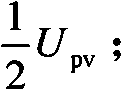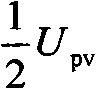Patents
Literature
1268results about How to "Reduce conduction loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
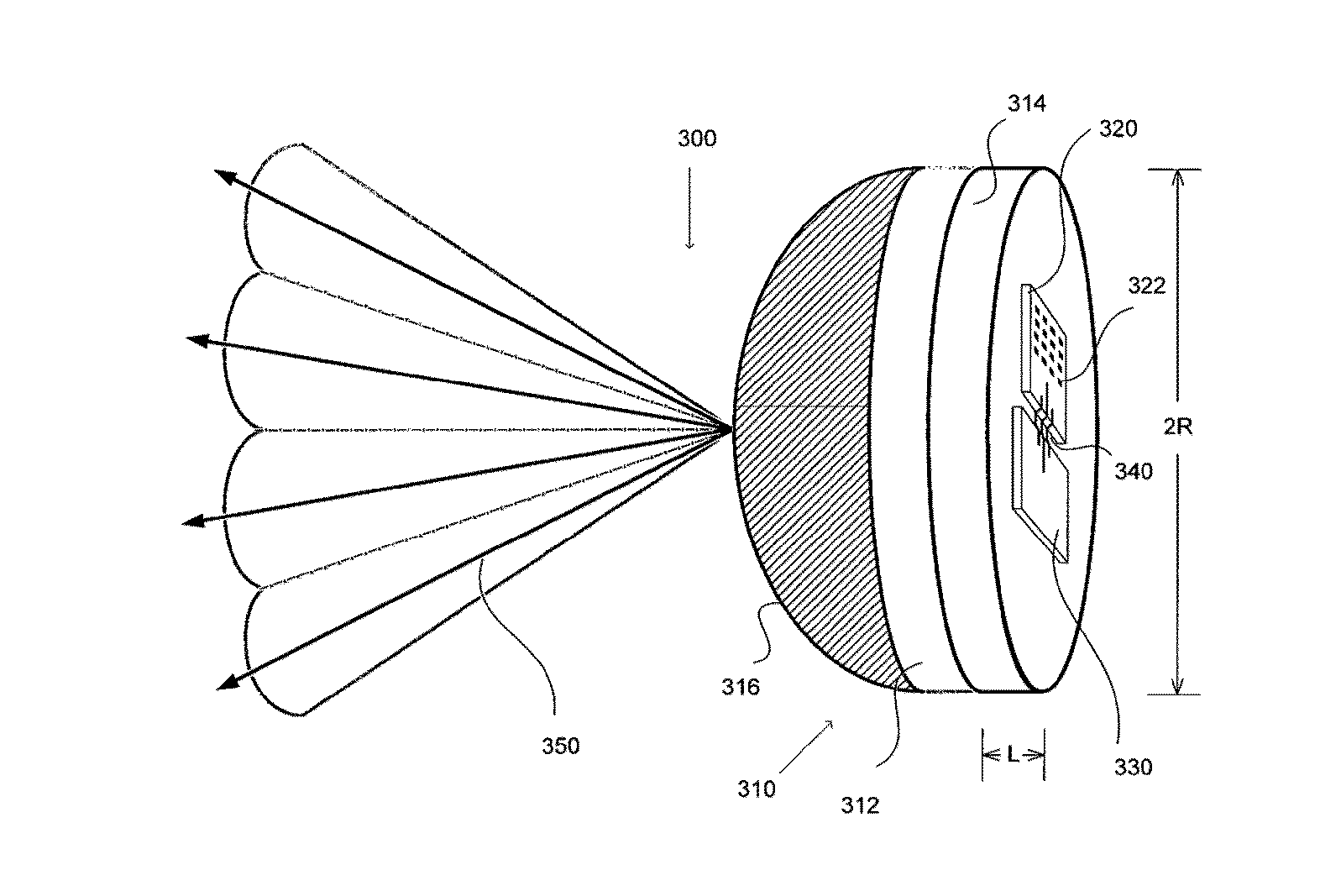
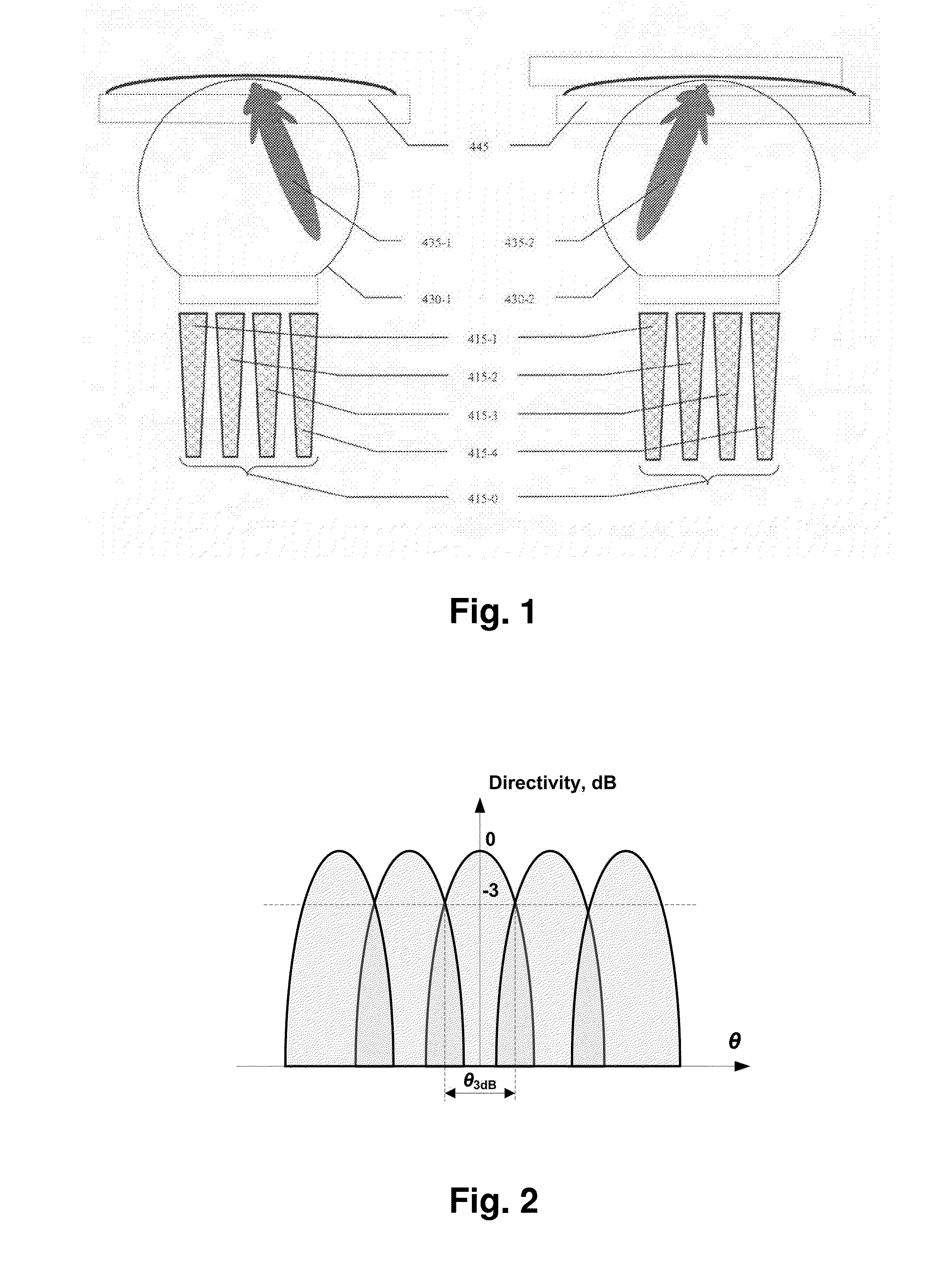
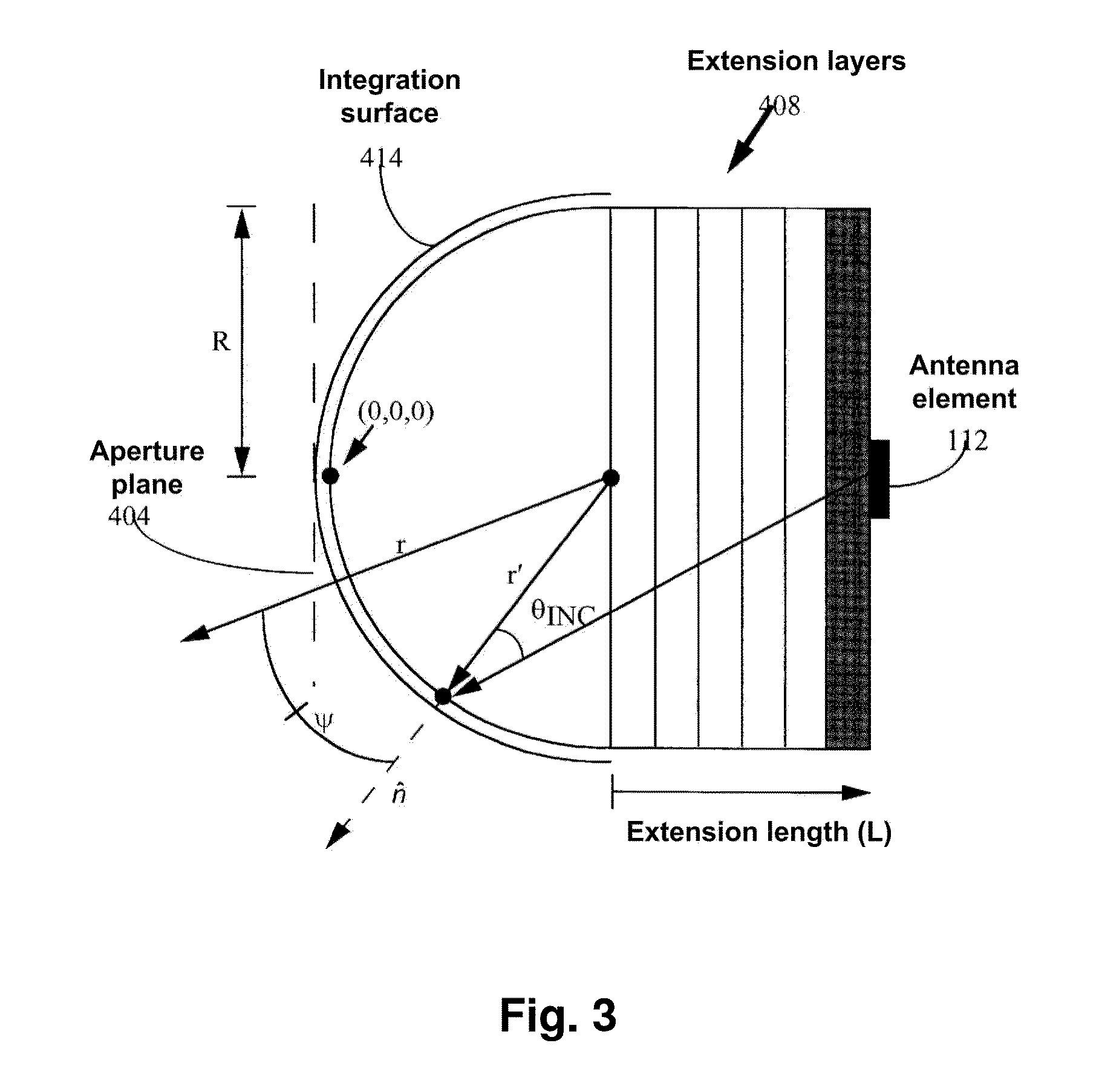
Lens antenna with electronic beam steering capabilities
InactiveUS20150116154A1Improve directivityImprove radiation efficiencyWaveguide hornsAntenna gainRadio relay
The invention discloses a lens antenna with high directivity intended for use in radio-relay communication systems, said antenna providing the capability of electronic steering of the main radiation pattern beam by switching between horn antenna elements placed on a plane focal surface of the lens. Electronic beam steering allows antenna to automatically adjust the beam direction during initial alignment of transmitting and receiving antennas and in case of small antenna orientation changes observed due to the influence of different reasons (wind, vibrations, compression and / or extension of portions of the supporting structures with the temperature changes, etc.). The technical result of the invention is the increase of the antenna directivity with simultaneously provided capability of scanning the beam in a continuous angle range and also the increase of the antenna radiation efficiency and, consequently, the increase of the lens antenna gain. This result is achieved by the implementation of horn antenna elements with optimized geometry.
Owner:OBSHCHESTVO S OGRANICHENNOJ OTVETSTVENNOSTYU RADIO GIGABIT
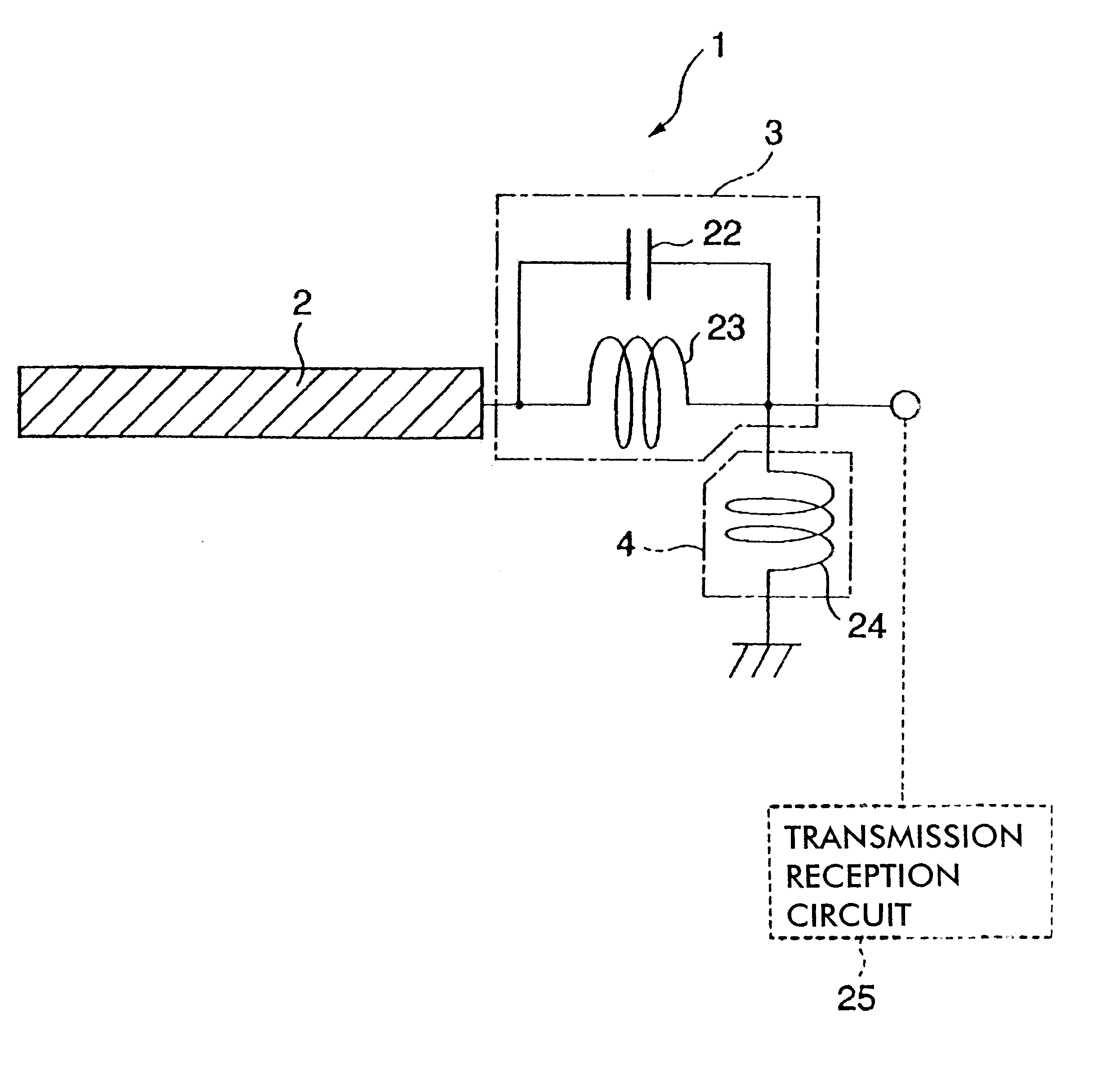
Antenna device and radio equipment having the same
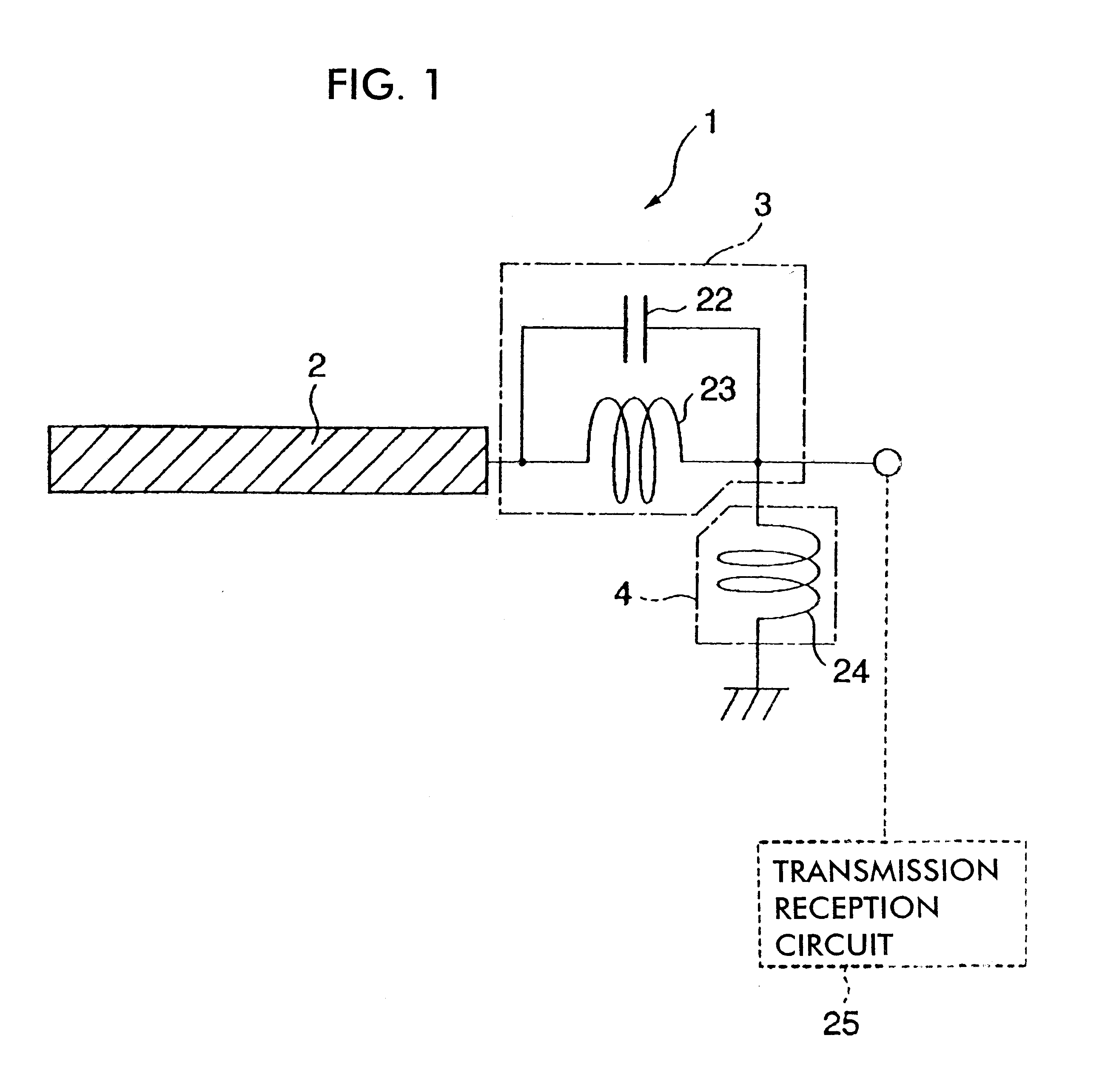
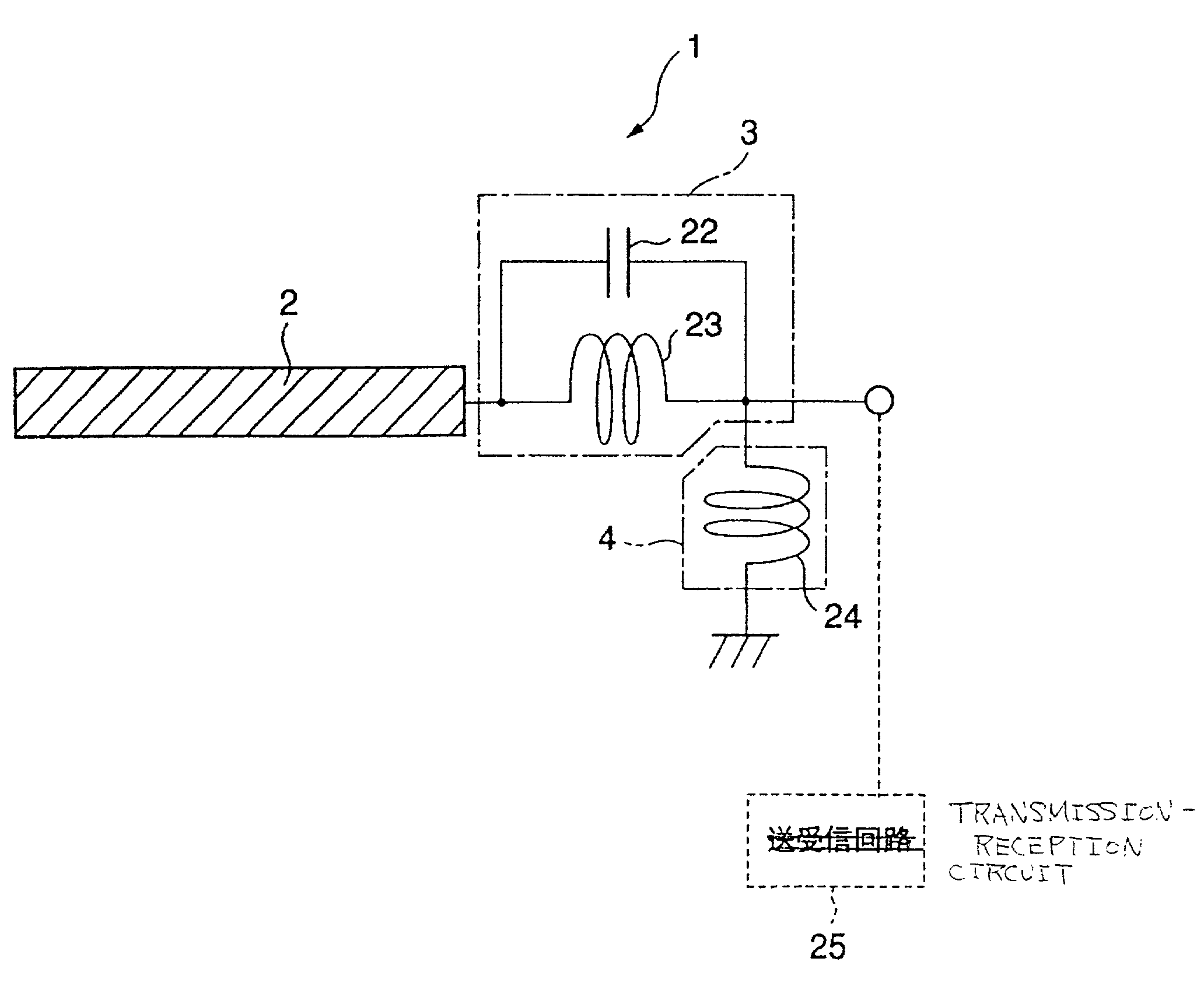
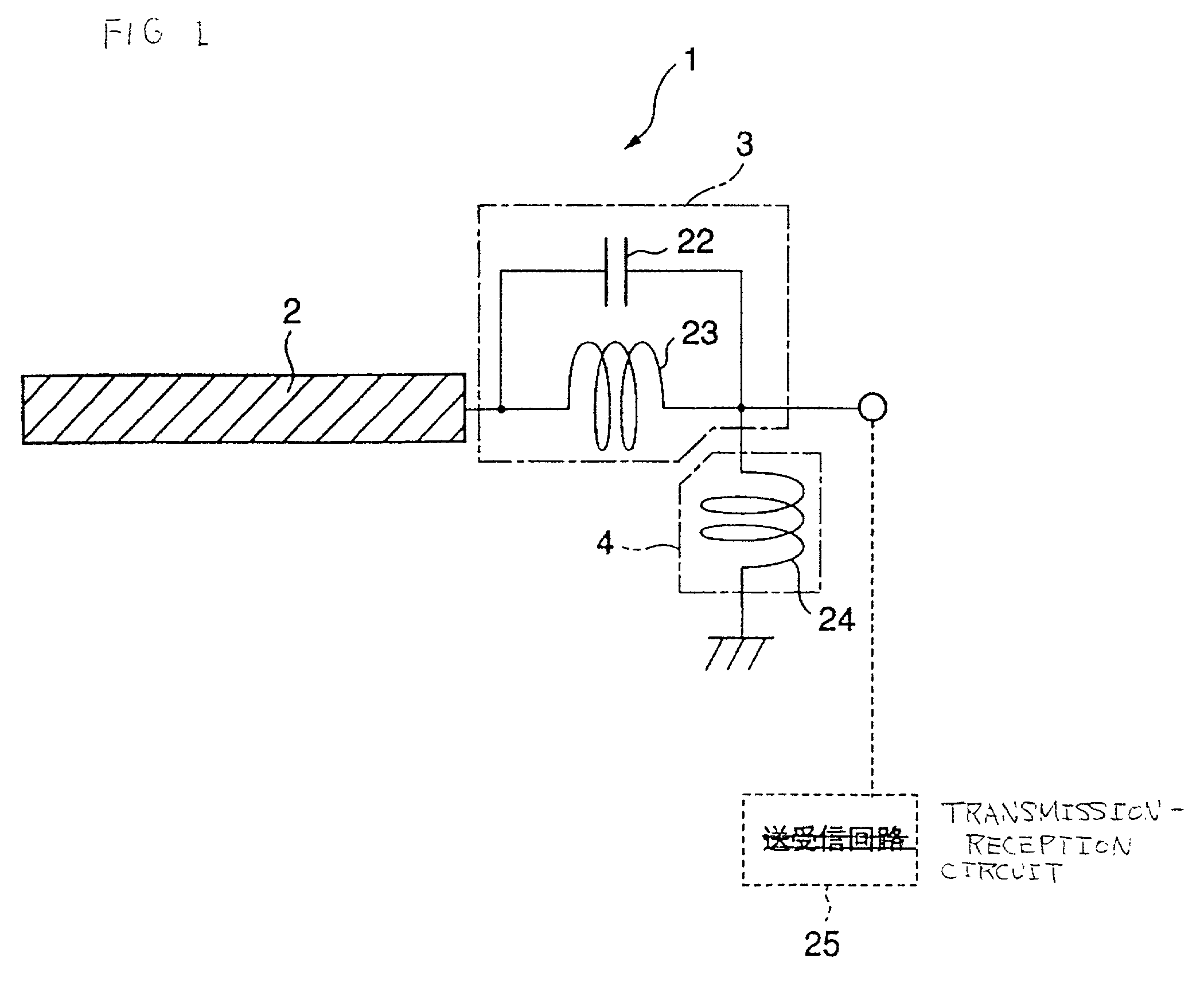
InactiveUS6462716B1Simple circuit configurationReduce conduction lossMultiple-port networksSimultaneous aerial operationsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Antenna device and radio equipment having the same
InactiveUS20020044092A1Simple circuit configurationReduce conduction lossMultiple-port networksSimultaneous aerial operationsCapacitanceElectrical conductor
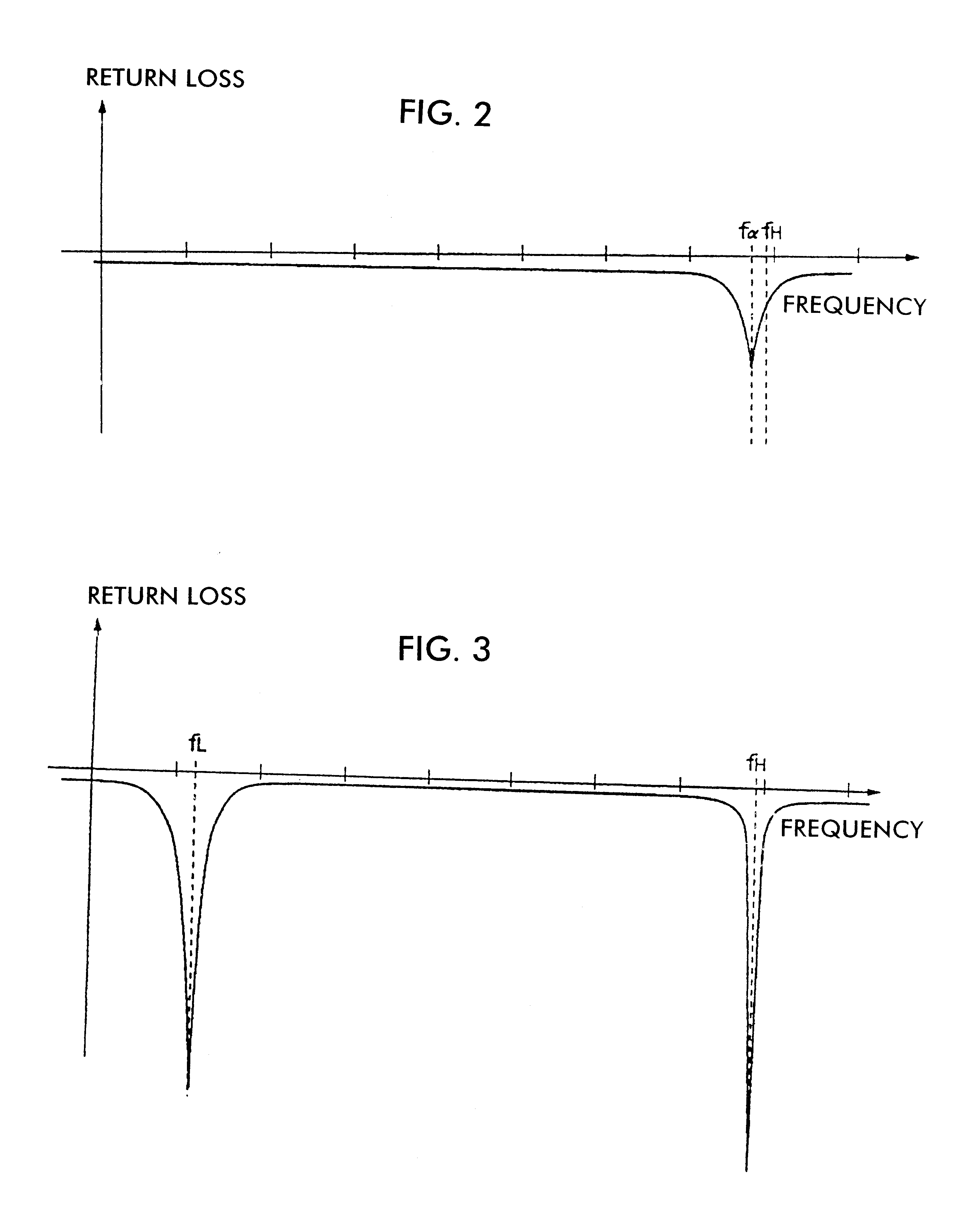
An LC parallel resonance circuit is connected in series with the power supply side of the antenna conductor portion. The antenna conductor portion is configured so as to resonate at a frequency slightly lower than the center frequency in the higher frequency band of two frequency bands for transmitting and receiving radio waves. The LC parallel resonance circuit is configured so as to resonate substantially at the center frequency in the lower frequency band for transmitting and receiving a radio wave and be capable of providing to the antenna conductor portion a capacitance for causing the antenna conductor portion to resonate at the center frequency in the higher frequency band. Thus, a circuit for changing the upper and lower frequency bands is not needed. Such a change-over circuit, which is complicated, causes problems in that the conduction loss increases, and the antenna sensitivity deteriorates. Without need of the change-over circuit, the conduction loss can be reduced, the antenna sensitivity can be enhanced and costs can be reduced.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Direct-current power supply and battery-powered electronic apparatus and equipped with the power supply
InactiveUS20060006850A1InhibitionSmall circuit sizeDc-dc conversionProtective switchesBoost chopperElectrical battery
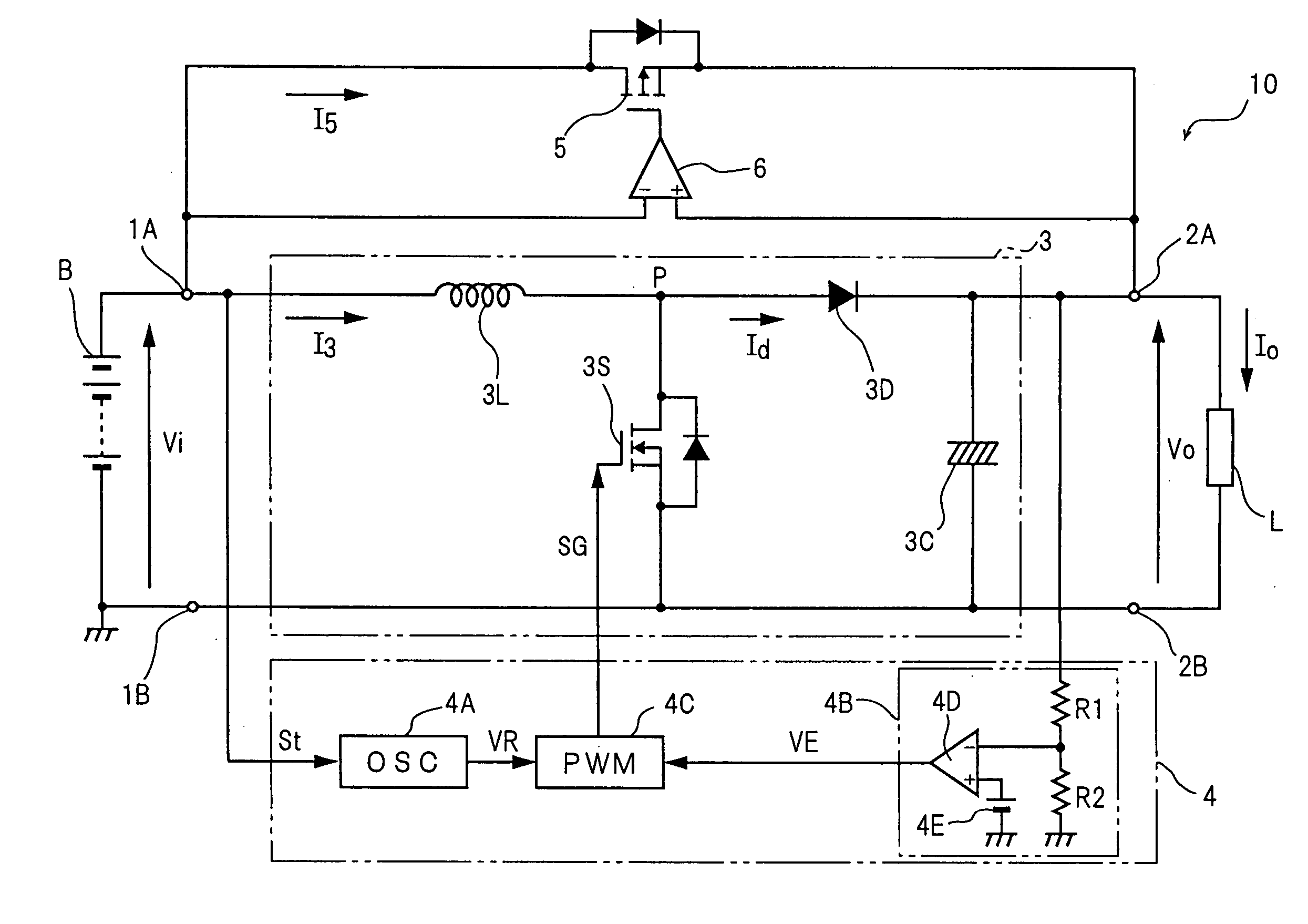
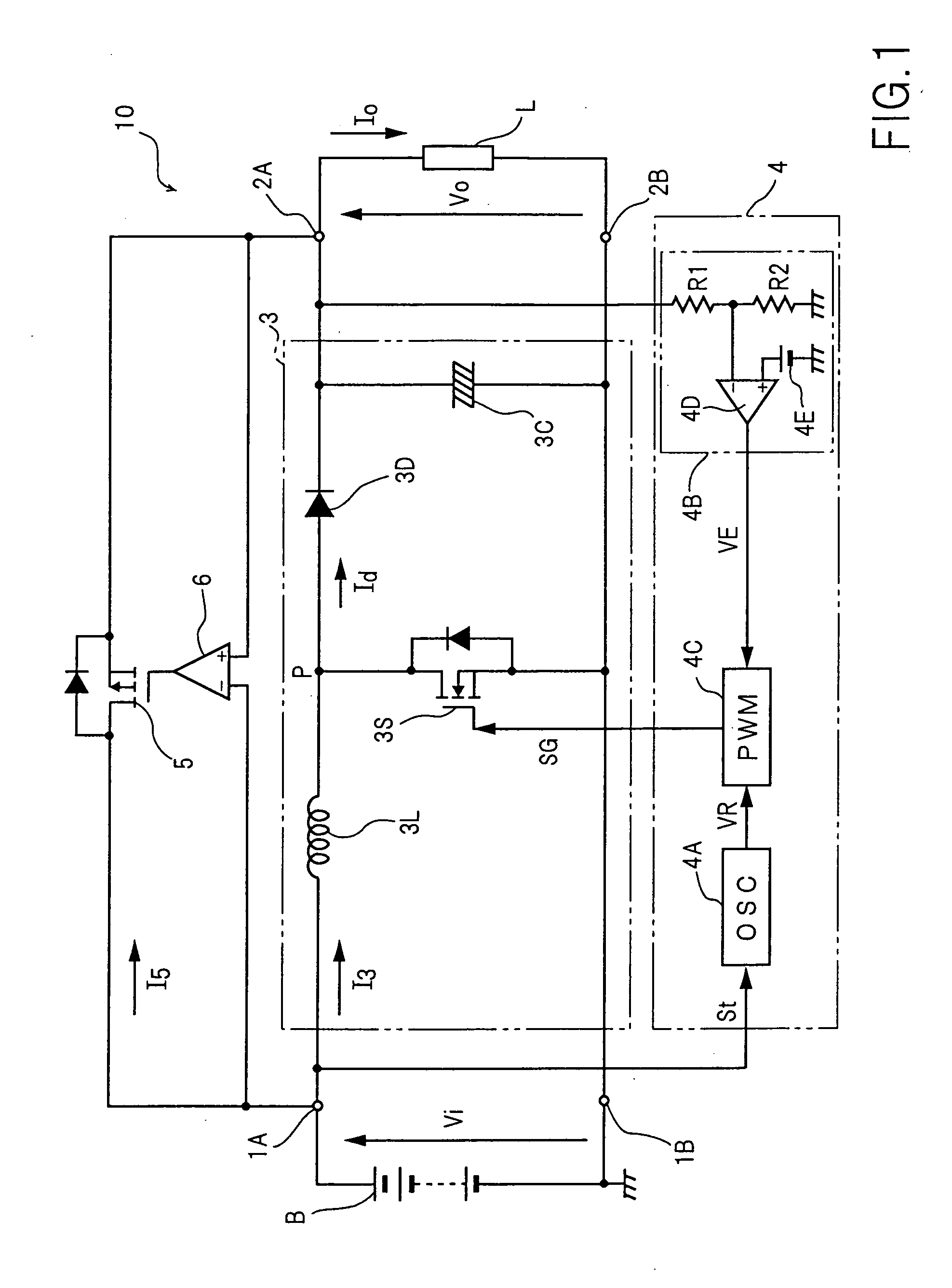
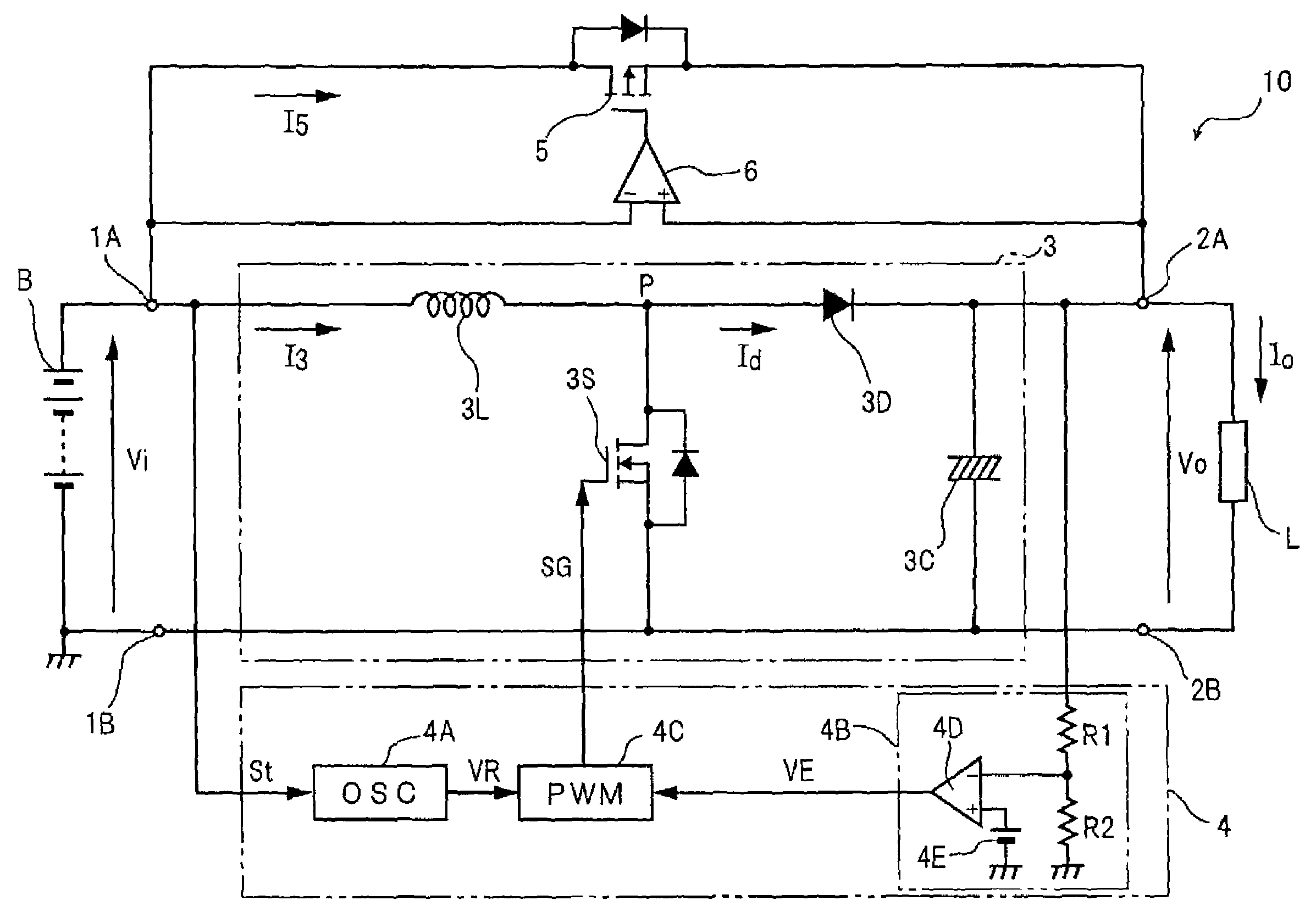
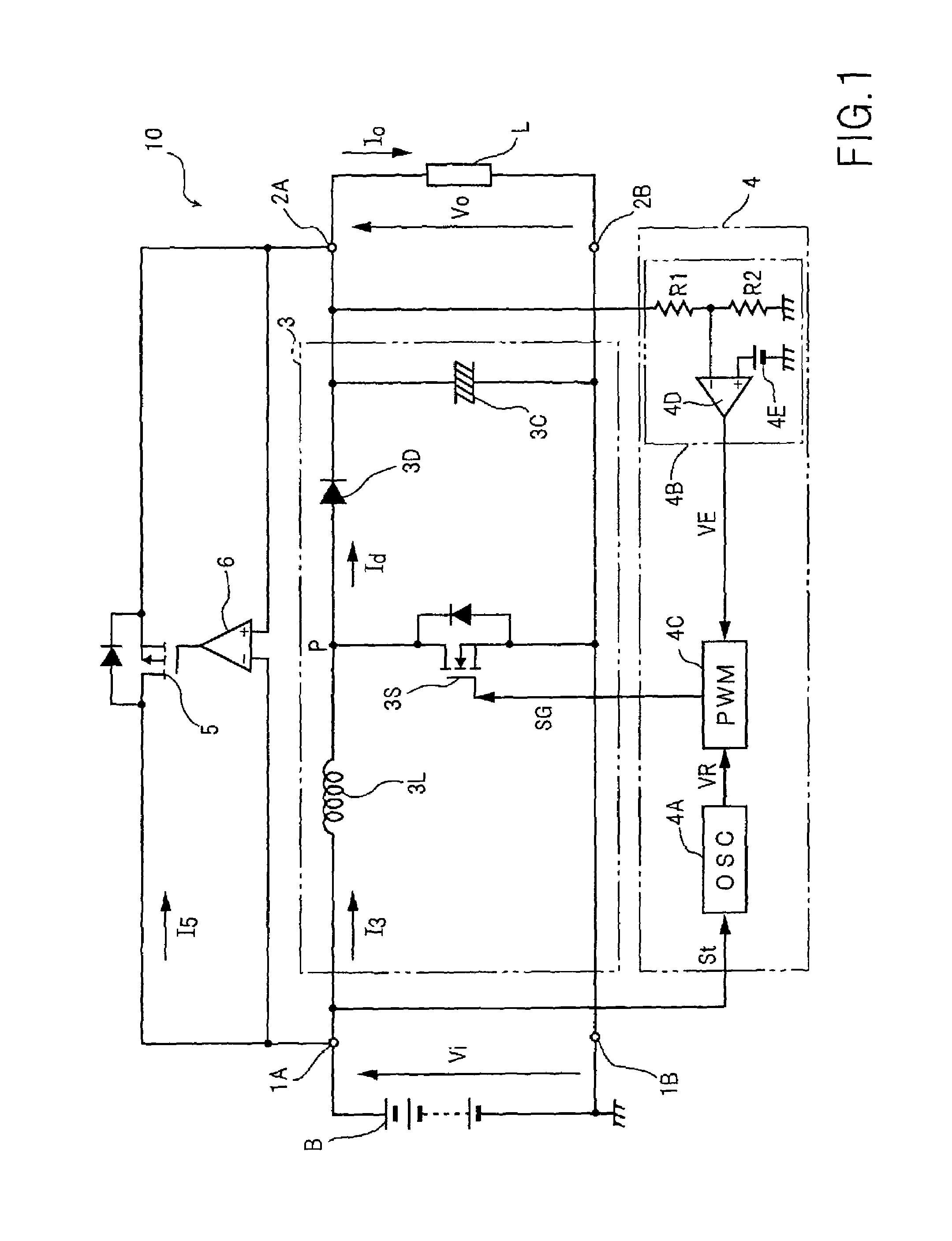
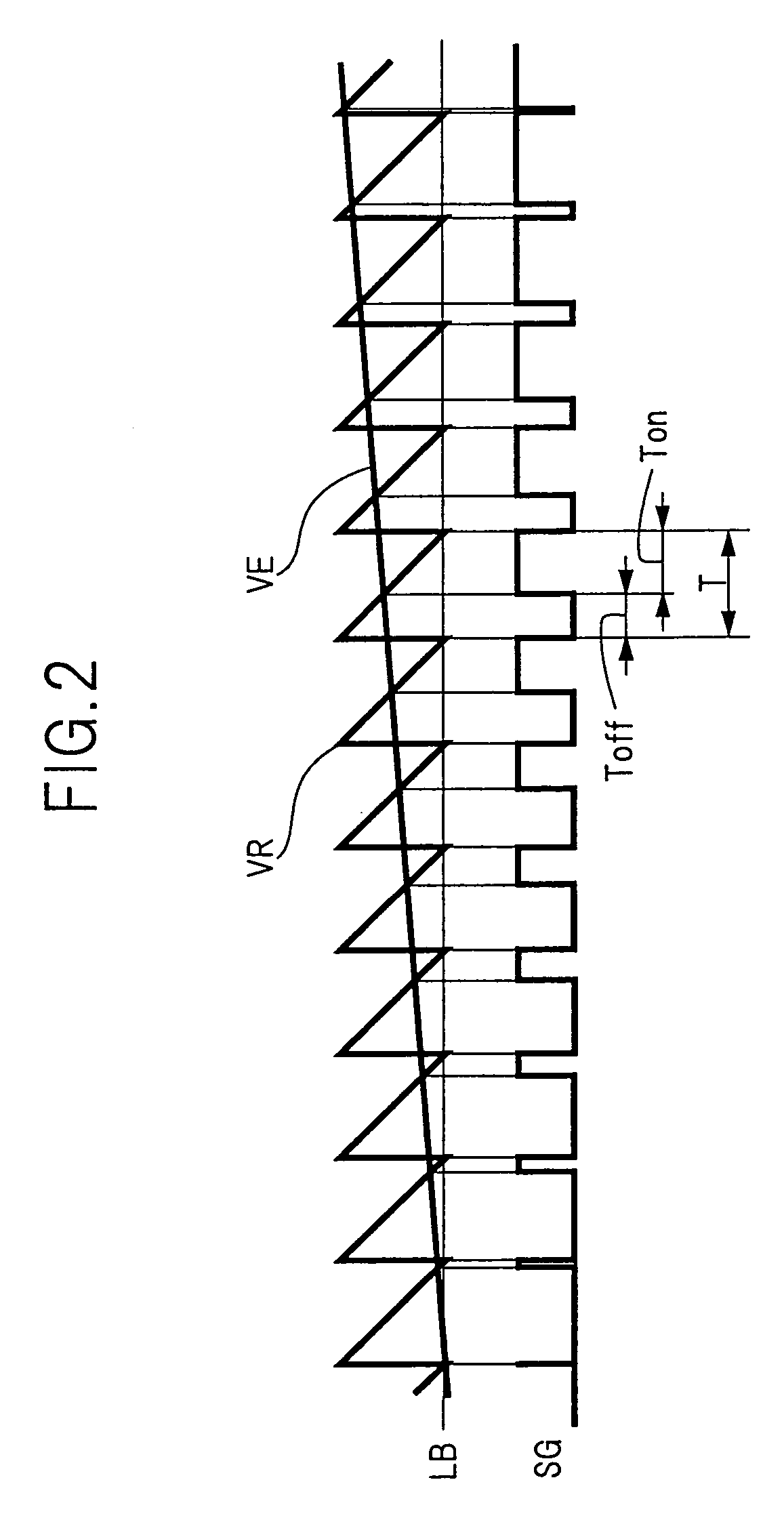
A bypass control section (6) maintains a bypass switch (5) in the ON state during the period when a battery voltage (Vi) is higher than the output voltage (Vo) to an external load (L). Upon falling of the output voltage (Vo) at a desired voltage (ET), a converter control section (4) starts switching control at once, and a step-up chopper (3) promptly starts boost operation. The bypass control section (6) maintains the bypass switch (5) in the ON state from the start of the boost operation of the step-up chopper (3) until the match between the battery voltage (Vi) and the output voltage (Vo).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
AC/DC flyback converter
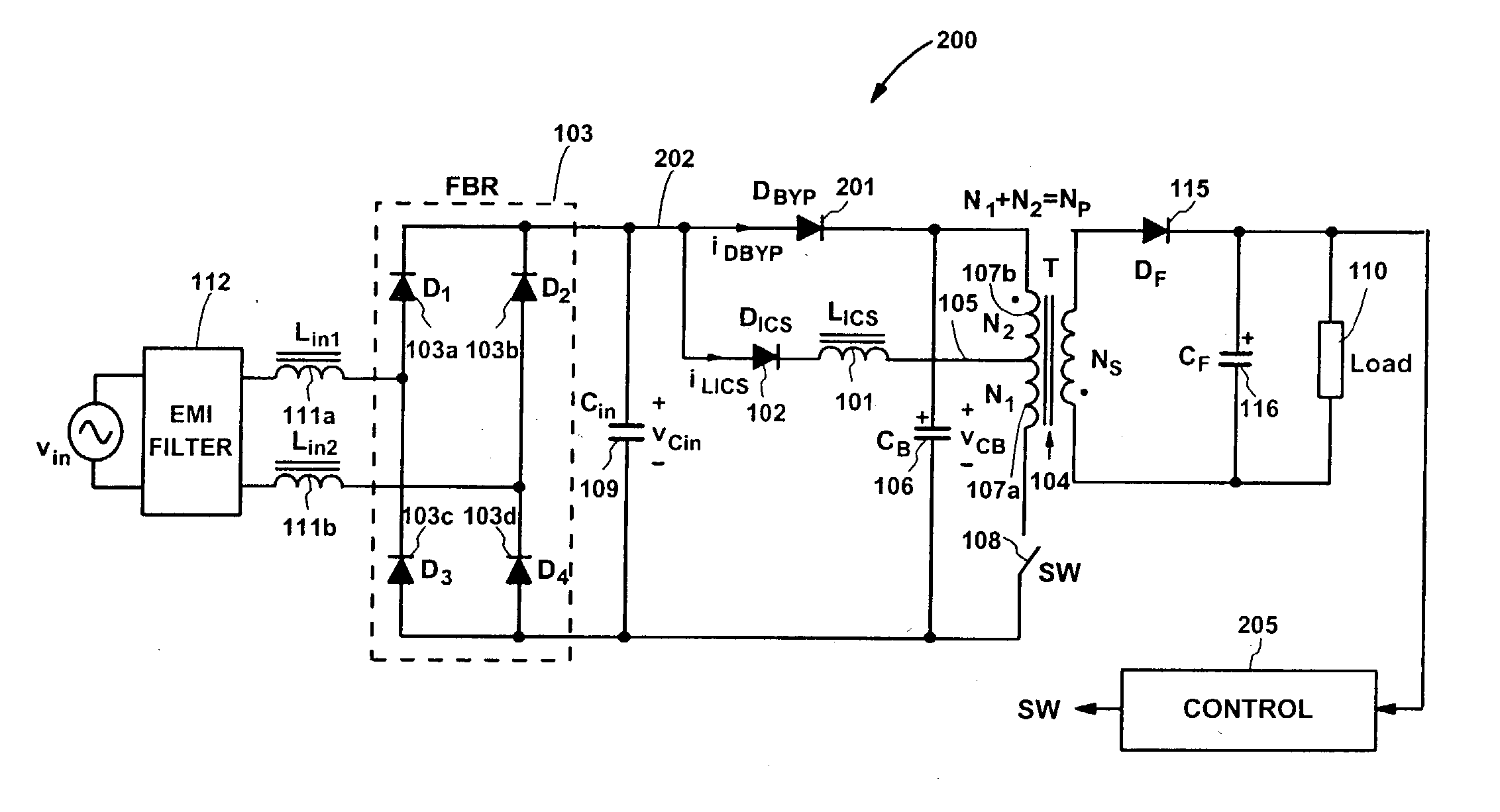
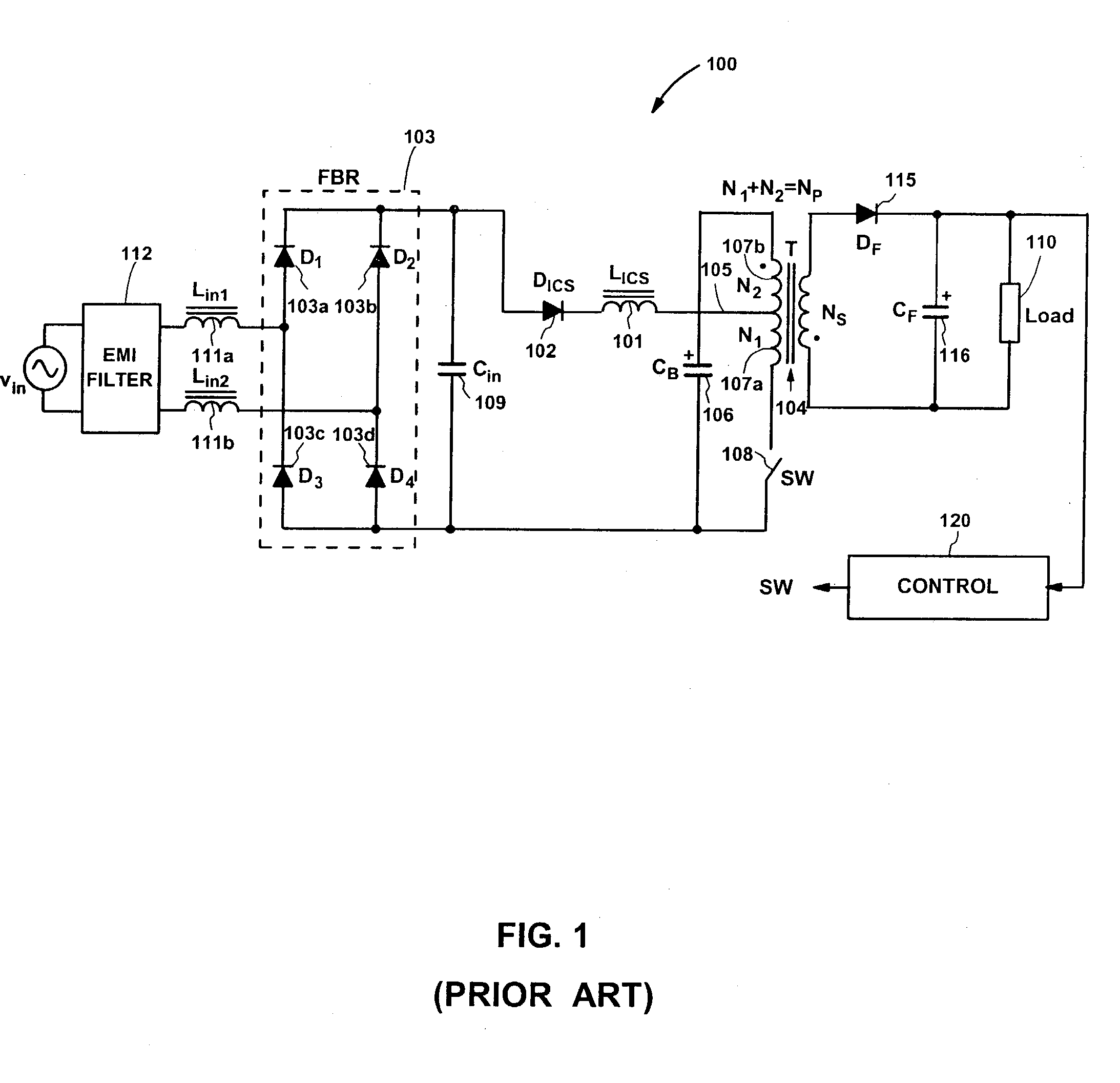
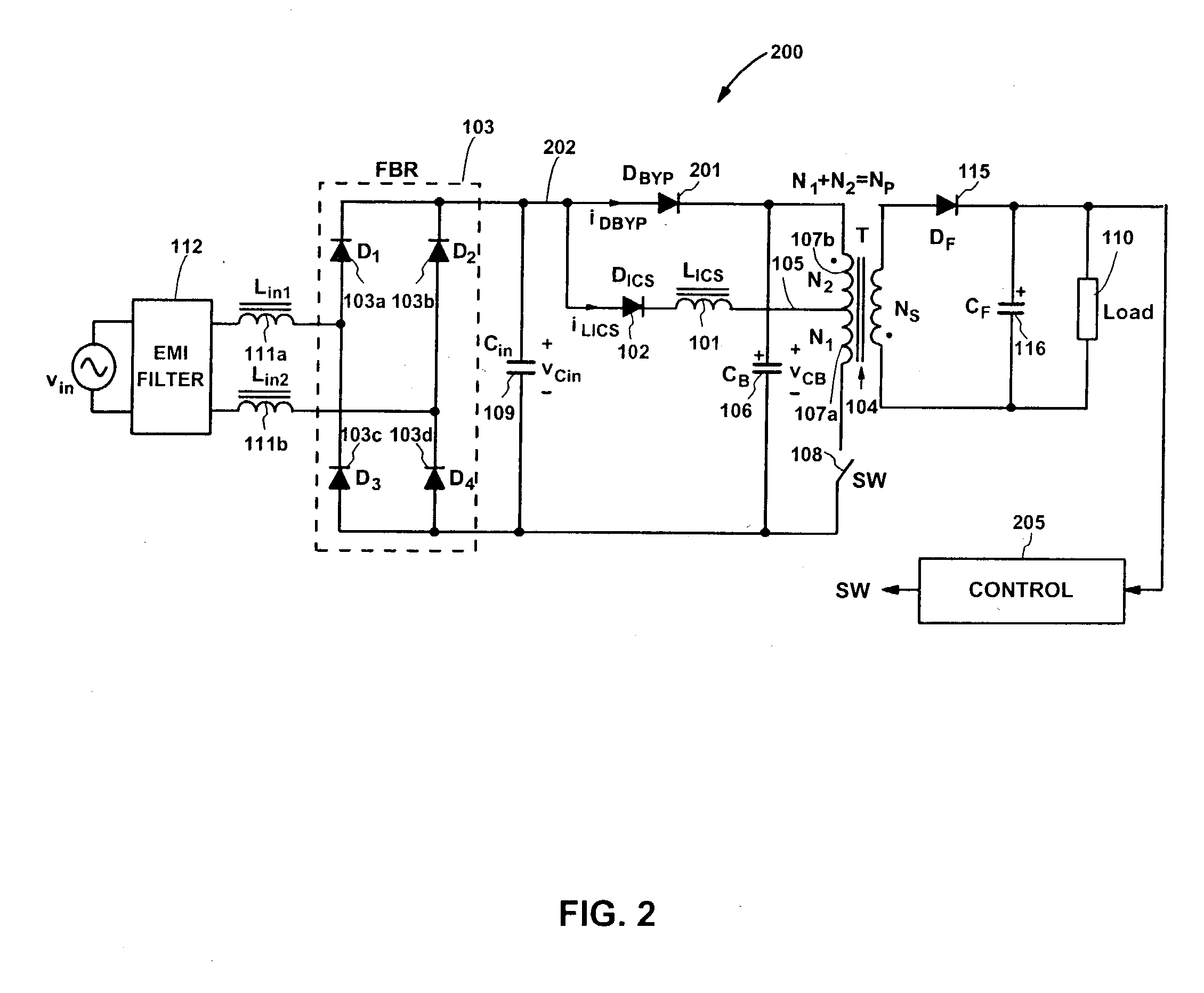
ActiveUS20040252529A1Reduce conduction lossImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionSingle stageFull bridge
A single-stage input-current-shaping (S<2>ICS) flyback converter achieves substantially reduced conduction losses in the primary side of the S<2>ICS flyback converter by connecting a bypass diode between the positive terminal of a full-bridge rectifier and the positive terminal of an energy-storage capacitor. An effective current interleaving between an energy-storage inductor and the bypass diode is thus obtained in the S<2>ICS flyback converter around the peak of the rectified line voltage, resulting in a significantly reduced input-current ripple and reduced current stress on the switch. Further, by rearranging the rectifiers in the ICS part of the S<2>ICS flyback converter in such a way that the energy-storage capacitor and the ICS inductor are connected to the ac line voltage through only two rectifiers, one diode forward-voltage drop is eliminated, which results in a substantially reduced conduction loss in the primary-side rectifiers.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
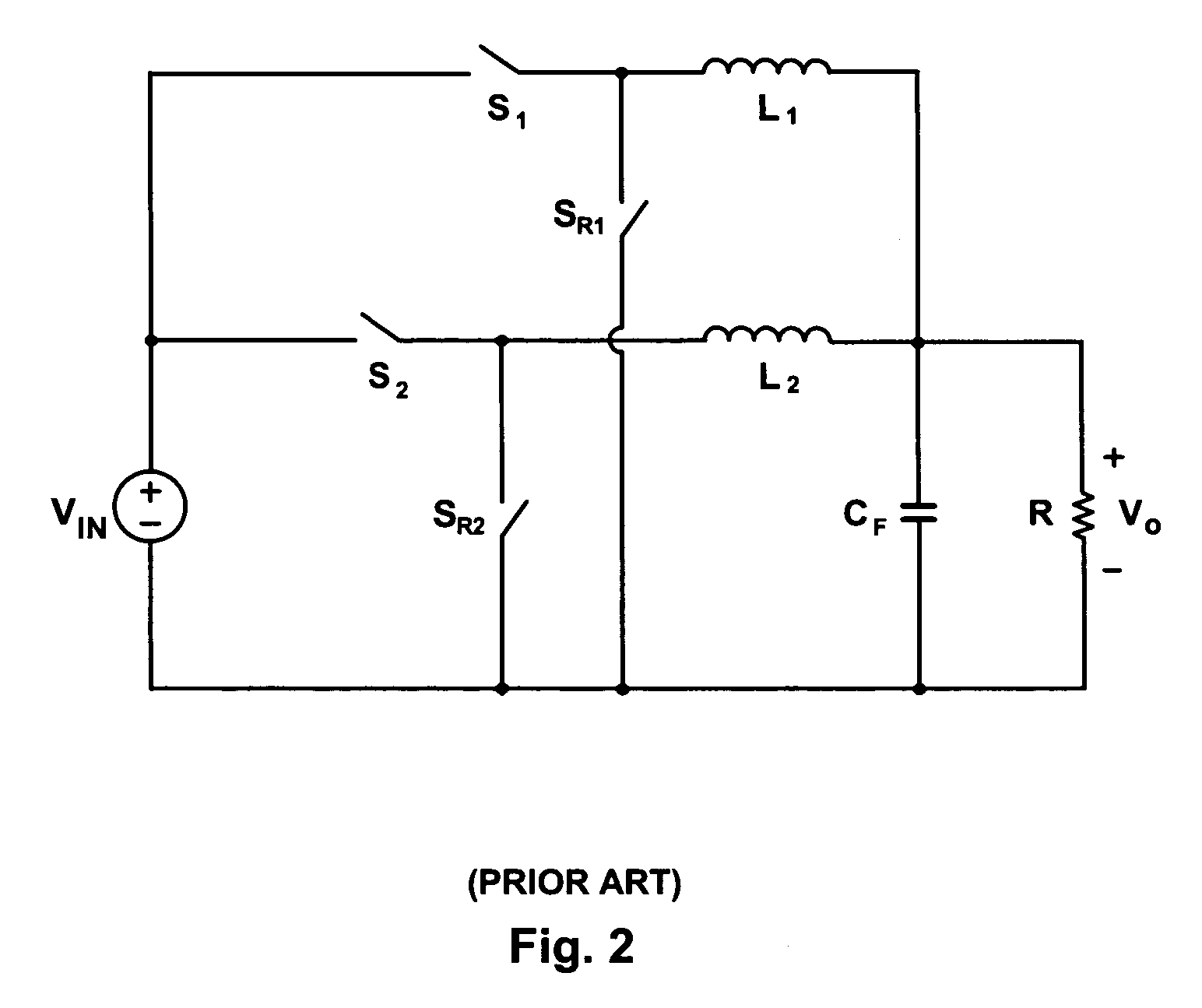
Switch voltage-stabilizing circuit and control method thereof
ActiveCN101552560APrevent fallingAvoid audio noiseDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationStored energyElectricity
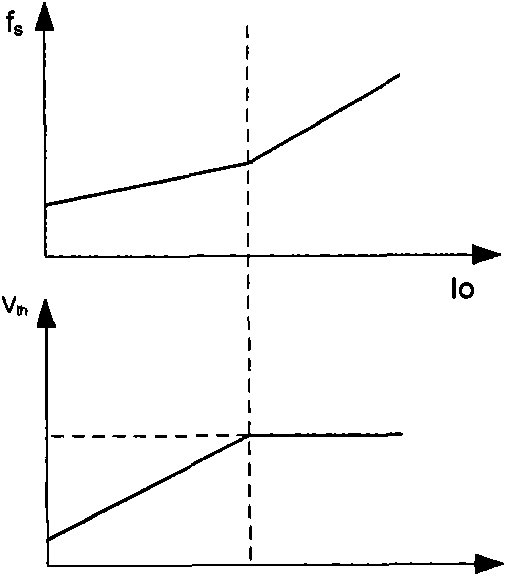
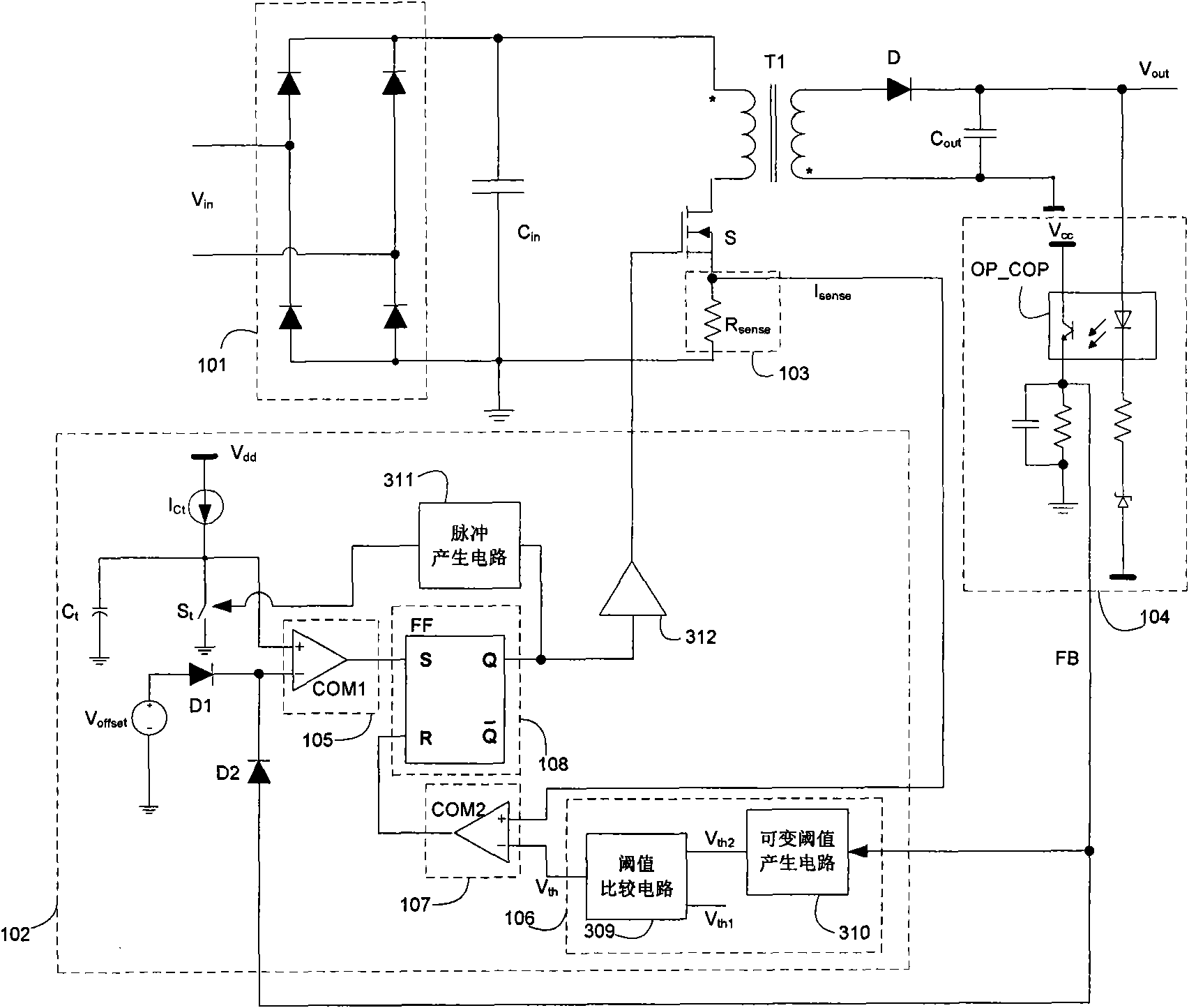
The invention discloses a switch voltage-stabilizing circuit which can regulate switching frequency as well as current peak, has high efficiency and has no audio-frequency noise generated in a state of light load, and method thereof. The switch voltage-stabilizing circuit comprises an energy storage component capable of storing energy; a switch electrically coupled to the energy storage component, wherein the energy storage component can store energy when the switch is on, and the energy stored in the energy storage component is transmitted to a load when the switch is off; a control circuit electrically coupled to the switch, wherein the control circuit compares current flowing through the switch with a current threshold, when the current flowing through the switch is more than the current threshold, the switch is off, and the control circuit determines on and off time of the switch according to the load of the switch voltage-stabilizing circuit, when the load becomes big, the on and off time of the switch is reduced, and when the load becomes small, the on and off time of the switch is increased. The current threshold is constant when the circuit has no light load and becomes low with the load reduced when the circuit has light load.
Owner:CHENGDU MONOLITHIC POWER SYST
Dielectric resonator, dielectric filter, dielectric duplexer, and communication device
InactiveUS6556101B1Reducing losses in dielectric resonatorsReduce conduction lossResonatorsWaveguidesElectrical conductorDielectric resonator
A small-sized low-loss dielectric resonator, dielectric filter, and dielectric duplexer, and a communication device using such an element. Through-holes are formed in a dielectric block. The inner surface of each through-hole is covered with a thin-film multilayer electrode consisting of an outermost conductive layer and a multilayer region including thin-film conductive layers and thin-film dielectric layers. An outer conductor having a similar thin-film multilayer electrode structure is formed on the outer surface of the dielectric block. An outer conductor in the form of a single-layer electrode is formed on a short-circuited end face of the dielectric block thereby connecting together the thin-film conductive layers of the inner and outer conductors.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Multiphase resonant converter for dc-dc applications
ActiveUS20080298093A1Small currentImprove efficiencyAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionPhase shiftedEngineering
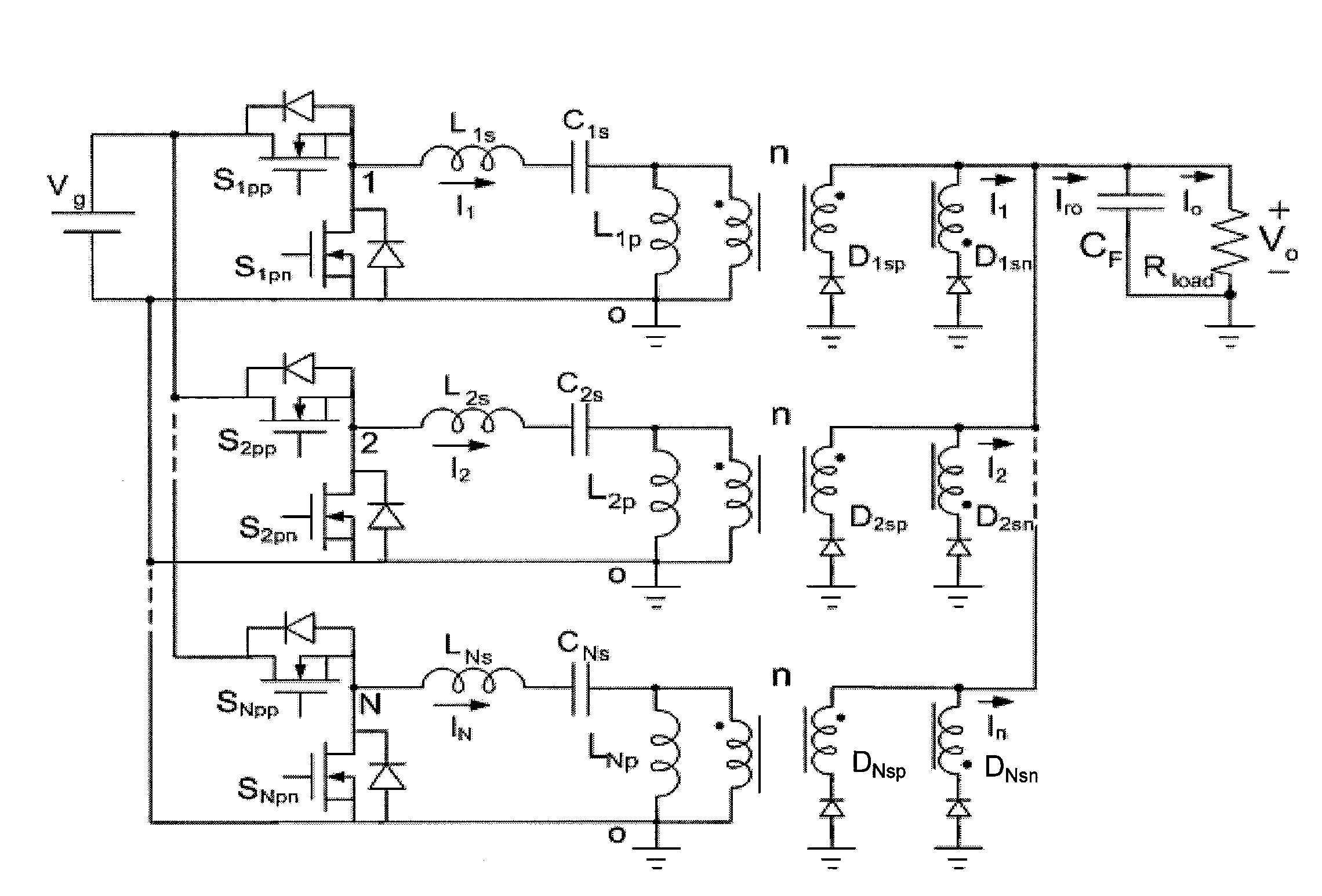
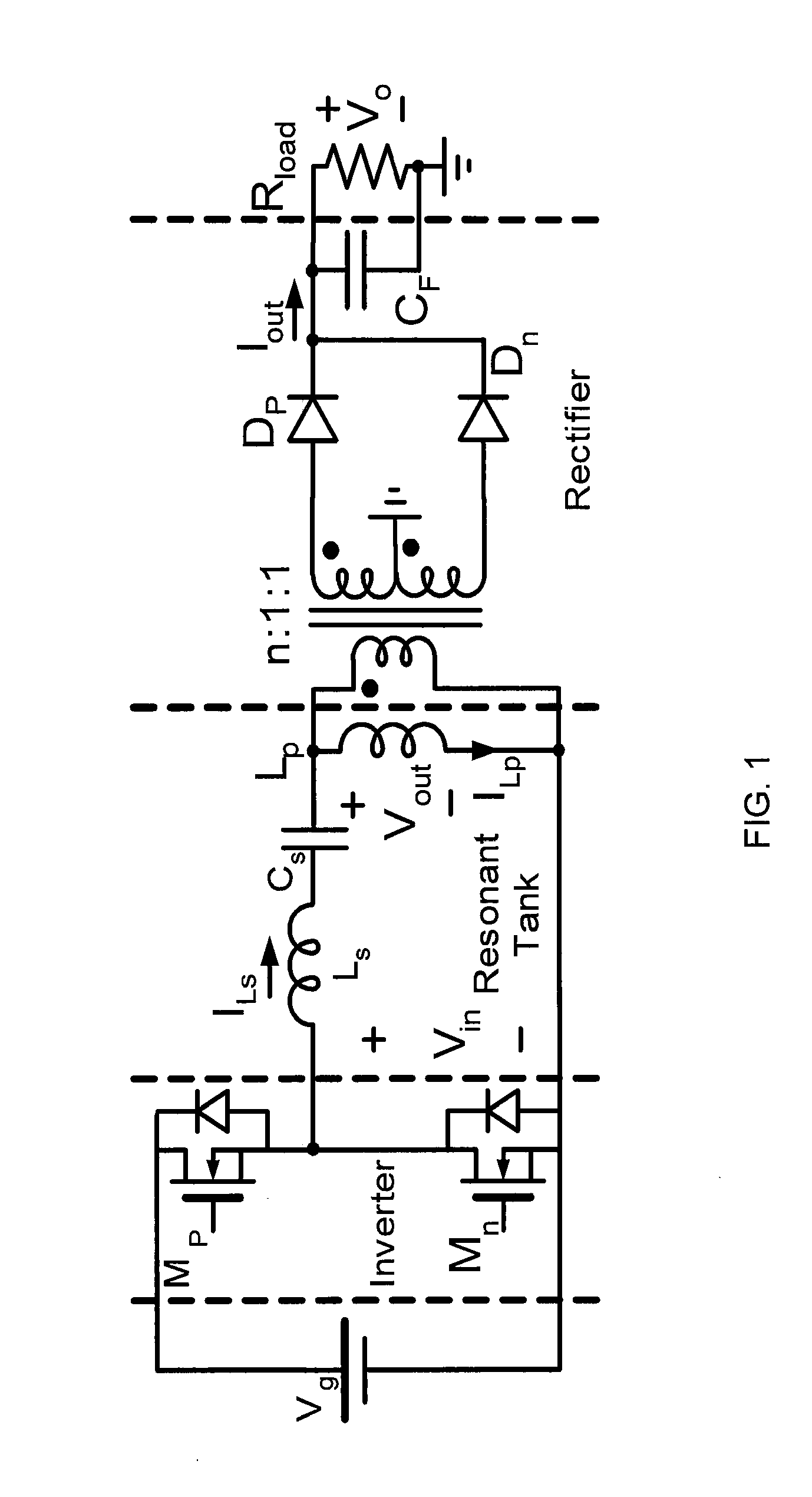
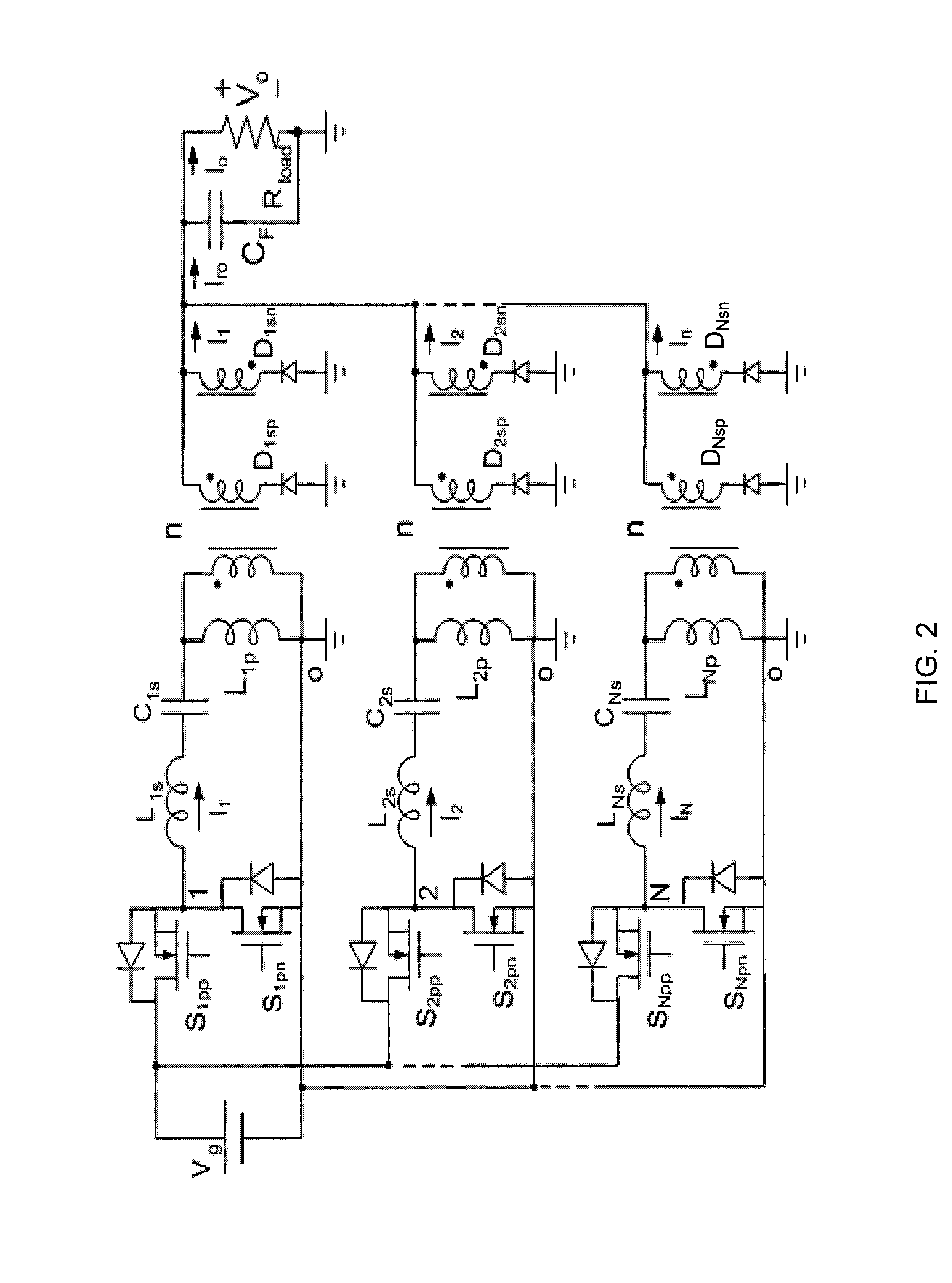
The various embodiments and example provided herein are generally directed to novel multiphase resonant converters. In an embodiment, a multiphase resonant converter comprises N unit resonant converters having inputs and outputs connected in parallel, respectively. Each unit converter comprises an inverter, a LLC series resonant tank, and a rectifier. In a preferred embodiment, the inverters of the N unit converters are driven by N drive signals phase-shifted 2π / N degrees apart. During operation, the current of the multiphase converter is shared among the unit converters, resulting in a smaller current in each unit converter. The smaller current in each unit converter reduces conduction losses, thereby increasing the efficiency of the multiphase converter. In addition, the smaller current in each unit converter reduces the amount of stress placed on individual components of the converter allowing for the use of lower tolerance components. Further, the multiphase converter has automatic current sharing ability.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multi-phase interleaving isolated DC/DC converter
InactiveUS6944033B1Reduces synchronous rectifier conduction loss lossReduces loss transformer winding lossDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceInductor
A converter has a transformer with primary and secondary windings each having n coils in a series-series arrangement connected to primary and secondary sides. The primary side has n primary legs each having a top switch and a bottom switch and connected to the primary winding therebetween. The secondary side has n secondary legs, each secondary leg has a synchronous rectifier switch and an output filter inductor connected to the secondary winding therebetween. A complimentary control for the primary side comprising a gate driver transformer with primary winding in series with a DC blocking capacitor connected to a drain and a source of the top switch of each primary leg, and a gate drive transformer, for each primary leg, with secondary winding containing a leakage inductor and in series with a DC blocking capacitor and a damping resistor connected to gate and source of the secondary side synchronous rectifier.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Electronic Ballast with High Power Factor
InactiveUS20120146526A1Minimizing componentLower current stress across the switchElectrical apparatusElectric light circuit arrangementEngineeringAlternating current
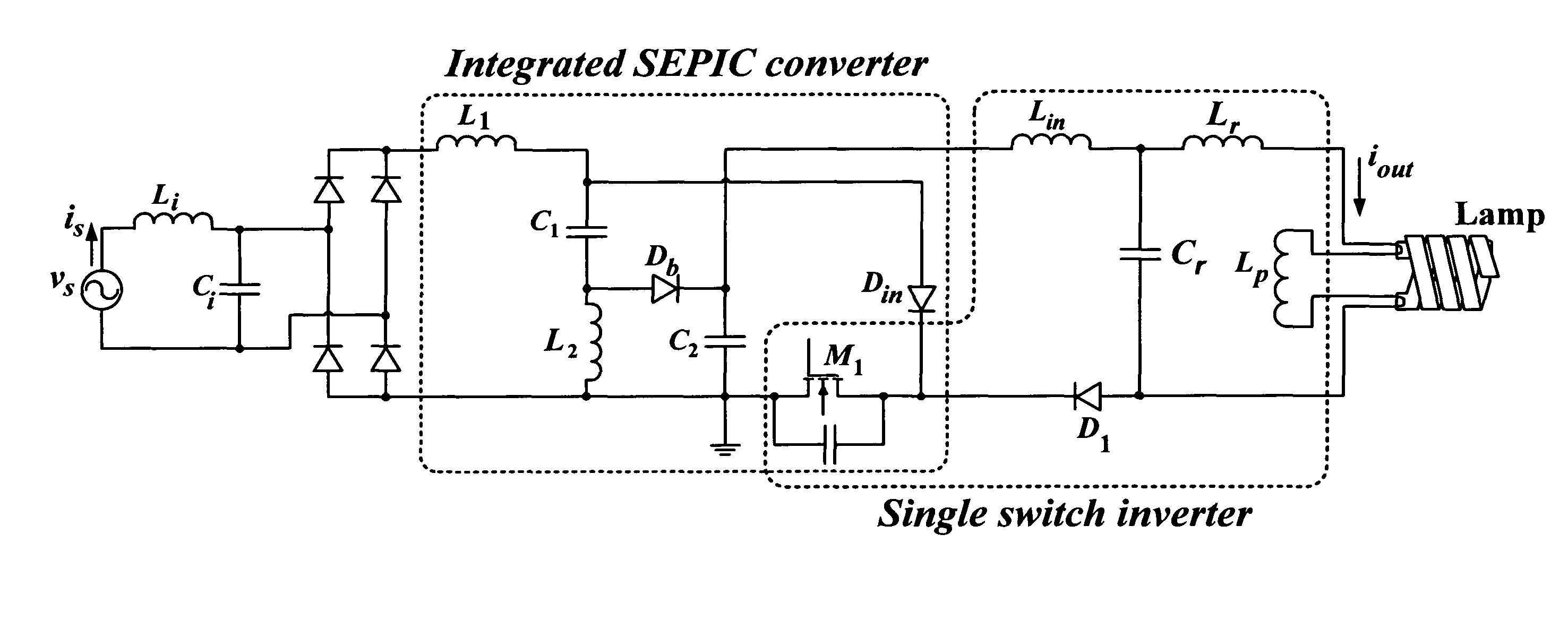
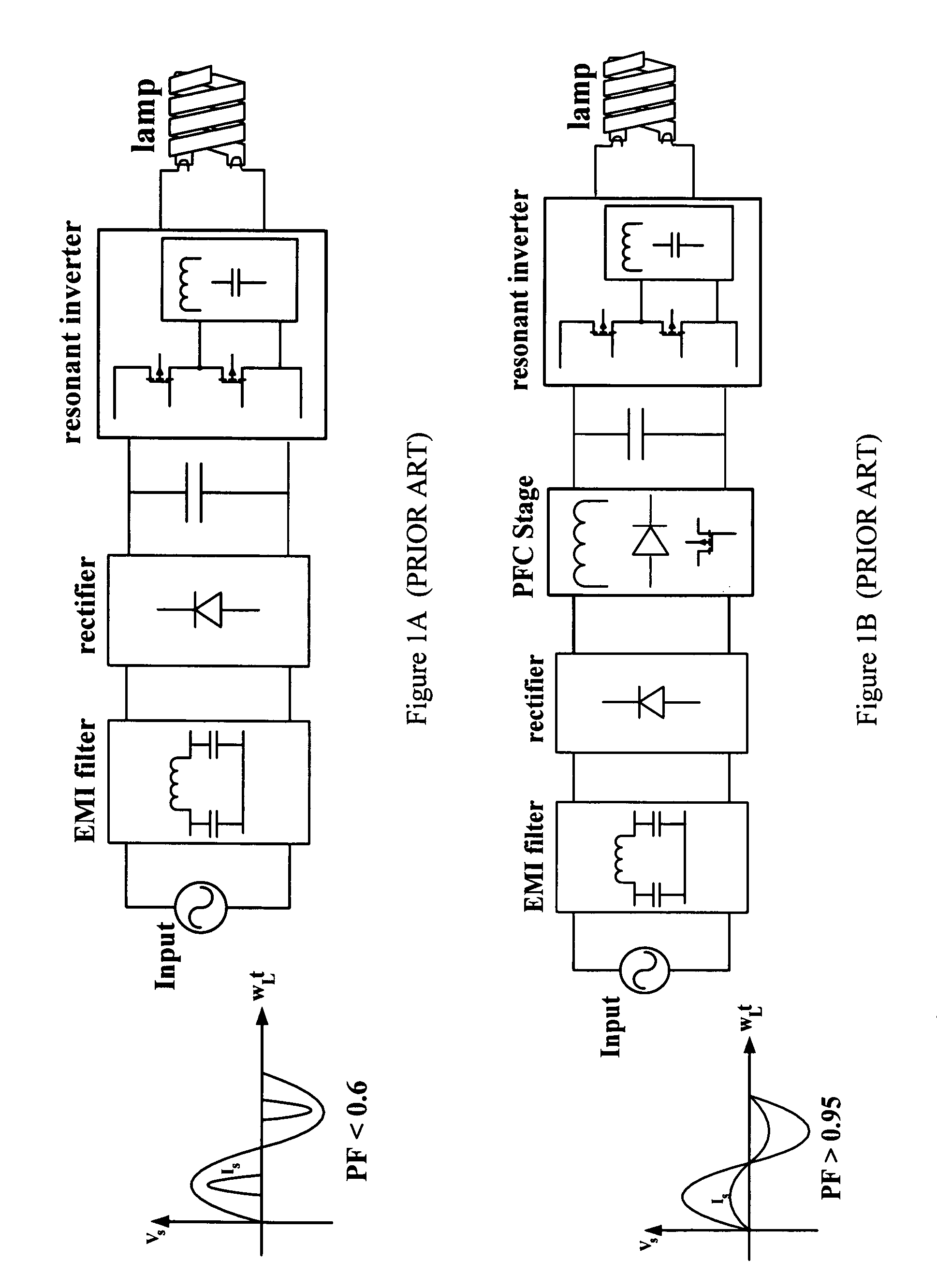
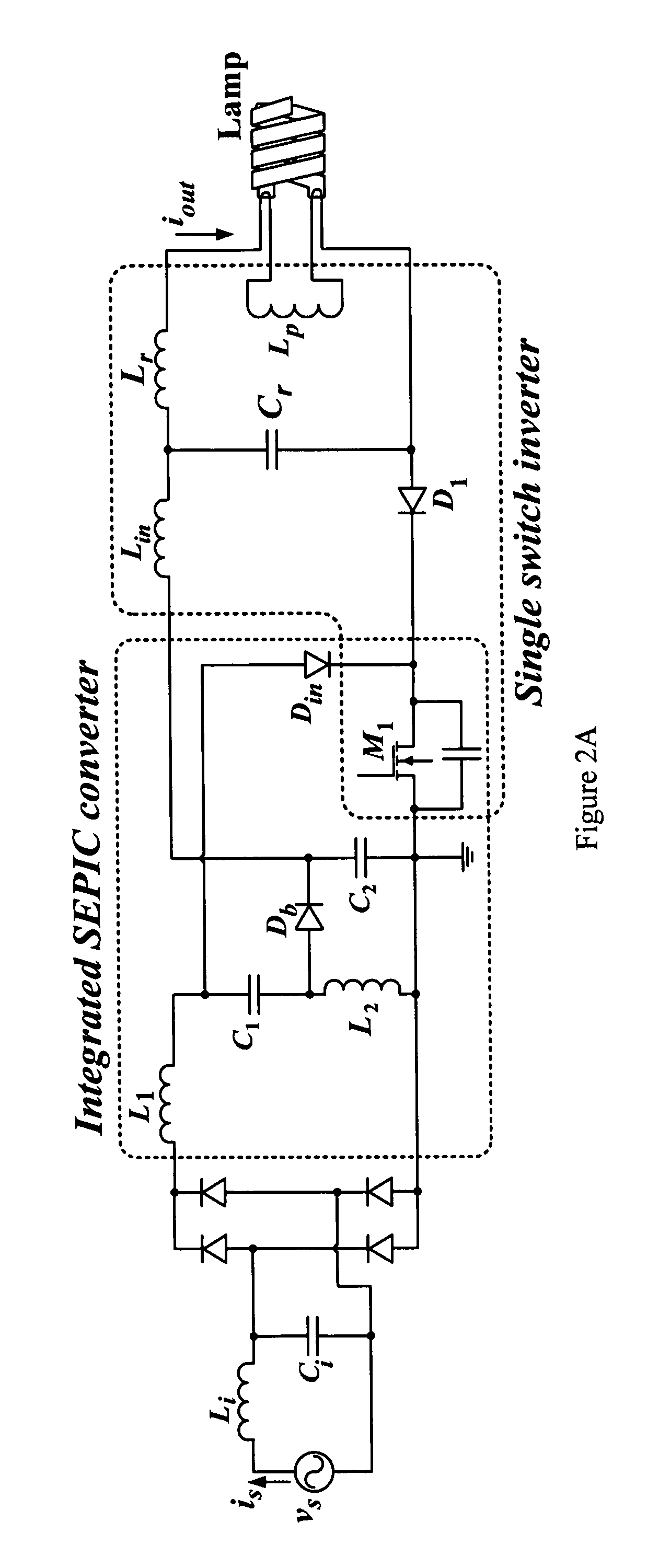
This invention provides an integrated power supply for a controller of an electronic ballast for a fluorescent lamp. The integrated power supply couples output power from the electronic ballast and uses the coupled power to provide power to the controller. In one embodiment, the electronic ballast may include a rectifier for converting an alternating current input voltage into a direct current output voltage, and a circuit including a combined power factor correction (PFC) stage and an inverter, wherein the PFC stage and the inverter share a switch. Also provided is a controller for an electronic ballast. The controller may include a voltage mode or current mode duty ratio controller that controls a duty ratio of a switch of the ballast. The controller and the ballast allow dimming of the fluorescent lamp while maintaining a high power factor.
Owner:JAIN PRAVEEN K +1
High-efficiency high-voltage difference ratio bi-directional converter
InactiveUS7382113B2Reduce conduction lossReduce voltageDc network circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversionTransformerLow voltage
The aim of this invention focuses on the development of a high-efficiency bidirectional converter for power sources with great voltage diversity. In traditional bidirectional converters, the circuit topology with transformer form is the common usual. Moreover, the soft-switching techniques including zero-voltage-switching (ZVS) or zero-current-switching (ZCS) are usually used for alleviating the corresponding switching losses. However, there are four and upward power semiconductor switches in these circuit schemes. By this way, it will result in the increase of production cost, and the degeneration of conversion efficiency. The coupled-inductor bidirectional scheme in the proposed converter only adopts three power semiconductor switches to accomplish the objective of bidirectional current control. Under the situation of non-isolation circuit topology, it still possesses the protection of electric safety for operators. Due to the characteristics of high step-up and step-down ratio, the battery module with low voltage could be injected into a high-voltage dc bus for the later utilization, e.g., high-voltage load, front-end of inverter. Since the techniques of voltage clamping, synchronous rectification and soft switching are manipulated in this circuit topology, and the corresponding device specifications are adequately performed, it can achieve the goal of high-efficiency bidirectional power conversion for power sources with great voltage diversity.
Owner:YUAN ZE UNIV
High power factor DCM Boost PFC converter
InactiveCN101764528AReduce conduction lossImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionVoltage sourceHigh input
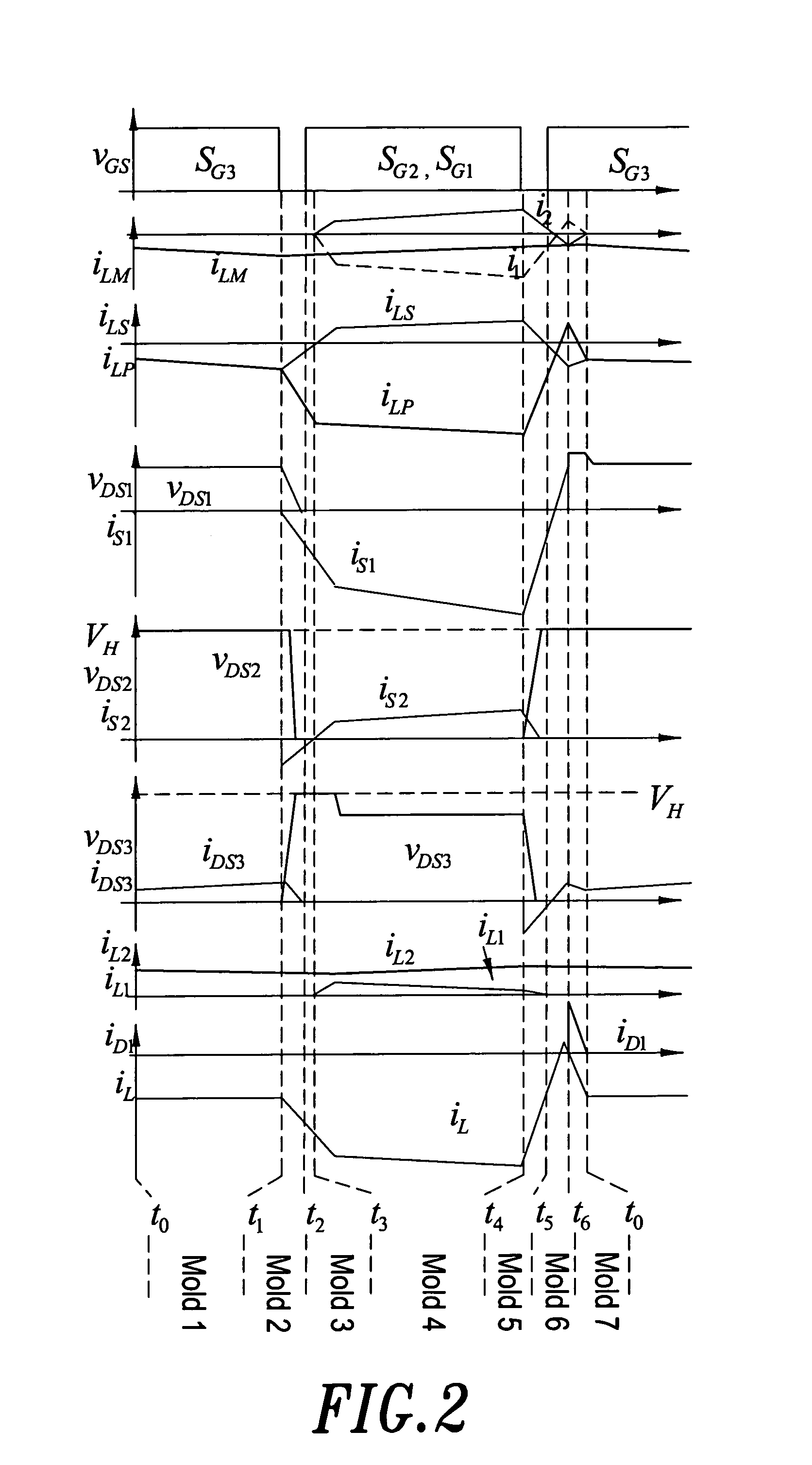
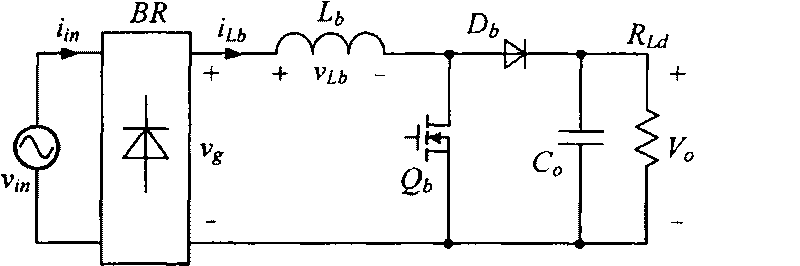
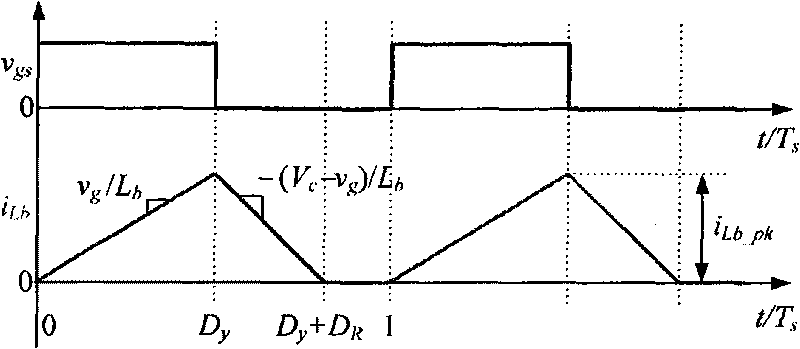
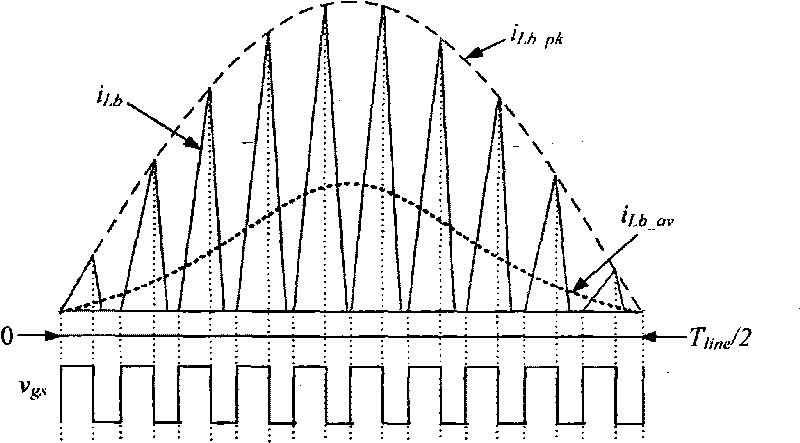
The invention relates to a high power factor DCM Boost PFC converter comprising a main power circuit and a control circuit. The main power circuit comprises an input voltage source vin, an EMI filter, a diode rectification circuit RB, a Boost inductor Lb, a switch tube Qb, a diode Db, an output capacitor Co and a load RLd. The high power factor DCM Boost PFC converter is characterized in that the control circuit adopts an output signal which adopts duty ratio as changing rule to drive the switch tube Qb. Adopting the varying duty ratio control, the high power factor DCM Boost PFC converter can improve the PF value to about 1 in the AC input voltage range of 90-265 V, increase the inductance capacity, obviously decrease the inductive current ripple, obviously reduce the effective value of the inductive current and correspondingly reduce the effective value of the current of the switch tube, has high input power factor and small output voltage ripple and contains less input current harmonic waves. The conduction loss of the high power factor DCM Boost PFC converter is reduced, and the efficiency is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Electronic ballast with high power factor
InactiveUS8212492B2Minimizing componentLower current stress across the switchElectrical apparatusElectric lightingPower inverterActive power factor correction
This invention provides an electronic ballast for a fluorescent lamp, including a rectifier for converting an alternating current input voltage into a direct current output voltage, and a circuit including a combined power factor correction (PFC) stage and an inverter, wherein the PFC stage and the inverter share a switch. Also provided is a controller for an electronic ballast, including a duty ratio controller that controls a duty ratio of a switch of the ballast, and means for adjusting the duty ratio according to a nonlinear function, so that an arc is sustained across the lamp. The controller and the ballast allow dimming of the fluorescent lamp while maintaining a high power factor.
Owner:JAIN PRAVEEN K +1
Junction termination structure of transverse high-pressure power semiconductor device
InactiveCN102244092AImprove breakdown voltageReduce widthSemiconductor devicesPower semiconductor deviceCMOS
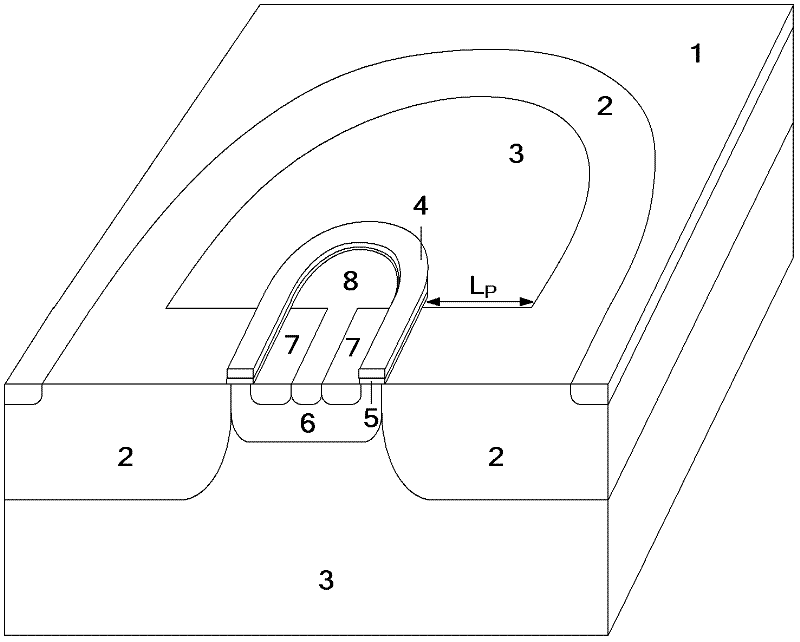
The invention relates to a junction termination structure of a transverse high-pressure power semiconductor device, belonging to the technical field of semiconductor power devices. An N-type drift region at a curvature termination of the transverse high-pressure power semiconductor device is shortened in length to ensure that the N-type drift region is spaced with a P-well region by a certain displace, wherein the spaced part is replaced by a P-type substrate, which is equivalent that additional electric charges of the P-type substrate are introduced so that the peak value of an electric field at a pn junction formed the original P-well region and the N-type drift region is reduced, meanwhile, a new peak value of the electric field is introduced at a pn junction formed by the P-type substrate and the N-type drift region, the radius of curvature of the curvature terminal is increased, the excessive concentration of a power line is avoided, and the puncture voltage of the device is increased, wherein the surface of the N-type drift region also can be combined with a surface RESURF structure or an ultra-junction structure. The junction termination structure has the advantages of being capable of decreasing the width of the curvature terminal of the device, saving the layout area of the device and being compatible with a CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-semiconductor Transistor) process, and can be used for manufacturing the transverse high-pressure power device with the advantages of excellent performance, high voltage, high speed and low conduction loss.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
High-efficiency high-voltage difference ratio bi-directional converter
InactiveUS20070216390A1Reduce conduction lossReduce voltageDc network circuit arrangementsAc-dc conversionLow voltageTransformer
The aim of this invention focuses on the development of a high-efficiency bidirectional converter for power sources with great voltage diversity. In traditional bidirectional converters, the circuit topology with transformer form is the common usual. Moreover, the soft-switching techniques including zero-voltage-switching (ZVS) or zero-current-switching (ZCS) are usually used for alleviating the corresponding switching losses. However, there are four and upward power semiconductor switches in these circuit schemes. By this way, it will result in the increase of production cost, and the degeneration of conversion efficiency. The coupled-inductor bidirectional scheme in the proposed converter only adopts three power semiconductor switches to accomplish the objective of bidirectional current control. Under the situation of non-isolation circuit topology, it still possesses the protection of electric safety for operators. Due to the characteristics of high step-up and step-down ratio, the battery module with low voltage could be injected into a high-voltage dc bus for the later utilization, e.g., high-voltage load, front-end of inverter. Since the techniques of voltage clamping, synchronous rectification and soft switching are manipulated in this circuit topology, and the corresponding device specifications are adequately performed, it can achieve the goal of high-efficiency bidirectional power conversion for power sources with great voltage diversity.
Owner:YUAN ZE UNIV
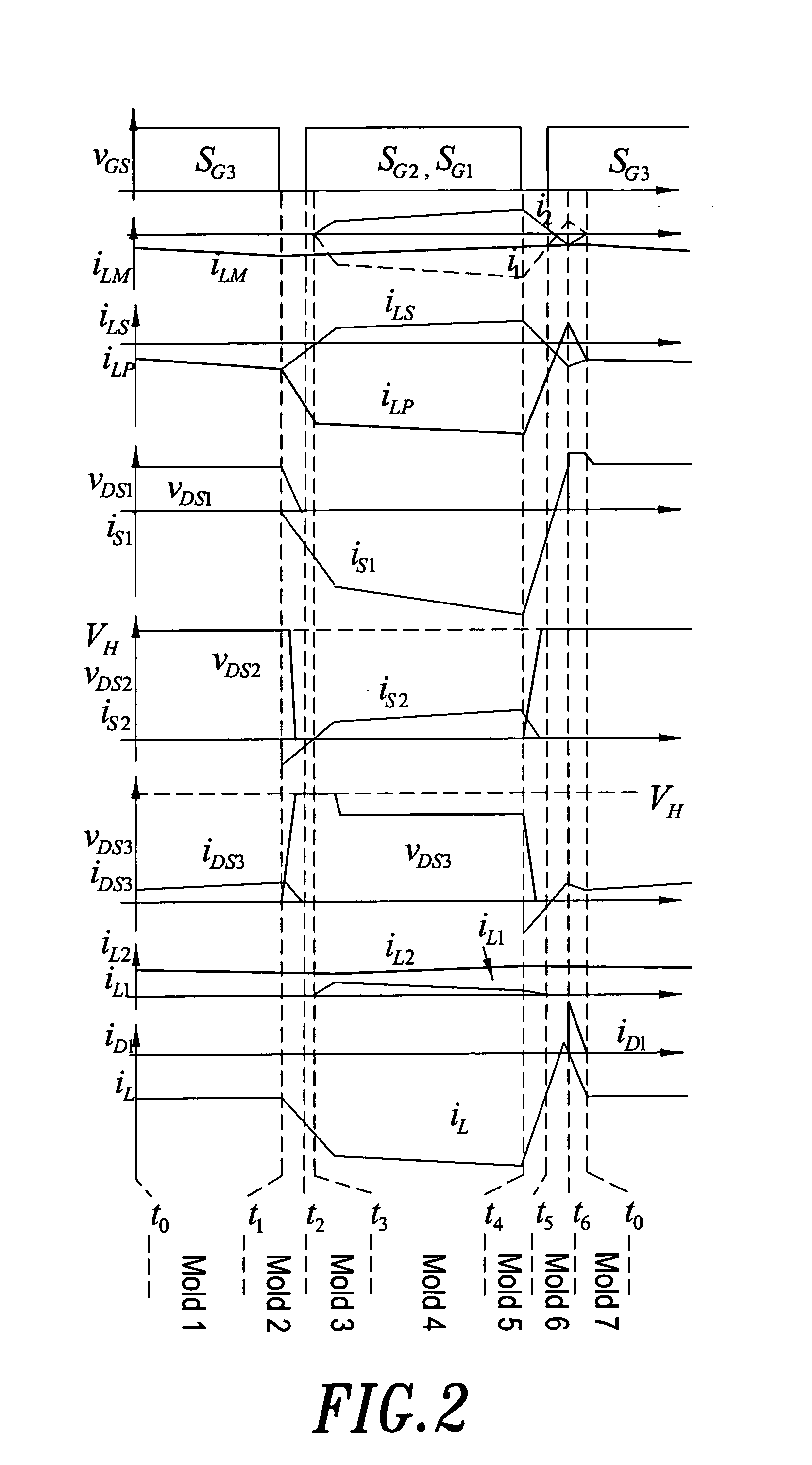
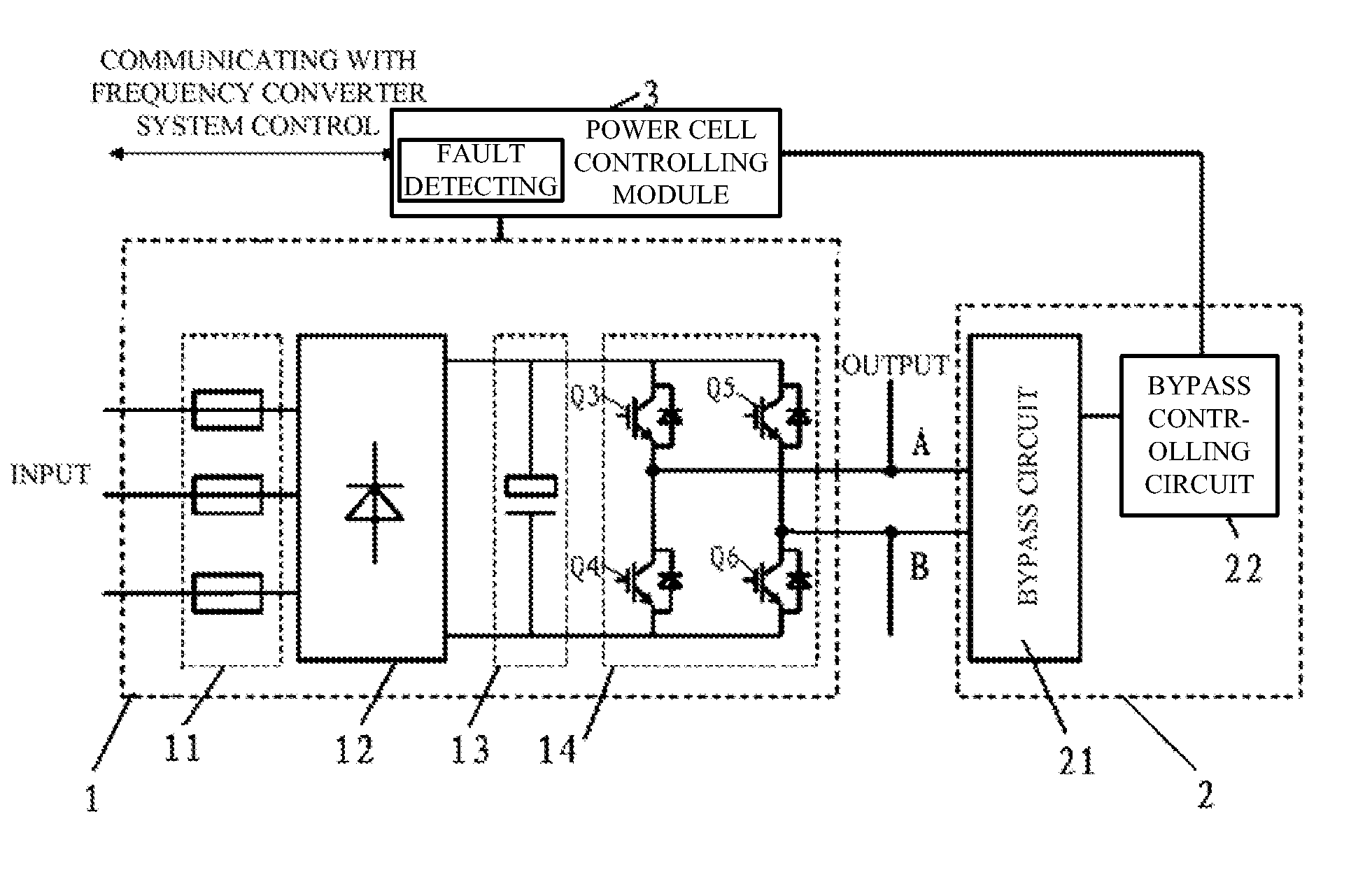
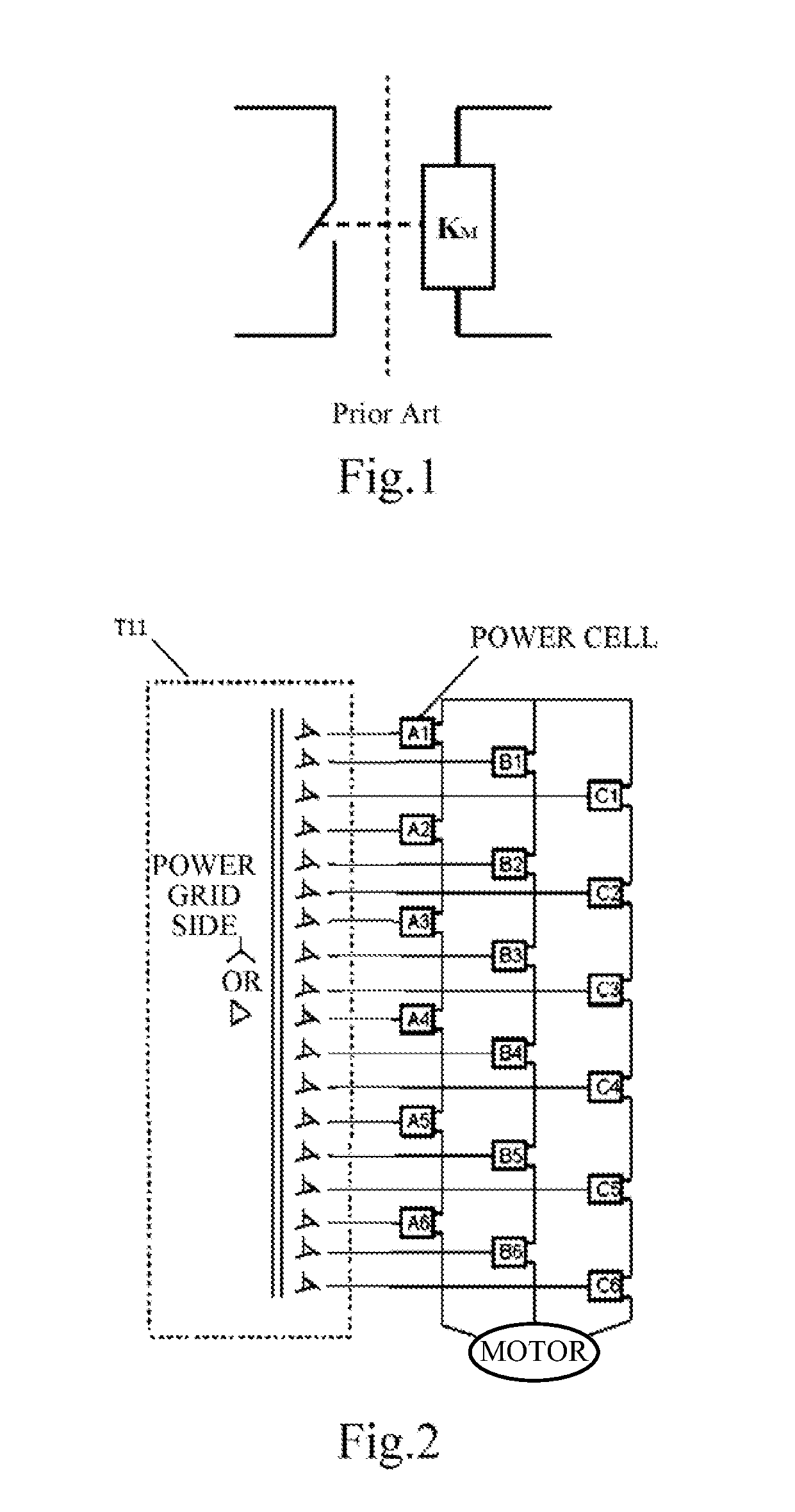
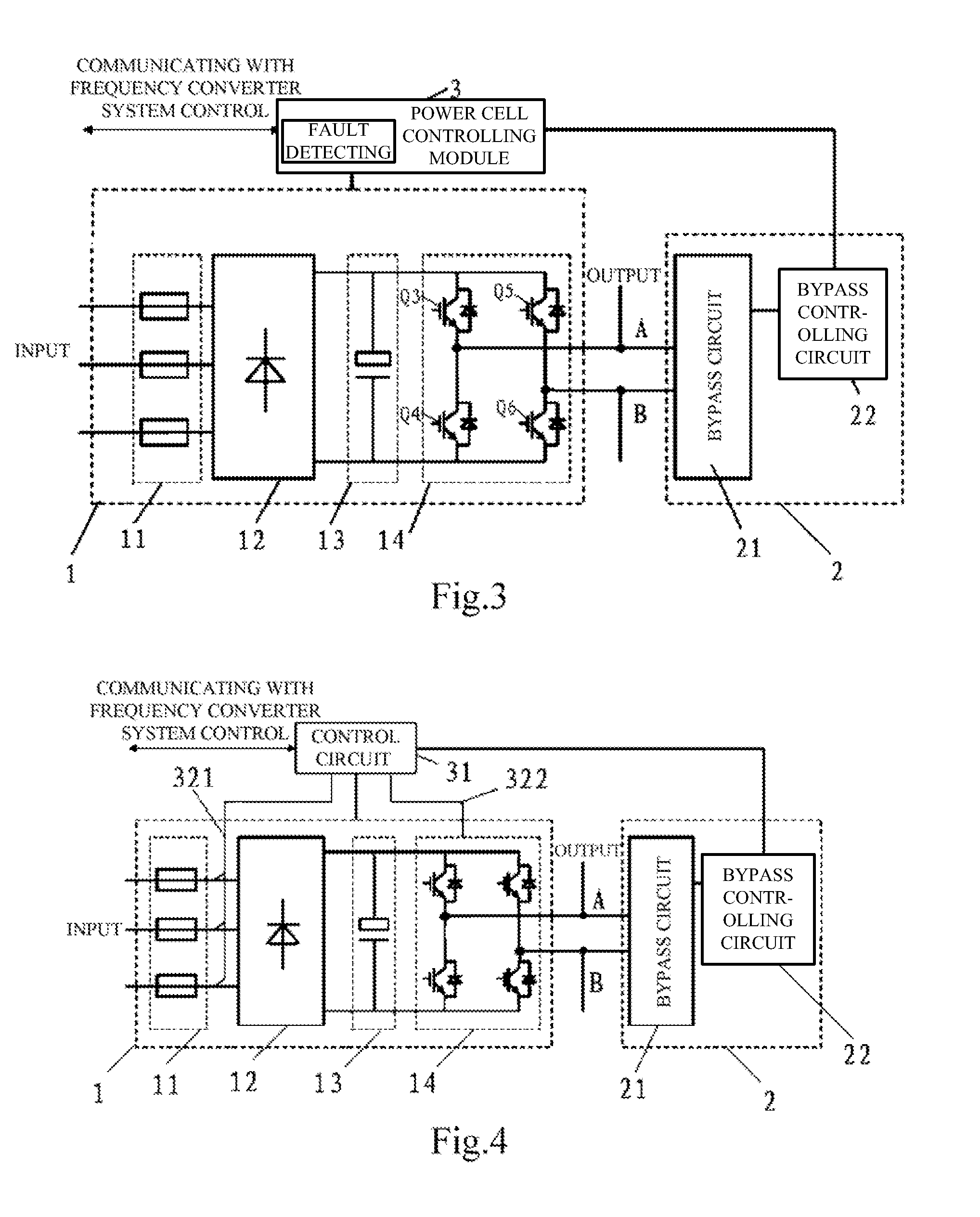
Cascaded h-bridge medium voltage drive, power cell and bypass module thereof
ActiveUS20130121042A1Low costSmall sizeAc-ac conversionDc-ac conversion without reversalComputer moduleEngineering
The present application relates to a cascaded H-Bridge medium voltage drive, a power cell, and a bypass module thereof, wherein the bypass module is configured for bypassing a major circuit module of the power cell, while the major circuit module comprises a fuse, a rectifier, a bus capacitor and an H-Bridge inverter, two points led from the H-Bridge inverter being configured as a first output end and a second output end; a bypass circuit comprises a first bridge arm and a second bridge arm; a point led from the first bridge arm is configured as a first input end of the bypass circuit, a point led from the second bridge arm is configured as a second input end of the bypass circuit, and the first input end is electrically connected with the first output end, the second input end is electrically connected with the second output end.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Direct-current power supply and battery-powered electronic apparatus equipped with the power supply
InactiveUS7274116B2InhibitionSmall circuit sizeDc-dc conversionProtective switchesBoost chopperEngineering
A bypass control section (6) maintains a bypass switch (5) in the ON state during the period when a battery voltage (Vi) is higher than the output voltage (Vo) to an external load (L). Upon falling of the output voltage (Vo) at a desired voltage (ET), a converter control section (4) starts switching control at once, and a step-up chopper (3) promptly starts boost operation. The bypass control section (6) maintains the bypass switch (5) in the ON state from the start of the boost operation of the step-up chopper (3) until the match between the battery voltage (Vi) and the output voltage (Vo).
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
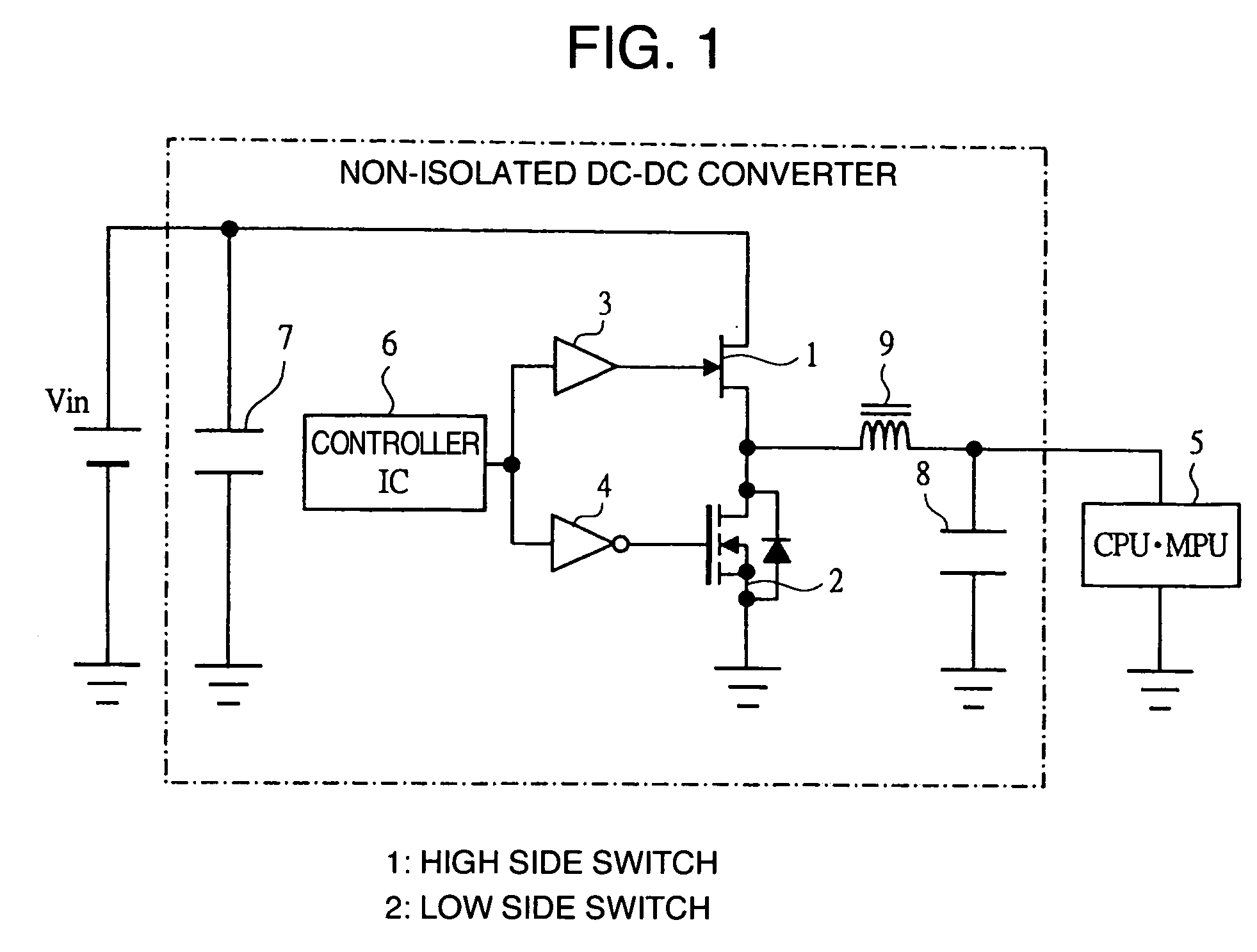
Power supply, multi chip module, system in package and non-isolated DC-DC converter
InactiveUS20060175627A1Reduce capacityLower on-resistanceEfficient power electronics conversionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDc dc converterComputer module
A power supply includes a non-isolated DC-DC converter for use in a power source system having a high side switch and a low side switch, in which HEMT or HFET or gallium nitride device with low capacity and low on-resistance is used for the high side switch and a vertical power MOSFET of silicon device with low on-resistance is used for the low side switch.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
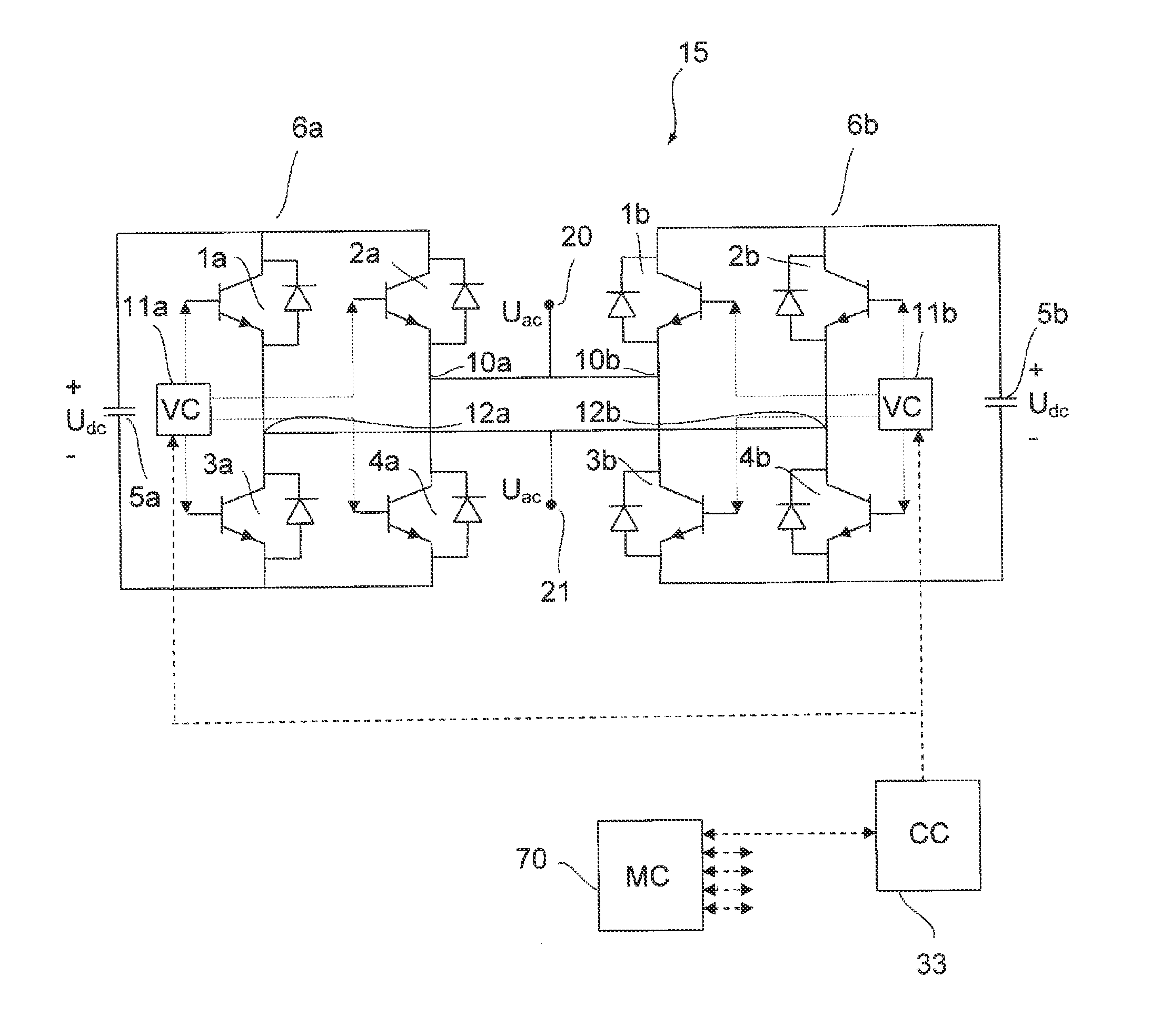
Voltage Source Converter And A Method For Fault Handling Thereof
InactiveUS20130026841A1Reduce conduction lossJeopardize functionalityDc network circuit arrangementsActive power filteringComputer moduleEngineering
A voltage source converter having a plurality of cell modules connected in series, each cell module including a converter unit having an ac-side and a dc-side, and the voltage source converter includes a control unit adapted to control the converter units, where at least one of the cell modules includes a second redundant converter unit having an ac-side which is connected in parallel with the ac-side of the first converter unit and the control unit is configured to substantially synchronously control the first and the second converter units.
Owner:ABB POWER GRIDS SWITZERLAND AG
Vertically Stacked Power FETS and Synchronous Buck Converter Having Low On-Resistance
InactiveUS20140063744A1Improve power densityReduce power consumptionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesBuck converterMetal
A power FET (100) comprising a leadframe including a pad (110), a first lead (111), and a second lead (112); a first metal clip (150) including a plate (150a), an extension (150b) and a ridge (150c), the plate and extension spaced from the leadframe pad and the ridge connected to the pad; a vertically assembled stack of FET chips in the space between the plate and the pad, the stack including a first n-channel FET chip (120) having the drain terminal on one surface and the source and gate terminals on the opposite surface, the drain terminal attached to the pad, the source terminal attached to a second clip (140) tied to the first lead; and a second n-channel FET chip (130) having the source terminal on one surface and the drain and gate terminals on the opposite surface, the source terminal attached to the second clip, its drain terminal attached to the first clip; wherein the drain-source on-resistance of the FET stack is smaller than the on-resistance of the first FET chip and of the second FET chip.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Heat sink and heat sink assembly
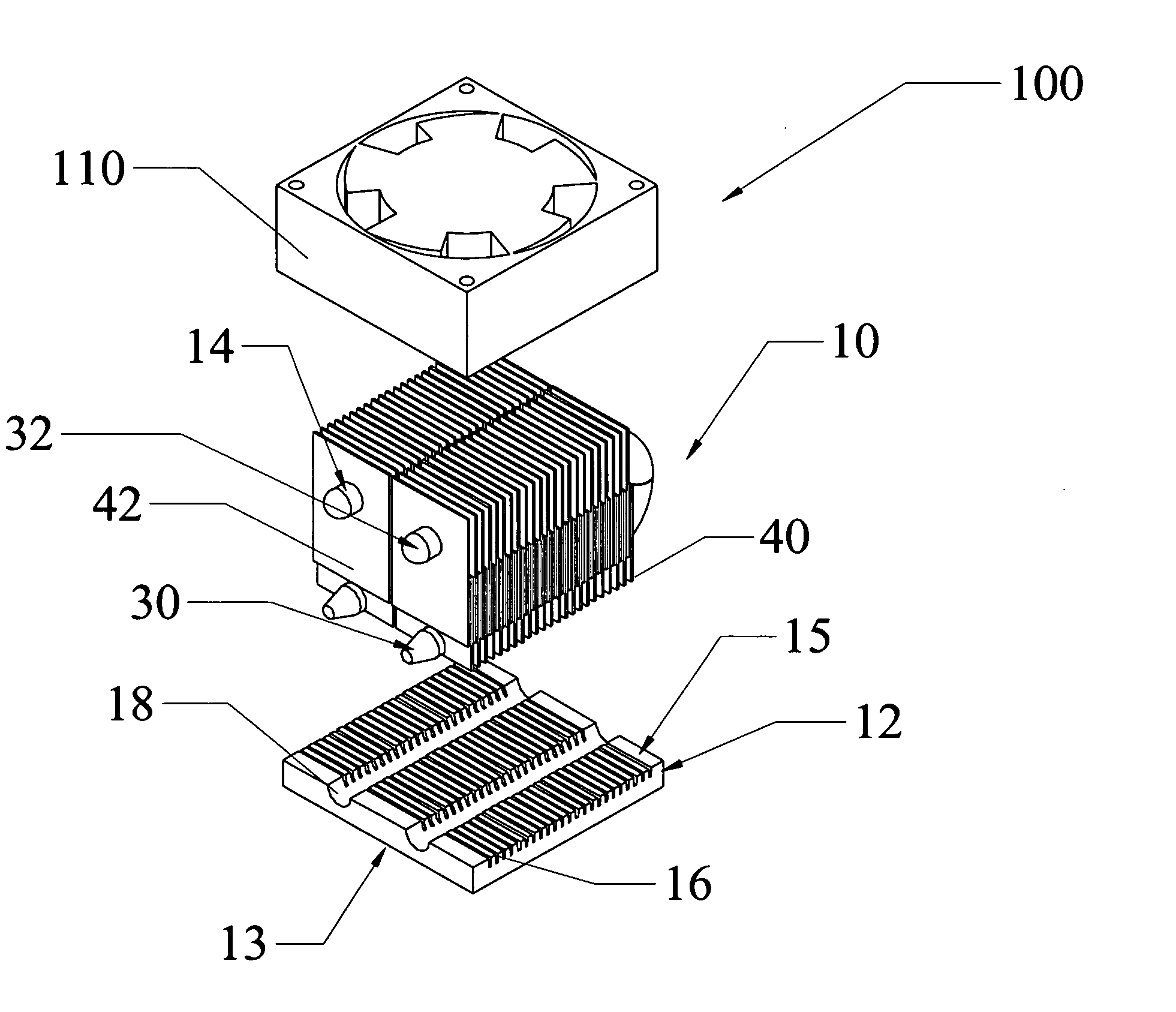
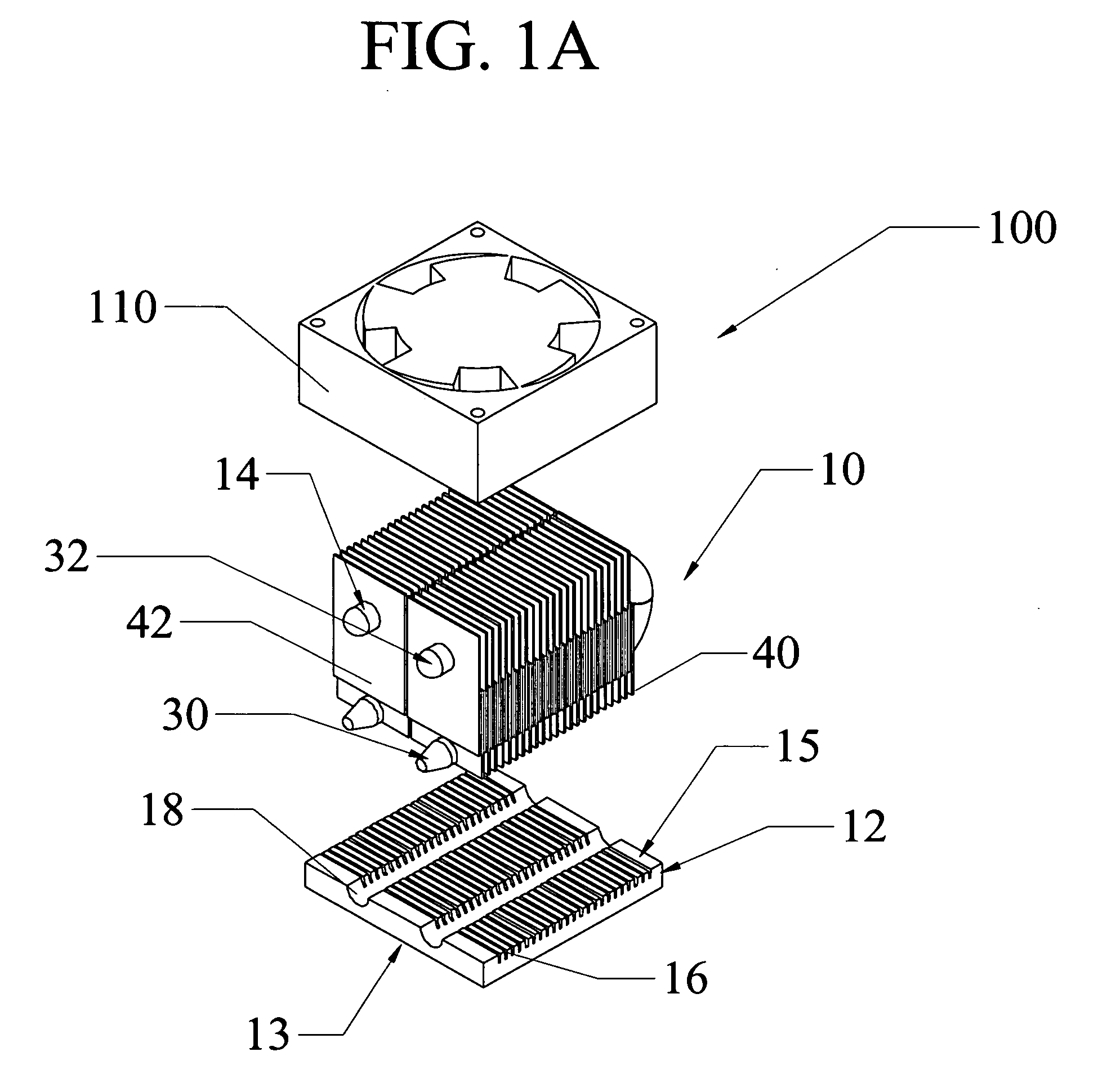
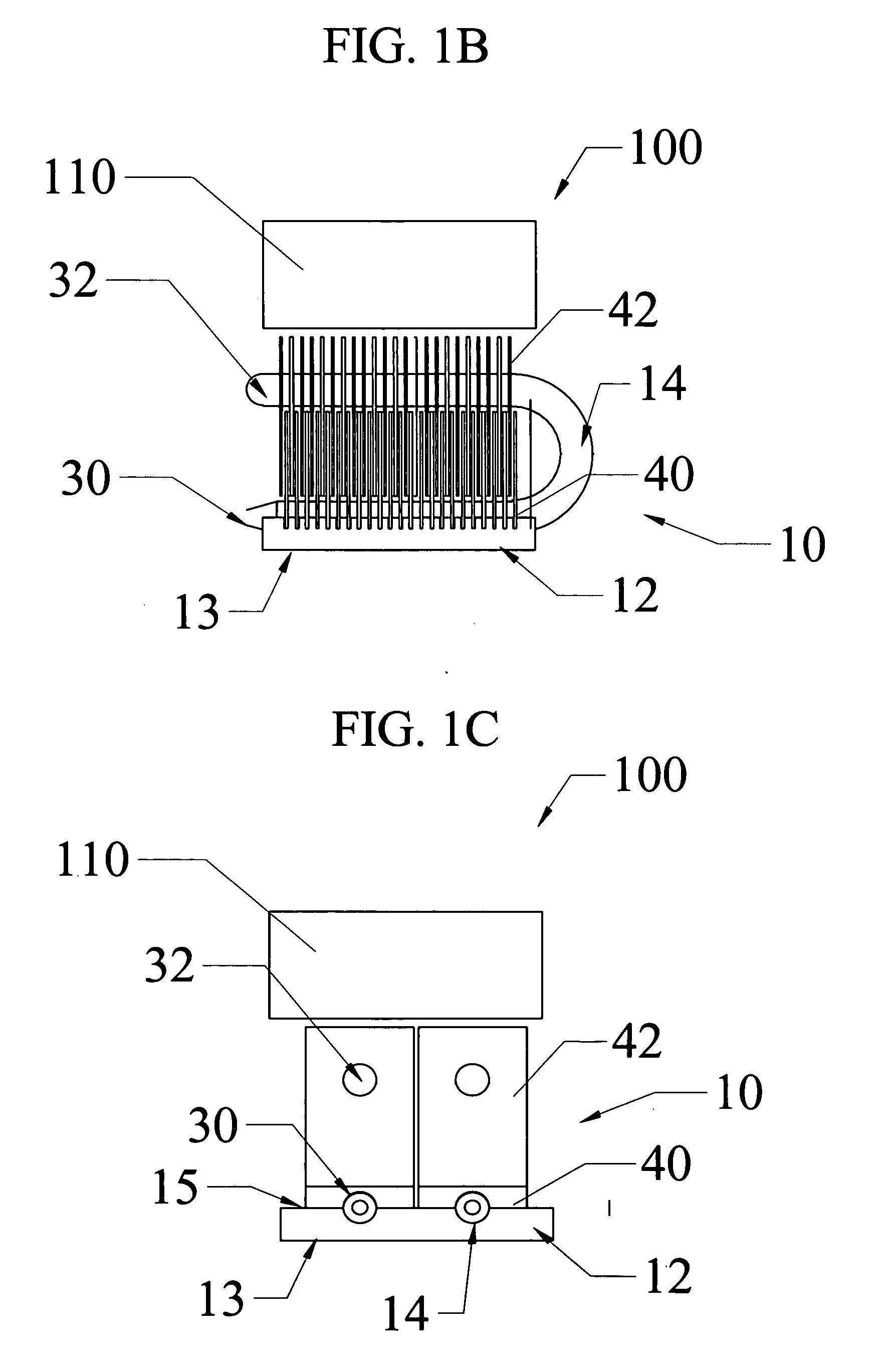
InactiveUS20060181848A1Reduce system sizeLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringThermal contact
A heat sink and a heat sink assembly that includes the heat sink and a source of flowing air, such as a fan. The heat sink includes a base from which a first plurality of convective surfaces extends. At least one heat pipe is in thermal contact with the base and extends therefrom. The heat pipe includes an evaporator portion in thermal contact with the base and a condenser portion. A second plurality of convective surfaces is in thermal communication with the condenser portion of the heat pipe.
Owner:KILEY RICHARD F +1
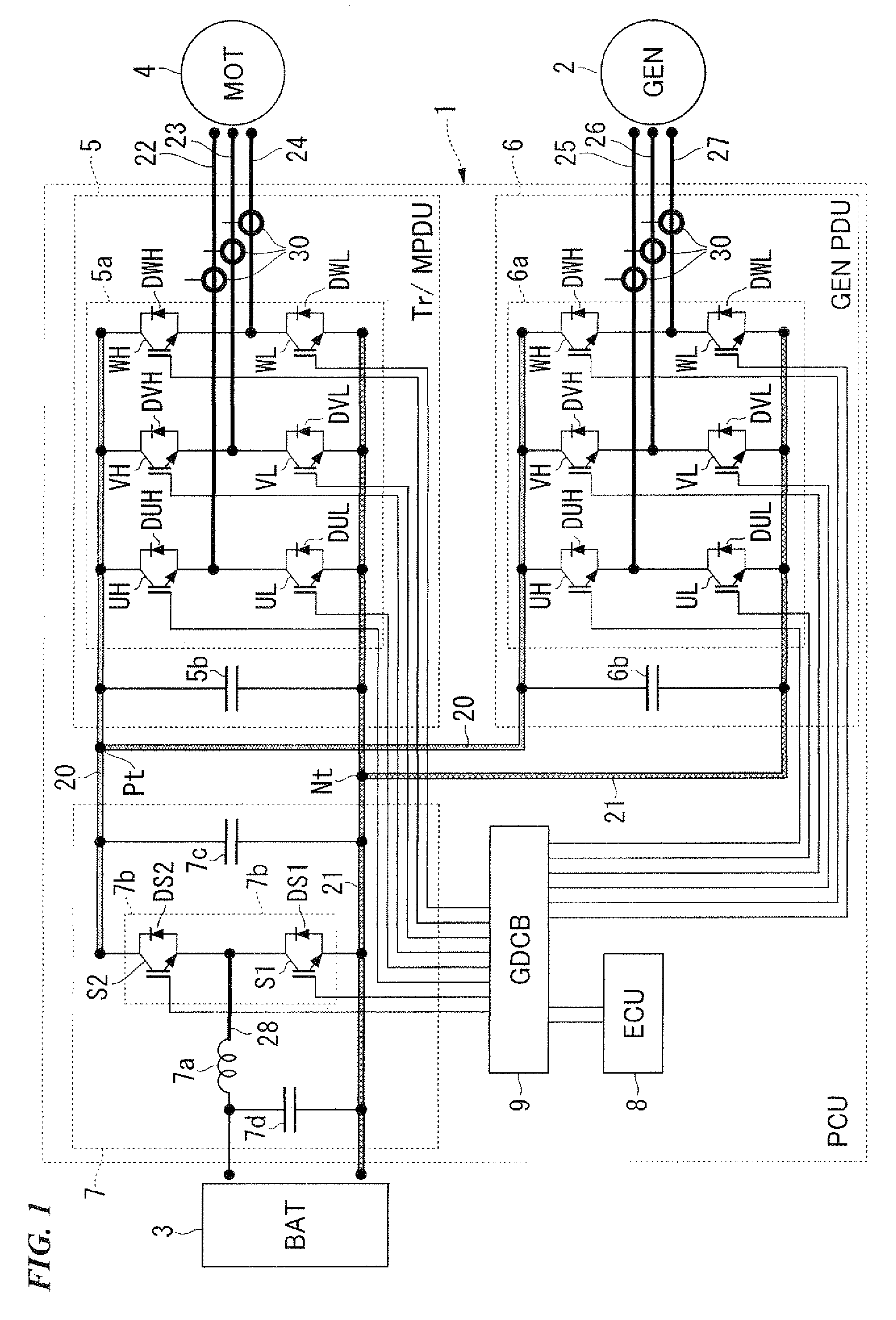
Power control unit and hybrid vehicle comprising same
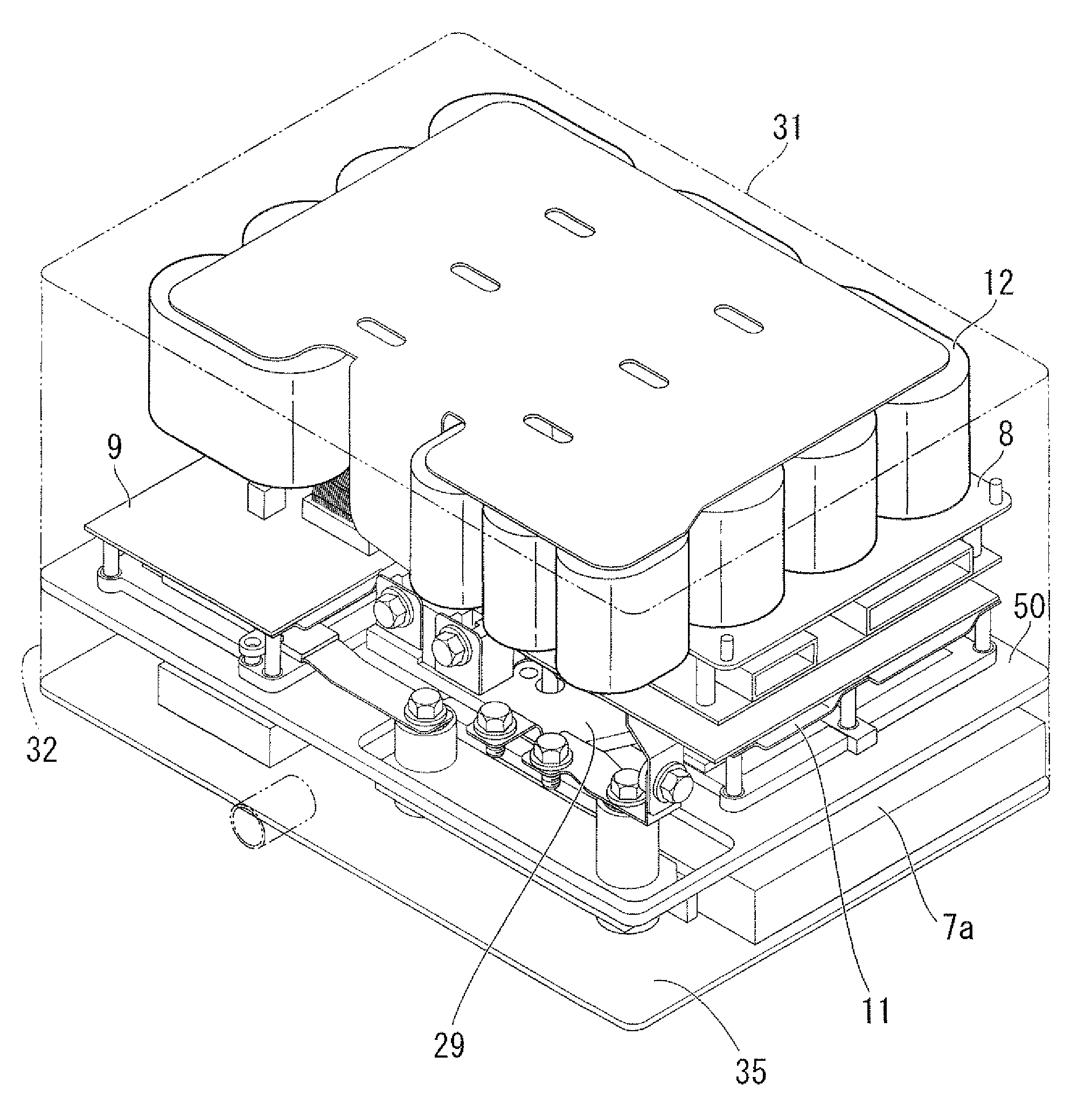
ActiveUS20090294195A1Reduce in sizeDecrease conduction lossElectric propulsion mountingGas pressure propulsion mountingPower controlHigh potential
A power control unit which comprises a plurality of semiconductor elements including a plurality of high-potential side semiconductor elements and a plurality of low-potential side semiconductor elements, and each having a first face and a second face, a collector terminal or an emitter terminal provided on the first face, or an emitter terminal and a gate terminal provided on the first face; a plurality of bus bars electrically connected with at least one of the semiconductor elements, and forming a power module together with the semiconductor elements; a terminal block having signal lines and a resin mold which supports the signal lines; and an engaging portion provided on at least one of the bus bars, and engaging with a portion of the terminal block, and also supporting the terminal block, the signal lines directly connected with the gate electrodes through the engaging portion.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Non-isolated power conversion system having multiple switching power converters
ActiveUS7230405B2Raise the ratioReduce compressive stressDc network circuit arrangementsIgnition automatic controlSwitching cycleEngineering
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
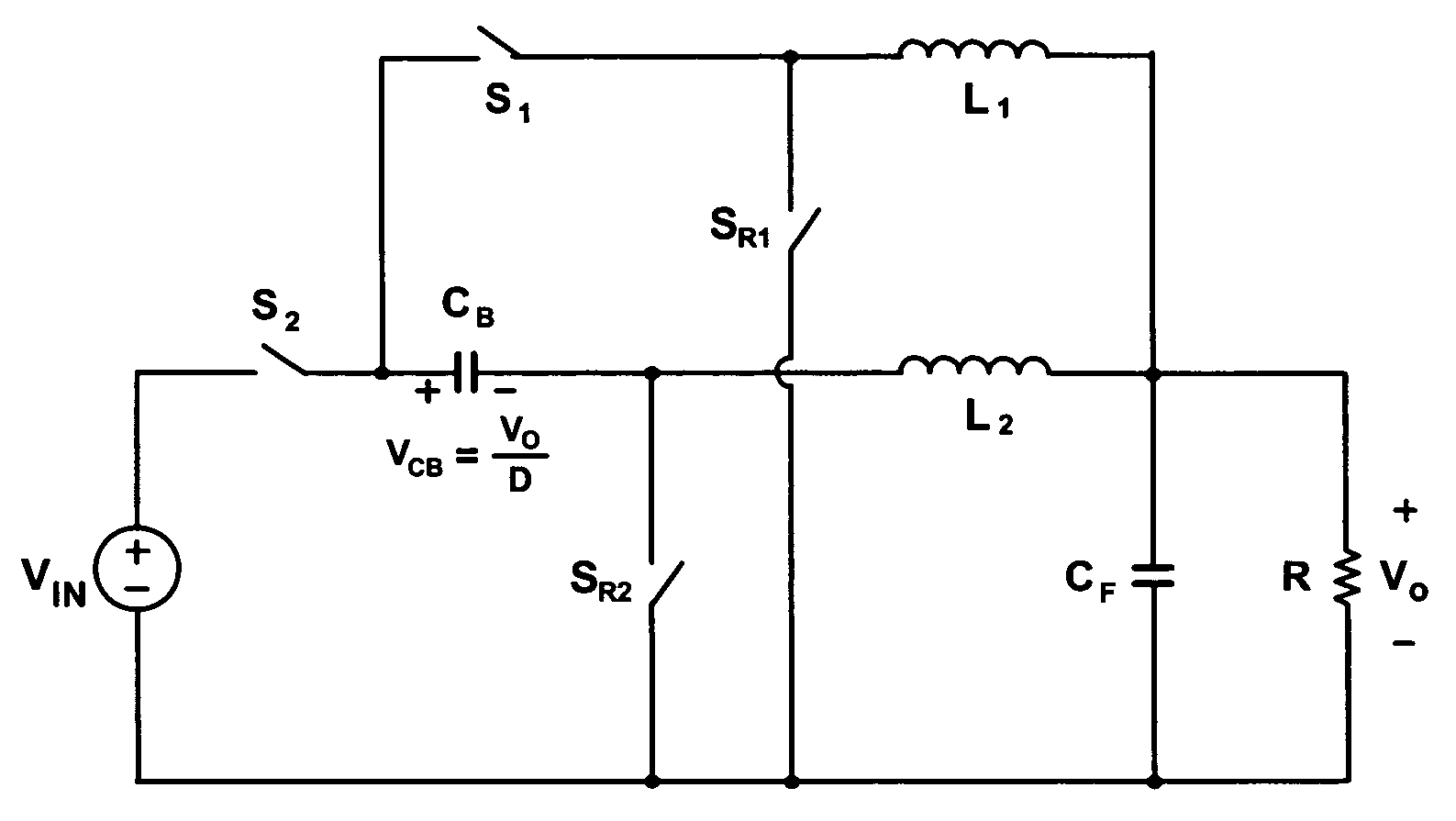
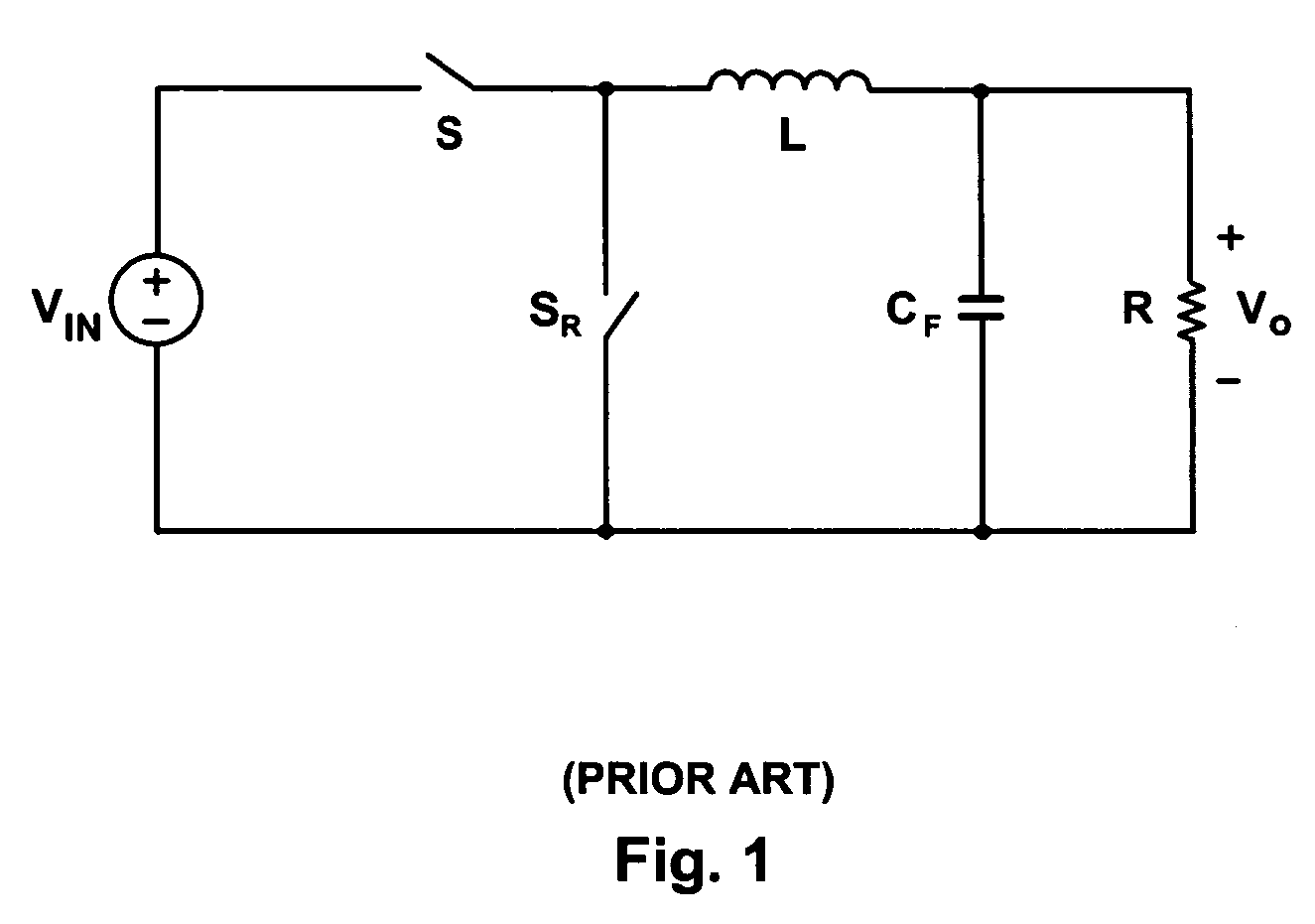
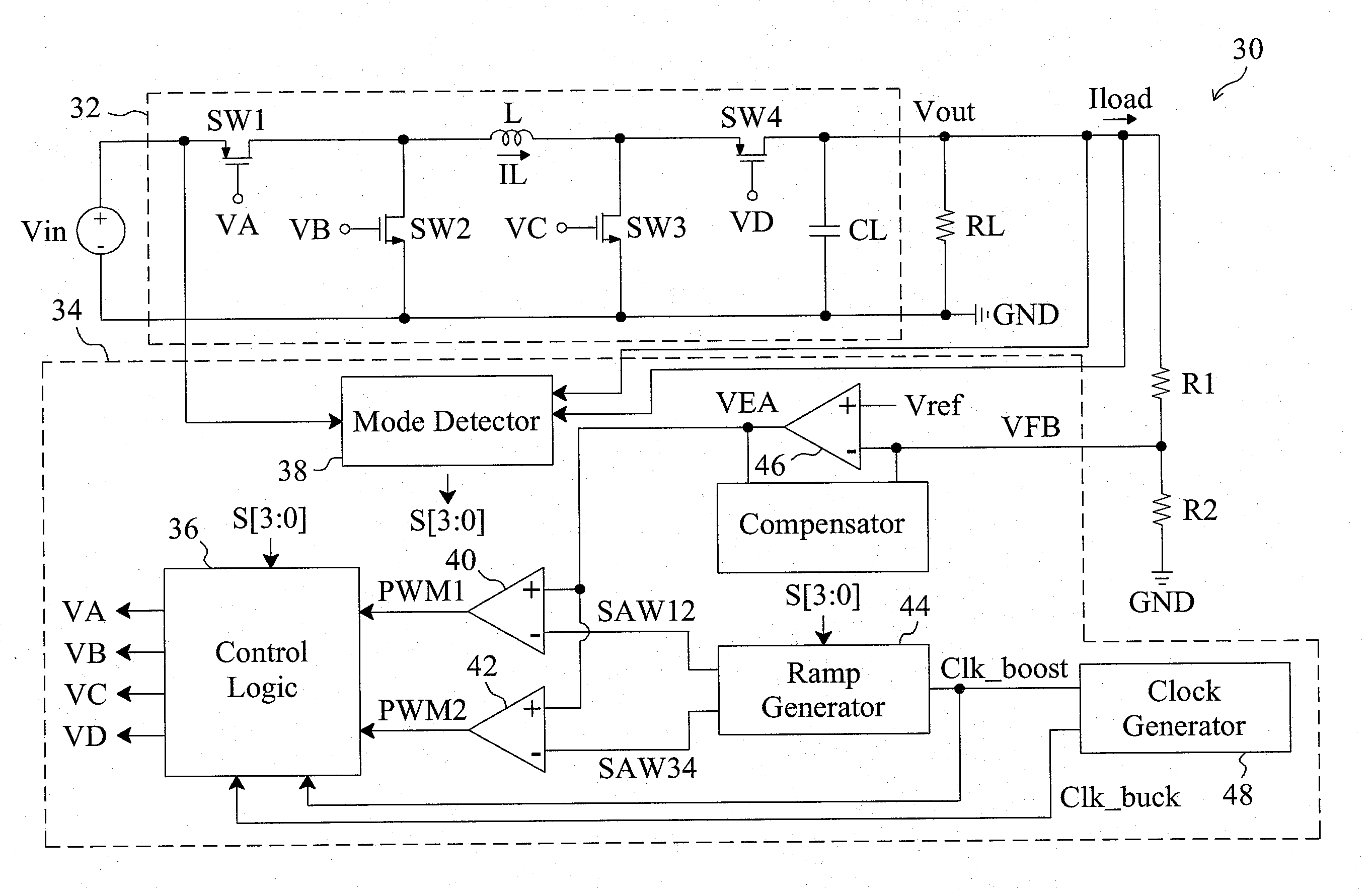
High efficiency buck-boost power converter
InactiveUS20100231189A1Reduce conduction lossExtend switching period of switchDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationEngineeringMode switching
A buck-boost power converter switches the switches thereof with a novel sequence and extends the switching periods of the switches to reduce the switching loss and conduction loss when the input voltage thereof approaches the output voltage thereof. The influence of the load current of the power converter on the duty thereof is taken into account to switch the power converter between modes at correct time points, so as to prevent the output voltage from being affected by the mode switching.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH +1
Method for Controlling Bidirectional DC-DC Converter
InactiveUS20080074905A1Reduce switching lossesReduce conduction lossDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationTransformer windingsConduction loss
A method for controlling a bidirectional DC-DC converter that reduces switching loss during a step-down operation and conduction loss caused by synchronous rectification, while enabling bidirectional operation with the same control. The DC-DC converter includes first and second switch elements for alternately applying voltage in opposite directions to a transformer winding during the step-down operation and performing synchronous rectification during a step-up operation. Third and fourth switch elements perform synchronous rectification during the step-down operation and alternately apply voltage in opposite directions to the transformer in the step-up operation. The method includes activating the first switch when the third switch is in an active state, activating the second switch when the fourth switch is in an active state, switching each of the third and forth switches between an active state and an inactive state while inactivating the third or fourth switch.
Owner:TOYOTA IND CORP
Power factor correction control circuit for reducing EMI (electro magnetic interference)
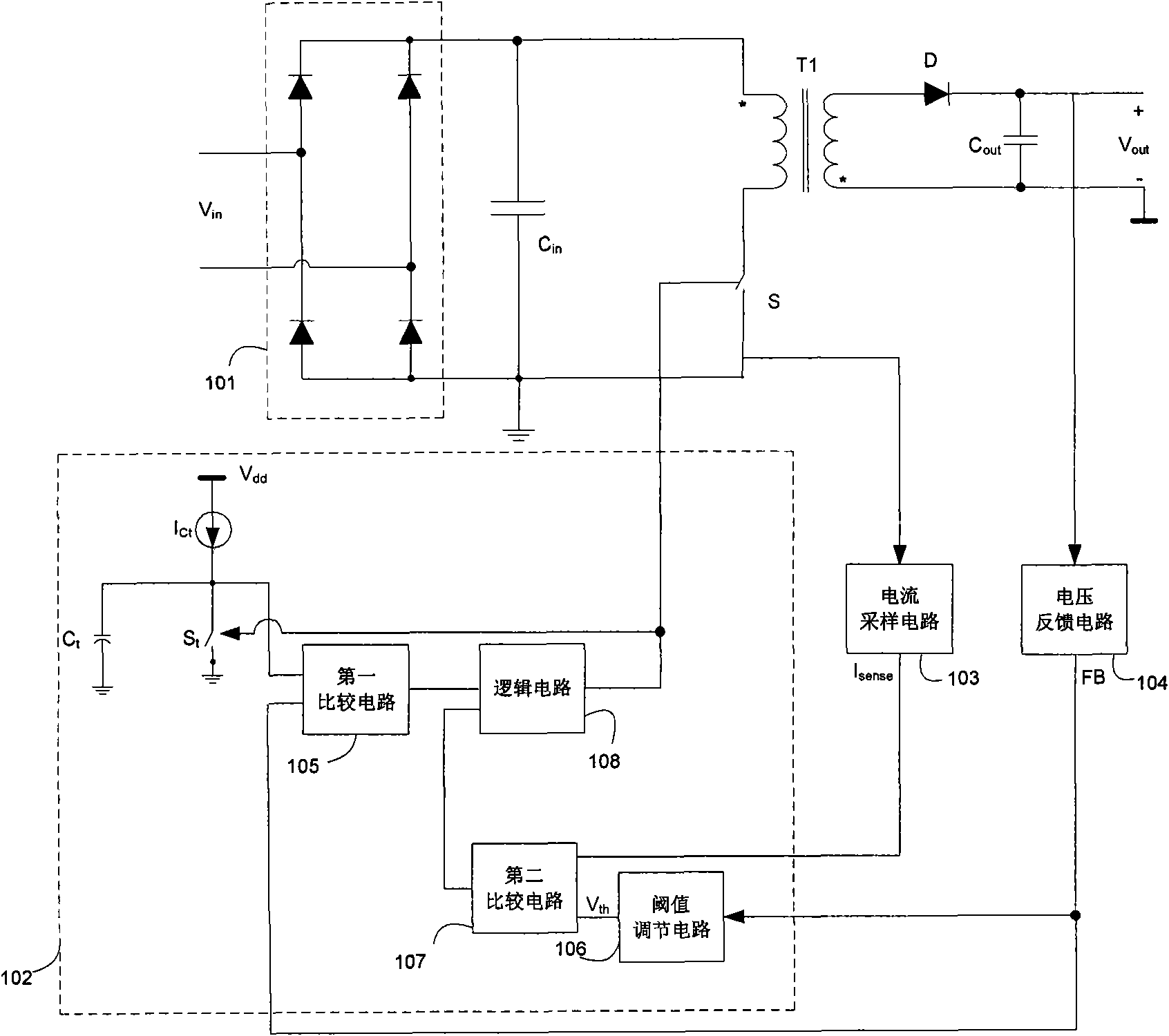
ActiveCN102332814ALighten the filtering burdenThe maximum peak current is reducedEfficient power electronics conversionEnergy industryHarmonicCurrent threshold
The invention discloses a power factor correction control circuit for reducing EMI (electro magnetic interference), which comprises an inductive current threshold value, wherein when an inductive current is less than the inductive current threshold value, a peak value of the inductive current is controlled to be changed along with an input voltage; and when the inductive current reaches the inductive current threshold value, the inductive current is limited to be the inductive current threshold value. In such a way, the maximum peak of the inductive current is reduced, so that an inductive ripple current is reduced; the power factor is ensured, and the EMI of the circuit is reduced simultaneously, so that circuit filtering can be carried out simply and easily; and the power factor correction control circuit is extremely suitable for occasions with middle or low power. In addition, the peak current stress of the circuit is low, so that a switch tube and other components have small loss, and the utilization ratio of a power supply is further improved. The power factor correction control circuit for reducing the EMI disclosed by the invention meets the requirements of high-power factor and IEC61000-3-2 on the harmonic of the power supply, and has low cost and a small size.
Owner:SILERGY SEMICON TECH (HANGZHOU) CO LTD
Lithium battery pack SOC (state of charge) equalization system and lithium battery pack SOC equalization method
ActiveCN106356927AAvoid diversionReduce equalization lossCharge equalisation circuitElectric powerEnergy transferDc dc converter
The invention discloses a lithium battery pack SOC (state of charge) equalization system and a lithium battery pack SOC equalization method. The equalization problems of lithium battery packs are divided into two levels, including intra-group equalization and intergroup equalization. Lithium batteries are divided into a plurality of groups, every lithium battery group is in parallel connection with a bidirectional DC-DC converter, the output ends of the bidirectional DC-DC converters are in series connection to serve as the output ends of a direct-current bus and a power generation system, and loads are in parallel connection. The batteries in every group are connected through bilateral switches and are in parallel connection with by-pass switches so as to be connected dynamically. Intergroup equalization is achieved by distributing output voltage of every group according to average SOC thereof; intra-group equalization can be achieved by controlling dynamic connection of every single battery in every group. The lithium battery pack SOC equalization system and the lithium battery pack SOC equalization method have the advantages that lithium battery pack SOC is equalized without an extra equalization circuit, so that energy transfer among the batteries is avoided, lithium battery pack equalization is achieved automatically in a charge-discharge process, the equalization speed is greatly increased and the equalization efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and circuit for reducing losses in DC-DC converters
InactiveUS6930473B2Reduction of gate capacitance switching lossReduce conduction lossElectronic switchingApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitanceLow load
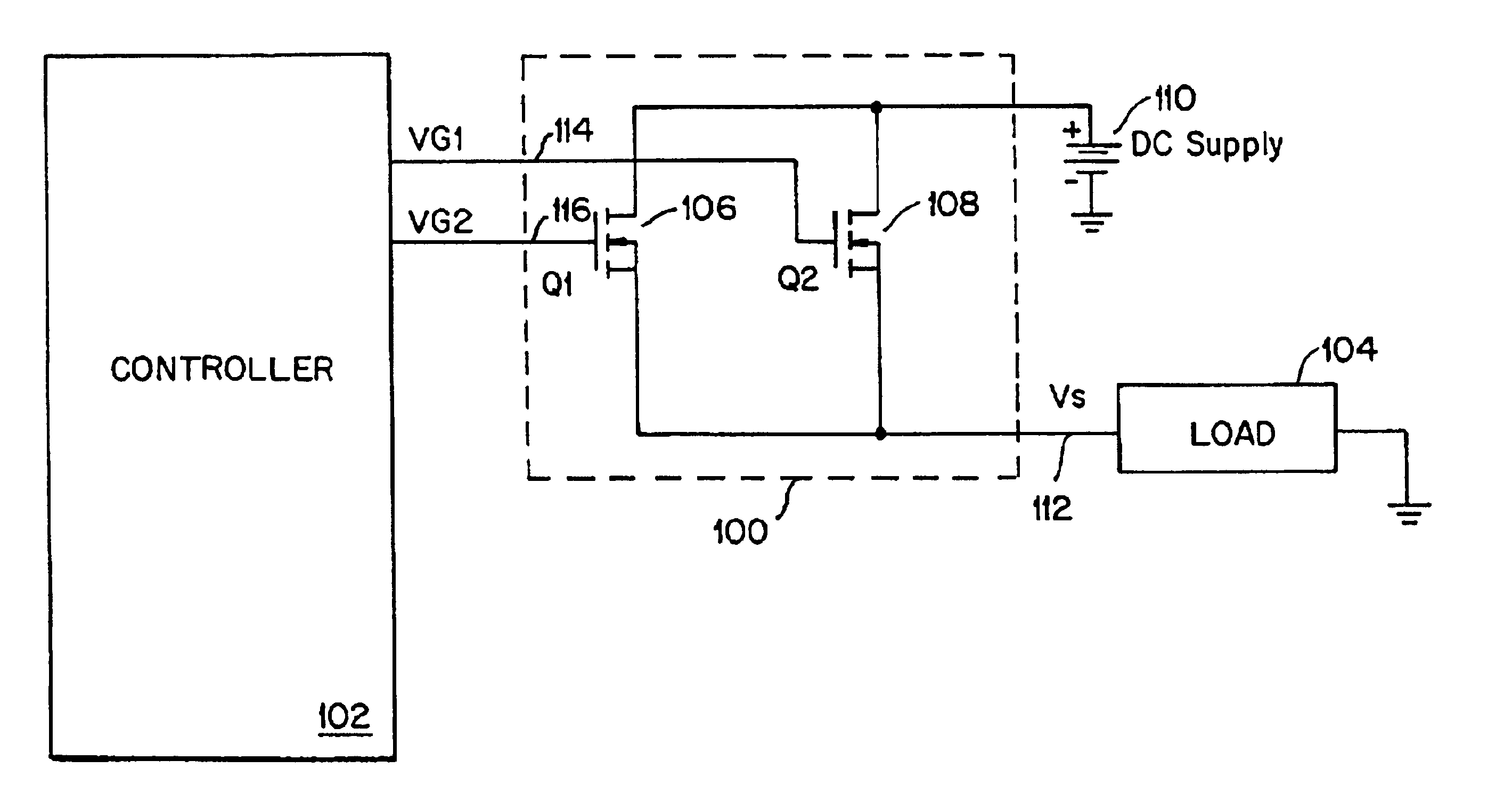
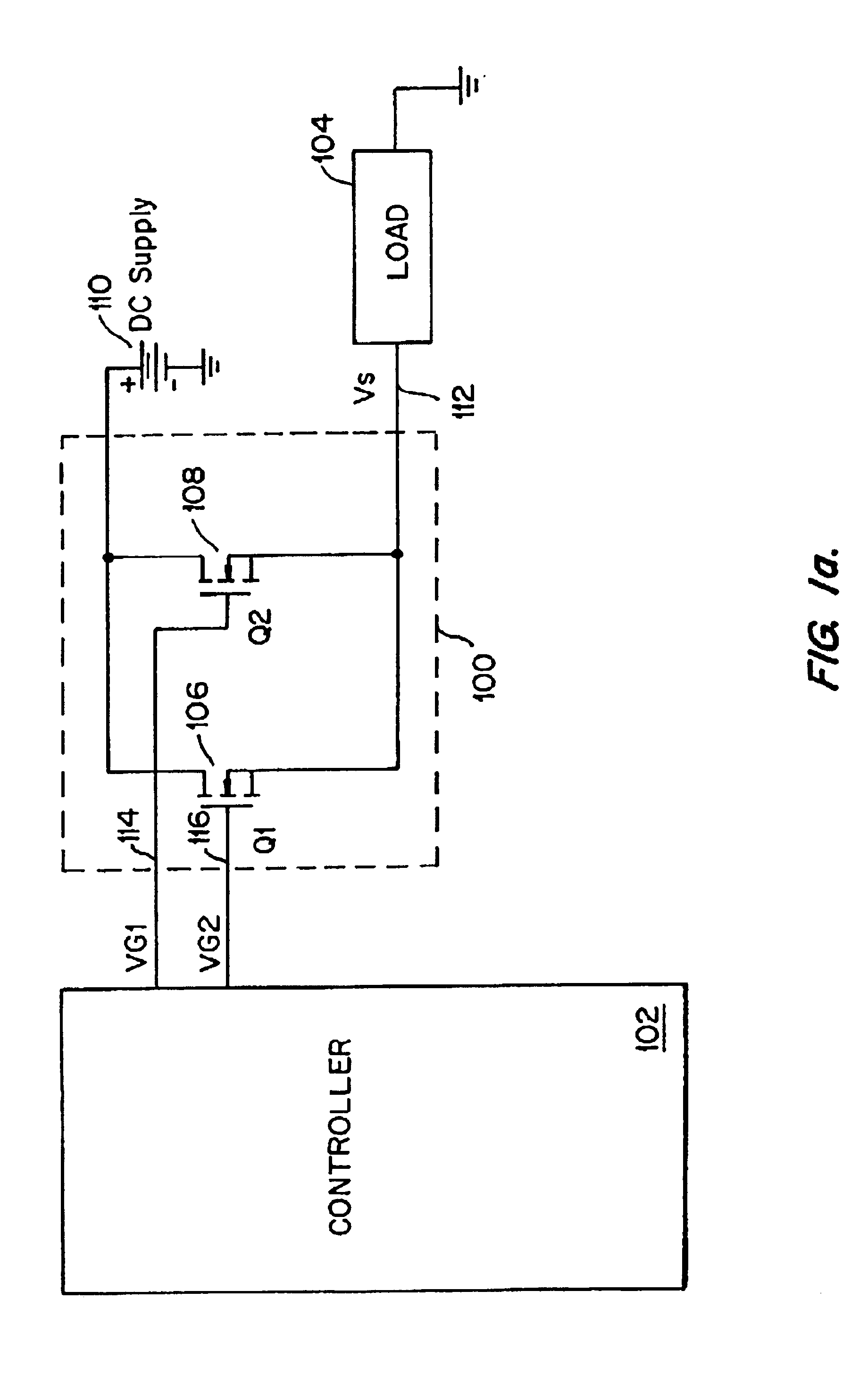
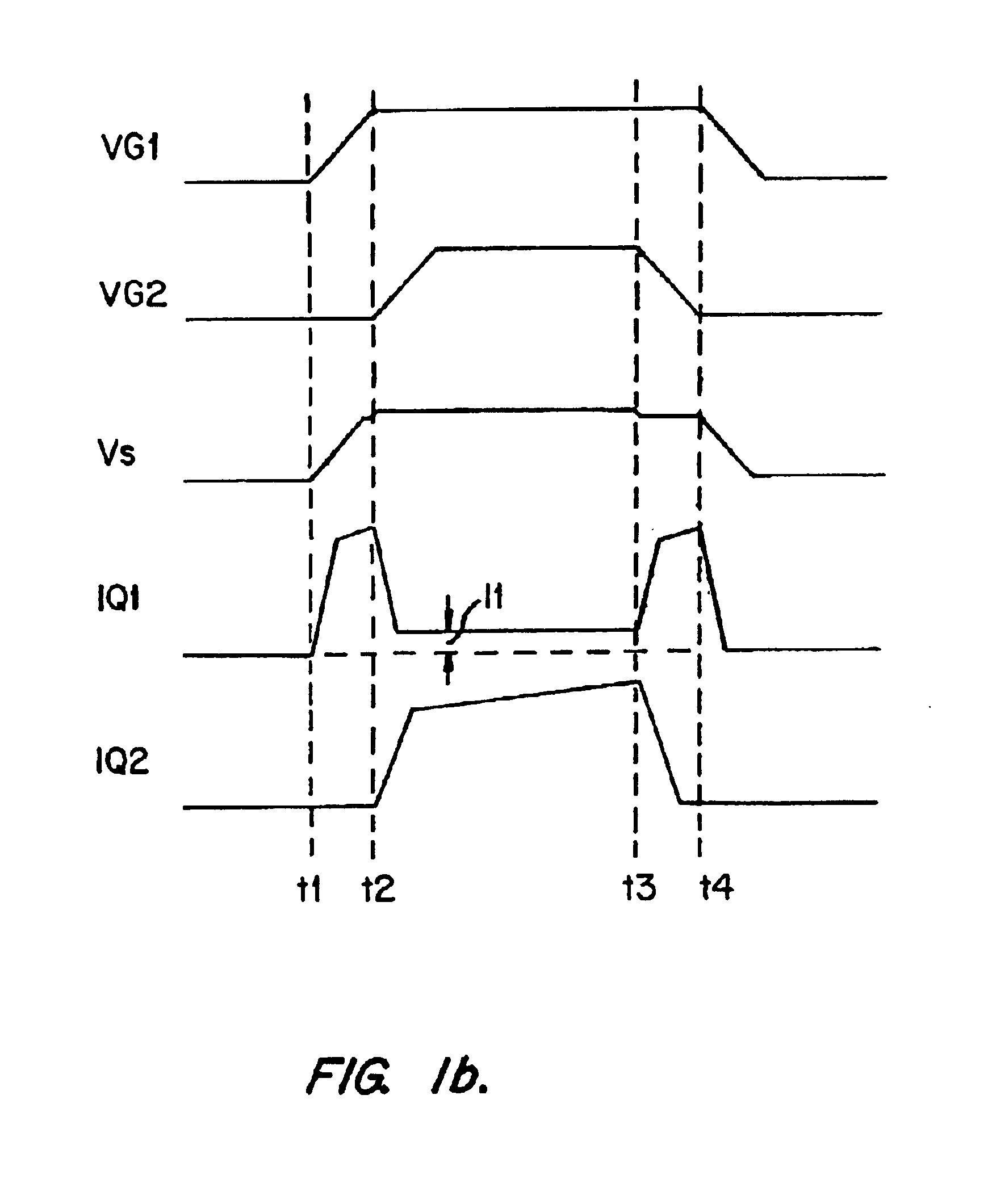
In accordance with the present invention, a switching converter includes two transistors Q1 and Q2 parallel-connected between two terminals. Transistor Q1 is optimized to reduce the dynamic loss and transistor Q2 is optimized to reduce the conduction loss. Q1 and Q2 are configured and operated such that the dynamic loss of the converter is dictated substantially by Q1 and the conduction loss of the converter is dictated substantially by Q2. Thus, the tradeoff between these two types of losses present in conventional techniques is eliminated, allowing the dynamic and conduction losses to be independently reduced. Further, the particular configuration and manner of operation of Q1 and Q2 enable reduction of the gate capacitance switching loss when operating under low load current conditions.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Non-isolated grid-connected inverter and switch control time sequence thereof
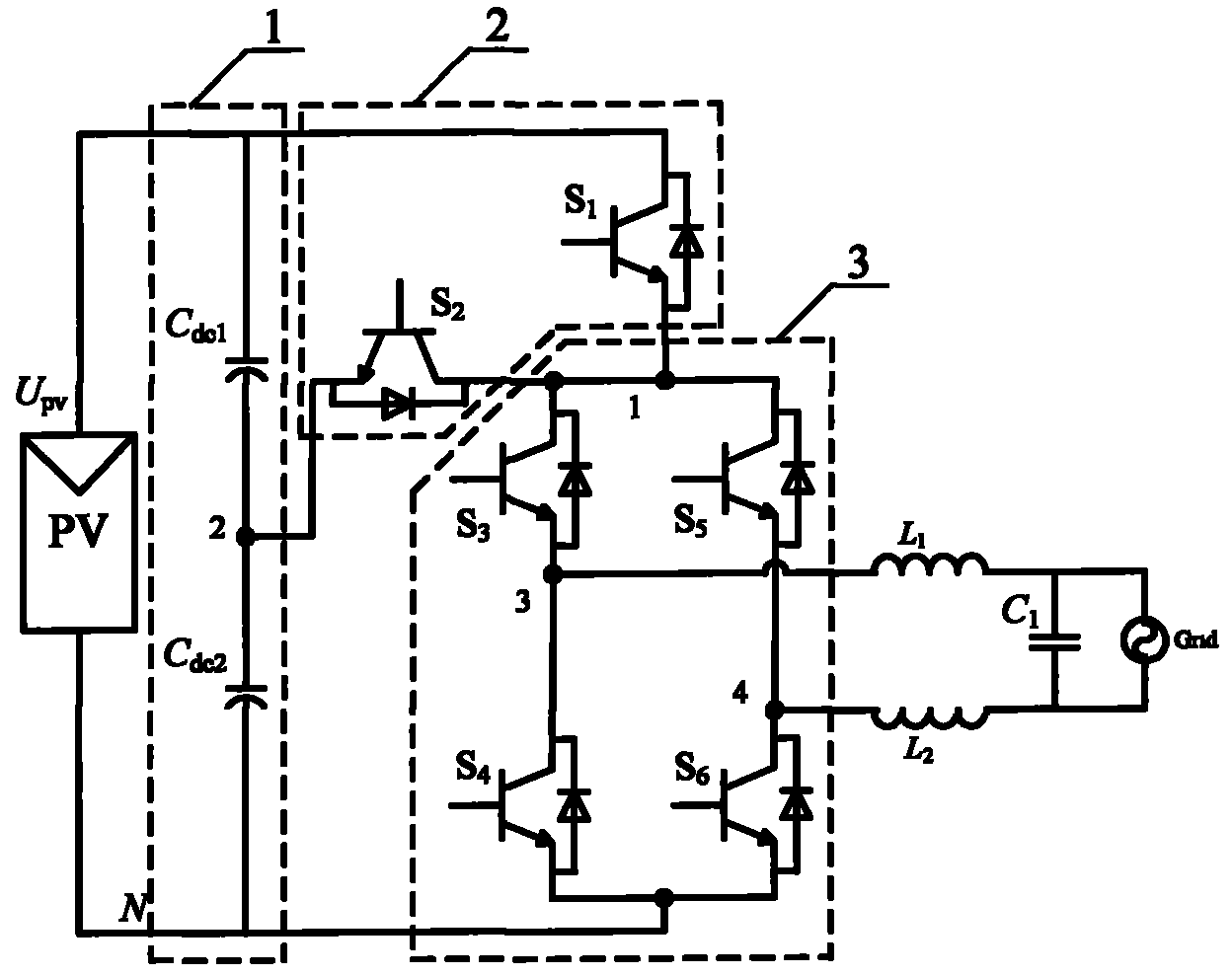
InactiveCN101814856AReduce conduction lossImprove efficiencyPhotovoltaic energy generationLight radiation electric generatorCapacitanceGrid connected inverter
The invention provides a non-isolated grid-connected inverter and a switch control time sequence thereof. The non-isolated grid-connected inverter comprises a voltage dividing capacitor branch (1), a clamping branch (2) and a full-bridge basic unit (3), wherein the voltage dividing capacitor branch (1) consists of a first voltage dividing capacitor (Cdc1) and a second voltage dividing capacitor (Cdc2), the clamping branch (2) consists of a first power switch pipe (S1) and a second power switch pipe (S2), and the full-bridge basic unit (3) consists of a third power switch pipe (S3), a fourth power switch pipe (S4), a fifth power switch pipe (S5) and a six power switch pipe (S6). The invention adds two controllable switch pipes and voltage dividing capacitors on the basis of a full-bridge circuit for forming a bidirectional clamping branch, is matched with the switch time sequence, and can realize the battery voltage at a half of the follow current loop potential in the follow current stage, so the leakage current of the non-isolated grid-connected inverter is eliminated, the output current only passes through three switch pipes in the power transmission stage is ensured, and the conduction consumption is effectively reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Novel efficient and reliable DC/AC converter for fuel cell power conditioning
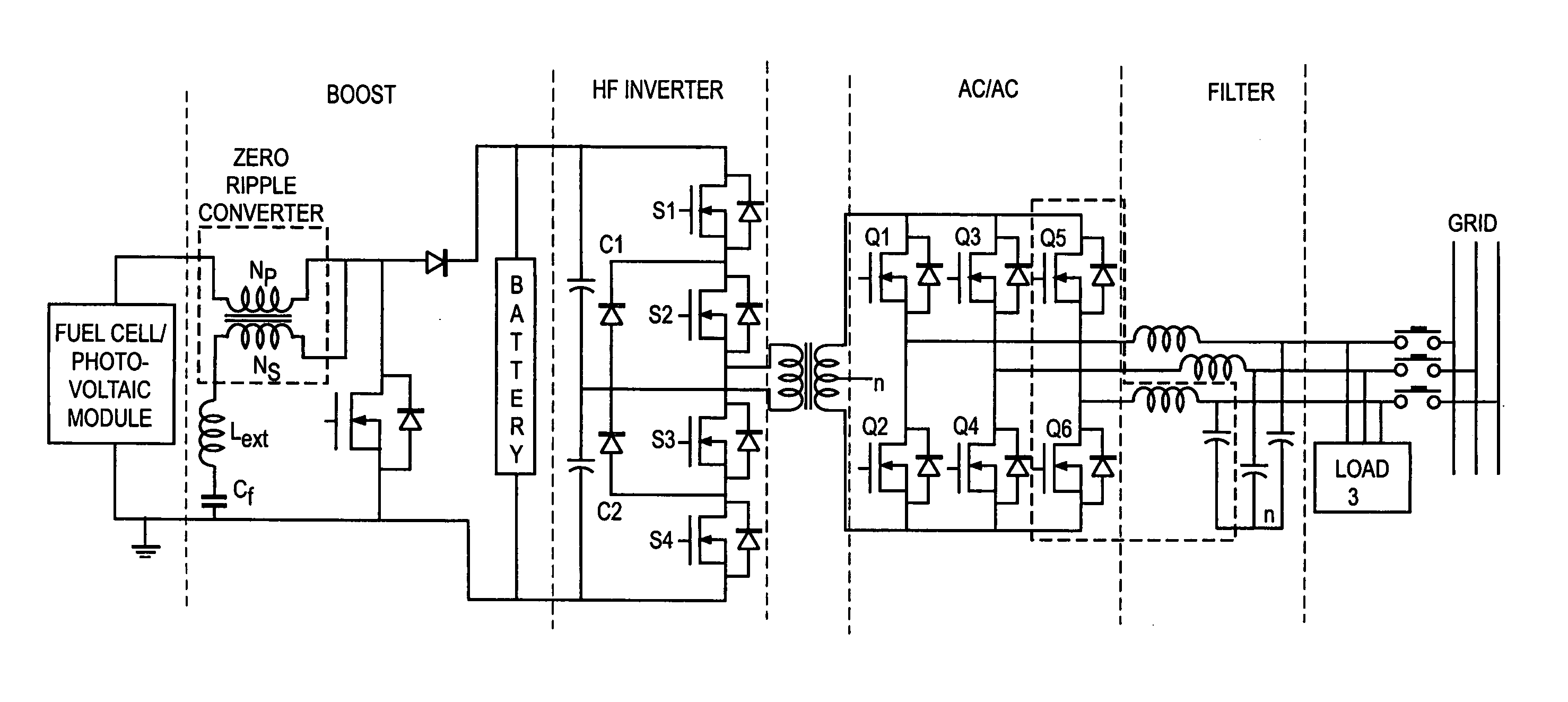
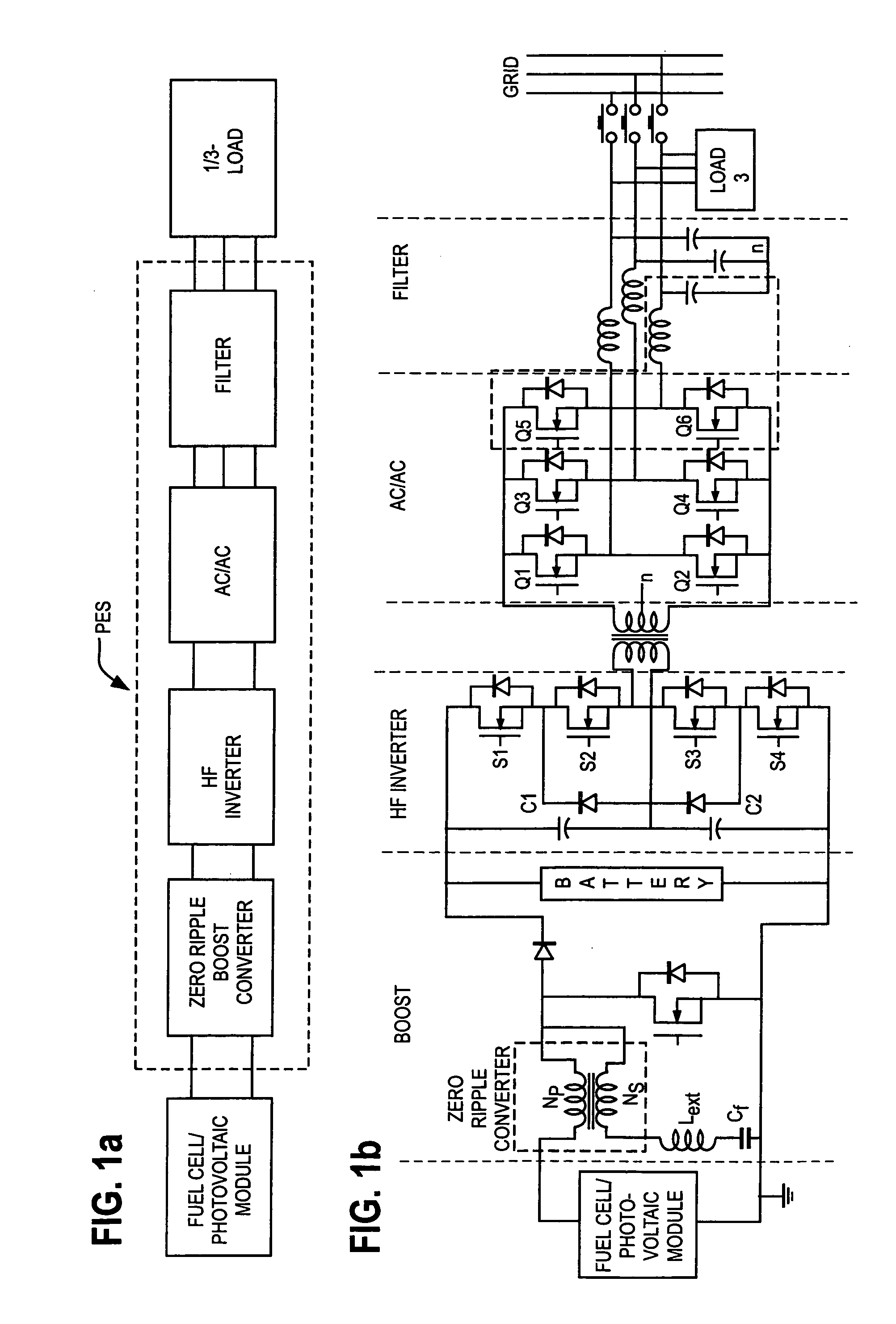
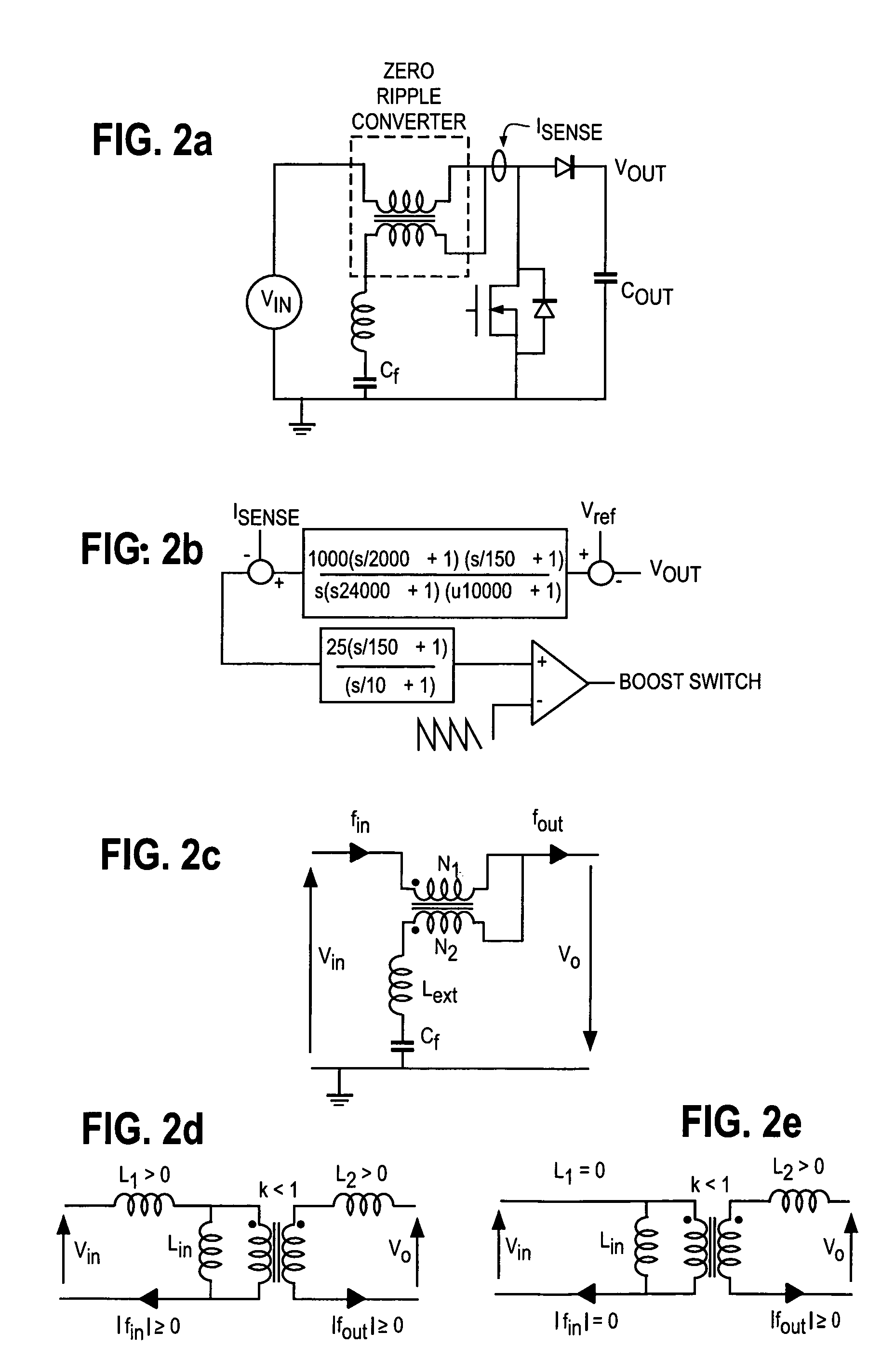
InactiveUS20050141248A1Reduce conduction lossReduced Thermal Management RequirementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsDc circuit to reduce harmonics/ripplesFuel cellsWork status
A novel power conditioning converter which provides a significant reduction in input current ripple (<1%), with efficiency above 90% and reduced thermal management is proposed. The converter in discussion has a sort-switched, multilevel, high frequency converter, which acts as an interface between the dc / dc boost and the ac / ac converter. This paper presents a detailed description of the operation of the converter and highlights the important features and advantages. SABER simulation results are presented to provide an improved understanding of the switching mechanisms. A discussion on the implementation of the converter and the status of ongoing work is presented.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com