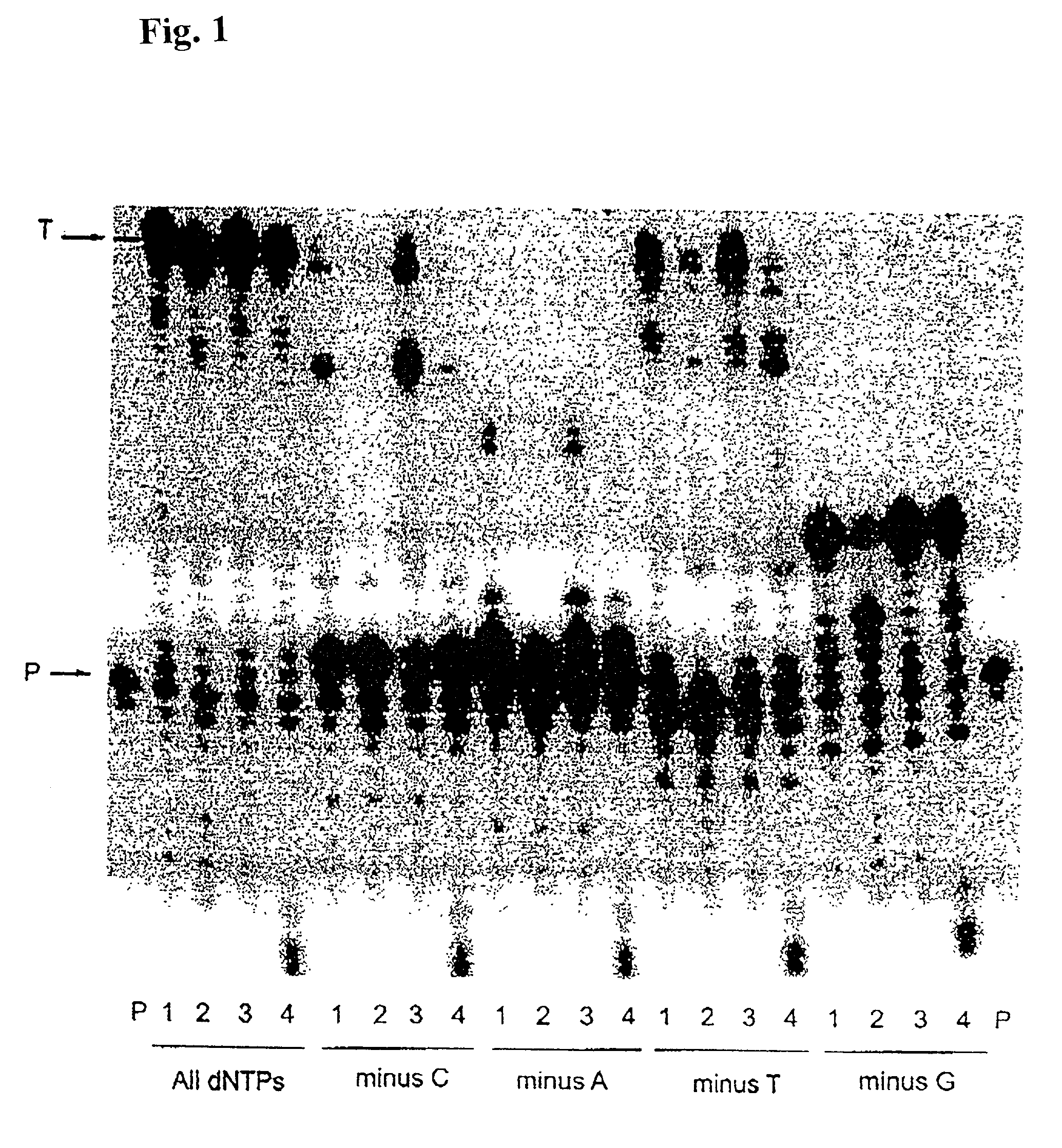
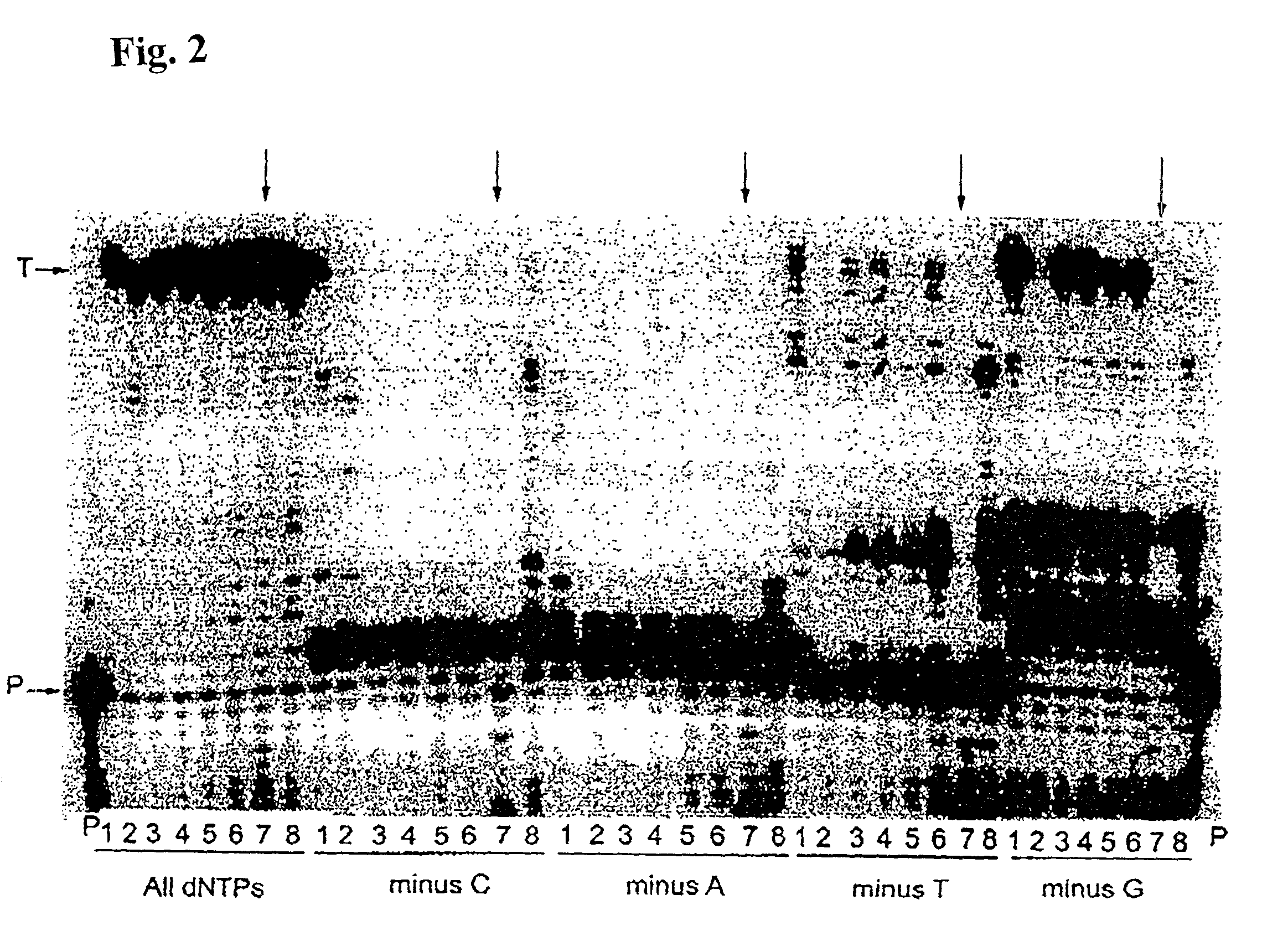
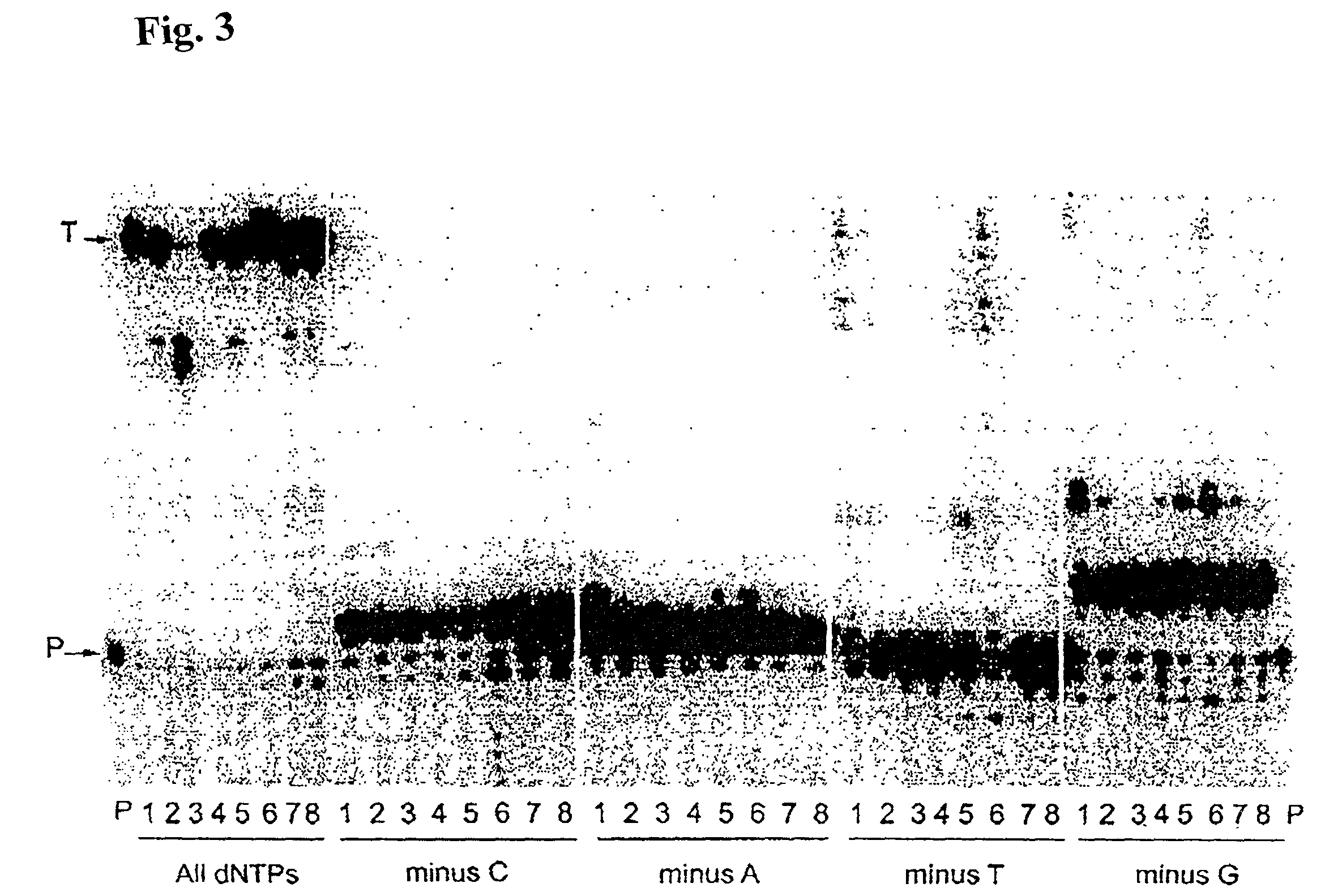
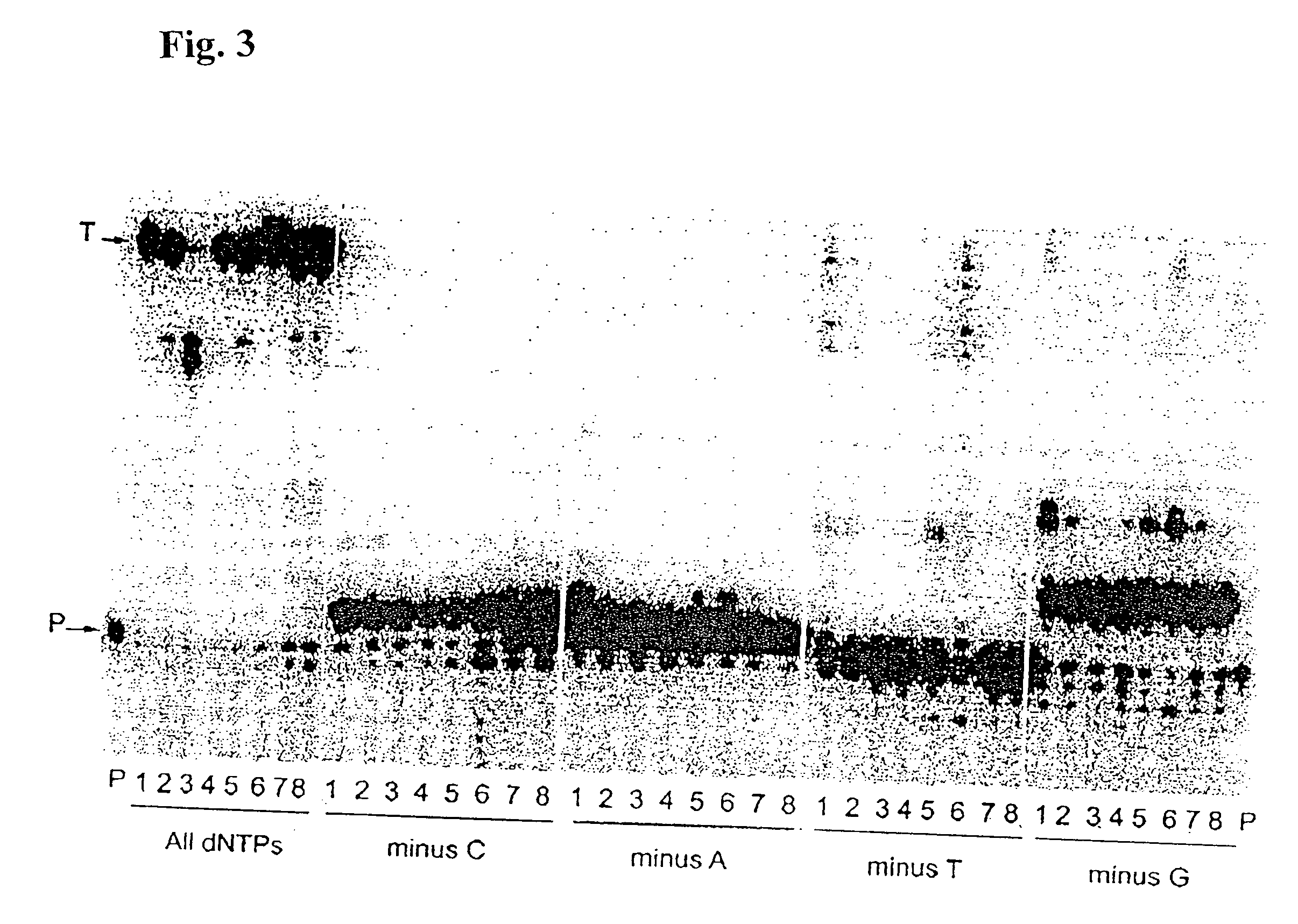
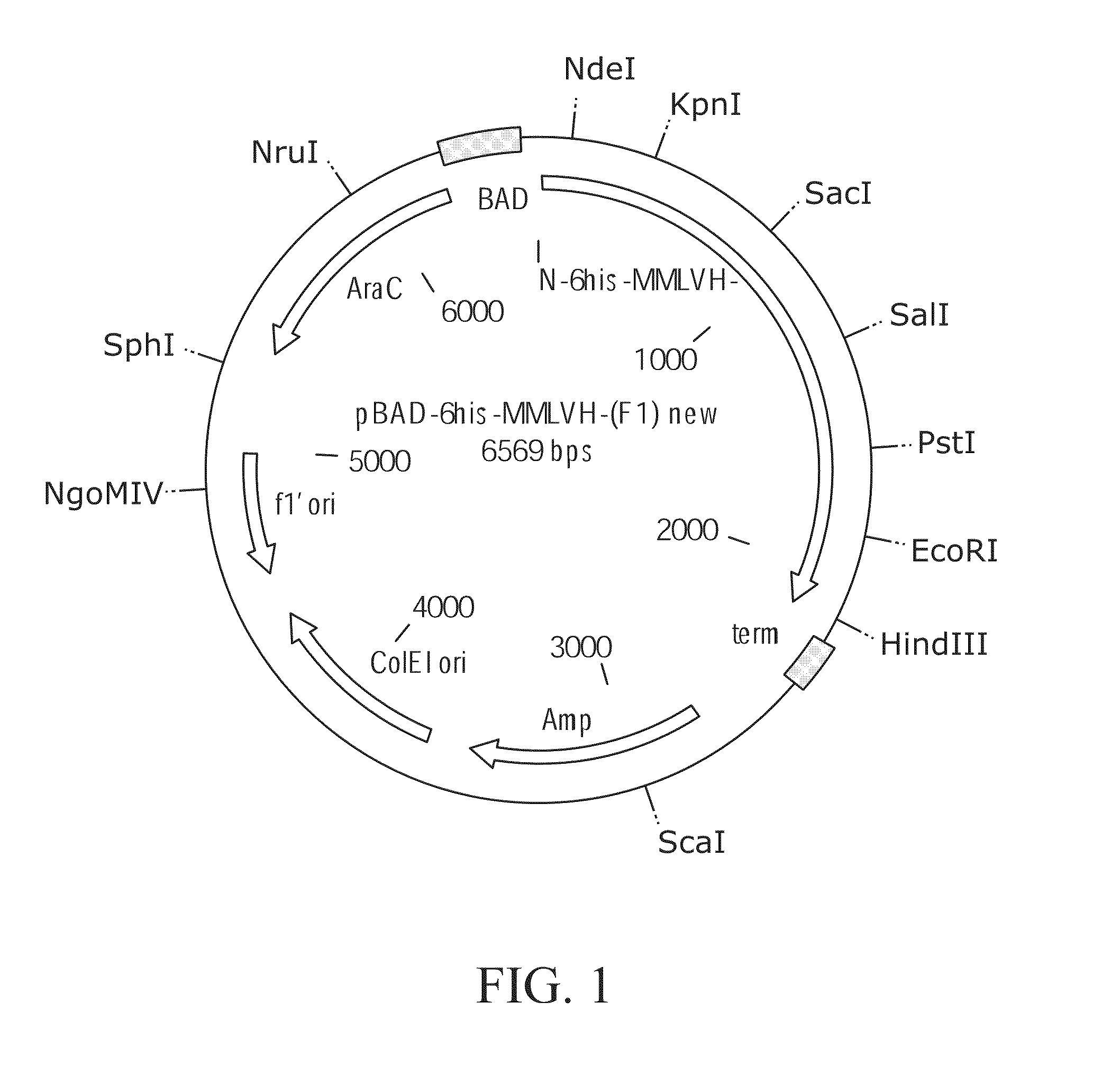
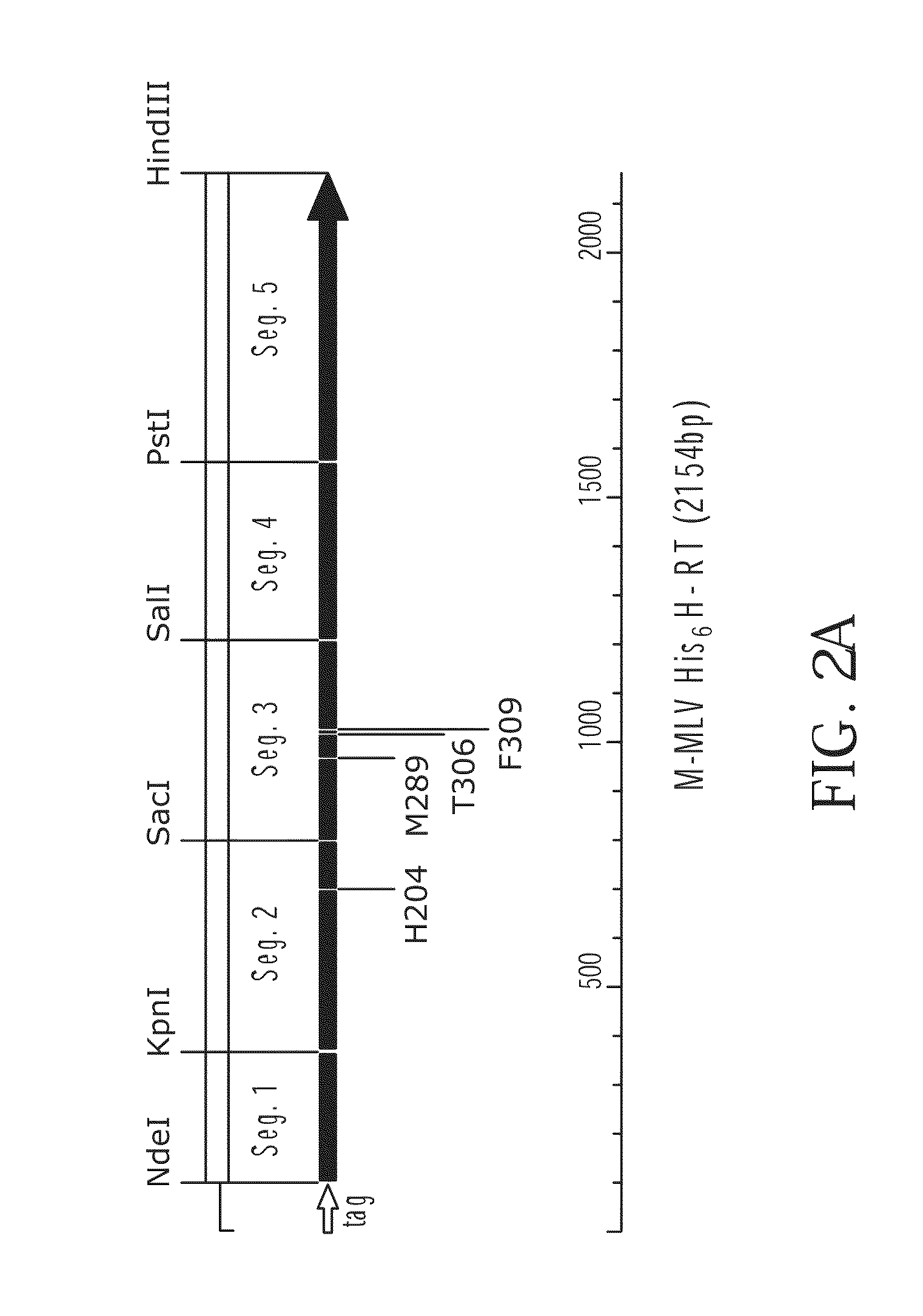
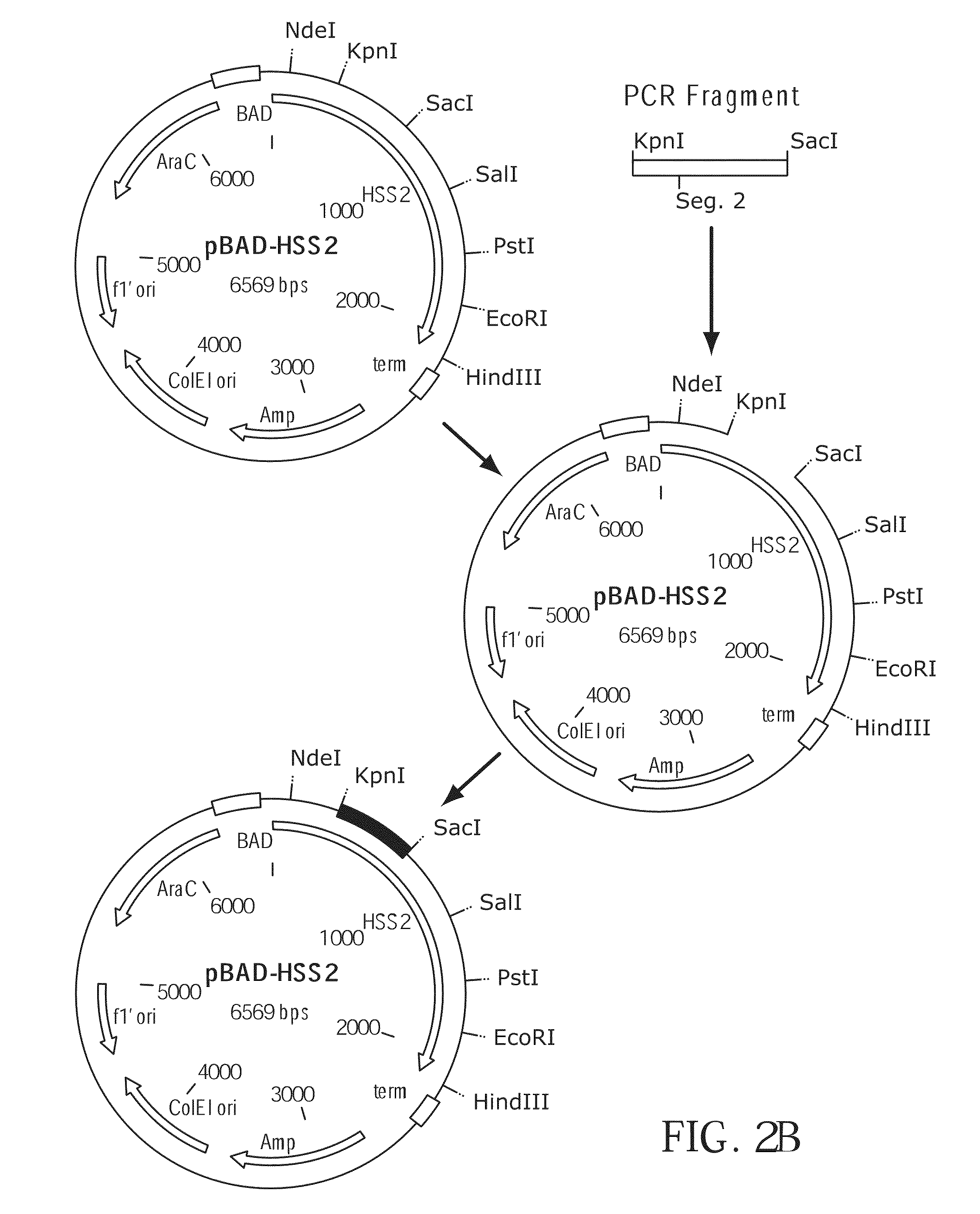
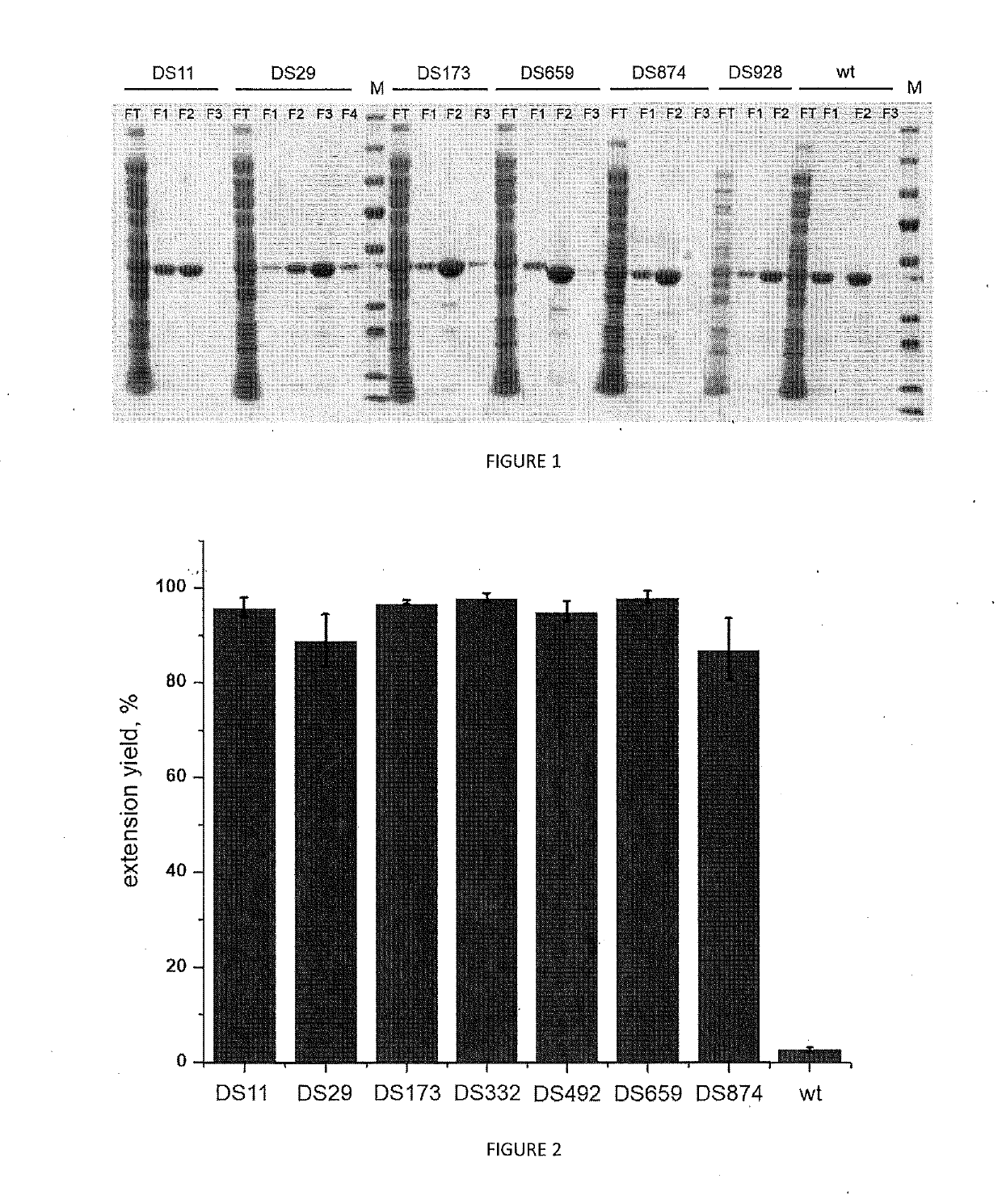
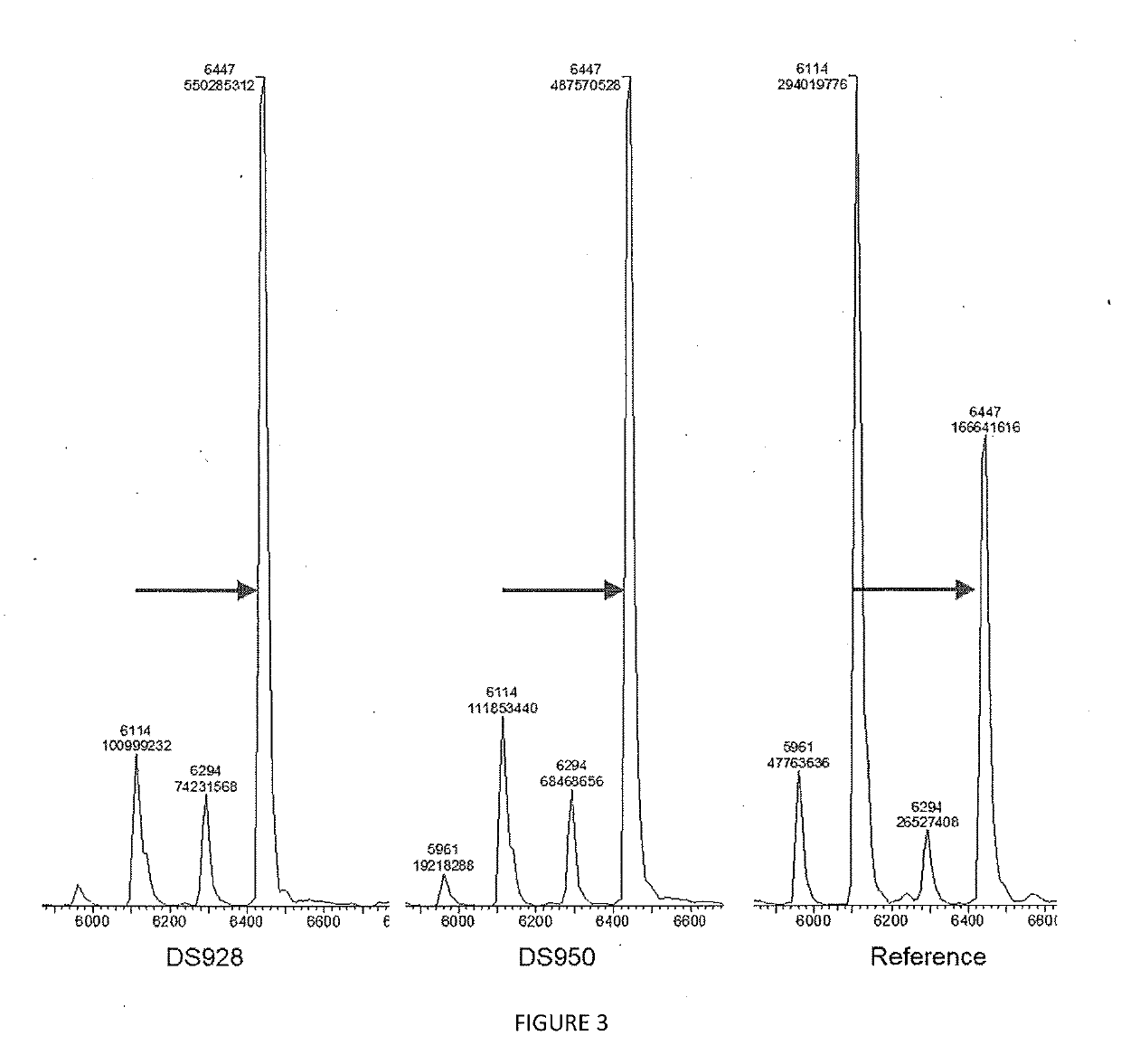
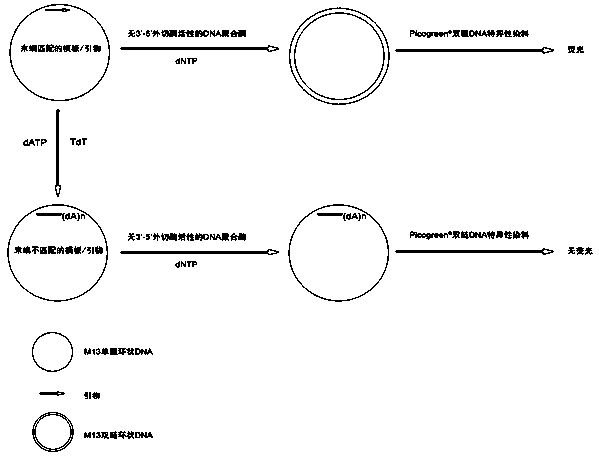
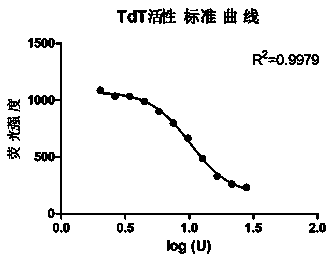
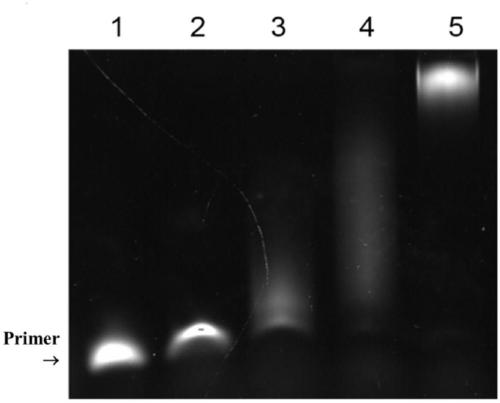
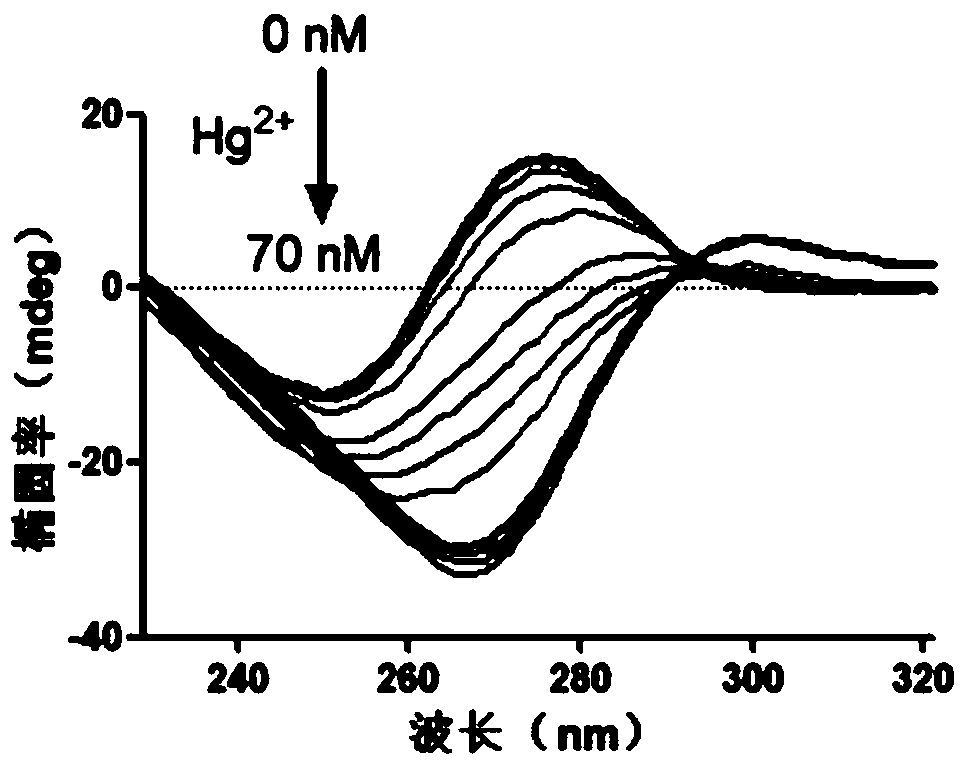
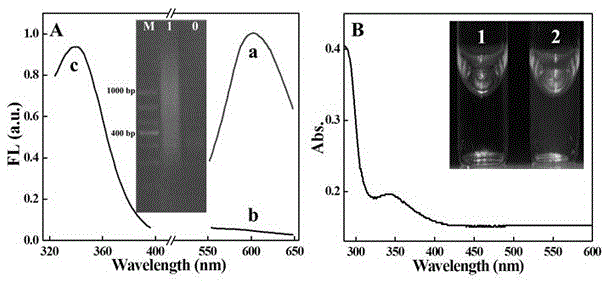
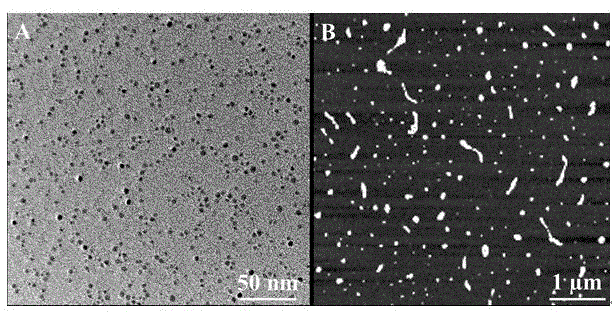
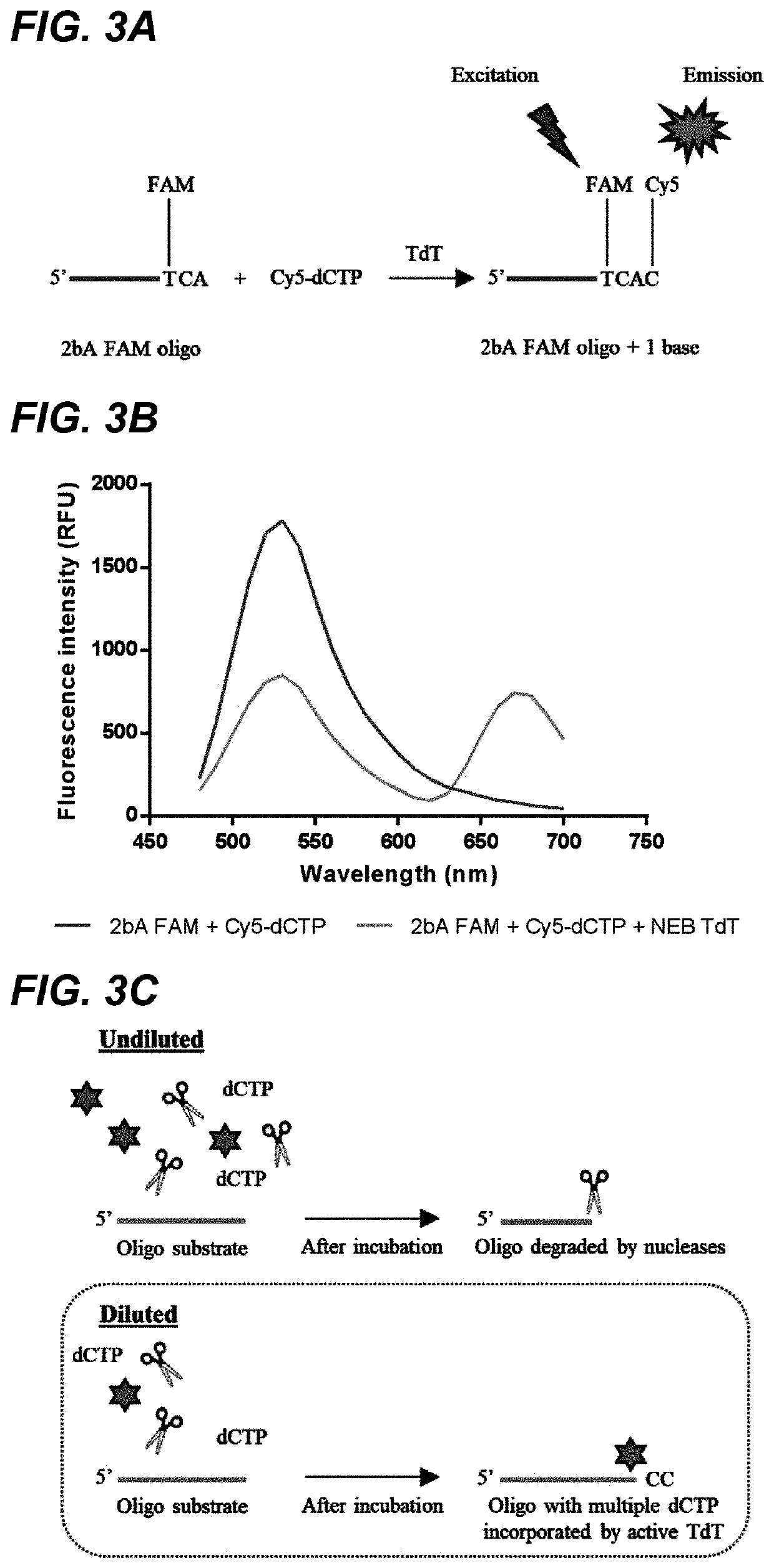
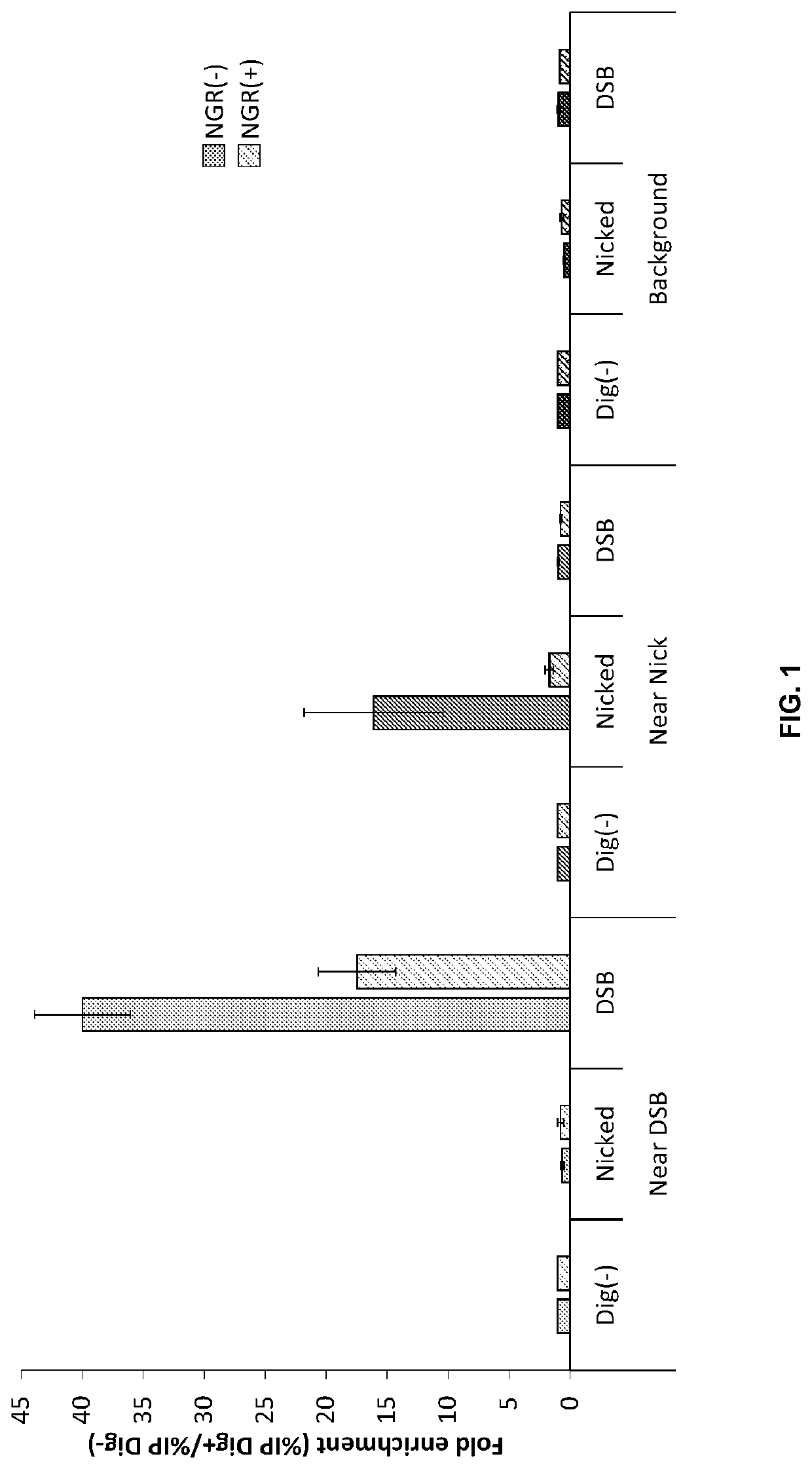
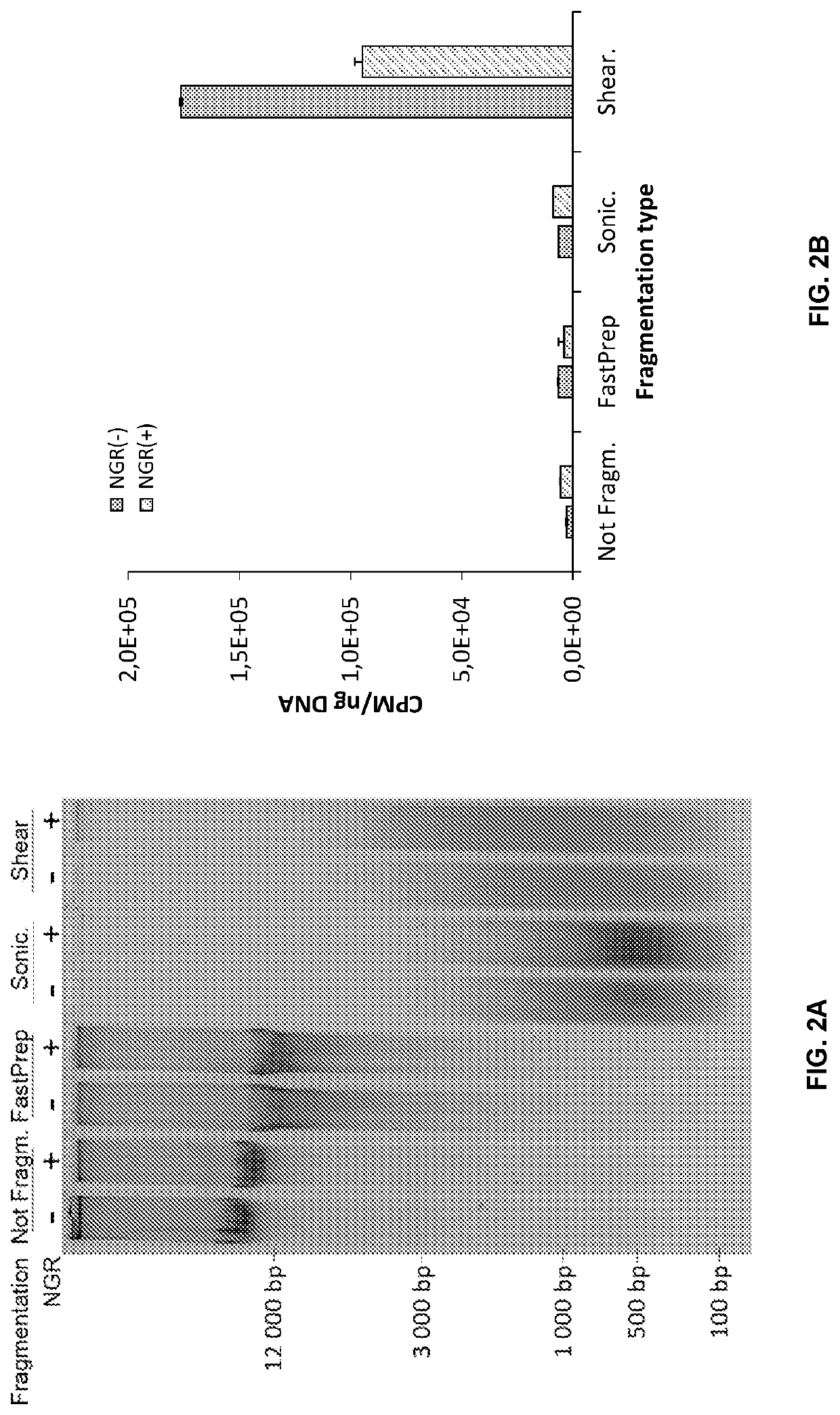
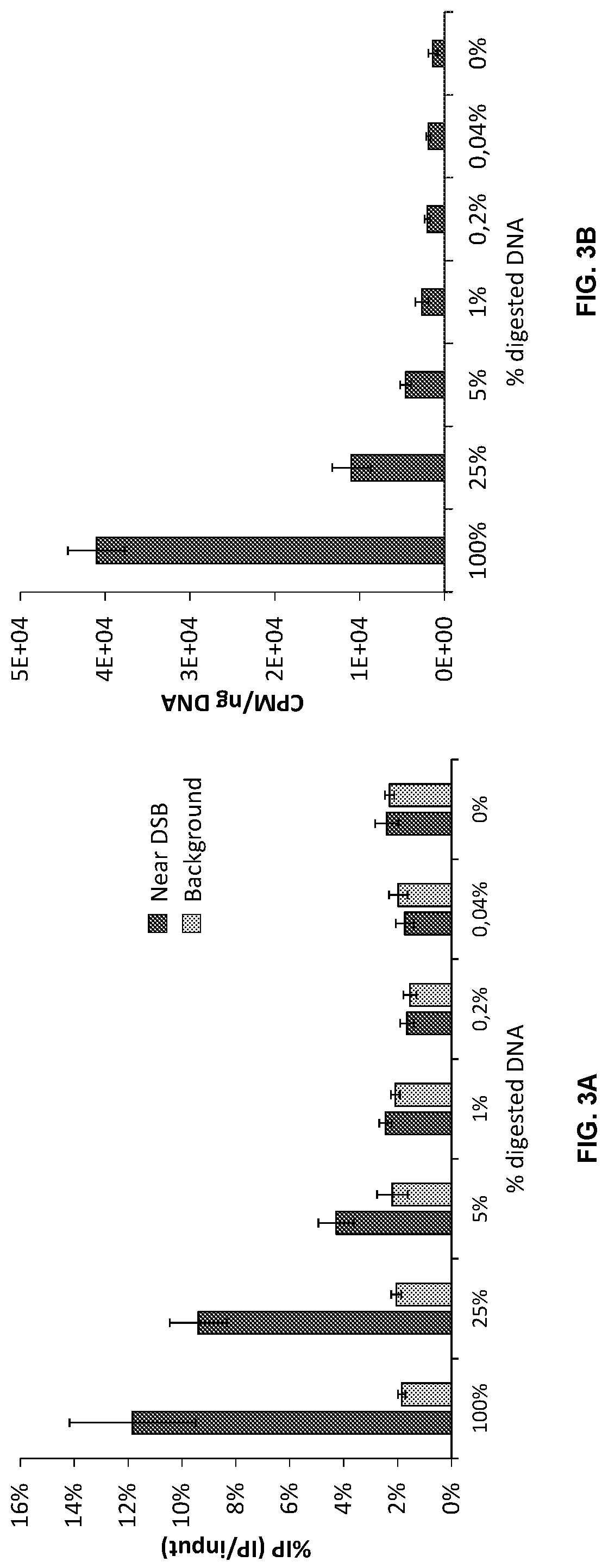
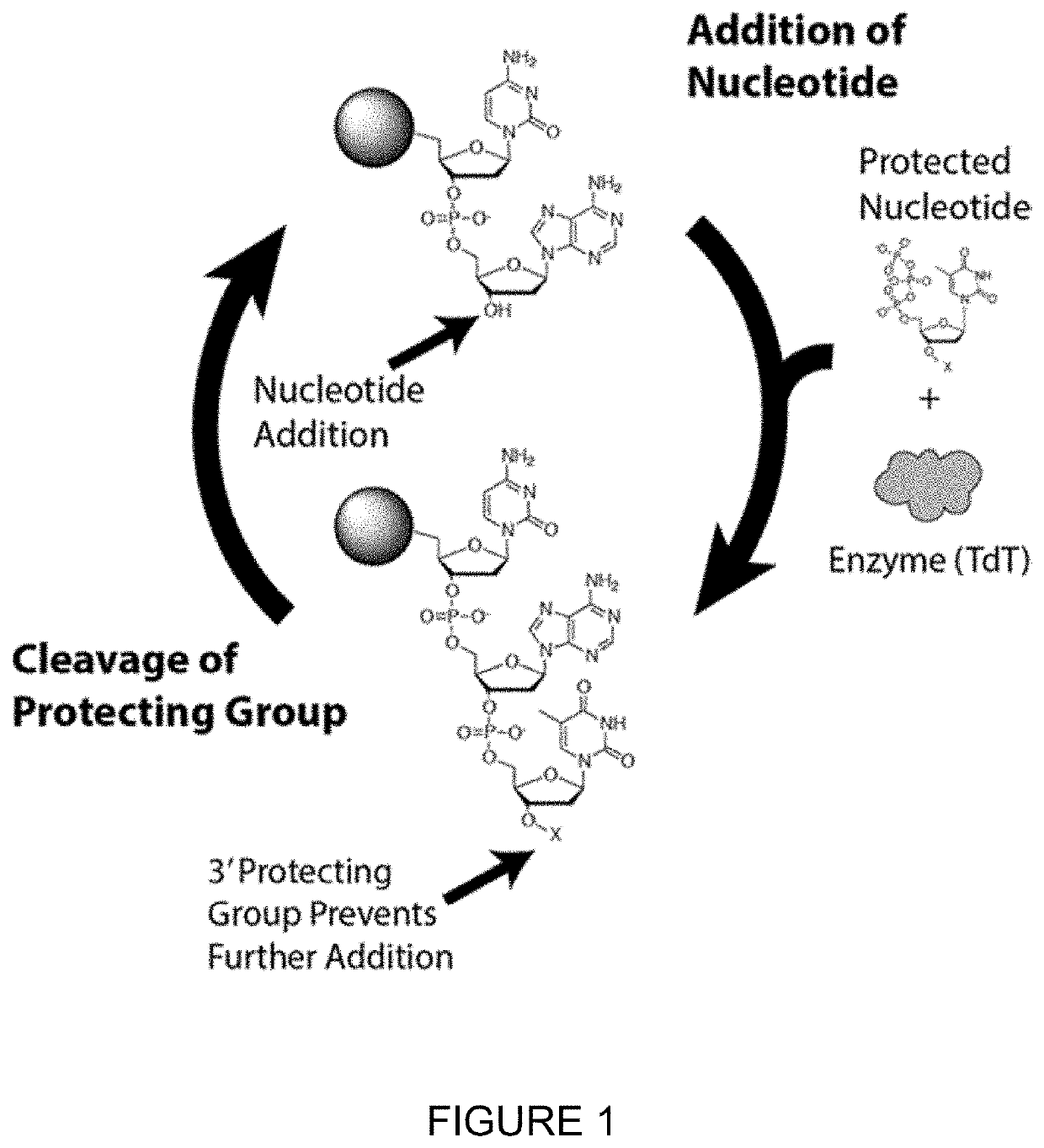
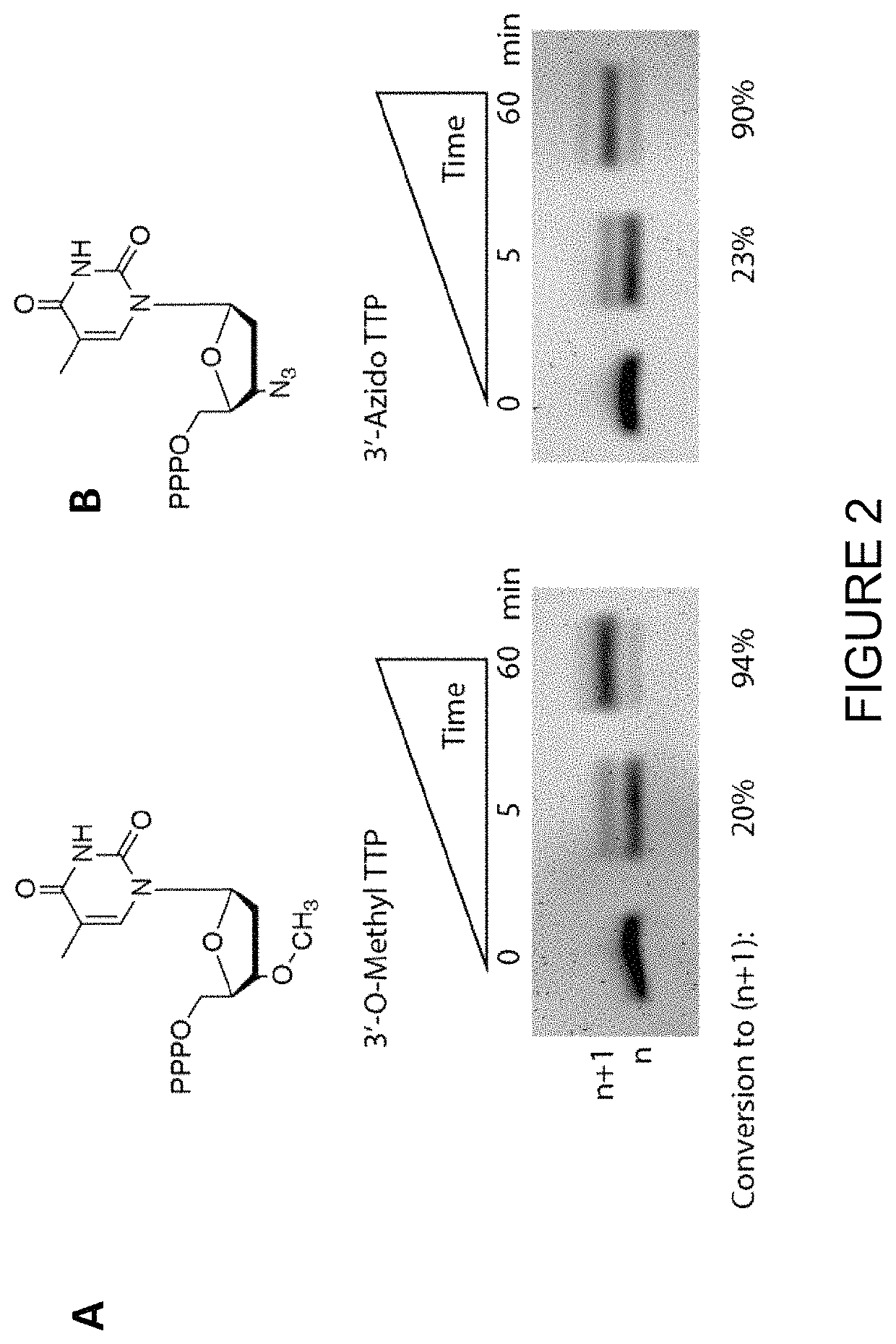
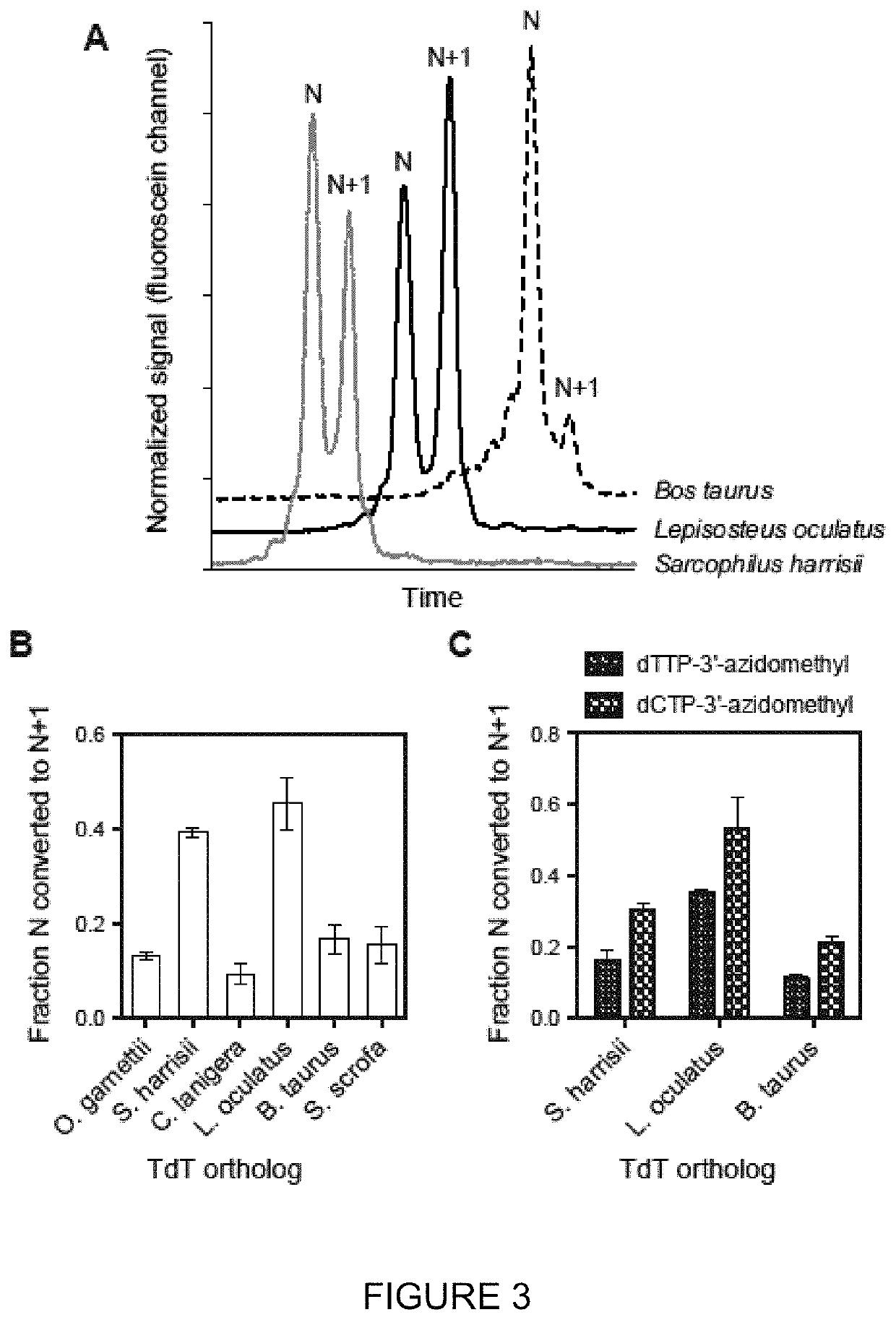
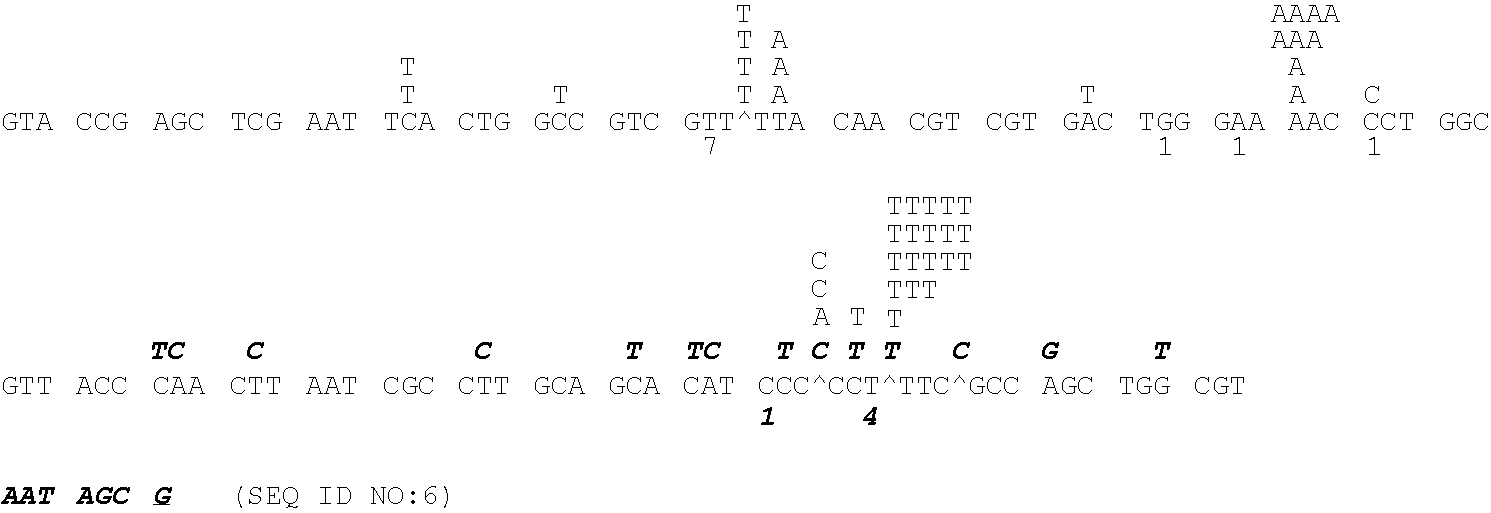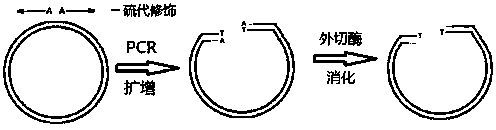Patents
Literature
47 results about "Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT), also known as DNA nucleotidylexotransferase (DNTT) or terminal transferase, is a specialized DNA polymerase expressed in immature, pre-B, pre-T lymphoid cells, and acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma cells. TdT adds N-nucleotides to the V, D, and J exons of the TCR and BCR genes during antibody gene recombination, enabling the phenomenon of junctional diversity. In humans, terminal transferase is encoded by the DNTT gene. As a member of the X family of DNA polymerase enzymes, it works in conjunction with polymerase λ and polymerase μ, both of which belong to the same X family of polymerase enzymes. The diversity introduced by TdT has played an important role in the evolution of the vertebrate immune system, significantly increasing the variety of antigen receptors that a cell is equipped with to fight pathogens. Studies using TdT knockout mice have found drastic reductions (10-fold) in T-cell receptor (TCR) diversity compared with that of normal, or wild-type, systems. The greater diversity of TCRs that an organism is equipped with leads to greater resistance to infection.
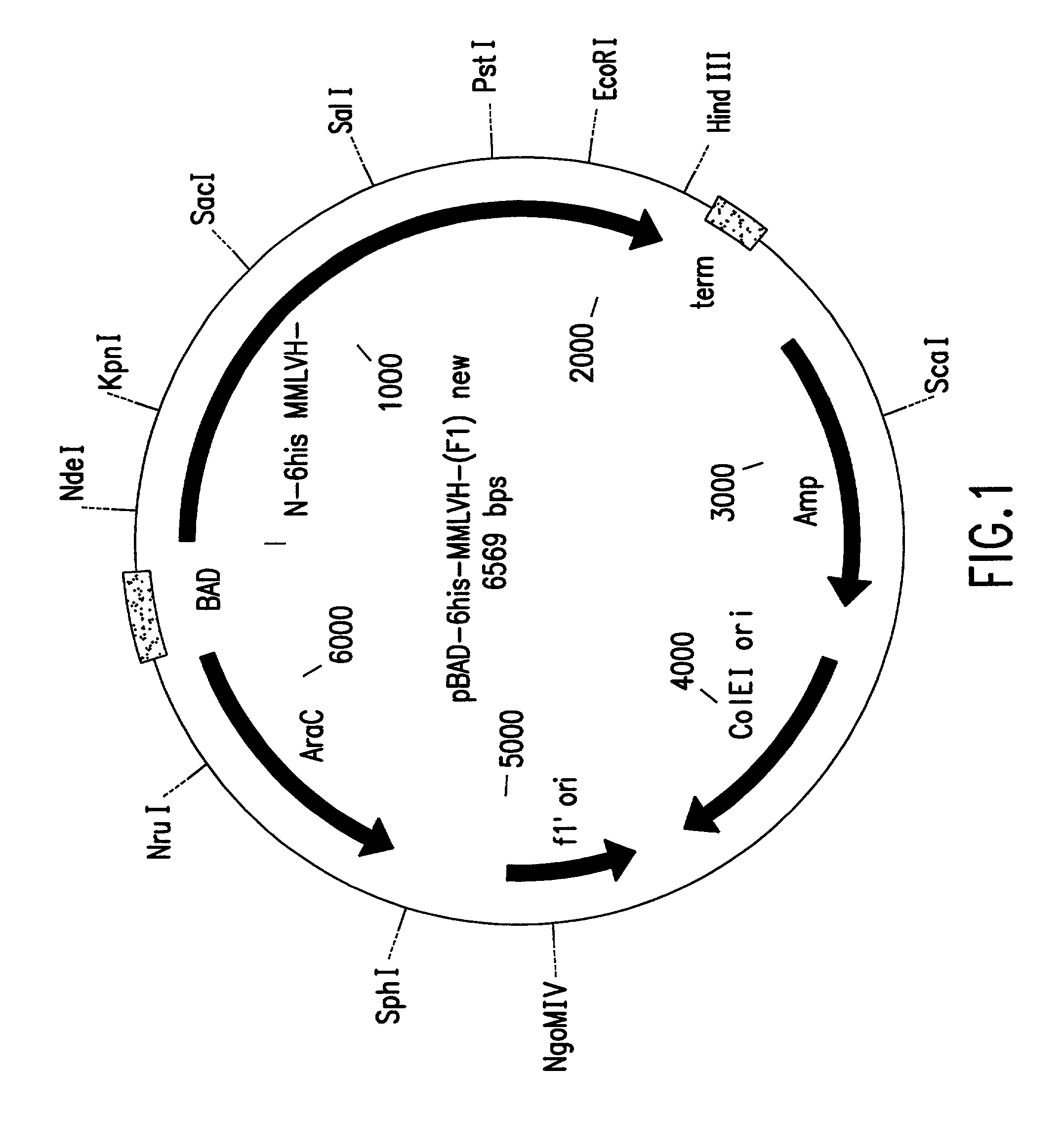
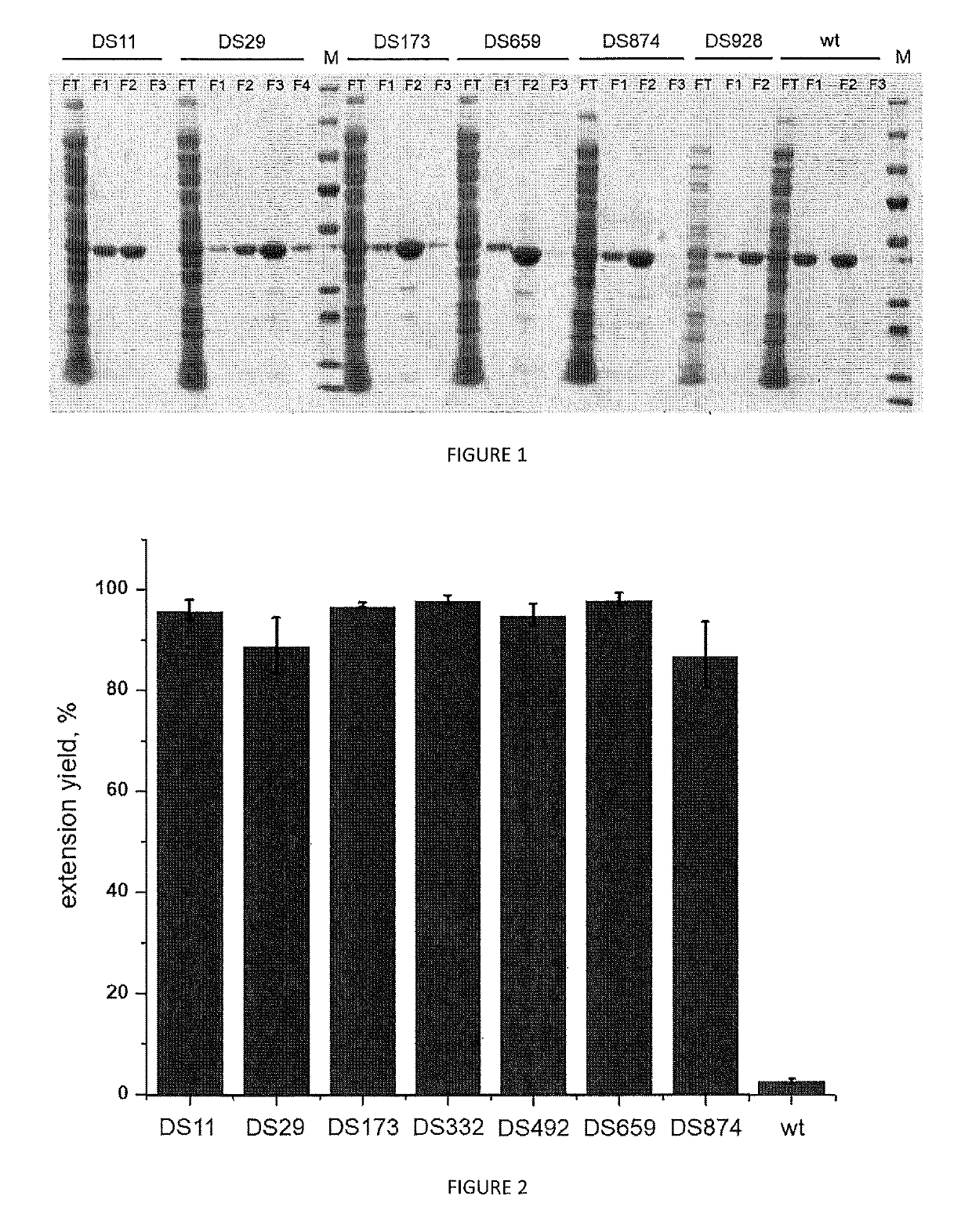
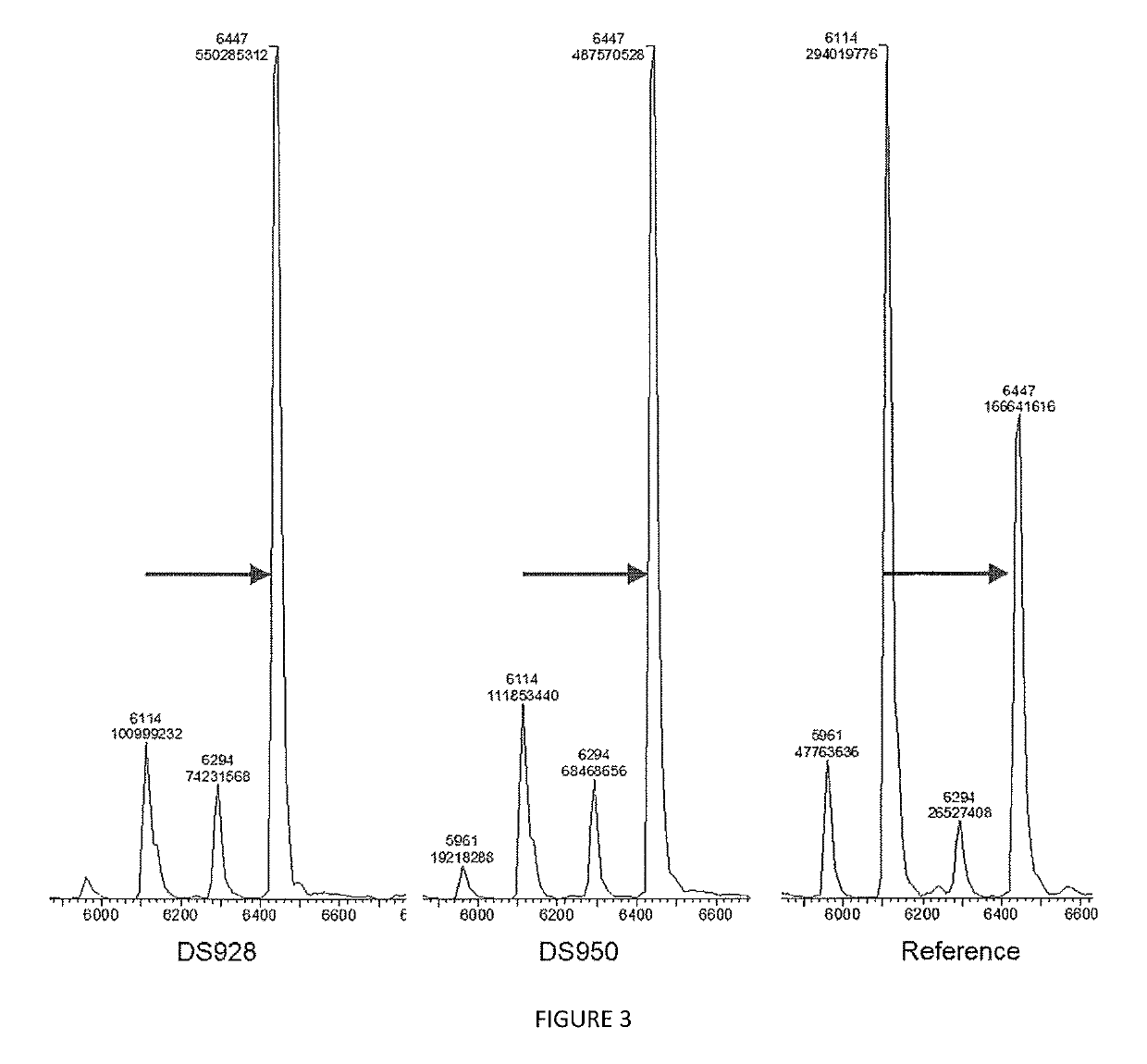
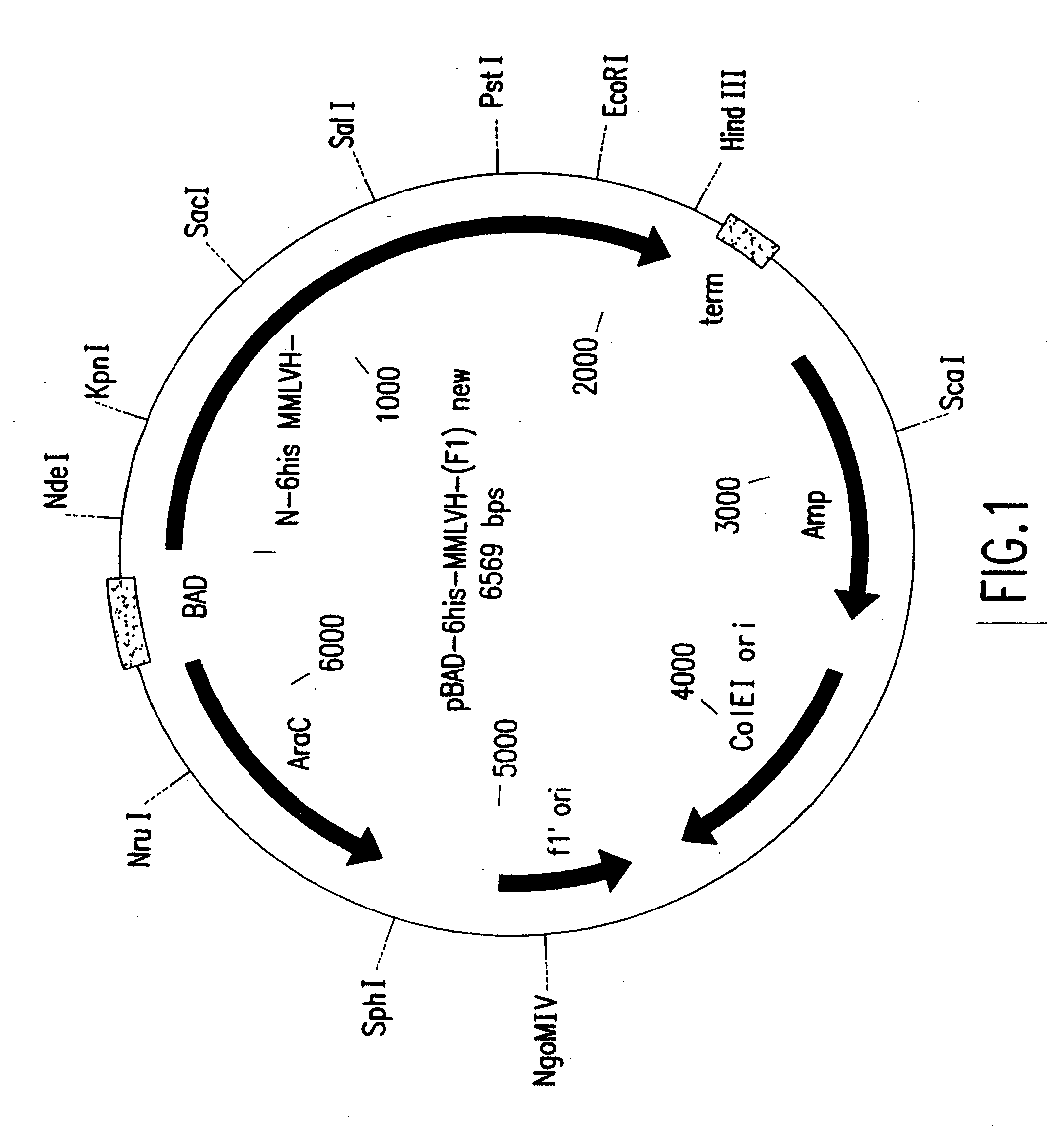
High fidelity reverse transcriptases and uses thereof
InactiveUS7056716B2FungiSugar derivativesReverse transcriptaseTerminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase activity
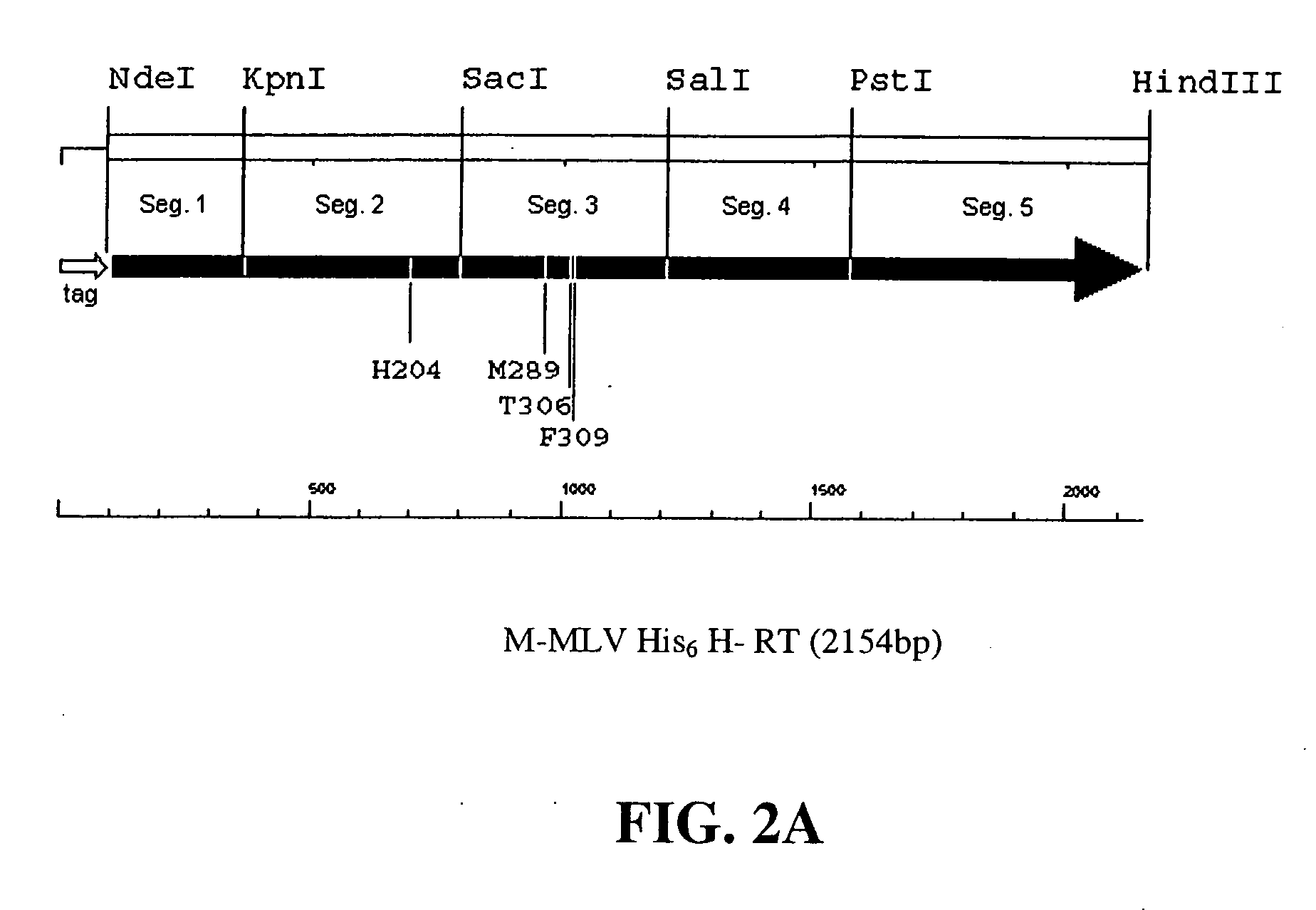
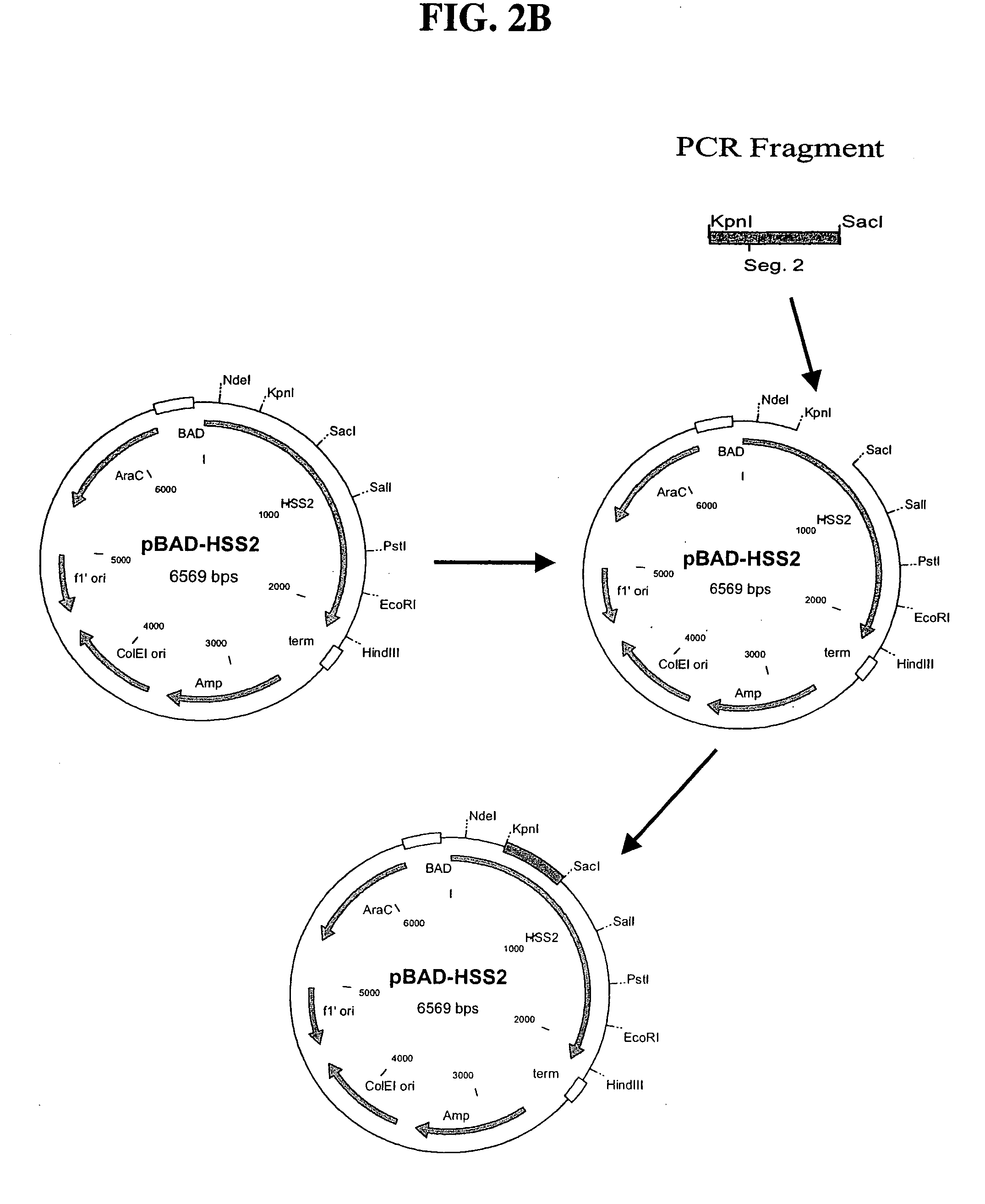
The invention relates to reverse transcriptases which have increased fidelity (or reduced misincorporation rate) and / or terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase activity. In particular, the invention relates to a method of making such reverse transcriptases by modifying or mutating specified positions in the reverse transcriptases. The invention also relates to nucleic acid molecules containing the genes encoding the reverse trancriptases of the invention, to host cells containing such nucleic acid molecules and to methods to make the reverse trancriptases using the host cells. The reverse transcriptases of the invention are particularly suited for nucleic acid synthesis, sequencing, amplification and cDNA synthesis.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Thermostable reverse transcriptases and uses thereof
InactiveUS7078208B2Reduced RNase H activityImprove fidelityFungiBacteriaMessenger RNAReverse transcriptase
The present invention is in the fields of molecular and cellular biology. The invention is generally related to reverse transcriptase enzymes and methods for the reverse transcription of nucleic acid molecules, especially messenger RNA molecules. Specifically, the invention relates to reverse transcriptase enzymes which have been mutated or modified to increase thermostability, decrease terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase activity, and / or increase fidelity, and to methods of producing, amplifying or sequencing nucleic acid molecules (particularly cDNA molecules) using these reverse transcriptase enzymes or compositions. The invention also relates to nucleic acid molecules produced by these methods and to the use of such nucleic acid molecules to produce desired polypeptides. The invention also concerns kits comprising such enzymes or compositions.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Selective isolation of bacterial mRNA
The invention provides methods and compositions for selectively isolating total bacterial mRNA. The general method comprises contacting a bacterial lysate comprising total bacterial mRNA and nonisolated bacterial polysomes with an exogenous enzyme under conditions wherein the enzyme selectively modifies the mRNA to form modified mRNA, and isolating the modified mRNA. In particular embodiments, the enzyme is selected from a poly(A) polymerase, a RNA ligase and a terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. Depending on the enzyme, the modified mRNA may have any of a variety of modifications, such as a 3' tail, particularly a poly(A) tail, a specific sequence tag, a detectably labeled nucleotide, etc.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Variants of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase and uses thereof
ActiveUS10435676B2Improve abilitiesLow costImmobilised enzymesTransferasesNucleotideAmino acid substitution
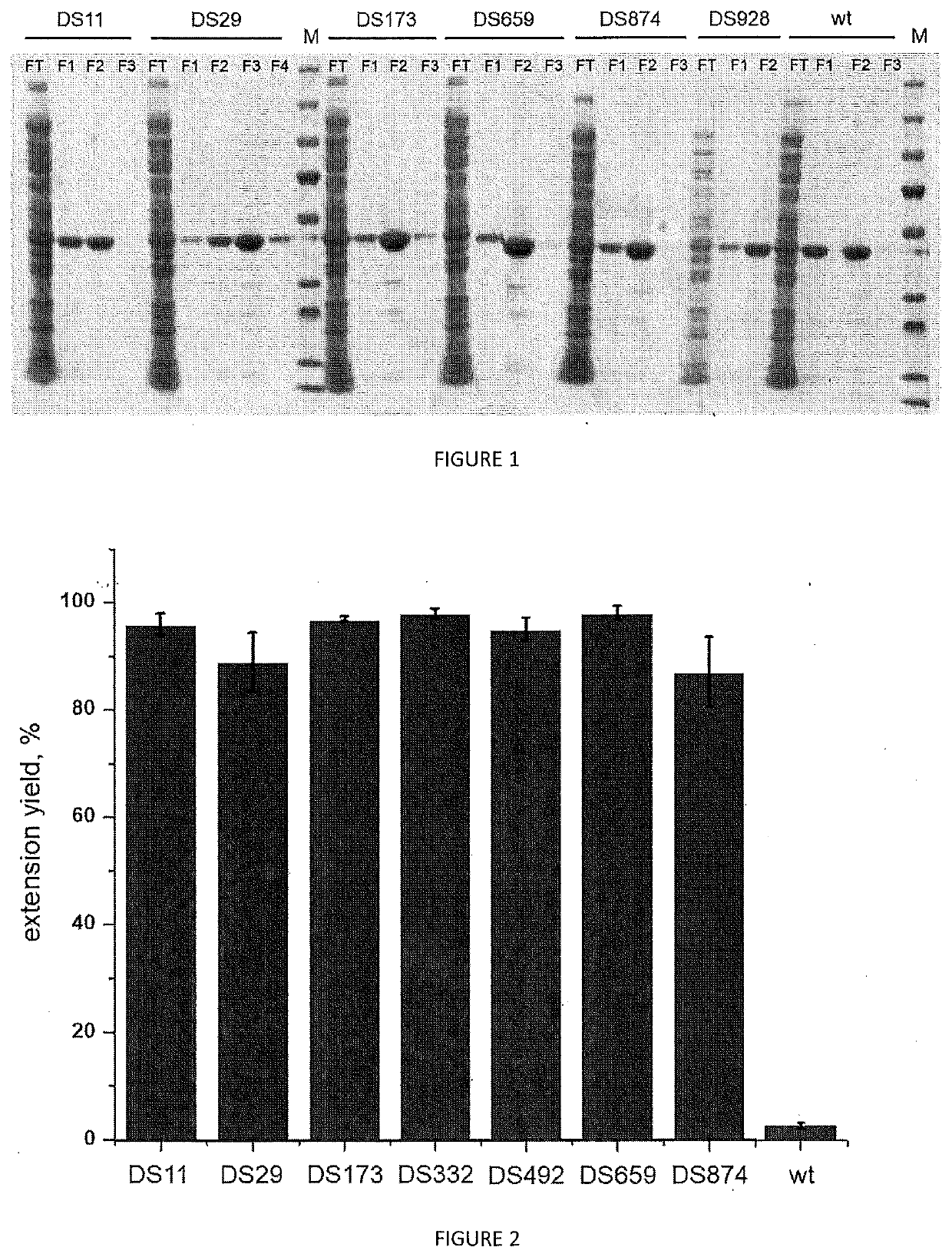
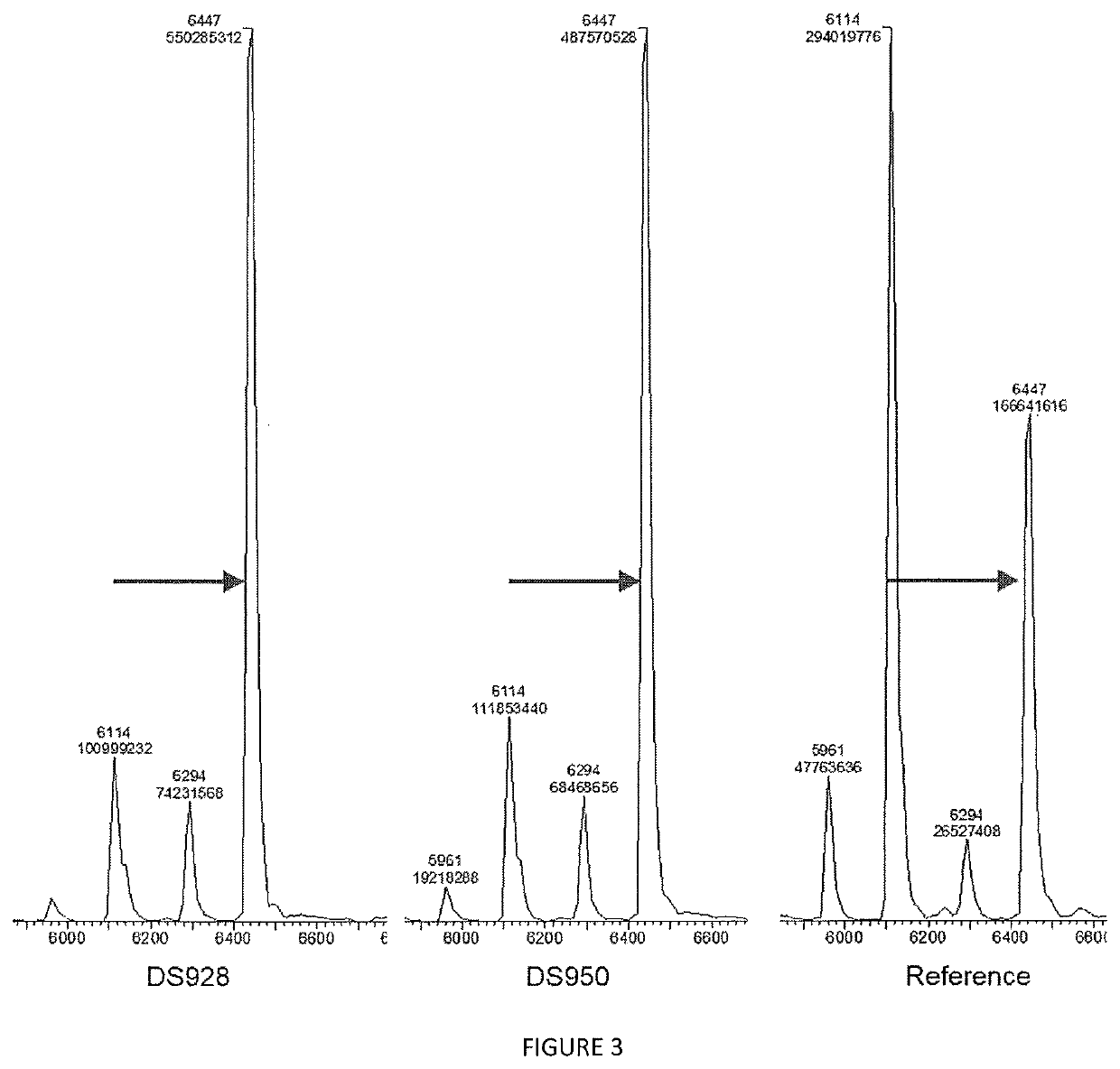
The present invention relates to a variant of Terminal deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT) which (i) comprises the amino acid sequence as set forth in SEQ ID Nº 2 or a functionally equivalent sequence, with at least an amino acid substitution at position corresponding to residue C302 or functionally equivalent residue, wherein the position is numbered by reference to the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID Nº 1, (ii) is able to synthesize a nucleic acid fragment without template and (iii) is able to incorporate a modified nucleotide into the nucleic fragment.
Owner:DNA SCRIPT SAS +2
Thermostable reverse transcriptases and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070141592A1Improve thermal stabilityReduced and eliminated RNase H activityFungiSugar derivativesMessenger RNAReverse transcriptase
The present invention is in the fields of molecular and cellular biology. The invention is generally related to reverse transcriptase enzymes and methods for the reverse transcription of nucleic acid molecules, especially messenger RNA molecules. Specifically, the invention relates to reverse transcriptase enzymes which have been mutated or modified to increase thermostability, decrease terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase activity, and / or increase fidelity, and to methods of producing, amplifying or sequencing nucleic acid molecules (particularly cDNA molecules) using these reverse transcriptase enzymes or compositions. The invention also relates to nucleic acid molecules produced by these methods and to the use of such nucleic acid molecules to produce desired polypeptides. The invention also concerns kits comprising such enzymes or compositions.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
High fidelity reverse transcriptases and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060094050A1Improve fidelityEffective limitFungiBacteriaReverse transcriptaseTerminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase activity
The invention relates to reverse transcriptases which have increased fidelity (or reduced misincorporation rate) and / or terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase activity. In particular, the invention relates to a method of making such reverse transcriptases by modifying or mutating specified positions in the reverse transcriptases. The invention also relates to nucleic acid molecules containing the genes encoding the reverse trancriptases of the invention, to host cells containing such nucleic acid molecules and to methods to make the reverse trancriptases using the host cells. The reverse transcriptases of the invention are particularly suited for nucleic acid synthesis, sequencing, amplification and cDNA synthesis.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Thermostable reverse transcriptases and uses thereof
InactiveUS20110081704A1Improve thermal stabilityExtended half-lifeTransferasesMessenger RNAReverse transcriptase
The present invention is in the fields of molecular and cellular biology. The invention is generally related to reverse transcriptase enzymes and methods for the reverse transcription of nucleic acid molecules, especially messenger RNA molecules. Specifically, the invention relates to reverse transcriptase enzymes which have been mutated or modified to increase thermostability, decrease terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase activity, and / or increase fidelity, and to methods of producing, amplifying or sequencing nucleic acid molecules (particularly cDNA molecules) using these reverse transcriptase enzymes or compositions. The invention also relates to nucleic acid molecules produced by these methods and to the use of such nucleic acid molecules to produce desired polypeptides. The invention also concerns kits comprising such enzymes or compositions.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Variants of Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20190211315A1Improve abilitiesLow costTransferasesFermentationNucleotideAmino acid substitution
The present invention relates to a variant of Terminal deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT) which (i) comprises the amino acid sequence as set forth in SEQ ID No 2 or a functionally equivalent sequence, with at least an amino acid substitution at position corresponding to residue C302 or functionally equivalent residue, wherein the position is numbered by reference to the amino acid sequence set forth in SEQ ID No 1, (ii) is able to synthesize a nucleic acid fragment without template and (iii) is able to incorporate a modified nucleotide into the nucleic fragment.
Owner:DNA SCRIPT SAS +2
Method for measuring activity of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
InactiveCN104293883ALow costEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LSingle strand
The invention discloses a method for measuring activity of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, synthesizing a primer according to a single stranded template, annealing the single stranded template, then performing a 3' end tailing reaction catalyzed by TdT enzyme in the presence of one of four deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, after the 3' end tailing reaction is completed, performing a polymerization reaction in the presence of enough DNA polymerase without 3'-5 'excision enzyme activity to generate double stranded DNA, finally measuring the relative quantity of the double stranded DNA or single stranded DNA in the reaction system after the polymerization reaction is finished, and deducing the activity degree of the Poly (A) polymerase according to the detection result, wherein the basic group at the first site on the used single stranded template in the 3' direction and the deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate used in the tailing reaction are not complementary. Compared with the existing method, the method disclosed by the invention is free of radioactive pollution, simple and quick to operate, low in reagent preparation cost and high in sensitivity.
Owner:VAZYME BIOTECH NANJING
Fluorescent chemical sensor and detection method for detecting oxidative damage in telomeres and application of fluorescent chemical sensor and detection method
ActiveCN110144384AReduce consumptionHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorophoreRepair enzymes
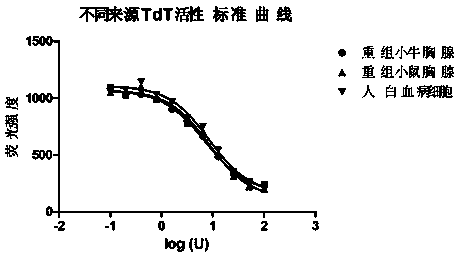
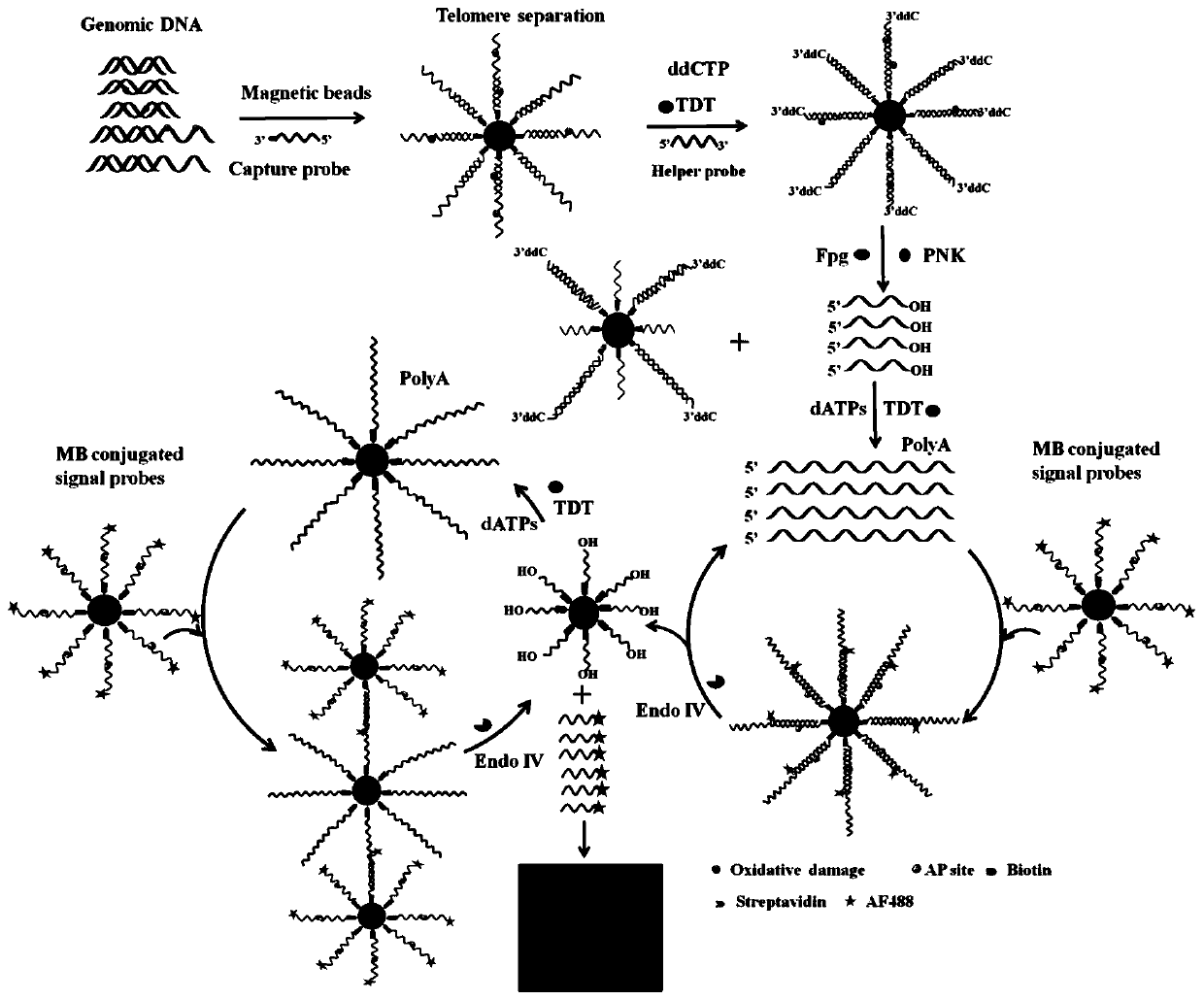
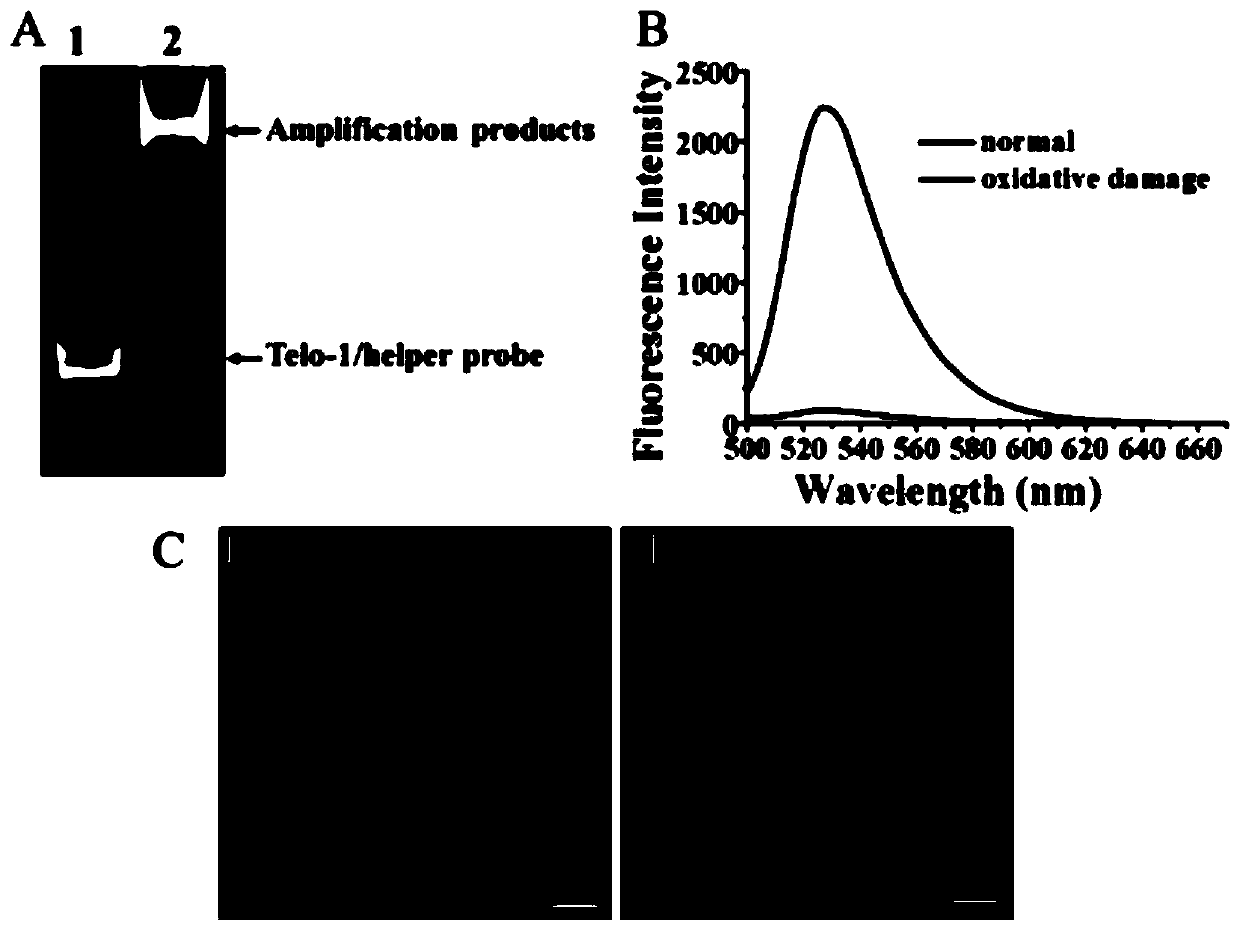
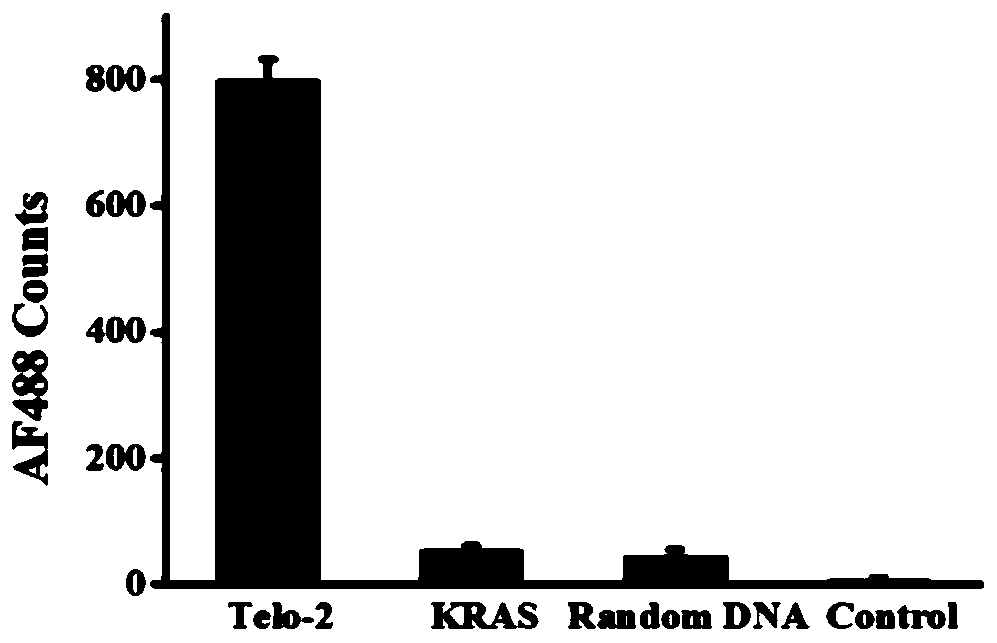
The invention provides a fluorescent chemical sensor and detection method for detecting oxidative damage in telomeres and an application of the fluorescent chemical sensor and the detection method. Specificity of a repair enzyme and polymerization mediated by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase are combined so as to start a cycle cutting signal probe induced by endonuclease IV, induce an AP sitein an Endo IV splitting signal probe, cause release of AF488 fluorophore on the signal probe, and besides, generate a signal probe having free 3'-OH end. Each signal probe having free 3'-OH can be effectively extended through TdT to generate a long poly-A sequence. The released poly-A sequence and a newly-generated poly-A sequence can induce the repeated cycle cutting of the signal probe so as torelease more AF488 fluorophore. Under magnetic separation, the fluorophore in supernatant can be imaged and quantified by unimolecule. The fluorescent chemical sensor and detection method have favorable actual application value.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Method for constructing strand-specific transcriptome library
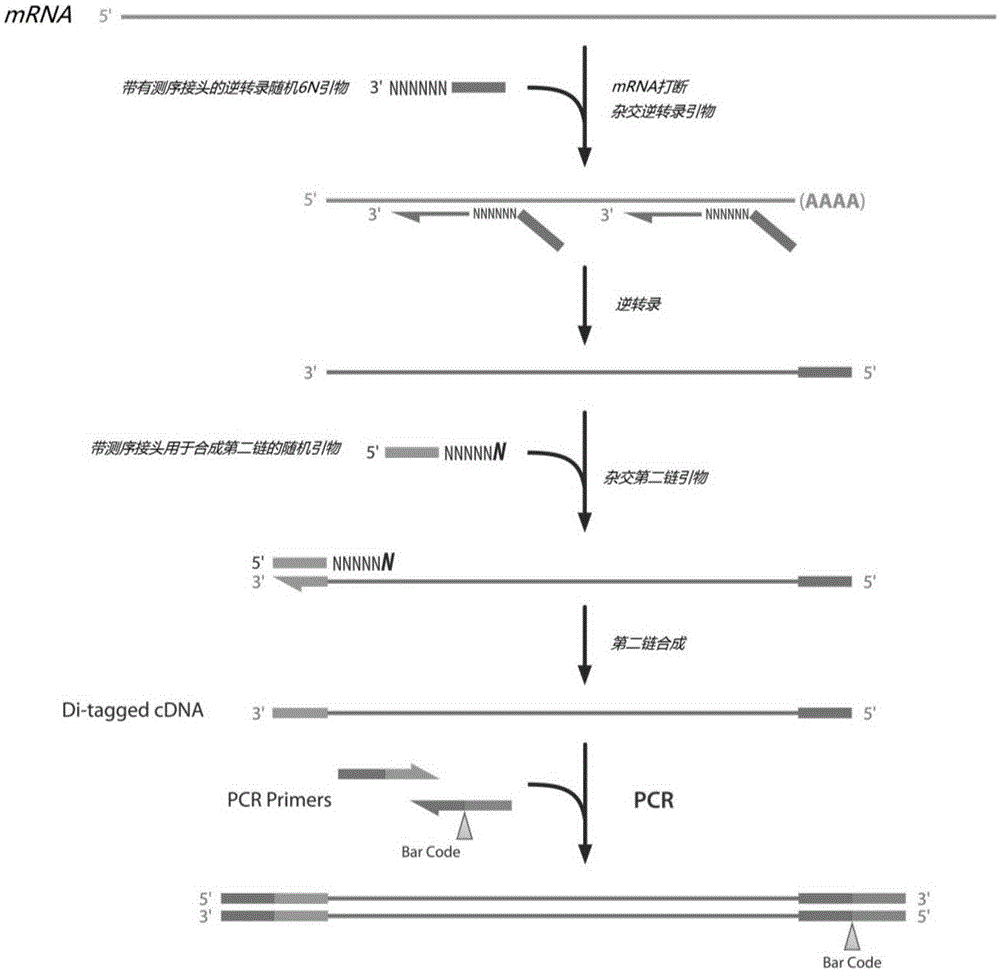
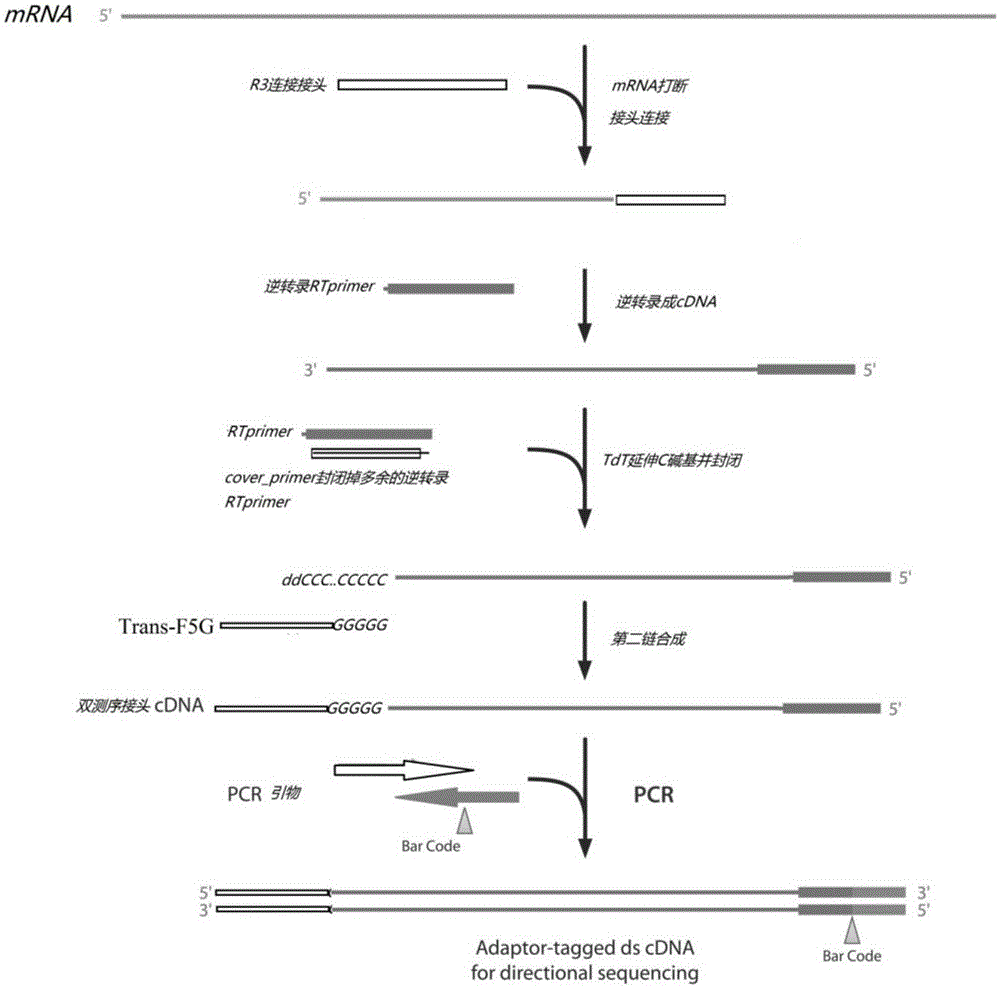
InactiveCN105349533AImprove uniformityQuality improvementMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationPolymerase LDesoxyribonucleic acid
The invention discloses a method for constructing a strand-specific transcriptome library. The method comprises steps as follows: step 1), mRNA (massager ribonucleic acid) fragmentation processing is performed; step 2), inverse transcription is performed: the fragmented mRNA 3' terminal is connected with an R3 joint with the known sequence; an RT primer and the R3 joint are subjected to annealing pairing for inverse transcription, and a first strand of cDNA (complementary desoxyribonucleic acid) is synthesized; step 3), cDNA 3' terminal marking is performed: after RNA is removed, TdT (terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase) is adopted to add multiple dC basic groups to the cDNA 3' terminal, ddCTP (2',3'-dideoxycytidine-5'-triphosphate) is adopted for end closing, pairing is performed with an F5G primer, and the first strand of cDNA is duplicated under the action of polymerase; step 4), PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification is performed; step 5), quality testing is performed. The fragmented mRNA is connected with the joint and then is synthesized, so that the synthetic efficiency and the homogeneity of cDNA are improved; after the first strand of cDNA is synthesized, multiple dC basic groups are added to the cDNA 3' terminal by adopting TdT and ddCTP is adopted for closing, pairing is performed with the F5G primer containing multiple dG basic groups, the first strand of cDNA is duplicated under the action of polymerase, therefore, production of self-linked dimers can be effectively reduced, and the homogeneity of the library is improved.
Owner:生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司
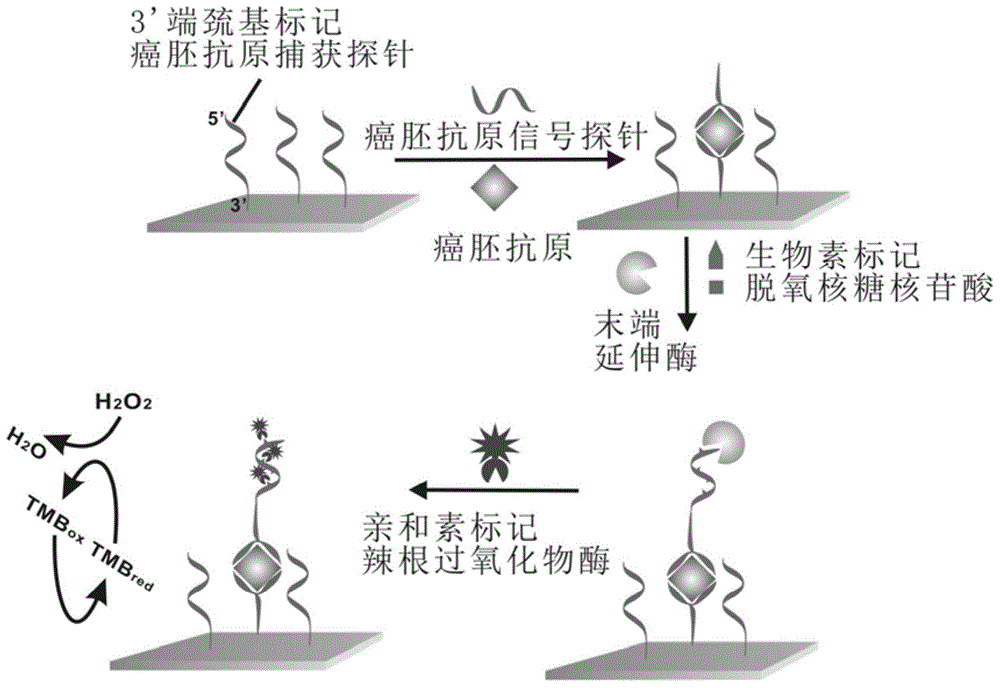
Method for detecting carcino-embryonic antigens by using electrochemical nucleic acid aptamer sensor on basis of terminal elongases
ActiveCN106525920AHigh detection sensitivityHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesWilms' tumorElongase
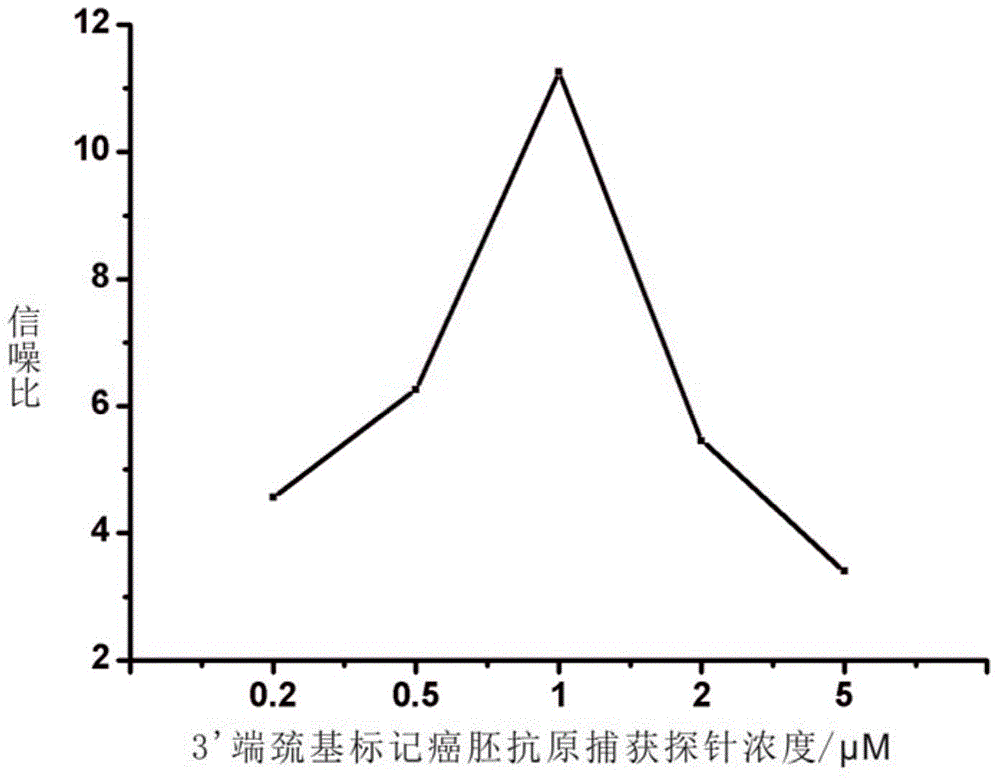
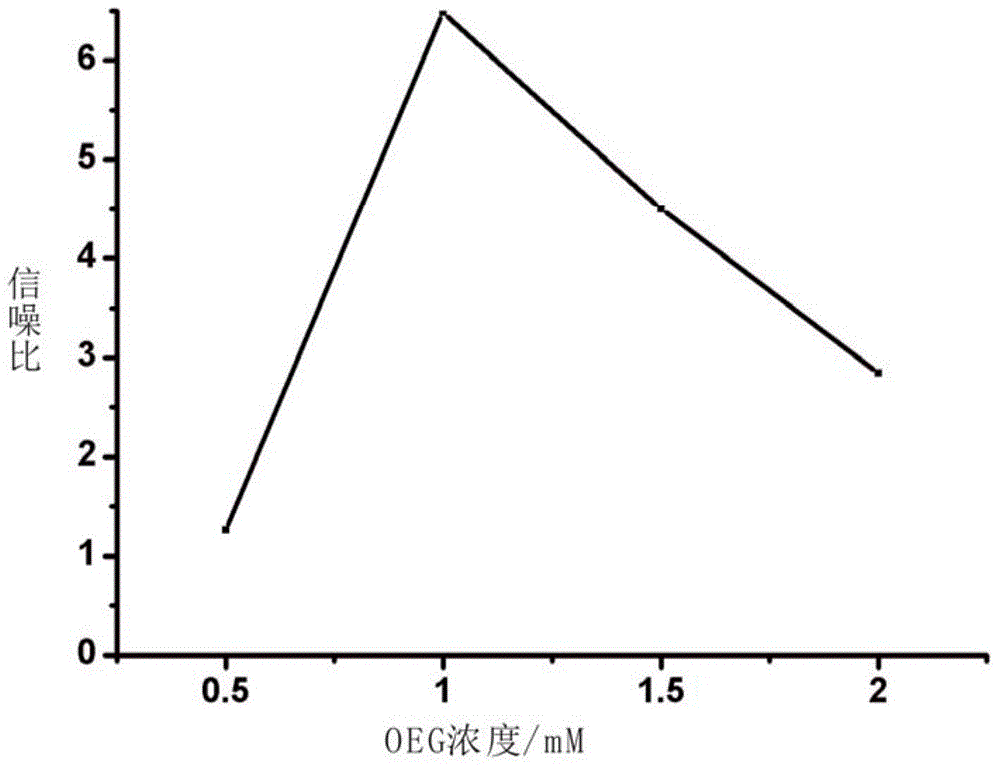
The invention discloses a method for detecting carcino-embryonic antigens by using an electrochemical nucleic acid aptamer sensor on the basis of terminal elongases. The method comprises the following steps: modifying a layer of 3' mercapto-terminated labeled carcino-embryonic antigen aptamer capturing probes on the surface of a gold electrode at first; then adding carcino-embryonic antigens and carcino-embryonic antigen aptamer signal probes, wherein the 3' mercapto-terminated labeled carcino-embryonic antigen aptamer capturing probes and the carcino-embryonic antigen aptamer signal probes can specifically recognize the carcino-embryonic antigens, so that a sandwich structure is formed on the surface of the electrode; extending biotin labeled nucleic acid long chains at 3' terminals of the carcino-embryonic antigen aptamer signal probes under the effect of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, wherein avidin labeled horse radish peroxidase can be combined to the biotin labeled nucleic acid long chains in a compatible manner; and detecting electrochemical signal change generated by horse radish peroxidase catalyzed electrolyte so as to realize high-sensitivity and high-specificity detection on the carcino-embryonic antigens. The method can be used for early diagnosis of tumors, curative effect judgment, progression of the disease, prognosis estimation and the like.
Owner:迈科若(苏州)医疗科技有限公司
Variants of Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20190390178A1Improve abilitiesIncrease synthesisTransferasesVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotideAmino acid substitution
The present invention relates to variants of Terminal deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT), each of which (i) has an amino acid sequence similarity to SEQ ID NO: 2. 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33 or 35 with corresponding amino acid substitutions, (ii) is capable of synthesizing a nucleic acid fragment without a template and (iii) is capable of incorporating a modified nucleotide into the nucleic acid fragment.
Owner:DNA SCRIPT SAS +3
Decoy compositions for treating and preventing brain diseases and disorders
InactiveUS20080207552A1Inhibit expressionAvoid damageSsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseStaining
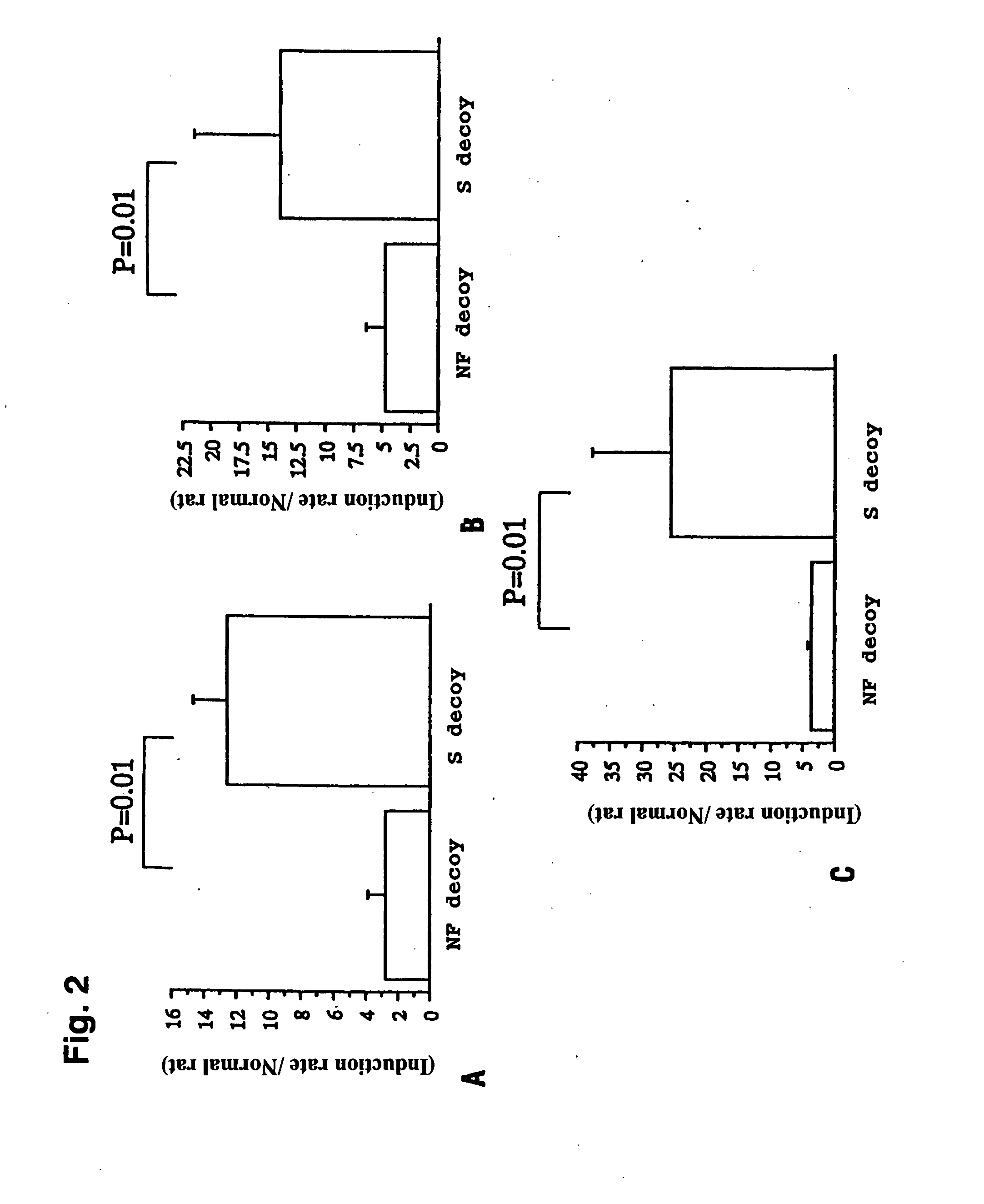
The present invention provides introduction of NF-κB decoy oligodeoxynucleotide into rat cranial nerve through a carotid artery during global brain ischemia. Polymerase chain reaction demonstrated that one hour after global brain ischemia, transfected NF-κB decoy oligodeoxynucleotide effectively suppressed expression of tumor necrosis factor α, interleukin 1β and intracellular adhesion molecule 1 messenger RNAs. Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated deoxyuridine nick-end labeling staining and immunohistochemistry using microtubule-associated protein 2 demonstrated that transfected NF-κB decoy oligodeoxynucleotide significantly attenuated neuronal damage seven days after global brain ischemia. Therapeutic transfection of NF-κB decoy oligodeoxynucleotide during brain ischemia may be effective for attenuation of neuronal damage, suggesting a strategy for protecting the cerebrum from global ischemia.
Owner:ANGES MG INC
MicroRNA detection method based on Hg<2+> assistance and double-polymerase isothermal nucleic acid amplification technology
ActiveCN106119343AAchieving Sensitive DetectionMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid amplification techniqueFluorescence
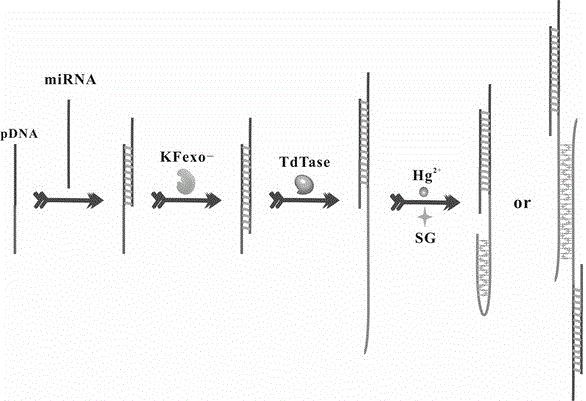
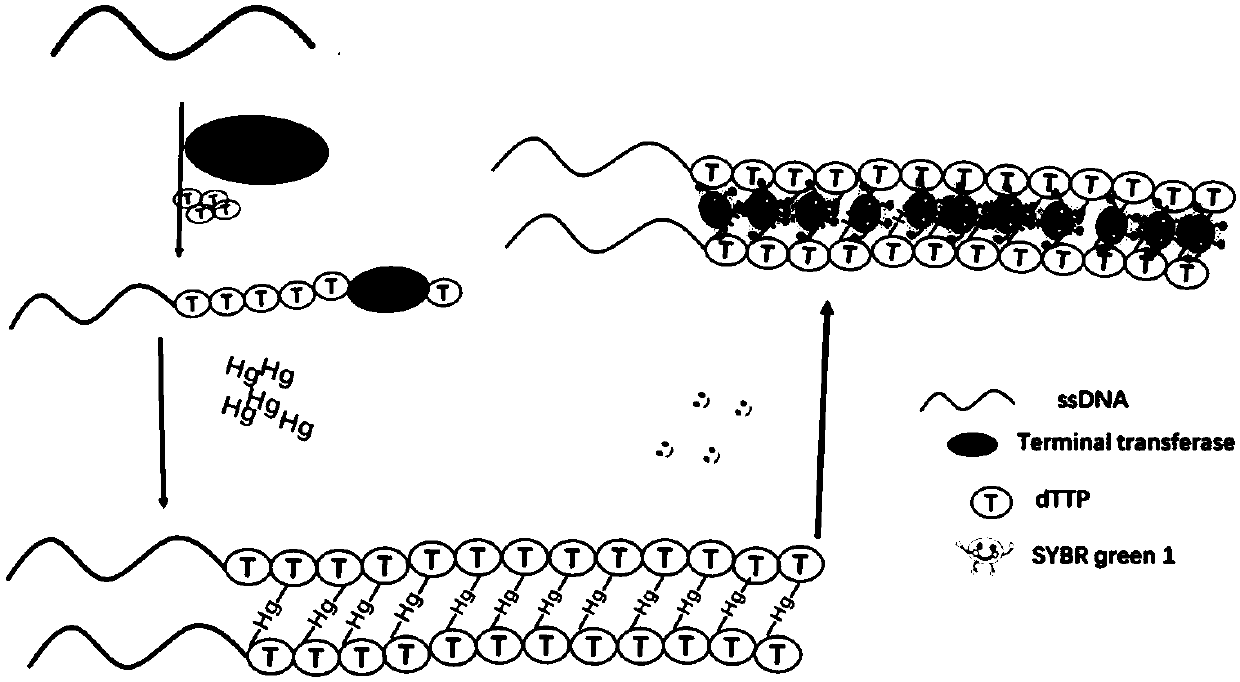
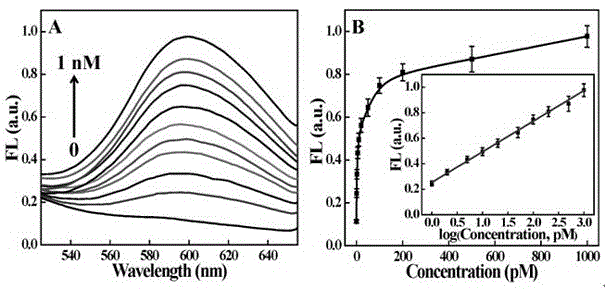
The invention discloses a microRNA detection method based on Hg<2+> assistance and a double-polymerase isothermal nucleic acid amplification technology, and belongs to the technical field of optical bio-sensing. On the basis of a combined catalytic action of a polymerase Klenow fragment and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, microRNA is effectively extended into a polythymine base sequence which is relatively long; Hg<2+> is added, so that a T-Hg<2+>-T double-stranded structure is formed; an SYBR Green I fluorescent dye is interpolated into the T-Hg<2+>-T double-stranded structure, so that the fluorescence of the SYBR Green I is enhanced; and a fluorescence enhancing degree is positively related to the concentration of the microRNA; therefore, the sensitive detection of the microRNA is achieved.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Variants of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase and uses thereof
ActiveUS10752887B2Improve abilitiesIncrease synthesisTransferasesFermentationNucleotideAmino acid substitution
The present invention relates to variants of Terminal deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT), each of which (i) has an amino acid sequence similarity to SEQ ID NO: 2. 11, 13, 15, 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29, 31, 33 or 35 with corresponding amino acid substitutions, (ii) is capable of synthesizing a nucleic acid fragment without a template and (iii) is capable of incorporating a modified nucleotide into the nucleic acid fragment.
Owner:DNA SCRIPT SAS +3
Methods and compositions for amplifying short DNA fragments
InactiveUS20200208143A1Reduce random errorImprove efficiencyNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMultiplexBase J
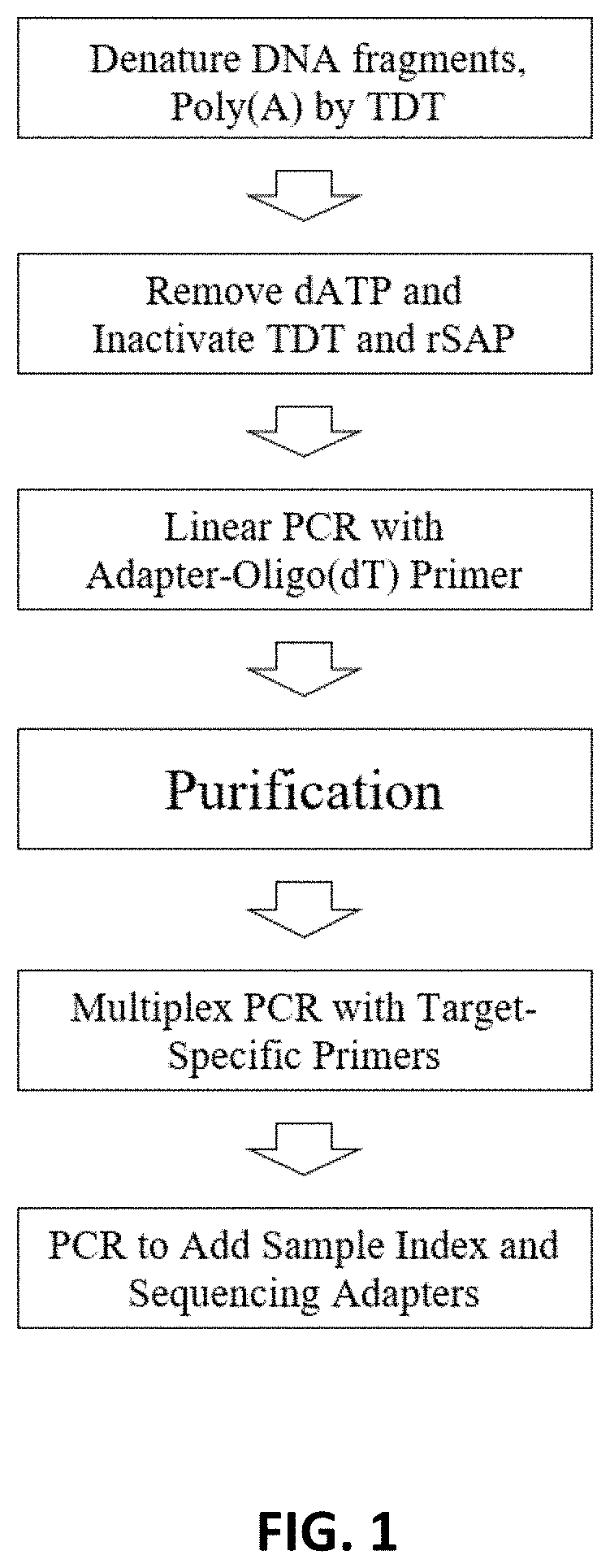
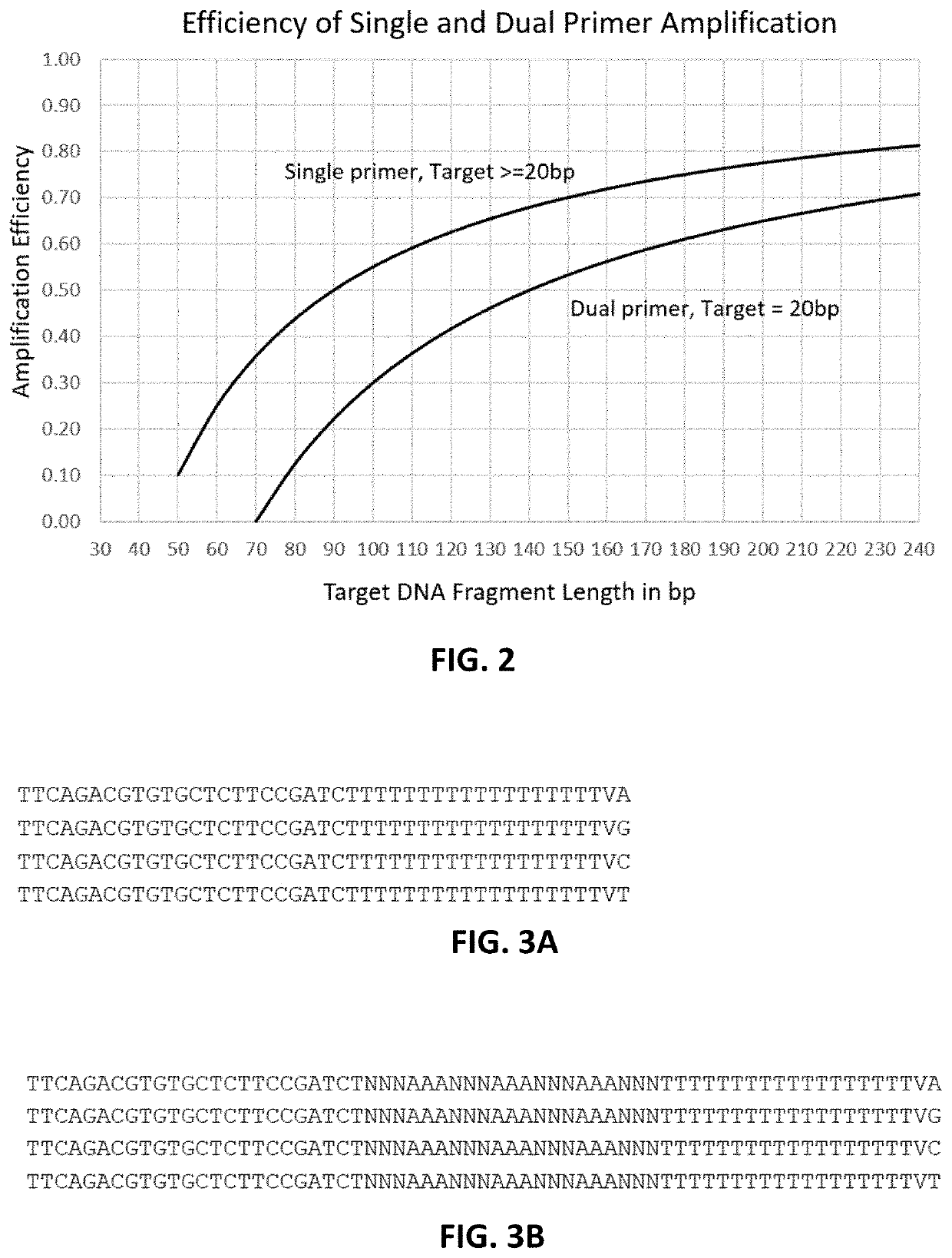
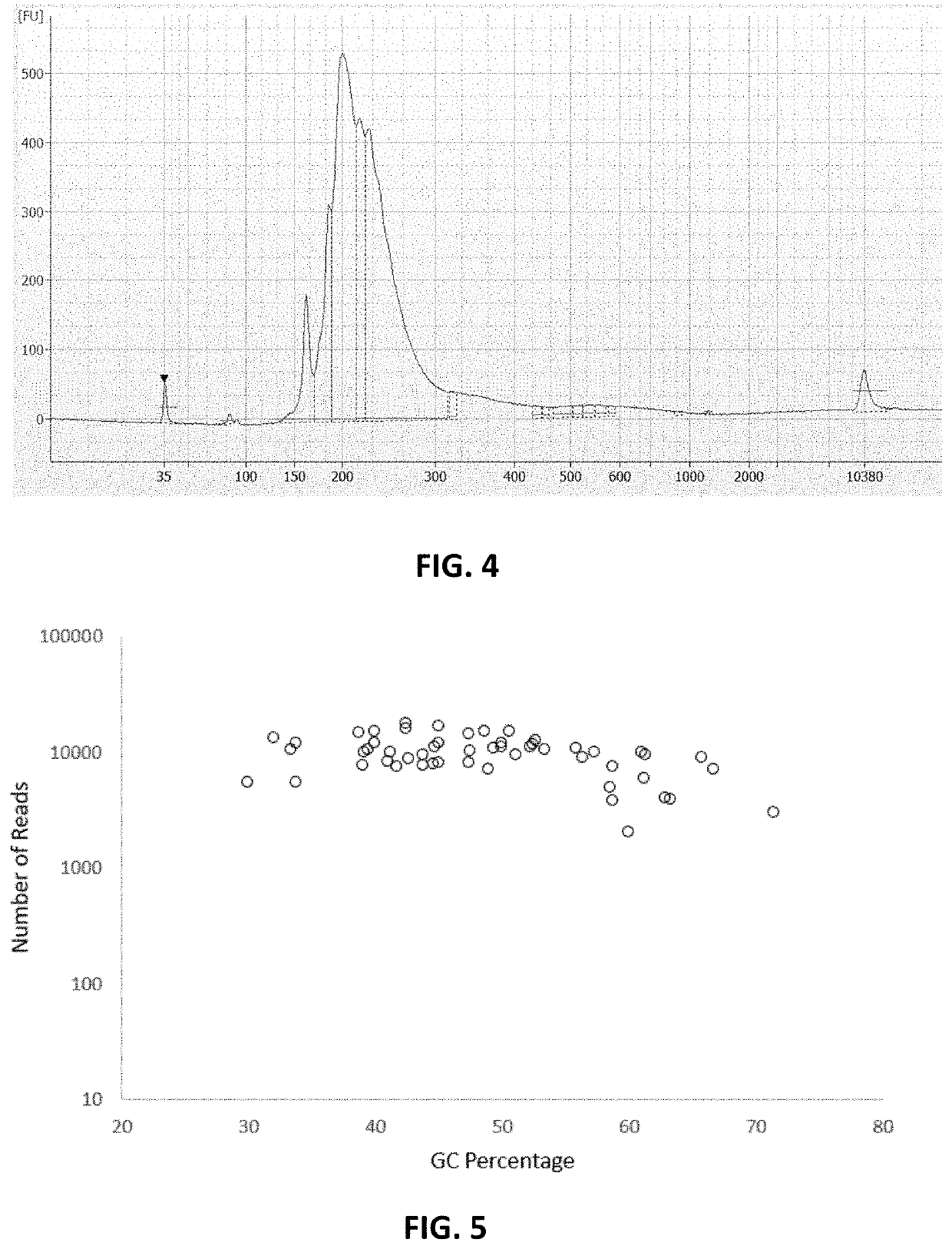
Methods, compositions and systems to amplify short DNA fragments, such as cfDNA, and to reduce random base errors formed in template-dependent primer extension reactions, and to find variant frequencies of mutations on the DNA fragments. The methods, compositions and systems described herein may include, or include the use of, poly(dA) tailing of short DNA fragments by a terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, linearly amplification and a multiplex primer extension reaction.
Owner:PARAGON GENOMICS INC
Method for determining activity of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase and application of method
ActiveCN109536577AQuick checkHigh fluorescence intensityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA SolutionsBiological studies
The invention discloses a method for determining activity of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) and application of the method. The method comprises the steps of: (1) designing a single-stranded DNA as a DNA probe; (2) incubating TdT with different final concentrations with DNA probes, CoCl2, dTTPs and a buffer solution separately to obtain a single-stranded probe DNA solution rich in a poly-T sequence; then adding a mercury salt to incubate to obtain a T-HgII-T structure-mediated double-stranded DNA solution; adding a nucleic acid dye to obtain a mixed solution; and finally detectinga fluorescence intensity signal of the mixed solution, and drawing a detection curve according to the fluorescence intensity signal and the final concentration of TdT; and (5) replacing the TdT with asample to be tested, repeating the above steps, and then comparing the detection result with the detection curve to calculate the content of TdT in the sample to be tested. The method has high sensitivity and good selectivity, and provides a new means for medical detection and biological research.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Detection method of microRNA (micro Ribonucleic Acid)
InactiveCN105648098ARealize detectionLow backgroundMicrobiological testing/measurementBase JSodium ascorbate
The invention discloses a detection method of microRNA (micro Ribonucleic Acid), and belongs to the field of optical biosensing techniques. A to-be-detected sample is mixed with template DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid), an obtained first mixture is annealed and hybridized, a buffer solution containing polymerase Klenow fragment, deoxyuracil nucleoside triphosphate and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase is added into a reaction product, an obtained second mixture is caused to react for 4h at 35 DEG C in a water bath, so as to prepare a polyuracil base sequence; sodium ascorbate is added into a polyuracil base sequence solution obtained in the step (4), and then CuCl2 is added into an obtained third mixture, and an obtained fourth mixture is caused to react for 10min at a room temperature, so as to prepare a red-fluorescence copper nano cluster which uses the polyuracil base sequence as a template, thereby obtaining a solution containing the red-fluorescence copper nano cluster. The intensity of the red fluorescence of the solution including the red-fluorescence copper nano cluster is measured by adopting a spectrofluorophotometer; by comparing the result about the intensity of the red fluorescence with a standard relation curve, the concentration of the microRNA is calculated and obtained.
Owner:吴滨
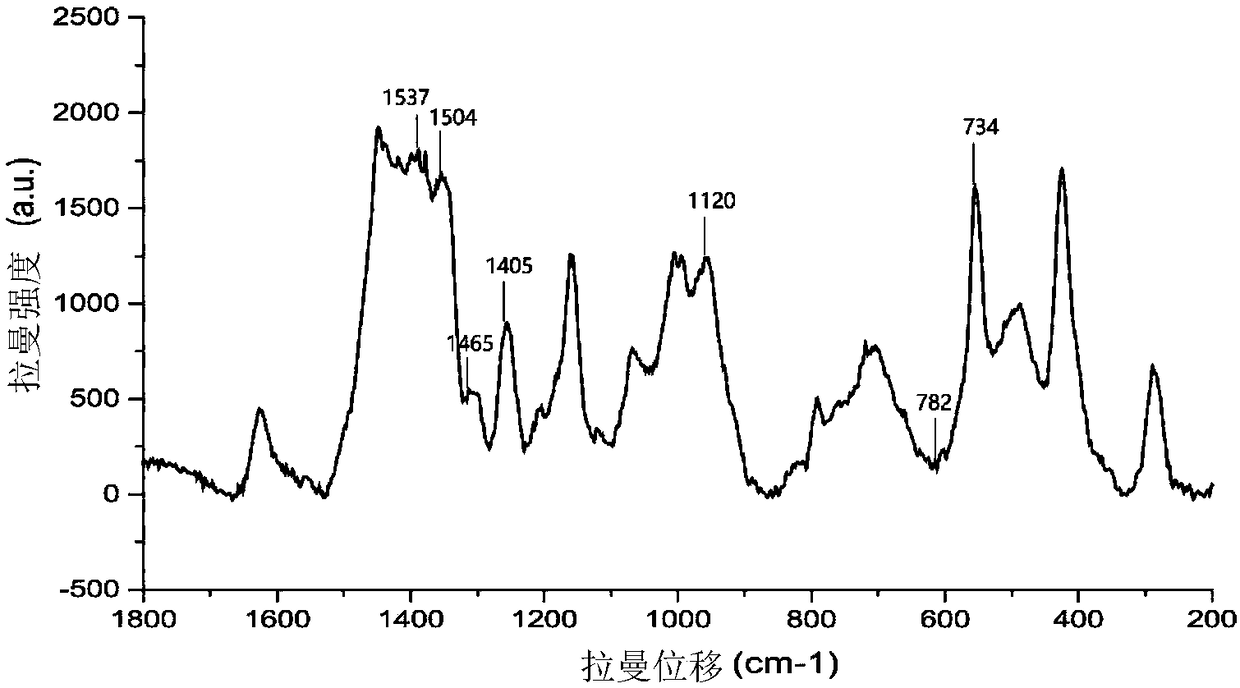
Method for preparing core-shell SERS structure based on amplification of nucleic acid strand by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
InactiveCN109307669AImprove adsorption stabilityIncrease the number of "hot spots"Raman scatteringSingle strand dnaBiology
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Fluorescence chemical method for detecting ALP (Alkaline Phosphatase) and application thereof
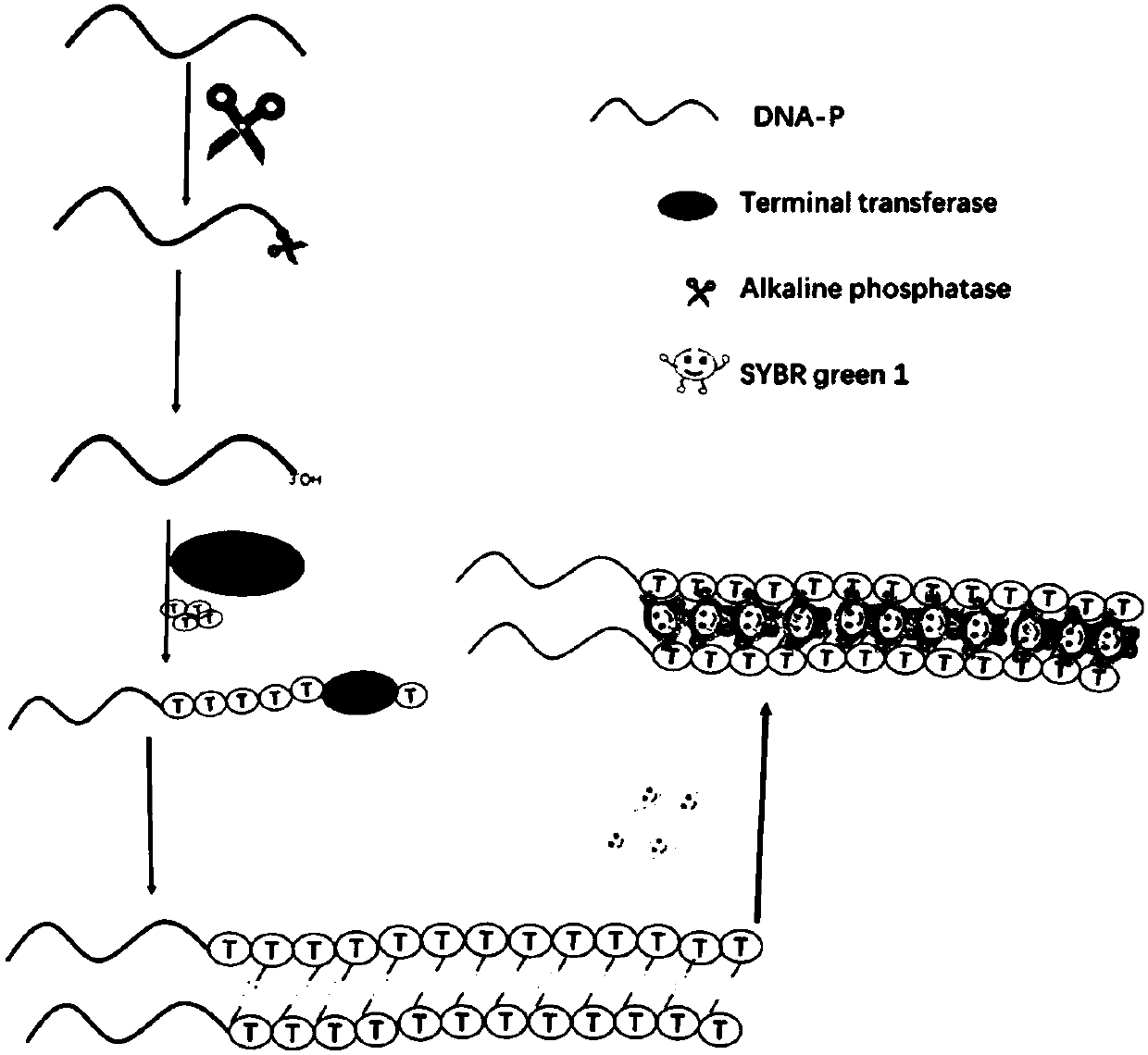
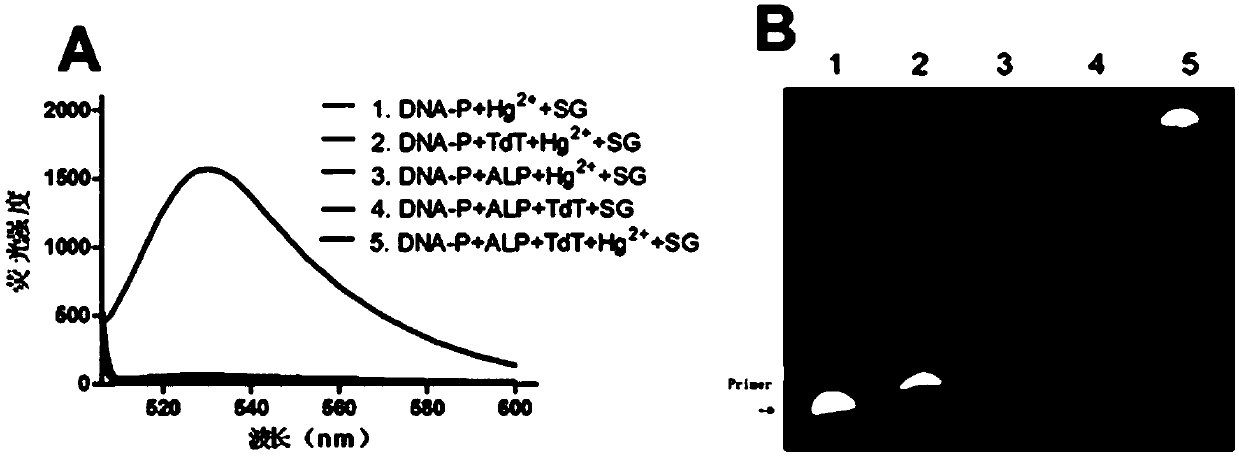
ActiveCN109576342AHigh fluorescence intensitySensitive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisPhosphorylationA-DNA
The invention discloses a fluorescence chemical method for detecting ALP (Alkaline Phosphatase) and application thereof. The fluorescence chemical method comprises the following steps of: firstly, designing a single-chain DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of which a 3' terminal is phosphorylated as a DNA probe, dephosphorylating the 3' terminal of the DNA probe and exposing a 3'-OH terminal when the ALPexists; secondly, performing catalytic addition on dTTPs (Deoxythymidine Triphosphates) at a 3'-OH terminal of the DNA probe by TdT (Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase), thus extending to generatea poly-T tail ssDNA, forming a dual-chain DNA mediated by T-HgII-T structure by the poly-T tail ssDNA and Hg ions, and drawing a detecting curve according to a detected fluorescence intensity signaland the concentration of the ALP after adding nucleic acid dye; finally, replacing the ALP with a to-be-detected sample, repeating the steps, and comparing a detecting result with the detecting curve,thus calculating the content of the ALP in the sample. The fluorescence chemical method disclosed by the invention is simple and convenient, is high in sensitivity and can be used for detecting the ALP or screening ALP inhibitors.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting HTLV-II DNA based on enzymatic catalysis controllable self-assembly bio-barcode
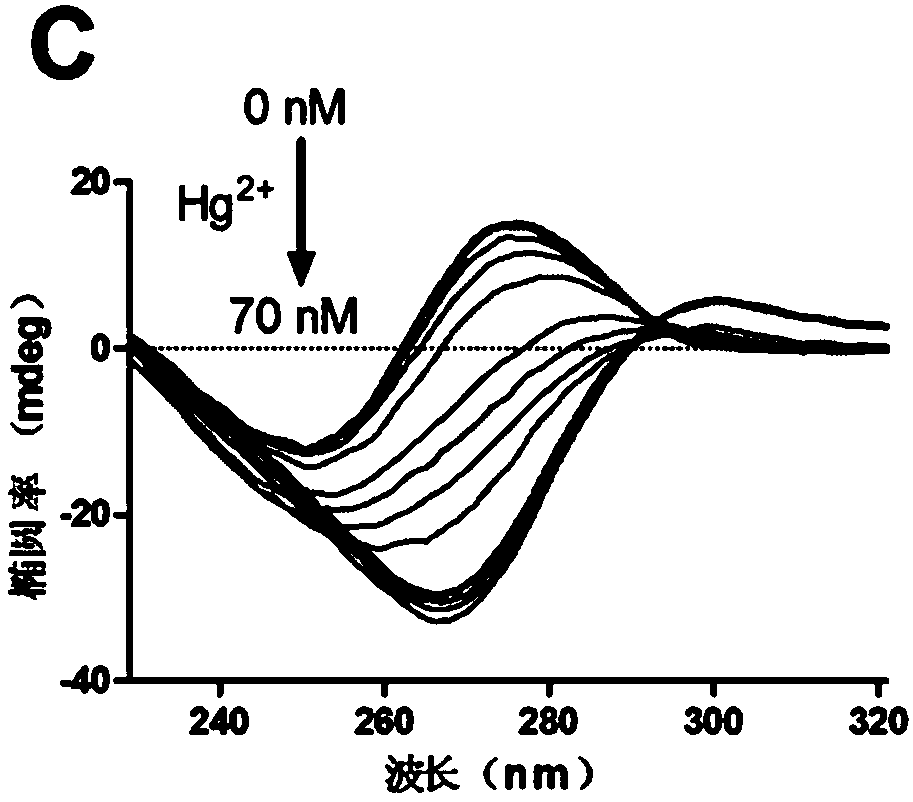
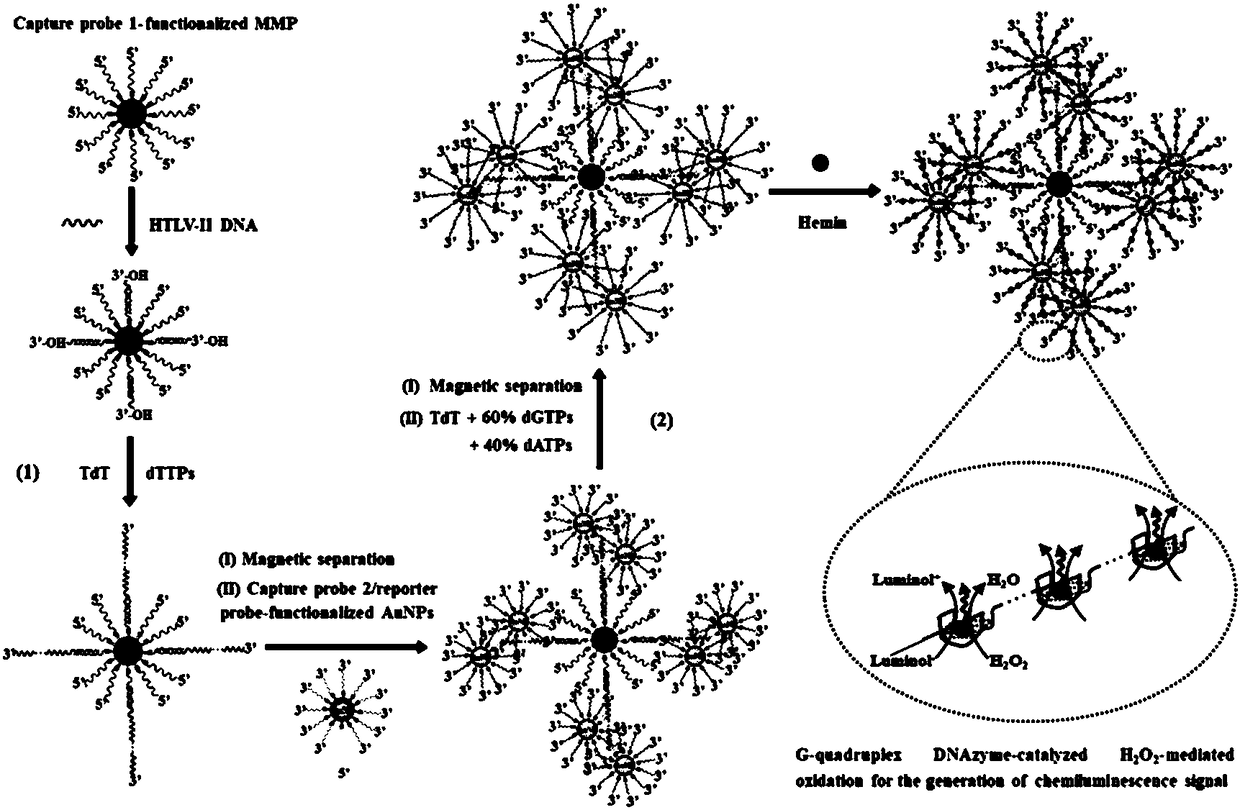
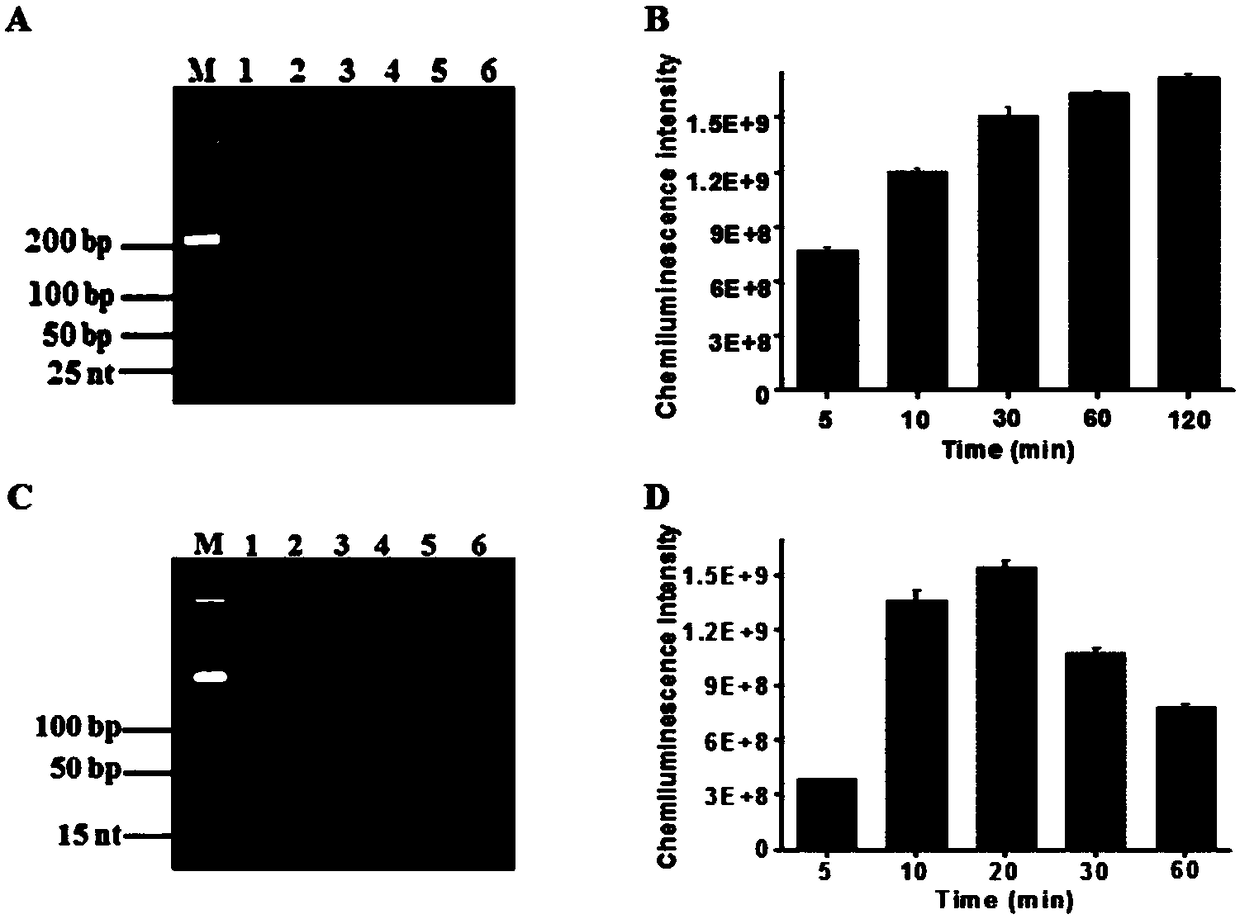
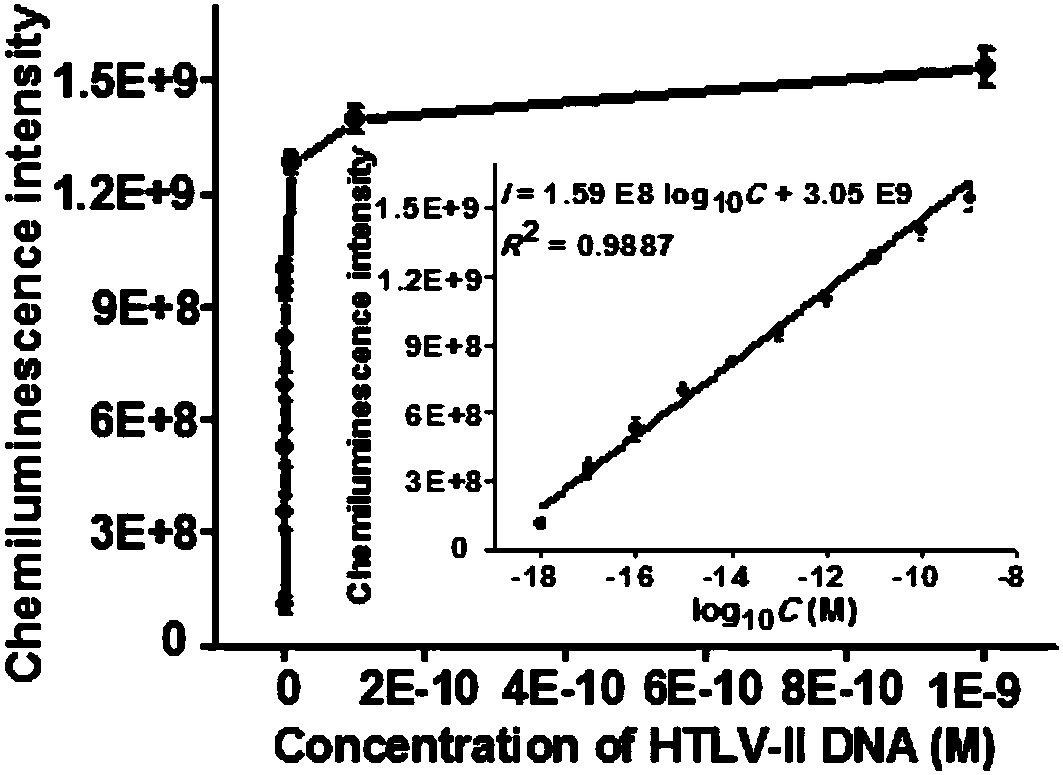
ActiveCN108588284ARapid detectionHigh sensitivity detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLower limitHeme
The invention provides a chemiluminescence method for performing dendritic amplified assay on human T-cell leukemia virus II (HTLV-II) DNA based on terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase catalysis self-assembly bio-barcode. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following two continuous reaction steps: (1) first, enzymatic extension and dendritic self-assembly of bio-barcode based on HTLV-II DNA induced terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase catalysis; (2) chemiluminescence detection in presence of second enzymatic extension heme based on terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase catalysis. According to the technical scheme in the invention, the lower limit of detection can reach 0.5*10<-18>mol / L, the sensitivity is greatly improved when being compared with that in the priorart, the specificity is good, and the operation is simple and convenient.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Reverse transcription PCR method mediated by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase and used for detecting micro RNA
PendingCN110055316AStrong specificityHigh detection sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementPcr methodSingle strand dna
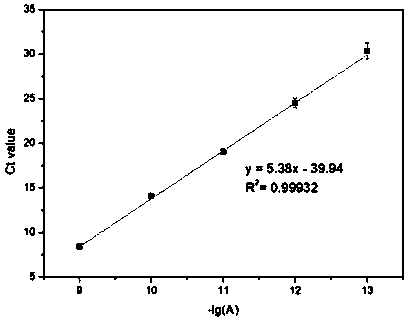
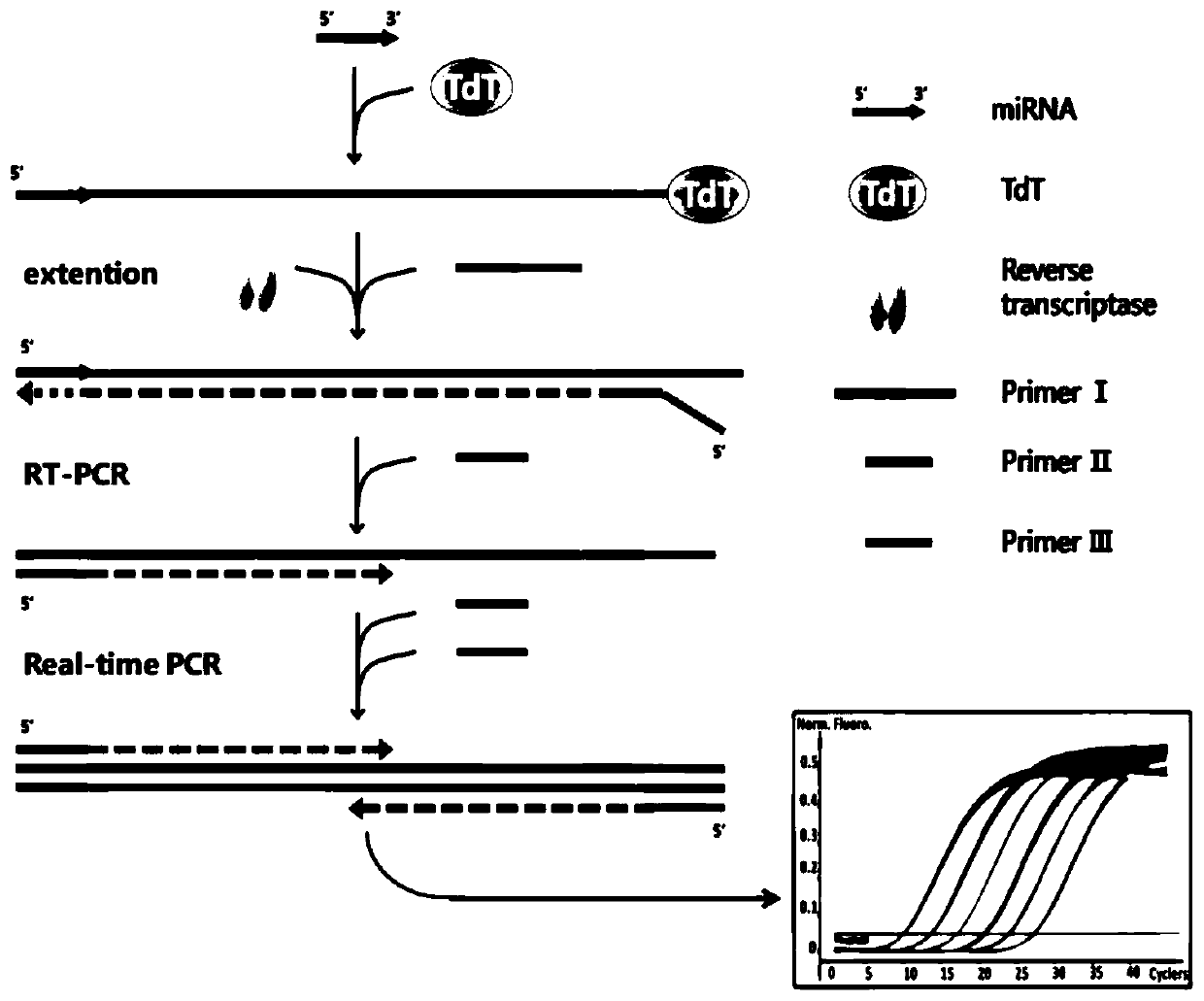
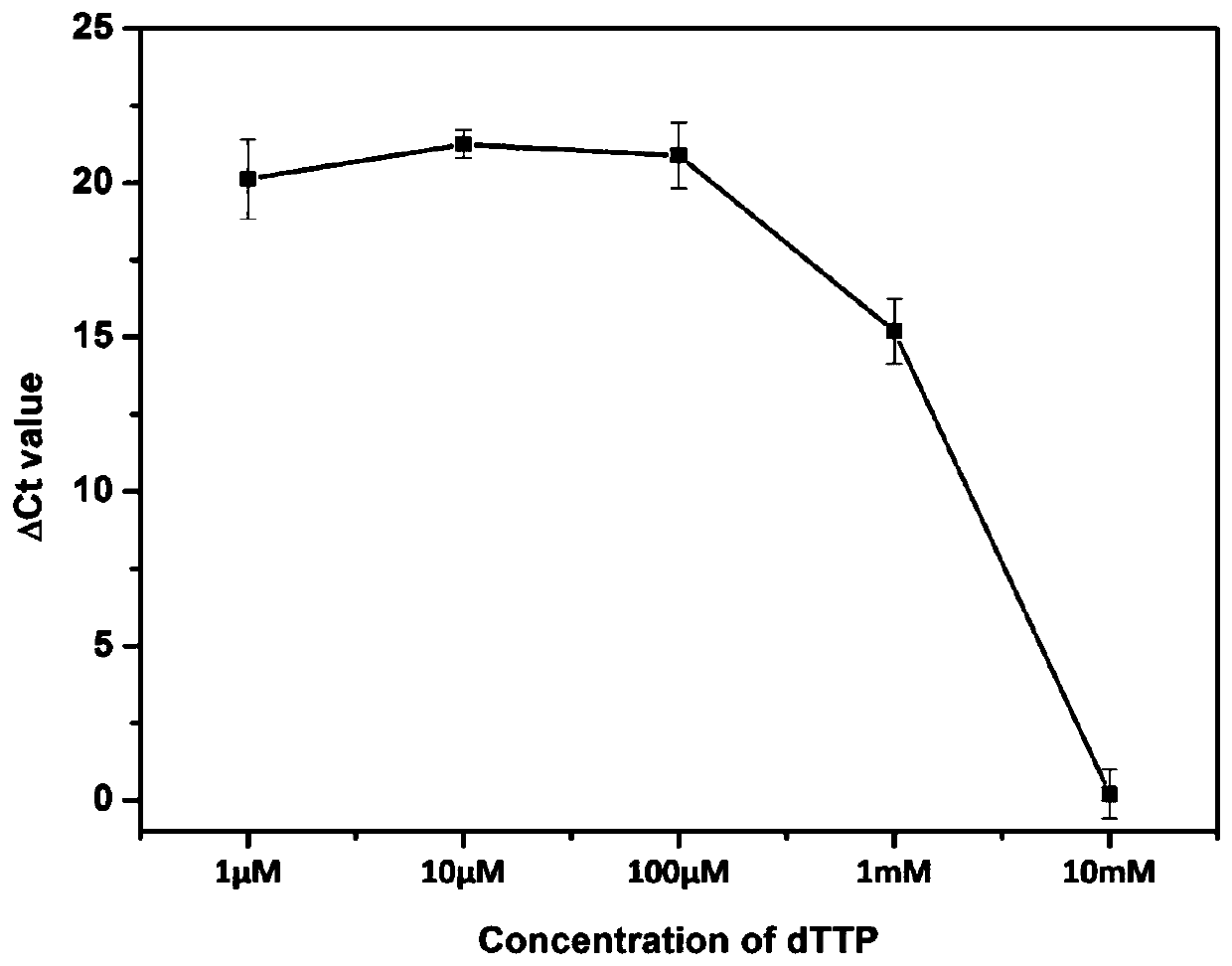
The invention discloses a reverse transcription PCR method mediated by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase for detecting microRNA, in particular to a reverse transcription PCR detection method of aliver injury microRNA marker miR-122, and belongs to the technical field of biology. Specifically, the method utilizes the function that TdT catalyzes RNA to extend out of single-stranded DNA so as toachieve miR-122 elongation; and then reverse transcription is carried out on the extension product by using a universal primer and rapid amplification is carried out by real-time quantitative PCR, sothat sensitive and specific quantitative detection on trace miRNA in a pure liquid phase system is achieved. The method has good specificity, sensitivity and anti-interference capability, and provides a new direction for establishing a sensitive and specific miRNA detection method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Enzyme DNA repair cascade drive fluorophore coding/de-coding-based biosensor and application thereof in telomerase detection
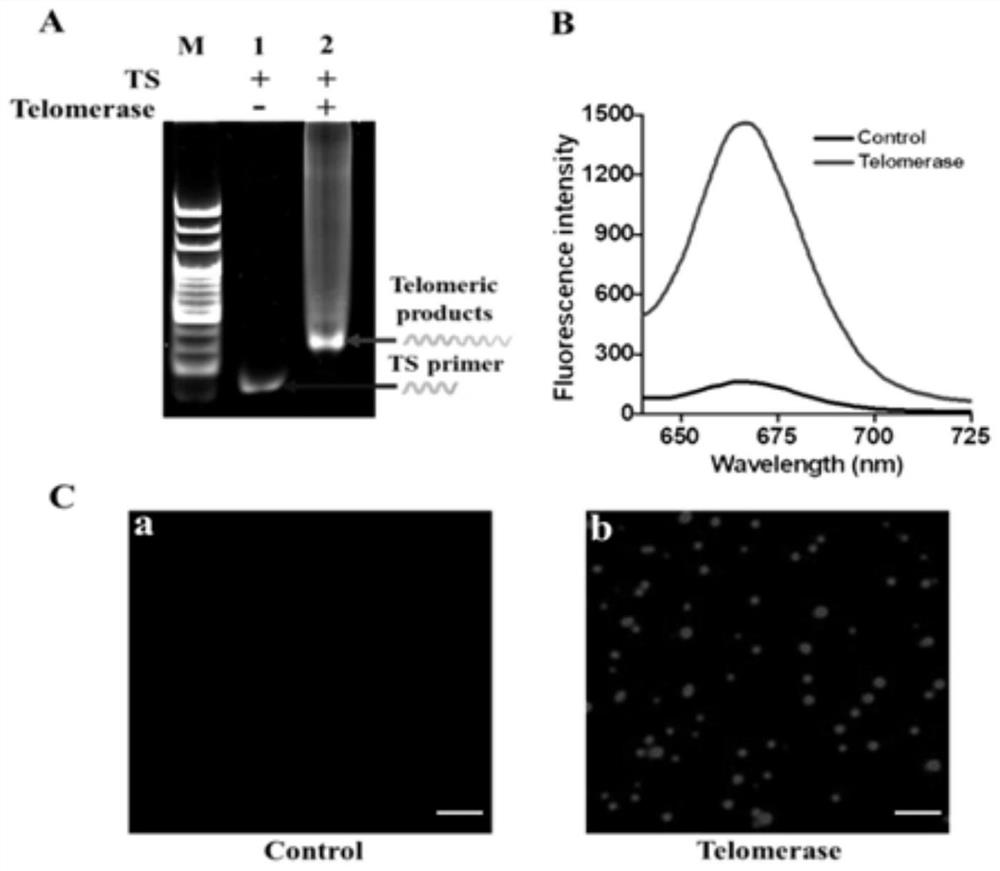
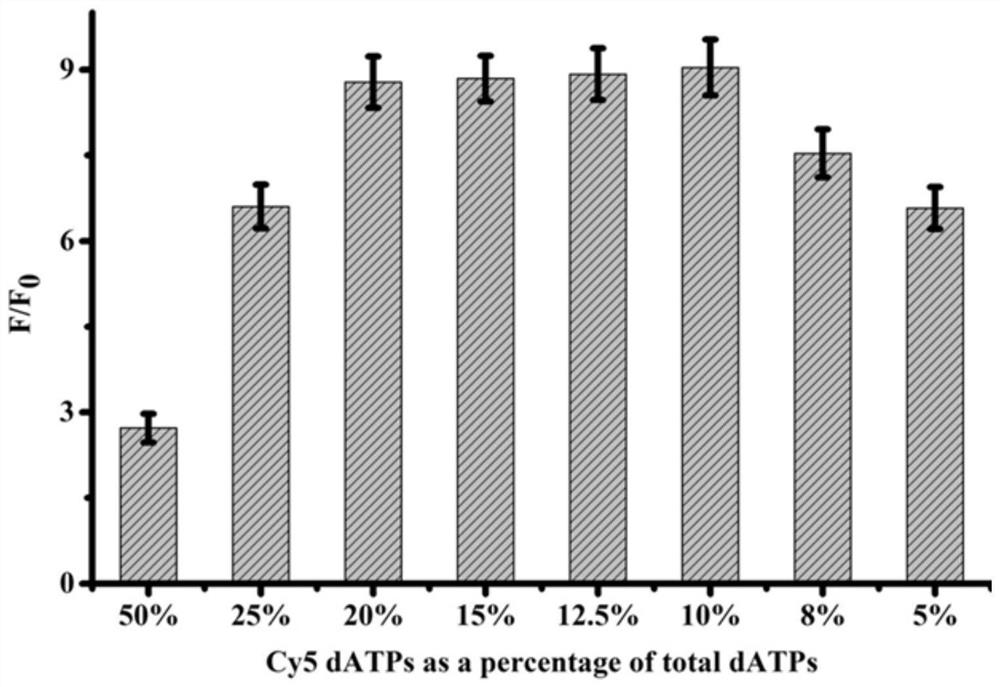
PendingCN114507706AAvoid non-specific amplificationNo extension reactionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisTelomeraseMagnetic bead
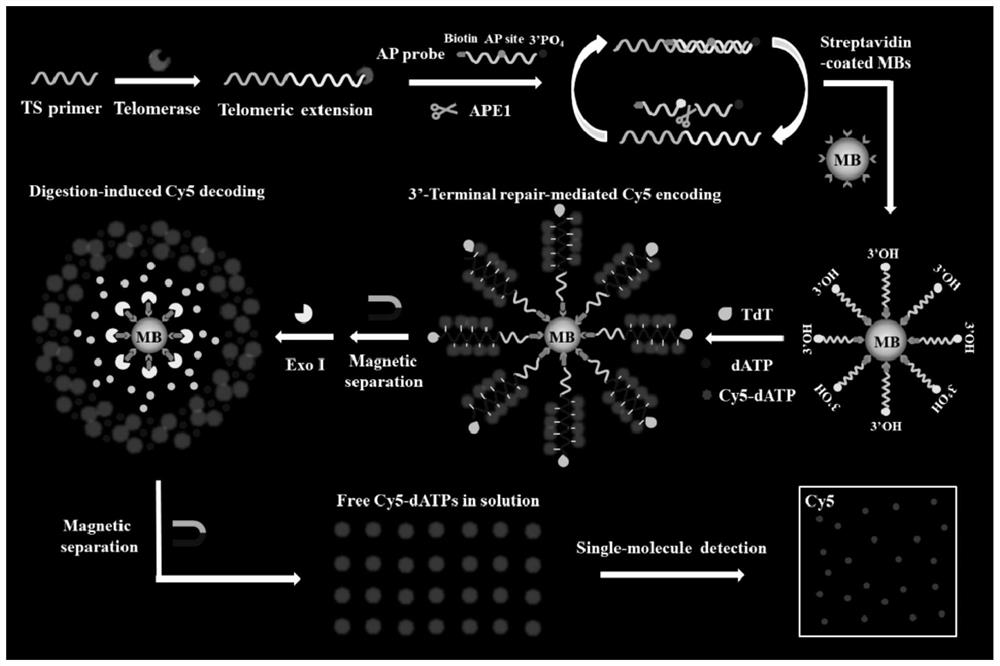
The invention provides a biosensor based on enzyme DNA repair cascade drive fluorophore coding / de-coding and application of the biosensor in telomerase detection, and belongs to the technical field of fluorescence detection. The biosensor at least comprises an AP probe, a TS primer, a purine-free / pyrimidine-free endonuclease (APE1), dATP modified by a fluorophore, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) and a magnetic bead coated by streptavidin. When the biosensor is used for telomerase detection, non-specific expansion can be effectively prevented, background signals are reduced, quantification is performed by using total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF)-based single molecule detection, and sensitive detection of telomerase at a single cell level can be realized, so that the biosensor has great potential in the aspects of early clinical diagnosis, anti-cancer drug development and the like; therefore, the method has good practical application value.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Method for identifying accessible binding sites on RNA
A method for identifying sites on a target RNA which are accessible to pairing by antisense DNA, ribozymes or DNAzymes. Native or in vitro-synthesized target RNA is incubated with defined ODNs and RNase H, or with a random or semi-random ODN library and RNase H, or with defined ribozymes or DNAzymes, or with a semi-random ribozyme or DNAzyme library, in a cell extract containing endogenous RNA-binding proteins, or in a medium which mimics a cell extract due to presence of one or more RNA-binding proteins. Any antisense ODN, ribozyme or DNAzyme which is complementary to an accessisble site in the target RNA hybridizes to that site and the RNA is cleaved at that site. Reverse transcription can be used to generate a first strand DNA from the RNA cleavage product, and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-dependent polymerase chain reaction (TDPCR) can be used to identify sites on target RNA to which antisense ODNs, ribozymes or DNAzymes have bound and cleavage has occurred.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
MODIFIED TERMINAL DEOXYNUCLEOTIDYL TRANSFERASE (TdT) ENZYMES
PendingCN113454212ASynthetic method implementationRobust terminal transferase abilityTransferasesNucleoside triphosphateTransferase
The invention relates to engineered terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) enzymes or the homologous amino acid sequence of Polmu, Polbeta, Pollambda, and Poltheta of any species or the homologous amino acid sequence of X family polymerases of any speciesand their use in a method of nucleic acid synthesis, to methods of synthesizing nucleic acids,and to the use of kits comprising said enzymes in a method of nucleic acid synthesis. Theinvention also relates to the use of new terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferases and 3'-blockednucleoside triphosphates in a method of template independent nucleic acid synthesis.
Owner:NUCLERA LTD
Thermostable terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
PendingUS20210355460A1TransferasesFusions for enhanced expression stability/foldingAmino acid substitutionTransferase
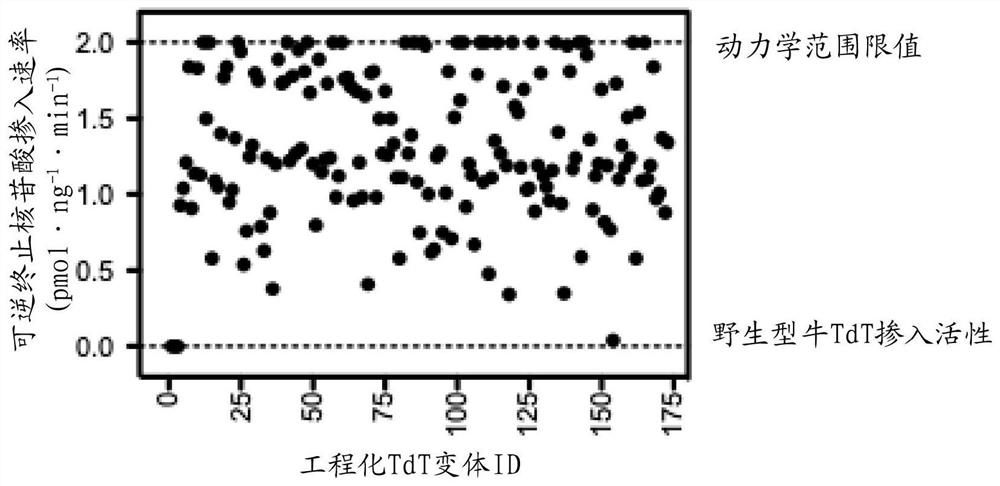
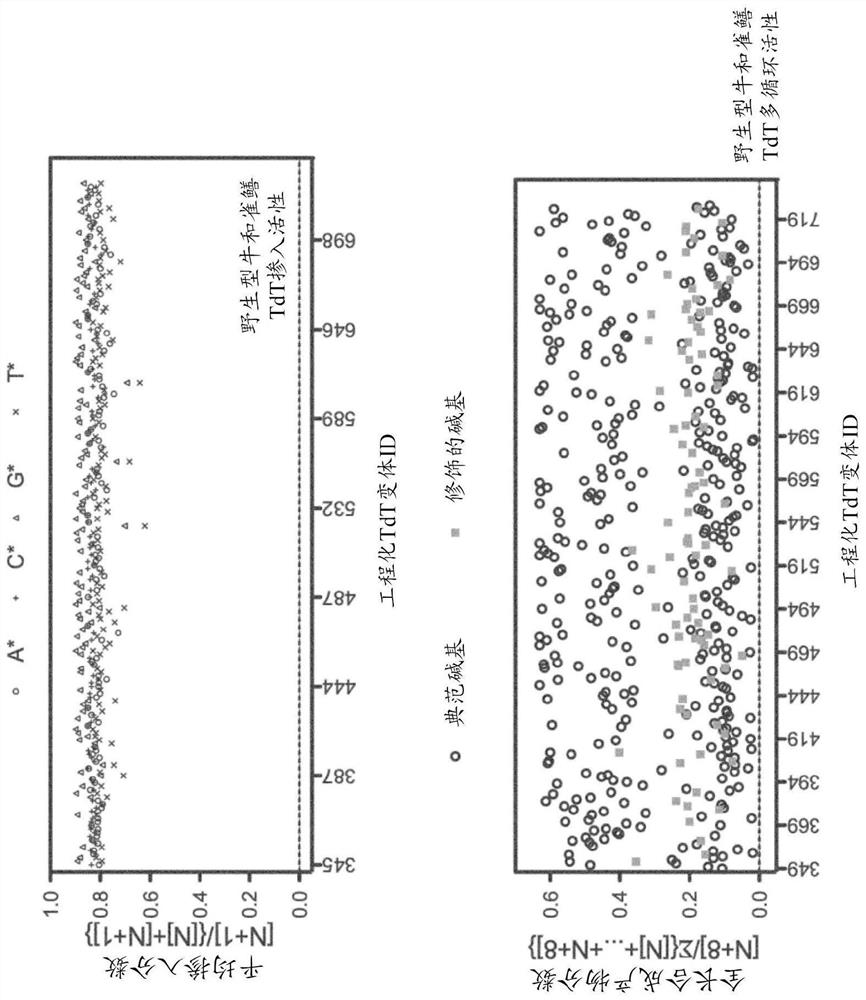
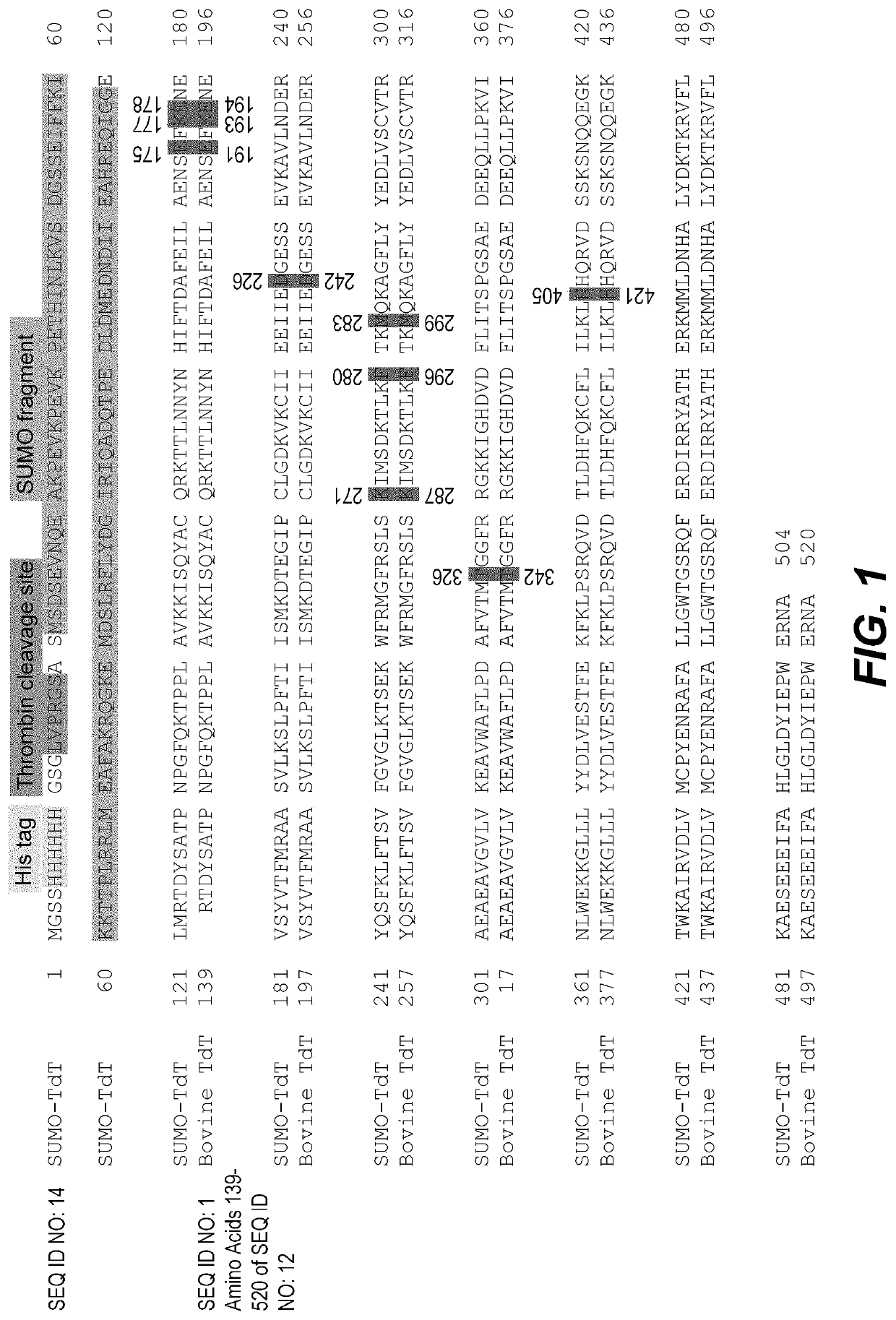
Disclosed herein include recombinant terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferases (TdTs). In some embodiments, the recombinant TdT comprises an amino acid sequence that is at least 80% identical to a bovine TdT, wherein the recombinant TdT comprises one or more amino acid substitution mutations at one or more positions functionally equivalent to Glu191, Lys193, Glu194, Asp242, Lys287, Phe296, Met299, Thr342, and His421 in the bovine TdT.
Owner:ILLUMINA SINGAPORE PTE LTD +2
Double-strand DNA break quantification method
The present disclosure provides the quantification of double-strand breaks in DNA molecules using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase using a preliminary step of nick gap and repair. This preliminary step comprising contacting the DNA molecules with both a DNA ligase and a DNA polymerase to repair DNA nicks and remove DNA gaps prior to using the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase.
Owner:SOCPRA SCI SANTE & HUMAINES S E C
Compositions and methods related to nucleic acid synthesis
Owner:NUCLERA NUCLEICS LTD
Preparation method of T carrier
InactiveCN109266672ANegative clone eliminationEliminate Technical DefectsVector-based foreign material introductionPlasmid VectorMicrobiology
The invention discloses a preparation method of a T carrier, which utilizes thio-modified primers to amplify a plasmid vector; digesting the template plasmid molecule with restriction endonuclease DpnI to eliminate the negative background clone caused by the circular plasmid template; the linearized vector amplified by PCR was digested with 5'exonuclease to obtain T carrier. By the method of theinvention, the linearized fragment of the T carrier can be prepared by direct and simple PCR amplification, the technical defects of the restriction endonuclease method and the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase method are eliminated, and the T carrier can be obtained by simple treatment.
Owner:苏州博睐恒生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com