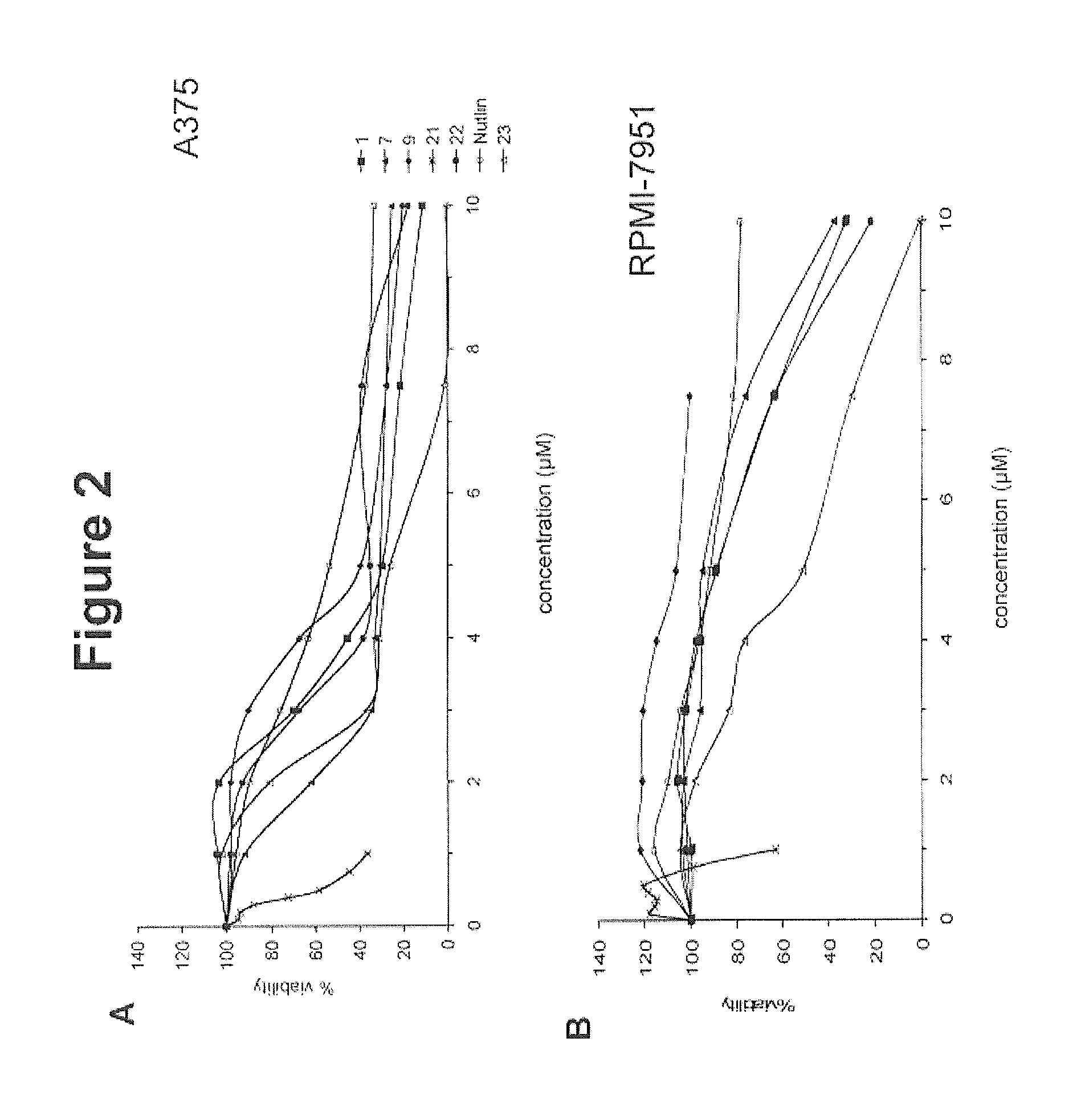
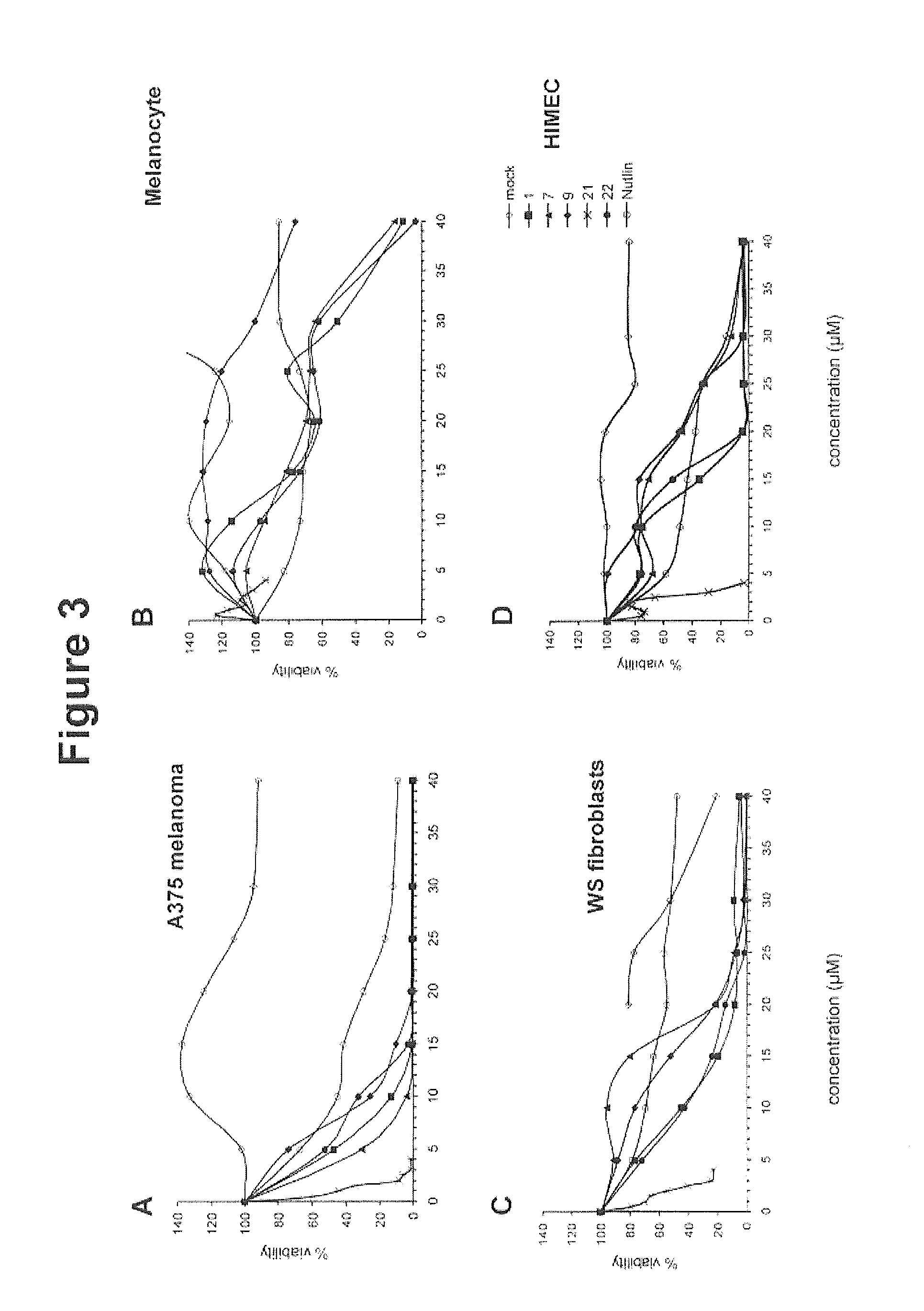
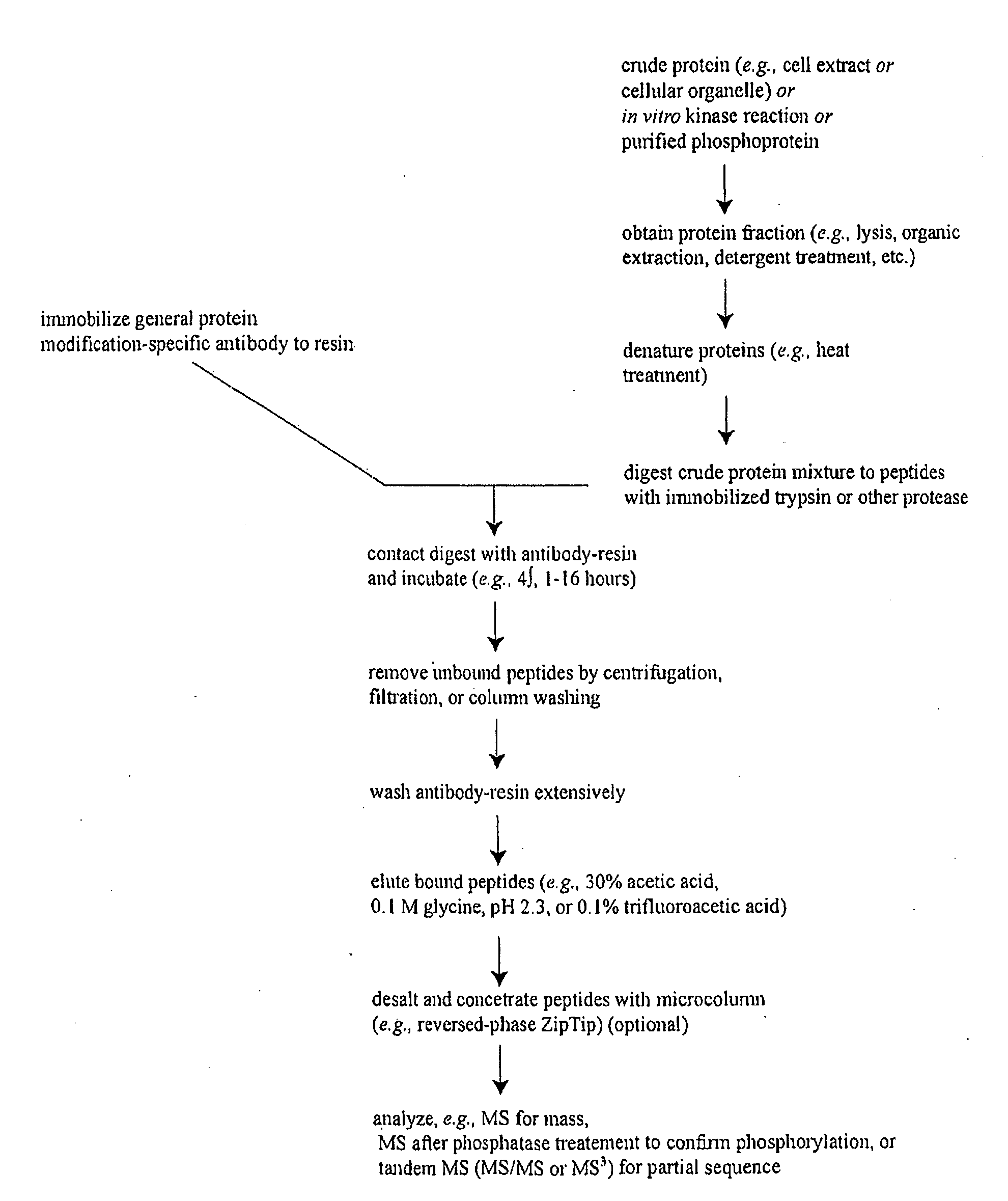
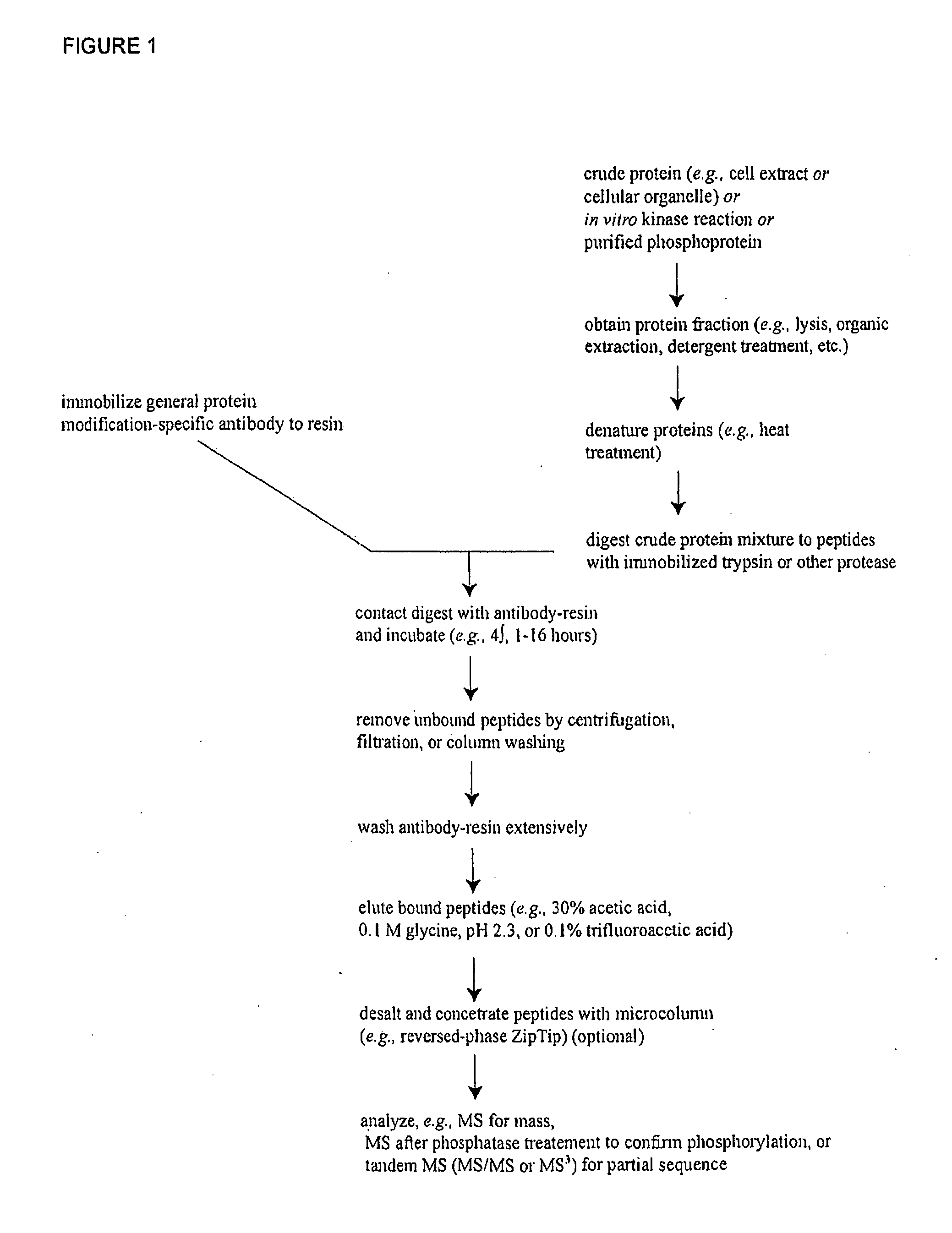
Patents
Literature
51 results about "Tumor suppressor proteins" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Compositions, kits, and methods relating to the human FEZ1 gene, a novel tumor suppressor gene
InactiveUS20070072230A1Increase stringencyInhibiting tumorigenesisSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsTumour suppressor geneHuman tumor
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Compositions, kits, and methods relating to the human FEZ1 gene, a novel tumor suppressor gene
InactiveUS7777005B2Increase stringencyInhibiting tumorigenesisSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsHuman tumorNucleotide
The invention relates to isolated polynucleotides homologous with a portion of one strand of the human tumor suppressor gene, FEZ1, and to the tumor suppressor protein encoded thereby, Fez1. The polynucleotides are useful, for example, as probes, primers, portions of expression vectors, and the like. The invention also includes diagnostic, therapeutic, cell proliferation enhancement, and screening methods which involve these polynucleotides and protein. The invention further includes kits useful for performing the methods of the invention.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Compositions, kits, and methods relating to the human FEZ1 gene, a novel tumor suppressor gene
InactiveUS7141417B1Increase stringencyInhibiting tumorigenesisSugar derivativesPeptidesHuman tumorNucleotide
The invention relates to isolated polynucleotides homologous with a portion of one strand of the human tumor suppressor gene, FEZ1, and to the tumor suppressor protein encoded thereby, Fez1. The polynucleotides are useful, for example, as probes, primers, portions of expression vectors, and the like. The invention also includes diagnostic, therapeutic, cell proliferation enhancement, and screening methods which involve these polynucleotides and protein. The invention further includes kits useful for performing the methods of the invention.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Co-feeding lipid nano-delivery system for medicine carrying
ActiveCN102114000AThe dosage can be controlledEasy to administerPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic effectOncoprotein p53
The invention belongs to the field of medicinal preparation, relates to a co-feeding delivery system, and particularly relates to a co-feeding lipid nano-delivery system for entrapping anticancer polypeptide and gene or chemotherapeutics or radiopharmaceutical simultaneously. The delivery system consists of a target searching material, a lipid component and medicaments, ensures that different medicaments are entrapped to the lipid nano-delivery system together by sufficiently utilizing character difference among components or entrapping through static electricity or a method of passively combining and actively carrying, and can simultaneously deliver the anticancer polypeptide and genetic medicament capable of restoring activity of tumor suppressor protein p53 or chemotherapeutics or radiopharmaceutical into a target cell so as to achieve the aim of co-therapy. By virtue of in-vitro activity evaluation, the system is proved to be superior to that of delivering single component at the same time, the anticancer activity of the system is remarkably improved, and the system has definite co-therapy effect.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
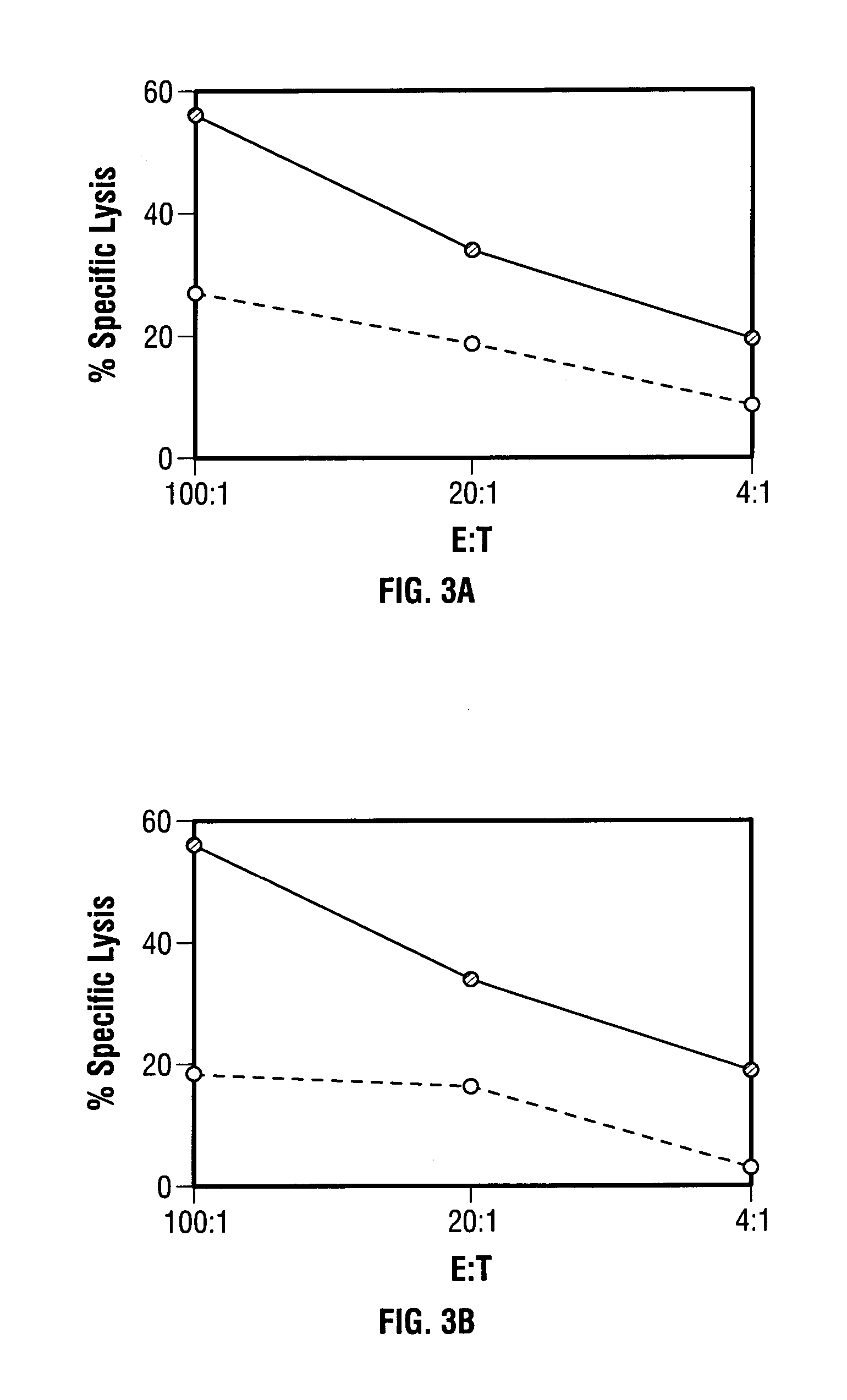
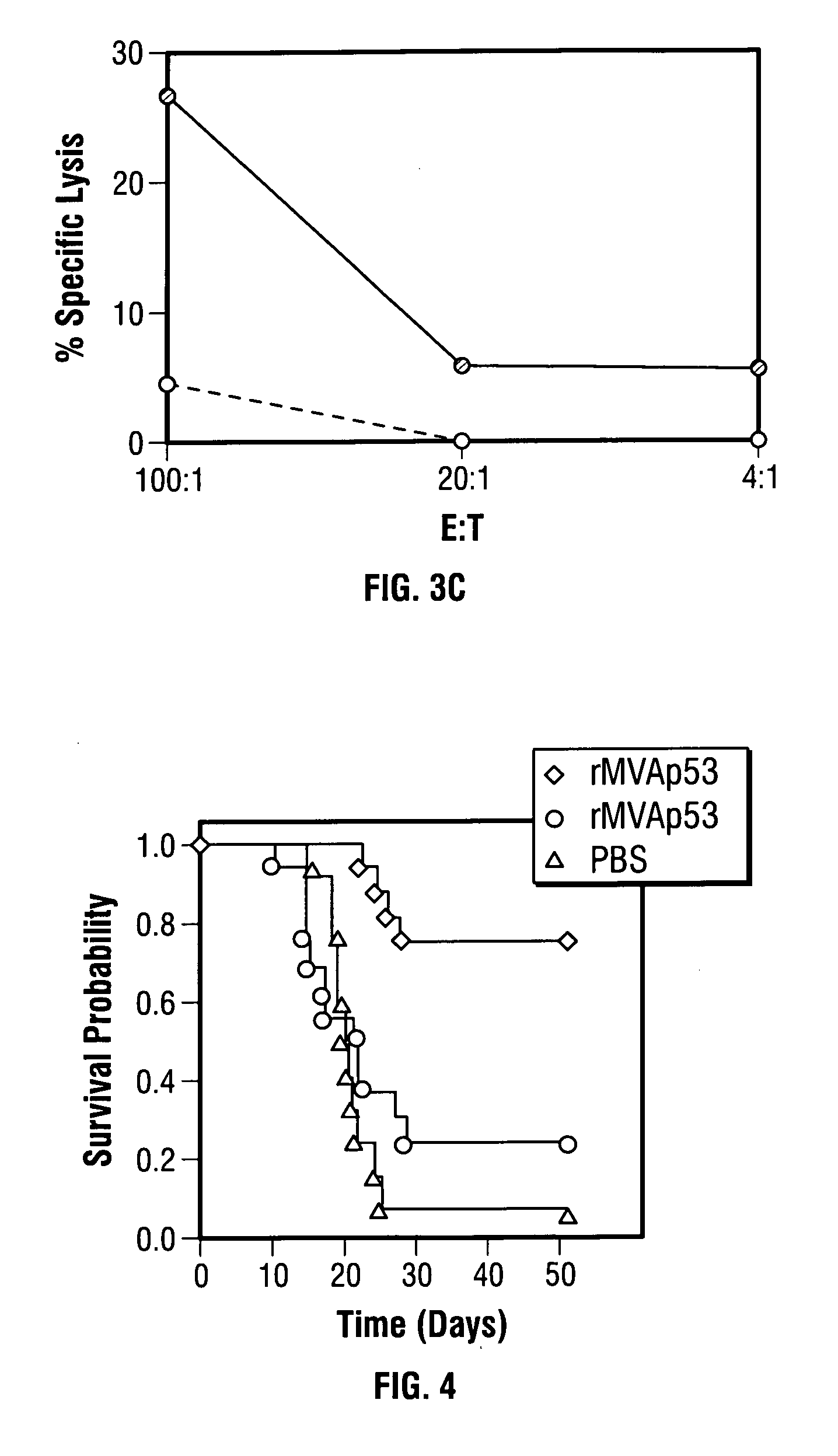
Modified vaccinia Ankara expressing p53 in cancer immunotherapy
ActiveUS7256037B2Limit therapeutic efficacyReduce developmentBiocideGenetic material ingredientsModified vaccinia AnkaraADAMTS Proteins
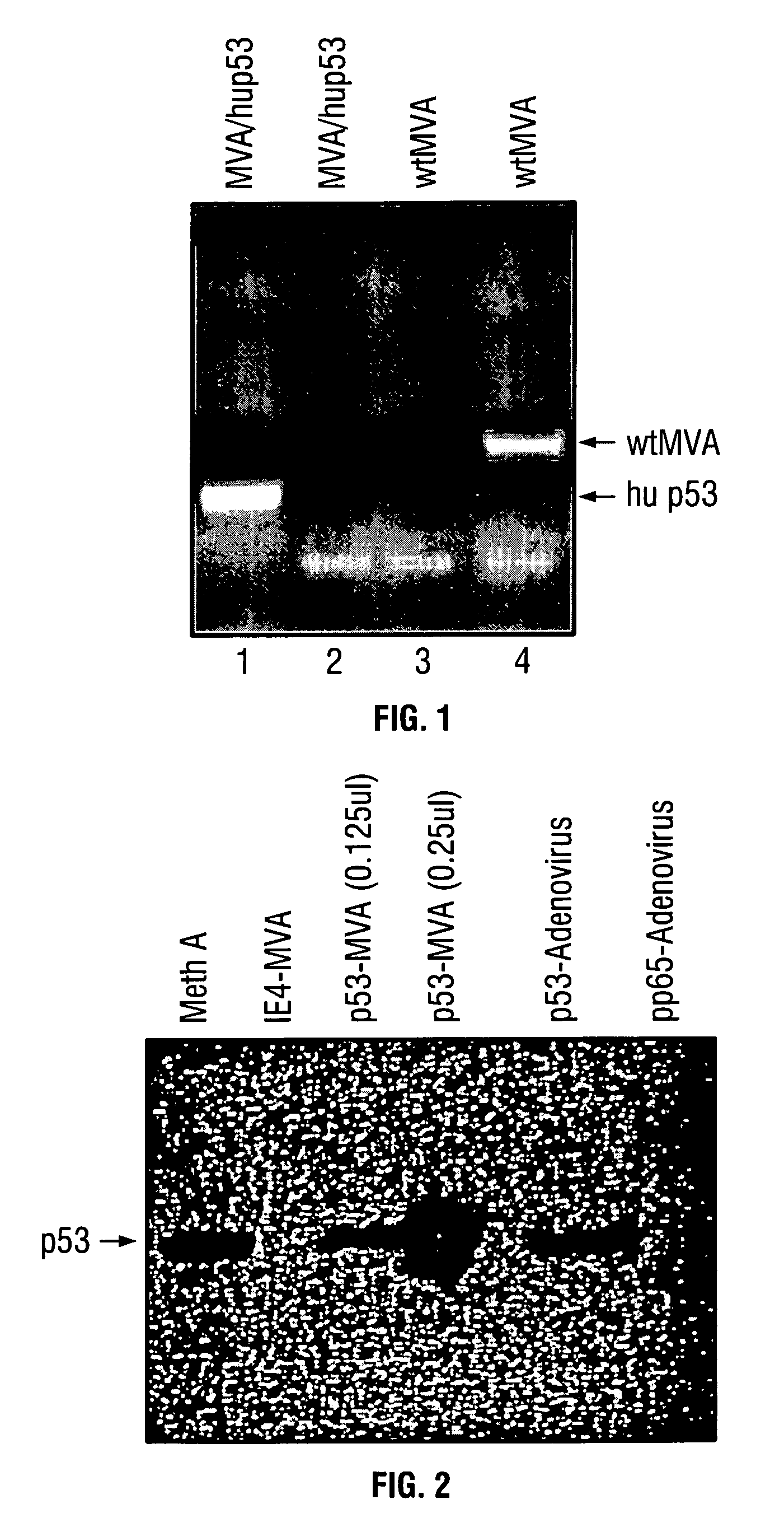
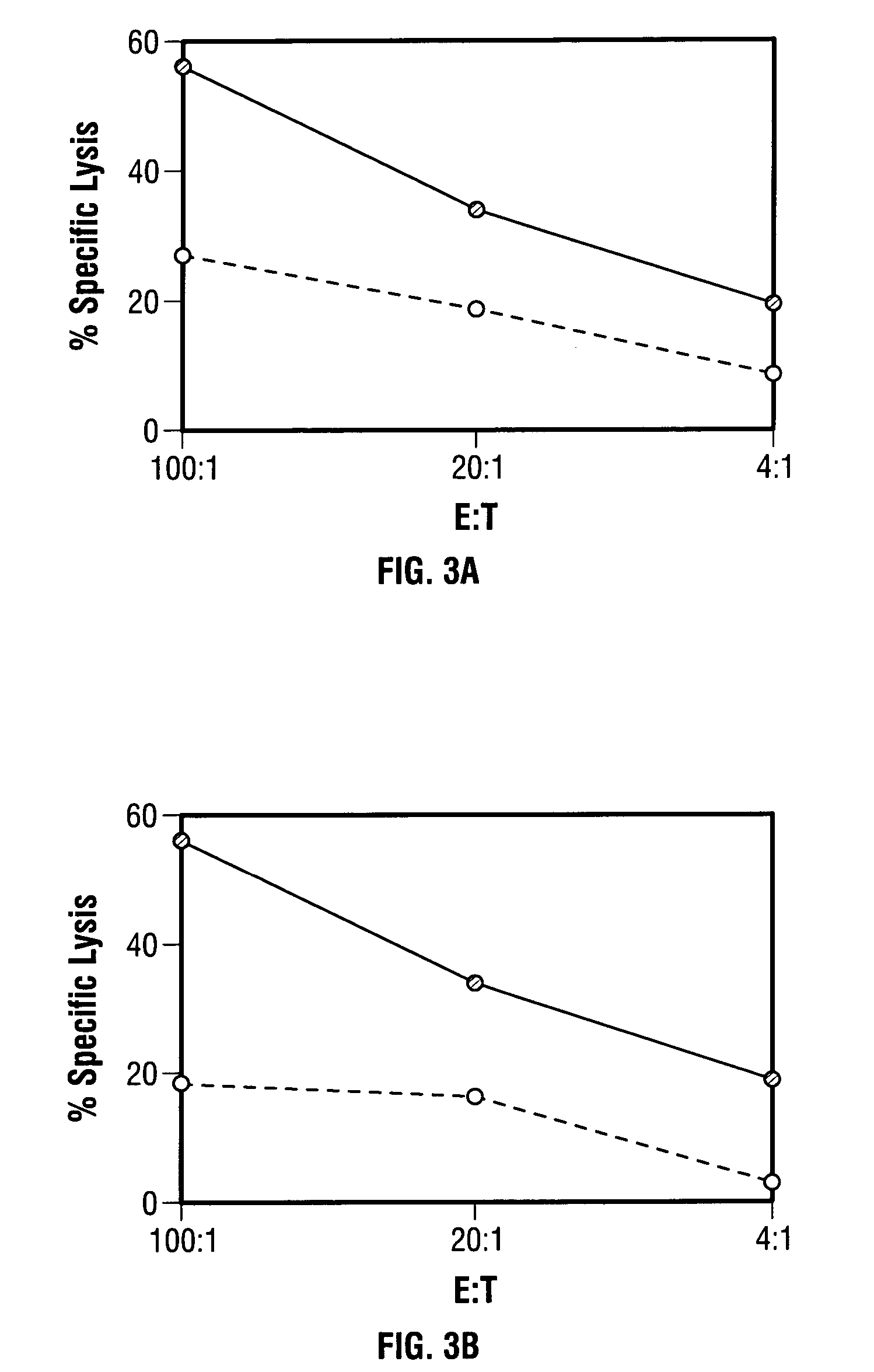
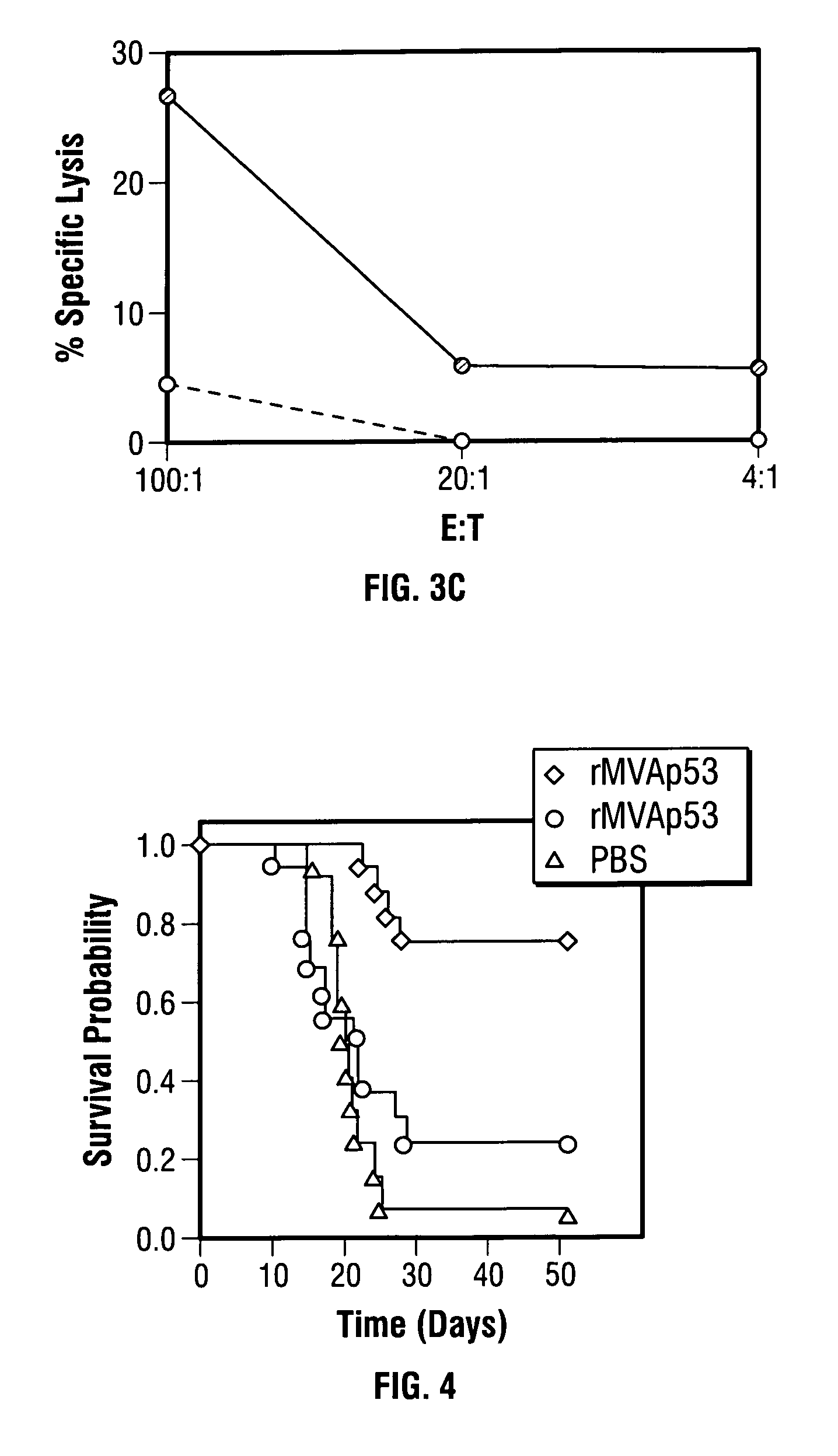
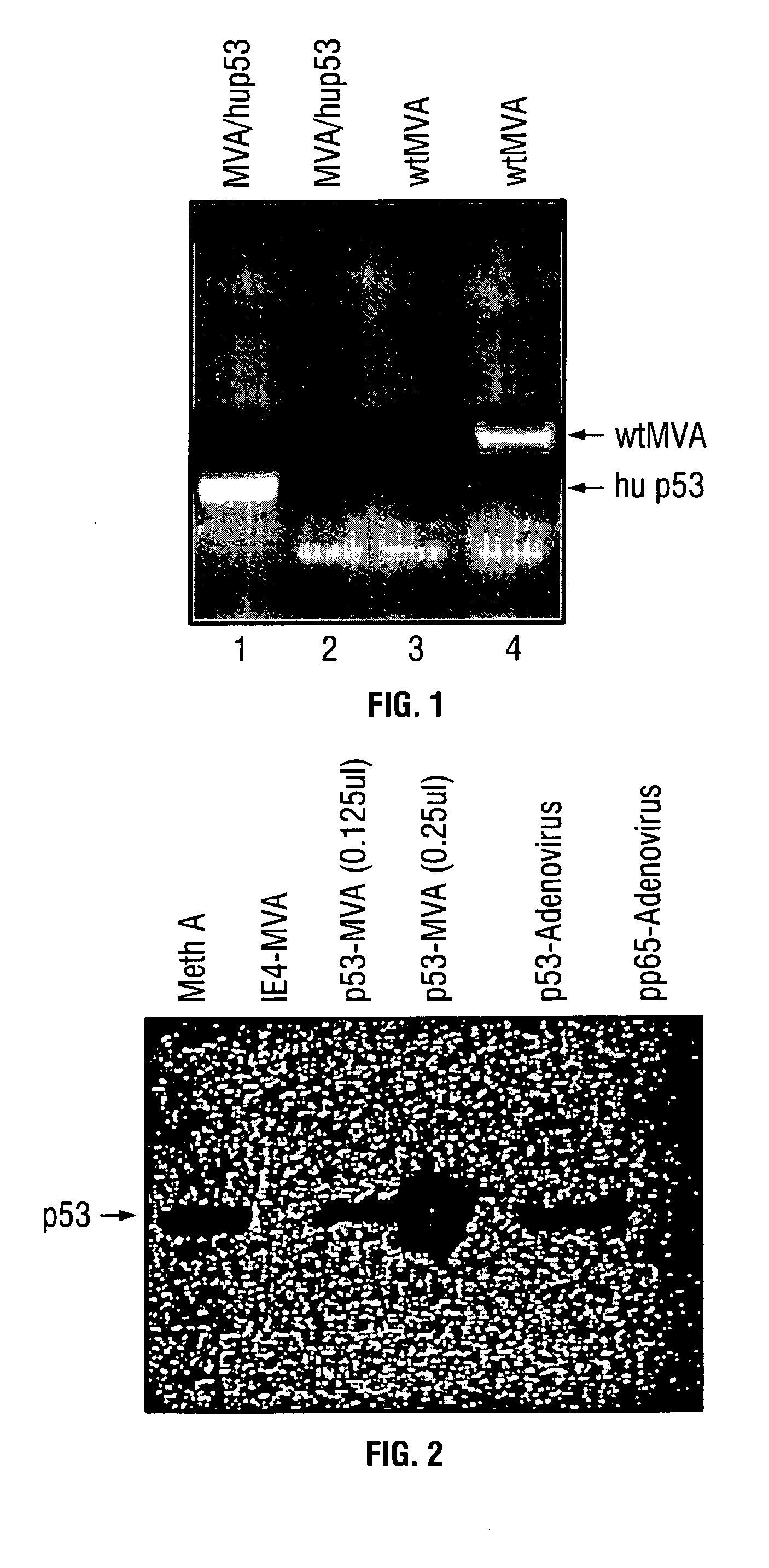
Mutations to the tumor suppressor protein p53 have been observed in 40-60% of all human cancers. These mutations are often associated with high nuclear and cytoplasmic concentrations of p53. Since many tumors exhibit highly elevated p53 levels, the protein is an attractive target for cancer immunotherapy. Unfortunately, p53 is an autoantigen that is likely to be tolerated as a self-protein by the immune system. The present invention is based on the discovery that this self-tolerance can be overcome by administration of recombinant modified vaccinia Ankara (MVA) containing a nucleic acid that encodes p53 (rMVAp53). The invention discloses a method of generating a p53-specific CTL-response to tumor cells expressing mutated p53 by administering a composition comprising rMVAp53. Administration of rMVAp53 decreases tumor development, tumor growth, and mortality in a variety of malignant cell types. These effects are enhanced by administration of CTLA-4 blocker and / or CpG oligodeoxynucleotide immunomodulators.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Modified vaccinia ankara expressing p53 in cancer immunotherapy
Mutations to the tumor suppressor protein p53 have been observed in 40-60% of all human cancers. These mutations are often associated with high nuclear and cytoplasmic concentrations of p53. Since many tumors exhibit highly elevated p53 levels, the protein is an attractive target for cancer immunotherapy. Unfortunately, p53 is an autoantigen that is likely to be tolerated as a self-protein by the immune system. The present invention is based on the discovery that this self-tolerance can be overcome by administration of recombinant modified vaccinia Ankara (MVA) containing a nucleic acid that encodes p53 (rMVAp53). The invention discloses a method of generating a p53-specific CTL-response to tumor cells expressing mutated p53 by administering a composition comprising rMVAp53. Administration of rMVAp53 decreases tumor development, tumor growth, and mortality in a variety of malignant cell types. These effects are enhanced by administration of CTLA-4 blocker and / or CpG oligodeoxynucleotide immunomodulators.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
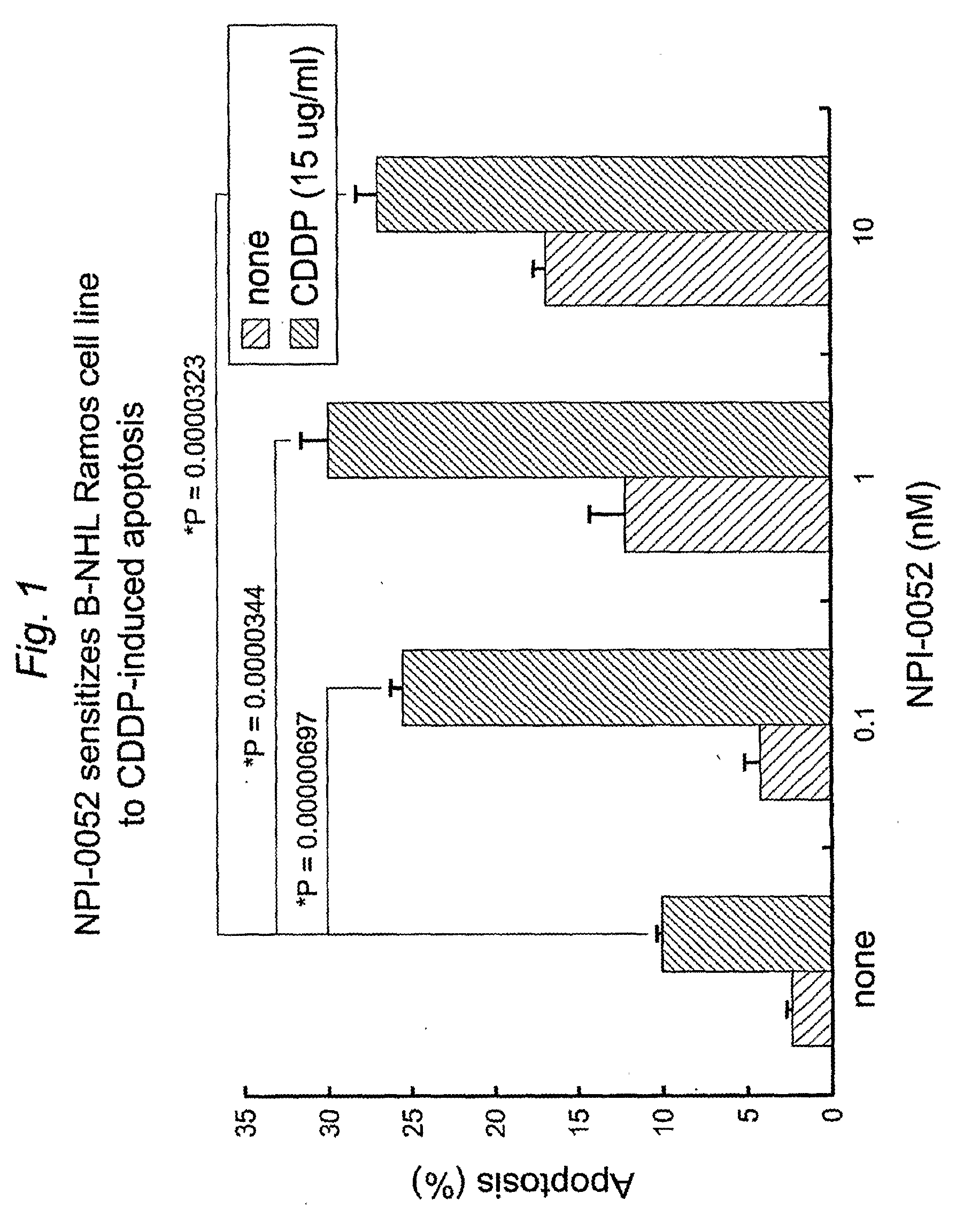
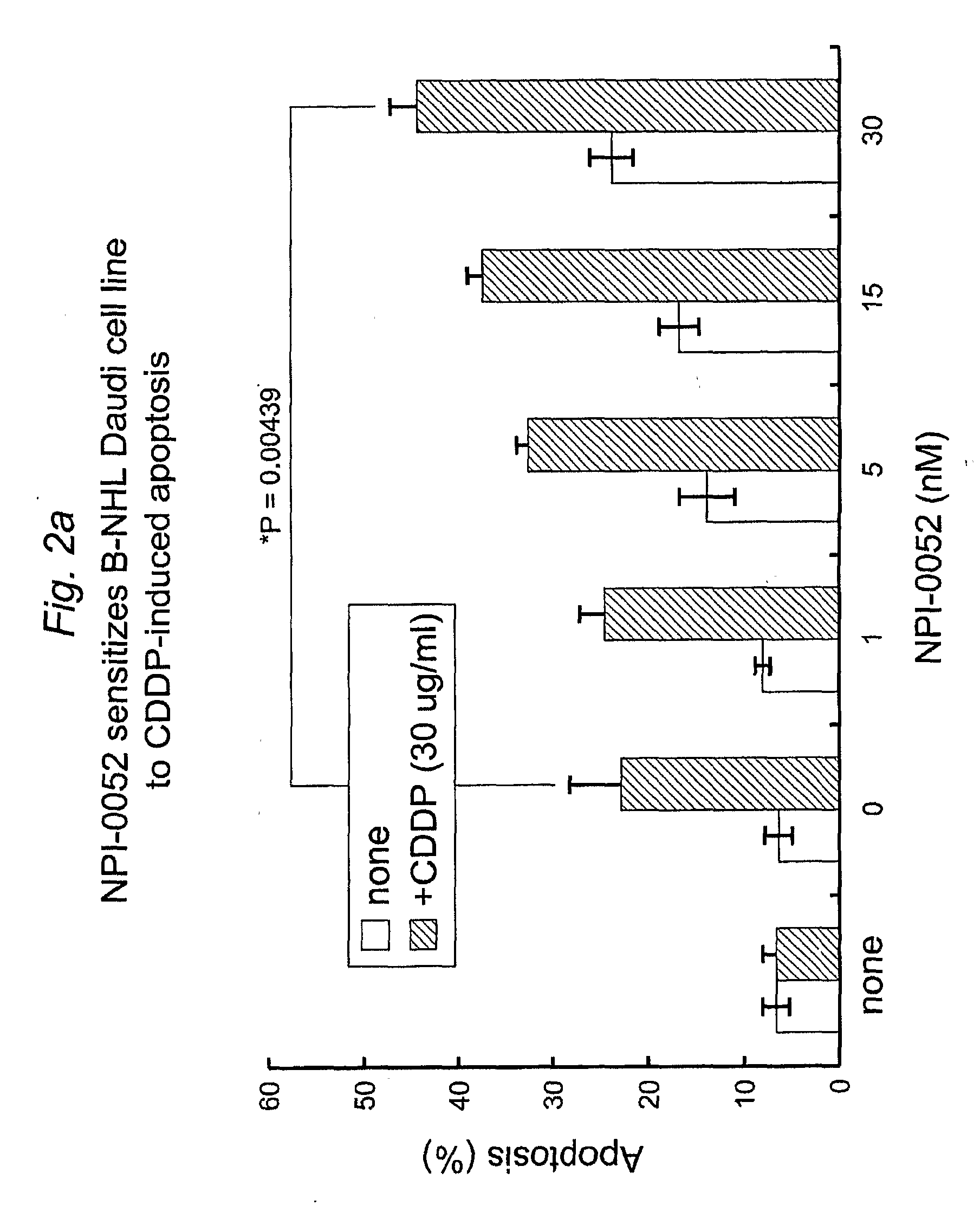
Methods of sensitizing cancer to therapy-induced cytotoxicity
InactiveUS20090148445A1Treating and preventing and inhibiting lymphomaPreventing and inhibiting lymphomaBiocideBoron compound active ingredientsSalinosporamide ATherapy resistant
Owner:TRIPHASE RES & DEV I +1
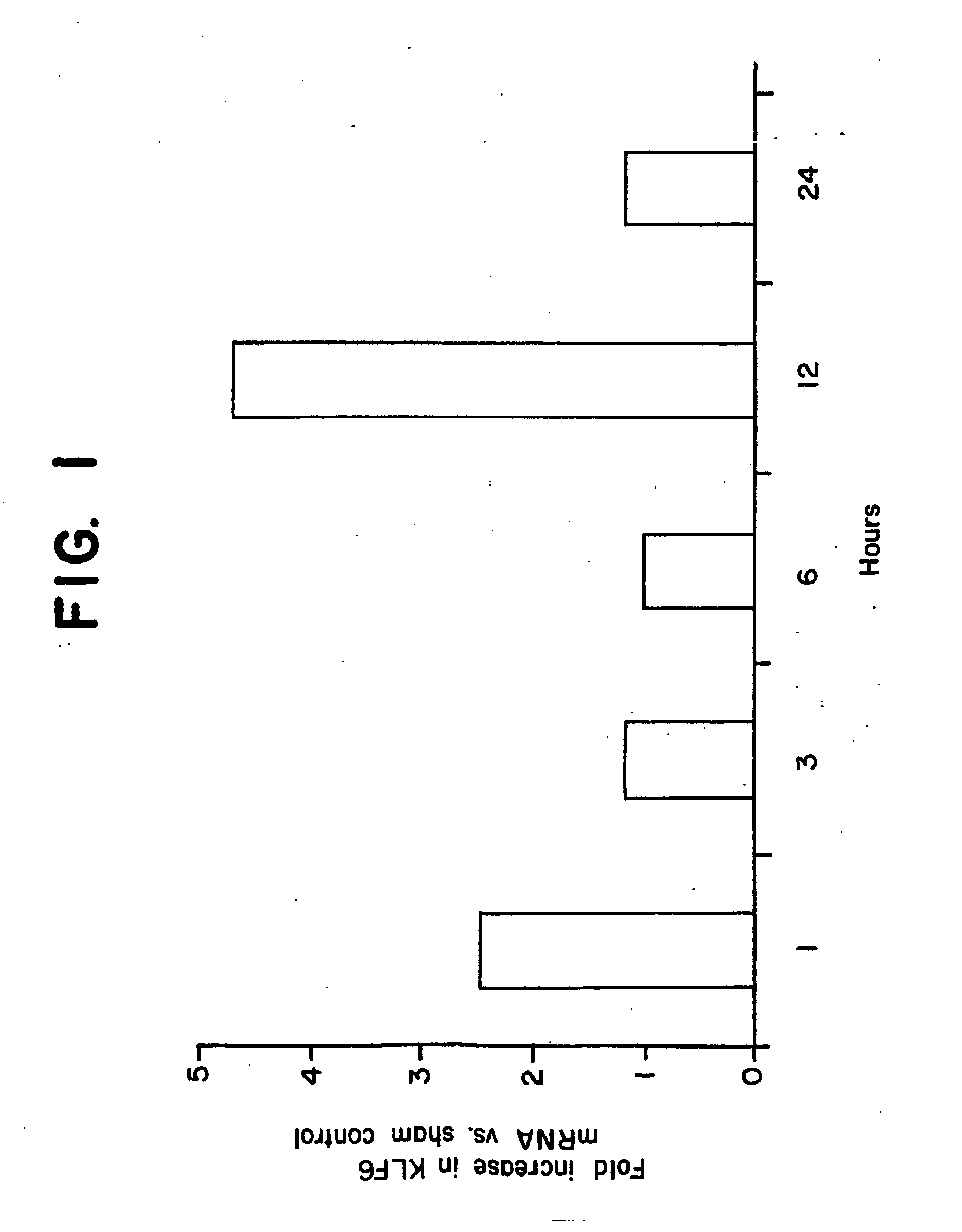
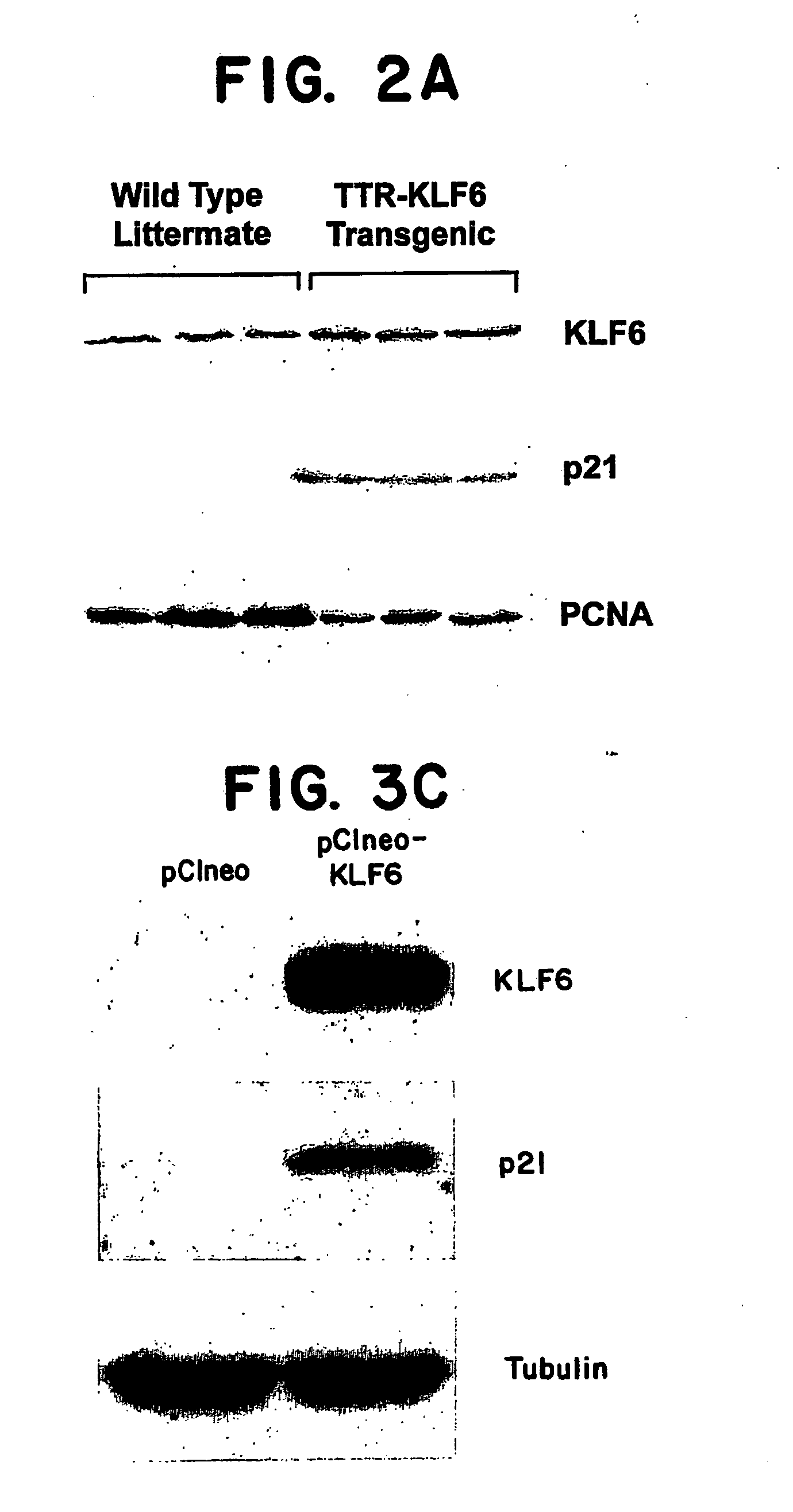
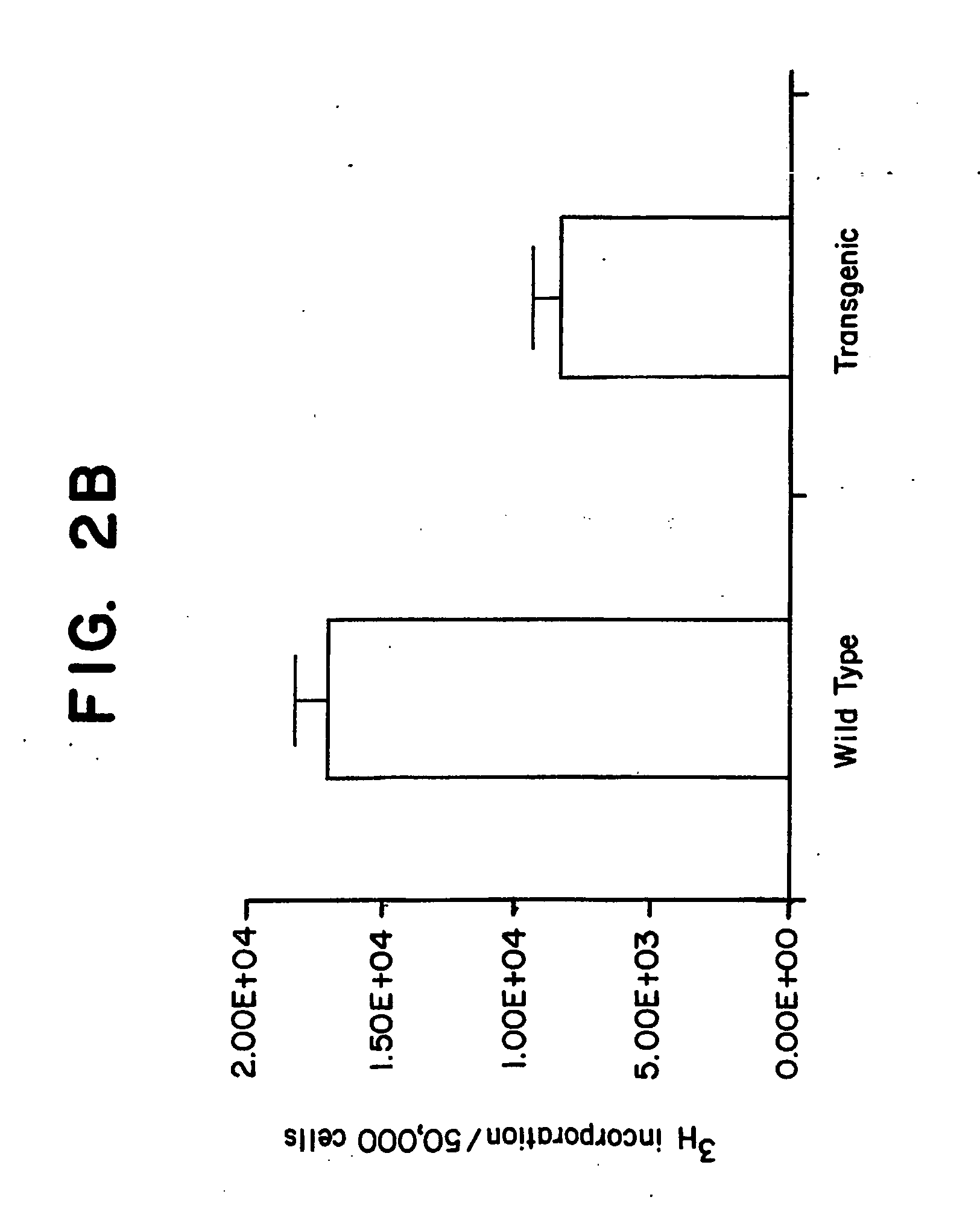
Kruppel-like factor 6 ( KLF6), a tumor suppressor protein, and diagnostics, therapeutics, and screening based on this protein
InactiveUS20050181374A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisGeneTumor suppressor activity
The present invention relates to identification of tumor suppressor activity of a protein, KLF6 (KLF6), and to related diagnostic and therapeutic compositions and methods. The discovery of this tumor suppressor activity provides screening targets as well, particularly screening for compounds that overcome gene inactivation or alteration.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Compounds and methods of early diagnosis of cervical cancer and genital condyloma with HPV, CHSP60 tumor suppressor h-ras, k-ras and PTEN derived peptides modified
InactiveUS20060154238A1Easy to synthesizeStrong specificityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsViral antigen ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthHuman papillomavirus
An isolated sequence or peptide isolated from an E2, E4, E6, E7 early or late coding region of human papillomavirus (HPV) that is soluble in aqueous medium, and characterized by a linkage to another protein sequence or peptide isolated from the E2, E4, E6, E7 early or late coding region of HPV by a spacer sequence, wherein the isolated protein sequence or peptide consists of more than 50% hydrophilic amino acids, and is recognized by a specific antibody of HPV. Also disclosed are isolated protein sequences or peptides from Harvey Ras (H-Ras), Kirsten Ras (K-Ras), and phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) tumor suppressor proteins and Chlamydia trachomatis heat shock protein 60 (CHSP60 groEL1) and methods for detecting or diagnosing cancer or cellular abnormalities.
Owner:HU YAO XIONG
Compounds and methods of early diagnosis of cervical cancer and genital condyloma with HPV, CHSP60 tumor suppressor H-Ras, K-Ras and PTEN derived peptides modified
InactiveUS7314630B2Easy to synthesizeStrong specificityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsViral antigen ingredientsHuman papillomavirusADAMTS Proteins
Owner:HU YAO XIONG
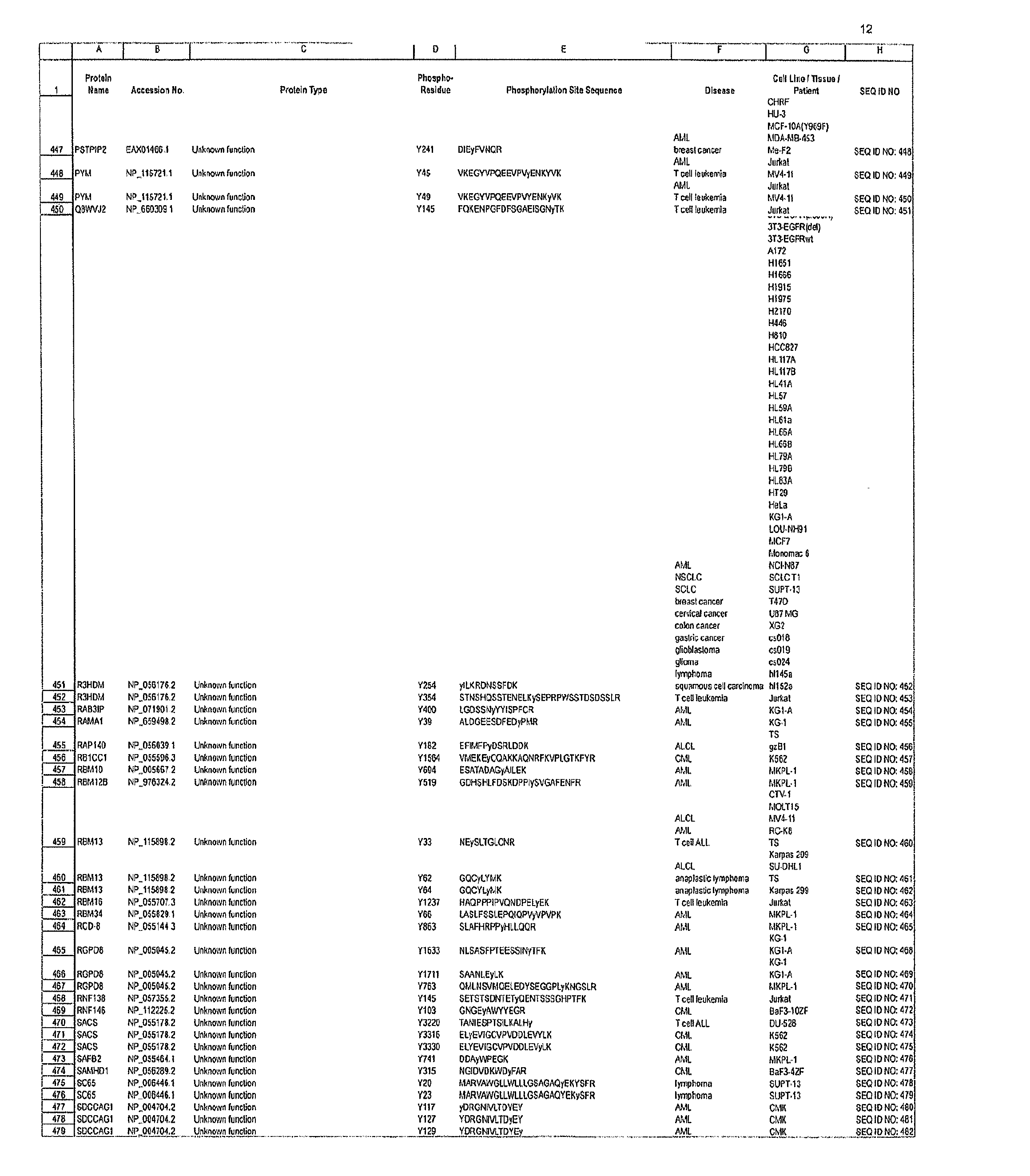
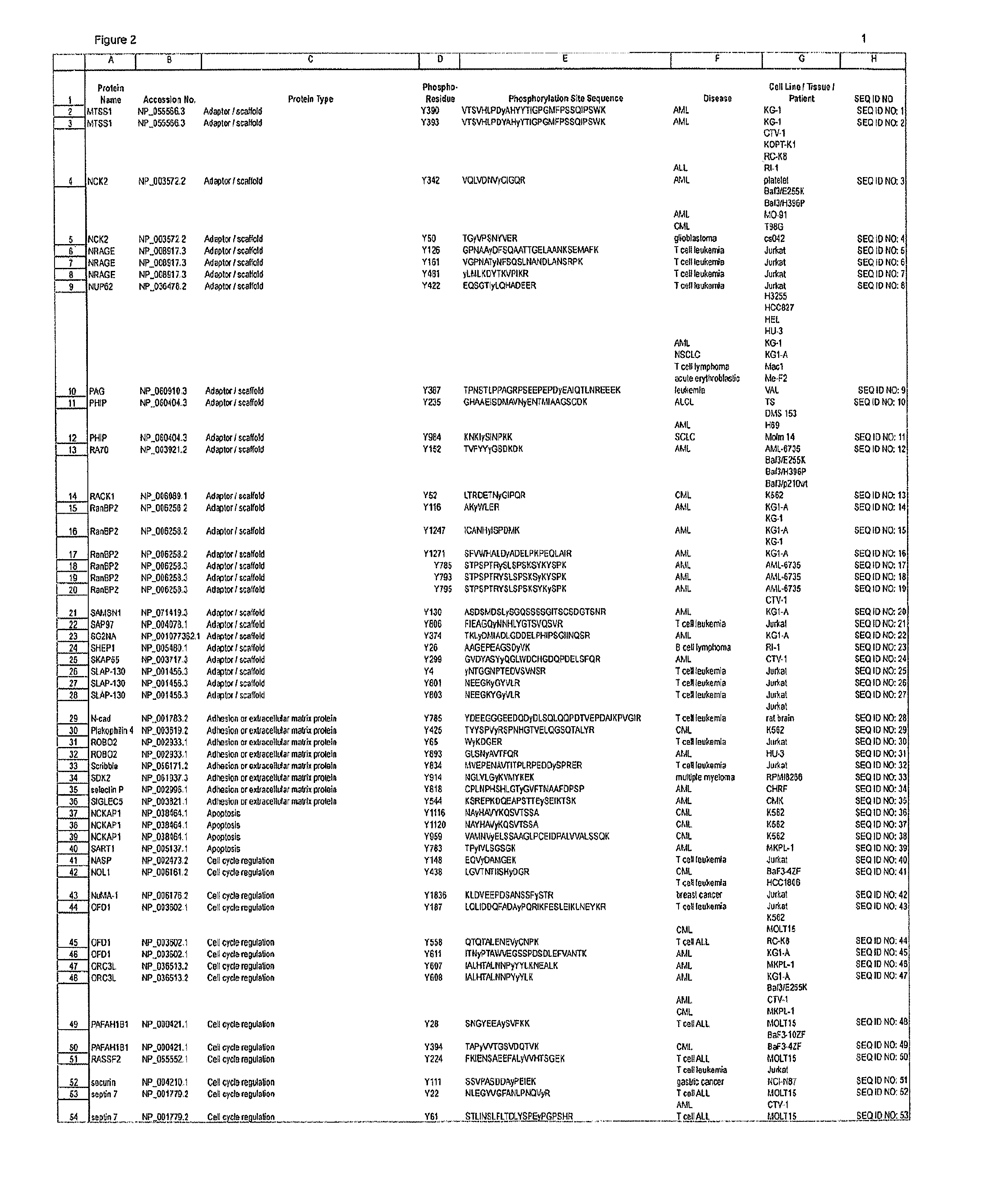
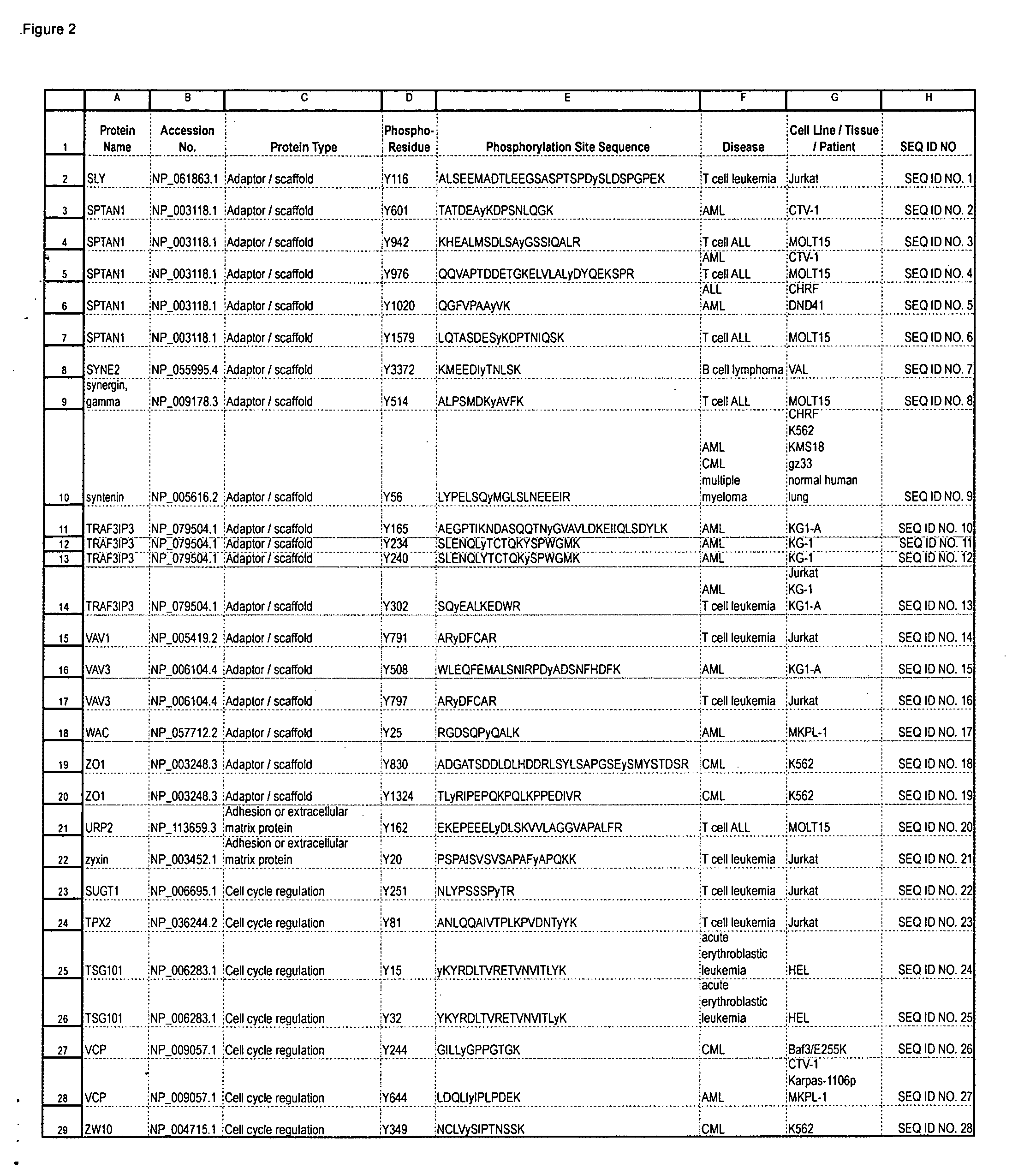
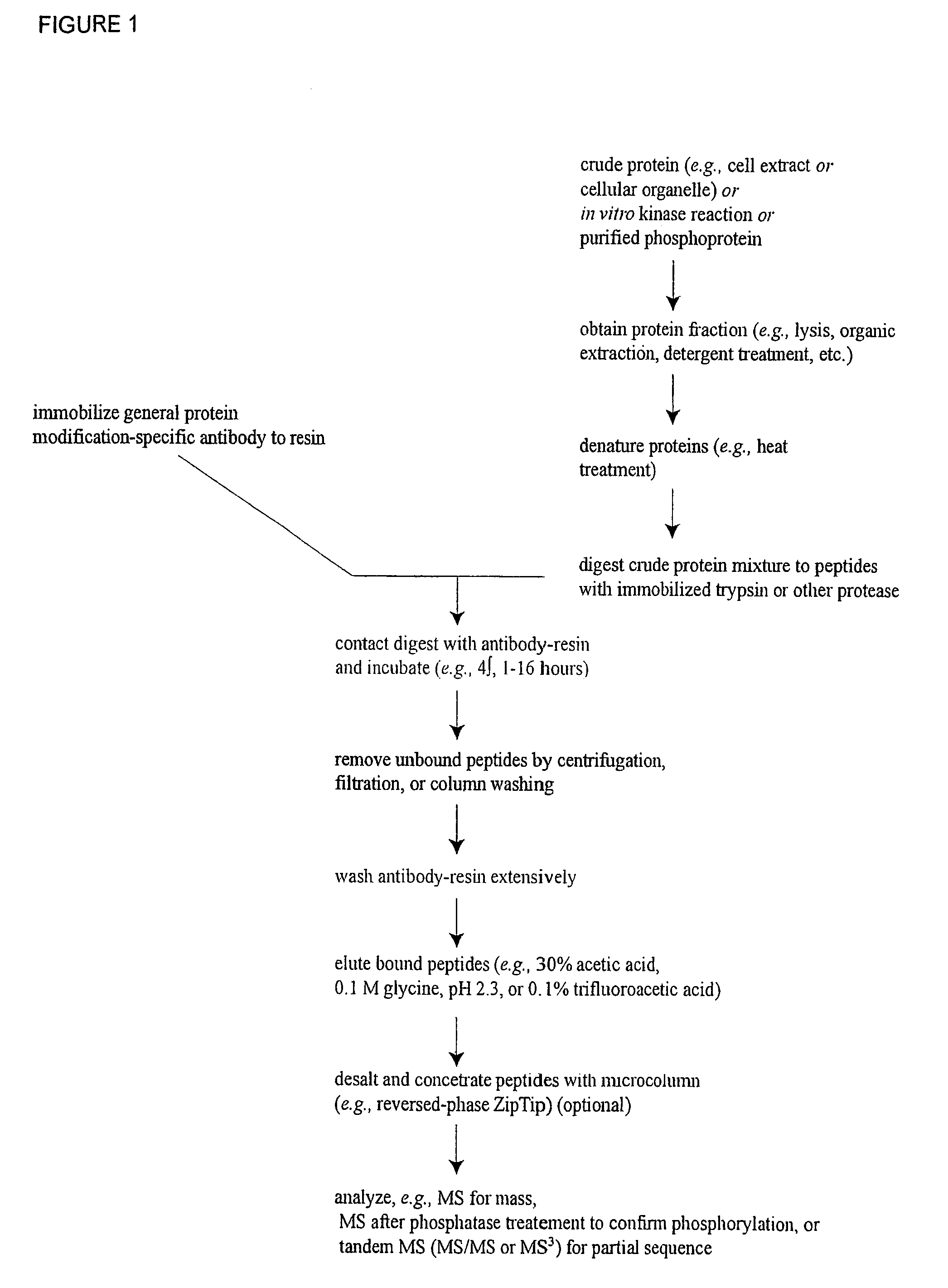
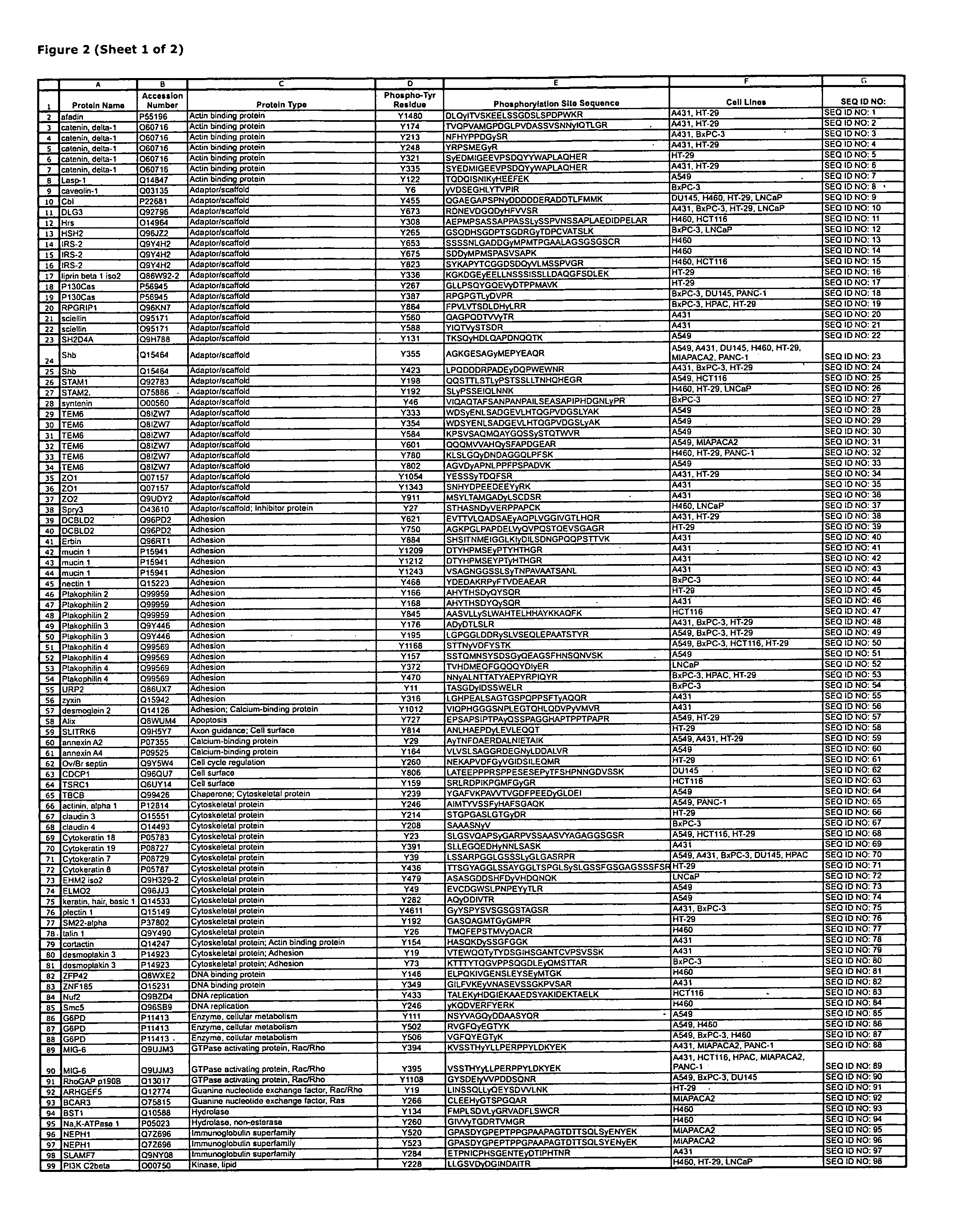
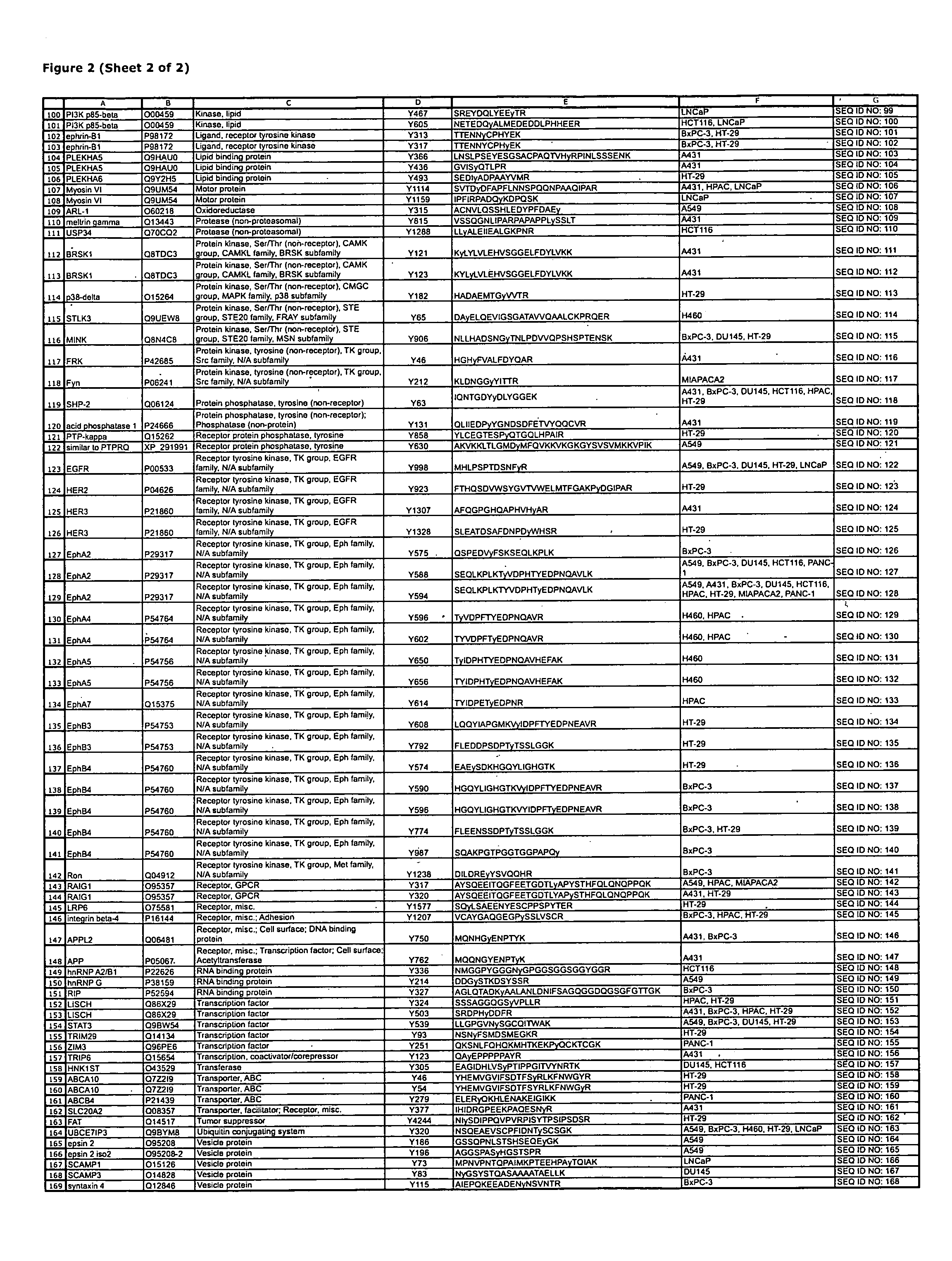
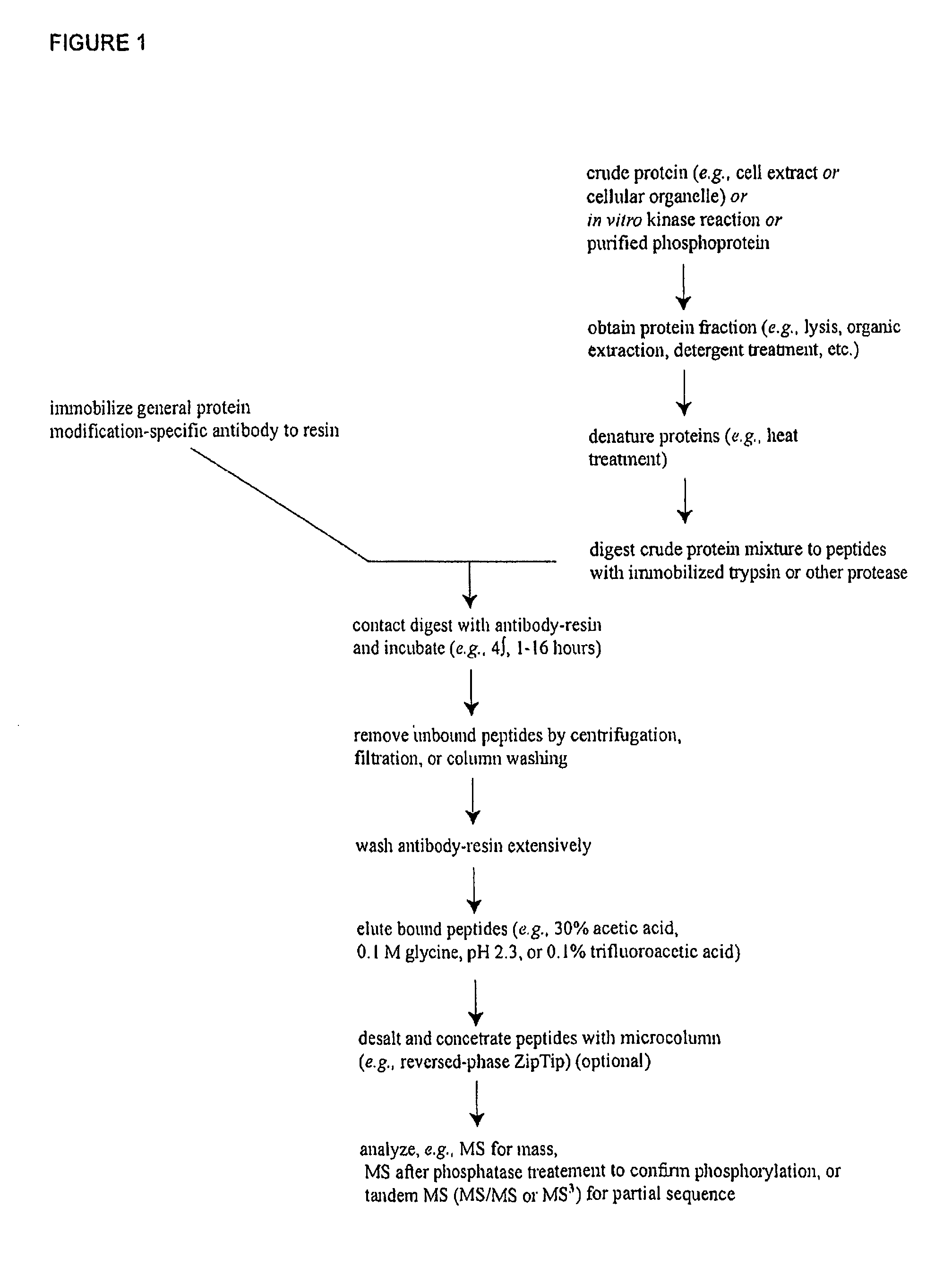
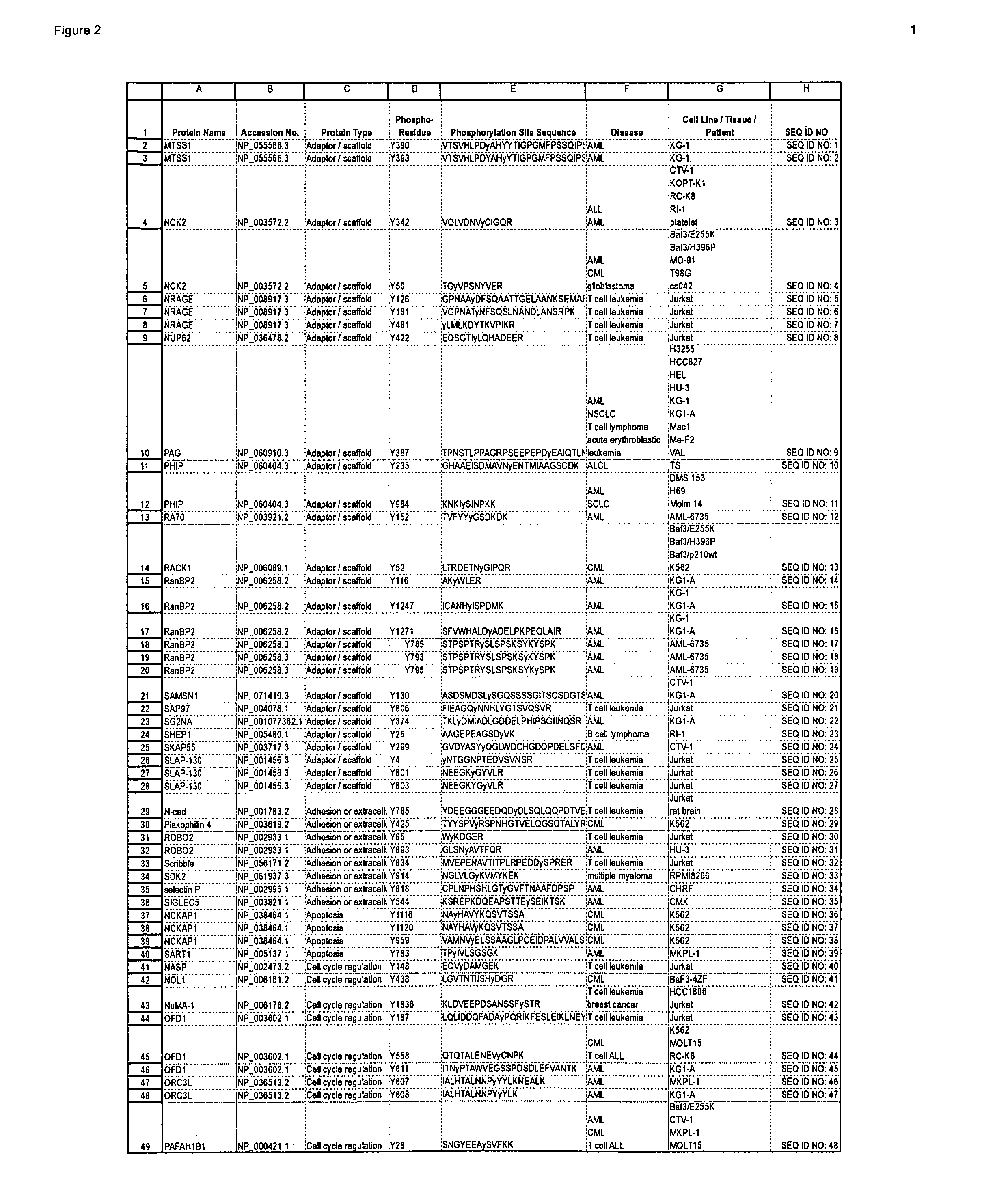
Reagents for the Detection of Protein Phosphorylation in Signaling Pathways
ActiveUS20090258436A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansEndoplasmic reticulumScaffold protein
The invention discloses novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: adaptor / scaffold proteins, adhesion / extracellular matrix protein, apoptosis proteins, calcium binding proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, chaperone proteins, chromatin, DNA binding / repair / replication proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, endoplasmic reticulum or golgi proteins, enzyme proteins, G / regulator proteins, inhibitor proteins, motor / contractile proteins, phosphatase, protease, Ser / Thr protein kinases, Protein kinase (Tyr)s, receptor / channel / cell surface proteins, RNA binding proteins, transcriptional regulators, tumor suppressor proteins, ubiquitan conjugating system proteins and proteins of unknown function.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Nanometer vesica capable of detecting wild type p53 protein and variant p53 protein in cells simultaneously
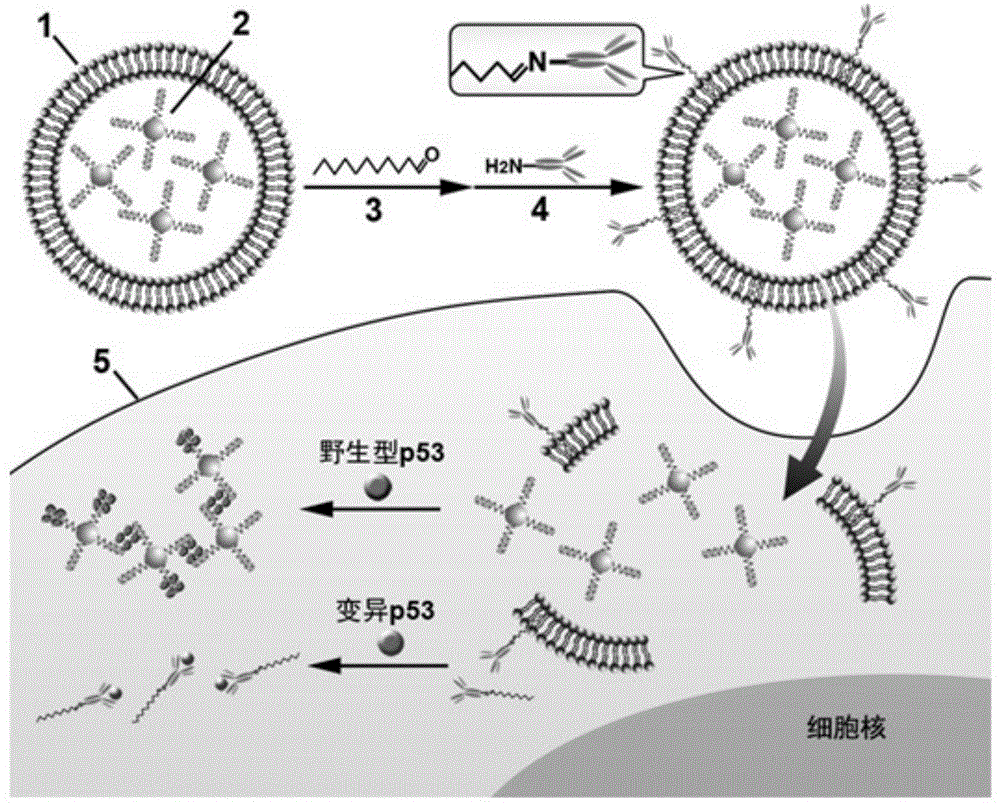
InactiveCN104977277AAchieving Simultaneous DetectionImprove featuresFluorescence/phosphorescenceCell layerWild type
The invention discloses a nanometer vesica capable of detecting wild type p53 protein and variant p53 protein in cells simultaneously. Nanogold capable of specifically recognizing wild type p53 protein wraps inside the vesica, and an antibody resisting variant p53 protein marked by fluorescein isothiocyanate decorates the surface of the vesica. The nanometer vesica has the advantages that (1) the nanometer vesica recognizes different types of tumor suppressor proteins p53 with high specificity, and the detection specificity and the sensitivity are improved; (2) plasma resonance imaging and fluorescence imaging technologies are adopted, after the vesica enters the cell, the cell is subjected to in-situ imaging by adopting a microscope, and wild type p53 protein and variant p53 protein on the single-cell layers are detected simultaneously; (3) the nanometer vesica designed according to the technical scheme is capable of carrying out in-situ monitoring on variation of expression of p53 protein in the cell under the action of medicine, and a novel method is provided for researching physiological process in the cell participated by the vesica.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
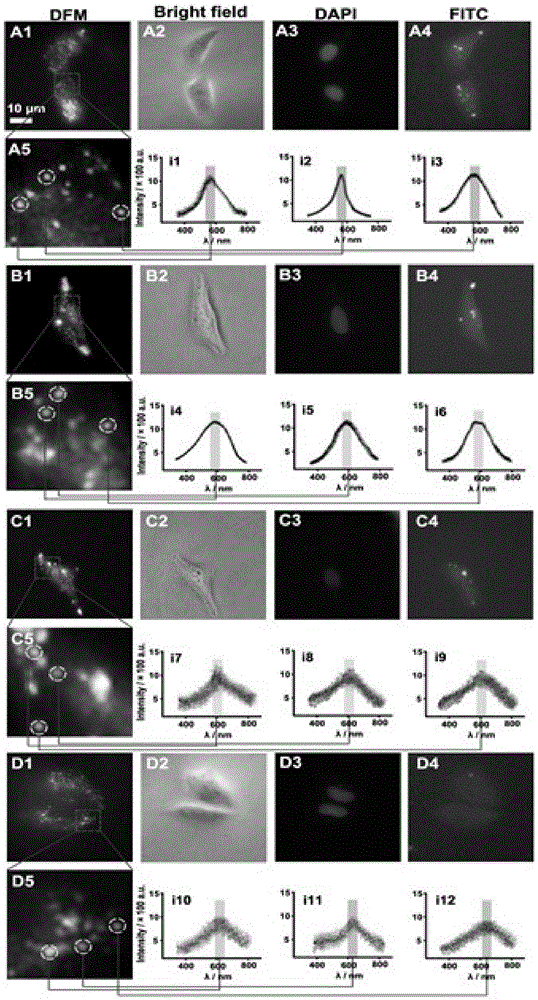
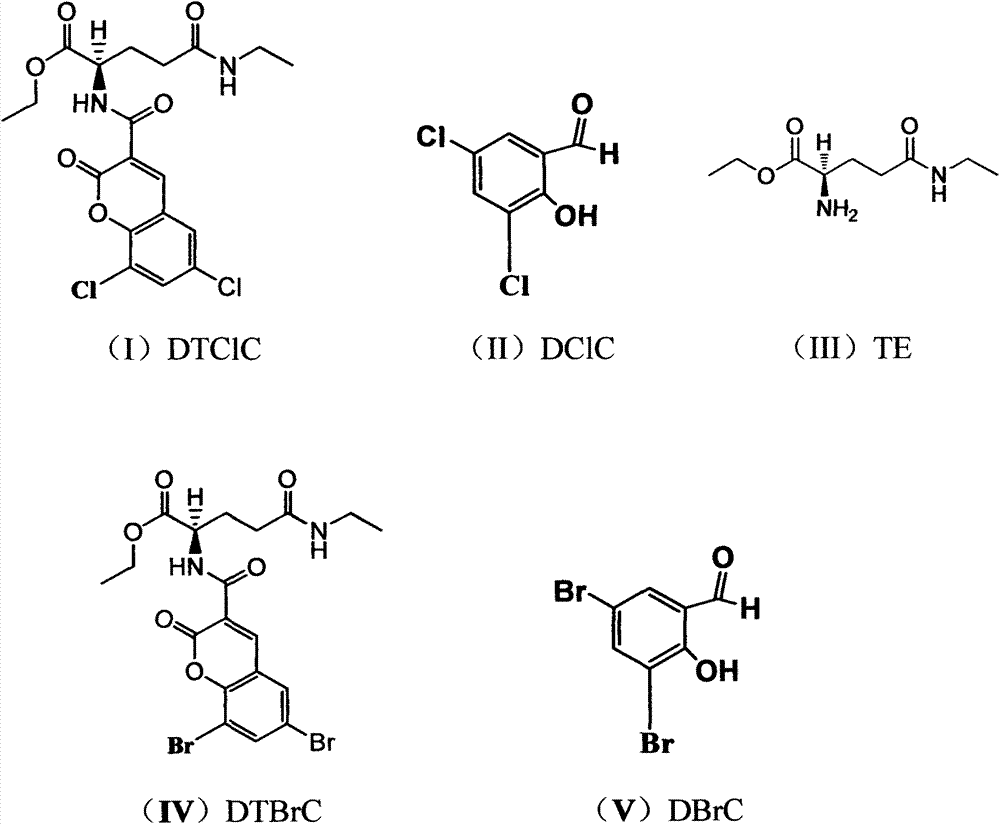
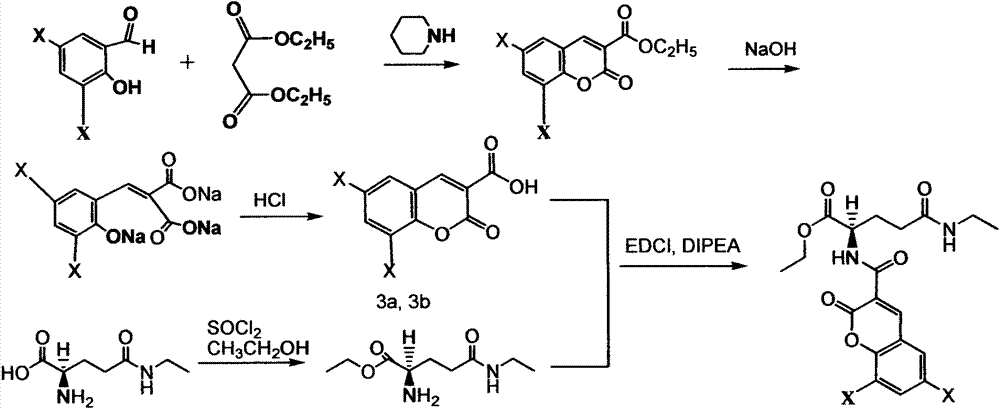
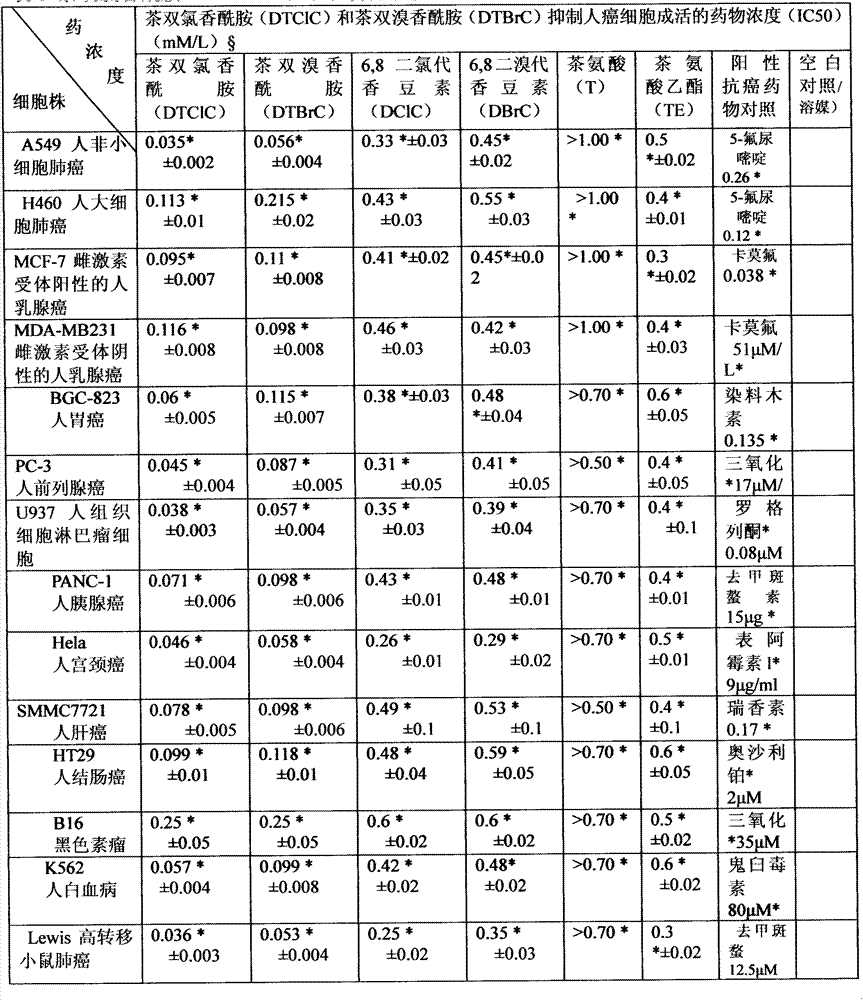
Applications of tea double-chlorine carboxamide and tea double-bromine carboxamide or like in preparation of products for prevention and treatment of diseases such as cancer
InactiveCN103110621AEfficient killingGood curative effectAntipyreticAnalgesicsDiseaseLymphatic Spread
The invention relates to the technical field of medical treatment. The tea double-chlorine carboxamide and tea double-bromine carboxamide are newly synthesized compounds which can inhibit growths and invasions of cancer cells such as lung cancer, breast cancer, liver cancer, stomach cancer, colon cancer, prostate cancer, pancreatic cancer, cervical cancer, lymphoma, leukemia, and melanoma, and can obviously inhibit the tumor growth and metastasis in the body, and the inhibition effect of the compound is better than that of an anticancer medicament; the mechanism of action involves a receptor which is closely related to down-regulation and inhibition of the growth, invasion and metastasis of a tumor, signal transduction and regulation protein and kinase levels and a binding of a nuclear factor and DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid), and up-regulation of factors such as tumor suppressor proteins and cell cycle inhibitor proteins simultaneously; double tea chlorine carboxamide and double tea chlorine carboxamide can directly inhibit activities of histone deacetylase and histone methyltransferase EZH2(Enhancer Of Zeste Homolog 2) and the binding of the inflammatory factor NF-kB and DNA, and the activities of tea double-chlorine carboxamide and tea double-bromine carboxamide are better than that of the clinical anti-cancer medicament. The invention provides new applications of tea double-chlorine carboxamide and tea double-bromine carboxamide and intermediate compounds in preventing and treating the diseases such as cancers, inflammation, cardiovascular and immune deficiencies.
Owner:YANTAI UNIV
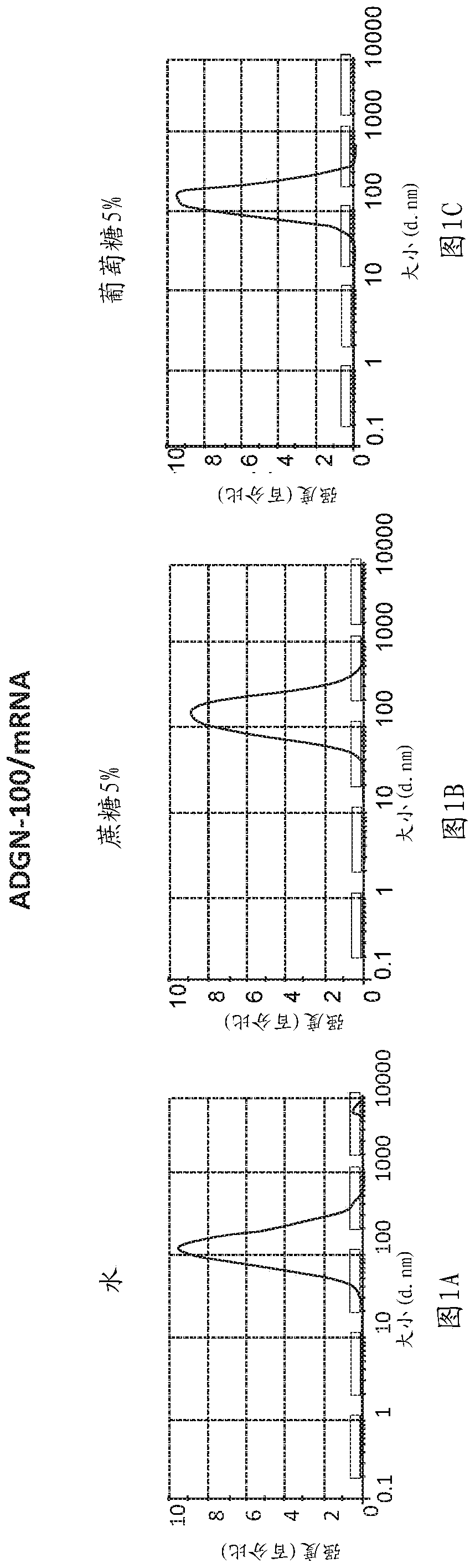
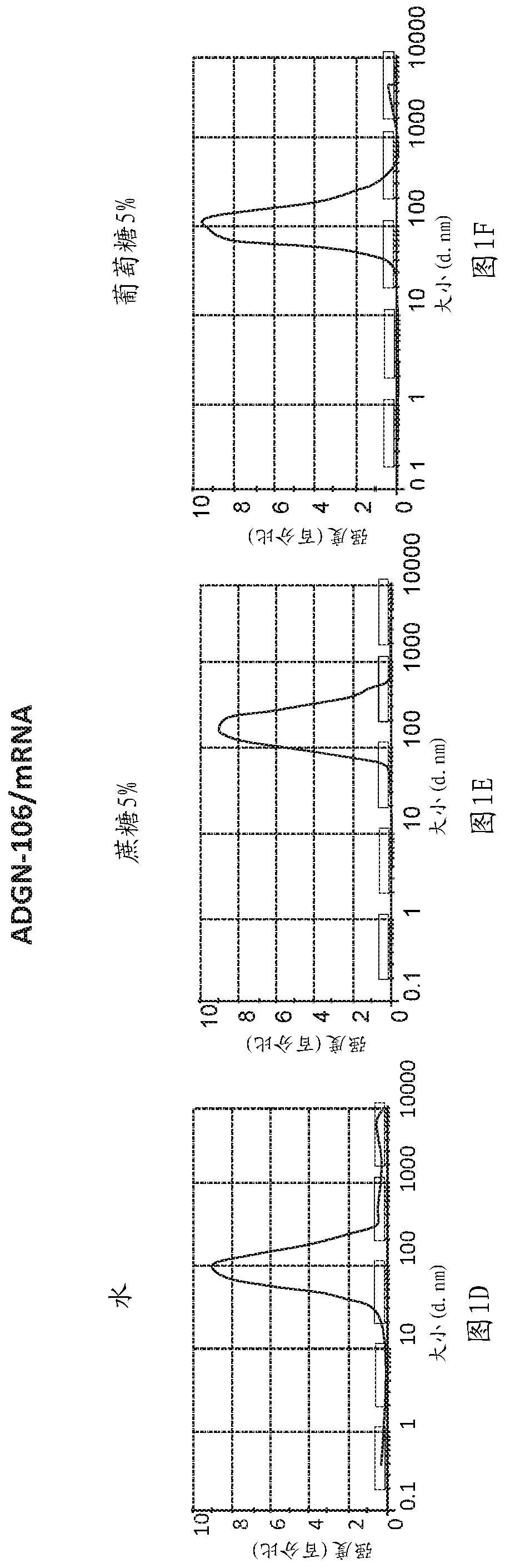
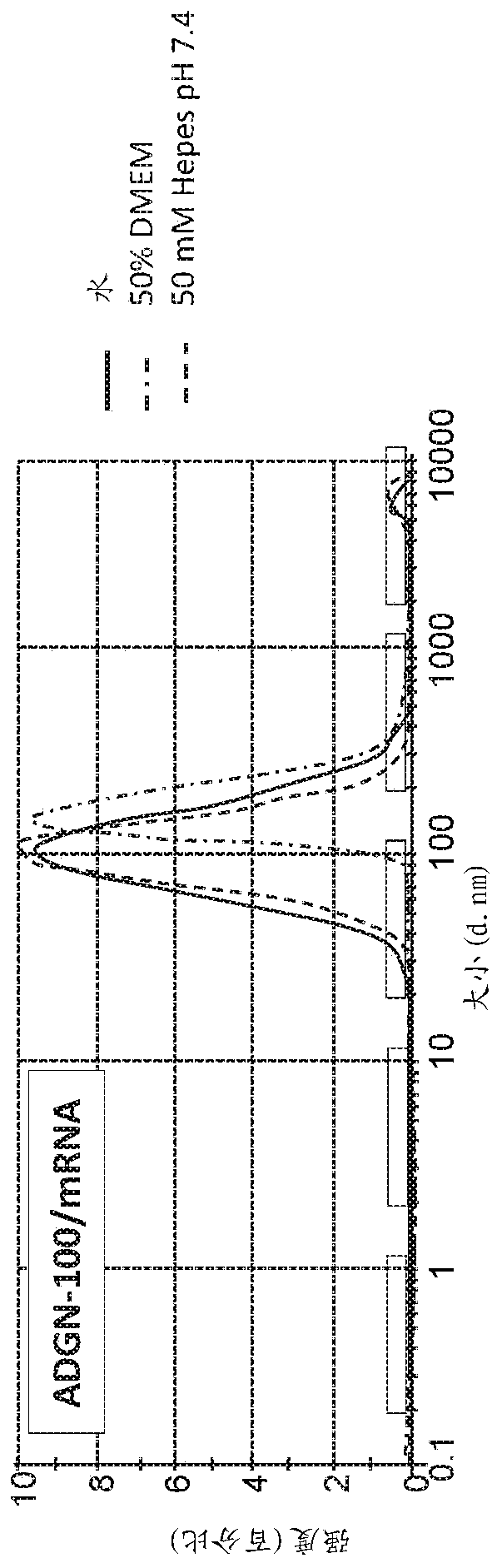
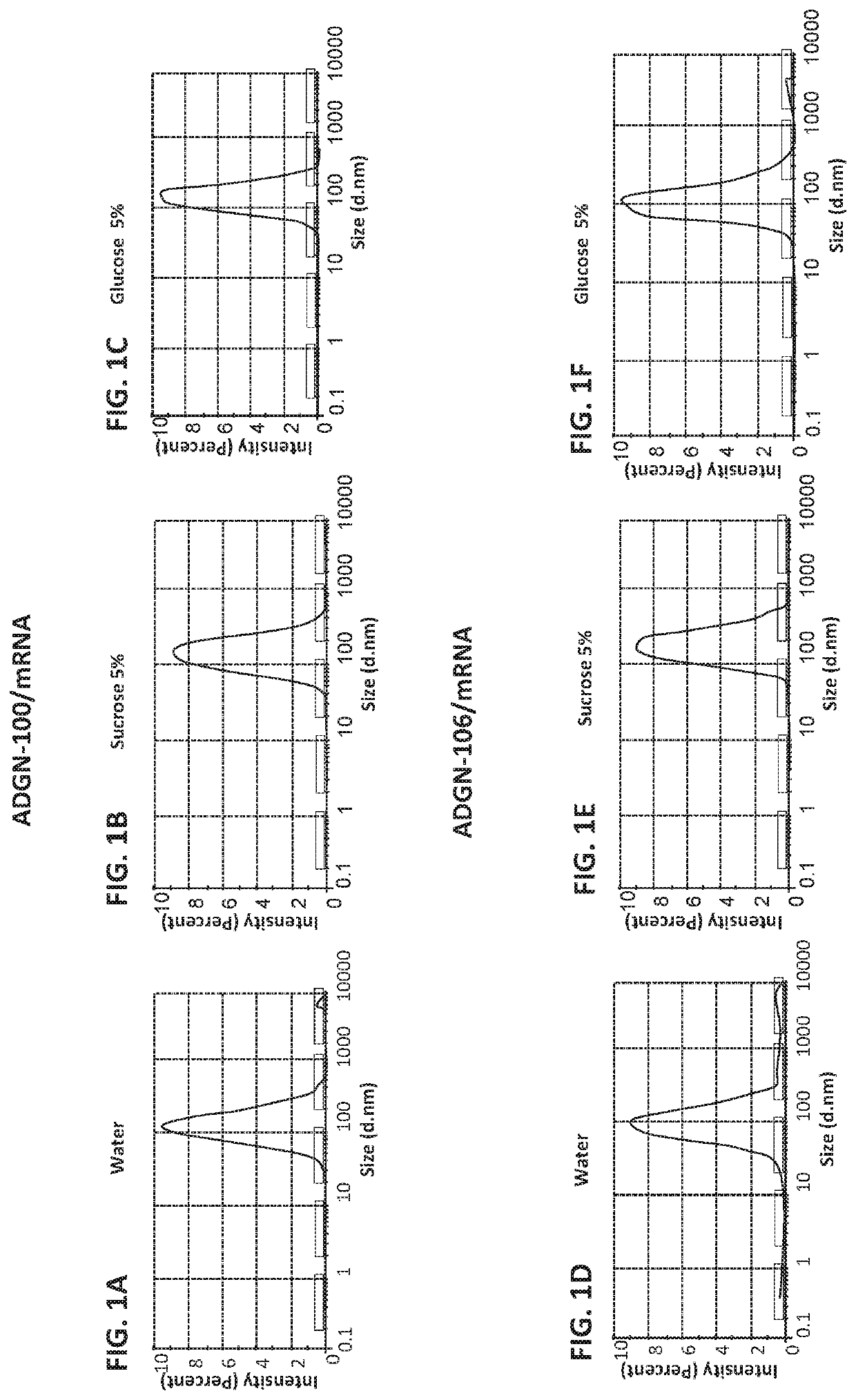
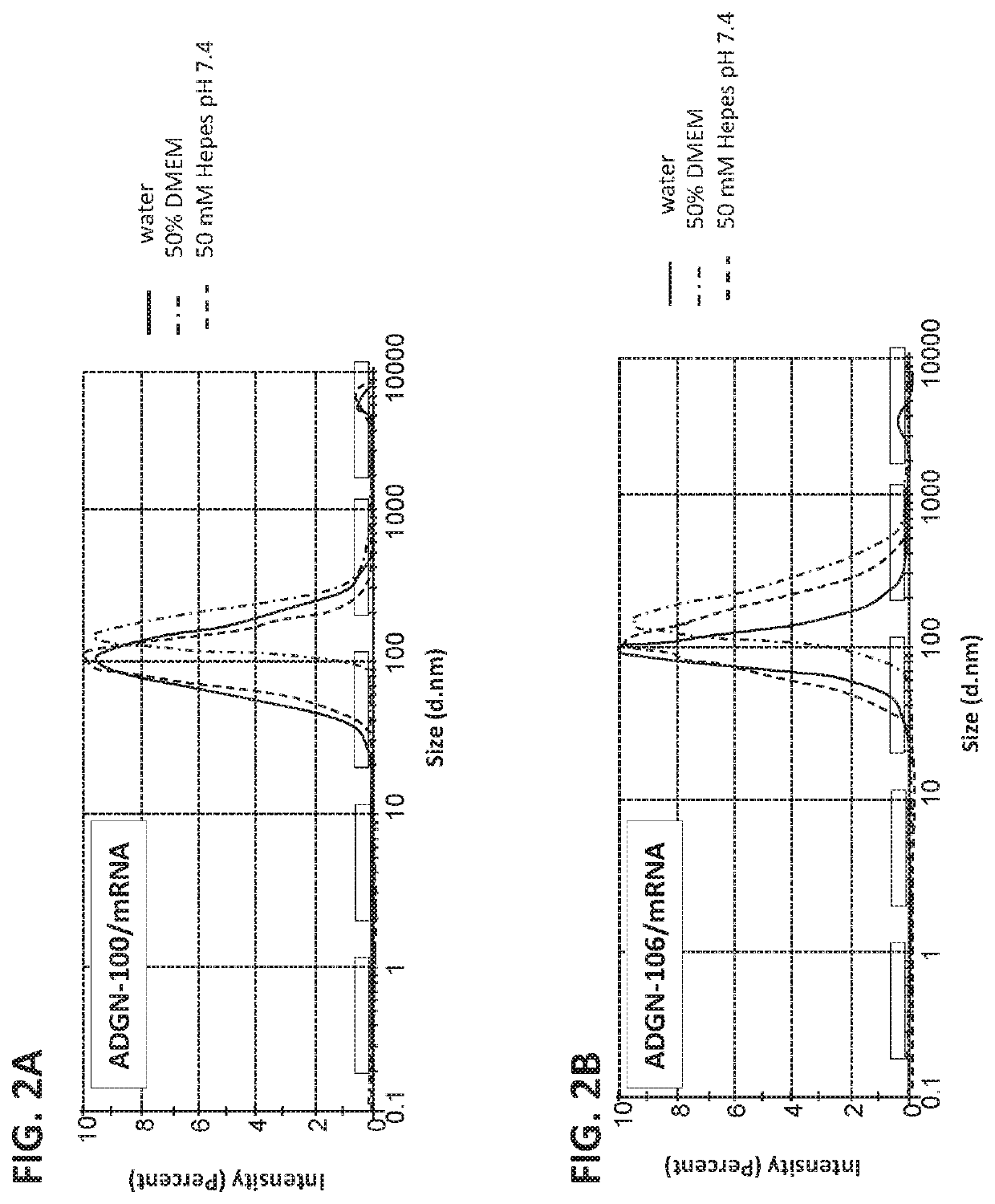
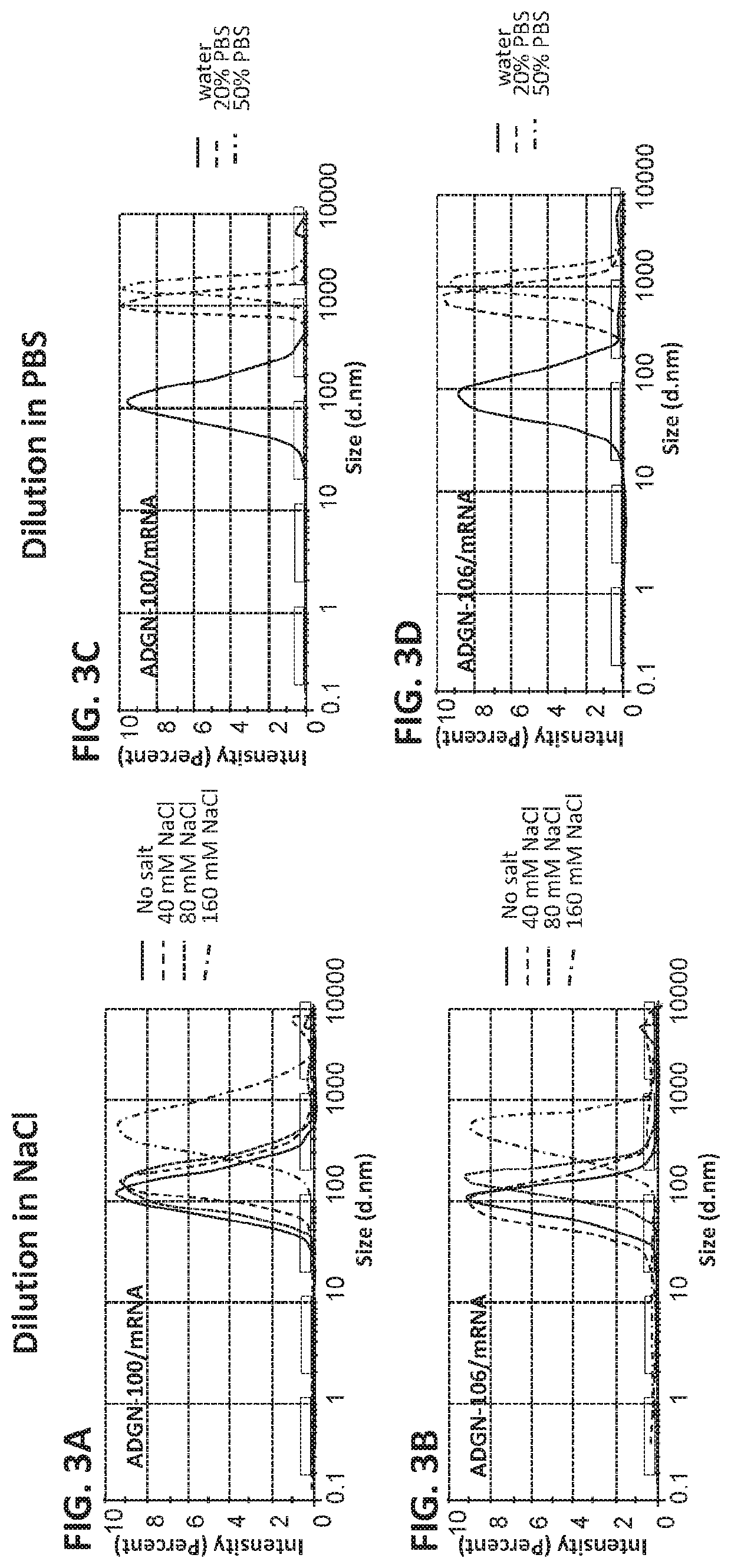
Peptides and nanoparticles for intracellular delivery of mRNA
The present invention pertains to peptide-containing complexes / nanoparticles that are useful for delivering into a cell one or more mRNA (such as therapeutic mRNA, e.g., mRNA encoding a tumor suppressor protein).
Owner:AADIGEN LLC
Activators and therapeutic applications thereof
The invention presents methods of identifying small molecule compounds that are activators of tumor suppressor protein p53 pathway, and its associated family members p63 and p73, function. The invention is further drawn to methods of killing tumor cells and treating cancers or other conditions requiring activation of the p53 family member pathways and DNA damage response pathways with the small molecules.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in signaling pathways
InactiveUS20100159477A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementGolgi componentCell Surface Proteins
The invention discloses novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: adaptor / scaffold proteins, adhesion / extracellular matrix protein, apoptosis proteins, calcium binding proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, chaperone proteins, chromatin, DNA binding / repair / replication proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, endoplasmic reticulum or golgi proteins, enzyme proteins, G / regulator proteins, inhibitor proteins, motor / contractile proteins, phosphatase, protease, Ser / Thr protein kinases, Protein kinase (Tyr)s, receptor / channel / cell suface proteins, RNA binding proteins, transcriptional regulators, tumor suppressor proteins, ubiquitan conjugating system proteins and proteins of unknown function.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 anti-tumor targeted engineering bacterial strain as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN109593693AImprove targetingImprove economyBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliTumor target
The invention discloses an escherichia coli Nissle 1917 anti-tumor targeted engineering bacterial strain as well as a construction method and application thereof. The escherichia coli Nissle 1917 anti-tumor targeted engineering bacterial strain is collected in China Center For Type Culture Collection on June 26, 2018, with the culture collection number of CCTCC NO: M 2018403; the classification name thereof is escherichia coli EcN (Tum 5-p53), and the Latin scientific name thereof is Escherichia coli Nissle (Tum 5-p53). The constructed escherichia coli EcN (Tum 5-p53) contains an anti-tumor hypoxic expression vector pET28a-Pvhb-SUMO-Tum 5-MMP-p53, can efficiently express bifunctional protein Tum 5-p53, can transmit an antiangiogenic factor Tum-5 and tumor suppressor protein p53 to a solidtumor, and plays a good anti-tumor therapeutic effect. The tumor inhibiting rate of the anti-tumor targeted engineering bacterial strain on a human liver cancer SMMC-7721 nude mouse is as high as 69.47%.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
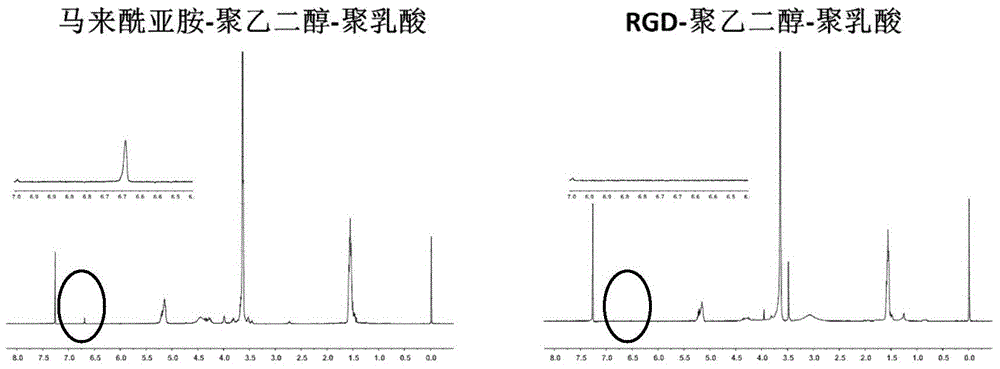
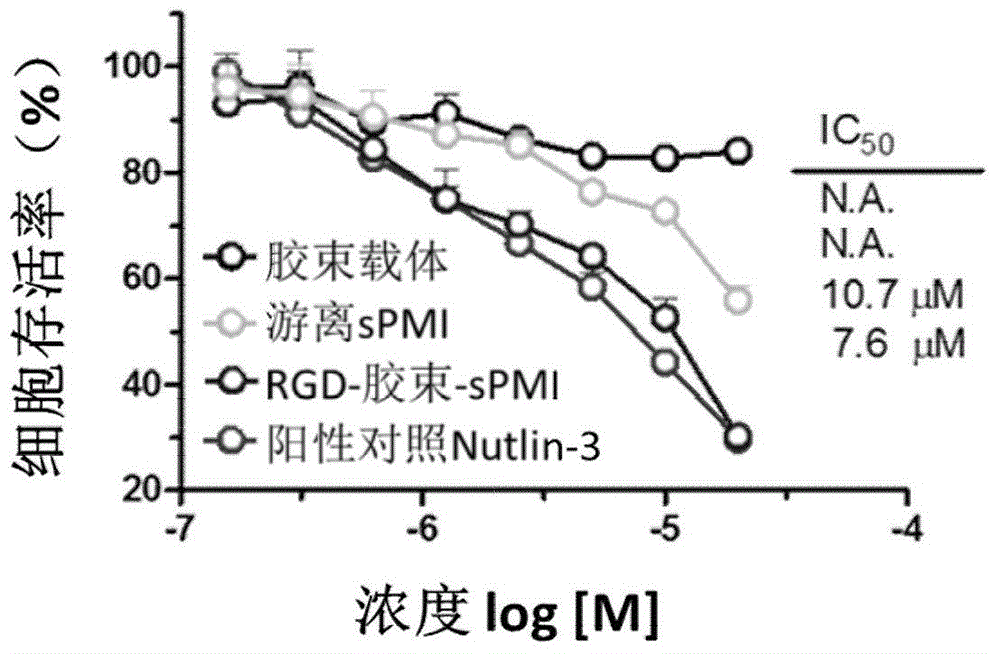
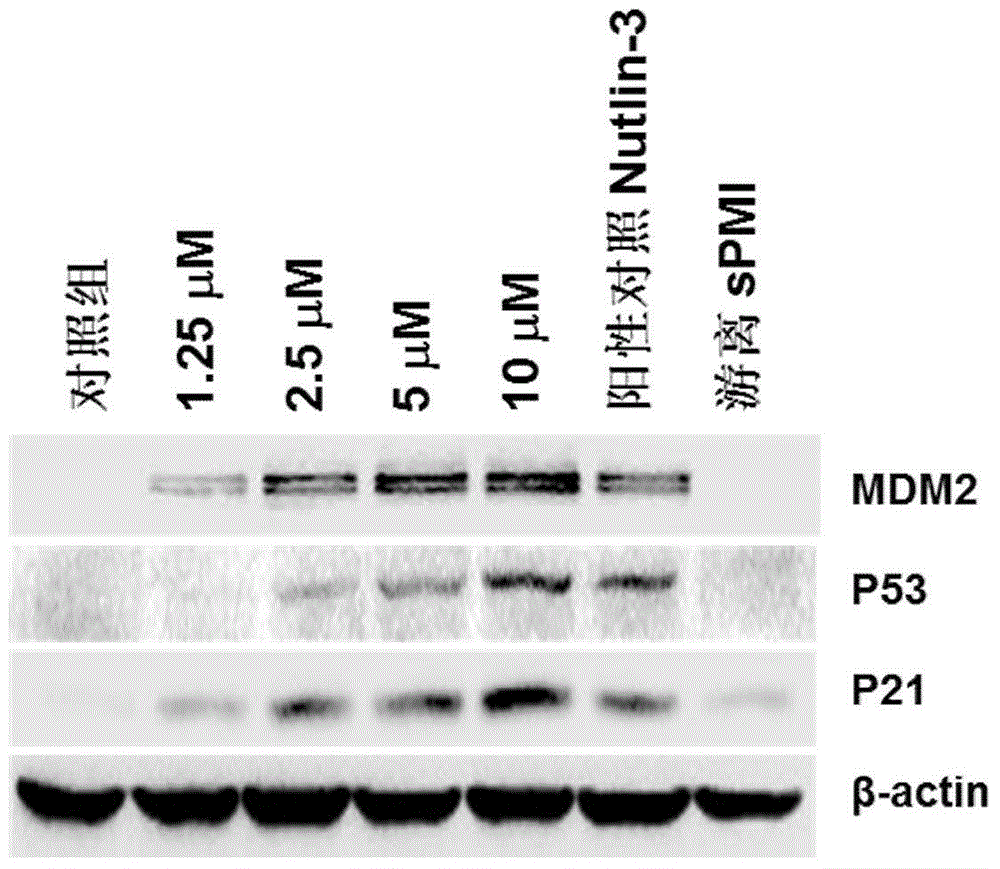
Micelle preparation entrapped with binding peptide polymer with specific anti-cancer activity
ActiveCN105853355AOvercoming selectivityOvercoming serum stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsEmulsion deliveryCancer cellBinding peptide
The present invention belongs to the field of pharmaceutical preparations, and relates to a polypeptide drug delivery system, particularly to a micelle preparation entrapped with binding peptide polymer with specific anti-cancer activity. The drug delivery system consists of a targeted functional material, an amphiphilic block copolymer and a binding peptide. By entrapping a binding peptide capable of restoring the activity of a tumor suppressor protein p53, the binding peptide is delivered into cancer cells to exert the activity of inhibiting tumor cell growth and increase targeted anti-cancer effect; and the binding peptide has better anti-cancer effect by combination with temozolomide. By in vivo and in vitro active valuation, the drug delivery system is proved to be able to successfully deliver binding peptides to the target site and send binding peptides into the target cells, and has clear therapeutic effect.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
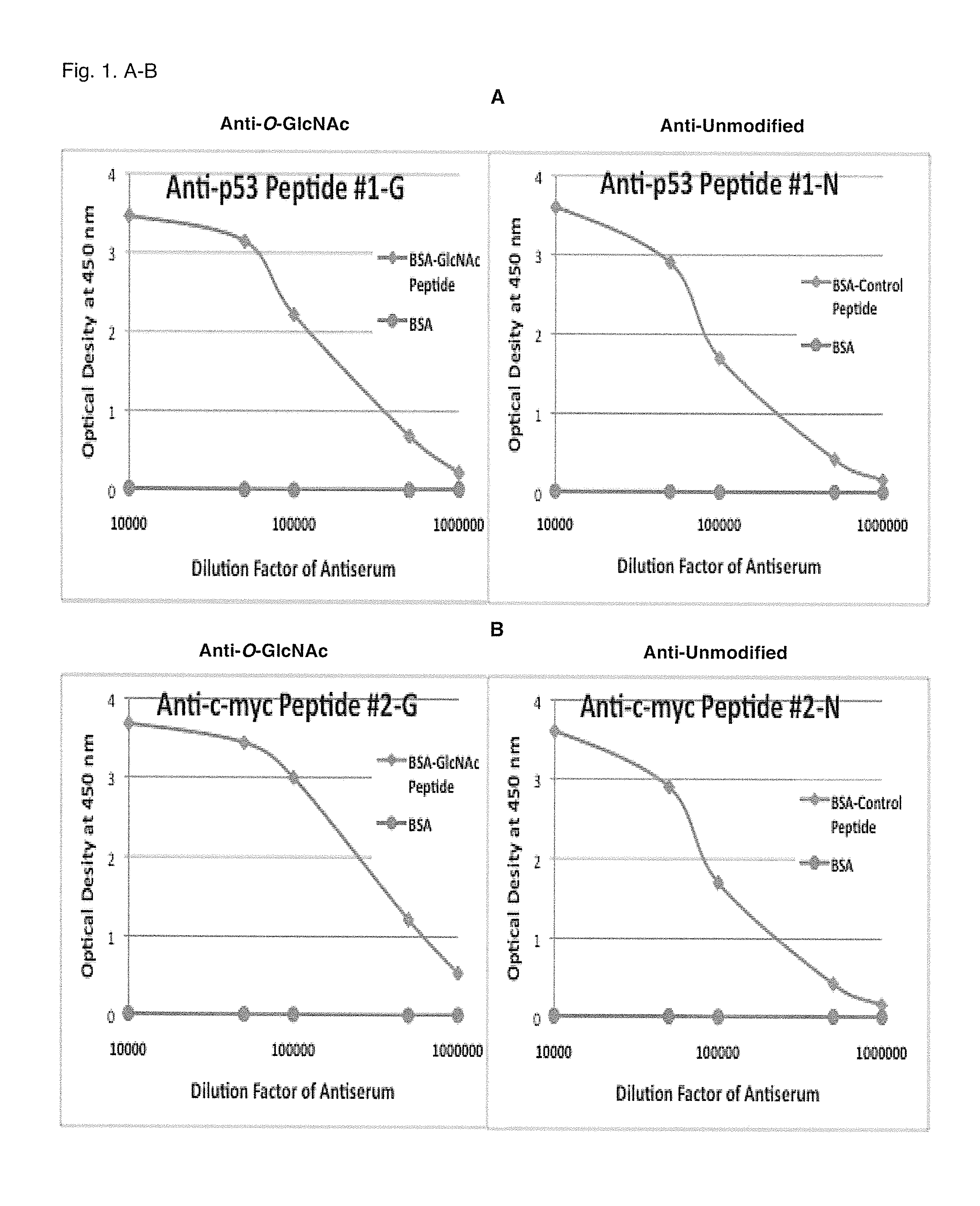
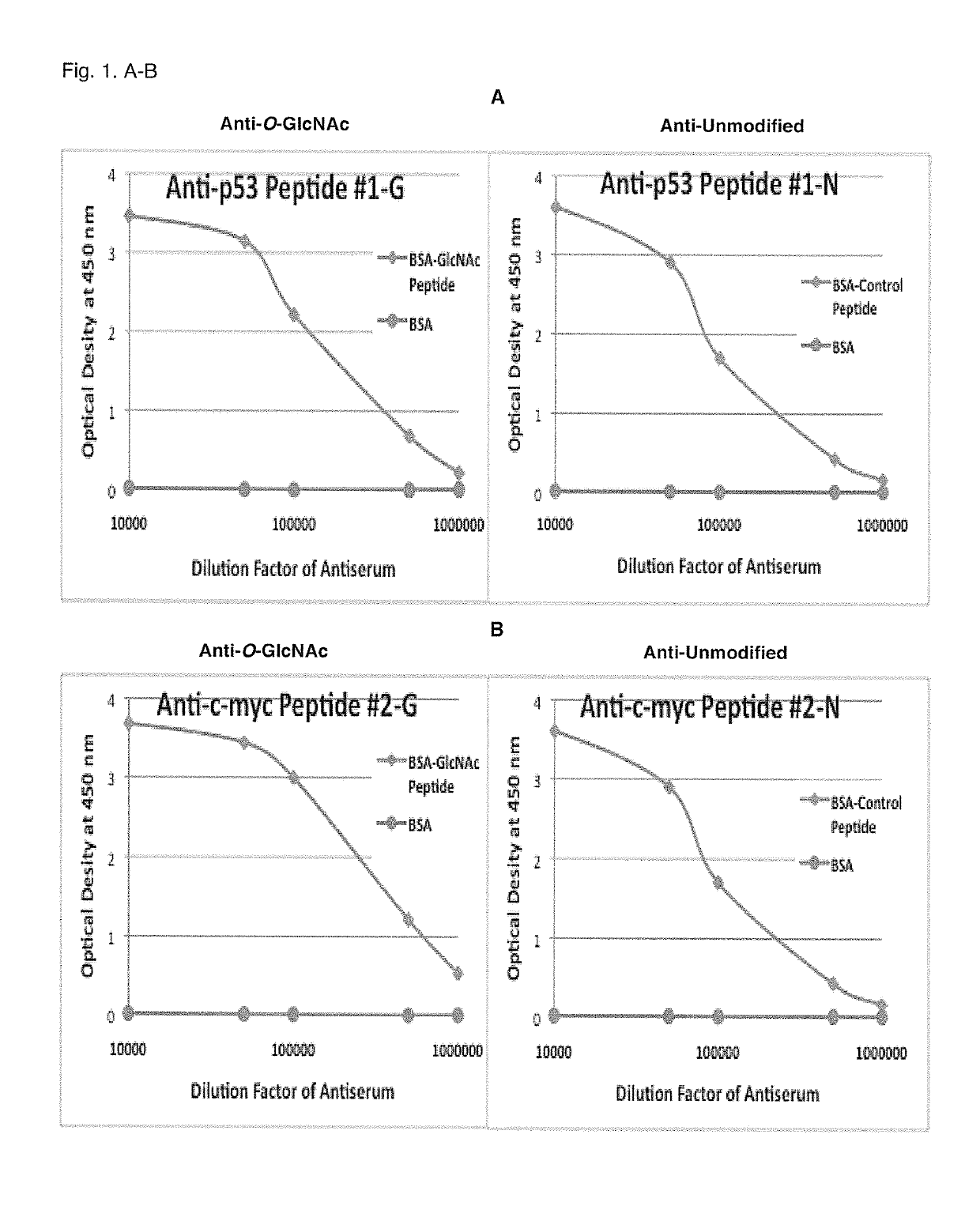
Glycosylation site-specific antibodies and Anti-cancer compounds
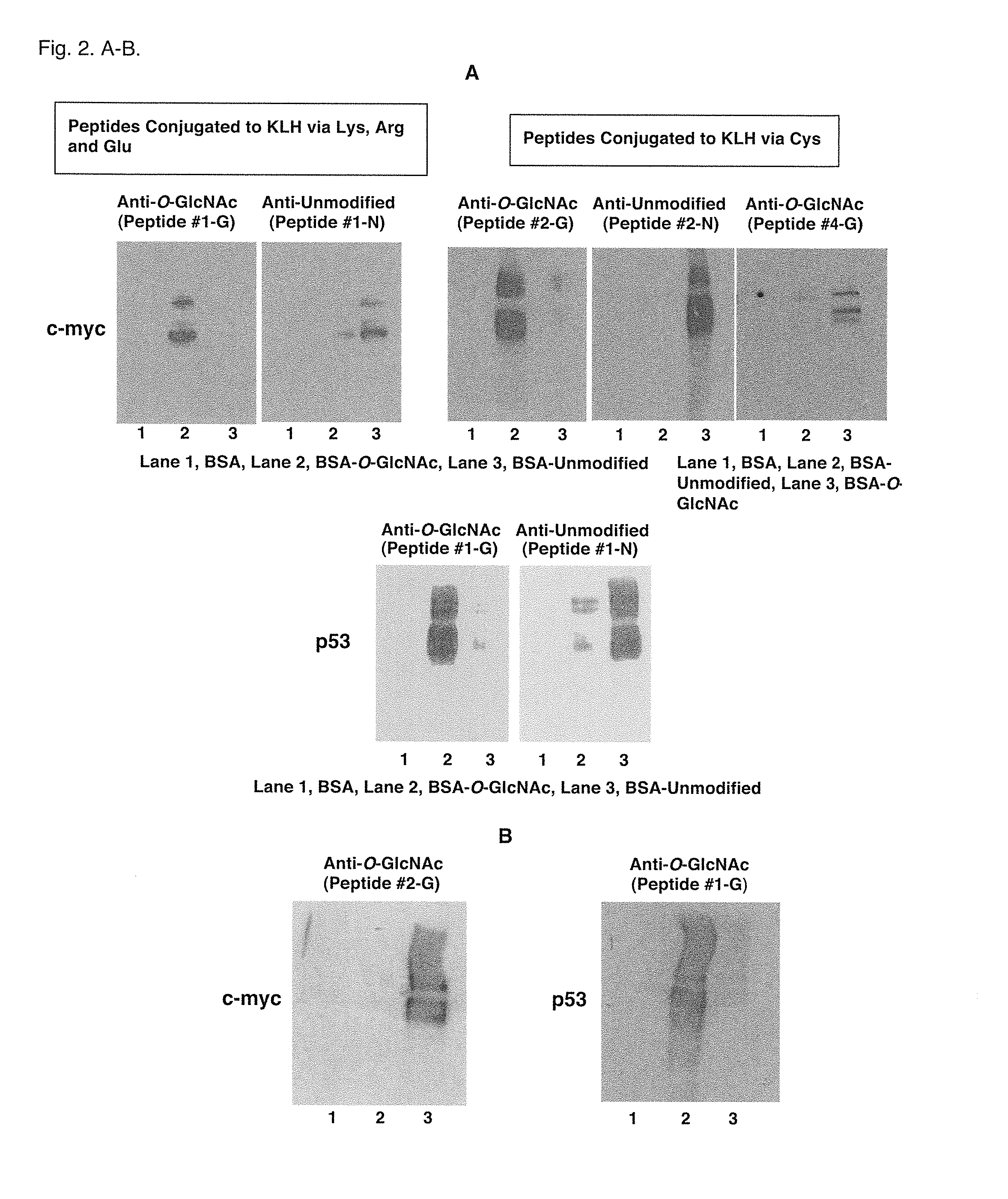
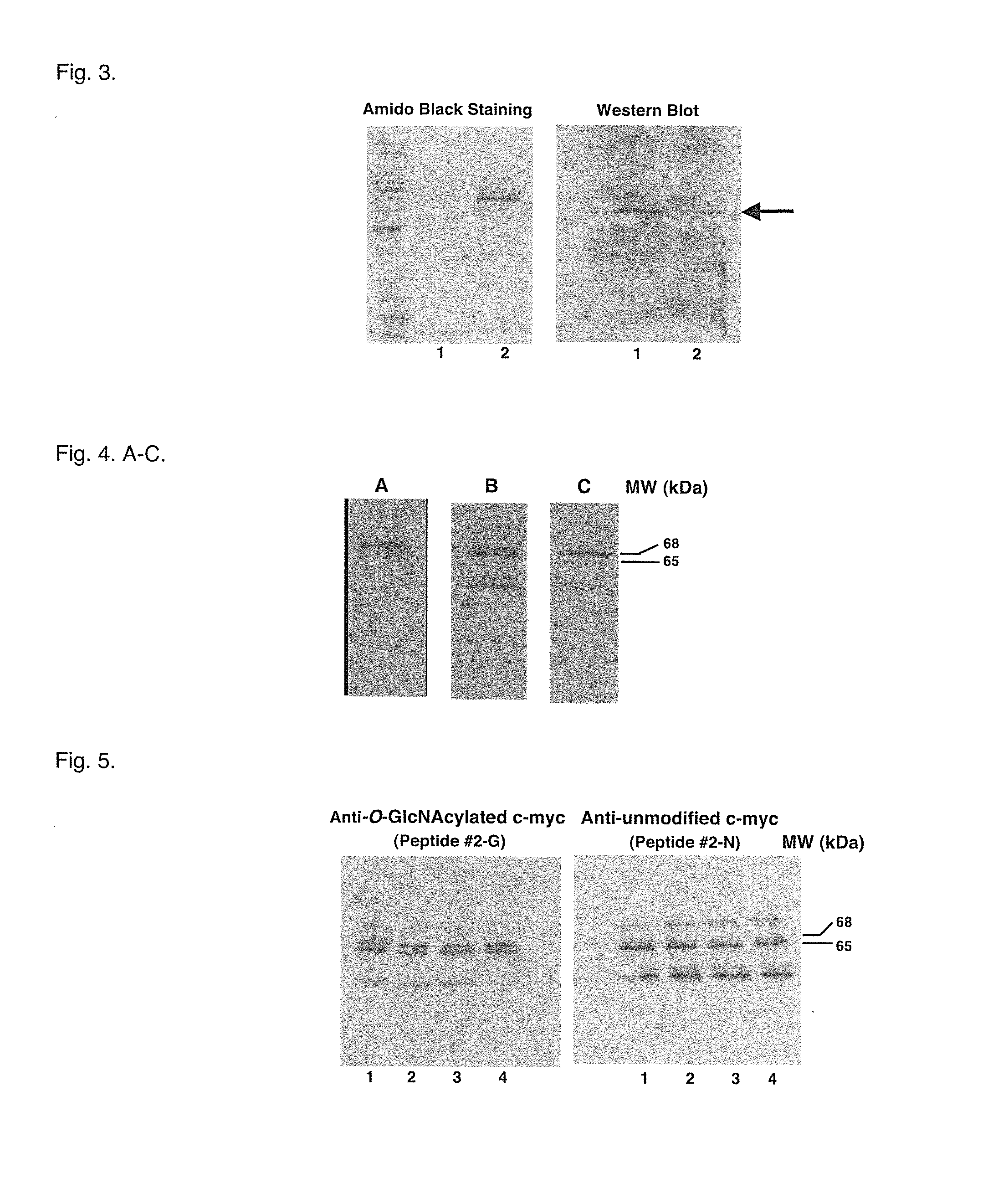
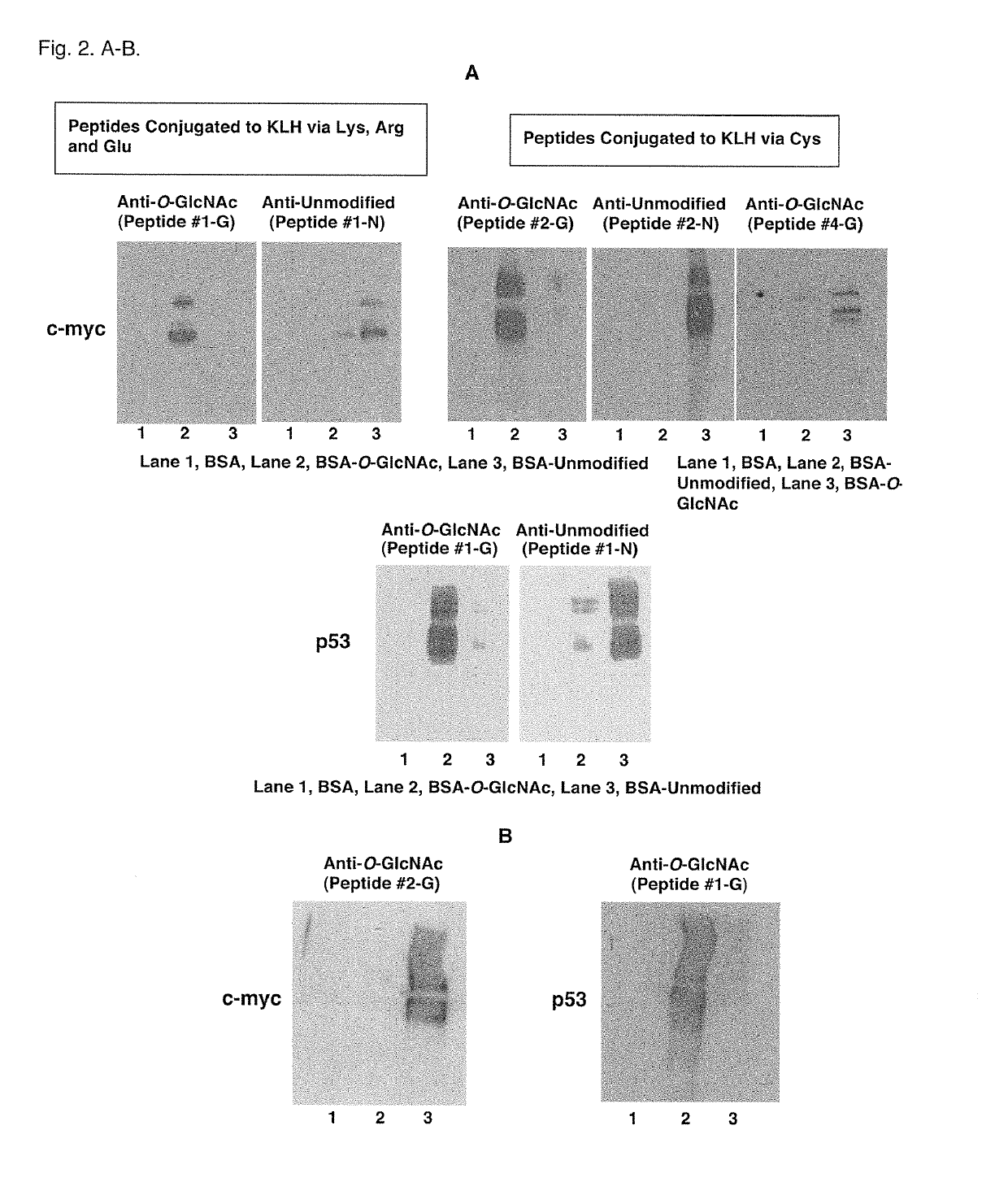
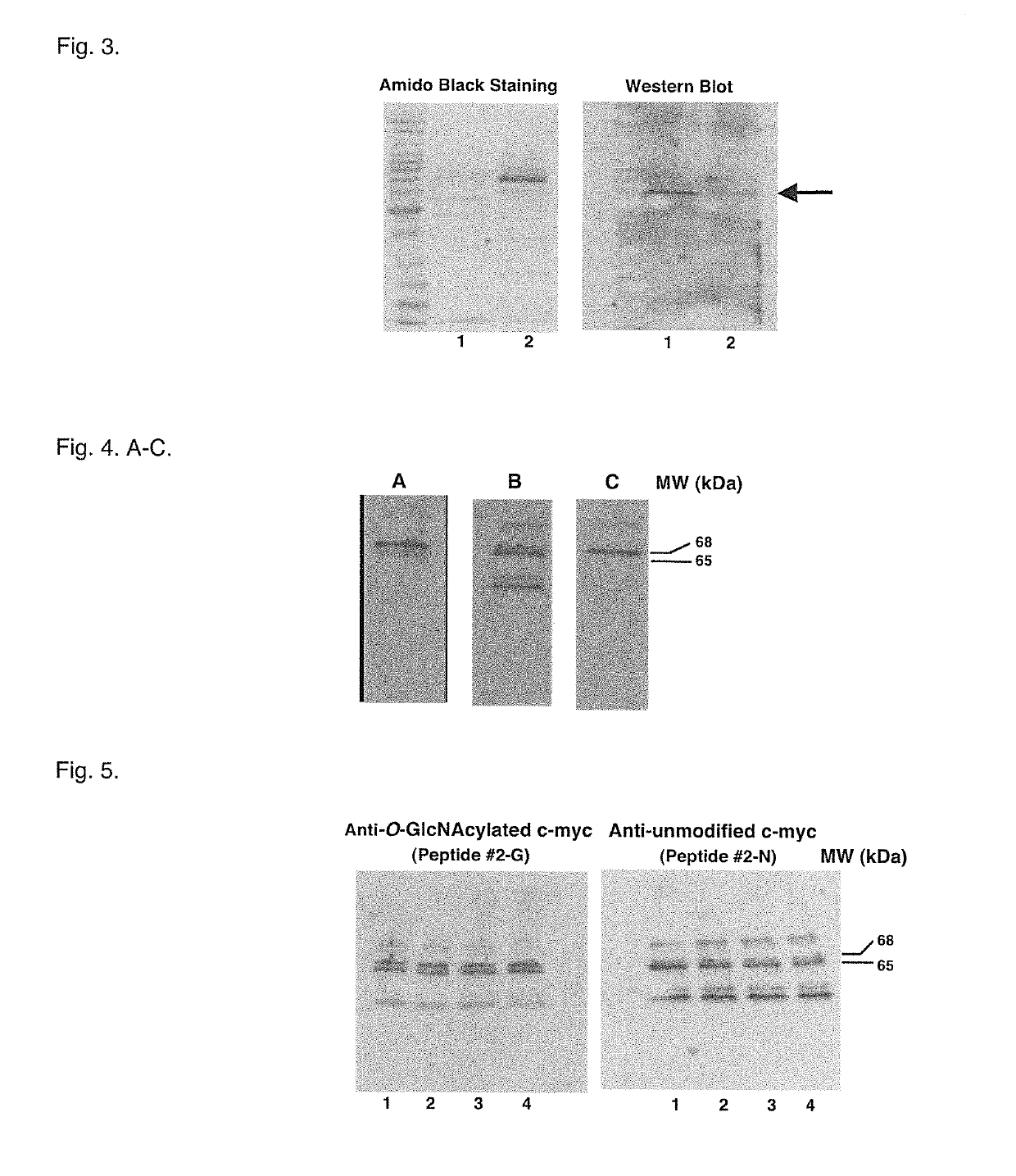
A method of characterizing the protein O-GlcNAcylation site-specificity of an antibody. A method of detecting or quantitating the expression of site-specific O-GlcNAcylated proteins expressed in cells and biological samples. A method of diagnosing cancer in a host based on the cellular expression of site-specific O-GlcNAcylated proteins. A method of screening anti-cancer compounds according to their ability to increase a level O-GlcNAcylation of oncogene or tumor suppressor proteins. Methods of treating cancer in an animal host by administering compounds that increase a level of O-GlcNAcylated c-myc or p53 in cancer cells. A method of distinguishing subclasses of pancreatic cancer according to the sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to an imidazole derivative, and a method of personalized pancreatic cancer treatment delivered according to the sensitivity subclasses.
Owner:DETROIT R&D
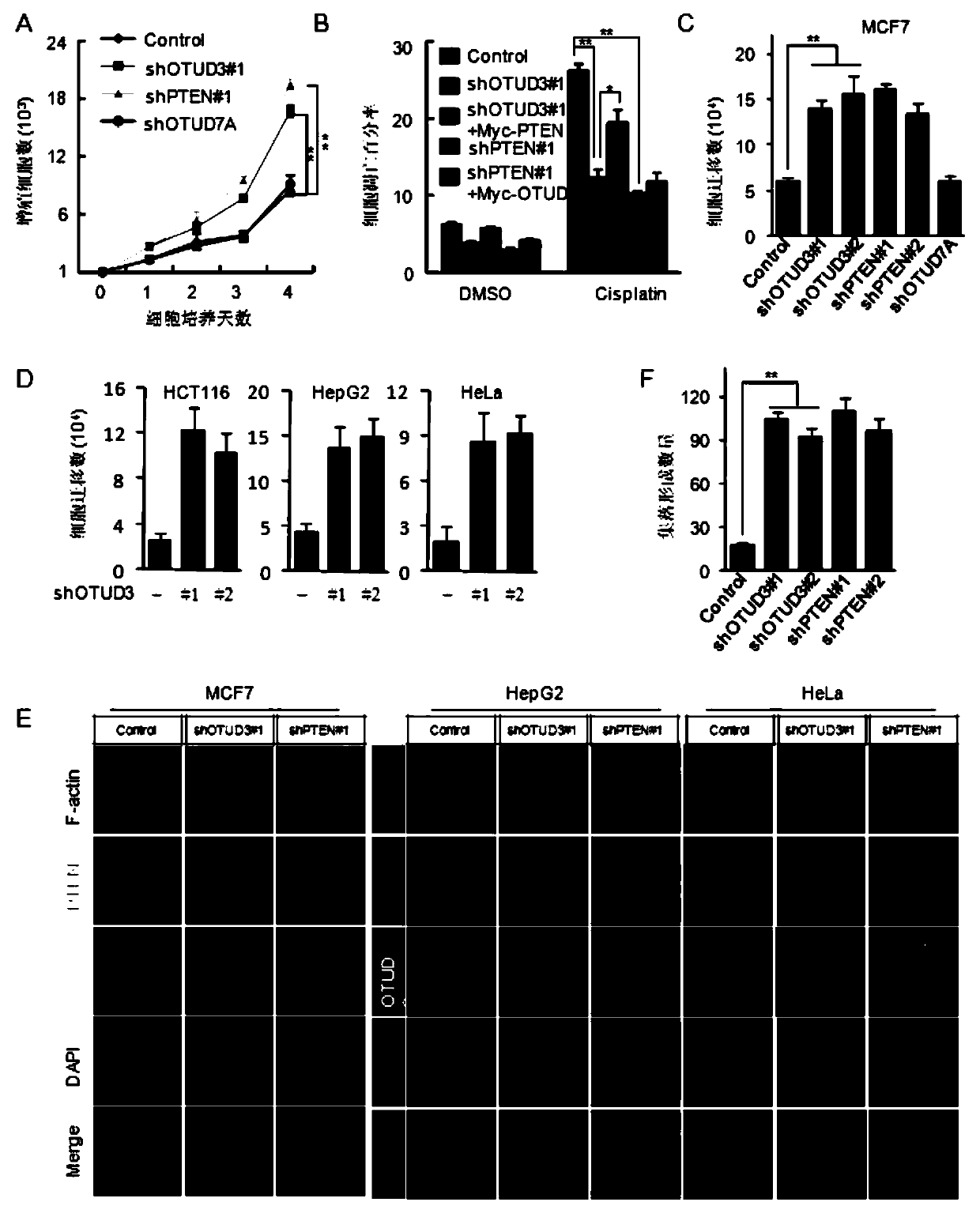
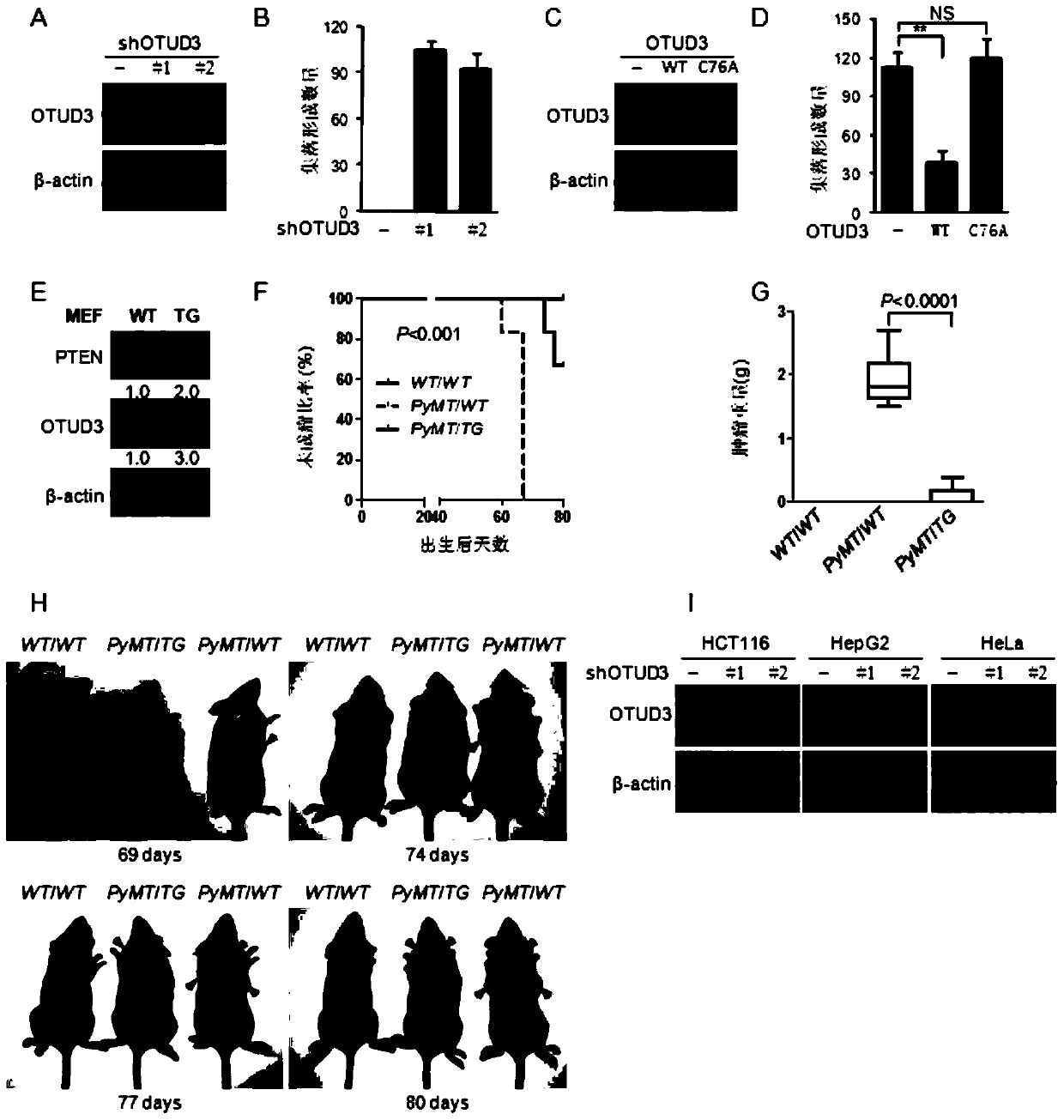
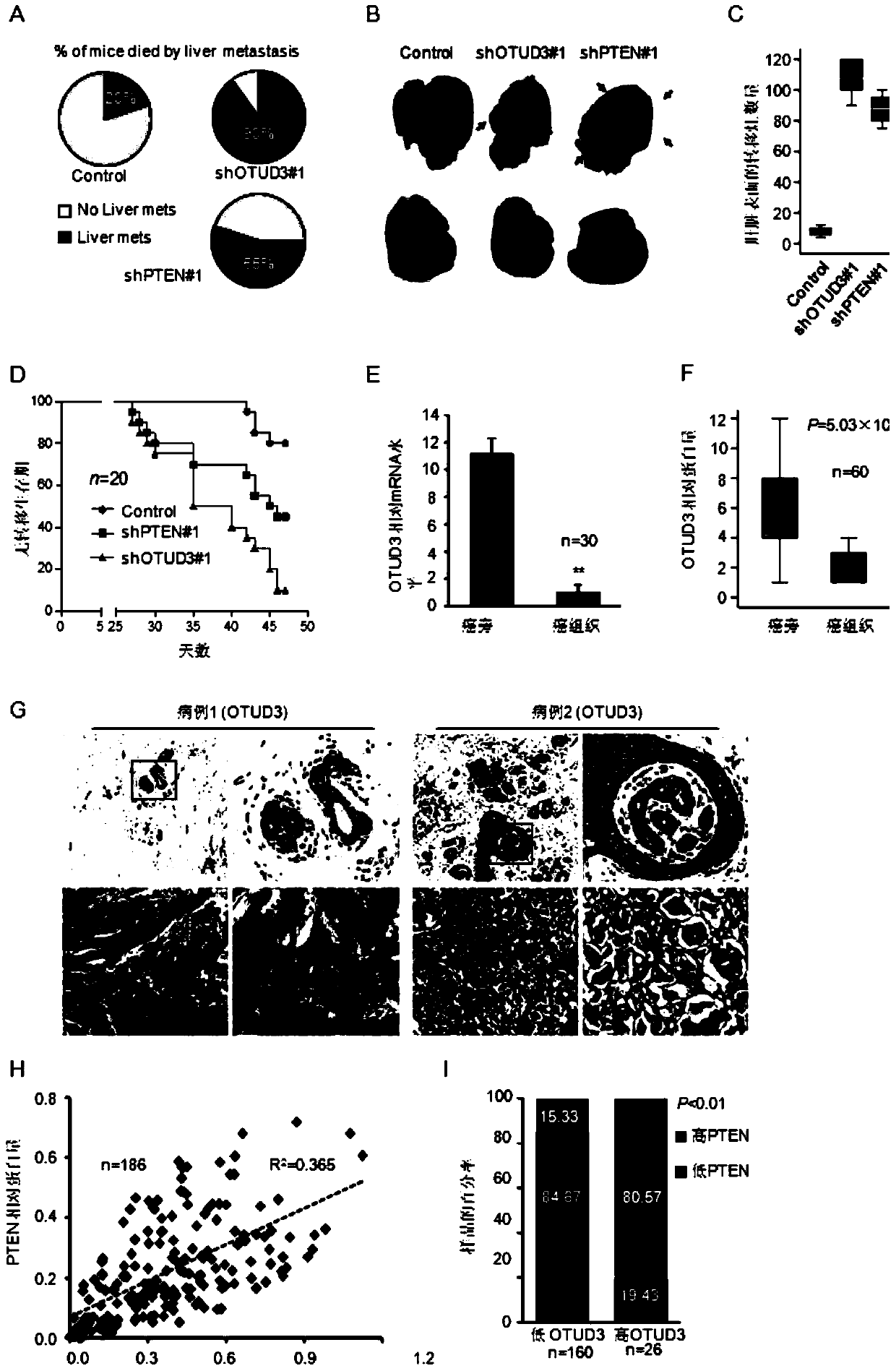
Application of OTUD3 protein in preparation of products for inhibiting tumor growth
ActiveCN104174012ASuppress generationInhibit transferPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsLentivirusLymphatic Spread
The invention discloses application of OTUD3 protein in preparing products for inhibiting tumor growth. The OTUD3 protein or an encoding gene of the OTUD3 or a recombinant vector containing the encoding gene of the OTUD3 or lentivirus expressing the OTUD3 protein can be applied to preparation of a product with at least one of the functions from (1) to (7) as shown in the specification. Experiments prove that the OTUD3 serving as a newly discovered important tumor suppressor protein is capable of inhibiting generation and metastasis of tumors, and discovery of the OTUD3 functions provides important scientific basis and application value to tumor diagnosis, prevention and treatment.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in EGFR-signaling pathways
ActiveUS7807789B2Isotope introduction to peptides/proteinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsADAMTS ProteinsLipid kinases
The invention discloses 168 novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways downstream of, and including, EGFR kinase, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: Actin Binding proteins, Adaptor / Scaffold proteins, Calcium-Binding Proteins, Cell Cycle Regulation proteins, Cytoskeletal proteins, DNA Binding and Replication Proteins, GTPase Activating proteins, Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factor proteins, Lipid Kinases, Receptor Tyrosine Kinases, Receptor Tyrosine Kinase ligands, Protein Kinases, Receptor and Protein Phosphatases, Transcription Factor proteins, Tumor Suppressor proteins, and Vesicle proteins.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
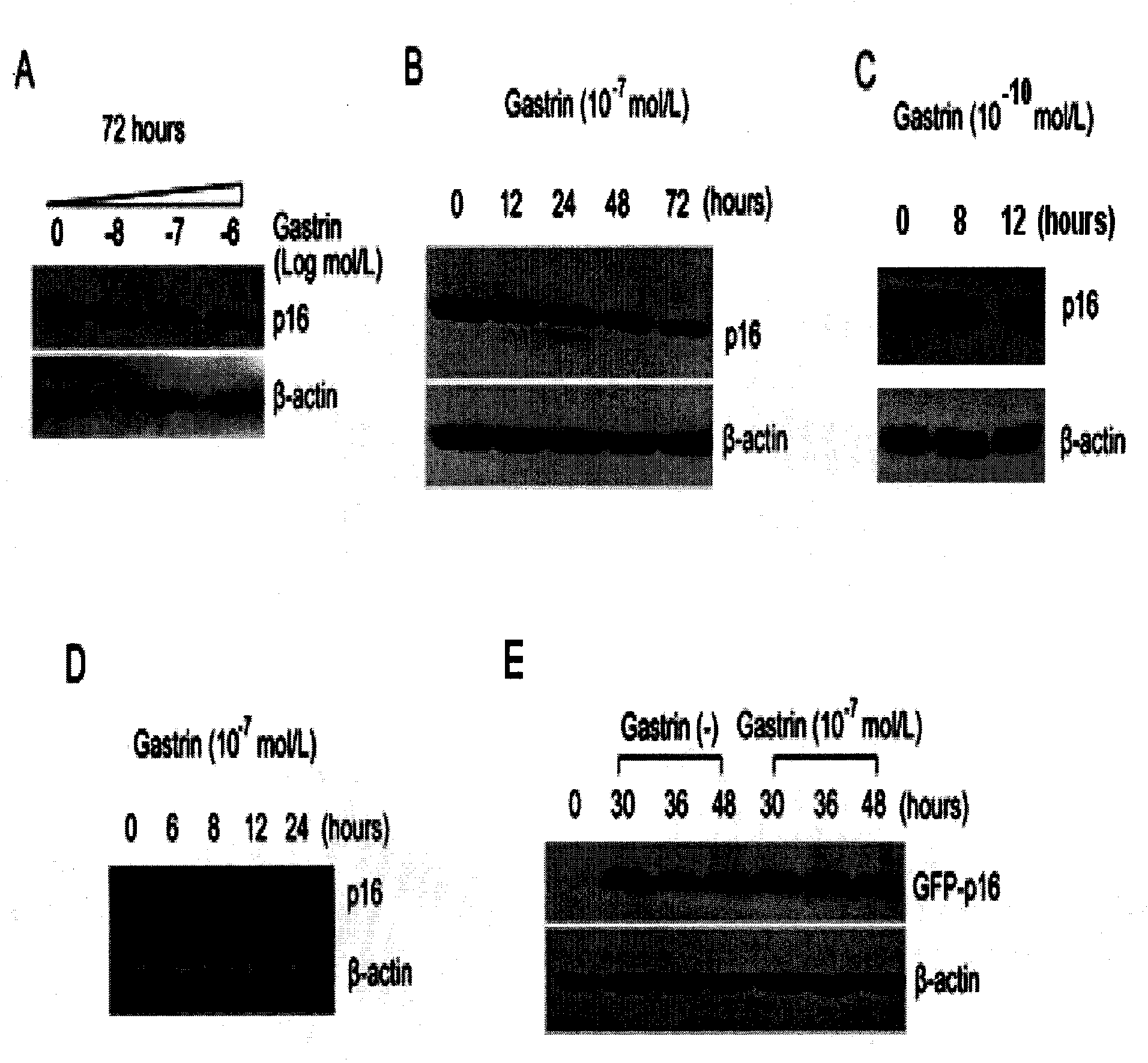
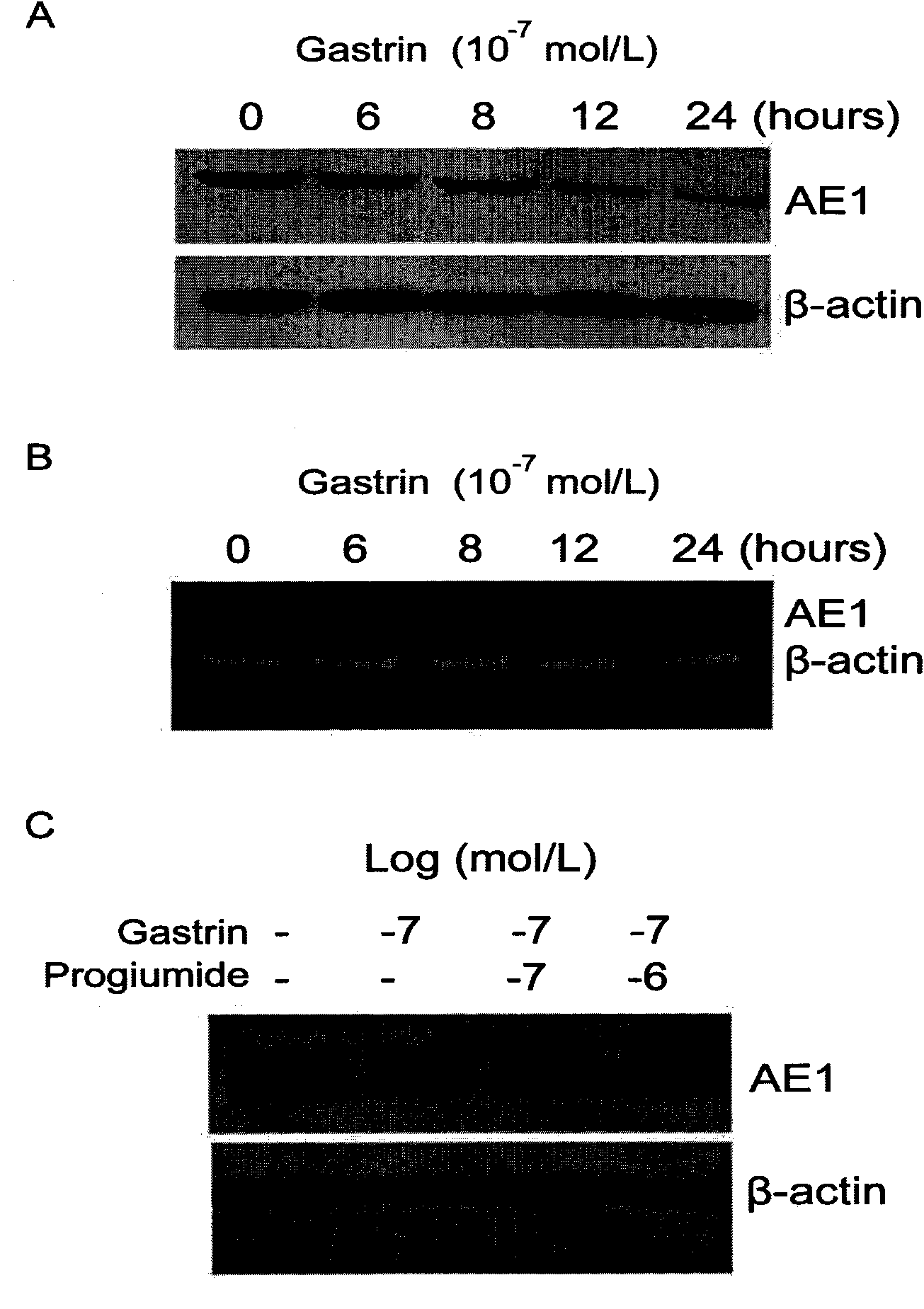
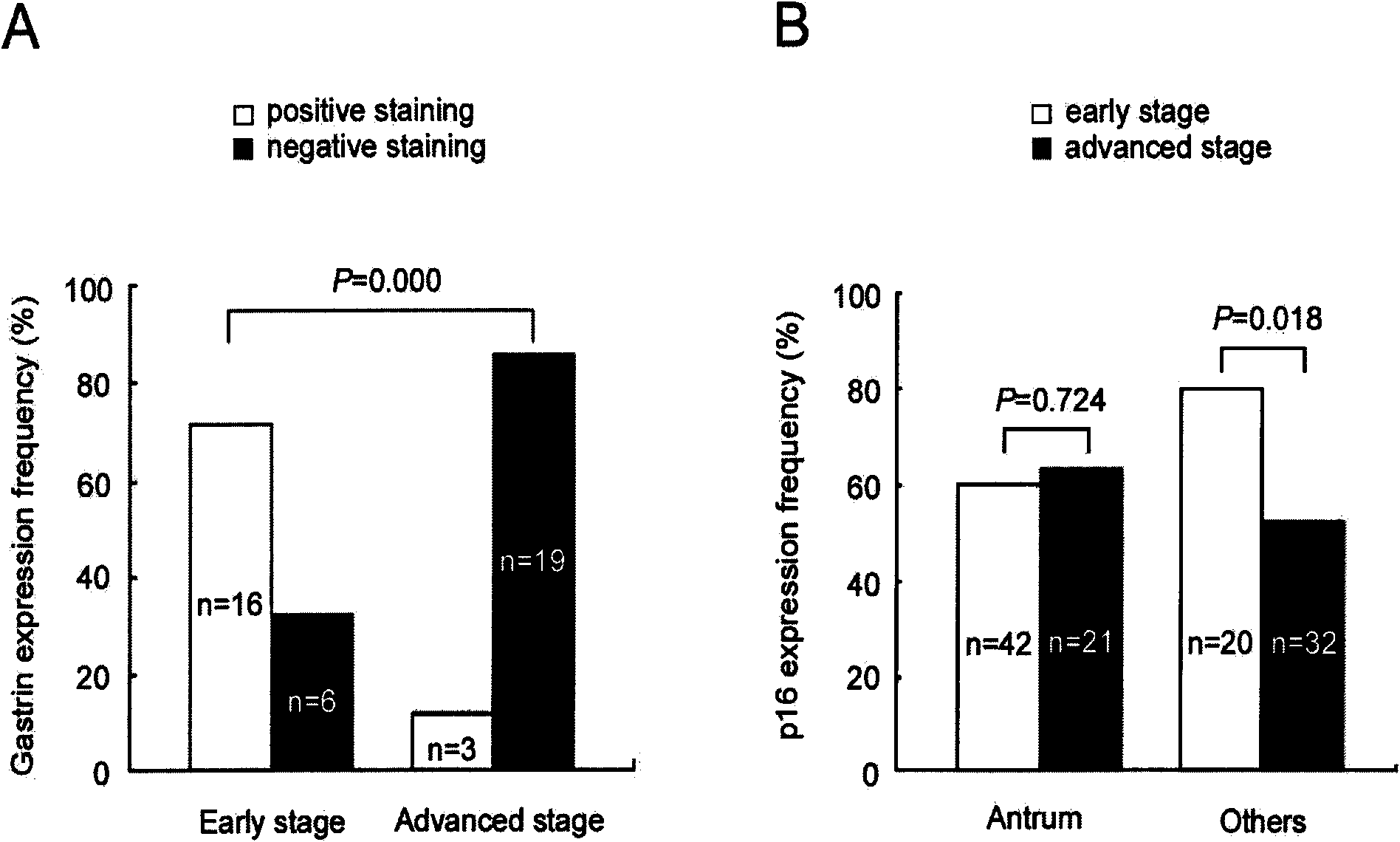
Application of gastrin in inhibiting gastrointestinal tumor tumors
ActiveCN101890157AHas therapeutic effectSignificant negative correlationPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemMultiple Tumor Suppressor-1Stomach cancer
The invention discloses a novel application of gastrin in inhibiting gastrointestinal tumor tumors. Gastric cancer target gene anion exchange protein 1 is interacted with tumor suppressor protein p16 so as to induce gastric cancer, however, 17 peptide gastrin (H-pGlu-Gly-Pro-Trp-Leu-Glu-Glu-Glu-Glu-Glu-Ala-Tyr-Gly-Trp-Met-Asp-Phe-NH2) can effectively inhibit expression of gastric cancer target gene AE1 and p16 and breaks through the traditional view that gastrin induces tumors, and clinical pathologies show that the gastrin has obvious negative correlation with AE1 and p16. The invention alsodiscloses that the gastrin with the concentration of 10-10mol / L-10-70mol / L has obvious inhibition effect on gastric cancer cell activity after a certain time, thus prompting that the gastrin has curing effect on gastric antrum cancer and providing a new direction for curing gastric cancer based on the test results.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Doc tumor suppressor protein and gene
InactiveUS6071741APrevent proliferationSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsFhit geneWilms' tumor
Disclosed is an isolated tumor suppressor protein inducible by tumor necrosis factor. Also disclosed are isolated cDNA molecules encoding the doc-1, a tumor suppressor protein, cells transformed with this cDNA, antibodies specific for and reactive with the doc-1 protein, and methods of using these proteins, cDNAs, and antibodies.
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH THE +1
Reagents for the detection of protein phosphorylation in signaling pathways
ActiveUS7999080B2Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansCell Surface ProteinsSignalling pathways
The invention discloses novel phosphorylation sites identified in signal transduction proteins and pathways, and provides phosphorylation-site specific antibodies and heavy-isotope labeled peptides (AQUA peptides) for the selective detection and quantification of these phosphorylated sites / proteins, as well as methods of using the reagents for such purpose. Among the phosphorylation sites identified are sites occurring in the following protein types: adaptor / scaffold proteins, adhesion / extracellular matrix protein, apoptosis proteins, calcium binding proteins, cell cycle regulation proteins, chaperone proteins, chromatin, DNA binding / repair / replication proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, endoplasmic reticulum or golgi proteins, enzyme proteins, G / regulator proteins, inhibitor proteins, motor / contractile proteins, phosphatase, protease, Ser / Thr protein kinases, Protein kinase (Tyr)s, receptor / channel / cell surface proteins, RNA binding proteins, transcriptional regulators, tumor suppressor proteins, ubiquitan conjugating system proteins and proteins of unknown function.
Owner:CELL SIGNALING TECHNOLOGY
Peptides and nanoparticles for intracellular delivery of mRNA
The present invention pertains to peptide-containing complexes / nanoparticles that are useful for delivering into a cell one or more mRNA (such as therapeutic mRNA, e.g., mRNA encoding a tumor suppressor protein).
Owner:AADIGEN
Activators and therapeutic applications thereof
The invention presents methods of identifying small molecule compounds that are activators of tumor suppressor protein p53 pathway, and its associated family members p63 and p73, function. The invention is further drawn to methods of killing tumor cells and treating cancers or other conditions requiring activation of the p53 family member pathways and DNA damage response pathways with the small molecules.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method for extracting tumour-inhibiting protein from amniotic fluid of pregnant woman
InactiveCN101250216AWill not harmFacilitate the elucidation of biological functionsPeptide preparation methodsObstetricsAmniotic fluid
The invention relates to a method for extracting tumor suppressor protein from the amniotic fluid of pregnant women, which comprises (1) collecting amniotic fluid, (2) filtering amniotic fluid, (3) centrifugally depositing, (4) first depressurizing and drying, (5) first dialysis: using the dialysis bag whose molecular weight cutoff is 10000Dalton, (6) second depressurizing and drying, (7) second dialysis: using the dialysis bag whose molecular weight cutoff is 3000Dalton, (8) third depressurizing and drying. The extraction method has the advantages that the invention can extract tumor suppressor protein from the amniotic fluid, thereby developing a new route of tumor suppressor protein, and test result proves that mice in tumor experiment can be healed, the tumor suppressor protein of the amniotic fluid of pregnant women can act the mice tumor, the protein has specific wide spectrum anti-tumor function and the invention is beneficial to express the biological function of amniotic fluid, providing the function of embryo growth information channel.
Owner:童兴龙
Tumor-inhibiting protein and the use thereof
InactiveUS20060116323A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthFull length cdna
The invention has disclosed a new tumor suppressor protein HCRP1, the polynucleotide sequences encoding this polypeptides, and methods for production of the polypeptide using the recombinant technology. The tumor suppression protein, HCRP1, is obtained through the positional candidate cloning strategy. It locates in 8p22 region of human chromosome. The full length cDNA for HCRP1 is 1917bp, which encodes a protein of 397 amino acids. When introduced into liver cancer cells, HCRP1 can inhibit the malignant transformation of liver cancer cells.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Glycosylation site-specific antibodies and anti-cancer compounds
A method of characterizing the protein O-GlcNAcylation site-specificity of an antibody. A method of detecting or quantitating the expression of site-specific O-GlcNAcylated proteins expressed in cells and biological samples. A method of diagnosing cancer in a host based on the cellular expression of site-specific O-GlcNAcylated proteins. A method of screening anti-cancer compounds according to their ability to increase a level O-GlcNAcylation of oncogene or tumor suppressor proteins. Methods of treating cancer in an animal host by administering compounds that increase a level of O-GlcNAcylated c-myc or p53 in cancer cells. A method of distinguishing subclasses of pancreatic cancer according to the sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to an imidazole derivative, and a method of personalized pancreatic cancer treatment delivered according to the sensitivity subclasses.
Owner:DETROIT R&D
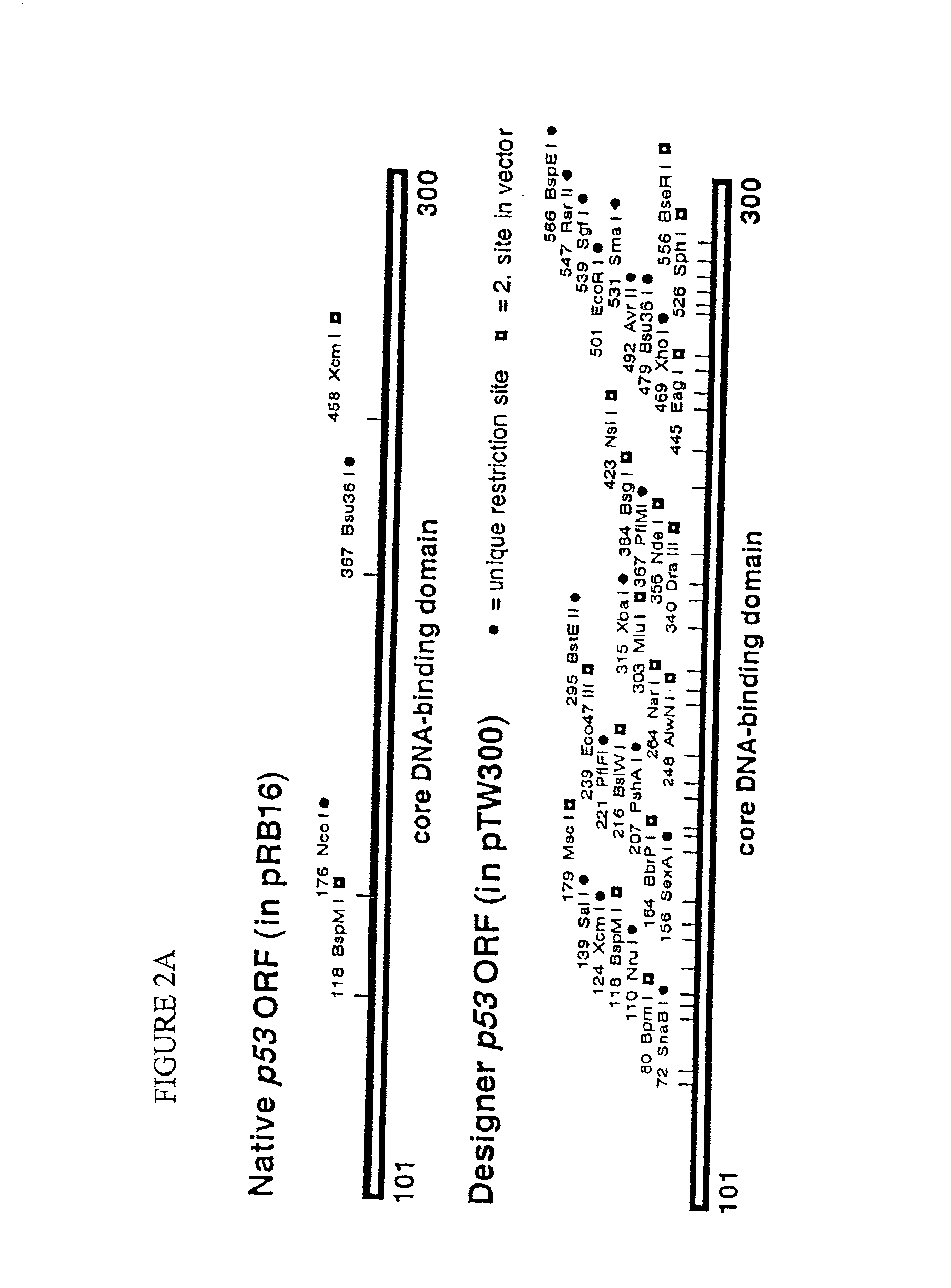
Engineered open reading frame for p53
The transcription factor and tumor suppressor protein p53 is inactivated in many human cancers. Approximately forty percent of cancers carry large amounts of mutated full-length p53 protein with one of over 900 reported single amino acid changes in the p53 core domain that recognizes p53 DNA binding sites. The ability to restore function to these inactive p53 proteins would dramatically improve cancer therapy. Alternative open reading frames that are more easily engineered encode a wild-type p53. The alternative open reading frames are optimized for codon usage and expression of p53 proteins in E. coli, yeast and mammalian cells. The alternative open reading frames may additionally contain mutations that are naturally found in human cancers, substitutions that correspond to polymorphic p53 alleles, or mutations in residues that can be post-translationally modified.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com