Patents
Literature
259 results about "Restriction site" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
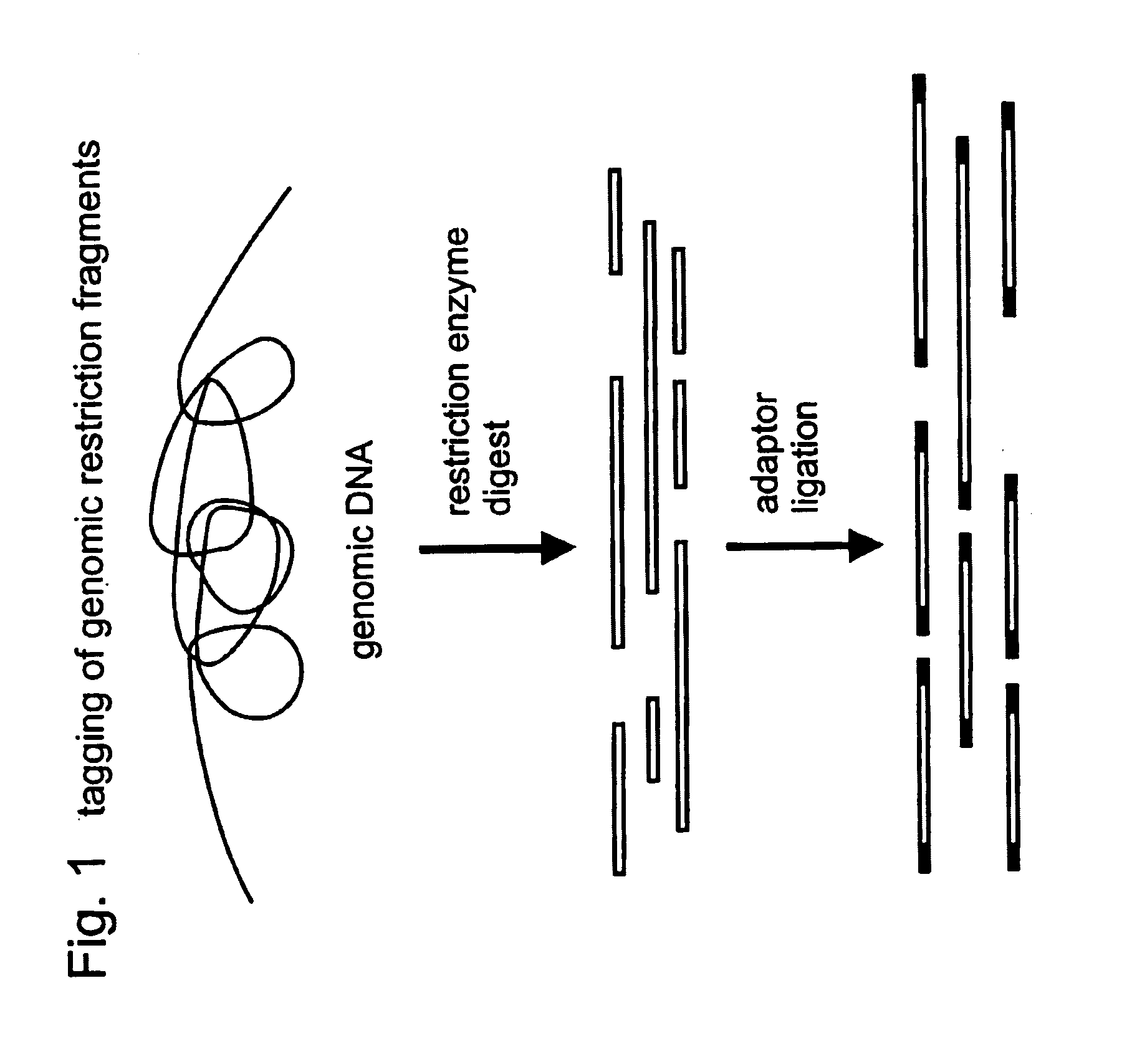
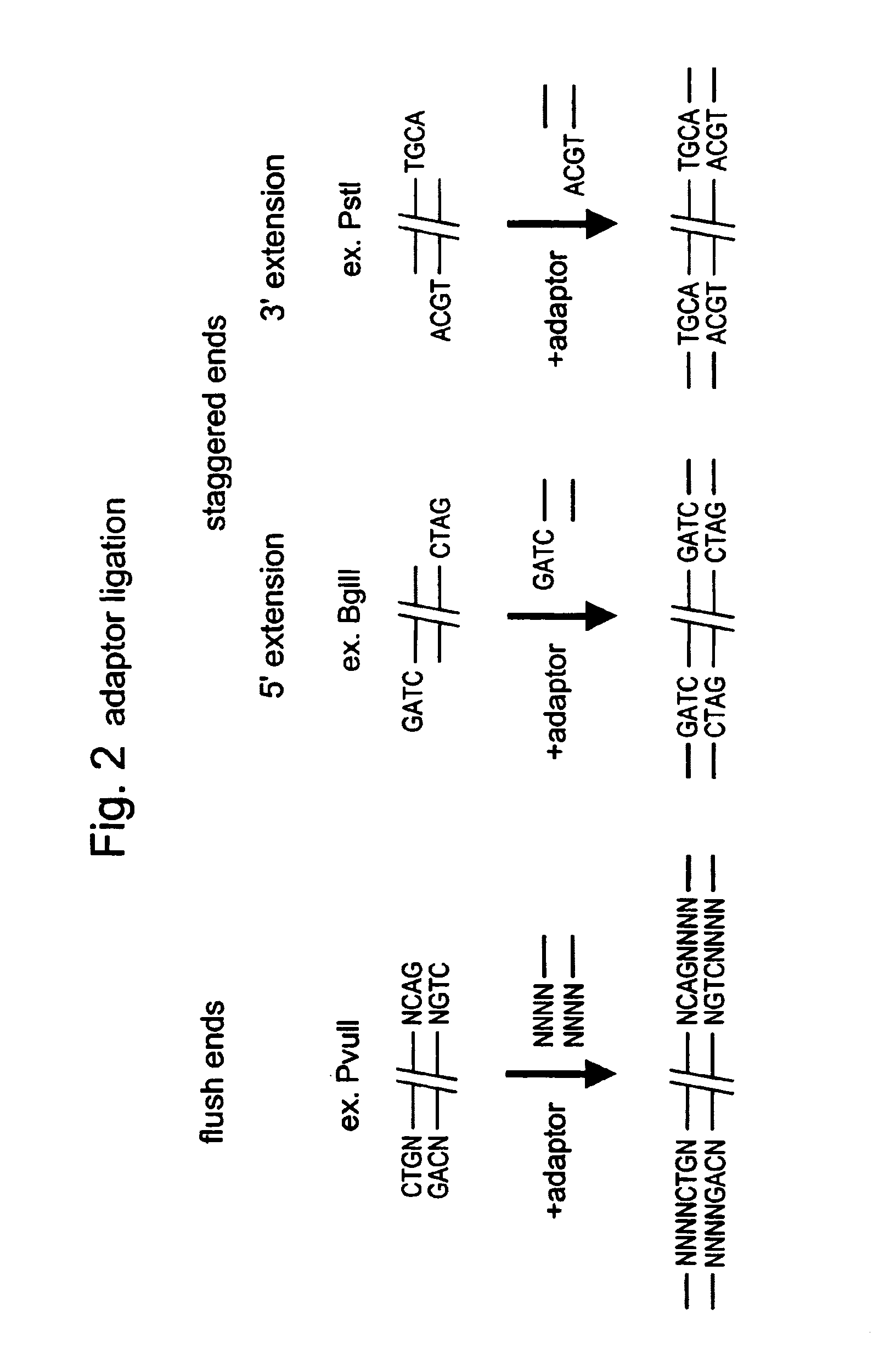
Restriction sites, or restriction recognition sites, are locations on a DNA molecule containing specific (4-8 base pairs in length) sequences of nucleotides, which are recognized by restriction enzymes. These are generally palindromic sequences (because restriction enzymes usually bind as homodimers), and a particular restriction enzyme may cut the sequence between two nucleotides within its recognition site, or somewhere nearby.
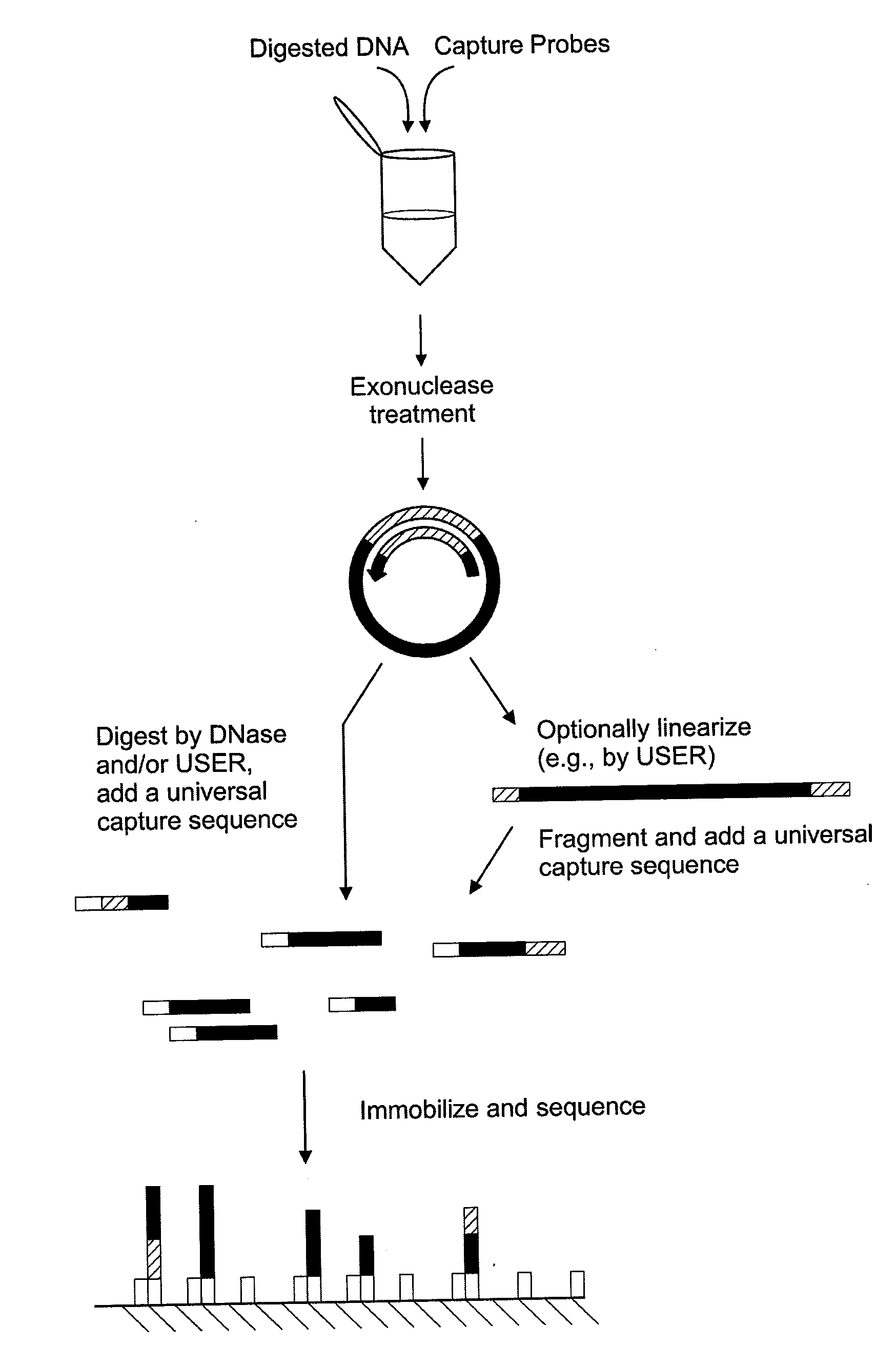
Surface-capture of target nucleic acids
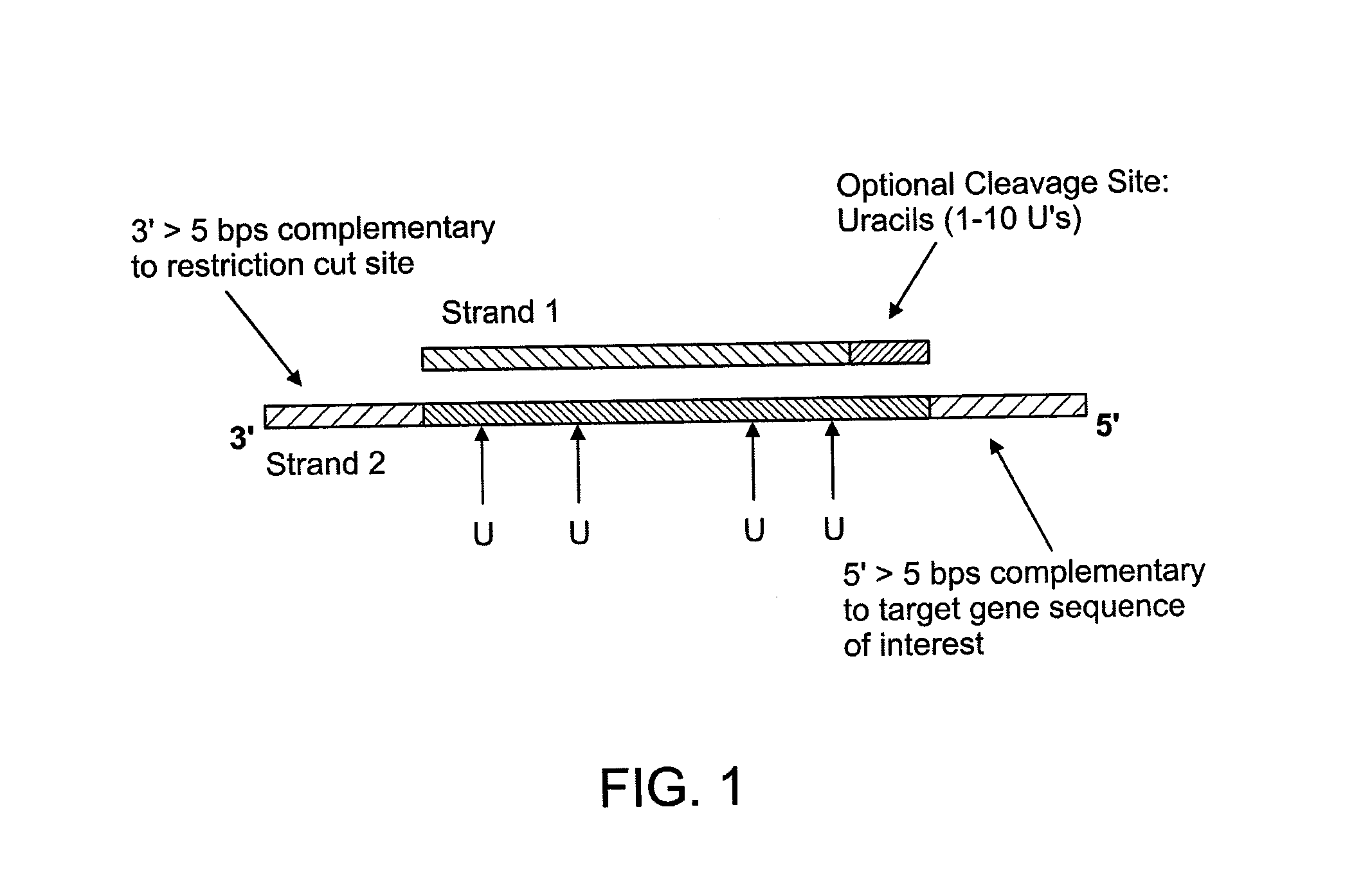
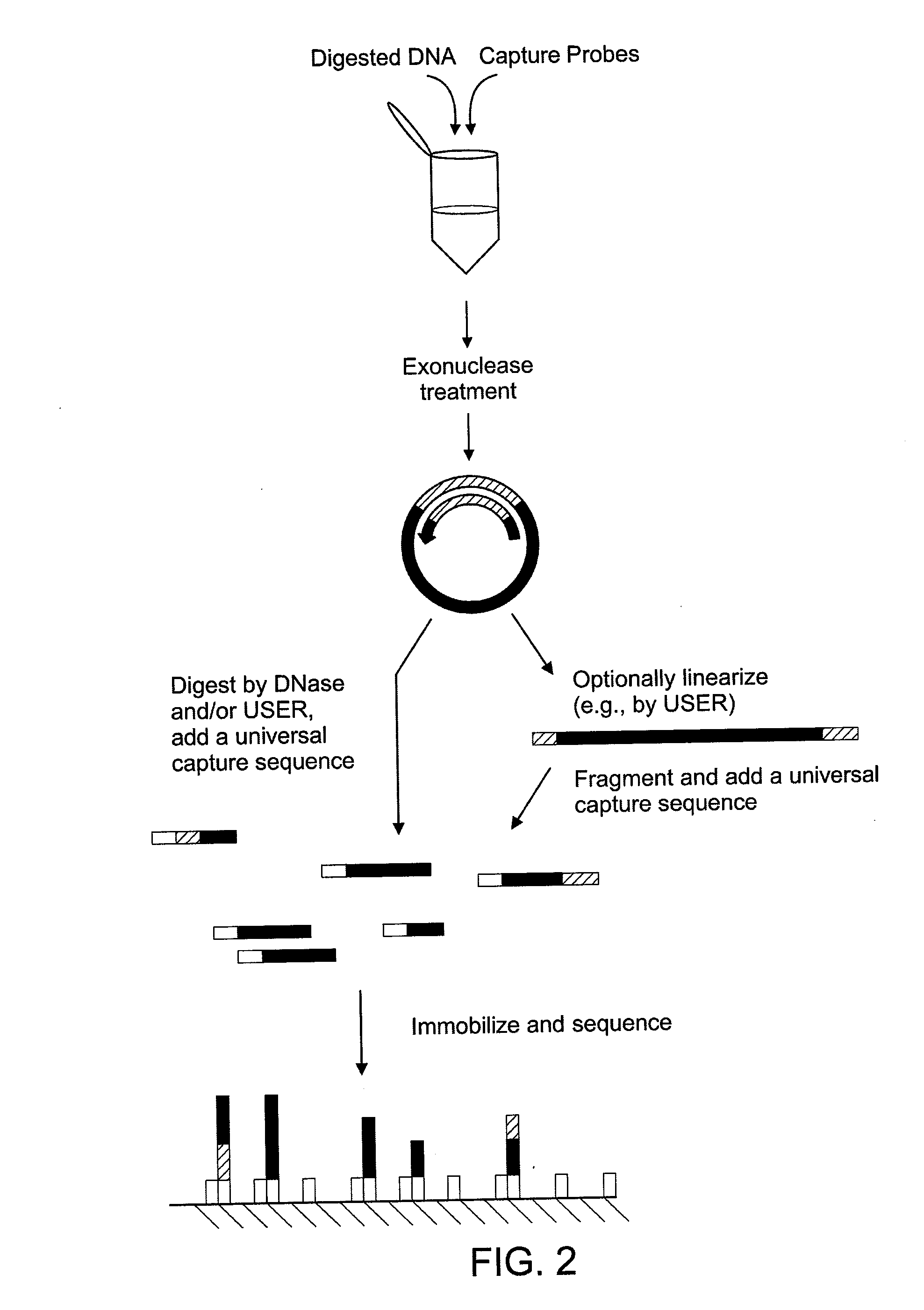
The disclosure provides methods of capturing target nucleic acids (e.g., gene or gene fragments) onto a solid support for further analysis. The disclosed methods utilize a capture probe that selectively circularizes only the target nucleic acid. Following the circularization of the target, the linear, non-target, nucleic acids are removed from the sample. Next, the circularized target is linearized and bound to a solid support. To allow for linearization, the capture probe may include a cleavage site that can be a noncanonical nucleotide(s) (e.g., uracil in DNA) and / or a rare-cutter site (e.g., the Not I restriction site). In some embodiments, the target nucleic acid is captured onto a support without an intermediate amplification step.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
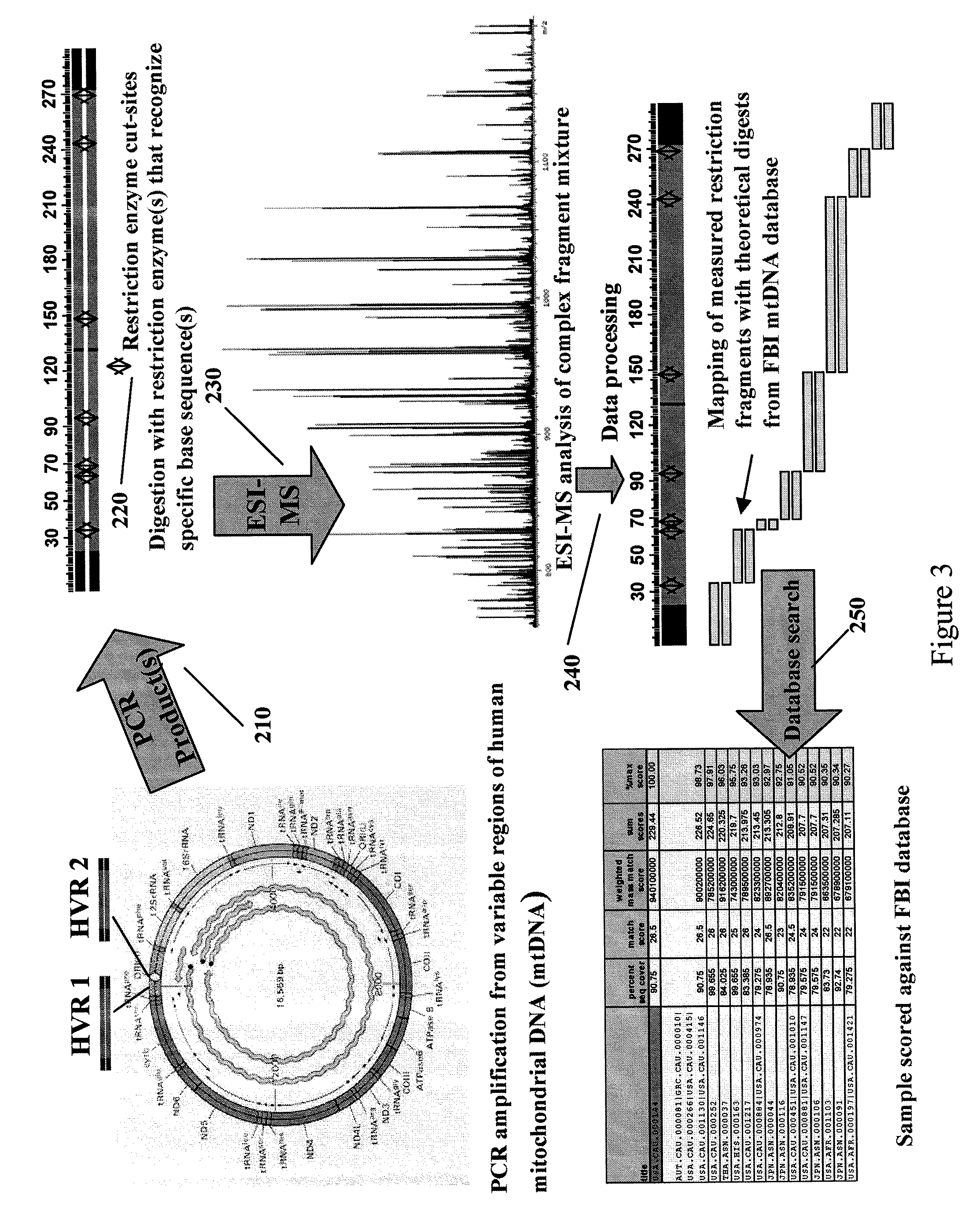
Methods for rapid forensic analysis of mitochondrial DNA
InactiveUS20050266411A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRestriction siteForensic science
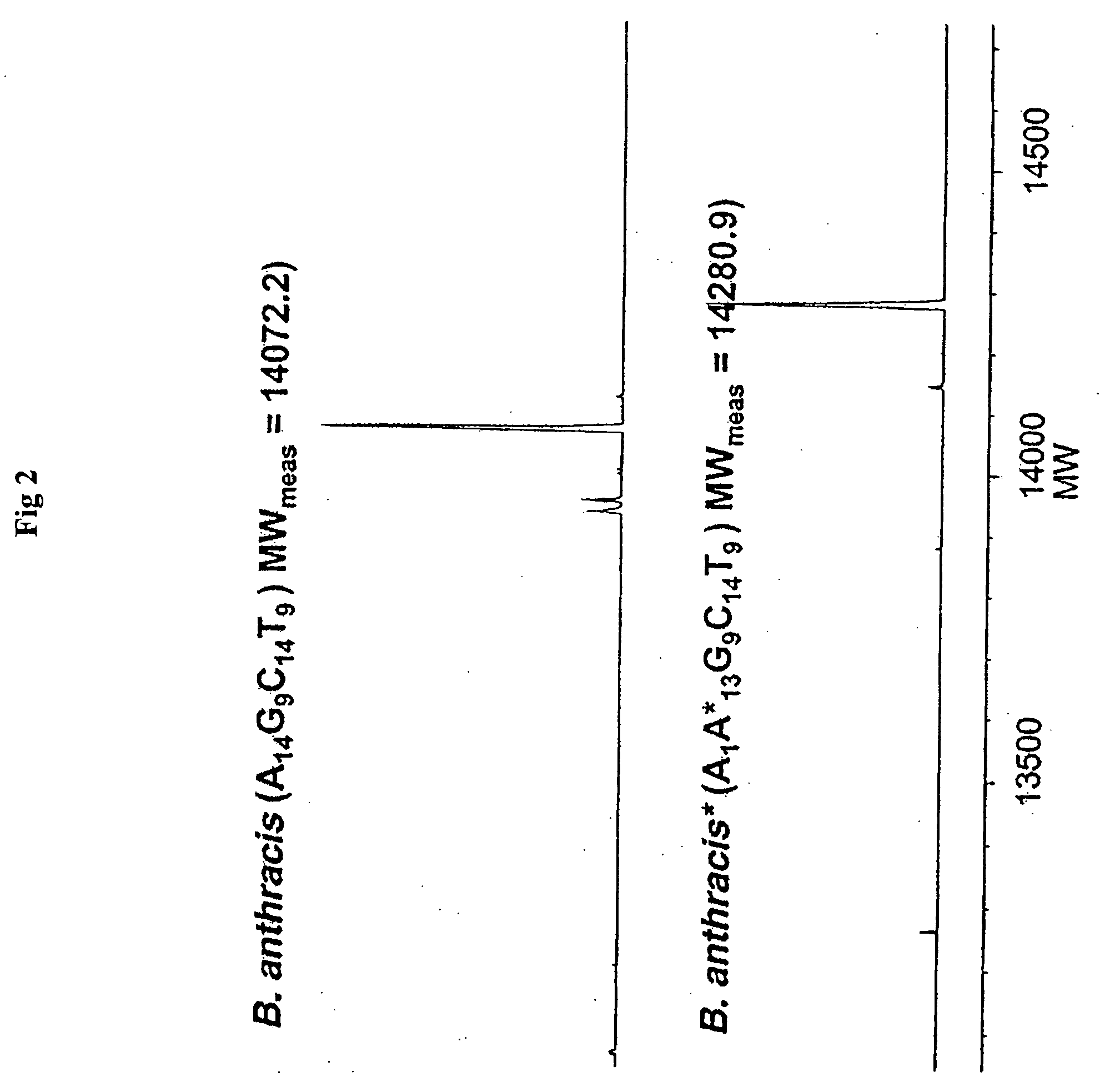
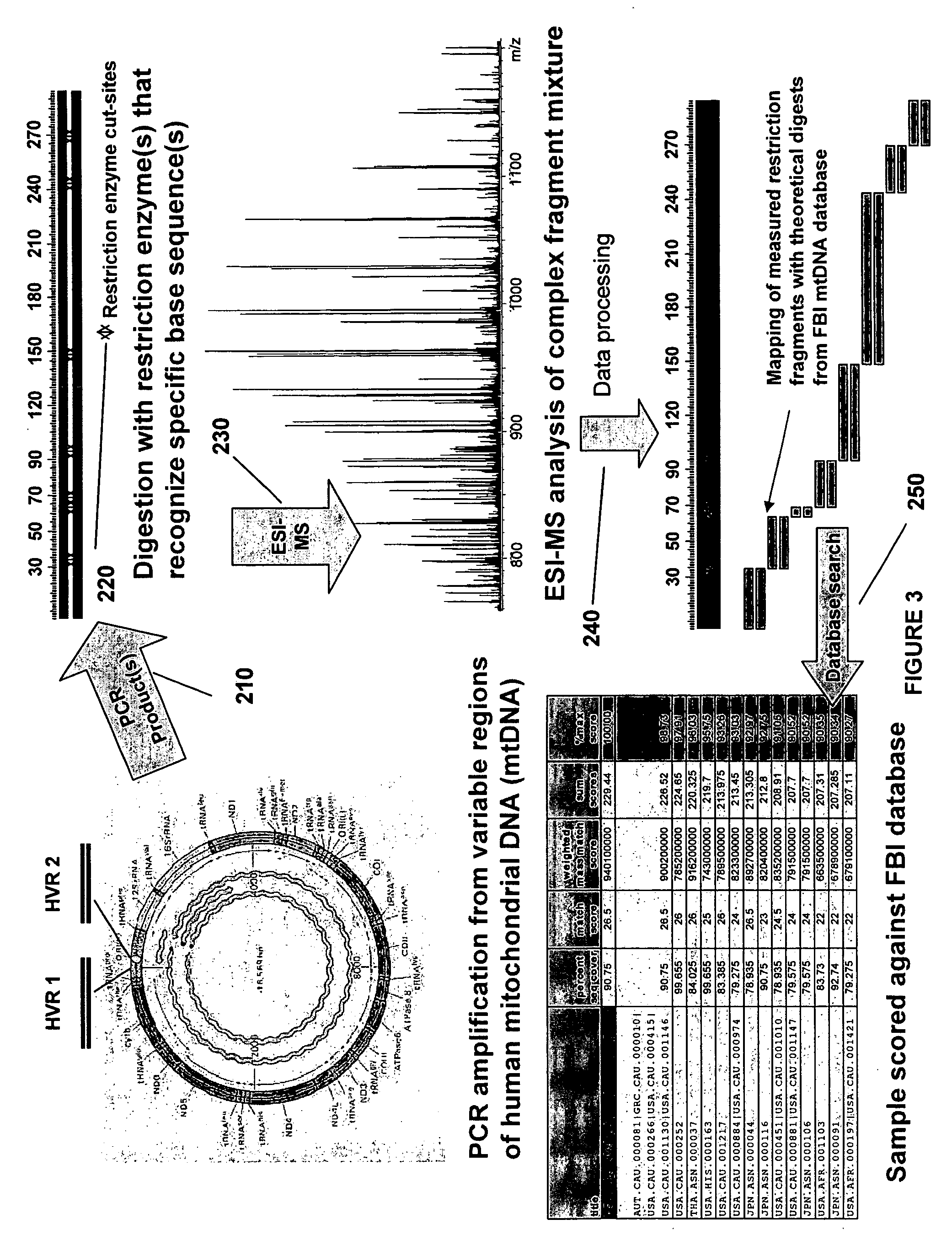
The present invention provides methods for rapid forensic analysis of mitochondrial DNA by amplification of a segment of mitochondrial DNA containing restriction sites, digesting the mitochondrial DNA segments with restriction enzymes, determining the molecular masses of the restriction fragments and comparing the molecular masses with the molecular masses of theoretical restriction digests of known mitochondrial DNA sequences stored in a database.
Owner:IBIS BIOSCI
Methods For Rapid Forensic Analysis Of Mitochondrial DNA
InactiveUS20090125245A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRestriction enzyme digestionRestriction site
The present invention provides methods for rapid forensic analysis of mitochondrial DNA by amplification of a segment of mitochondrial DNA containing restriction sites, digesting the mitochondrial DNA segments with restriction enzymes, determining the molecular masses of the restriction fragments and comparing the molecular masses with the molecular masses of theoretical restriction digests of known mitochondrial DNA sequences stored in a database.
Owner:IBIS BIOSCI +1
Methods and compositions for DNA manipulation
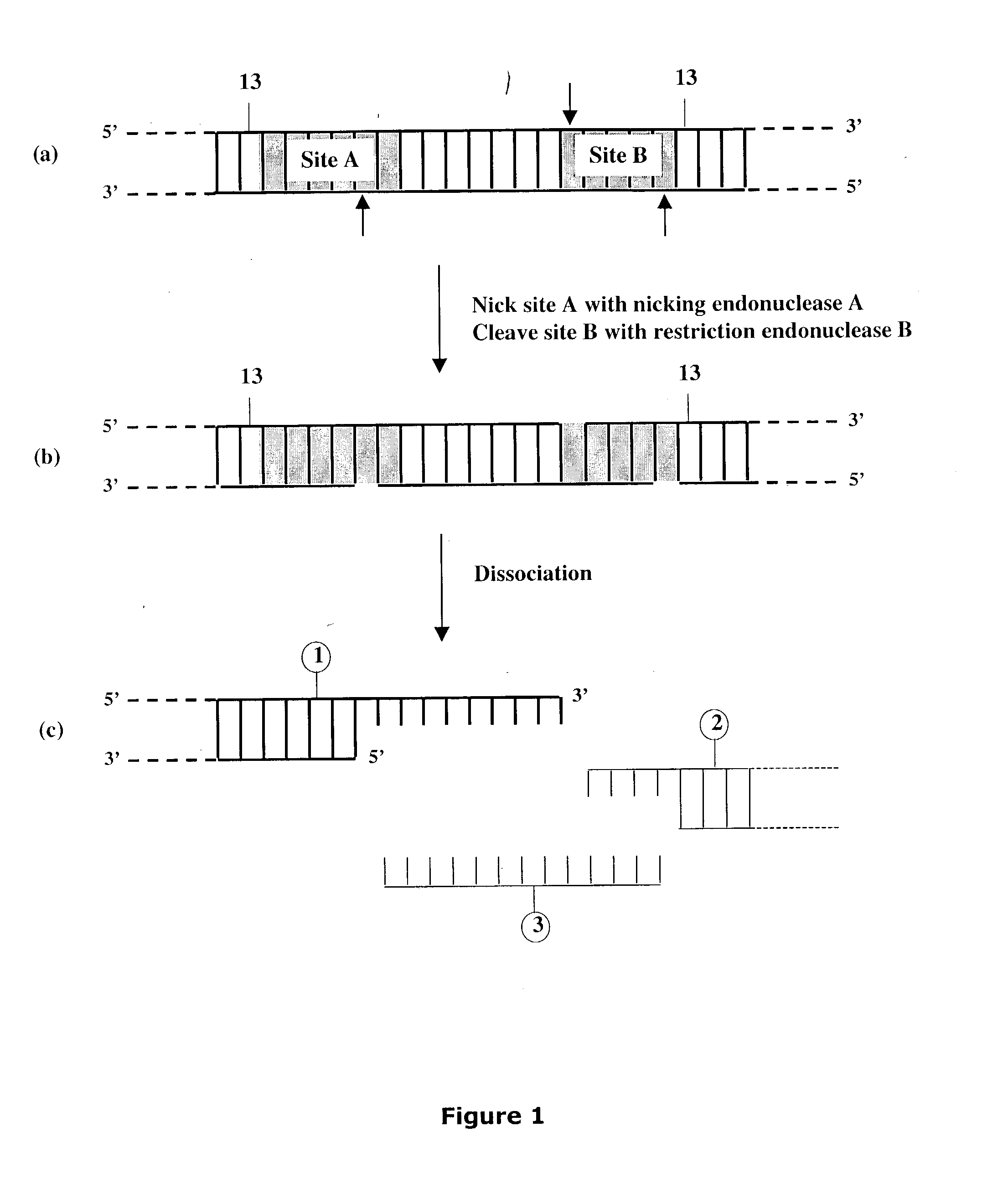
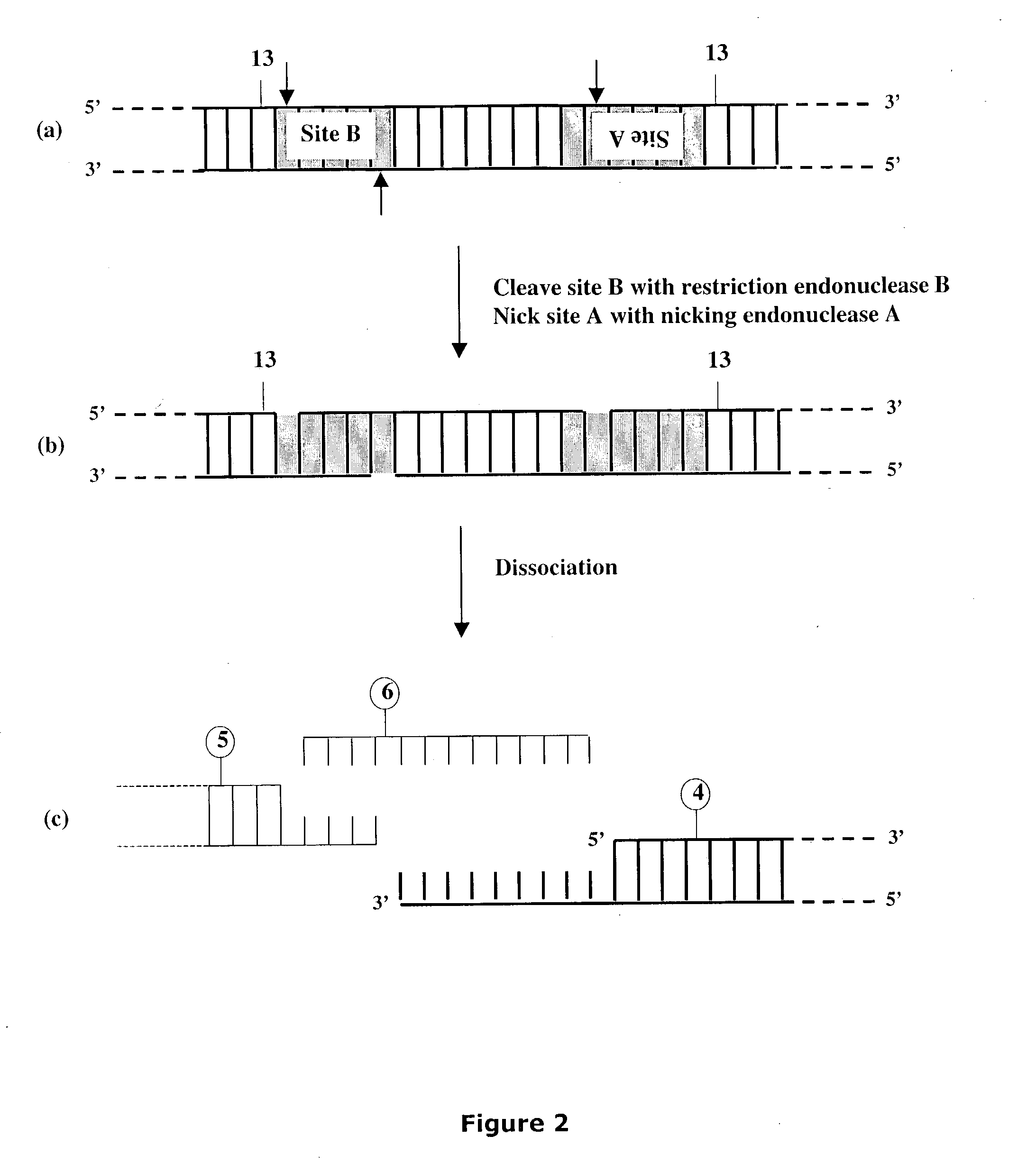
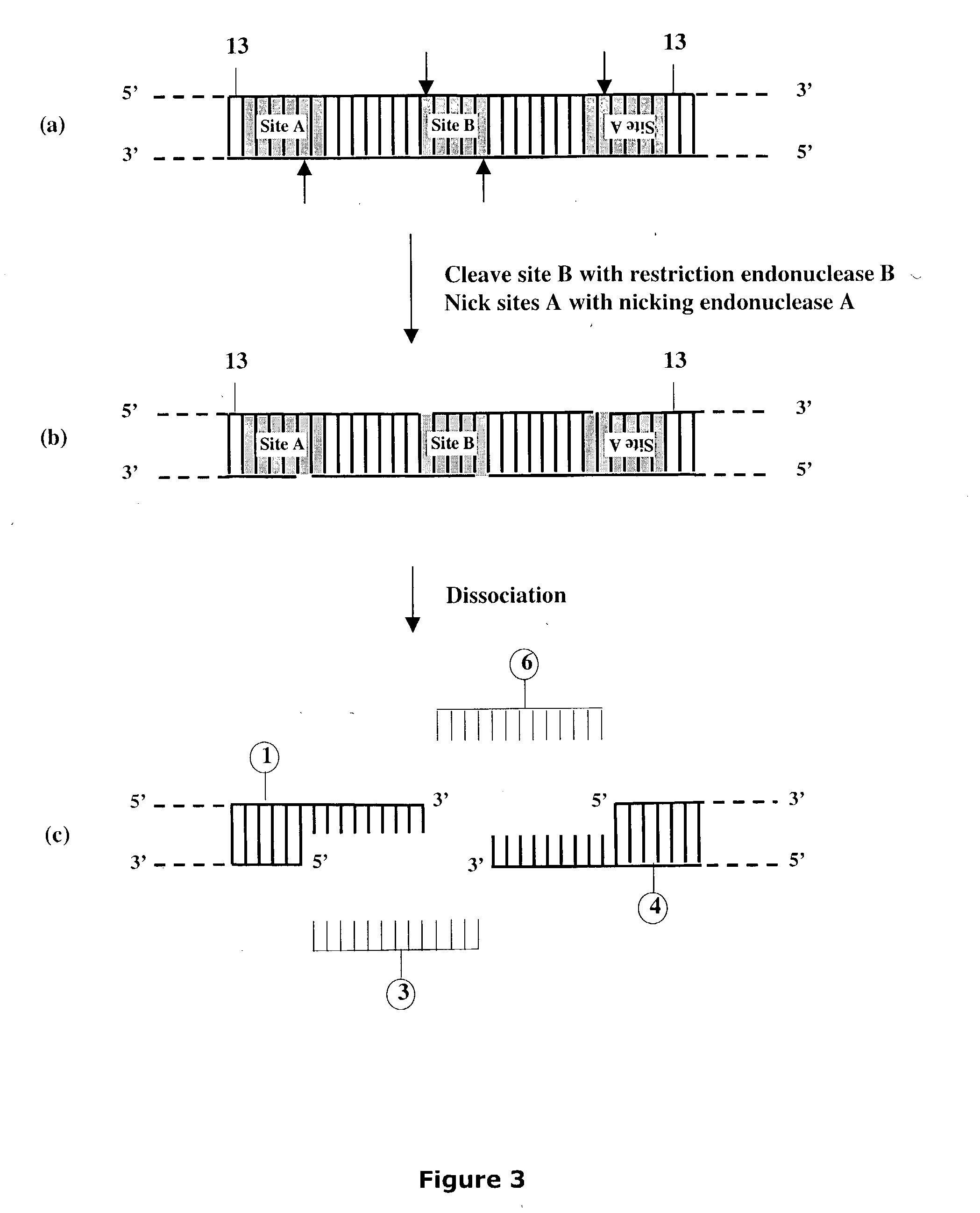
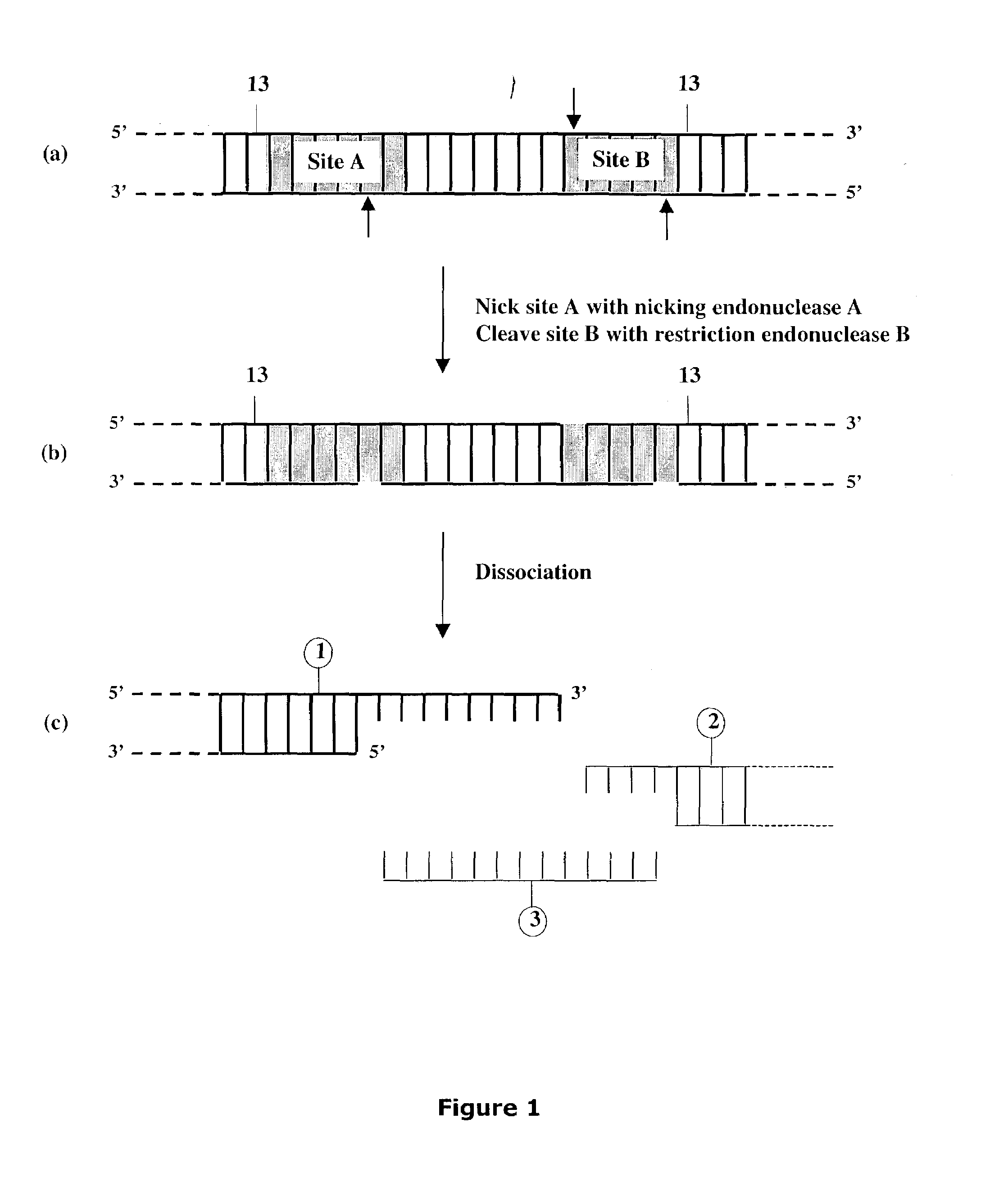
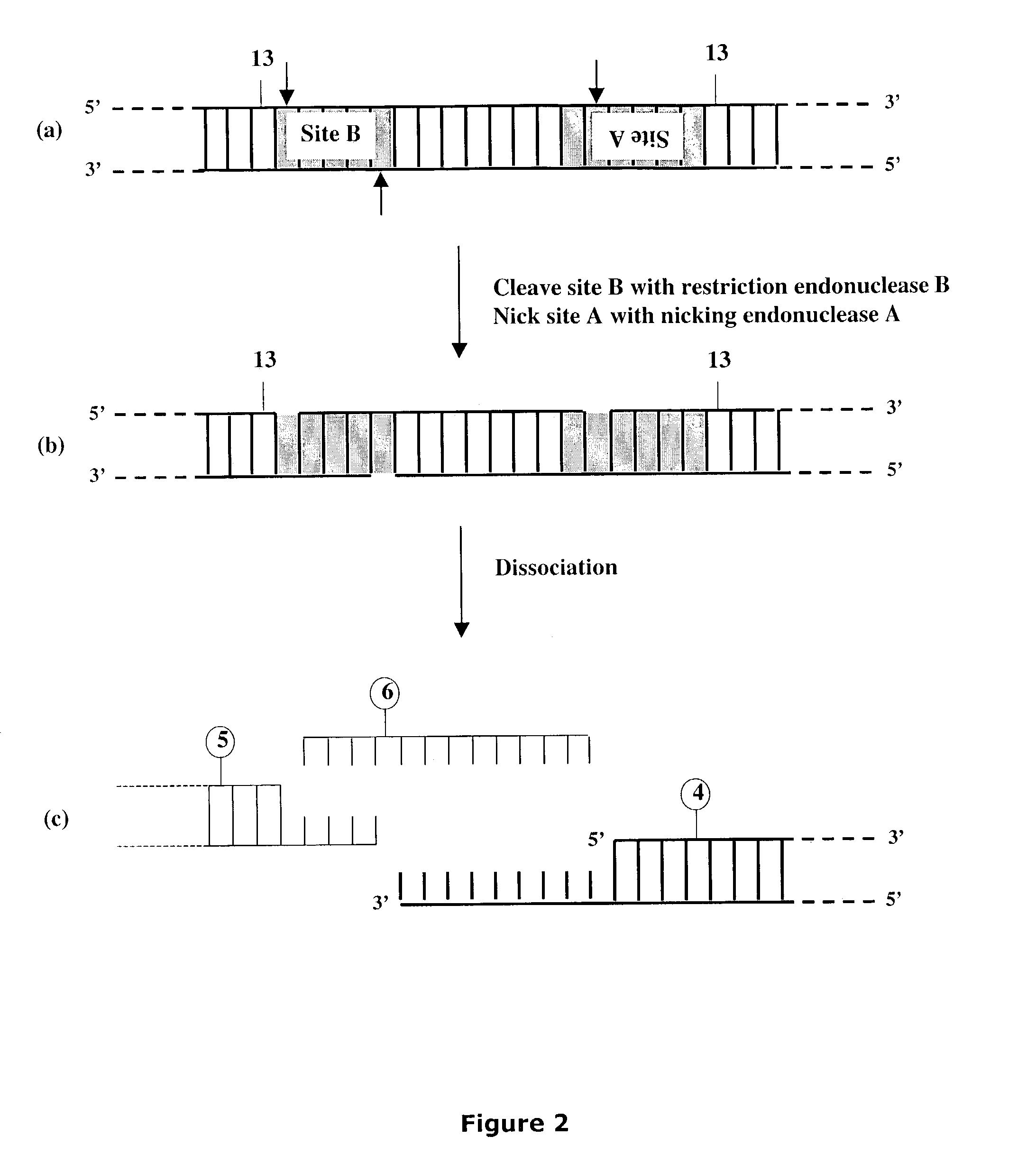
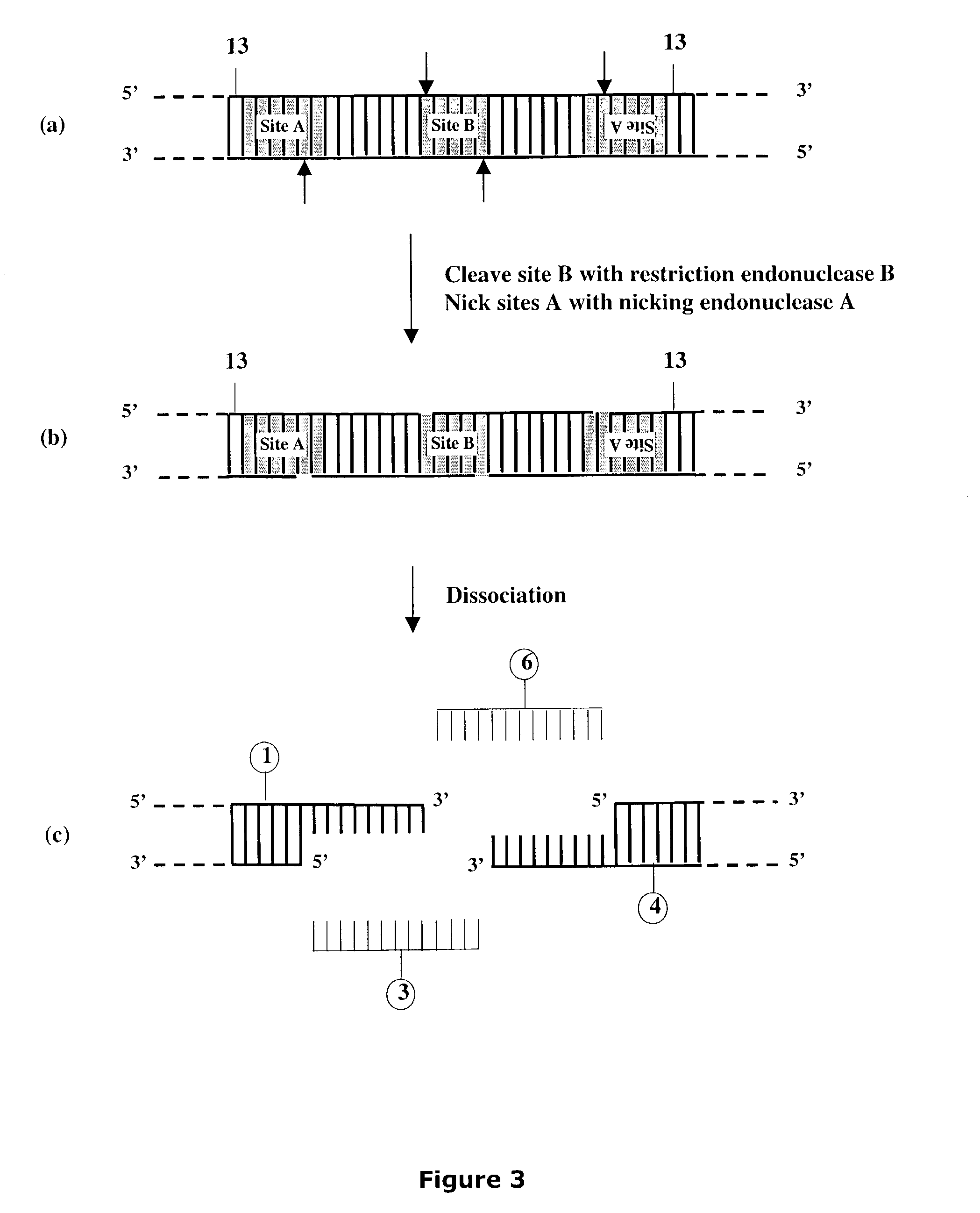
Methods and compositions are provided for generating a single-stranded extension on a polynucleotide molecule, the single-stranded extension having a desired length and sequence composition. Methods for forming single-stranded extensions include: the use of a cassette containing at least one nicking site and at least one restriction site at a predetermined distance from each other and in a predetermined orientation; or primer-dependent amplification which introduces into a polynucleotide molecule, a modified nucleotide which is excised to create a nick using a nicking agent. The methods and compositions provided can be used to manipulate a DNA sequence including introducing site specific mutations into a polynucleotide molecule and for cloning any polynucleotide molecule or set of joined polynucleotide molecules in a recipient molecule such as a vector of choice.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
POLYMERIC IMMUNOGLOBULIN FUSION PROTEINS THAT TARGET LOW AFFINITY FCyRECEPTORS
InactiveUS20090117133A1Small size range and conformationPromote generationSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsLow affinityNACHT domain
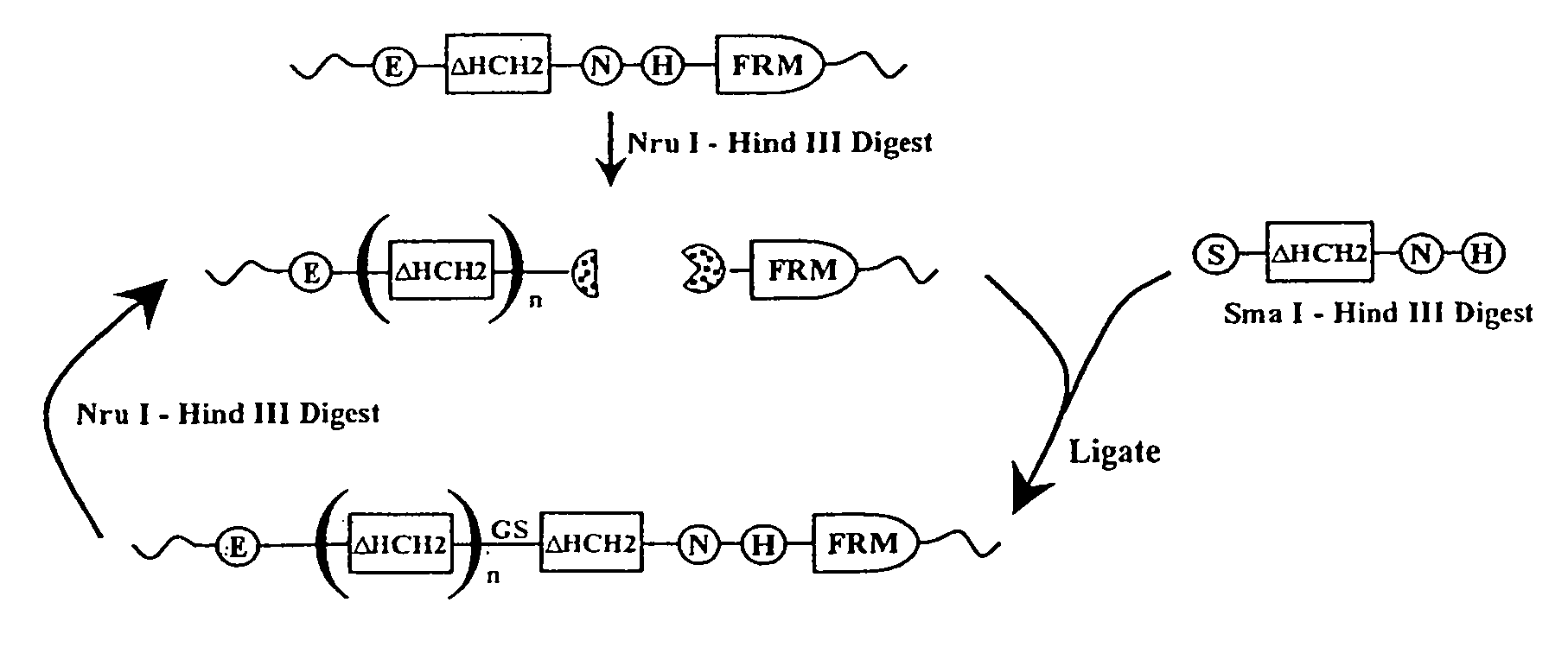
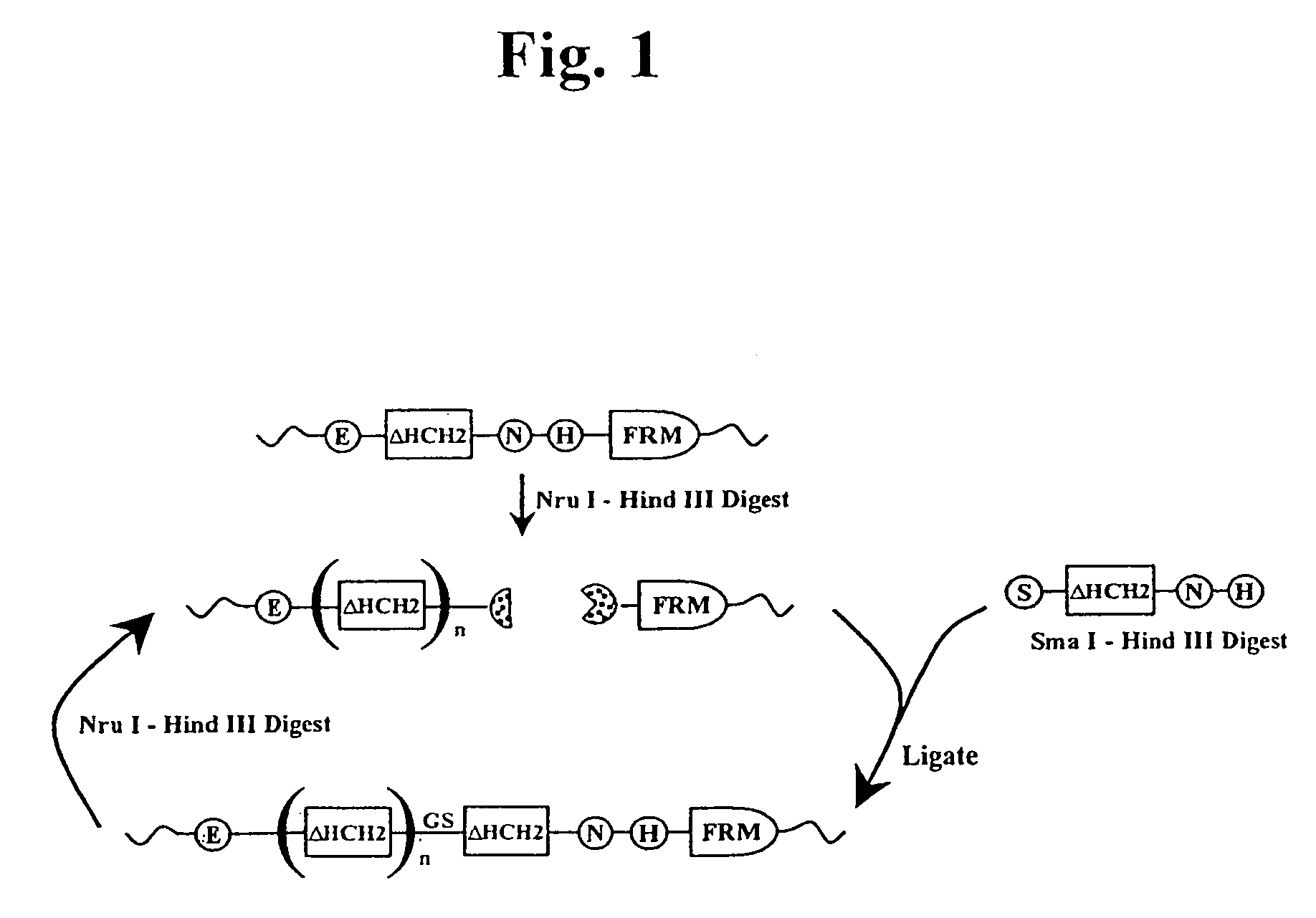
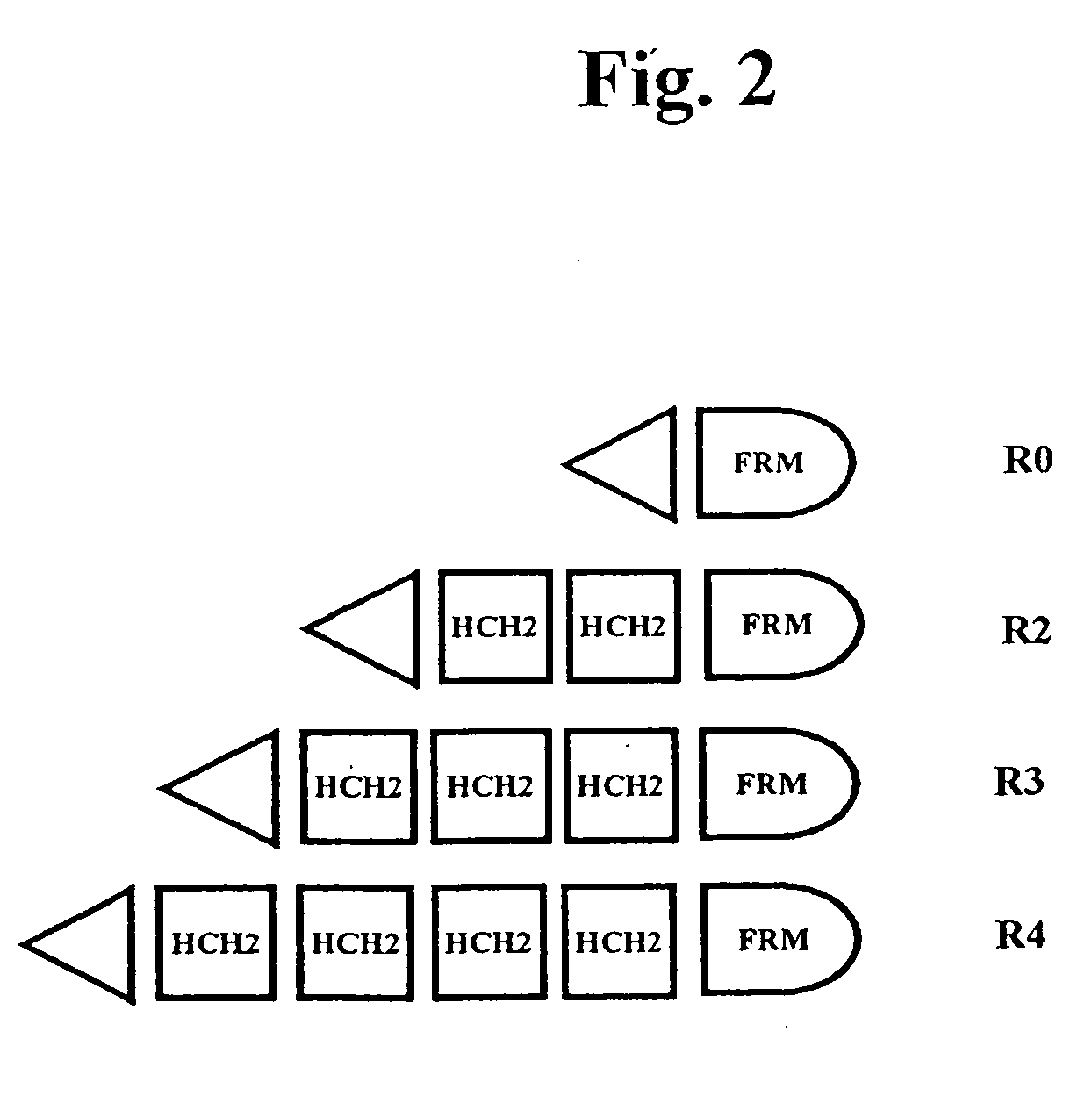
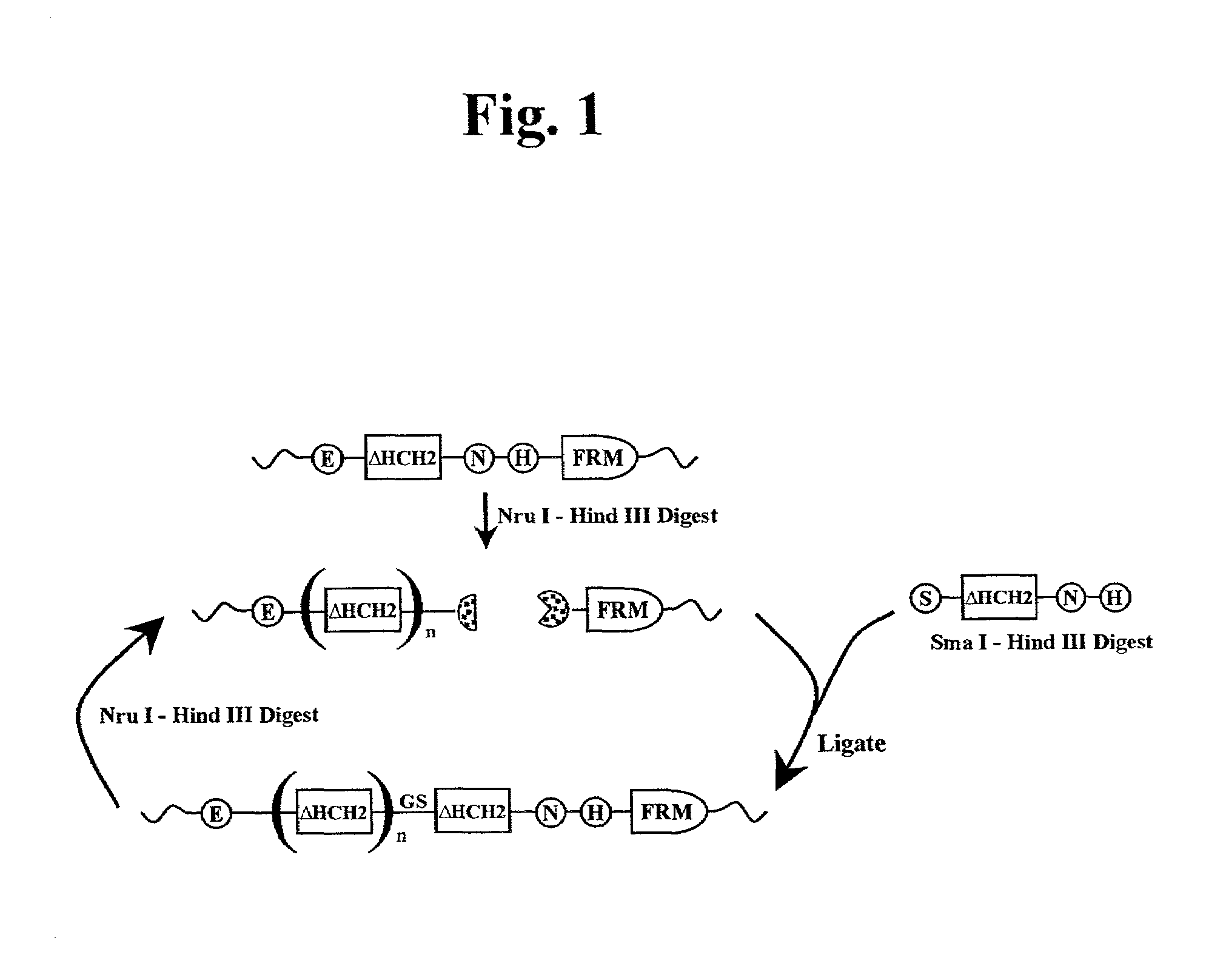
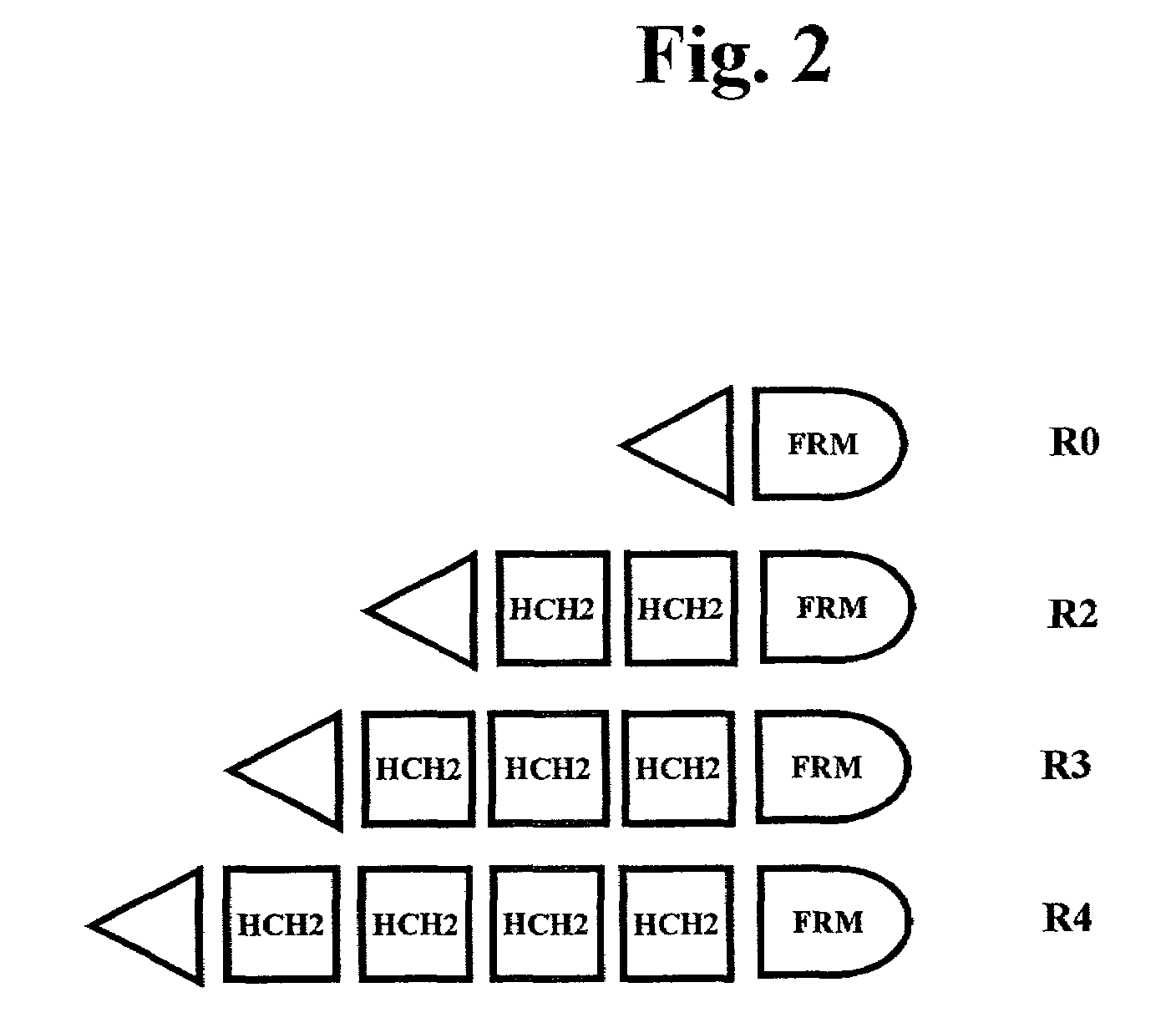
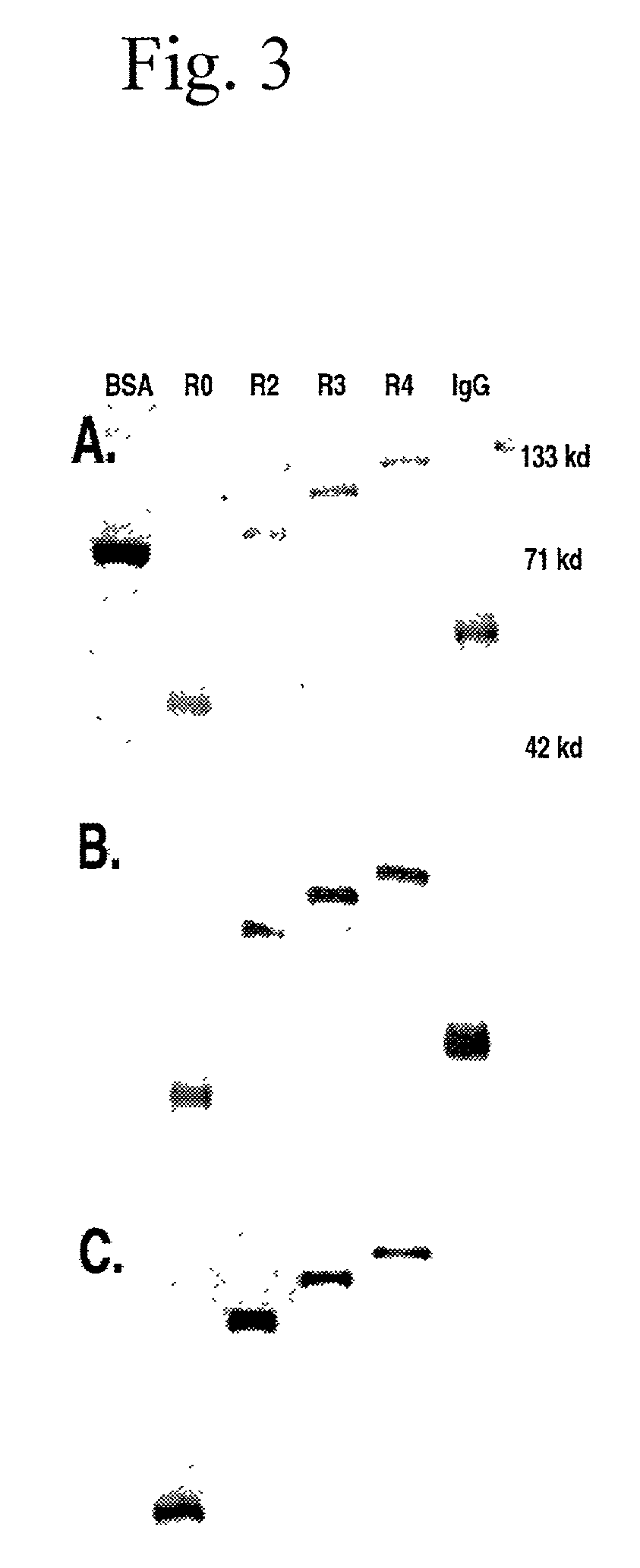
The present invention concerns a family of nucleic acids, polypeptides and cloning vectors which direct expression of fusion proteins that can mimic aggregated IgG (AIG) and immune complex function with respect to their interactions with FcγR and which allow for the inclusion and targeting of a second protein domain to cells expressing FcγR. This was accomplished by expressing multiple linear copies of the hinge and CH2 domains (HCH2) of human IgG1 fused to the framework region of human IgG1. Convenient restriction sites allow for the facile introduction of additional amino-terminal domains. Methods for treating patients using fission proteins are also disclosed. The HCH2 polymers described here represent a new strategy in the design of recombinant proteins for the therapeutic targeting of FcγR in autoimmune disorders.
Owner:ITERATIVE THERAPEUTICS
Polymeric immunoglobulin fusion proteins that target low-affinity Fcγreceptors
ActiveUS7511121B2Improve effectivenessModerating disease severitySenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsFusion Protein ExpressionLow affinity
The present invention concerns a family of nucleic acids, polypeptides and cloning vectors which direct expression of fusion proteins that can mimic aggregated IgG (AIG) and immune complex function with respect to their interactions with FcγR and which allow for the inclusion and targeting of a second protein domain to cells expressing FcγR. This was accomplished by expressing multiple linear copies of the hinge and CH2 domains (HCH2) of human IgG1 fused to the framework region of human IgG1. Convenient restriction sites allow for the facile introduction of additional amino-terminal domains. Methods for treating patients using fusion proteins are also disclosed. The HCH2 polymers described here represent a new strategy in the design of recombinant proteins for the therapeutic targeting of FcγR in autoimmune disorders.
Owner:ITERATIVE THERAPEUTICS
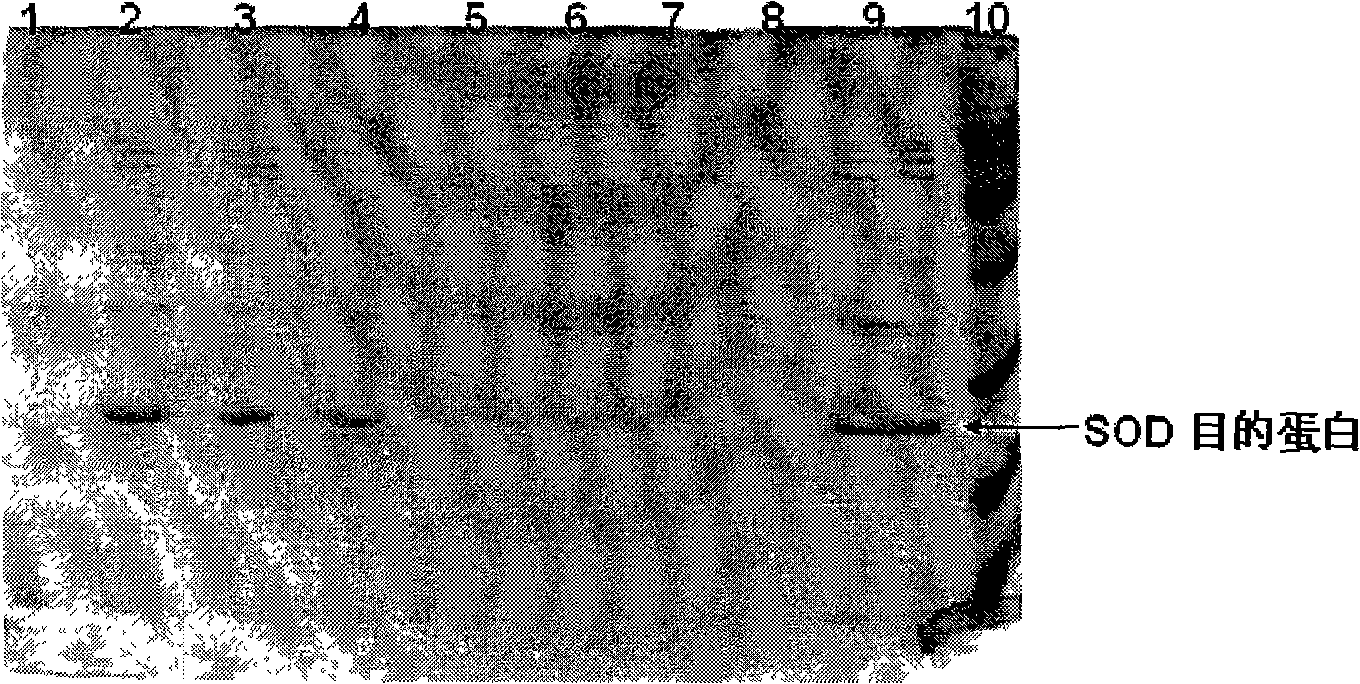
High-density fermentation and purification process for recombination high temperature-resistant hyperoxide dismutase
InactiveCN101275144AAvoid pollutionSimple purification processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliDismutase
The present invention provides a high density fermentation and a purification process of a recombination high temperature resistance superoxide dismutase, the construction method of the invention includes: using gene coded for SOD in a thermophilic bacteria as a template, designing specific primer amplification target gene having restriction enzyme sites, after double digestion, connecting to plasmid vector pET28a after the same double digestion, constructing a recombinant plasmid, named for pSOD, transforming plasmid pSOD to competence escherichia coli BL21(DE3) by chemical transformation method, obtaining strain having high SOD yield after screening, completing the construction of SOD engineering bacteria; the fermentation process includes four steps of first order seed culture, secondary order feed culture, batch fermentation and induced expression, fermentation product SOD is finally obtained; the fermentation process realizes high level expression of SOD, the expression of the target protein is more than 60% of the bacterial protein total; SOD has excellent thermal stability and heat resistance, the expression product accounts for more than 60% of the whole proteins, and fully soluble protein, avoiding any trouble in the course of inclusion body renaturation; the purification process is simple, having high yield, lower cost, the final product SOD has high purification, high activity and strength stability.
Owner:YANGTZE DELTA REGION INST OF TSINGHUA UNIV ZHEJIANG +1
Concatemers of differentially expressed multiple genes
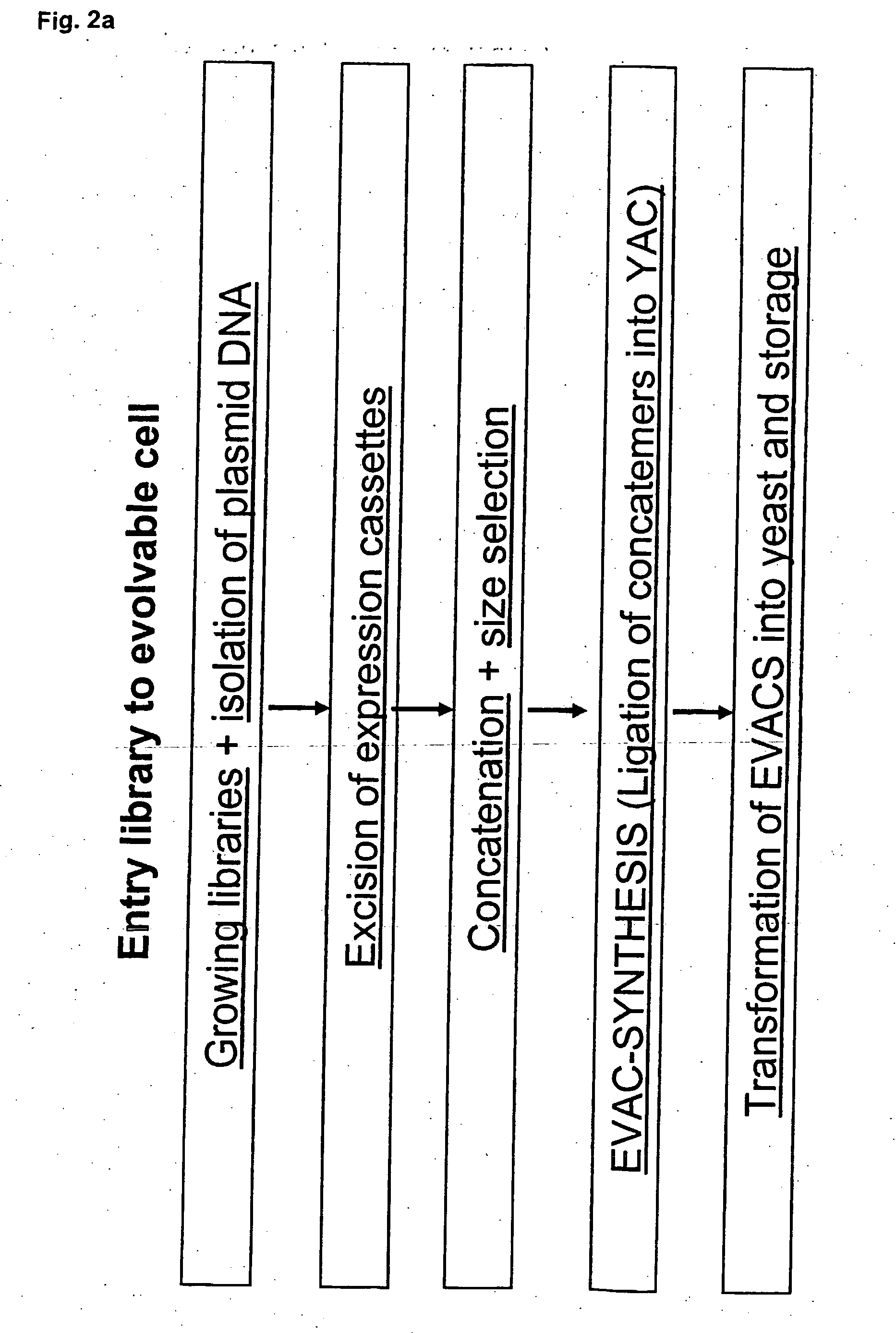
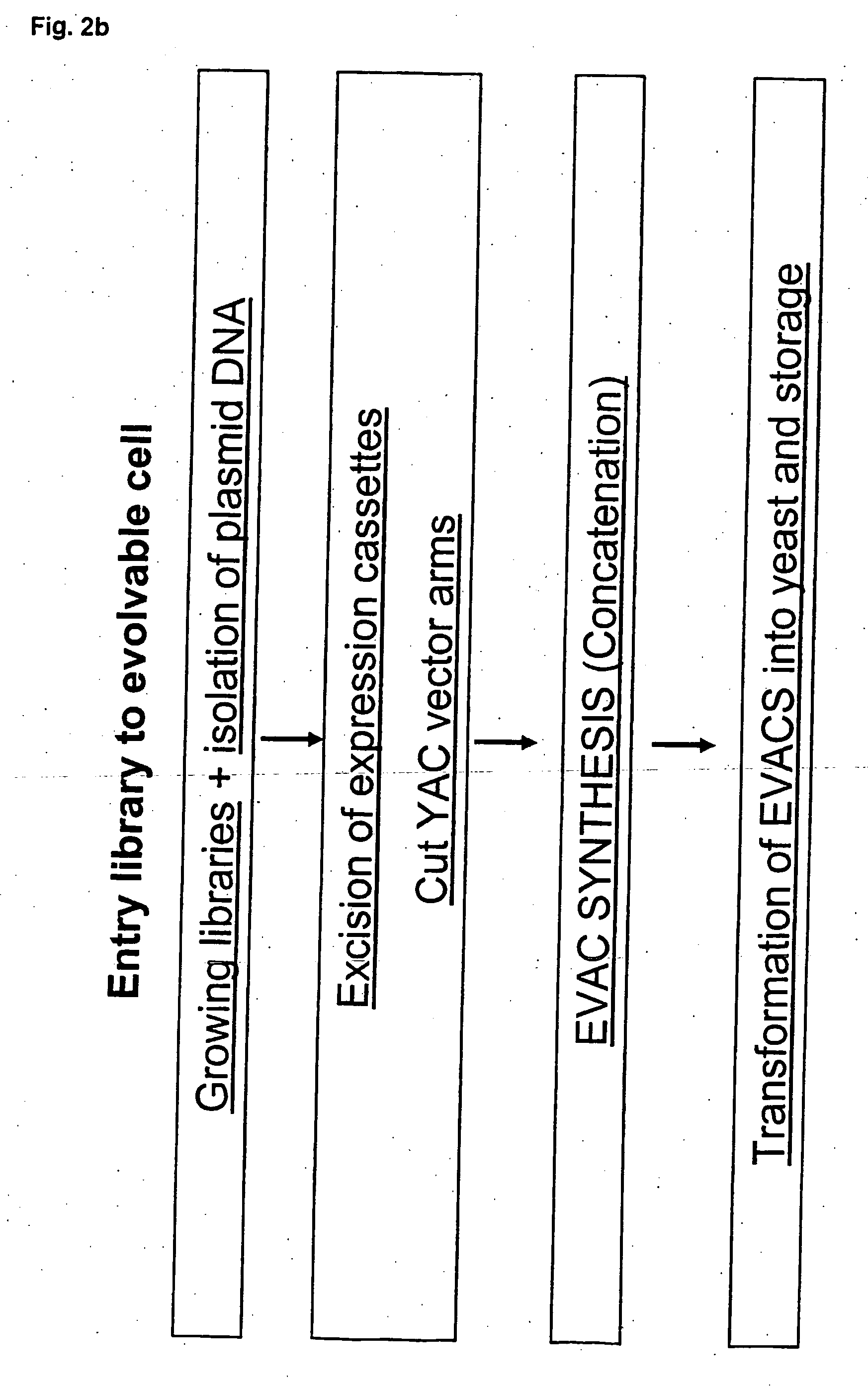
In the present invention are disclosed concatemers of concatenated expression cassettes and vectors that enable the synthesis of such concatemers. The concatemer comprises in the 5′→3′ direction a cassette of nucleotide sequence of the general formula [rs2-SP-PR-X-TR-SP-rs1]n wherein rs1 and rs2 together denote a functional restriction site, SP individually denotes a spacer of at least two nucleotide bases, PR denotes a promoter, capable of functioning in a cell, X denotes an expressible nucleotide sequence, TR denotes a terminator, and SP individually denotes a spacer of at least two nucleotide bases, and n> / =2, and wherein at least a first cassette is different from a second cassette. The main purpose of these concatemers is the controllable and co-ordinated expression of large numbers of heterologous genes in a single host. Furthermore, the invention relates to a concatemer of cassettes of nucleotide sequences and a method for preparing the concatemers. In a further aspect, the invention relates to transgenic host cells comprising at least one concatemer according to the invention, as well as to a method for preparing the transgenic host cells. Finally, the invention relates to a vector comprising a cassette of nucleotides, a method for preparing said vector, a nucleotide library comprising at least two primary vectors each comprising a cassette of nucleotides, a method for preparing the library.
Owner:EVOLVA SA
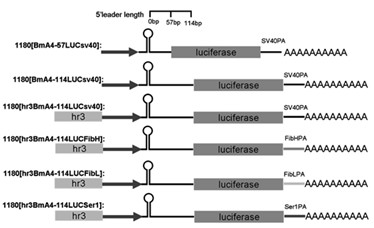
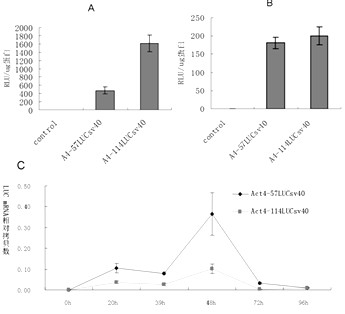
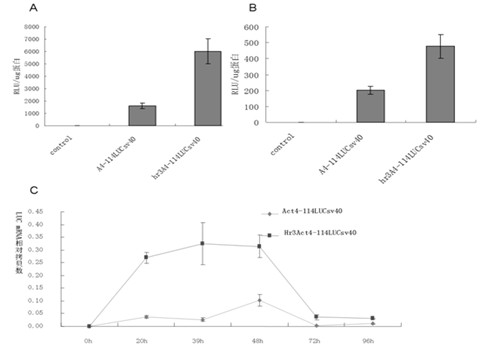
Enhancer Hr3
ActiveCN102492692AIncrease transcriptional activityImprove expression levelVector-based foreign material introductionDNA preparationRestriction sitePromoter
The invention relates to enhancer Hr3 adopting the nucleotide sequence shown in the SEQIDNO: 1. The enhancer Hr3 can be used for preparing and recombining heterologous protein by bombyx mori. The invention further relates to a recombination carrier containing the enhancer Hr3, and the recombination carrier is prepared in such a manner that the enhancer Hr3 is connected with a Nco1 restriction site at the upstream of a promoter of a carrier containing no enhancer through the Nco1 restriction site of the enhancer Hr3. In the invention, functional elements such as the first grade enhancer, activating transcription factor IE1, untranslated region sequences (5' UTR and 3' UTR) and the like which are expressed by intensifier are identified in the cellular level, and an efficient and stable sericin I expression system is built by integrating optimum elements on the basis, so that efficient expression recombination heterologous protein can be made of middle silk gland of transgenic bombyx mori.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Viral Vectors with Improved Properties
InactiveUS20120220492A1Increase infectivityGenetic therapy composition manufacturePeptidesMutated proteinADAMTS Proteins
Methods to improve the tropism or other features of a virus are disclosed. Such methods can be used to prepare, e.g., DNA or plasmid libraries of variants of a gene encoding a viral capsid or envelope protein having a randomly inserted restriction site, libraries of viral clones with such variant genes with a randomly inserted restriction site or polypeptide sequence targeting a receptor expressed by a specific type of mammalian cells. Described are also methods to prepare mosaic viruses, i.e., viral particles wherein copies of one or more capsid or envelope proteins originate from different sources. These methods can be used to prepare mosaic viruses of a specific mixture of wild-type and mutant proteins, or of different types of mutant proteins.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Process for producing activated human ALT
The present invention relates to an altered-type human ALT gene in which the codons for the five amino acids in the human ALT (alanine aminotransferase) gene are replaced, i. e. the fourth amino acid codon from the initiation codon for methionine (Met) is replaced by a codon for serine (Ser), the fifth by a codon for threonine (Thr), the seventh by a codon for aspartic acid (Asp), the 39th by a codon for glycine (Gly) and the 222nd by a codon for alanine (Ala), and concurrently, restriction sites are added at the upstream and downstream of said gene.The active human ALT having properties similar to those of the native enzyme can be effectively produced by culturing E. coli transformed with a recombinant plasmid in which the altered-type human ALT gene of the present invention is ligated to a vector.
Owner:ORIENTAL YEAST
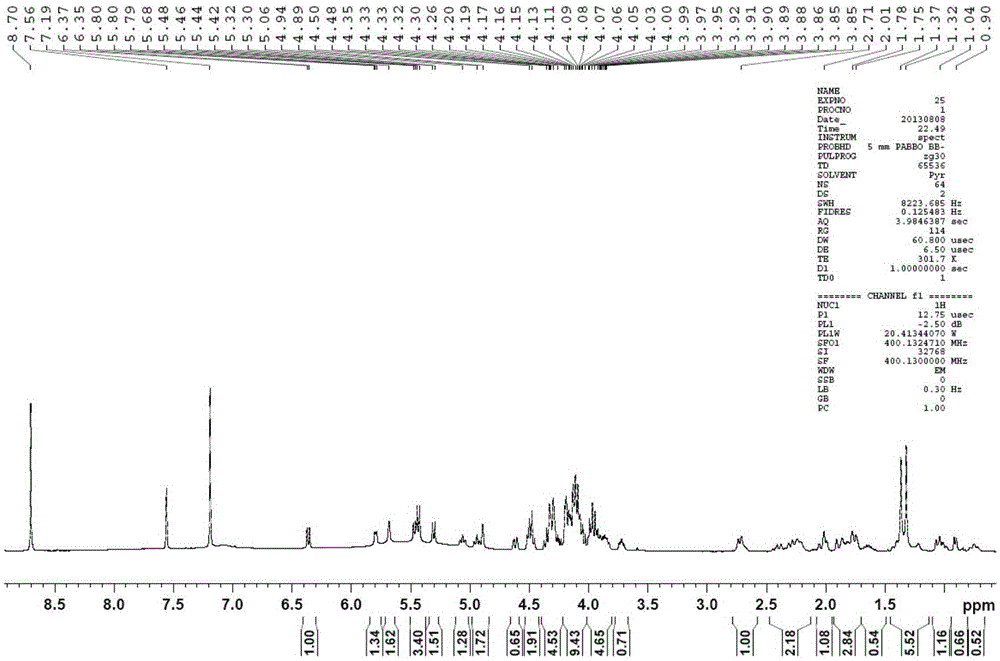
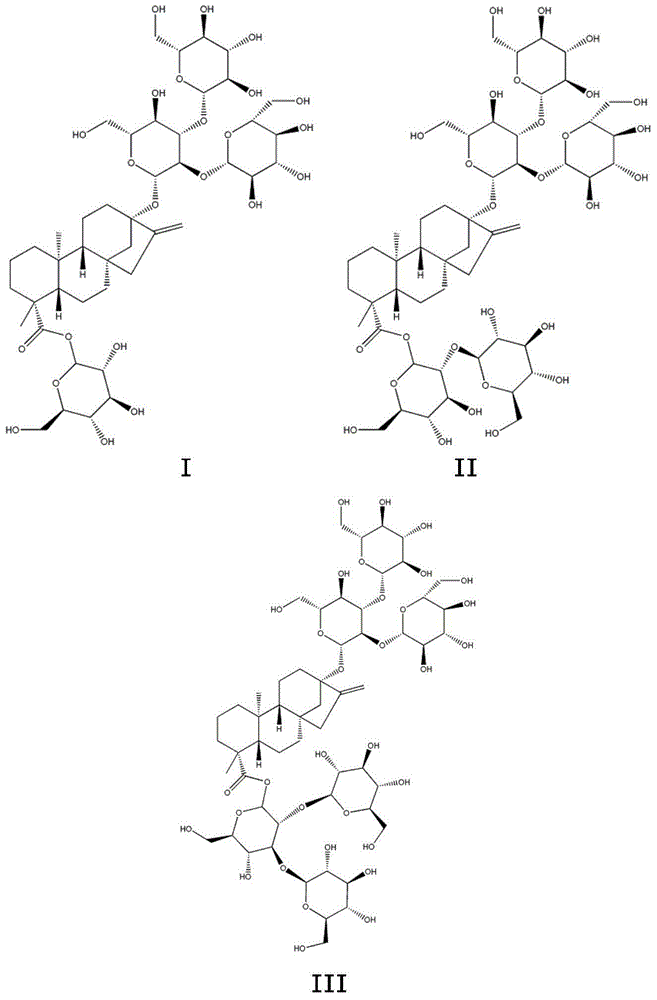
Method for preparing rebaudioside M according to saccharomyces cerevisiae enzymatic method
InactiveCN105200098AImprove securitySave fermentation timeMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesFood additiveUdp glucosyltransferase
The invention discloses a method for preparing rebaudioside M according to a saccharomyces cerevisiae enzymatic method. The method for preparing rebaudioside M comprises the following steps: utilizing recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae containing UDP-glucosyltransferase or UDP-glucosyltransferase prepared from the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae to catalyze rebaudioside A or rebaudioside D in the presence of a glucosyl group donor, so as to generate rebaudioside M. The recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae is obtained by introducing a strong promoter into a plasmid to obtain a vector plasmid, inserting a UDP-glucosyltransferase gene into the vector plasmid through a restriction site to obtain an expression vector under the control the strong promoter, and carrying out saccharomyces cerevisiae transformation. The method for preparing rebaudioside M has the advantages that the high-safety recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae is utilized for catalytic production; the produced UDP-glucosyltransferase is higher in expression level and activity; the produced rebaudioside M can be directly utilized as a food additive, and is short in production period, higher in yield, and relatively low in cost.
Owner:PEPSICO INC
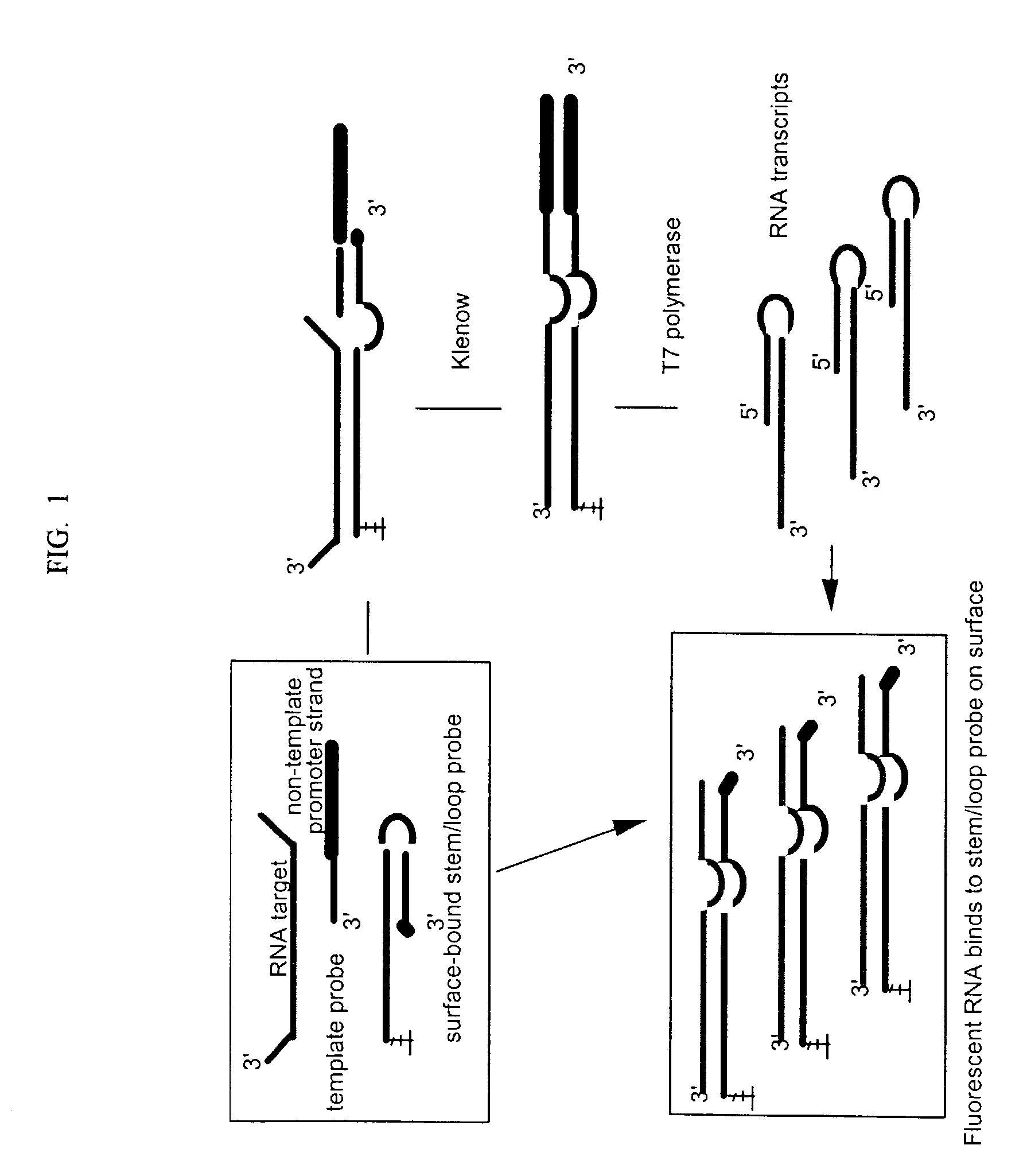
Isothermal amplification in nucleic acid analysis
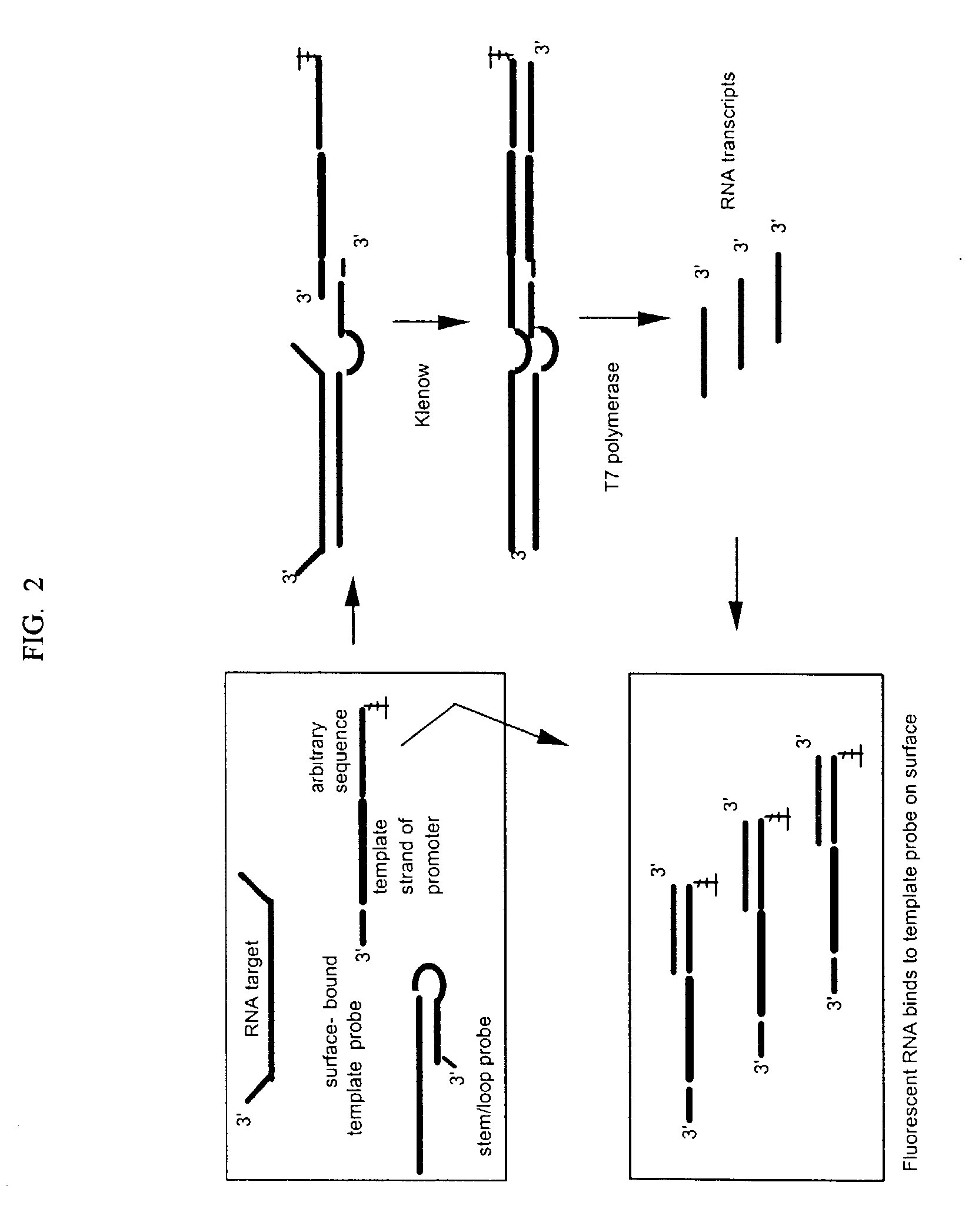
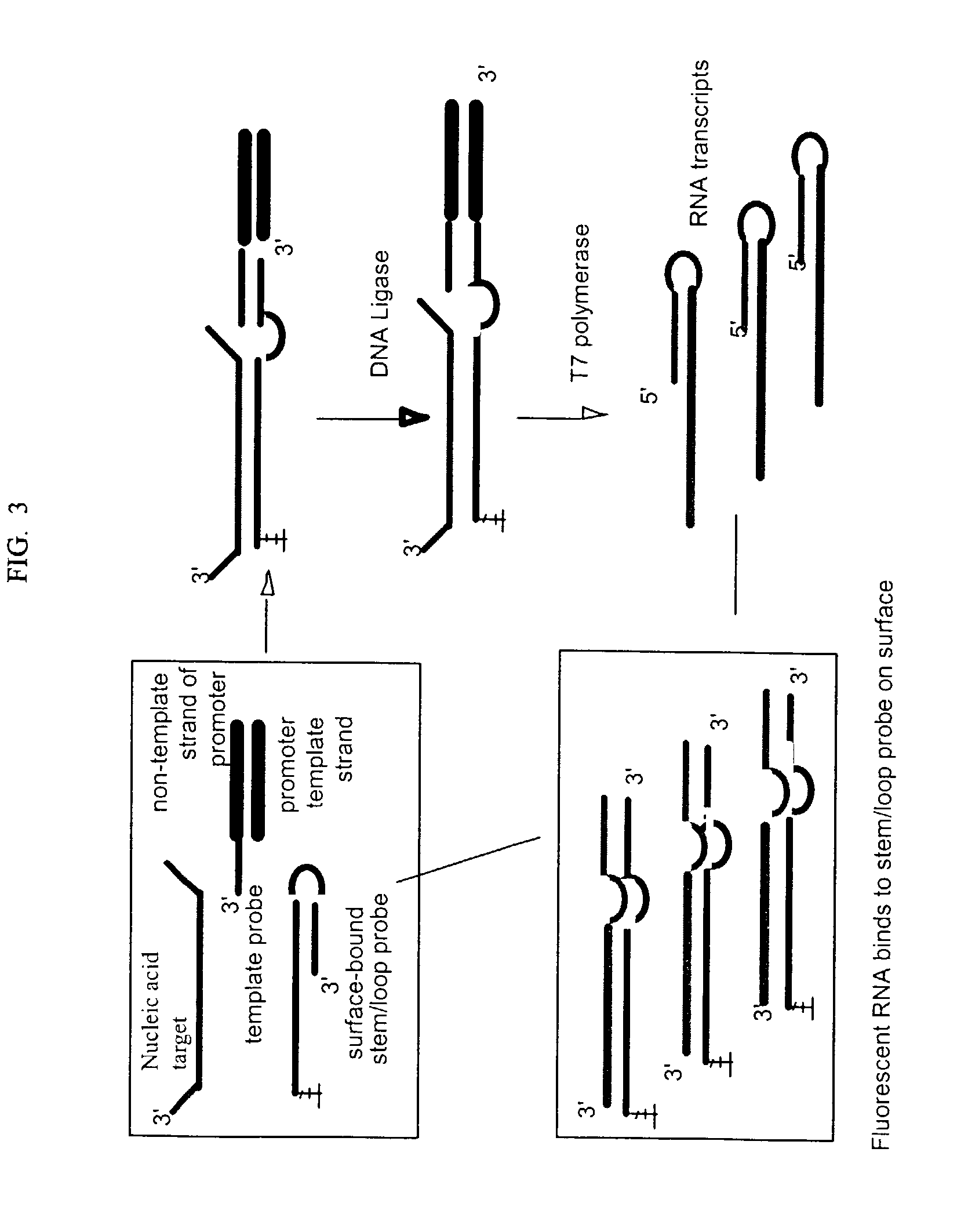
A method for detection of nucleic acid targets using as reagents: (1) a stem loop probe having a long strand for hybridizing to a target, a short strand, usually with a free 3'-end for extension, hybridized to a portion of the long strand and a linker forming a loop and joining the short and long strands; and (2) a hybridizing reagent that hybridizes to the short strand when released by the target. The target is detected by extension of one or both the probe or hybridizing reagent along each other. A circular hybridizing reagent can be employed with DNA polymerase for concatenated extension of the probe 3'-end or extension of the 3'-end of the probe along a hybridizing reagent having a promoter sequence for forming transcripts of at least a portion of the long strand or the hybridizing reagent. A non-cleavable restriction site consensus sequence in the linker, where the hybridizing reagent is extended with dNTPs and DNA polymerase and the extended sequence is cleaved with a restriction enzyme, so that chains may be repetitively produced and cleaved. The presence of the target nucleic acid is established by detecting the concatenated chain, the RNA transcripts or the repetitively produced chains.
Owner:DISCOVEX
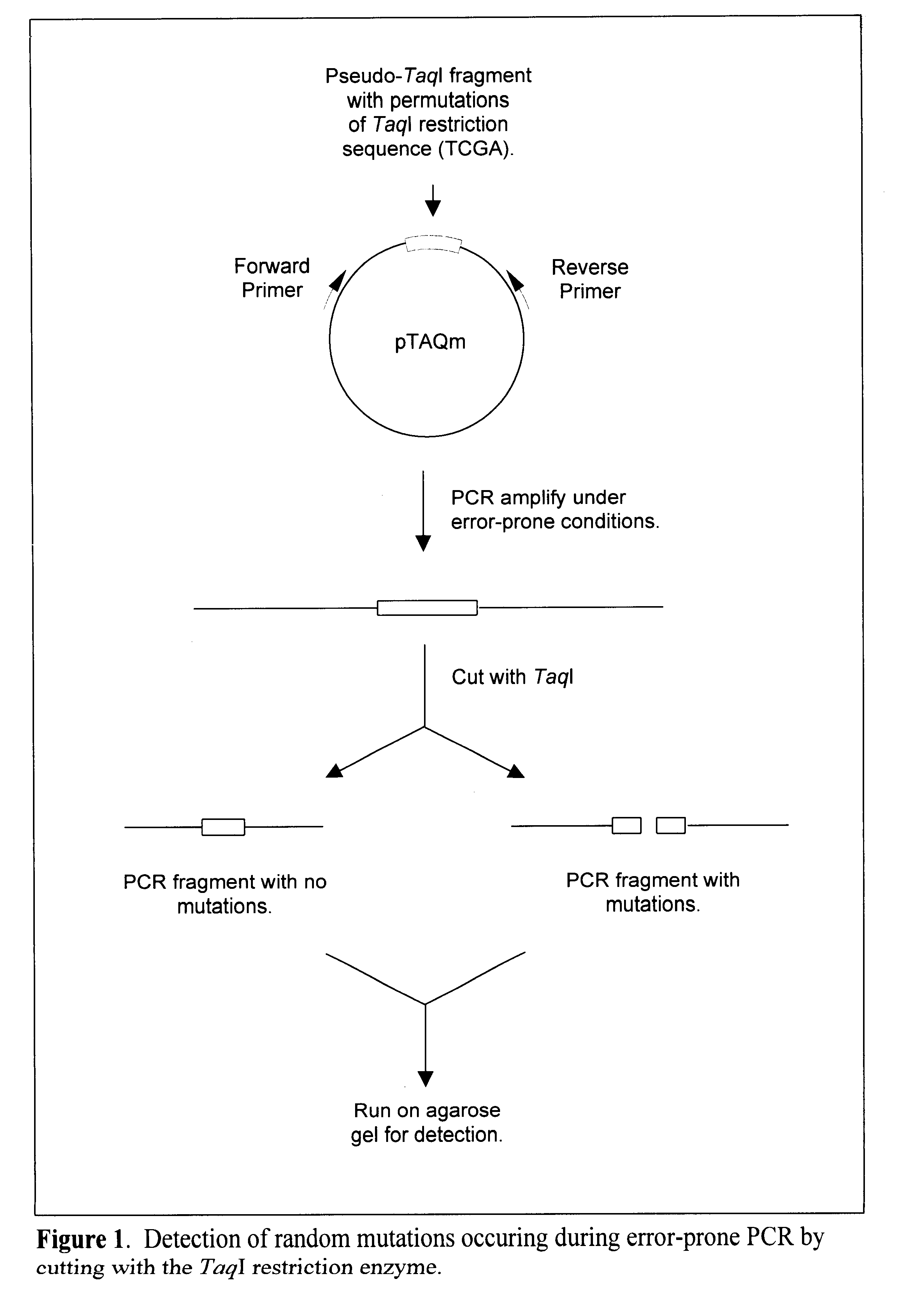
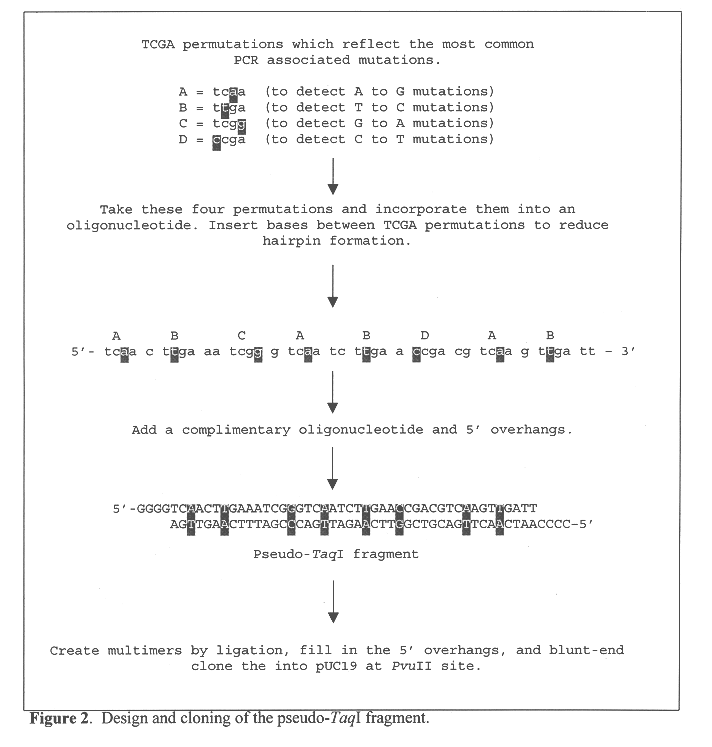
Methods and kits for determining the fidelity of polymerase chain reaction conditions
Methods are provided for evaluating the fidelity of a given set of polymerase chain reaction conditions. In the subject methods, a template polydeoxyribonucleotide is amplified under the to be evaluated polymerase chain reaction conditions, where the template polydeoxyribonucleotide includes a pseudo restriction endonuclease restriction site. The resultant amplified product population is then contacted with the corresponding restriction endonuclease and resultant cleavage products, if any, are detected. The fidelity of the polymerase chain reaction conditions is then derived from the detected cleavage products (or absence thereof). Also provided are kits for use in practicing the subject methods. The subject methods are suited for determining the fidelity of a given polymerase under PCR conditions, and are particularly suited for determining the fidelity of a thermostable polymerase under PCR conditions.
Owner:CLONTECH LAB
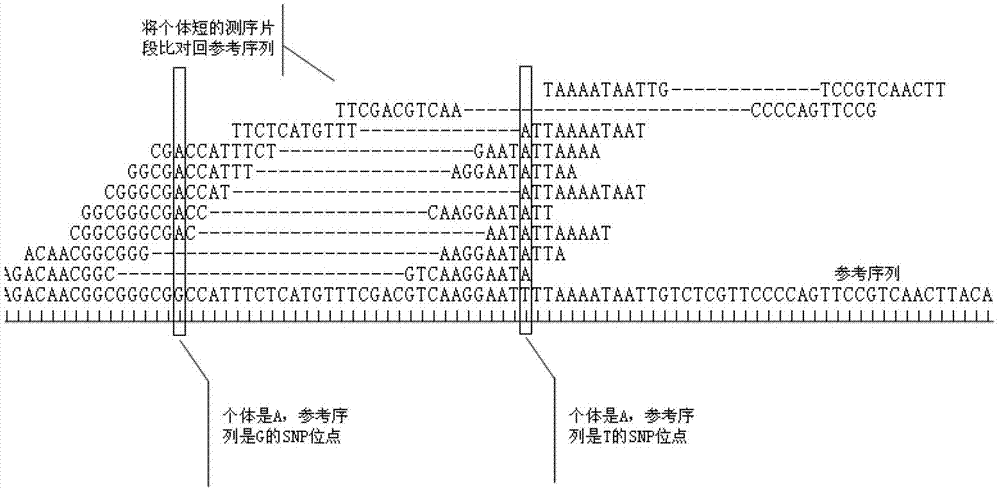
Single nucleotide polymorphism site identification method based on digestion library-establishing and sequencing and bayesian statistics
ActiveCN103114150ALow costThe result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementNon model organismRestriction site
The invention discloses a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) site identification method based on digestion library-establishing and sequencing and bayesian statistics. The method is used for processing RAD (restriction site associated deoxyribonucleic acid) sequencing data, searching candidate SNP on an RAD sequencing fragment, and identifying the SNP reliability by employing a bioinformatics analysis method based on bayesian statistics. The method can be used for model and non-model organisms to eliminate the limitation that lots of species are lack of reference sequences and reduce the sequencing cost, and can be used for solving the bottleneck that a reliable statistical method is absent in the process of performing SNP identification by utilizing the RAD data at present, so that the obtained SNP site accuracy is greatly improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI MAJORBIO BIO PHARM TECH
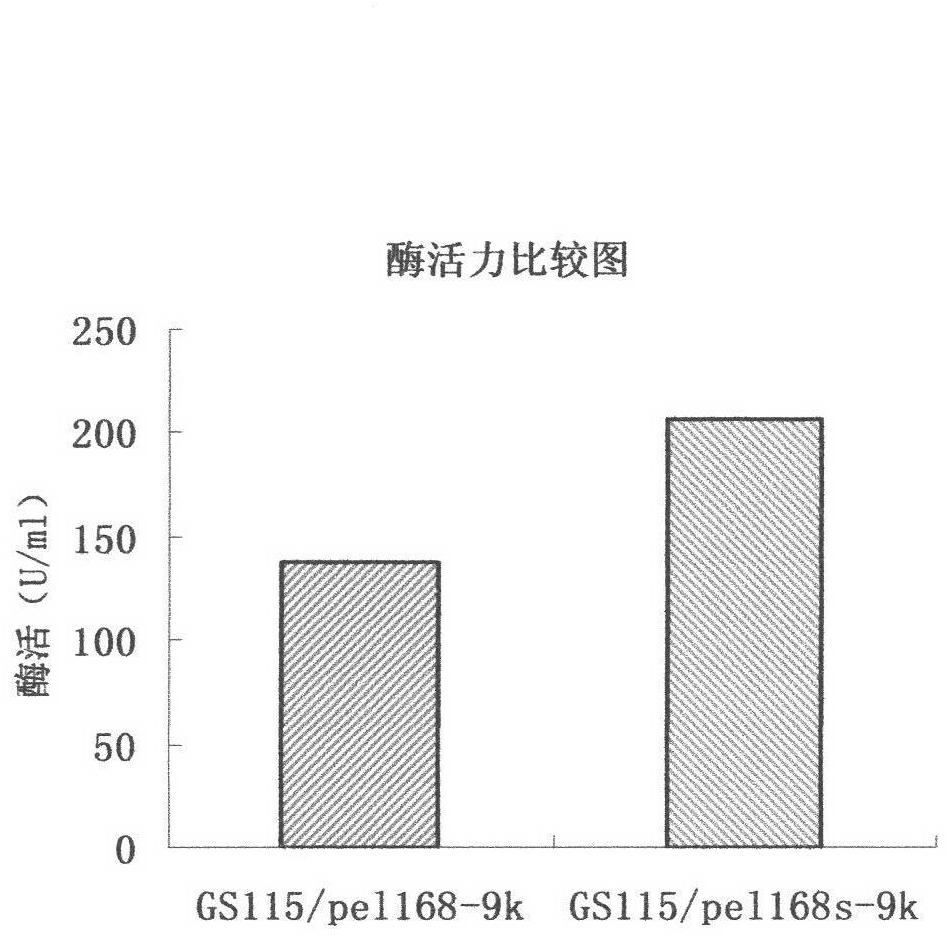
Optimized nucleotide sequence of alkaline pectinase pell68s and high-level expression method thereof
ActiveCN102604977AEasy to purifyHigh activityMicroorganism based processesEnzymesPectinaseBiotechnology
The invention provides and discloses an optimized nucleotide sequence of alkaline pectinase pel168s and a high-level expression method thereof. According to the method, a pel168 gene sequence (wherein the gene is Bacillus subtilis 168 the accession number of which in a GenBank is AL009126) is optimized by DNA works software, restriction enzyme cutting sites SalI and PmeI are shielded, a restriction enzyme cutting site EcoRI is added at the 3' end of a primer, and a restriction enzyme cutting site NotI is introduced at the 5' end of the primer. After the procedures of PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification, connection transformation and sequencing verification, the optimized gene sequence of the alkaline pectinase pel168s is obtained. Recombinant plasmid pel168s-9k is constructed according to the sequence, and then is transformed into pichia yeast GS115, thereby obtaining a positive recombinant strain GS115 / pel168s-9k. According to the invention, when alkaline pectinase is produced by adopting the optimized nucleotide sequence of the alkaline pectinase pel168s and utilizing the pichia yeast, the target protein expression index is high, the purge process is simple, the production cost of the alkaline pectinase is reduced greatly, and the utilization rate of an enterprise on the alkaline pectinase is enhanced.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
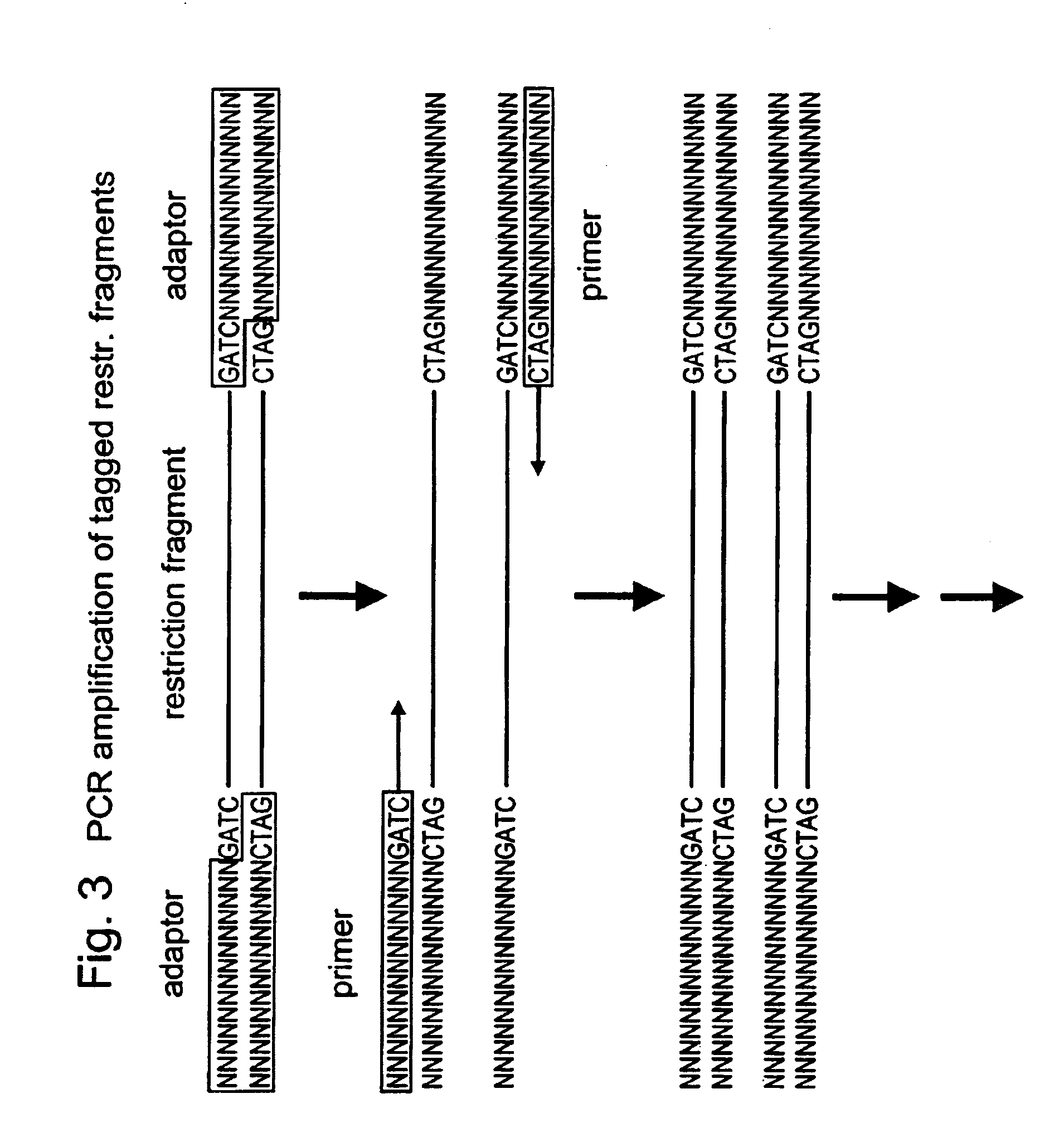
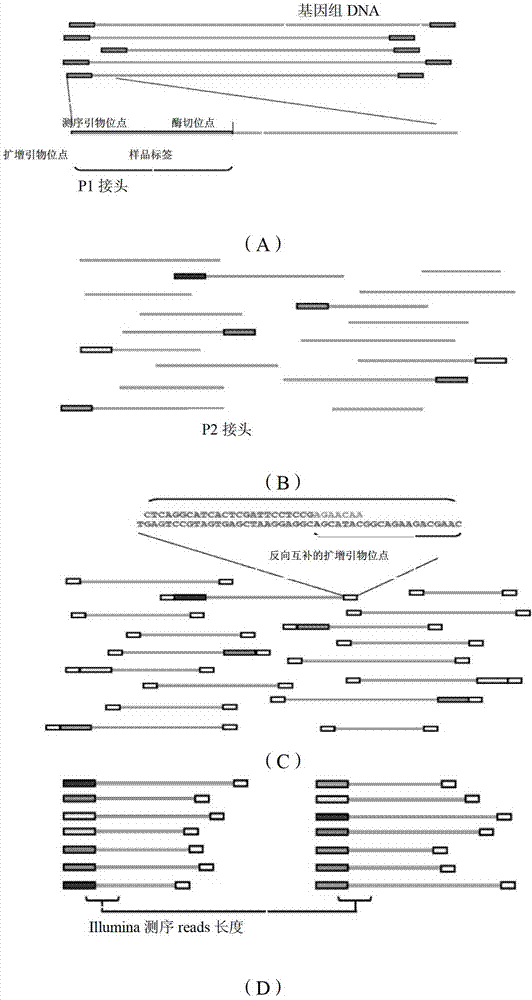
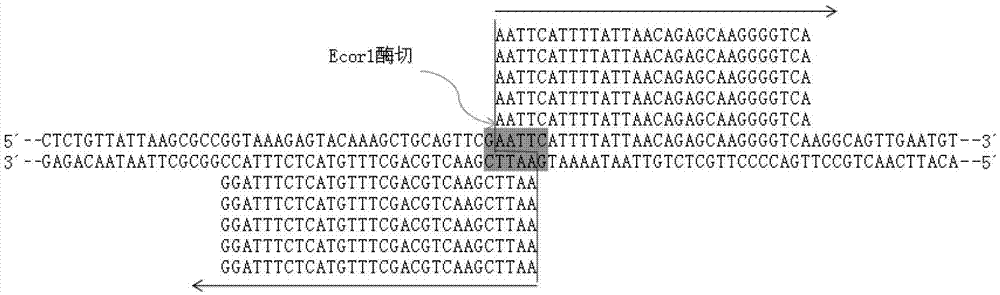
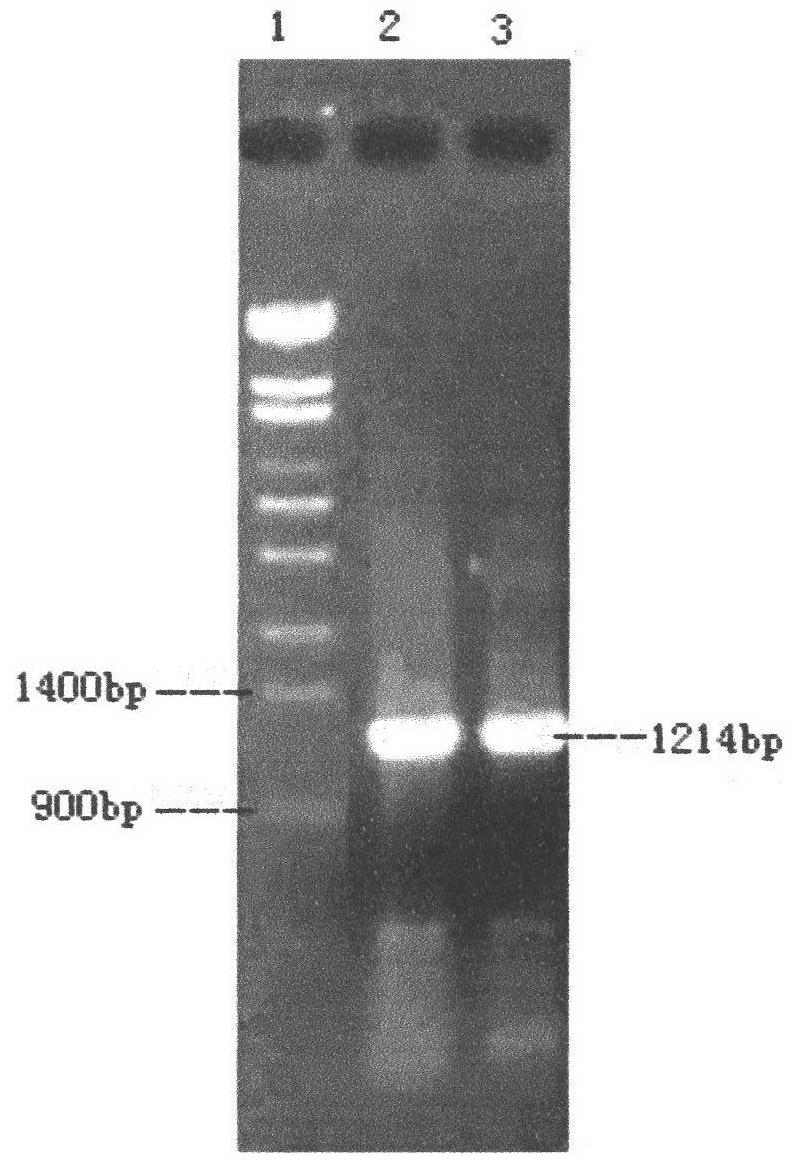
Method for constructing series connection RAD [restriction-site-associated DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)] tag sequencing libraries
ActiveCN106192021AIncrease label densityAdd one step enzyme ligation reactionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationEnzyme digestionBarcode
The invention discloses a method for constructing series connection RAD [restriction-site-associated DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)] tag sequencing libraries. The method includes steps of 1), carrying out enzyme digestion reaction on DNA by the aid of incision enzymes; 2), respectively connecting linkers to enzyme digestion fragments; 3), amplifying connection products, to be more specific, carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification by the aid of biotin primer and common primer combinations, enriching PCR products, recycling the PCR products by means of gel incision, amplifying the PCR products again, equivalently mixing the PCR products with one another and equivalently purifying the PCR products; 4), serially connecting tag libraries with one another, to be more specific, carrying out enzyme digestion on the PCR products by the aid of SapI enzymes and sequentially serially connecting the PCR products with one another; 5) enriching series connection long tags, to be more specific, purifying the series connection long tags by the aid of gel, then carrying out PCR amplification by the aid of primers and introducing barcode to construct the libraries; 6), carrying out library sequencing. The linkers are provided with enzyme digestion sites of the SapI enzymes, signature sequences for serially connecting the tags with one another and universal sequences for binding the amplification primers. The method has the advantage that genetic markers and epigenetic variation can be screened and detected in whole genome ranges by the aid of the method in a high-throughput and low-cost manner.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Viral vectors with improved properties
InactiveUS20060286545A1Efficient retargetingIncrease infectivityVectorsGenetic therapy composition manufactureMutated proteinRestriction site
Methods to improve the tropism or other features of a virus is disclosed. Such methods can be used to prepare, e.g., DNA or plasmid libraries of variants of a gene encoding a viral capsid or envelope restriction site, libraries of viral clones with such variant genes with a randon-dy inserted restriction site or polypeptide sequence targeting a receptor expressed by a specific type of mammalian cells. Described are also methods to prepare mosaic viruses, i.e., viral particles wherein copies of one or more capsid or envelope proteins originate from different sources. These methods can be used to prepare mosaic viruses of a specific mixture of wild-type and mutant proteins, or of different types of mutant proteins.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods of Making Modular Fusion Protein Expression Products
InactiveUS20090123973A1The process is simple and fastSugar derivativesBacteriaFusion Protein ExpressionOpen reading frame
The invention relates to methods of making modular chimeric protein expression products and compositions utilized in the methods. In particular, the invention relates to sequential, directional cloning of polynucleotides encoding polypeptide modules. Each clonable element or module contains an open reading frame of interest flanked by predetermined restriction sites. The methods include using modules and vectors containing these modules as starting materials for recombinant DNA techniques. One advantage of the invention is that it allows for many variations of fusion proteins to be made quickly and easily without needing to design and evaluate each subsequent cloning step.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Proviral Plasmids and Production of Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus
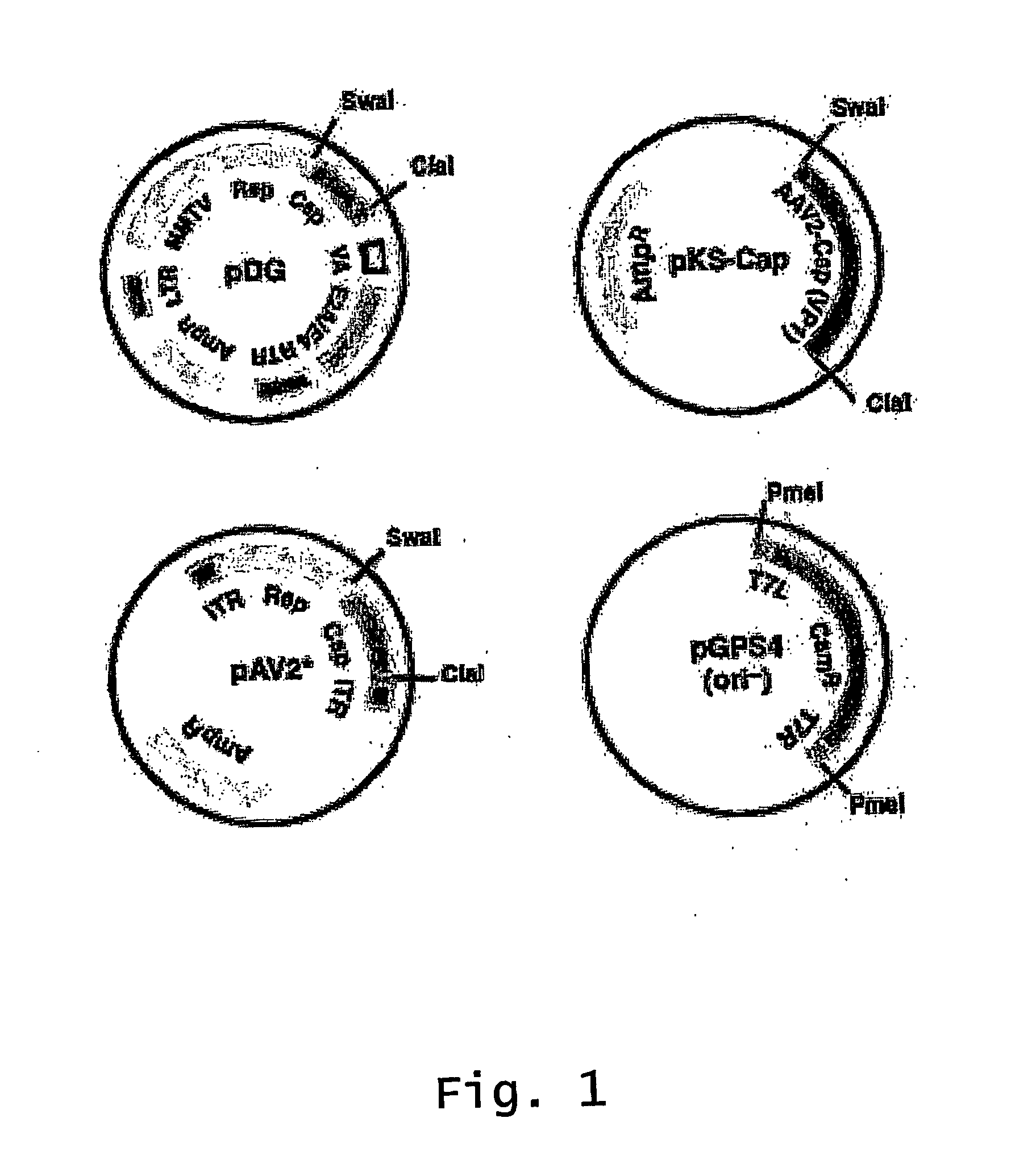
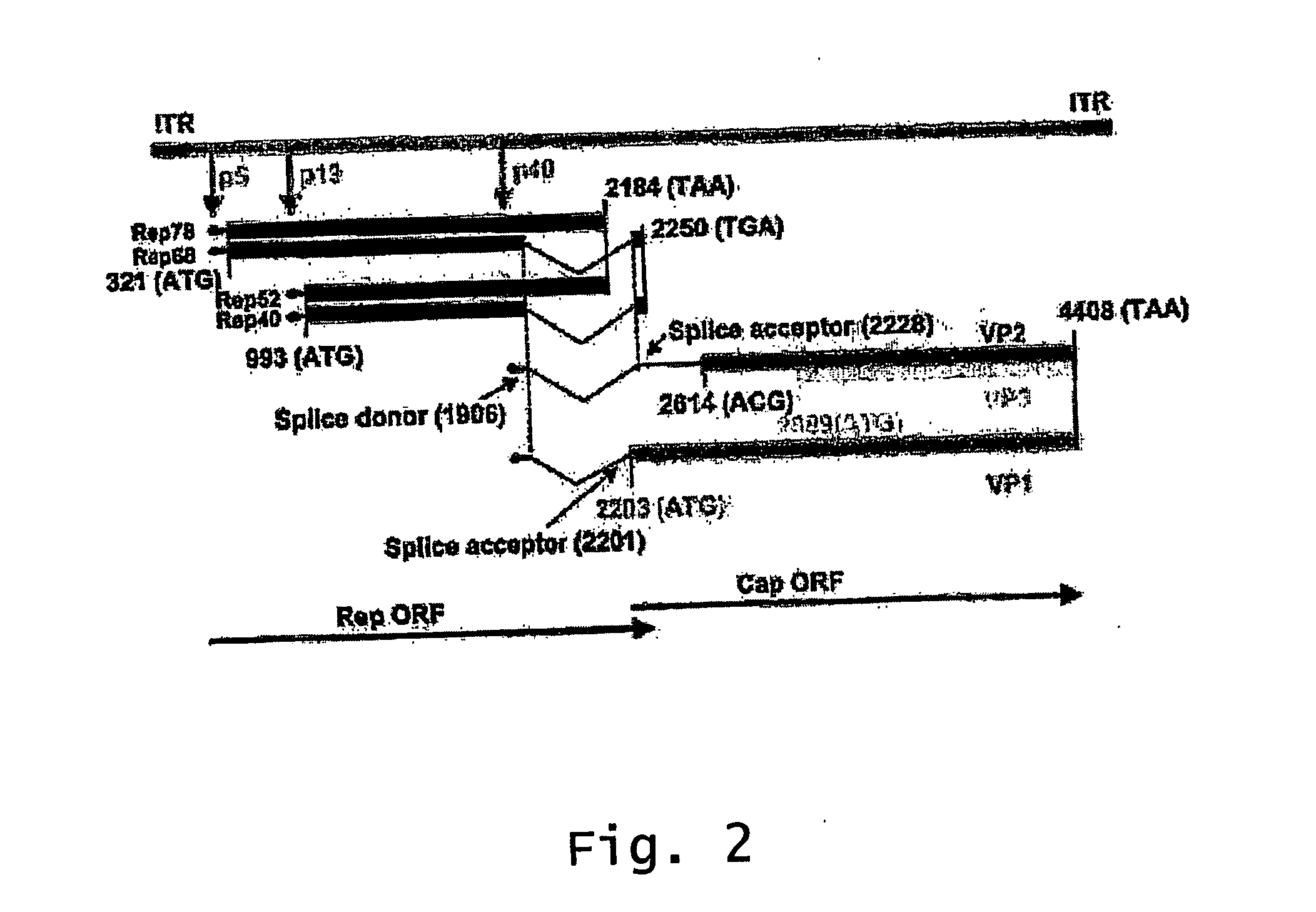
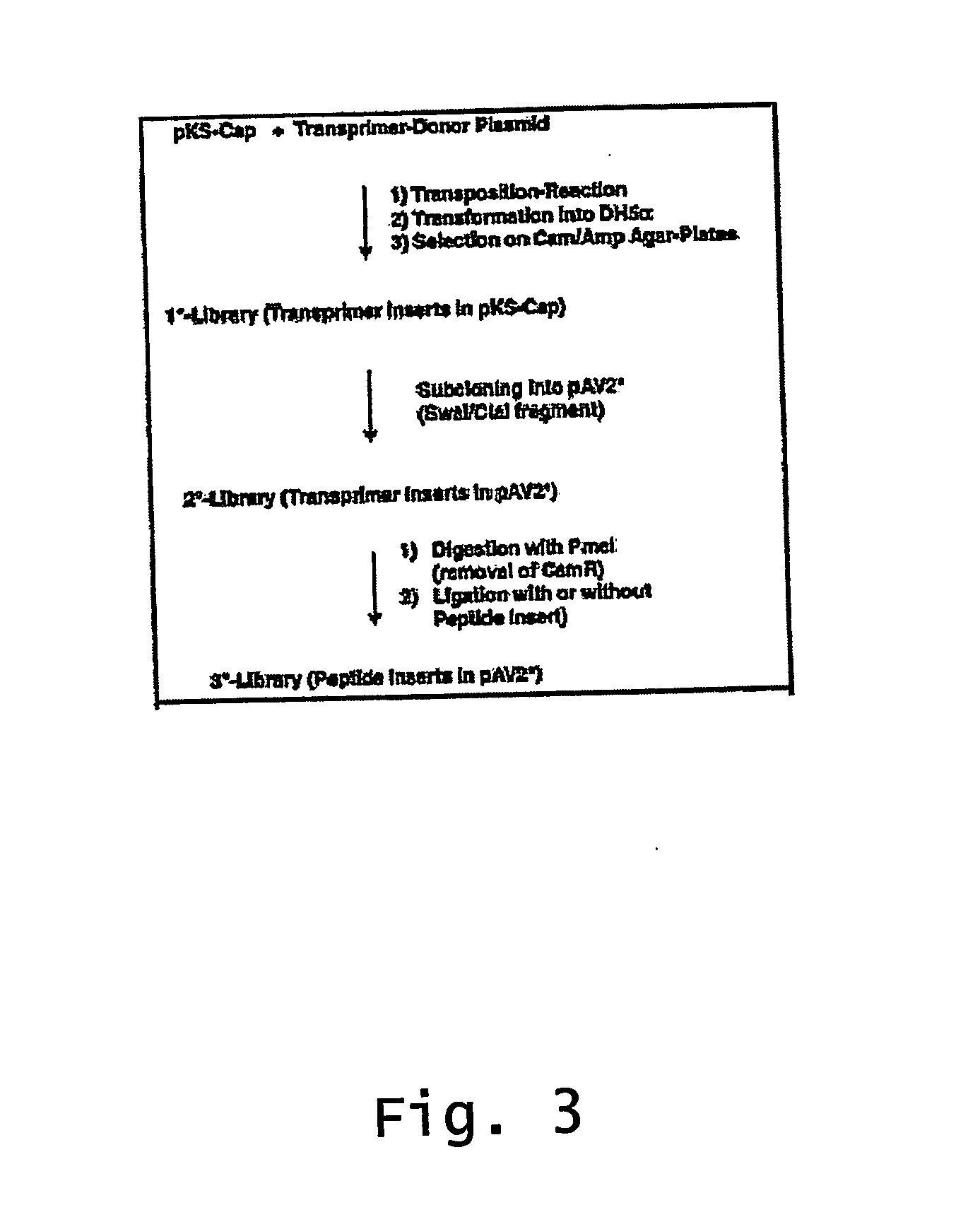
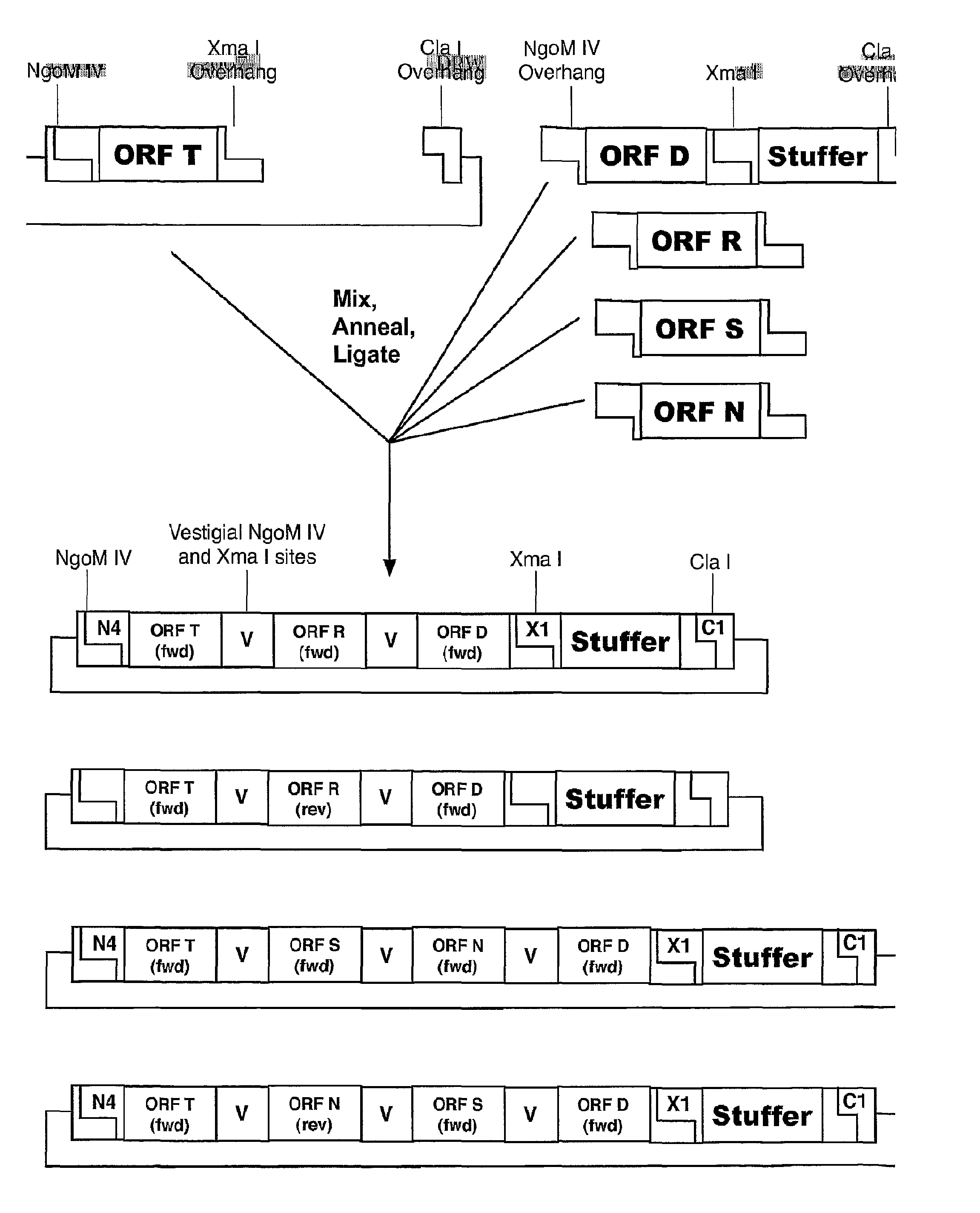
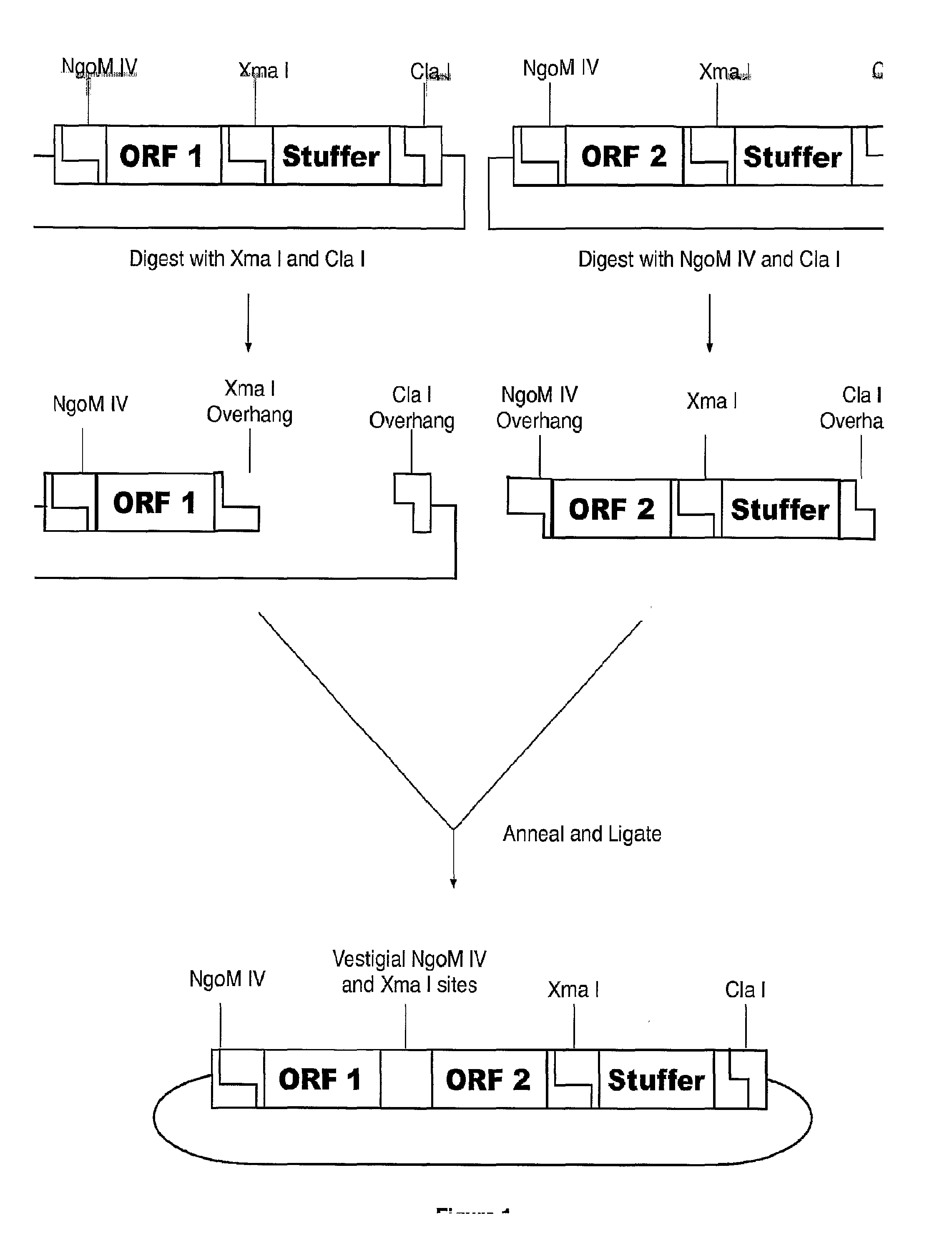
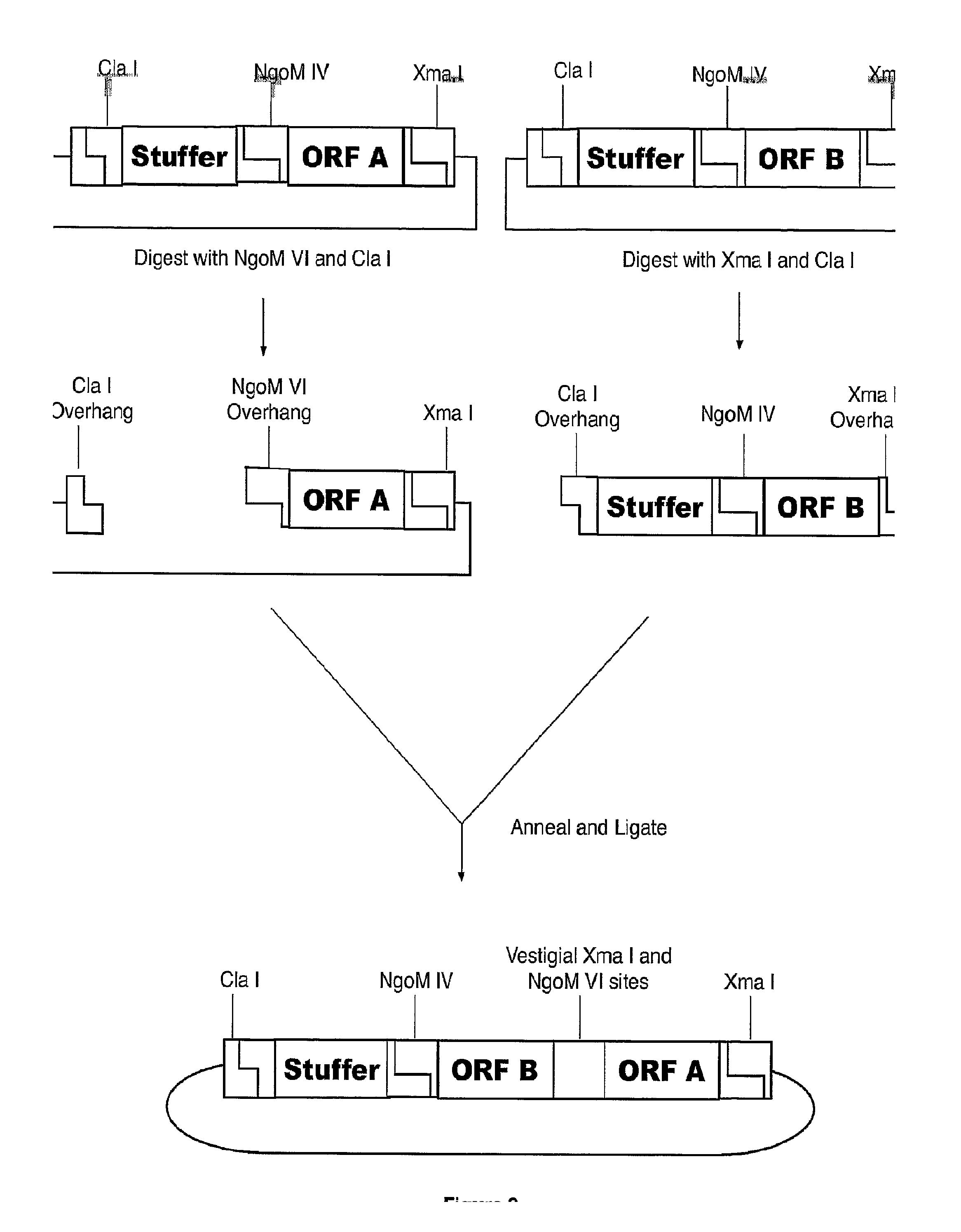
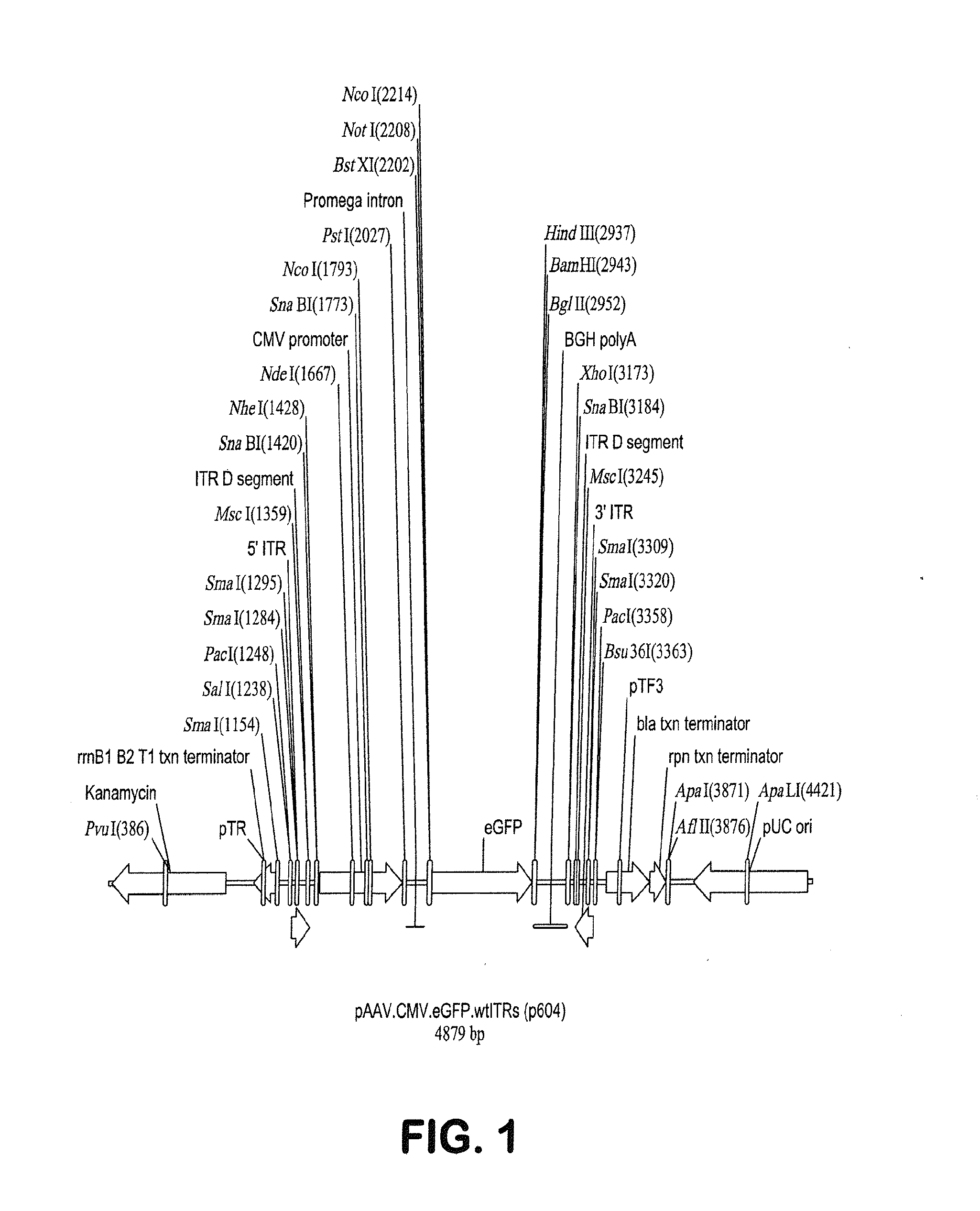
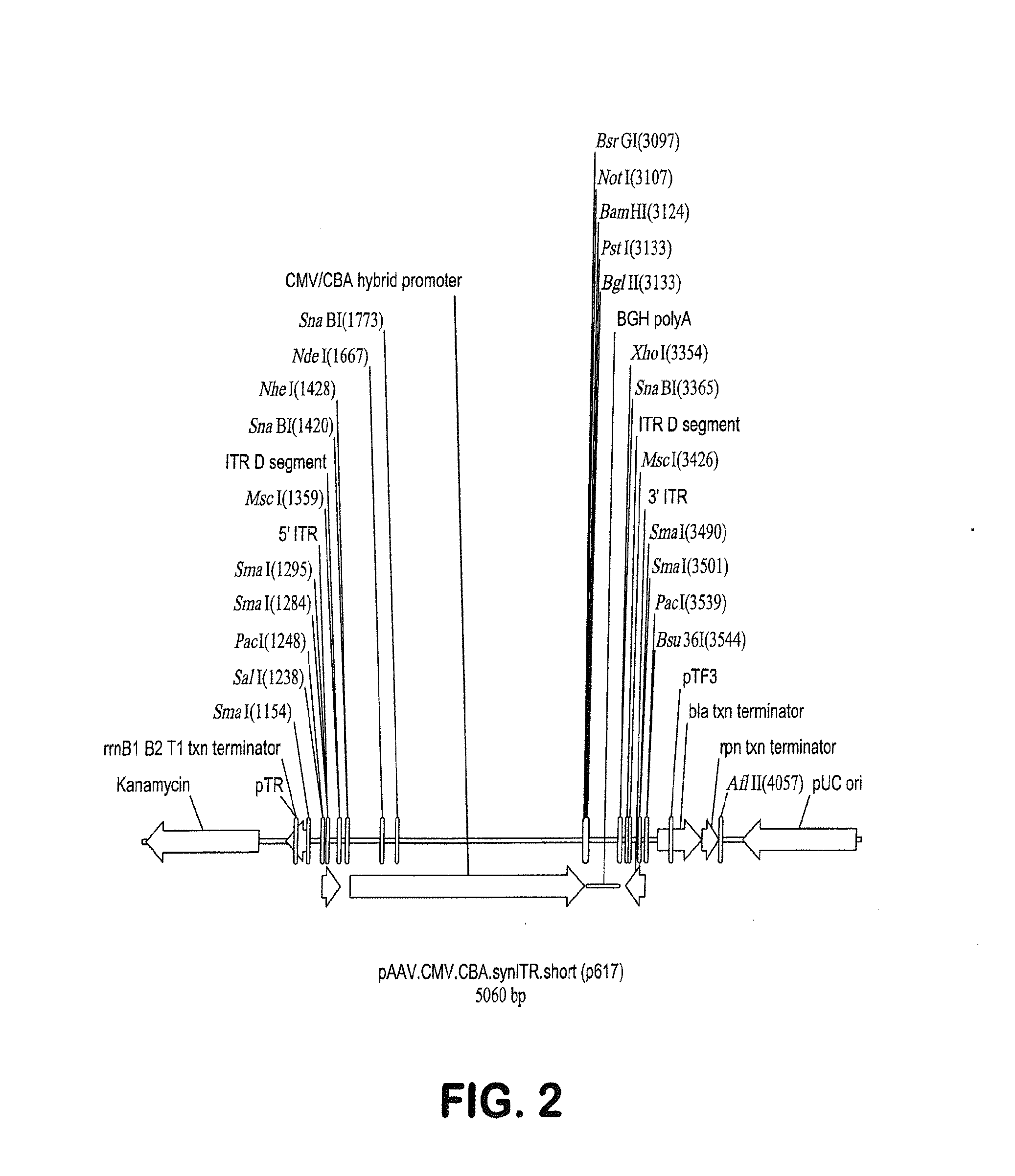
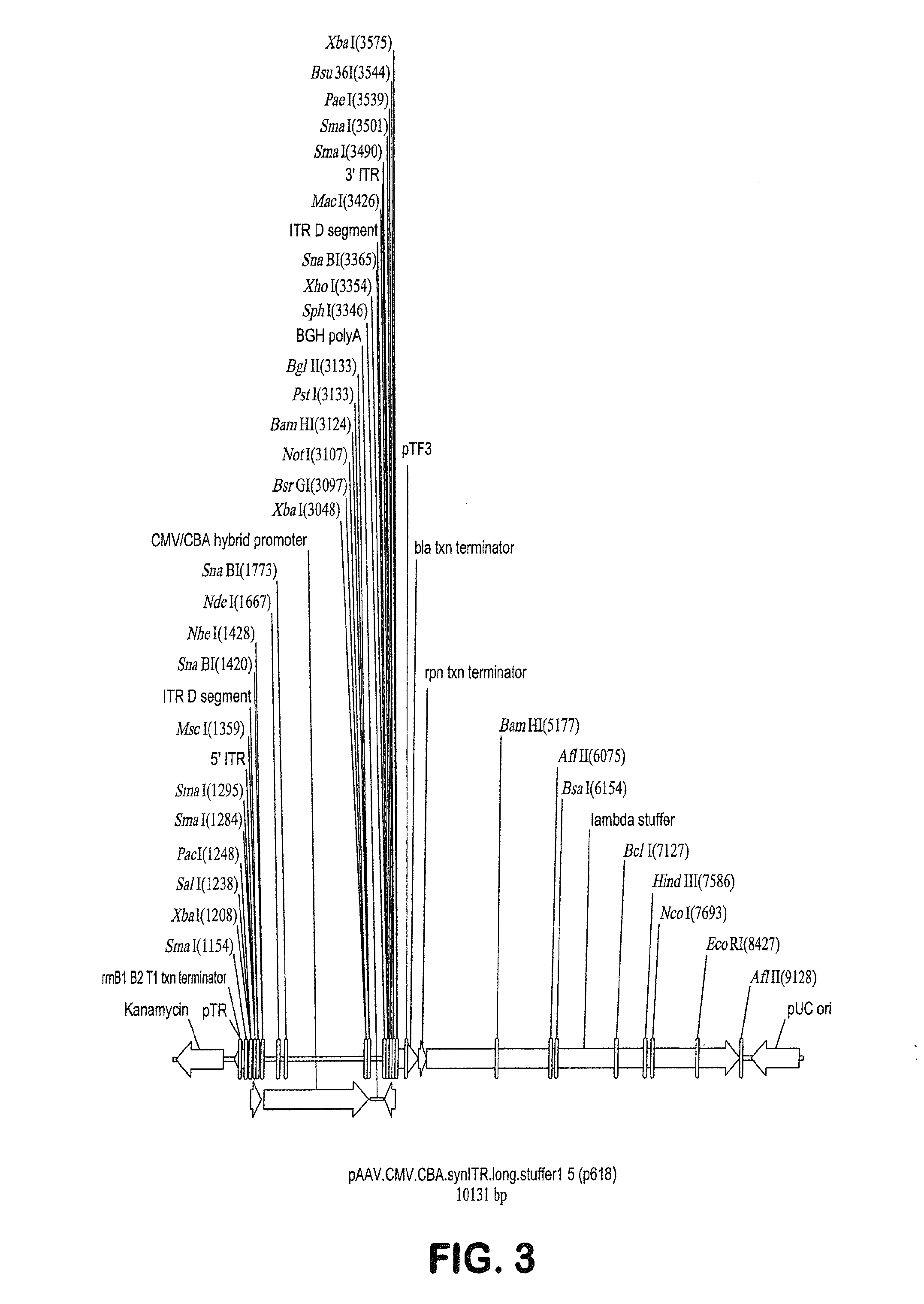
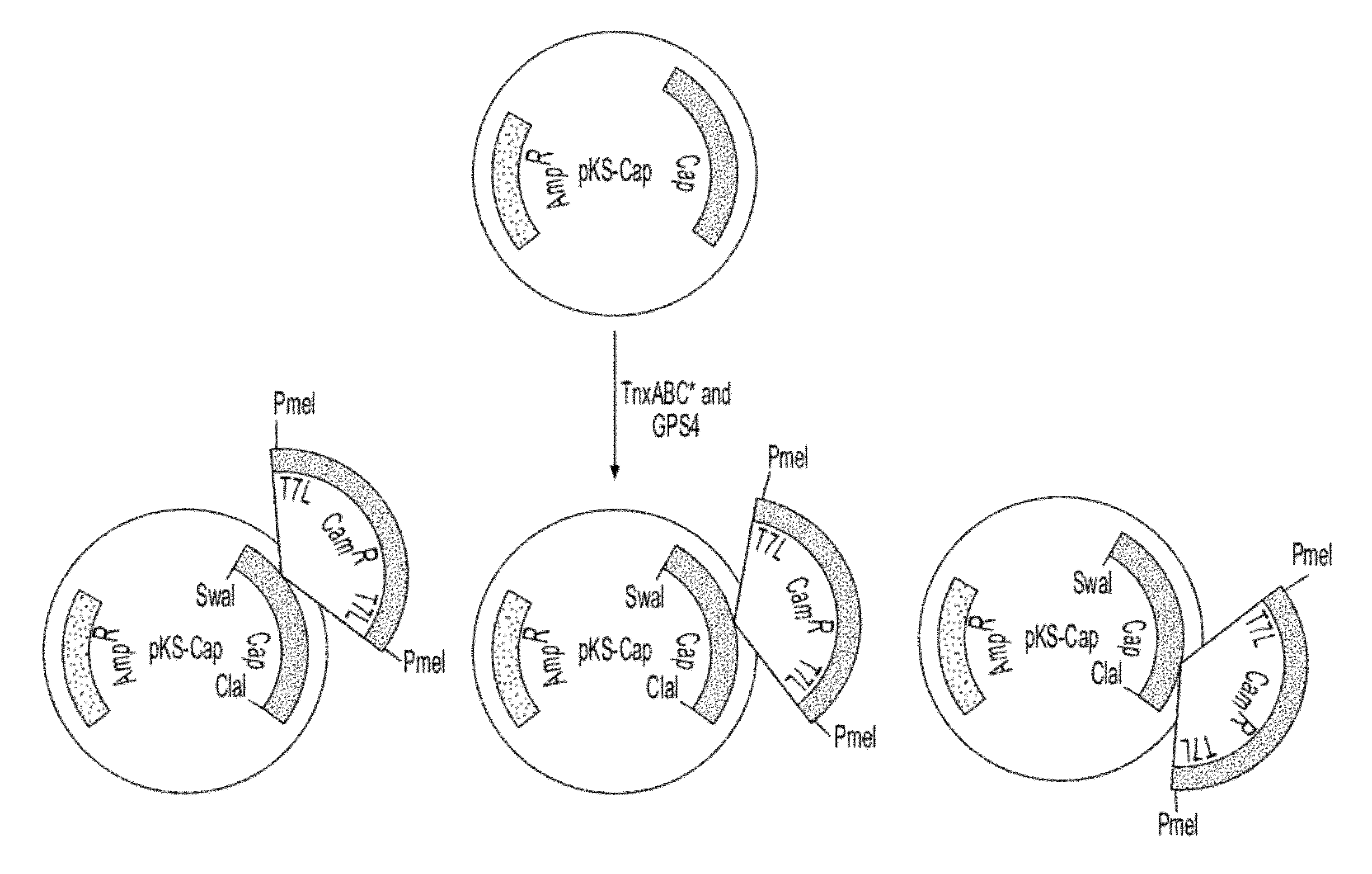
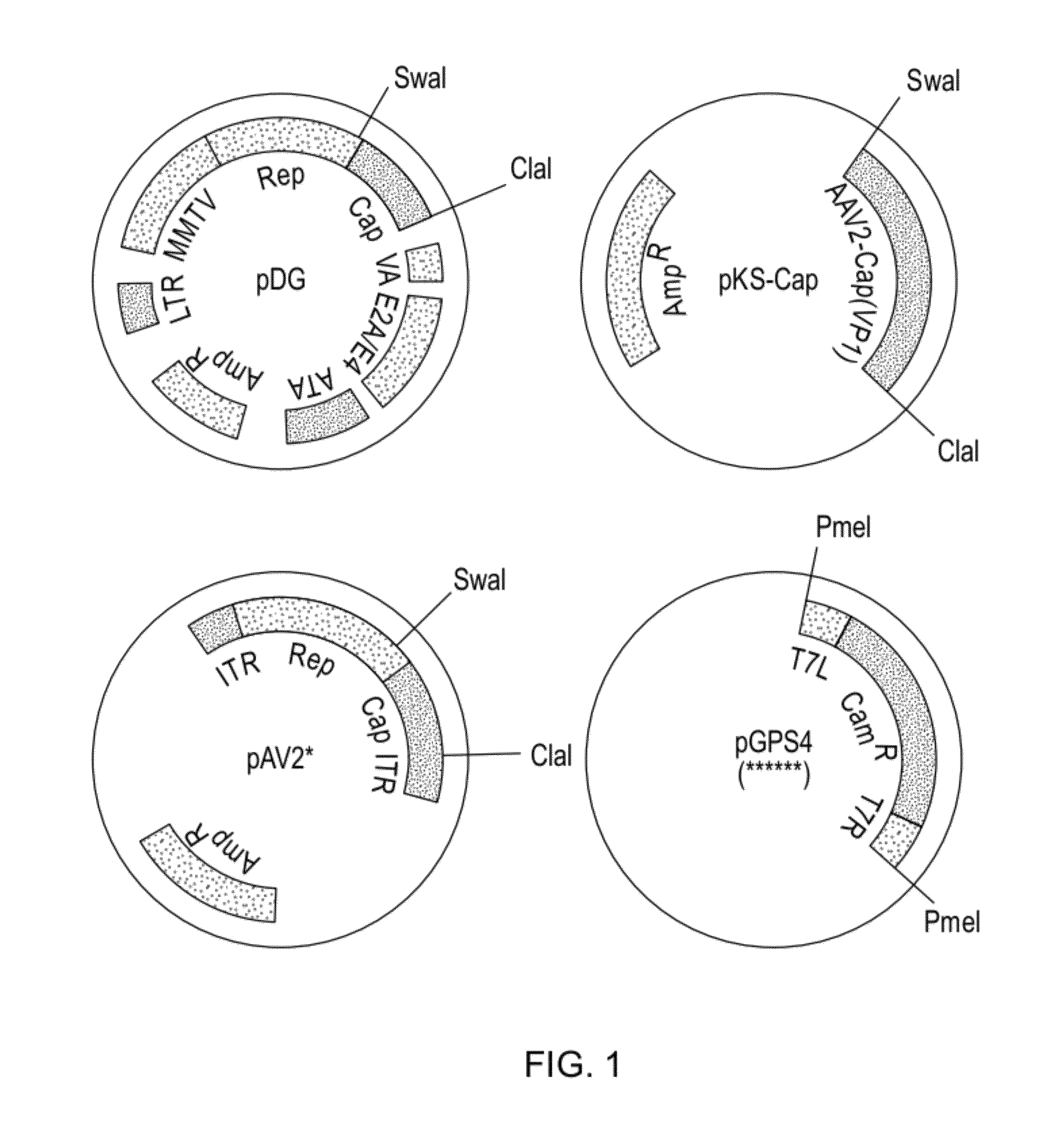
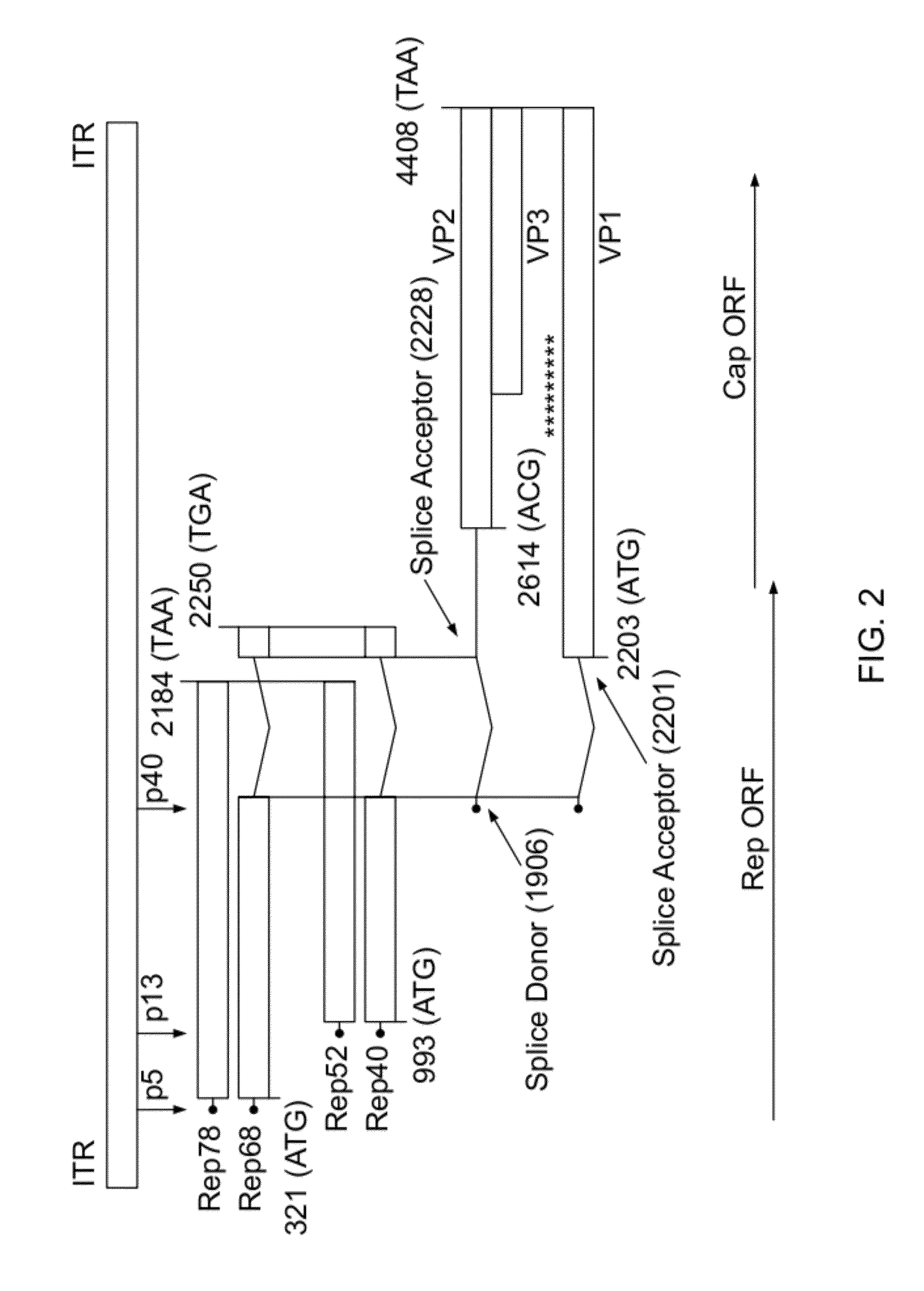
ActiveUS20140087444A1Facilitate ready substitutionImprove efficiencyAnimal cellsBacteriaPoly-A RNARestriction site
Proviral plasmids contain a modular gene expression cassette with one or a combination of (i) a wildtype 5′ AAV2 ITR sequence flanked by unique restriction sites that permit ready removal or replacement of said ITR; (ii) a promoter flanked by unique restriction sites that permit ready removal or replacement of the entire promoter sequence; (iii) a polylinker sequence that permits insertion of a gene coding sequence without modification thereof, wherein the gene is operatively linked to, and under the regulatory control of, the aforementioned promoter; (iv) a bovine growth hormone polyadenylation sequence flanked by unique restriction sites that permit ready removal or replacement of said polyA sequence; and (v) a wildtype 3′ AAV2 ITR sequence flanked by unique restriction sites that permit ready removal or replacement of the 3′ ITR. These plasmids enable rapid manipulation of the components of the cassette, e.g., rapid mutation and / or replacement of any component, and thereby increase the efficiency of recombinant viral vector, e.g., rAAV, production.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
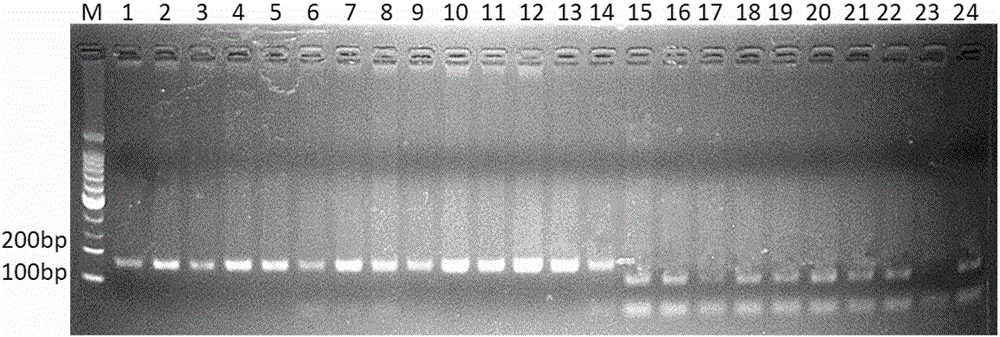
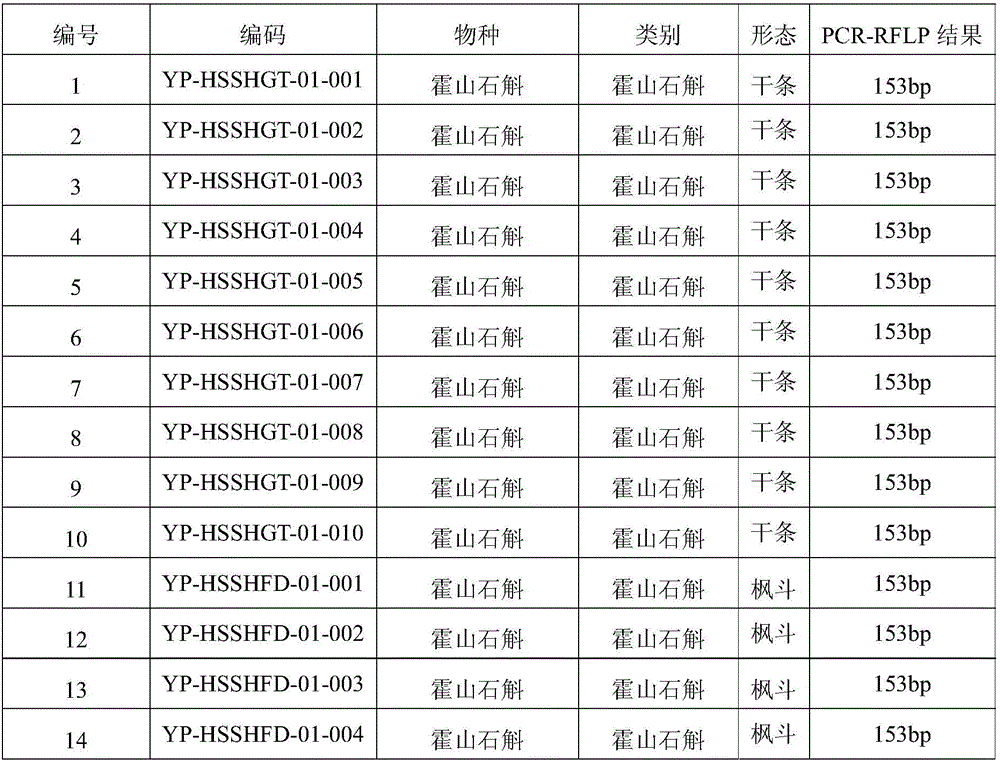
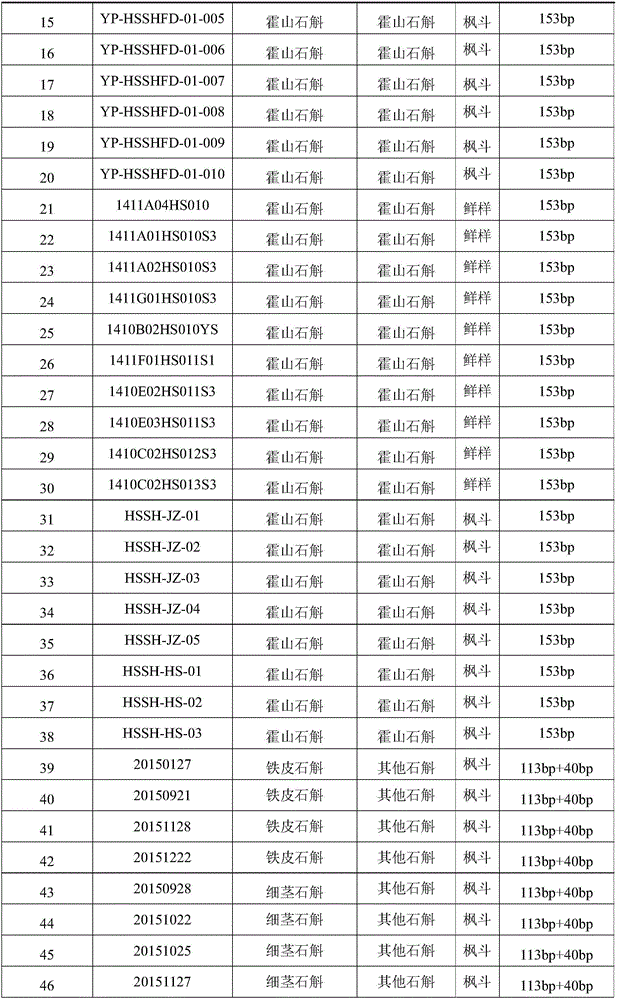
SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) marker for identifying dendrobium huoshanense C.Z. Tang et S.J.Cheng and molecular detection method for SNP marker
ActiveCN105779628AAchieve accurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSequence analysisDendrobium huoshanense
The invention discloses an SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) marker for identifying dendrobium huoshanense C.Z. Tang et S.J.Cheng and a molecular detection method for the SNP marker, and provides application of SNP of the following SNP site in a dendrobium genome or a substance for detecting the SNP of the following SNP site in the dendrobium genome to identification or auxiliary identification of dendrobium. The SNP site in the dendrobium genome corresponds to the 113th site of a nucleotide sequence shown in sequence 3 in a sequence table; a nucleotide at the SNP site is T or G. According to the SNP marker and the molecular detection method, sequencing analysis is performed on 27 kinds of dendrobium samples comprising all species of dendrobium huoshanense C.Z. Tang et S.J.Cheng complexes to find the functional SNP molecular marker only existing in the dendrobium huoshanense C.Z. Tang et S.J.Cheng by virtue of an RAD (Restriction Site Associated) technology, and the detection method for the SNP marker is established to accurately identify the dendrobium huoshanense C.Z. Tang et S.J.Cheng and other dendrobium (comprising hybrids of the dendrobium huoshanense C.Z. Tang et S.J.Cheng and the other dendrobium).
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI +1
Alternate current-aided efficient protein enzymolysis method
InactiveCN101280334AShorten the enzymatic digestion timeImprove work efficiencyFermentationProtein moleculesRestriction site
The invention belongs to the proteomics technology field, in particular relates to an efficient enzymolysis method of alternating current accessory protein. Protein and proteolytic enzymes such, as trypsin, are solubilized in buffer solution in a certain proportion by the method, and the solution is ensured to contact with an electrode applied by alternating voltage; the charged protein, enzyme and inorganic ions, etc. change the direction of motion in the electric field immediately, and the motions, such as vibration, collision, rotation and friction, etc., of the molecules such as protein and enzyme, etc., are caused. Simultaneously, shakings also occurs to the charged group in the peptide chain of the protein molecules under the exertion of the alternating electric field, and more restriction sites are exposed. The motions improve the energy level and interaction frequency of the protein and enzyme molecules, in order to increase the protein enzymolysis efficiency greatly. By adopting the alternating current accessory protein enzymolysis, the enzymolysis time is greatly shortened from twelve hours of traditional solution enzymolysis to five to ten minutes, and the enzymolysis efficiency is improved remarkably.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for preparing chicken genetic engineering immunopotentiator by akirin2 gene sequence
InactiveCN102240402AImprove immune efficiencyReduce manufacturing costGenetic material ingredientsAntibody medical ingredientsPhosphateRestriction site
The invention provides a method for preparing a chicken genetic engineering immunopotentiator by an akirin2 gene sequence, relating to a method for preparing a chicken genetic engineering immunopotentiator. The invention solves the problem that the existing genetic engineering immunoenhancement nucleic acid vaccines can not extensively improve the immunity effects of vaccines and bacterins. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring a chicken akirin2 gene coded sequence; acquiring a recombinant pMD18-T vector containing the chicken akirin2 gene; designing a primer and enabling the 5'- terminals to have HindIII and EcoRI restriction sites, subcloning the chicken akirin2 gene in the recombinant pMD18-T vector into an expression vector to construct a recombinant expression vector; and diluting the recombinant expression vector by a sterile PBS (phosphate buffer solution). The chicken genetic engineering immunopotentiator provided by the invention can improve the expression levels of multiple immunity related factors such as IL-1, IL-6, toll-like receptors and the like, and has the characteristics of wide applicable range and the like for various vaccines and bacterins.
Owner:HARBIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for targeted sequencing
InactiveUS20150284789A1Avoid short lengthImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationNucleotideGenetics
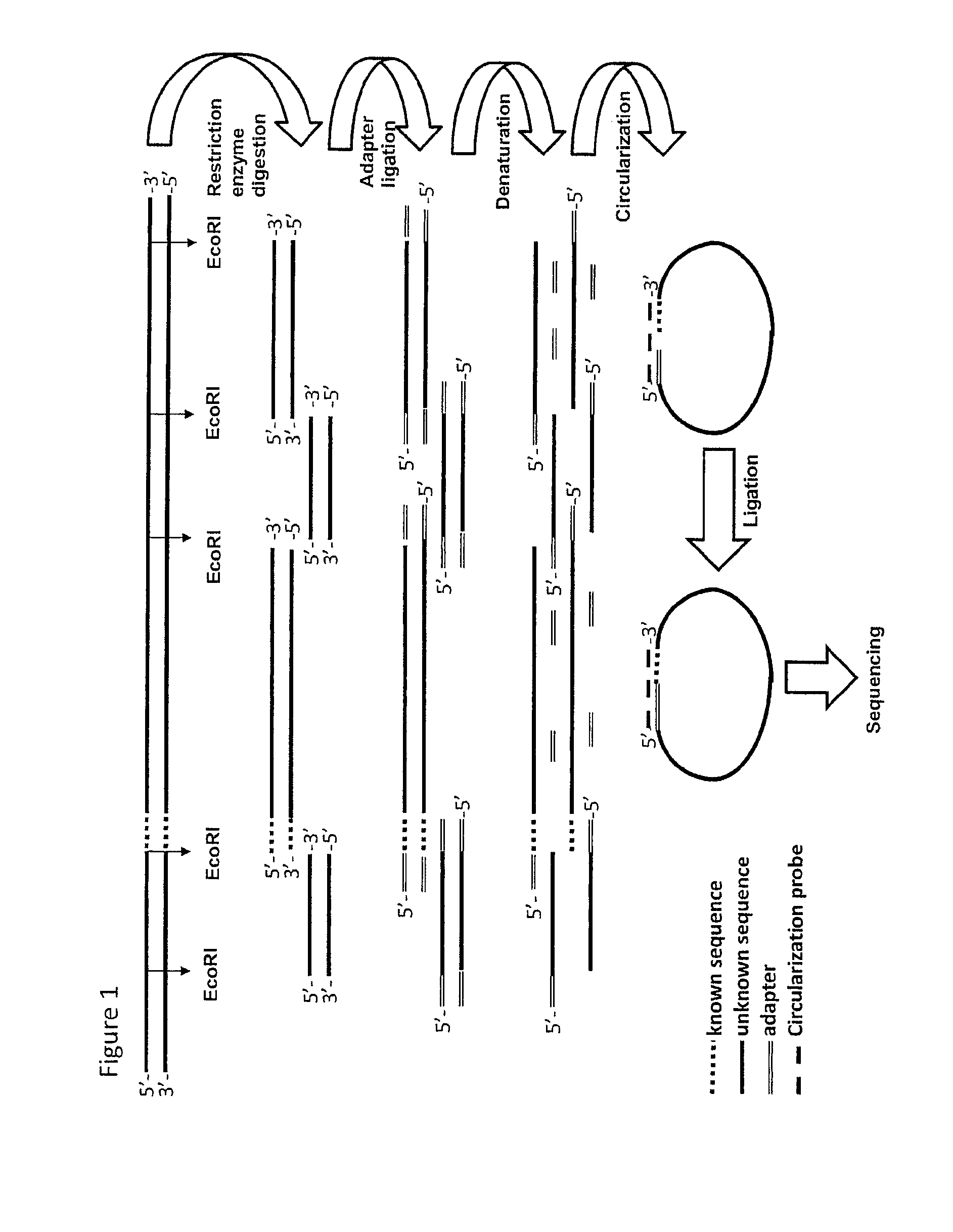
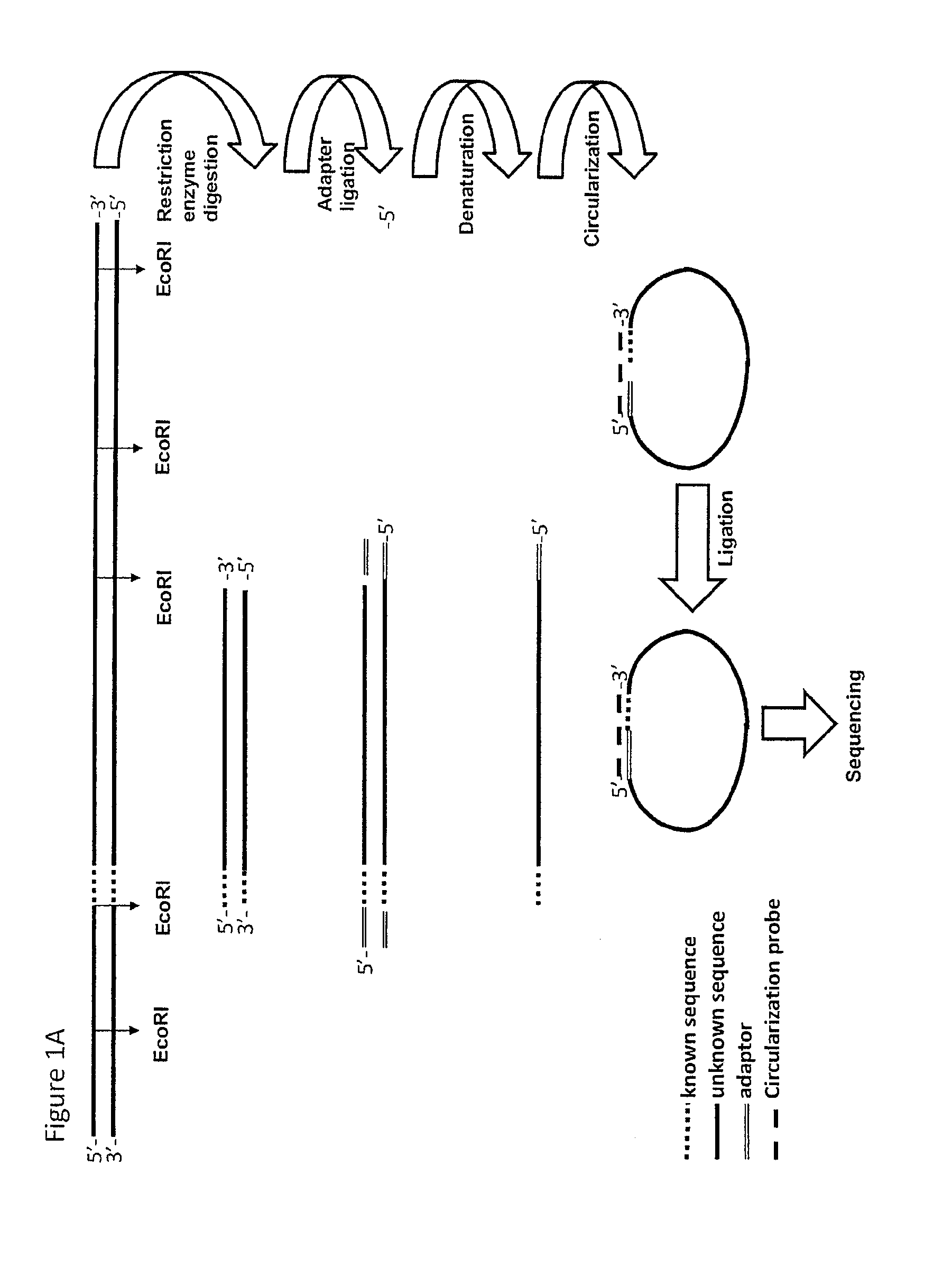
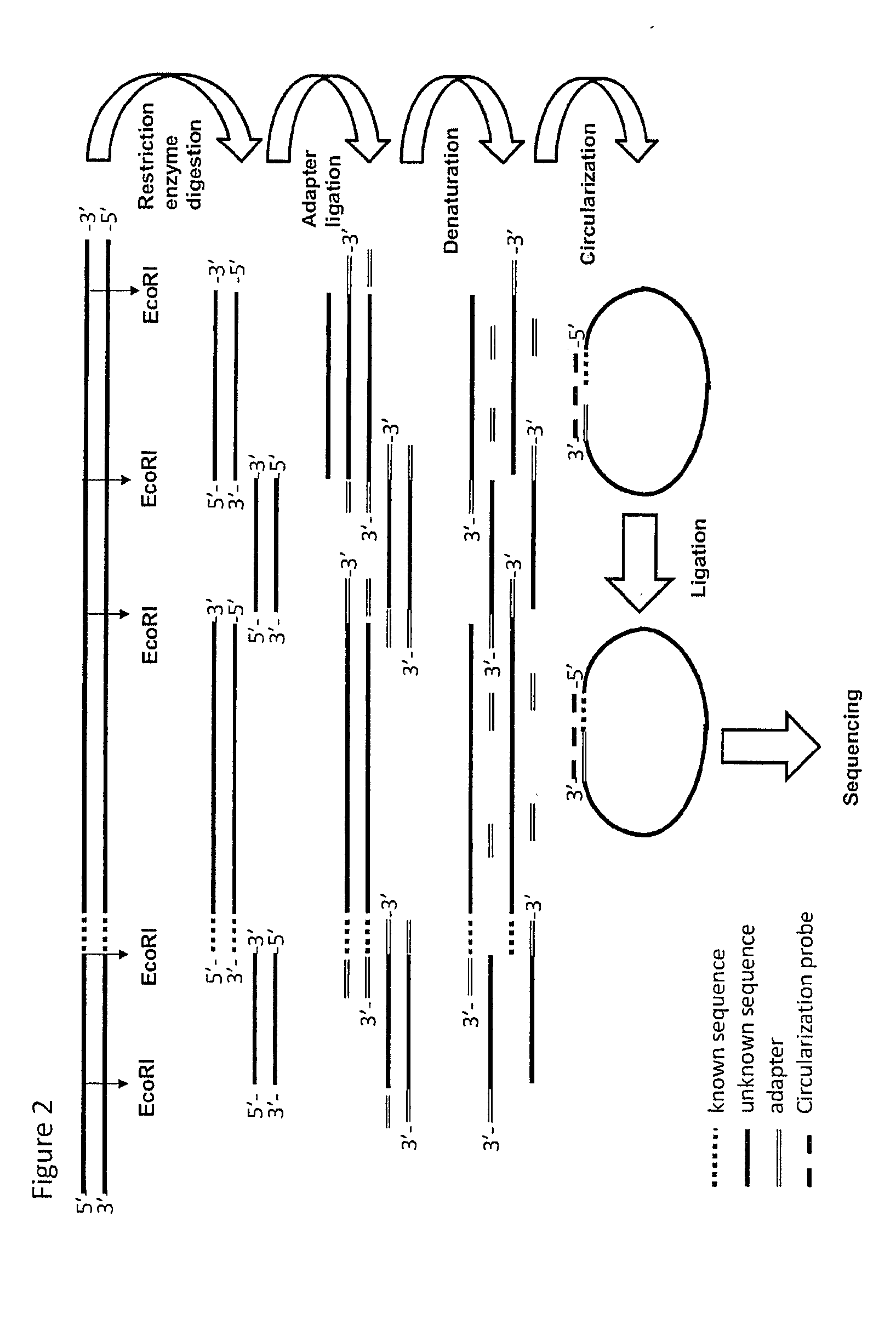
The method of the present invention now provides a technique for generating sequence information from nucleic acid samples based on knowledge from part(s) of the nucleotide sequence. The knowledge of the partial sequence may include knowledge about the presence of restriction sites. The knowledge of the partial sequence can be used to generate adaptor ligated or nucleotide-elongated fragments. From the combination of information on the ligated adaptor and the Known Nucleotide Sequence Section, probes can be designed. The probes can be used in the provision of circularised fragments that can be sequenced. Combining the known and determined sequences adds sequence information to the already existing sequence information and complements the available genomic sequence information.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Recombinant pichiapastoris for producing FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenase as well as construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN107460138AIncrease enzyme activityFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisRestriction site
The invention provides recombinant pichiapastoris for producing FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenase as well as a construction method and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The invention provides a recombinant plasmid pMD-GDH containing FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenase genes. After the FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenase genes are subjected to codon preference adjustment, EcoRI restriction sites and NotI restriction sites are added at two ends of the sequence, and six histidine tags are added at the 3' end. The recombinant pichiapastoris takes Pichia pastoris as an expression host and comprises the recombinant plasmid. The invention further provides application of the recombinant pichiapastoris for producing FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenase in fermentation production of the FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenase. The embodiments show that when the recombinant pichiapastoris is subjected to induction culture for 136 hours during culture in a 10L of fermentation tank, the enzyme activity reaches 257600U / L and is 5.3 times that of the enzyme activity reported in the prior art.
Owner:河北省微生物研究所有限公司
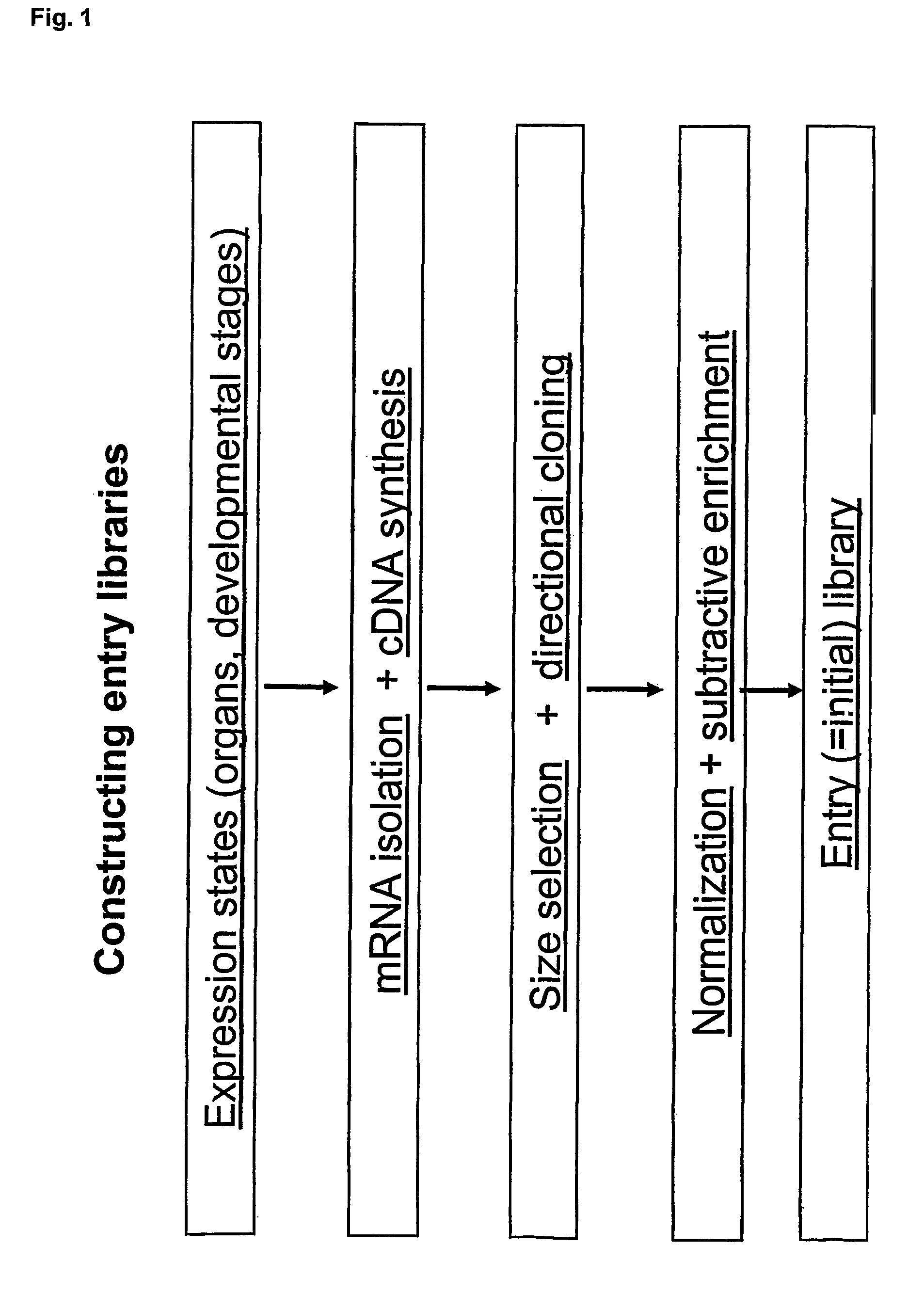
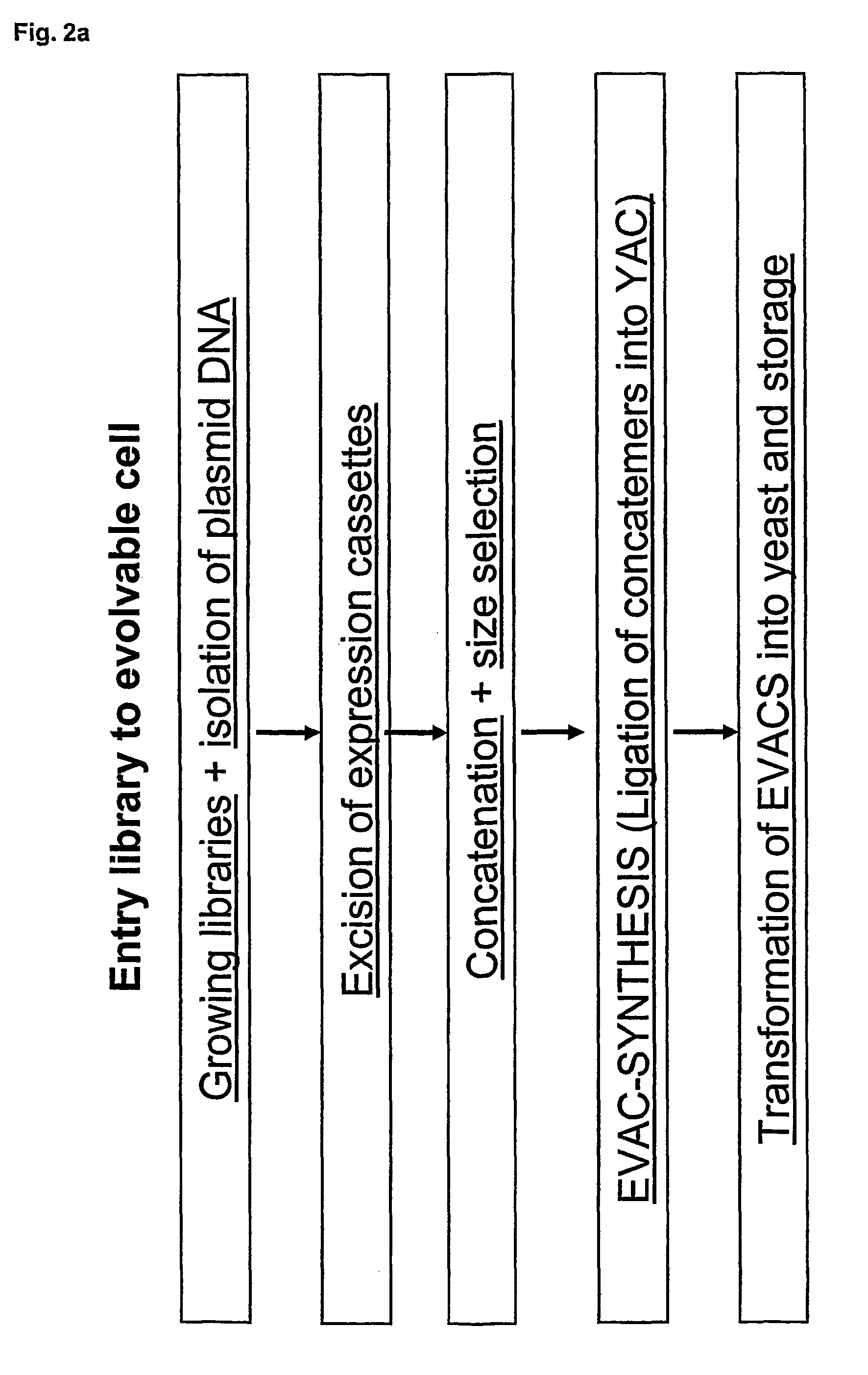
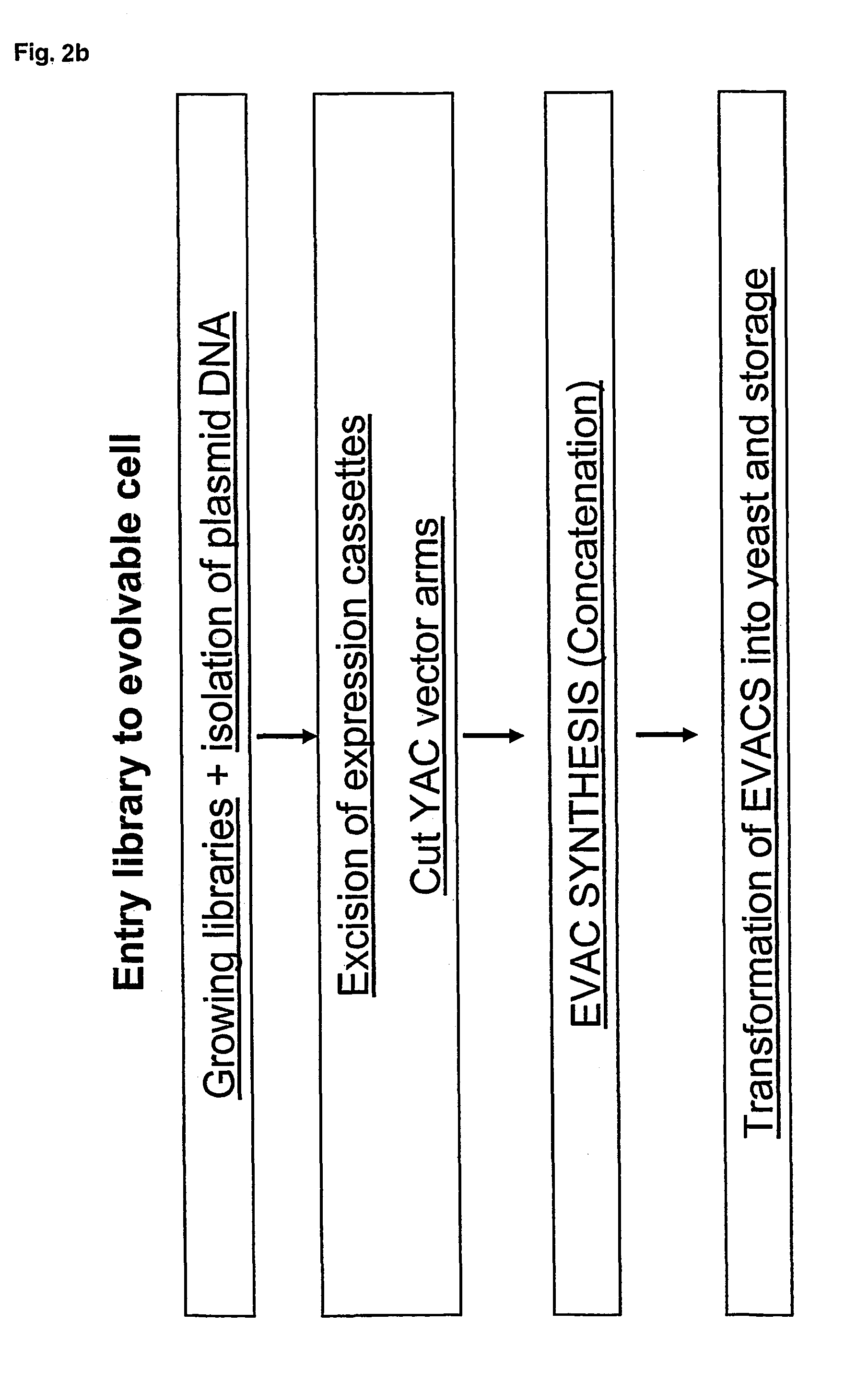
Method for evolving a cell having desired phenotype and evolved cells
The present invention relates to evolution of a cell or a composition of cells having a desired property or functionally. The principle behind the evolution of cells according to the invention is to produce a great diversity of genes in each cell subjected to evolution and a great diversity of genes among the cells in a composition according to the invention and to exchange the genes between the cells from time to time. In preferred embodiments the genes are arranged in expression cassettes in concatemers in the cells, as well as in artificial chromosomes. Said methods comprising the steps of a) obtaining a composition of cells, at least one cell of said composition comprising a1) at least two expressible nucleotide sequences, at least one of said sequences being incorporated into an artificial chromosome in the cell and / or a2) at least two expression cassettes of the following formula: [rs2-SP-PR-X-TR-SP-rs11 wherein rs1 and rs2 together denotes a restriction site, SP individually denotes a spacer, PR denotes a promoter, capable of functionning in the first cell, X denotes an expressible nucleotide sequence, TR denotes a terminator, and / or a3) at least two expressible nucleotide sequences, said sequences being heterologous to the cell, determining at least one screening functionality. The genes are preferably co-ordinately controllable for increasing diversity. The desired property of functionality is preferably a compound, or a series of compounds synergistically acting to each other.
Owner:EVOLVA SA
Selective restriction fragment amplification: fingerprinting
InactiveUS7026115B1Enable amplificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRestriction siteRFLP - Restriction fragment length polymorphism
The invention relates to a process for the controlled amplification of at least one part of a starting DNA containing a plurality of restriction sites for a determined specific restriction endonuclease, and of which at least part or its nucleic acid is unknown.Application of this process to human, animal or plant DNA fingerprinting, to identification of restriction fragment length polymorphisms.Kit for the application of the process.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
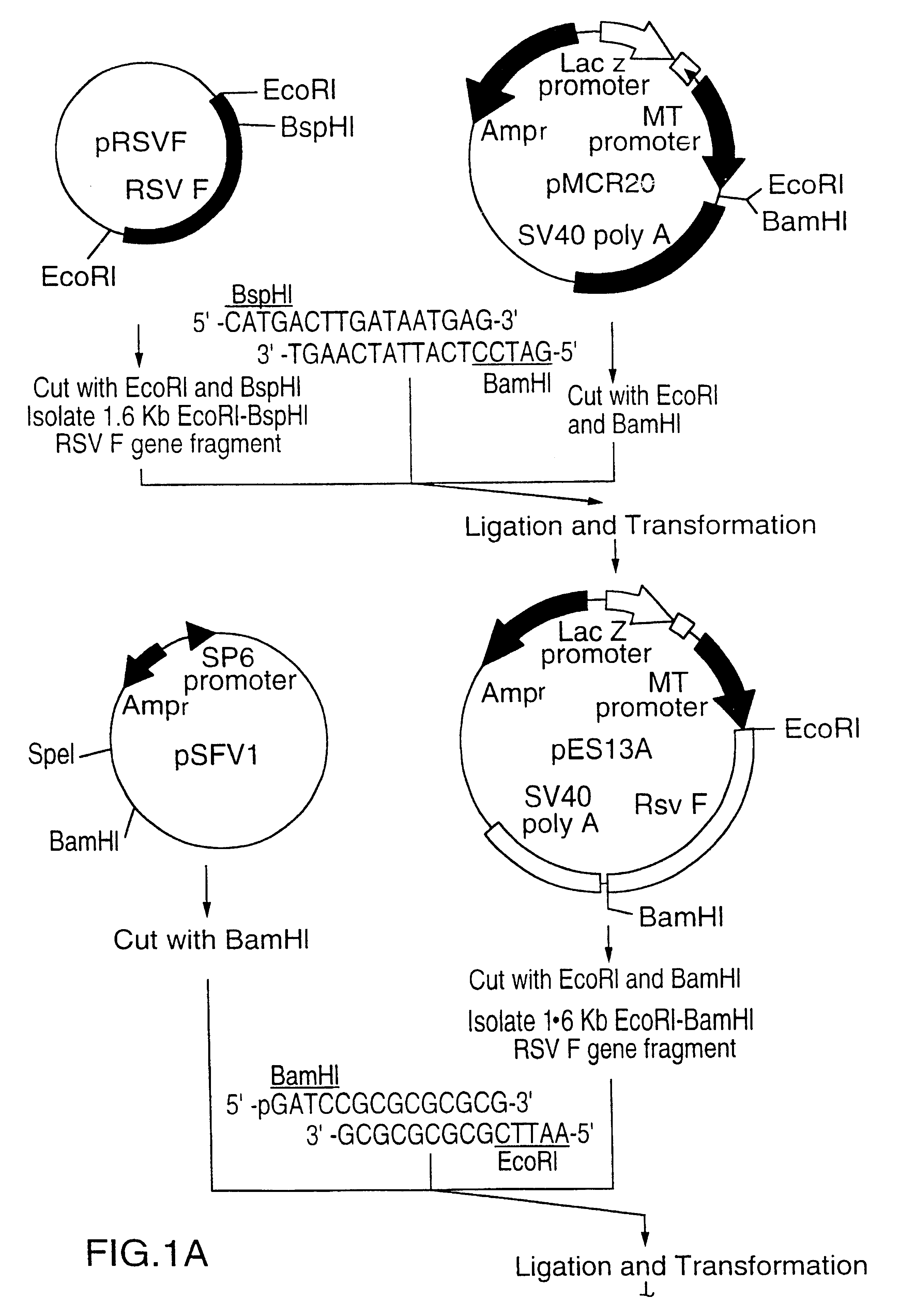
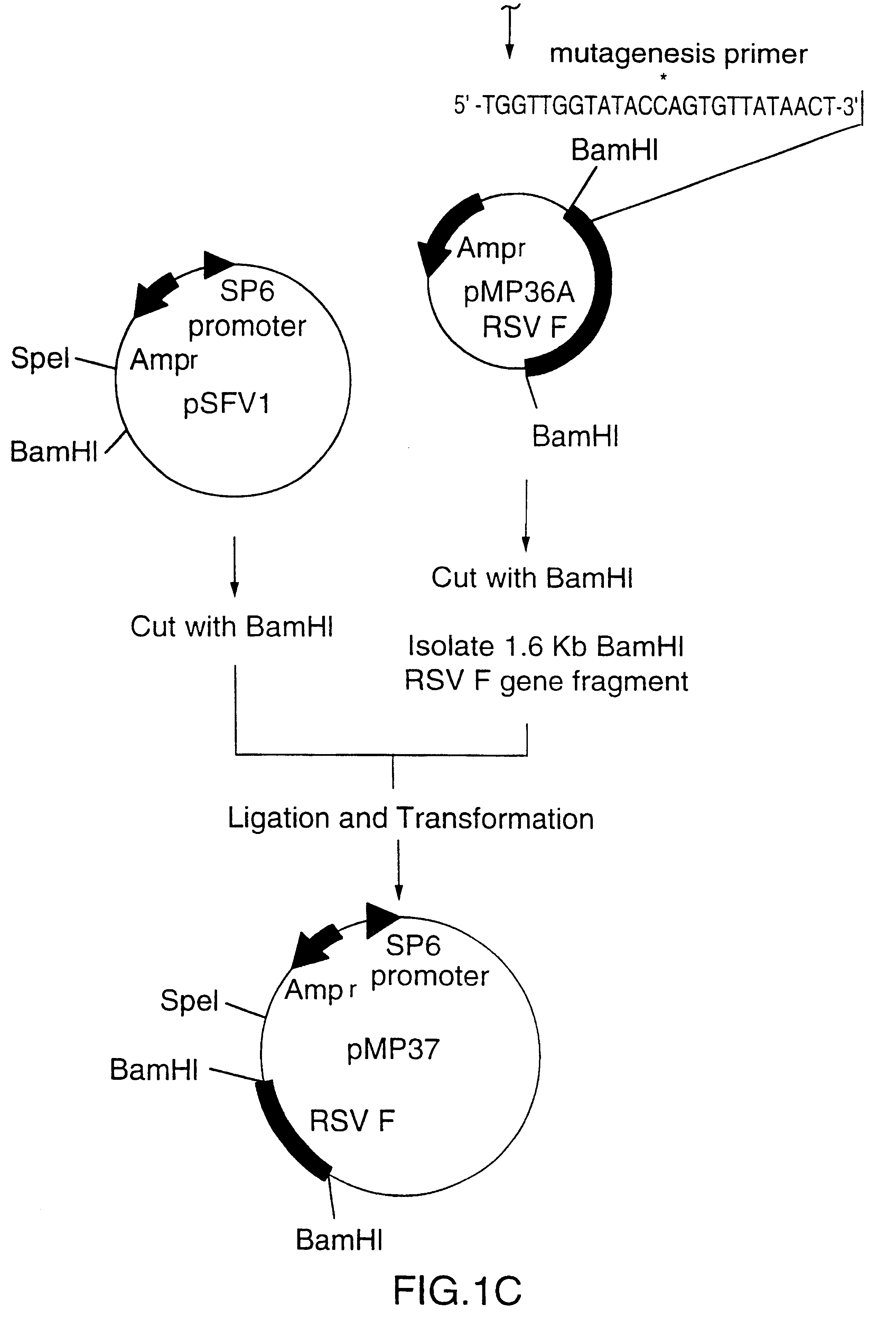
RNA respiratory syncytial virus vaccines
InactiveUS6428324B1Faster replicationImprove efficiencySsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsF proteinRestriction site
Owner:AVENTIS PASTEUR LTD
Methods and compositions for DNA manipulation
Methods and compositions are provided for generating a single-stranded extension on a polynucleotide molecule, the single-stranded extension having a desired length and sequence composition. Methods for forming single-stranded extensions include: the use of a cassette containing at least one nicking site and at least one restriction site at a predetermined distance from each other and in a predetermined orientation; or primer-dependent amplification which introduces into a polynucleotide molecule, a modified nucleotide which is excised to create a nick using a nicking agent. The methods and compositions provided can be used to manipulate a DNA sequence including introducing site specific mutations into a polynucleotide molecule and for cloning any polynucleotide molecule or set of joined polynucleotide molecules in a recipient molecule such as a vector of choice.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Bioinformatics data processing systems
InactiveUS20180247012A1Saving in computational timeSave spaceSequence analysisSpecial data processing applicationsData processing systemFragment size
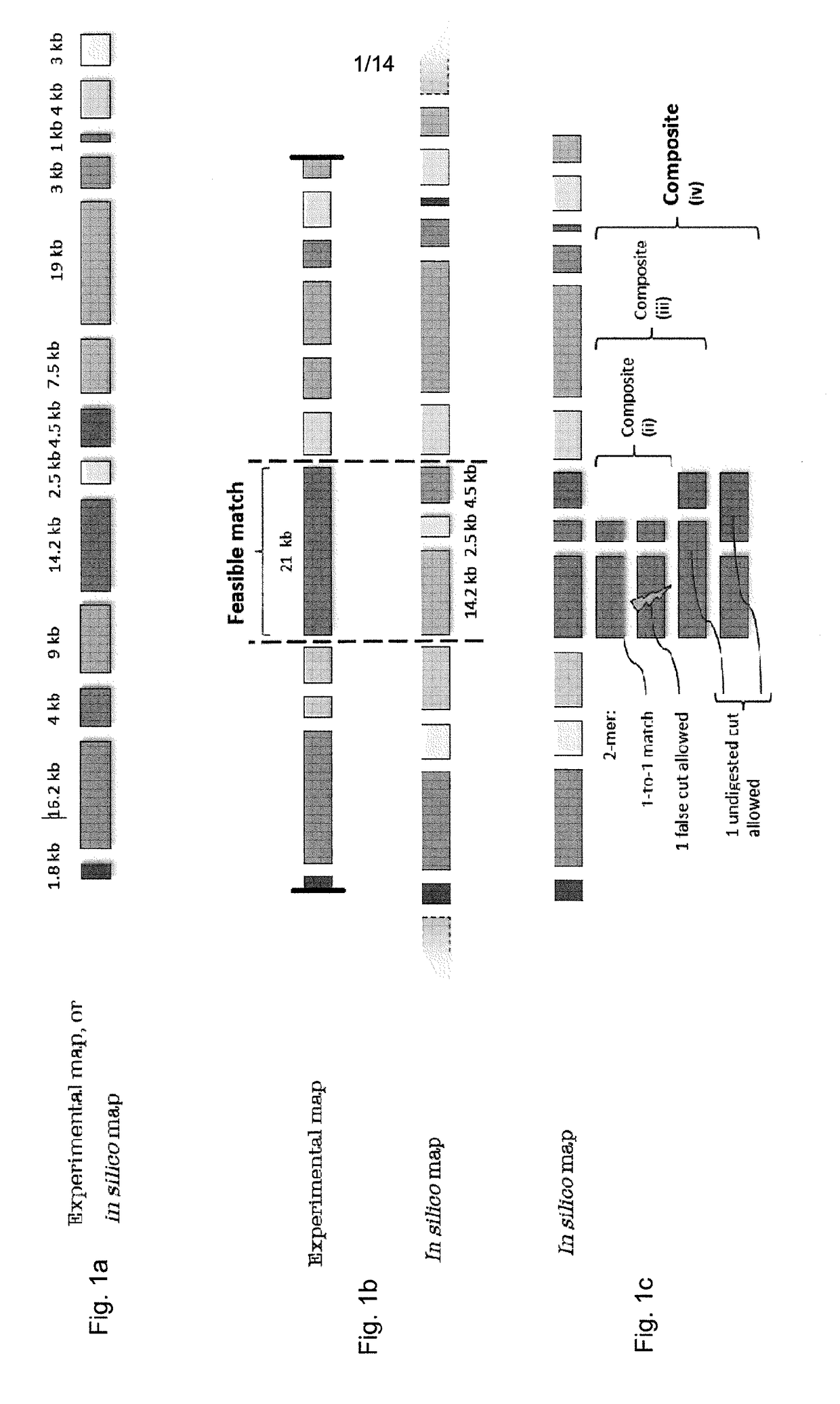
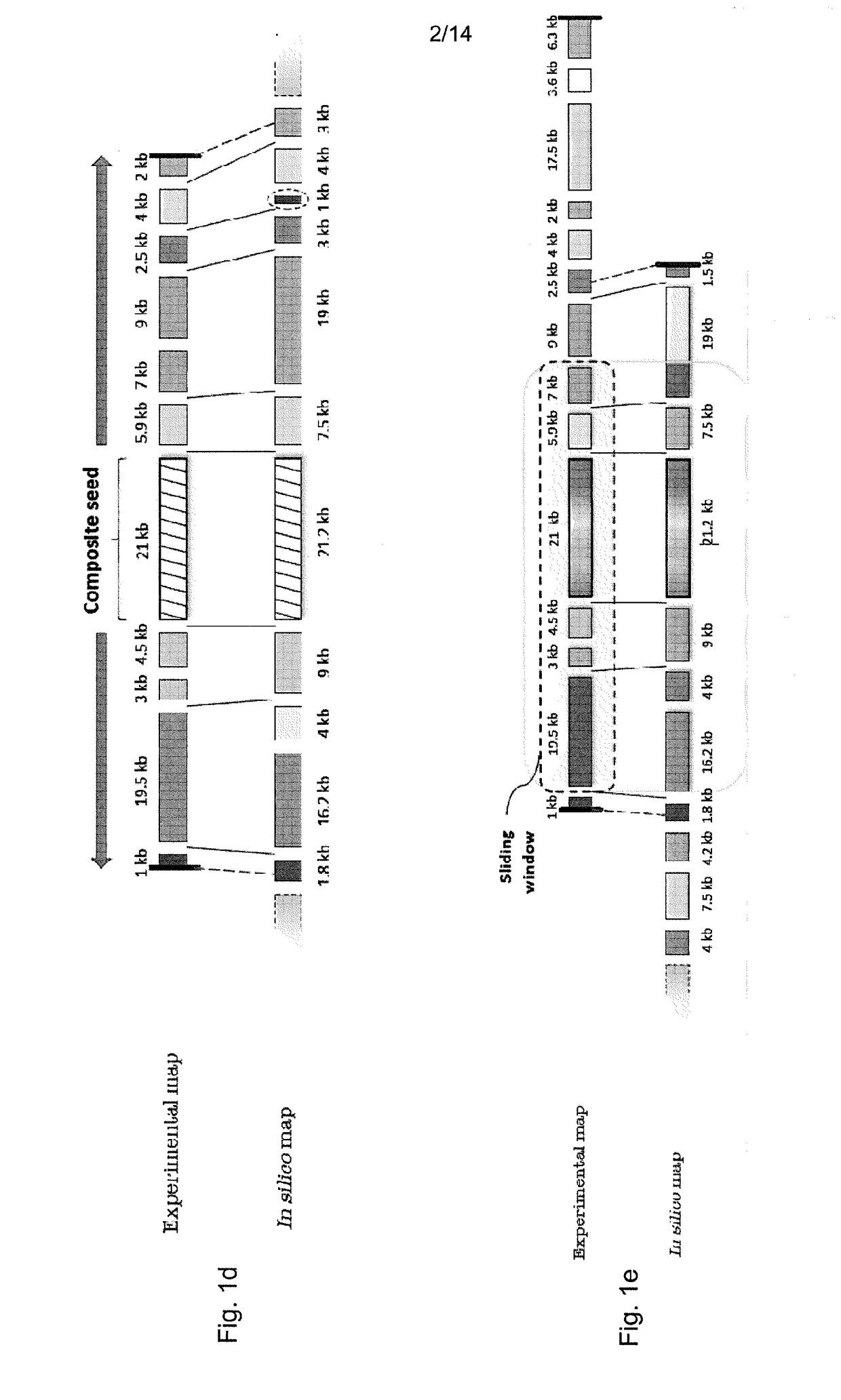
Disclosed is a computer-implemented method of determining at least one optimal alignment of at least part of a first map to at least part of a second map or a plurality of second maps, wherein the maps are physical genome maps and / or restriction maps. The method comprises: receiving first map data indicative of a first ordered list of distances between features of the first map, receiving second map data indicative of a second ordered list of distances between features of the second map or second maps; generating, from the second map data, seed data indicative of a plurality of seeds, each seed comprising at least one of the distances in the second ordered list, wherein the features are restriction sites and distances are fragment sizes. The said method further comprises generating a plurality of candidate alignments from the seed data by searching at least part of the first ordered list to find at least approximate matches for respective seeds, and extending the approximate matches by dynamic programming; determining respective alignment scores for respective candidate alignments; and selecting one or more of the candidate alignments as an optimal alignment or optimal alignments, based on the alignment scores.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
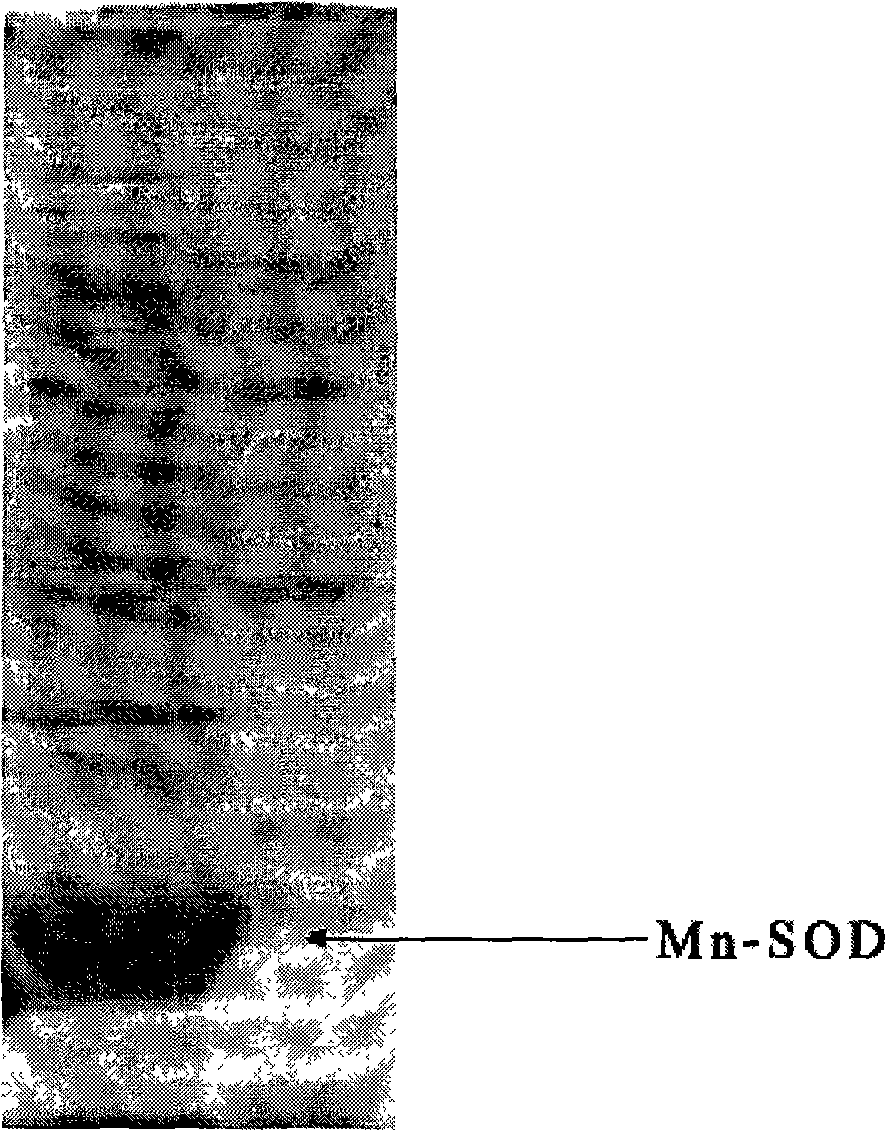

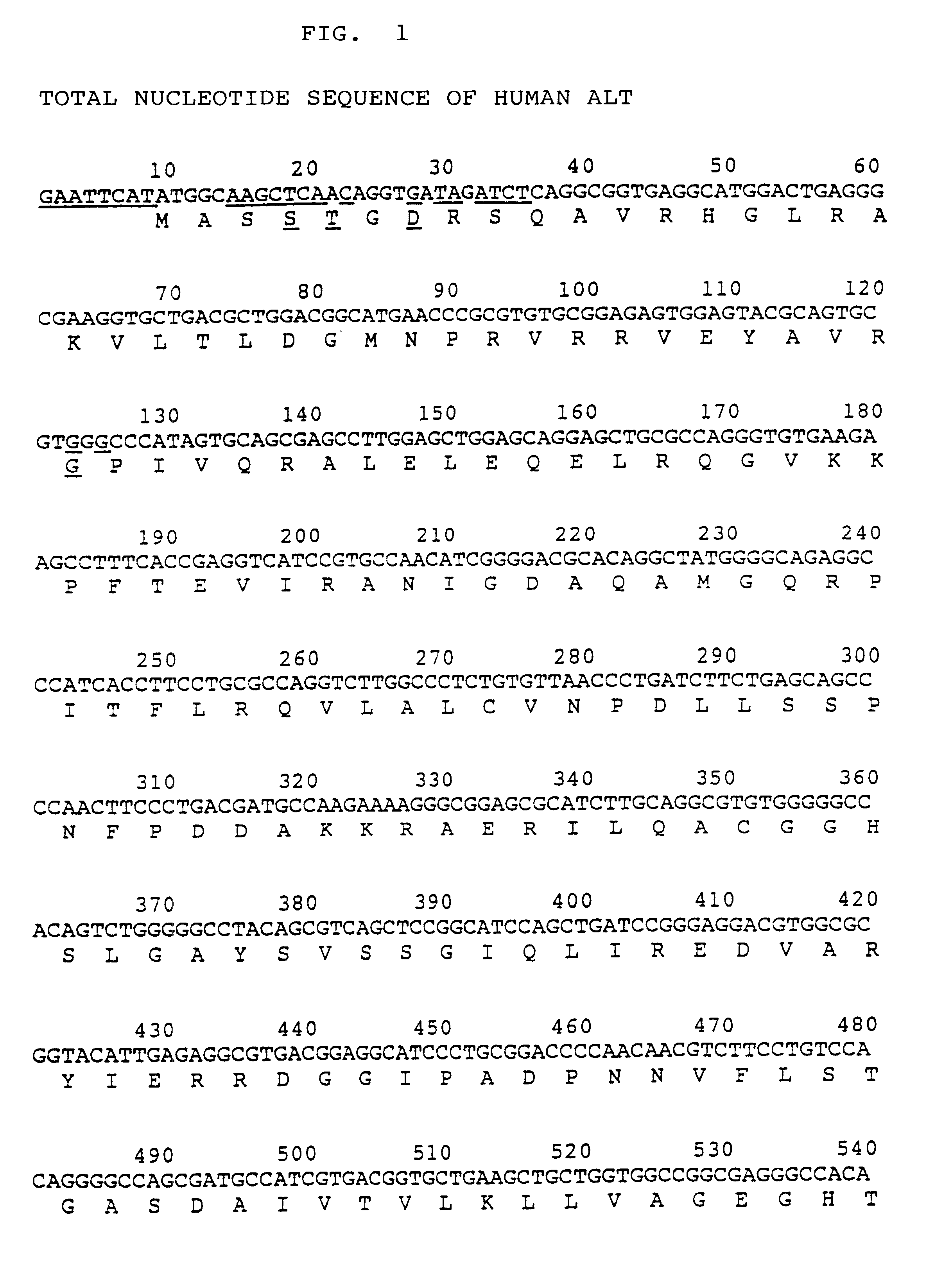


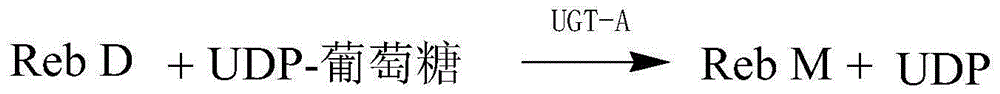

![Method for constructing series connection RAD [restriction-site-associated DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)] tag sequencing libraries Method for constructing series connection RAD [restriction-site-associated DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)] tag sequencing libraries](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/b240cc49-4537-4413-ae94-2905a37c4c32/160802164511.PNG)
![Method for constructing series connection RAD [restriction-site-associated DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)] tag sequencing libraries Method for constructing series connection RAD [restriction-site-associated DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)] tag sequencing libraries](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/b240cc49-4537-4413-ae94-2905a37c4c32/BDA0001067799170000141.PNG)
![Method for constructing series connection RAD [restriction-site-associated DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)] tag sequencing libraries Method for constructing series connection RAD [restriction-site-associated DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)] tag sequencing libraries](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/b240cc49-4537-4413-ae94-2905a37c4c32/BDA0001067799170000151.PNG)