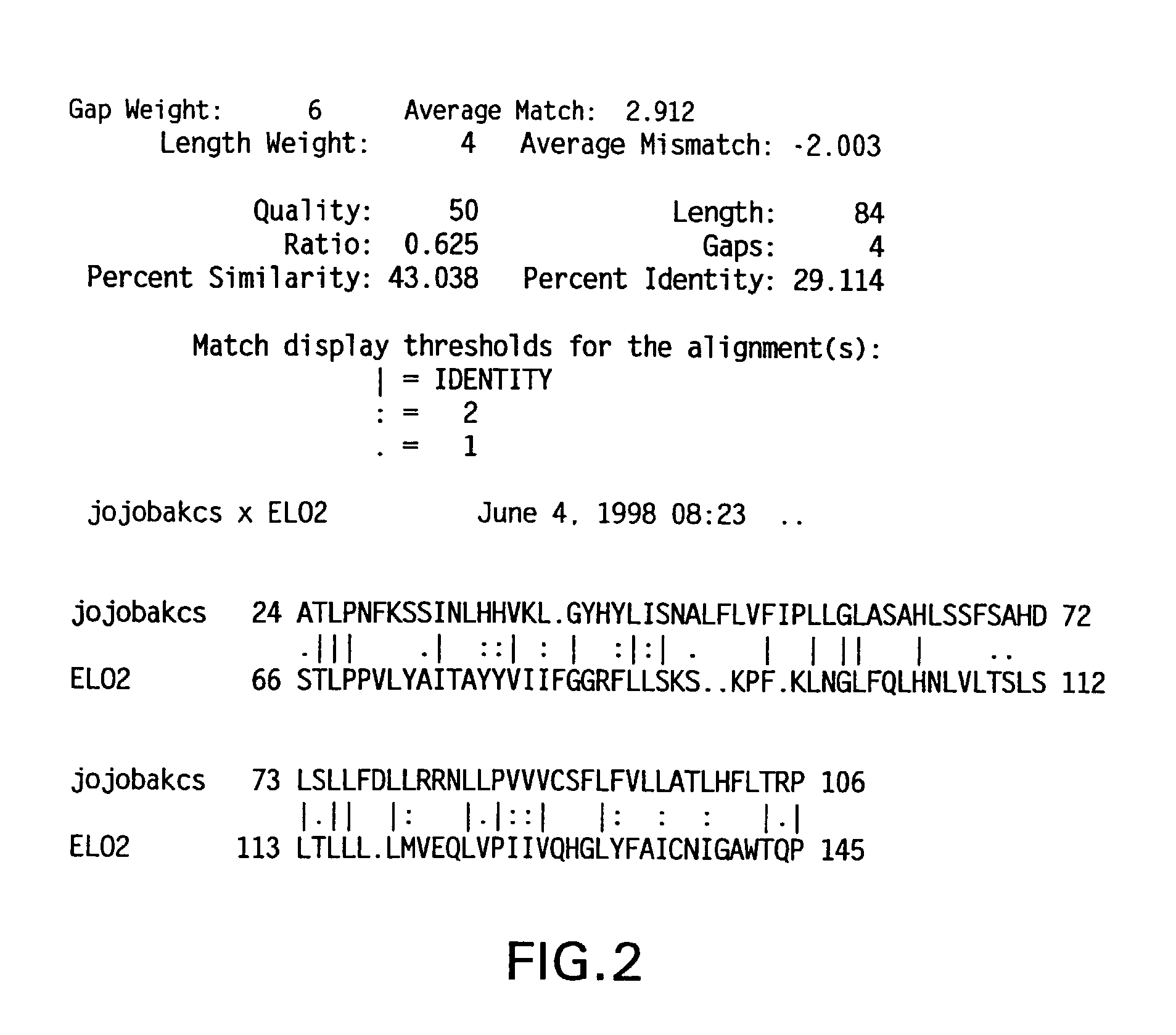
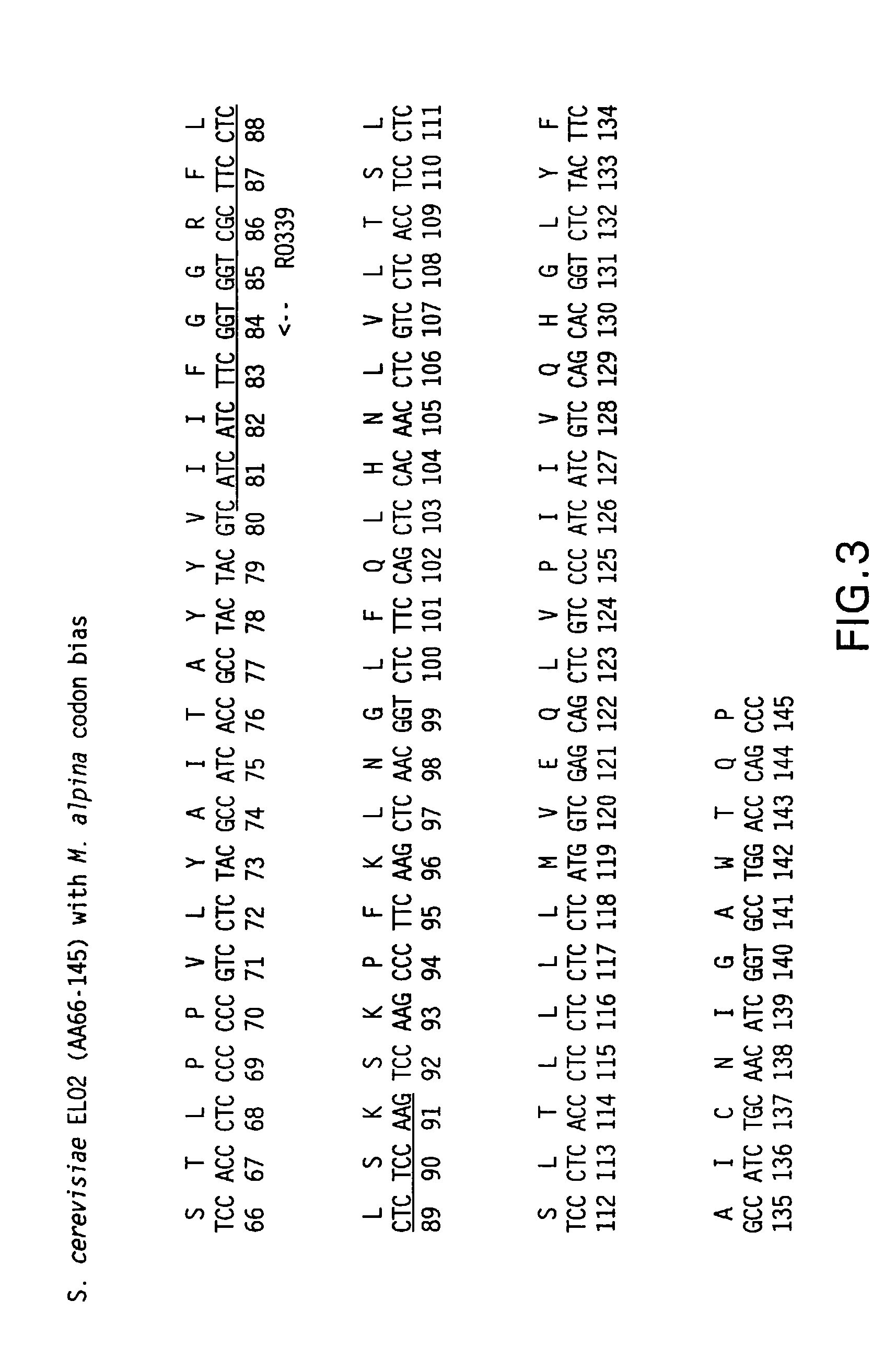
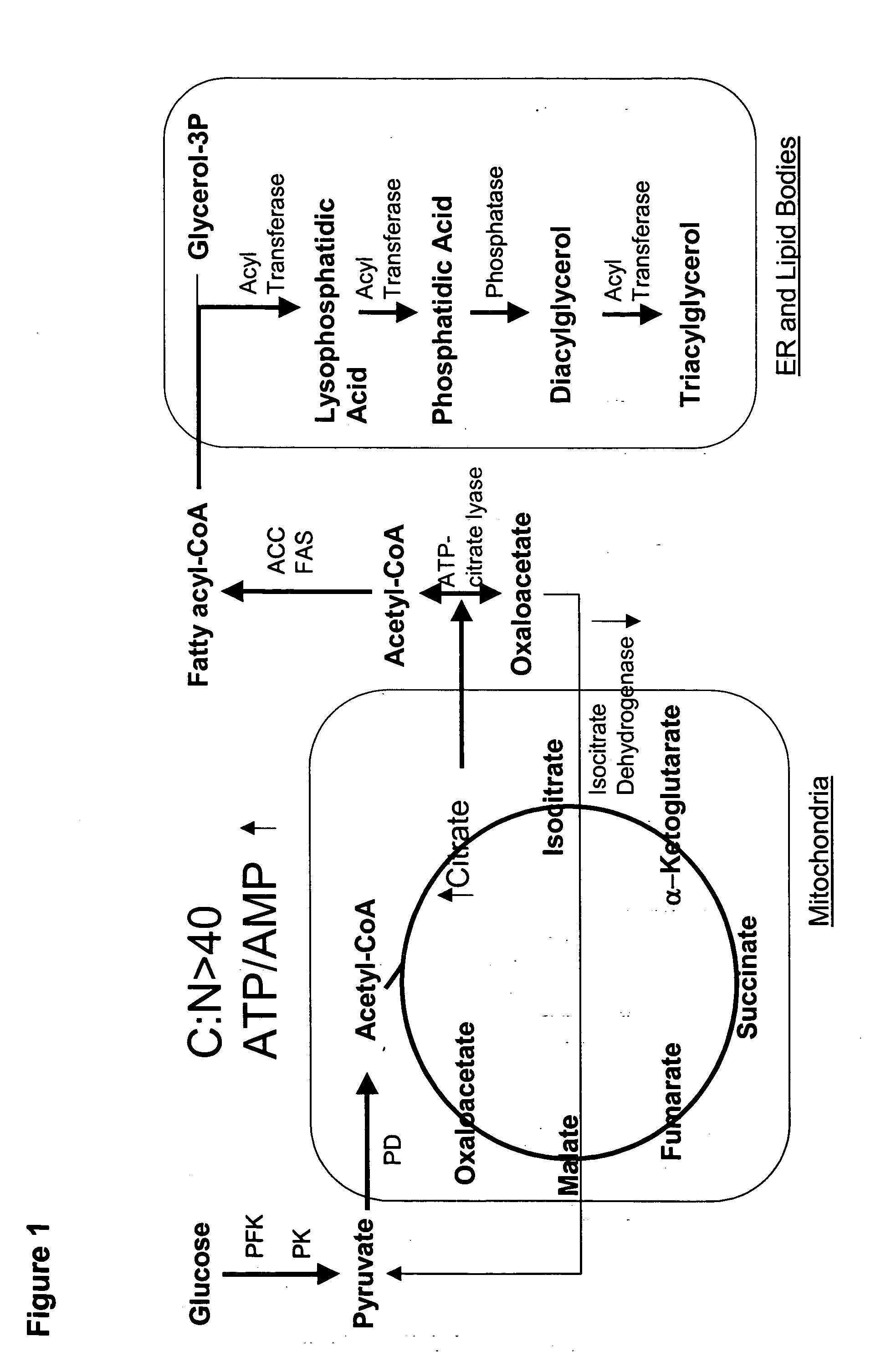
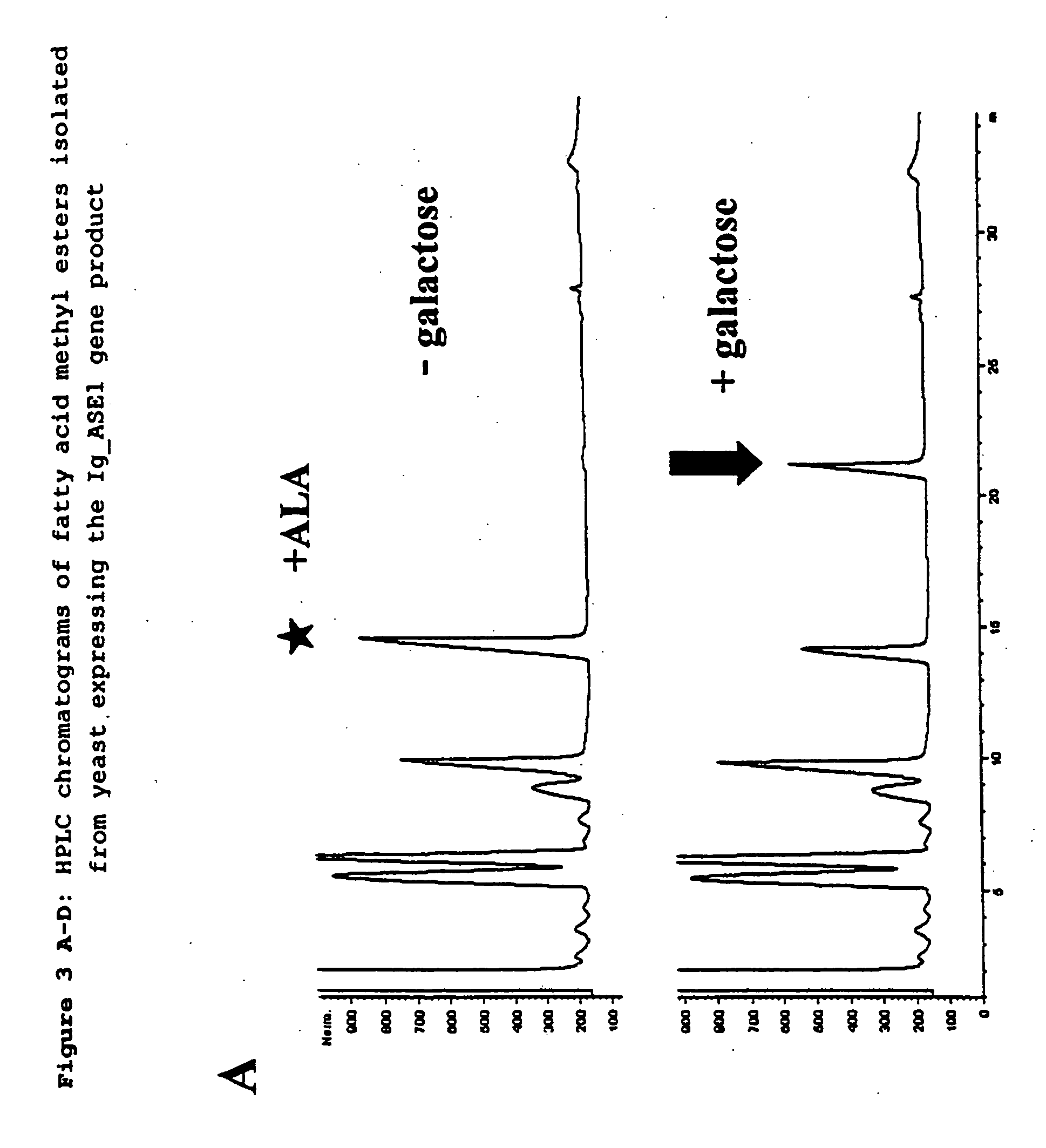
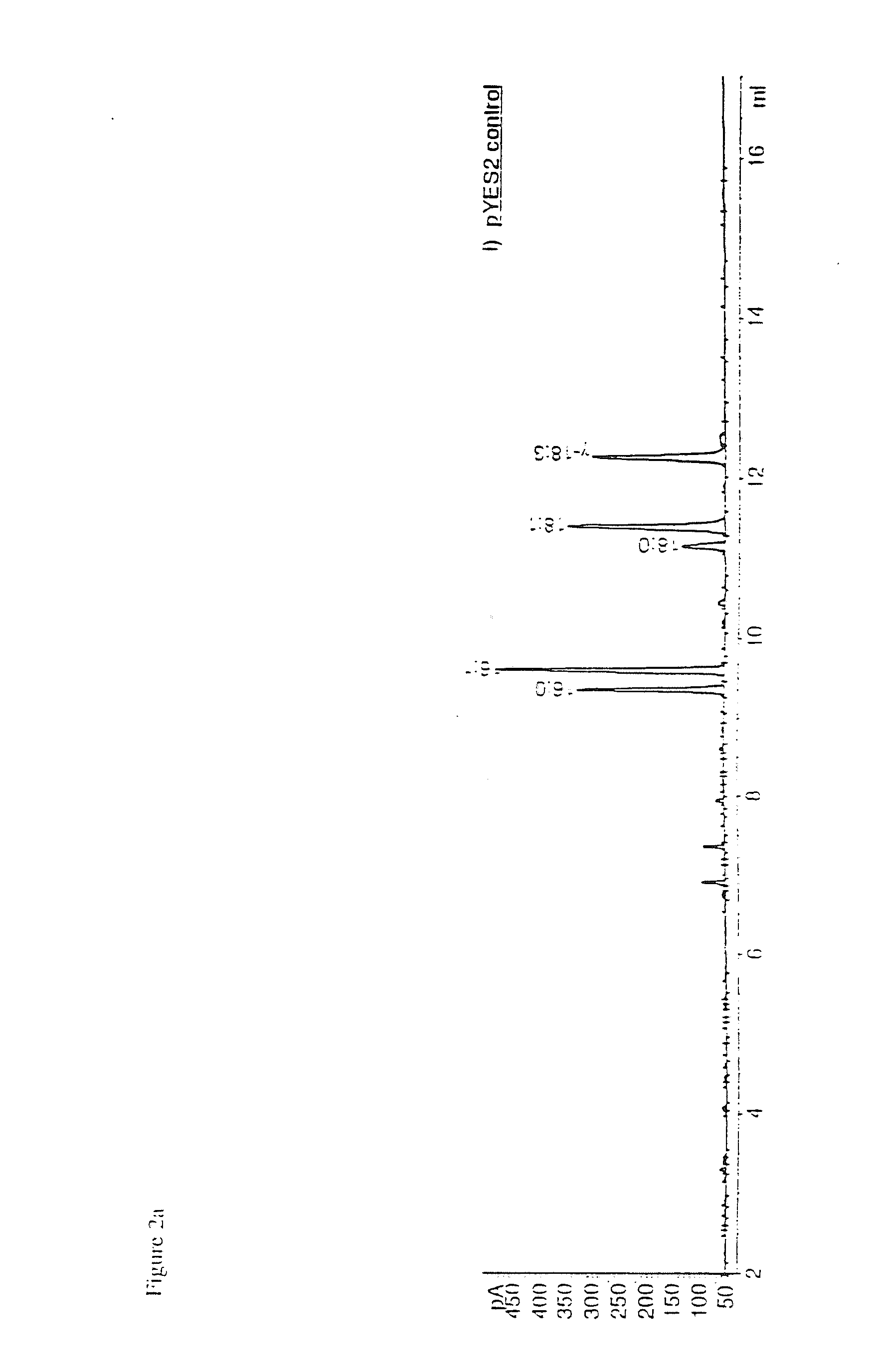
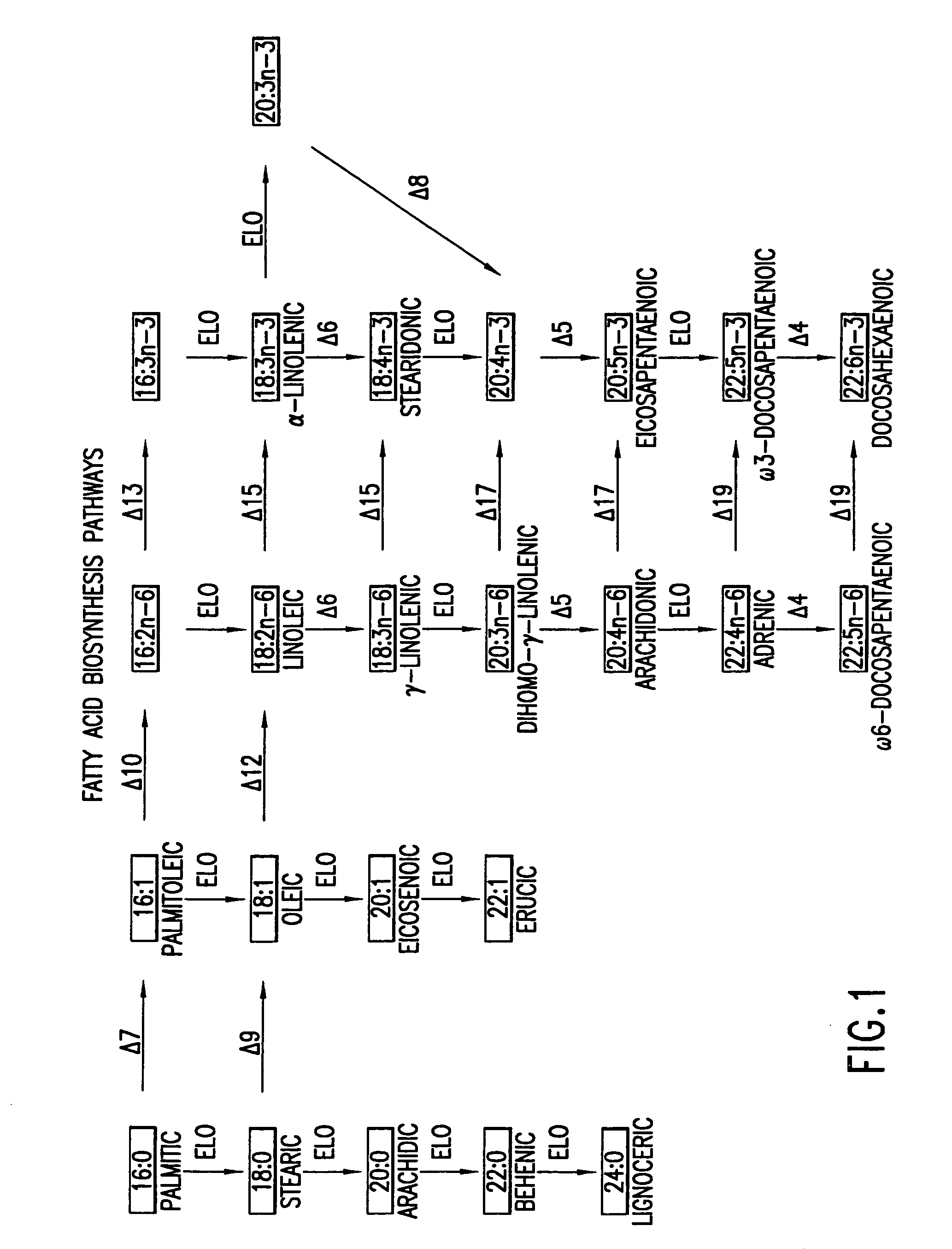
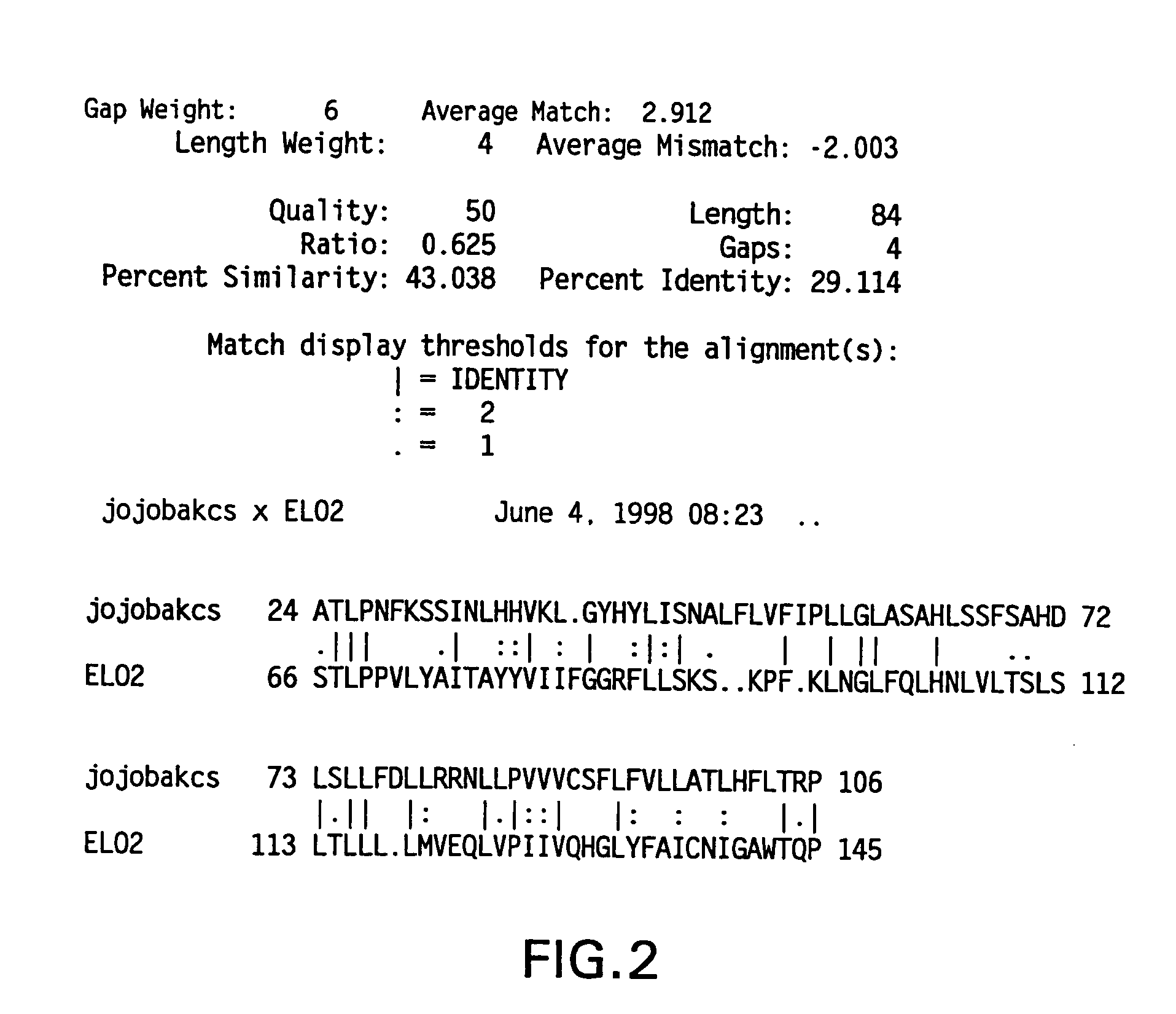
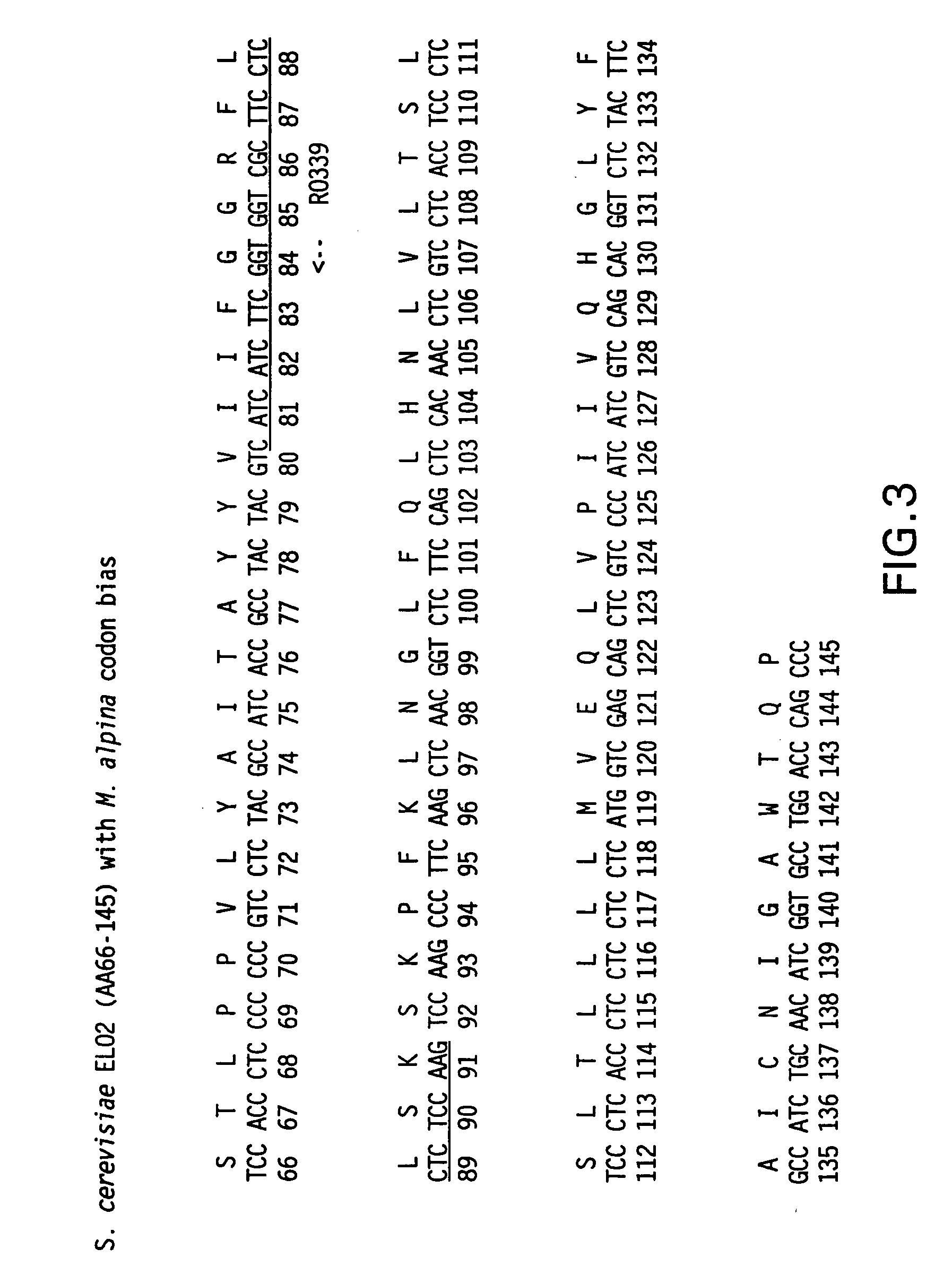
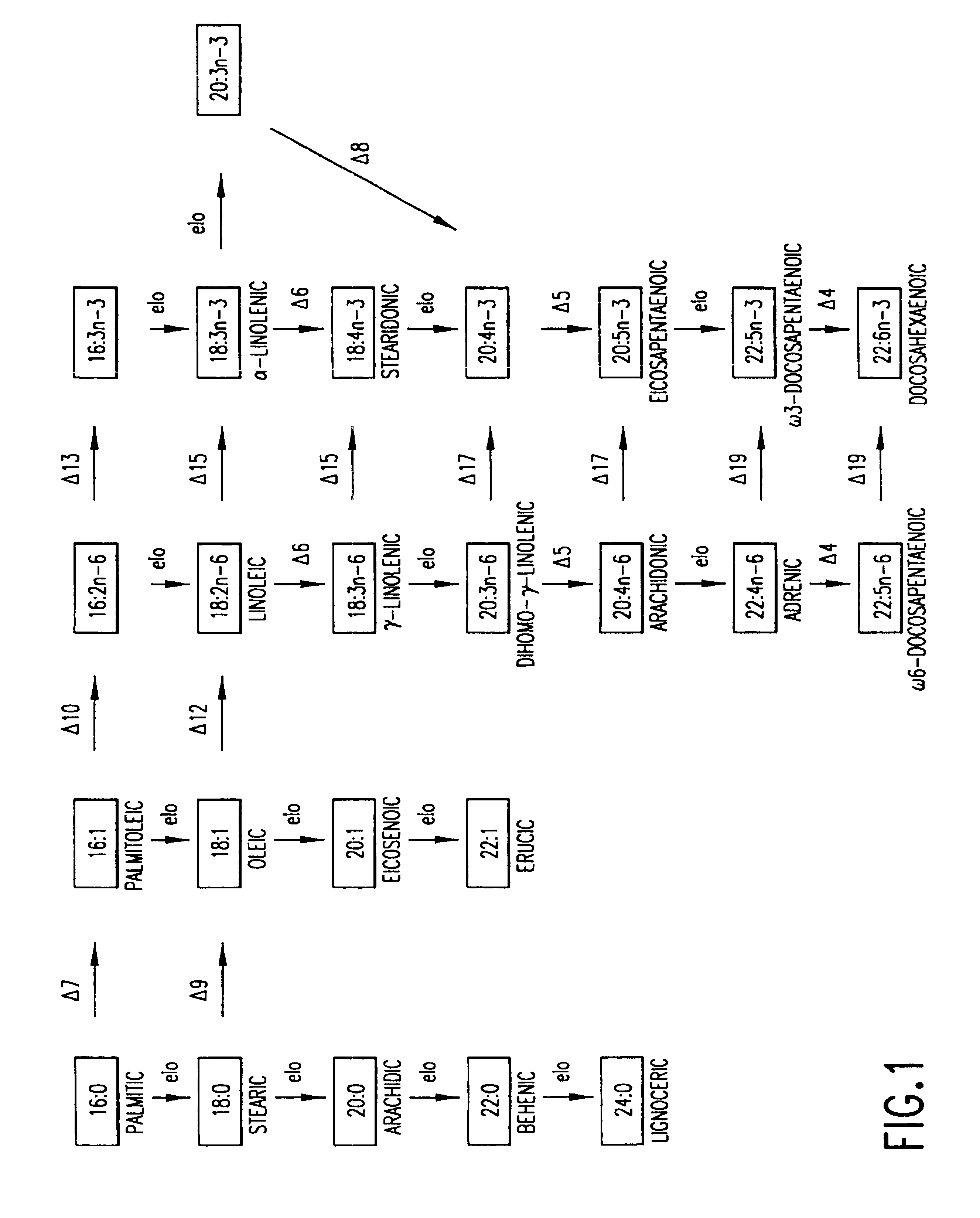
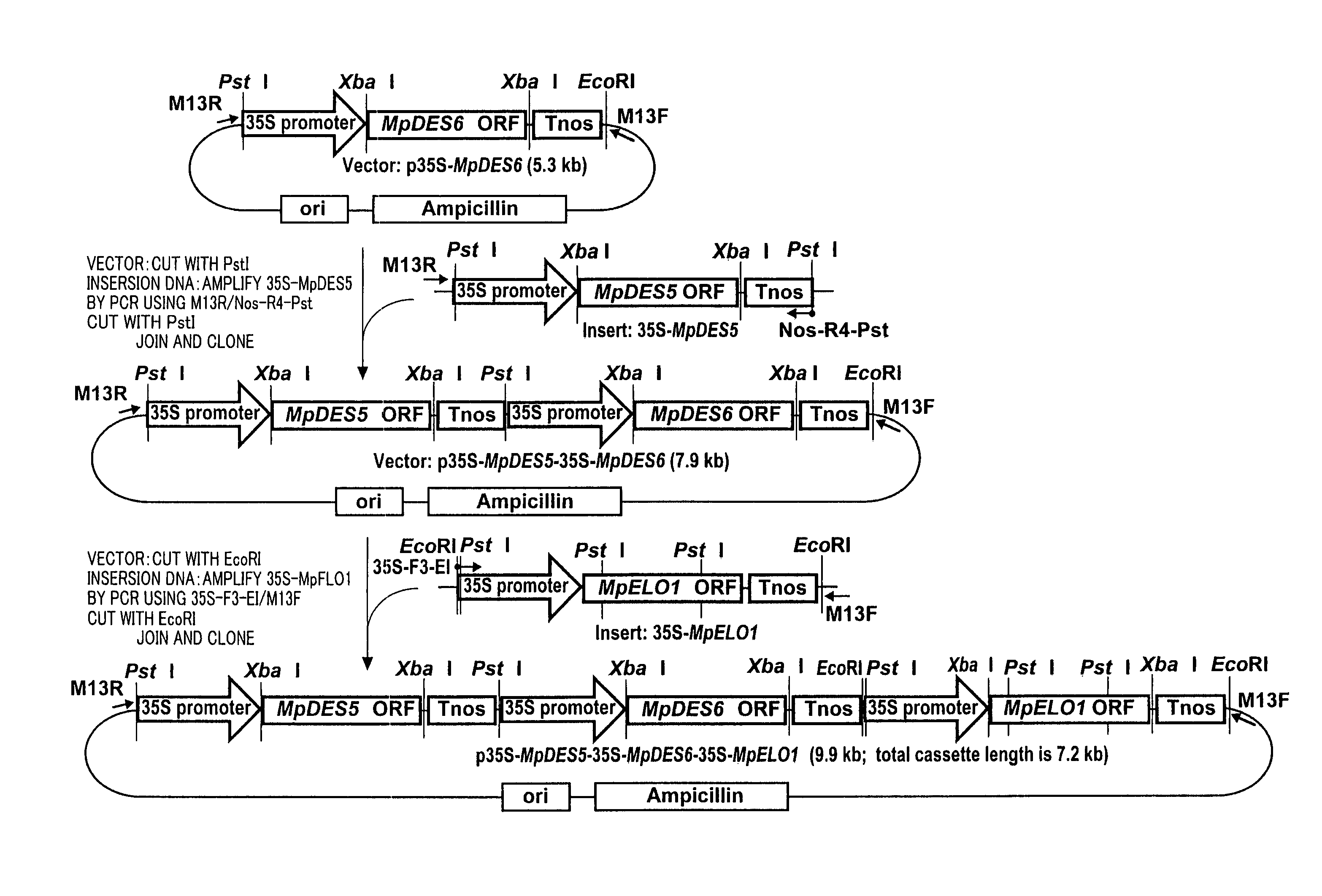
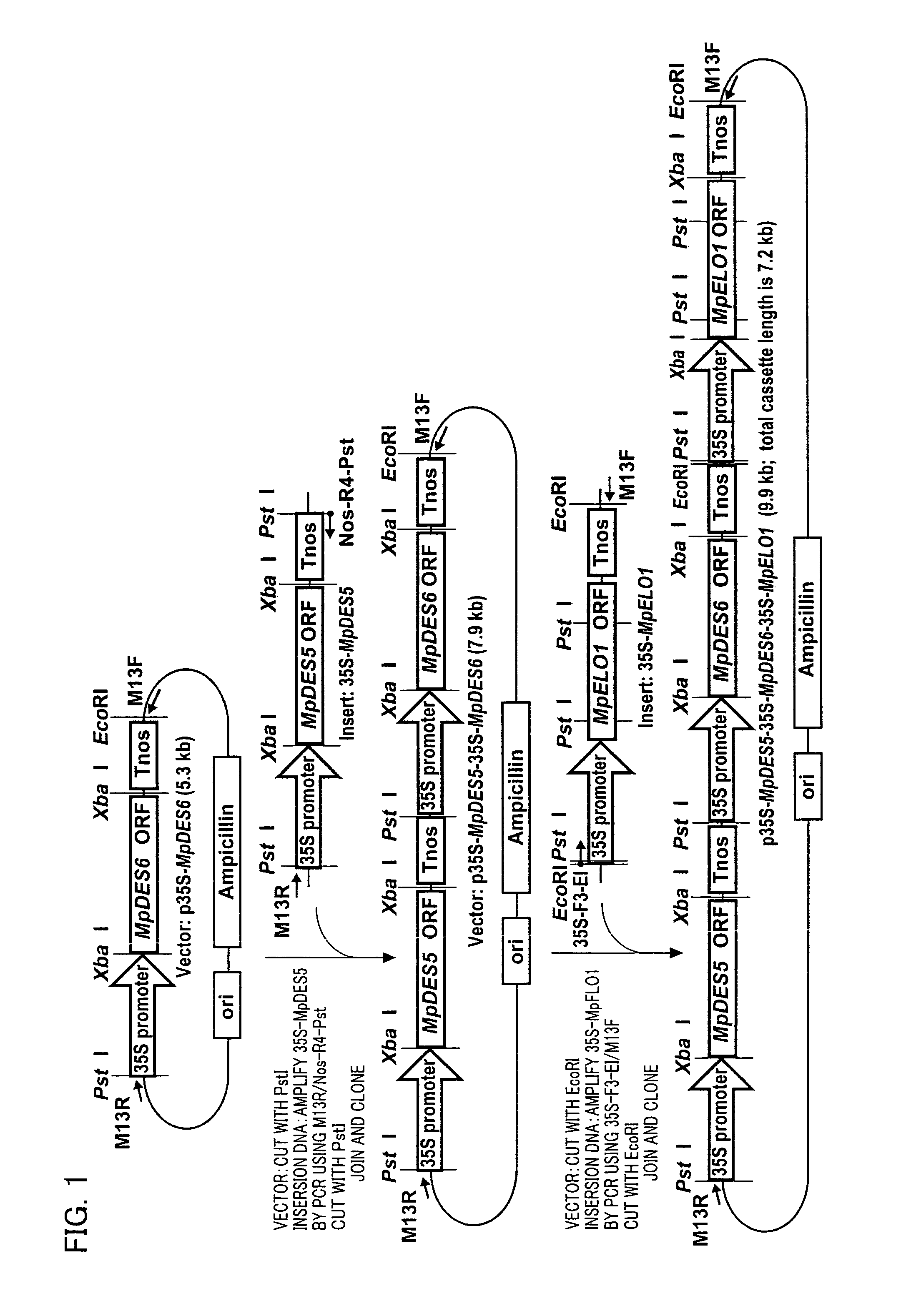
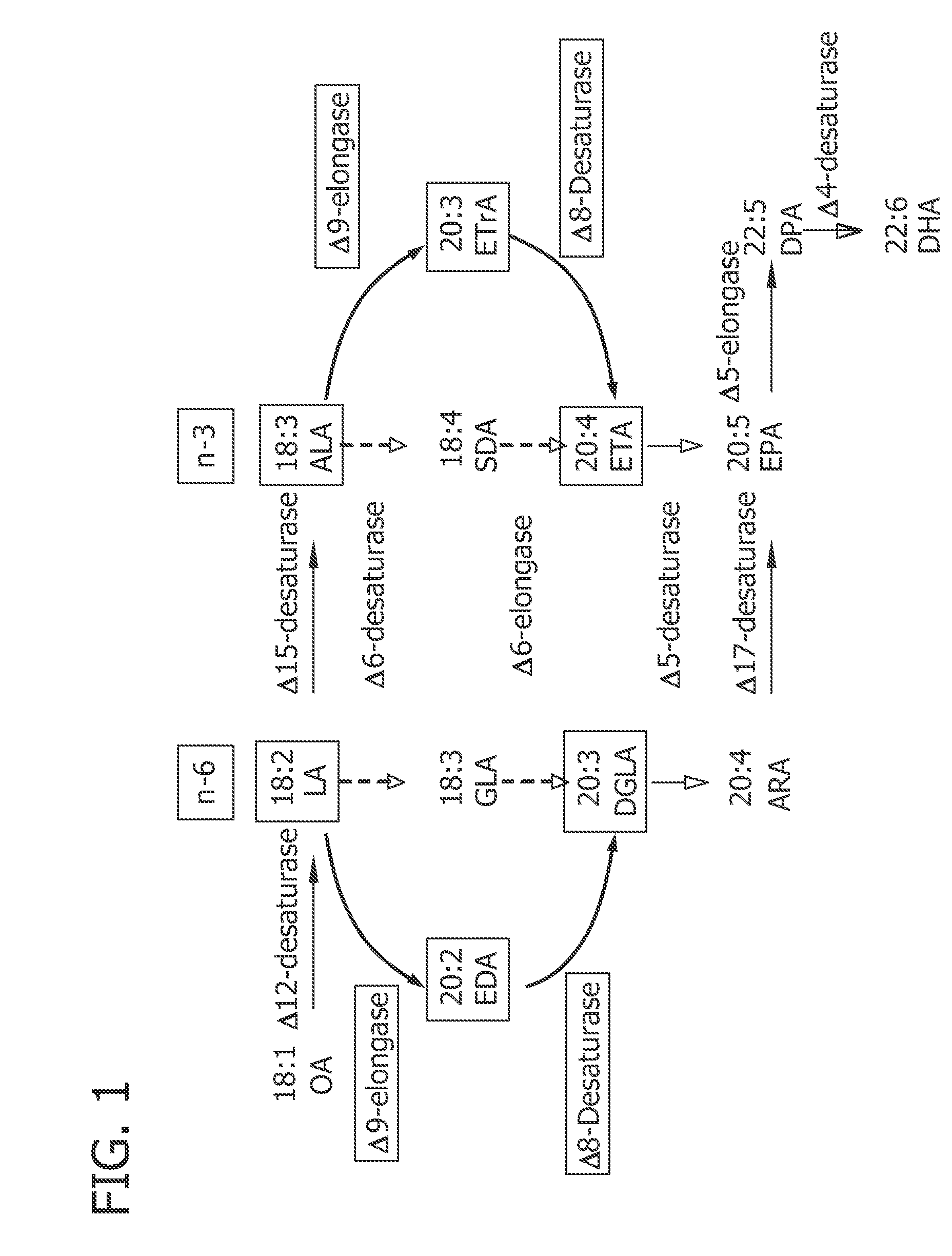
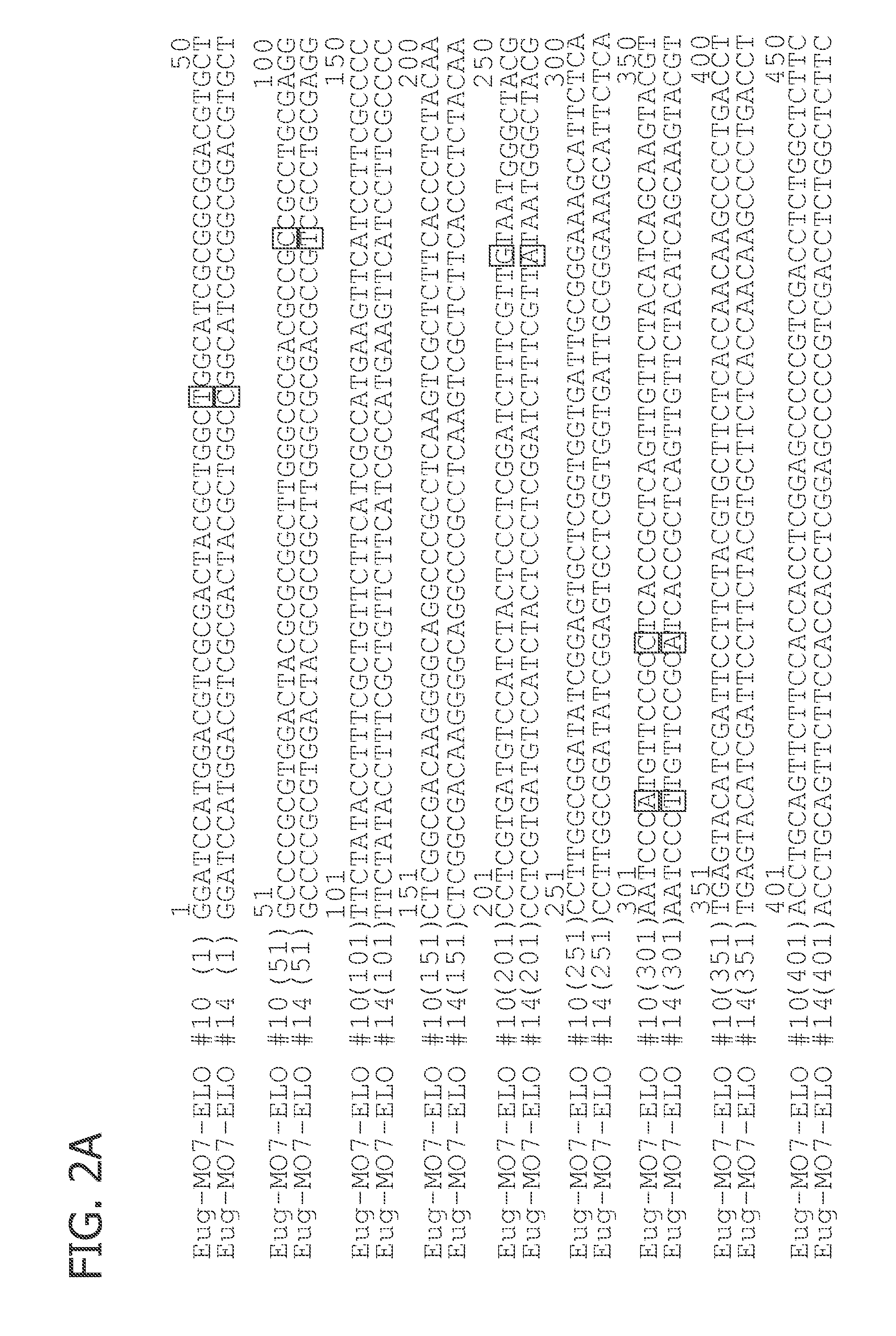
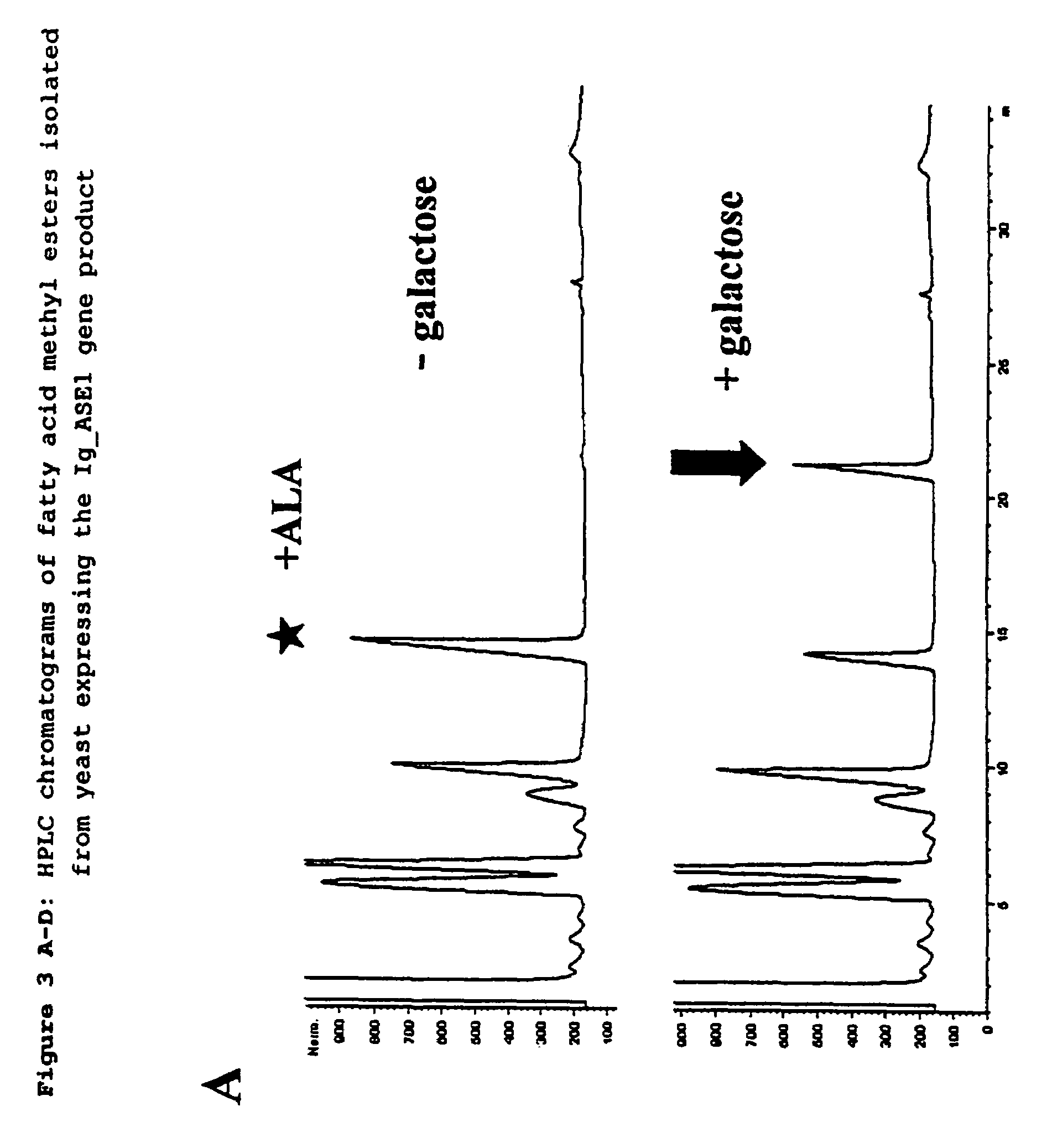
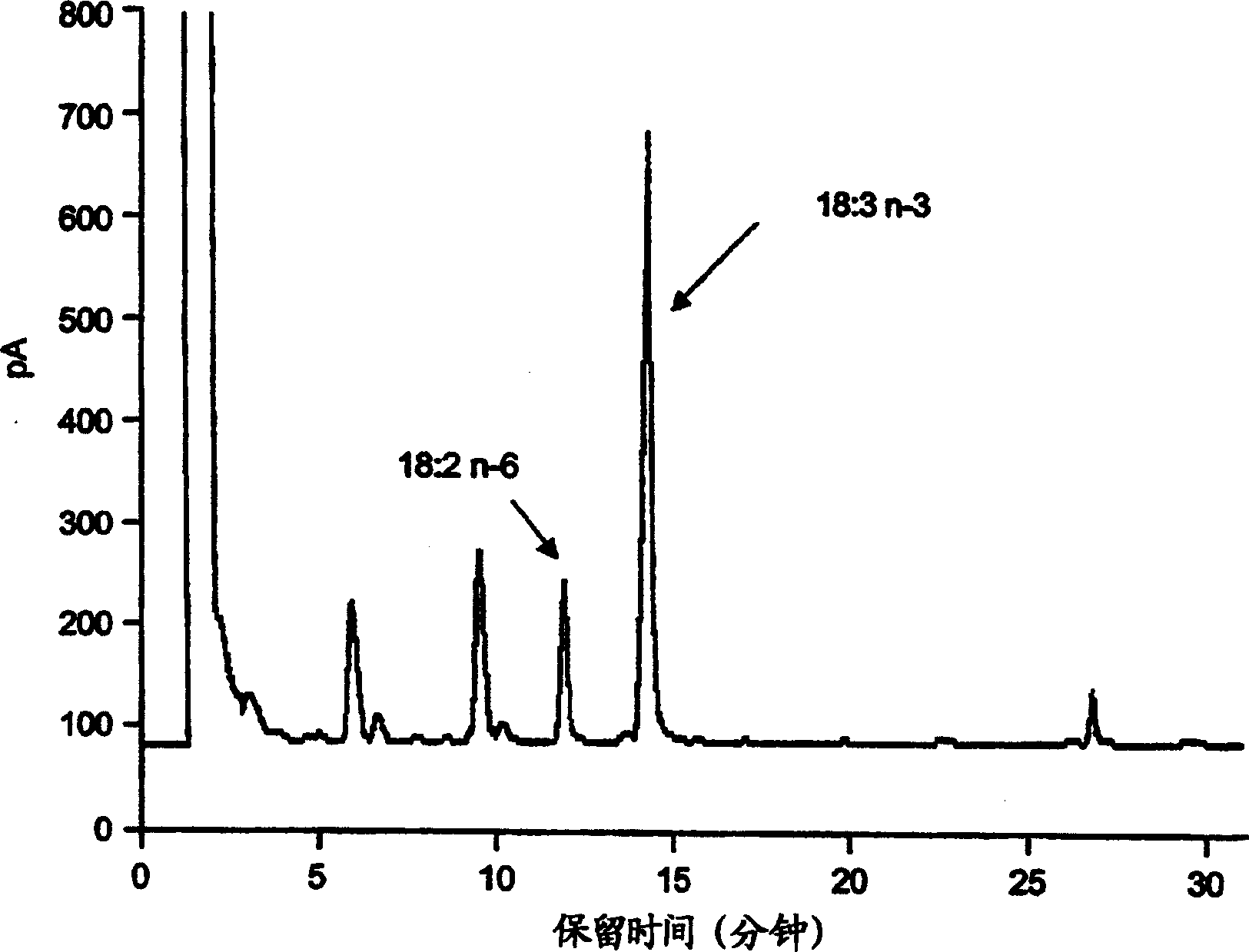
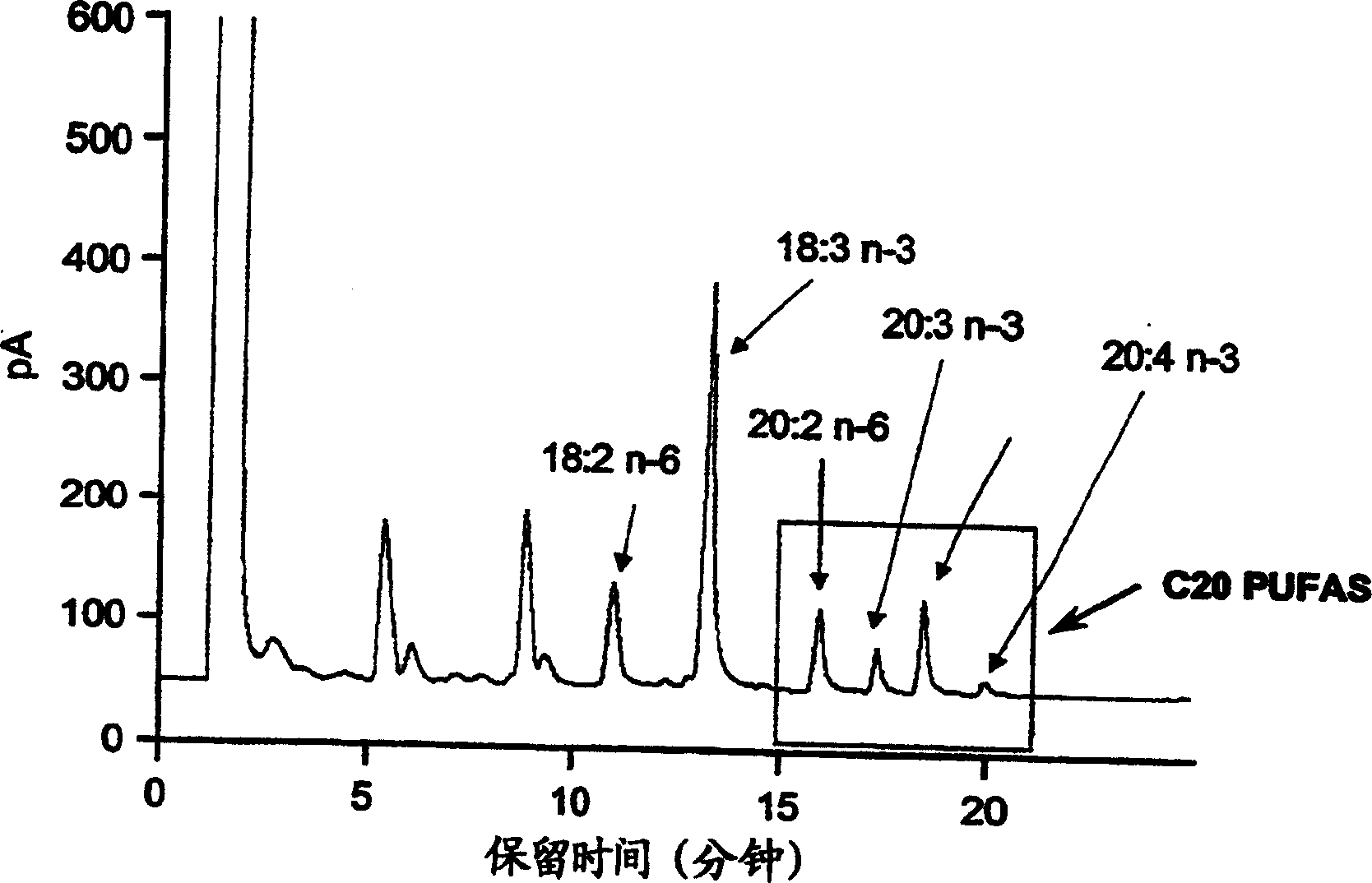
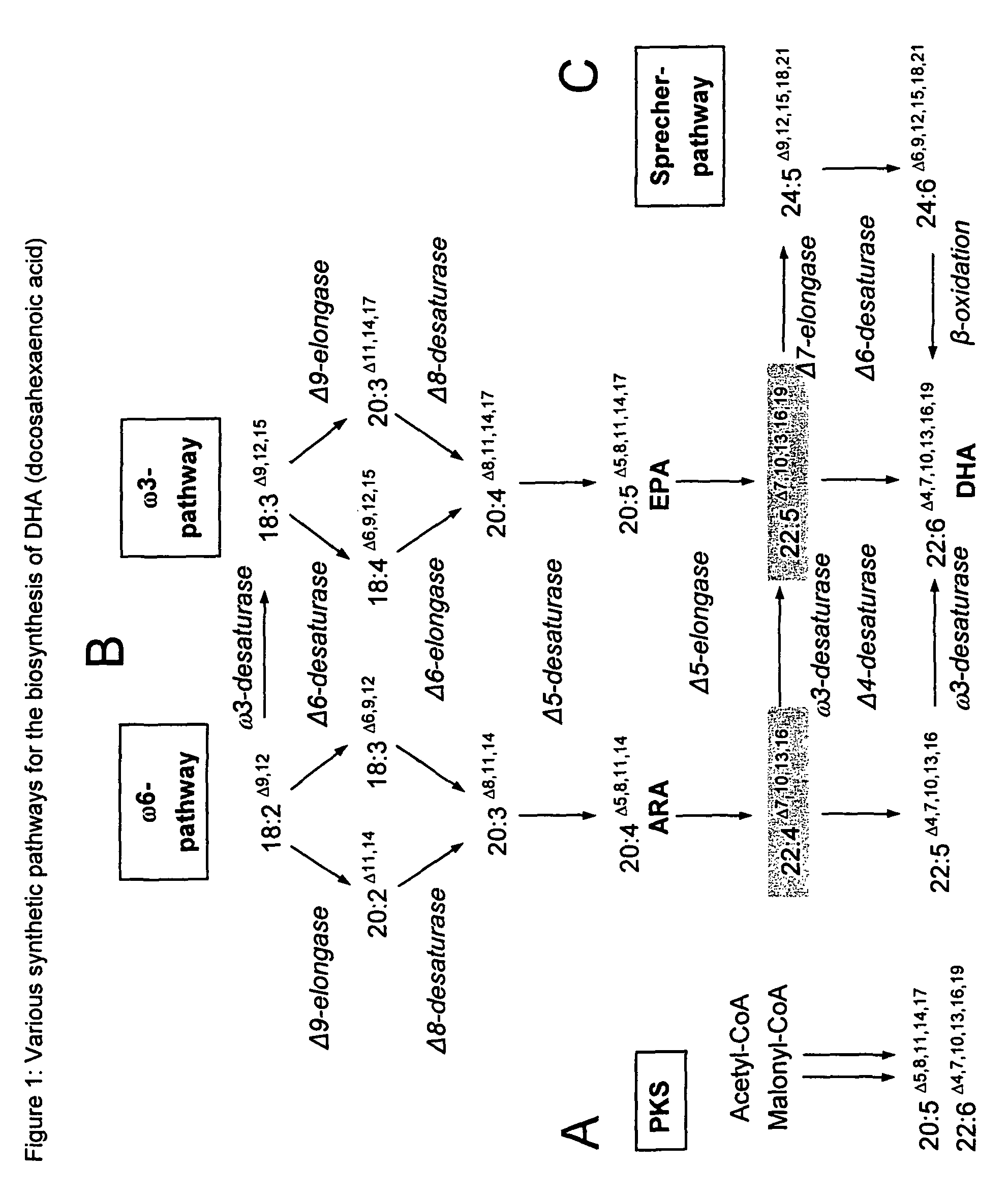
Patents
Literature
72 results about "Elongase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
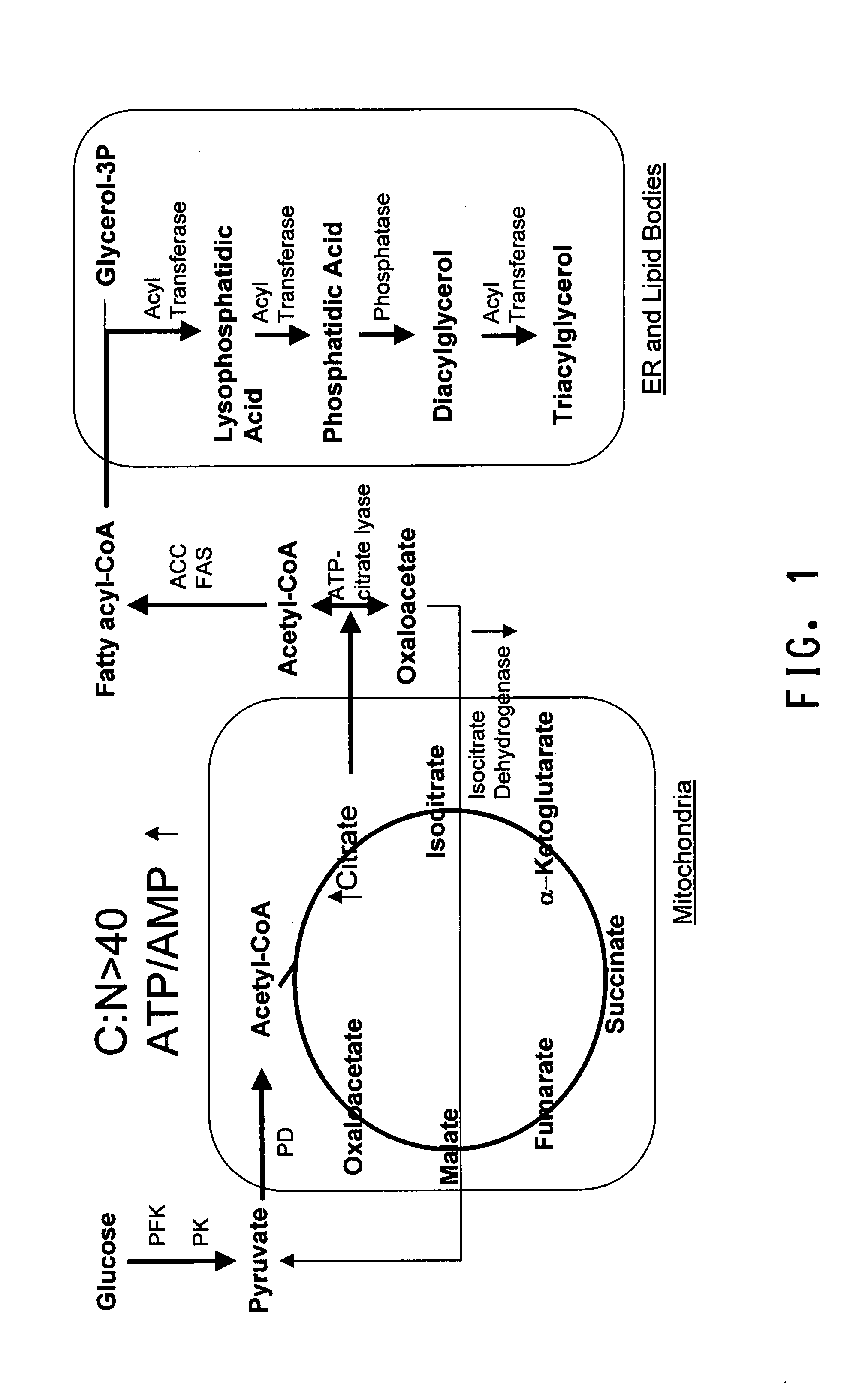
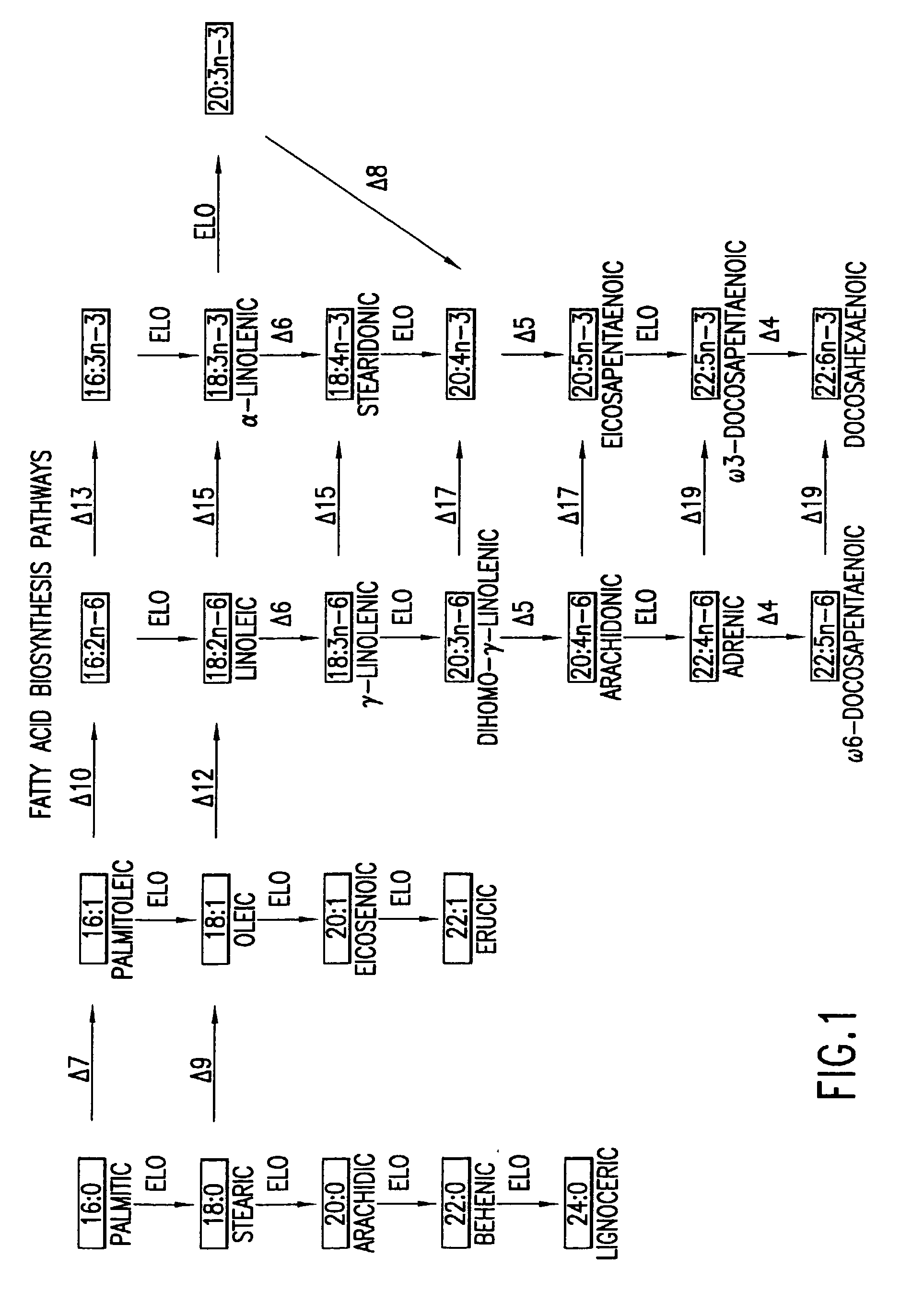
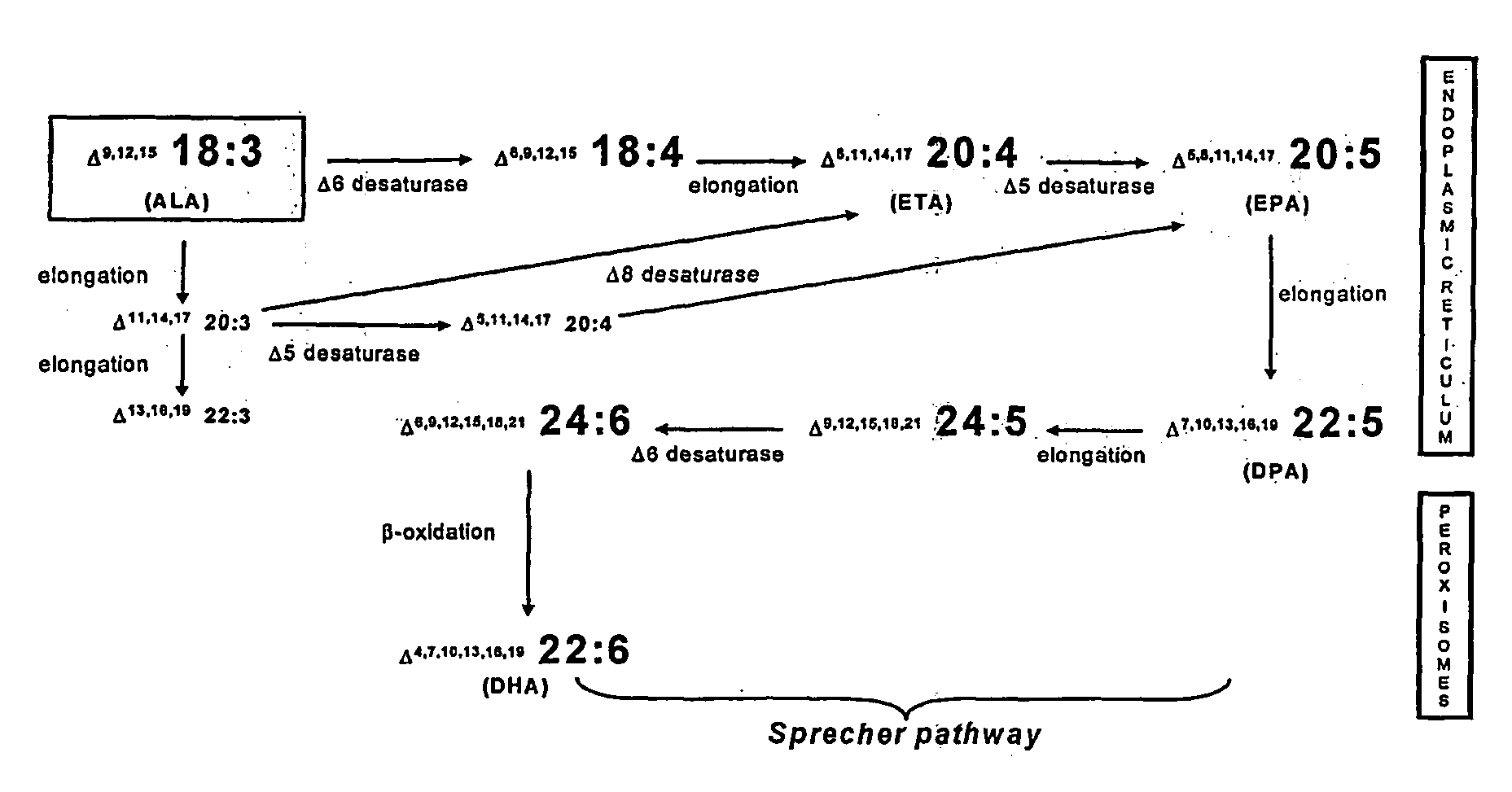
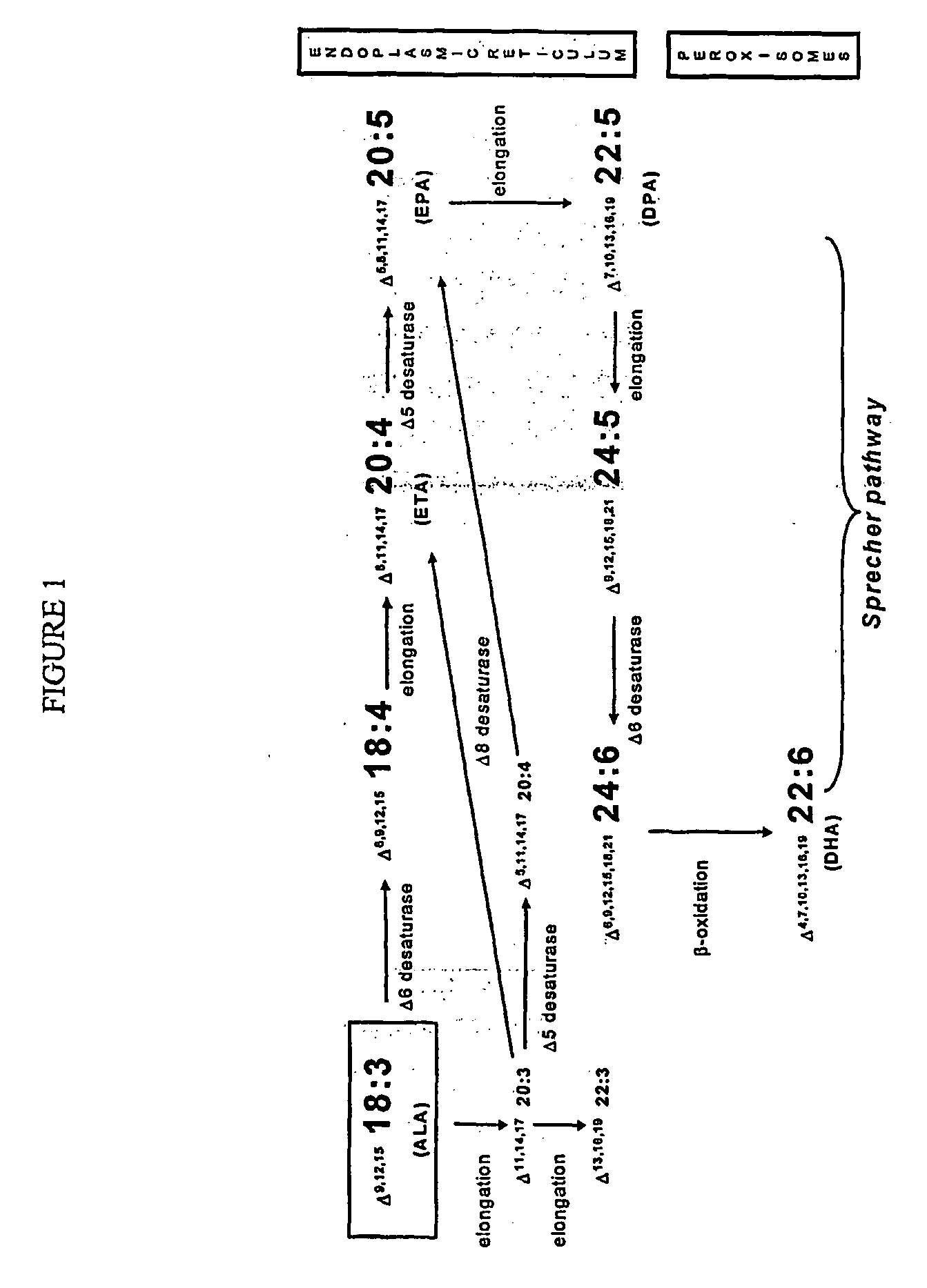
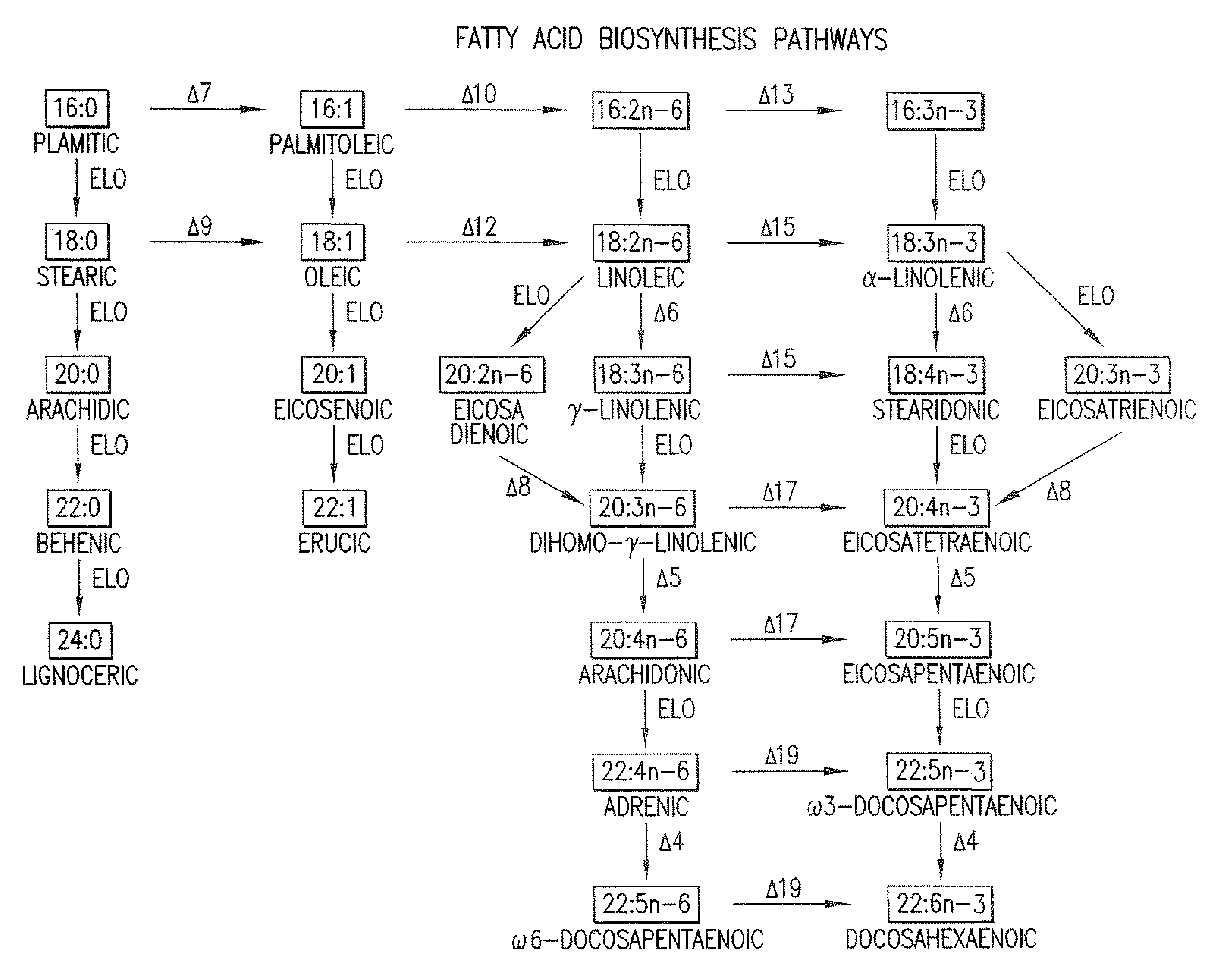
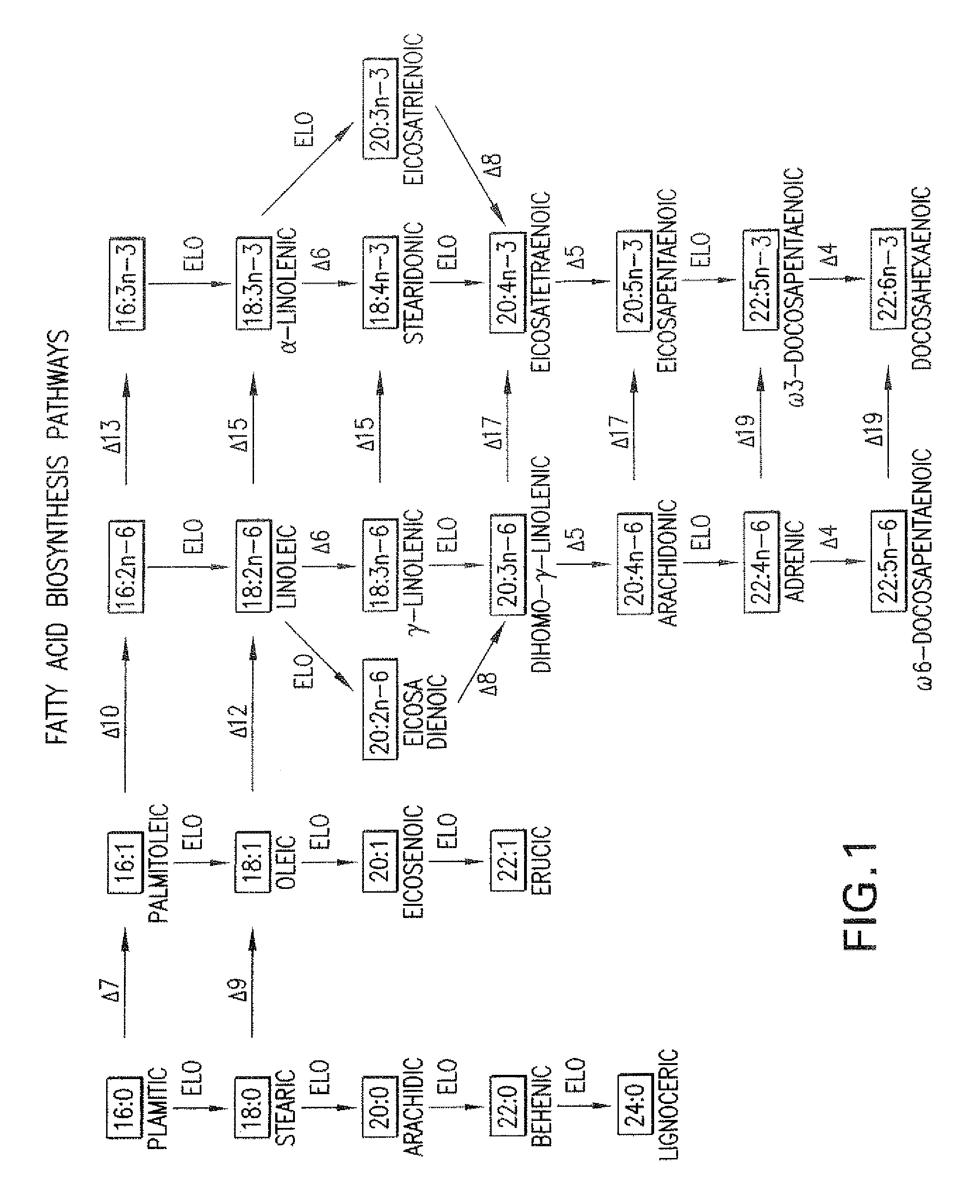
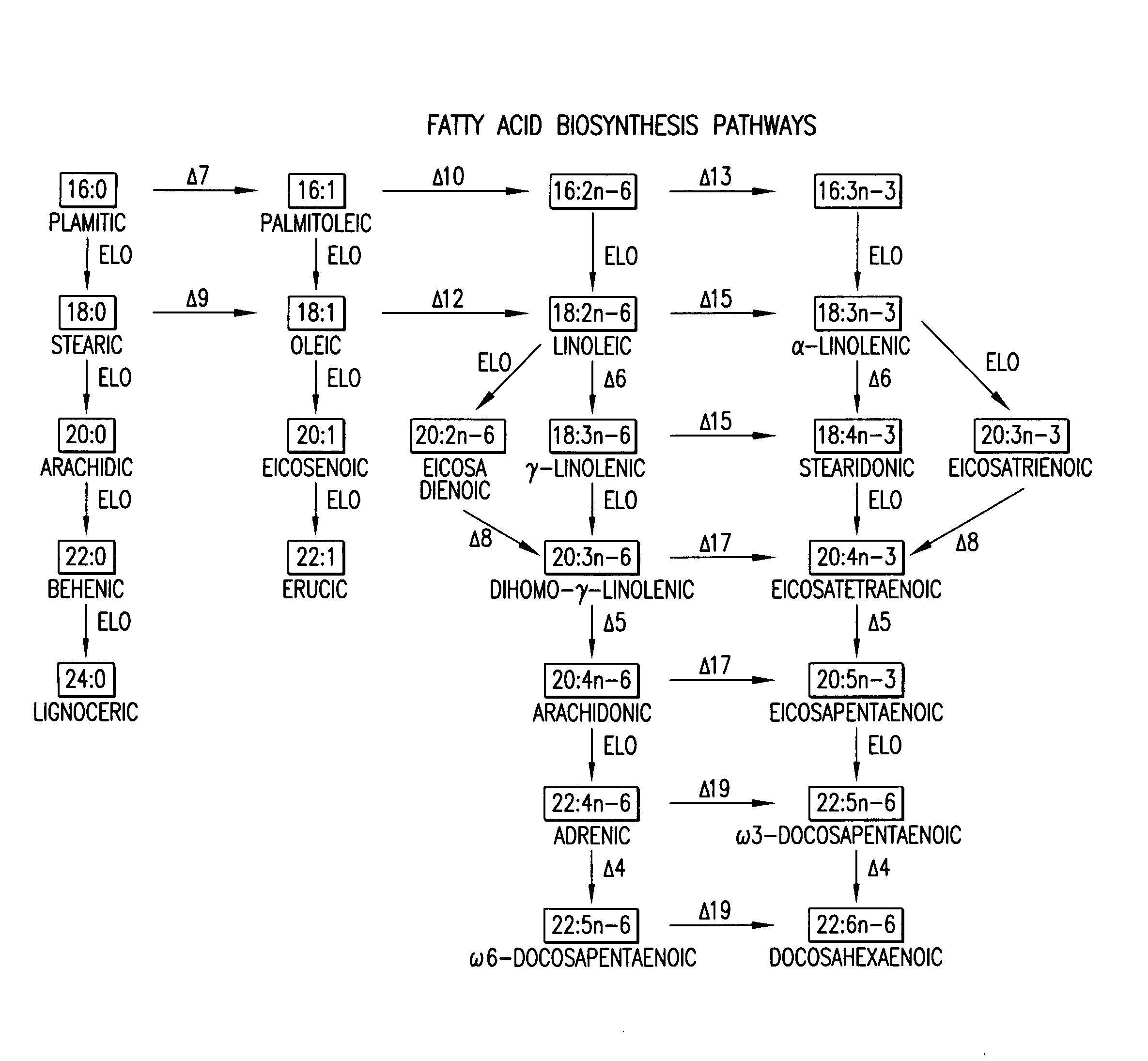
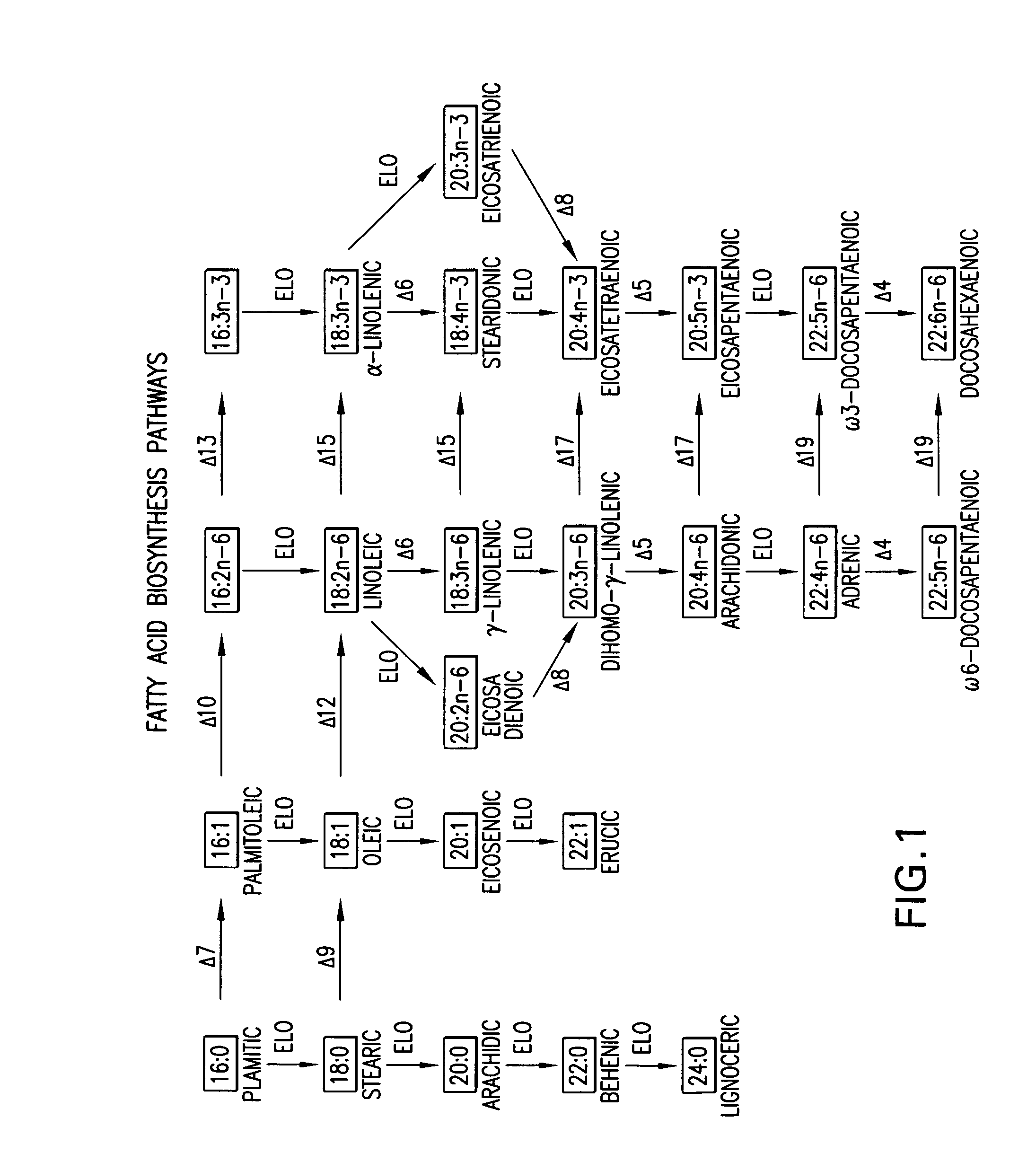
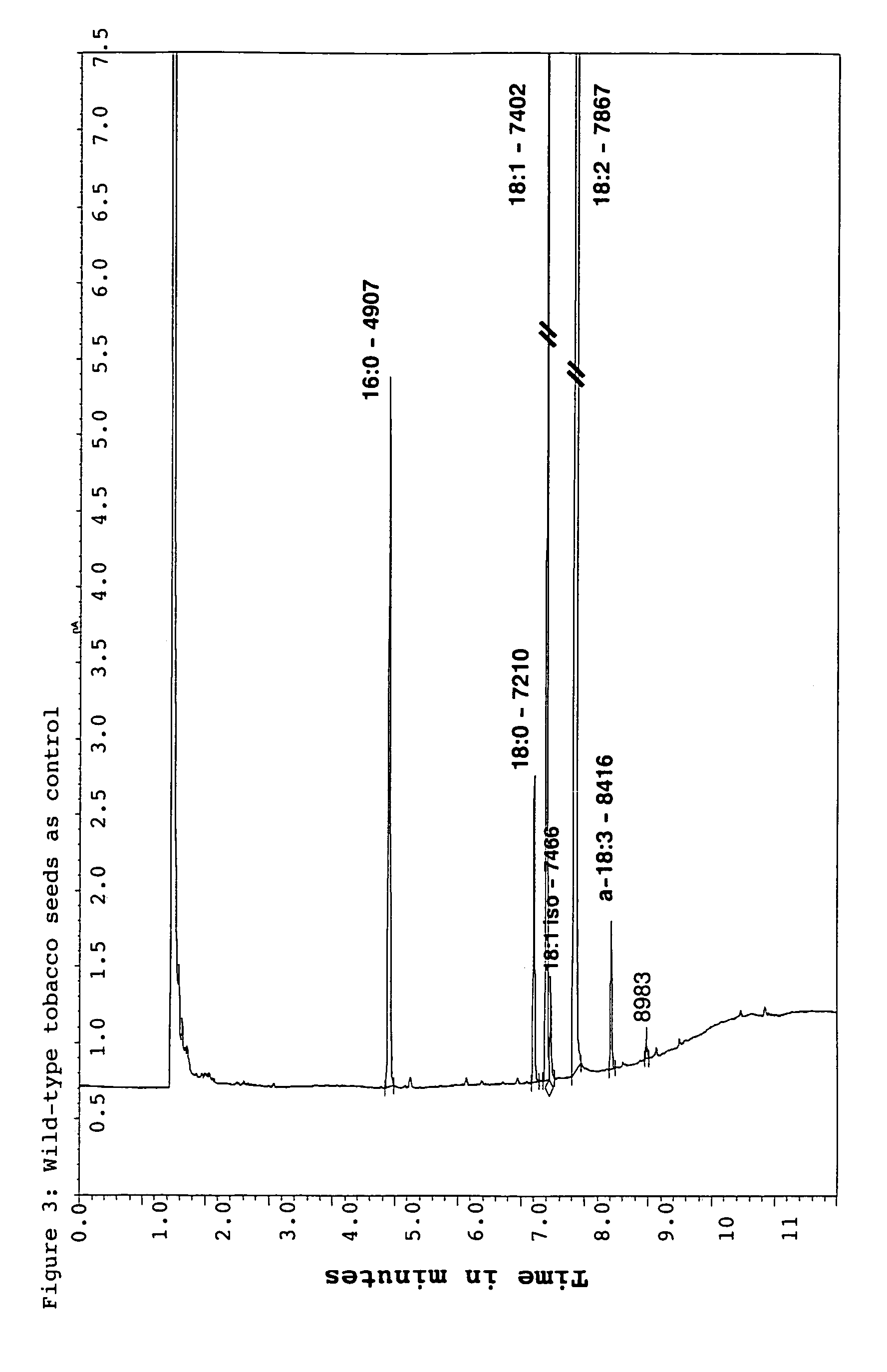
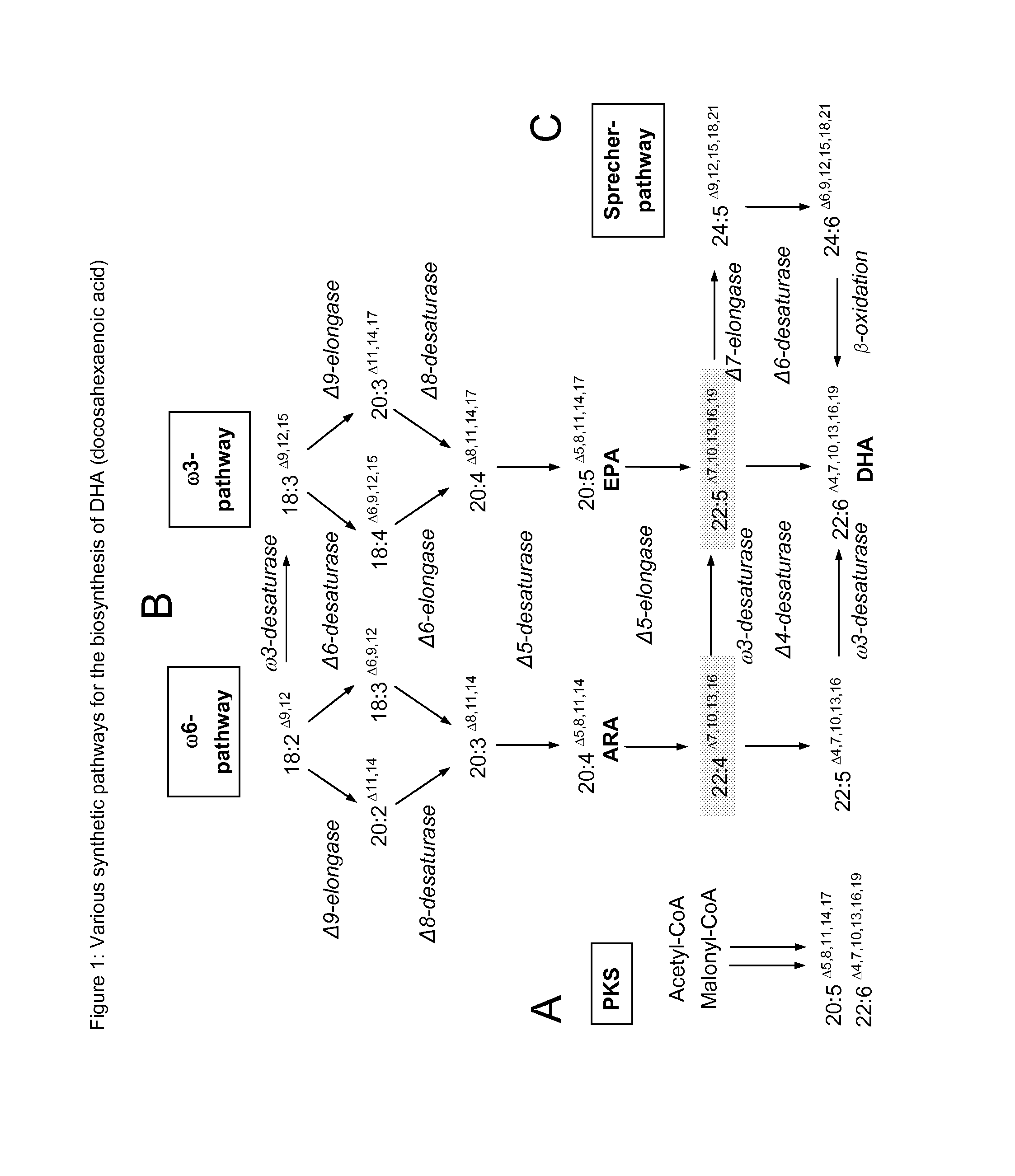
Elongase is a generic term for an enzyme that catalyzes carbon chain extension of an organic molecule, especially a fatty acid. Elongases play a variety of roles in mammalian organisms, accounting for changes in tissue function, lipid regulation, and the overall physiology of an organism.
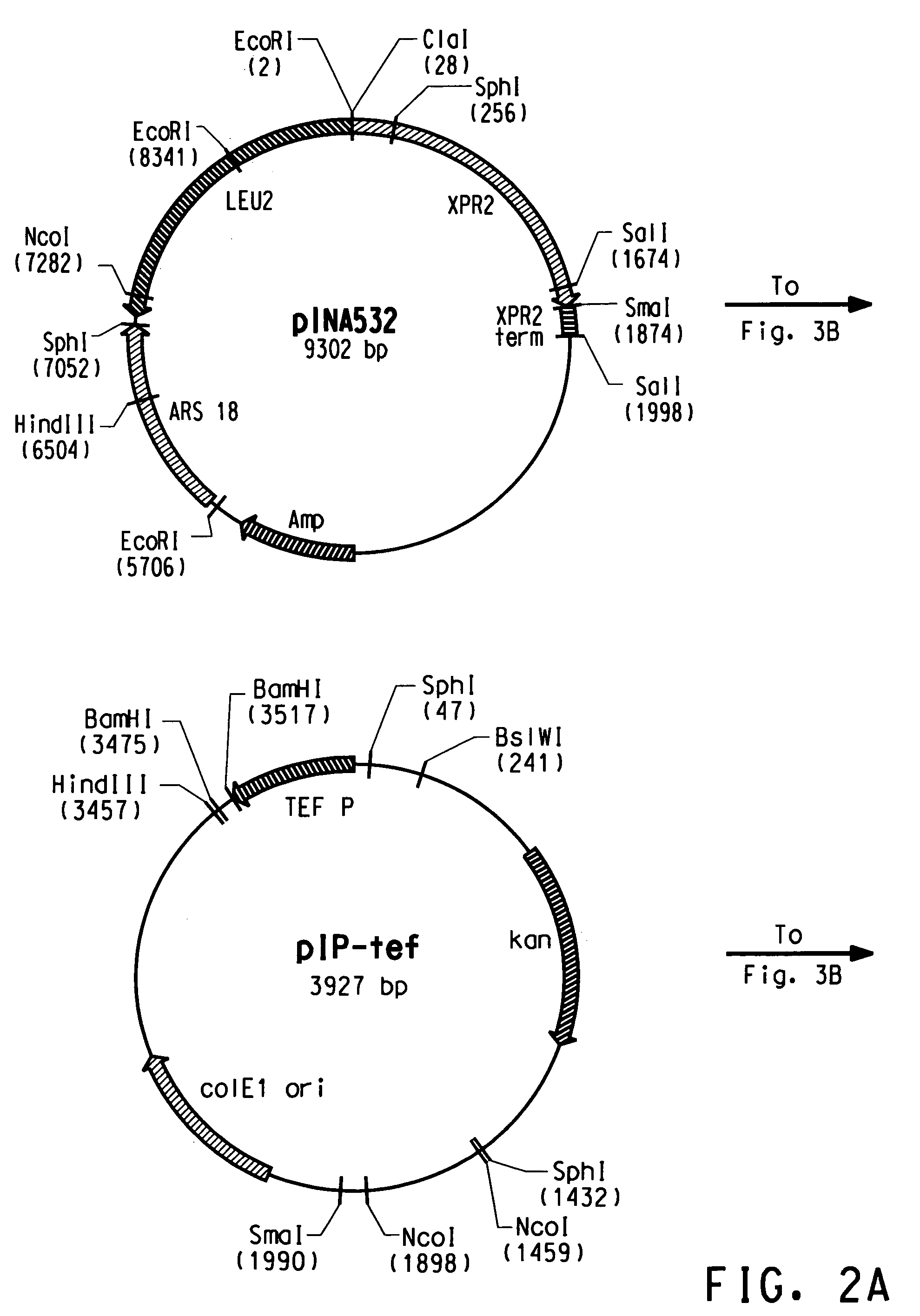
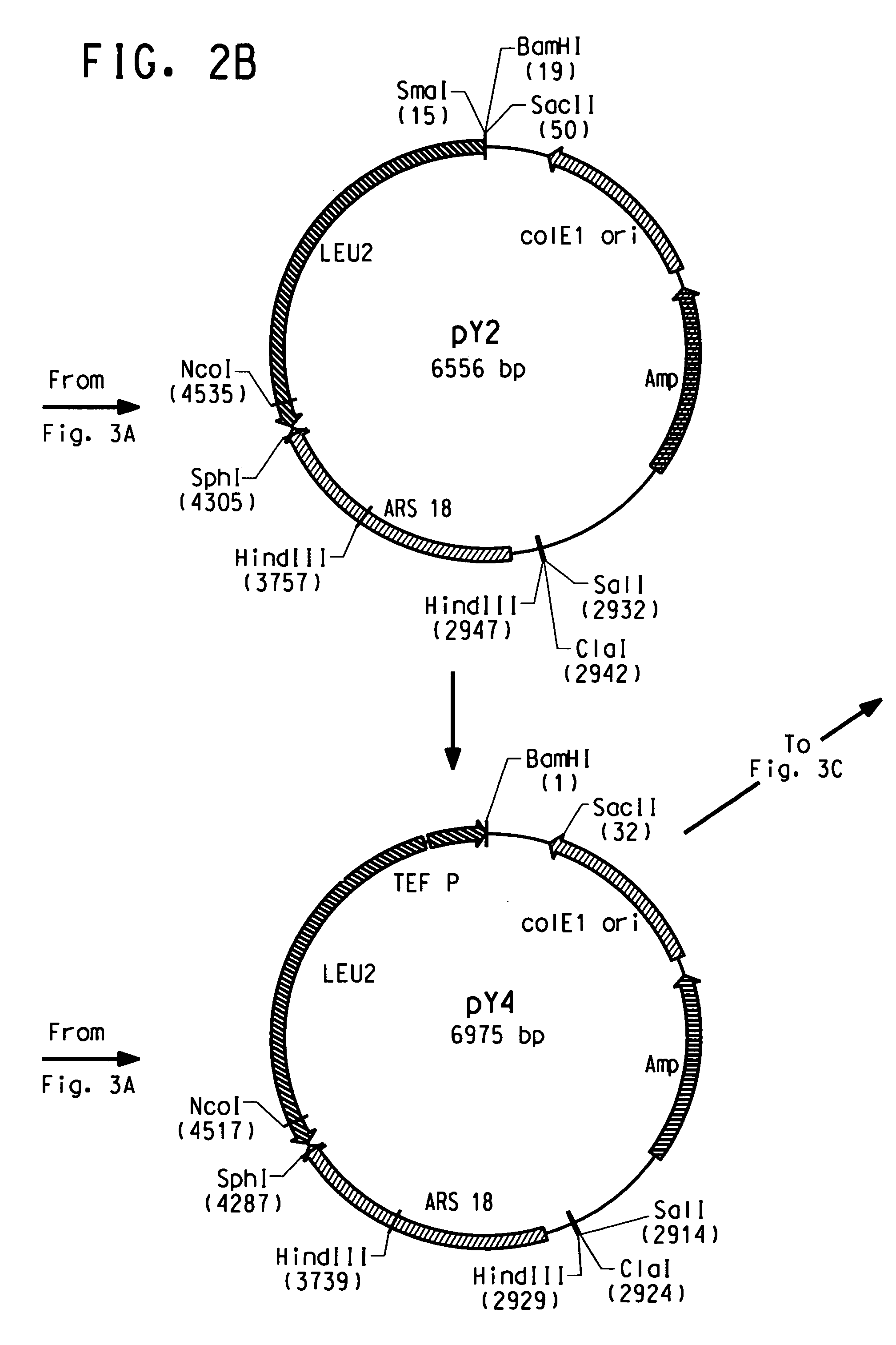
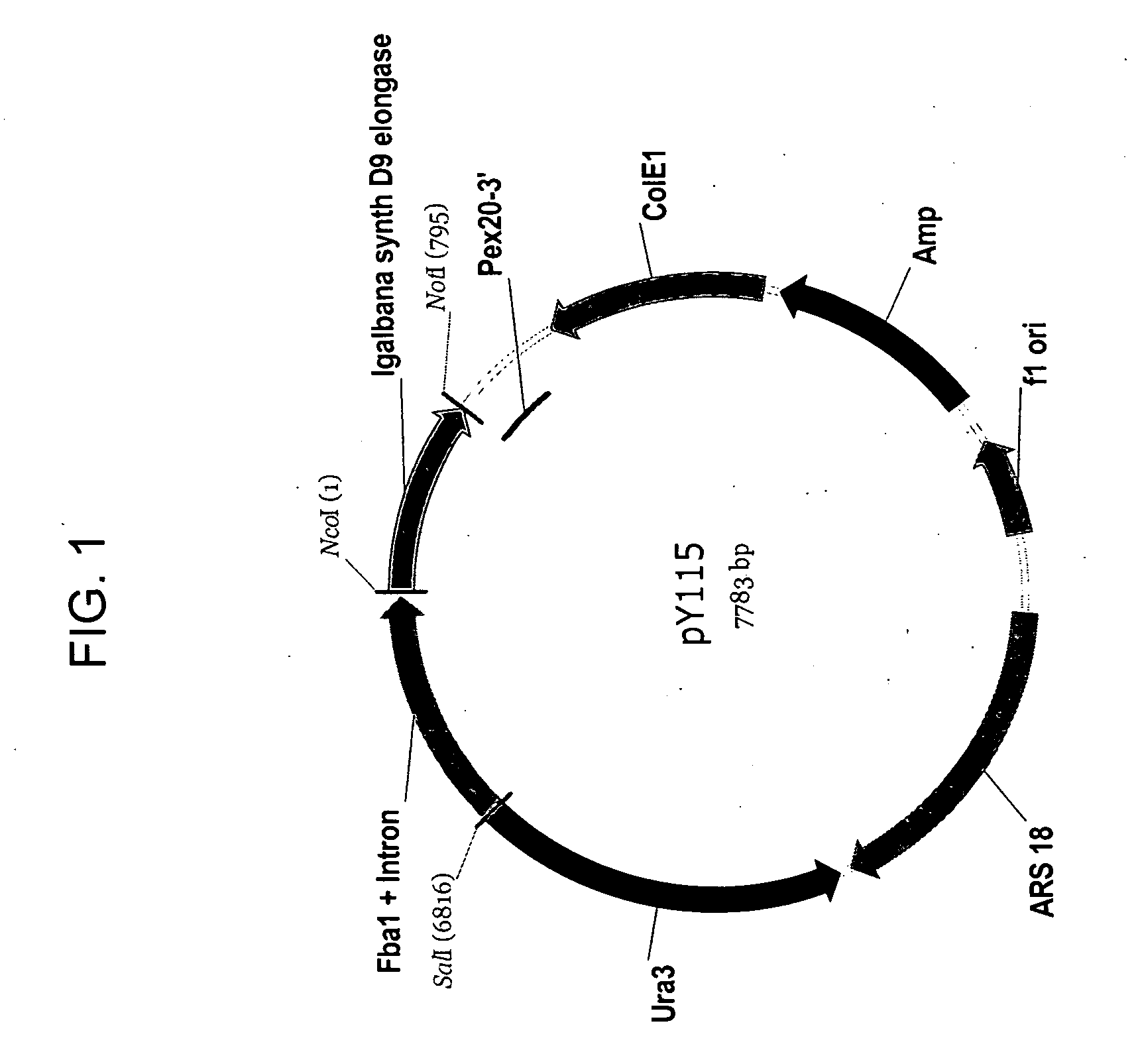
High eicosapentaenoic acid producing strains of Yarrowia lipolytica
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
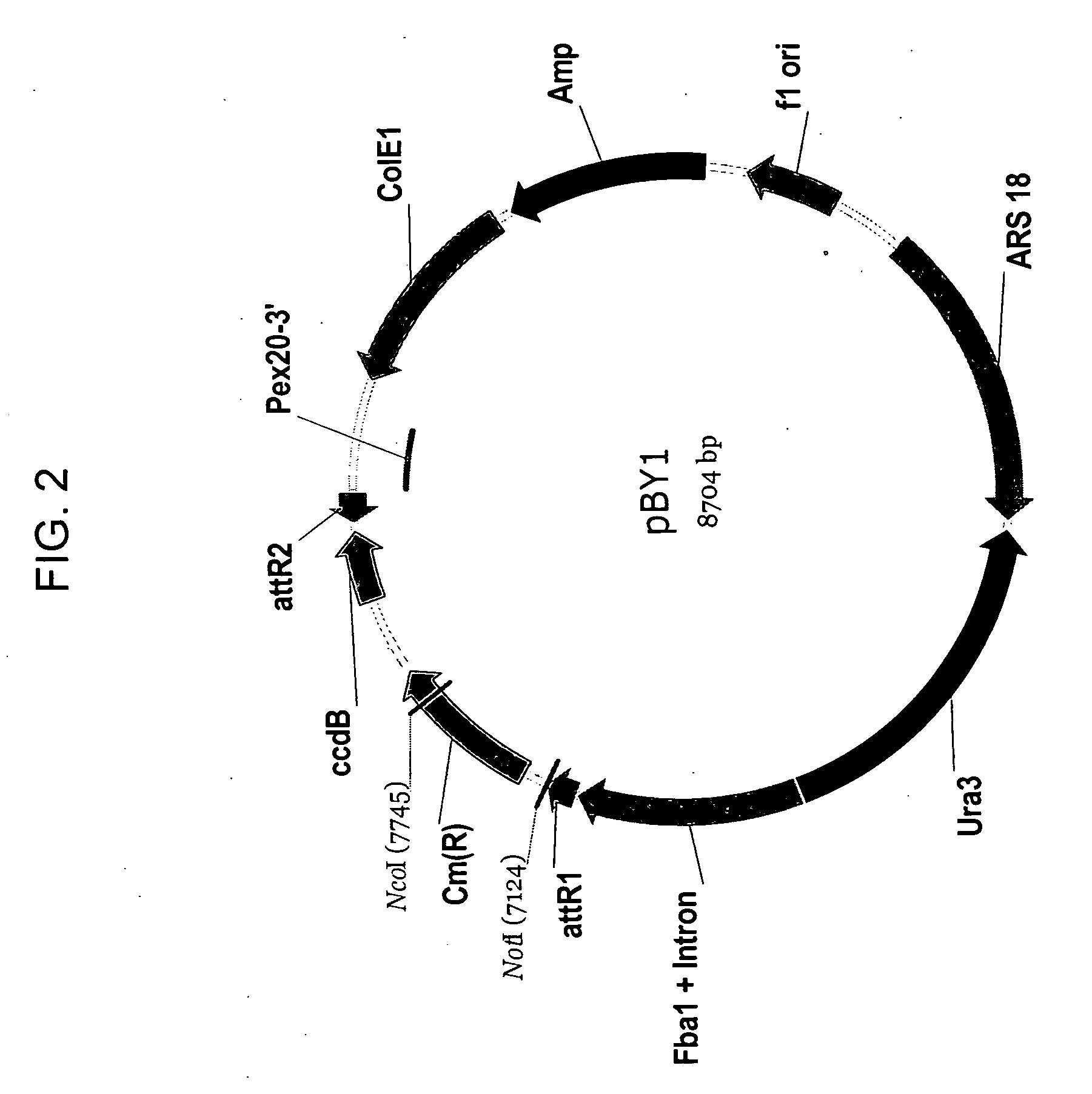
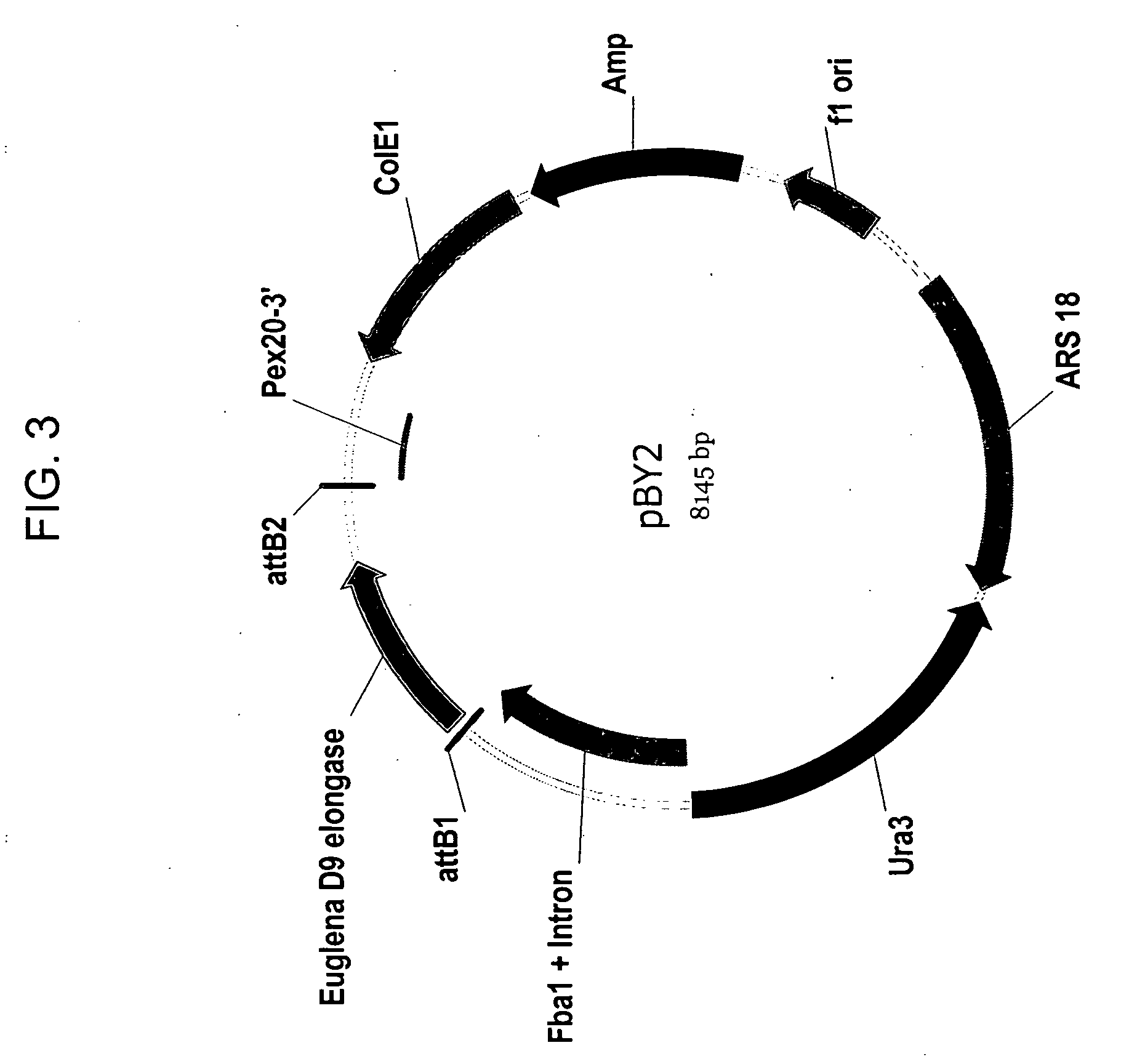
Codon-optimized genes for the production of polyunsaturated fatty acids in oleaginous yeasts
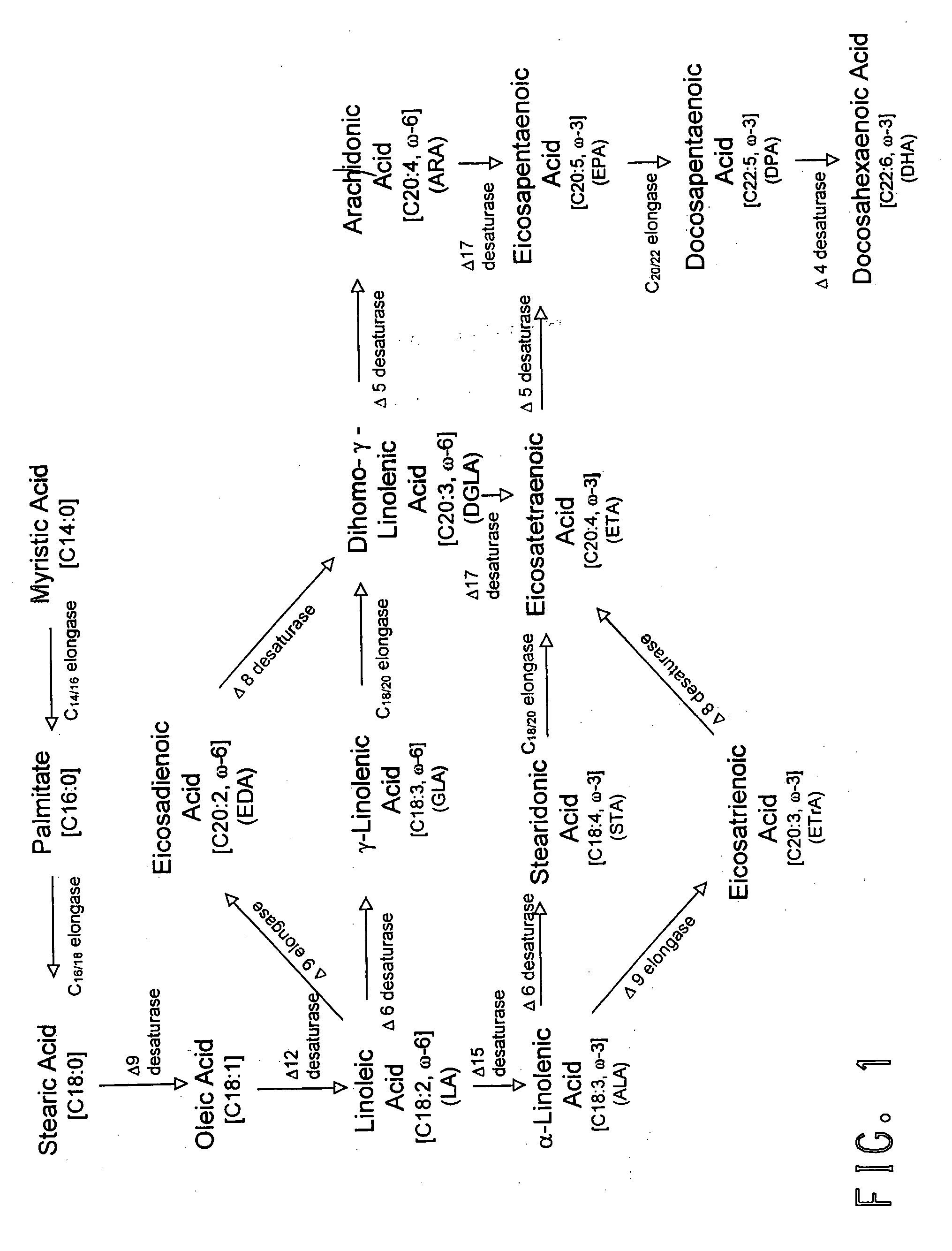
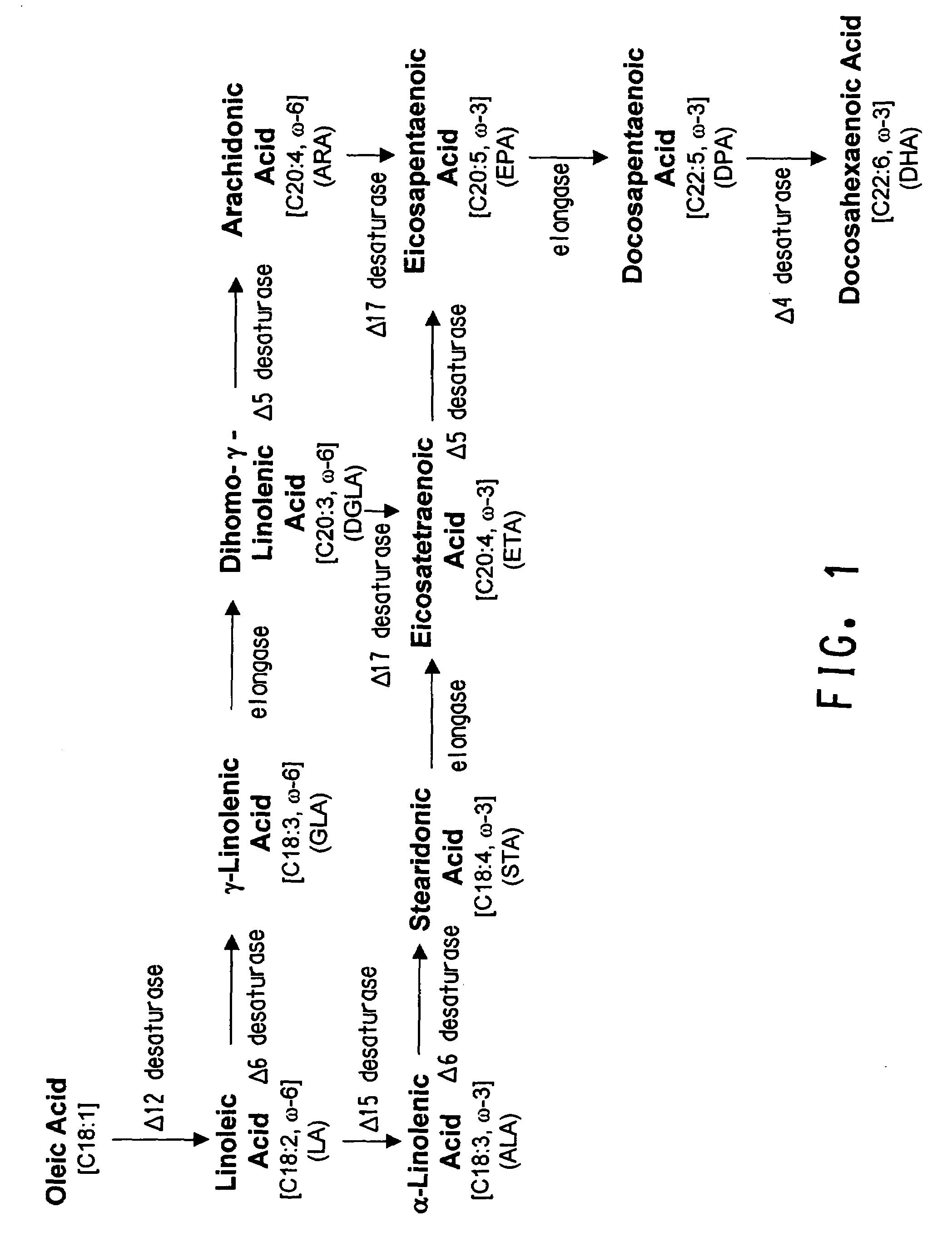
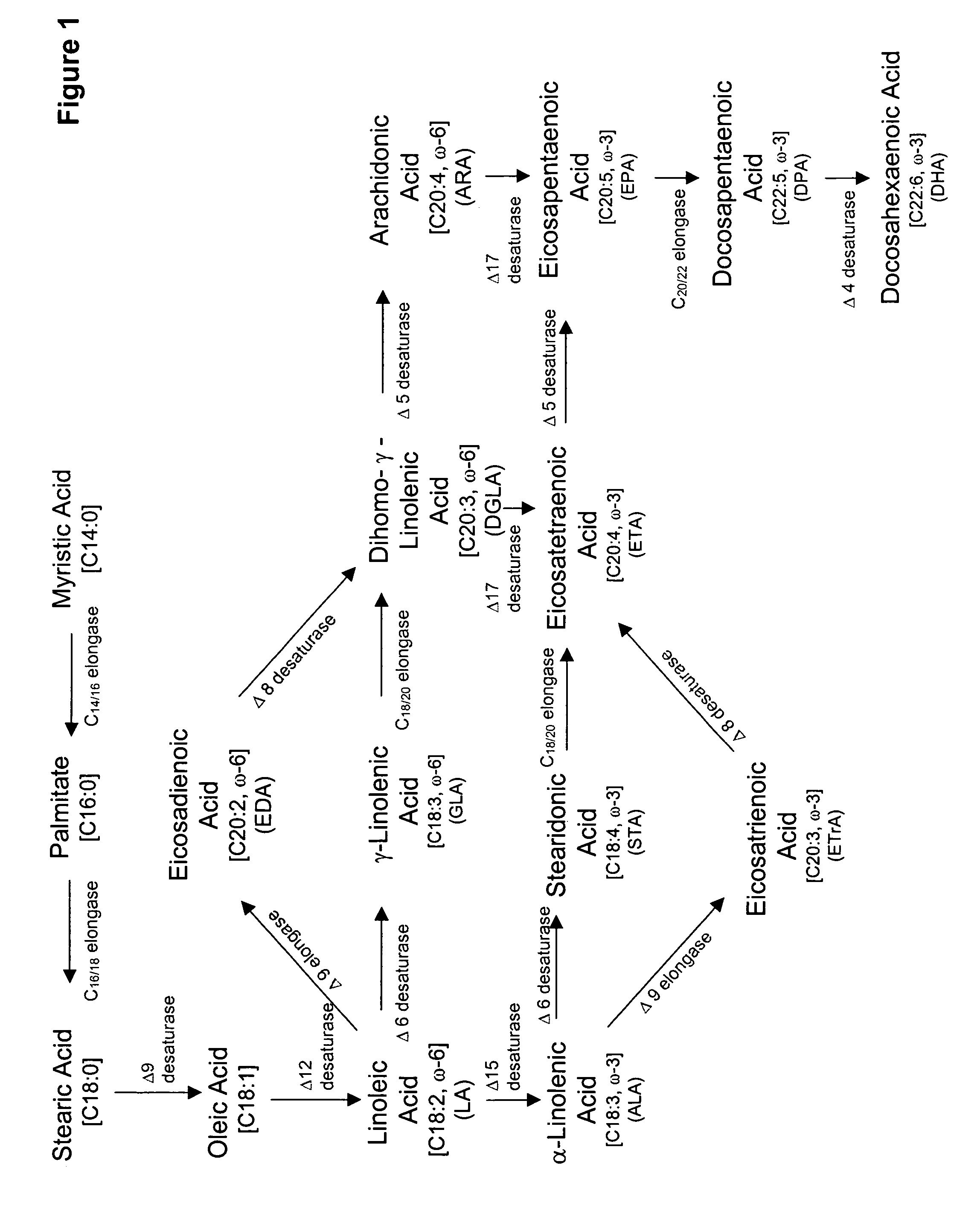
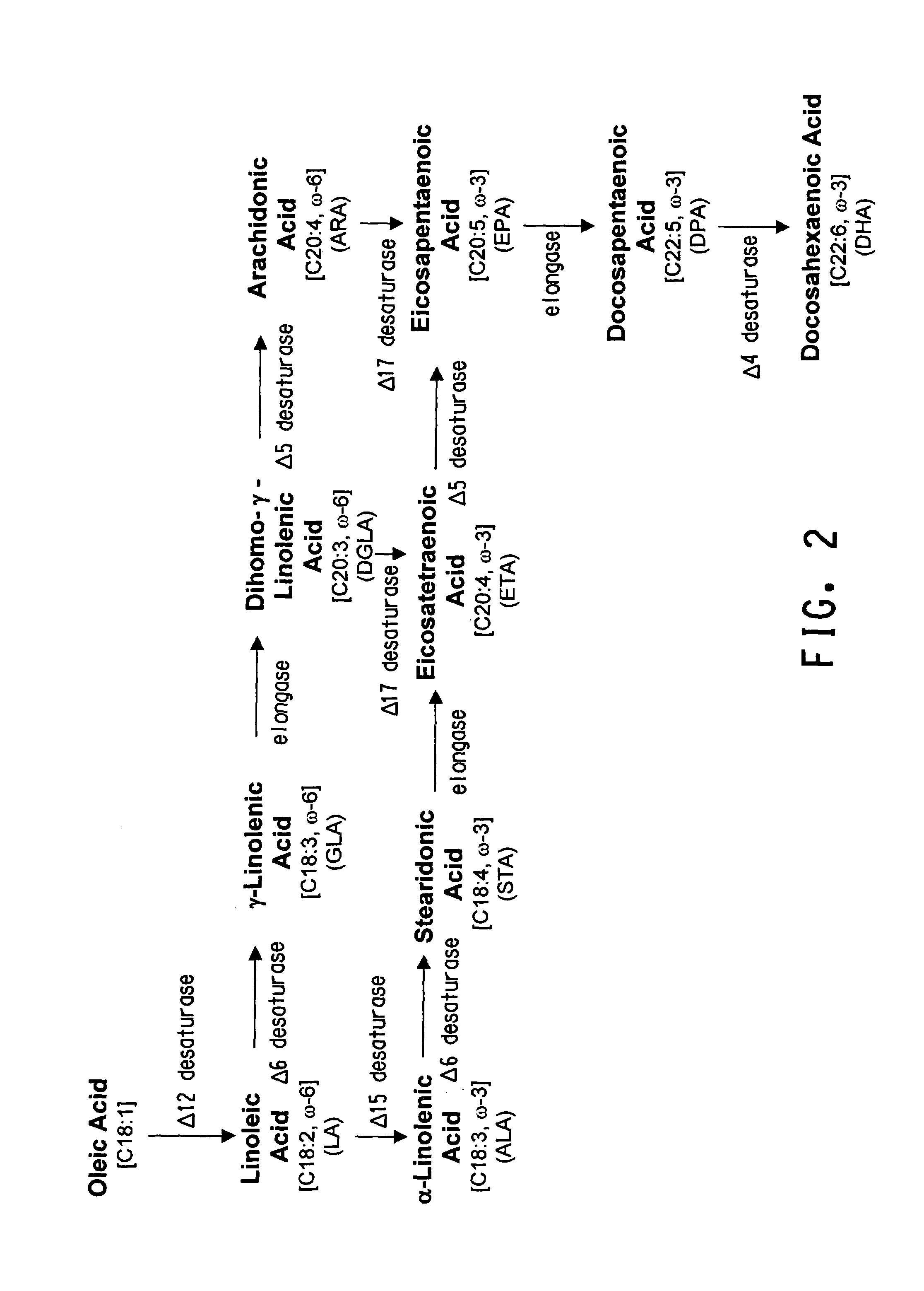
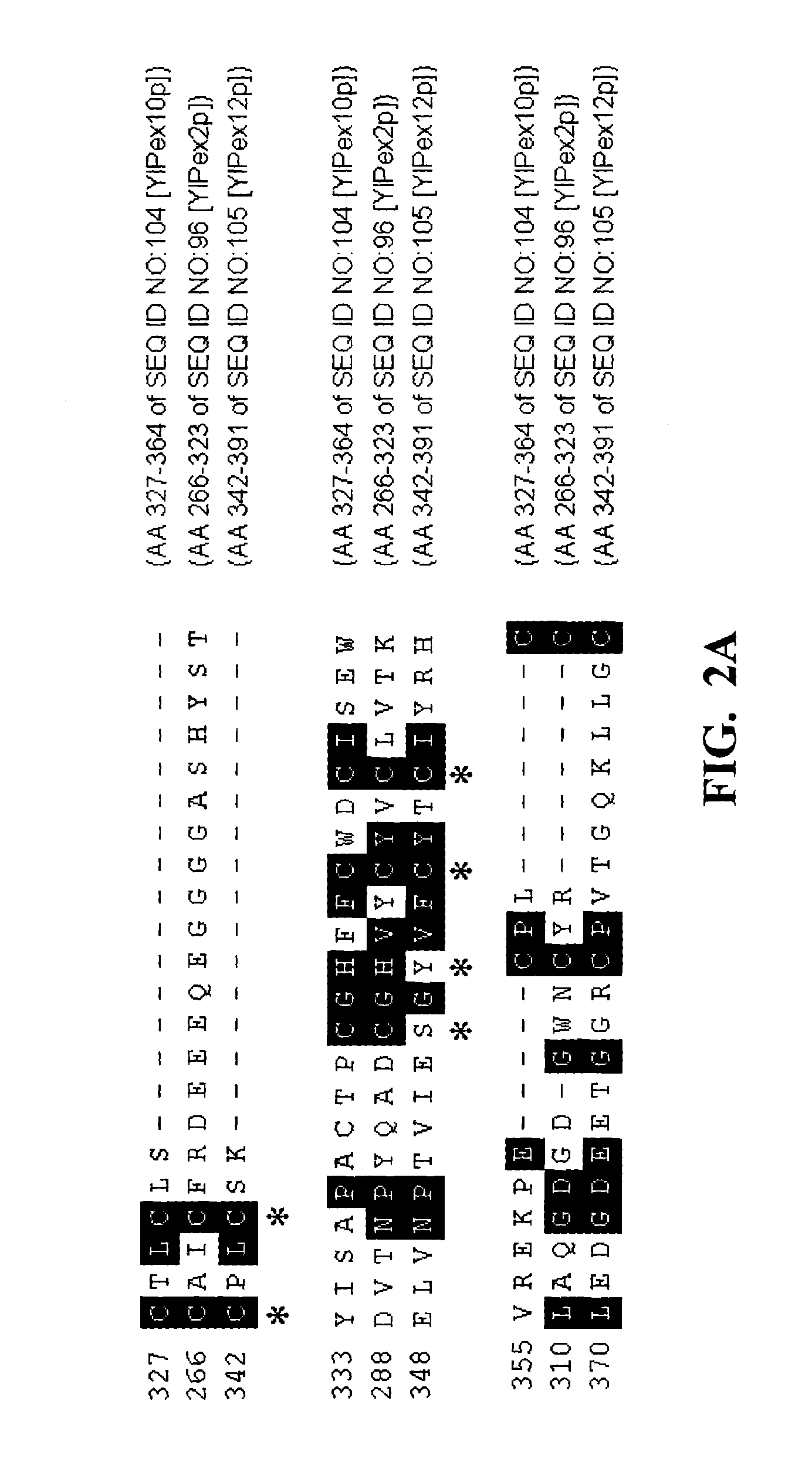
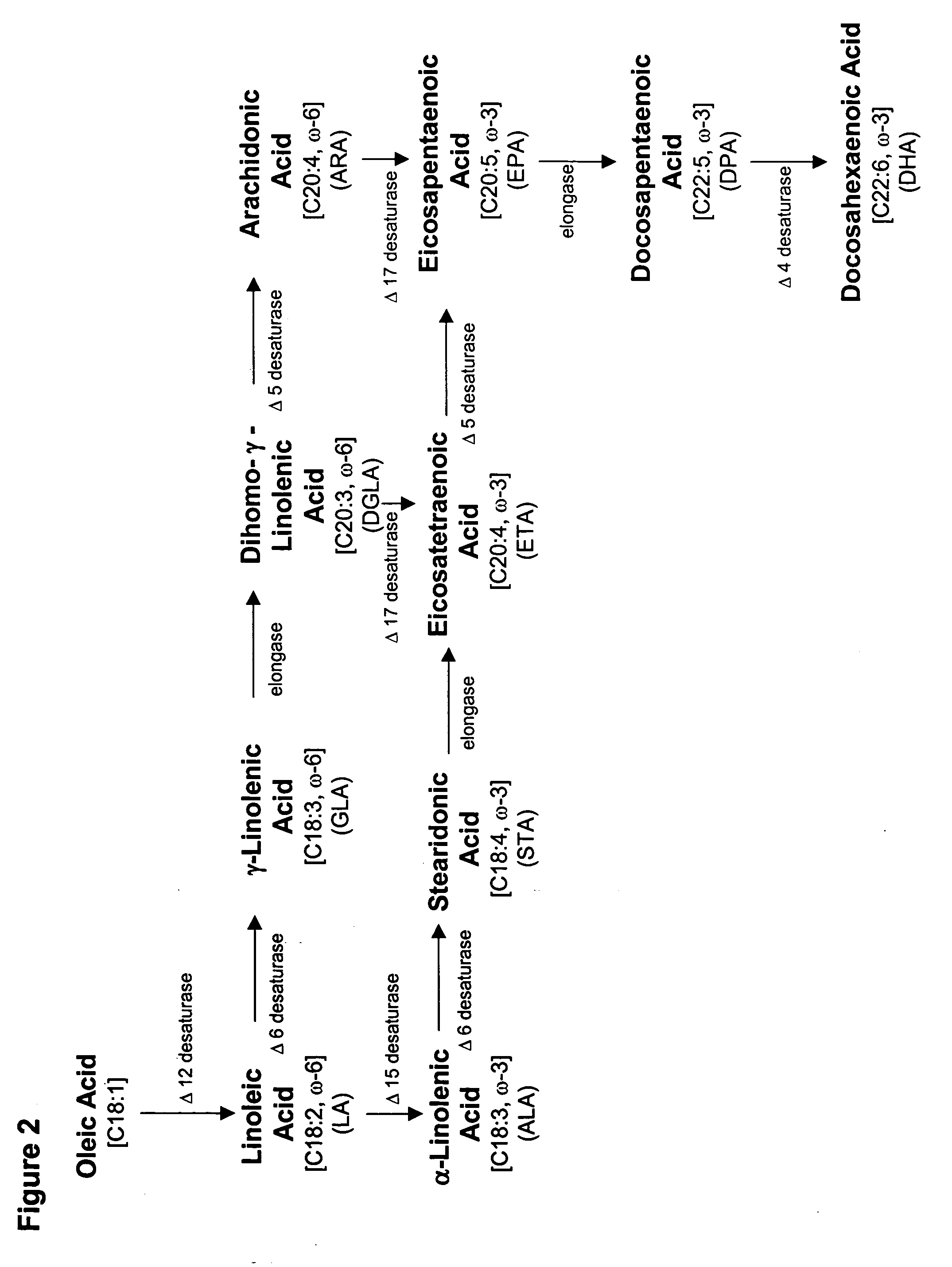
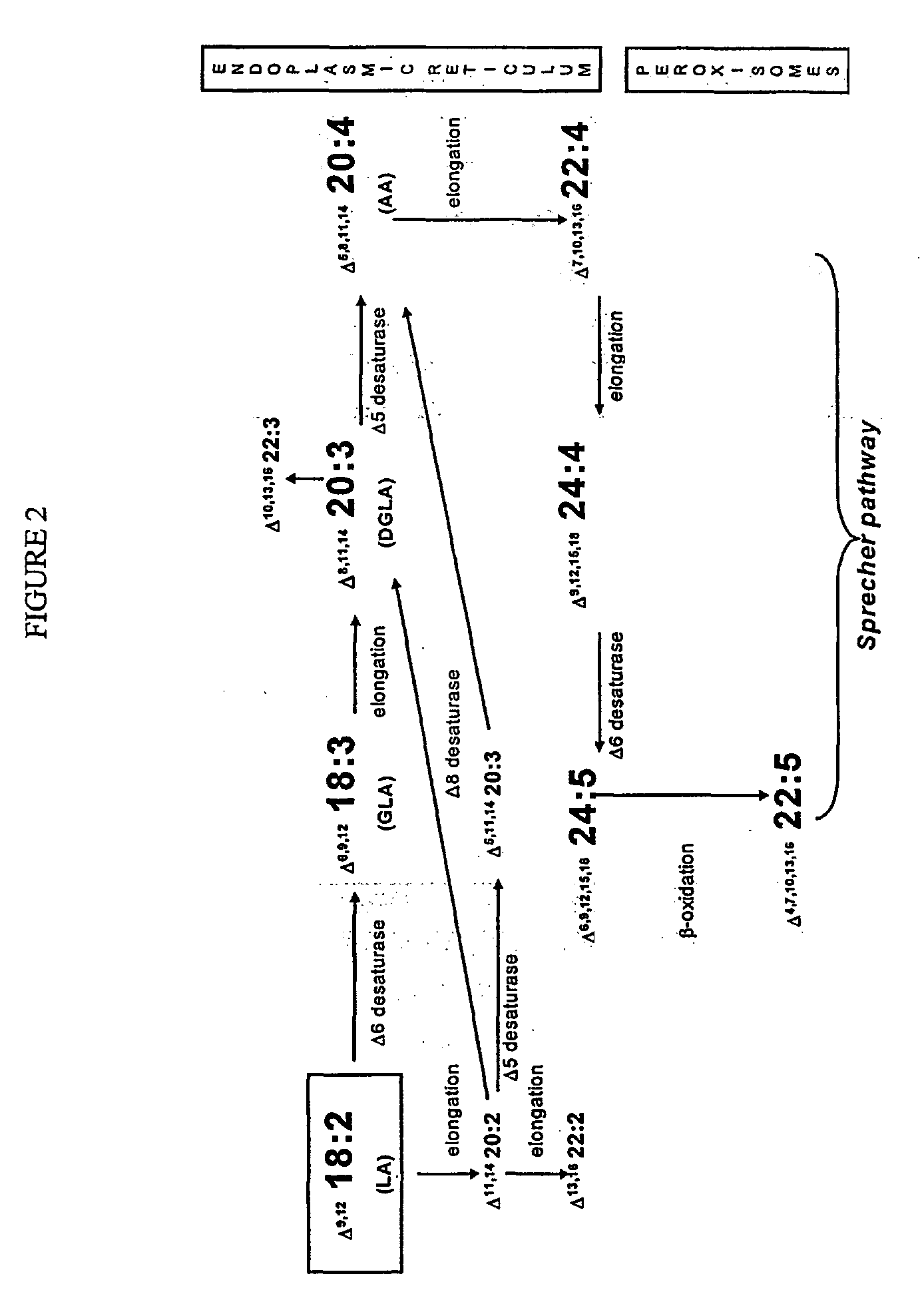
The present invention relates to fatty acid desaturases and elongases able to catalyze the conversion of linoleic acid (LA) to γ-linolenic acid (GLA); α-linoleic acid (ALA) to stearidonic acid (STA); GLA to dihomo-γ-linoleic acid (DGLA); STA to eicosatetraenoic acid (ETA); DGLA to ETA; eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) to docosapentaenoic acid (DPA); and arachidonic acid (ARA) to EPA. Nucleic acid sequences encoding codon-optimized desaturases and elongases, nucleic acid sequences which hybridize thereto, DNA constructs comprising the codon-optimized desaturase or elongases, and recombinant host microorganisms expressing increased levels of desaturase or elongase are described.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
High arachidonic acid producing strains of Yarrowia lipolytica
Engineered strains of the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica capable of producing greater than 10% arachidonic acid (ARA, an ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid) in the total oil fraction are described. These strains comprise various chimeric genes expressing heterologous desaturases, elongases and acyltransferases, and optionally comprise various native desaturase and acyltransferase knockouts to enable synthesis and high accumulation of ARA. Production host cells are claimed, as are methods for producing ARA within said host cells.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Docosahexaenoic acid producing strains of Yarrowia lipolytica
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Production of polyunsaturated fatty acids in oleaginous yeasts
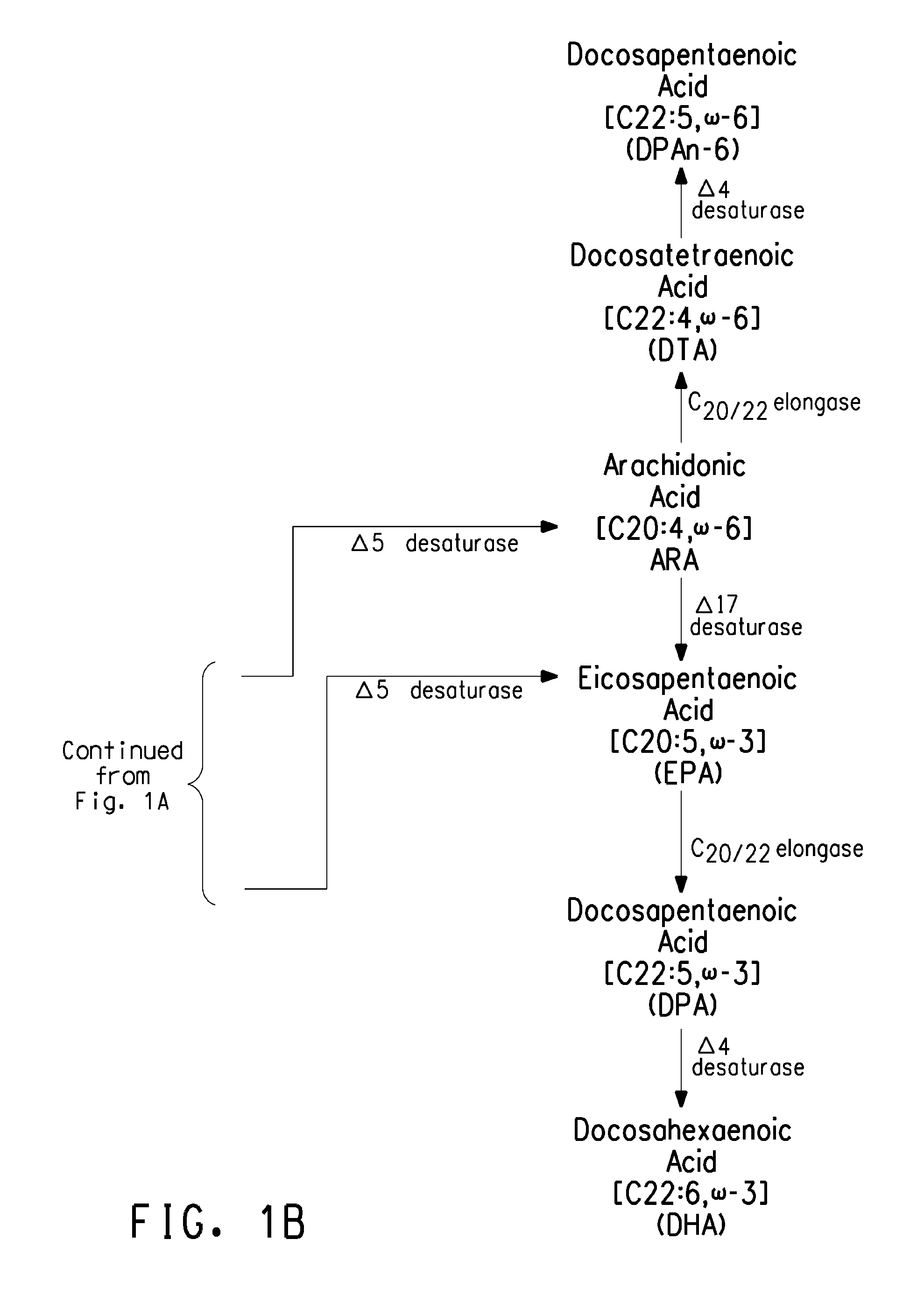
The present invention relates to methods for the production of ω-3 and / or ω-6 fatty acids in oleaginous yeast. Thus, desaturases and elongases able to catalyze the conversion of linoleic acid (LA) to γ-linolenic acid (GLA); α-linoleic acid (ALA) to stearidonic acid (STA); GLA to dihomo-γ-linoleic acid (DGLA); STA to eicosatetraenoic acid (ETA); DGLA to arachidonic acid (ARA); ETA to eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA); DGLA to ETA; EPA to docosapentaenoic acid (DPA); and ARA to EPA have been introduced into the genome of Yarrowia for synthesis of ARA and EPA.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Optimized strains of yarrowia lipolytica for high eicosapentaenoic acid production
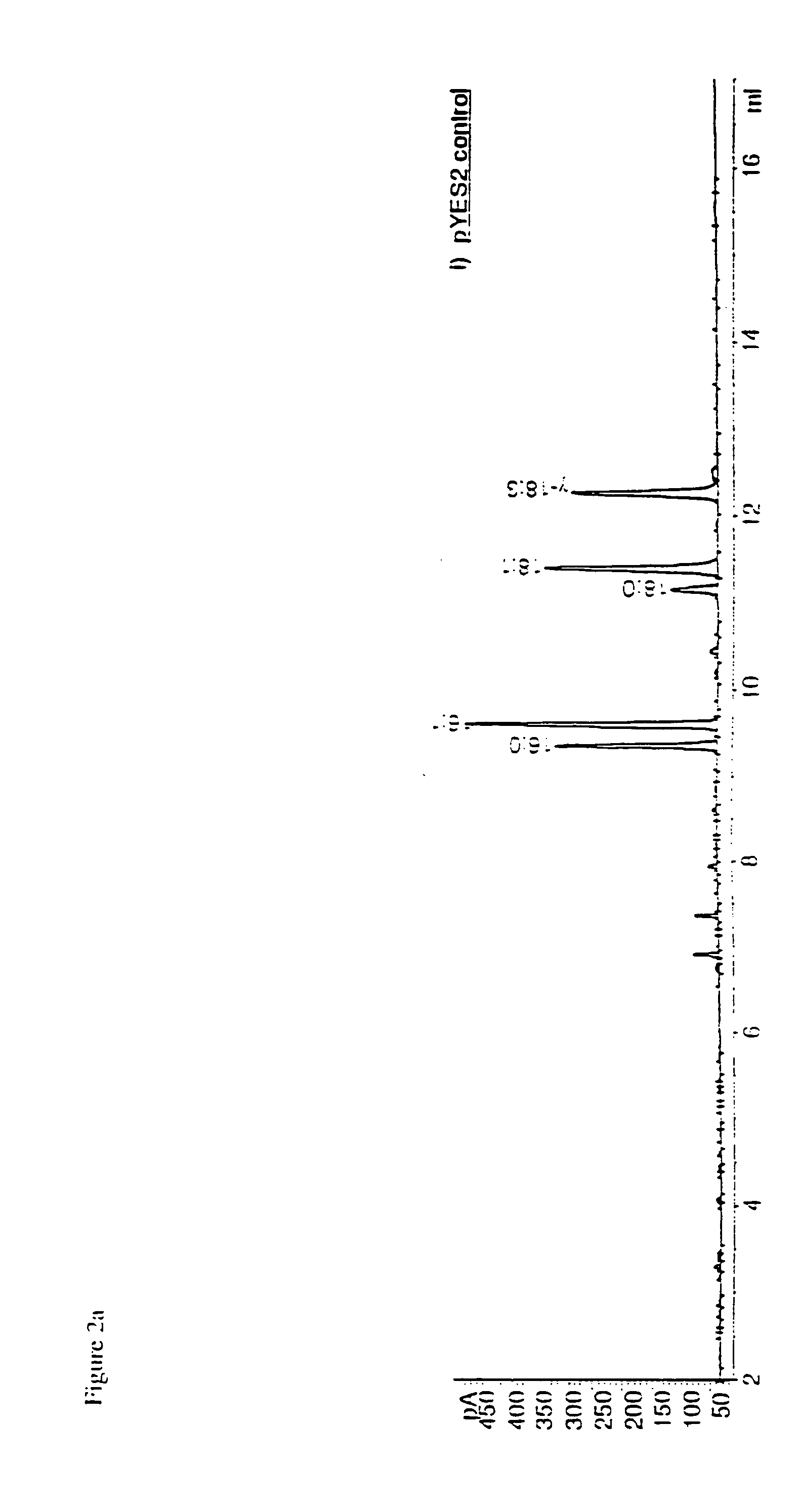
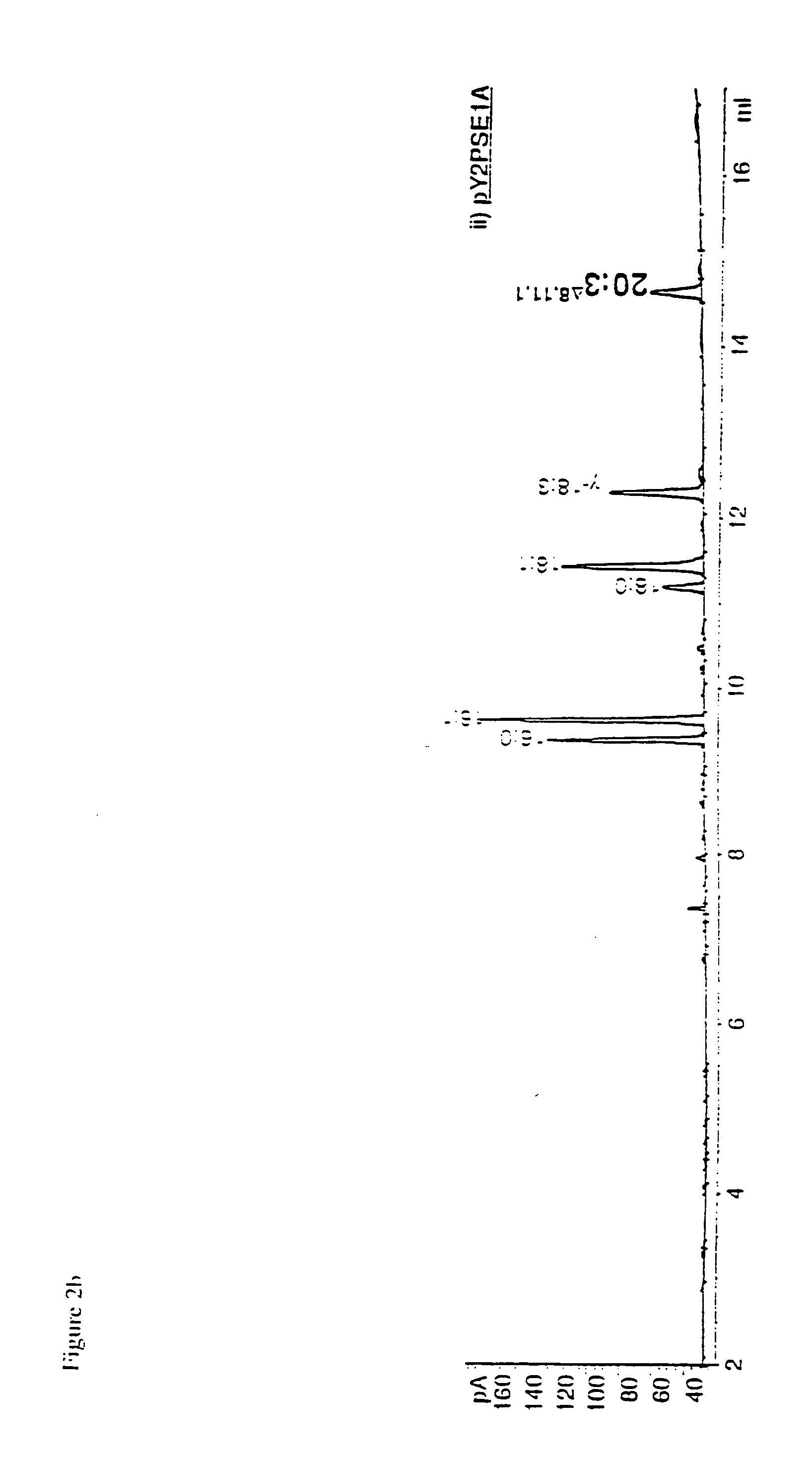
Engineered strains of the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica capable of producing greater than 50 weight percent of eicosapentaenoic acid [“EPA”], an ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid, in the total oil fraction are described. These strains over-express heterologous Δ9 elongases, Δ8 desaturases, Δ5 desaturases, Δ17 desaturases, Δ12 desaturases and C16 / 18 elongases, and optionally over-express diacylglycerol cholinephosphotransferases. Preferred gene knockouts are also described. Production host cells, methods for producing EPA within said host cells, and products comprising EPA from the optimized Yarrowia lipolytica strains are claimed.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
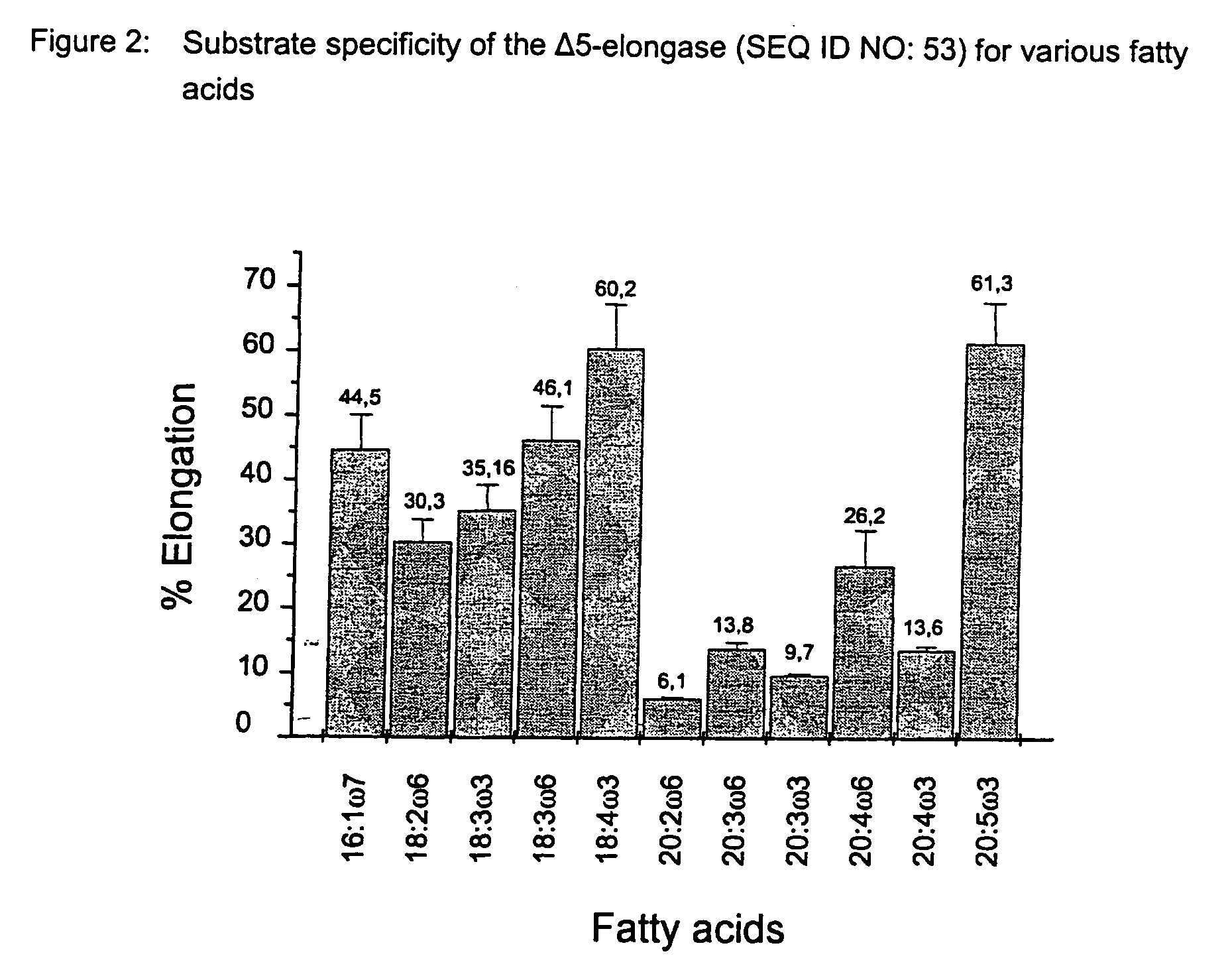
Novel elongase gene and method for producing multiple-unsaturated fatty acids
InactiveUS20040111763A1Improve efficiencyIncrease productionCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsElongaseTriacylglycerol VLDL
The invention relates to a novel elongase gene with the sequences stated in sequence SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 7 or their homologs, derivatives or analogs, to a gene construct comprising this gene or its homologs, derivatives and analogs, and to its use. The invention also relates to vectors or transgenic organisms comprising an elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 7 or its homologs, derivatives and analogs. The invention furthermore relates to the use of the elongase gene sequences alone or in combination with further elongases and / or further fatty acid biosynthesis genes. The present invention relates to a novel elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID NO:1 or its homologs, derivatives and analogs. Furthermore, the invention relates to a process for the preparation of polyunsaturated fatty acids and to a process for introducing DNA into organisms which produce large amounts of oils and, in particular, oils with a high content of unsaturated fatty acids. Moreover, the invention relates to an oil and / or a fatty acid preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds and / or a triacylglycerol preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds.
Owner:BASF AG
Delta-9 elongases and their use in making polyunsaturated fatty acids
Isolated nucleic acid fragments and recombinant constructs comprising such fragments encoding delta-9 elongases along with a method of making long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) using these delta-9 elongases in plants.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Elongase genes and uses thereof
The subject invention relates to the identification of several genes involved in the elongation of polyunsaturated acids (i.e., "elongases") and to uses thereof. At least two of these genes are also involved in the elongation of monounsaturated fatty acids. In particular, elongase is utilized in the conversion of gamma linolenic acid (GLA) to dihomogamma linolenic acid (DGLA) and in the conversion of AA to adrenic acid (ADA), or eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) to omega3-docosapentaenoic acid (DPA). DGLA may be utilized in the production of polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as arachidonic acid (AA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), EPA, adrenic acid, omega6-docosapentaenoic acid or omega3-docosapentaenoic acid which may be added to pharmaceutical compositions, nutritional compositions, animal feeds, as well as other products such as cosmetics.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Production of polyunsaturated fatty acids in oleaginous yeasts
The present invention relates to methods for the production of ω-3 and / or ω-6 fatty acids in oleaginous yeast. Thus, desaturases and elongases able to catalyze the conversion of linoleic acid (LA) to γ-linolenic acid (GLA); α-linoleic acid (ALA) to stearidonic acid (STA); GLA to dihomo-γ-linoleic acid (DGLA); STA to eicosatetraenoic acid (ETA); DGLA to arachidonic acid (ARA); ETA to eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA); DGLA to ETA; EPA to docosapentaenoic acid (DPA); and ARA to EPA have been introduced into the genome of Yarrowia for synthesis of ARA and EPA.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
Elongase genes and uses thereof
The subject invention relates to the identification of four genes involved in the elongation of polyunsaturated acids (i.e., “elongases”) and to uses thereof. Two of these genes are also involved in the elongation of monounsaturated fatty acids. In particular, elongase is utilized in the conversion of gamma linolenic acid (GLA) to dihomogamma linolenic acid (DGLA) and in the conversion of DGLA or 20:4n-3 to eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). DGLA may be utilized in the production of polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as arachidonic acid (AA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), EPA, adrenic acid, ω6-docosapentaenoic acid or ω3-docosapentaenoic acid which may be added to pharmaceutical compositions, nutritional compositions, animal feeds, as well as other products such as cosmetics.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Elongase gene and production of delta9-polyunsaturated fatty acids
This invention relates to a new elongase gene having the sequence SEQ ID NO: 1 or its derivatives, to a gene construct comprising this sequence or its derivatives and to its use. The inventive nucleic acid sequence encodes a polypeptide which elongates α-linolenic acid (C18:3 d9, 12, 15) by at least two carbon atoms whereas γ-linolenic acid (C18:3 d6, 9, 12) is not elongated. The invention additionally relates to vectors or organisms comprising an elongase gene having the sequence SEQ ID NO: 1 or its derivatives. The invention further relates to a process for the production of polyunsaturated fatty acids (=PUFAs) with an organism which comprises the elongase gene and which organism produces high amounts of oils and especially oils with a high content of unsaturated fatty acids. Additionally the invention relates to an oil and / or fatty acid composition with a higher content of polyunsaturated C20 or C22 fatty acids with at least two double bonds and / or to a triacylglycerol composition with a higher content of said polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Owner:UNIV OF BRISTOL
Novel elongase gene, and process for the preparation of polyunsaturated fatty acids
InactiveUS20080160054A1Improve efficiencyIncrease productionOrganic active ingredientsFatty acid chemical modificationBiotechnologyFatty acid biosynthesis
The invention relates to a novel elongase gene with the sequences stated in sequence SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 7 or their homologs, derivatives or analogs, to a gene construct comprising this gene or its homologs, derivatives and analogs, and to its use. The invention also relates to vectors or transgenic organisms comprising an elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 7 or its homologs, derivatives and analogs. The invention furthermore relates to the use of the elongase gene sequences alone or in combination with further elongases and / or further fatty acid biosynthesis genes. The present invention relates to a novel elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID NO:1 or its homologs, derivatives and analogs.Furthermore, the invention relates to a process for the preparation of polyunsaturated fatty acids and to a process for introducing DNA into organisms which produce large amounts of oils and, in particular, oils with a high content of unsaturated fatty acids. Moreover, the invention relates to an oil and / or a fatty acid preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds and / or a triacylglycerol preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds.
Owner:BASF AG
Elongase genes and uses thereof
The subject invention relates to the identification of several genes involved in the elongation of polyunsaturated acids (i.e., "elongases") and to uses thereof. At least two of these genes are also involved in the elongation of monounsaturated fatty acids. In particular, elongase is utilized in the conversion of gamma linolenic acid (GLA) to dihomogamma linolenic acid (DGLA) and in the conversion of AA to adrenic acid (ADA), or eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) to omega3-docosapentaenoic acid (DPA). DGLA may be utilized in the production of polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as arachidonic acid (AA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), EPA, adrenic acid, omega6-docosapentaenoic acid or omega3-docosapentaenoic acid which may be added to pharmaceutical compositions, nutritional compositions, animal feeds, as well as other products such as cosmetics.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Elongase genes and uses thereof
The subject invention relates to the identification of several genes involved in the elongation of polyunsaturated acids (i.e., “elongases”) and to uses thereof. At least two of these genes are also involved in the elongation of monounsaturated fatty acids. In particular, elongase is utilized in the conversion of gamma linolenic acid (GLA) to dihomogama linolenic acid (DGLA) and in the conversion of DGLA or 20:4n-3 to eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA). DGLA may be utilized in the production of polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as arachiodonic acid (AA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), EPA, adrenic acid, ω6-docosapentaenoic acid or ω3-docosapentaenoic acid which may be added to pharmaceutical compositions, nutritional compositions, animal feeds, as well as other products such as cosmetics.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Marchantiales-Derived Unsaturated Fatty Acid Synthetase Genes And Use Of The Same
InactiveUS20080057495A1ImmunoglobulinsOxidoreductasesUnsaturated fatty acid synthesisEicosapentaenoic acid
A Δ5 fatty acid desaturase gene, a Δ6 fatty acid desaturase gene, and a Δ6 fatty-acid-chain elongase gene are isolated from a single species of Marchantiales. By introducing these genes into higher plants, transformed plants which can produce arachidonic acid and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) are obtained.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Novel delta9-elongase for production of polyunsaturated fatty acid-enriched oils
The present disclosure relates to isolated polynucleotides encoding a delta 9-elongase, delta 9-elongases encoded by the isolated polynucleotides, expression vectors comprising the isolated polynucleotides, host cells comprising the expression vectors, and methods for producing delta 9-elongase and polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Elongase gene and method for producing polyunsaturated fatty acids
InactiveUS7179647B2High trafficImprove abilitiesCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsBiological bodyBiotechnology
The invention relates to a novel elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID NO: 1 or its homologs, derivatives or analogs, to a gene construct comprising this gene or its homologs, derivatives and analogs, and to its use. The invention also relates to vectors or organisms comprising an elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID No: 1 or its homologs, derivatives or analogs. Furthermore, the invention relates to a process for the preparation of polyunsaturated fatty acids and to a process for introducing DNA into organisms which produce large amounts of oils and, in particular, oils with a high content of unsaturated fatty acids. Moreover, the invention relates to an oil and / or a fatty acid preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds and / or a triacyiglycerol preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Human elongase genes and uses thereof
The present invention relates to elongase genes, their polypeptides and their control regions, and the use of such genes, polypeptides and control regions in determining compositions for use in the treatment of disease. The identified compositions regulate the expression of the elongase genes or modulate the activity of their protein products. The nucleotide and amino acid sequences are taught for ELG4, ELG6 and ELG7. The control sequences and function are taught for ELG1, ELG2, ELG3, ELG4, ELG5, ELG6 and ELG7.
Owner:XENON PHARMACEUTICALS INC +1
Elongase Gene and Uses Thereof
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
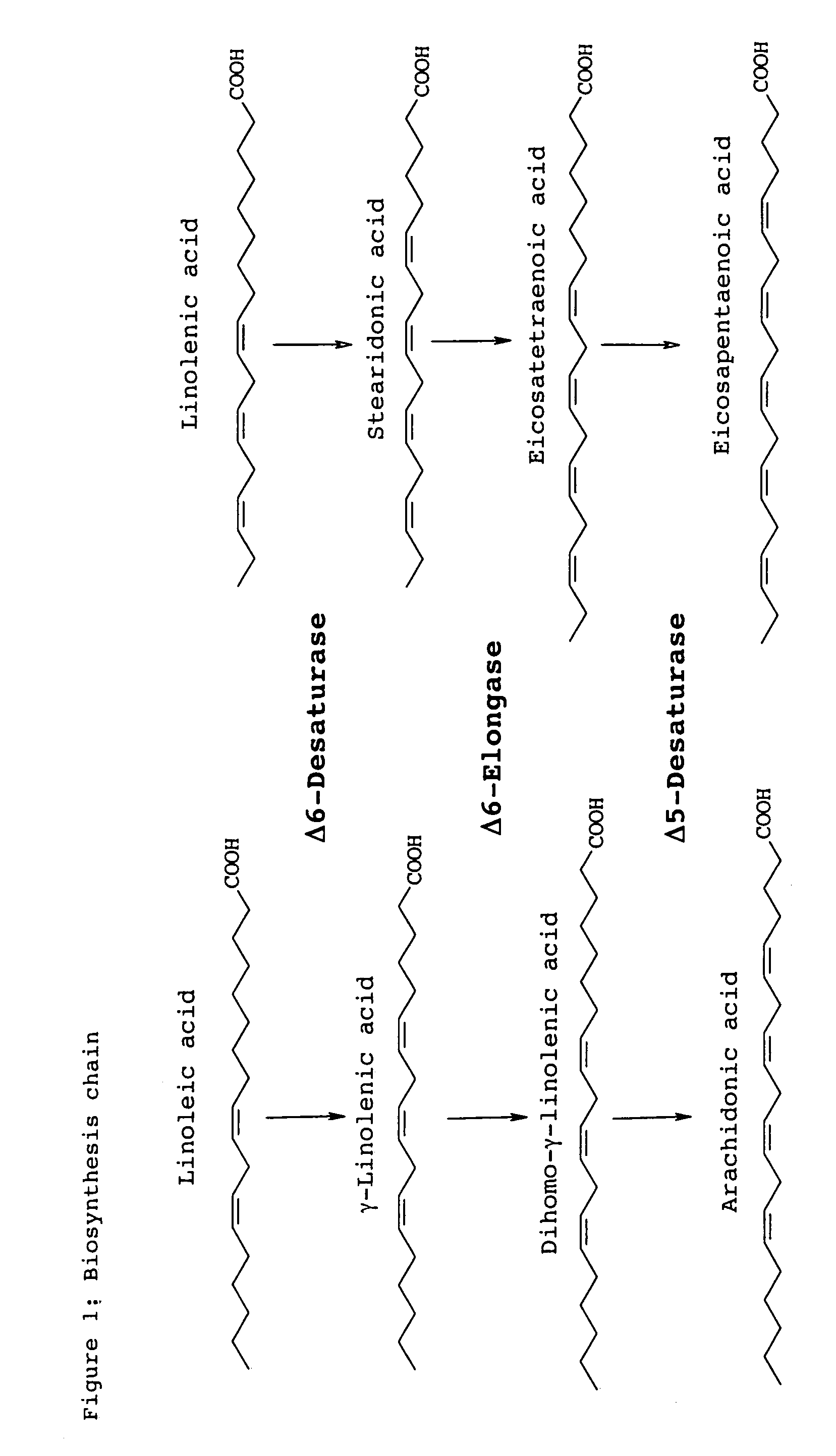
Method for producing arachidonic acid and/or eicosapentaenoic acid in useful transgenic plants
InactiveUS8134046B2Simple and inexpensive and economicalHigh nutritional valueCosmetic preparationsBiocideBiotechnologyTransgene
The present invention relates to a process for producing arachidonic acid and / or eicosapentaenoic acid in transgenic useful plants by introducing into the plant nucleic acids coding for polypeptides having Δ6-desaturase, Δ6-elongase or Δ5-desaturase activity. Furthermore, a gene coding for an ω3-desaturase is advantageously expressed in said useful plants. In another advantageous embodiment of the process, further nucleic acid sequences coding for polypeptides of fatty acid or lipid metabolism biosynthesis may be expressed in the plants. Particularly advantageous nucleic acid sequences here are those coding for a Δ8-desaturase, Δ12-desaturase, Δ15-desaturase, Δ4-desaturase, Δ9-elongase and / or Δ5-elongase activity.The invention further relates to the use of the oils, lipids and / or fatty acids produced in the process according to the invention in feedstuffs or foodstuffs, cosmetics or pharmaceuticals.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Elongase gene and uses thereof
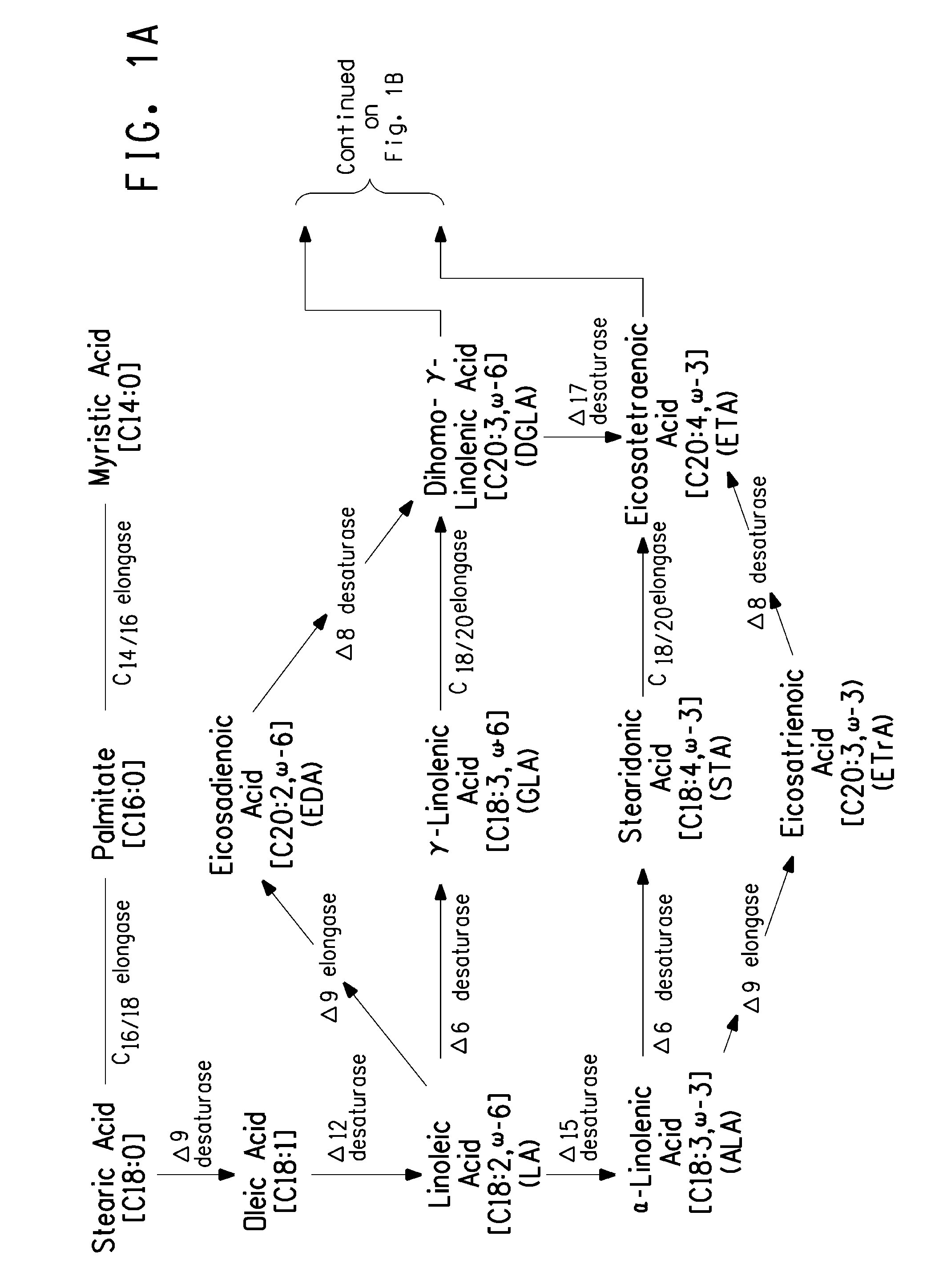
The subject invention relates to the identification of a gene involved in the elongation of polyunsaturated fatty acids containing unsaturation at the carbon 9 position (i.e., “Δ9-elongase”) and to uses thereof. In particular, Δ9-elongase may be utilized, for example, in the conversion of linoleic acid (LA, 18:2n-6) to eicosadienoic acid (EDA, 20:2n-6). The production of dihomo-γ-linolenic acid (DGLA, 20:3n-6) from eicosadienoic acid (EDA, 20:2n-6), and arachidonic acid (AA, 20:4n-6) from dihomo-γ-linolenic acid (DGLA, 20:3n-6) is then catalyzed by Δ8-desaturase and Δ5-desaturase, respectively. AA or polyunsaturated fatty acids produced therefrom may be added to pharmaceutical compositions, nutritional compositions, animal feeds, as well as other products such as cosmetics.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Elongase gene and production of Delta9-polyunsaturated fatty acids
This invention relates to a new elongase gene having the sequence SEQ ID NO: 1 or its derivatives, to a gene construct comprising this sequence or its derivatives and to its use. The inventive nucleic acid sequence encodes a polypeptide which elongates α-linolenic acid (C18:3 d9, 12, 15) by at least two carbon atoms whereas γ-linolenic acid (C18:3 d6, 9, 12) is not elongated. The invention additionally relates to vectors or organisms comprising an elongase gene having the sequence SEQ ID NO: 1 or its derivatives.The invention further relates to a process for the production of polyunsaturated fatty acids (=PUFAs) with an organism which comprises the elongase gene and which organism produces high amounts of oils and especially oils with a high content of unsaturated fatty acids. Additionally the invention relates to an oil and / or fatty acid composition with a higher content of polyunsaturated C20 or C22 fatty acids with at least two double bonds and / or to a triacylglycerol composition with a higher content of said polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Owner:UNIV OF BRISTOL
Novel method for the production of polyunsaturated fatty acids
The present invention relates to an improved process for the specific production of poly-unsaturated omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids and a process for the production of triglycerides having an increased content of unsaturated fatty acids, in particular omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids having at least two double bonds and a 20 or 22 carbon atom chain length. The invention relates to the produc-tion of a transgenic organism, preferably a transgenic plant or a transgenic microorganism, hav-ing an increased content of fatty acids, oils or lipids containing C20- or C22- fatty acids with a delta-5, 7, 8, 10 double bond, respectively due to the expression of a delta-8-desaturase and a delta-9- elon-gase from organisms such as plants preferably Algae like Isochrysis galbana or Euglena gracilis. In addition the invention relates to a process for the production of poly unsaturated fatty acids such as Eicosapentaenoic, Arachidonic, Docosapentaenoic or Docosahexaenoic acid through the co- expression of a delta -8-desaturase, a delta-9-elongase and a delta-5 desaturase in organisms such as microorganisms or plants.The invention additionally relates to the use of specific nucleic acid sequences encoding for the aforementioned proteins with delta-8-desaturase-, delta-9-elongase- or delta-5-desaturase-activity, nucleic acid constructs, vectors and organisms containing said nucleic acid sequences. The invention further relates to unsaturated fatty acids and triglycerides having an increased content of at least 1 % by weight of unsaturated fatty acids and use thereof.
Owner:UNIV OF BRISTOL
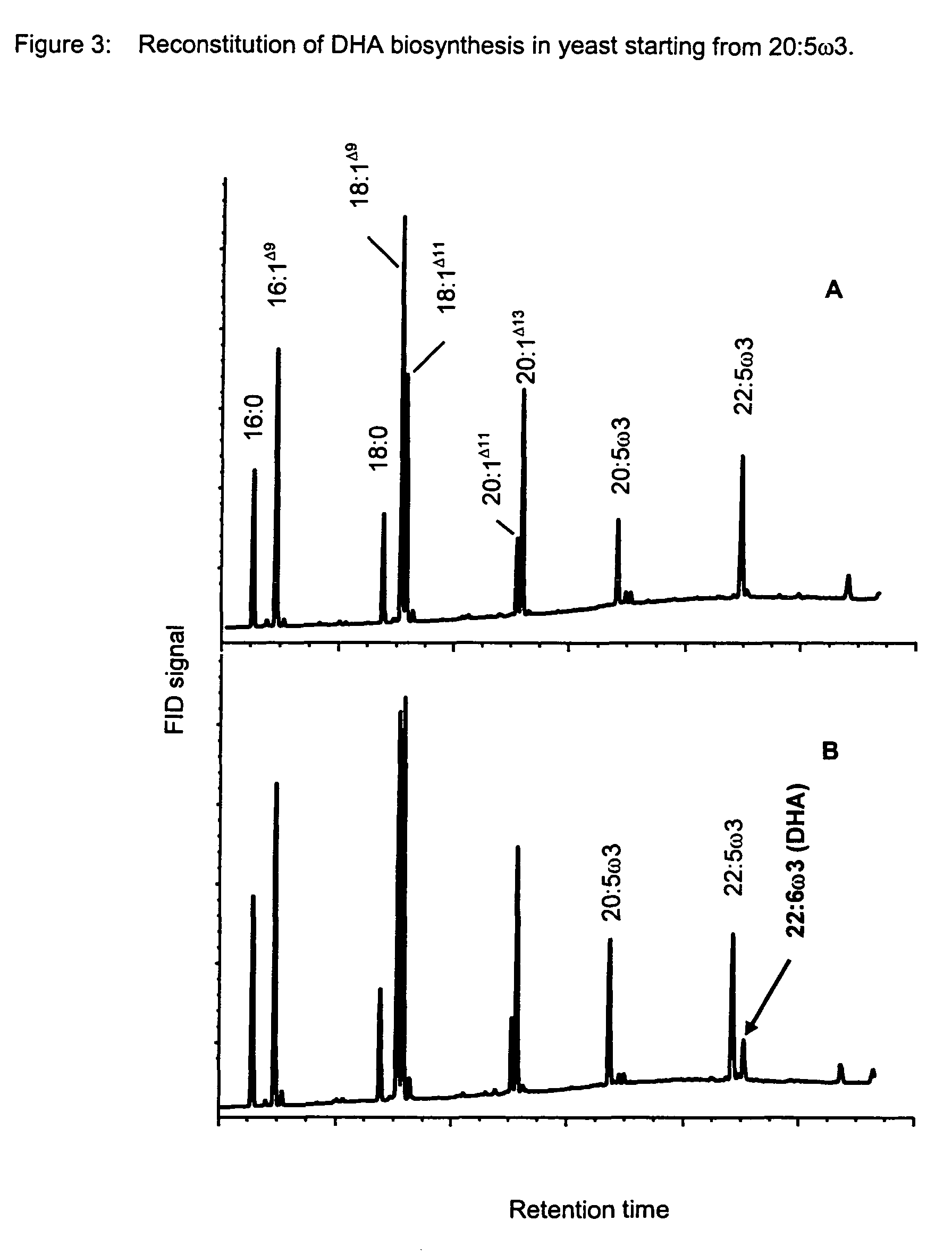
Method for the production of multiple-unsaturated fatty acids in transgenic organisms
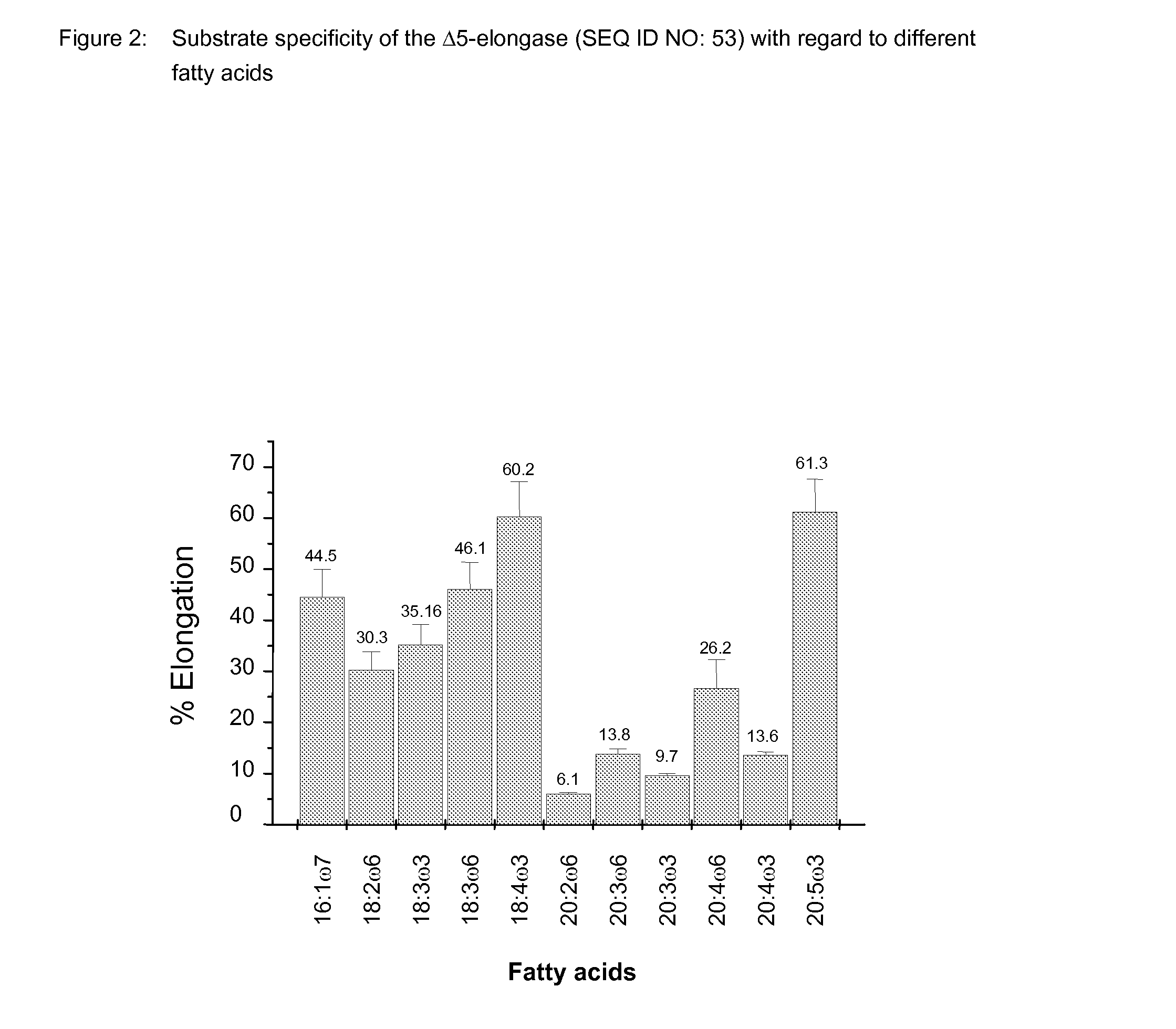
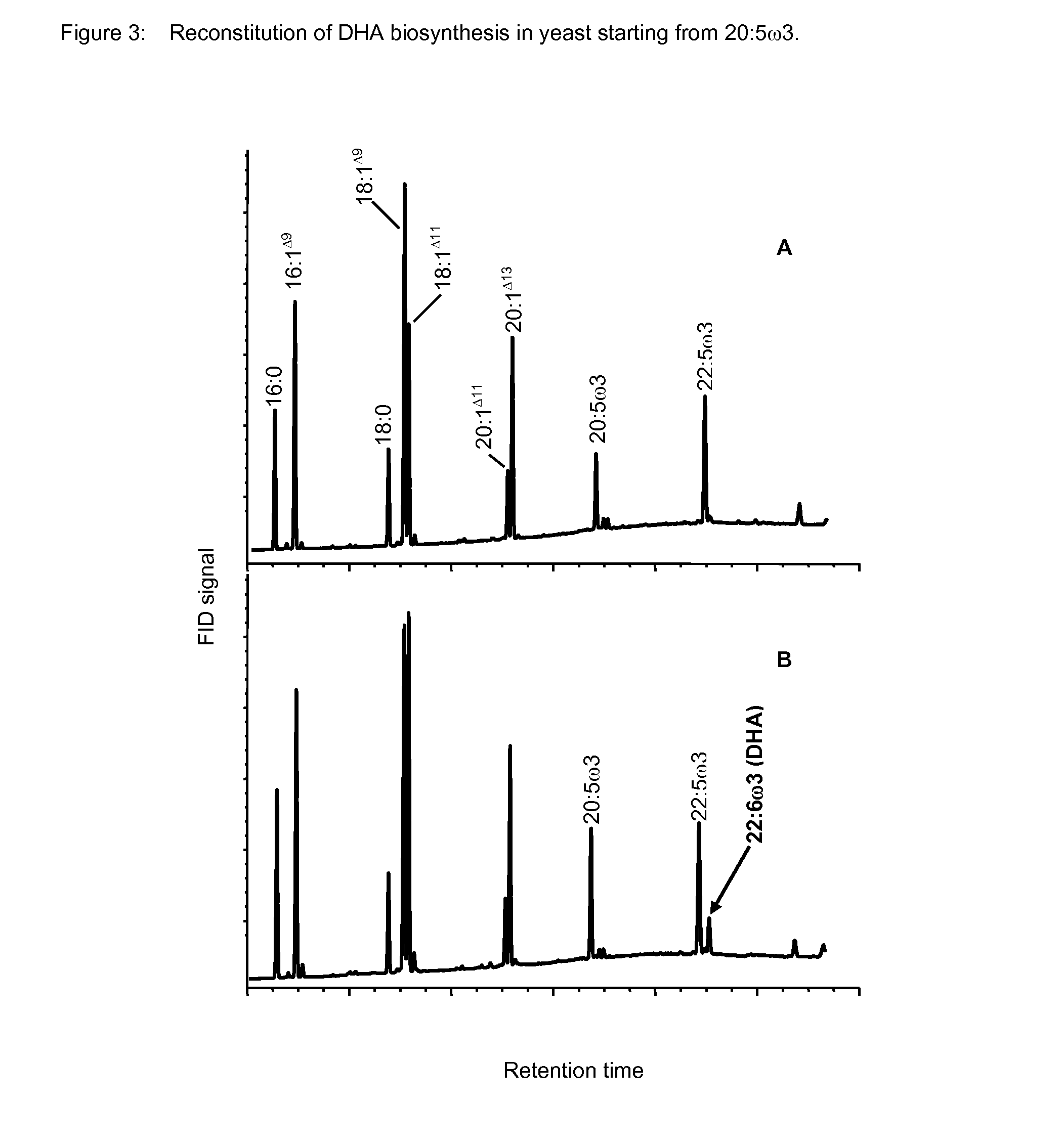
The invention relates to a method for the production of multiply-unsaturated fatty acids in an organism, into which nucleic acids have been introduced, which code for polypeptides with Δ-5 elongase activity. Said nucleic acid sequences, optionally with further nucleic acid sequences, coding for polypeptides for the biosynthesis of fatty acids and lipid metabolism, are advantageously expressed in the organism. Nucleic acid sequences coding for a Δ-6 desaturase, a Δ-5 desaturase, Δ-4 desaturase and / or Δ-6 elongase activity are particularly advantageous and, advantageously, said saturases and elongases are derived from Thalassiosira, Euglena or Ostreococcus. The invention further relates to a method for the production of oils and / or triacylglycerides with an increased content of long-chain, multiply-unsaturated fatty acids. A particular embodiment of the invention is a method for the production of unsaturated ω-3 fatty acids and a method for the production of triglycerides with an increased content of unsaturated fatty acids, in particular, of Δ-3 fatty acids with more than three double bonds. Also disclosed is the production of a transgenic organism, preferably a transgenic plant, or a transgenic microorganism with increased content of ω-3 fatty acids, oils or lipids with ω-3 double bonds as a result of the expression of the elongases and desaturases employed in the above method, preferably in combination with ω-3 desaturases, for example a ω-3 desaturase from fungi of the family Pythiaceae such as the genus Phytophtora, for example, the genus and species Phytophtora infestans, or a ω-3 desaturase from algae such as the family Prasinophyceae, for example, the genus Ostreococcus and, particularly, the genus and species Ostreococcus tauri or diatomaceæ such as the genus Thalassiosira and, particularly, the genus and species Thalassiosira pseudonana. The invention also relates to the nucleic acid sequences, nucleic acid constructs, vectors and organisms containing the nucleic acid sequences and / or the nucleic acid constructs and transgenic organisms containing said nucleic acid sequences, nucleic acid constructs and / or vectors. A further part of the invention relates to oils, lipids and / or fatty acids produced according to the above method and use thereof and, furthermore, unsaturated fatty acids and triglycerides with an increased content of unsaturated fatty acids and use thereof.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Method for producing multiple unsaturated fatty acids in plants
InactiveUS7893320B2Other foreign material introduction processesOxidoreductasesDouble bondNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to a method for the production of fatty acid esters which comprise unsaturated fatty acids with at least three double bonds, and to free unsaturated fatty acids with a content of at least 1% by weight based on the total fatty acids present in the plants, by expressing at least one nucleic acid sequence which encodes a polypeptide with Δ6-desaturase activity and at least one nucleic acid sequence which encodes a polypeptide with Δ6-elongase activity. Advantageously, these nucleic acid sequences can, if appropriate, be expressed in the transgenic plant together with a third nucleic acid sequence which encodes a polypeptide with Δ5-desaturase activity. The invention furthermore relates to the use of defined nucleic acid sequences which encode polypeptides with a Δ6-desaturase activity, Δ6-elongase activity or Δ5-desaturase activity selected from a group of nucleic acid sequences, and / or to the use of nucleic acid constructs comprising the abovementioned nucleic acid sequences.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
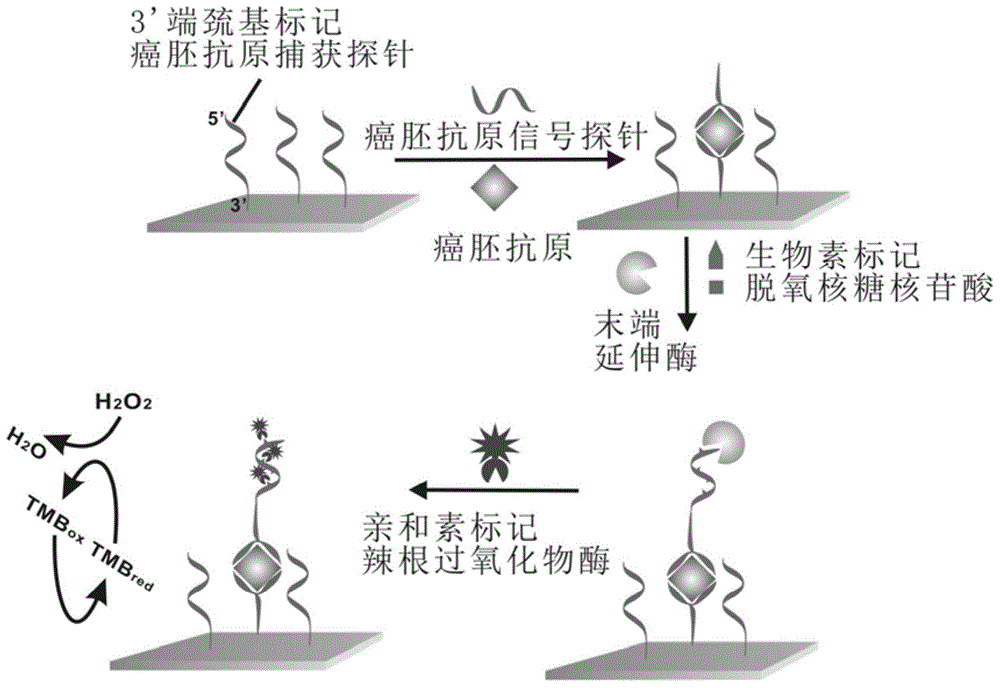
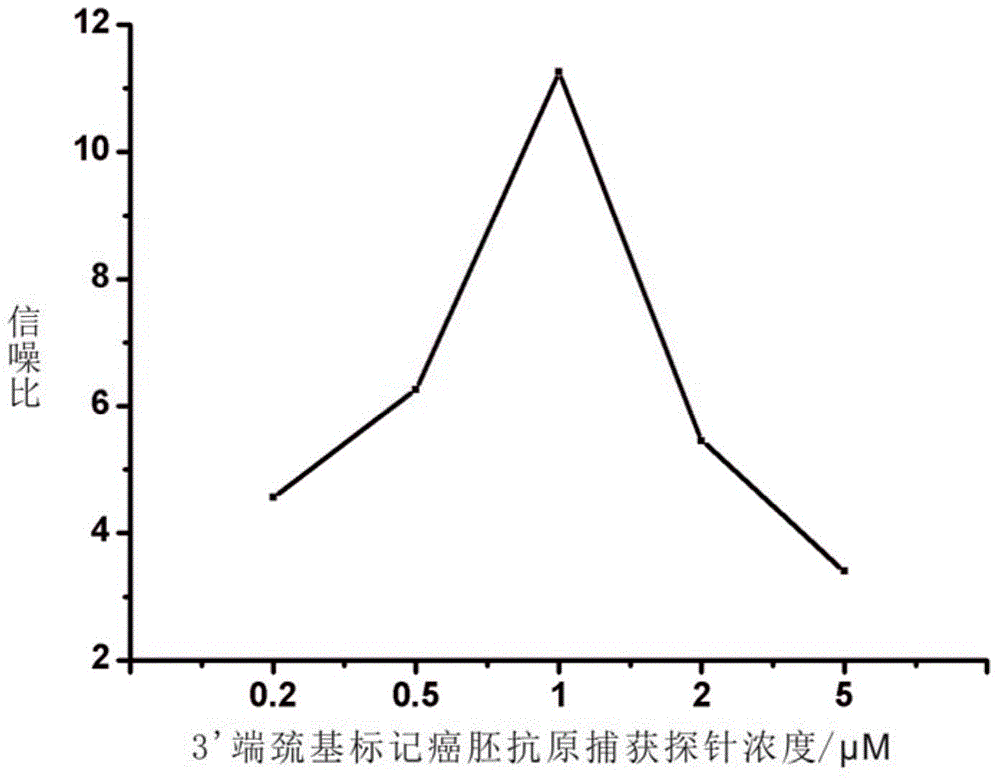
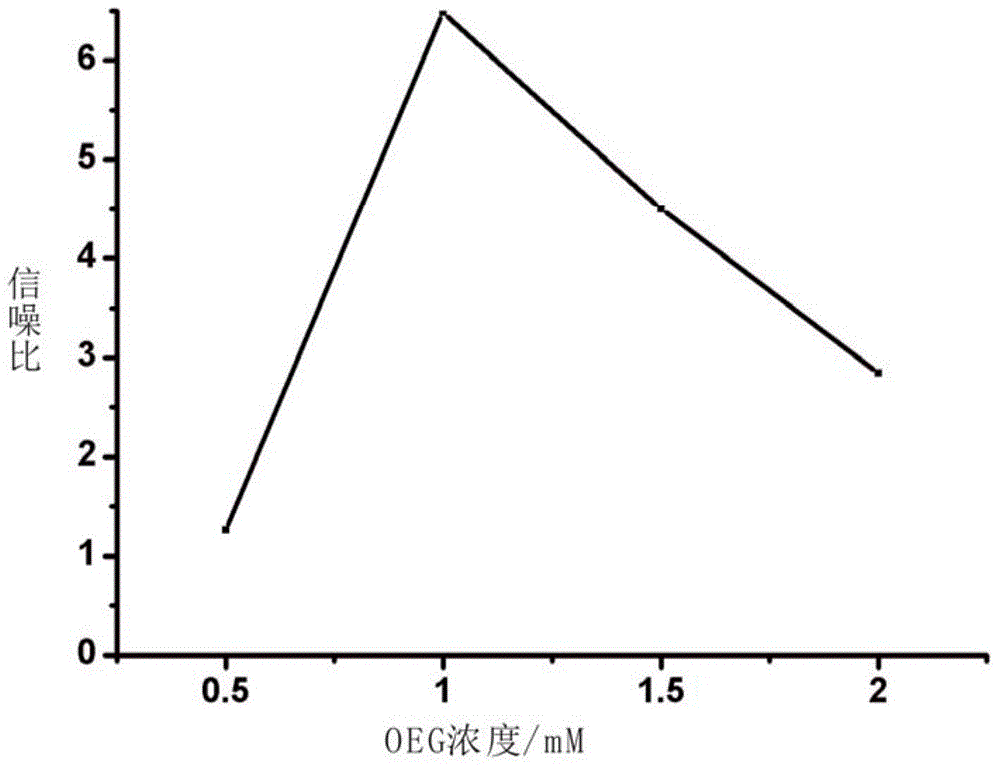
Method for detecting carcino-embryonic antigens by using electrochemical nucleic acid aptamer sensor on basis of terminal elongases
ActiveCN106525920AHigh detection sensitivityHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesWilms' tumorElongase
The invention discloses a method for detecting carcino-embryonic antigens by using an electrochemical nucleic acid aptamer sensor on the basis of terminal elongases. The method comprises the following steps: modifying a layer of 3' mercapto-terminated labeled carcino-embryonic antigen aptamer capturing probes on the surface of a gold electrode at first; then adding carcino-embryonic antigens and carcino-embryonic antigen aptamer signal probes, wherein the 3' mercapto-terminated labeled carcino-embryonic antigen aptamer capturing probes and the carcino-embryonic antigen aptamer signal probes can specifically recognize the carcino-embryonic antigens, so that a sandwich structure is formed on the surface of the electrode; extending biotin labeled nucleic acid long chains at 3' terminals of the carcino-embryonic antigen aptamer signal probes under the effect of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, wherein avidin labeled horse radish peroxidase can be combined to the biotin labeled nucleic acid long chains in a compatible manner; and detecting electrochemical signal change generated by horse radish peroxidase catalyzed electrolyte so as to realize high-sensitivity and high-specificity detection on the carcino-embryonic antigens. The method can be used for early diagnosis of tumors, curative effect judgment, progression of the disease, prognosis estimation and the like.
Owner:迈科若(苏州)医疗科技有限公司
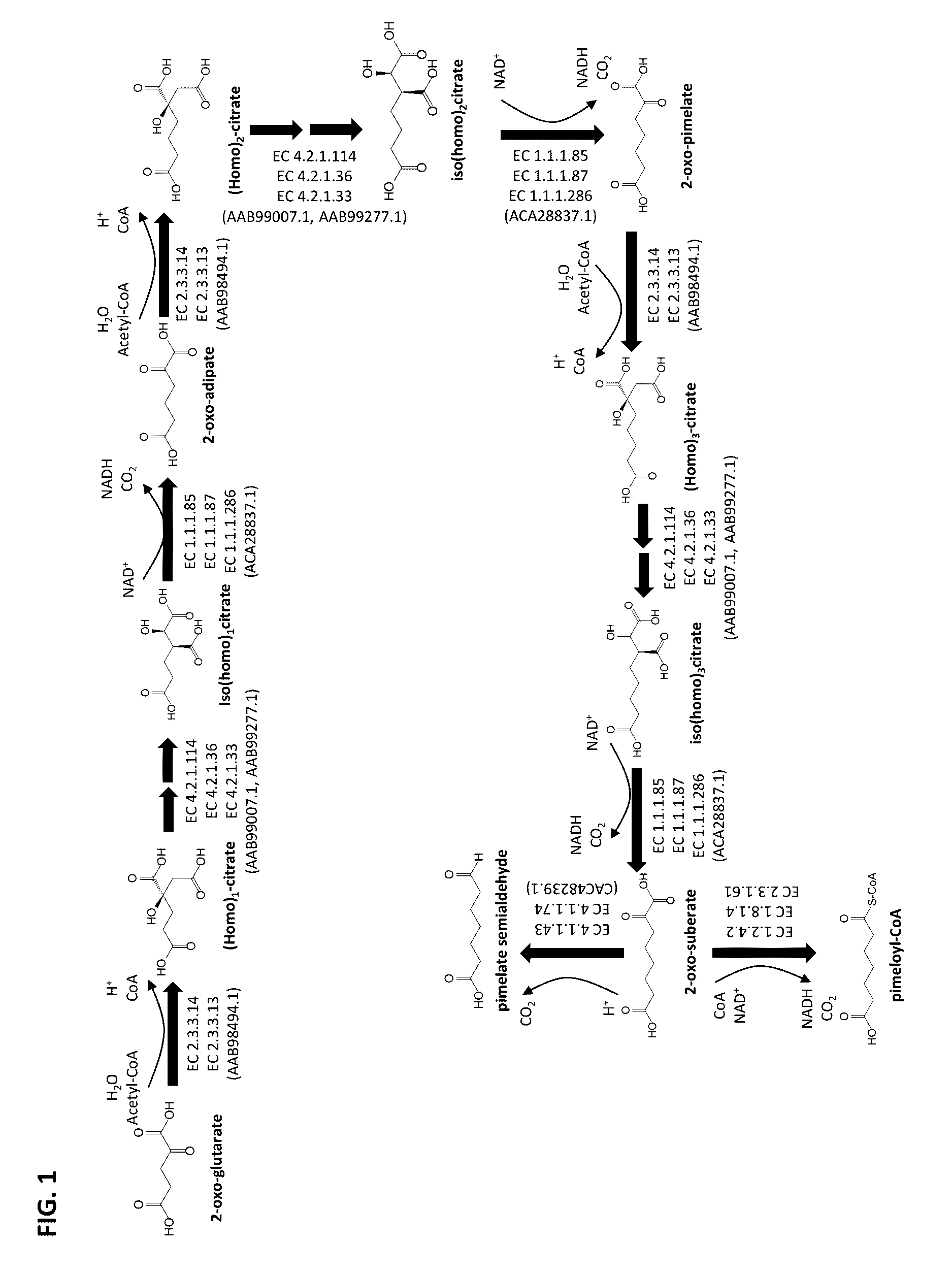
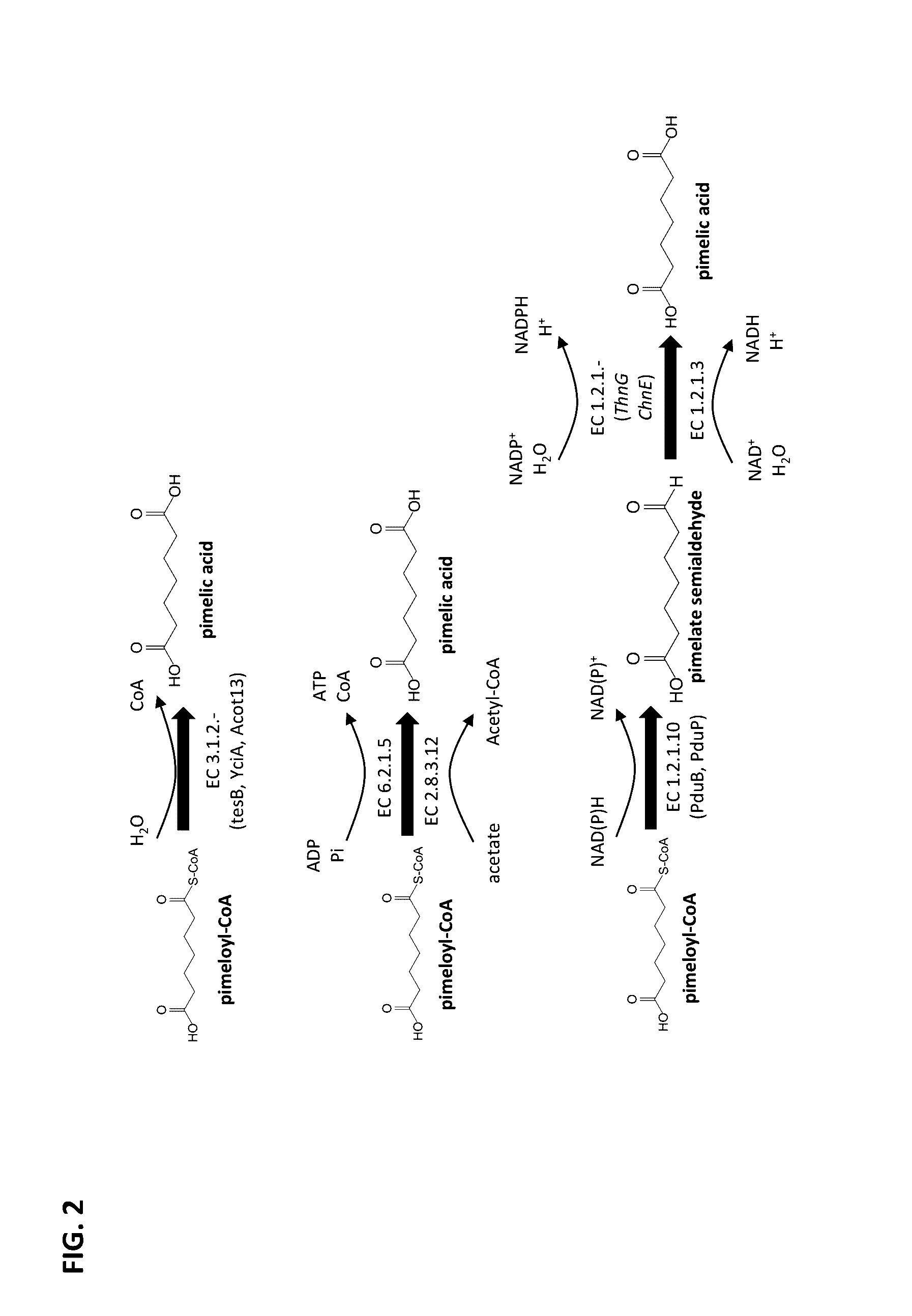
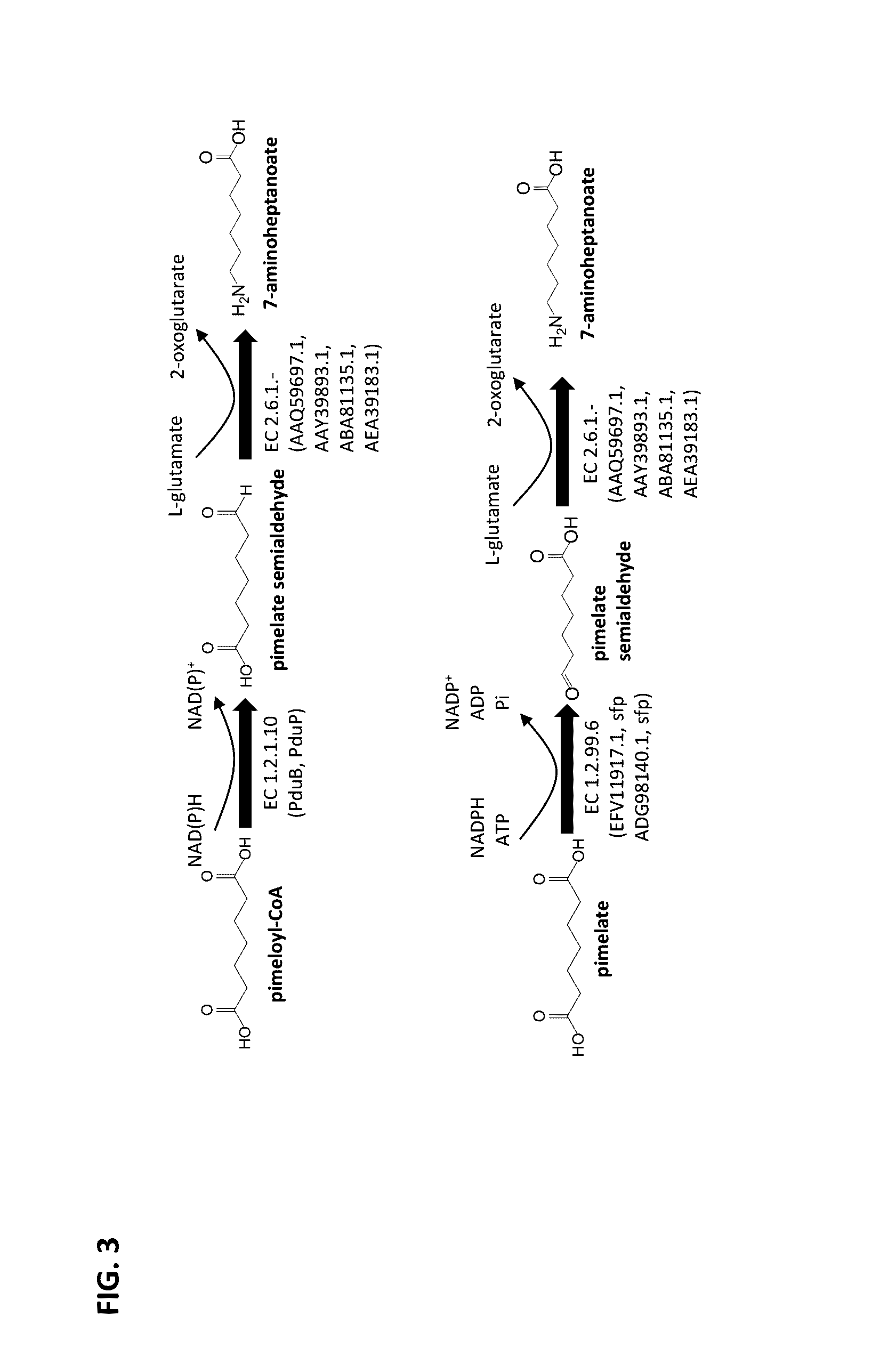
Methods of producing 7-carbon chemicals via c1 carbon chain elongation associated with coenzyme B synthesis
ActiveUS9580731B2High activityTolerance to high concentrations of a C7 building block can be improvedHydrolasesOxidoreductasesCarbon chainCoenzyme B
This document describes biochemical pathways for producing pimelic acid, 7-aminoheptanoic acid, 7-hydroxyheptanoic acid, heptamethylenediamine or 1,7-heptanediol by forming one or two terminal functional groups, each comprised of carboxyl, amine or hydroxyl group, in a C7 aliphatic backbone substrate. These pathways, metabolic engineering and cultivation strategies described herein rely on the C1 elongation enzymes or homolog associated with coenzyme B biosynthesis.
Owner:INV NYLON CHEM AMERICAS LLC
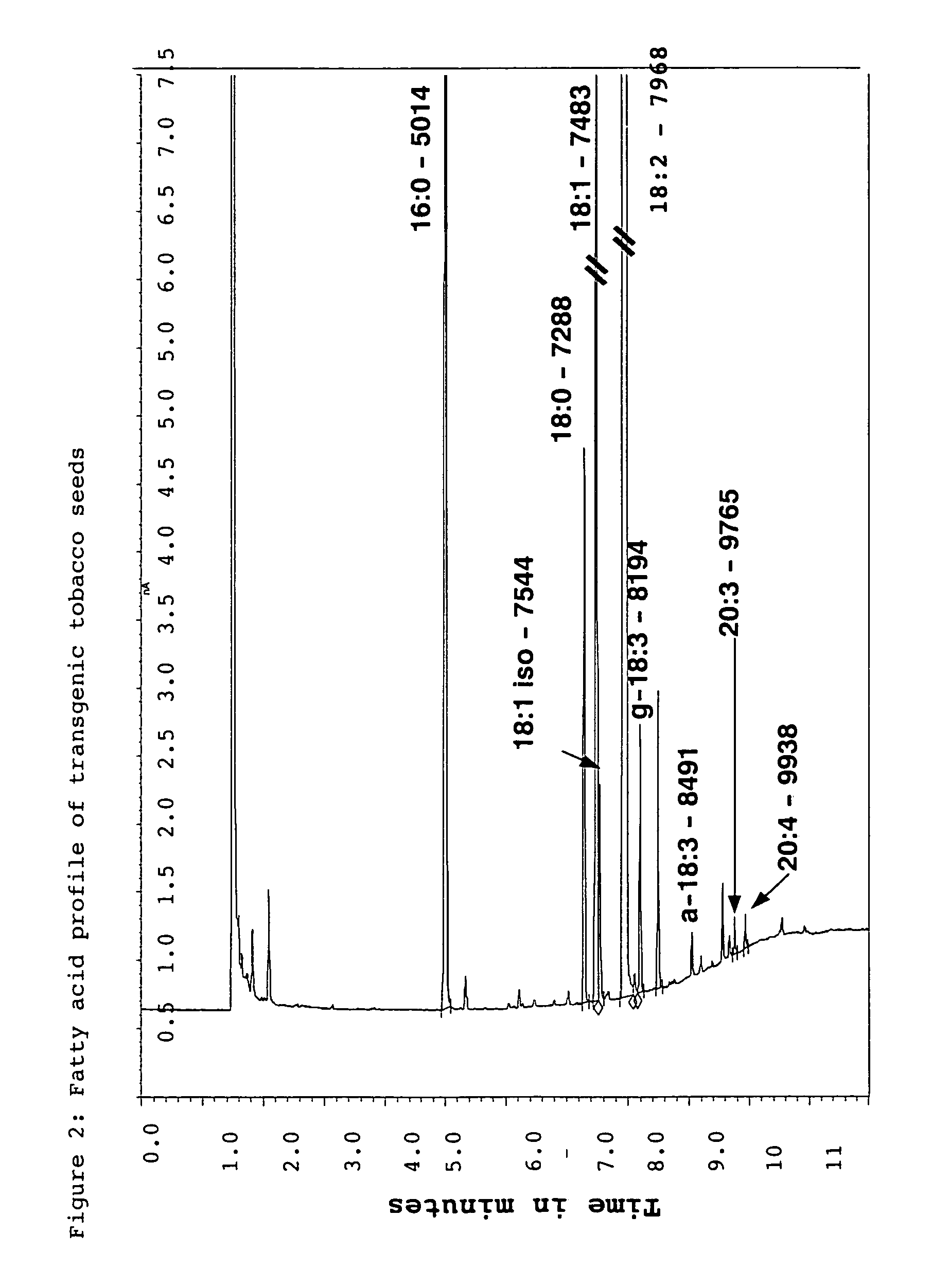
Method for producing polyunsaturated fatty acids in transgenic plants
ActiveUS20150361404A1Organic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsArachidonic acid supplementationTransgene
The present invention relates to a process for the production of polyunsaturated fatty acids in the seed of transgenic plants by introducing, into the organism, nucleic acids which encode polypeptides with a ω3-desaturase, Δ12-desaturase, Δ6-desaturase, Δ6-elongase, Δ5-desaturase, Δ5-elongase and / or Δ4-desaturase activity. The invention furthermore relates to recombinant nucleic acid molecules comprising the nucleic acid sequences which encode the aforementioned polypeptides, either jointly or individually, and transgenic plants which comprise the aforementioned recombinant nucleic acid molecules. Furthermore, the invention relates to the generation of a transgenic plant and to oils, lipids and / or fatty acids with an elevated content of polyunsaturated fatty acids, in particular arachidonic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid and / or docosahexaenoic acid, as the result of the expression of the elongases and desaturases used in the process according to the invention.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
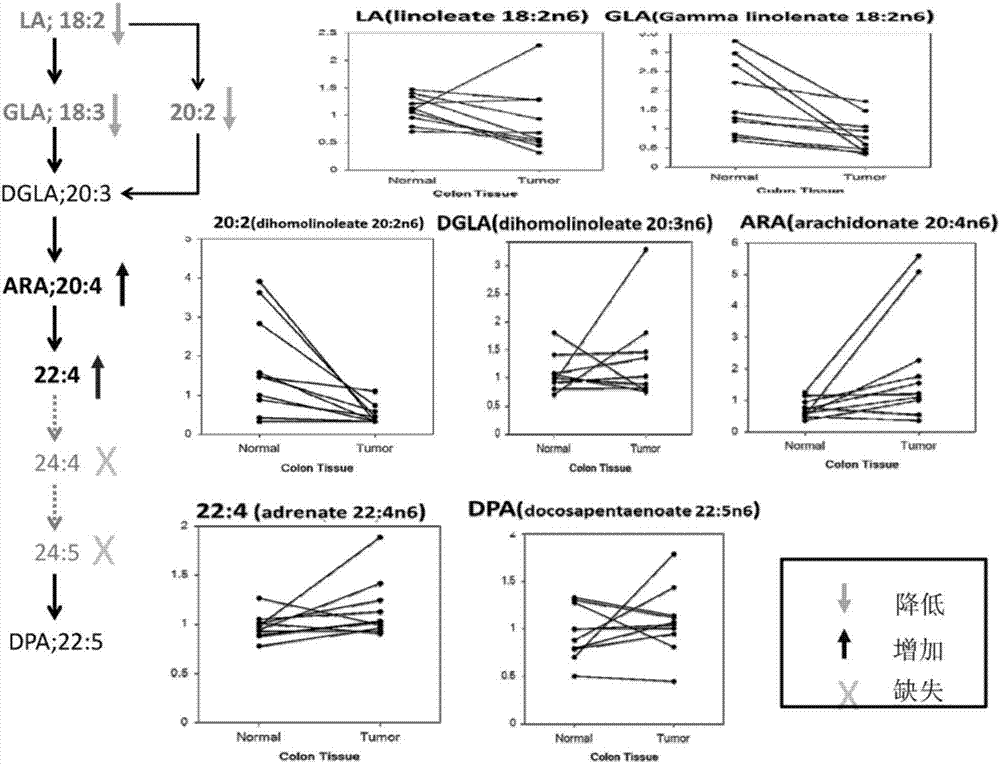
Method for detecting content of linoleic acid in tissues by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and diagnostic kit of colorectal cancer
ActiveCN106872590AQuick checkAccurate detectionComponent separationVery long chain fatty acidMetabolic enzymes
The invention provides a method for detecting the content of linoleic acid in tissues by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and a diagnostic kit of colorectal cancer. The method comprises the following steps: grinding a tissue sample into powder in liquid nitrogen; homogenizing the tissue powder with iced methanol containing BHT (Butylated Hydroxytoluene) and centrifuging; adding an interior label into supernatant and carrying out derivatization treatment with n-butanol; dispersing and dissolving the mixture by a mobile phase again to obtain a sample to be loaded and detected; analyzing the sample to be loaded and detected with the liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry to obtain the content of the linoleic acid in the tissue sample. Furthermore, a metabolic enzyme of a linoleic acid pathway is subjected to expression analysis and a result shows that gene expression of FADS1 (Fatty Acid Desaturase 1), FADS2 (Fatty Acid Desaturase 2), ELOVL2 (elongase of very long chain fatty acid 2) and ELOVL5 (elongase of very long chain fatty acid 5) in the linoleic acid pathway is increased. The method provided by the invention can be used for detecting changes of the content of the linoleic acid of tumor tissues and normal tissues of patients with the colorectal cancer and expression changes of genes in a related metabolism pathway, and important reference is provided for diagnosis and treatment of the colorectal cancer and post-period nutrition support.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com