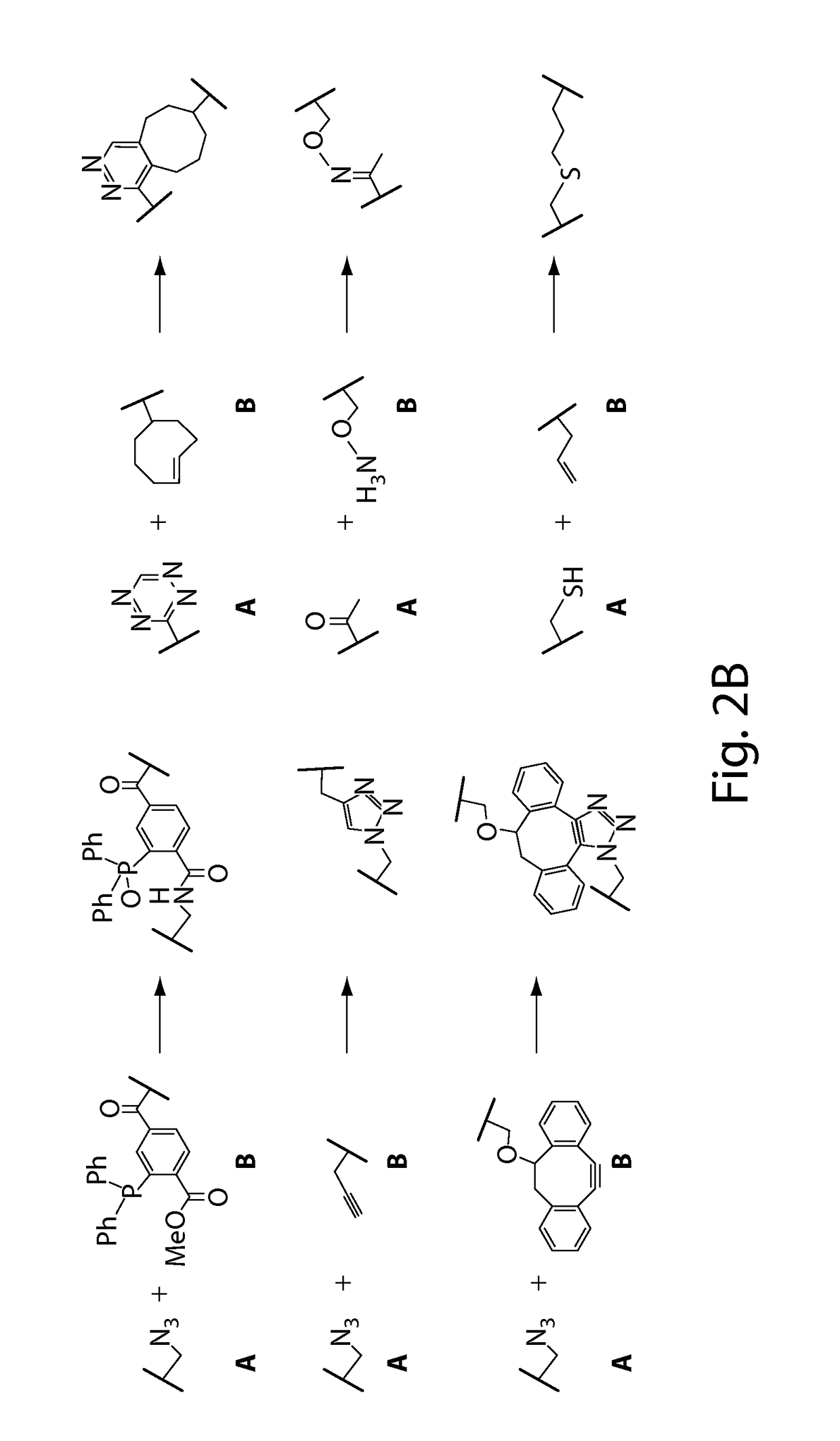
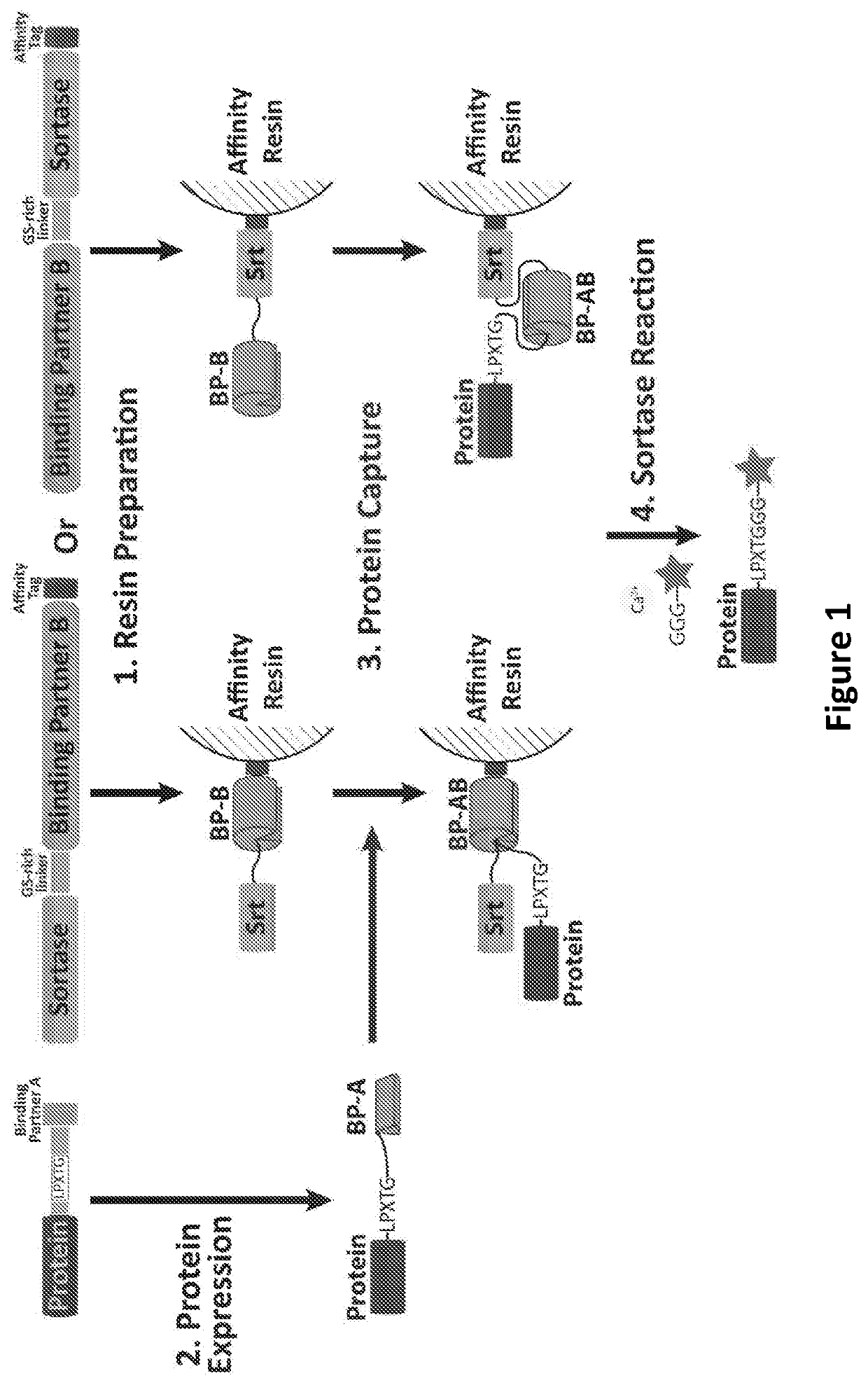
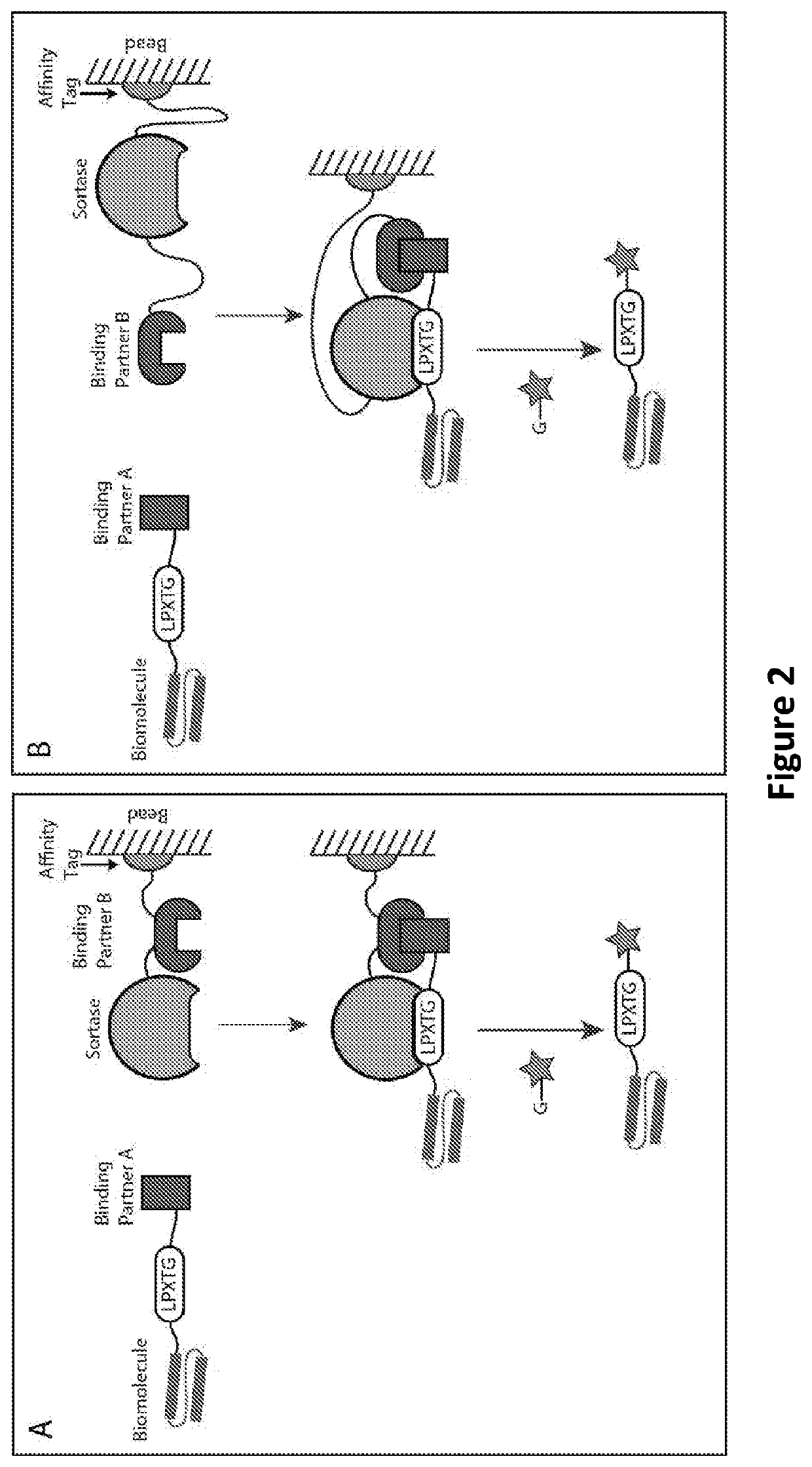
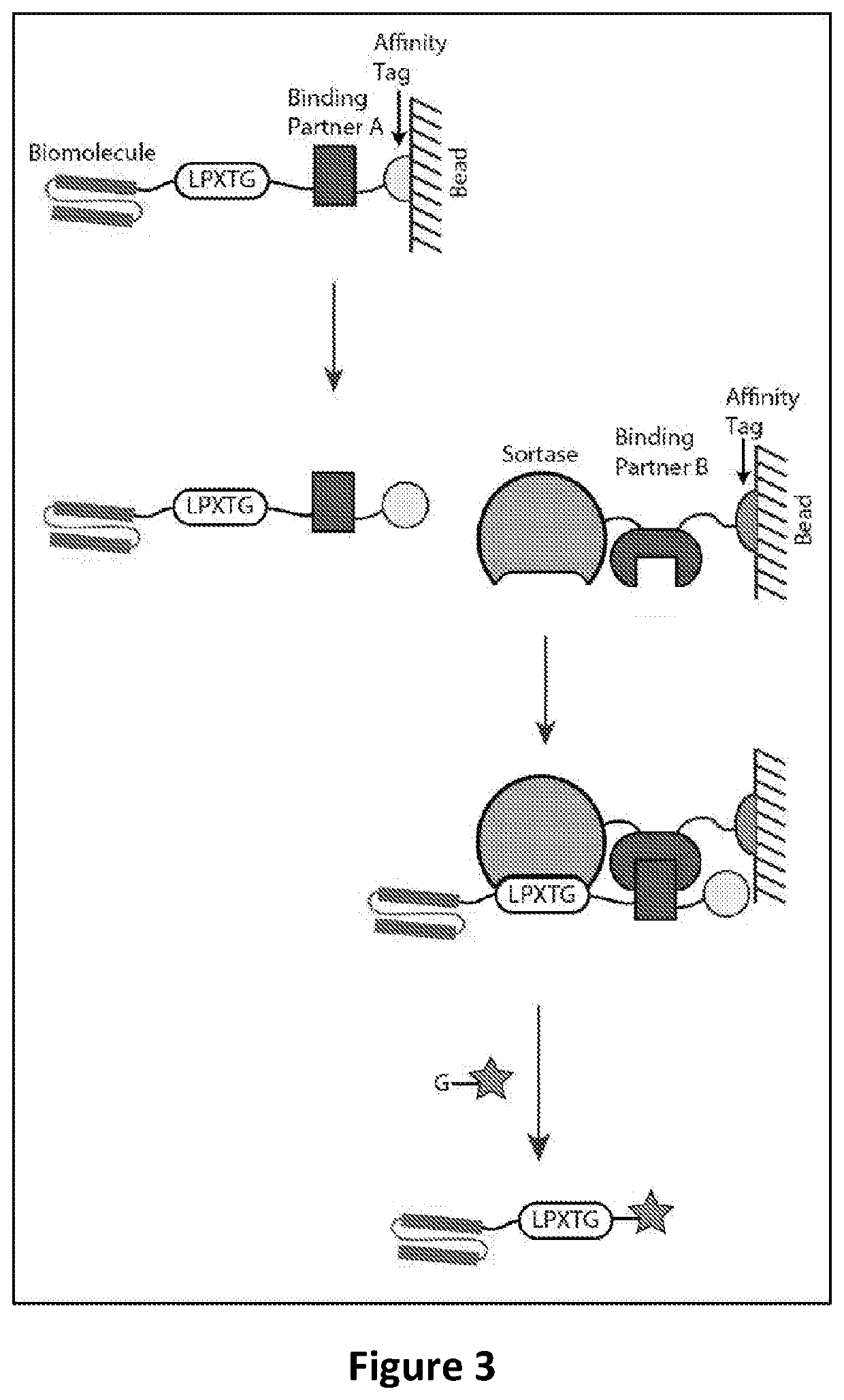
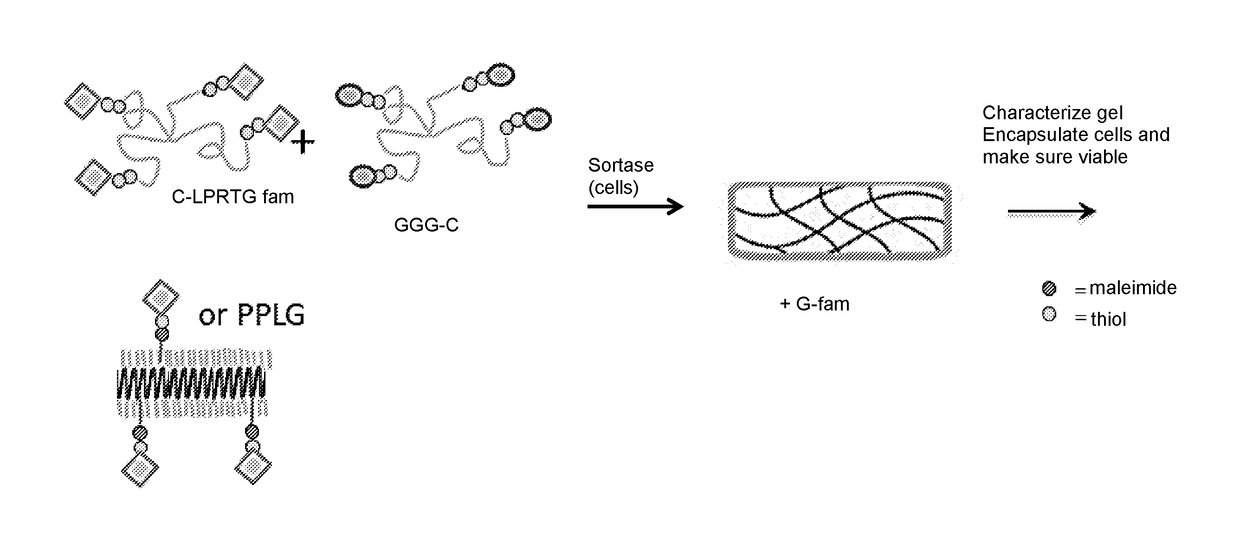
Patents
Literature
79 results about "Sortase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
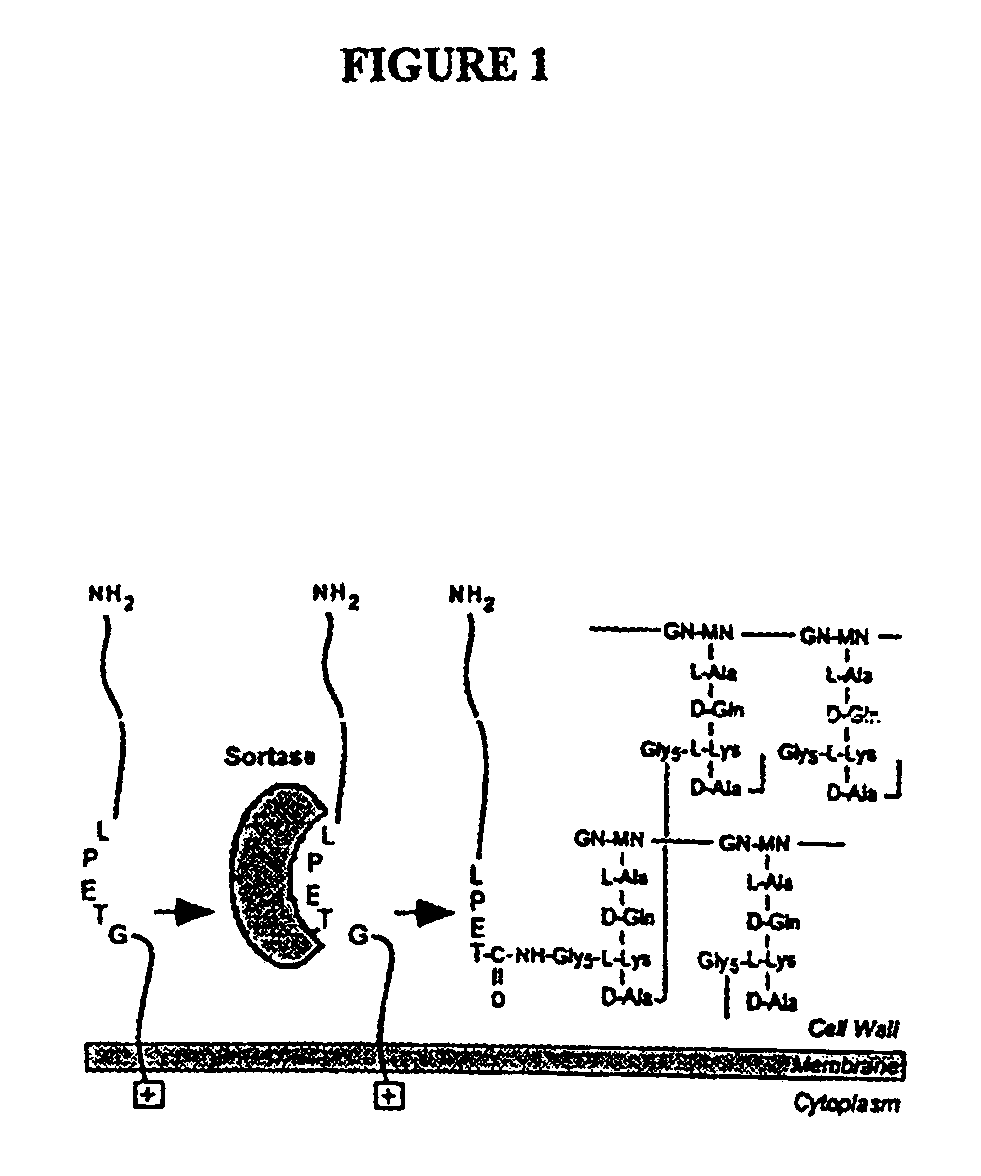
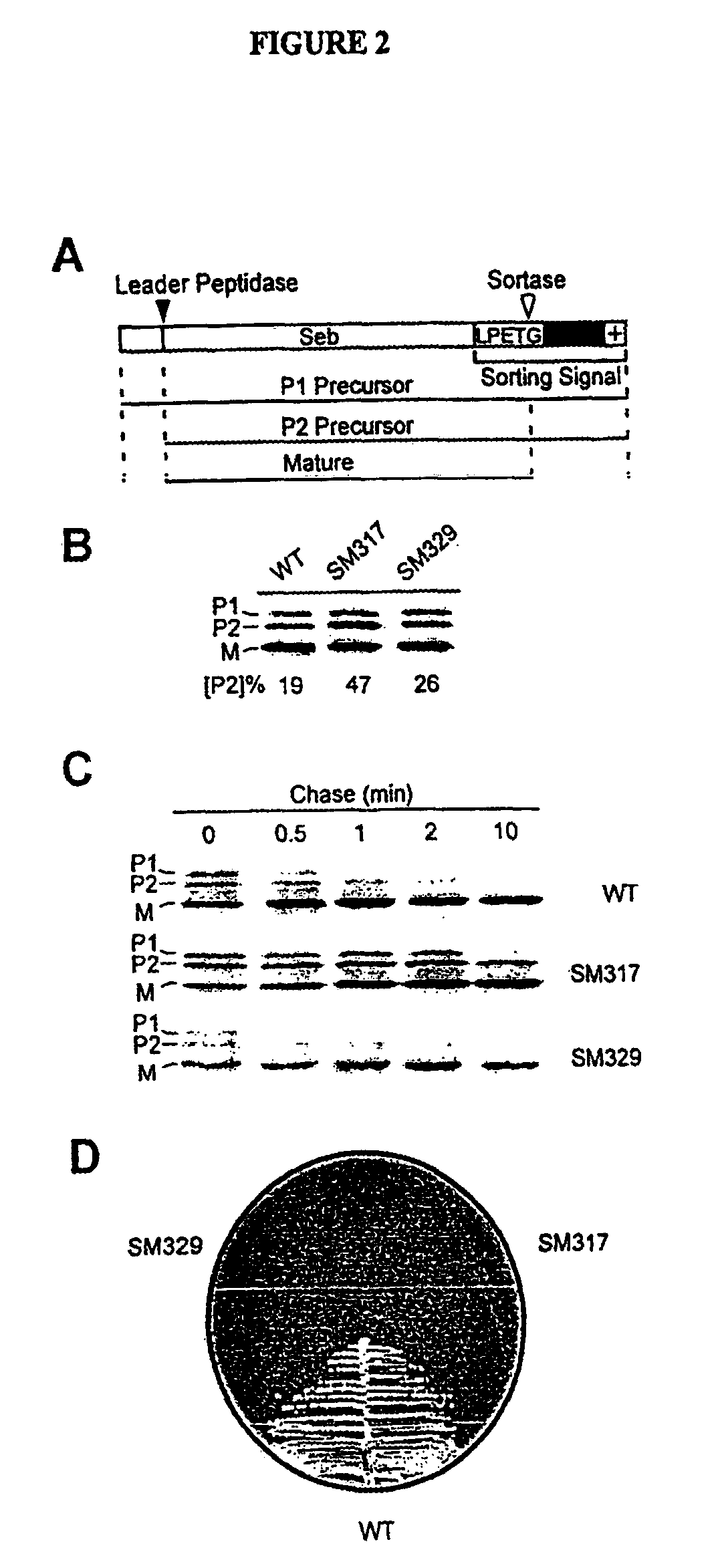
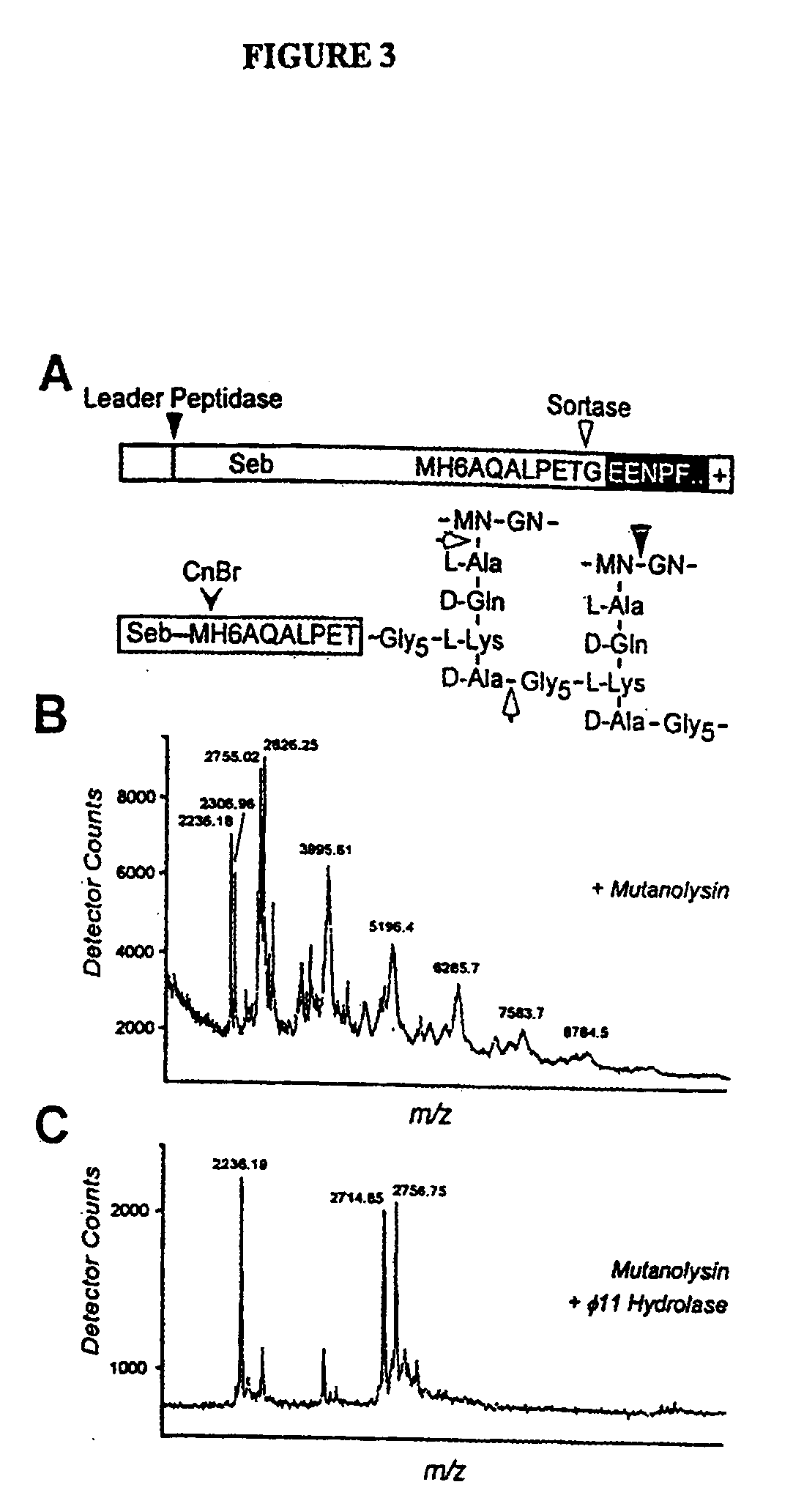
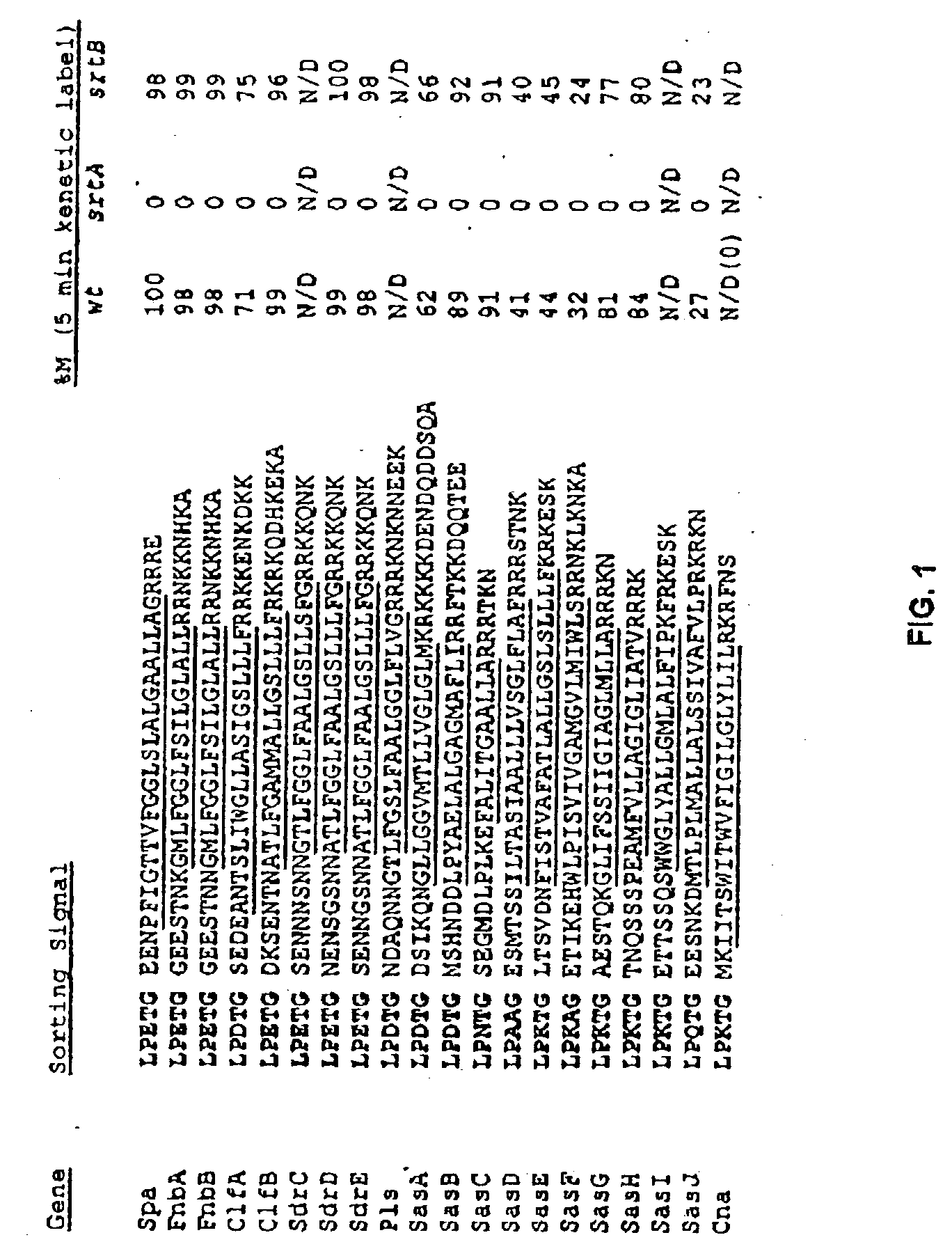
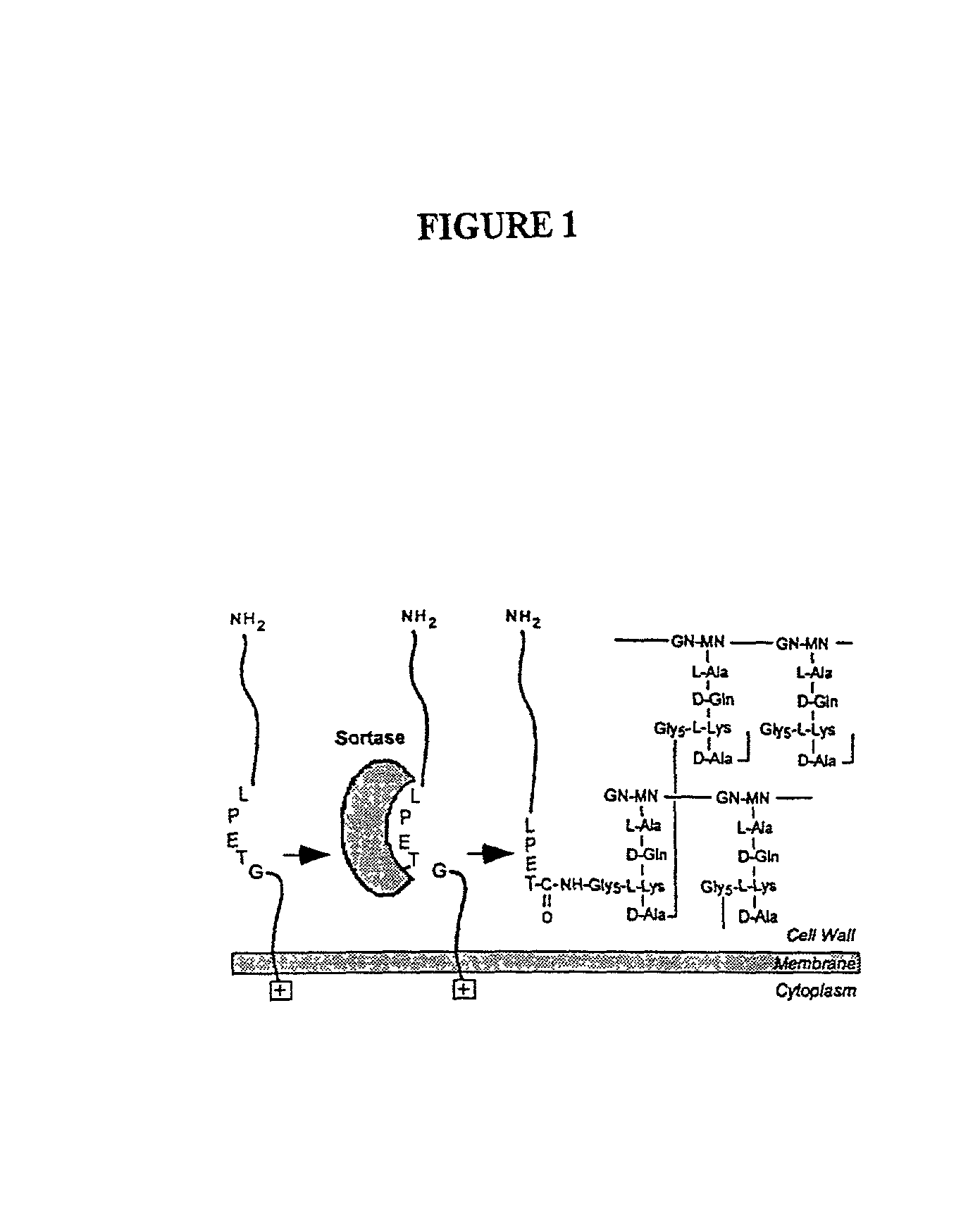
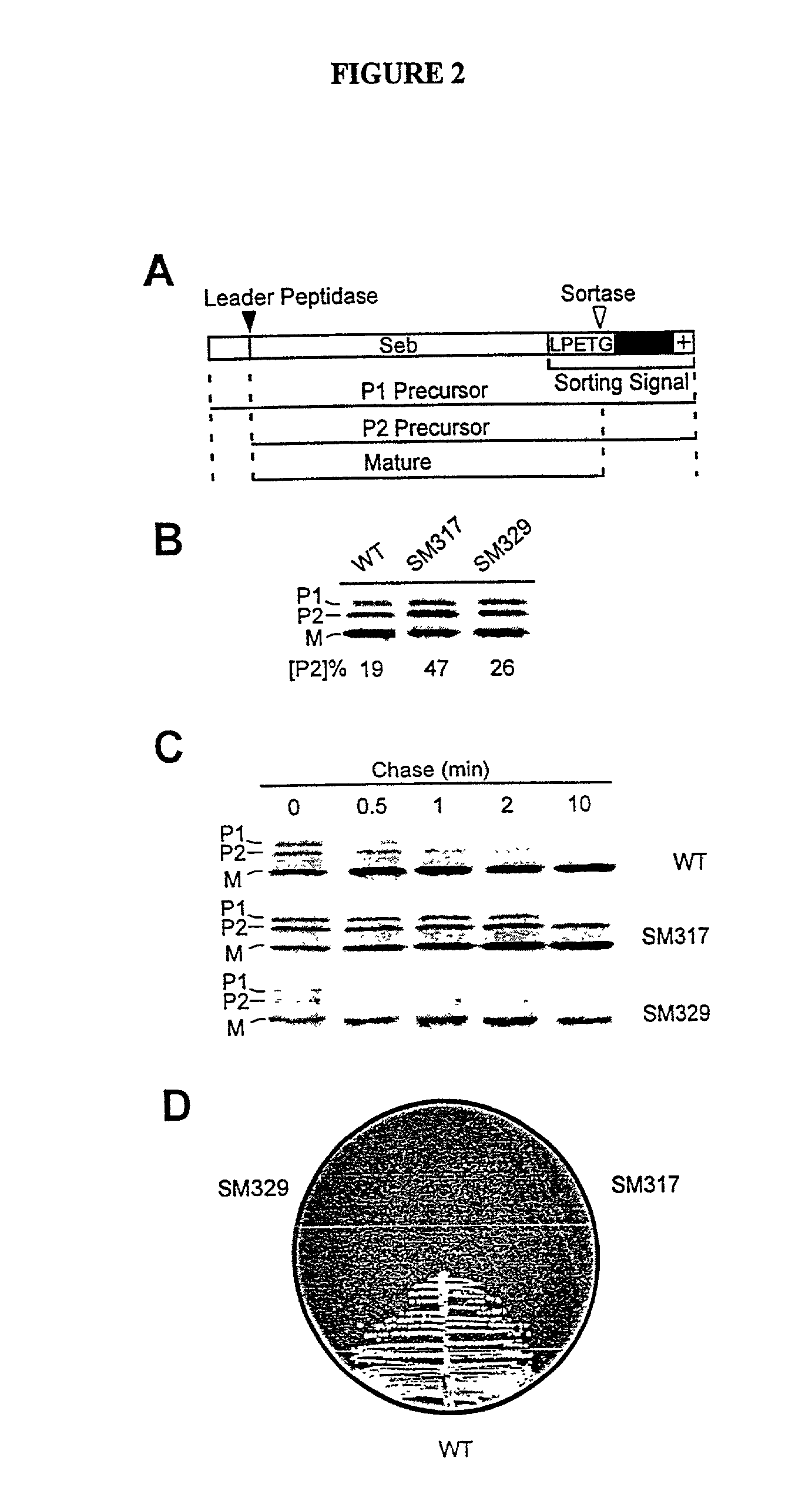
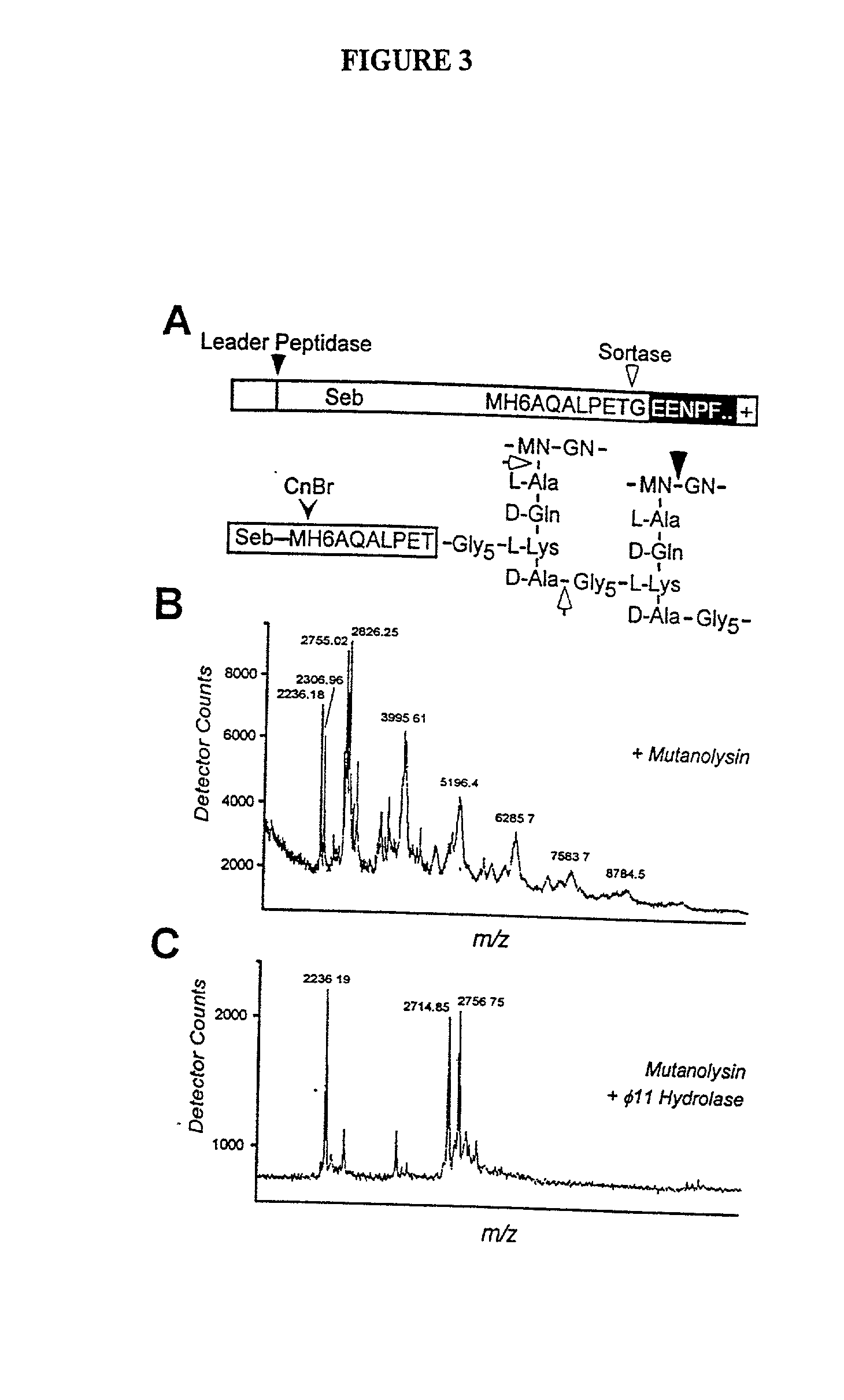
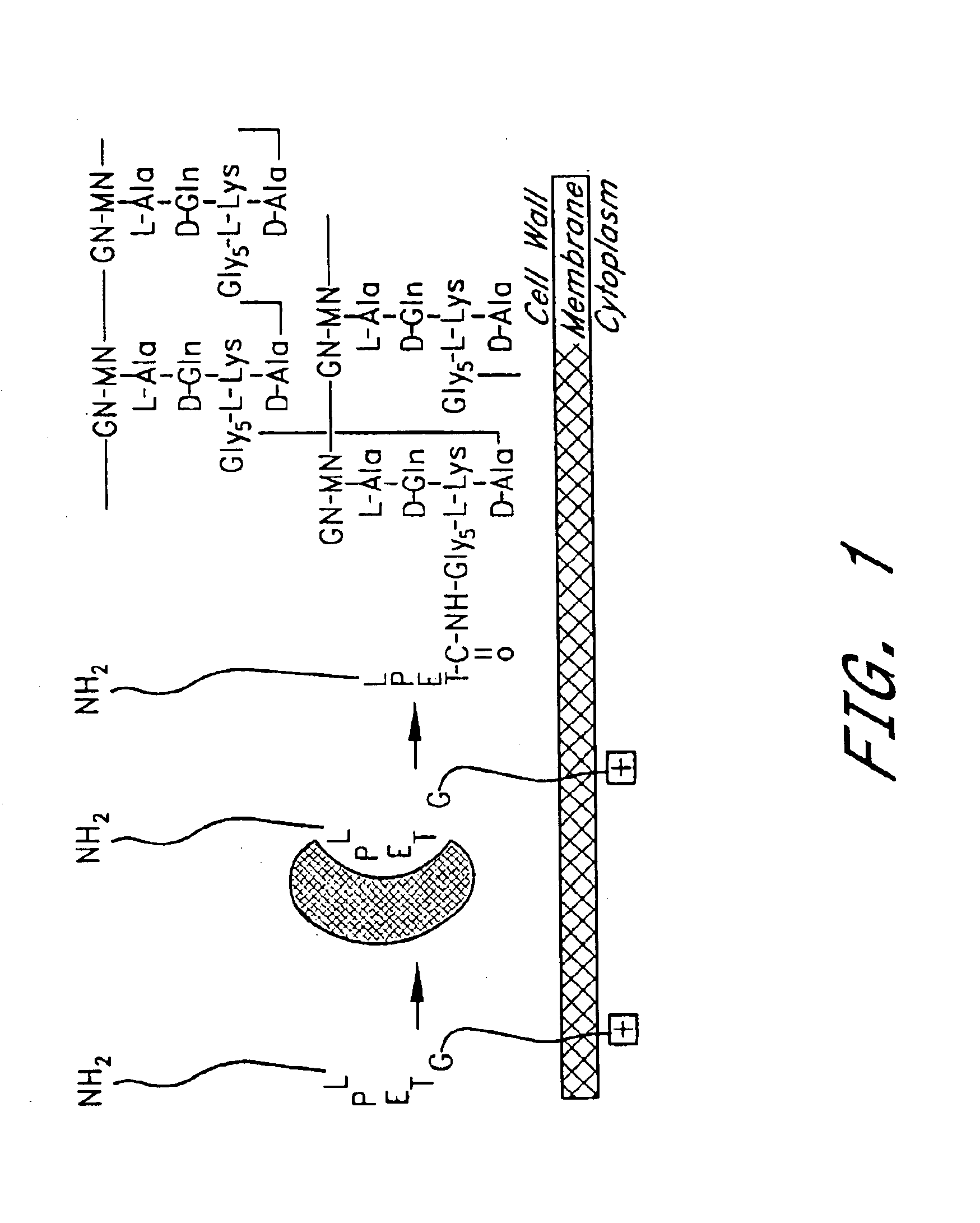
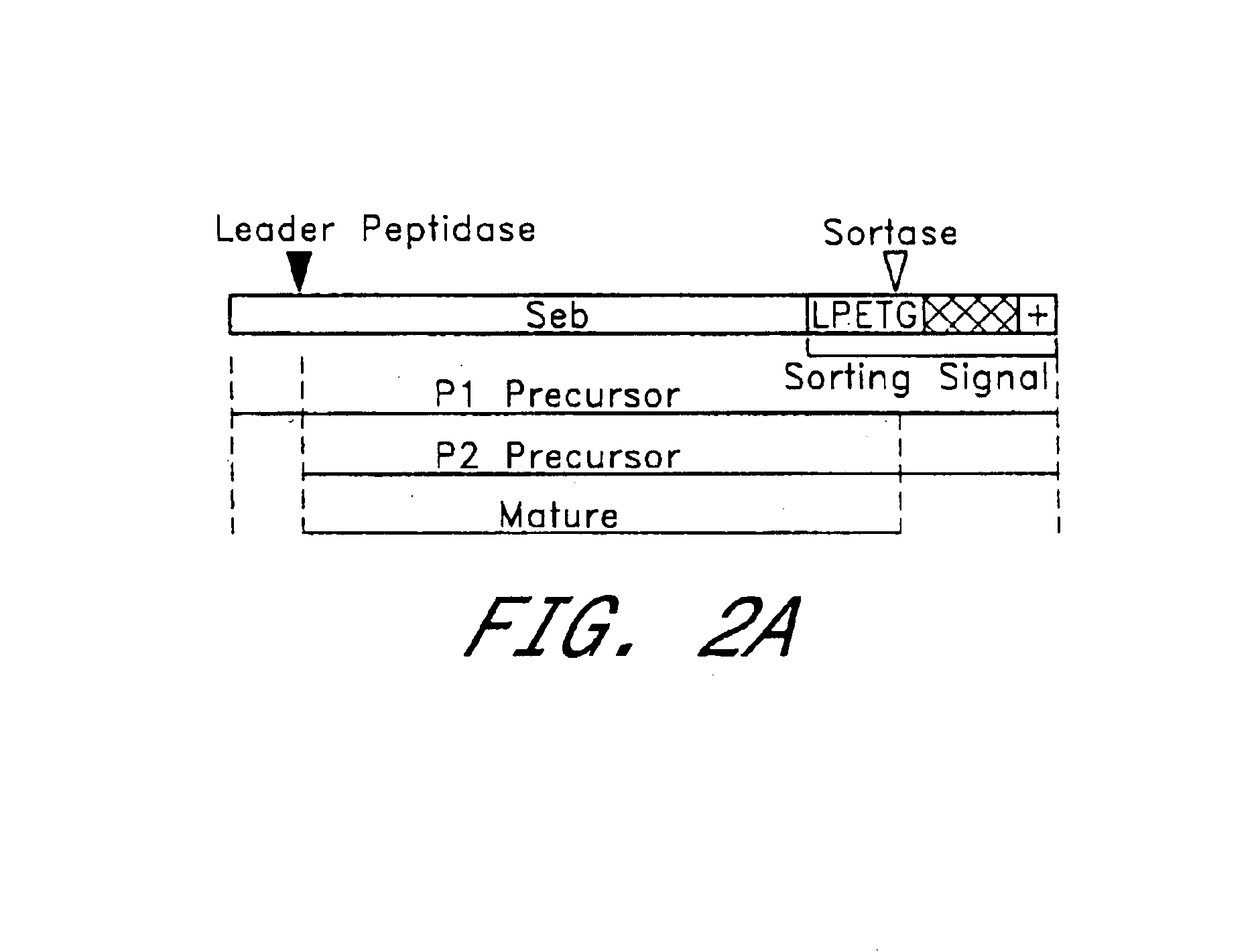
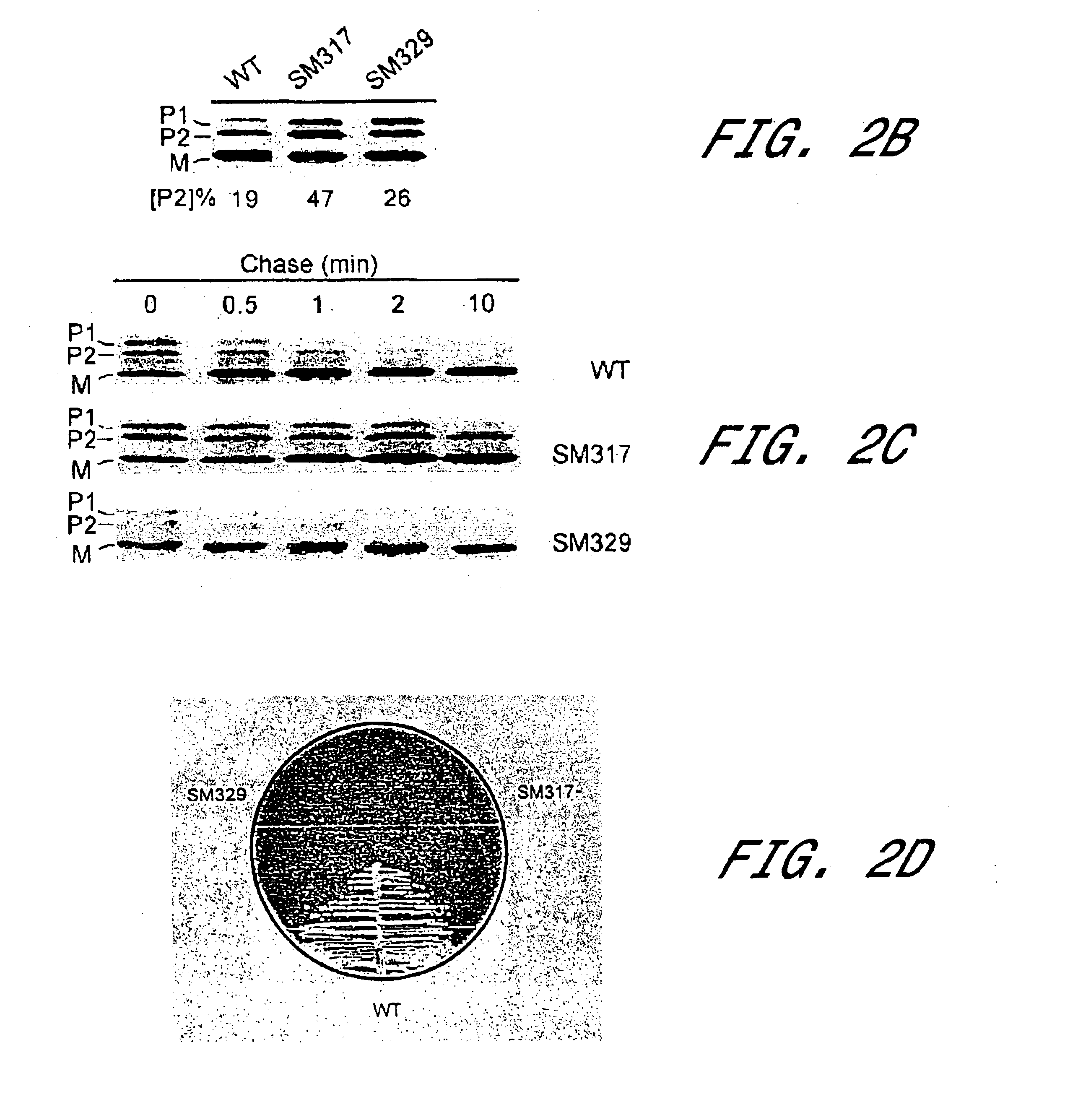
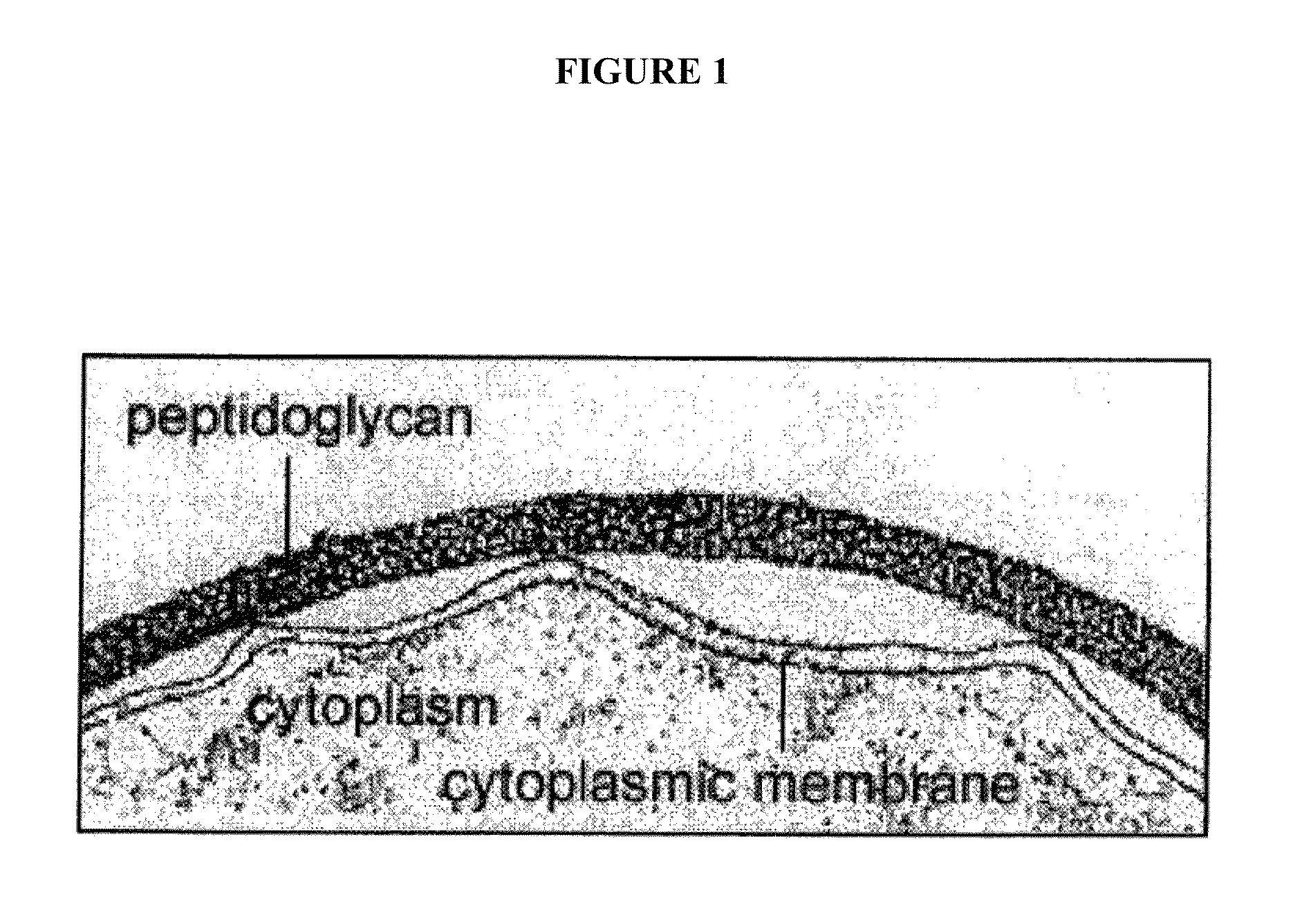
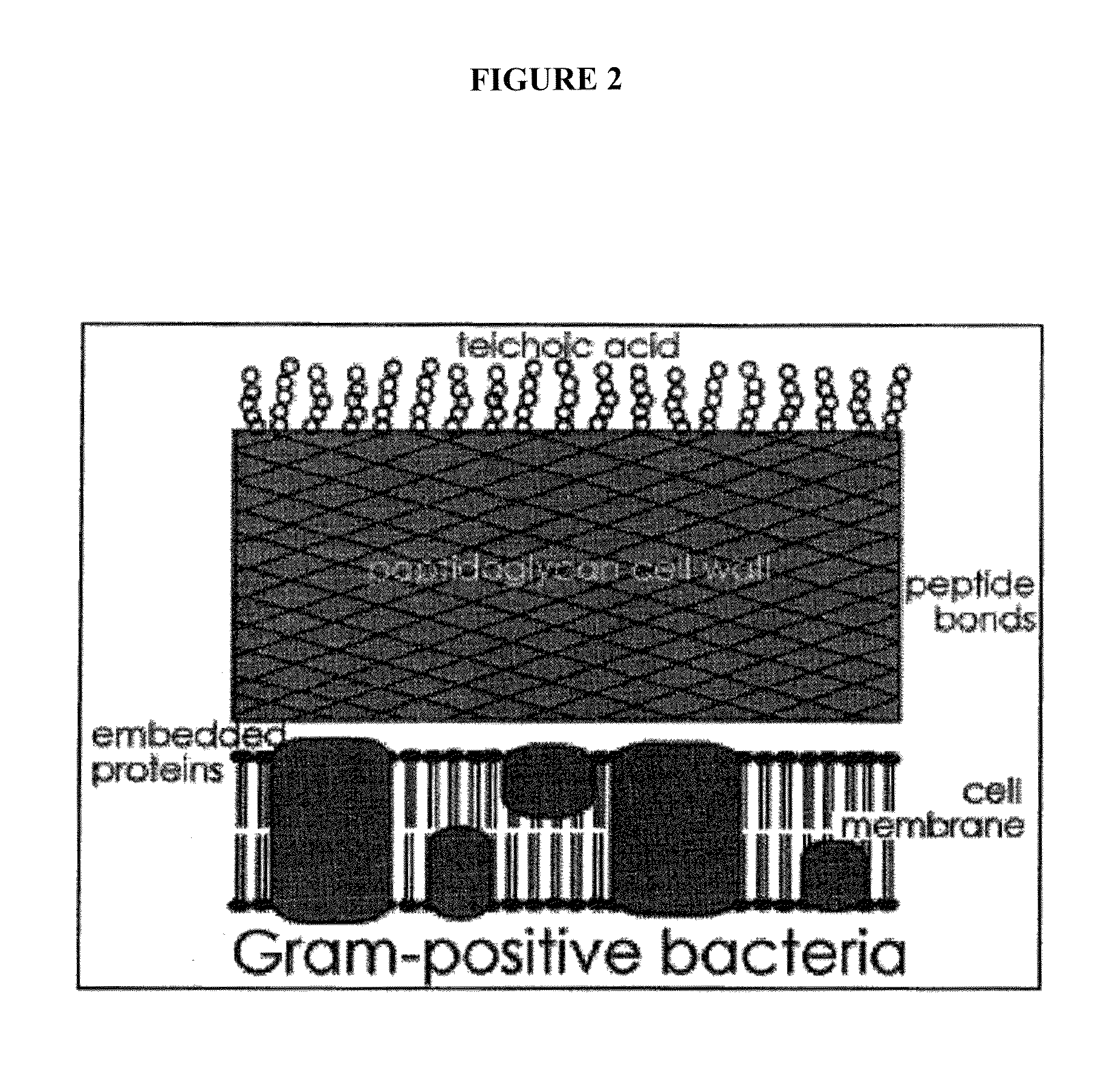
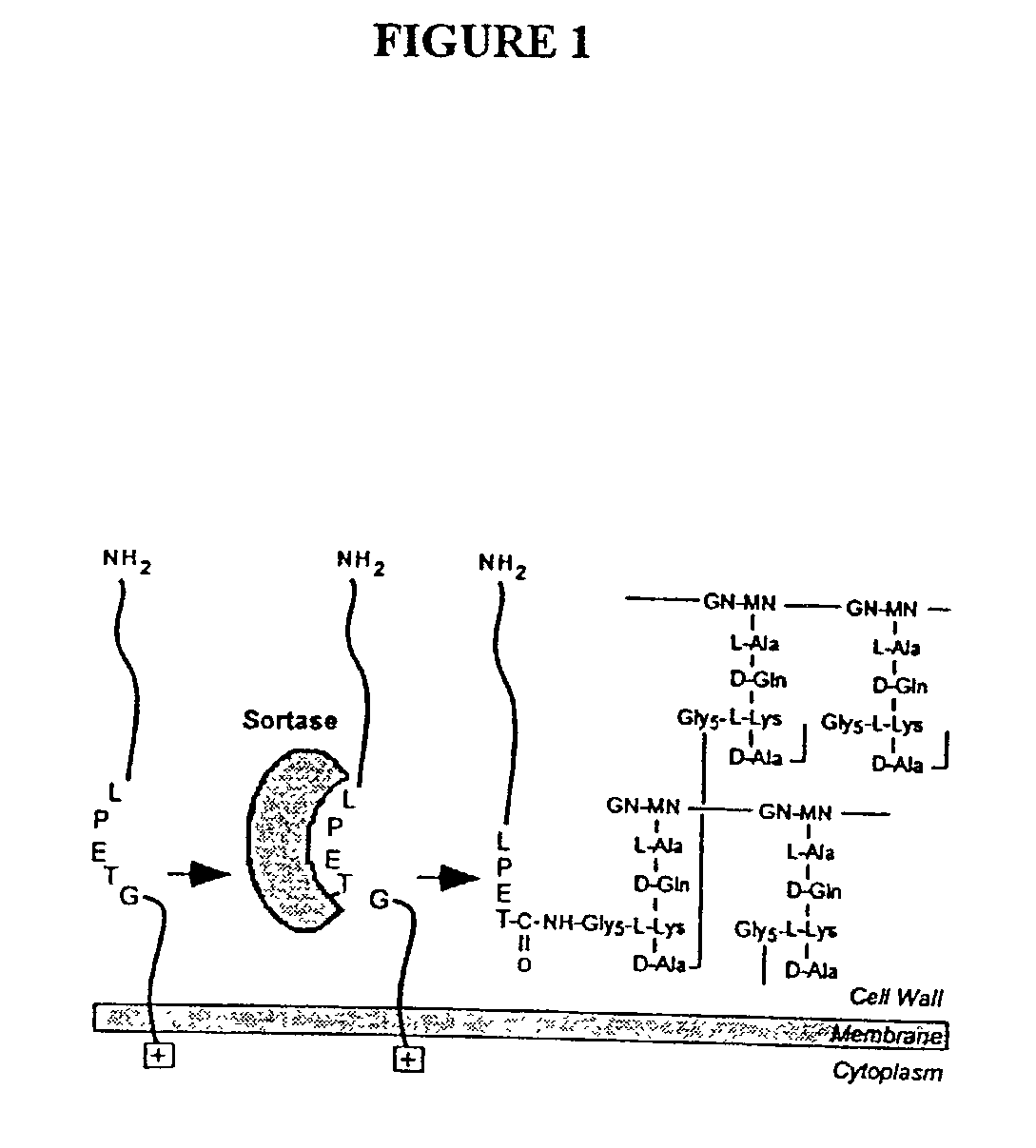
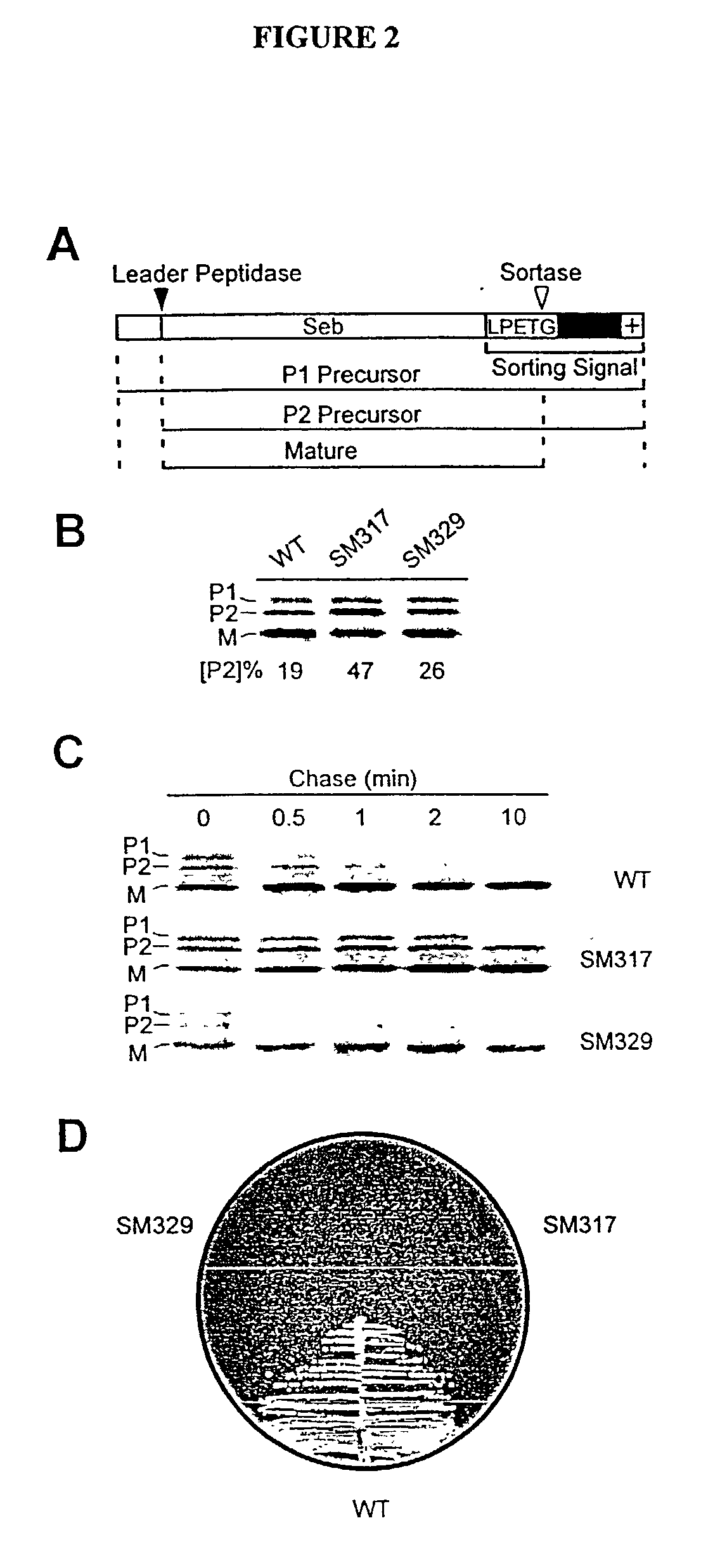
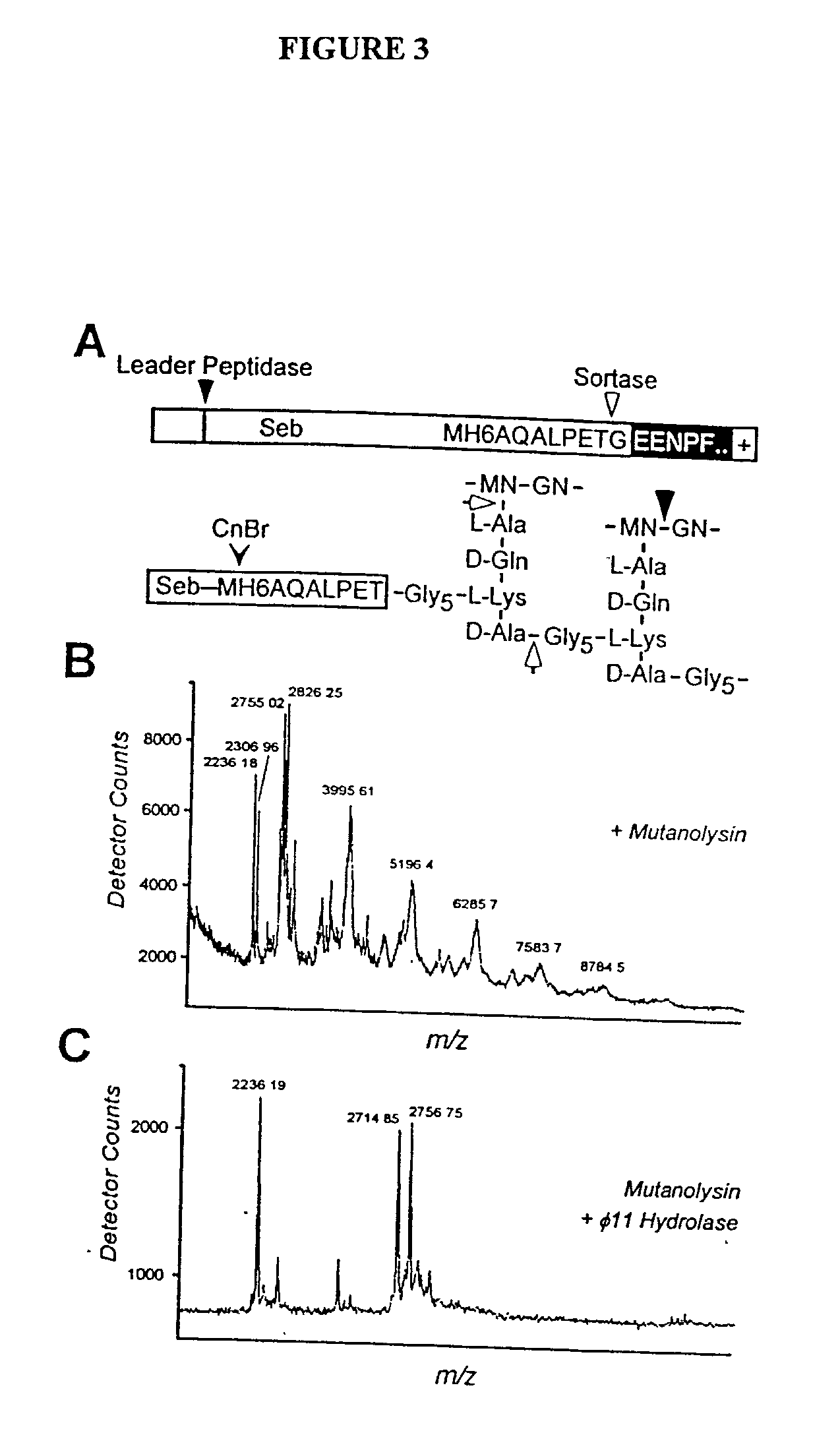
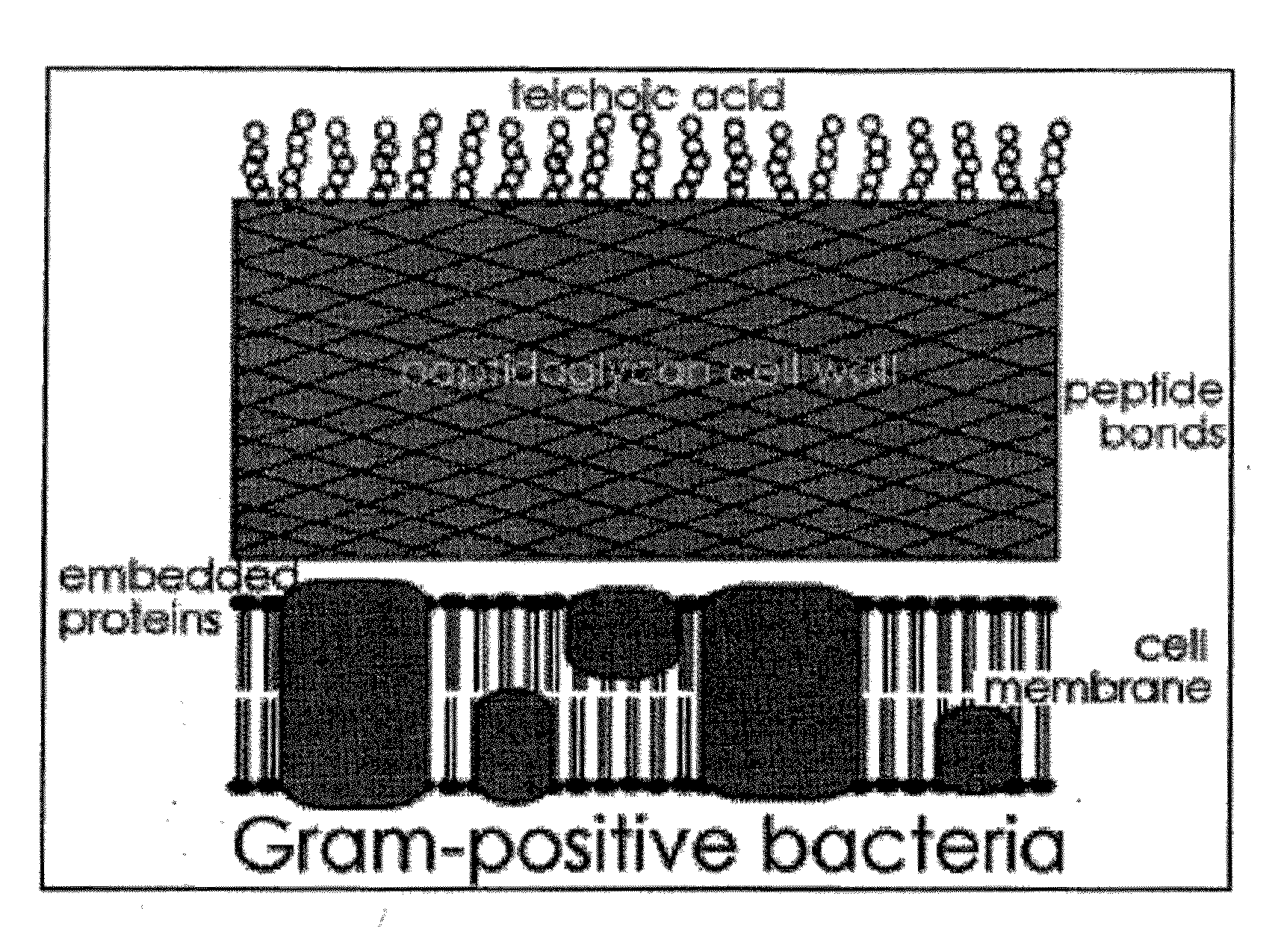
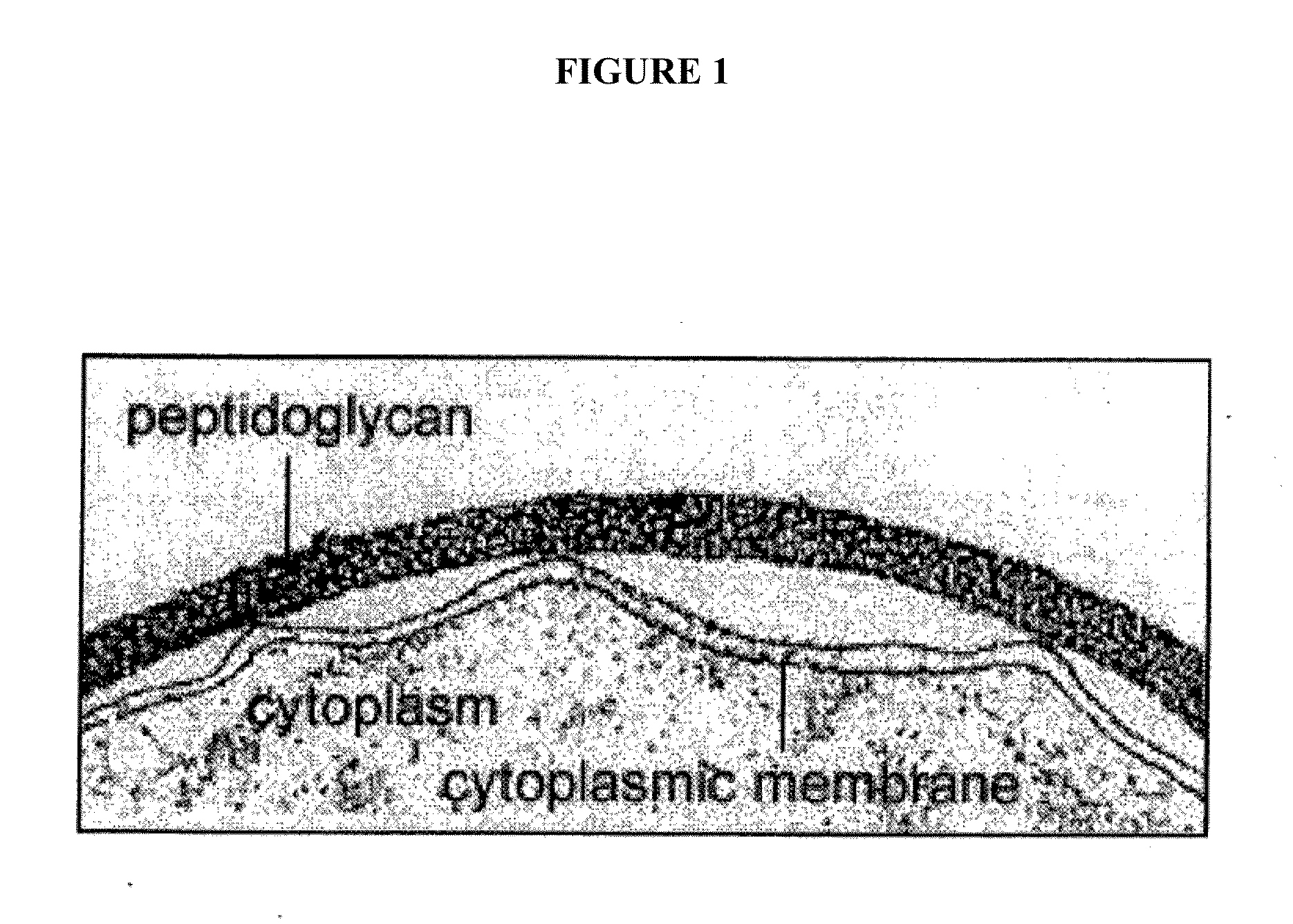
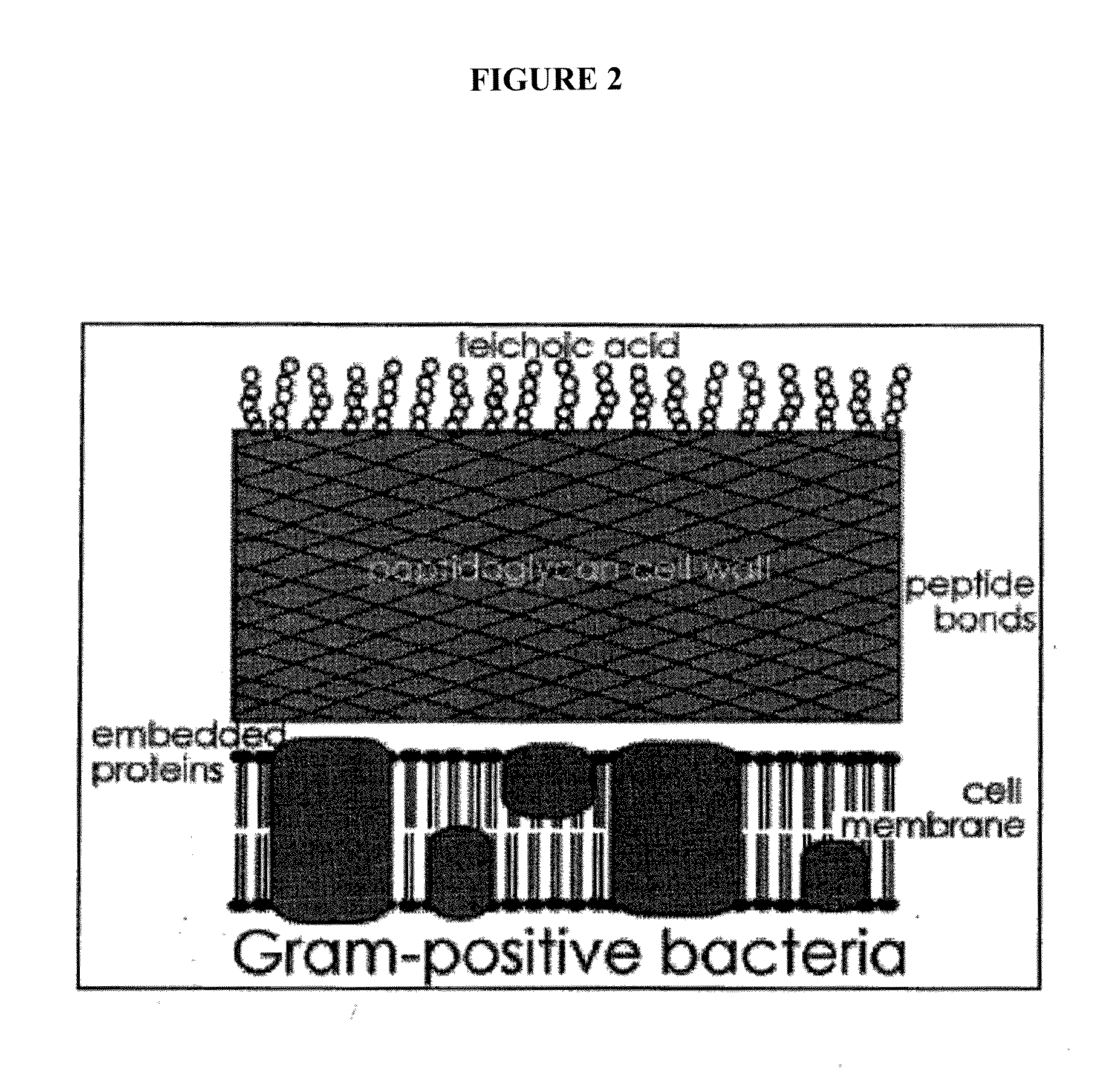
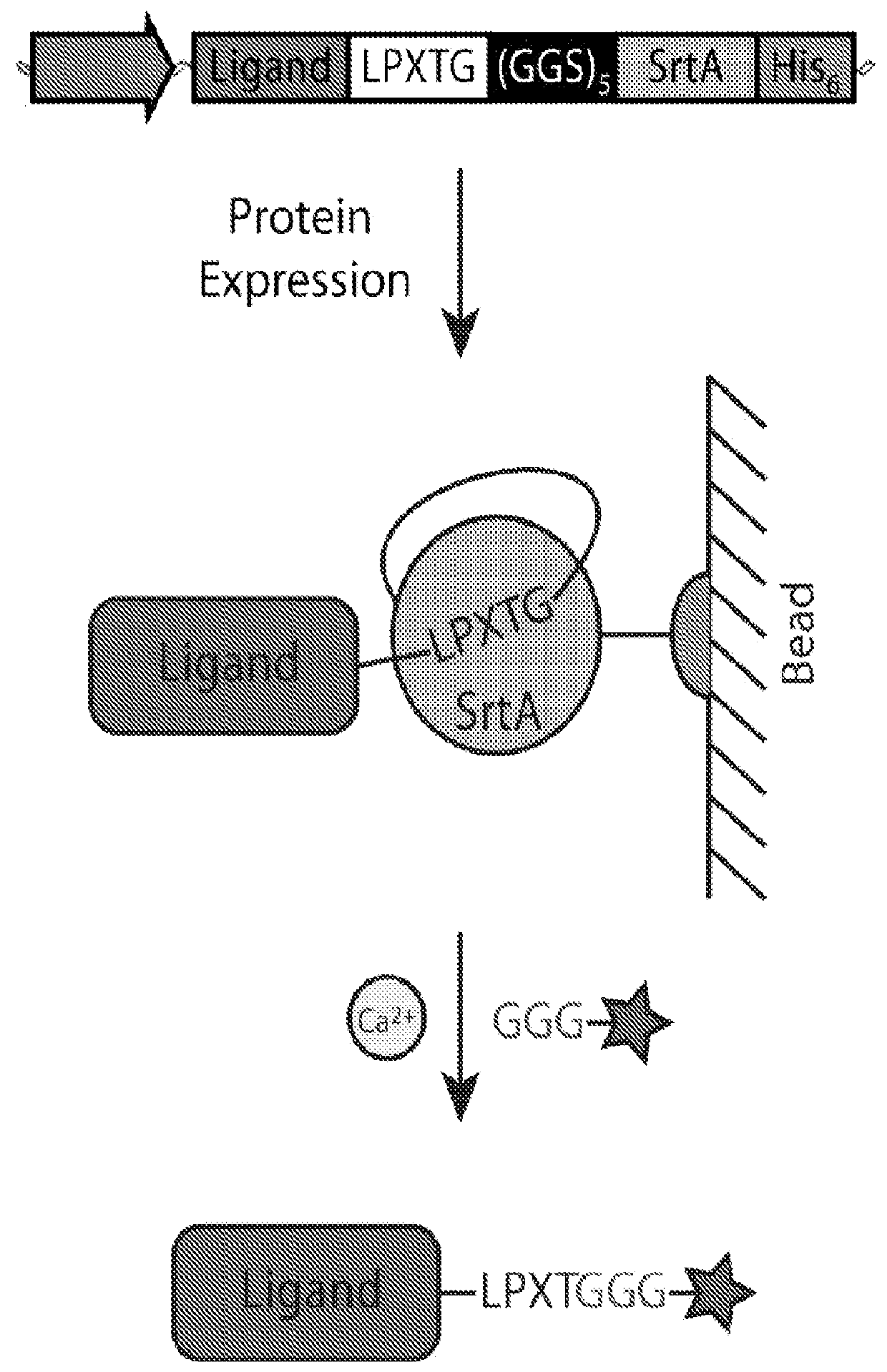
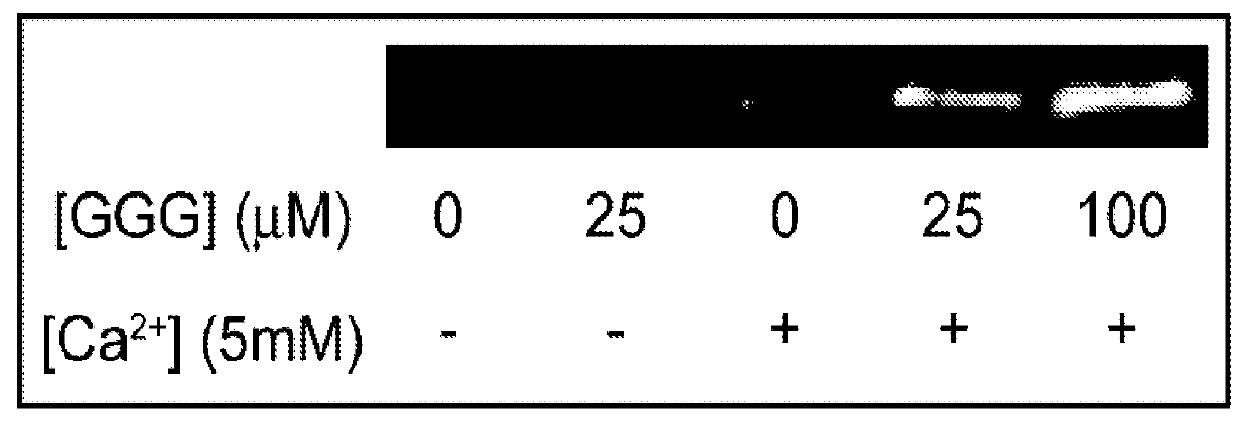
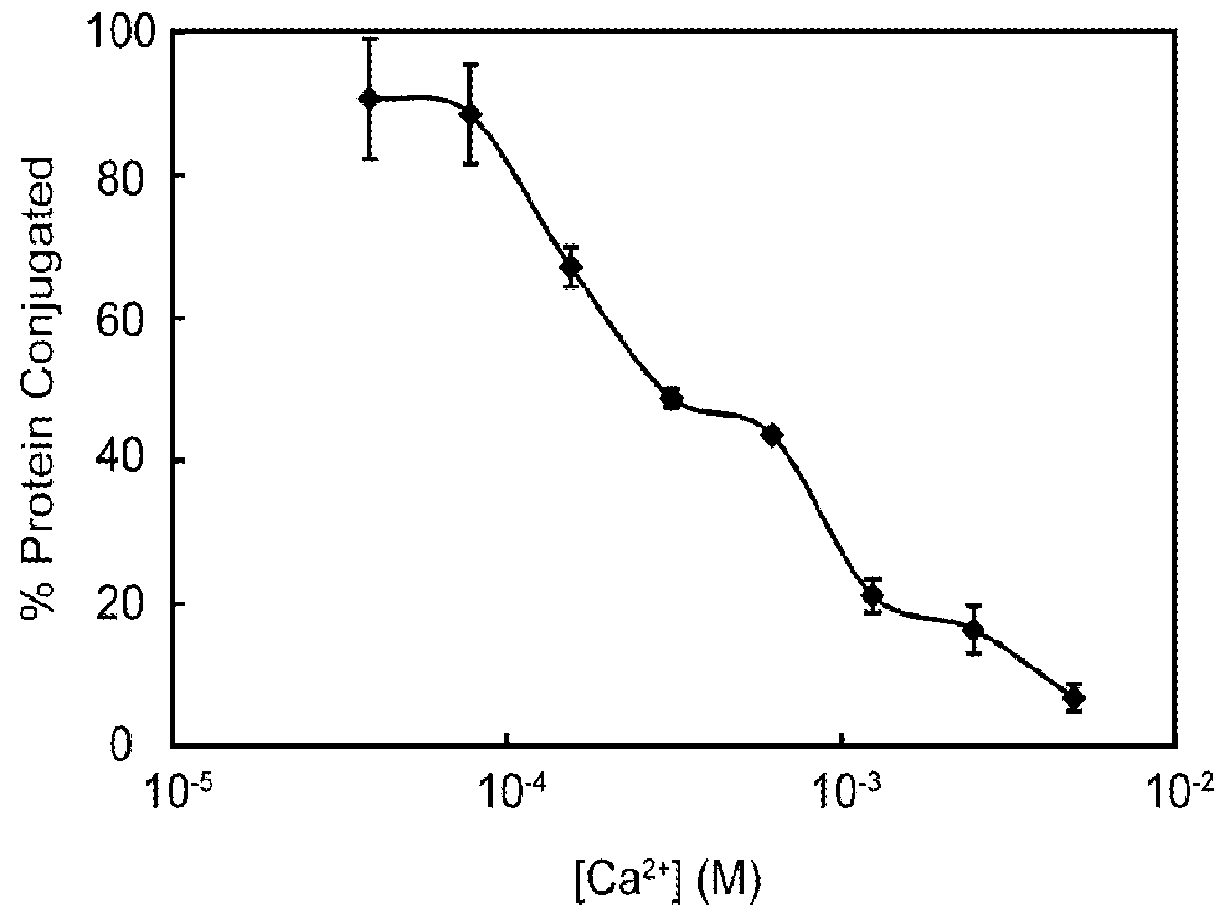
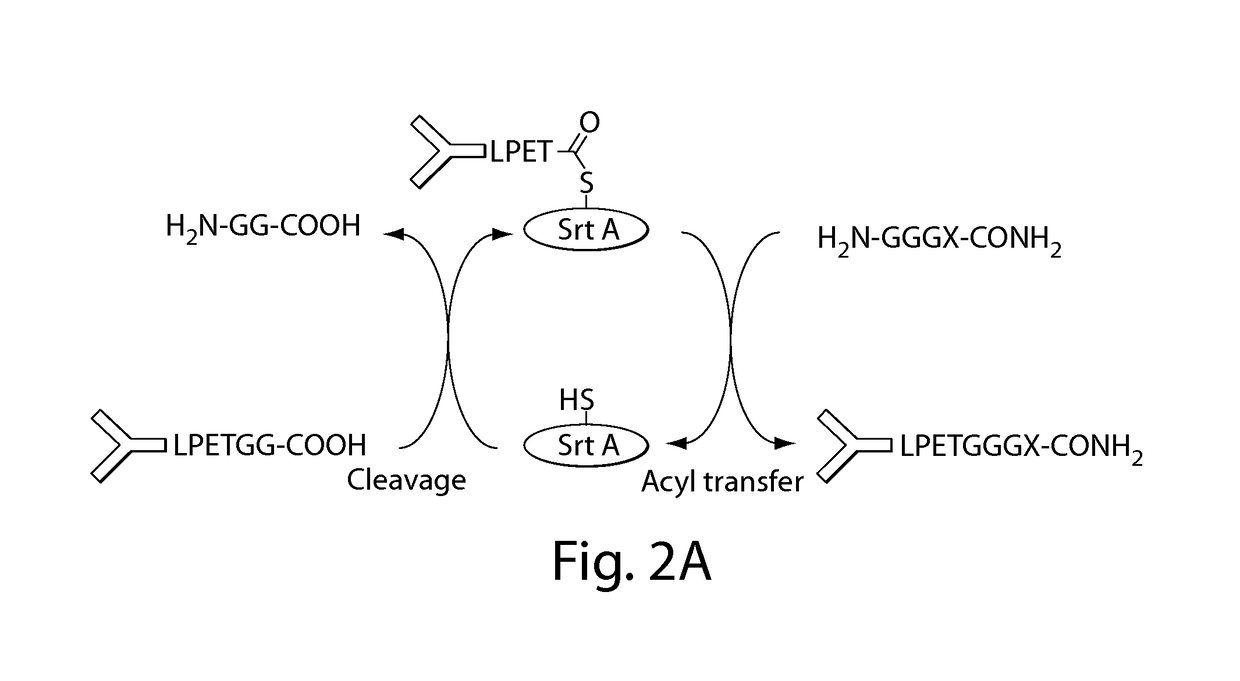
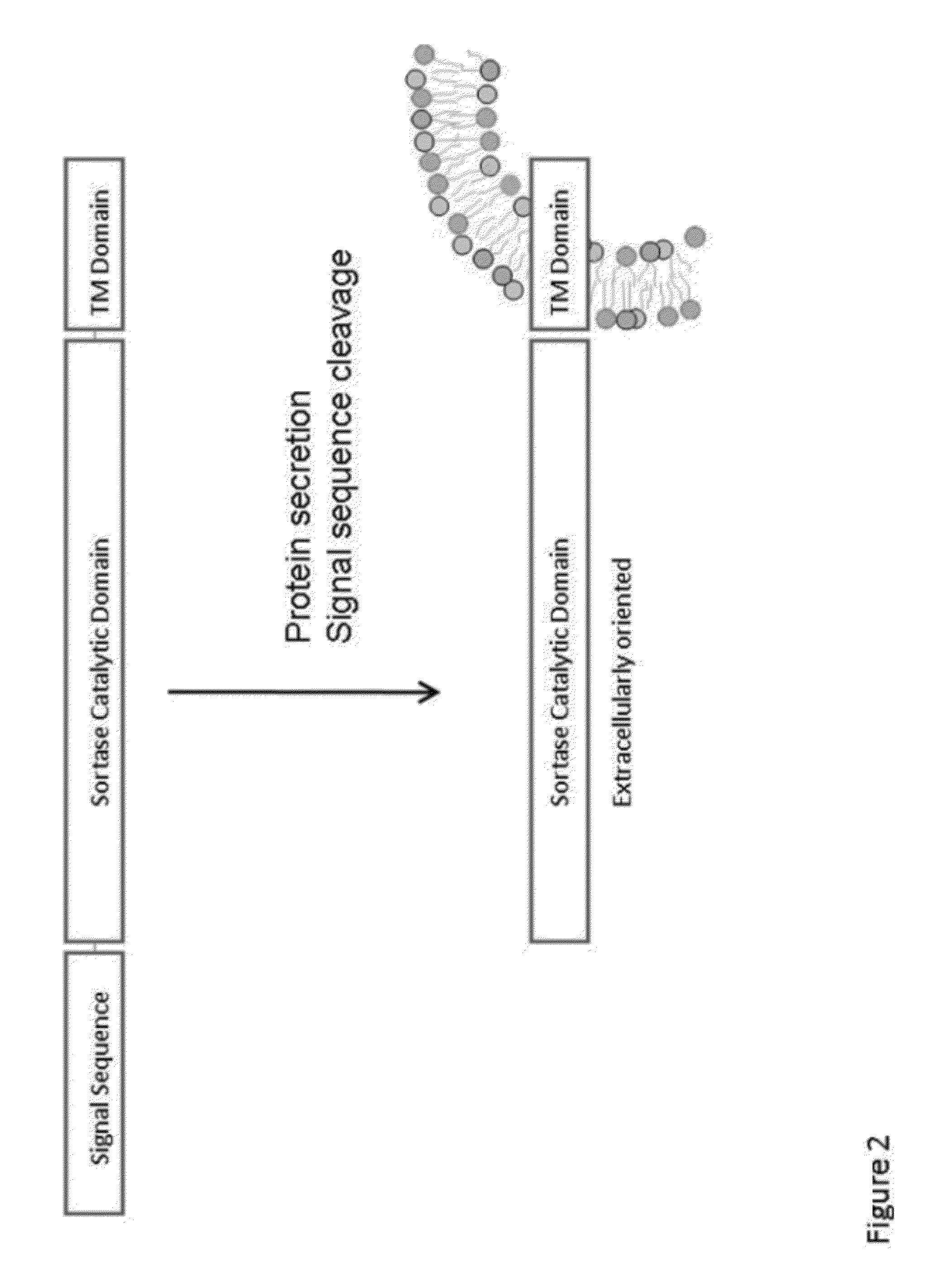
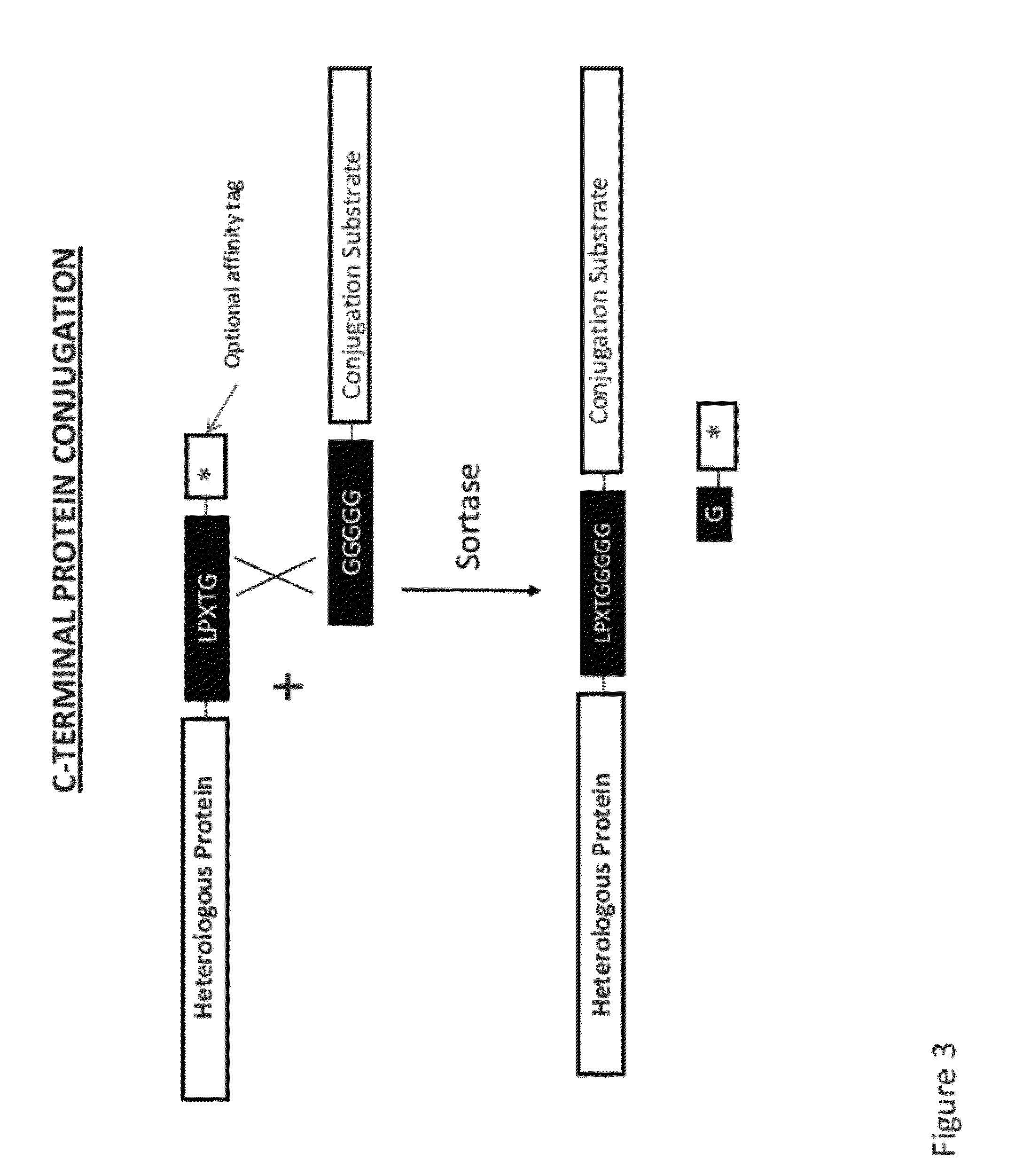
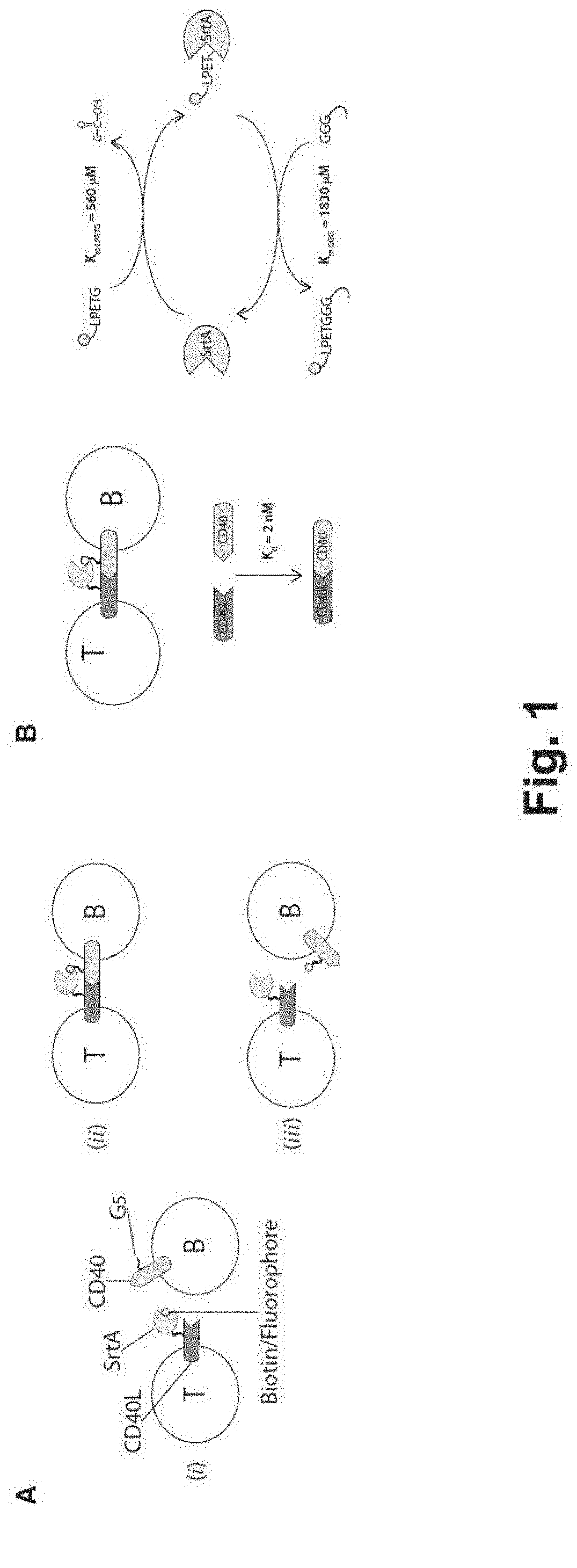
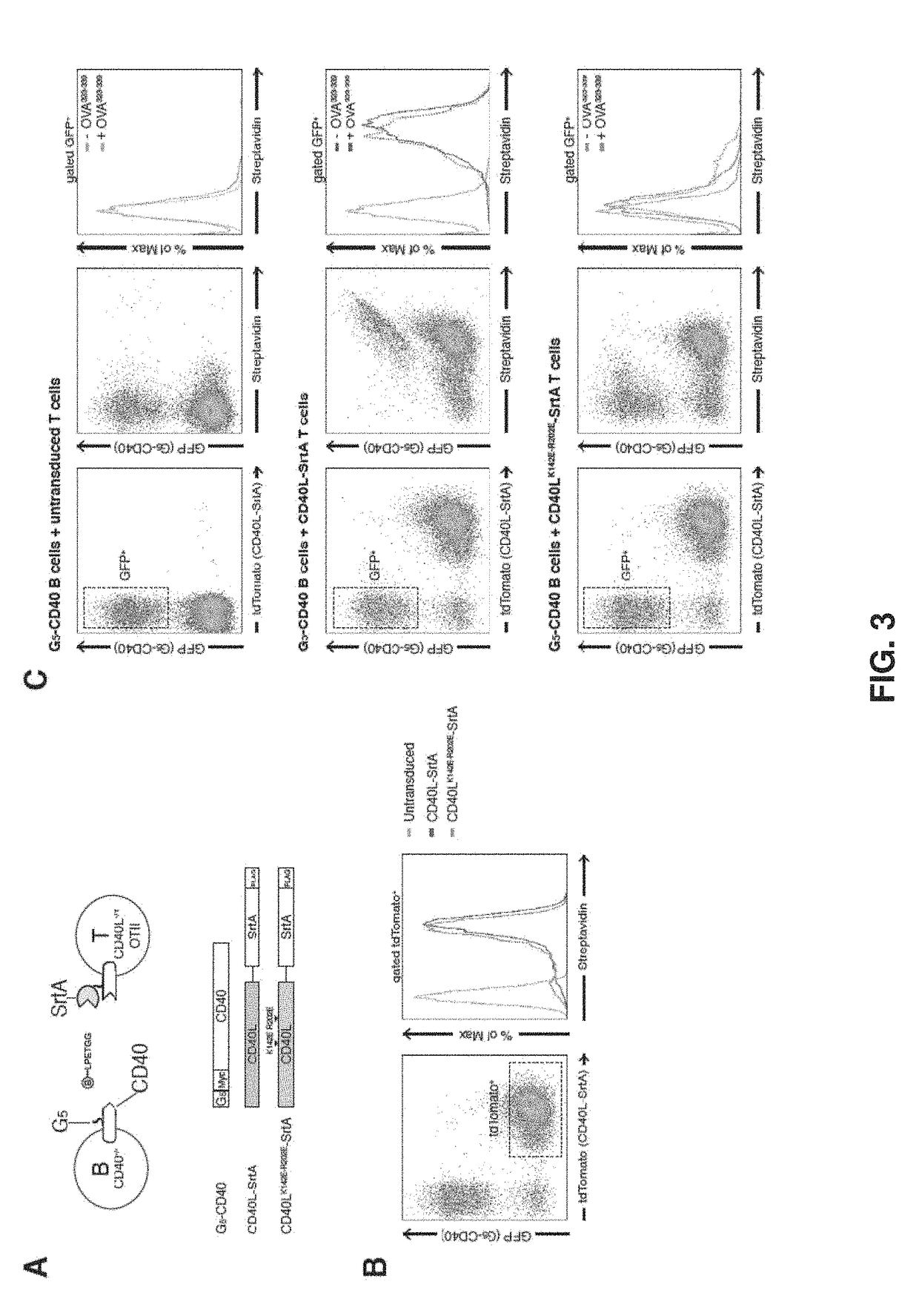
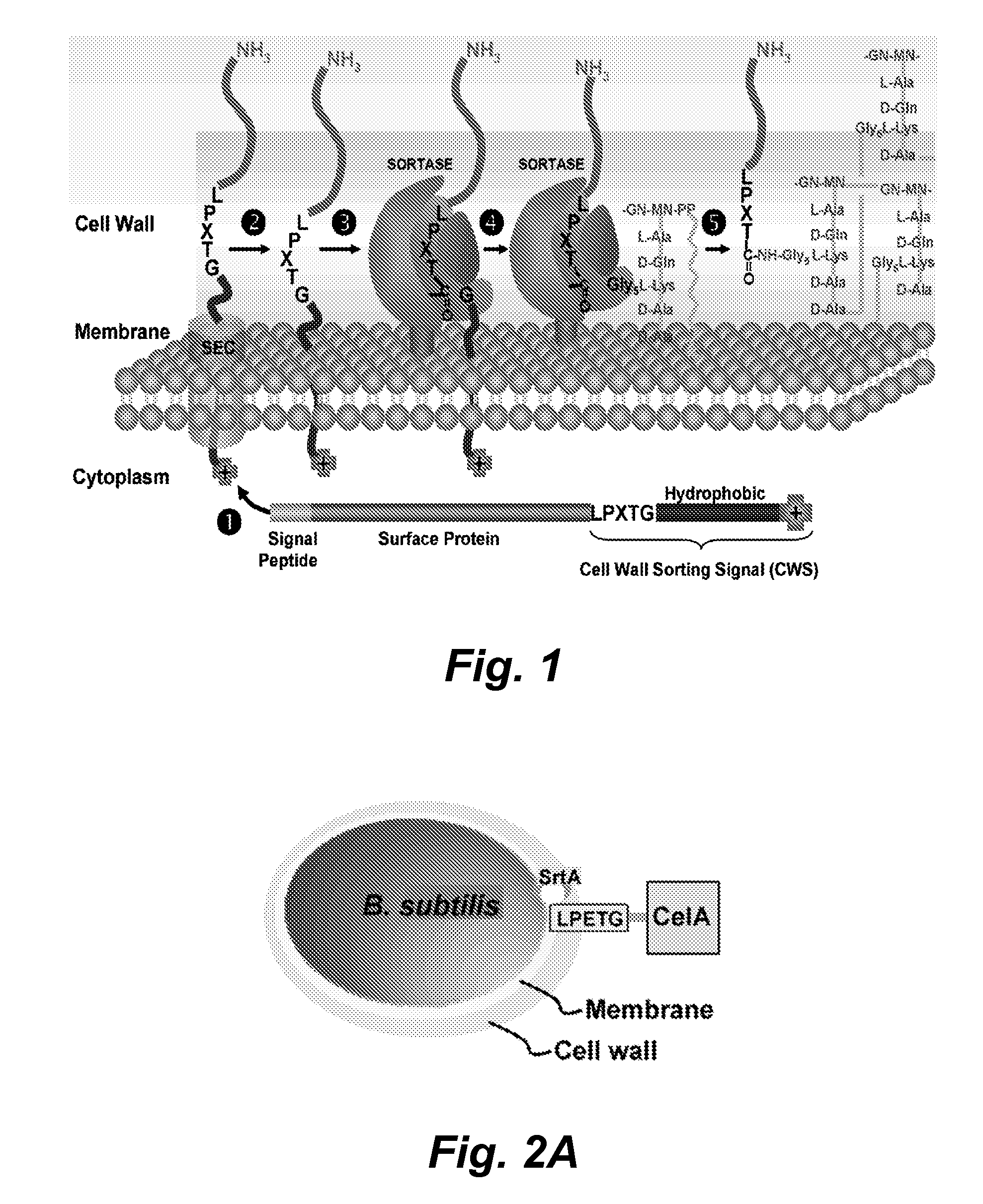
Sortase refers to a group of prokaryotic enzymes that modify surface proteins by recognizing and cleaving a carboxyl-terminal sorting signal. For most substrates of sortase enzymes, the recognition signal consists of the motif LPXTG (Leu-Pro-any-Thr-Gly), then a highly hydrophobic transmembrane sequence, followed by a cluster of basic residues such as arginine. Cleavage occurs between the Thr and Gly, with transient attachment through the Thr residue to the active site Cys residue, followed by transpeptidation that attaches the protein covalently to cell wall components. Sortases occur in almost all Gram-positive bacteria and the occasional Gram-negative (e.g. Shewanella putrefaciens) or Archaea (e.g. Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum), where cell wall LPXTG-mediated decoration has not been reported. Although sortase A, the "housekeeping" sortase, typically acts on many protein targets, other forms of sortase recognize variant forms of the cleavage motif, or that catalyze the assembly of pilins into pili.
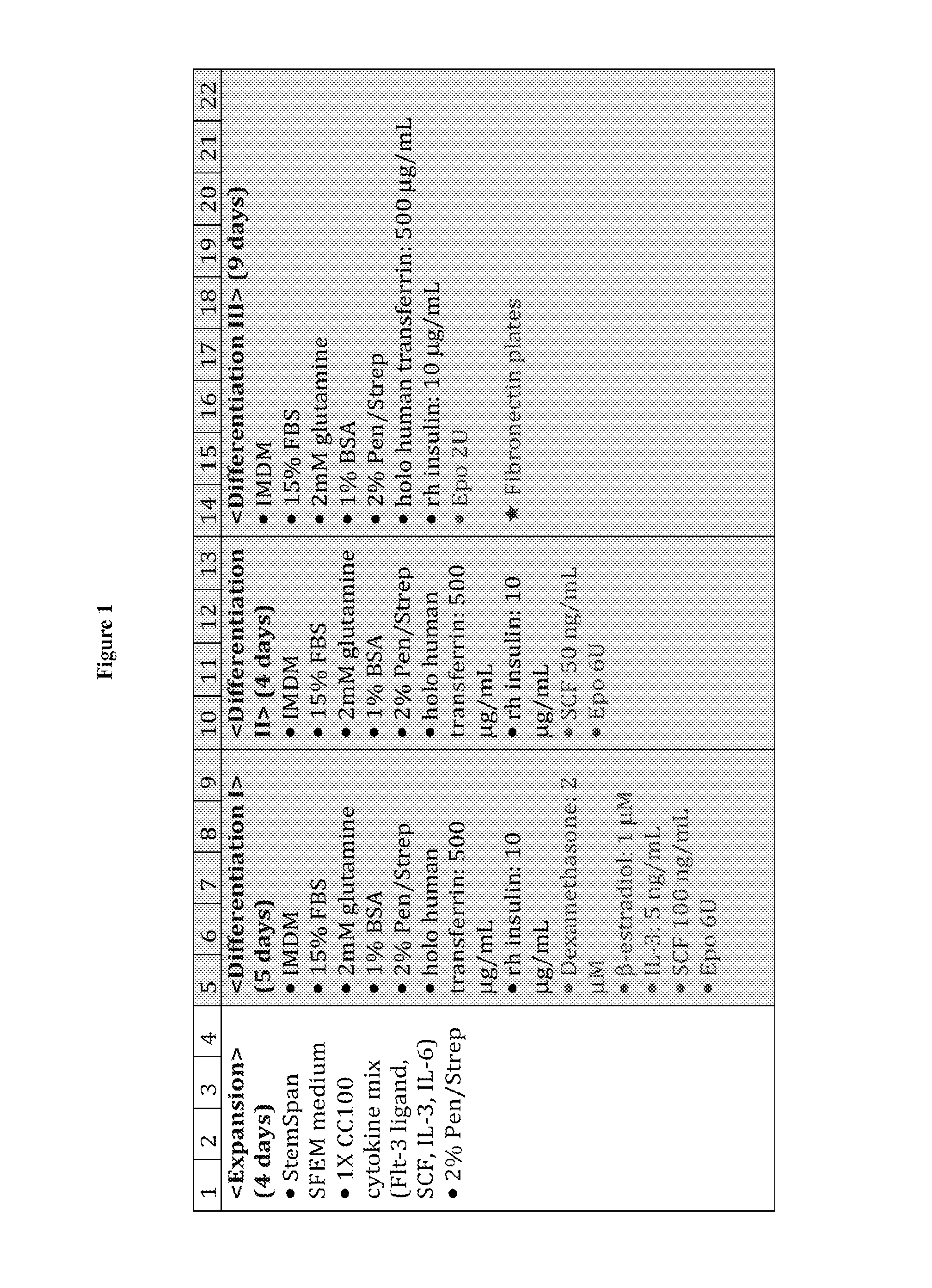
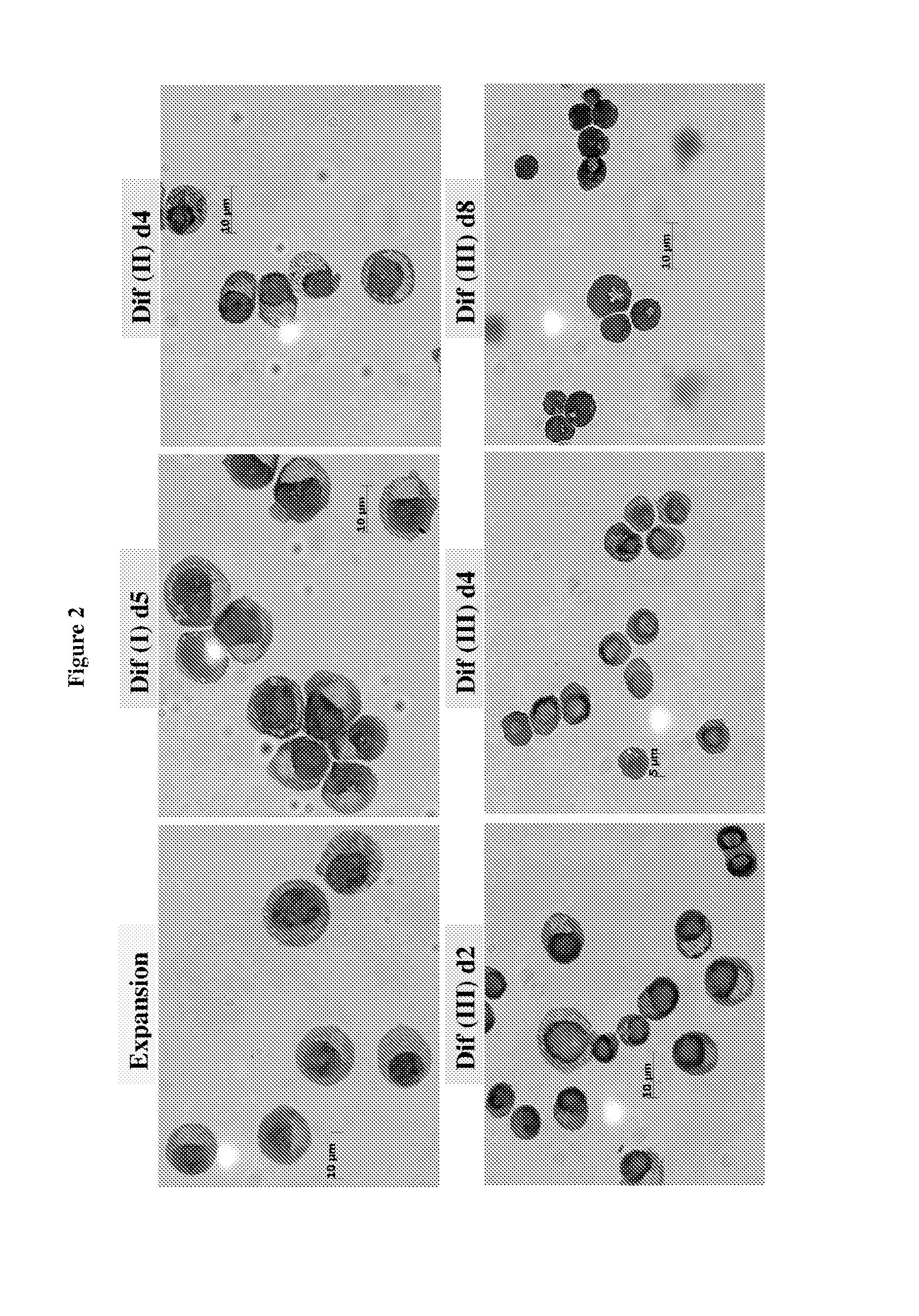
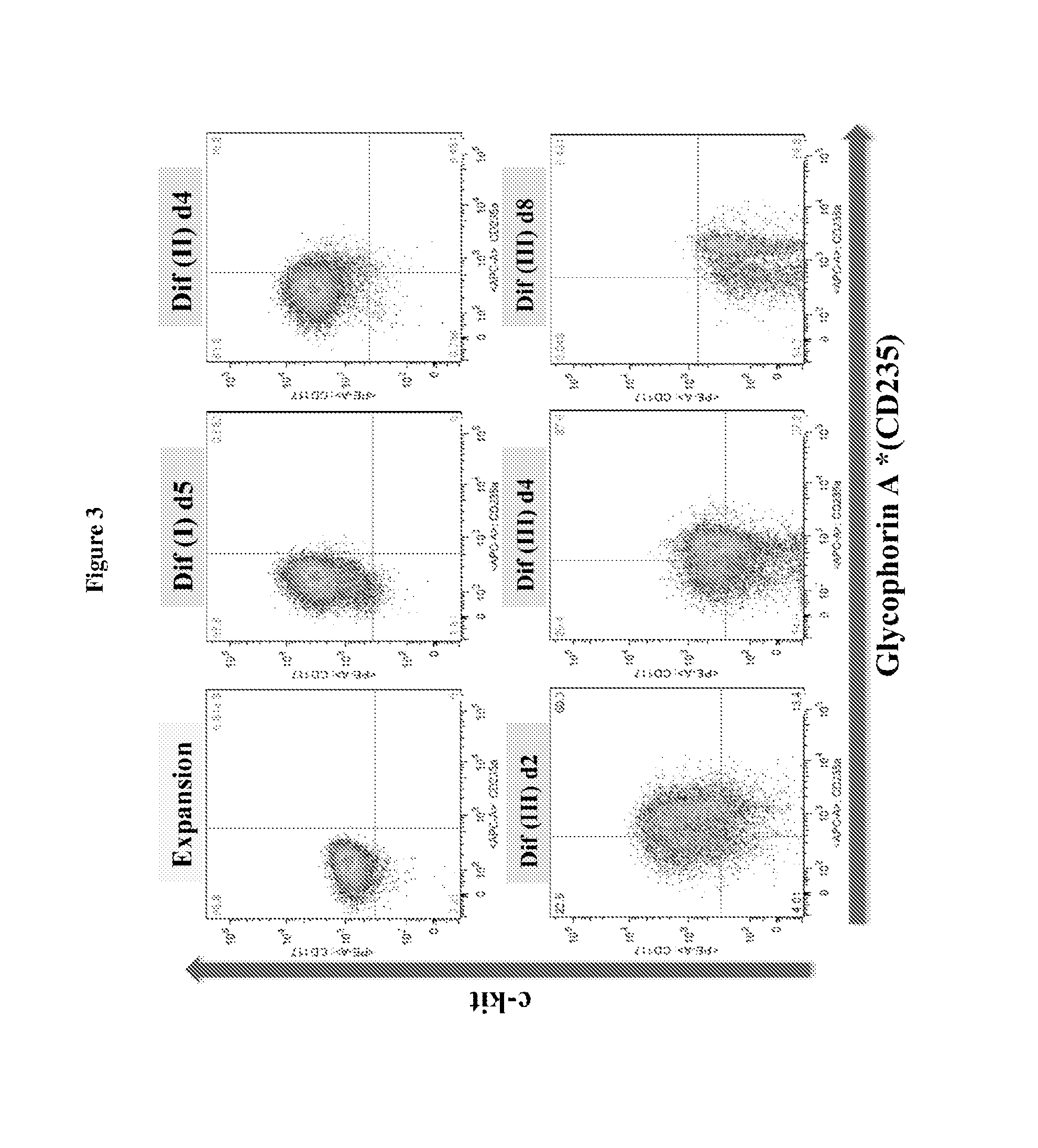
In vitro production of red blood cells with sortaggable proteins
Methods for the in vitro production of enucleated red blood cells and the enucleated red blood cells thus prepared are provided. Such enucleated red blood cells may express a sortaggable surface protein, which allows for surface modification in the presence of a sortase. Also described herein are surface modified enucleated red blood cells, e.g., conjugated with an agent of interest such as a peptide, a detectable label, or a chemotherapeutic agent, and uses thereof in delivering the agent to a subject.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Identification of sortase gene
The present invention is a substantially purified sortase-transamidase enzyme from Gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus. A specific sortase-transamidase enzyme disclosed has a molecular weight of about 29,076 daltons and catalyzes a reaction that covalently cross-links the carboxyl terminus of a protein having a sorting signal to the peptidoglycan of a Gram-positive bacterium, where the sorting signal has a a motif of NPQ / KTN / G therein. Variants of the enzyme, methods for cloning the gene encoding the enzyme and expressing the cloned gene, and methods of use of the enzyme, including for screening for antibiotics and for display of proteins or peptides on the surfaces of Gram-positive bacteria, are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
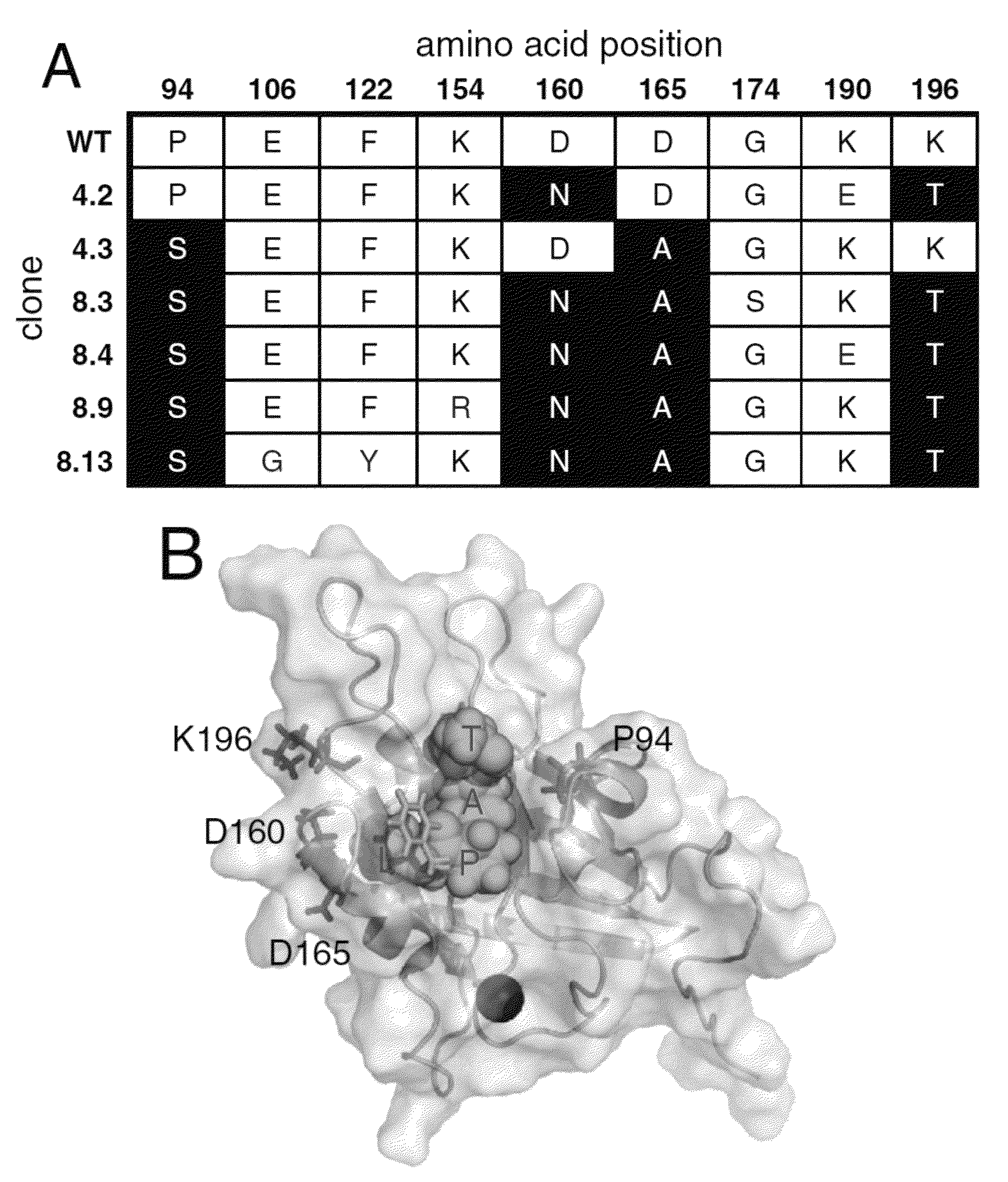
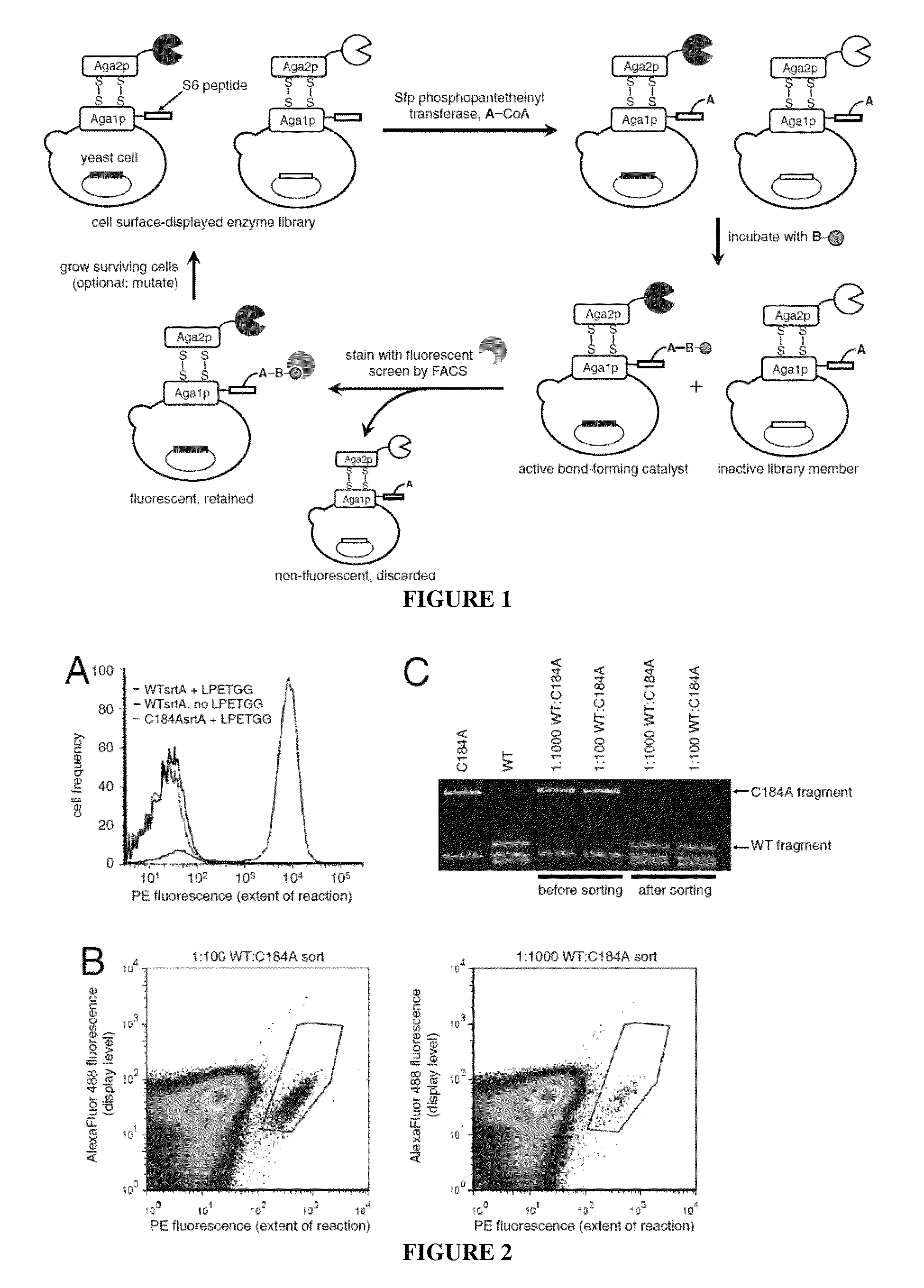
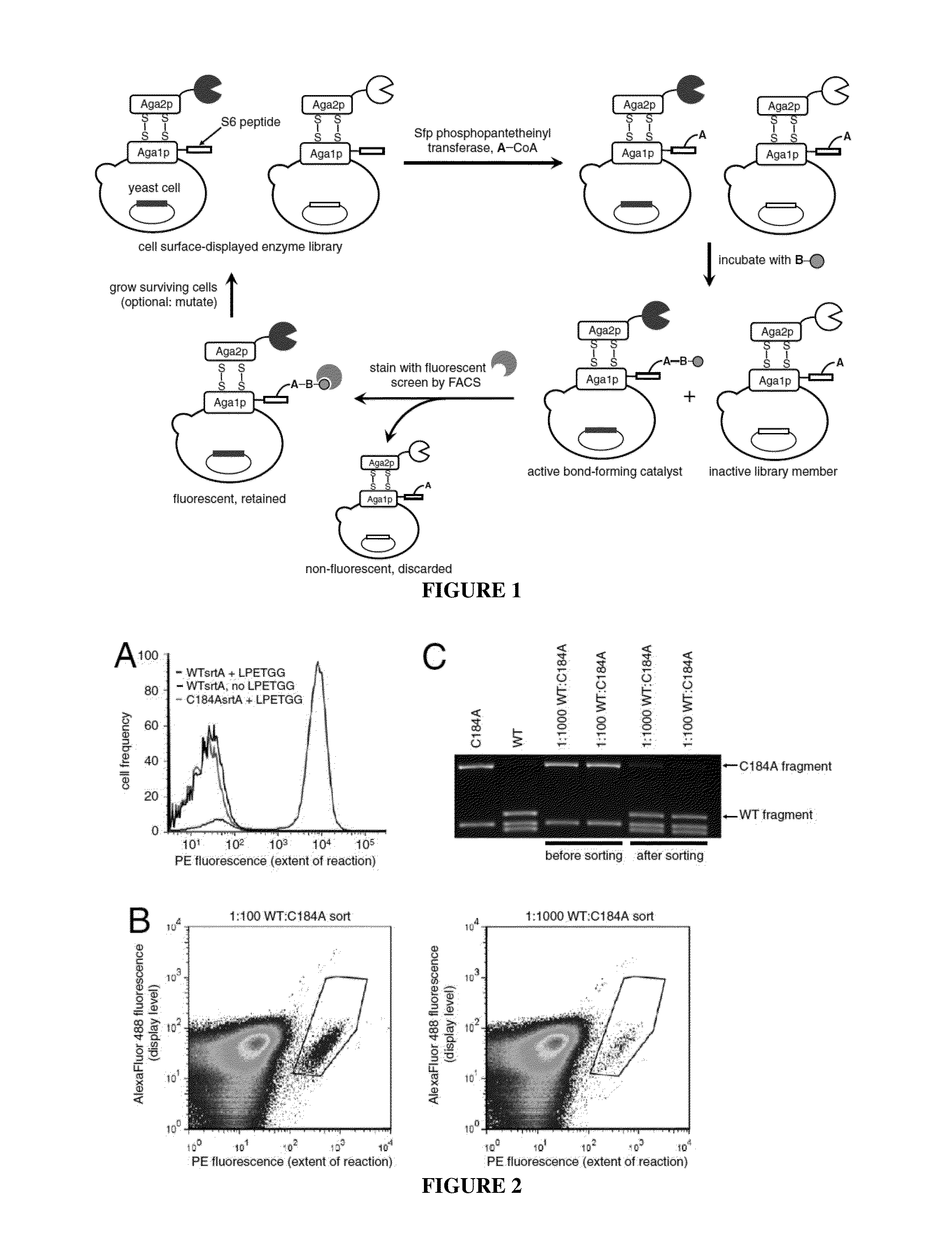
Evolution of bond-forming enzymes
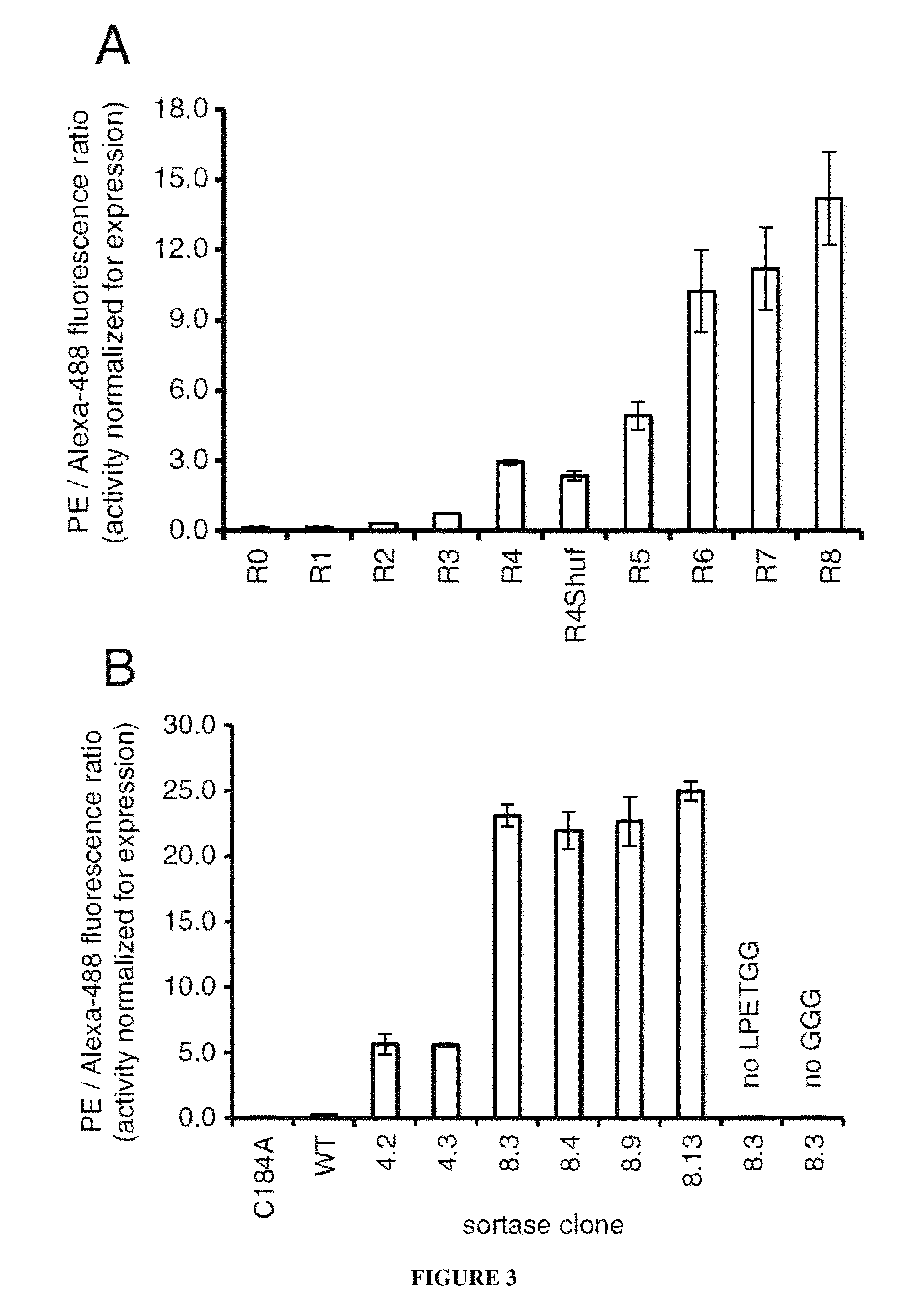
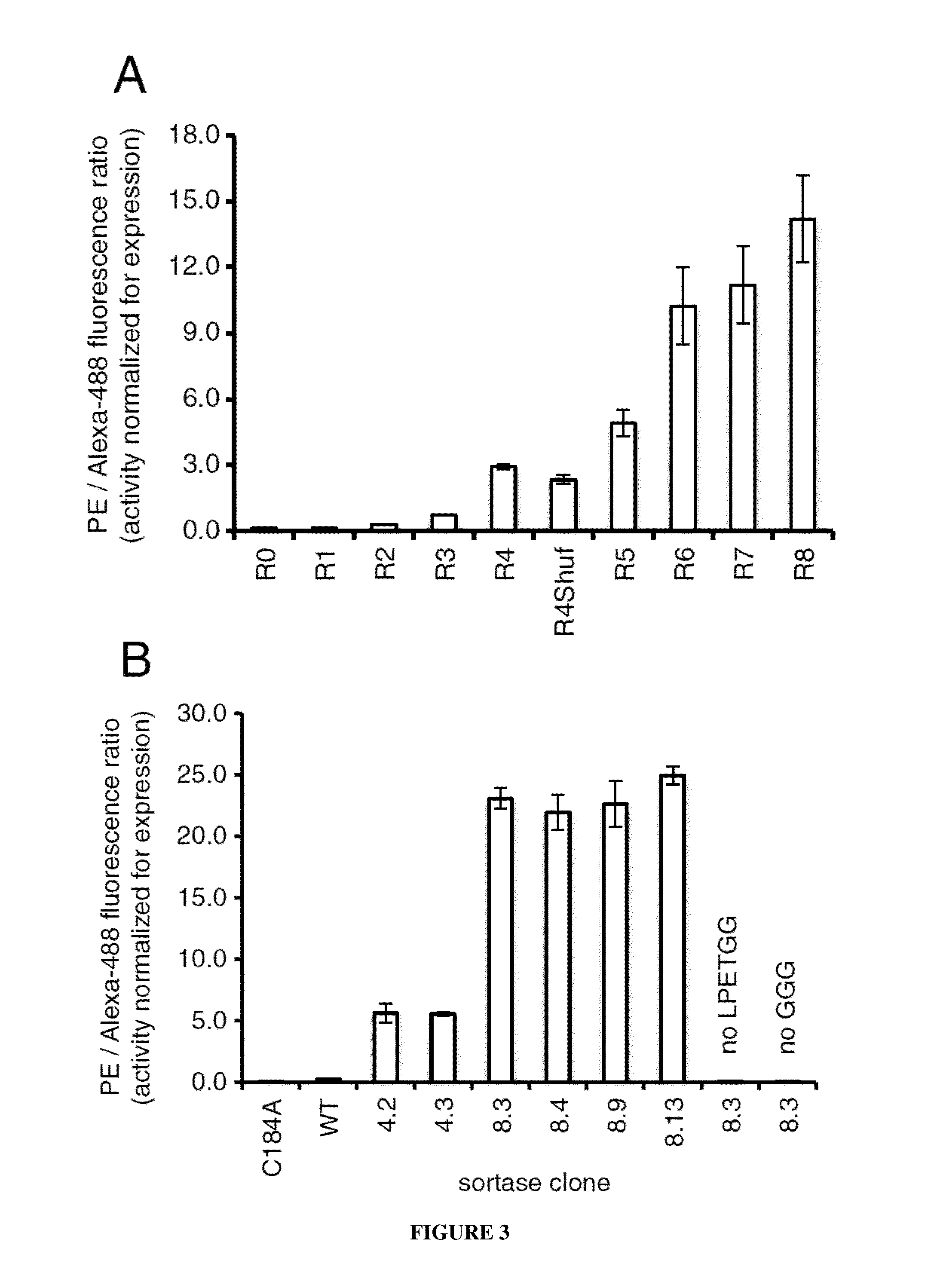
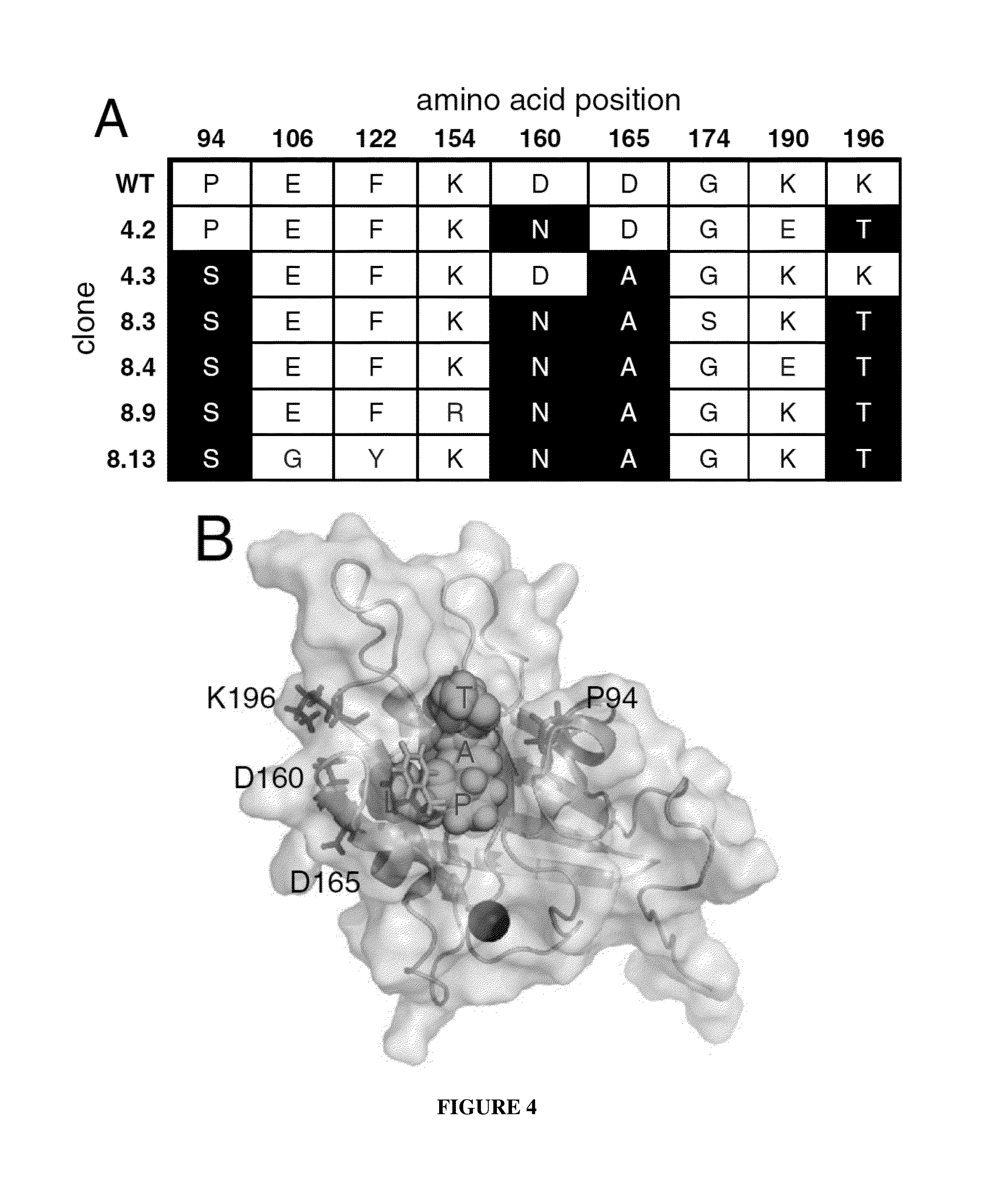
Strategies, systems, methods, reagents, and kits for the directed evolution of bond-forming enzymes are provided herein. Evolution products, for example, evolved sortases exhibiting enhanced reaction kinetics and / or altered substrate preferences are also provided herein, as are methods for using such evolved bond-forming enzymes. Kits comprising materials, reagents, and cells for carrying out the directed evolution methods described herein are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
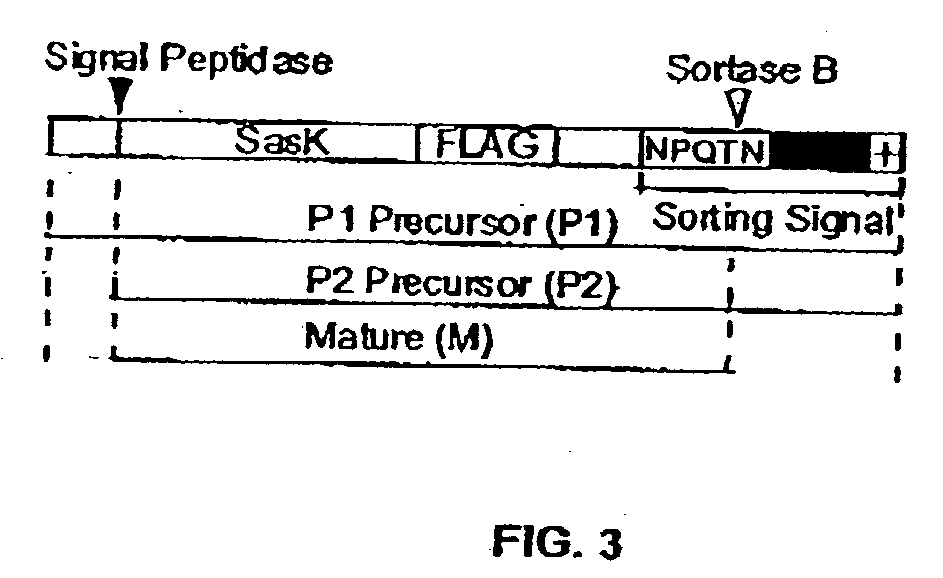
Methods and compositions involving sortase B
The present invention provides methods and compositions involving sortase-transamidases, including sortase B, and polypeptides that include a signal sorting sequence of NPQ / KTN / G. Methods of screening for inhibitors of Gram-positive bacteria as well as therapeutic, preventative, and research methods focusing on Gram-positive bacteria are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO +1
Identification of sortase gene
InactiveUS20030022178A1Fluorescence enhancementIncreased cleavageAntibacterial agentsFungiEnzyme GeneCarboxyl radical
The present invention is a substantially purified sortase-transamidase enzyme from Gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus. The enzyme having a molecular weight of about 23,539 or about 29,076 daltons and catalyzing a reaction that covalently cross-links the carboxyl terminus of a protein having a sorting signal to the peptidoglycan of a Gram-positive bacterium, the sorting signal having: (1) a motif of LPX3X4G therein; (2) a substantially hydrophobic domain of at least 31 amino acids carboxyl to the motif; and (3) a charged tail region with at least two positively charged residues carboxyl to the substantially hydrophobic domain, at least one of the two positively charged residues being arginine, the two positively charged residues being located at residues 31-33 from the motif, wherein X3 is any of the twenty naturally-occurring L-amino acids and X4 is selected from the group consisting of alanine, serine, and threonine, and wherein sorting occurs by cleavage between the fourth and fifth residues of the LPX3X4G motif. Variants of the enzyme, methods for cloning the gene encoding the enzyme and expressing the cloned gene, and methods of use of the enzyme, including for screening for antibiotics and for display of proteins or peptides on the surfaces of Gram-positive bacteria, are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Evolution of bond-forming enzymes
ActiveUS20140057317A1High catalytic activityAltered substrate preferenceFermentationPeptidasesReagentDirected evolution
Strategies, systems, methods, reagents, and kits for the directed evolution of bond-forming enzymes are provided herein. Evolution products, for example, evolved sortases exhibiting enhanced reaction kinetics and / or altered substrate preferences are also provided herein, as are methods for using such evolved bond-forming enzymes. Kits comprising materials, reagents, and cells for carrying out the directed evolution methods described herein are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Sortase-modified vhh domains and uses thereof
In some aspects, polypeptides comprising single domain antibodies and methods of identifying single domain antibodies are provided. In some embodiments polypeptides comprising a single domain antibody and a sortase recognition sequence, are provided. In some aspects, products and methods of use in modulating the immune system, e.g., modulating an immune response, are provided.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Sortase-modified VHH domains and uses thereof
In some aspects, polypeptides comprising single domain antibodies and methods of identifying single domain antibodies are provided. In some embodiments polypeptides comprising a single domain antibody and a sortase recognition sequence, are provided. In some aspects, products and methods of use in modulating the immune system, e.g., modulating an immune response, are provided.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Identification of sortase gene
The present invention is a substantially purified sortase-transamidase enzyme from Gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus. The enzyme having a molecular weight of about 23,539 or about 29,076 daltons and catalyzing a reaction that covalently cross-links the carboxyl terminus of a protein having a sorting signal to the peptidoglycan of a Gram-positive bacterium, the sorting signal having: (1) a motif of LPX3X4G therein; (2) a substantially hydrophobic domain of at least 31 amino acids carboxyl to the motif; and (3) a charged tail region with at least two positively charged residues carboxyl to the substantially hydrophobic domain, at least one of the two positively charged residues being arginine, the two positively charged residues being located at residues 31-33 from the motif, wherein X3 is any of the twenty naturally-occurring L-amino acids and X4 is selected from the group consisting of alanine, serine, and threonine, and wherein sorting occurs by cleavage between the fourth and fifth residues of the LPX3X4G motif. Variants of the enzyme, methods for cloning the gene encoding the enzyme and expressing the cloned gene, and methods of use of the enzyme, including for screening for antibiotics and for display of proteins or peptides on the surfaces of Gram-positive bacteria, are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods and compositions for enhanced immunological therapy and targeting of gram-positive bacteria
ActiveUS9005579B2Promote growthImprove targetingAntibacterial agentsCompound screeningVirulent characteristicsGram
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for use in modulating, including inhibiting the growth and / or reducing the virulence of gram-positive bacteria. The present invention provides methods and compositions for disrupting the cell wall and / or cell membrane in gram-positive bacteria such that cell wall or cell membrane target(s) are rendered exposed or accessible and sensitive to a modulation thereof. Methods for modulation of one or more gram-positive bacterial cell wall or cell membrane targets in a gram-positive bacteria are provided comprising disrupting the cell wall such that the cell wall or cell membrane target, which is particularly a sortase, is rendered exposed or accessible and sensitive to a modifying, modulating or binding agent, which is particularly an antibody or fragment thereof, wherein the cell wall or cell membrane target is inaccessible or relatively insensitive to the modifying, modulating or binding agent in the absence of cell wall disruption.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV +1
In vitro production of red blood cells with proteins comprising sortase recognition motifs
Methods for the in vitro production of enucleated red blood cells and the enucleated red blood cells thus prepared are provided. Such enucleated red blood cells may express a sortaggable surface protein, which allows for surface modification in the presence of a sortase. Also described herein are surface modified enucleated red blood cells, e.g., conjugated with an agent of interest such as a peptide, a detectable label, or a chemotherapeutic agent, and uses thereof in delivering the agent to a subject.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Evolved sortases and uses thereof
Evolved sortases exhibiting enhanced reaction kinetics and / or altered substrate preferences are provided herein, for example evolved sortases that bind recognitions motifs comprising a LAXT or LPXS sequence. Also provided are methods (e.g., orthogonal transpeptidation and diagnostics methods) for using such sortases. Kits comprising materials, reagents, and cells for carrying out the methods described herein are also provided.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Identification of sortase gene
InactiveUS20030153020A1Fluorescence enhancementIncreased cleavageBacteriaHydrolasesCross-linkStaphylococcus aureus
The present invention is a substantially purified sortase-transamidase enzyme from Gram-positive bacteria, such as Staphylococcus aureus. A specific sortase-transamidase enzyme disclosed has a molecular weight of about 29,076 daltons and catalyzes a reaction that covalently cross-links the carboxyl terminus of a protein having a sorting signal to the peptidoglycan of a Gram-positive bacterium, where the sorting signal has a a motif of NPQ / KTN / G therein. Variants of the enzyme, methods for cloning the gene encoding the enzyme and expressing the cloned gene, and methods of use of the enzyme, including for screening for antibiotics and for display of proteins or peptides on the surfaces of Gram-positive bacteria, are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for catalyzing to generate L-theanine by using recombinant Bacillus subtilis secreted gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase
The invention relates to a method for catalyzing L-glutamine and ethylamine to generate L-theanine by using recombinant Bacillus subtilis secreted gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. The method provided by the invention is used for amplifying genes of gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase (GGT) in bacillus subtilis and cloning overexpression in bacillus subtilis 168. According to the method, a bacillus subtilis engineering strain capable of secreting gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase is established for the first time and the enzyme activity of the strain and the fermenting property of enzyme are researched: the supernatant enzyme activity of recombinant bacteria reaches 49.8 U / mg which is 20 times of that of an original strain. By using 80mML-glutamine as a donor and 640mMZ ethylamine as a receptor, the conversion ratio of L-theanine can reach over 86%. The method provided by the invention uses the safe strain, has the advantages of being high in conversion ratio, simple in production method and the like, and facilitates production of L-theanine produced by an industrial scaled enzymic method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Bacterial surface display and screening of thioether-bridge-containing peptides
The invention relates to bacterial cell surface display of post-translationally modified heterologous proteins. Provided is an isolated nucleic acid construct encoding a proteinaceous substance comprising, from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, at least (a) an N-terminal a lantibiotic leader sequence; (b) an amino acid sequence of interest to be post-translationally modified to a dehydroresidue- or thioether-bridge containing polypeptide; (c) a hydrophilic cell-wall spanning domain; (d) a sortase recognition motif; (e) a hydrophobic membrane spanning domain and (f) a C-terminal charged membrane anchoring domain. Also provided is a Gram-positive host cell expressing the construct, as well as a library of host cells.
Owner:LANTHIO PEP
Methods and compositions for enhanced immunological therapy and targeting of gram-positive bacteria
ActiveUS20130045211A1Promote growthImprove targetingAntibacterial agentsCompound screeningVirulent characteristicsGram
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for use in modulating, including inhibiting the growth and / or reducing the virulence of gram-positive bacteria. The present invention provides methods and compositions for disrupting the cell wall and / or cell membrane in gram-positive bacteria such that cell wall or cell membrane target(s) are rendered exposed or accessible and sensitive to a modulation thereof. Methods for modulation of one or more gram-positive bacterial cell wall or cell membrane targets in a gram-positive bacteria are provided comprising disrupting the cell wall such that the cell wall or cell membrane target, which is particularly a sortase, is rendered exposed or accessible and sensitive to a modifying, modulating or binding agent, which is particularly an antibody or fragment thereof, wherein the cell wall or cell membrane target is inaccessible or relatively insensitive to the modifying, modulating or binding agent in the absence of cell wall disruption.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV +1
Electrochemical detection method of Staphylococcus aureus
ActiveCN106501337ALarge specific surface areaLarge pore volumeMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCarbon paste electrodeParaffin oils
The invention discloses an electrochemical detection method of Staphylococcus aureus. The method comprises the following steps: preparing an ordered mesoporous carbon nano material CMK-3 by a template process, and carrying out surface carboxyl functionalization modification to obtain a carboxyl-functionalized mesoporous carbon nano material O-CMK-3; immobilizing sortase A (Srt A) onto the carboxyl-functionalized mesoporous carbon nano material O-CMK-3 by a chemical covalent binding technique to obtain an immobilized sortase nano composite material O-CMK-3-M; and preparing a carbon paste electrode from the immobilized sortase nano composite material, graphite, paraffin and other materials, immersing the carbon paste electrode into Staphylococcus aureus solutions with different concentrations, and detecting Staphylococcus aureus by using a tri-electrode detection system. Compared with the existing detection technique, the method has the advantages of short detection time and the like, is convenient to operate, is recyclable, and thus, has favorable application prospects.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
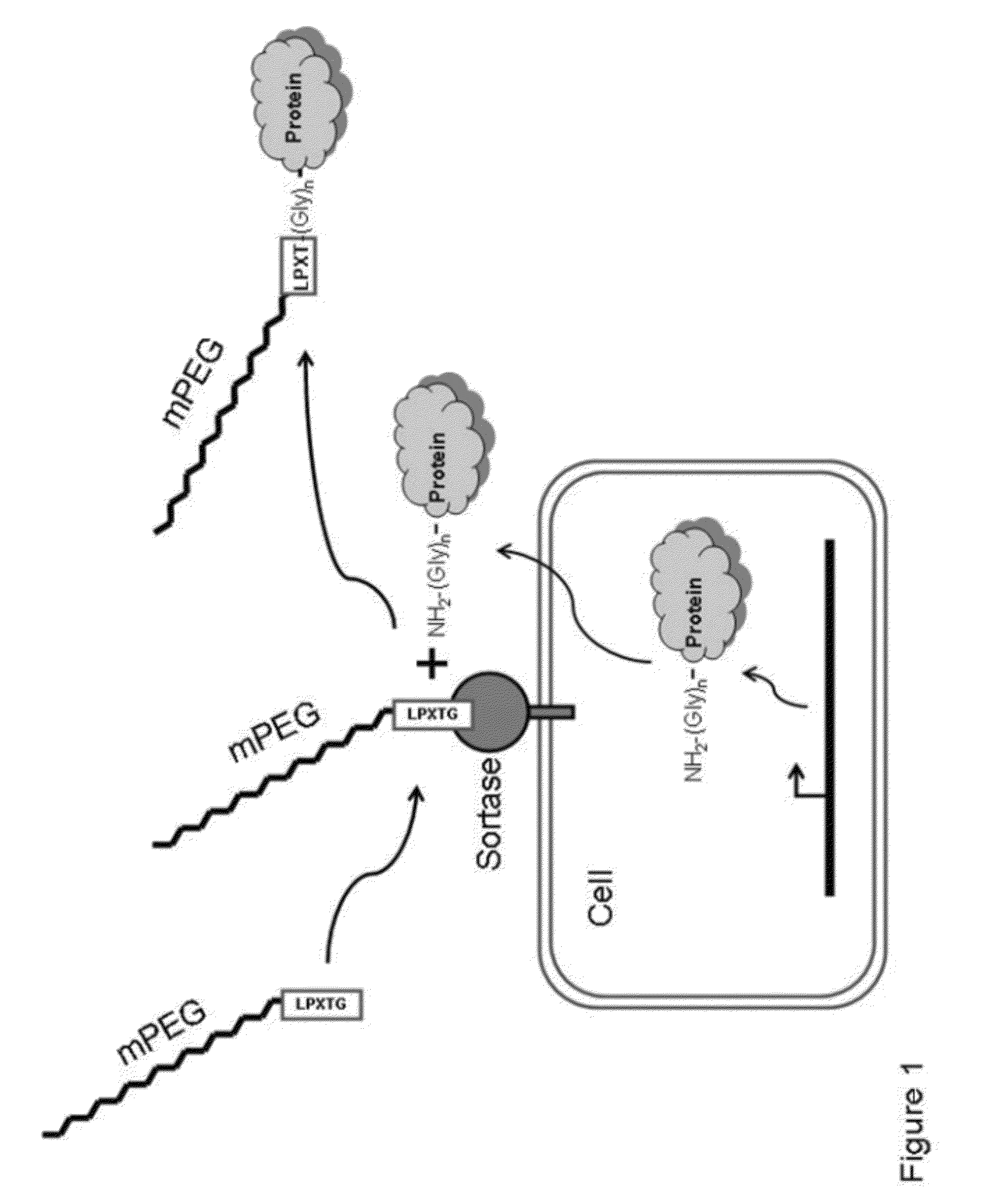
Protein designated PEG modification method and obtained PEG modified protein
InactiveCN104130308AExtended half-lifeEasy to operatePeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsESA ProteinBio engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological engineering, and discloses a protein designated PEG modification method and an obtained PEG modified protein. The protein designated PEG modification method of the invention is as below: acquiring a protein, fusing a sorting motif recognized by a sortase at the C terminal of the protein to obtain a recombinant protein; mixing a PEG modifier, the recombinant protein and sortase, conducting peptide bond cutting and connection reaction to obtain a PEG modified protein, wherein the PEG modifier has a structure shown in a formula (I). The invention utilizes the sortase to realize designated PEG modification at the C terminal of the protein; the whole operation is simple and low in cost, avoids multisite modification in protein PEG modification, is more conducive to application of PEG modification in protein modification; m represents the degree of polymerization, and satisfies the relation of 1<=m<= 5; and n represents the degree of polymerization, and satisfies the relation of 110<= n<=1100.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
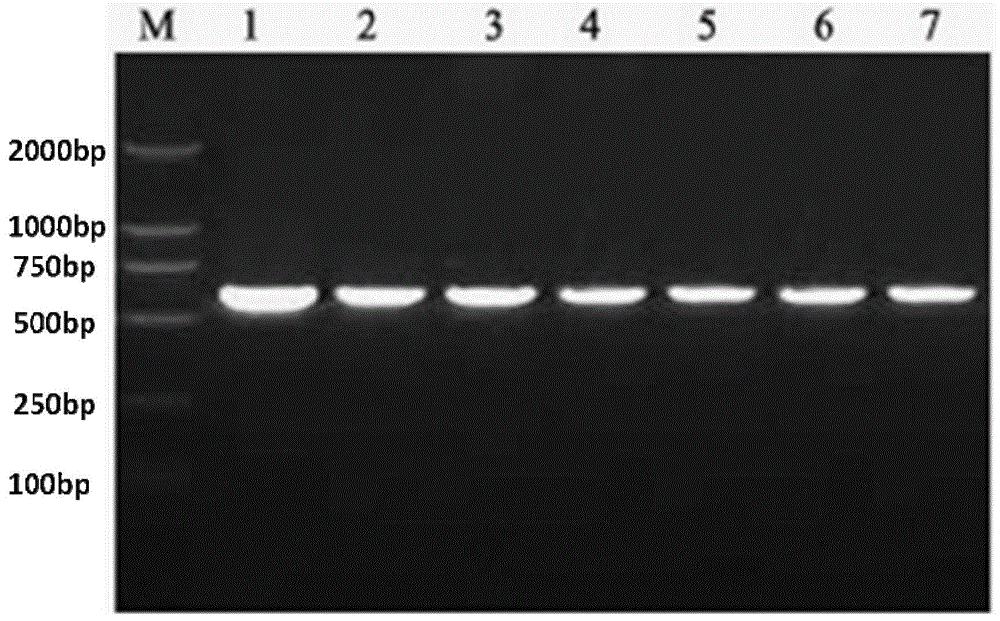
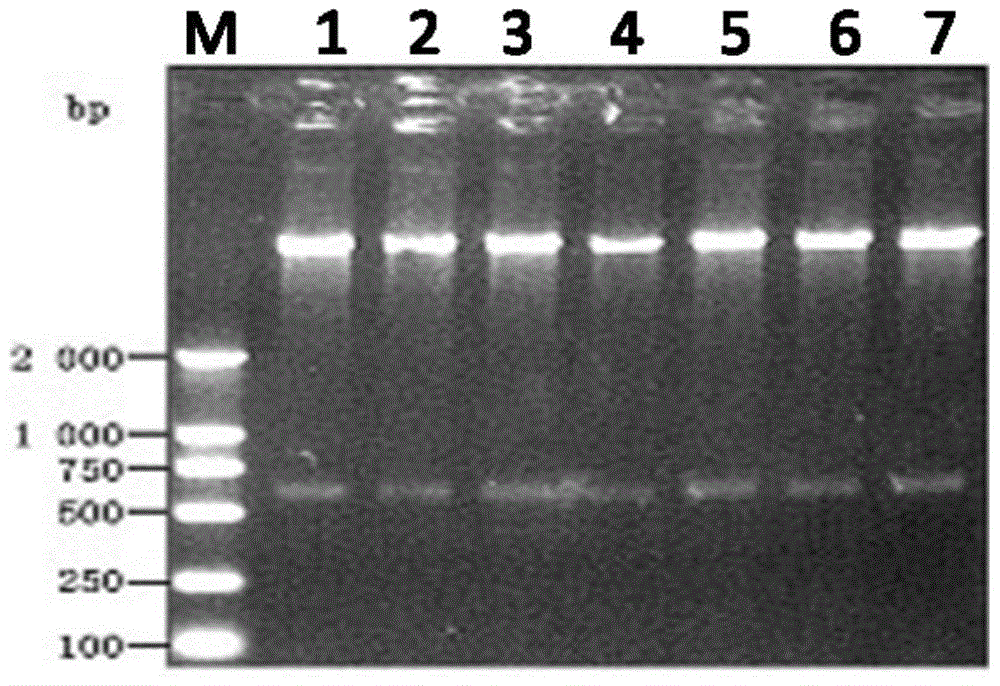
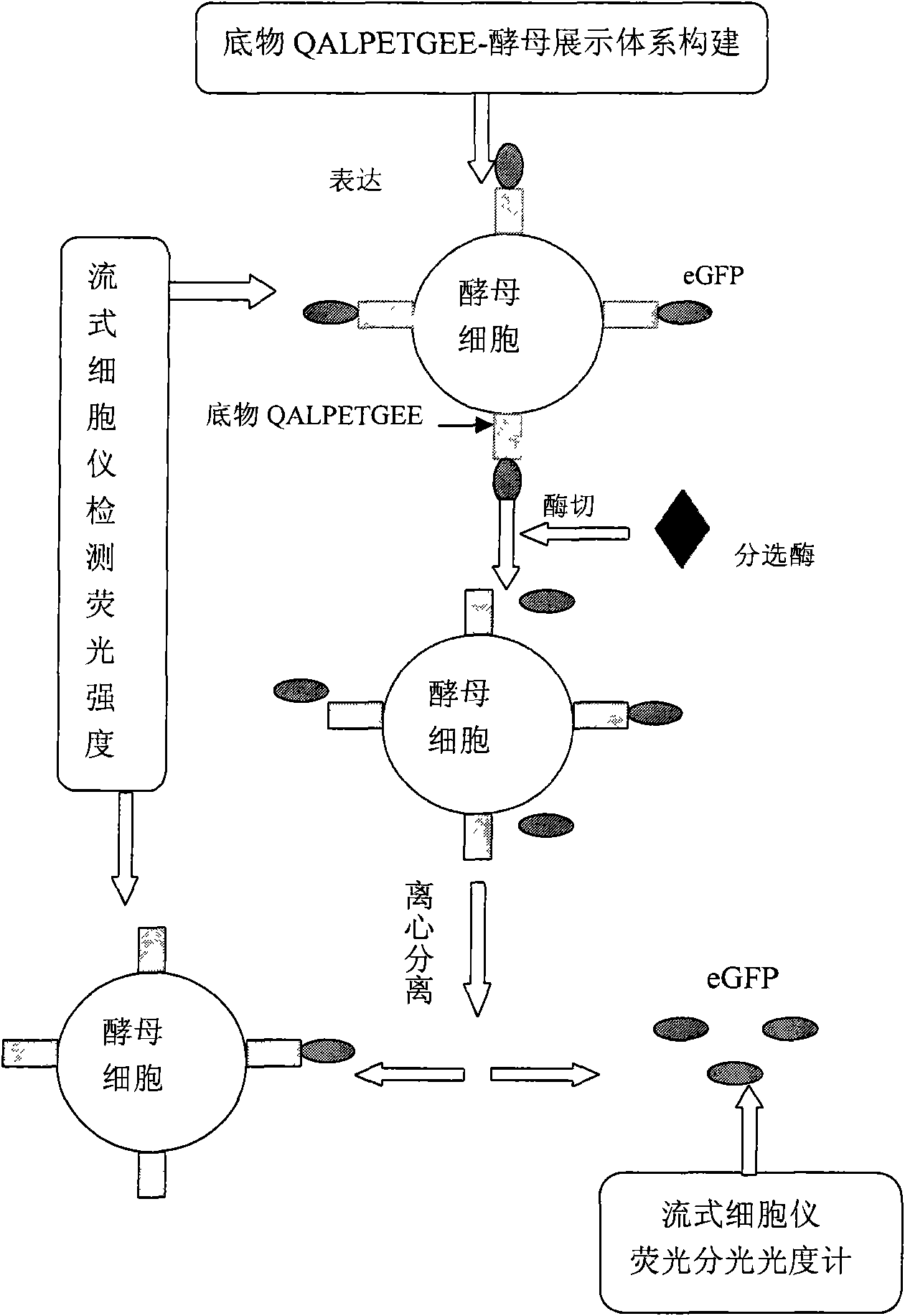
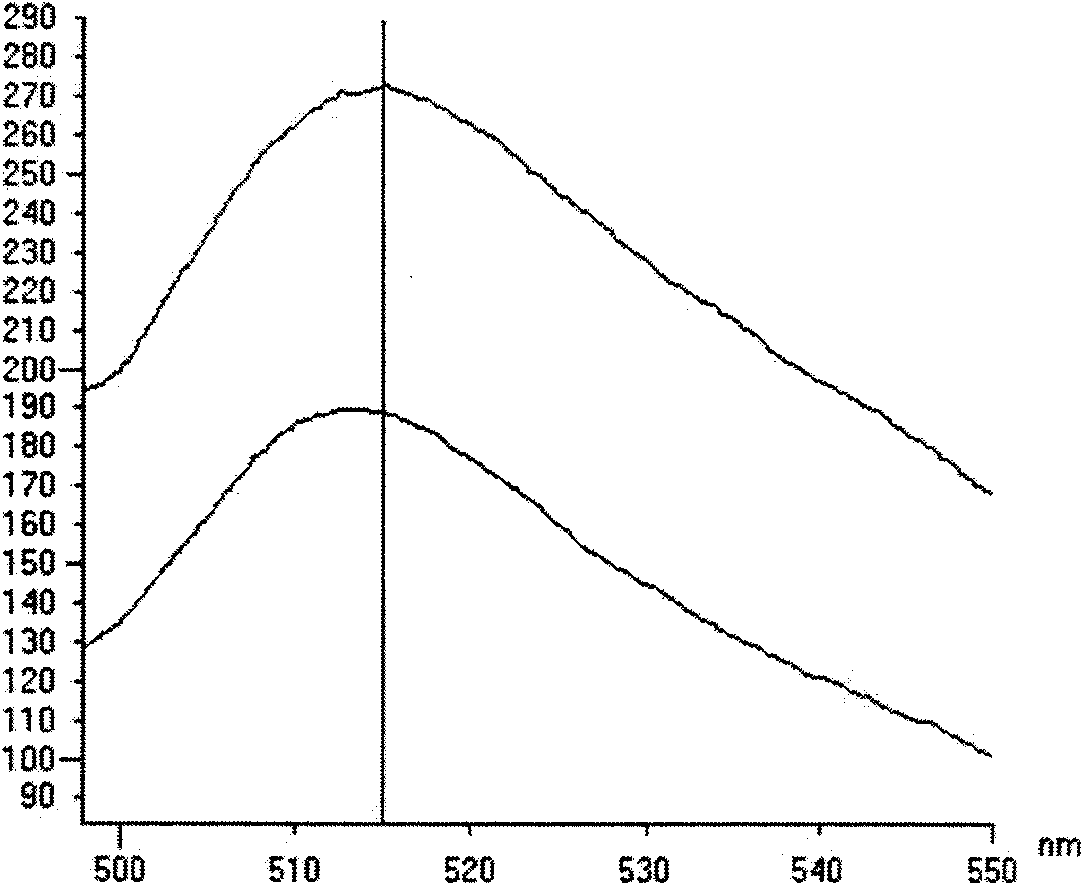
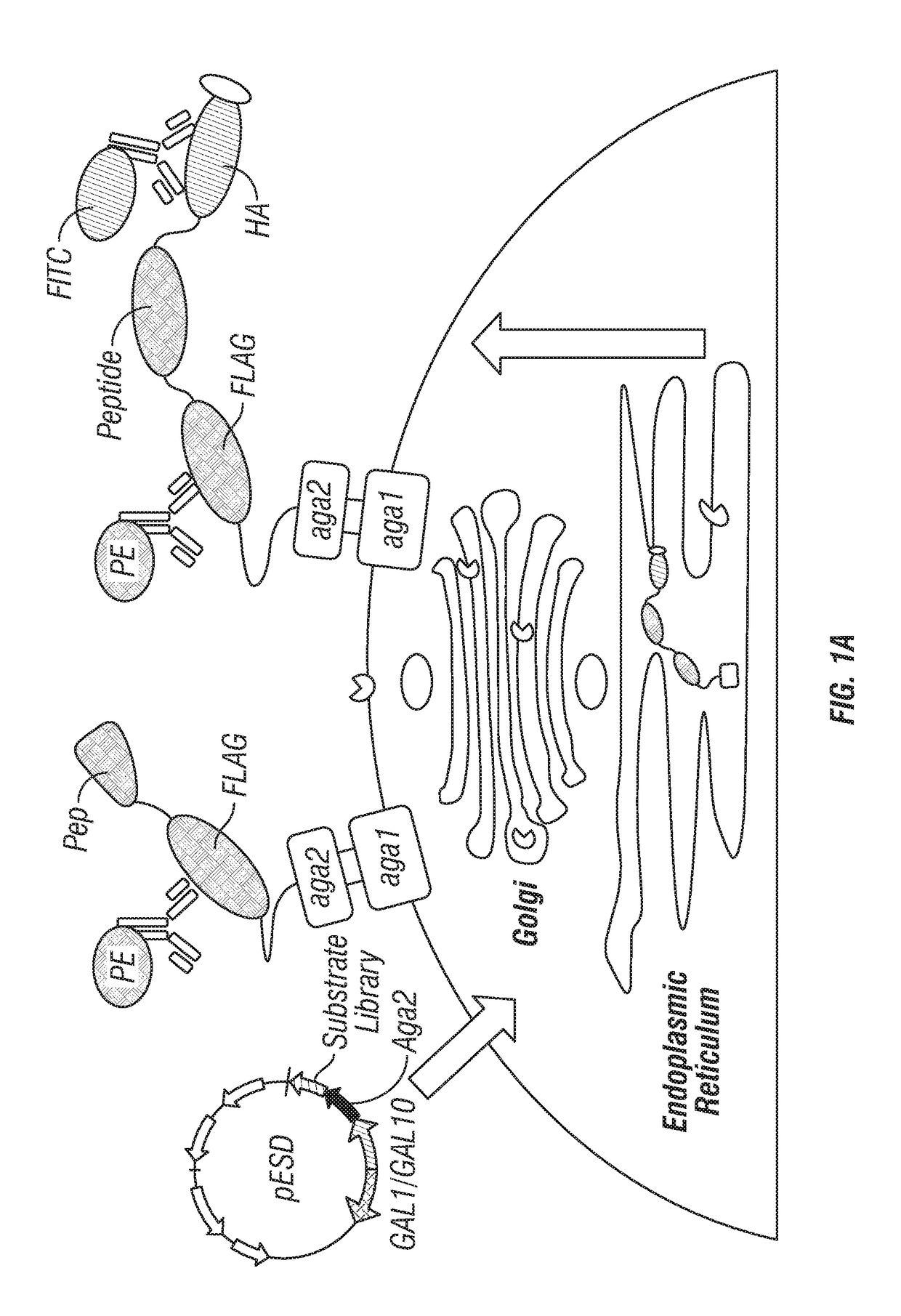
Method for measuring sortase based on yeast surface display
InactiveCN101603075ALow costMaterial prices are lowMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesPichia pastorisSurface display
The invention discloses a method for measuring sortase based on pichia pastoris surface display, comprising the following steps: A. infusing target gene QALPETGEE and linker-eGFP gene into QALPETGEE-linker-eGFP; B. constructing an expression carrier for constructing QALPETGEE-linker--eGFP; C. converting the expression carrier pKFS-QALPETGEE-linker-eGFP into pichia pastoris; D. expressing yeast surface protein: inoculating and culturing positive transformant by YPD and BGMY liquid culture medium, and inducing expression in BMMY liquid culture medium; E. measuring the yeast surface protein; F. expressing sortase; and G. testing activatedly the sortase. The invention uses the yeast surface display technology, fluorospectrophotometer and flow cytometry are adopted for measuring, and the used materials are lower in price, thus greatly reducing the measuring cost of sortase and facilitating operation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Methods for generating engineered enzymes
ActiveUS20170233781A1Accurate identificationPrevent unwanted cleavageMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesYeastProteinase activity
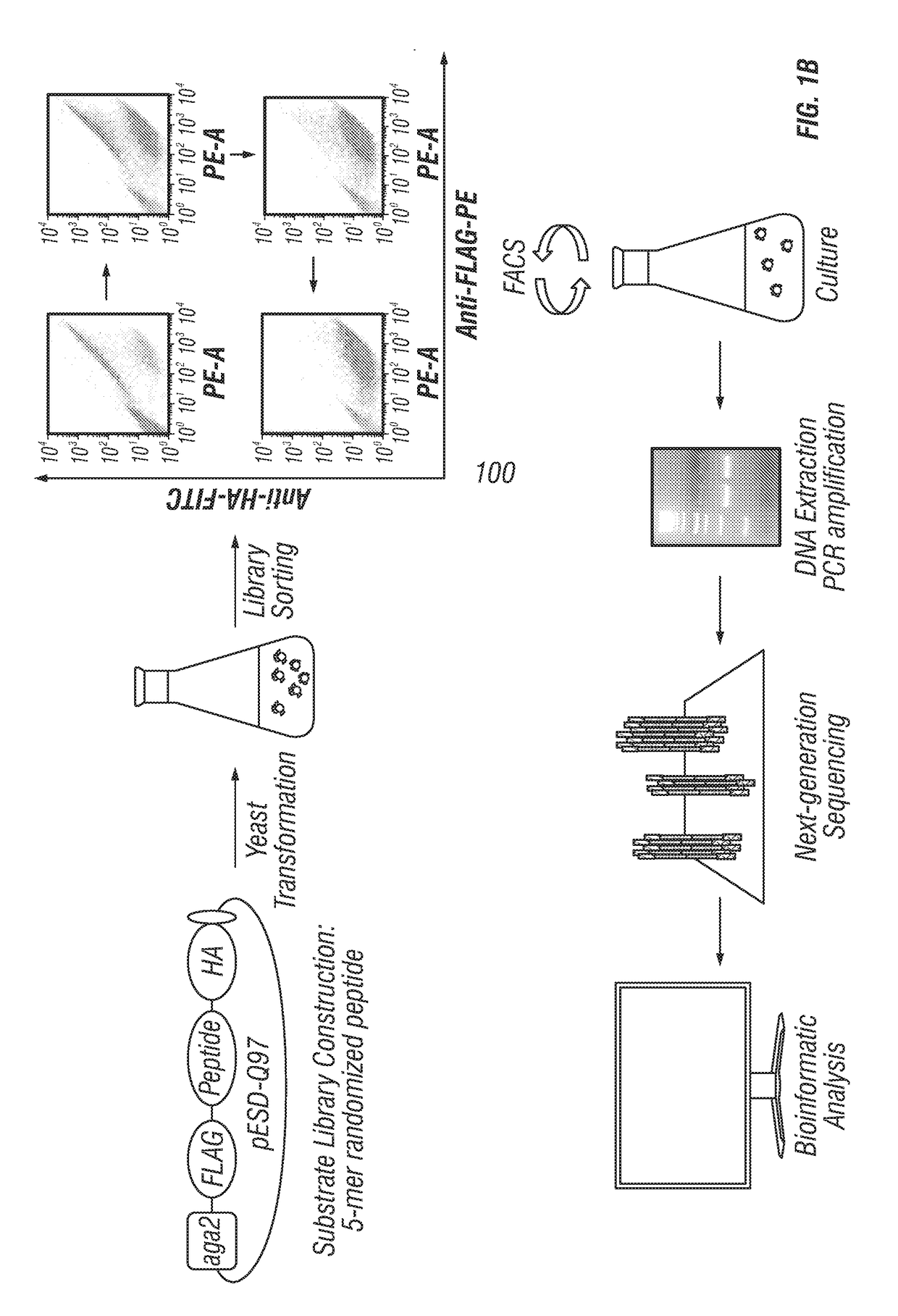
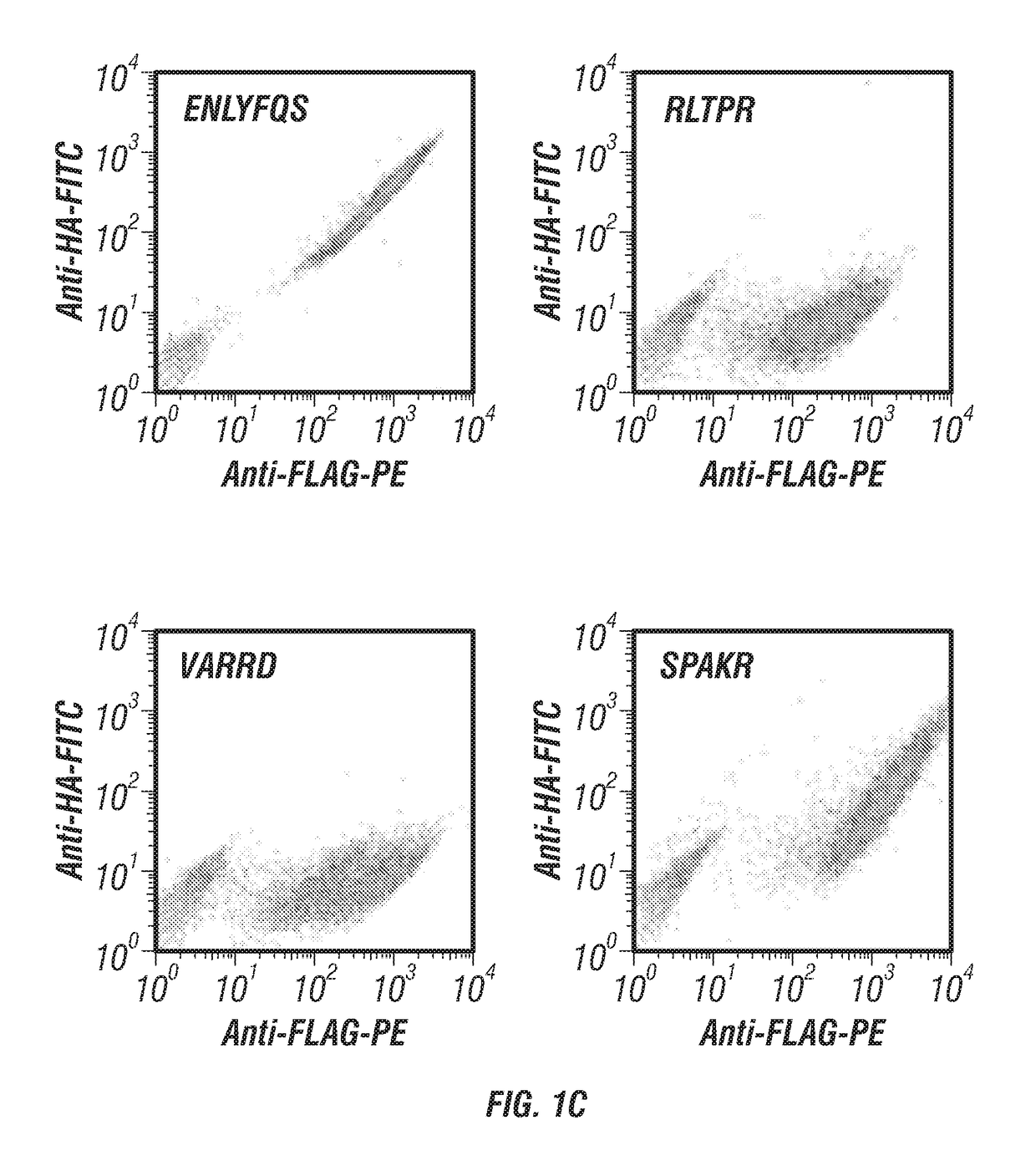
Provided are improved methods for identifying the substrate recognition specificity or activity of a protease, convertase (sortase), or kinase. In some embodiments, methods are provided for identifying the endogenous protease or convertase cleaving patterns (e.g., “cleaveOme”) inside the secretory pathway of a living cell. Select embodiments involve aspects of yeast endoplasmic reticulum sequestration screening and next generation sequencing. Methods of producing polypeptides in Kex2 knockout yeast are also provided.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
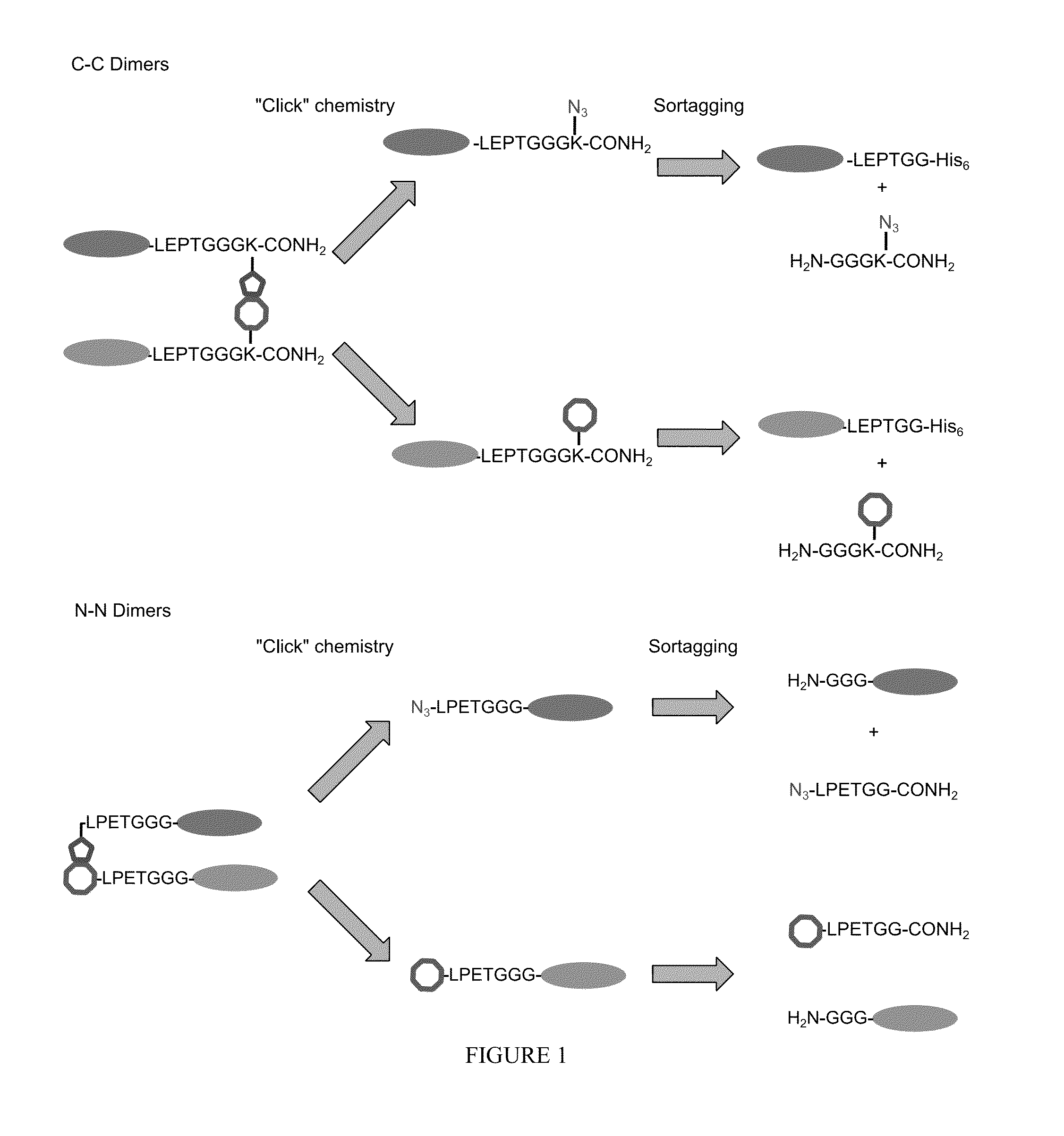
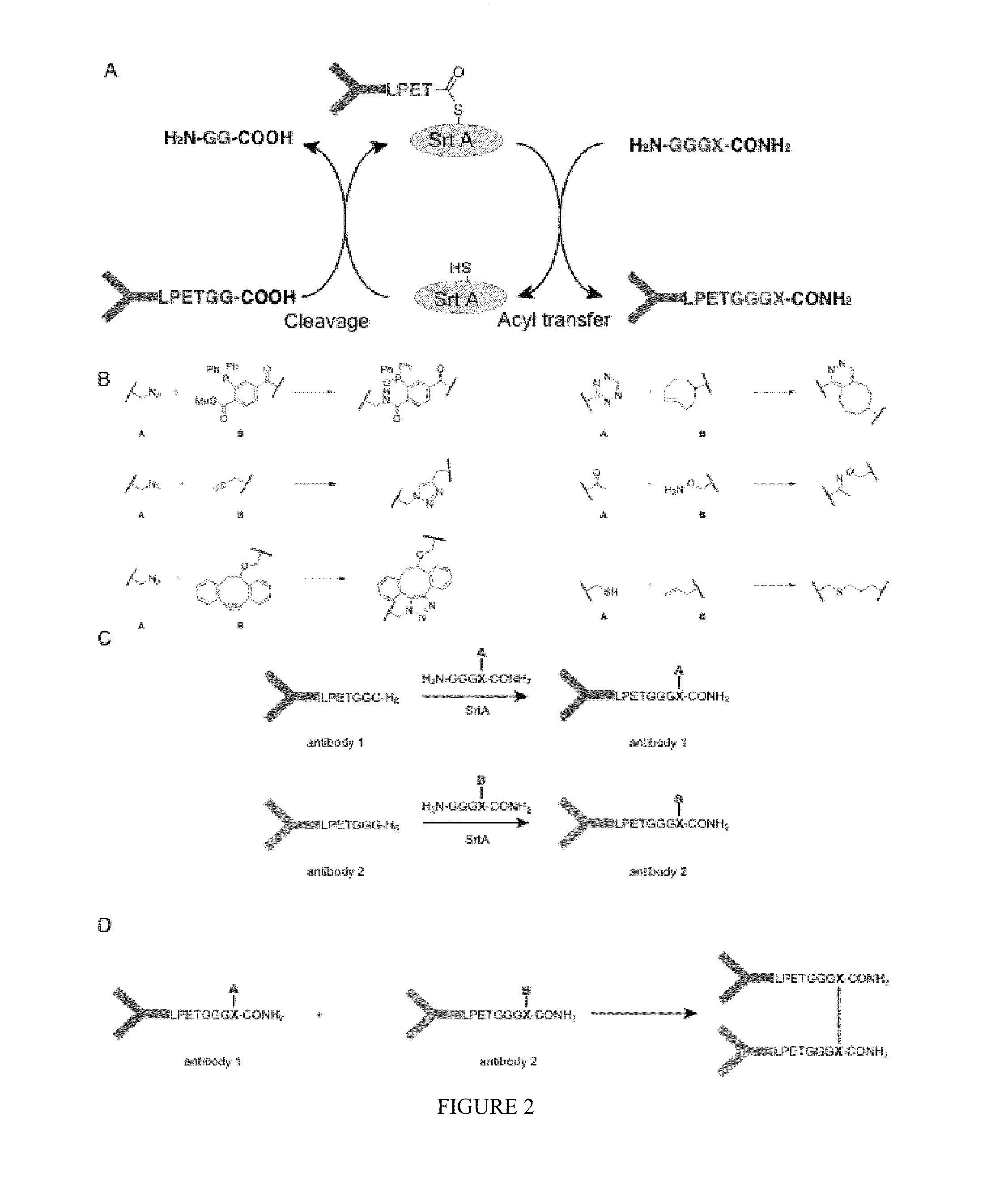
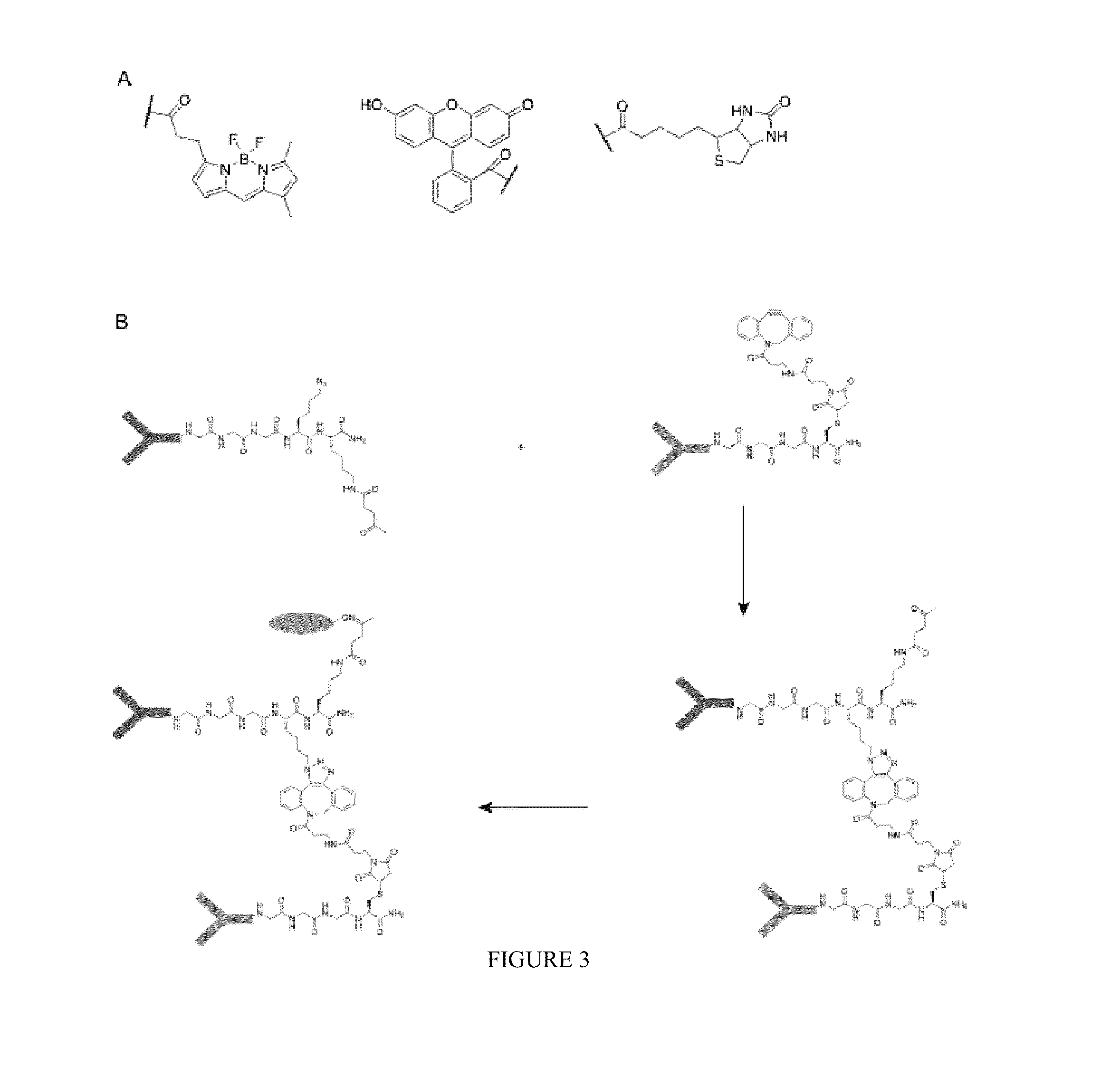
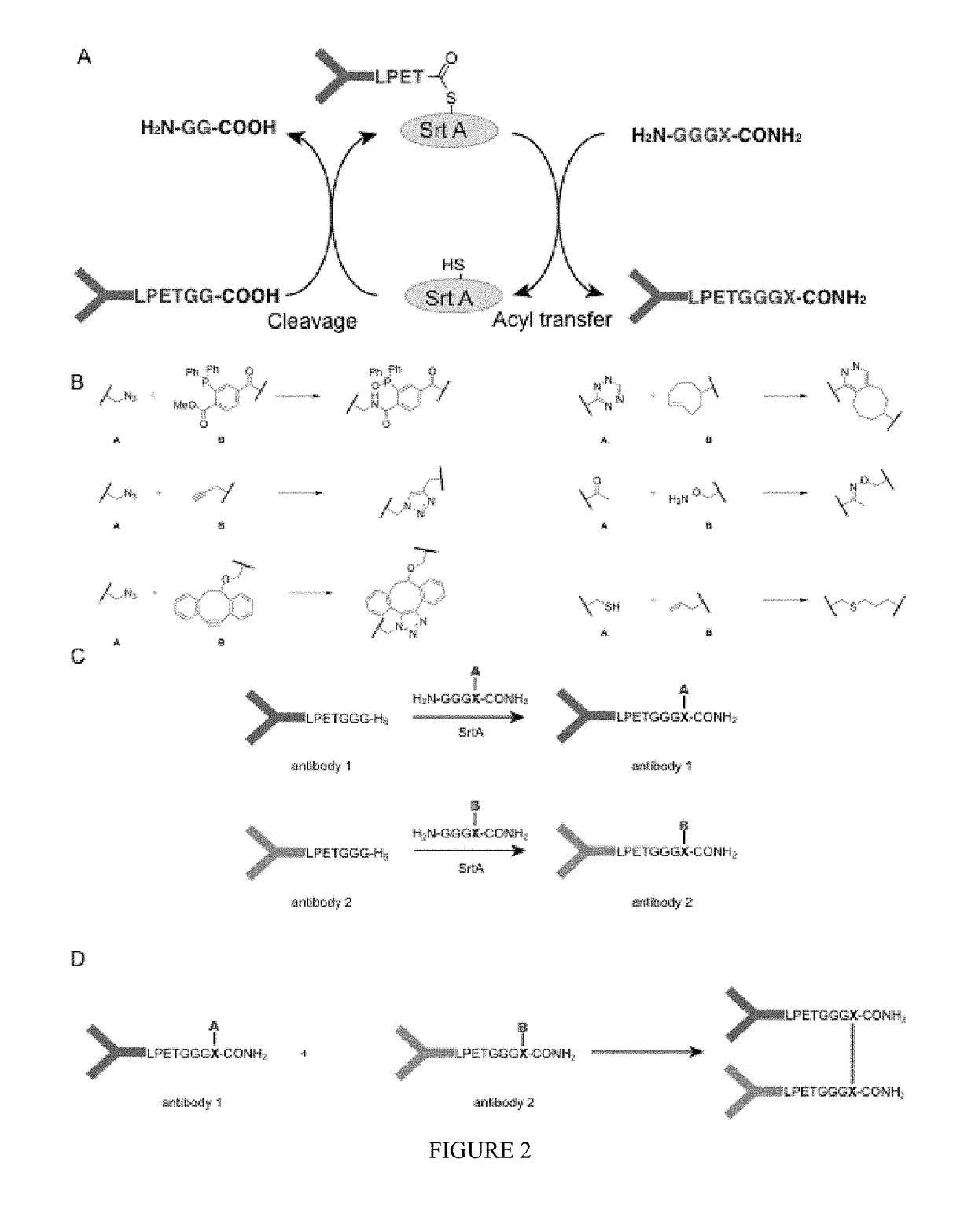
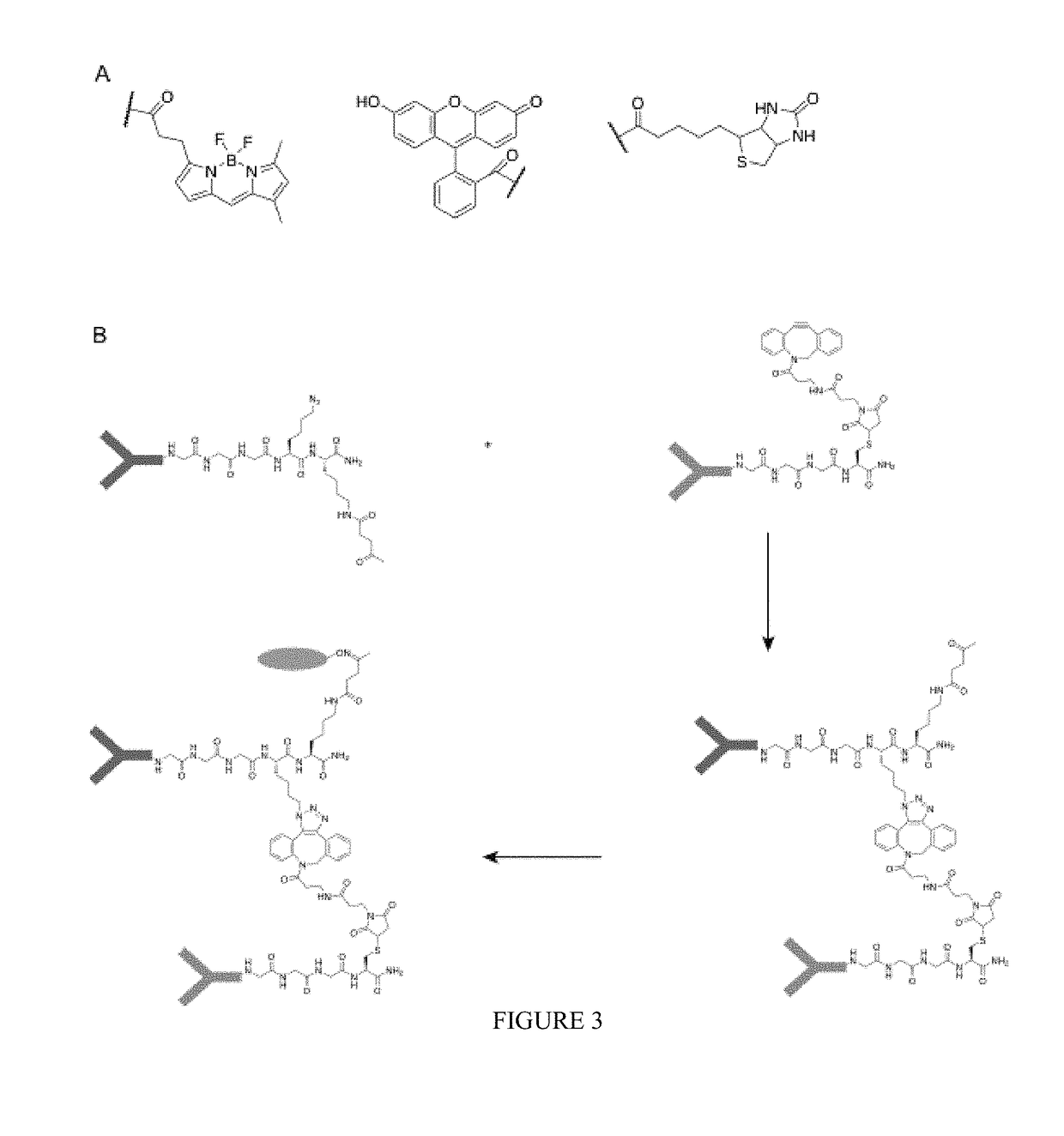
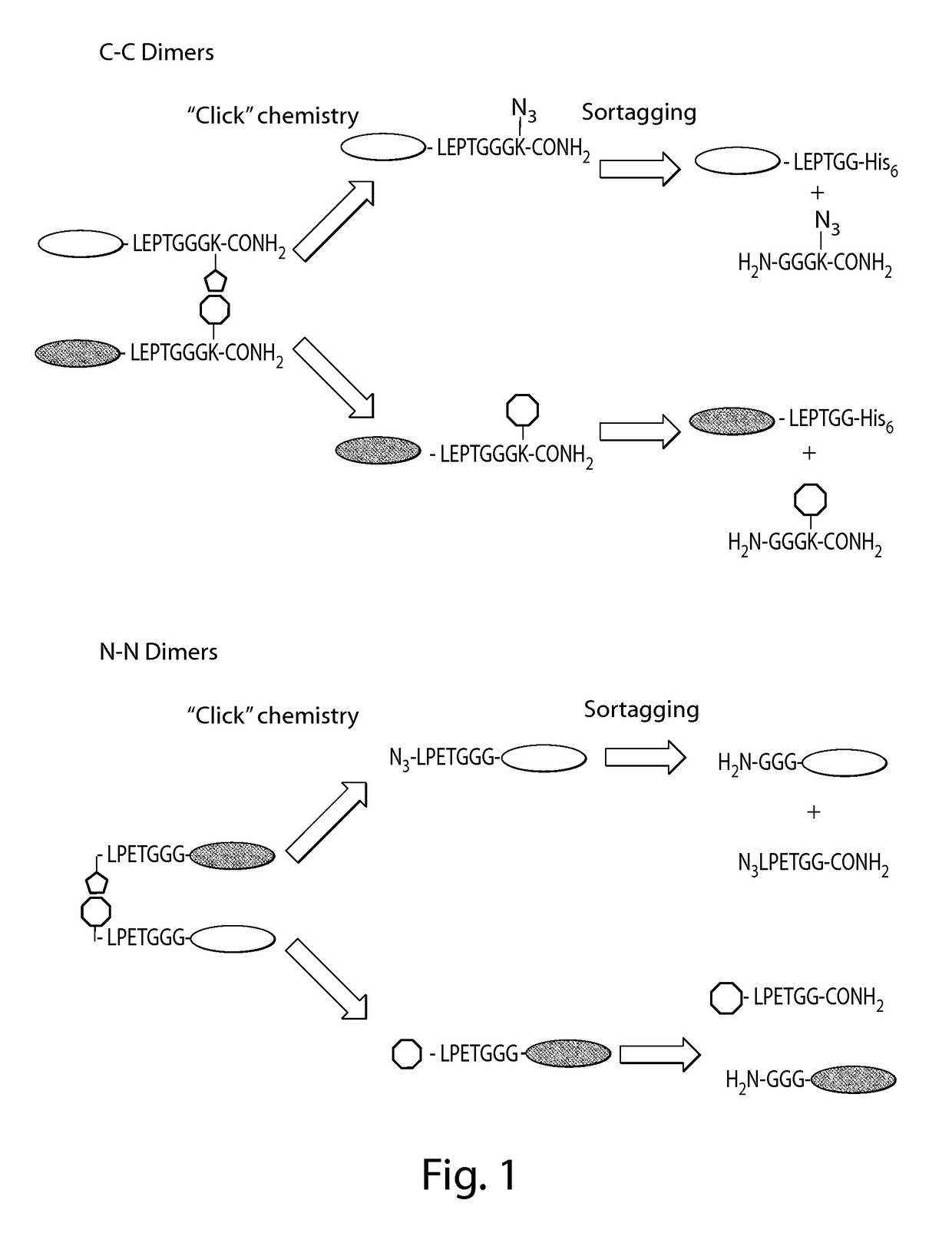
Using sortases to install click chemistry handles for protein ligation
Methods and reagents for the installation of click chemistry handles on target proteins are provided, as well as modified proteins comprising click chemistry handles. Further, chimeric proteins, for example, bi-specific antibodies, that comprise two proteins conjugated via click chemistry, as well as methods for their generation and use are disclosed herein.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
In vitro production of red blood cells with sortaggable proteins
ActiveUS20180280440A1Genetically modified cellsMammal material medical ingredientsRed CellProtein methods
Methods for the in vitro production of enucleated red blood cells and the enucleated red blood cells thus prepared are provided. Such enucleated red blood cells may express a sortaggable surface protein, which allows for surface modification in the presence of a sortase. Also described herein are surface modified enucleated red blood cells, e.g., conjugated with an agent of interest such as a peptide, a detectable label, or a chemotherapeutic agent, and uses thereof in delivering the agent to a subject.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Compositions and methods for enhancing production of a biological product
Provided herein are methods, nucleic acids, polypeptides, compositions, and kits relating to the conjugation of a heterologous polypeptide to a molecule of interest during production of the polypeptide in cell culture. In various embodiments, the heterologous polypeptide is linked to a sortase ligation sequence and the molecule of interest is linked to a complementary sortase ligation sequence, such that expression of the heterologous protein in the presence of the molecule of interest and cells expressing a surface-associated sortase with the sortase catalytic domain exposed to the extracellular medium results in ligation of the heterologous polypeptide to the molecule of interest to form a conjugated polypeptide.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARMA INC
Intercellular labeling of ligand-receptor interactions
InactiveUS20180346899A1Facilitate purification and isolationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiological material analysisAntigenT cell
An sortase-mediated intercellular labeling method allowing for tracking ligand-receptor interaction both in vitro and in vivo; and uses thereof for tracking molecule interactions both in vitro and in vivo, identifying modulators of ligand-receptor interaction, identifying potential binding partners of a protein of interest, identifying B cells expressing high affinity B cell receptors to antigens, and identifying the antigen to which a T cell of interest binds.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
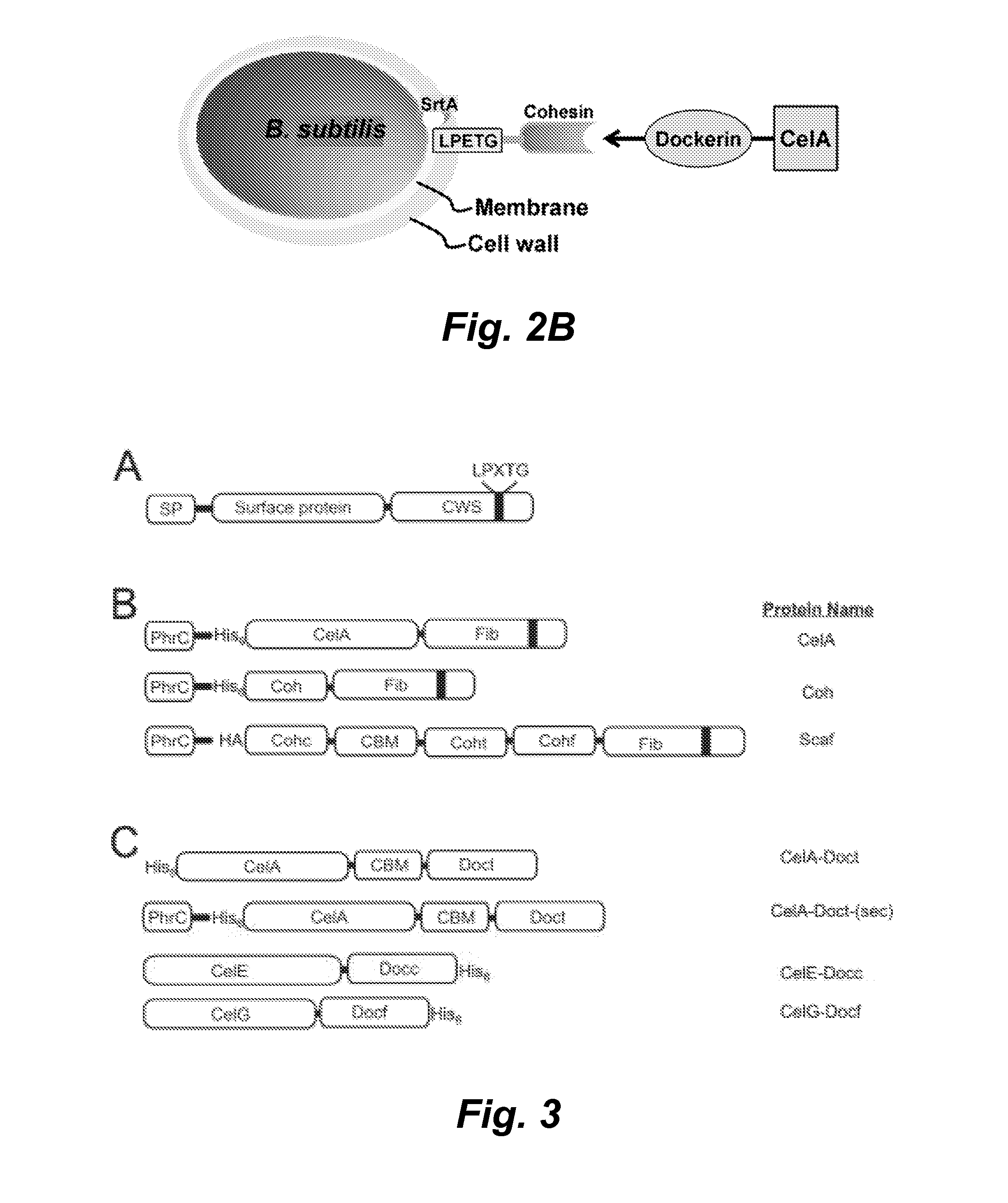
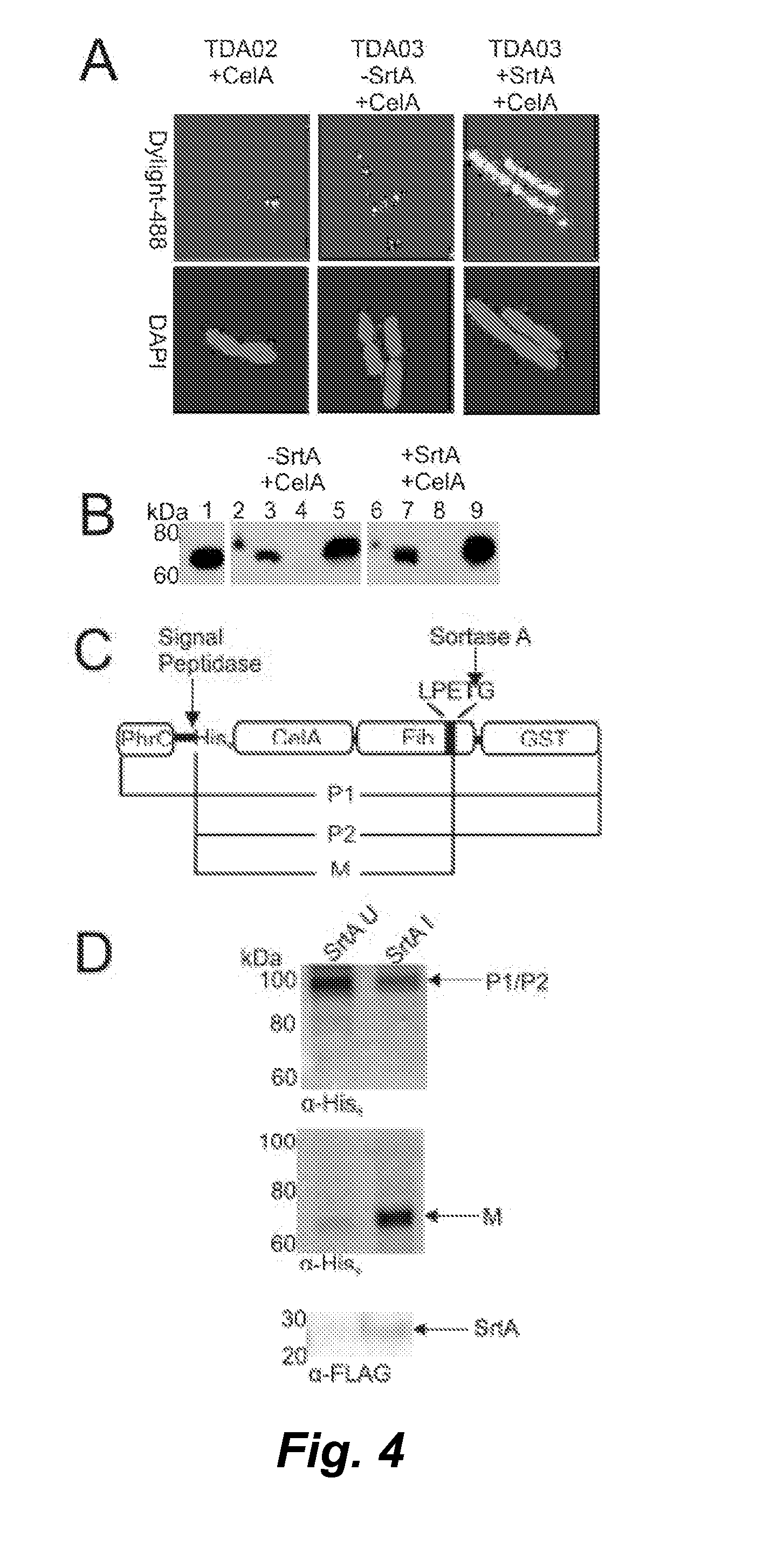
Surface display of cellulolytic enzymes and enzyme complexes on gram-positive microorganisms
InactiveUS20140147873A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBacteroidesSurface display
In various embodiments a system is provided that displays heterologous proteins on the surface of a Gram-positive microorganism. In certain embodiments the system displays proteins using a sortase transpeptidase to covalently anchor proteins to the cell wall of the microbe. Novel bacterial strains are provided to exploit this system to display cellulase enzymes and multi-enzyme complexes on the surface of Gram-positive microorganisms (e.g., Bacillus subtilis) through their non-covalent interaction with a scaffoldin protein that is covalently anchored to the cell wall by the sortase transpeptidase. The surface displayed protein complexes contain enzymes capable of degrading cellulose into its component sugars at accelerated rates as compared to solutions of purified enzymes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Proximity-based sortase-mediated protein purification and ligation
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
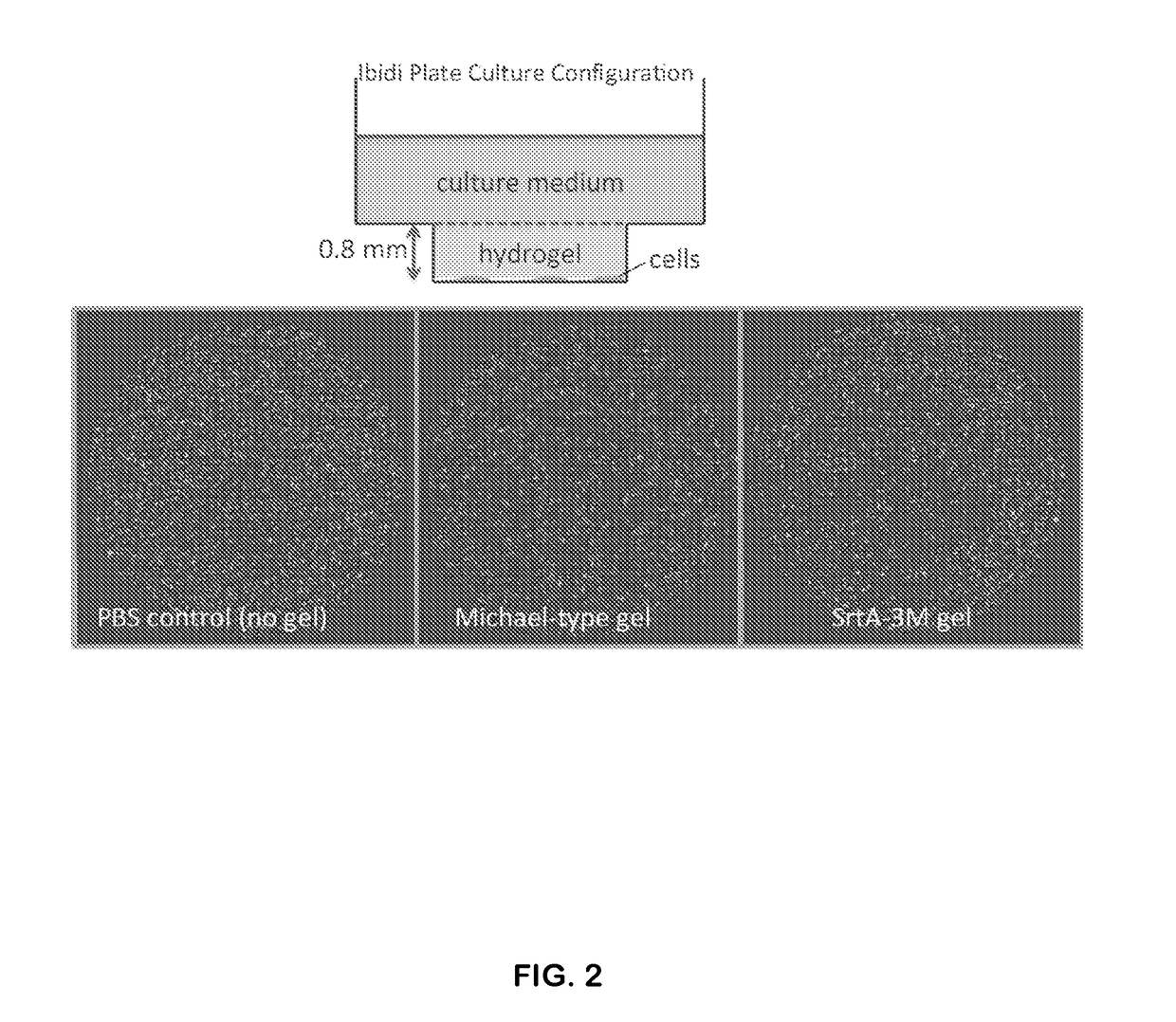
Hydrogel Comprising A Scaffold Macromer Crosslinked With A Peptide And A Recognition Motif
InactiveUS20180010091A1Accurate analysisAccurate interpretationPeptide/protein ingredientsOintment deliveryCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
Methods of forming, dissolving, and functionalizing an extracellular matrix gel on demand based on cross-linking, modification, and dissolution of hydrogels using transpeptidase (e.g. sortase) are disclosed. Also provided are hydrogels comprising one or more macromers crosslinked to a mixture of peptides, wherein all or a portion of the peptides in the mixture comprise a recognition motif cleavable by a transpeptidase (e.g., sortase).
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Fusion protein and use thereof
ActiveCN111848816APrecise targetingEasy to prepareCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsESA ProteinEffector cell
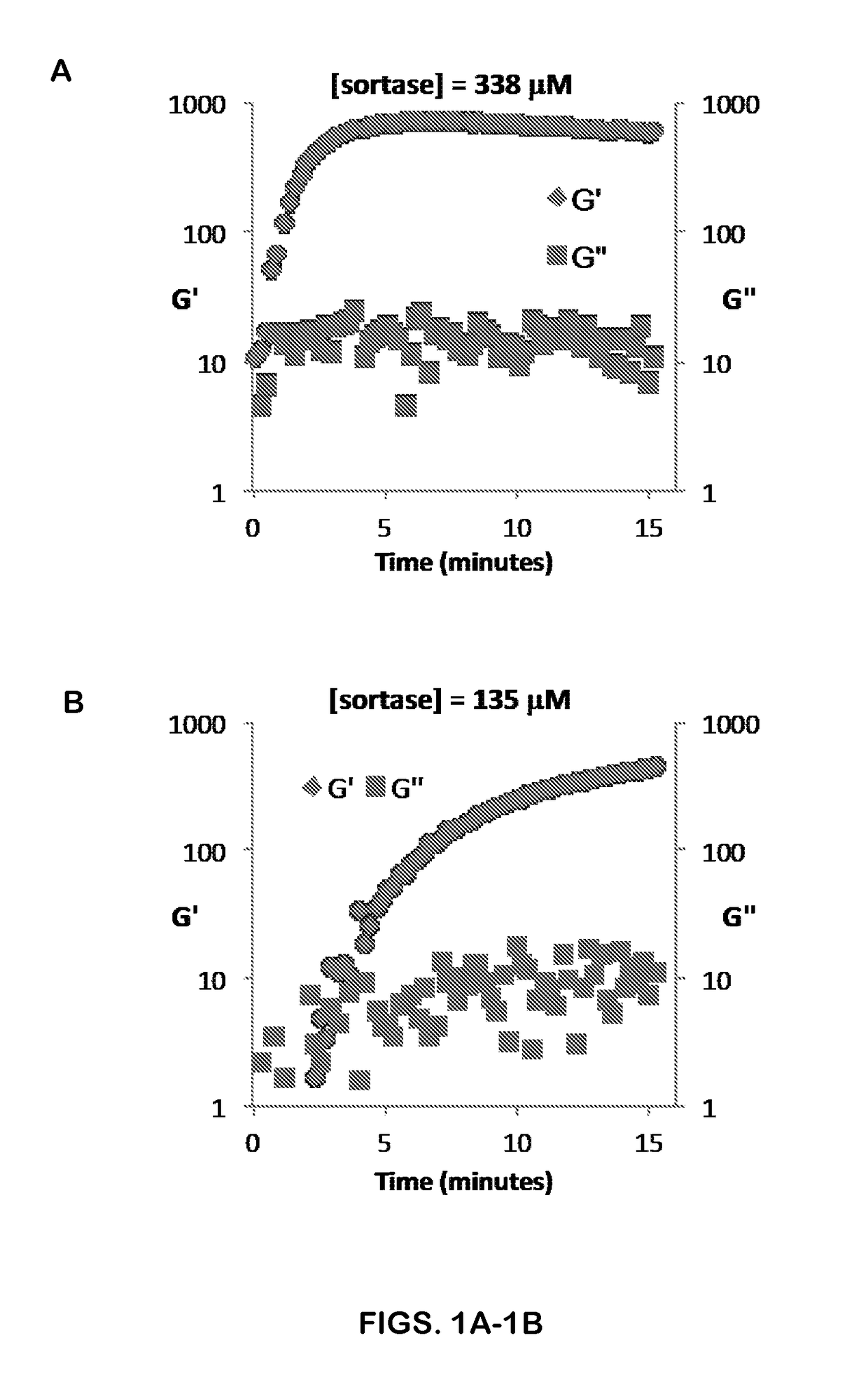
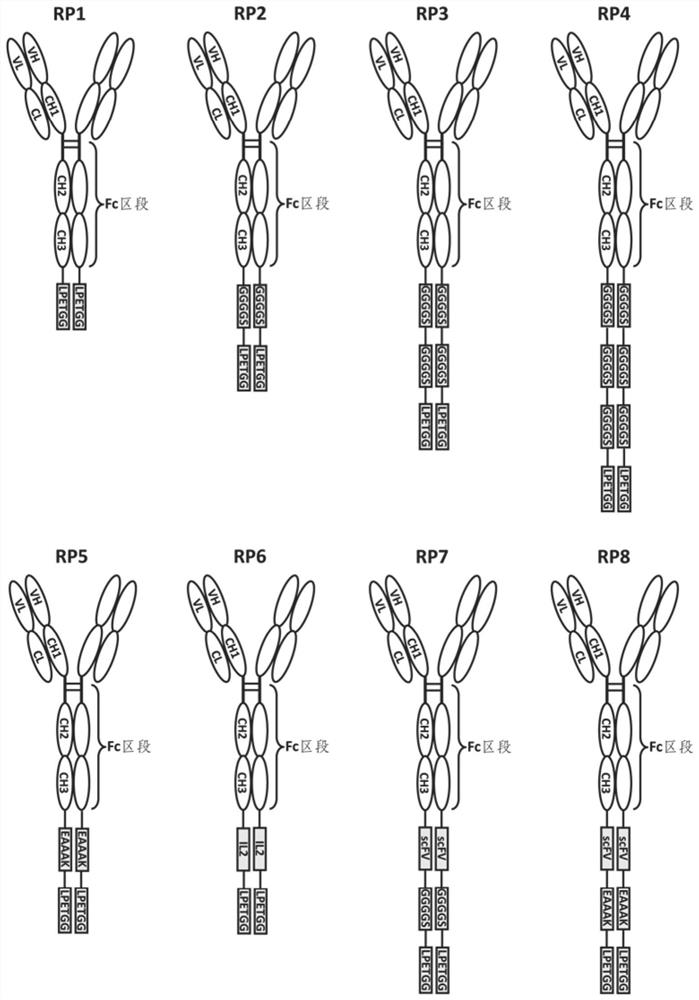
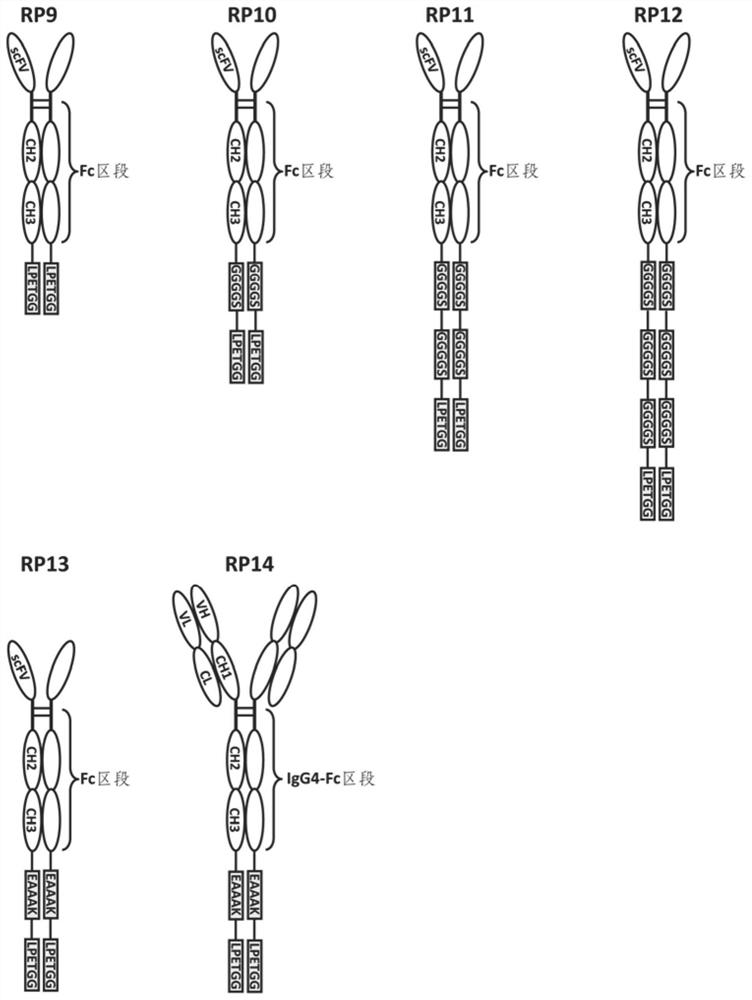
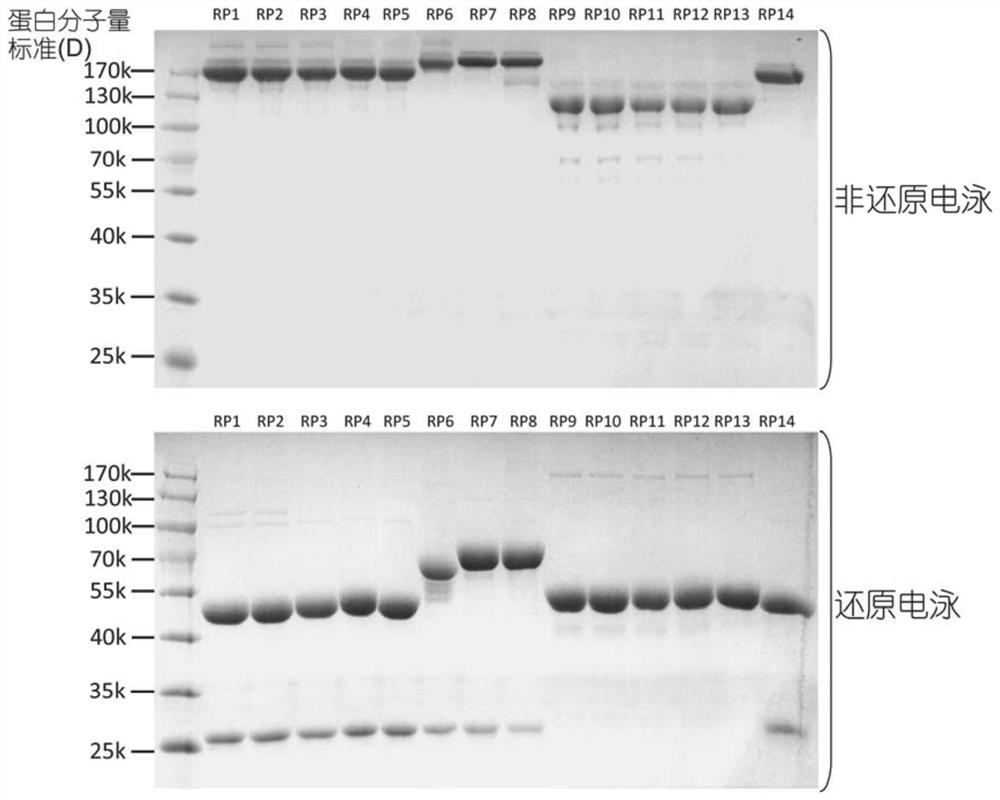
The invention relates to a fusion protein and use thereof. The fusion protein comprises, from N to C terminals, a first moiety, an Fc segment, a linker moiety comprising a moiety selected from the group consisting of a linker and a protein or polypeptide selected from the group consisting of IL2 or scFv, and a substrate moiety of transpeptidase A; the linker comprises a sequence selected from thegroup consisting of (1) (GGGGS) n, wherein when the linker moiety comprises the protein or polypeptide and linker, n>=1; when the linker moiety only comprises the joint, n>=3; and (2) (EAAK) n, n >= 1; the substrate moiety comprises a sequence as shown in LPXTG. The fusion protein can be directly connected to cells to enable the cells to have targeting property, is simpler than an existing methodfor preparing targeting cells through cell transfection, and can also reduce the risk possibly generated by effector cell genome operation at the same time.
Owner:SUPERMAB (BEIJING) BIOTECH CO LTD
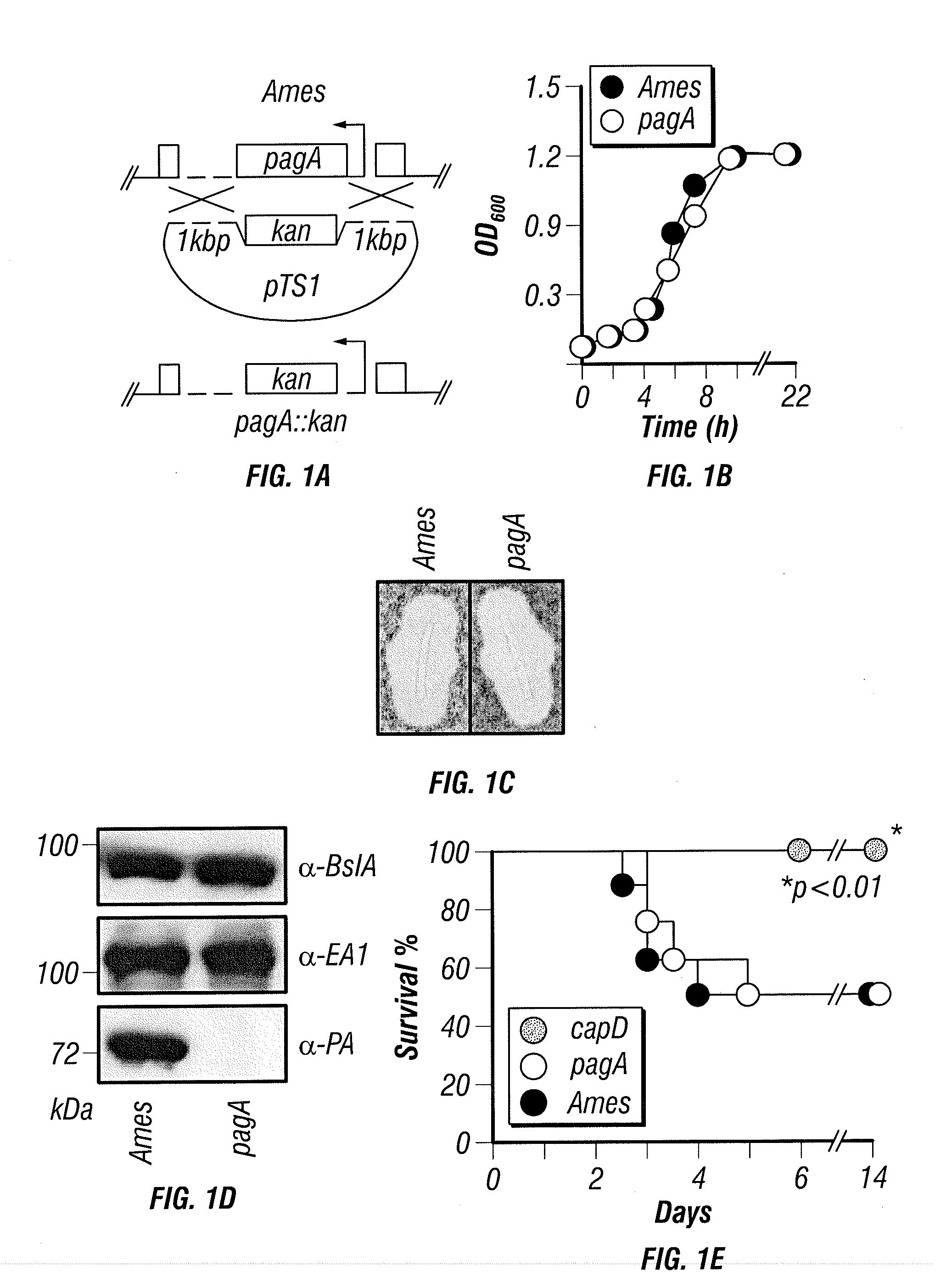
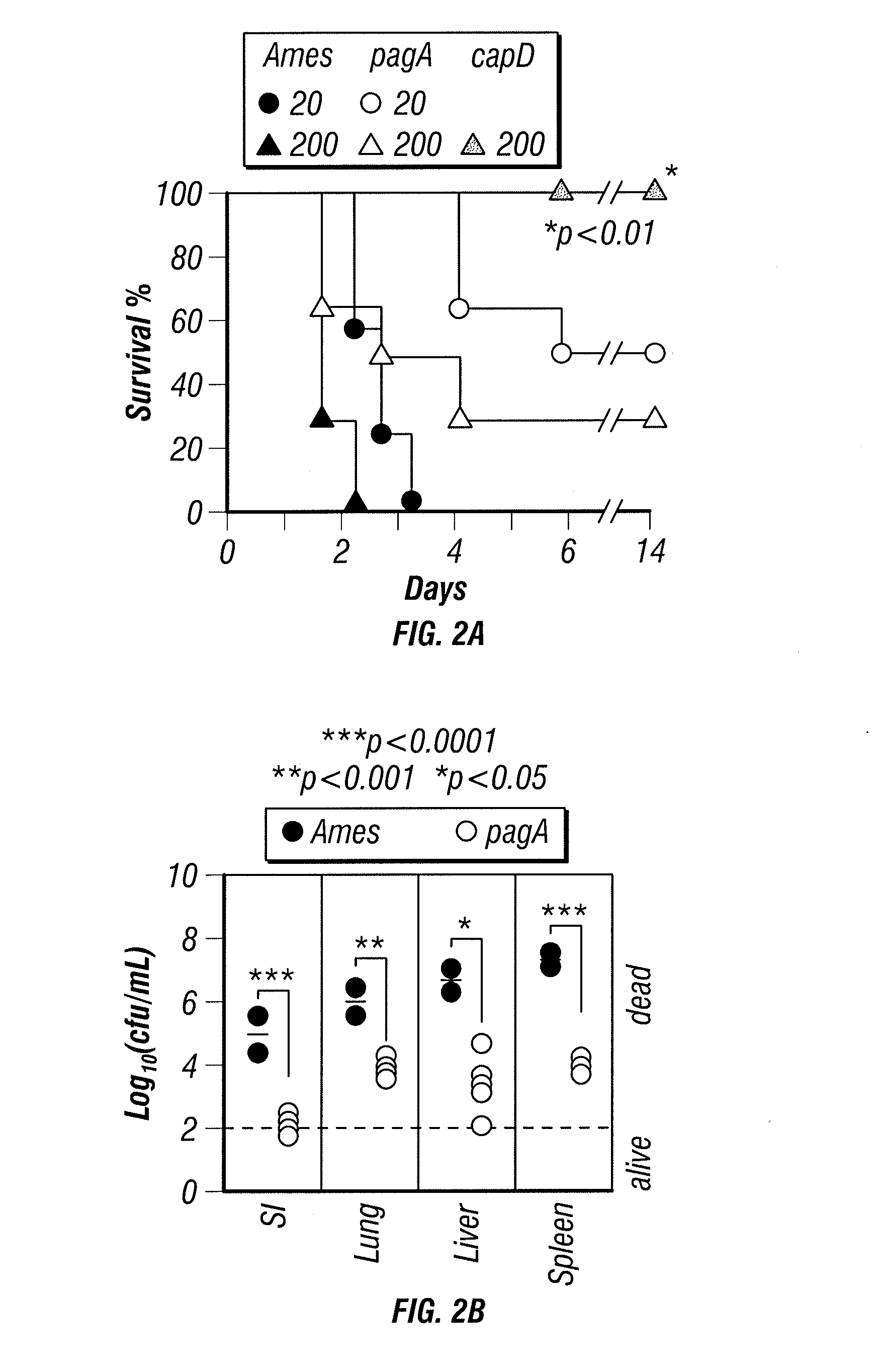
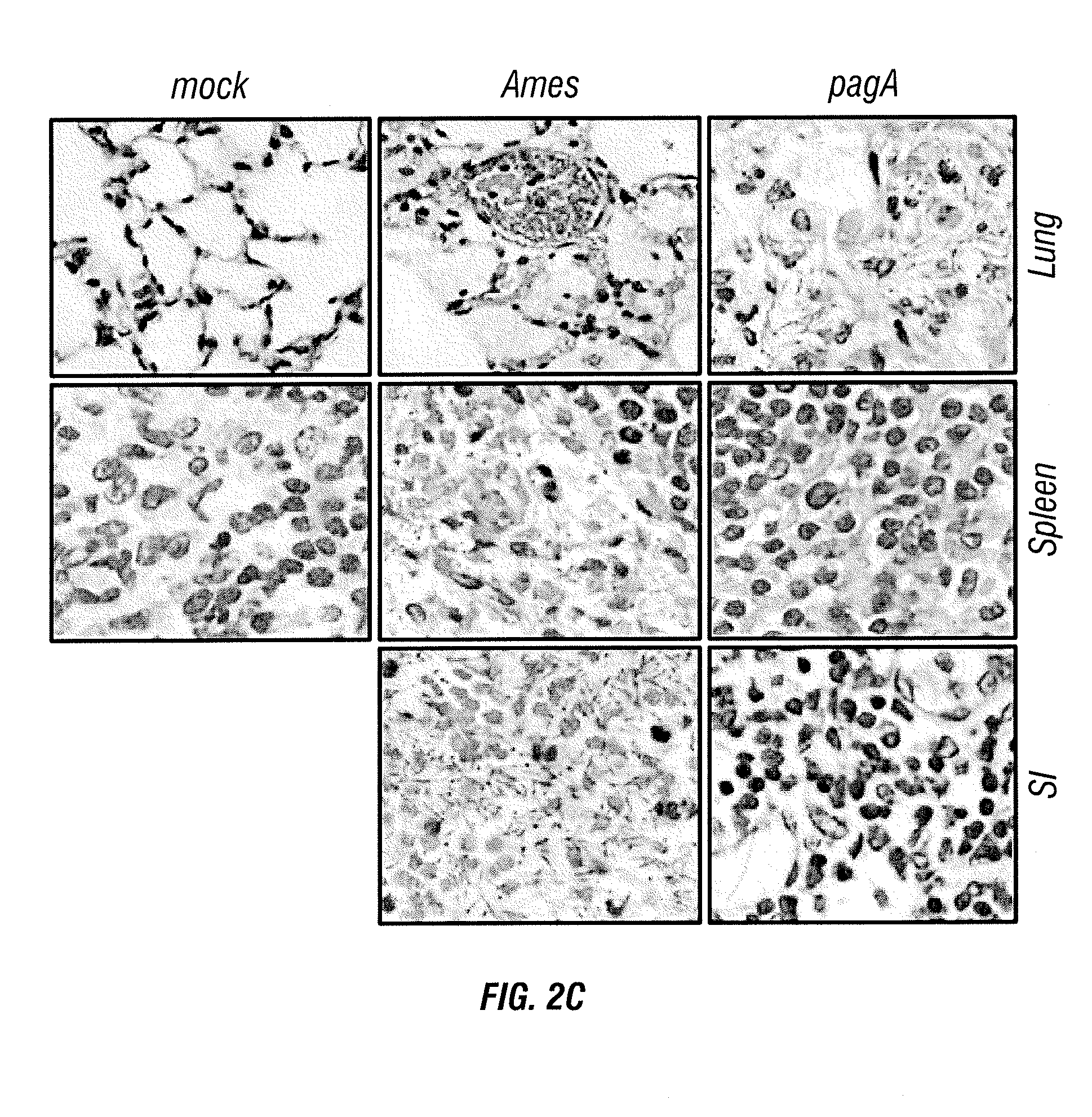
Immunogenic protein conjugates and method for making and using the same
InactiveUS20140302084A1Maximum protectionEnhance immune responseBacterial antigen ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsProtective antigenConjugate vaccine
Production of protein conjugate vaccines by use of transpeptidase enzymes, such as sortase enzymes. For example, homogenous immunoconjugates (e.g., a population of molecules having the same structure) formed by conjugating an antigenic polypeptide and a bacterial capsule component are provided. In certain aspects, methods for generating an immune response to B. anthracis by use of protective antigen-PDGA immunoconjugates are provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com