Patents
Literature
226results about "Fusion with post-translational modification motif" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
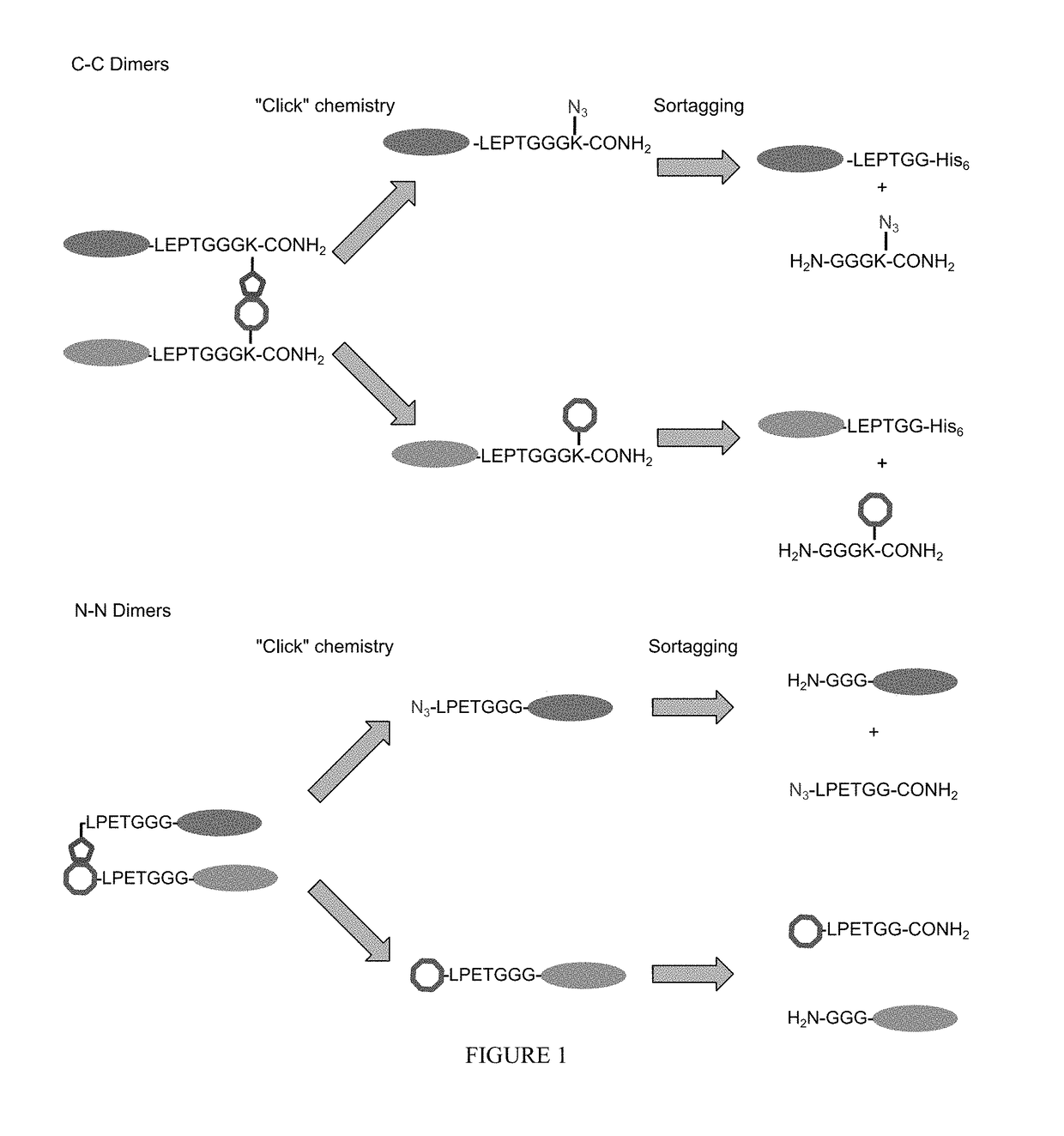
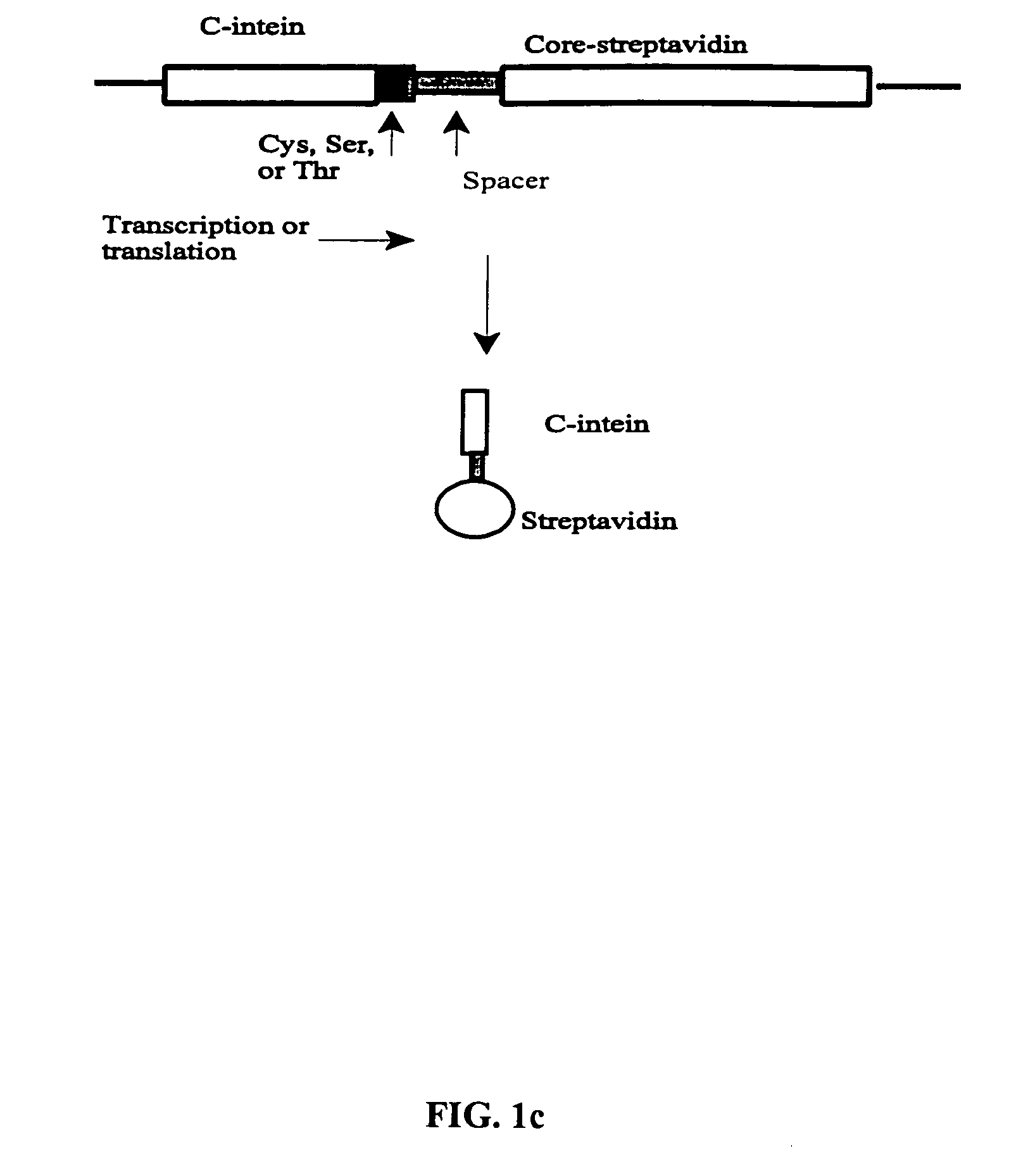
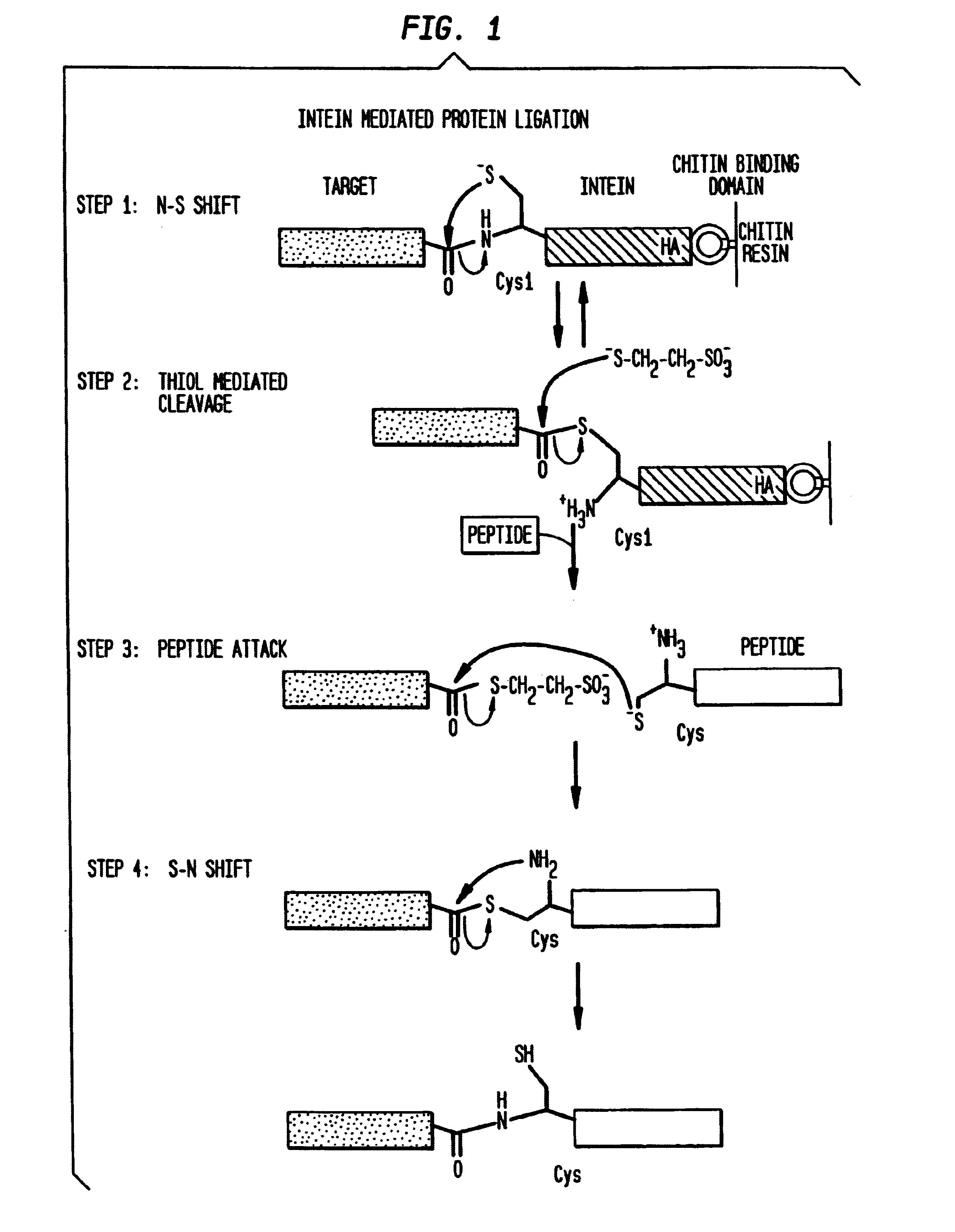
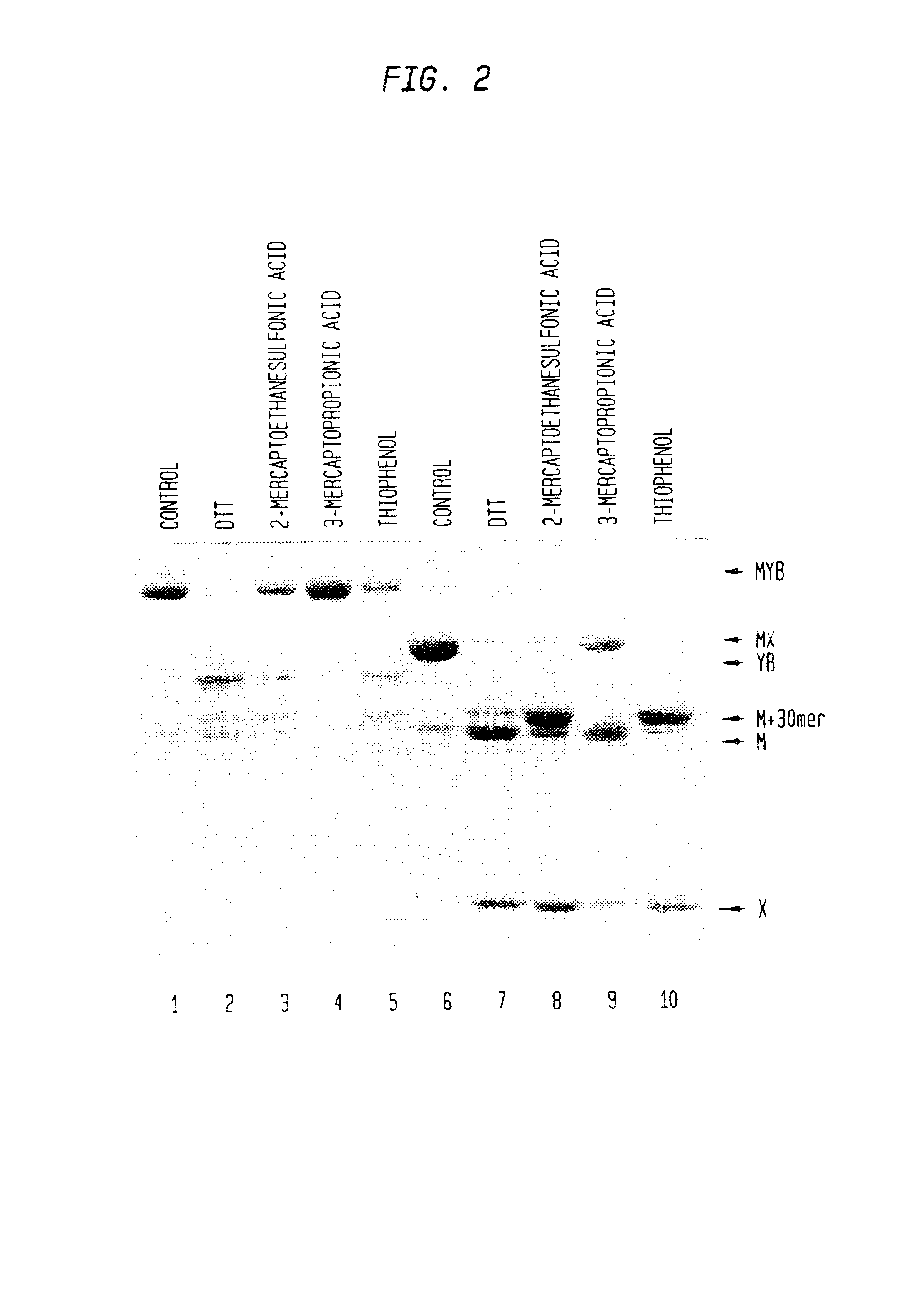
Intein-mediated protein ligation of expressed proteins
InactiveUS6849428B1Eliminate needBacteriaFusion with post-translational modification motifProtein targetIntein
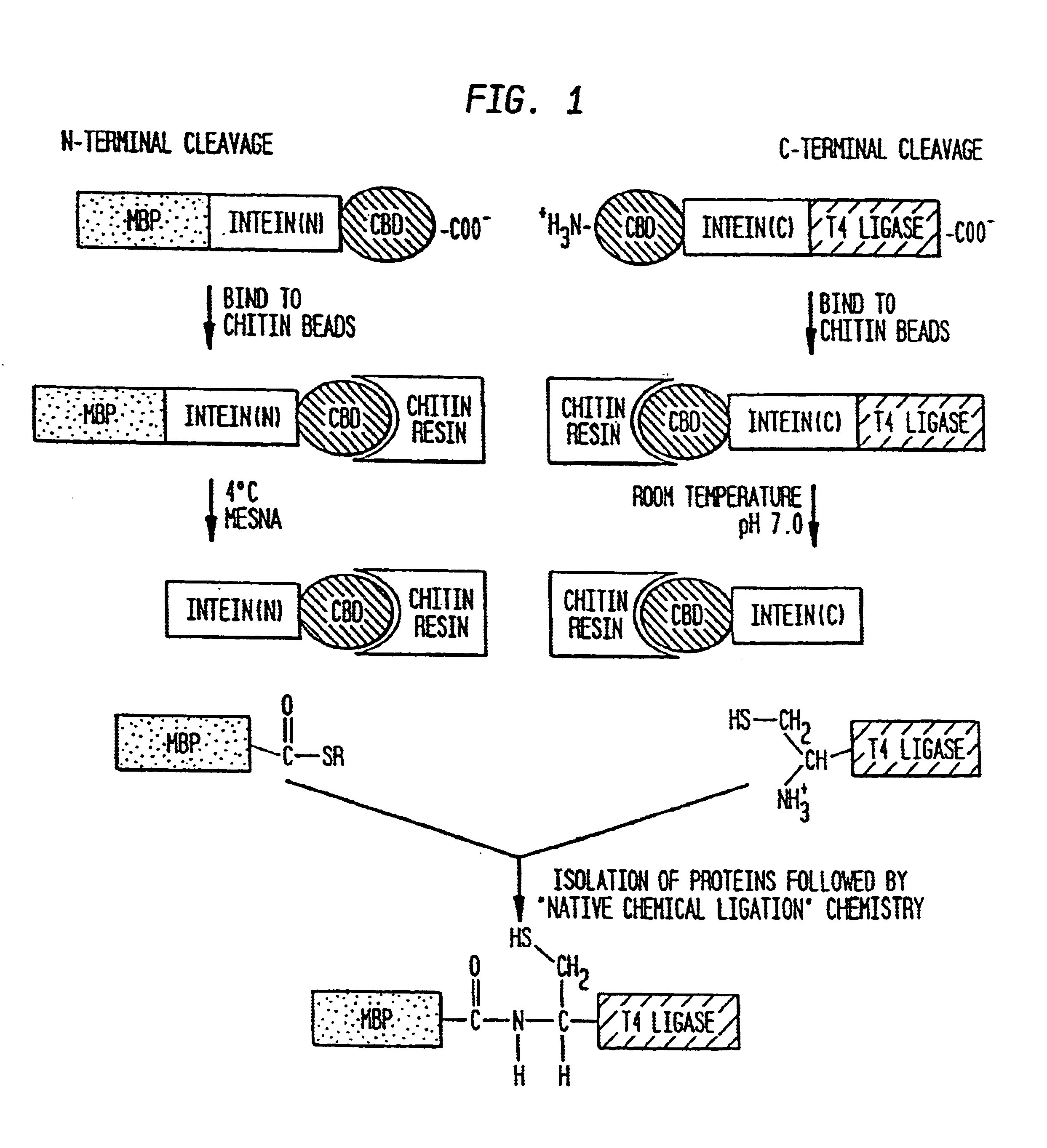
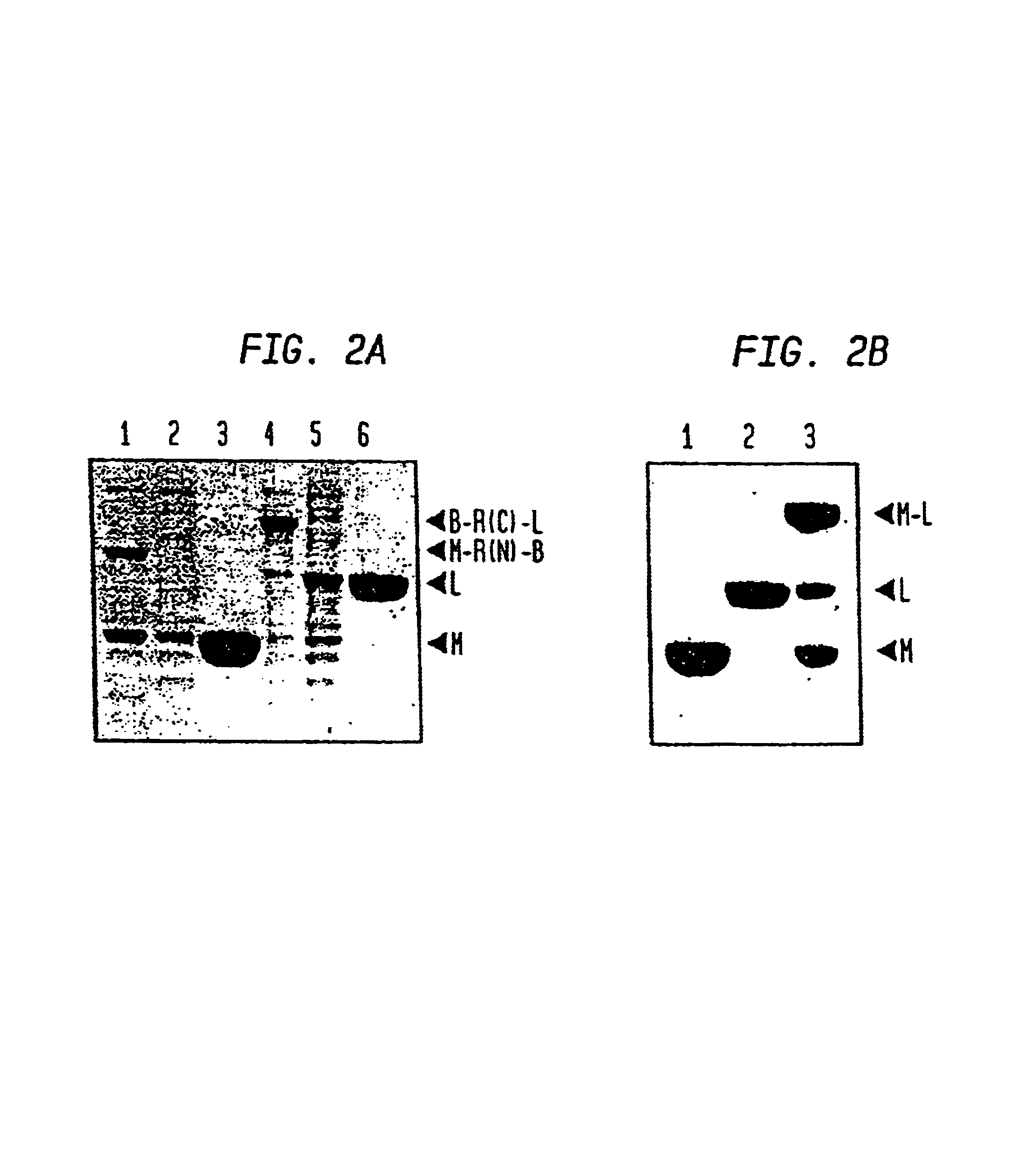
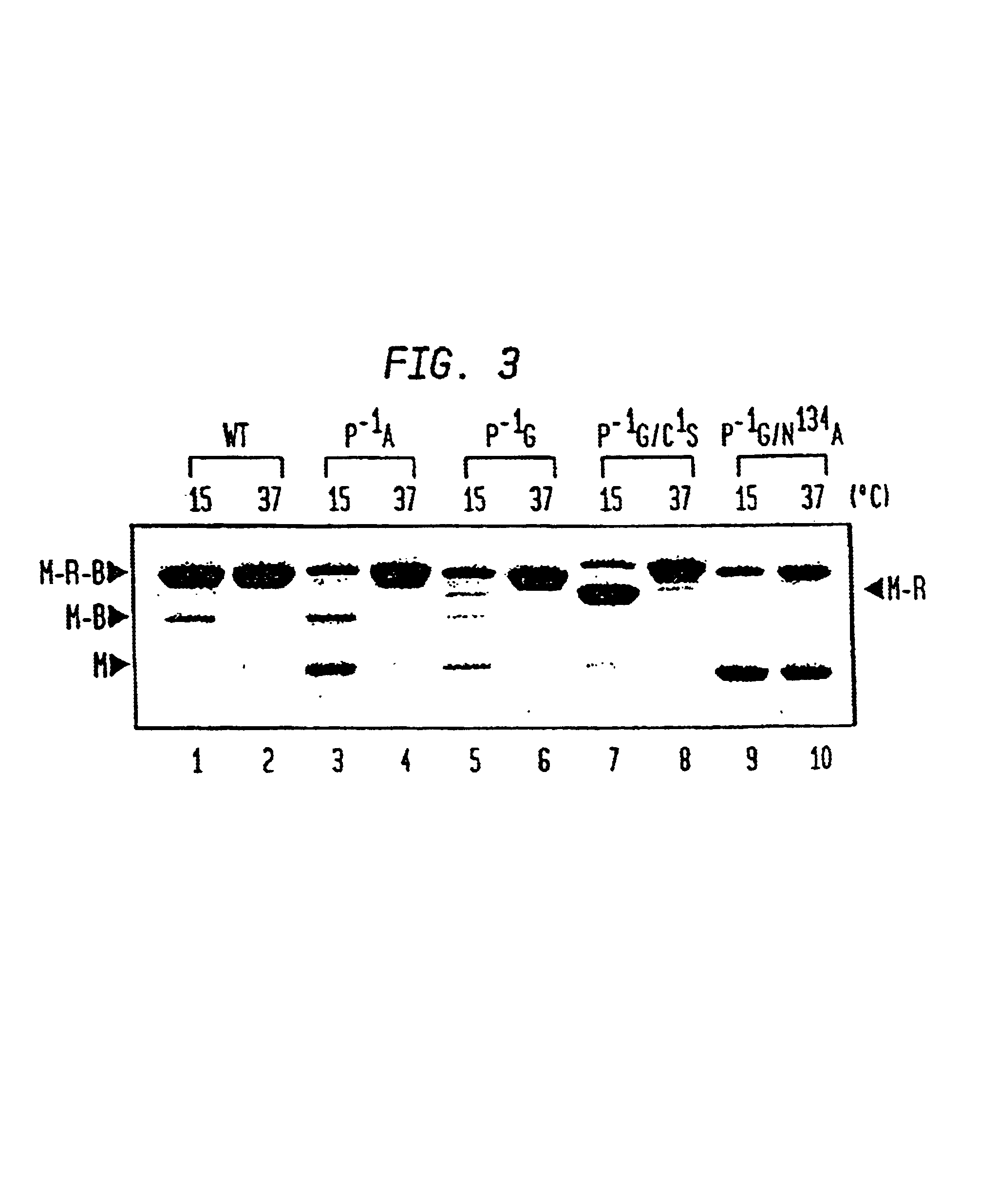
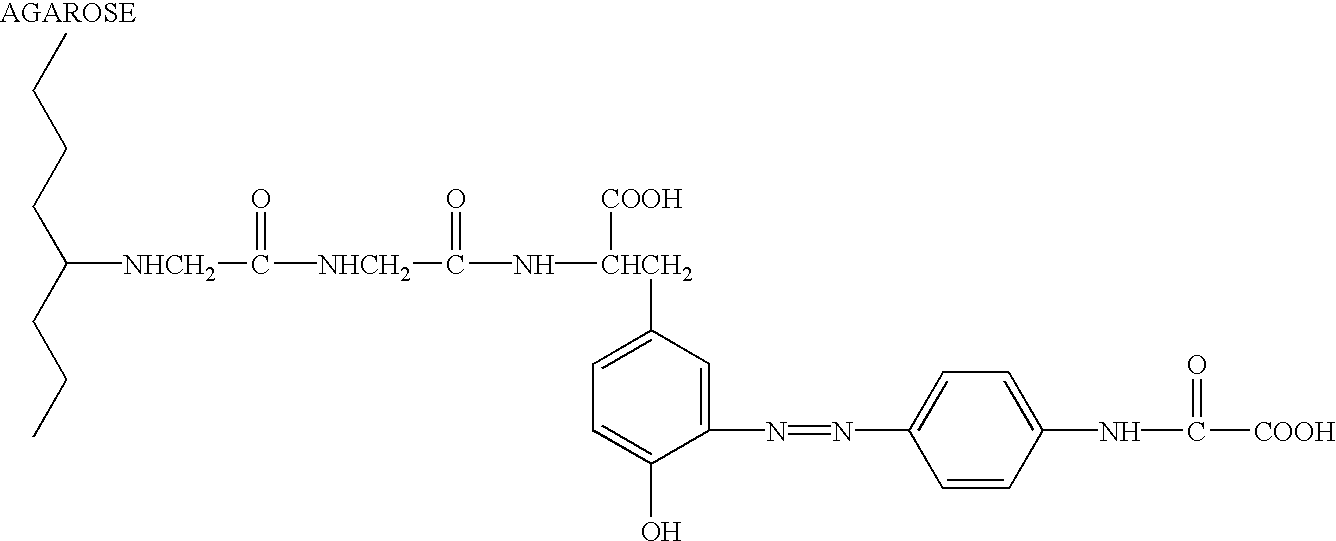
A method for the ligation of expressed proteins which utilizes inteins, for example the RIR1 intein from Methanobacterium thermotrophicum, is provided. Constructs of the Mth RIR1 intein in which either the C-terminal asparagine or N-terminal cysteine of the intein are replaced with alanine enable the facile isolation of a protein with a specified N-terminal, for example, cysteine for use in the fusion of two or more expressed proteins. The method involves the steps of generating a C-terminal thioester-tagged target protein and a second target protein having a specified N-terminal via inteins, such as the modified Mth RIR1 intein, and ligating these proteins. A similar method for producing a cyclic or polymerized protein is provided. Modified inteins engineered to cleave at their C-terminus or N-terminus, respectively, and DNA and plasmids encoding these modified inteins are also provided.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Neuraminidase-supplemented compositions
InactiveUS6485729B1Less importancePrevents and lessens HA immunodominanceSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNasal cavityAdjuvant
An anti-influenza vaccine composition wherein the improvement is that the vaccine includes, as an additive, neuraminidase (NA). The base anti-influenza vaccine can be any commercially available anti-influenza vaccine. The composition can include and be administered with an adjuvant. The vaccine composition provides protection in a host, animal or human, against influenza infection, including viral replication and systemic infection. Oral, nasal or other mucosal or per needle administration, including intracutaneous, intradermal, intramuscular, intravascular, and intravenous, are included.
Owner:PROTEIN SCI
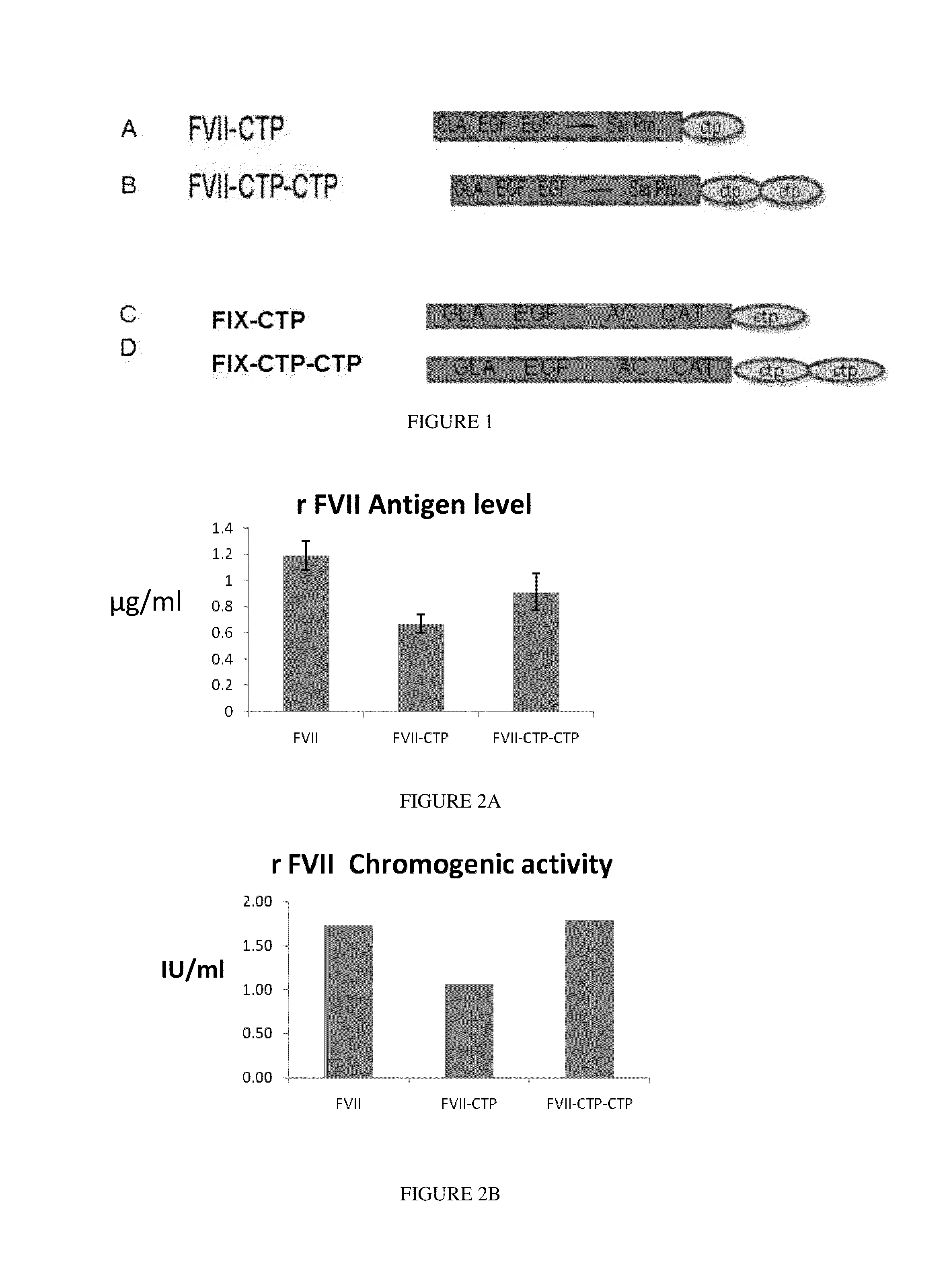
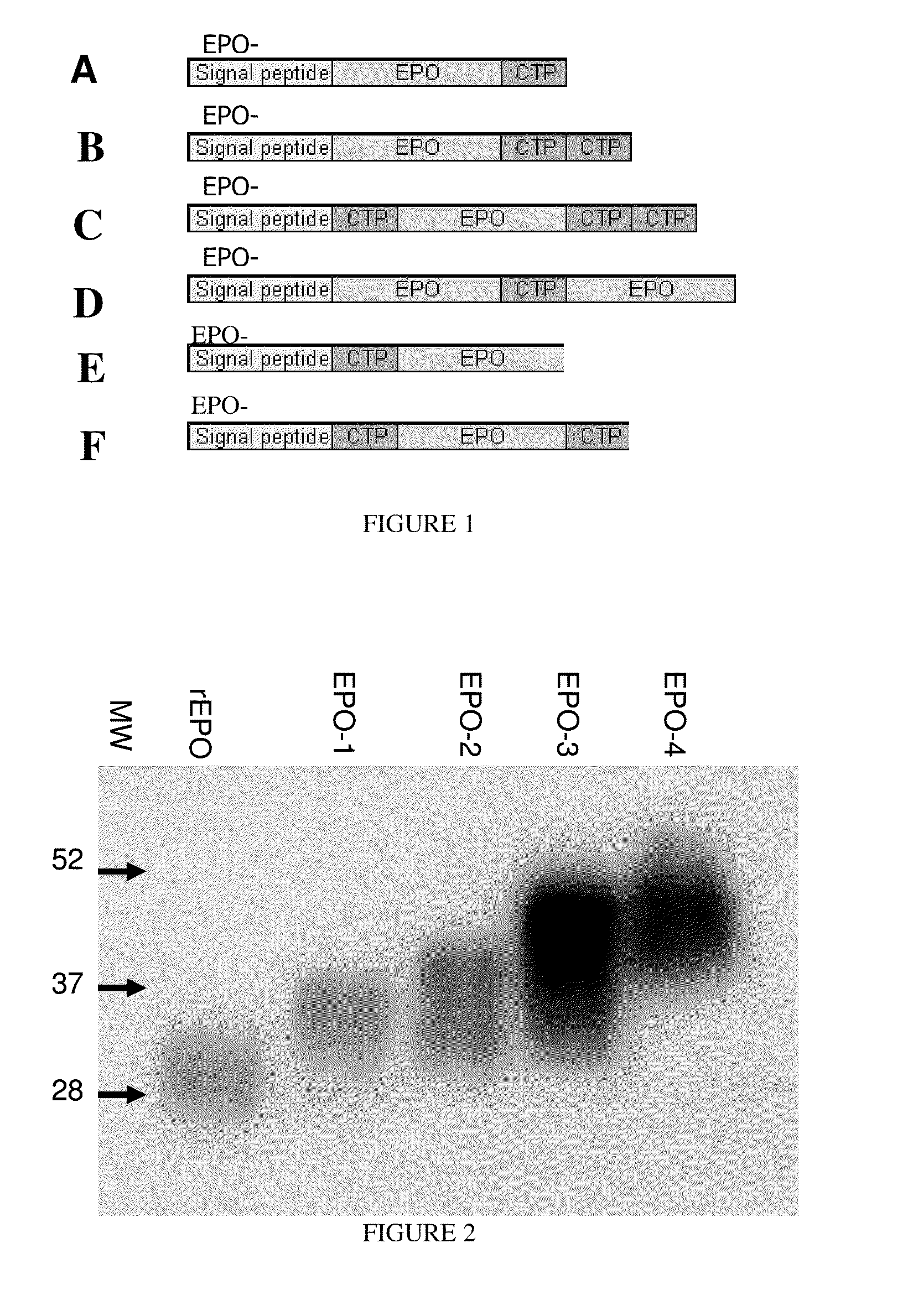
Long-acting coagulation factors and methods of producing same
ActiveUS20130243747A1Prevent coagulationPreventing hemophiliaBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotidePolynucleotide
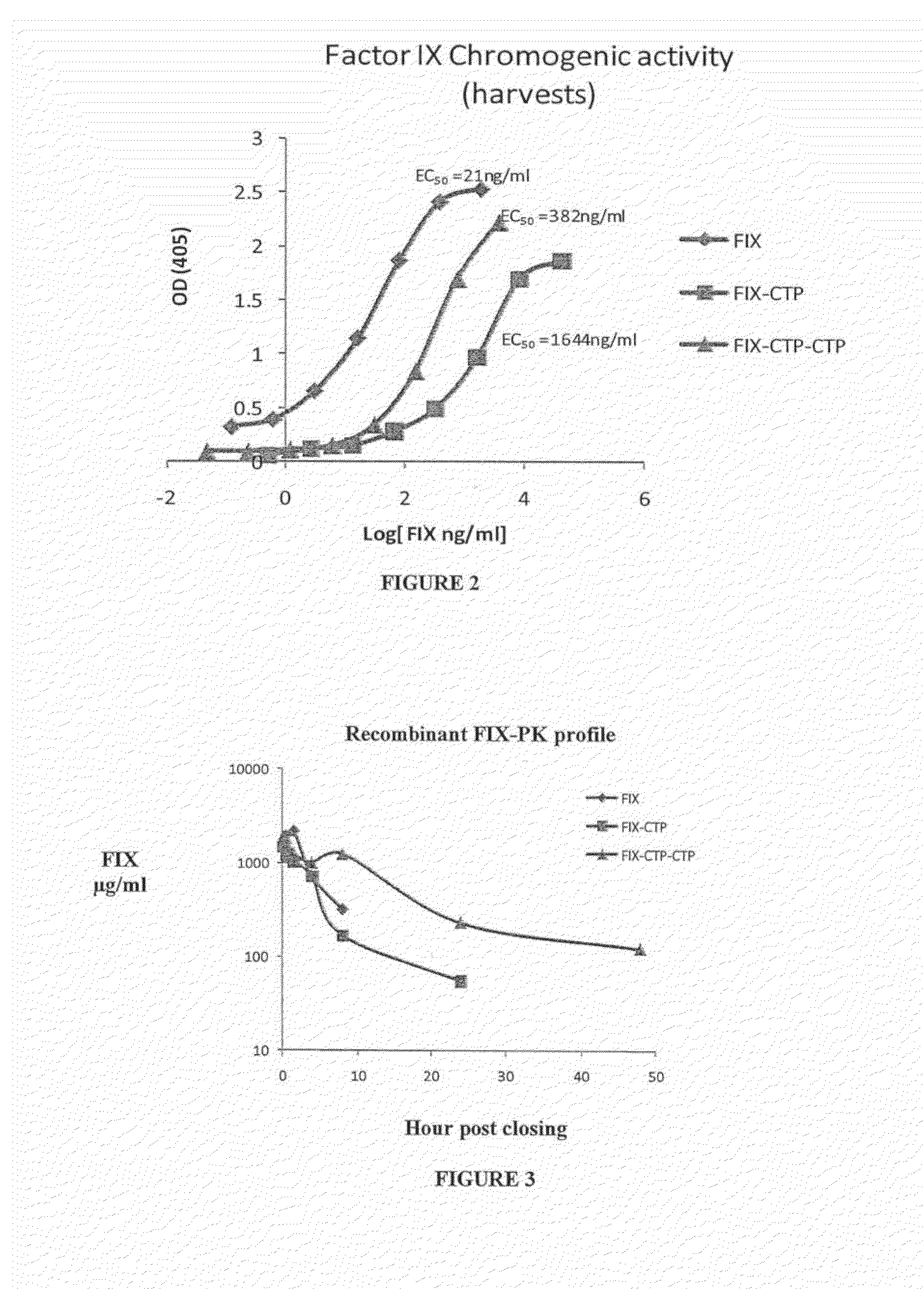
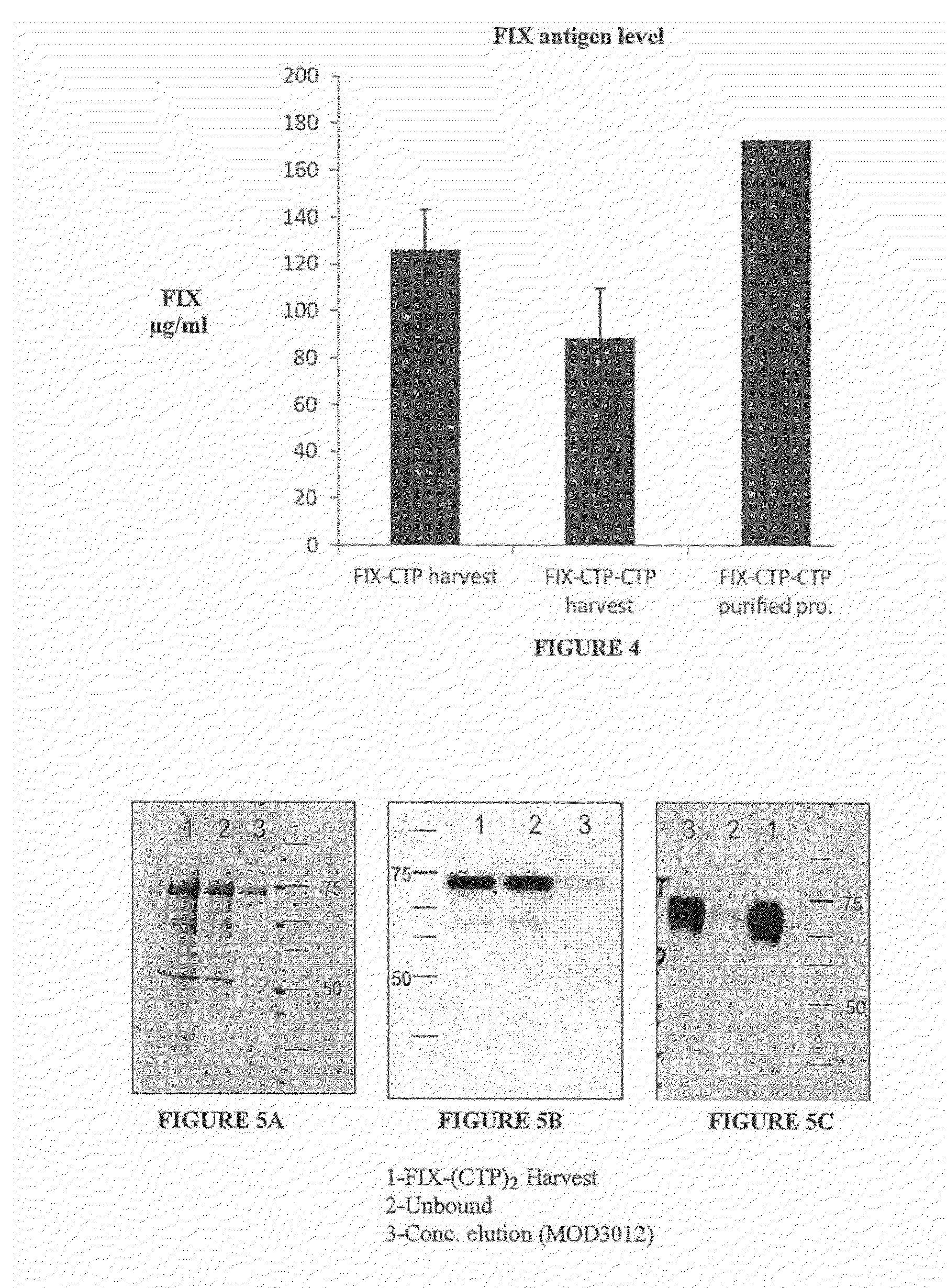
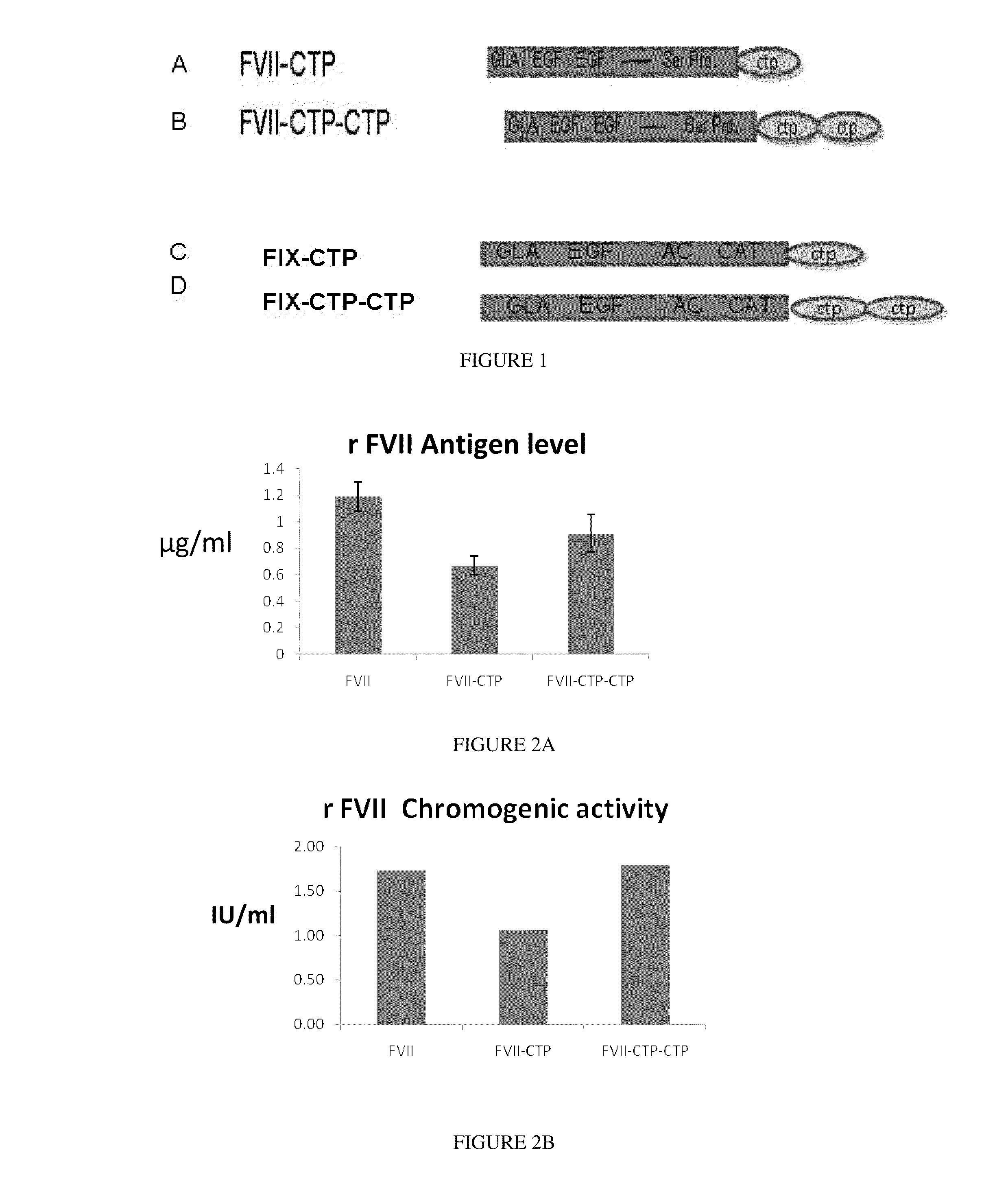
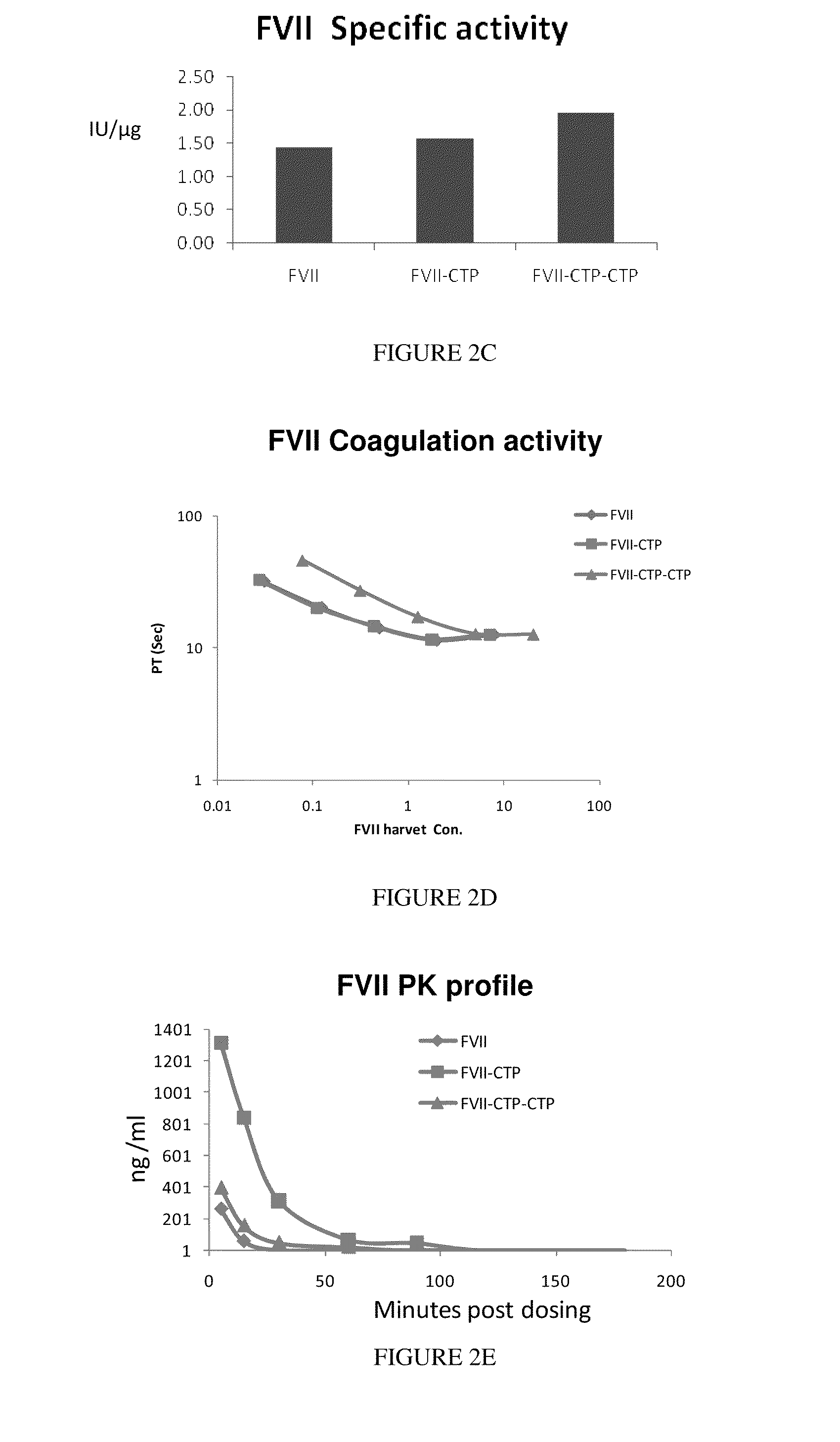
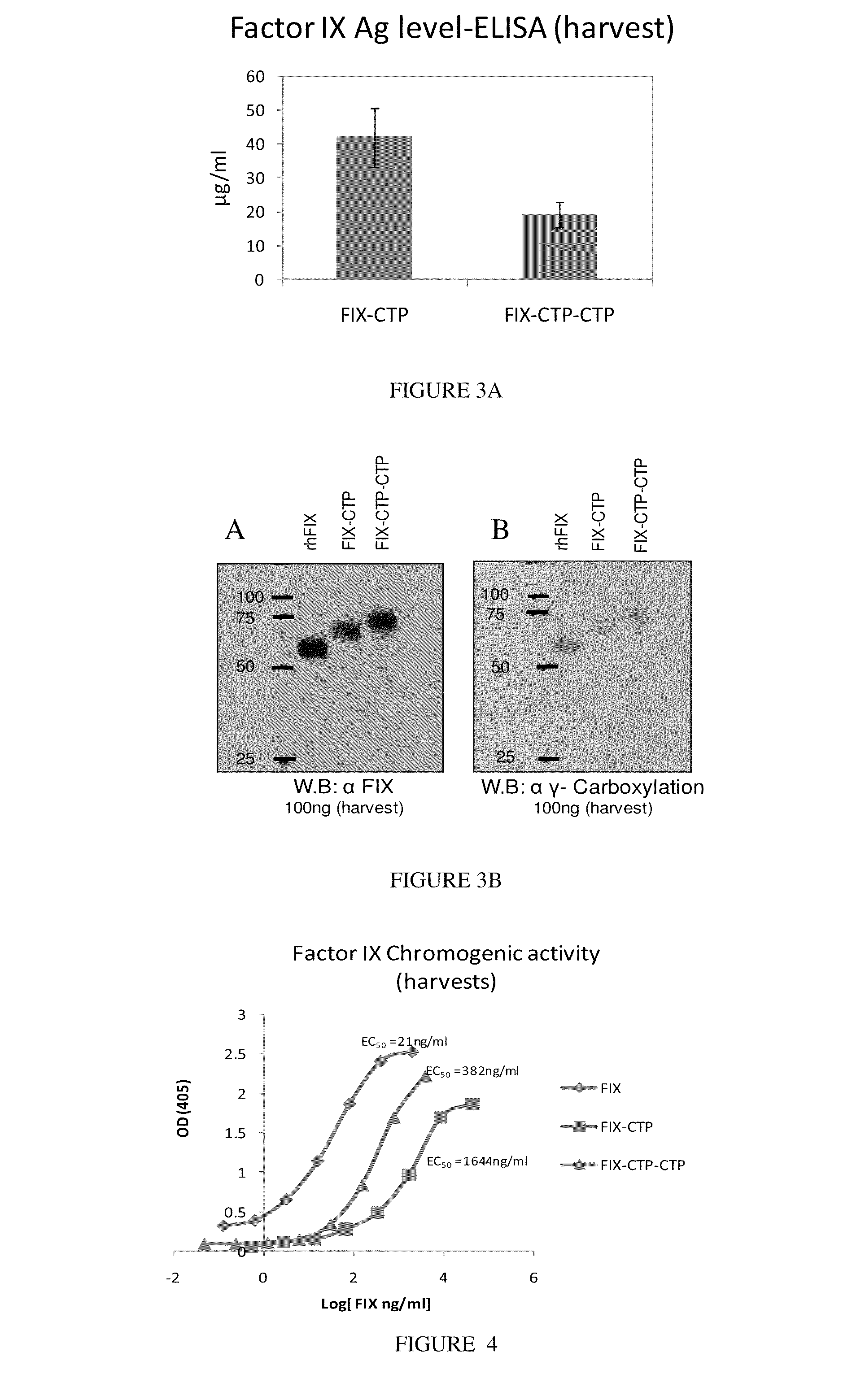
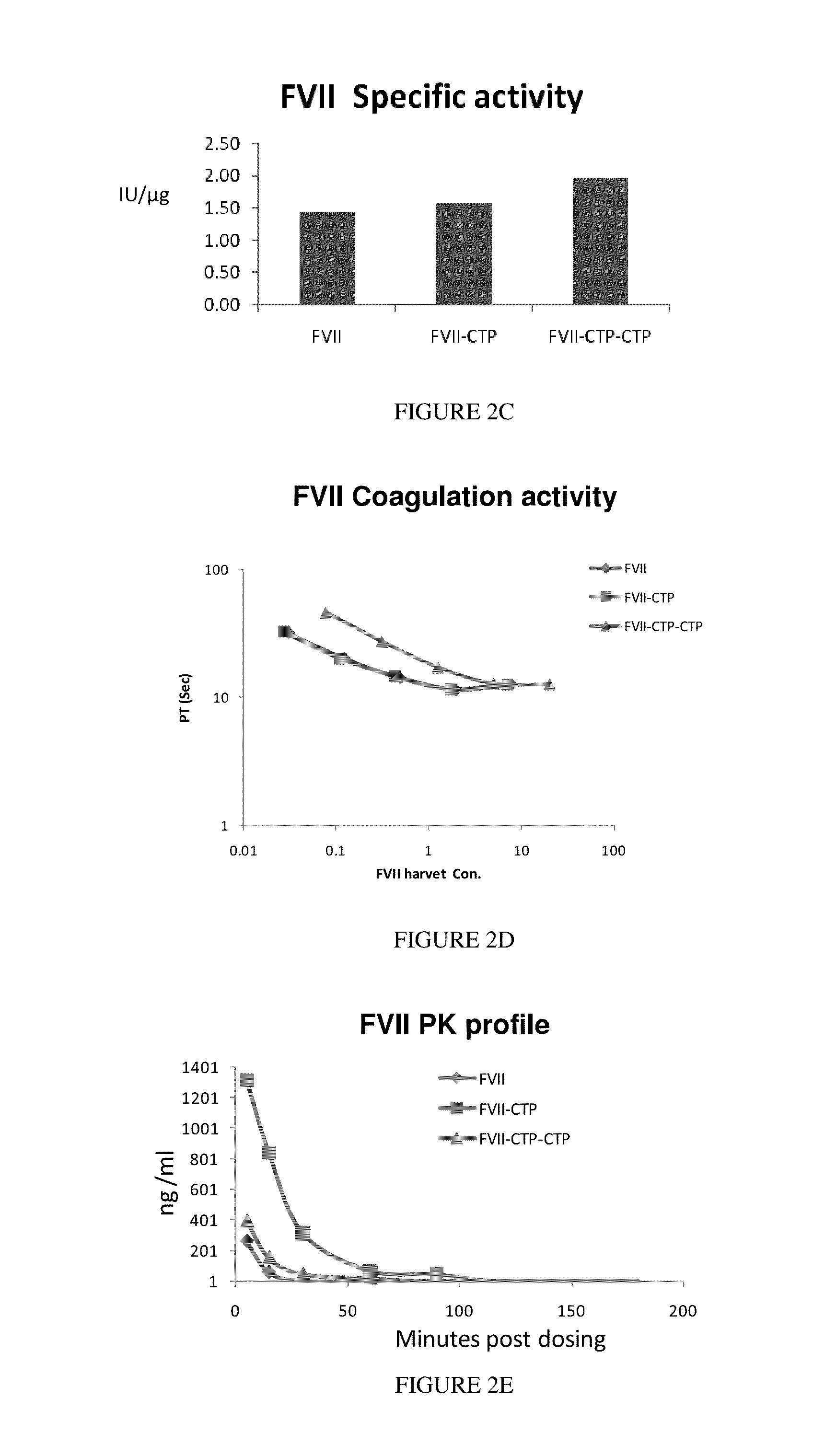
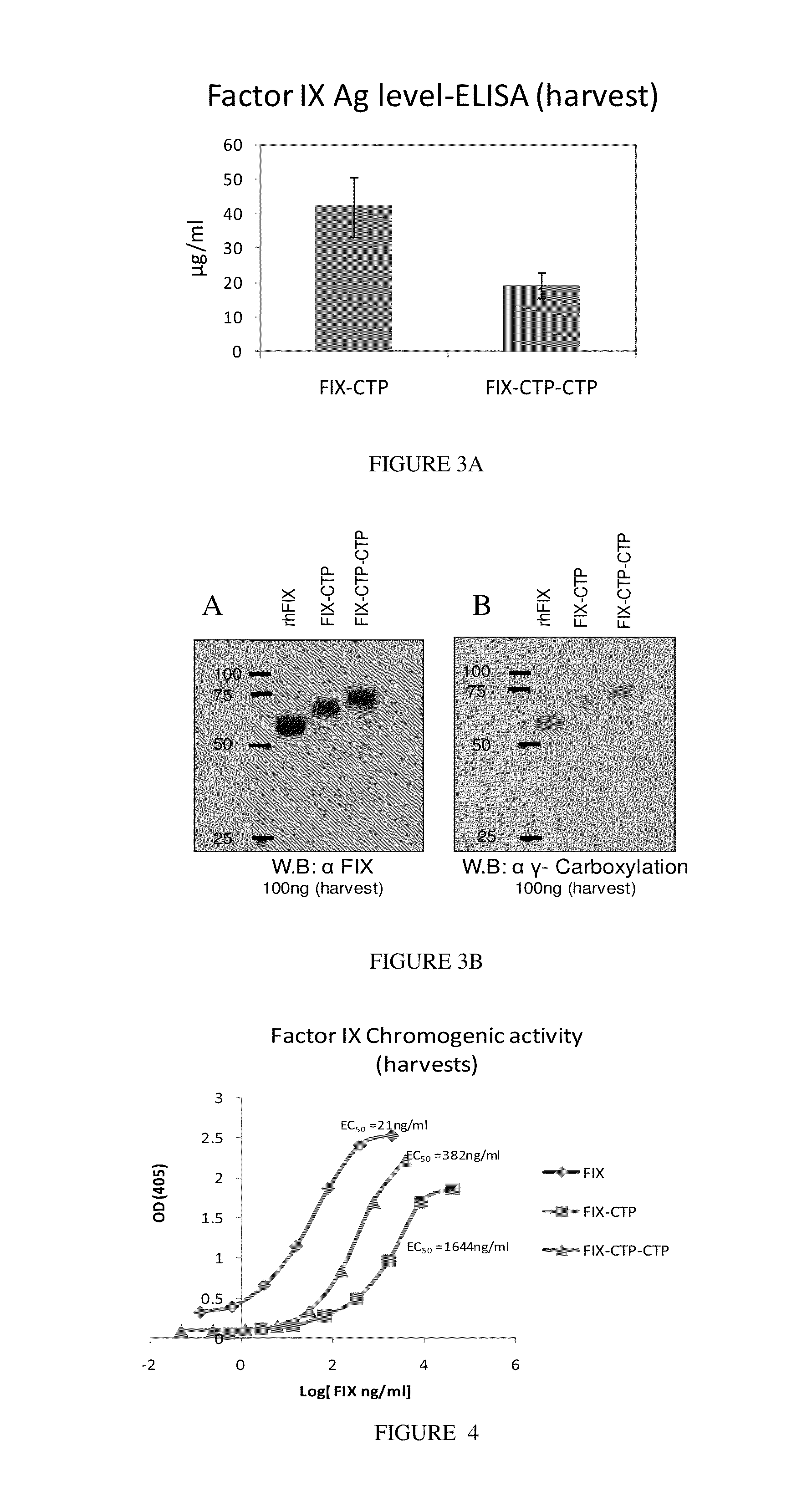
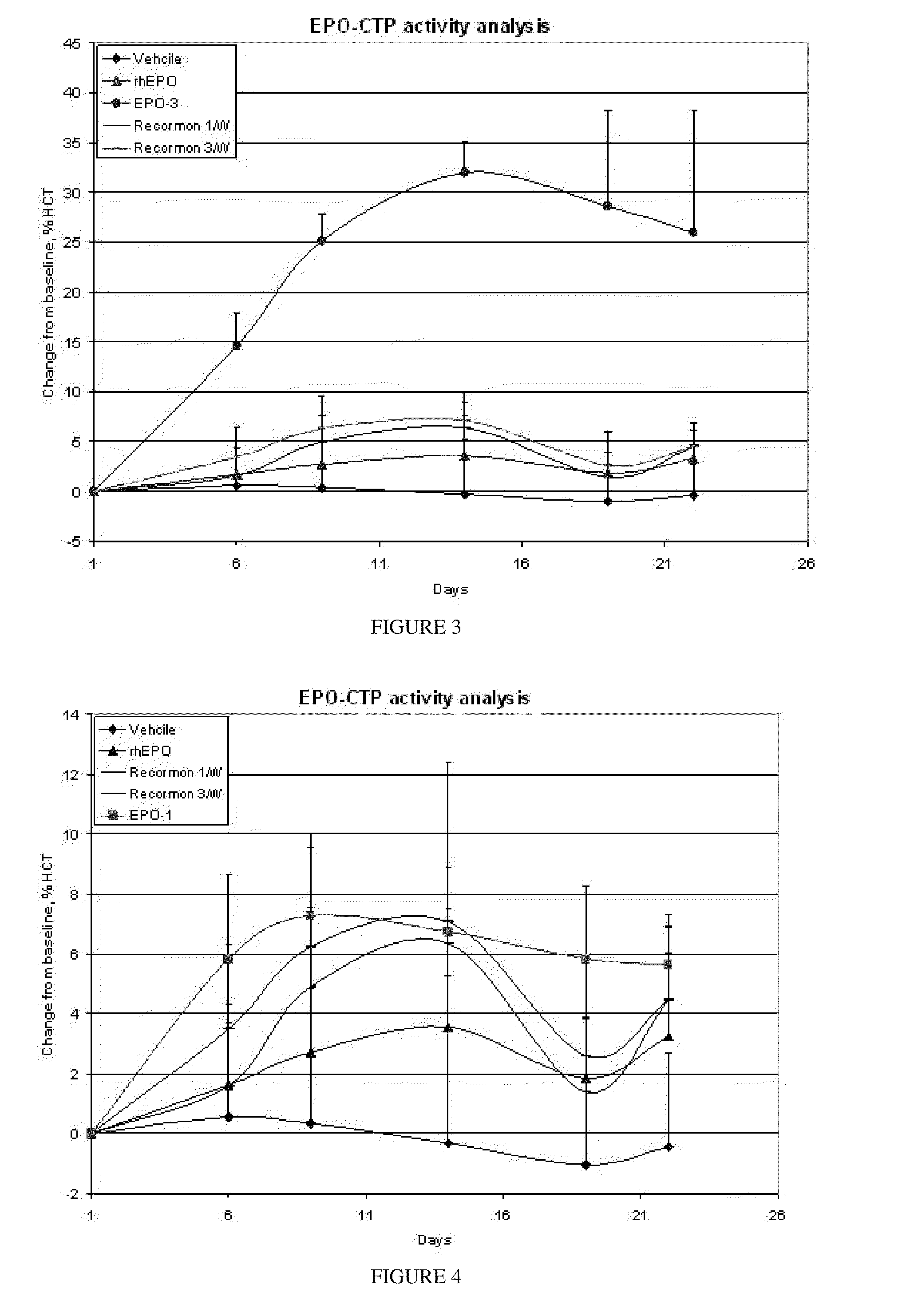
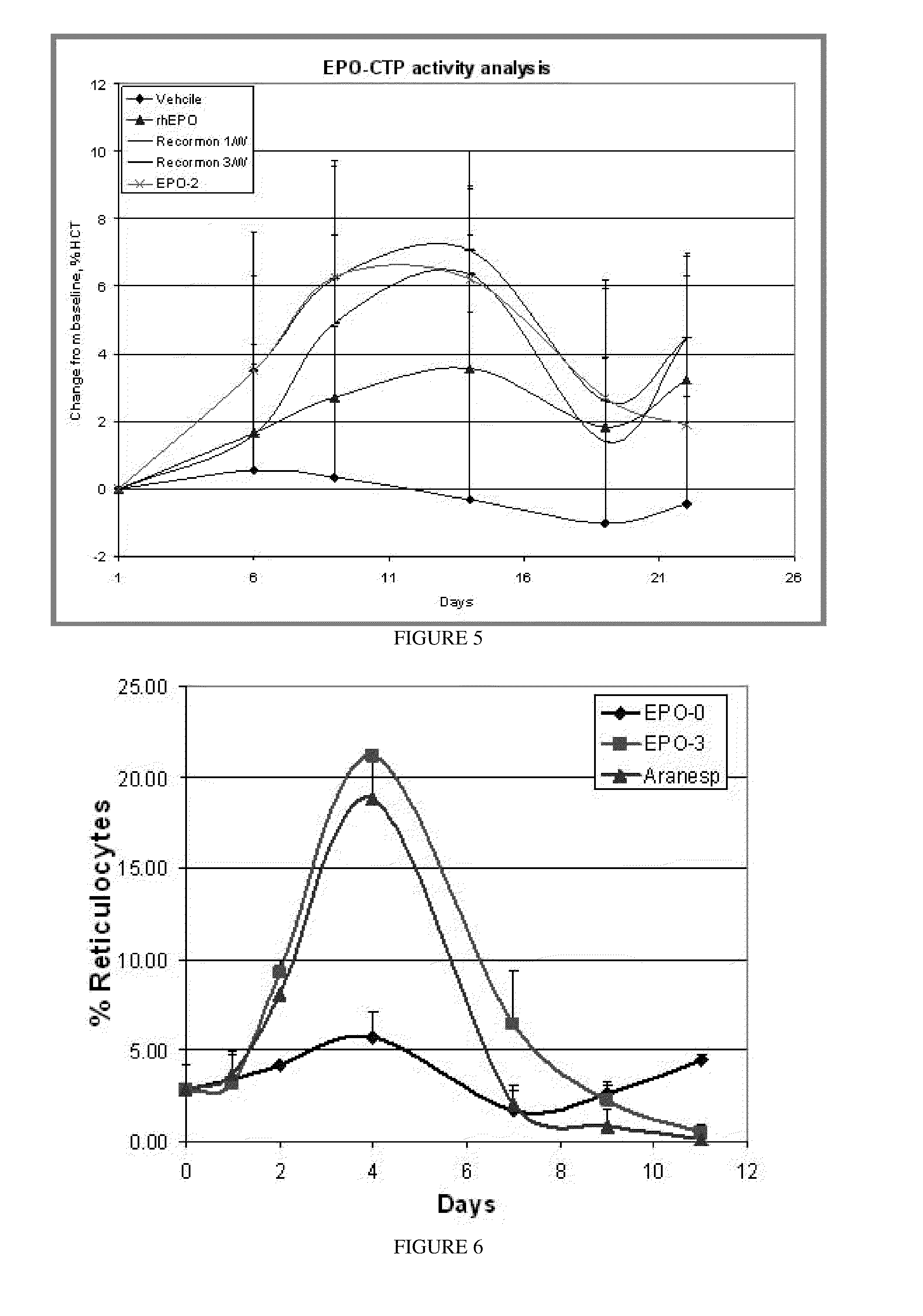
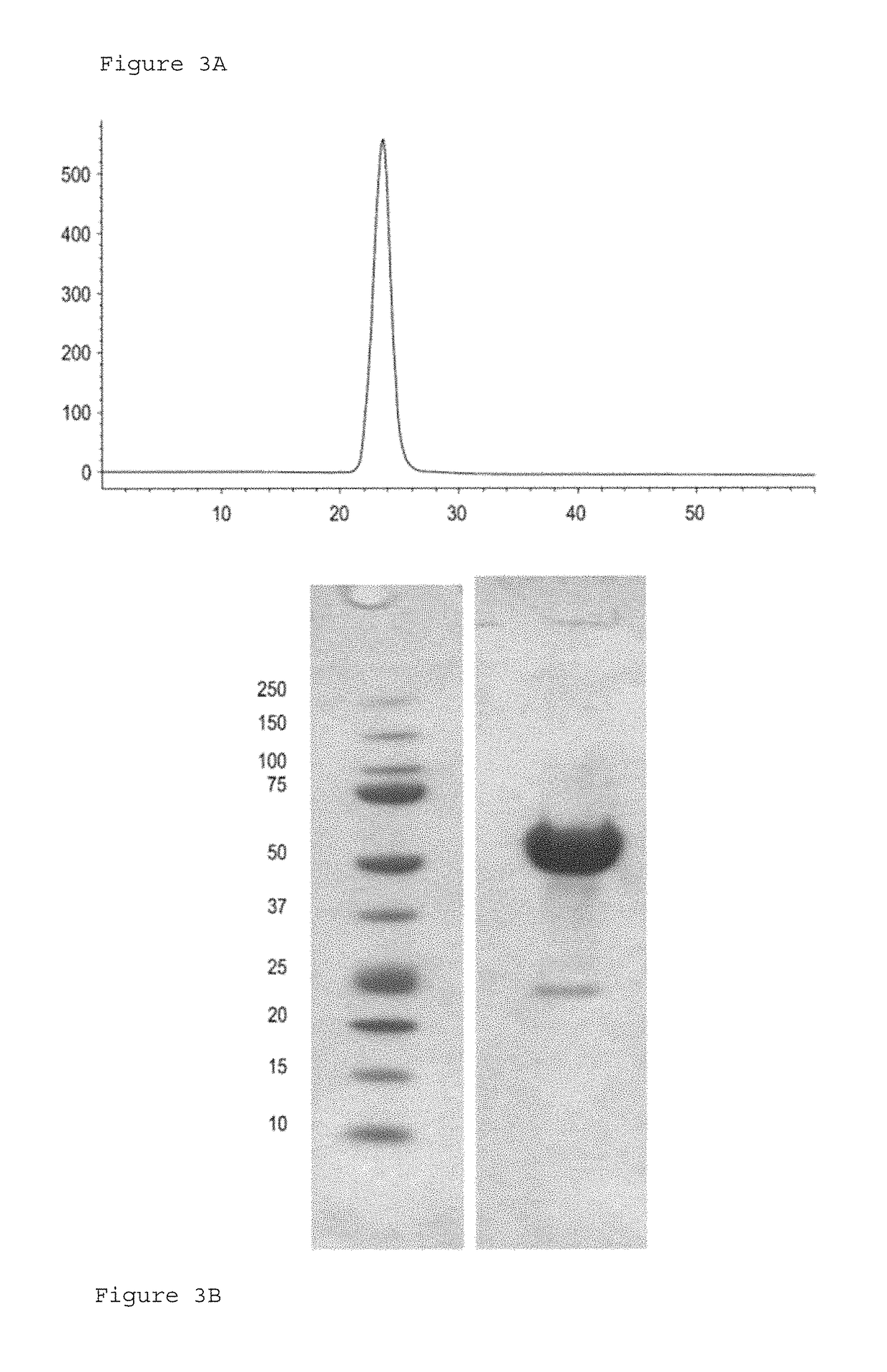
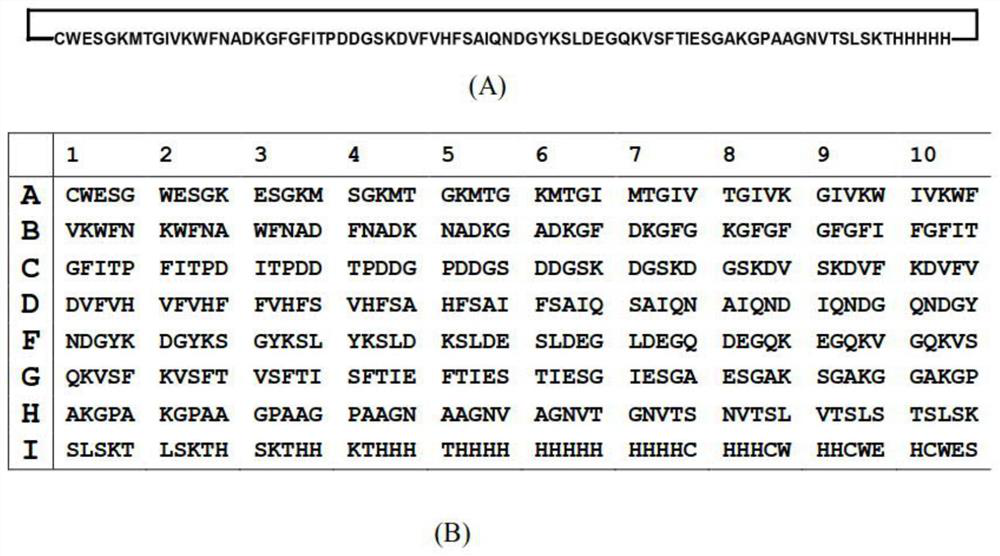
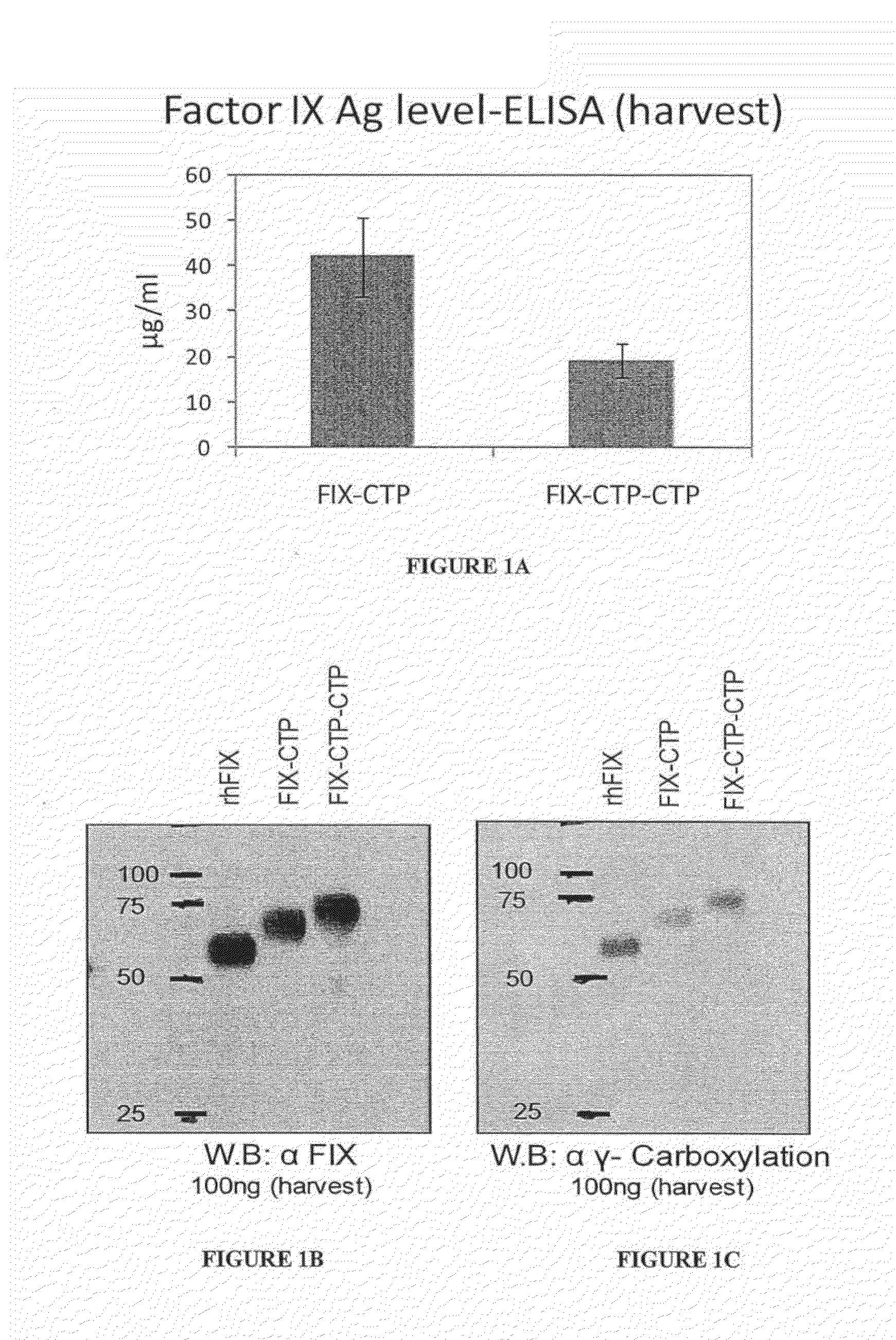
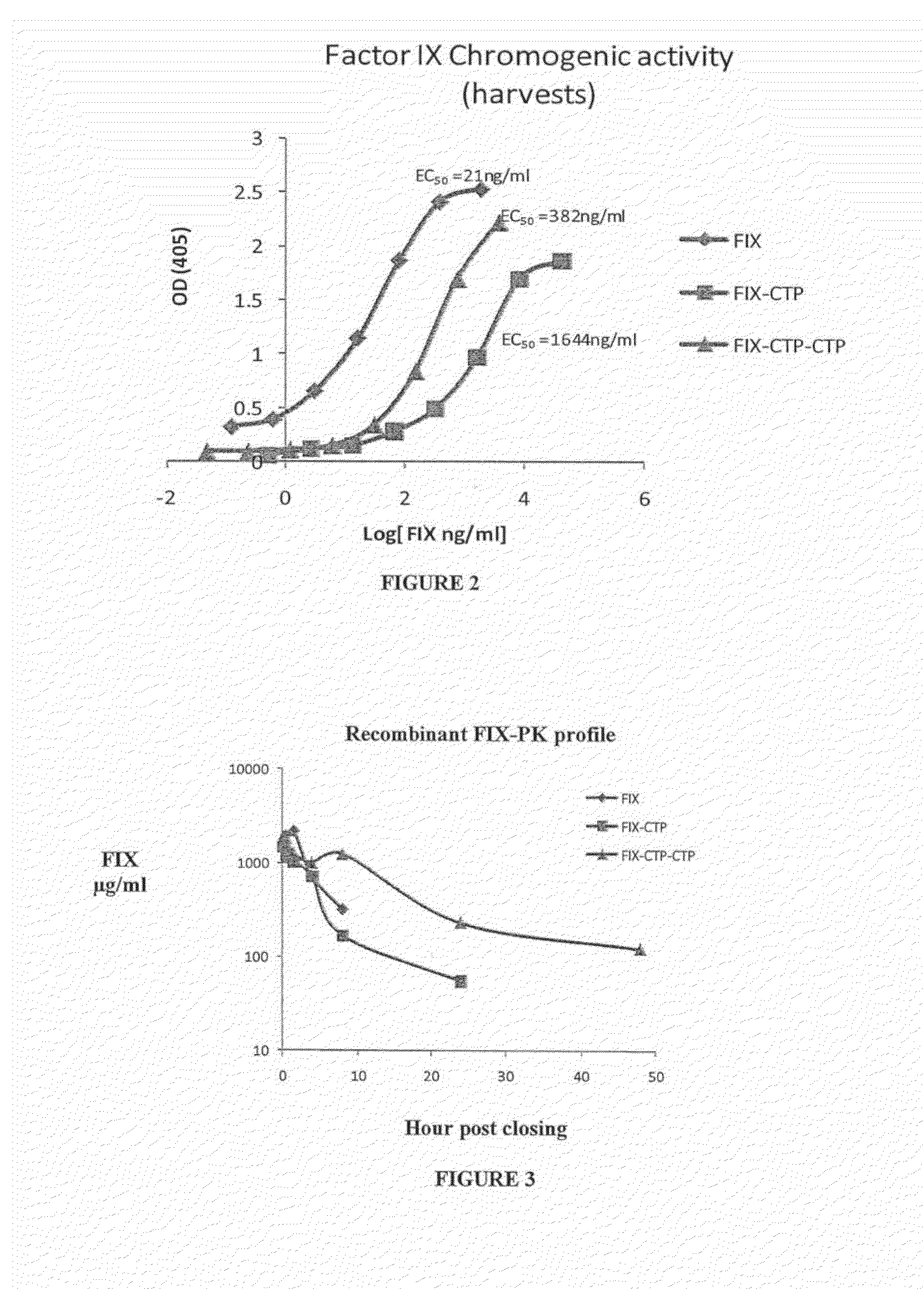
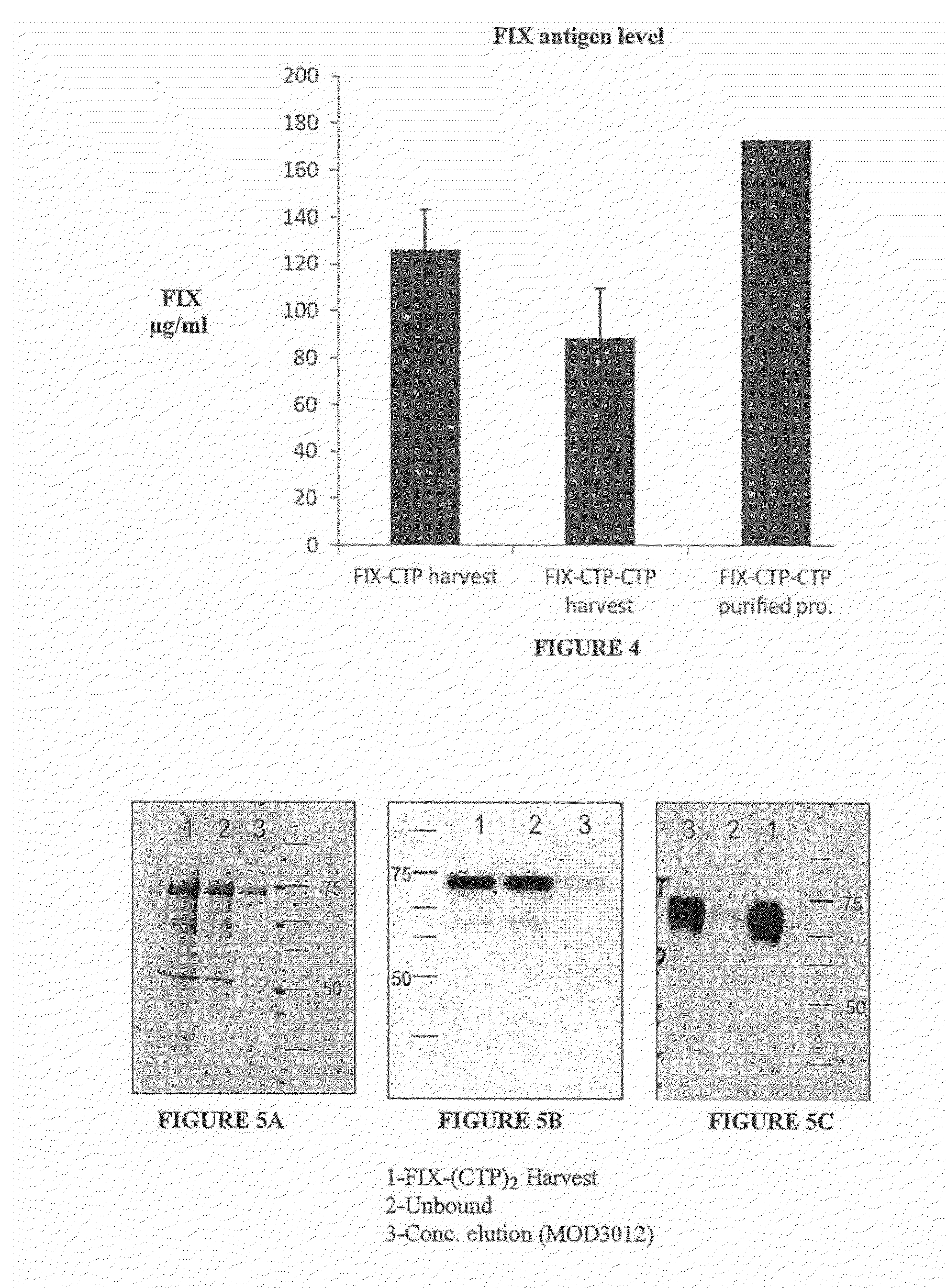
Polypeptides comprising at least one carboxy-terminal peptide (CTP) of chorionic gonadotrophin attached to the carboxy terminus but not to the amino terminus of a coagulation factor and polynucleotides encoding the same are disclosed. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the polypeptides and polynucleotides of the invention and methods of using and producing same are also disclosed.
Owner:OPKO BIOLOGICS
Long-acting coagulation factors and methods of producing same
ActiveUS20100317585A1Improving biological half lifeImproving area under curve (AUC)Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleotideChorionic gonadotrophin
Polypeptides and polynucleotides encoding same comprising at least one carboxy-terminal peptide (CTP) of chorionic gonadotrophin attached to a carboxy terminus of a coagulation factor and not to an amino terminus are disclosed. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the polypeptides and polynucleotides of the invention and methods of using same are also disclosed.
Owner:OPKO BIOLOGICS
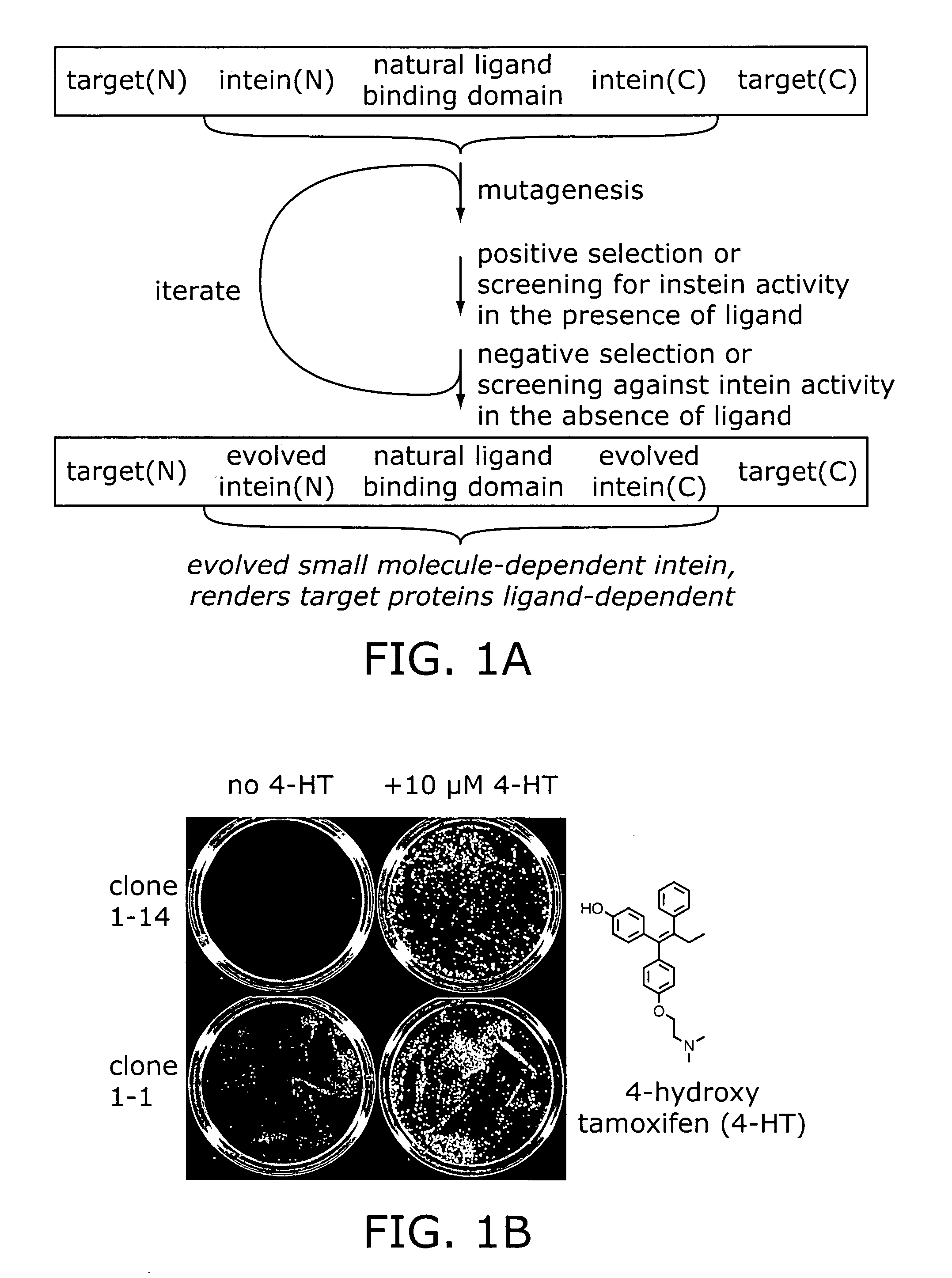
Small molecule-dependent inteins and uses thereof
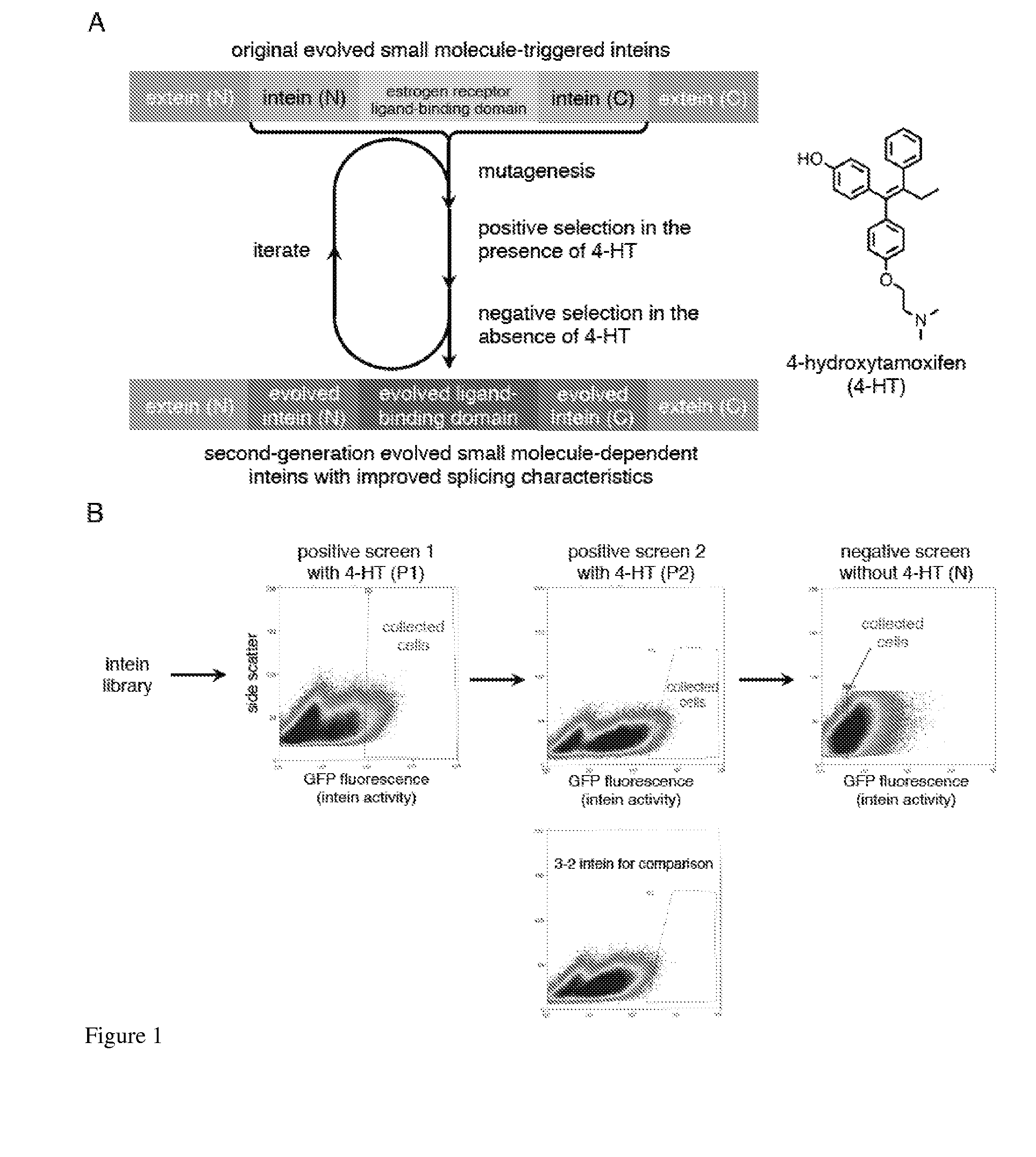
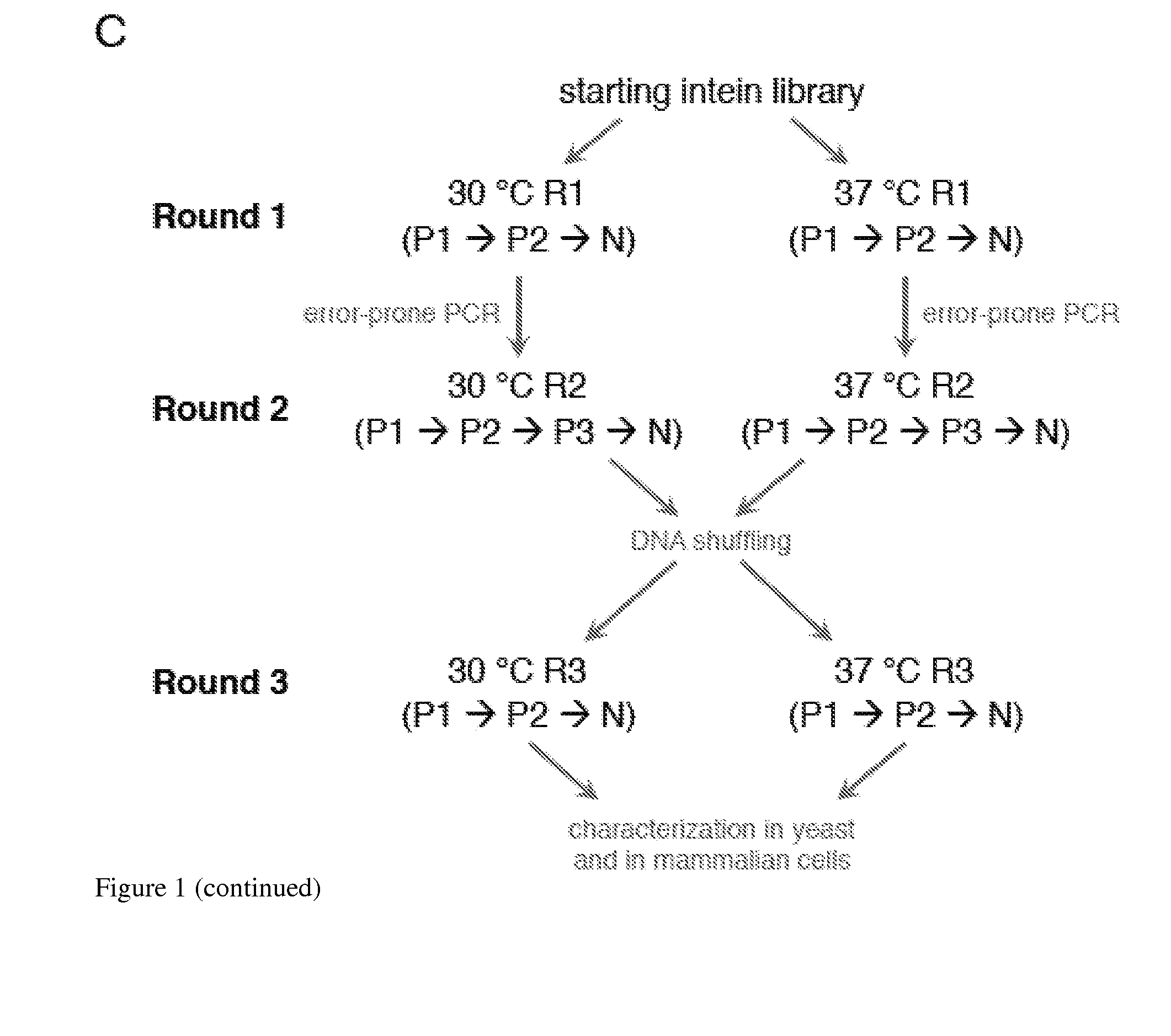
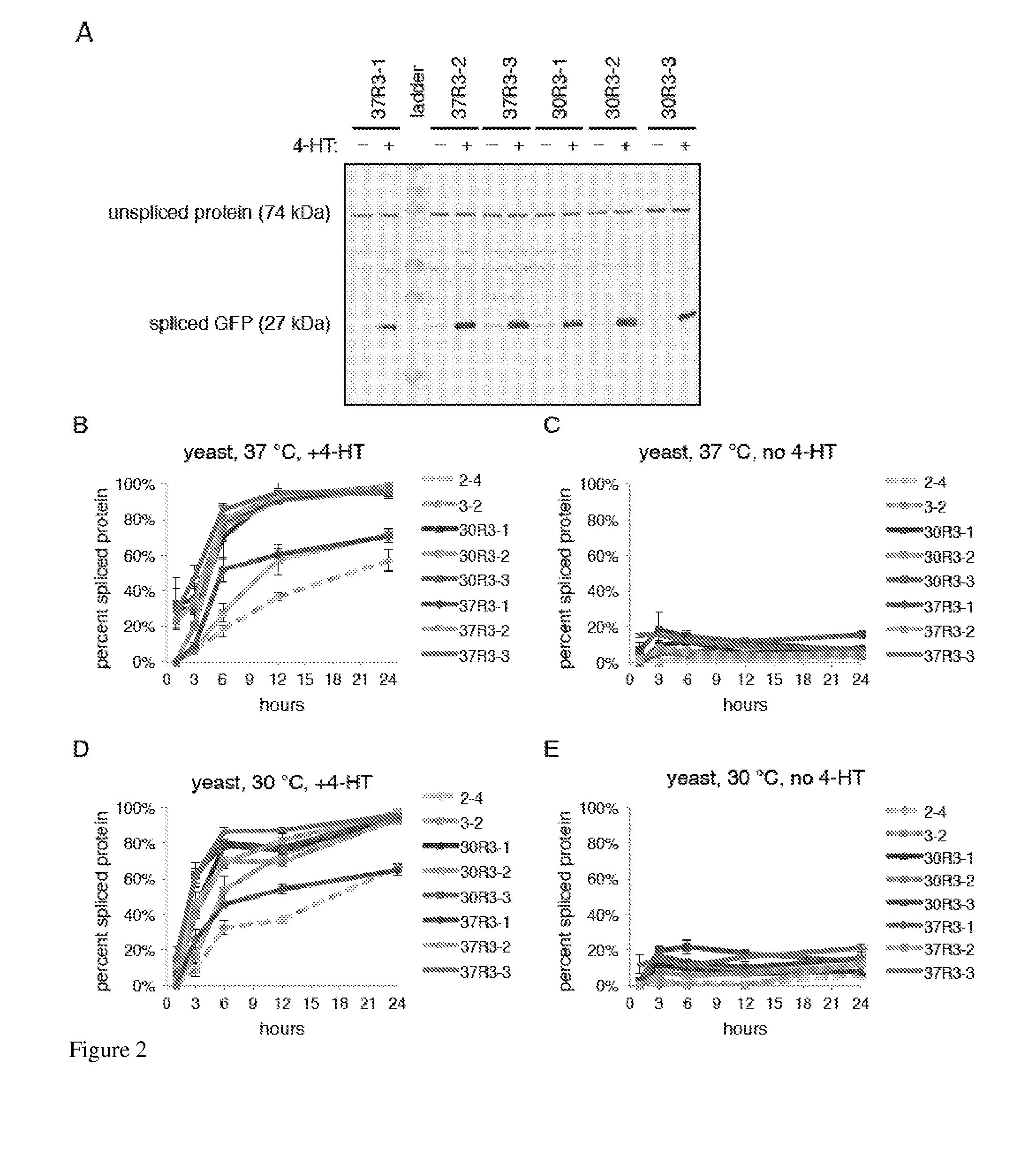
ActiveUS20140065711A1Low splicing efficiencySlow splicingHydrolasesFusion with post-translational modification motifInteinNatural state
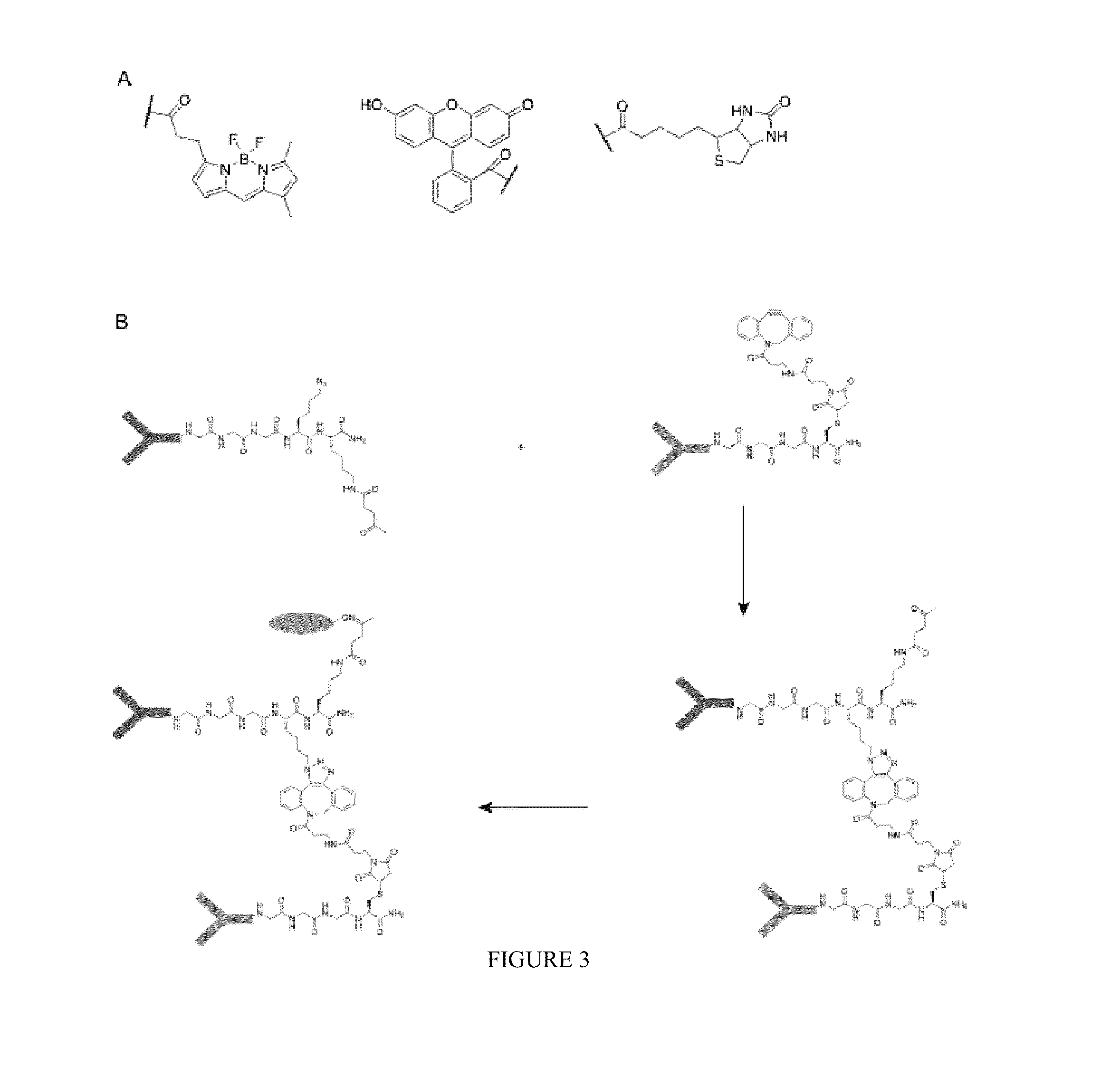
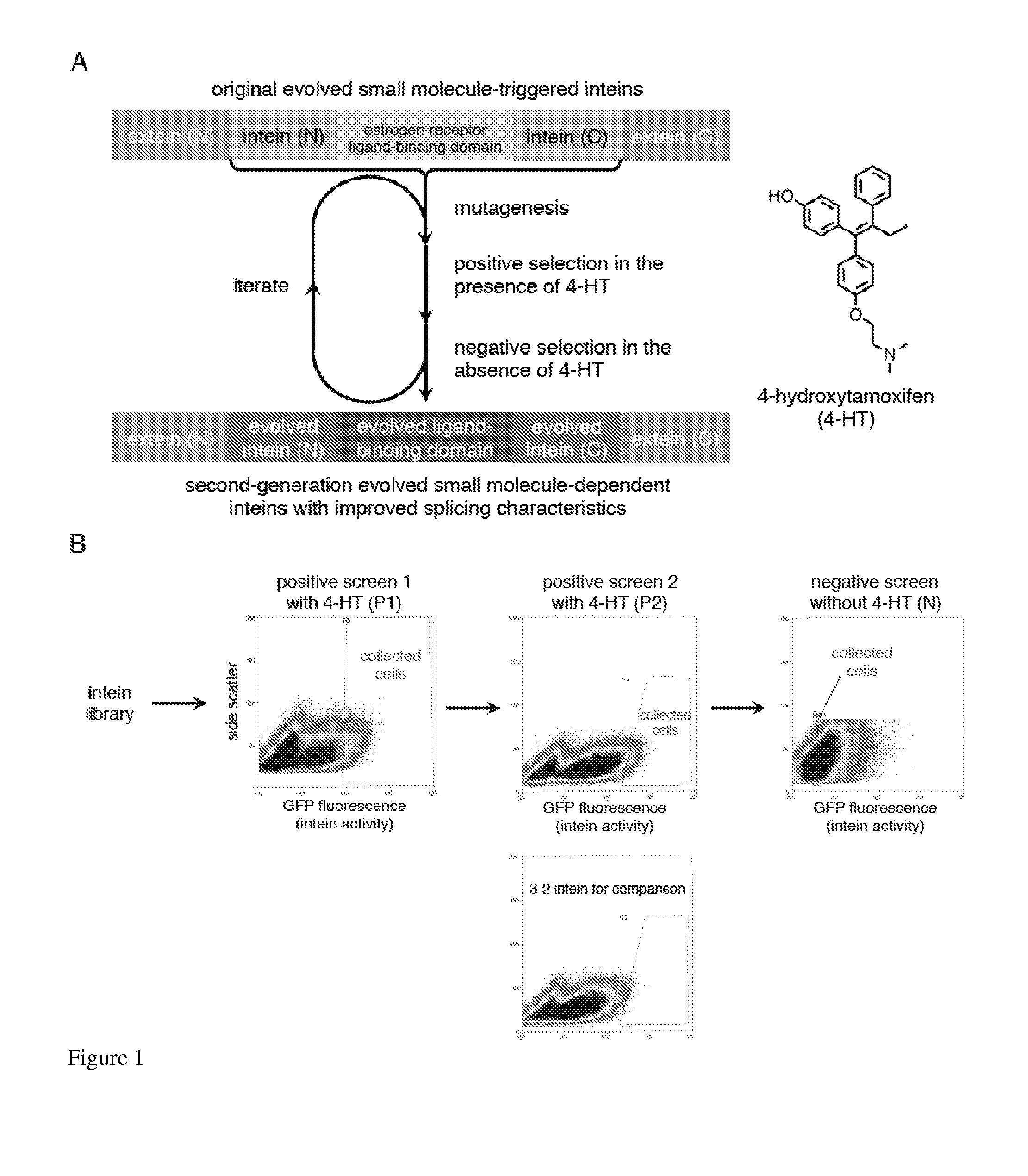
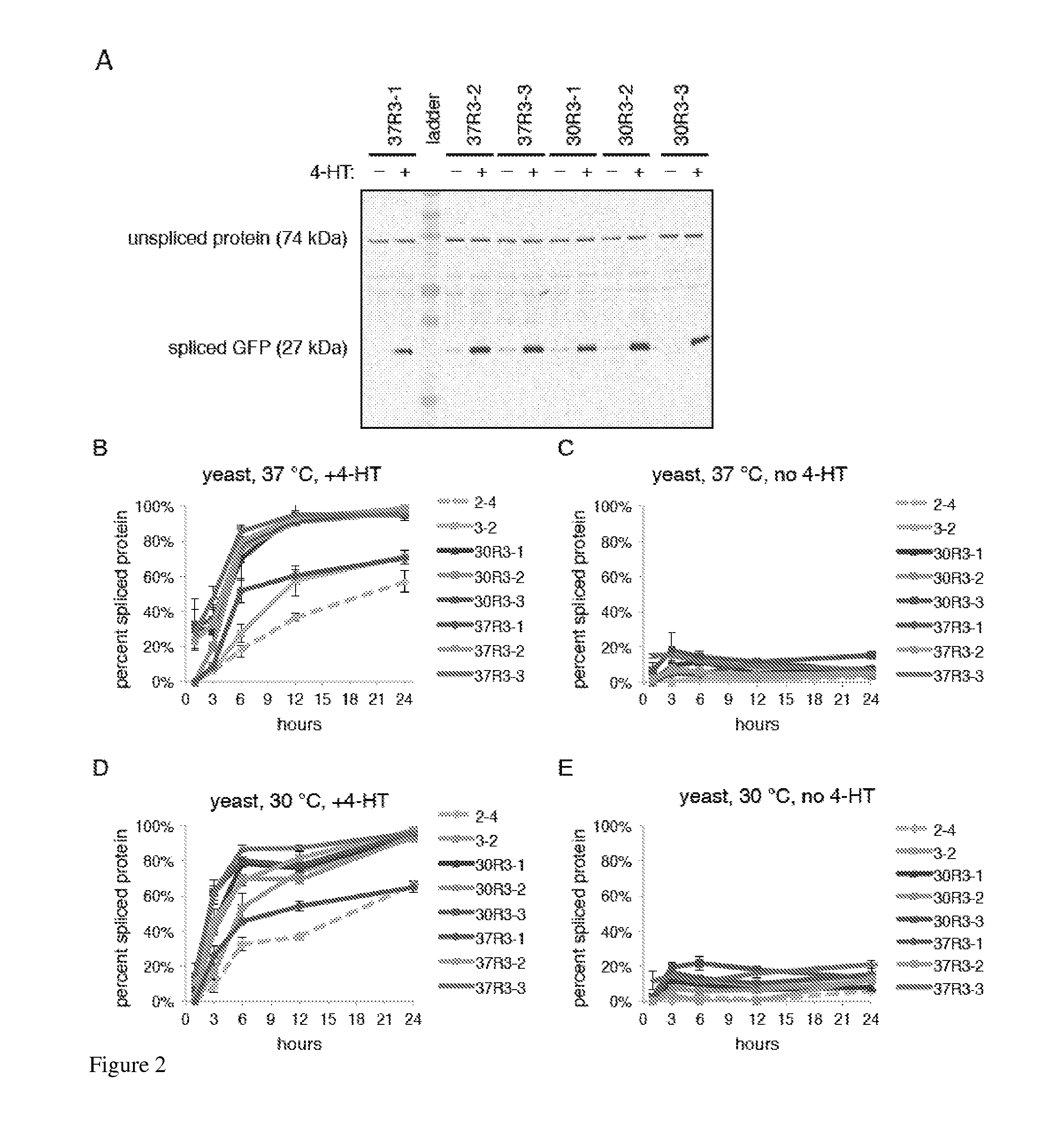
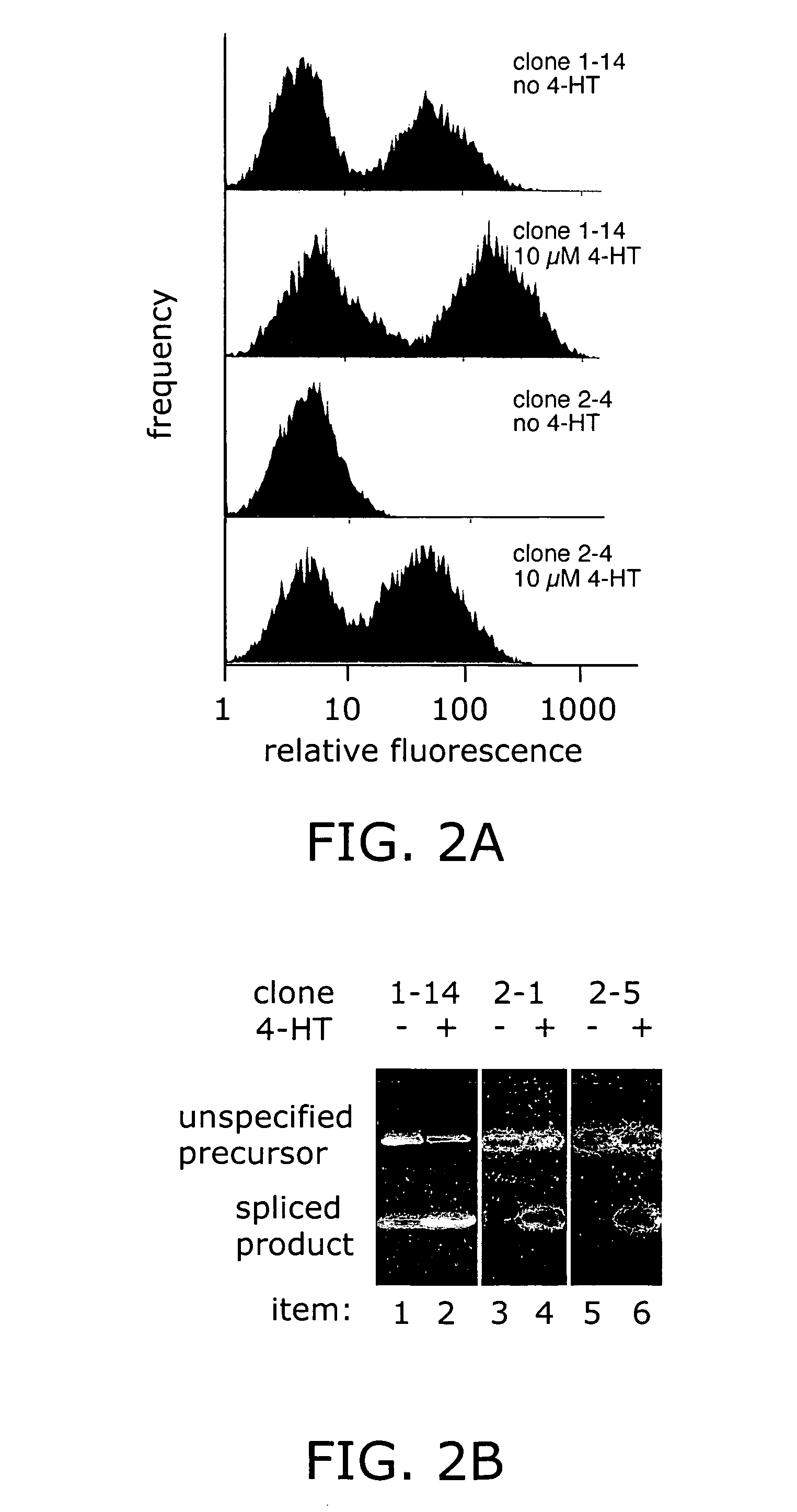
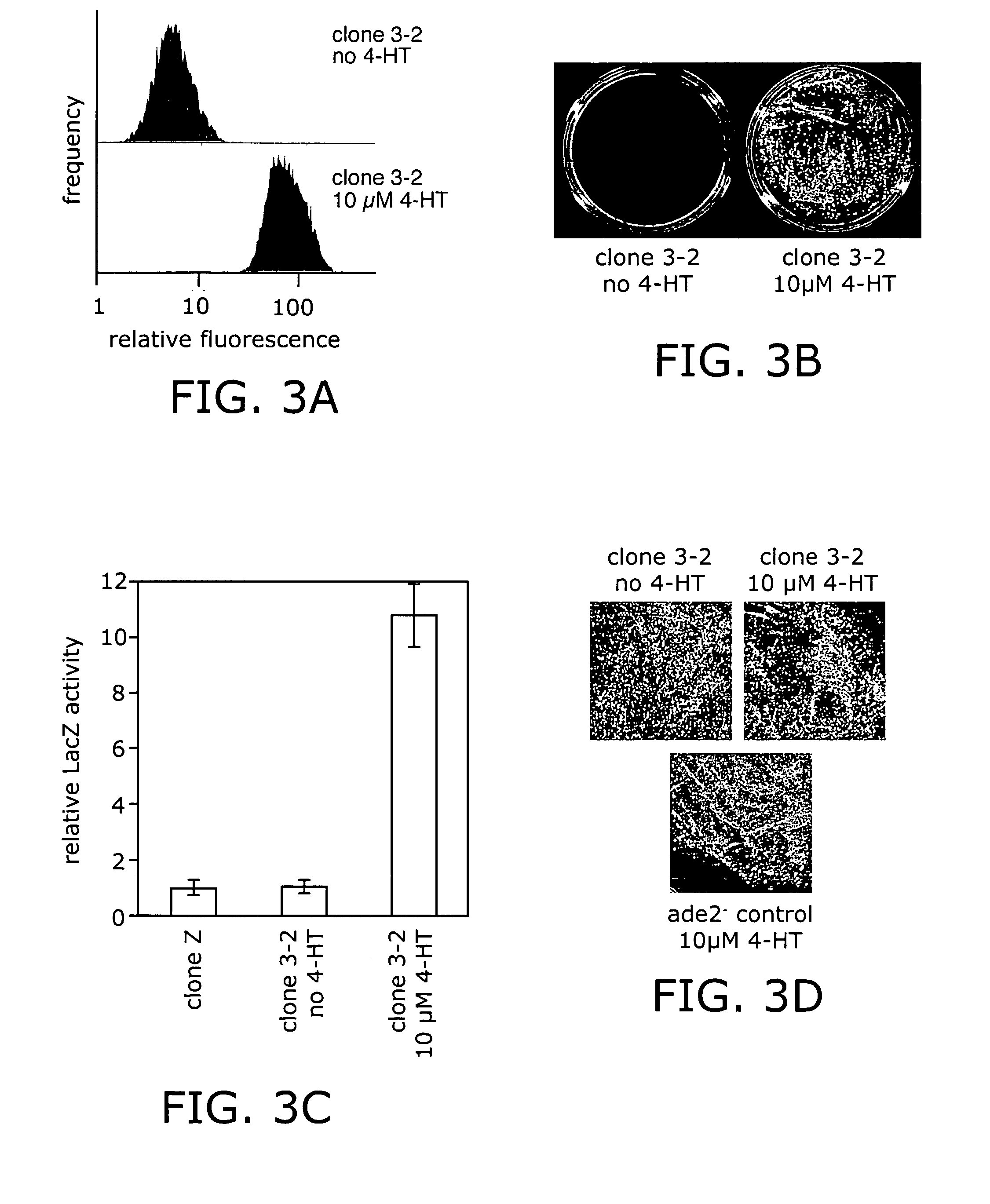
Elucidating the function of proteins in mammalian cells is particularly challenging due to the inherent complexity of these systems. Methods to study protein function in living cells ideally perturb the activity of only the protein of interest but otherwise maintain the natural state of the host cell or organism. Ligand-dependent inteins offer single-protein specificity and other desirable features as an approach to control protein function in cells post-translationally. Some aspects of this invention provide second-generation ligand-dependent inteins that splice to substantially higher yields and with faster kinetics in the presence of the cell-permeable small molecule 4-HT, especially at 37° C., while exhibiting comparable or improved low levels of background splicing in the absence of 4-HT, as compared to the parental inteins. These improvements were observed in four protein contexts tested in mammalian cells at 37° C., as well as in yeast cells assayed at 30° C. or 37° C. The newly evolved inteins described herein are therefore promising tools as conditional modulators of protein structure and function in yeast and mammalian cells.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Antigen delivery platforms
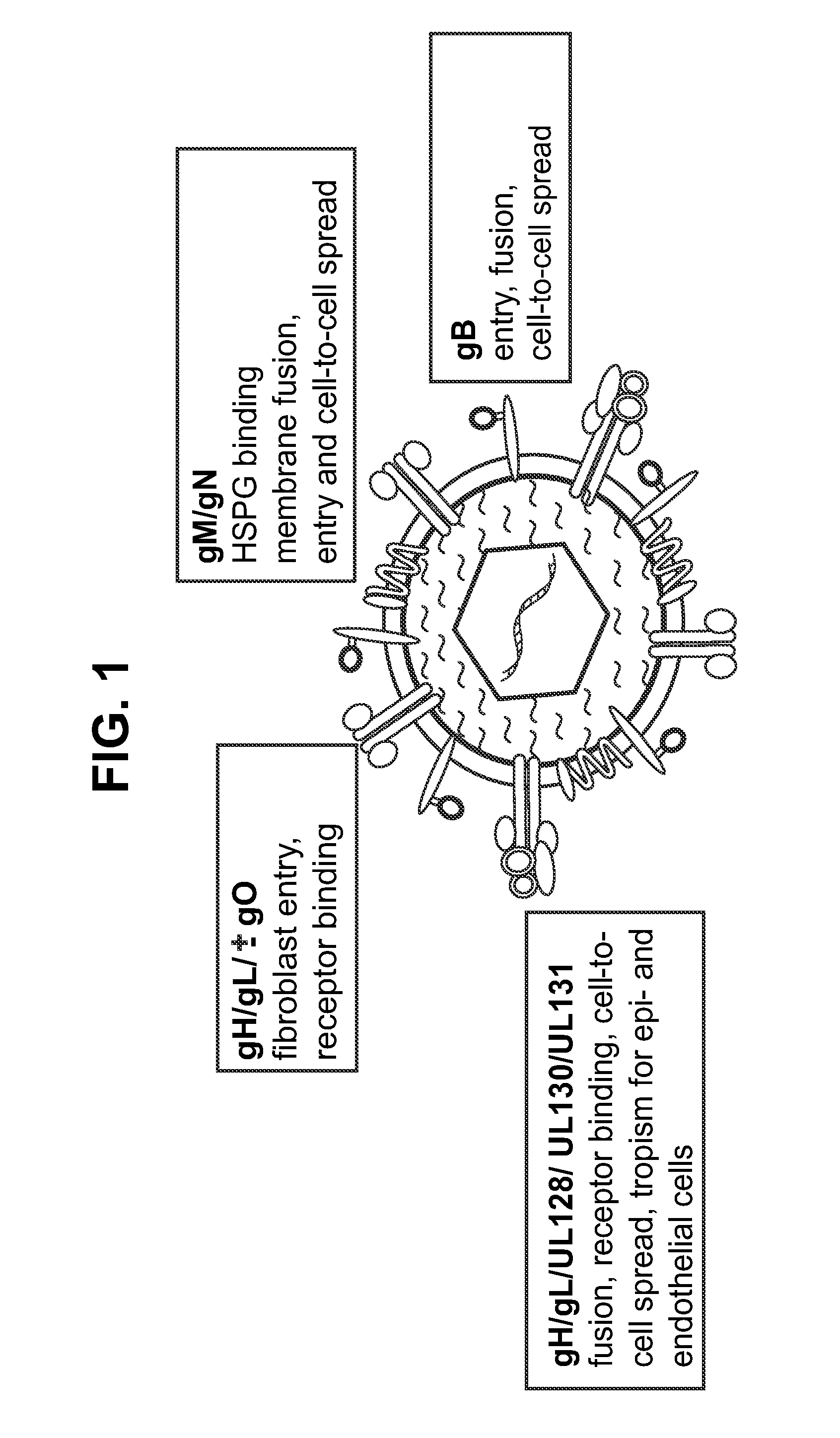
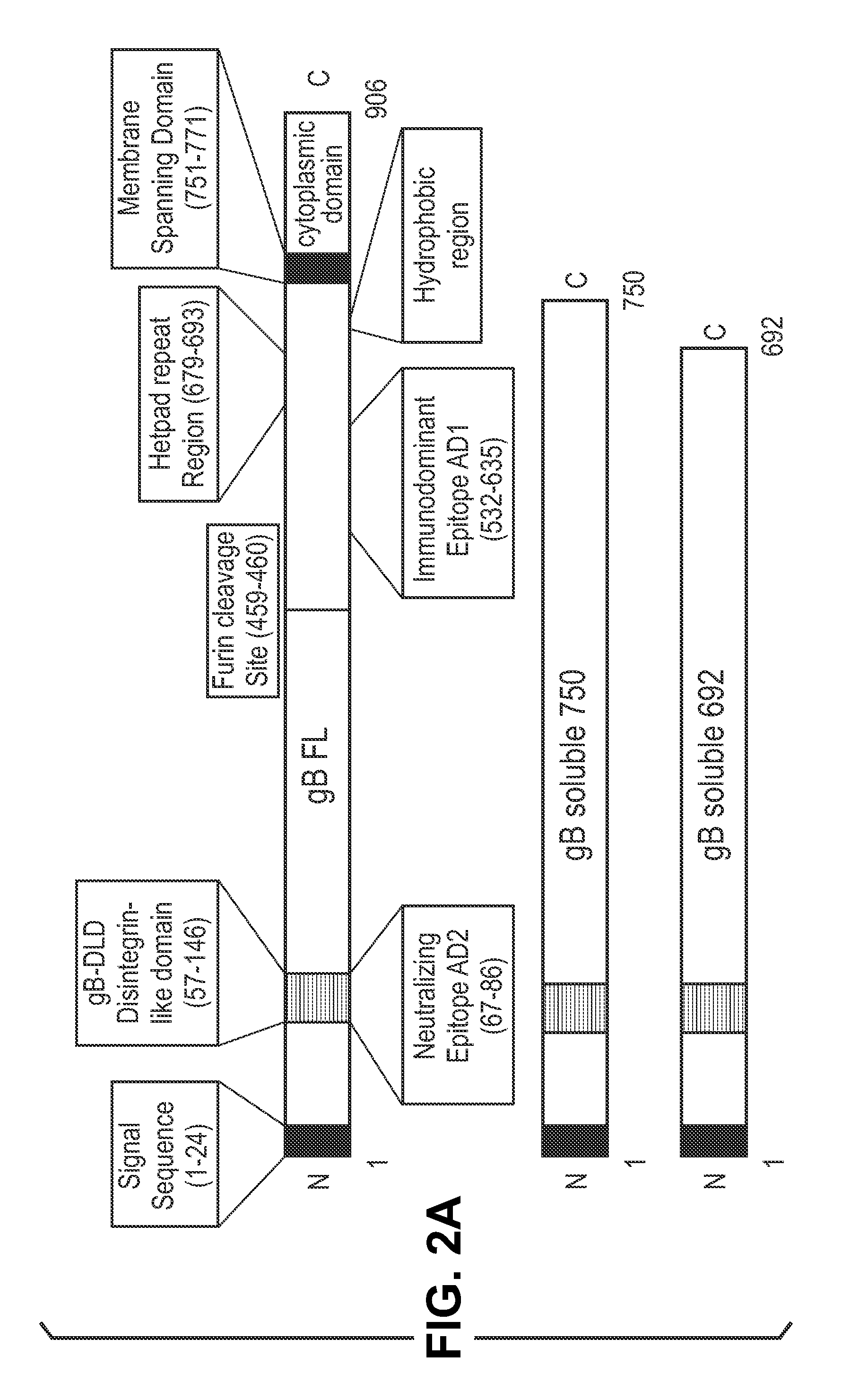
InactiveUS20140030292A1Improve stabilityAvoid reduce stimulationSsRNA viruses positive-senseFusion with post-translational modification motifAntigen deliveryHerpes simplex virus DNA
This disclosure provides platforms for delivery of herpes virus proteins to cells, particularly proteins that form complexes in vivo. In some embodiments these proteins and the complexes they form elicit potent neutralizing antibodies. Thus, presentation of herpes virus proteins using the disclosed platforms permits the generation of broad and potent immune responses useful for vaccine development.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Control of Protein Glycosylation and Compositions and Methods Relating Thereto
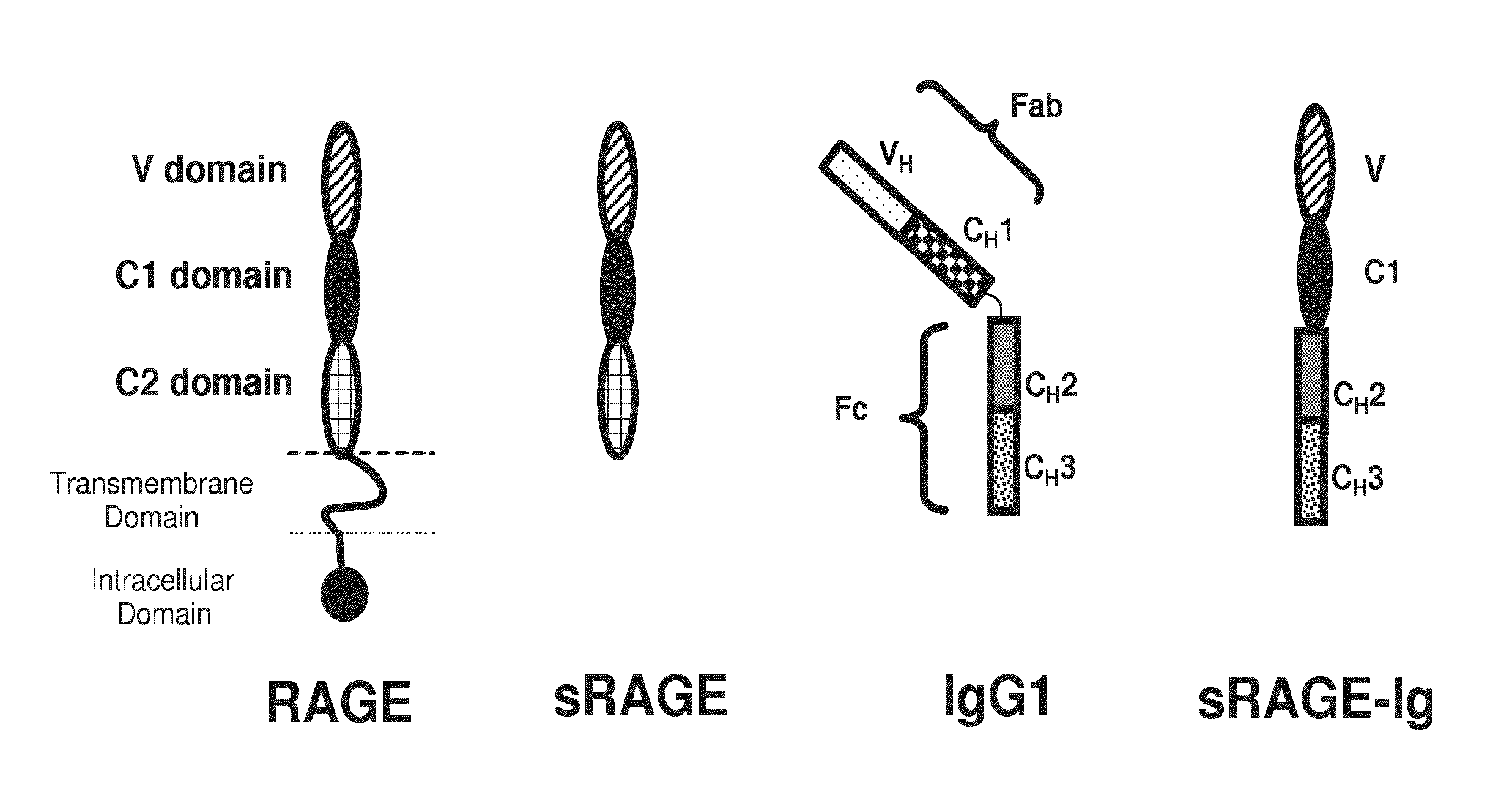
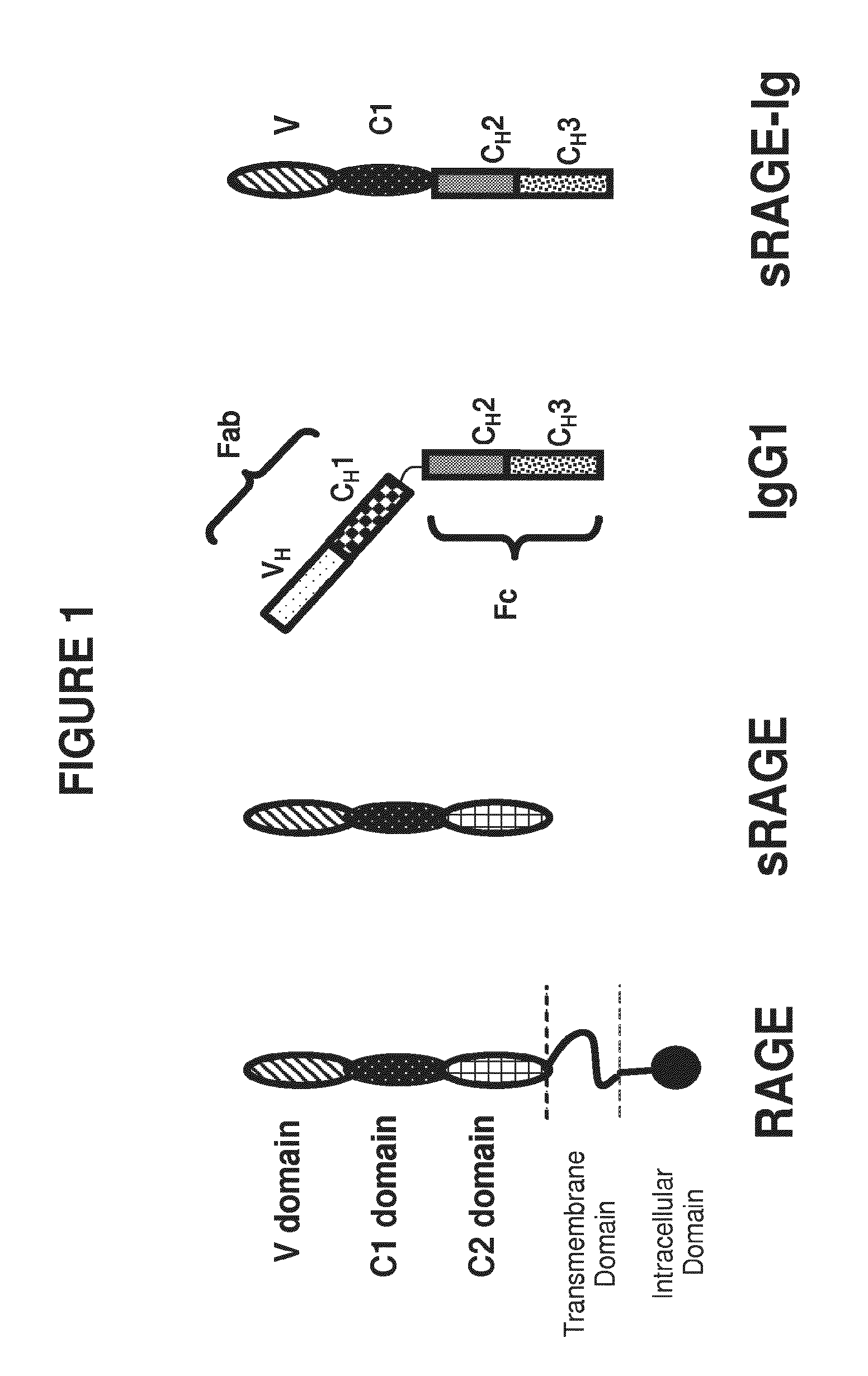
InactiveUS20120039908A1Lower Level RequirementsControlling glycosylation levelSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsTargeting ligandsProtein glycosylation
The invention relates to novel methods for controlling the glycosylation of a protein and the protein produced thereby. An exemplary method of the invention comprises producing a protein comprising a decreased level of glycosylation, e.g., the protein comprises fewer glycans or fewer saccharides at the glycosylation site, by culturing a host cell expressing the protein in the presence of a glycosylation inhibitor. In an exemplary method of the invention, the biological characteristics of the protein are altered by the decreased level of glycosylation, e.g., the binding of the protein with its target ligand is modified.
Owner:VTV THERAPEUTICS LLC
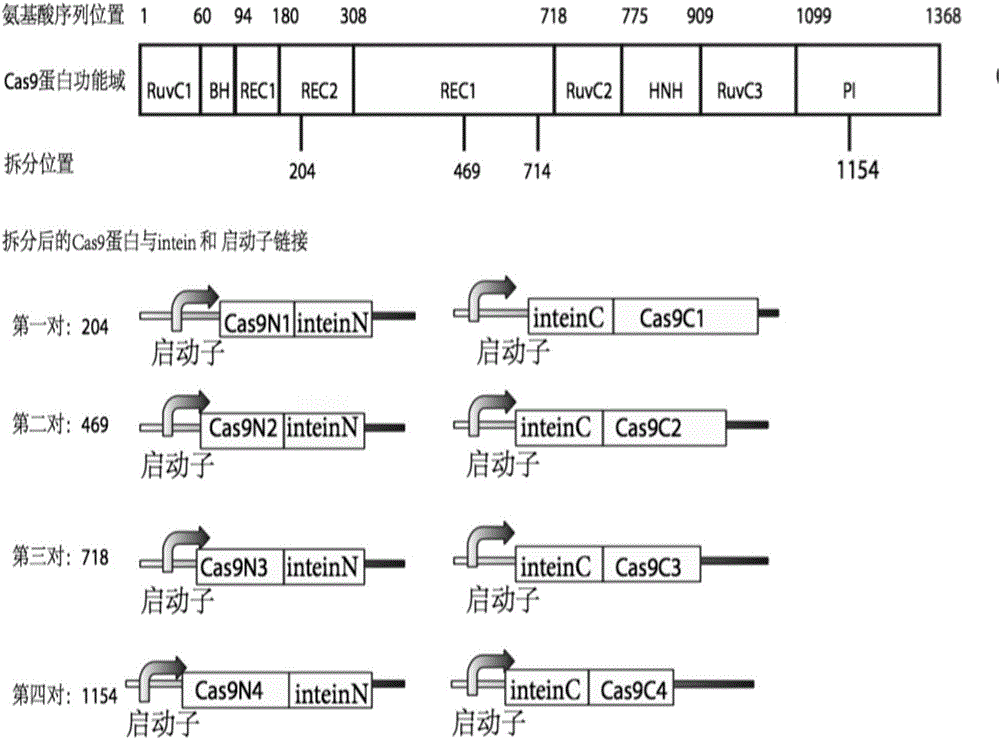
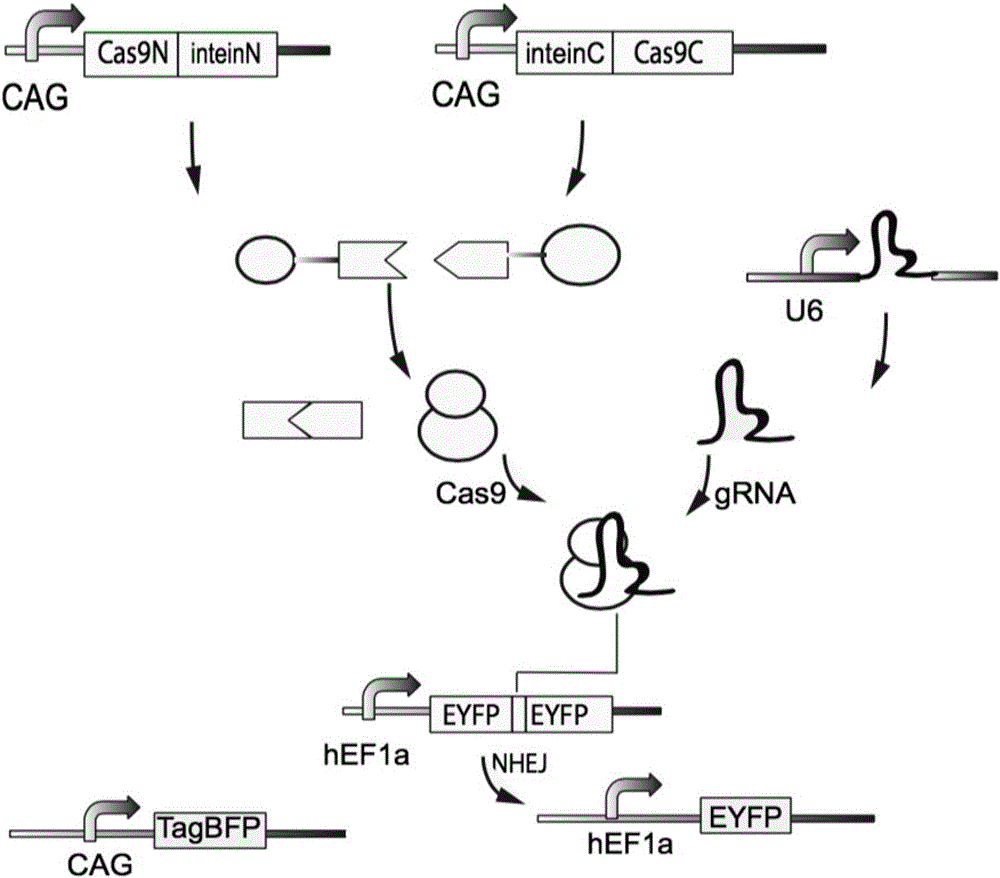
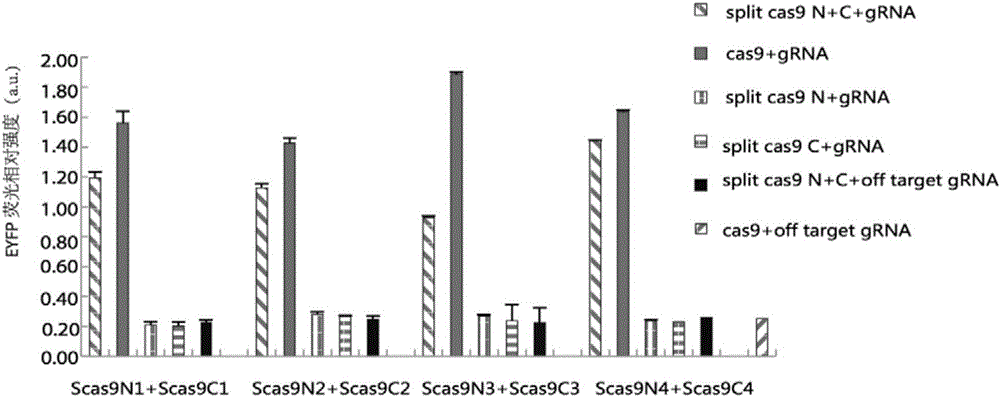
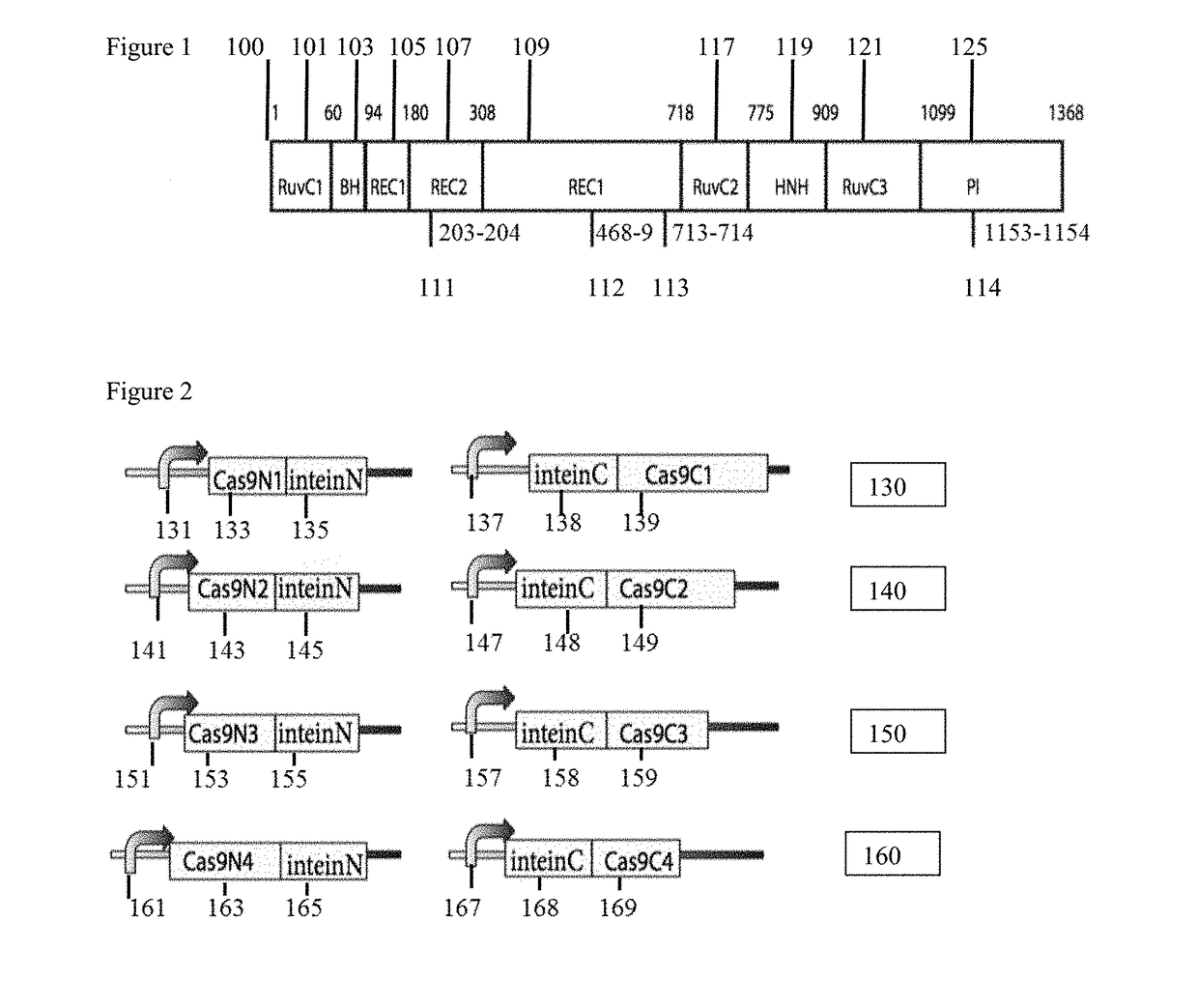
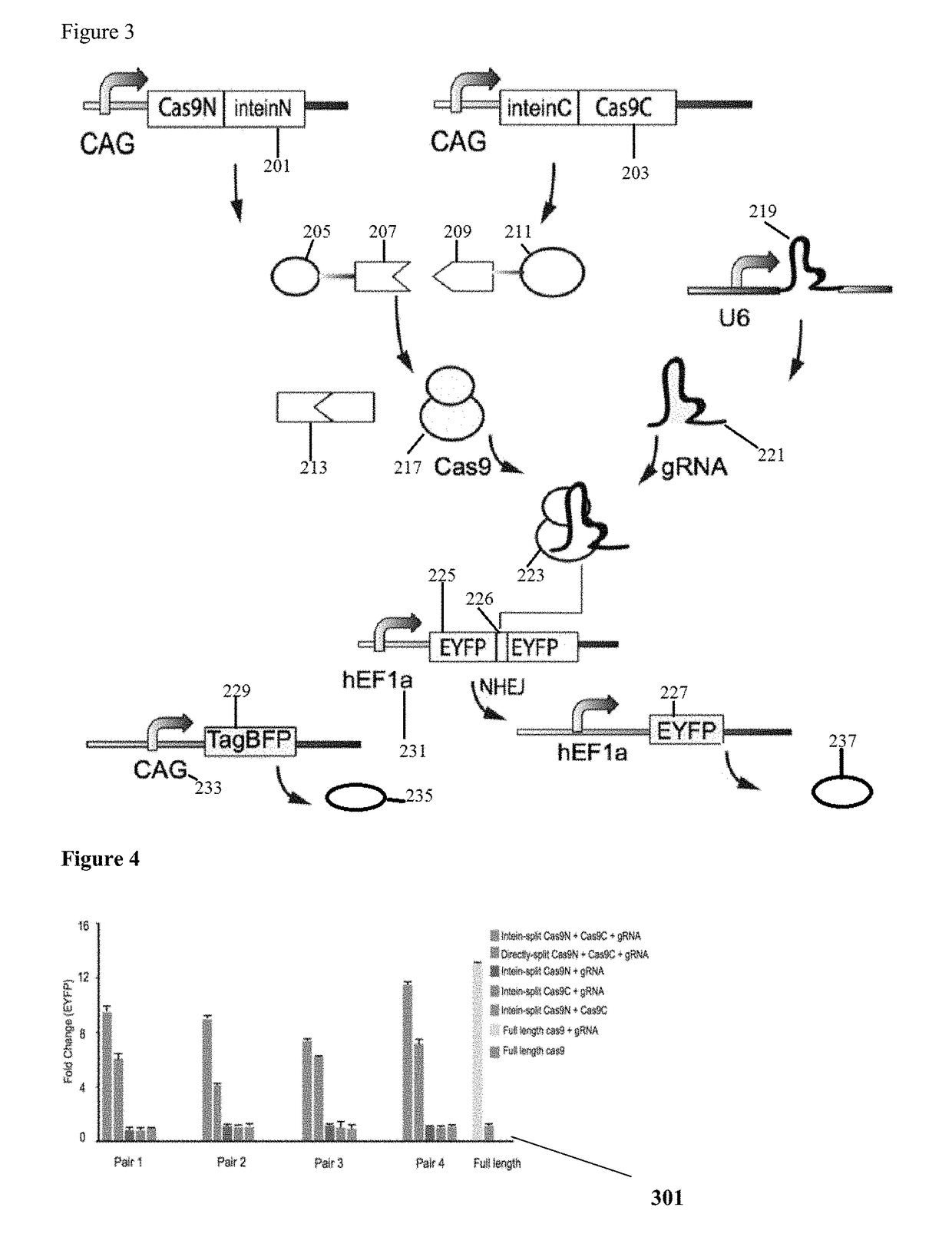
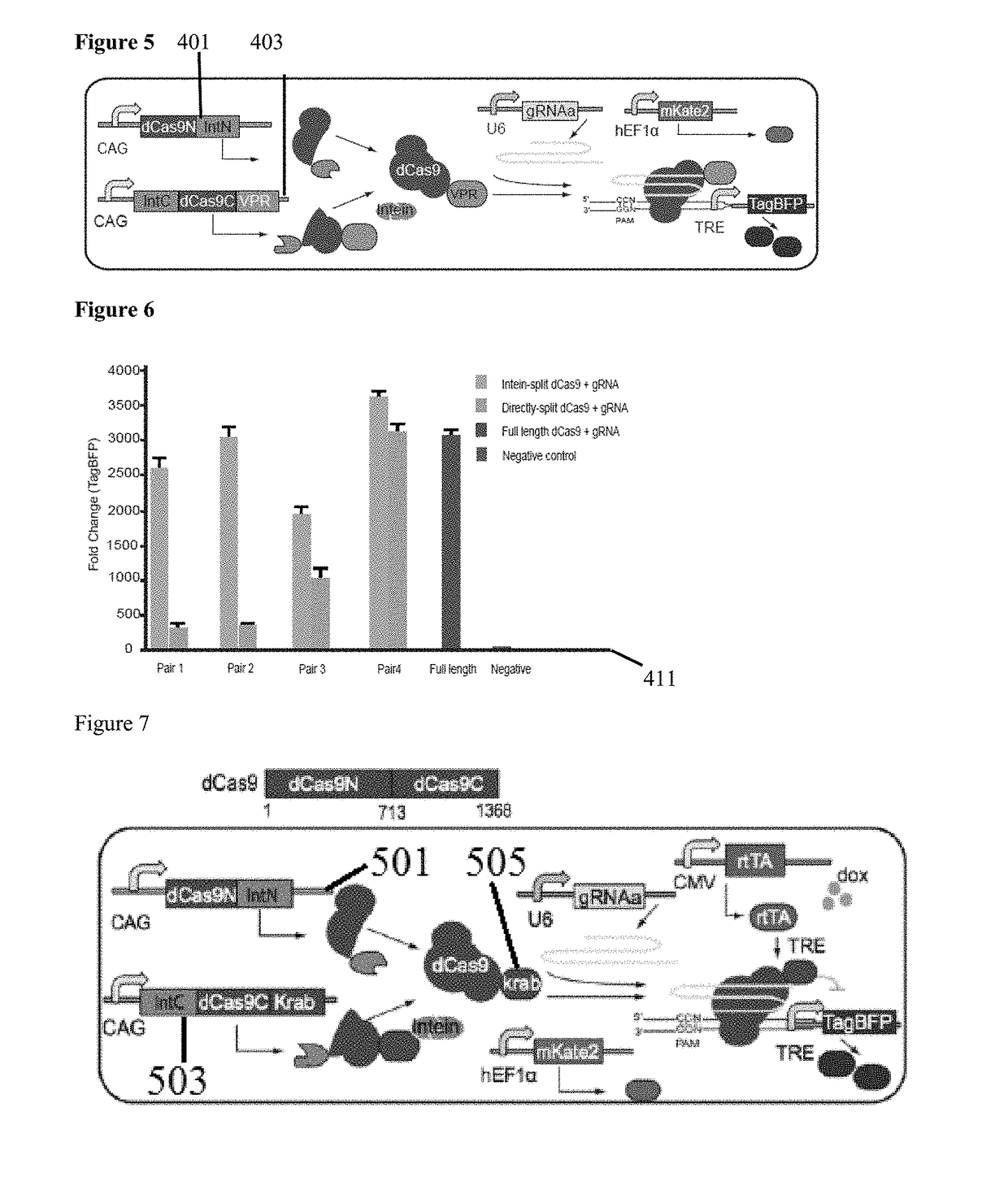
Method for carrying out gene editing and expression regulation by utilizing Cas splitting system
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Long-acting coagulation factors and methods of producing same
ActiveUS8476234B2Prolong lifeImproving area under curve (AUC)Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleotideClotting factor
Polypeptides and polynucleotides encoding same comprising at least one carboxy-terminal peptide (CTP) of chorionic gonadotrophin attached to a carboxy terminus of a coagulation factor and not to an amino terminus are disclosed. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the polypeptides and polynucleotides of the invention and methods of using same are also disclosed.
Owner:OPKO BIOLOGICS
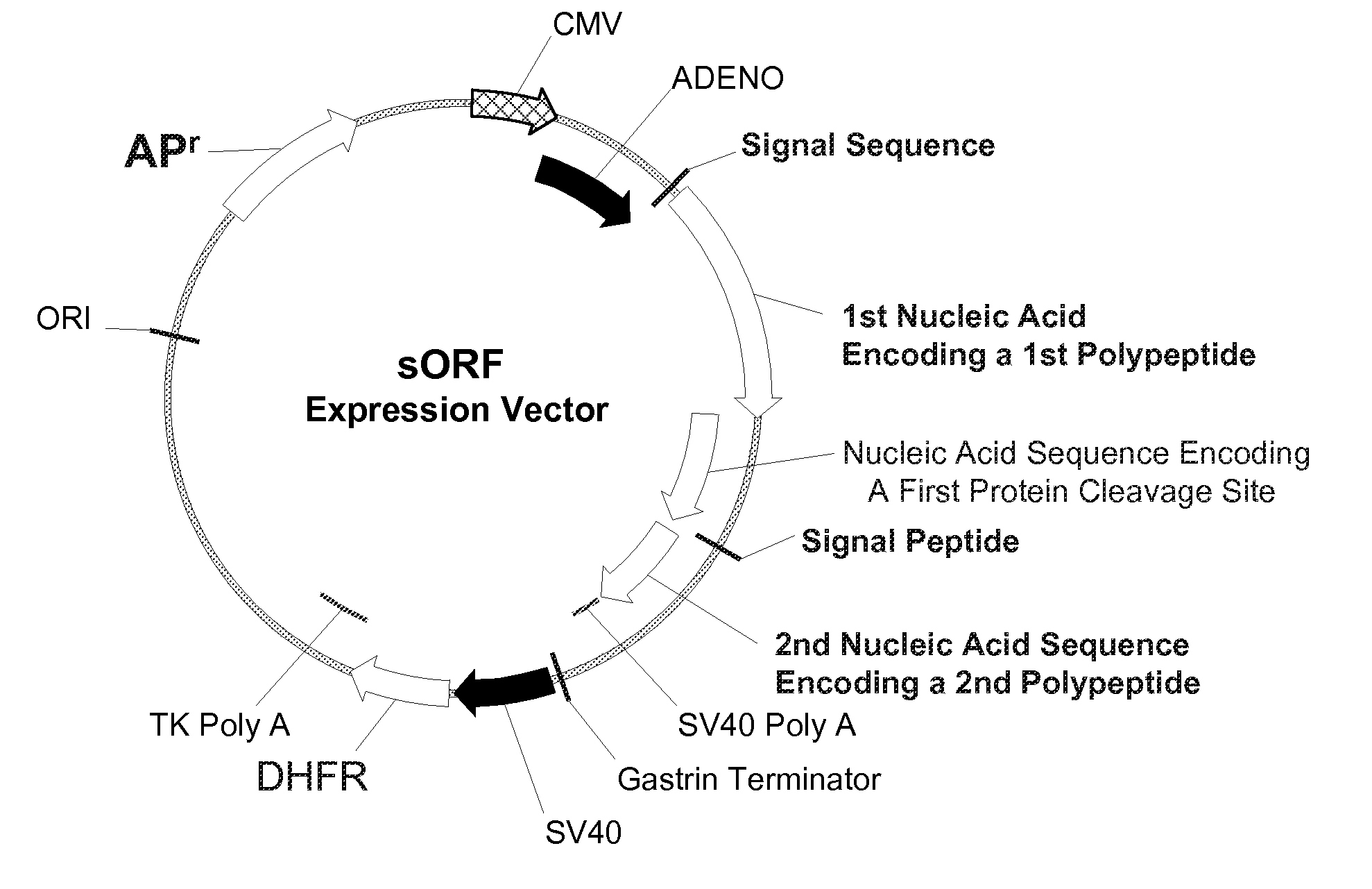
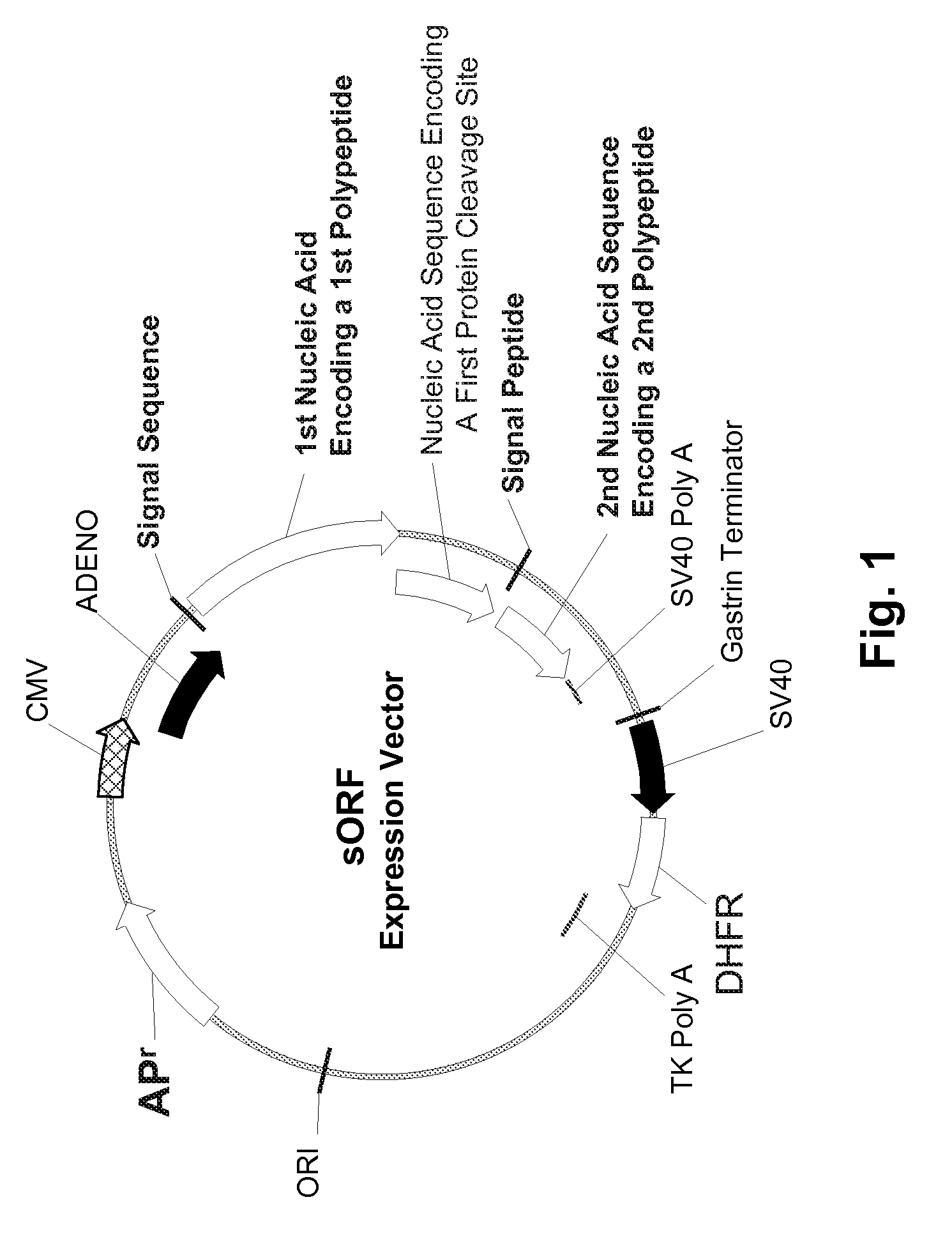
Multiple Gene Expression including sORF Constructs and Methods with Polyproteins, Pro-Proteins, and Proteolysis
InactiveUS20070065912A1Efficient expressionImprove economyFungiFusion with post-translational modification motifOpen reading frameADAMTS Proteins
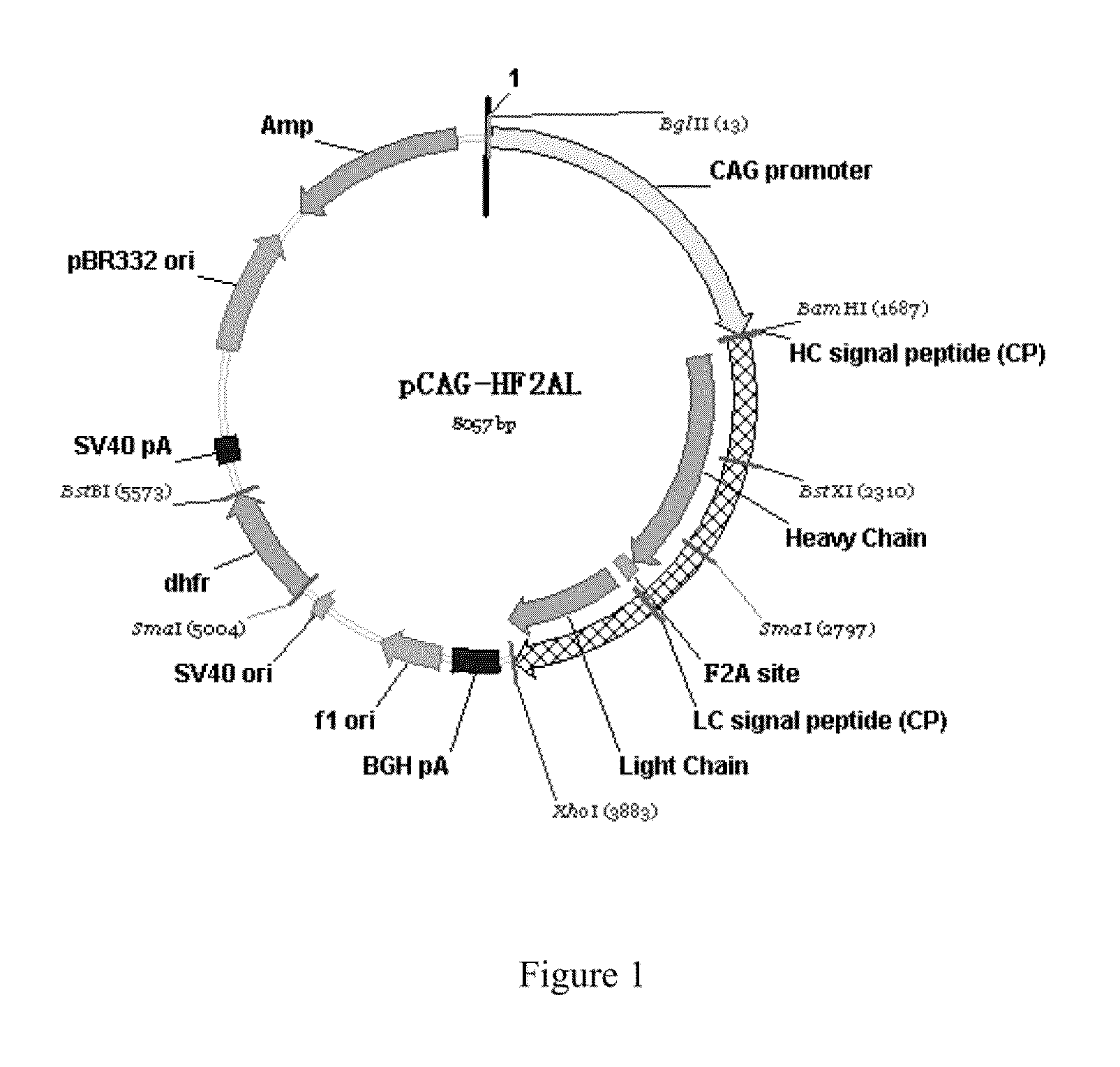
Disclosed are useful constructs and methods for the expression of proteins using primary translation products that are processed within a recombinant host cell. Constructs comprising a single open reading frame (sORF) are described for protein expression including expression of multiple polypeptides. A primary translation product (a pro-protein or a polyprotein) contains polypeptides such as inteins or hedgehog family auto-processing domains, or variants thereof, inserted in frame between multiple protein subunits of interest. The primary product can also contain cleavage sequences such as other proteolytic cleavage or protease recognition sites, or signal peptides which contain recognition sequences for signal peptidases, separating at least two of the multiple protein subunits. The sequences of the inserted auto-processing polypeptides or cleavage sites can be manipulated to enhance the efficiency of expression of the separate multiple protein subunits. Also disclosed are independent aspects of conducting efficient expression, secretion, and / or multimeric assembly of proteins such as immunoglobulins. Where the polyprotein contains immunoglobulin heavy and light chain segments or fragments capable of antigen recognition, in an embodiment a selectable stoichiometric ratio is at least two copies of a light chain segment per heavy chain segment, with the result that the production of properly folded and assembled functional antibody is made. Modified signal peptides, including such from immunoglobulin light chains, are described.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Long-acting polypeptides and methods of producing same
ActiveUS20090312254A1Reduce dosing frequencyImprove compliancePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleotideChorionic gonadotrophin
A polypeptide and polynucleotides encoding same comprising one carboxy-terminal peptide (CTP) of chorionic gonadotrophin attached to an amino terminus of a cytokine and two carboxy-terminal peptides (CTP) of chorionic gonadotrophin attached to a carboxy terminus of a cytokine are disclosed. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the polypeptide and polynucleotides of the invention and methods of using same are also disclosed.
Owner:MODIGENE LLC +1
Genetic indicator and control system and method utilizing split Cas9/CRISPR domains for transcriptional control in eukaryotic cell lines
PendingUS20170233703A1Facilitated engineeringIncrease the number ofHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLiving systemsPlant cell
While genetic engineering has undergone rapid advancement with the discovery of CRISPR / Cas9, there is room for improvement for genetic circuit control, precision (reducing circuit ‘leakiness’) and delivery into living systems. The claimed invention offers programmable and precise regulation of dCas9 functions in response to multiple molecular signals by using synthetic gene circuits, greatly expanding applications. Moreover, using the system to greatest therapeutic potential has been greatly limited by the restrictive cargo size of existing viral delivery systems. By splitting dCas9 into multiple sections, the delivery size of synthetic gene circuits is greatly reduced. By exchanging split dCas9 domains, differential regulation on one gene, or activating two different genes in response to cell-type specific microRNAs is illustrated. Practical applications of the illustrative examples include engineered sensory switches including indicators for bladder cancer as well as enhanced systems for adenovirus delivery, cellular regulation, plant cell modification and potential therapeutic applications.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Long-acting polypeptides and methods of producing same
ActiveUS8048849B2Reduce dosing frequencyImprove compliancePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleotideCytokine
A polypeptide and polynucleotides encoding same comprising one carboxy-terminal peptide (CTP) of chorionic gonadotrophin attached to an amino terminus of a cytokine and two carboxy-terminal peptides (CTP) of chorionic gonadotrophin attached to a carboxy terminus of a cytokine are disclosed. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the polypeptide and polynucleotides of the invention and methods of using same are also disclosed.
Owner:MODIGENE LLC +1
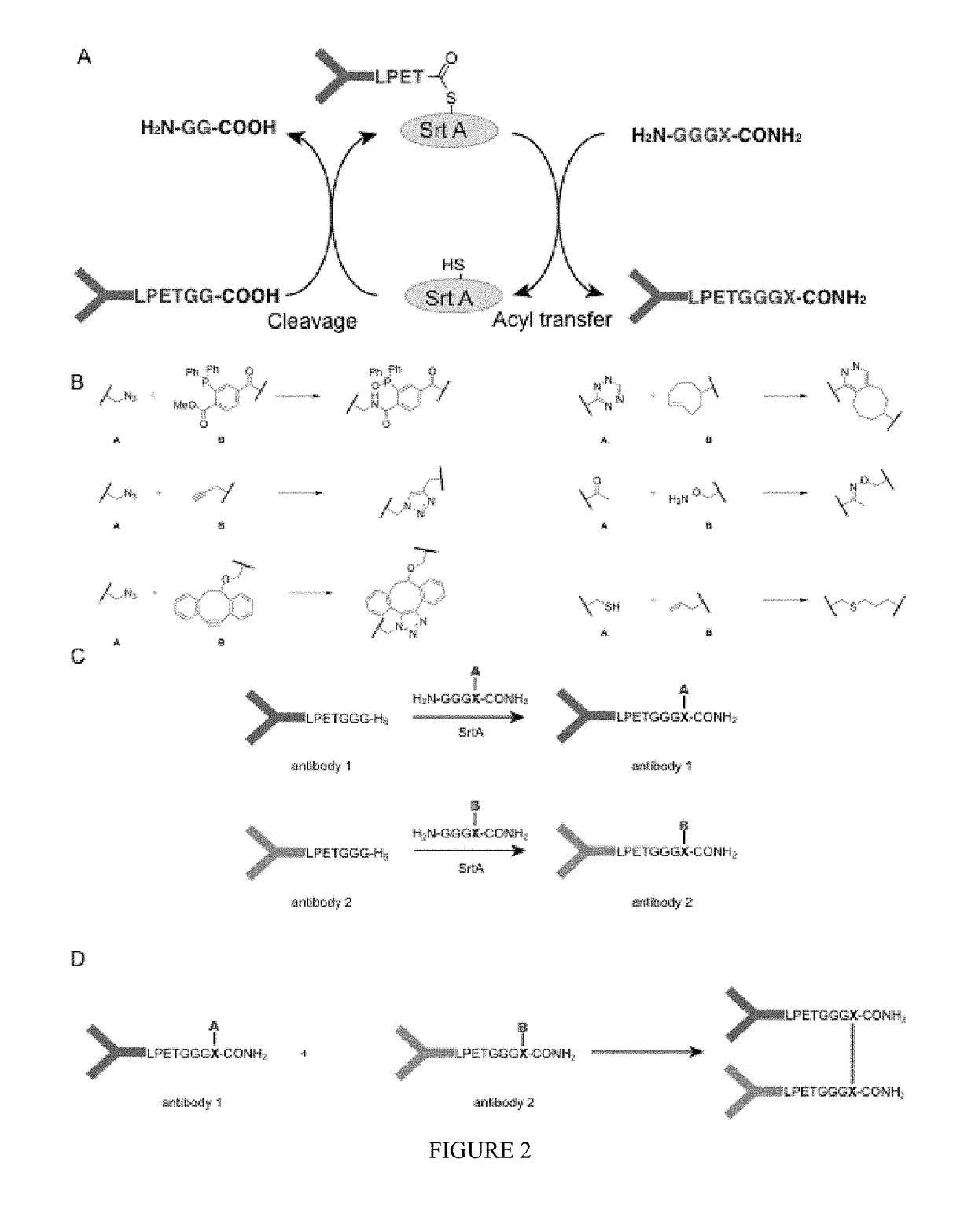
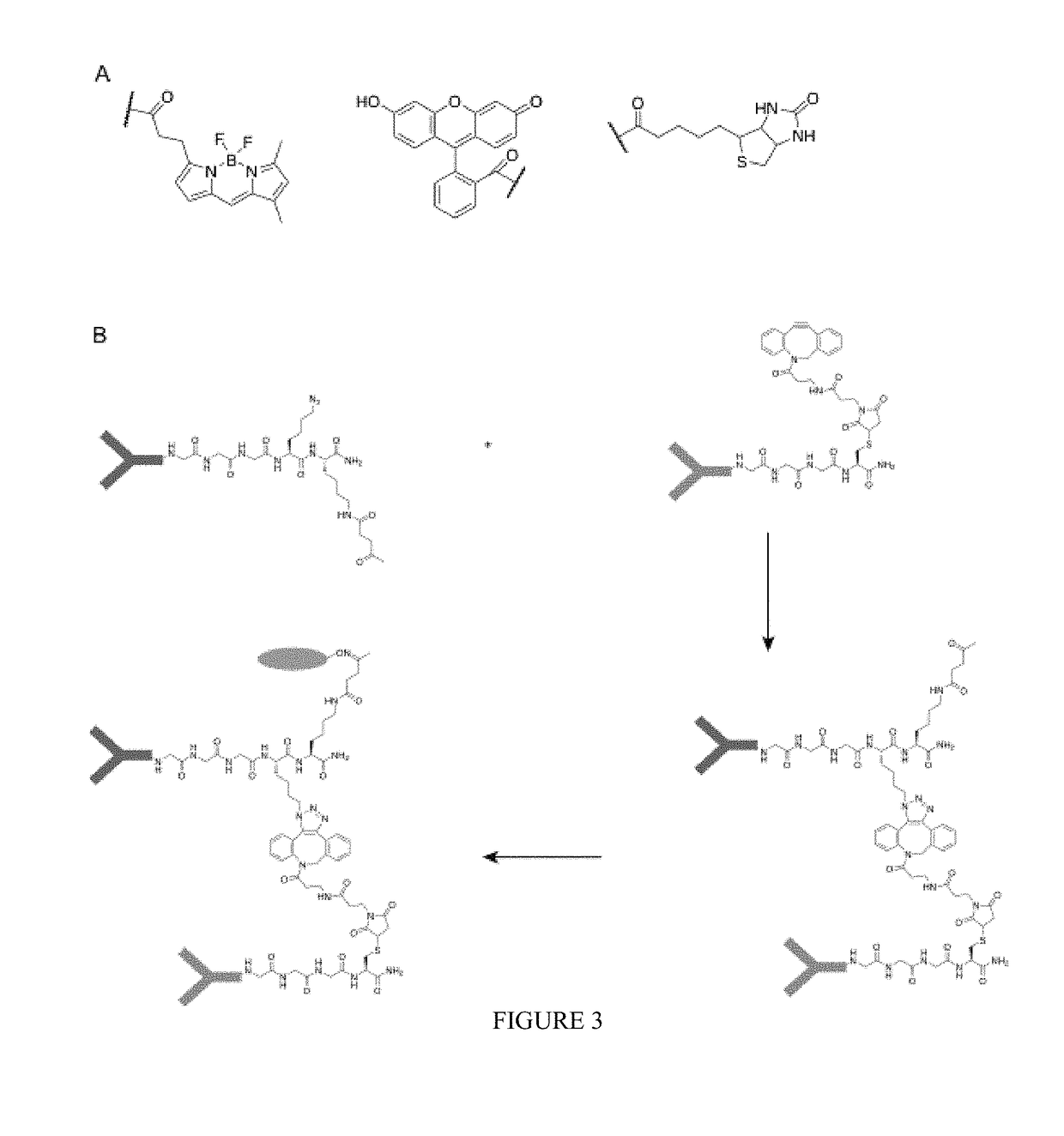
Sortase-modified vhh domains and uses thereof
In some aspects, polypeptides comprising single domain antibodies and methods of identifying single domain antibodies are provided. In some embodiments polypeptides comprising a single domain antibody and a sortase recognition sequence, are provided. In some aspects, products and methods of use in modulating the immune system, e.g., modulating an immune response, are provided.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Small molecule-dependent inteins and uses thereof
ActiveUS9200045B2Low efficiencySlow splicingHydrolasesFusion with post-translational modification motifInteinNatural state
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Sortase-modified VHH domains and uses thereof
In some aspects, polypeptides comprising single domain antibodies and methods of identifying single domain antibodies are provided. In some embodiments polypeptides comprising a single domain antibody and a sortase recognition sequence, are provided. In some aspects, products and methods of use in modulating the immune system, e.g., modulating an immune response, are provided.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Ligand-dependent protein splicing
Ligand-dependent inteins allow for modulation of a protein's activity in vivo. Upon binding of the ligand to the ligand-dependent intein inserted into the protein of interest, the hybrid protein undergoes protein splicing removing the intein. The activity of the spliced protein is then restored. A 4-hydroxytamoxifen-dependent intein based on the M. tuberculosis RecA intein is prepared and demonstrated in a variety of exteins contexts. The invention provides a system for engineering other ligand-dependent inteins and using them, including the ligand-dependent inteins themselves, hybrid proteins with the inserted ligand-dependent inteins, polynucleotides encoding inteins and hybrid proteins, and engineered cells. Kits with the materials and reagents necessary for preparing and using ligand-dependent inteins are also included.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
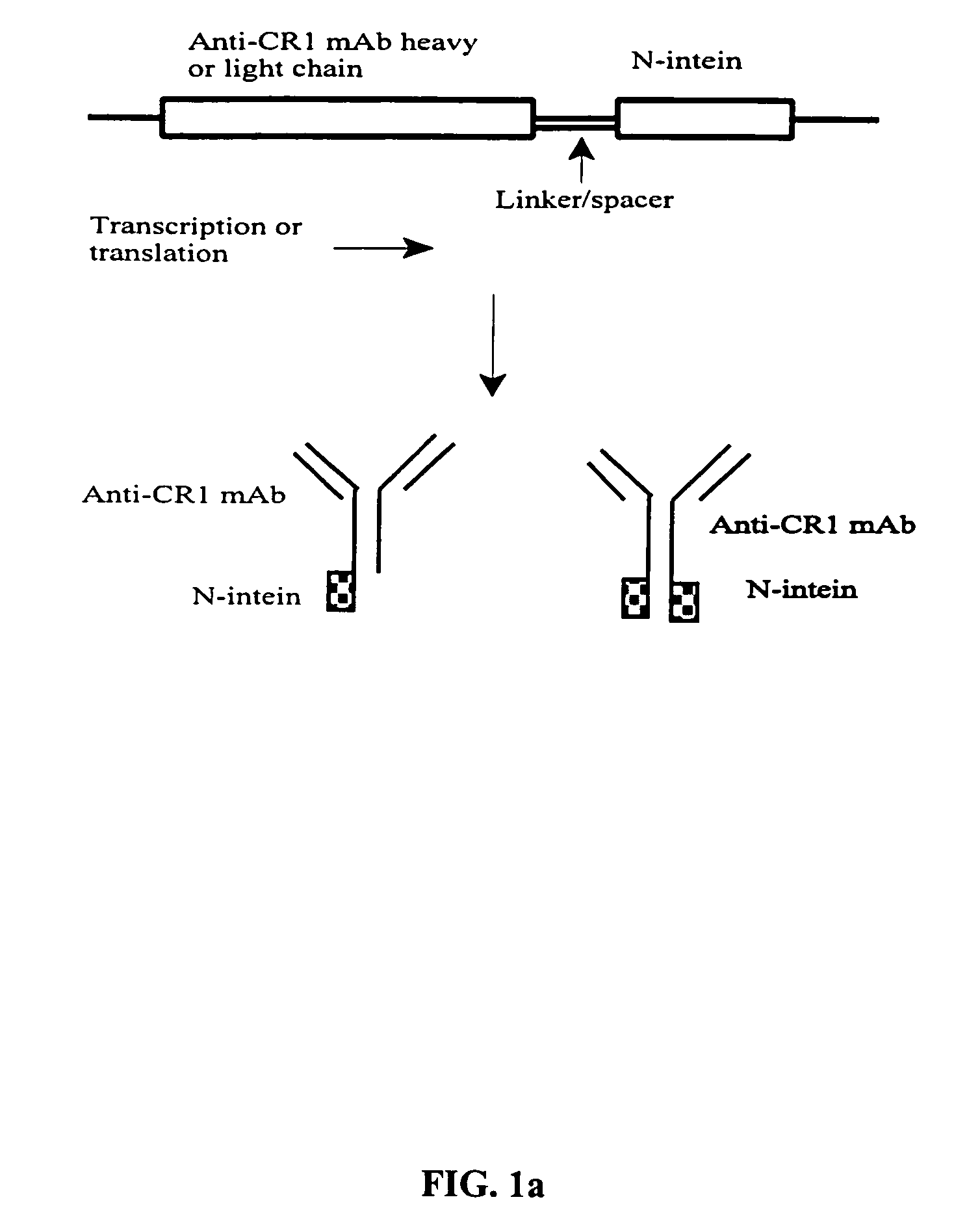
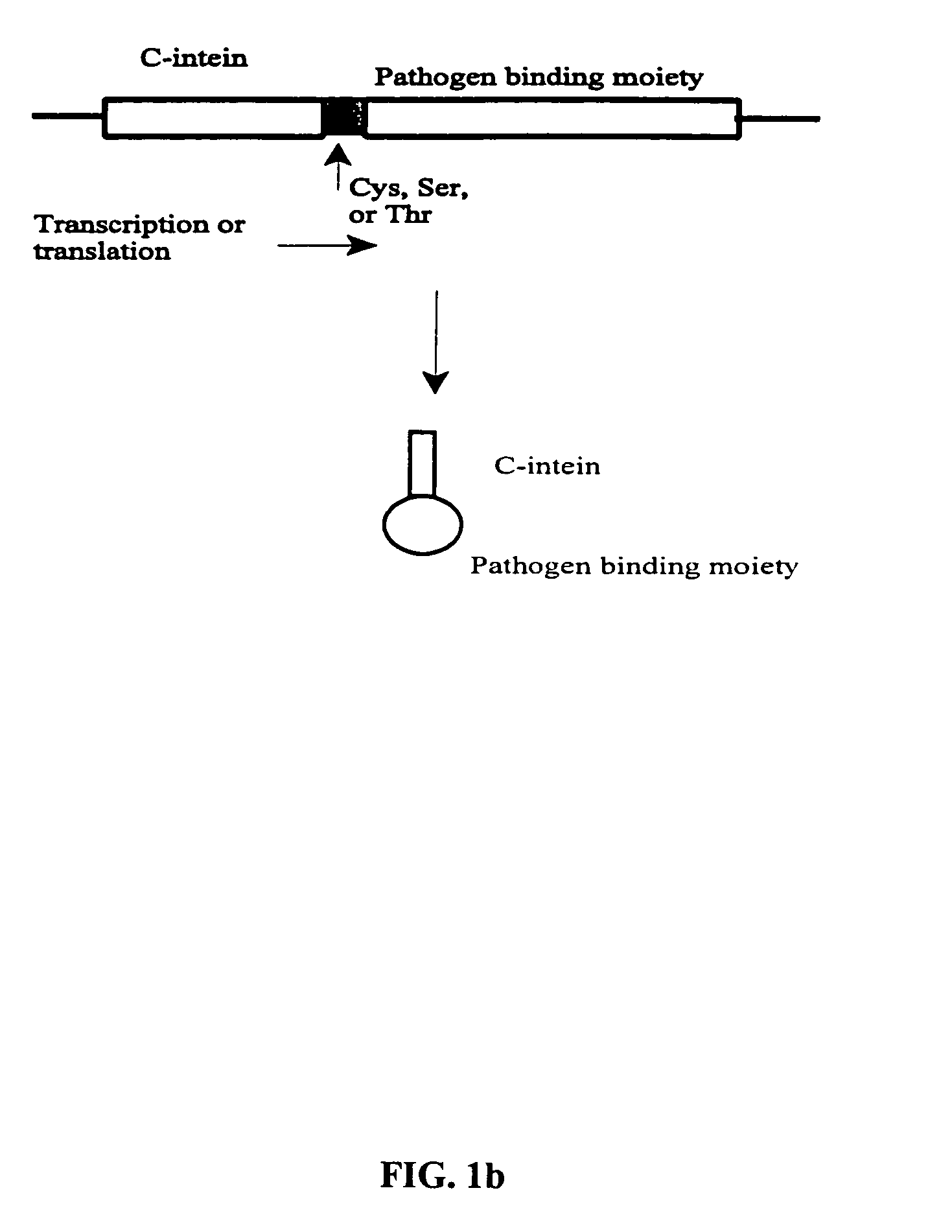
Method of producing biospecific molecules by protein trans-splicing
The invention provides methods of using protein trans-splicing for the production of bispecific molecule which has a first antigen recognition portion that binds a C3b-like receptor and a second antigen recognition portion that binds an antigenic molecule present in the circulatory system of a mammal. The invention also provides bispecific molecules produced by protein trans-splicing. The bispecific molecules of the invention can be used for the clearance of pathogenic antigenic molecules from the circulatory system of a mammal. The invention further provides methods of using protein trans-splicing for the production of polyclonal libraries of bispecific molecules, which comprise populations of bispecific molecules with different antigen recognition specificities. Such polyclonal libraries of bispecific molecules can be used for targeting multiple epitopes of a pathogenic antigenic molecule and / or multiple variants of a pathogenic antigenic molecule.
Owner:ELUSYS THERAPEUTICS
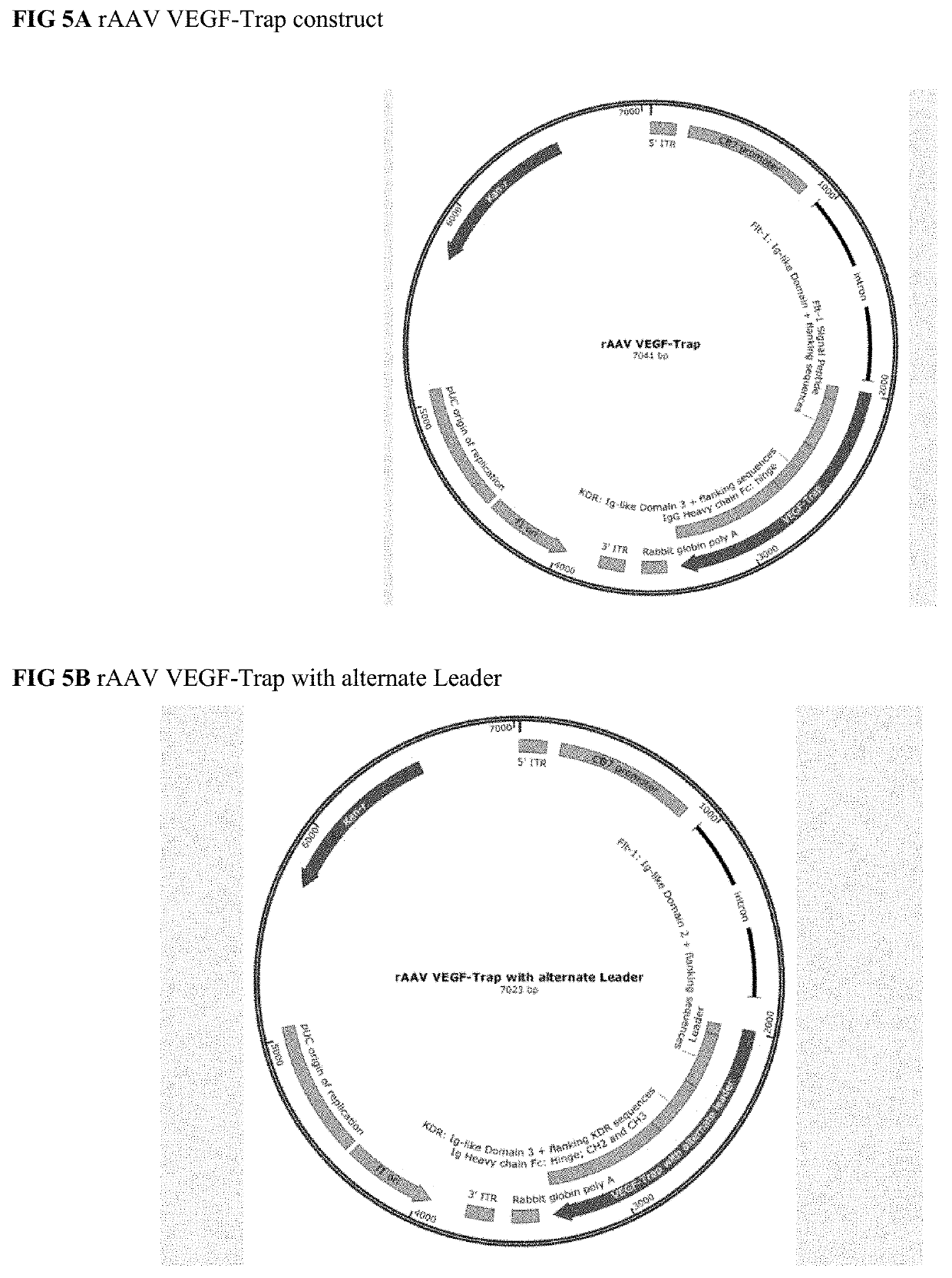
Treatment of ocular diseases with human post-translationally modified vegf-trap
PendingUS20210010025A1Maintain stabilityReduced half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseOncology
Compositions and methods are described for the delivery of a fully human post-translationally modified (HuPTM) therapeutic VEGF-Trap (VEGF-TrapHuPTM)—to a human subject diagnosed with an ocular disease or condition or cancer associated with neovascularization and indicated for treatment with the therapeutic mAb. Delivery may be advantageously accomplished via gene therapy—e.g., by administering a viral vector or other DNA expression construct encoding the VEGF-TrapHuPTM to a patient (human subject) diagnosed with an ocular condition or cancer indicated for treatment with the VEGF-Trap—to create a permanent depot in a tissue or organ of the patient that continuously supplies the VEGF-TrapHuPTM, i.e., a human-glycosylated transgene product. Alternatively, the VEGF-TrapHuPTM, for example, produced in cultured human cell culture, can be administered to the patient for treatment of the ocular disease or cancer.
Owner:REGENXBIO
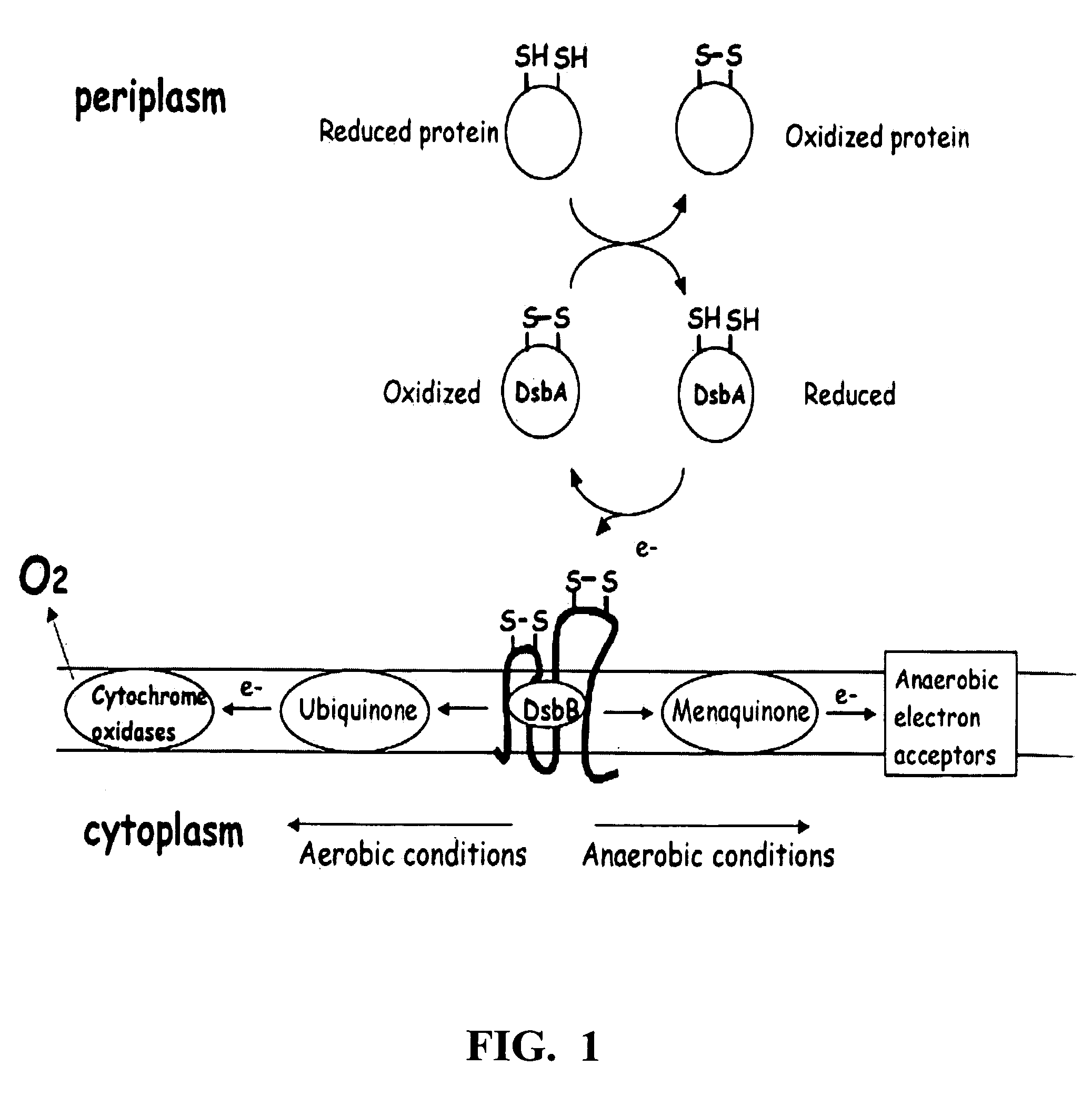
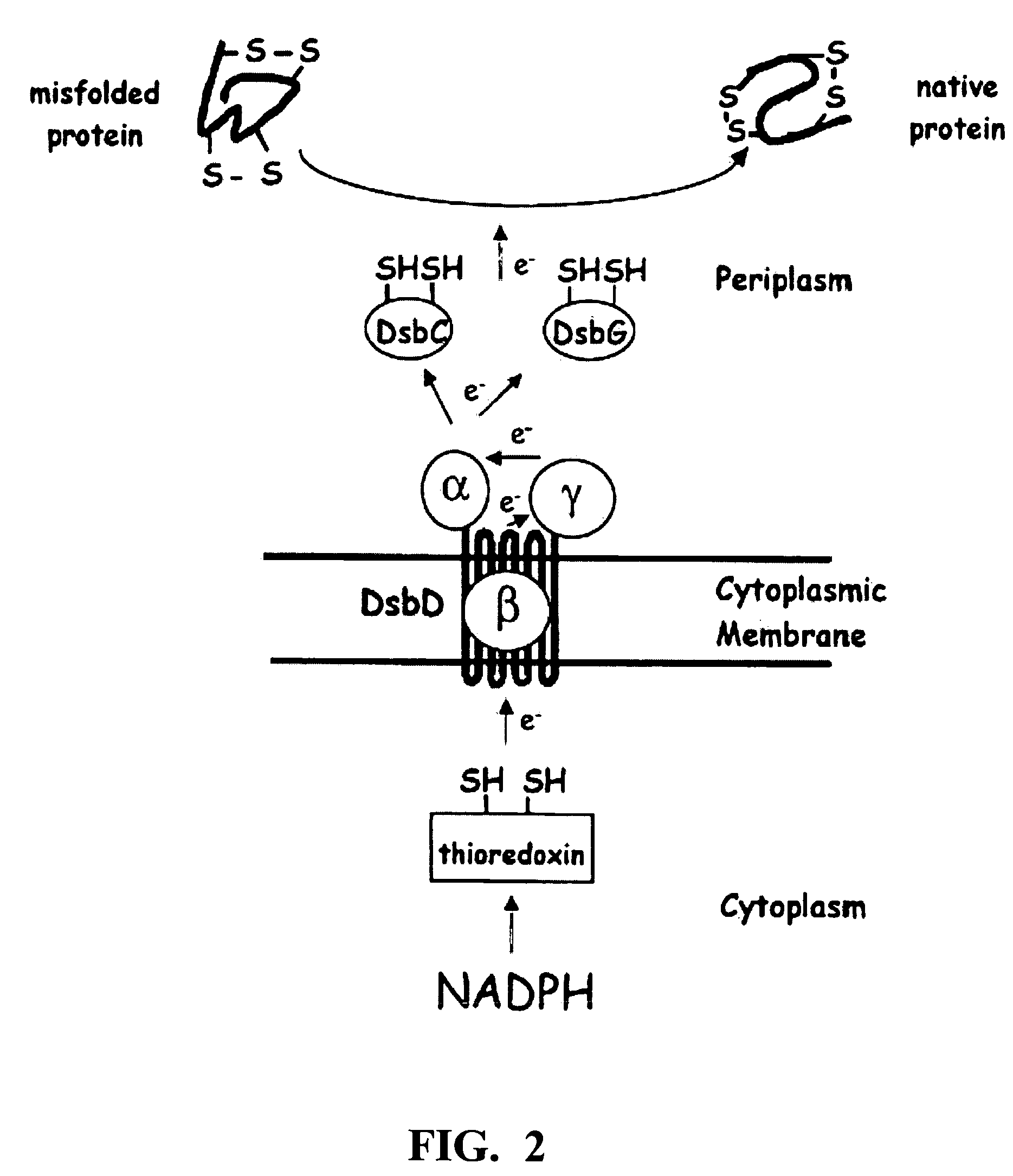
Method of expressing proteins with disulfide bridges
InactiveUS20060246541A1High affinityFacilitate the proper folding of nascent recombinant CN disintegrin domainBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyADAMTS Proteins
This invention relates to methods of expressing eukaryotic proteins in prokaryotic hosts, particularly eukaryotic proteins that require formation of disulfide bridges for biological activity. Various approaches are used including fusion to thioredoxin, cytoplasmic expression of disulfide isomerases, deficiencies in thioredoxin and / or glutathione reductases, deficiencies in proteases, and the like. The method is applicable to express monomeric and dimeric forms of the eukaryotic protein with biological activity such as monomeric and dimeric forms of a disintegrin or a disintegrin domain. Included are the vectors, host cells expressing the proteins, the expressed proteins and methods of using the proteins.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Recognition tags for tgase-mediated conjugation
ActiveUS20150284713A1Low production costImprove responsePeptide librariesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseSpecific antibody
The present application relates to methods for the functionalization of antibodies using transglutaminase, in particular antibodies lacking Fc regions. Also disclosed herein are peptide tags for transglutaminase, linking reagents, functionalized antibodies, multi-specific antibodies, pharmaceutical compositions, and method of treating disease and / or conditions.
Owner:INNATE PHARMA SA +1
Methods and compositions for treating ulcers
ActiveUS20160039922A1Increase productionIncreased erythropoiesisPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsRed blood cellCanker
The present disclosure provides compositions and methods for treating or preventing ulcers in subjects having low red blood cell levels and / or hemoglobin levels (e.g, anemia). In some embodiments, the compositions of the disclosure may be used to treat or prevent ulcers associated with anemia.
Owner:ACCELERON PHARMA INC
Intein-mediated protein purification using in vivo expression of an elastin-like protein
InactiveUS20060263855A1Successful useFunction increaseConnective tissue peptidesBacteriaInteinIn vivo
Purification of recombinant proteins is performed by expressing in a host cell a fusion protein comprising: (a) a product protein domain, (b) an intein, and (c) at least one aggregator protein domain, wherein the aggregator protein domain comprises a self-aggregating protein such as elastin-like proteins (ELPs).
Owner:PRINCETON UNIV
Intein mediated peptide ligation
InactiveUS7001745B1High yieldReturn to normal activitiesBacteriaFusion with post-translational modification motifOxidative stressIntein
The present invention provides methods that utilize compositions containing colostrinin, an constituent peptide thereof, an active analog thereof, and combinations thereof, as an oxidative stress regulator.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
Methods for treating ulcers in thalassemia syndrome with an ActRIIB polypeptide
ActiveUS9850298B2Undesired effectPromote growthPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsThalassemia syndromeRed blood cell
The present disclosure provides compositions and methods for treating or preventing ulcers in subjects having low red blood cell levels and / or hemoglobin levels (e.g, anemia). In some embodiments, the compositions of the disclosure may be used to treat or prevent ulcers associated with anemia.
Owner:ACCELERON PHARMA INC
Peptide library constructing method
ActiveCN111727194AReduce in quantityNo need for elutionPolypeptide with affinity tagFusion with post-translational modification motifCyclic peptideChemical synthesis
An improved peptide library preparation method is provided for constructing complete virtual peptide libraries such as a complete virtual tripeptide library, tetrapeptide library, pentapeptide library, hexapeptide library, heptapeptide library, or a complete octapeptide library, etc. The method includes constructing an expression vector for the expression of cyclic peptides. Each cyclic peptide displays an array of peptides of different sizes and sequences, and the number of cyclic peptides needed for constructing a complete virtual peptide library can be dramatically reduced compared with conventional chemical peptide synthesis. Furthermore, the cyclic peptide libraries can be readily reproduced by the expression and purification of the cyclic peptides using the constructed gene libraries.
Owner:HUNAN ZONSEN PEPLIB BIOTECH CO LTD
Long-acting coagulation factors and methods of producing same
ActiveUS20150368630A9Reduce dosing frequencyIncrease the areaBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotidePolynucleotide
Polypeptides comprising at least one carboxy-terminal peptide (CTP) of chorionic gonadotrophin attached to the carboxy terminus but not to the amino terminus of a coagulation factor and polynucleotides encoding the same are disclosed. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the polypeptides and polynucleotides of the invention and methods of using and producing same are also disclosed.
Owner:OPKO BIOLOGICS
Humanized monoclonal antibodies against the extracellular domain of human death receptor 5
ActiveUS20150353638A1Enhance anti-cancer efficacyInhibition formationOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDiseaseCancer cell
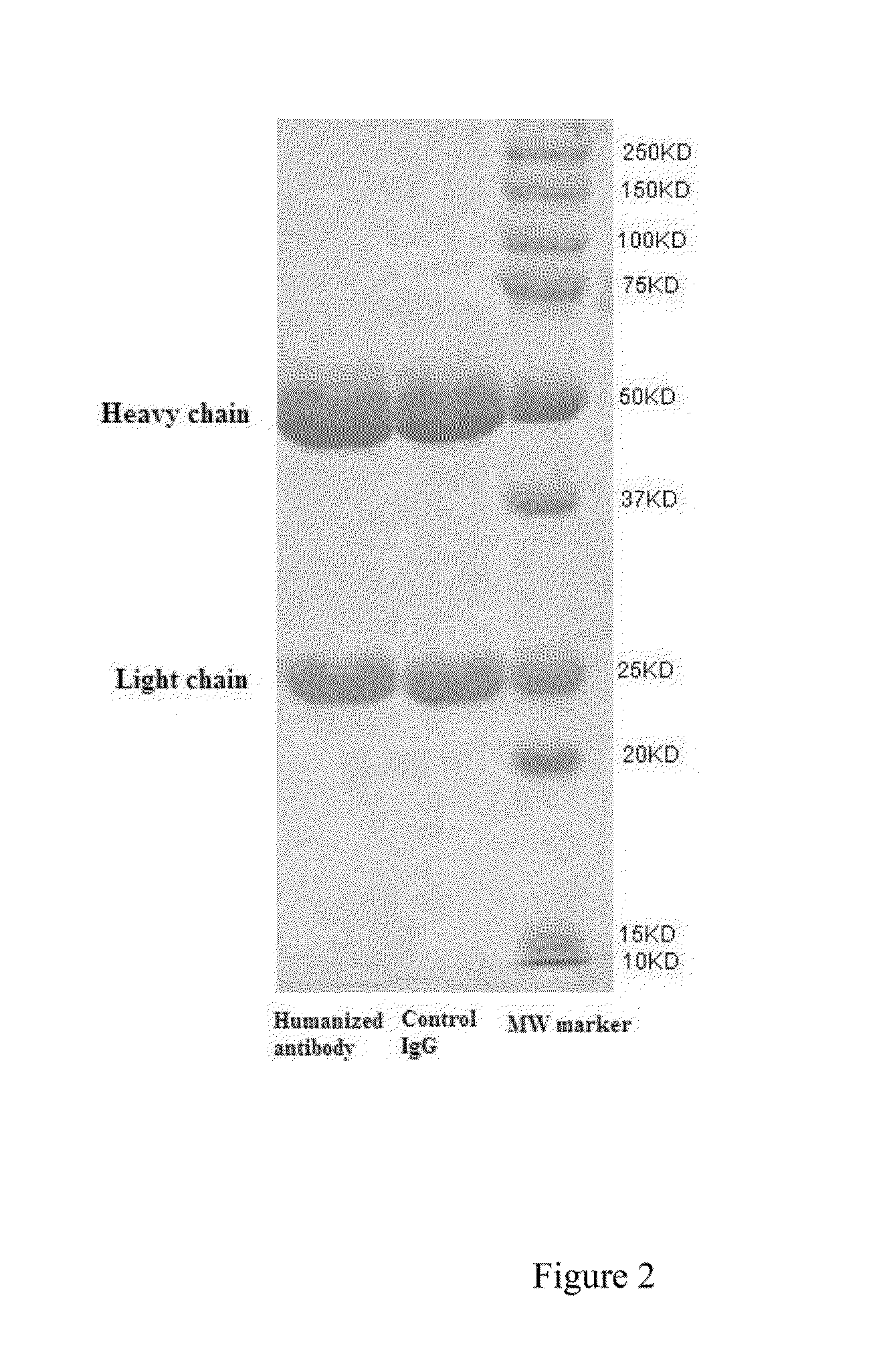
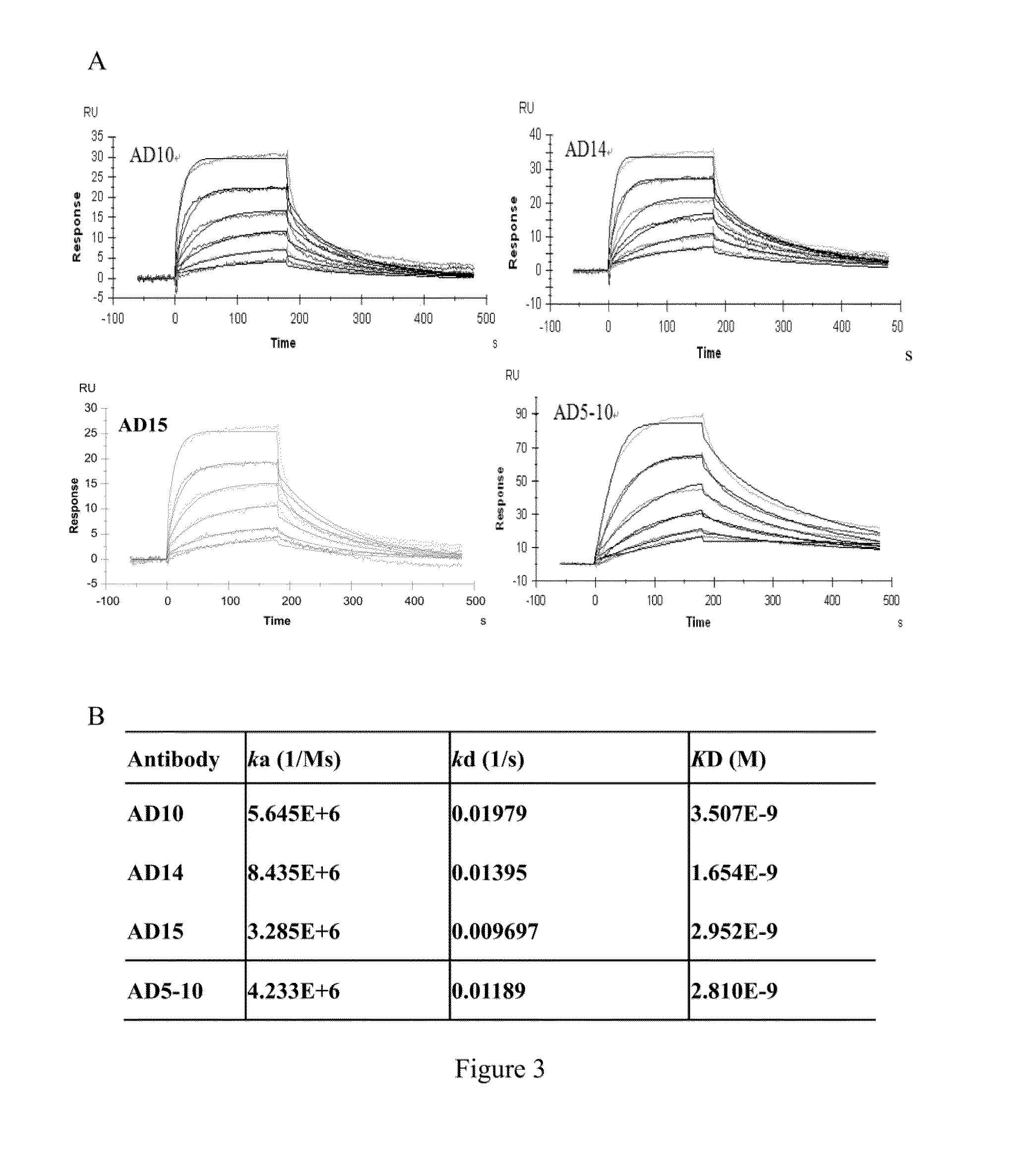
The present invention provides a humanized monoclonal antibody against extracellular domain of human death receptor 5, comprising a light chain variable region, whose amino acid sequence has at least 90% identity with the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, a heavy chain variable region, whose amino acid sequence has at least 90% identity with the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 2, and constant region derived from human antibody. The present invention also provides nucleotide sequence encoding said humanized monoclonal antibody, a recombinant eukaryotic expression vector, a process for preparing the humanized monoclonal antibody, and the composition and use therefore. Said humanized monoclonal antibody of the present invention shows specific apoptosis-inducing activity against various cancer cells both in vivo and in vitro, and thus it can be used alone or in combination with natural ligand of DR5, apoptosis-inducing ligand associated with tumor nerosis factor or other medicaments for the treatment of a variety of cancers as well as other diseases associated with high DR5 expression.
Owner:YANTAI OBIOADC BIOMEDICAL TECH LTD
Compositions and methods of use for treating metabolic disorders
Methods of treating individuals with a glucose metabolism disorder and / or a body weight disorder, and compositions associated therewith, are provided.
Owner:NGM BIOPHARMLS
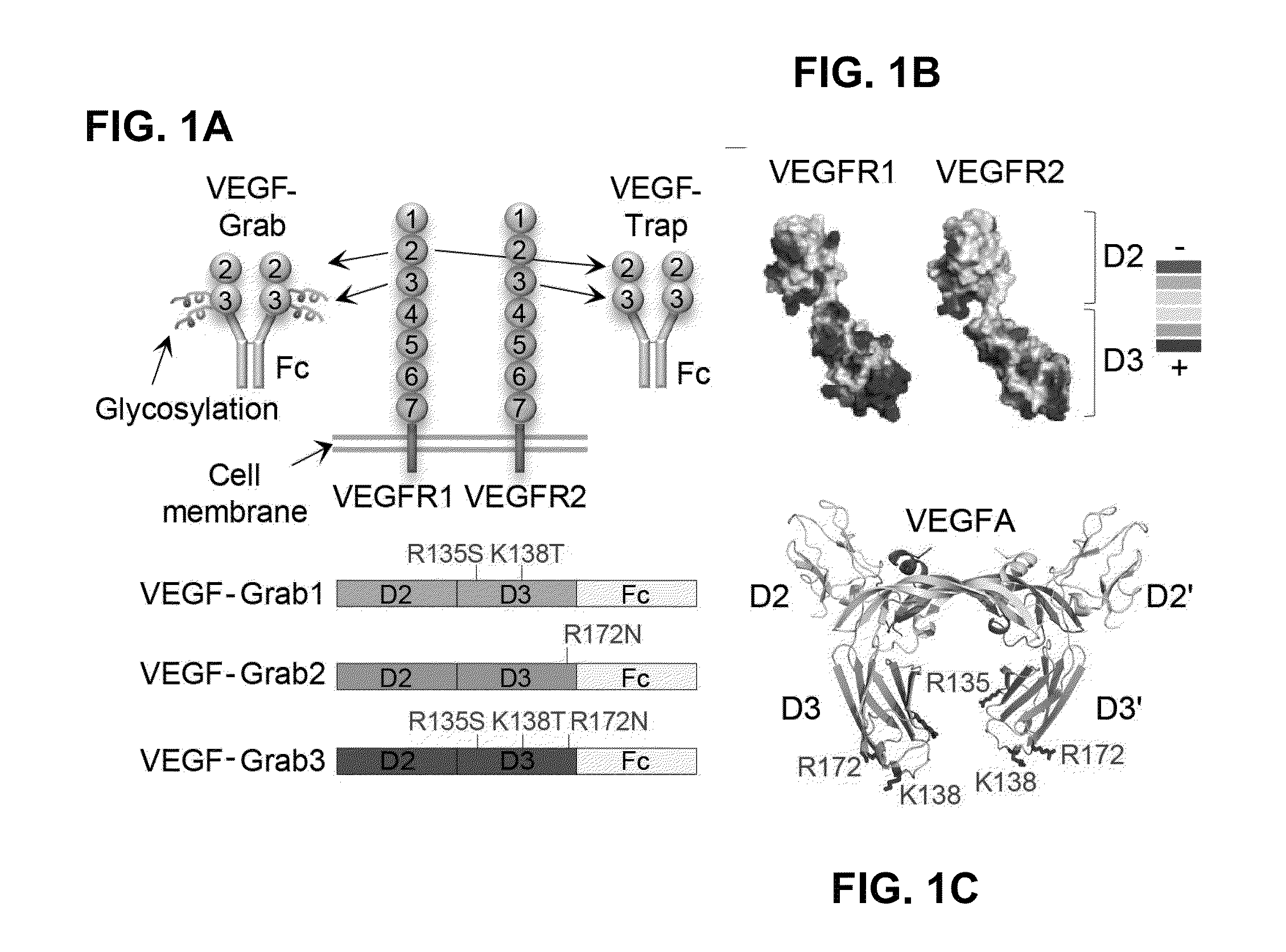
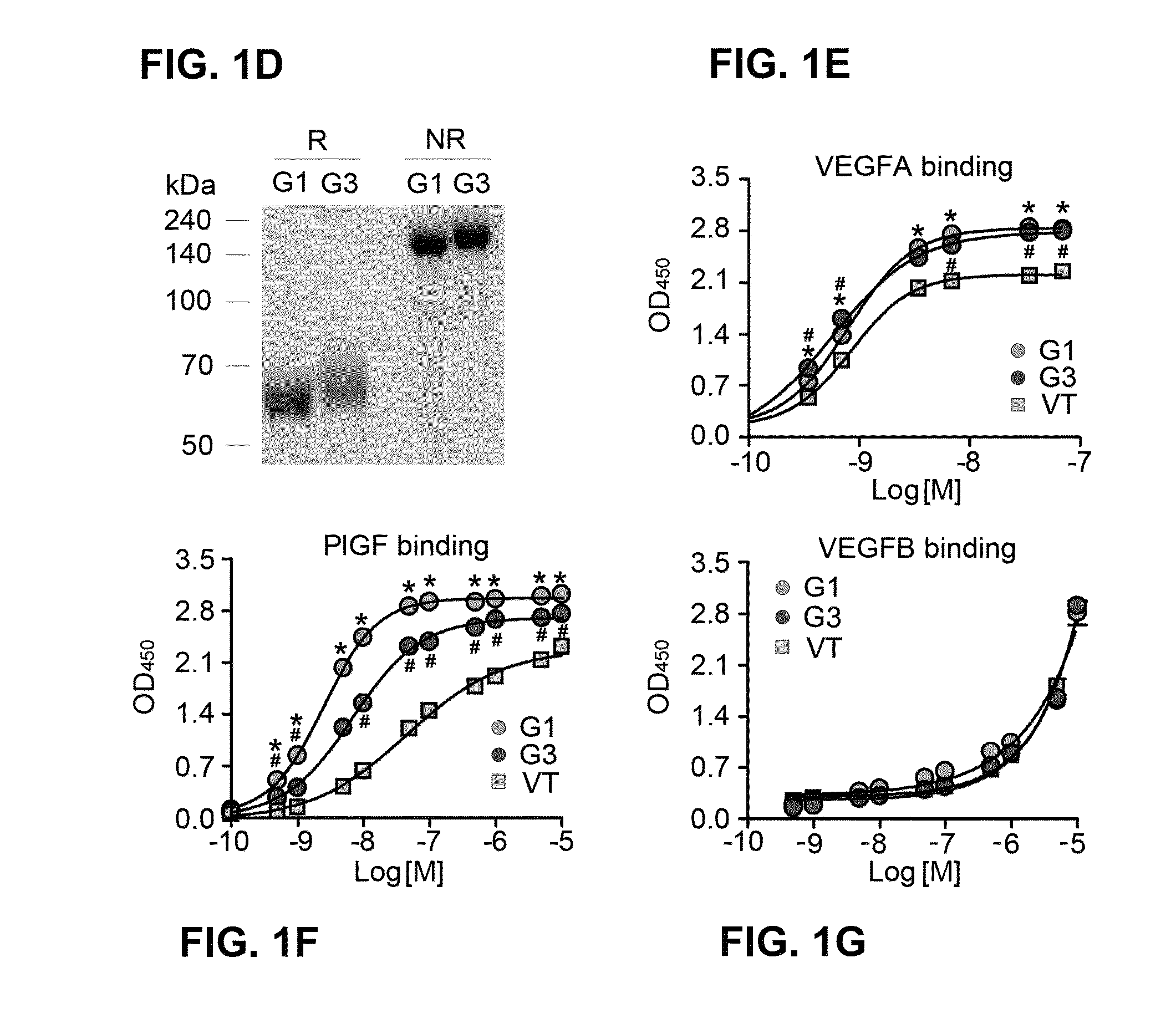
Method of treating eye disease using glycosylated VEGF decoy receptor fusion protein
ActiveUS20160024483A1Improved pharmacokinetic profileStrong and durable anti-angiogenicSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDecoy receptorsNucleotide
The present application describes an isolated nucleic acid molecule encoding a polypeptide capable of synchronously binding VEGF polypeptide and placenta growth factor (PIGF) polypeptide comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding a VEGFR1 component.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com