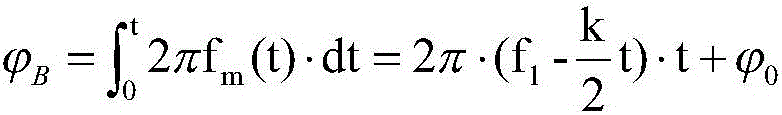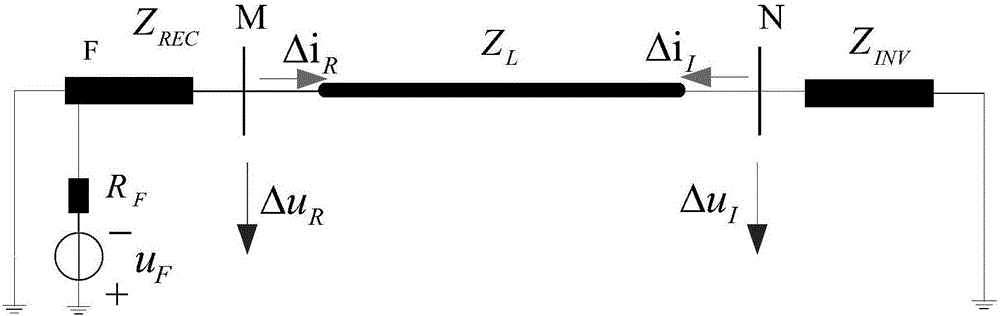Patents
Literature
390 results about "Phase angle difference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
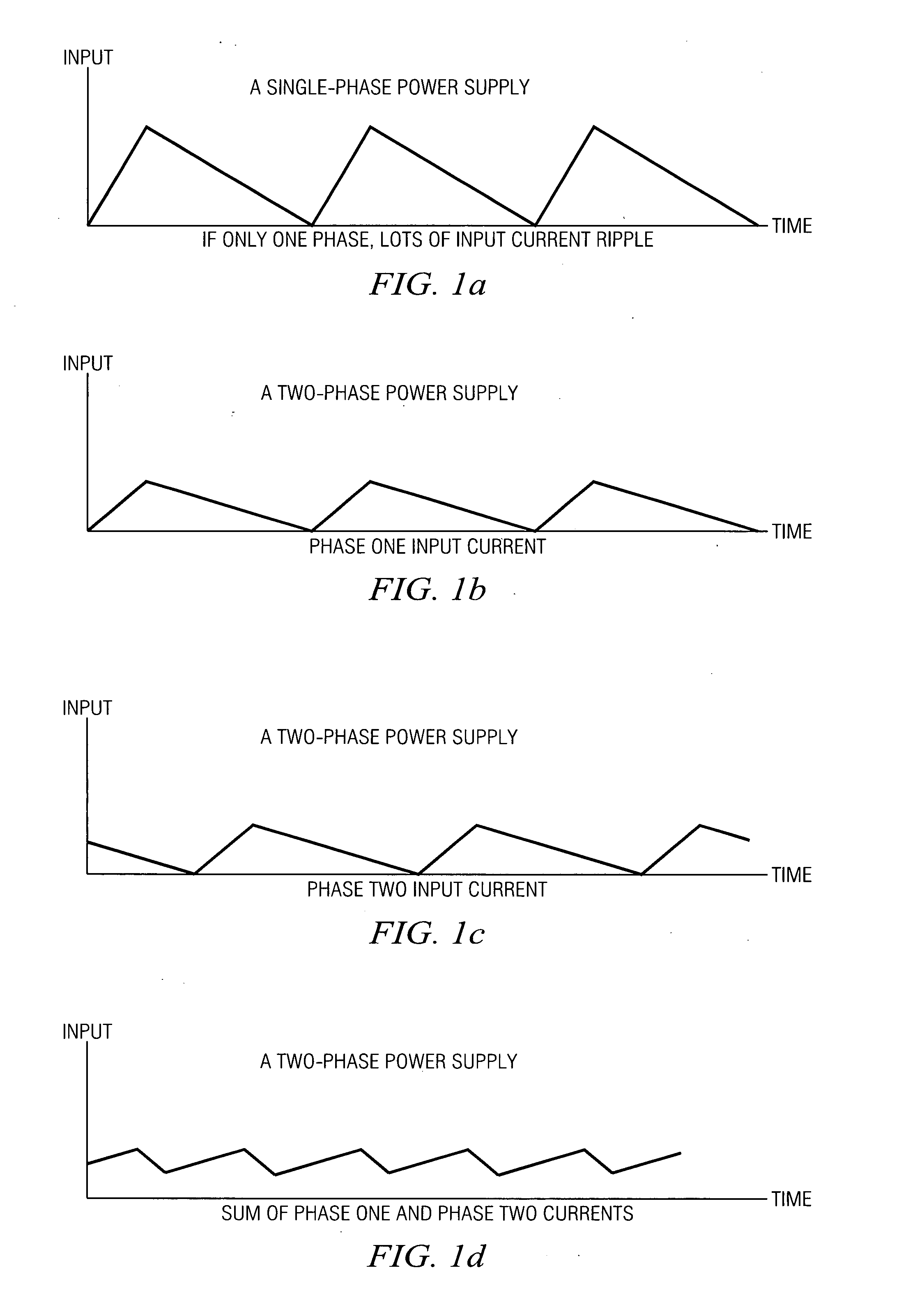
Phase difference , also called phase angle , in degrees is conventionally defined as a number greater than -180, and less than or equal to +180. Leading phase refers to a wave that occurs "ahead" of another wave of the same frequency. Lagging phase refers to a wave that occurs "behind" another wave of the same frequency.
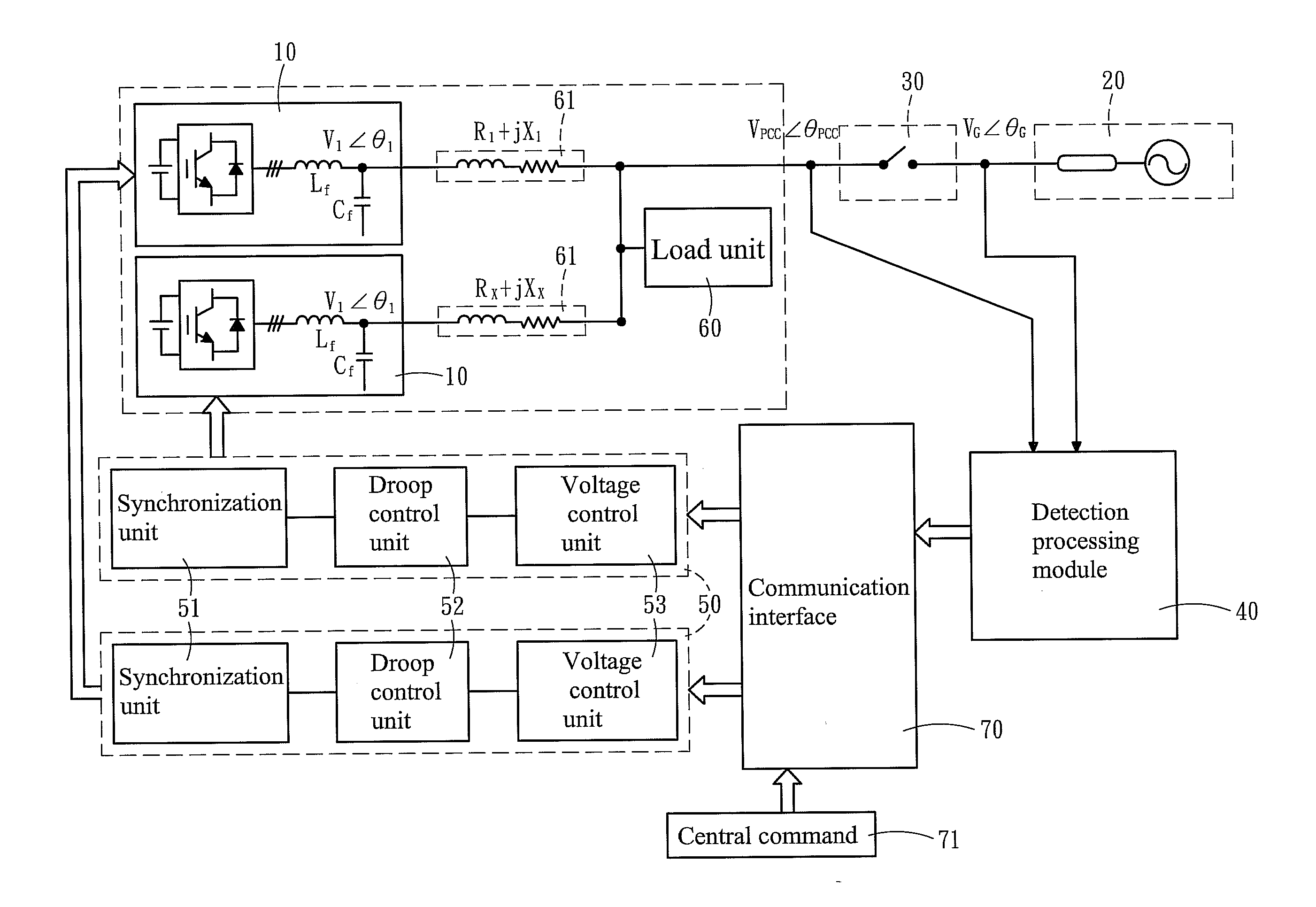
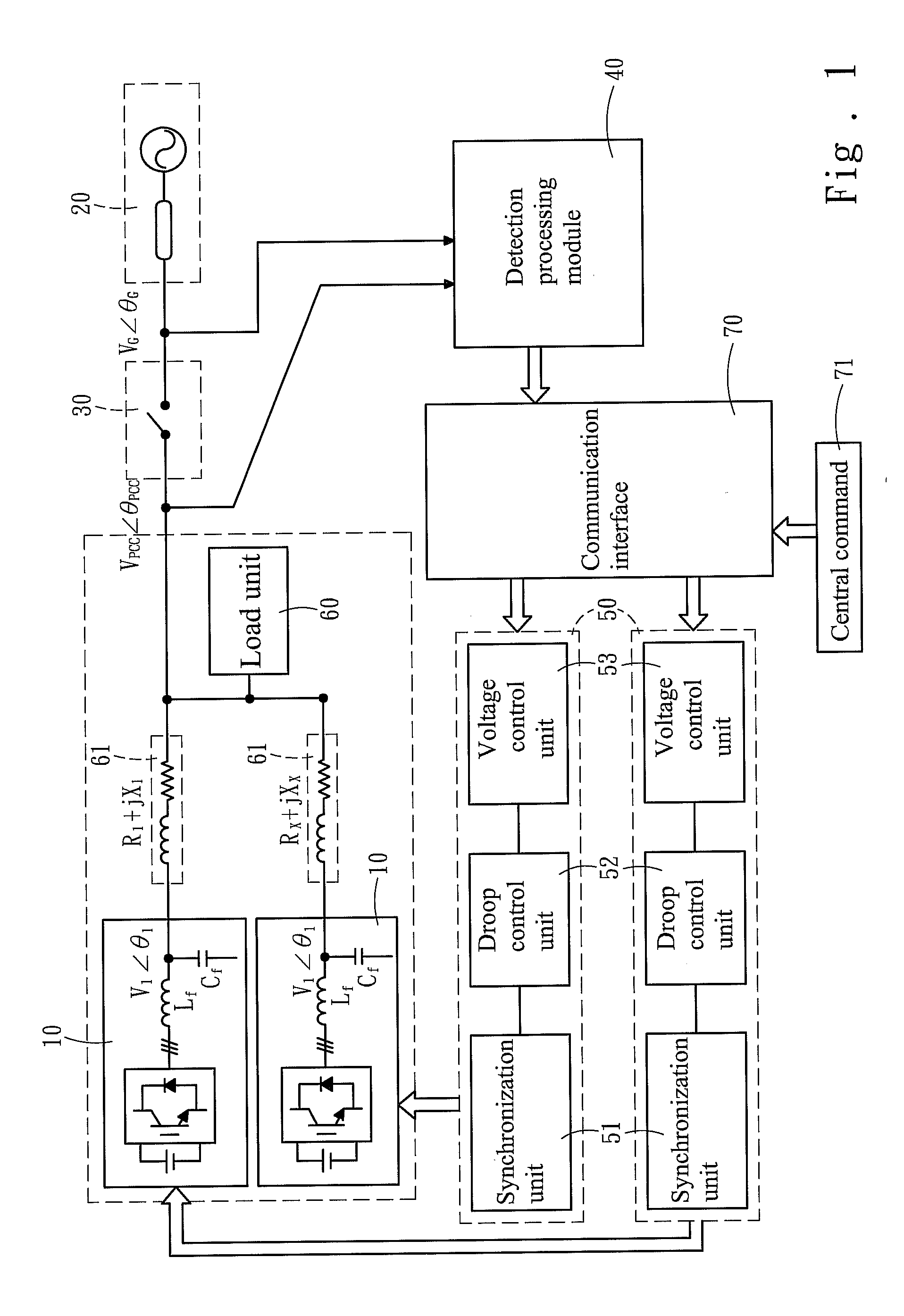
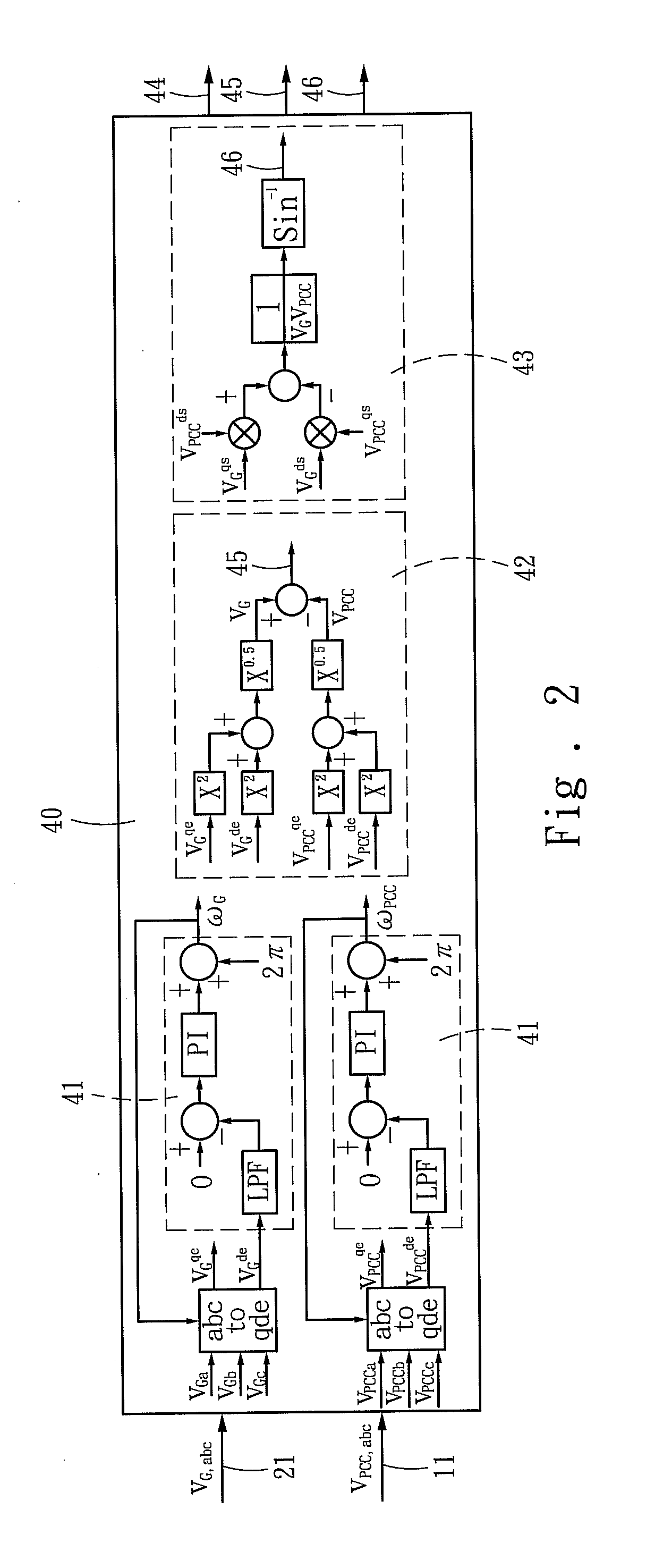
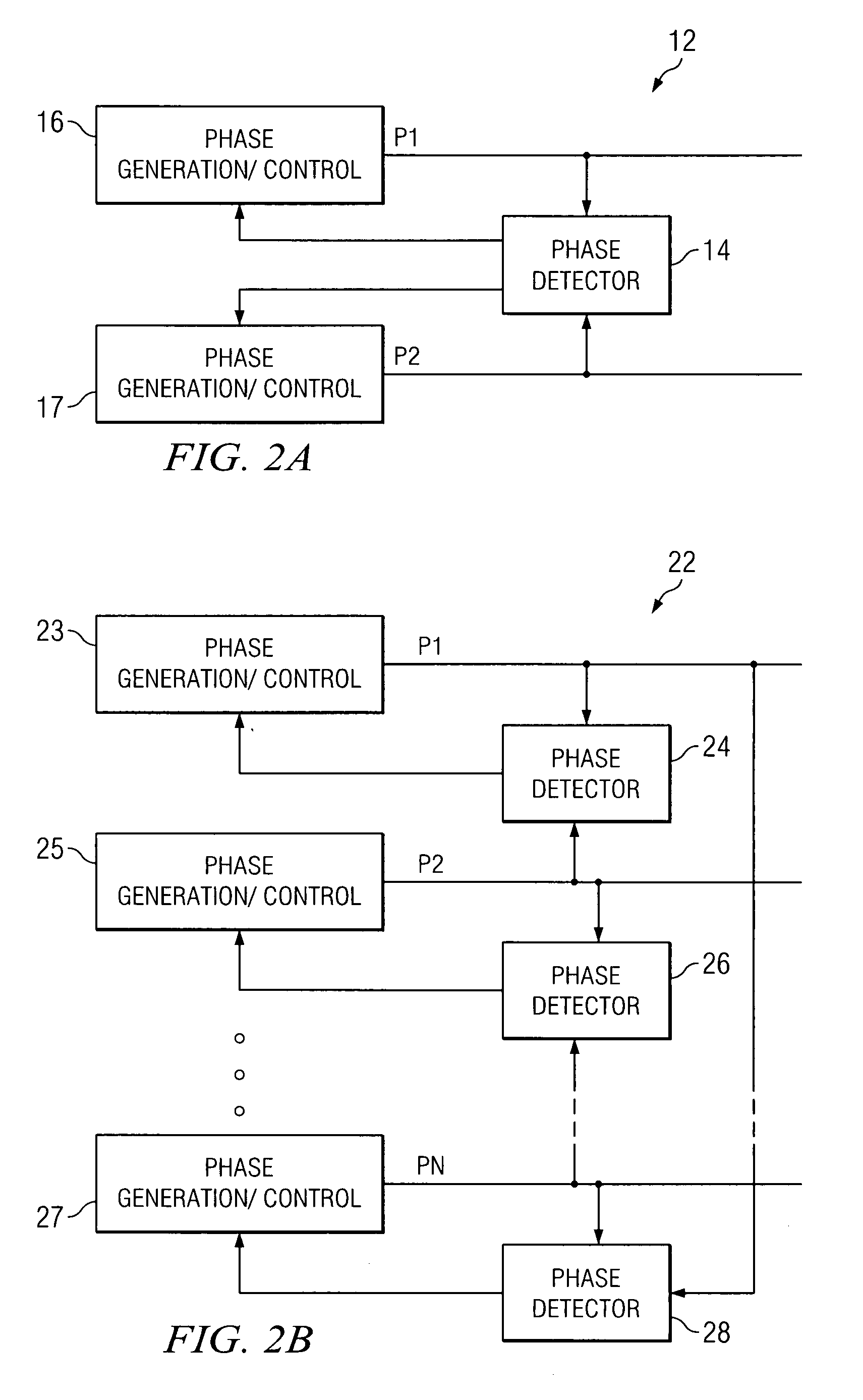
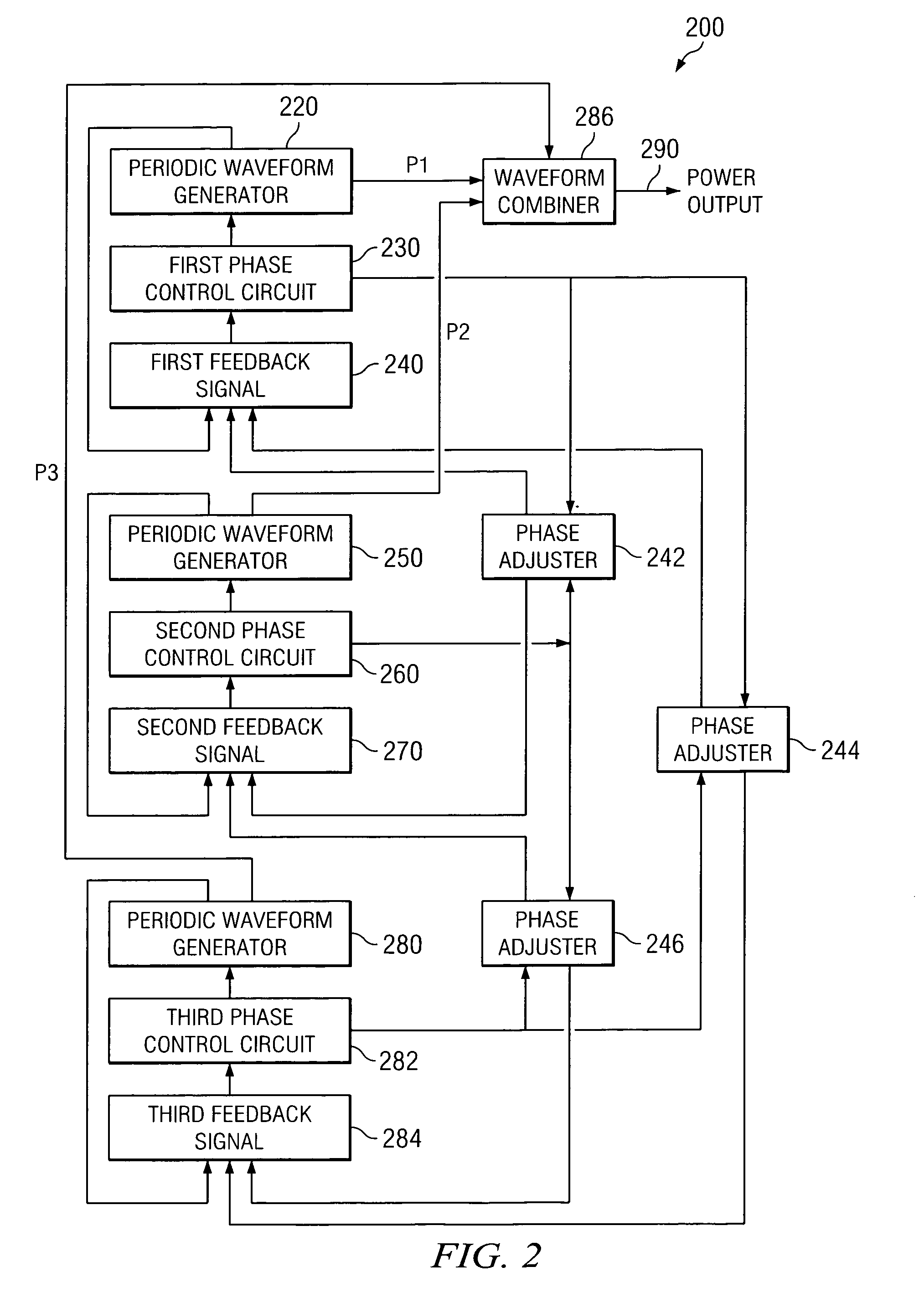
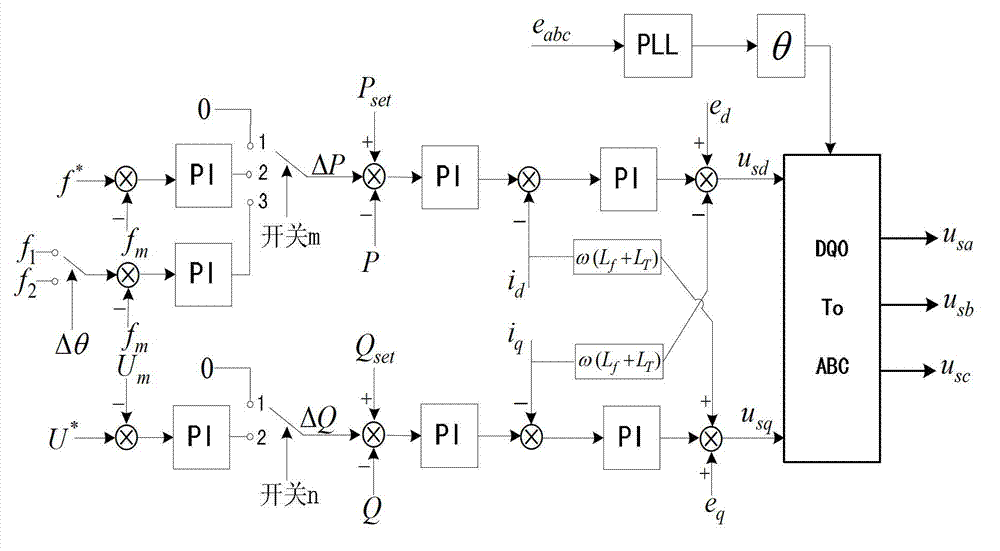
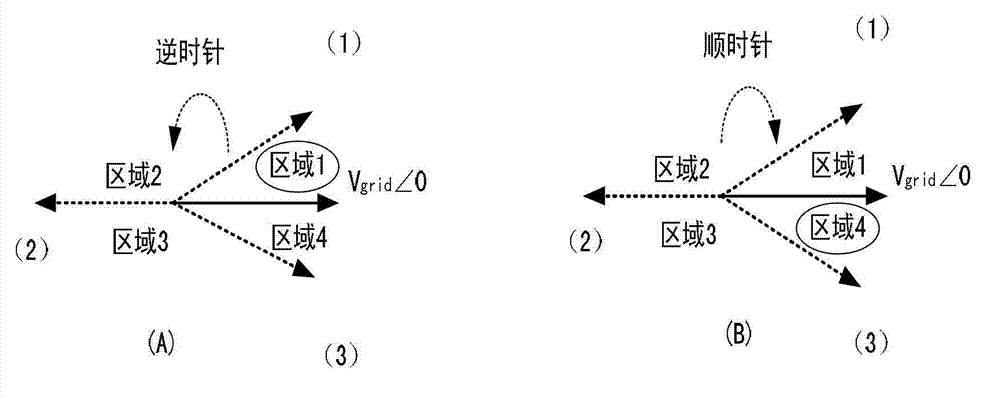
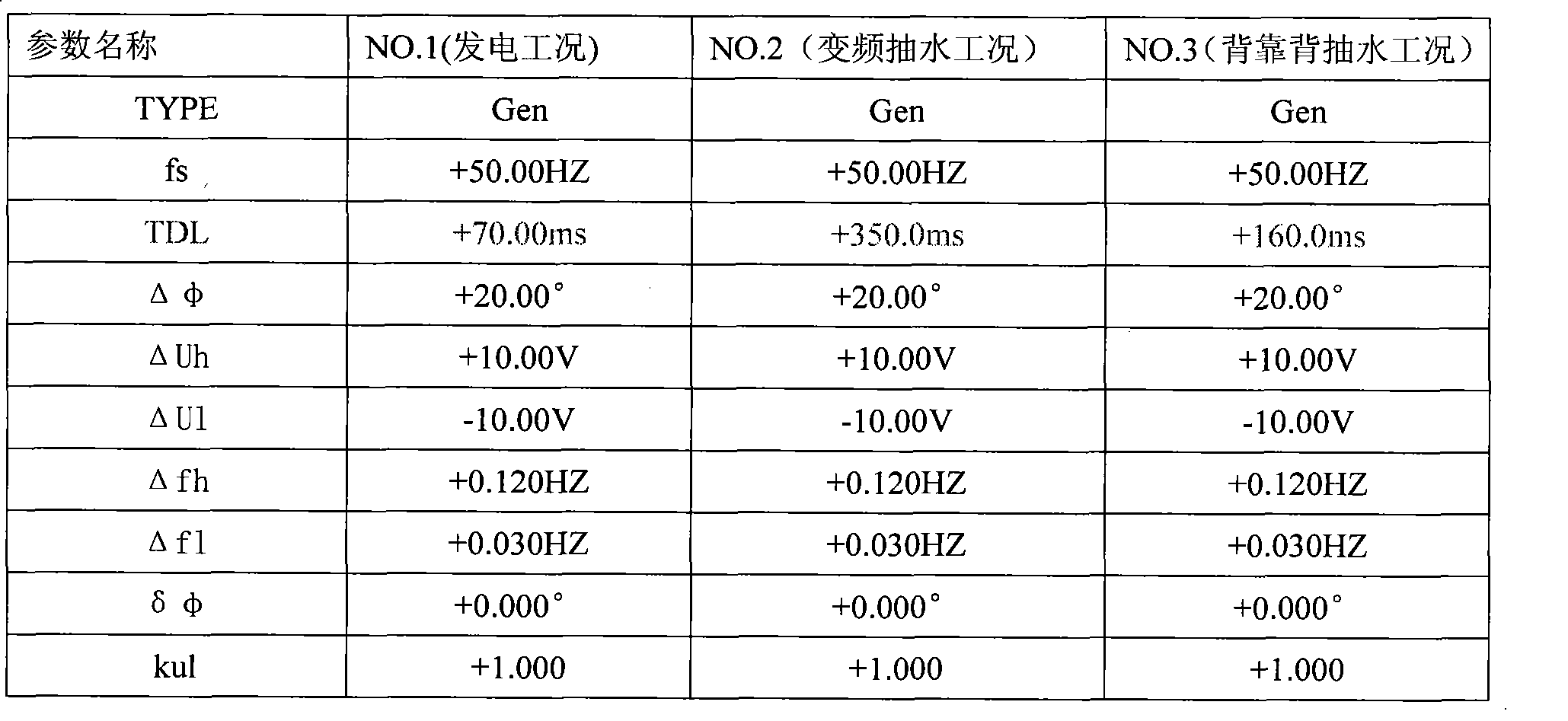
Droop control system for grid-connected synchronization
InactiveUS20130073109A1Minimizes voltage fluctuationGood effectMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlProcess moduleElectric power system
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
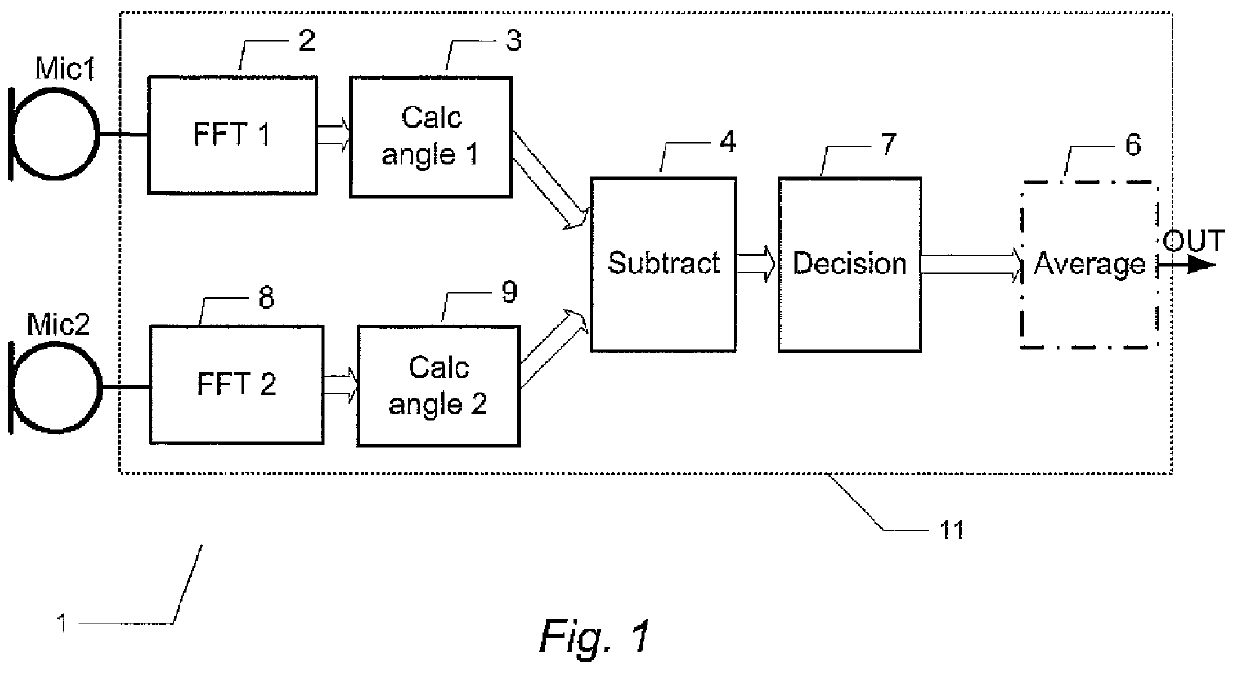
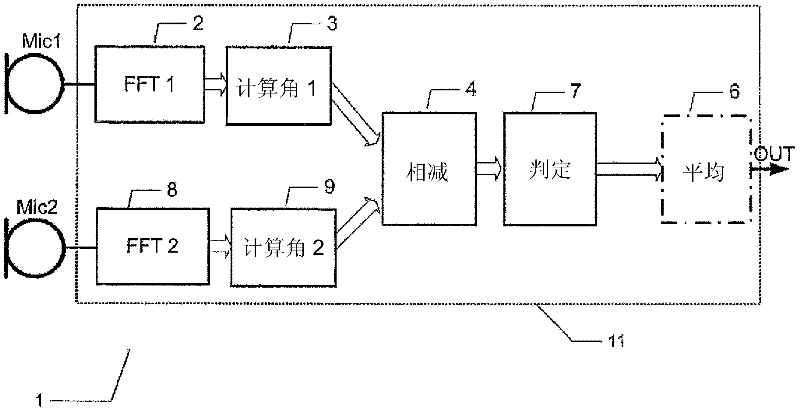
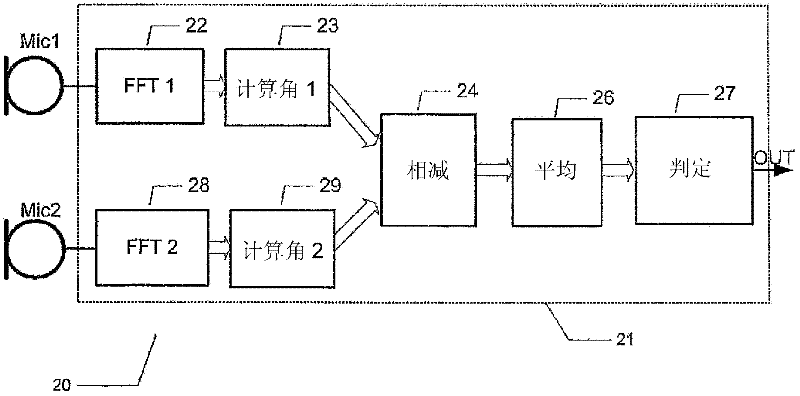
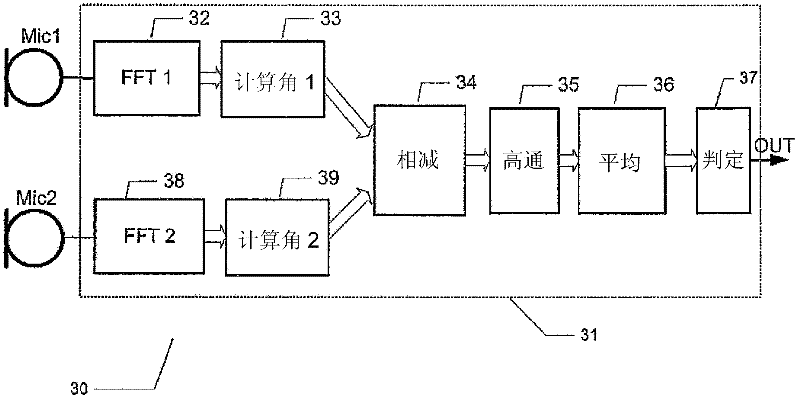
Wind noise detection method and system
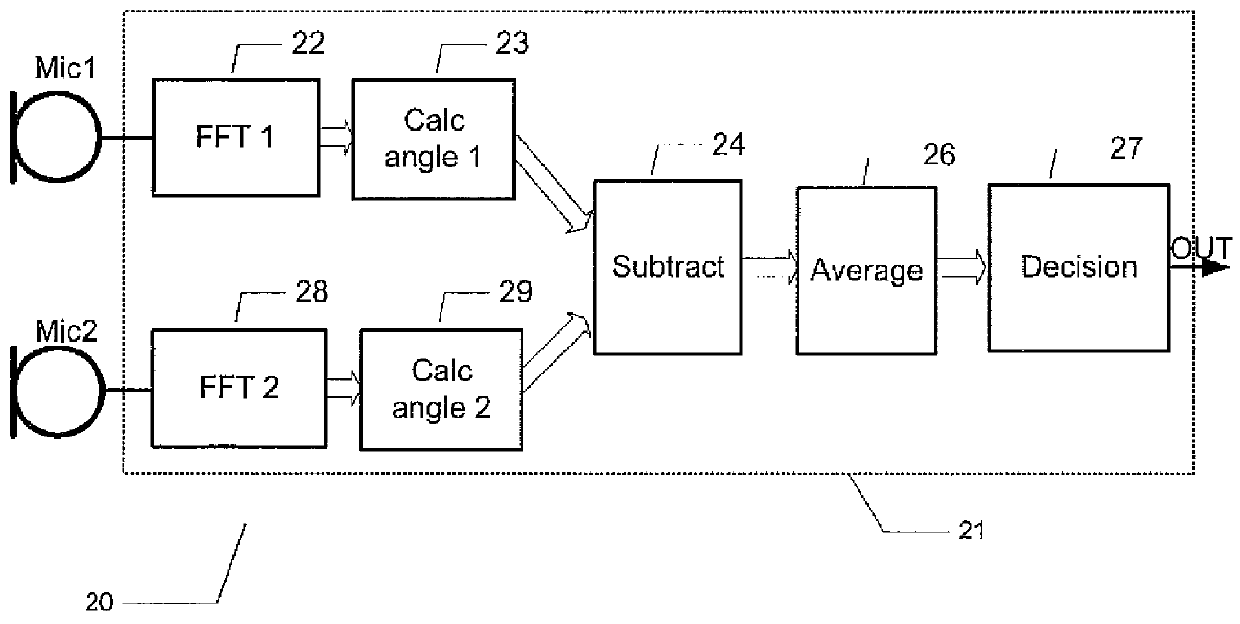
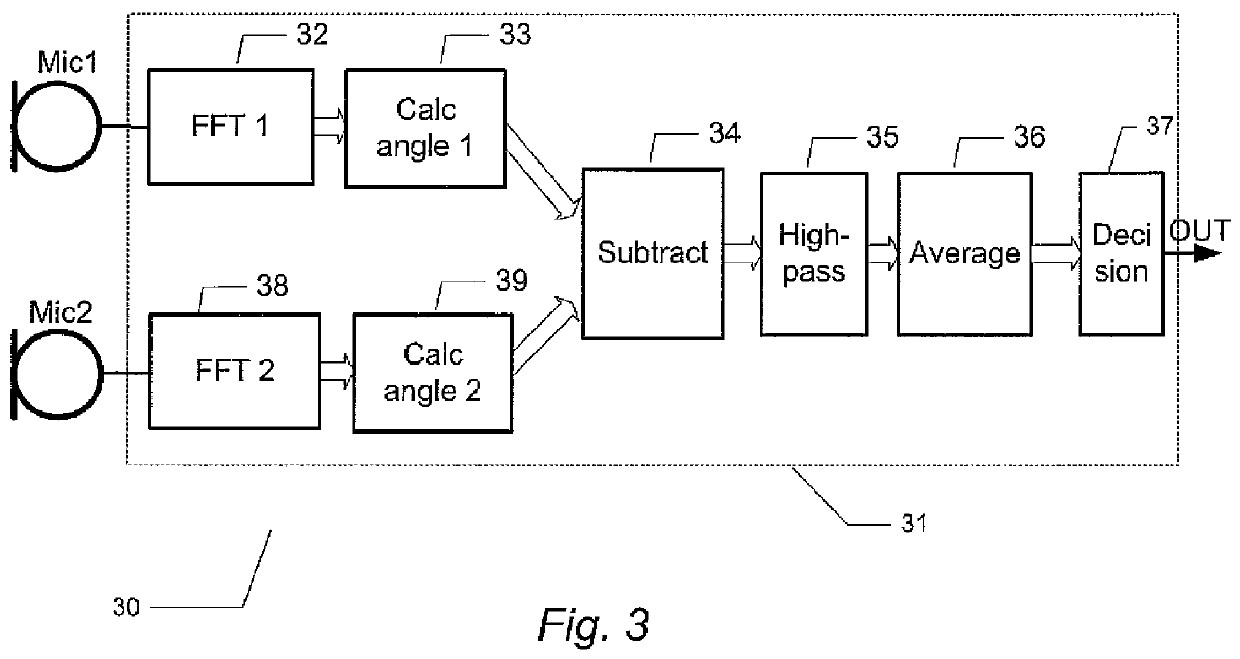
ActiveUS20120148067A1Save computing resourcesReduce power consumptionMicrophonesMicrophones signal combinationPhase differencePhase angle difference
The present invention relates to a multi-microphone system and method adapted to determine phase angle differences between a first microphone and a second microphone signal to detect presence of wind noise.
Owner:INVENSENSE
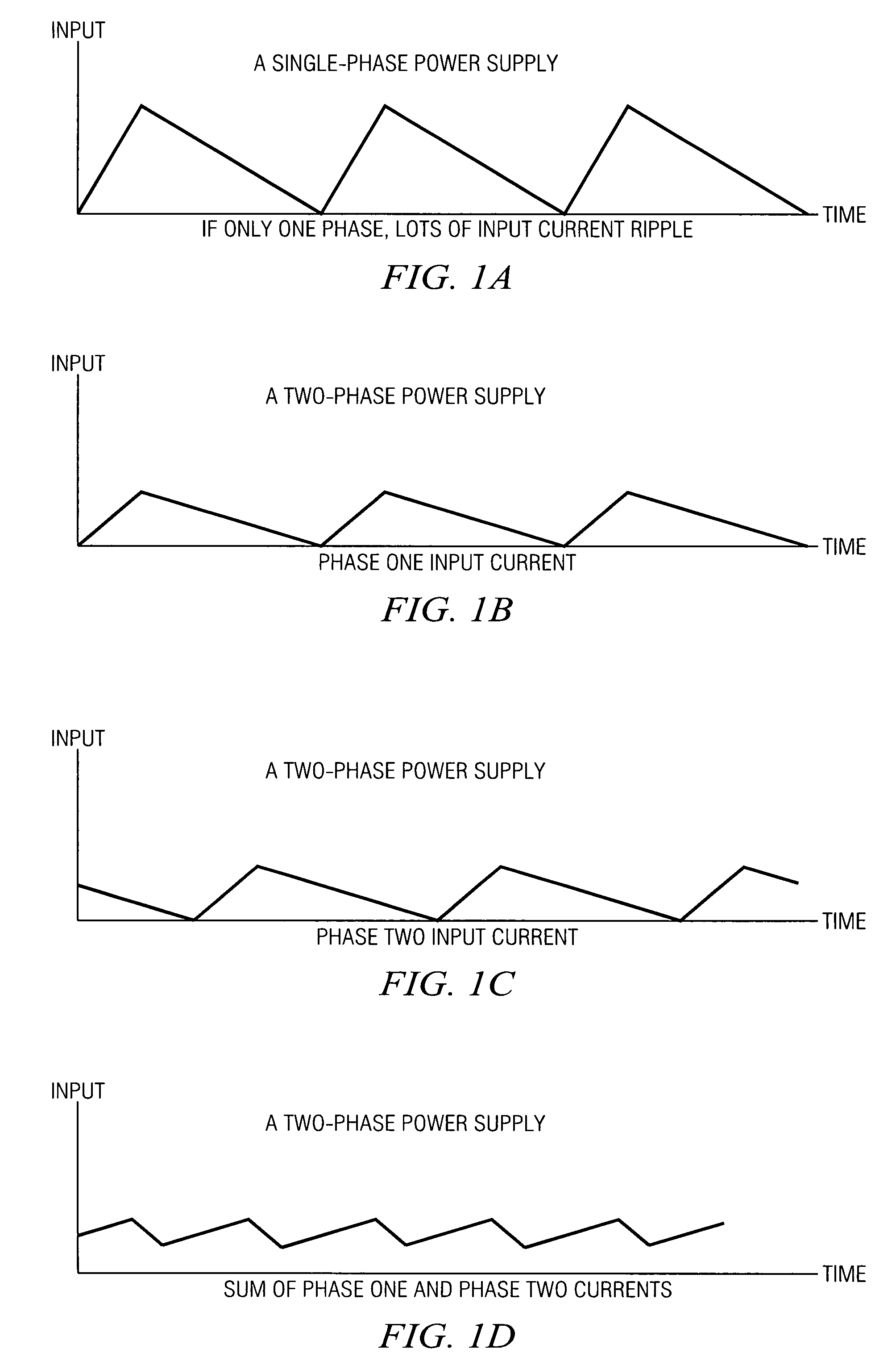
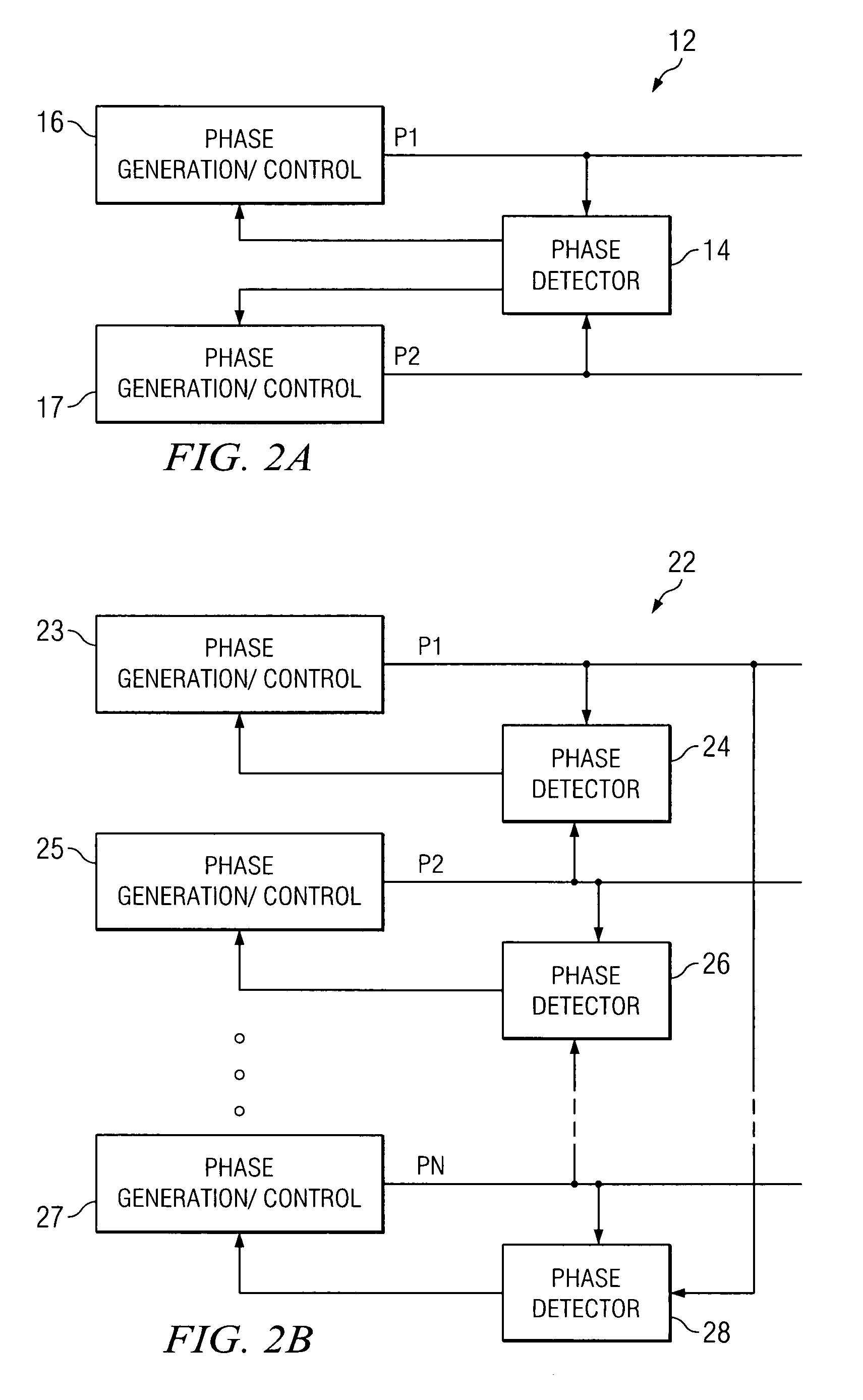
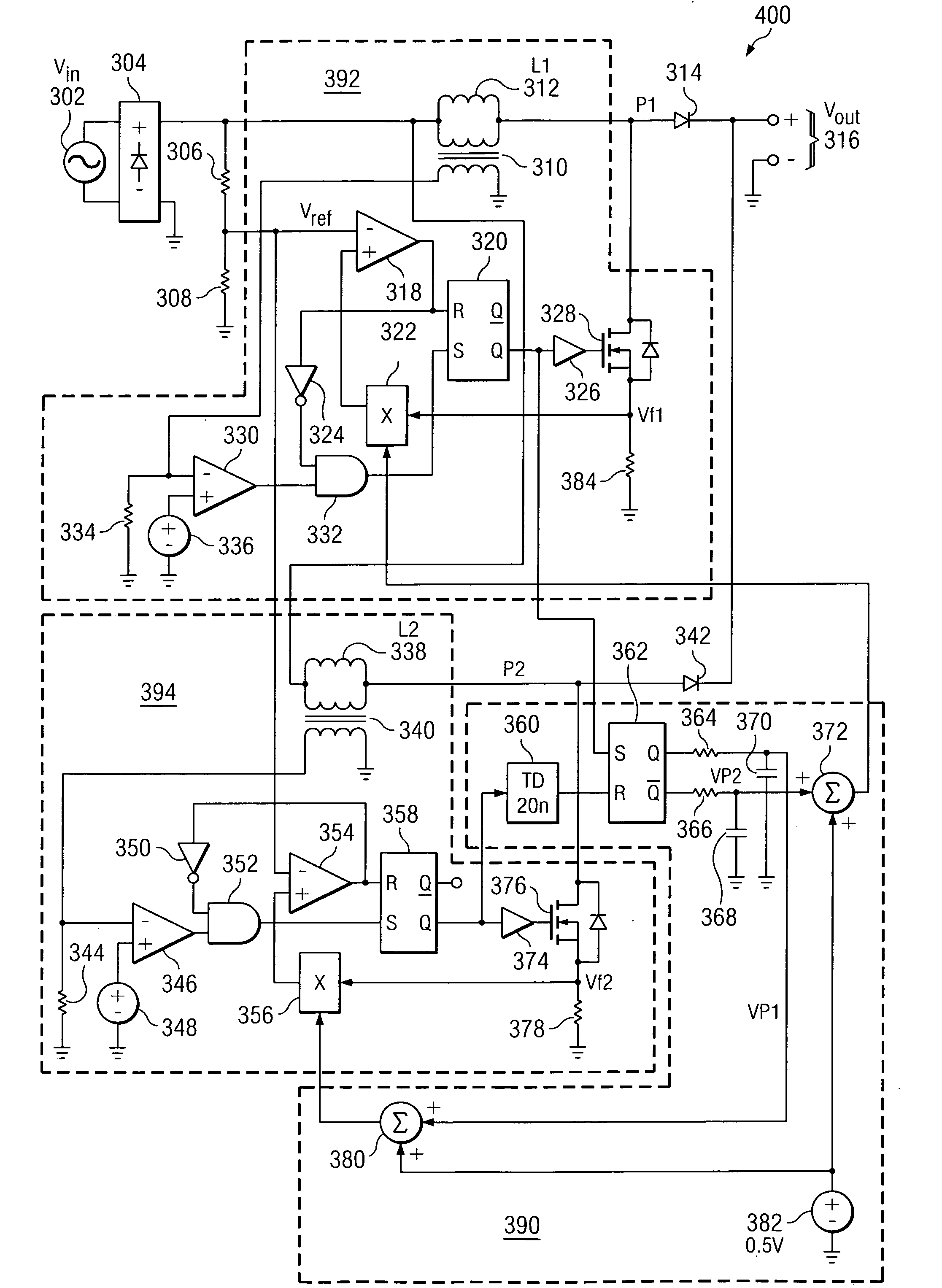
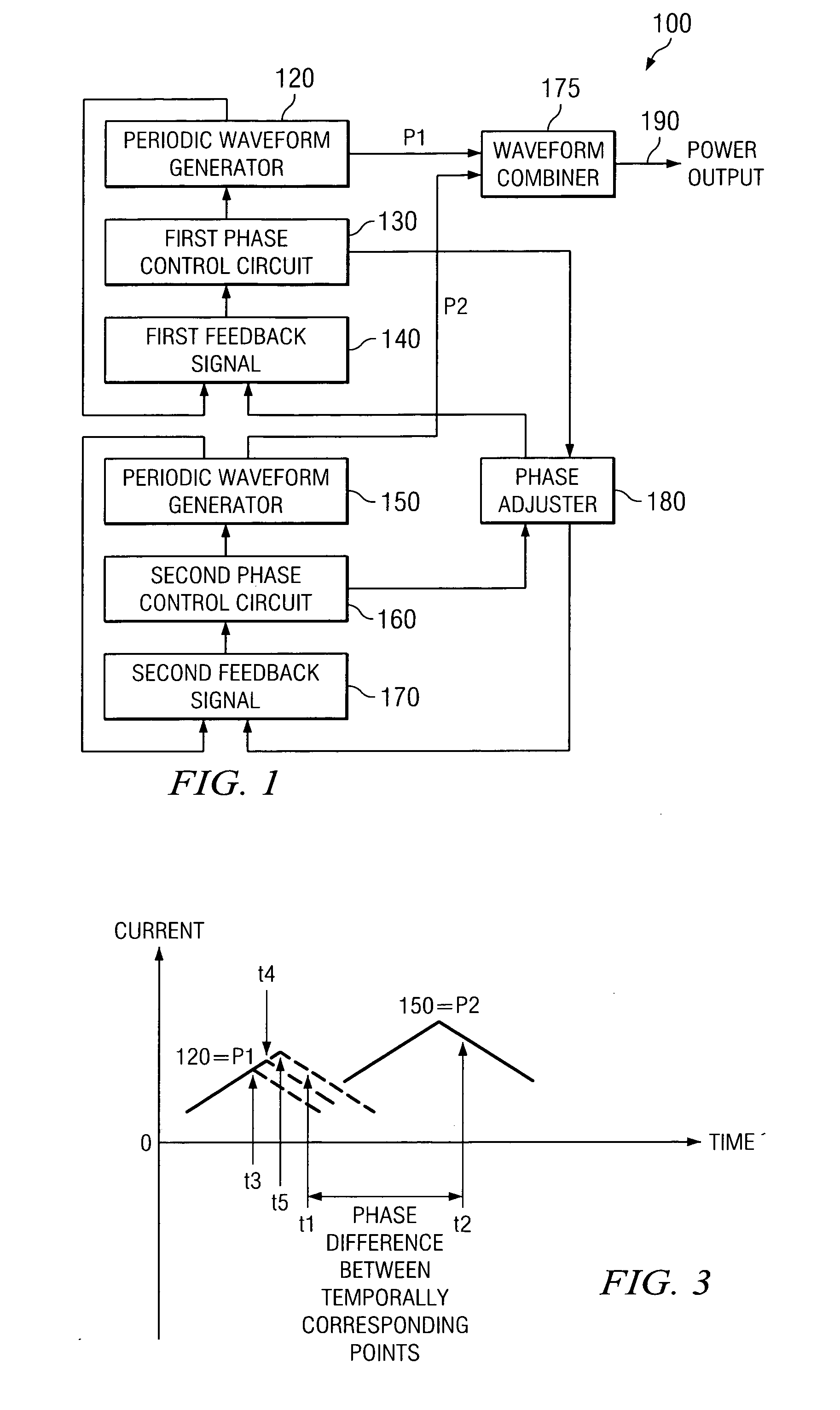
Method and apparatus for multi-phase power conversion
ActiveUS20070253223A1Improve circuit efficiencyReduce and eliminate impactEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionEngineeringSwitching frequency
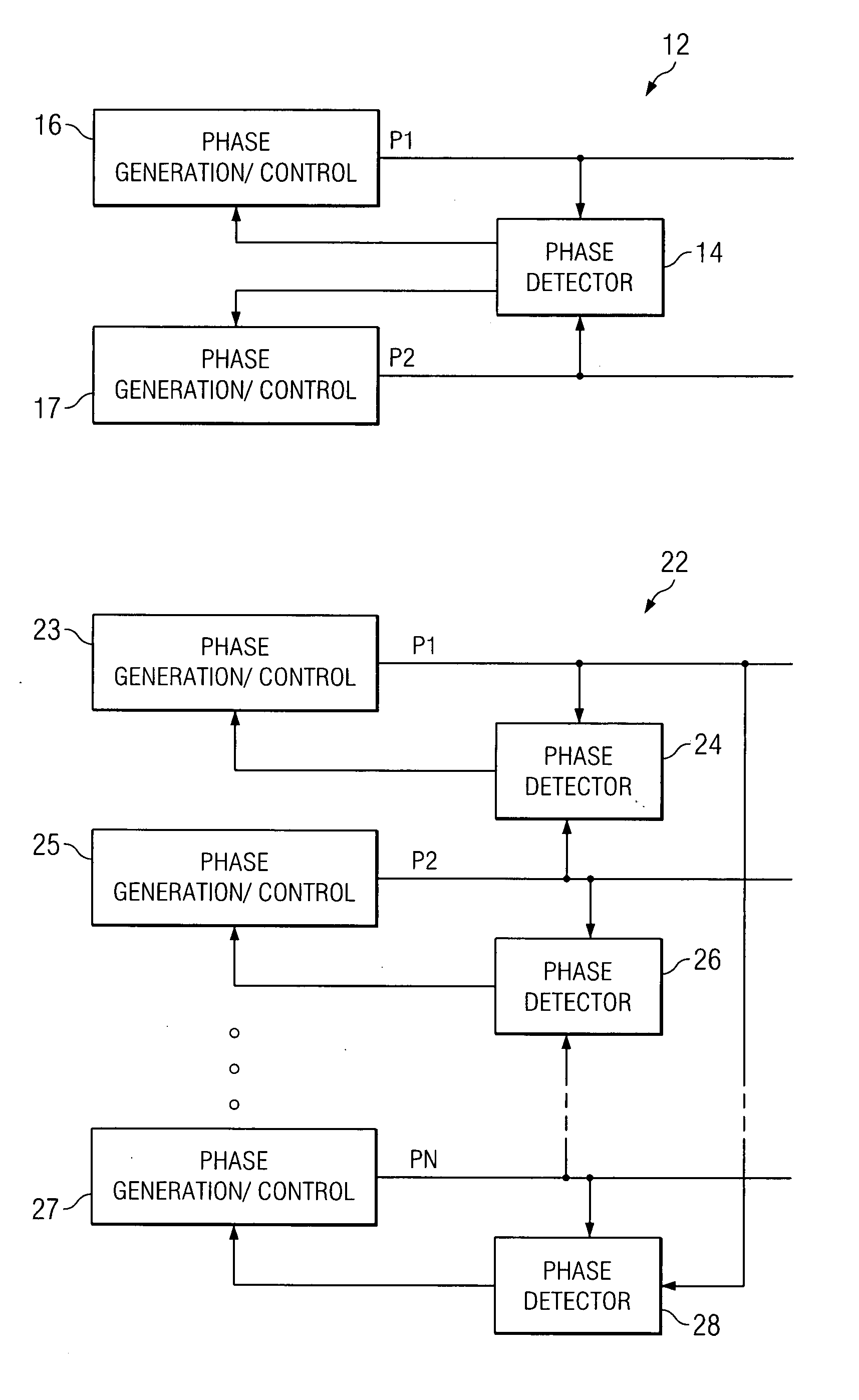
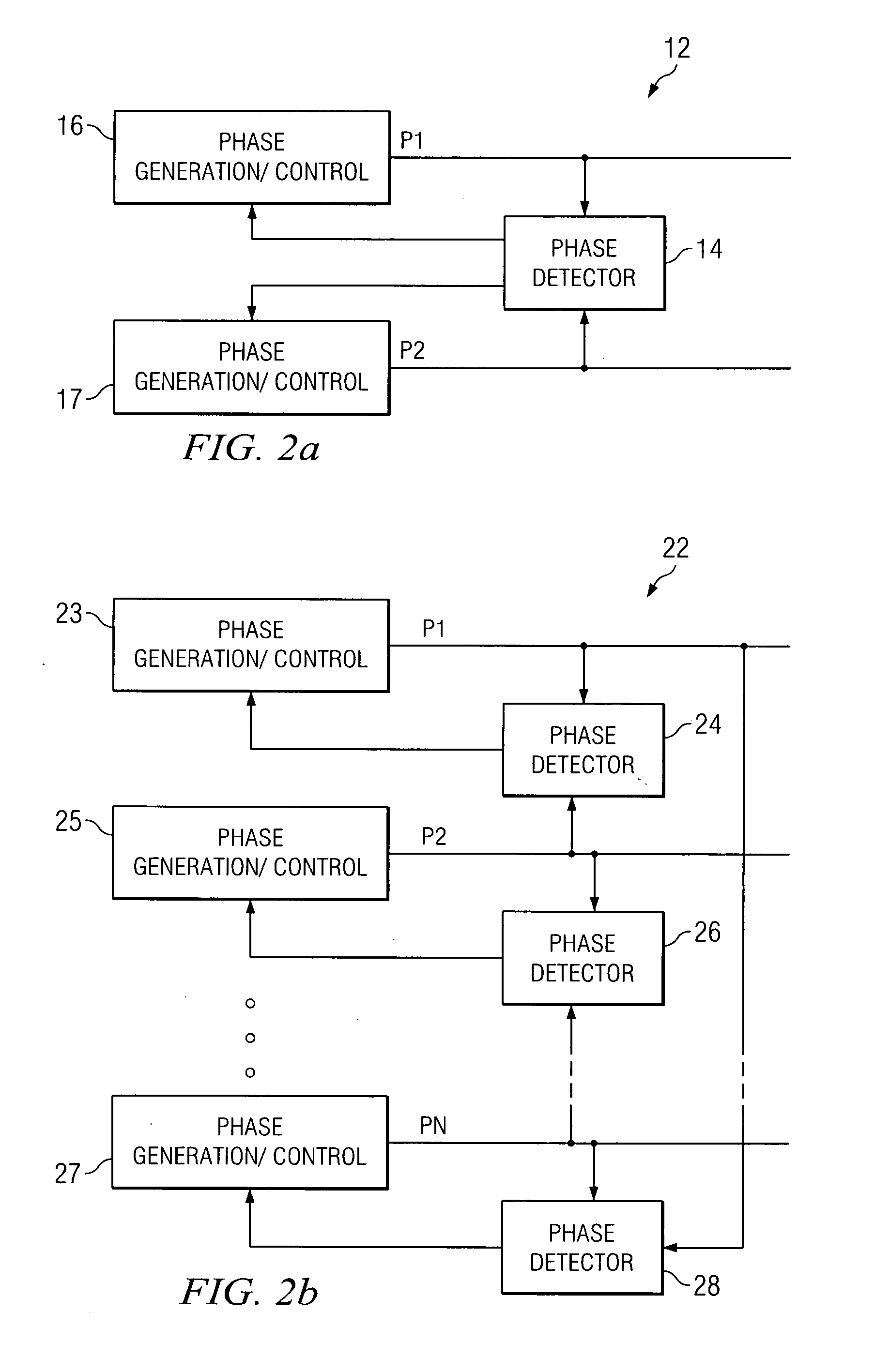
A system and method for power conversion synchronizes multiple phases at a desired phase angle difference. The power conversion involves variable frequency switching, fixed on-time and provides power factor correction. A relative measure of a phase angle difference between two phases permits each phase to be controlled to obtain the desired phase angle difference. The power conversion involves transition mode switching to help reduce switching losses. A phase angle difference detector may be provided for each phase. The various phases may have different inherent frequencies that vary with switching frequency, and are synchronized to an average frequency. Current measures can be taken with a single component, such as a resistor. A maximum frequency control limits period width to avoid high frequency switching. An added switch on time improves input voltage crossover distortion. One or more phases can be deactivated in light load conditions.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Apparatus and method for determining a faulted phase of a three-phase ungrounded power system
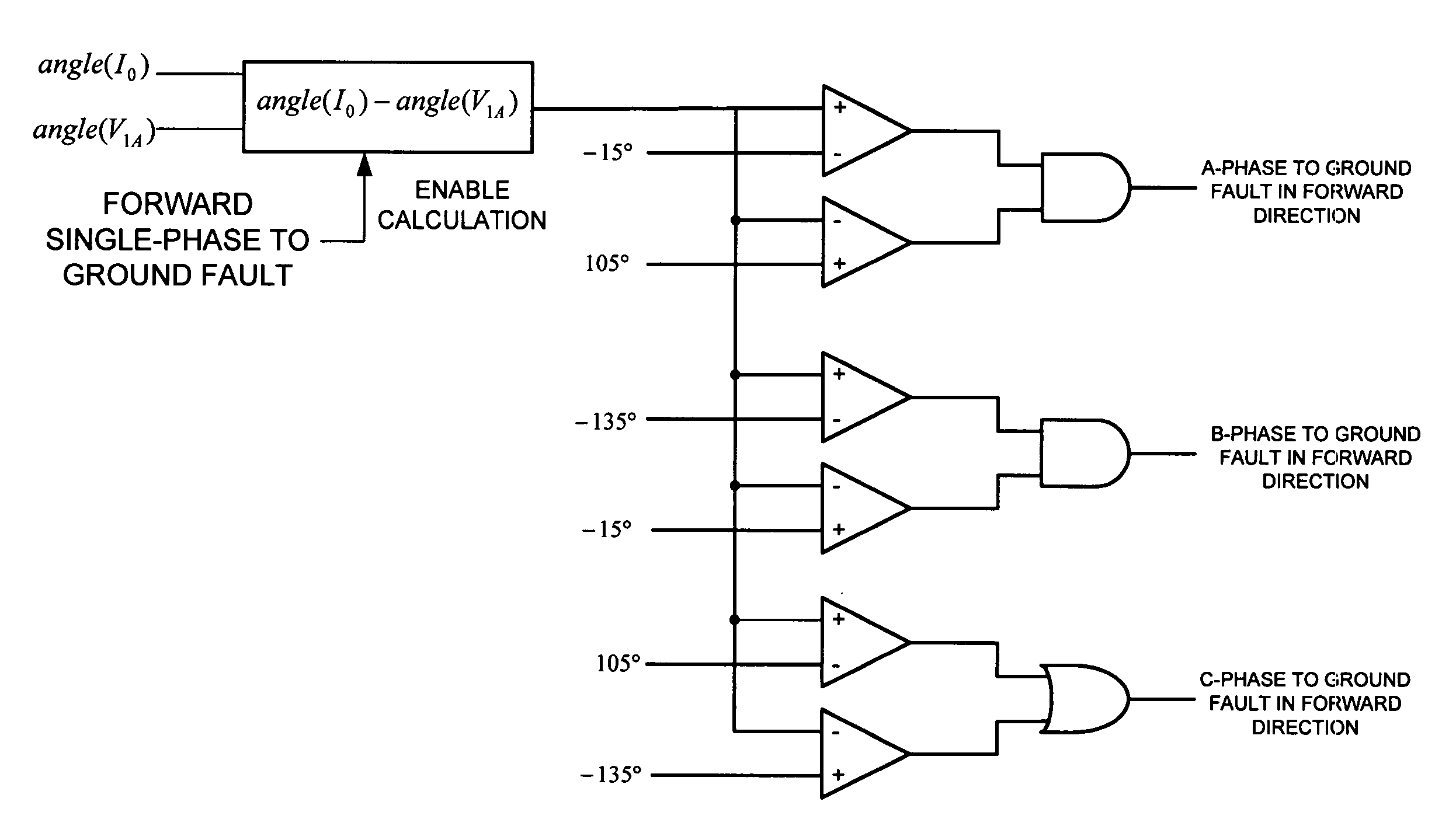
ActiveUS20070085549A1Assist understandingShort-circuit testingEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionPhase angle differenceEngineering
Provided is an apparatus and method for determining a faulted phase resulting from a fault in a three-phase ungrounded power system. The method includes comparing a phase angle of an operating phasor to a phase angle of a fixed reference phasor. The operating phasor is derived from a digitized signal sample of a plurality of measured signals of the power system. The method also includes comparing a phase angle difference between the operating phasor and the fixed reference phasor to at least one threshold to determine the faulted phase. The fixed reference phasor may be a phase-to-phase voltage or a positive sequence voltage of the plurality of measured signals of the power system. The operating phasor may be a zero sequence current, a zero sequence voltage or a combination of a zero sequence current and a zero sequence voltage of the plurality of measured signals of the power system.
Owner:SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES
Flow meter with a rectifying module having a plurality of mesh members
ActiveUS7415895B2Conveniently performedThe effect is accurateFluid dynamicsVolume meteringPhase angle differenceSmall hole
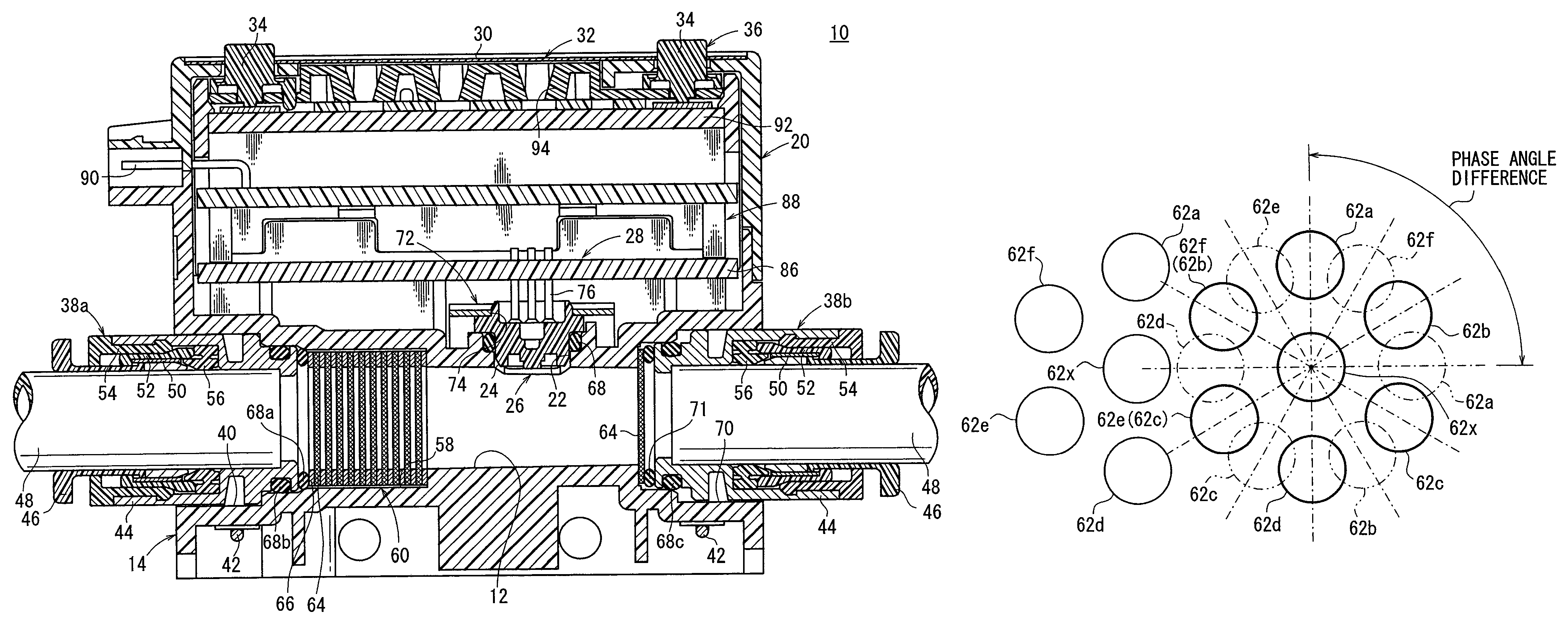
A rectifying module is arranged on an upstream side of a flow passage containing a flow velocity sensor. The rectifying module includes mesh members each having a plurality of circular small holes and ring-shaped spacers, wherein the mesh members and the spacers are alternately stacked in an axial direction and integrally joined to one another by means of thermal diffusion bonding. The mesh members have identical structures, in which the plurality of small holes are arranged concentrically at angles of separation of 60 degrees in the circumferential direction about the center of a reference small hole. The small holes are formed over the entire surface of the mesh member continuous with adjoining other small holes. The small holes of one mesh member and another mesh member adjacent thereto in the axial direction are arranged so as to have a phase angle difference of 90 degrees in the circumferential direction.
Owner:SMC CORP
Method and apparatus for multi-phase power conversion
ActiveUS7706151B2Reduce switching lossesTempo syncEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionSwitching frequencyEngineering
A system and method for power conversion synchronizes multiple phases at a desired phase angle difference. The power conversion involves variable frequency switching, fixed on-time and provides power factor correction. A relative measure of a phase angle difference between two phases permits each phase to be controlled to obtain the desired phase angle difference. The power conversion involves transition mode switching to help reduce switching losses. A phase angle difference detector may be provided for each phase. The various phases may have different inherent frequencies that vary with switching frequency, and are synchronized to an average frequency. Current measures can be taken with a single component, such as a resistor. A maximum frequency control limits period width to avoid high frequency switching. An added switch on time improves input voltage crossover distortion. One or more phases can be deactivated in light load conditions.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
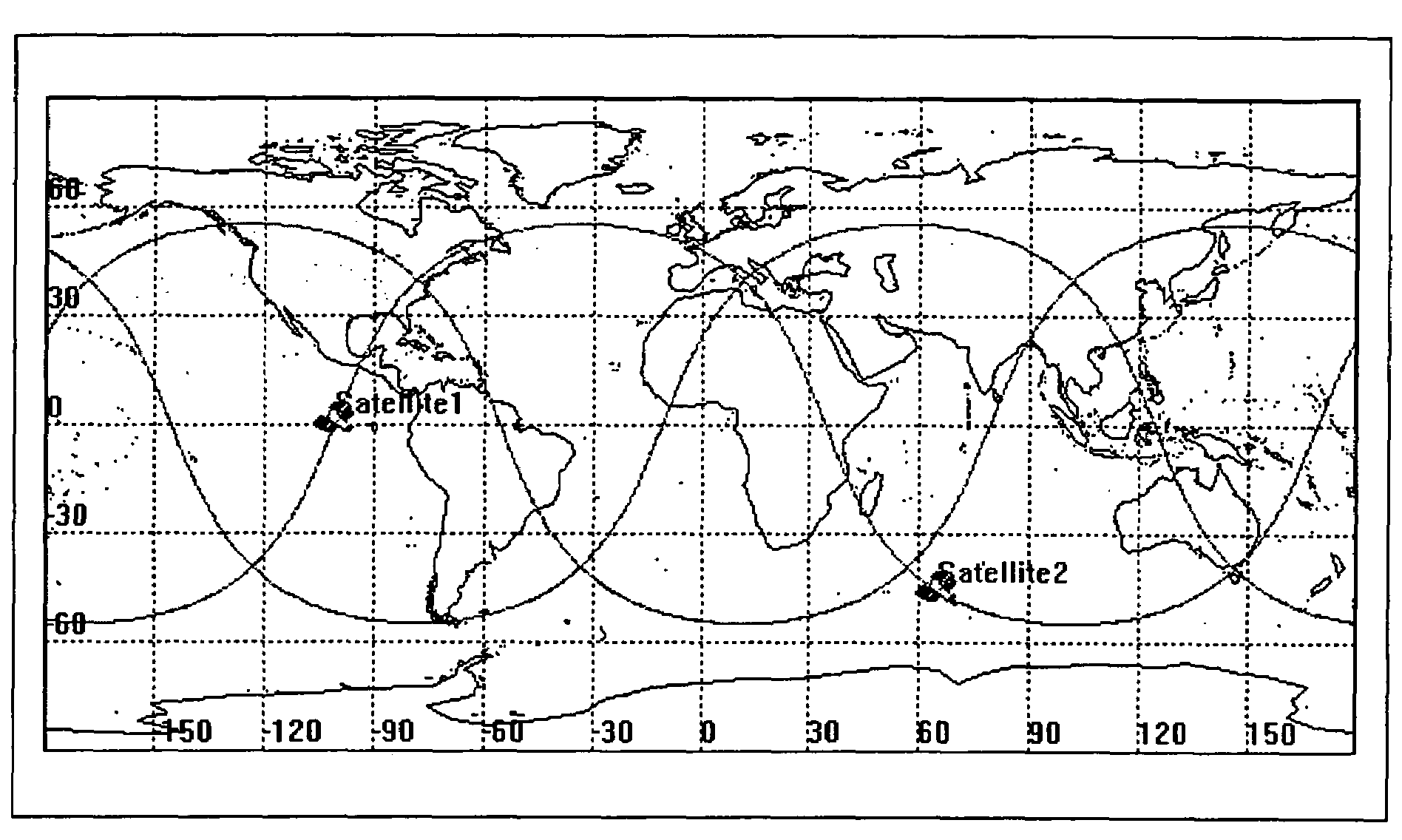
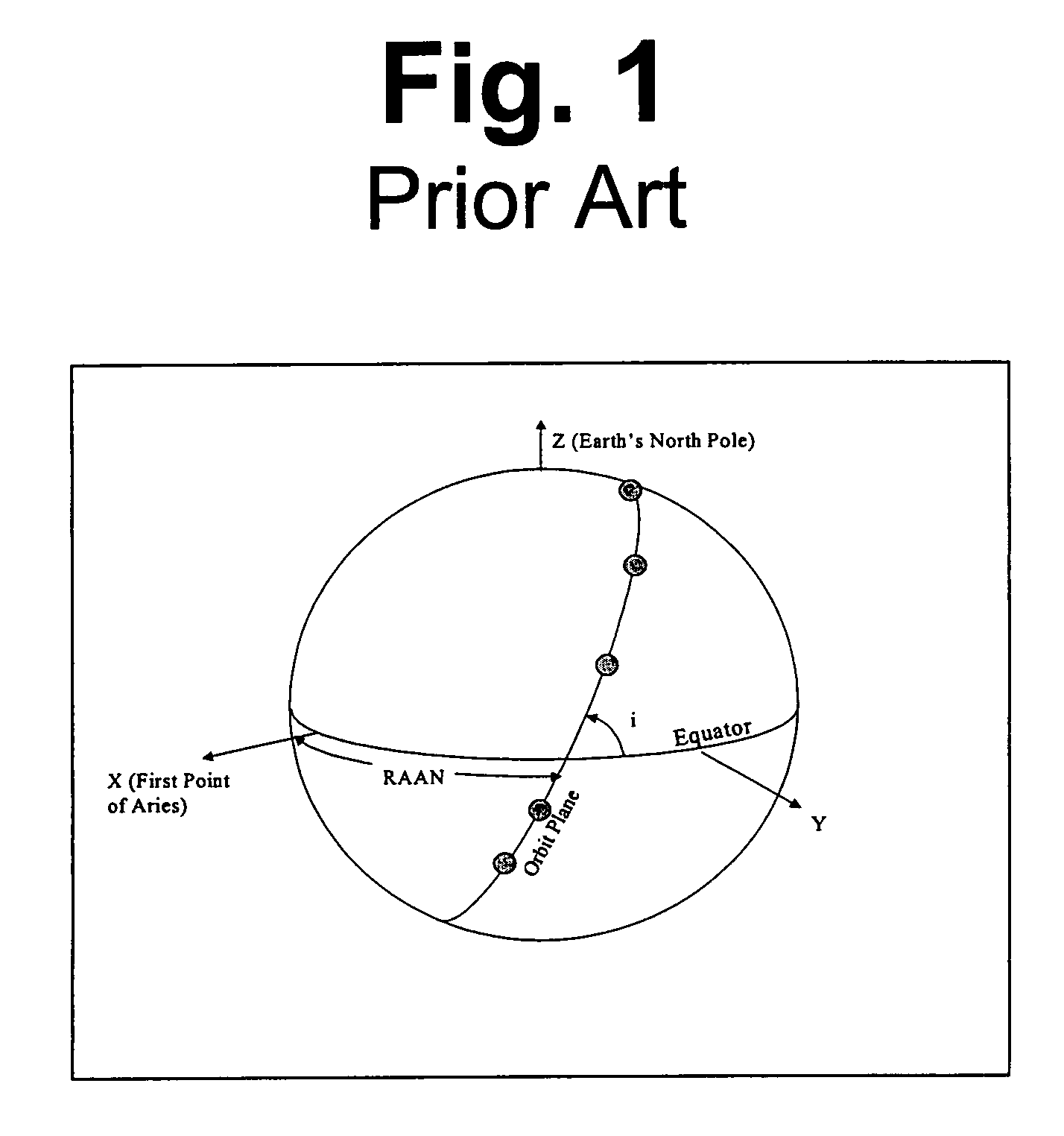
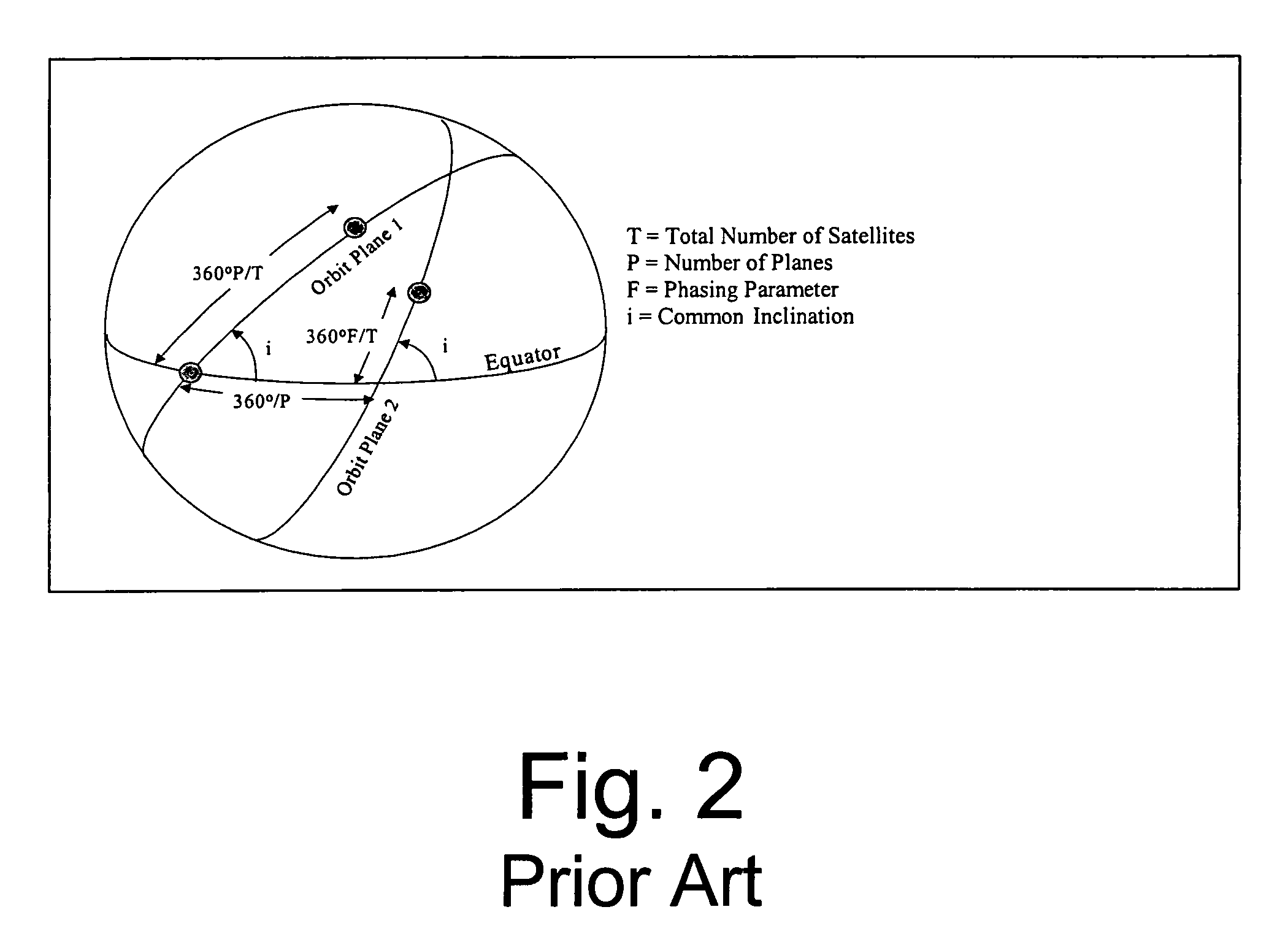
Space based change detection using common ground track constellations
InactiveUS7270299B1Minimal image blurring and distortionReduce in quantityCosmonautic partsArtificial satellitesEarth's rotationPhase angle difference
A new approach for designing satellite constellations whereby each satellite follows a common ground track is being proposed for performing high-precision change detection imagery for long periods of time. By precisely prescribing the orbital parameters, i.e., the relationship between the right ascension of the ascending nodes (RAAN) and the phase angle difference between successive satellites, for example, sharpened change detection images may be taken from successive satellites in the constellation without the need to process out blurring by any special image re-working software. The relationship between the orbital parameters of the satellites is precisely tuned to the earth's rotation rate for the altitude of the satellites. A reduction in the total satellite count is achievable due to tiling the satellite coverage in near optimal arrangements. Such high-precision change detection imaging by successive satellites in orbit around the earth is at least useful in the detection of underground facilities activities and the detection of slow moving objects.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
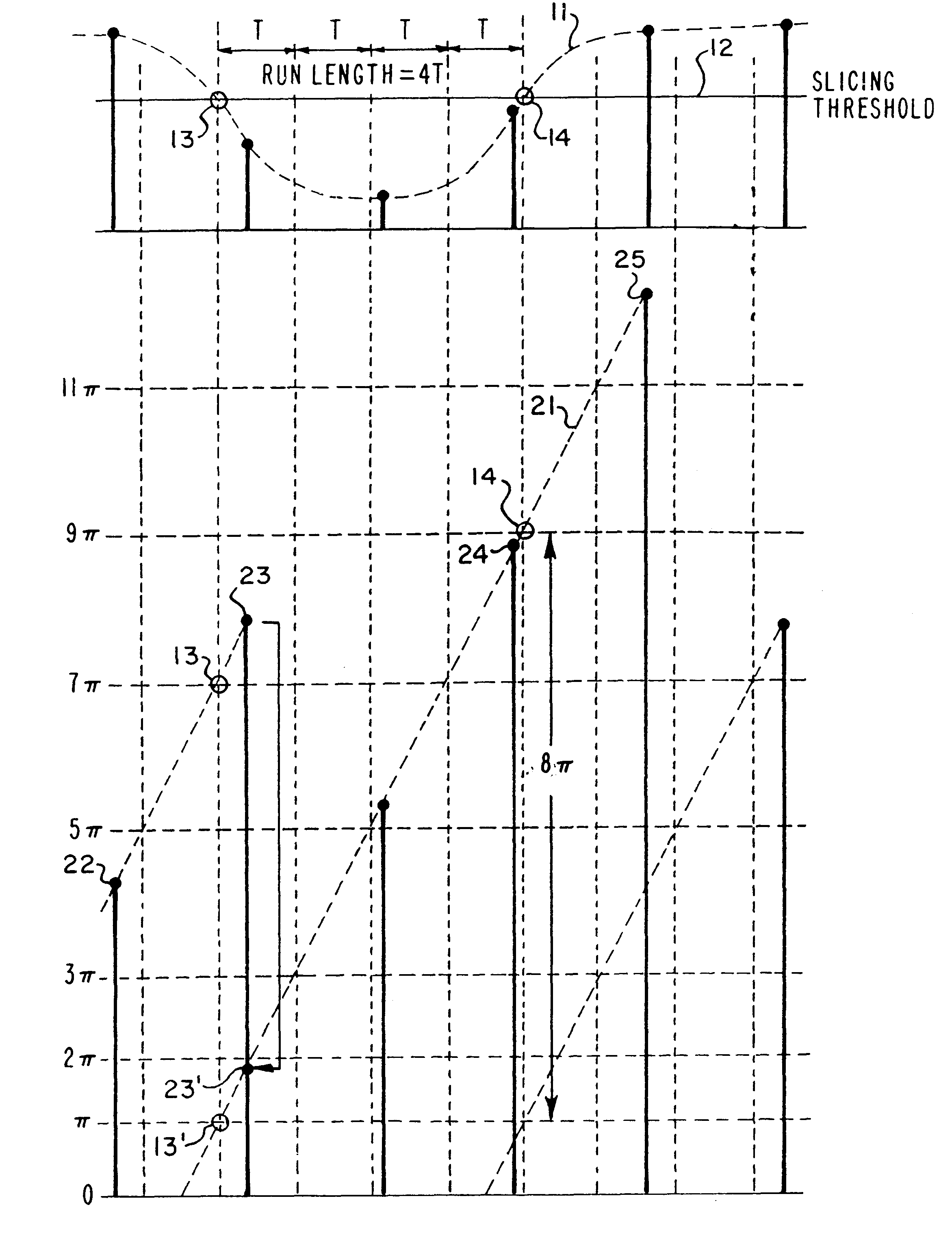
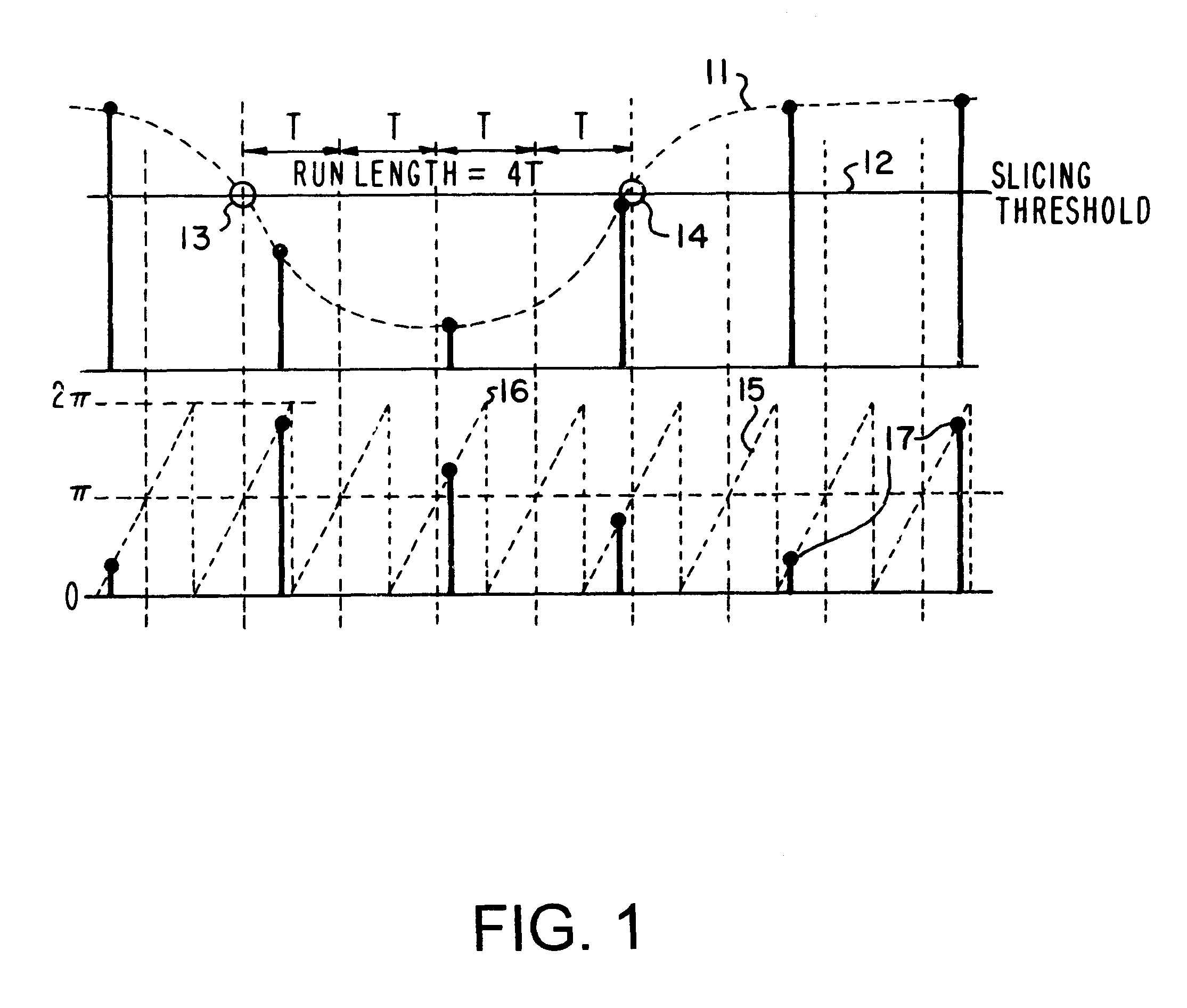
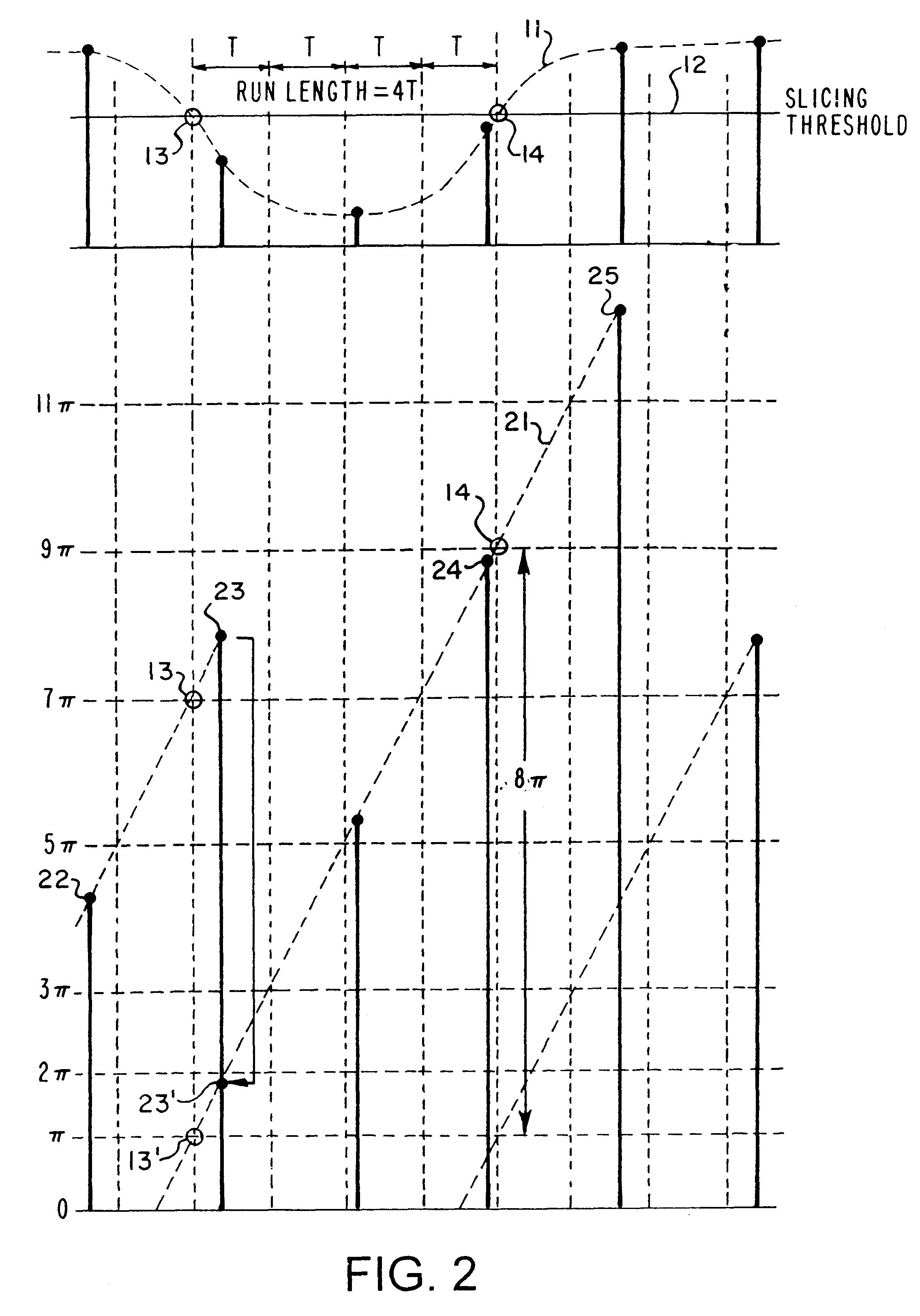
Pulse run-length measurement for HF data signal by dividing accumulated phase difference between first and second zero-crossings by single-cycle range using multiple cycle range sawtooth waveform
InactiveUS6389548B1Modulated-carrier systemsDigital data processing detailsPhase differenceLength measurement
A system and method for accurately measuring a pulse run length in a high frequency (HF) data signal while utilizing a low analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) sampling rate. Four bits are added to the most significant end of an oscillator's accumulator register so that the oscillator generates a sawtooth clock waveform ranging in phase from zero (0) to 32pi radians. An interpolator detects a first zero-crossing transition of the HF data signal at the leading edge of the pulse run length, and a phase detector measures a first phase increment at that time. The MSBs of the accumulator register is then initialized to place the measured first phase increment in a range between zero (0) and 2pi radians. The accumulator register then accumulates phase increments until the interpolator detects a second zero-crossing transition of the HF data signal at the trailing edge of the pulse run length, and the phase detector measures a second phase increment when the second zero-crossing transition is detected. An accumulated phase difference is calculated by subtracting the initialized first phase increment from the measured second phase increment. The pulse run length is then obtained by dividing the accumulated phase difference by 2pi.
Owner:CEVA IRELAND +1
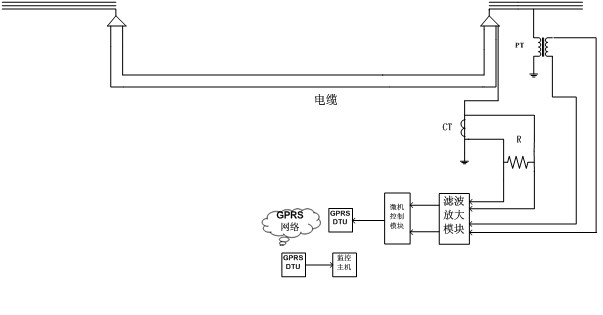
On-line monitoring method and device for insulating state of power cable
InactiveCN101975914AAffect operational safetyTesting dielectric strengthPower cablePhase angle difference
The invention discloses on-line monitoring method and device for the insulating state of a power cable. Two factors are mainly considered for the monitoring of the insulating state of the cable, wherein one factor is a low-frequency current value generated by low-frequency oscillation of a power system; and the other factor is a cable medium loss factor value acquired by calculating the phase angle difference between a low-frequency voltage signal and the current signal, which is generated by the oscillation of the power system and seeking an arctangent value. If any one of the two factors is greater than the corresponding insulated safety threshold, the cable has the insulated ageing hidden trouble. By using the low-frequency signal to monitor, the invention has high detection precision and can remarkably reflect the ageing state of the cable; and in addition, the extra superposition power supply is avoided, so that the invention avoids the damage to the safety of a power grid.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and apparatus for power converters having phases spaced at desired phase angles
ActiveUS20070253224A1Reduce switching lossesTempo syncEfficient power electronics conversionAC/AC convertorsPhase angle differencePhase space
A system and method for power conversion synchronizes multiple phases at a desired phase angle difference. The power conversion involves variable frequency switching, fixed on-time and provides power factor correction. A relative measure of a phase angle difference between two phases permits each phase to be controlled to obtain the desired phase angle difference. The power conversion involves transition mode switching to help reduce switching losses. A phase angle difference detector may be provided for each phase. The various phases may have different inherent frequencies that vary with switching frequency, and are synchronized to an average frequency.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
System and method for synchronizing multiple oscillators
ActiveUS20070262823A1Tempo syncReduce complexityPulse automatic controlPulse generation by logic circuitsPhase angle differencePhysics
A system and method for synchronizing an oscillator with multiple phases at a desired phase angle difference. A relative measure of a phase angle difference between two phases permits each phase to be controlled to obtain the desired phase angle difference. The various phases may have different inherent frequencies that are synchronized to a common frequency such as an average of the different frequencies.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Adaptive fault section positioning method of power distribution network containing distributed power supply
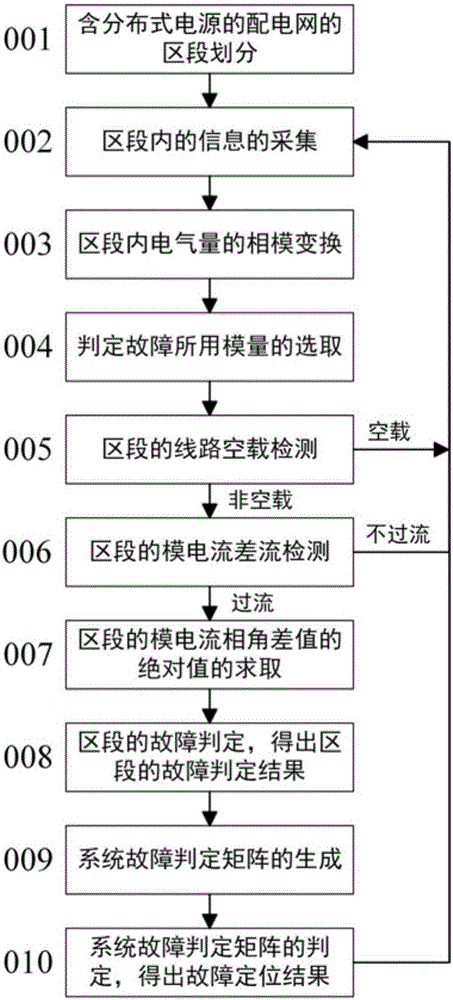
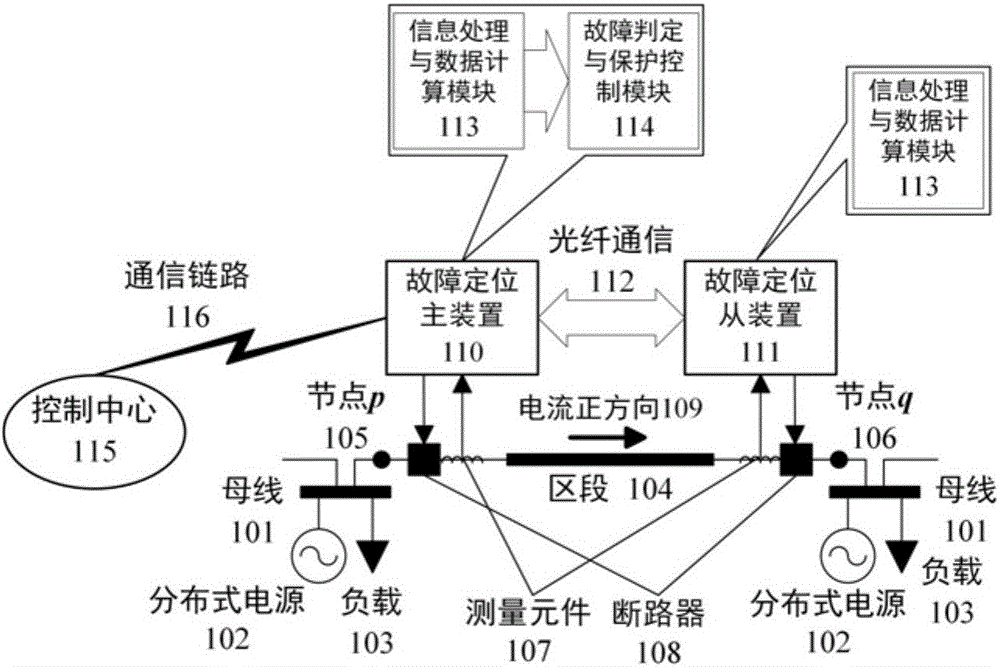
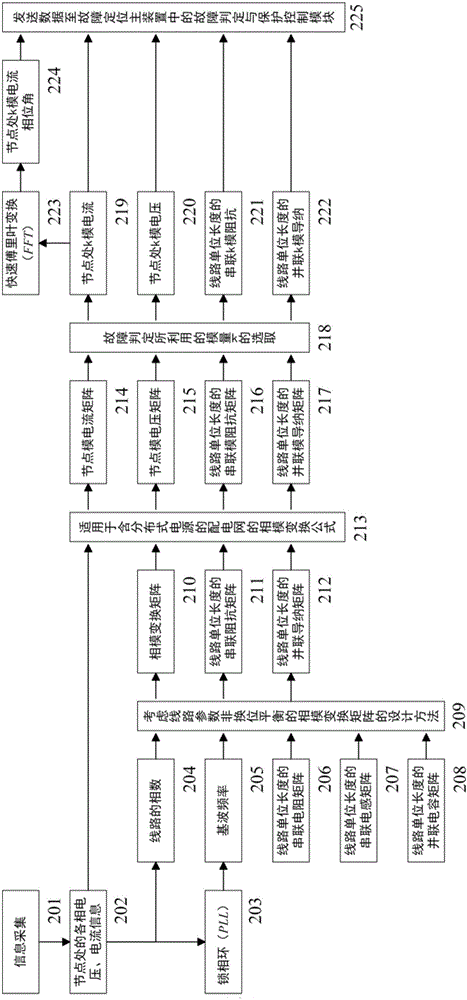
ActiveCN105759173ARapid positioningPrecise positioningFault location by conductor typesInformation technology support systemPhase angle differenceMode transformation
The invention relates to an adaptive fault section positioning method of a power distribution network containing a distributed power supply, and the power distribution network containing the distributed power supply is divided into a plurality of sections with no branches at double ends. Under the condition of knowing line parameters of all the sections, voltage and current information at nodes of both ends of each section is collected, mode voltage, mode current and mode parameters of a line at the nodes are obtained through phase-mode transformation, and Fourier transform is performed on node mode current to obtain a node mode current phase angle. No-load detection of a line and differential current detection of mode current of a section are utilized, only under the condition that the line in the section is loaded and mode current differential current of the section is overflowing is fault judgment of the section started, and through comparison of a mode current phase angle difference value absolute value of the section with a judgment threshold value, a fault judgment result of the section is obtained. Fault judgment results of all the sections in the power distribution network containing the distributed power supply are utilized to generate a system fault judgment matrix, and through judgment of element values in the system fault judgment matrix, the section where a fault point is is obtained.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
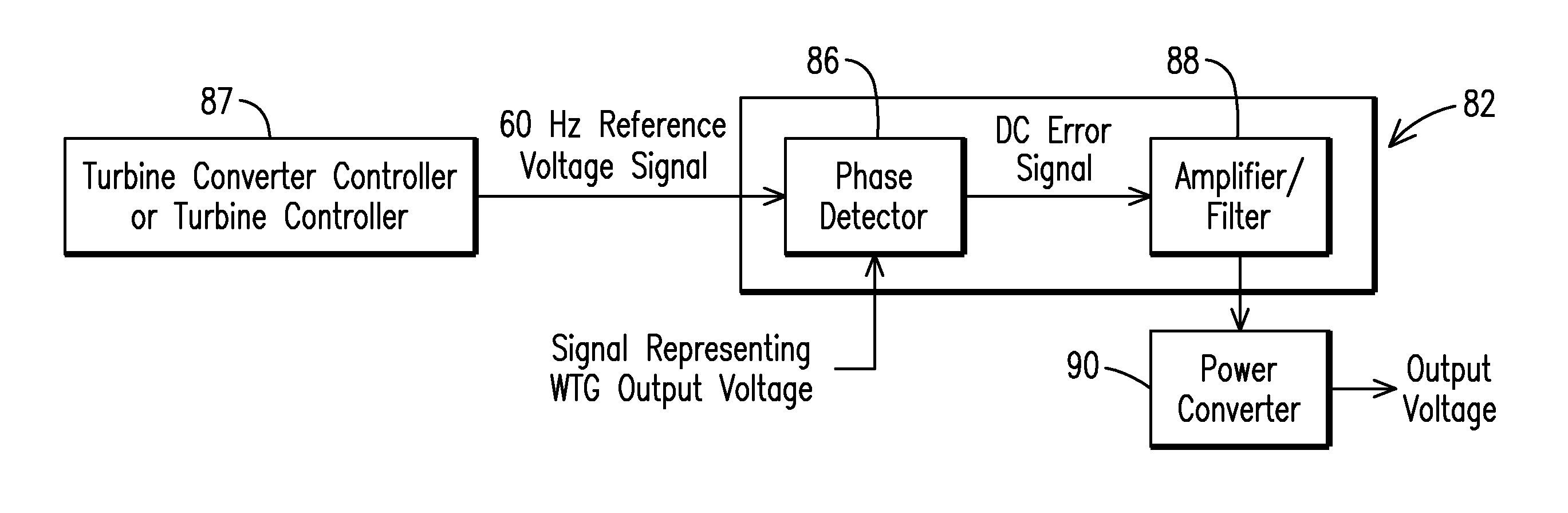
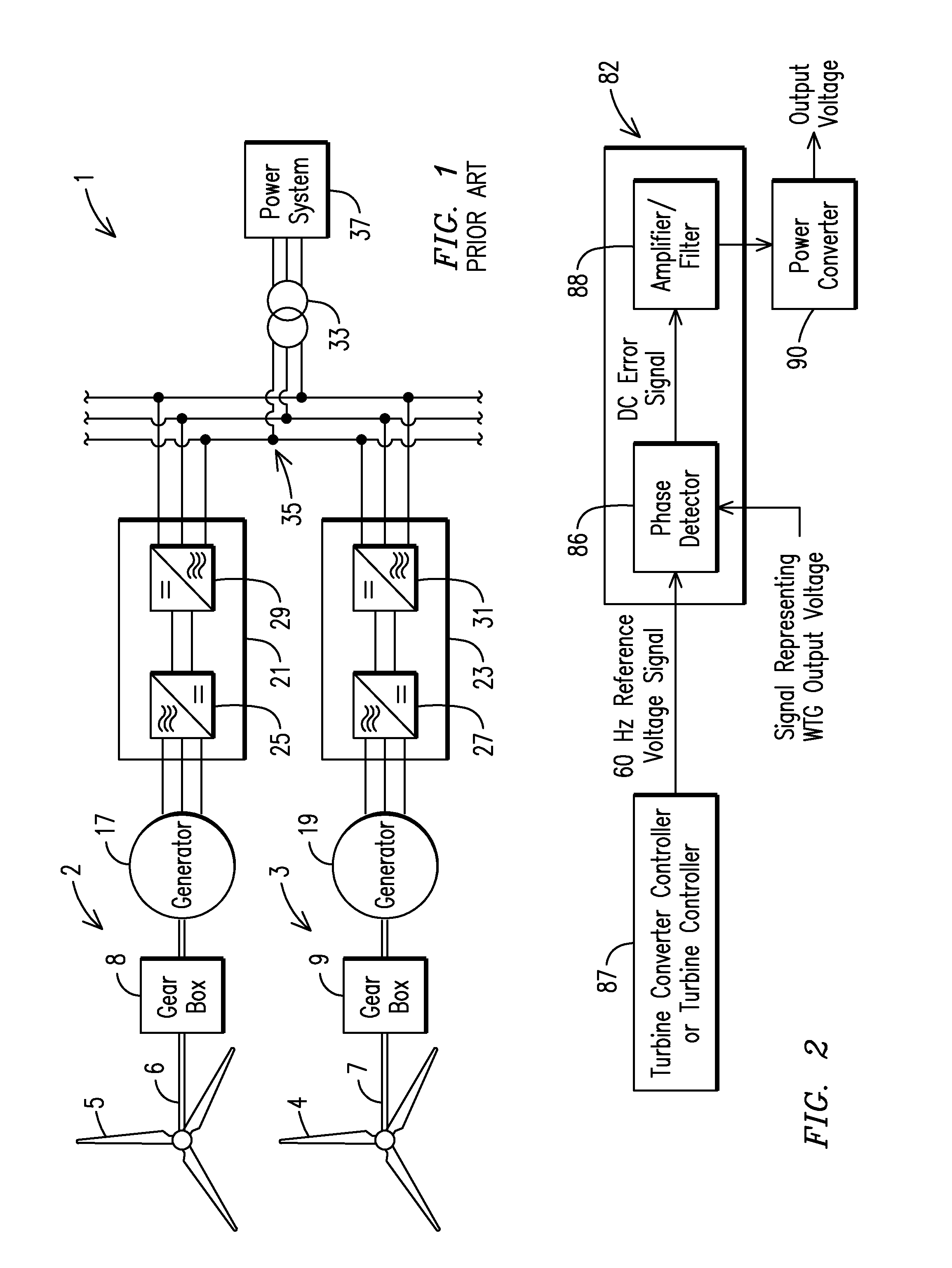
Isochronous wind turbine generator capable of stand-alone operation
InactiveUS20150042092A1Wind motor controlConversion with intermediate conversion to dcElectric power systemPhase angle difference
A power generating device (2, 3) for supplying power to a power system (37). The power generating device includes a first component (87) for generating a first signal representing a frequency of a voltage on the power system, a power converter (90) for generating an output voltage, a second component (82) responsive to the first signal and to a second signal representing the output voltage, the second component producing an error signal representing a phase angle difference between the first and second signals, and the error signal being an input to the power converter for controlling the power converter to maintain the phase angle difference between the output voltage and the first signal.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Method for rapidly and accurately judging false wiring of metering device
ActiveCN104316822ATroubleshooting Voltage Reference IssuesSolve the discrimination problemElectrical testingPhase differencePower factor
The invention discloses a method for rapidly and accurately judging false wiring of a metering device. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, it is ensured that the measuring conditions that the voltage of a three-phase and three-wire circuit is symmetrical, and the three-phase load power factor angles are equal are met; secondly, six phase angle differences on the three-phase, three-wire and two-element metering device are measured through a phase position voltammeter; the relation of the current phase angle of the three-phase, three-wire and two-element metering device is analyzed, the current phase difference is determined, the voltage phase angle relation is analyzed, the voltage phase sequence is determined, the relation of the voltage and the current phase angle is analyzed, the voltage phase difference is determined through the phase crossing method, the voltage and current phase angle relation is analyzed finally, and the current direction is determined. The method has the advantages that the algorithm is simple, the data size is small, using is convenient, and the method is rapid and accurate.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Apparatus and method for determining a faulted phase of a three-phase ungrounded power system
ActiveUS7345488B2Short-circuit testingEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionPhase angle differenceEngineering
Provided is an apparatus and method for determining a faulted phase resulting from a fault in a three-phase ungrounded power system. The method includes comparing a phase angle of an operating phasor to a phase angle of a fixed reference phasor. The operating phasor is derived from a digitized signal sample of a plurality of measured signals of the power system. The method also includes comparing a phase angle difference between the operating phasor and the fixed reference phasor to at least one threshold to determine the faulted phase. The fixed reference phasor may be a phase-to-phase voltage or a positive sequence voltage of the plurality of measured signals of the power system. The operating phasor may be a zero sequence current, a zero sequence voltage or a combination of a zero sequence current and a zero sequence voltage of the plurality of measured signals of the power system.
Owner:SCHWEITZER ENGINEERING LABORATORIES
Micro-grid combination control method based on inverter in energy storage unit
InactiveCN102904282ASmall fluctuationGuaranteed frequencySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsAc network load balancingVoltage amplitudeMicrogrid
The invention discloses a micro-grid combination control method based on an inverter in an energy storage unit. The control method is characterized in that inverter power supplies (of a micro-grid) which operate in a parallel manner before the micro-grid combination all adopt droop control policies; the inverter power supplies adopting the droop control policies adopt an operation mode of peer-to-peer control; a static switch which is used as a grid combination switch-on switch is adopted between the micro-grid and a power frequency power grid; the micro-grid combination control method comprises the following steps of: measuring and calculating a voltage amplitude value difference and a frequency difference at two sides of a public coupling point of the micro-grid and the power frequency power grid; adding the energy storage unit for adjusting so as to enable the voltage phase angle difference to meet voltage phase angle constraint conditions; closing a grid combination switch when all constraint conditions are met; and switching over inverter control policies of the energy storage unit to accomplish the whole process of the grid combination after the switch is closed. According to the method, the impact caused by the grid combination is reduced, and the micro-grid is smoothly combined into the power frequency power grid.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
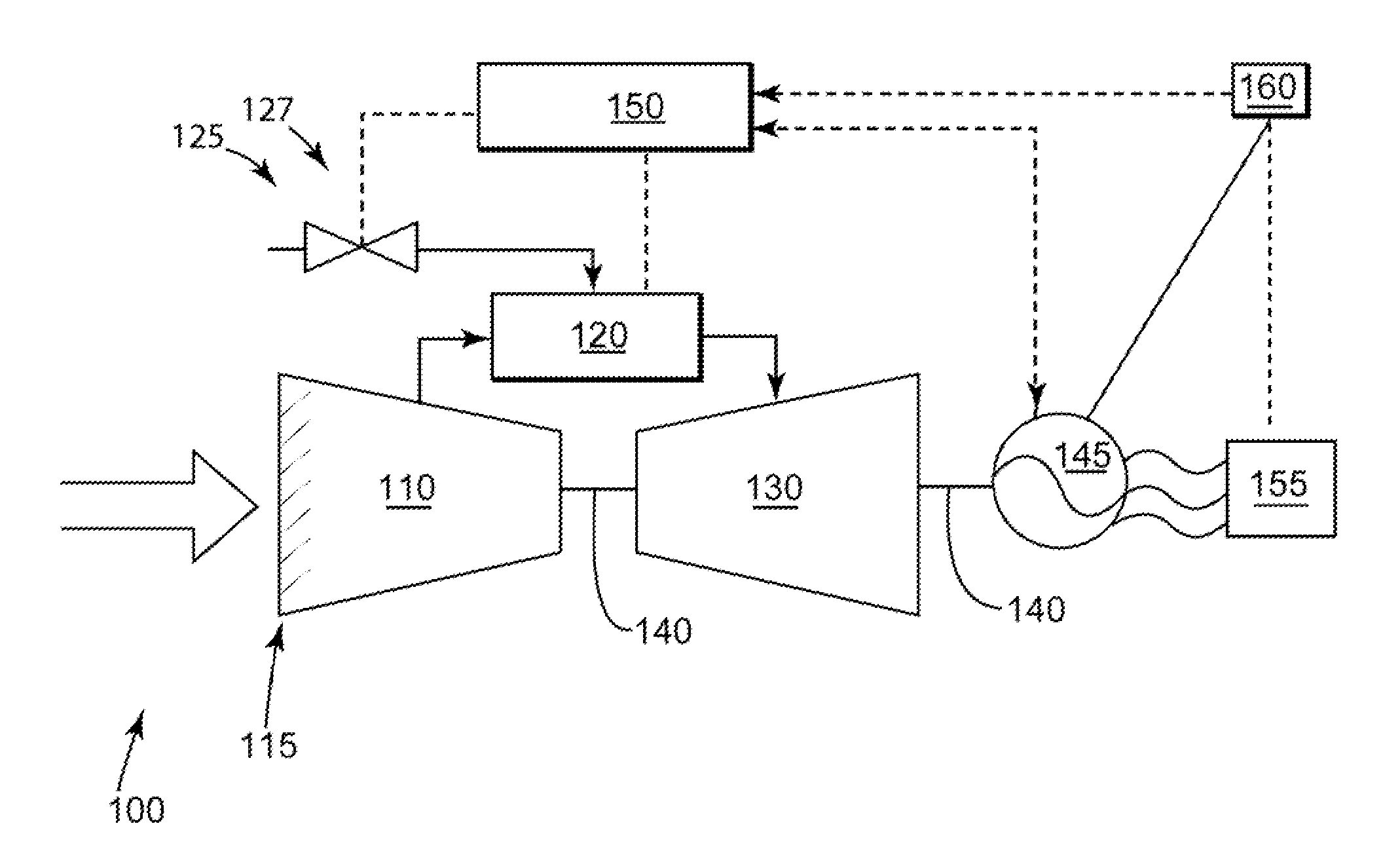
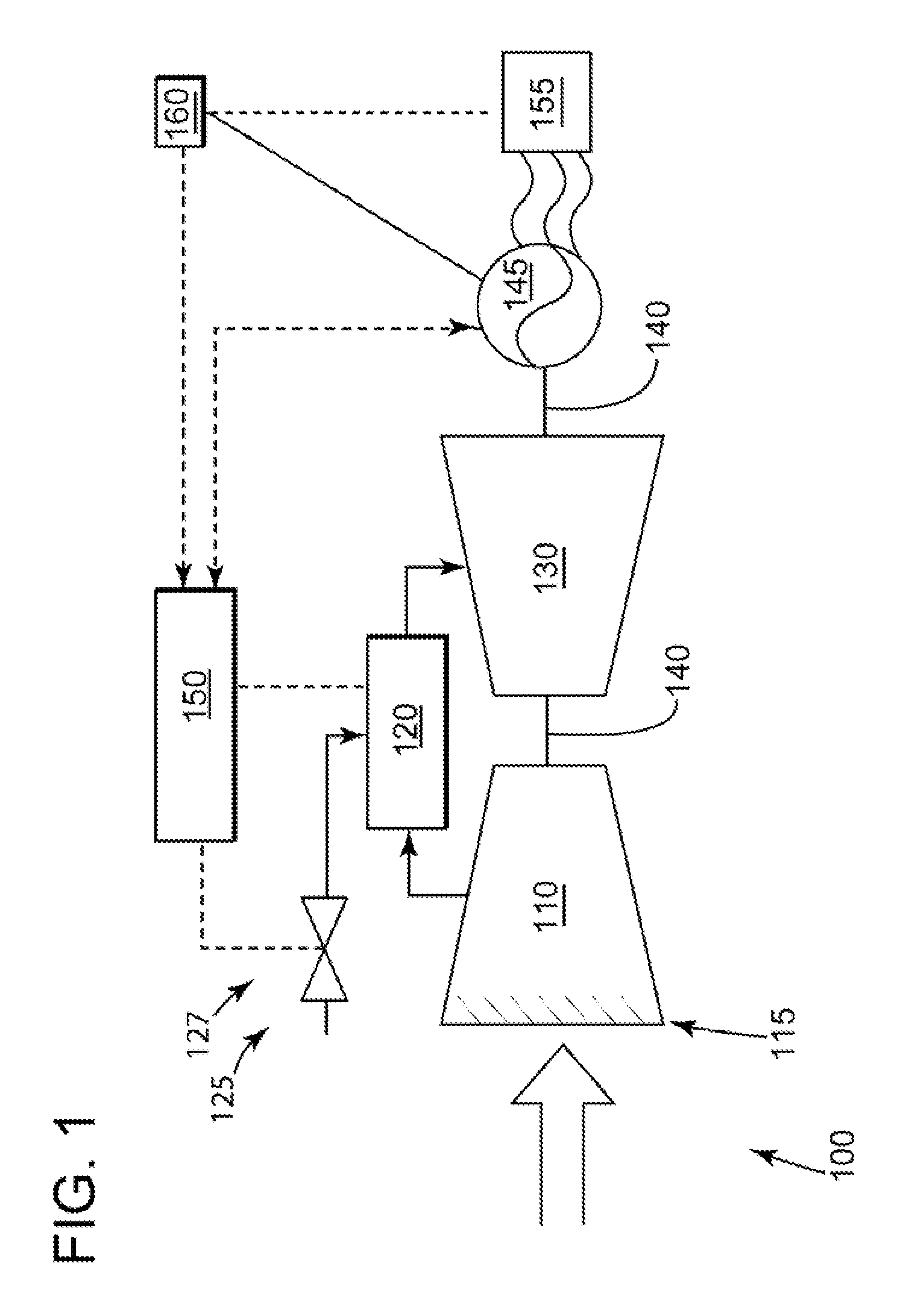
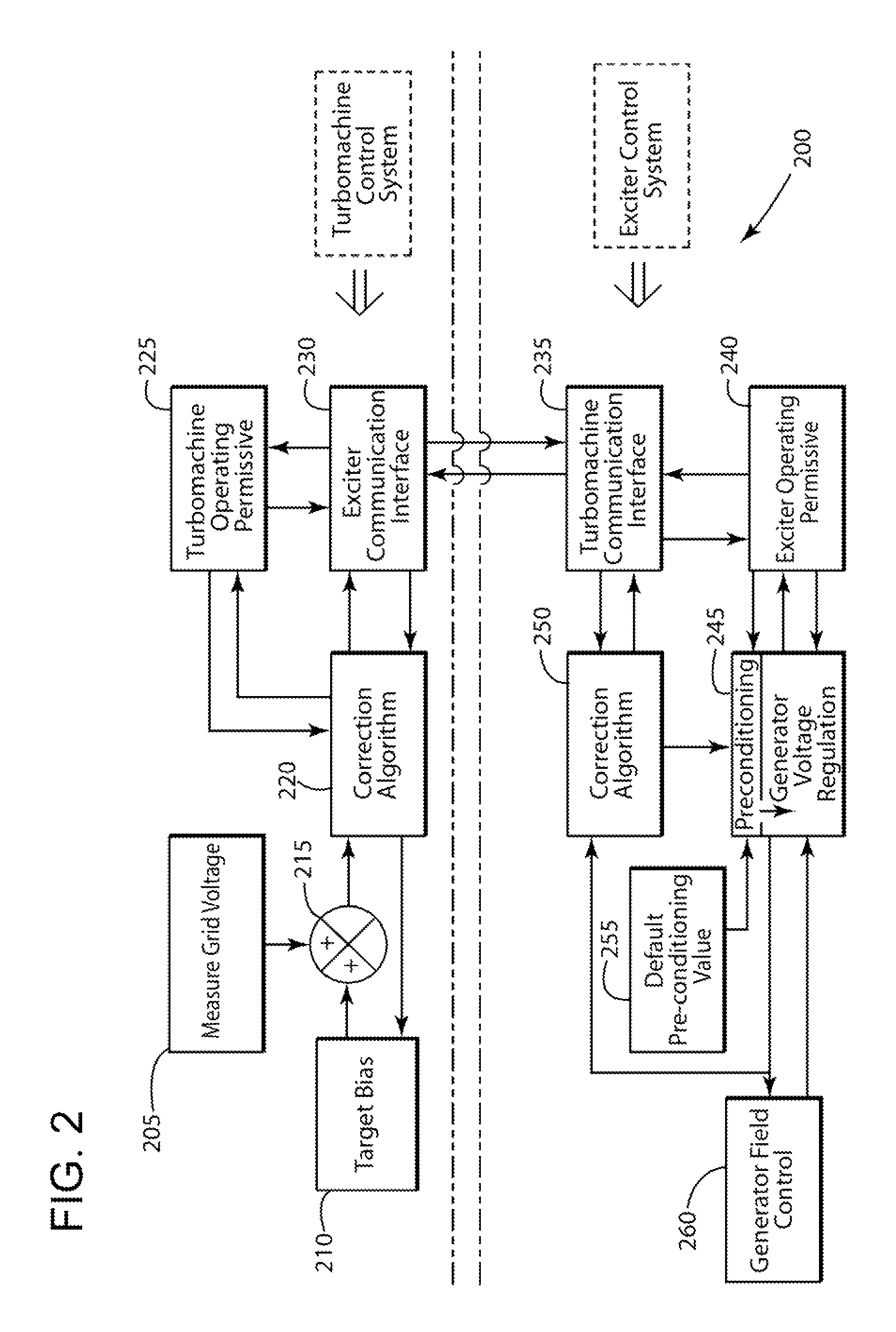
Method of synchronizing a turbomachine generator to an electric grid
ActiveUS7915868B1Reduce time synchronization requirementsHigh voltage accuracyMotor/generator/converter stoppersEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPower gridPhase angle difference
An embodiment of the present invention may seek to match the generator and grid voltages before the powerplant machine reaches the grid matching speed during the start-up process. An embodiment of the present invention may provide a predictive algorithm, or the like, to control the acceleration rate of the powerplant machine to target a particular phase angle differential between the powerplant machine and the grid when the powerplant machine reaches the grid matching speed. Here, the phase angle difference may be targeted such that a generator breaker may be closed immediately after the powerplant machine accelerates beyond the grid matching speed. This may avoid the generator experiencing a phase angle differential, which may add to the power transient associated with the generator breaker closure.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
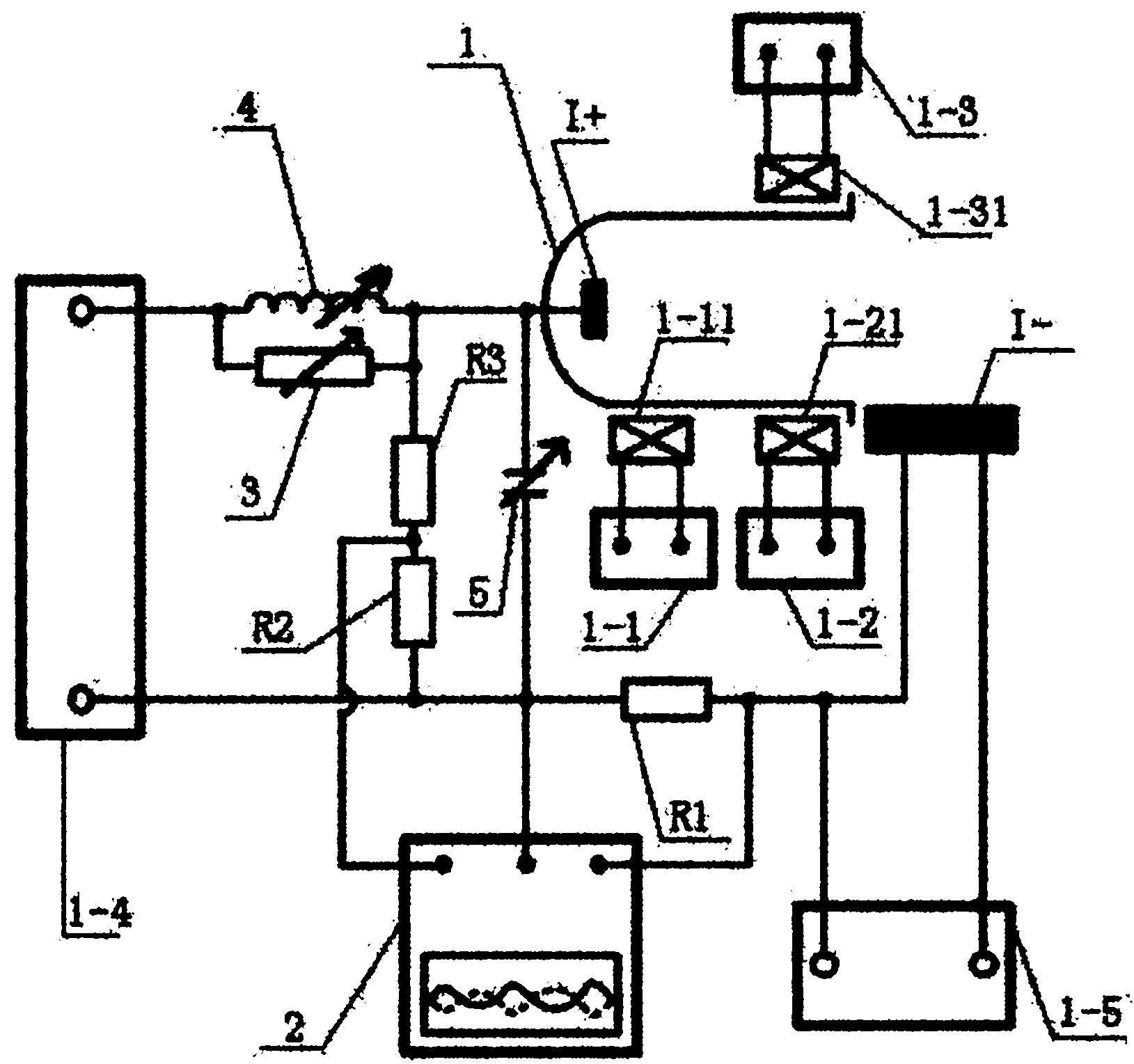
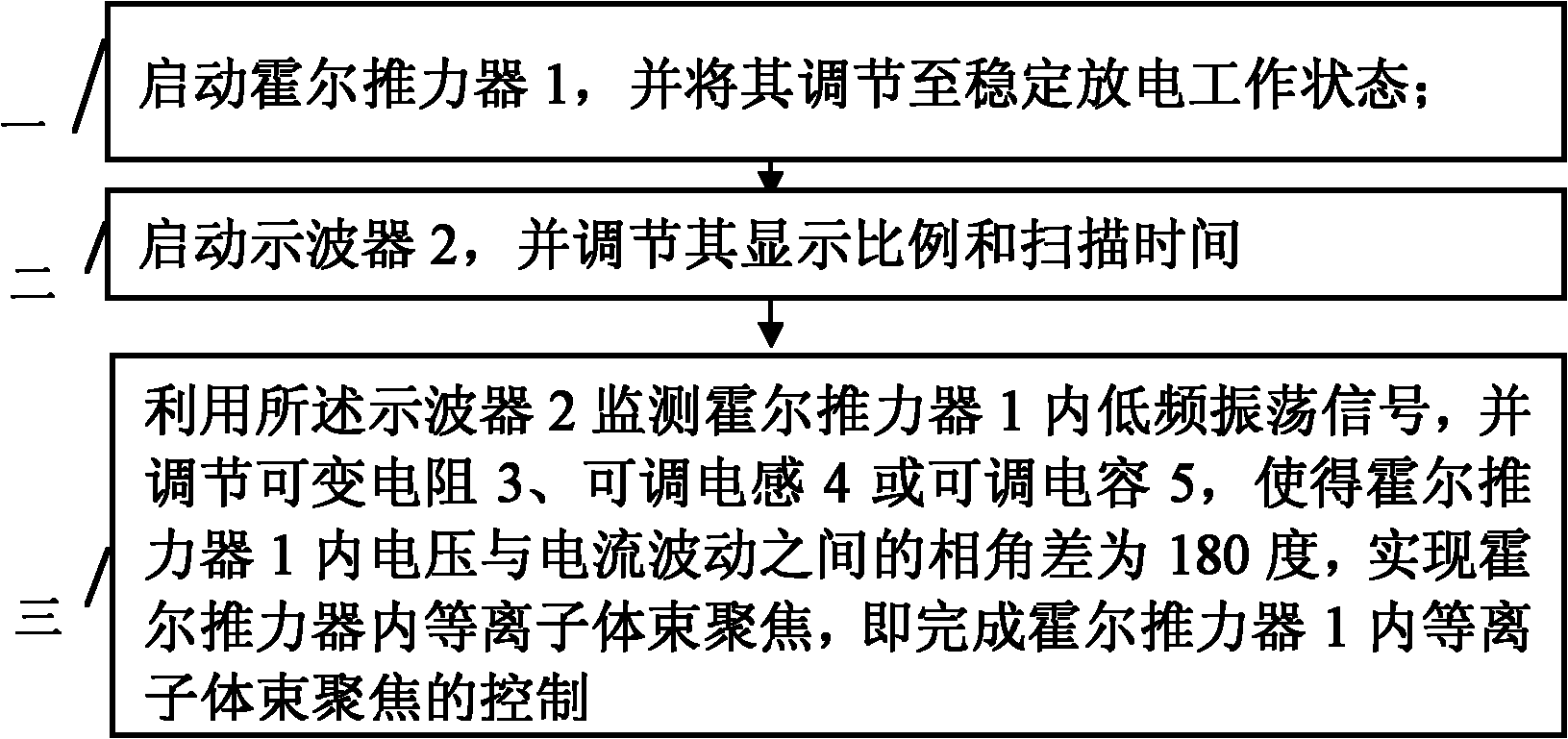
Outside loop control device and method for realizing plasma beam focusing in Hall thruster
InactiveCN101969737AAchieve focusEasy to implementNuclear energy generationMachines/enginesCapacitanceLoop control
The invention provides an outside loop control device and a method for realizing plasma beam focusing in a Hall thruster and relates to a plasma beam focusing technology in the Hall thruster. The device and method solve the problem that the calculation and adjustment are complex and the problem that the controllability is poor in the conventional method for realizing plasma beam focusing in a Hall thruster. The device of the invention comprises an externally powered loop system, an oscillograph, a variable resistor, an adjustable inductance and an adjustable capacitor. The method of the invention includes the following steps of: firstly, starting the Hall thruster and adjusting the Hall thruster to a stable discharge operational state; secondly, starting the oscillograph and adjusting the display scale and the scanning time of the oscillograph so as to clearly display low-frequency oscillation signal on the oscillograph; and finally, adjusting the value of the variable resistor, the adjustable inductance and the adjustable capacitor, keeping the phase-angle difference between the voltage and current fluctuation in the Hall thruster at 180 degrees so as to realize and control the plasma beam focusing in the Hall thruster. The device and the method are suitable for the plasma beam focusing in the Hall thruster.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Synchronization control for reconnecting microgrid to main grid after islanding
A method and system are provided. The method includes synchronously reconnecting a microgrid to a main grid after islanding of the microgrid. The synchronously reconnecting step includes calculating a phase angle difference between synchrophasor measurements collected from a common coupling on the main grid and synchrophasor measurements collected from a common coupling on the microgrid. The synchronously reconnecting step further includes calculating, by a controller, a frequency reference deviation based on the phase angle difference. The synchronously reconnecting step also includes adjusting a frequency of the diesel generator based on the frequency reference deviation.
Owner:NEC CORP
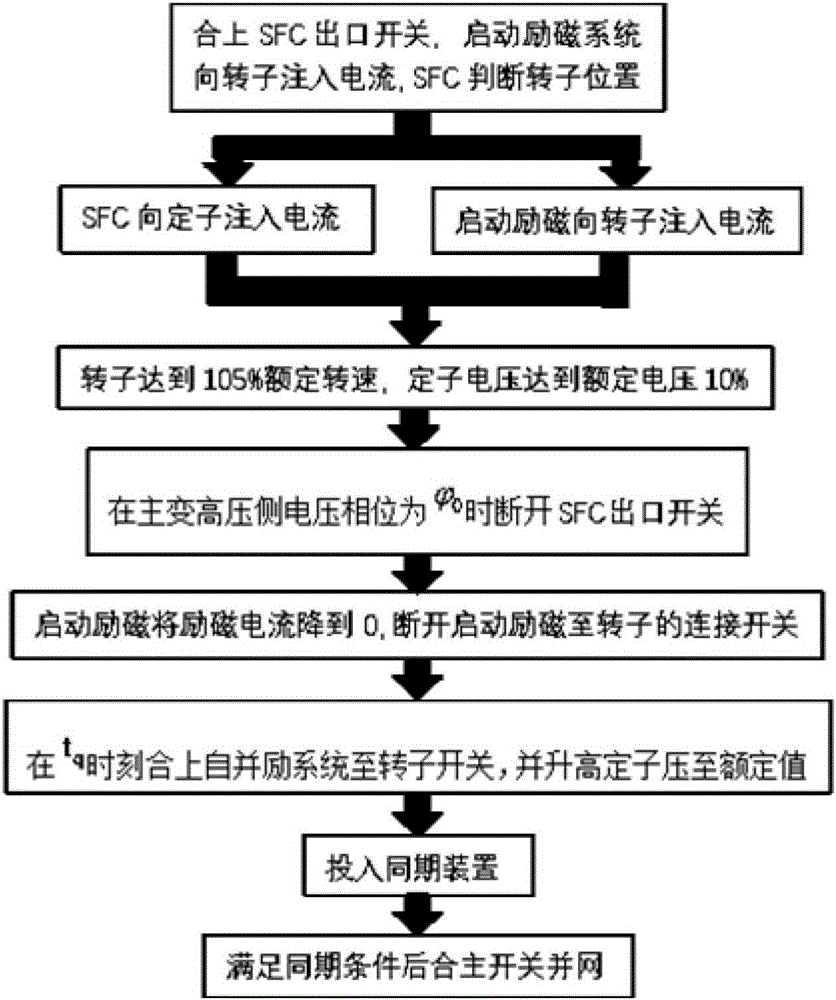
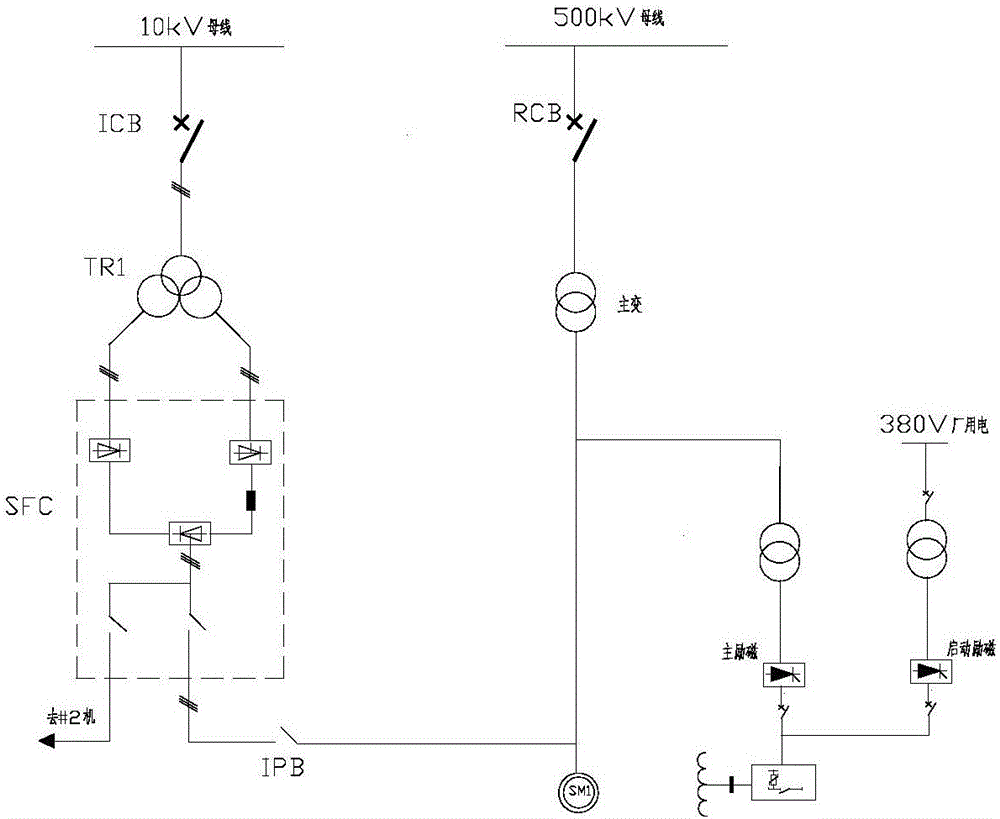
Large phase modifier start grid-connected control method
ActiveCN106849180AEnsure safetyReduce shockSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsStarter arrangementsPhase angle differenceGrid connection
The invention provides a large phase modifier start grid-connected control method, belongs to the technical field of motor controls. The method targets the problems that the large phase modifier when started is dragged by a SFC to a 105% rated speed then gets into the running down state, and boosted grid causes frequency difference and phase angle difference uncontrollable issues, and proposes a control strategy for controlling the SFC removal angle and excitation system at reclosing time, to maximally reduce phase modifier grid-connected impact on the device body and the system. The method can effectively solve the problem that under the condition of unit turning down, the switch of phase modifier start excitation and the self-shunt excitation exciting mode cause grid connecting process to be uncontrollable, the controllability of poor frequency and poor phase angle at grid connection is improved while success rate is ensured, and the impact problem caused by phase modifier grid connection is greatly reduced, the security stability and grid success rate of large phase modifier are improved, the method has significances on the security, efficiency and reliability of running large phase modifier.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
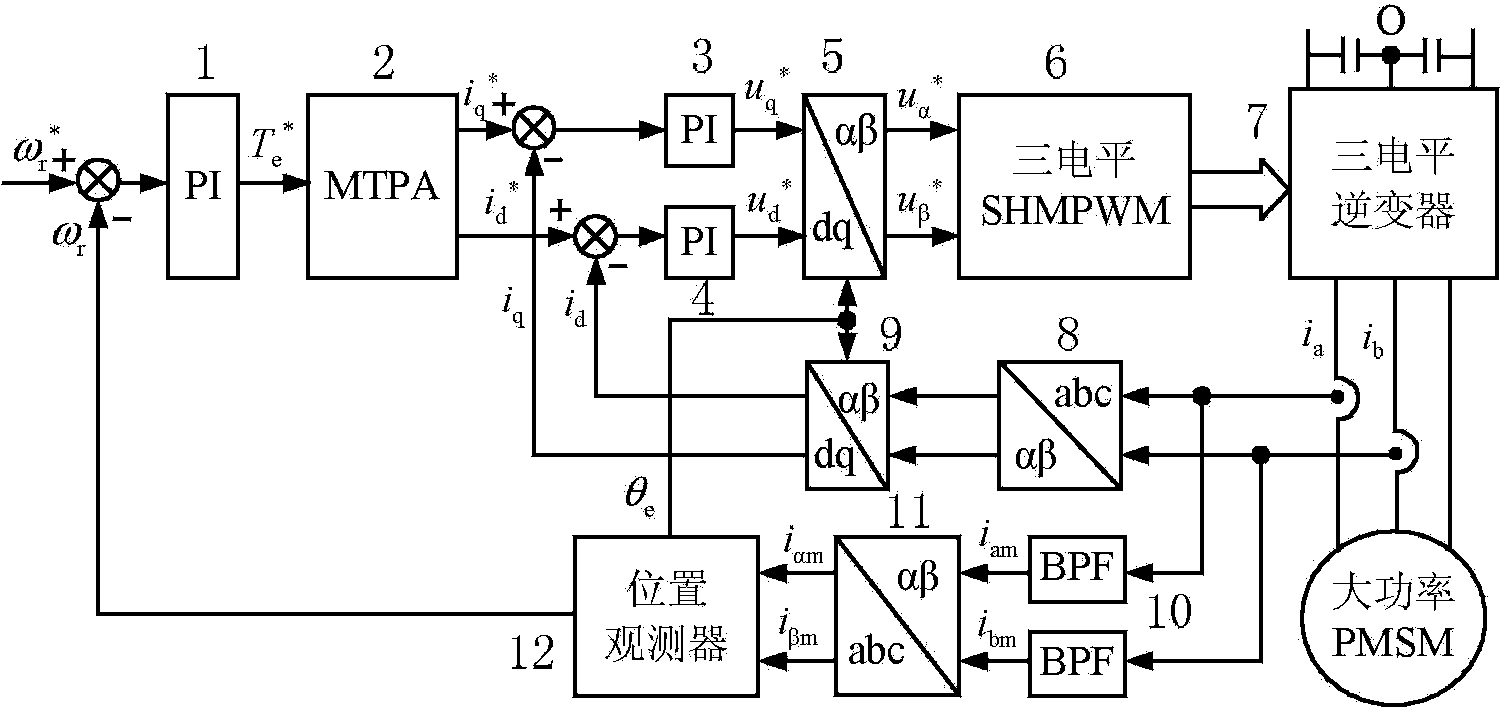
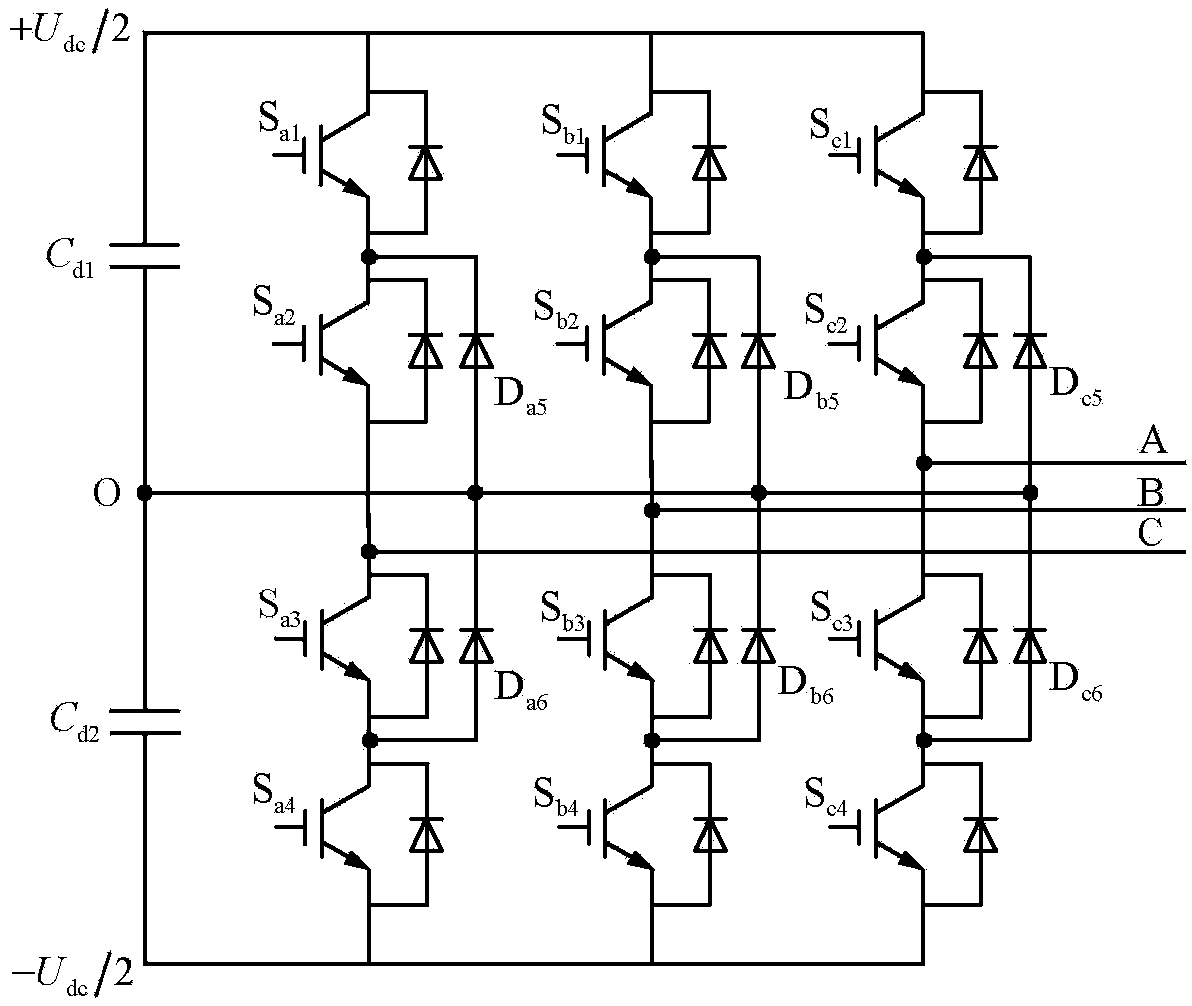
High-power built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor position-sensorless control system and control method
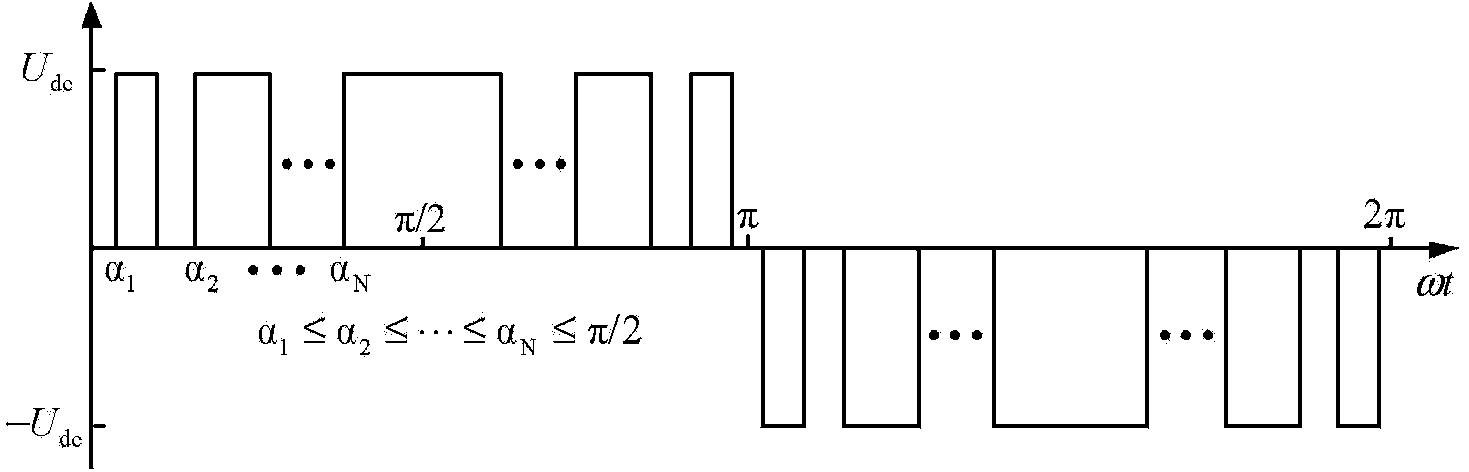
InactiveCN103929109AAdd constraintsFilter out the problem of increased low-order harmonic componentsElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsVoltage vectorHarmonic mitigation
The invention provides a high-power built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor position-sensorless control system and a control method, and belongs to the field of motor control. The control system solves the problem that when a traditional high-power built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor system works at a low switch frequency, low-order harmonic content increases, and meets the requirements that low-order harmonic waves are weakened and meanwhile, rotating voltage vector control with constant amplitude values is produced. An SHMPWM technique is adopted, it is guaranteed that on a low-switch-frequency work condition, harmonic waves of a high-power permanent magnet synchronous motor system are inhibited, constraint conditions of SHMPWM non-linear transcendental equation sets are increased, and three-phase specific harmonic wave content signals with constant amplitude values and 120-degree phase angle differences are extracted from the weakened harmonic wave content to be used for estimation of a rotor position; specific harmonic currents are obtained through a band-pass filter; by means of a position observer, the estimated rotation speed and the rotor position of a permanent magnet synchronous motor are obtained, and position-sensorless rotation speed closed loop vector control of a motor is achieved. The control system and the control method are suitable for control of the motor.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
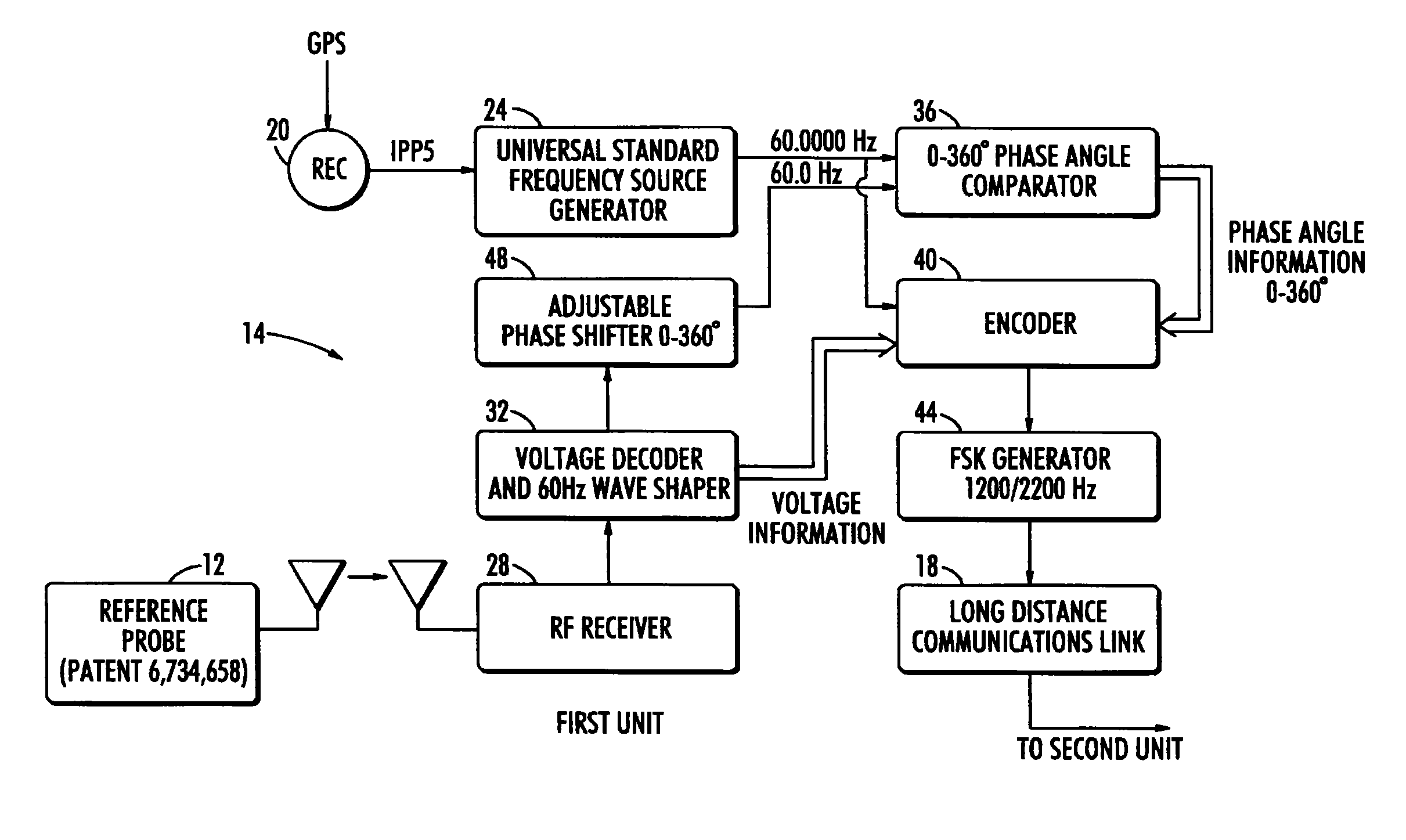
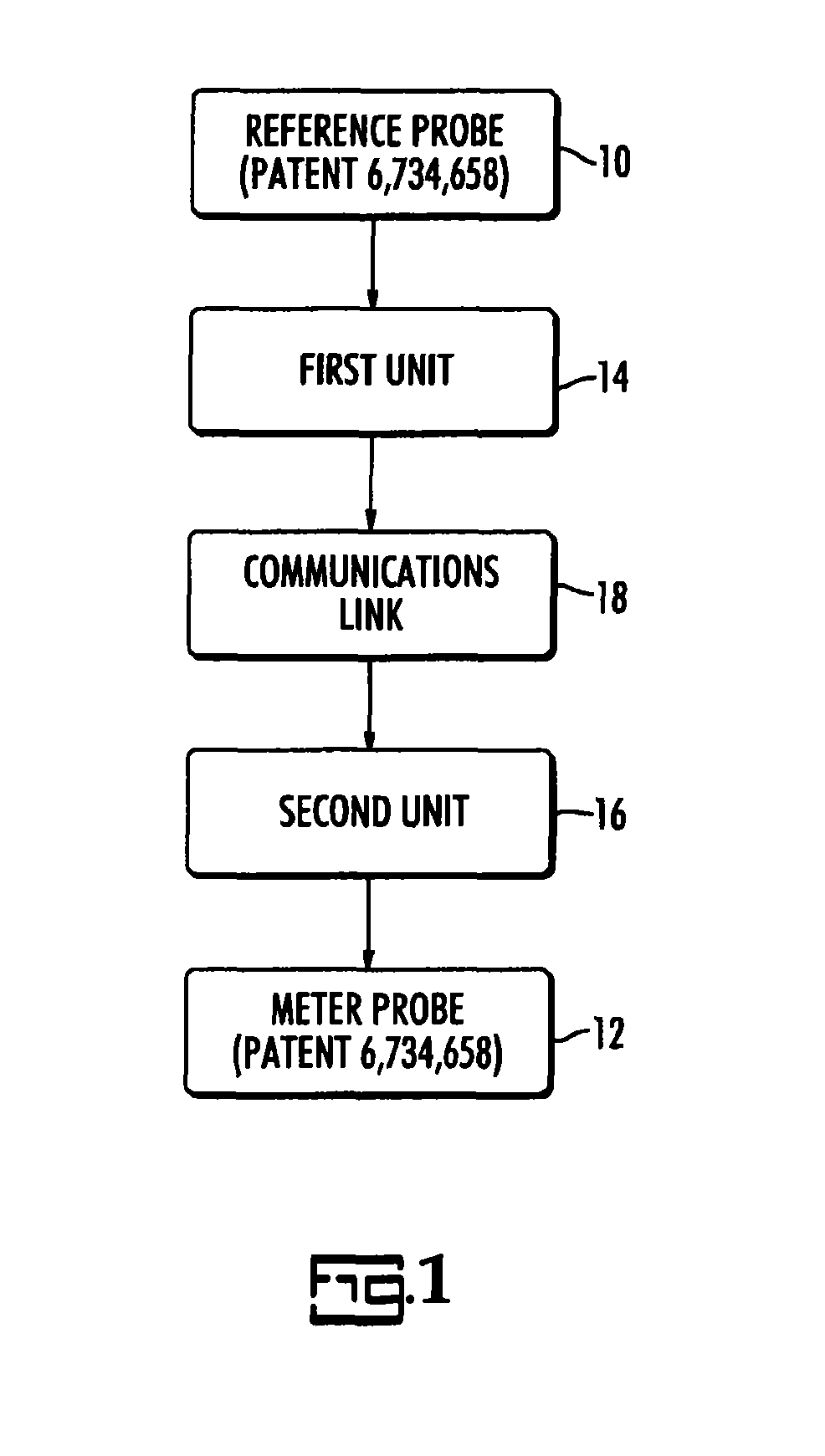
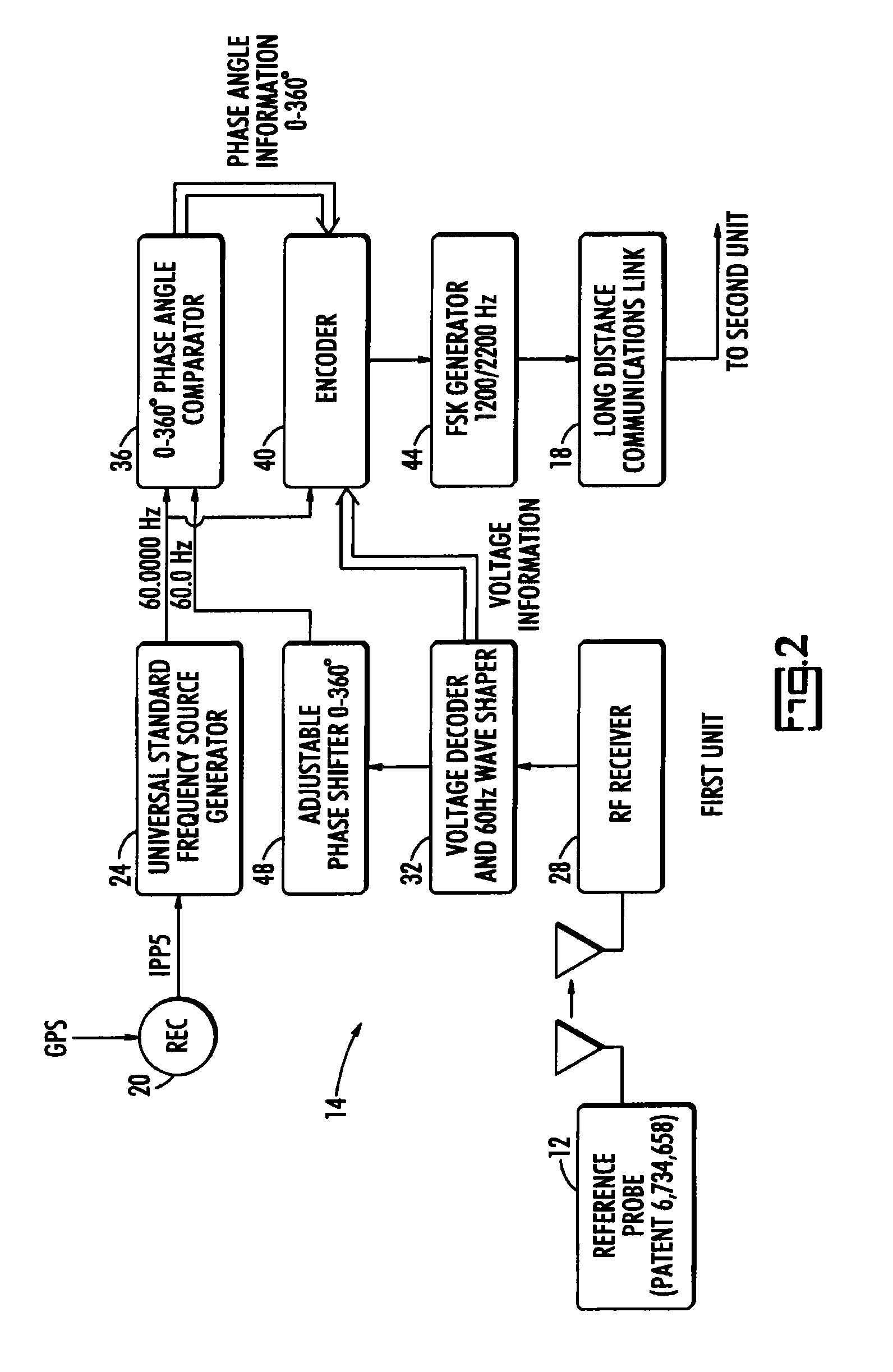
Long range phasing voltmeter
ActiveUS8283911B1Accurate measurementCurrent/voltage measurementVoltage-current phase angleElectrical conductorPhase difference
A long range wireless phasing voltmeter determines the phase difference between the time-varying voltage carried on a reference electrical conductor and another, field conductor. The voltage signal from the reference conductor is measured by a reference probe and compared by a first unit in communication with that reference probe to a precision 60 Hz signal generated from a GPS receiver. The phase difference between these, in the form of a nine-bit, audible signal using frequency shift keying to modulate the carrier frequency, is transmitted by the first unit to a second unit perhaps miles away. A receiver in the second unit decodes the signal and uses another precision 60 Hz signal generated from another GPS receiver to re-create a surrogate of the original reference voltage signal. This surrogate signal is forwarded to a meter probe that is measuring the signal on a field conductor. The meter probe can then compare the two signals to determine the phase angle difference between them.
Owner:BIERER WALTER S
Motor for directly driving electric drum
ActiveCN104600881ASimple structureWork reliablyMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic circuit stationary partsElectric machinePhase angle difference
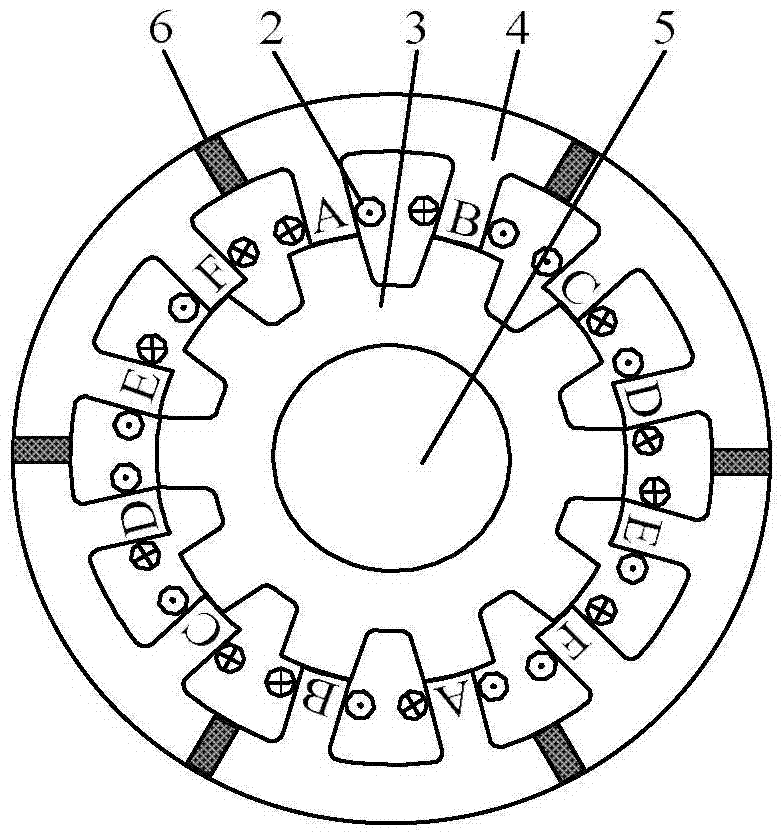
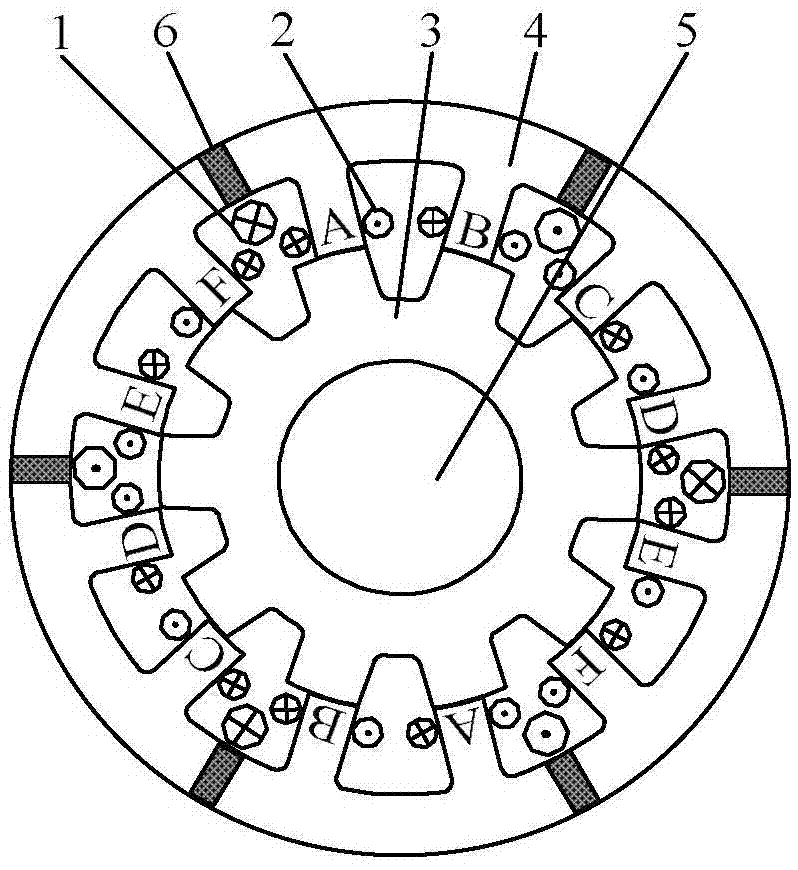
The invention provides a motor for directly driving an electric drum. The motor for directly driving the electric drum comprises a stator iron core, a rotor iron core, a drum wall, an exciting winding, an armature winding, a shaft and the like. The motor for directly driving the electric drum is of an outer rotor structure. The outer side of the rotor iron core and the drum wall are fixed together. When the stator pole number of the motor for directly driving the electric drum is 6N and the rotor pole number of the motor for directly driving the electric drum is 7N, a pole arc coefficient of a stator of the motor for directly driving the electric drum is 0.333, and a pole arc coefficient of a rotor of the motor for directly driving the electric drum is 0.5. When the stator pole number of the motor for directly driving the electric drum is 6N and the rotor pole number of the motor for directly driving the electric drum is 5N, the pole arc coefficient of the stator of the motor for directly driving the electric drum is 0.4, and the pole arc coefficient of the rotor of the motor for directly driving the electric drum is 0.5. The motor for directly driving the electric drum is provided with a six phase winding, and phase angle difference of the six phase winding is 60 electrical degrees. The six phase winding is divided into two channels which are isolated from each other, and when one phase or one channel of the six phase winding breaks down, the other channel can run in fault tolerant mode, and accordingly reliability of a system is improved, and the motor for directly driving the electric drum can be used to directly drive the drum.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Pilot protection method of high-voltage direct current transmission line based on S transformation
ActiveCN105098738AQuick actionReliable identificationEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPhase angle differenceTransmission line
The invention discloses a pilot protection method of a high-voltage direct current transmission line based on S transformation. The pilot protection method comprises: collecting voltage and current of a protection element connected with positive and negative electrodes of the direct current transmission line, and filtering the voltage and the current; extracting voltage and current mutation data within a set time after a fault, and carrying out S transformation on the mutation data to obtain a complex time-frequency S matrix of voltage and current signals; calculating S transformation phase angles of the voltage and current mutations at each sampling point and a mean of the phase angle difference thereof; establishing a protection criterion of the direct current transmission line, and identifying faults inside and outside the sample space based on the S transformation phase angles of the voltage and current mutations according to the protection criterion; if the fault is a fault inside the sample space, comparing the transient energy of S transformation zero frequency bands of the voltage mutations of the positive and negative electrodes via a rectifying side protection device to judge a fault pole. The pilot protection method disclosed by the invention does not need to synchronize data on both ends of the direct current transmission line and only requires an inversion side to transmit a fault direction identification result to the rectifying side.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Self-adapting combiner delay time and synchronous electronic mutual inductor steady state checking device
ActiveCN101556318AAvoid Fixed Phase Angle DifferencesElectrical measurementsProcess moduleTime delays
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +1
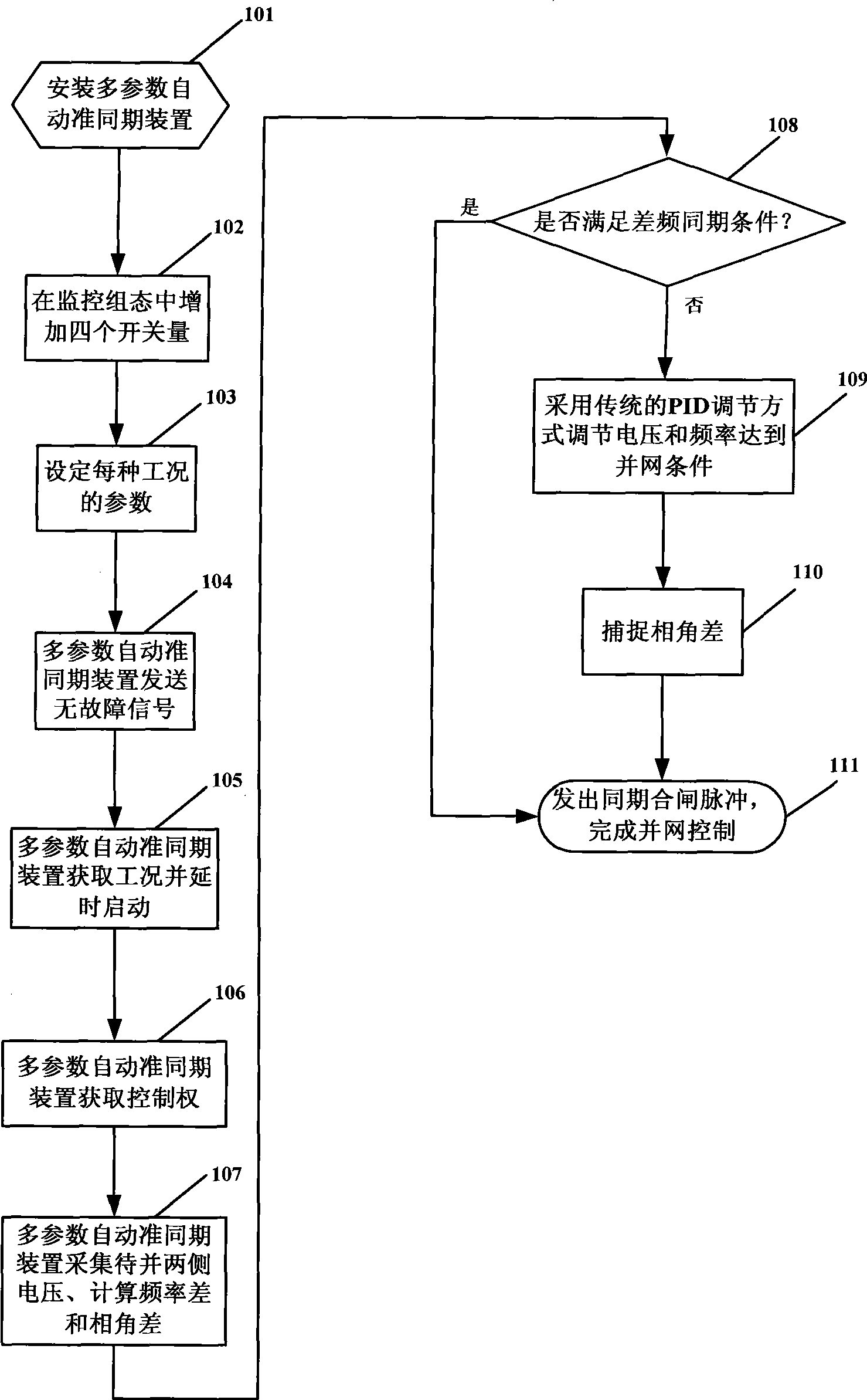
Multi-parameter automatic presynchronization control method
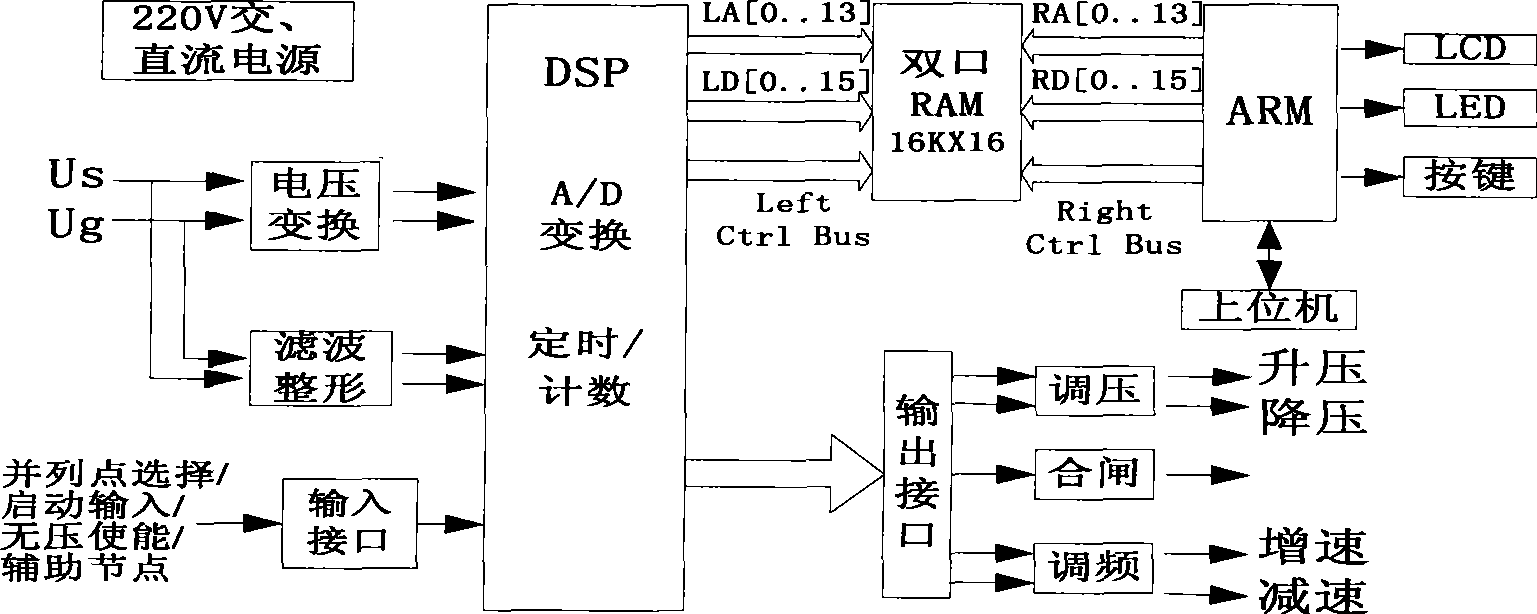
InactiveCN101369732AShorten the grid connection time in the same periodShorten grid connection timeSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsFrequency changerAutomatic control
The invention discloses a multi-parameter automatic quasi synchronization control method of the electric power system automatic control technology field. The technical scheme is that the multi-parameter automatic quasi synchronization apparatus, where setting the work condition and synchronization parameter, is mounted in the prior synchronization control loop; then the apparatus acquires two-side voltage, and calculates a frequency difference and phase angle difference; synchronization types is captured, and engine speed is regulated; the synchronization condition is judged whether meeting or not based on the different synchronization types combining setting synchronization parameter; when meeting the synchronization condition, a switching-in pulse is sent to implement network-connection; otherwise, the voltage and the frequency are regulated based on traditional PID regulation mode to meet the network-connection condition, and capturing the phase angle difference as well as forecasting the synchronization point, and the network-connection control is implemented ultimately. The invention implements the optimum matching of the synchronization apparatus and the speed governor system, an excitation system, a frequency converter control system; reduces unit network-connection electric impact, and improves the service lifetime of the generators and a GIS combinational switch system.
Owner:华北电网有限公司北京十三陵蓄能电厂
Rotary dual-cylinder compressor using exhaust middle partition board
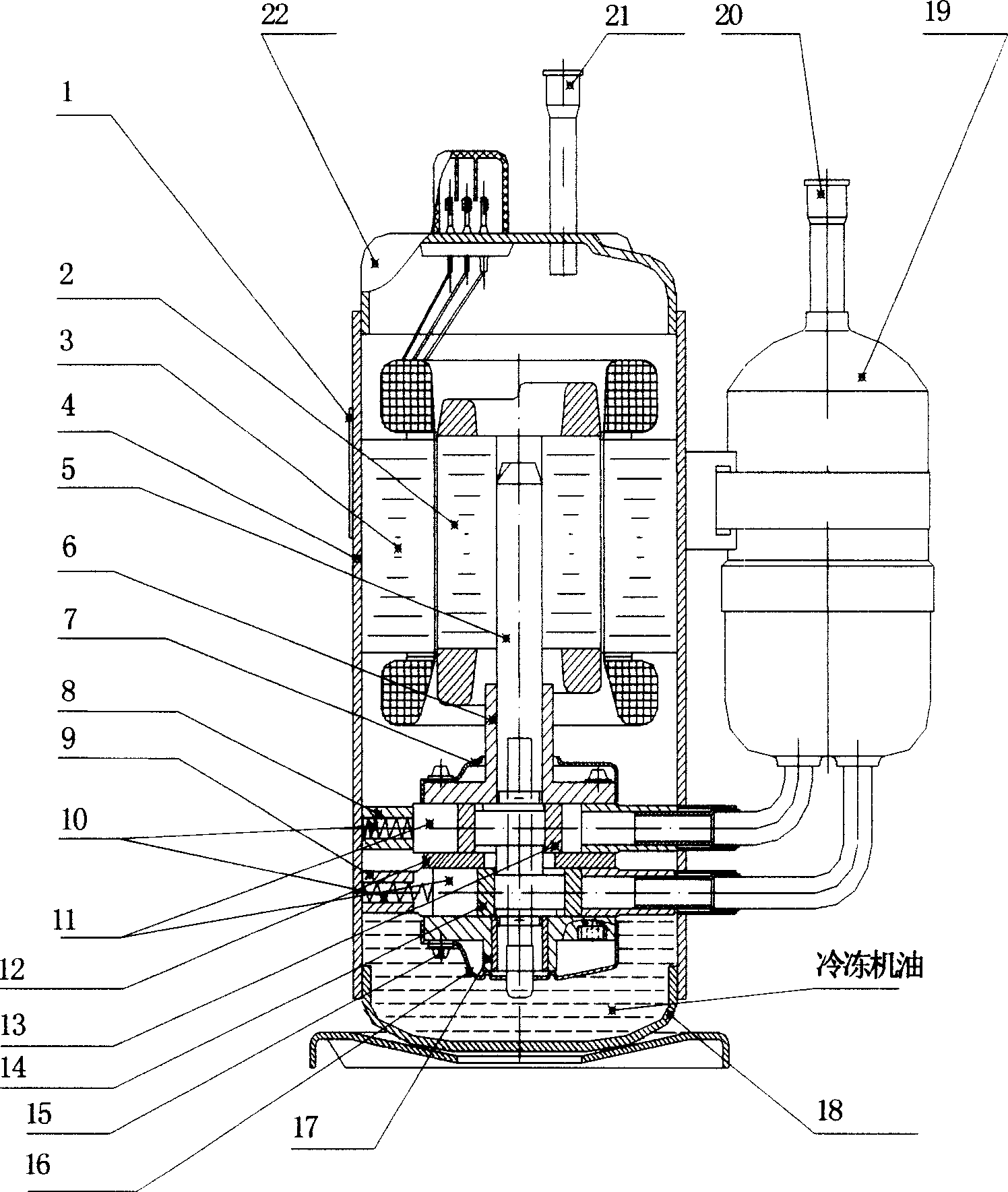
InactiveCN1676938AImprove pumping efficiencyImprove machine efficiencyRotary/oscillating piston combinations for elastic fluidsRotary piston pumpsLow noisePhase angle difference
The invention discloses a rotate dual-cylinder compressor adopted with a exhaust intermediate baffle plate. The compressor is a normal rotate dual-cylinder compressor with it intermediate baffle plate additionally set a valve base slot on which set exhaust port, exhaust fin and other components and a concave cavity acquiring exhausting function for the baffle plate. In this way the compressor exhausting resistance is alleviated so the whole efficiency is enhanced. Moreover in consequence that two eccentric radius is arranged on two side of the eccentric shaft with a angle of 180 degrees, the lower exhaustion and the upper exhaustion are just opposite when in the baffle plate with a phase angle difference of 180 degrees, the crest and the hollow of the exhaustion pulsing lapping over so to reduce the exhausting noise. The experiment shows that 5HP rotate dual-cylinder compressor adopted with this invention has a 4 percents higher efficiency and a 5 to 6 dB lower noise than the normal one.
Owner:XIAN QINGAN REFRIGERATION EQUIP CO LTD
Wind noise detection method and system
The present invention relates to a multi-microphone system and method adapted to determine phase angle differences between a first microphone and a second microphone signal to detect presence of wind noise.
Owner:INVENSENSE
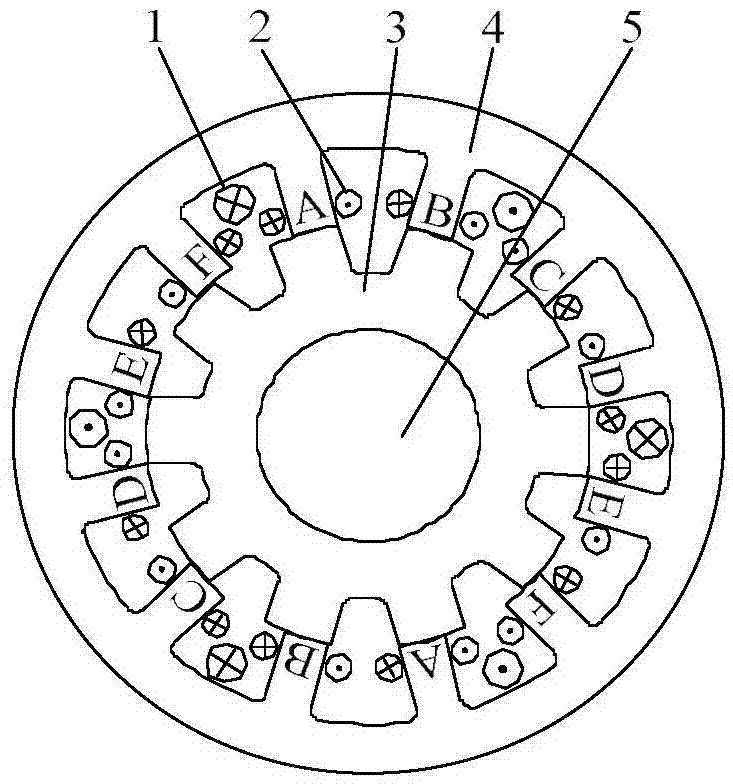
Low-mutual-inductance fault tolerance type six-phase double-salient-pole brushless DC motor
ActiveCN105449881ASmall mutual inductanceAchieve electrical isolationMagnetic circuit stationary partsWindings conductor shape/form/constructionFault toleranceElectrical polarity
The invention discloses a low-mutual-inductance fault tolerance type six-phase double-salient-pole brushless DC motor, and the motor comprises a stator assembly and a rotor core, which share one rotating shaft. The stator assembly comprises a stator core, excitation elements, and six-phase stator windings. The stator core is provided with 12N stator poles, wherein N is a natural number. The rotor core is provided with 10N or 14N rotor poles, and the number of excitation elements is 6N. Each excitation element is arranged to be across two stator poles, and the adjacent excitation elements are opposite in polarity. Each stator winding is formed by the series connection or parallel connection of 2N stator coils with the same phase, wherein the phase angle difference among the stator windings is 60 degrees. Each excitation element is in turn linkage with the stator coils of the corresponding two stator windings, and the polarity of each excitation element is consistent with the polarity of the stator windings in turn linkage with the excitation element. The motor achieves the electrical isolation among the six-phase stator windings, is better in fault tolerance performances, and is small in phase-switching torque pulsation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Bilinearization-based all-distributed robust state estimation method for multi-regional power network
ActiveCN105552904ASmall scaleImprove protectionElectric testing/monitoringComplex mathematical operationsElectric power systemEngineering
The invention relates to a bilinearization-based all-distributed robust state estimation method for a multi-regional power network, and belongs to the fields of power system operation and control. The method is divided into three states: preprocessing a measurement to obtain pre-estimation of an intermediate state variable in the first stage; carrying out nonlinear conversion on the intermediate state variable in the second stage to obtain new measurements, namely a phase-angle difference between voltages at two ends of each branch and twice of the sum of logarithmic magnitudes of the voltages; and estimating the final state variable on the basis of these new measurements in the third stage. Through nonlinear conversion in the second stage, parallel solving can be carried out in various regions and communication with the other regions is not needed. State estimation in the first stage and the third stage is aimed at a linearized system; and each control region determines the local state quantity by communication of the local and a neighbor by an alternating direction multiplier method. The bilinearization-based all-distributed robust state estimation method provided by the invention is suitable for large-scale multi-regional state estimation, can well protect the data privacy of various regions and has very high agility, flexibility and robustness.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com