Patents
Literature
2618results about How to "Reduce switching losses" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
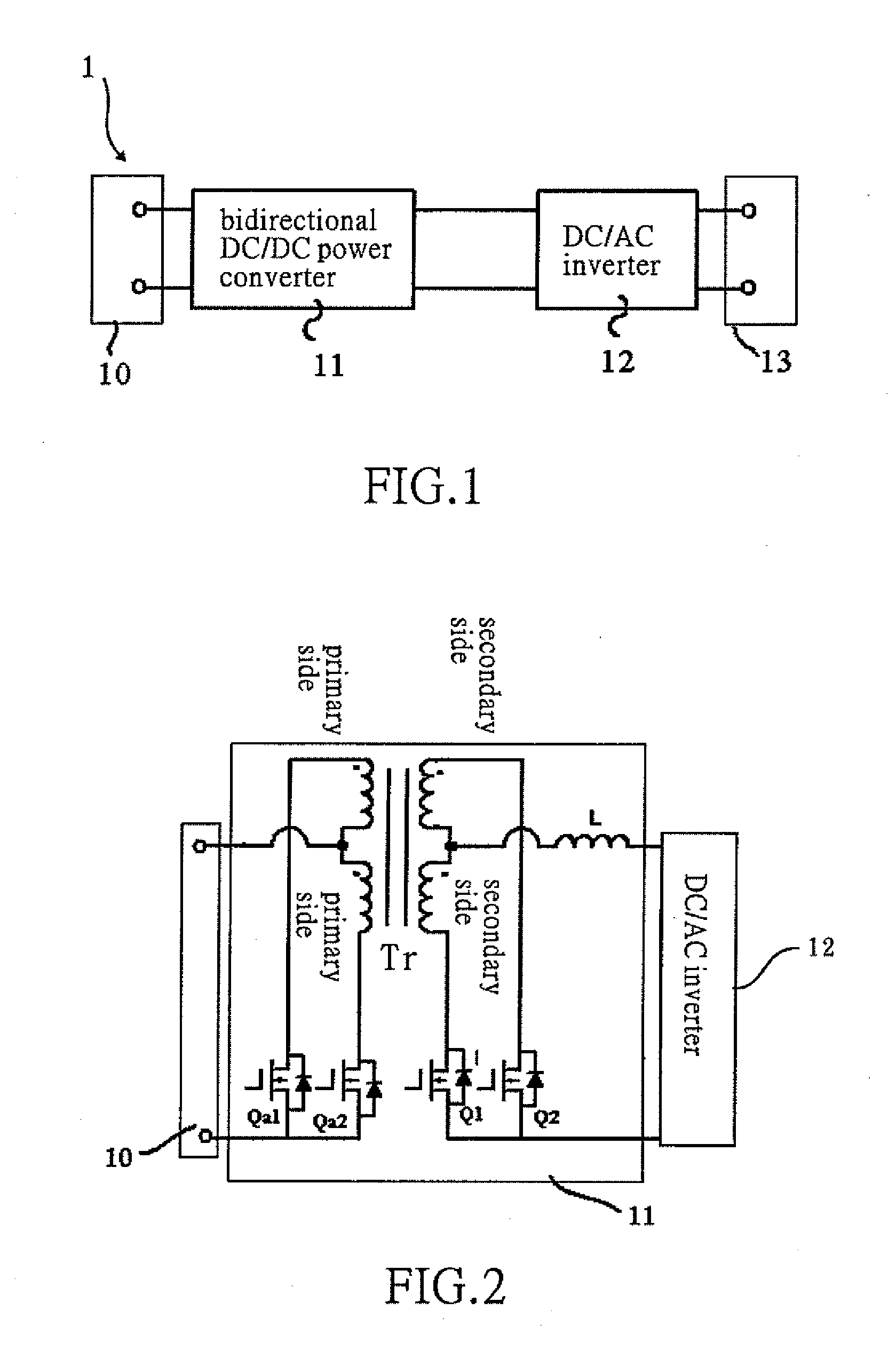
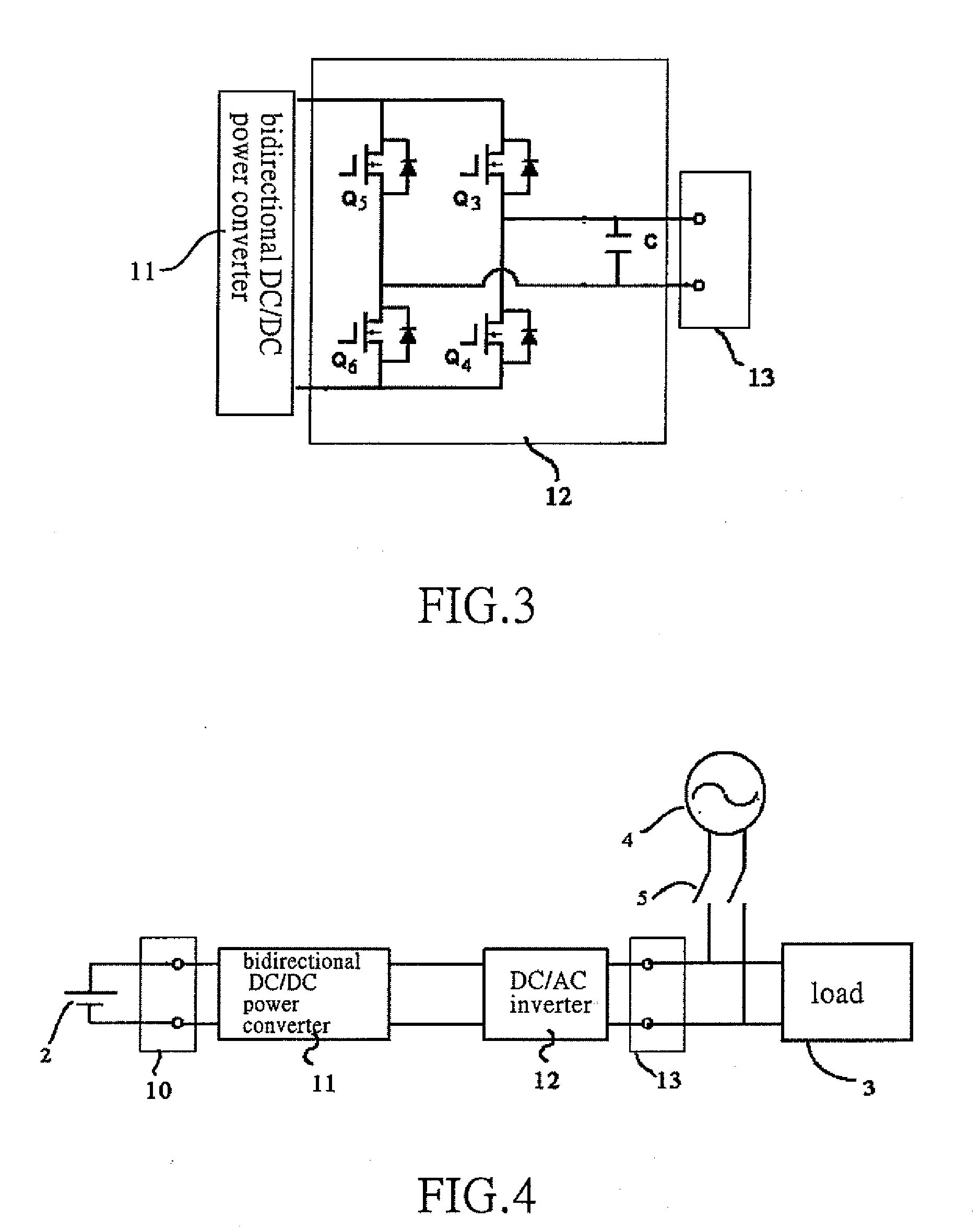
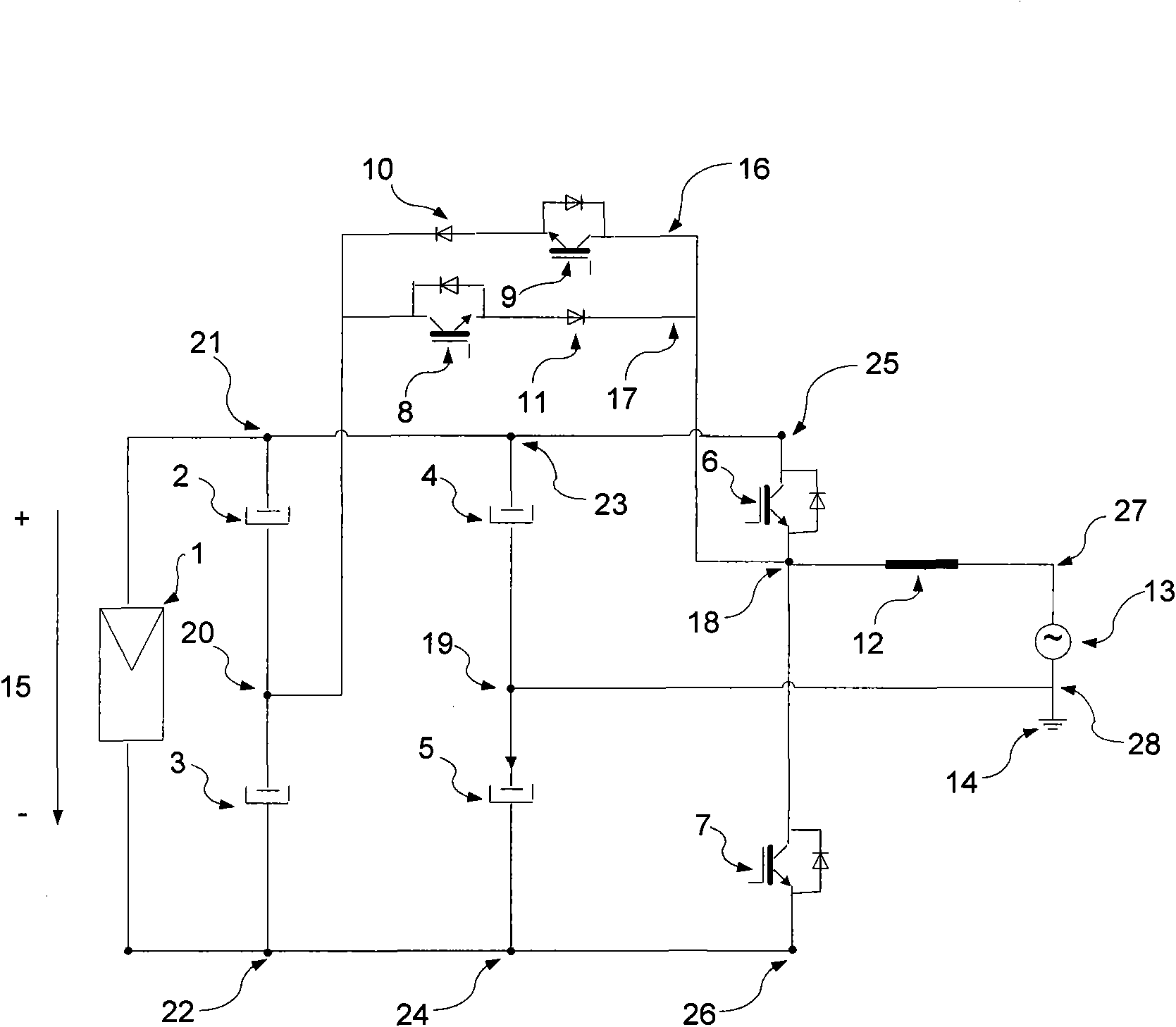
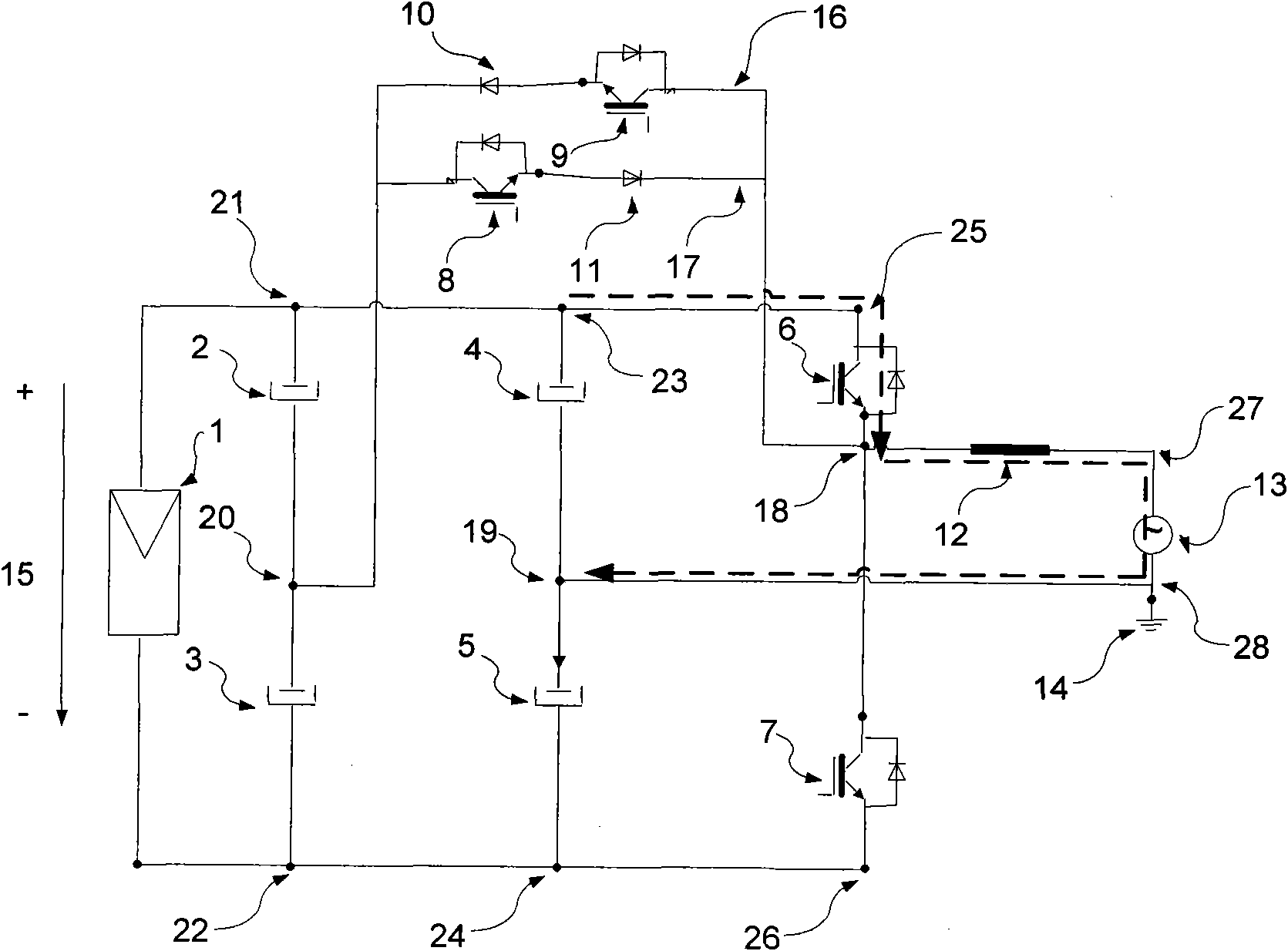
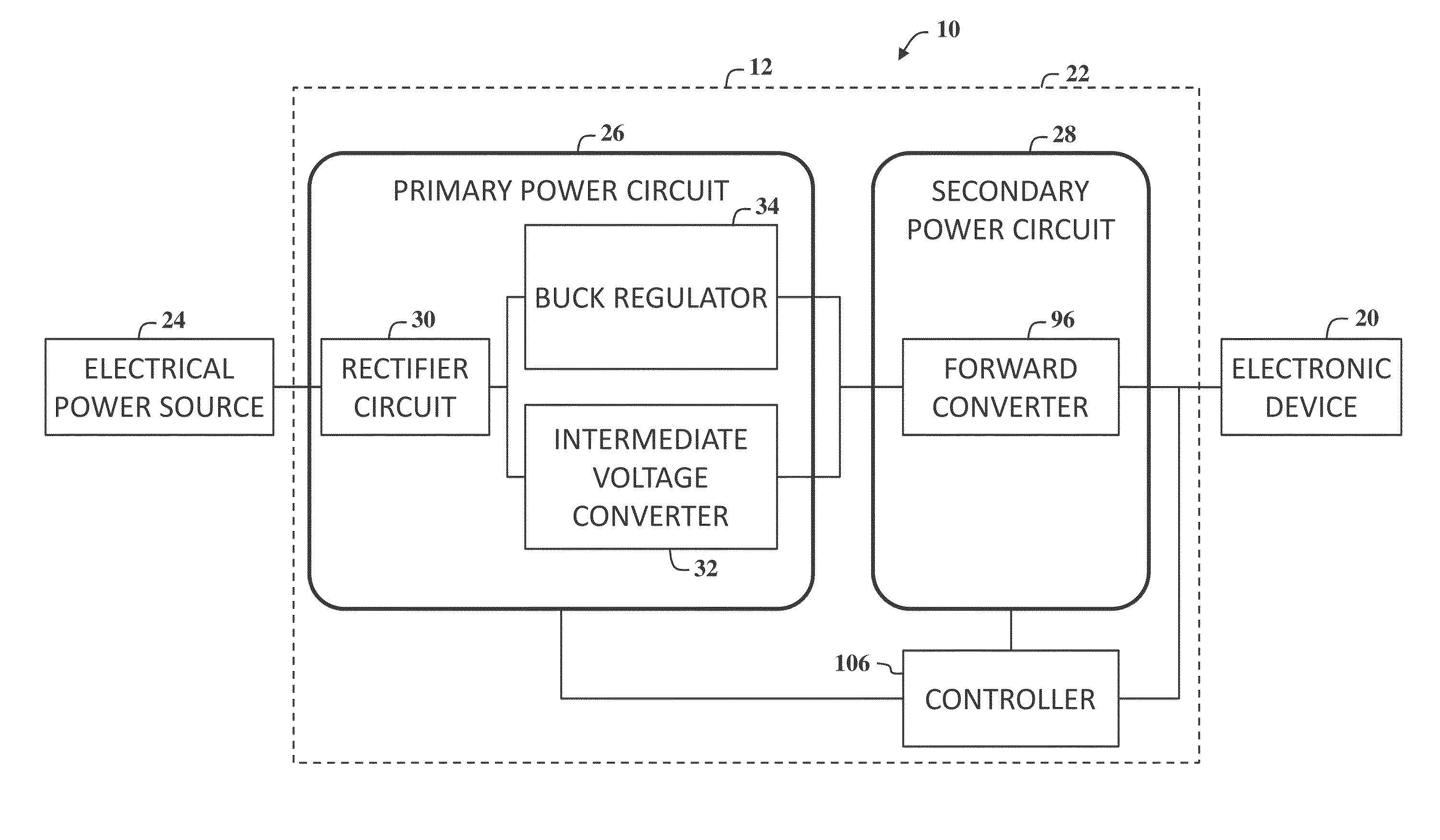
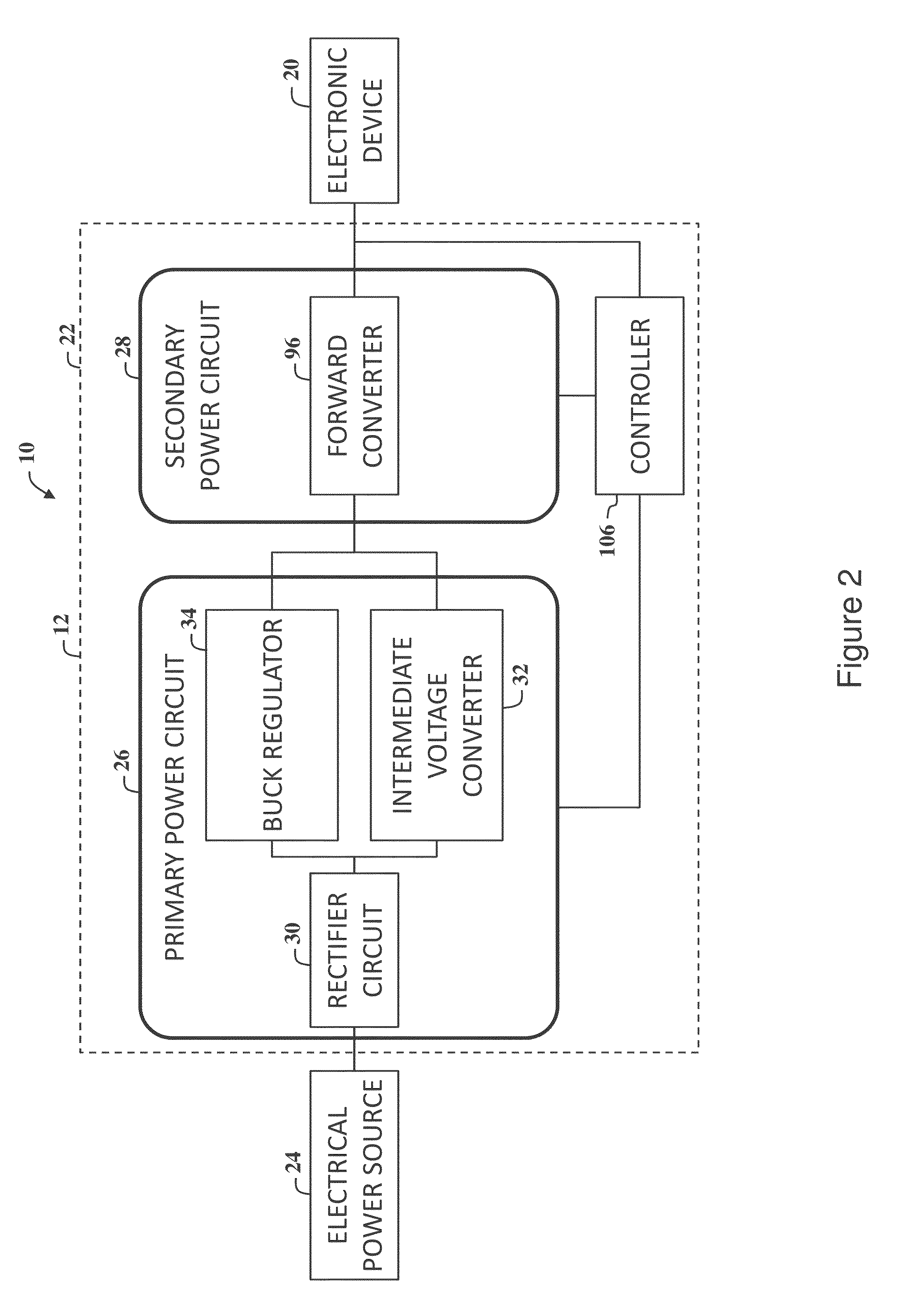
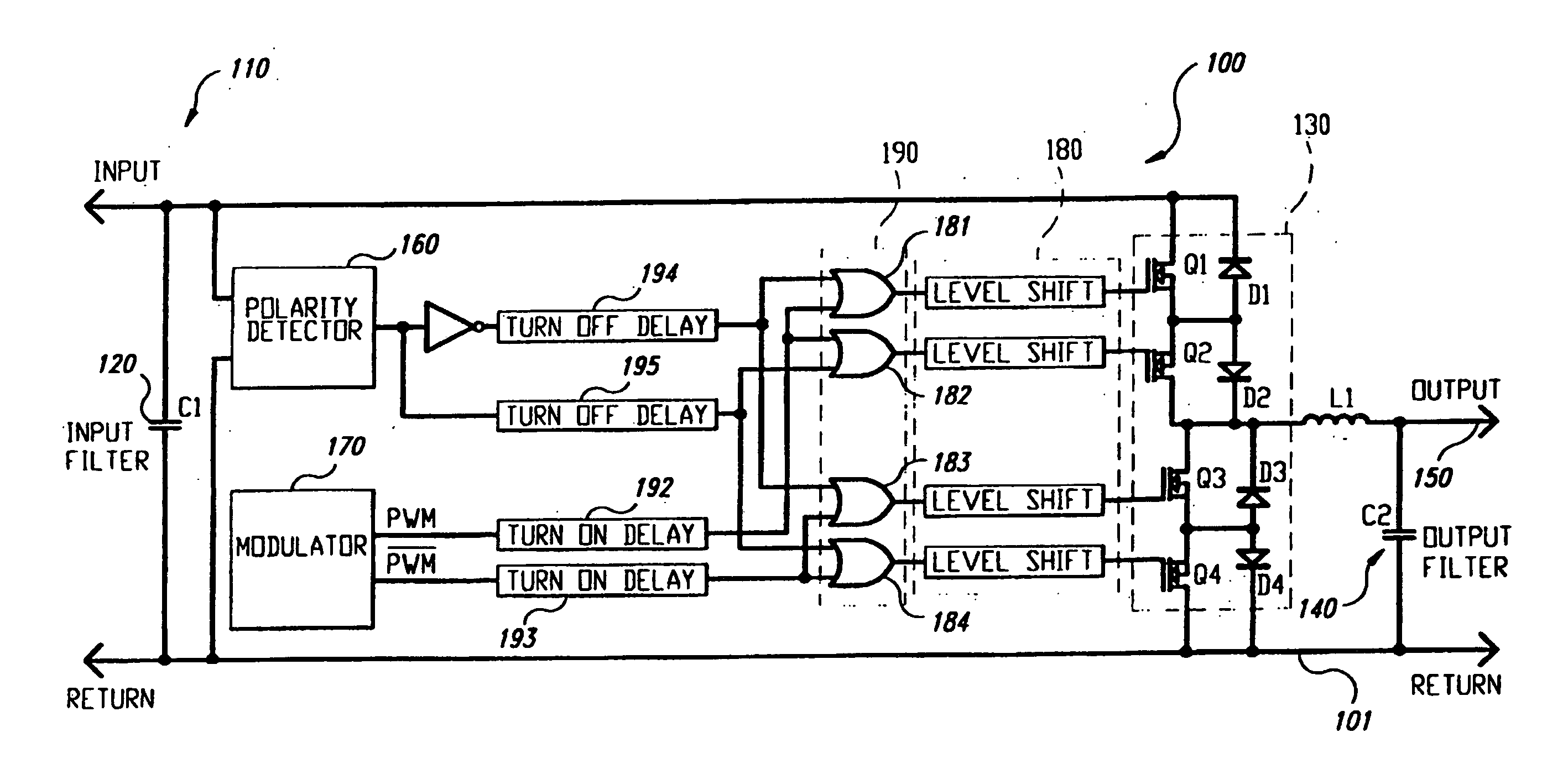
Bidirectional active power conditioner
InactiveUS20080062724A1Reduce switching lossesImprove power efficiencyDc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsPower conditionerDc current
A bidirectional active power conditioner includes a DC side, a bidirectional DC / DC power converter, a DC / AC inverter and an AC side. The DC side electrically connects with a DC source while the AC side electrically connects with a load and an AC source. The bidirectional DC / DC power converter is controlled via high-frequency pulse width modulation (PWM) switching so as to generate a predetermined DC voltage or DC current while the DC / AC inverter is controlled to convert the predetermined DC voltage or DC current into a predetermined AC voltage or AC current.
Owner:ABLEREX ELECTRONICS CO LTD
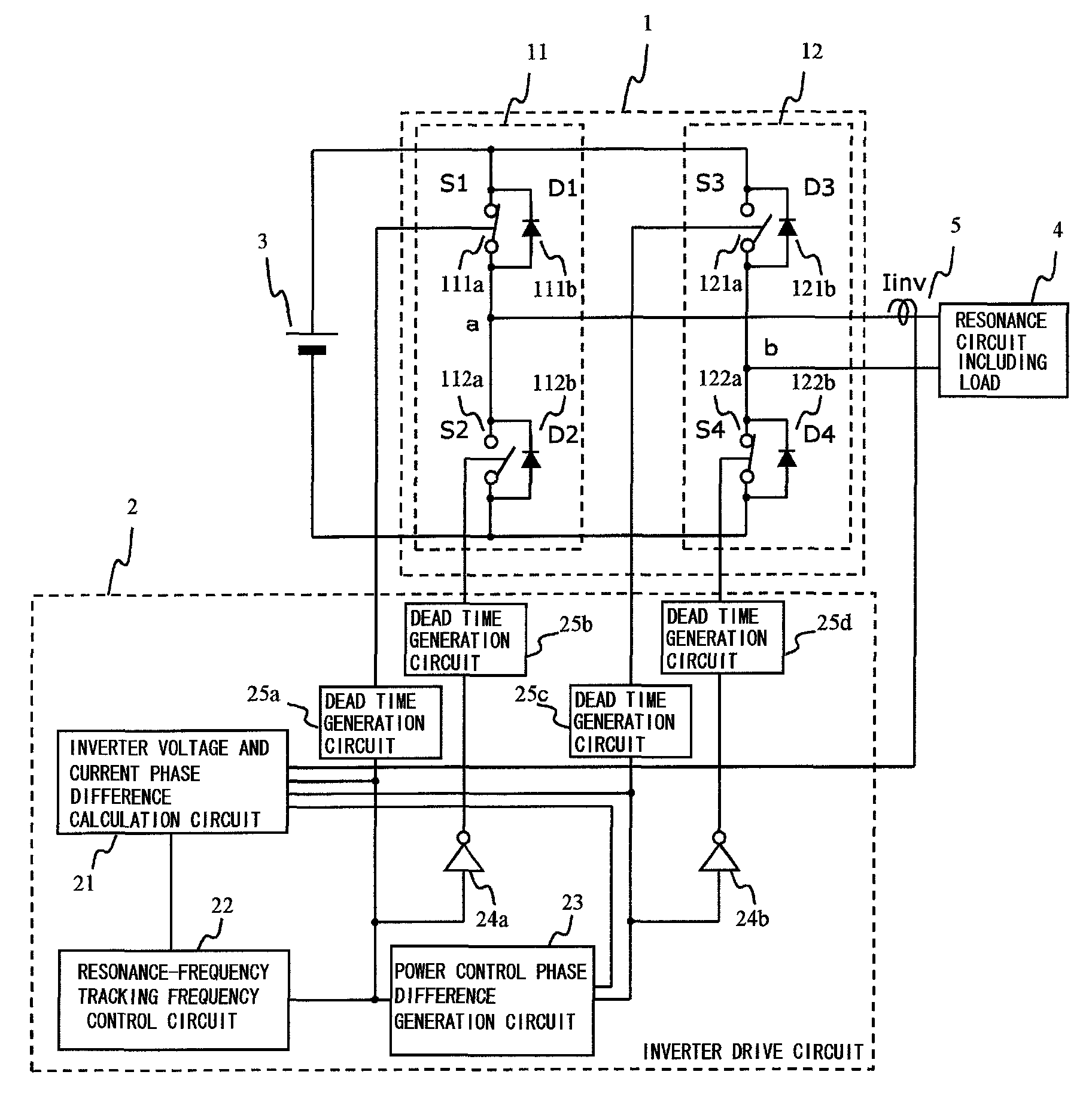
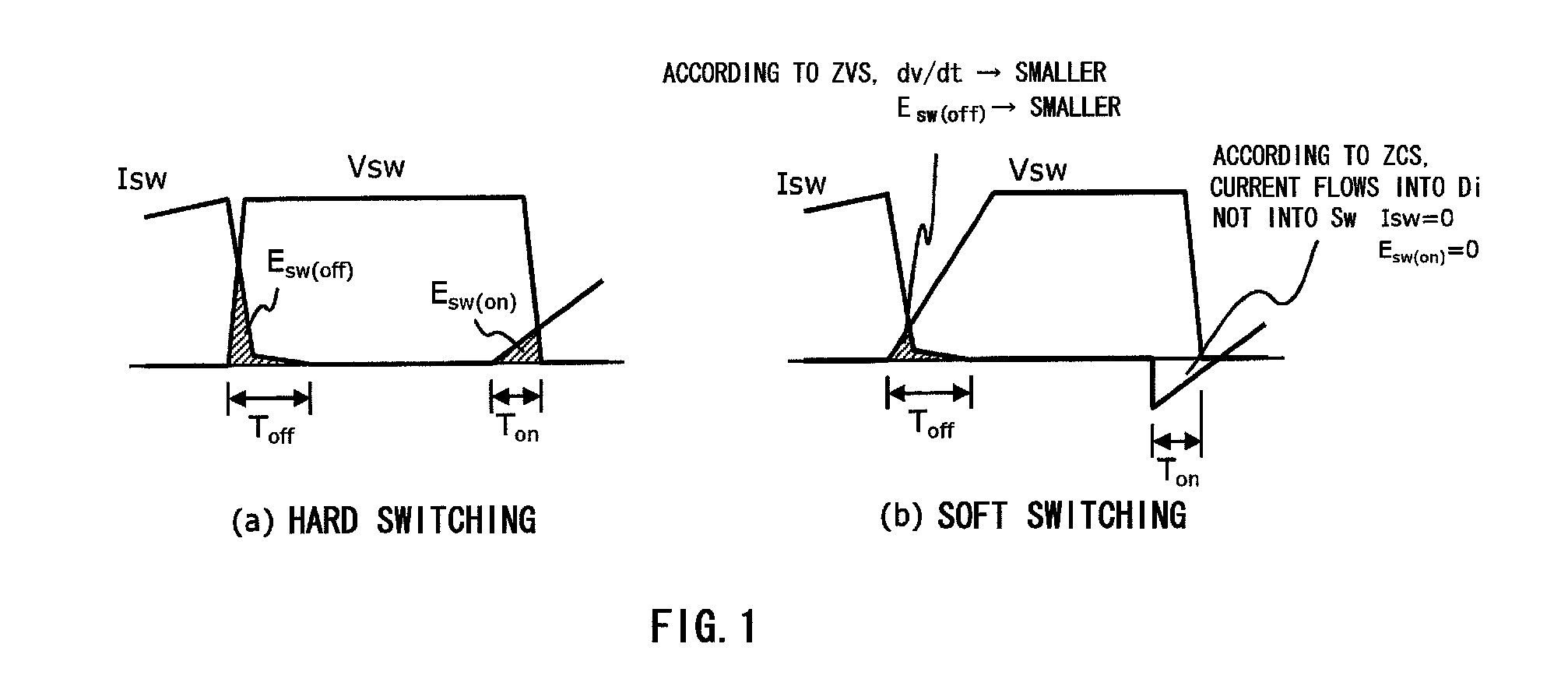
Phase shift inverter, X-ray high-voltage device using same, X-ray CT device, and X-ray imaging device
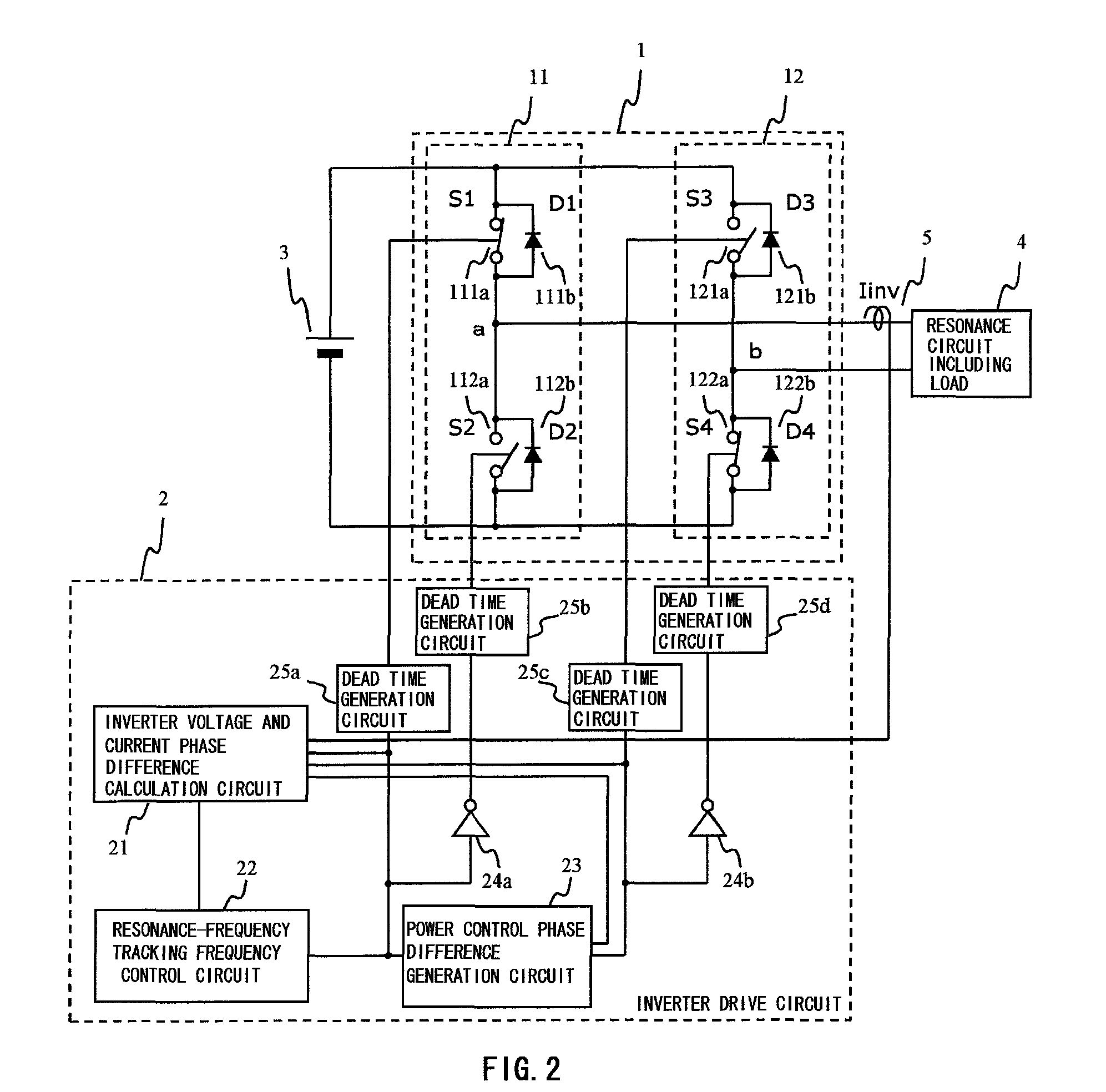
InactiveUS8588371B2Reduce weightAddress rising pricesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationEfficient power electronics conversionLoad circuitPhase difference
An inverter circuit allowing a single drive circuit to perform both tracking control for tracking resonance frequency fluctuations caused by load fluctuations, and power control, thereby reducing switching loss. An inverter drive circuit part obtains a phase difference between output current and output voltage directed to a load circuit connected to a midpoint of two arm circuits of the inverter circuit, and controls a phase of the driving signal directed to each semiconductor switch such that the phase difference becomes zero or a predetermined value, enabling an operating frequency of the inverter circuit part to track a resonance frequency of the load circuit, and enabling a current phase to be delayed with respect to a voltage phase, thereby achieving ZCS. Since the phase difference is used, an auxiliary circuit is not necessary for measuring a current value in proximity to the semiconductor switches.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Dual-mode PFM boost converter
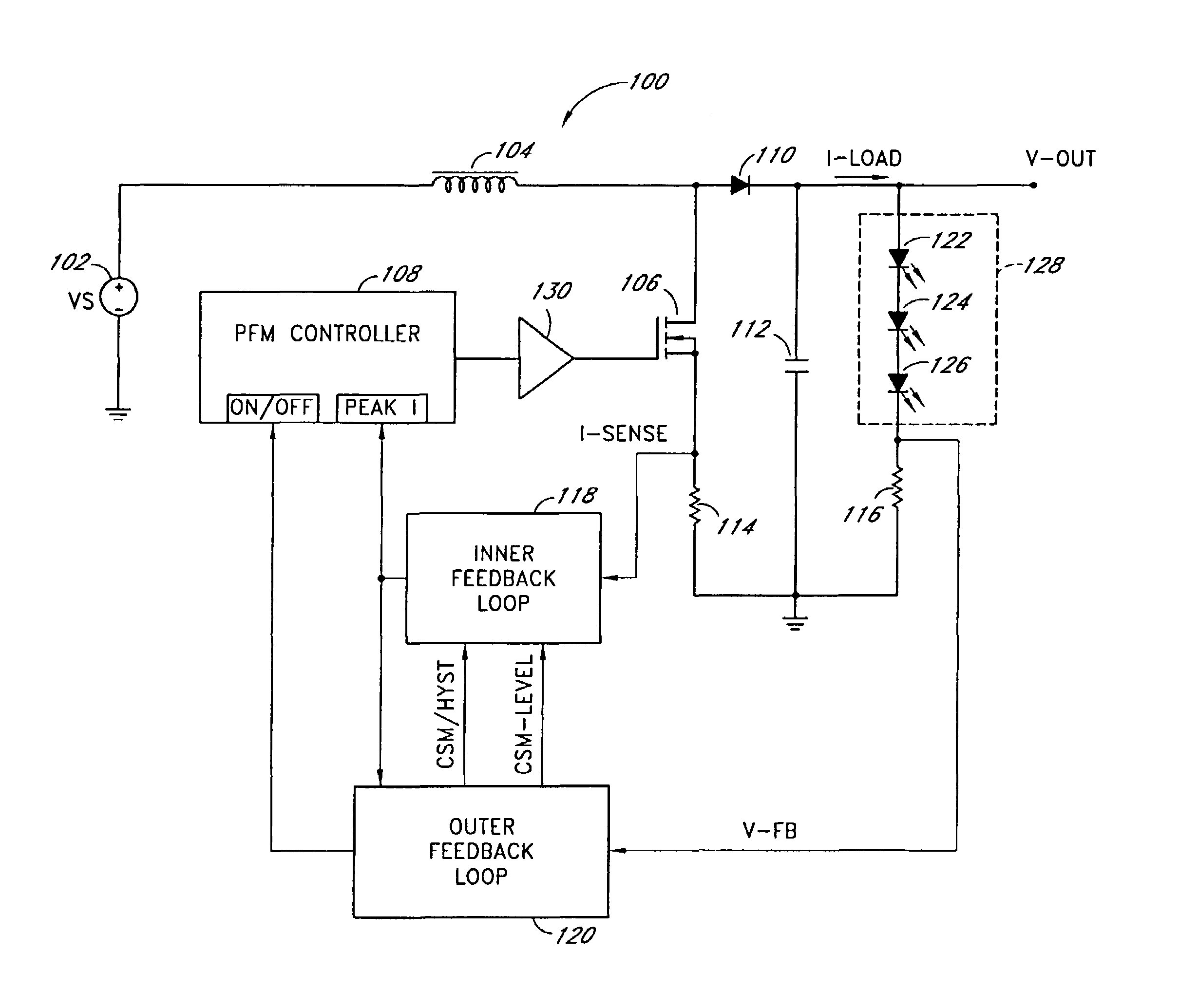
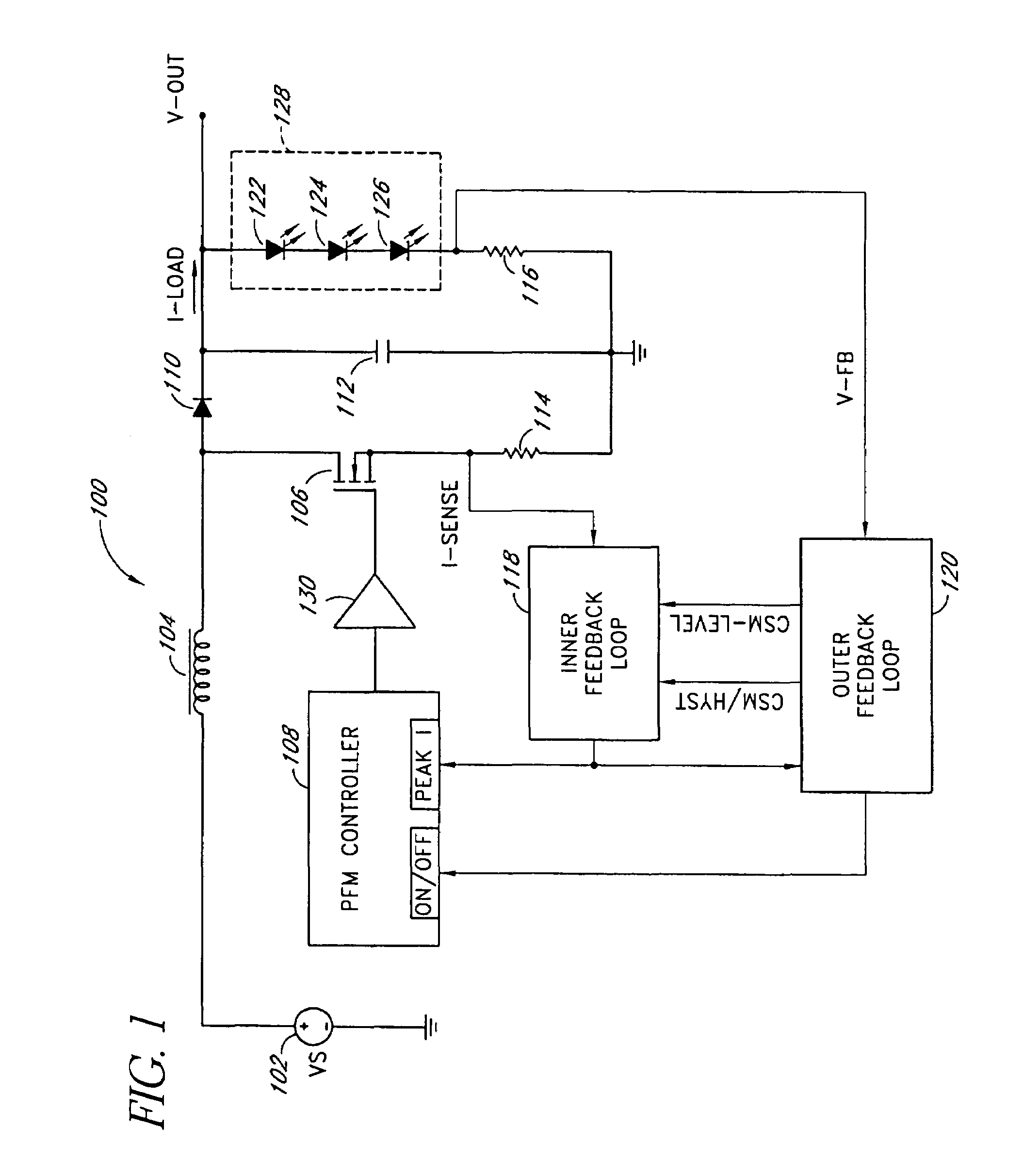
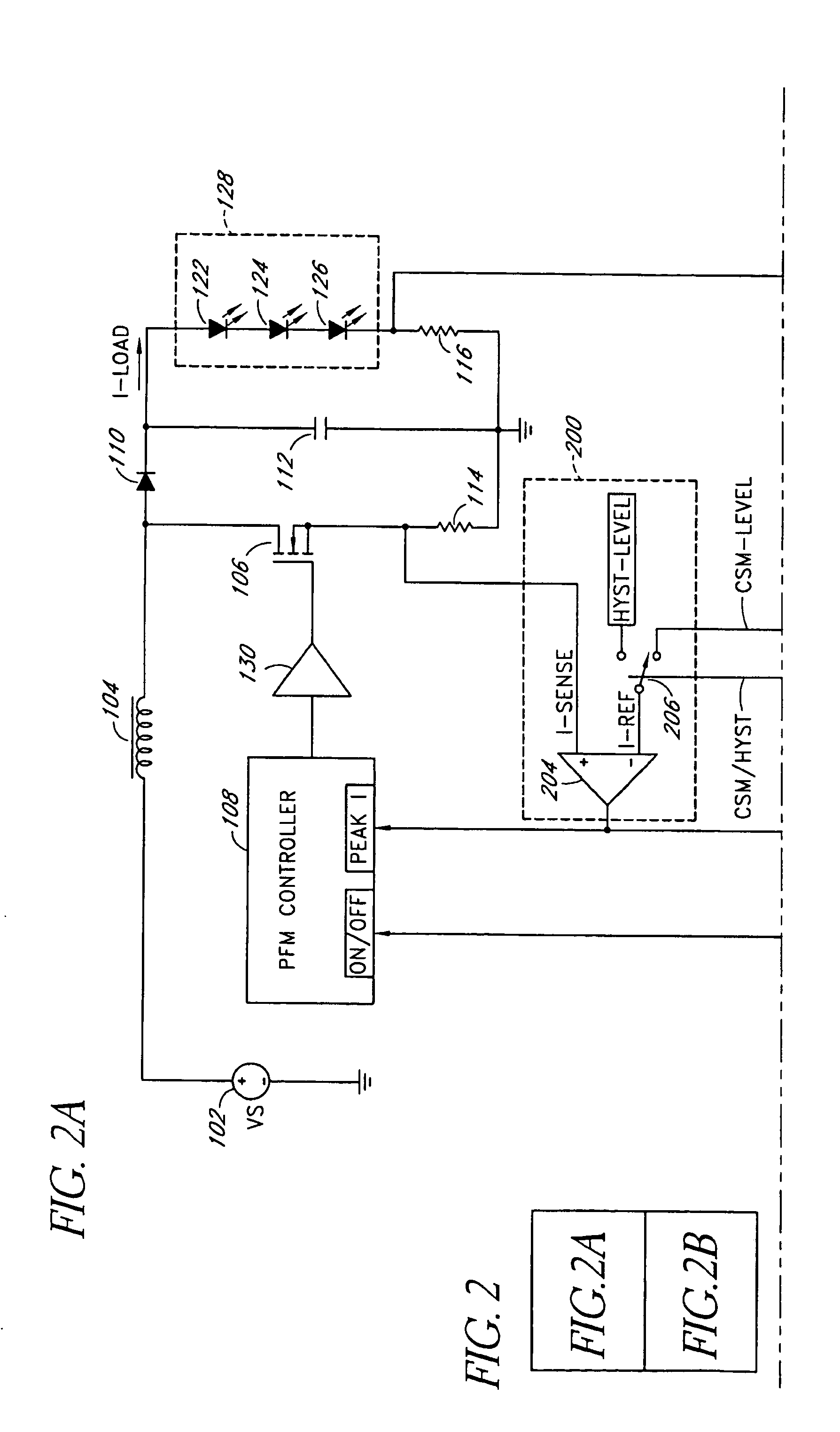
InactiveUS7102340B1Conduction loss downReduce switching lossesElectric lighting sourcesDc-dc conversionSwitched currentDual mode
A dual-mode pulse frequency modulation boost converter operates in a hysteretic mode during light load currents to regulate an output voltage using a substantially fixed peak switching current and operates in a continuous mode during heavy load currents to regulate the output voltage using a variable peak switching current. The boost converter senses load power to automatically switch between the hysteretic mode and the continuous mode.
Owner:MICROSEMI
Driving circuit for high intensity discharge lamp electronic ballast
InactiveUS6020691AImprove performanceAvoiding excessive currentElectric light circuit arrangementGas discharge lamp usageLamp currentEngineering
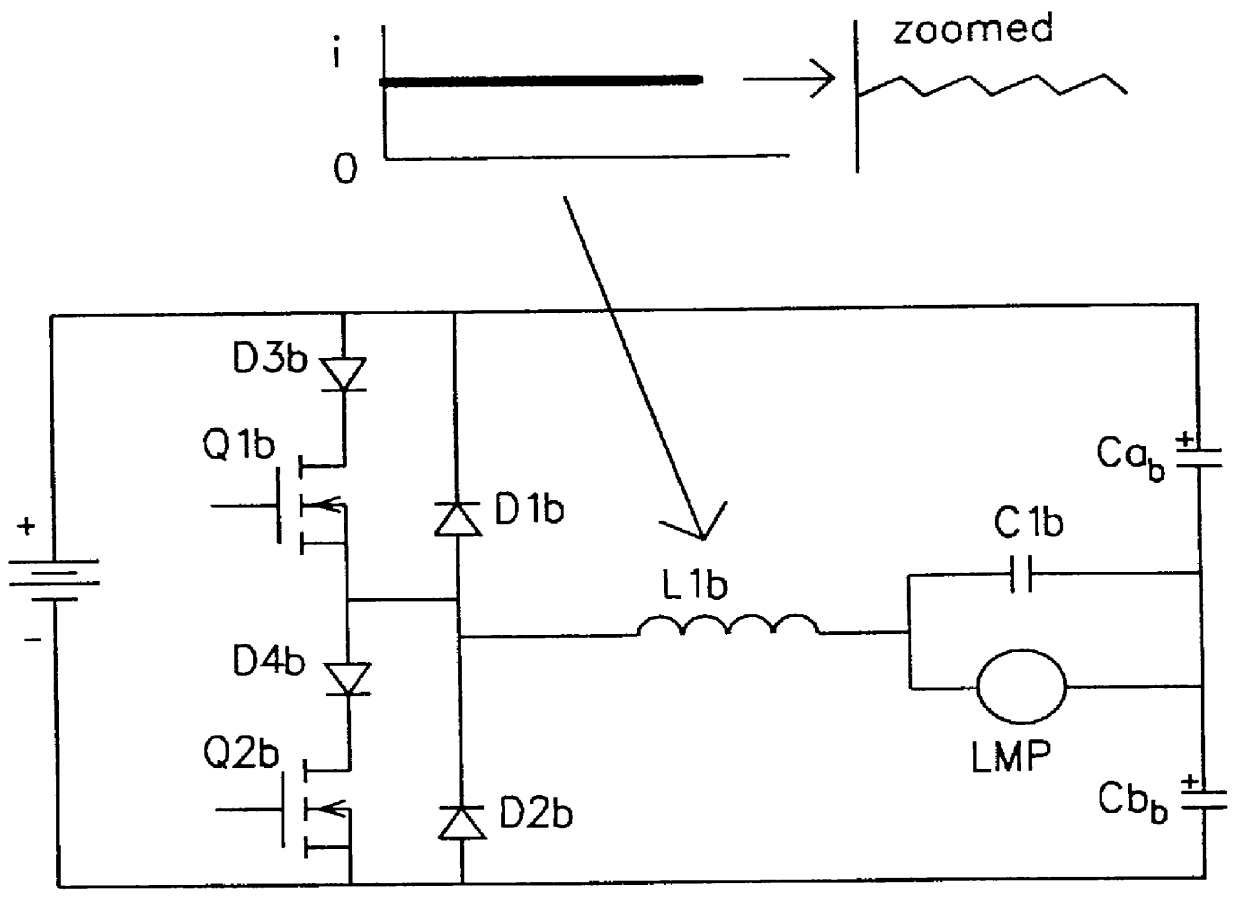
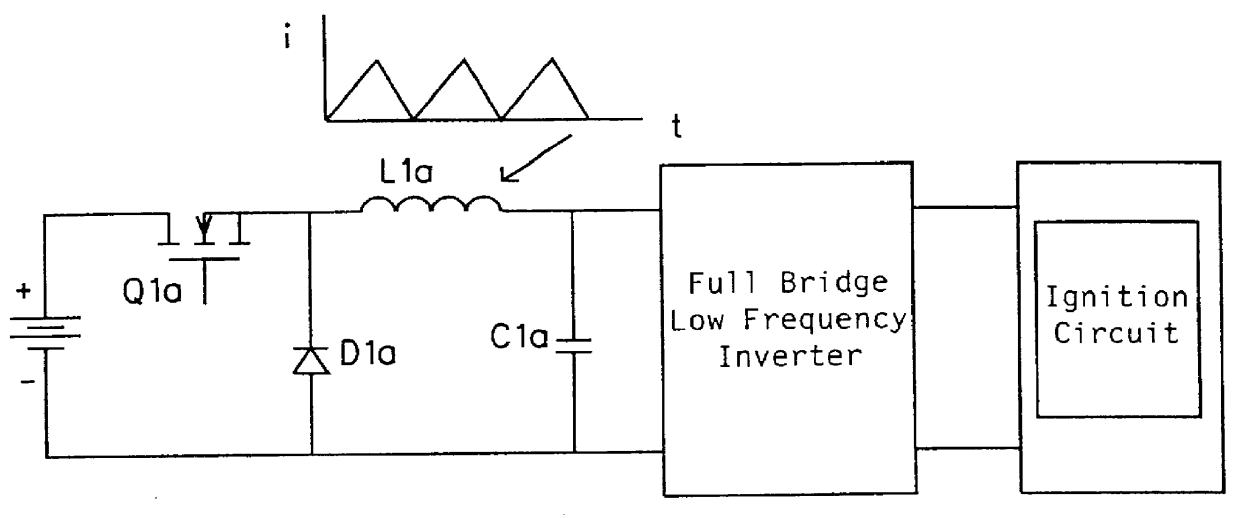
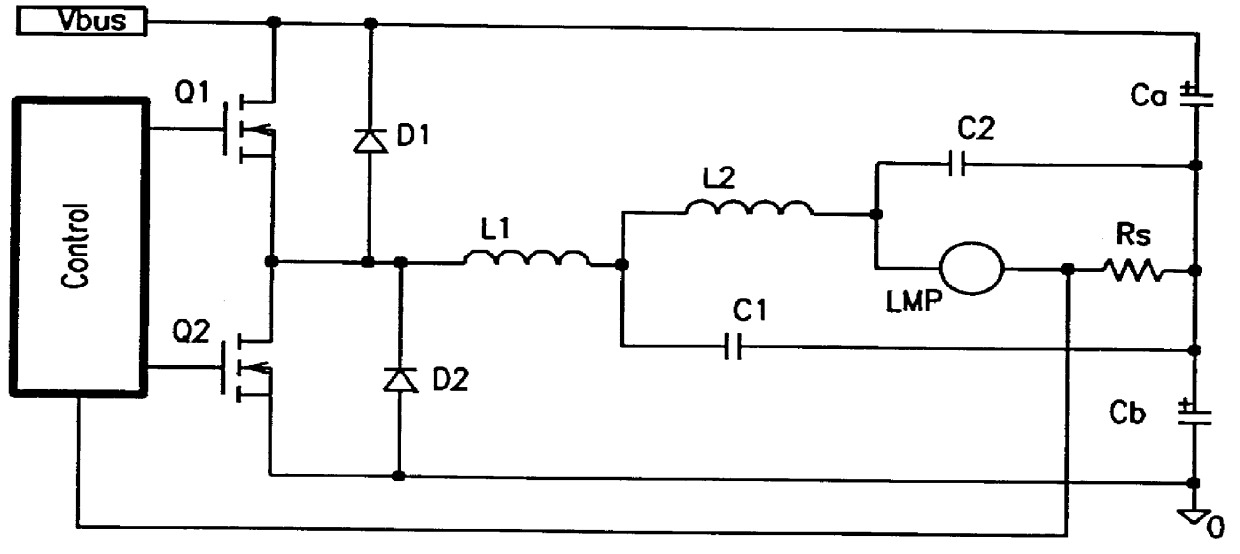
A circuit arrangement and control thereof for igniting a high intensity discharge (HID) lamp, for reducing the high frequency ripple superimposed on the low frequency rectangular waveform lamp current after ignition, and for increased circuit efficiency. The high frequency ignition voltage is only applied to the lamp during ignition phase and is mainly generated by the second stage of the low pass (LP) filter. The first stage of the LP filter whose resonant frequency is below the second stage further attenuates the high frequency ripple current through the lamp in normal operation. The resulting lamp current is a low frequency rectangular wave with less than 10% high frequency ripple. Acoustic resonance is avoided. The inductor in the first stage of LP filter is operated in discontinuous current mode. Doing so, the active switches are in zero current switching (ZCS) to maximize the circuit efficiency.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Switch mode power supply and driving method thereof
ActiveUS20080130324A1Reduce switching lossesReduce noiseAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionTransformerBurst switching
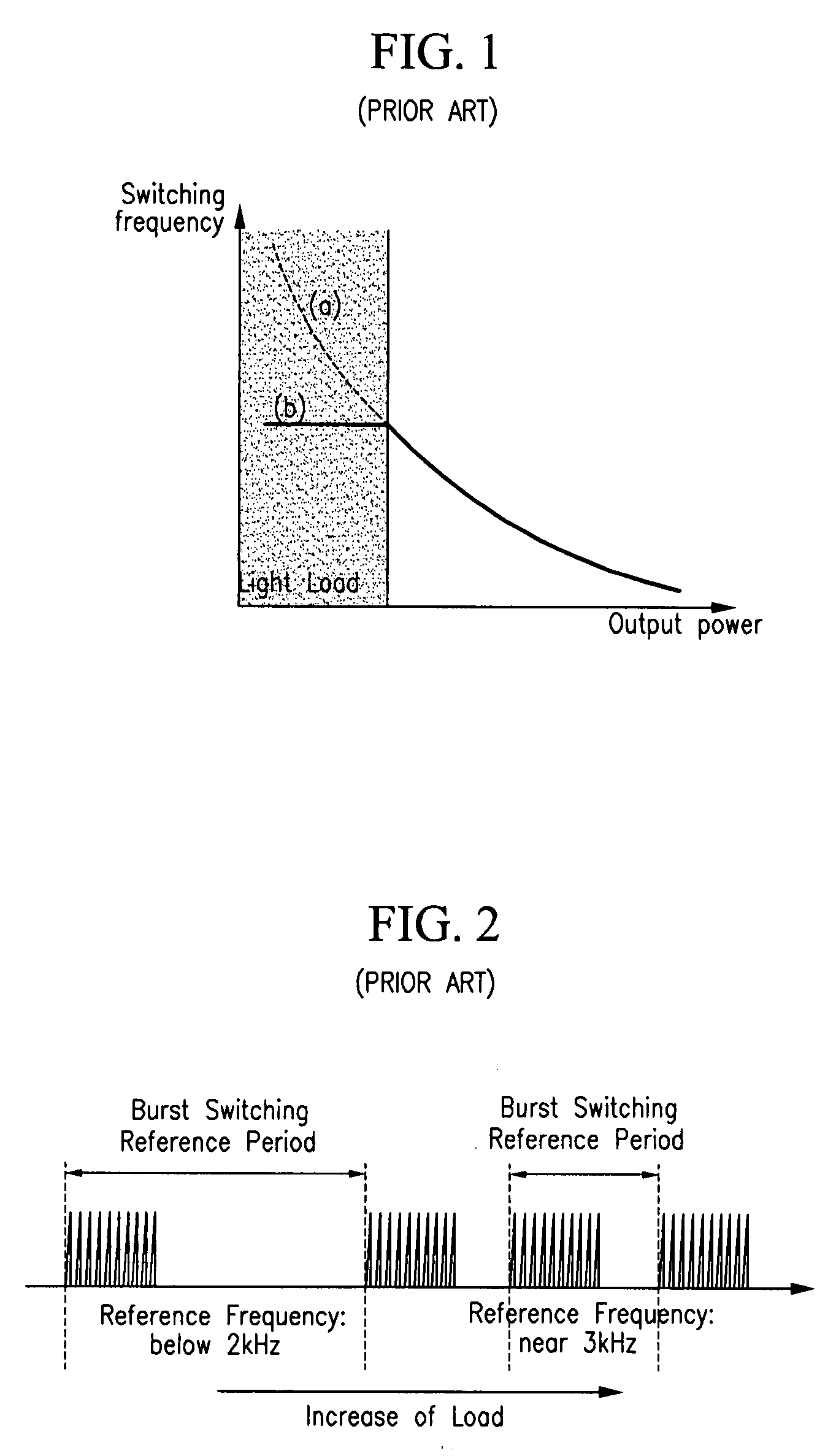
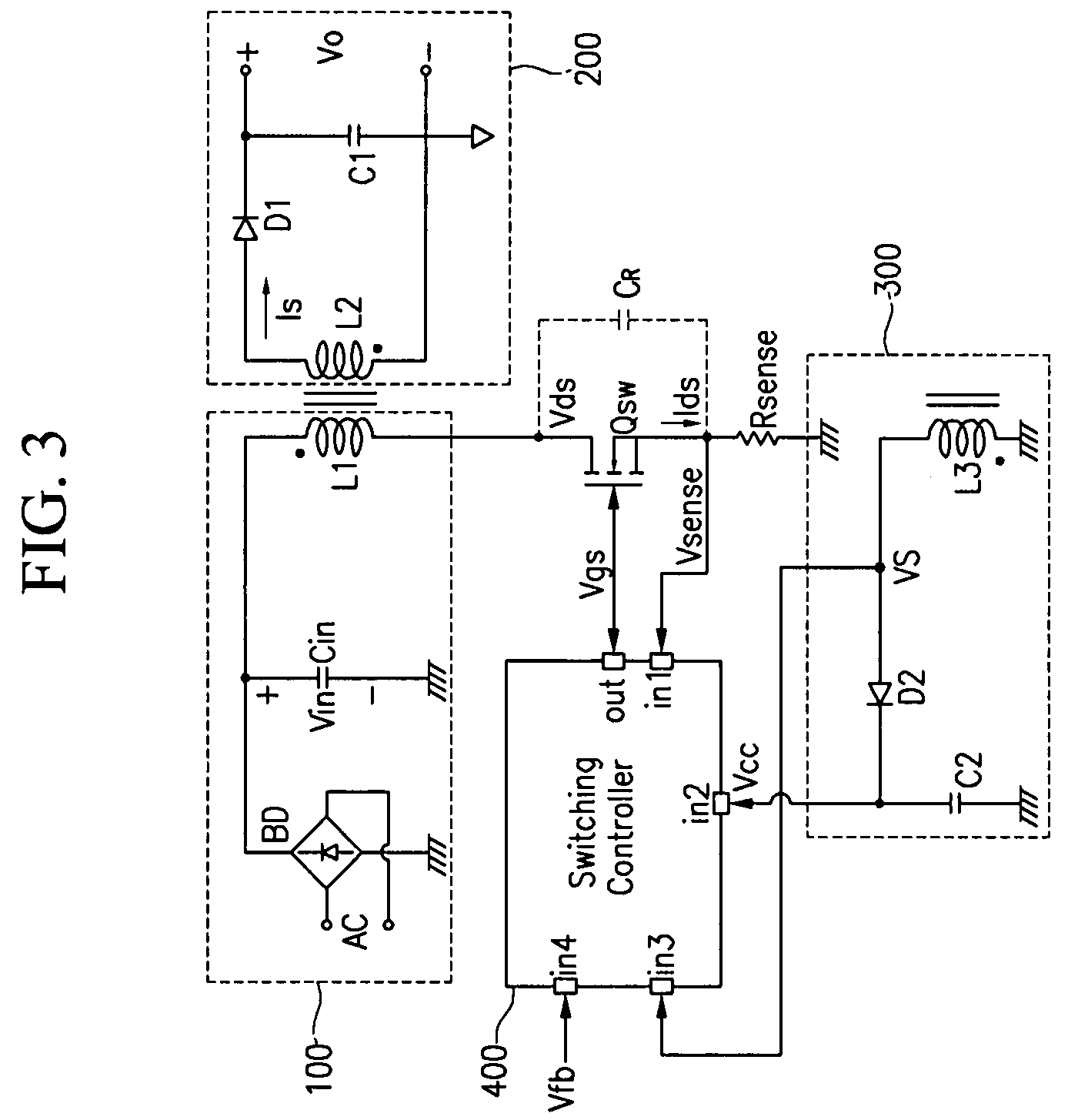
The present invention relates to a switch mode power supply and a driving method for reducing switching loss and audible noise in the burst mode. The switch mode power supply includes a main switch, a power supply, an output unit, and a switch controller. The power supply includes a transformer having a primary coil connected to the main switch, and supplies power to a secondary coil of the transformer according to the operation of the main switch. The output unit is connected to the secondary coil of the transformer and outputs power supplied to the secondary coil of the transformer. The switch controller receives a feedback signal corresponding to the output voltage of the output unit, a sense signal corresponding to the current flowing to the main switch, and a sync signal corresponding to the voltage difference at the main switch, controls the on / off of the main switch, and determines whether to start the burst mode by using the feedback signal, and maintains the switching operation forcibly off period in the burst mode so that the reference frequency of burst switching may be less than a predetermined value.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Switch voltage-stabilizing circuit and control method thereof
ActiveCN101552560APrevent fallingAvoid audio noiseDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationStored energyElectricity
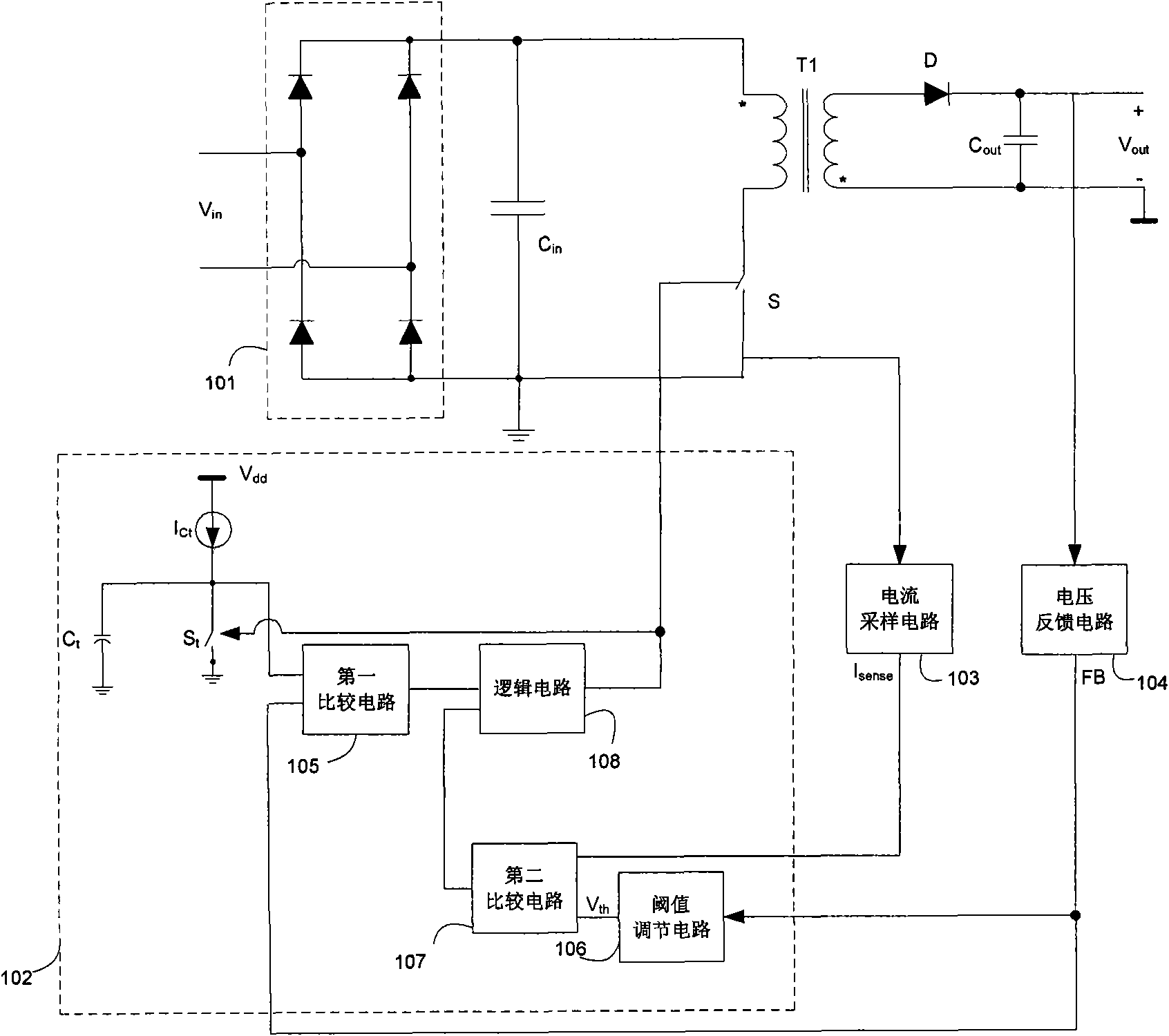
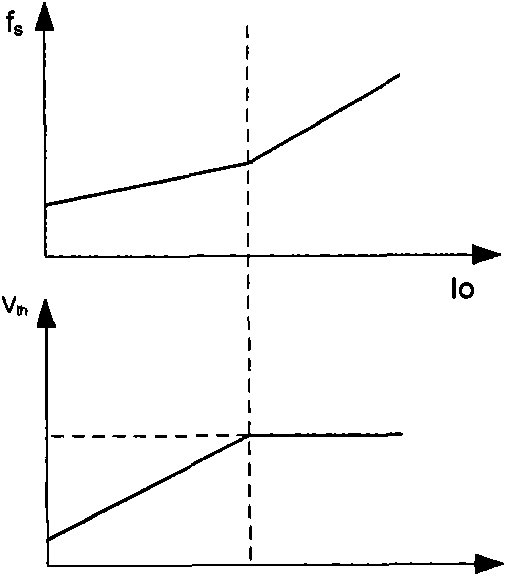
The invention discloses a switch voltage-stabilizing circuit which can regulate switching frequency as well as current peak, has high efficiency and has no audio-frequency noise generated in a state of light load, and method thereof. The switch voltage-stabilizing circuit comprises an energy storage component capable of storing energy; a switch electrically coupled to the energy storage component, wherein the energy storage component can store energy when the switch is on, and the energy stored in the energy storage component is transmitted to a load when the switch is off; a control circuit electrically coupled to the switch, wherein the control circuit compares current flowing through the switch with a current threshold, when the current flowing through the switch is more than the current threshold, the switch is off, and the control circuit determines on and off time of the switch according to the load of the switch voltage-stabilizing circuit, when the load becomes big, the on and off time of the switch is reduced, and when the load becomes small, the on and off time of the switch is increased. The current threshold is constant when the circuit has no light load and becomes low with the load reduced when the circuit has light load.
Owner:CHENGDU MONOLITHIC POWER SYST
Switching power source device
InactiveUS7035119B2Reduce the oscillation frequencyImprove conversion efficiencyConversion with intermediate conversion to dcApparatus with intermediate ac conversionEngineeringVoltage reference
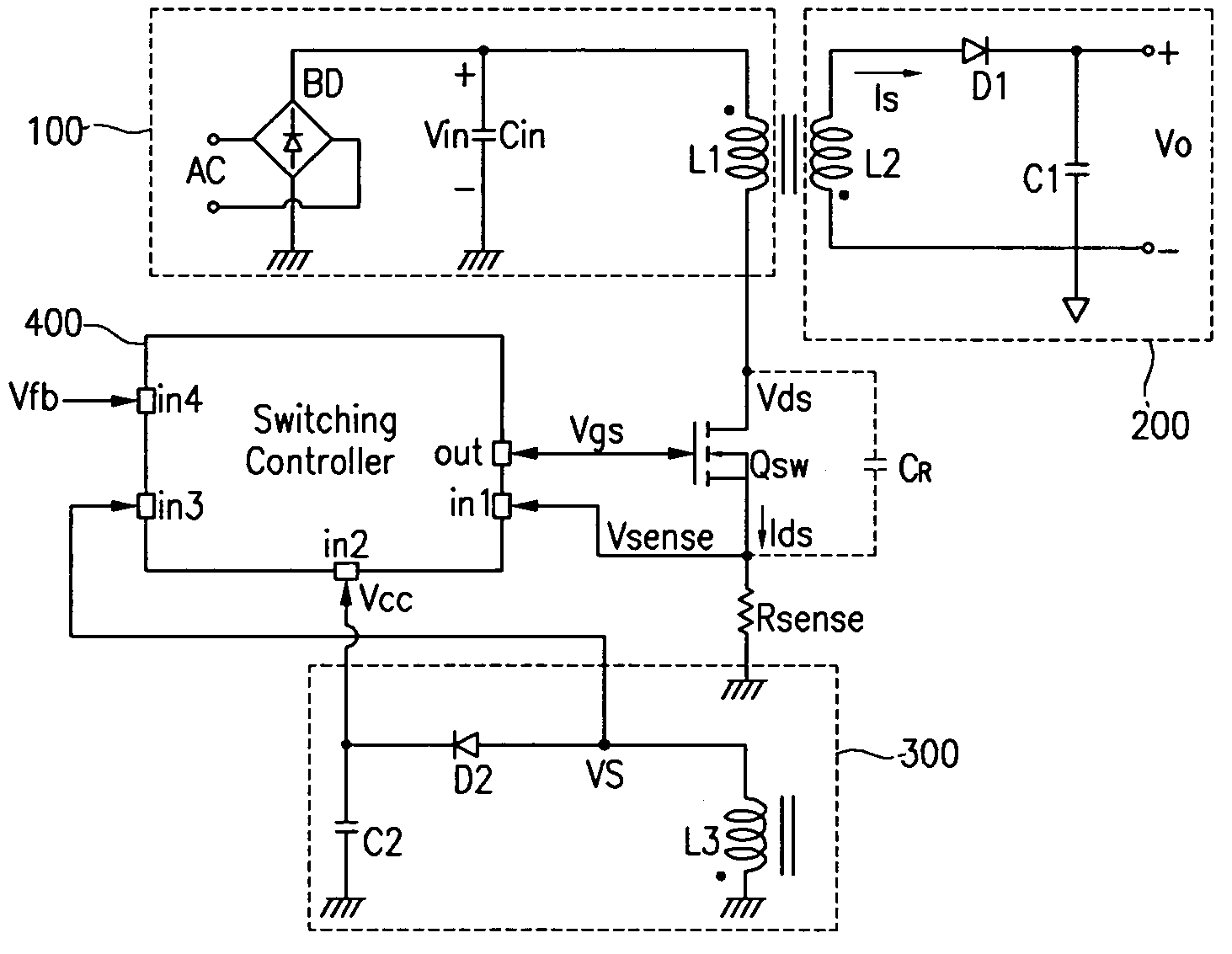
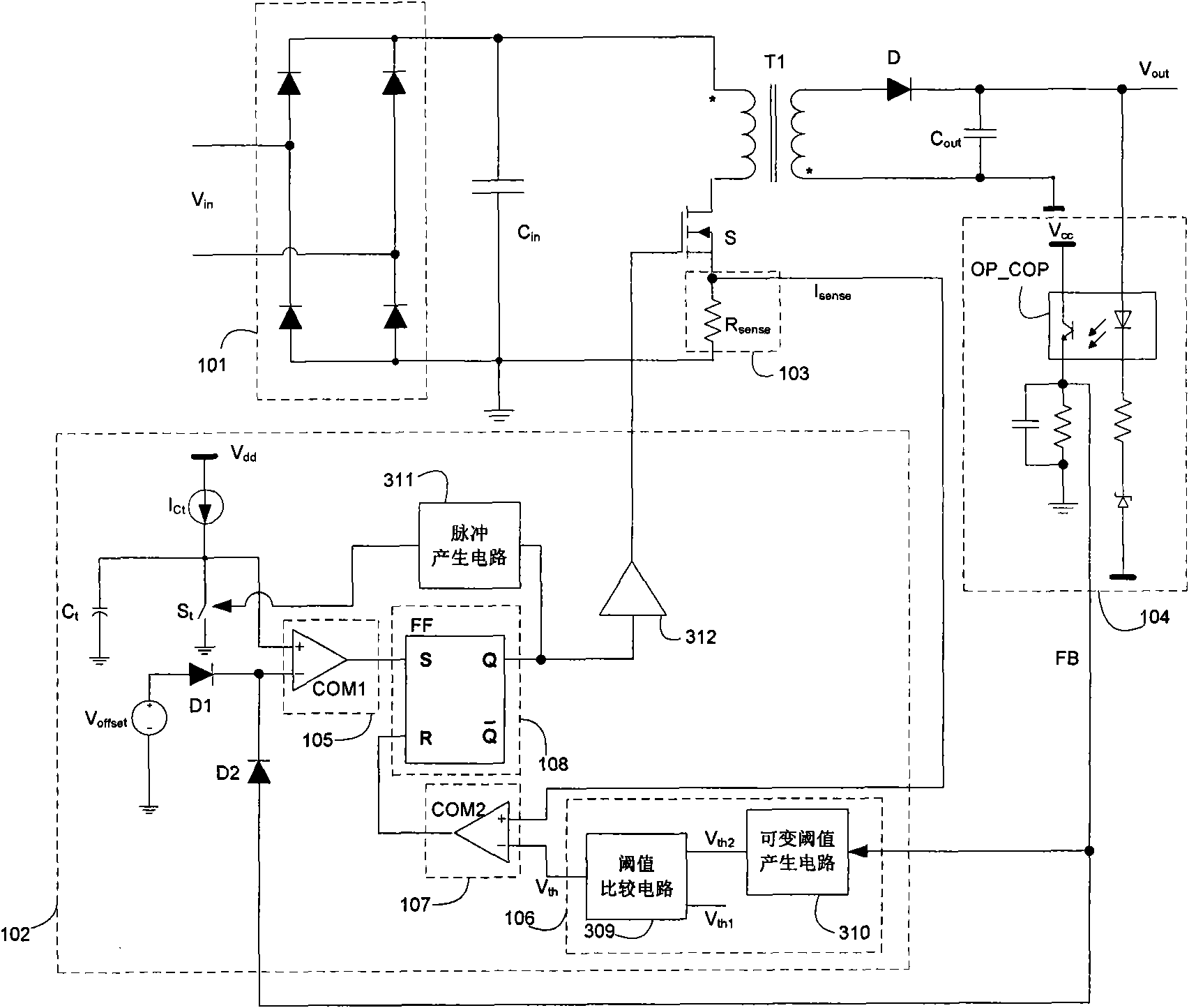
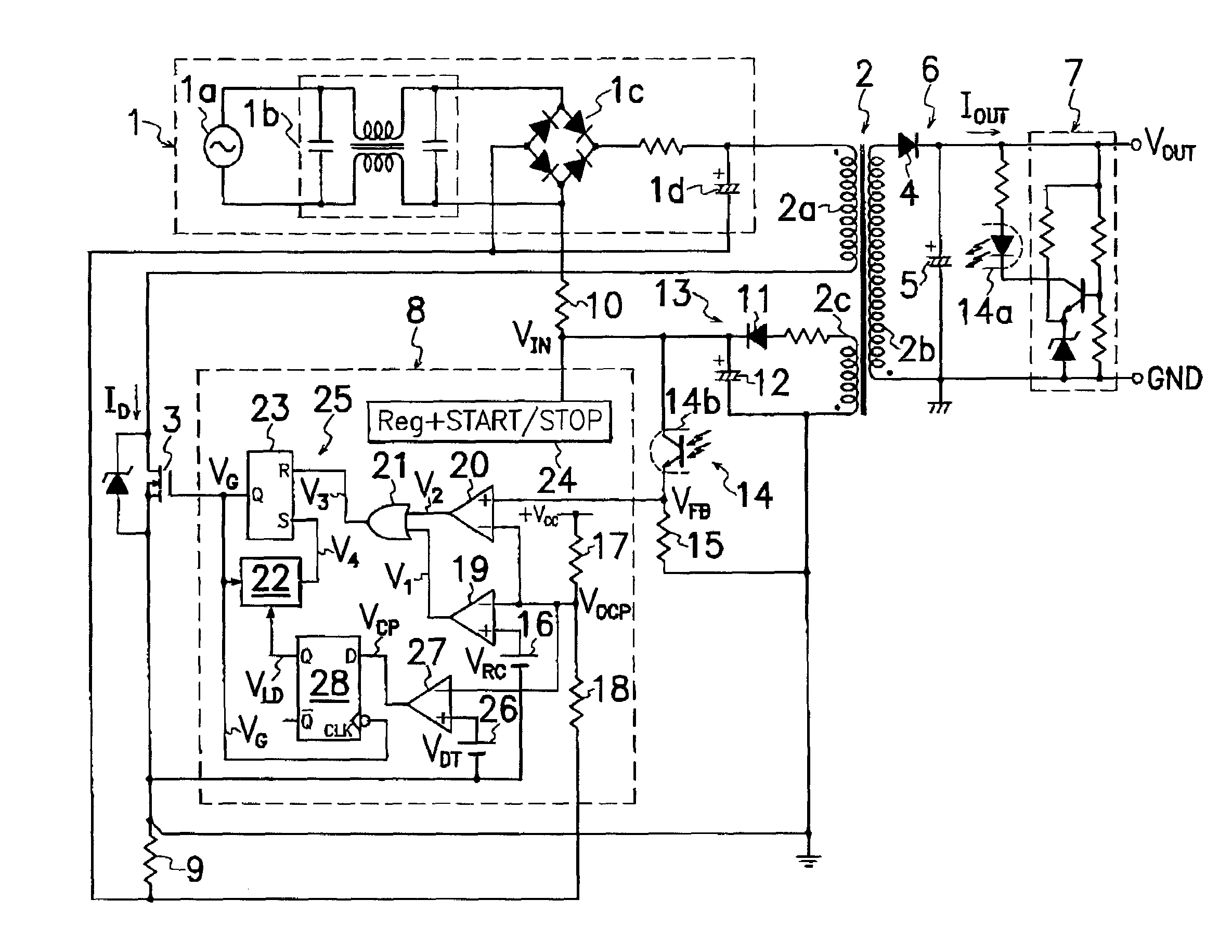
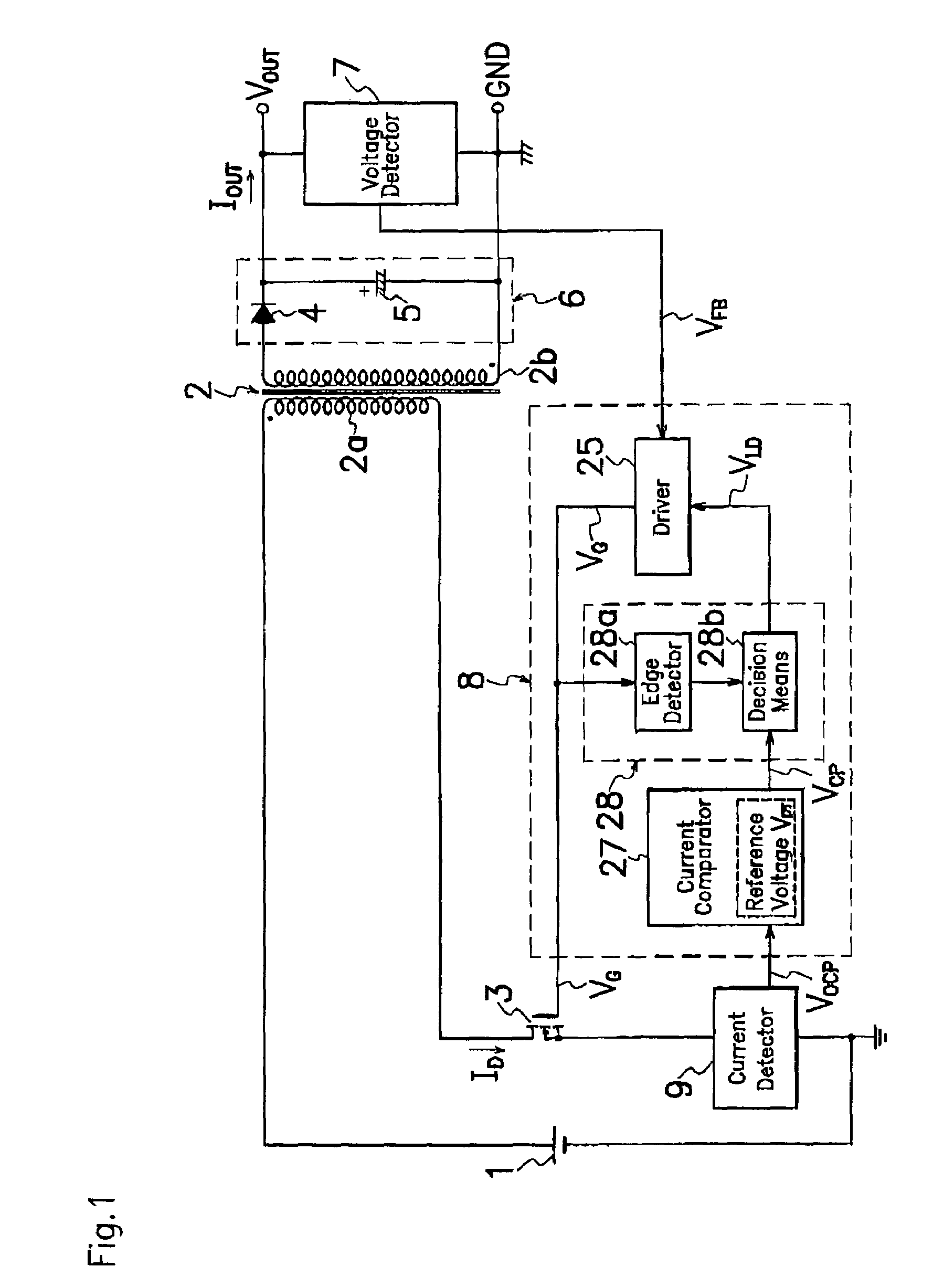
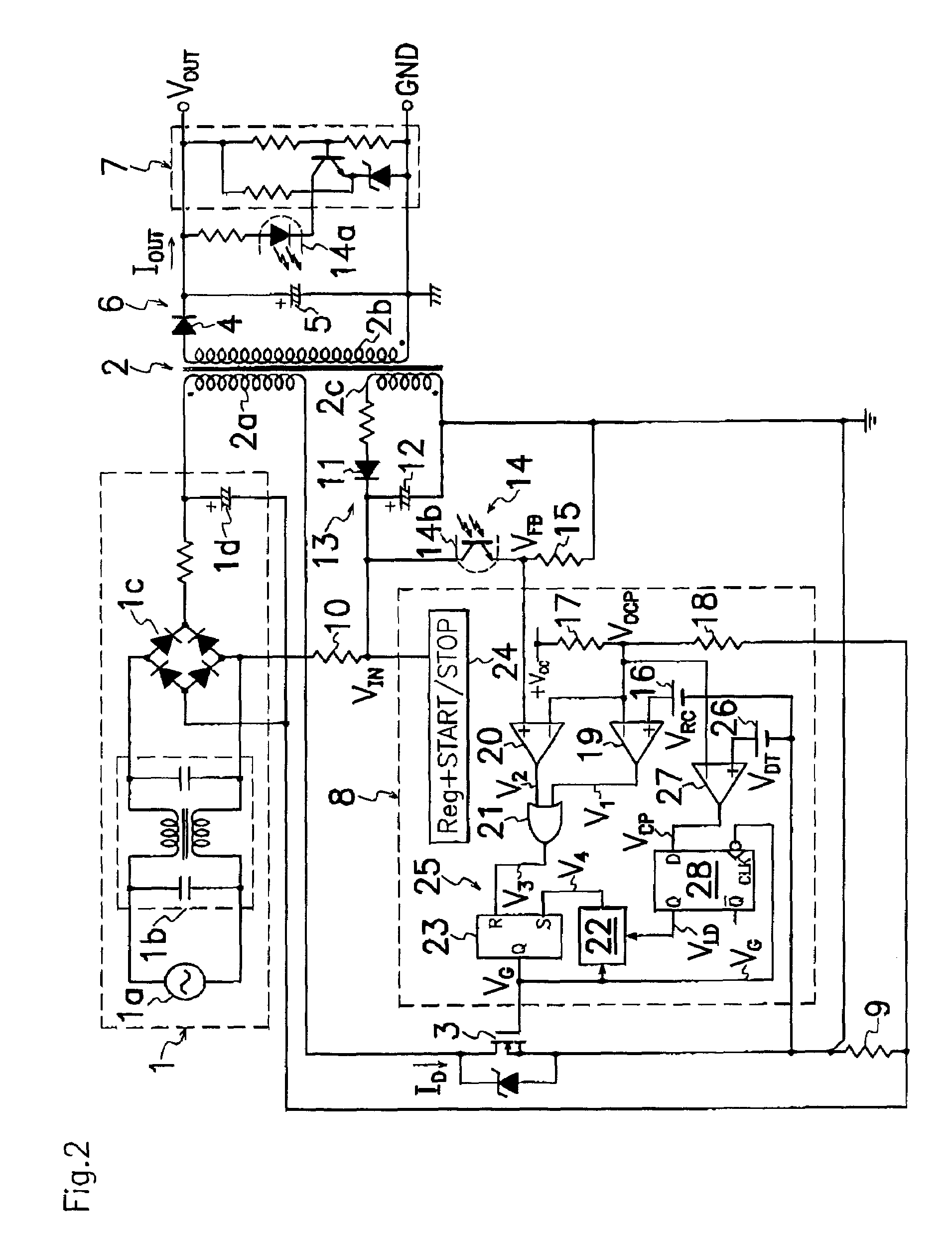
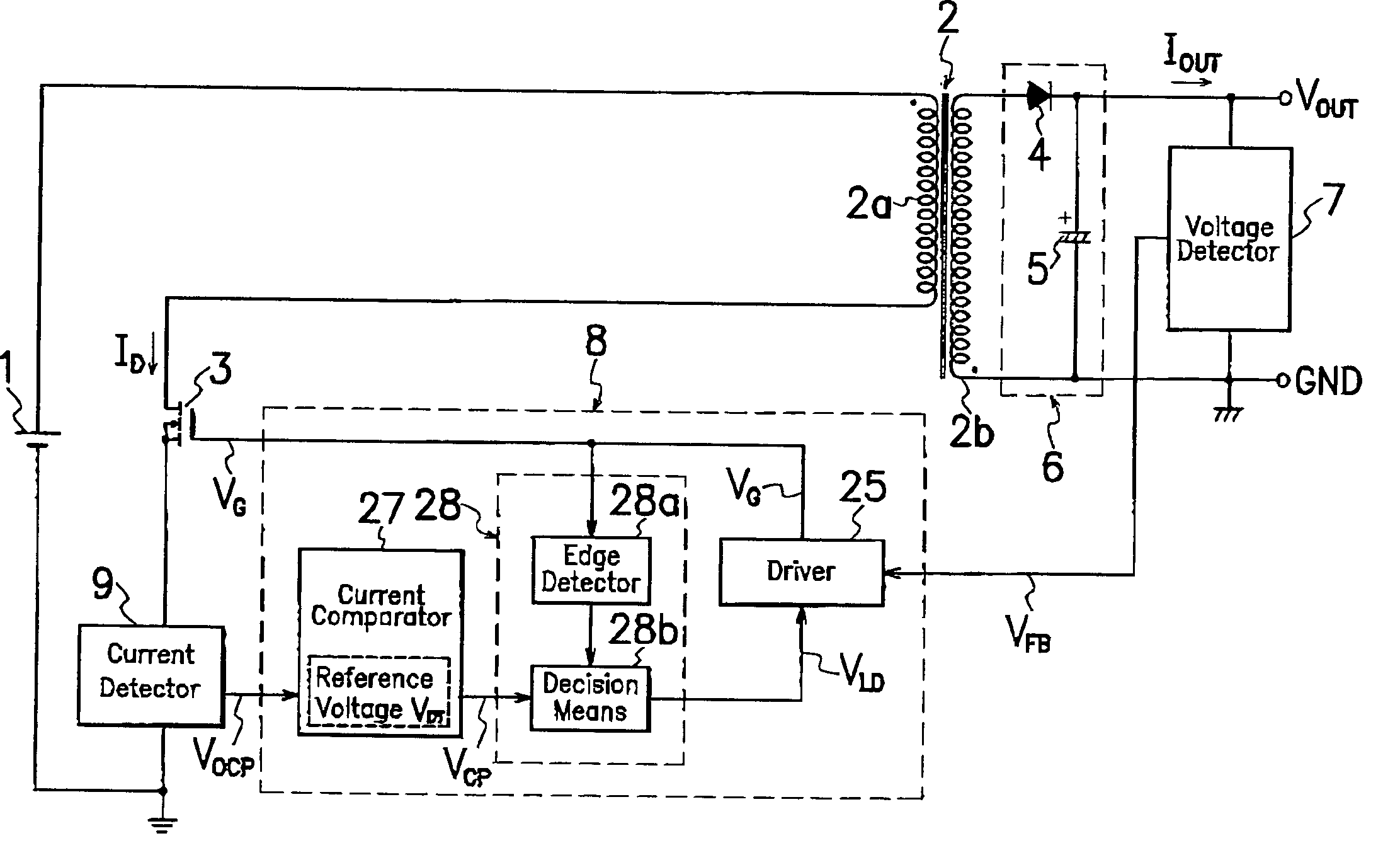
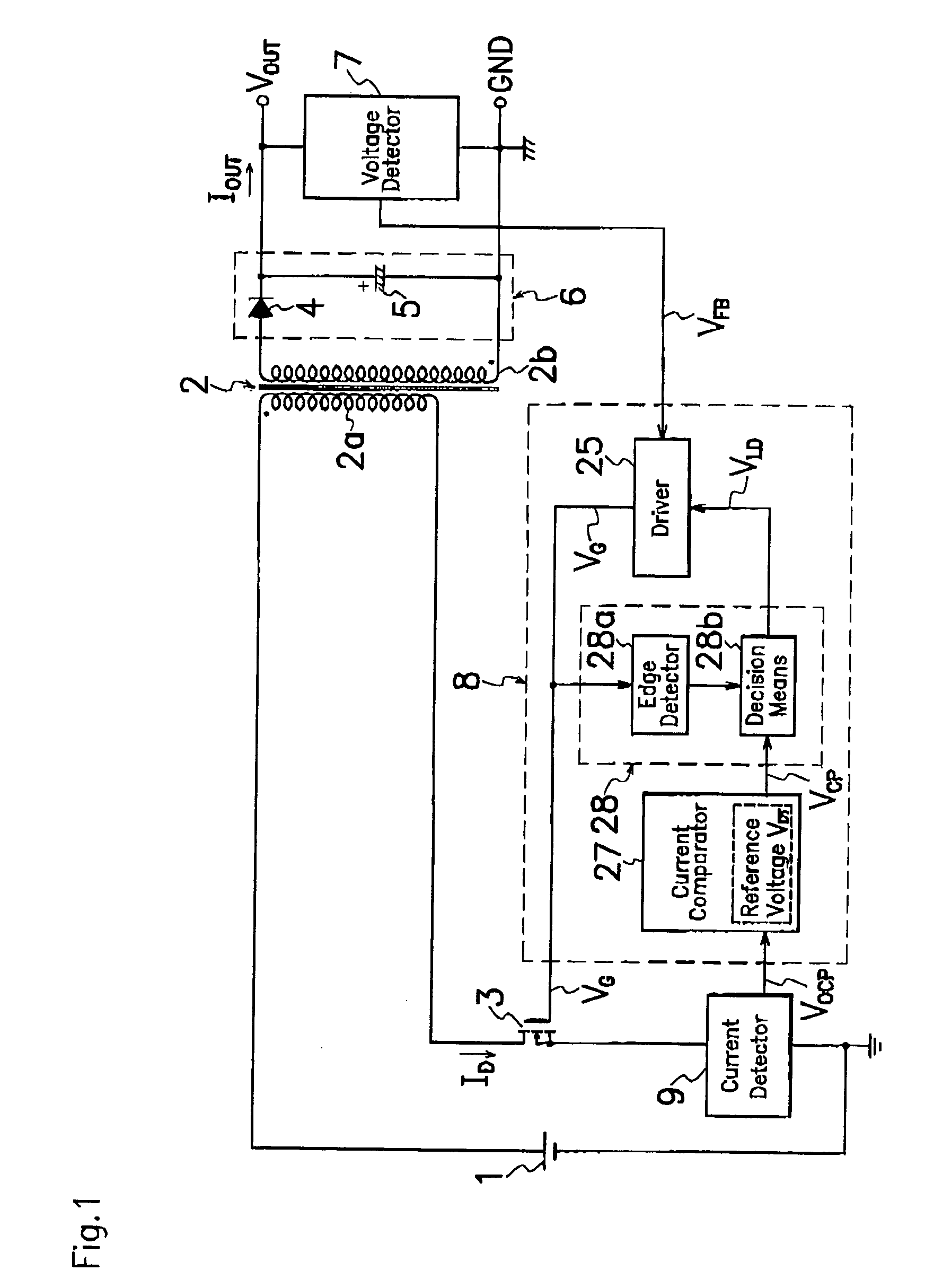
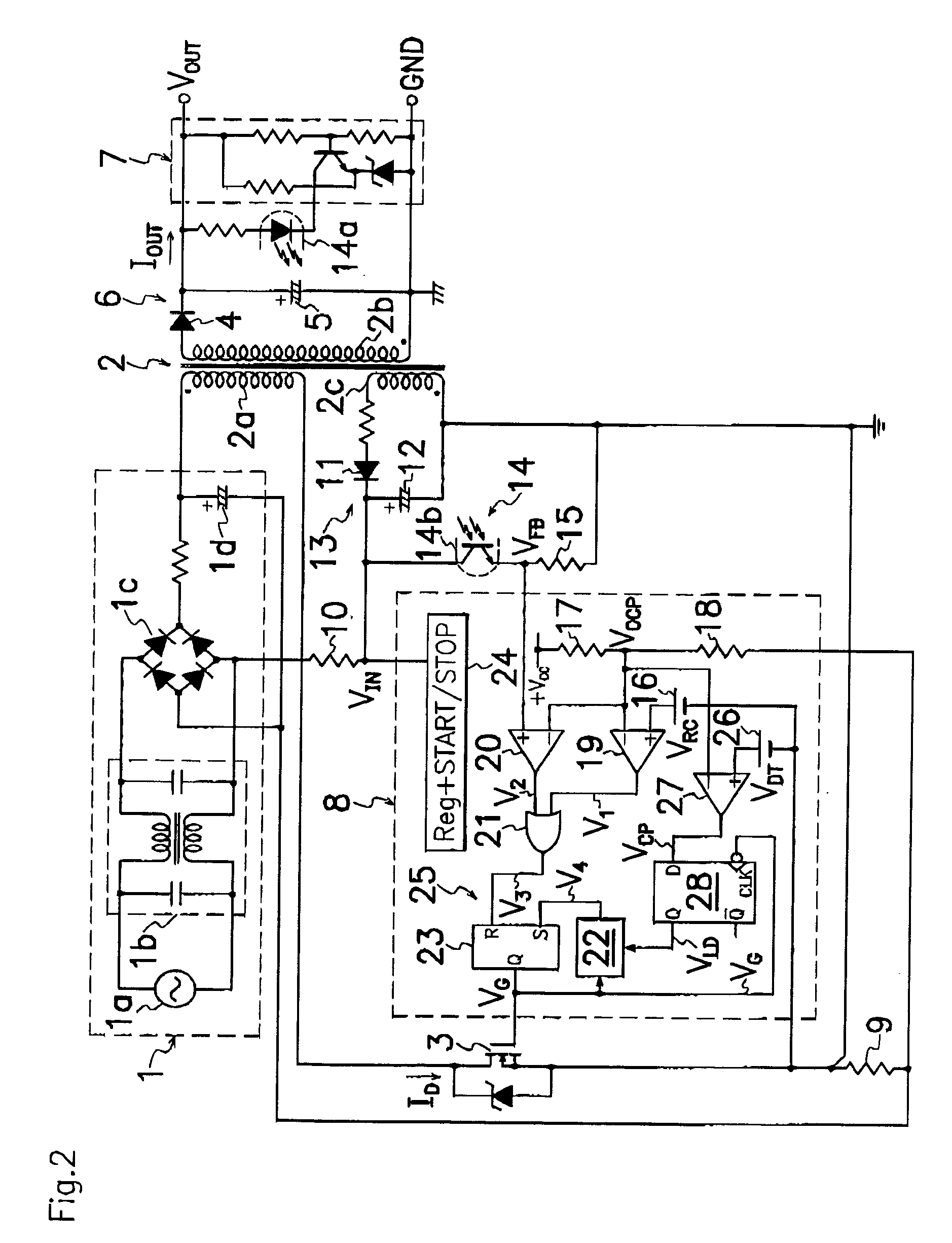
A switching power source comprises a current comparator 27 for comparing a voltage level of signals acquired by a current detector 9 with a reference voltage level VDT to produce detection signals VCP of first or second level L or H; an edge detector 28a for sensing an edge of drive signal VG supplied to a gate terminal of MOS-FET 3 during the period of transition from turning on to off of MOS-FET 3; and a decision means 28b for receiving a current detection signal VCP from current comparator 27 to produce an output signal VLD when edge detector 28a catches an edge of drive signal VG; wherein decision means 28b produces different output signals VLD of respectively first and second voltage levels L and H under the light and heavy load conditions to precisely and certainly detect on the primary side of transformer 2 the load condition on the secondary side of transformer 2 for improvement in conversion efficiency.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Grid-connected photovoltaic inverter
InactiveCN101980409ALow switching voltageReduce switching lossesAc-dc conversionSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsFull bridge inverterAC power
The invention discloses a grid-connected photovoltaic inverter and relates to equipment which employs irreversible DC power input conversion as AC power output for a semiconductor device with a control electrode and is used for being used together with a power supply system of a power supply. The equipment consists of a photovoltaic array module, four identical switching tubes, two identical diodes, four identical capacitors, an inductor and a power grid; and the topology ensures not to generate DC component or common mode current for the power grid. Meanwhile, the inverter has low output current ripple and higher efficiency, and overcomes the defects that the conventional full-bridge inverters and other types of transformerless photovoltaic inverters generate DC component in the power grid and generate common mode current or / and higher current ripple. Compared with a half-bridge inverter, the grid-connected photovoltaic inverter reduces the differential mode voltage and current ripple by half.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
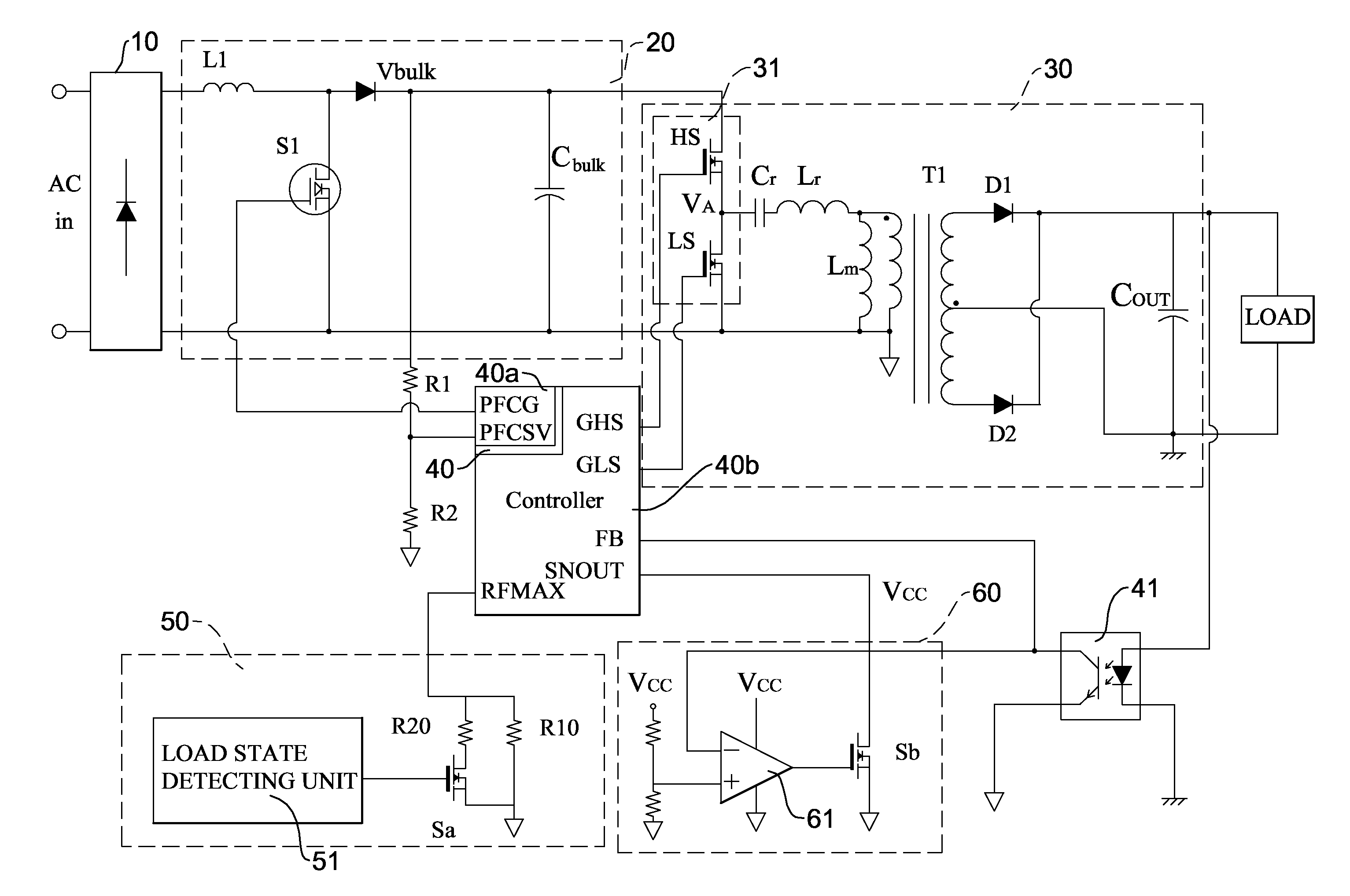
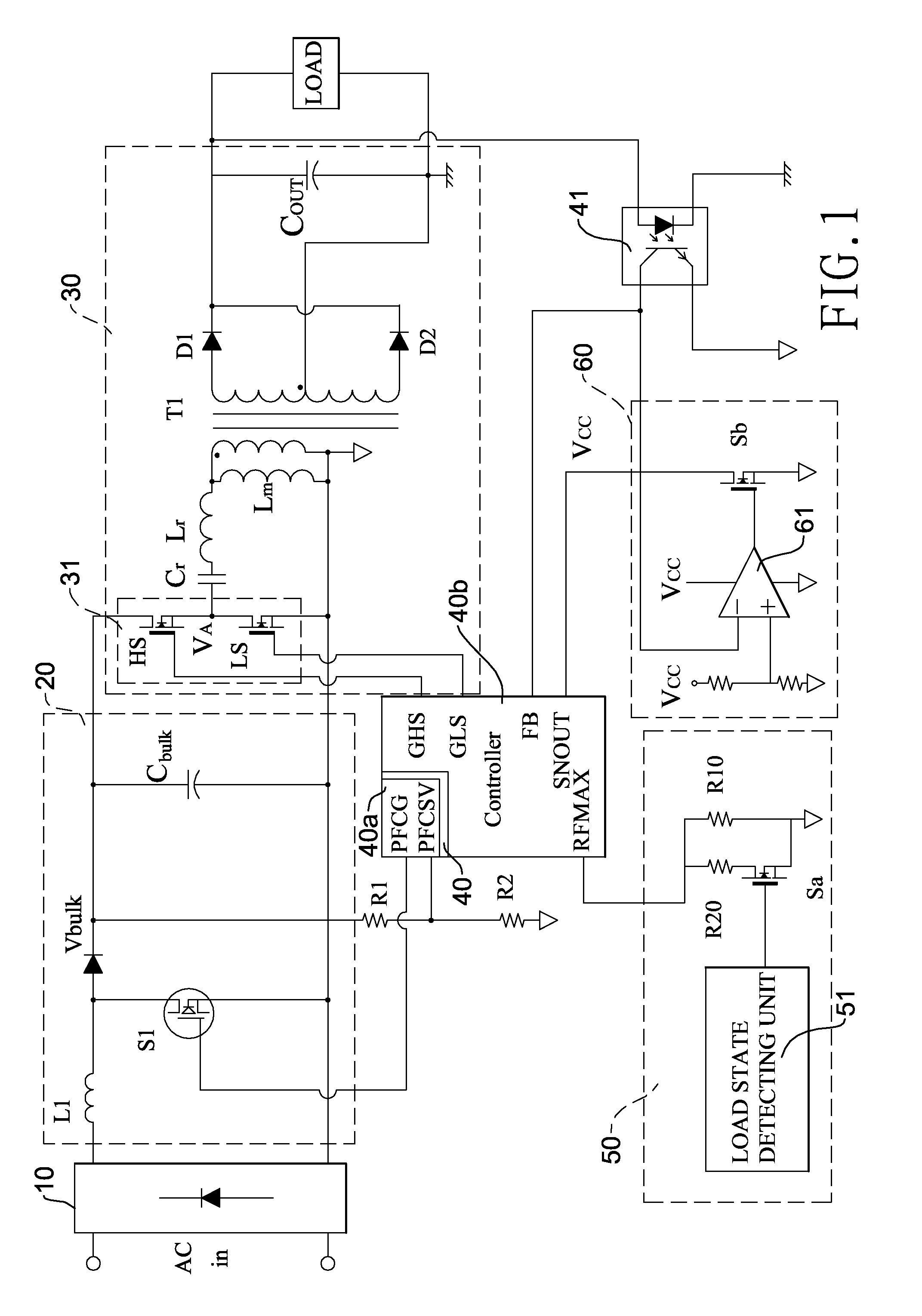
Burst mode resonant power converter with high conversion efficiency
InactiveUS20110085354A1Improve conversion efficiencyLowering maximum switch frequencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionTransformerResonant power converters
A burst mode resonant power converter with high conversion efficiency has a rectifier, a power factor correction circuit, a resonant circuit, a controller, and a burst mode triggering unit. The maximum frequency switching end of the controller is connected to a maximum frequency variable circuit. When the load is medium or heavy, the maximum frequency variable circuit increases the maximum switch frequency of the controller. When the load is in the no-load or the light conditions, it reduces the maximum switch frequency thereof. Therefore, the controller reduces the number of times that the resonant circuit switches the bridge switch circuit. The conduction cycle of the 50% pulse signal output to the bridge switch circuit becomes longer. Larger energy can be transmitted at a time to the secondary coil of the transformer. This increases the overall efficiency.
Owner:ACBEL POLYTECH INC
Method and apparatus to switch operating modes in a PFM converter
InactiveUS7102339B1Conduction loss downReduce switching lossesDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationSwitched currentDual mode
A dual-mode pulse frequency modulation boost converter operates in a hysteretic mode during light load currents to regulate an output voltage using a substantially fixed peak switching current and operates in a continuous mode during heavy load currents to regulate the output voltage using a variable peak switching current. The boost converter senses load power to automatically switch between the hysteretic mode and the continuous mode.
Owner:MICROSEMI
DC-DC converter and bi-directional DC-DC converter and method of controlling the same
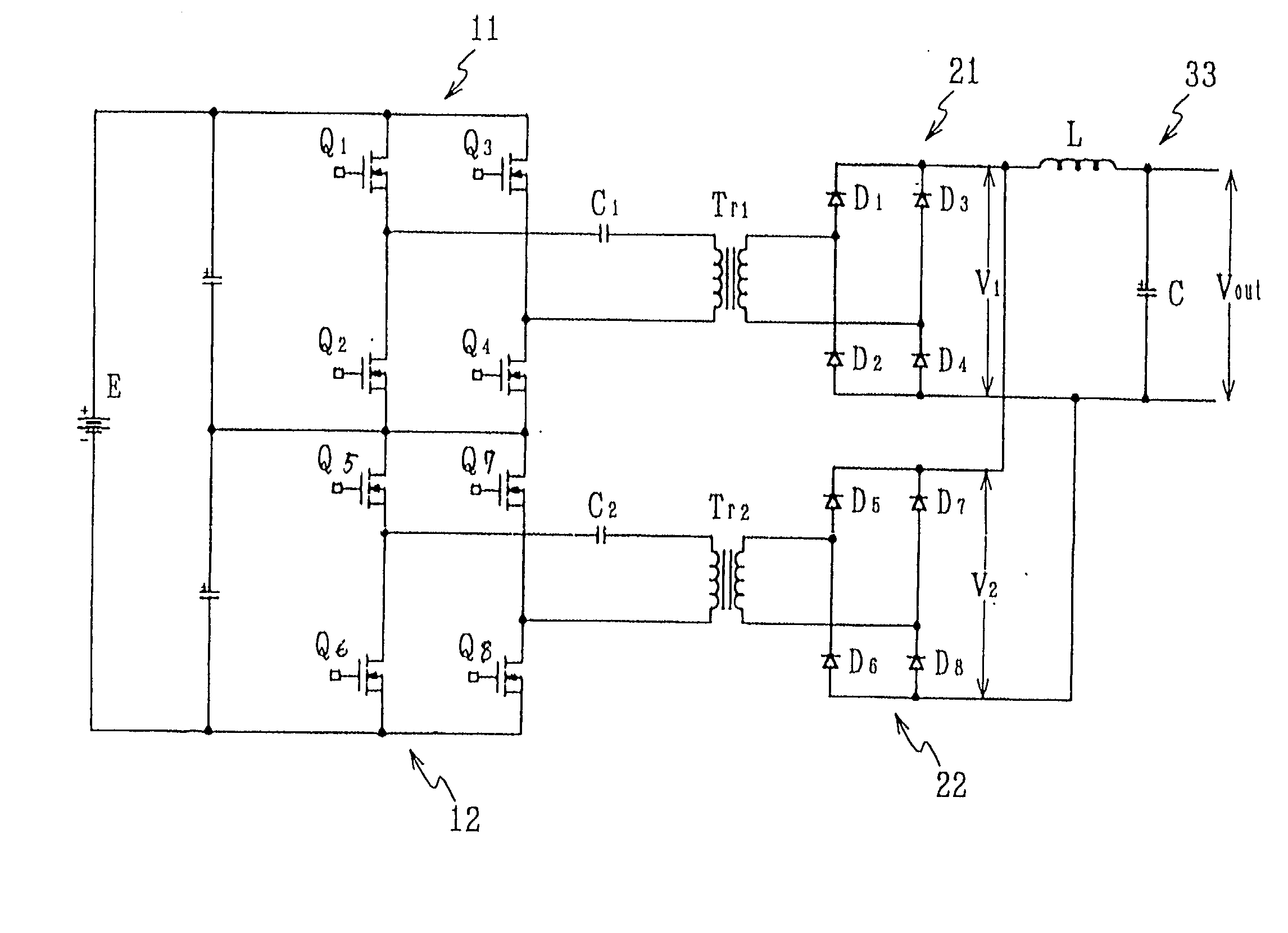
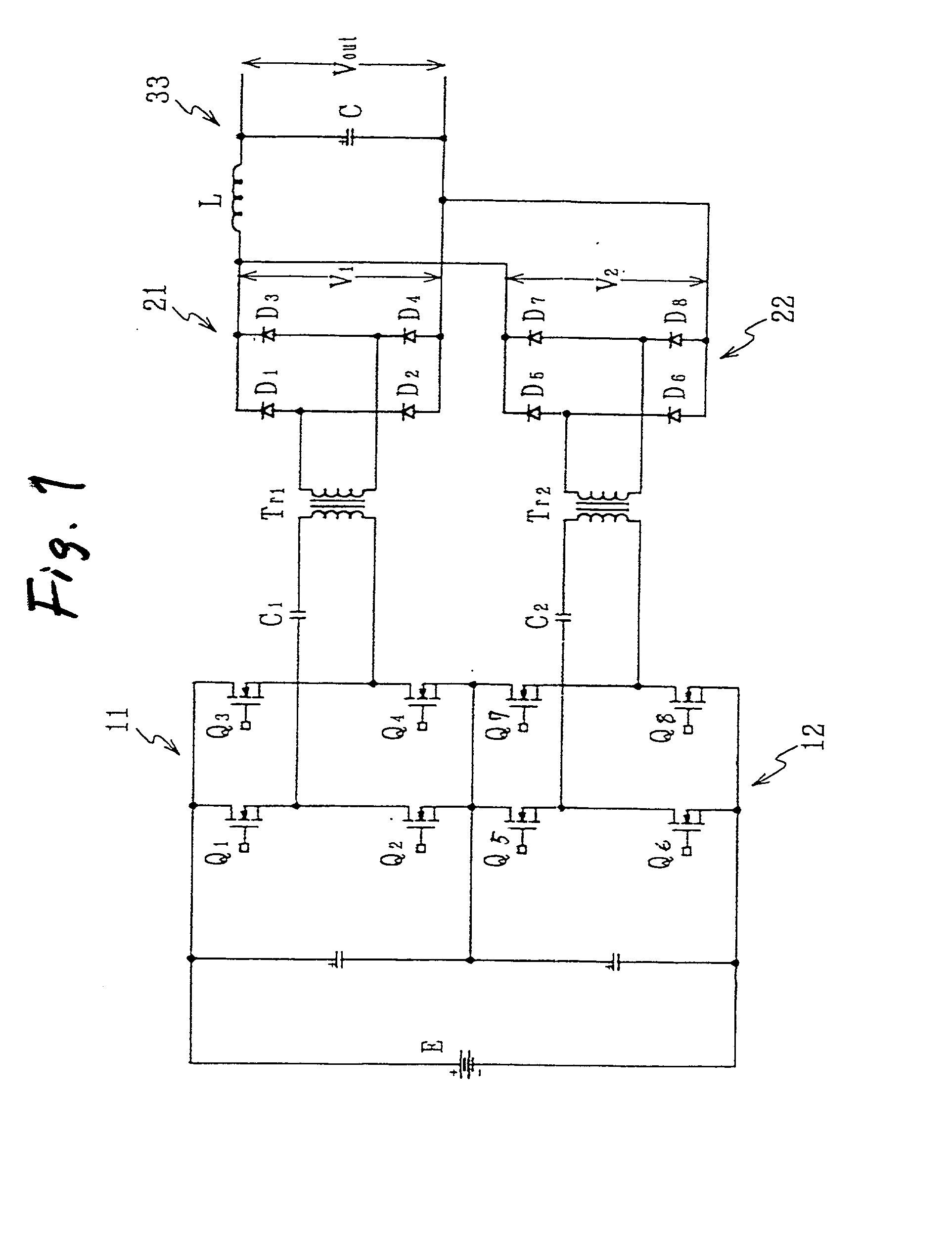
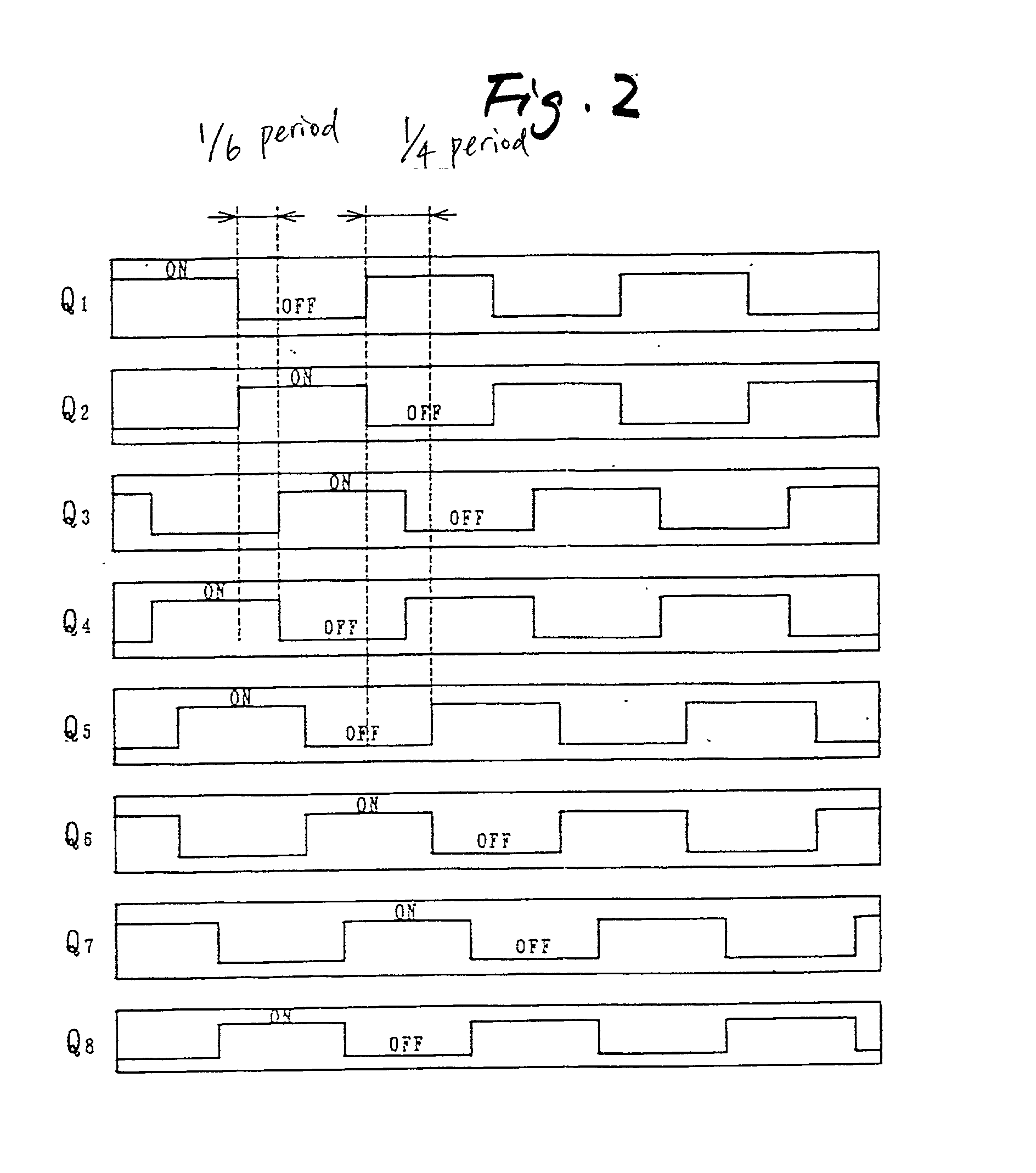
InactiveUS20020126517A1Lower on-resistanceReduce switching lossesAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcDc dc converterTransverter
A DC-DC converter has converter circuit portions 11 and 12, transformers Tr.sub.1 and T r.sub.2, and rectifier circuit portions 21 and 22. Two sets of converter circuit portions 11 and 12 respectively include two pairs of switching elements Q.sub.1 to Q.sub.4, and two pairs of switching elements Q.sub.5 to Q.sub.8 connected in full bridge configuration, series capacitors C.sub.1 and C.sub.2 are inserted and connected between the converter circuit portions 11 and 12 and the transformers Tr.sub.1 and Tr.sub.2 respectively. The switching phase of one switching element Q.sub.4 or Q.sub.8 is shifted by a 1 / 3n period from the switching phase of the other switching element Q.sub.1 or Q.sub.5 in the pair of switching elements. The switching phases of corresponding switching elements Q.sub.1 and Q.sub.5 in the converter circuit portions 11 and 12 are shifted by a 1 / 2n period from each other.
Owner:NISSIN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Circuitry for supplying a load with an output current
ActiveUS20070024254A1Efficient and interference-free operationEasy to adjustPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectroluminescent light sourcesElectricityForms of energy
A circuitry comprises a converter means for generating an alternating current signal from an energy from an energy source, a piezo transformer with an input and an output, wherein the input of the piezo transformer is electrically coupled to the converter means, to receive the alternating current signal as an excitation on the input side from the converter means, and wherein the output of the piezo transformer is designed to provide an output current, and a load, which is coupled to the output of the piezo transformer, so that output current flows through the same. The load is designed to convert at least part of the electrical energy supplied by the output current flowing through the load into another form of energy. The load is further designed such that a useful power provided in the form of useful energy is substantially proportional to the output current. The circuitry is designed to adjust the output current to a predetermined value. The described circuitry allows the supply of a load with particularly high efficiency, low interference emission and good regulation characteristics.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG +1
High-reliability MOSFET drive circuit
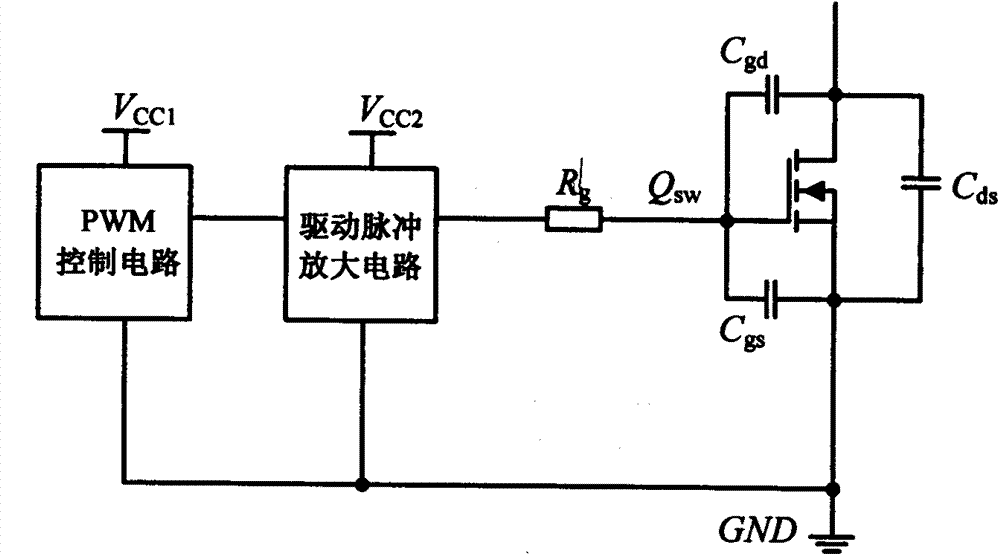
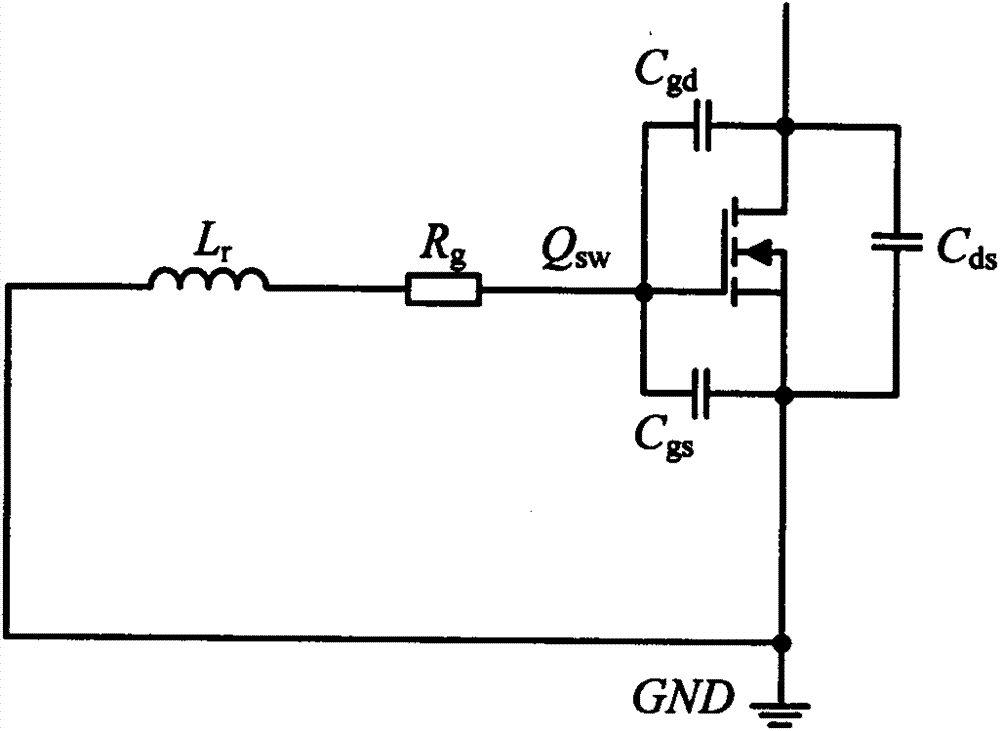
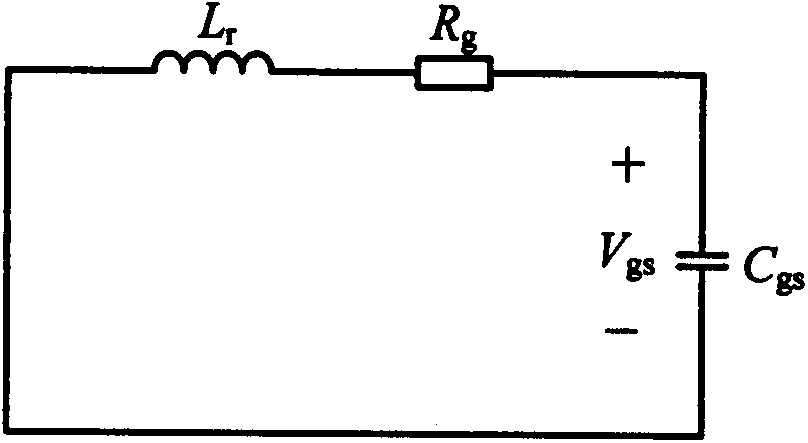
The invention relates to a drive circuit applied to a power switch tube MOSFET, in particular to a drive circuit of a silicon carbide MOSFET, and belongs to the technical field of drive circuits. The drive circuit aims to solve the problem that when an MOSFET in an existing drive circuit is turned off, the reliability is poor. The drive circuit comprises a PWM control circuit, a drive pulse amplifying circuit, a drive resistor Rg, a first diode D1, a resistor R1, a PNP triode Qoff, a second diode D2 and a capacitor C. According to the drive circuit, the PNP triode Qoff, the resistor R1 and the capacitor C form an MOSFET turn-off circuit; when the MOSFET is turned off quickly, a gate pole positive voltage spike caused by Miller currents is effectively suppressed; meanwhile, a gate pole negative voltage spike can also be suppressed through the second diode D2 and the capacitor C, it is guaranteed that the MOSFET is turned off safely and reliably, and the performance advantages of the silicon carbide MOSFET can be given to full play.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Electrical circuit for delivering power to consumer electronic devices
ActiveUS20160116925A1Lower resistanceReduce conductionAc-dc conversion without reversalBoards/switchyards circuit arrangementsData centerEngineering
An electrical circuit for providing electrical power for use in powering electronic devices, such as monitors, televisions, white goods, data centers, and telecom circuit boards, is described herein. The electrical circuit includes a voltage reduction circuit cell that includes a first capacitor, a second capacitor, a switching circuit, and a hold capacitor. The switching circuit includes a plurality of switching devices that are coupled to the first and the second capacitors for delivering power from an input terminal to an output terminal. The plurality of switching devices includes at least two switching devices that are coupled to ground. The voltage reduction circuit cell also includes a controller for operating the switching circuit in a plurality of operational modes to deliver an output power signal at a desired voltage level.
Owner:SMART PRONG TECH INC
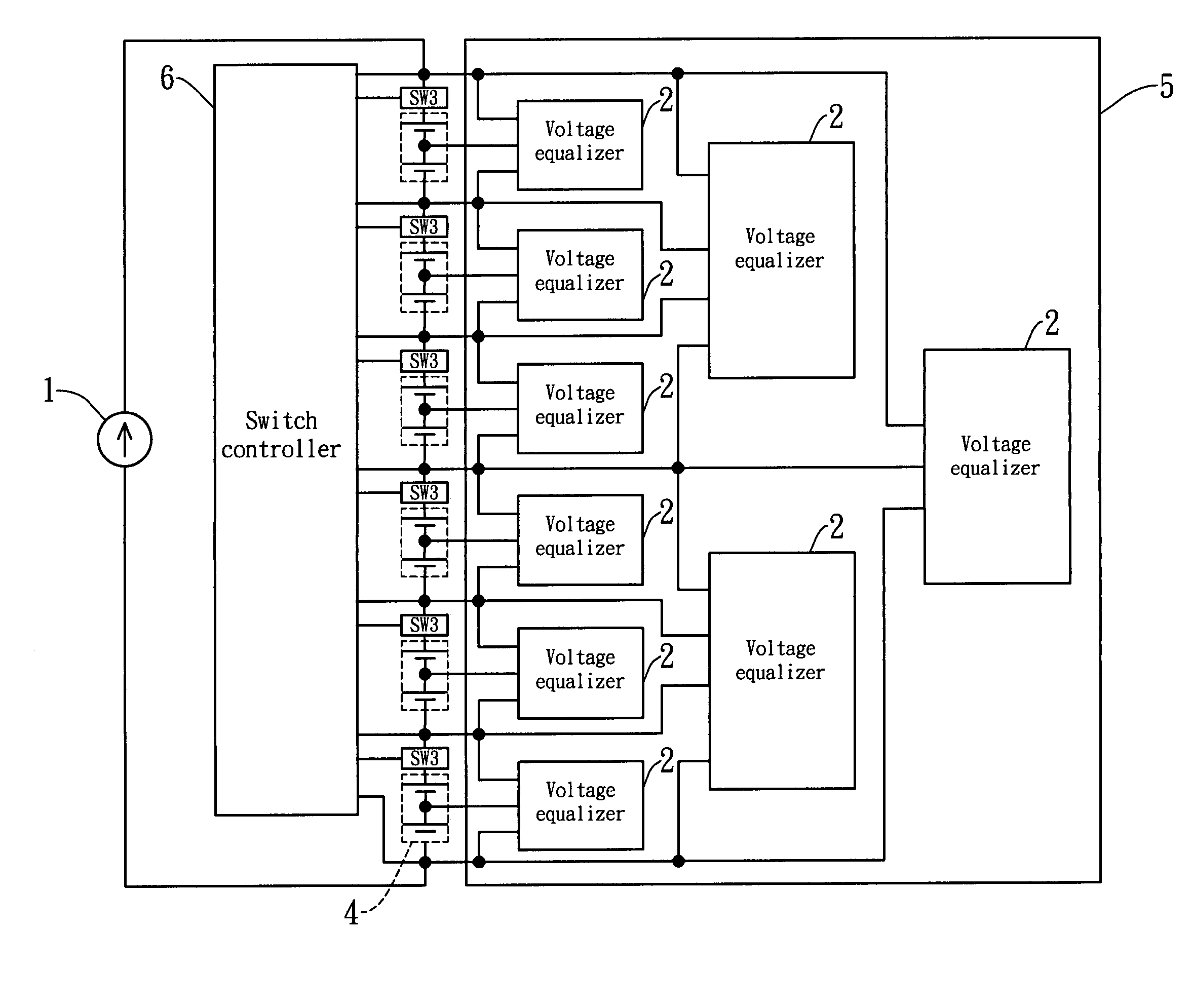
Bridge battery voltage equalizer
ActiveUS20080116850A1Easy to assembleSimple circuit structureCharge equalisation circuitElectric powerEnergy transferInductor
This present invention provides a bridge battery voltage equalizer to equalize the voltages of the serially connected battery strings, comprising at least one battery crossing over an energy-transferring circuit. A plurality of the energy-transferring circuits are interconnected in a bridge architecture. Each energy-transferring circuit having four nodes comprises a first semiconductor switch, a first diode, a second semiconductor switch, a second diode, and an inductor. One end of the first element switch is connected to a negative pole of the first diode thereto. A positive pole of the second diode is connected to one end of the second element switch thereto. The inductor is an energy storing element that crosses over between the negative pole of the first diode and the positive pole of the second diode.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
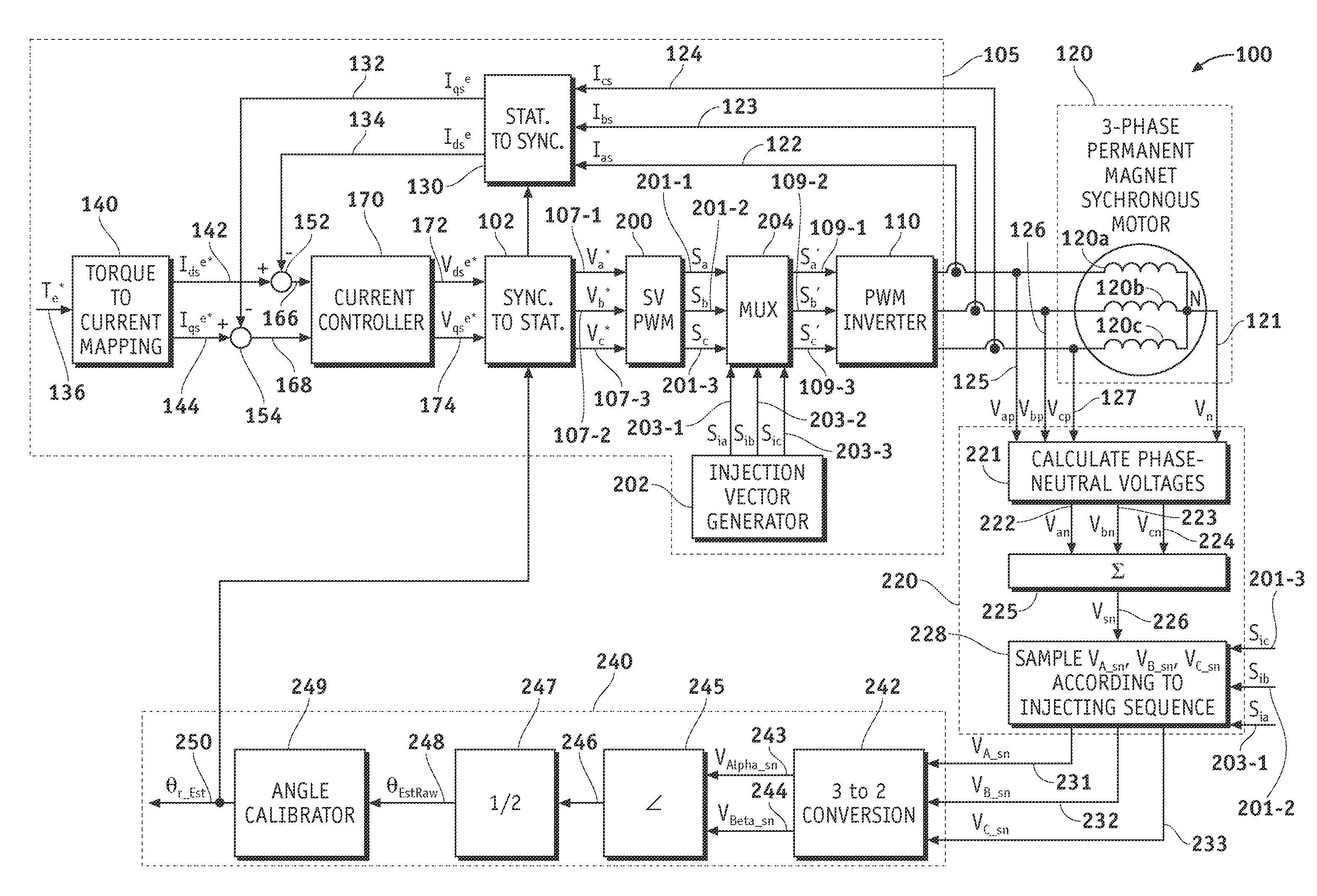
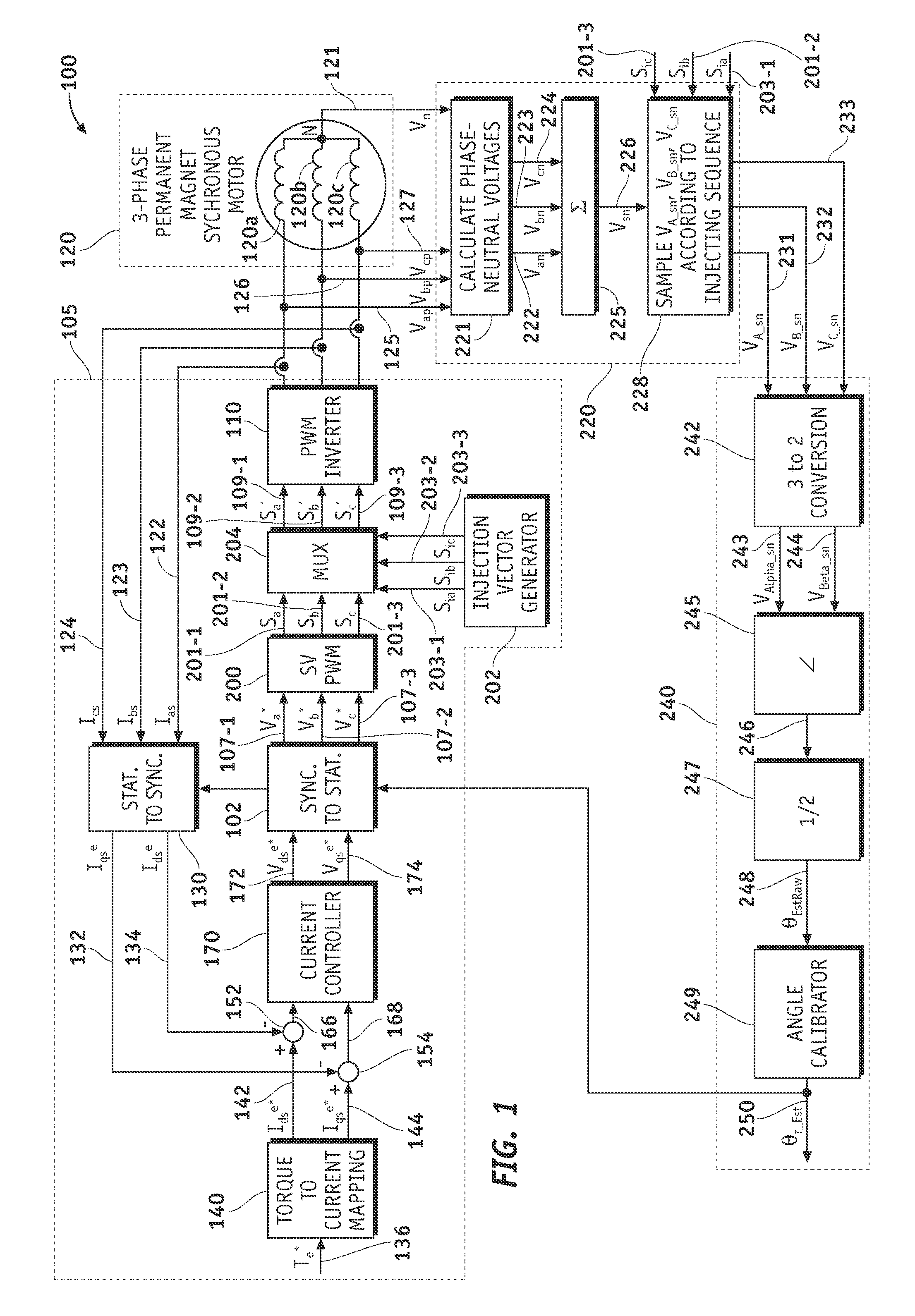
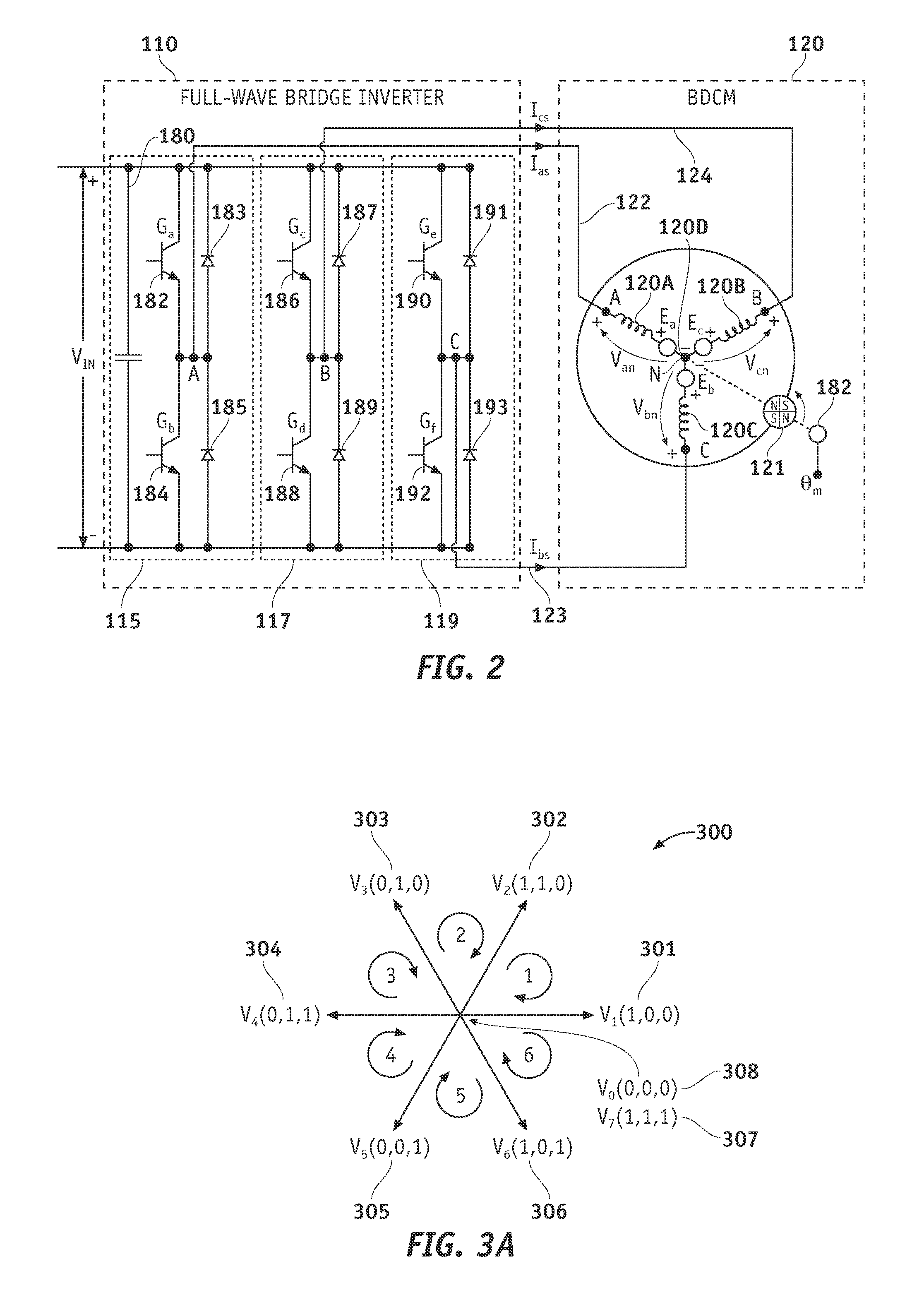
Methods, systems and apparatus for sensorless rotor angular position estimation implementing reduced switching loss pulse width modulated (PWM) waveforms
ActiveUS20110012544A1Decreased numberReduce in quantityAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersLow speedWave shape
Methods, system and apparatus are provided for low speed sensorless rotor angular position estimation that implements reduced switching loss PWM waveforms.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
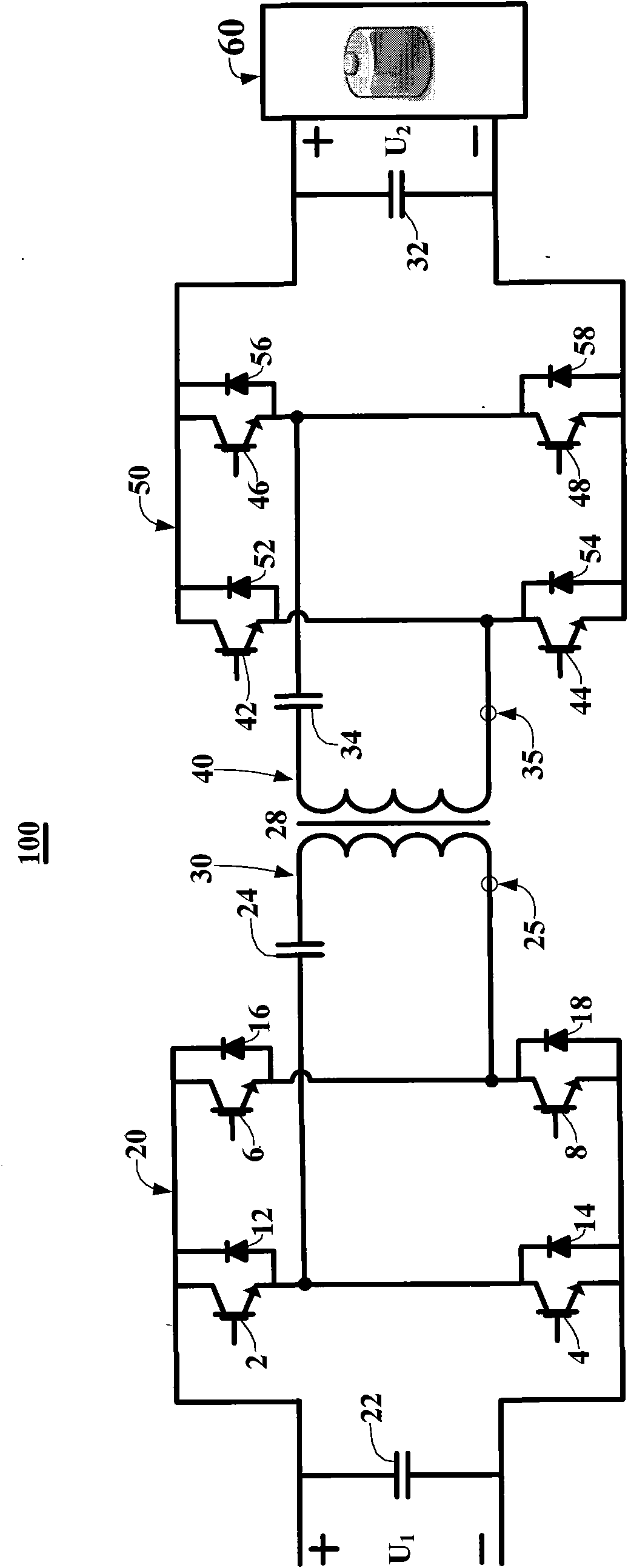
Bidirectionally isolating type series resonance DC/DC converter
InactiveCN102064702ALarge change rangeExtended service lifeEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionTransformerEngineering
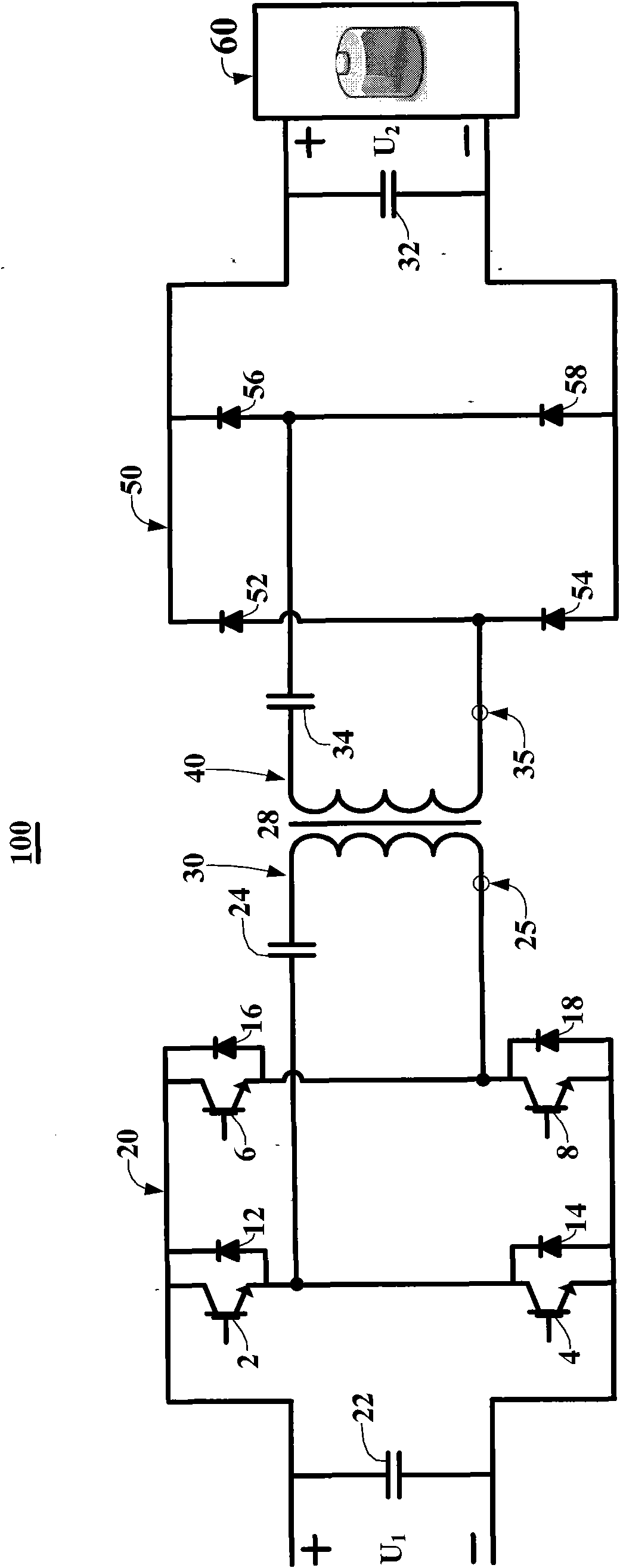
The invention relates to a bidirectionally isolating type series resonance DC / DC converter (100) which comprises voltage-stabilizing capacitors (22, 32), high-frequency converters (20, 50), series resonance circuits (30, 40), a high-frequency transformer (28) and an energy storage unit (60), wherein the voltage-stabilizing capacitors (22, 32) are used for enhancing the stability of a DC voltage; the high-frequency converters (20, 50) have the same structure and comprise four switching elements inversely connected in parallel with a rapid diode and can be used for inversion and rectification; the series resonance circuits are used for converting three kinds of discrete levels output by corresponding high-frequency converters into sinusoidal waveforms and can be used for softly switching the switching elements of the corresponding high-frequency converters, at the same time, only one series resonance circuit (30 or 40) acts; and the high-frequency transformer (28) can be used for isolation and transformation. The transformer (100) can be used for greatly converting the DC voltage, has high efficiency, and can be applied to an electric vehicle power supply, standby power supplies of large-scale equipment, and the like.
Owner:刘闯
Quasi-resonant DC-DC converters with reduced body diode loss
InactiveUS6989997B2Reduce output voltageGreater duty cycleEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionSoft switchingDc dc converter
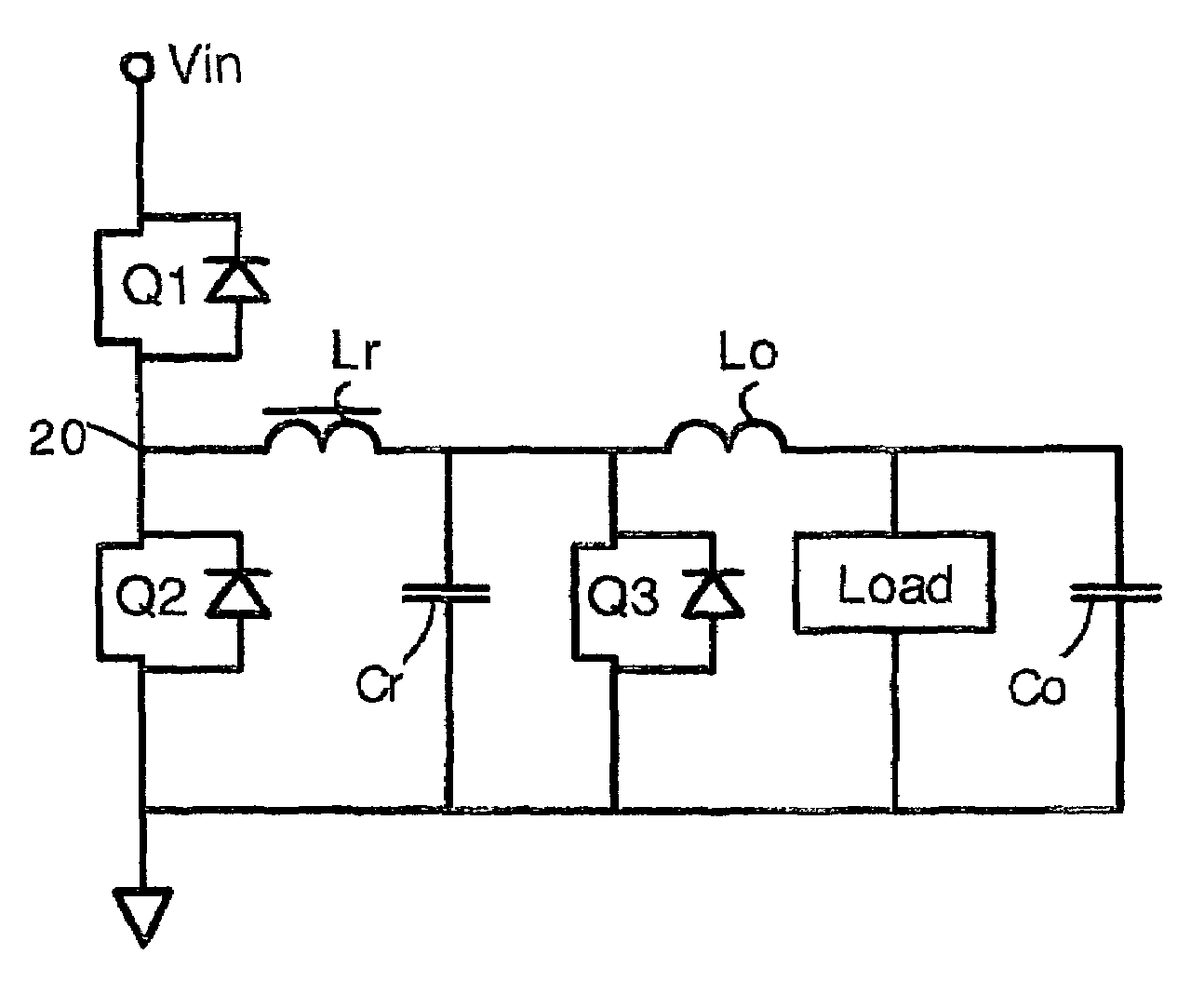
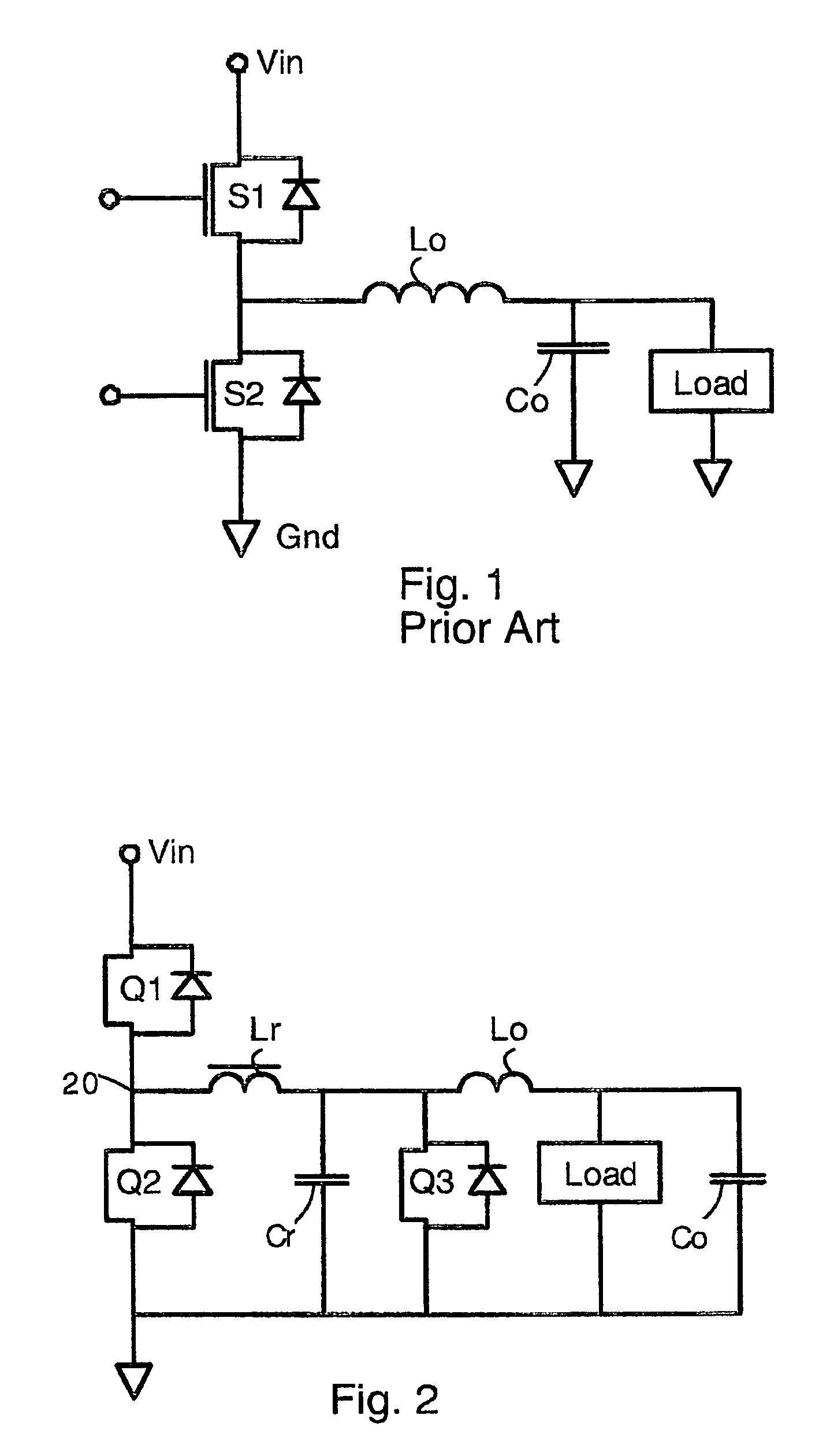
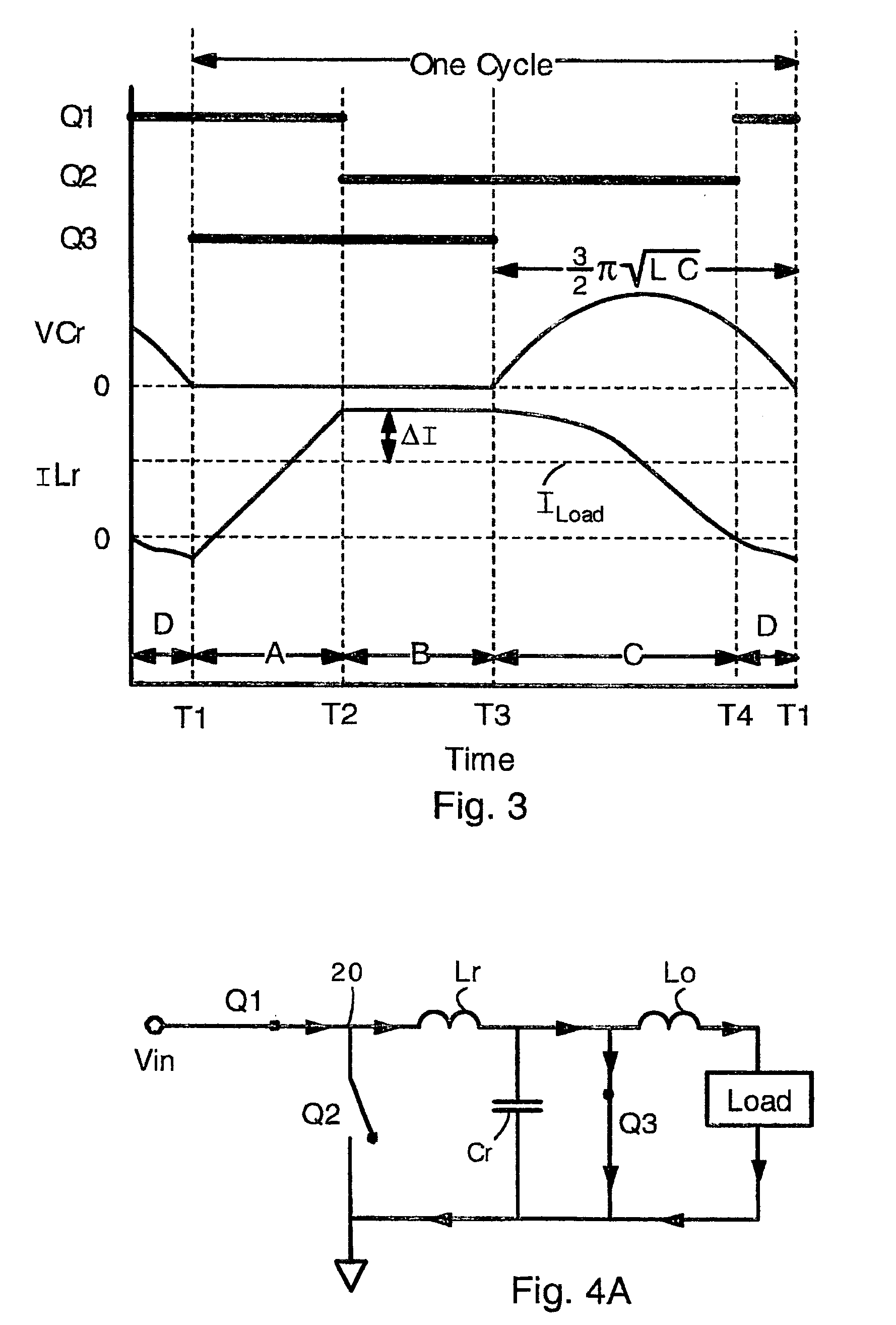
Buck converters having a resonant inductor Lr, resonant capacitor Cr, and synchronous switch Q3 that together provide reduced switching loss and soft switching. In operation, the resonant inductor Lr is charged during a time period A. Then, Lr is freewheeling and provides current to an output inductor Lo. Then, Q3 is turned OFF, and energy from the resonant inductor Lr charges the resonant capacitor Cr. Finally, energy from the resonant capacitor Cr is provided to the output inductor and load. The output power can be adjusted by phase control of the operation of switch Q3. In alternative embodiments, the circuit has a pair of coupled inductors L1 L2 or an isolation transformer 40. The coupled inductors have a polarity selected so that the output voltage is reduced, thereby allowing top switch Q1 to have a greater duty cycle. These circuits feature no body diode loss in the switch Q3.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC +1
Method and apparatus for electronic power control
InactiveUS20070052397A1Low in electricalLight weightEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEngineeringGalvanic isolation
The method of the invention in one aspect involves electronic power control by varying the amplitude of an electrical power supply voltage, independent of frequency, whereby the output frequency will always be the same as the input frequency. An electrical circuit apparatus for accomplishing this function in a specific embodiment is also disclosed herein. The specific circuitry of this aspect of the invention uses eight solid state switches, such as IGBT's, eight diodes, an inductor, input and output filters and novel controlling circuitry. The controller apparatus and methods of the invention may be used to implement all otherwise conventional converter types, buck, boost, and inverting (and duals of these) versions to obtain different regulating characteristics, including galvanic isolation of the output from the input. Indeed, the eight-switch controller can act to either buck or boost the input voltage, and can switch between bucking and boosting during a cycle, thus providing more control of the regulated output voltage. The inventive methods and devices may be used in power factor correction, voltage and / or current harmonic filtering and neutralization, line and load conditioning, control of power transfer between two power grids, and programmable control of surges, sags, dropouts and most other voltage regulation problems.
Owner:MICROPLANET
Method and apparatus for multi-phase power conversion
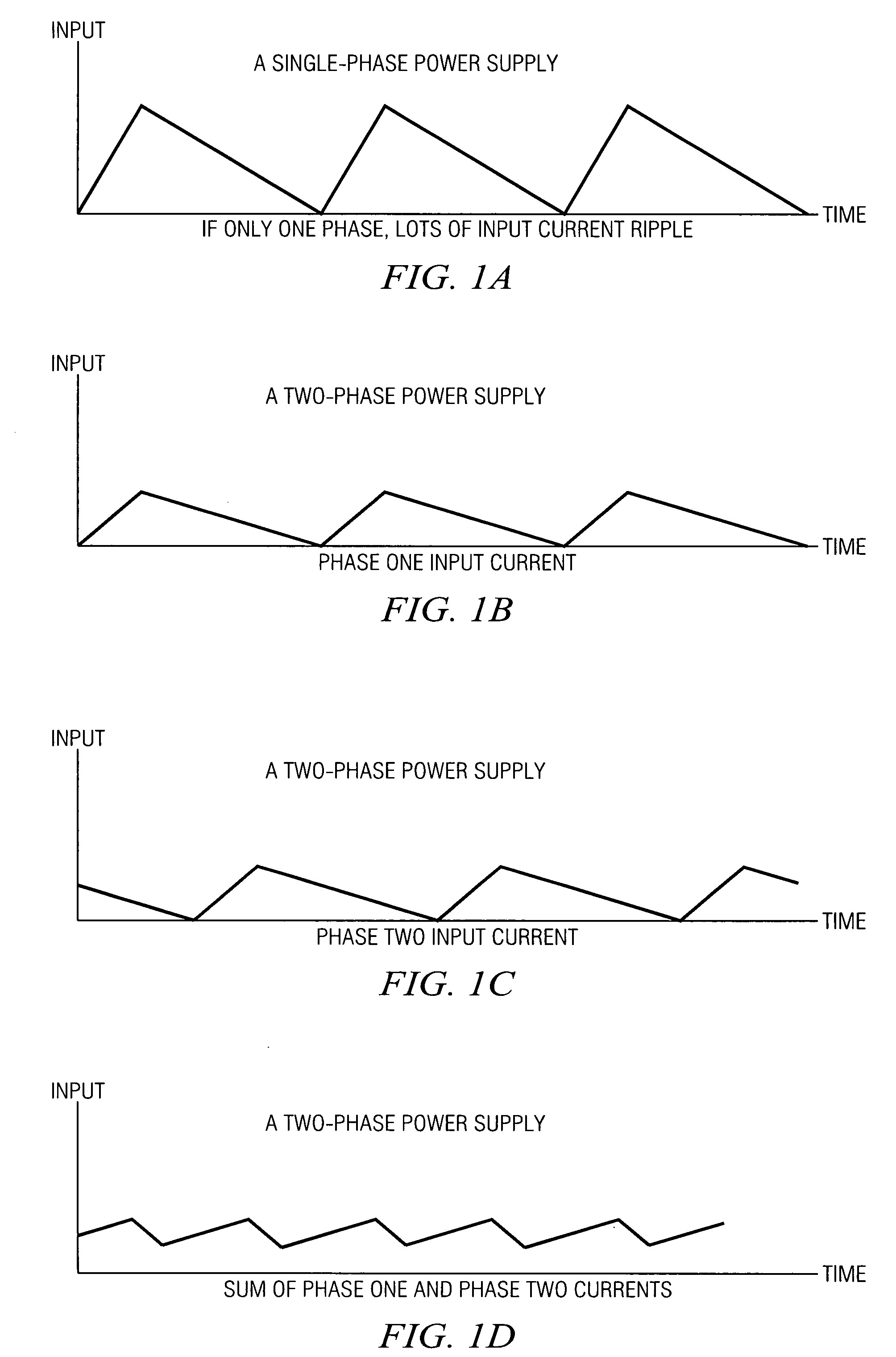
ActiveUS20070253223A1Improve circuit efficiencyReduce and eliminate impactEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionEngineeringSwitching frequency
A system and method for power conversion synchronizes multiple phases at a desired phase angle difference. The power conversion involves variable frequency switching, fixed on-time and provides power factor correction. A relative measure of a phase angle difference between two phases permits each phase to be controlled to obtain the desired phase angle difference. The power conversion involves transition mode switching to help reduce switching losses. A phase angle difference detector may be provided for each phase. The various phases may have different inherent frequencies that vary with switching frequency, and are synchronized to an average frequency. Current measures can be taken with a single component, such as a resistor. A maximum frequency control limits period width to avoid high frequency switching. An added switch on time improves input voltage crossover distortion. One or more phases can be deactivated in light load conditions.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Synchronous electric motor system
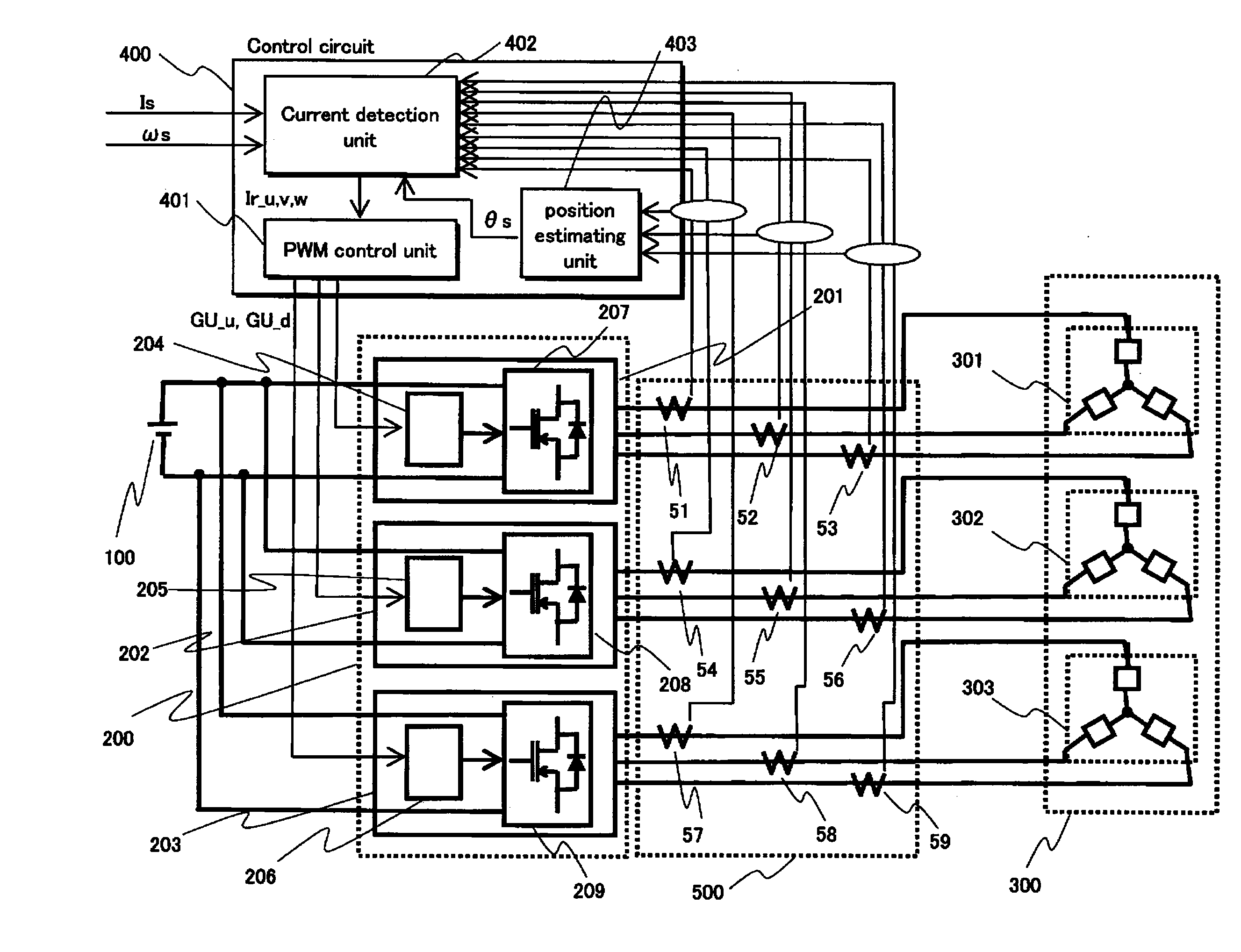
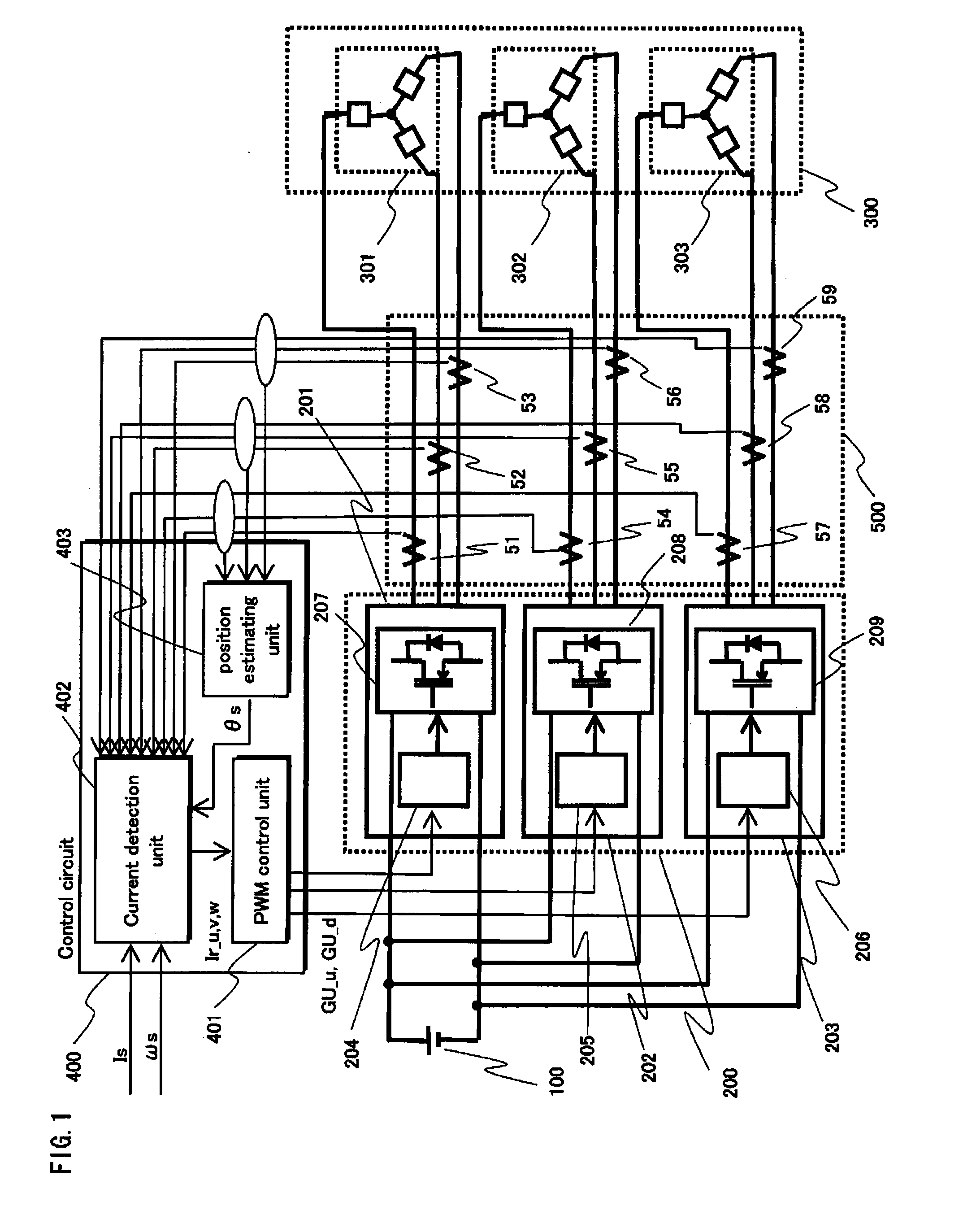
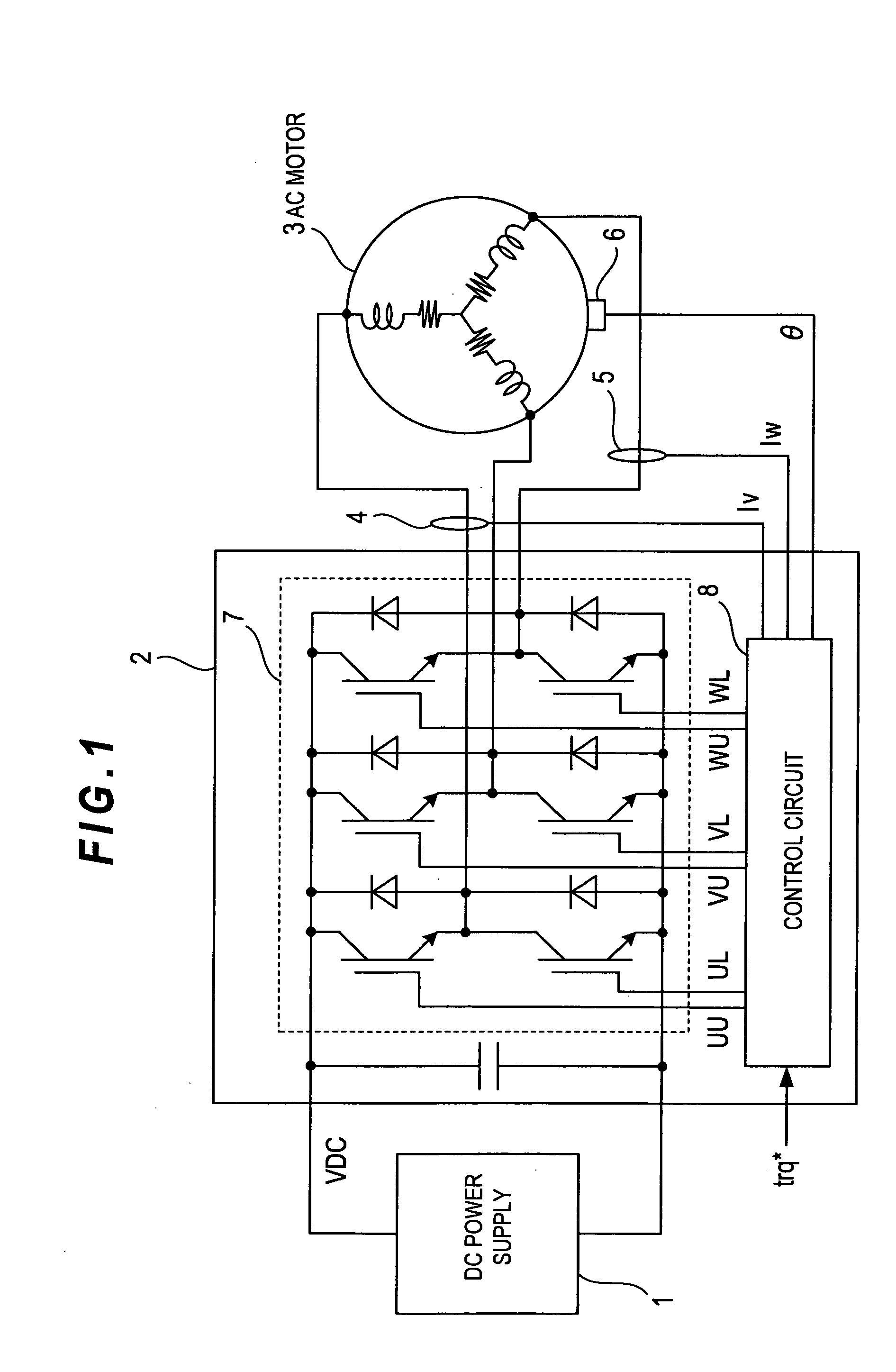
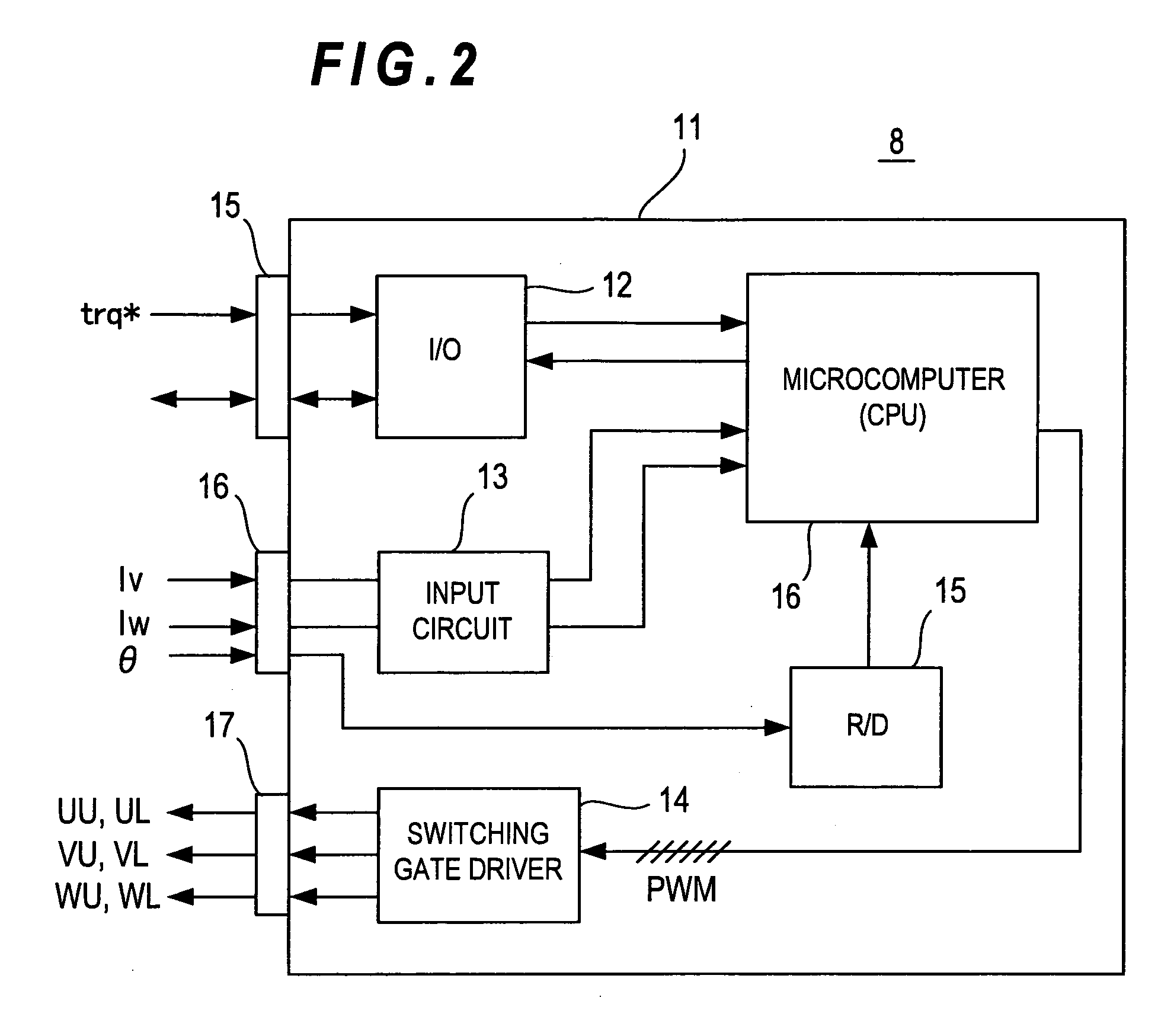
InactiveUS20110101906A1Reduce switching lossesSuppress rippleElectronic commutation motor controlAssociation with control/drive circuitsSynchronous motorThree-phase
The present invention aims to provide a synchronous motor drive system that is capable of suppressing ripples in current while reducing switching loss. The system includes three-phase inverters 201-203, a control circuit 400 for controlling the operations of the three-phase inverters and a synchronous motor 300 including a plurality of three-phase coils. To control the operations of the three-phase inverters, the control circuit 400 causes the three-phase inverters 201 and 203 and the three-phase inverter 202 to use different carrier frequencies to generate three-phase AC power, and each of the three-phase inverters supplies a different one of the three-phase coils with three-phase AC power.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Control circuit and method for a constant on-time PWM switching converter
ActiveUS20080030181A1Reduce switching lossesImprove efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionControl signalSwitching frequency
A control circuit provides a control signal for a constant on-time PWM switching converter to produce an output voltage, such that the converter operates with a constant on-time at a first state and operates with a variable on-time at a second state, so as to decrease the switching frequency and thereby the switching loss, to increase the efficiency of the converter, to improve the transient response, and to reduce the recovery time of the output voltage.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
Switching power source device
InactiveUS20050259448A1Reduce the oscillation frequencyImprove conversion efficiencyConversion with intermediate conversion to dcApparatus with intermediate ac conversionVoltage referenceSecondary side
A switching power source comprises a current comparator 27 for comparing a voltage level of signals acquired by a current detector 9 with a reference voltage level VDT to produce detection signals VCP of first or second level L or H; an edge detector 28a for sensing an edge of drive singal VG supplied to a gate terminal of MOS-FET 3 during the period of transition from turning on to off of MOS-FET 3; and a decision means 28b for receiving a current detection signal VCP from current comparator 27 to produce an output signal VLD when edge detector 28a catches an edge of drive signal VG; wherein decision means 28b produces different output signals VLD of respectively first and second voltage levels L and H under the light and heavy load conditions to precisely and certainly detect on the primary side of transformer 2 the load condition on the secondary side of transformer 2 for improvement in conversion efficiency.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD
Frequency converter for high-speed generators
InactiveUS7180270B2Simple and flexibleReduce switching lossesAc-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcFrequency changerPower grid
The present invention relates to a method and to a device for adapting the alternating current generated by a generator (1) and the alternating voltage generated by a generator (1) to a grid (8), whereby the generator (1) has at least one excitation coil (2). The power fed into the grid (8) can be flexibly adapted while entailing low switching losses in that a static frequency converter (9) is employed for the adaptation between the generator (1) and the grid (8), and in that, in order to control the power fed into the grid (8), means (3) are provided with which, on the one hand, the strength of the excitation field generated by the at least one excitation coil (2) is regulated and, on the other hand, the phase angle between the frequency converter voltage and the generator or grid voltage is appropriately controlled.
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
Submodule topology for modular multi-level transverter and application of modular multi-level transverter
ActiveCN104052026AReduce in quantityReduce switching lossesConversion with intermediate conversion to dcEmergency protective circuit arrangementsCapacitanceTransverter
The invention discloses a submodule topology for a modular multi-level transverter. The submodule topology comprises a first switching module, a second switching module, a direct current capacitor and a third switching module, wherein the first switching module and the second switching module are connected in series, the negative end of the first switching module is connected with the positive end of the second switching module, and the first switching module and the second switching module are formed by connecting full-controlled devices and diodes in an antiparallel mode. The positive electrode and the negative electrode of the direct current capacitor are connected with the positive end of the first switching module and the negative end of the second switching module. The third switching module is electrically connected with the first switching module and the second switching module, so that a full-controlled device of the third switching module applies trigger pulses all the time during normal operation and is in a conducting state all the time, and currents of direct current faults can be blocked by locking the trigger pulses of the third switching module when direct current faults happen. The invention further comprises the transverter comprising a submodule and application of the transverter. By means of the submodule topology for the modular multi-level transverter and application of the modular multi-level transverter, a function of isolating the direct current faults is achieved, quantity and switching losses of switching devices in the submodule are decreased, and requirements on trigger simultaneity are reduced.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and apparatus for electronic power control
InactiveUS7102334B2Low in electrical and audible noiseLight weightEfficient power electronics conversionAc-ac conversionGalvanic isolationPower control
The method of the invention in one aspect involves electronic power control by varying the amplitude of an electrical power supply voltage, independent of frequency, whereby the output frequency will always be the same as the input frequency. An electrical circuit apparatus for accomplishing this function in a preferred embodiment is also disclosed herein. The preferred circuitry of this aspect of the invention uses four solid state switches, such as IGBT's, four diodes, an inductor, input and output filters and novel controlling circuitry. The controller apparatus and methods of the invention may be used to implement all otherwise conventional converter types, buck, boost, and inverting (and duals of these) versions to obtain different regulating characteristics, including galvanic isolation of the output from the input. The inventive methods and devices may be used in power factor correction, voltage and / or current harmonic filtering and neutralization, line and load conditioning, control of power transfer between two power grids, and programmable control of surges, sags, dropouts and most other voltage regulation problems.
Owner:MICROPLANET
Switching power supply device and the semiconductor integrated circuit for power supply control
InactiveUS7158392B2Reduce switching lossesReduce lossesAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionDc dc converterFull bridge
It is aimed at decreasing losses not only in a synchronous rectifier circuit provided at a secondary side of a DC-DC converter, but also in a full-bridge switching circuit provided at a primary side thereof. The DC-DC converter comprises a transformer for voltage conversion, a synchronous rectifier circuit at the secondary side, and a full-bridge switching circuit at the primary side. The DC-DC converter performs synchronous rectifier control which uses switch transistors to change paths of currents flowing through the secondary coil in synchronization with switching operations at the primary side. The DC-DC converter detects currents flowing through a load at the secondary side, primary-side currents varying with the load currents, or primary-side input voltages to dynamically control off-timings of a synchronous rectification transistor at the secondary side. In addition, the DC-DC converter detects primary-side input voltages and currents flowing through the secondary-side load to dynamically control on-timings of a transistor in the primary-side switching circuit.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Apparatus for controlling three-phase AC motor on two-phase modulation technique
ActiveUS20050194925A1Reduce switching lossesSingle-phase induction motor startersElectronic commutation motor control
An apparatus is provided to control a three-phase AC motor and comprises an inverter and a controller. The inverter powers the motor in response to a three-phase PWM command. The control circuit controls the inverter based on two modulation techniques selectively switched from one the other depending on information indicative of an operation state of the motor. One modulation technique gives the PWM command a first two-phase modulation allowing each phase voltage to be fixed at a predetermined voltage level in turn at intervals of an electrical angle of 2π / 3. The other modulation technique gives the PWM command a second two-phase modulation allowing each phase voltage to be fixed at a predetermined voltage in turn at intervals of an electrical angle of π / 3. The switchover can be made between the two-phase and three-phase modulations or can be made with consideration of temperature at switching elements.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Power converter
ActiveUS20120188712A1Reduce power lossImprove equipment efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConversion constructional detailsLow inductanceSemiconductor
In a power converter in which semiconductor modules are arranged on both surfaces of a cooler for downsizing, an excellent connection between control boards and a low inductance connection between smoothing capacitors and the semiconductor modules are performed at the same time. The semiconductor modules are disposed on both surfaces of the cooler, and control boards that control the semiconductor modules are arranged opposite to the respective semiconductor modules. The semiconductor modules and the cooler are held between the control boards. A current detector or a terminal block is disposed at a position perpendicular to a surface on which the cooler and the semiconductor modules contact each other, opposite to the cooler. The respective control boards disposed on both surfaces of the cooler are electrically connected by using wirings provided in the current detector or the terminal block.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
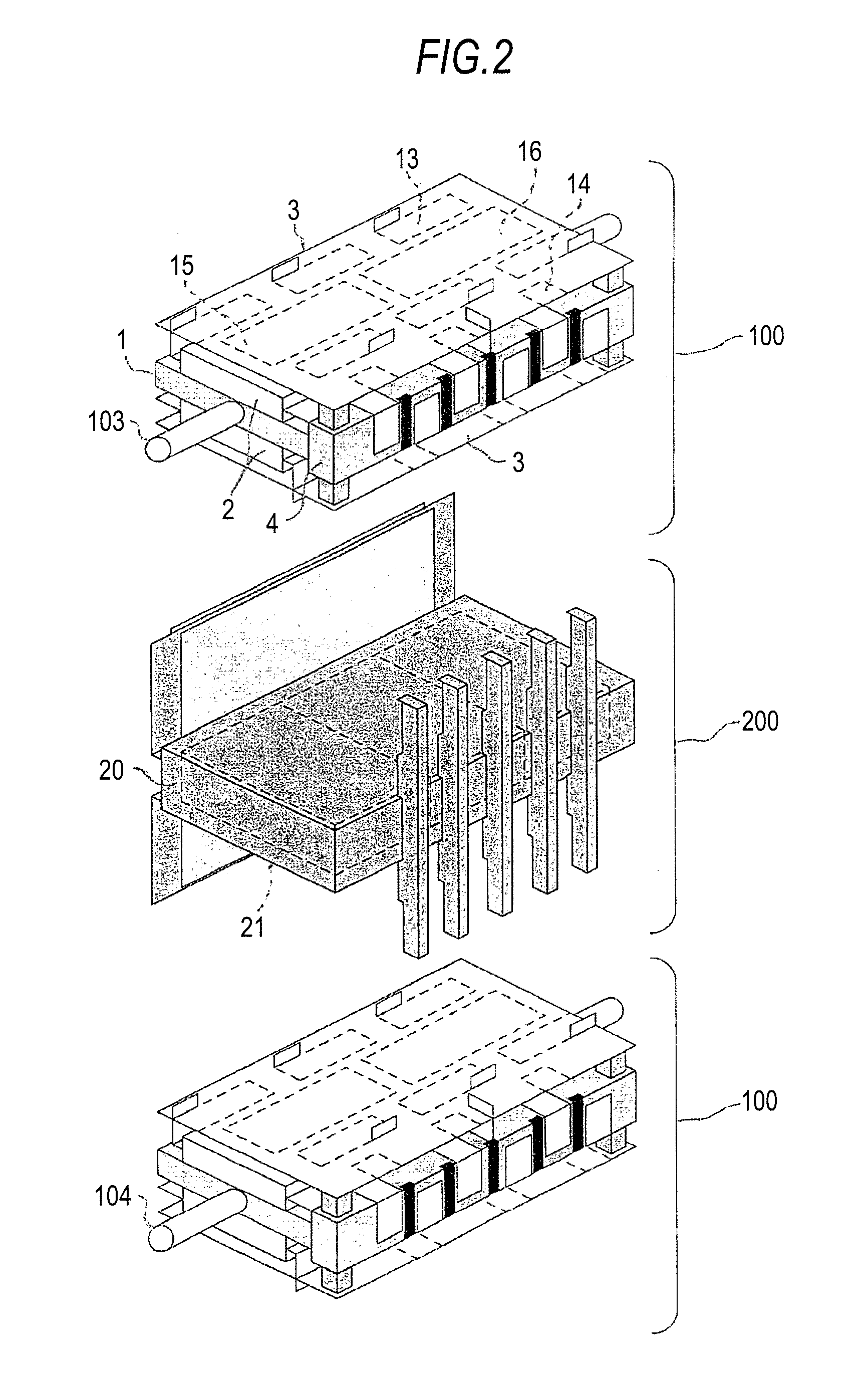
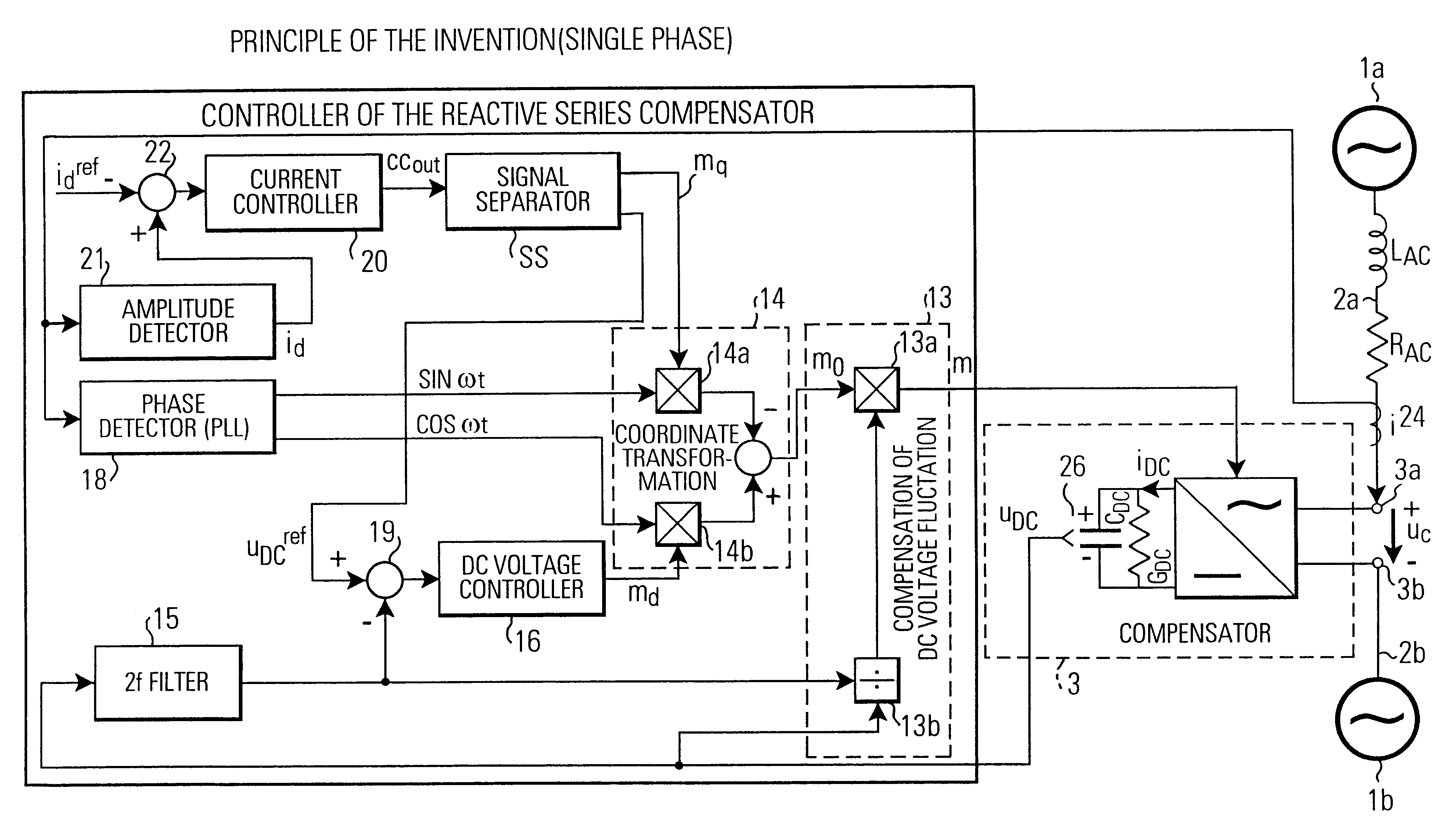
Controller of adjustable DC voltage for a transformerless reactive series compensator
InactiveUS6242895B1Avoids zero voltageHarmonics are still reducedReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationElectric variable regulationTransformerEngineering
A controller for controlling a reactive series compensator serially inserted at compensator terminals into a power transmission line for controlling the line current. The controller includes a current control loop and a voltage control loop. A current controller outputs a control voltage (cc.sub.out) indicating a desired compensator terminal output voltage (u.sub.c). A control method selector means generates, in a low output voltage region, a constant reference voltage (u.sub.DC.sup.ref) for the voltage control loop and a variable modulation index mq of a modulation signal m=m.sub.d cos (.omega.t) -m.sub.q sin (.omega.t). In a high output voltage range, the control method selector outputs a constant modulation index m.sub.q and a variable reference voltage (u.sub.DC.sup.ref). The voltage controller outputs the modulation index m.sub.d of the modulation signal m. Furthermore, the control method selector can include a rate limiter for limiting the change rate of the reference voltage (u.sub.DC.sup.ref). In connection with the control method selection and / or the rate limiter, a decoupling control for making the voltage and current control loops independent from each other can be used. The controllers find particular application in transformerless reactive series compensators for single-phase or three-phase control.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com