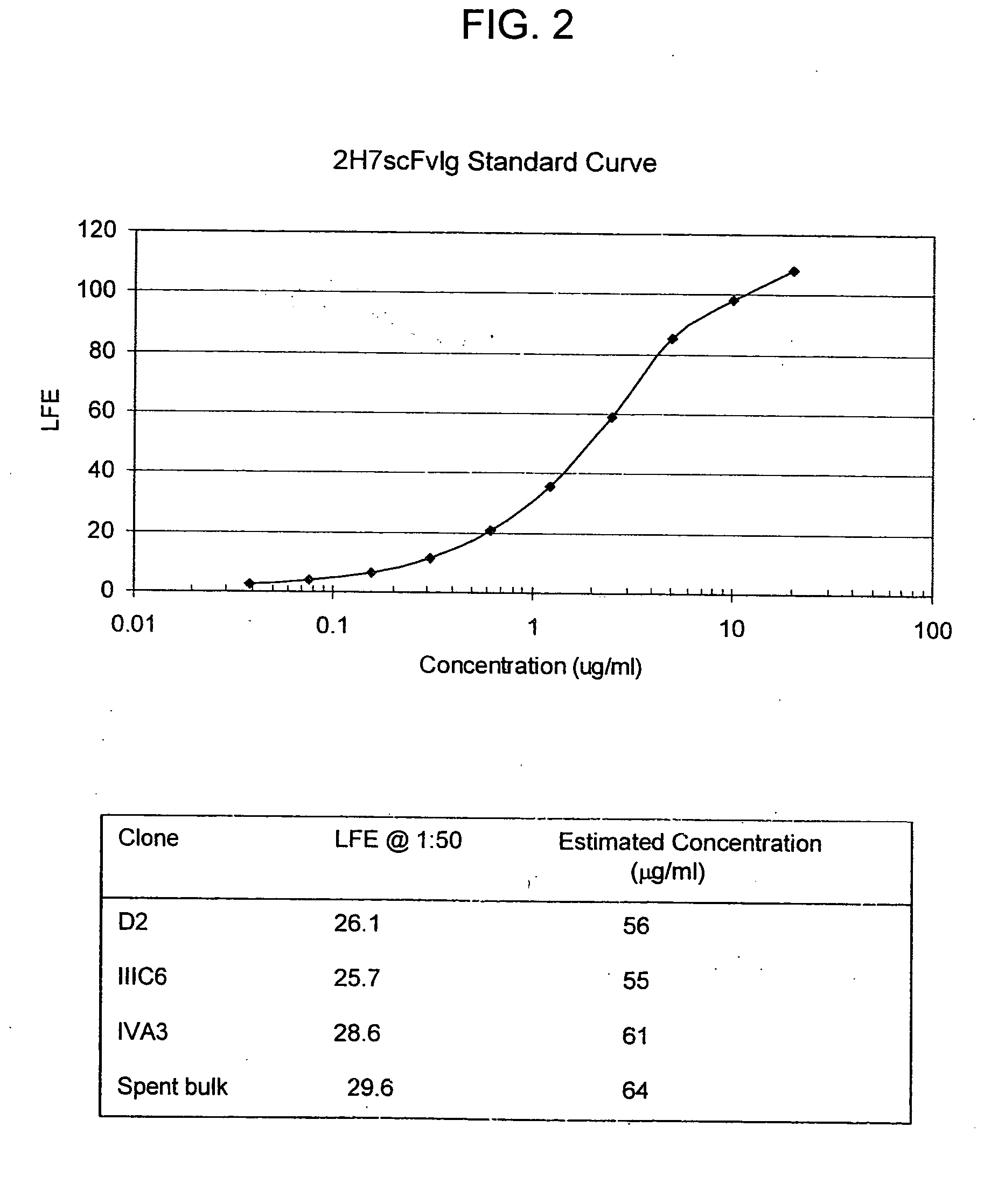
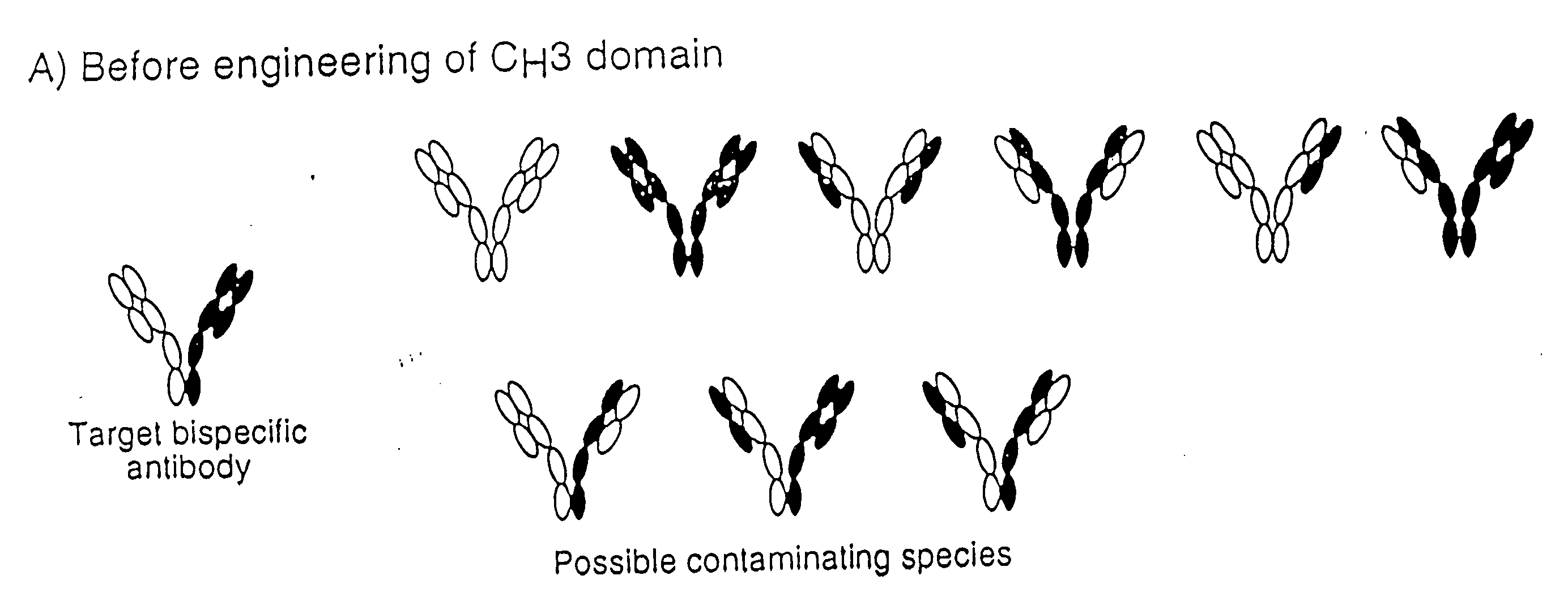
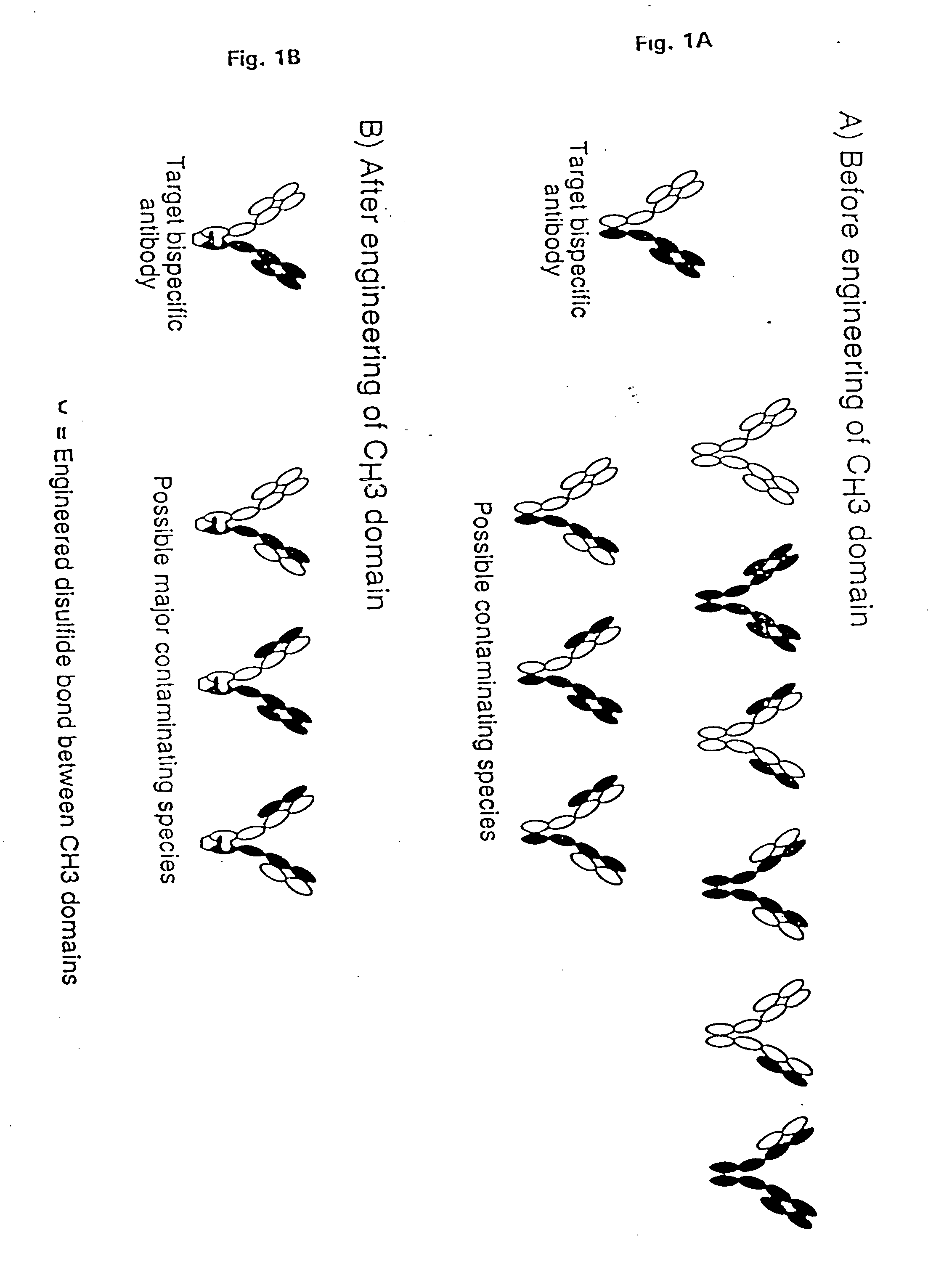
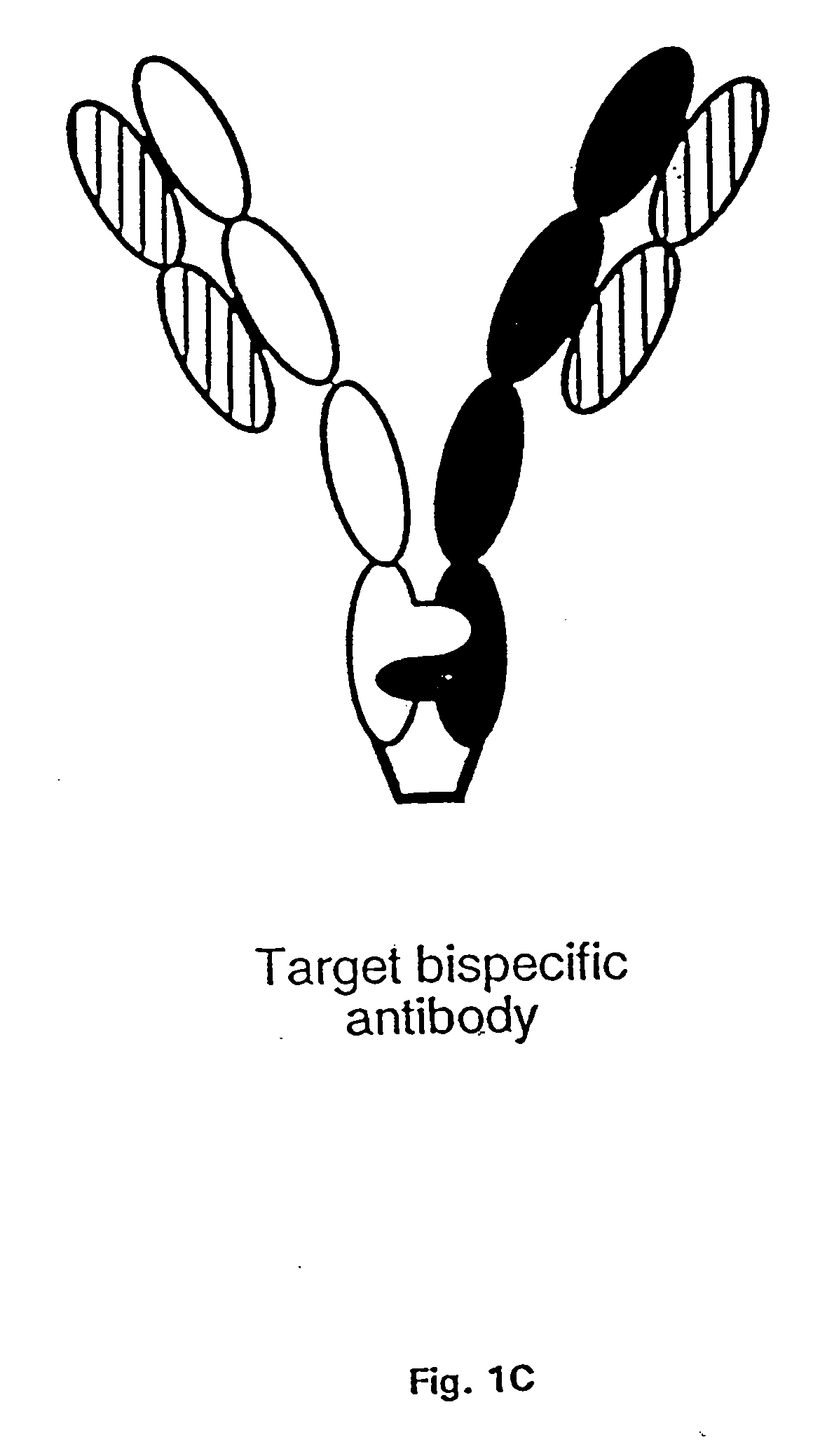
Patents
Literature
2371 results about "Homomeric" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A homomeric substance is one which is made out of any number of identical products or molecules. e.g. A homomeric peptide = glutathione A peptide which is made up of only a single type of amino acid subunit; e.g., alanylalanylalanine. ALA-ALA-ALA e.g. A homomeric channel = α7-Nicotinic receptor channel can be made from 5 α nicotinic subunits and is therefore said to be homomeric.
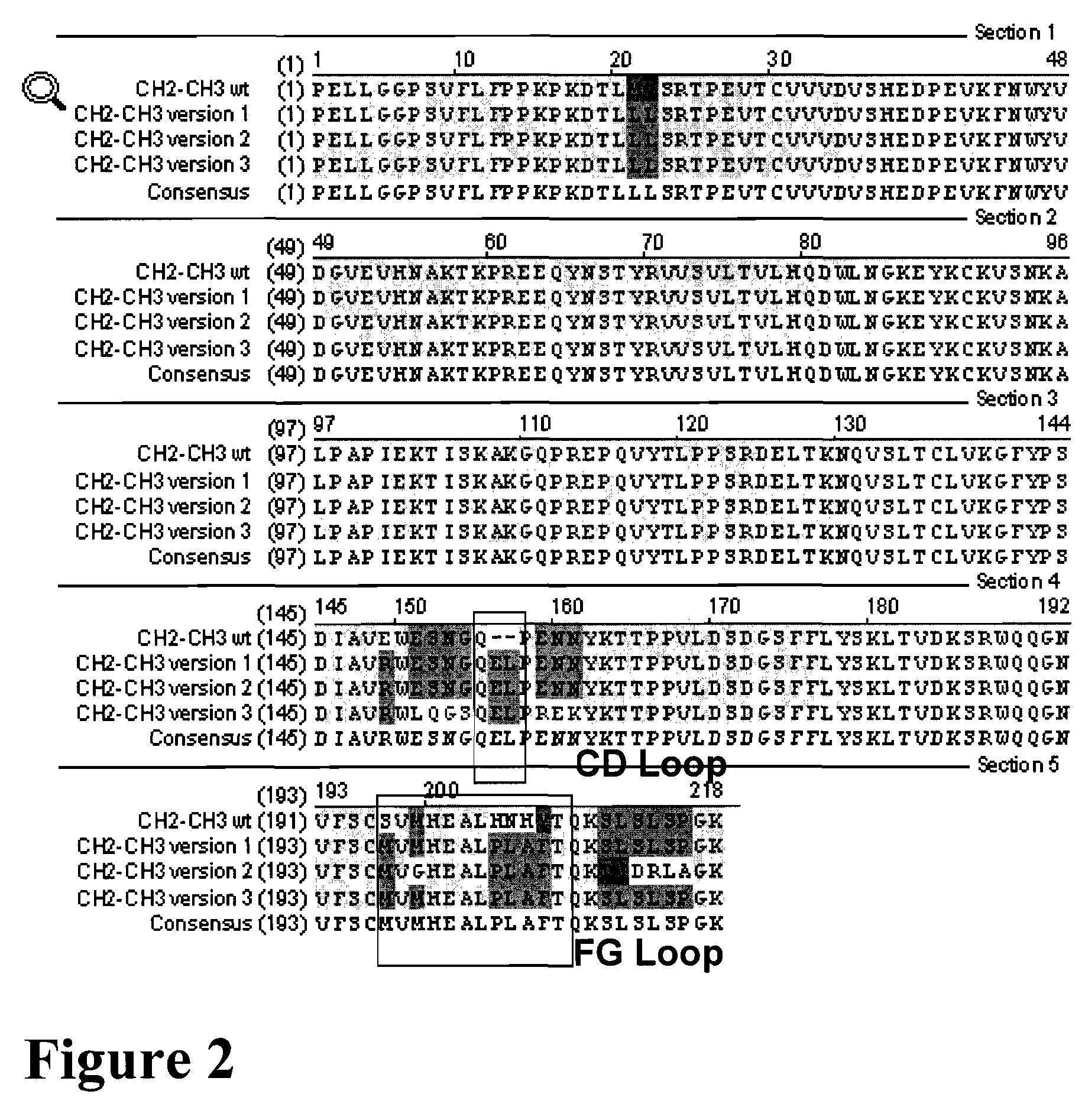
Binding domain-immunoglobulin fusion proteins
InactiveUS20050175614A1Reduced ability to dimerizeHybrid immunoglobulinsAntipyreticCrystallographyAntigen
The invention relates to novel binding domain-immunoglobulin fusion proteins that feature a binding domain for a cognate structure such as an antigen, a counterreceptor or the like, a hinge region polypeptide having either zero or one cysteine residue, and immunoglobulin CH2 and CH3 domains, and that are capable of ADCC and / or CDC while occurring predominantly as monomeric polypeptides. The fusion proteins can be recombinantly produced at high expression levels. Also provided are related compositions and methods, including immunotherapeutic applications.
Owner:TRUBION PHARM INC
Method for Making Multispecific Antibodies Having Heteromultimeric and Common Components
InactiveUS20070178552A1Increased formationIncrease productionAnimal cellsHybrid immunoglobulinsSpecific immunityBiology
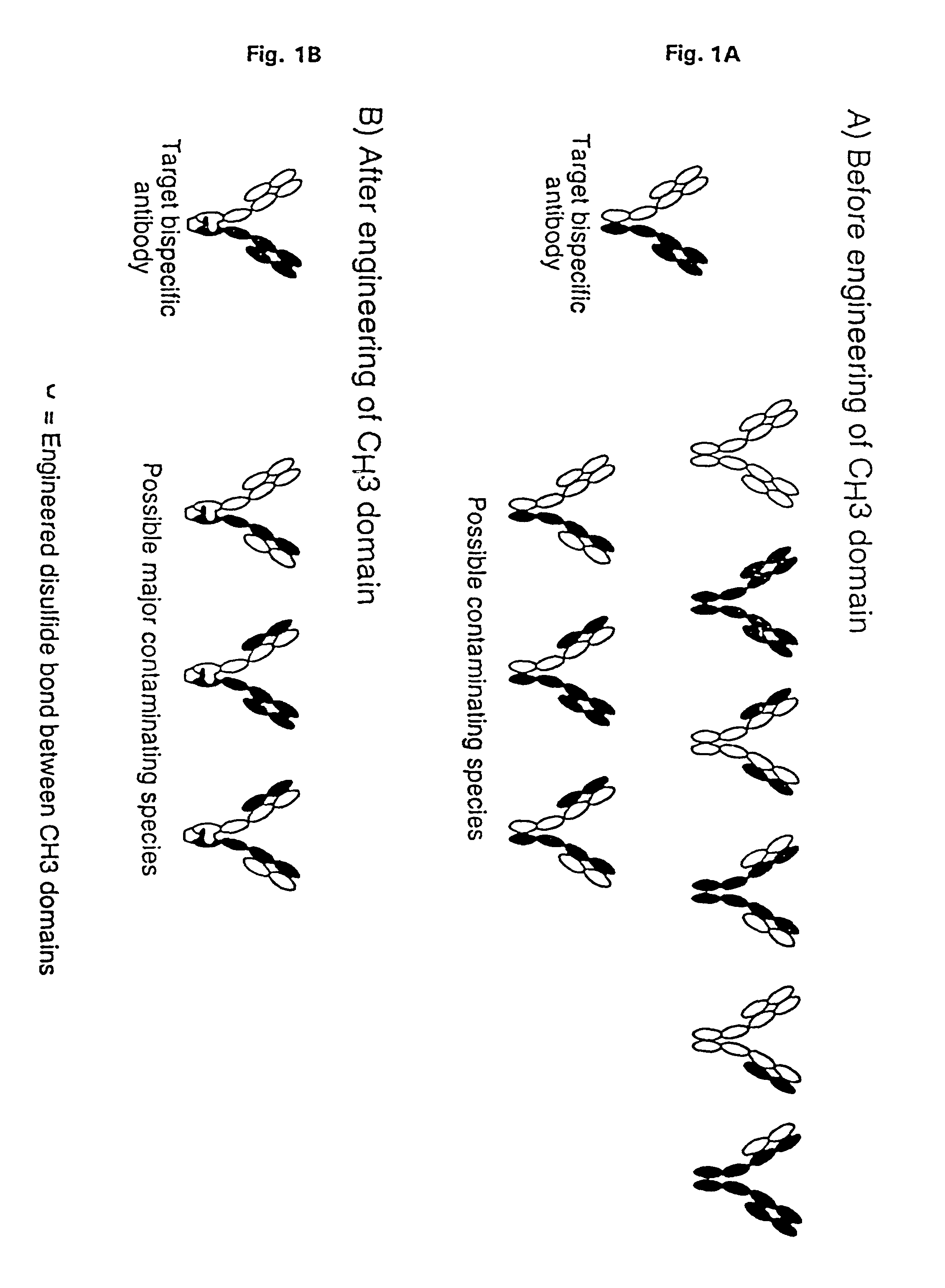
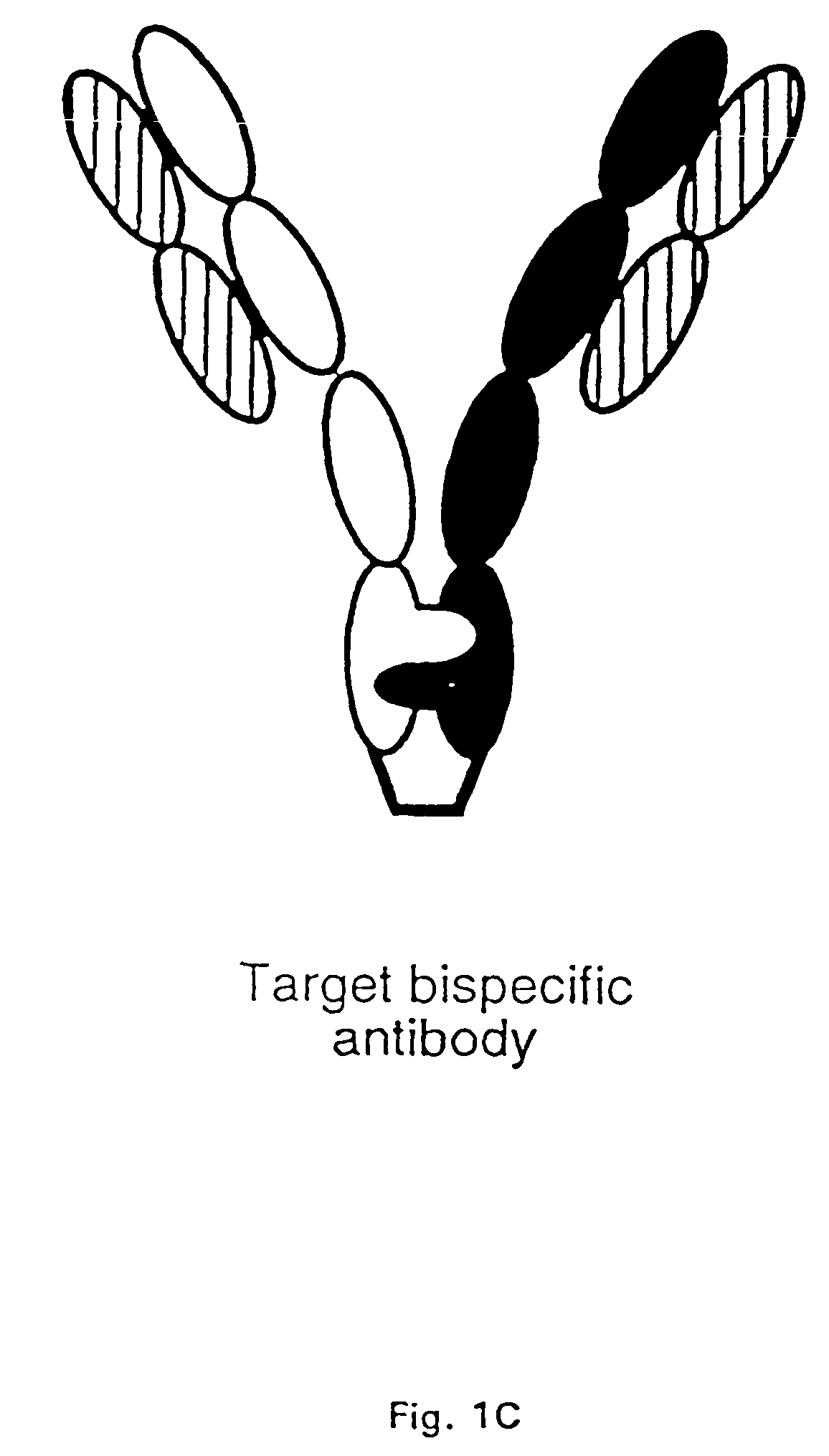
The invention relates to a method of preparing heteromultimeric polypeptides such as bispecific antibodies, bispecific immunoadhesins and antibody-immunoadhesin chimeras. The invention also relates to the heteromultimers prepared using the method. Generally, the method provides a multispecific antibody having a common light chain associated with each heteromeric polypeptide having an antibody binding domain. Additionally the method further involves introducing into the multispecific antibody a specific and complementary interaction at the interface of a first polypeptide and the interface of a second polypeptide, so as to promote heteromultimer formation and hinder homomultimer formation; and / or a free thiol-containing residue at the interface of a first polypeptide and a corresponding free thiol-containing residue in the interface of a second polypeptide, such that a non-naturally occurring disulfide bond is formed between the first and second polypeptide. The method allows for the enhanced formation of the desired heteromultimer relative to undesired heteromultimers and homomultimers.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method for making multispecific antibodies having heteromultimeric and common components
InactiveUS7951917B1Increased formationIncrease productionHybrid immunoglobulinsAntibody ingredientsSpecific immunityBispecific antibody
The invention relates to a method of preparing heteromultimeric polypeptides such as bispecific antibodies, bispecific immunoadhesins and antibody-immunoadhesin chimeras. The invention also relates to the heteromultimers prepared using the method. Generally, the method provides a multispecific antibody having a common light chain associated with each heteromeric polypeptide having an antibody binding domain. Additionally the method further involves introducing into the multispecific antibody a specific and complementary interaction at the interface of a first polypeptide and the interface of a second polypeptide, so as to promote heteromultimer formation and hinder homomultimer formation; and / or a free thiol-containing residue at the interface of a first polypeptide and a corresponding free thiol-containing residue in the interface of a second polypeptide, such that a non-naturally occurring disulfide bond is formed between the first and second polypeptide. The method allows for the enhanced formation of the desired heteromultimer relative to undesired heteromultimers and homomultimers.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
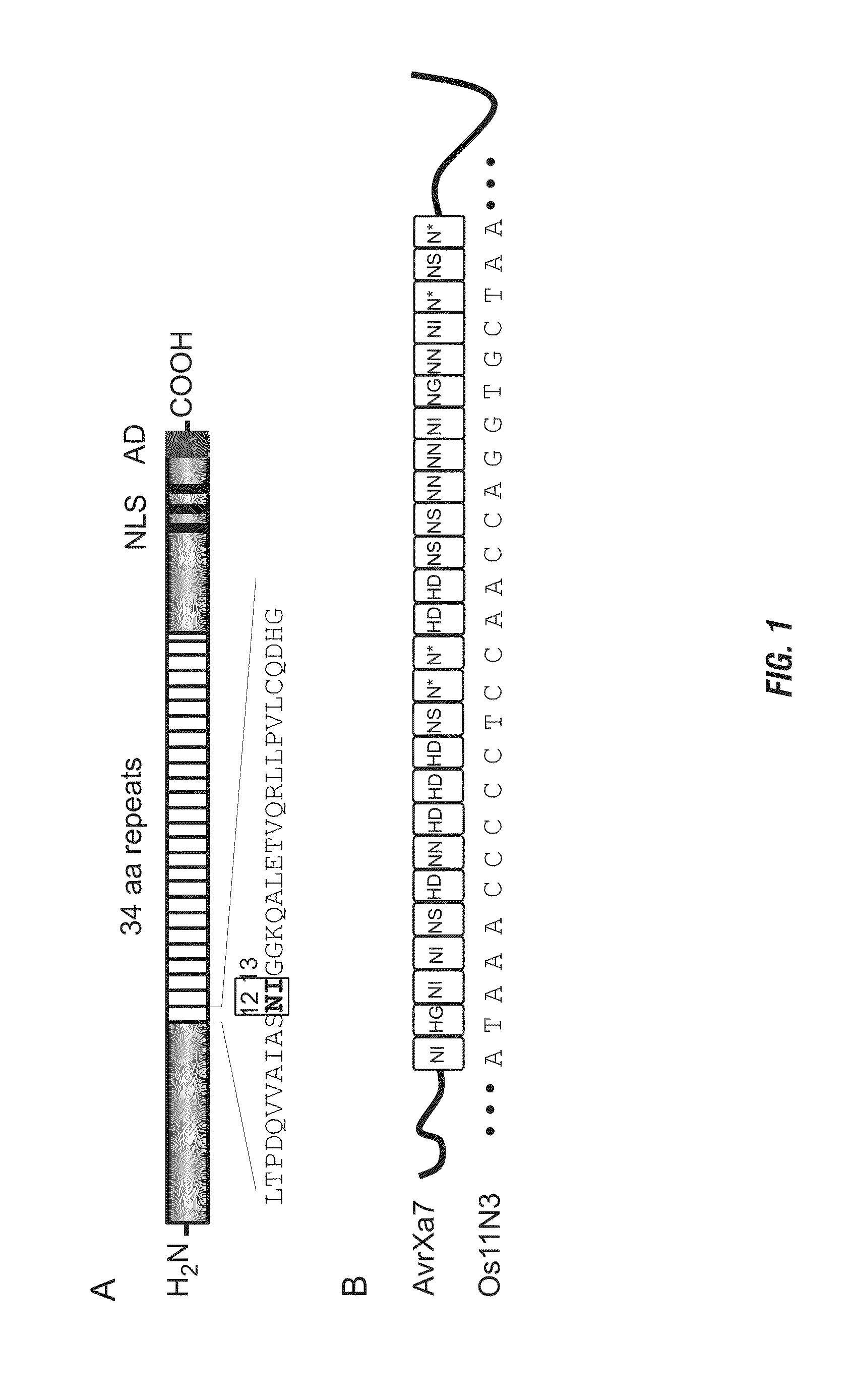
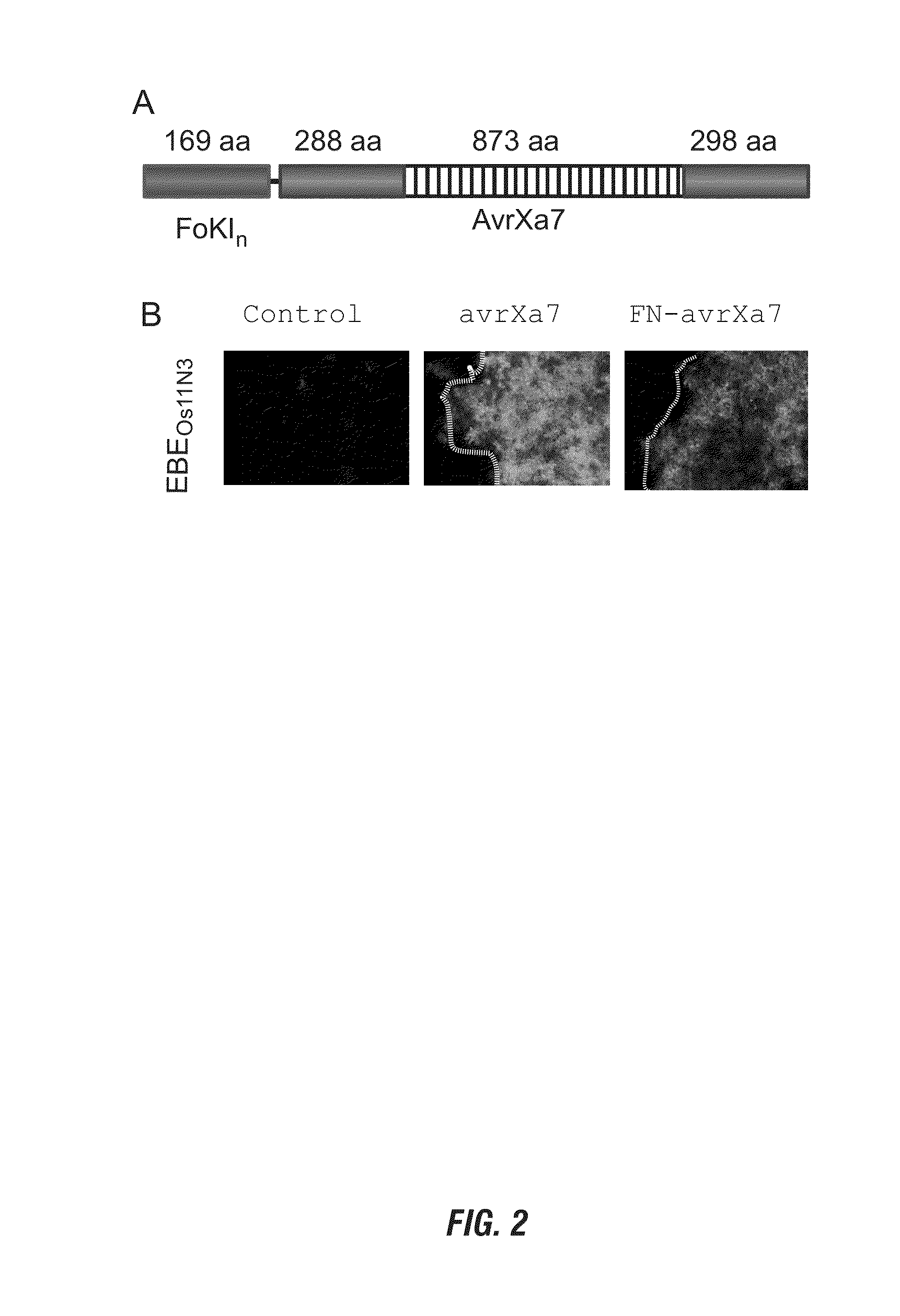
Nuclease activity of tal effector and foki fusion protein
The present invention provides compositions and methods for targeted cleavage of cellular chromatin in a region of interest and / or homologous recombination at a predetermined site in cells. Compositions include fusion polypeptides comprising a TAL effector binding domain and a cleavage domain. The cleavage domain can be from any endonuclease. In certain embodiments, the endonuclease is a Type IIS restriction endonuclease. In further embodiments, the Type IIS restriction endonuclease is FokI.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
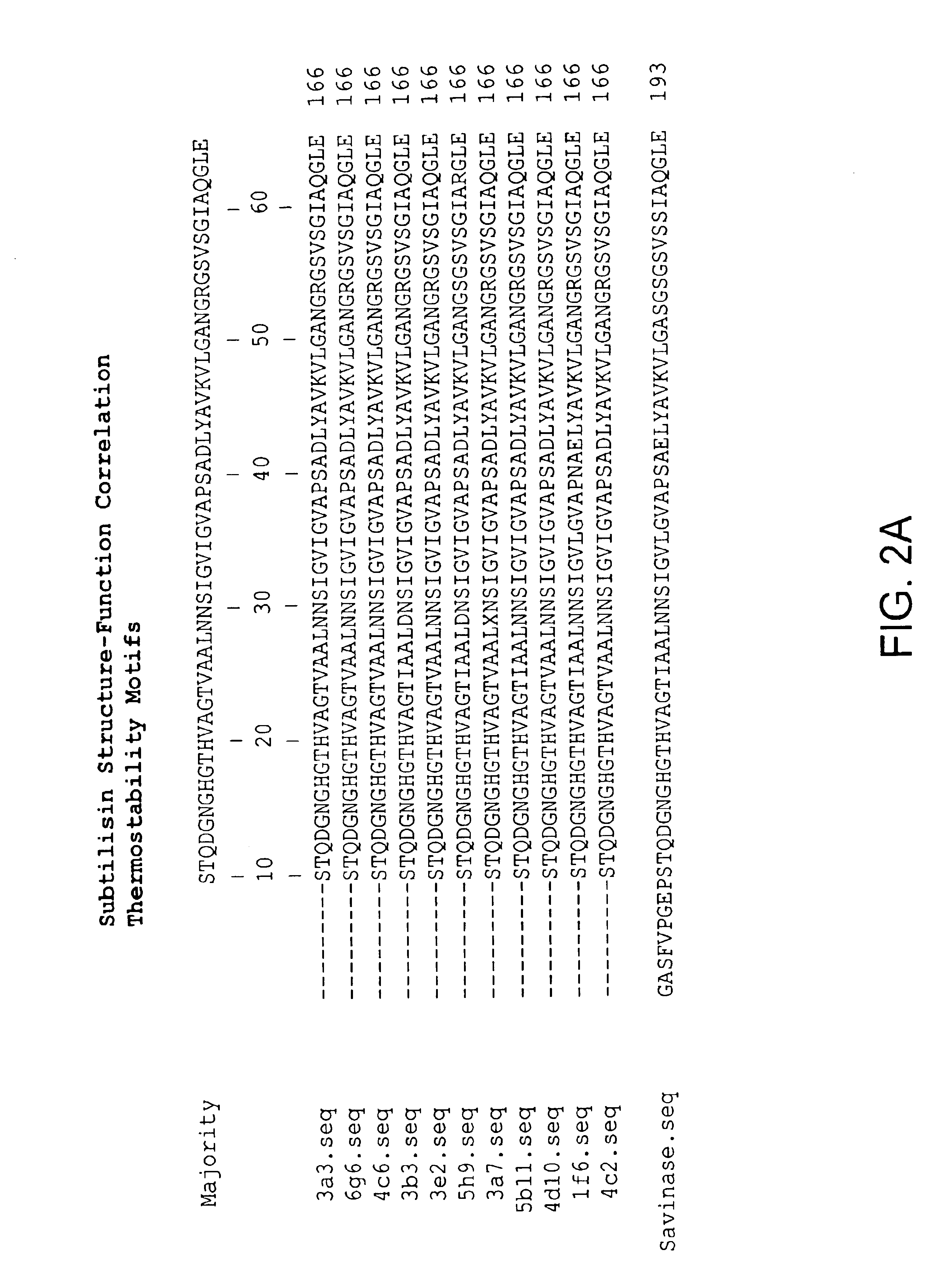
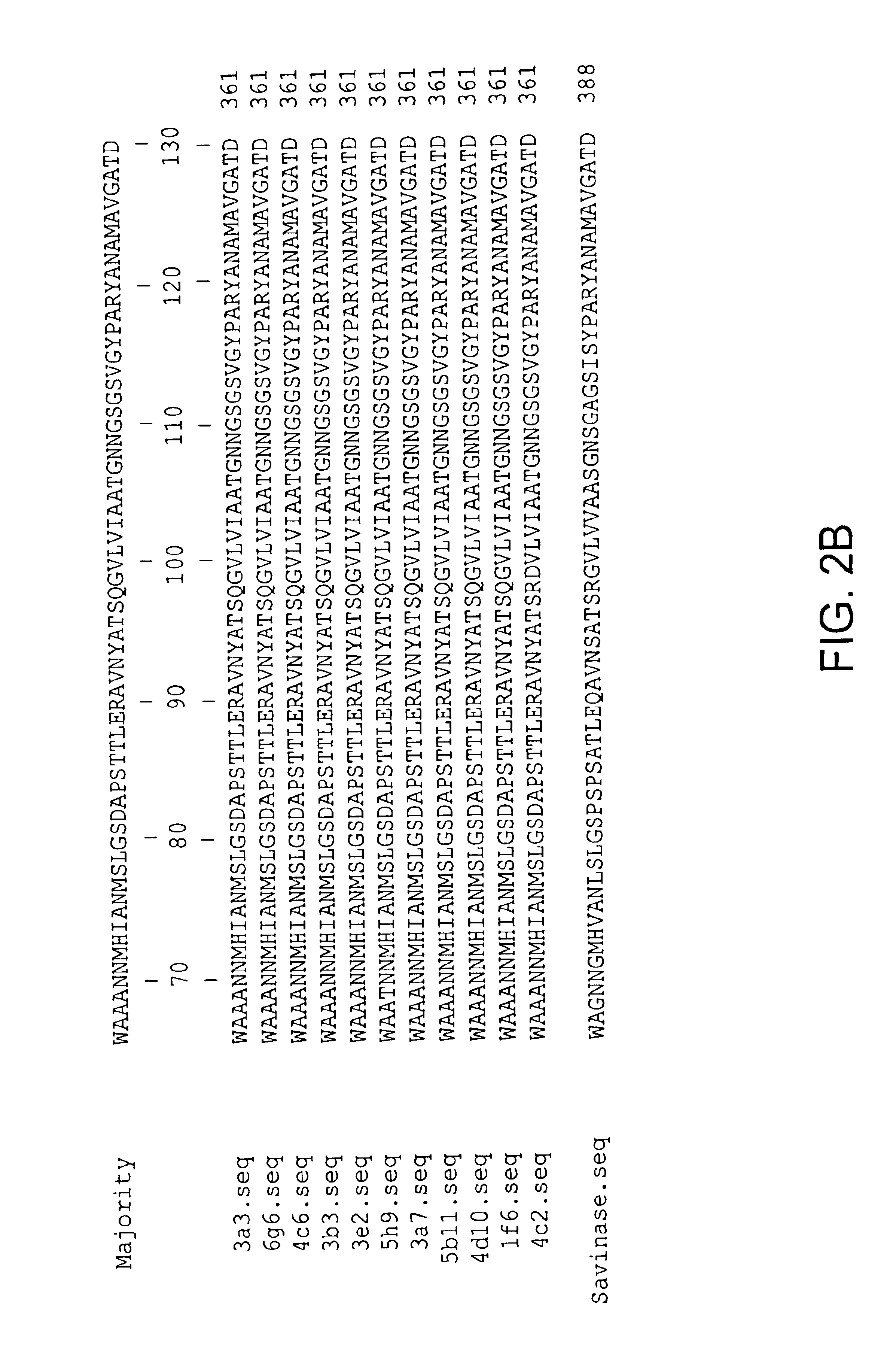
Subtilisin variants
New subtilisin homologues (both nucleic acids and proteins) are provided. Compositions which include these new proteins, recombinant cells, shuffling methods involving the new homologues, antibodies to the new homologues, and methods of using the homologues are also provided.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS +1
Methods for protein labeling based on acyl carrier protein
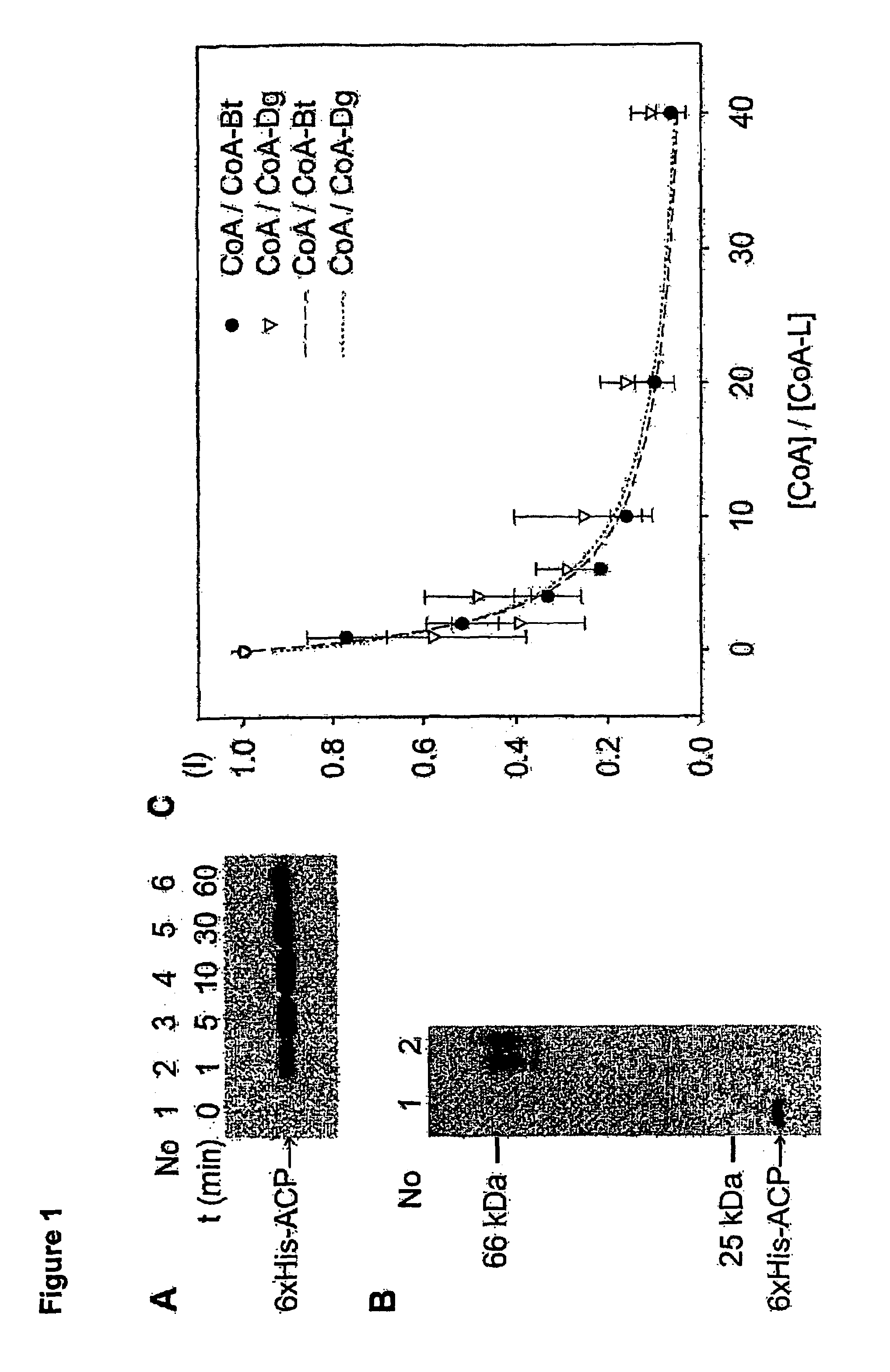
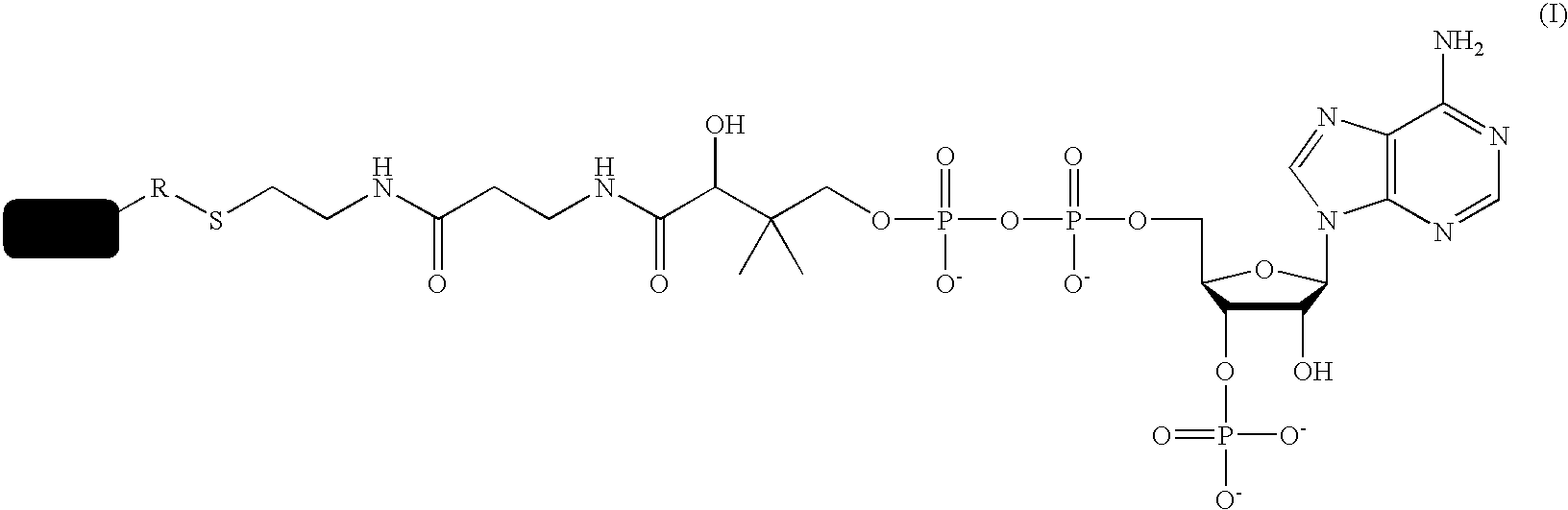
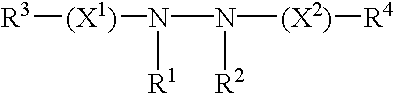
InactiveUS7666612B2Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesCoenzyme A biosynthesisCarrier protein
A method for labeling acyl carrier protein (ACP) fusion proteins with a wide variety of different labels is disclosed. The method relies on the transfer of a label from a coenzyme A type substrate to an ACP fusion protein using a holo-acyl carrier protein synthase (ACPS) or a homologue thereof. The method allows detecting and manipulating the fusion protein, both in vitro and in vivo, by attaching molecules to the fusion proteins that introduce a new physical or chemical property to the fusion protein. Examples of such labels are, among others, spectroscopic probes or reporter molecules, affinity tags, molecules generating reactive radicals, cross-linkers, ligands mediating protein-protein interactions or molecules suitable for the immobilization of the fusion protein.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Homogeneous preparations of IL-28 and IL-29
ActiveUS7157559B2Improve expression levelIncrease productionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticMutated proteinPolynucleotide
Homogeneous preparations of IL-28A, IL-28B, and IL-29 have been produced by mutating one or more of the cysteine residues in the polynucleotide sequences encoding the mature proteins. The cysteine mutant proteins can be shown to either bind to their cognate receptor or exhibit biological activity. One type of biological activity that is shown is an antiviral activity.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Methods for modulating expression of exogenous genes in mammalian systems
InactiveUS7045315B2Short half-lifeImprove pharmacokineticsBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsHormones regulationGene transfer
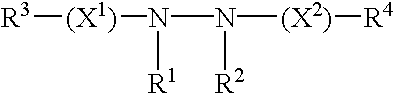
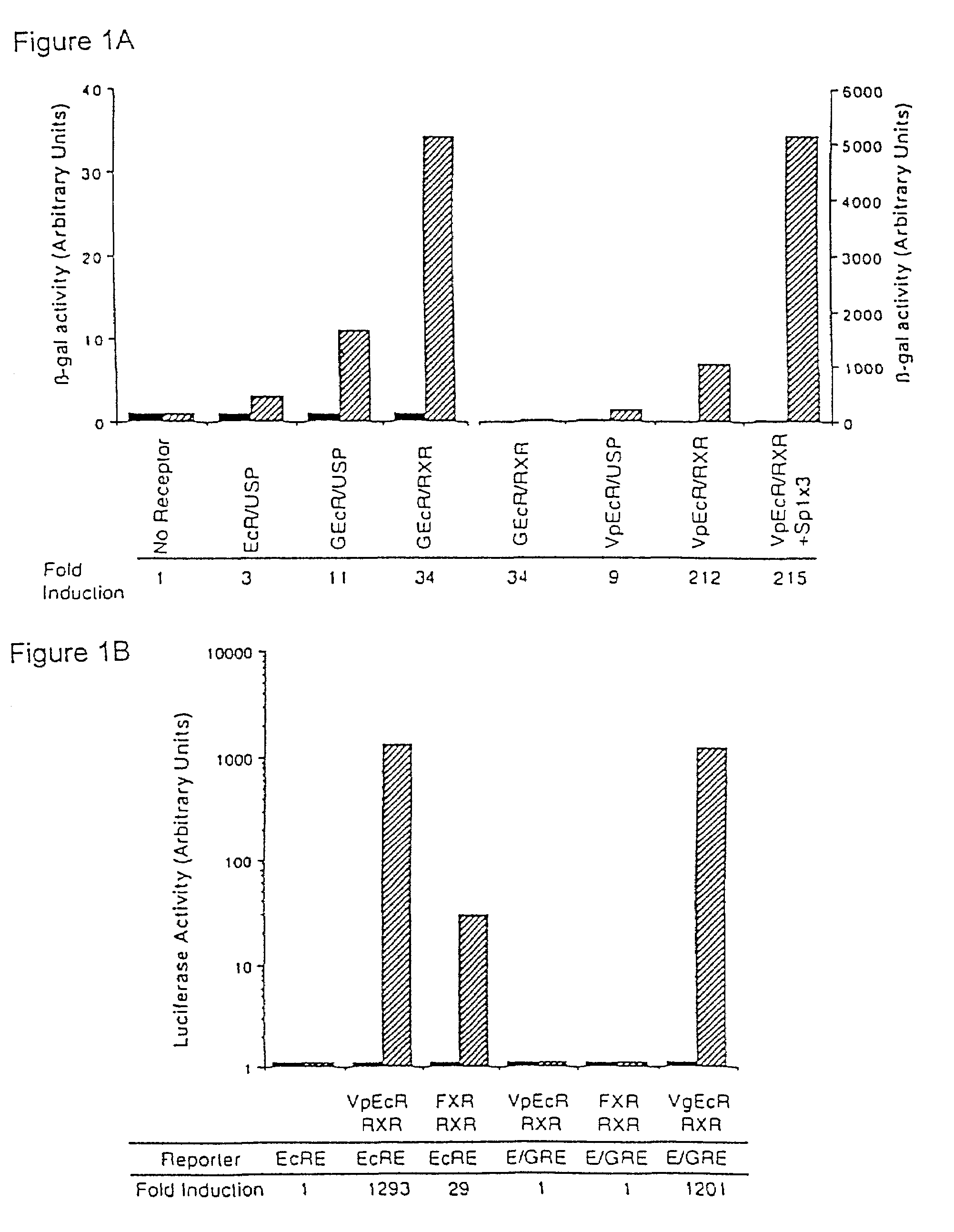
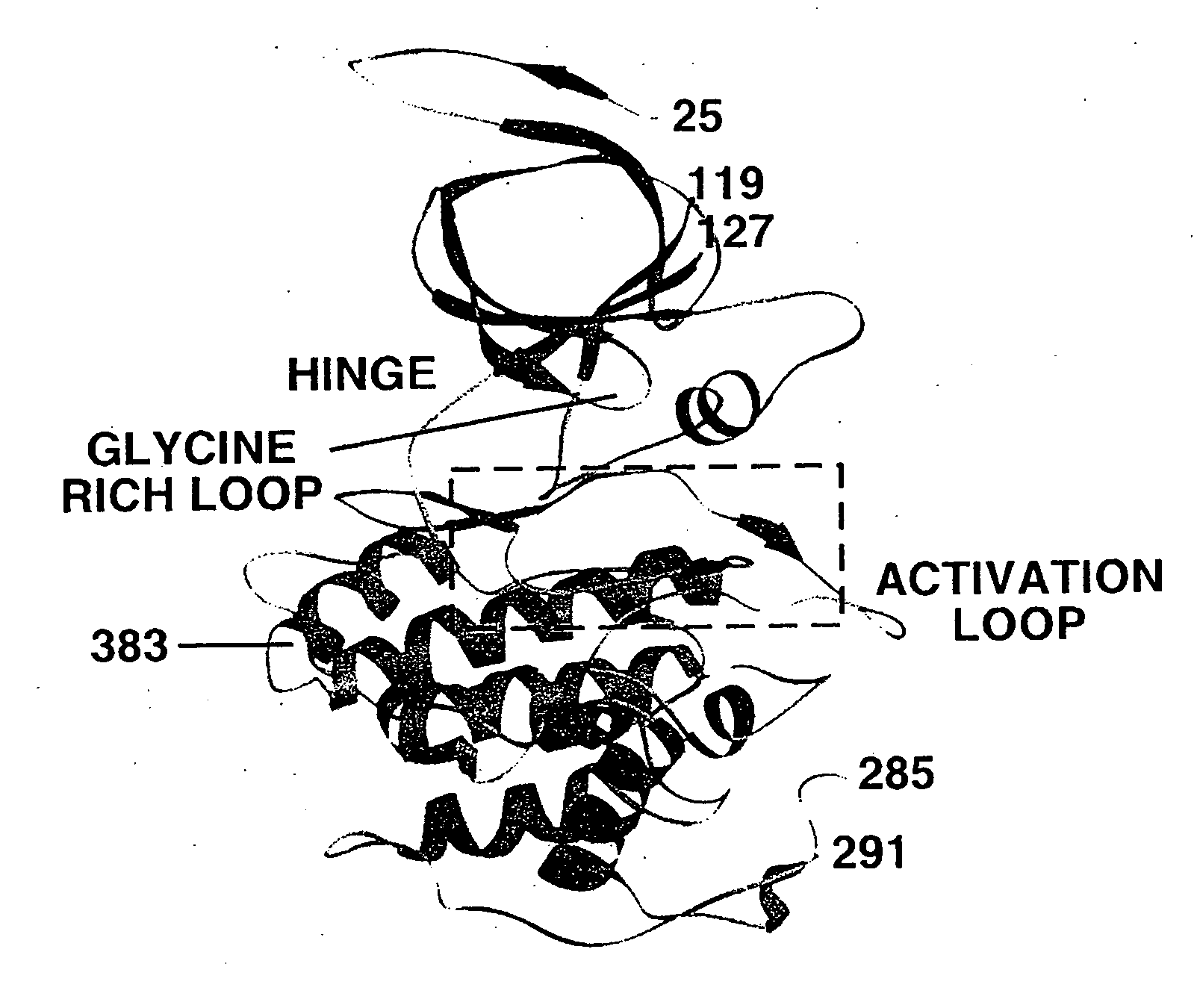
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided various methods for modulating the expression of an exogenous gene in an isolated cell and in a mammalian subject employing modified ecdysone receptors. Also provided are modified ecdysone receptors, as well as homomeric and heterodimeric receptors containing same, nucleic acids encoding invention modified ecdysone receptors, modified hormone response elements, gene transfer vectors, recombinant cells, and transgenic animals containing nucleic acids encoding invention modified ecdysone receptor.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Inhibitors of GSK-3 and crystal structures of GSK-3beta protein and protein complexes
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
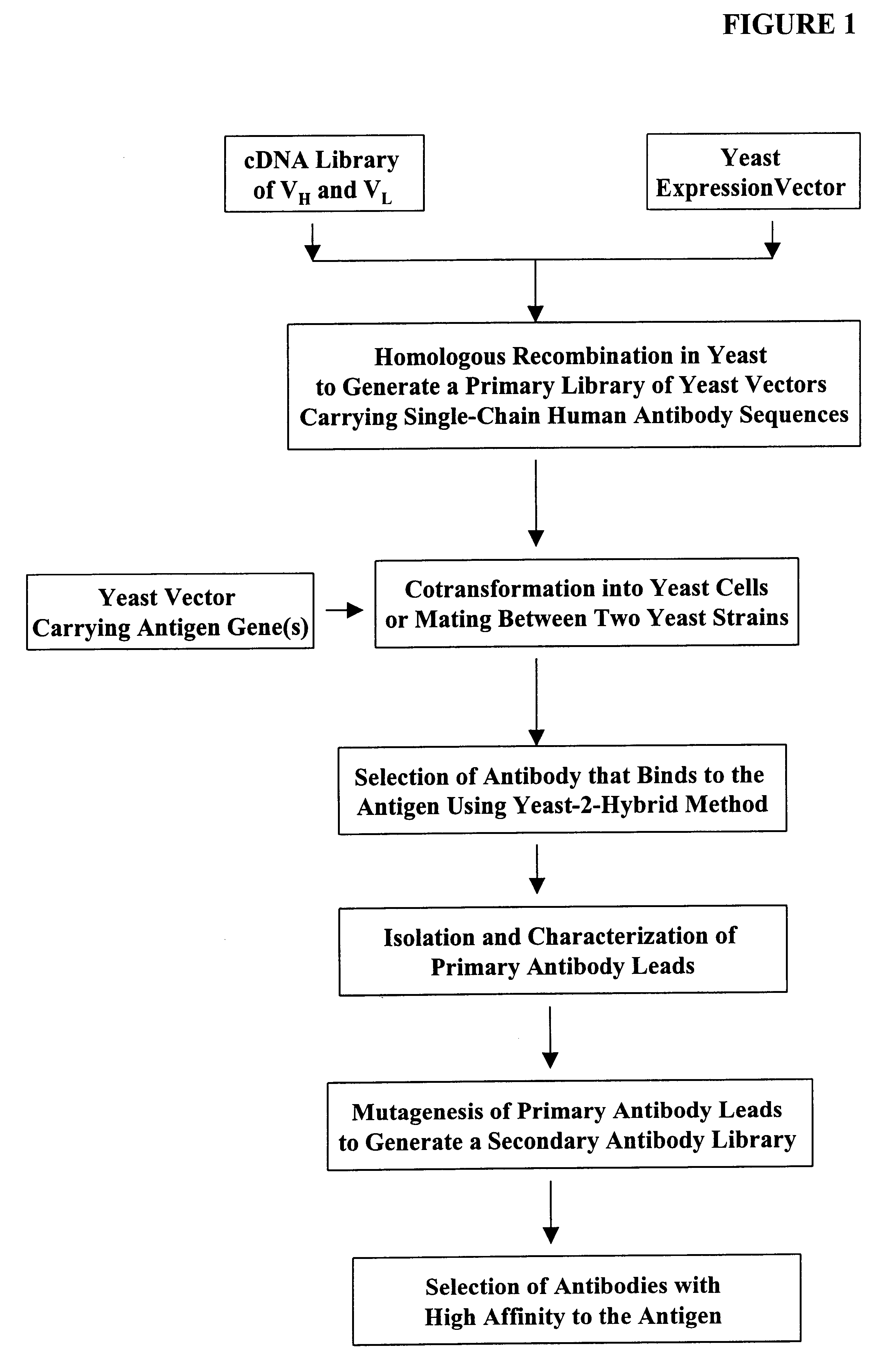
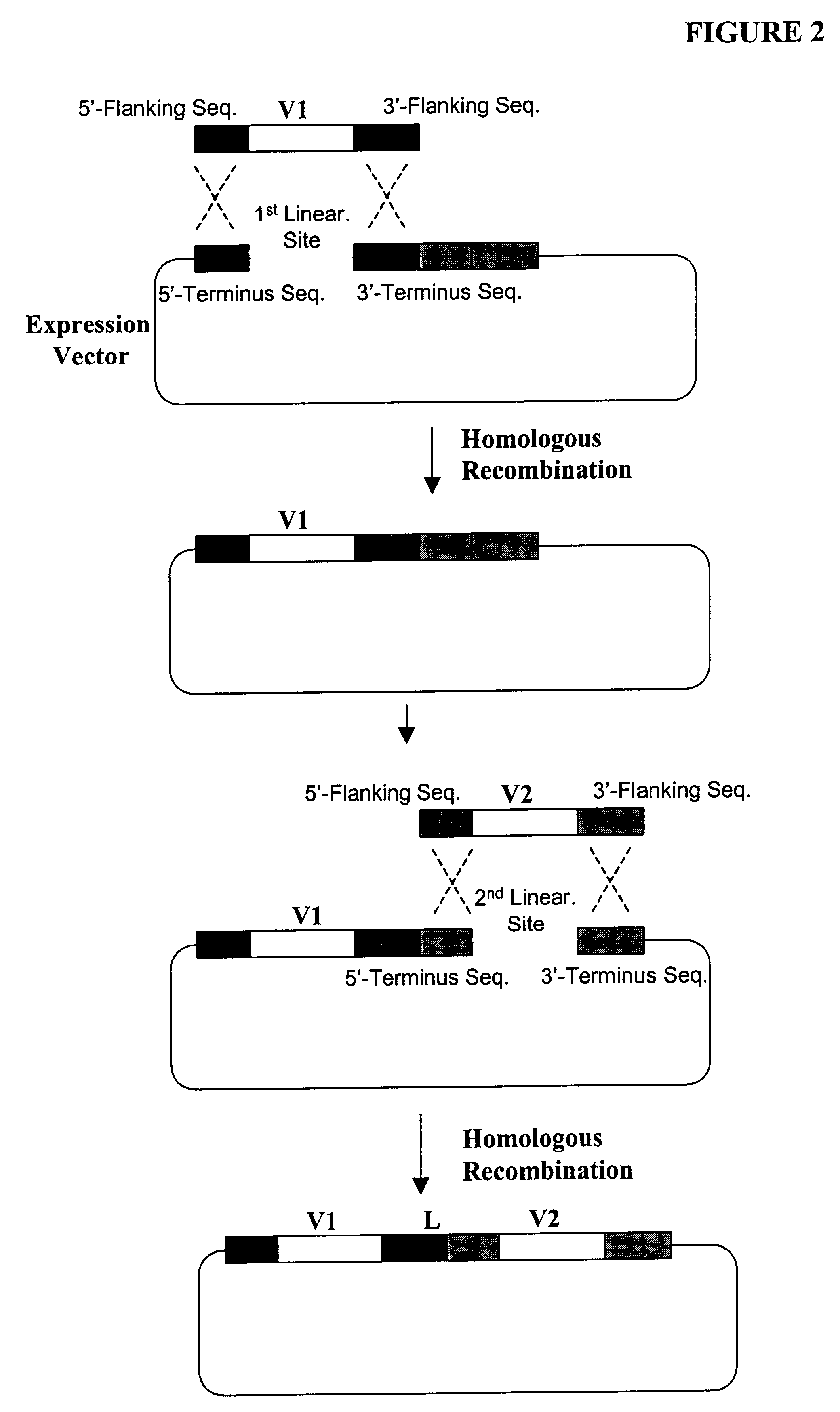
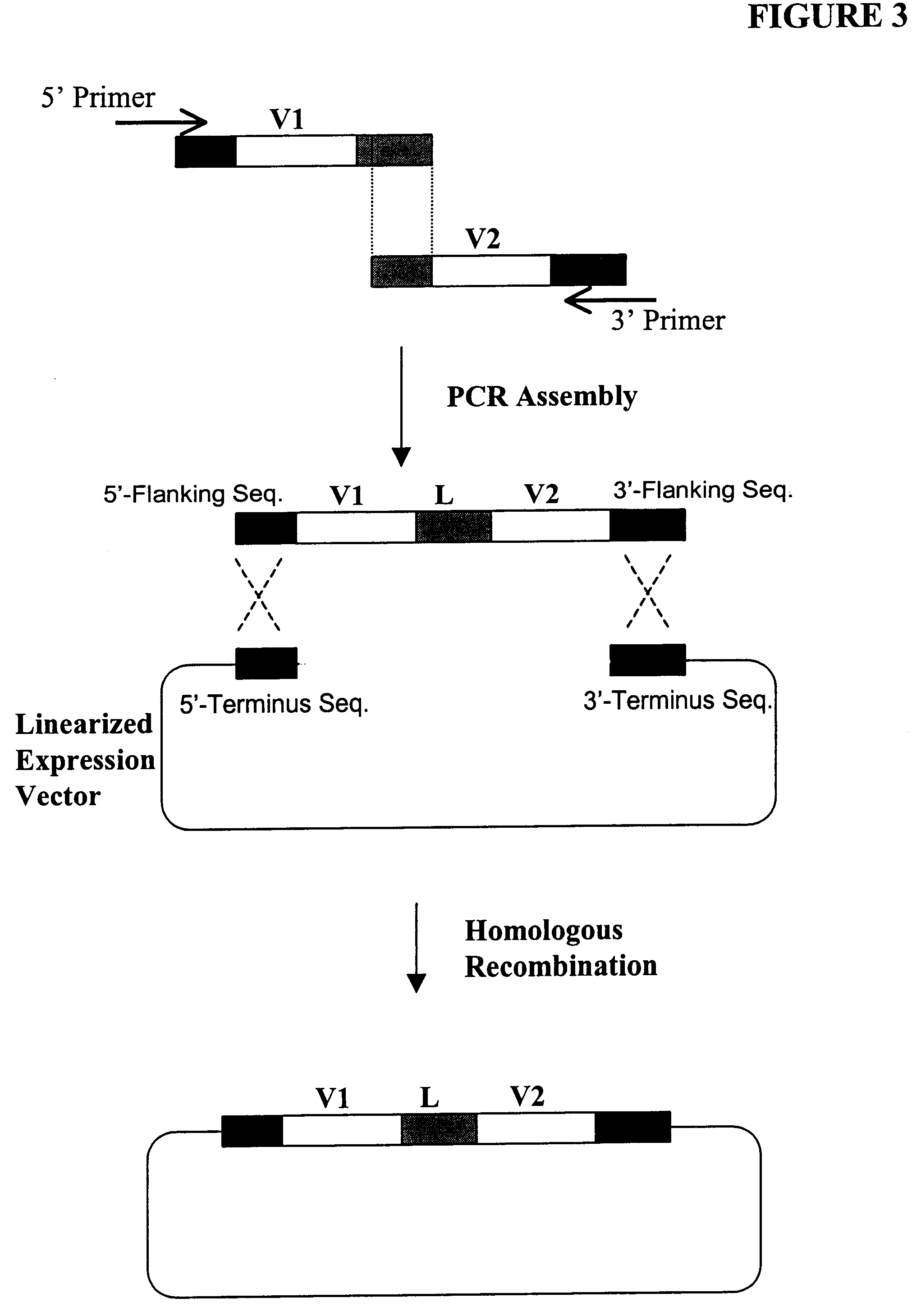
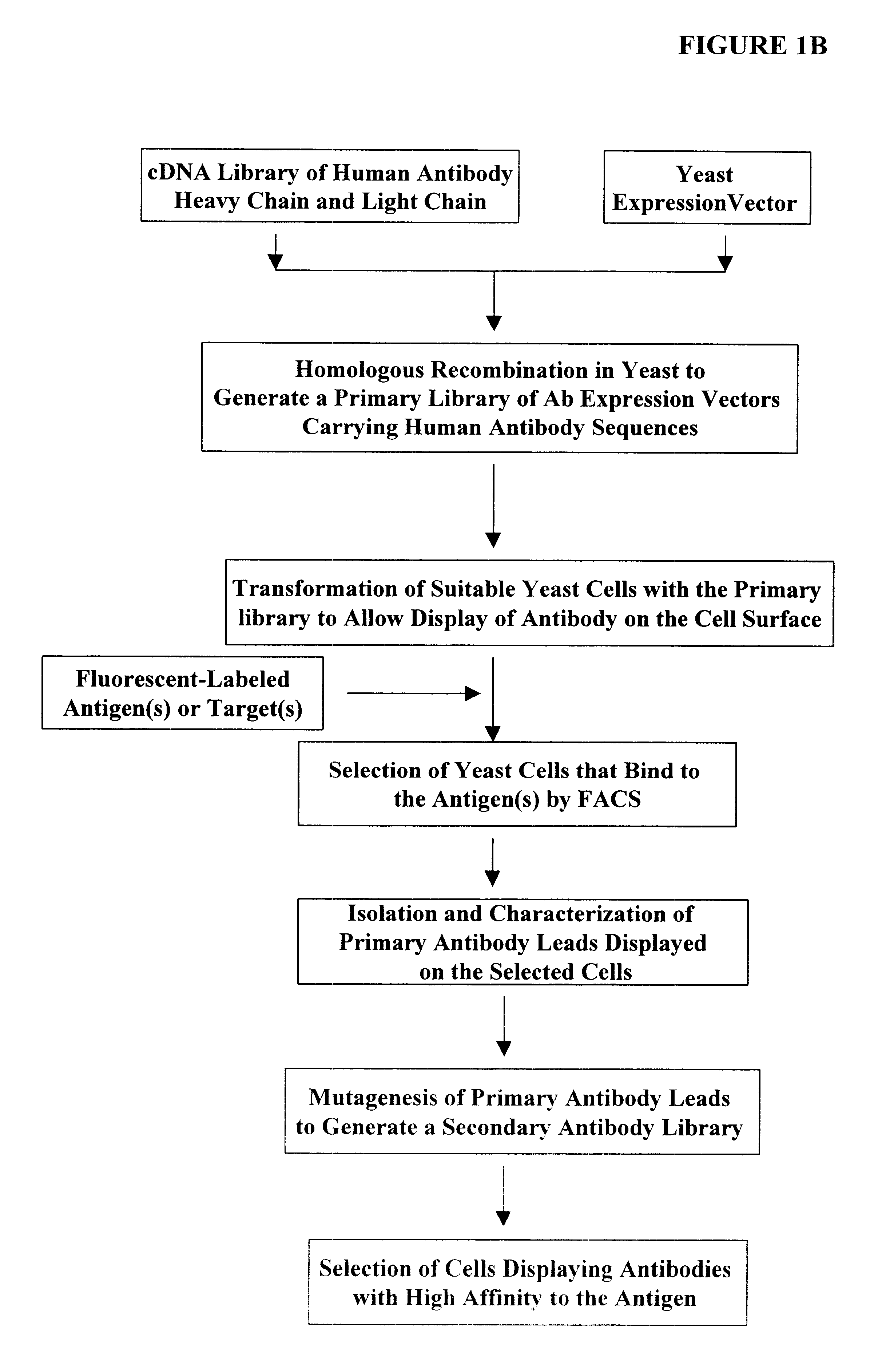
High throughput generation and screening of fully human antibody repertoire in yeast
InactiveUS6406863B1High affinityEasy to assembleMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulinsTarget peptideIn vivo
Compostions, kits and methods are provided for generating highly diverse libraries of proteins such as antibodies via homologous recombination in vivo, and screening these libraries against protein, peptide and nucleic acid targets using a two-hybrid method in yeast. The method for screening a library of tester proteins against a target protein or peptide comprises: expressing a library of tester proteins in yeast cells, each tester protein being a fusion protein comprised of a first polypeptide subunit whose sequence varies within the library, a second polypeptide subunit whose sequence varies within the library independently of the first polypeptide, and a linker peptide which links the first and second polypeptide subunits; expressing one or more target fusion proteins in the yeast cells expressing the tester proteins, each of the target fusion proteins comprising a target peptide or protein; and selecting those yeast cells in which a reporter gene is expressed, the expression of the reporter gene being activated by binding of the tester fusion protein to the target fusion protein.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
Novel elongase gene and method for producing multiple-unsaturated fatty acids
InactiveUS20040111763A1Improve efficiencyIncrease productionCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsElongaseTriacylglycerol VLDL
The invention relates to a novel elongase gene with the sequences stated in sequence SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 7 or their homologs, derivatives or analogs, to a gene construct comprising this gene or its homologs, derivatives and analogs, and to its use. The invention also relates to vectors or transgenic organisms comprising an elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 7 or its homologs, derivatives and analogs. The invention furthermore relates to the use of the elongase gene sequences alone or in combination with further elongases and / or further fatty acid biosynthesis genes. The present invention relates to a novel elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID NO:1 or its homologs, derivatives and analogs. Furthermore, the invention relates to a process for the preparation of polyunsaturated fatty acids and to a process for introducing DNA into organisms which produce large amounts of oils and, in particular, oils with a high content of unsaturated fatty acids. Moreover, the invention relates to an oil and / or a fatty acid preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds and / or a triacylglycerol preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds.
Owner:BASF AG
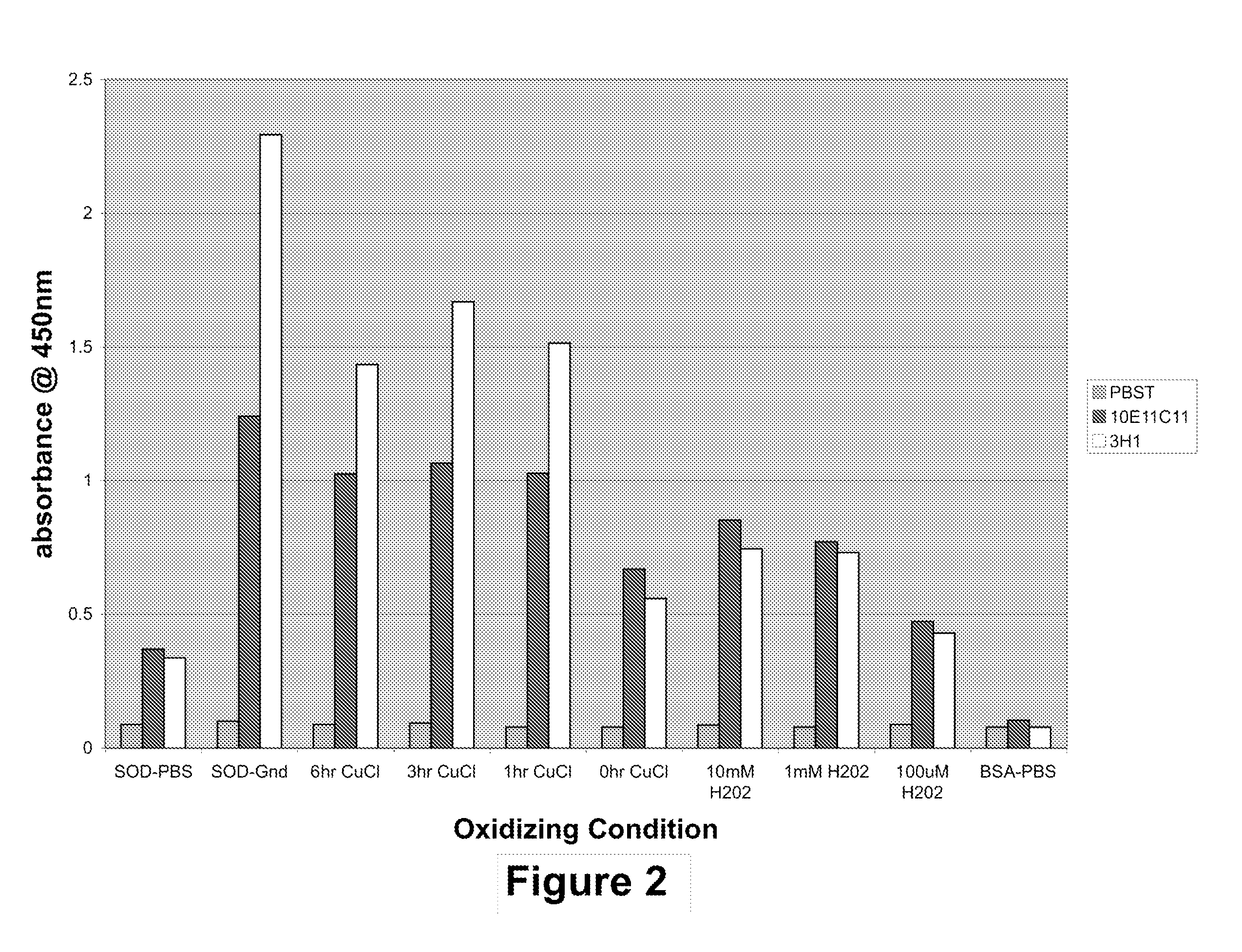
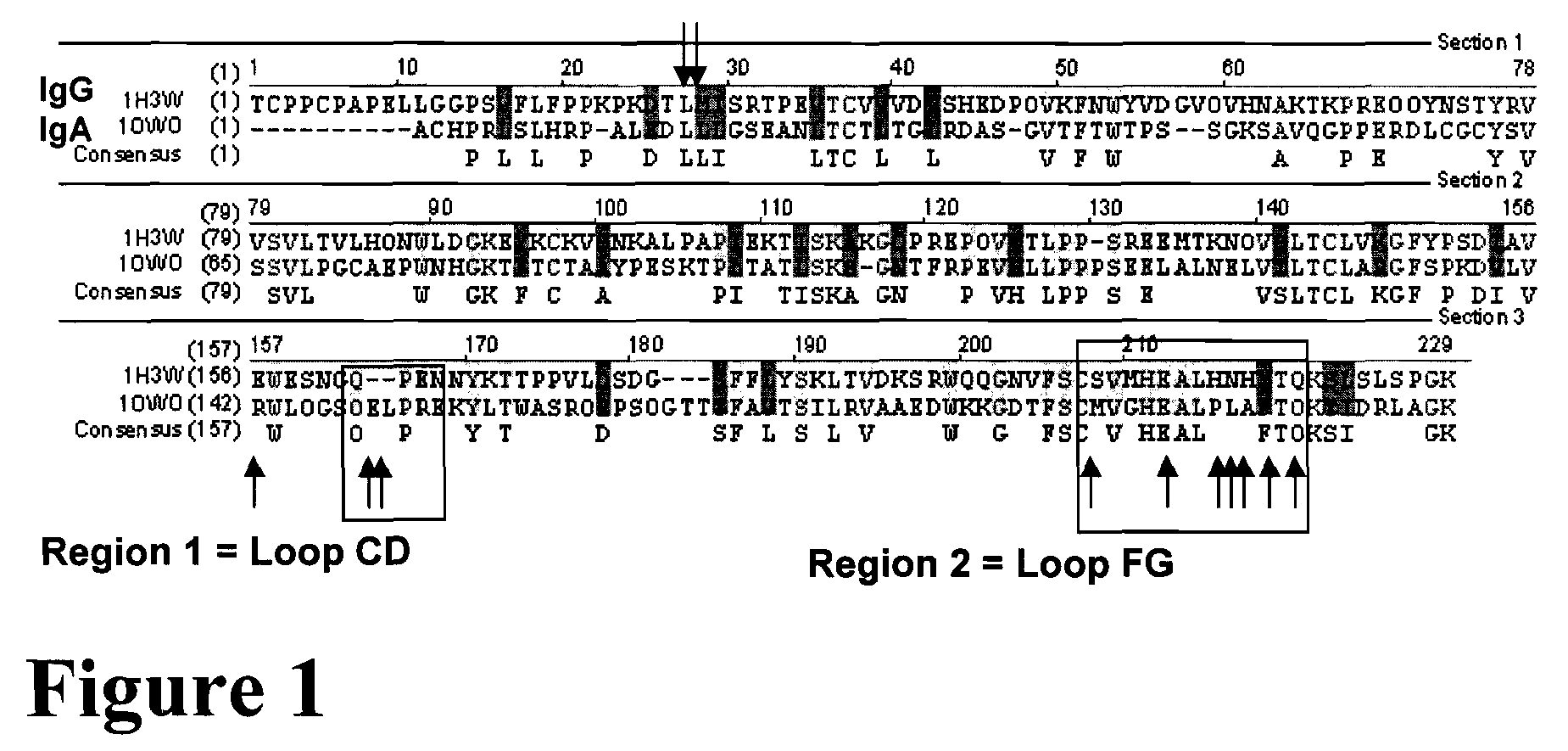
Methods and compositions to treat and detect misfolded-SOD1 mediated diseases
ActiveUS20070292410A1Inhibit and neutralize toxic effectInhibition of disease progressionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsOrganic active ingredientsEpitopeSOD1
The invention provides a method for treating a medical condition, disease, or disorder mediated by a misfolded form of superoxide dismutase (SOD) in a subject in need of treatment. The method optionally comprises administering to the subject a composition comprising a pharmaceutically acceptable vehicle and an agent selected from (1) an exogenous antibody or fragment thereof that binds selectively to the misfolded form of SOD, and / or (2) an immunogen that elicits production of an endogenous antibody that binds selectively to the misfolded form of SOD, and / or (3) a nucleic acid sequence encoding (1) or (2). In certain embodiments, the invention provides methods of treating diseases such as Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using amyotrophic disease-specific epitopes, and compositions including these epitopes. The invention also provides antibodies that bind to monomeric or misfolded SOD1, and not on the molecular surface of native homodimeric SOD1. In addition, the invention includes methods of diagnosing Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in a subject. Also, the invention provides methods of identifying substances for the treatment or prevention of Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and kits using the binding proteins of the invention.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK +1
Detection of nucleic acids by target-specific hybrid capture method
InactiveUS20060051809A1Rapid and sensitive and accurateFunction increaseSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionDNA
Target-specific hybrid capture (TSHC) provides a nucleic acid detection method that is not only rapid and sensitive, but is also highly specific and capable of discriminating highly homologous nucleic acid target sequences. The method produces DNA:RNA hybrids which can be detected by a variety of methods.
Owner:QIAGEN GAITHERSBURG
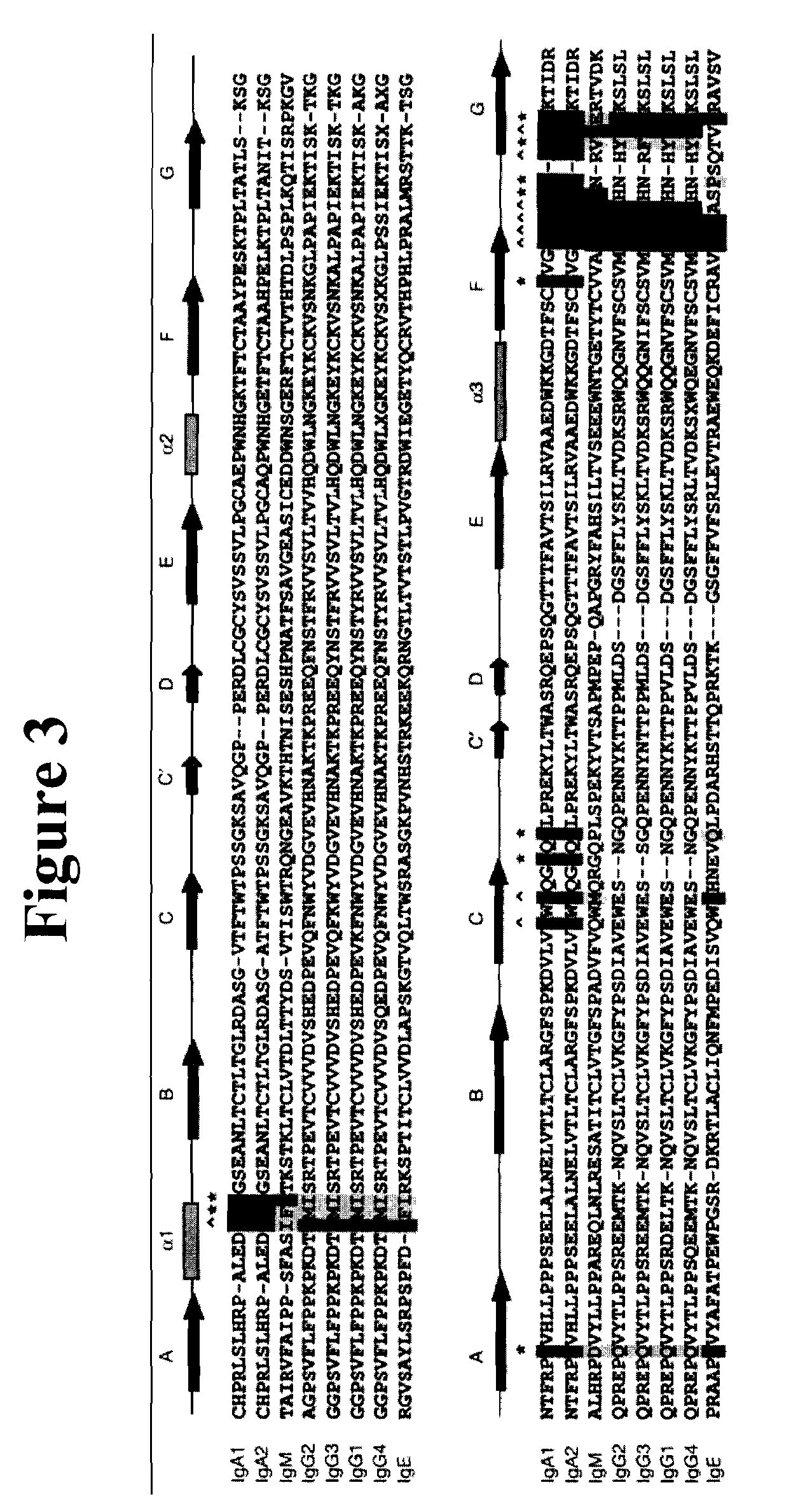
Binding proteins comprising immunoglobulin hinge and fc regions having altered fc effector functions
Provided herein are binding proteins comprising one or more immunoglobulin Fc region hinge, CH2, and / or CH3 domain wherein one or more hinge and / or constant region CH2 and / or CH3 domain is modified to alter the binding protein's binding affinity and / or specificity for a cognate receptor (e.g., an Fc receptor) and / or to impart one or more new binding specificity(ies) to the hinge and / or constant region that the corresponding unmodified immunoglobulin does not possess (e.g., affinity for distinct class of cognate receptor distinct from the class of cognate receptor to which the unmodified binding protein specifically binds). Binding proteins according to the present invention include, for example, modified antibodies, antibody fragments, recombinant binding proteins, and molecularly engineered binding domain-immunoglobulin fusion proteins, including small modular immunopharmaceutical products (SMIP™ products).
Owner:TRUBION PHARM INC
Compounds and methods for crispr/cas-based genome editing by homologous recombination
The present invention relates to guide RNAs comprising adaptor segments having one or more modifications, and their use in homologous recombination by CRISPR:Cas systems. The modified adaptor segments are resistant to degradation by RNaseH. The present invention also relates to a dual guide RNA strategy in which a first guide RNA directs a Cas enzyme to make a double-strand break at a first target sequence, and a second guide RNA comprises an adaptor segment attached to a donor polynucleotide, and binds a second target sequence that is offset from the first target sequence.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Gene products of bacillus licheniformis which form odorous substances and improved biotechnological production methods based thereon
InactiveUS20070190605A1Reduce formationImprove filtering effectBacteriaHydrolasesBacillus licheniformisPropanoic acid
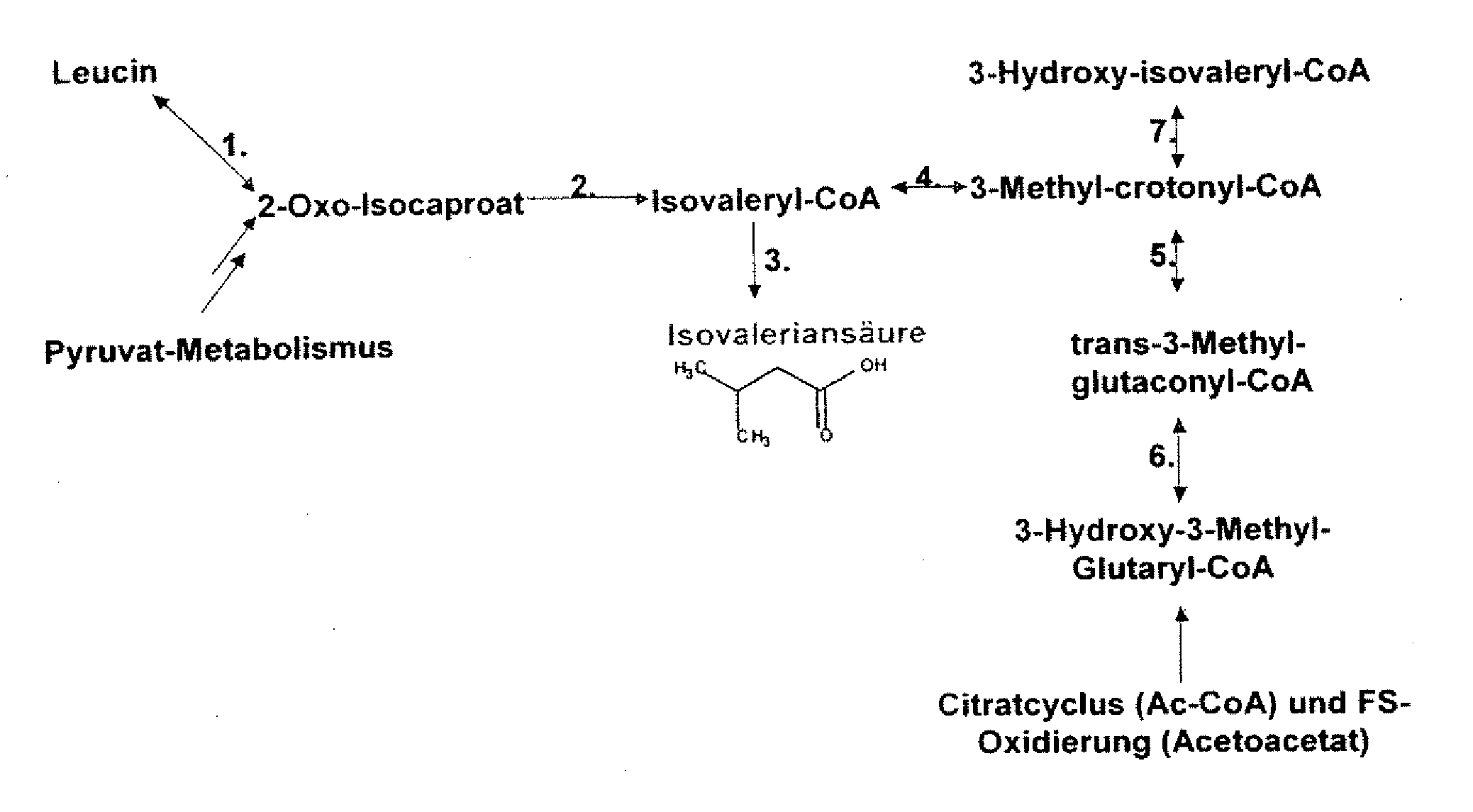
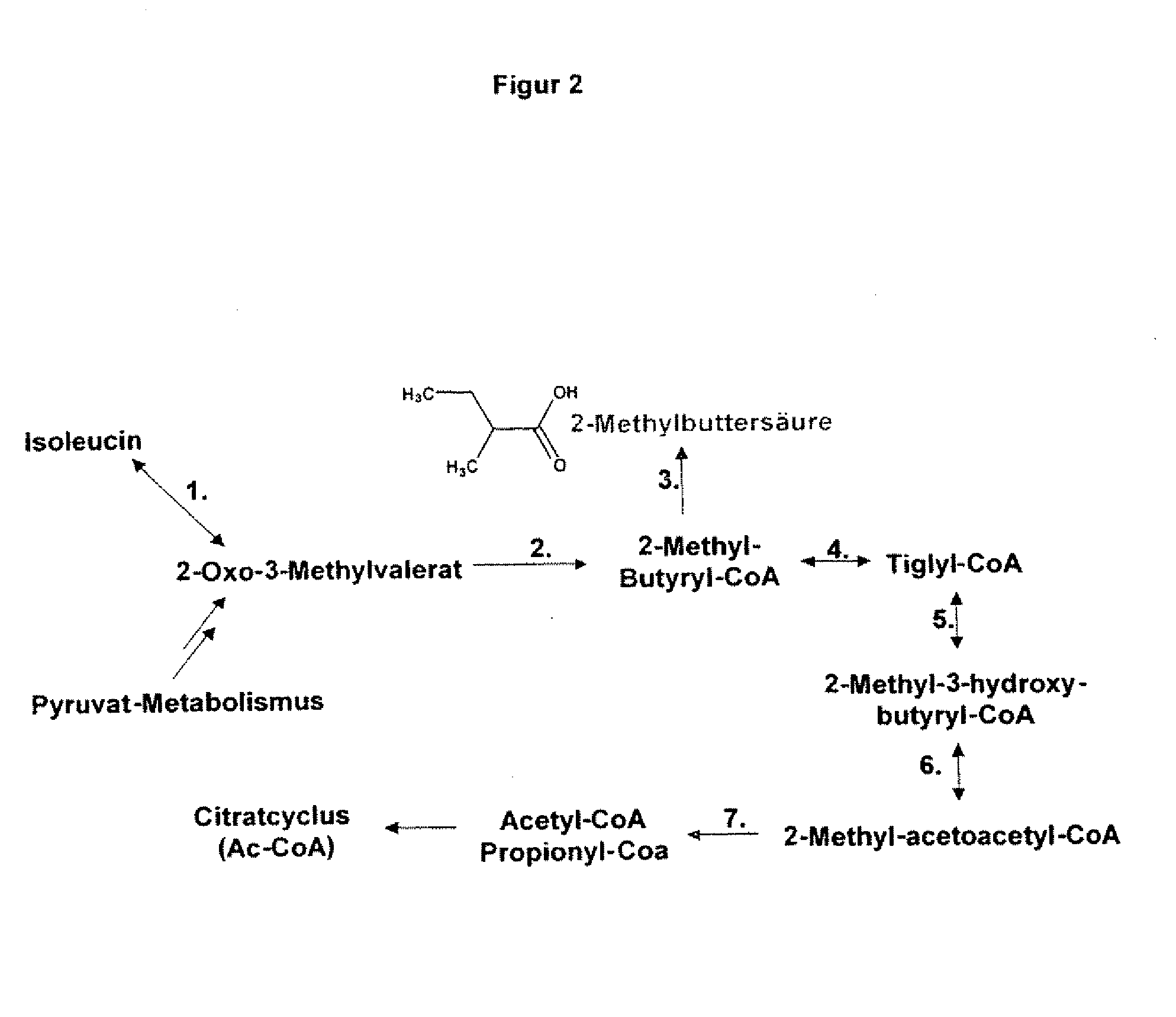
The present invention relates to 25 hitherto undescribed genes of B. licheniformis and gene products derived therefrom and all sufficiently homologous nucleic acids and proteins thereof. They occur in five different metabolic pathways for the formation of odorous substances. The metabolic pathways in question are for the synthesis of: 1) isovalerian acid (as part of the catabolism of leucine), 2) 2-methylbutyric acid and / or isobutyric acid (as part of the catabolism of valine and / or isoleucine), 3) butanol and / or butyric acid (as part of the metabolism of butyric acid), 4) propyl acid (as part of the metabolism of propionate) and / or 5) cadaverine and / or putrescine (as parts of the catabolism of lysine and / or arginine). The identification of these genes allows biotechnological production methods to be developed that are improved to the extent that, to assist these nucleic acids, the formation of the odorous substances synthesized via these metabolic pathways can be reduced by deactivating the corresponding genes in the micro-organism used for the biotechnological production. In addition, these gene products are thus available for preparing reactions or for methods according to their respective biochemical properties.
Owner:BASF AG
Novel root specific promoter driving the expression of a novel lrr receptor-like kinase
The present invention relates to the field of plant molecular biology, more particularly to the root-specific gene expression in plants. The invention provides nucleic acids for a novel transcriptional regulatory root-specific promoter and nucleic acid and protein sequences coding for a new LRR receptor-kinase protein, further specified as a root clavata 1 homolog (RCH1). Further provided are compositions comprising nucleic acids, polypeptides, antibodies and vectors. The invention further provides for methods for modifying cell fate and / or plant development and / or plant morphology and / or plant biochemistry and / or plant physiology comprising the modification of expression in particular cells, tissues or organs of a plant of the novel LRR receptor-like kinase or comprising the expressing of a gene of interest under the control of the novel transcriptional regulatory root-specific promoter. Further are provided compounds interacting with the new polypeptides for use as herbicides or growth regulators.
Owner:SCHERES BEN +1
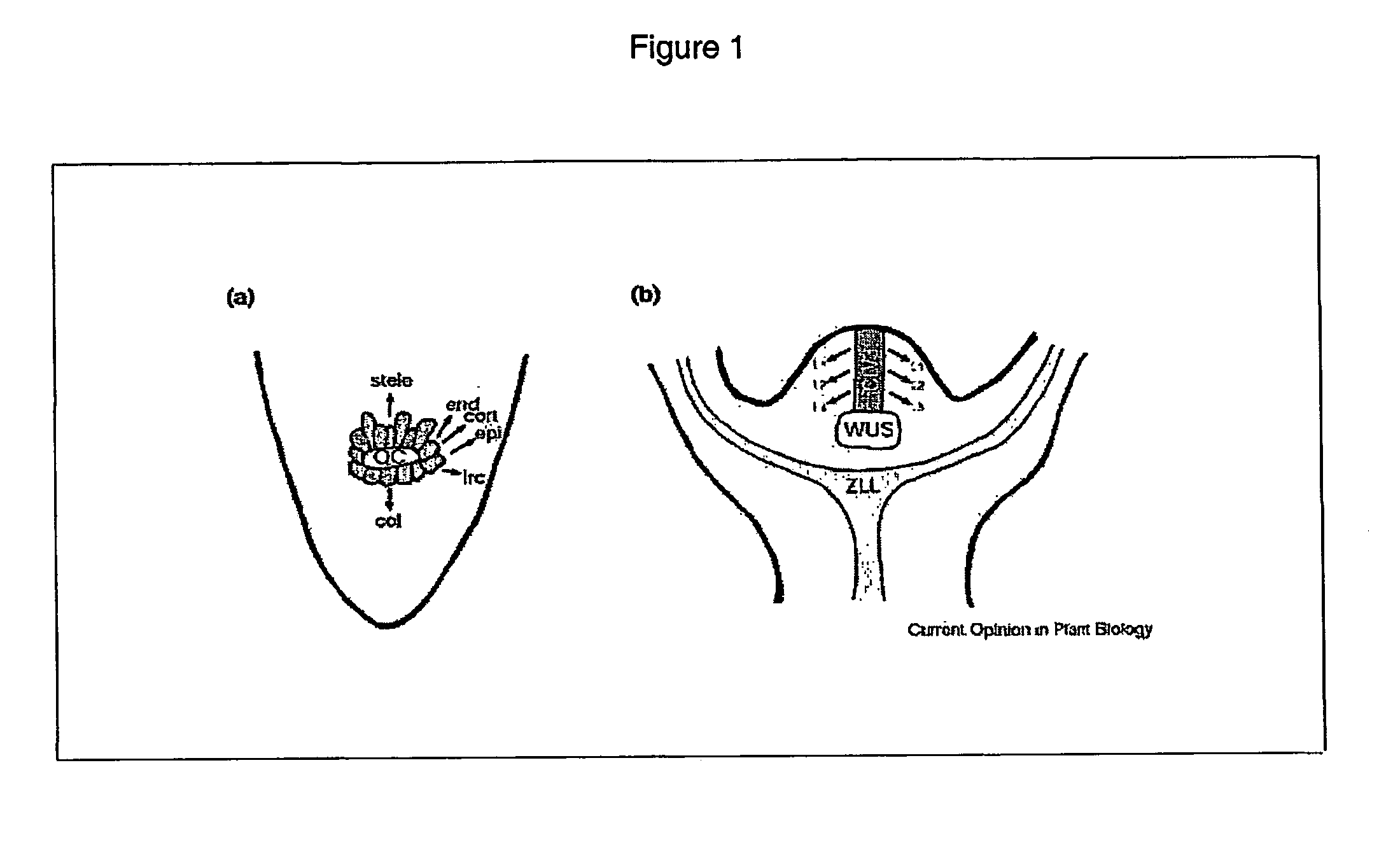
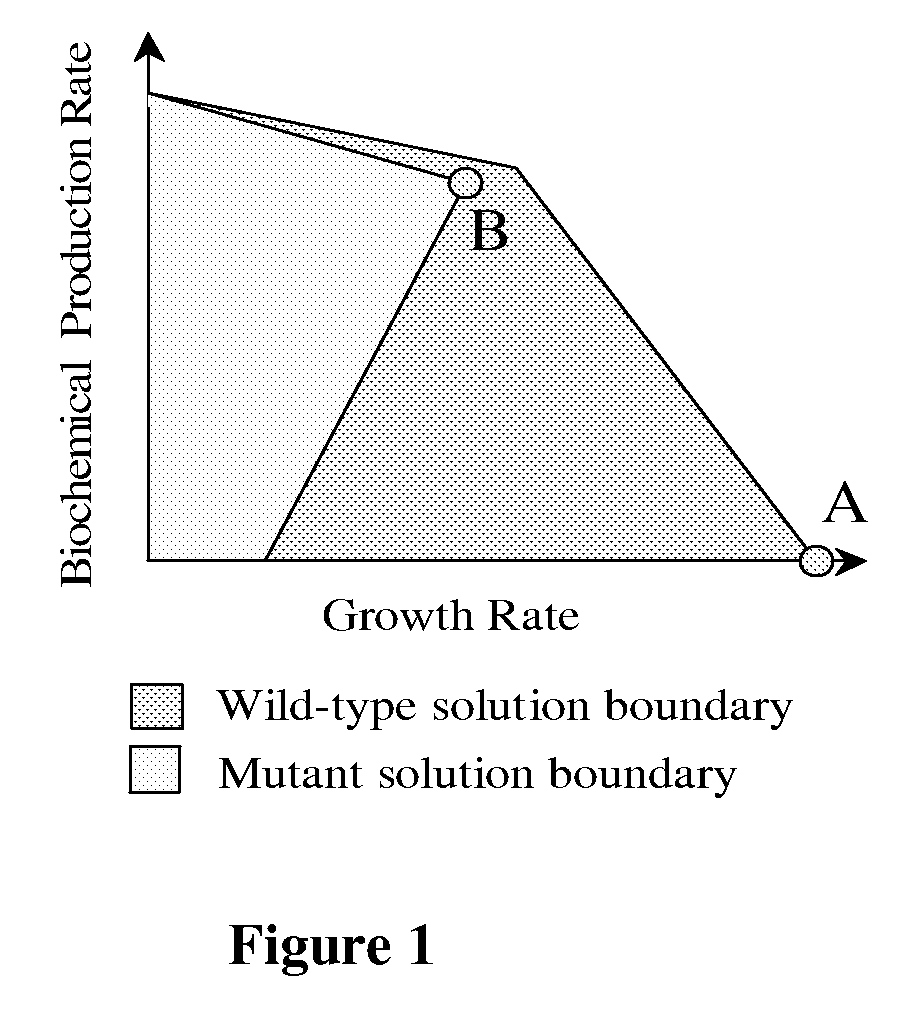
Methods and Organisms for Growth-Coupled Production of 3-Hydroxypropionic Acid
The invention provides a non-naturally occurring microorganism having one or more gene disruptions, the one or more gene disruptions occurring in genes encoding an enzyme obligatory coupling 3-hydroxypropionic acid production to growth of the microorganism when the gene disruption reduces an activity of the enzyme, whereby the one or more gene disruptions confers stable growth-coupled production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid onto the non-naturally occurring microorganism. Also provided is a non-naturally occurring microorganism comprising a set of metabolic modifications obligatory coupling 3-hydroxypropionic acid production to growth of the microorganism, the set of metabolic modifications having disruption of one or more genes including: (a) the set of genes selected from: (1) adhE, ldhA, pta-ackA; (2) adhE, ldhA, frdABCD; (3) adhE, ldhA, frdABCD, ptsG; (4) adhE, ldhA, frdABCD, pntAB; (5) adhE, ldhA, fumA, fumB, fumC; (6) adhE, ldhA, fumA, fumB, fumC, pntAB; (7) pflAB, ldhA, or (8) adhE, ldhA, pgi in a microorganism utilizing an anaerobic β-alanine 3-HP precursor pathway; (b) the set of genes selected from: (1) tpi, zwf; (2) tpi, ybhE; (3) tpi, gnd; (4) fpb, gapA; (5) pgi, edd, or (6) pgi, eda in a microorganism utilizing an aerobic glycerol 3-HP precursor pathway; (c) the set of genes selected from: (1) eno; (2) yibO; (3) eno, atpH, or other atp subunit, or (4) yibO, atpH, or other atp subunit, in a microorganism utilizing a glycerate 3-HP precursor pathway, or an ortholog thereof, wherein the microorganism exhibits stable growth-coupled production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid. The disruptions can be complete gene disruptions and the non-naturally occurring organisms can include a variety of prokaryotic or eukaryotic microorganisms. A method of producing a non-naturally occurring microorganism having stable growth-coupled production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid is further provided. The method includes: (a) identifying in silico a set of metabolic modifications requiring 3-hydroxypropionic acid production during exponential growth, and (b) genetically modifying a microorganism to contain the set of metabolic modifications requiring 3-hydroxypropionic acid production.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Tol1 factor transposase and DNA introduction system using the same
InactiveUS8598328B2High transposition frequencyEffectively actSugar derivativesHydrolasesGene defectNucleotide
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY +1
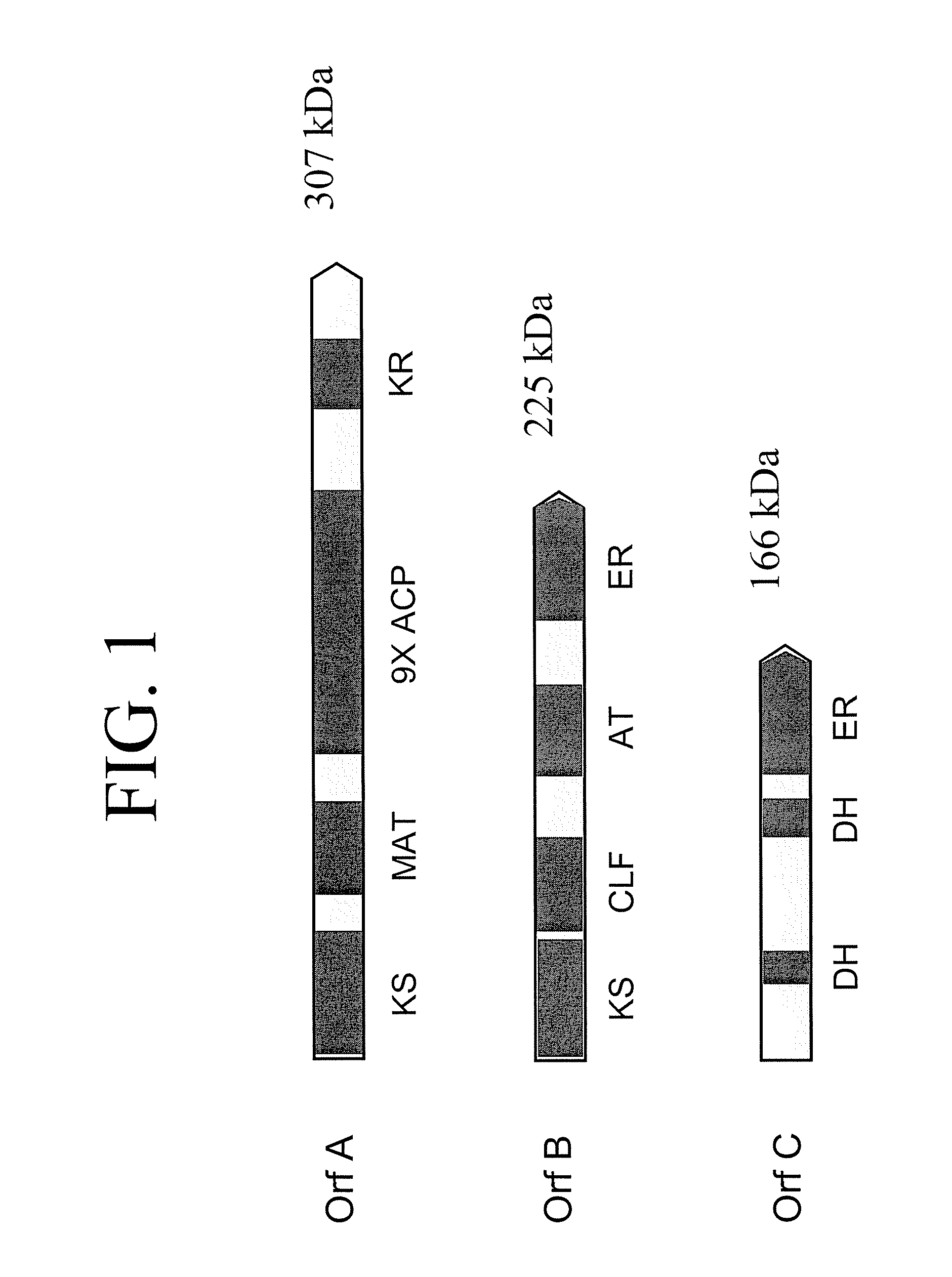
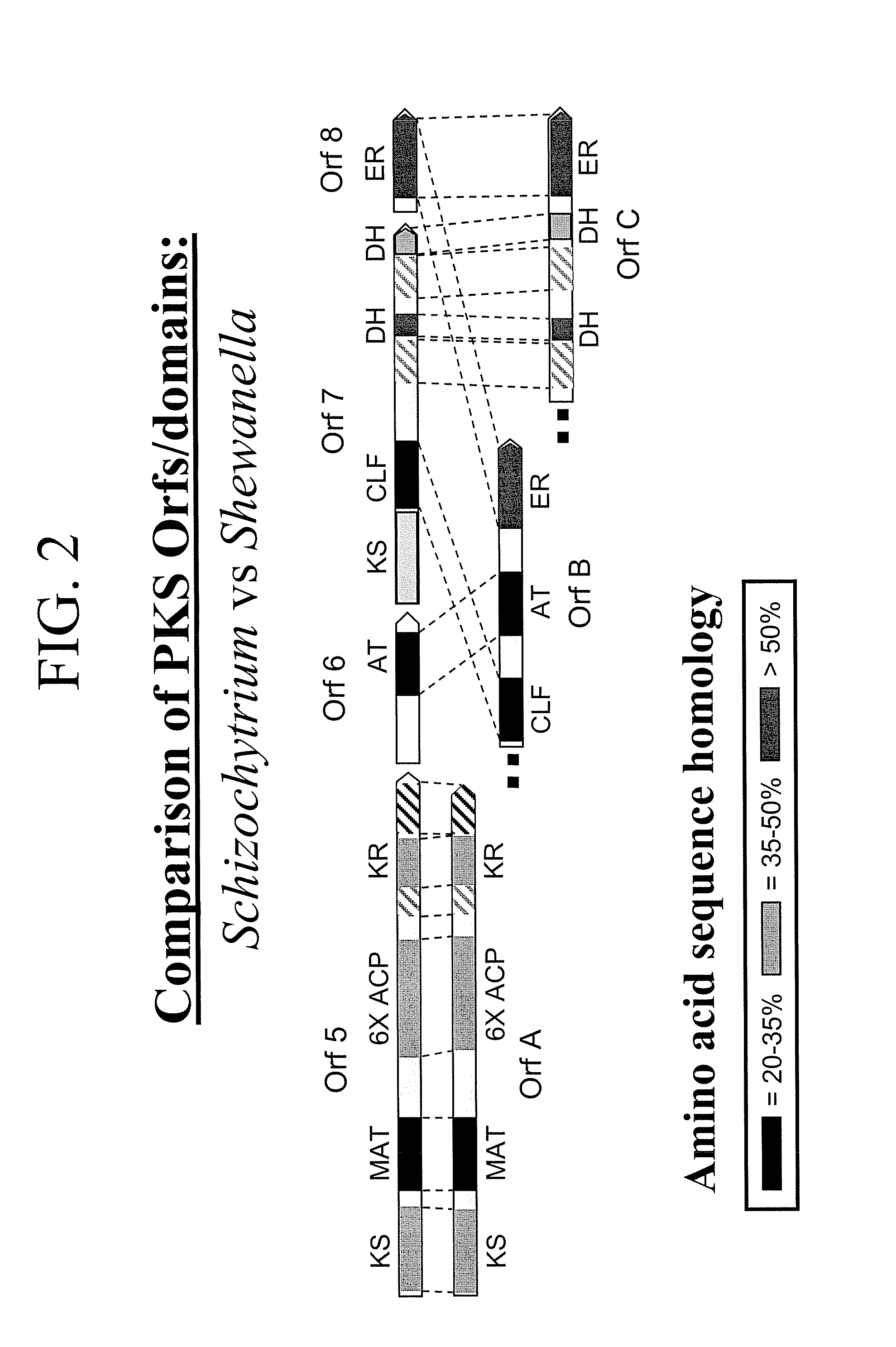
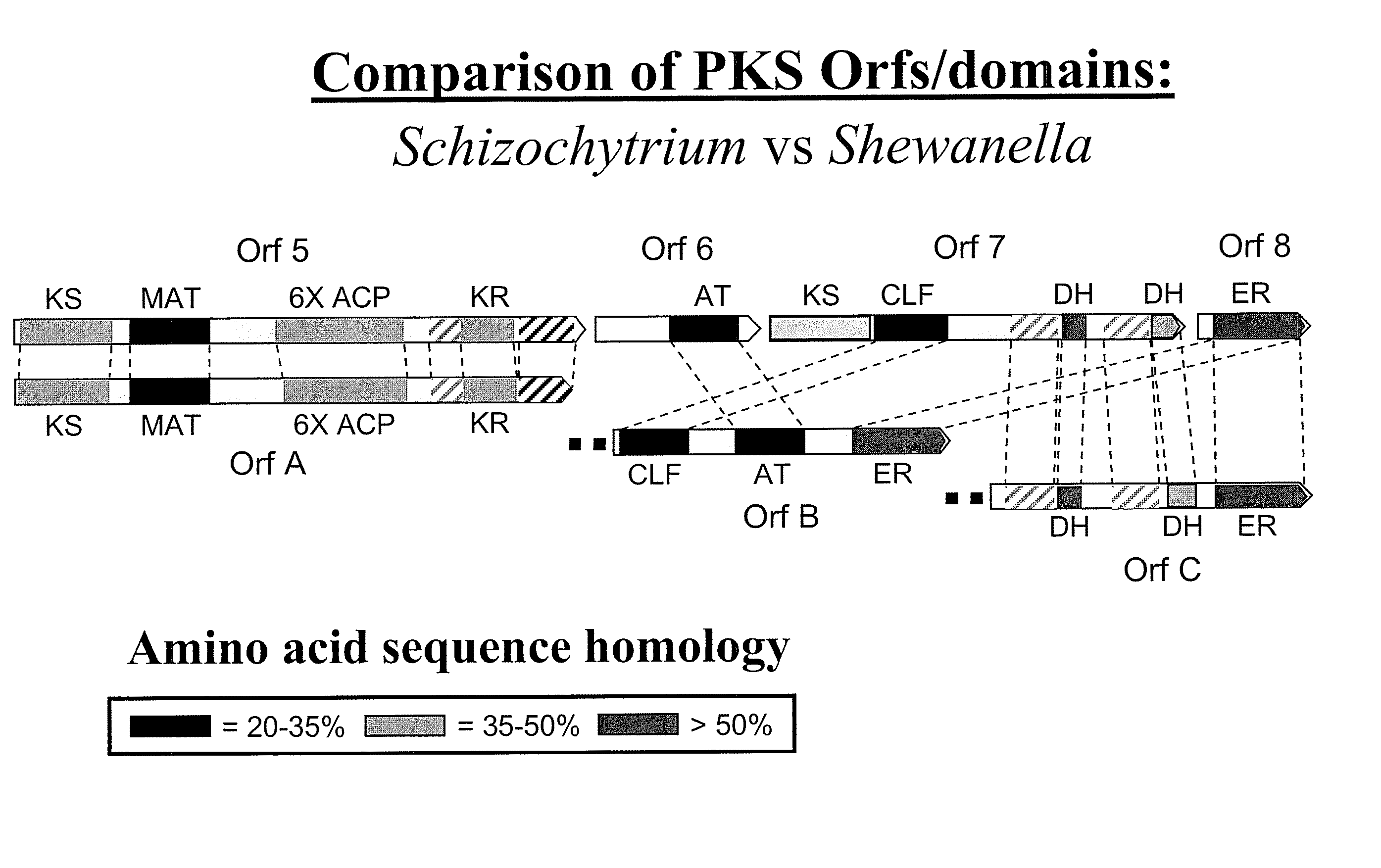
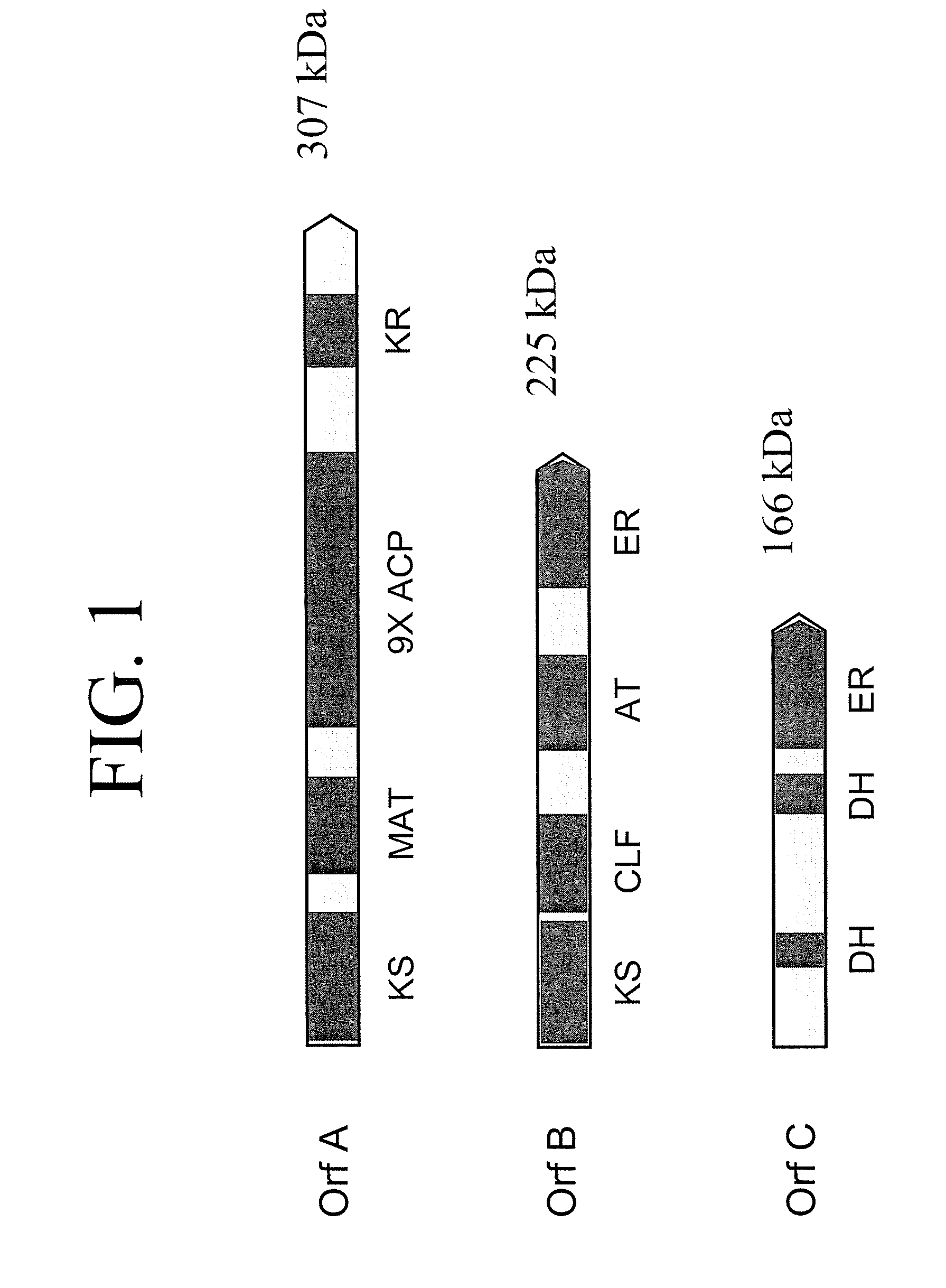
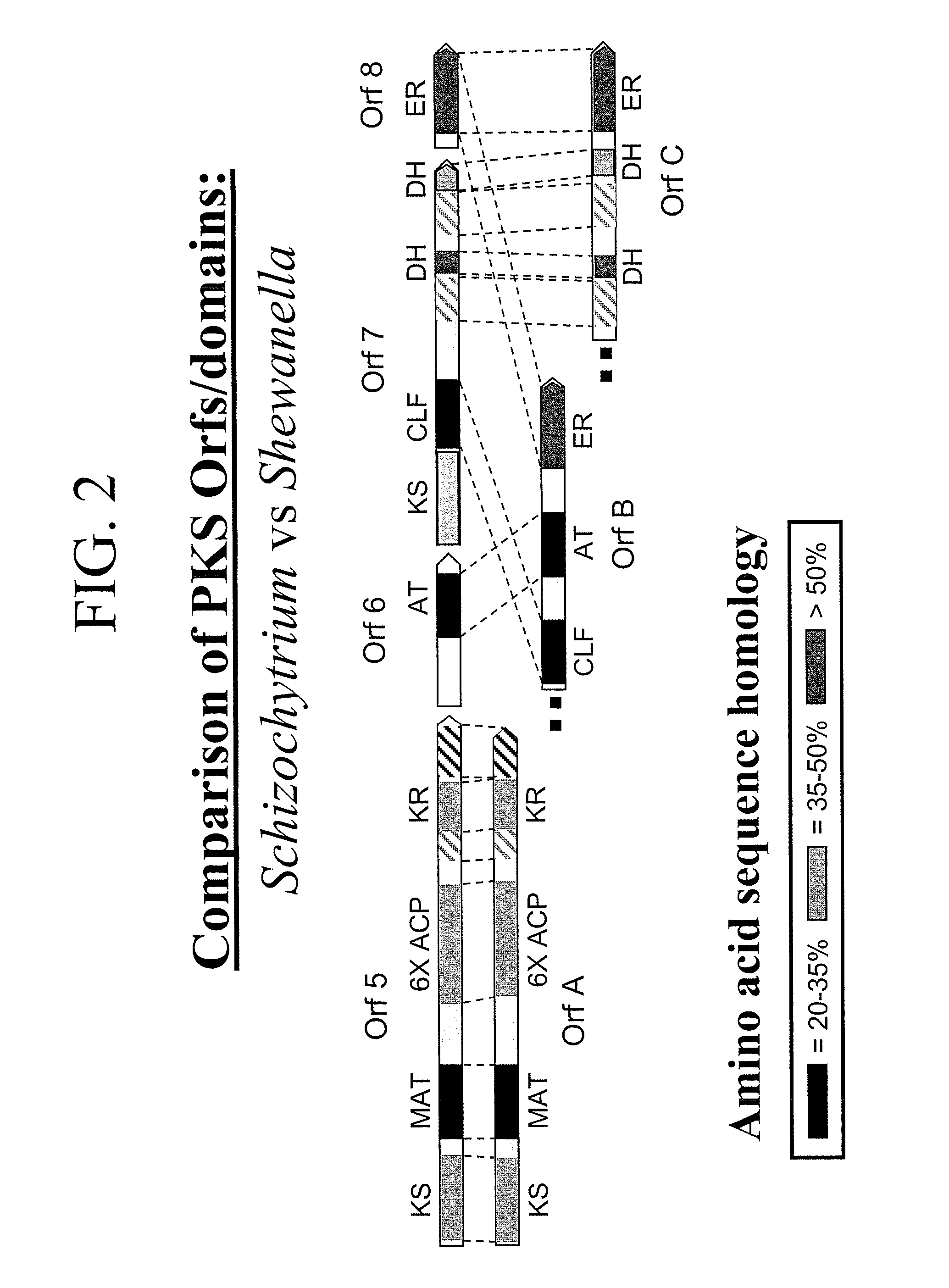
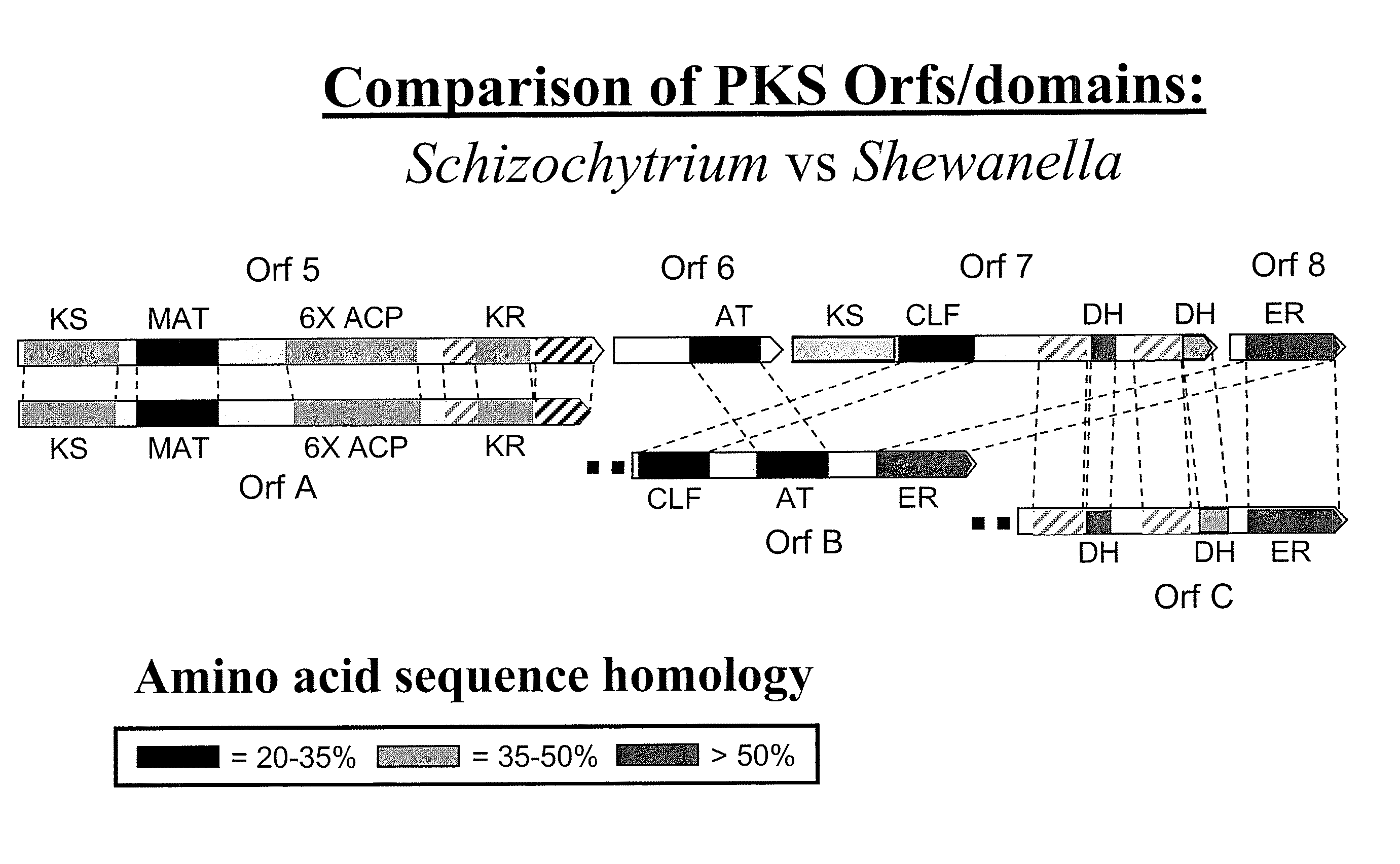
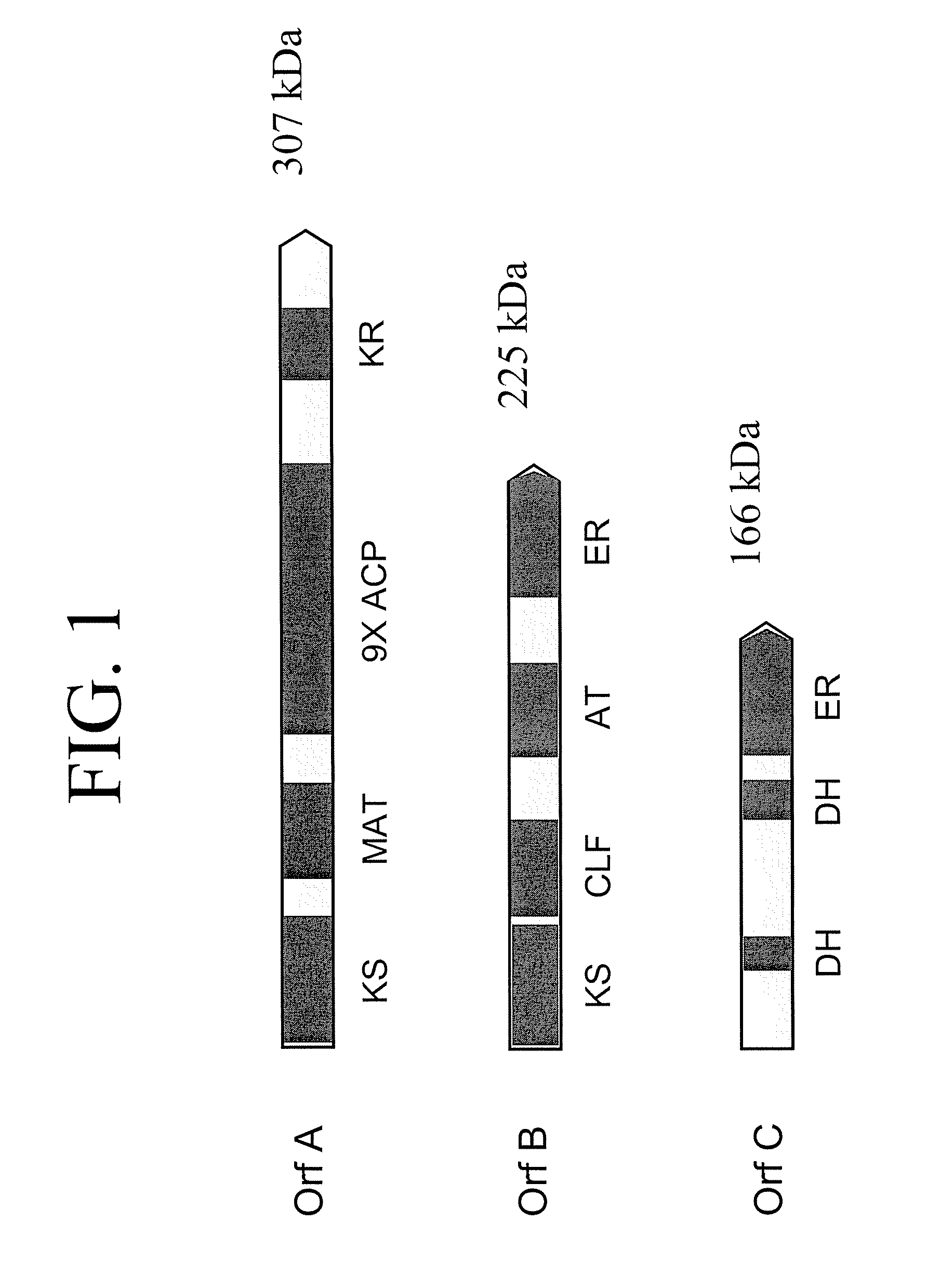
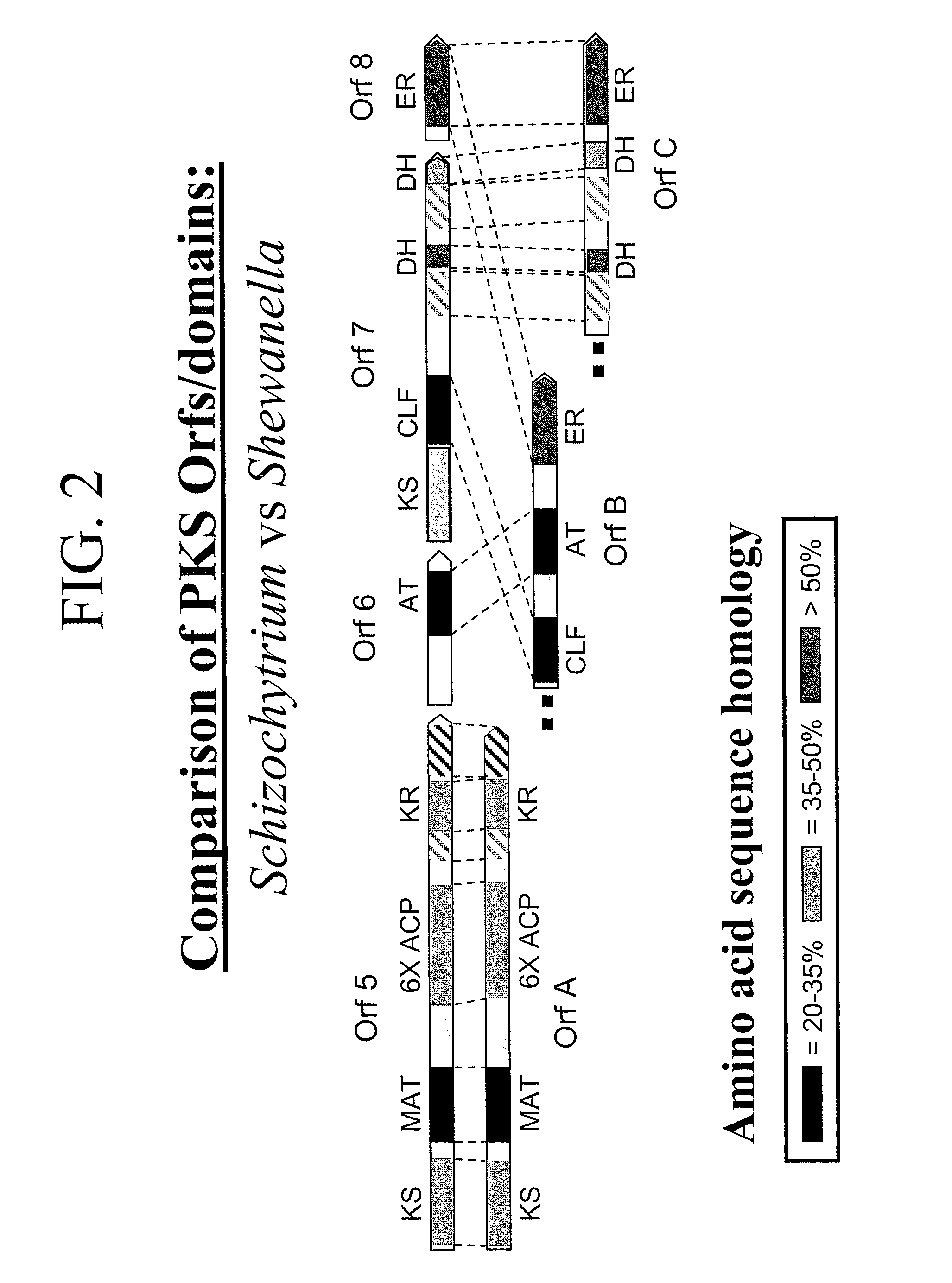
Pufa polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
The invention generally relates to polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems, to homologues thereof, to isolated nucleic acid molecules and recombinant nucleic acid molecules encoding biologically active domains of such a PUFA PKS system, to genetically modified organisms comprising PUFA PKS systems, to methods of making and using such systems for the production of bioactive molecules of interest, and to novel methods for identifying new bacterial and non-bacterial microorganisms having such a PUFA PKS system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Disease treatment via antimicrobial peptides or their inhibitors
The invention provides methods for the treatment of disease and promotion of healing that include providing a therapeutically effective amount of a mammalian antimicrobial peptide (AMP) or analog thereof, in particular a cathelicidin or cathelicidin fragment or cathelicidin analog, thereby treating the disease in the subject in need thereof. The invention also provides specific analogs or fragments of cathelicidin that function as agonists, as do endogenous cathelicidins, or as either dominant negatives or as inhibitors to endogenous cathelicidin or to other endogenous AMPs or that compete with pro-inflammatory agents or fragments of AMPs on cognate receptors without inducing disease.
Owner:HILLMAN YITZCHAK
Pufa polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
The invention generally relates to polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems, to homologues thereof, to isolated nucleic acid molecules and recombinant nucleic acid molecules encoding biologically active domains of such a PUFA PKS system, to genetically modified organisms comprising PUFA PKS systems, to methods of making and using such systems for the production of bioactive molecules of interest, and to novel methods for identifying new bacterial and non-bacterial microorganisms having such a PUFA PKS system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Pufa polyketide synthase systems and uses thereof
The invention generally relates to polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) polyketide synthase (PKS) systems, to homologues thereof, to isolated nucleic acid molecules and recombinant nucleic acid molecules encoding biologically active domains of such a PUFA PKS system, to genetically modified organisms comprising PUFA PKS systems, to methods of making and using such systems for the production of bioactive molecules of interest, and to novel methods for identifying new bacterial and non-bacterial microorganisms having such a PUFA PKS system.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Error reduction in automated gene synthesis
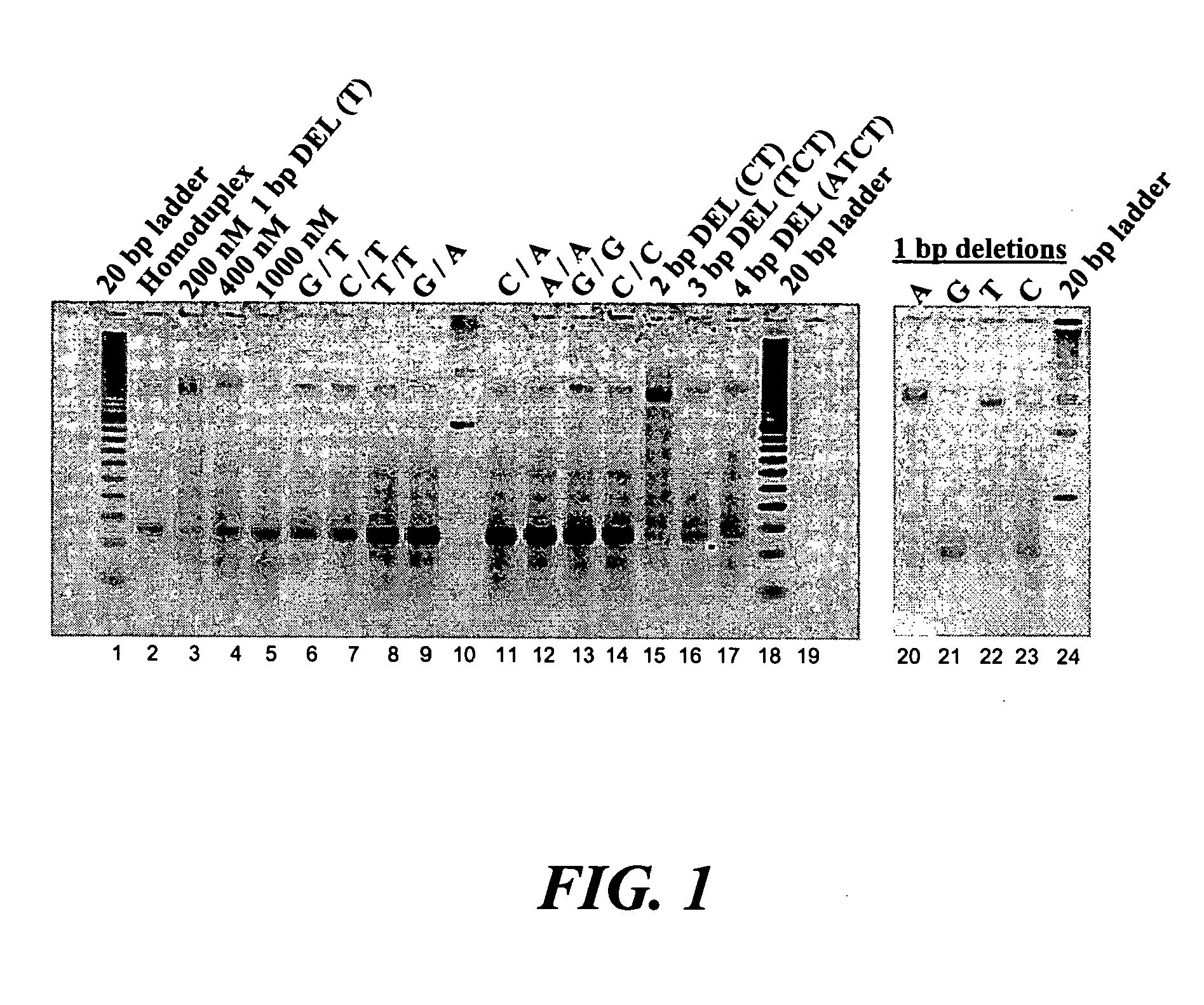
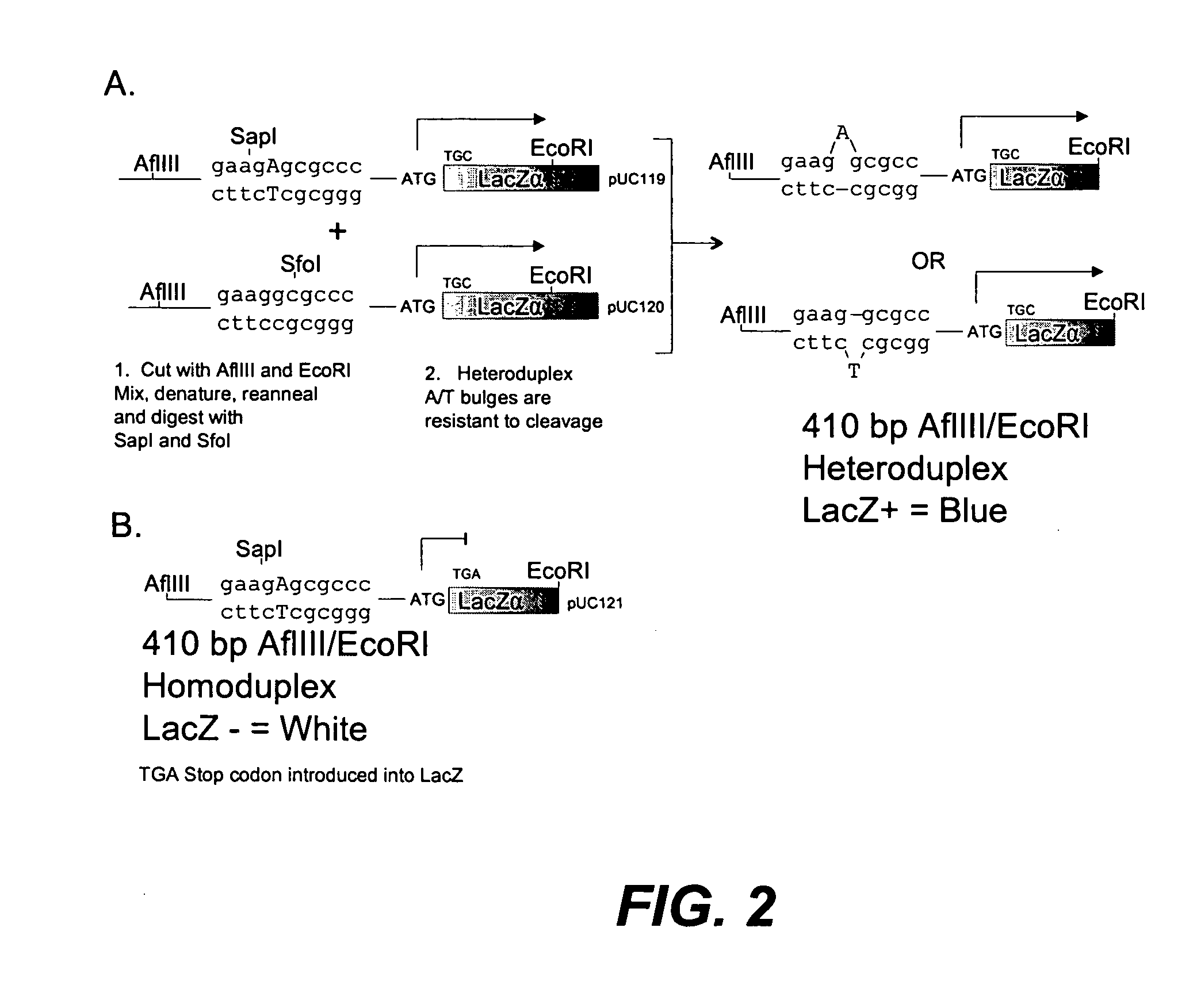
In embodiments of the present invention, methods are provided for removing double-stranded oligonucleotide (e.g., DNA) molecules containing one or more sequence errors, generated during nucleic acid synthesis, from a population of correct oligonucleotide duplexes. In one embodiment, the oligonucleotides are generated enzymatically. Heteroduplex (containing mismatched bases) oligonucleotides may be created by denaturing and reannealing the population of duplexes. The reannealed oligonucleotide duplexes are contacted with a mismatch recognition protein that interacts with (e.g., binds and / or cleaves) the duplexes containing a base pair mismatch. The oligonucleotide heteroduplexes that have interacted with such a protein are separated, simultaneously with contacting or sequentially in a separate step, from homoduplexes. These methods are also used in another embodiment to remove heteroduplex oligonucleotides (e.g., DNA) that are formed directly from chemical nucleic acid synthesis. In other embodiments of the present invention, kits and compositions useful for the methods are provided.
Owner:BLUE HERON BIOTECH
Method of cloning reproductive and respiratory syndrome resisting pig
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Compositions and methods for the identification and selection of nucleic acids and polypeptides
InactiveUS20050089913A1Efficient rapid identification selectionQuickly and accurately identify and selectPeptide librariesGenetic material ingredientsComputational biologyPsoralen
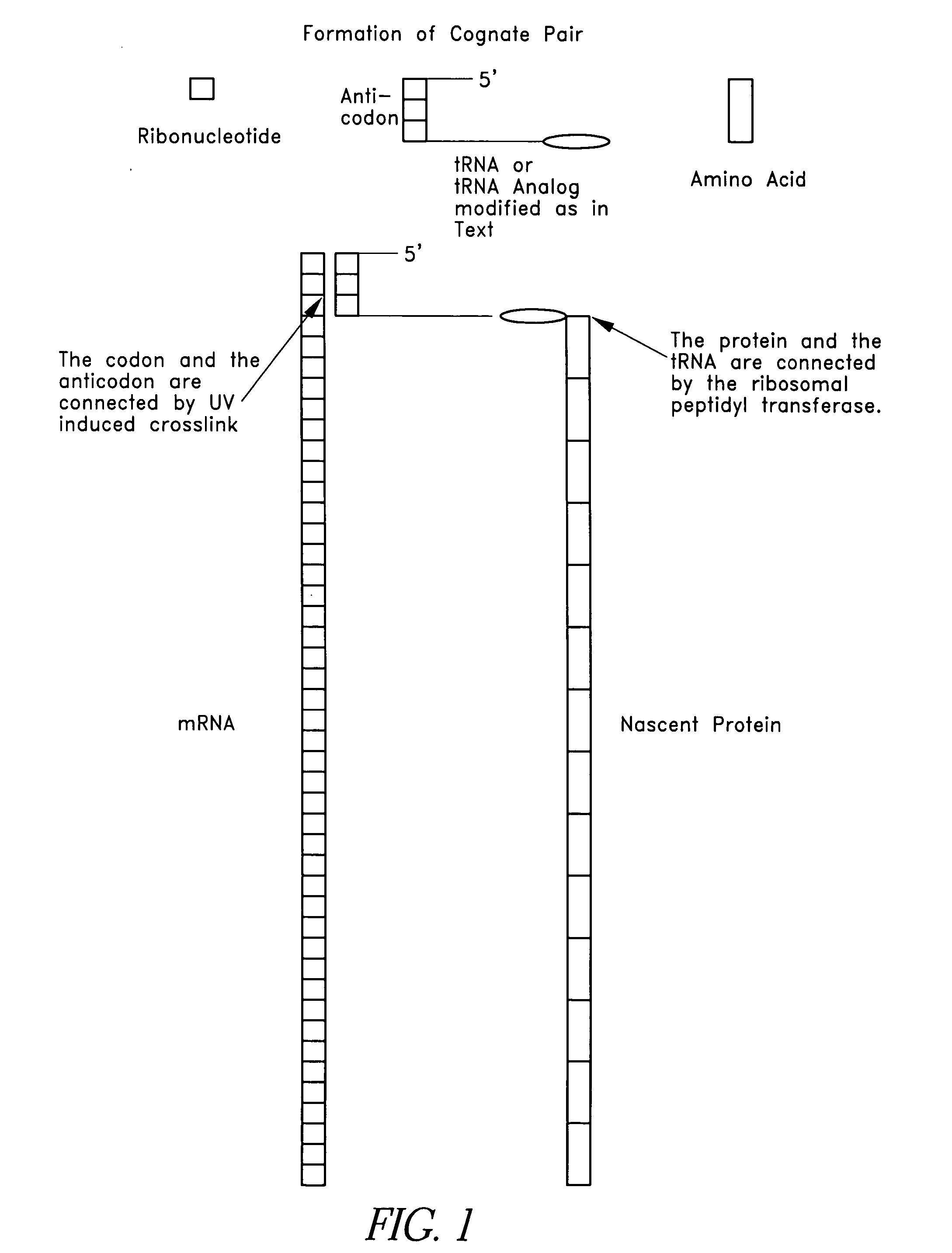
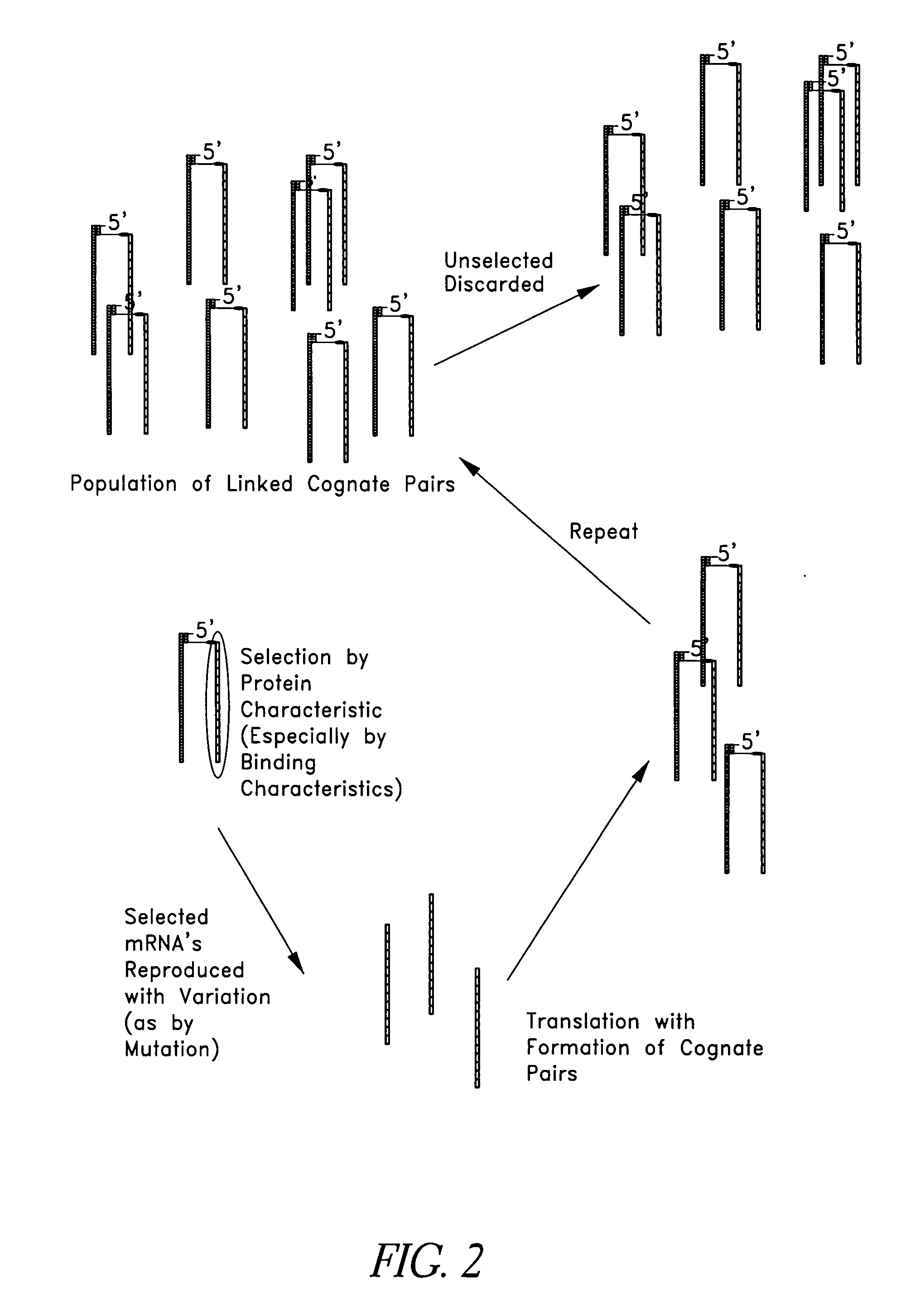
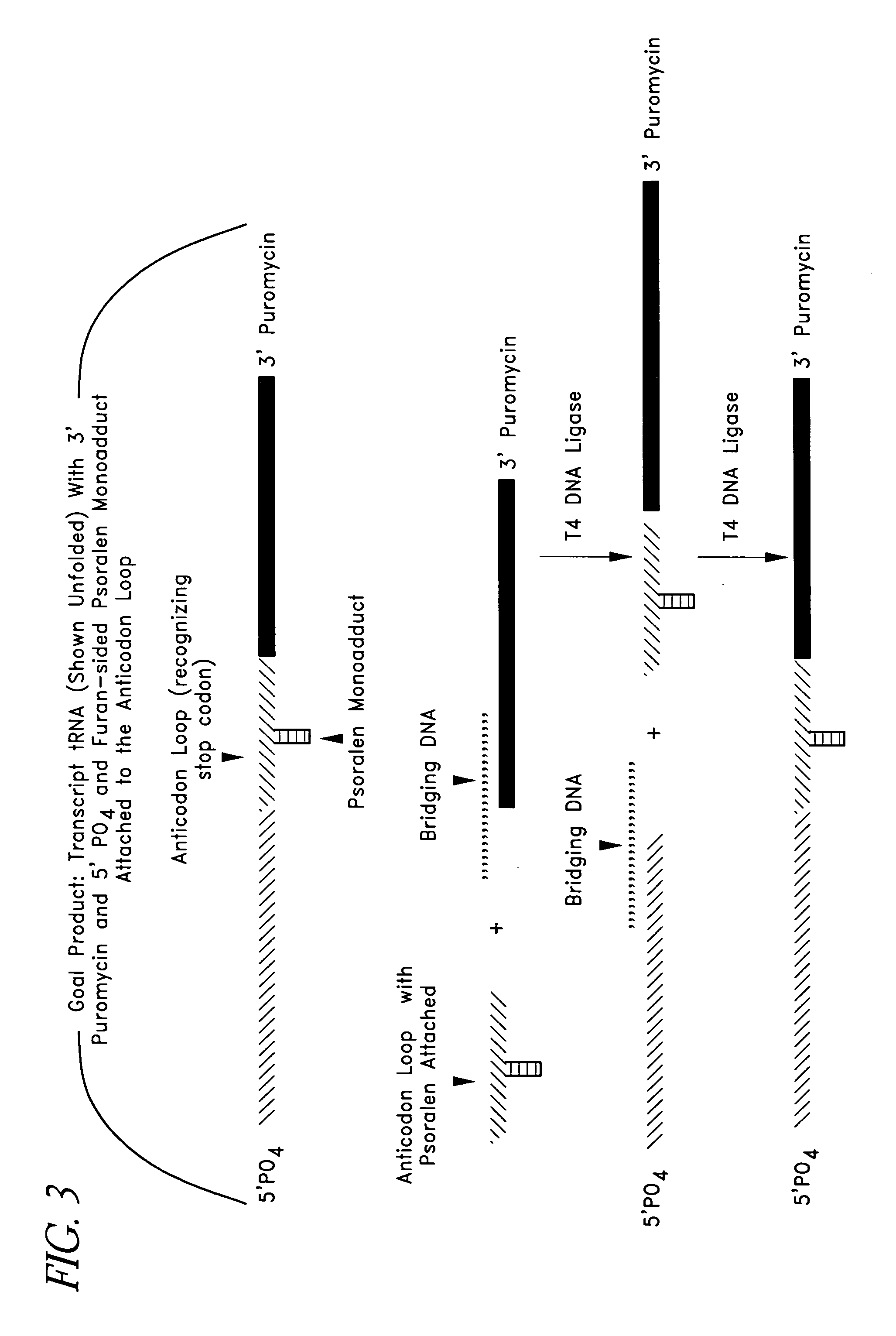
This invention relates generally to systems and methods for identifying and selecting, desired proteins or nucleic acid molecules by linking mRNA, with known or unknown sequences, to its translated protein to form a cognate pair. The cognate pair is selected based upon desired properties of the protein or the nucleic acid. This method also includes the evolution of a desired protein or nucleic acid molecule by amplifying the nucleic acid portion of the selected cognate pair, introducing variation into the nucleic acid, translating the nucleic acid, attaching the nucleic acid to its protein to form a second cognate pair, and re-selecting this cognate pair based upon desired properties. Modified mRNAs operable to crosslink to tRNAs are also provided. Methods of producing a psoralen monoadduct or a crosslink are also provided.
Owner:PROTEONOVA
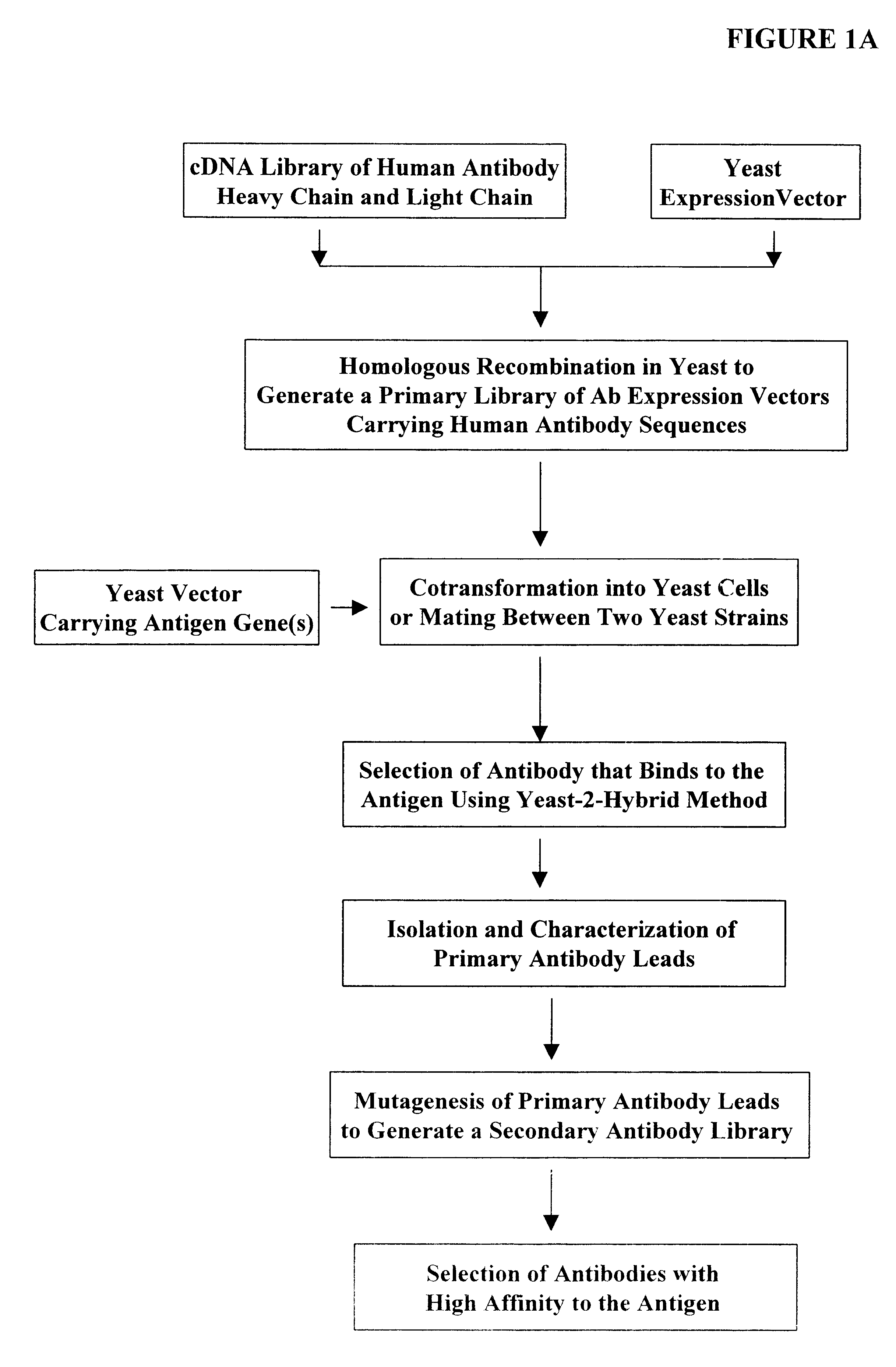
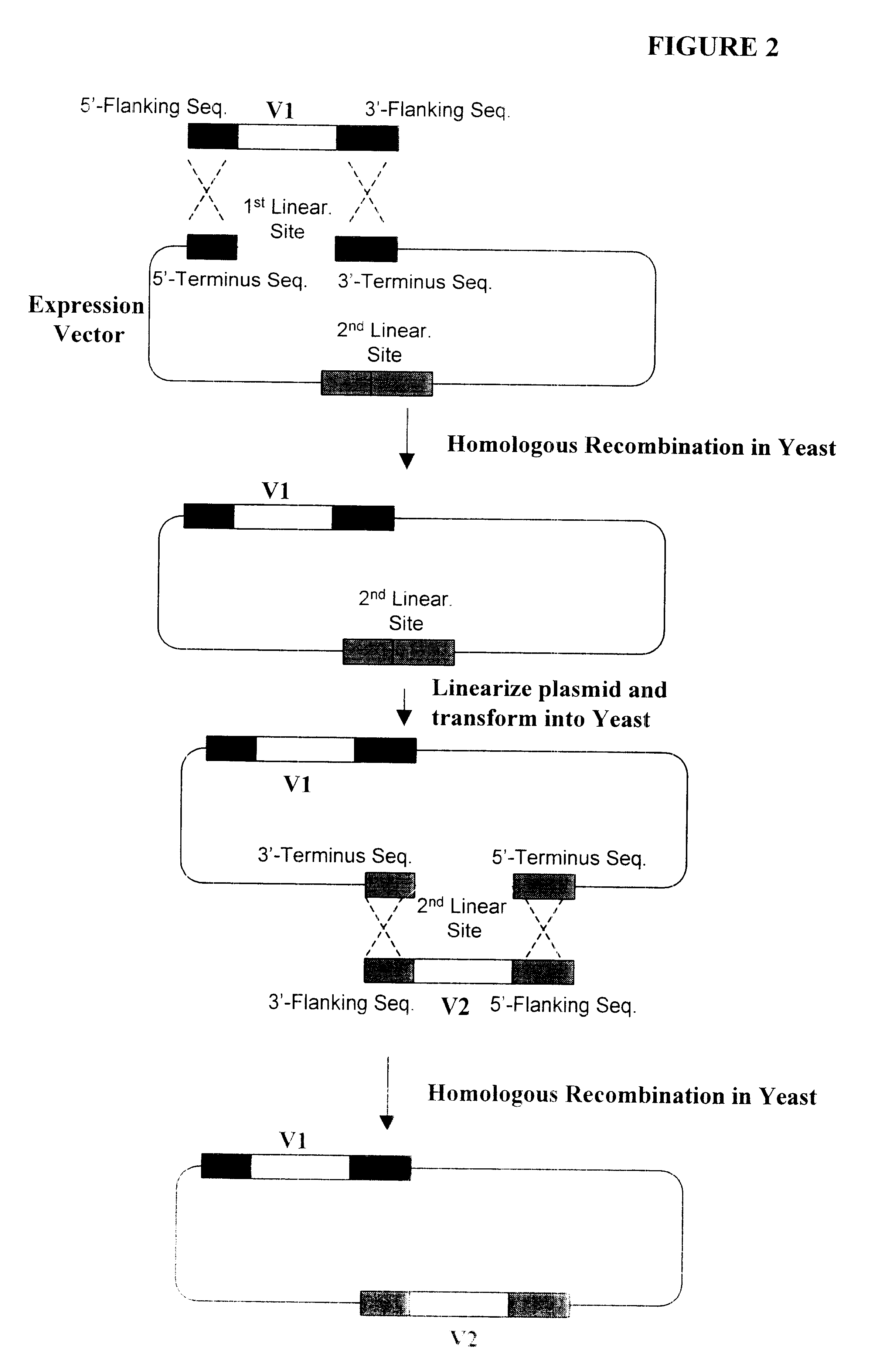
Assembly and screening of highly complex and fully human antibody repertoire in yeast
InactiveUS6610472B1High affinityEasy to assembleFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsNucleotide
Compositions, methods, and kits are provided for efficiently generating and screening a library of highly diverse protein complexes for their ability to bind to other proteins or oligonucleotide sequences. In one aspect of the invention, a library of expression vectors is provided for expressing the library of protein complexes. The library comprises a first nucleotide sequence encoding a first polypeptide subunit; and a second nucleotide sequence encoding a second polypeptide subunit. The first and second nucleotide sequences each independently varies within the library of expression vectors. In addition, the first and second polypeptide subunit are expressed as separate proteins which self-assemble to form a protein complex, such as a double-chain antibody fragment (dcFv or Fab) and a fully assembled antibody, in cells into which the library of expression vectors are introduced. The library of expression vectors can be efficiently generated in yeast cells through homologous recombination; and the encoded proteins complexes with high binding affinity to their target molecule can be selected by high throughput screening in vivo or in vitro.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
Inducible Eukaryotic Expression System
ActiveUS20090162901A1Suitable for mass productionInhibit transcriptionVectorsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
Compositions and methods for the inducible expression of genes in eukaryotic cells are provided. Expression of a nucleotide sequence of interest encoding a protein of interest is controlled by a regulatory fusion protein that consists of a transcription blocking domain and a ligand-binding domain. When a cognate ligand for the ligand-binding domain is present, transcription of the nucleotide sequence of interest is blocked. Upon removal of the cognate ligand, the nucleotide sequence of interest is transcribed. The method is useful for large scale bioreactor production of a desired protein of interest in eukaryotic cells.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
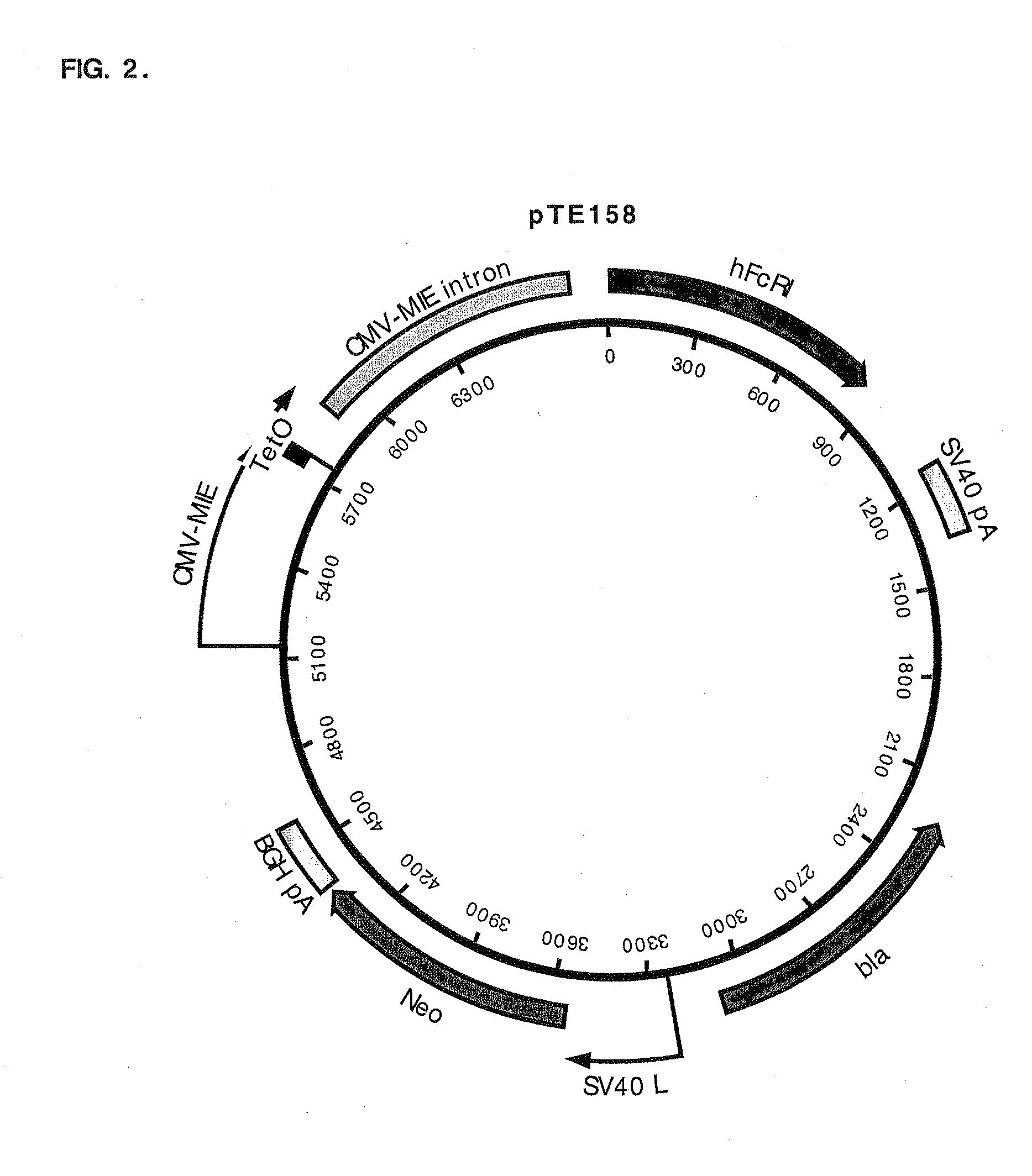
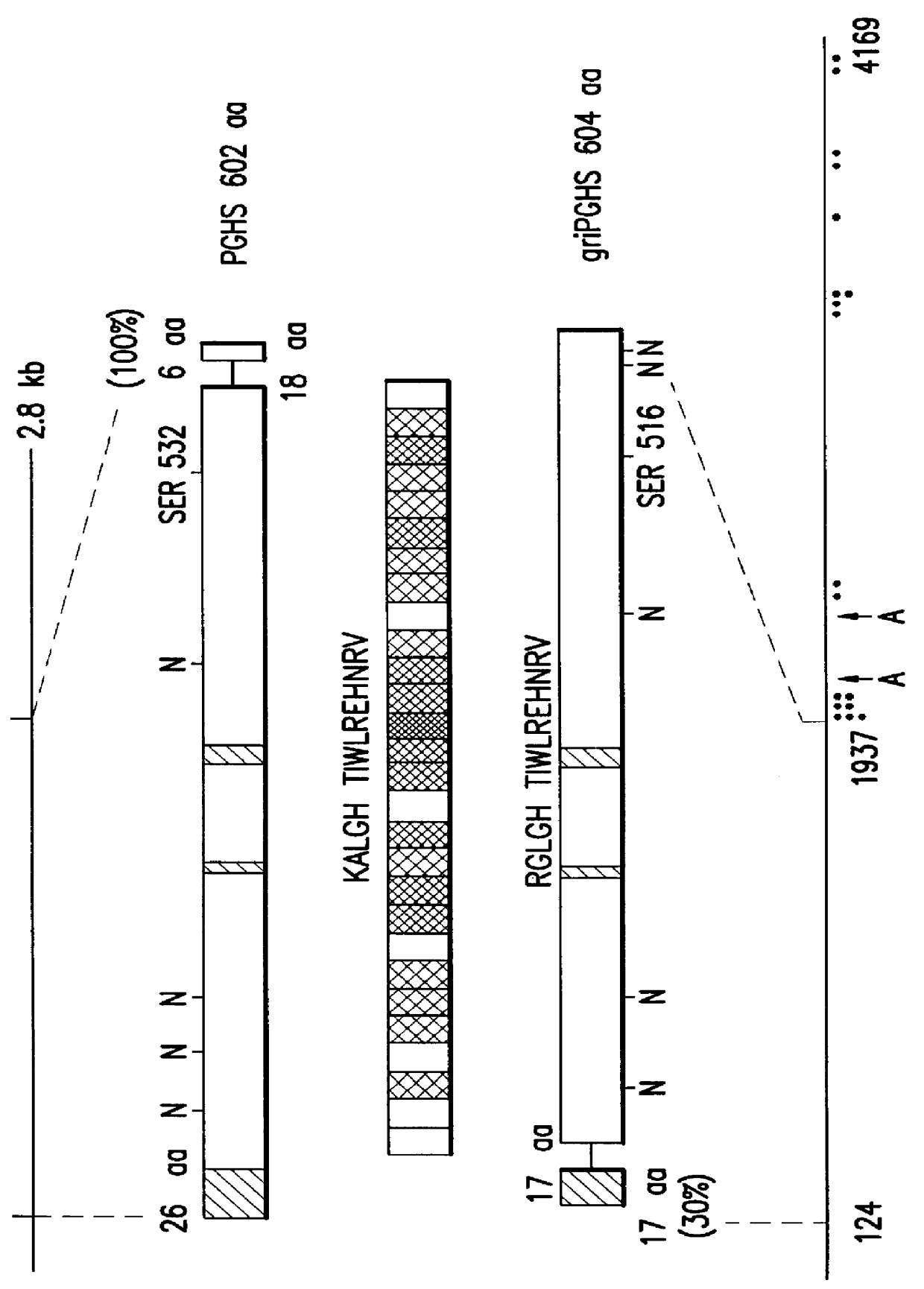
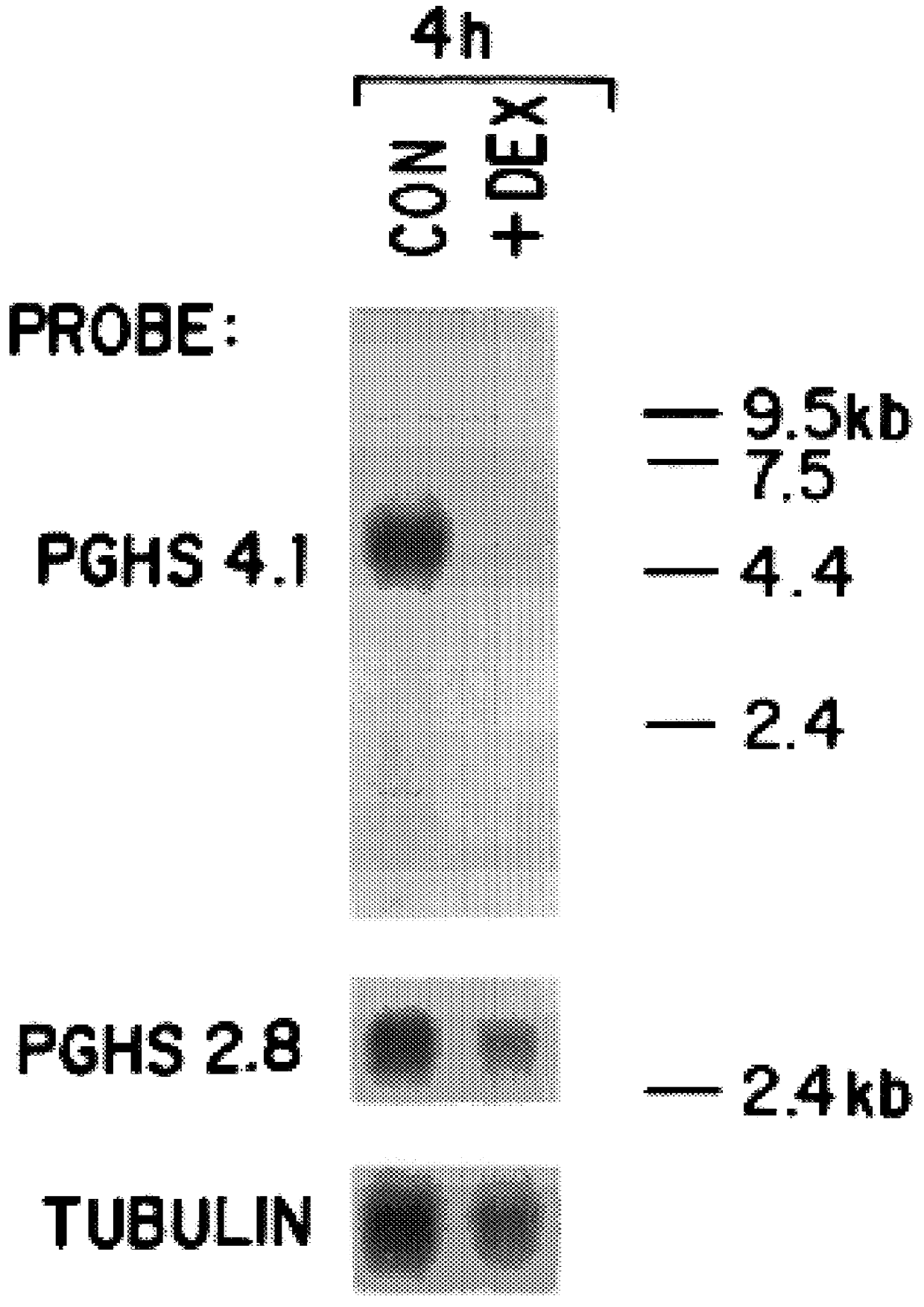
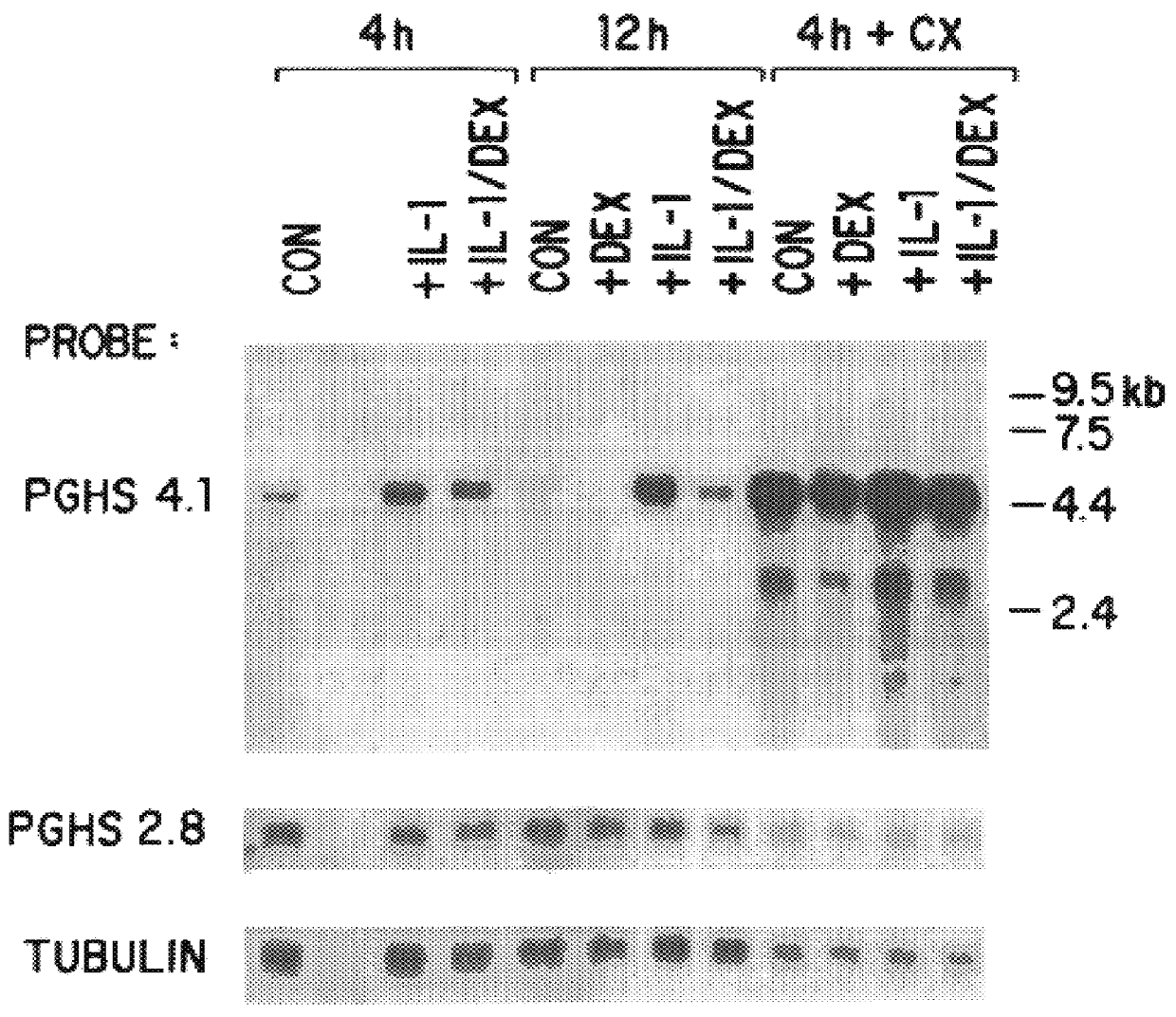
Method of inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis in a human host
The invention relates to the gene encoding the mammalian prostaglandin H synthase-2 and its product. More specifically, the invention relates to the diagnosis of aberrant PGHS-2 gene or gene product; the identification, production, and use of compounds which modulate PGHS-2 gene expression or the activity of the PGHS-2 gene product including but not limited to nucleic acid encoding PGHS-12 and homologues, analogues, and deletions thereof, as well as antisense, ribozyme, triple helix, antibody, and polypeptide molecules as well as small inorganic molecules; and pharmaceutical formulations and routes of administration for such compounds.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Hybrids of M. tuberculosis antigens
InactiveUS20020176867A1Improving immunogenicityEasy to transportBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsMycobacterial antigenMycobacterium
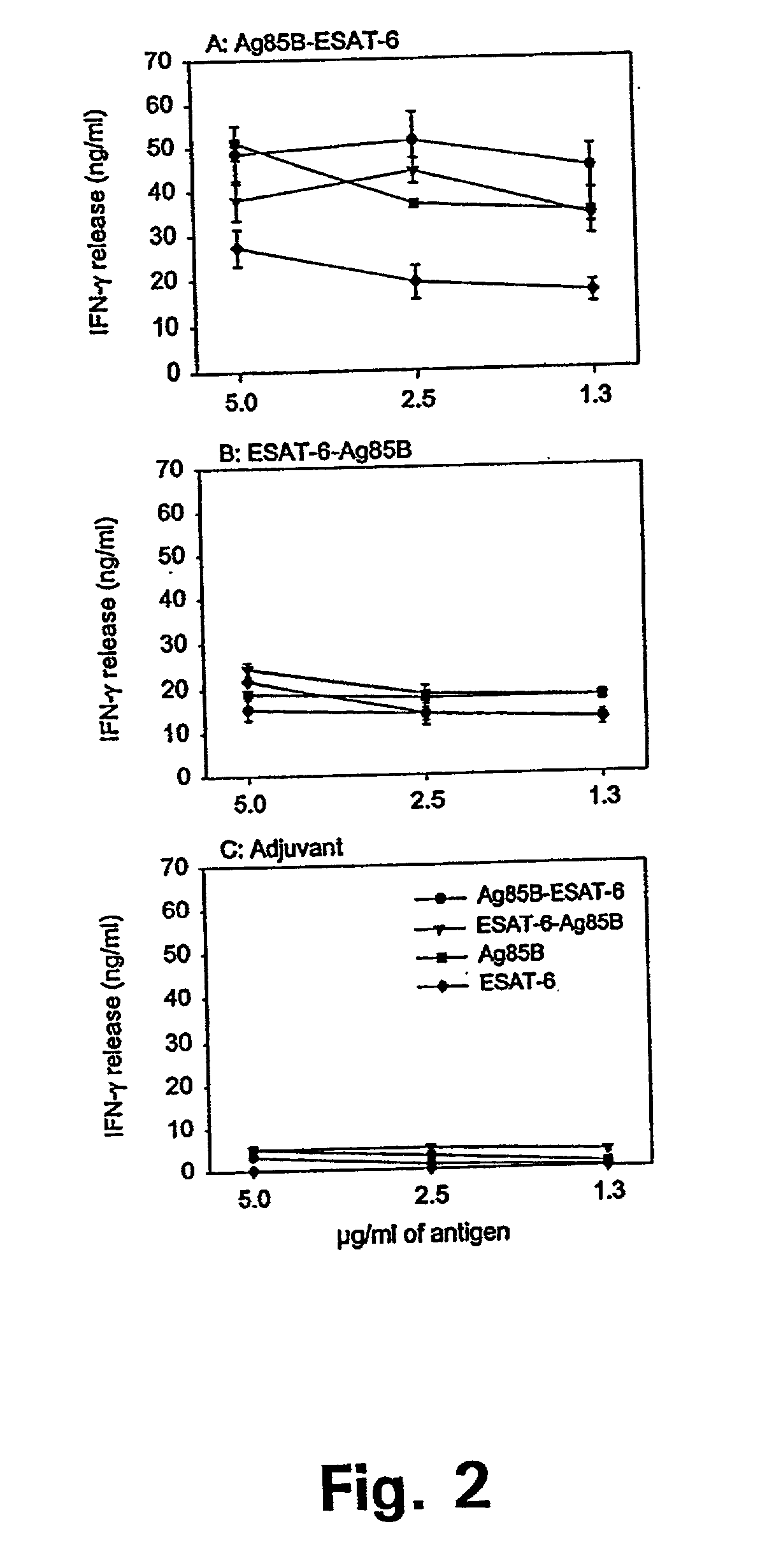
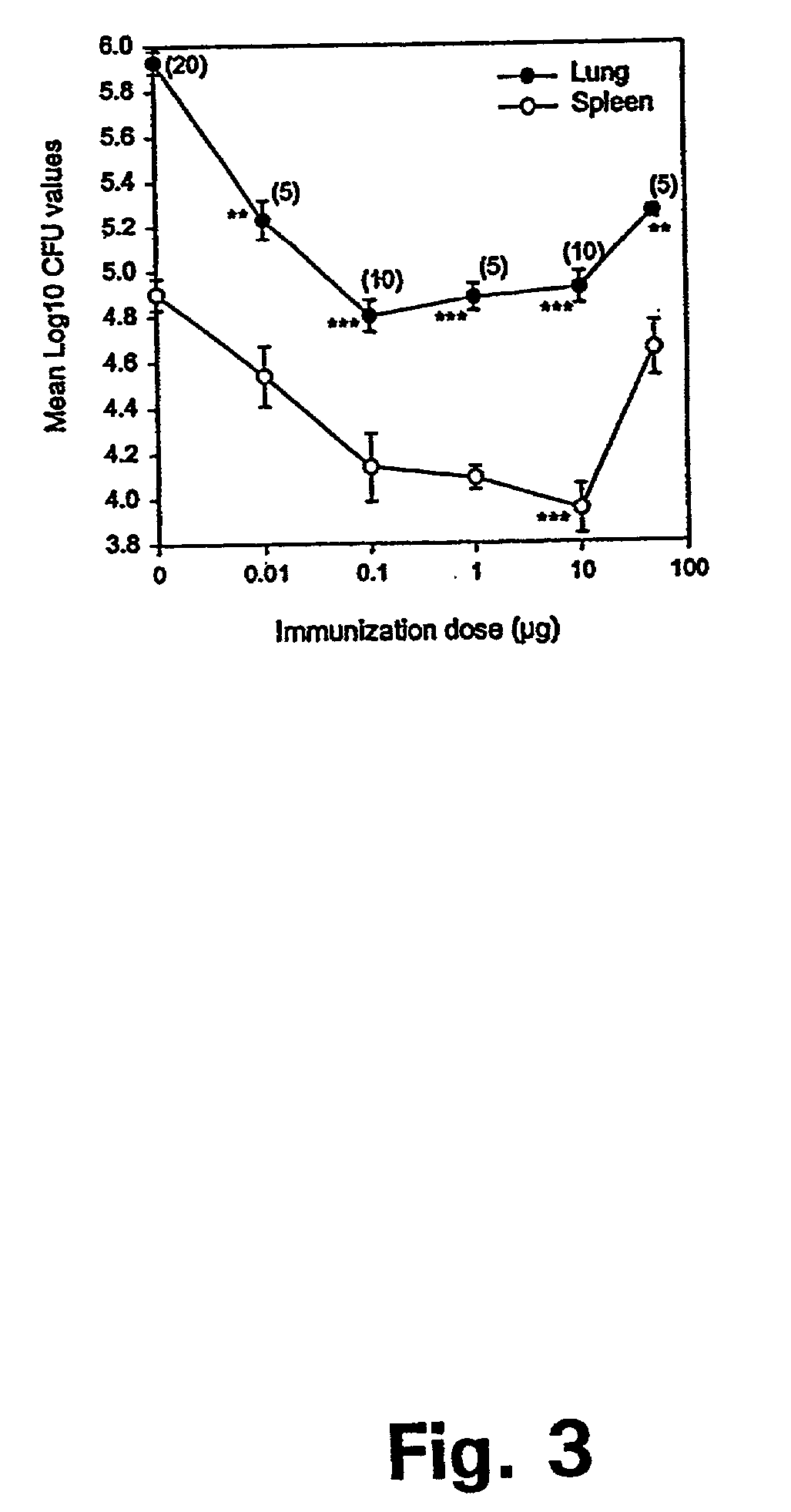
The present invention discloses fusion proteins of the immunodominant antigens ESAT-6 and Ag85B from Mycobacterium tuberculosis or homologues thereof, and a tuberculosis vaccine based on the fusion proteins, which vaccine induces efficient immunological memory.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com