Patents
Literature
620 results about "Frequency oscillation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The frequency of oscillation definition is simply the number of oscillations performed by the particle in one second. In T seconds, the particle completes one oscillation.
Temperature estimation and tissue detection of an ultrasonic dissector from frequency response monitoring
InactiveUS20130331875A1SurgeryThermometers using physical/chemical changesMicrocontrollerSonification
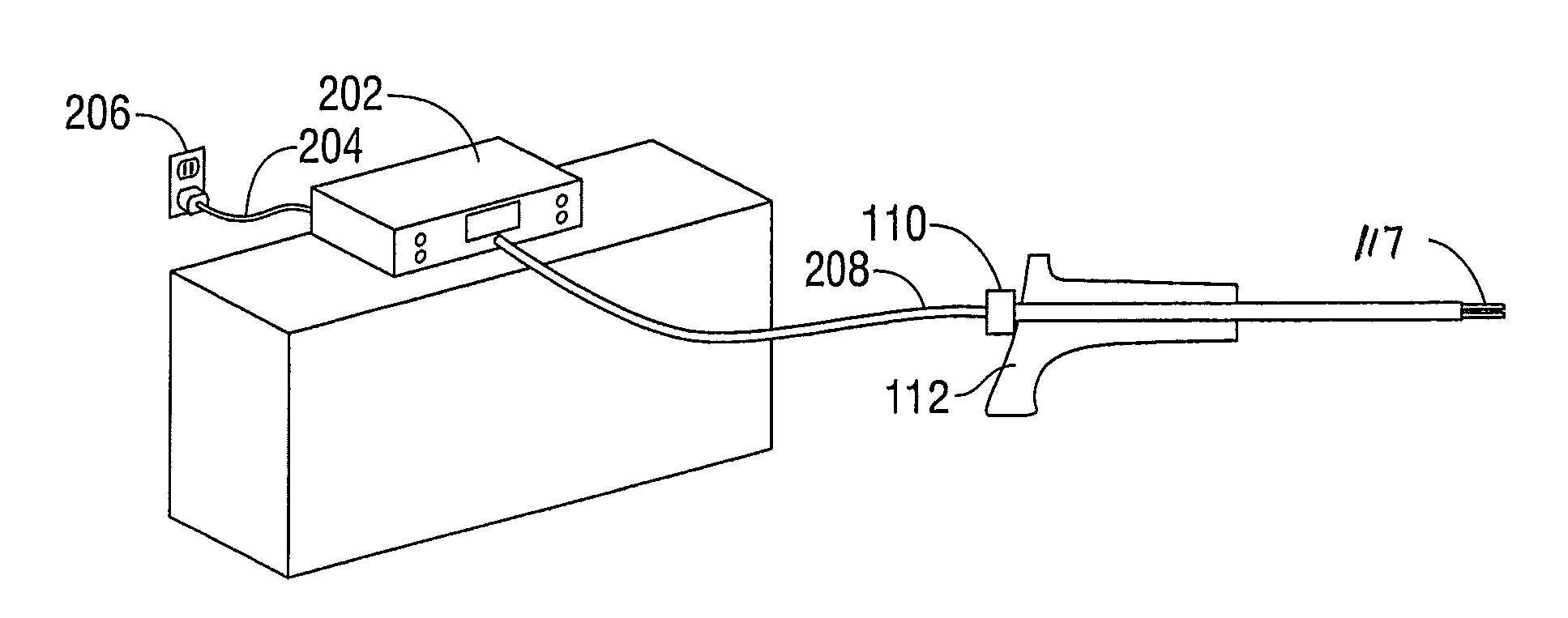
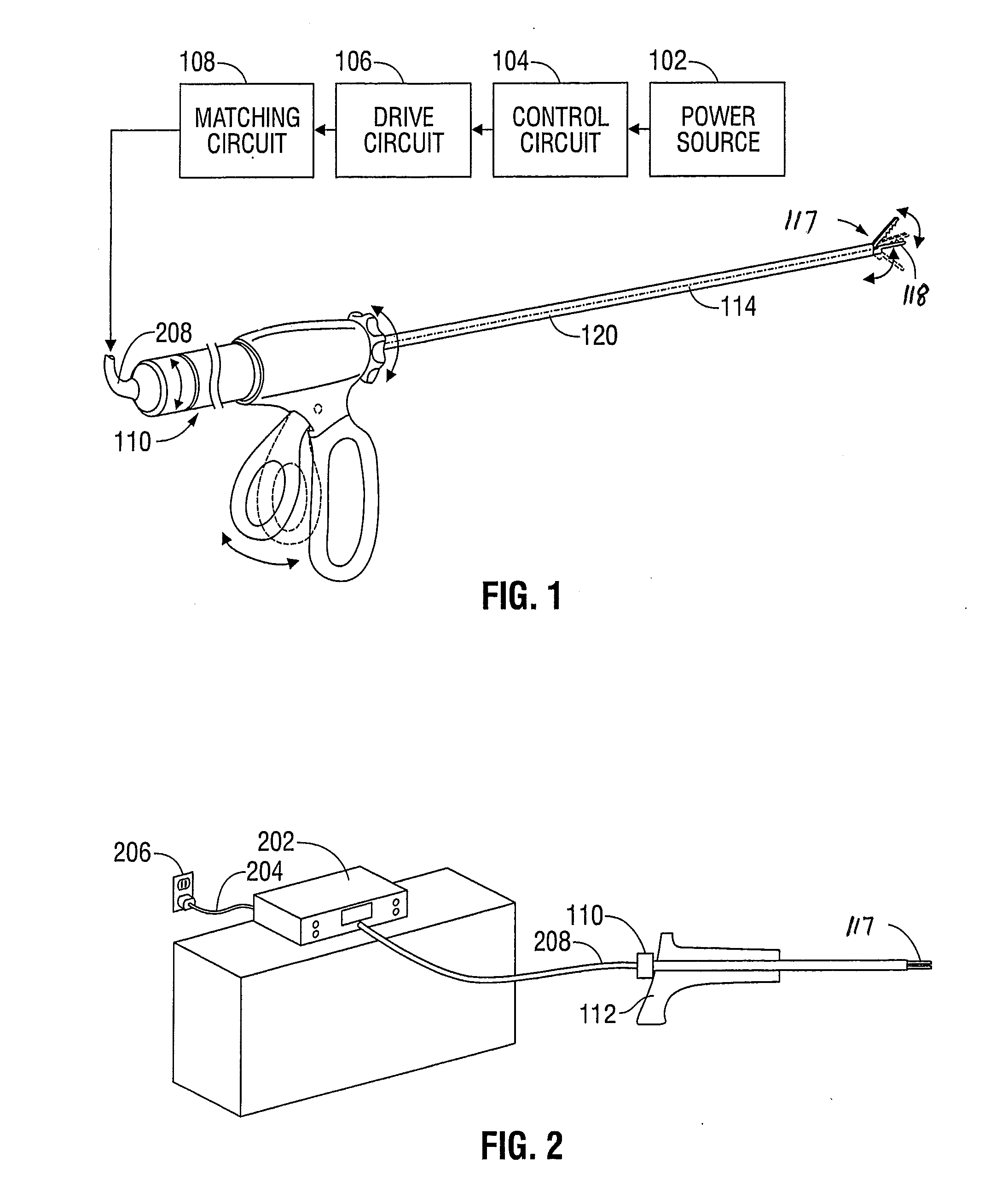
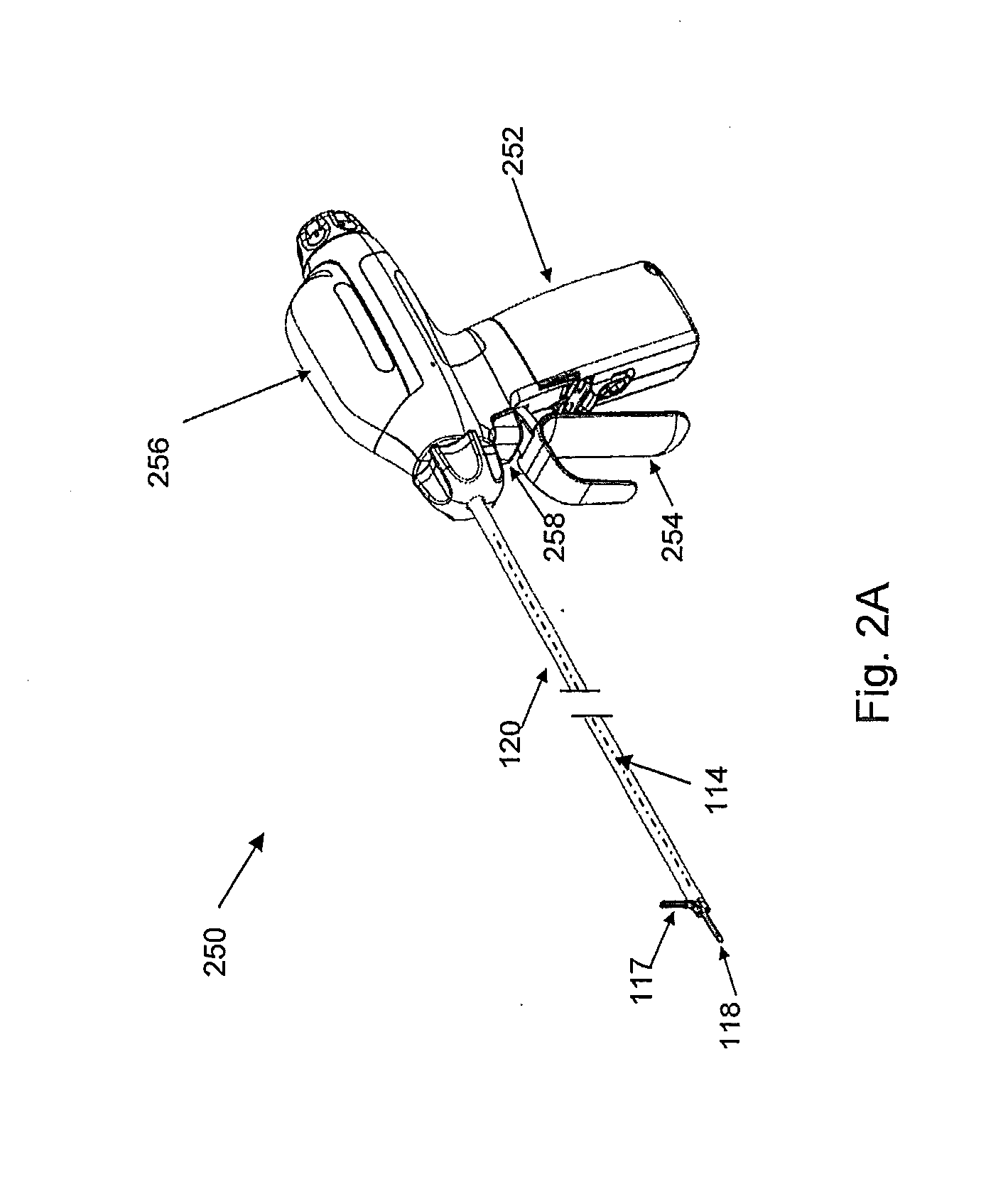
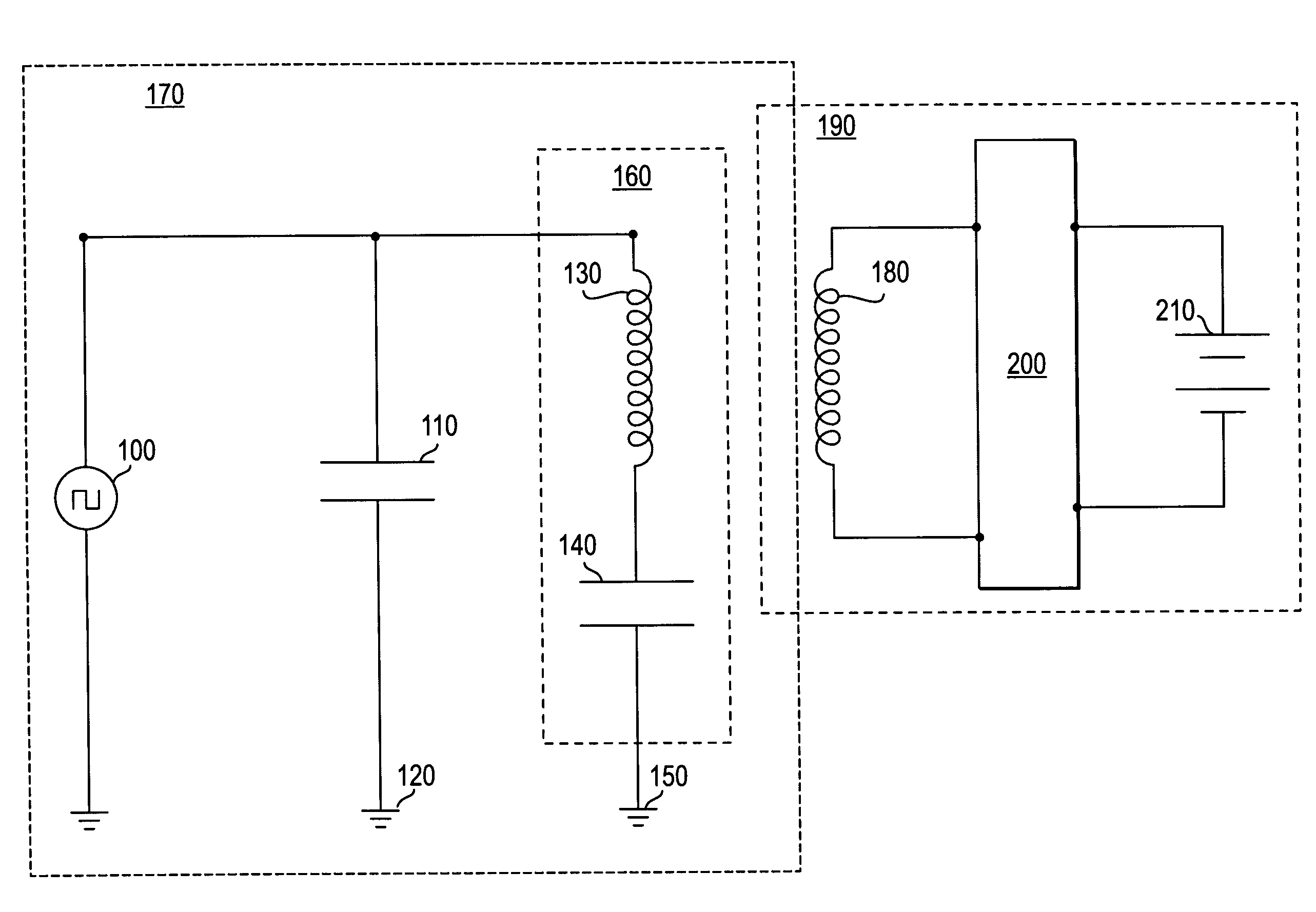
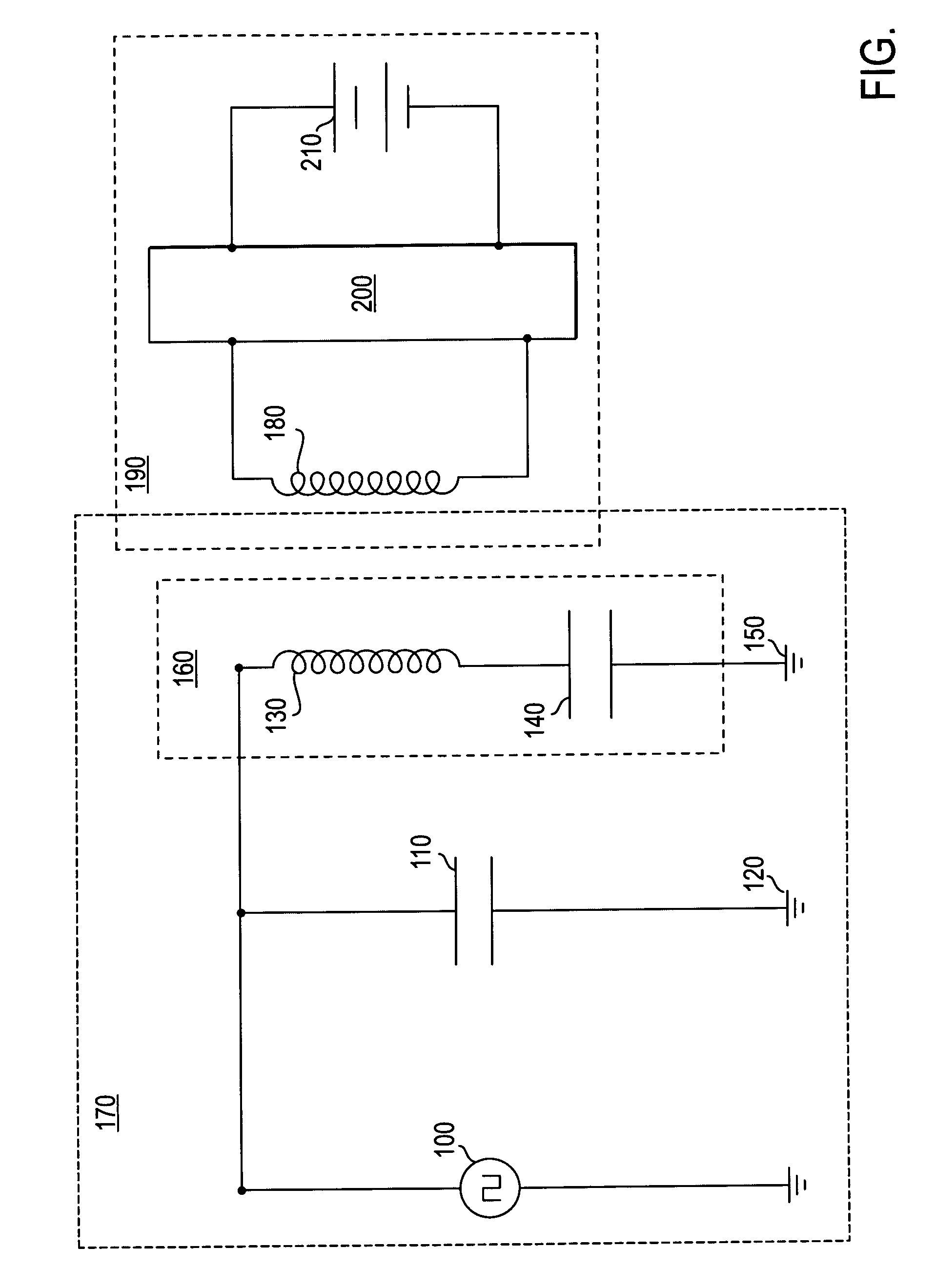
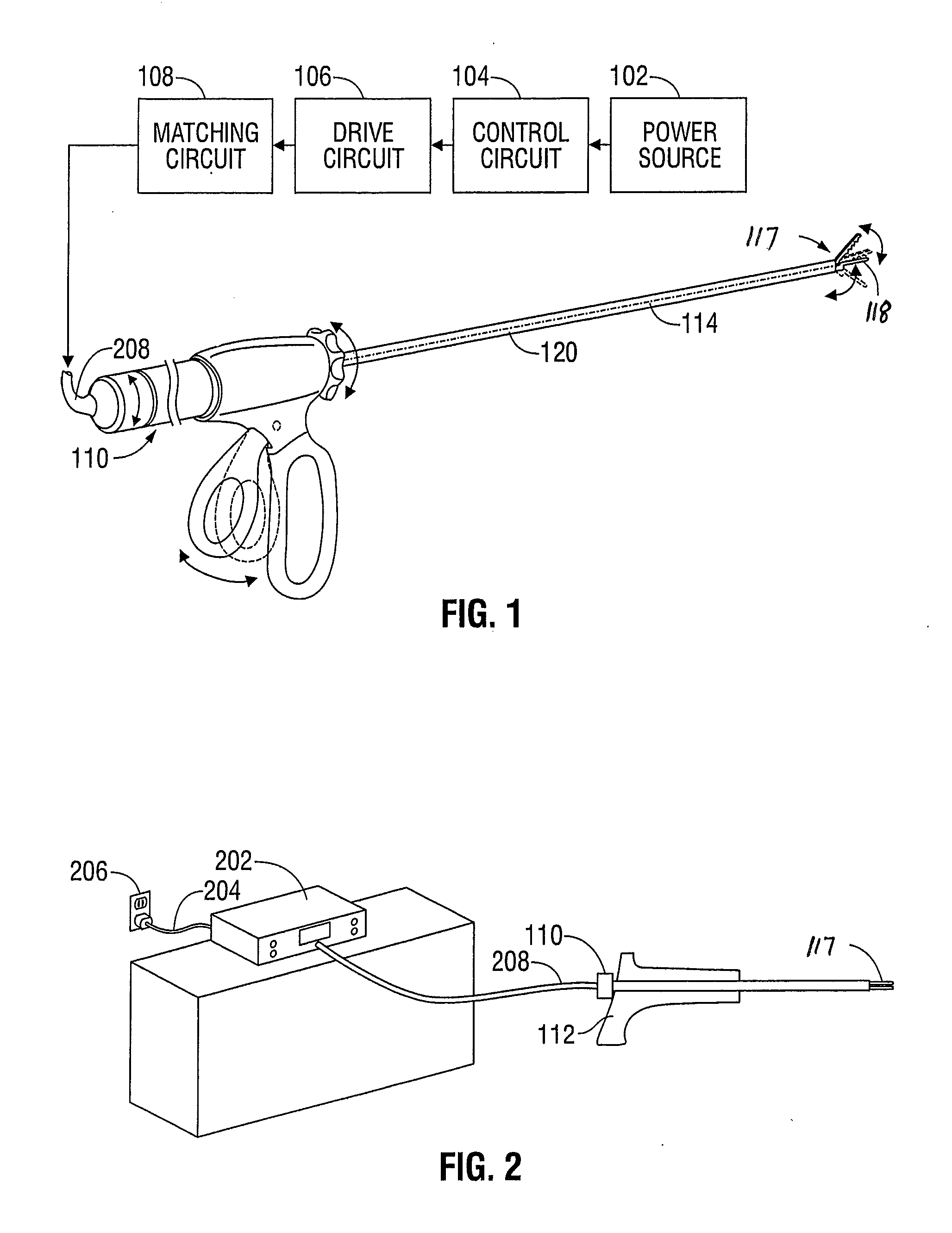
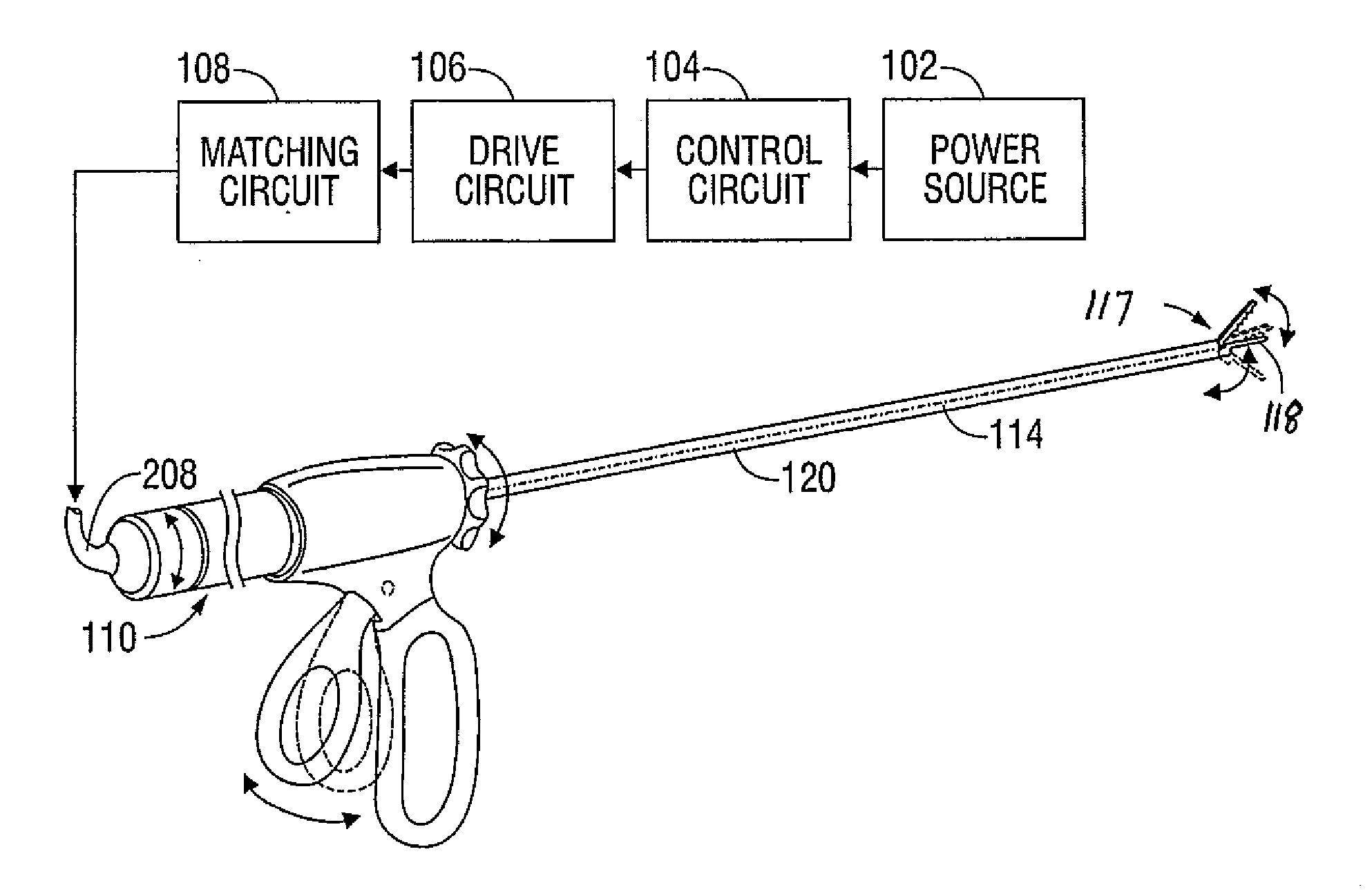
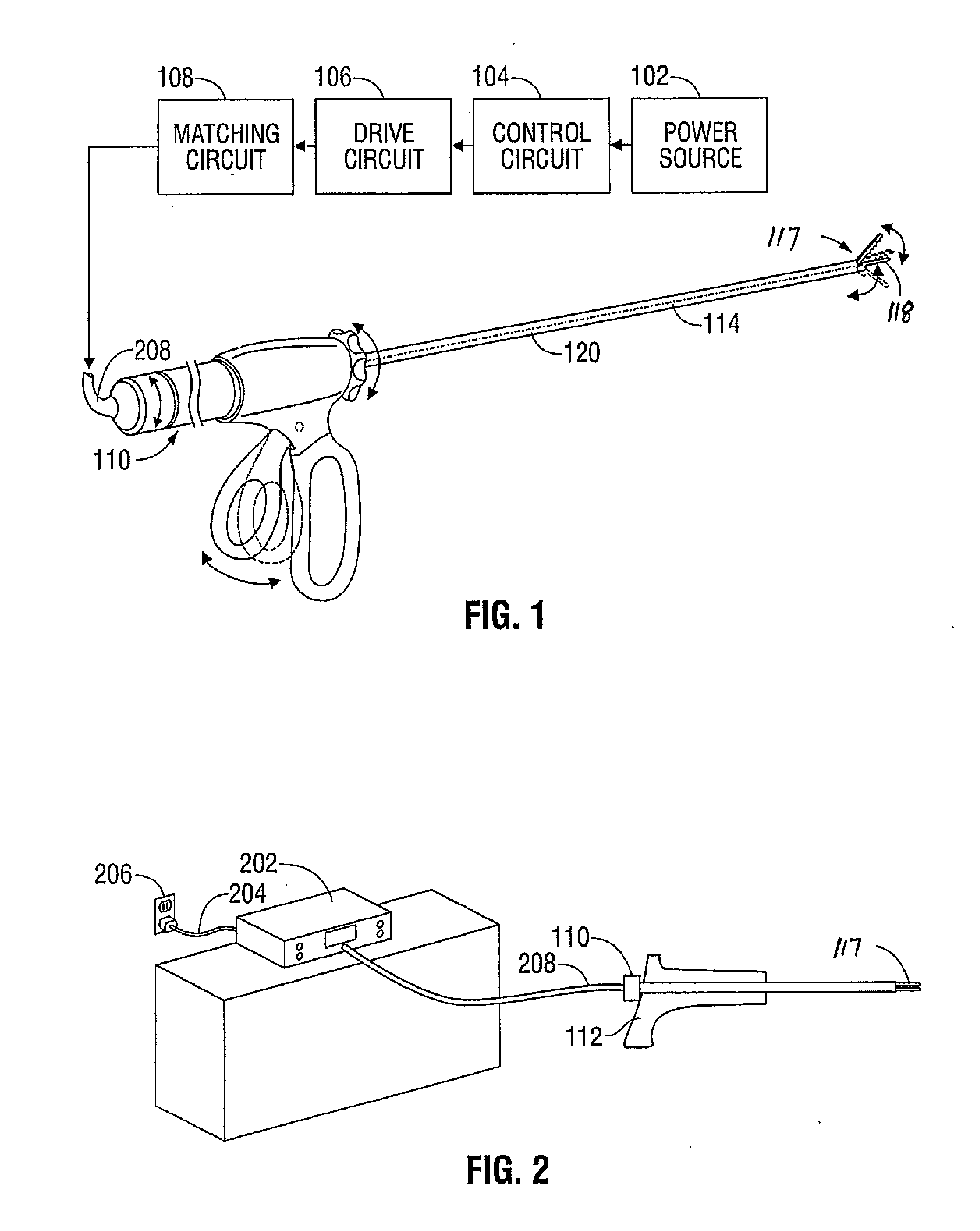
An ultrasonic surgical apparatus and method of use including a signal generator outputting a drive signal having a frequency, an oscillating structure, receiving the drive signal and oscillating at the frequency of the drive signal, a bridge circuit, detecting the mechanical motion of the oscillating structure and outputting a signal representative of the mechanical motion, and a microcontroller receiving the signal output by the bridge circuit, the microcontroller determining an instantaneous frequency at which the oscillating structure is oscillating based on the received signal, and comparing the instantaneous frequency to a known frequency value and estimating a temperature of the oscillating structure based on the comparison.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
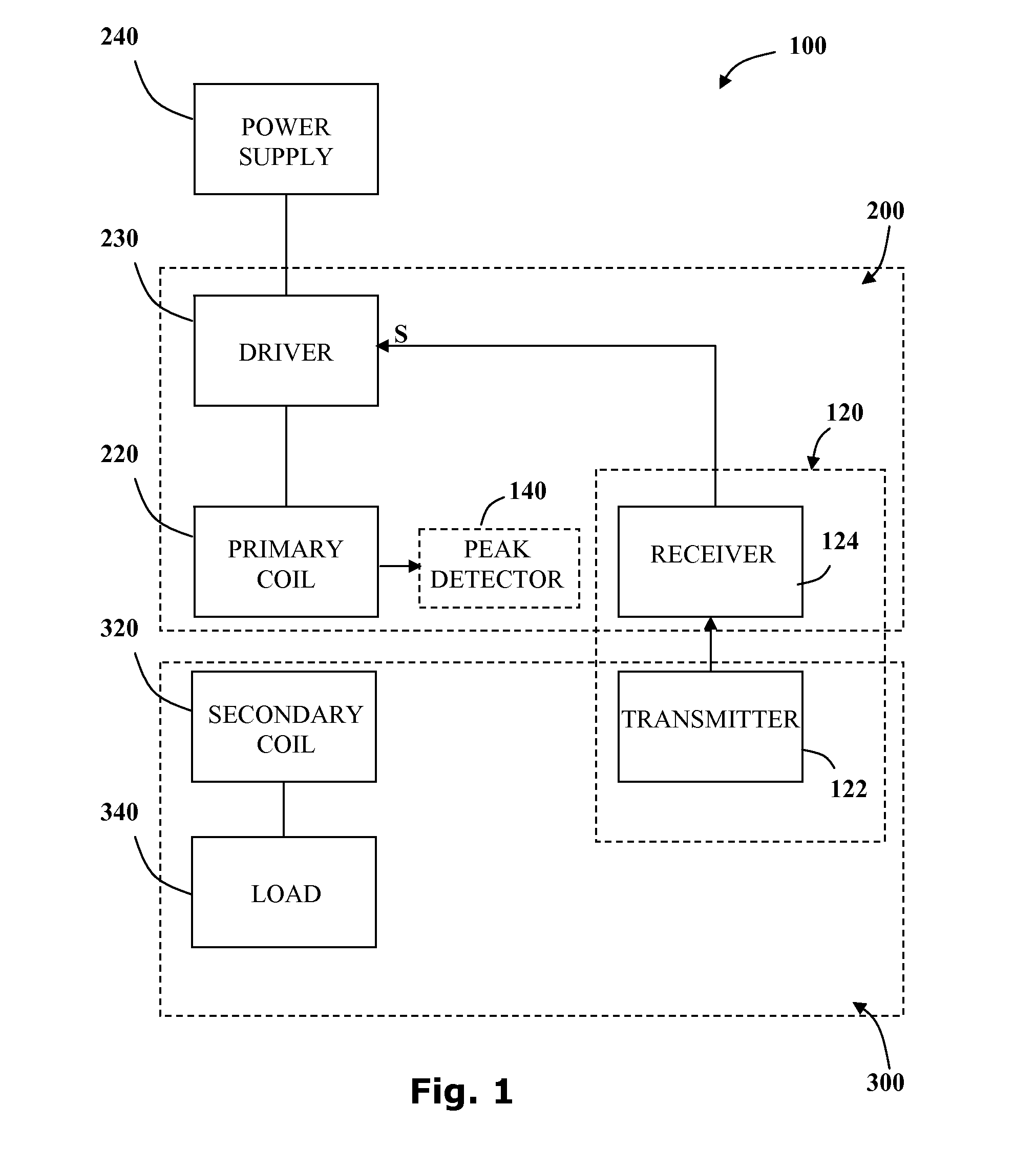
Series resonant inductive charging circuit
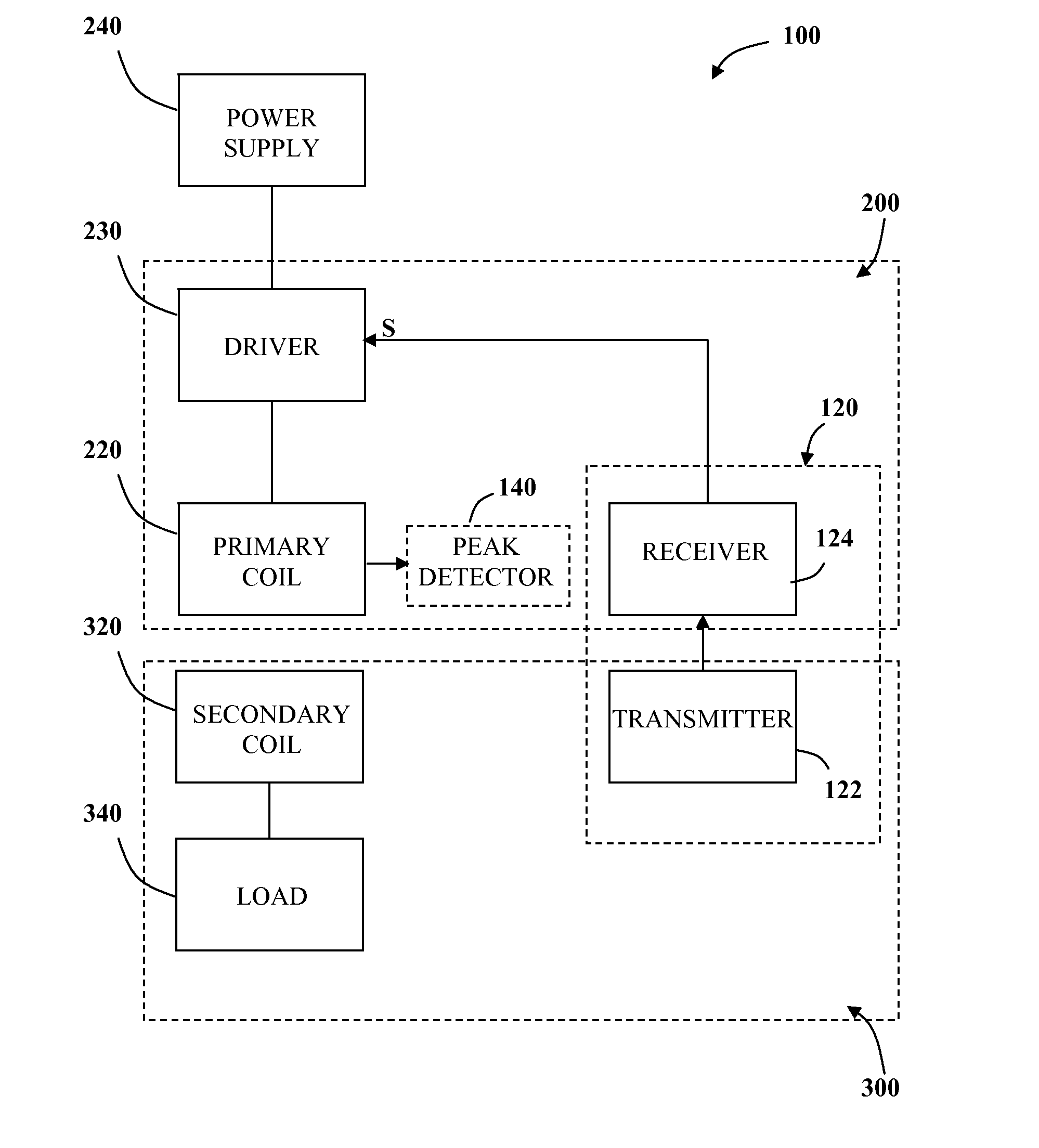
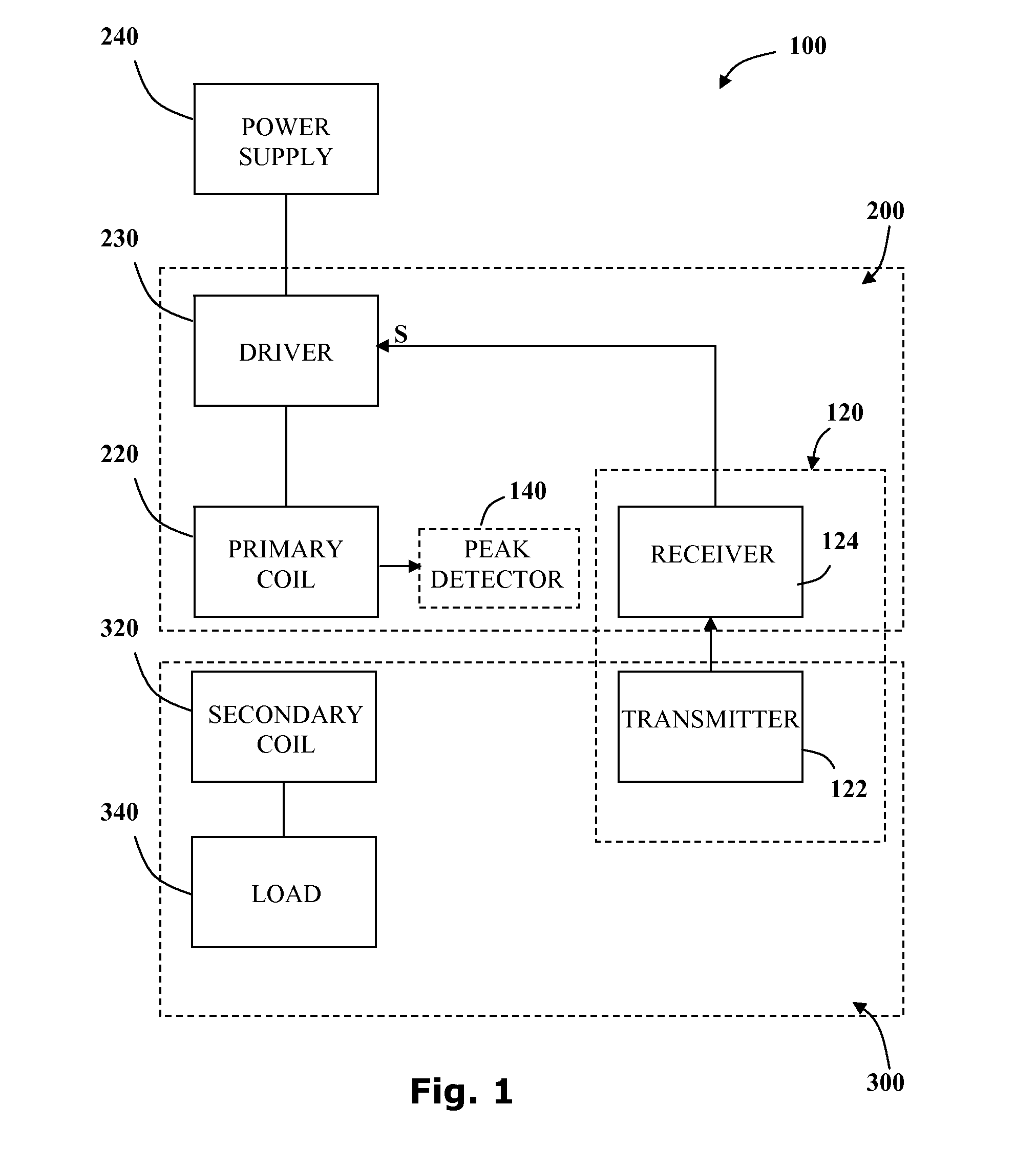
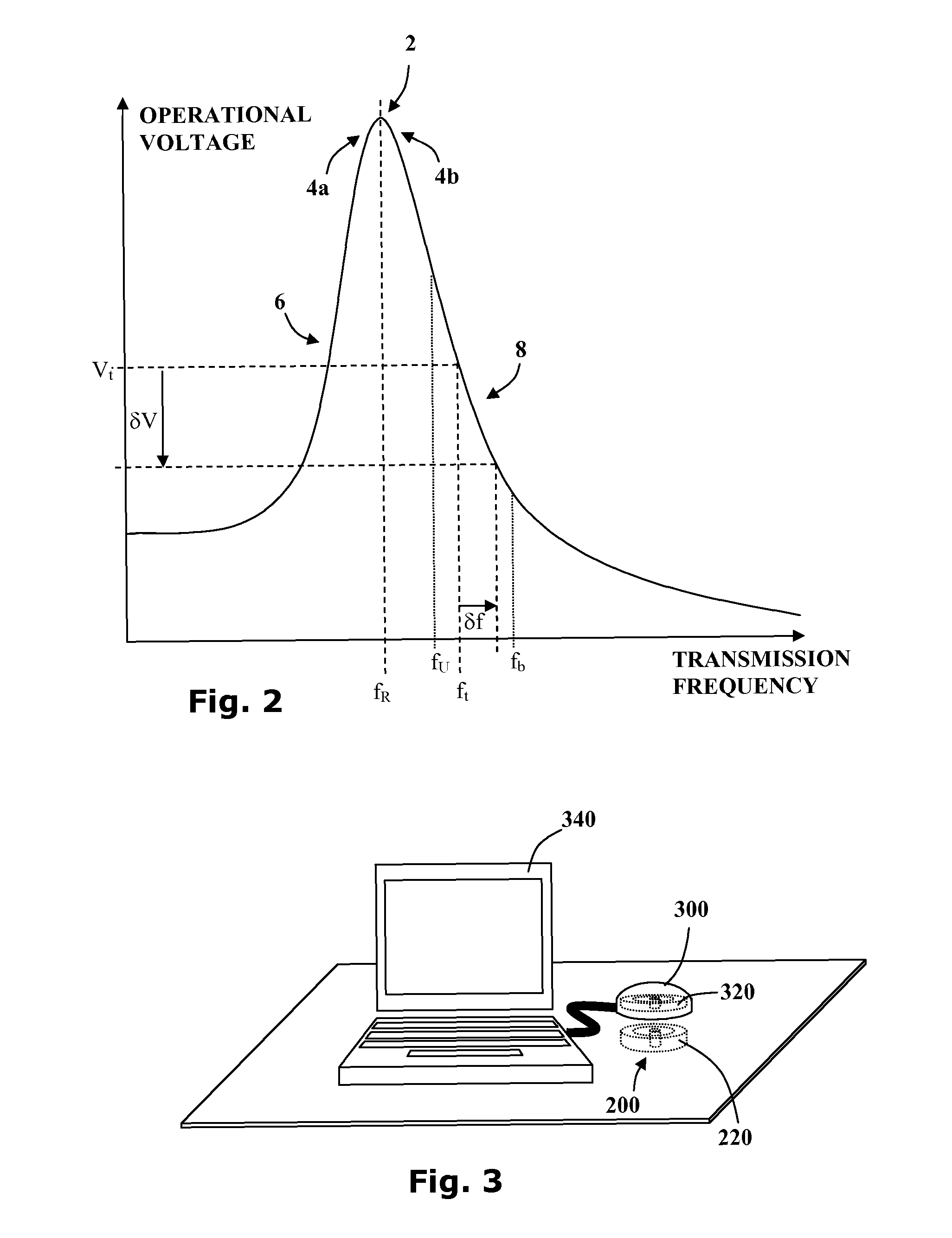
An apparatus to charge a power supply inductively, with increased efficiency due to resonance, comprises an LC series resonance circuit formed by a capacitor and a primary inductive coil coupled in series with the capacitor, and a secondary inductive coil positioned such that power is inductively transferred from the primary coil to the secondary coil. The LC circuit has a natural resonant frequency, wherein the primary coil of the resonance circuit is coupled to receive power from a source oscillating at the natural resonant frequency. The secondary coil is further coupled to the power supply so that power induced in the secondary coil causes the power supply to be charged.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Temperature estimation and tissue detection of an ultrasonic dissector from frequency response monitoring
An ultrasonic surgical apparatus including a first signal generator outputting a drive signal at a predetermined voltage and frequency, a first oscillating structure receiving the drive signal and oscillating at the frequency of the drive signal, and a bridge circuit, detecting the mechanical motion of the first oscillating structure and outputting a signal representative of the mechanical motion. The apparatus also includes a second oscillating structure integrally formed within a portion of the first oscillating structure, the second oscillating structure outputting an electrical signal, and a microcontroller receiving the signal output by the bridge circuit and output by the second oscillating structure, the microcontroller determining an instantaneous frequency at which the first oscillating structure is oscillating based on the received signal, comparing the electrical signal from the second oscillating structure with a known signal value and determining the temperature of the second oscillating structure based on a the comparison.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
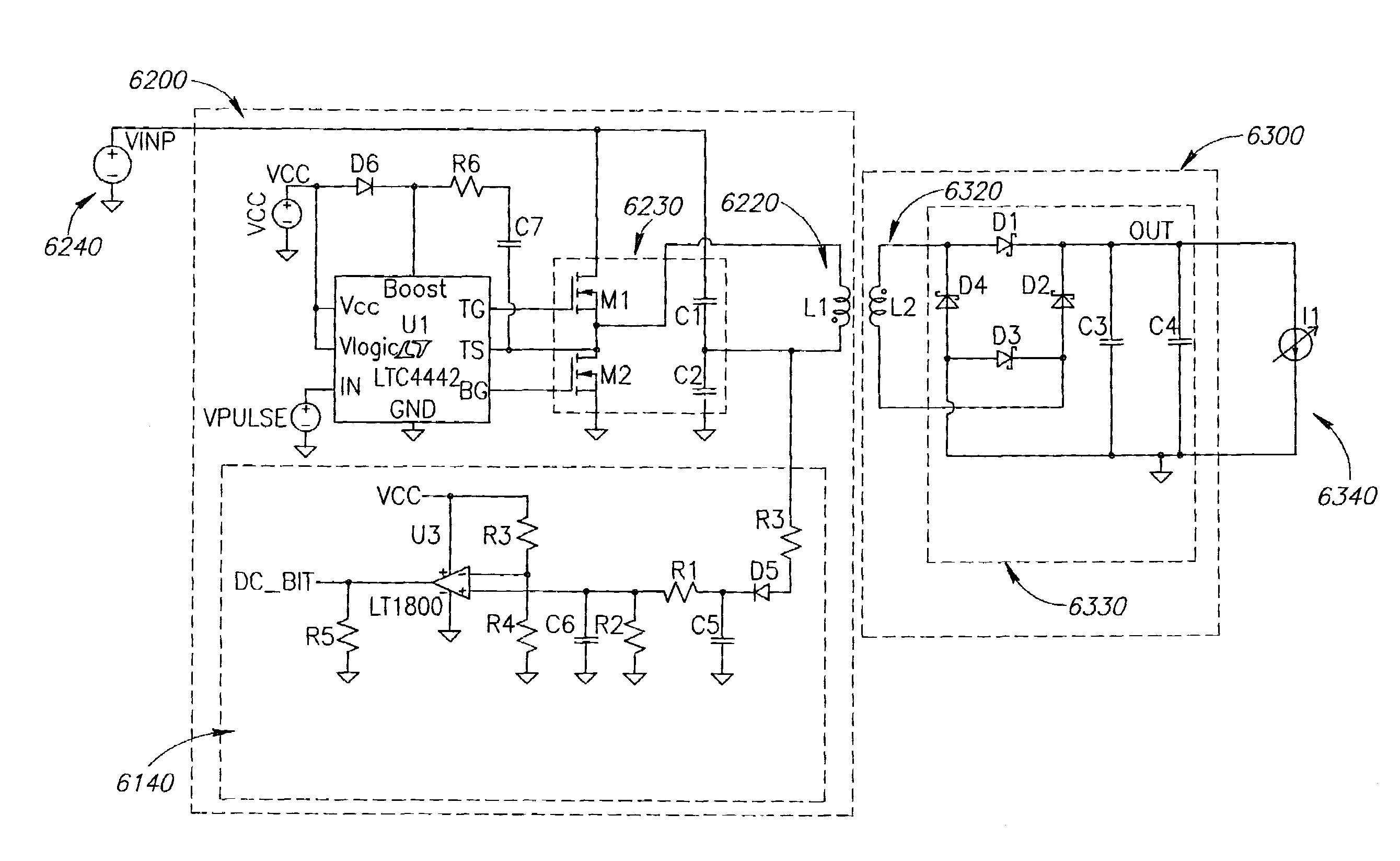
Non resonant inductive power transmission system and method
ActiveUS20100066176A1TransformersEfficient power electronics conversionElectric power transmissionEngineering
Non-resonant inductive power transmission wherein the driving voltage across a primary inductor oscillates at a frequency significantly different from the resonant frequency of the inductive coupling system. Embodiments of the invention include systems and methods for: power regulation using frequency control, fault detection using voltage peak detectors and inductive communication channels.
Owner:POWERMAT TECHNOLOGIES
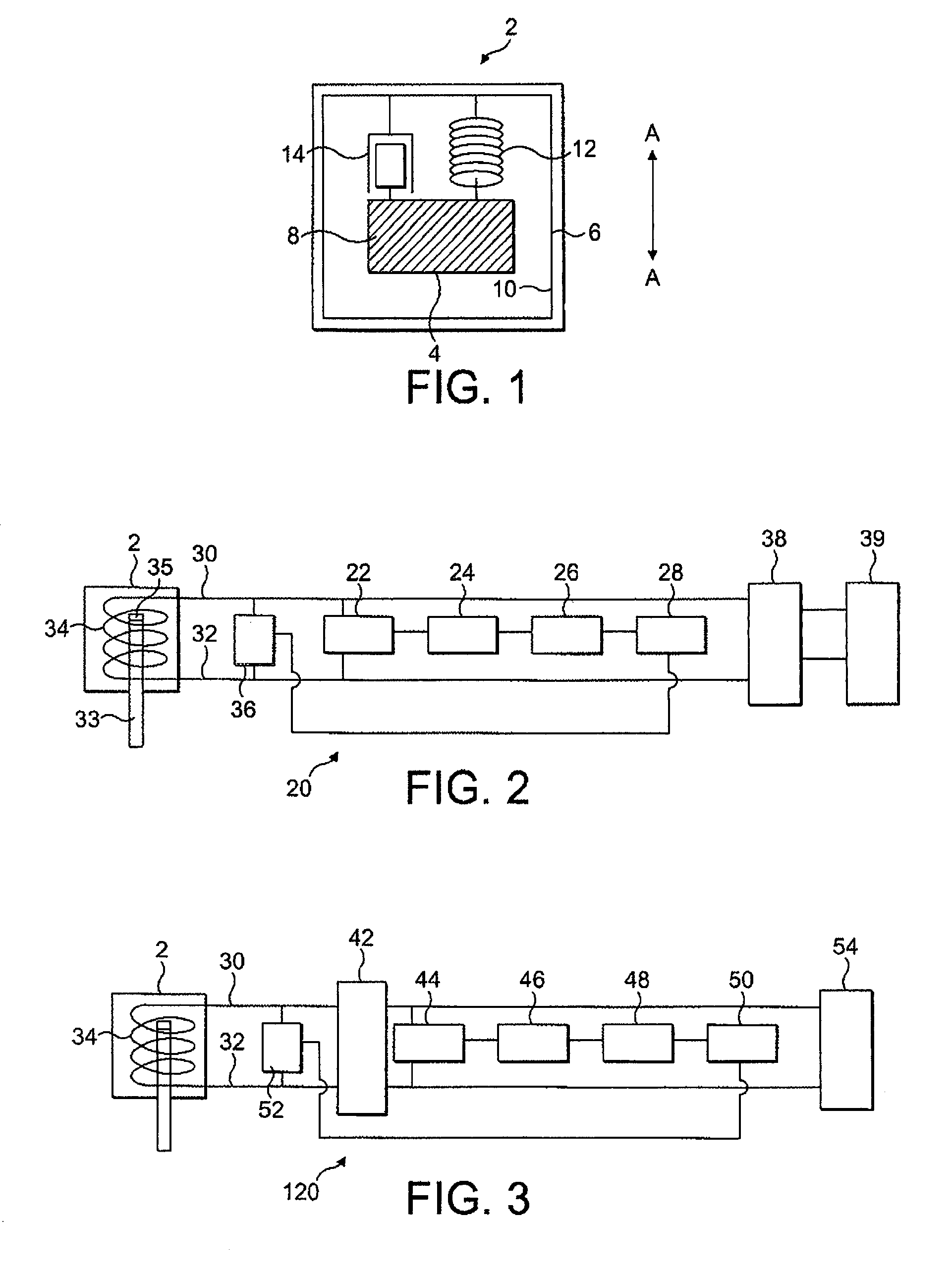
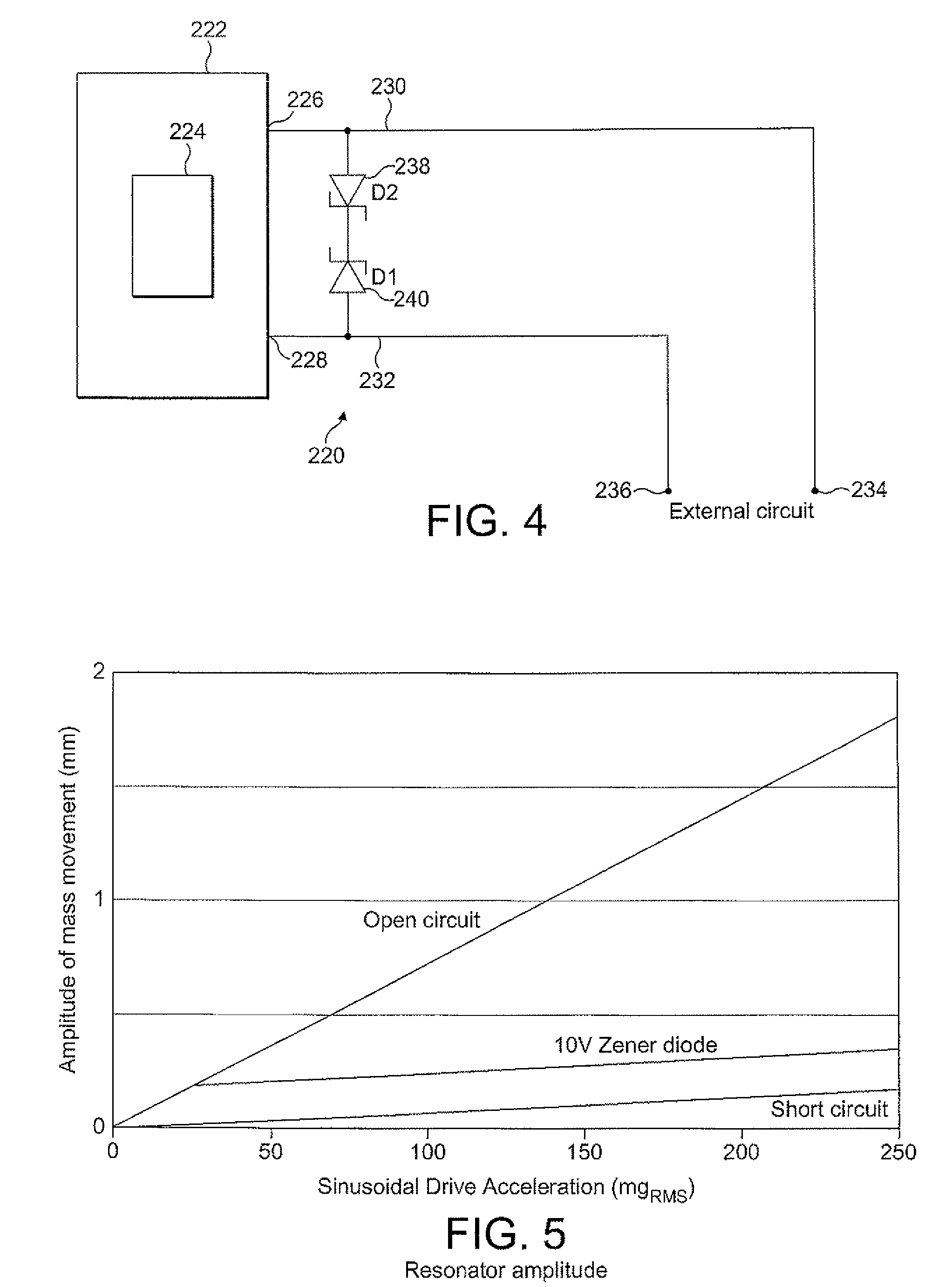
Electromechanical generator for, and method of, converting mechanical vibrational energy into electrical energy
ActiveUS7345372B2Reduce the possibility of damageEasy to operateGeneration protection through controlMachines/enginesEngineeringFrequency oscillation
An electromechanical generator comprising an electromechanical device for converting mechanical vibrational energy into electrical energy, the electromechanical device having a vibratable mass adapted to resonate with an oscillation amplitude at a frequency and a regulator for regulating the oscillation amplitude to a value not greater than a maximum threshold.
Owner:PERPETUUM +1
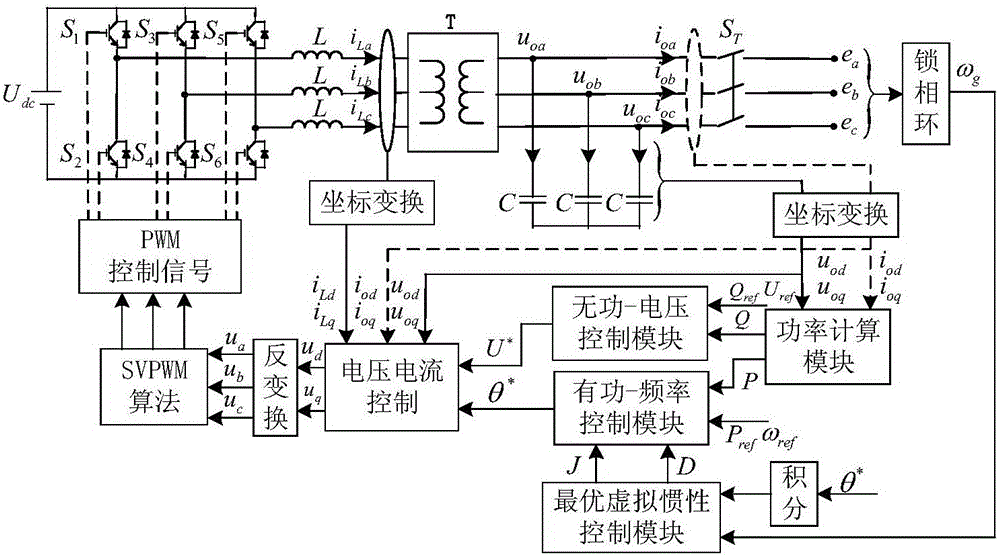
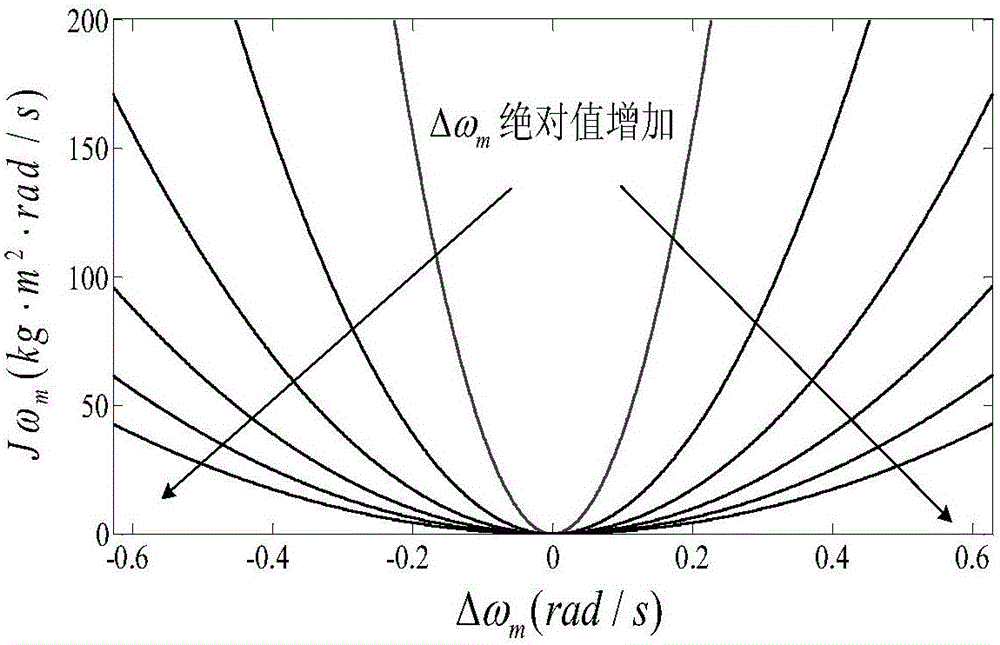
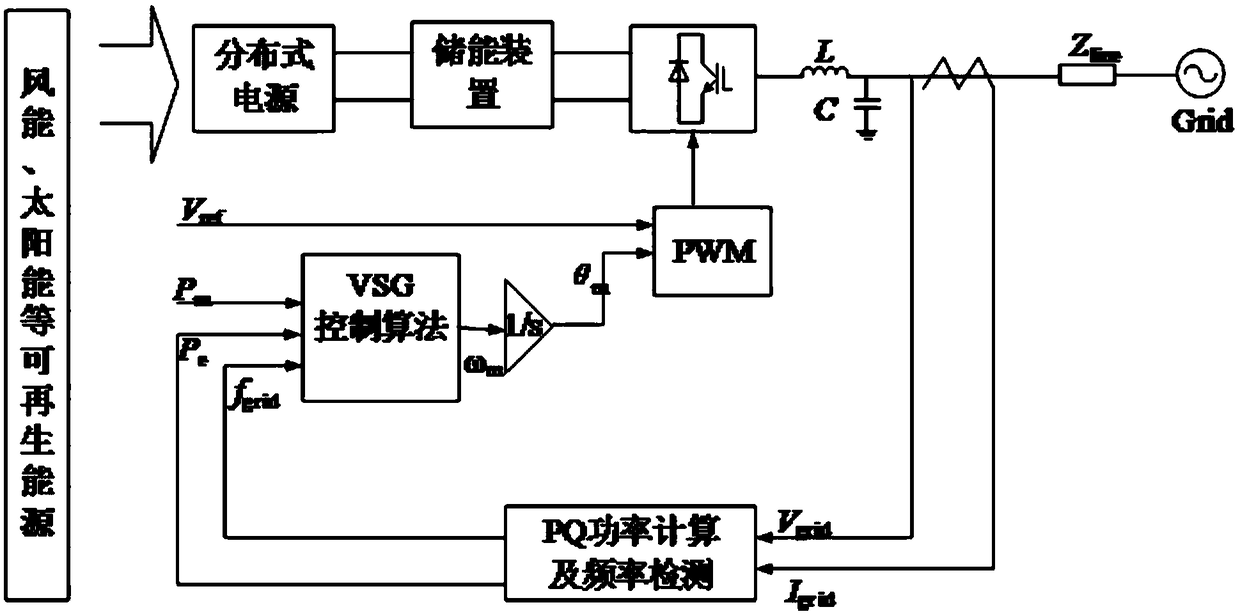
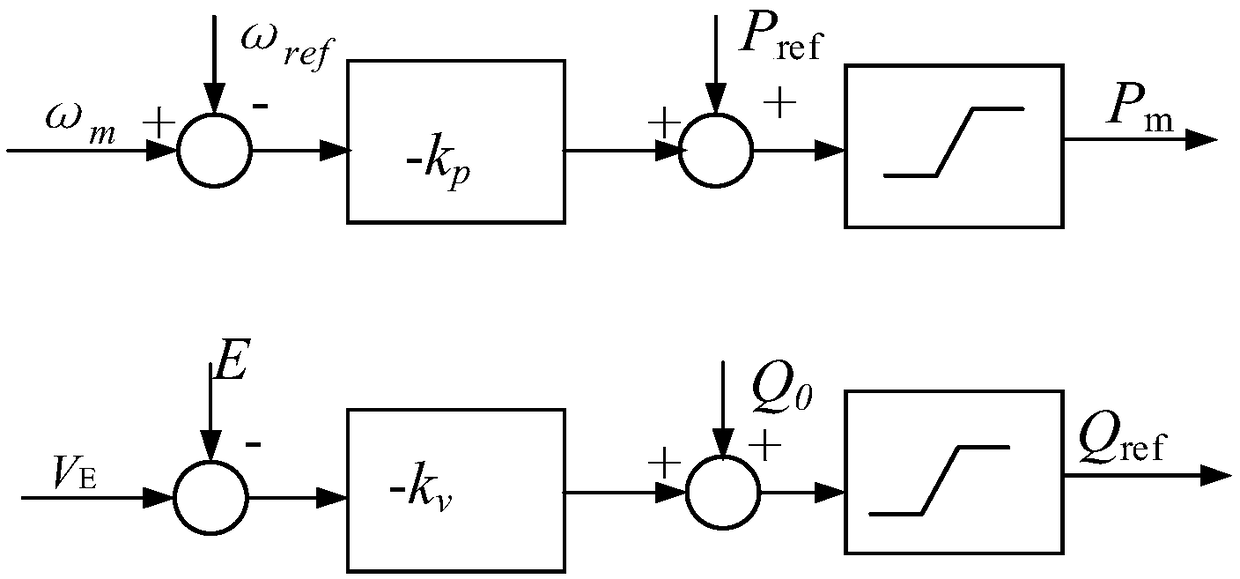
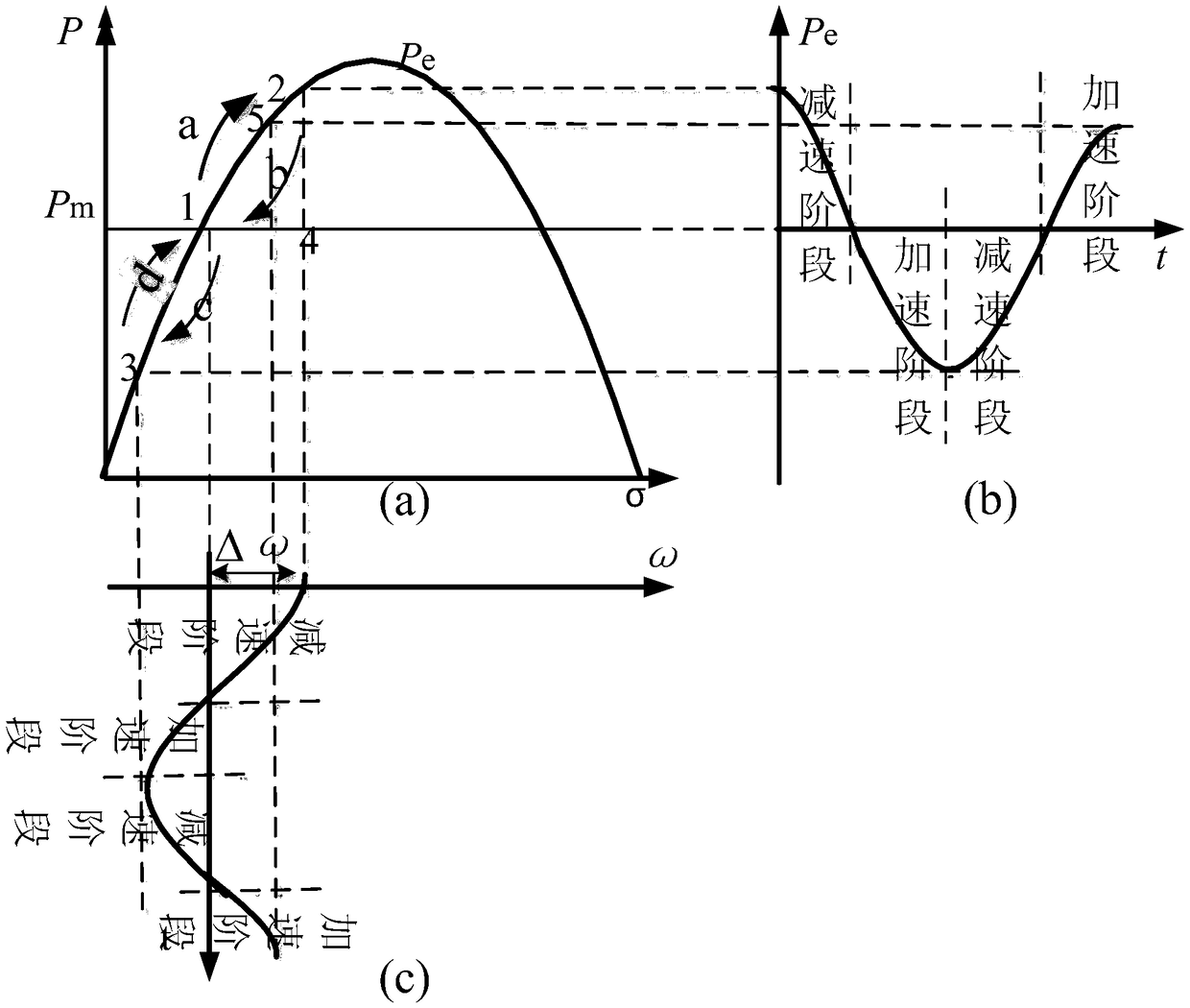
Optimal virtual inertia control method based on virtual synchronous generator
ActiveCN105006834AFully reflect the inertia advantageImprove stabilityEnergy industrySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsVirtual synchronous generatorSimulation
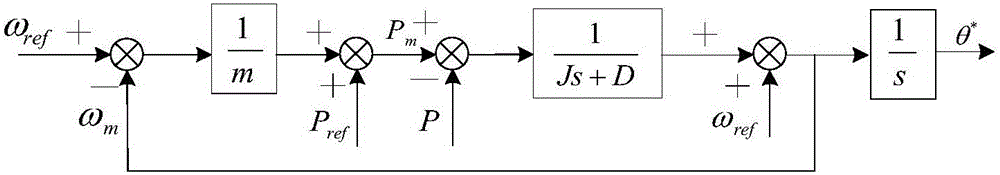
The invention discloses an optimal virtual inertia control method based on a virtual synchronous generator in the distributed power generation control field. According to the method, a control strategy of a virtual synchronous generator is employed for a micro-grid inverter to organically combine three control degrees of freedom including a droop coefficient m, a virtual inertia J and a virtual damping D, and thus optimization of key parameters of the virtual synchronous generator is achieved. Through adoption of the method, the inertia advantage of a conventional synchronous generator is fully exhibited, and the stability and the inherent dynamic performance of an inverter are also taken into consideration. Moreover, the output power and frequency oscillation problems brought by virtual inertia are solved while the power and the capacity configuration of an energy storage apparatus are considered.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Device for RF control
InactiveUS6417634B1High RF electrode voltageNuclear energy generationMagnetic resonance acceleratorsAudio power amplifierResonance
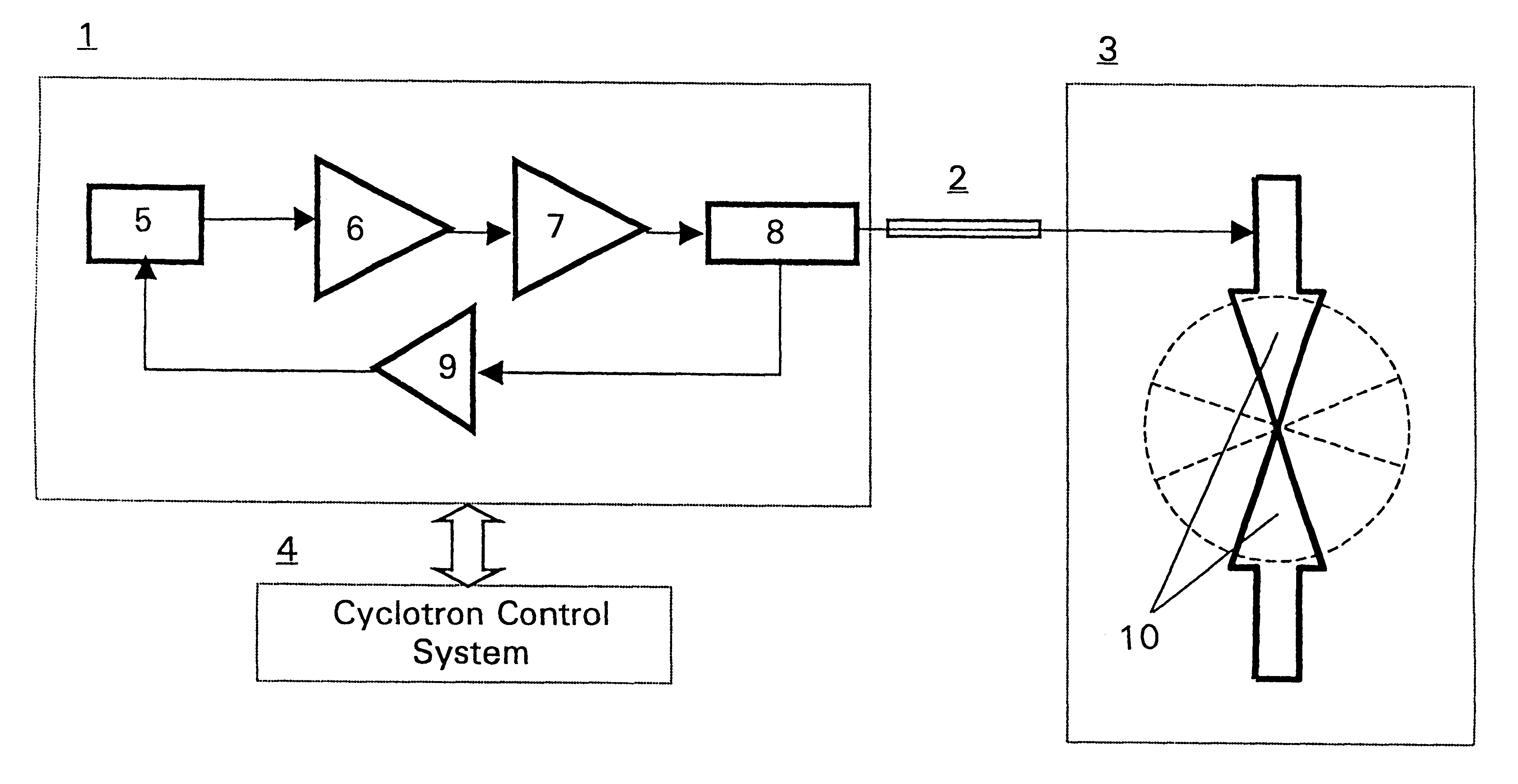
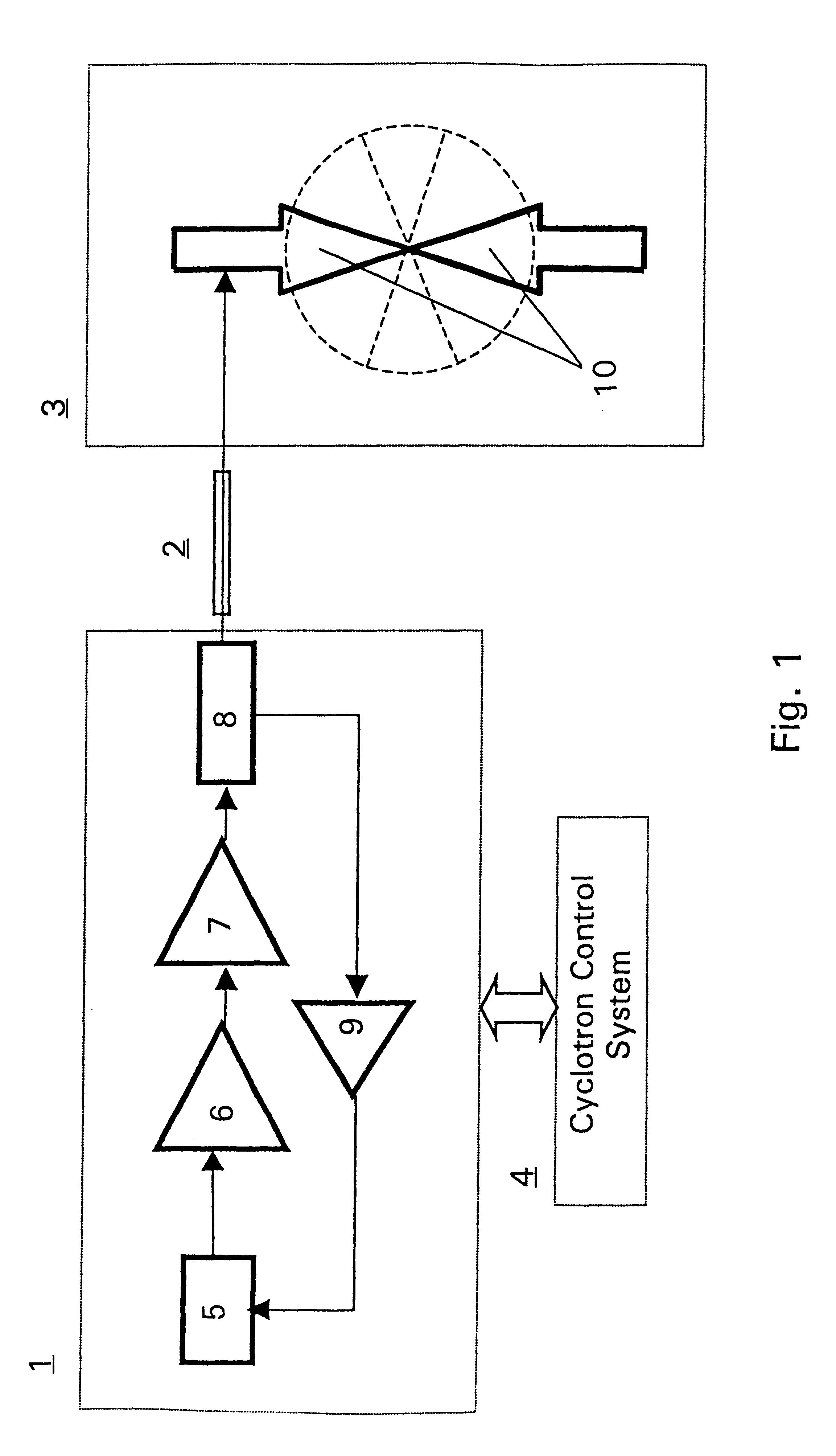
A method and a system for obtaining a proper resonance of the RF electrodes when using a preset or predetermined stable frequency oscillator in a cyclotron accelerator without using mechanical tuning devices. In order to maintain a high RF electrode voltage during operation the RF electrode system resonance is monitored and the frequency of the stable frequency generator is controlled by a feedback system continuously monitoring the matching of the oscillator output frequency and the resonance of the RF electrode system. Necessary small adjustments of the stable oscillator frequency to maintain a maximum matching to the resonance frequency of the RF electrode system are obtained by means of the feedback system to the stable oscillator. The feedback system relies on measured values obtained by a load phase sensor monitoring the output of the final RF power amplifier. A cyclotron control system in turn obtains the set and corrected oscillator frequency value and fine tunes further the magnetic field created in the accelerator device according to the frequency information obtained.
Owner:GEMS PET SYST
Nanomechanical Oscillator
ActiveUS20090294638A1Easy to detectHigh-frequency oscillationSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansResonanceFrequency oscillation
A mechanical oscillator has components with dimensions in a sub-micron range to produce resonance mode oscillations in a gigahertz range. A major element is coupled to a minor, sub-micron element to produce large amplitude gigahertz frequency oscillation that is detected with readily available techniques. The mechanical structure can be formed according to a number of geometries including beams and rings and is excited with electrostatic, magnetic and thermal related forces, as well as other excitation techniques. The mechanical structure can be arranged in arrays for applications such as amplification and mixing and is less sensitive to shock and radiative environments than electrical or optical counterparts.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Electromechanical generator for, and method of, converting mechanical vibrational energy into electrical energy
ActiveUS20070210580A1Reduce the possibility of damageExtended service lifeGeneration protection through controlMachines/enginesEngineeringFrequency oscillation
An electromechanical generator comprising an electromechanical device for converting mechanical vibrational energy into electrical energy, the electromechanical device having a vibratable mass adapted to resonate with an oscillation amplitude at a frequency and a regulator for regulating the oscillation amplitude to a value not greater than a maximum threshold.
Owner:PERPETUUM +1
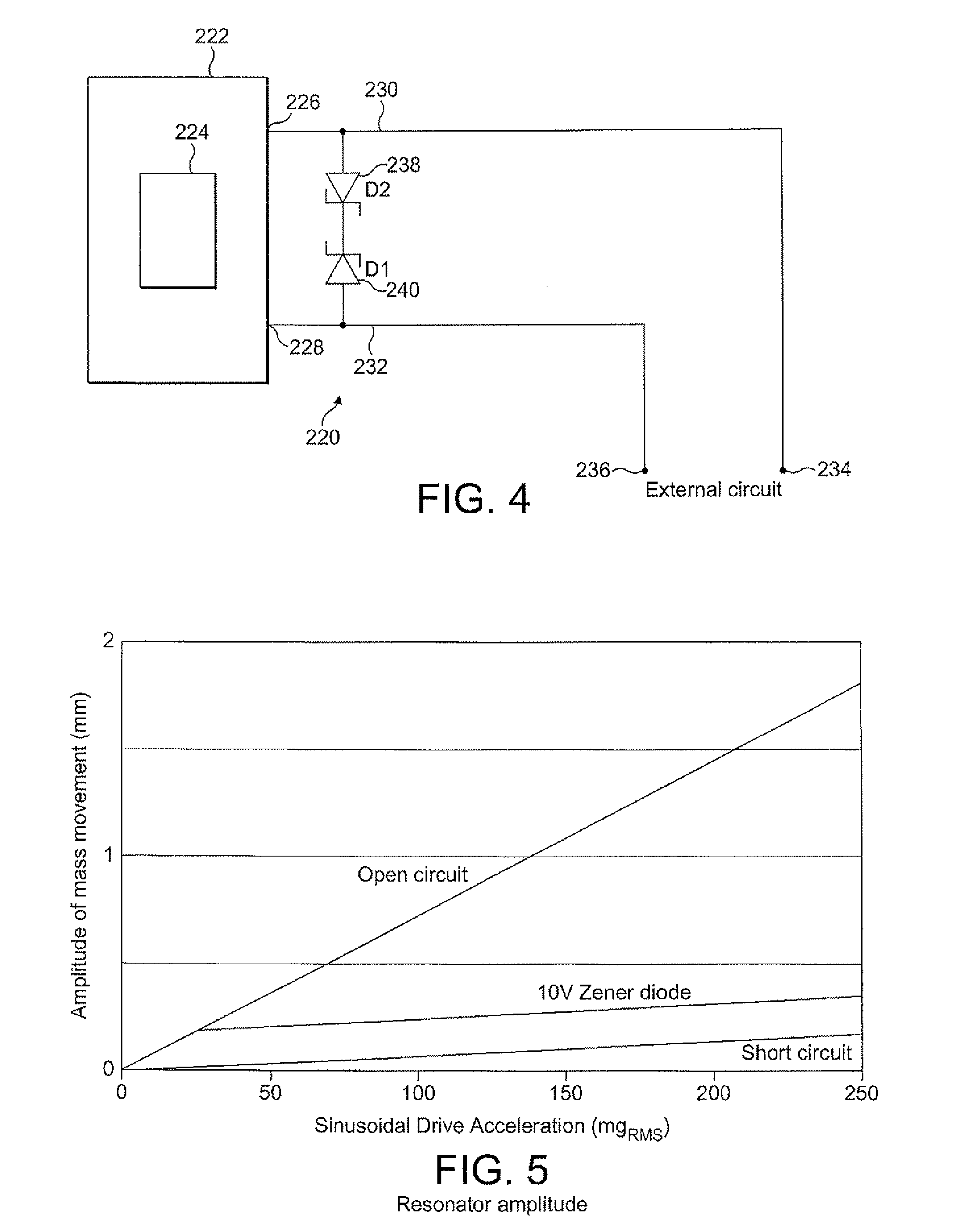
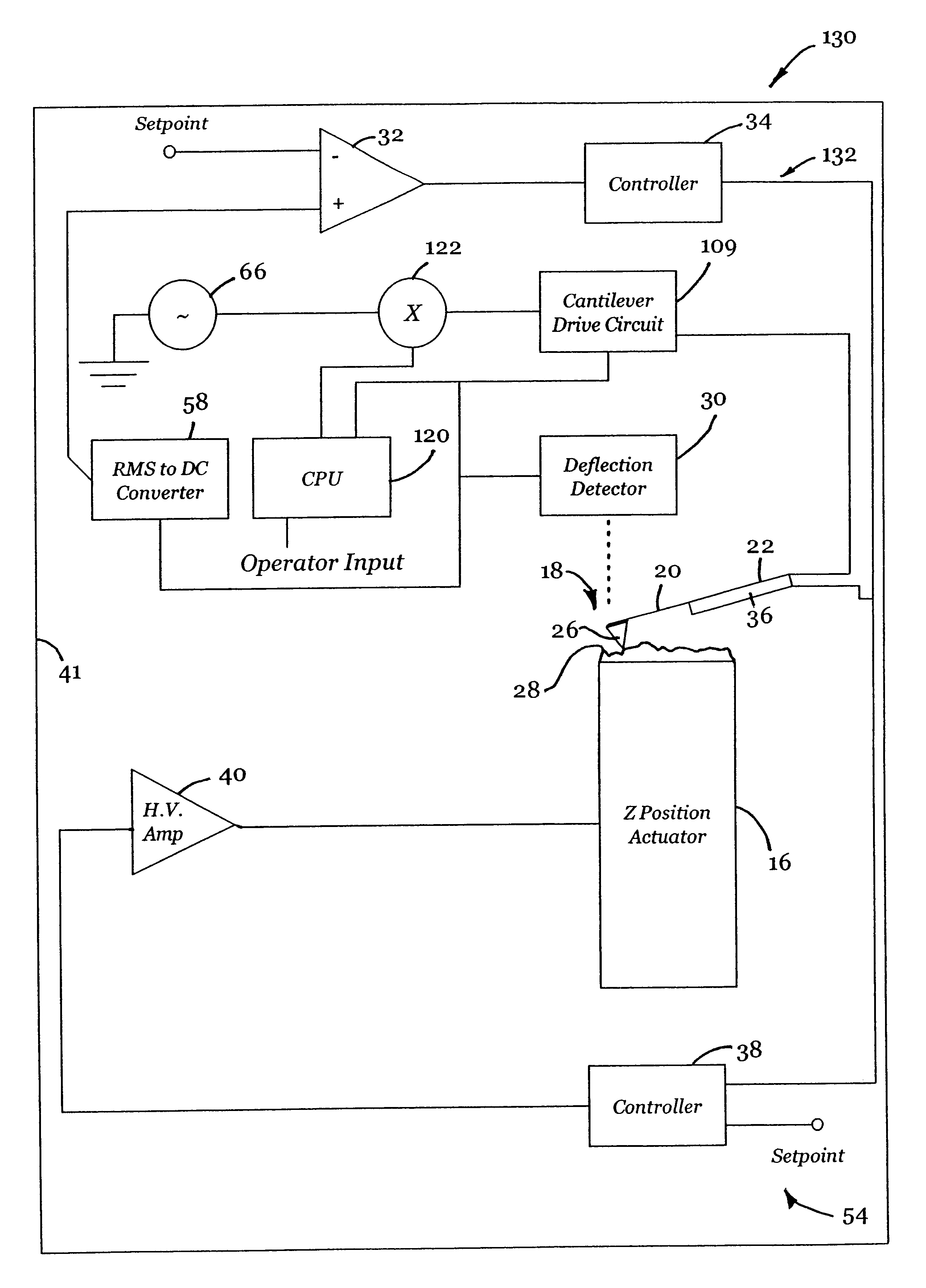
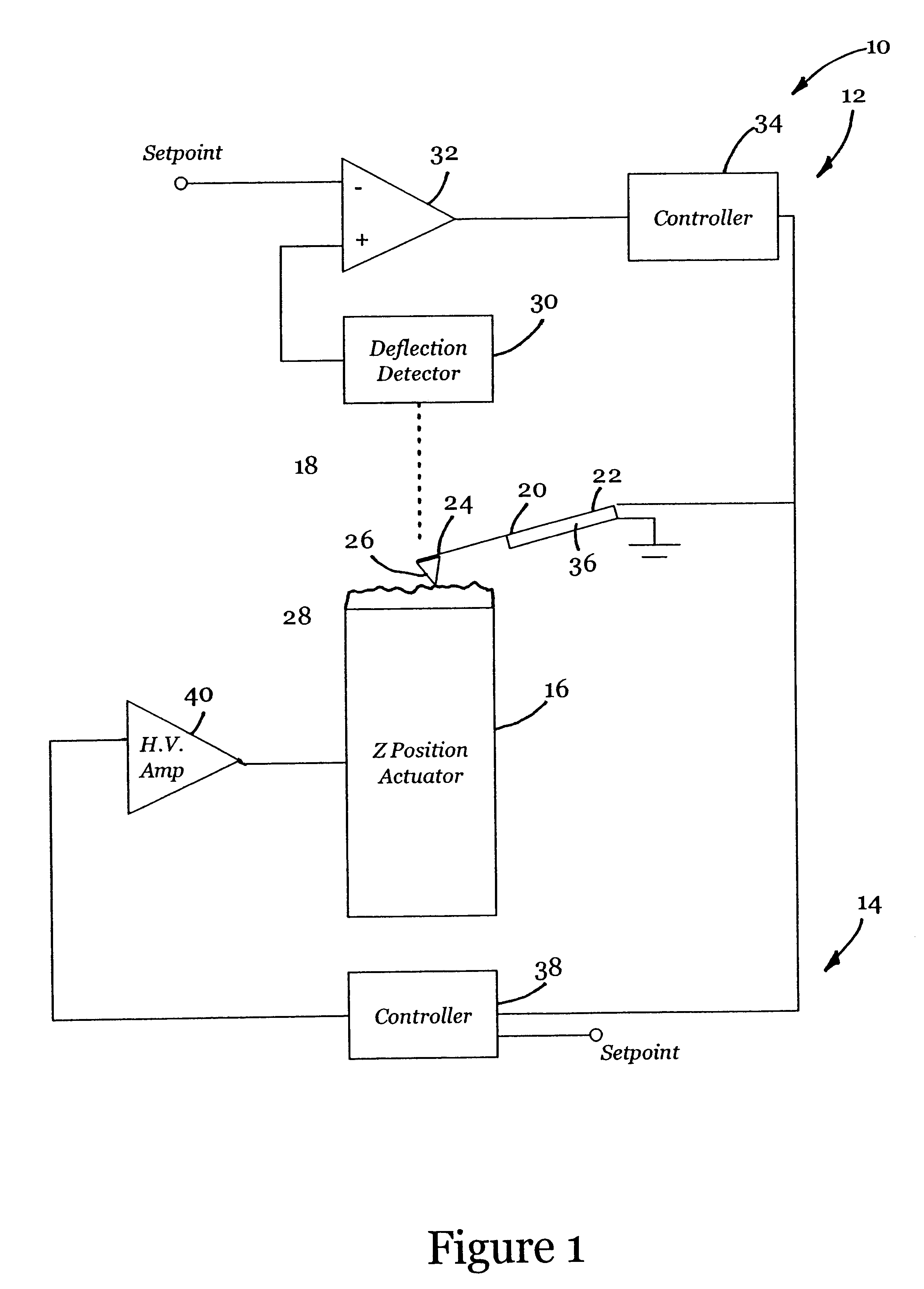
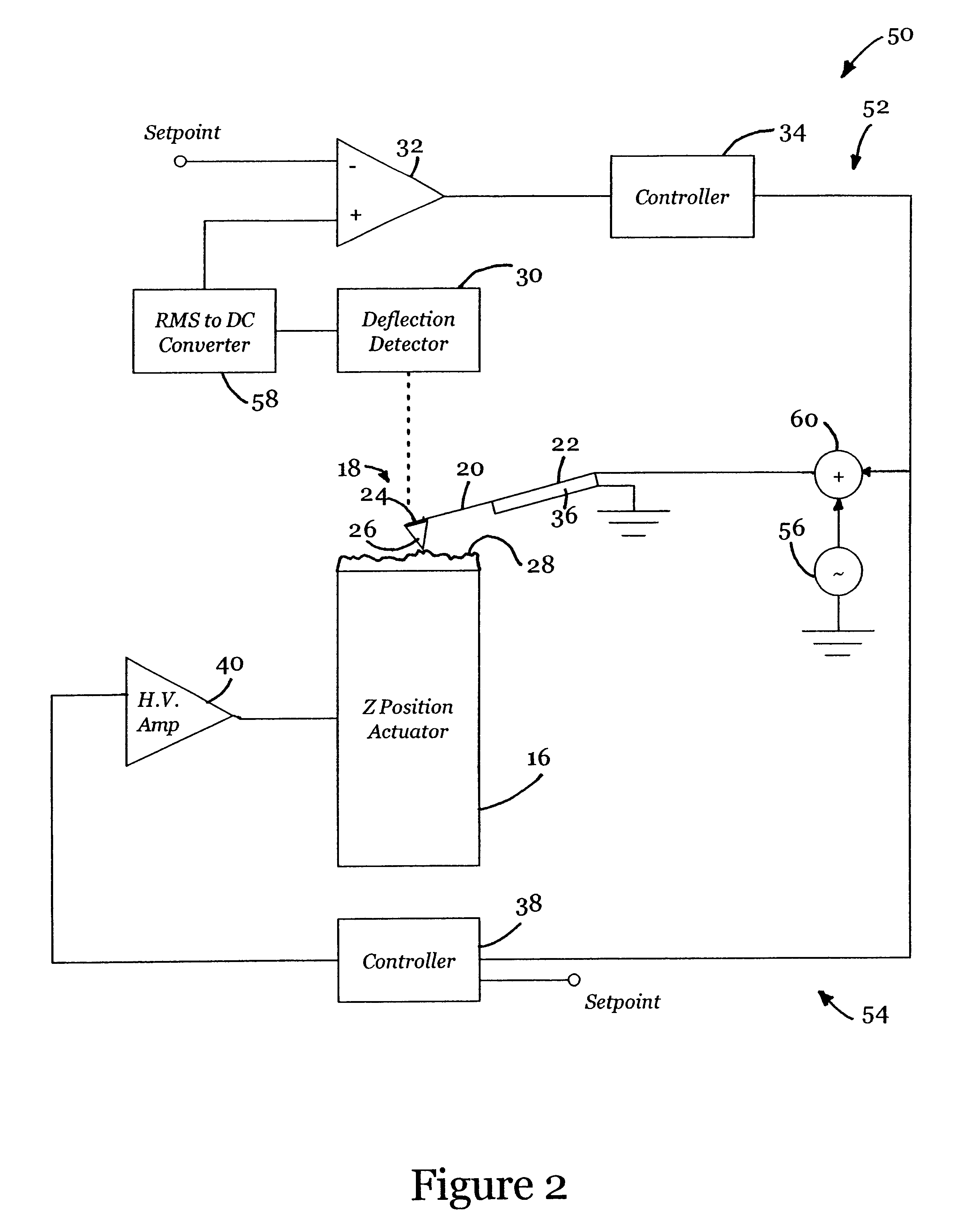
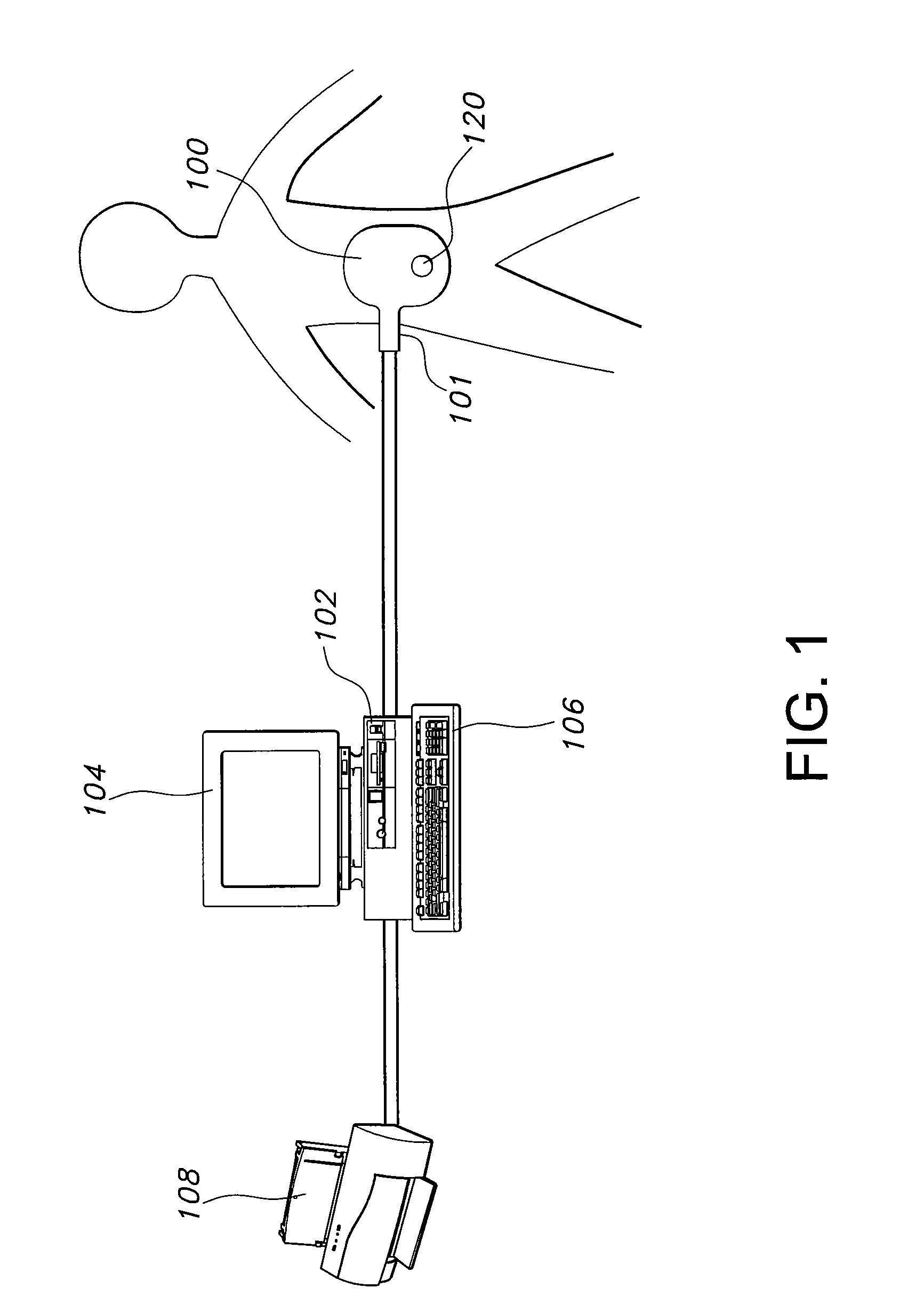
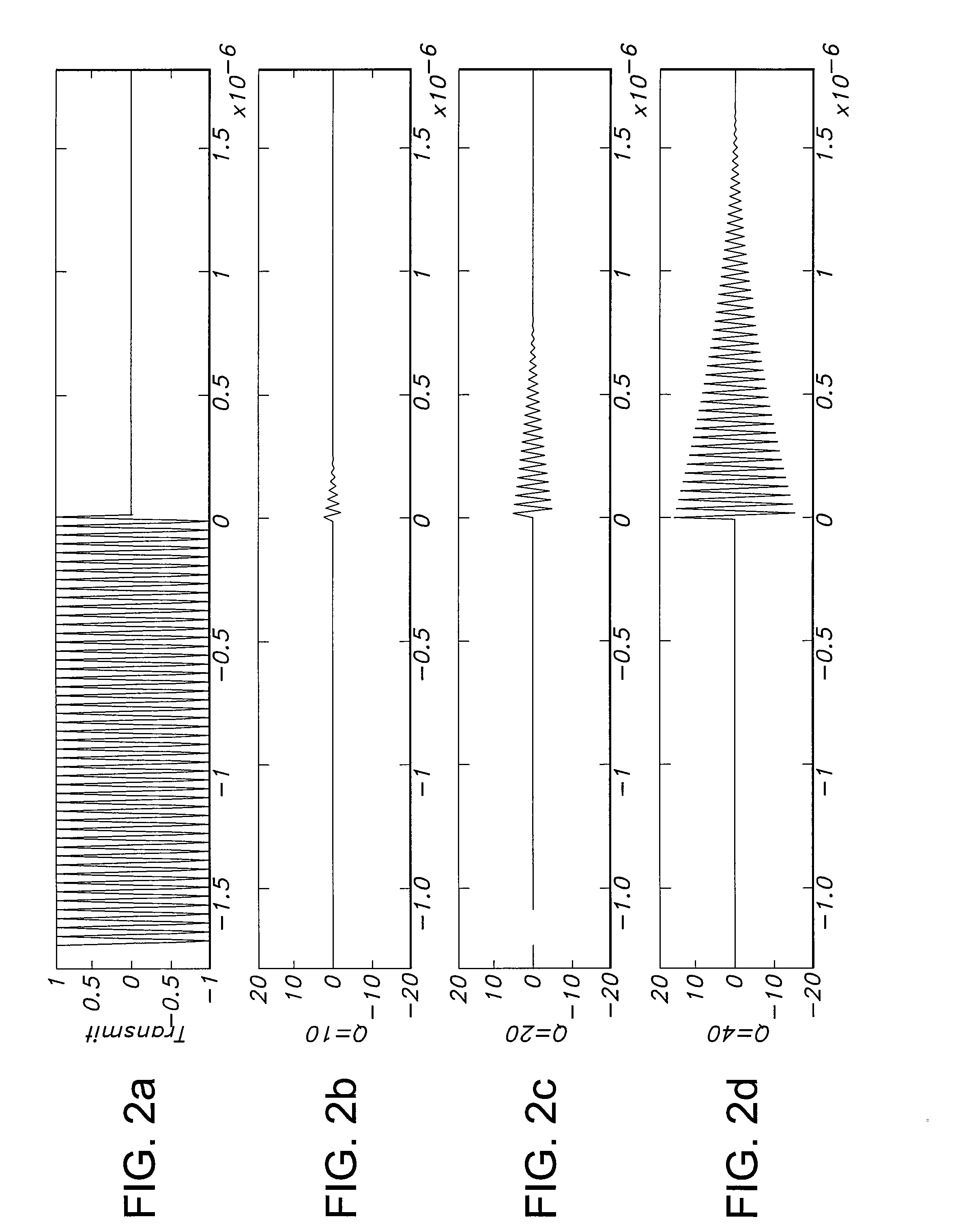
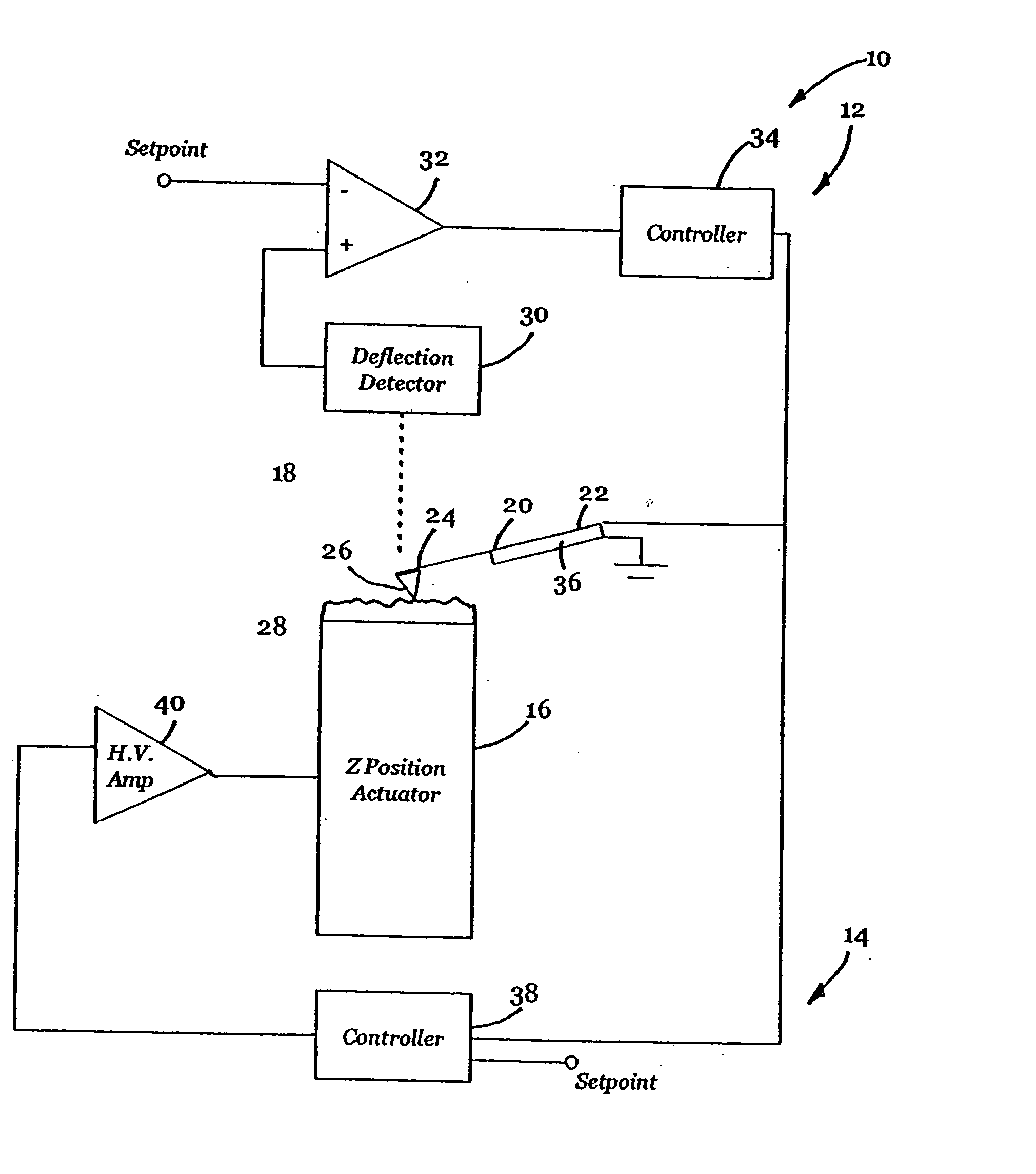
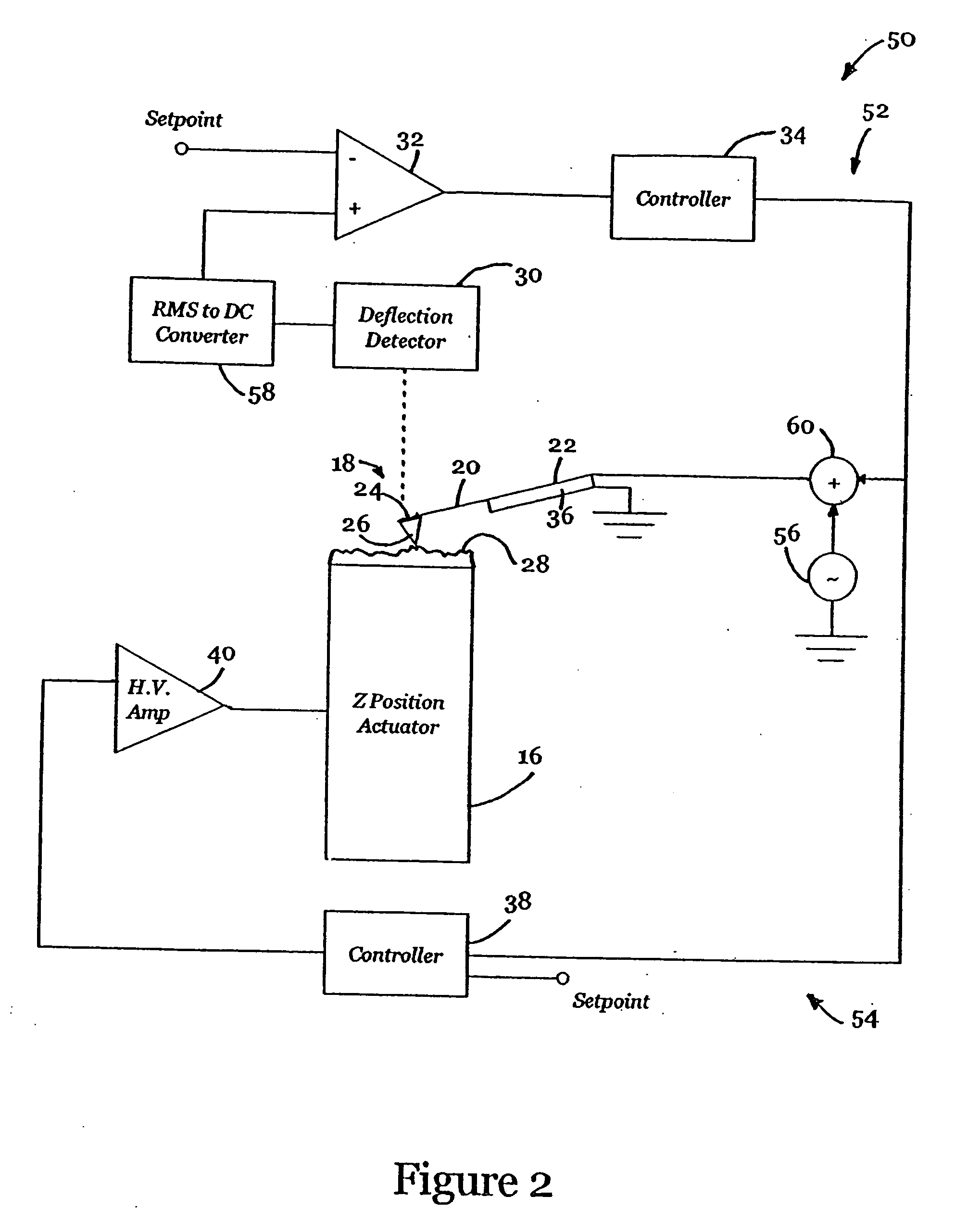
Active probe for an atomic force microscope and method of use thereof
InactiveUS6530266B1High-speed imagingAccurate Z position measurementNanotechElectric discharge tubesFrequency oscillationCantilever
An AFM that combines an AFM Z position actuator and a self-actuated Z position cantilever (both operable in cyclical mode and contact mode), with appropriate nested feedback control circuitry to achieve high-speed imaging and accurate Z position measurements. A preferred embodiment of an AFM for analyzing a surface of a sample in either ambient air or fluid includes a self-actuated cantilever having a Z-positioning element integrated therewith and an oscillator that oscillates the self-actuated cantilever at a frequency generally equal to a resonant frequency of the self-actuated cantilever and at an oscillation amplitude generally equal to a setpoint value. The AFM includes a first feedback circuit nested within a second feedback circuit, wherein the first feedback circuit generates a cantilever control signal in response to vertical displacement of the self-actuated cantilever during a scanning operation, and the second feedback circuit is responsive to the cantilever control signal to generate a position control signal. A Z position actuator is also included within the second feedback circuit and is responsive to the position control signal to position the sample. In operation, preferably, the cantilever control signal alone is indicative of the topography of the sample surface. In a further embodiment, the first feedback circuit includes an active damping circuit for modifying the quality factor ("Q") of the cantilever resonance to optimize the bandwidth of the cantilever response.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Standing wave pump
InactiveUS6079214AStirling type enginesCompression machines with non-reversible cycleStored energyResonant cavity
A standing wave pump in which a standing compression wave is produced by a pair of diametrically opposing transducers. The vibrating surfaces of the transducers are oscillated at a frequency sufficient to generate a substantially cylindrical compression wave having substantially planar wave fronts between the transducer pair. The length of pump housing is made to be equal to an integer times half the wavelength of the compression wave and the pump housing acts as a resonant cavity having a standing wave pattern set up in it. Waves are simultaneously produced and reflected by the oscillating surface and are superimposed upon one another and travel to the opposing oscillating surface where this process is repeated, substantially multiplying the intensity of the standing compression wave, which provides a stored-energy effect. The high-intensity standing compression wave has pressure nodes and antinodes, whose pressure differential is used to pump a medium through inlets and outlets advantageously located at the nodes and antinodes.
Owner:FACE INT
Communicating with an implanted wireless sensor
ActiveUS7439723B2Increase opportunitiesAvoid breakingModulated-carrier systemsEndoradiosondesLine sensorRing down
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG II S A R L SJM LUX II
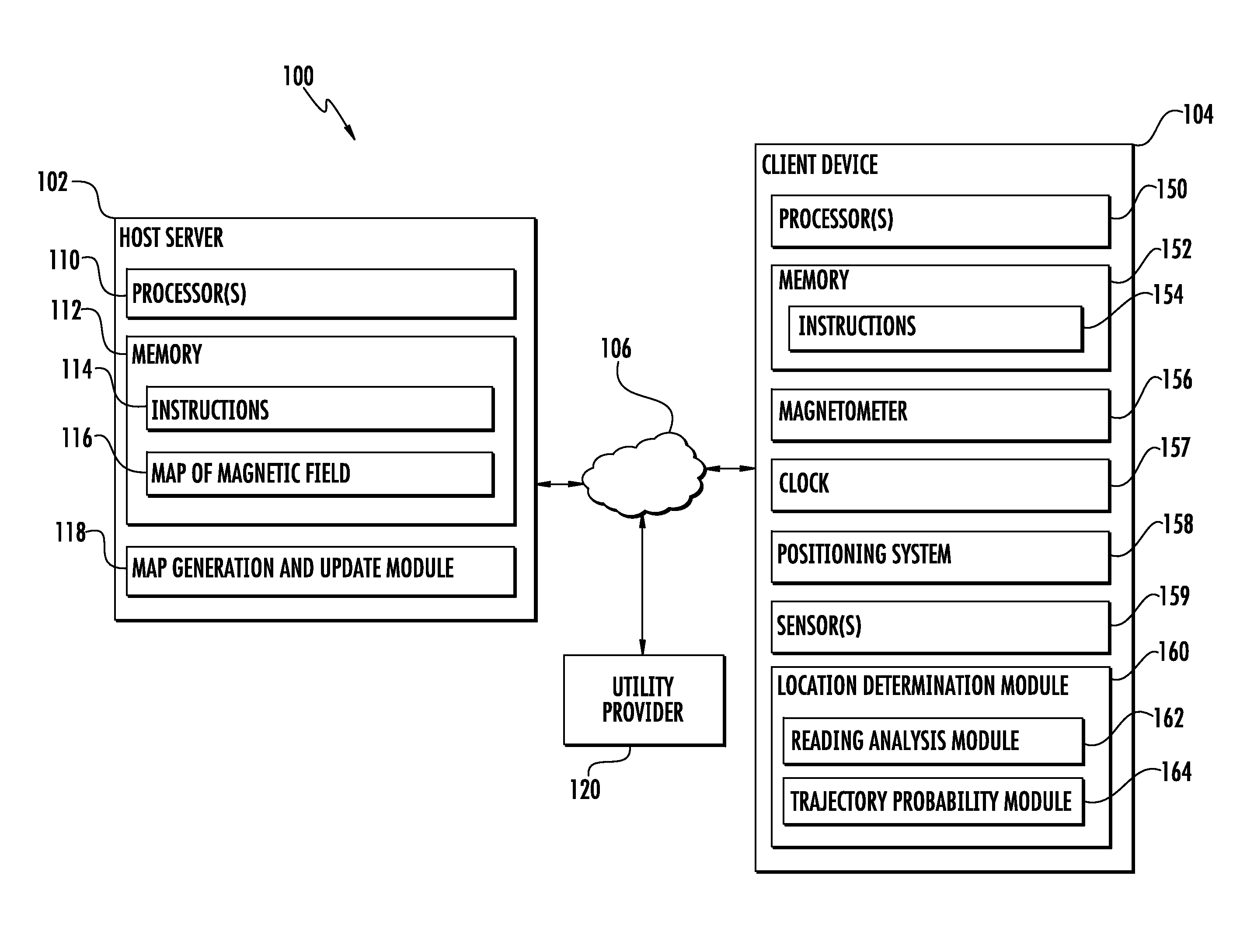
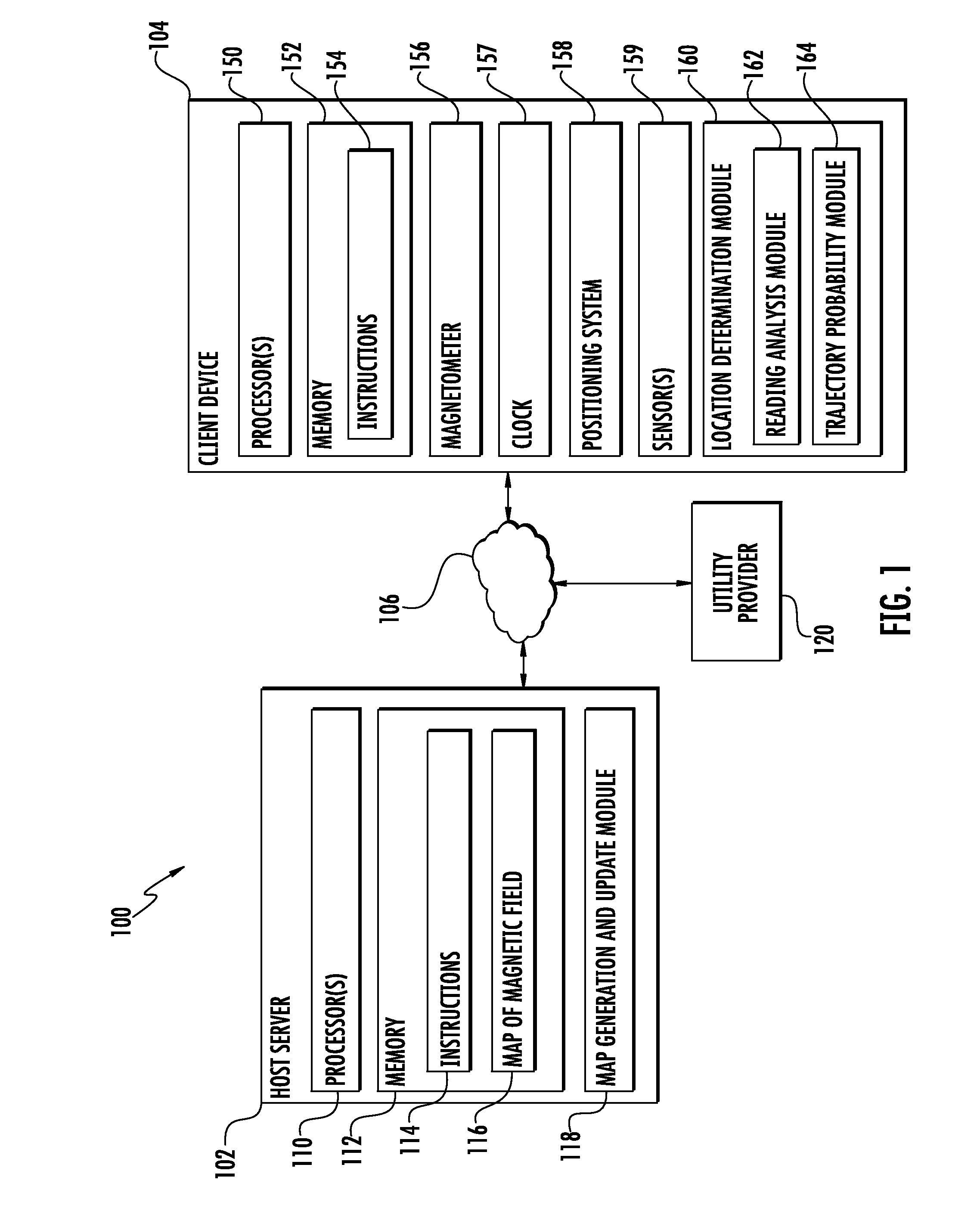
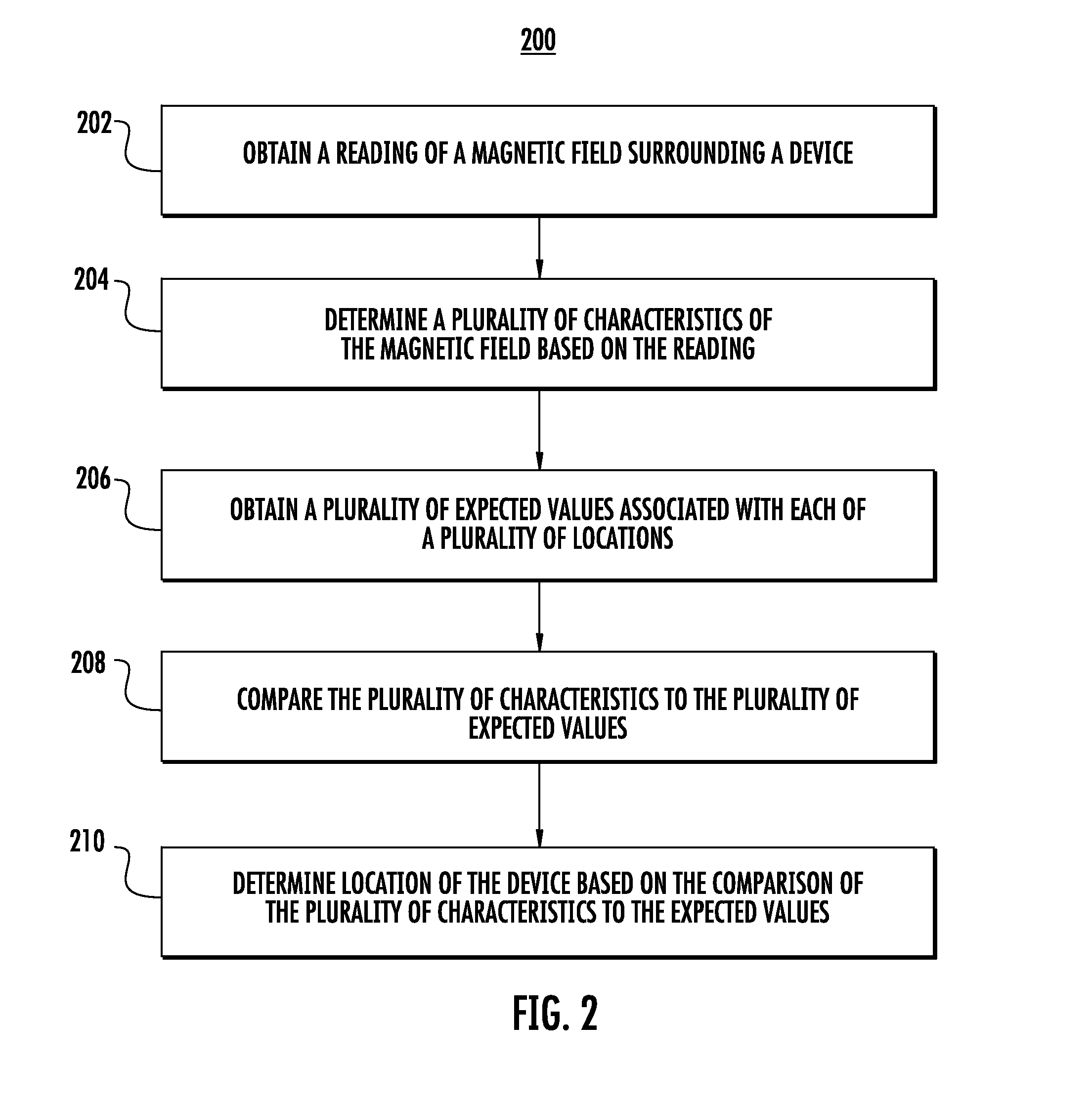
Determining Location Using Magnetic Fields From AC Power Lines
ActiveUS20150153151A1Digital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsPosition dependentFrequency oscillation
Systems and methods for determining location using magnetic fields from AC power lines are provided. As an example, each magnetic field reading collected by the device over time can be analyzed to determine a plurality of characteristics of the magnetic field. One or more of the plurality of characteristics can describe a component of the magnetic field that oscillates at a frequency associated with the AC power lines. The plurality of characteristics can be compared to expected values respectively associated with a plurality of locations and provided by a map of the magnetic field to determine a location at which each magnetic field reading was collected. In further embodiments, magnetic field readings collected by the device over time can be analyzed in conjunction with other data or constraints to determine a trajectory of the device. In addition, the map can be updated using the collected readings and the determined trajectory.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
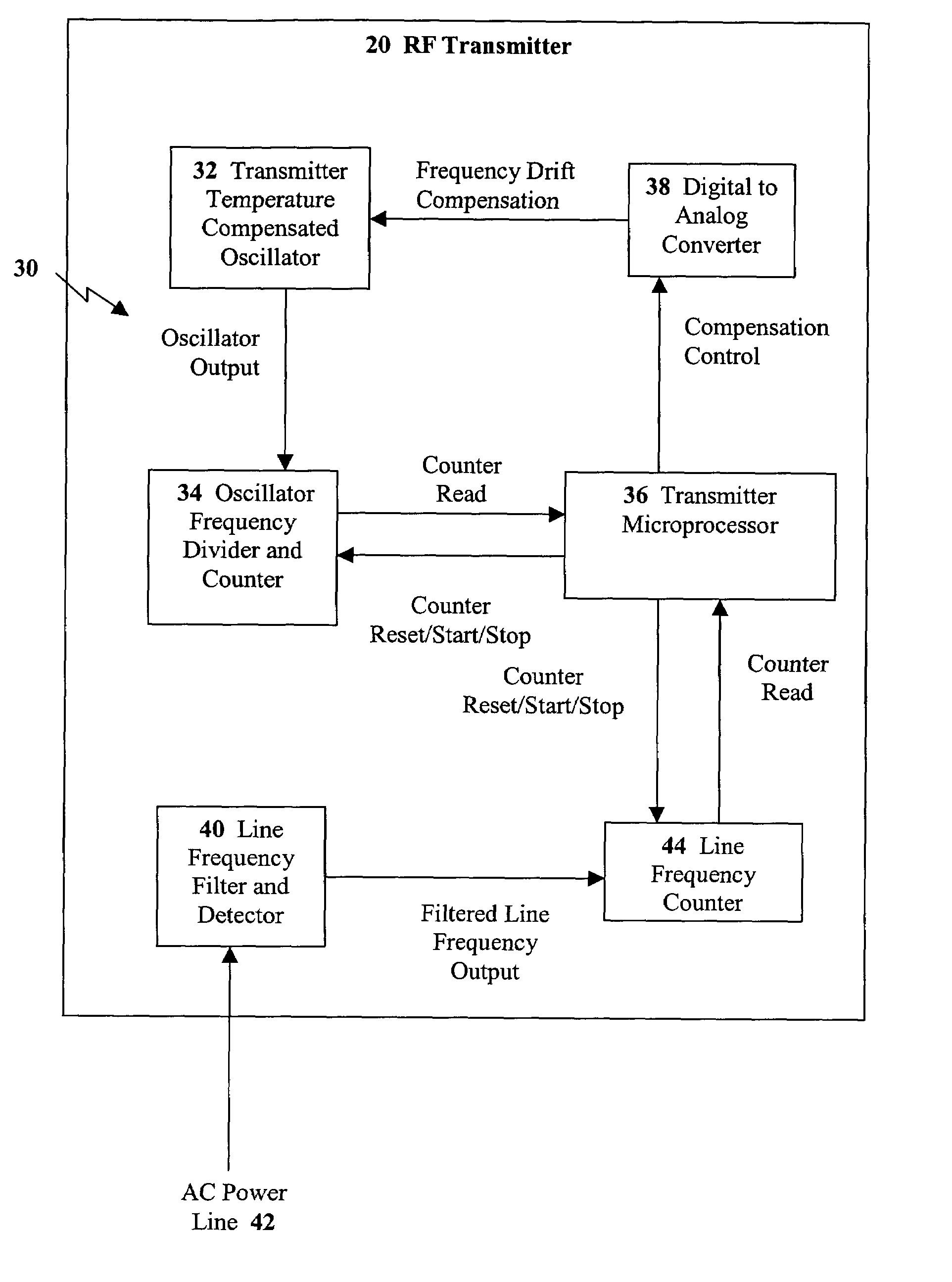
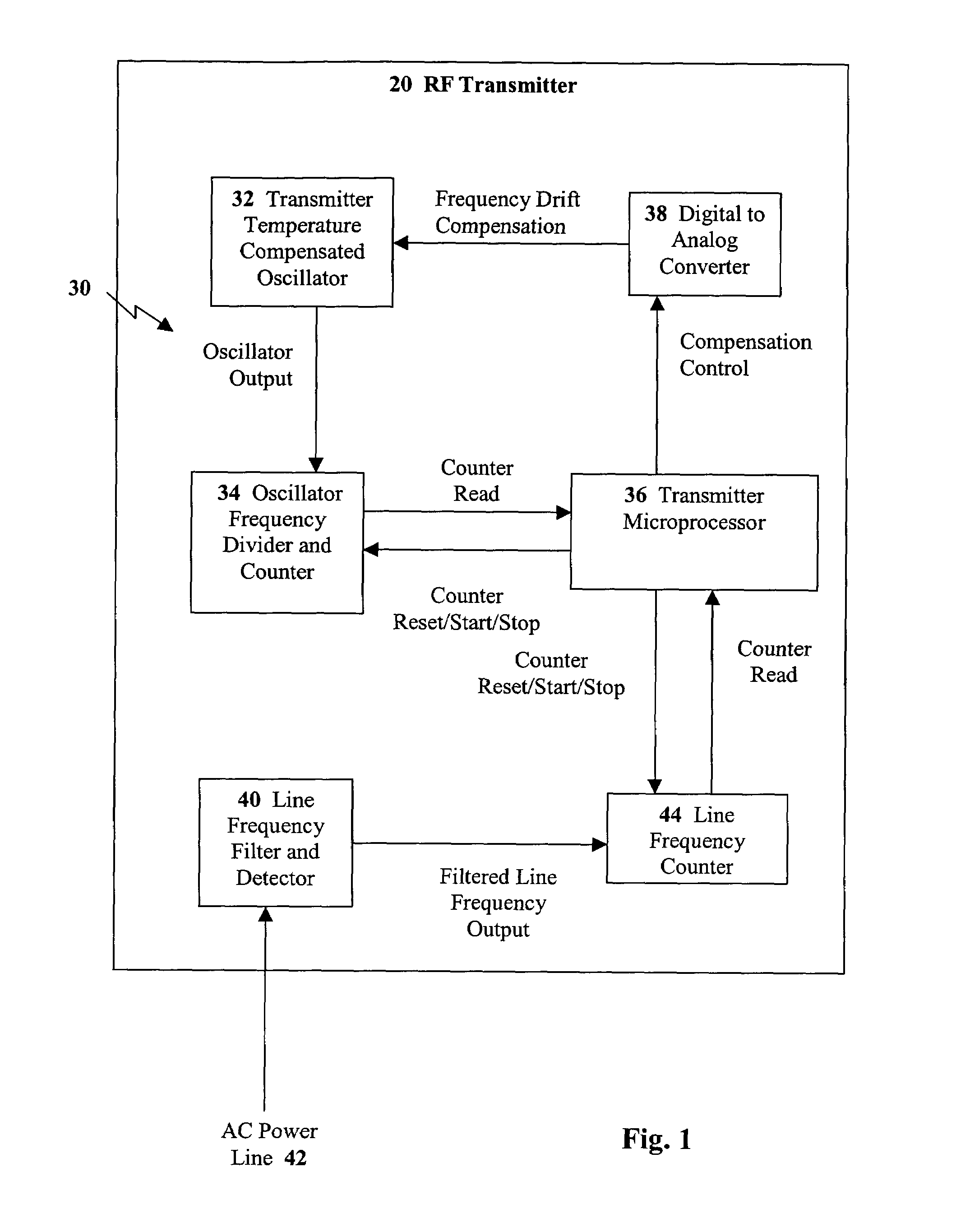
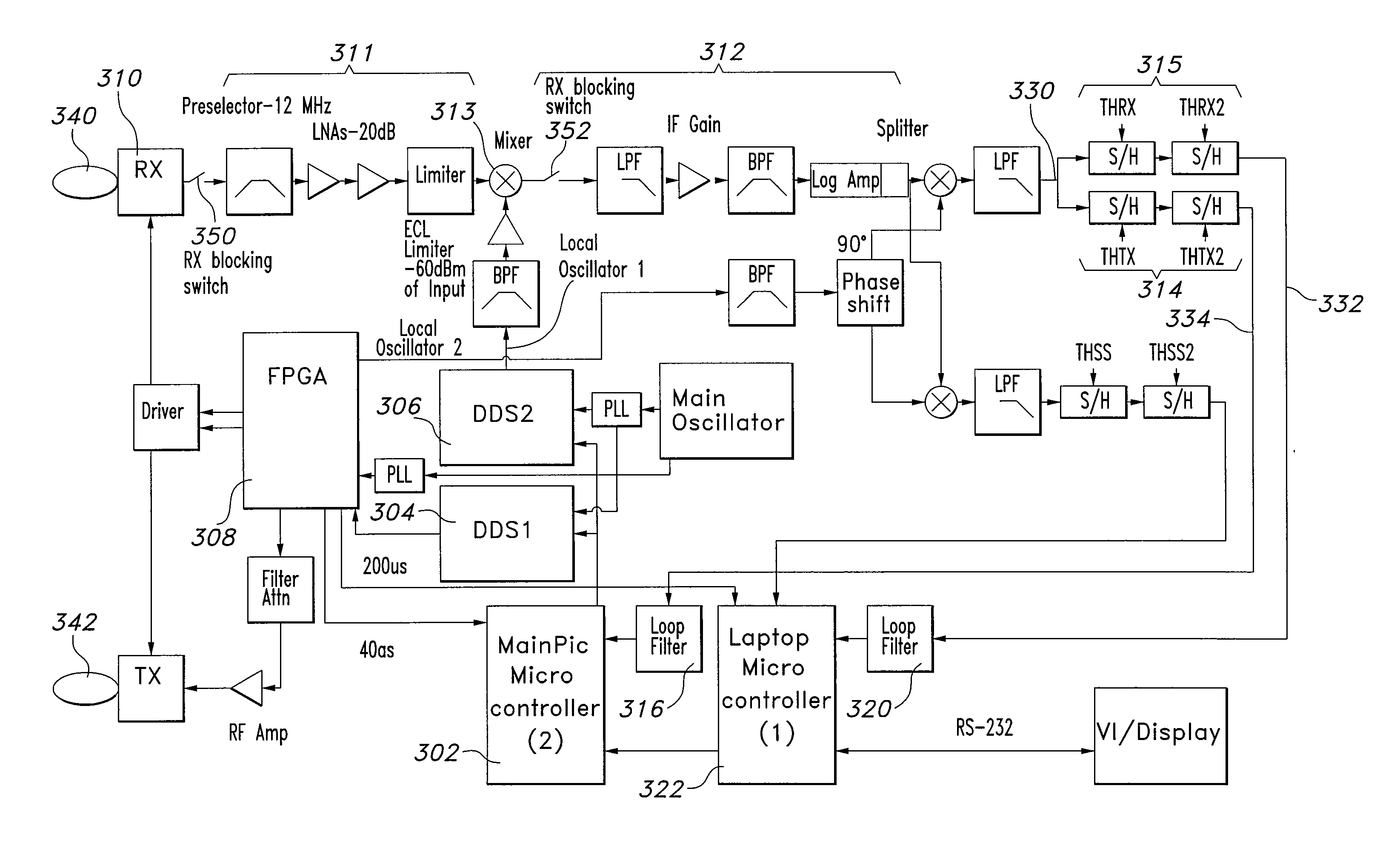
System and method for oscillator self-calibration using AC line frequency
InactiveUS6973400B2Pulse automatic controlDigital data processing detailsFrequency counterFrequency oscillation
Owner:ITRON
Temperature estimation and tissue detection of an ultrasonic dissector from frequency response monitoring
ActiveUS20130331874A1Simple methodSurgeryProcessing detected response signalMicrocontrollerMaterial type
An ultrasonic surgical apparatus and method, the apparatus including a signal generator outputting a drive signal having a frequency, an oscillating structure, receiving the drive signal and oscillating at the frequency of the drive signal, and a bridge circuit, detecting the mechanical motion of the oscillating structure and outputting a signal representative of the mechanical motion. The ultrasonic surgical apparatus also includes a microcontroller receiving the signal output by the bridge circuit, the microcontroller determining an instantaneous frequency at which the oscillating structure is oscillating based on the received signal, and determining a frequency adjustment necessary to maintain the oscillating structure oscillating at its resonance frequency, the microcontroller further determining the quality (Q value) of the signal received from the bridge circuit and determining material type contacting the oscillating structure.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Communicating with an Implanted Wireless Sensor
ActiveUS20070210786A1Avoid breakingIncrease opportunitiesModulated-carrier systemsEndoradiosondesRing downLine sensor
The present invention determines the resonant frequency of a sensor by adjusting the phase and frequency of an energizing signal until the frequency of the energizing signal matches the resonant frequency of the sensor. The system energizes the sensor with a low duty cycle, gated burst of RF energy having a predetermined frequency or set of frequencies and a predetermined amplitude. The energizing signal is coupled to the sensor via magnetic coupling and induces a current in the sensor which oscillates at the resonant frequency of the sensor. The system receives the ring down response of the sensor via magnetic coupling and determines the resonant frequency of the sensor, which is used to calculate the measured physical parameter. The system uses a pair of phase locked loops to adjust the phase and the frequency of the energizing signal.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG II S A R L SJM LUX II
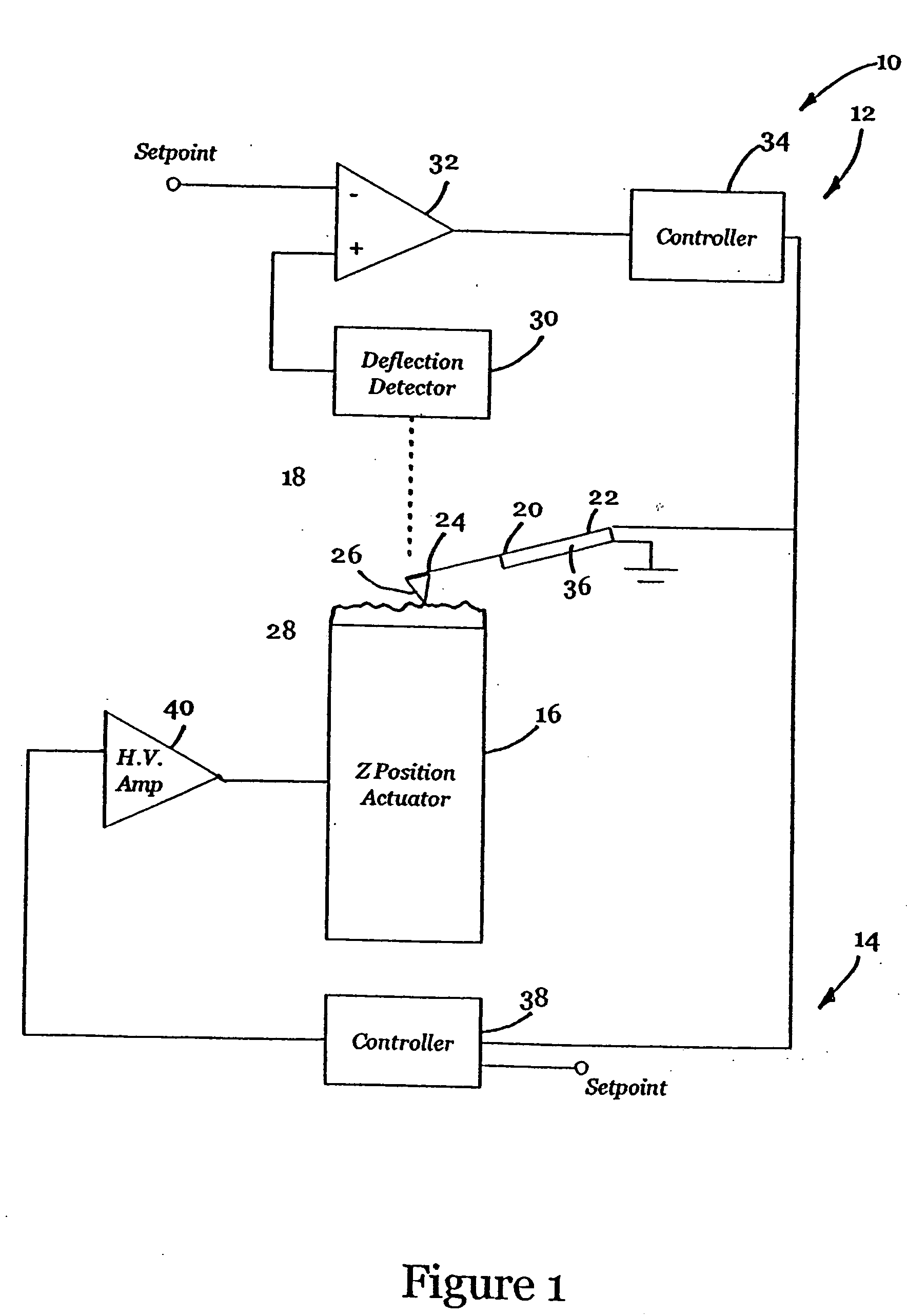
Active probe for an atomic force microscope and method for use thereof
InactiveUS20050066714A1High-speed imagingAccurate measurementNanotechElectric discharge tubesControl signalFeedback circuits
An AFM that combines an AFM Z position actuator and a self-actuated Z position cantilever (both operable in cyclical mode and contact mode), with appropriate nested feedback control circuitry to achieve high-speed imaging and accurate Z position measurements. A preferred embodiment of an AFM for analyzing a surface of a sample in either ambient air or fluid includes a self-actuated cantilever having a Z-positioning element integrated therewith and an oscillator that oscillates the self-actuated cantilever at a frequency generally equal to a resonant frequency of the self-actuated cantilever and at an oscillation amplitude generally equal to a setpoint value. The AFM includes a first feedback circuit nested within a second feedback circuit, wherein the first feedback circuit generates a cantilever control signal in response to vertical displacement of the self-actuated cantilever during a scanning operation, and the second feedback circuit is responsive to the cantilever control signal to generate a position control signal. A Z position actuator is also included within the second feedback circuit and is responsive to the position control signal to position the sample. In operation, preferably, the cantilever control signal alone is indicative of the topography of the sample surface. In a further embodiment, the first feedback circuit includes an active damping circuit for modifying the quality factor (“Q”) of the cantilever resonance to optimize the bandwidth of the cantilever response.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
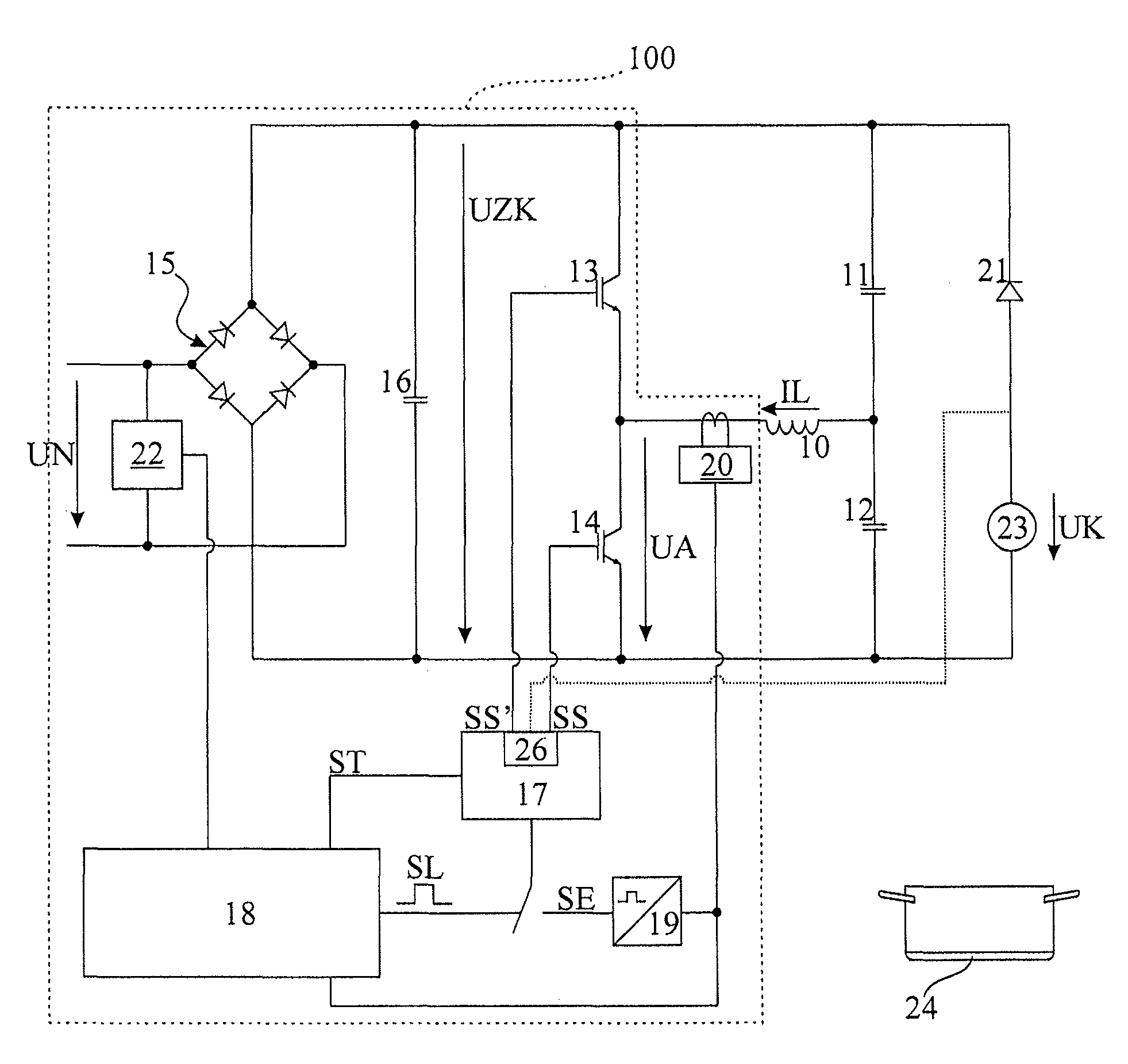
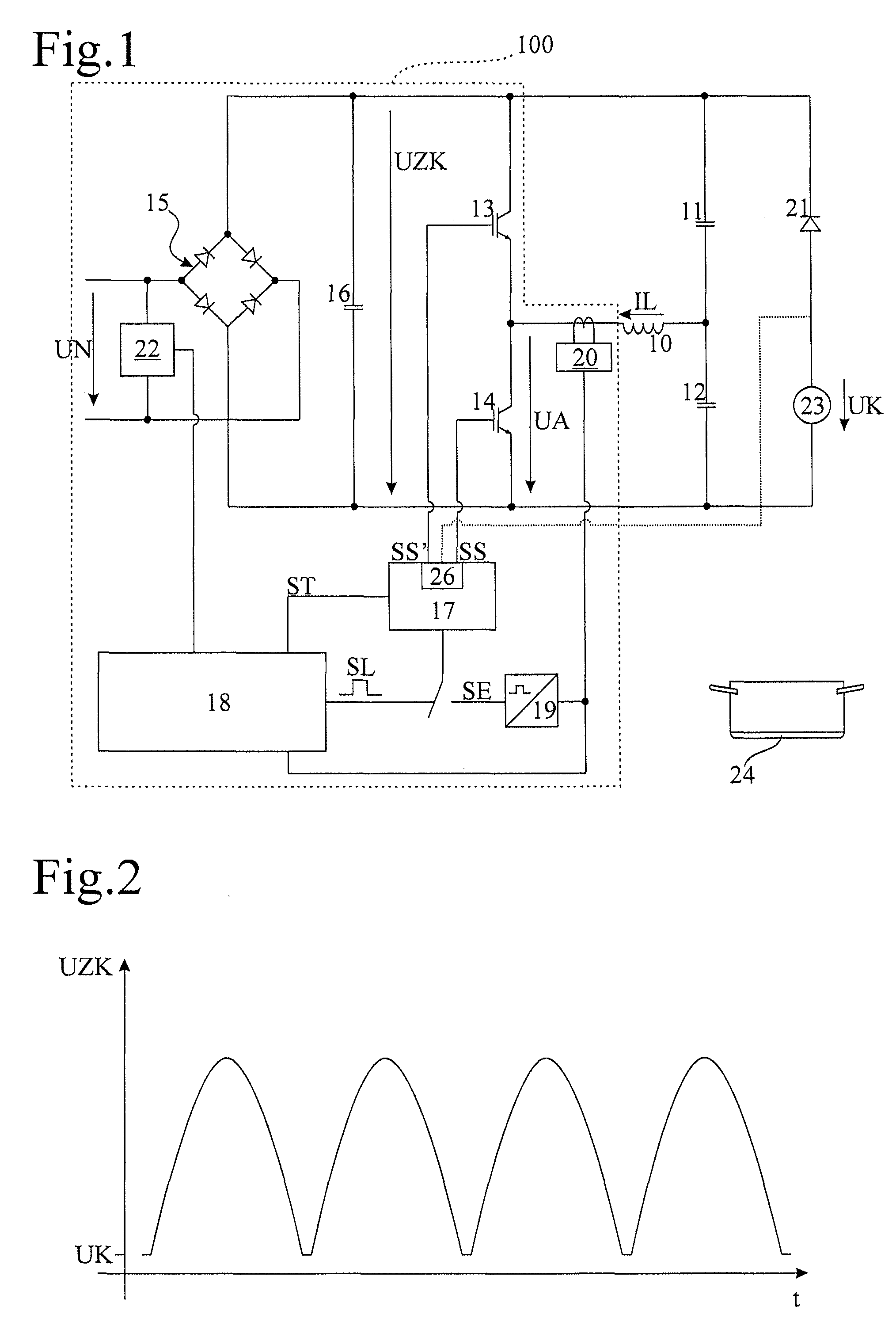
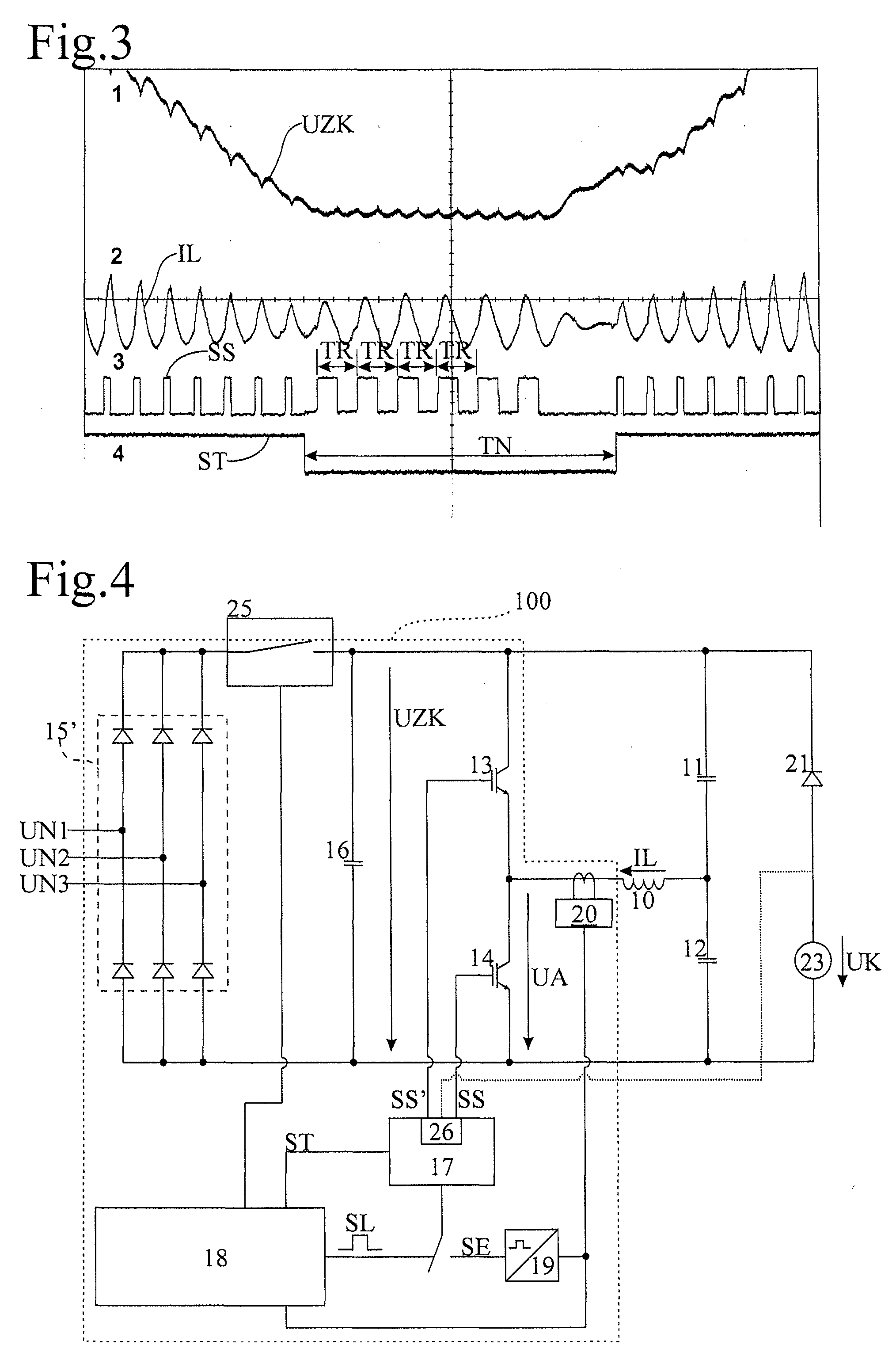
Method and induction heating device for determining a temperature of a cooking vessel base which is heated by means of an induction heating coil
ActiveUS20110120989A1Avoid switchingAvoid noiseThermometers using physical/chemical changesInduction current sourcesEngineeringFrequency oscillation
An induction heating device comprises a frequency converter that generates a high-frequency drive voltage from an intermediate circuit voltage generated at least temporarily as a function of an AC mains voltage, a resonant circuit having an induction heating coil, with the drive voltage applied to the resonant circuit, and a temperature detection device that determines a temperature of a cooking vessel base which is heated by means of the induction heating coil. An auxiliary voltage source generated the intermediate circuit voltage over predefined time periods at a constant level. The frequency converter generates the drive voltage over time periods such that the resonant circuit oscillates at a natural resonant frequency in a substantially de-attenuated manner, and the temperature detection device further measuring at least one oscillation parameter over the time periods, and to evaluate the at least one measured oscillation parameter in order to determine the temperature.
Owner:E G O ELEKTRO GERAETEBAU GMBH
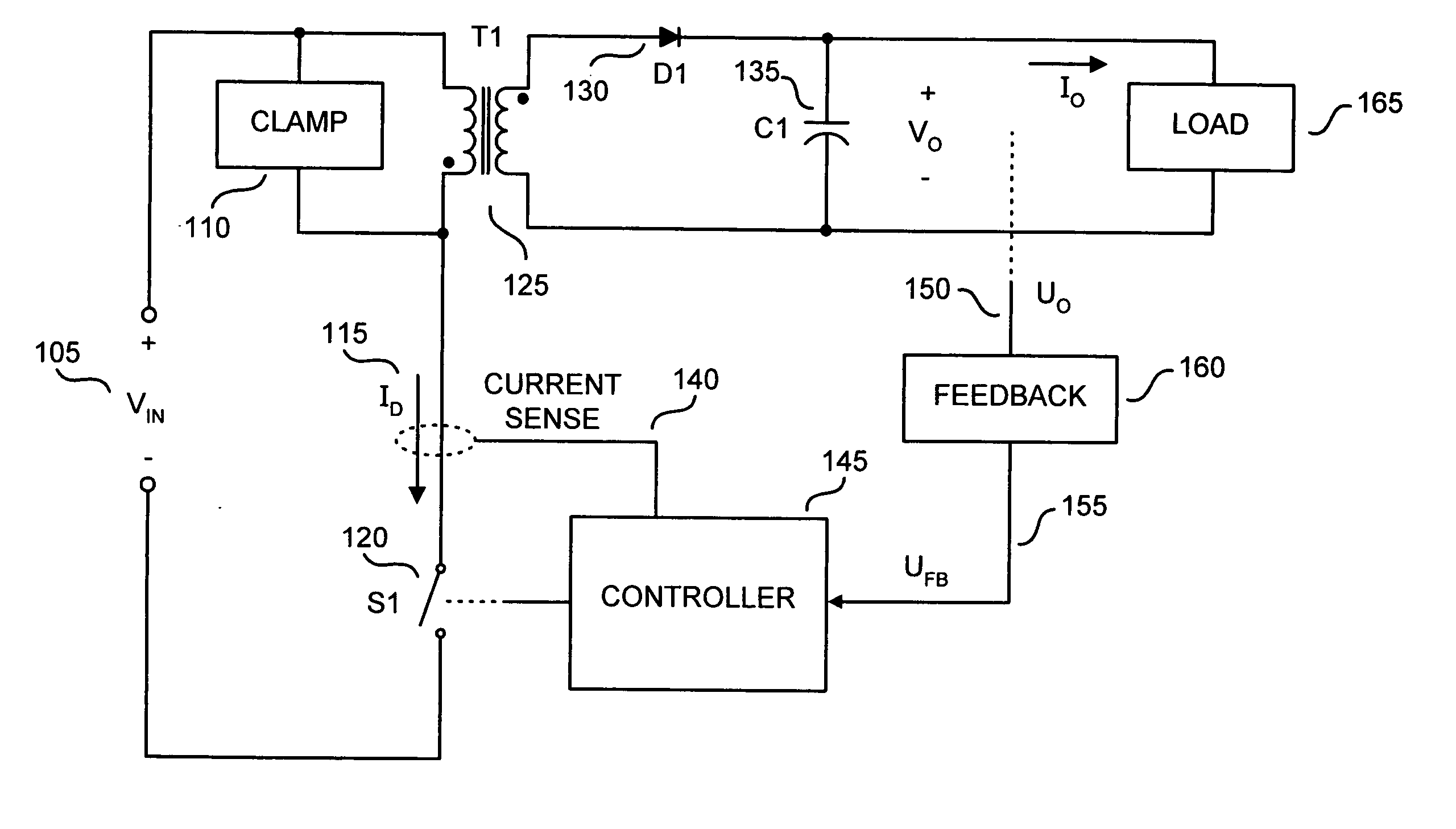
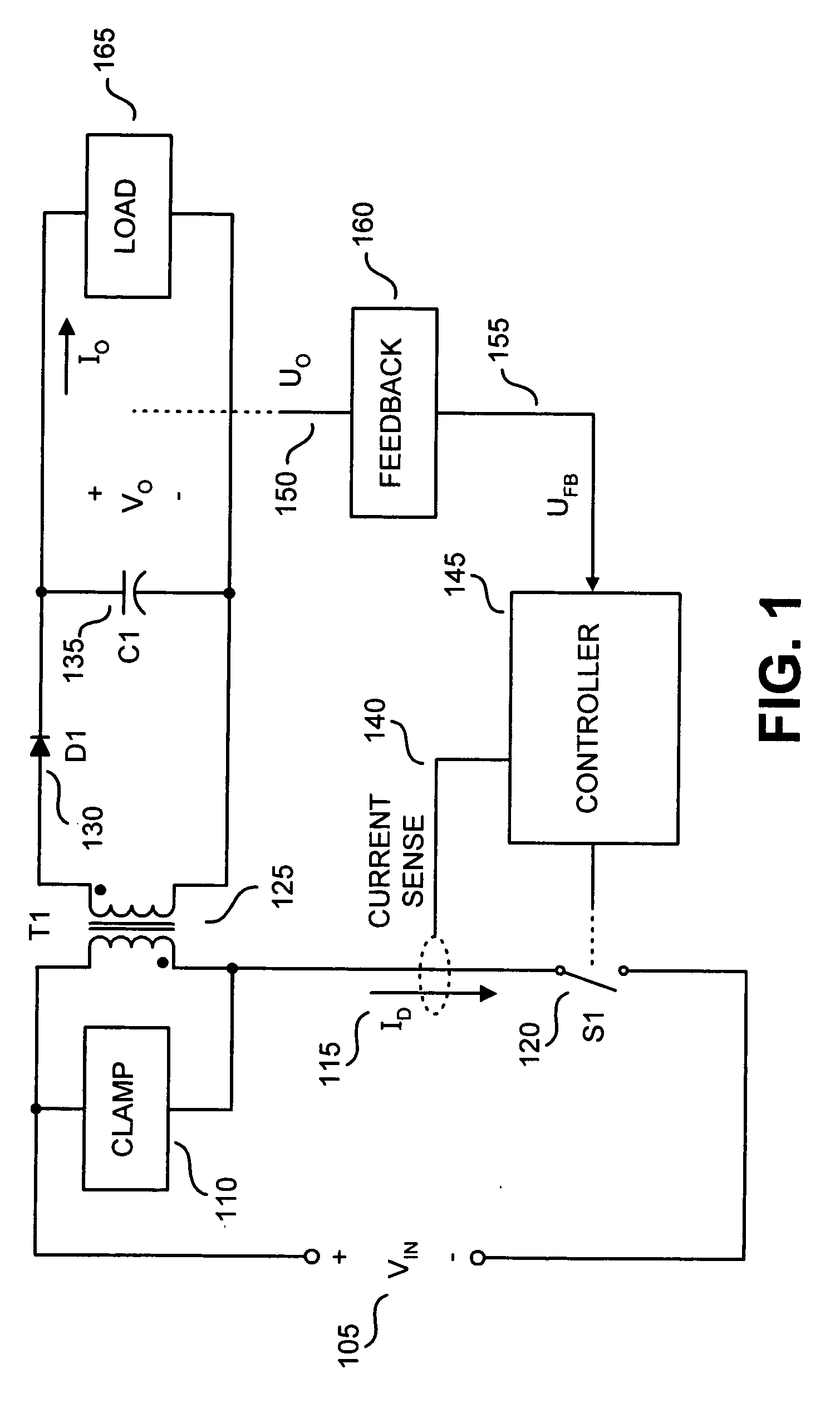
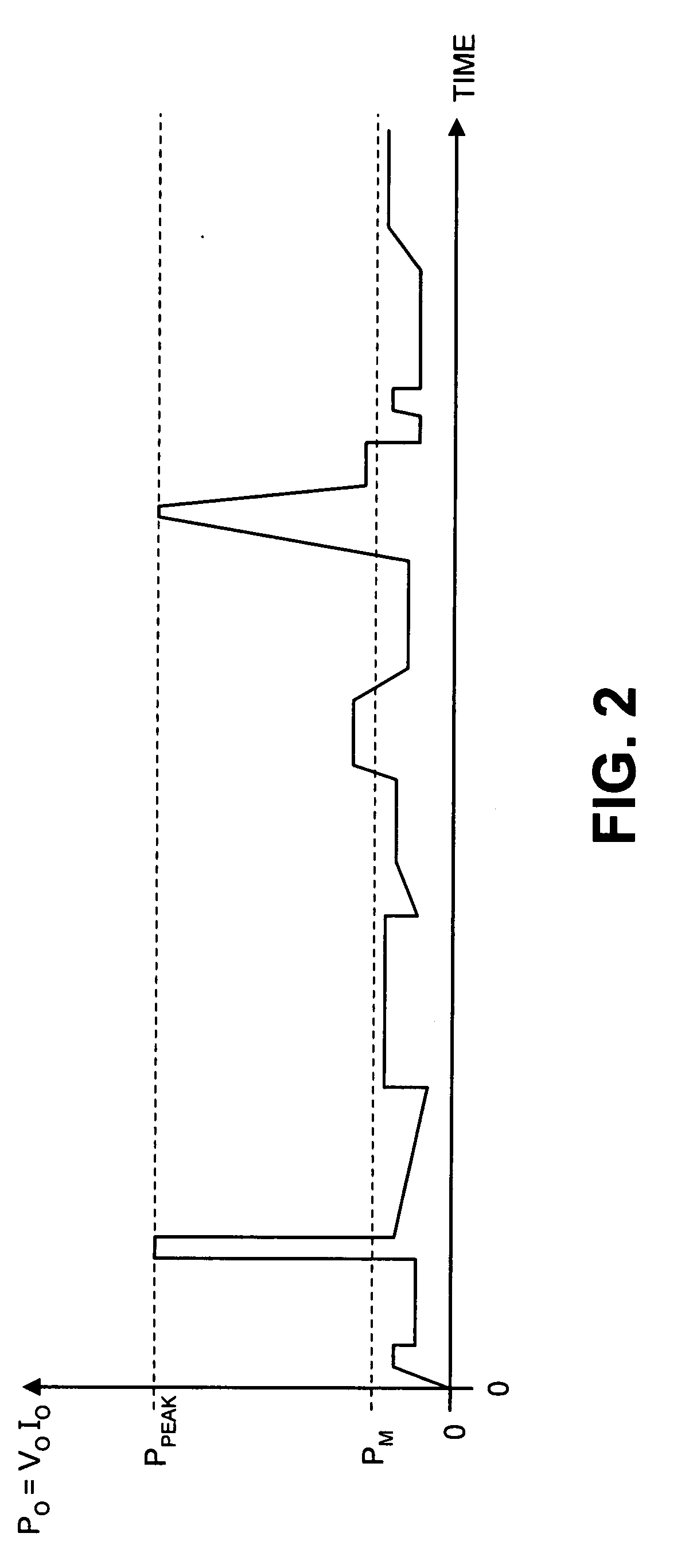
Method and apparatus to provide temporary peak power from a switching regulator
ActiveUS20060098463A1Emergency protective circuit arrangementsDc-dc conversionEnergy transferEngineering
Various techniques directed to providing temporary peak power from a switching regulator are disclosed. In one aspect, a switching regulator includes a switch that is to be coupled between a power supply input and an energy transfer element of the power supply. A controller is coupled to be responsive to a feedback signal to be received from an output of the power supply. The controller is coupled to switch the switch in response to the feedback signal to regulate the output of the power supply. An oscillator is coupled to provide an oscillating signal to the controller to determine a maximum switching frequency of the switch. The oscillating signal is coupled to oscillate at a first frequency under a first moderate load condition at the power supply output. The oscillating signal is coupled to oscillate at a second frequency under a second peak load condition at the power supply output.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC
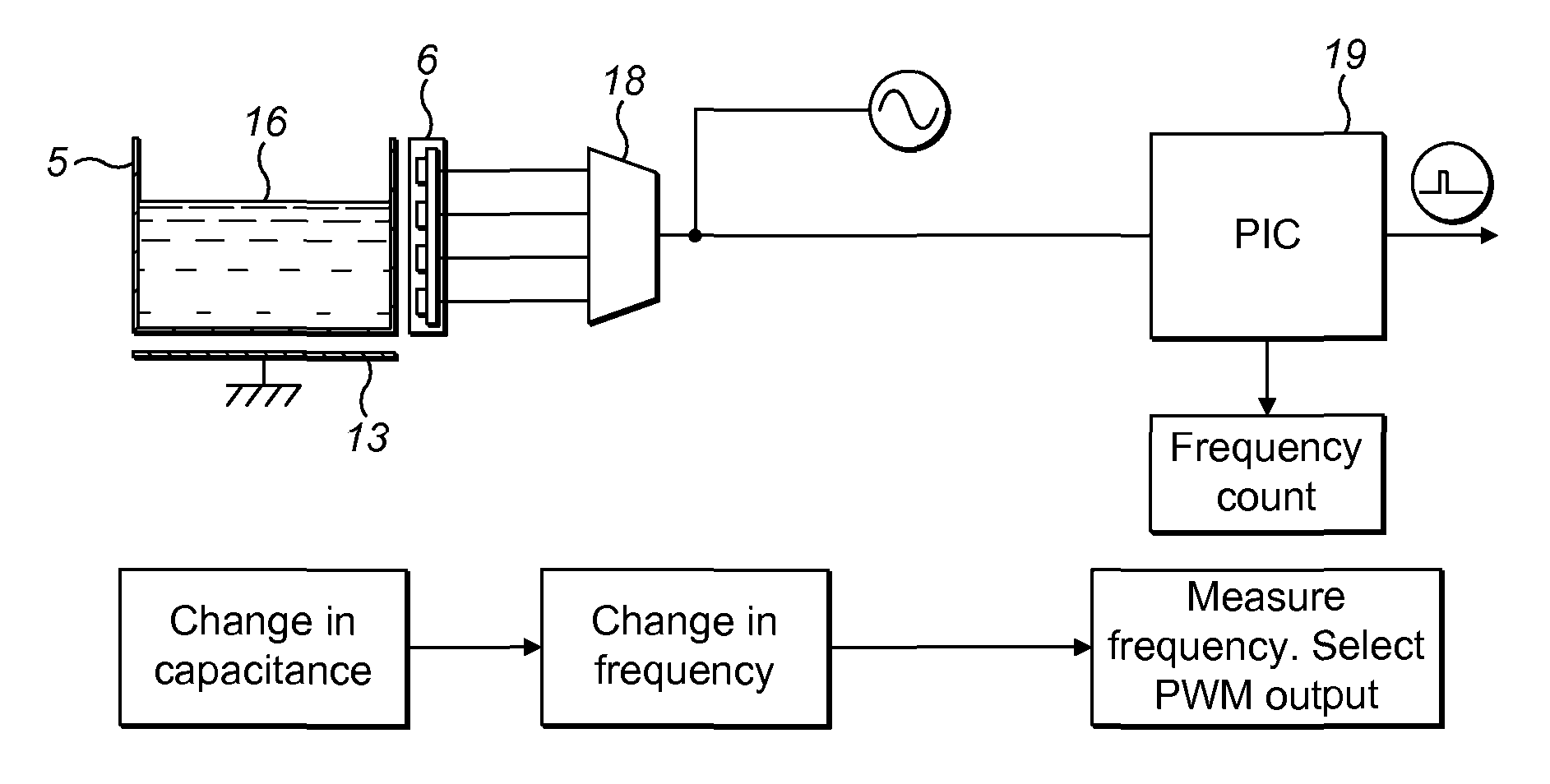
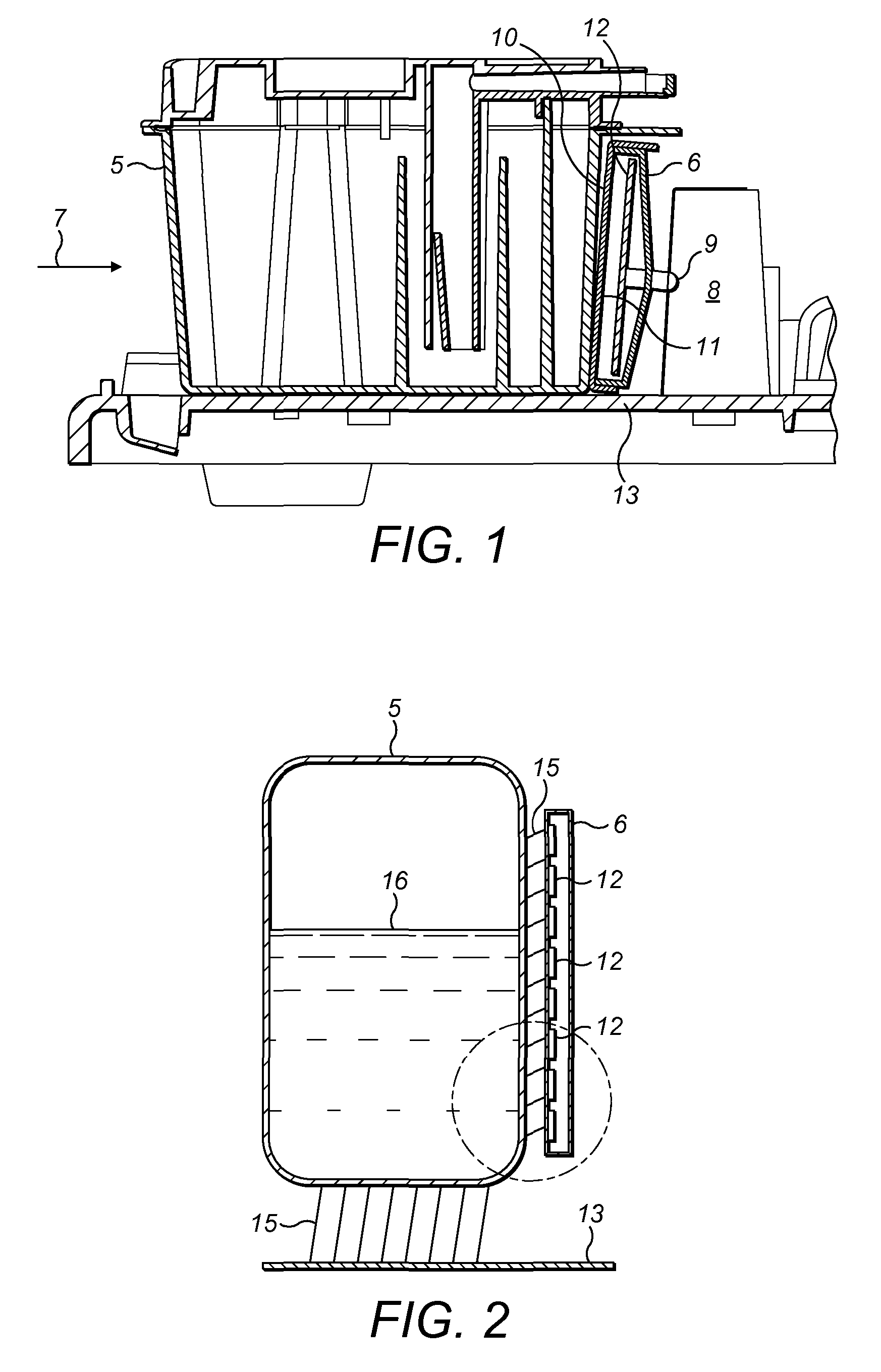
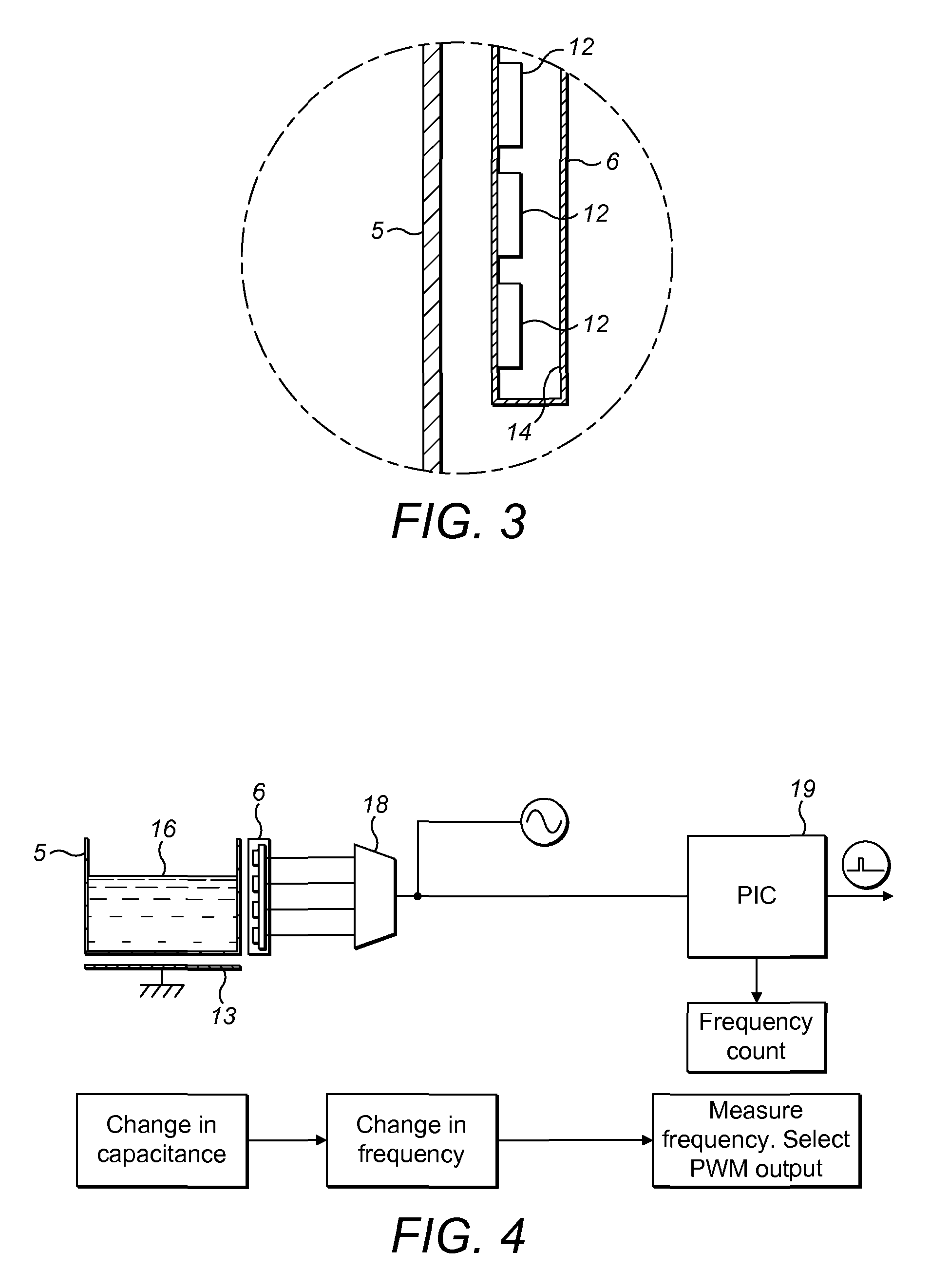
Inkjet printers
The invention provides a method and system for determining fluid levels in an inkjet printer. A non-contact sensor array is provided external to the container in which the levels are to be determined and each sensor in the array is sequentially switched into a sensing circuit until a change in capacitance is noted. The sensing circuit is preferably a frequency oscillation circuit whose frequency is defined by circuit capacitance.
Owner:DOMINO PRINTING SCIENCES
Method for operating a mass flowmeter
A method is disclosed for operating a mass flowmeter that employs the Coriolis principle and that incorporates a measuring tube through which flows a fluid medium, which measuring tube is stimulated to oscillate in a predefined pattern, allowing the resulting oscillatory response of the measuring tube to be detected and measured. The drive power level required for stimulating the measuring tube to oscillate at a predefined frequency is quantified and with the aid of the quantified drive power, the presence of a multiphase flow of the medium traveling through the measuring tube is detected. In this fashion, it is possible to significantly improve the measuring accuracy and dependability of the measuring procedure.
Owner:KRONE GMBH
Reference timing signal apparatus and method
ActiveUS7424069B1Easy to trackIncrease currentPulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationTraining periodAdaptive filter
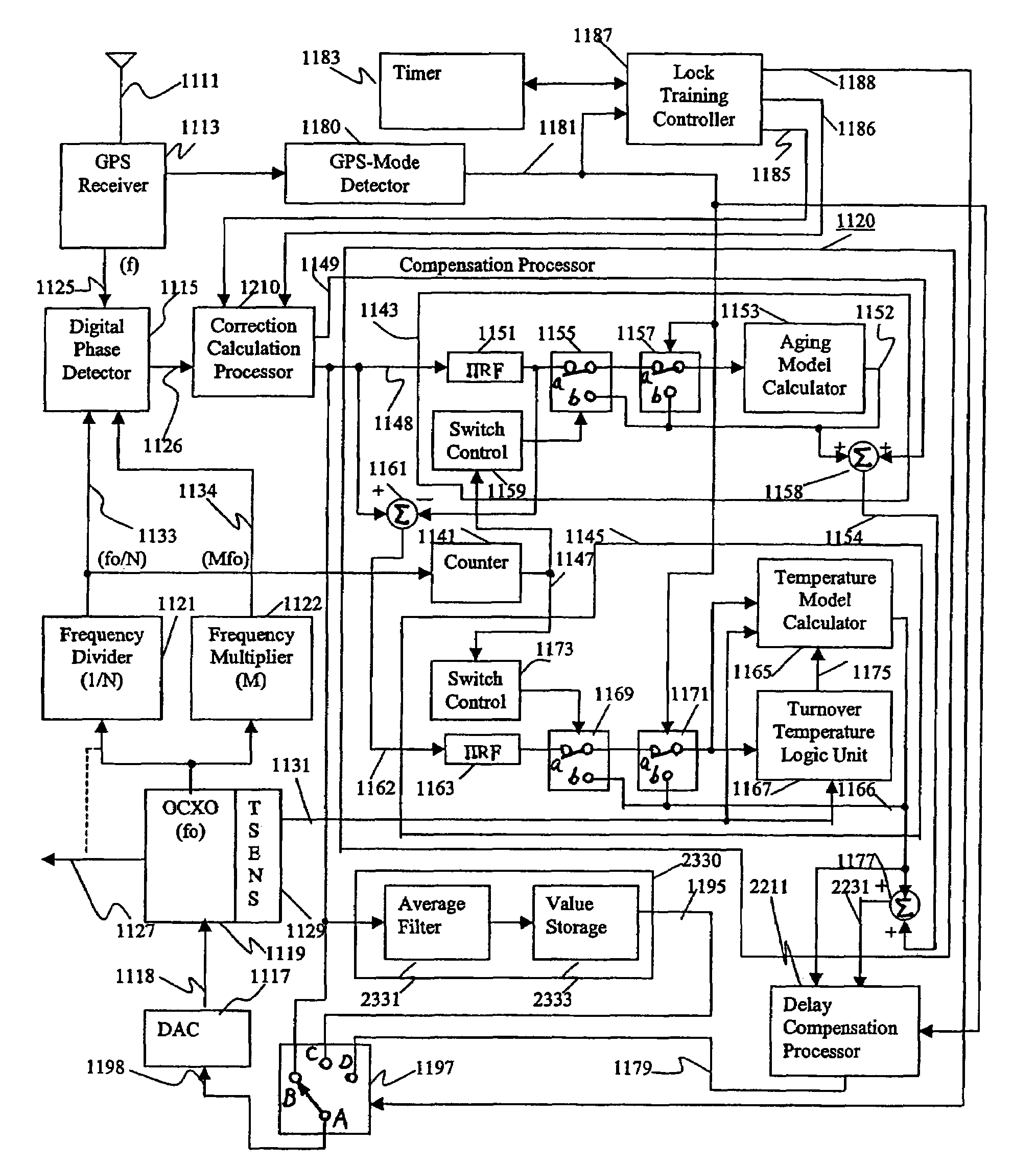
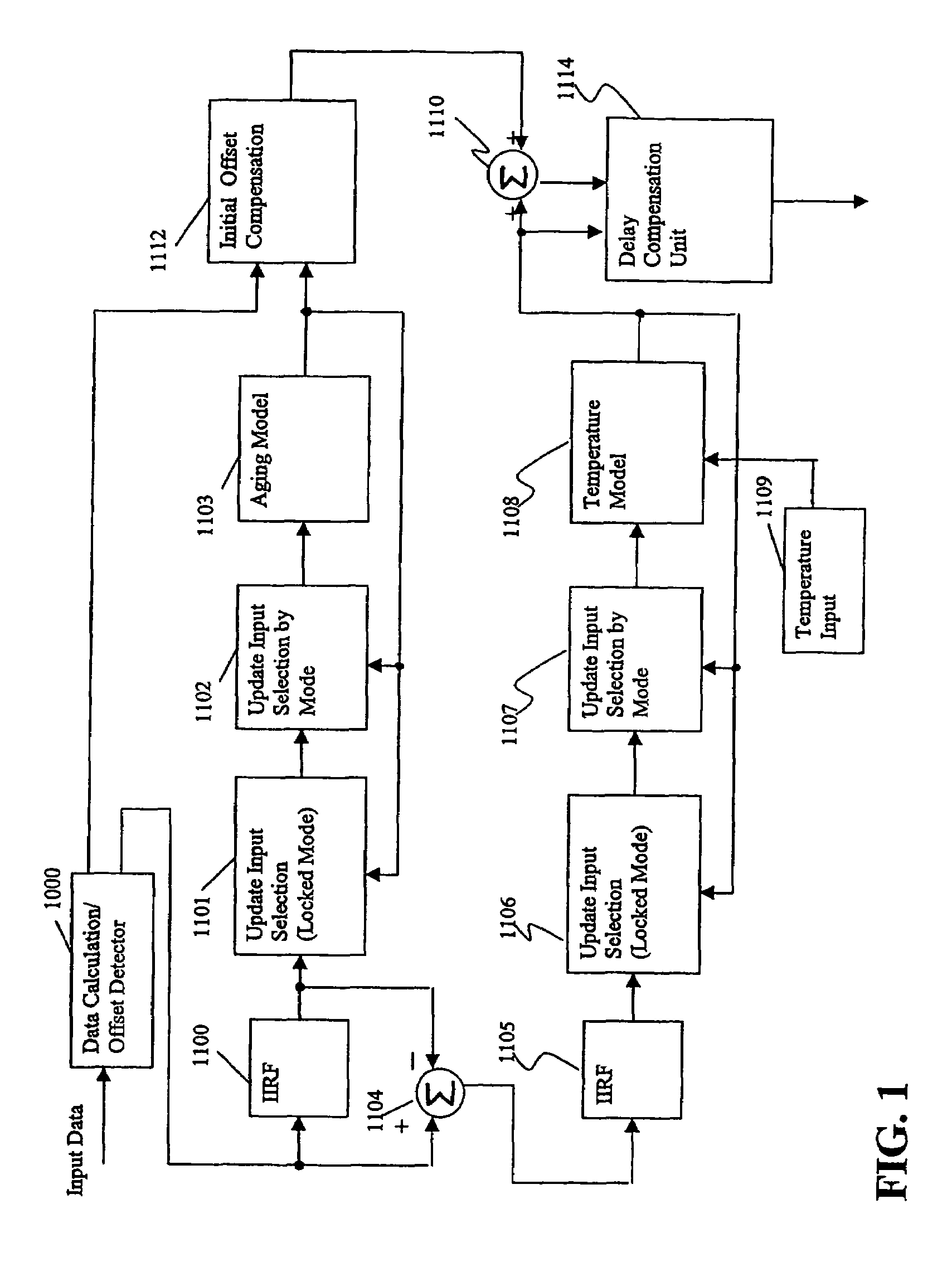
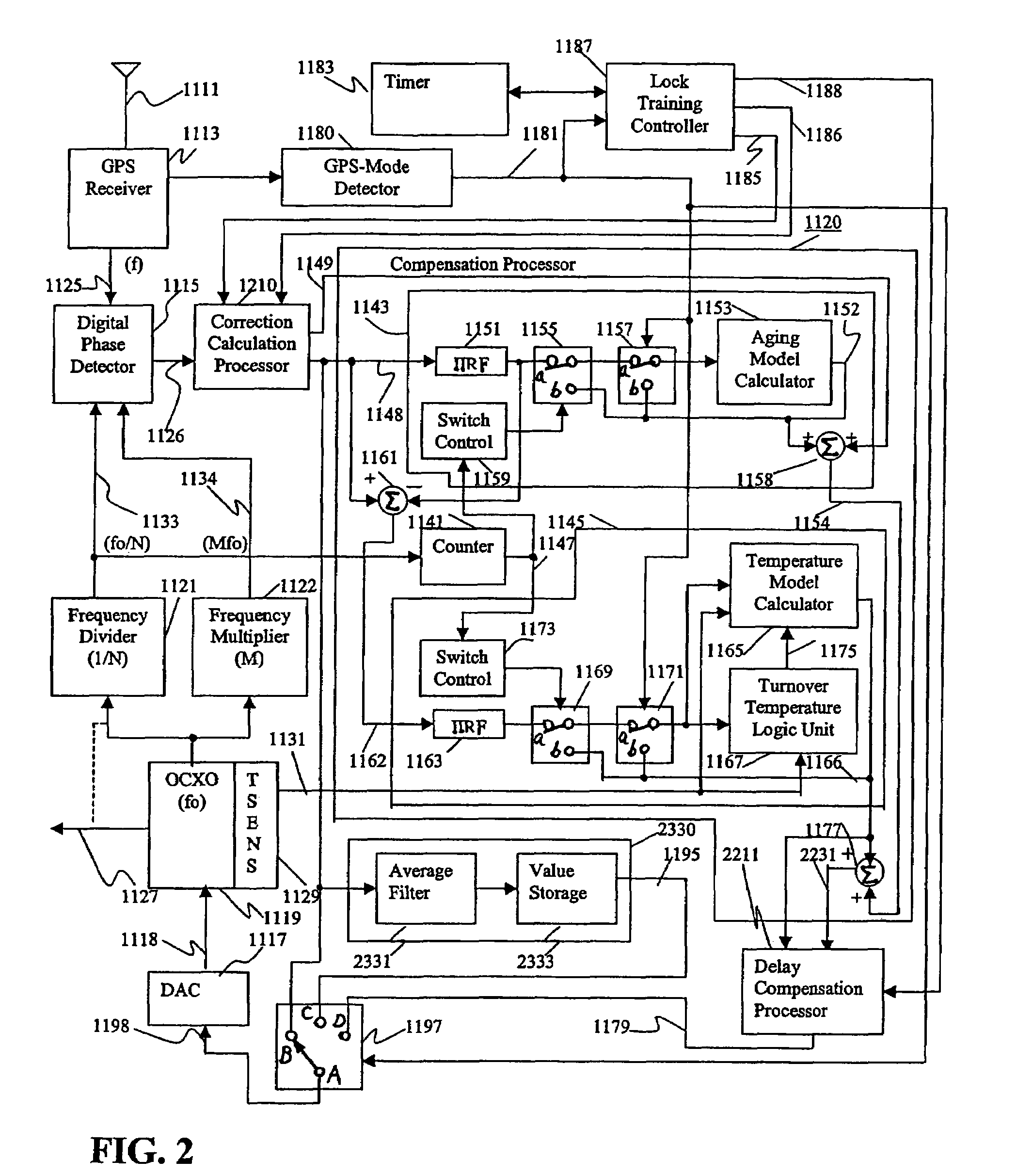
A reference timing signal apparatus with a phase-locked loop has a computer algorithm which adaptively models the multiple frequencies of an oscillator following a training period. The oscillation frequency of the oscillator is controlled in response to a phase detector output. The computer algorithm processes the control signal applied to the oscillator. The computer algorithm updates the characteristics of the model relating to the aging and temperature of the oscillator, using for example, a Kalman filter as an adaptive filter. By the algorithm, the subsequent model predicts the future frequency state of the oscillator on which it was trained. The predicted frequency of the model functions as a reference to correct the frequency of the oscillator in the event that no input reference timing signal is available. In a case of using pre-processing infinite impulse response filters (IIRFs) before the adaptive processor, the time delay caused by the filters are compensated after the adaptive processor. Without pre-processing IIRFs, aging and temperature update rates are adaptively controlled by dynamically changing the rates depending upon the loop condition to achieve a wider tracking bandwidth. With the model updating algorithm, oscillators of low stability performance may be used as cellular base station reference oscillator.
Owner:APPLE INC
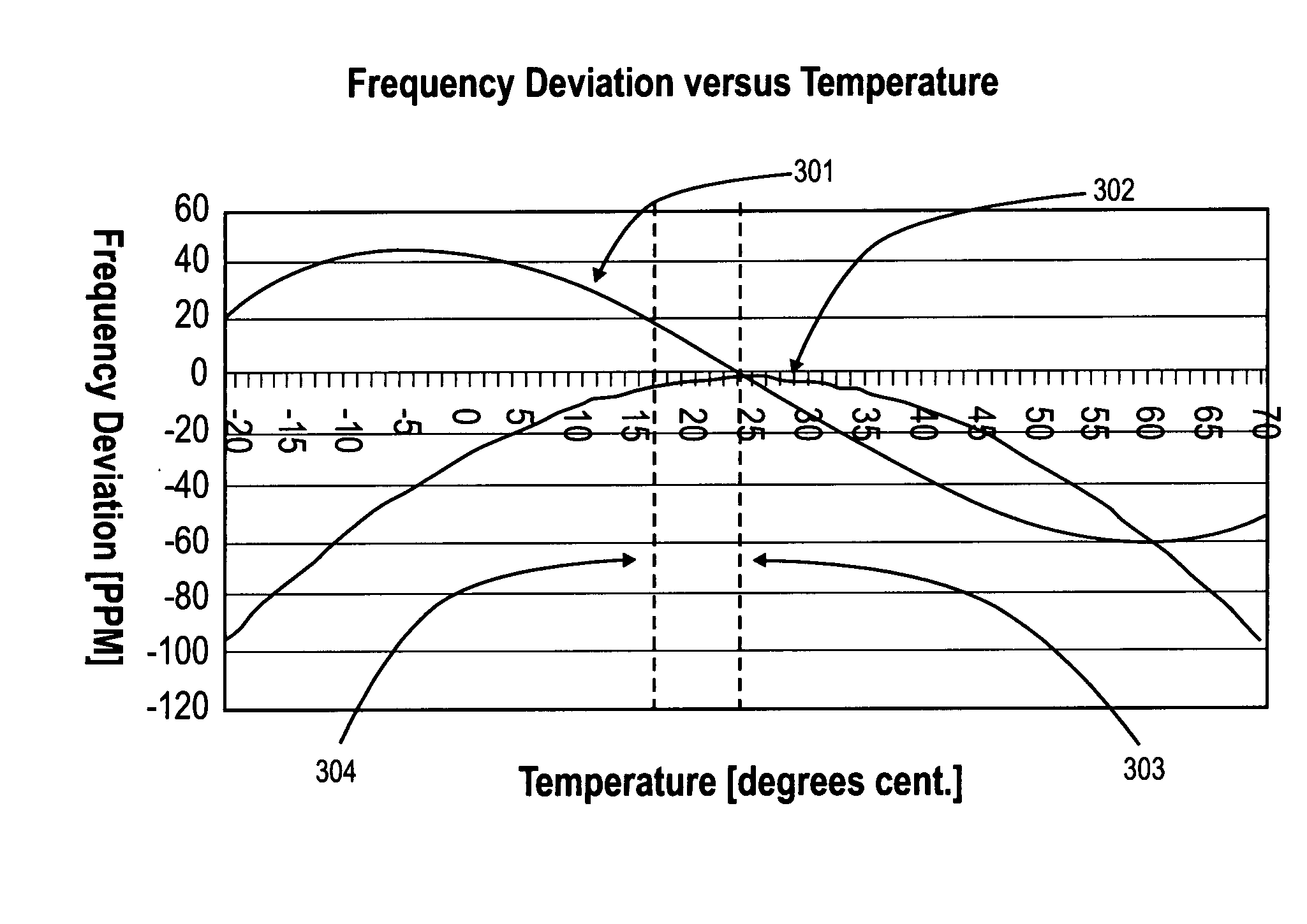
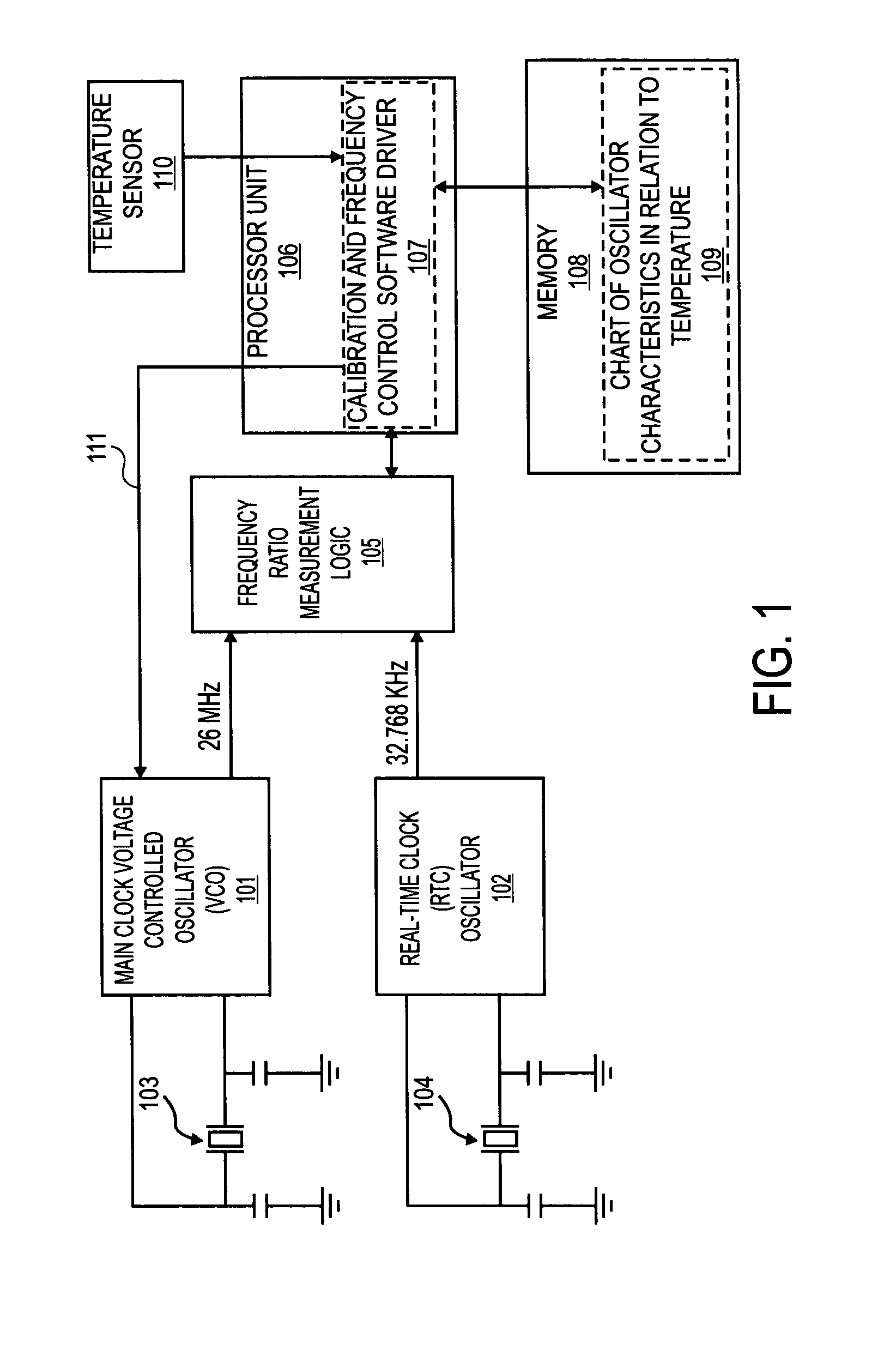
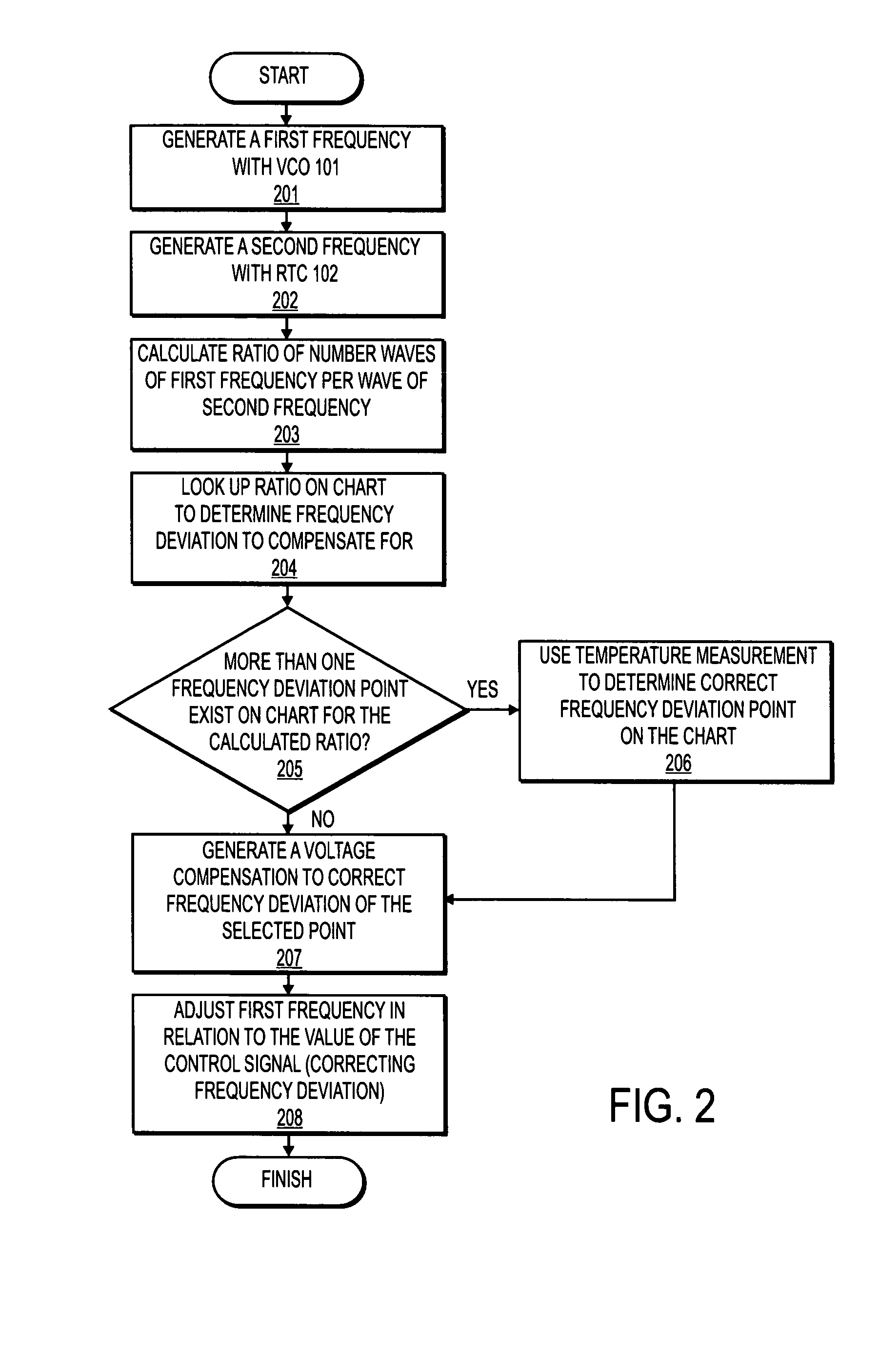
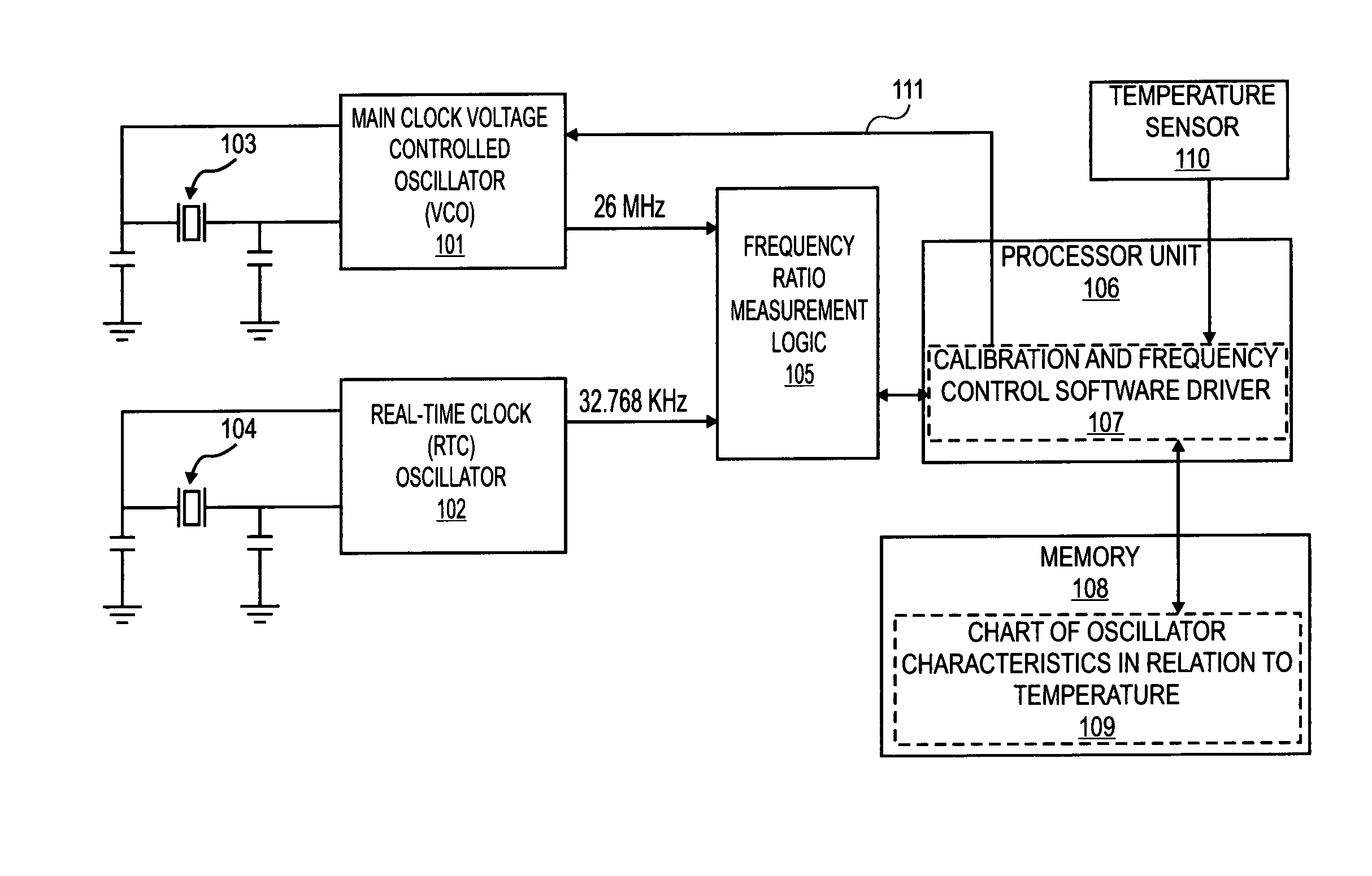
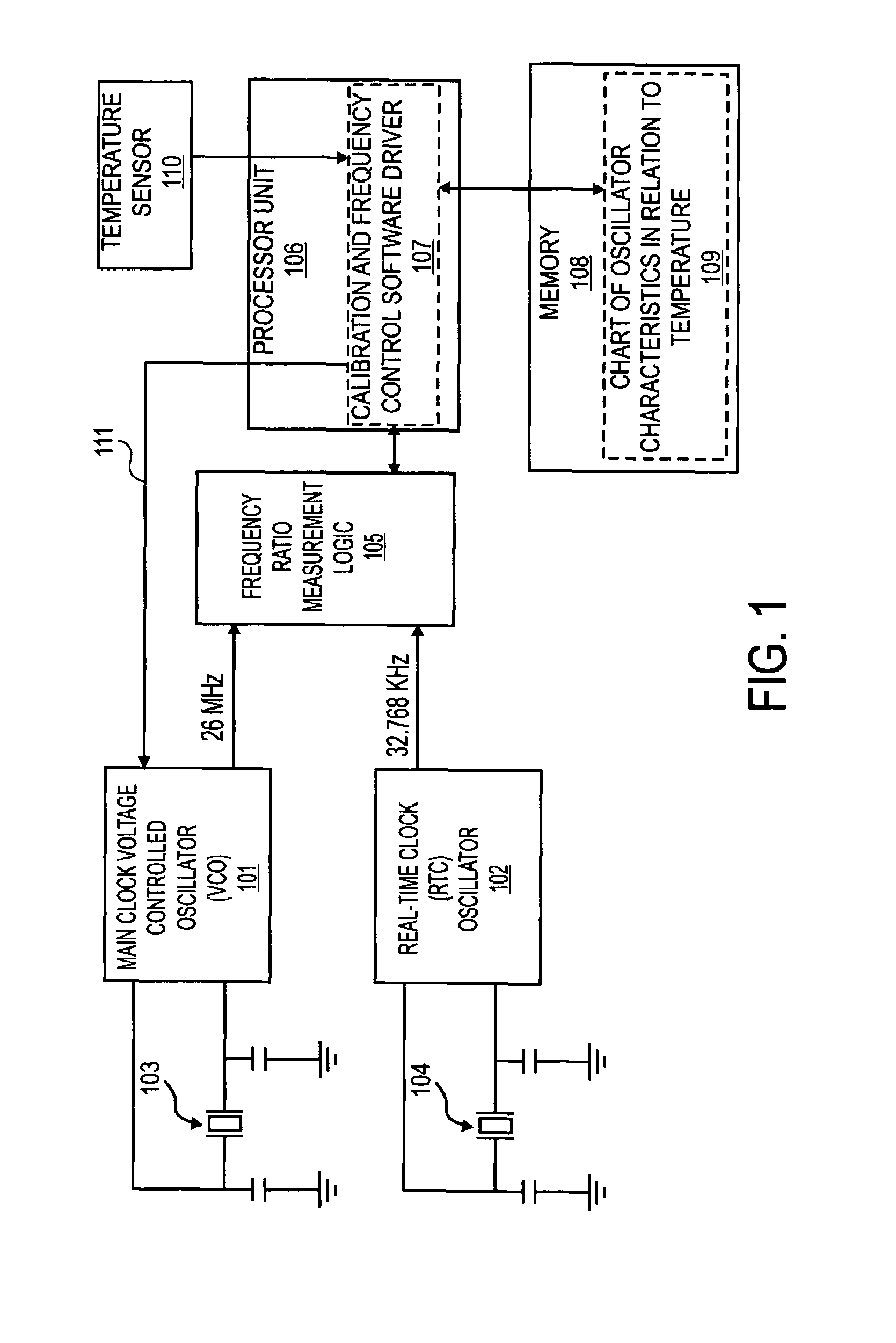
Temperature compensated crystal oscillator
InactiveUS20070155341A1Pulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationFrequency oscillationComparator
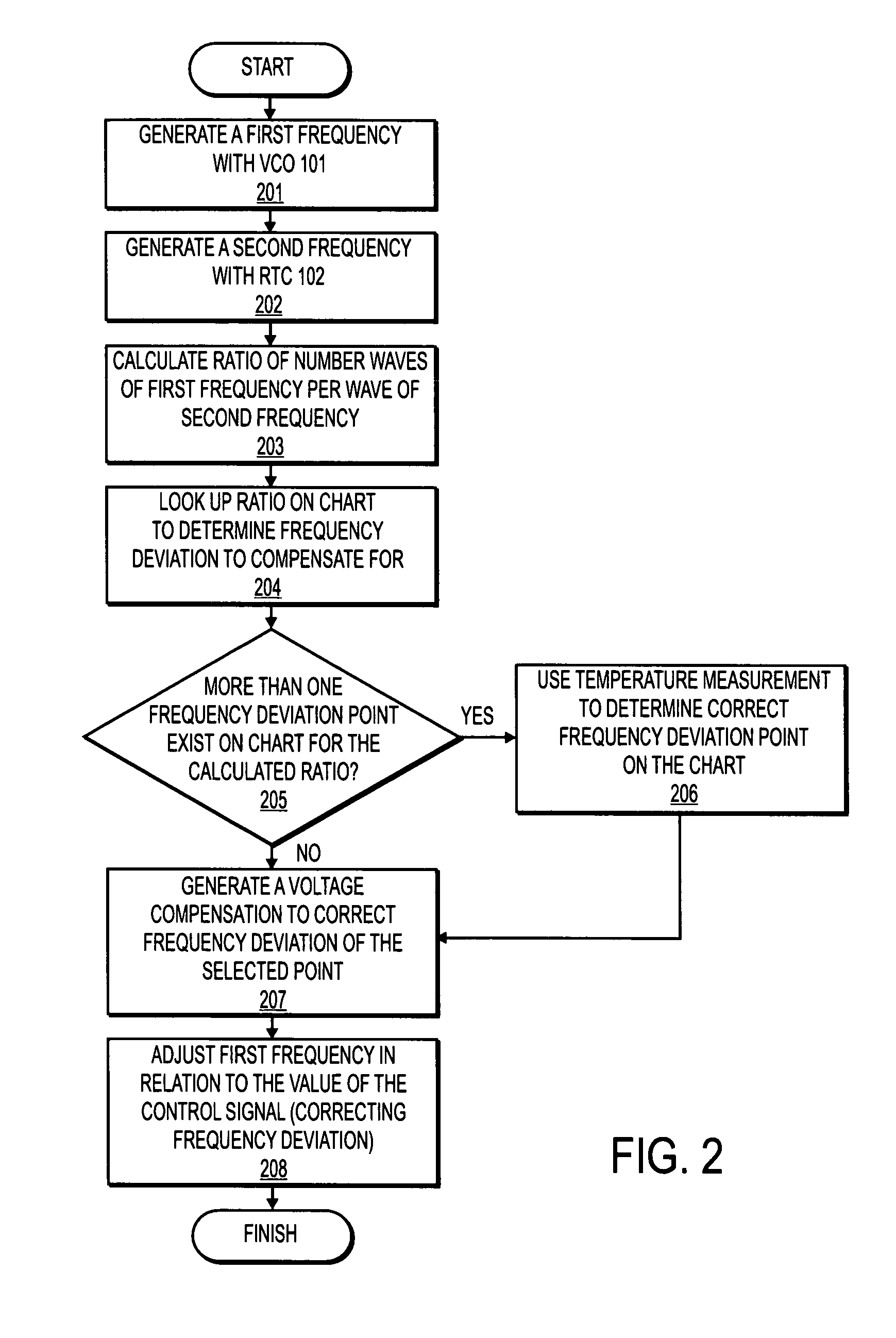
An apparatus, comprising: a first oscillator made from piezoelectric material to oscillate at a first frequency; a second oscillator to oscillate at a second frequency; a comparator to compare the first frequency to the second frequency; and a controller to change the first frequency in response to the comparing of the first frequency to the second frequency.
Owner:INTEL CORP
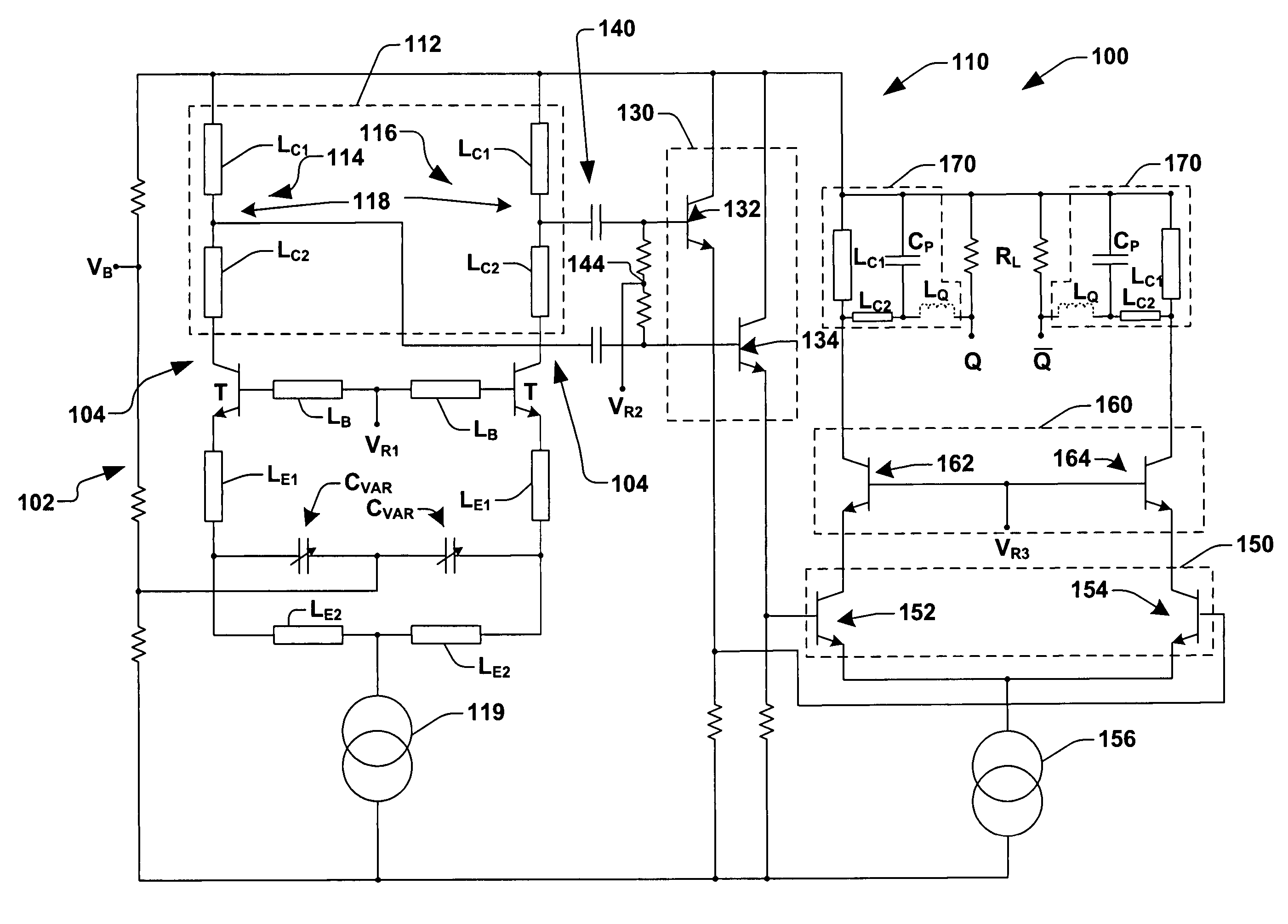
Voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) with output buffer
An oscillator system is disclosed and includes an oscillator circuit having a differential output producing a differential output signal thereat having a frequency that is a function of an input voltage. The oscillator system further includes an output buffer coupled to the differential output of the oscillator circuit. The output buffer includes an inductive voltage divider circuit configured to weaken a loading at the oscillator differential output and it increases the output power.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Frequency generator and communication system using the same
InactiveUS20050059373A1Highly stable oscillation frequencyOscillation frequency is stableMultiple-port networksAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationVoltage generatorCommunications system
A frequency generator which can perform stable frequency oscillation unaffected by temperature variation. A frequency generator having a differential amplifier (1) having an LC resonance circuit (10) as a load and buffer circuits (21, 22) feeding back an output of the differential amplifier to its input, wherein a temperature coefficient converter (5) converting an output voltage of a reference voltage generator (4) and its temperature dependence to a voltage having a predetermined voltage and temperature coefficient and outputting it is provided to control bias currents IEF of emitter follower circuits to be in proportion to temperature variation. There are a characteristic in which delay time of the emitter follower circuits constructing the buffer circuits is in inverse proportion to a transconductance of transistors and a characteristic in which the transconductance is in inverse proportion to temperature and is in proportion to the bias currents IEF. An oscillation frequency stable to temperature variation can be obtained.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Resonant Difference-Frequency Atomic Force Ultrasonic Microscope
InactiveUS20080295584A1NanotechnologyMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsResonanceFrequency oscillation
A scanning probe microscope and methodology called resonant difference-frequency atomic force ultrasonic microscopy (RDF-AFUM), employs an ultrasonic wave launched from the bottom of a sample while the cantilever of an atomic force microscope, driven at a frequency differing from the ultrasonic frequency by one of the contact resonance frequencies of the cantilever, engages the sample top surface. The nonlinear mixing of the oscillating cantilever and the ultrasonic wave in the region defined by the cantilever tip-sample surface interaction force generates difference-frequency oscillations at the cantilever contact resonance. The resonance-enhanced difference-frequency signals are used to create images of nanoscale near-surface and subsurface features.
Owner:NASA
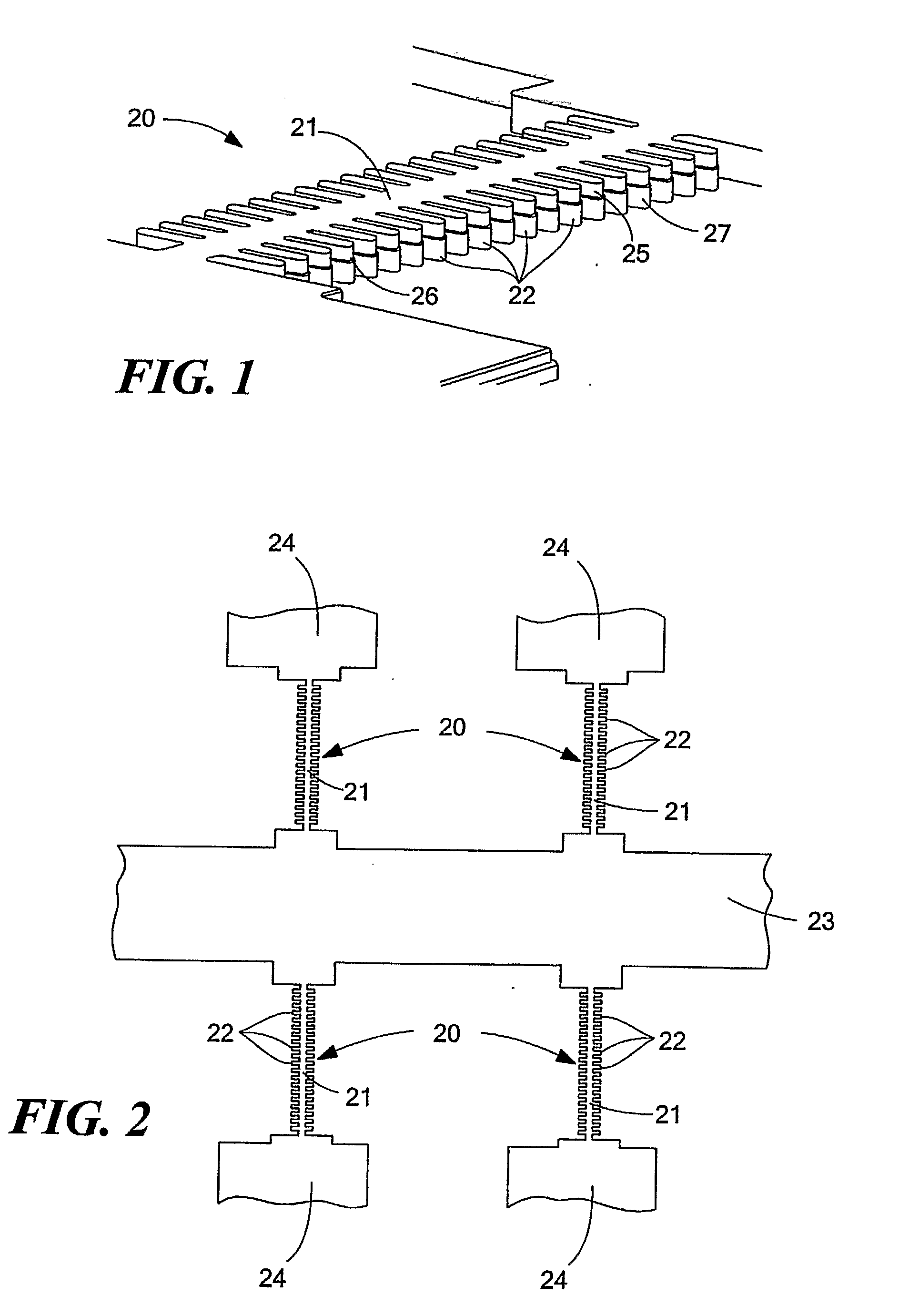
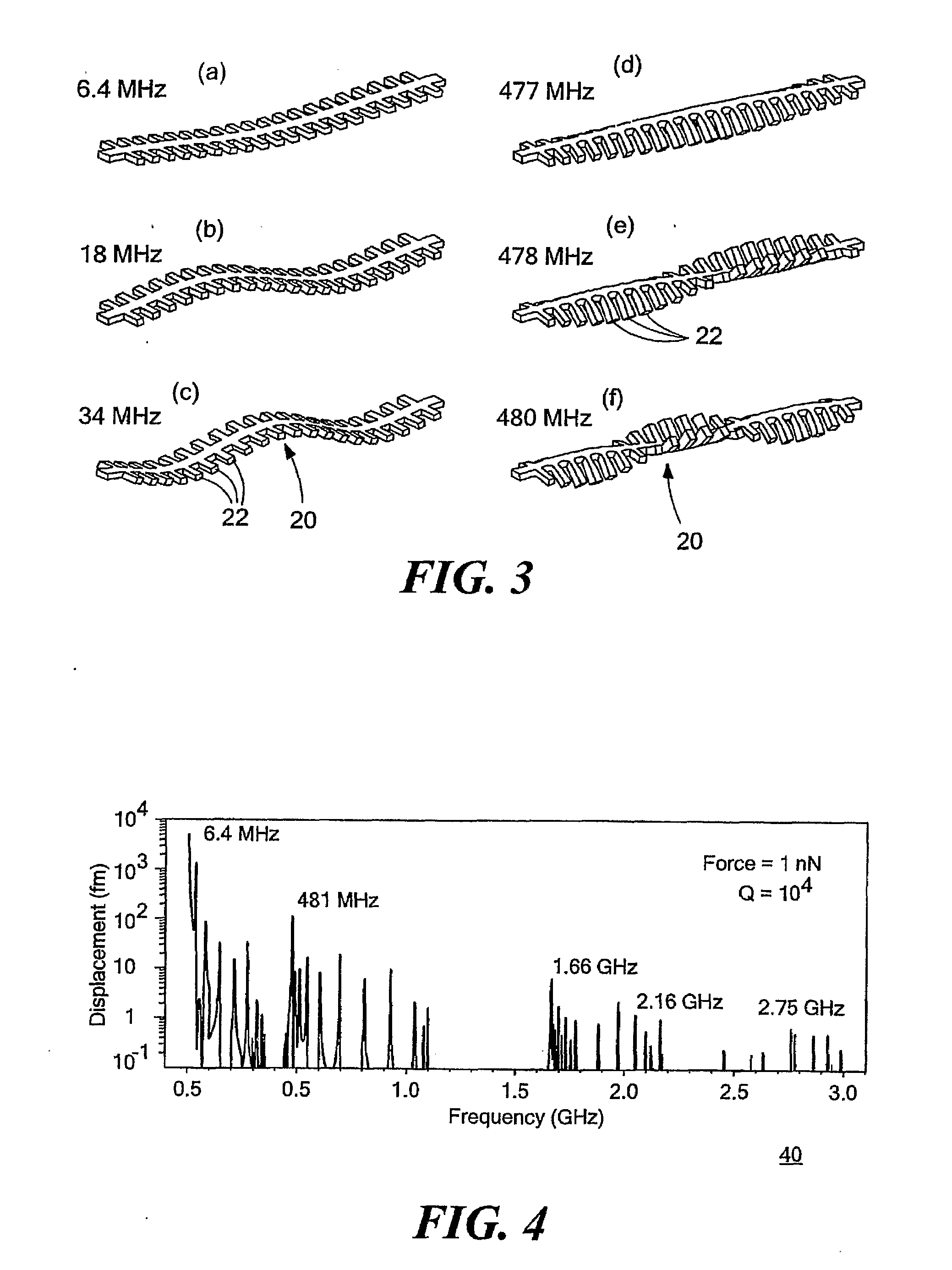
MEMS resonator array structure and method of operating and using same
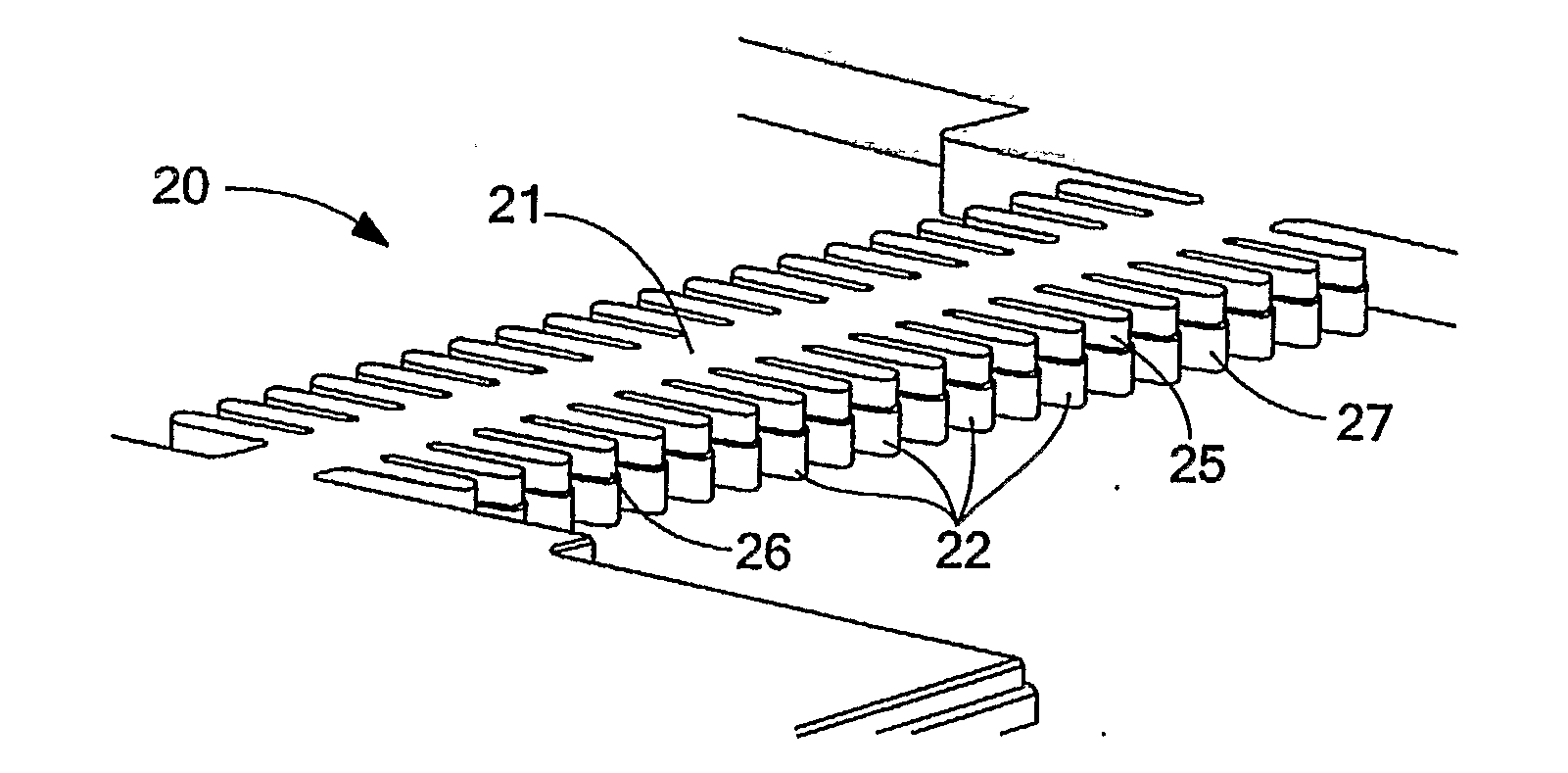
Each one of resonators arranged in an N×M MEMS array structure includes substantially straight elongated beam sections connected by curved / rounded sections and is mechanically coupled to at least one adjacent resonator of the array via a coupling section, each elongated beam section connected to another elongated beam section at a distal end via the curved / rounded sections forming a geometric shape (e.g., a rounded square), and the coupling sections disposed between elongated beam sections of adjacent resonators. The resonators, when induced, oscillate at substantially the same frequency, in combined elongating / breathing and bending modes, i.e., beam sections exhibiting elongating / breathing-like and bending-like motions. One or more of the array structure's resonators may include one or more nodal points (i.e., that are substantially stationary and / or experience little movement), which are suitable and / or preferable locations to anchor the resonator / array to the substrate, in one or more areas of the structure's curved sections.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
A transient adaptive parameter control strategy for microgrid based on VSG
ActiveCN109149605ASimple structureImprove dynamic stabilityPower oscillations reduction/preventionDamping factorMicrogrid
The invention discloses a microgrid transient adaptive parameter control strategy based on VSG, belonging to the field of microgrid frequency control. The invention comprises the following steps: a dynamic model of a microgrid system based on VSG is constructed; The virtual inertial torque and virtual damping factor of the system model are controlled adaptively. The stability of the system energyfunction is evaluated. Matlab / simulink software is used to simulate and analyze the numerical example. By analyzing the frequency oscillation process, the method of the invention establishes the dynamic relationship between the system inertia and the system frequency offset, and changes the virtual inertia factor in real time according to the frequency change, thereby effectively suppressing the frequency oscillation, enabling the system to better cope with the transient disturbance and providing the system frequency stability.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Temperature compensated crystal oscillator
InactiveUS7541878B2Pulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationFrequency oscillationCrystal oscillator
An apparatus, comprising: a first oscillator made from piezoelectric material to oscillate at a first frequency; a second oscillator to oscillate at a second frequency; a comparator to compare the first frequency to the second frequency; and a controller to change the first frequency in response to the comparing of the first frequency to the second frequency.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Non resonant inductive power transmission system and method
ActiveUS8188619B2TransformersEfficient power electronics conversionElectric power transmissionPeak value
Non-resonant inductive power transmission wherein the driving voltage across a primary inductor oscillates at a frequency significantly different from the resonant frequency of the inductive coupling system. Embodiments of the invention include systems and methods for: power regulation using frequency control, fault detection using voltage peak detectors and inductive communication channels.
Owner:POWERMAT TECHNOLOGIES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com