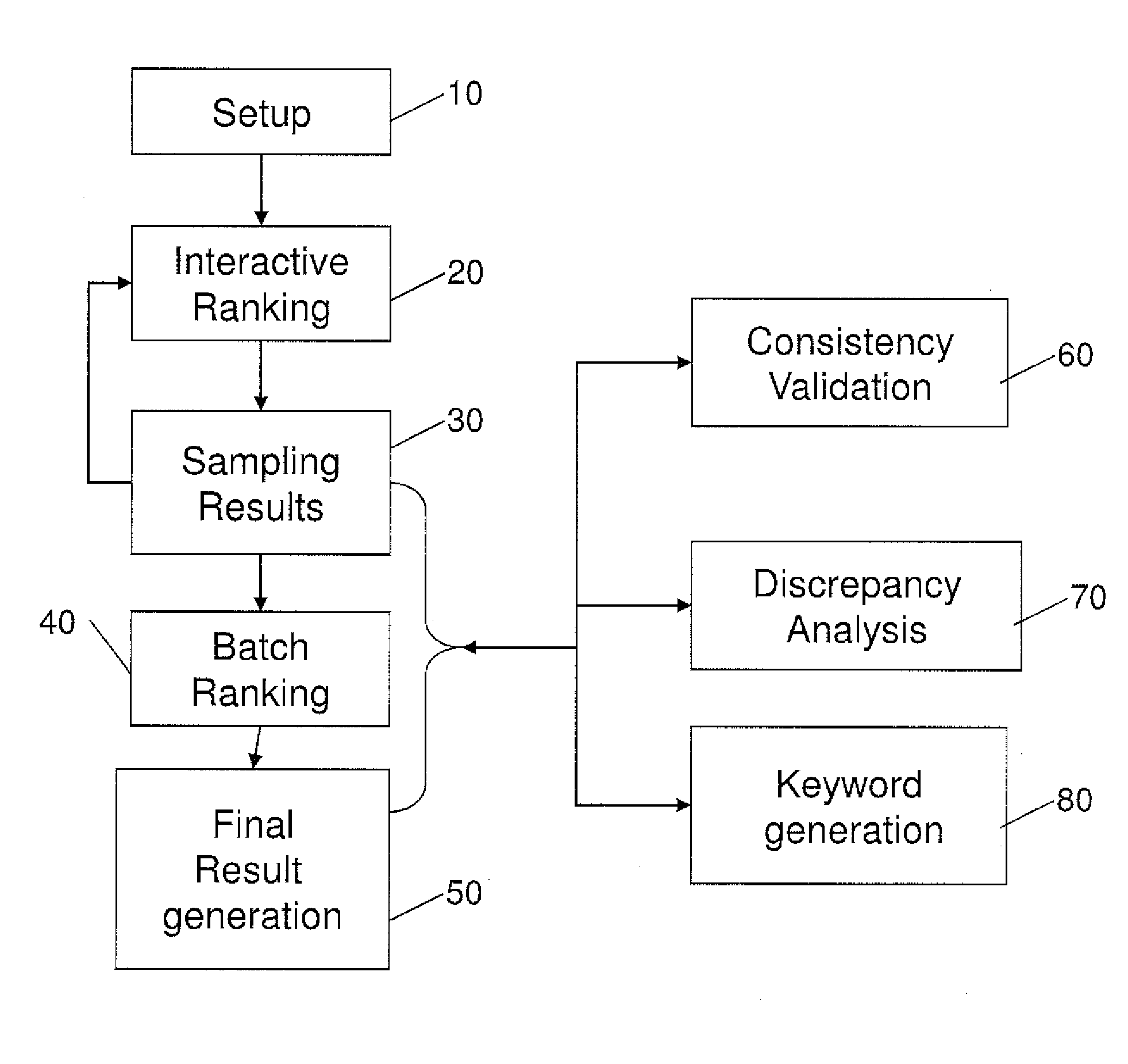
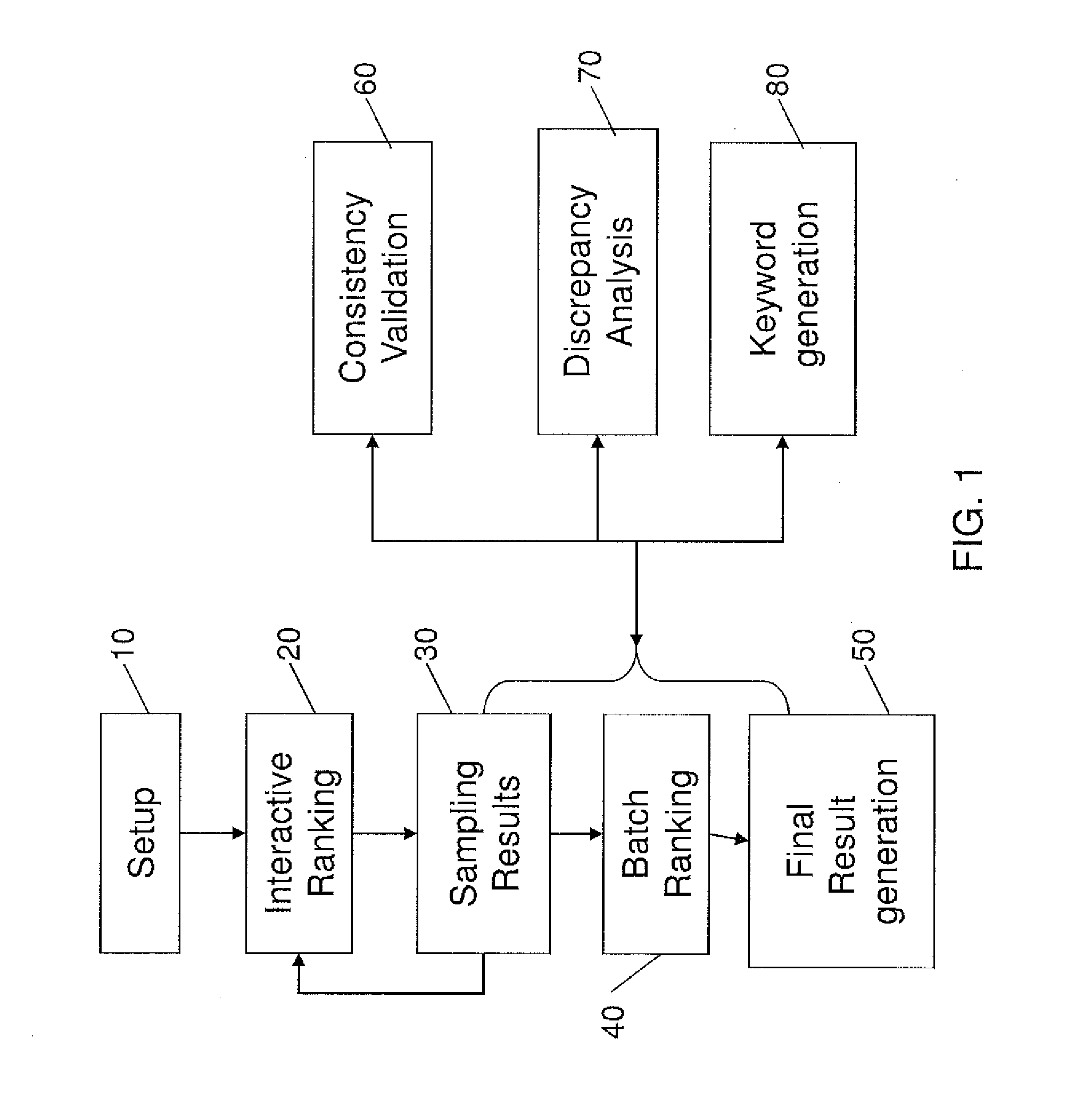
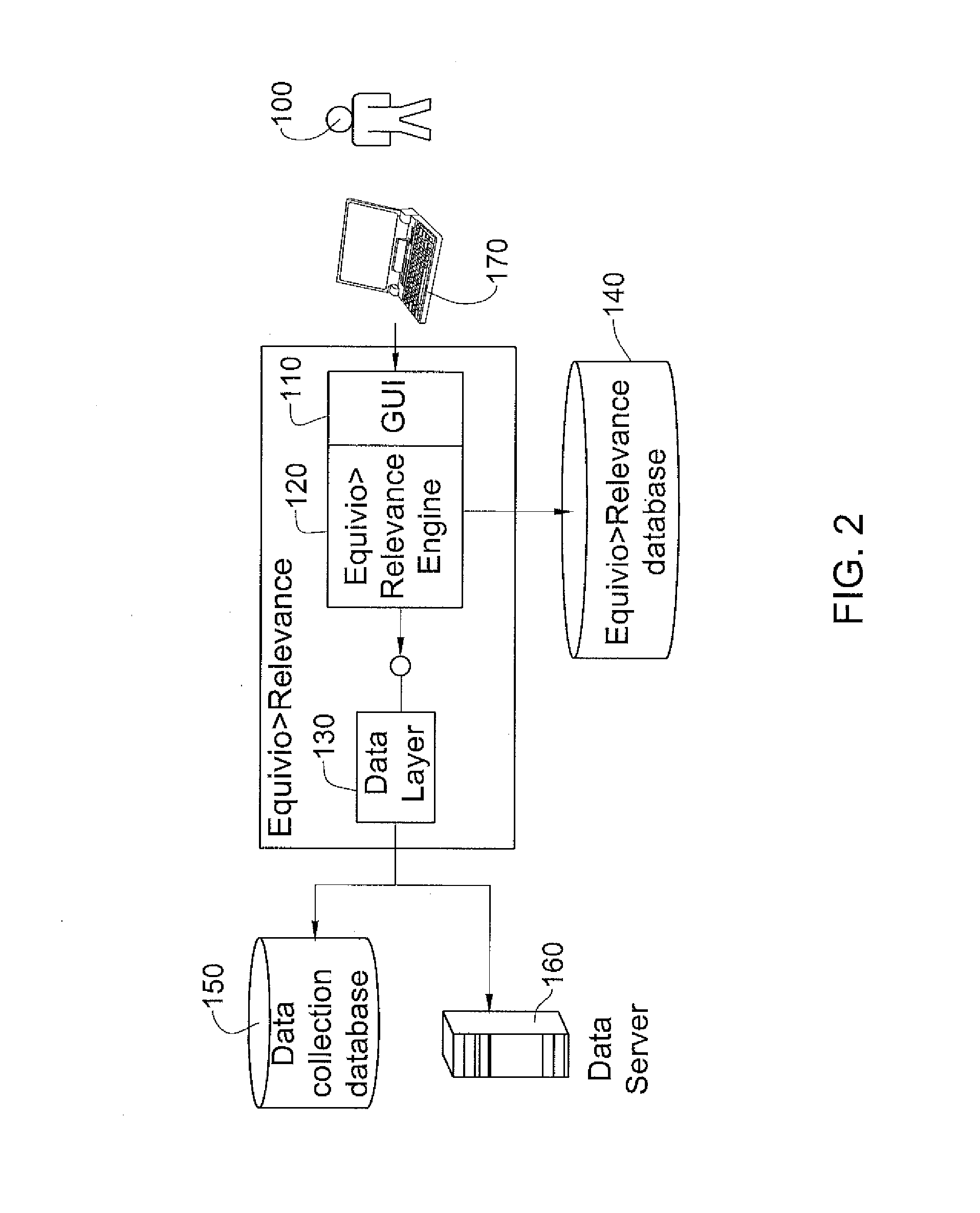
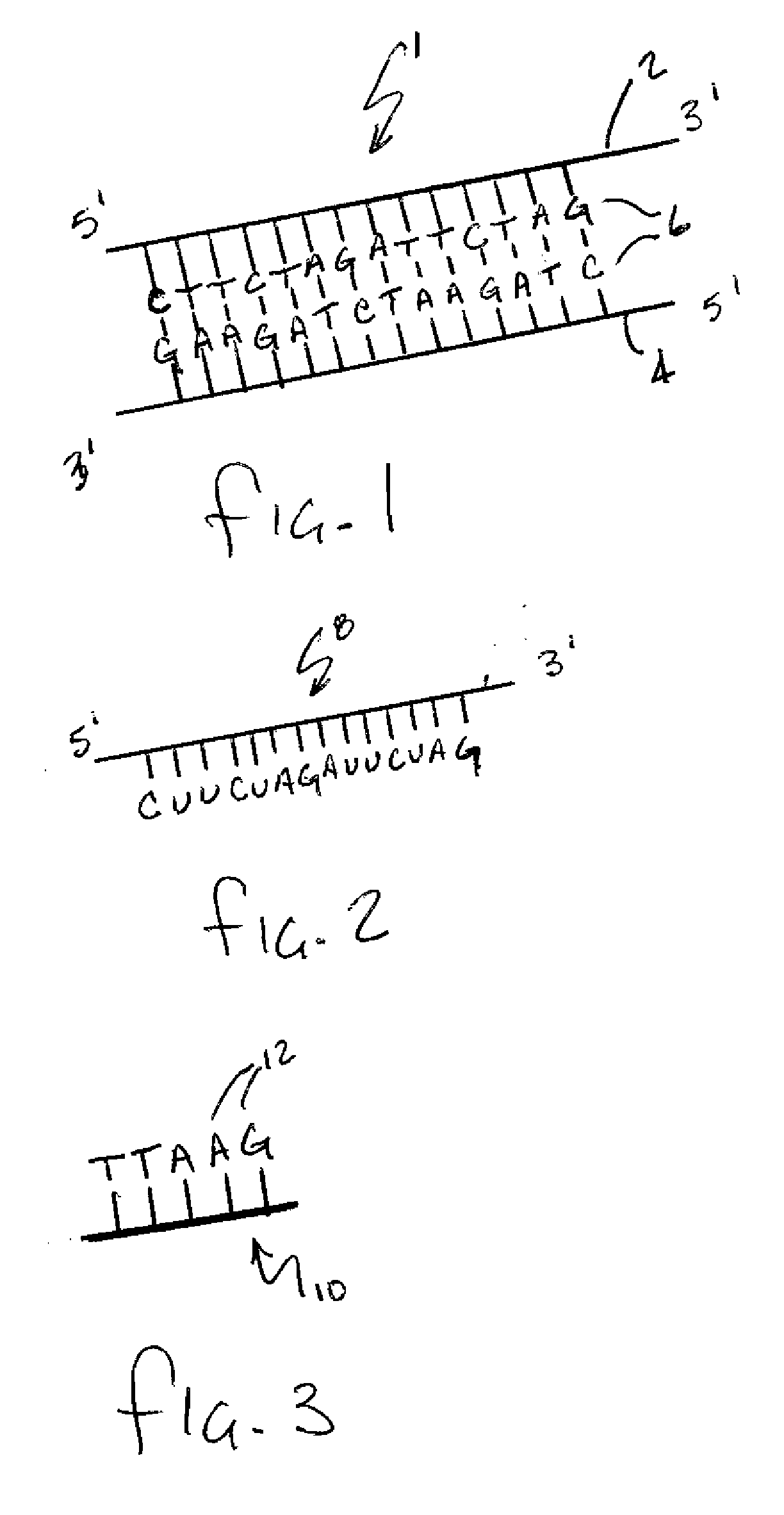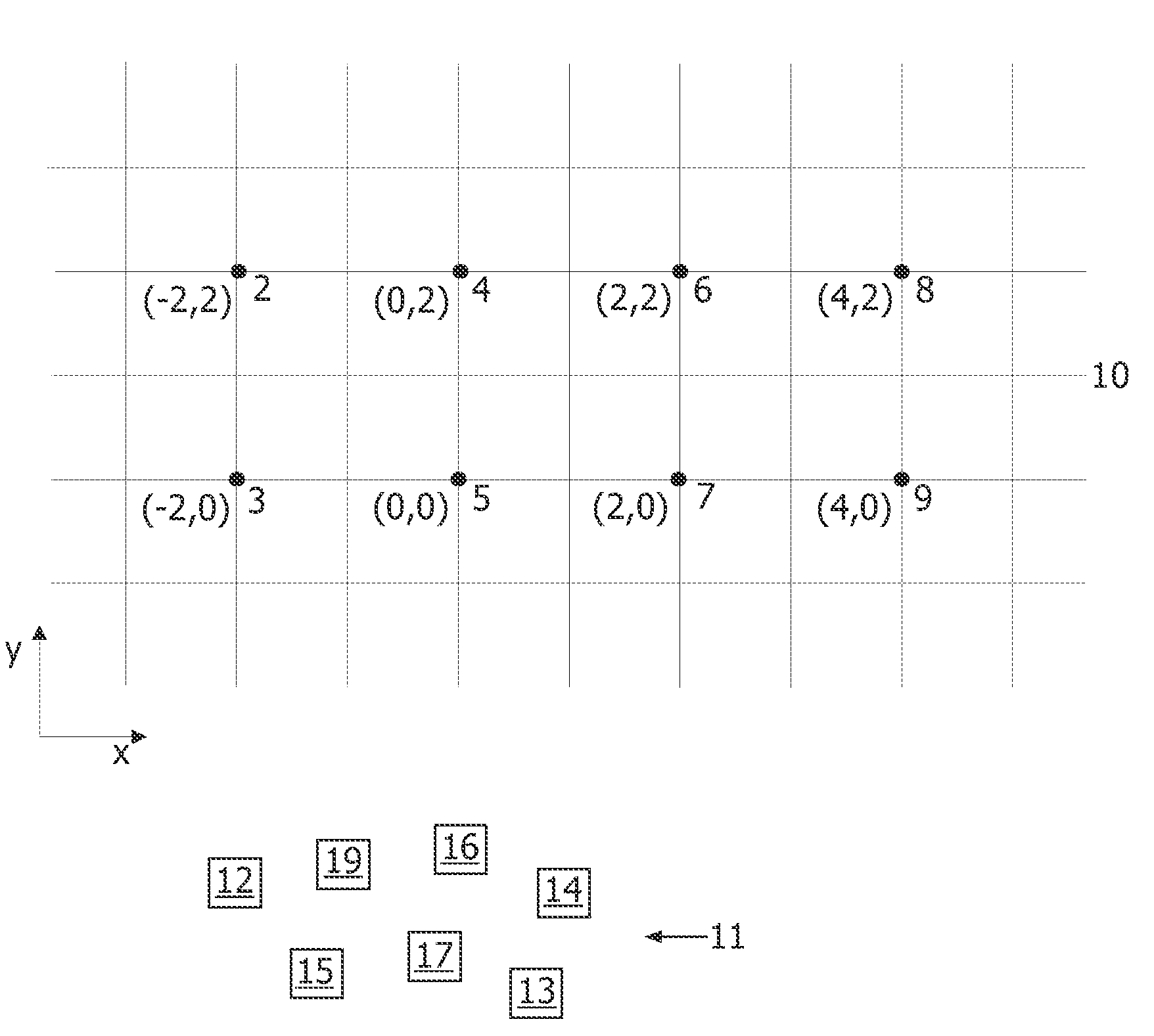Patents
Literature
255 results about "Computer algorithm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A computer algorithm is a sequence of steps that is followed to achieve a particular outcome. An algorithm is just step-by -step instructions for doing something. An algorithm is a series of steps that, if followed precisely, is guaranteed to solve a specific problem in a finite amount of time.
Flexible instrument
InactiveUS7214230B2Small diameterSufficient flexibilitySuture equipmentsProgramme-controlled manipulatorRemote controlMaster station
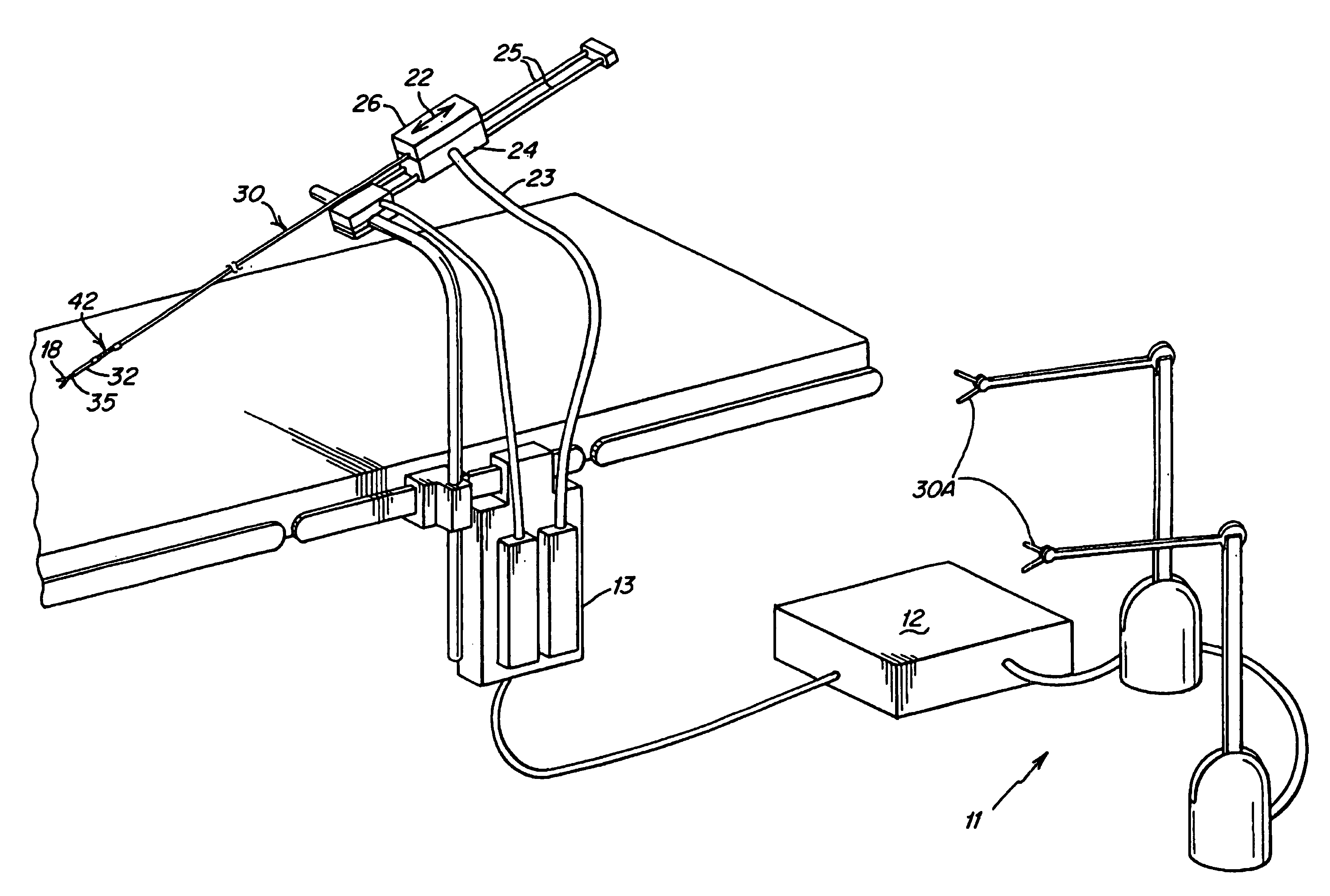
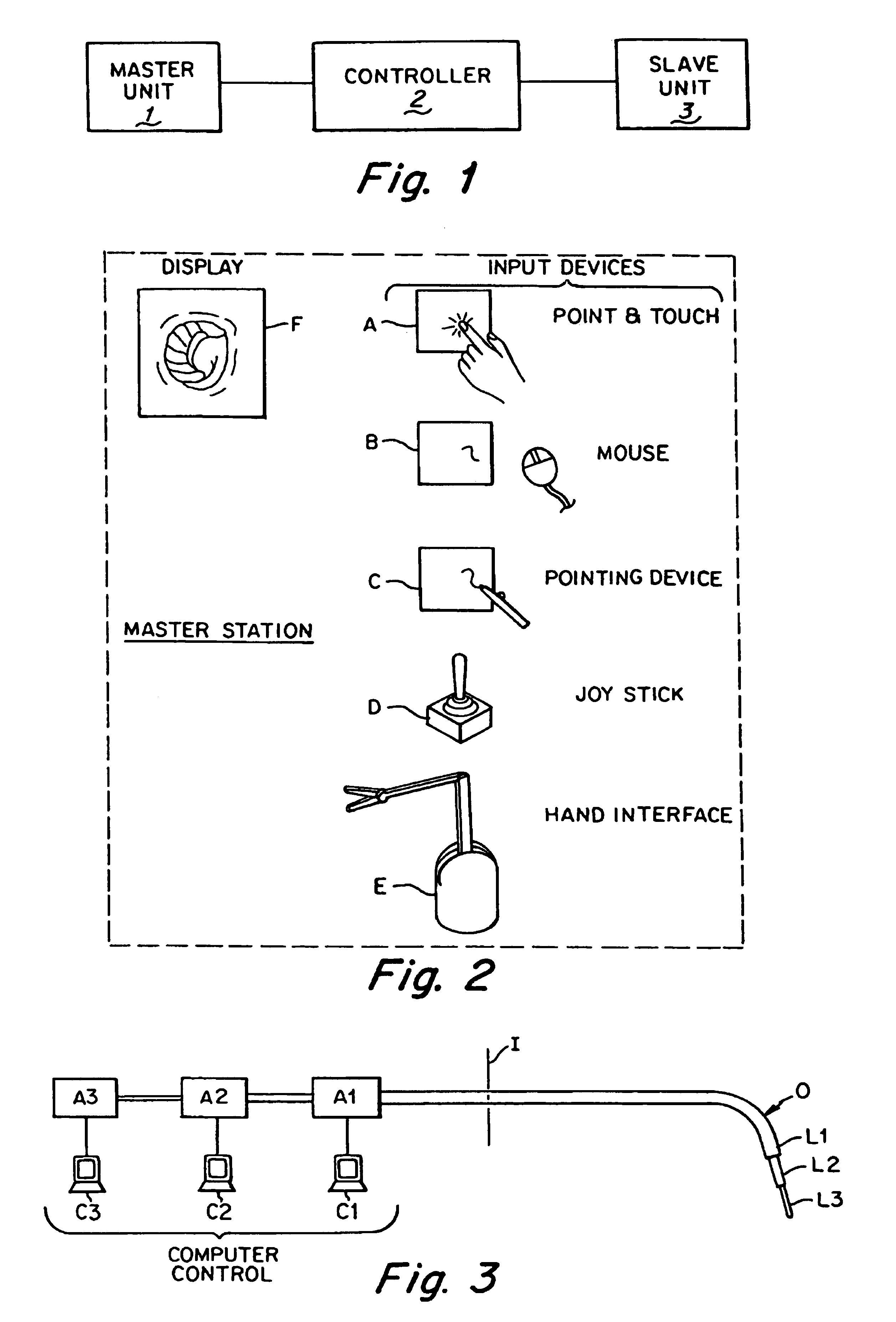
A remote control flexible instrument system, employing a shaft which supports a tool, is described in which the has proximal and distal ends with at least a portion thereof extending through a lumen of the human body so as to locate the shaft at an internal target site. A master station including an input device provides control of the instrument situated at a slave station. The master station can control at least one degree-of-freedom of the flexible instrument. A controller intercouples the master and slave stations and is operated in accordance with a computer algorithm that receives a command from the input device for controlling at least one degree-of-freedom of the catheter so as to respond in accordance with action at the input device. The flexible instrument further comprises a controlled flexible segment along the shaft, for controlled bending at the flexible segment to guide the shaft and to dispose the tool at an operative site.
Owner:AURIS HEALTH INC
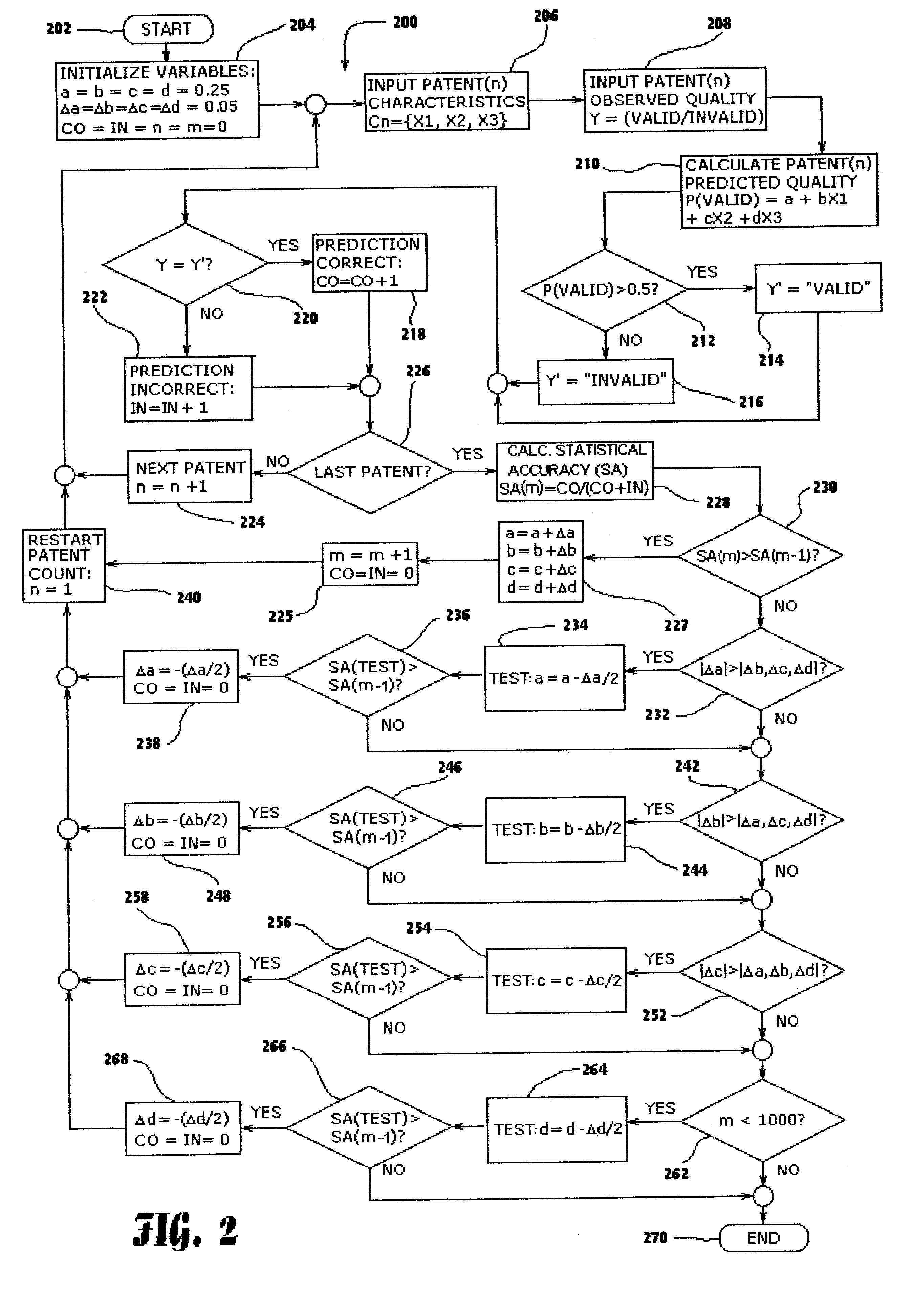
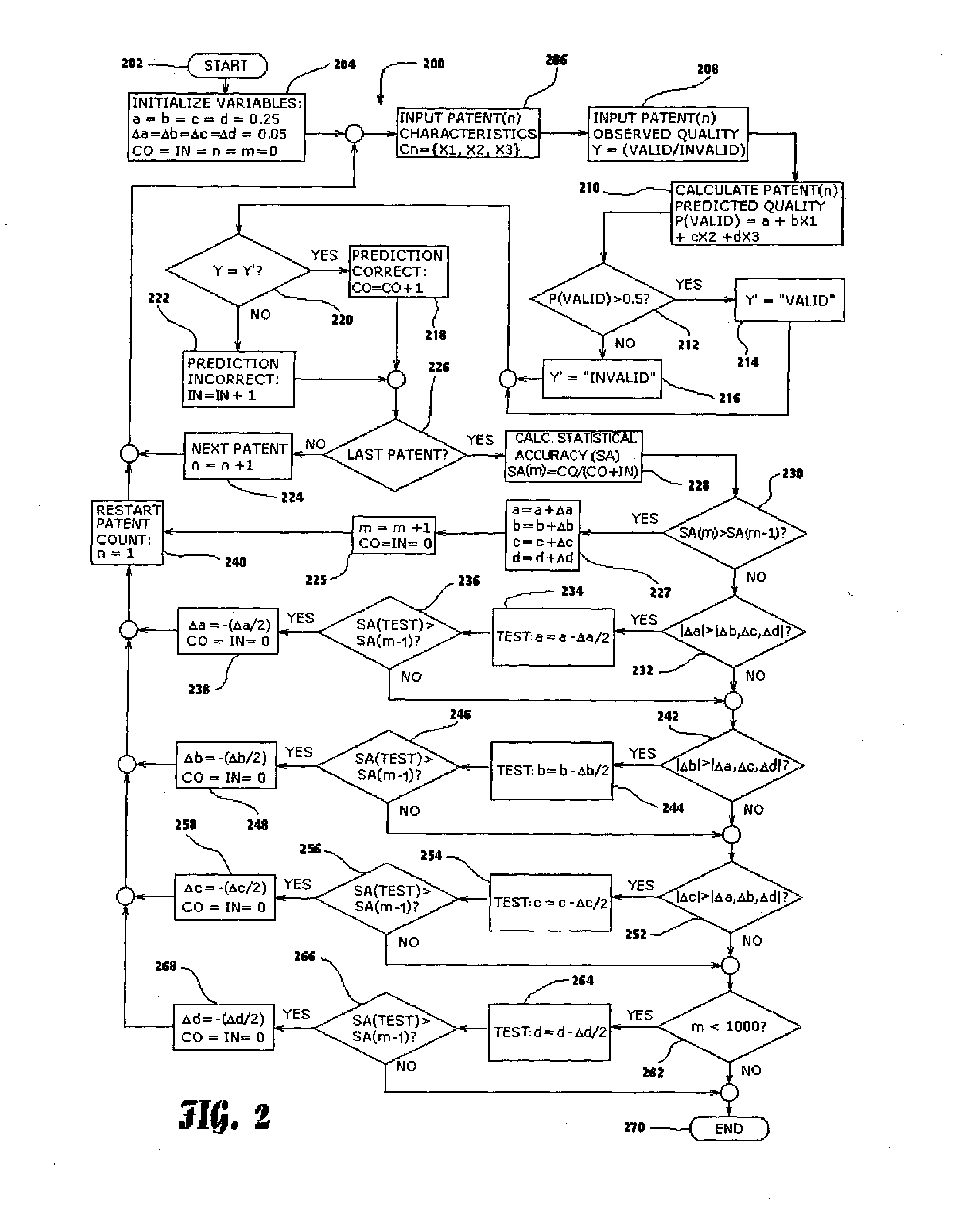
Method and system for rating patents and other intangible assets
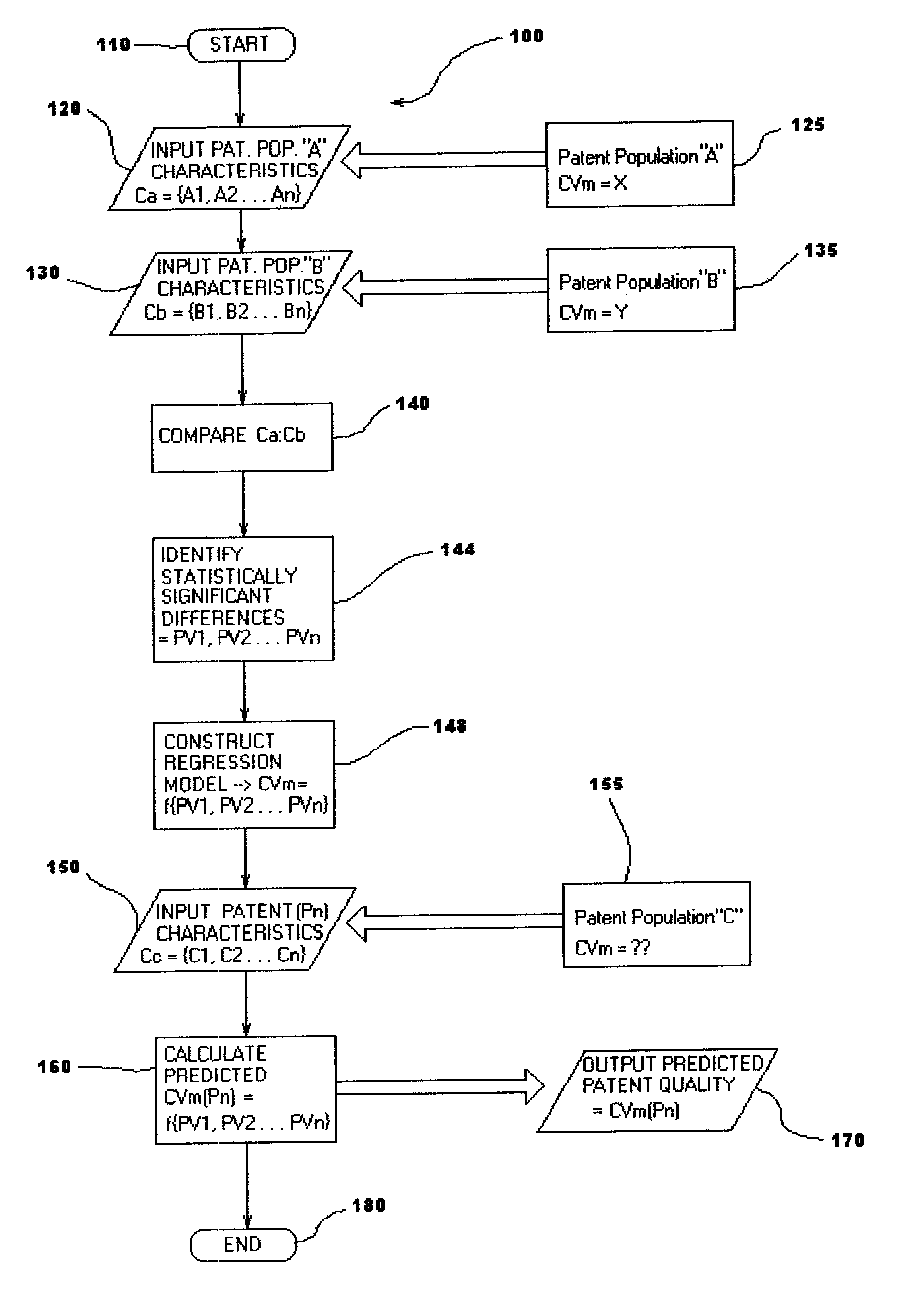
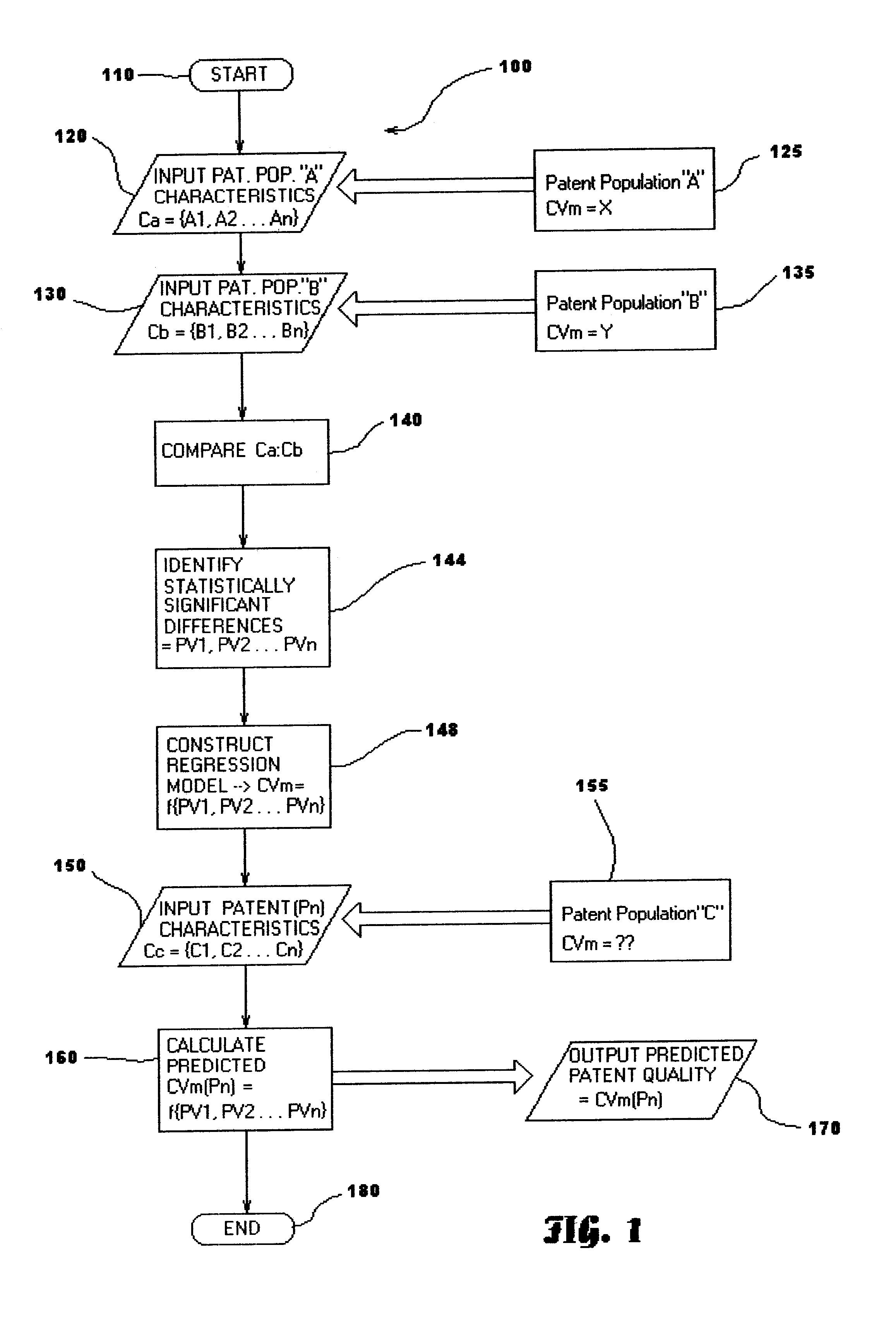
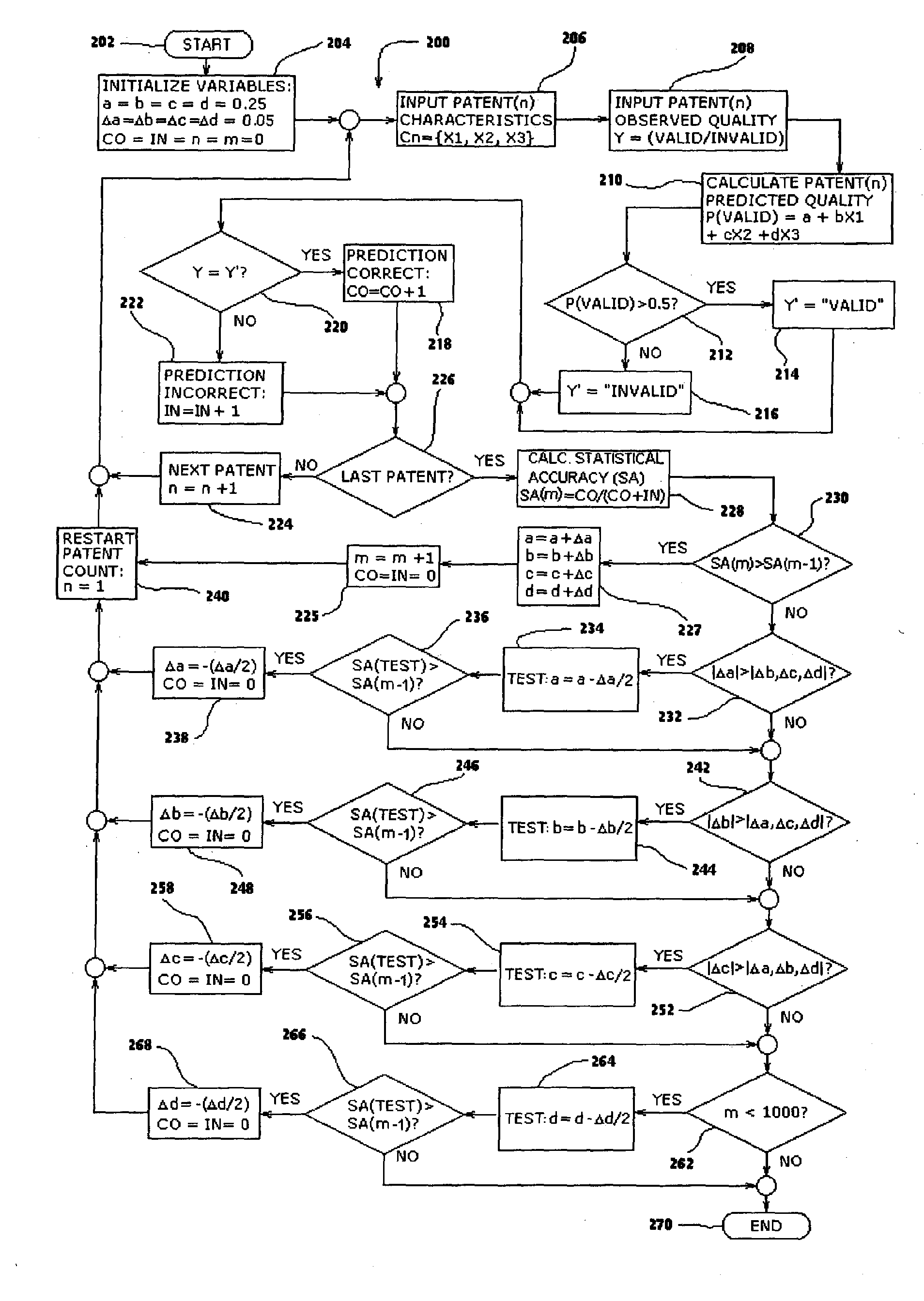
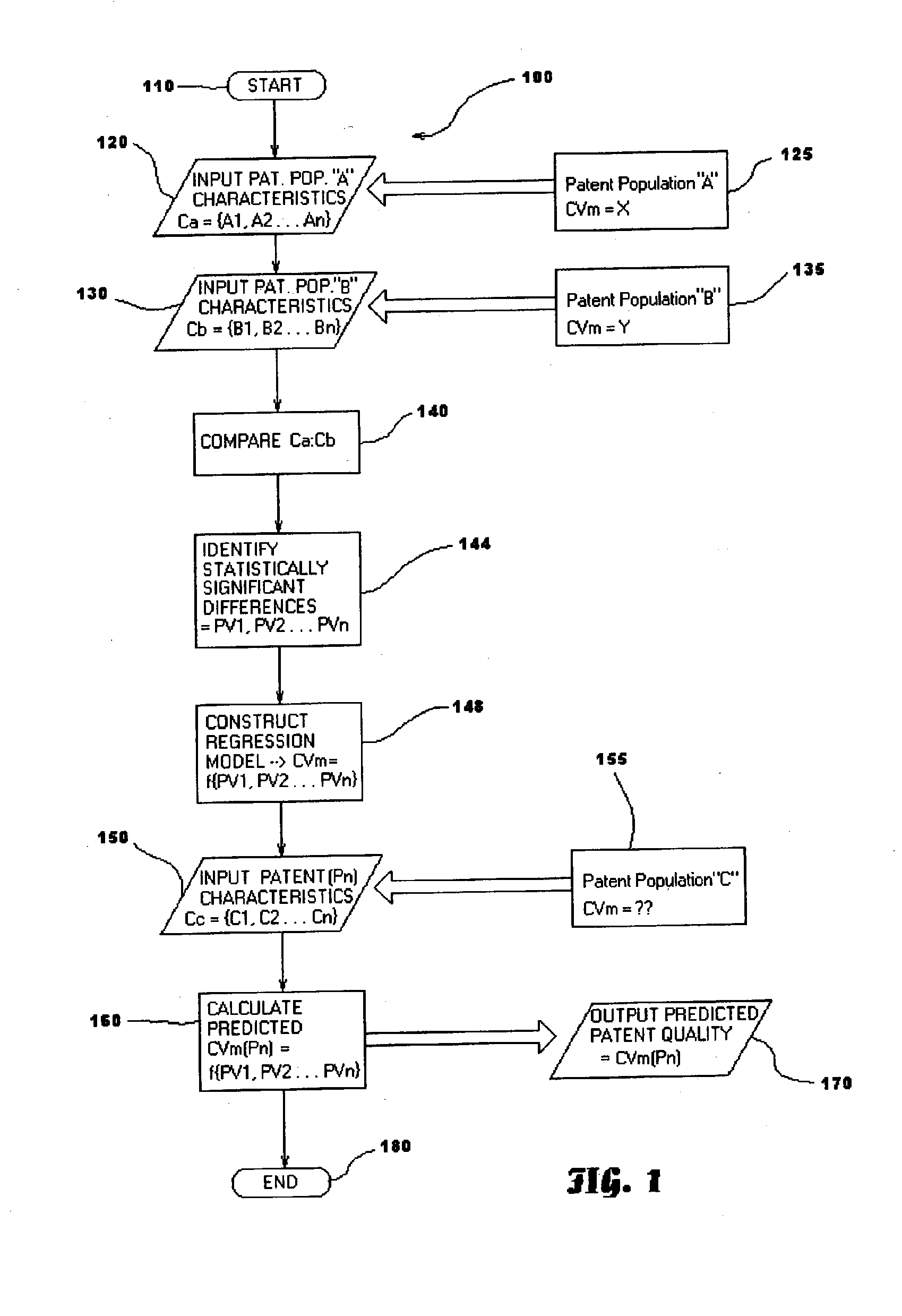
A statistical patent rating method and system is provided for independently assessing the relative breadth ("B"), defensibility ("D") and commercial relevance ("R") of individual patent assets and other intangible intellectual property assets. The invention provides new and valuable information that can be used by patent valuation experts, investment advisors, economists and others to help guide future patent investment decisions, licensing programs, patent appraisals, tax valuations, transfer pricing, economic forecasting and planning, and even mediation and / or settlement of patent litigation lawsuits. In one embodiment the invention provides a statistically-based patent rating method and system whereby relative ratings or rankings are generated using a database of patent information by identifying and comparing various characteristics of each individual patent to a statistically determined distribution of the same characteristics within a given patent population. For example, a first population of patents having a known relatively high intrinsic value or quality (e.g. successfully litigated patents) is compared to a second population of patents having a known relatively low intrinsic value or quality (e.g. unsuccessfully litigated patents). Based on a statistical comparison of the two populations, certain characteristics are identified as being more prevalent or more pronounced in one population group or the other to a statistically significant degree. Multiple such statistical comparisons are used to construct and optimize a computer model or computer algorithm that can then be used to predict and / or provide statistically-accurate probabilities of a desired value or quality being present or a future event occurring, given the identified characteristics of an individual patent or group of patents.
Owner:PATENTRATINGS
Pobabilistic methods for mapping and localization in arbitrary outdoor environments
InactiveUS20080033645A1Maximize likelihoodNavigational calculation instrumentsPosition fixationTerrainLand based
Systems and methods which provide mapping an arbitrary outdoor environment and positioning a ground-based vehicle relative to this map. In one embodiment, a land-based vehicle travels across a section of terrain, recording both location data from sensors such as GPS as well as scene data from sensors such as laser scanners or cameras. These data are then used to create a high-resolution map of the terrain, which may have well-defined structure (such as a road) or which may be unstructured (such as a section of desert), and which does not rely on the presence of any “landmark” features. In another embodiment, the vehicle localizes itself relative to this map in a subsequent drive over the same section of terrain, using a computer algorithm that incorporates incoming sensor data from the vehicle by attempting to maximize the likelihood of the observed data given the map.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
System for enhancing expert-based computerized analysis of a set of digital documents and methods useful in conjunction therewith
ActiveUS8706742B1Efficient budgetingReduce riskDigital data processing detailsInference methodsDiscriminatorComputer algorithm
A system including an electronic repository having a multiplicity of accesses to a respective multiplicity of electronic documents and metadata; a document rater using a processor to run a first computer algorithm on the multiplicity of electronic documents which yields a score which rates each of the multiplicity of electronic documents to an issue; and a metadata-based document discriminator to run a second computer algorithm on at least some of the metadata which yields leads, each lead having at least one metadata value for at least one metadata parameter, whose value correlates with the score of the electronic documents to the issue, typically used in combination with an electronic document analysis method receiving N electronic documents pertaining to a case encompassing a set of issues including at least one issue and establishing relevance of at least the N documents to at least one individual issue in the set of issues.
Owner:MICROSOFT ISRAEL RES & DEV 2002 LTD
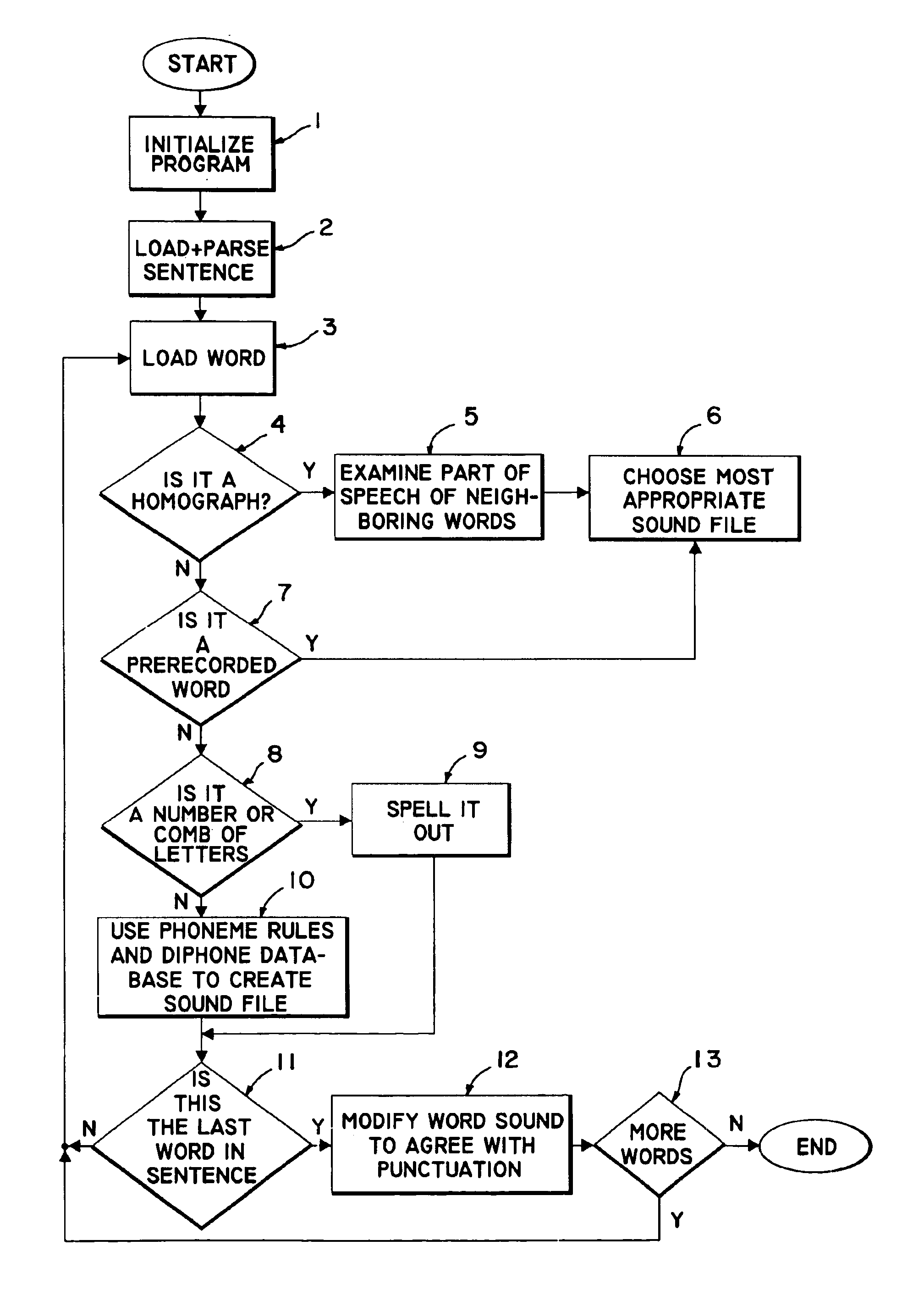
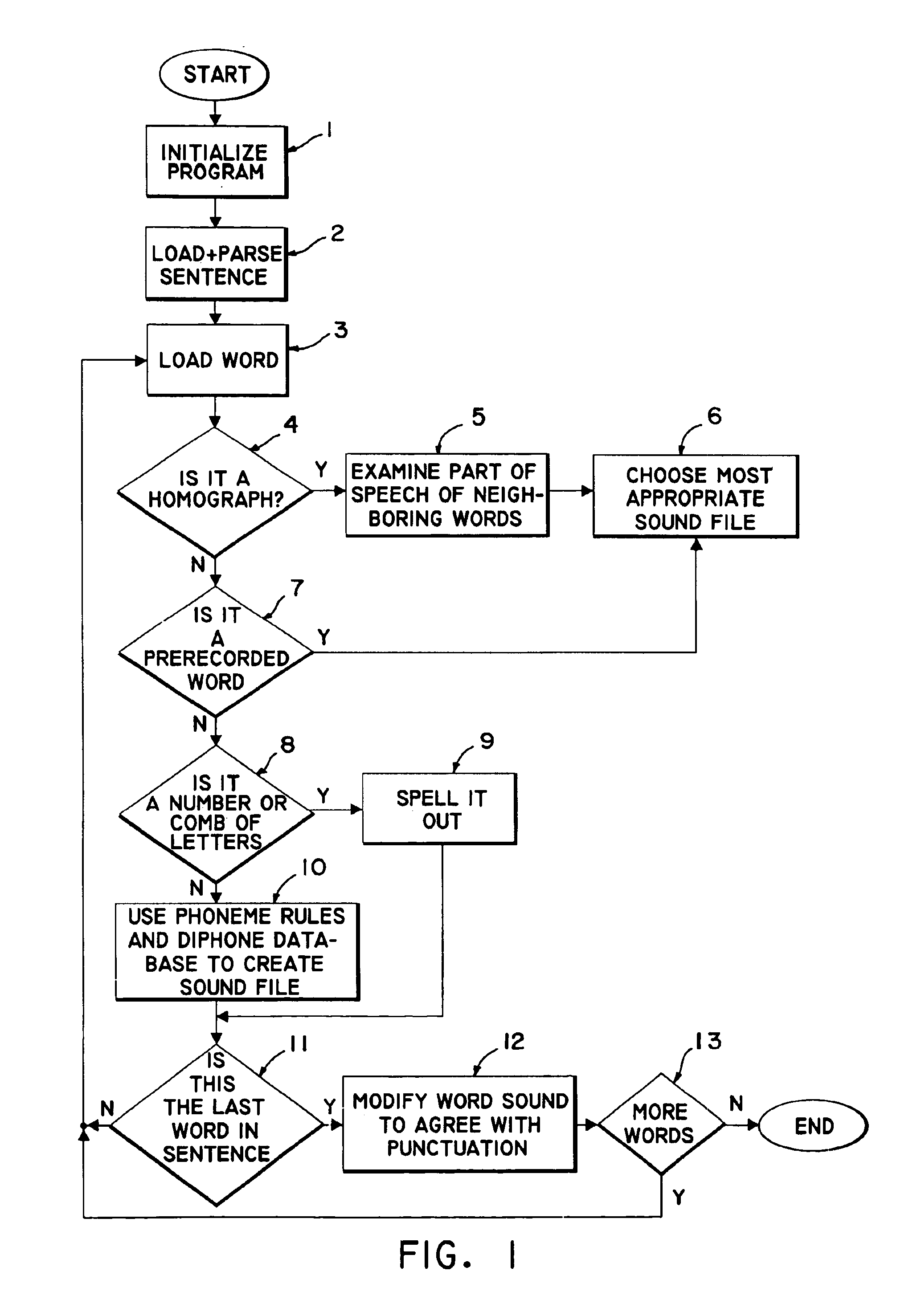
Method for producing a speech rendition of text from diphone sounds
A text-to-speech system utilizes a method for producing a speech rendition of text based on dividing some or all words of a sentence into component diphones. A phonetic dictionary is aligned so that each letter within each word has a single corresponding phoneme. The aligned dictionary is analyzed to determine the most common phoneme representation of the letter in the context of a string of letters before and after it. The results for each letter are stored in phoneme rule matrix. A diphone database is created using a way editor to cut 2,000 distinct diphones out of specially selected words. A computer algorithm selects a phoneme for each letter. Then, two phonemes are used to create a diphone. Words are then read aloud by concatenating sounds from the diphone database. In one embodiment, diphones are used only when a word is not one of a list of pre-recorded words.
Owner:ASAPP INC
Hybridization assisted nanopore sequencing
InactiveUS20070190542A1Eliminate needEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresHybridization probeNucleic Acid Probes
A method of employing a nanopore structure in a manner that allows the detection of the positions (relative and / or absolute) of nucleic acid probes that are hybridized onto a single-stranded nucleic acid molecule. In accordance with the method the strand of interest is hybridized with a probe having a known sequence. The strand and hybridized probes are translocated through a nanopore. The fluctuations in current measured across the nanopore will vary as a function of time corresponding to the passing of a probe attachment point along the strand. These fluctuations in current are then used to determine the attachment positions of the probes along the strand of interest. This probe position data is then fed into a computer algorithm that returns the sequence of the strand of interest.
Owner:NABSYS 2 0 +1
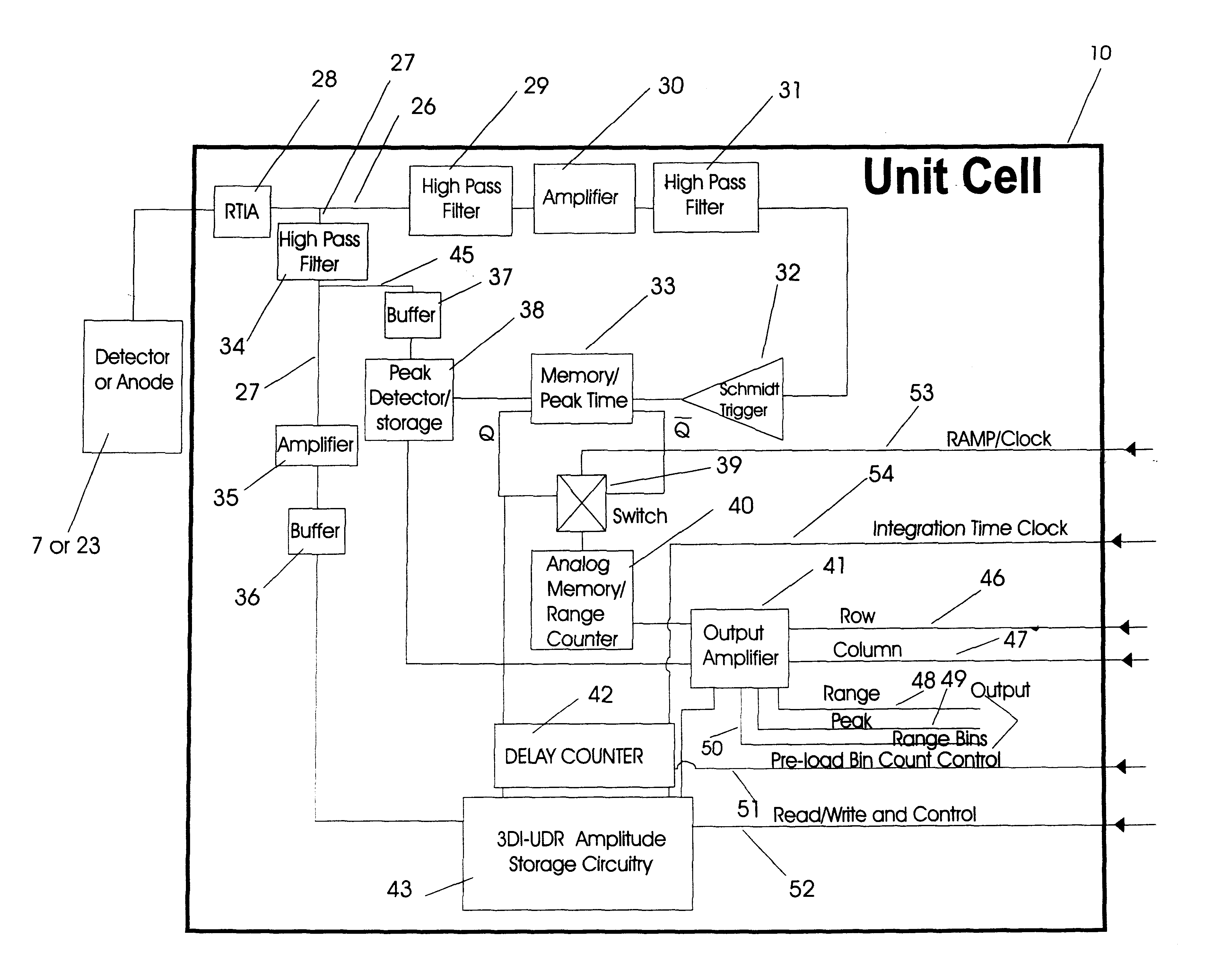
3-D imaging multiple target laser radar
InactiveUS6414746B1Accurately determineOptical rangefindersSolid-state devicesElectronIntegrated circuit
A three dimensional imaging device is presented which uses a single pulse from a pulsed light source to detect objects which are obscured by camouflage, fog or smoke but otherwise enveloped by a light-transmitting medium. The device simultaneously operates in two modes, light reflected from the nearest object is processed to form a three-dimensional image by an array of pixels. This first image is based upon the light-pulse transit time recorded in each pixel. Each pixel also contains a high-speed analog memory that sequentially stores reflected signals at a repeated time interval. The first reflection acts as a time base that controls when the analog memory begins or ends the storage sequence. The first return could be from a camouflage net and the amplitudes of the return signals, after the first return, would then be from objects behind the net. Computer processing these amplitudes reveals the three-dimensional nature of the obscured objects.The device consists of the pulsed light source, optics for collecting the reflected light, a sensor for detecting the light and converting it to electrical data, drive and output electronics for timing and signal conditioning of data generated by the sensors and a computer for processing the sensor data and converting it to a three dimensional image. The sensor collects and processes the light data in a unique manner, first converting it to electricity by a number of alternate detector technologies and then using integrated circuit chips which consist of a two dimensional array of electronic pixels also called unit cells. The two dimensional array defines two dimensions of the image. Stored within each unit cells is data associated with the third dimension, ranges of targets, and amplitudes of target reflections. This data is read out of the integrated circuit chip in the time interval between laser pulses to a processing computer. The processing computer corrects the data and, by means of computer algorithms specific to the device, converts the data to a three-dimensional image of one or more targets. This image may be viewed or processed electronically to isolate targets.
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTONOMOUS MOBILITY US LLC
Simian immunodeficiency virus peptides with antifusogenic and antiviral activities
InactiveUS6017536ASsRNA viruses negative-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsSimian immunodeficiency viruses SIVDefective virus
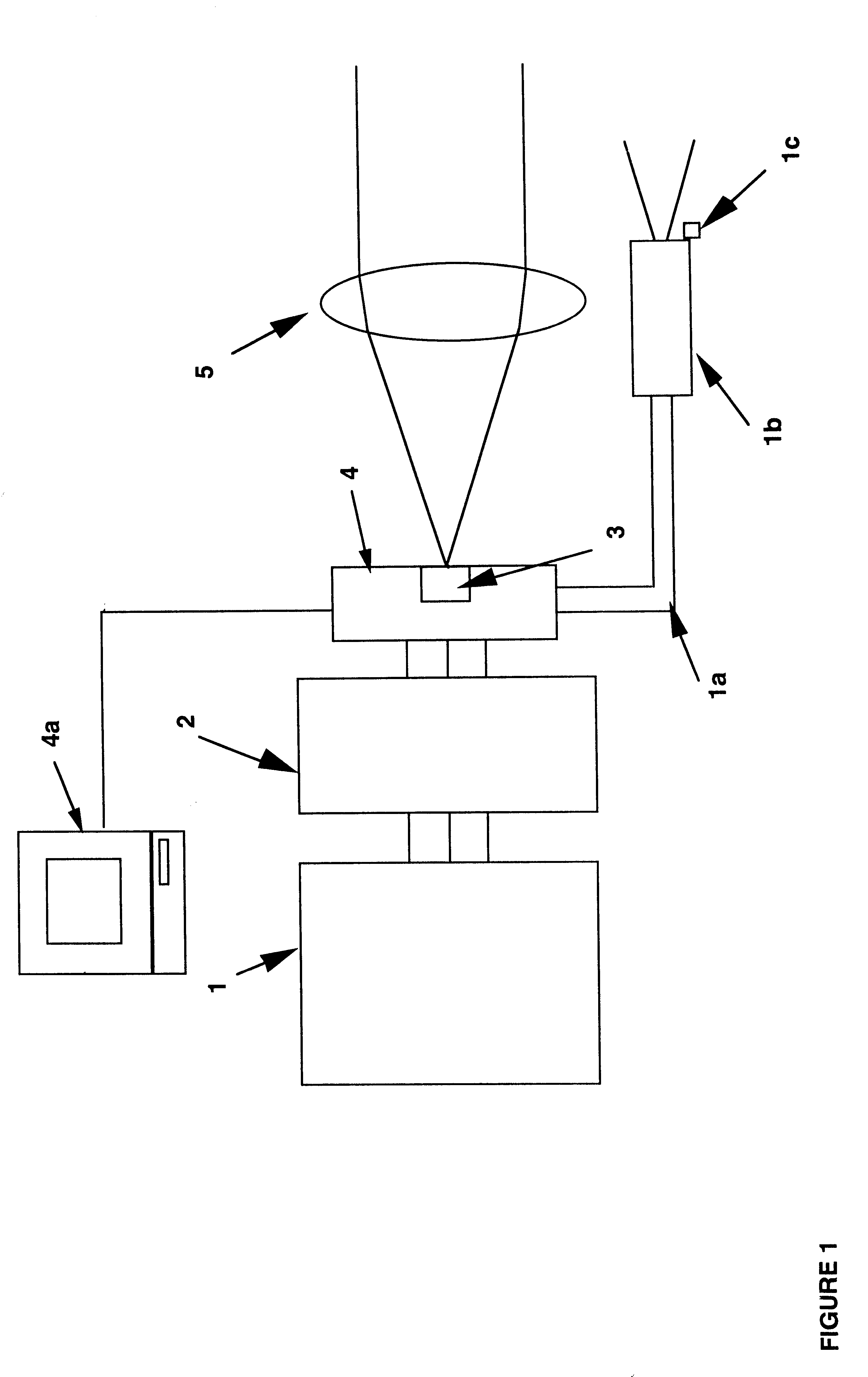
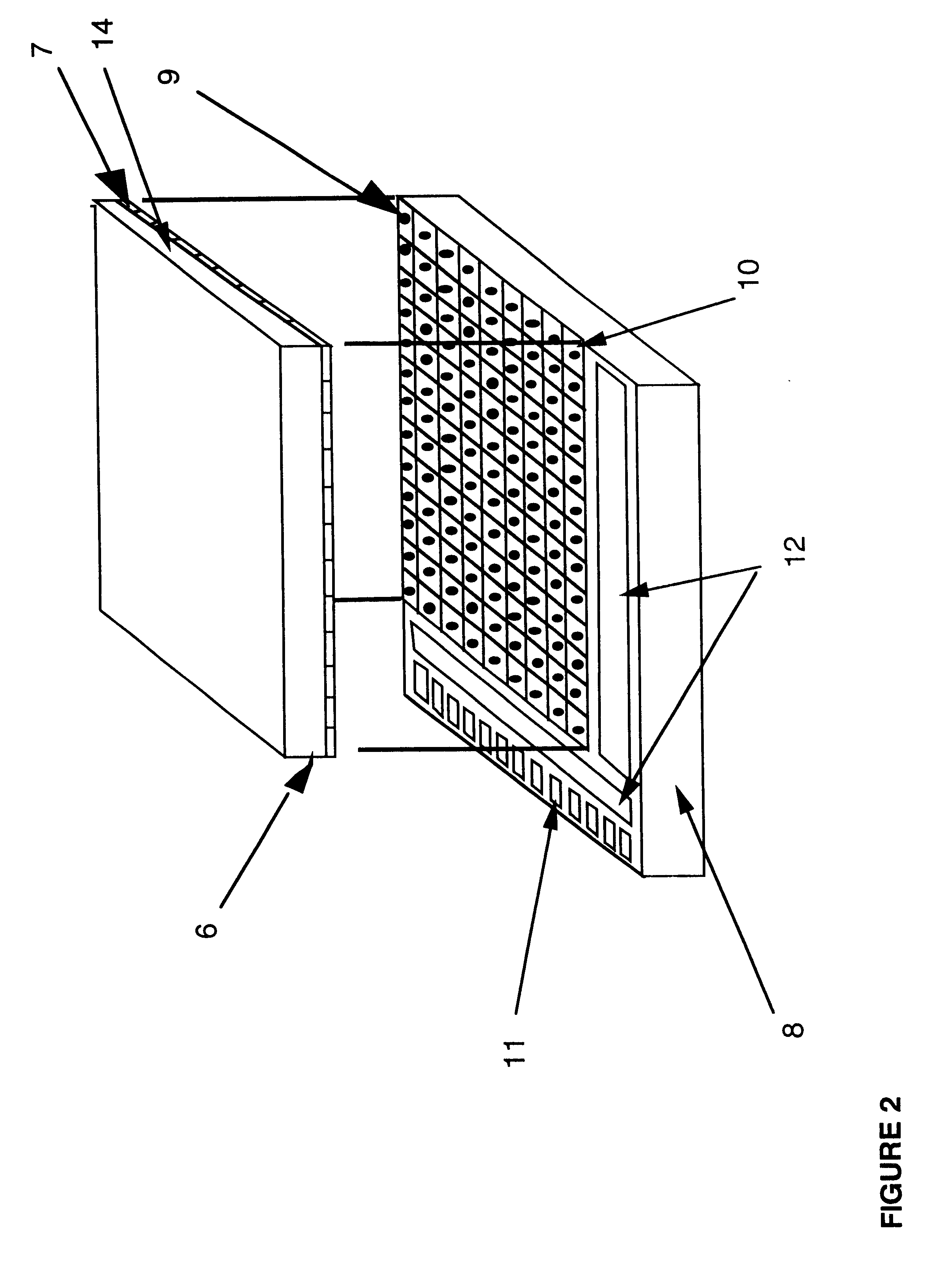
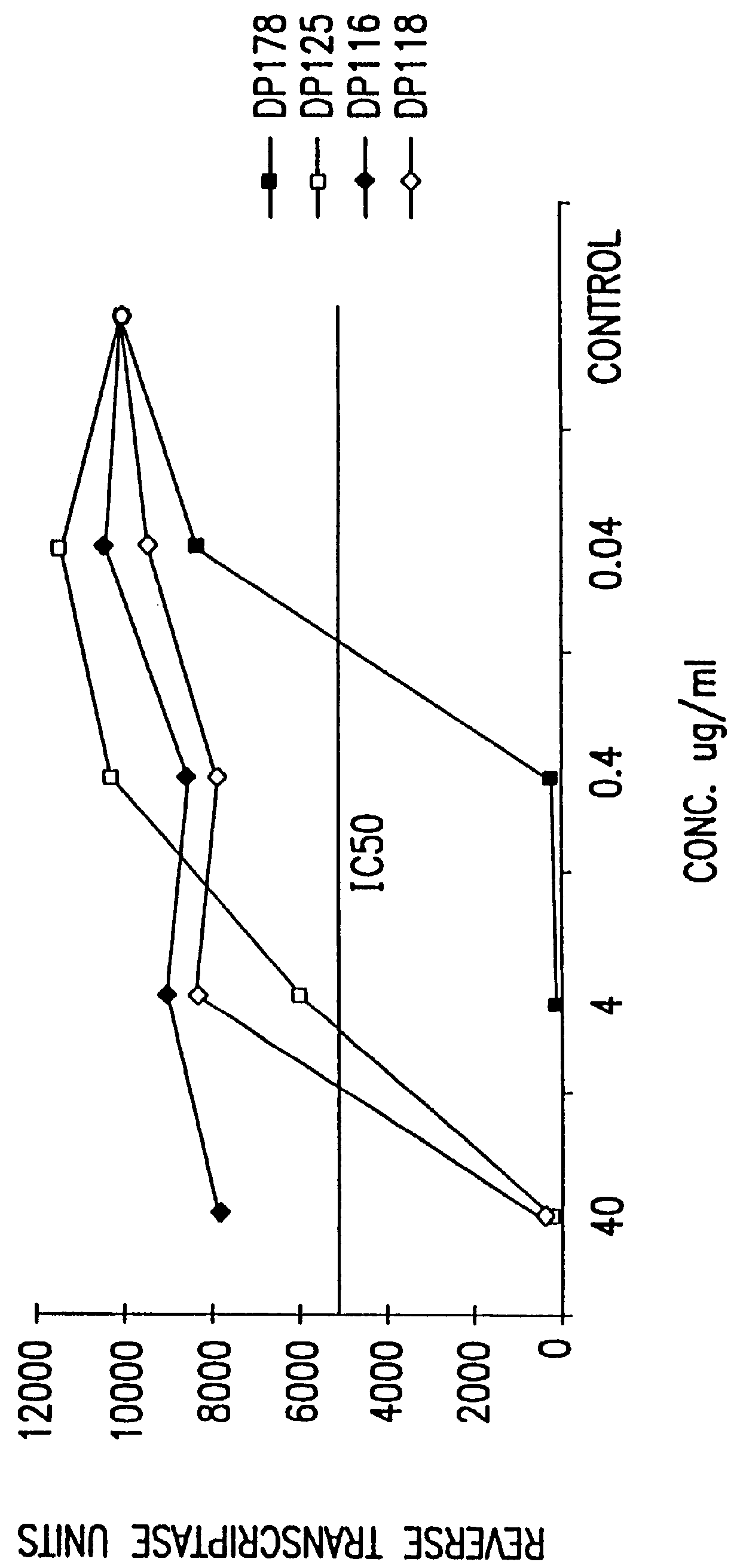
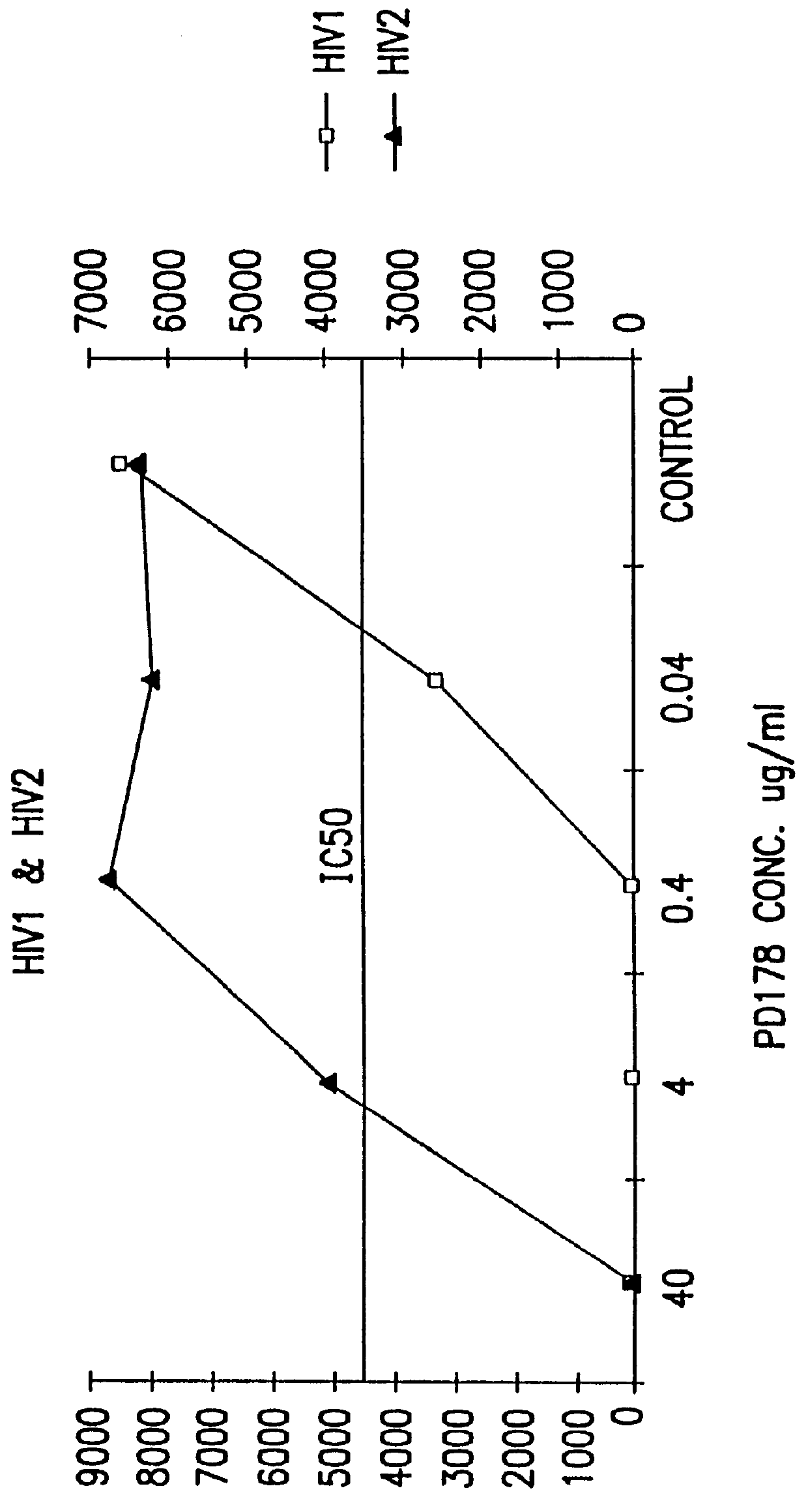
The present invention relates to peptides which exhibit antifusogenic and antiviral activities. The peptides of the invention consist of a 16 to 39 amino acid region of a simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) protein. These regions were identified through computer algorithms capable of recognizing the ALLMOTI5, 107x178x4, or PLZIP amino acid motifs. These motifs are associated with the antifusogenic and antiviral activities of the claimed peptides.
Owner:TRIMERIS +1
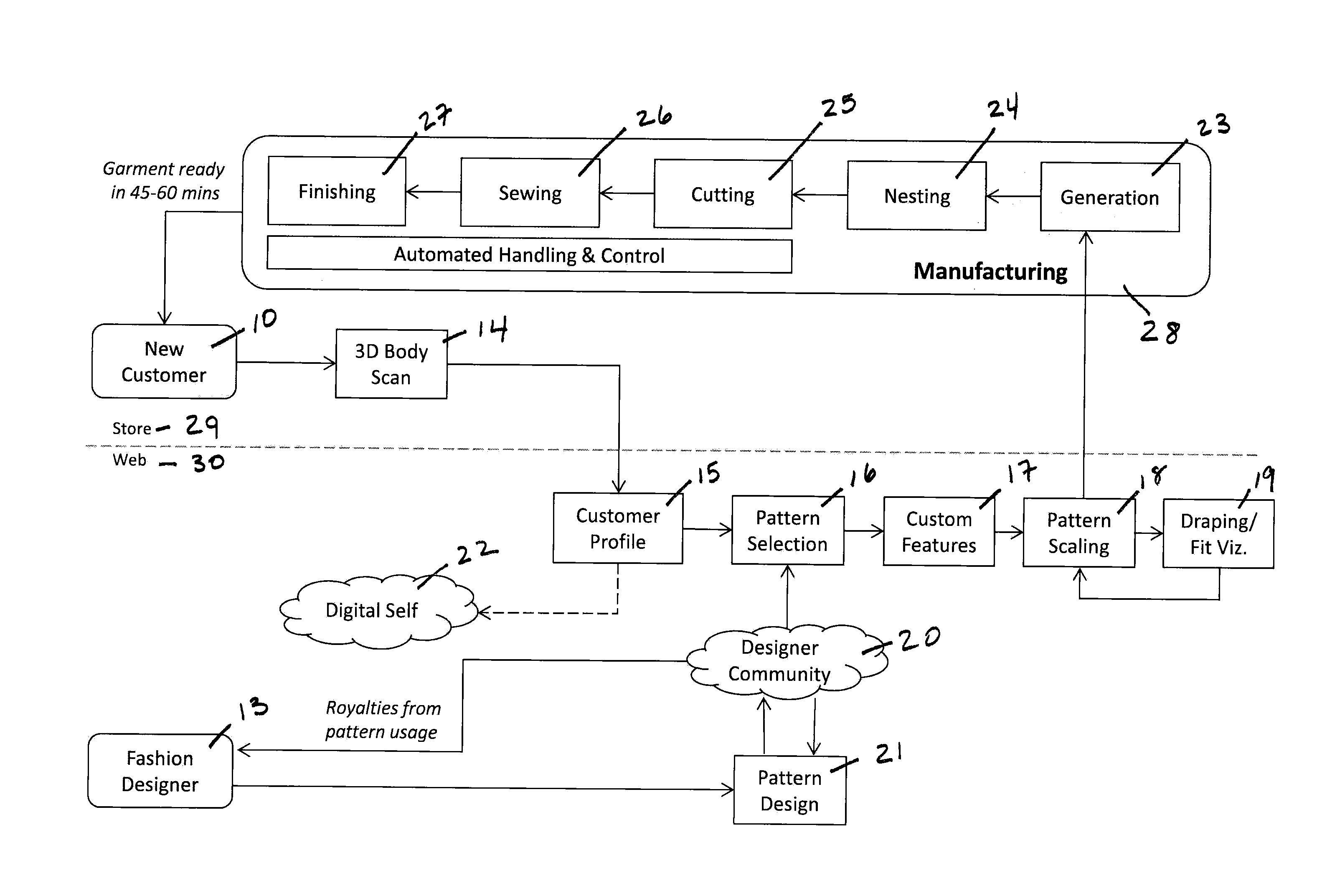
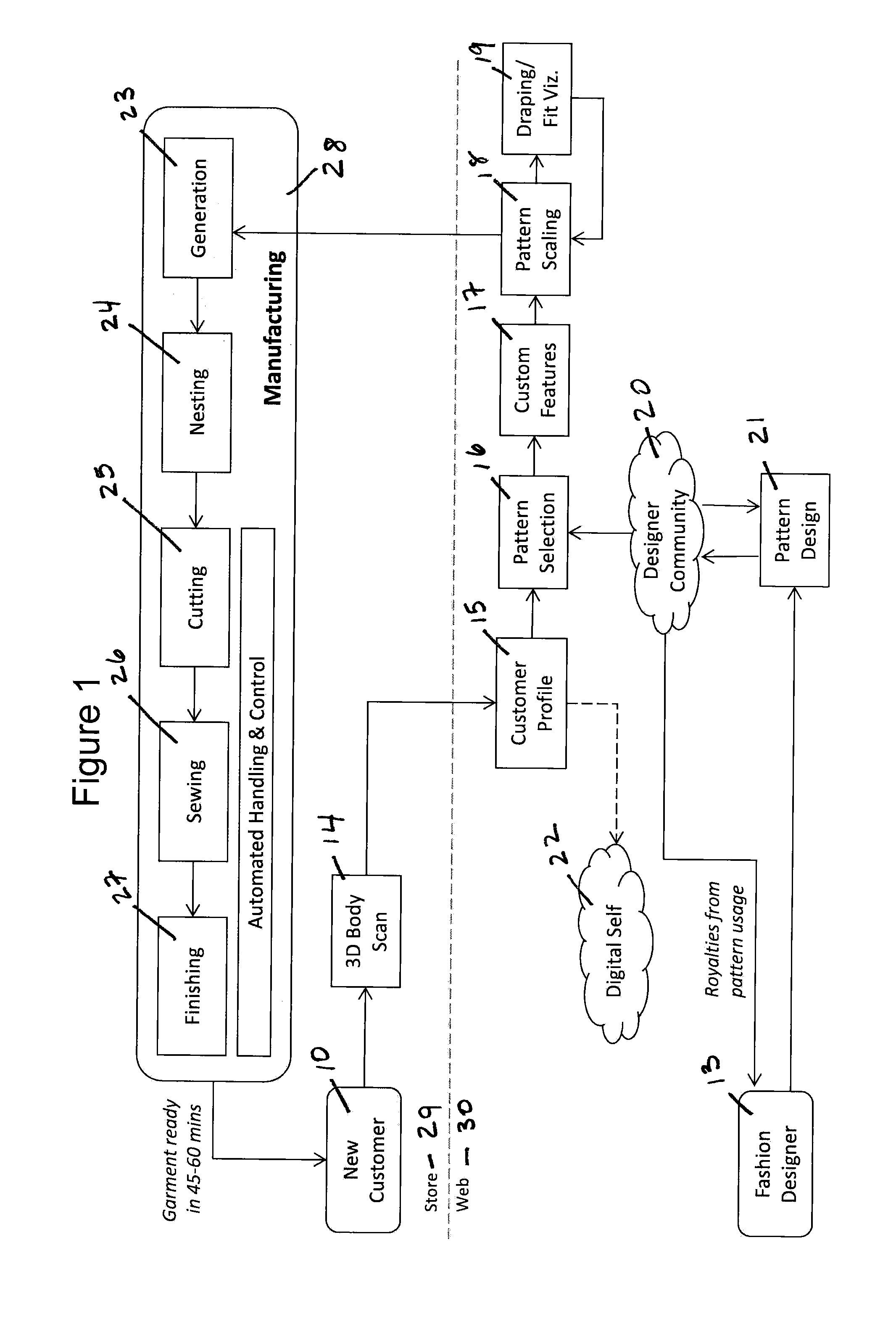
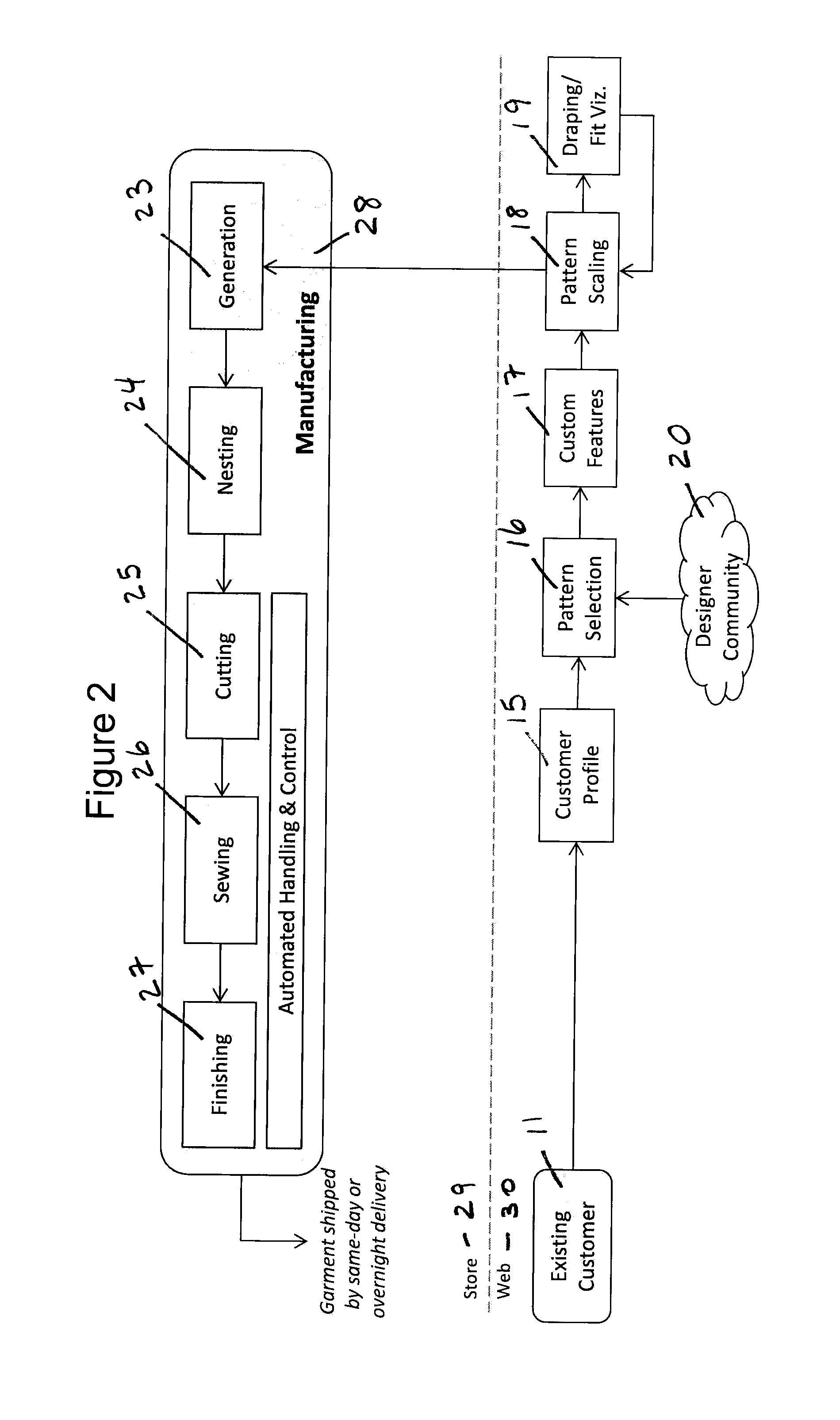
System and Method for Creating Custom-Fit Apparel Designs
InactiveUS20140277663A1Rapid visualizationShort amount of timeCommerceComputer aided designBody shapePersonalization
An automated system for the production of a personalized custom-fit garment comprises a scanner for obtaining a three-dimensional model of a customer's body shape; a computer having non-transitory computer algorithms for scaling a digital design to the customer's body shape, customizing the digital pattern with the customer's fit and style preferences, and visualizing the drape and fit of the garment; a database comprising a set of digital design patterns; and an automated garment manufacturing system networked to a central controller. A method for creating a personalized custom-fit garment comprises obtaining three-dimensional body measurements of a customer, having the customer select and customize a particular garment design, and manufacturing the personalized garment using an automated manufacturing process. The system and method can be used to prepare any kind of garments without substantive manual intervention or touch labor.
Owner:3D TECH LLC
Imaging-based distance measurement and three-dimensional profiling system
A method and apparatus for determining the distance of each pixel or a set of pixels in images acquired by cameras and thus imaging the three-dimensional profiles of objects in the images is described A source of illumination is projected through a mask of two-dimensional pattern onto the objects and images from predetermined and different view points are captured by a camera or cameras. A computer algorithm is used to identify a pixel or a set of pixels in each area of the pattern in each acquired image. The distance of the pixel or the set of pixels in the images is uniquely calculated by using the X, Y coordinates of the pixel or the set of pixels in the images of different view points and the positional relationship of the different view points. The three-dimensional profile of objects in the images is determined by collecting the distance information of each pixel or an area of pixels in the images.
Owner:PARK SEUJEUNG P
Reference timing signal apparatus and method
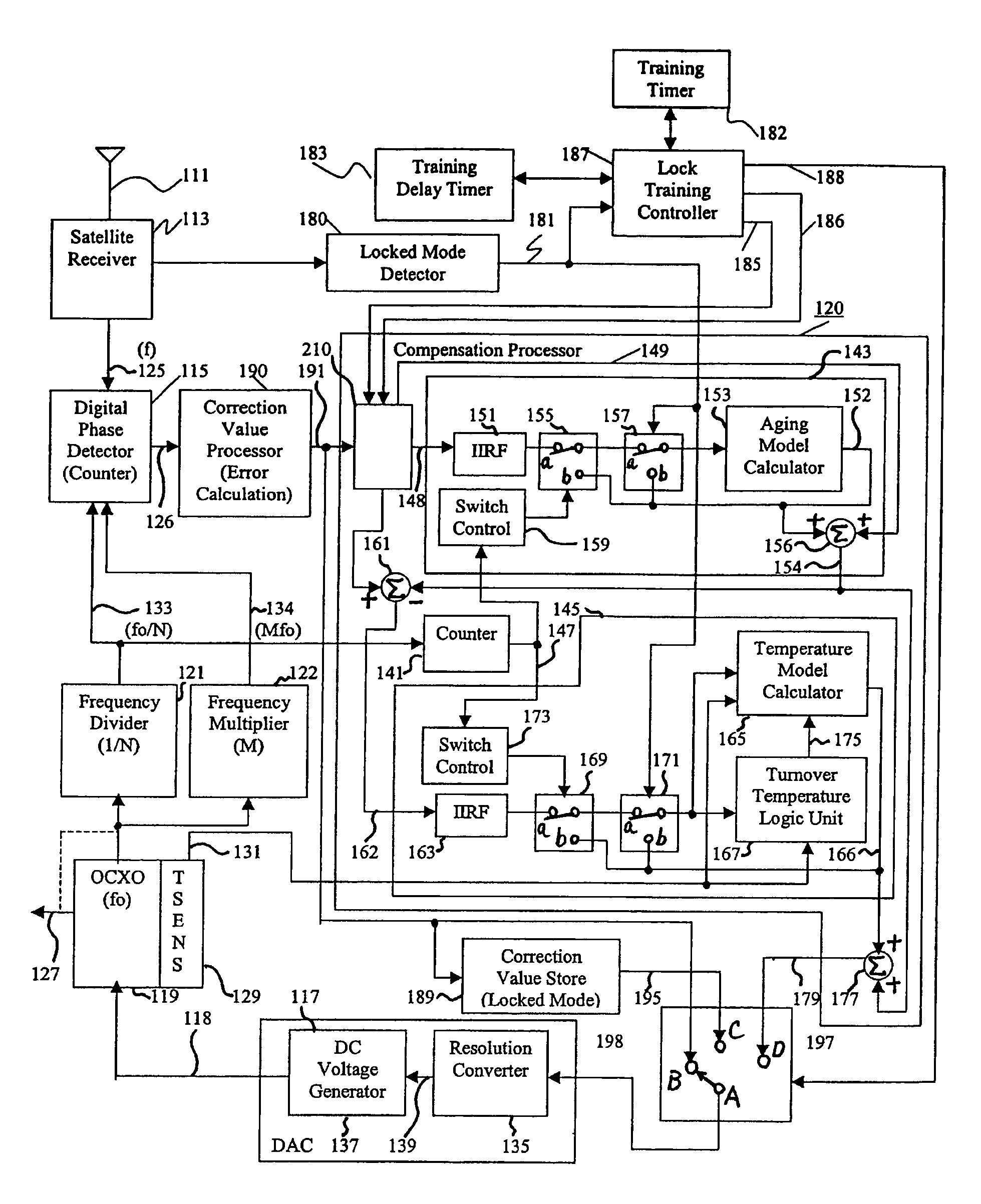
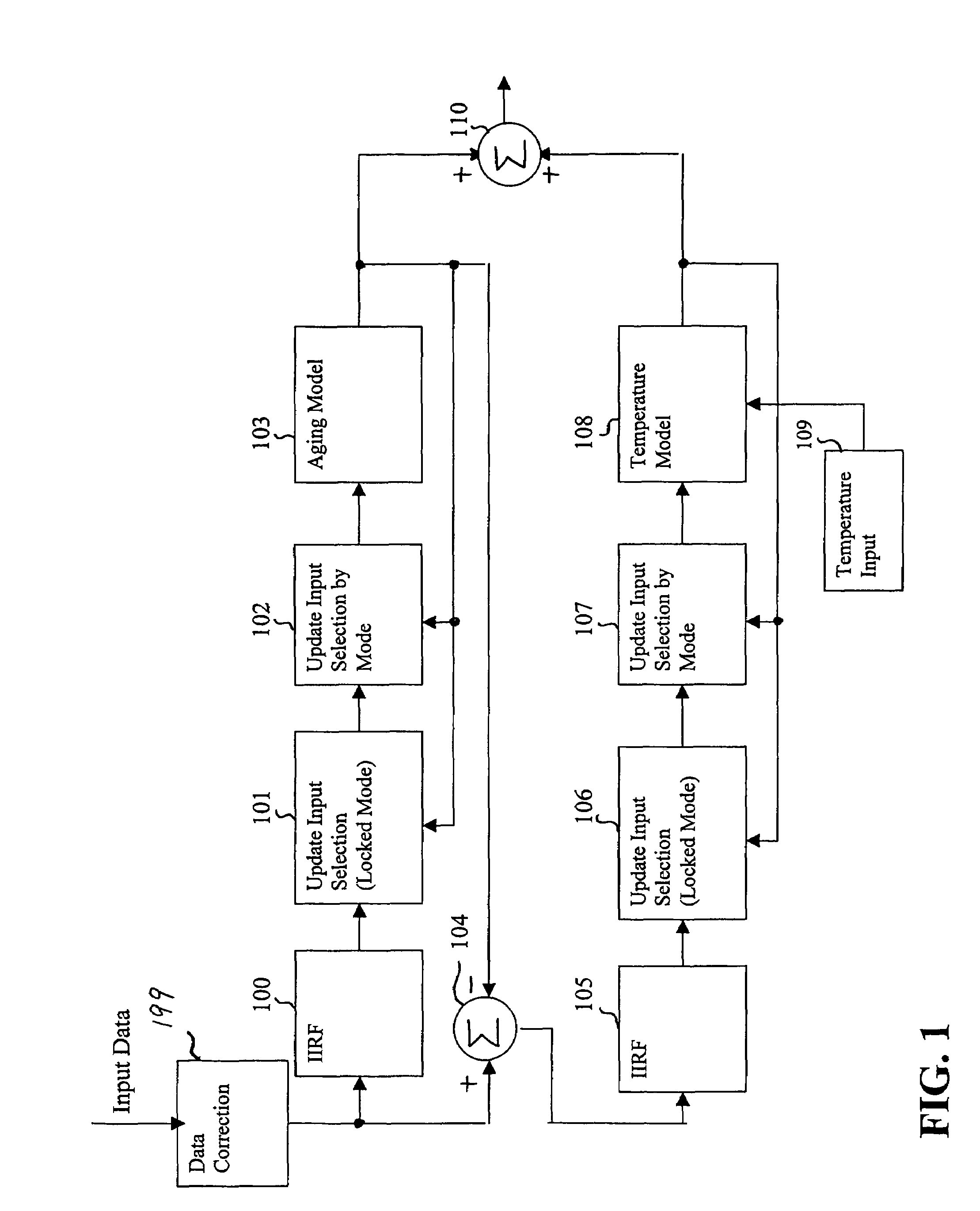
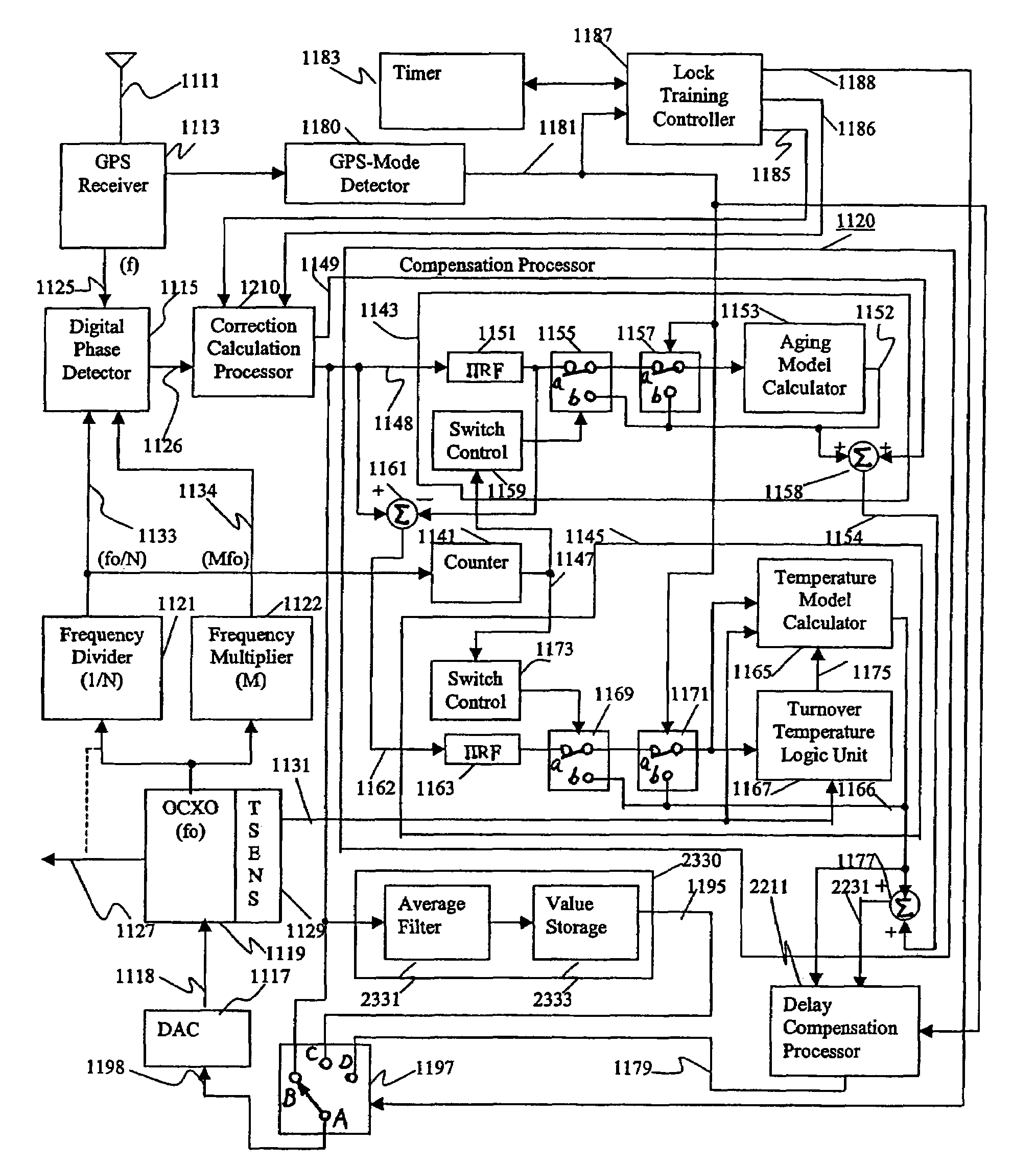
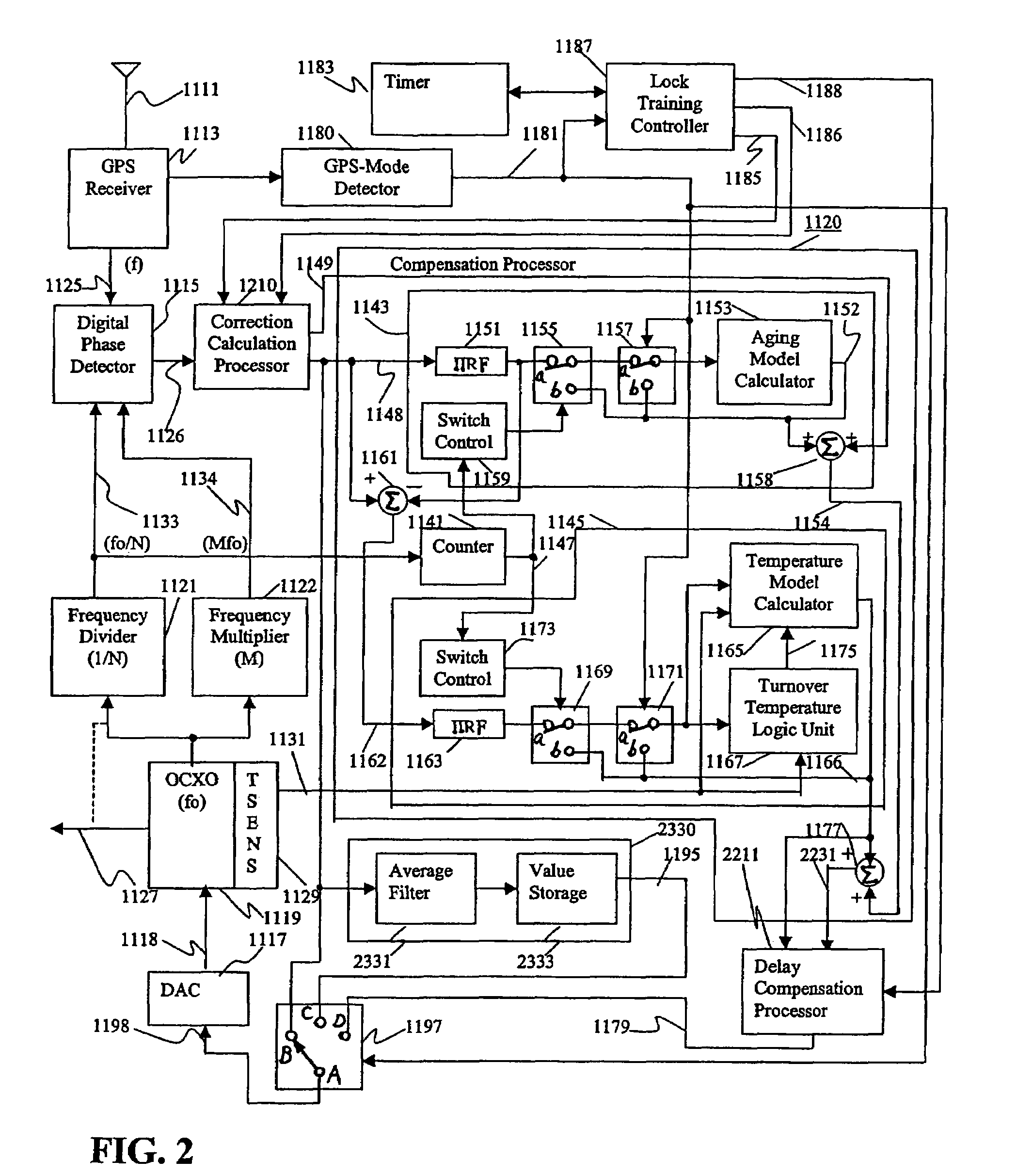
ActiveUS7015762B1Increase currentGood compensationRadiation pyrometryPulse automatic controlTraining periodAdaptive filter
A reference timing signal apparatus with a phase-locked loop (PLL) has a computer algorithm which adaptively models the multiple frequencies of an oscillator following a training period. The oscillator is part of a PLL and the oscillation frequency thereof is controlled in response to the phase detector output. The computer algorithm processes the control signal applied to the oscillator. The computer algorithm updates the characteristics of the model relating to the aging and temperature of the oscillator, using for example, a Kalman filter as an adaptive filter, in accordance with a cumulative phase error in the PLL calculated during a given time interval. By the algorithm, the subsequent model predicts the future frequency state of the oscillator on which it was trained. The predicted frequency of the model functions as a reference to correct the frequency of the oscillator in the event that no input reference timing signal is available. Also, the calculated phase error is stored and is used while no input reference timing signal or accurate predicted frequency value is available. With the model updating algorithm, oscillators of low stability performance may be used as cellular base station reference oscillator, which is based on satellite systems, for example, GPS, GLONASS or Galileo systems.
Owner:APPLE INC
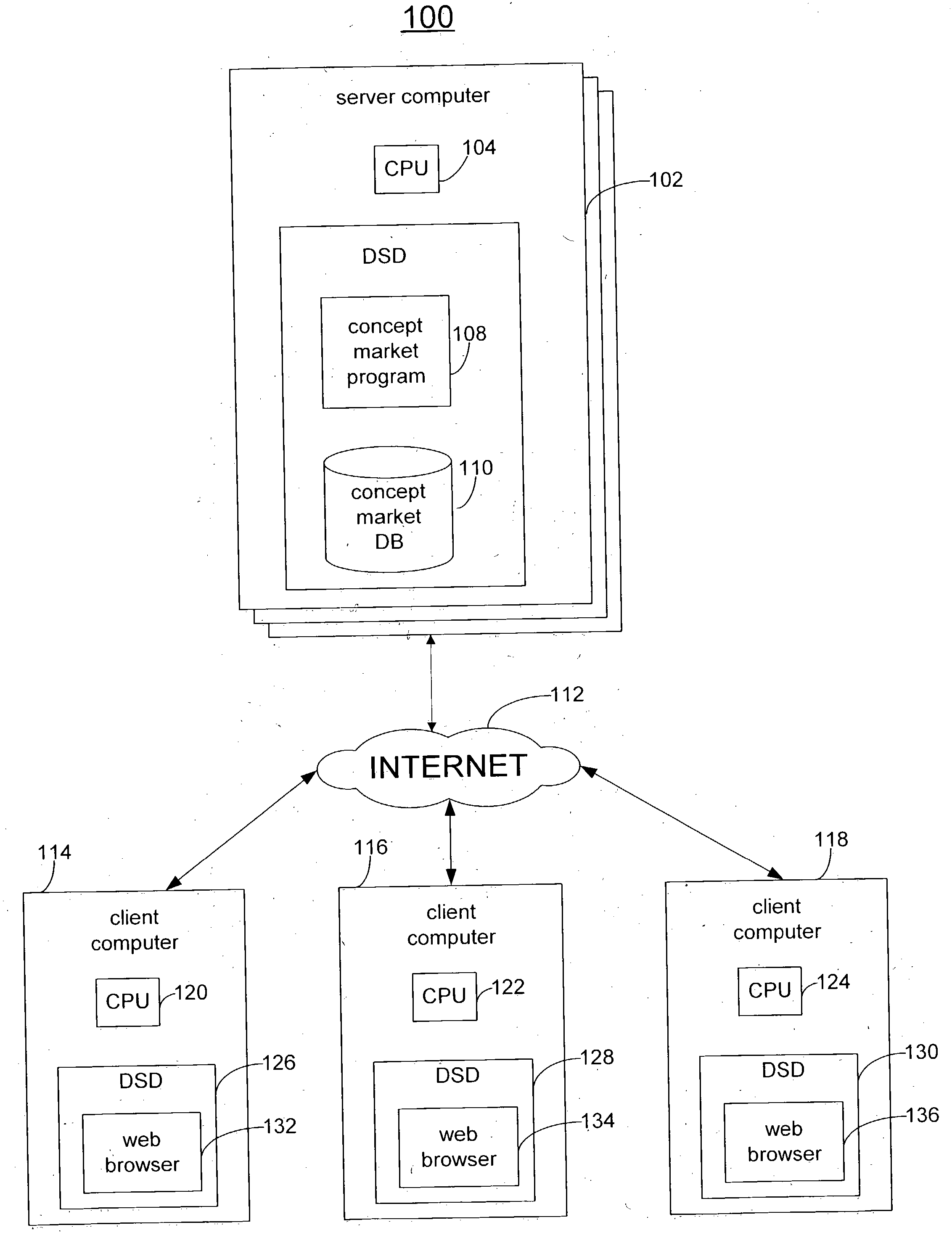
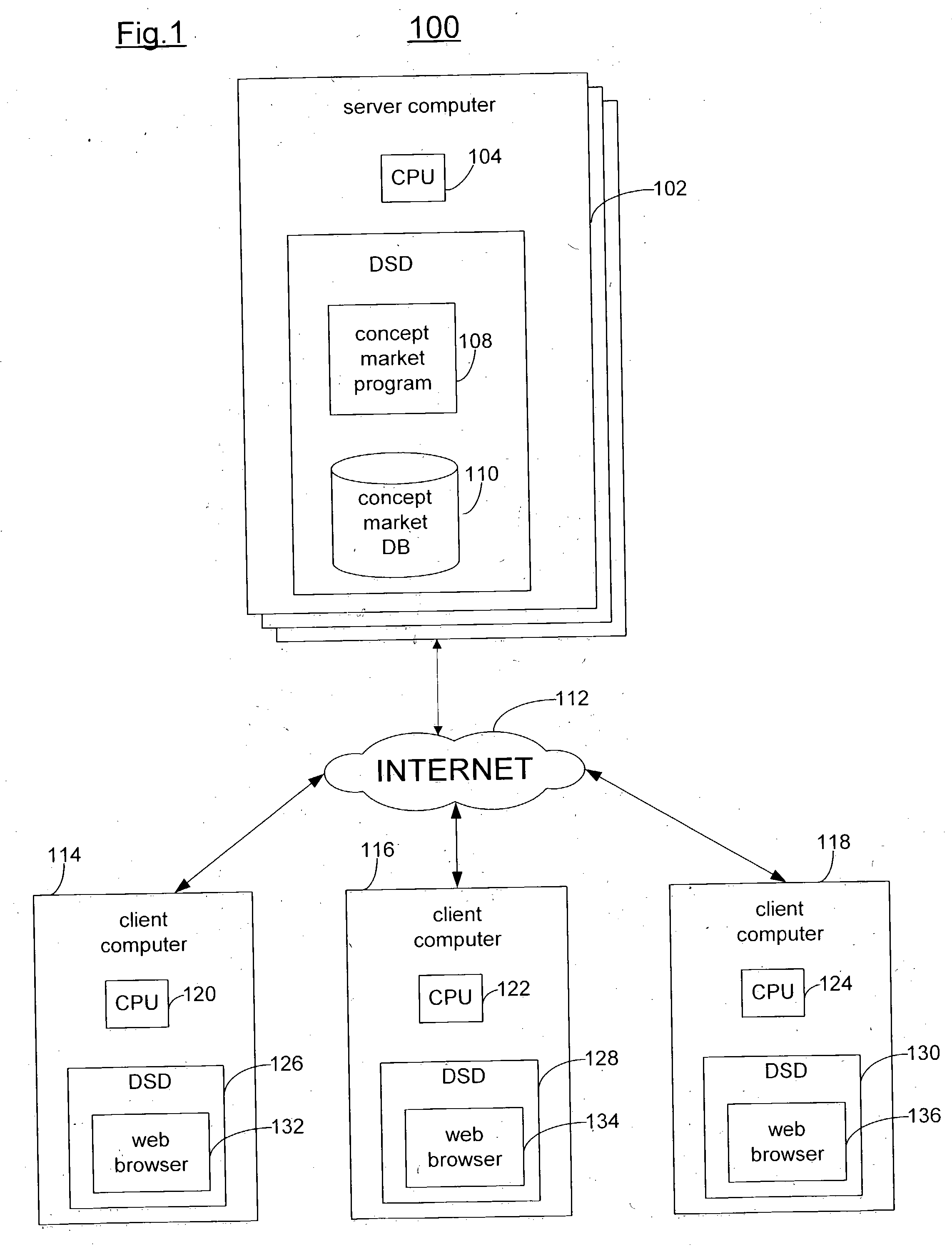
Concept valuation in a term-based concept market
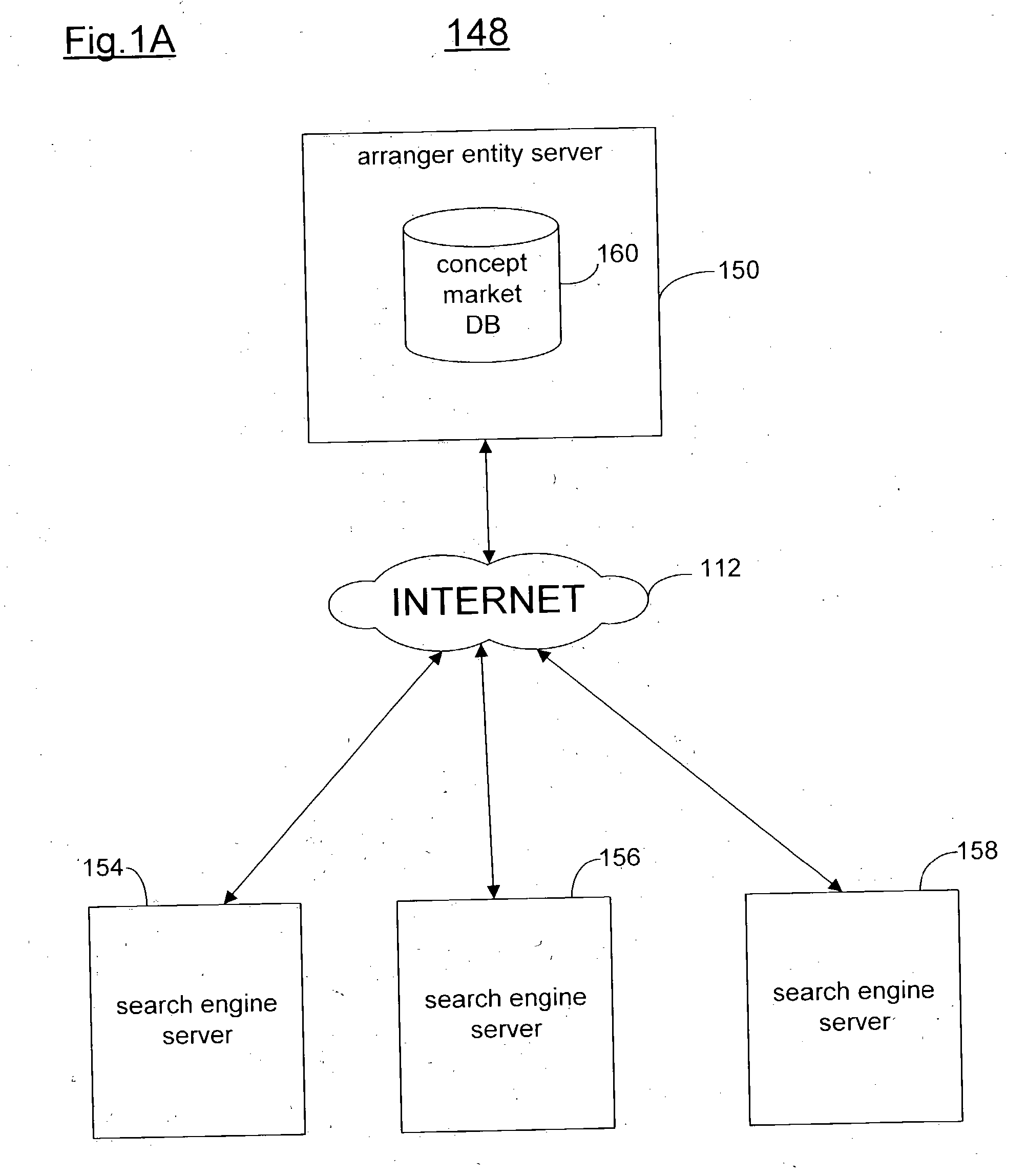
InactiveUS20050021441A1FinanceSpecial data processing applicationsSubject specificComputer algorithm
The present invention provides methods and systems for allowing transactions in instruments relating to term-based concepts in a networked computer system. Concepts may be defined as a set of terms, such as words or phrases, that relate to a theme. The terms are useable in computerized searches. The set of terms may be determined manually, using a computer algorithm, or both. Concepts are valued, such as by a measure of advertising value. Instruments include concept futures as well as bets. Concept-based instruments can be used, for example, as hedging tools, speculating tools, market forecasting tools, or data generating tools.
Owner:OATH INC
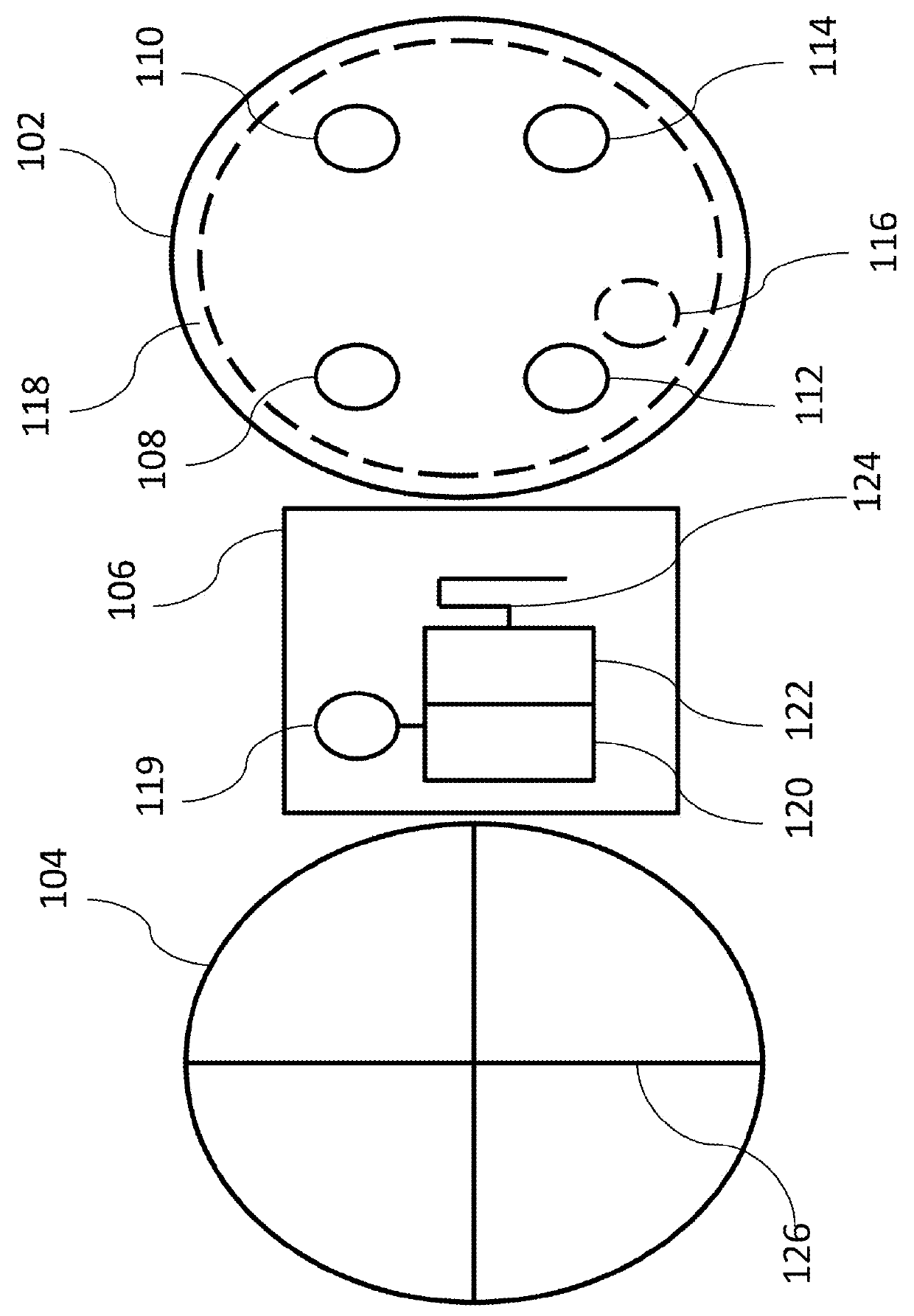
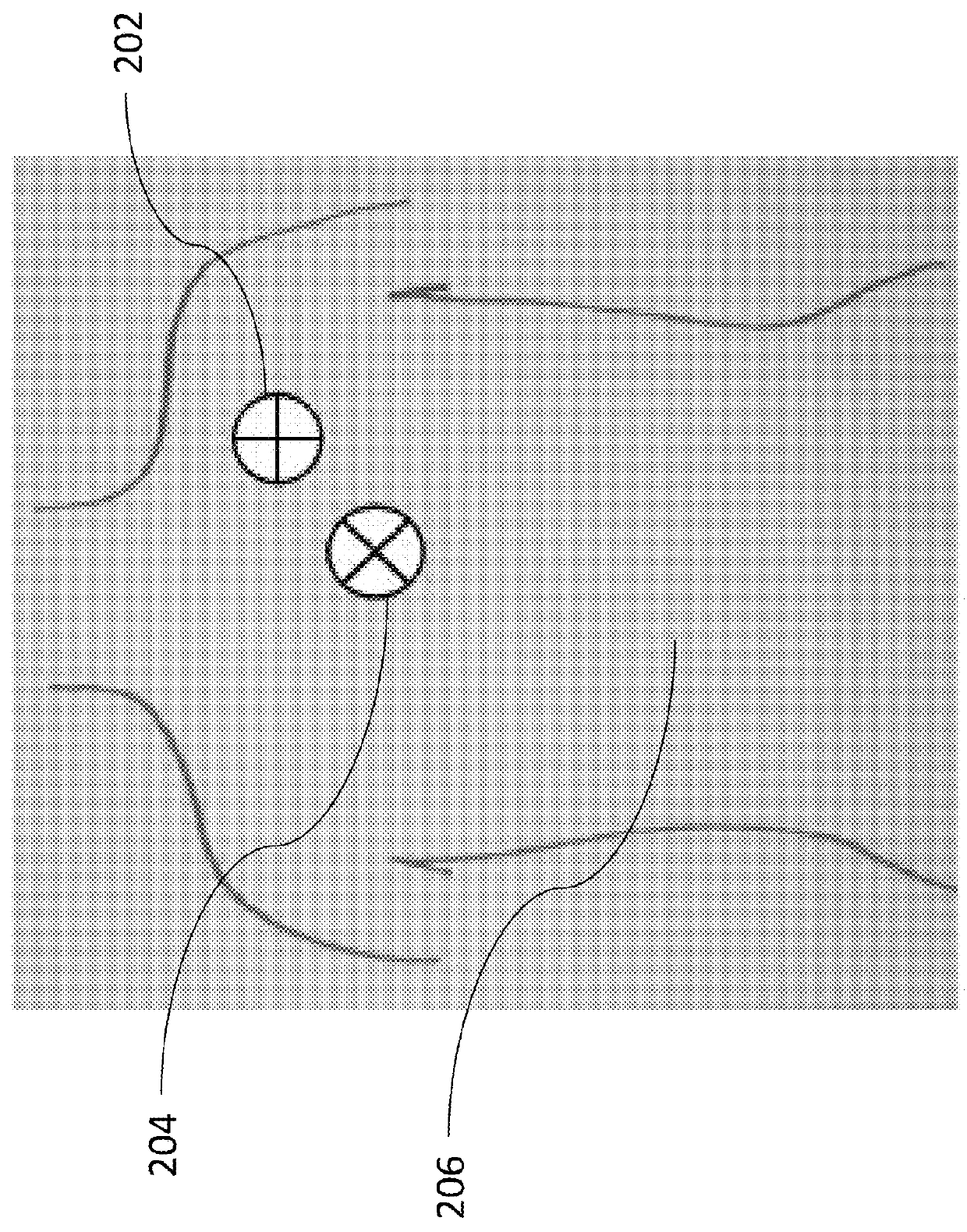
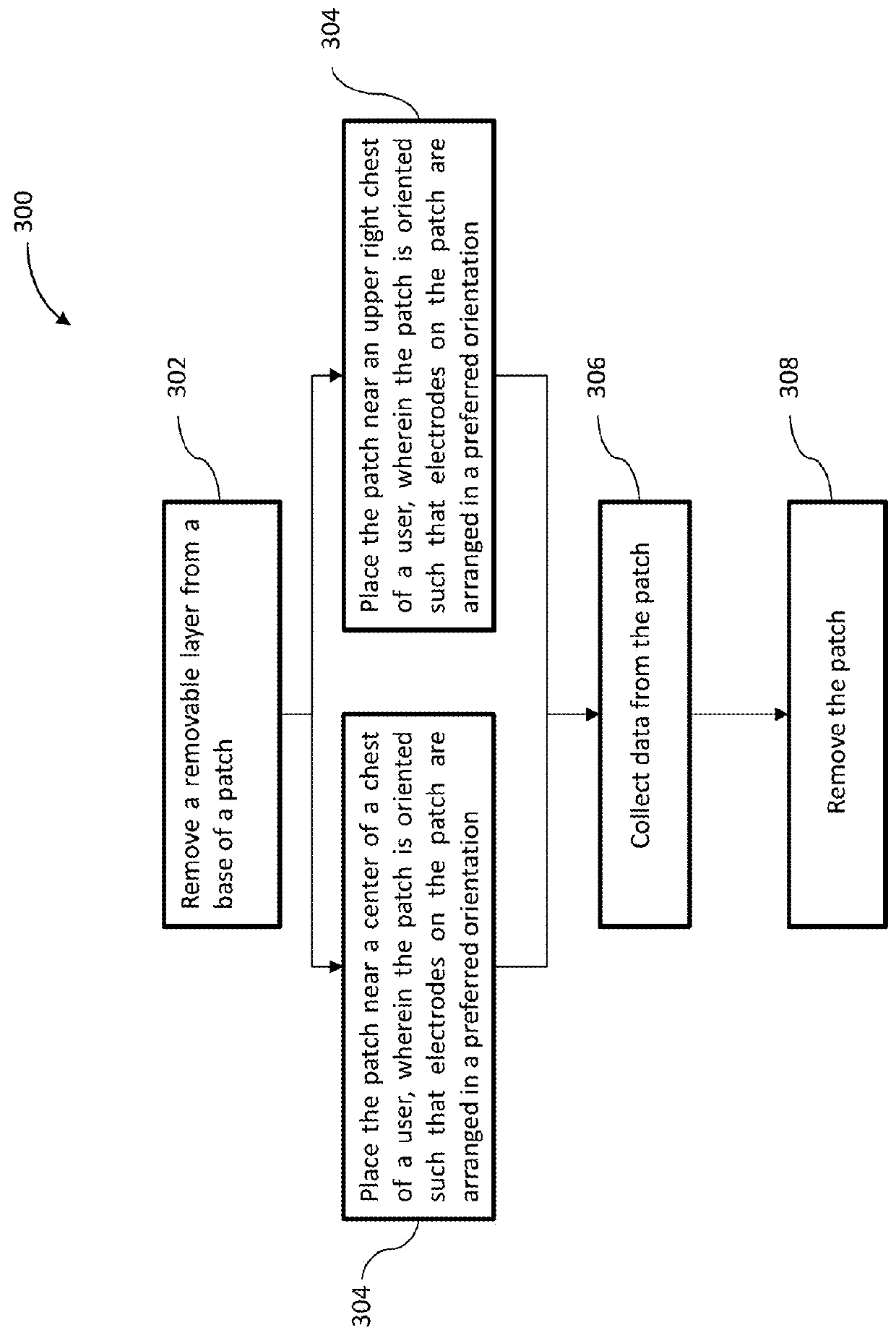
ECG patch and methods of use
A compact integrated patch may be used to collect physiological data. The patch may be wireless. The patch may be utilized in everyday life as well as in clinical environments. Data acquired by the patch and / or external devices may be interpreted and / or be utilized by healthcare professionals and / or computer algorithms (e.g., third party applications). Data acquired by the patch may be interpreted and be presented for viewing to healthcare professionals and / or ordinary users.
Owner:LIFESIGNALS INC
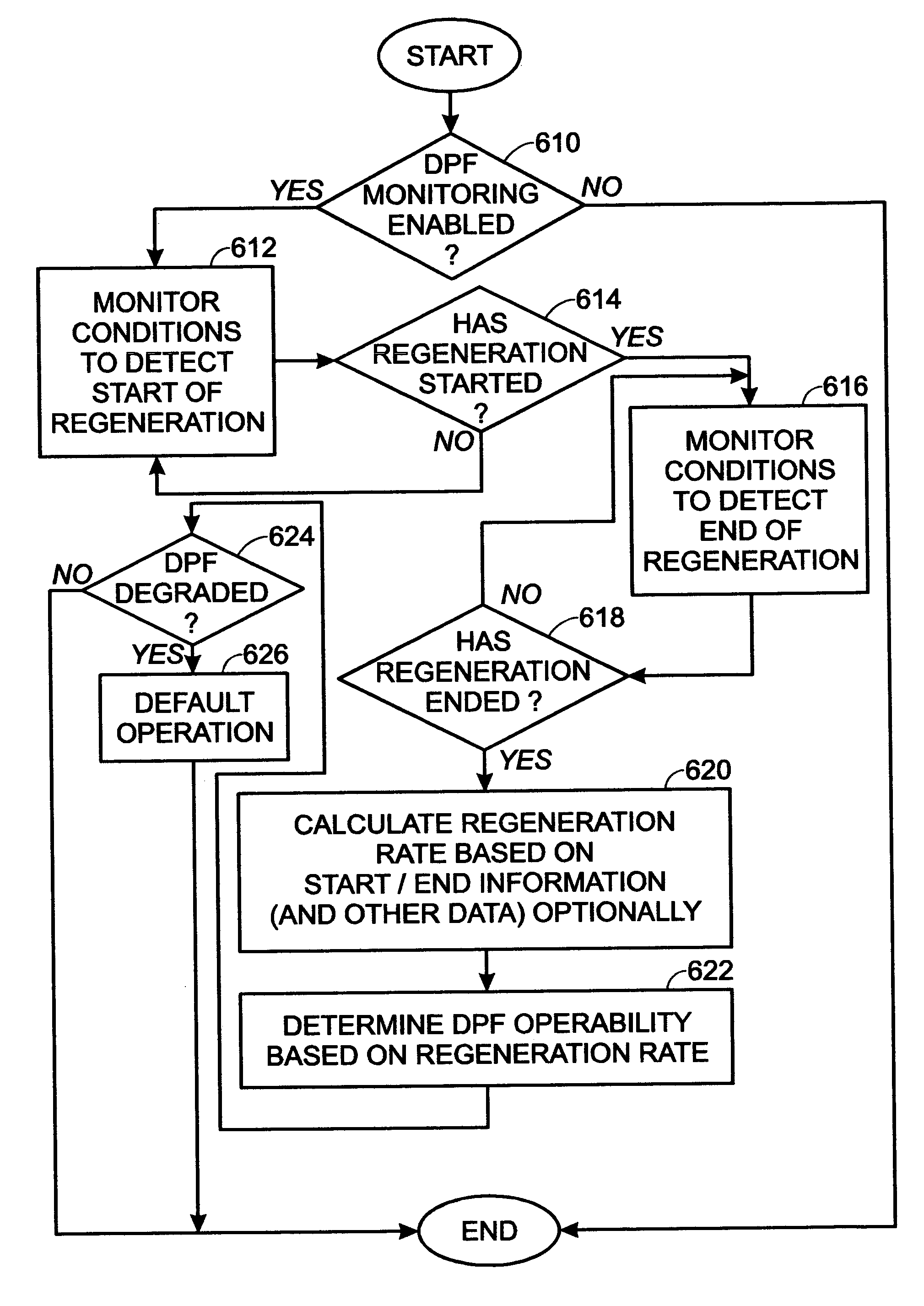
Computer algorithm to estimate particulate filter regeneration rates
InactiveUS7031827B2Analogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlMicroparticleDiesel particulate filter
A system and method is described for determining degradation of a diesel particulate filter in an engine exhaust system. The method uses information indicative of a regeneration rate, such as regeneration duration. From this, it is possible to determine when particulate filter operation has degraded.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Use of decision trees for automatic commissioning
InactiveUS20090045971A1Circuit arrangementsDigital computer detailsTheoretical computer scienceEffect light
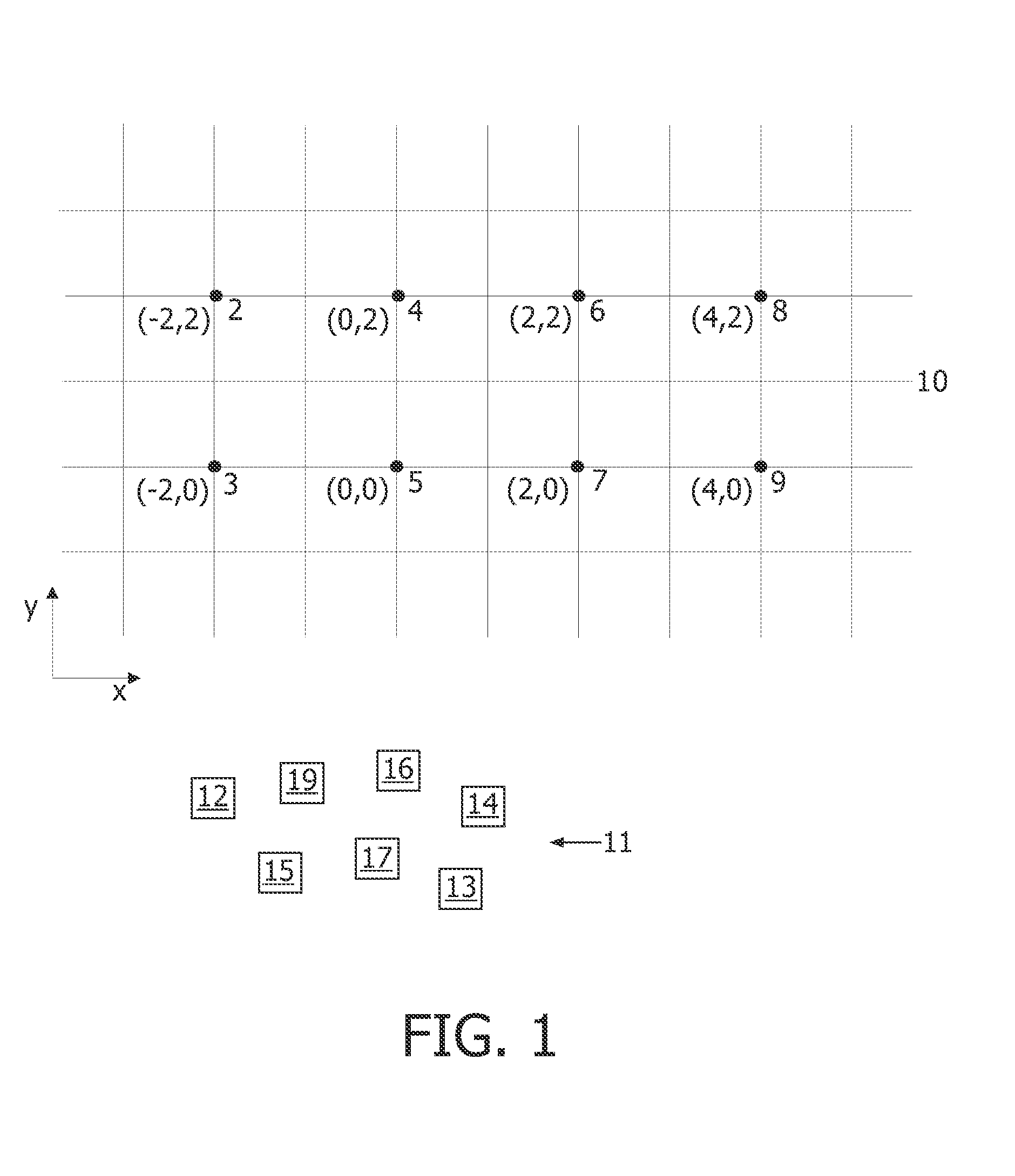
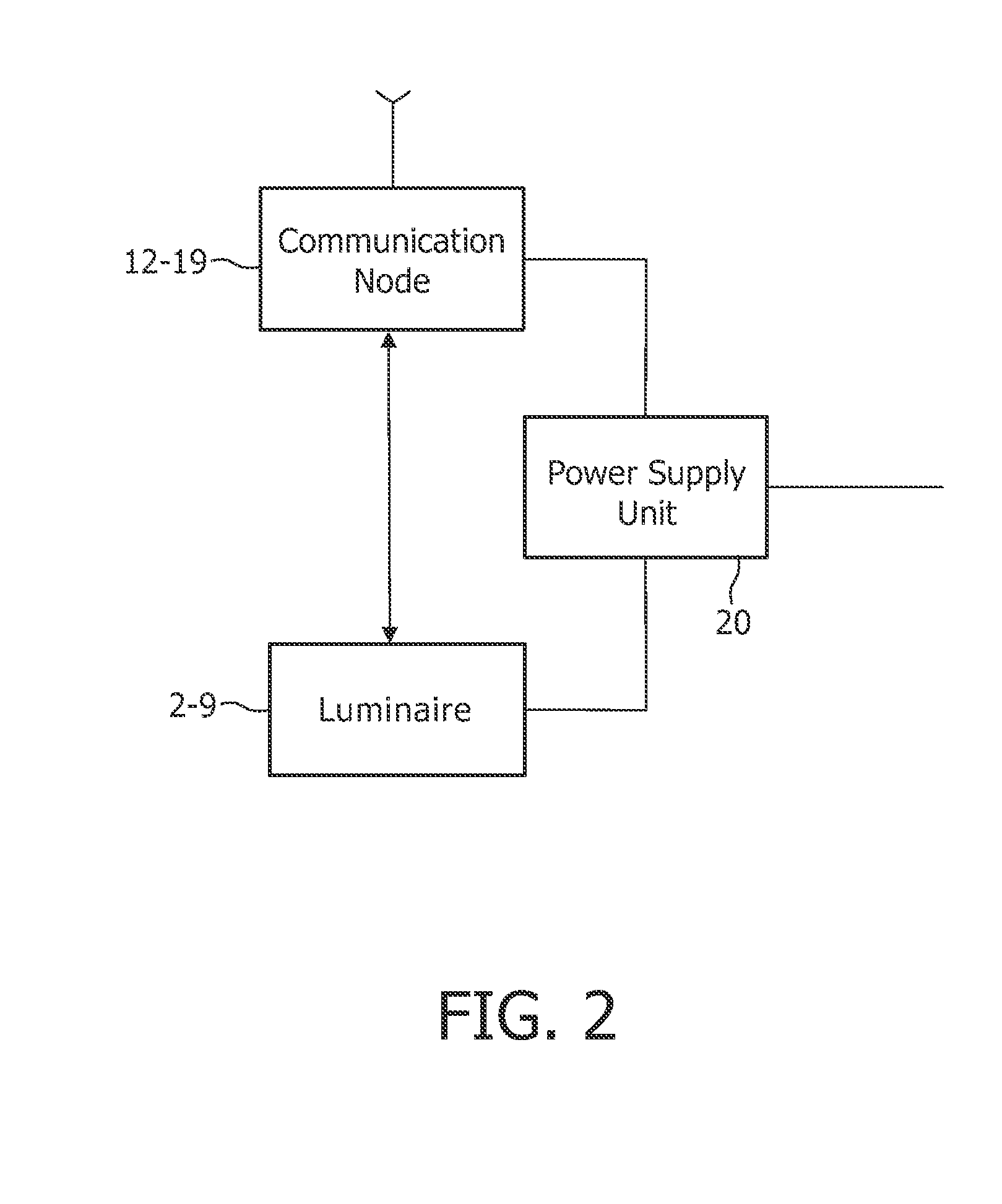
A computer algorithm (36) employing decision trees in order to assign wireless communication nodes (12-19,39-43) in a derived spatial arrangement. In a first embodiment, the algorithm (36) assigns nodes to an array of positions corresponding to the positions of luminaires (2-9) in a lighting array (1) to enable the lighting array (1) to be commissioned automatically. In a second embodiment, the algorithm (36) assigns nodes to control groups (49-51) such that the member nodes of a particular control group (49-51) may be controlled by a single switch or sensor (46-48). The use of decision trees allows the final assignment of nodes to be delayed until more information has been taken into account, thus, the algorithm (36) is able to select the best overall configuration.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and system for rating patents and other intangible assets
A statistical patent rating method and system is provided for independently assessing the relative breadth (“B”), defensibility (“D”) and commercial relevance (“R”) of individual patent assets and other intangible intellectual property assets. The invention provides new and valuable information that can be used by patent valuation experts, investment advisors, economists and others to help guide future patent investment decisions, licensing programs, patent appraisals, tax valuations, transfer pricing, economic forecasting and planning, and even mediation and / or settlement of patent litigation lawsuits. In one embodiment the invention provides a statistically-based patent rating method and system whereby relative ratings or rankings are generated using a database of patent information by identifying and comparing various characteristics of each individual patent to a statistically determined distribution of the same characteristics within a given patent population. For example, a first population of patents having a known relatively high intrinsic value or quality (e.g. successfully litigated patents) is compared to a second population of patents having a known relatively low intrinsic value or quality (e.g. unsuccessfully litigated patents). Based on a statistical comparison of the two populations, certain characteristics are identified as being more prevalent or more pronounced in one population group or the other to a statistically significant degree. Multiple such statistical comparisons are used to construct and optimize a computer model or computer algorithm that can then be used to predict and / or provide statistically-accurate probabilities of a desired value or quality being present or a future event occurring, given the identified characteristics of an individual patent or group of patents.
Owner:PATENTRATINGS
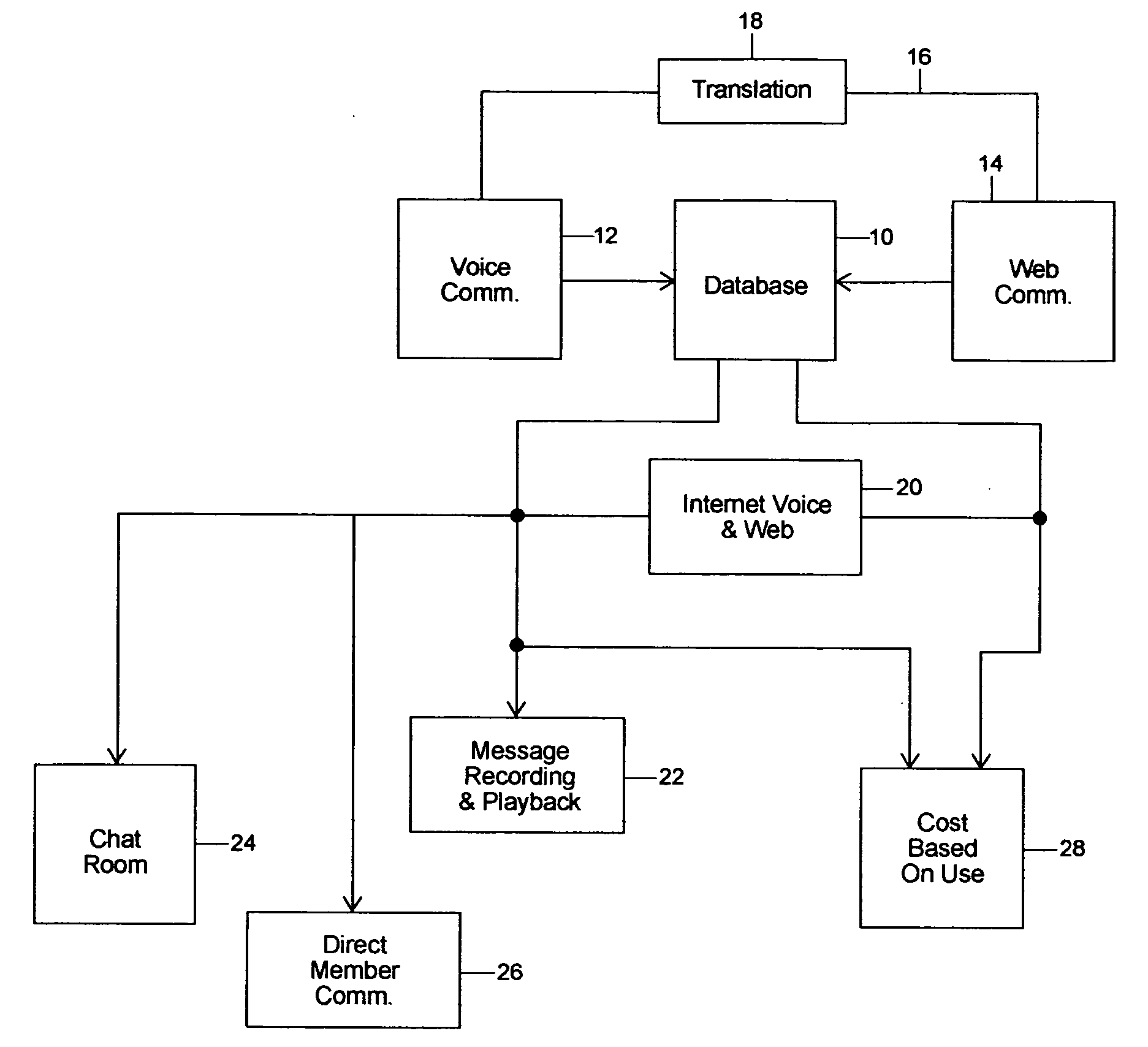
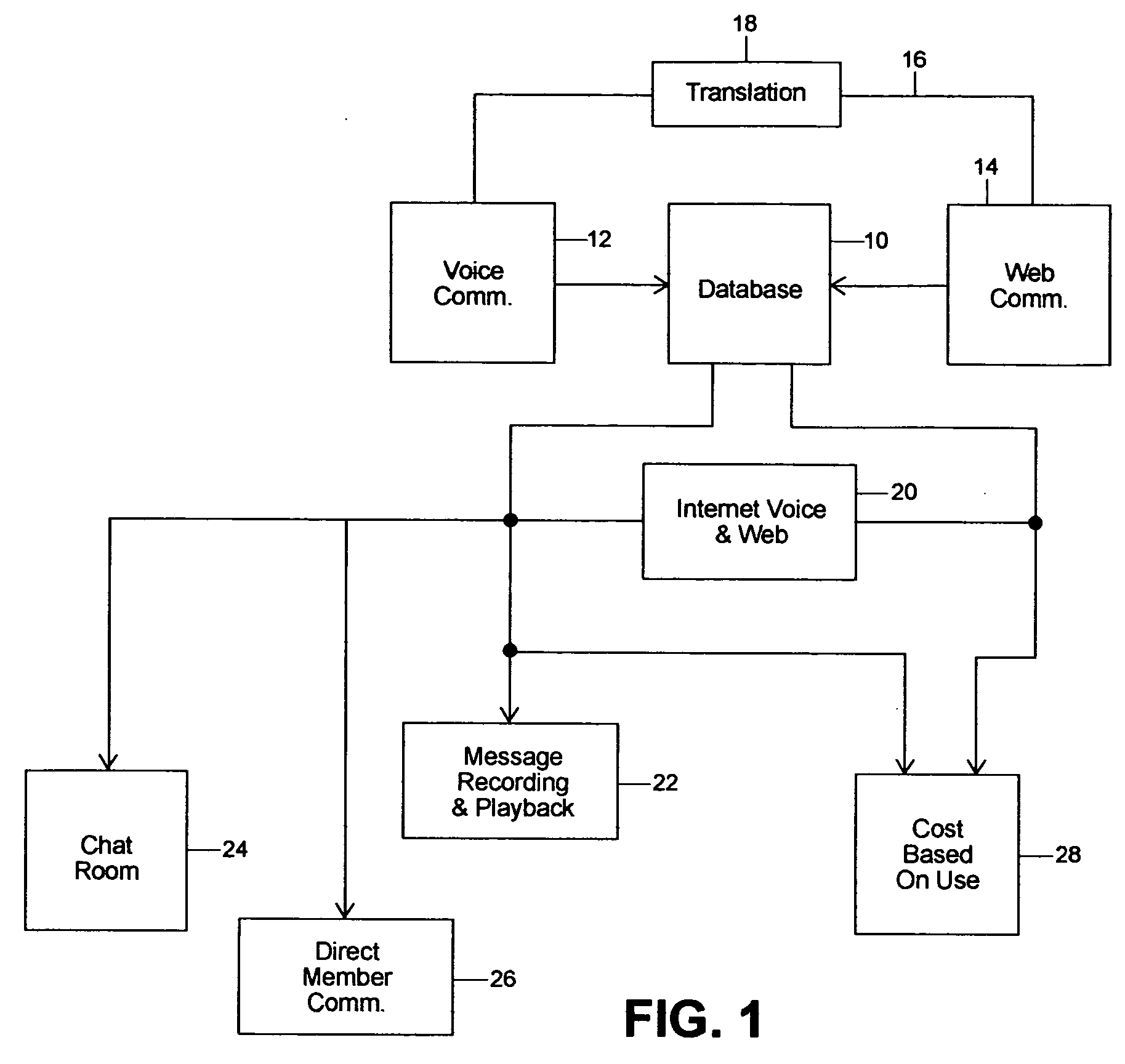
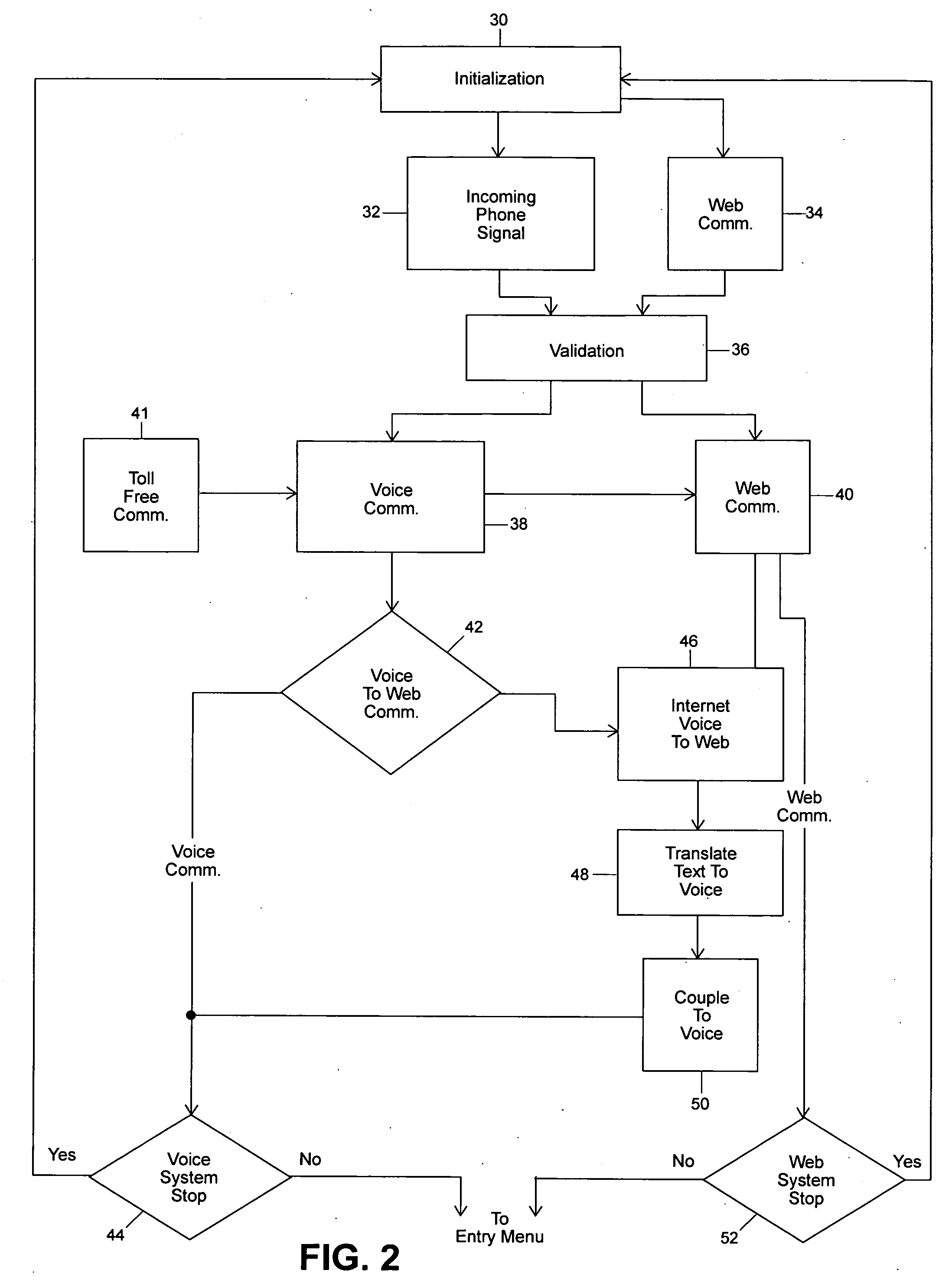
Computer algorithm and method for facilitating the networking of individuals
InactiveUS20040184445A1Easy to useSpecial service provision for substationTelephone data network interconnectionsVoice communicationDirect communication
An algorithm and method for using computer services for facilitating the meeting and communication of individuals in a social networking environment. The algorithm and method allow for individuals using differing modes of communication, for example one using voice communication and another using computer communication, to be in direct communication with one another. The algorithm and method also facilitate direct communication when one party locates a potential candidate and is desirous of being in direct communication with that candidate. Message recording and playback are also facilitated as well as other advantages arising from the use of the algorithm and software program derived therefrom as well as the method of the invention.
Owner:BURNE JEFFREY K
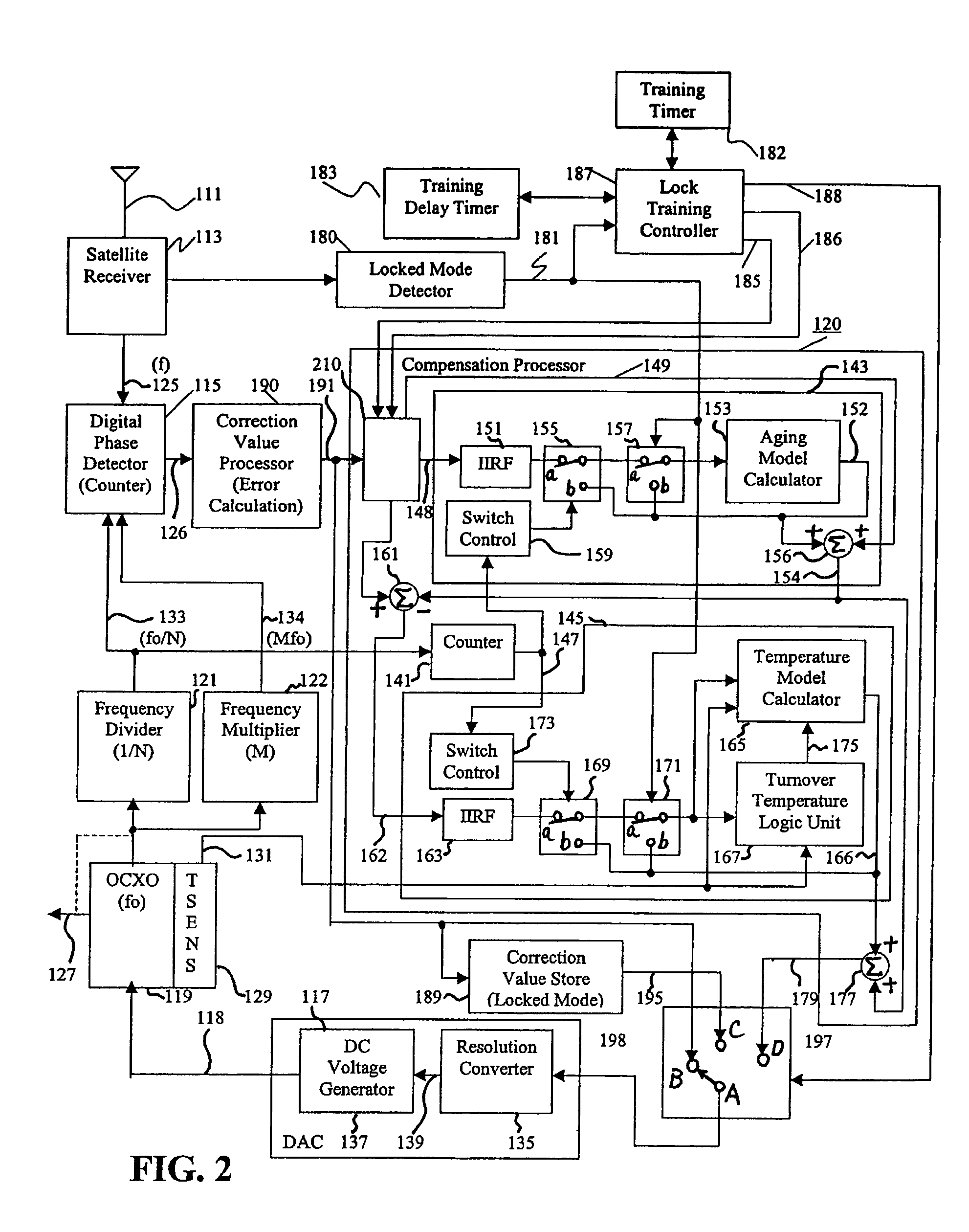
Reference timing signal apparatus and method
ActiveUS7424069B1Easy to trackIncrease currentPulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationTraining periodAdaptive filter
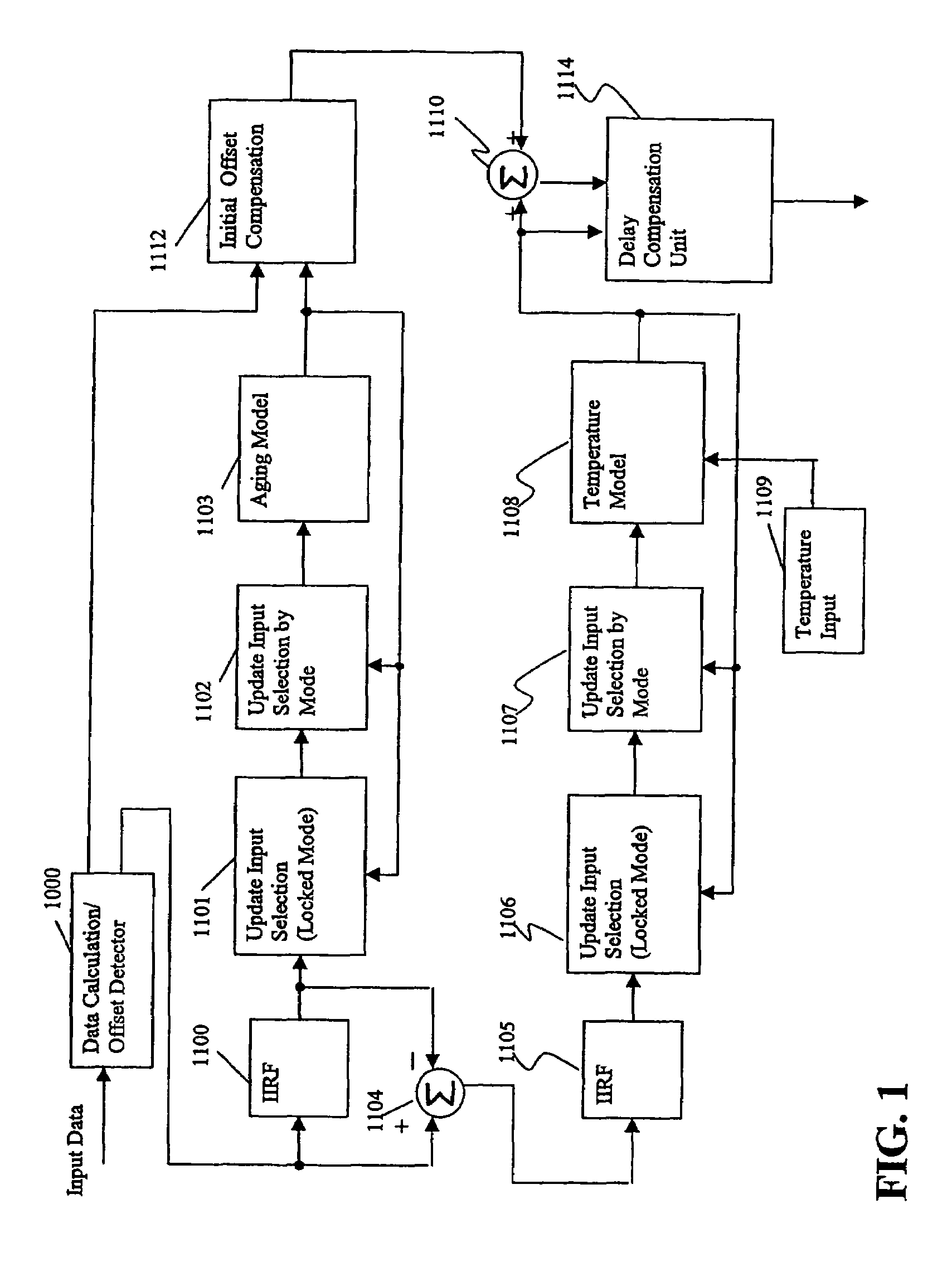
A reference timing signal apparatus with a phase-locked loop has a computer algorithm which adaptively models the multiple frequencies of an oscillator following a training period. The oscillation frequency of the oscillator is controlled in response to a phase detector output. The computer algorithm processes the control signal applied to the oscillator. The computer algorithm updates the characteristics of the model relating to the aging and temperature of the oscillator, using for example, a Kalman filter as an adaptive filter. By the algorithm, the subsequent model predicts the future frequency state of the oscillator on which it was trained. The predicted frequency of the model functions as a reference to correct the frequency of the oscillator in the event that no input reference timing signal is available. In a case of using pre-processing infinite impulse response filters (IIRFs) before the adaptive processor, the time delay caused by the filters are compensated after the adaptive processor. Without pre-processing IIRFs, aging and temperature update rates are adaptively controlled by dynamically changing the rates depending upon the loop condition to achieve a wider tracking bandwidth. With the model updating algorithm, oscillators of low stability performance may be used as cellular base station reference oscillator.
Owner:APPLE INC
Micro-video personalized recommendation algorithm based on social network credibility
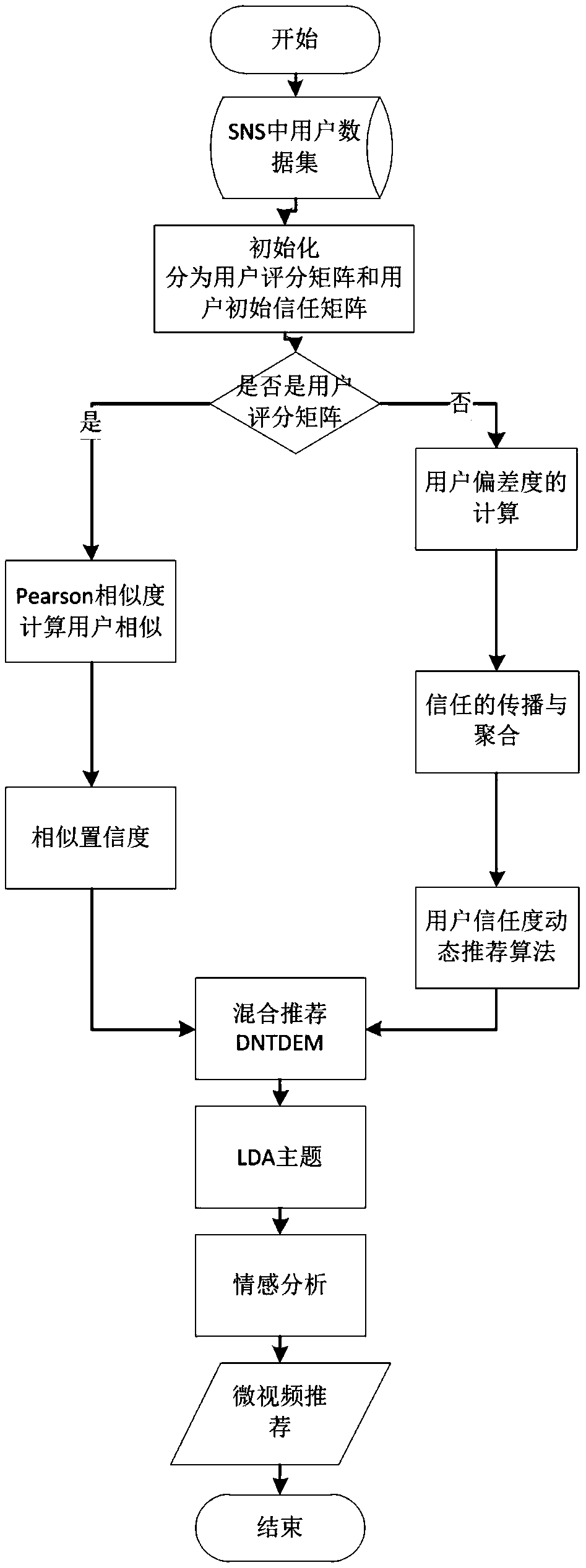
The invention provides a micro-video personalized recommendation algorithm based on social network credibility and belongs to the field of computer algorithms. The micro-video personalized recommendation algorithm includes the steps of firstly, calculating user deviation degree according to the difference of global credibility and local trust; secondly, adding a confidence degree factor into a traditional similarity calculation method; thirdly, using the dependence of trust on time to allow a trust network to dynamically evolve; fourthly, creating a dual network time domain evolution model (DNTDEM) comprising a user similarity network and a user trust network; fifthly, acquiring a brand new user trust network according to the DNTDEM; sixthly, using an LDA model to supplement recommendationcontent; seventhly, allowing predicted users to be similar to the emotion neighbors of the users, and using a minimum error square value to optimize the similarity. The micro-video personalized recommendation algorithm has the advantages that high-quality new-form user-generated content (UGC) can be effectively identified and recommended to appropriate users; influence of the subjective prejudices of other users on the recommendation content can be relieved, and high-quality recommendation content can be objectively provided for target users.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Systems and methods for identifying and extracting data from HTML pages
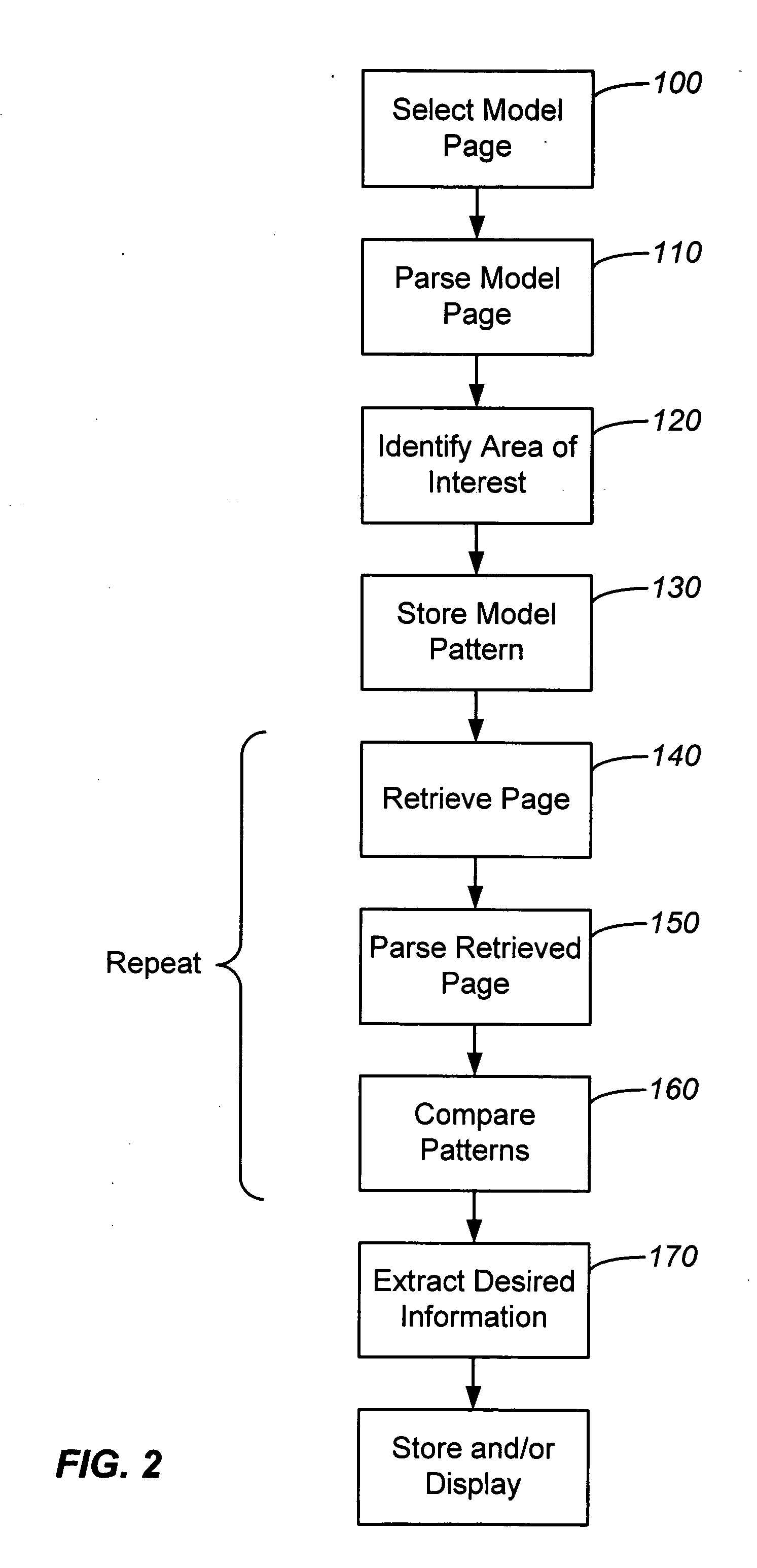
InactiveUS20050273706A1The extraction process is fastData processing applicationsWeb data indexingDatabaseComputer algorithm
Systems and methods for analyzing HTML formatted web pages to automatically identify and extract desired information. A computer algorithm identifies and extracts different pieces of information from different web pages automatically after minimal manual setup. The algorithm automatically analyzes pages with different content if they have the same, or similar, formats. The algorithm is fast and efficient and performs the extraction process quickly in real-time. The systems and methods are useful to build databases from unstructured web information. The algorithm can be used as an agent that captures information about products, and compares prices or other characteristics. It can also be used to populate structured databases that, given the different pieces of information, can analyze products and their characteristics. And it can also be used for data mining applications looking for patterns useful for marketing analyses, or other uses.
Owner:OATH INC
Railroad car lateral instability and tracking error detector
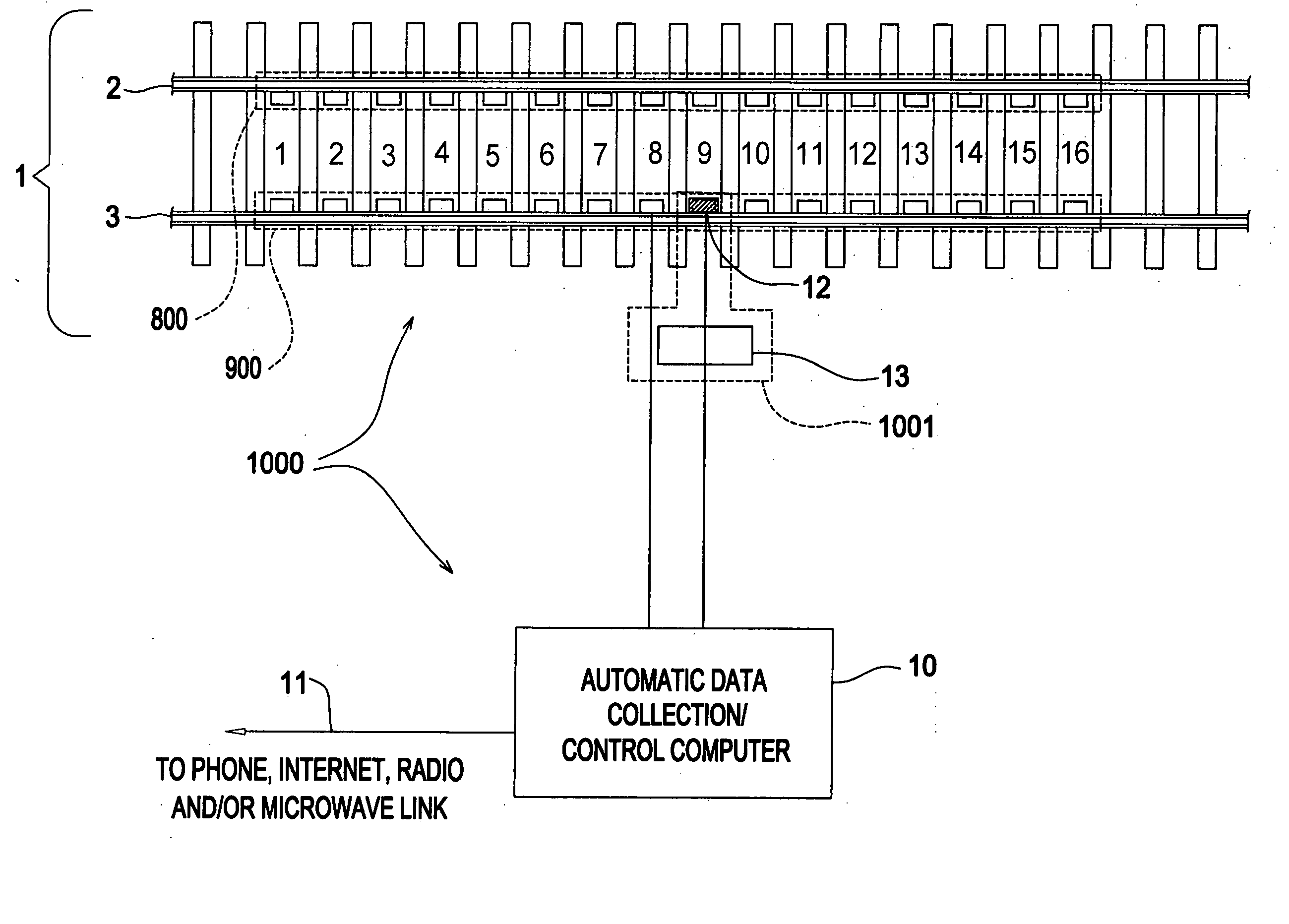
InactiveUS20060261218A1Wheel-rims surveying/measuringRail derailment preventionProximity sensorRailroad wheel
The current invention is intended to be installed in revenue service railroad tracks to detect railroad cars exhibiting wheel set lateral instability. The invention utilizes an array of inductive proximity sensors mounted at regular intervals in a section of railroad track. Each proximity sensor is oriented to sense the lateral position of railroad car wheel sets. The invention employs a computer algorithm to extrapolate the trajectory from the set of proximity sensor signals for each wheel set. A second algorithm evaluates the shape of the trajectory to detect oscillating lateral motion of the wheel set. A third algorithm assesses the severity of any wheel set lateral oscillations that are detected. An additional function of the invention is to detect railroad car trucks that exhibit “tracking errors”.
Owner:PROGRESSIVE RAIL TECH
Aircraft engine reliability business model
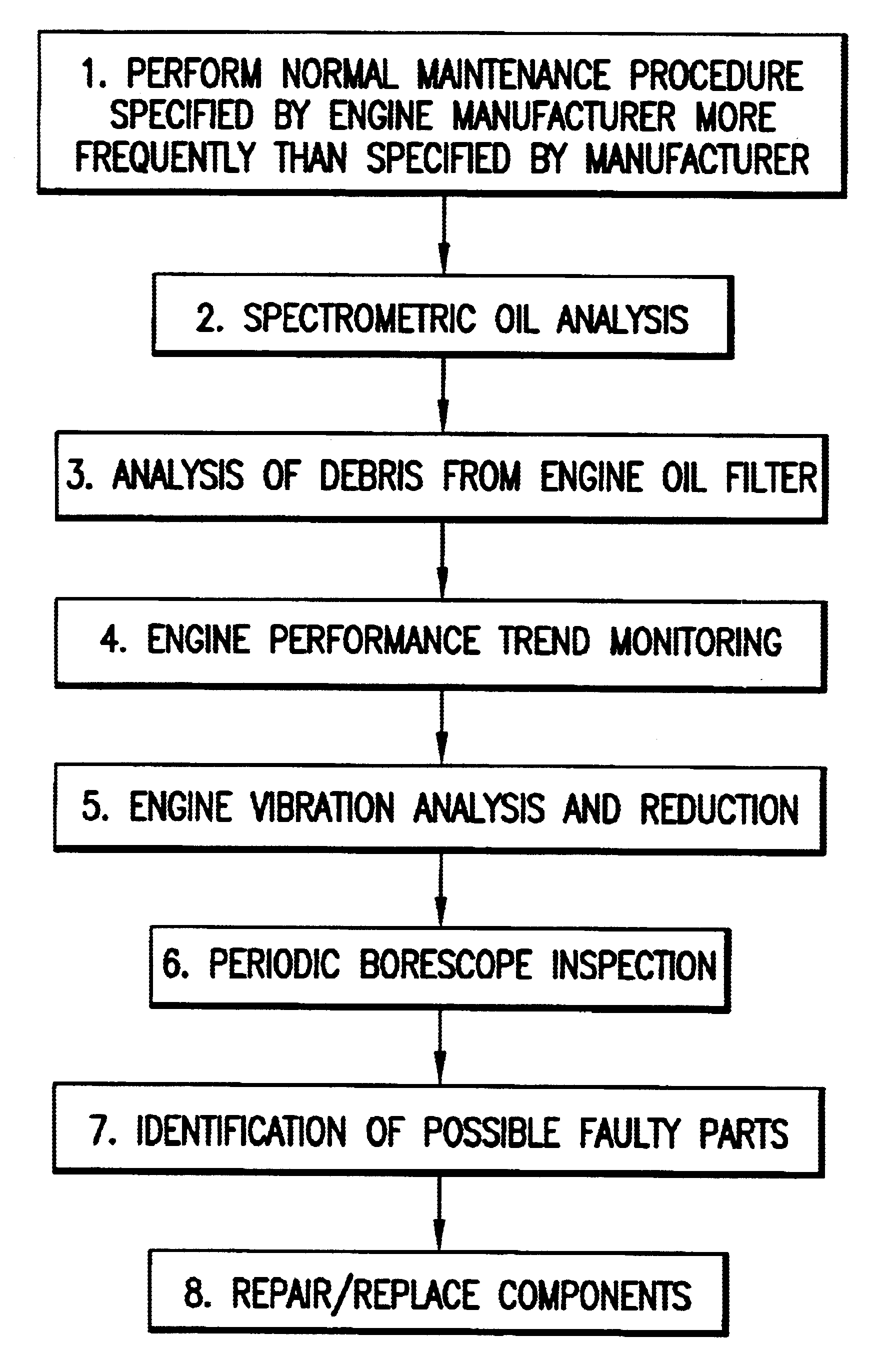
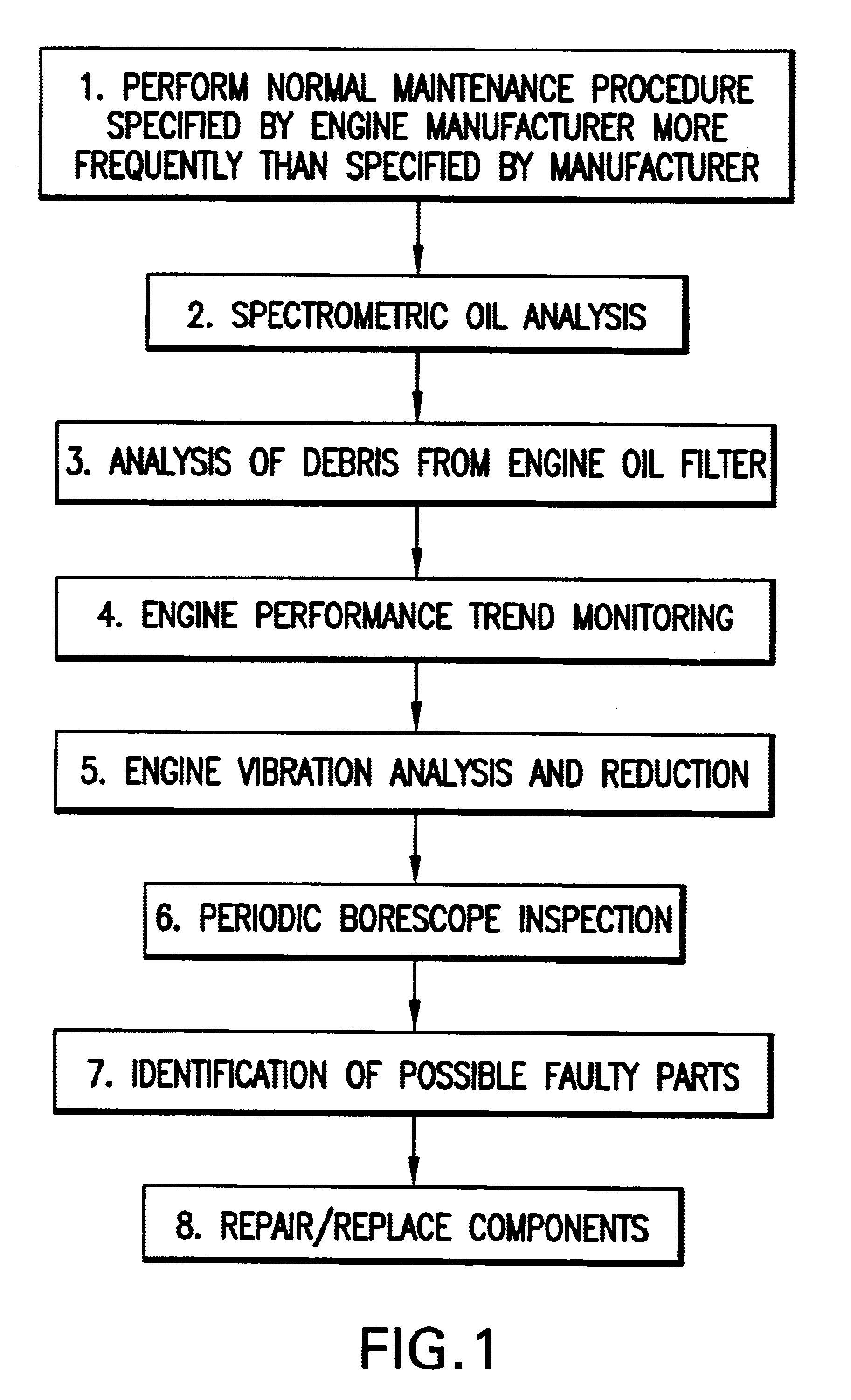
A business model algorithm for maintaining aircraft engines in reliable and safe operating condition without the necessity of performing major engine overhaul in which engine manufacturers' maintenance procedures are enhanced and performed more frequently and supplemented by engine trend analysis, engine oil analysis, engine vibration analysis, borescope inspection and computer algorithm forecasting to identify, repair, and / or replace engine components without necessity of major engine overhaul.
Owner:BANGERT BARRY +1
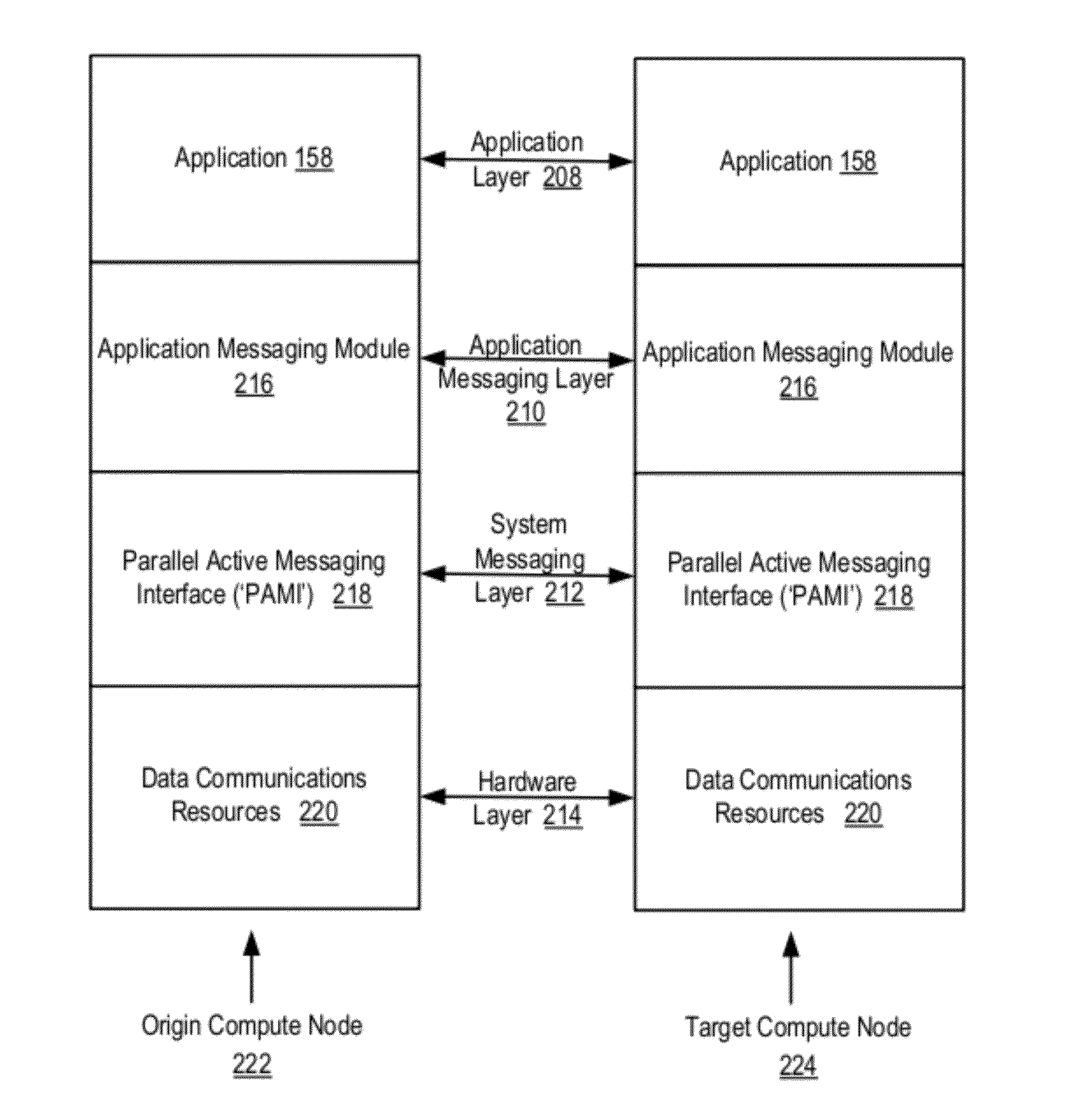
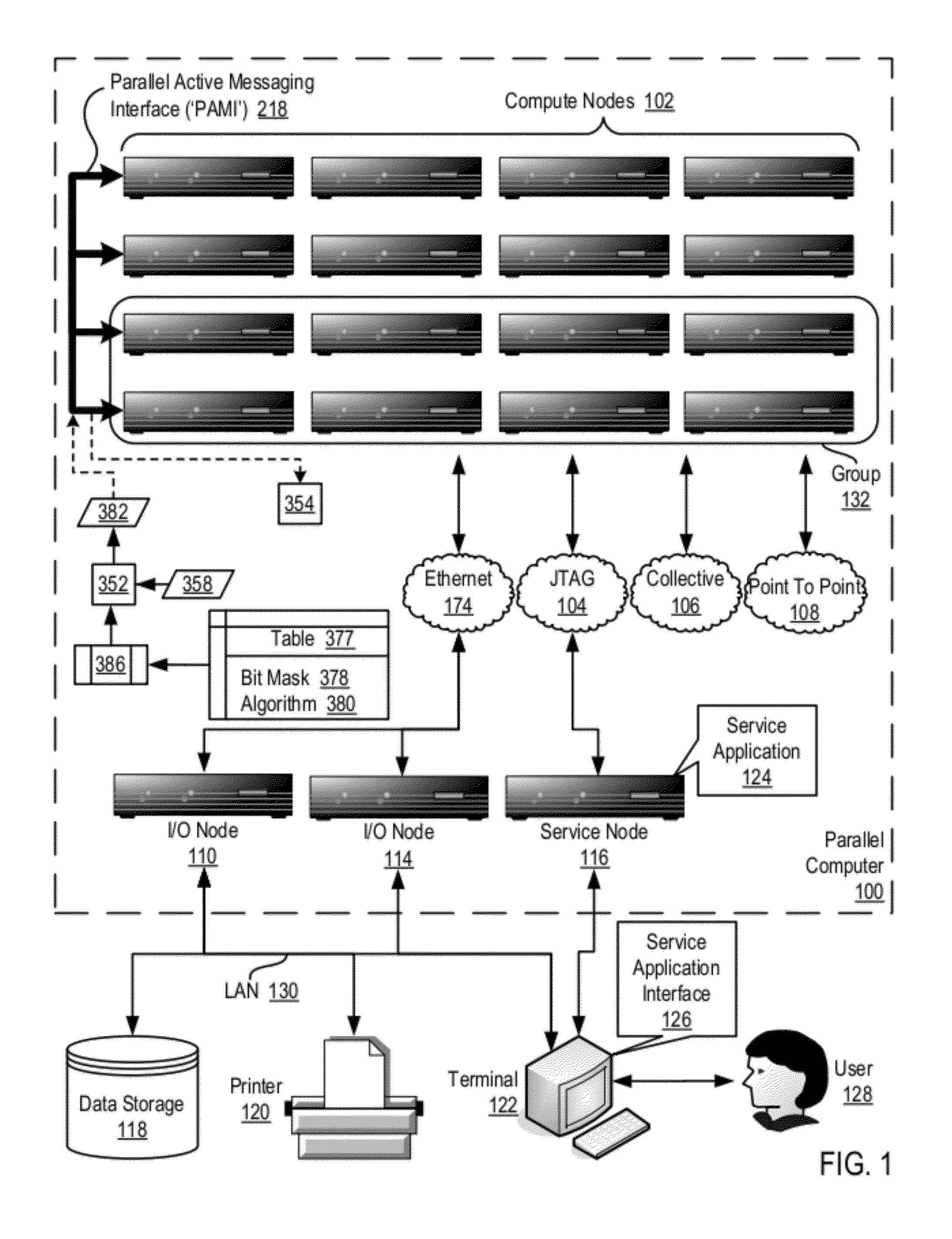
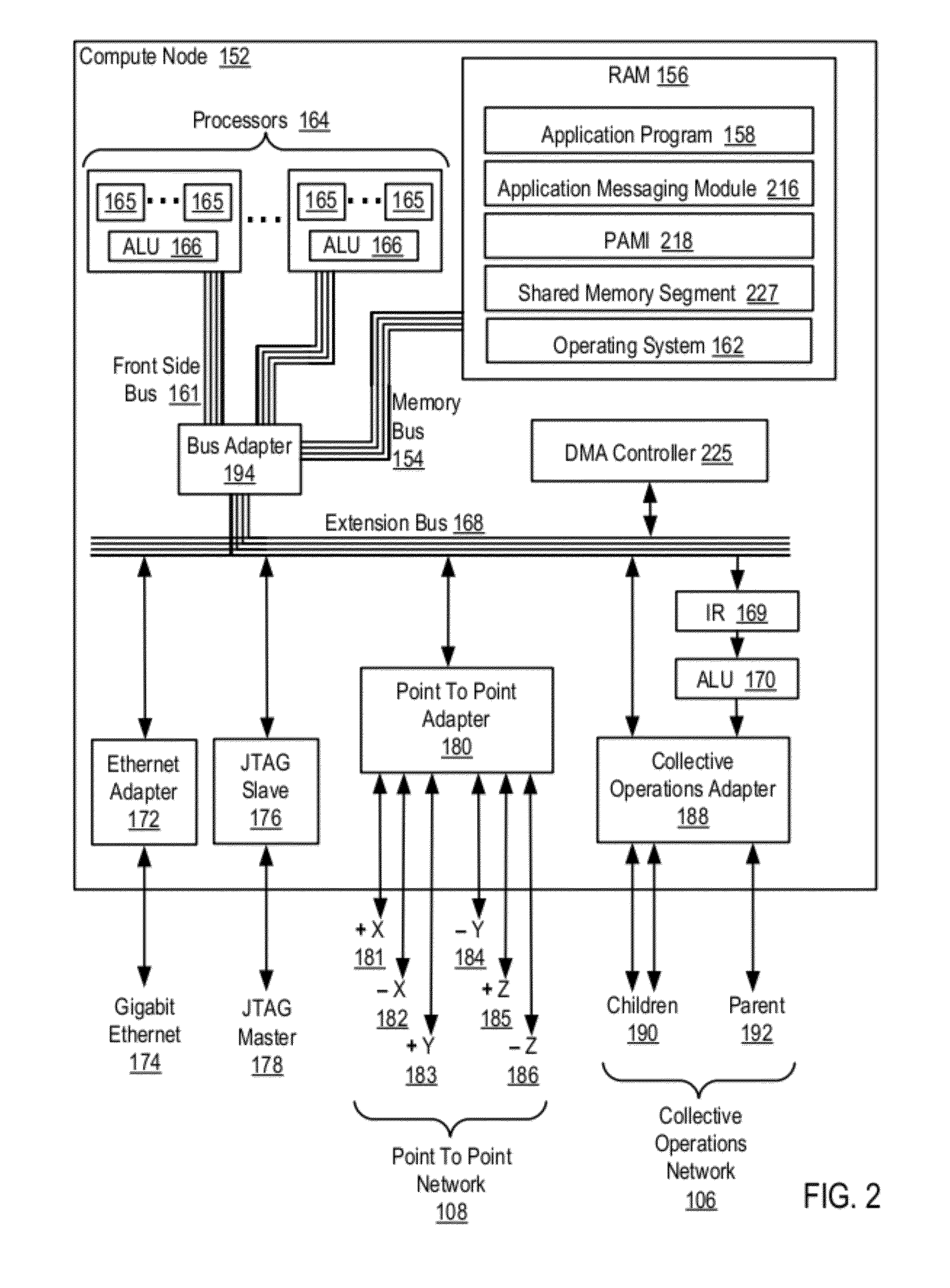
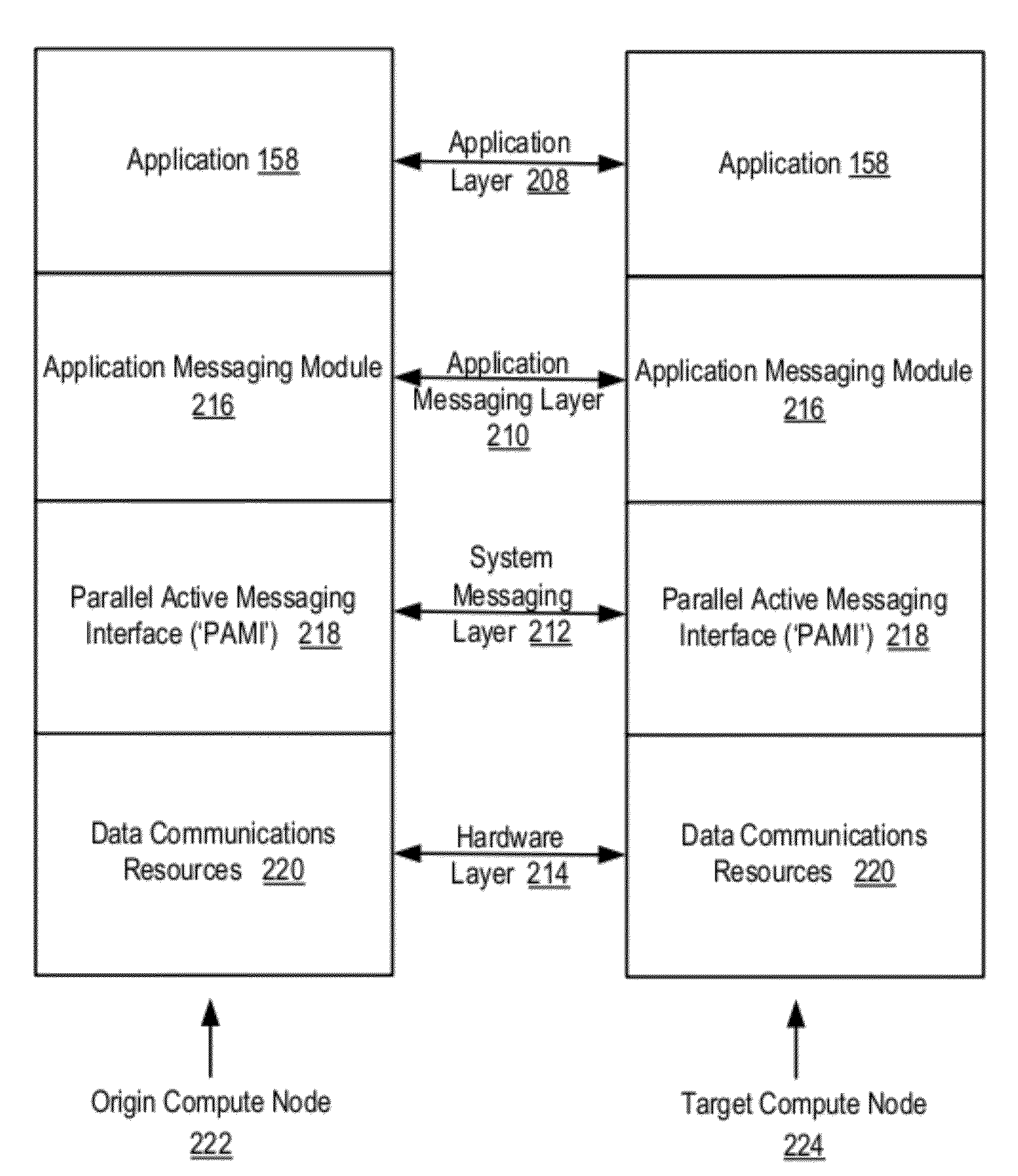
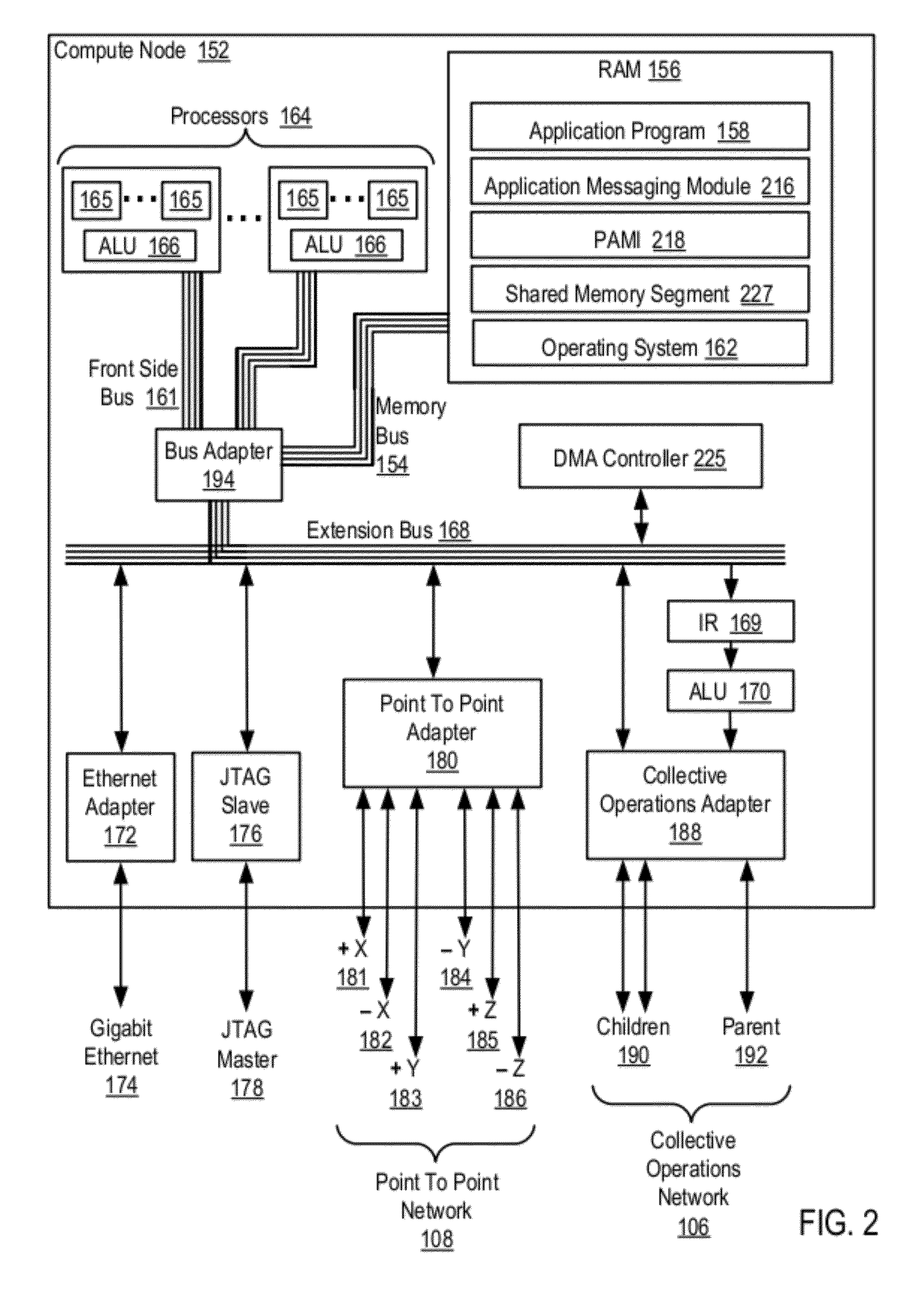
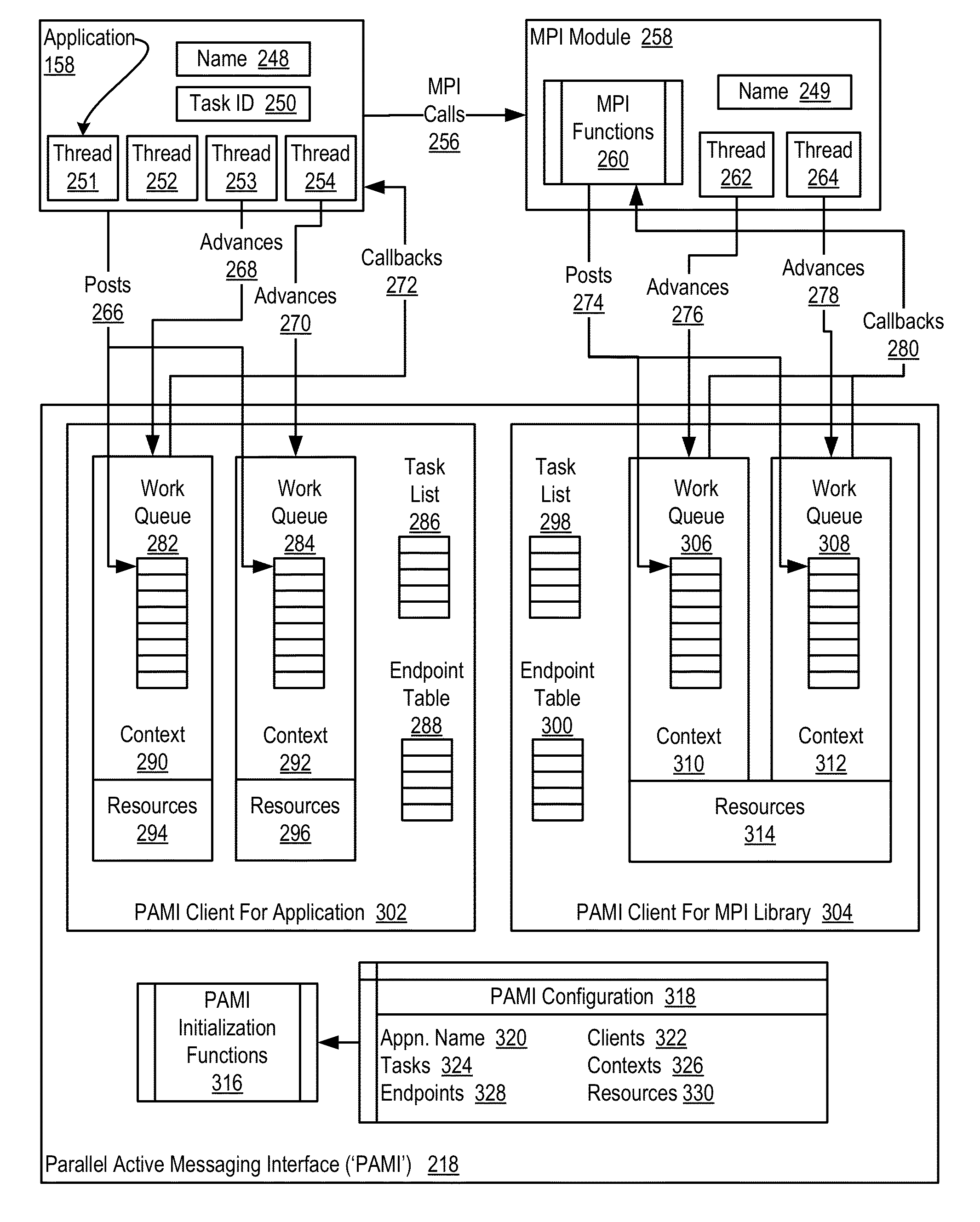
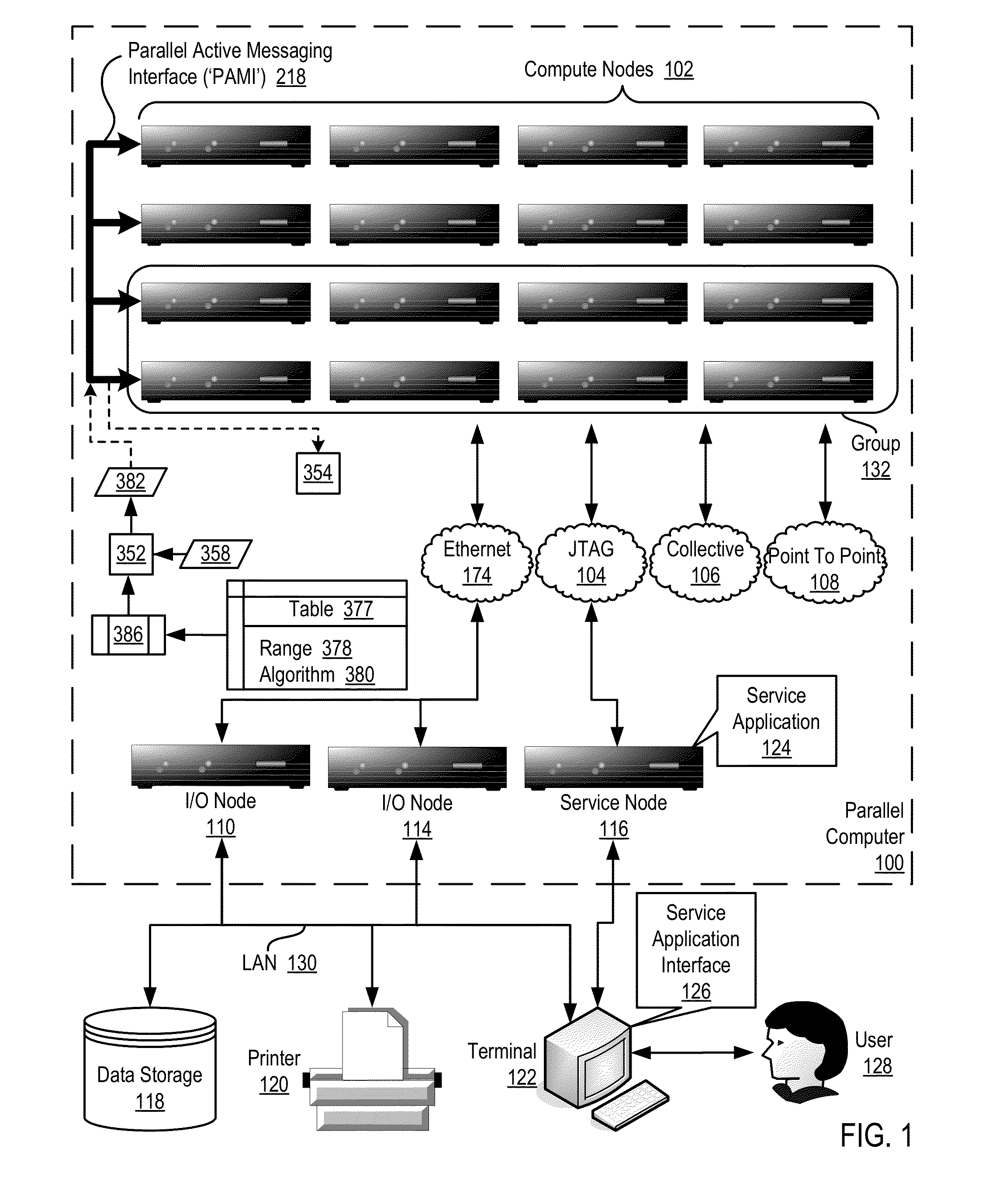
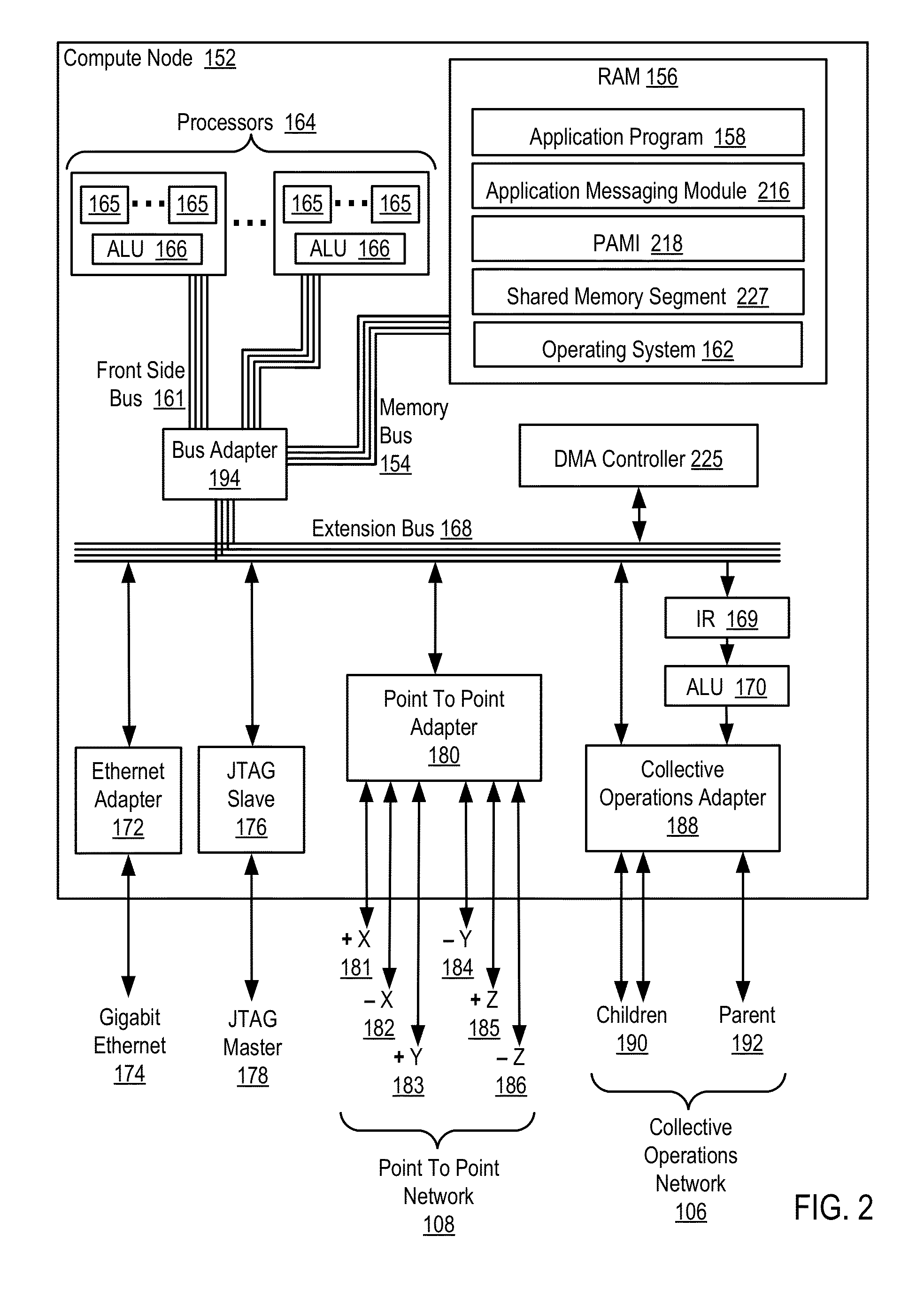
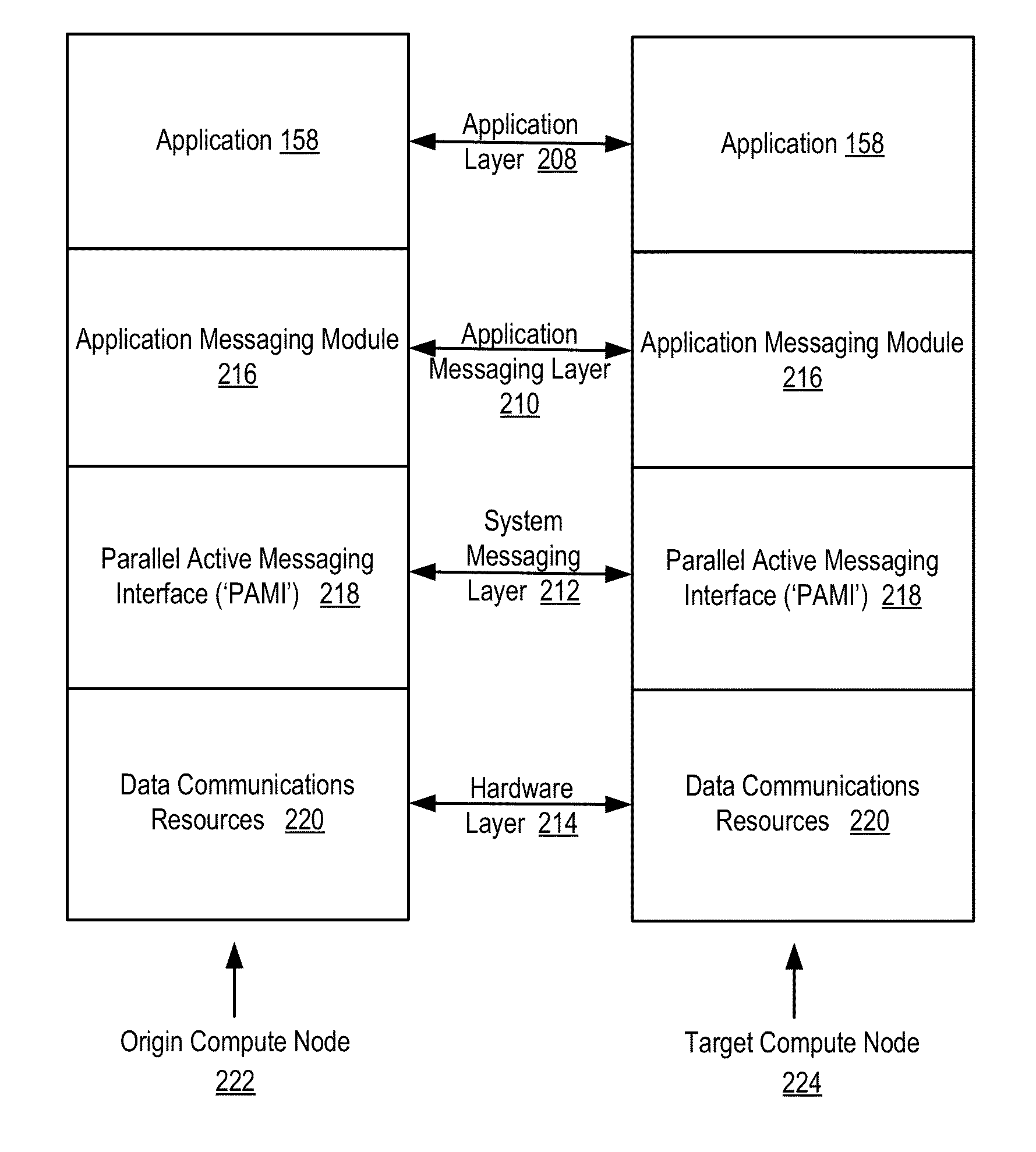
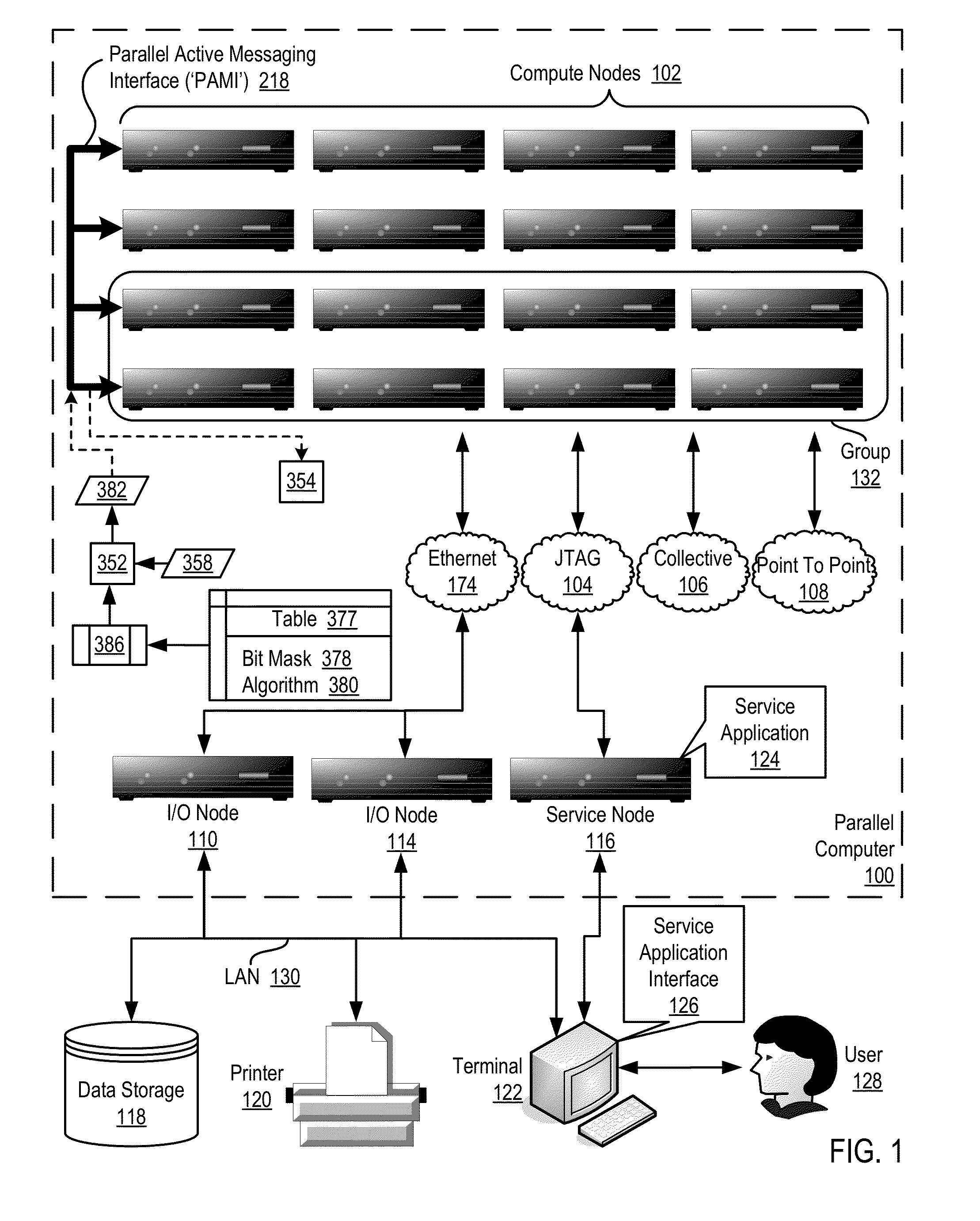
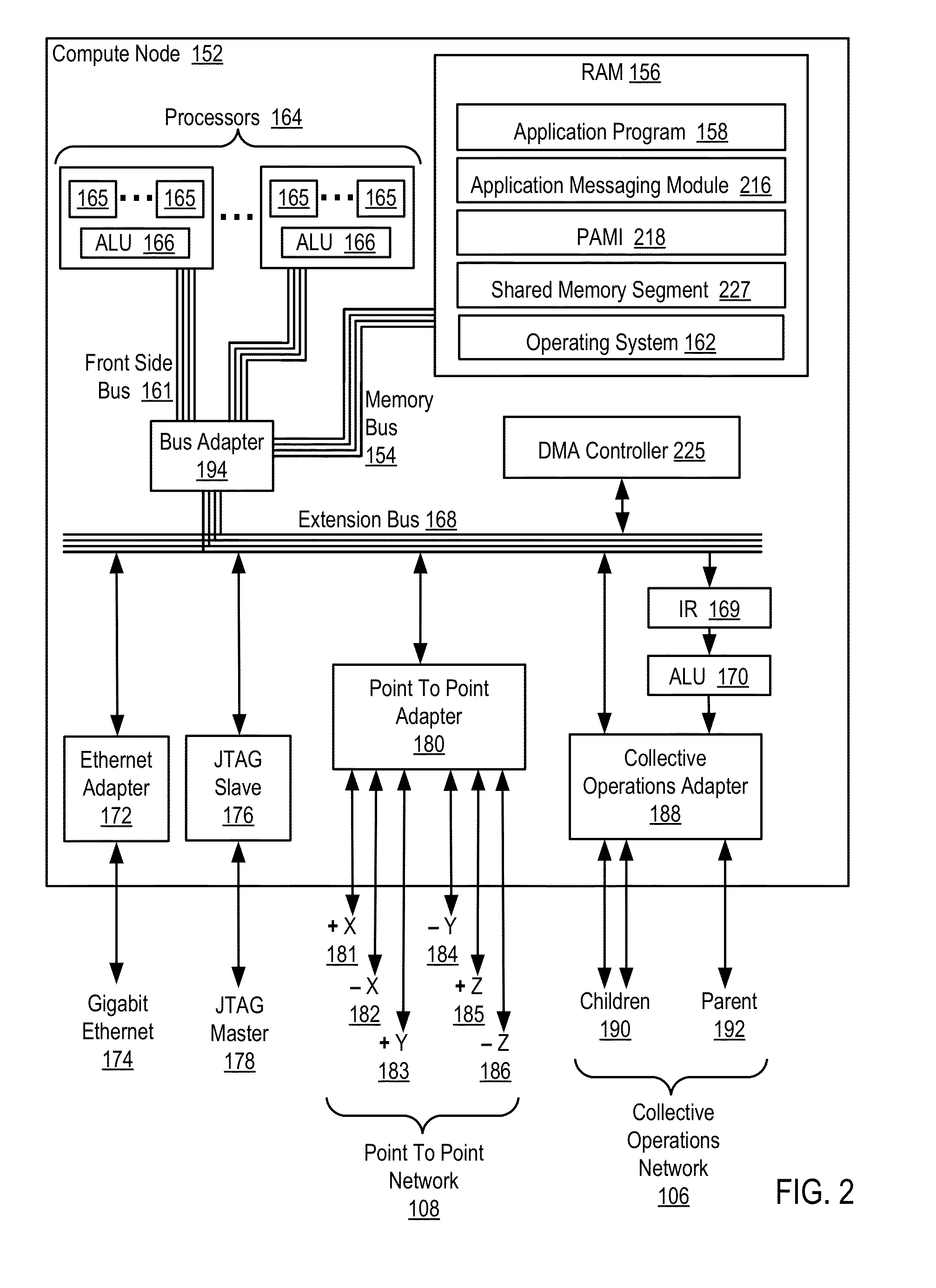
Data Communications For A Collective Operation In A Parallel Active Messaging Interface Of A Parallel Computer
InactiveUS20120144401A1Interprogram communicationDigital computer detailsCommunication endpointClient-side
Algorithm selection for data communications in a parallel active messaging interface (‘PAMI’) of a parallel computer, the PAMI composed of data communications endpoints, each endpoint including specifications of a client, a context, and a task, endpoints coupled for data communications through the PAMI, including associating in the PAMI data communications algorithms and bit masks; receiving in an origin endpoint of the PAMI a collective instruction, the instruction specifying transmission of a data communications message from the origin endpoint to a target endpoint; constructing a bit mask for the received collective instruction; selecting, from among the associated algorithms and bit masks, a data communications algorithm in dependence upon the constructed bit mask; and executing the collective instruction, transmitting, according to the selected data communications algorithm from the origin endpoint to the target endpoint, the data communications message.
Owner:IBM CORP
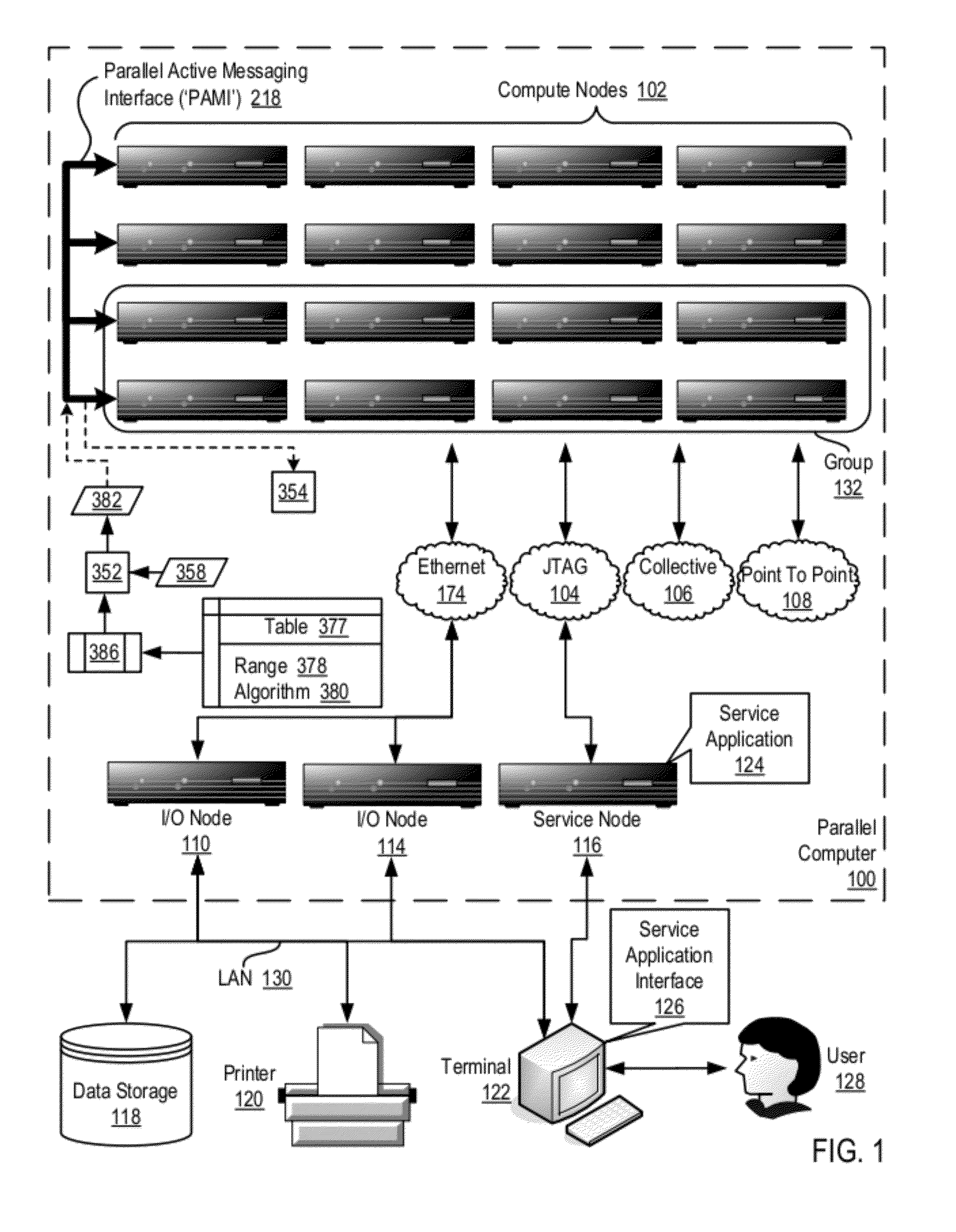
Data Communications In A Parallel Active Messaging Interface Of A Parallel Computer
InactiveUS20120144400A1Digital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsCommunication endpointParallel computing
Algorithm selection for data communications in a parallel active messaging interface (‘PAMI’) of a parallel computer, the PAMI composed of data communications endpoints, each endpoint including specifications of a client, a context, and a task, endpoints coupled for data communications through the PAMI, including associating in the PAMI data communications algorithms and ranges of message sizes so that each algorithm is associated with a separate range of message sizes; receiving in an origin endpoint of the PAMI a data communications instruction, the instruction specifying transmission of a data communications message from the origin endpoint to a target endpoint, the data communications message characterized by a message size; selecting, from among the associated algorithms and ranges, a data communications algorithm in dependence upon the message size; and transmitting, according to the selected data communications algorithm from the origin endpoint to the target endpoint, the data communications message.
Owner:IBM CORP
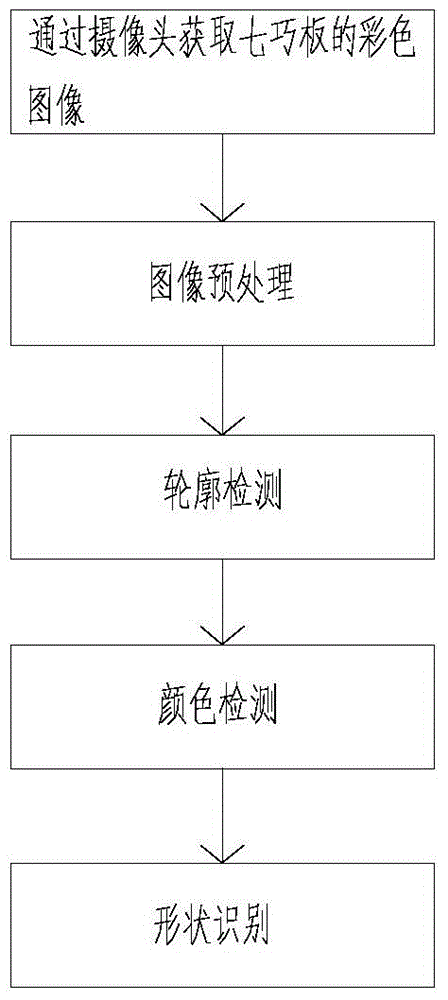
Seven-piece puzzle identification method based on contours and colors
The invention discloses a seven-piece puzzle identification method based on contours and colors. The seven-piece puzzle identification method comprises the following steps: S1, obtaining the color image of a seven-piece puzzle through a camera; S2, preprocessing the color image in the step S1; S3, carrying out contour detection on the color image in the step S1; S4, carrying out color detection on contour information in the step S3; S5, carrying out shape identification. The seven-piece puzzle identification method has the beneficial effects that the method is suitable for any electronic equipment and platforms, such as human-computer interaction, and a physical toy in traditional games and electronic equipment are skillfully combined together through an advanced computer algorithm, so that a game of combining the real world with a virtual technology together is realized, and the limitation problem for seven-piece puzzle game when an embedded platform is low in processing speed and limited in memory resources is effectively solved.
Owner:SICHUAN CHANGHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
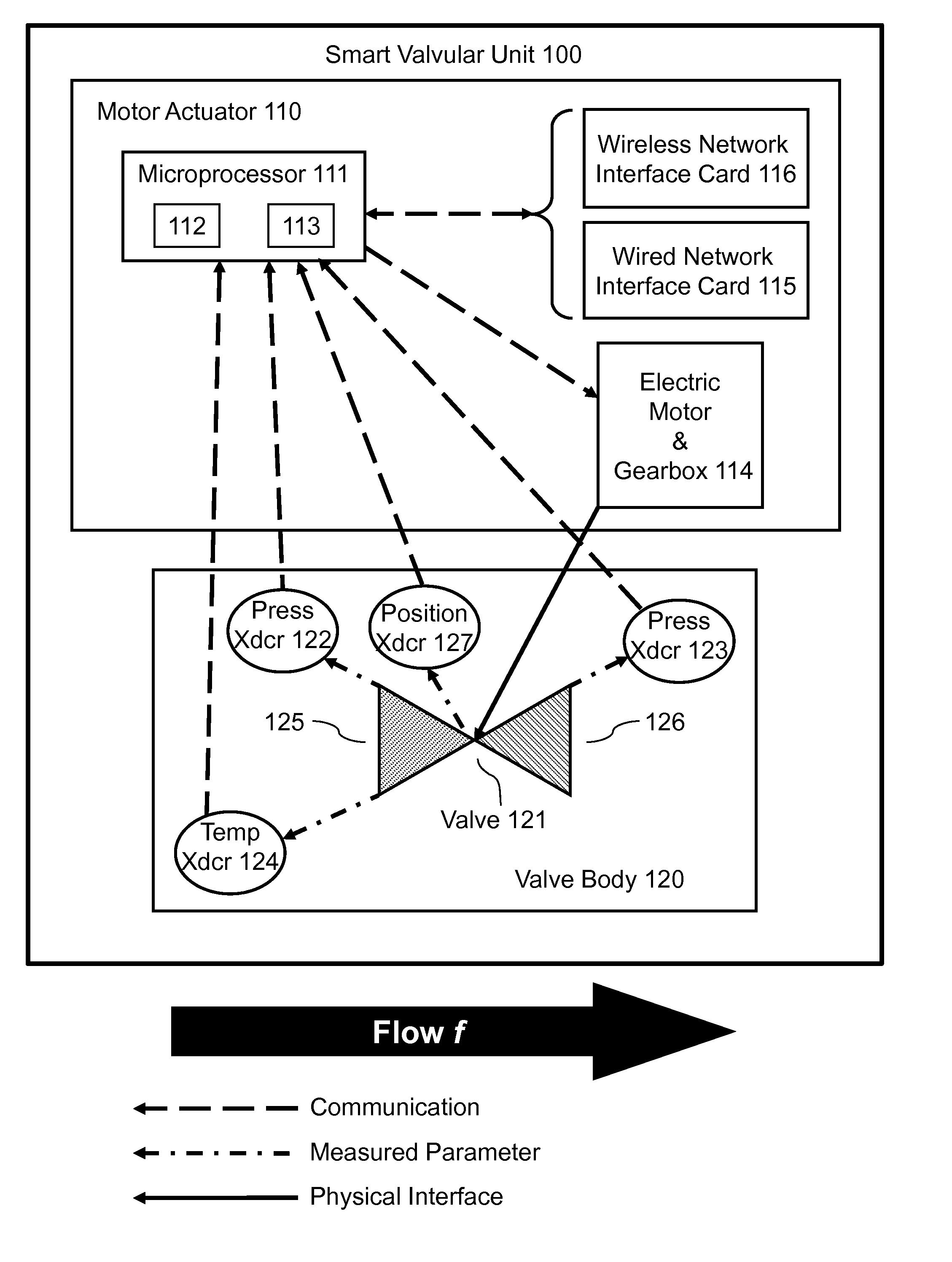
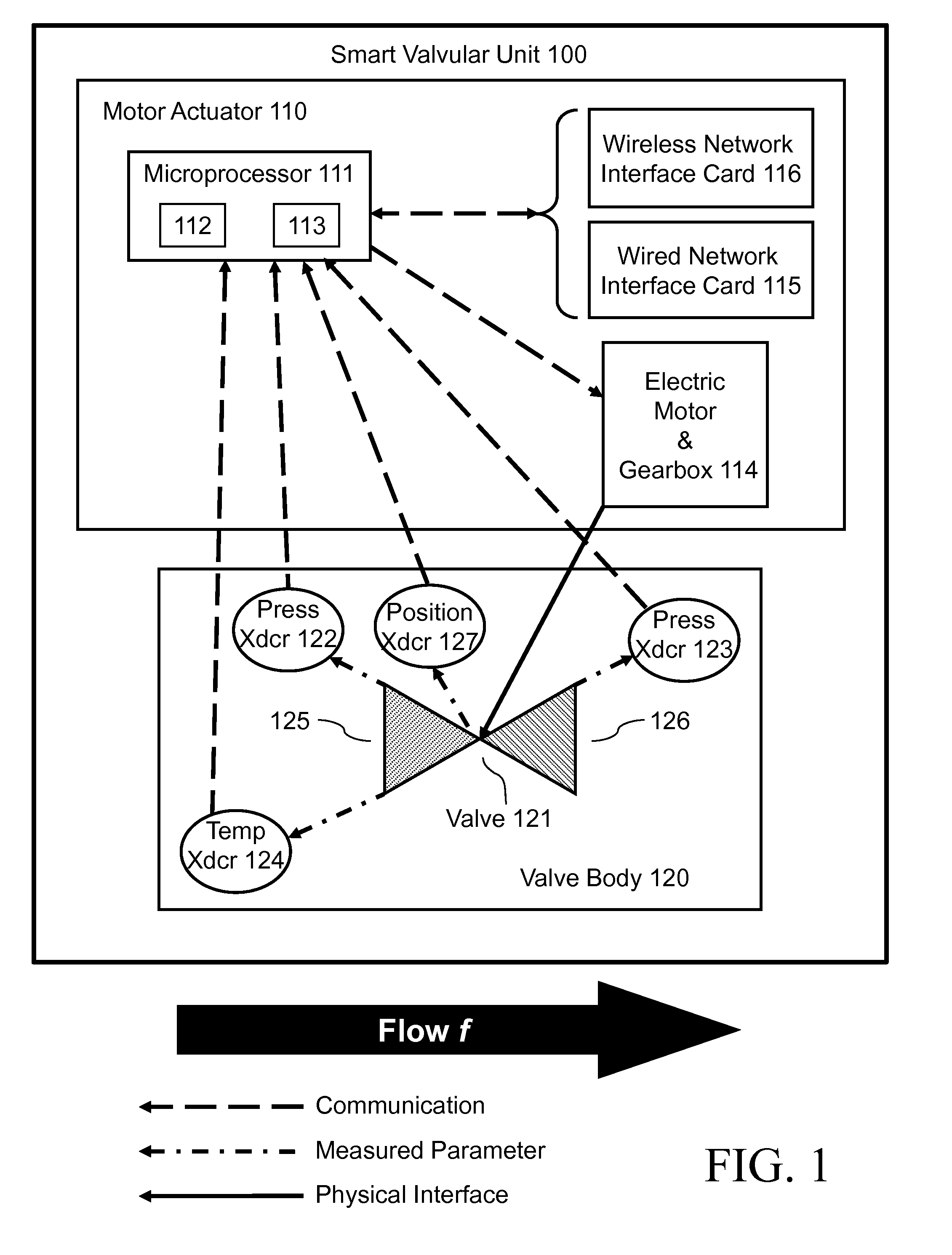
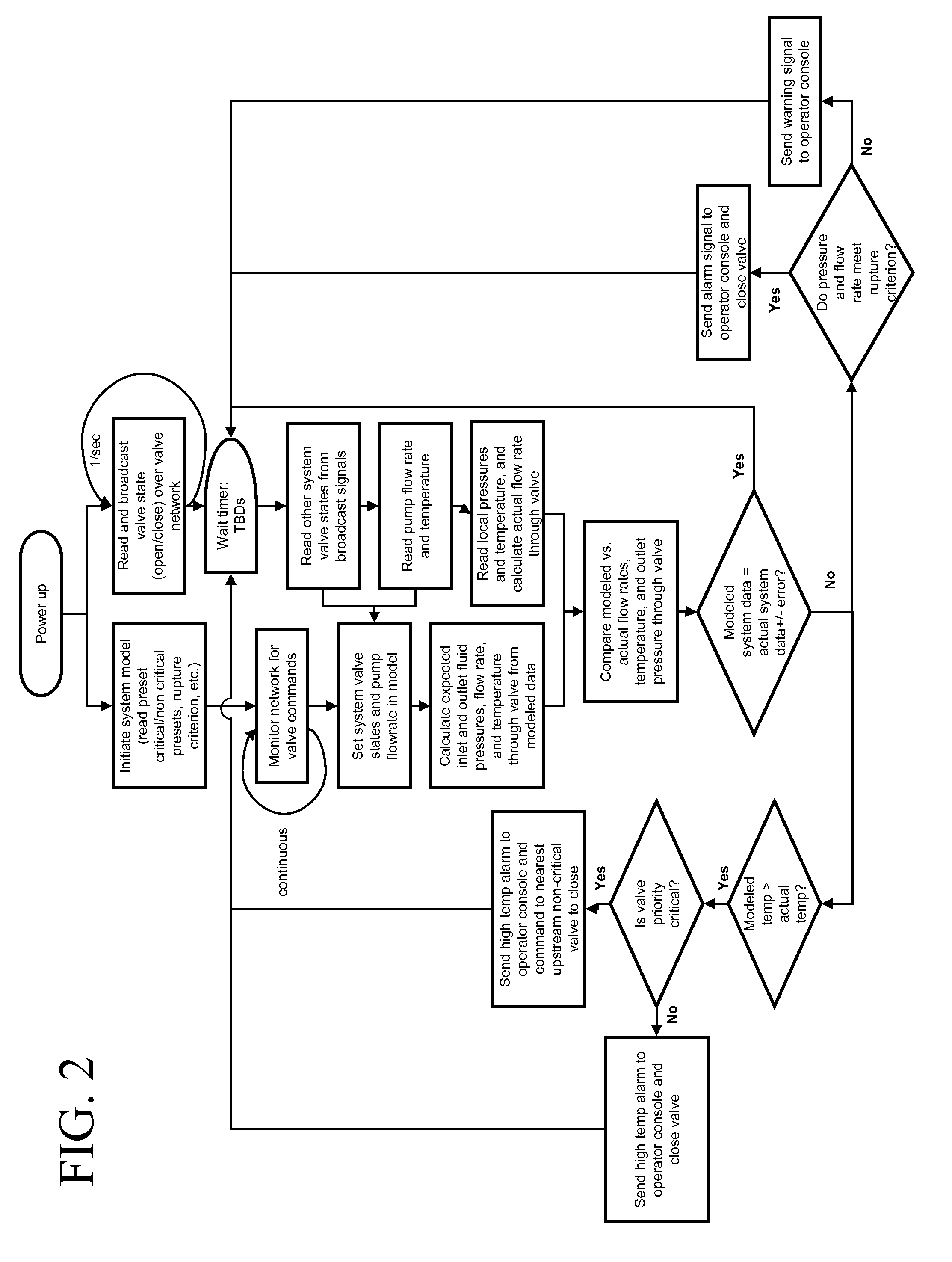
Thermal management smart valve with rupture detection and isolation
InactiveUS8600566B1Improve the realignment of a cooling systemImprove usabilityValve arrangementsTemperatue controlEngineeringComputer algorithm
The condition of a fluid piping system is monitored by multiple intercommunicative smart valves, each executing a computer algorithm that designates smart valves as critical or non-critical, compares measurement data versus simulation data, and makes decisions based on the critical-or-noncritical designations and the measurement-versus-simulation comparisons. Initial measurement-versus-simulation comparisons are made for downstream pressure, flow rate, and temperature. If a measurement-versus-simulation discrepancy is found in either the downstream pressure or the flow rate, then the algorithm compares a measurement rupture determinant versus a simulation rupture determinant; if a measurement-versus-simulation discrepancy is found in the rupture determinant, then the smart valve is closed. If a measurement-versus-simulation discrepancy is found in the temperature, then the smart valve, if non-critical, is closed; however, if the smart valve is critical, then the nearest upstream non-critical smart valve is closed. Any measurement-versus-simulation discrepancy results, at least, in an alarm or warning.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Data communications in a parallel active messaging interface of a parallel computer
InactiveUS20130061244A1Digital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsCommunication endpointParallel computing
Algorithm selection for data communications in a parallel active messaging interface (‘PAMI’) of a parallel computer, the PAMI composed of data communications endpoints, each endpoint including specifications of a client, a context, and a task, endpoints coupled for data communications through the PAMI, including associating in the PAMI data communications algorithms and ranges of message sizes so that each algorithm is associated with a separate range of message sizes; receiving in an origin endpoint of the PAMI a data communications instruction, the instruction specifying transmission of a data communications message from the origin endpoint to a target endpoint, the data communications message characterized by a message size; selecting, from among the associated algorithms and ranges, a data communications algorithm in dependence upon the message size; and transmitting, according to the selected data communications algorithm from the origin endpoint to the target endpoint, the data communications message.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Data communications for a collective operation in a parallel active messaging interface of a parallel computer
ActiveUS20130061245A1Interprogram communicationDigital computer detailsCommunication endpointAlgorithm Selection
Algorithm selection for data communications in a parallel active messaging interface (‘PAMI’) of a parallel computer, the PAMI composed of data communications endpoints, each endpoint including specifications of a client, a context, and a task, endpoints coupled for data communications through the PAMI, including associating in the PAMI data communications algorithms and bit masks; receiving in an origin endpoint of the PAMI a collective instruction, the instruction specifying transmission of a data communications message from the origin endpoint to a target endpoint; constructing a bit mask for the received collective instruction; selecting, from among the associated algorithms and bit masks, a data communications algorithm in dependence upon the constructed bit mask; and executing the collective instruction, transmitting, according to the selected data communications algorithm from the origin endpoint to the target endpoint, the data communications message.
Owner:IBM CORP
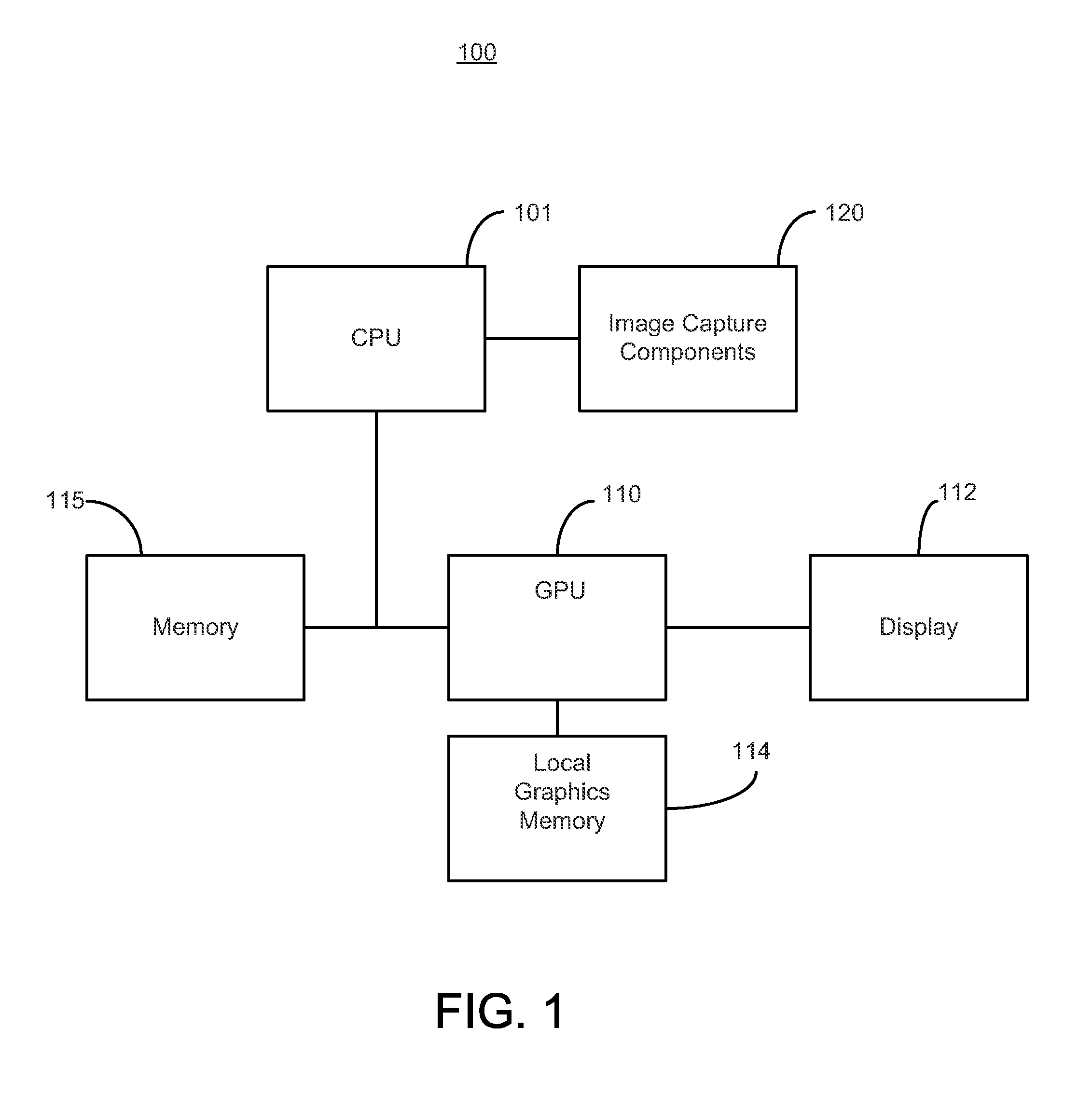
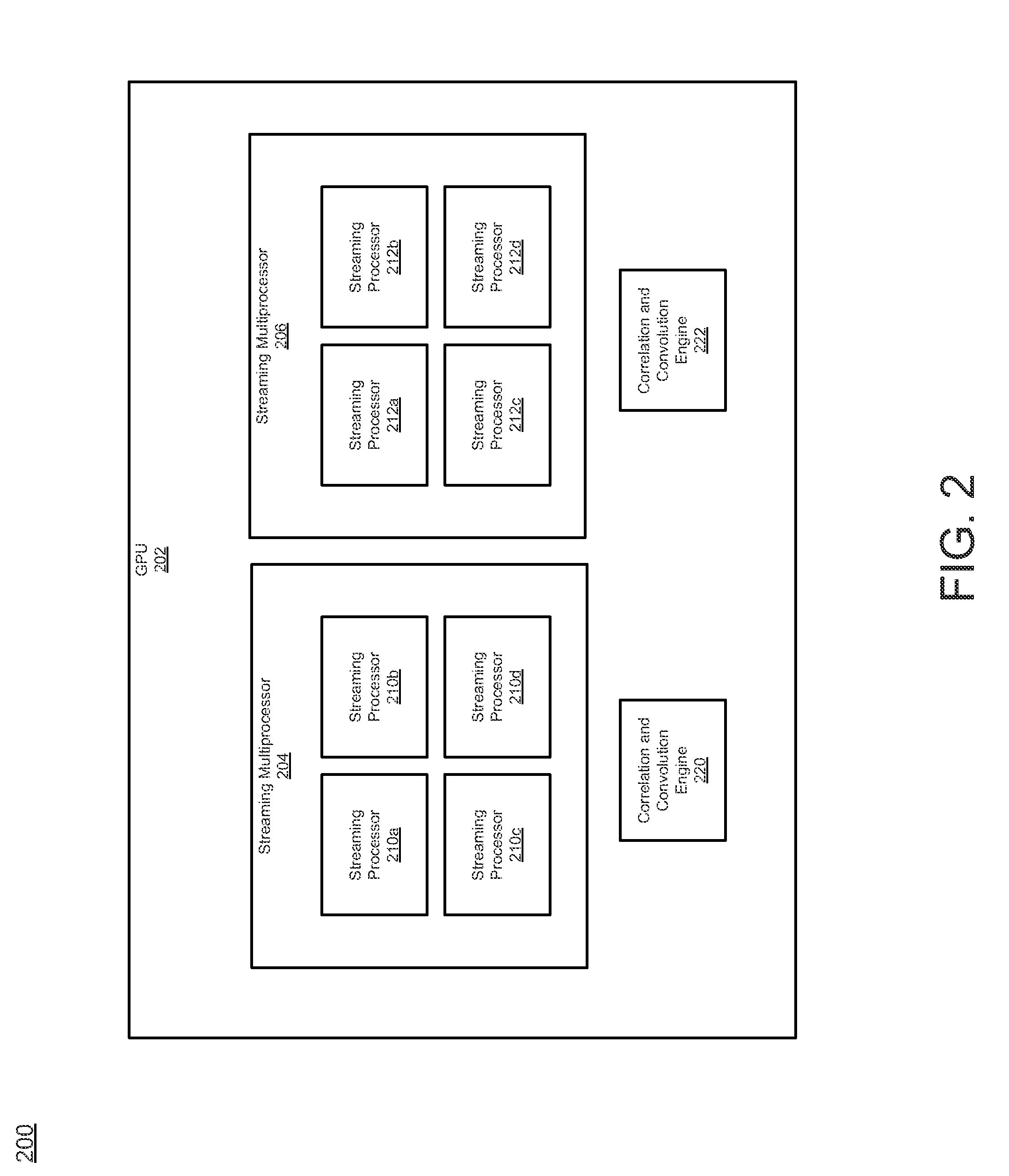
Parallel processor with integrated correlation and convolution engine
ActiveUS20140192066A1High performance correlationDelay problemProcessor architectures/configurationSpecial data processing applicationsComputational scienceGraphics
A system and method for performing computer algorithms. The system includes a graphics pipeline operable to perform graphics processing and an engine operable to perform at least one of a correlation determination and a convolution determination for the graphics pipeline. The graphics pipeline is further operable to execute general computing tasks. The engine comprises a plurality of functional units operable to be configured to perform at least one of the correlation determination and the convolution determination. In one embodiment, the engine is coupled to the graphics pipeline. The system further includes a configuration module operable to configure the engine to perform at least one of the correlation determination and the convolution determination.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
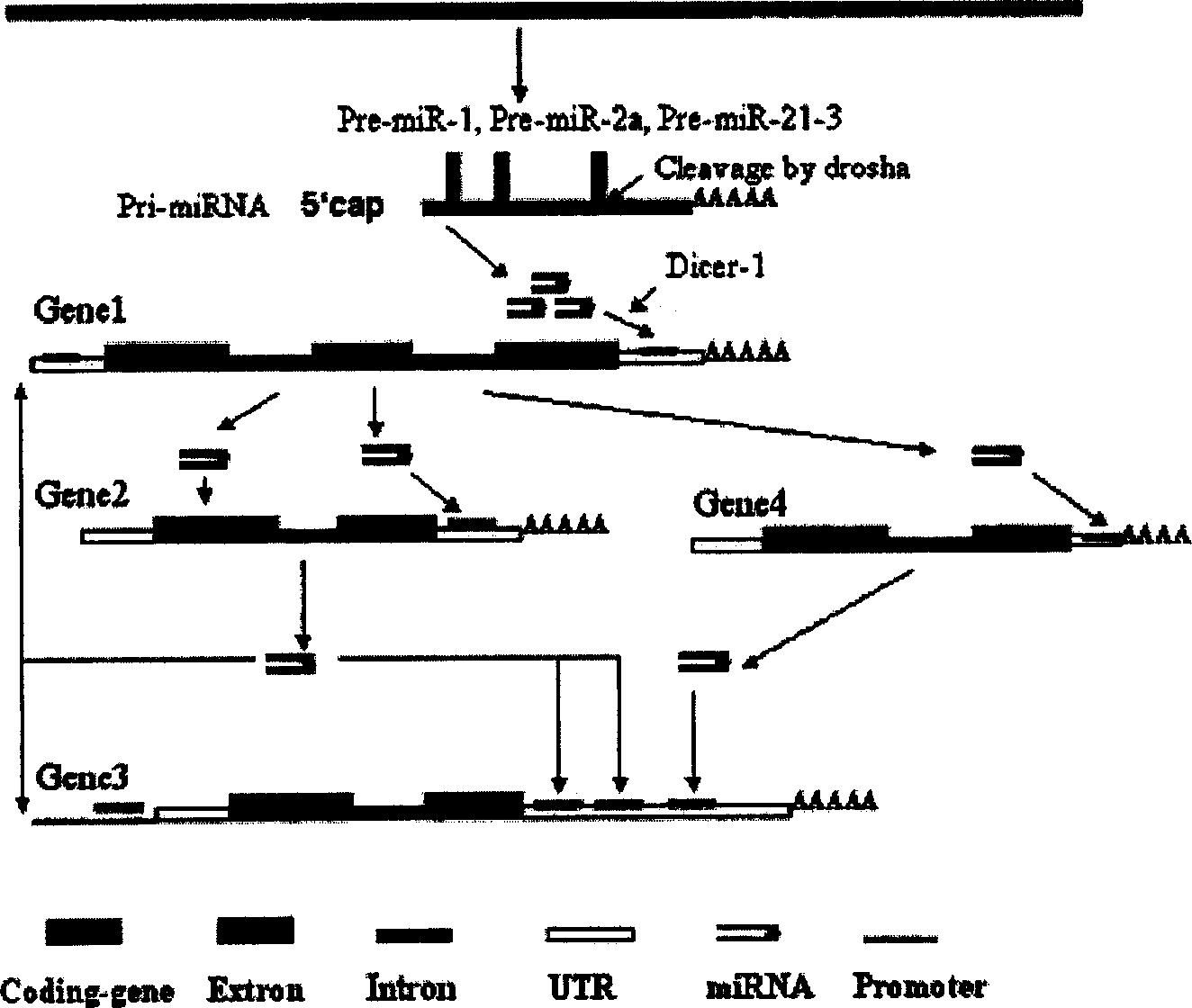
Human autogenous siRNA sequence, its application and screening method
The invention relates to a computer algorithmic language and relative application software. It could rapidly select and predict internal source siRNA gene and siRNA molecule. Especially, it relates to an entire finding method for internal source siRNA gene and internal source siRNA molecule, and gaining 255 new siRNAs and target mRNAs from coding gene intron. The siRNA molecules could be used to research develop, differentiation and growth of cell, organization and organic, discuss the function and express adjusting network and discuss function of genes. It also could be used to develop medicines to prevent and cure kinds of disease.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com