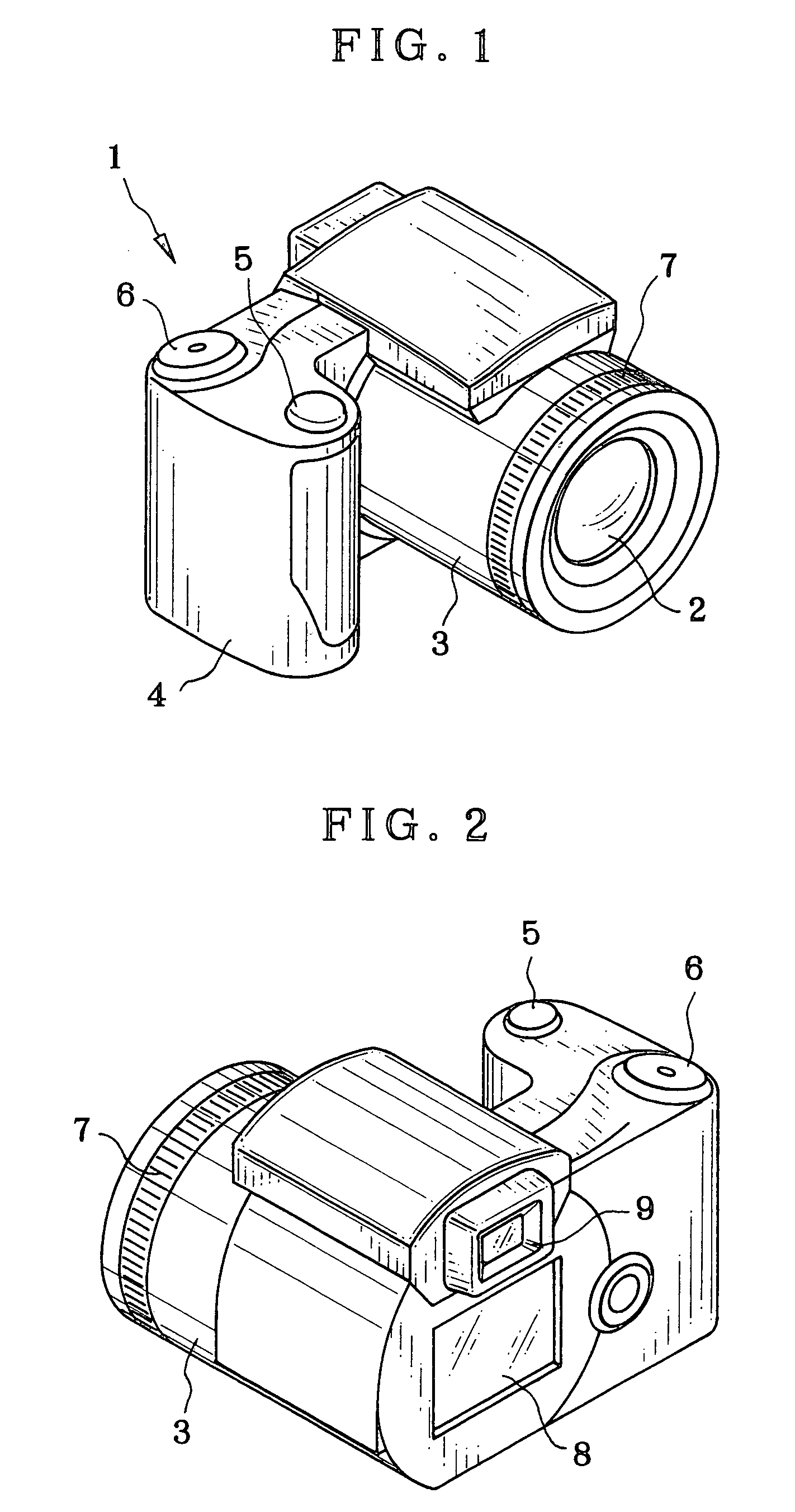
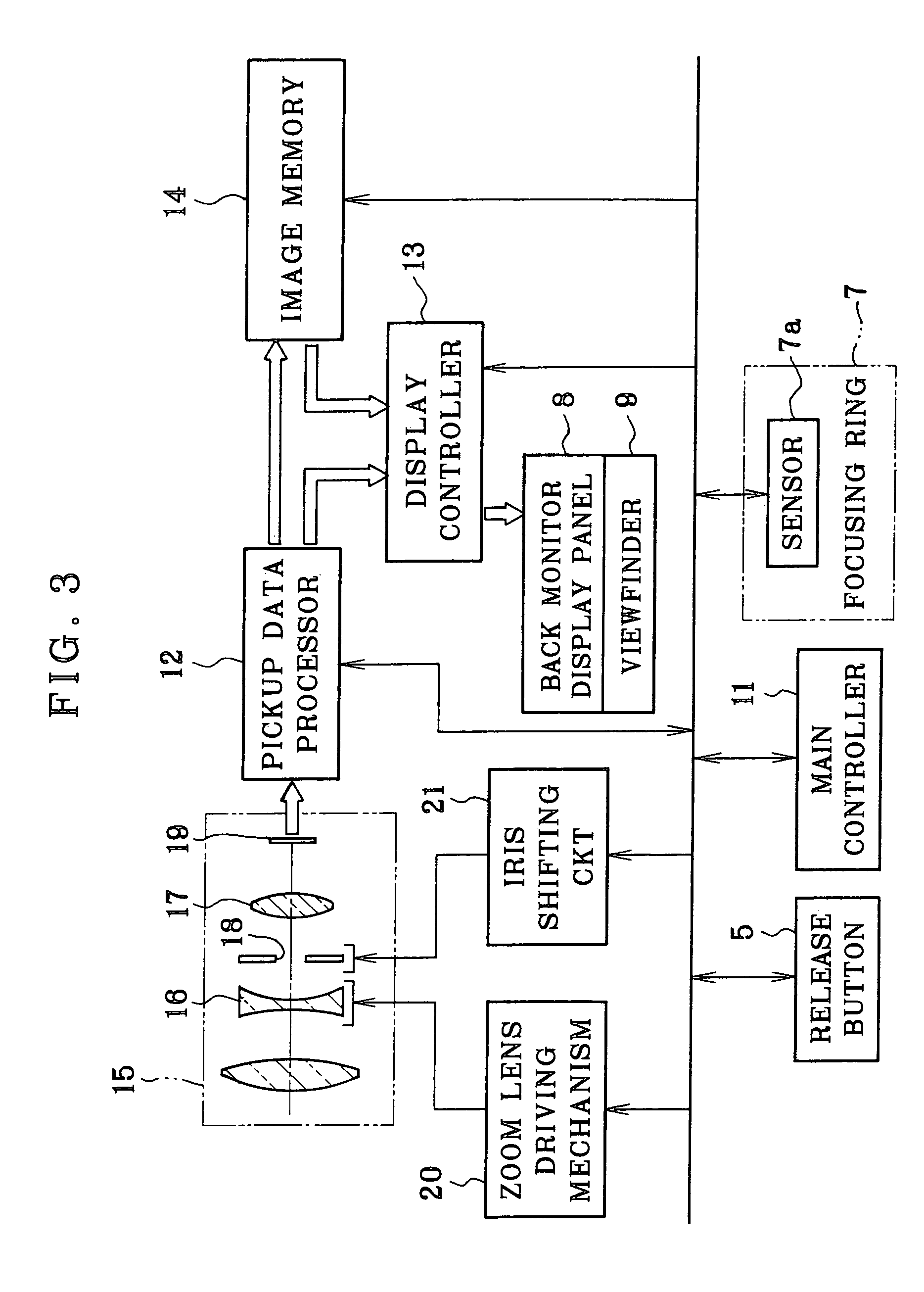
InactiveUS20050191047A1Intuitive effectEasily effectedTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementOptical axisVisual inspection
A digital still camera includes an aperture stop opening, a taking lens system, and a CCD pickup element. In a manual focus device, an iris shifting mechanism sets the aperture stop opening in an aperture stop unit with reference to a first light amount gravity center by shifting the aperture stop opening to the right relative to a lens optical axis, and sets the aperture stop opening with reference to a second light amount gravity center by shifting the aperture stop opening to the left. First and second sample pickup data are obtained by the CCD pickup element in the setting of the aperture stop opening at the two light amount gravity centers. A display panel displays first and second sample images according to the sample pickup data, to indicate a present deviation of the taking lens system from an in-focus position in simulation. A focusing ring is externally operable, for moving the taking lens system on the optical axis, and for actuation while the two sample images are checked visually, to position the taking lens system when the two sample images inform a reach to the in-focus position.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Devices incorporating electrochromic elements and optical sensors
InactiveUS6963437B2Easy to installEasy and inexpensive to manufactureTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesTransmittanceElectrochromism
The device of the present invention includes an electrochromic element having a transmittance that varies in response to an electrical signal, a base substrate disposed in spaced relation to the electrochromic element, a seal disposed between the base substrate and the electrochromic element, and an optical sensor. The seal, base substrate, and electrochromic element form a sealed cavity therebetween, in which the optical sensor is disposed. According to another embodiment, an electrochromic device is provided that includes a first substrate, an electrochromic medium disposed on the first substrate, a pair of electrodes in contact with the electrochromic medium, a pair of conductive clips, each in electrical contact with a respective one of the electrodes, and two pairs of electrical lead posts for mounting the first substrate to the circuit board. Each pair of lead posts is attached to, and extends from, a respective one of the conductive clips. According to another embodiment, an imaging device is disclosed having an image recorder for recording a scene or object, and an electrochromic element positioned between the image recorder and the object or scene to be imaged. The electrochromic element is configured to exhibit a non-uniform transmittance in response to an applied electrical signal.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
Lens driving device
InactiveUS20040130808A1Projector focusing arrangementCamera focusing arrangementCamera lensOptical axis
A lens driving device includes a moving body equipped with a lens and a driving magnet attached to the lens, and a fixed body that is equipped with a driving coil that forms together with the driving magnet a magnetic circuit and moves the moving body in an optical axis direction of the lens between a first lens retaining position and a second lens retaining position, and at least one magnetic member disposed adjacent to at least one of two end sections in the optical axis direction of the driving magnet. The moving body is retained at the first lens retaining position by magnetic attraction caused by the driving magnet and the magnetic member when energization of the driving coil is stopped. Accordingly, the driving coil does not need to be energized while the lens is retained at the first lens retaining position.
Owner:SANKYO SEIKI MFG CO LTD
Monocular three-dimensional imaging
Owner:MEDIT CORP
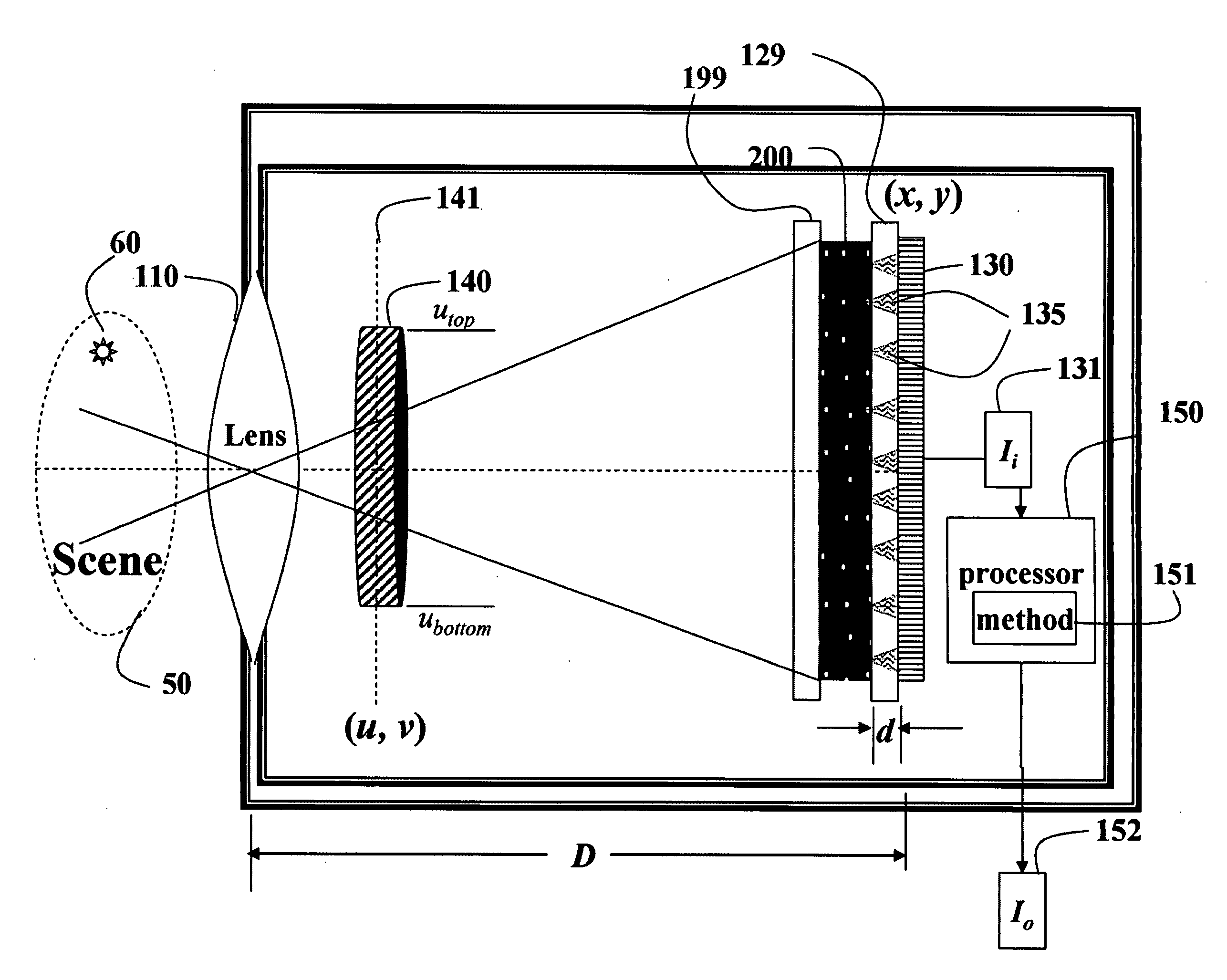
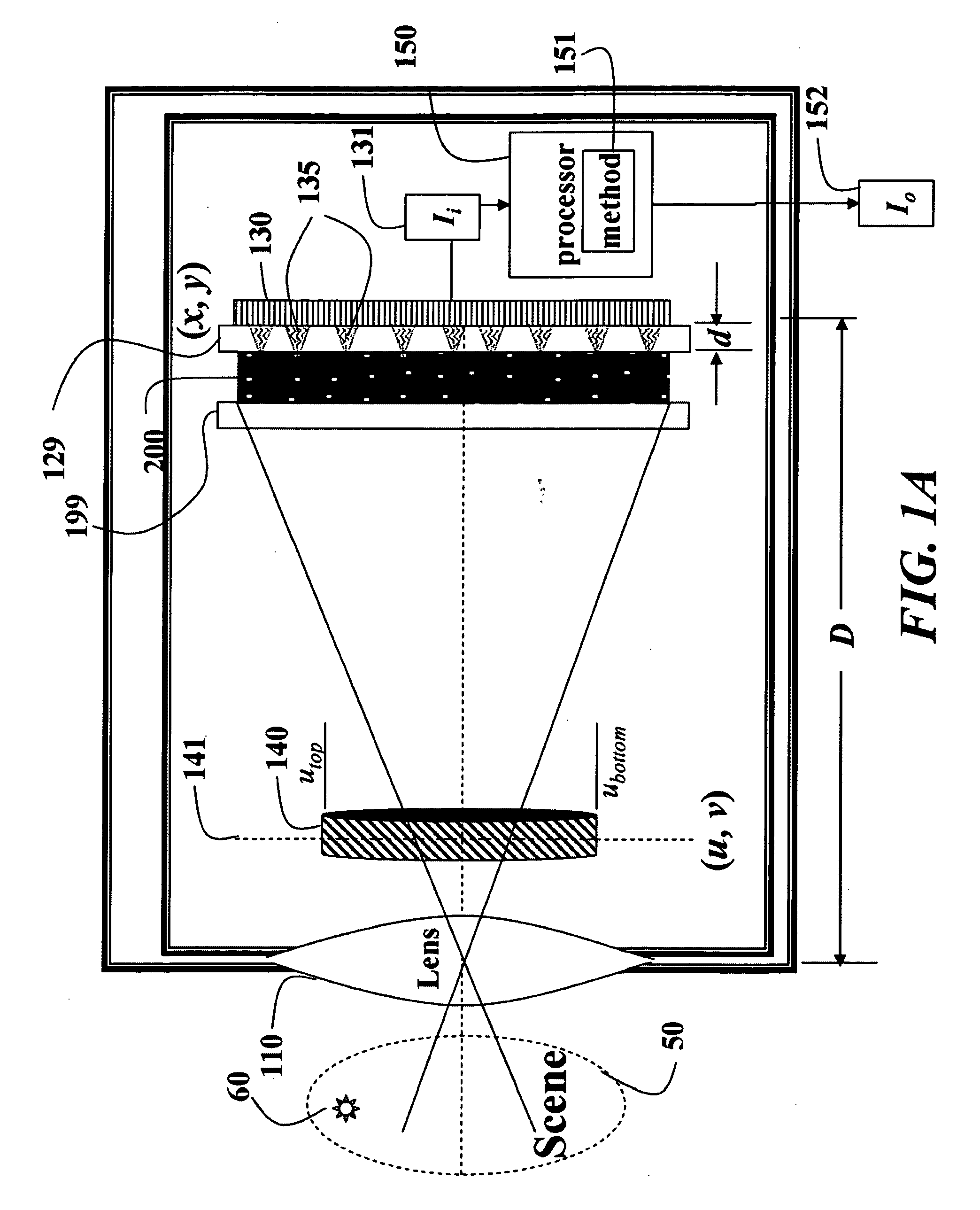
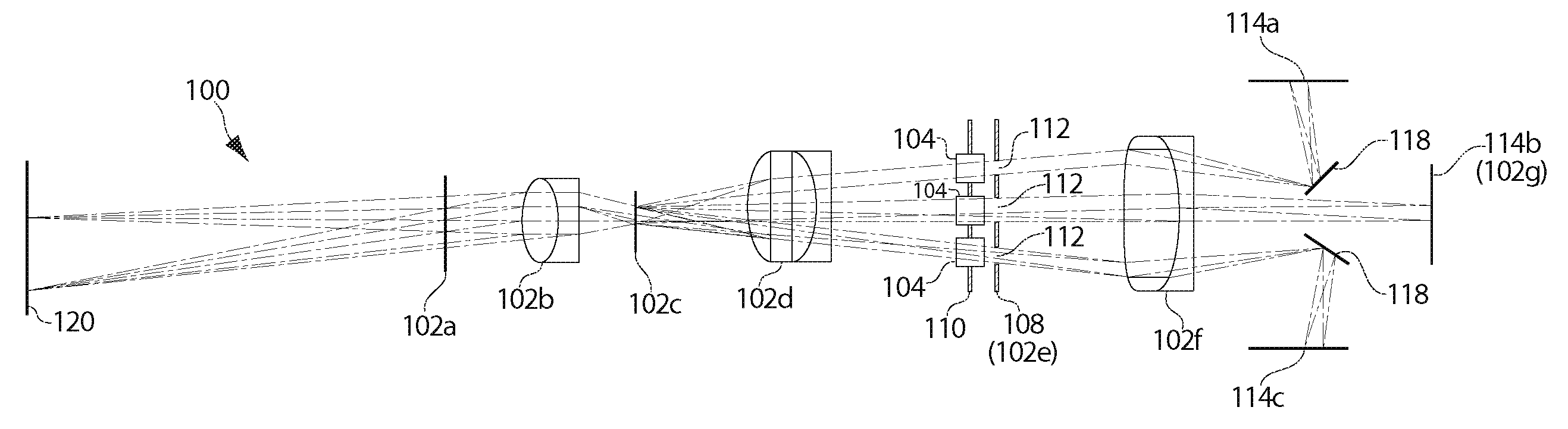
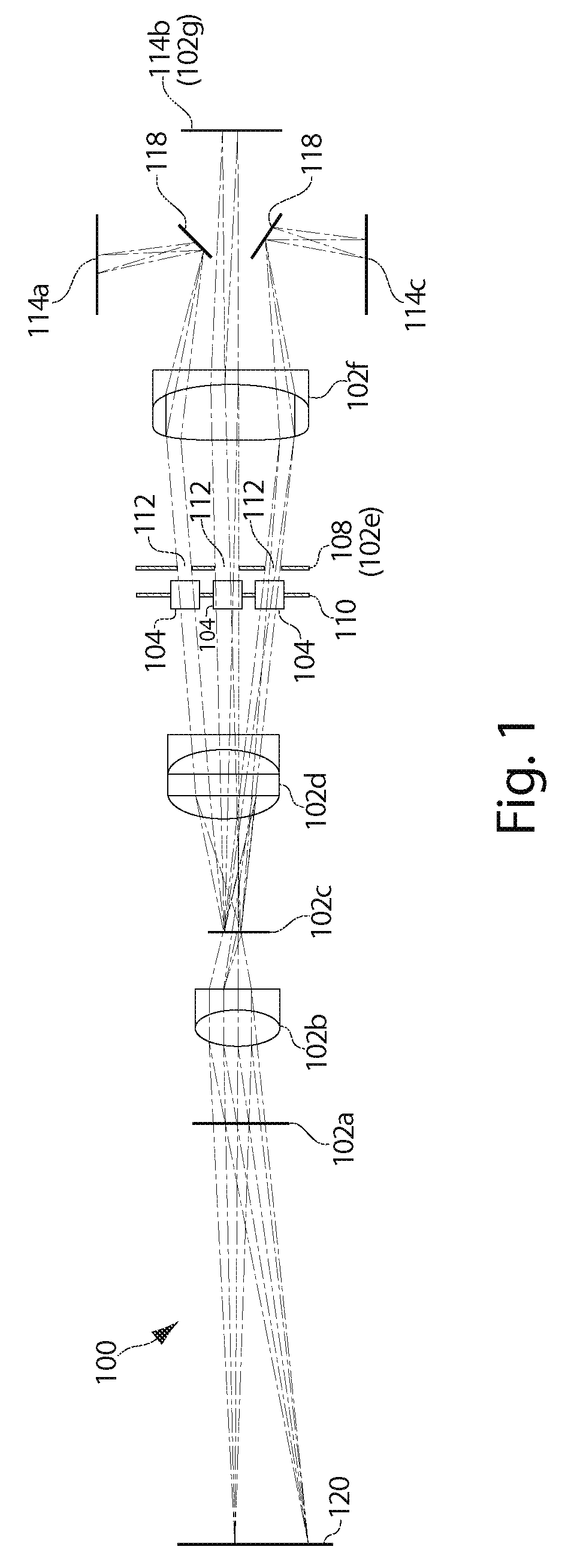
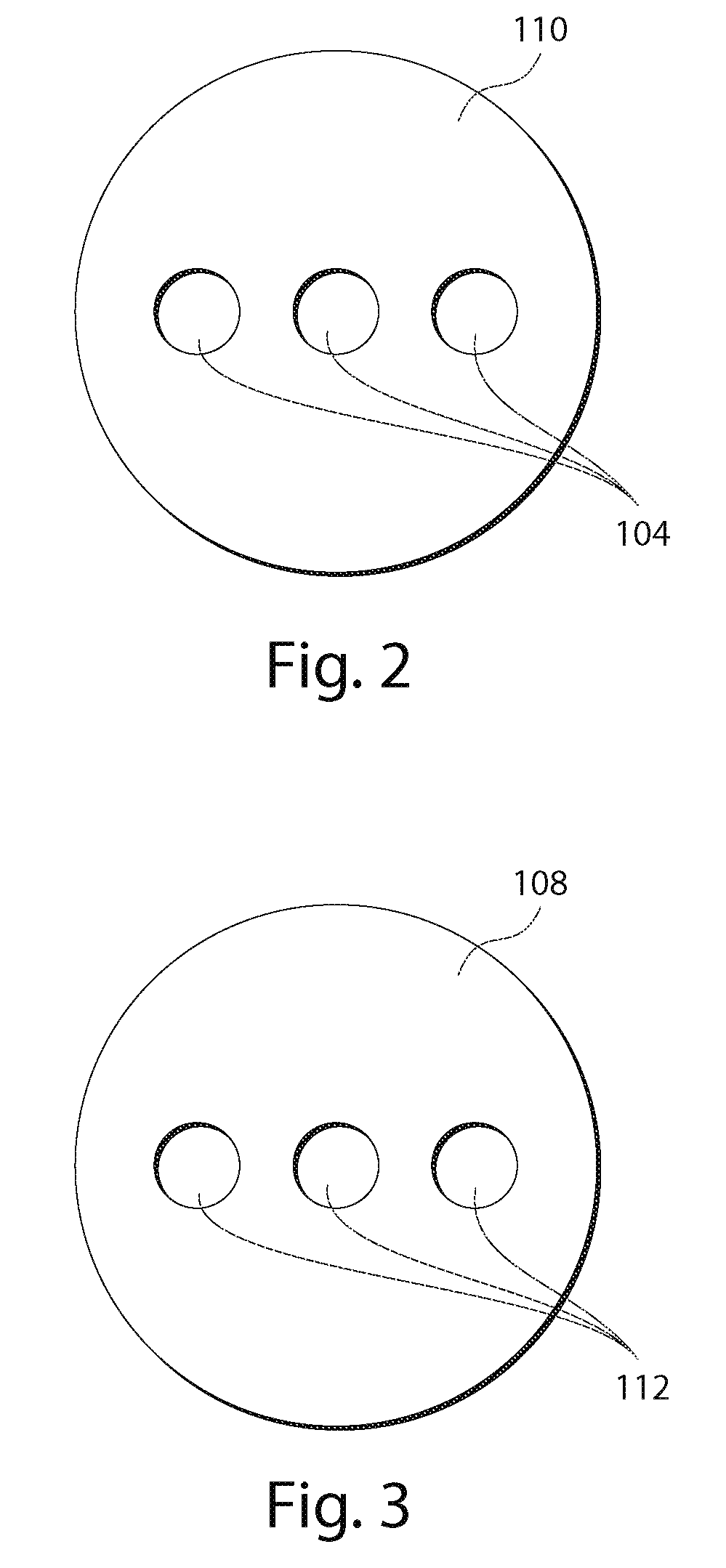
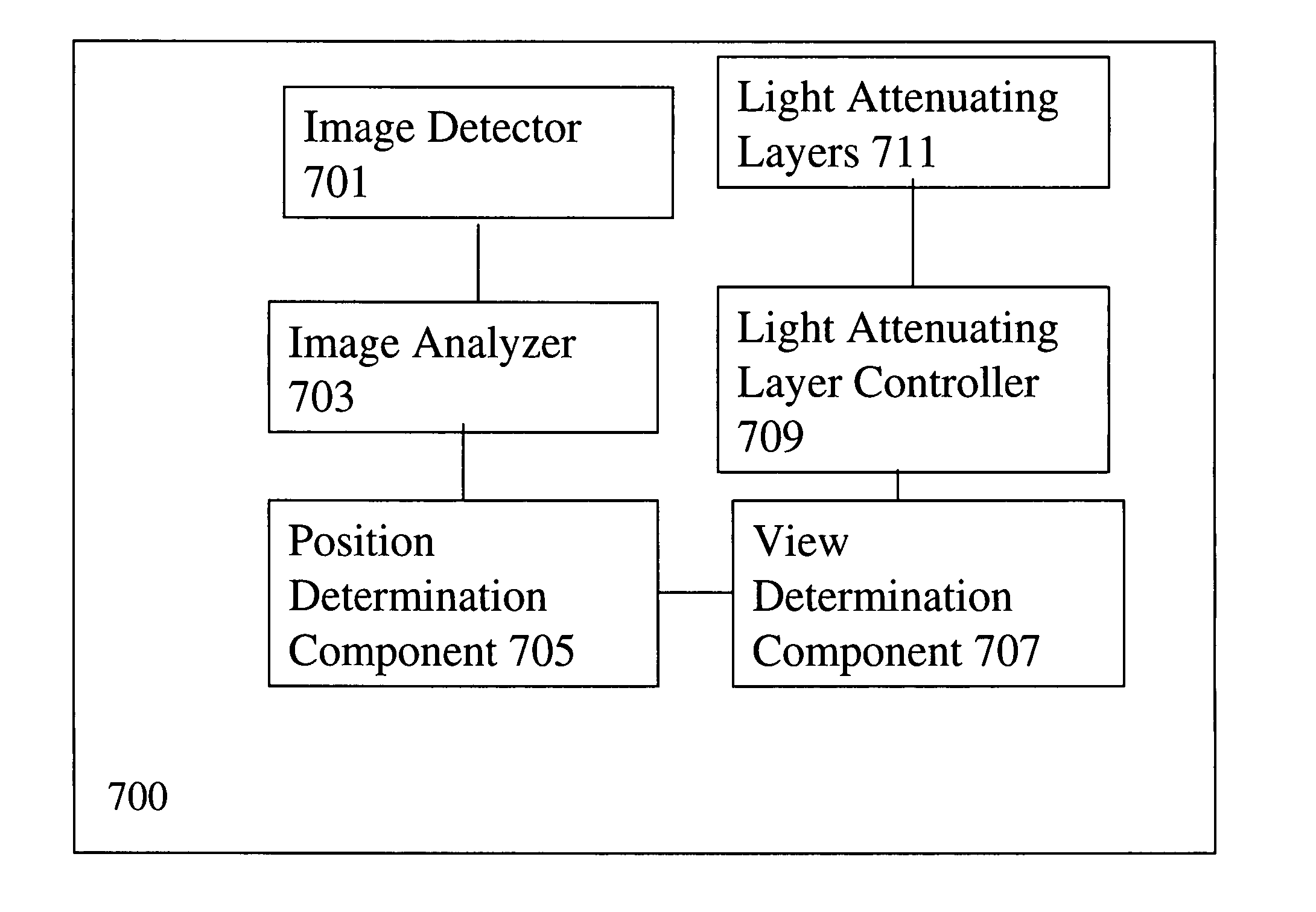
Lensless imaging with controllable apertures
InactiveUS20070081200A1Increase flexibilityOvercome limitationsTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionTransmittanceImage detector
Embodiments of the present invention provide a lensless optical device for acquiring an image. The device can include a light attenuating layer having a plurality of elements, where transmittance of each of the plurality of elements is controllable, and an image detector disposed at a distance from the light attenuating layer, the image detector configured to acquire an image with light that passes through the light attenuating layer. The device also can include a light attenuating layer controller configured to simultaneously control transmittance of each of the plurality of elements independent of each other. Methods of detecting and tracking an object in a scene are also disclosed.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
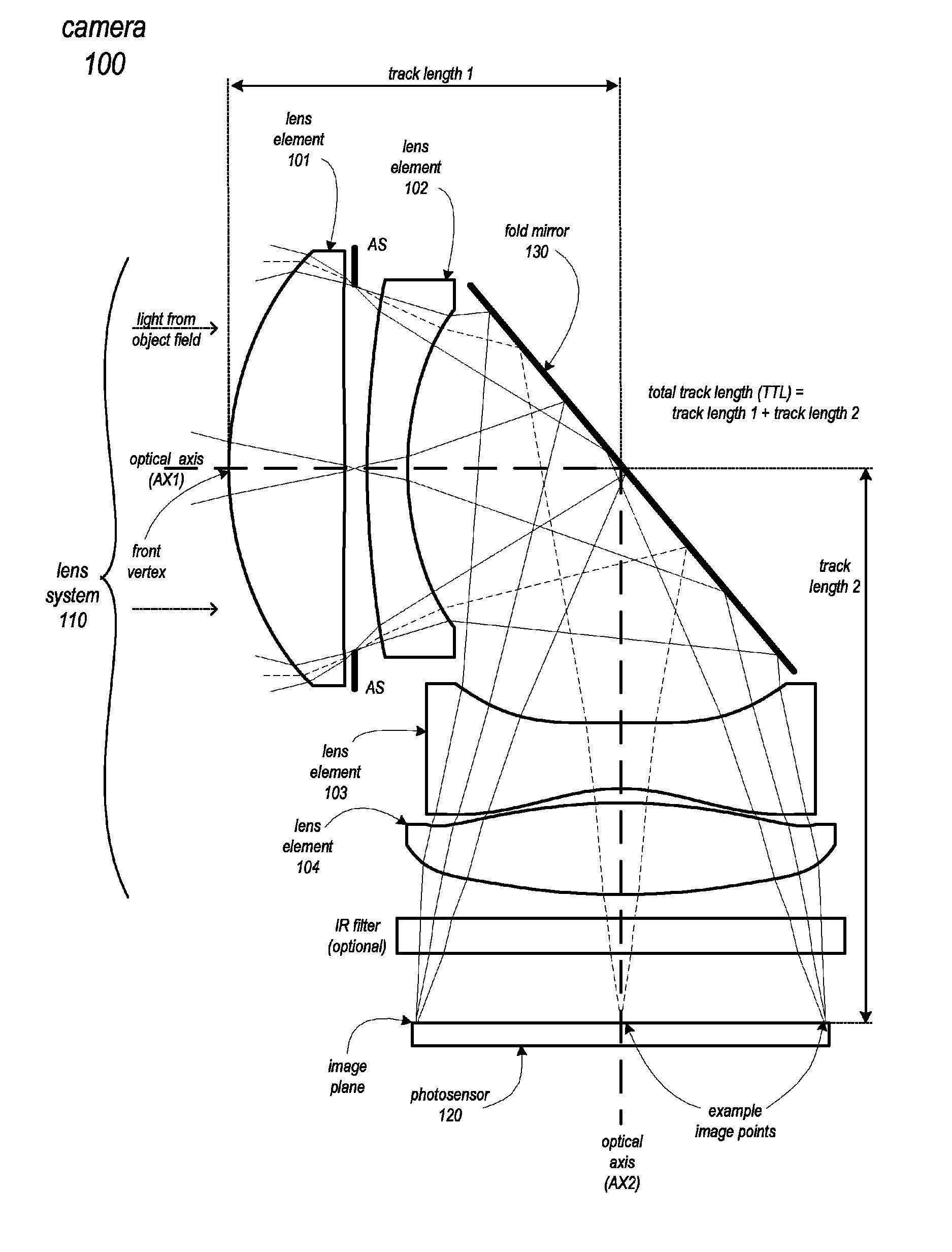
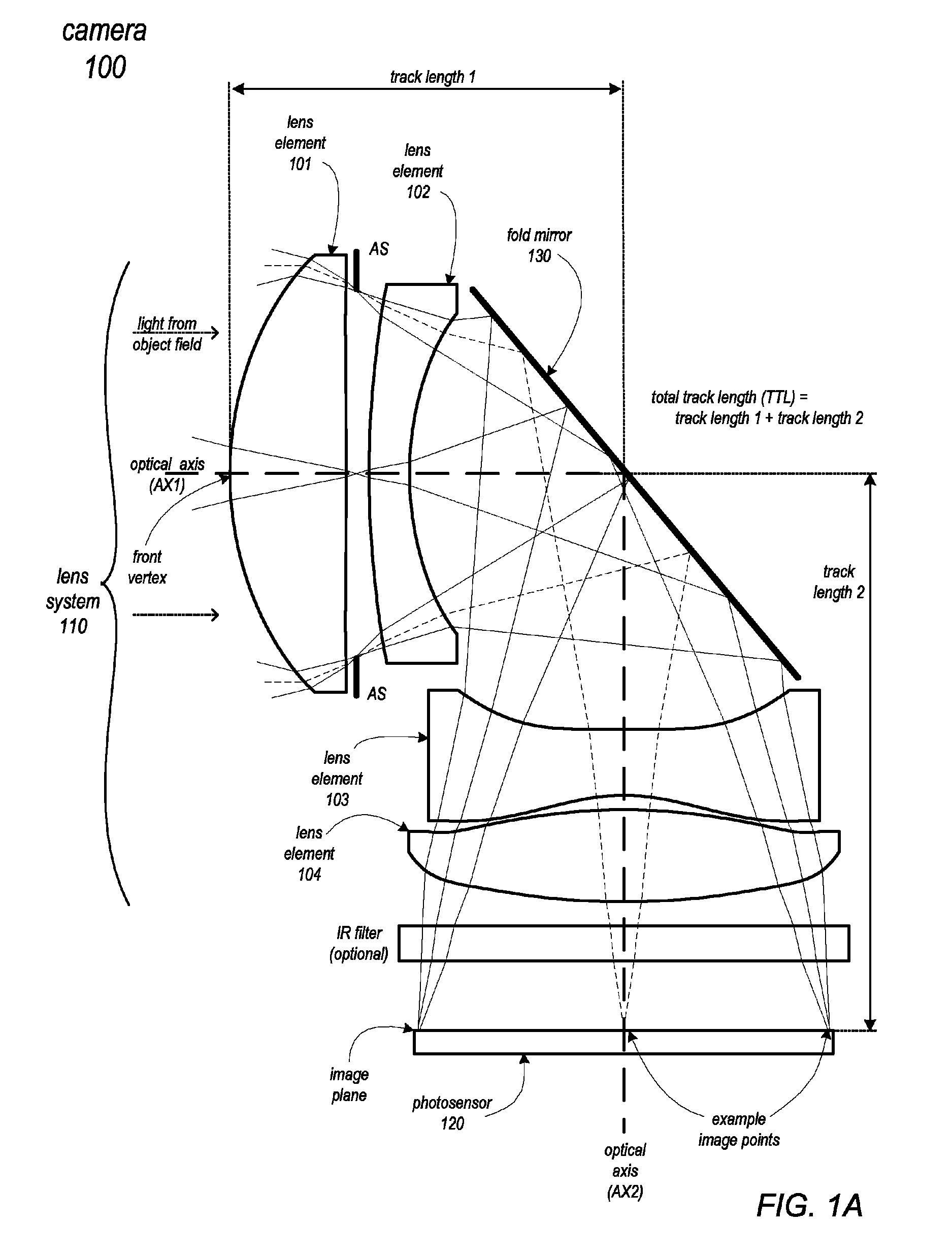
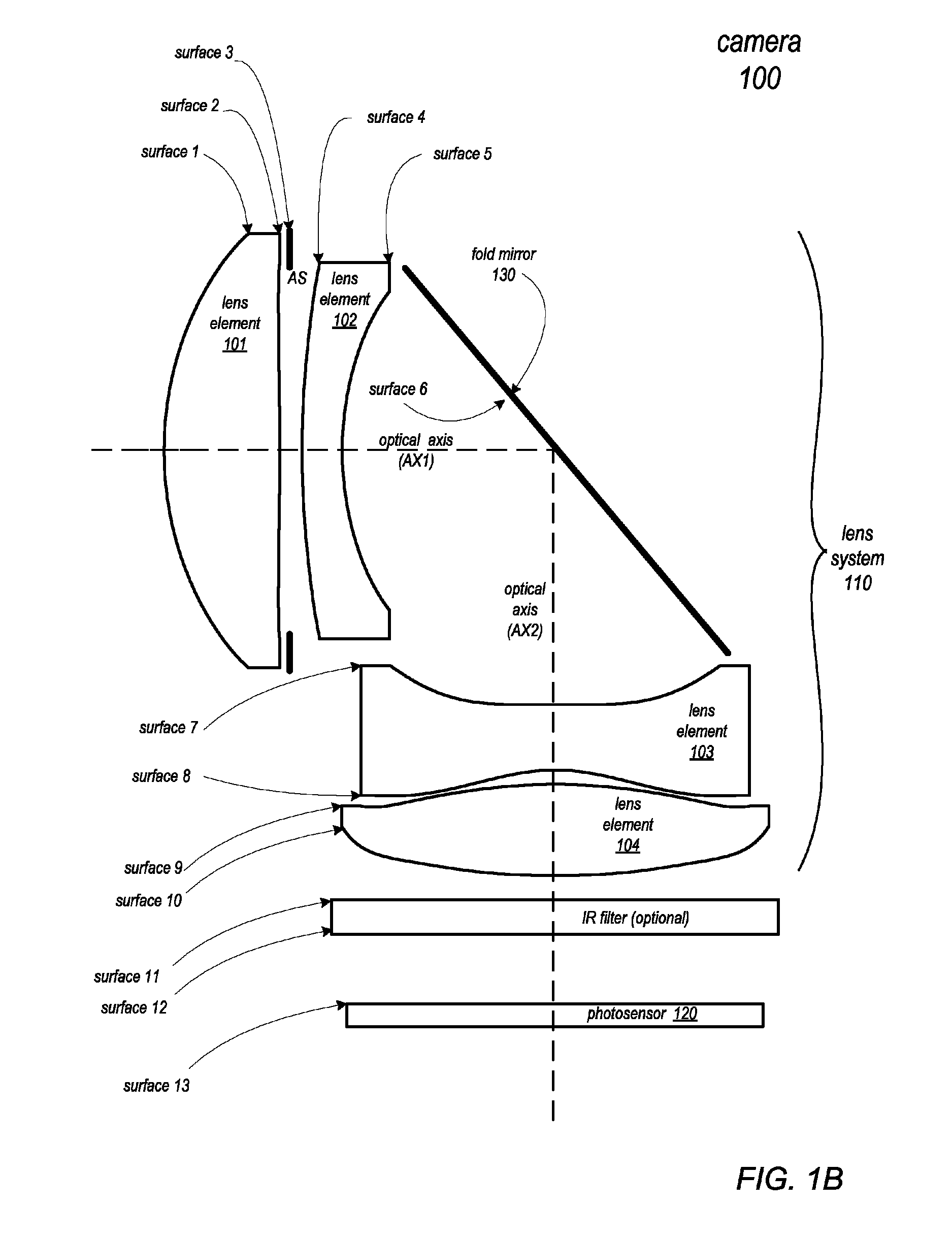
Folded telephoto camera lens system
ActiveUS9316810B2Small sizeEasy to implementTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensTelephoto lens
Owner:APPLE INC
Image pickup apparatus
InactiveUS20070065135A1Improve image qualityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical axisLight filter
Owner:CANON KK
Small imaging lens and imaging apparatus
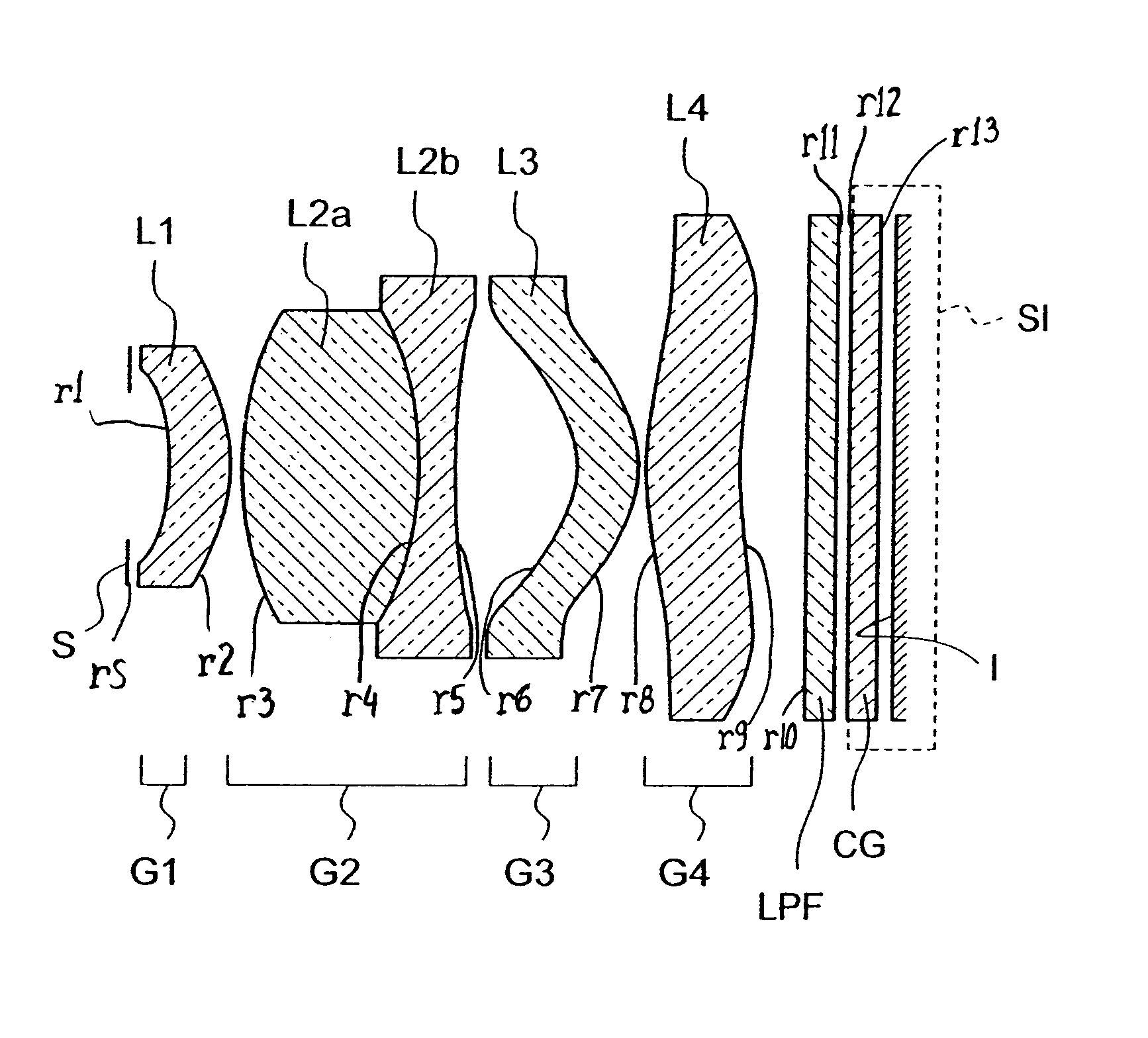
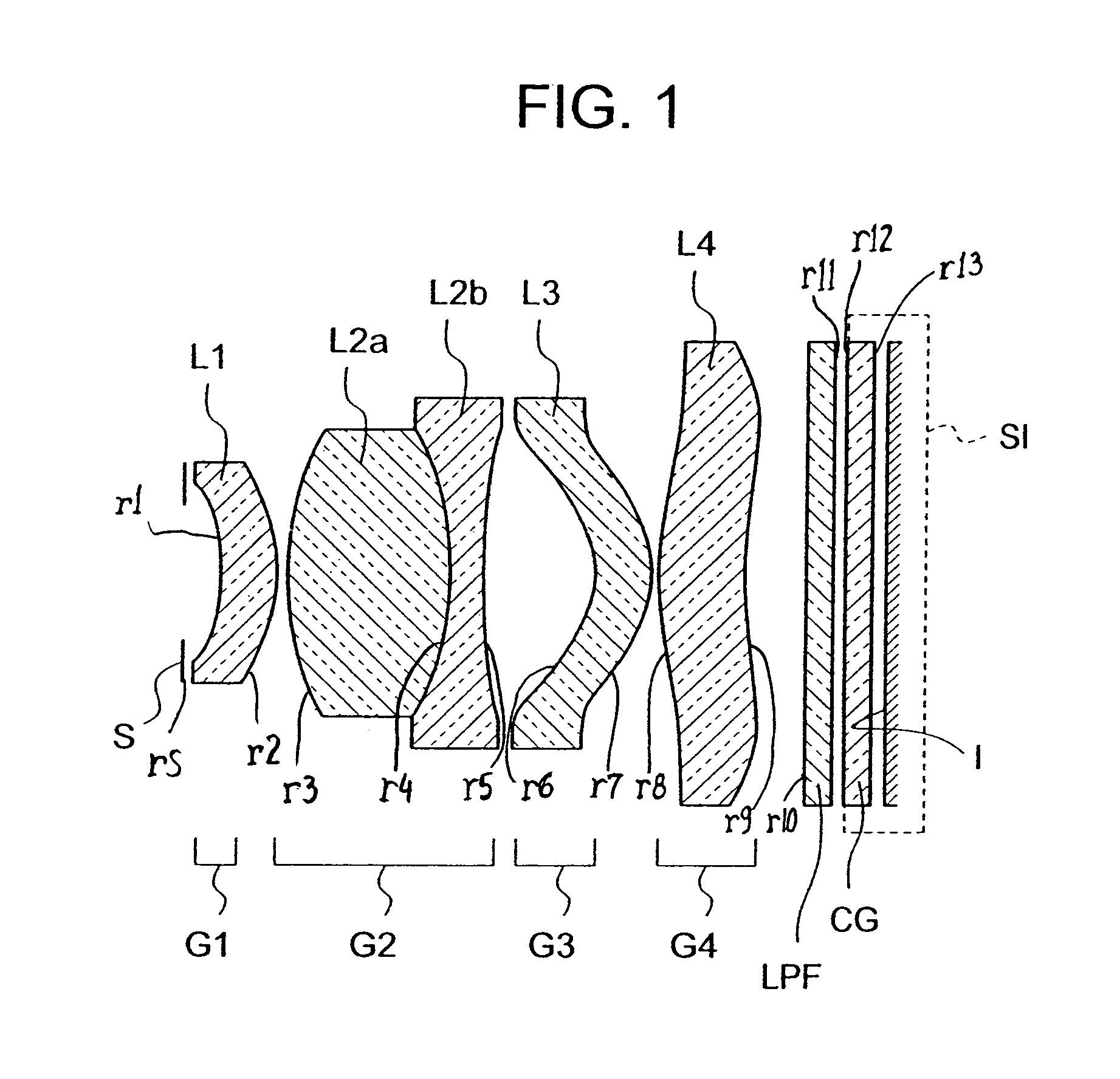
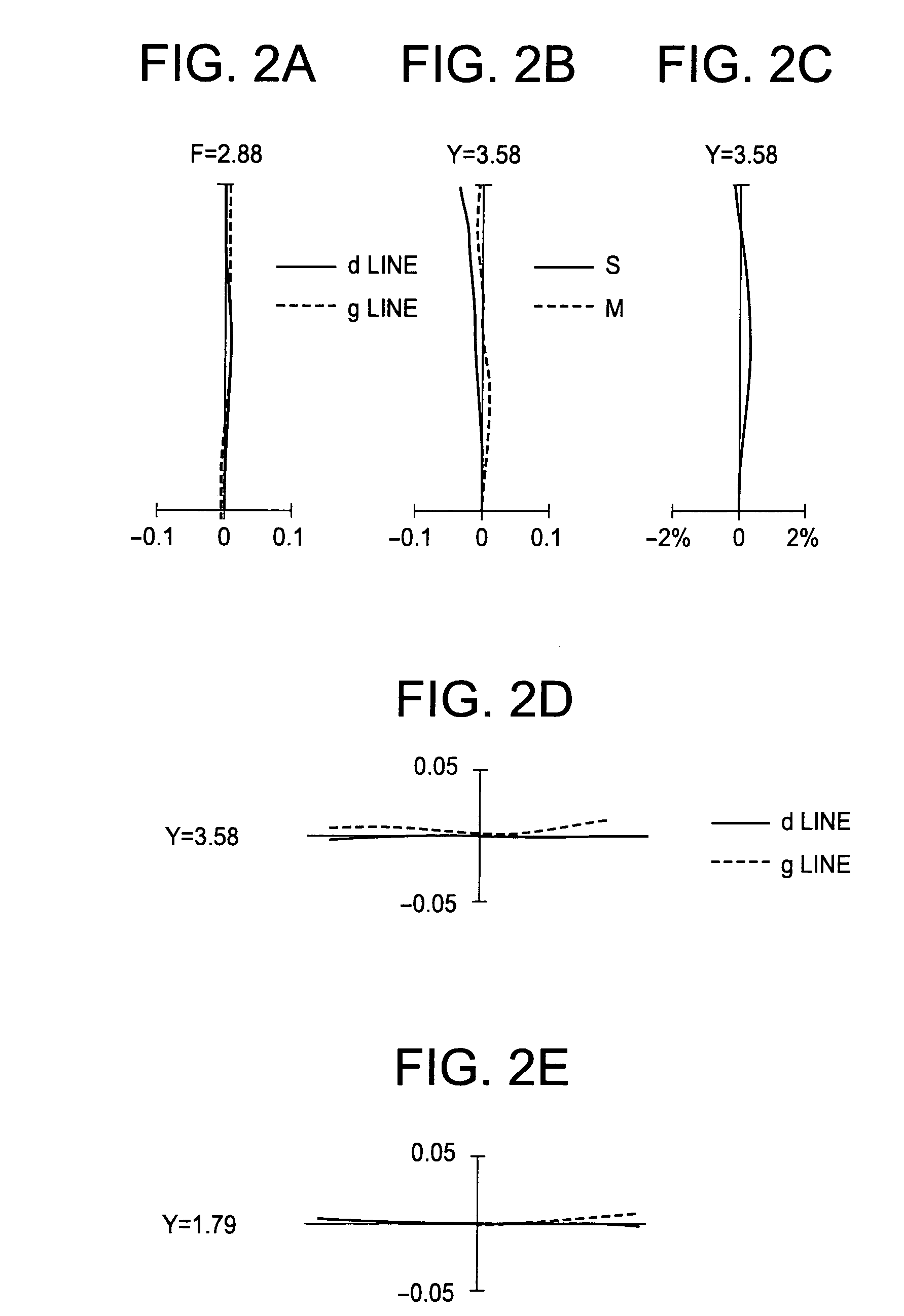
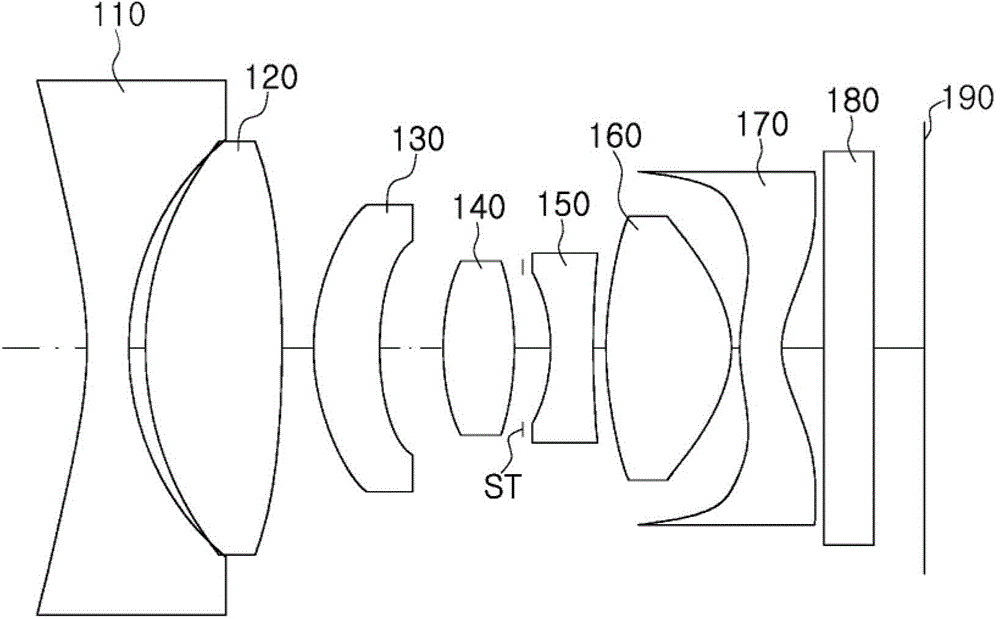
InactiveUS7110188B2Small sizeGood image-side telecentric characteristicCamera diaphragmsLensImaging lensImaging equipment
An imaging lens includes sequentially, from an object side, a first lens group, a second lens group, a third lens group, and a fourth lens group. The first lens group includes only a first lens having a meniscus shape with a concave surface facing the object side. The second lens group has positive refracting power as a whole and includes sequentially, from the object side, a second-first lens having positive refracting power and a second-second lens cemented to or separated from the second-first lens and having negative refracting power. The third lens group includes only a third lens having a meniscus shape with a concave surface facing the object side. The fourth lens group includes only a fourth lens.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Control method and device of light ring
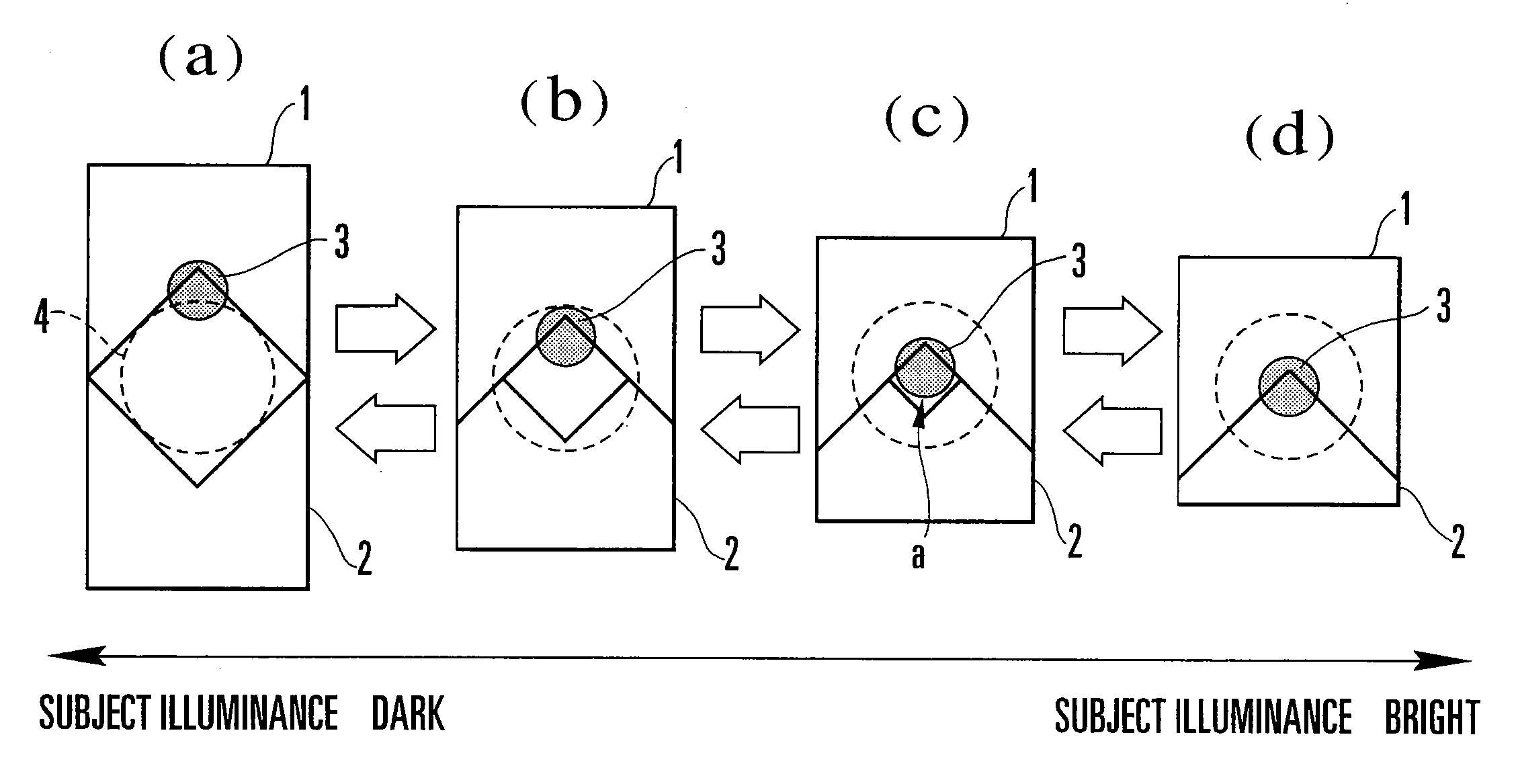
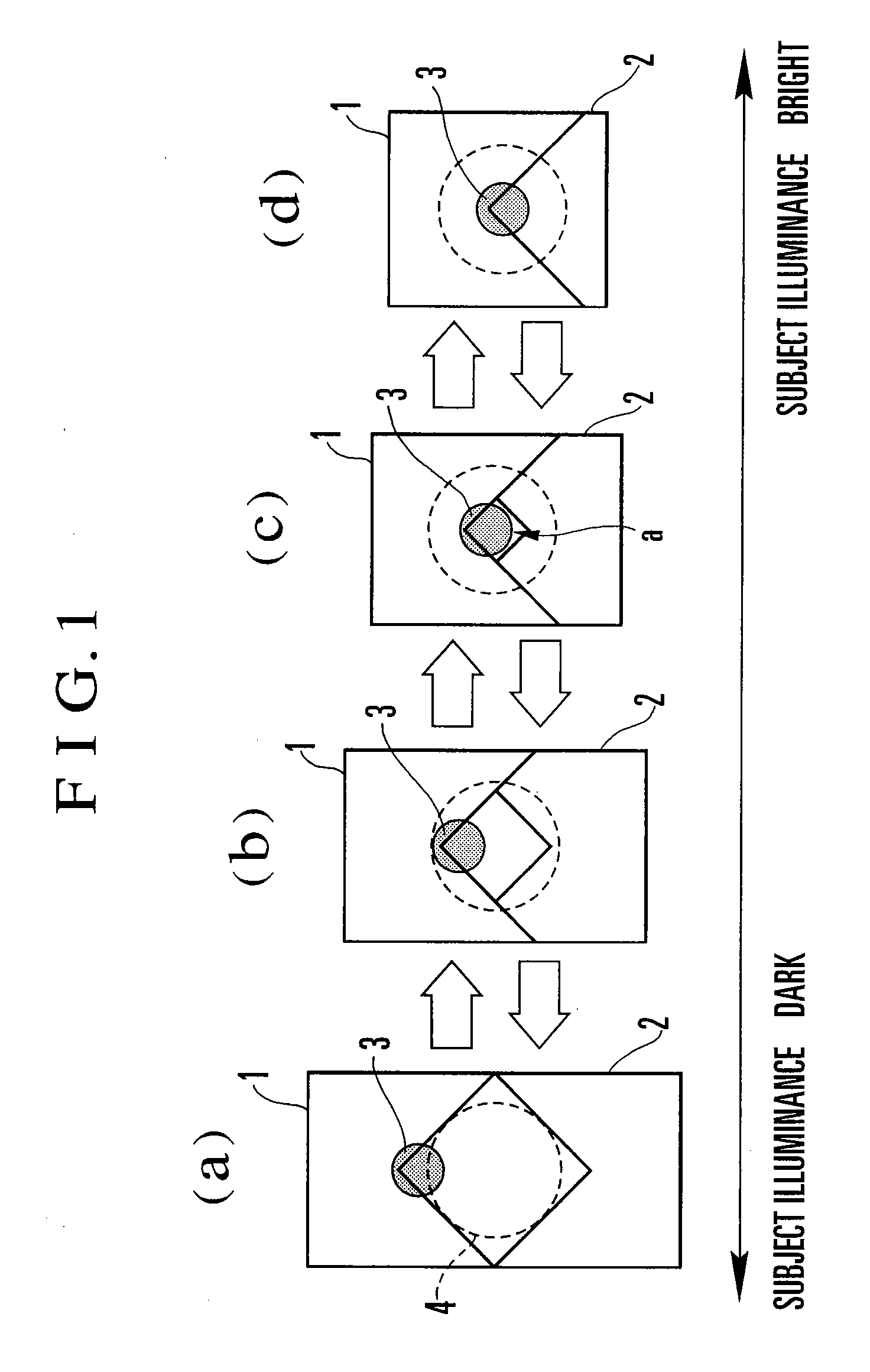
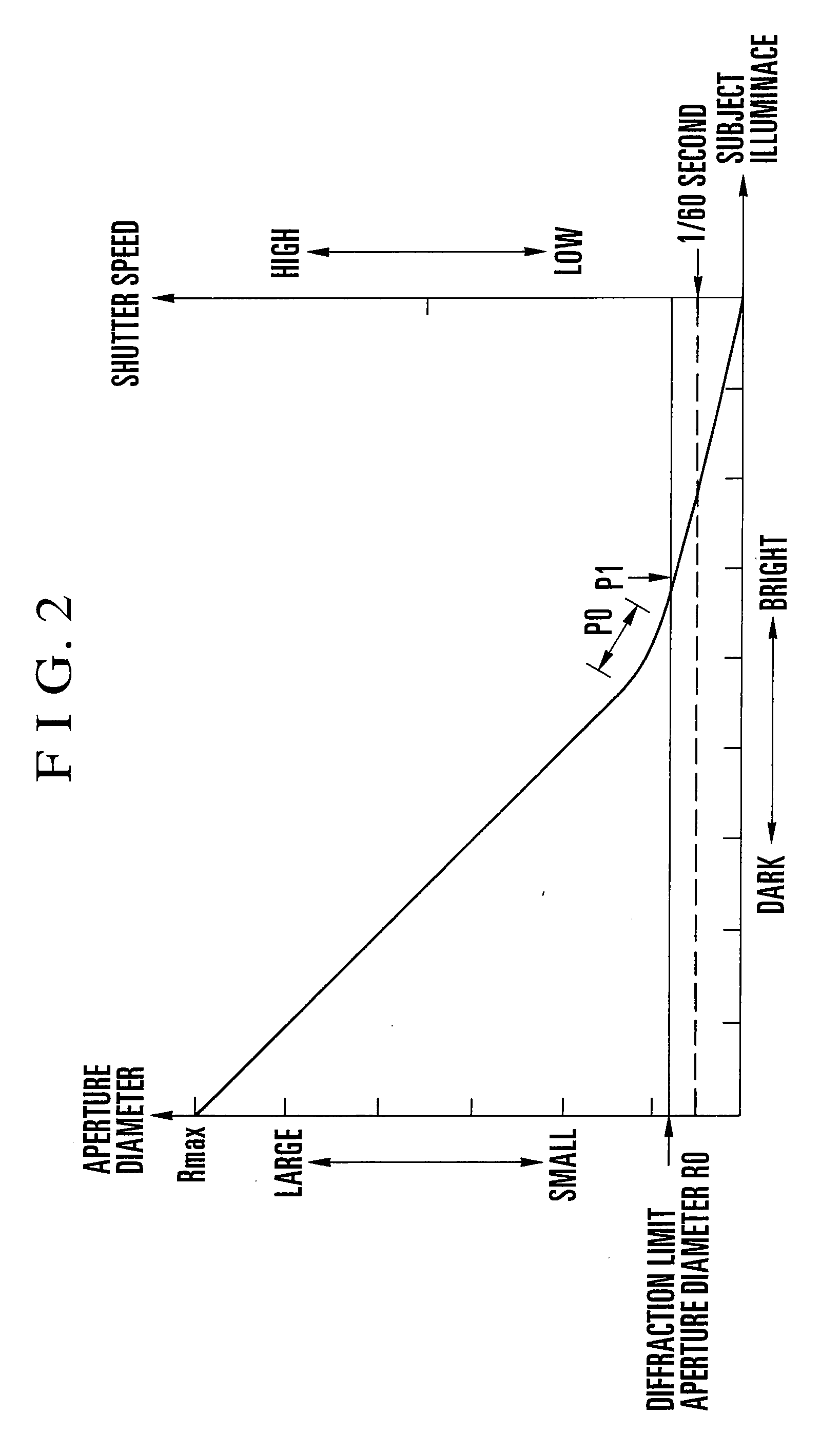
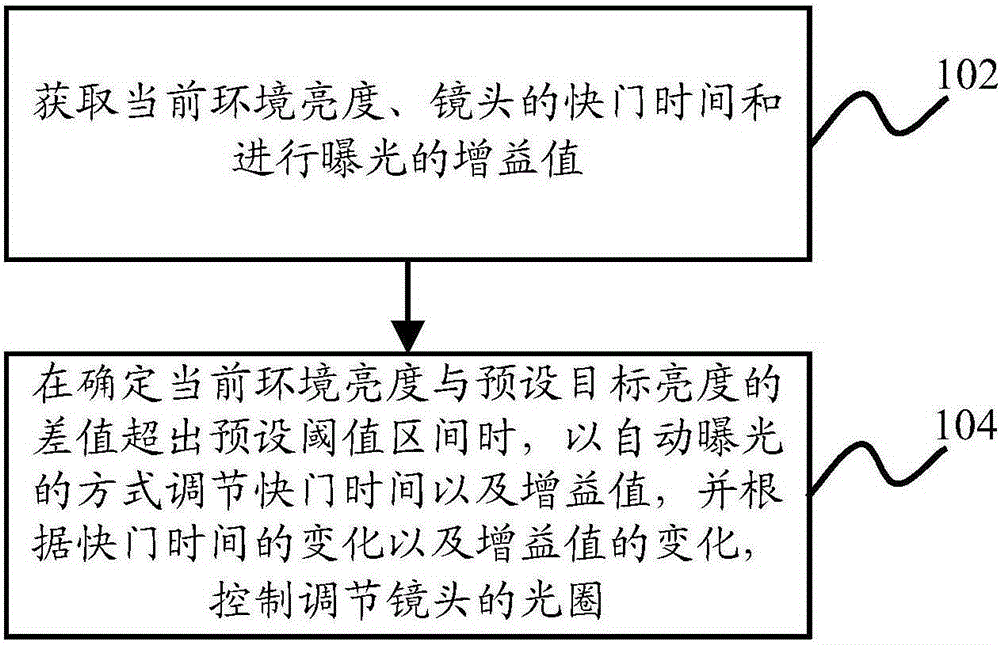
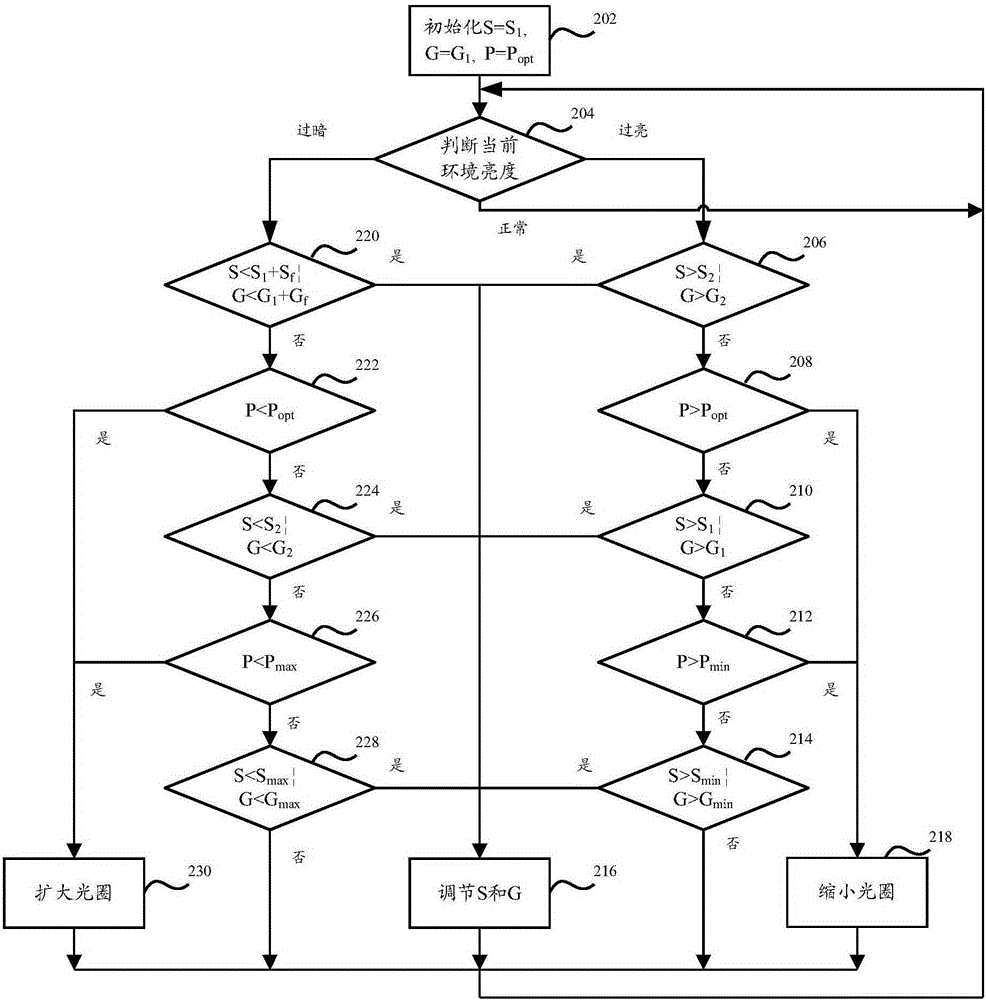
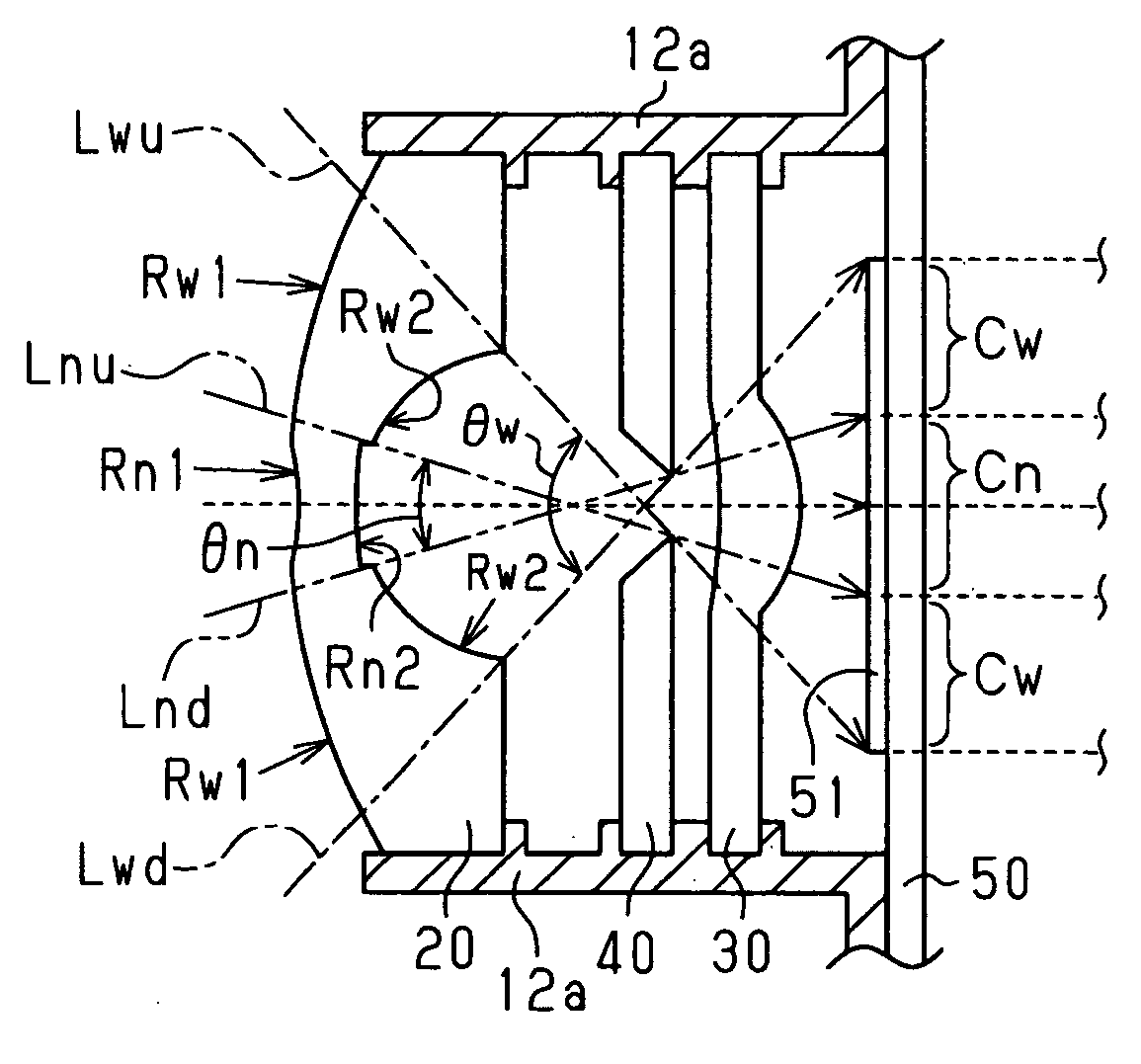
ActiveCN105242481AFlexible configurationAdapt to the diverse needs of application scenariosExposure controlCamera diaphragmsBrightness perceptionPhysics
The invention discloses a control method and device of a light ring. According to change of shutter time and change of a gain value, the light ring of an adjustment lens is controlled so as to be adaptive to versatile demands of an application scene. The control method of the light ring comprises the following steps of acquiring current environment brightness, the shutter time of the lens and the gain value during exposure; adjusting the shutter time and the gain value in an automatic exposure mode when the difference between the current environment brightness and the preset target brightness is determined to exceed a preset threshold interval; and controlling the light ring of the adjustment lens according to the change of the shutter time and the change of the gain value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DAHUA TECH CO LTD
Imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20070153120A1Less easily transmittedImprove reliabilityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsEngineeringImaging equipment
Owner:SONY CORP
Optical apparatus
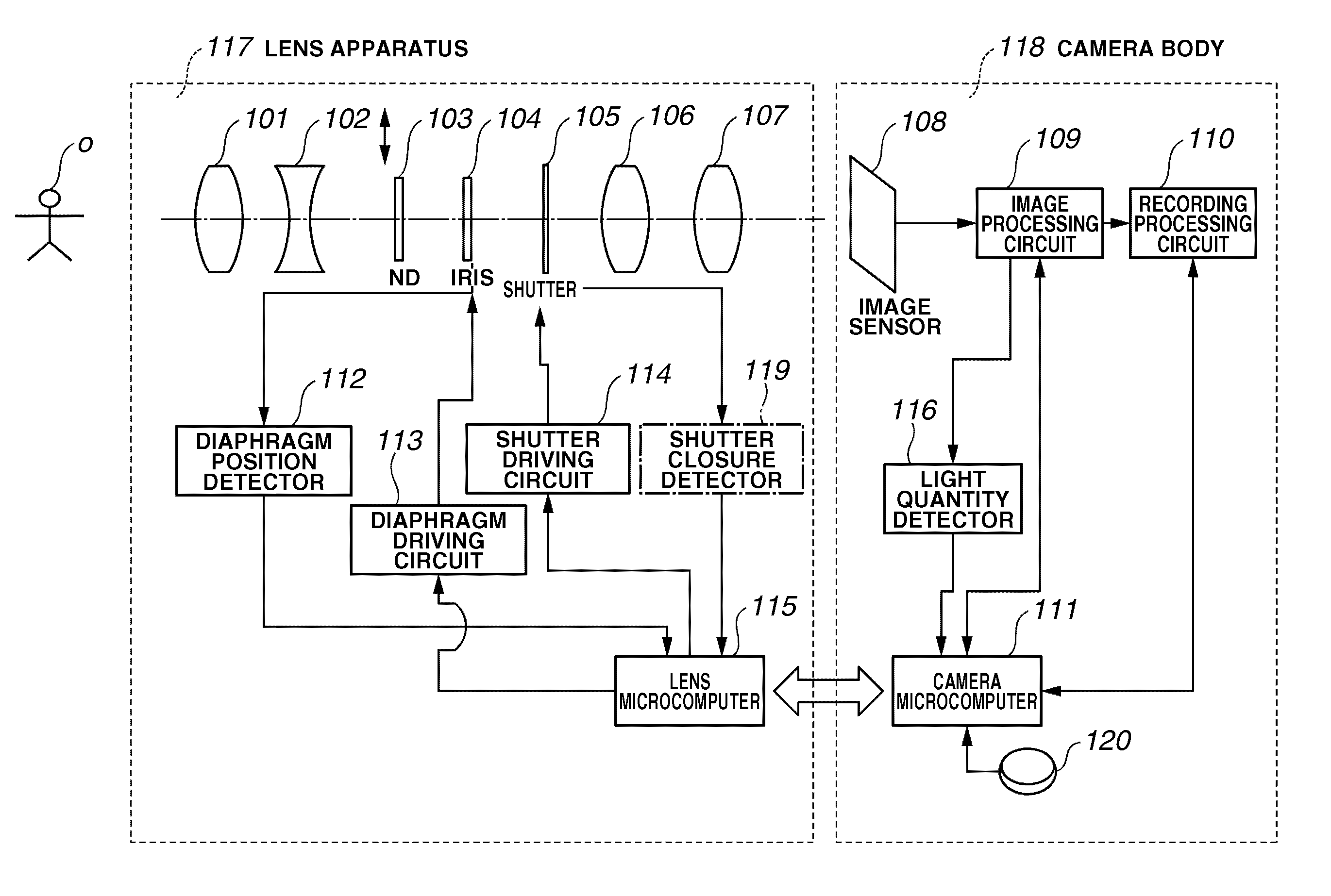
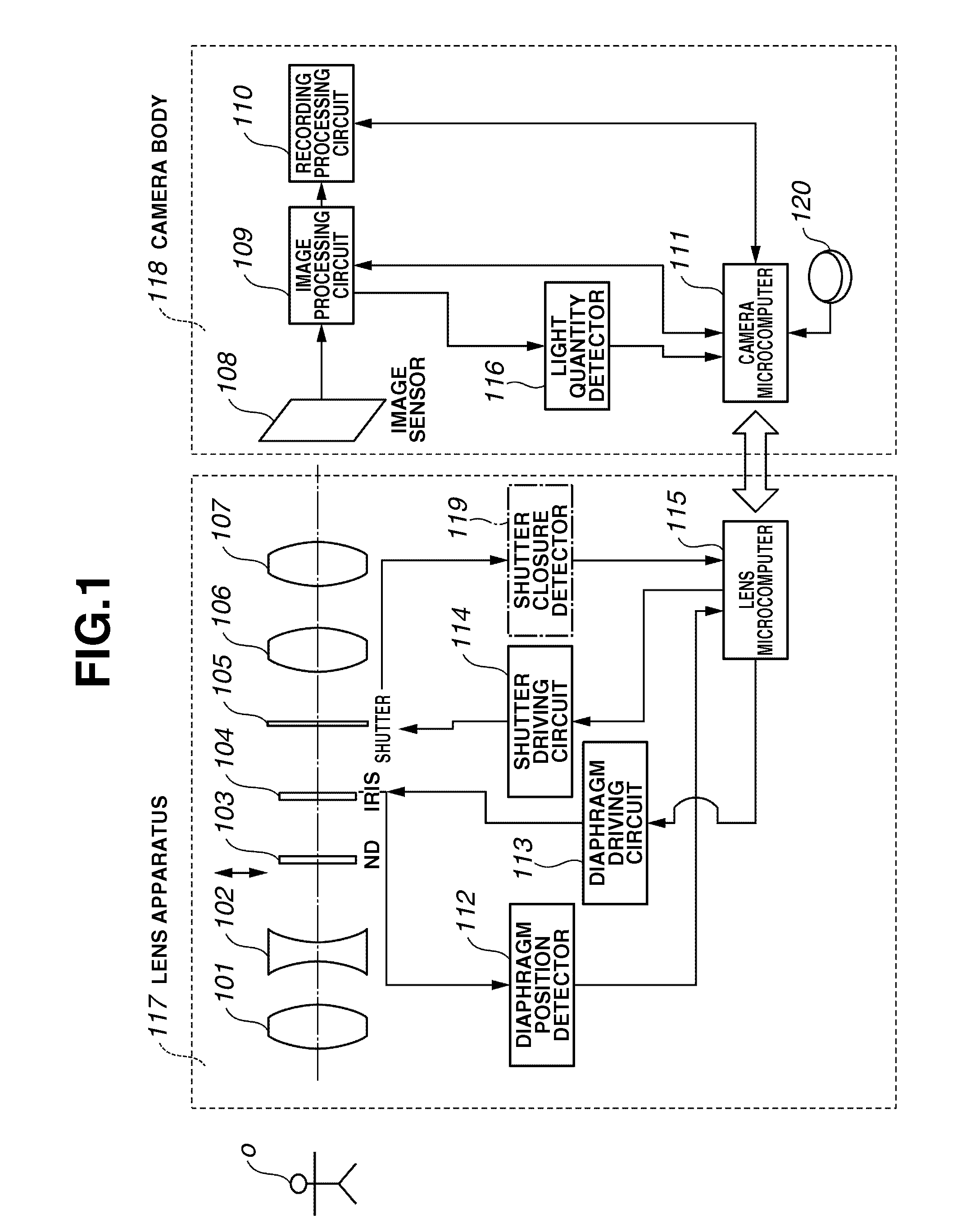
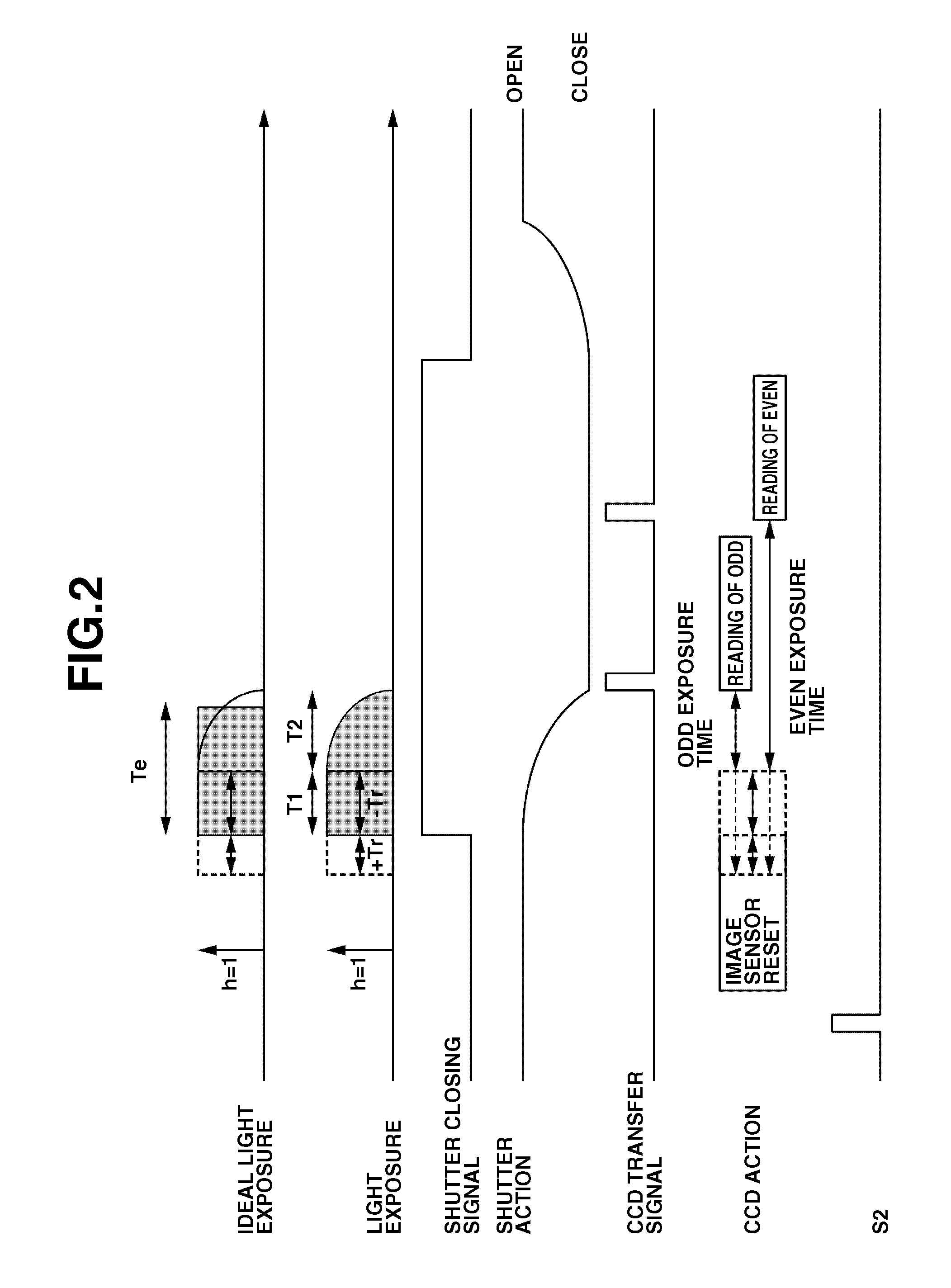
InactiveUS20070116453A1Accurate calculationExposure timeTelevision system detailsShuttersLight exposureAcoustics
An optical apparatus includes a mechanical shutter in addition to a mechanical diaphragm. The optical apparatus obtains a shutter shifting amount based on acceleration data of the shutter, obtains a total light exposure in a period of time required for the shutter to completely close an aperture of the diaphragm having a predetermined F-number, and calculates an actual exposure time by dividing the total light exposure by a light exposure per unit time calculated from an aperture area of the diaphragm having the predetermined F-number in an opened state.
Owner:CANON KK
Blade driving device for use in cameras
InactiveUS7156564B2Simple processSimple structureShuttersCamera diaphragmsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:COPAL CO LTD
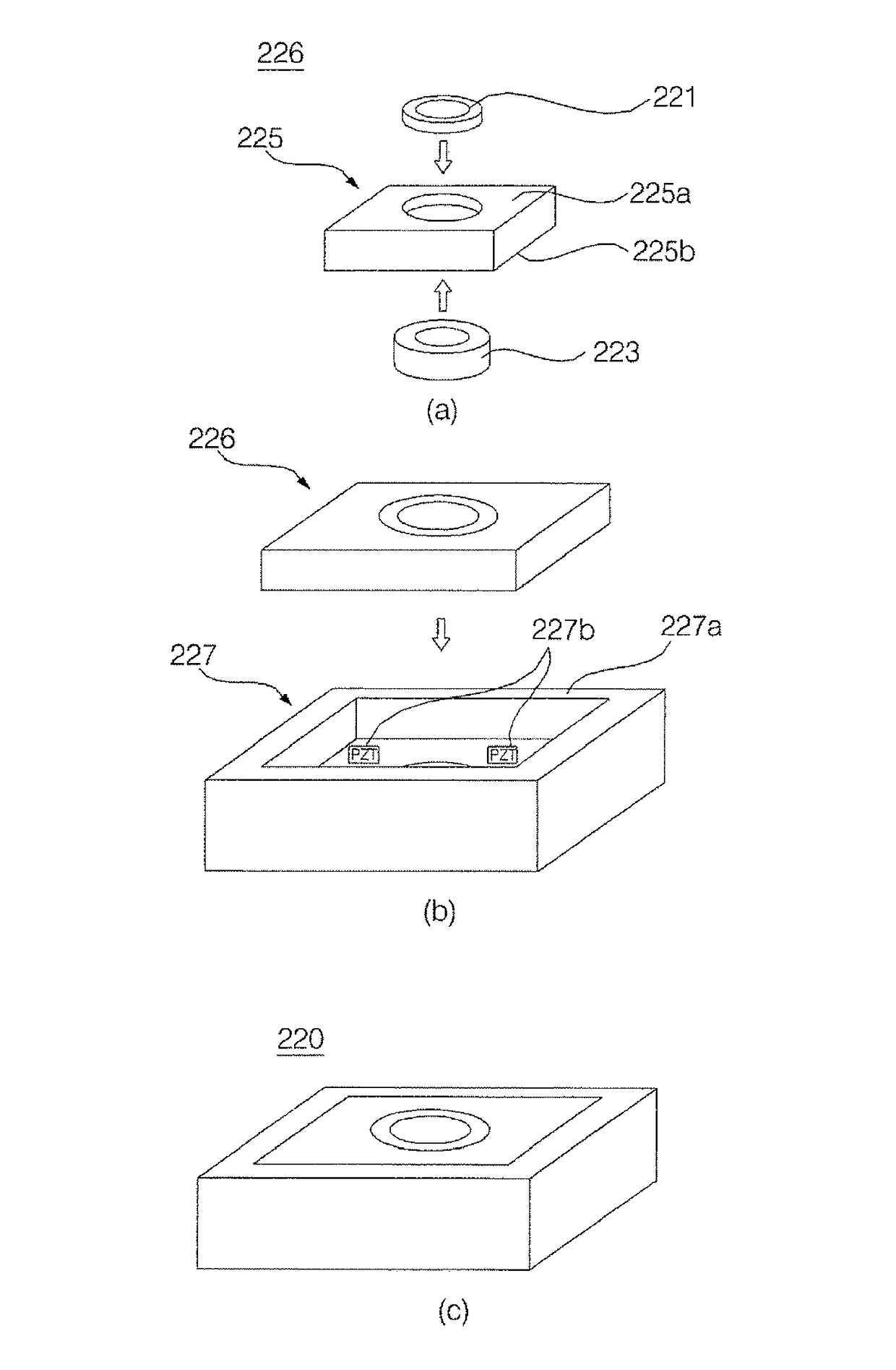
Optical element, lens unit and image pickup apparatus
ActiveUS20060047039A1Maintaining light transmissionMaintain performanceTelevision system detailsProjector focusing arrangementElectrolysisOptical property
An optical element and a lens unit each includes: a liquid container transmitting light at least in a predetermined optical axis direction, the liquid container containing an insulating liquid and an ionic liquid being mutually immiscible and optically transparent, and having different refractive indices; a first electrode contacting the ionic liquid in the liquid container; and a second electrode insulated from the ionic liquid in the liquid container. The ionic fluid is not subject to electrolysis and does not evaporate easily even at high temperature. Accordingly, the optical element, the lens unit and an image taking apparatus having the optical element can maintain high light-transmission and optical characteristics over a long period even in a high temperature environment.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +2
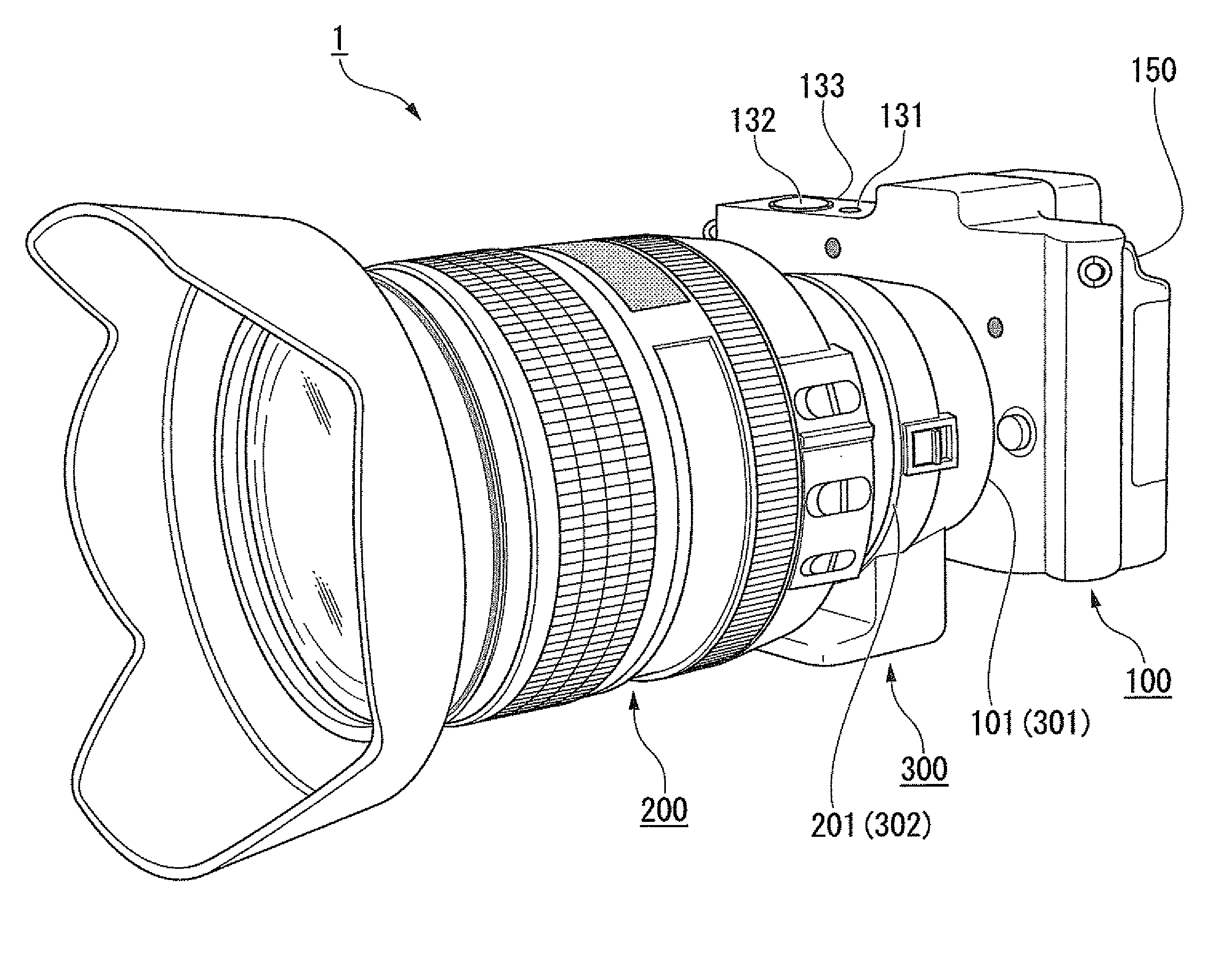
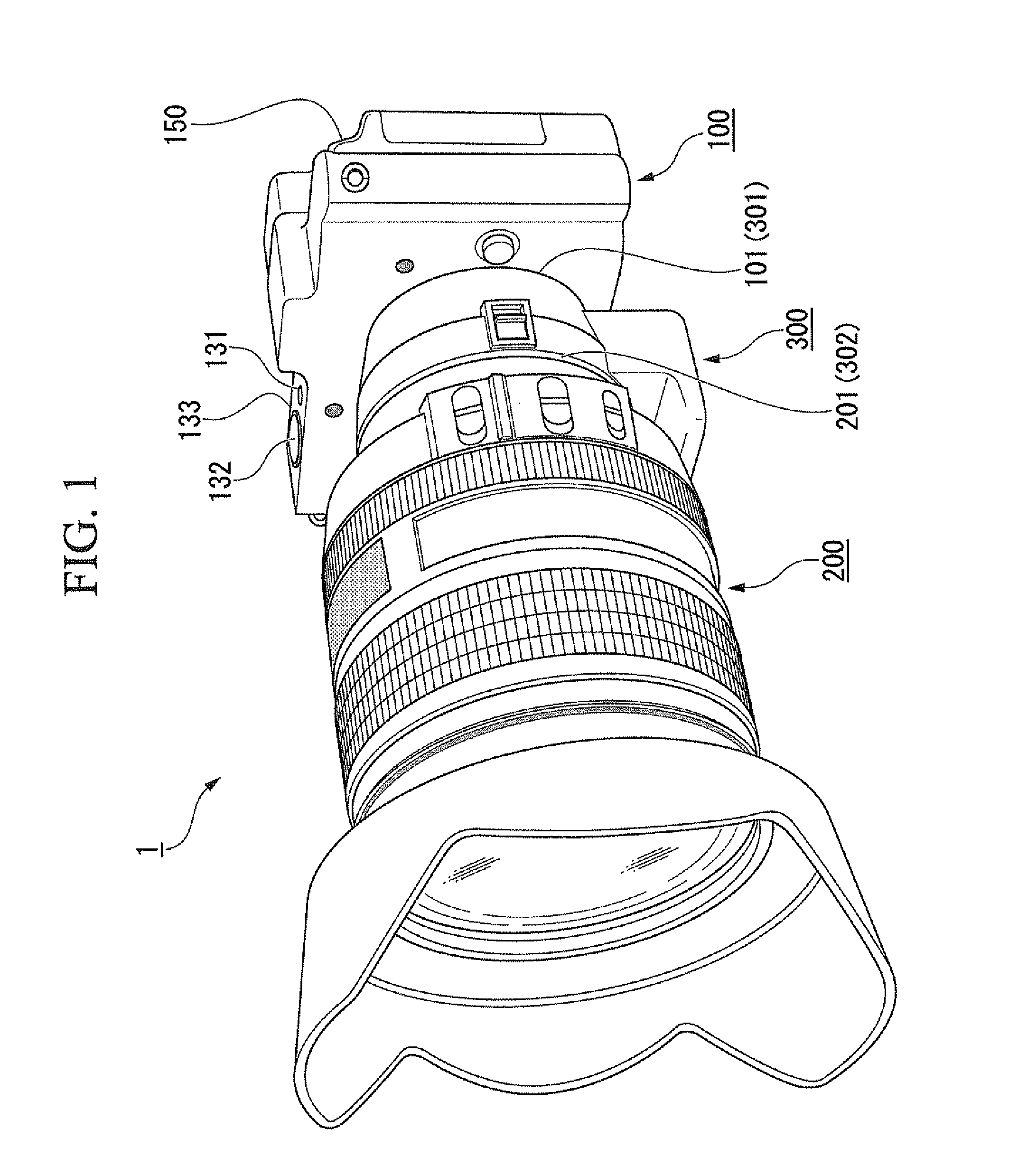
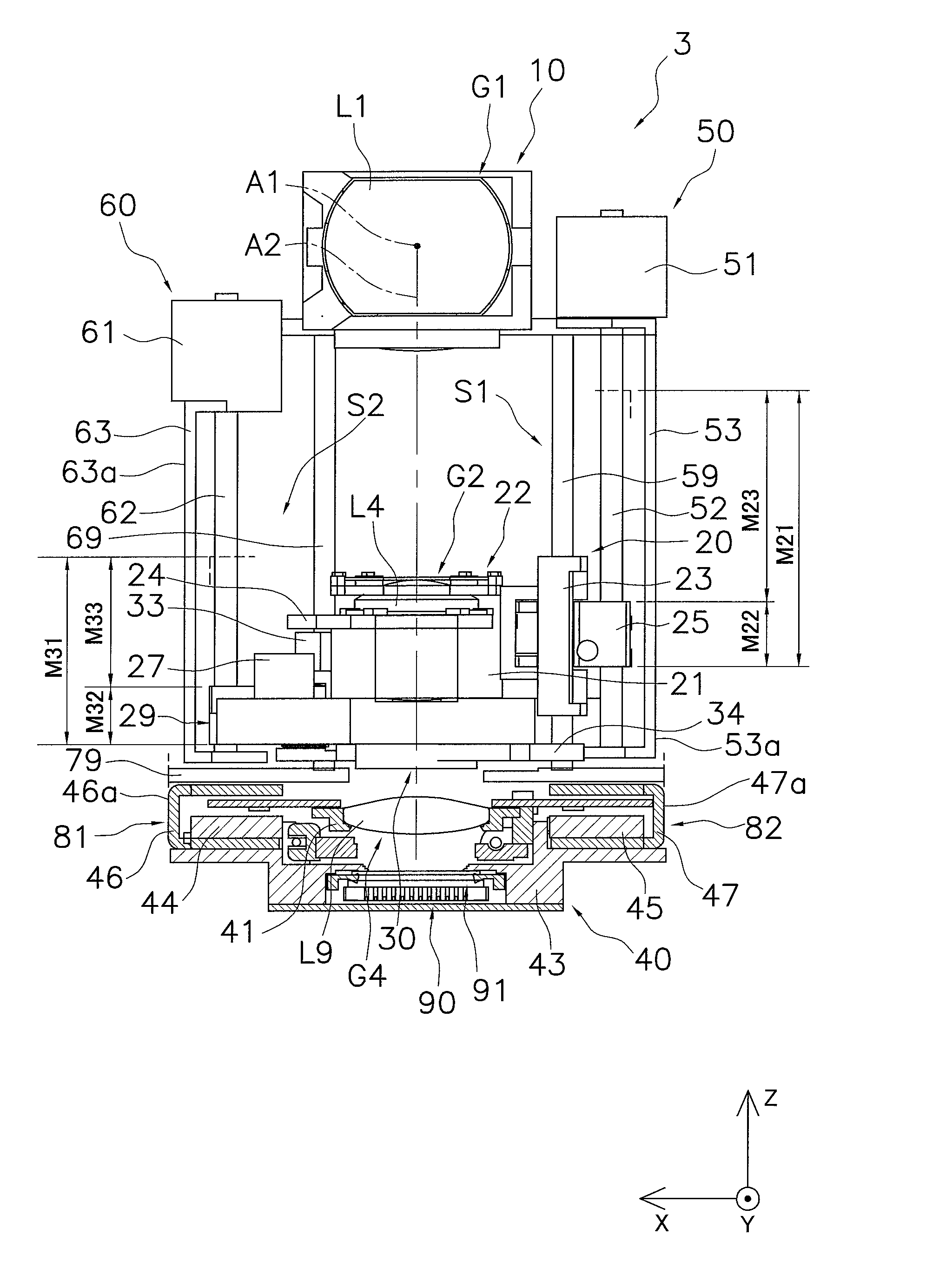
Lens barrel and lens support structure
ActiveUS20100277813A1Wide angleHigh magnificationMountingsCamera diaphragmsCamera lensManufacturing cost reduction
A lens barrel is provided with which manufacturing costs can be reduced. The lens barrel (3) has a first lens group (G1), a second lens group (G2), a third lens group (G3), a first support frame (10) that supports the first lens group (G1), a second support frame (20) that supports the second lens group (G2), a third support frame (30) that supports the third lens group (G3), a first driving unit (50), a second driving unit (60), and a shutter unit (29) that is fixed to the second support frame (20). The first lens group (G1) has an overall negative refractive power, and includes a prism (PR). The second support frame (20) is driven along a second optical axis (A2) by the first driving unit (50). The third support frame (30) is driven along the second optical axis (A2) by the second driving unit (60).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Image capture apparatus and control method therefor
InactiveUS7430369B2Television system detailsProjector focusing arrangementImaging processingStill camera
Owner:CANON KK
Optical system
An optical system includes a first lens having negative refractive power and having two concave surfaces, a second lens having positive refractive power, a third lens having refractive power, a fourth lens having refractive power, a fifth lens having refractive power, a sixth lens having refractive power, and a seventh lens having refractive power. The first to seventh lenses are sequentially disposed from an object side. Whereby an aberration improvement effect may be increased and high resolution and a wide angle may be implemented.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Imaging module
InactiveUS20060266835A1High resolutionMinimal loadingTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionOptics
An imaging module having an imager comprised of a group of imaging elements arrayed in a square lattice and an optical system for forming two kinds of light images, a light image of a careful looking region and a light image of a surrounding region, on the imager in a lens-barrel. The optical system of the imaging module includes a plurality of lenses arranged in a cylinder direction of the lens-barrel, and one of the lenses is formed as an aspherical lens such that a sectional radius of curvature of a center part of the lens is smaller than the sectional radius of curvature of a peripheral part of the lens.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Camera module
ActiveUS20180149833A1High-quality bright imageImage can be preventedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera moduleOptic system
The present invention relates to a camera module mounted in a mobile terminal, comprising: a first lens group having a first lens, which has a positive (+) refractive power, and a second lens, which has a negative (−) refractive power, in order from the object side, wherein the first and second lenses are integrally formed through a first lens barrel; a variable aperture for controlling the quantity of light incident into an optical system; and a second lens group having a third lens having a negative (−) refractive power, a fourth lens having a positive (+) refractive power, and a fifth lens having a positive (+) refractive power, wherein the third to fifth lenses are integrally formed through a second lens barrel.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Lens shutter and aperture control devices
ActiveUS20090147340A1MountingsPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesCamera lensElectroactive polymer actuators
The present invention provides optical systems, devices and methods which utilize one or more electroactive polymer actuators to provide shutter and / or aperture control.
Owner:BAYER MATERIALSCIENCE AG
Camera, aperture controlling method and apparatus, lens controlling method and apparatus, and edging amount controlling method and apparatus
InactiveUS7292280B2Image qualityImprove vibrationTelevision system detailsPrintersCamera lensImage resolution
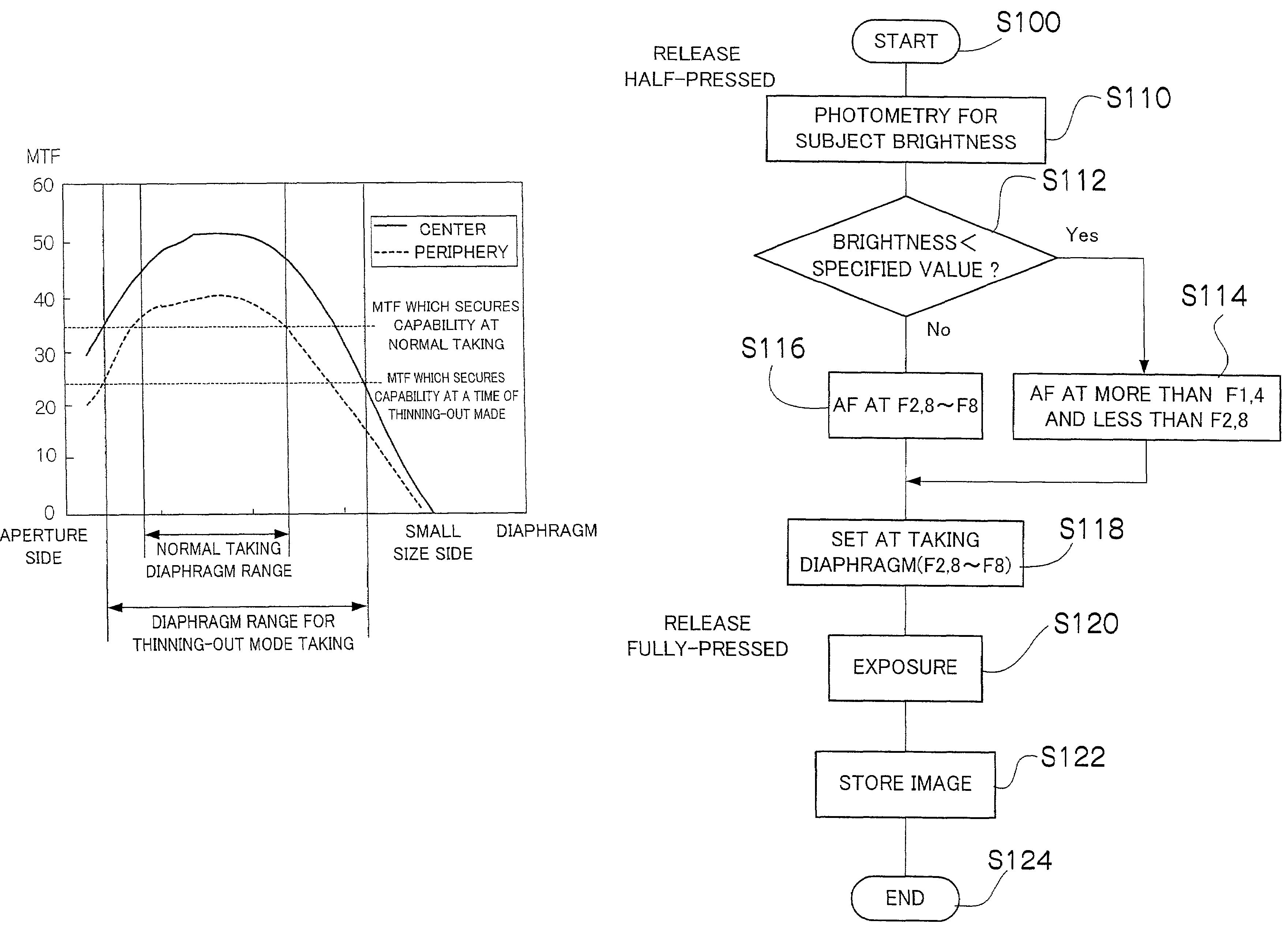
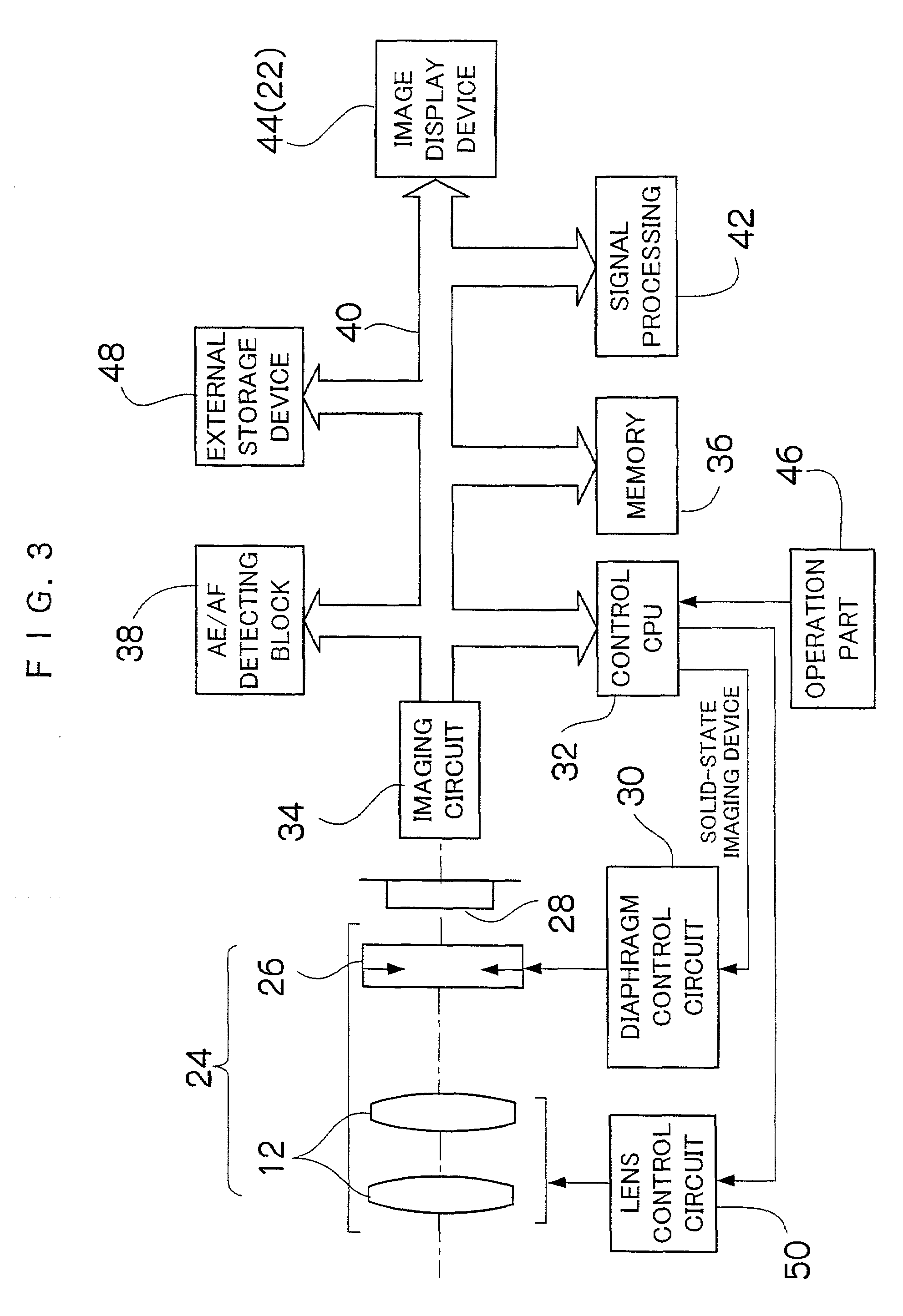
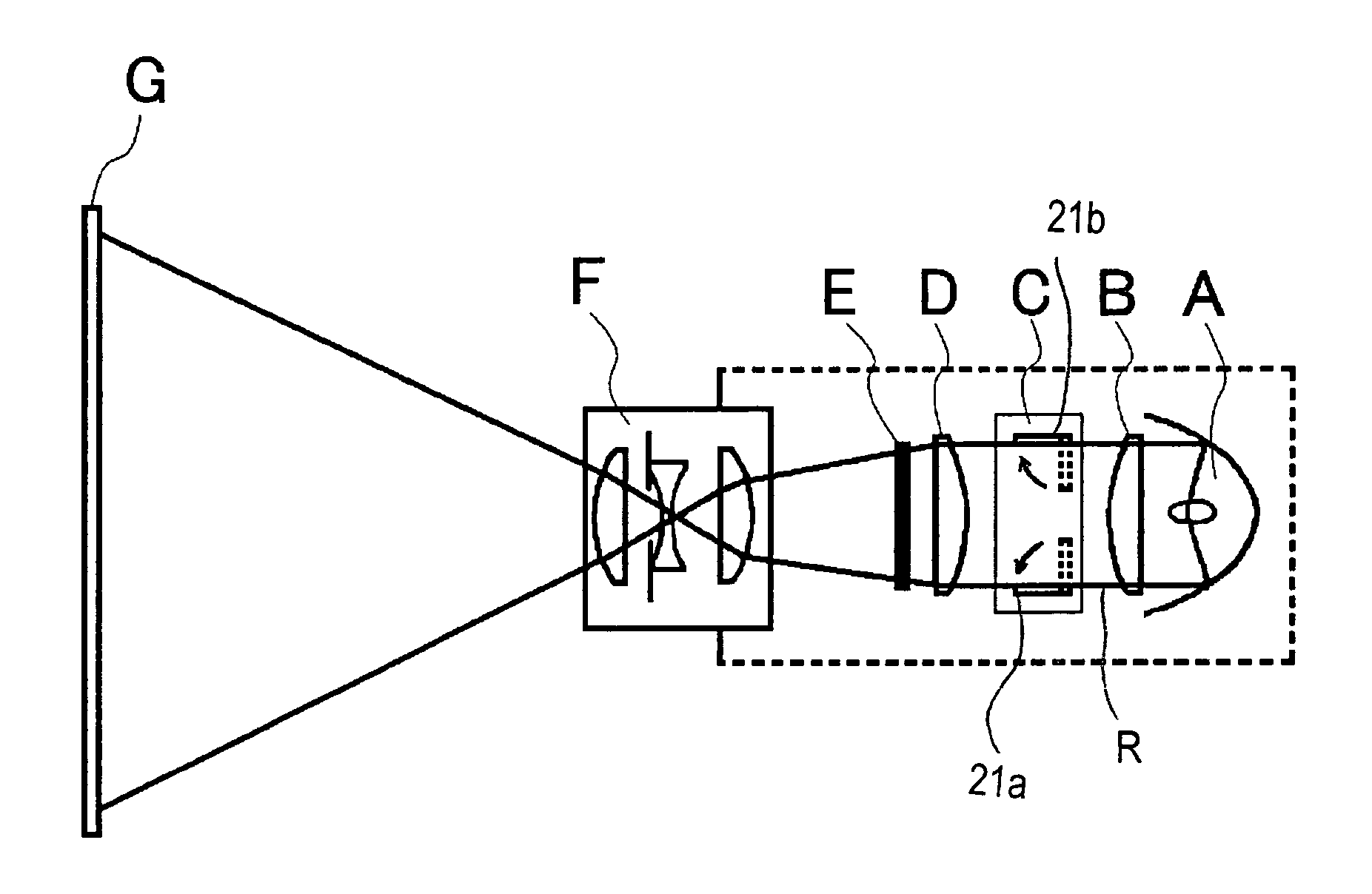
Maximum and minimum aperture sizes are regulated with regard to a diaphragm in order to secure predetermined optical capability in an optical unit which includes a taking lens and the diaphragm. In a normal taking, the diaphragm is used within a normal taking range from the maximum to the minimum aperture sizes. In the present invention, an aperture size which is larger than the maximum size and a size which is smaller than the minimum size (extra aperture size or extra small size) are respectively set at outside the range that secures the capability. The aperture sizes of the diaphragm at outside the specified range are used at least for one of the following: automatic exposure (AE) adjustment, auto focus (AF) adjustment, electronic zoom, displaying a moving image, taking for recording the moving image, and taking under a low resolution by thinning out pixels.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
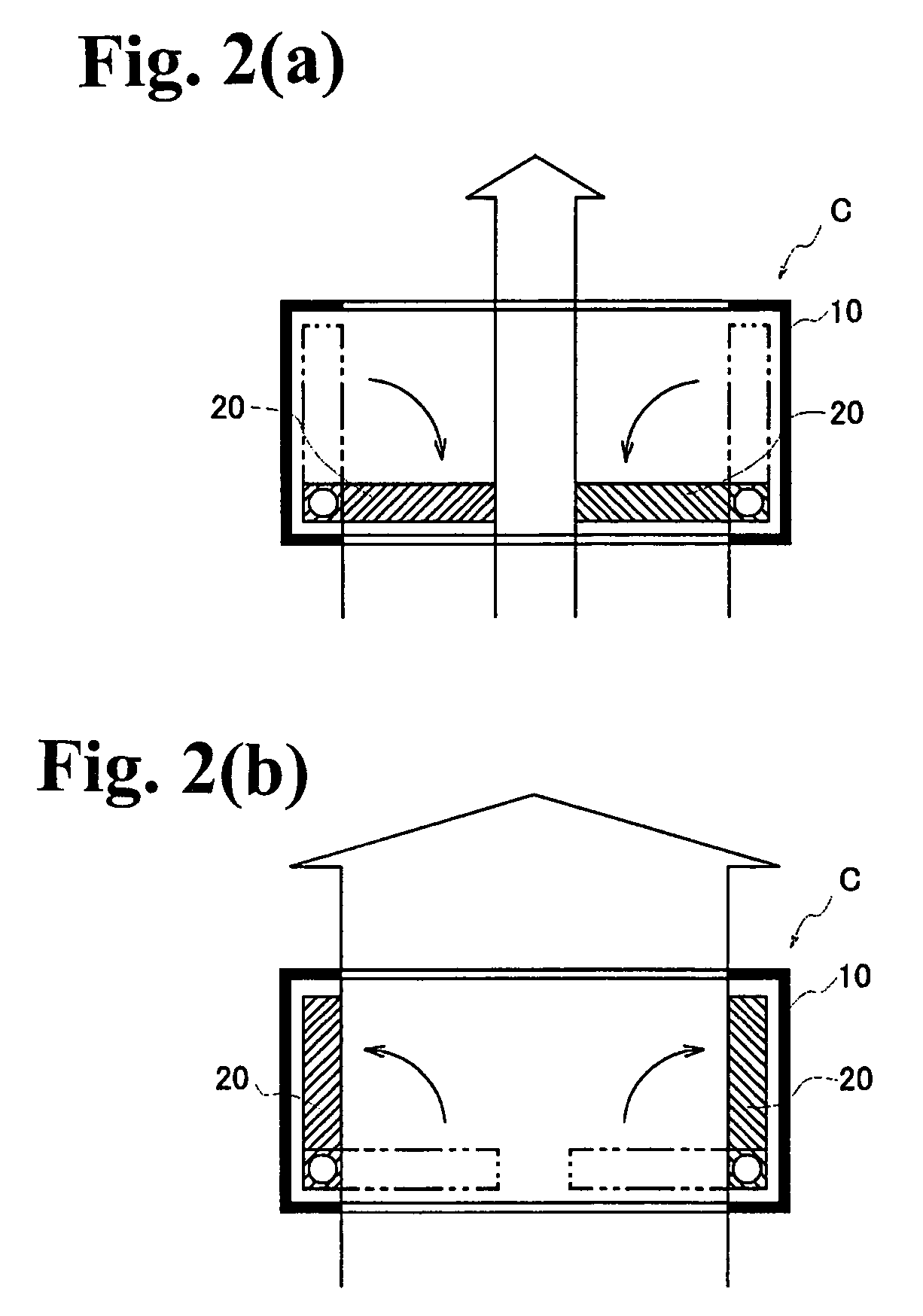
Light amount adjusting apparatus and projector using the same
At least a pair of light amount adjusting plates is allocated at peripheral side rim portions of a light path through which light from a light source is projected. These light amount adjusting plates are drivable between a narrow-down position in which they enter into the light path and a retreat position in which they retreat to outside of the light path. A restriction member such as a stopper member restricts a rotation of the light amount adjusting plate at the retreat position, and a holding unit holds the light amount adjusting plate to this restriction member. The restriction member blocks a predetermined angle or further rotation of the light amount adjusting plate, and the holding unit, such as a spring or a magnet, biases the light amount adjusting plate to the restriction member.
Owner:NISCA KK
Light quantity adjusting device and projector apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20050264770A1Reduce stepsReduce frictionTelevision system detailsProjectorsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A light quantity adjusting device for adjusting light quantity of a projector apparatus. The adjusting device includes a substrate having an optical path opening and a blade guide surface having level differences in a direction perpendicular to the optical path; a plurality of blade members arranged at a circumferential edge of the optical path opening for rotating along the blade guide surface in an inclined state with respect to the optical path; and a plurality of pins disposed on the substrate for supporting base end portions of the blade members to rotate around the base end portions for opening and closing the optical path opening. A transmission member is mounted on the substrate for engaging the blade members, and a drive device drives the transmission member to rotate the blade members to open and close the optical path opening.
Owner:NISCA KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com