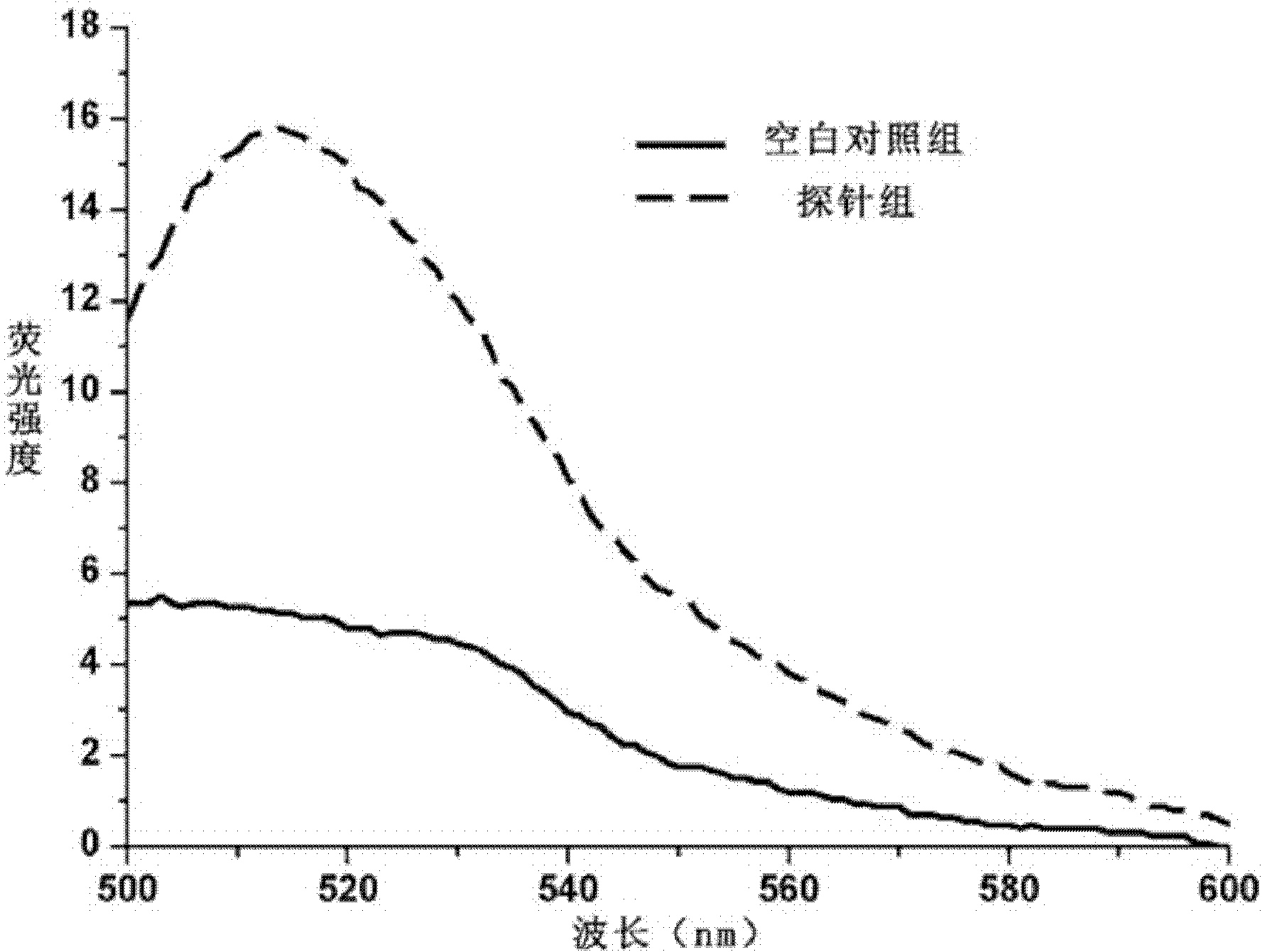
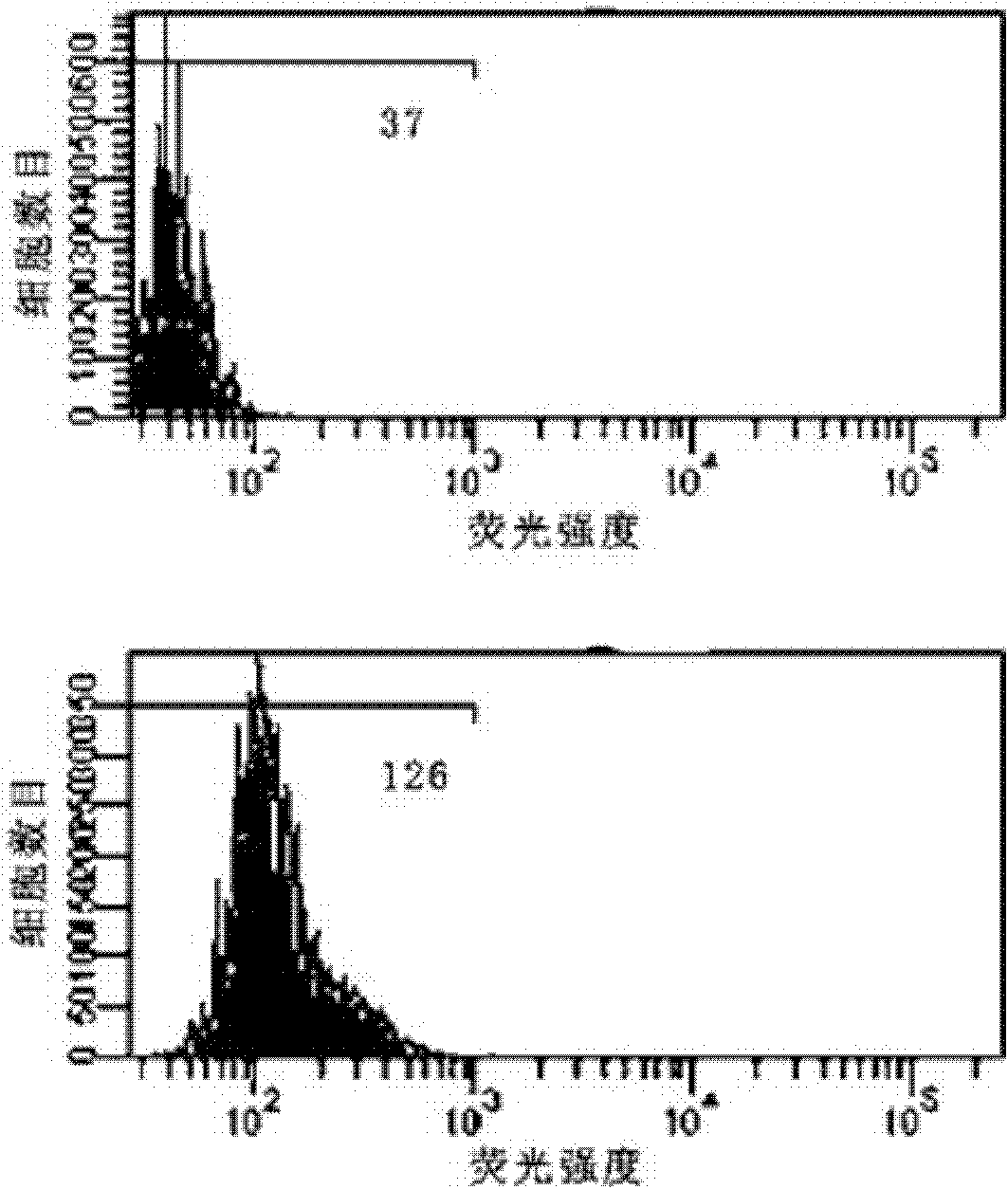
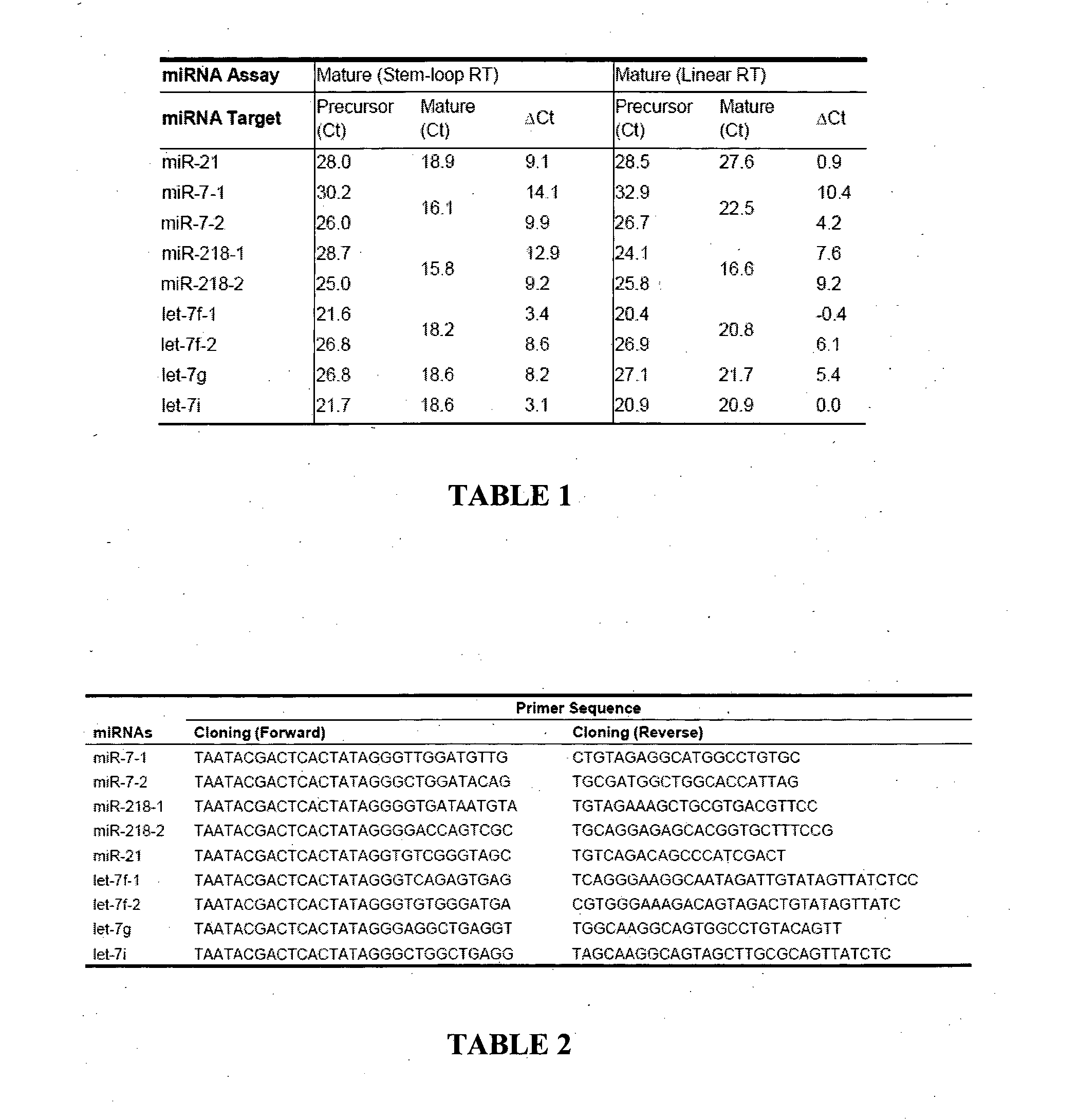
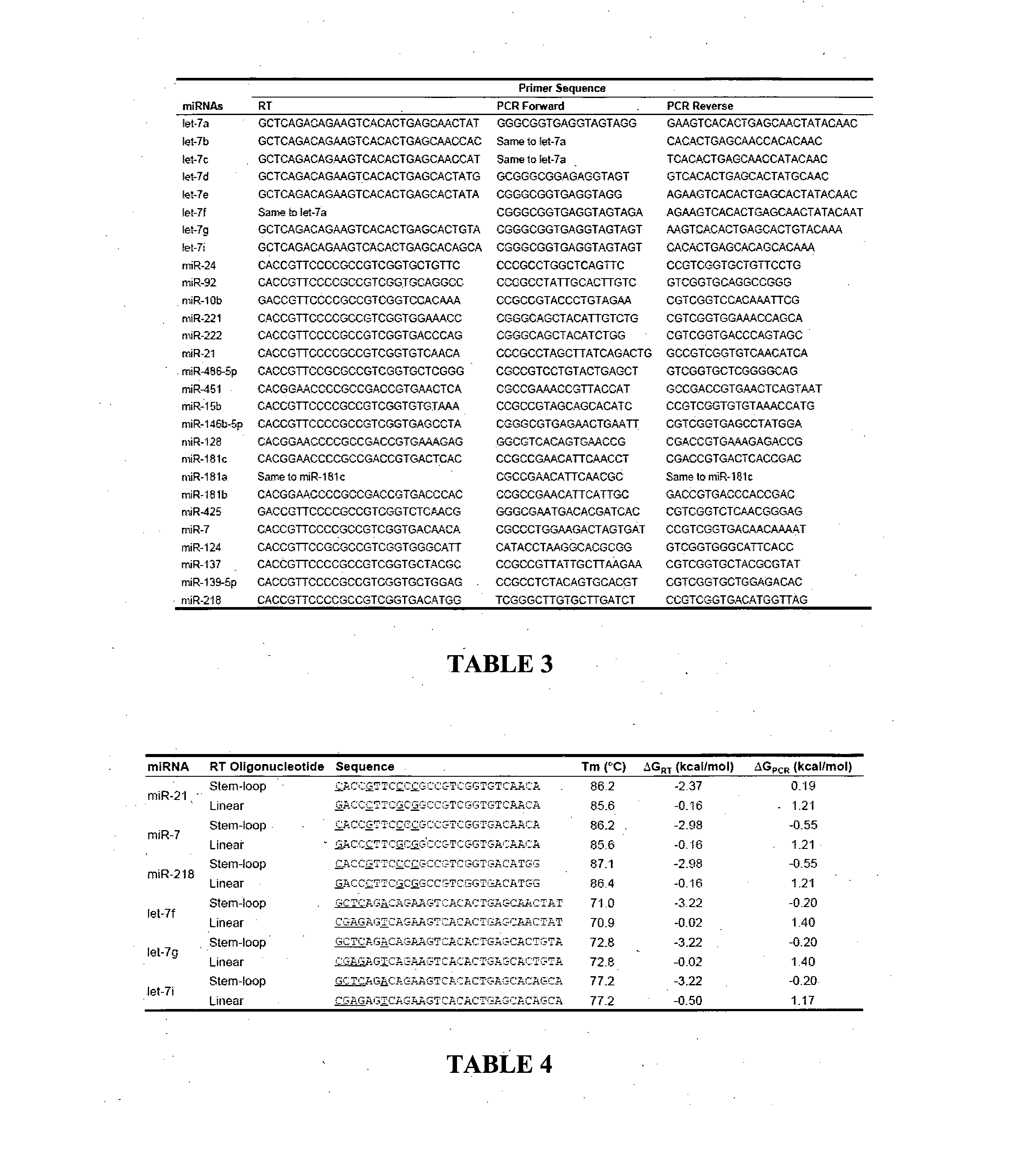
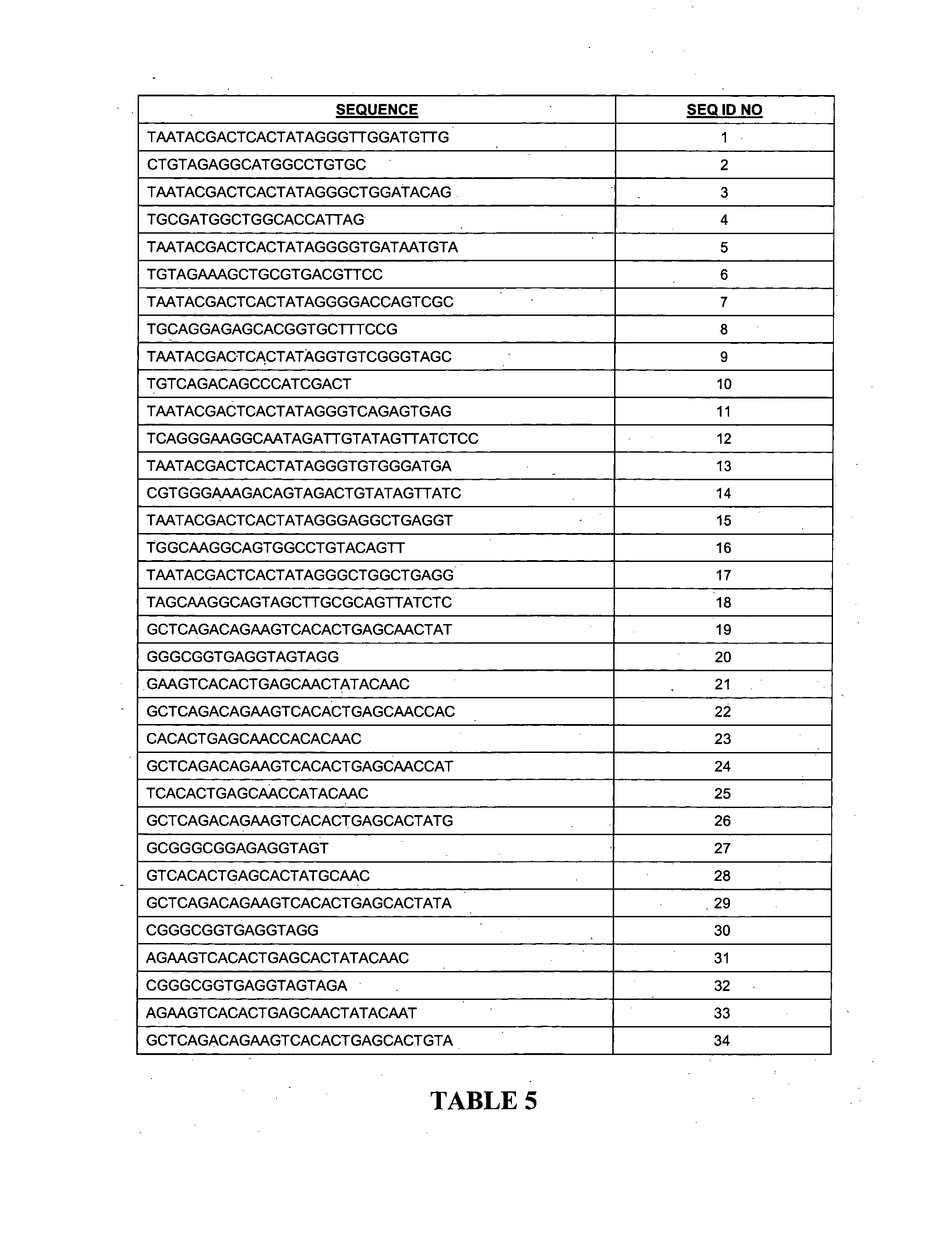
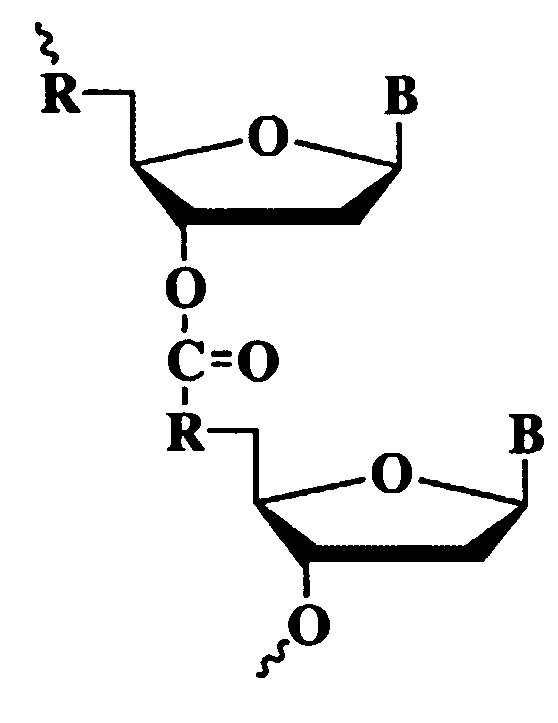
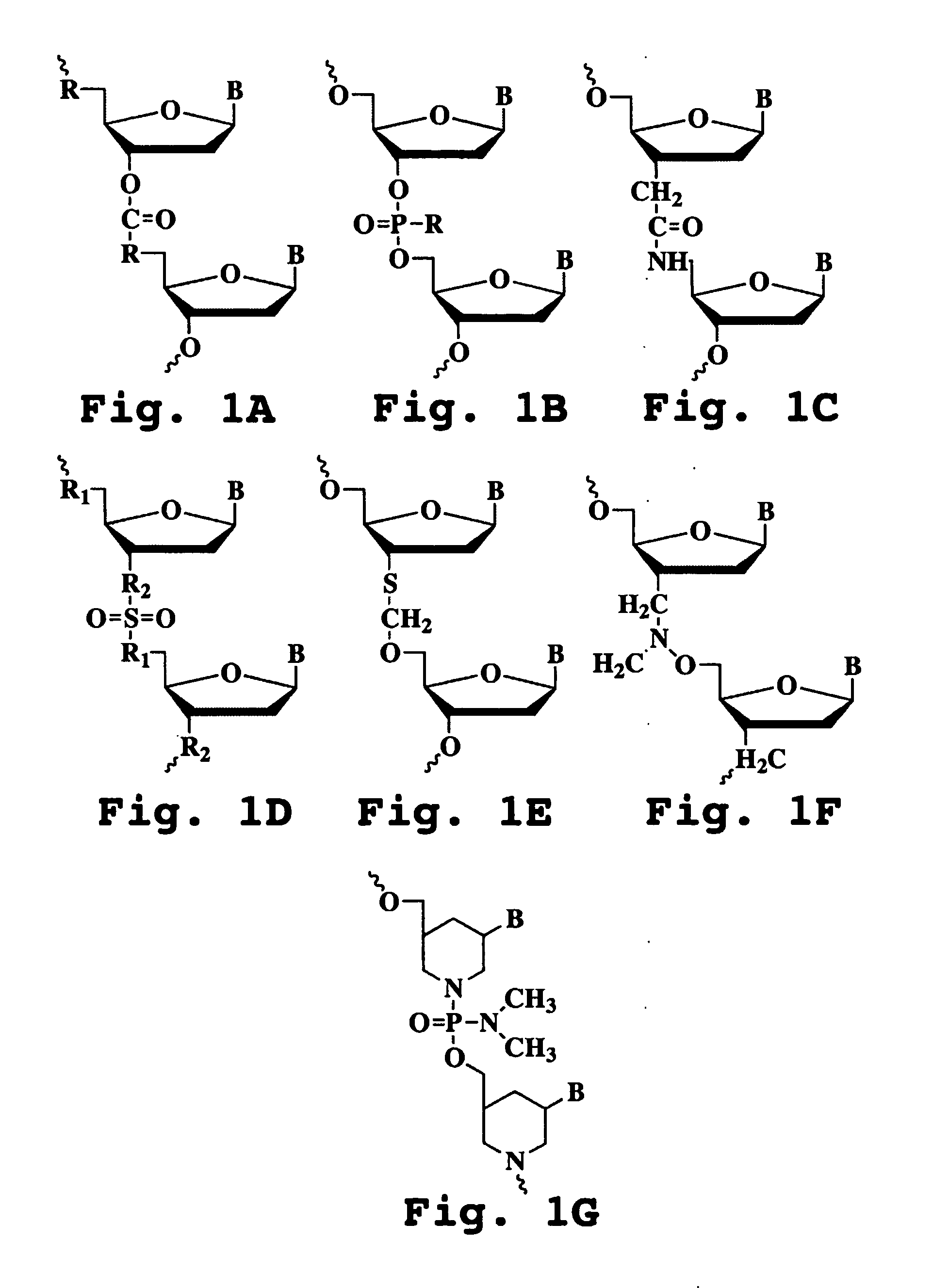
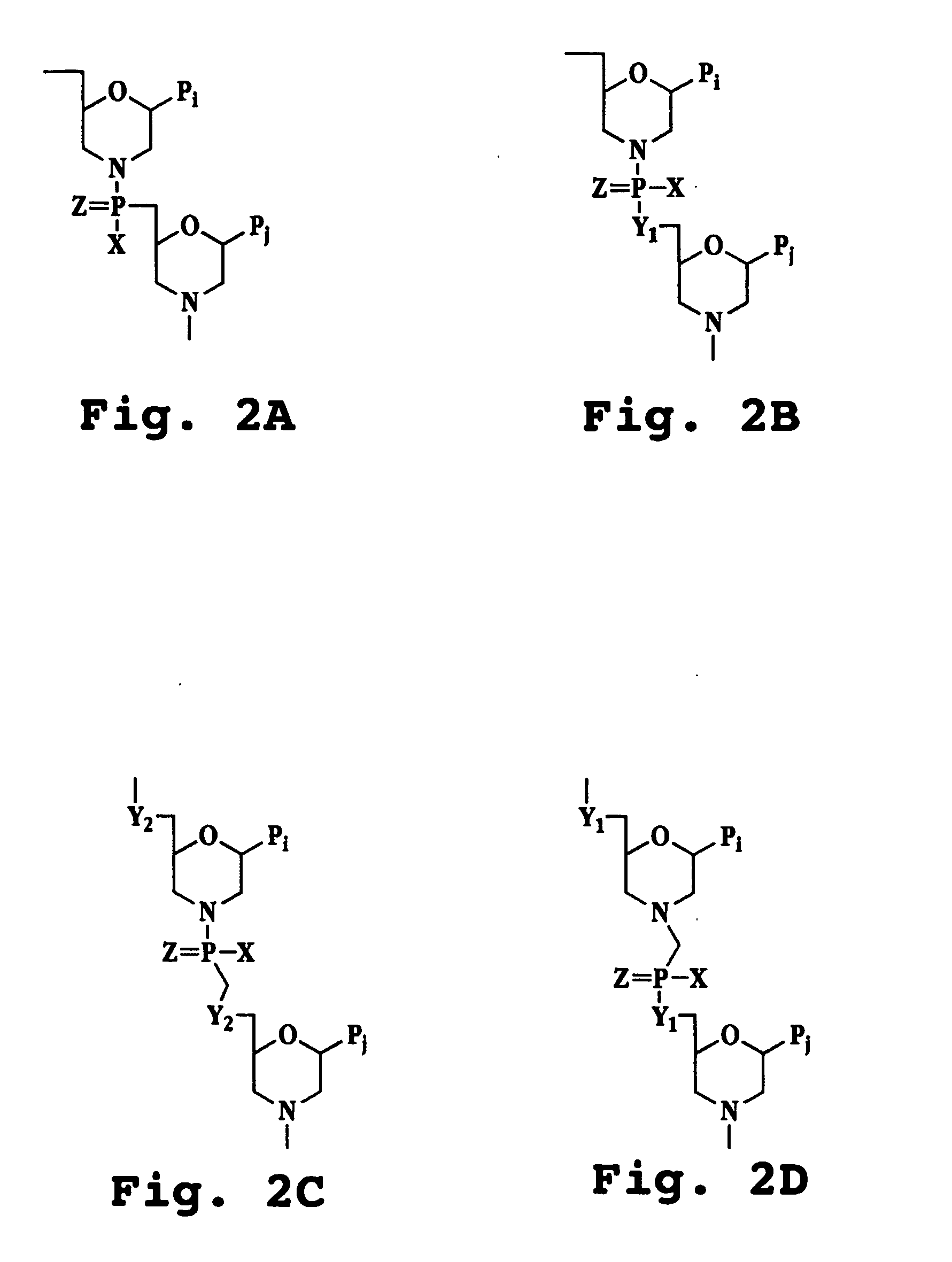
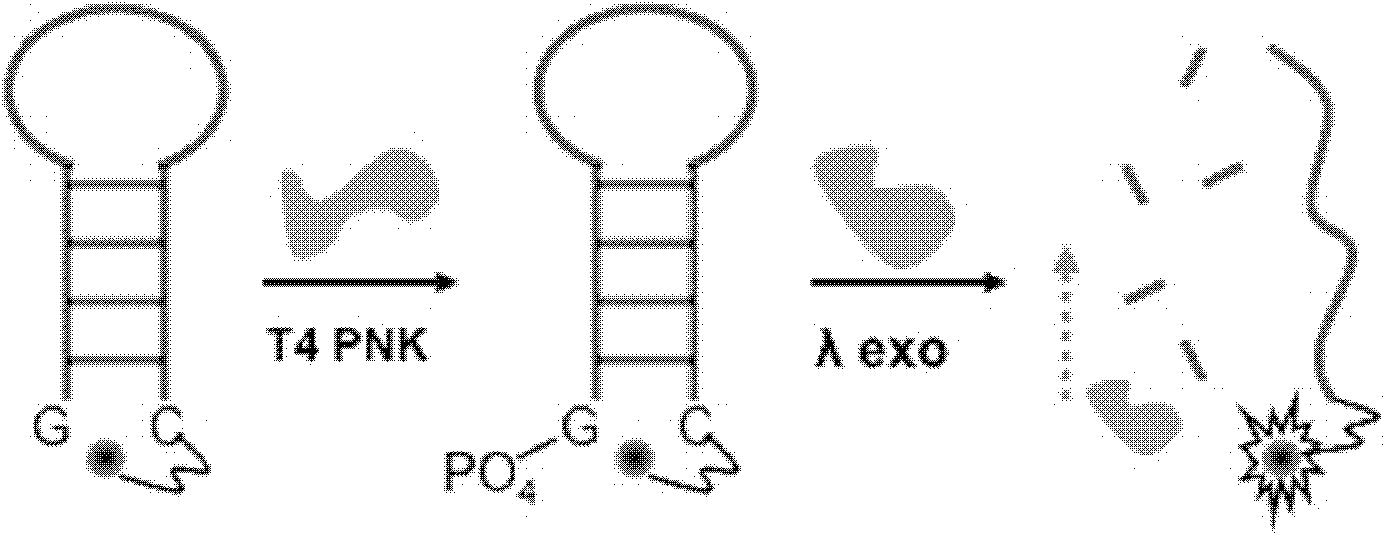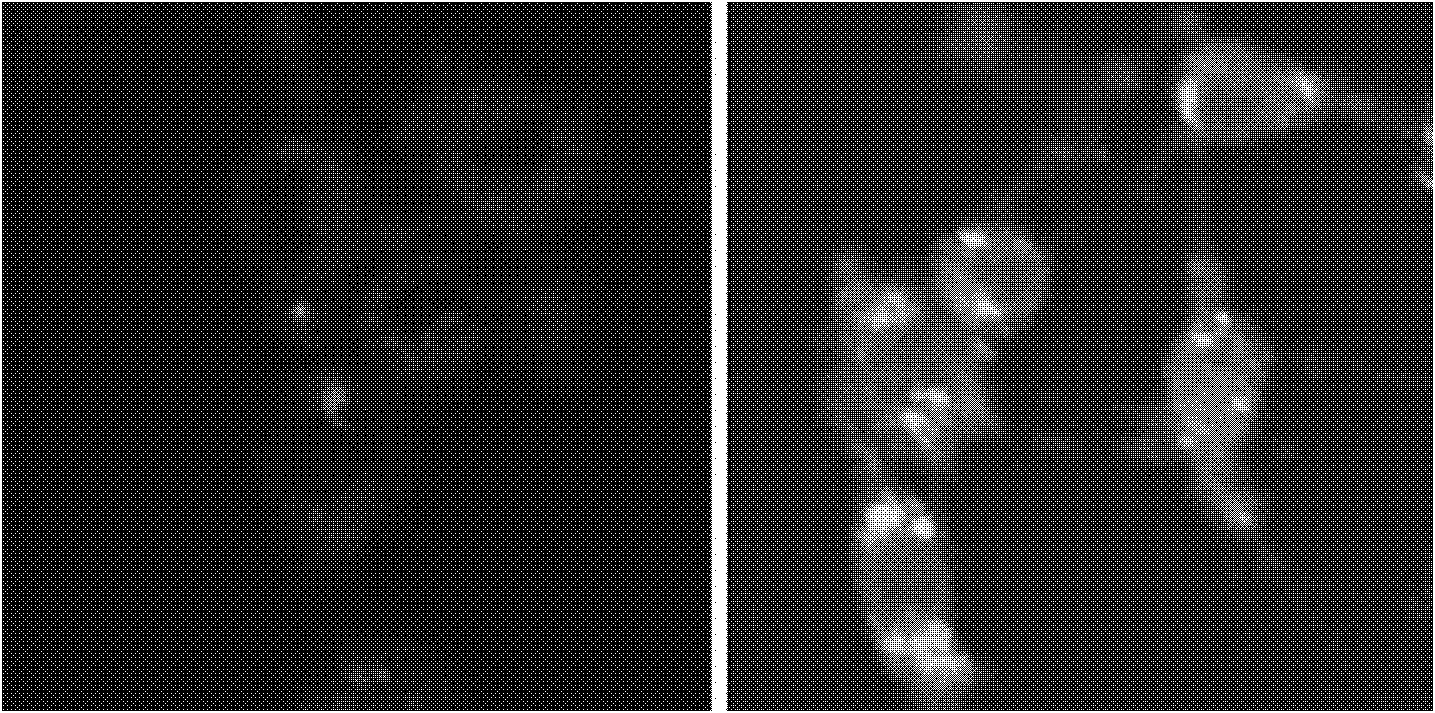Patents
Literature
322 results about "Stem-loop" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
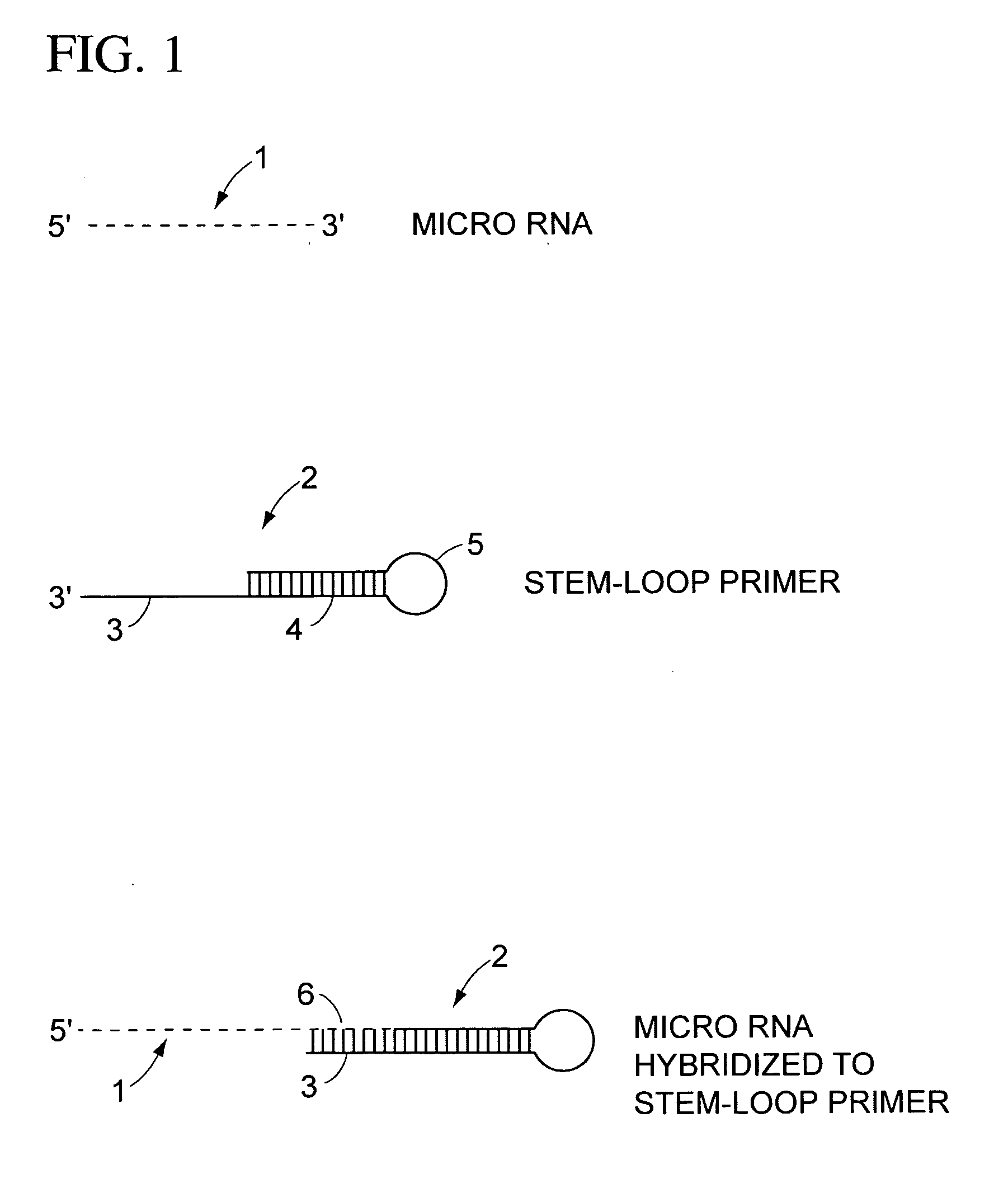
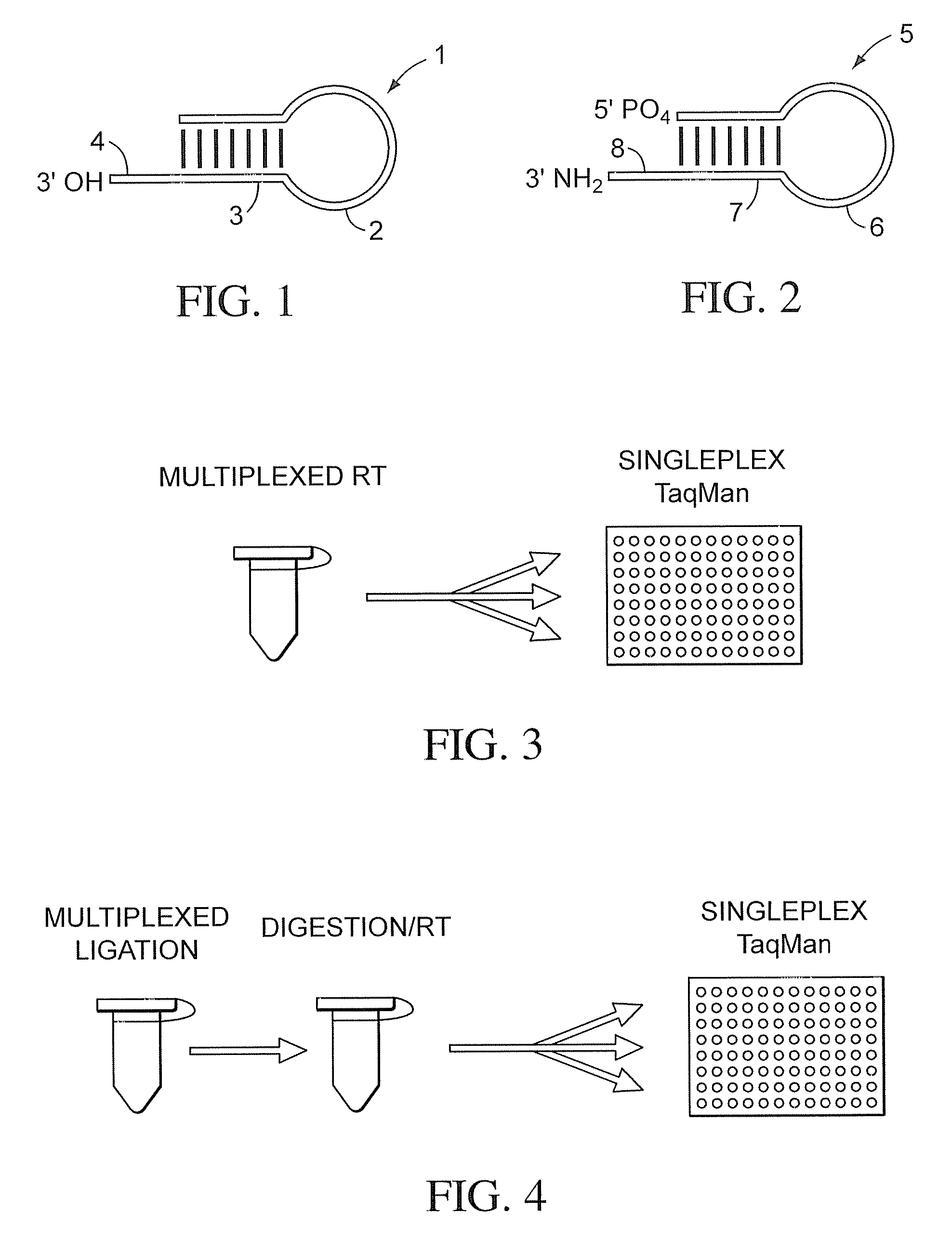
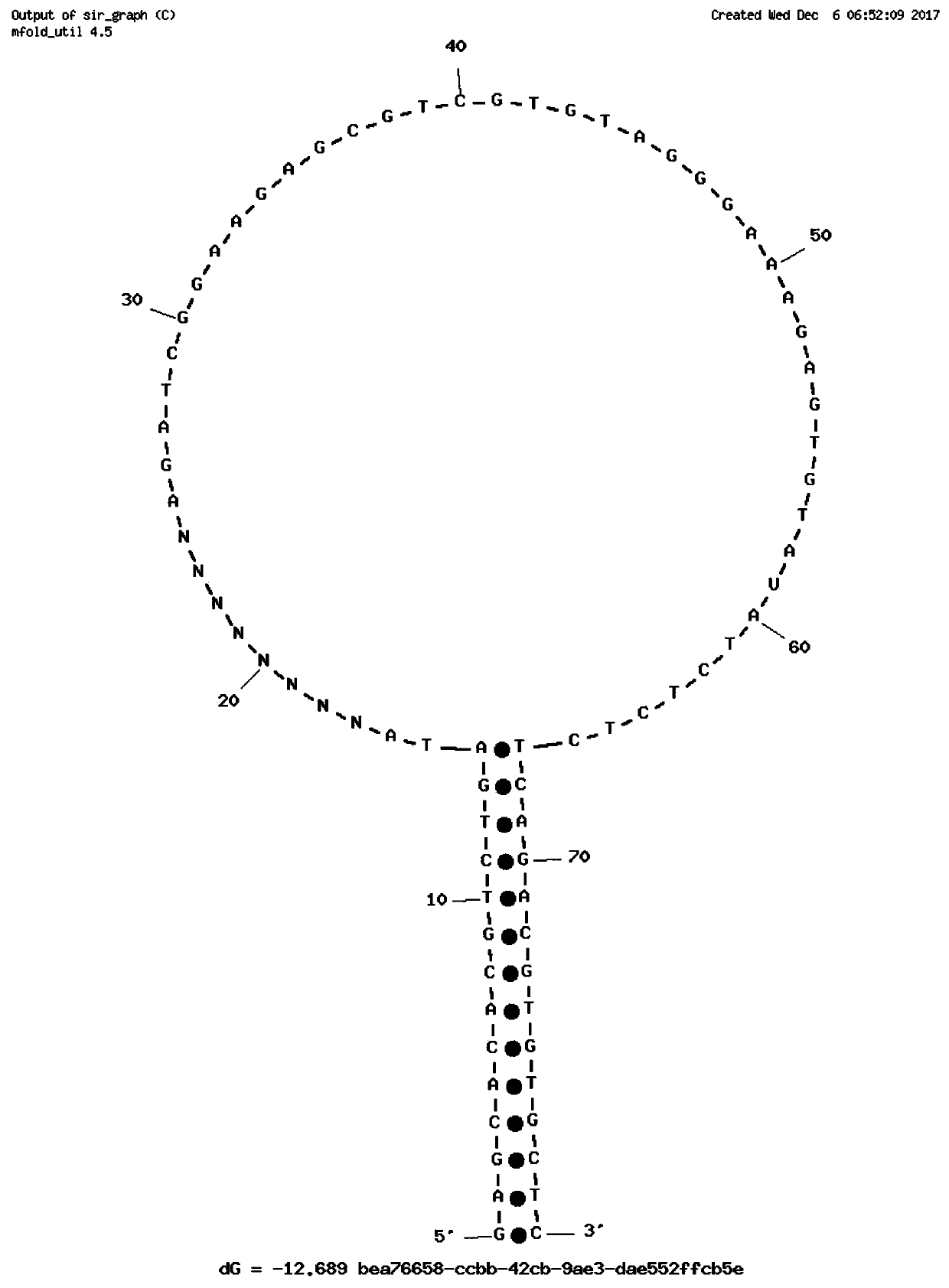
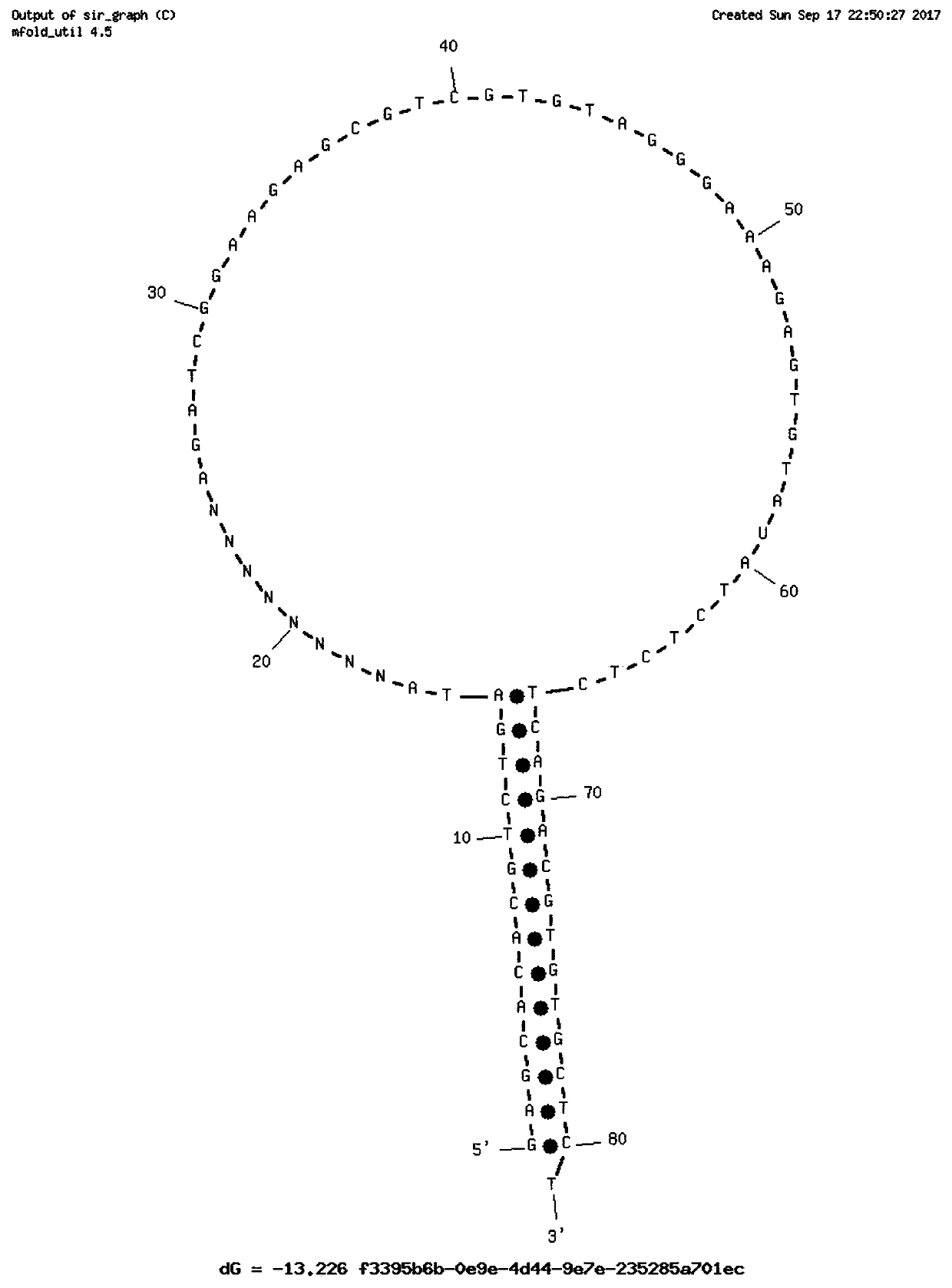
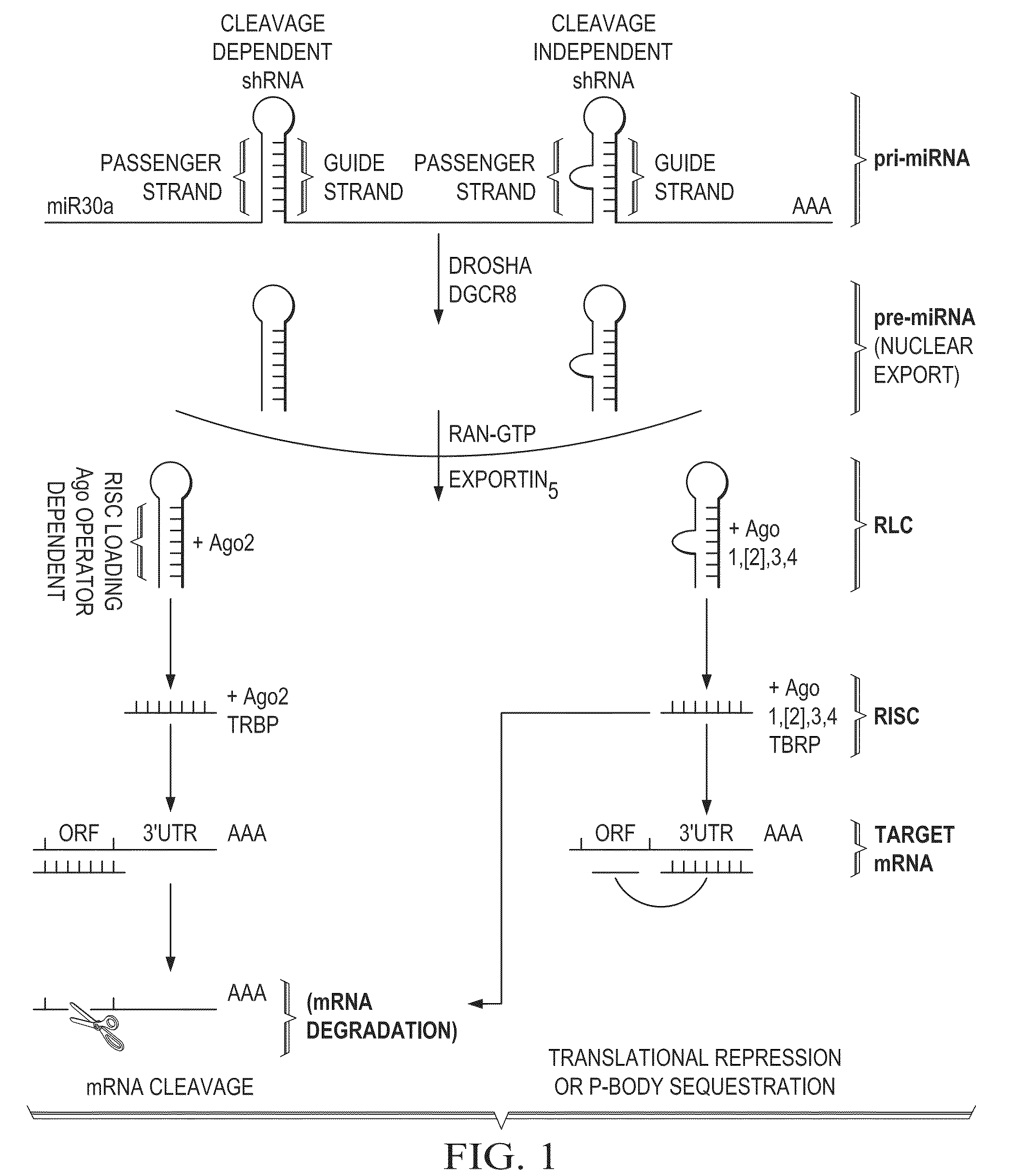
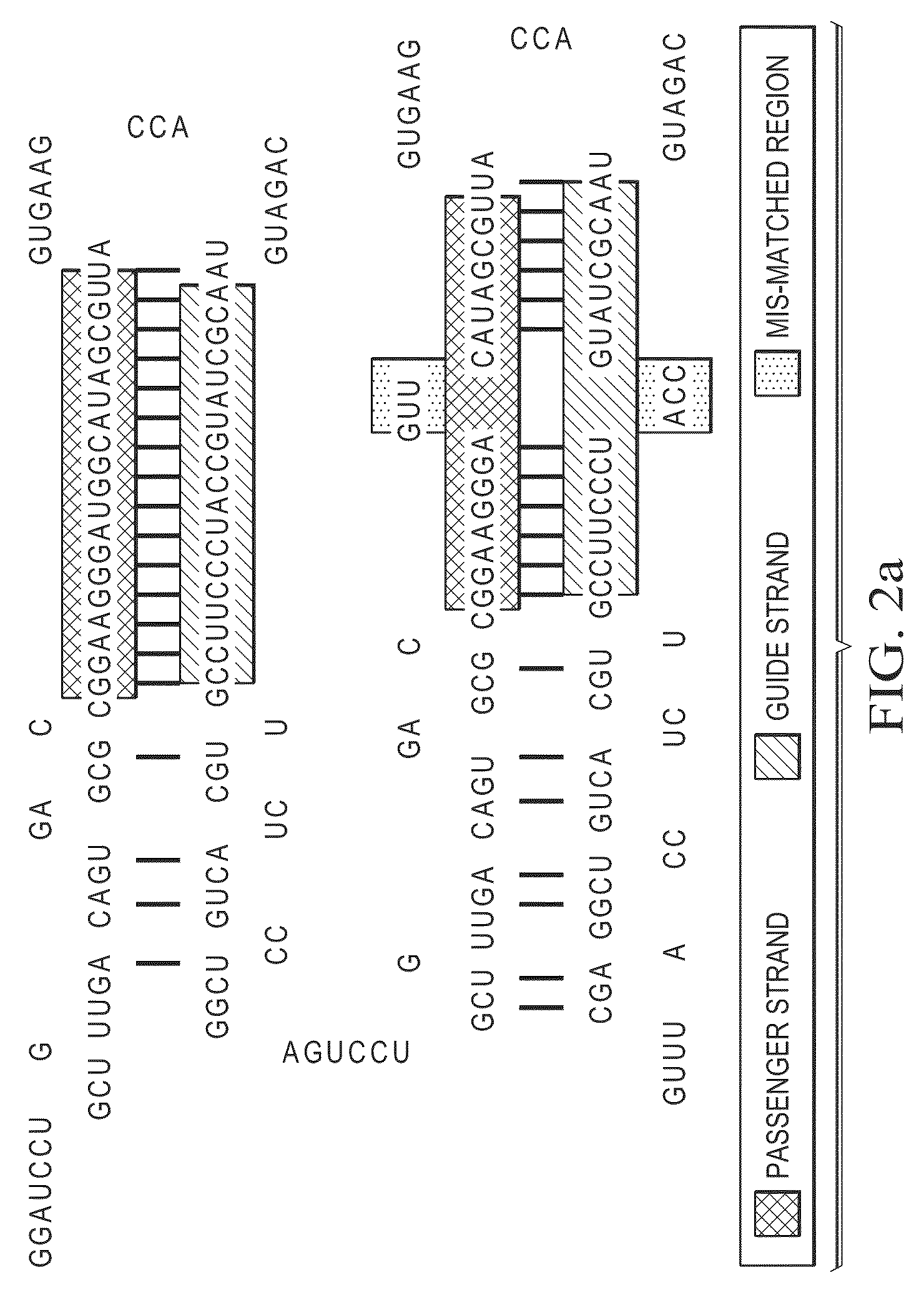
Stem-loop intramolecular base pairing is a pattern that can occur in single-stranded DNA or, more commonly, in RNA. The structure is also known as a hairpin or hairpin loop. It occurs when two regions of the same strand, usually complementary in nucleotide sequence when read in opposite directions, base-pair to form a double helix that ends in an unpaired loop. The resulting structure is a key building block of many RNA secondary structures. As an important secondary structure of RNA, it can direct RNA folding, protect structural stability for messenger RNA (mRNA), provide recognition sites for RNA binding proteins, and serve as a substrate for enzymatic reactions.
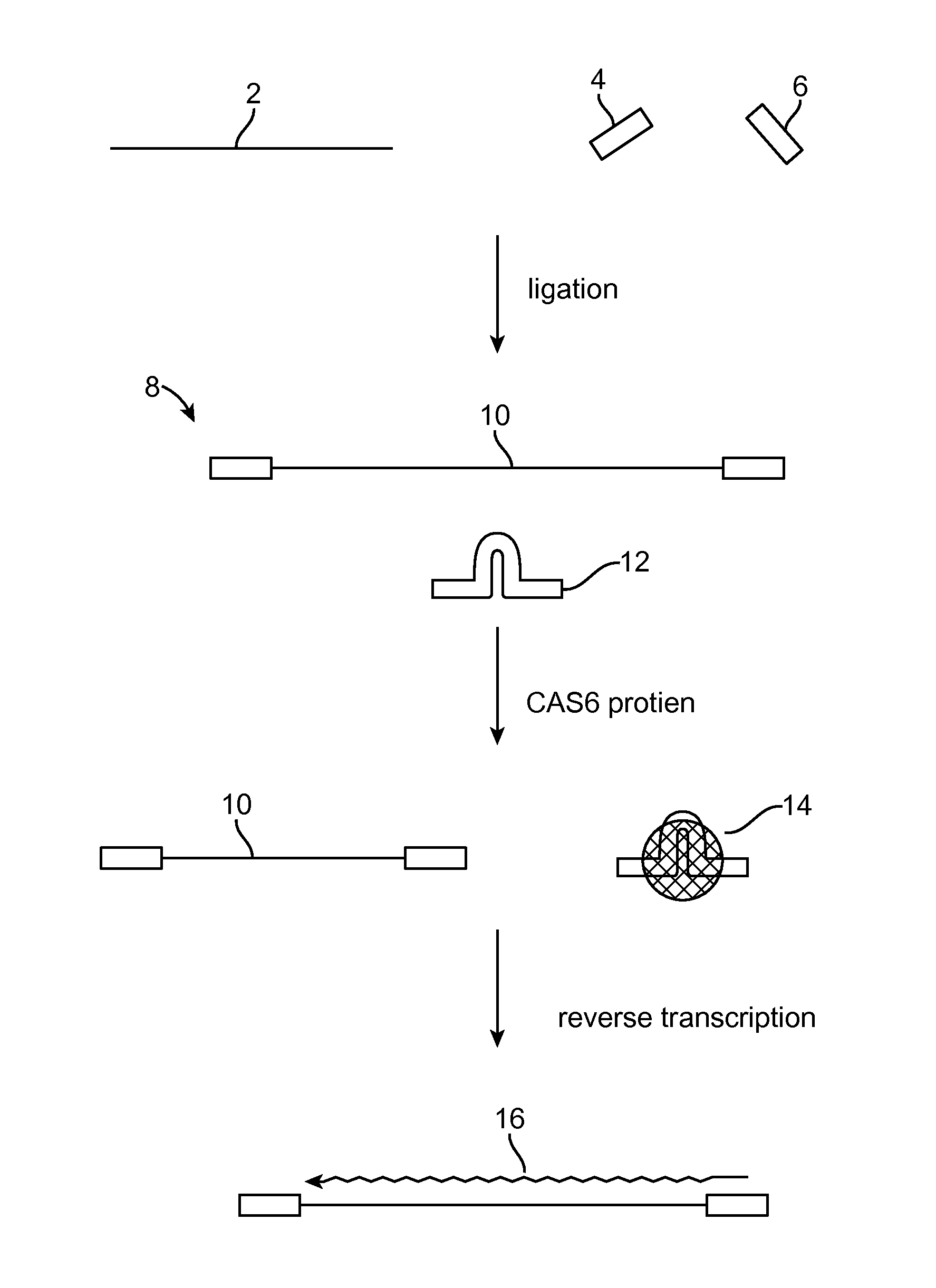
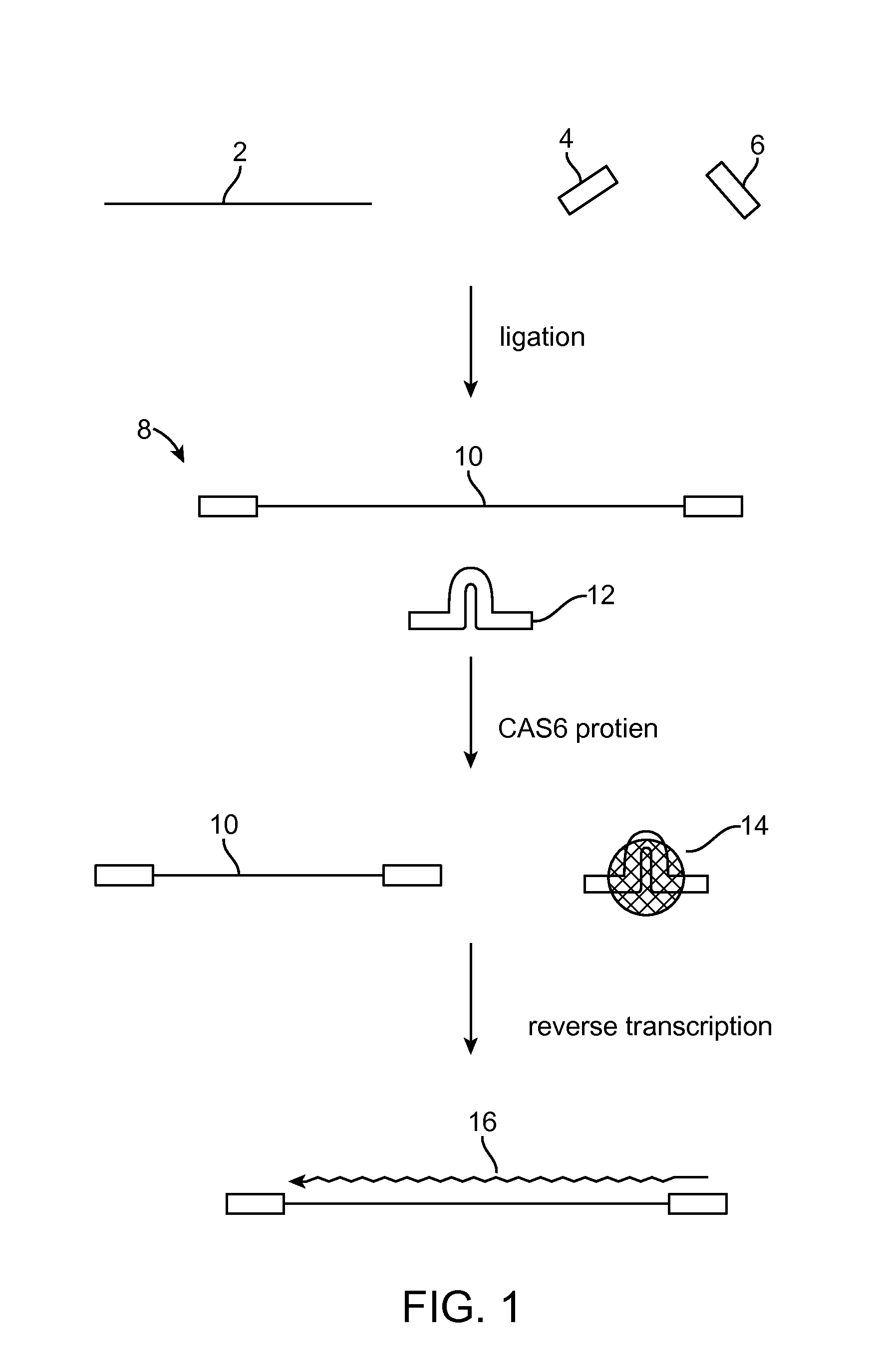
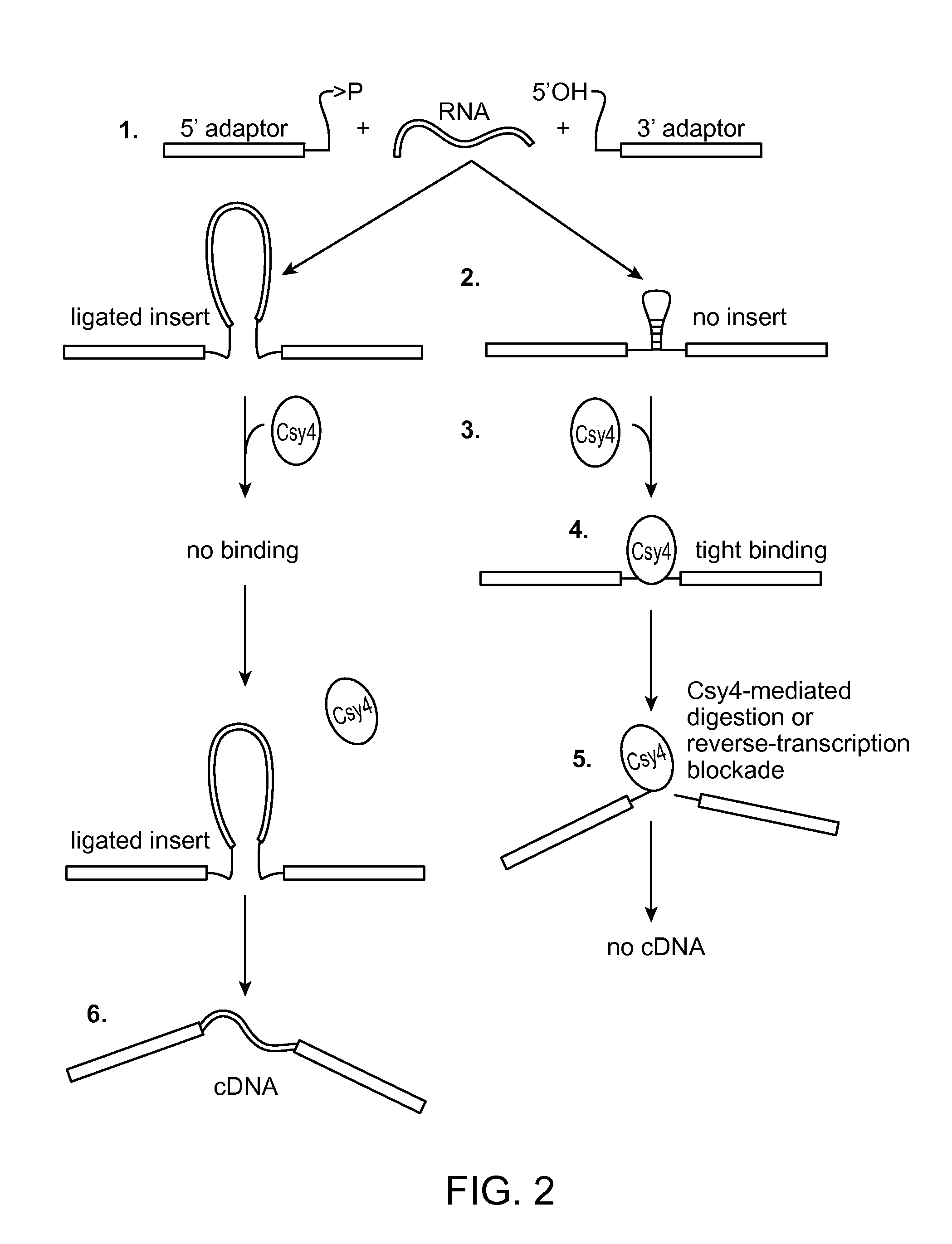
Method of adaptor-dimer subtraction using a crispr cas6 protein
A method of processing a target RNA is provided. In certain embodiments, this method comprises: contacting the products of an RNA ligase-mediated ligation reaction with an CAS6 protein, wherein: (i) the RNA ligase-mediated ligation reaction comprises: a target RNA, an RNA ligase, and first and second adaptors that can ligate together to produce an adaptor dimer that contains a CRISPR stem loop; and (ii) the CAS6 protein recognizes the CRISPR stem loop; thereby preventing the adaptor dimer from being reverse transcribed.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
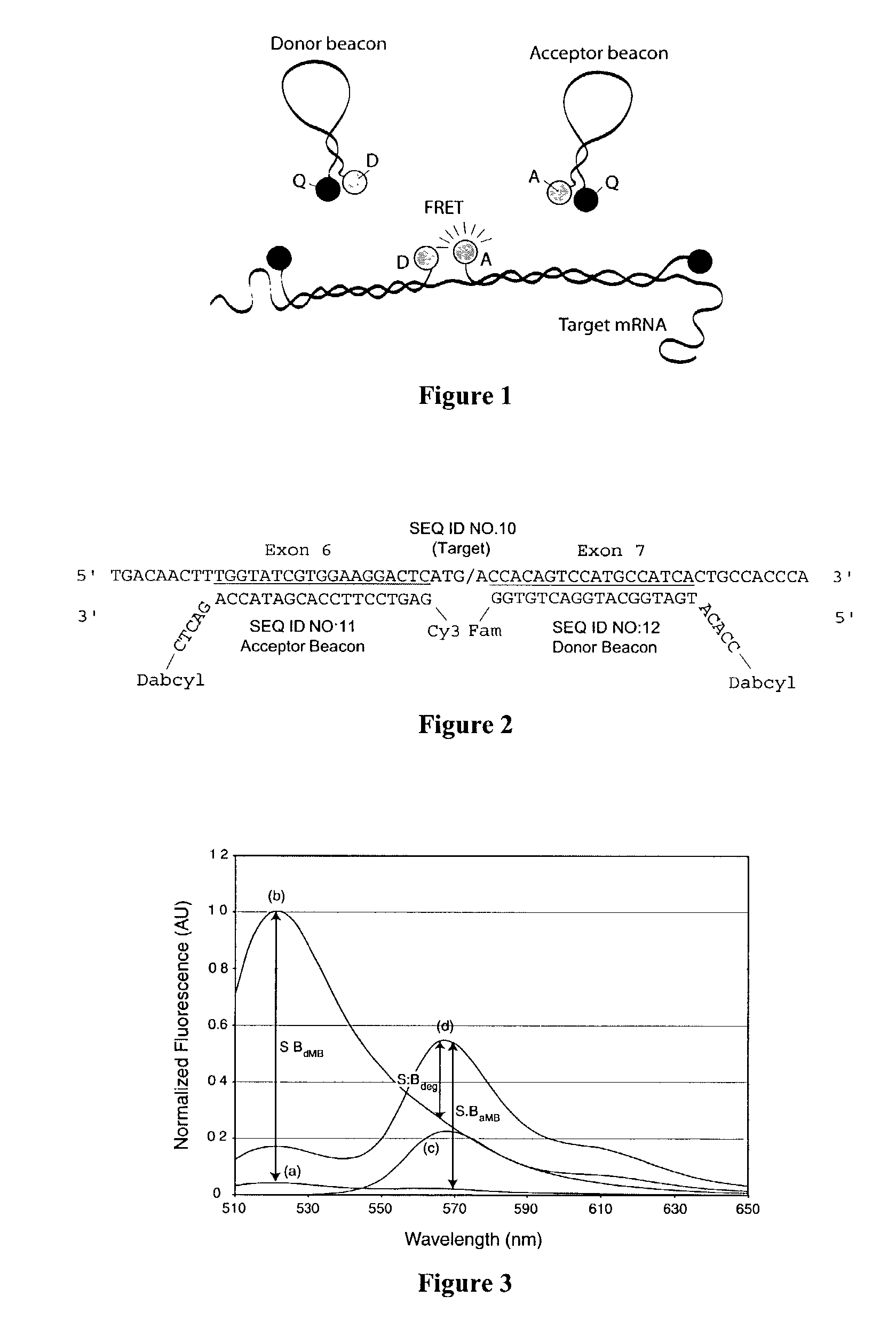
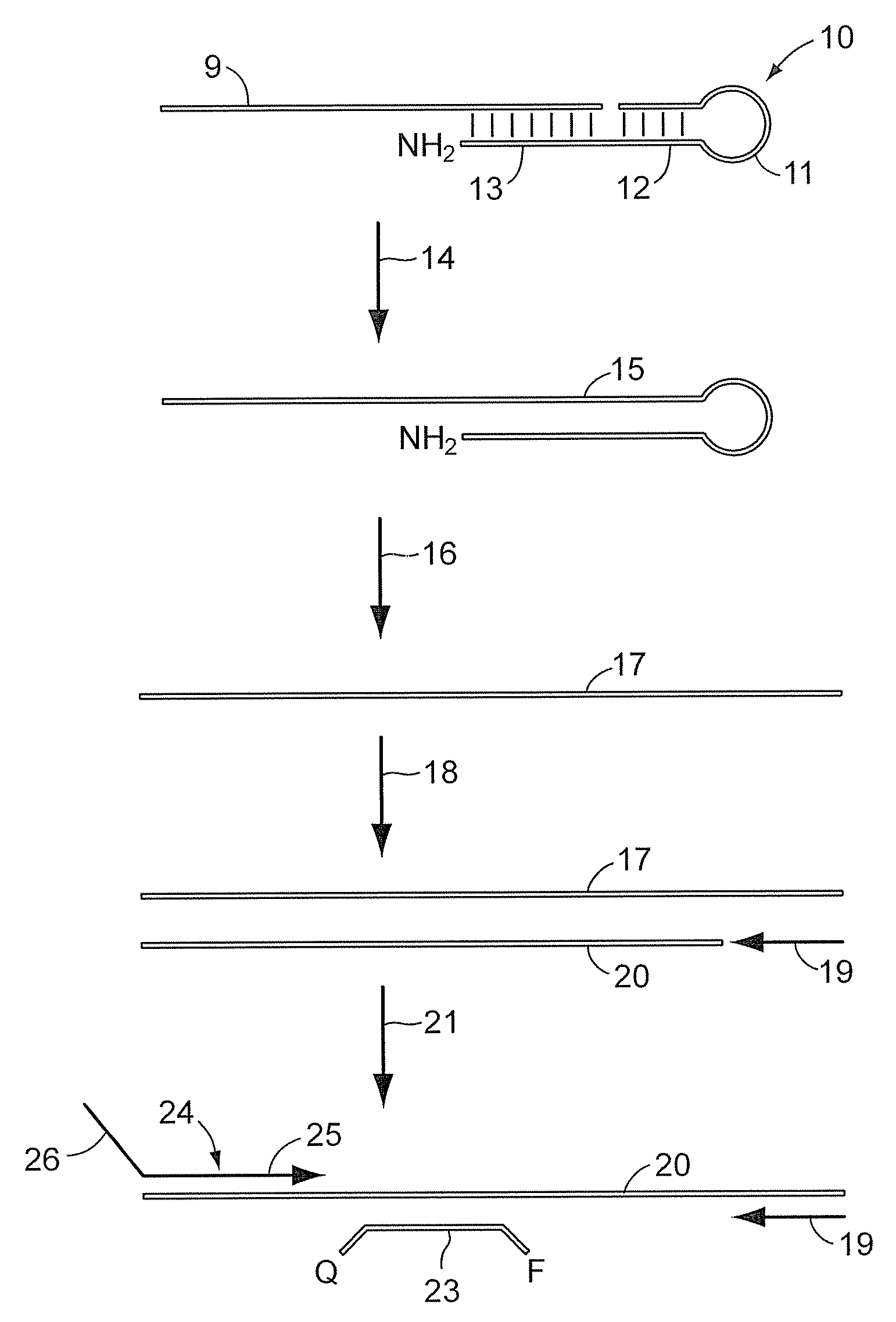
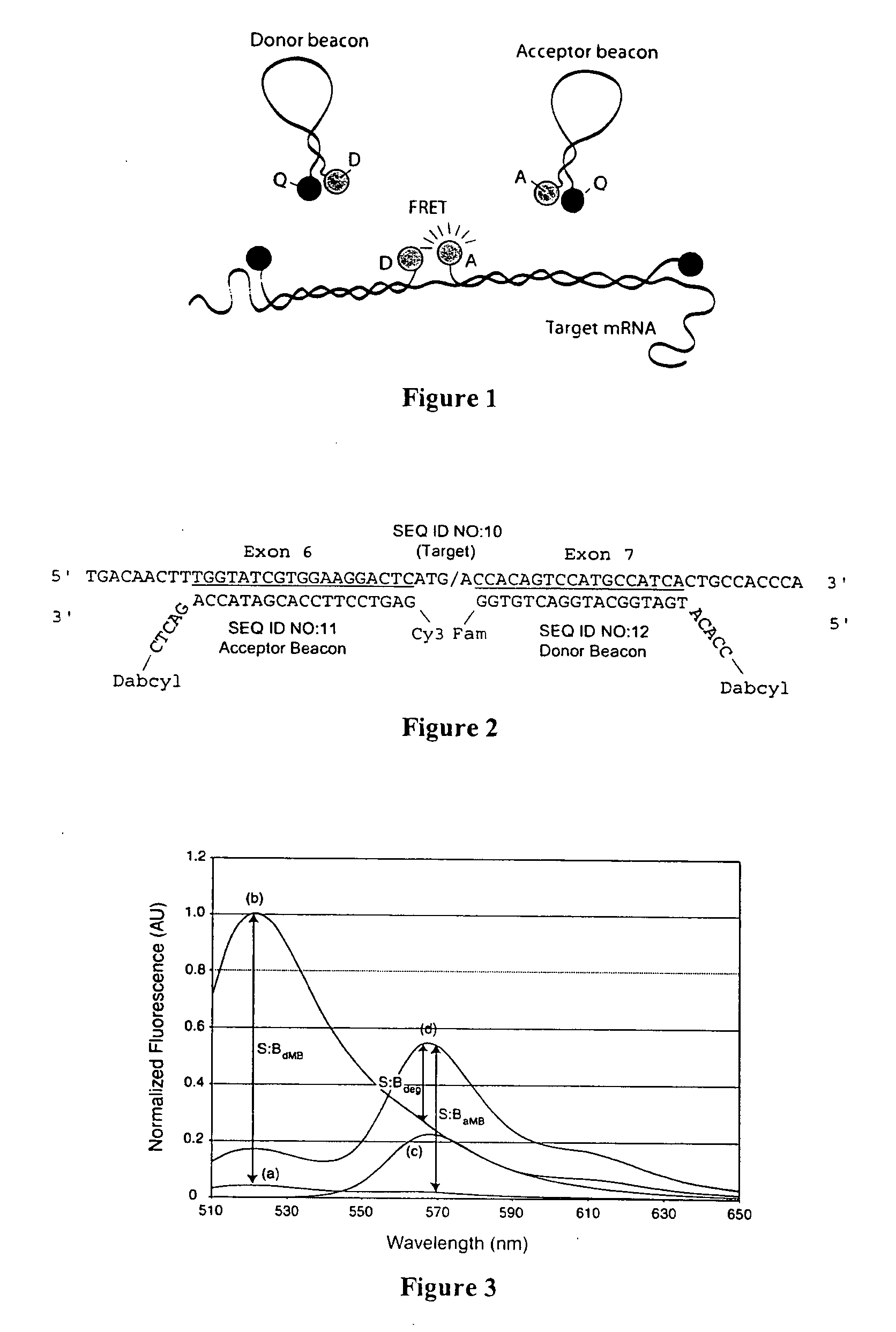
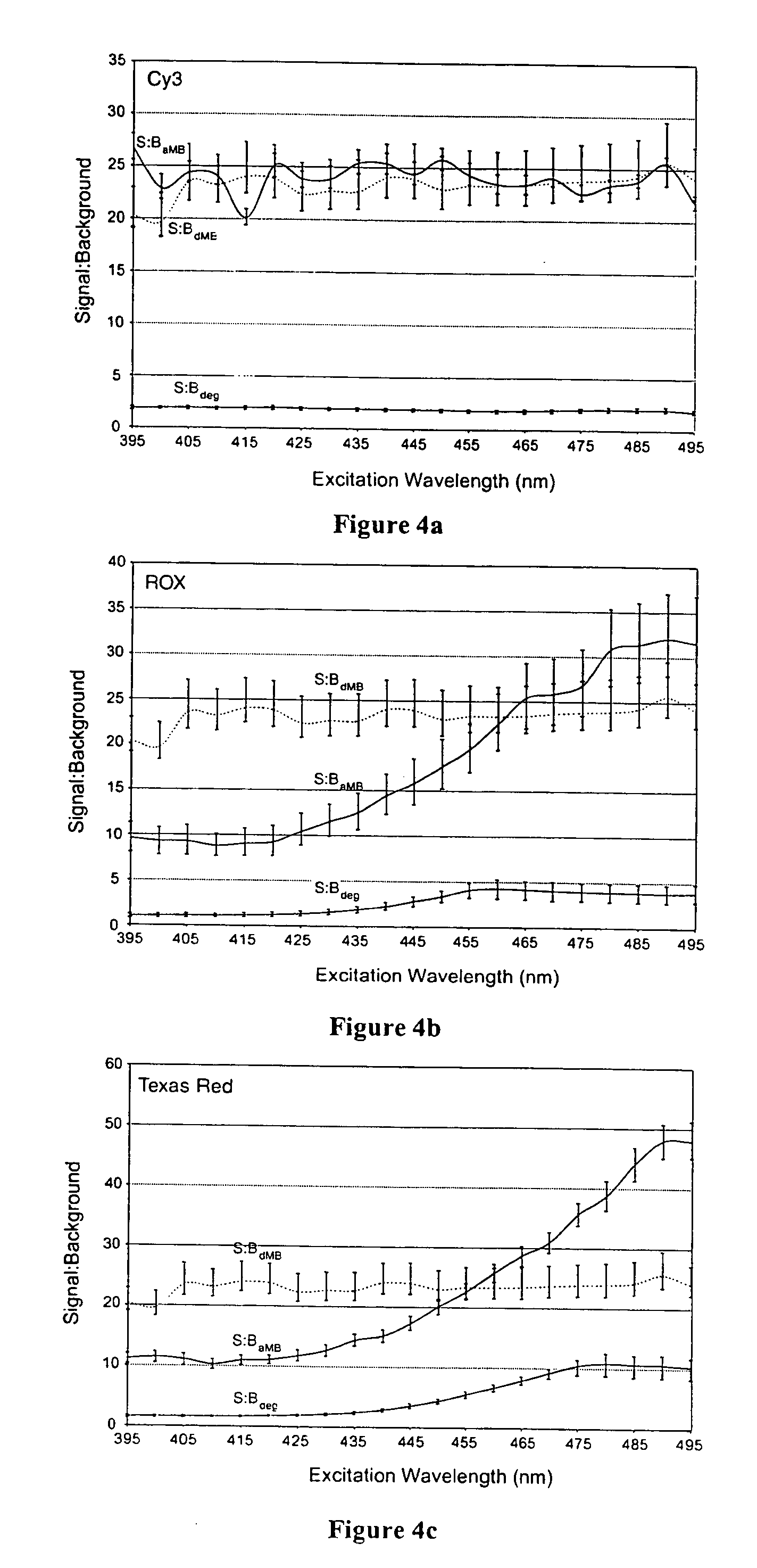
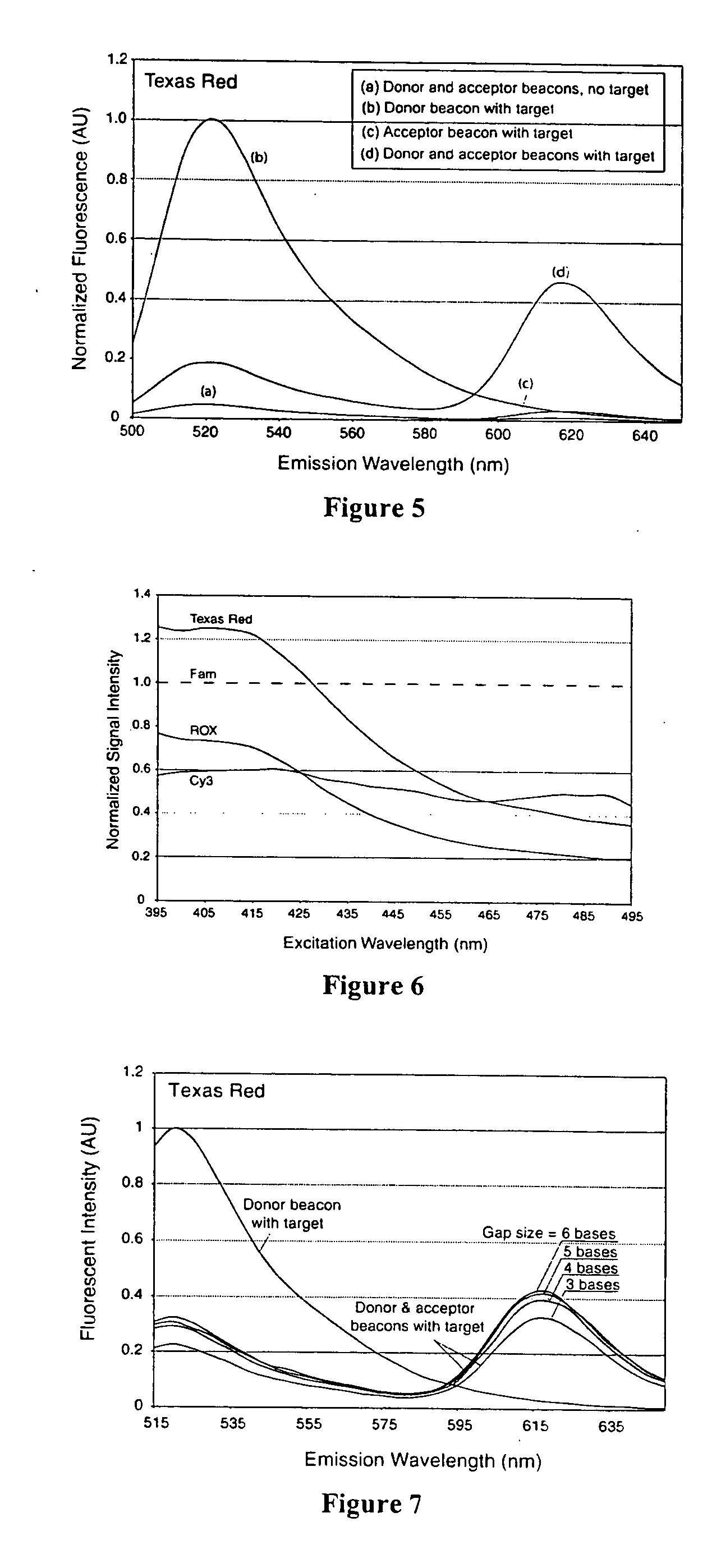
Dual resonance energy transfer nucleic acid probes
InactiveUS7081336B2Quick checkEasy to useSugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDiseaseCell specific
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
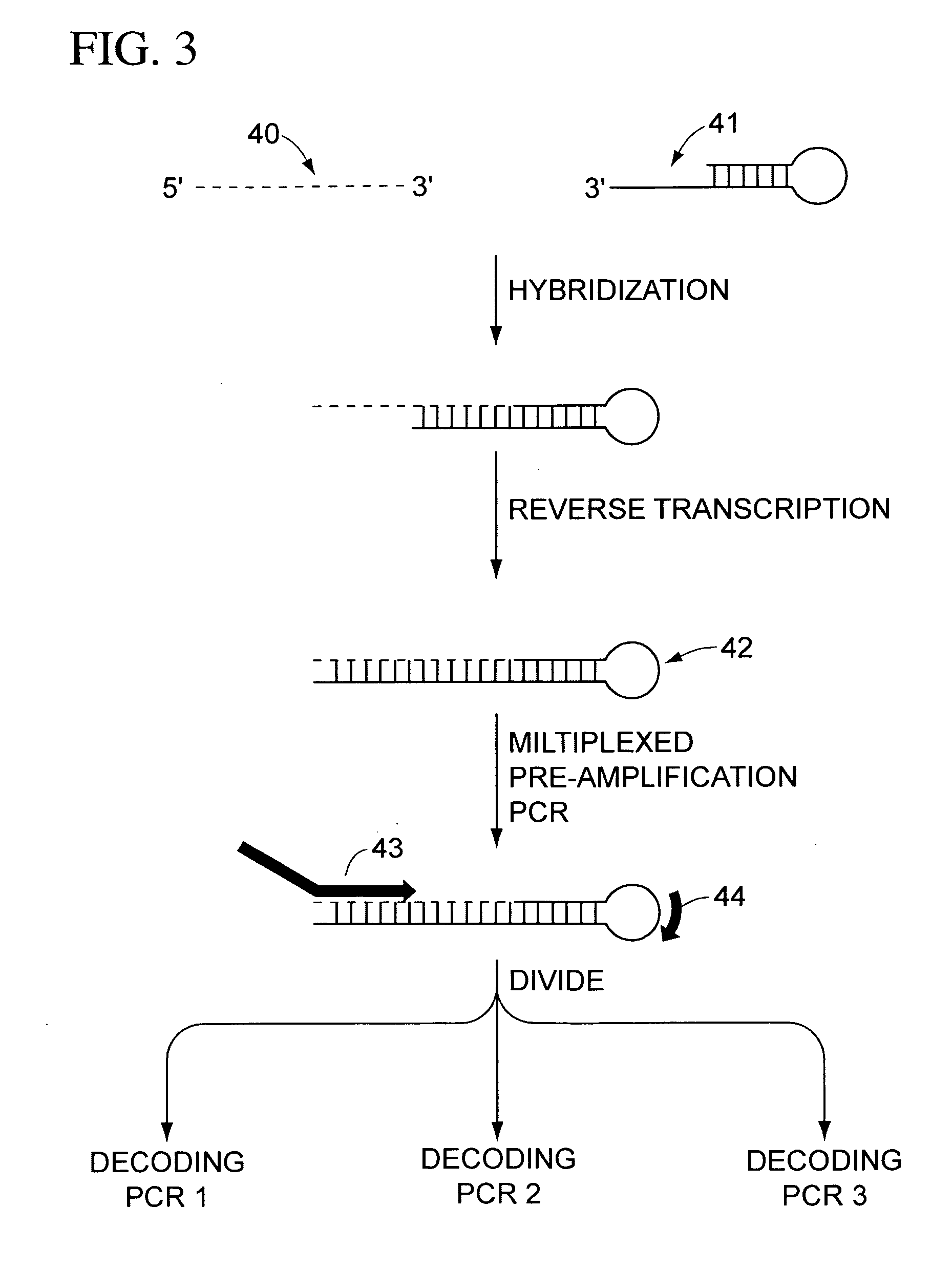
Multiplexed amplification of short nucleic acids
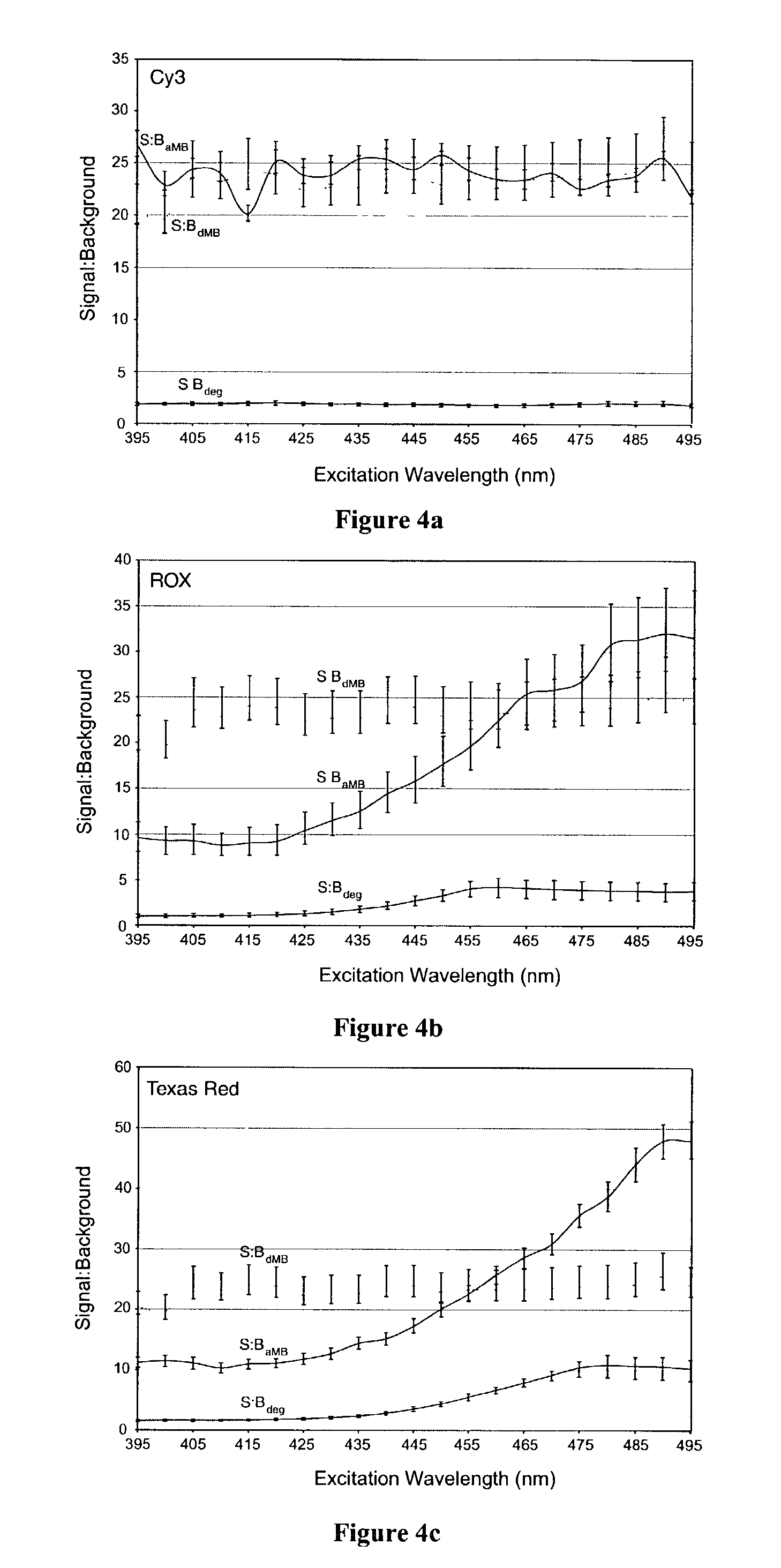
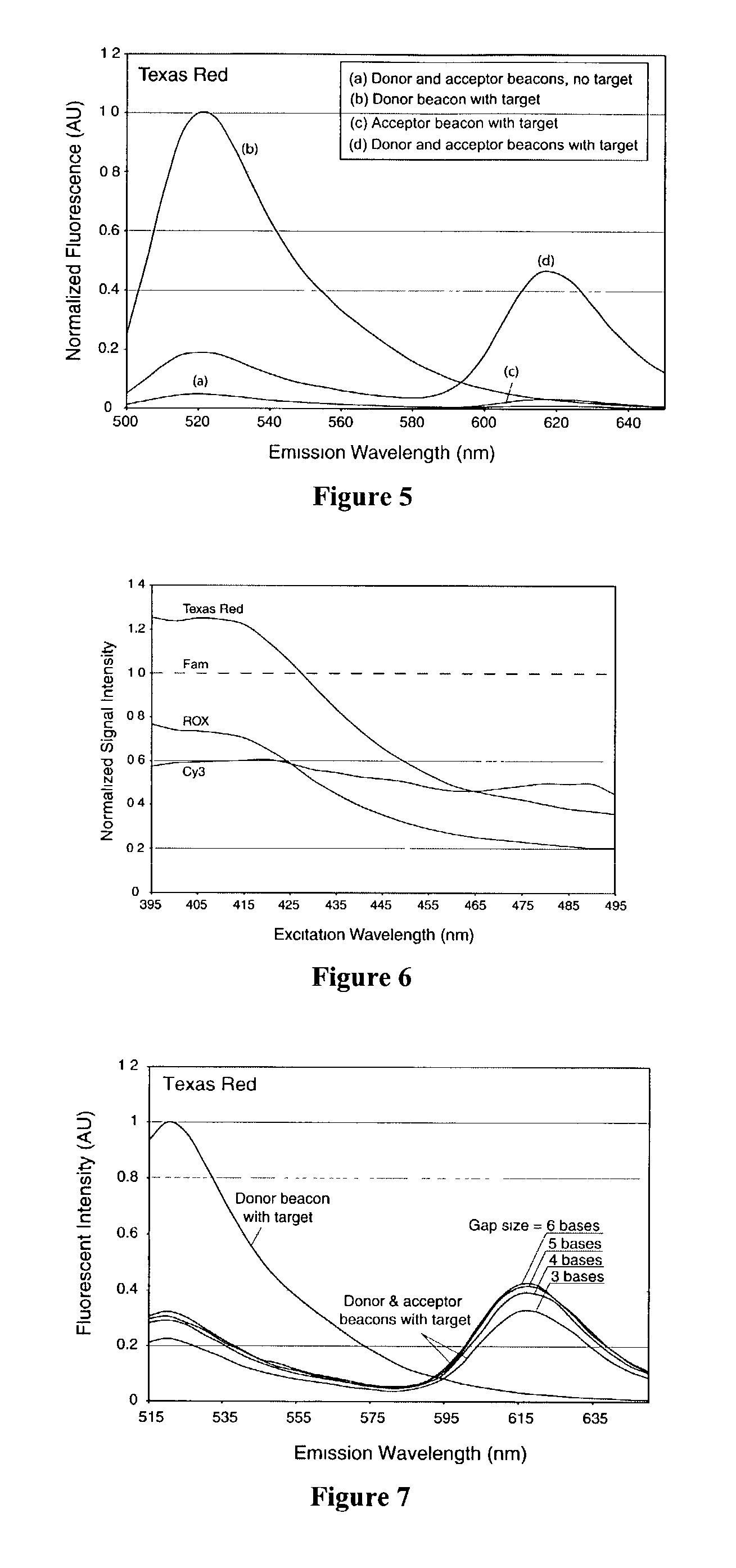
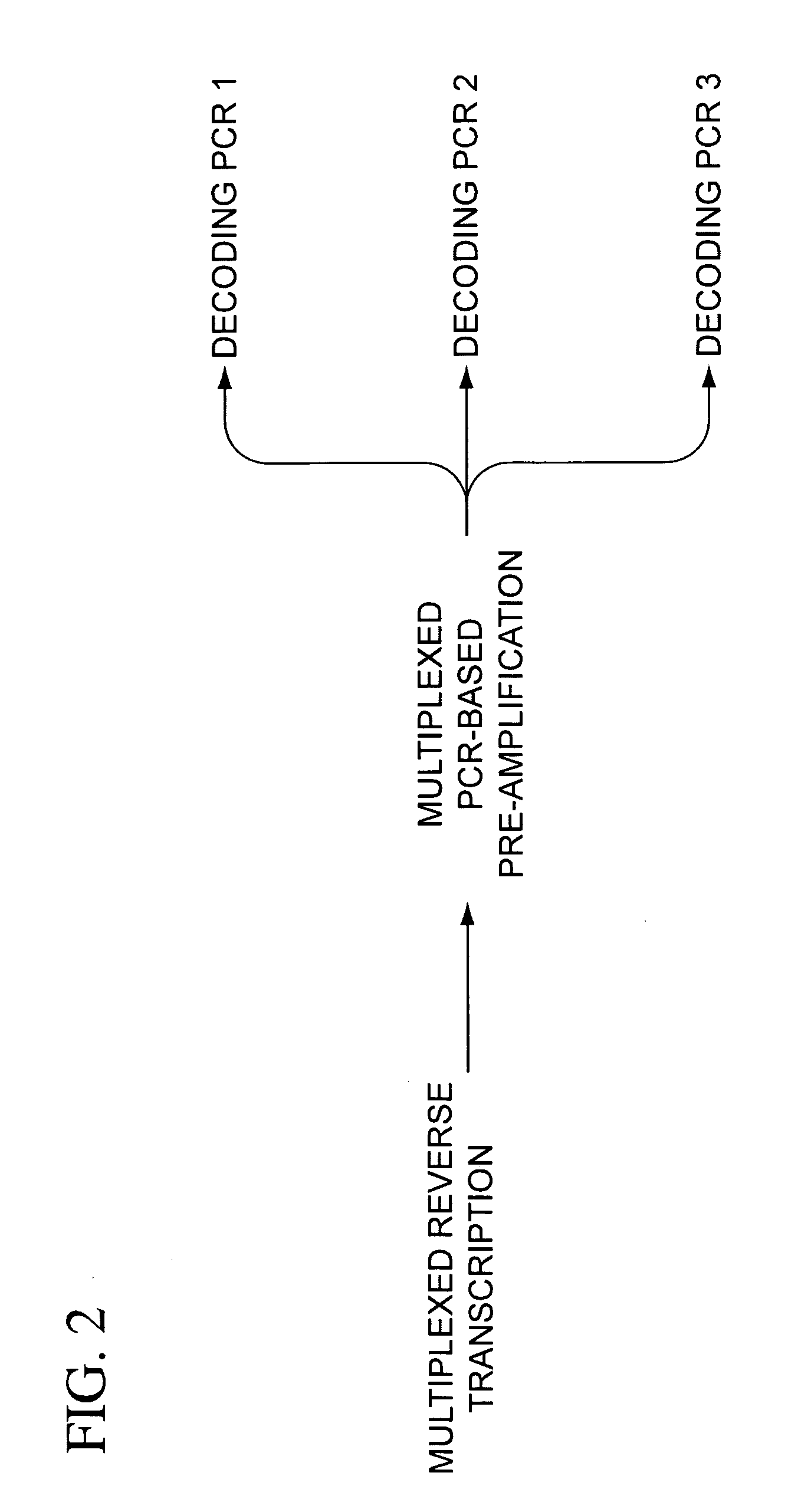
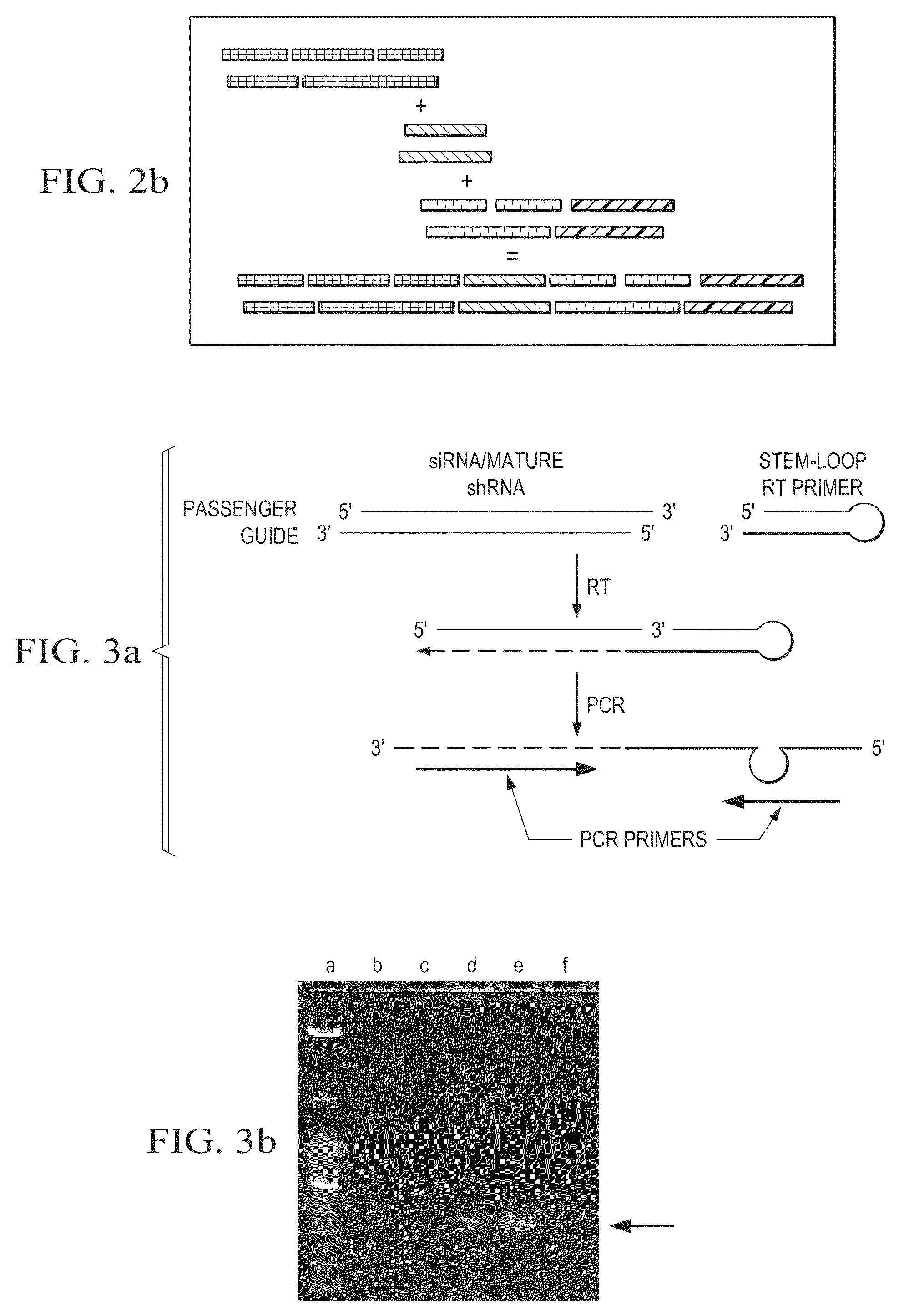
The present teachings provide methods, compositions, and kits for reverse transcribing and amplifying small nucleic acids such as micro RNAs. High levels of multiplexing are provided by the use of a zip-coded stem-loop reverse transcription primer, along with a PCR-based pre-amplification reaction that comprises a zip-coded forward primer. Detector probes in downstream decoding PCRs can take advantage of the zip-code introduced by the stem-loop reverse transcription primer. In some embodiments, further amplification is achieved by cycling the reverse transcription reaction. The present teachings also provide compositions and kits useful for performing the reverse transcription and amplification reactions described herein.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
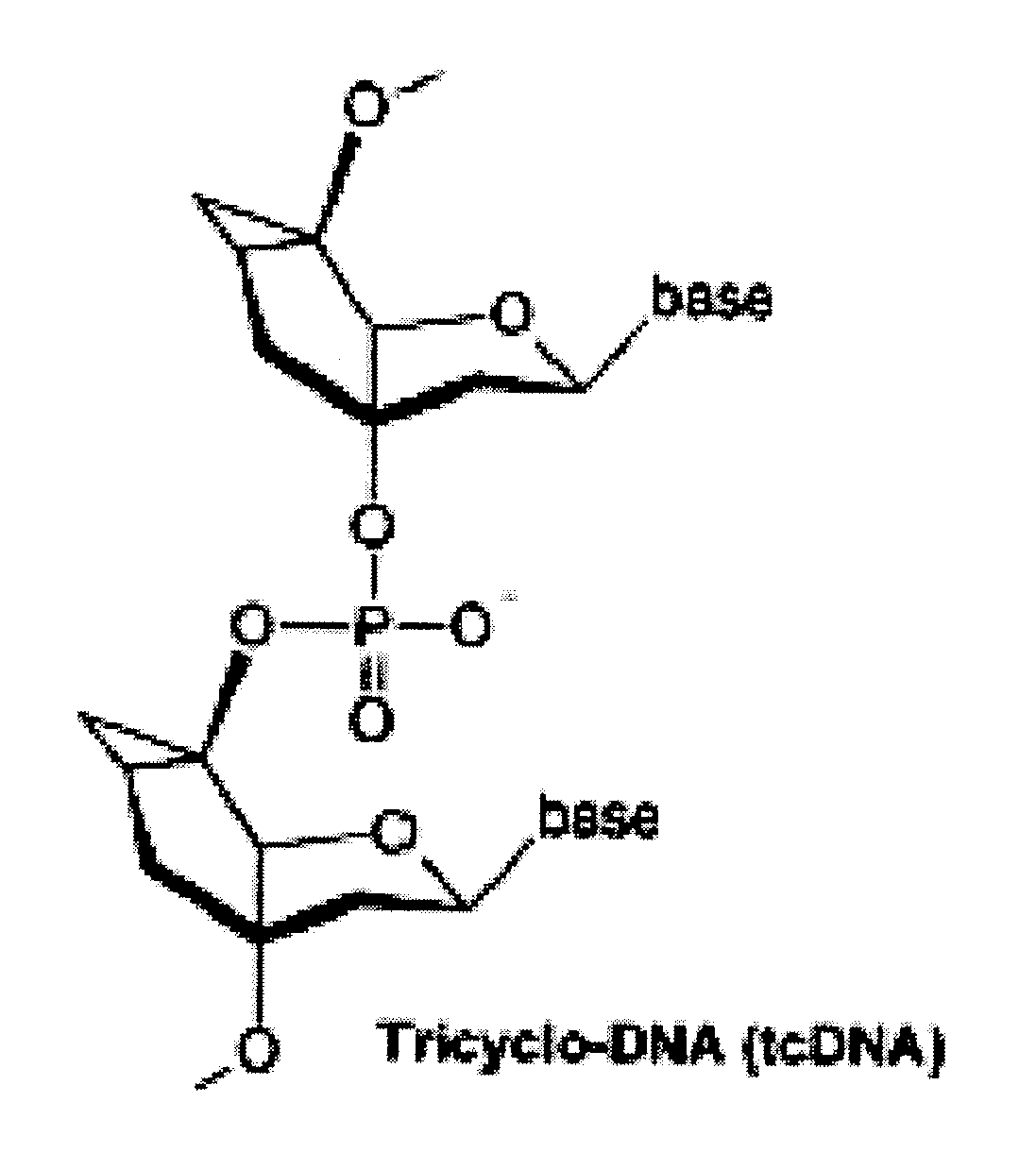
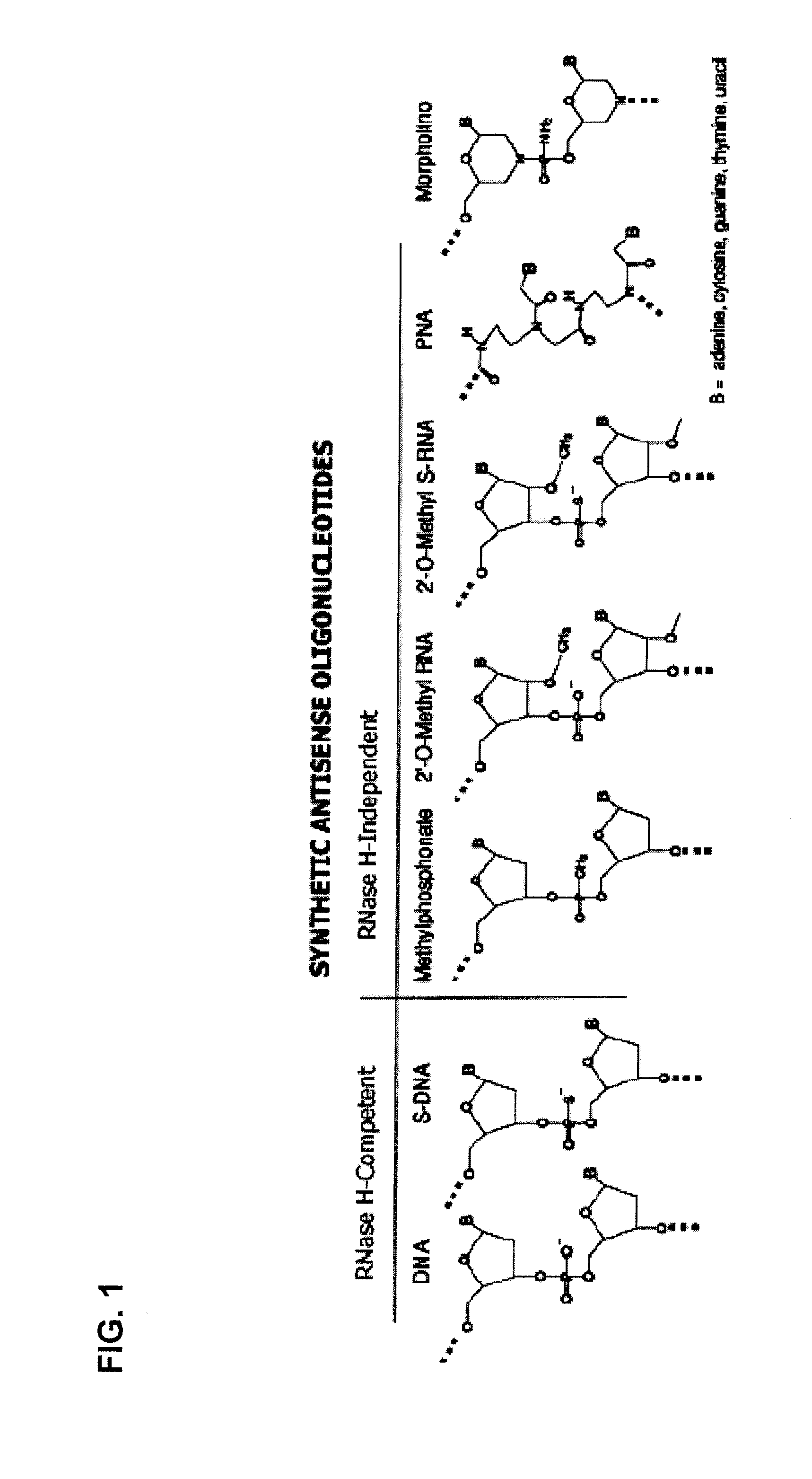
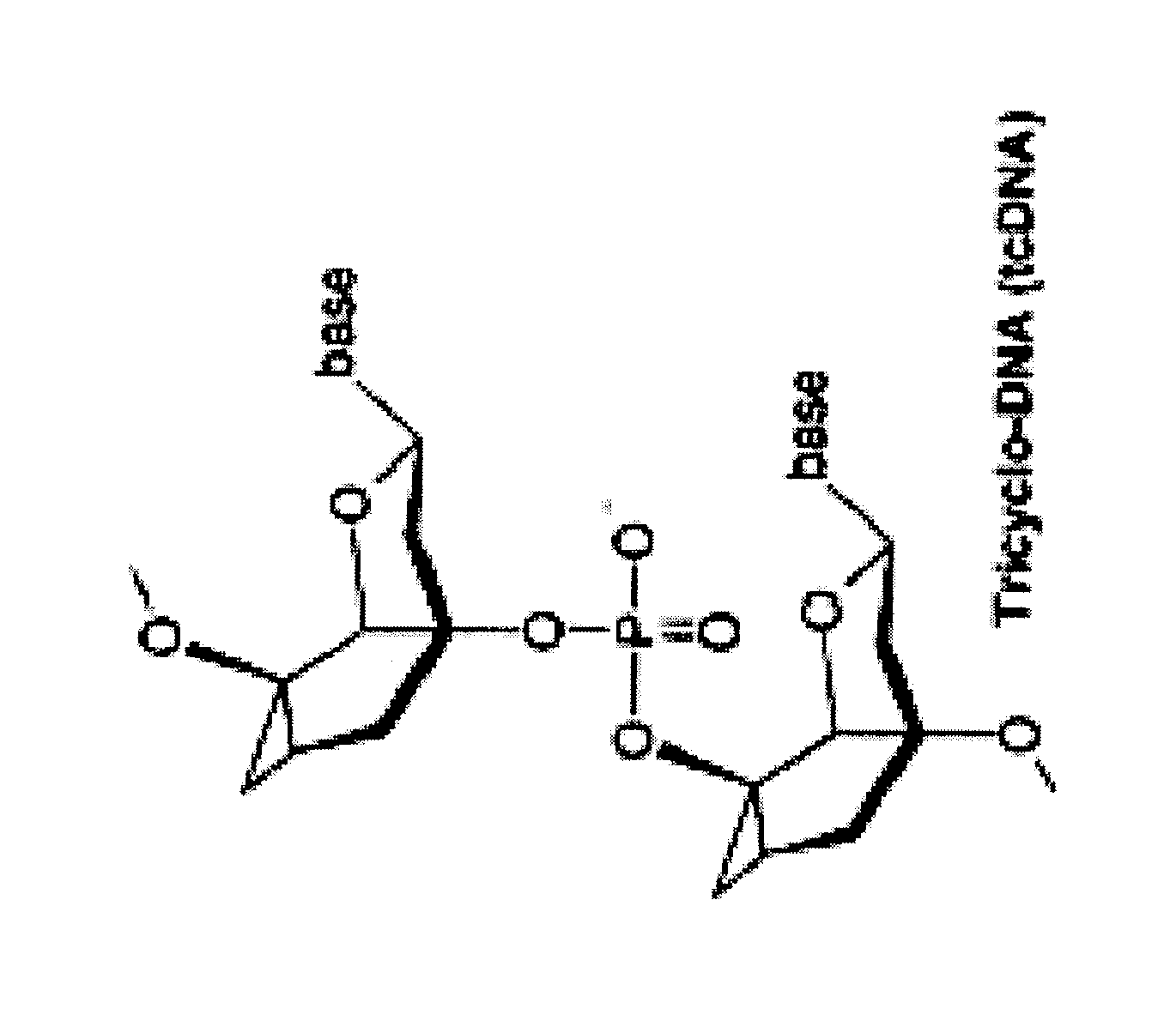
Tricyclo-dna antisense oligonucleotides, compositions, and methods for the treatment of disease
InactiveUS20120149756A1Find utilityFacilitates inclusionOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationDiseasePre mrna processing
Provided are tricyclo-DNA (tc-DNA) AON and methods employing tc-DNA AON for modifying splicing events that occur during pre-mRNA processing. Tricyclo-DNA (tc-DNA) AON are described that may be used to facilitate exon skipping or to mask intronic silencer sequences and / or terminal stem-loop sequences during pre-mRNA processing and to target RNase-mediated destruction of processed mRNA. Tc-DNA AON described herein may be used in methods for the treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy by skipping a mutated exon 23 or exon 51 within a dystrophin gene to restore functionality of a dystrophin protein; in methods for the treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy by masking an intronic silencing sequence and / or a terminal stem-loop sequence within an SMN2 gene to yield modified functional SMN2 protein, including an amino acid sequence encoded by exon 7, which is capable of at least partially complementing a non-functional SMN1 protein; and in methods for the treatment of Steinert's Myotonic Dystrophy by targeting the destruction of a mutated DM1 mRNA comprising 3′-terminal CUG repeats.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +4
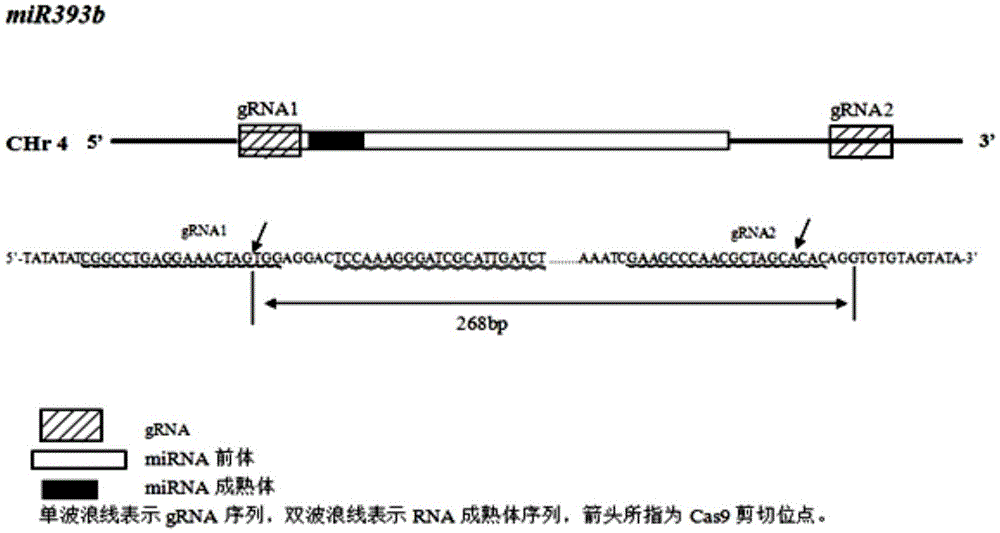
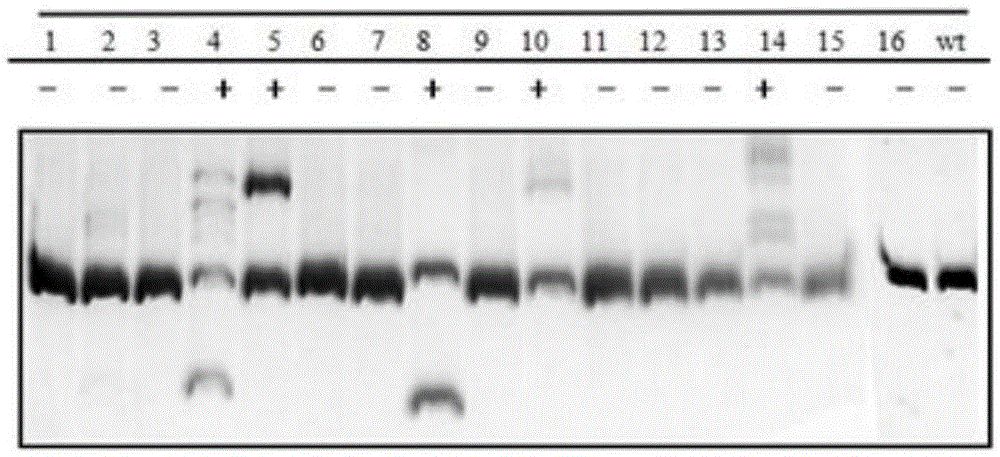
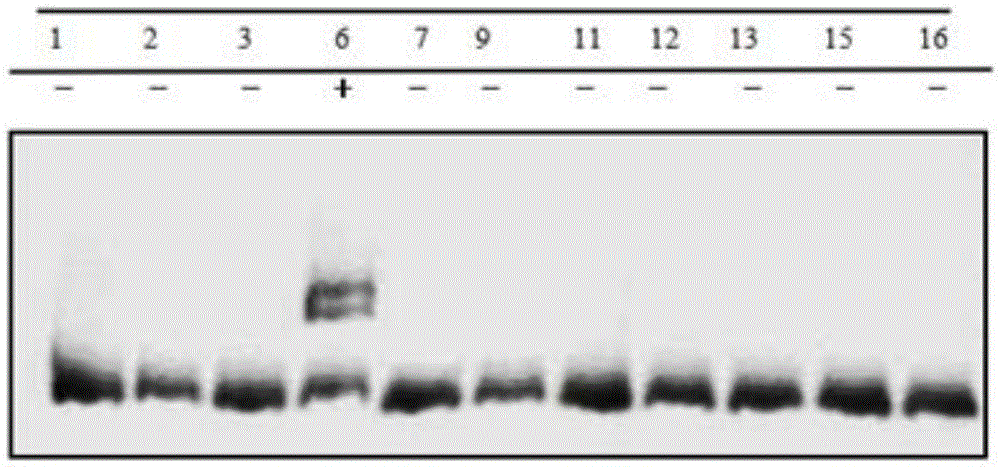
Gene editing method for knocking out rice MIRNA393b stem-loop sequences with application of CRISPR(clustered regulatory interspersed short palindromic repeat)-Cas9 system
InactiveCN105647962AKnockout worksNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to construction of rice transgenic materials and aims to provide a gene editing method for knocking out rice MIRNA393b stem-loop sequences with application of a CRISPR(clustered regulatory interspersed short palindromic repeat)-Cas9 system. The gene editing method comprises steps as follows: gRNA target sites are selected for cloning and GG linking, enzyme digestion is performed after amplification, and a product is linked with a pGREB 32 vector; escherichia coli competent cells are transformed; plasmids with a correct sequencing result are used for transforming agrobacteria, transgenic plants are obtained through mediated transformation of rice calli, and transgenic positive lines are obtained; the T0-generation mutant plant seeds are collected for seeding, and the T1-generation plants are subjected to homozygote screening; homozygous lines which are discovered to be negative through MIRNA393b expression are rice mutants completely losing the MIRNA393b stem-loop sequences and MIRNA393b stem-loop sequence expression. According to the gene editing method, MIRNA stem-loop sequences can be effectively knocked out, and loss-of-function mutants of different members in the same MIRNA family can be prepared; the mutant plant propagates to obtain a large number of seeds and is an ideal material for acquiring rice MIRNA393b gene functions successfully.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method to Quantify siRNAs, miRNAs and Polymorphic miRNAs
The present teachings provide methods, compositions, and kits for quantifying target polynucleotides. In some embodiments, a reverse stem-loop ligation probe is ligated to the 3′ end of a target polynucleotide, using a ligase that can ligate the 3′ end of RNA to the 5′ end of DNA using a DNA template, such as T4 DNA ligase. Following digestion to form an elongated target polynucleotide with a liberated end, a reverse transcription reaction can be performed, followed by a PCR. In some embodiments, the methods of the present teachings can discriminate between polymorphic polynucleoitides that vary by as little as one nucleotide.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Molecular barcoding on opposite transcript ends
ActiveUS20190338278A1Microbiological testing/measurementDNA preparationBarcodeMolecular hybridization
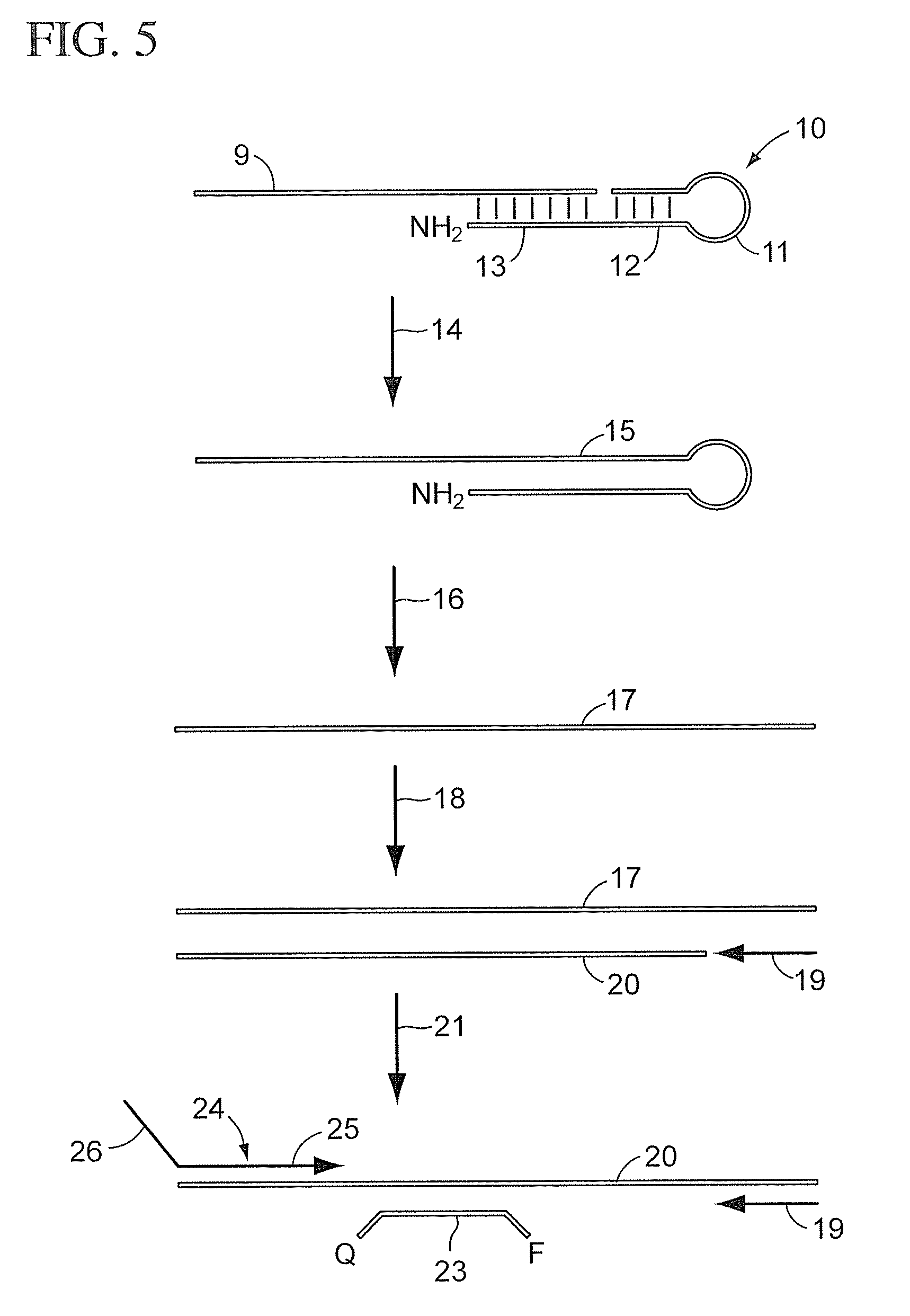
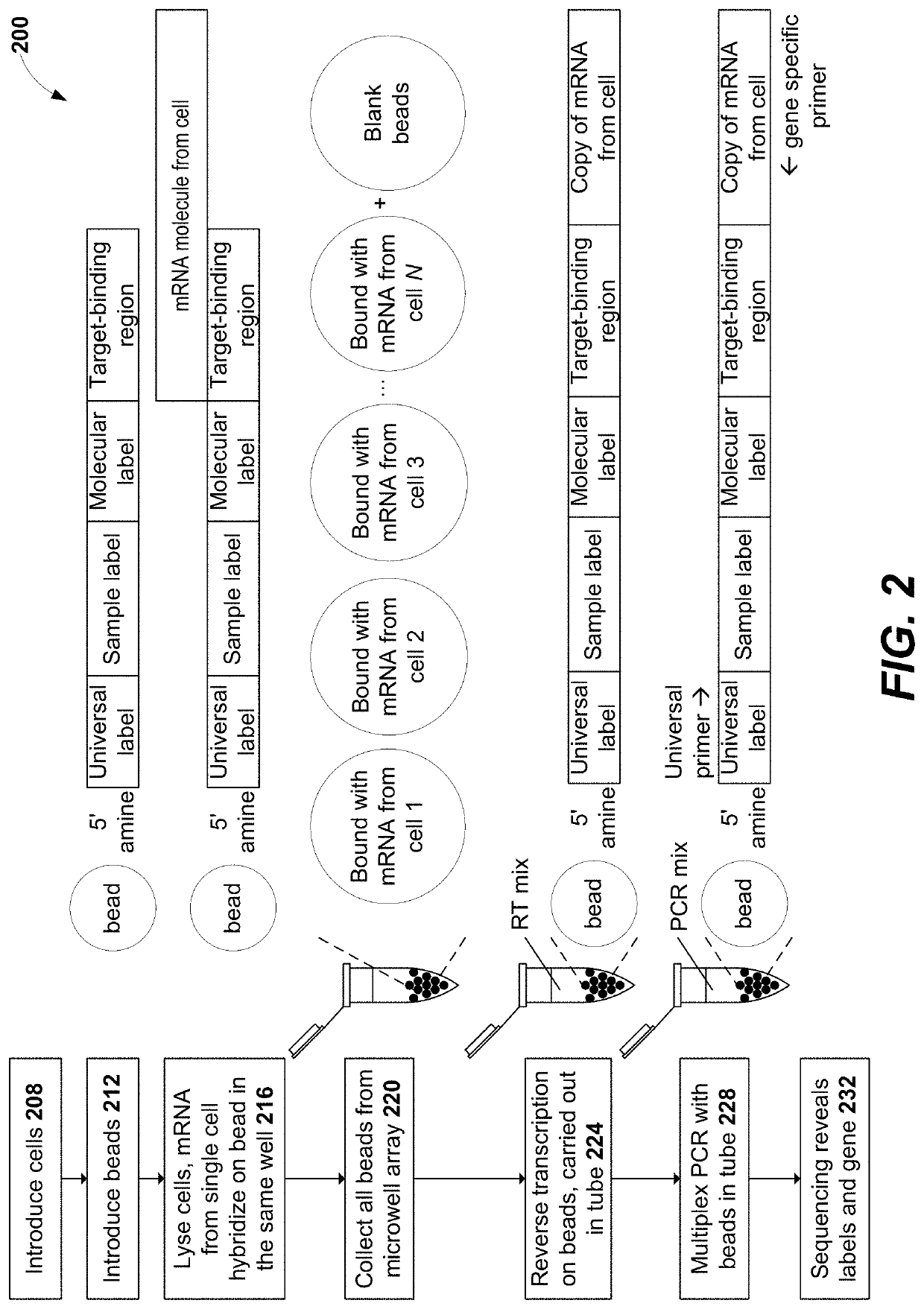
Disclosed herein include systems, methods, compositions, and kits for molecular barcoding on the 5′-end of a nucleic acid target. After barcoding a nucleic acid target using an oligonucleotide barcode comprising a target binding region and a molecular label to generate a barcoded nucleic acid molecule, an oligonucleotide comprising a complement of the target binding region can be added to generate a barcoded nucleic acid molecule comprising the target-binding region and the complement of the target-binding region. A stem loop is formed with intra-molecular hybridization of the barcoded nucleic acid molecule, which can be extended to generate an extended barcoded nucleic acid molecule comprising the molecular label and a complement of the molecular label.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Self-folding amplification of target nucleic acid
ActiveUS20130040344A1Eliminate needReduce signalingMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideSingle strand
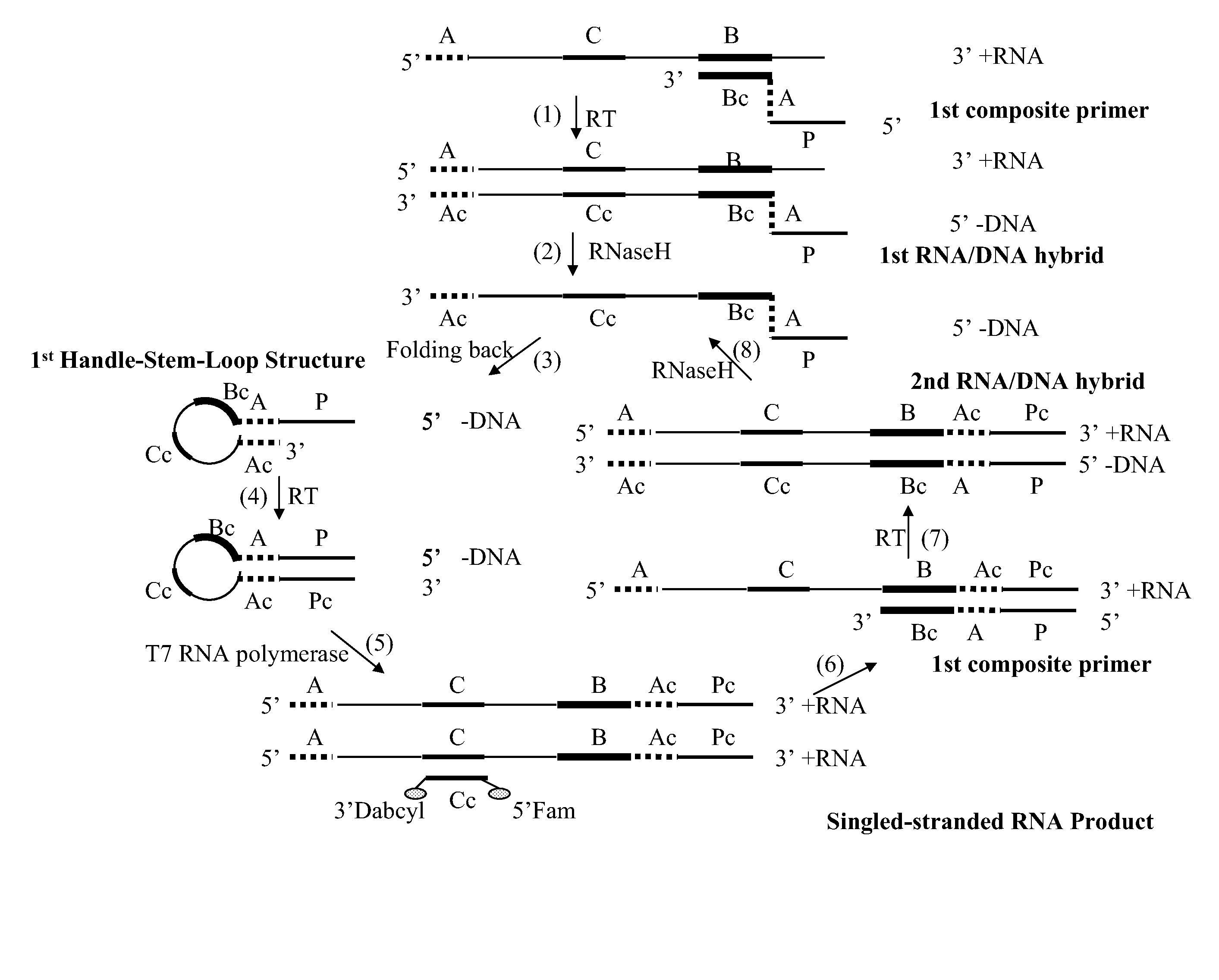
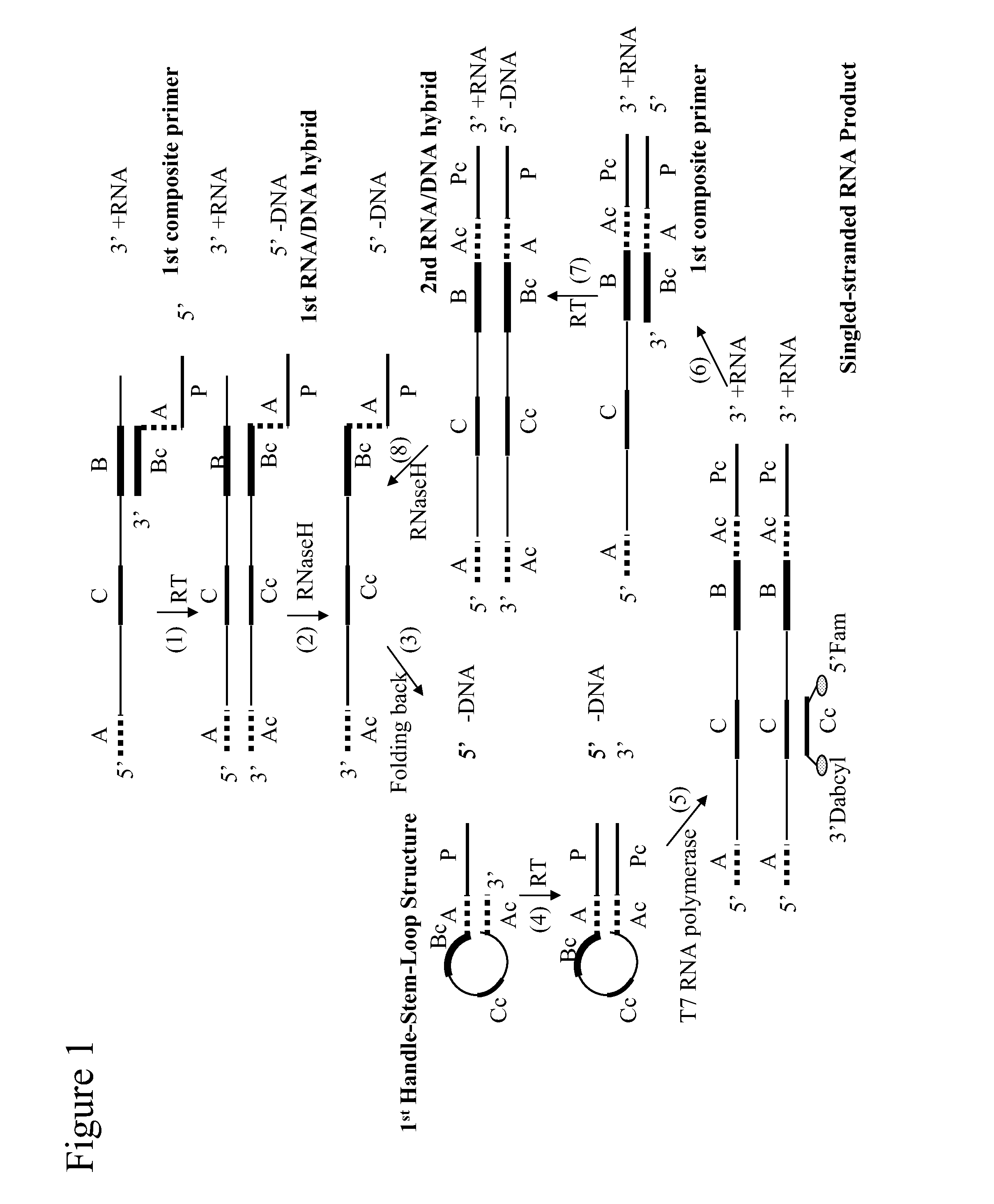
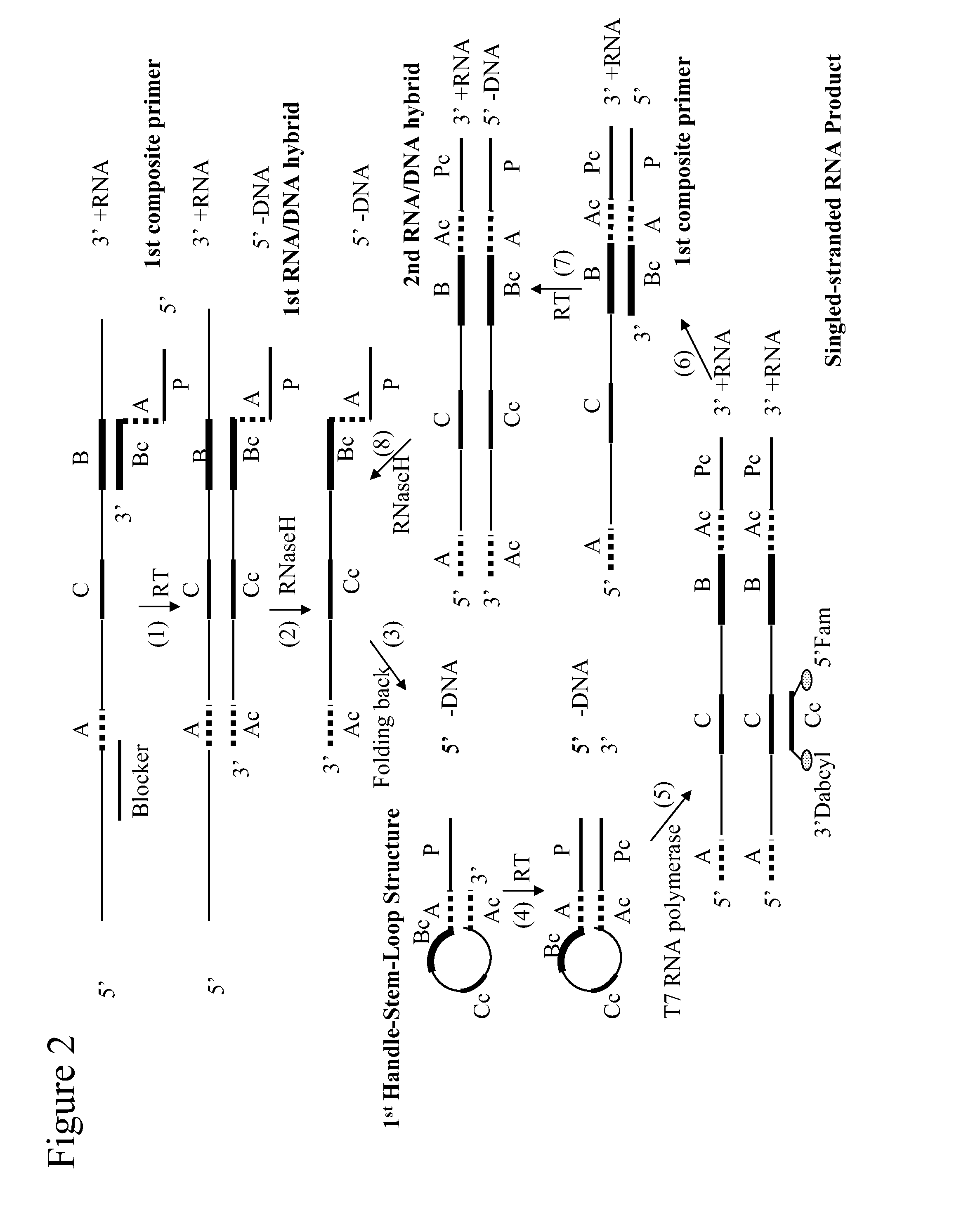
The application relates generally to methods useful for the selective amplification of one or more target nucleic acid or fragments thereof, as well as compositions and kits comprising said amplification reaction mixtures. More specifically, the application relates to a composite primer that comprises a 5′ promoter portion and a 3′ target-recognition portion which is complementary to the 3′ end portion of a target polynucleotide sequence; and optionally, a means for identifying the 5′ end portion of the target polynucleotide sequence. The amplification reaction mixture comprises at least one handle-stem-loop structure which comprises a 5′ single-stranded handle comprising the promoter portion and a double-stranded stem comprising at least one pair of self-folding segments hybridized to each other, and optionally, a single-stranded loop comprising the sequence between the pair of self-folding segments.
Owner:RENDU USA INC
Singly labeled oligonucleotide fluorescent probe and method for detecting nuclease
ActiveCN102154489ASimple and fast operationDesign and synthesis cost reductionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceSide chain
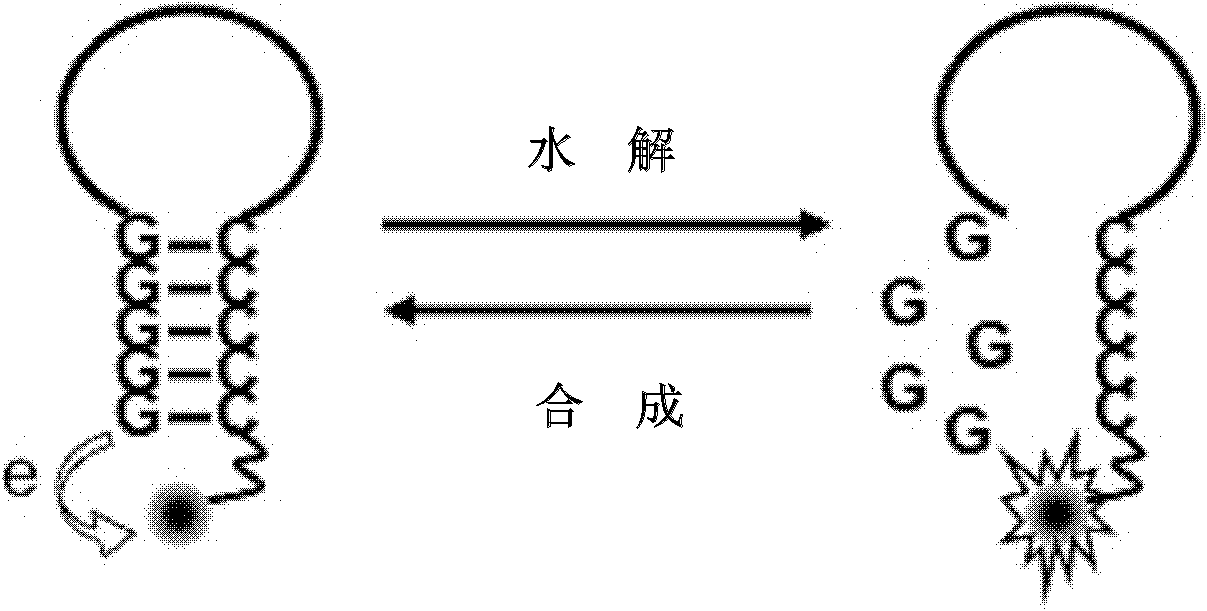
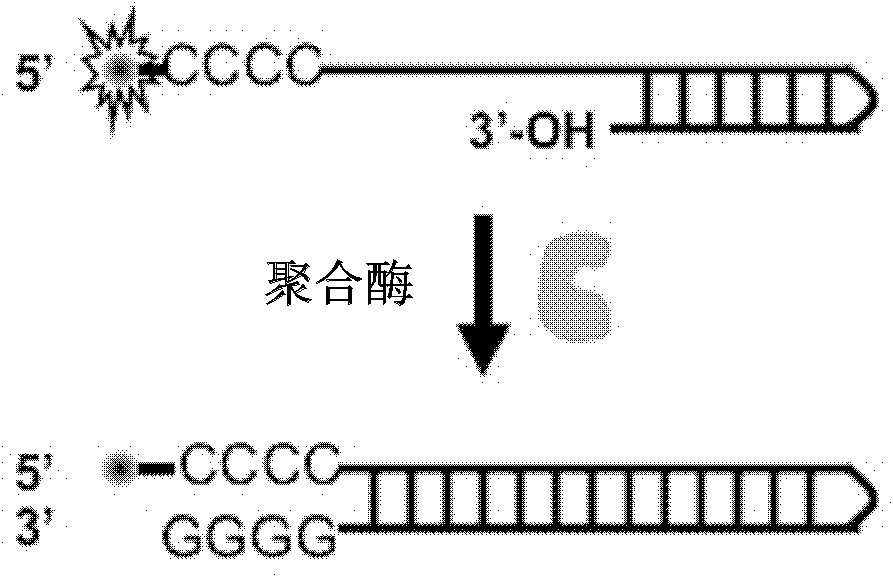
The invention discloses a singly labeled oligonucleotide fluorescent probe and a method for detecting nuclease. The singly labeled oligonucleotide fluorescent probe has a stem loop structure, wherein a loop part consists of 5-24 nucleotide residues; a stem part is in a hydrolysis mode or a synthesis mode according to the activity of nuclease to be detected; in the hydrolysis mode, the stem part has a double-chain structure, the tail end is provided with at least three continuous G-C base pairs, the C base ends are labeled with fluorescence groups, the G base ends have quenching effects, one chain of the stem part is hydrolyzed under the action of the nuclease to release a fluorescence signal; and in the synthesis mode, the stem part consists of a section of double chains and a 5'-(dC)4-8side chain, the 5'- end is labeled with a fluorescence group, the 3'- end reacts with the nuclease, 4-8 continuous guanine deoxyribonucleotides are produced by polymerization extension, the fluorescence group at the 5'- end is quenched, and the activity of the nuclease to be detected is analyzed according to the change condition of the fluorescence signal.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Nucleic acids for down-regulation of gene expression
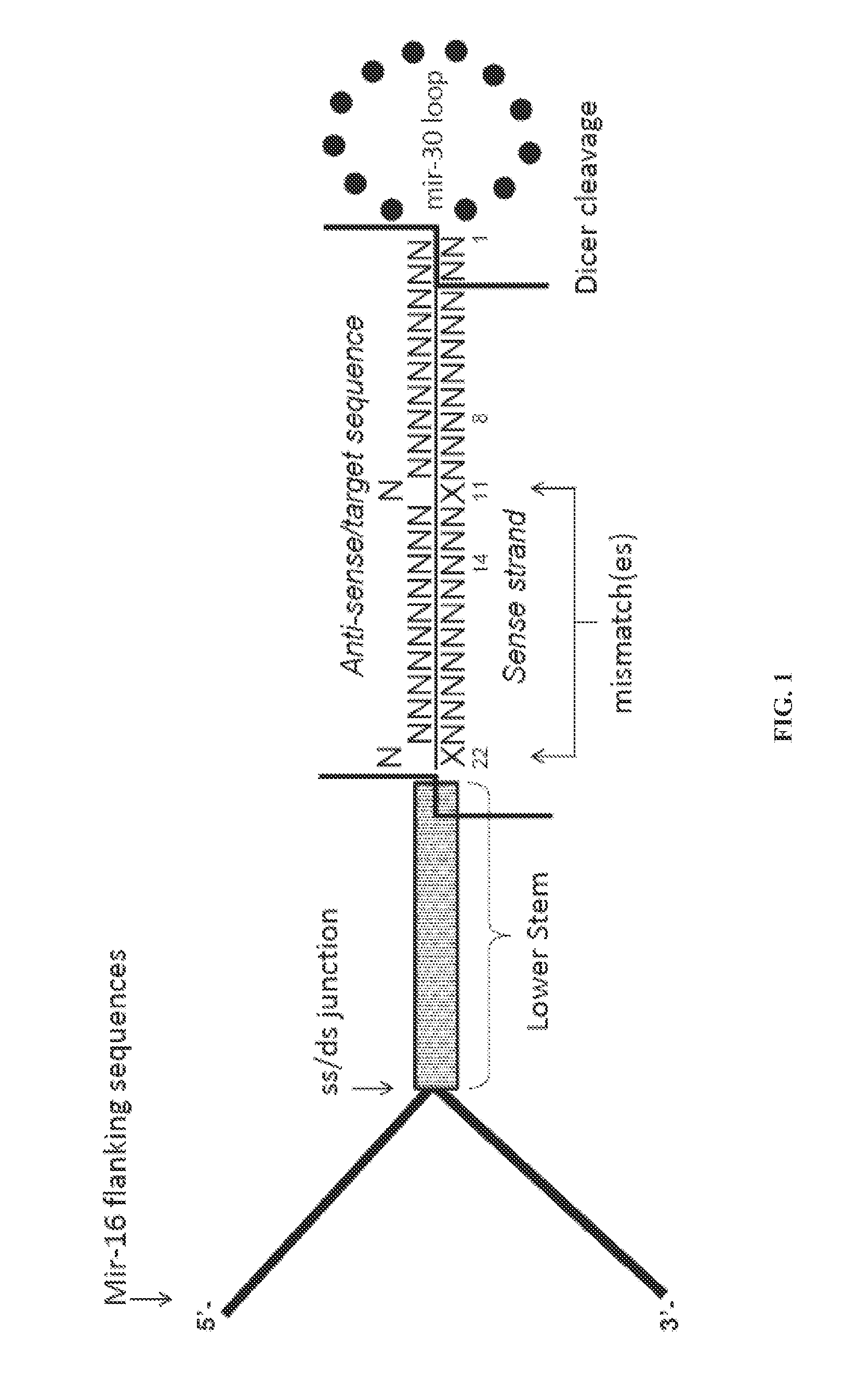
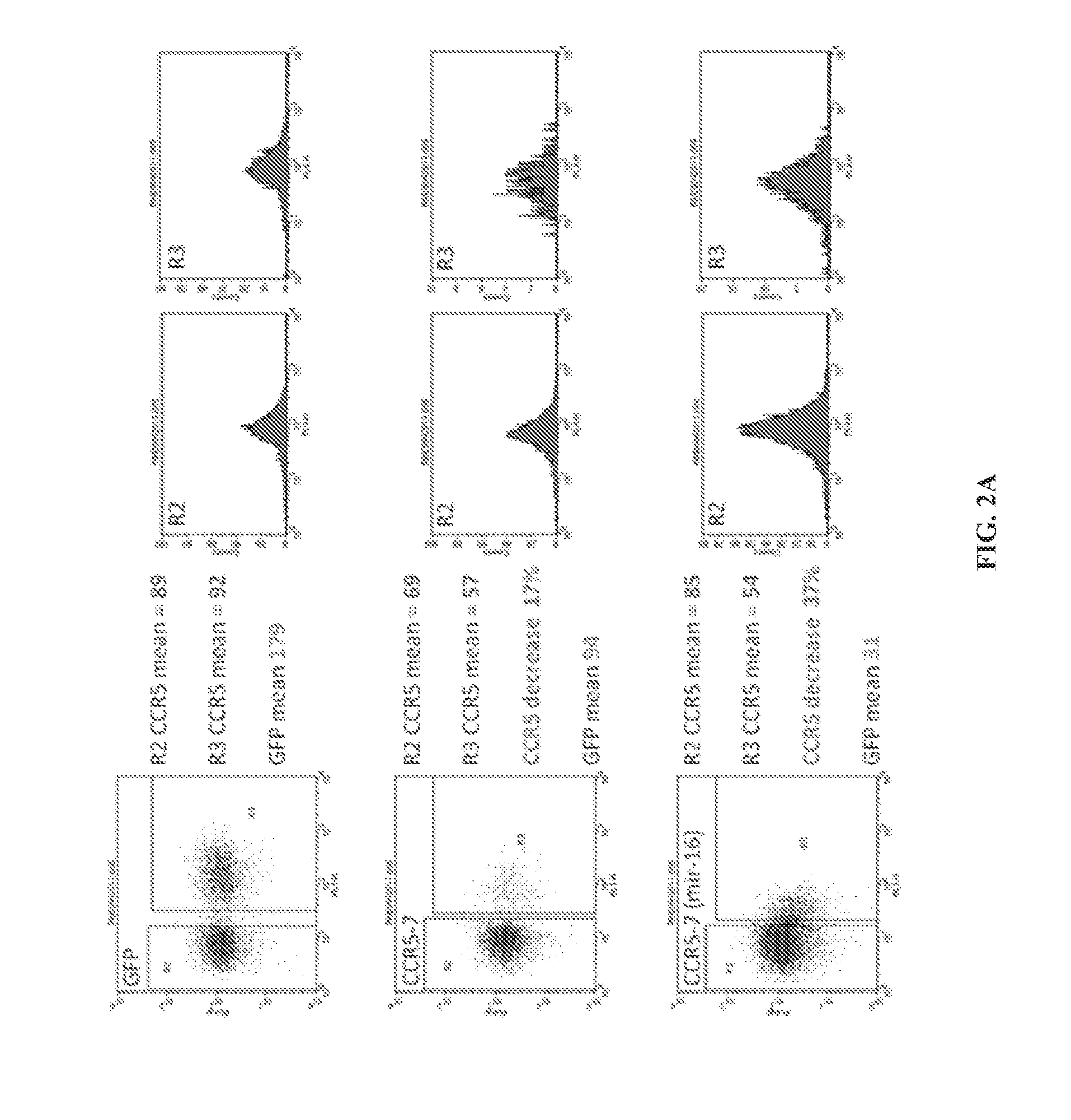
Recombinant nucleic acid molecules are provided that form hair pin structures and can be used to down-regulate gene expression. For example, a nucleic acid molecule can comprise a flanking and lower stem loop sequence from a mir-16 gene; an antisense target sequence; a mir-30 loop sequence; a complement of the anti-sense target sequence; and a lower stem loop complementary to the mir-16 sequence. Methods for down regulating gene expression in a cell using such recombinant nucleic acid molecules are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GENEVA +1
Dual resonance energy transfer nucleic acid probes
InactiveUS20060127940A1Rapid and specific and sensitive hybridization detectionEasy to useSugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDiseaseCell specific
Dual nucleic acid probes with resonance energy transfer moieties are provided. In particular, fluorescent or luminescent resonance energy transfer moieties are provided on hairpin stem-loop molecular beacon probes that hybridize sufficiently near each other on a subject nucleic acid, e.g. mRNA, to generate an observable interaction. The invention also provides lanthanide chelate luminescent resonance energy transfer moieties on linear and stem-loop probes that hybridize sufficiently near each other on a subject nucleic acid to generate an observable interaction. The invention thereby provides detectable signals for rapid, specific and sensitive hybridization determination in vivo. The probes are used in methods of detection of nucleic acid target hybridization for the identification and quantification of tissue and cell-specific gene expression levels, including response to external stimuli, such as drug candidates, and genetic variations associated with disease, such as cancer.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Probe for detecting nucleic acid in living cells and application method thereof
InactiveCN102220431AEasy to detectReal-time detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementSpatial OrientationsDisease
The invention relates to the field of nanotechnology and biotechnology, in particular to a probe for detecting nucleic acid in living cells and an application method thereof. The probe is characterized in that the probe comprises three parts, namely hair clip-shaped oligonucleotide, a fluorescent labeling matter and nano-gold, wherein the hair clip-shaped oligonucleotide contains a base sequence being complimentary with target nucleic acid and has a stem-loop structure, the fluorescent labeling matter is arranged at one end of the hair clip-shaped oligonucleotide in a covalence way, and nano-gold particles are in coordination connection with hydrosulphonyl modified at the other end of the hair clip-shaped oligonucleotide. By adopting the method, the target nucleic acid in living cell samples can be simply detected in real-time, and spatial orientation can be performed on the target nucleic acid for realizing real-time in-situ detection; furthermore, transfection and a transmembrane reagent or technology are not required, thereby having important significance and extensive application prospect in the aspects of developing disease nosogenesis, tumor early diagnosis and treatment and medicament target points.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Modified stem-loop oligonucleotide mediated reverse transcription and base-spacing constrained quantitative PCR
ActiveUS20130177915A1Strong specificityRetain specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDna polymerasenGenetics
There is provided a method for detecting a target RNA molecule in a sample. The method comprises reverse transcribing the target RNA contained in the sample using an RT oligonucleotide, the RT oligonucleotide comprising a stem-loop portion containing one or more nucleotides modified or modifiable to block DNA polymerase extension and a target annealing portion that is complementary to a downstream portion of the target RNA, the target annealing portion located 3′ to the stem-loop portion, to produce a reverse transcription product that comprises the RT oligonucleotide and a 3′ extended region; amplifying the reverse transcription product using (i) a first amplification primer that anneals to a downstream portion of the 3′ extended region of the reverse transcription product and (ii) a second amplification primer that anneals to an interface portion of a DNA strand complementary to the reverse transcription product, the interface portion comprising a region that is complementary to a 3′ portion of the RT oligonucleotide and a 5′ portion of the 3′ extended region in the reverse transcription product, to produce an amplification product; and detecting the amplification product; wherein the stem-loop portion adopts a stem-loop structure under conditions used for said reverse transcribing but does not adopt the stem-loop structure under conditions used for said amplifying and wherein when the stem-loop portion contains one or more nucleotides that are modifiable to block DNA polymerase extension, the method further comprises modifying the modifiable nucleotide prior to said amplifying.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
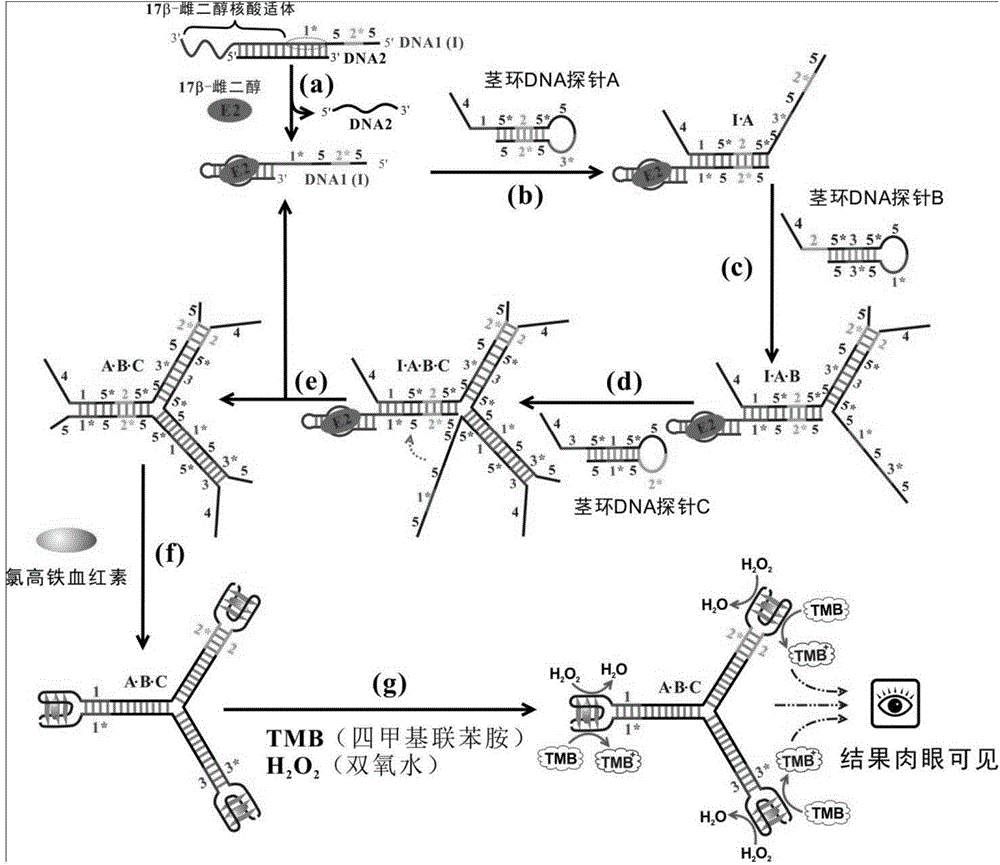
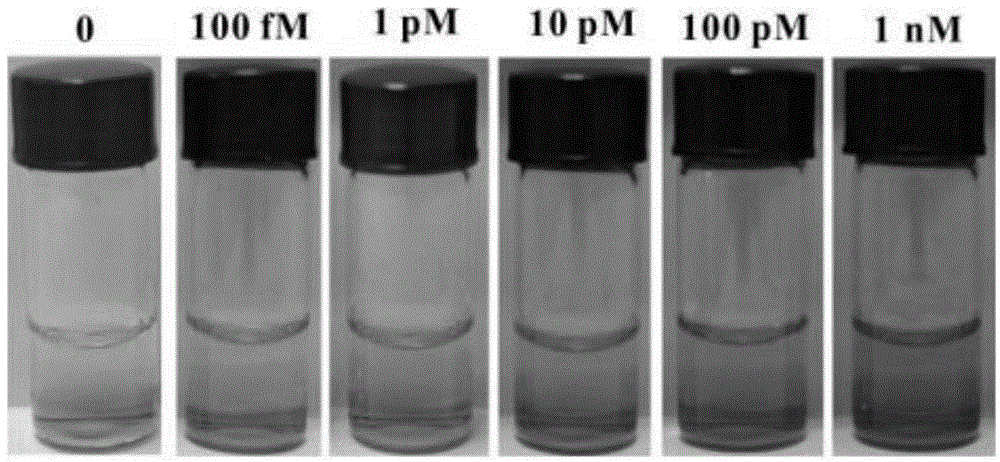
17beta-estradiol visualization detection method based on DNA nano-structure, and 17beta-estradiol visualization detection kit based on DNA nano-structure
ActiveCN104975079AHigh sensitivityQuick analysisMicrobiological testing/measurement17beta estradiolNano structuring
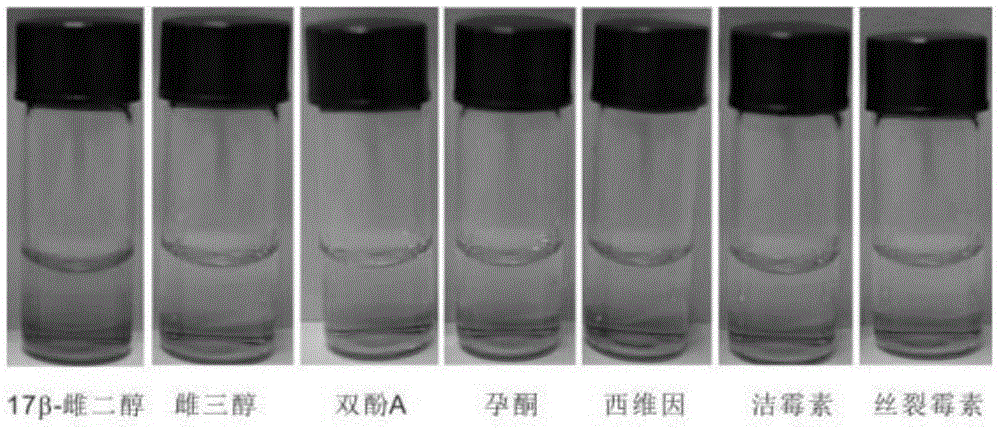
The present invention discloses a 17beta-estradiol visualization detection method based on DNA nano-structure, and a 17beta-estradiol visualization detection kit based on DNA nano-structure. The working principle is that 17b-estradiol interacts with aptamer, a strand displacement reaction is started, three groups of stem-loop DNA probes are constantly opened to form DNA nano-structures, a G tetramer having catalysis activity is formed on the terminals of the three DNA arms in the DNA nano-structures, the G tetramer is bound with hemin so as to form a compound having catalysis activity and similar to HRP, TMB is subjected to catalytic oxidation, and a blue substrate is produced, wherein the result is visible, and the concentration of 17b-estradiol is directly related to the blue shade. According to the present invention, the operation is simple, the whole reaction can be completed at the room temperature, the high sensitivity is provided, the detection limit on 17b-estradiol is 100 fM, the good specificity is provided, the detection result is directly visible without any detection equipment, and the method and the kit can be used for the on-site rapid detection of 17b-estradiol.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
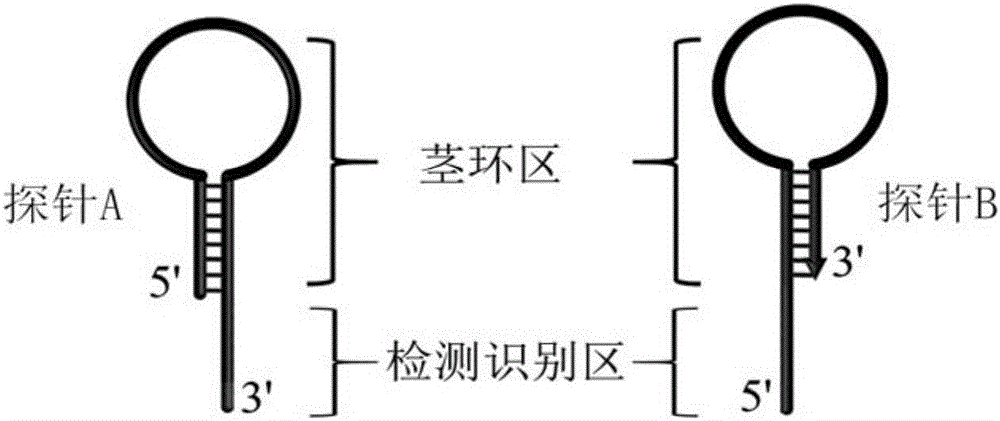
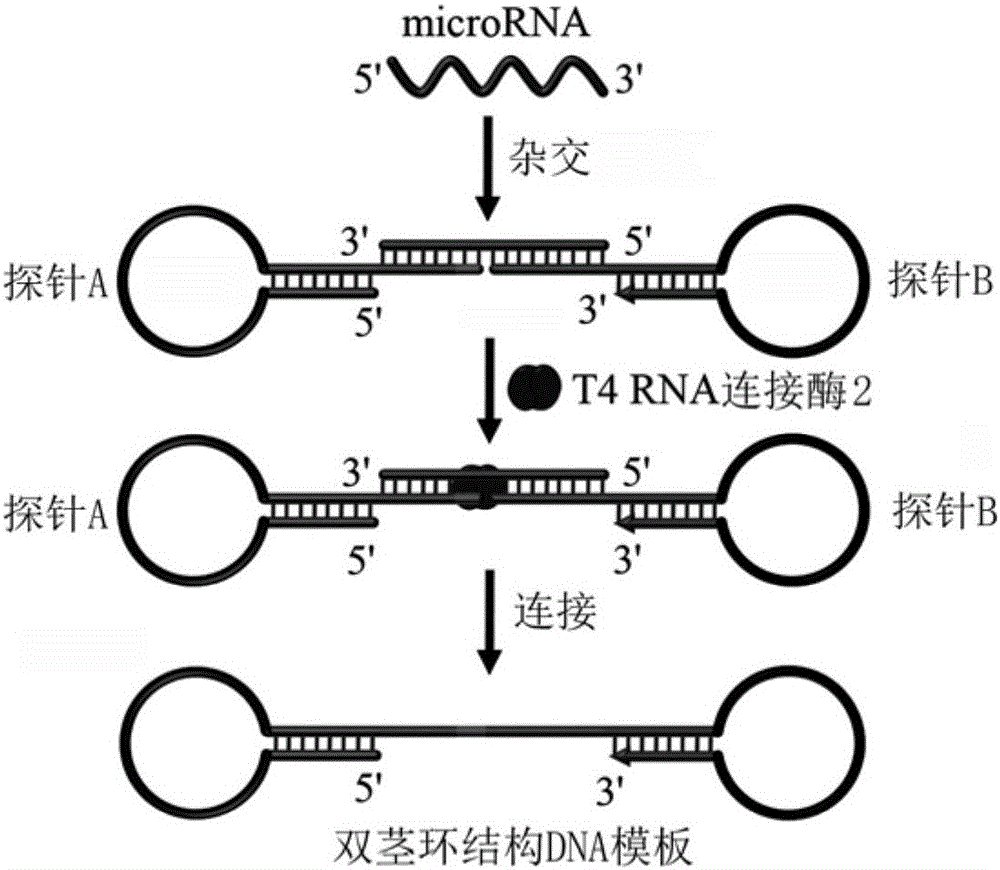
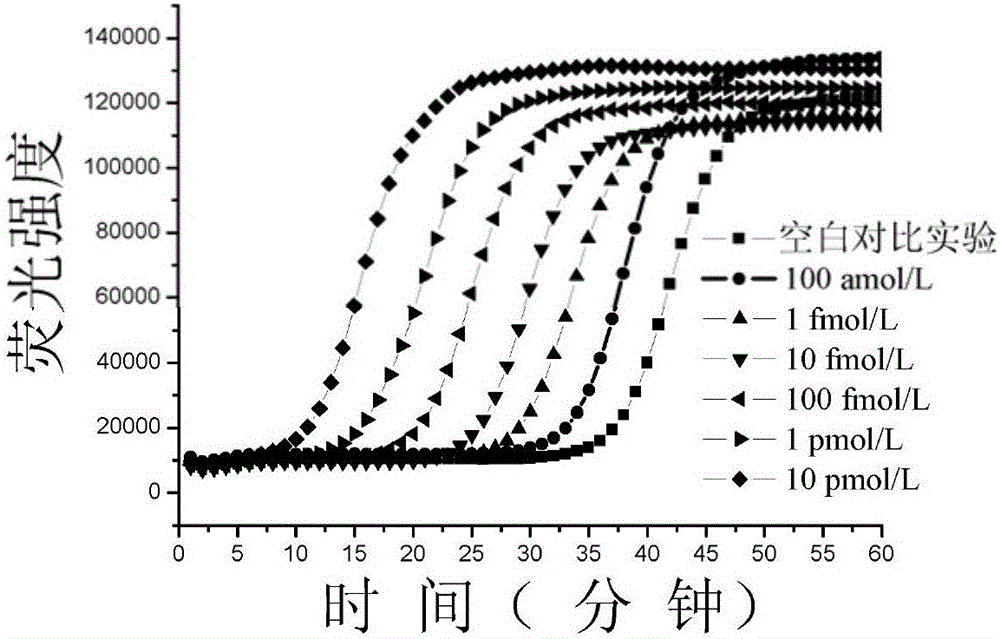
Method for constructing double-stem-loop structure DNA template to detect nucleic acid based on ligation reaction
InactiveCN105821138AAvoid Radiation HazardsLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for constructing a double stem loop structure DNA template to detect nucleic acid based on a ligation reaction. The method includes the steps that ligase is used for connecting a probe containing a stem-loop structure and complemented with nucleic acid to be detected to form a double-stem-loop structure DNA template, the template can guide fast and efficient loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction to achieve high-sensitivity nucleic acid detection, and meanwhile the method can specifically distinguish nucleic acid with single-base difference. It is provided for the first time that double stem loop structure DNA is constructed through the high-specificity ligation reaction, the specificity template is provided for the loop-mediated isothermal amplification reaction in the next step, fluorescence labeling is not needed in the method, cost is low, the precise heat cycle process in the PCR process is avoided, and fast amplification of the nucleic acid to be detected can be realized at constant temperature. The method can be used for quantitative analysis, methylation detection, SNP detection and the like on RNA or DNA and provides a new strategy for high-sensitivity nucleic acid analysis, early cancer diagnosis and other researches.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Sense Antiviral Compound and Method for Treating Ssrna Viral Infection
InactiveUS20080311556A1Disruption of secondary structureInhibition of replicationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSsRNA virusesViral infection
The invention provides sense antiviral compounds and methods of their use in inhibition of growth of viruses of the Flaviviridae, Picornoviridae, Caliciviridae, Togaviridae, Coronaviridae families and hepatitis E virus in the treatment of a viral infection. The sense antiviral compounds are substantially uncharged morpholino oligonucleotides having a sequence of (12-40) subunits, including at least (12) subunits having a targeting sequence that is complementary to a region associated with stem-loop secondary structure within the 3′-terminal end (40) bases of the negative-sense RNA strand of the virus.
Owner:AVI BIOPHARMA
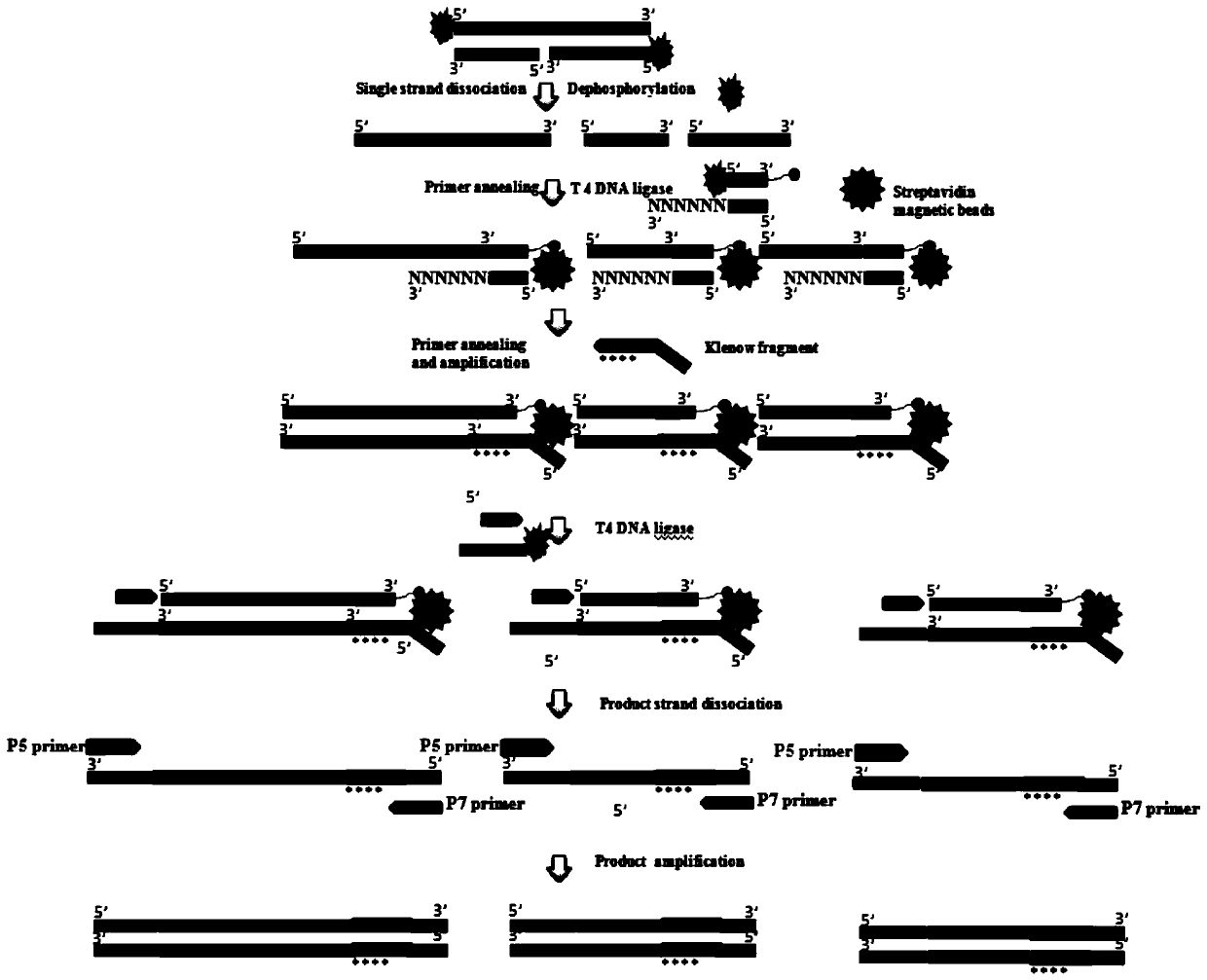
Single-chain molecular identifier adapter and single-chain DNA database creating method and application thereof to circulating tumor DNA detection
InactiveCN109797197AReduce dosageHigh-resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary linkersDNA databaseSingle strand dna
The invention discloses a single-chain molecular identifier adapter and a single-chain DNA database creating method and application thereof to circulating tumor DNA detection. The single-chain molecular identifier adapter comprises a stem structure formed by 14 base pairing, a sequencing primer sequence and a molecular identifier sequence formed by 8 random nucleotides, wherein a base 'U' is inserted between the sequencing primer sequence and a stem structure sequence, and a stem-loop structure can be formed by annealing denaturation of the single-chain nucleotide sequence. By single-chain DNAdatabase creating, technical problems of low sensitivity, fragmentation, low concentration and short ctDNA fragments in liquid biopsy in application of an existing detection technique are solved. Accurately distinguishing whether sequencing reads identical in genome coordinate beginning and end loci come from cfDNA released by the same one or multiple germinal cell is realized, sequencing reads derived from original positive and negative chains of the same cell are paired for analysis, and accordingly sequencing rehandling is reduced, and the distinguishing rate of false positive mutation isincreased.
Owner:HANGZHOU NEOANTIGEN THERAPEUTICS CO LTD
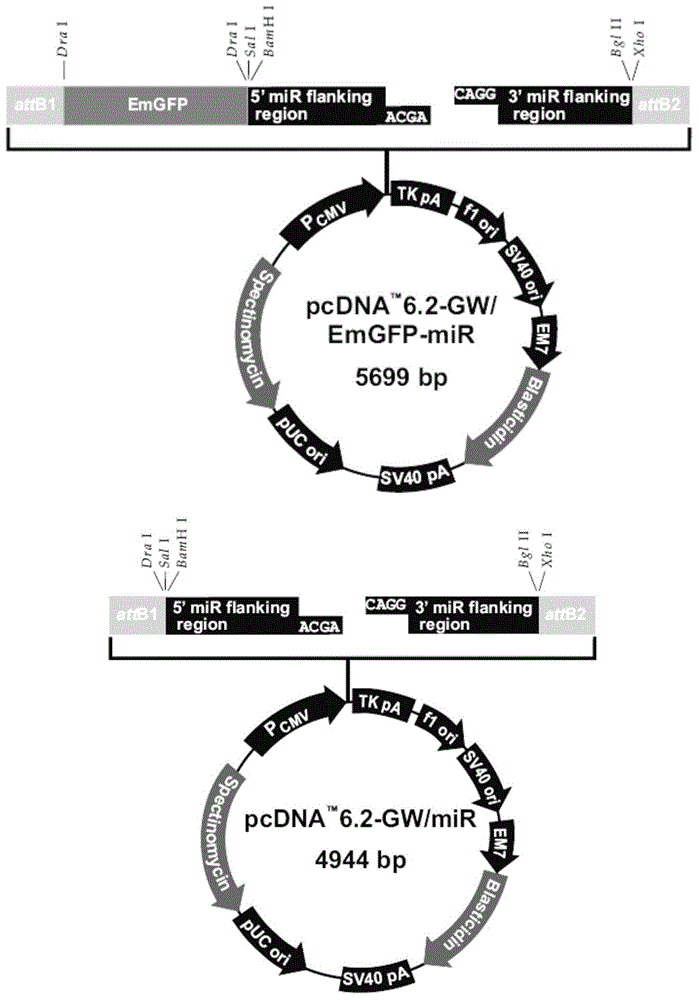
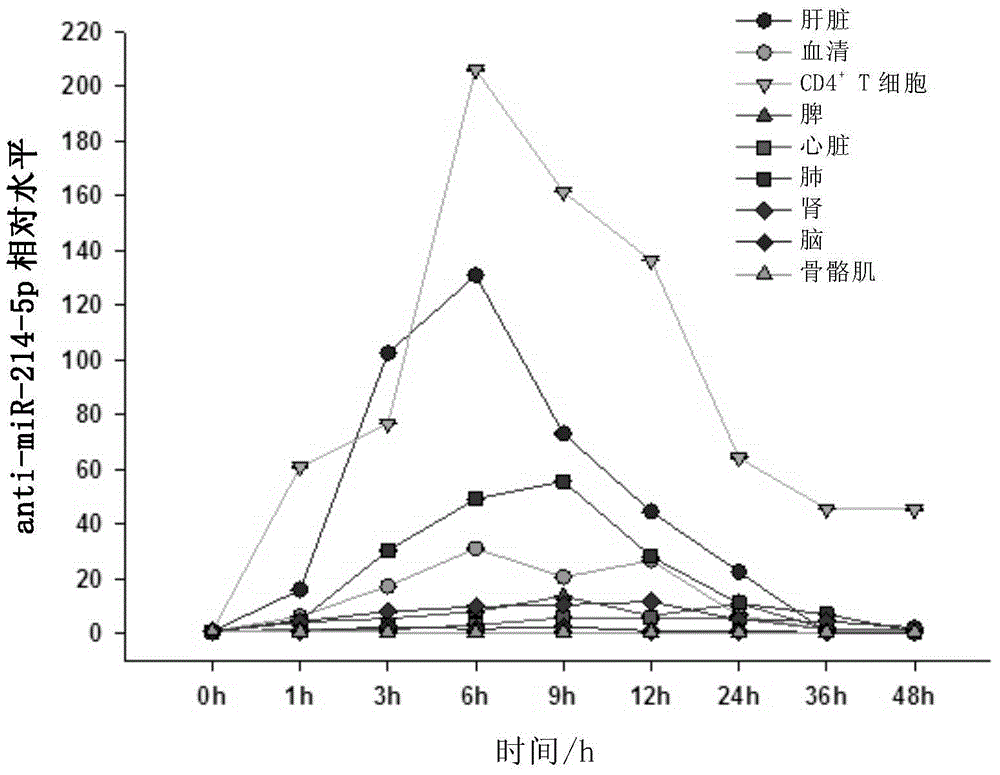
New precursor miRNA and applications of new precursor miRNA in tumor treatment
ActiveCN106177990AAvoid interferenceEffective therapeutic effectOrganic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryRNA SequenceWilms' tumor
The present invention discloses a new precursor miRNA and applications of the new precursor miRNA in tumor treatment. Specifically the present invention provides a precursor miRNA, wherein the structure represented by a formula I exists at the 5' to 3' terminal, B1 is anti-miRNA-214-5p, B2 is a sequence substantially complementary or completely complementary to B1, B2 and C are not complementary, C is a stem-loop structural sequence, A1 and A2 respectively are none, optionally RNA sequences comprising 4-5 bases, the precursor miRNA can be processed in a host to form anti-miRNA-214, and in the anti-miRNA-214, only the anti-miRNA-214-5p is expressed while the anti-miRNA-214-3p is not expressed. The formula I is defined in the specification.
Owner:JIANGSU MICROMEDMARK BIOTECH
Isothermal amplification in nucleic acid analysis
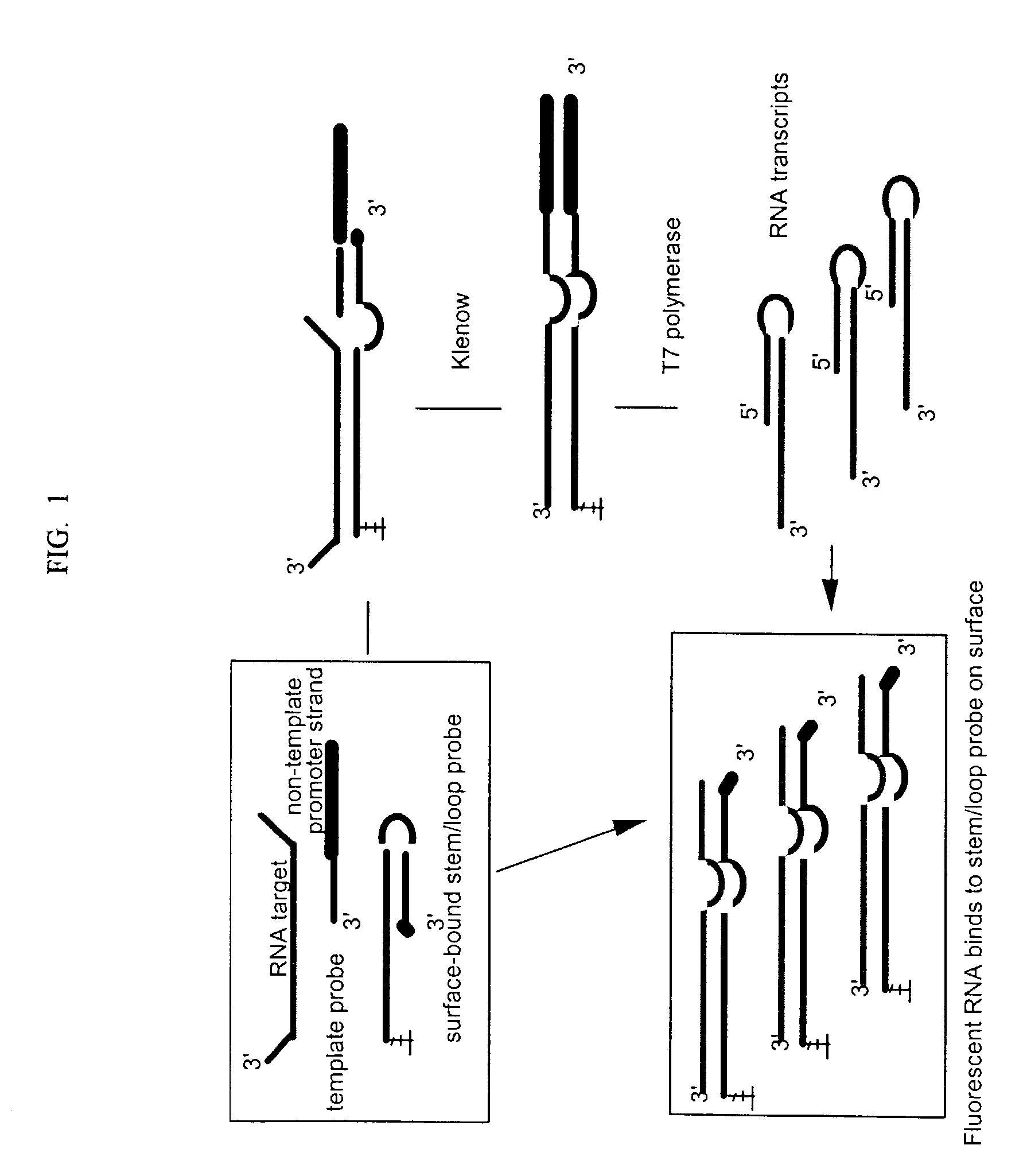
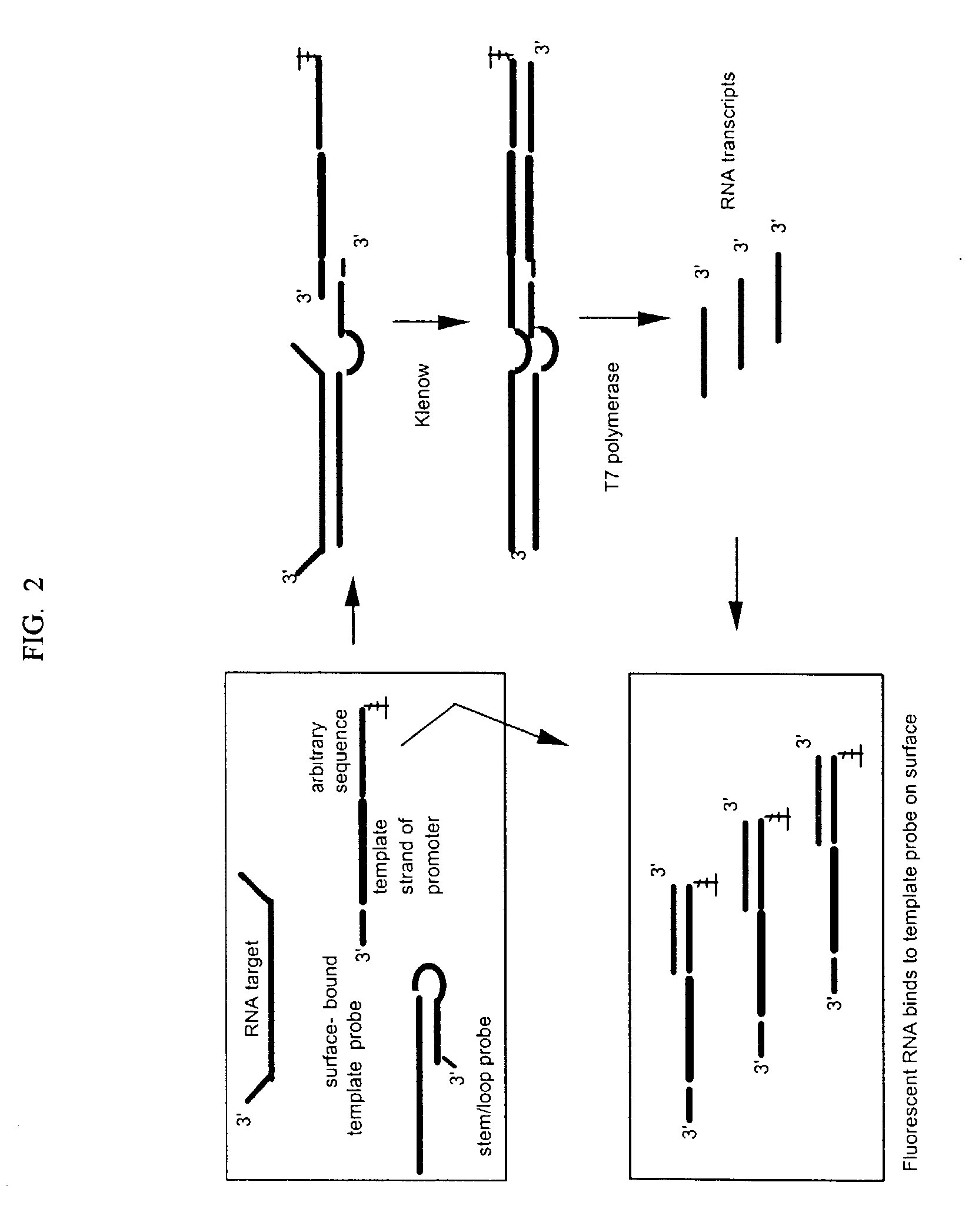
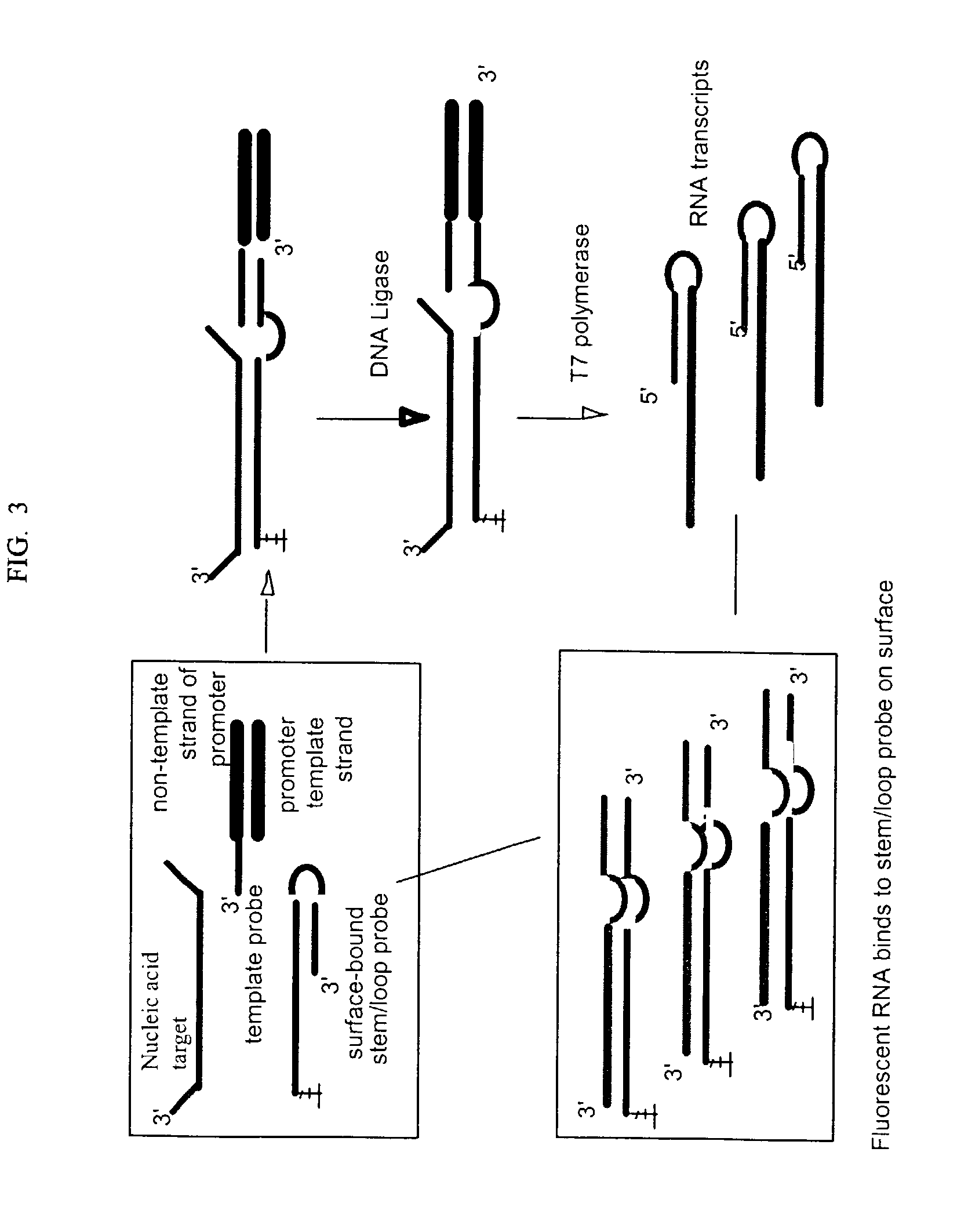
A method for detection of nucleic acid targets using as reagents: (1) a stem loop probe having a long strand for hybridizing to a target, a short strand, usually with a free 3'-end for extension, hybridized to a portion of the long strand and a linker forming a loop and joining the short and long strands; and (2) a hybridizing reagent that hybridizes to the short strand when released by the target. The target is detected by extension of one or both the probe or hybridizing reagent along each other. A circular hybridizing reagent can be employed with DNA polymerase for concatenated extension of the probe 3'-end or extension of the 3'-end of the probe along a hybridizing reagent having a promoter sequence for forming transcripts of at least a portion of the long strand or the hybridizing reagent. A non-cleavable restriction site consensus sequence in the linker, where the hybridizing reagent is extended with dNTPs and DNA polymerase and the extended sequence is cleaved with a restriction enzyme, so that chains may be repetitively produced and cleaved. The presence of the target nucleic acid is established by detecting the concatenated chain, the RNA transcripts or the repetitively produced chains.
Owner:DISCOVEX
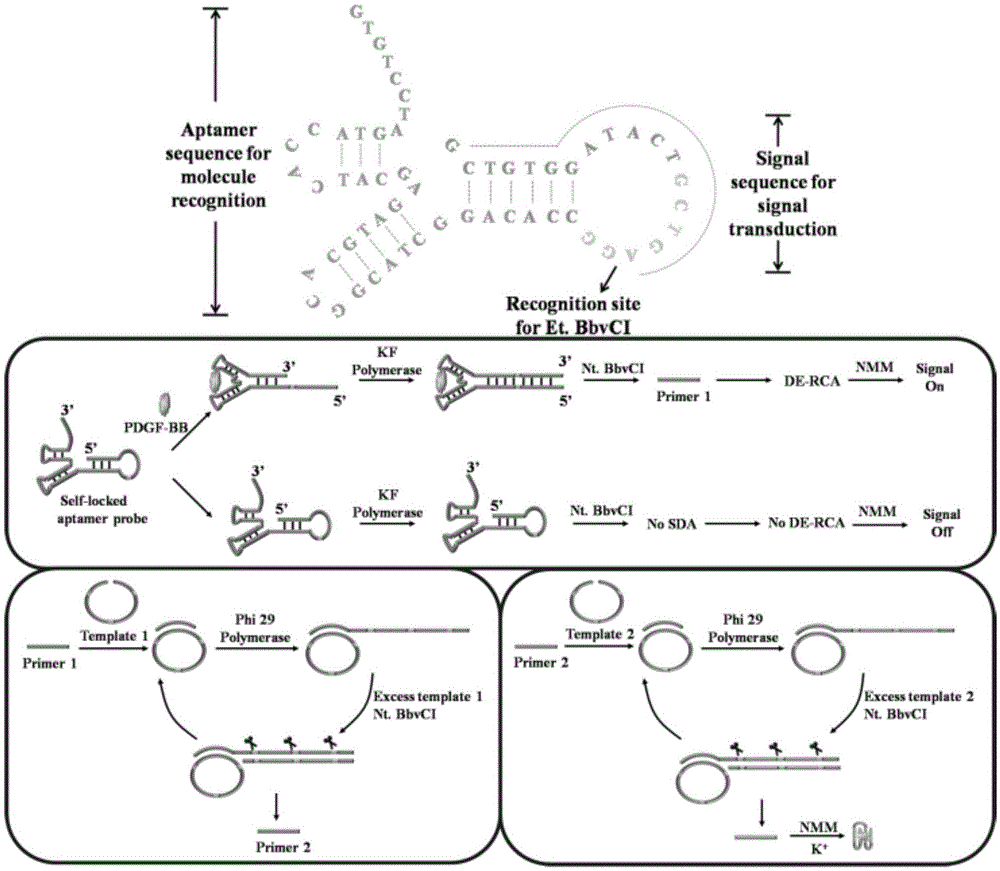
Cascade amplifying-strategy biomolecule detecting method based on self-locking aptamer probe
ActiveCN105624165AImprove versatilityGreat application potentialMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingSpecific detectionAdenosine
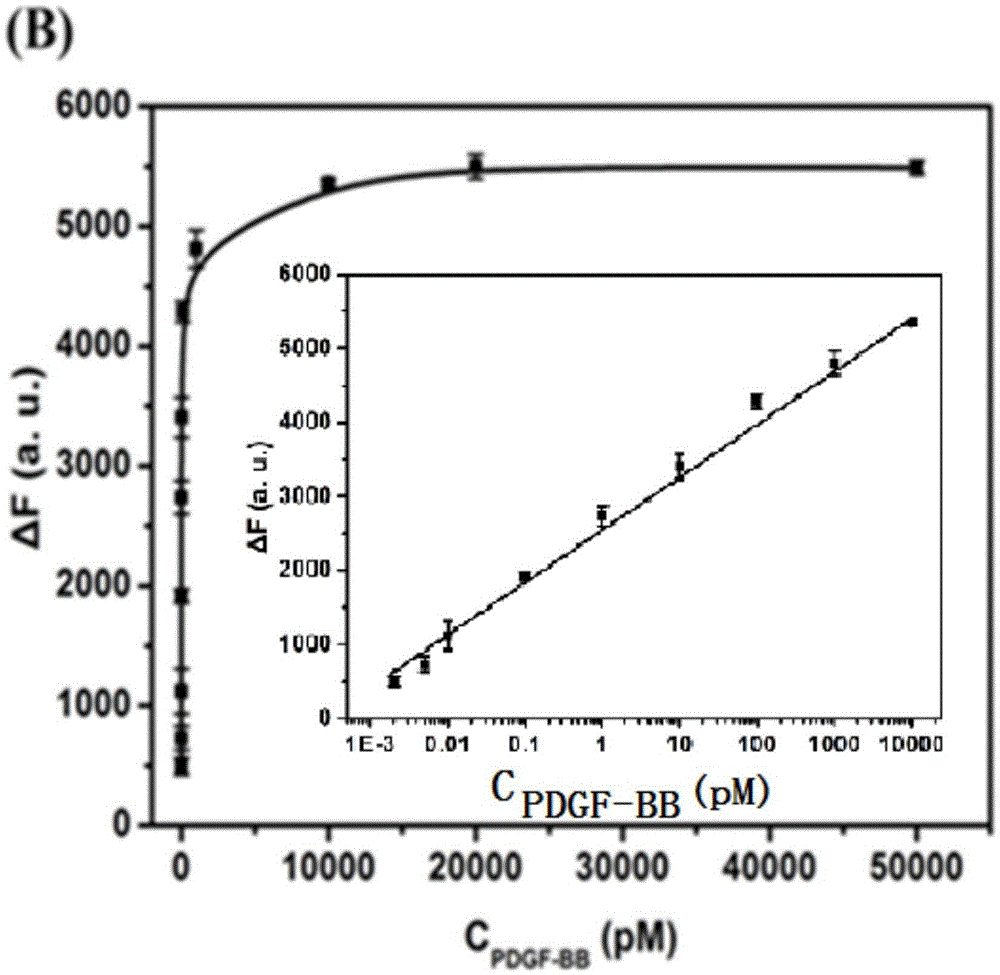
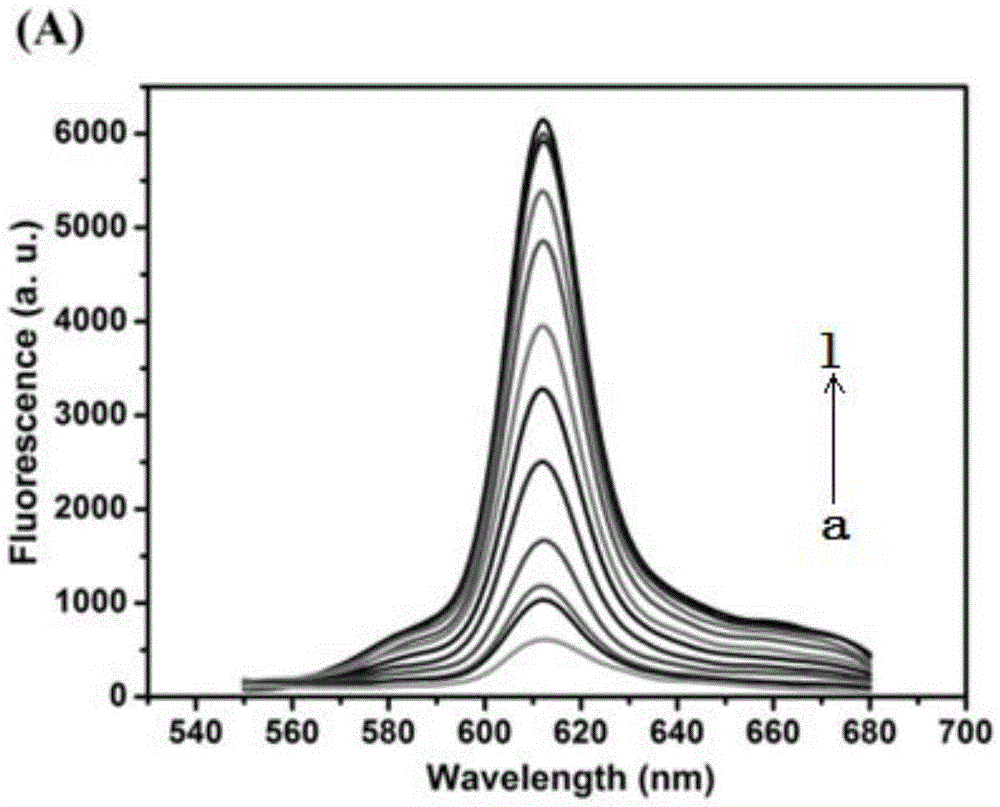
The invention discloses a cascade amplifying-strategy biomolecule detecting method based on a self-locking aptamer probe. The probe at least comprises two parts of an aptamer sequence of a 3(minute) terminal having specific recognition on a target and a signal transduction sequence of a 5(minute) terminal, wherein the signal transduction sequence of the 5(minute) terminal is hybridized with a part of the aptamer sequence to form a stem-loop structure of the 5(minute) terminal, and the signal transduction sequence of the 5(minute) terminal comprises a recognition site of Cech endonuclease. The probe combines strand displacement amplification (SDA) with a double-exponential rolling circle amplification (DE-RCA) strategy to achieve ultra-sensitive and high-specific detection on protein-PDGF-BB and micromolecule-adenosine, wherein the detection limit reaches 3.8*10<-16>mol / L and 4.8*10<-8>mol / L respectively.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
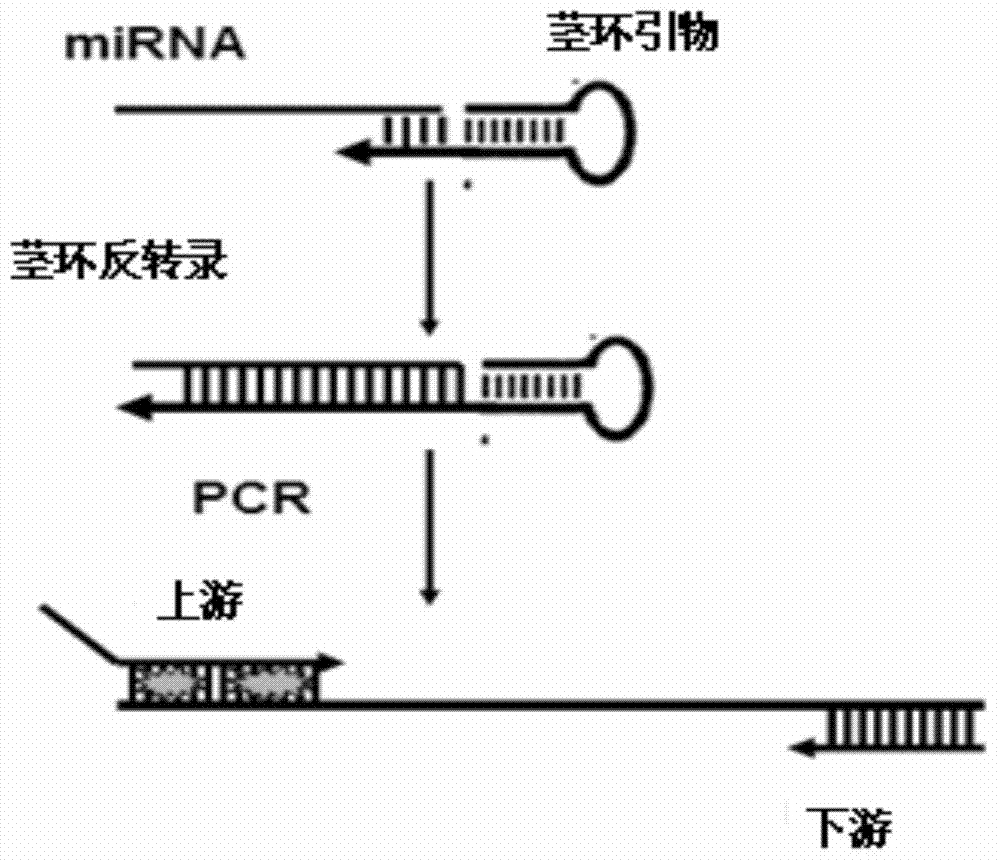
Method for detecting miRNA (micro Ribose Nucleic Acid) by improved stem-lop primer qRT-PCR (Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction)
InactiveCN103866009ALow technical costStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceComplementary pair
The invention relates to a method for detecting miRNA (micro Ribose Nucleic Acid) by an improved stem-lop primer qRT-PCR (Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction). The method comprises the steps: (1), designing a miRNA detection primer, wherein a stem-loop primer comprises two parts of a general stem loop sequence and a specific primer sequence which is in complementary pairing with a 3' end of a target miRNA, a base number which is in complementary pairing with the target miRNA is 11bp, a downstream primer needle of qPCR is specific to a general stem loop sequence, an upstream primer needle is specific to a 5' end of the target miRNA, a GC tail is added in the 5' end of the upstream primer so that the annealing temperatures of the upstream primer and the downstream primer are close; (2), performing inverse transcription on the target miRNA into cDNA (complementary Desoxvribose Nucleic Acid); and (3), performing a quantitative PCR amplification and detecting by adopting an SYBR Green qPCR detection method. The method disclosed by the invention is good in specificity, and high in sensitivity; and one downstream primer is only synthesized, and an SYBR Green I fluorochrome method is adopted, and thus the cost is greatly saved.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Application of serum ssc-miR-215 as molecular marker on detecting stress injury of intestinal tract of pigling
ActiveCN104975093AStress injury did not occurMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerAnti stress
The invention belongs to the field of biology, and relates to an application of serum ssc-miR-215 as a molecular marker on detecting stress injury of the intestinal tract of a pigling. A nucleotide sequence of serum ssc-miR-215 is represented as SEQ ID NO.1. A nucleotide sequence of a stem-loop primer required by reverse transcription of ssc-miR-215 is represented as SEQ ID NO.2. A nucleotide sequence of a forward primer required by augmentation of ssc-miR-215 is represented as SEQ ID NO.3. Diagnosis of stress injury of the intestinal tract of a weaned pigling is realized by adopting the above primers. A diagnostic method comprises extraction of serum total RNA, separation of small molecular RNA, synthesis of cDNA, and augmentation and authentication of PCR. The invention provides guidance for prevention, diagnosis and treatment of stress injury of the intestinal tract of a pigling, and provides a novel molecular marker for marker assisted selection of an anti-stress pig line.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Quantitative biomolecule detection method
InactiveCN102653789AGet rid of dependenceMild reaction conditionsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceNucleic Acid Probes
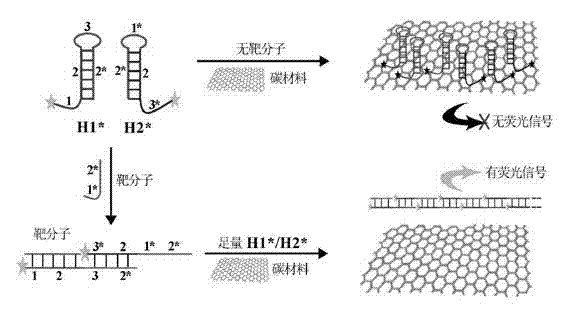
The invention discloses a quantitative biomolecule detection method comprising the following steps of: firstly, designing fluorescently-labeled H1* and H2* probes according to a target biomolecule sequence; secondly, heating solution with set concentration of fluorophore-labeled stem-loop-structure nucleic acid probes H1* and H2* on PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) instrument for 2 minutes at 95 DEG C, and then placing the solution away from light for 1 hour to 2 hours at a room temperature so as to allow a stem-loop structure to close fully; thirdly, preparing solution with set specification concentration from target biomolecules, respectively adding the biomolecule solution with different specification concentration and the H1* and H2* solution in a plurality of centrifuge tubes, and performing HCR (Hybridization Chain Reaction) on the biomolecule solution and the H1* and H2* solution which are mixed uniformly at the room temperature; after the HCR is finished, adding a proper amount of carbon materials in the mixed solution according to the concentration of the H1* and H2* in the second step, reacting the solution for 30 minutes at a room temperature, and detecting and recording fluorescent signals of the system; and finally, performing quantitative analysis on the target biomolecules by virtue of the fluorescent signals. According to the quantitative biomolecule detection method, the cost is low, the sensitivity is high, and the operation is simple.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
New micro ribonucleic acid quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method
ActiveCN101082060AIncrease the Tm valueAvoid formingMicrobiological testing/measurementReverse transcriptaseFluorescence
The new quantitative PCR detection process of micro RNAs (microRNAs) and small interference RNAs (siRNAs) includes: complementing the bases near the 5' end and the 3' end of retroprimer to form a stem-loop structure, combining the 3' end of retroprimer and target nucleic acid complementarily, and performing reverse transcription reaction with reverse transcriptase; amplifying cDNA obtained through the reverse transcription reaction with partial sequence of the retroprimer as one of the PCR primers; and real-time monitoring quantitative PCR with fluorescence labeled molecular beacon probe.
Owner:SUZHOU GENEPHARMA
microRNA biomarker and application thereof
InactiveCN102002494AEasy to get materialsNon-invasiveMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGeneticsMicroRNA
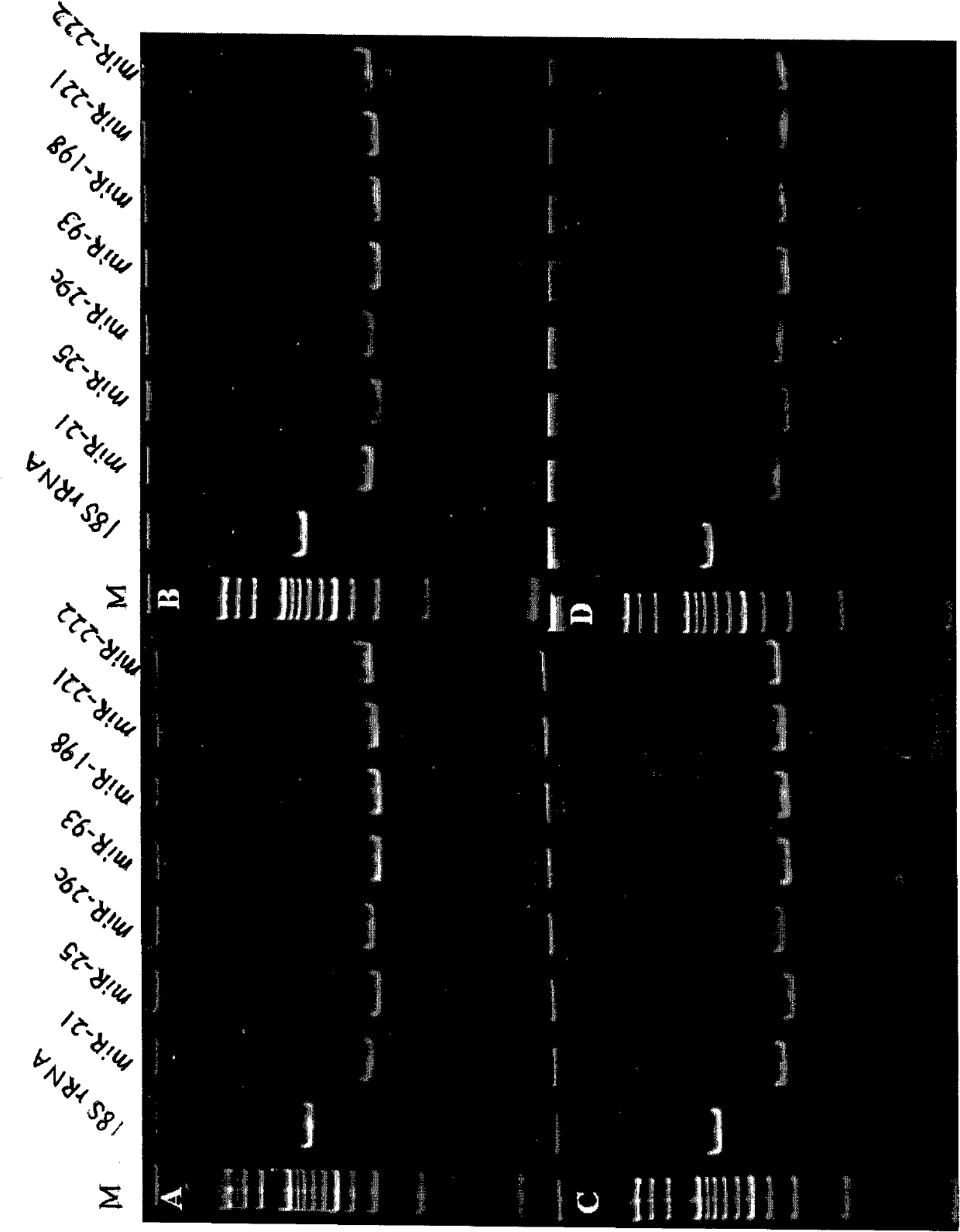
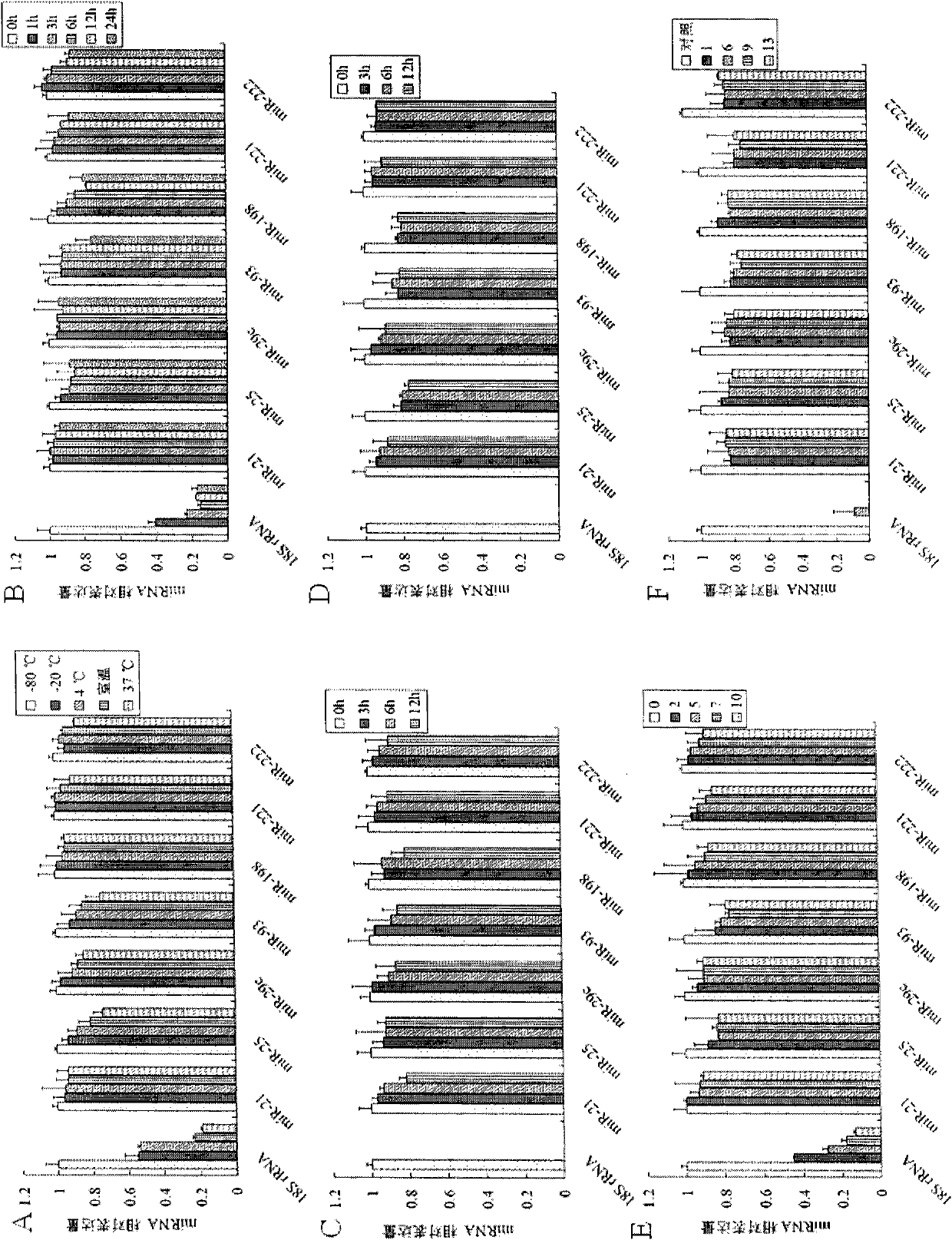
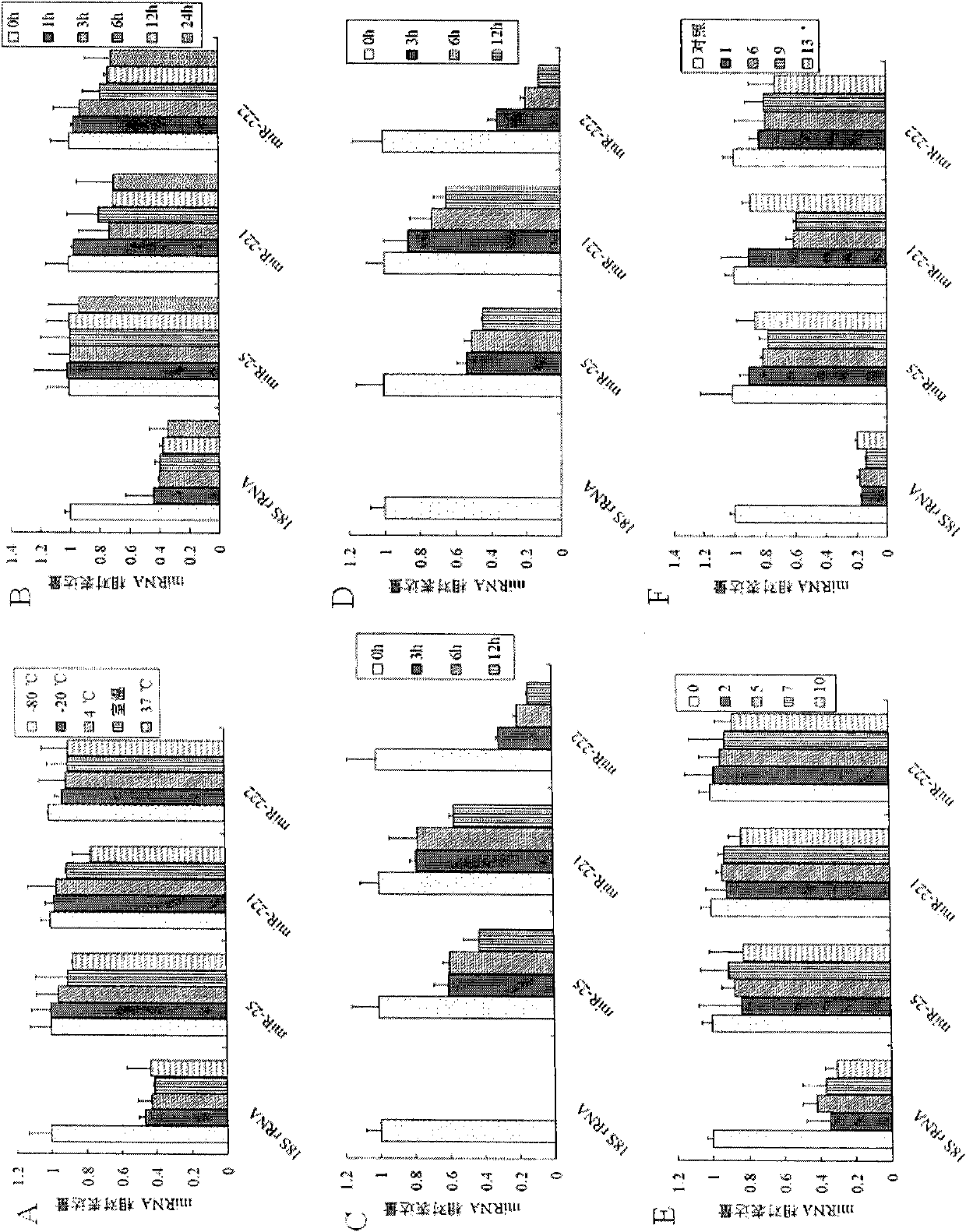
The invention discloses a microRNA biomarker. The microRNA biomarker is one of miR-21, miR-25, miR-29c, miR-93, miR-198, miR-221 and miR-222 the sequences of which are correspondingly shown in SEQ ID NO:1-SEQ ID NO:7. The invention also discloses an application of the microRNA biomarker in preparing a kit capable of detecting liver cancer. The invention simultaneously discloses a kit capable of detecting liver cancer. The kit consists of a reverse transcription system, an amplification system and a primer system, wherein the primer system comprises the stem-loop primer and amplification primer of one of the miR-21, the miR-25, the miR-29c, the miR-93, the miR-198, the miR-221 and the miR-222. The invention can be used for screening and diagnosing the liver cancer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Aptamer EpCAM (epithelial cell adhesion molecule) Ccut of EpCAM and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103387988AMaintain native conformationNo toxicityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationProtein targetNeural cell adhesion molecule
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
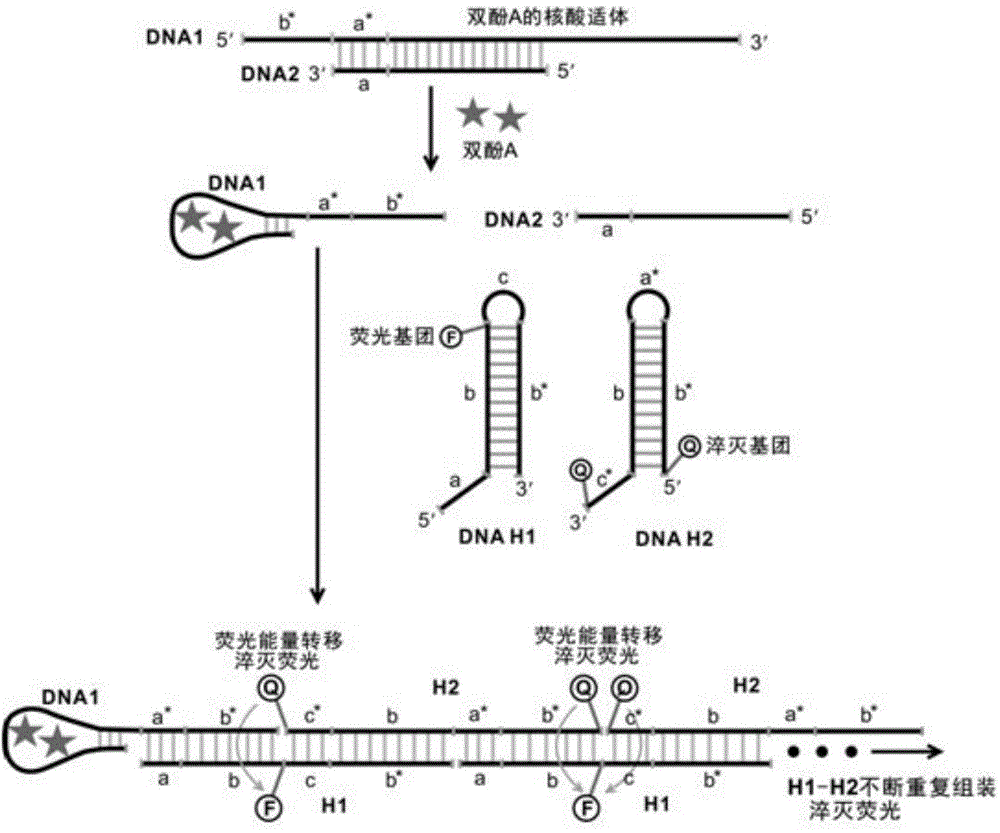
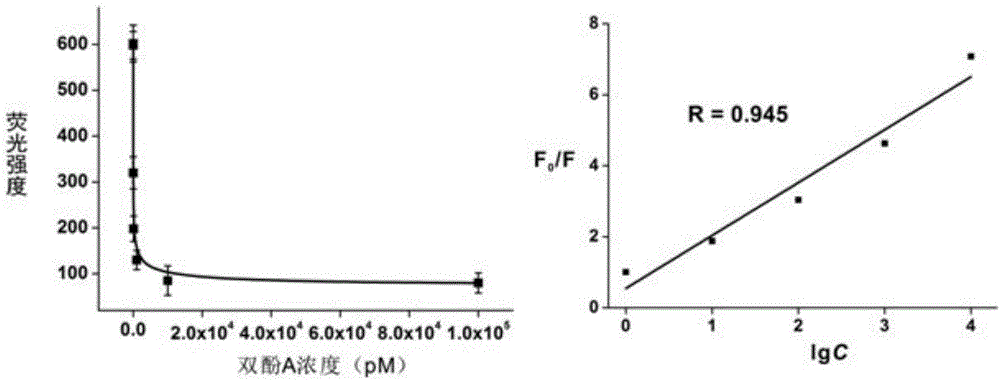
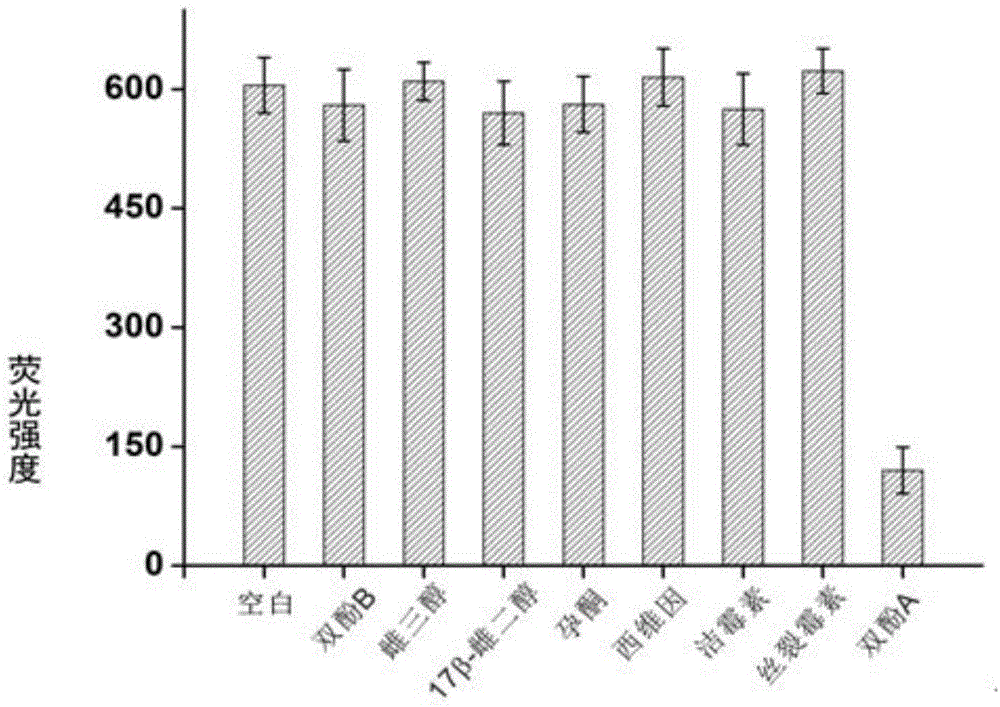
Bisphenol A detecting method and detecting kit based on dual-quenching-group nucleic acid self-assembling technology
ActiveCN104962608AQuenching is effectiveEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorophoreBiology
The invention discloses a bisphenol A detecting method and detecting kit based on the dual-quenching-group nucleic acid self-assembling technology. Two DNAs of stem loop structures are designed, wherein one DNA of the stem loop structure is used for modifying a fluorophore, and the other DNA of the stem loop structure is used for modifying two quenching groups; and under the condition that bisphenol A exists, loop opening hybridization can be continuously carried out on the two DNAs of the stem loop structures, so that the fluorophore and the quenching groups get close to each other, fluorescence energy transferring happens, and fluorescence is accordingly quenched. According to the detecting method, signal amplification is sourced from continuous loop opening complementation of the two DNAs of the stem loop structures, and no protease is needed to be used, so that operation is easy, a reaction can be completed at the room temperature, the sensitivity is high, and the selectively is good. The two quenching groups exist on one DNA of the stem loop structure at the same time, and the fluorophore on the other DNA of the stem loop structure can be quenched more effectively, so that the fluorescence background is effectively reduced, the detection sensitivity is greatly improved, and the detection limit is 0.4 pM.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
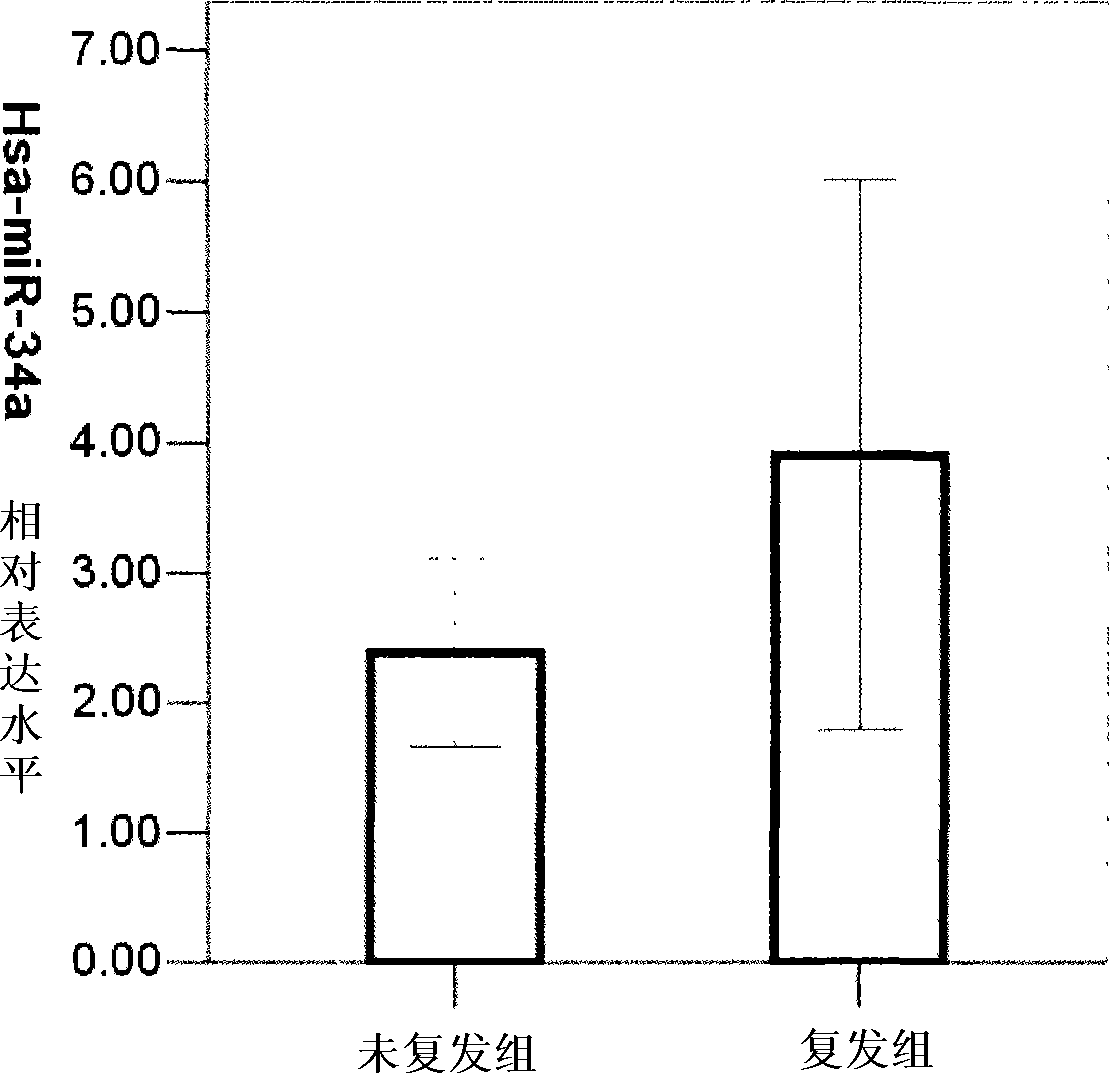
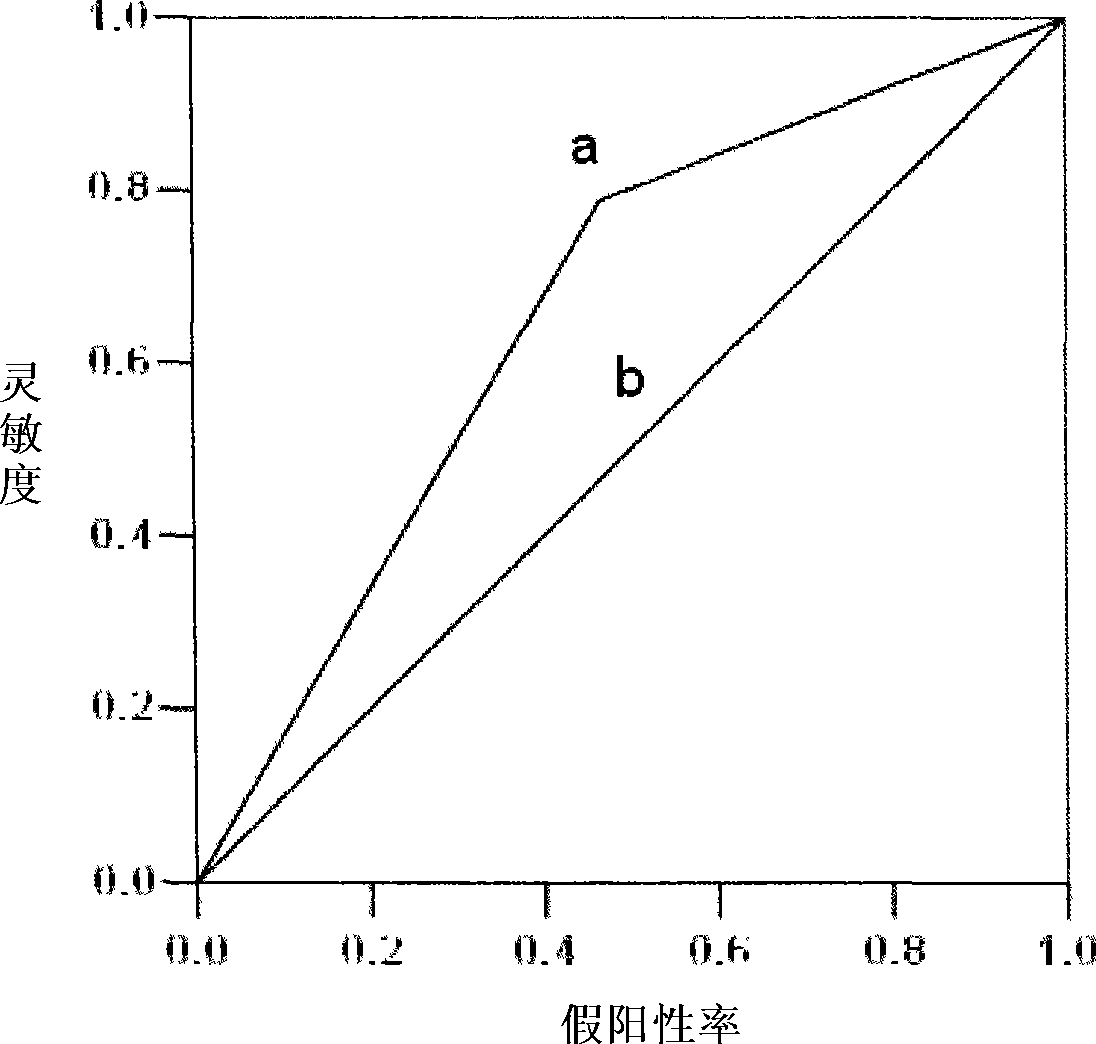
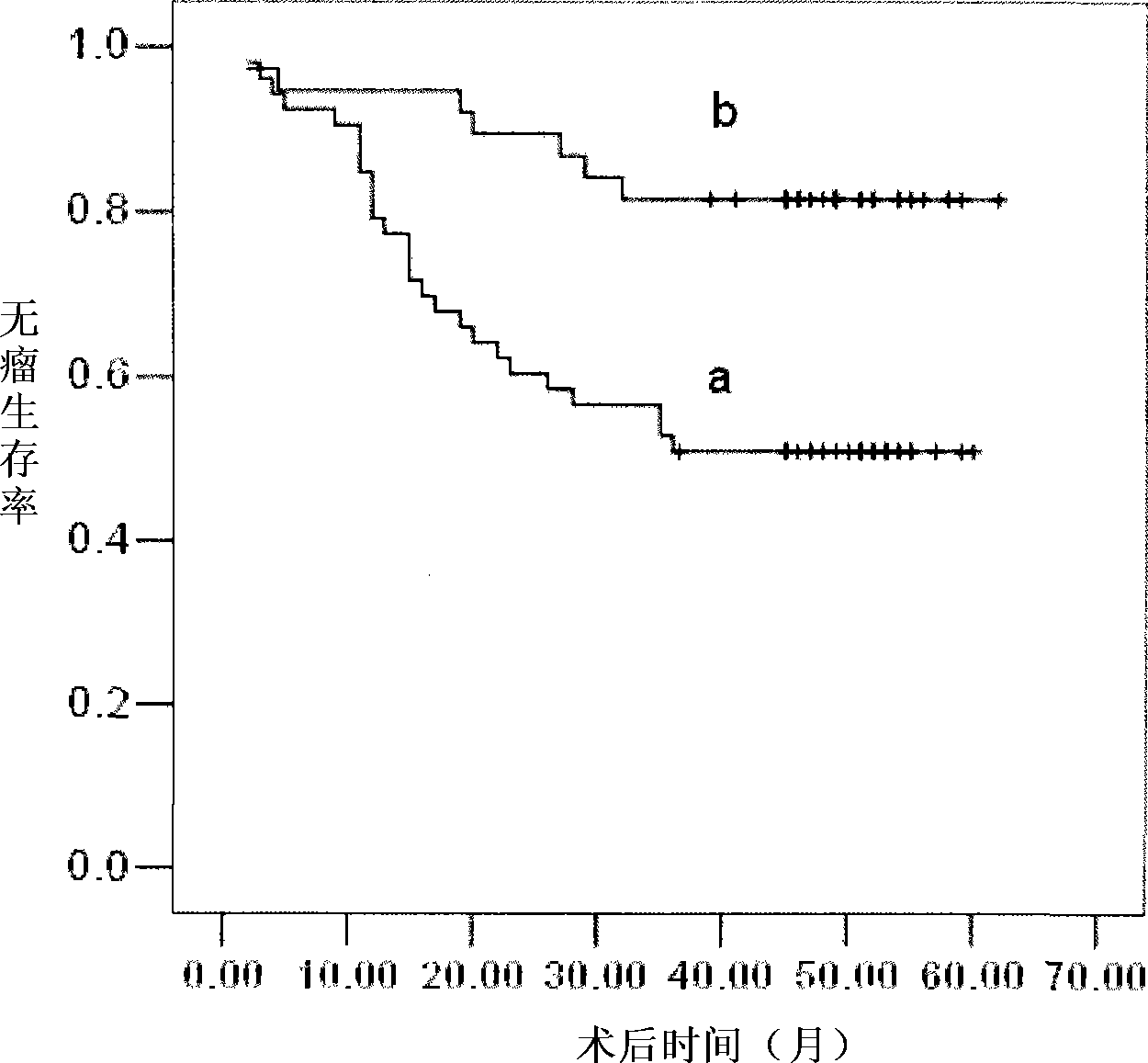
Application of miRNA in predicting postoperative recurrence for early primary hepatocarcinoma patient and kit thereof
InactiveCN101418343AQuantitatively accurateSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementQuantitative determinationReverse transcriptase
The invention provides a kit for predicting postoperative liver cancer relapse of early primary liver cancer patients, which comprises a reverse transcription system, an amplification system and a primer and probe system, wherein the reverse transcription system consists of reverse transcriptase, a reverse transcription system buffer solution and an RNA enzyme inhibitor; the amplification system consists of a miRNA expressive quantitative determination mixture containing Taq enzymes; and the primer and probe system comprises an has-miR-34a stem-loop structure primer, an has-miR-34a amplification primer, a fluorescent marker probe, an RNU6B stem-loop structure primer, an RNU6B amplification primer and a fluorescent marker probe. The kit is accurate in detection and quantification, is simple, quick, convenient, economic and practical, can be further combined with other molecular indexes, provides a comprehensive molecular index kit for diagnosis, prognosis and prediction of early primary liver cancer relapse, and is convenient for clinic application.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN HOSPITAL FUDAN UNIV +1
Construction of bifunctional short hairpin RNA
ActiveUS8758998B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBioinformaticsExpression cassette
A method for designing a bi-shRNA expression cassette encoding a bi-shRNA comprising: selecting one or more target site sequences; providing a backbone sequence comprising a first and a second stem-loop structure, inserting a first passenger strand and a second passenger strand and providing for synthesis of the bi-shRNA expression cassette.
Owner:GRADALIS
Mercuric ion detection kit based on constant-temperature cascading nucleic acid amplification and detection method thereof
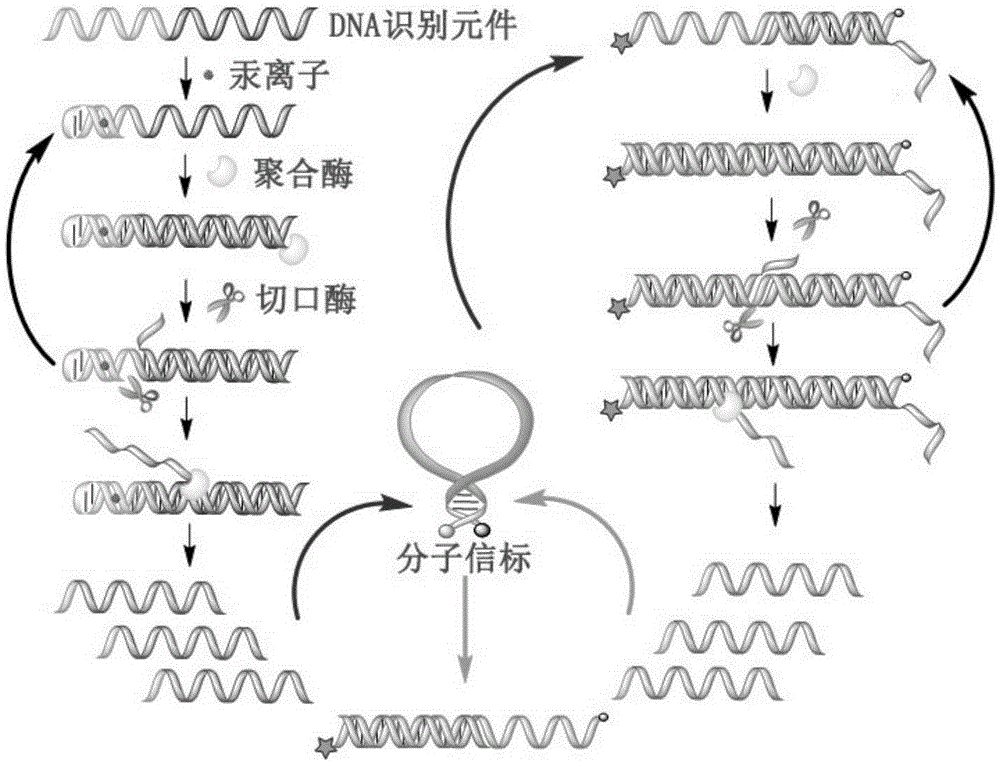
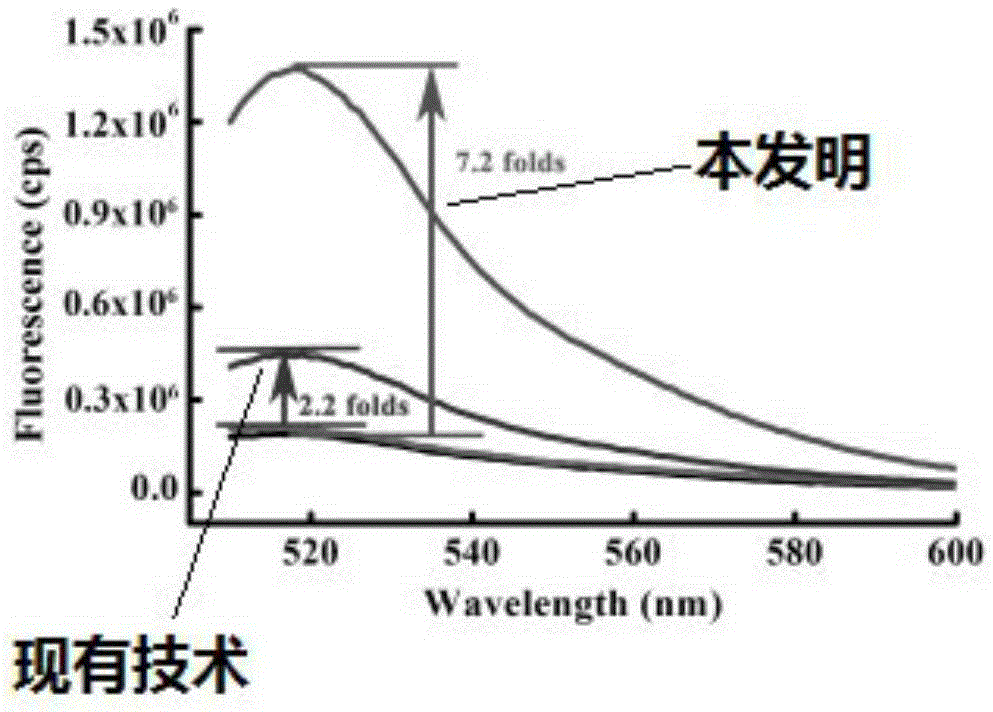
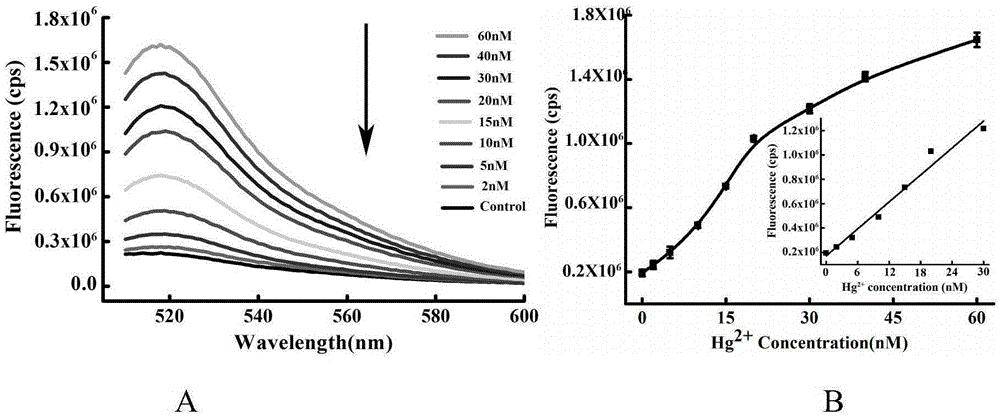
InactiveCN105256033ASimple designNo need to add system complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementMercuric ionFluorescence
The invention provides a mercuric ion detection kit based on constant-temperature cascading nucleic acid amplification and a detection method thereof. Thymine-containing DNA identification elements are specifically bound with mercuric ions and then are folded to form an intra-molecular stem-loop structure; The 3' terminal of the DNA can be identified by polymerase, the DNA itself serves as a template to start strand displacement amplification reaction so as to produce a large amount of single-stranded DNA products; the single-stranded DNA products can open a restriction enzyme cutting site containing molecular beacon stem-loop structure to produce fluorescence signals; at the same time, the single-stranded DNA products can be also used as primers, and hybridization combined molecular beacons are used as templates to trigger secondary strand displacement amplification reaction, and released SDA products can form heteroduplexes with new molecular beacons so as to produce cascaded-amplified fluorescent signals. The detection method is high in sensitivity, ingeniously achieves cascading amplification of strand displacement amplification reaction without system complexity increase, is high in amplification efficiency and response speed and can achieve mercuric ion quantification within 30 minutes, and the detection limit is as low as 2 nM.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com