High fidelity reverse transcriptases and uses thereof
a reverse transcriptase, high-fidelity technology, applied in the field of molecular and cellular biology, can solve the problems of low fidelity of rts, inability to copy rna templates, inefficient use of unmodified rts to catalyze reverse transcription, etc., and achieve high fidelity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Mutation Frequency of M-MLV High Fidelity Mutants
[0144] Mutation frequency Data and Calculation of Error Rates. Mutation frequency (MF) is determined by dividing the number of mutant plaques (light blue or white) by the total number of plaques and then subtracting the background mutation frequency of the starting DNA.
[0145] All mutant reverse transcriptases tested also contained the point mutations to remove RNase H activity, as in SuperScript II (SS II, U.S. Pat. Nos. 5,244,797; 5,405,776; 5,668,005 and 6,063,608). Point mutations were made in the M-MLV RT gene to remove RNase H activity. The point mutations include D524G, D583N, and E562Q. Briefly, the RT gene from pRT601 was inserted into a pUC plasmid and then the above point mutations were made in the RNase H domain of the RT gene. pRT601 is described in U.S. Pat. Nos. 5,244,797; 5,405,776; 5,668,005 and 6,063,608 and was deposited at the ATCC under Accession No. 67007 (See U.S. Pat. No. 5,017,492). This RNase H— mutant is re...
example 2
Misinsertion Assays with DNA Template
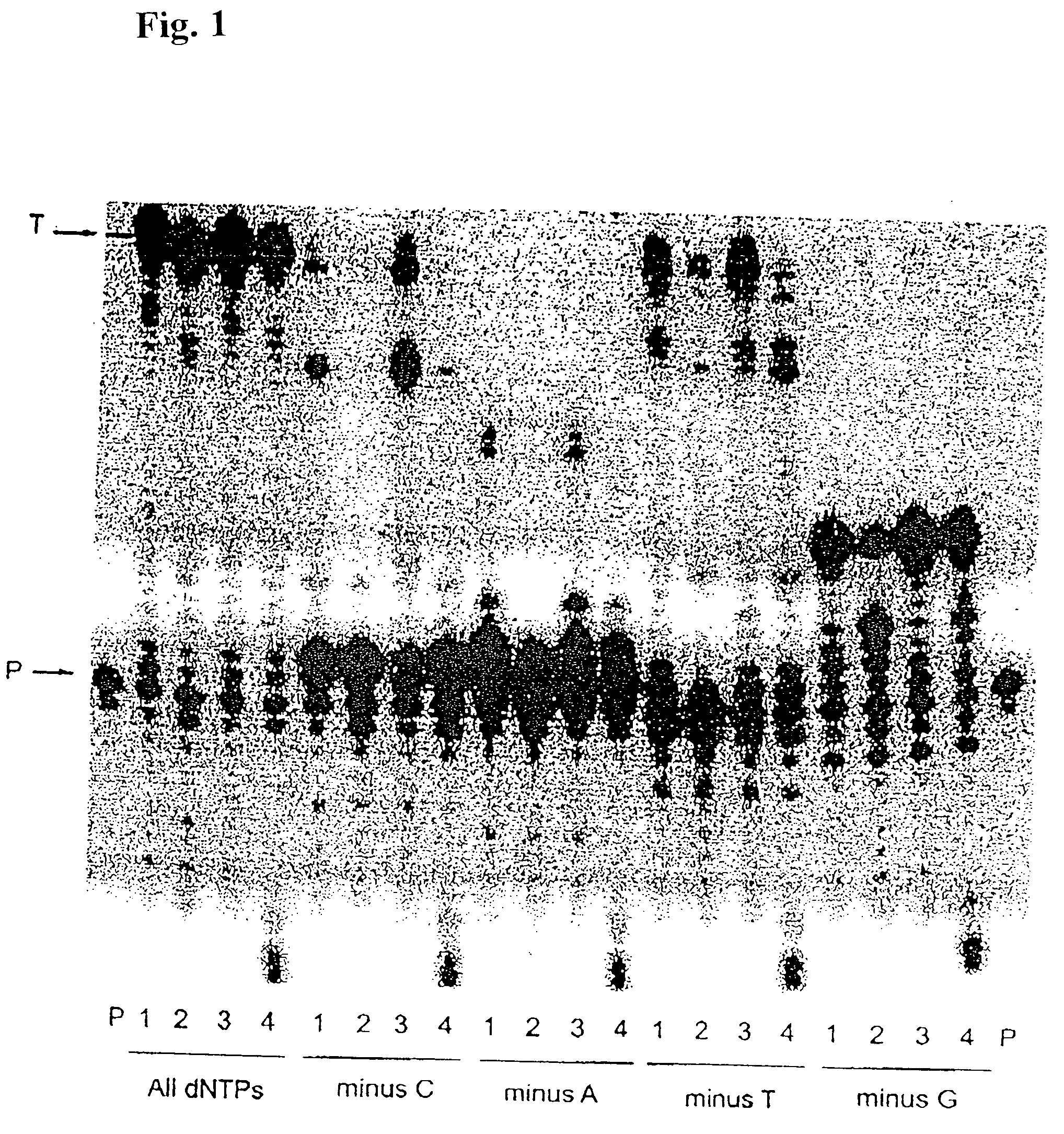
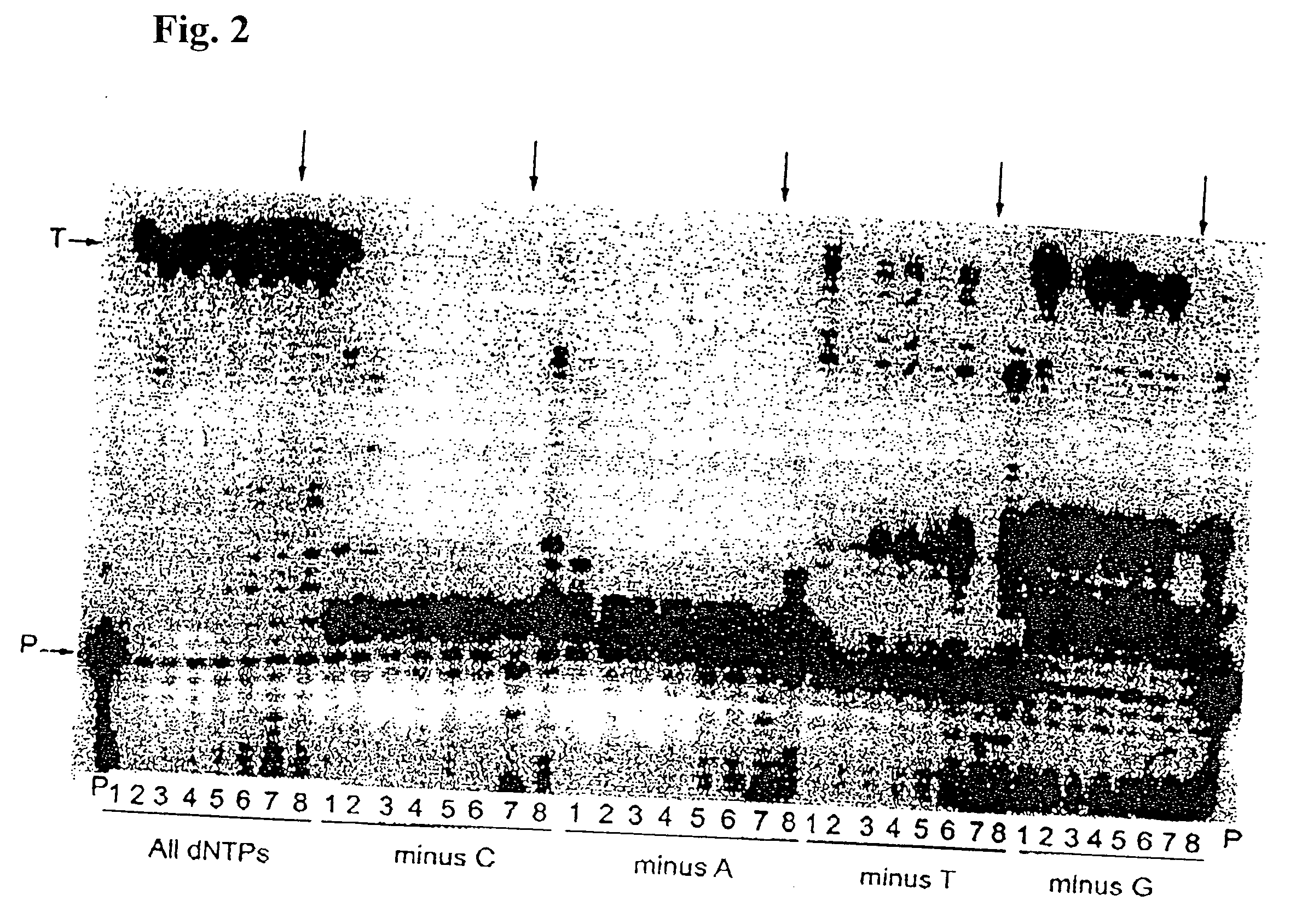
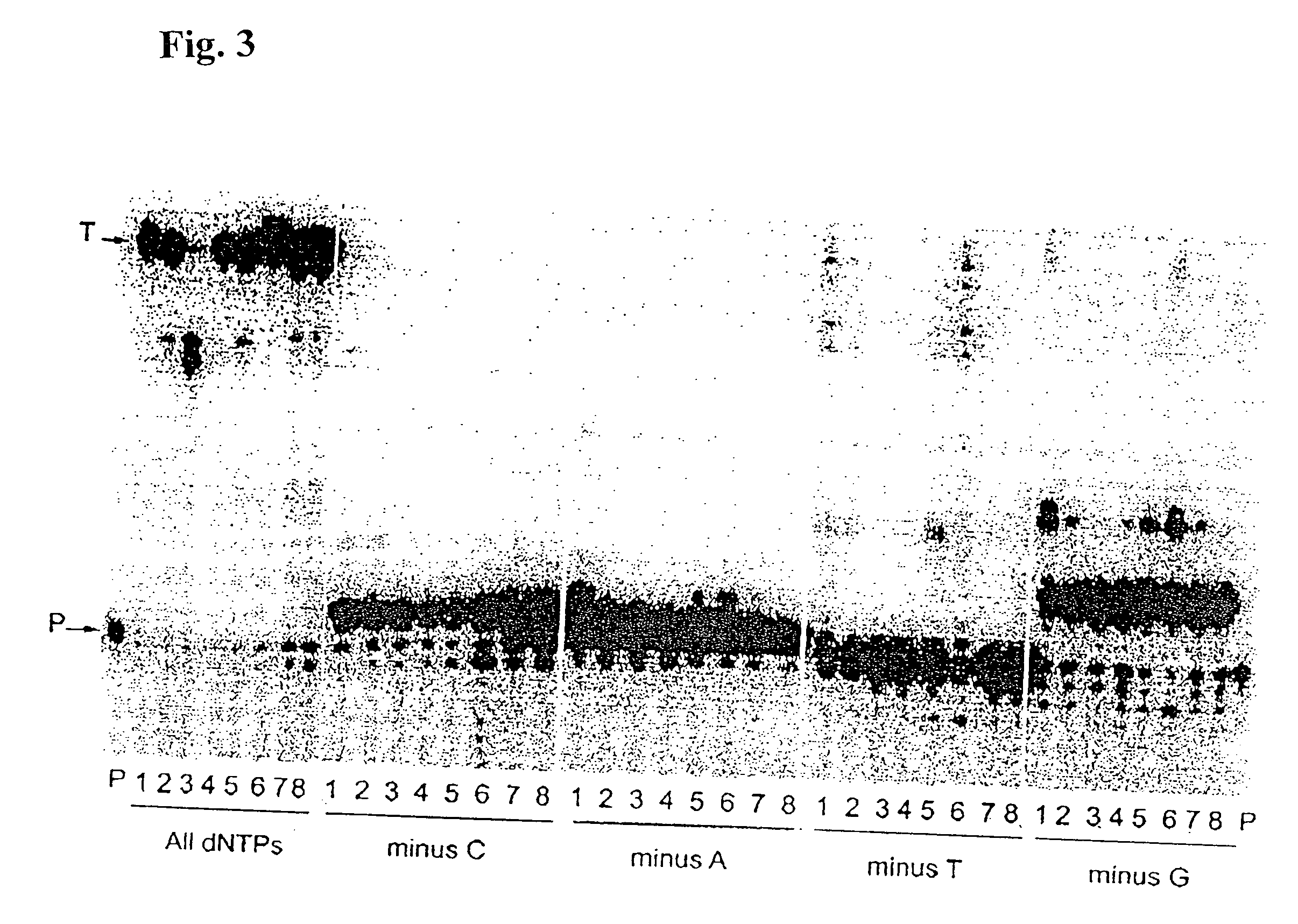
[0147] Misinsertion assay of Y64W, R116M, K152R, Q190F, T197A, V223H M-MLV RNase H− RT with DNA template. This assay was employed to compare the misincorporation capability of the mutants to Superscript II (M-MLV RNase H− RT). The assay is a primer extension assay using synthetic DNA template-primer and biased dNTP pools containing only three of the four dNTPs. The reactions are displayed on a gel in FIGS. 1-3. In this assay, higher efficiency of primer extension in the absence of one dNTP denotes lower fidelity. As shown in FIGS. 1-3, in the presence of all 4 dNTPs, SuperScript II and all the selected mutants were able to extend the primer approximately equally, with some variance in the addition of non-template nucleotides at the end of the primer. However when incubated with biased pools of nucleotides, SS II was able to catalyze substantial extension past template nucleotides for which a complementary dNTP was missing, indicating use of inco...
example 3
TdT Reverse Transcriptase Mutants
[0148] In checking fidelity mutants of reverse transcriptase (RT) for misextension in a 3 dNTP assay, it was observed that SS II RT extended 2-3 bases past the end of the template in the presence of 3 and 4 dNTPs. This non-template directed extension or TdT activity is reduced in many mutants, but in a few such as F309N and T197E it appears that this activity is severely reduced or eliminated. These mutants are probably in close proximity or in contact with the template-primer as determined by homology to HIV reverse transcriptase and its crystal structure with bound template-primer.
Methods
[0149] For F309N:
[0150] Primers were designed corresponding to the mutant position F309 with the silent insertion of a NgoMIV restriction site at amino acid positions 310-311. The primers encoded a random NNK sequence for this position generating a random library of F309 mutants, where N is any of the four bases and K is T or G. The primers along w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com