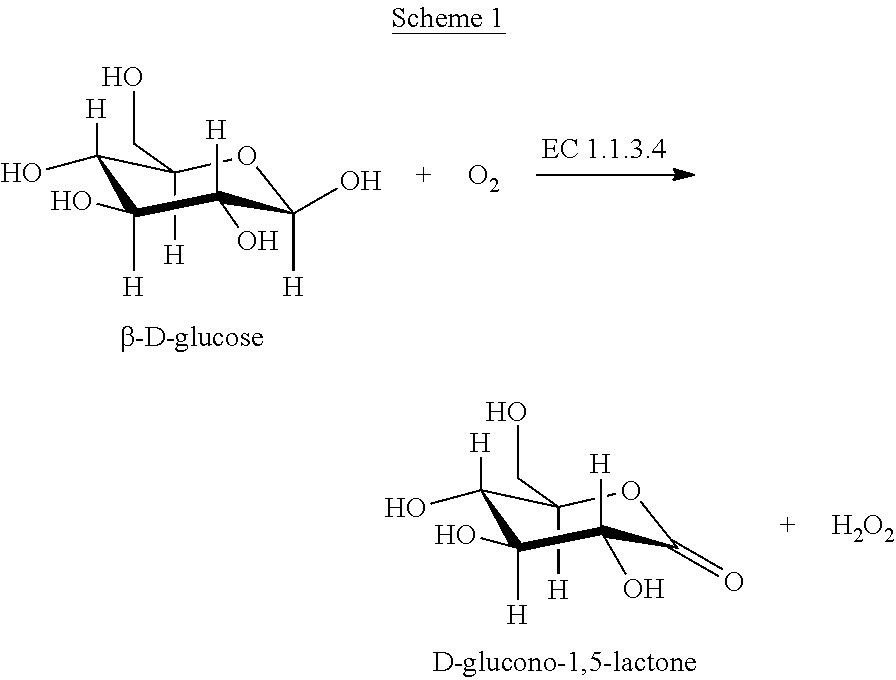
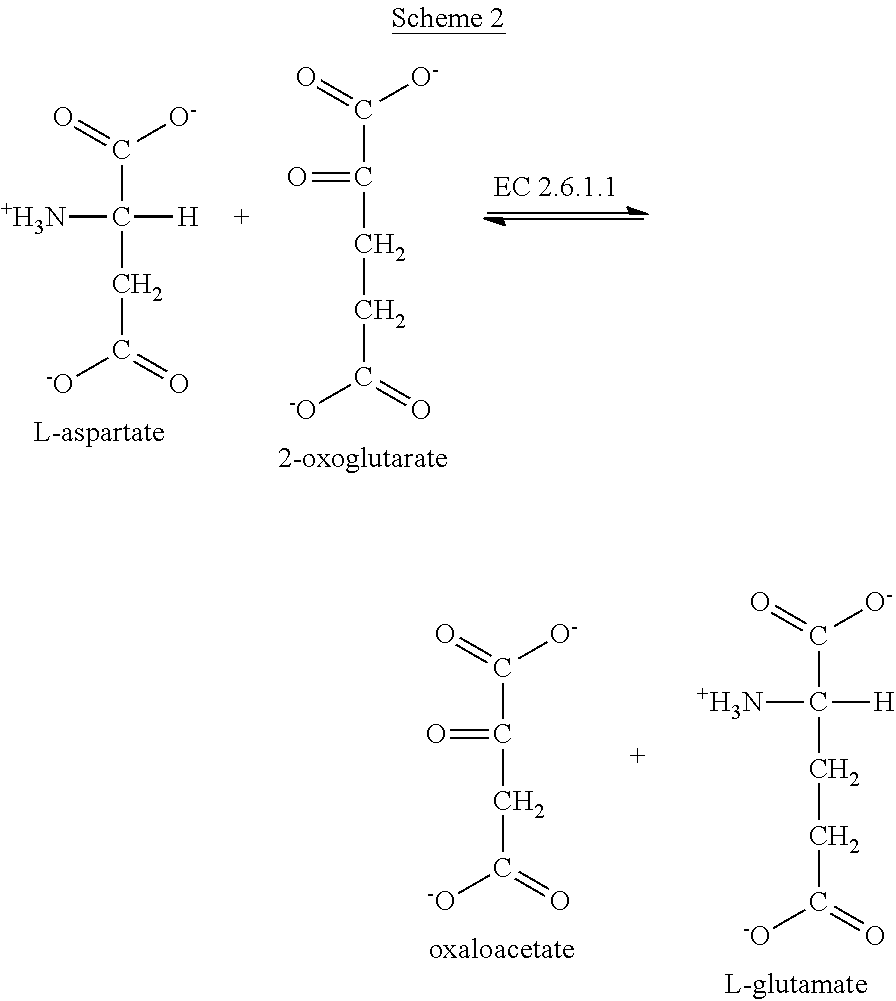
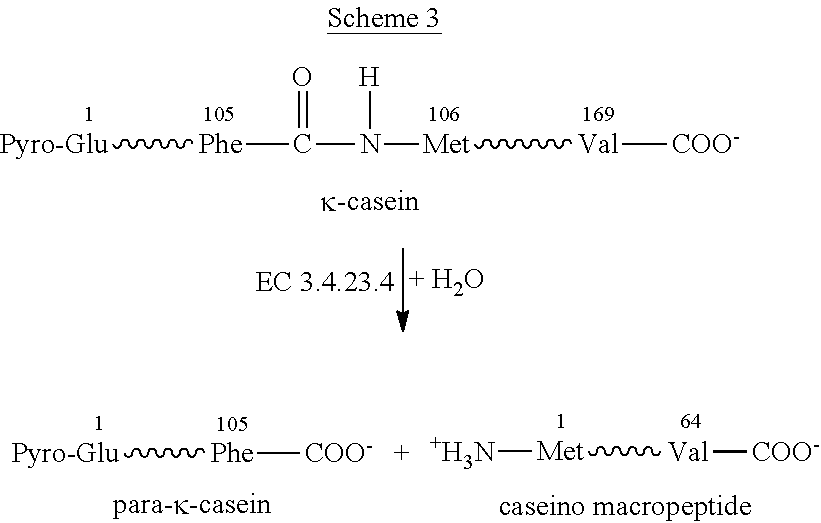
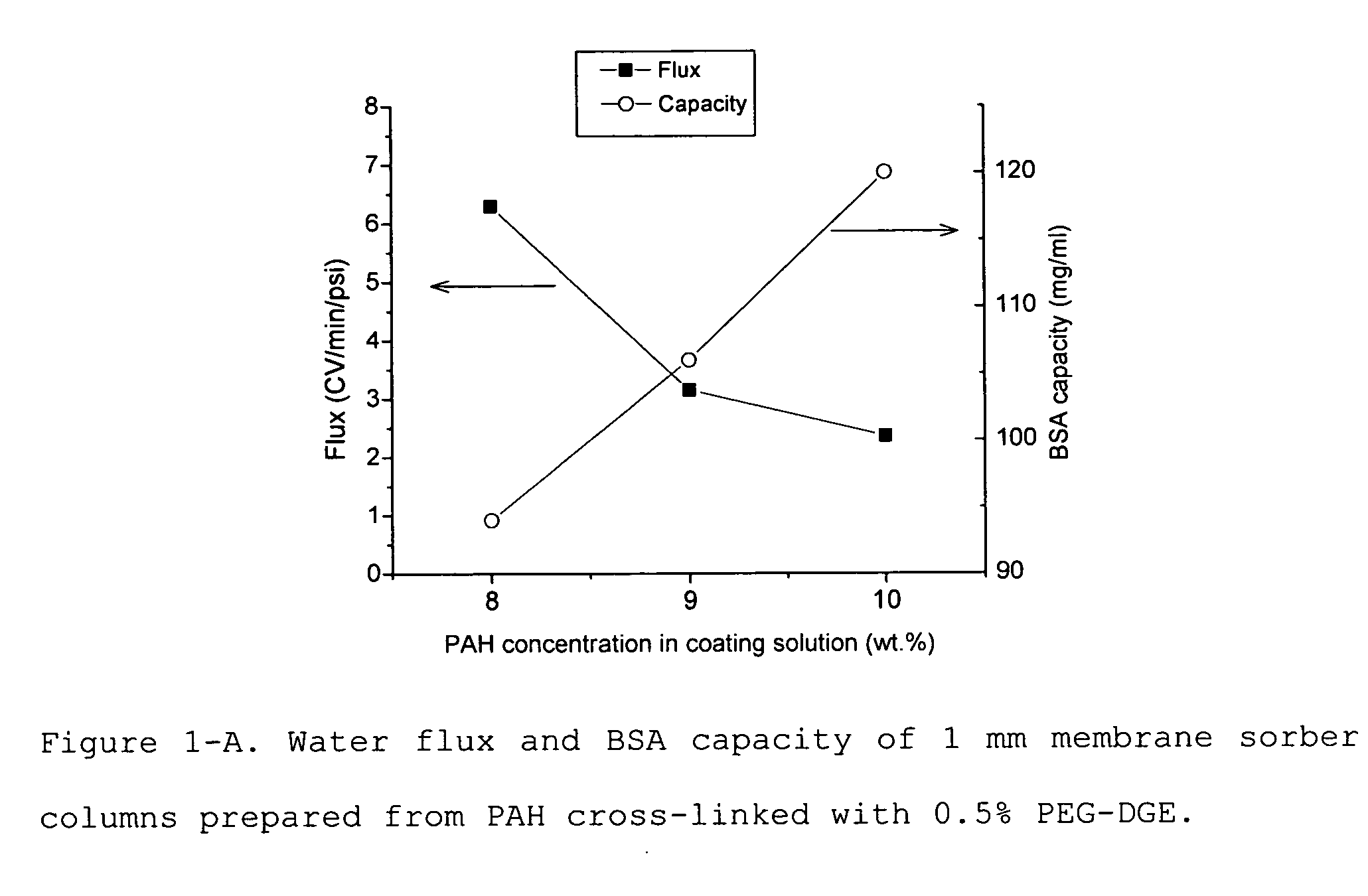
Patents
Literature
1175 results about "Protein A" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
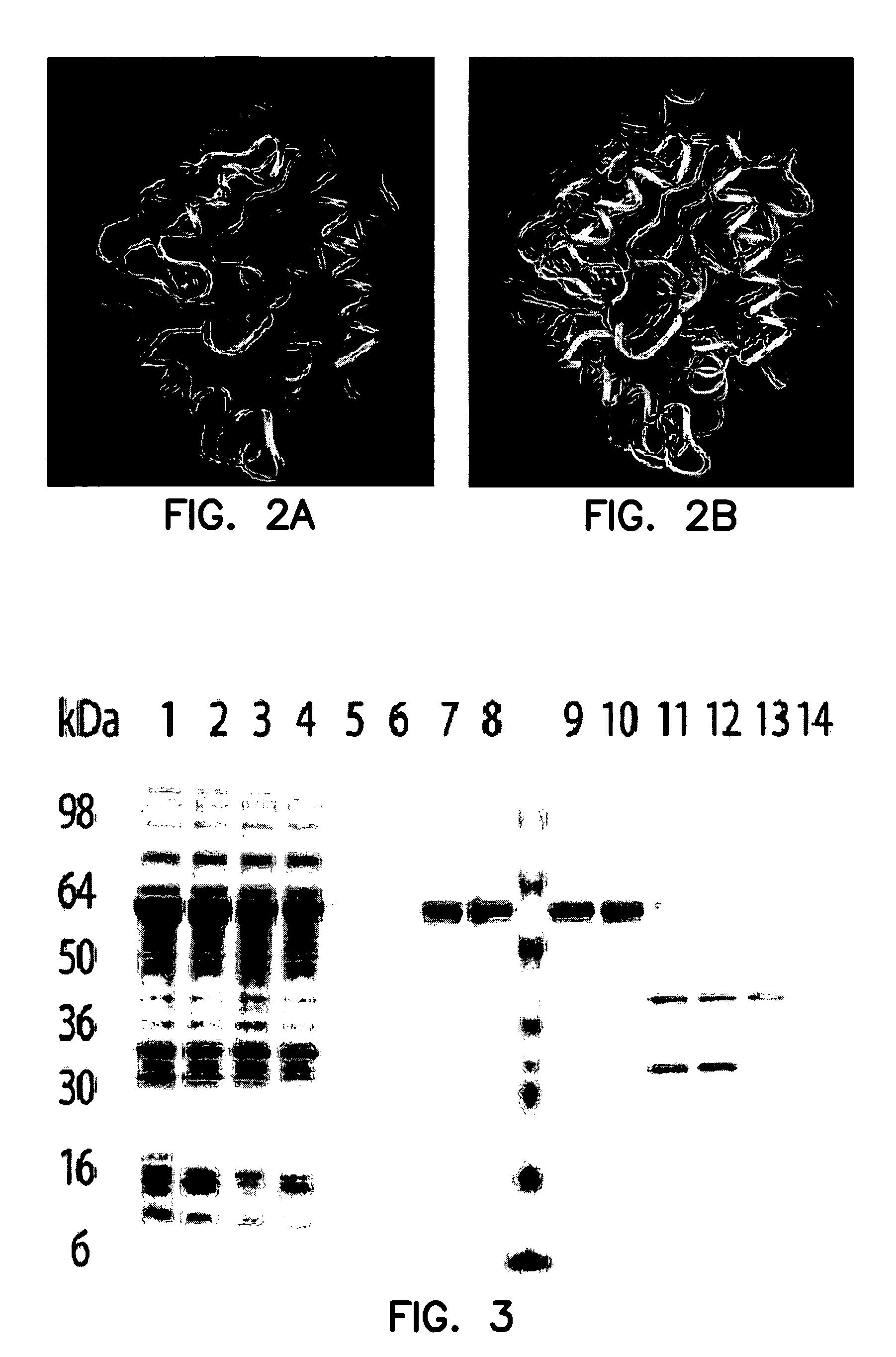
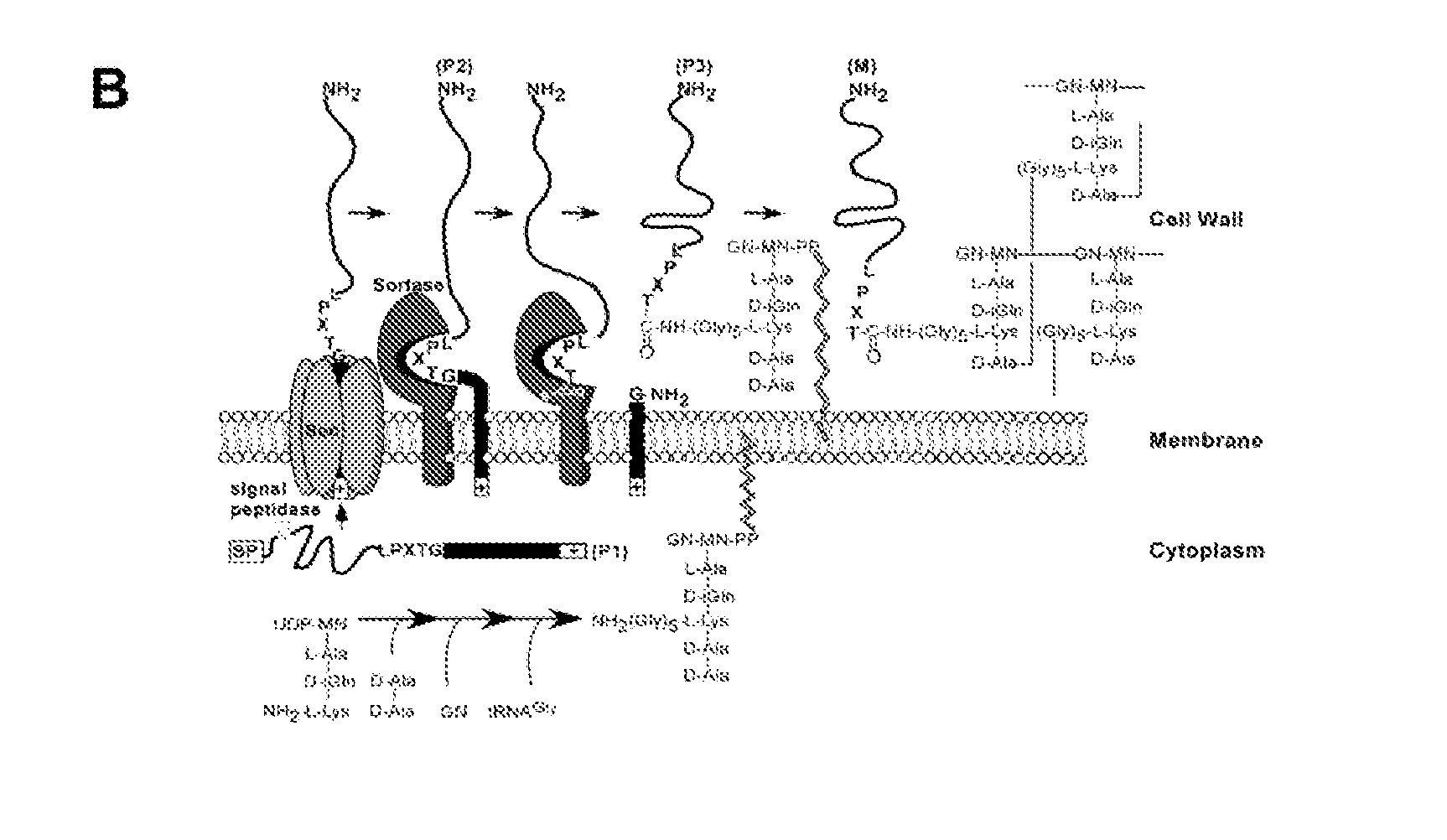
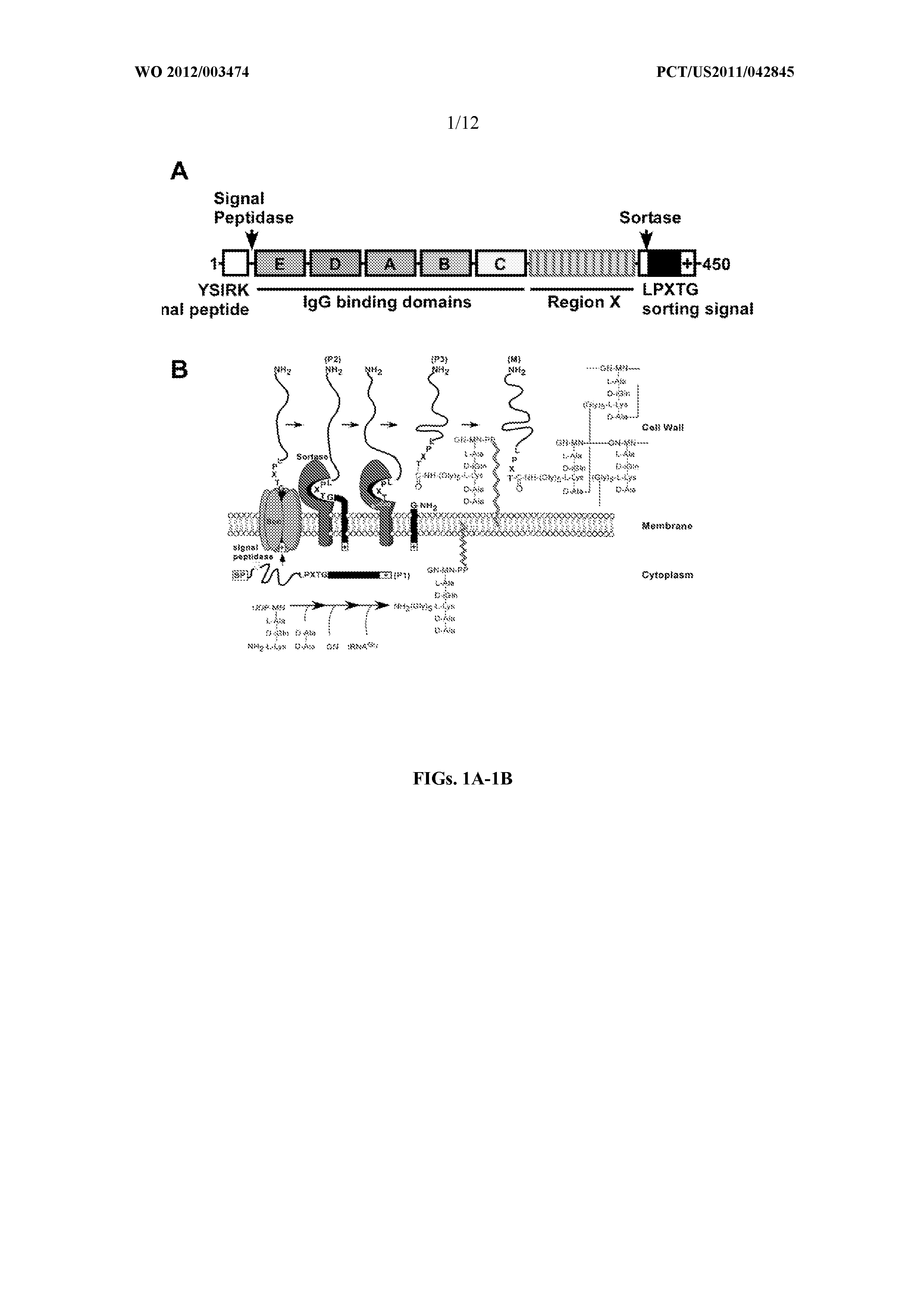
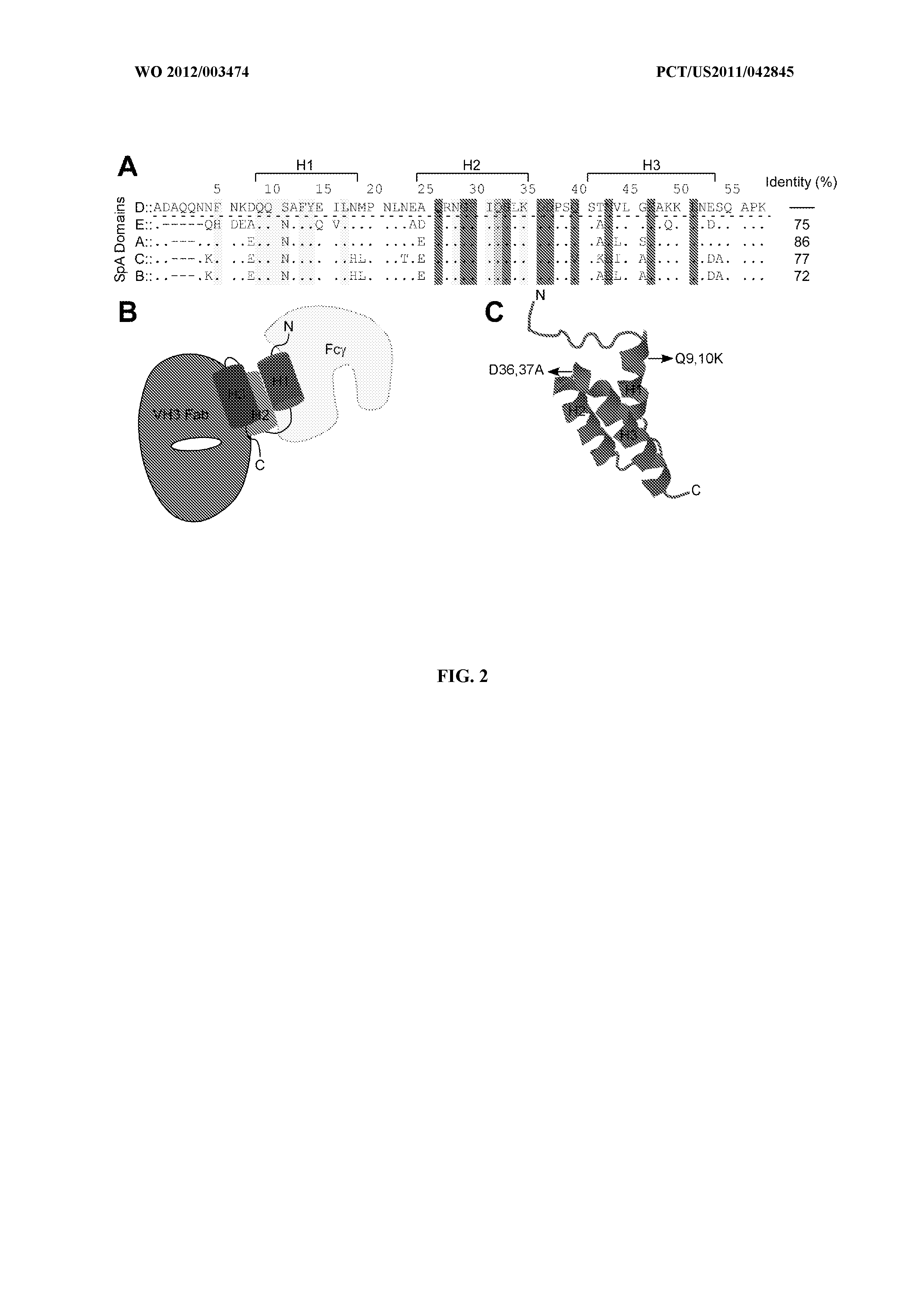
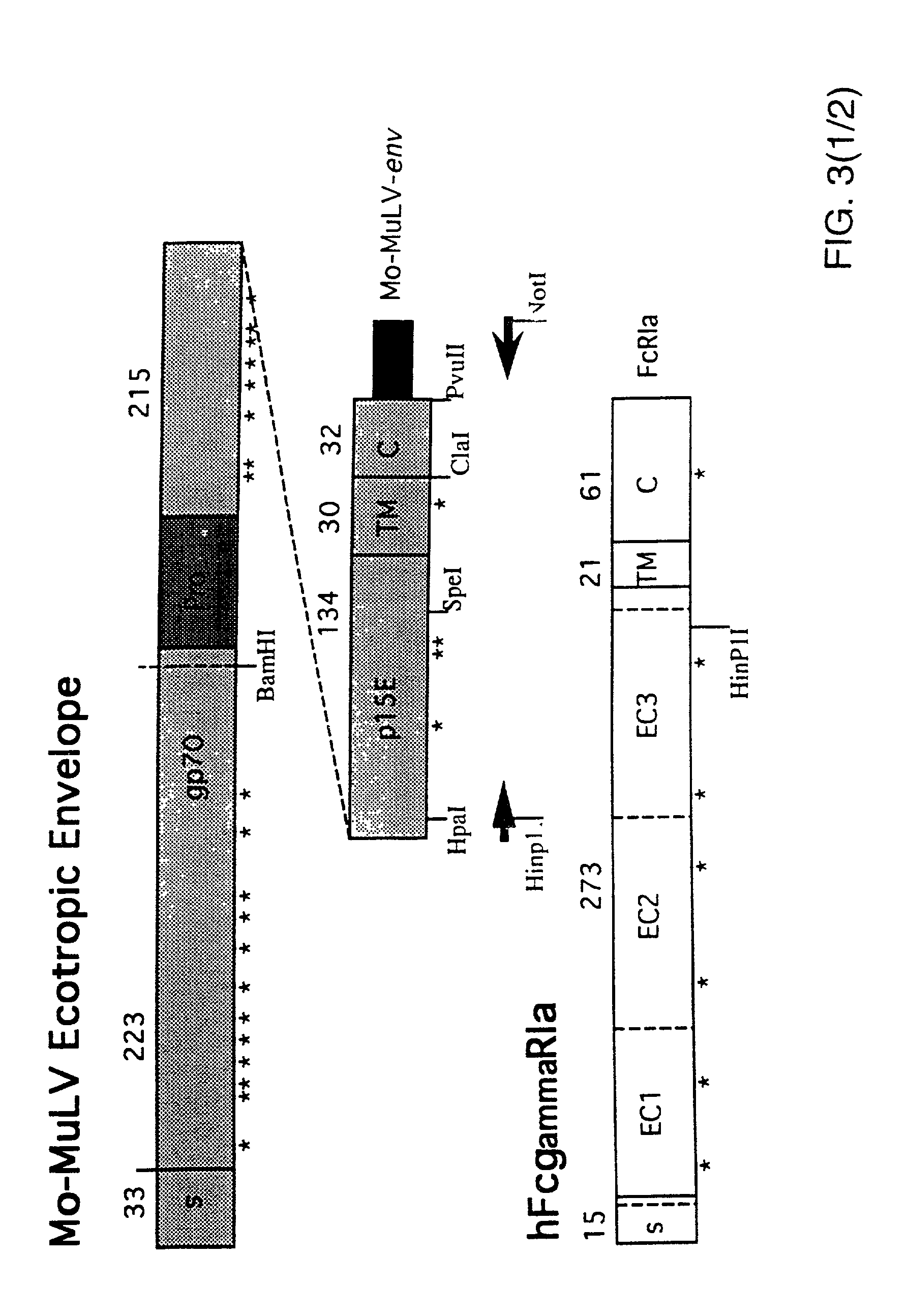
Protein A is a 42 kDa surface protein originally found in the cell wall of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. It is encoded by the spa gene and its regulation is controlled by DNA topology, cellular osmolarity, and a two-component system called ArlS-ArlR. It has found use in biochemical research because of its ability to bind immunoglobulins. It is composed of five homologous Ig-binding domains that fold into a three-helix bundle. Each domain is able to bind proteins from many mammalian species, most notably IgGs. It binds the heavy chain within the Fc region of most immunoglobulins and also within the Fab region in the case of the human VH3 family. Through these interactions in serum, where IgG molecules are bound in the wrong orientation (in relation to normal antibody function), the bacteria disrupts opsonization and phagocytosis.
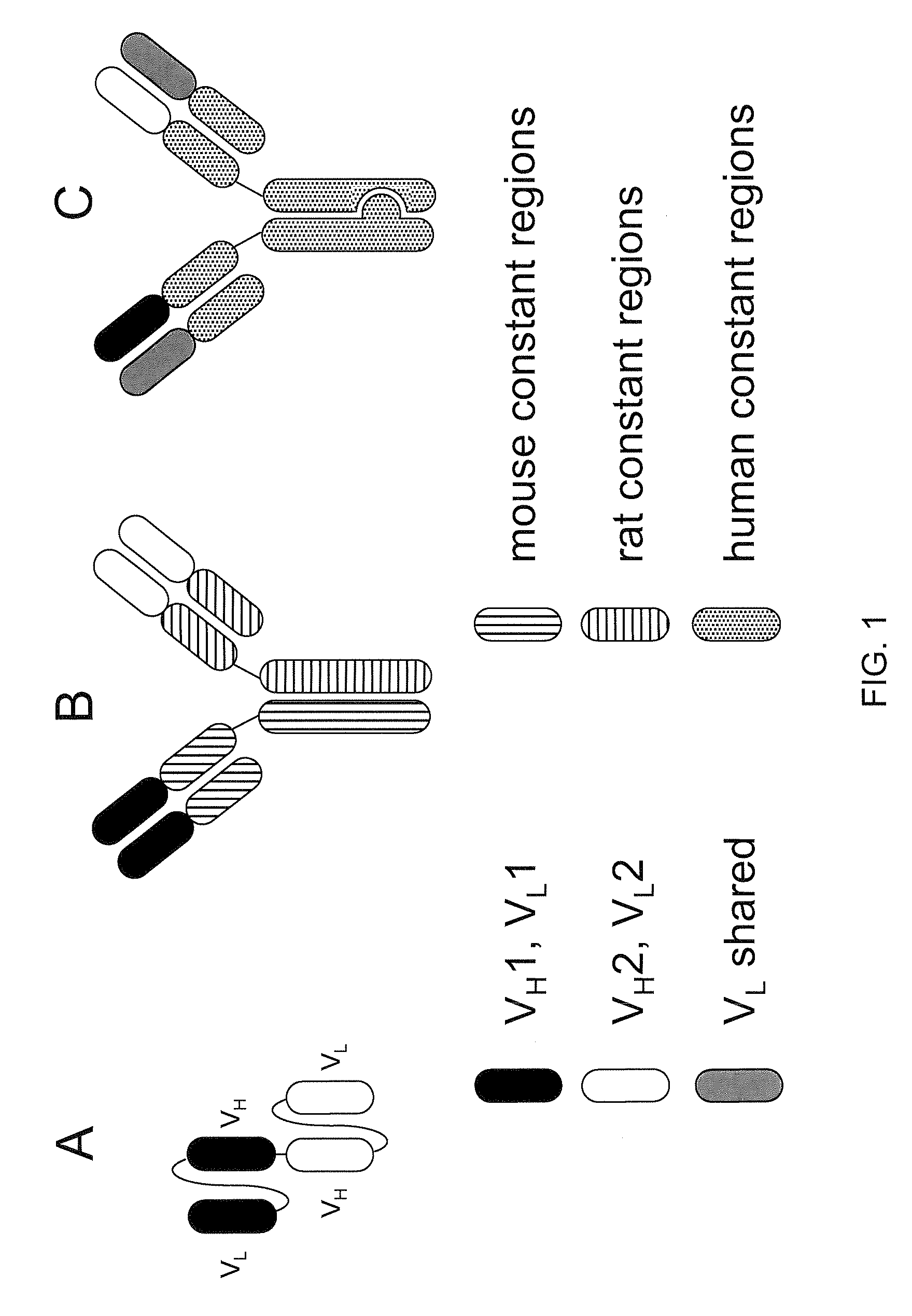
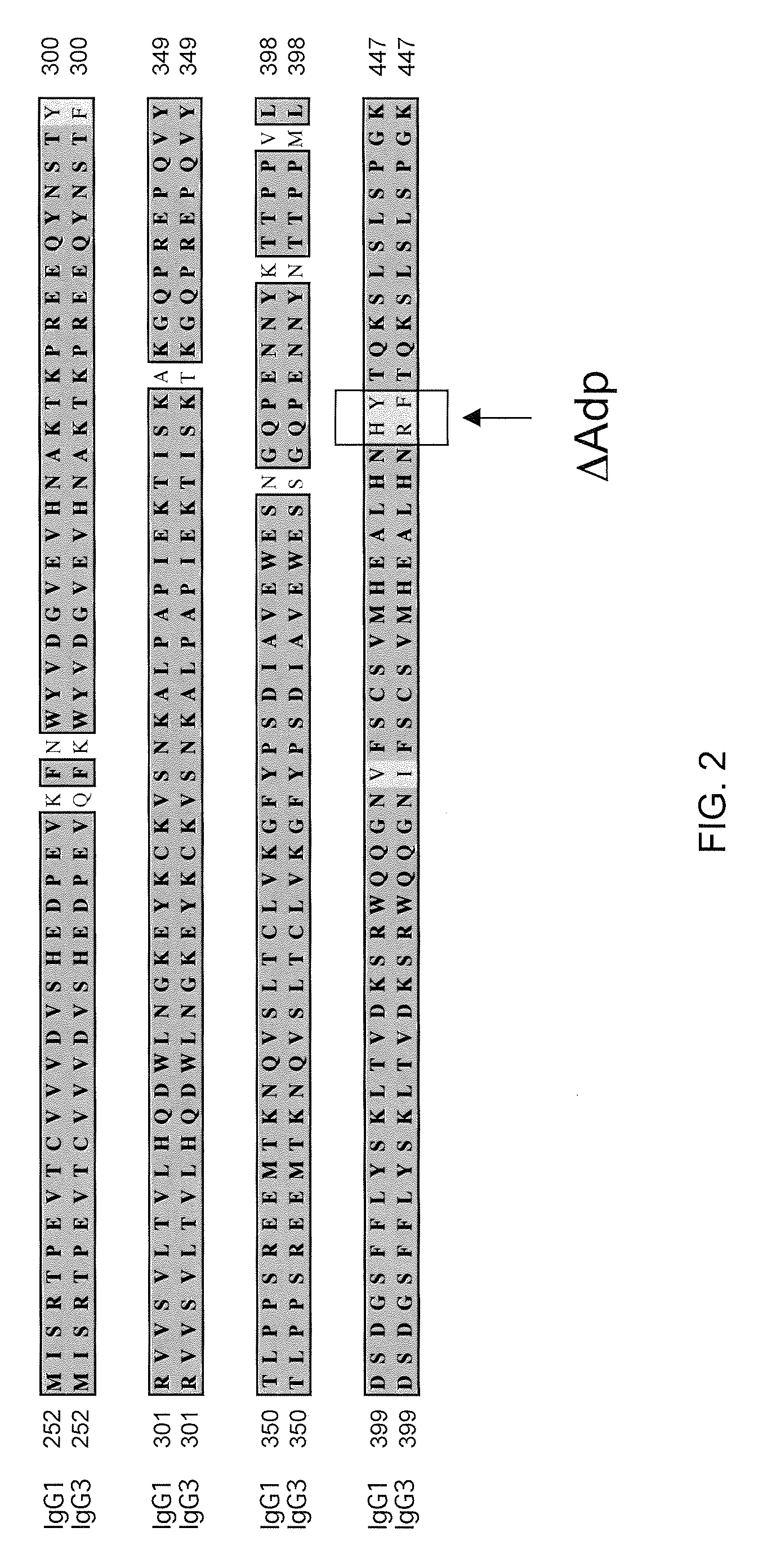
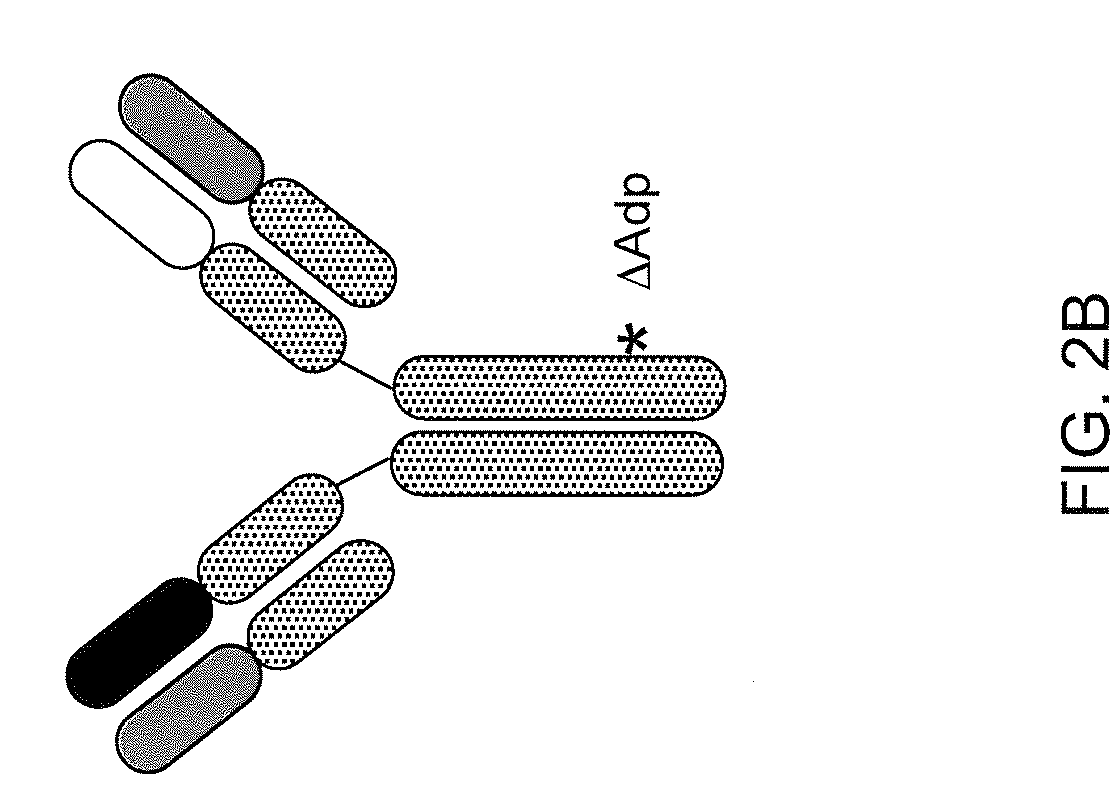
Readily Isolated Bispecific Antibodies with Native Immunoglobulin Format
ActiveUS20100331527A1Improve abilitiesReduces and eliminates bindingHybrid immunoglobulinsSerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulin heavy chainHeavy chain
A bispecific antibody format providing ease of isolation is provided, comprising immunoglobulin heavy chain variable domains that are differentially modified in the CH3 domain, wherein the differential modifications are non-immunogenic or substantially non-immunogenic with respect to the CH3 modifications, and at least one of the modifications results in a differential affinity for the bispecific antibody for an affinity reagent such as Protein A, and the bispecific antibody is isolable from a disrupted cell, from medium, or from a mixture of antibodies based on its affinity for Protein A.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Treatment of neuropathic pain with zinc finger proteins
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
IGG separation medium
A separation medium having a base matrix and matrix-bound groups which exhibit recombinant Protein A containing a cysteine. The groups are of formula:where B is a bridge which binds to the base matrix and X includes a heteroatom N or S from rProtein A-cys. In a preferred embodiment X is a thioether sulphur and / or a secondary amine (-NH-). An alternative embodiment features a variant of Protein A in which the C-terminal residue is cysteine.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIOPROCESS R&D
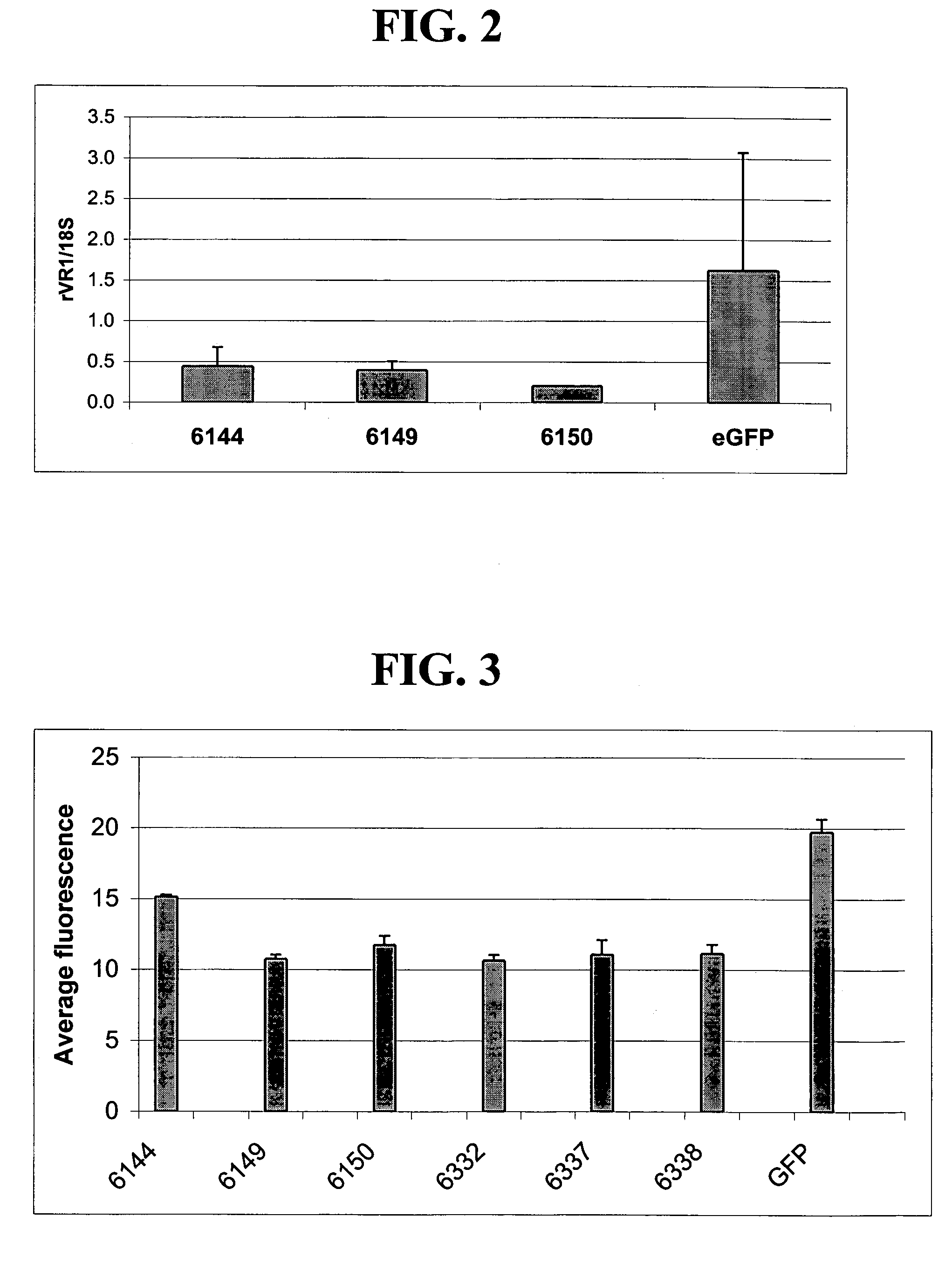
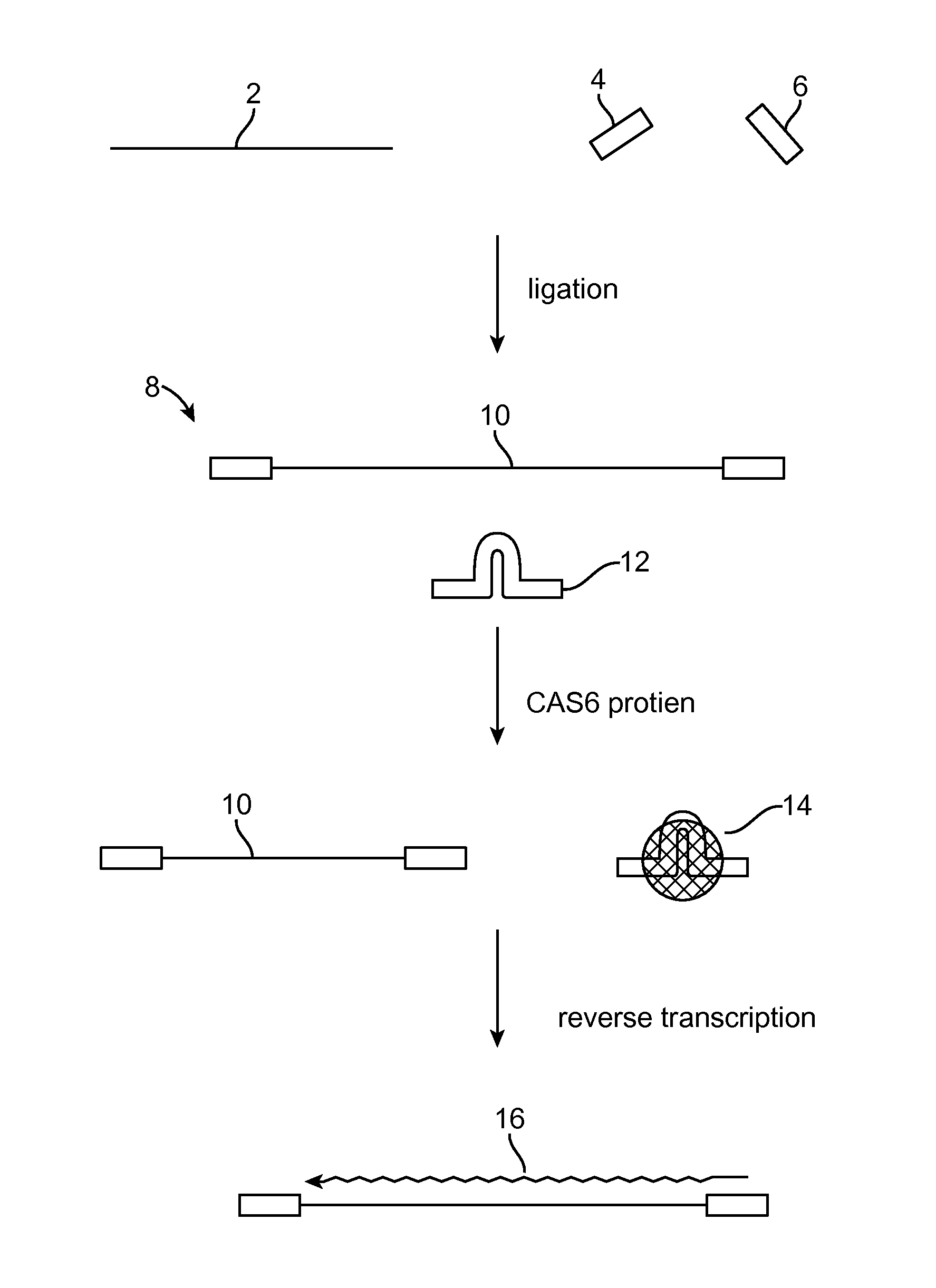
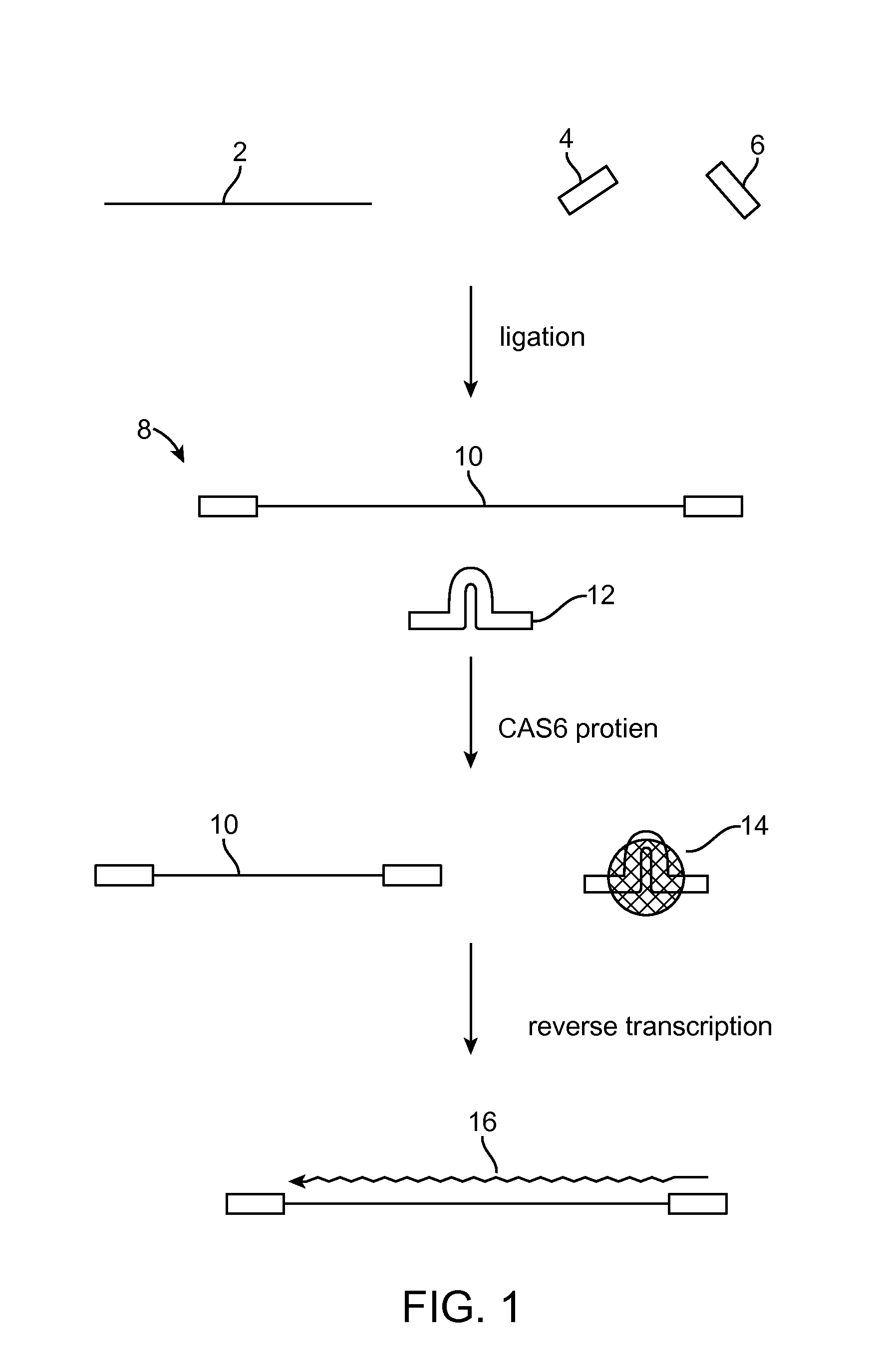
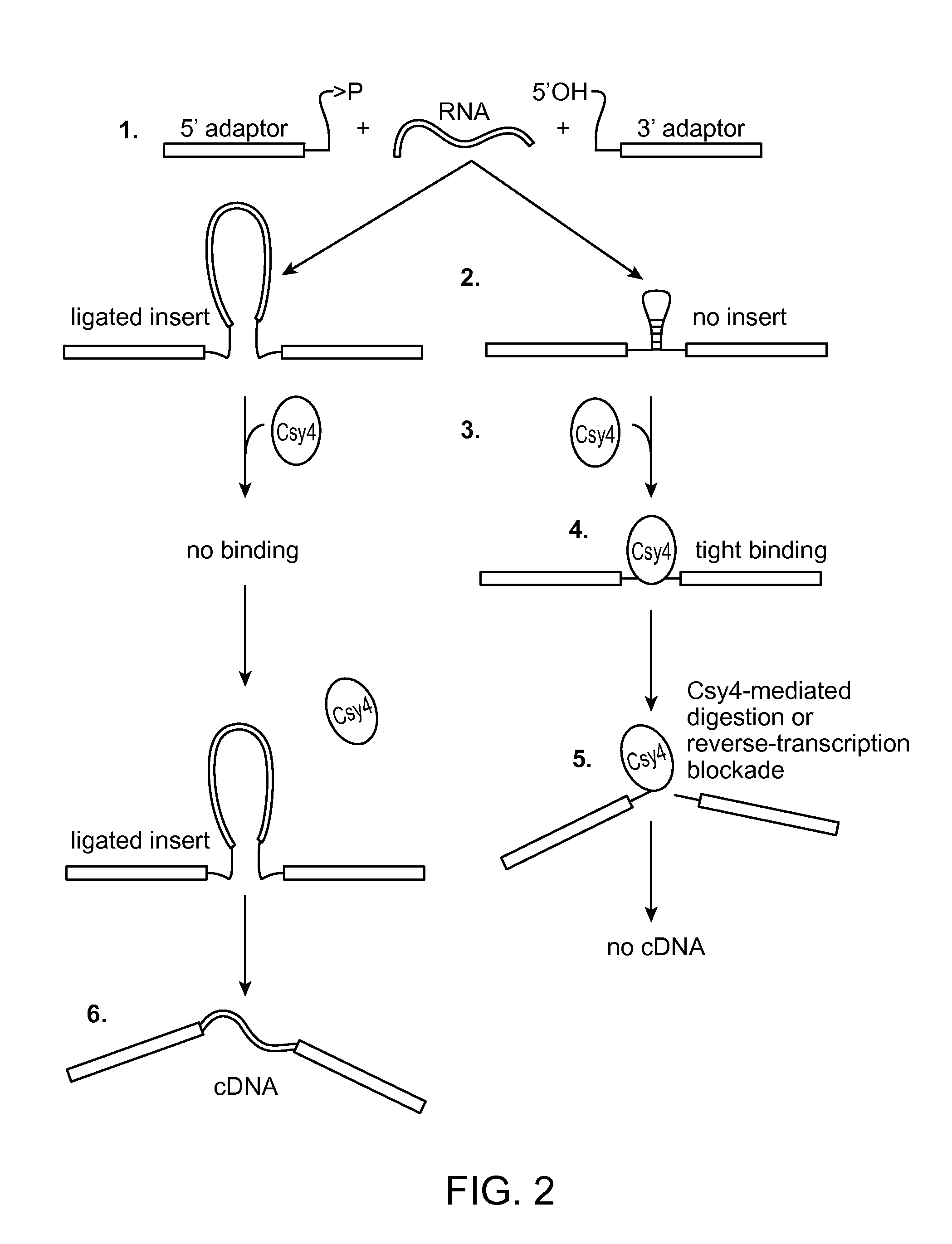
Method of adaptor-dimer subtraction using a crispr cas6 protein
A method of processing a target RNA is provided. In certain embodiments, this method comprises: contacting the products of an RNA ligase-mediated ligation reaction with an CAS6 protein, wherein: (i) the RNA ligase-mediated ligation reaction comprises: a target RNA, an RNA ligase, and first and second adaptors that can ligate together to produce an adaptor dimer that contains a CRISPR stem loop; and (ii) the CAS6 protein recognizes the CRISPR stem loop; thereby preventing the adaptor dimer from being reverse transcribed.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
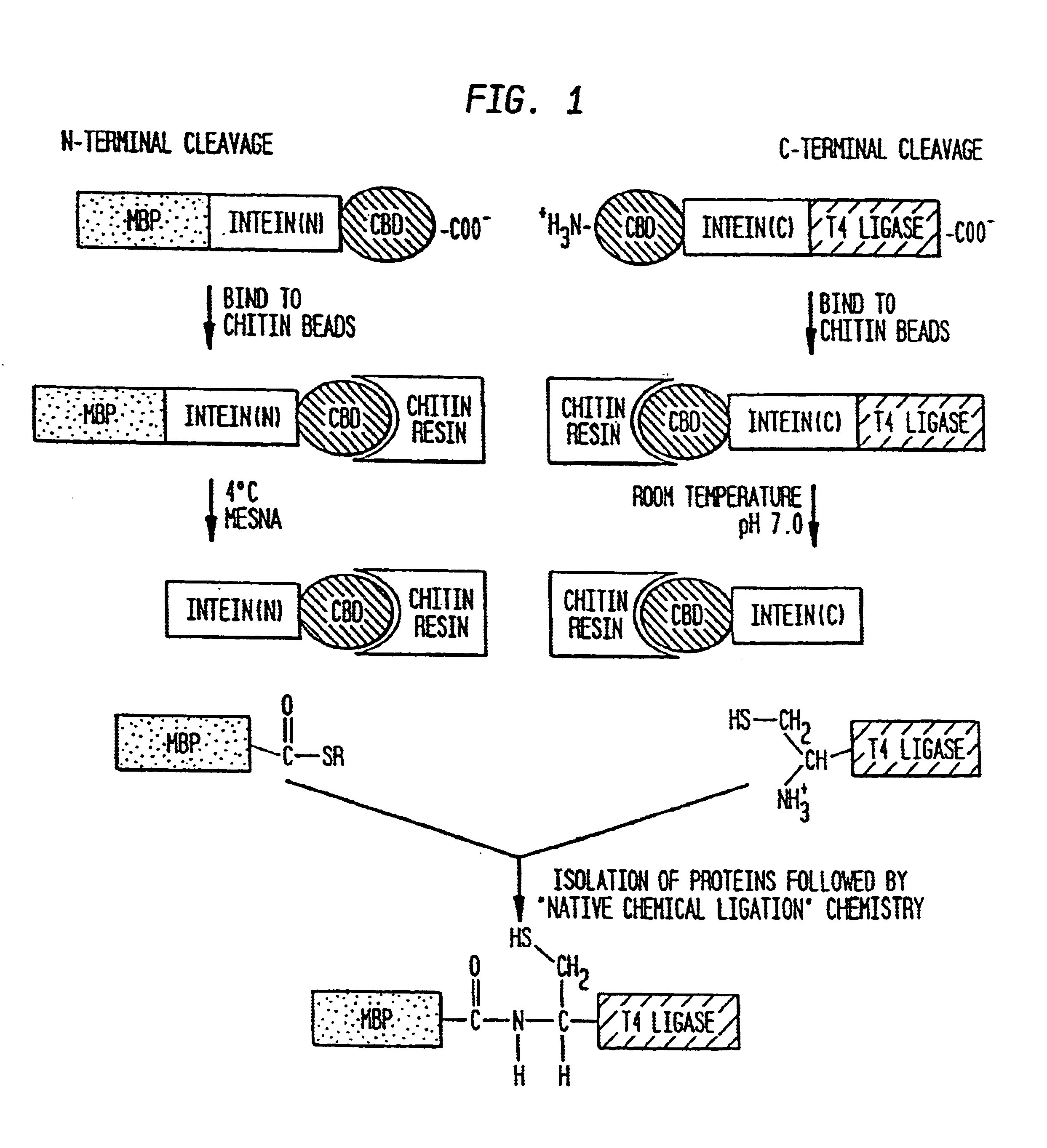
Intein-mediated protein ligation of expressed proteins
InactiveUS6849428B1Eliminate needBacteriaFusion with post-translational modification motifProtein targetIntein
A method for the ligation of expressed proteins which utilizes inteins, for example the RIR1 intein from Methanobacterium thermotrophicum, is provided. Constructs of the Mth RIR1 intein in which either the C-terminal asparagine or N-terminal cysteine of the intein are replaced with alanine enable the facile isolation of a protein with a specified N-terminal, for example, cysteine for use in the fusion of two or more expressed proteins. The method involves the steps of generating a C-terminal thioester-tagged target protein and a second target protein having a specified N-terminal via inteins, such as the modified Mth RIR1 intein, and ligating these proteins. A similar method for producing a cyclic or polymerized protein is provided. Modified inteins engineered to cleave at their C-terminus or N-terminus, respectively, and DNA and plasmids encoding these modified inteins are also provided.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Isolating cells expressing secreted proteins
InactiveUS6919183B2Easy to detectImprove isolationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionSecretory proteinCell sheet
A method for identifying and isolating cells which produce secreted proteins. This method is based upon a specific characteristic or the expression level of the secreted protein by transiently capturing the secreted protein on the surface of an individual cell, allowing selection of rare cell clones from a heterogeneous population. Also provided is the use of this method to generate cells which produce a desired level of secreted protein or secreted protein of a particular characteristic(s), and organisms which possess such cells. In particular, the method allows rapid isolation of high expression recombinant antibody-producing cell lines, or may be applied directly to rapid isolation of specific hybridomas, or to the isolation of antibody-producing transgenic animals. This method is applicable for any cell which secretes protein.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Methods for purifying protein
ActiveUS7122641B2Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsNGF/TNF-superfamilyAntibody Affinity ChromatographyImmunoglobulin domain
A method is provided for separating a protein from one or more other proteins using hydroxyapatite chromatography in which the protein does not bind to hydroxyapatite but the other protein(s) does. In some embodiments, a second protein affixed to a solid support has been used previously to purify the protein by affinity chromatography, and small amounts of the second protein are introduced in the sample during this process. The protein being purified can comprise at least one constant antibody immunoglobulin domain. The second protein can bind to proteins comprising such a domain.
Owner:IMMUNEX CORP
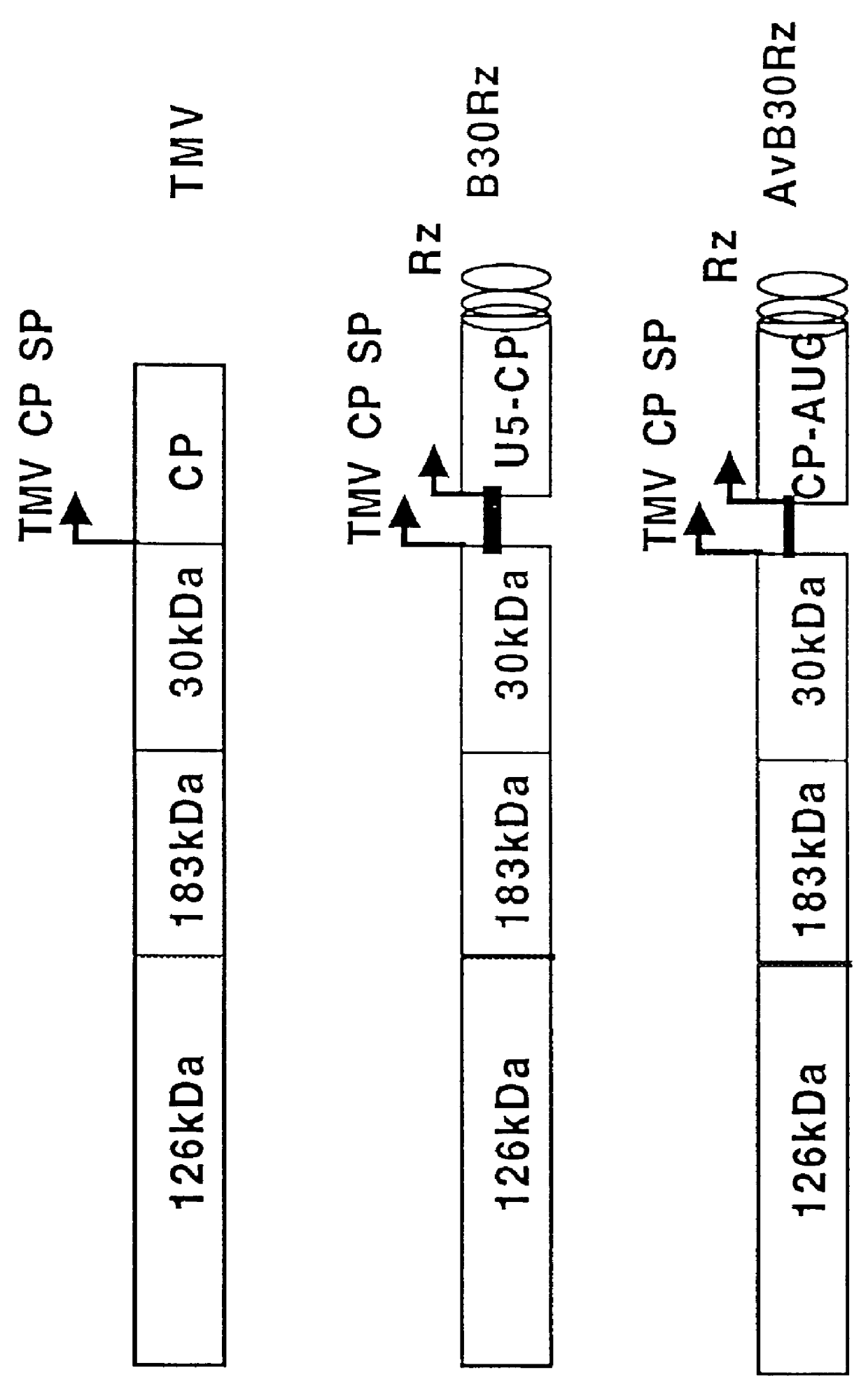
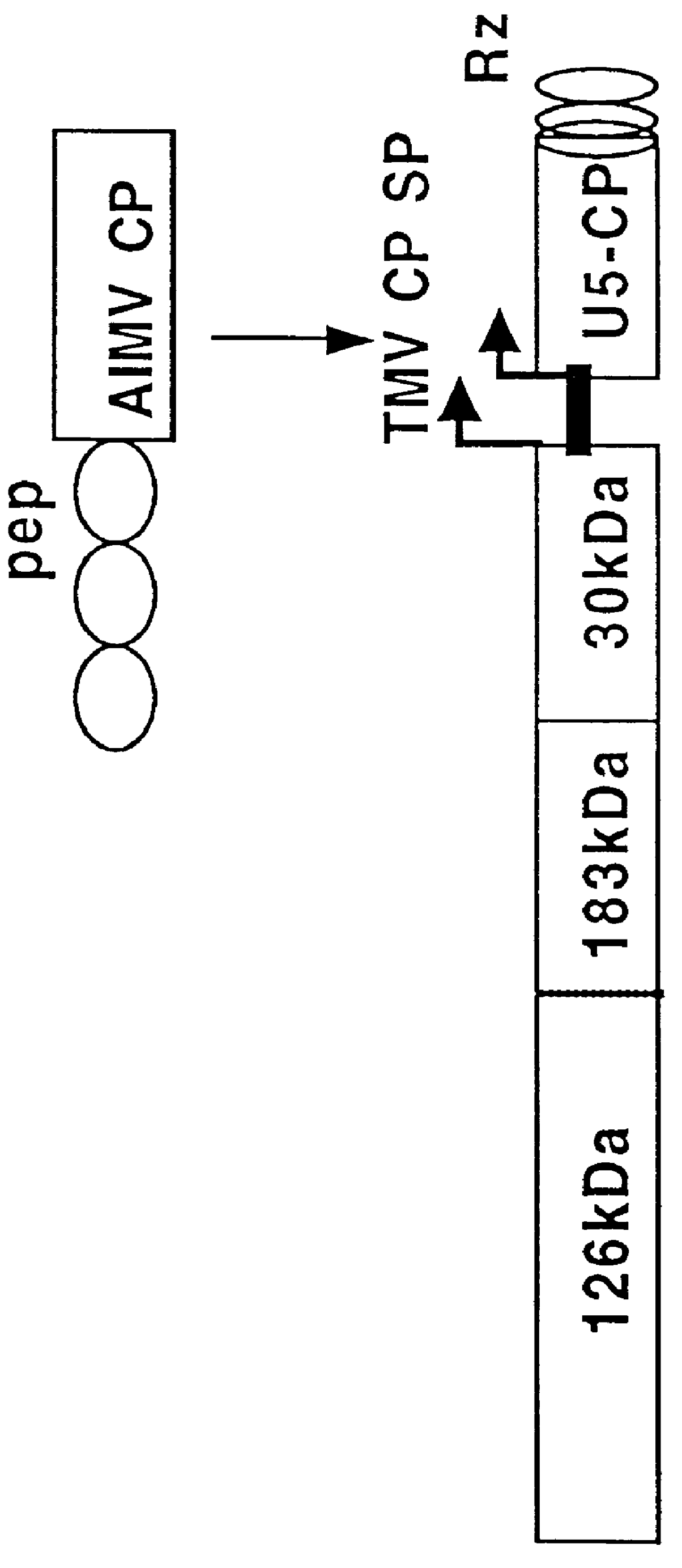
Polypeptides fused with alfalfa mosaic virus or ilarvirus capsid proteins
InactiveUS6042832AEfficient presentation of antigenImprove protectionSsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntigenIlarvirus
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Methods of purifying Fc region containing proteins
ActiveUS20070072307A1Efficient removalDecrease and prevent nonspecific adherenceImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPeptide preparation methodsProtein GFc binding
The present application provides methods of purifying polypeptides having a Fc region, for example, antibodies or antibody fusions, by adsorbing the polypeptides to a Fc binding agent, such as, for example, Protein A or Protein G, followed by a wash with a divalent cation salt buffer to remove impurities and subsequent recovery of the adsorbed polypeptides. The present application also features methods of eluting the purified polypeptide as well as the incorporation of the methods within a purification train. Kits comprising components for carrying out the methods and instructions for use are also provided.
Owner:JANSSEN ALZHEIMER IMMUNOTHERAPY +1
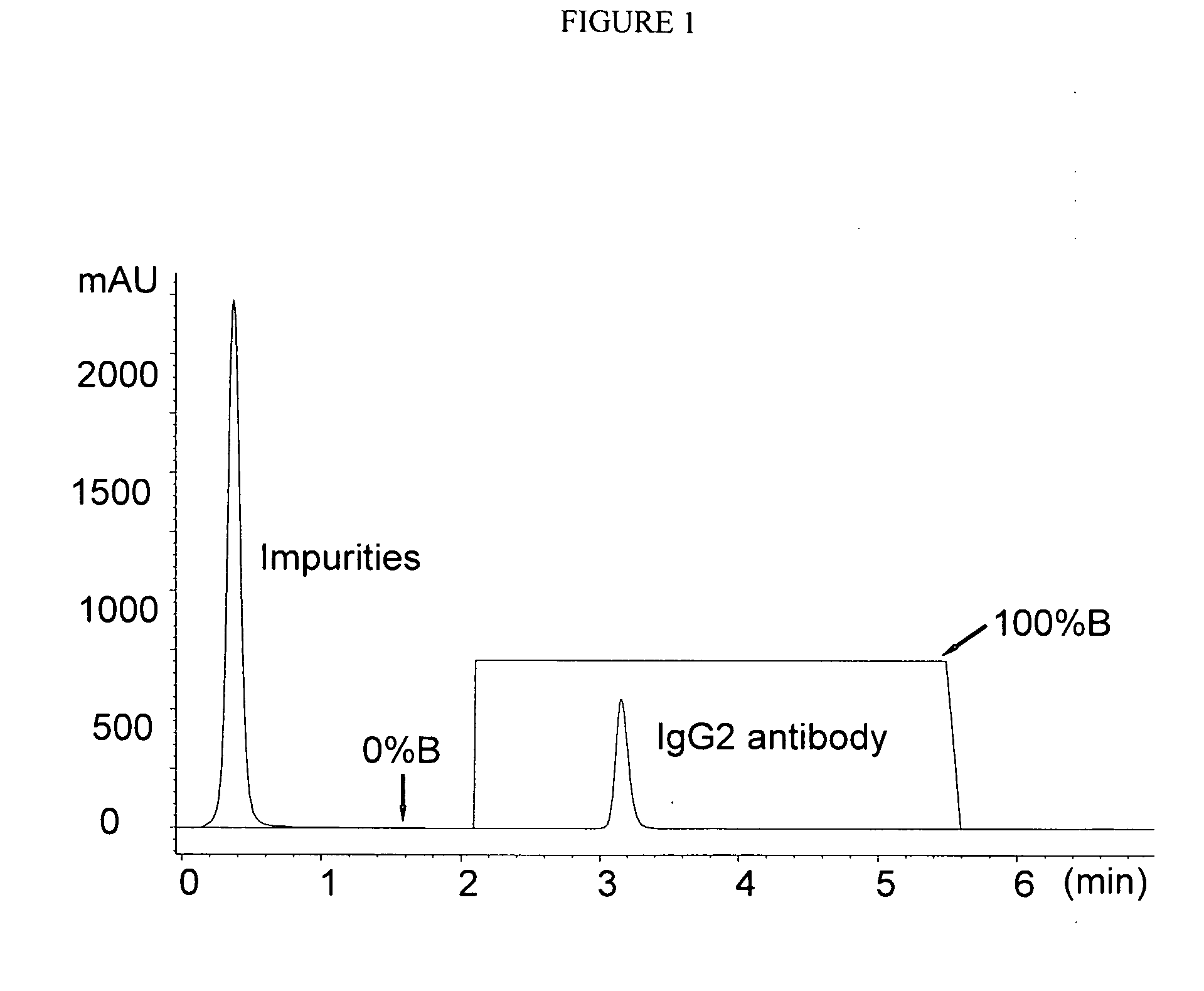
Isolation and purification of antibodies using protein a affinity chromatography
ActiveUS20100135987A1Easy to disassembleReduce or inactivate pH-sensitive virusesAntipyreticAnalgesicsIon exchangeAntibody Affinity Chromatography
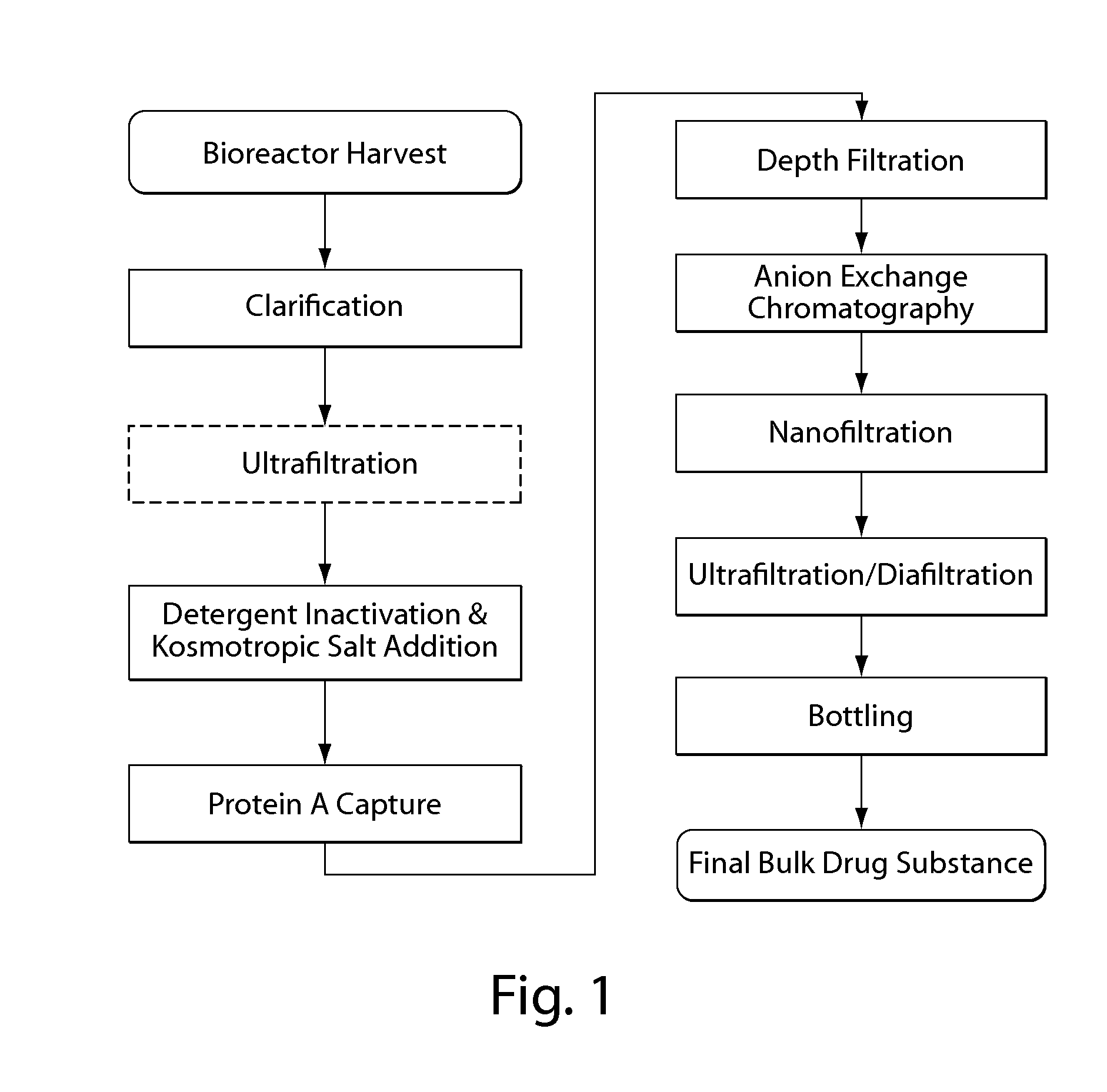
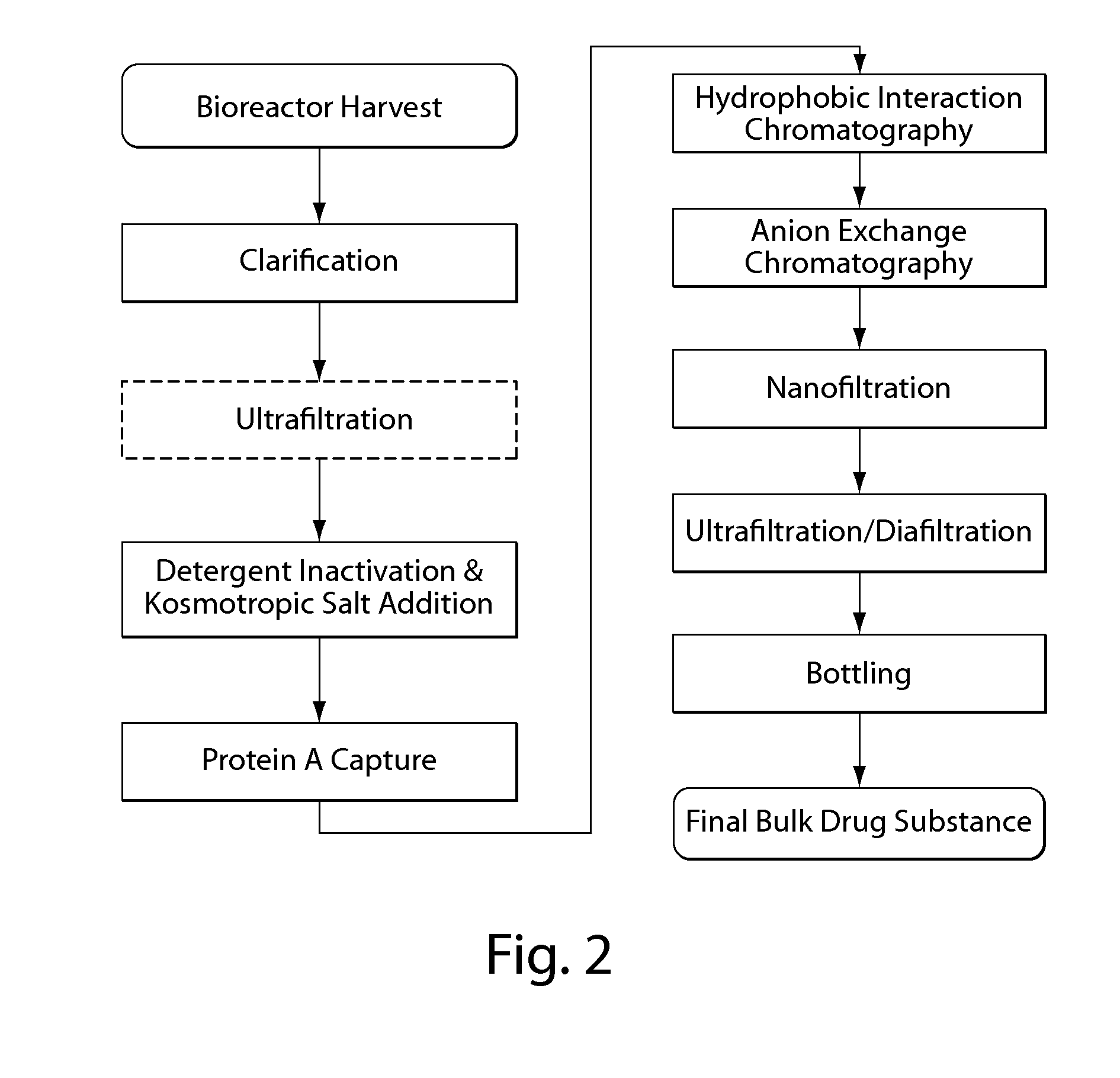
Disclosed herein are methods for the isolation and purification of antibodies wherein the use of an affinity chromatographic step results in an antibody composition sufficiently pure for pharmaceutical uses. The methods described herein comprise pH viral reduction / inactivation, ultrafiltration / diafiltration, affinity chromatography, preferably Protein A affinity, ion exchange chromatography, and hydrophobic chromatography. Further, the present invention is directed toward pharmaceutical compositions comprising one or more antibodies of the present invention.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Monolayer modification to gold coated stents to reduce adsorption of protein
A stent has a body and a surface with at least a portion of the surface comprising metal with a coating thereon. The coating is selected from the group consisting of thiols and disulfides and combinations thereof. The thiols are of the form R-SH and the disulfide of the form R-S-S-R'' where R is an alkyl group and R'' is an alkyl group. The metal is selected from the group consisting of noble metals, silver and copper.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Substrates for covalent tethering to proteins
ActiveUS20050272114A1Efficient loadingLoad is outside loadMaterial nanotechnologyHydrolasesAmino acid substitutionWild type
A mutant hydrolase optionally fused to a protein of interest is provided. The mutant hydrolase is capable of forming a bond with a substrate for the corresponding nonmutant (wild-type) hydrolase which is more stable than the bond formed between the wild-type hydrolase and the substrate and has at least two amino acid substitutions relative to the wild-type hydrolase. Substrates for hydrolases comprising one or more functional groups are also provided, as well as methods of using the mutant hydrolase and the substrates of the invention. Also provided is a fusion protein capable of forming a stable bond with a substrate and cells which express the fusion protein.
Owner:PROMEGA
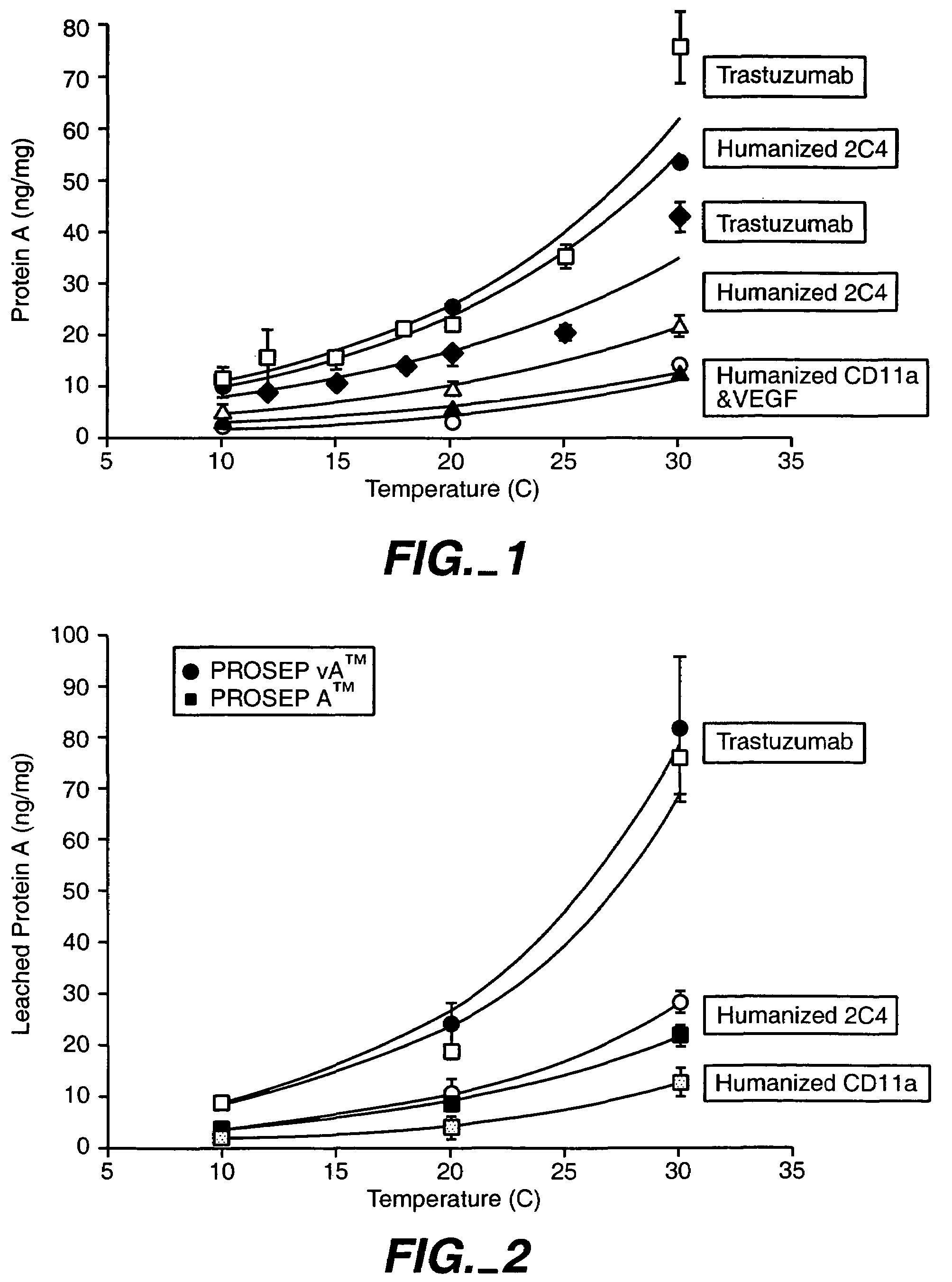
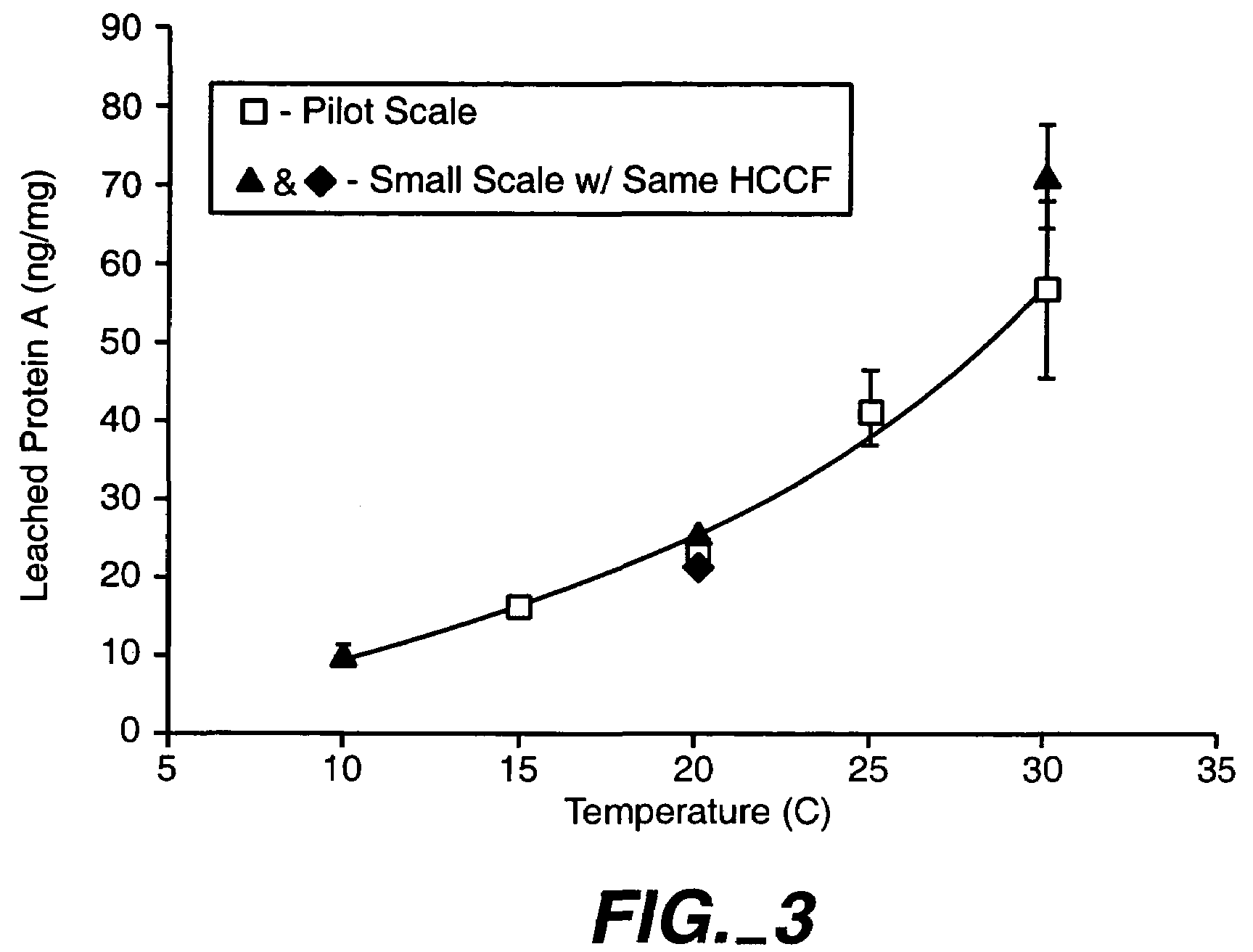
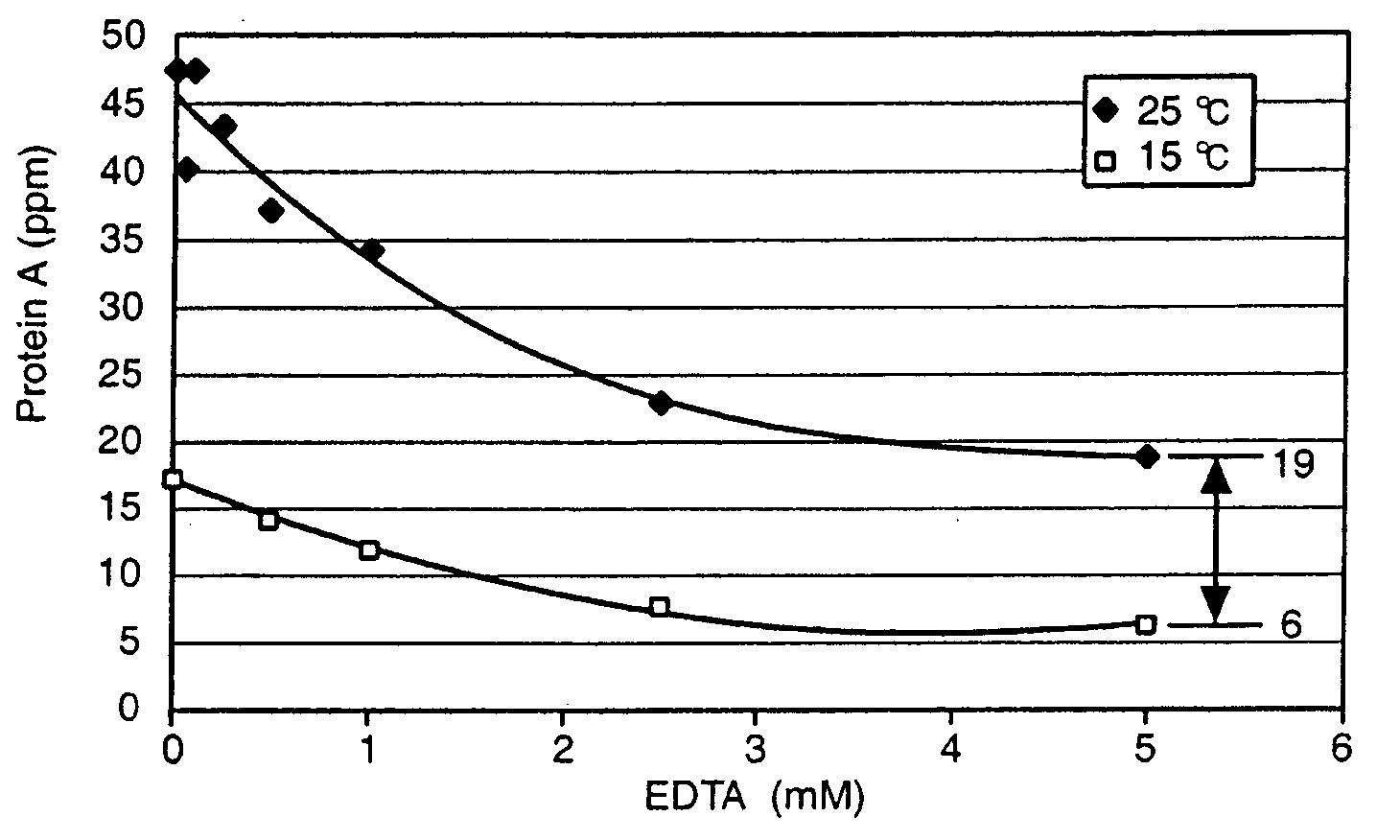
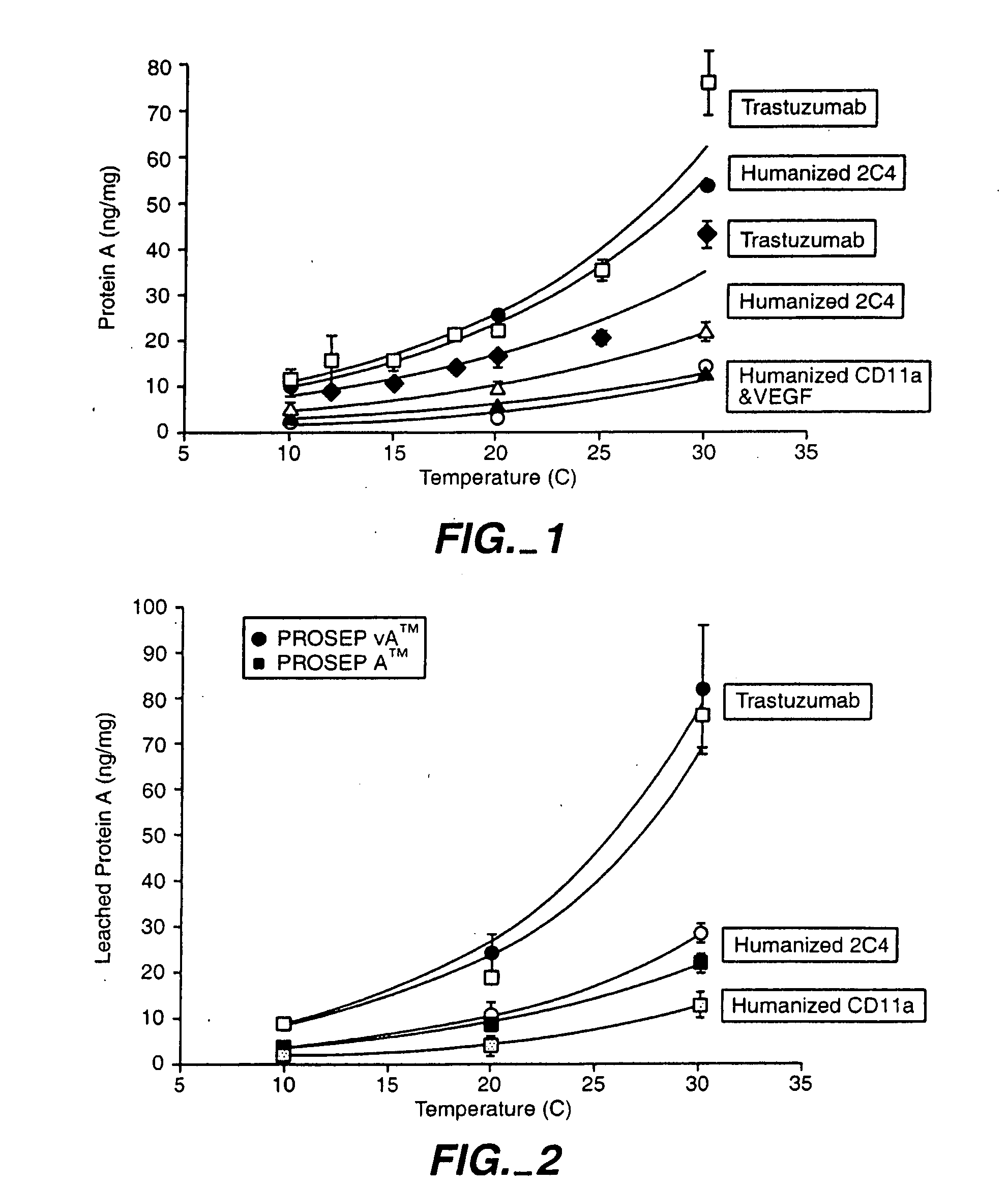
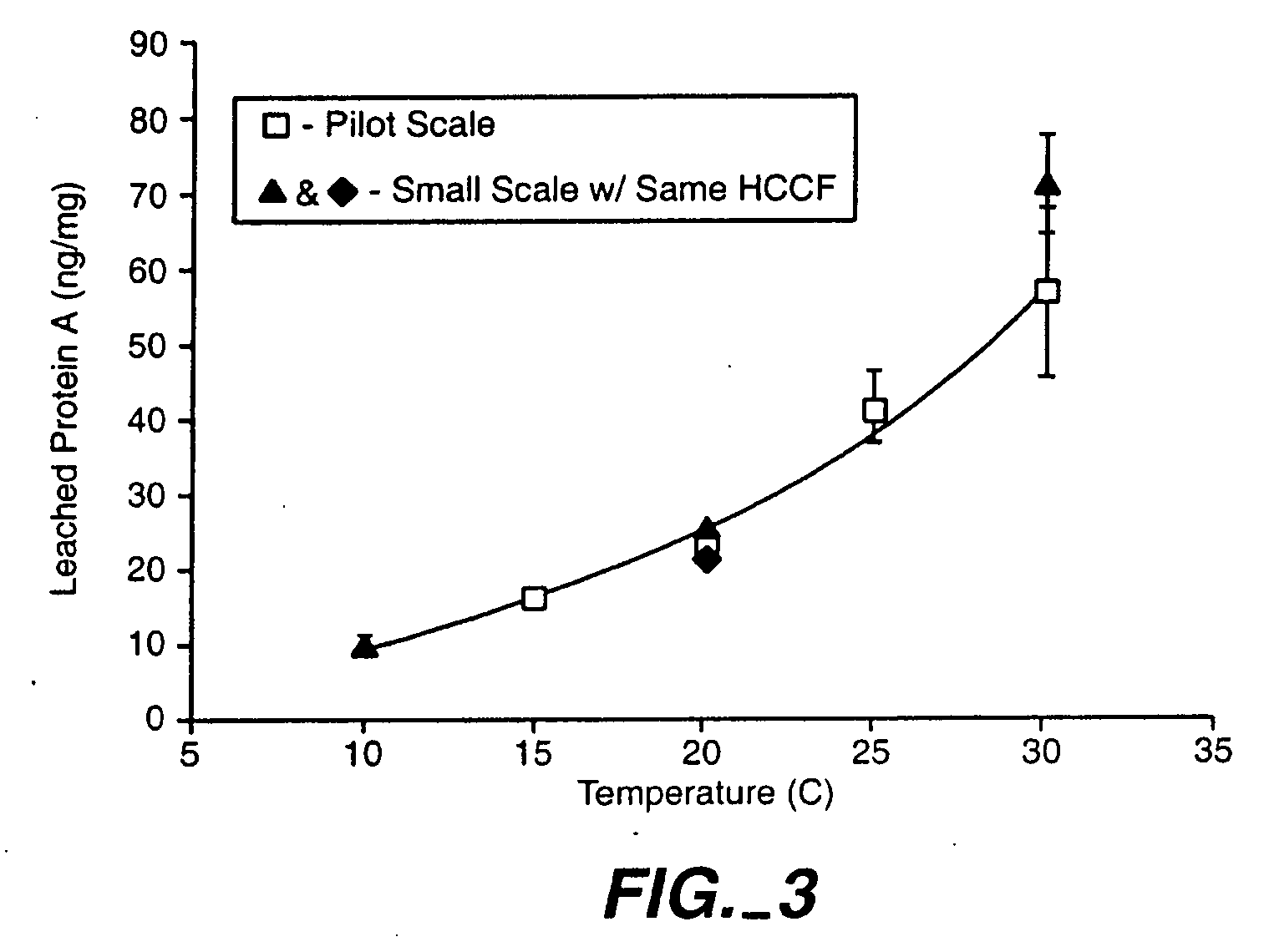
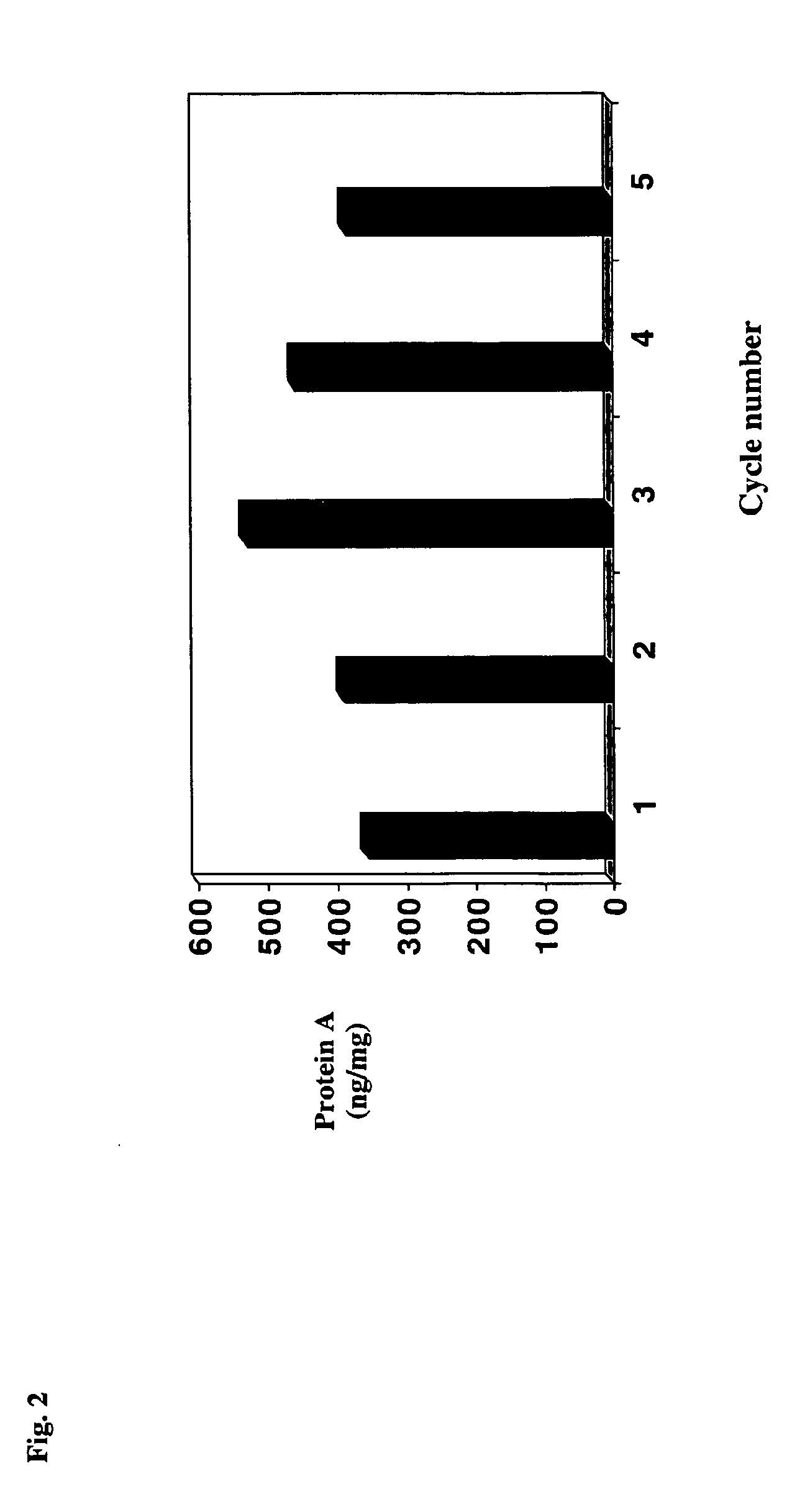
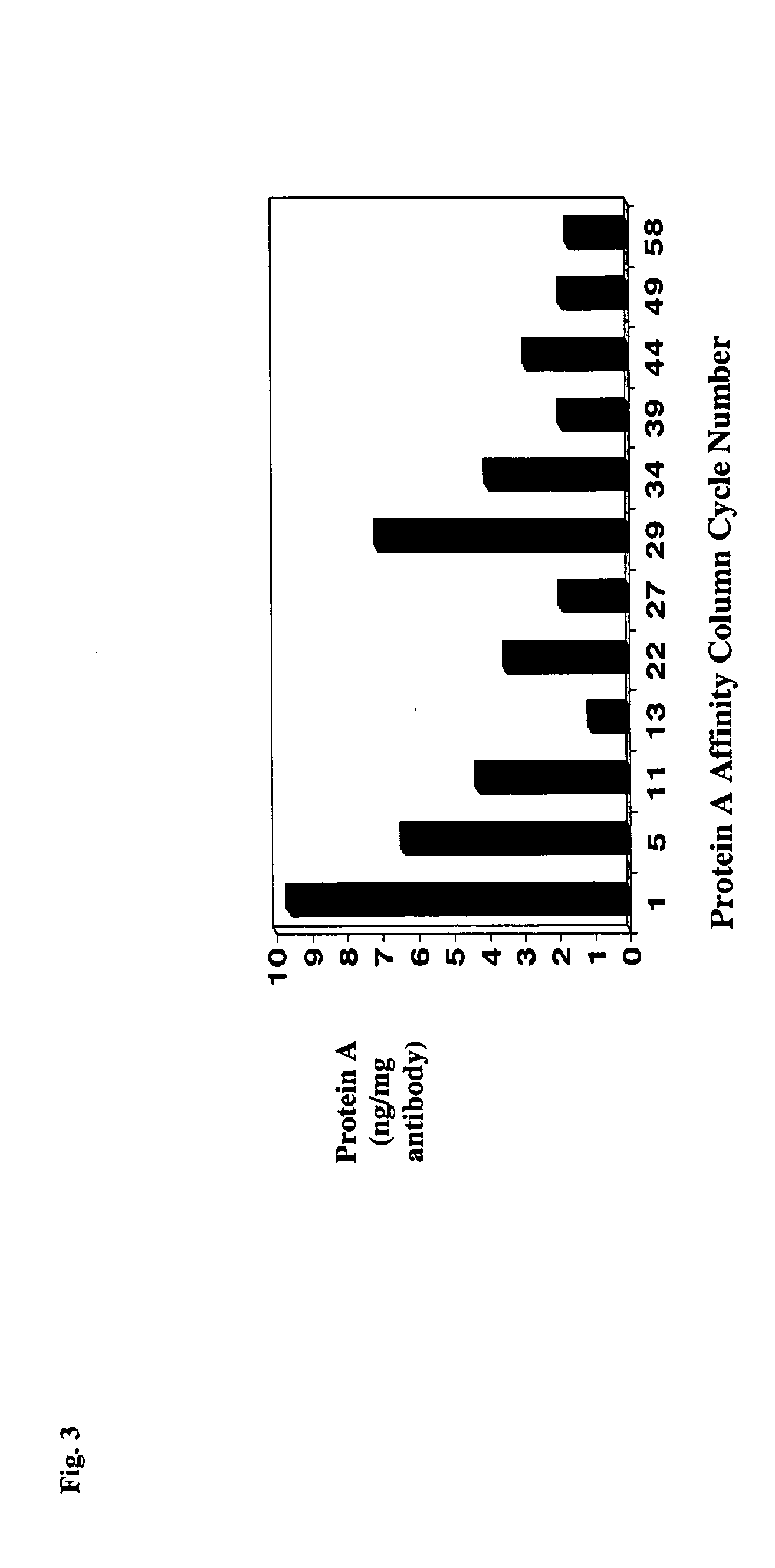
Reducing protein A leaching during protein A affinity chromatography
ActiveUS7485704B2Reduce the temperatureProtein A leaching is reduced.Serum immunoglobulinsSolid sorbent liquid separationProteinase activityAntibody Affinity Chromatography
A method for reducing leaching of protein A during protein A affinity chromatography is described which involves reducing temperature or pH of, or by adding one or more protease inhibitors to, a composition that is subjected to protein A affinity chromatography.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Modified Proteins
InactiveUS20080108557A1Prolonged Circulatory Half-LifeReduce in quantityPeptide/protein ingredientsAlbumin peptidesGlycosyltransferasePeptide
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Covalent tethering of functional groups to proteins
ActiveUS7238842B2Rapidly and efficiently loaded intoRapidly and efficiently loaded into and washed outCarbamic acid derivatives preparationHydrolasesTetheringWild type
A mutant hydrolase optionally fused to a protein of interest is provided. The mutant hydrolase is capable of forming a bond with a substrate for the corresponding nonmutant (wild-type) hydrolase which is more stable than the bond formed between the wild-type hydrolase and the substrate. Substrates for hydrolases comprising one or more functional groups are also provided, as well as methods of using the mutant hydrolase and the substrates of the invention. Also provided is a fusion protein capable of forming a stable bond with a substrate and cells which express the fusion protein.
Owner:PROMEGA
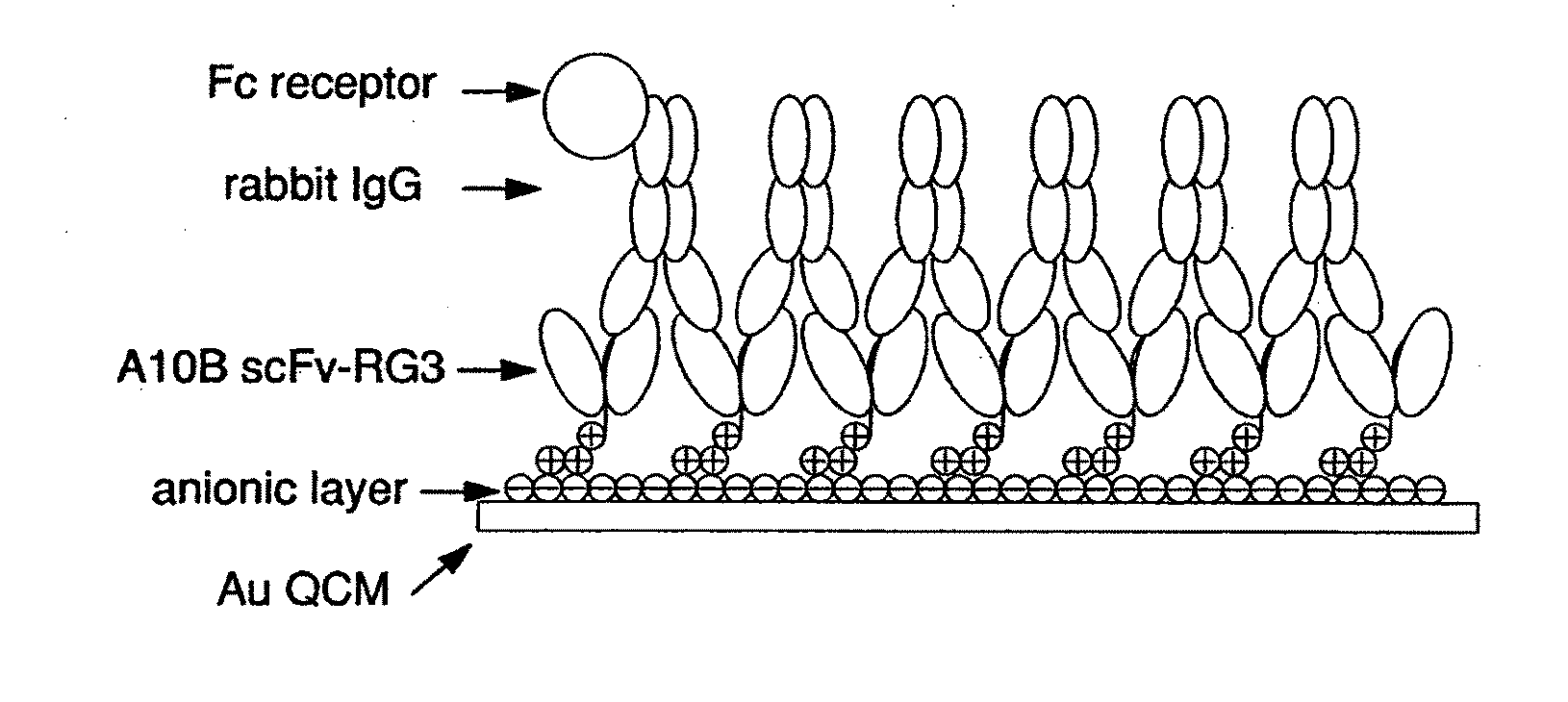
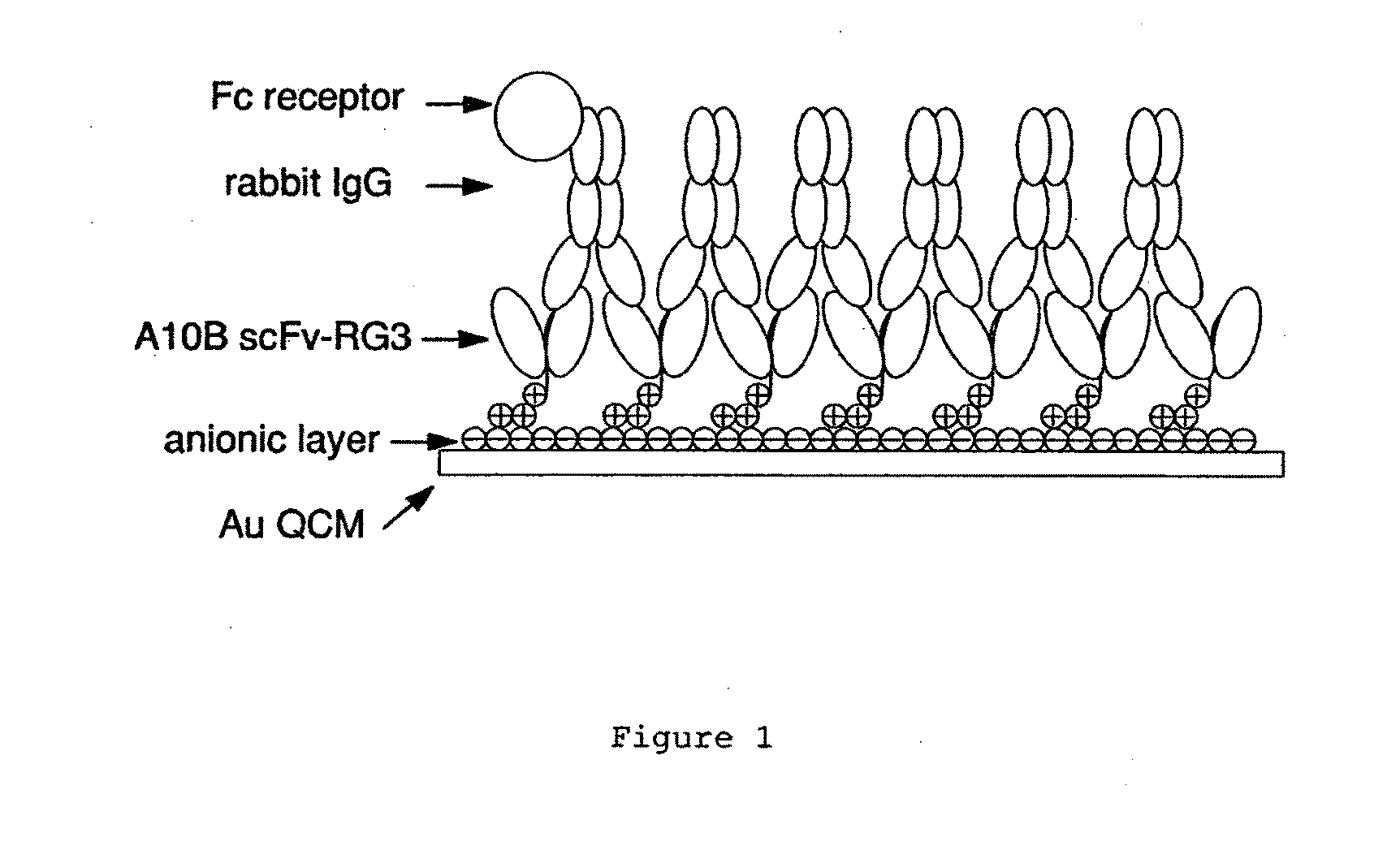
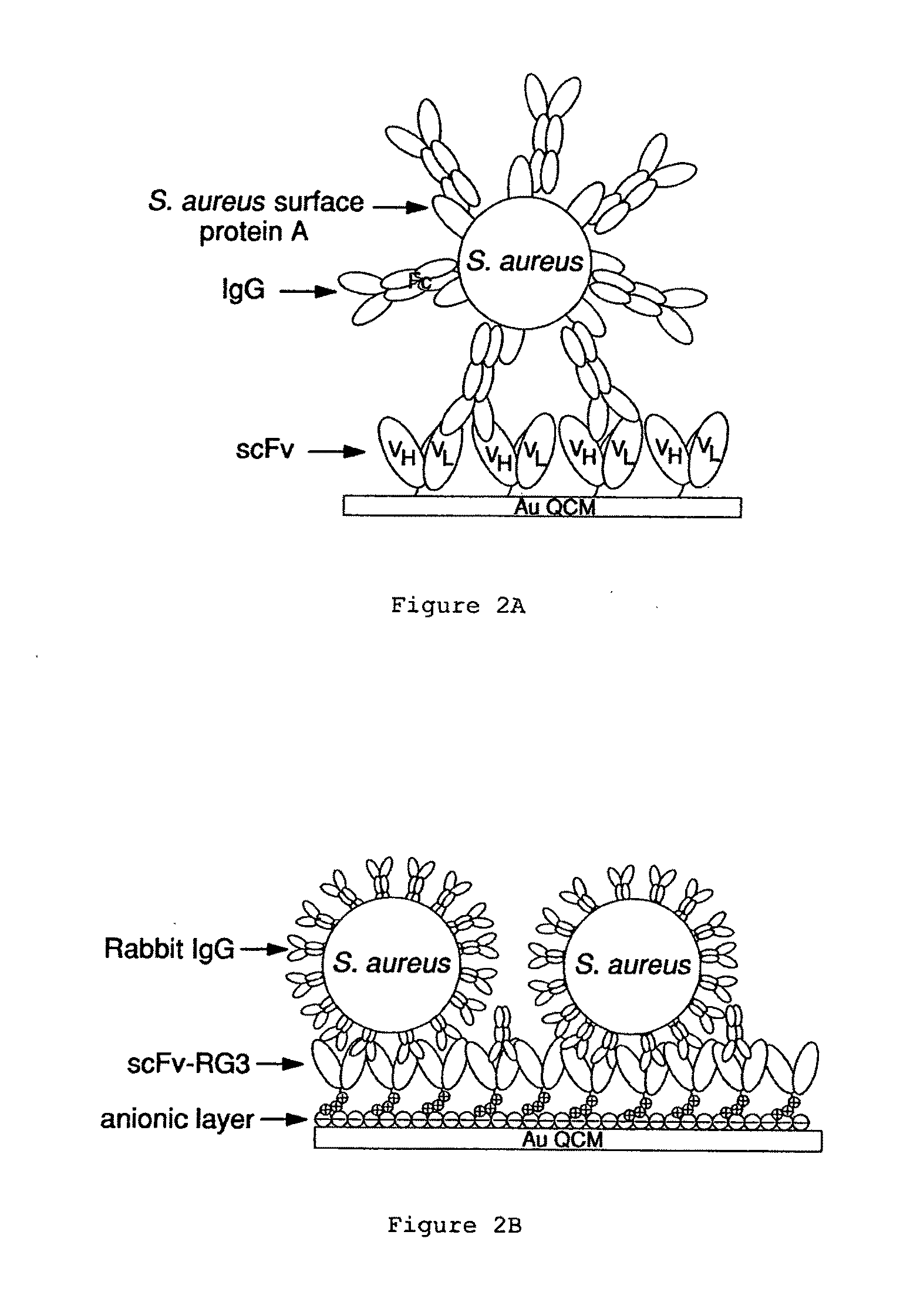
Immunosensors: scFv-linker design for surface immobilization
InactiveUS20110201032A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologySingle-Chain AntibodiesSide chain
An apparatus and methods for binding an analyte of interest in a sample are provided. The apparatus comprises a substrate with an exposed surface with an compound, that is electrostatically charged or capable of forming hydrogen bonds, provided bound to the solid substrate. A recombinant single chain antibody (scFv) molecule specific for the analyte of interest, having one or more amino acids with charged or hydrogen-bond forming sidechains in a linker polypeptide portion, is bound to the layer on the solid substrate. When the analyte of interest is present in the sample the scFv binds the analyte to the solid substrate. The apparatus can be used with an immunoglobulin layer to detect Fc receptors, so as to detect microorganisms such as Staphylococcus aureus having protein A or protein G.
Owner:OAKLAND UNIVESITY +1
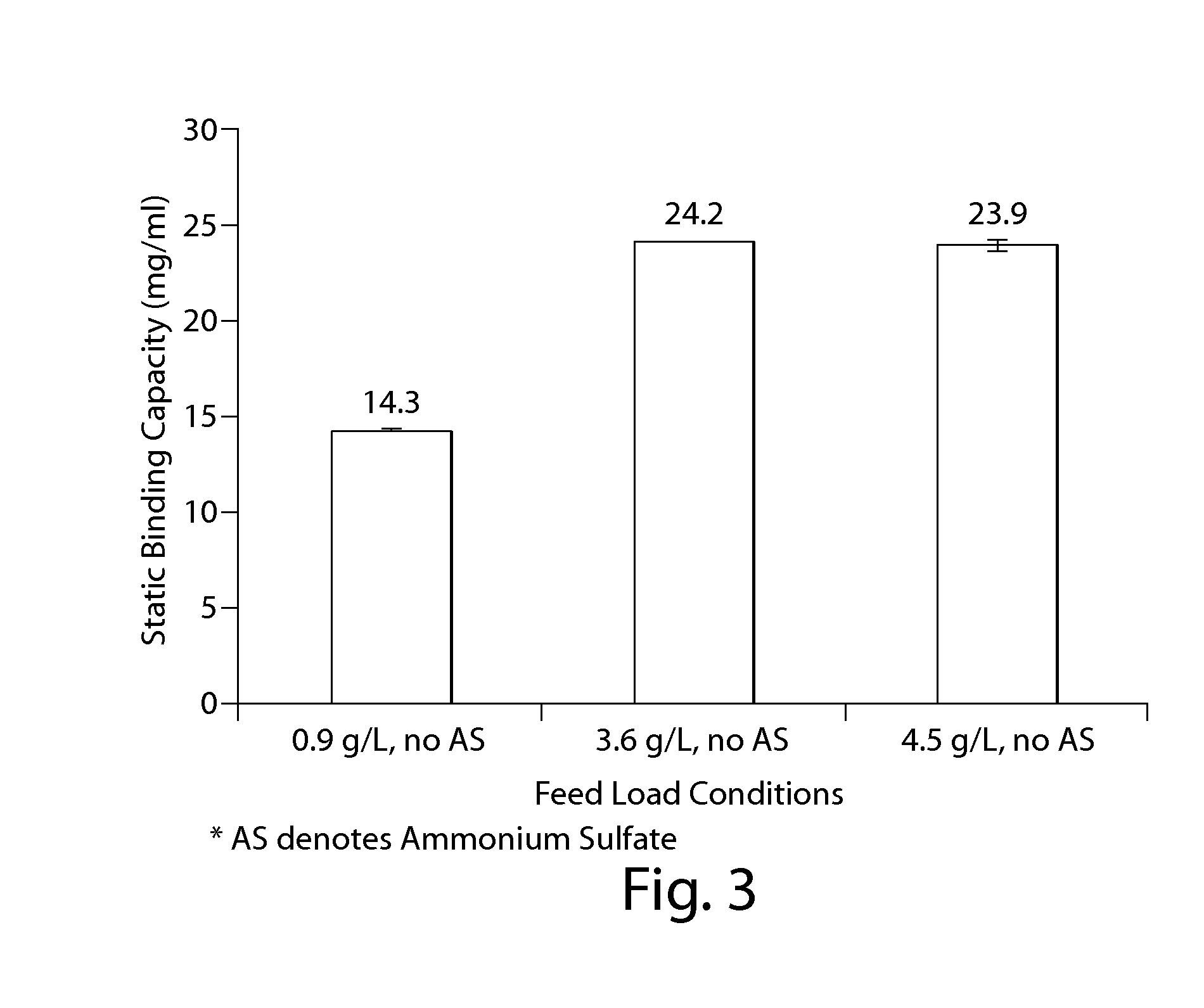
Purification of non-human antibodies using kosmotropic salt enhanced protein a affinity chromatography
InactiveUS20140154270A1Solid sorbent liquid separationPeptide preparation methodsKosmotropicWeak binding
The present invention is directed to methods for purifying a non-human antibody, or antigen binding portion thereof, exhibiting weak binding strength and low binding capacity for Protein A chromatography media. In one aspect, a kosmotropic salt solution is employed to promote the hydrophobic interaction between the non-human antibody, or antigen binding portion thereof, and the Protein A ligand, thereby enhancing the binding of the non-human antibody, or antigen binding portion thereof, to the Protein A chromatography media. In another aspect, the concentration of the non-human antibody, or antigen binding portion thereof, in a sample comprising the antibody, or antigen binding portion thereof, exposed to a Protein A chromatography media is increased to enhance the binding of the non-human antibody, or antigen binding portion thereof, on the Protein A chromatography media.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
VEGF-related protein
InactiveUS20030166873A1Organic active ingredientsSenses disorderPhosphorylationDrug biological activity
A human VEGF-related protein (VRP) has been identified and isolated that binds to, and stimulates the phosphorylation of, the receptor tyrosine kinase Flt4. The VRP is postulated to be a third member of the VEGF protein family. Also provided are antibodies that bind to VRP and neutralize a biological activity of VRP, compositions containing the VRP or antibody, methods of use, chimeric polypeptides, and a signal polypeptide for VRP.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
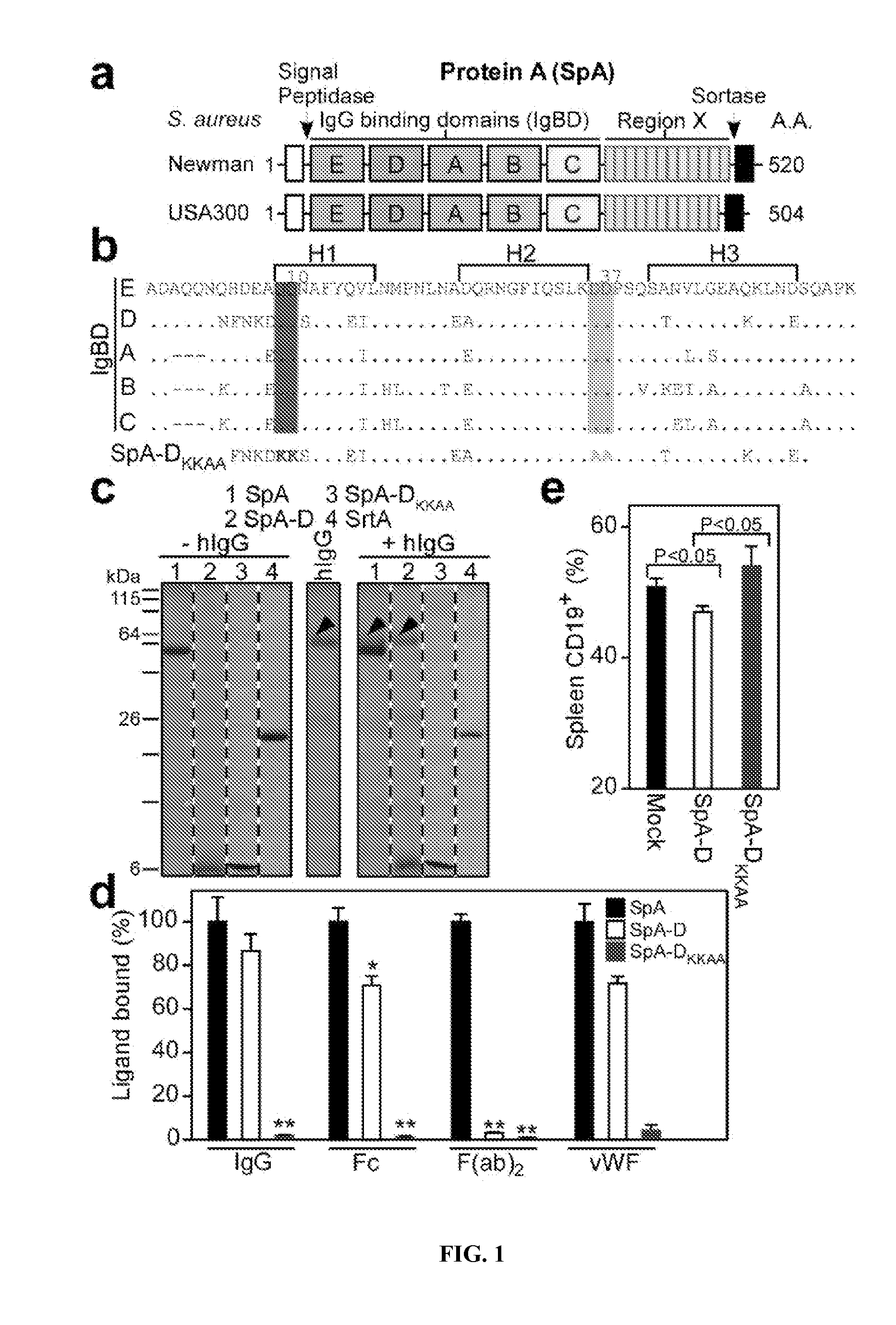
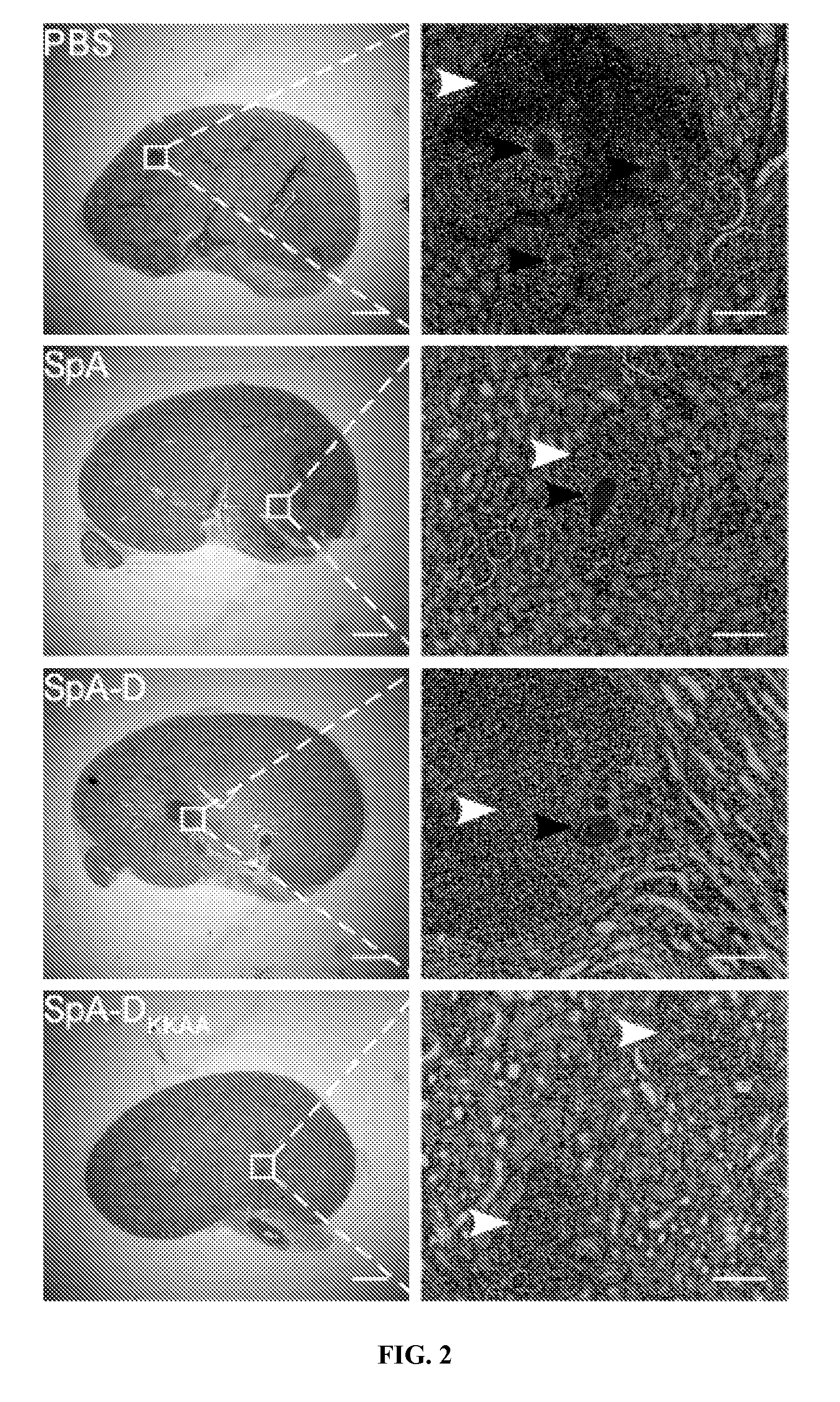
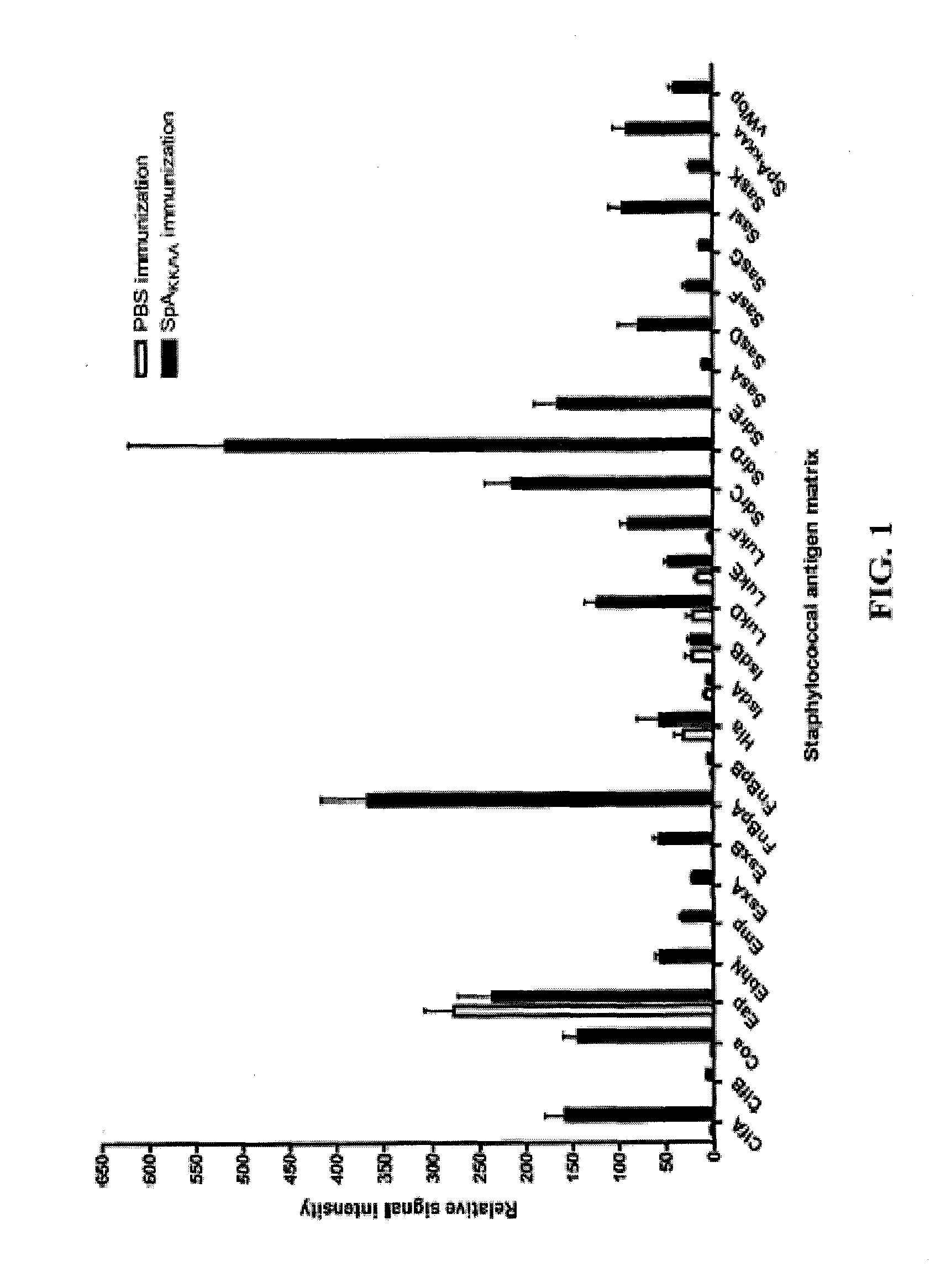
Compositions and methods related to protein a (SPA) variants
ActiveUS20120114686A1Reduced activityPrevents alleviates ameliorates symptomAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsStaphylococcus xylosusProtein A
Disclosed are methods and compositions for treating or preventing a Staphylococcus bacterial infection using a non-toxigenic Protein A (SpA) variant.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Compositions and methods related to protein a (SPA) variants
ActiveUS20130171183A1Prevents alleviates ameliorates symptomImprove survivalAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsStaphylococcusVirology
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for treating or preventing a bacterial infection, particularly infection by a Staphylococcus bacterium. The invention provides methods and compositions for stimulating an immune response against the bacteria. In certain embodiments, the methods and compositions involve a non-toxigenic Protein A (SpA) variant.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Isolating Cells Expressing Secreted Proteins
InactiveUS20090137416A1Easy to detectImprove isolationLibrary screeningBiological material analysisSurface displayVariable domain
A method of detecting and isolating cells that produce a secreted protein of interest (POI) that has a T cell receptor variable domain, comprising: a) constructing a cell line transiently or stably expressing a cell surface capture molecule, which binds the POI, by transfecting the cell line with a nucleic acid that encodes such cell surface capture molecule; b) transfecting said cell simultaneously or subsequently with a second nucleic acid that encodes a POI wherein such POI is secreted; c) detecting the surface-displayed POI by contacting the cells with a detection molecule, which binds the POI; and d) isolating cells based on the detection molecule.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Reducing protein a leaching during protein a affinity chromatography
ActiveUS20090099344A1Reduce the temperatureProtein A leaching is reducedSerum immunoglobulinsSolid sorbent liquid separationProteinase activityEnzyme inhibitor
A method for reducing leaching of protein A during protein A affinity chromatography is described which involves reducing temperature or pH of, or by adding one or more protease inhibitors to, a composition that is subjected to protein A affinity chromatography.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS RELATED TO PROTEIN A (SpA) ANTIBODIES AS AN ENHANCER OF IMMUNE RESPONSE
ActiveUS20130136746A1Limiting staphylococcal abscess formationLimiting persistenceAntibacterial agentsAntibody ingredientsBacilliVirology
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Antibody purification by protein a and ion exchange chromatography
ActiveUS20060194953A1Serum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansIon exchangeAntibody Affinity Chromatography
A novel method for selectively removing leaked protein A from antibody purified by means of protein A affinity chromatography is disclosed.
Owner:LONZA BIOLOGICS PLC
Classification of Protein Sequences and Uses of Classified Proteins
A searchable protein database is disclosed. The protein database comprises a plurality of entries, each entry having a sufficiently short predicting sequence and a protein classifier corresponding to the predicting sequence. An unclassified protein sequence can be classifiable by the database via searching therein for a motif of amino acids matching a predicting sequence of the database, thereby attributing to the unclassified protein a protein classifier.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Media for membrane ion exchange chromatography based on polymeric primary amines, sorption device containing that media, and chromatography scheme and purification method using the same
ActiveUS20090050566A1Improve bindingGood removal effectCation exchanger materialsIon-exchanger regenerationPurification methodsSorbent
Media and devices, such as anion exchangers including such media, wherein the media is a membrane having a surface coated with a polymer such as a polyallylamine. The resulting membrane offers stronger binding of protein impurities and superior removal of host cell proteins from biological samples than conventional ligands based on quaternary ammonium salts, including trimethylammonium ligands. Also described is a chromatography scheme and method for purifying monoclonal antibodies, wherein the anion exchange sorber is placed downstream of an affinity column (such as Protein A or Protein G affinity column) and optionally one or more polishing devices such as cationic exchange columns. Little or no dilution of the cation exchanger pool (or affinity column exchange pool where no cation exchanger is used) is necessary to lower the conductivity of the sample. The sorber functions well to strongly bind host cell proteins and other impurities in biological samples even at high conductivities and pH.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Methods and means for targeted gene delivery
InactiveUS7033834B2Efficient introductionEfficiently introducedBiocideGenetic material ingredientsGene deliveryDelivery vehicle
A method for producing viral gene delivery vehicles which can be transferred to pre-selected cell types by using targeting conjugates. The gene delivery vehicles comprise: 1) the gene of interest; and 2) a viral capsid or envelope carrying a member of a specific binding pair, the counterpart of which is not directly associated with the surface of the target cell. These vehicles can be rendered unable to bind to their natural cell receptor. The targeting conjugates include the counterpart member of the specific binding pair, linked to a targeting moiety which is a cell-type specific ligand (or fragments thereof). The number of the specific binding pair present on the viral vehicles can be, for example, an immunoglobulin binding moiety (e.g., capable of binding to a Fc fragment, protein A, protein G, FcR or an anti-Ig antibody), or biotin, avidin or streptavidin. The virus' outer membrane or capsid may contain a substance which mediates entrance of the gene delivery vehicle into the target cell. Due to the specificity of the ligand, the binding pair's high affinity, and the gene delivery vehicle's inability to be targeted when used alone, the universality of the method for gene delivery, together with its high cell type selectively can be achieved by using various targeting conjugates.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Method for treating and processing lupine seeds containing alkaloid, oil and protein
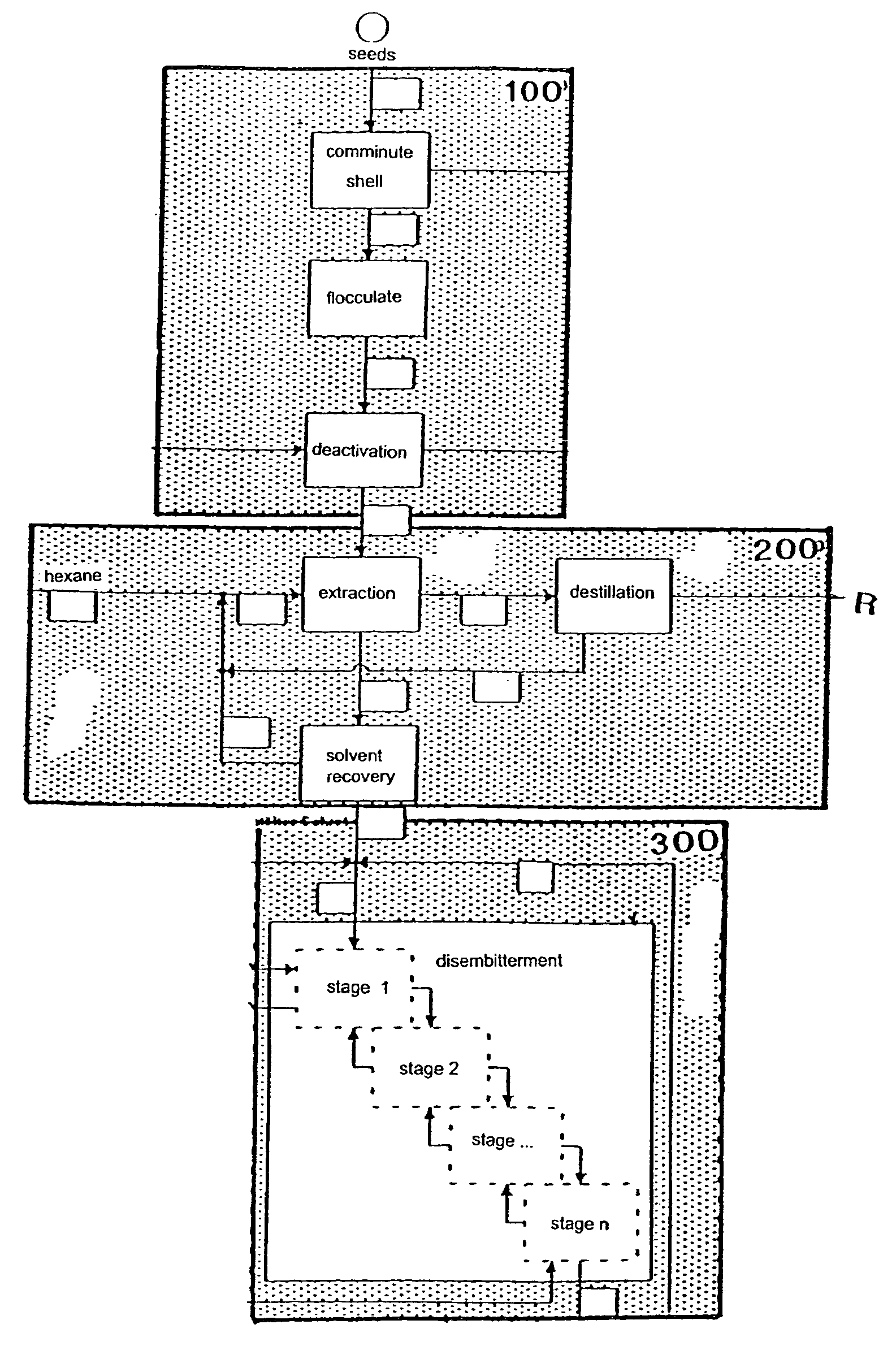
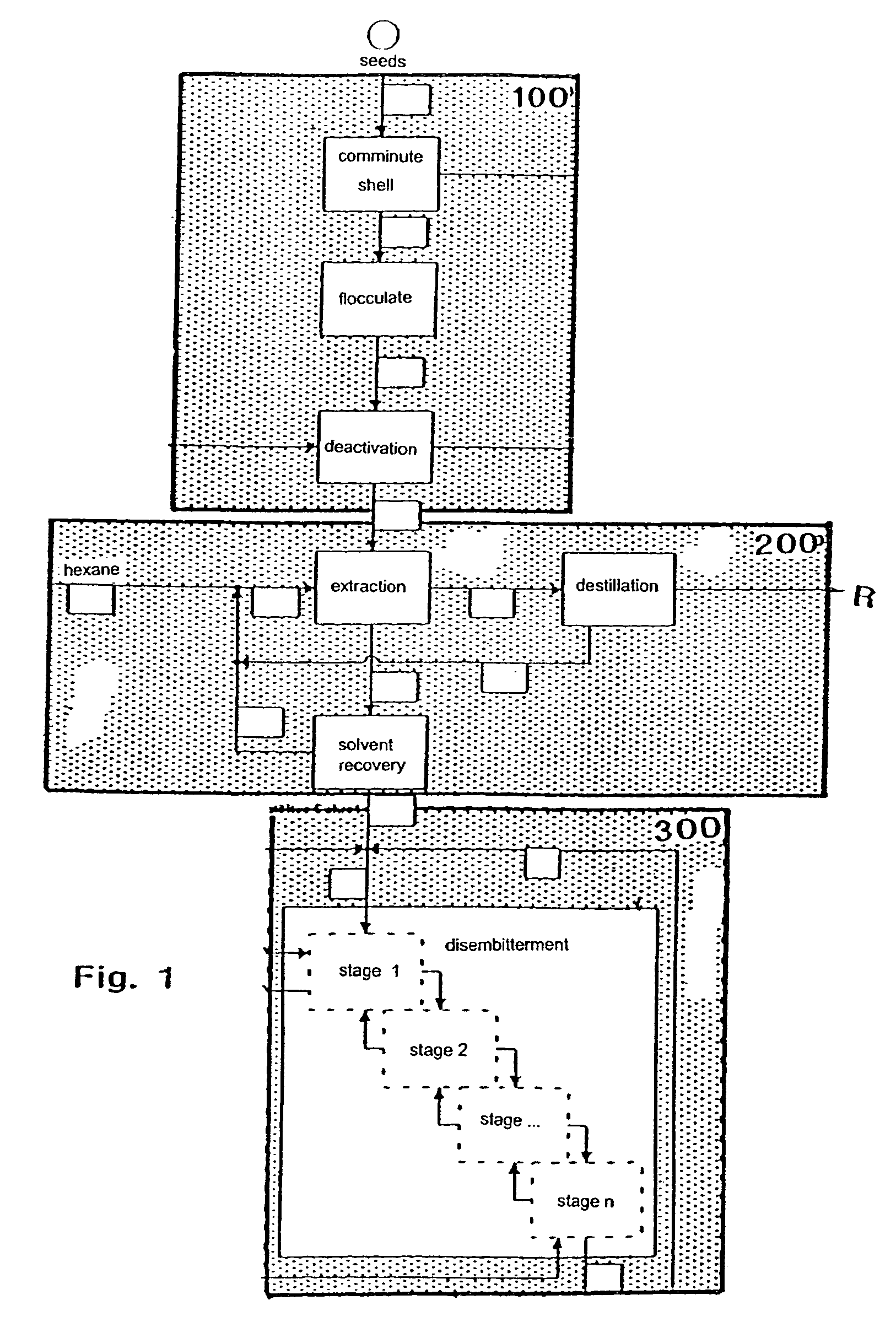
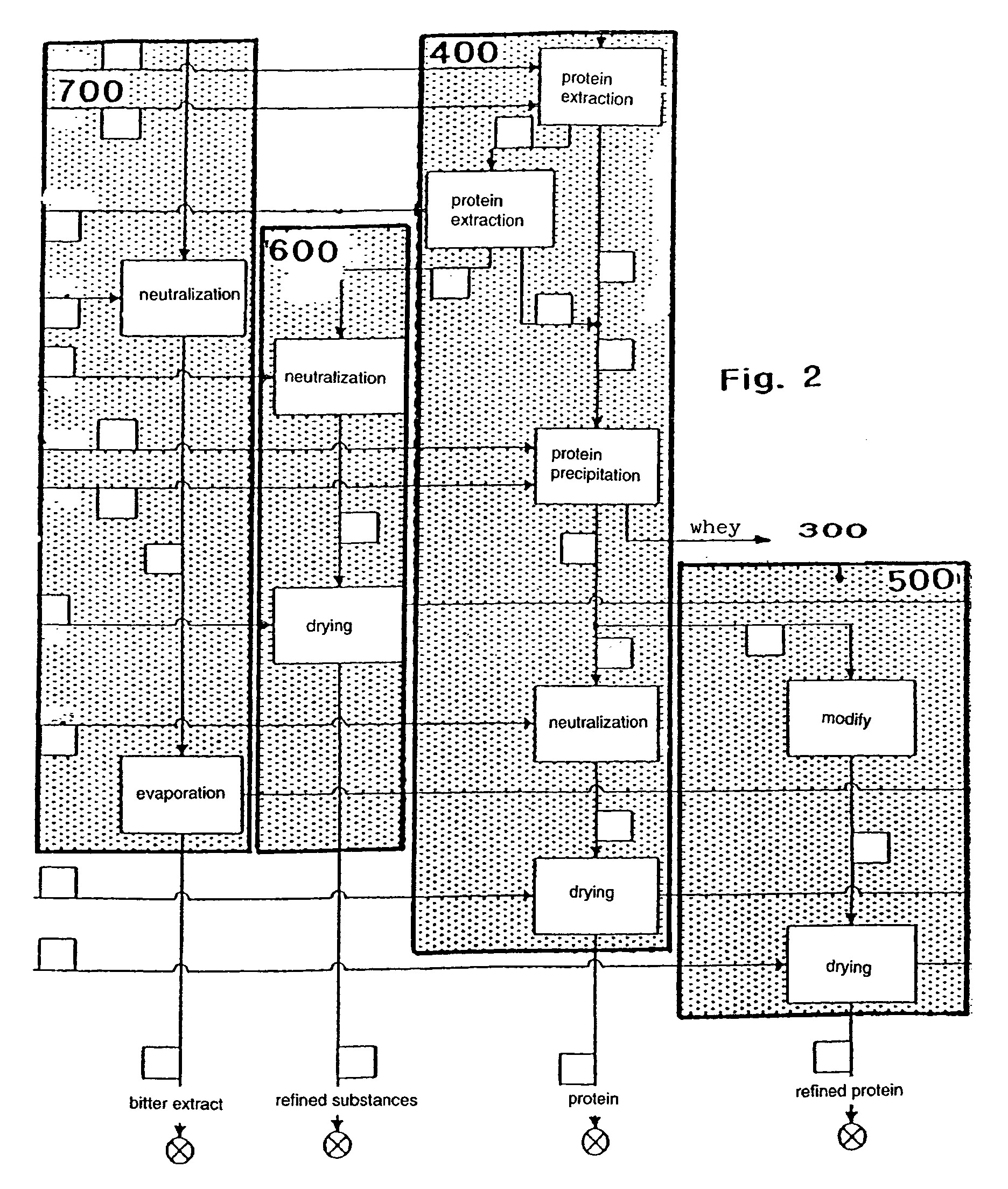
InactiveUS7074449B1Water being largely excludedAvoid heatProtein composition from vegetable seedsFood preparationFractionationPlanting seed
A method of treating and processing alkaloid, oil and protein-containing lupine seeds for the extraction of products from the lupine seeds by means of targeted fractionation is described, whereby the comminuted lupine seed is de-oiled by introducing a solvent and the residue is depleted of substances soluble in the acid range, preferably of alkaloids, by adding acids. The invention is characterized by the provisions that the lupine seeds are comminuted and / or shaped to form discoid flakes in such a way that after pre-crushing of the shelled or non-shelled seed containing the plant seeds the comminution of the plant seeds is carried out by means of a cooled flocculating roller, and the seed is heated by indirect supply of heat, largely with exclusion of water, and that after de-oiling the depletion of the flakes of substances soluble in the acid range, preferably of alkaloids, is performed by aqueous extraction, with a refined product of reduced alkaloid level and an aqueous extract being obtained.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
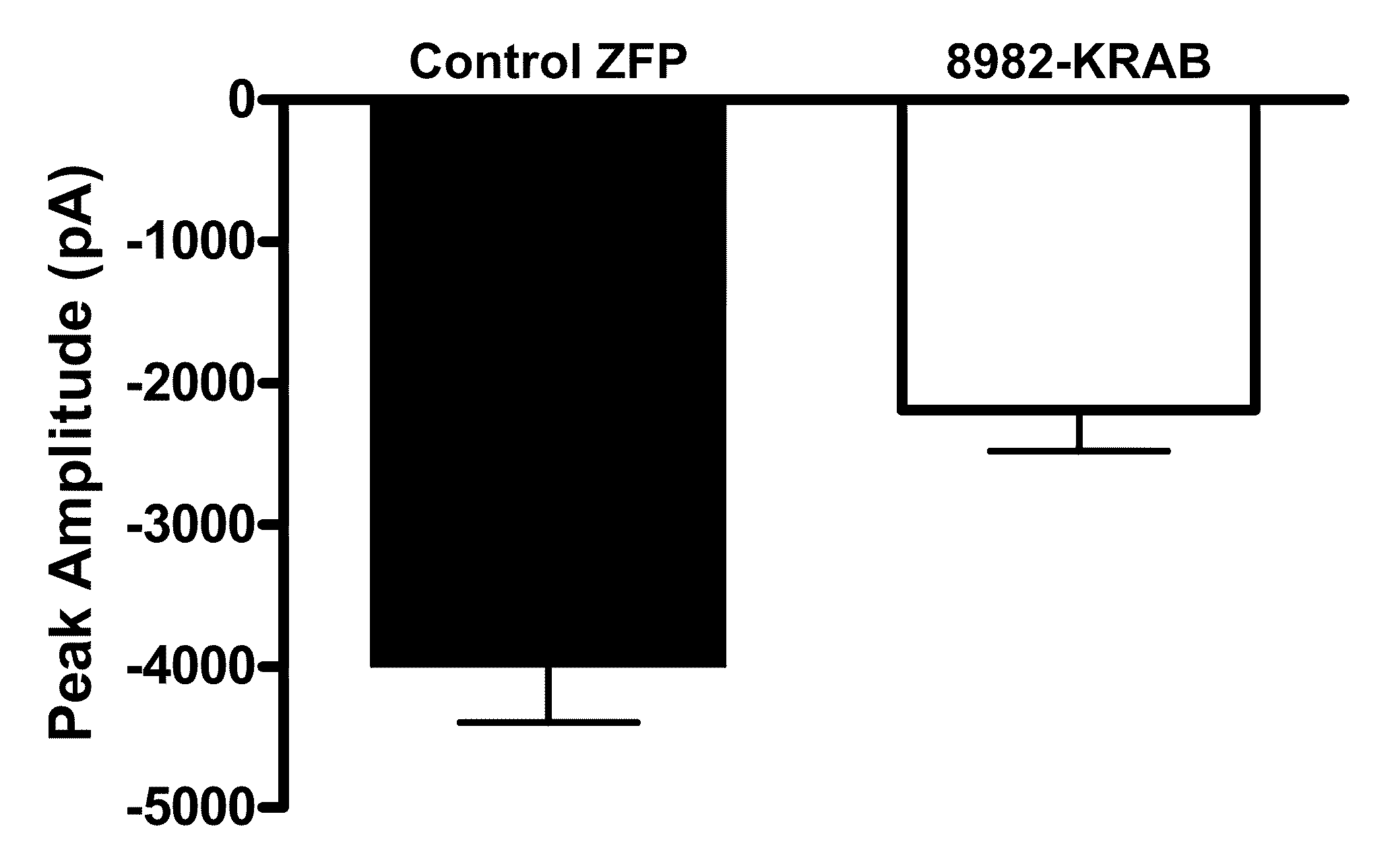
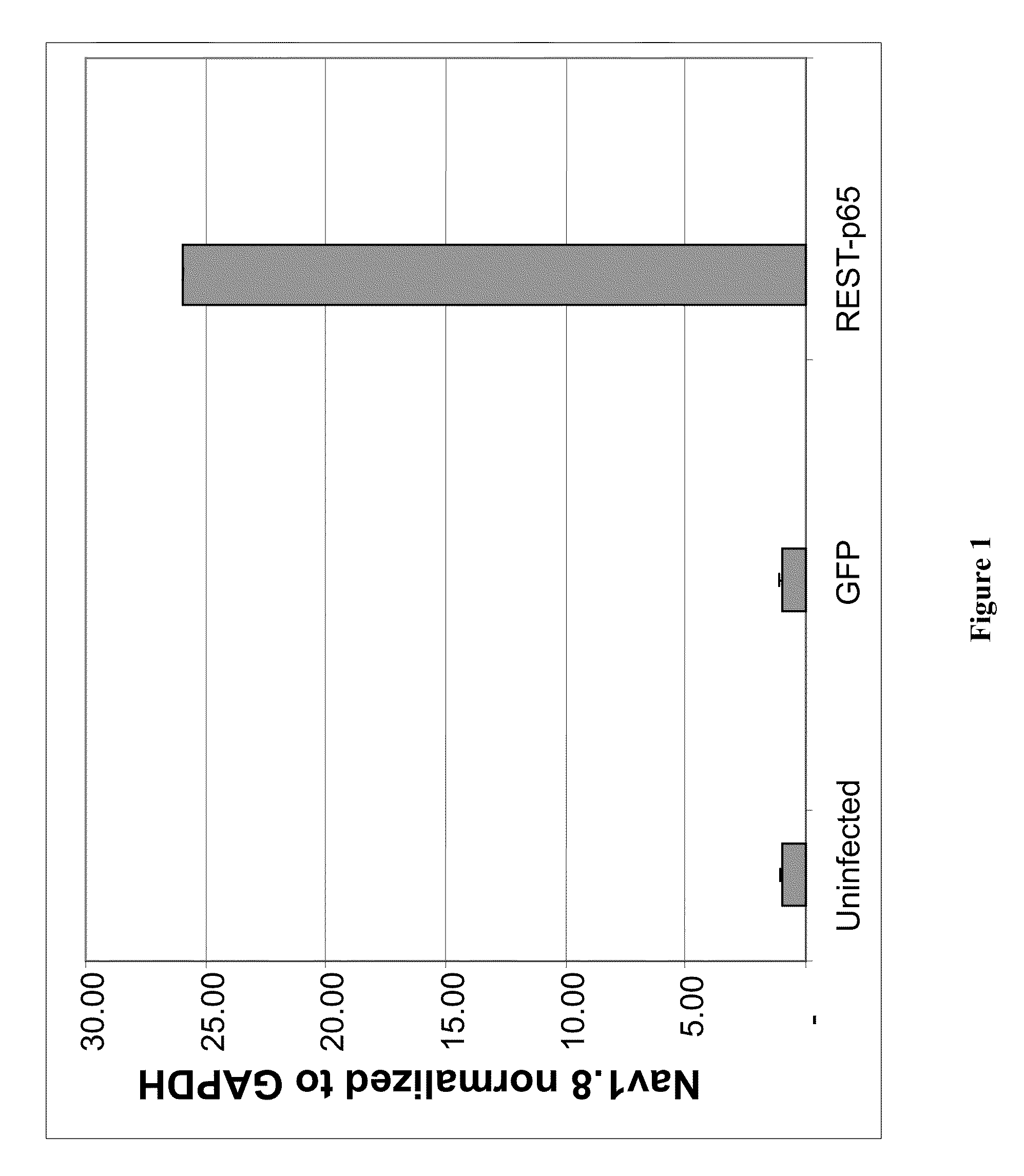
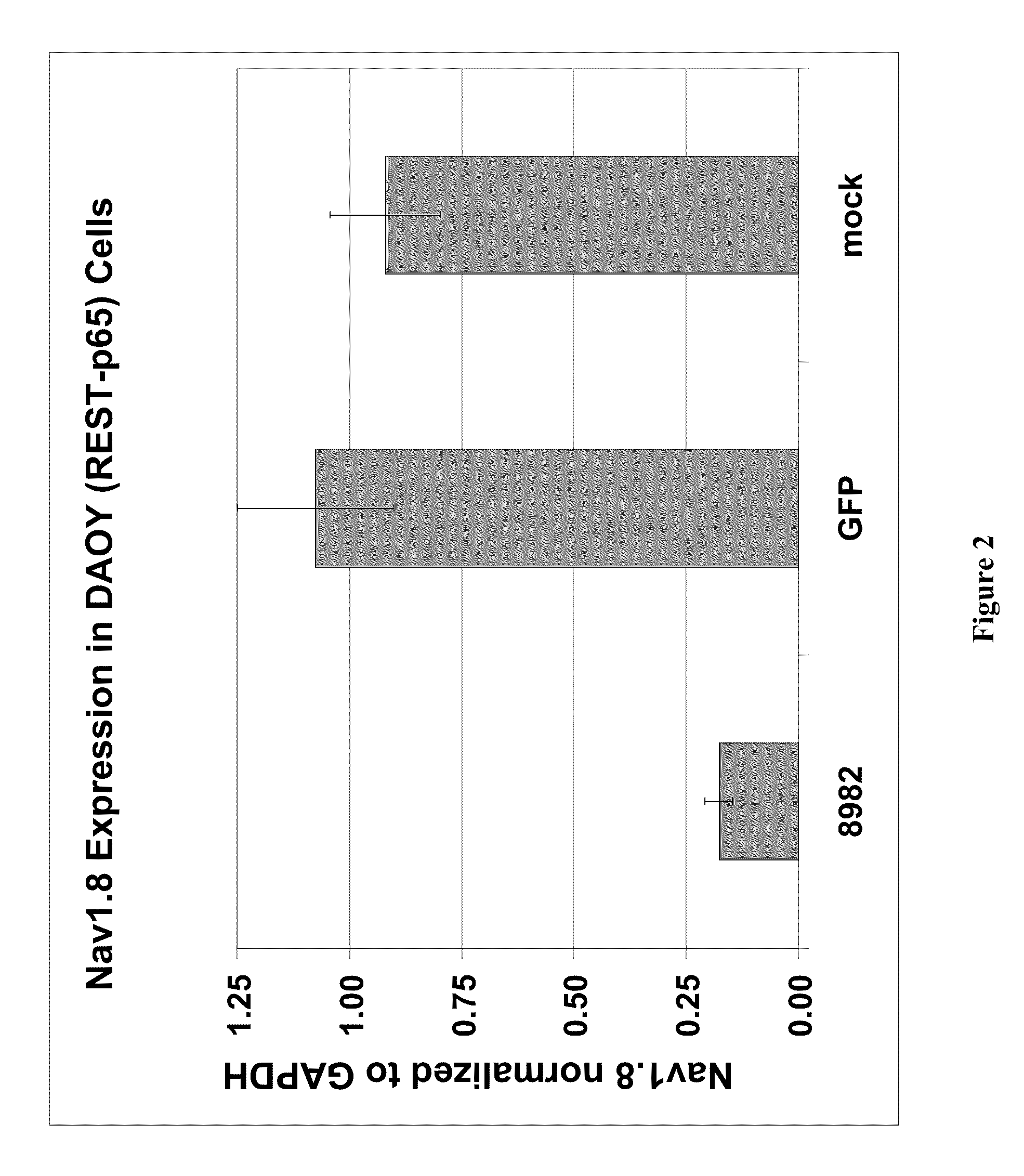
Treatment of chronic pain with zinc finger proteins
InactiveUS20090215878A1Suppress gene expressionModulate physiological processes correlatedOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNormal levelPain patient
A variety of zinc finger proteins (ZFPs) and methods utilizing such proteins are provided for use in treating chronic pain. ZFPs that bind to a target site in genes that are aberrantly expressed in subjects having chronic pain are described. In addition, ZFPs that bind to a target site in genes expressed at normal levels in subjects experiencing chronic pain, modulation of whose expression results in decreased pain perception, are also provided. For example, genes that are over-expressed in the dorsal root ganglia (DRG) of pain patients (e.g., Nav1.8) can be repressed.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
Methods of purifying proteins
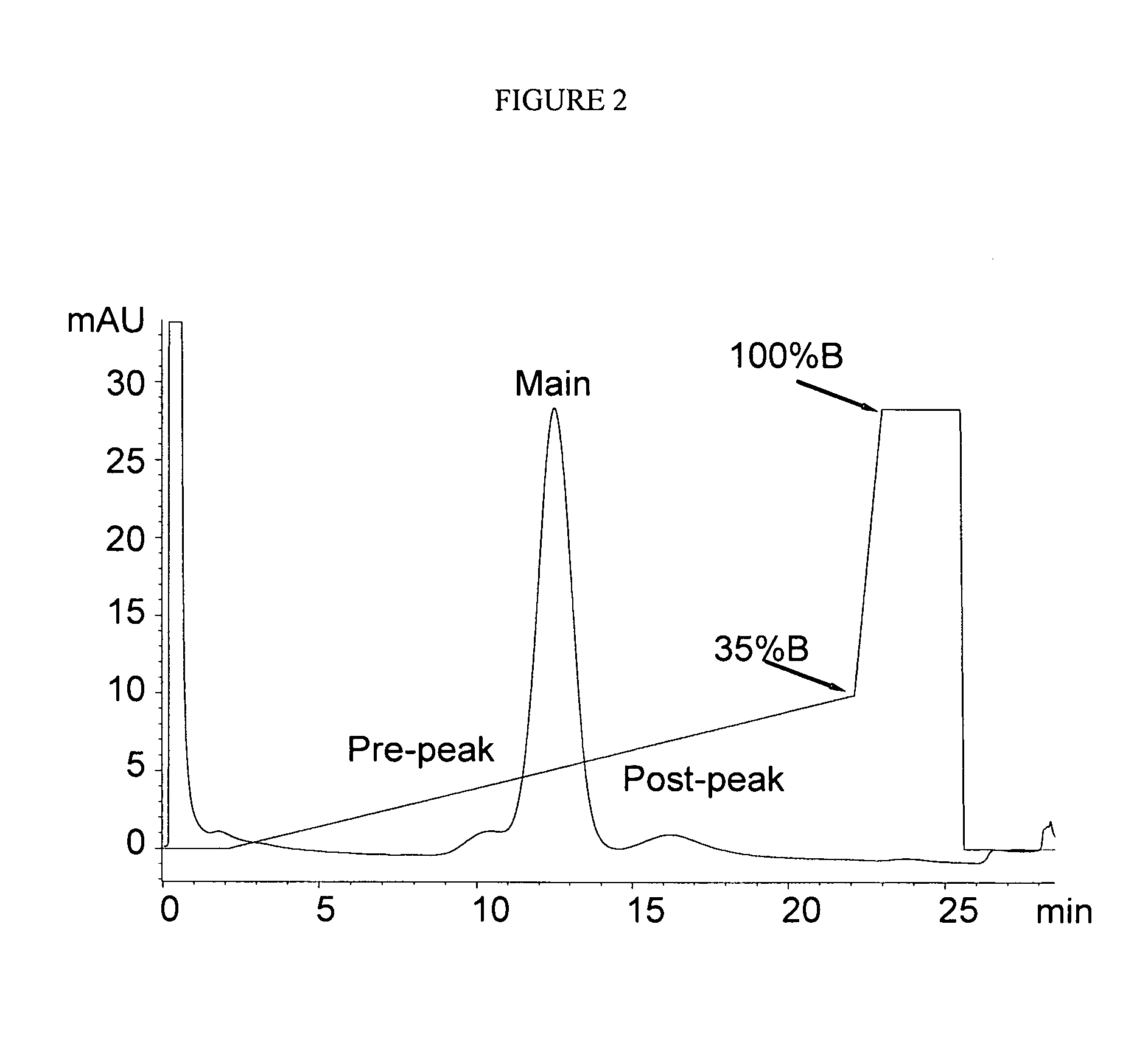
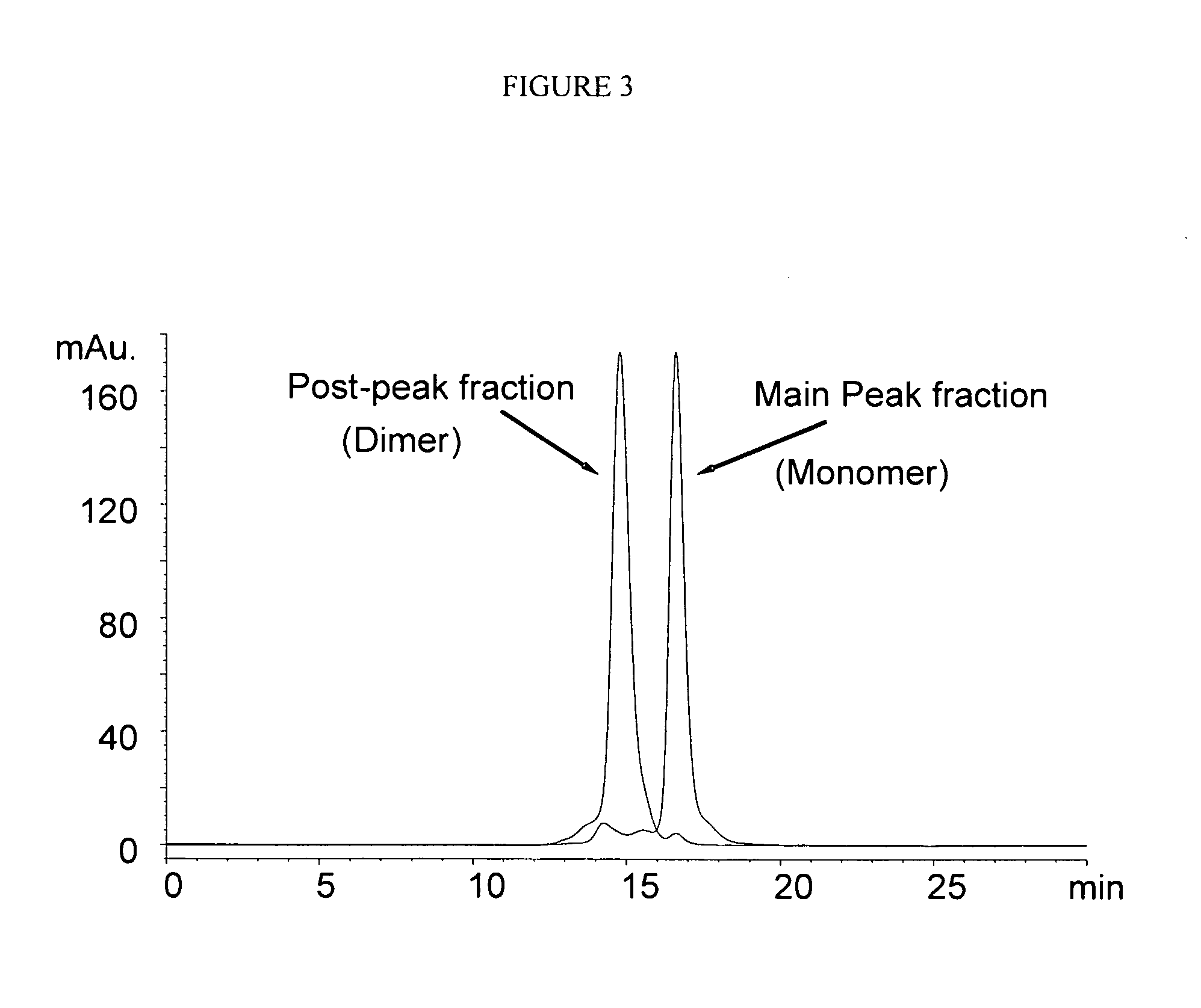
InactiveUS20080167450A1Improve homogeneityUnderstand product qualityPeptide preparation methodsImmunoglobulinsElutionPh gradient
The present invention relates to methods of purifying and analyzing preparations of Fc domain containing polypeptides comprising binding said polypeptide to protein A, more particularly to a protein A column, and eluting with a pH gradient elution system. This method enhances separation of aggregates, multimers and modified versions of the protein from the single Fc domain containing polypeptide.
Owner:AMGEN INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com