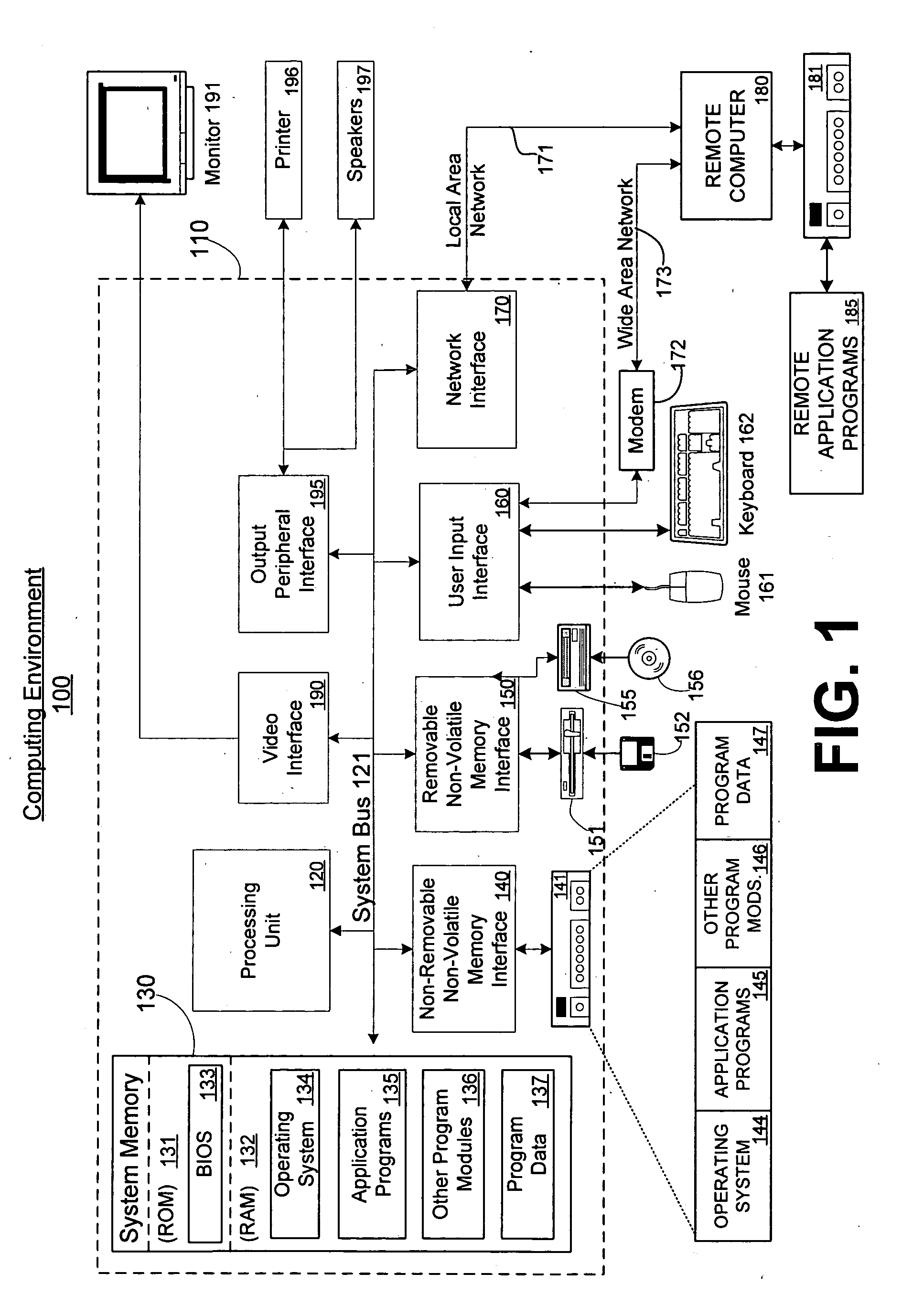
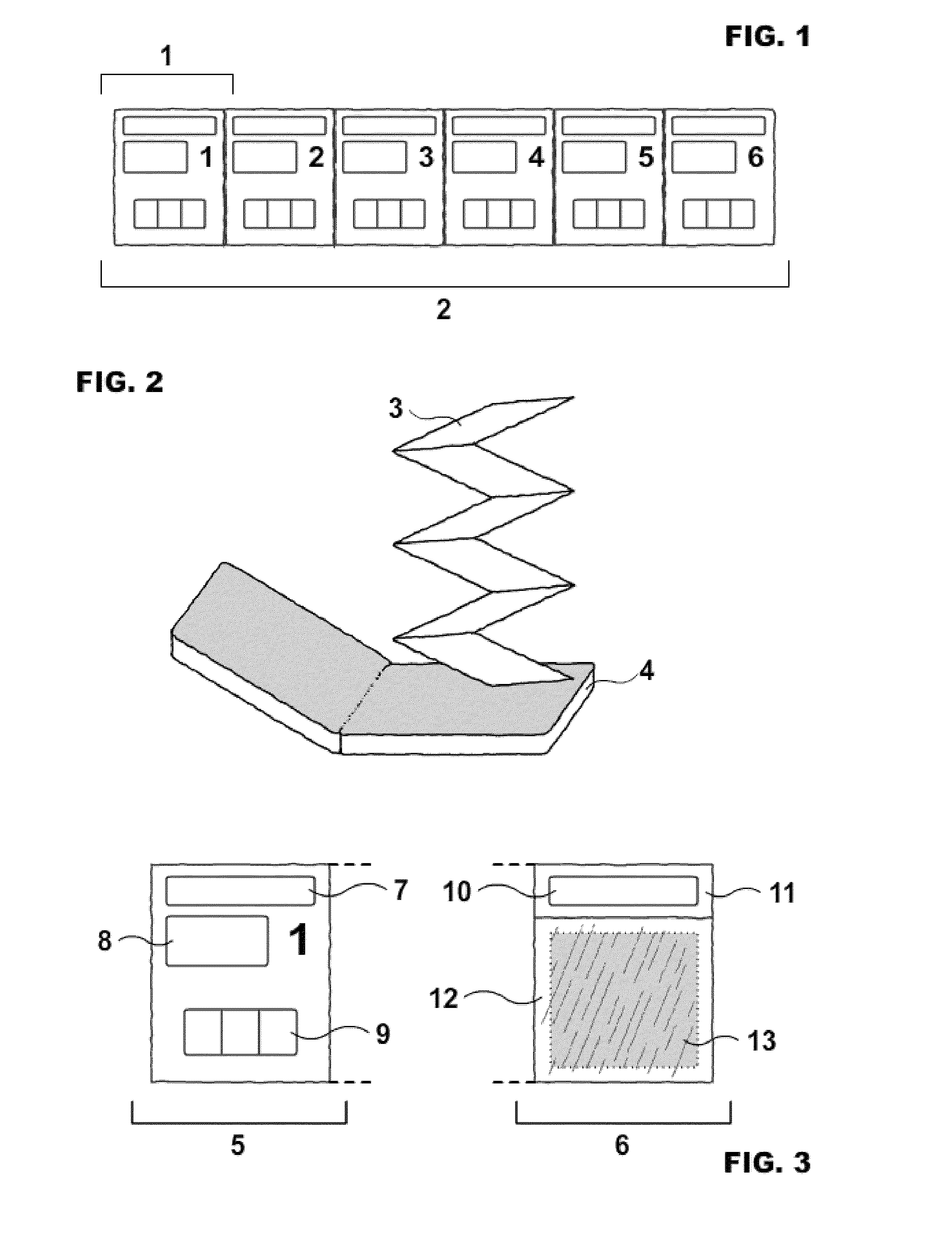
Patents
Literature
48results about How to "Rapid visualization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
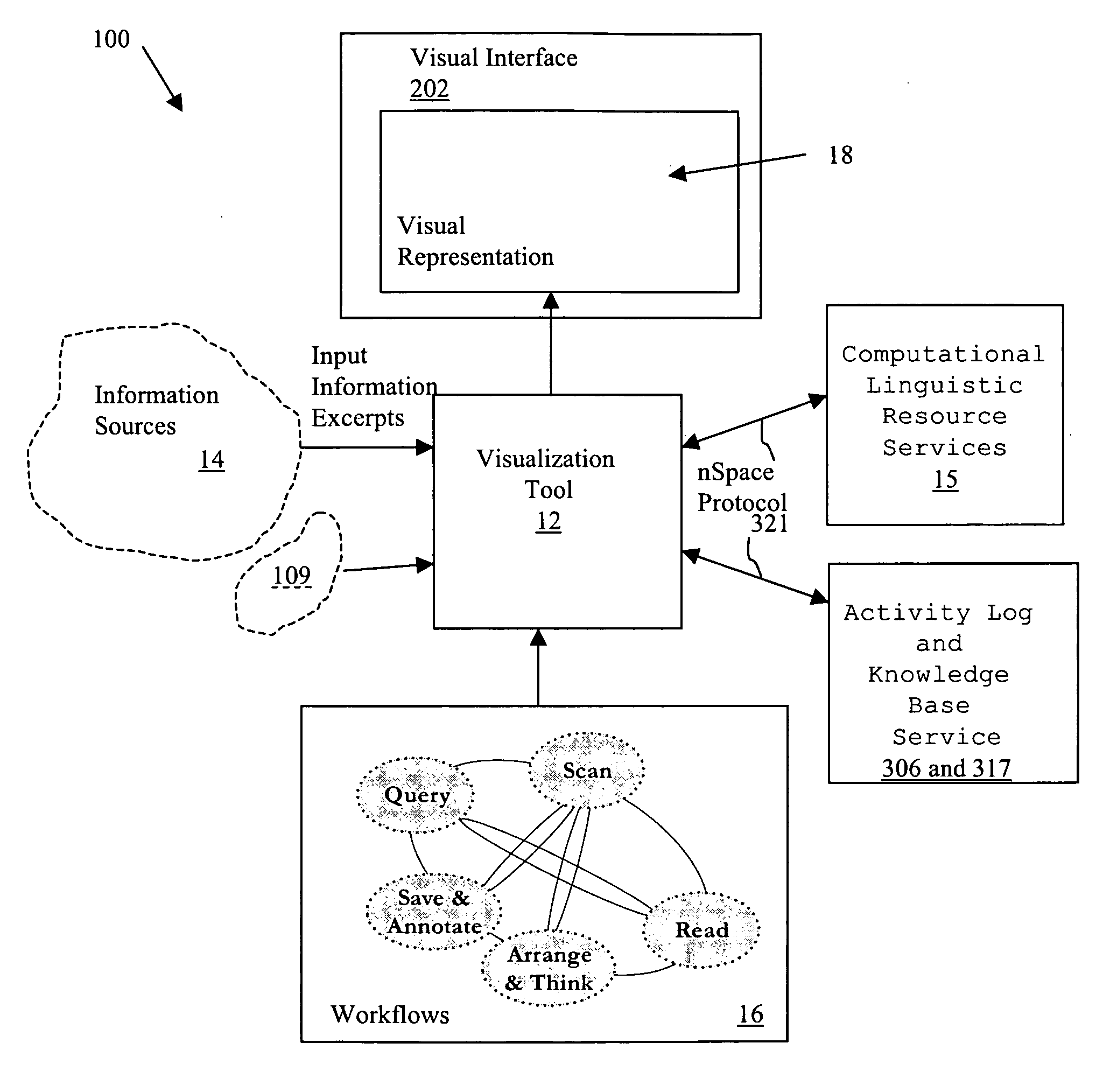
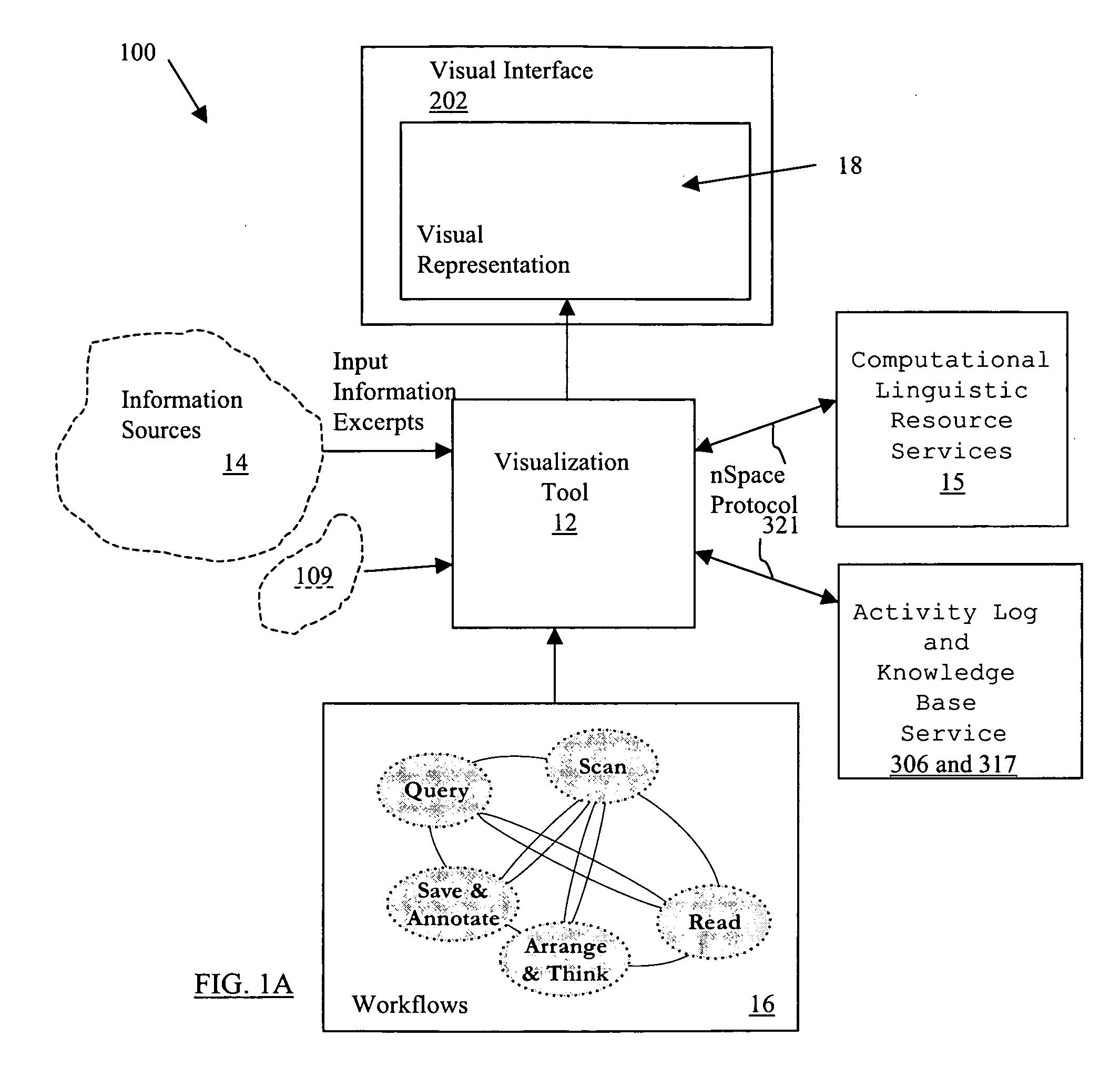
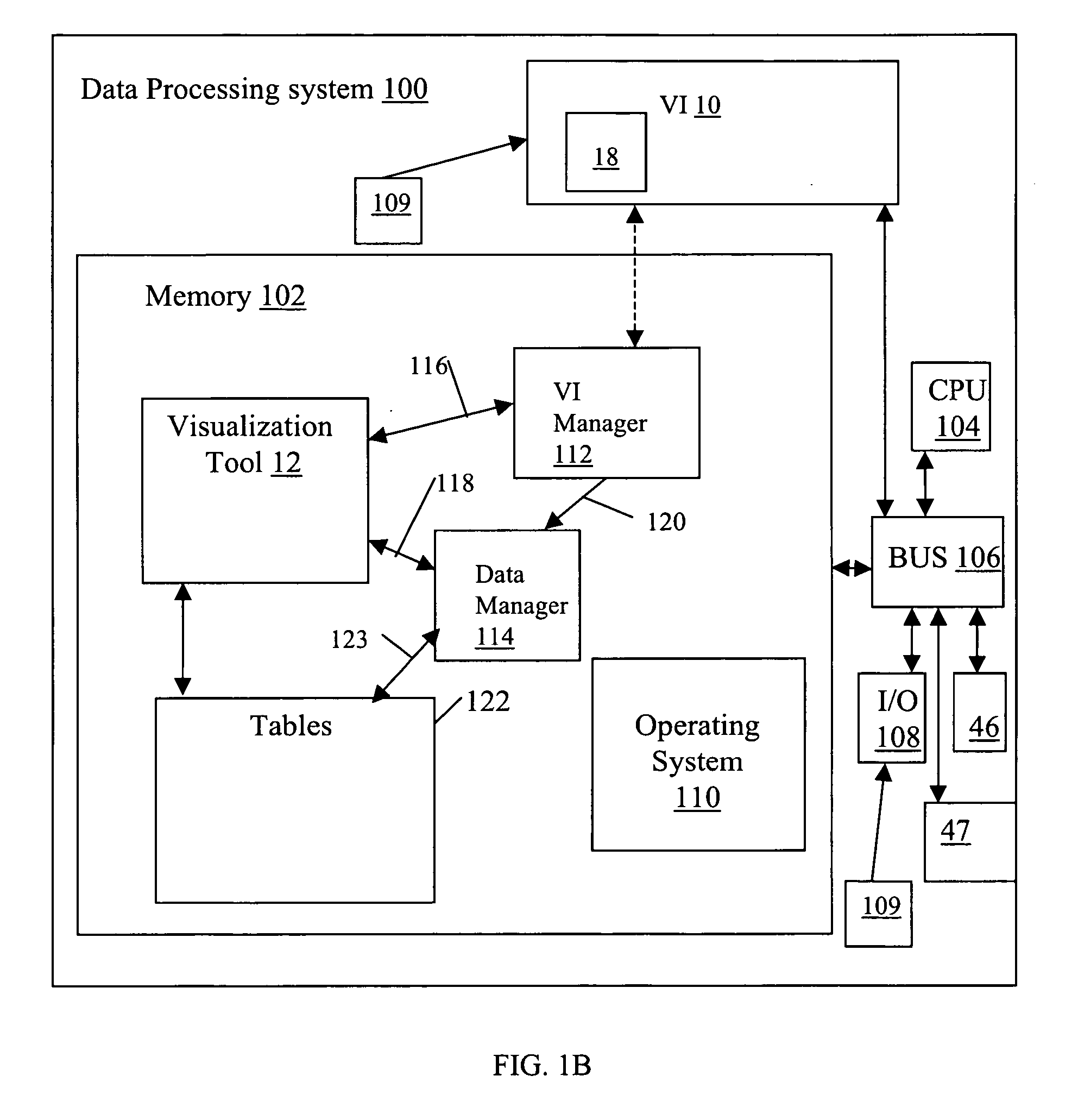
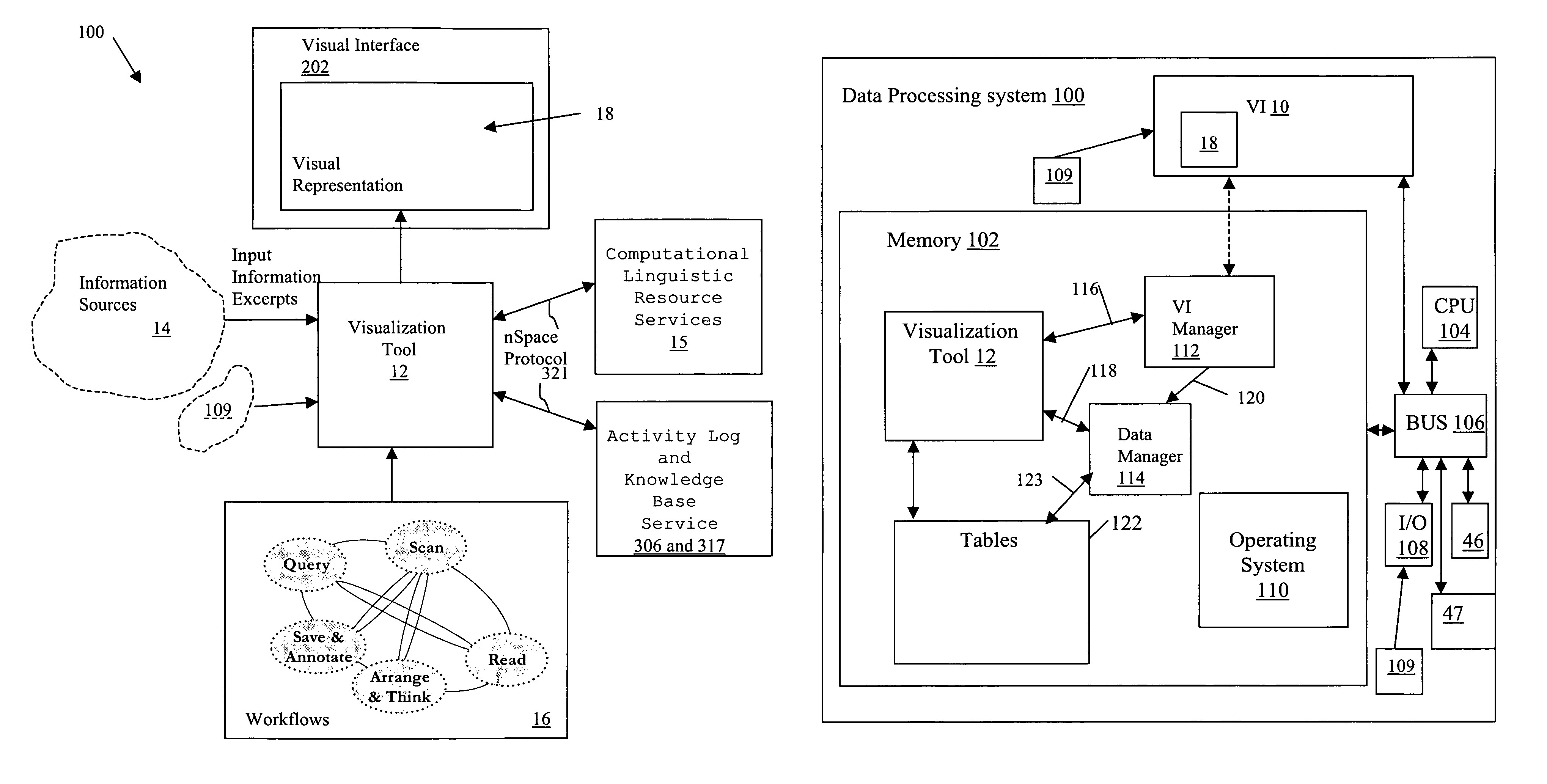
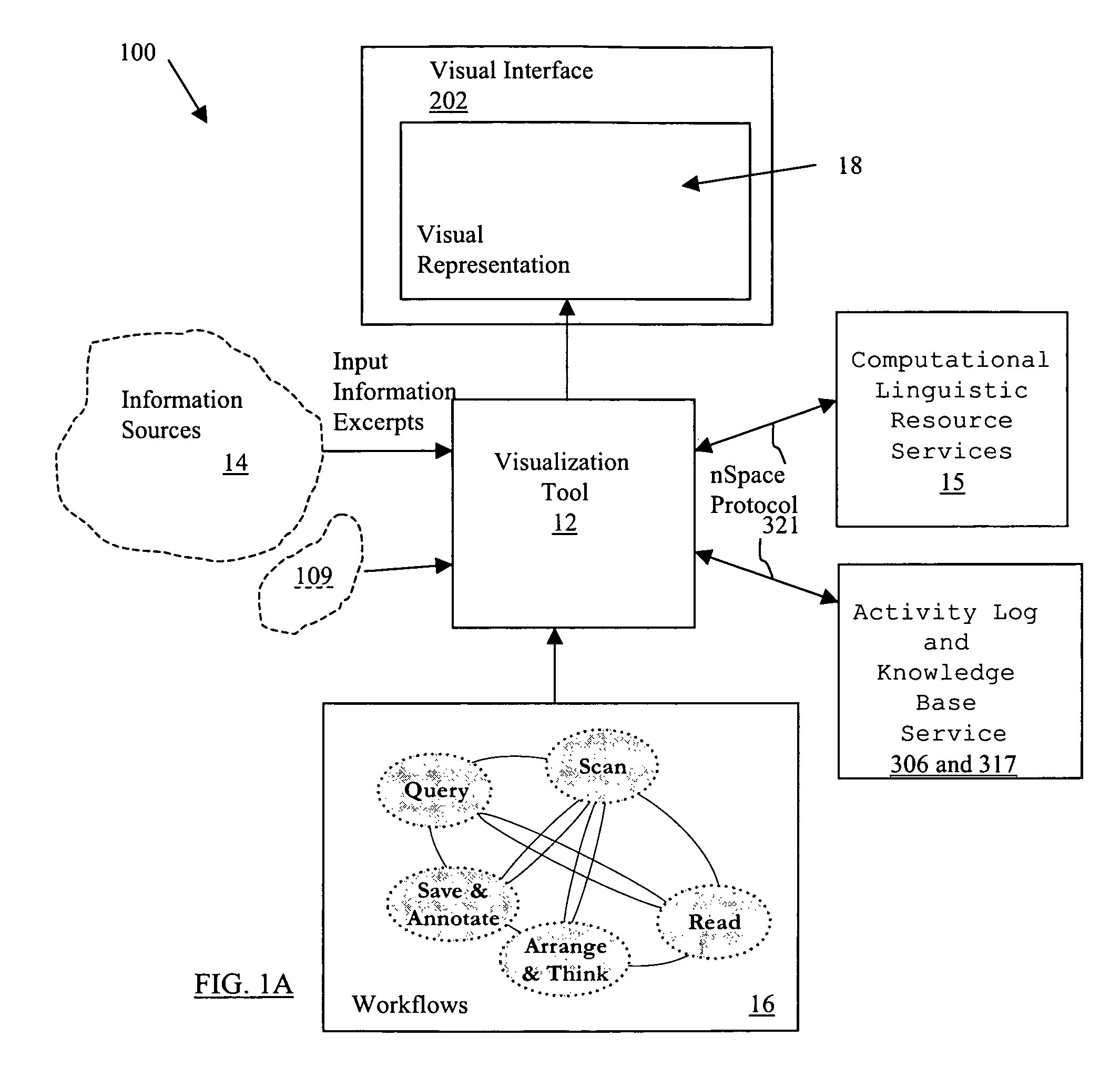
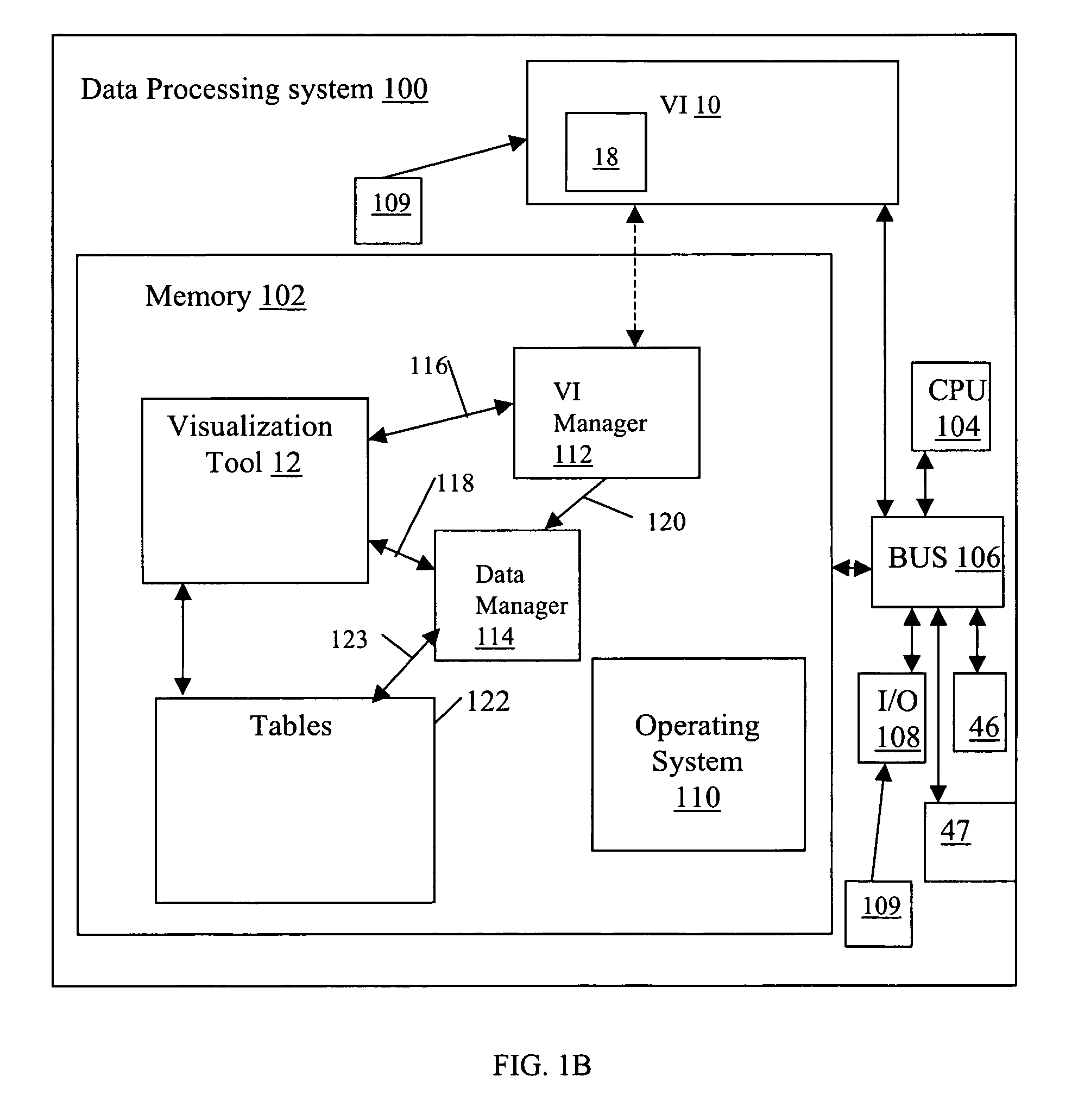
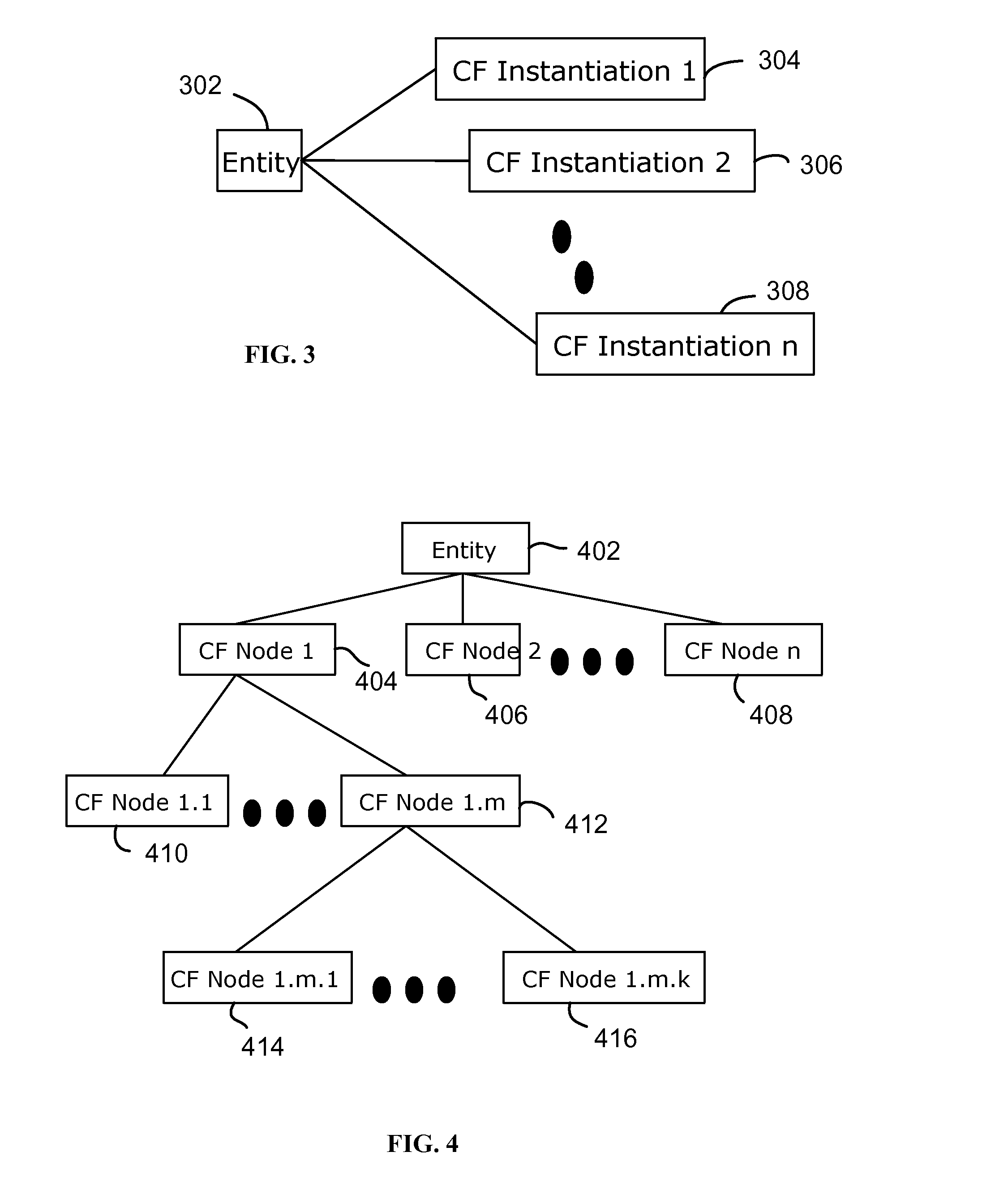
System and method for interactive multi-dimensional visual representation of information content and properties
ActiveUS20060116994A1Rapid visualizationImprove performanceDigital data processing detailsMultimedia data retrievalTriageInformation analysis
A system and method of information retrieval and triage for information analysis provides an for interactive multi-dimensional and linked visual representation of information content and properties. A query interface plans and obtains result sets. A dimension interface specifies dimensions with which to categorize the result sets. Links among results of a result set or results of different sets are automatically generated for linked selection viewing. Entities may be extracted and viewed and entity relations determined to establish further links and dimensions. Properties encoded in representations (e.g. icons) of the results in the multidimensional views maximizes display density. Multiple queries may be performed and compared. An integrated browser component responsive to the links is provided for viewing documents. Documents and other information from the result set may be used in an analysis component providing a space for visual linking, to arrange the information in the space while maintaining links automatically.
Owner:UNCHARTED SOFTWARE INC
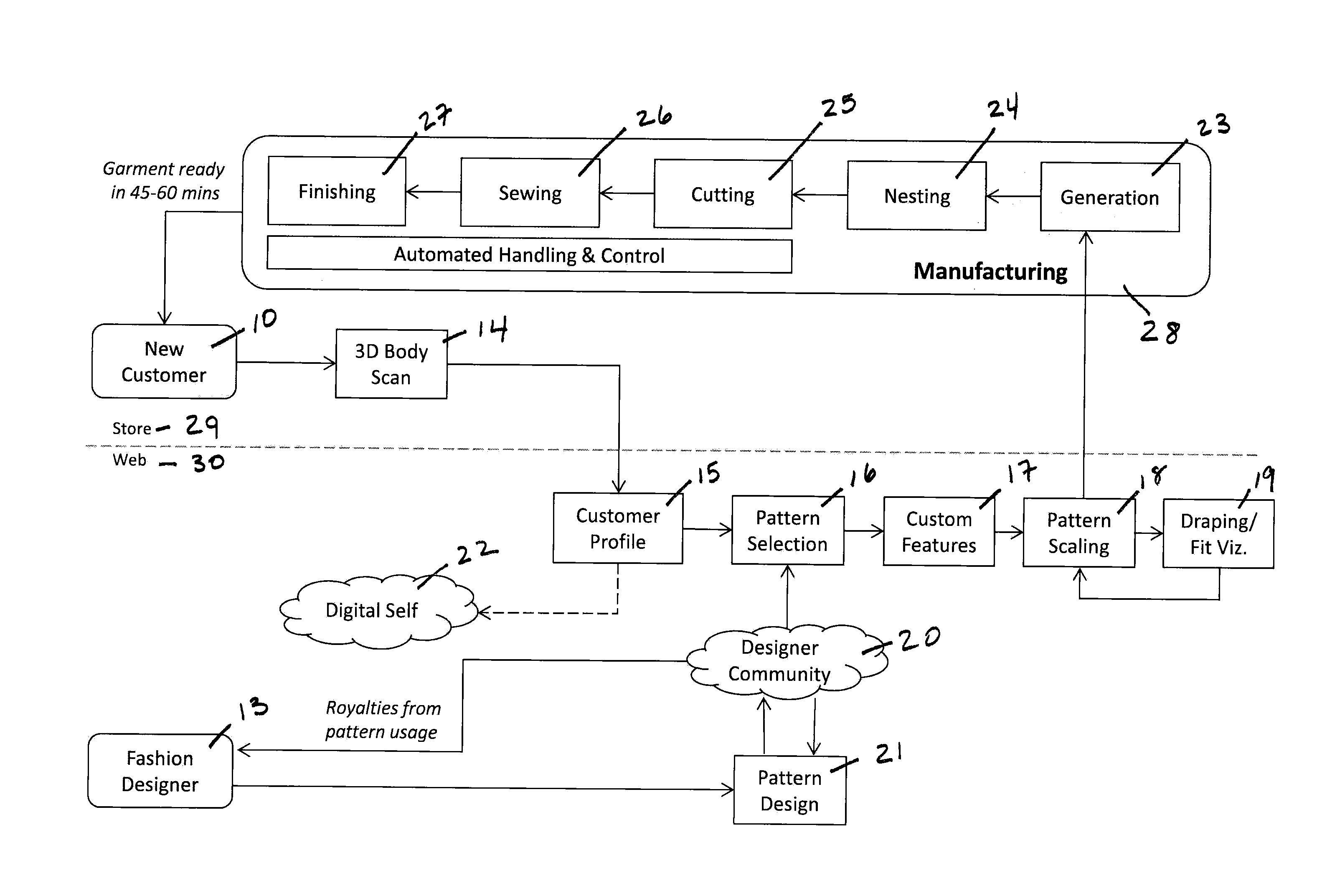
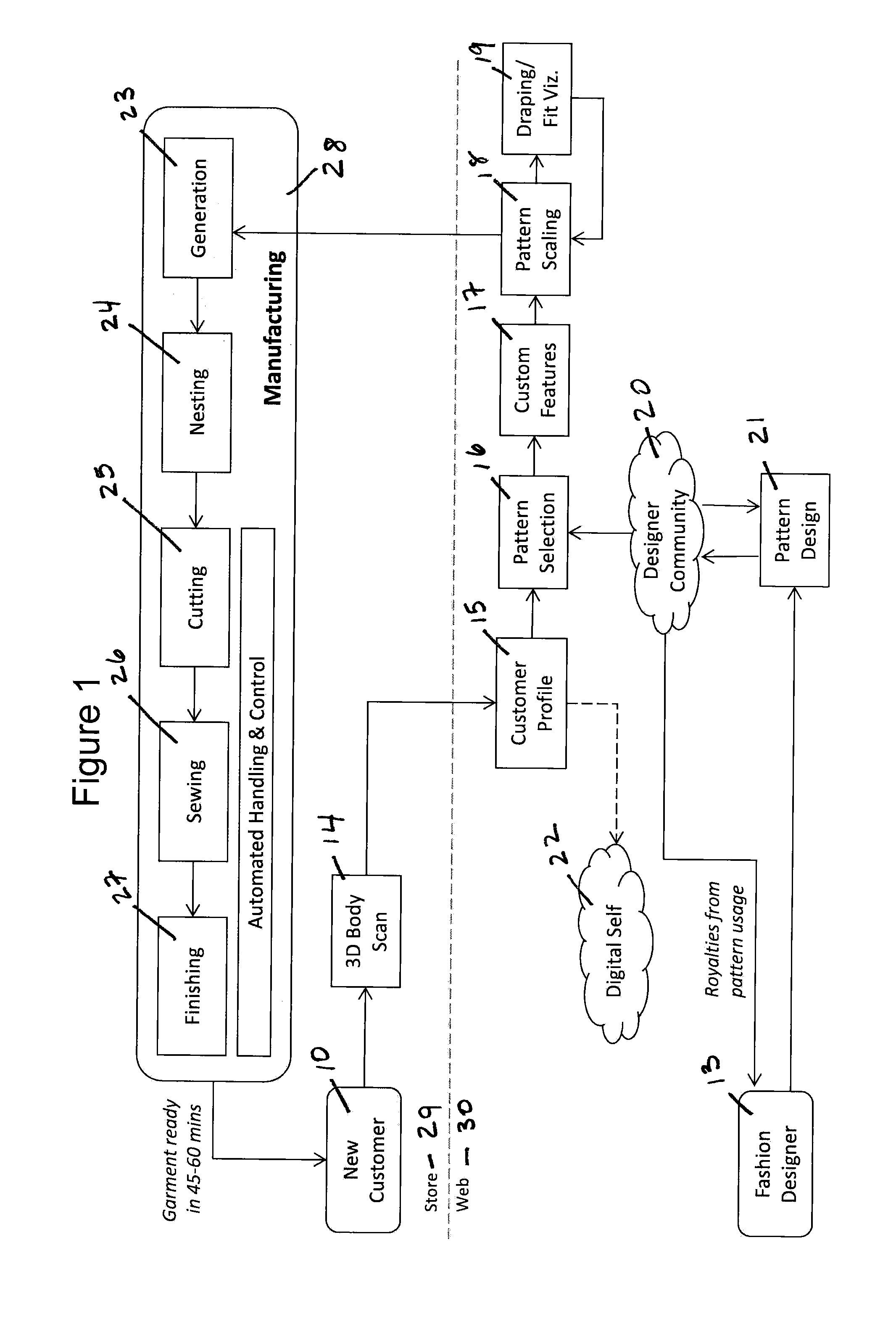
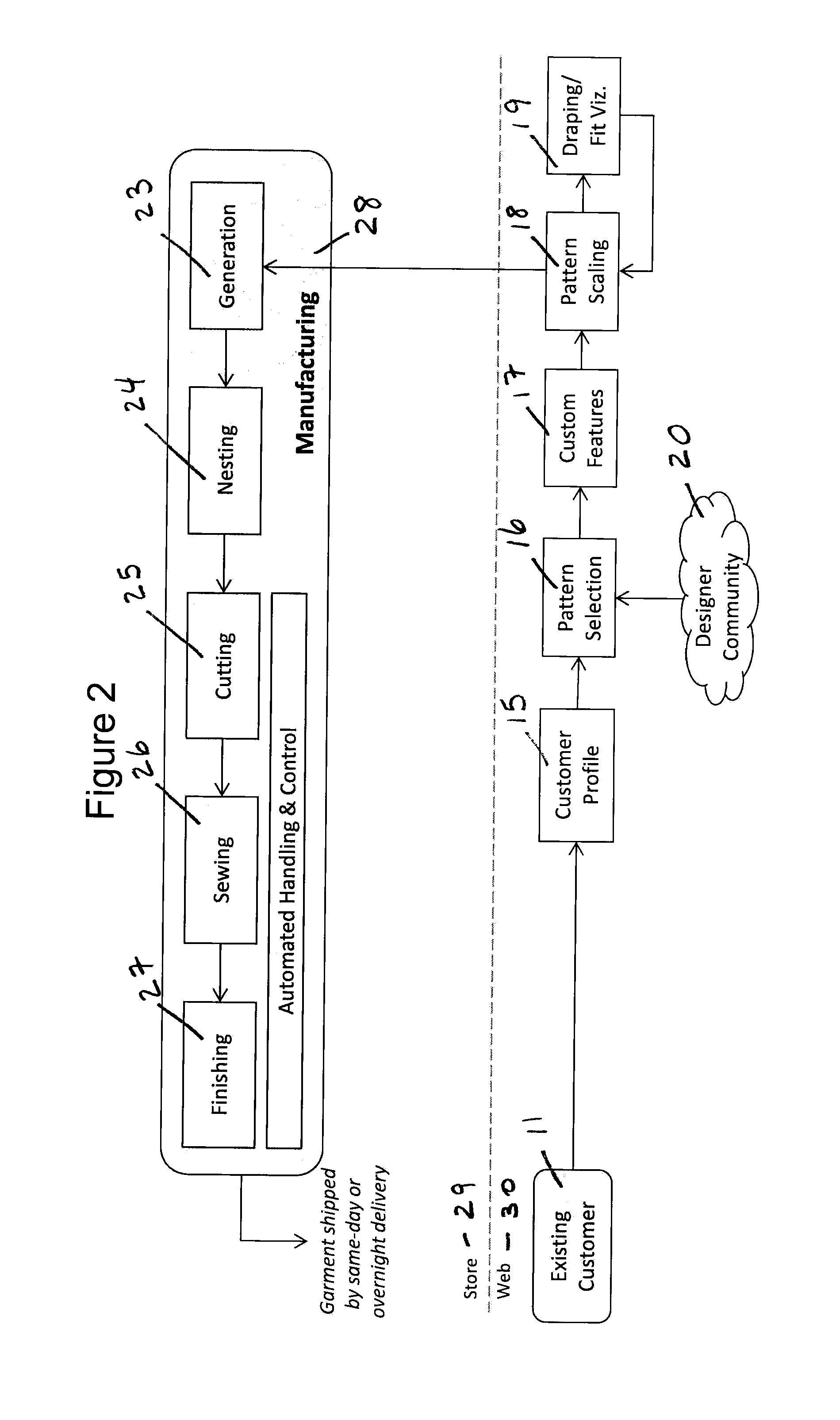
System and Method for Creating Custom-Fit Apparel Designs
InactiveUS20140277663A1Rapid visualizationShort amount of timeCommerceComputer aided designBody shapePersonalization
An automated system for the production of a personalized custom-fit garment comprises a scanner for obtaining a three-dimensional model of a customer's body shape; a computer having non-transitory computer algorithms for scaling a digital design to the customer's body shape, customizing the digital pattern with the customer's fit and style preferences, and visualizing the drape and fit of the garment; a database comprising a set of digital design patterns; and an automated garment manufacturing system networked to a central controller. A method for creating a personalized custom-fit garment comprises obtaining three-dimensional body measurements of a customer, having the customer select and customize a particular garment design, and manufacturing the personalized garment using an automated manufacturing process. The system and method can be used to prepare any kind of garments without substantive manual intervention or touch labor.
Owner:3D TECH LLC
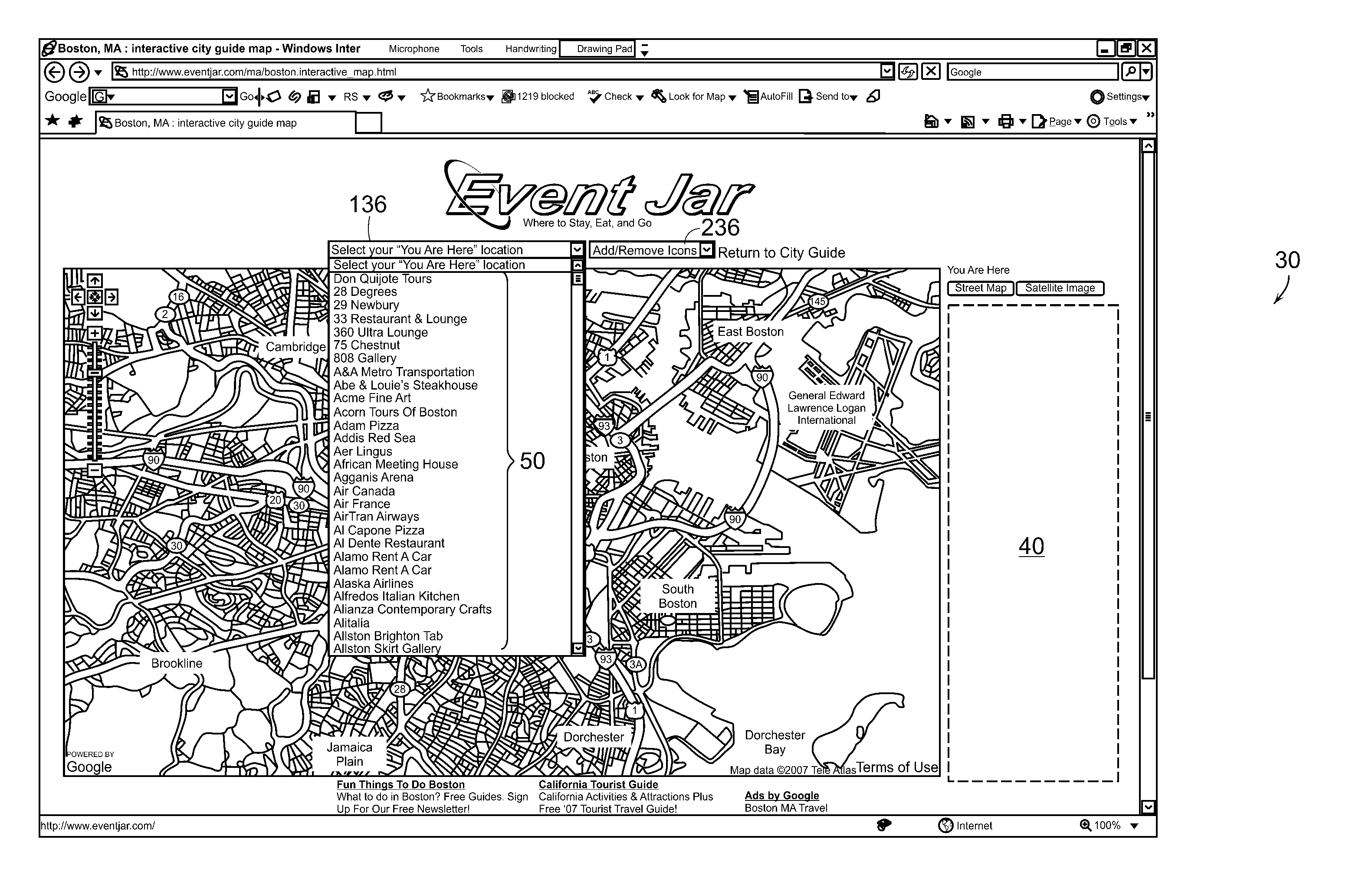
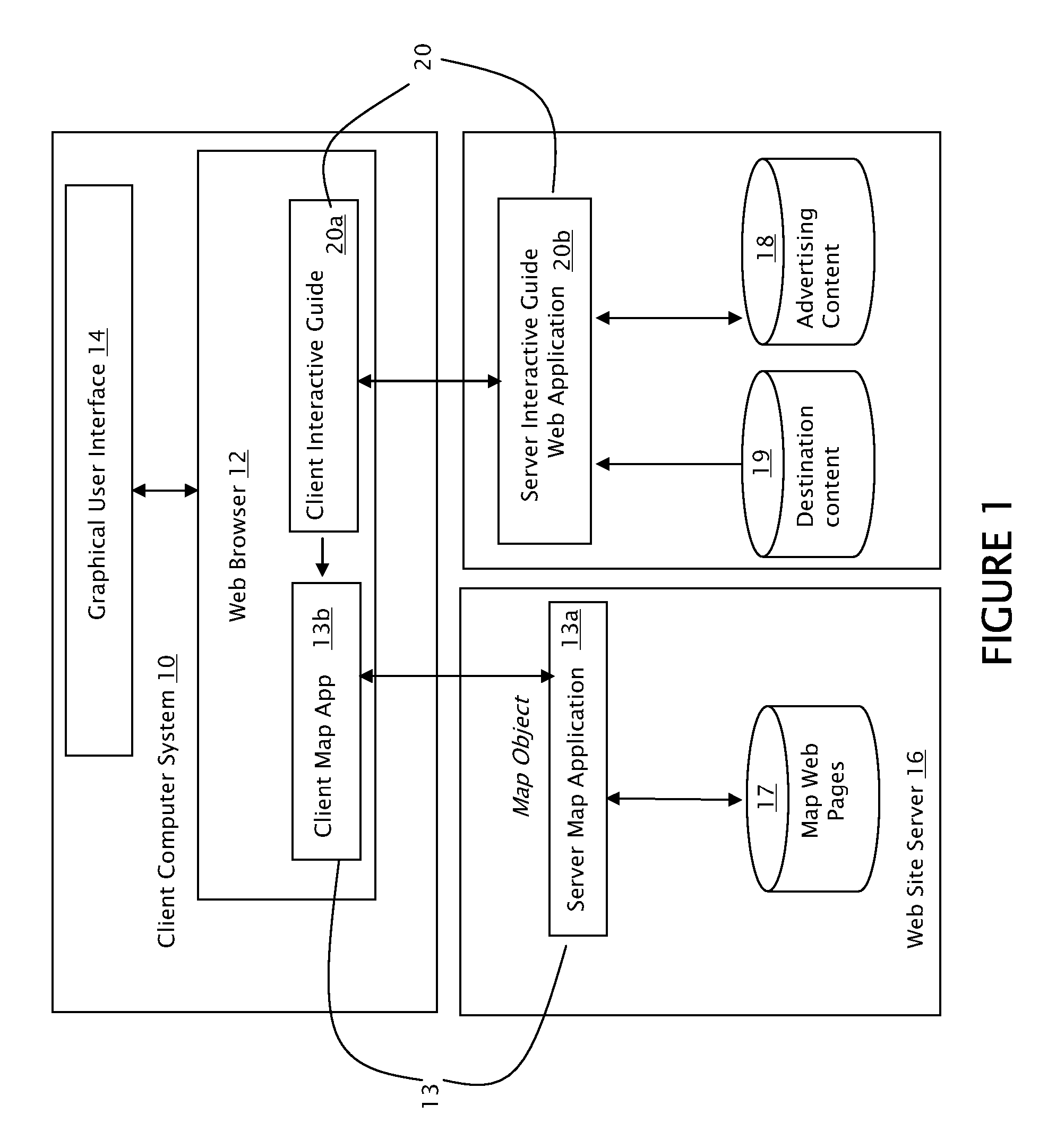
Interactive Area Guide Method, System and Apparatus
InactiveUS20080040678A1Quick distinctionAvoid difficult choicesInput/output processes for data processingVisual perceptionComputer science
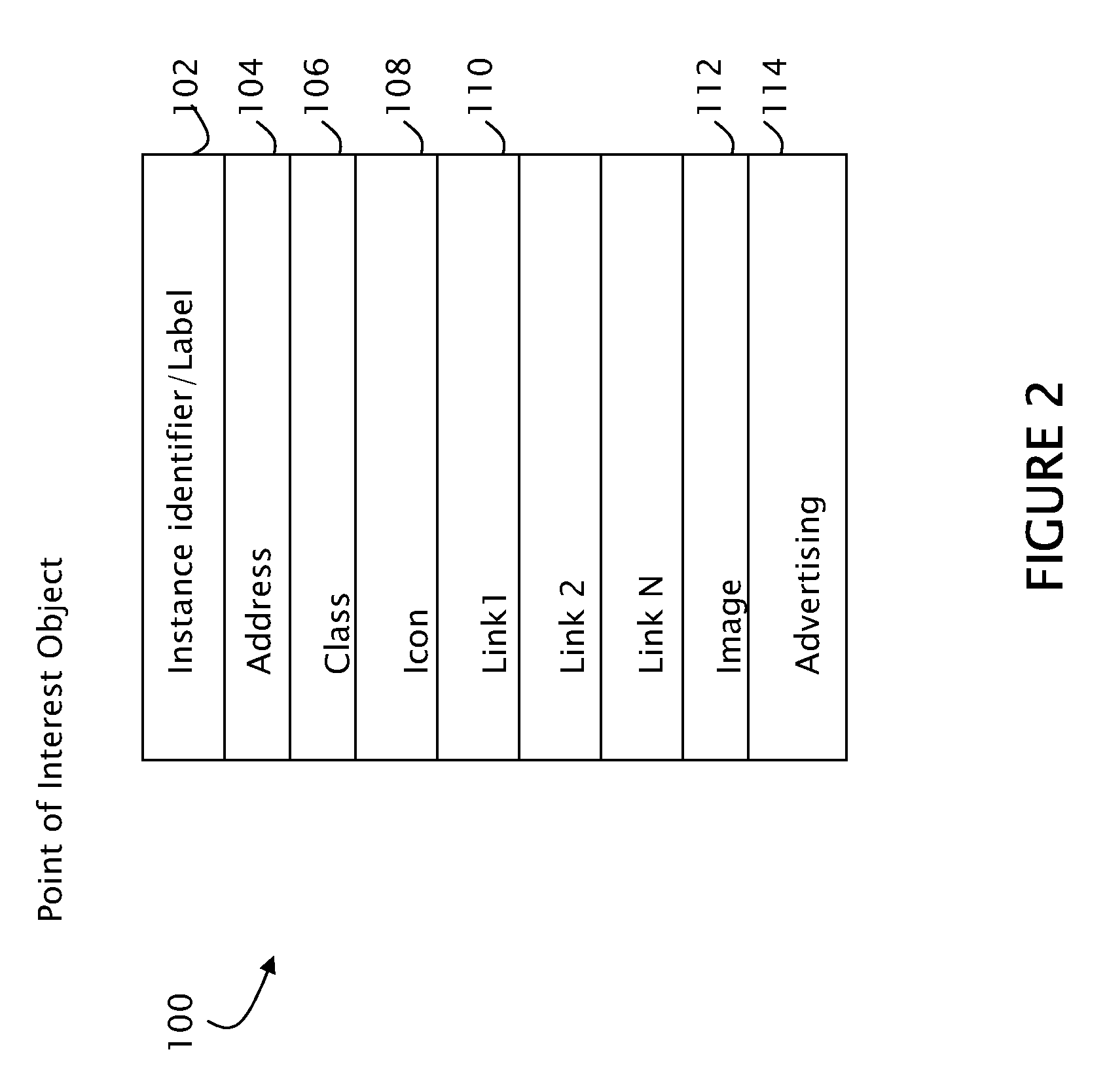
An interactive map web-based tool is provided which gives the user the ability to customize their use of a map. The present invention includes a customized overlay of point of interest information on an existing map. The information overlay includes icons, drop down lists, information panels, advertising content, pop-up windows and hypertext links which are associated with points of interest, where each point of interest is associated with a class. Drop down lists permit the user to display one or more points of interest by location or class. Visual cues, including color coding, icon shaping and text differentiation for different classes of points of interest allow a user of the map to quickly differentiate area resources. With such an arrangement a traveler can easily select for display only those particular resources that are of interest to the traveler and thereby create a local search experience focused on their specific travel needs.
Owner:CRUMP RICHARD
Intuitive hierarchical time-series data display method and system
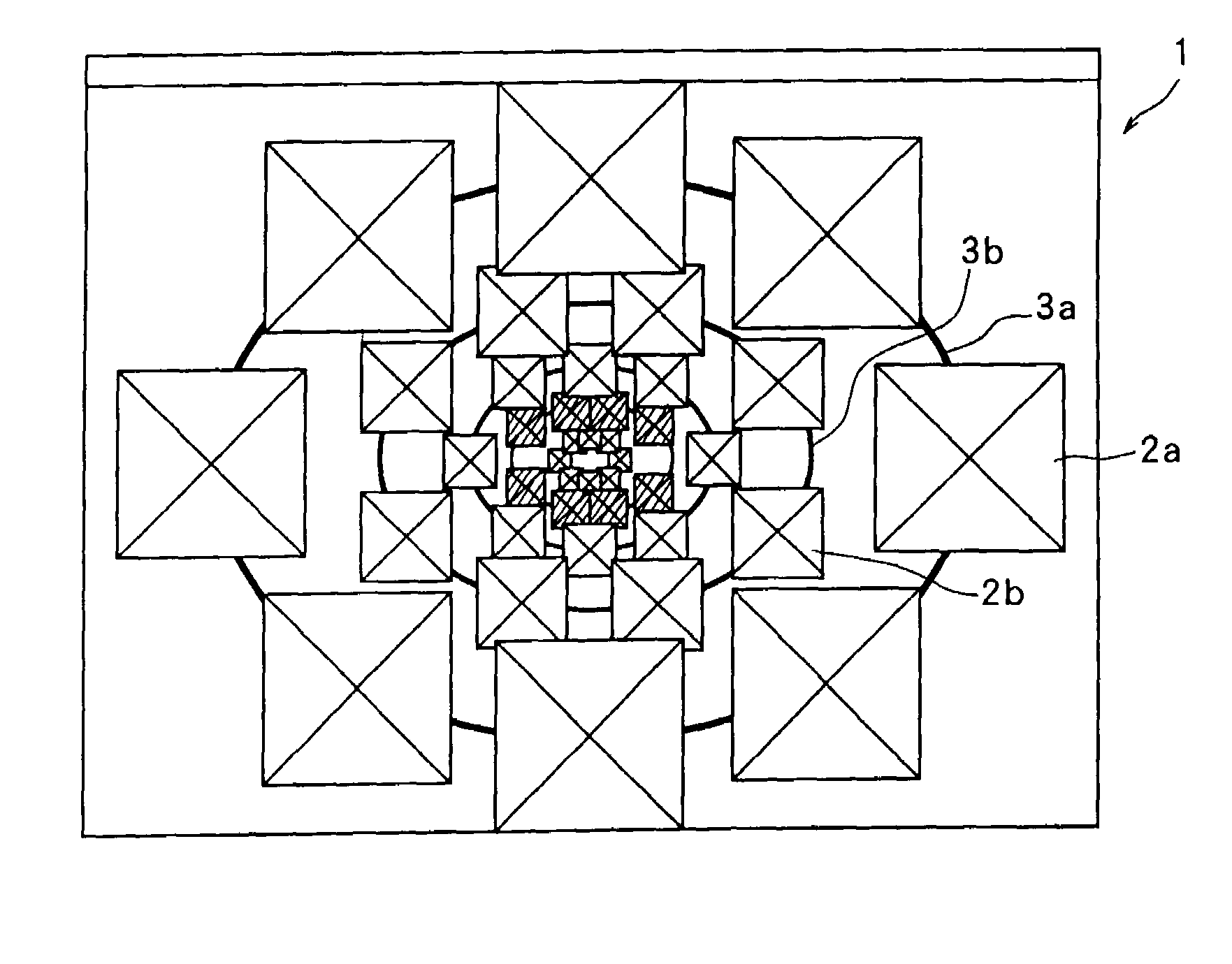
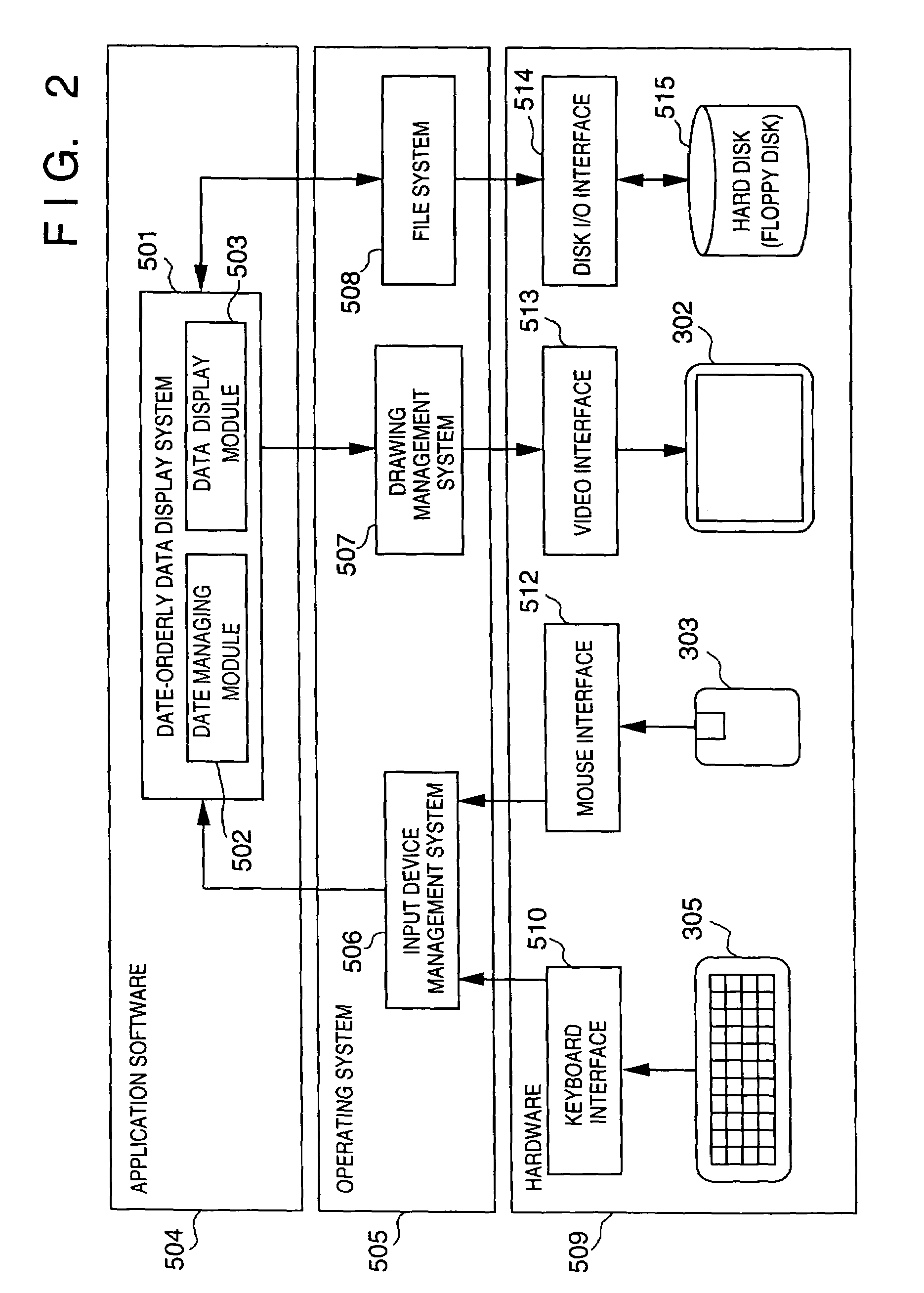
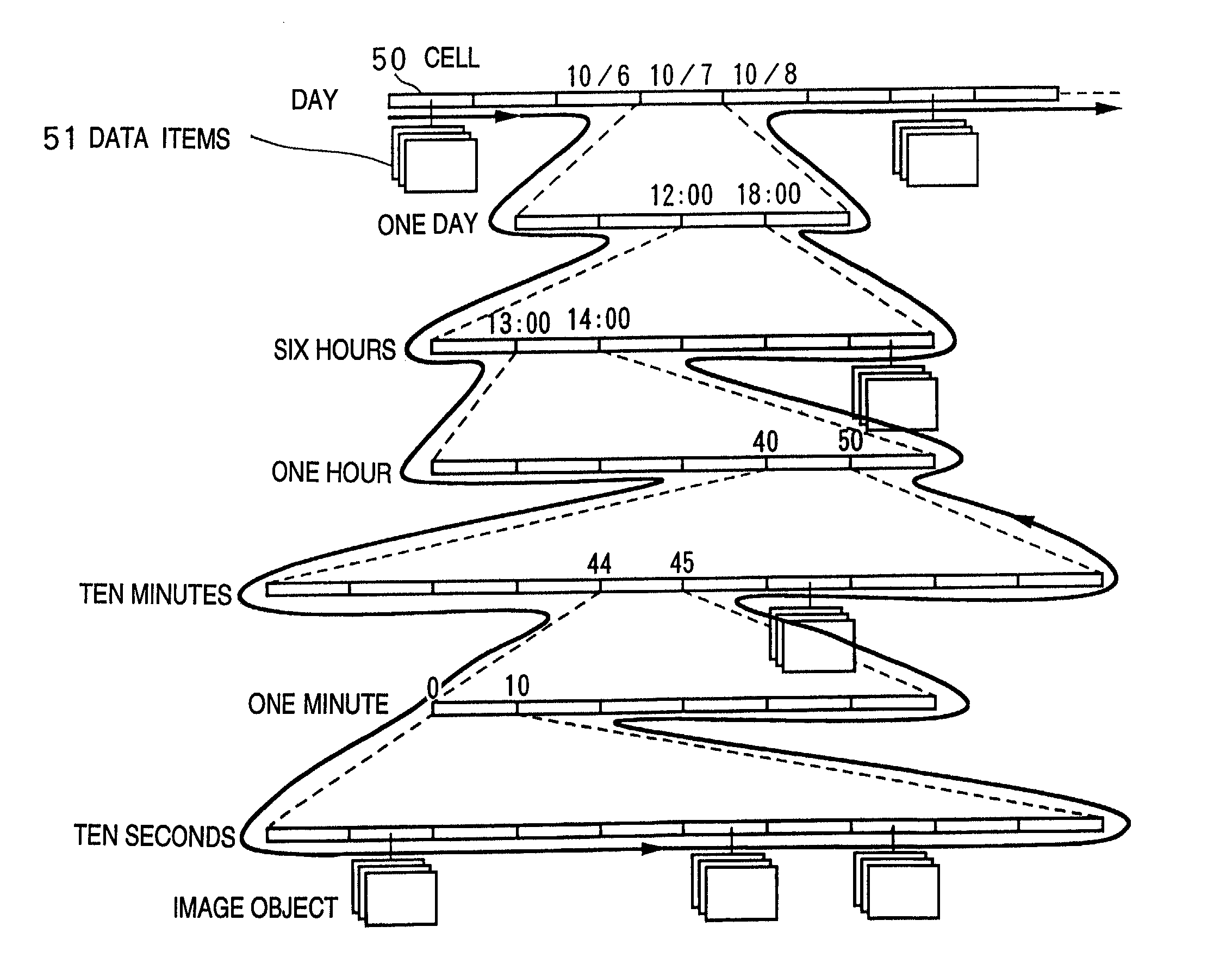
InactiveUS7336279B1Precise positioningRapid visualizationStill image data browsing/visualisationAnimationData displayImage extraction
The present invention provides a time-series data display method and system for displaying time-series data items so that a user can grasp time more intuitively. First data associated with a desired date is retrieved and displayed, second data associated with a contiguous date is retrieved, and a display screen for the second data is displayed smaller than that for the first data in a temporal direction starting with the desired date. Third data is associated with a date contiguous to the second date retrieved, and is displayed inside the second data with a smaller display area. Also, in a hierarchical data display method and browser system, a display area is divided into an area where icons representing data items belonging to one level are displayed, and an area where child levels are displayed. As hierarchical depth increases, the data icons are made smaller and simpler. The hierarchical structure of a file system or data base can be displayed as a Venn diagram. Data items belonging to child levels are not hidden but displayed as reduced images, whereby intended data can be located effortlessly. A cutout form and image are registered mutually independently. An identifier, position, and size of the cutout form are specified as the attributes of the image. Thus, an image can be fetched into album software by performing a simple operation, or a cutout can be changed in size.
Owner:CANON KK
Methods and systems for identification of DNA patterns through spectral analysis
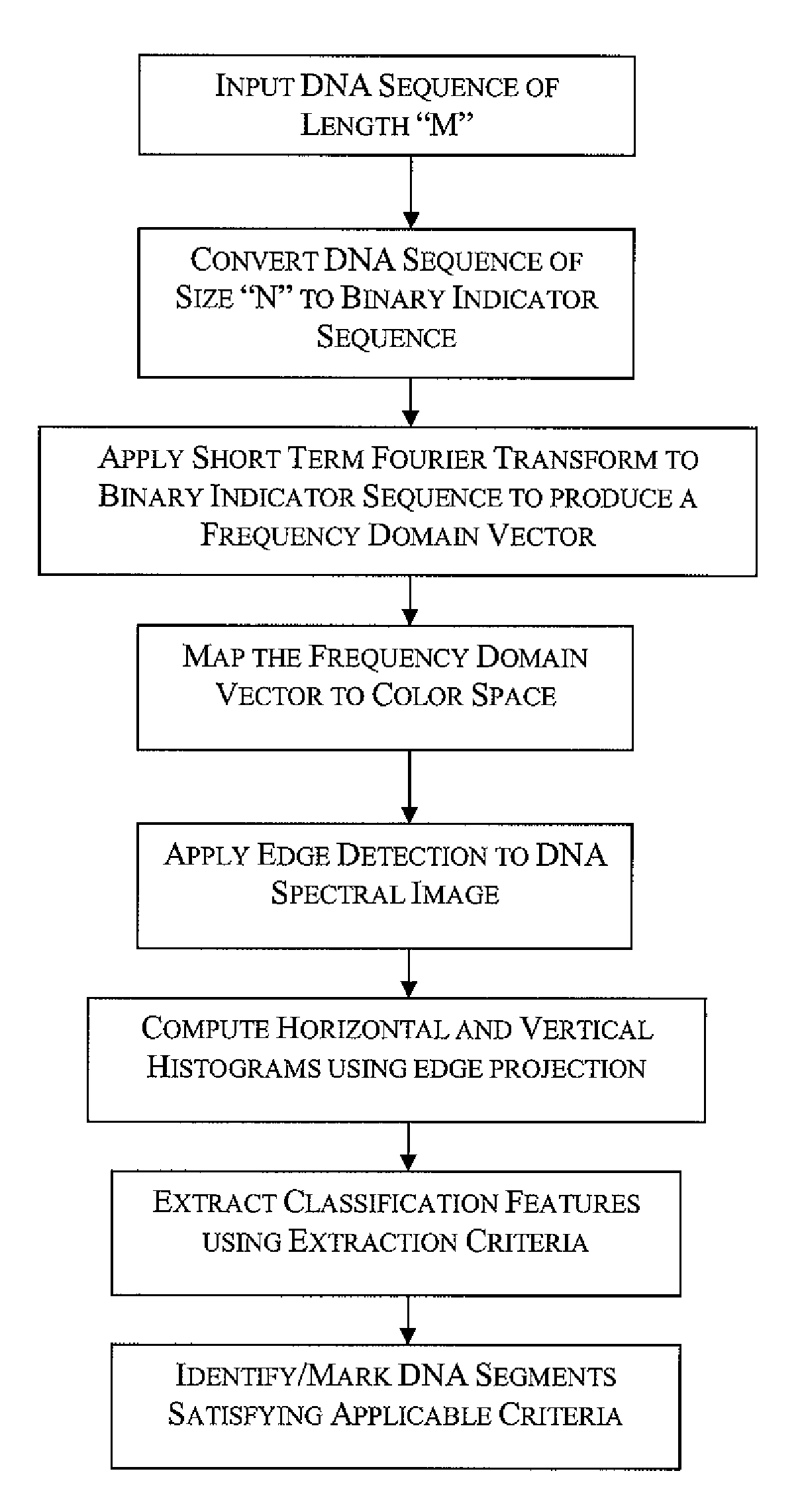
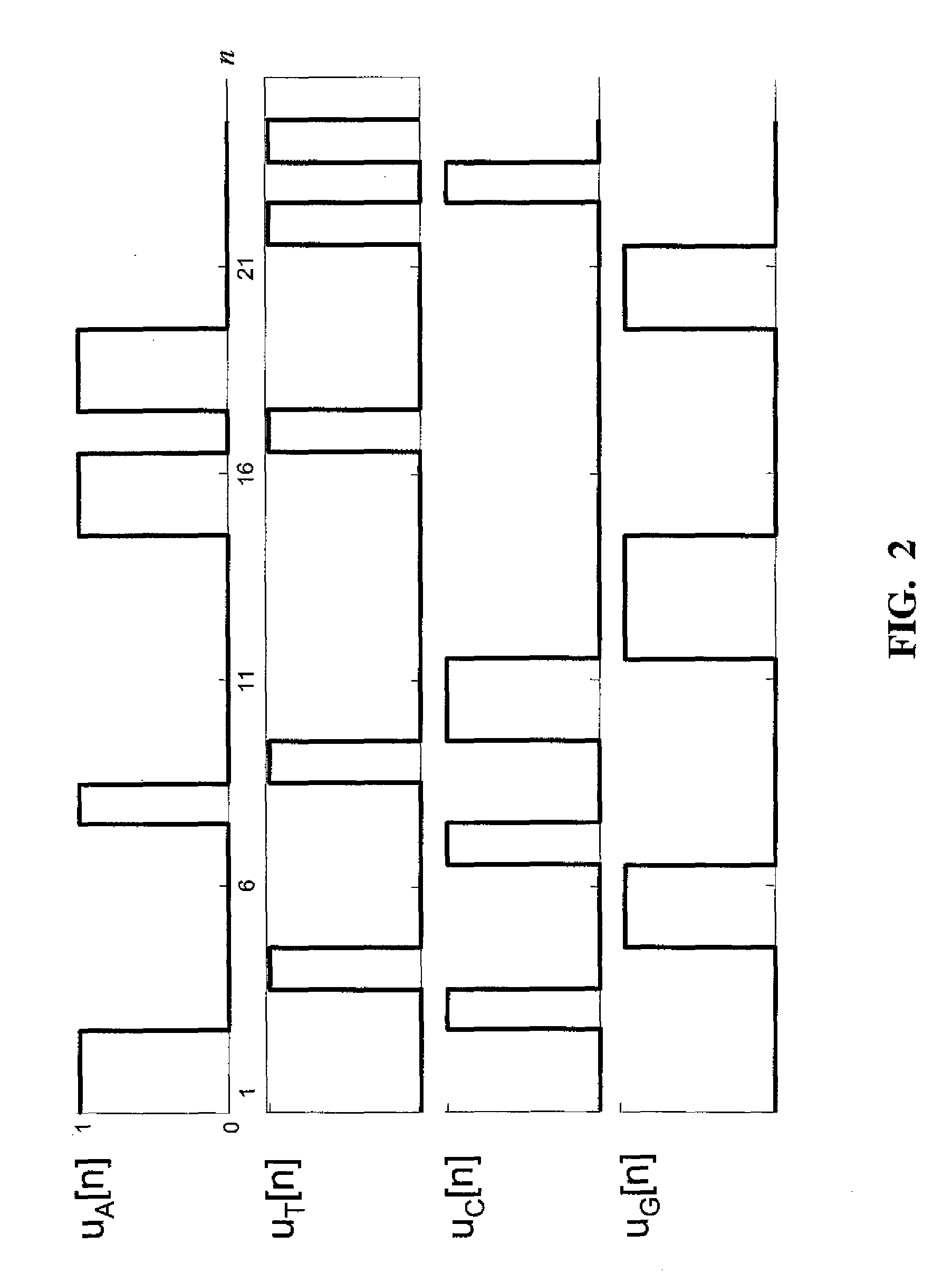
InactiveUS20090129647A1Improve visualizationHigh resolutionData visualisationBiostatisticsDNA PatternsCo-occurrence
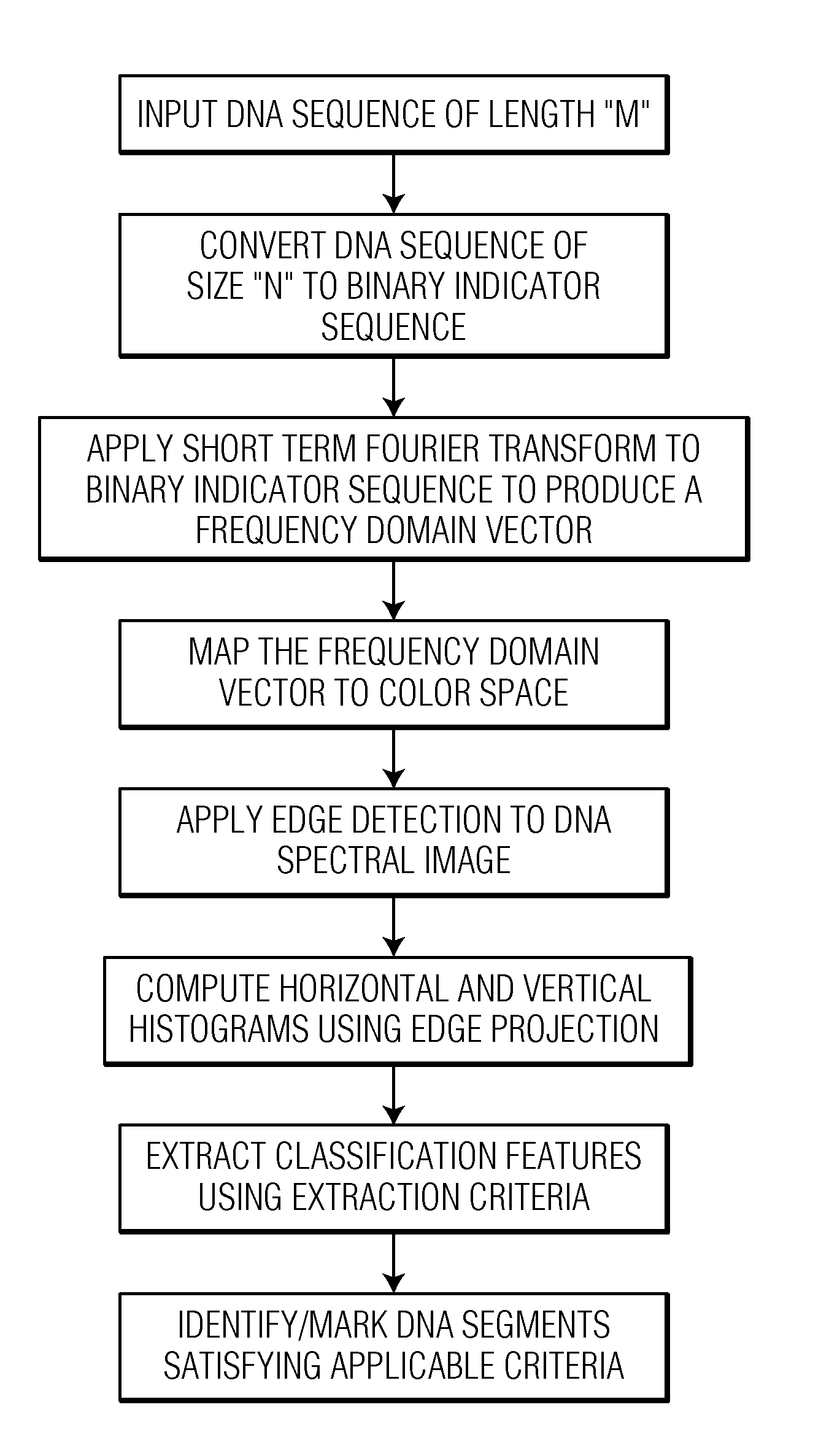
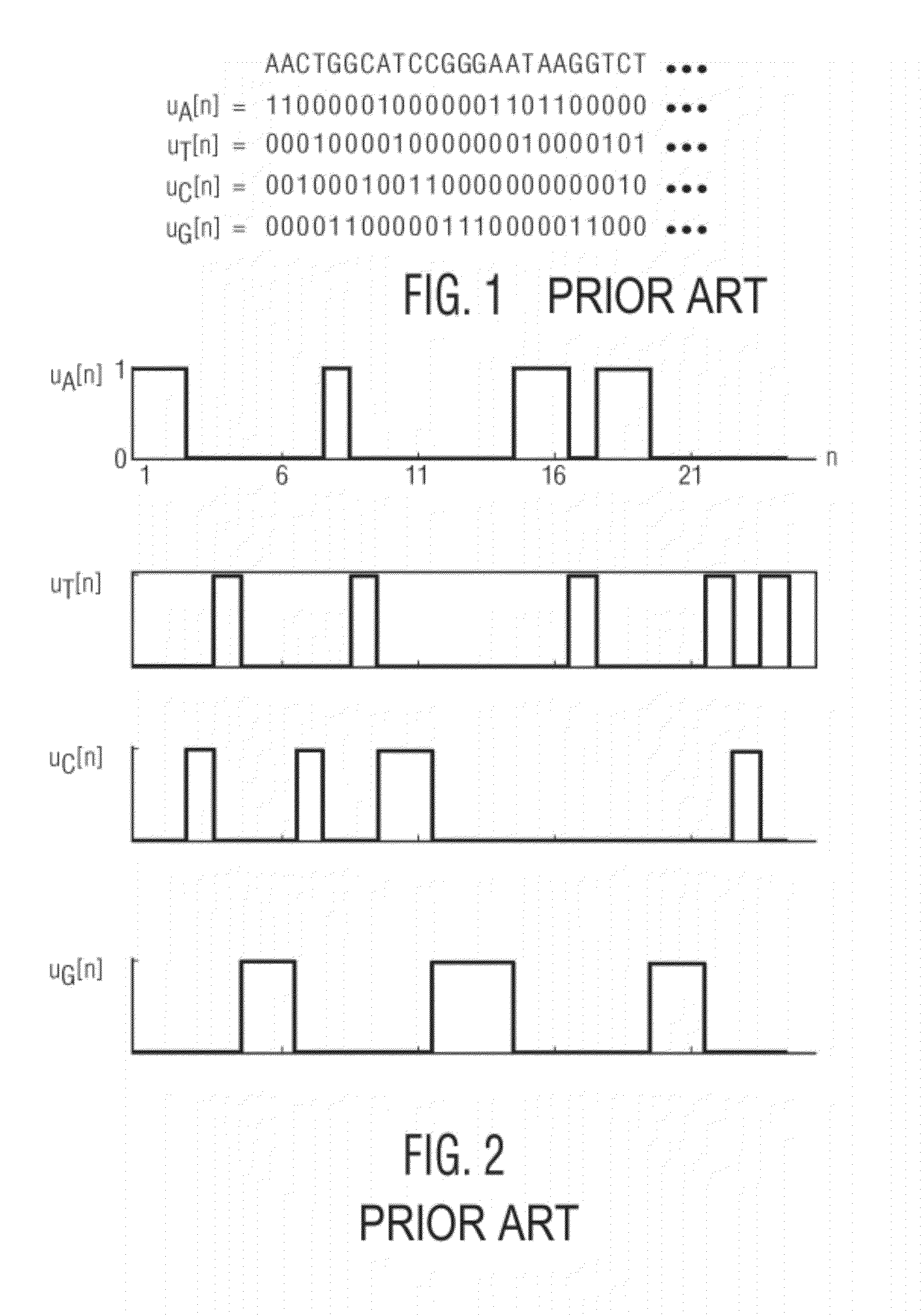
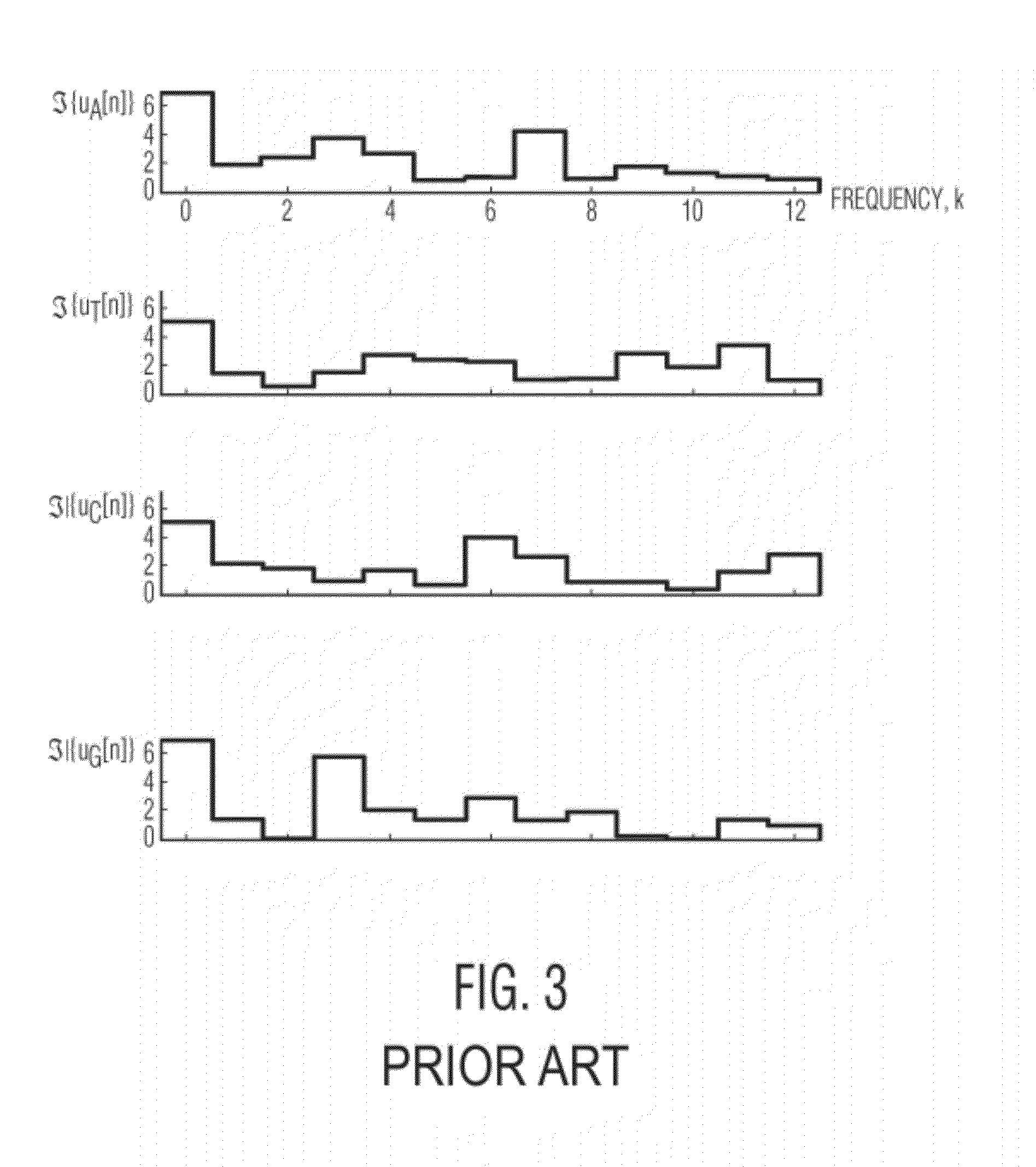
Spectrogram extraction from DNA sequence has been known since 2001. A DNA spectrogram is generated by applying Fourier transform to convert a symbolic DNA sequence consisting of letters A, T, C, G into a visual representation that highlights periodicities of co-occurrence of DNA patterns. Given a DNA sequence or whole genomes, with this method it is easy to generate a large number of spectrogram images. However, the difficult part is to elucidate where are the repetitive patterns and to associate a biological and clinical meaning to them. The present disclosure provides systems and methods that facilitate the location and / or identification of repetitive DNA patterns, such as CpG islands, Alu repeats, tandem repeats and various types of satellite repeats. These repetitive elements can be found within a chromosome, within a genome or across genomes of various species. The disclosed systems and methods apply image processing operators to find prominent features in the vertical and horizontal direction of the DNA spectrograms. Systems and methods for fast, full scale analysis of the derived images using supervised machine learning methods are also disclosed. The disclosed systems and methods for detecting and / or classifying repetitive DNA patterns include: (a) comparative histogram method, (b) feature selection and classification using support vector machines and genetic algorithms, and (c) generation of spectrovideo from a plurality of spectral images.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
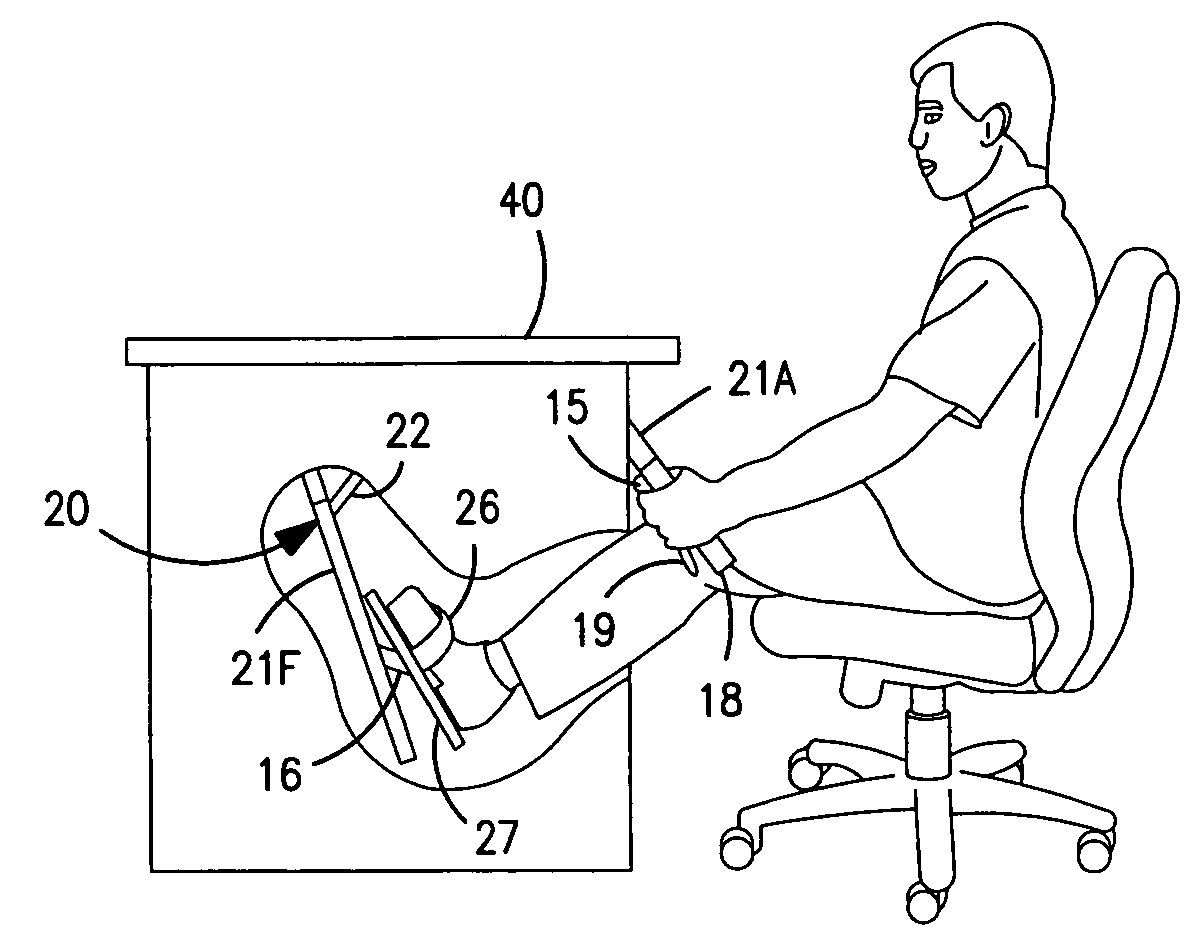
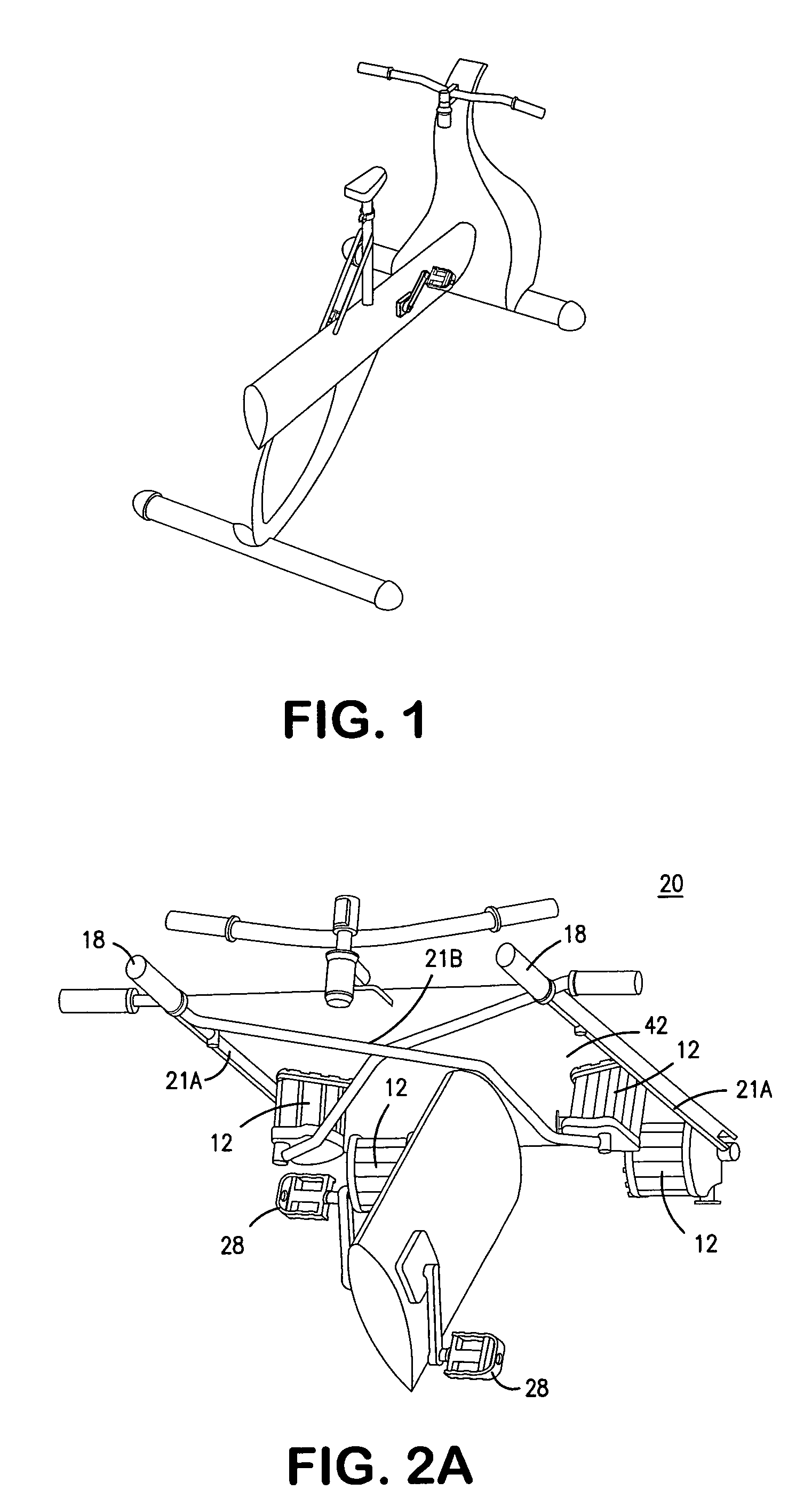
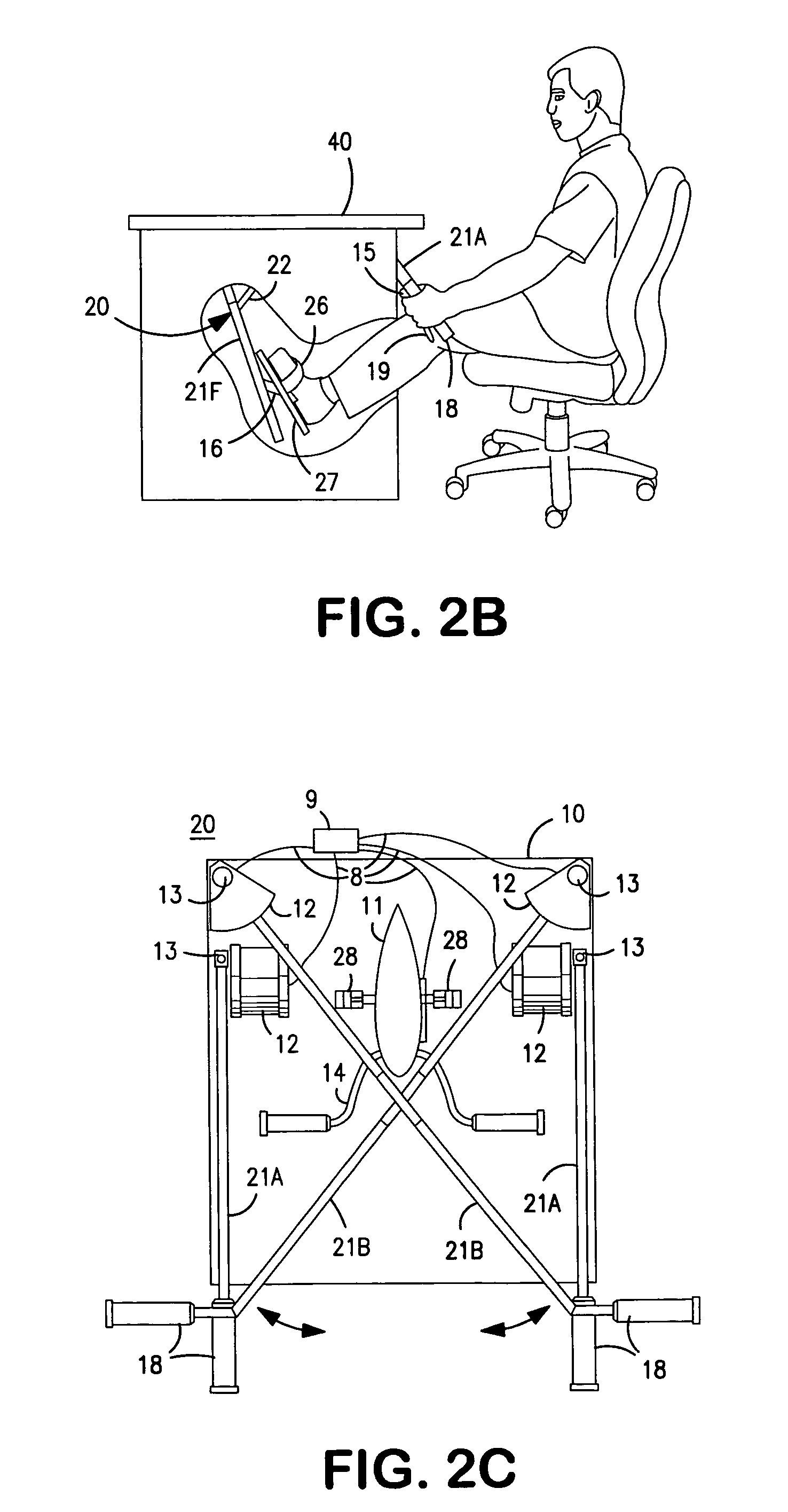
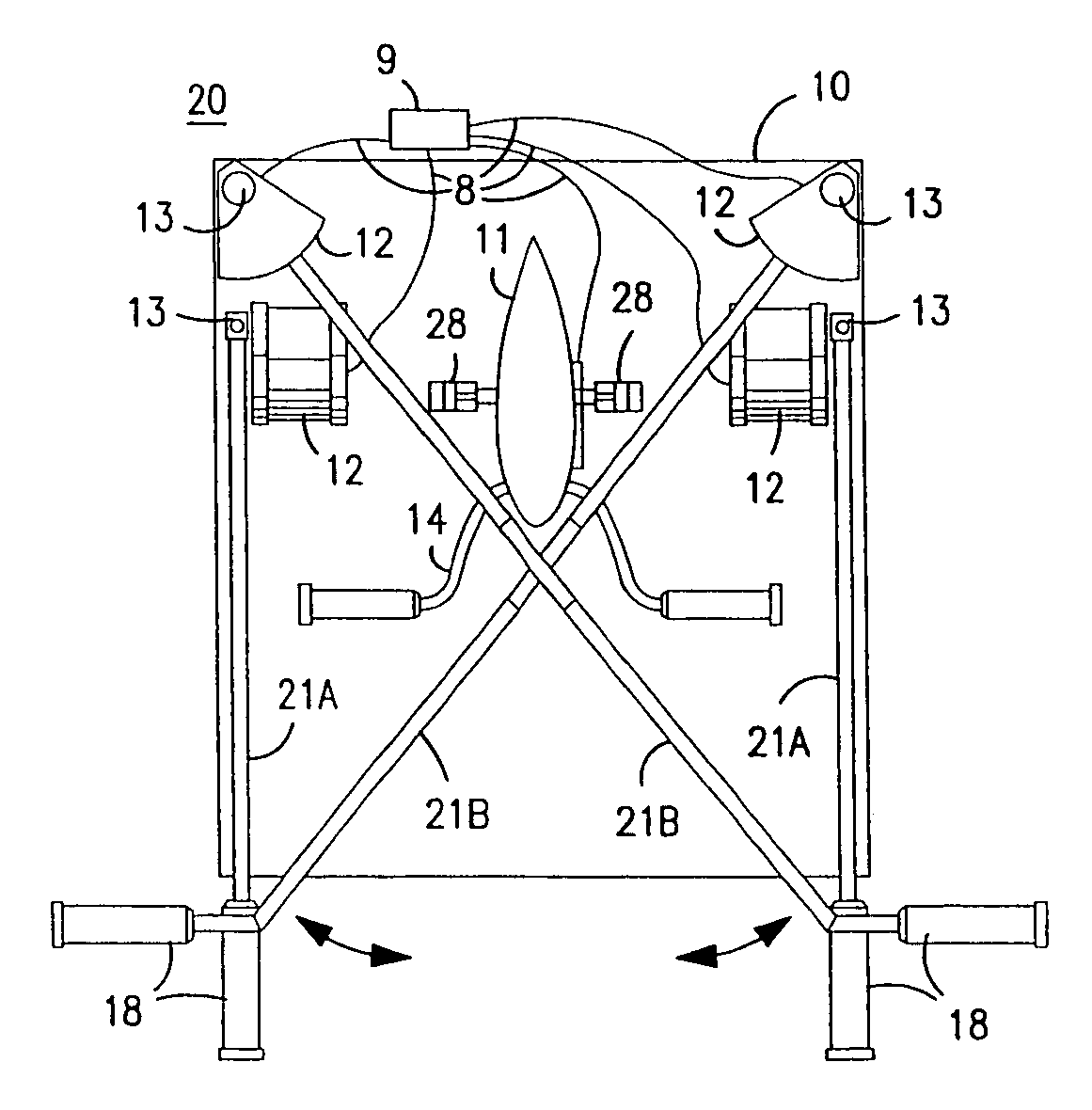
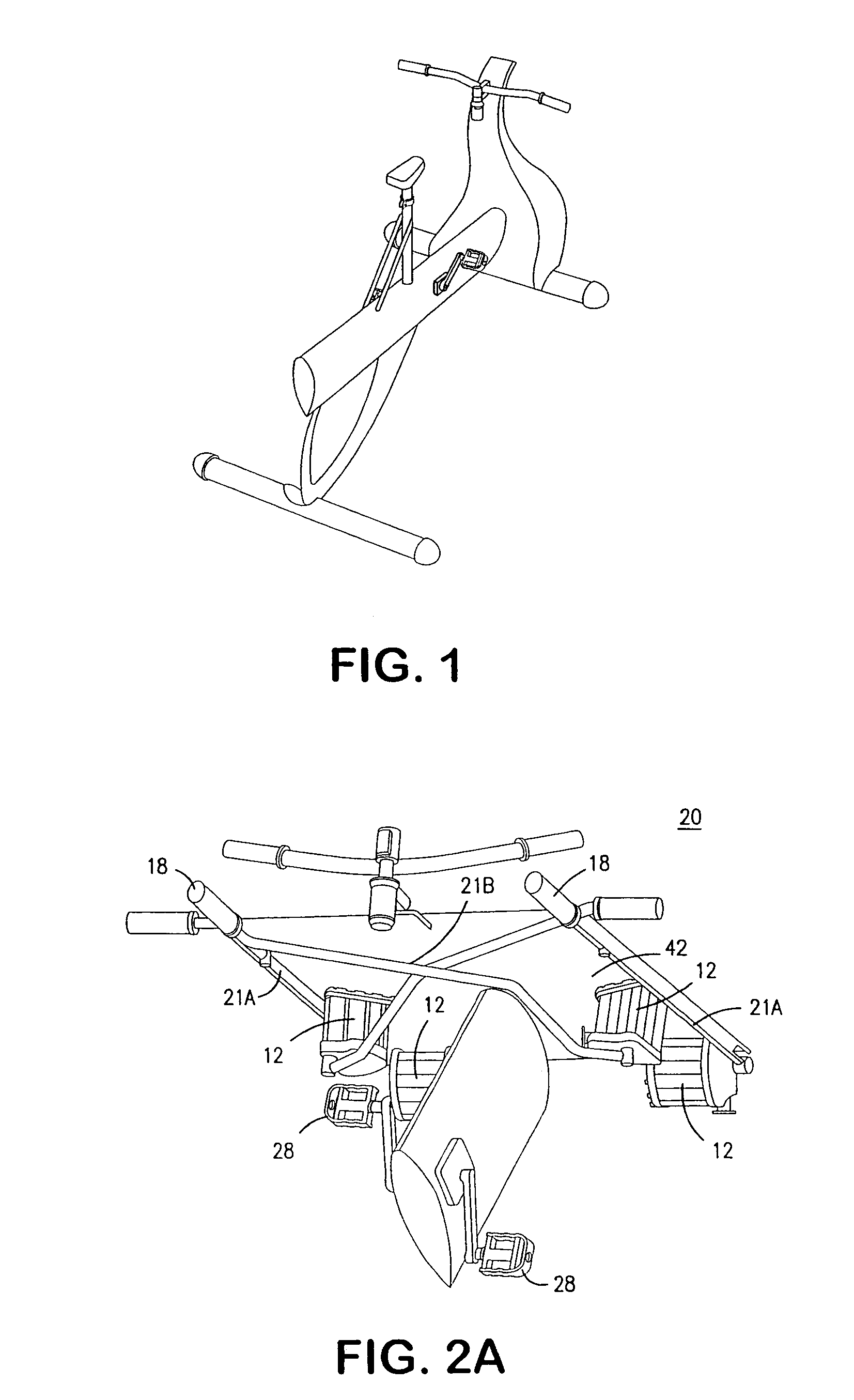
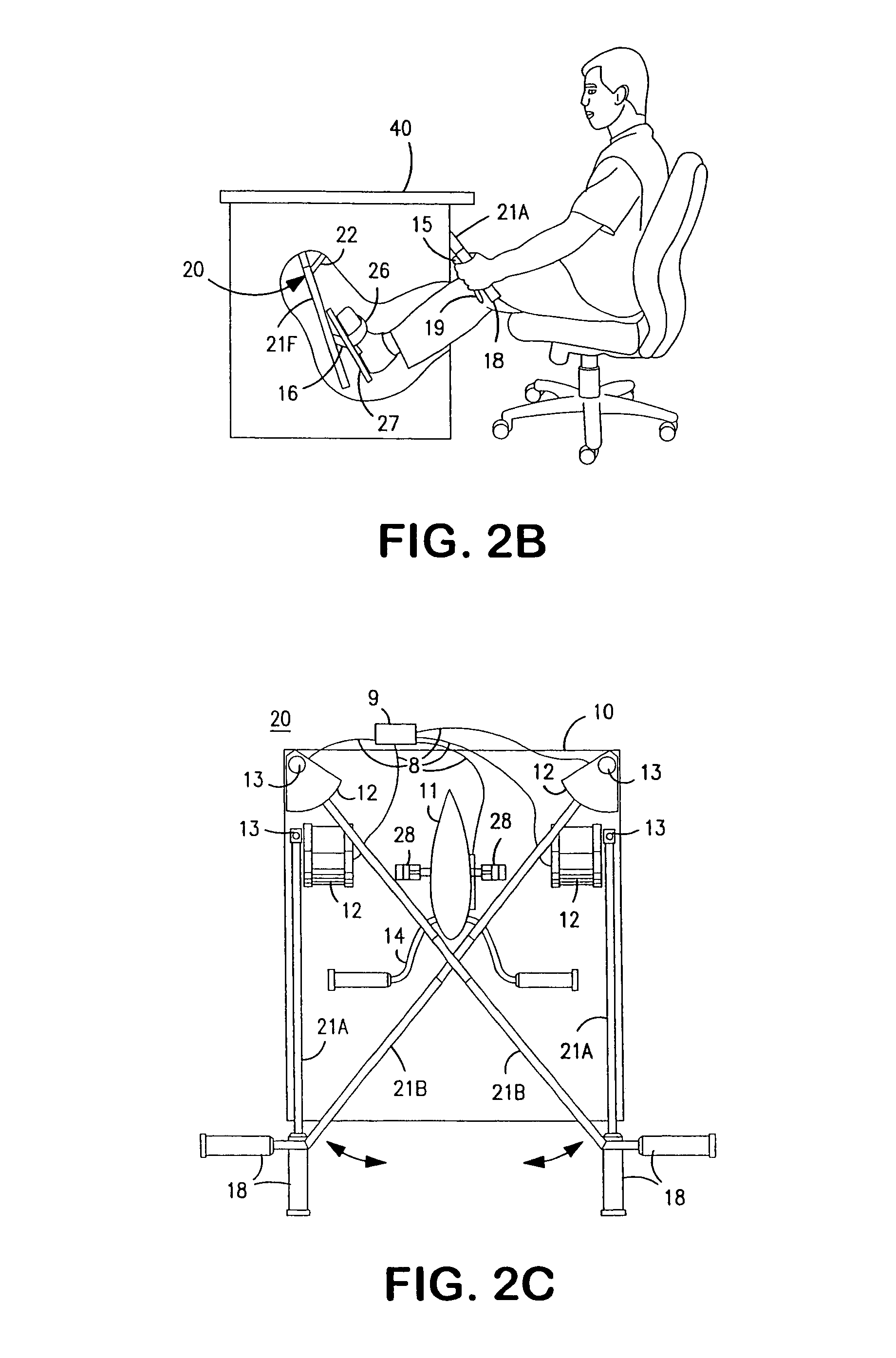
Interactive computer simulation enhanced exercise machine
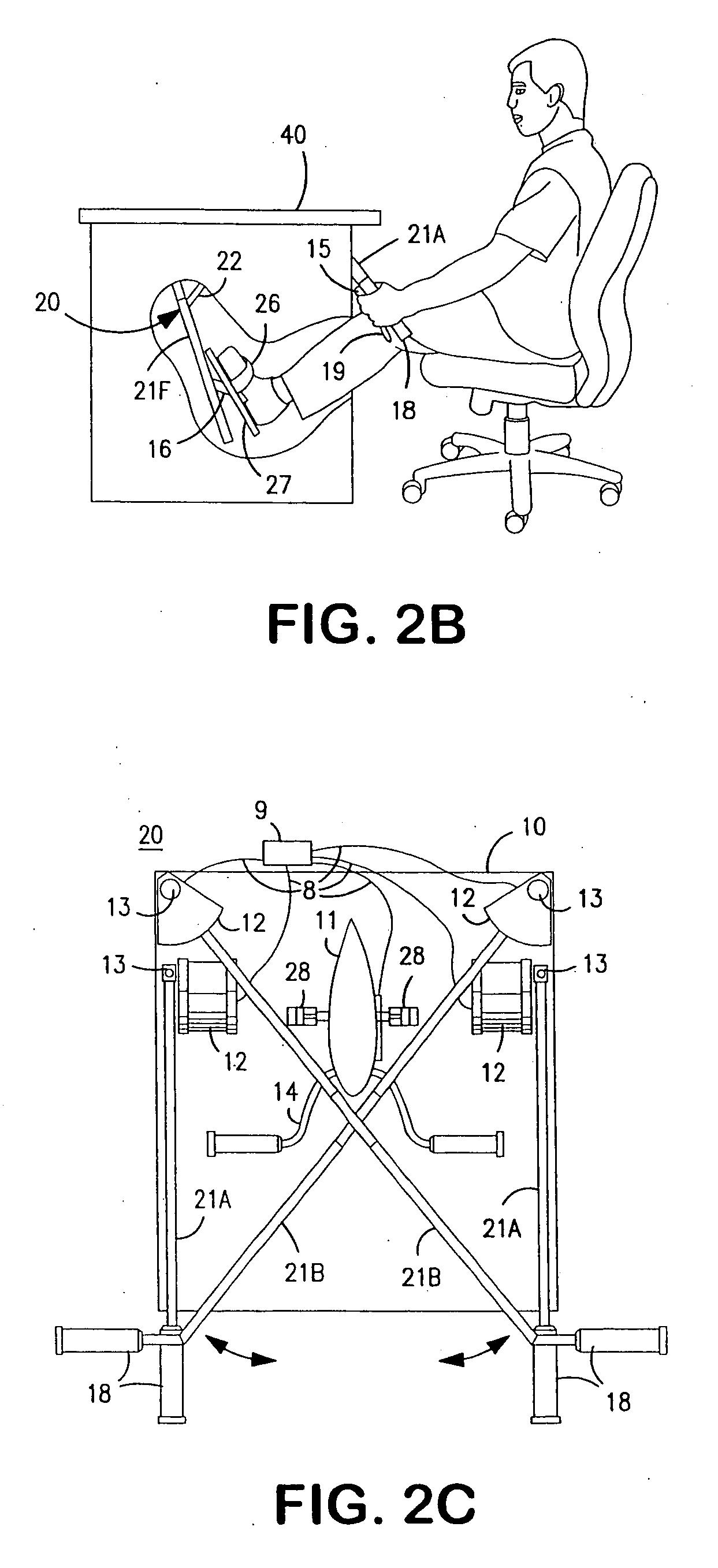
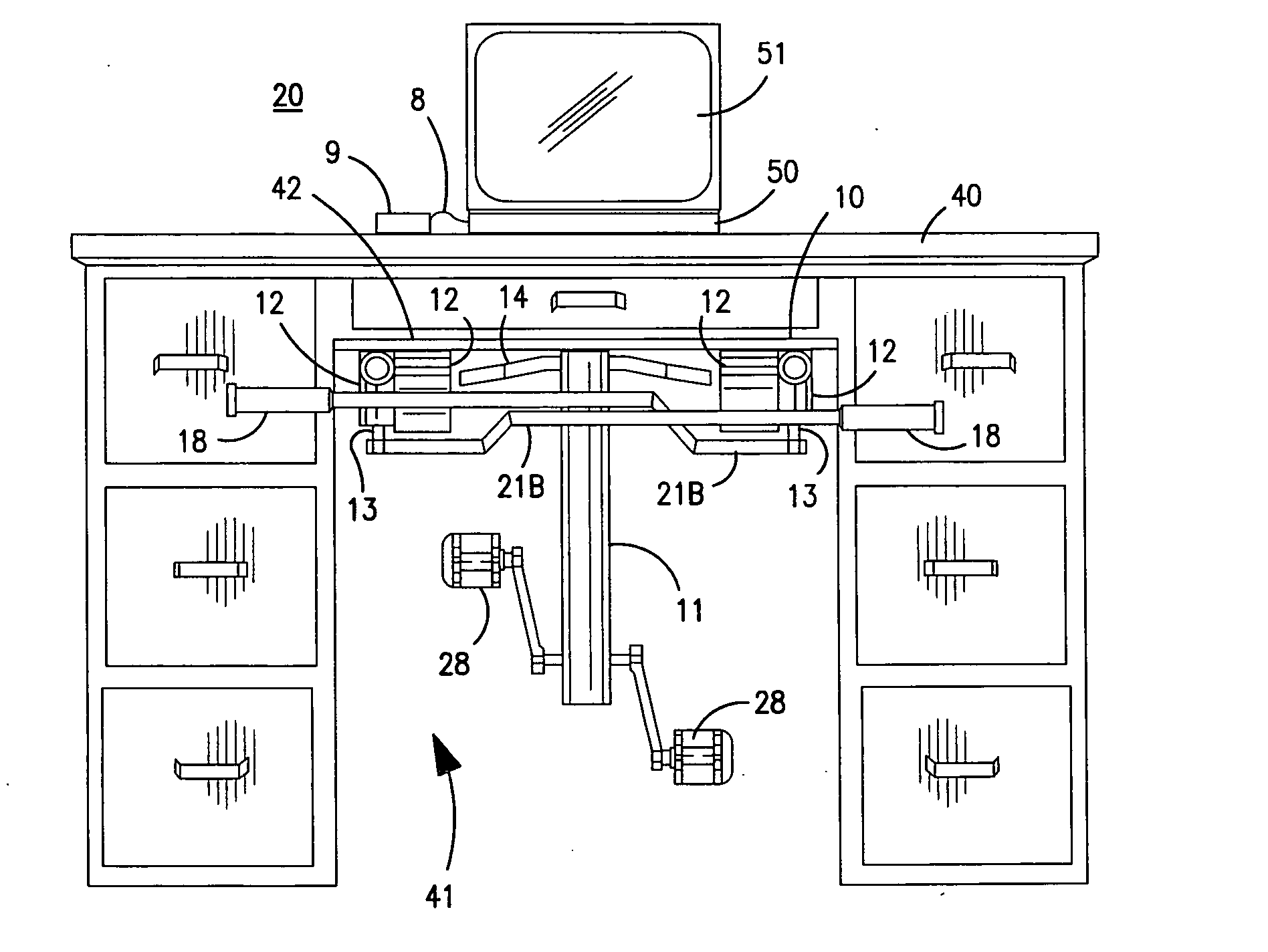
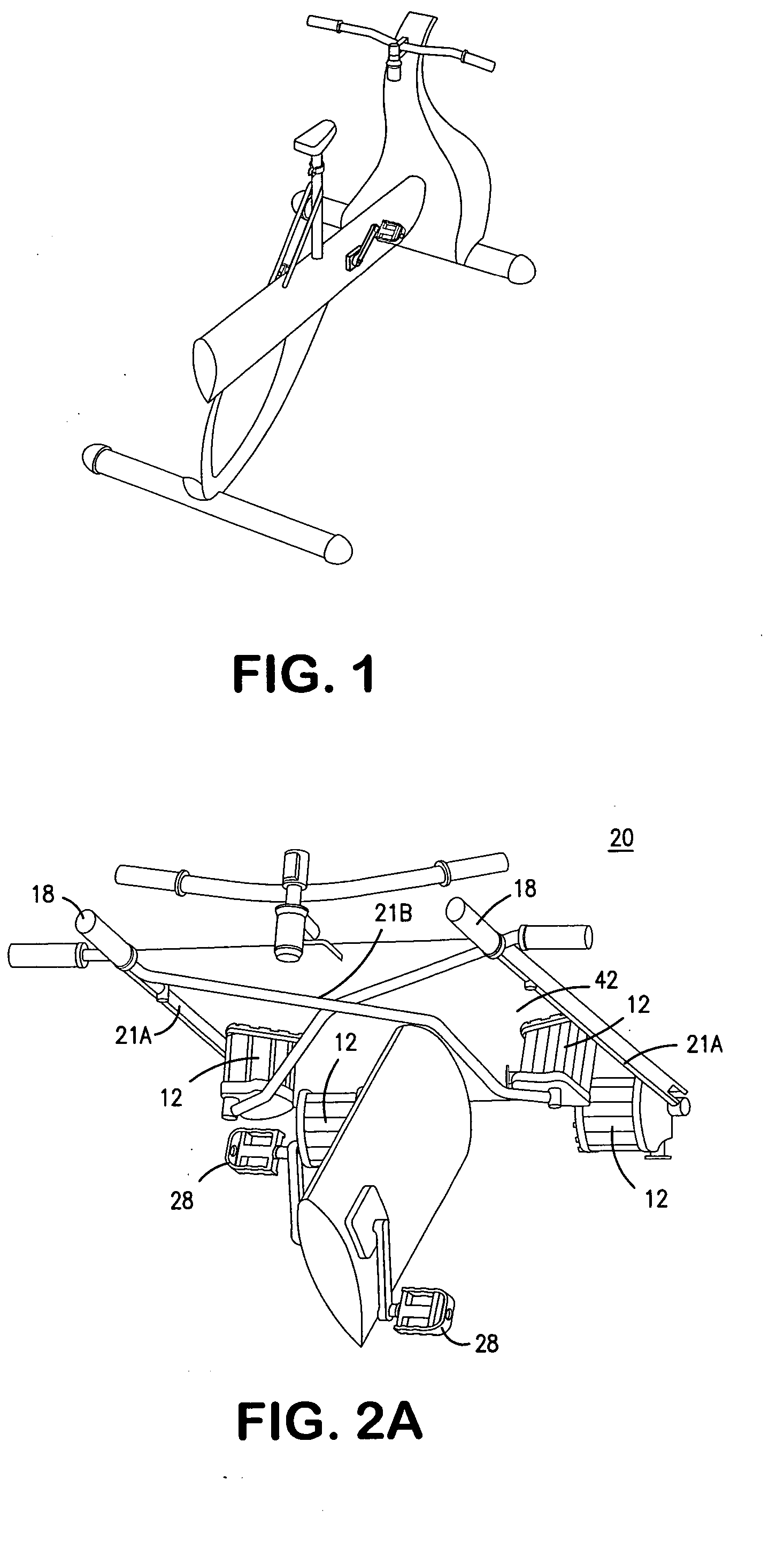
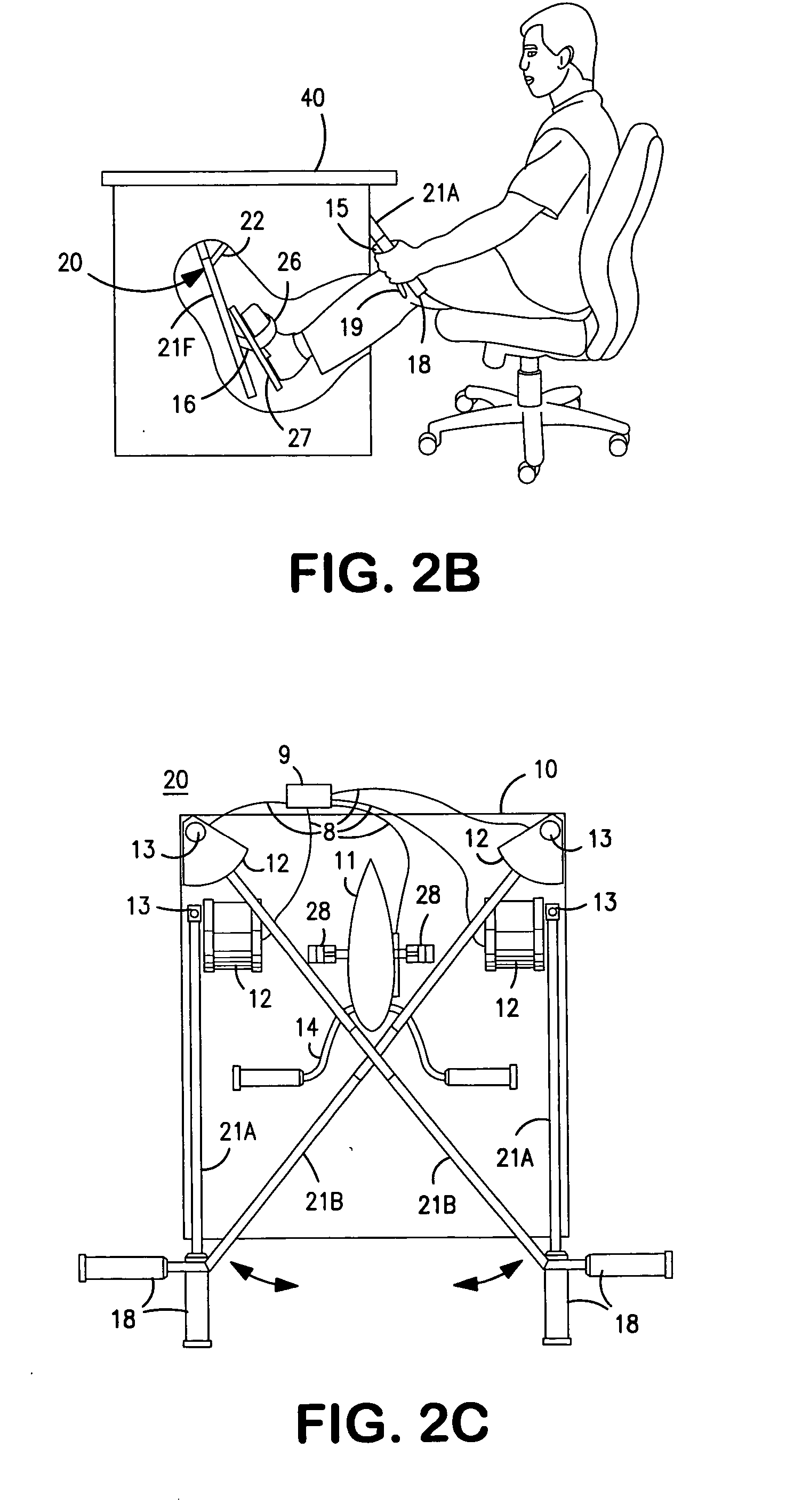
InactiveUS20070117680A1Improve sports experienceEfficient executionIndoor gamesSpace saving gamesExercise machineVisual perception
A computer simulation enhanced exercise device is provided which engages the user by directly relating the users exercise motion in real time to a visual simulation or interactive game. The exercise device may comprise any variety of machines including, stationary bikes, rowing machines, treadmills, stepper, elliptical gliders or under desk exercise. These exercise devices are configured with sensors to measure physical movements as the user exercises and are coupled to computer hardware with modeling and virtualization software to create the system. These sensor measurements are then sent to a computer for use in the physics based modeling and real-time visual simulation. The computer simulation enhanced exercise device is further provided with features including manual and automatic adjustment of resistance levels, visualization of accurate caloric burn rates and correlation to everyday food items, and network connectivity providing for multiplayer network simulations and directed advertising.
Owner:CUBEX
Interactive computer simulation enhanced exercise machine
InactiveUS20070093360A1Enhancement of exercise experienceReduce computational costInput/output for user-computer interactionIndoor gamesPhysical exerciseAutomatic tuning
A computer simulation enhanced exercise device is provided which engages the user by directly relating the users exercise motion in real time to a visual simulation or interactive game. The exercise device may comprise any variety of machines including, stationary bikes, rowing machines, treadmills, stepper, elliptical gliders or under desk exercise. These exercise devices are configured with sensors to measure physical movements as the user exercises and are coupled to computer hardware with modeling and virtualization software to create the system. These sensor measurements are then sent to a computer for use in the physics based modeling and real-time visual simulation. The computer simulation enhanced exercise device is further provided with features including manual and automatic adjustment of resistance levels, visualization of accurate caloric bum rates and correlation to everyday food items, and network connectivity providing for multiplayer network simulations and directed advertising.
Owner:CUBEX
Interactive computer simulation enhanced exercise machine
InactiveUS7497812B2Improve sports experienceLow costInput/output for user-computer interactionIndoor gamesPhysics basedVirtualization
A computer simulation enhanced exercise device is provided which engages the user by directly relating the users exercise motion in real time to a visual simulation or interactive game. The exercise device may comprise any variety of machines including, stationary bikes, rowing machines, treadmills, stepper, elliptical gliders or under desk exercise. These exercise devices are configured with sensors to measure physical movements as the user exercises and are coupled to computer hardware with modeling and virtualization software to create the system. These sensor measurements are then sent to a computer for use in the physics based modeling and real-time visual simulation. The computer simulation enhanced exercise device is further provided with features including manual and automatic adjustment of resistance levels, visualization of accurate caloric burn rates and correlation to everyday food items, and network connectivity providing for multiplayer network simulations and directed advertising.
Owner:CUBEX
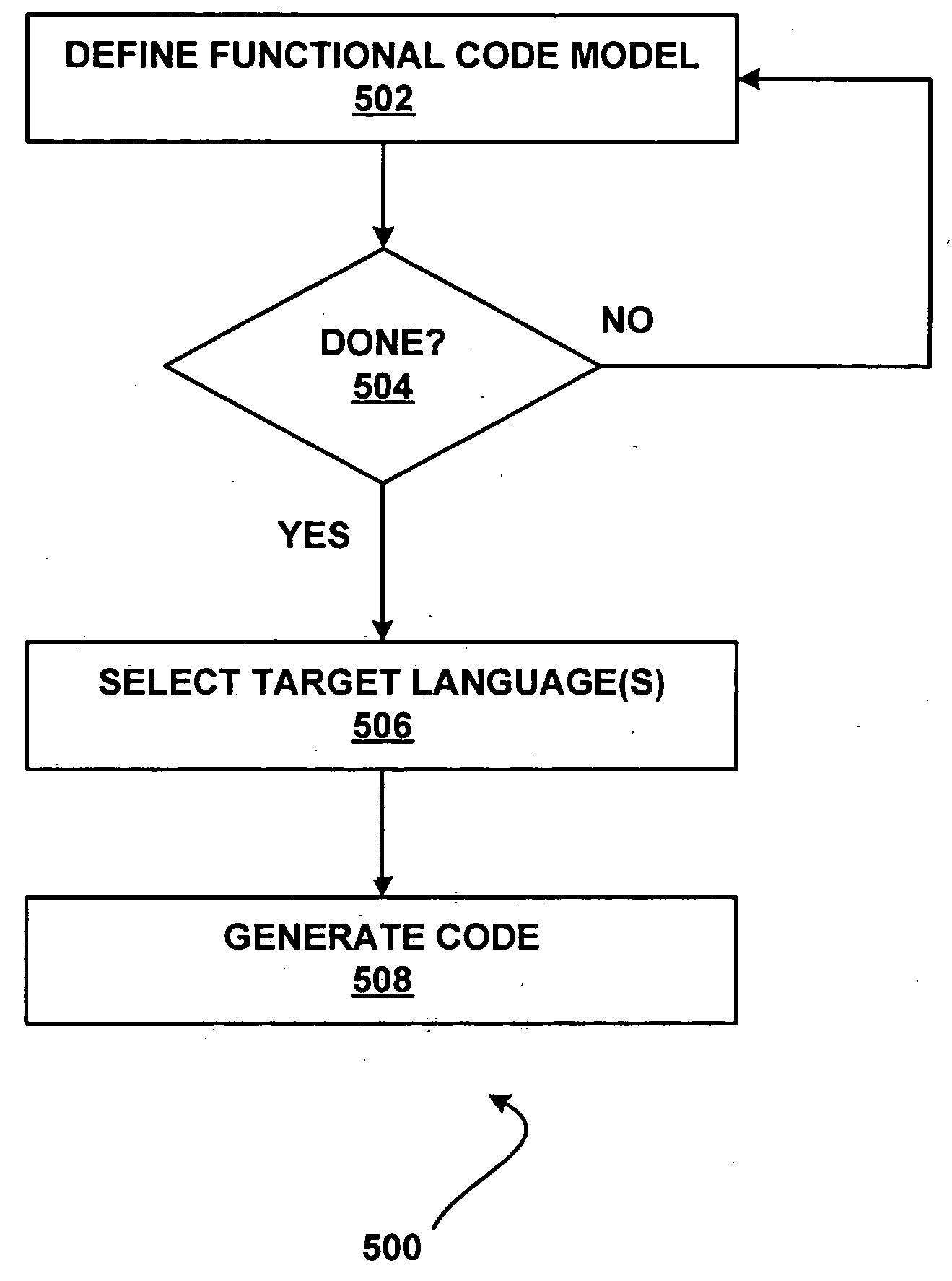
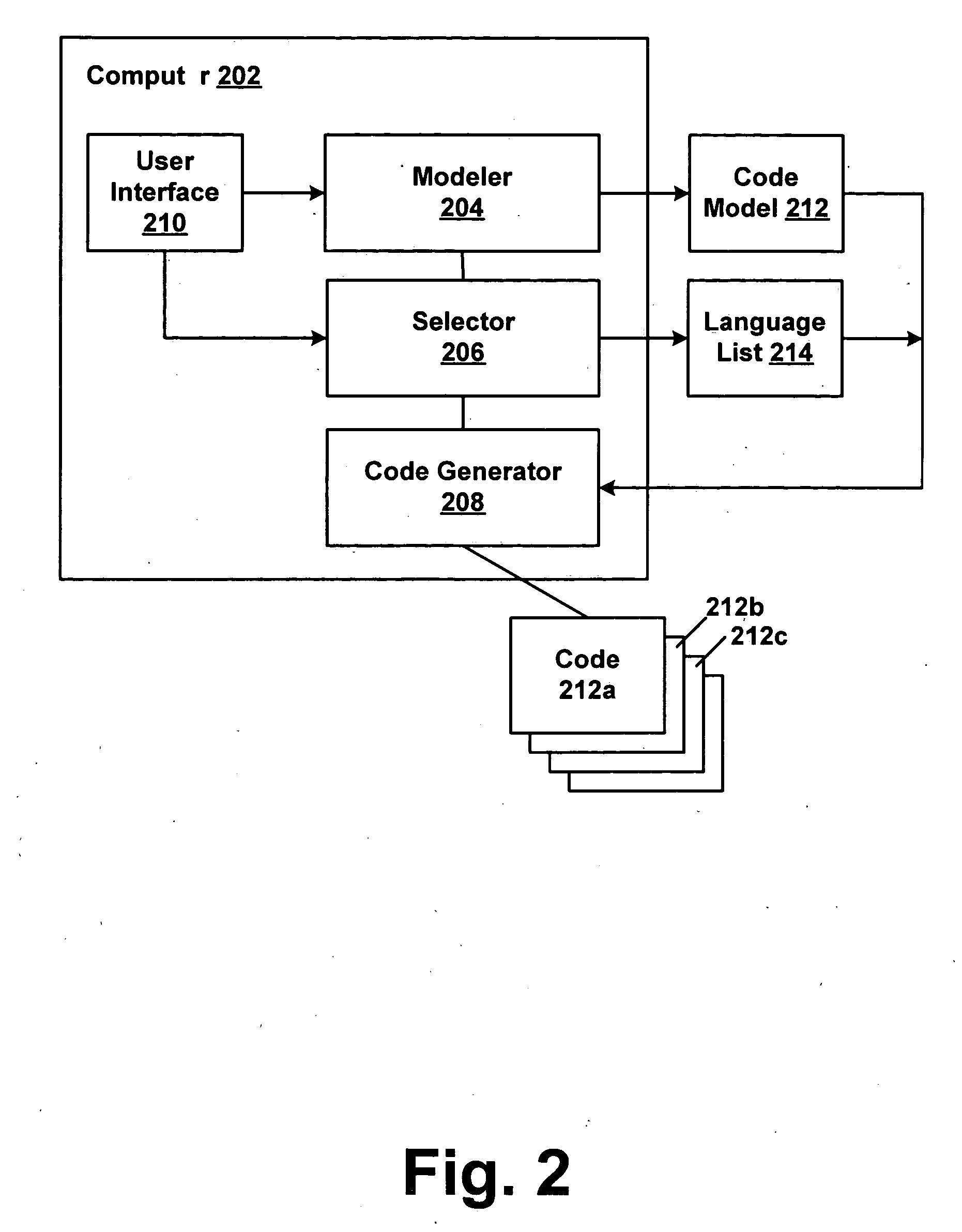
Automatically generating program code from a functional model of software
InactiveUS20050114832A1Rapid visualizationCode structure and flowVisual/graphical programmingSpecific program execution arrangementsProgramming languageCoded element
Modeling of the code elements and structure of a block of programming code enables code structure and flow to be visualized, eliminating language-specific aspects. One or more programming languages for which code is to be generated are selected. Code in the selected language(s) is generated from the functional model.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for interactive multi-dimensional visual representation of information content and properties
ActiveUS8131779B2Rapid visualizationImprove performanceDigital data processing detailsMultimedia data retrievalTriageInformation analysis
A system and method of information retrieval and triage for Information analysis provides an for interactive multi-dimensional and linked visual representation of information content and properties. A query Interface plans and obtains result sets. A dimension interface specifies dimensions with which to categorize the result sets. Links among results of a result set or results of different sets are automatically generated for linked selection viewing. Entitles may be extracted and viewed and entity relations determined to establish further links and dimensions. Properties encoded in representations of the results in the multi-dimensional views maximizes display density. Multiple queries may be performed and compared. An integrated browser component responsive to the links is provided for viewing documents. Documents and other information from the result set may be used in an analysis component providing a space for visual thinking, to arrange the information in the space while maintaining links automatically.
Owner:UNCHARTED SOFTWARE INC
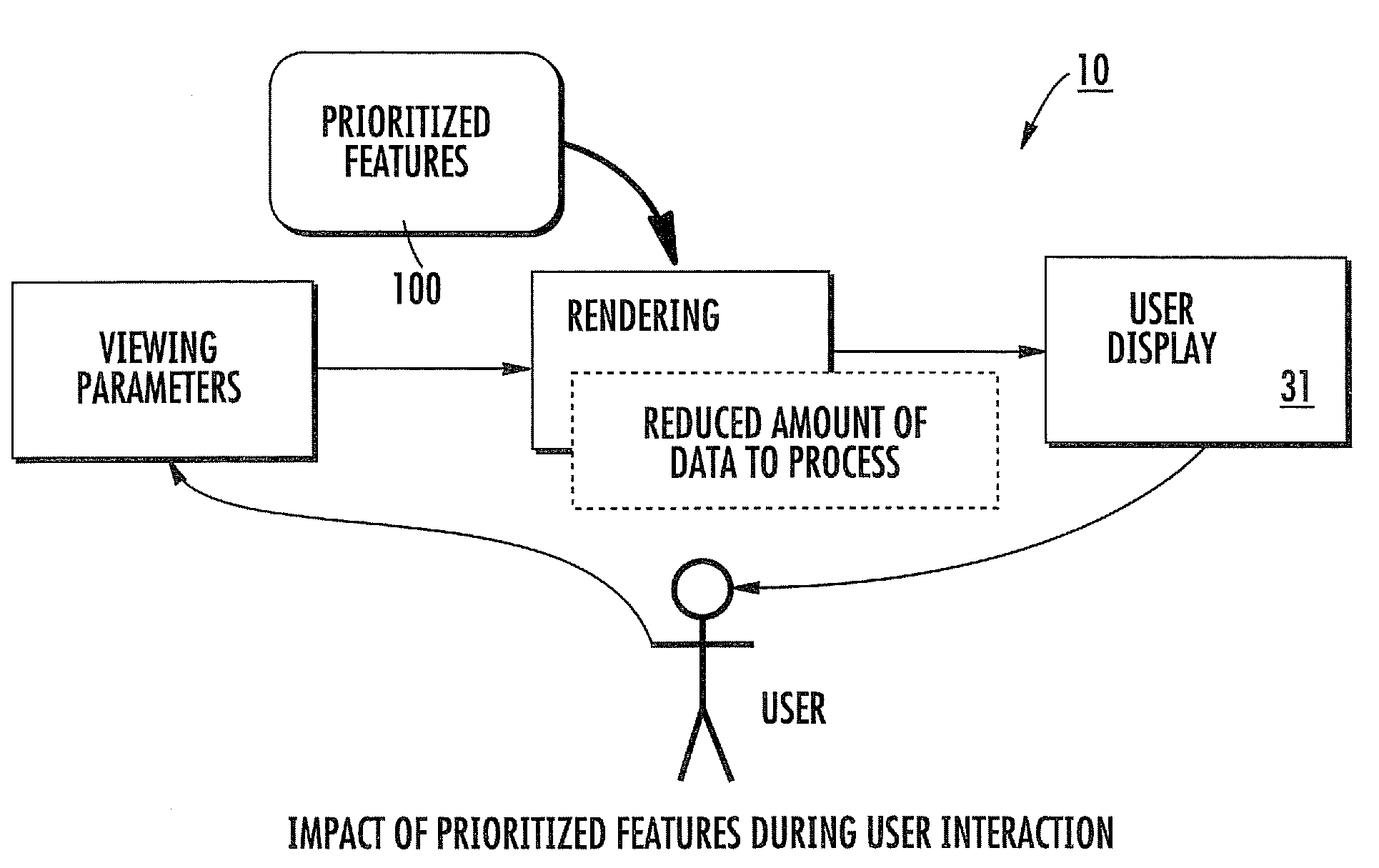
Systems for visualizing images using explicit quality prioritization of a feature(s) in multidimensional image data sets, related methods and computer products
ActiveUS7830381B2Rapid visualizationQuality improvementCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringData setLevel of detail
Visualization systems for rendering images from a multi-dimensional data set, include an interactive visualization system configured to accept user input to define at least one explicit prioritized feature in an image rendered from a multi-dimensional image data set. The at least one prioritized feature is automatically electronically rendered with high or full quality in different interactively requested rendered images of the image data while other non-prioritized features are rendered at lower quality. The visualization system may optionally include a rendering system configured to render images by electronically assigning a level of detail for different tiles associated with an image, each level of detail having a number of pixel samples to be calculated to thereby accelerate image processing.
Owner:SECTRA
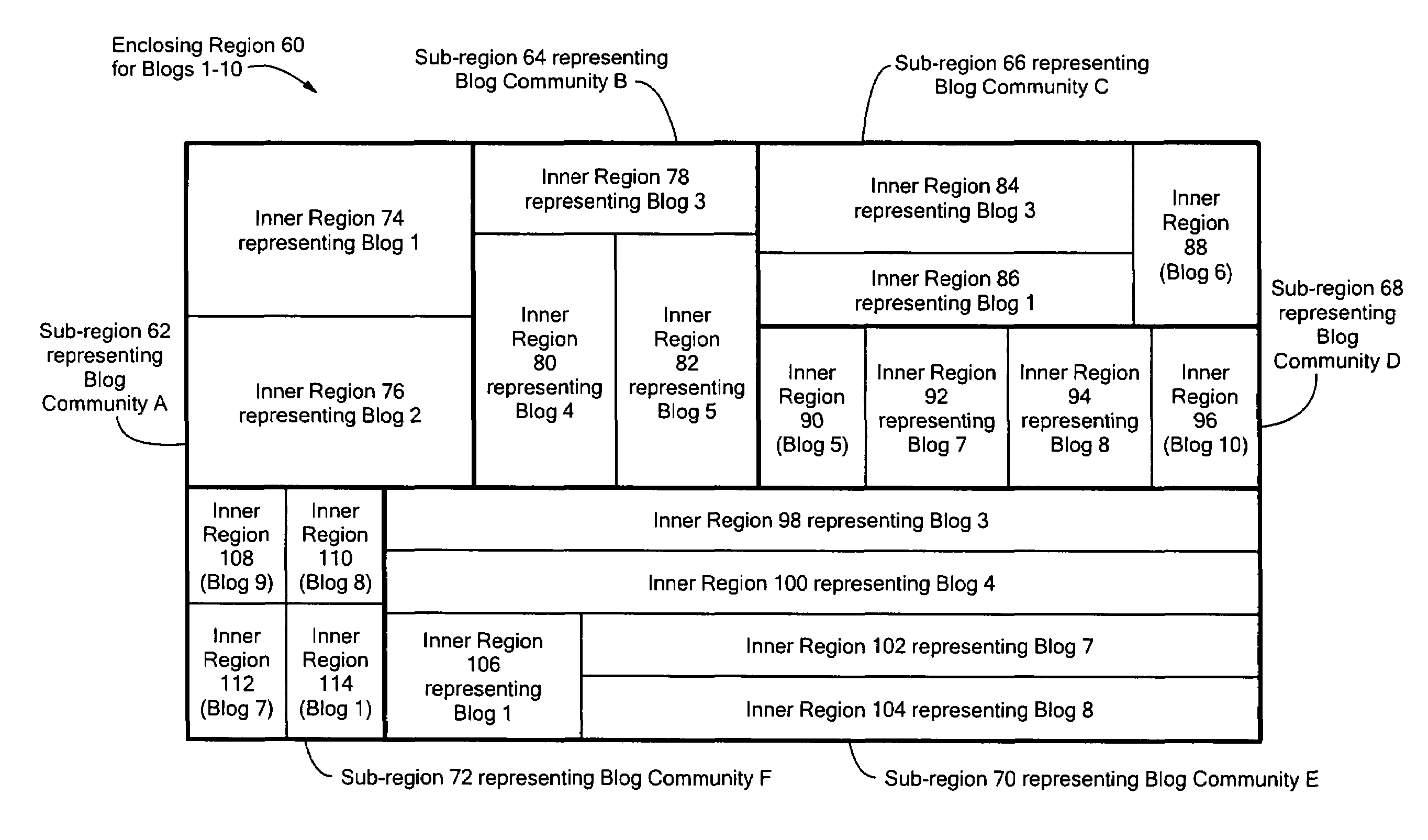
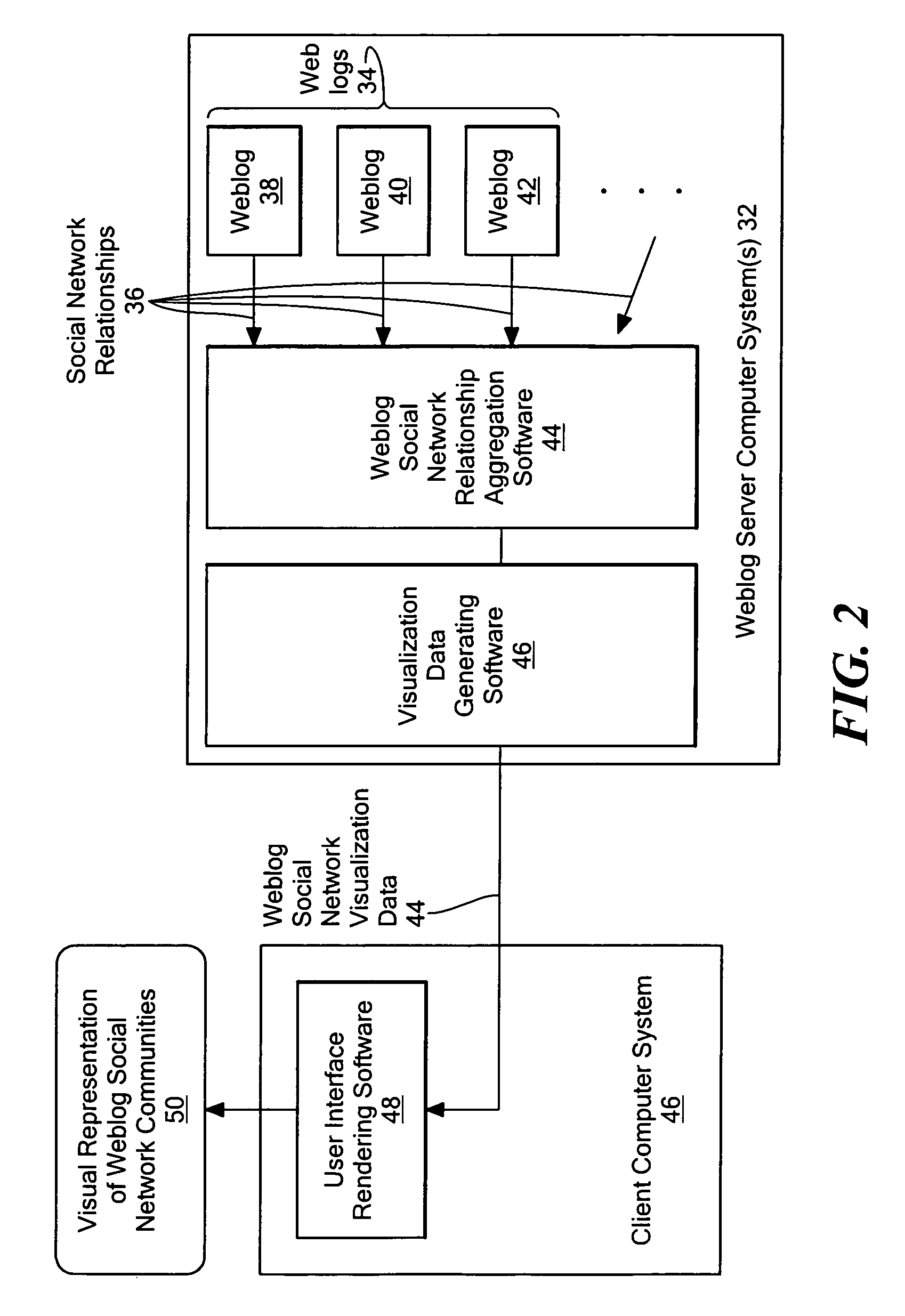
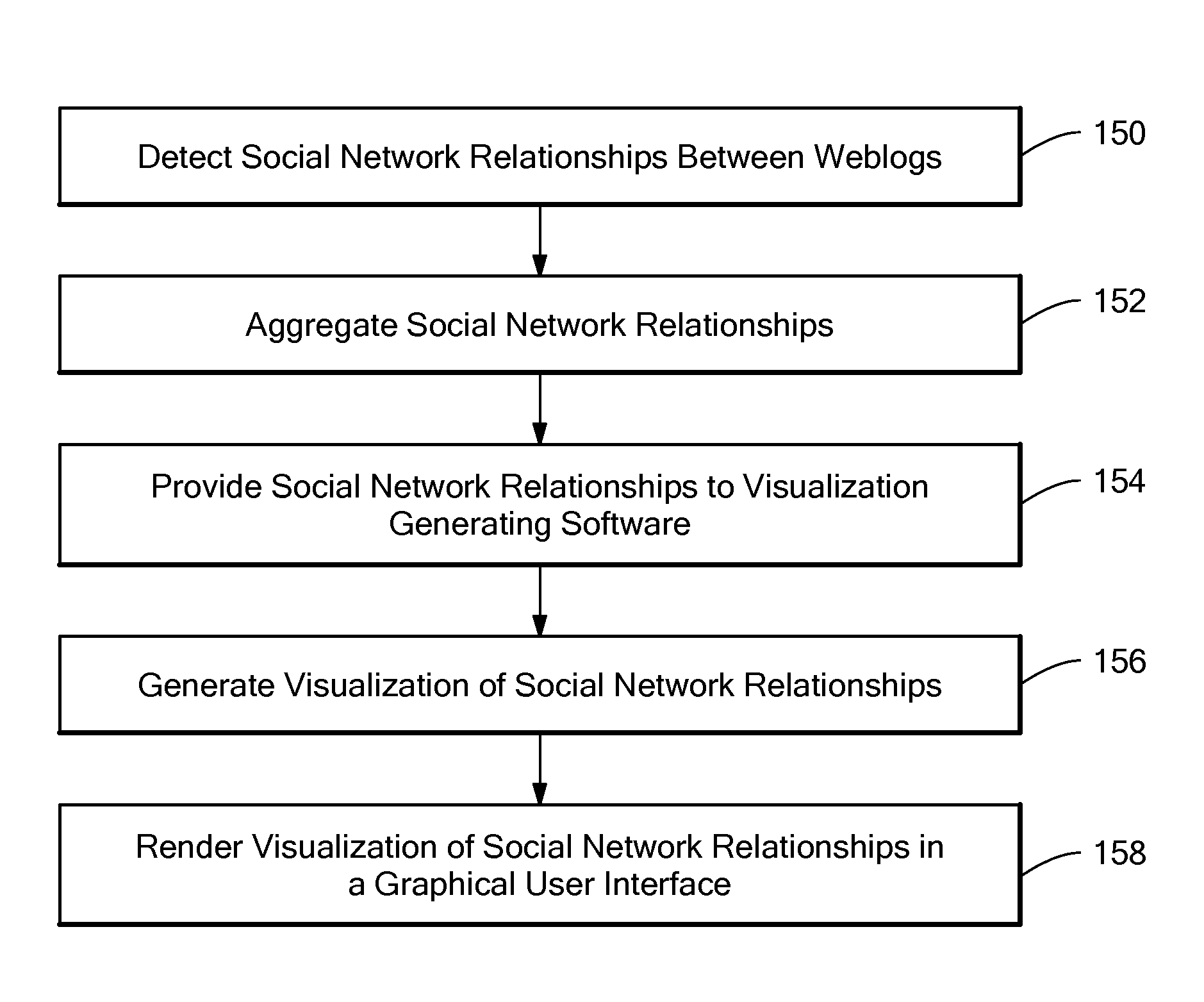
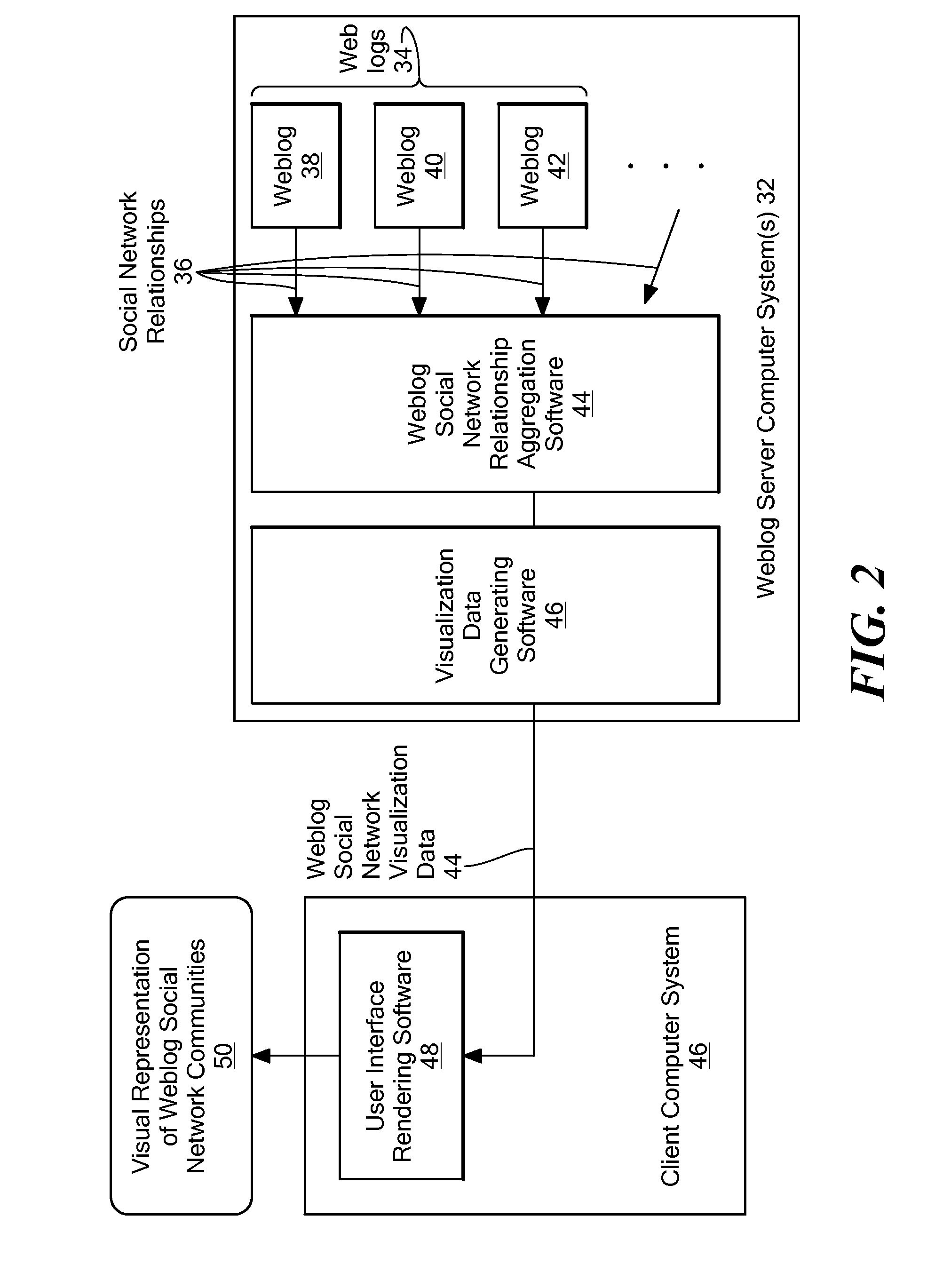
Method for visualizing weblog social network communities
ActiveUS7373606B2Rapid visualizationWebsite content managementSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsGraphical user interface
A method and system for providing a visual representation of electronic, on-line journals, such as those generally referred to as “Weblogs” or “Blogs”, that uses a treemap display object in a graphical user interface to represent social networking characteristics discovered in, and aggregated from a set of on-line journals. The generated display object includes on-line journal representations shown within the social network communities to which they belong. This visual organization is provided through a treemap representation, in which an enclosing region for a set of journals is broken up into sub-regions corresponding to social network communities. Representations of individual on-line journals are provided as inner regions within the sub-regions for the communities. The enclosing region, sub-regions and inner regions may be rectangular, or any other specific geometric shape as appropriate for a given application. The relative size of an inner region representing a specific journal may be determined based on how strongly related that journal is to the other members of the community, or on how active that journal is in terms of reads or writes, or based on some other criteria.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Interactive computer simulation enhanced exercise machine
InactiveUS7497807B2Improve sports experienceLow costIndoor gamesSpace saving gamesVirtualizationPhysics based
A computer simulation enhanced exercise device is provided which engages the user by directly relating the users exercise motion in real time to a visual simulation or interactive game. The exercise device may comprise any variety of machines including, stationary bikes, rowing machines, treadmills, stepper, elliptical gliders or under desk exercise. These exercise devices are configured with sensors to measure physical movements as the user exercises and are coupled to computer hardware with modeling and virtualization software to create the system. These sensor measurements are then sent to a computer for use in the physics based modeling and real-time visual simulation. The computer simulation enhanced exercise device is further provided with features including manual and automatic adjustment of resistance levels, visualization of accurate caloric burn rates and correlation to everyday food items, and network connectivity providing for multiplayer network simulations and directed advertising.
Owner:CUBEX
System and Method for Priority-Based Management of Patient Health for a Patient Population
InactiveUS20150186602A1Easy data entryEasy to sortData processing applicationsHealth-index calculationNursingHealth management system
Efficient management of patient health of a population of patients, such as chronically ill patients living at home and monitored with remote continuous wearable or implantable physiology telemetry, is provided by means of a computer application for rendering a prioritized list of patients sortable according to a number of distinct criteria.
Owner:VGBIO
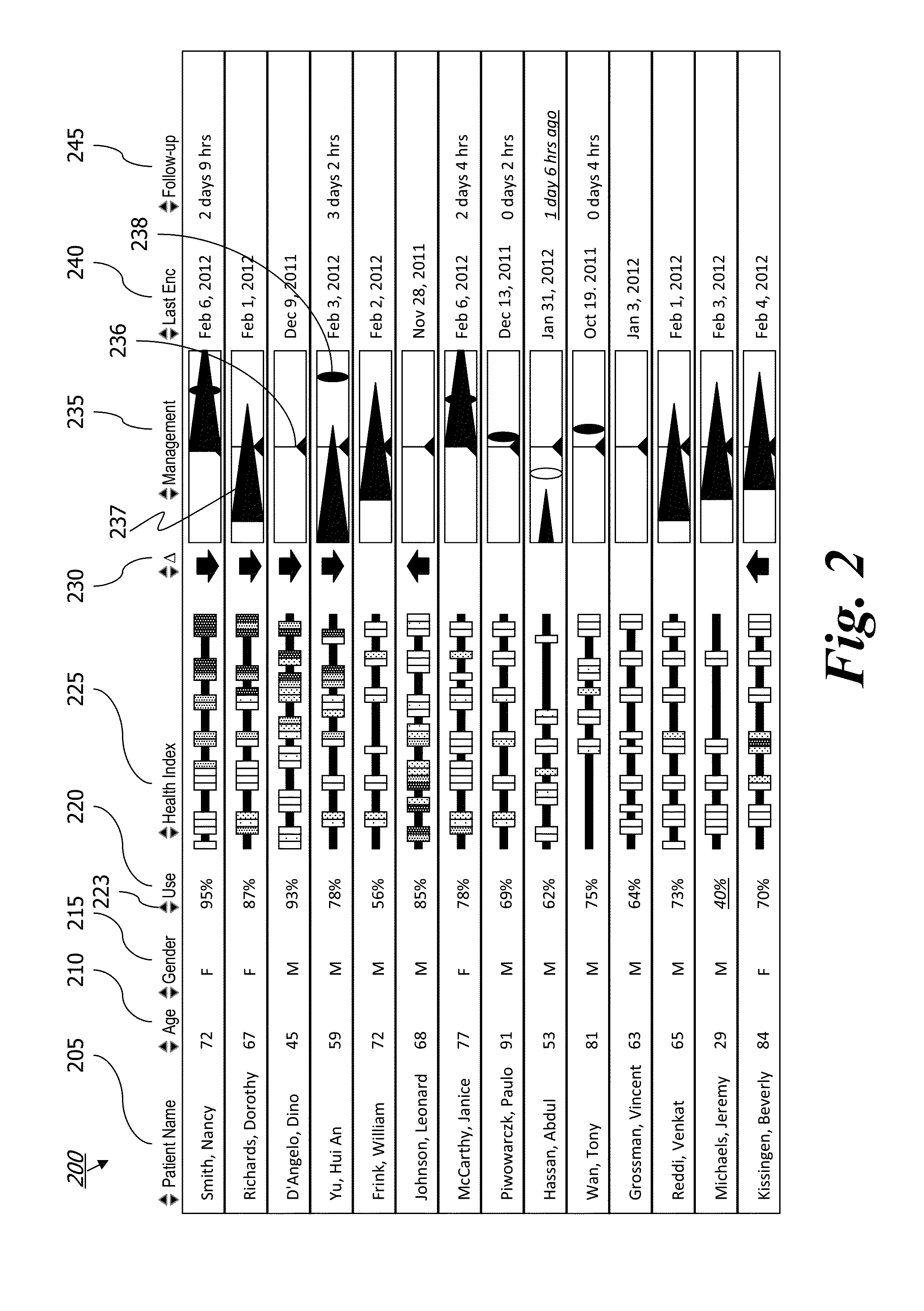
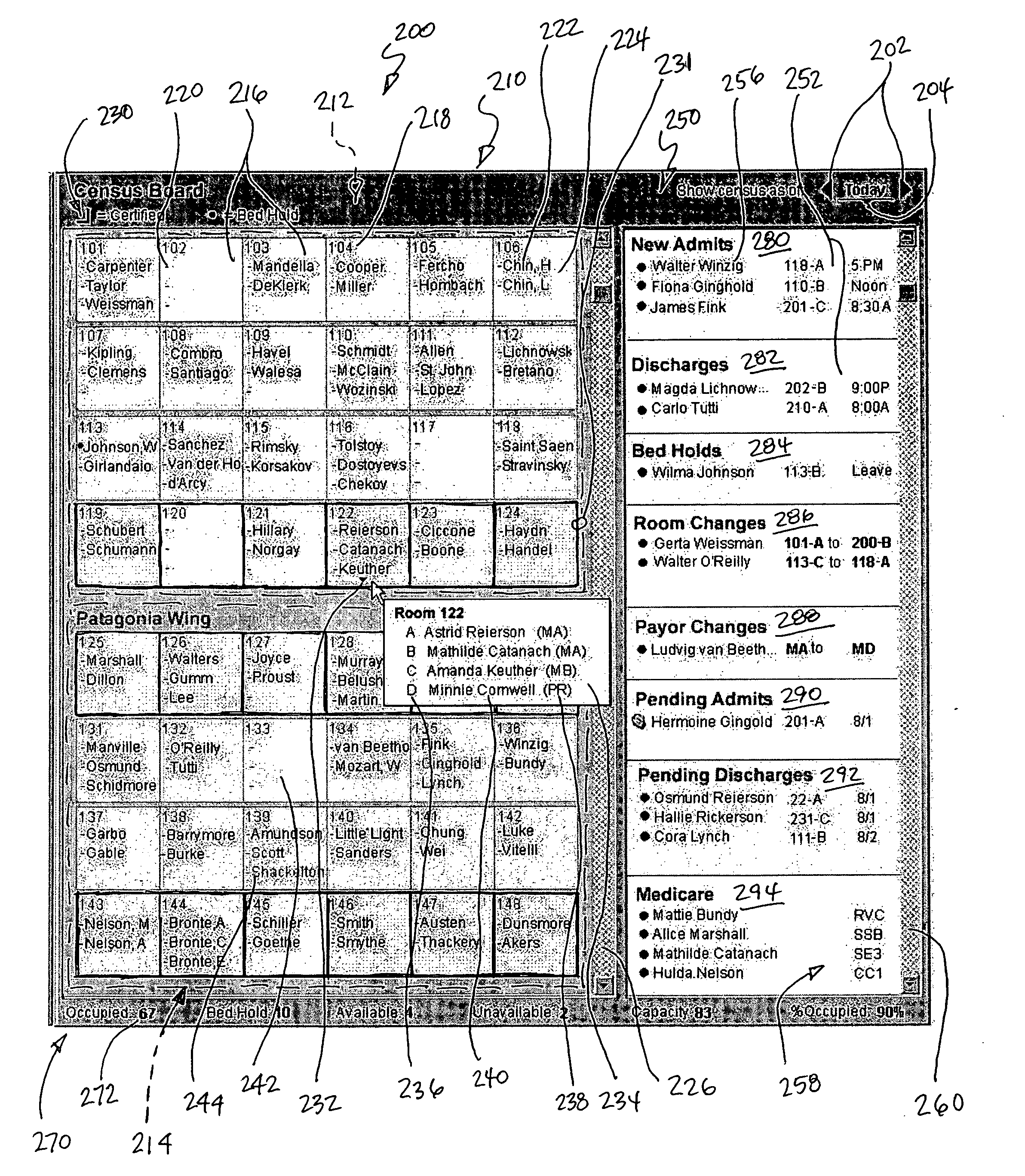
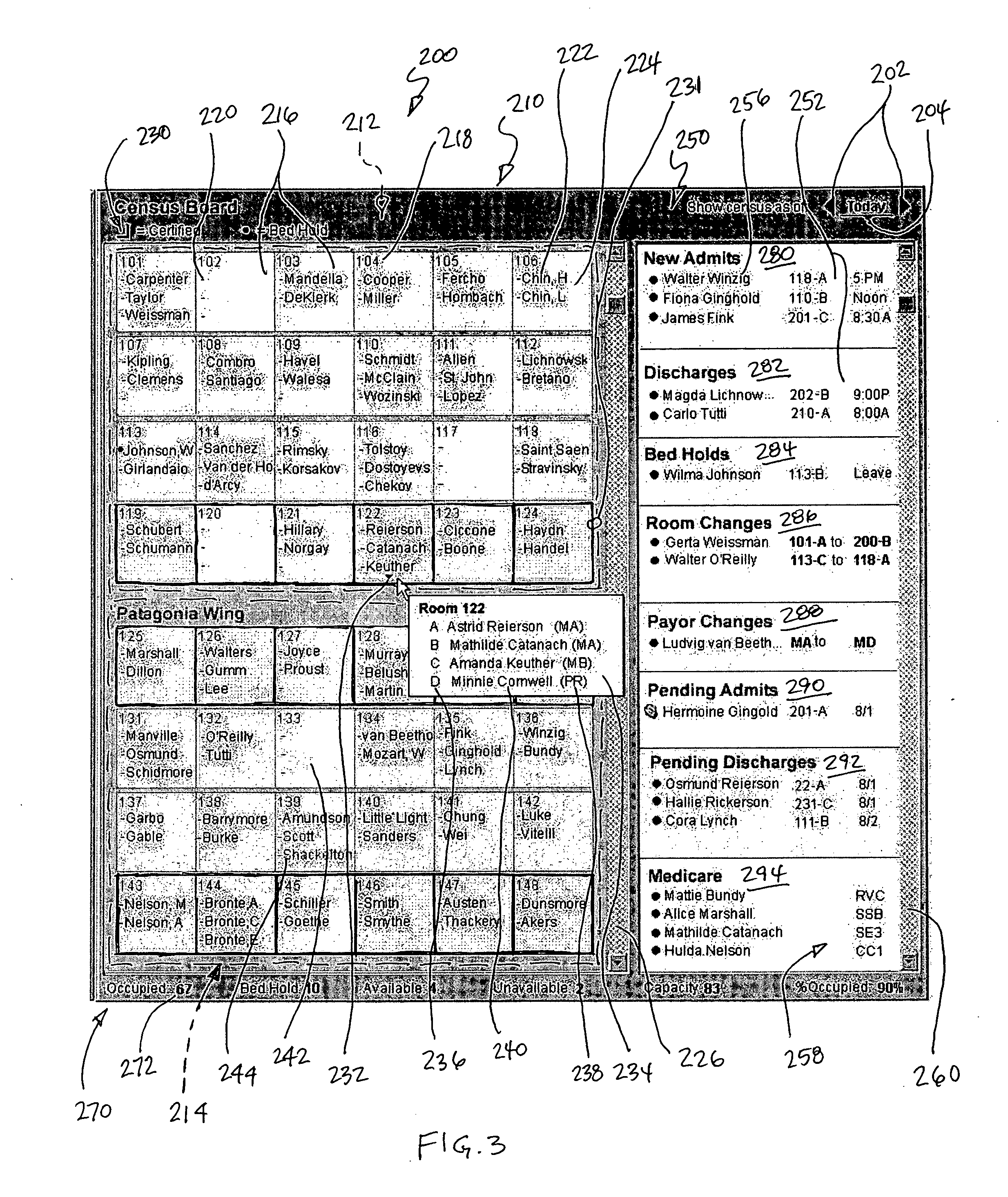
System and method for displaying the census of a healthcare facility
InactiveUS20050010441A1Rapid visualizationOffice automationHealthcare resources and facilitiesGraphicsGraphical user interface
Computer executable software code stored on a computer readable medium of a computer, the code for generating a graphical user interface. The graphical user interface includes a plurality of room representations that each correspond to a room in a healthcare facility. Each of the room representations communicates a number of beds in a corresponding room and identifiers of occupants of the beds in the corresponding room. The graphical user interface also includes an area communicating at least one of admits, discharges, bed holds, and room changes.
Owner:WHEELER JUDY
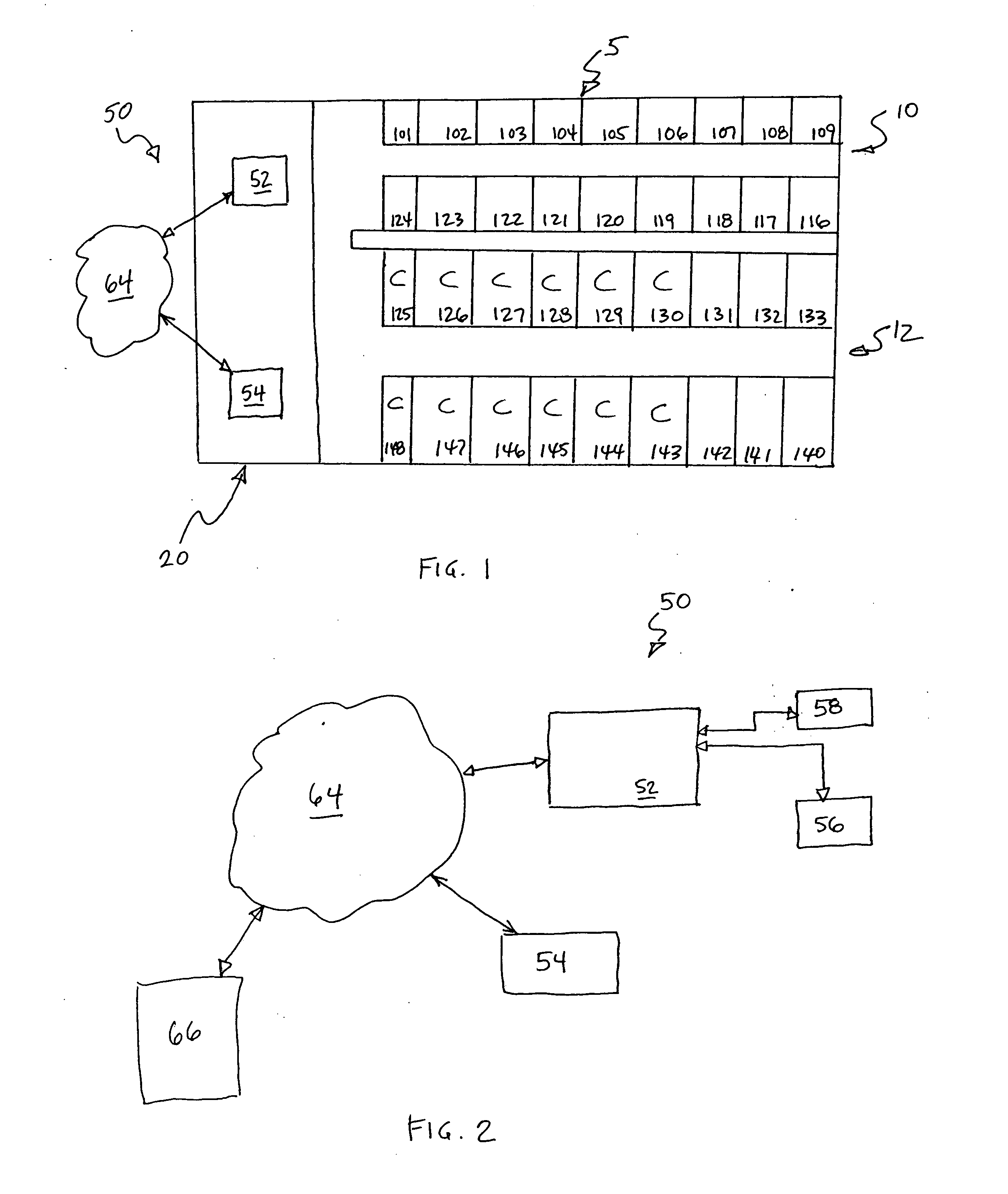
Graphics-based inventory control system
InactiveUS20050261975A1Rapid visualizationAccurate representationHand manipulated computer devicesPayment architectureGraphicsControl system
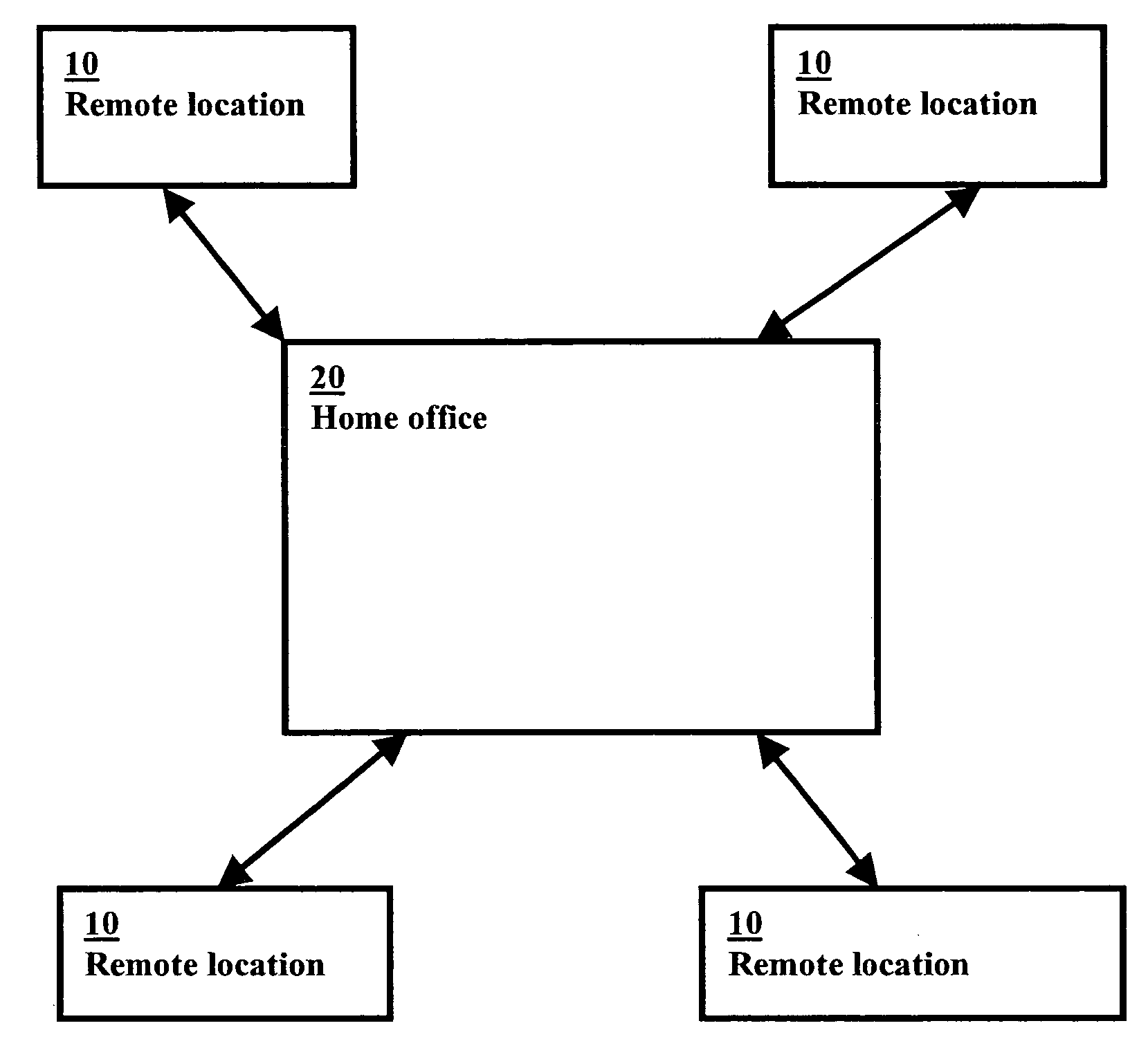
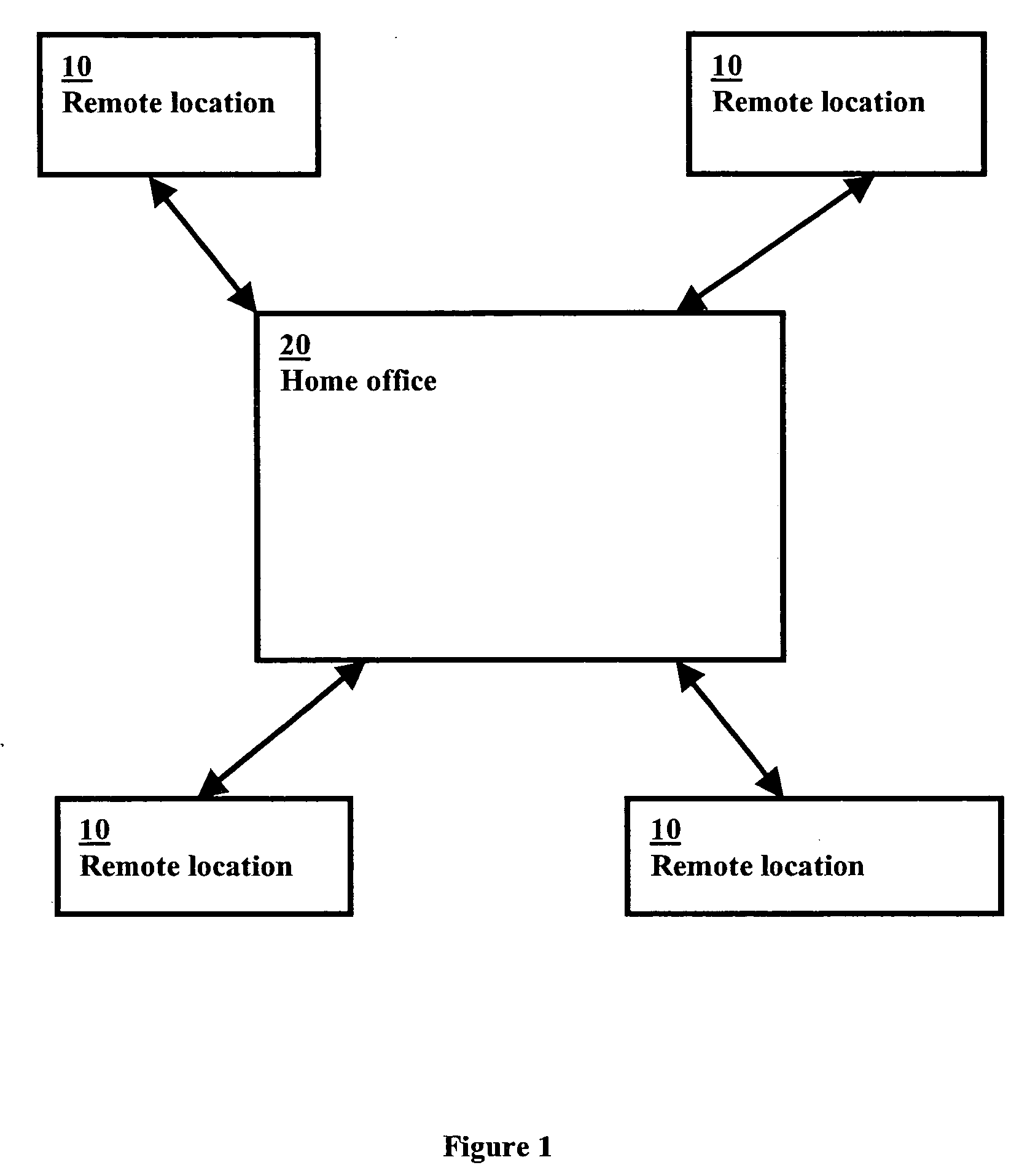
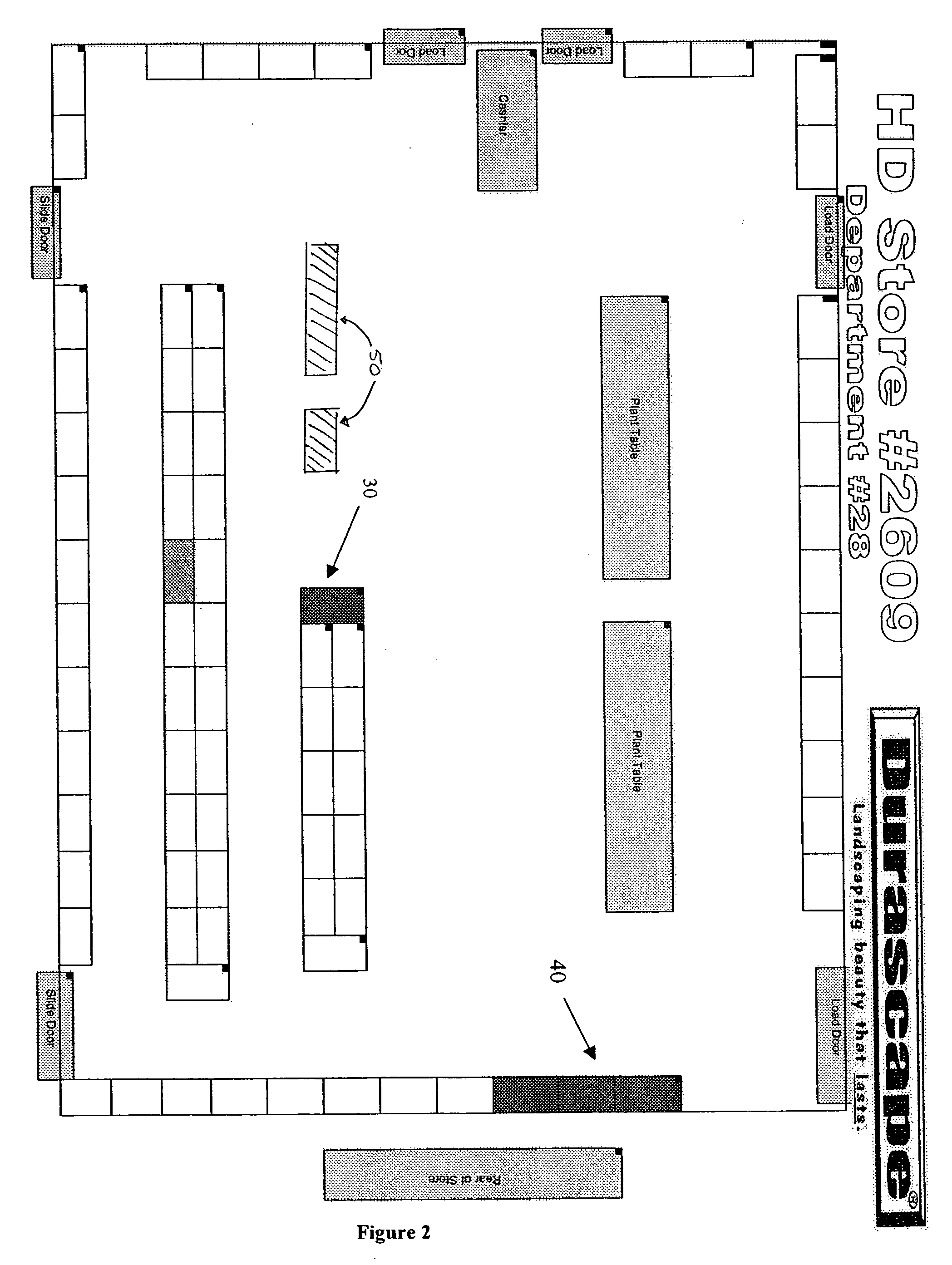
A graphics-based inventory control system for creating a visional graphics-based blueprint representation indicating the current placement of product in the sales bays and aisles in a particular location for the tracking of inventory and sales as well as to ensure the accurate placement of the product in accordance to the best practice agreement is disclosed. The graphics-based inventory control system is used to quickly alter off-site the configuration of the visional graphics-based blueprint representation to assist in the planning of future product placement in the remote location is also disclosed. The graphics-based inventory control system can further assist in determining the optimal product placement in the warehouse to streamline the shipping of the products to the individual remote locations by placing the products in the most efficient location in the warehouse for shipping the product out.
Owner:OLDCASTLE ARCHITECTURAL
Rapid Deployment First Aid Kit and System For Refilling
ActiveUS20110017633A1Fast contentEasy accessFirst-aid kitsContainer/bottle contructionDiseaseVisual presentation
A first aid kit organized with pockets containing first aid and emergency preparedness supplies and equipment and a system for refilling. Each pocket in the kit contains supplies and equipment useful in providing initial care for a particular illness or injury and is quickly identified through textual labels and transparent elements. The pockets are connected into a strip of pockets which is folded to fit within a case. The strip of pockets is easily deployed from the case facilitating rapid and accurate identification, selection, and acquisition of items appropriate for initial care of a particular illness or injury by comprehensive visual presentation of the organizational scheme and the supplies and pieces of equipment themselves.
Owner:GENUINE FIRST AID INT
Method for the detection of viable microorganisms
InactiveUS20050202523A1Enhancing bacteria absorptionRapid visualizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismExternal energy
Method for the detection and enumeration of viable microorganisms. A liquid that comprises one or more markers incorporated in a liquid sol-gel precursor, is provided. A transparent slide is coated with a thin uniform layer of the liquid sol-gel precursor composition. The microorganisms are separated from liquid sample to be analyzed by passing the sample through a filter, and then bringing the filter into close contact with the sol-gel coated slide. The filter is co-incubated with the sol-gel coated slide for a period of time and at a temperature suitable to promote uptake of the markers by the microorganisms. The gel-coated slide irradiated with an external energy source, so as to generate detectable signals emitted from the markers uptaken by the microorganisms. Image of the detectable signals emitted from the microorganisms are acquired, and analyzed using a computer system, in order to provide the identification and enumeration of the microorganisms.
Owner:BIOGEM OPTICAL LTD
Intuitive hierarchical time-series data display method and system
InactiveUS7639254B2Precise positioningRapid visualizationCathode-ray tube indicatorsStill image data browsing/visualisationImage extractionData display
The present invention provides display that permits a user to grasp time more intuitively. Data associated with respective dates is retrieved and displayed, each set of data being displayed in a display screen that is displayed smaller than that for preceding data in the series (in any temporal direction). Each set of data is displayed inside the preceding set with a smaller display area. Also, a display area may be divided into an area where icons representing data items belonging to one level are displayed, and an area where child levels are displayed. As hierarchical depth increases, the data icons are made smaller and simpler. The hierarchical structure of a file system or database can be displayed as a Venn diagram. Data items belonging to child levels are displayed as reduced images instead of being hidden. A cutout form and image are registered mutually and independently. An identifier, position, and size of the cutout form are specified as attributes of the image, permitting an image to be fetched into album software by performing a simple operation.
Owner:CANON KK
Compounds and methods of early diagnosis of cervical cancer and genital condyloma with HPV, CHSP60 tumor suppressor h-ras, k-ras and PTEN derived peptides modified
InactiveUS20060154238A1Easy to synthesizeStrong specificityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsViral antigen ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthHuman papillomavirus
An isolated sequence or peptide isolated from an E2, E4, E6, E7 early or late coding region of human papillomavirus (HPV) that is soluble in aqueous medium, and characterized by a linkage to another protein sequence or peptide isolated from the E2, E4, E6, E7 early or late coding region of HPV by a spacer sequence, wherein the isolated protein sequence or peptide consists of more than 50% hydrophilic amino acids, and is recognized by a specific antibody of HPV. Also disclosed are isolated protein sequences or peptides from Harvey Ras (H-Ras), Kirsten Ras (K-Ras), and phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) tumor suppressor proteins and Chlamydia trachomatis heat shock protein 60 (CHSP60 groEL1) and methods for detecting or diagnosing cancer or cellular abnormalities.
Owner:HU YAO XIONG
Compounds and methods of early diagnosis of cervical cancer and genital condyloma with HPV, CHSP60 tumor suppressor H-Ras, K-Ras and PTEN derived peptides modified
InactiveUS7314630B2Easy to synthesizeStrong specificityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsViral antigen ingredientsHuman papillomavirusADAMTS Proteins
Owner:HU YAO XIONG
Rapid deployment first aid kit and system for refilling
ActiveUS8167130B2Rapid visualizationEasy accessFirst-aid kitsContainer/bottle contructionVisual presentationKit first aid
Owner:GENUINE FIRST AID INT
Methods and systems for identification of DNA patterns through spectral analysis
InactiveUS8189892B2Improve visualizationHigh resolutionData visualisationBiostatisticsDNA PatternsTandem repeat
Systems and methods facilitate the location and / or identification of repetitive DNA patterns, such as CpG islands, Alu repeats, tandem repeats and various types of satellite repeats. These repetitive elements can be found within a chromosome, within a genome or across genomes of various species. The systems and methods apply image processing operators to find prominent features in the vertical and horizontal direction of the DNA spectrograms. The systems and methods for detecting and / or classifying repetitive DNA patterns include: (a) a comparative histogram method, (b) feature selection and classification using support vector machines and genetic algorithms, and (c) generation of a spectrovideo from a plurality of spectral images.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method for the detection of viable microorganisms
InactiveUS7312073B2Rapid visualizationPromote absorptionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismExternal energy
Method for the detection and enumeration of viable microorganisms. A liquid that comprises one or more markers incorporated in a liquid sol-gel precursor, is provided. A transparent slide is coated with a thin uniform layer of the liquid sol-gel precursor composition. The microorganisms are separated from liquid sample to be analyzed by passing the sample through a filter, and then bringing the filter into close contact with the sol-gel coated slide. The filter is co-incubated with the sol-gel coated slide for a period of time and at a temperature suitable to promote uptake of the markers by the microorganisms. The gel-coated slide irradiated with an external energy source, so as to generate detectable signals emitted from the markers uptaken by the microorganisms. Image of the detectable signals emitted from the microorganisms are acquired, and analyzed using a computer system, in order to provide the identification and enumeration of the microorganisms.
Owner:BIOGEM OPTICAL LTD
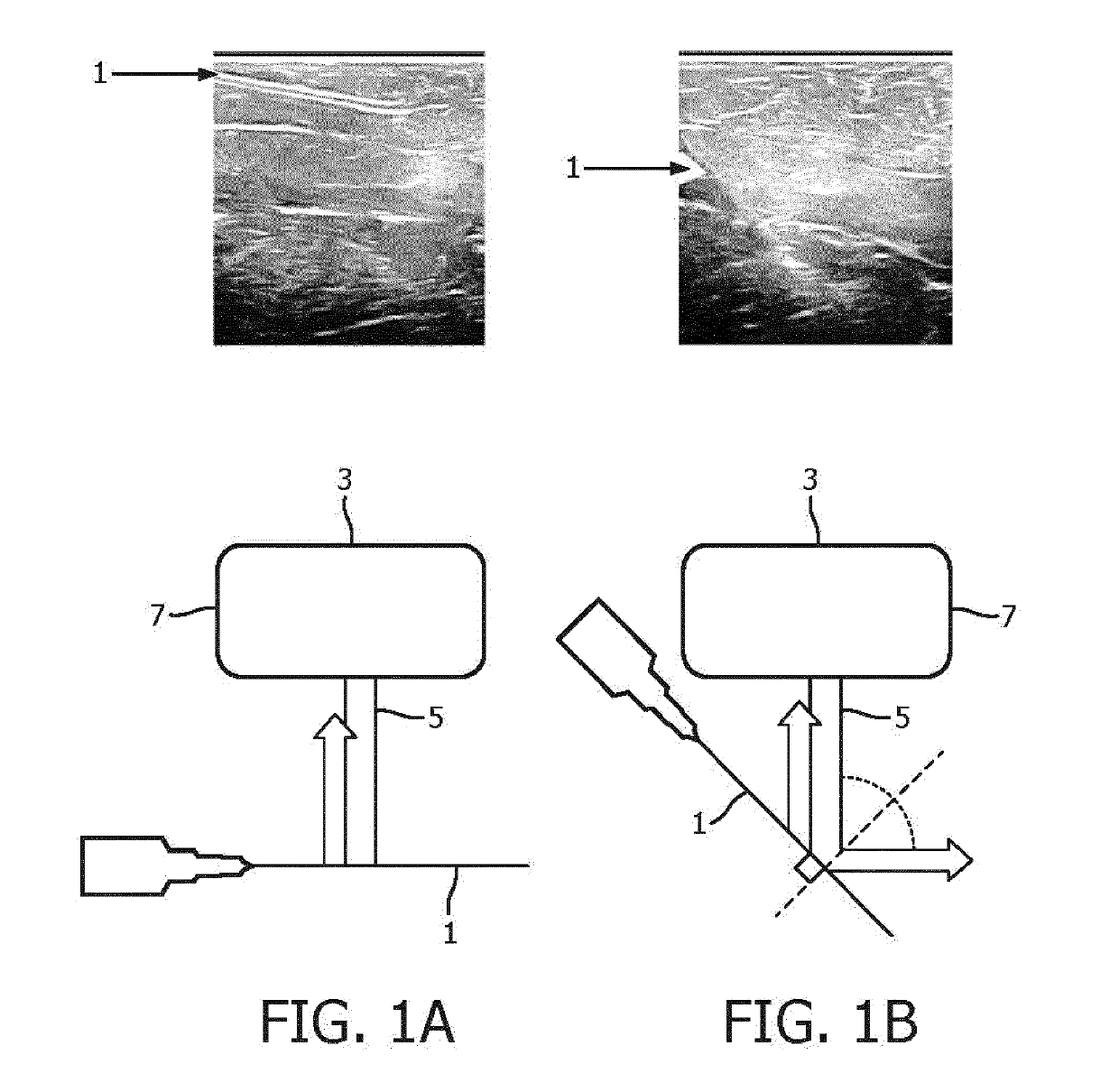
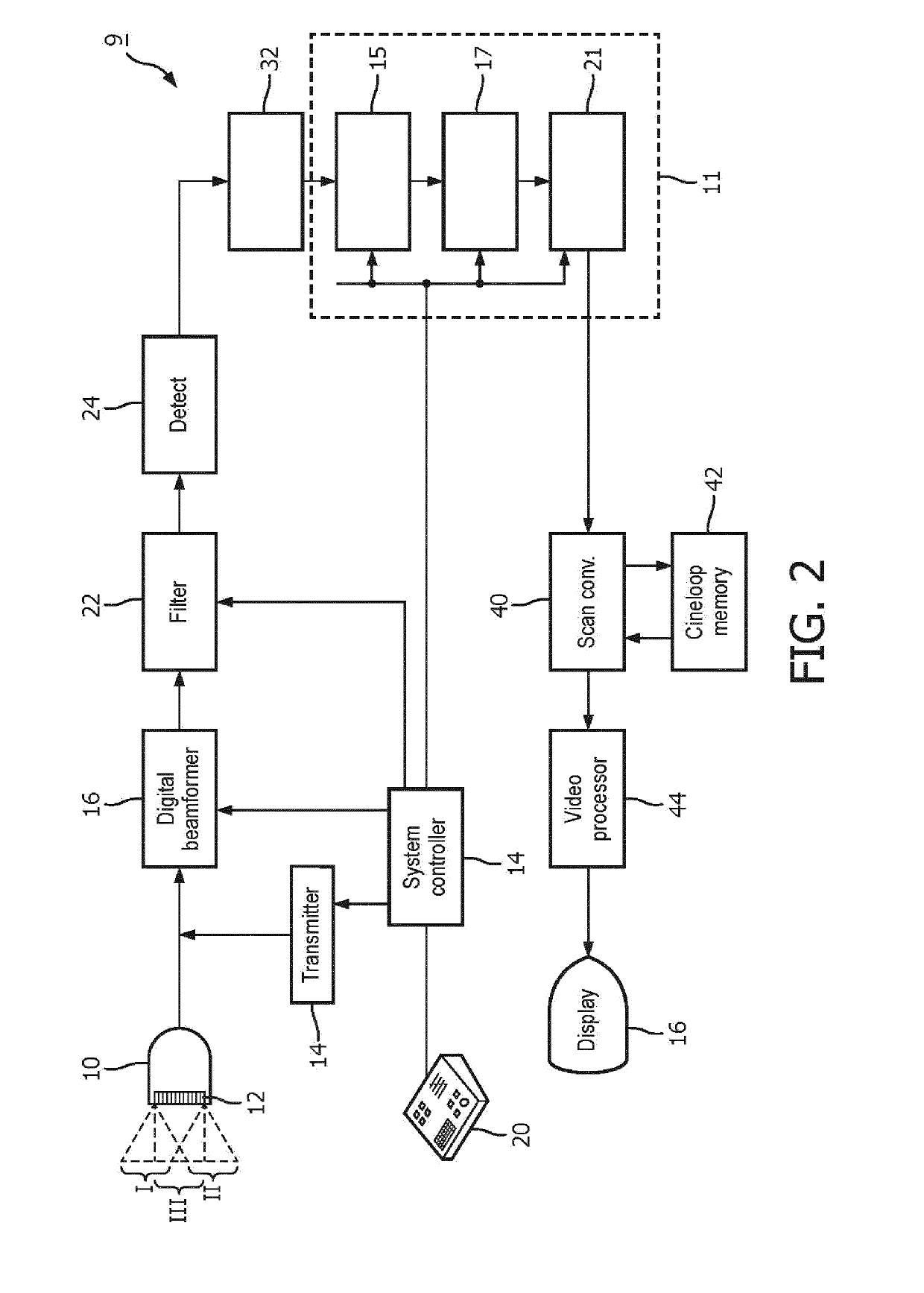
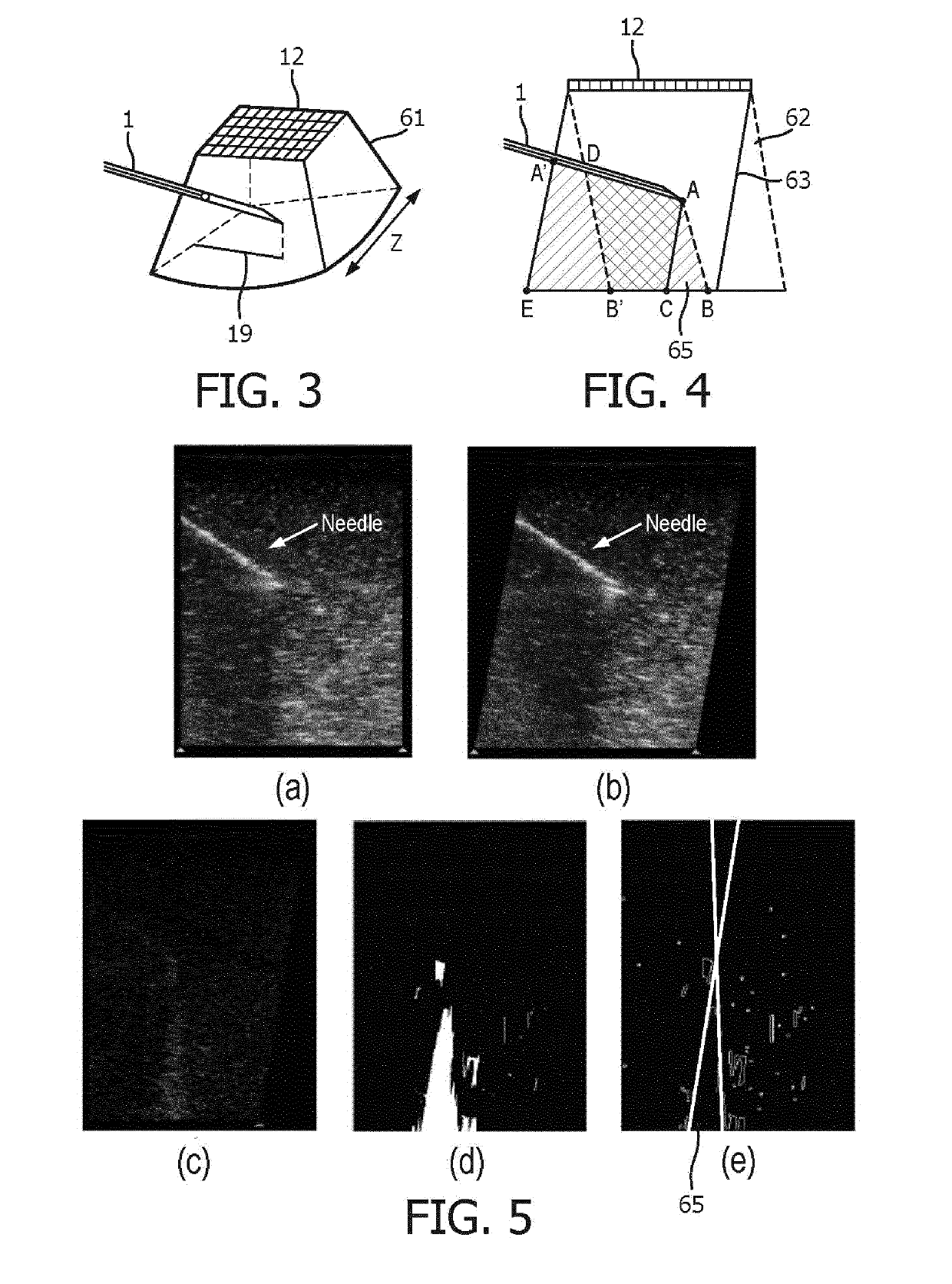
An apparatus and method for detecting an interventional tool
ActiveUS20190201110A1High precisionGood precisionImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingBeam steering
The apparatus is adapted to detect a tip of an interventional tool based on at least two ultrasound images reconstructed for different beam steering angles within a volumetric region comprising said tool. The apparatus comprises an image processing unit, which includes a tip detection module configured to perform a tip tool detection procedure. The tip tool detection procedure involves identifying shadow regions of the tool in the at least two ultrasound images and calculating the position of the tip of the tool within the volumetric region.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
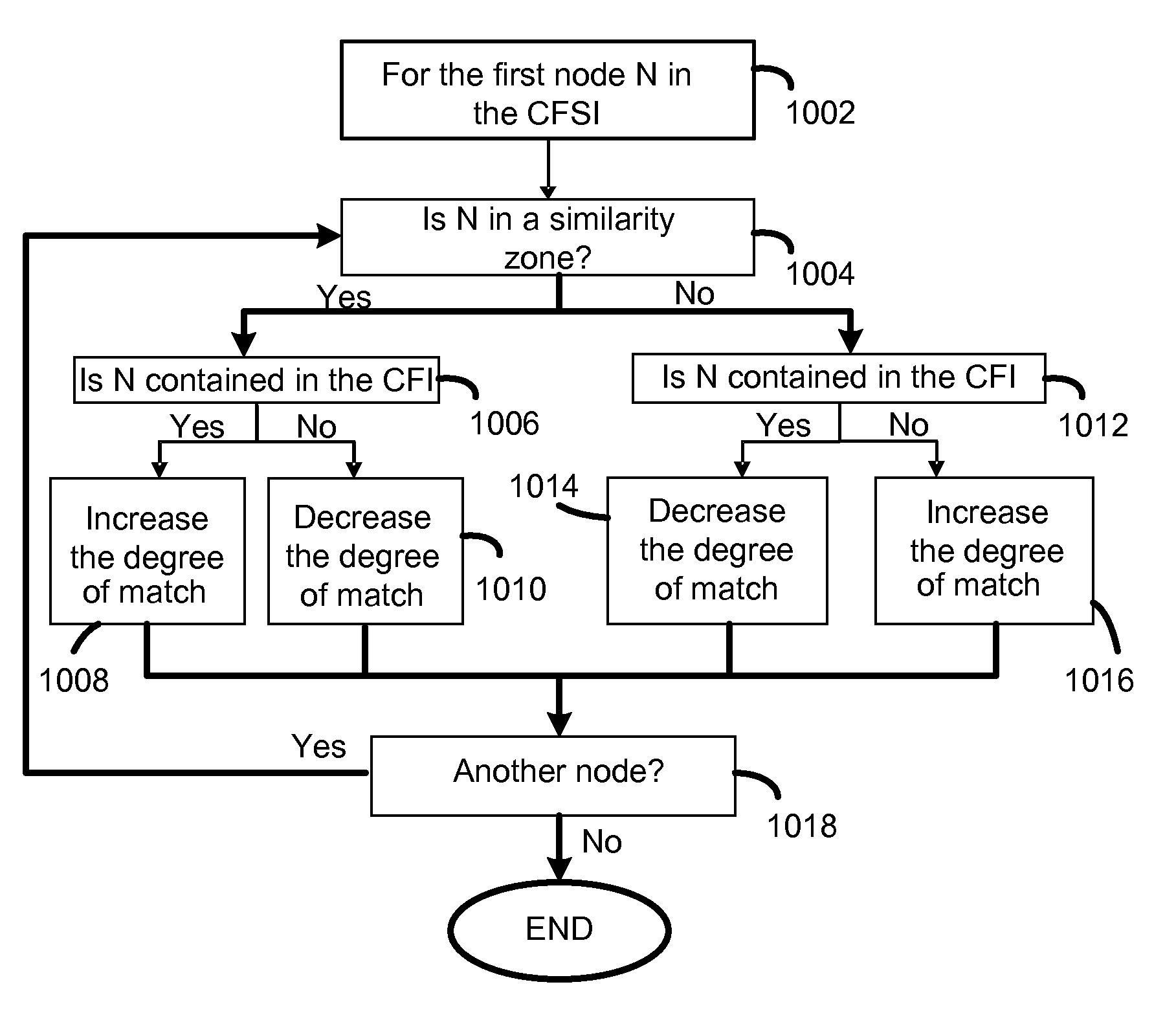
Methods and systems for managing similar and dissimilar entities
InactiveUS20080082519A1Improve refinementRapid visualizationDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsMatching methodsVisual interface
Search criteria and potential targets of searches are each represented by a classification of attributes. The search classifications and target classifications are compared to determine whether a target matches or loosely matches the search criteria. The search classifications and target classifications may be modified to increase the chance of a match or loose match. A user can request to modify a classification using a visual interface in which information about the classification is presented. The matching approach may be implemented in conjunction with conventional matching methods to provide classifications. The matching approach is capable of interacting with users of the approach to dynamically alter the classifications being searched based on any given set of search results.
Owner:AUBICE
Method and system for visualizing weblog social network communities
ActiveUS20080163068A1Rapid visualizationWebsite content managementSpecial data processing applicationsGraphicsGraphical user interface
A system for providing a visual representation of electronic, on-line journals, such as those generally referred to as “Weblogs” or “Blogs”, that uses a treemap display object in a graphical user interface to represent social networking characteristics discovered in, and aggregated from a set of on-line journals. The generated display object includes on-line journal representations shown within the social network communities to which they belong. This visual organization is provided through a treemap representation, in which an enclosing region for a set of journals is broken up into sub-regions corresponding to social network communities. Representations of individual on-line journals are provided as inner regions within the sub-regions for the communities. The enclosing region, sub-regions and inner regions may be rectangular, or any other specific geometric shape as appropriate for a given application. The relative size of an inner region representing a specific journal may be determined based on how strongly related that journal is to the other members of the community, or on how active that journal is in terms of reads or writes, or based on some other criteria.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Device For the Growth of Macromolecular Crystals and Drug Screening
InactiveUS20090129983A1Improve efficiencyMinimal handlingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsInterior spaceCapillary Tubing
The invention is a device for counter-diffusion applications comprising a removable cartridge having a plurality of capillary tubes that may be disposed between first and second members. The first member may be moveable into at least a first and second position. The second member may be moveable into a sealing position wherein the distal ends of the capillary tubes contact a sealant material. In the first position, the proximal ends of the capillary tubes may contact a macromolecular solution, which may cause the macromolecular solution to diffuse into the interior space of the capillary tube. In the second position, the proximal ends of the capillary tubes may be inserted into a corresponding reservoir well having a precipitating solution. The macromolecular solution and the precipitating solution may then counter diffuse against each other in each capillary tube. The removable cartridge may then be removed and replaced with a new removable cartridge.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
Methods and systems for managing similar and dissimilar entities
InactiveUS20090327289A1Improve refinementRapid visualizationDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsMatching methodsVisual interface
Search criteria and potential targets of searches are each represented by a classification of attributes. The search classifications and target classifications are compared to determine whether a target matches or loosely matches the search criteria. The search classifications and target classifications may be modified to increase the chance of a match or loose match. A user can request to modify a classification using a visual interface in which information about the classification is presented. The matching approach may be implemented in conjunction with conventional matching methods to provide classifications. The matching approach is capable of interacting with users of the approach to dynamically alter the classifications being searched based on any given set of search results.
Owner:ZENTNER MICHAEL G
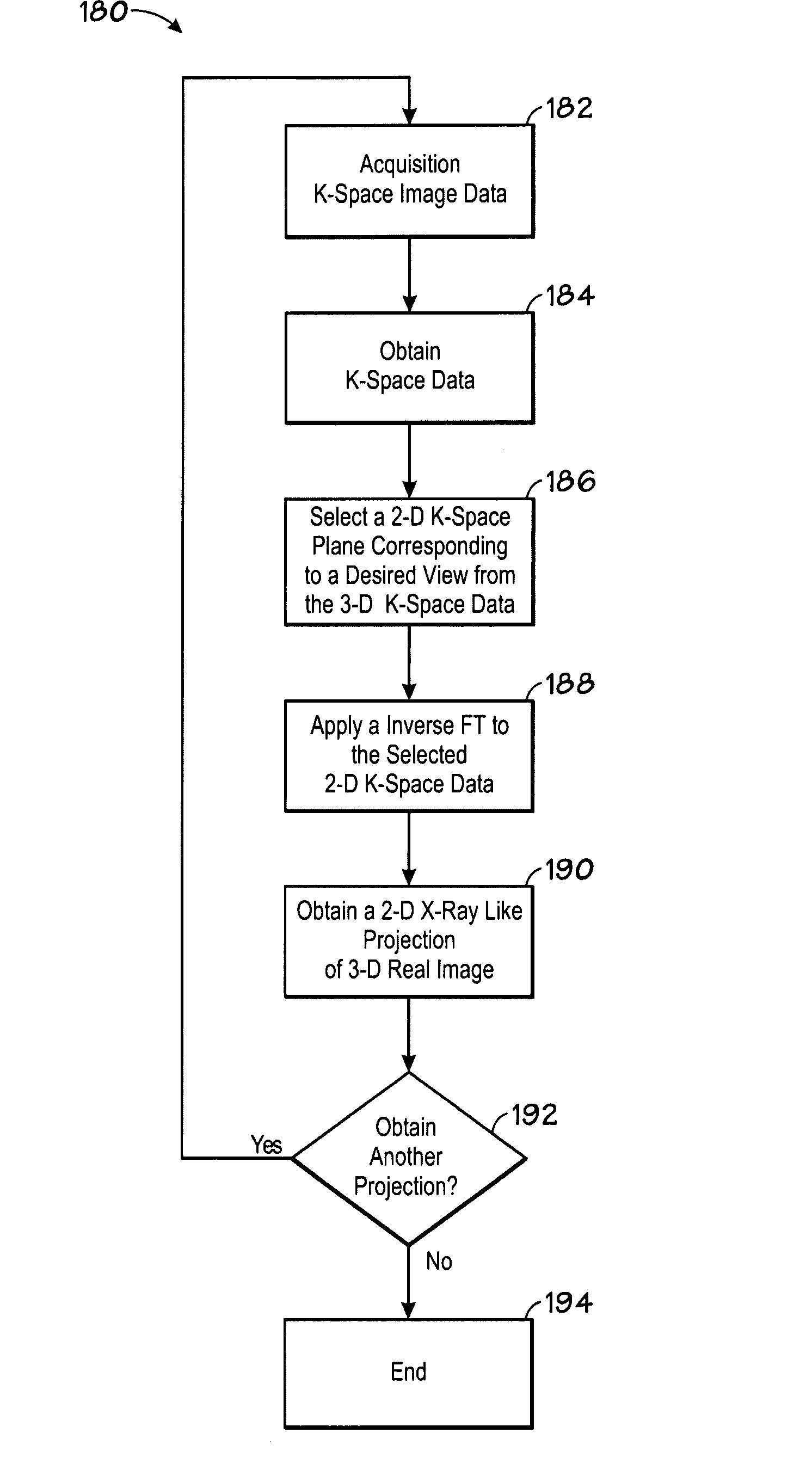
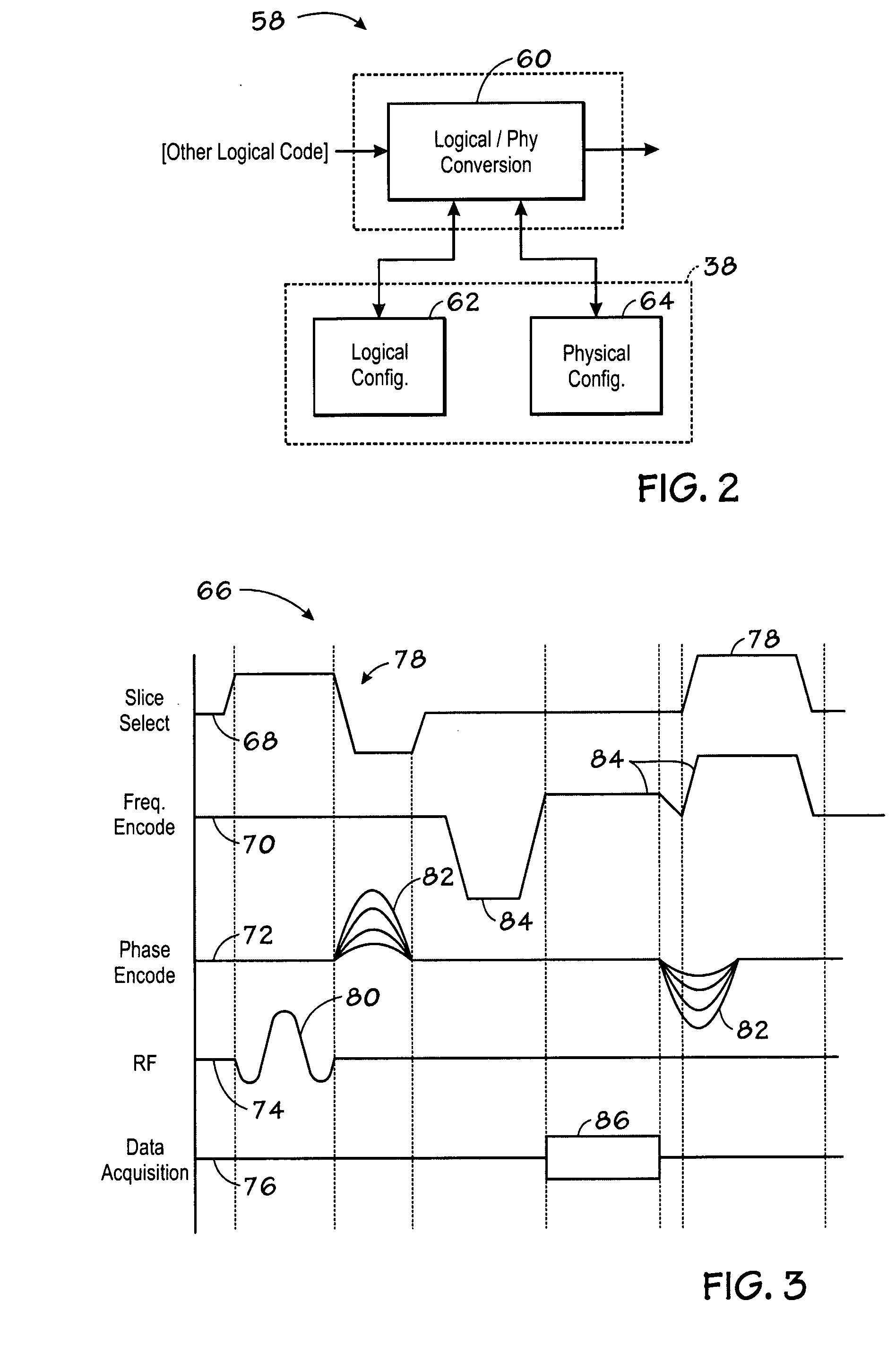
Magnetic resonance imaging visualization method and system
ActiveUS20080258724A1Rapid visualizationCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsThree-dimensional spaceX-ray
The present technique provides a system and method for processing an image. Particularly the method comprises acquiring image data in frequency space (k-space) of an imaged volume and obtaining a three-dimensional (3-D) k-space volume representative of the imaged volume based on the acquired k-space data. The method further comprises selecting a two-dimensional (2-D) plane from the 3-D k-space volume and applying an inverse Fourier transform to the selected 2-D plane to obtain a real 2-D X-ray-like (or enhanced rendering) projection of the imaged volume offering insights into the 3-D data.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com