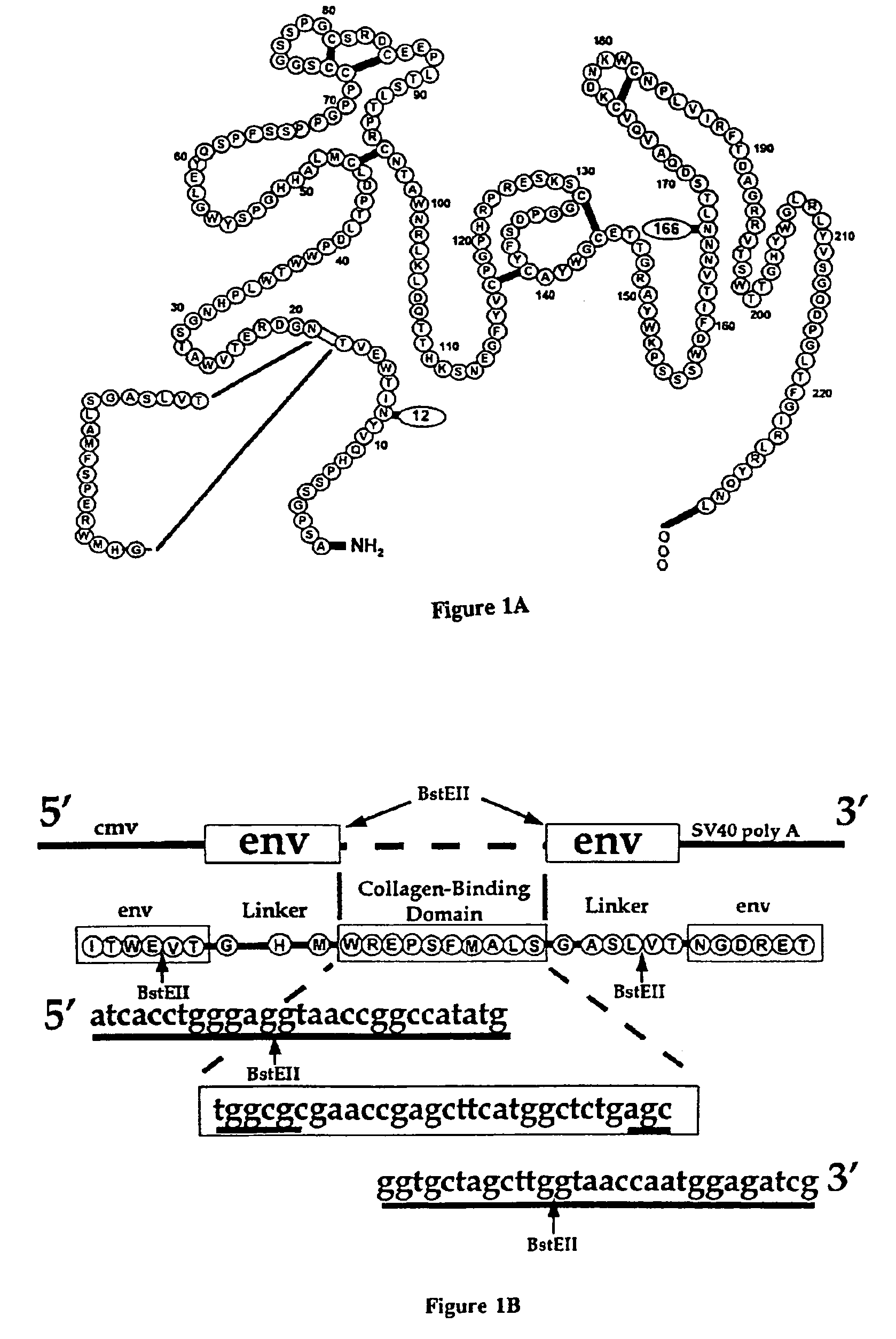
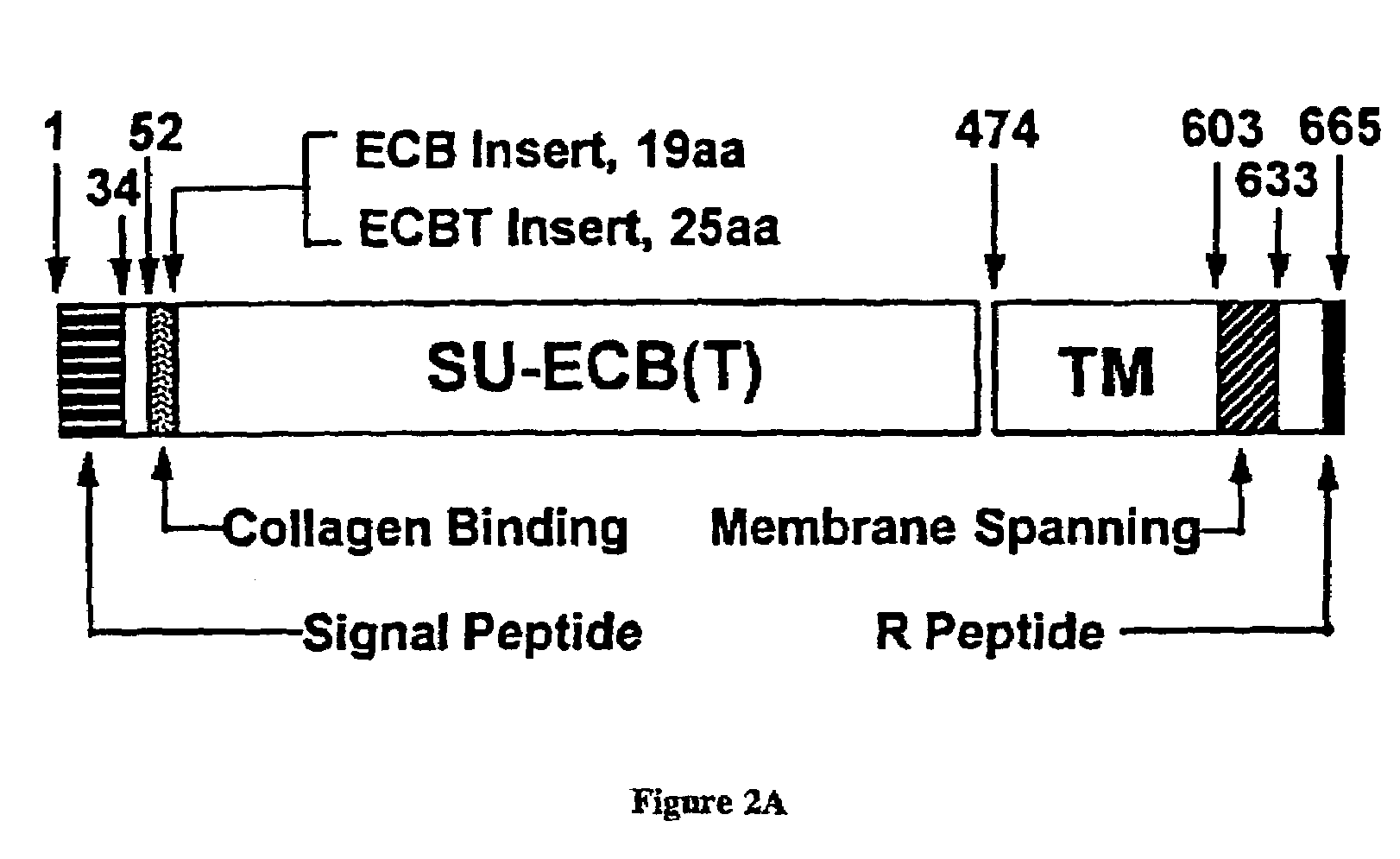
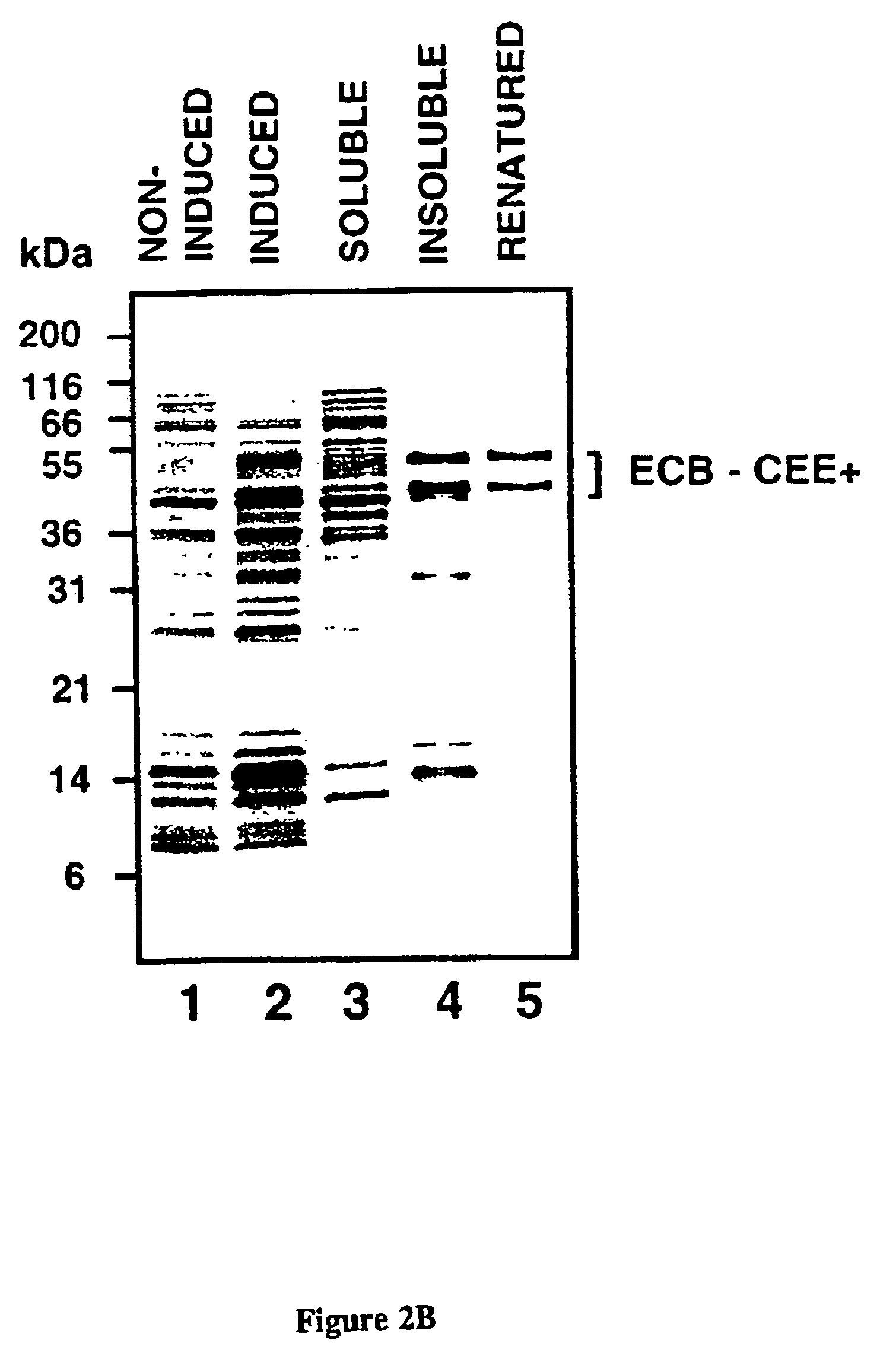
Patents
Literature
579 results about "Surface protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Surface Proteins. Cell surface proteins are proteins that are embedded in or span the layer of cell membranes of more complex organisms. These proteins are integral to the way in which a cell interacts with the environment around it, including other cells. Some of these proteins, especially ones that are exposed to the external side of the membrane,...
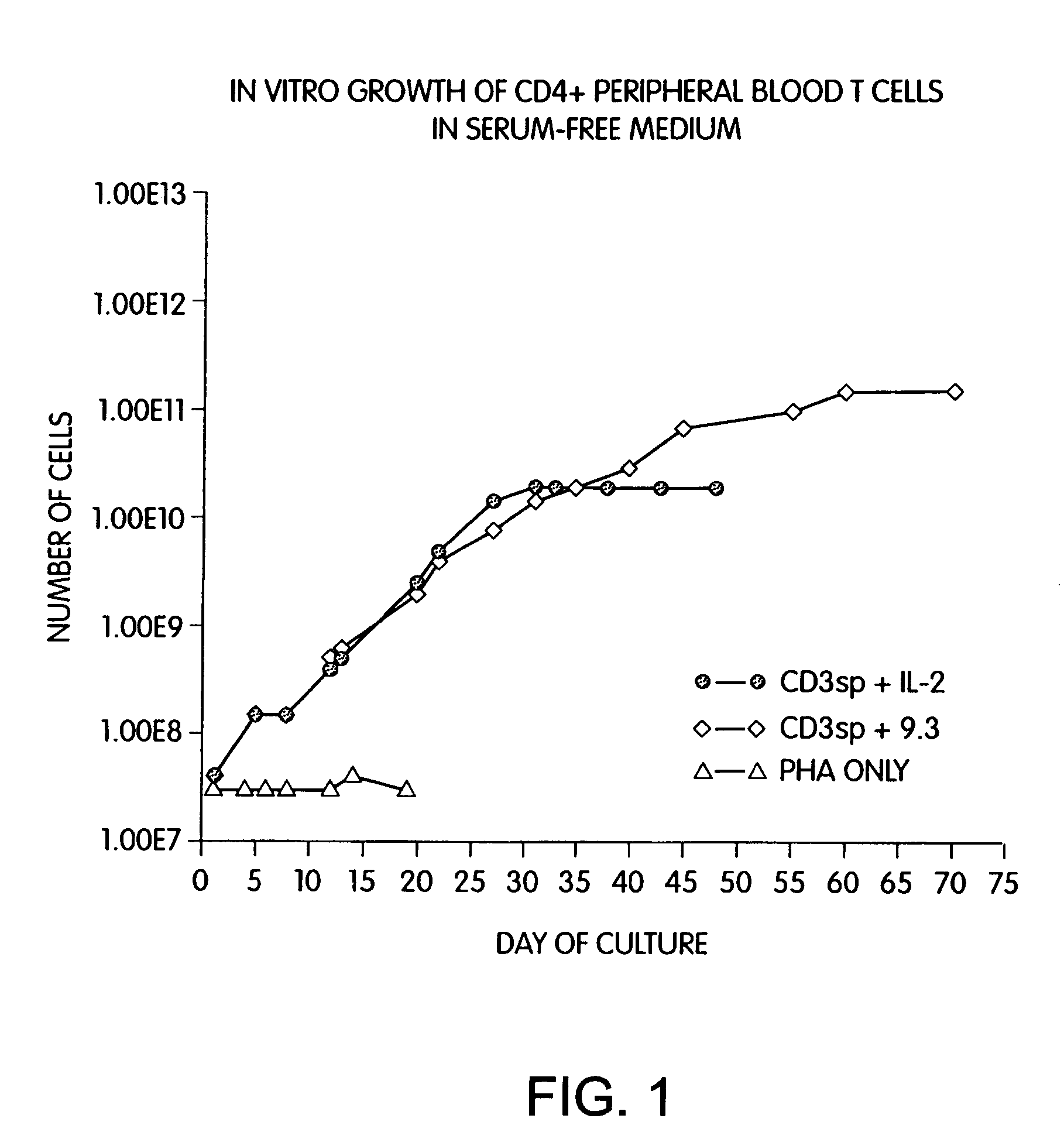
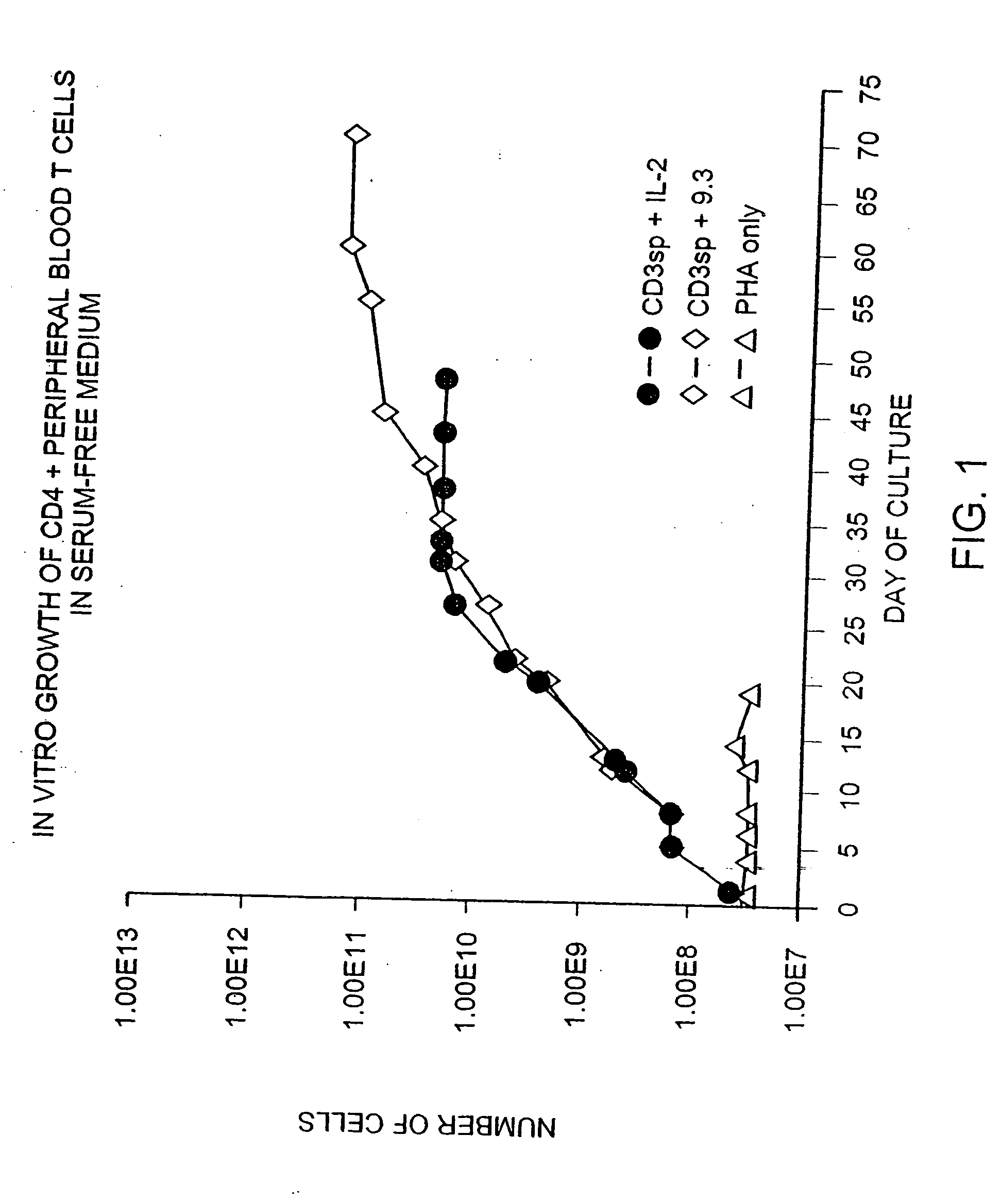
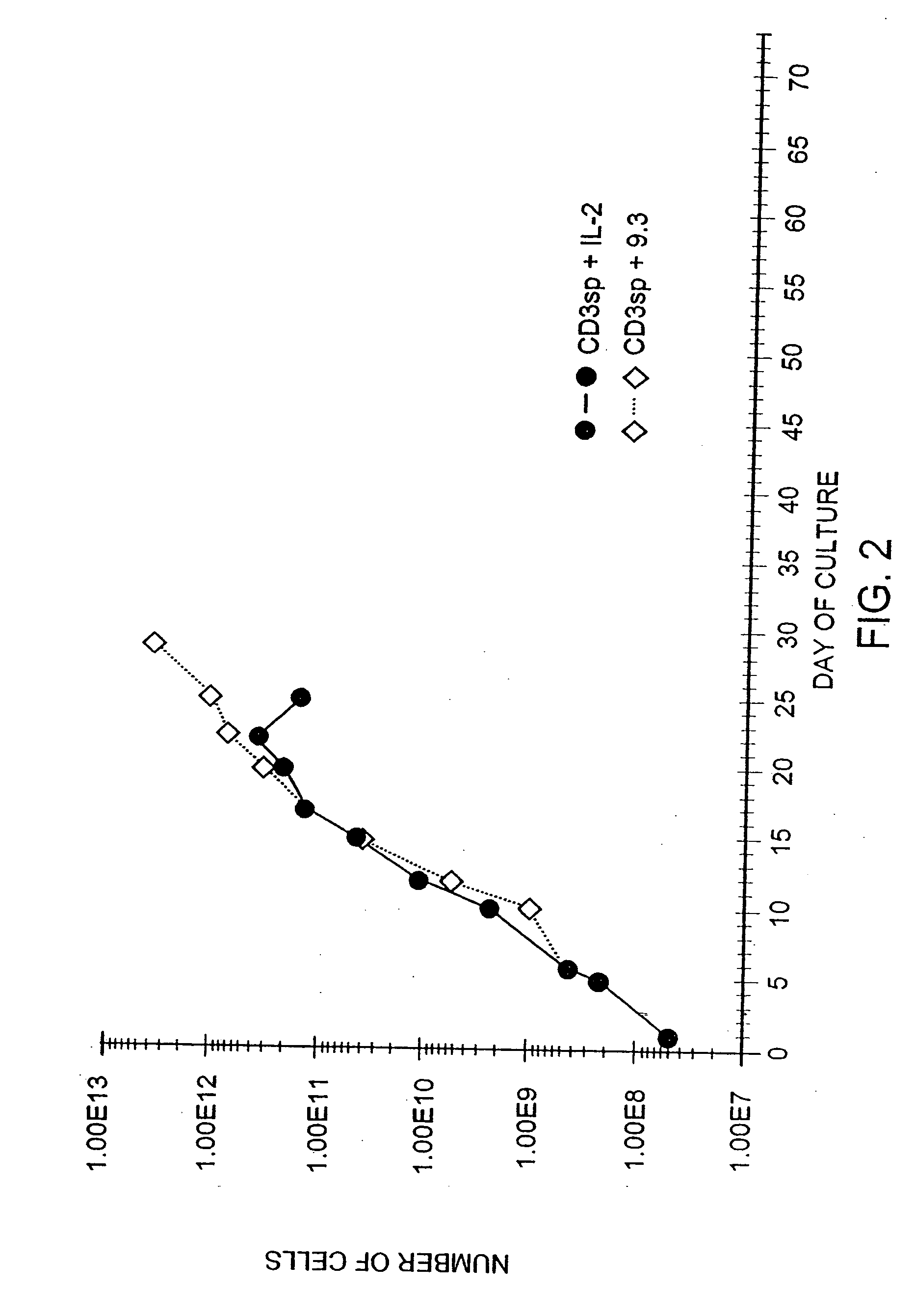
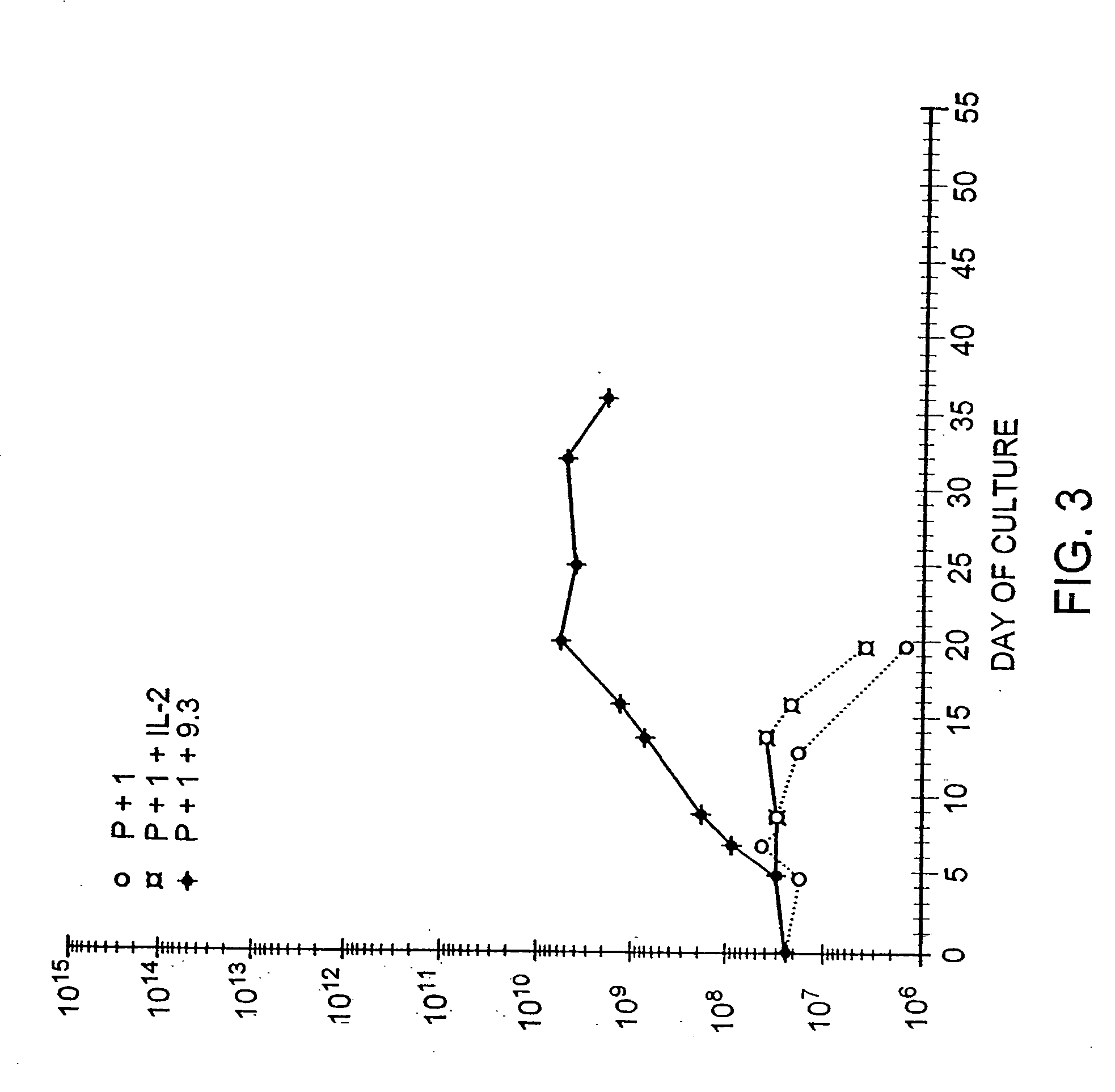
Methods for selectively stimulating proliferation of T cells
InactiveUS6905681B1Increase the number ofVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsAccessory moleculeExogenous growth
Owner:GENETICS INST INC +2
Methods for selectively stimulating proliferation of T cells
InactiveUS6887466B2Expanding population of cellIncrease the number ofVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsAccessory moleculeExogenous growth
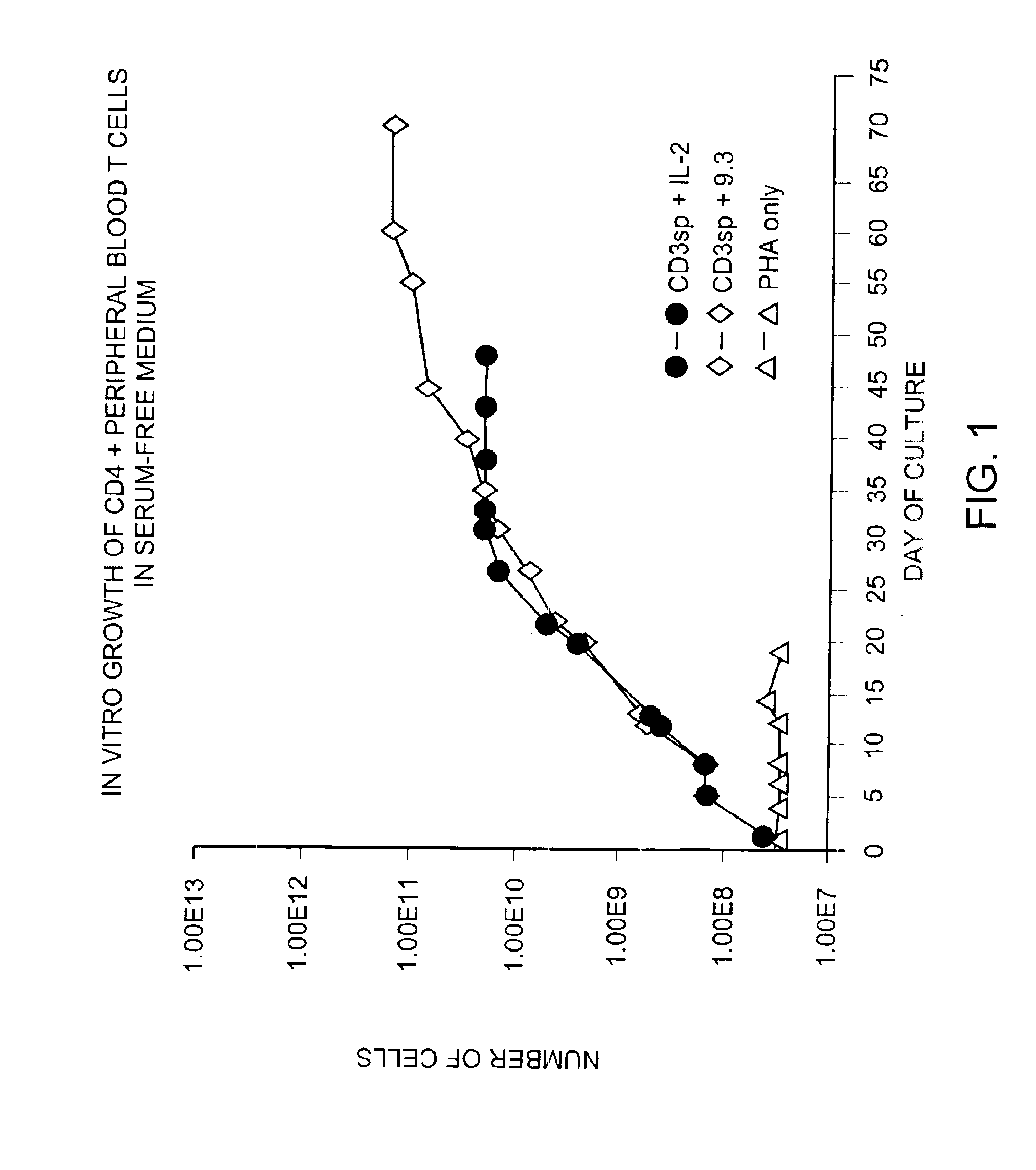
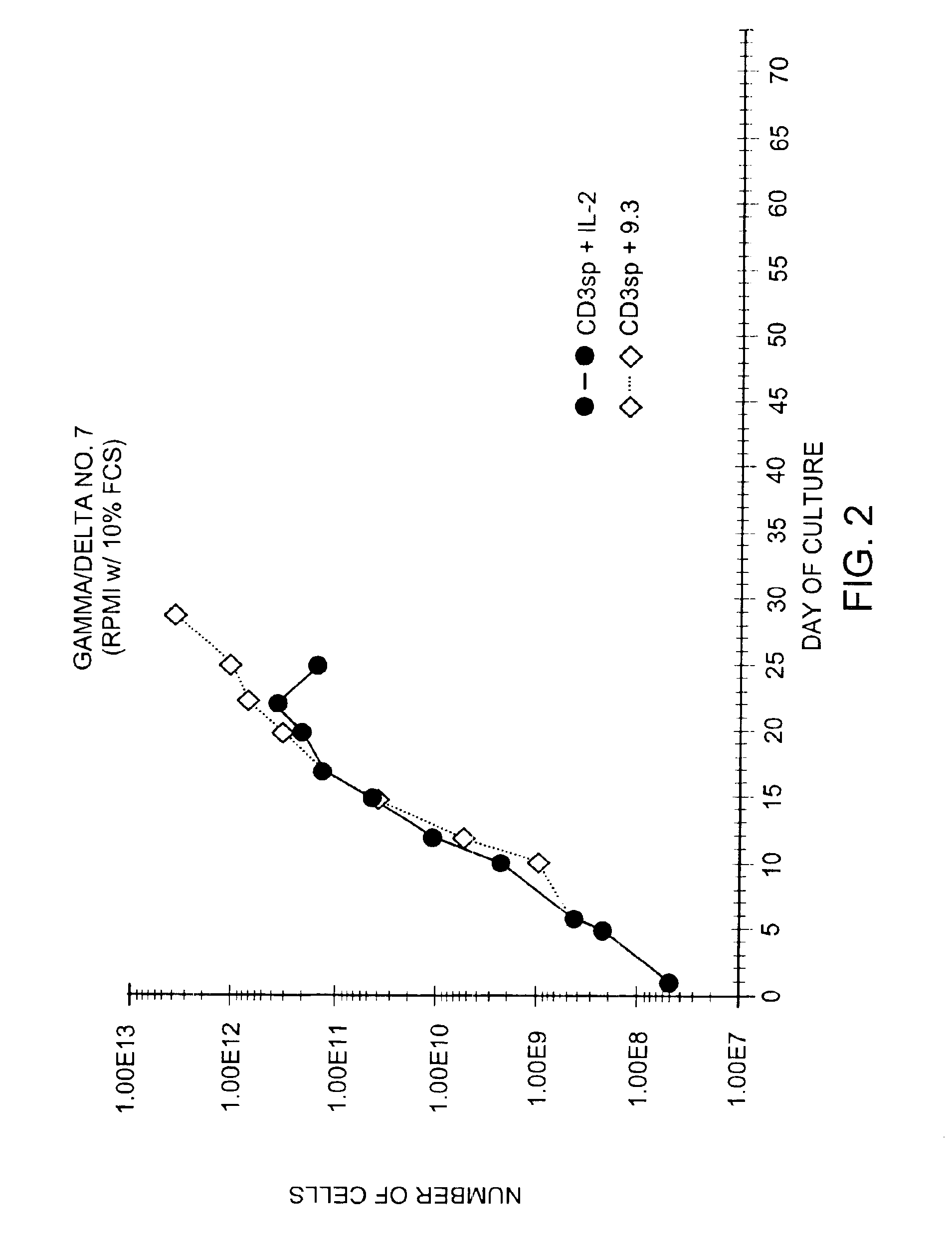
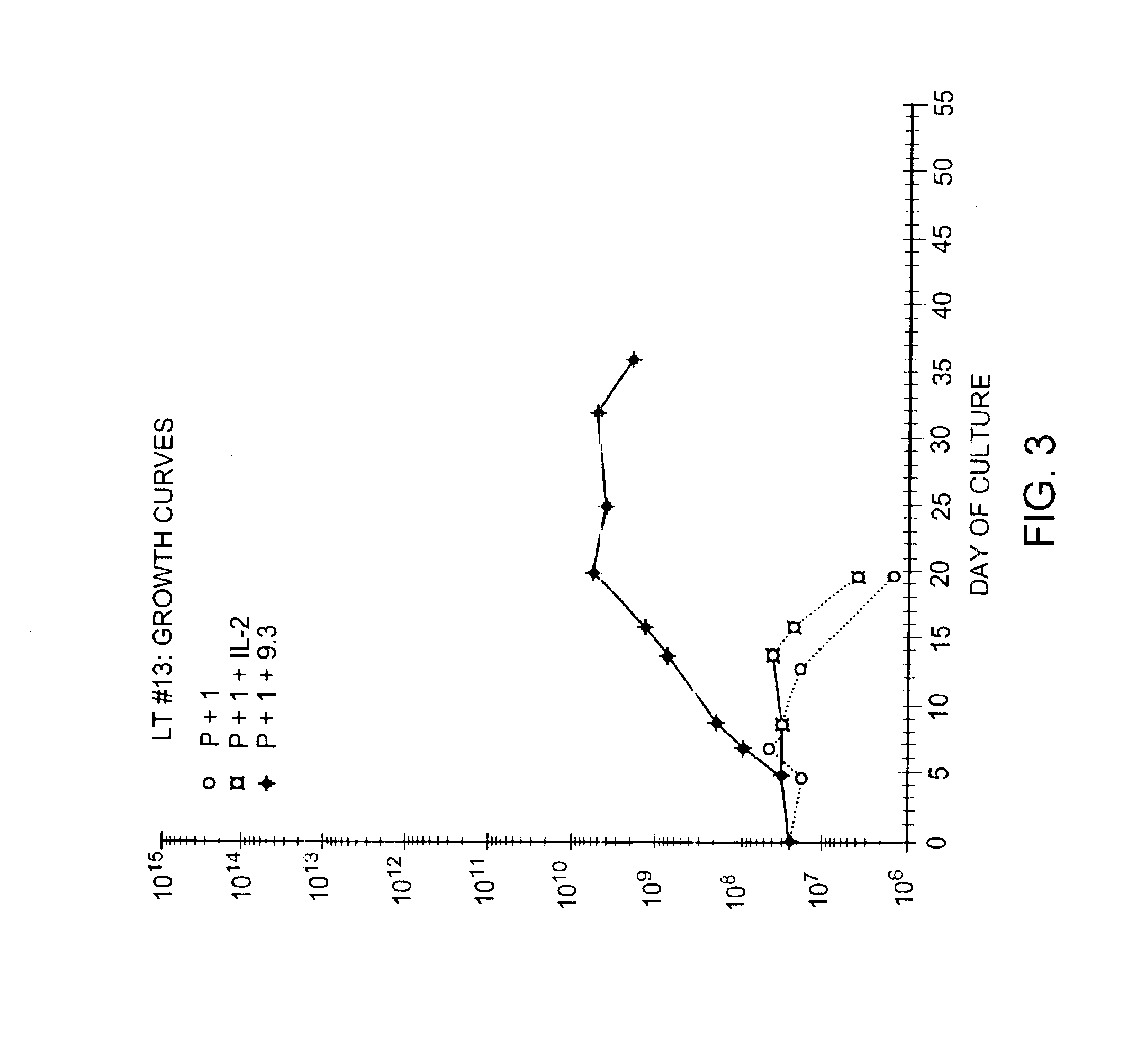
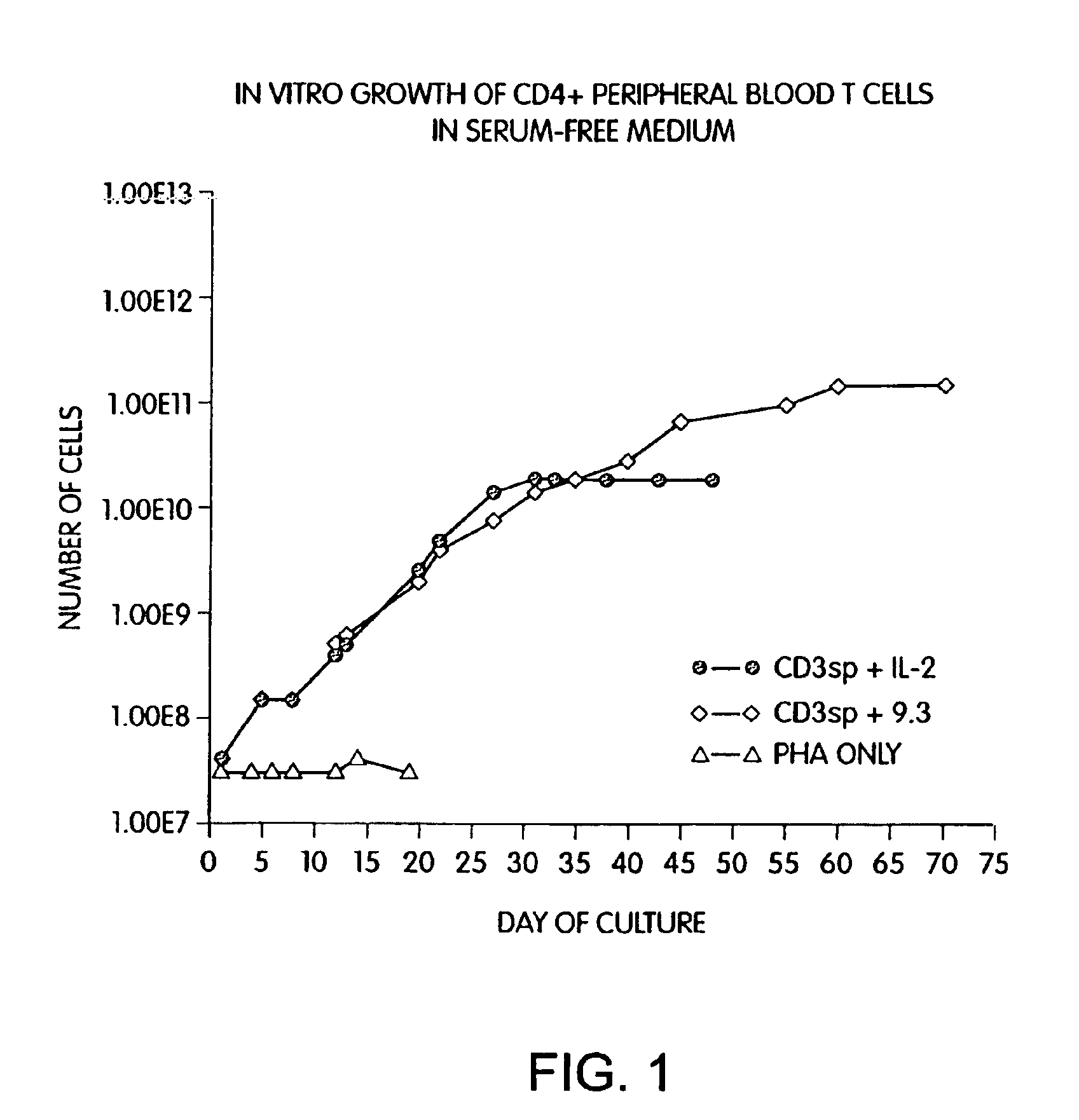
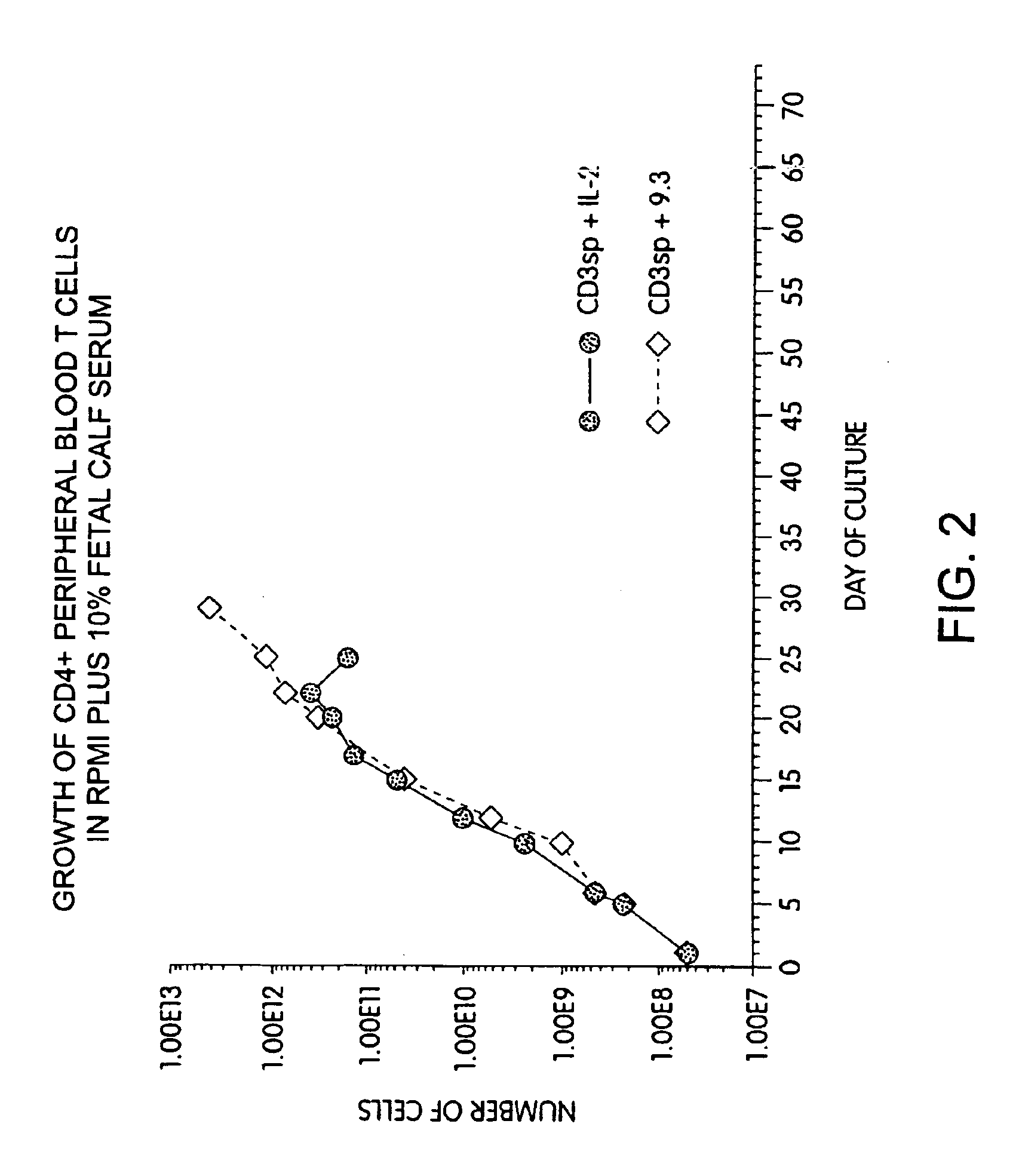
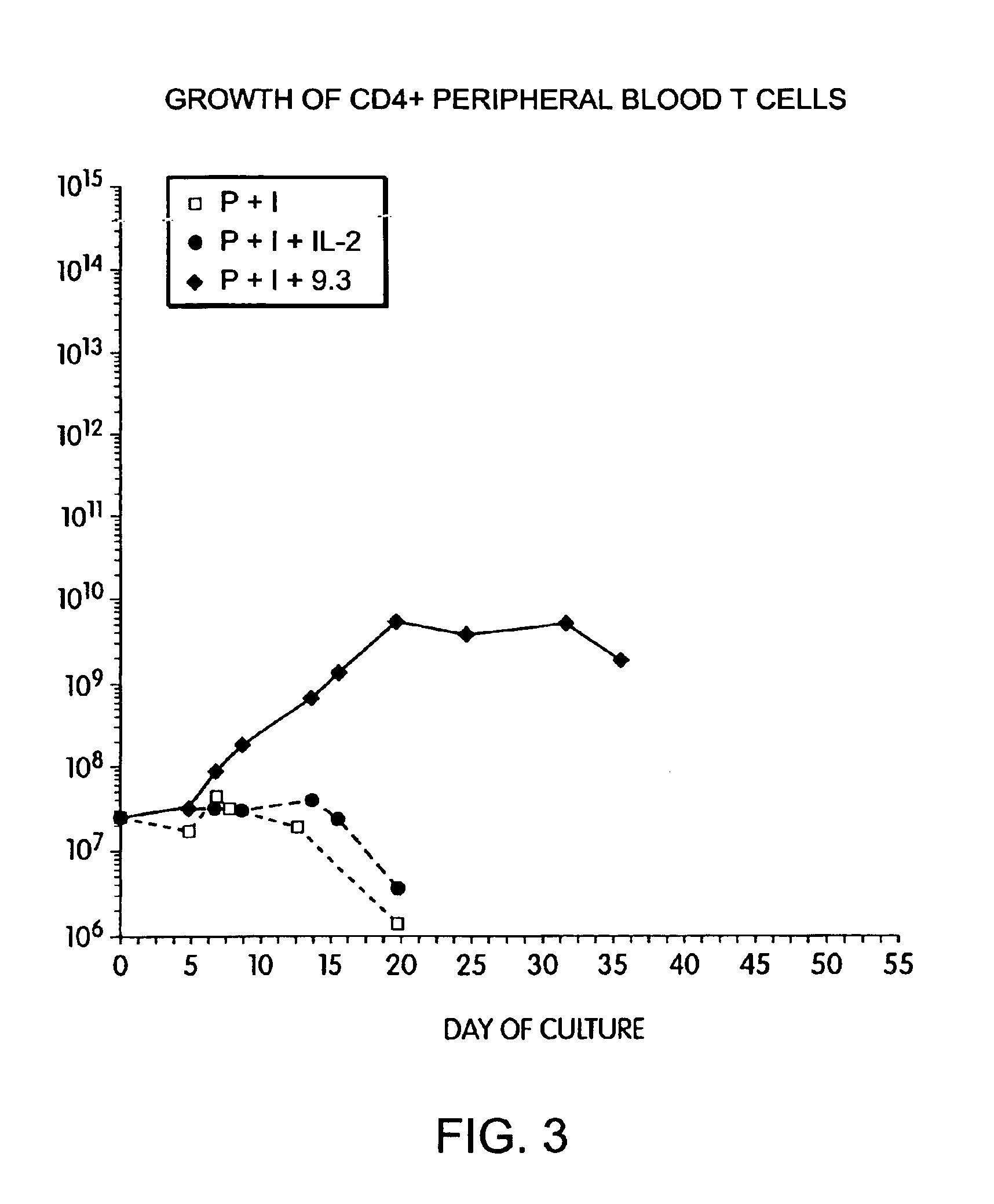
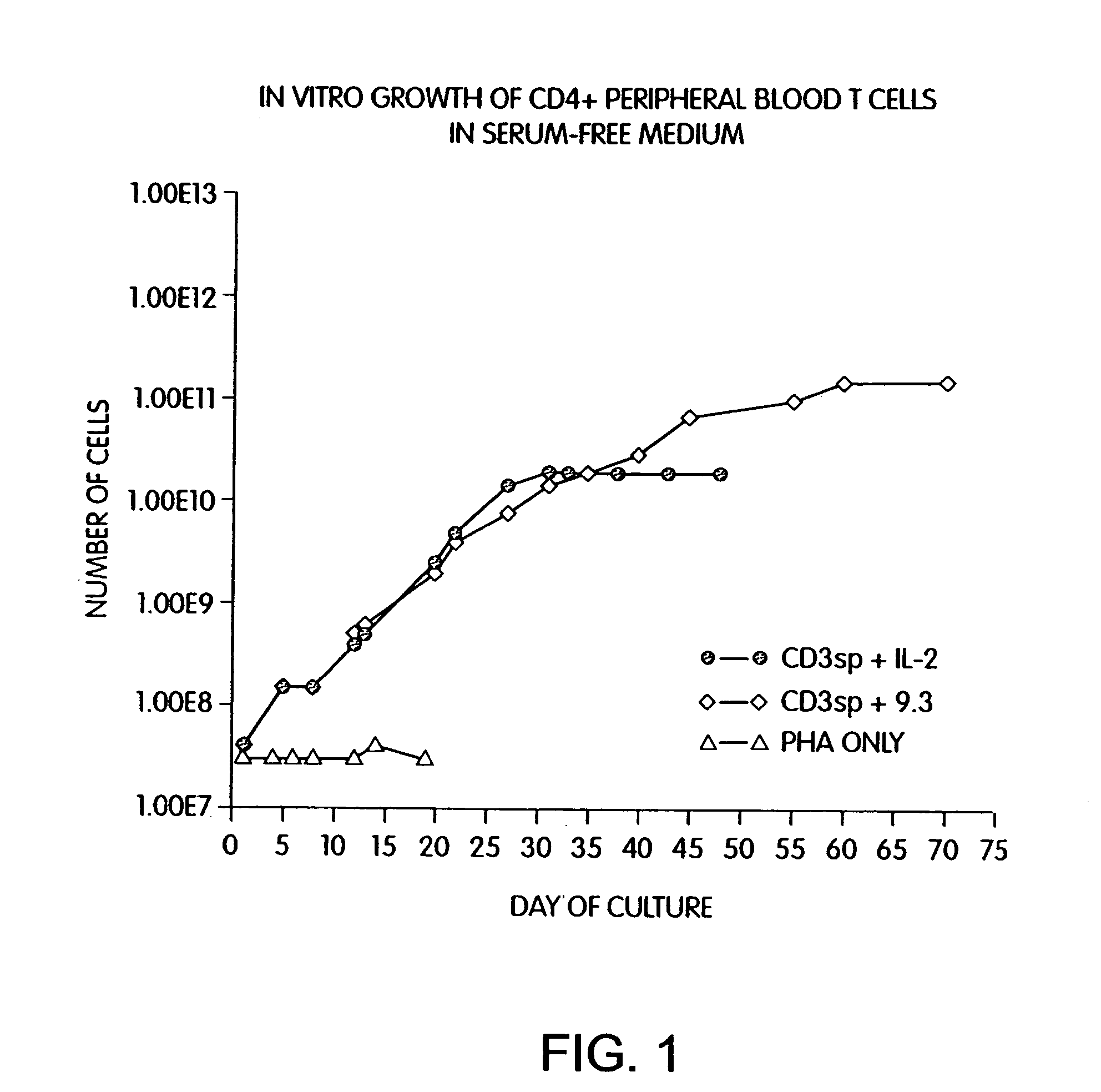
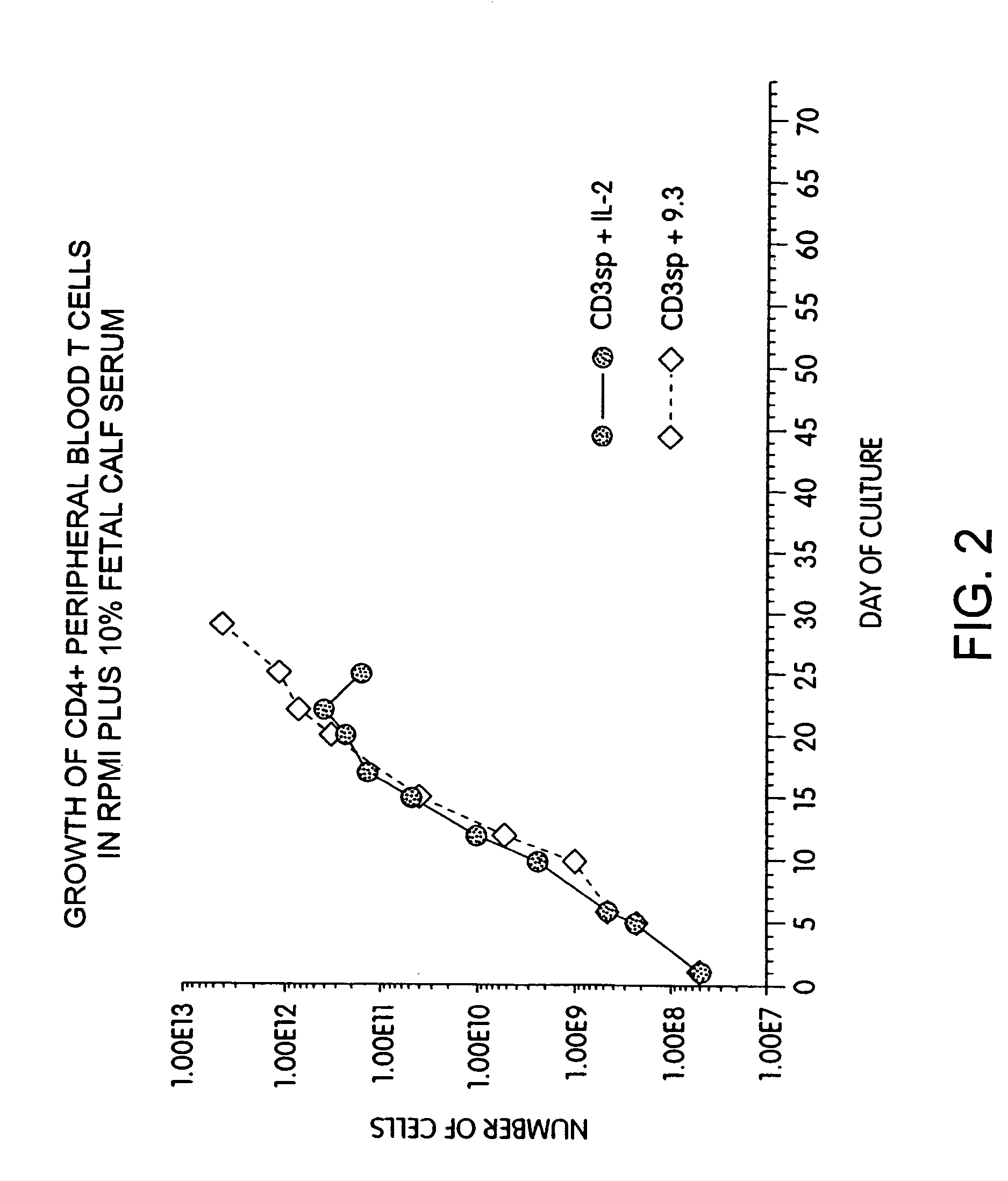
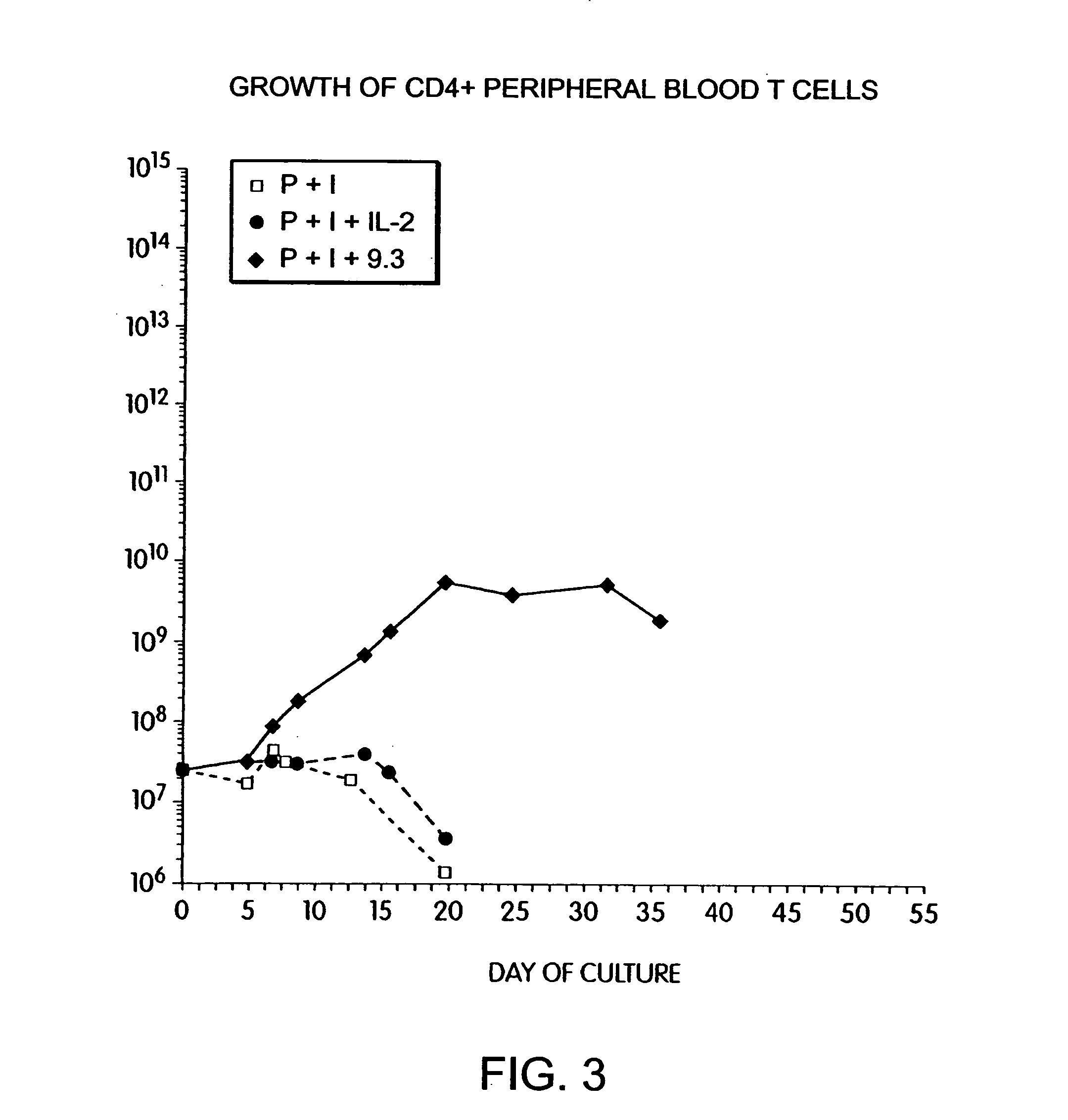
Methods for inducing a population of T cells to proliferate by activating the population of T cells and stimulating an accessory molecule on the surface of the T cells with a ligand which binds the accessory molecule are described. T cell proliferation occurs in the absence of exogenous growth factors or accessory cells. T cell activation is accomplished by stimulating the T cell receptor (TCR) / CD3 complex or the CD2 surface protein. To induce proliferation of an activated population T cells, an accessory molecule on the surface of the T cells, such as CD28, is stimulated with a ligand which binds the accessory molecule. The T cell population expanded by the method of the invention can be genetically transduced and used for immunotherapy or can be used in methods of diagnosis.
Owner:GENETICS INST INC +2
Methods for selectively stimulating proliferation of T cells
InactiveUS7175843B2Increase the number ofBiocideCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAccessory moleculeExogenous growth
Owner:GENETICS INST LLC +2
Methods of treating HIV infected subjects
InactiveUS6905680B2Expanding population of cellIncrease the number ofVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsAccessory moleculeExogenous growth
Methods for inducing a population of T cells to proliferate by activating the population of T cells and stimulating an accessory molecule on the surface of the T cells with a ligand which binds the accessory molecule are described. T cell proliferation occurs in the absence of exogenous growth factors or accessory cells. T cell activation is accomplished by stimulating the T cell receptor (TCR) / CD3 complex or the CD2 surface protein. To induce proliferation of an activated population T cells, an accessory molecule on the surface of the T cells, such as CD28, is stimulated with a ligand which binds the accessory molecule. The T cell population expanded by the method of the invention can be genetically transduced and used for immunotherapy or can be used in methods of diagnosis.
Owner:GENETICS INST INC +2
Methods for selectively stimulating proliferation of T cells
InactiveUS7144575B2Increase the number ofBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAccessory moleculeExogenous growth
Methods for inducing a population of T cells to proliferate by activating the population of T cells and stimulating an accessory molecule on the surface of the T cells with a ligand which binds the accessory molecule are described. T cell proliferation occurs in the absence of exogenous growth factors or accessory cells. T cell activation is accomplished by stimulating the T cell receptor (TCR) / CD3 complex or the CD2 surface protein. To induce proliferation of an activated population T cells, an accessory molecule on the surface of the T cells, such as CD28, is stimulated with a ligand which binds the accessory molecule. The T cell population expanded by the method of the invention can be genetically transduced and used for immunotherapy or can be used in methods of diagnosis.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY +2
CE7-specific redirected immune cells
Genetically engineered, CE7-specific redirected immune cells expressing a cell surface protein having an extracellular domain comprising a receptor which is specific for CE7, an intracellular signaling domain, and a transmembrane domain, and methods of use for such cells for cellular immunotherapy of CE7+ neuroblastoma are disclosed. In one embodiment, the immune cell is a T cell and the cell surface protein is a single chain FvFc:ζ receptor where Fv designates the VH and VL chains of a single chain monoclonal antibody to CE7 linked by peptide, Fc represents a hinge —CH2—CH3 region of a human IgG1, and ζ represents the intracellular signaling domain of the zeta chain of human CD3. DNA constructs encoding a chimeric T-cell receptor and a method of making a redirected T cell expressing a chimeric T cell receptor by electroporation using naked DNA encoding the receptor are also disclosed.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
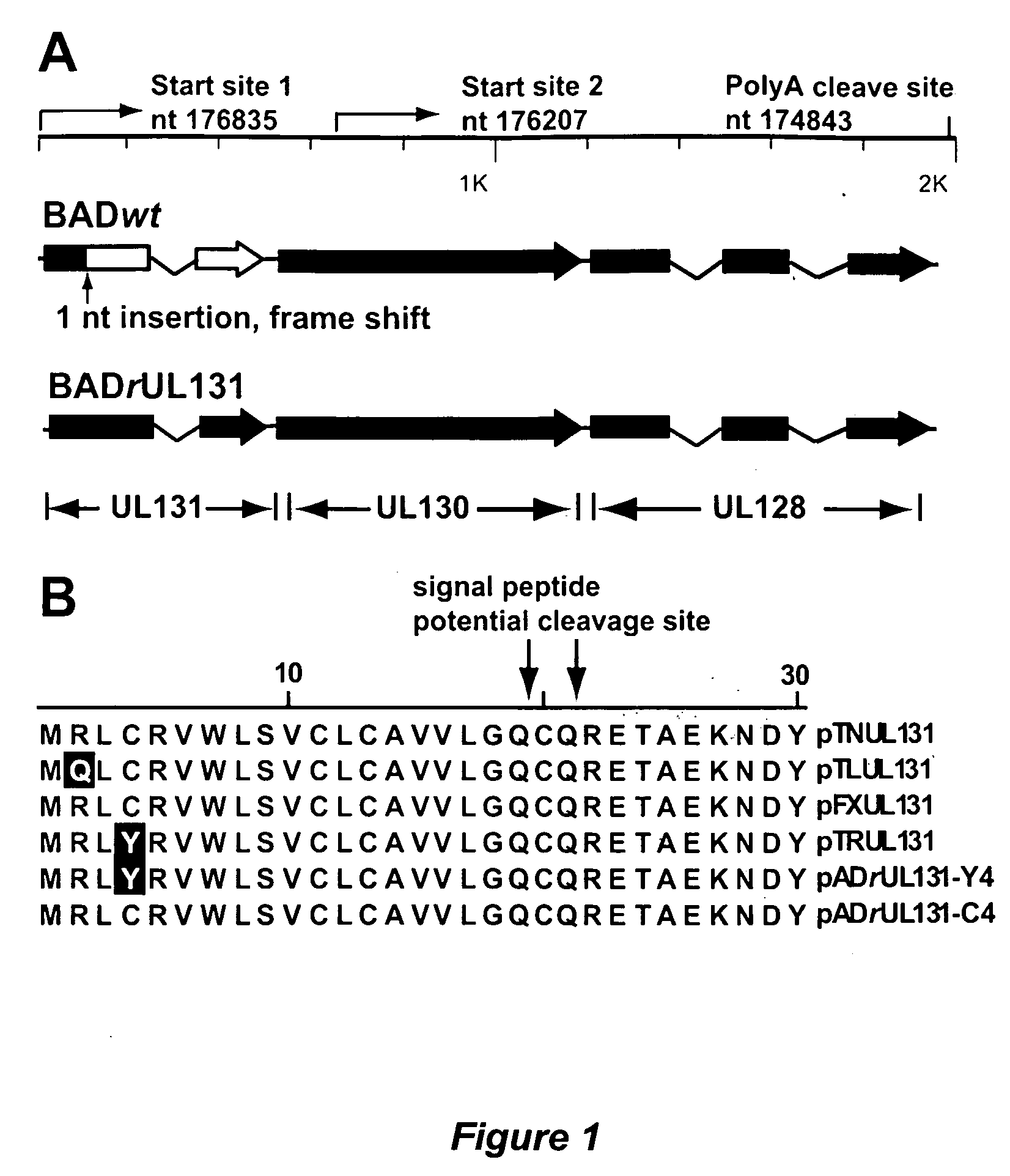
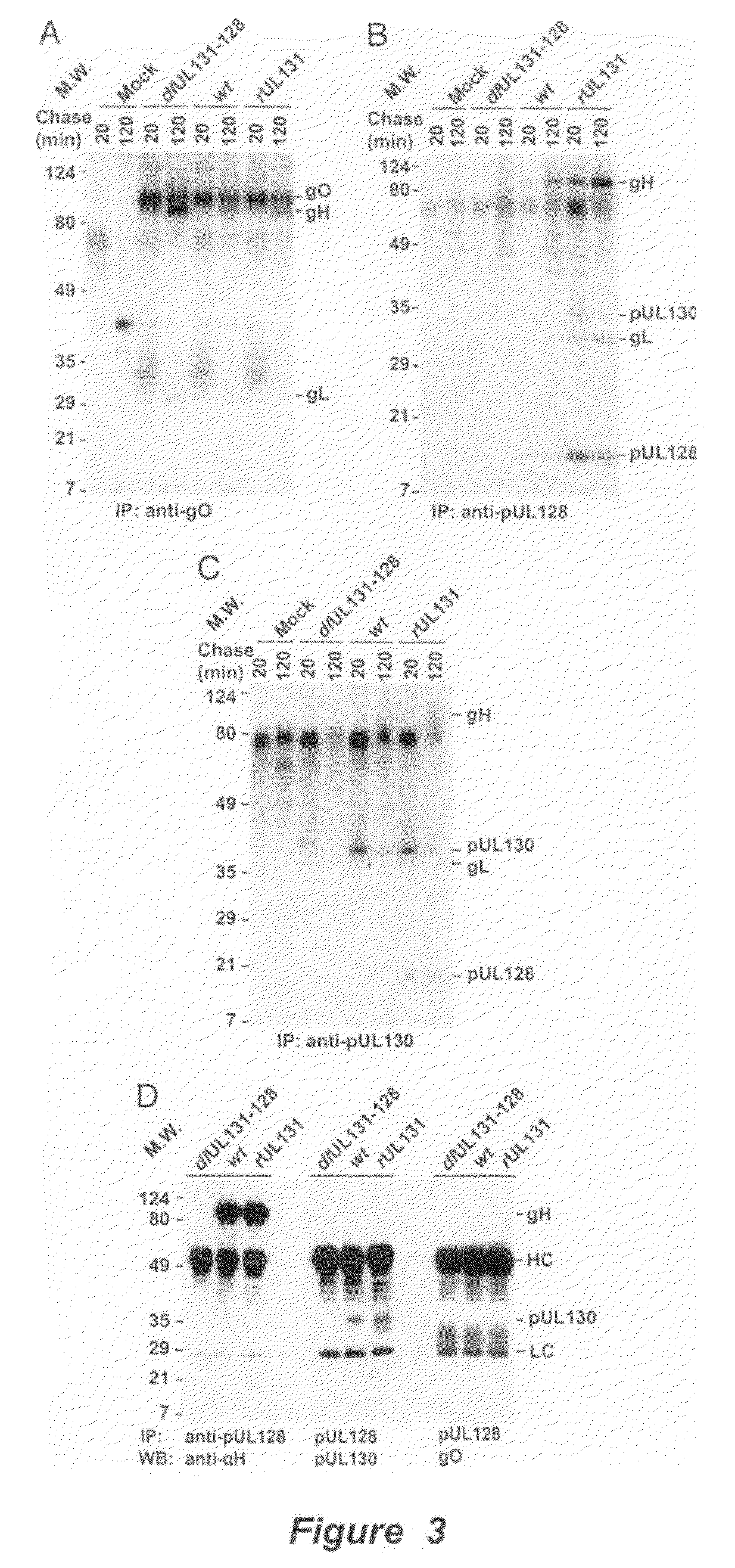
Cytomegalovirus surface protein complex for use in vaccines and as a drug target
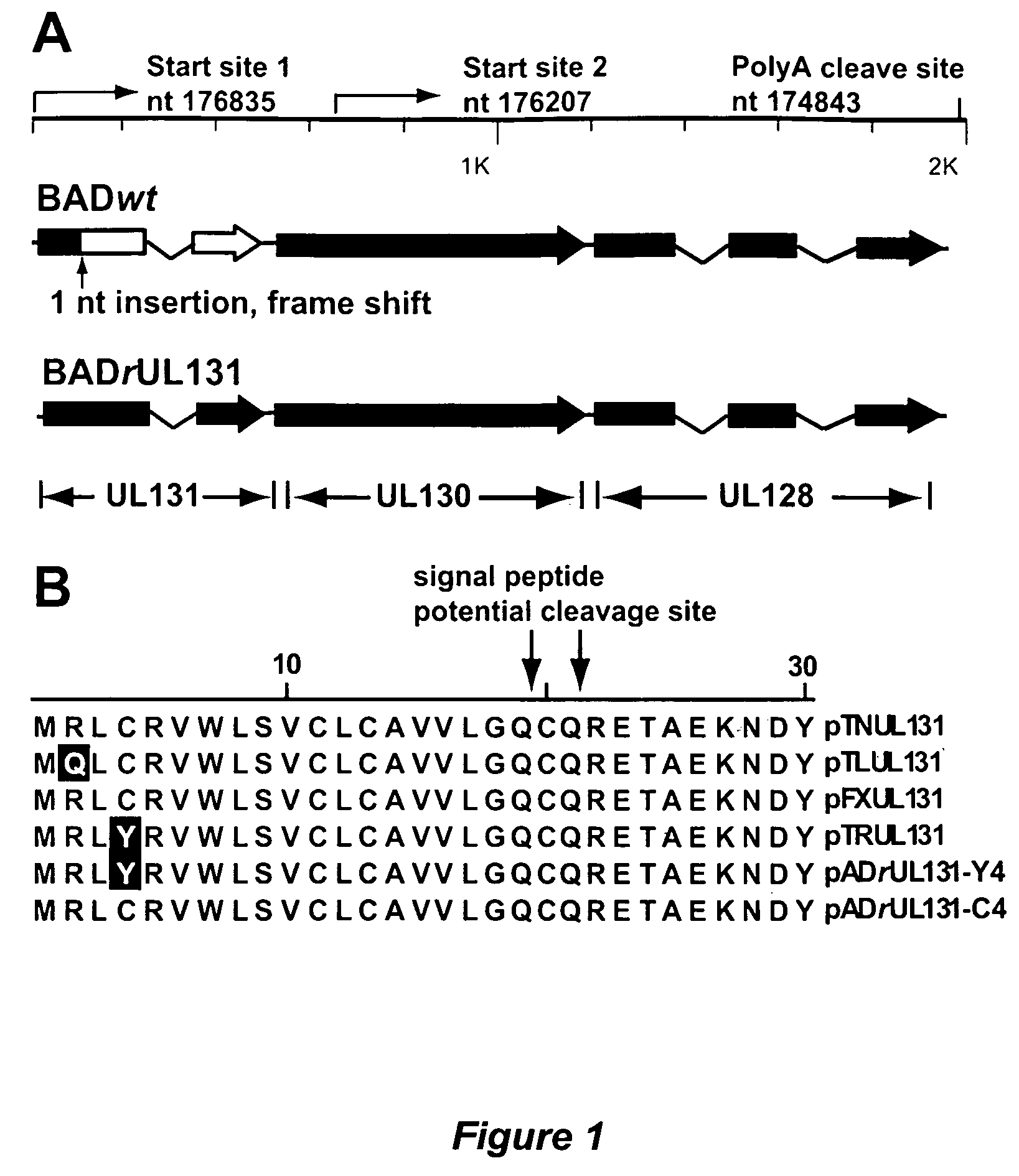
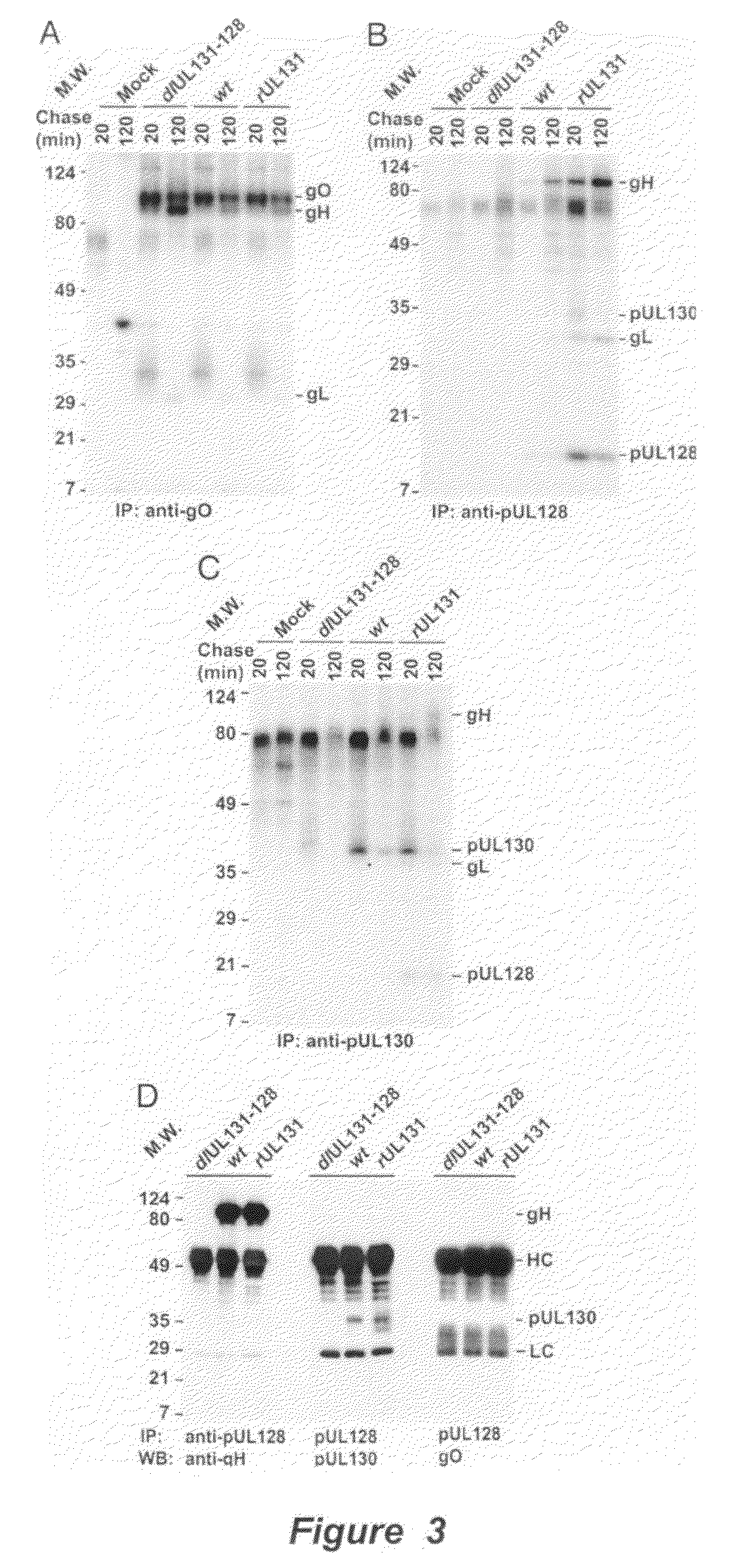
Immunogenic compositions and prophylactic or therapeutic vaccines for use in protecting and treating against human cytomegalovirus (CMV) are disclosed. Subunit vaccines comprising a human CMV protein complex comprising pUL128 or pUL130, and nucleic acid vaccines comprising at least one nucleic acid encoding a CMV protein complex comprising pUL128 or pUL130 are described. Also disclosed are therapeutic antibodies reactive against a CMV protein complex comprising pUL128 or pUL130, as well as methods for screening compounds that inhibit CMV infection of epithelial and endothelial cells, methods for immunizing a subject against CMV infection, methods for determining the capability of neutralizing antibodies to inhibit human CMV infection of cell types other than fibroblasts, and methods of diminishing an CMV infection.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
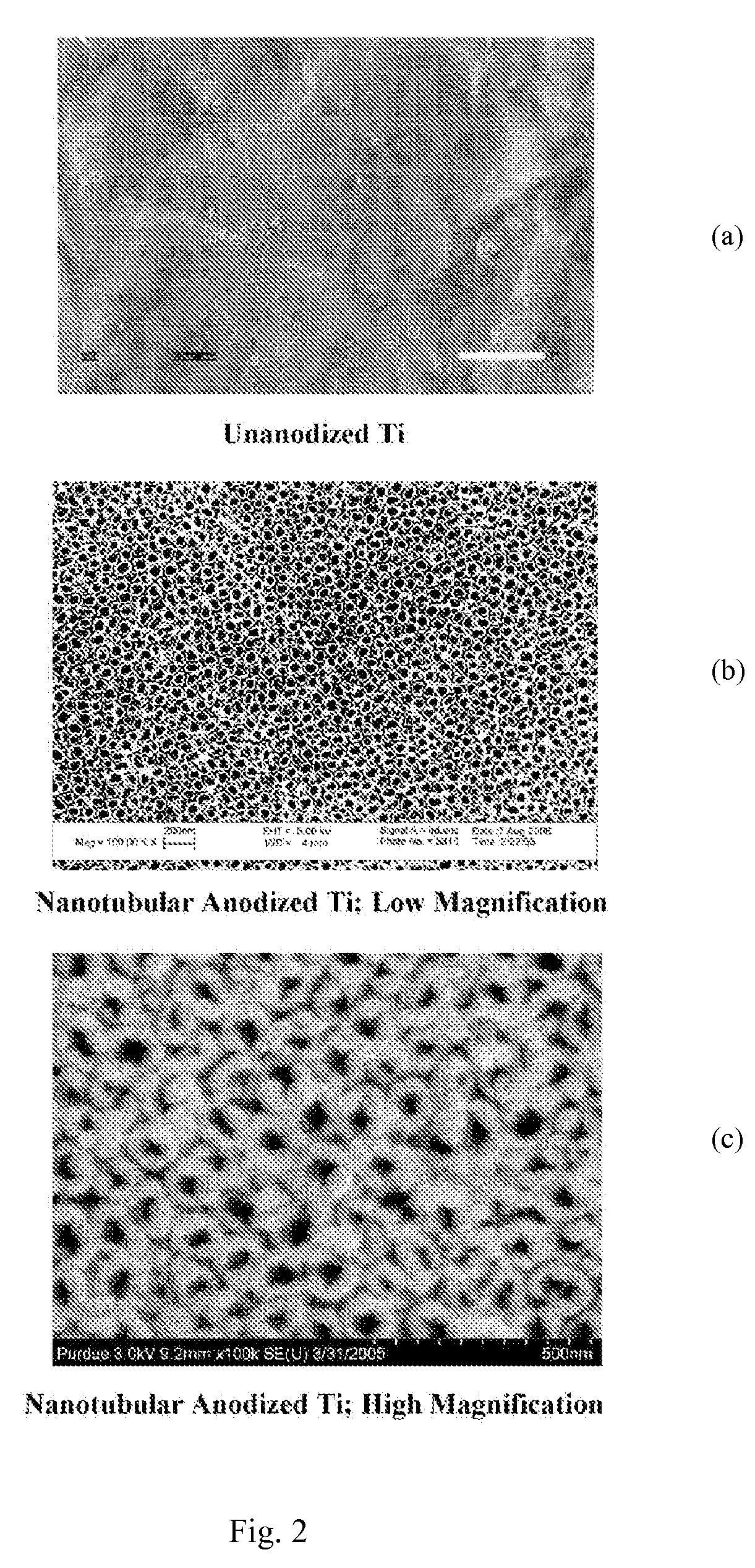
Method for producing nanostructures on a surface of a medical implant
InactiveUS20110125263A1Enhanced and increased in vivo chondrocyte functionalityImprove adhesionSurface reaction electrolytic coatingPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPorosityIn vivo
A method for treating a surface of a medical implant to create nanostructures on the surface that results in increased in-vivo chondrocyte adhesion to the surface. Further, disclosed is a method to fabricate a drug delivery system. The drug delivery system includes a medical implant that has undergone a surface treatment process that results in the modification of the surface configuration and topography. The modified surface acts as a depot or reservoir for loaded biological material, biologic agents or pharmaceutical products. Additionally, a device for delivering pharmaceutical products or other biological materials is disclosed. The device includes integrally attached nanostructures that retain or adsorb the loaded pharmaceutical products and / or biological materials. Further disclosed is a medical implant that includes a surface configured to allow for and regulate protein adsorption. The surface of the medical implant has a layer of nanostructures rigidly attached with varying porosity and orientation that allow for surface protein adsorption to be controlled.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
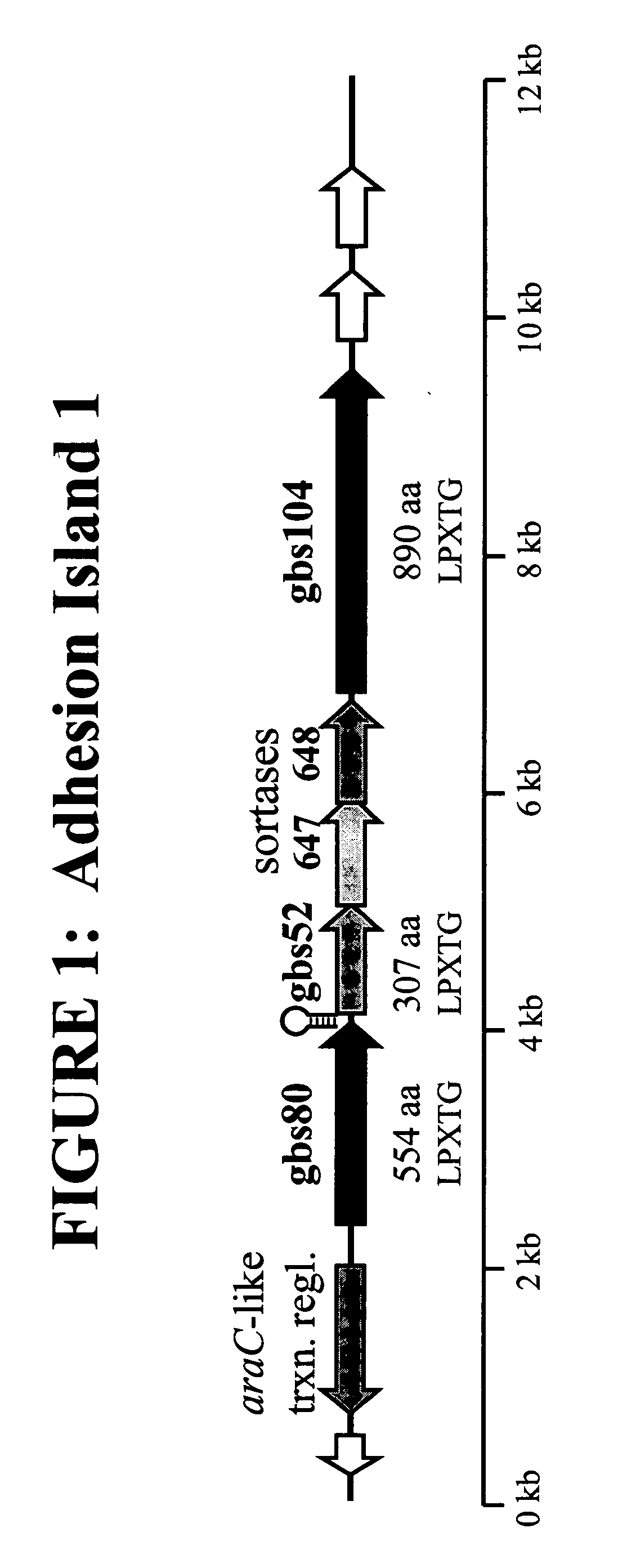
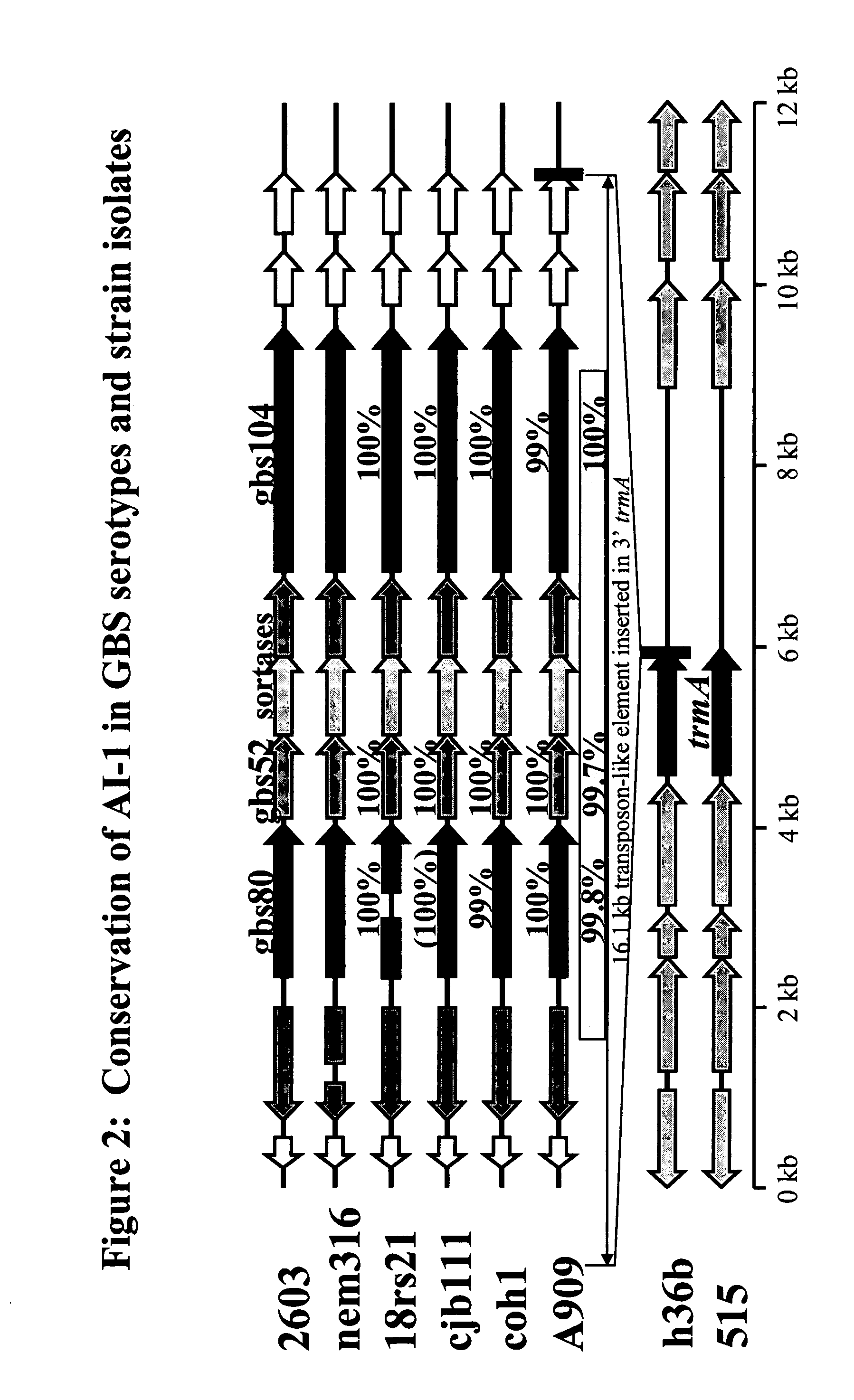
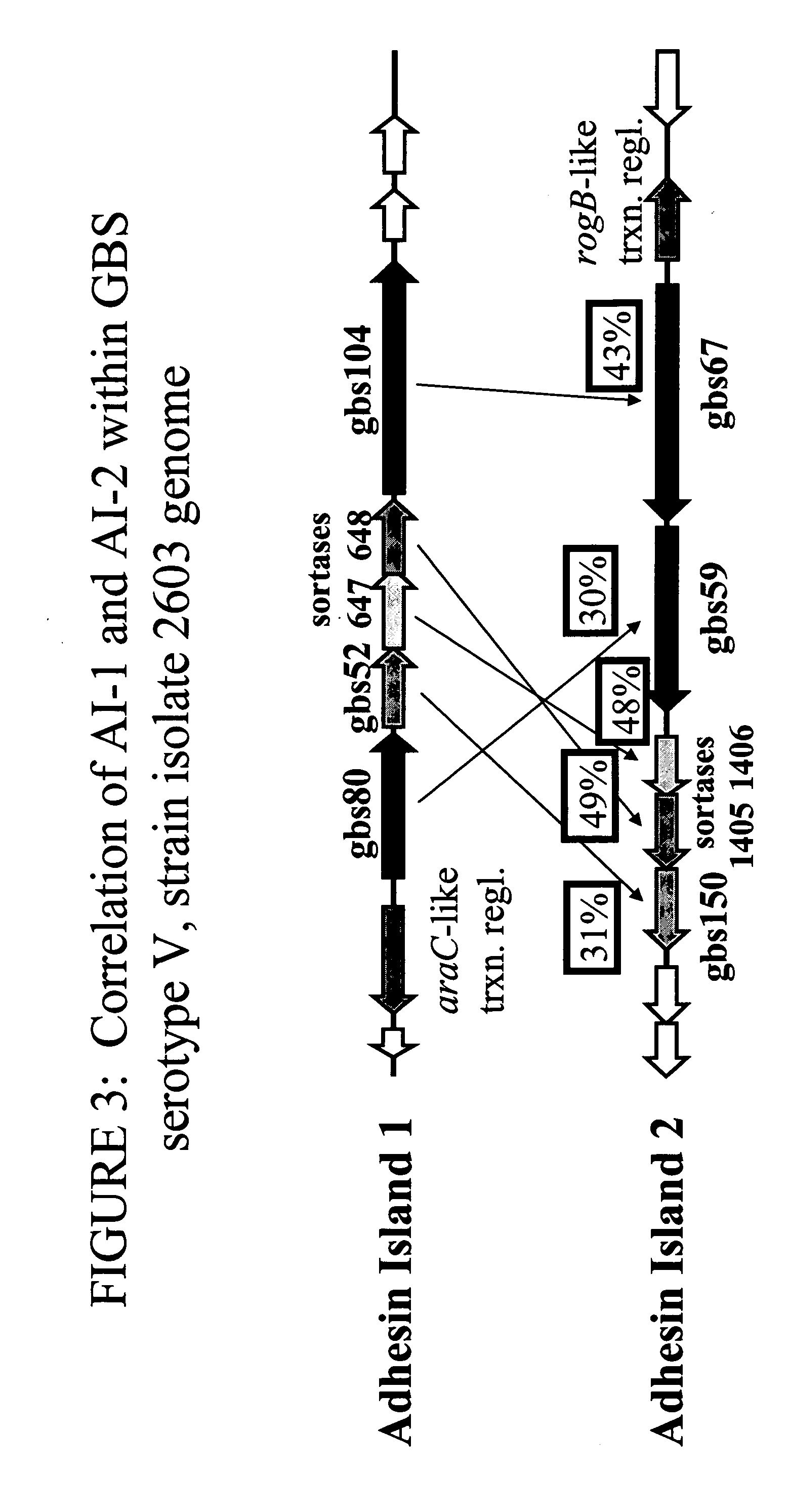
Immunogenic compositions for gram positive bacteria such as streptococcus agalactiae
InactiveUS20060165716A1InhibitionEasy to eliminateAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesVirulent characteristics
The invention relates to the identification of a new adhesin islands within the genomes of several Group A and Group B Streptococcus serotypes and isolates. The adhesin islands are thought to encode surface proteins which are important in the bacteria's virulence. Thus, the adhesin island proteins of the invention may be used in immunogenic compositions for prophylactic or therapeutic immunization against GAS or GBS infection. For example, the invention may include an immunogenic composition comprising one or more of the discovered adhesin island proteins.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Human antibodies that have MN binding and cell adhesion-neutralizing activity
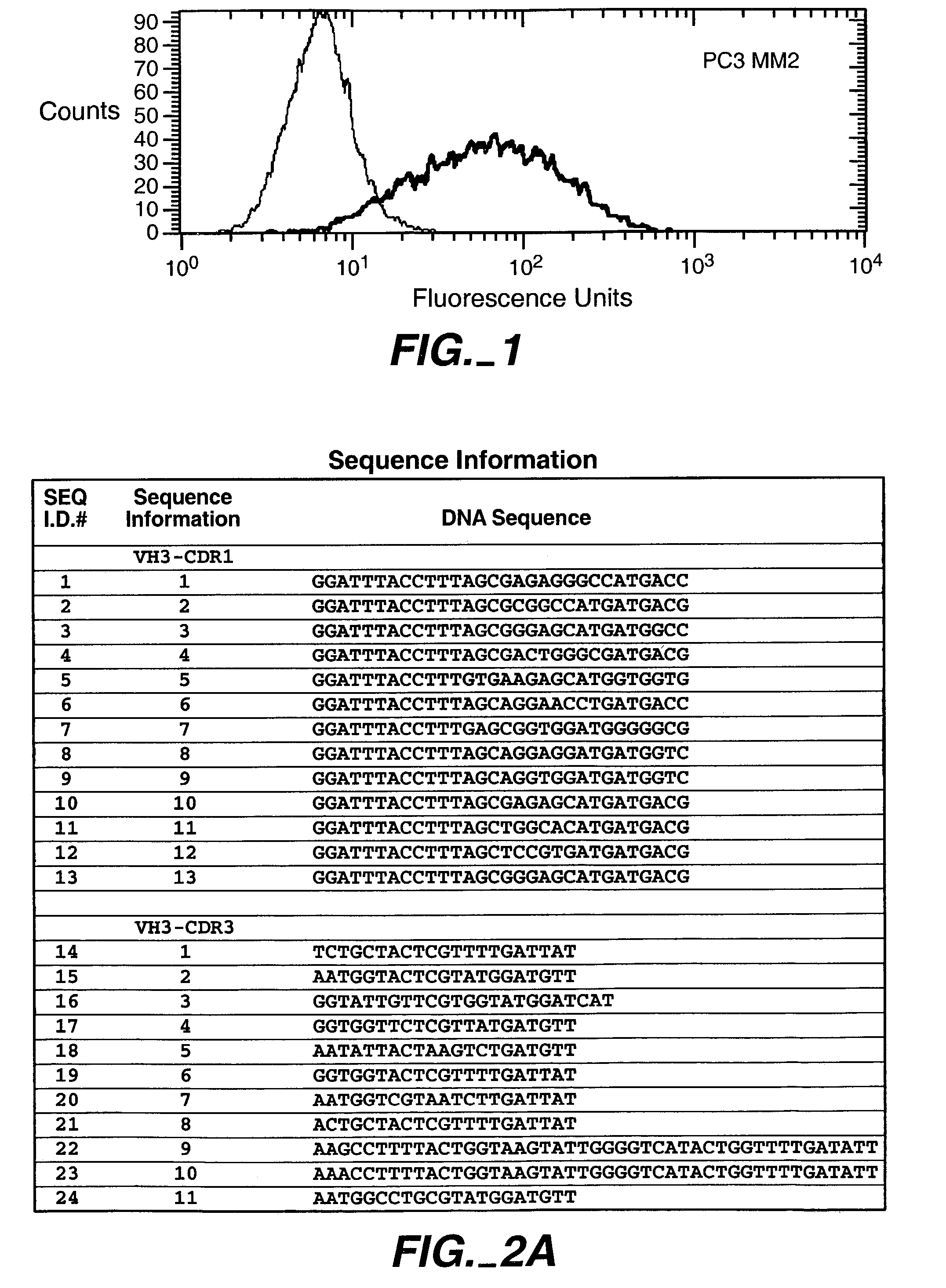
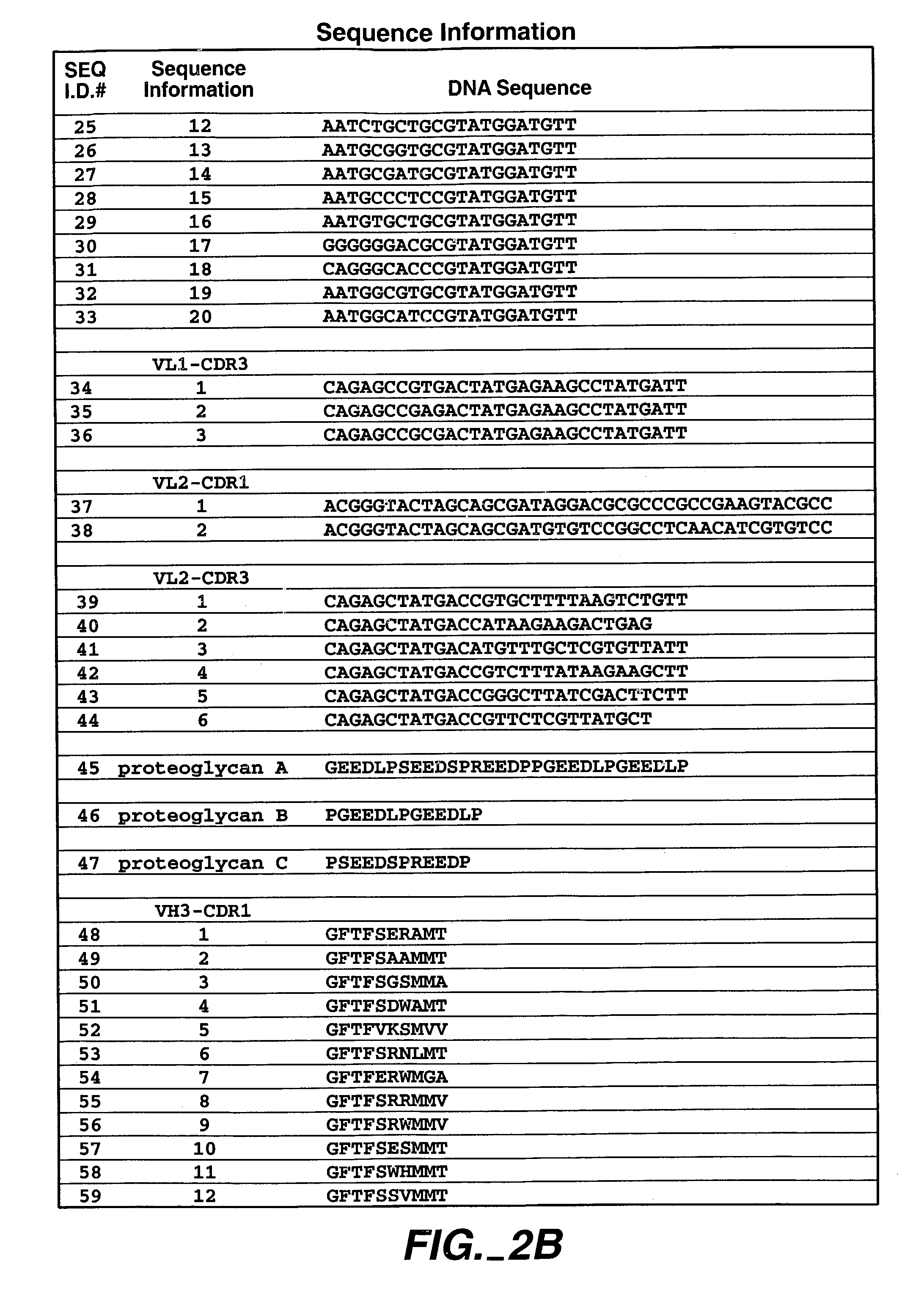
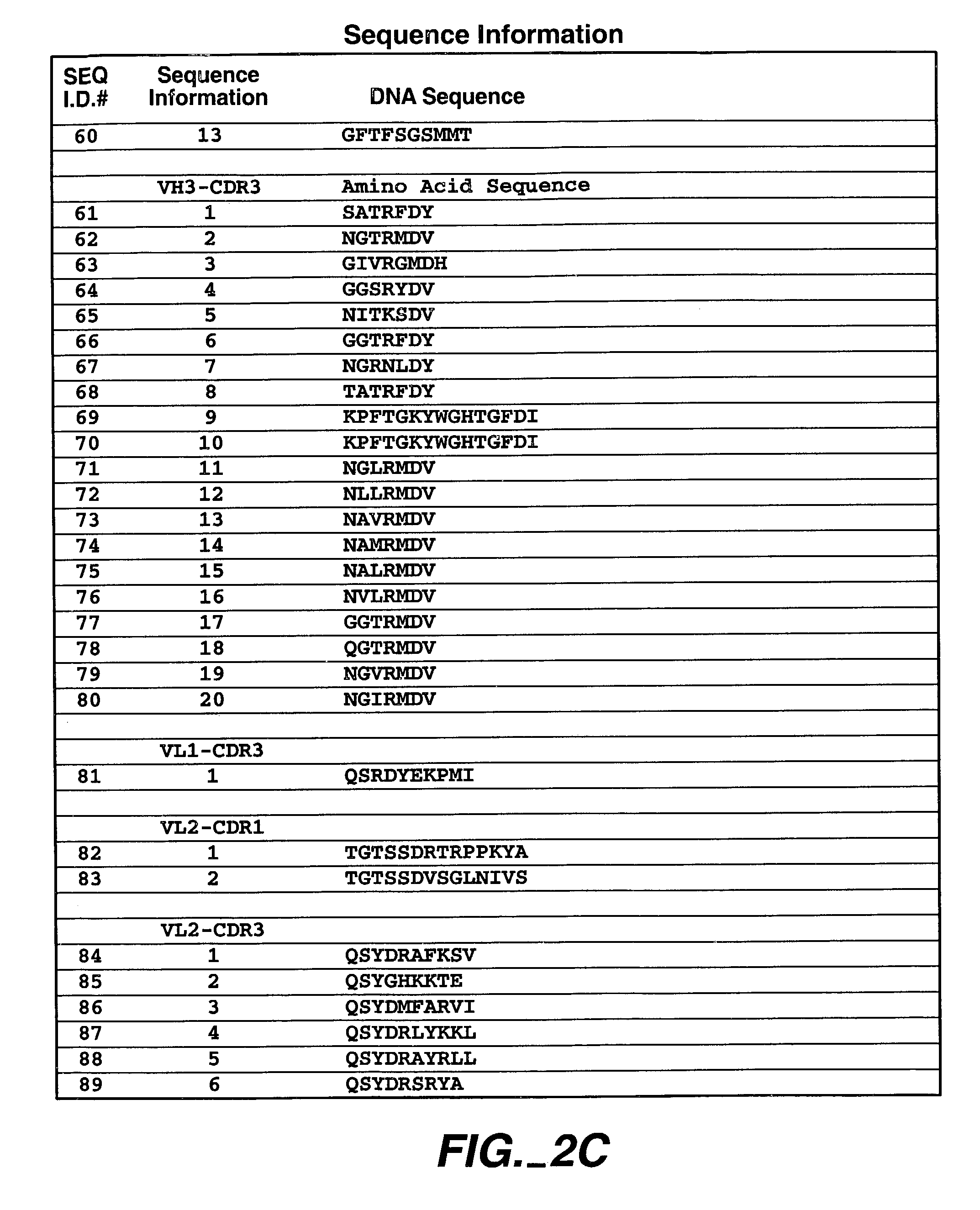
The invention is composed of monoclonal human MN antibodies or MN antibody fragments that target the GEEDLP (SEQ ID NO: 118) repeat within the proteoglycan domain. The proteoglycan domain of the MN cell surface protein contains four of these identical GEEDLP (SEQ ID NO: 118) repeats. Binding to the desired epitope is verified by competition ELISA, where ELISA signal can be attenuated by co-incubation with a peptide containing this repeat (PGEEDLPGEEDLP (SEQ ID NO: 119)). This inhibition of binding can also be verified using Biacore assays, where binding of desired antibodies to immobilized MN or proteoglycan peptides can be inhibited by the peptide repeat. In addition to binding to the peptide repeat, human anti-MN antibodies can inhibit the cell adhesion of CGL-1 cells to MN coated plastic plates. Human anti-MN antibodies have been used to diagnose and quantify MN expression in cancer cells and tumors using FACS and immunohistochemical methods. An example is also provided where a human anti-MN IgG1 mediates tumor cell lysis though antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Therefore, these antibodies will be useful for the treatment of cancers in which MN is upregulated or can be useful for the diagnosis of cancers in which MN is upregulated.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
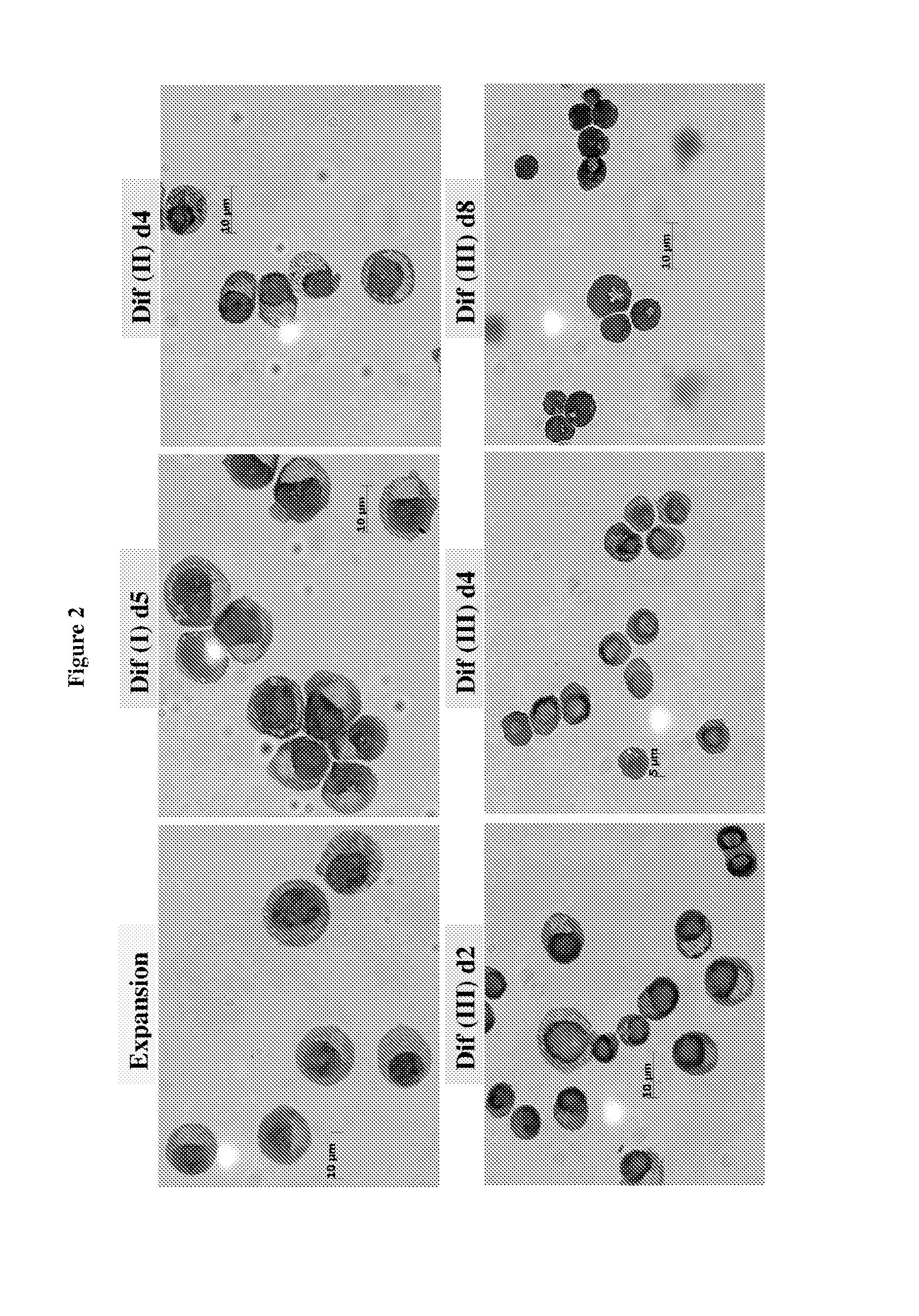
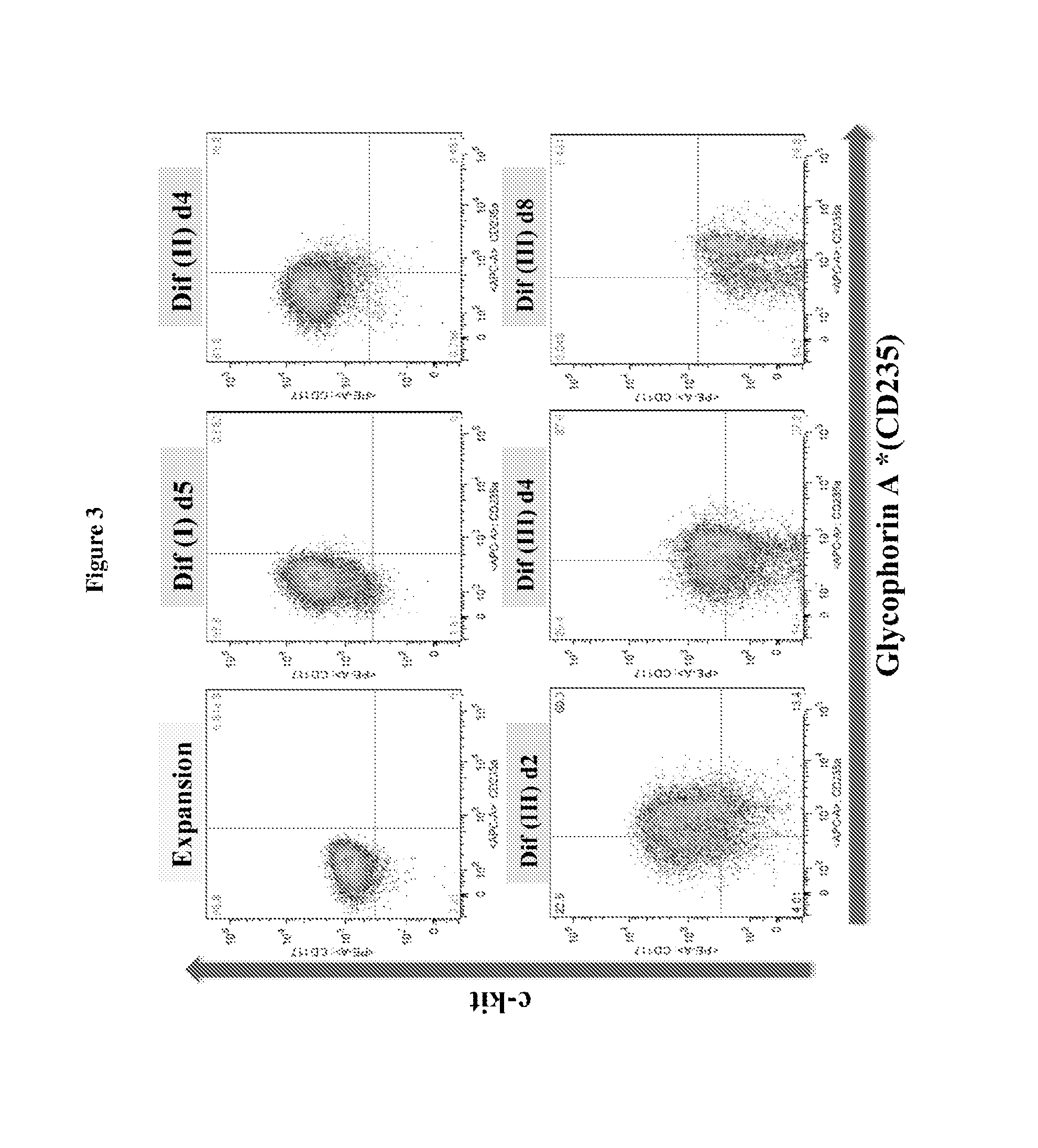
In vitro production of red blood cells with sortaggable proteins
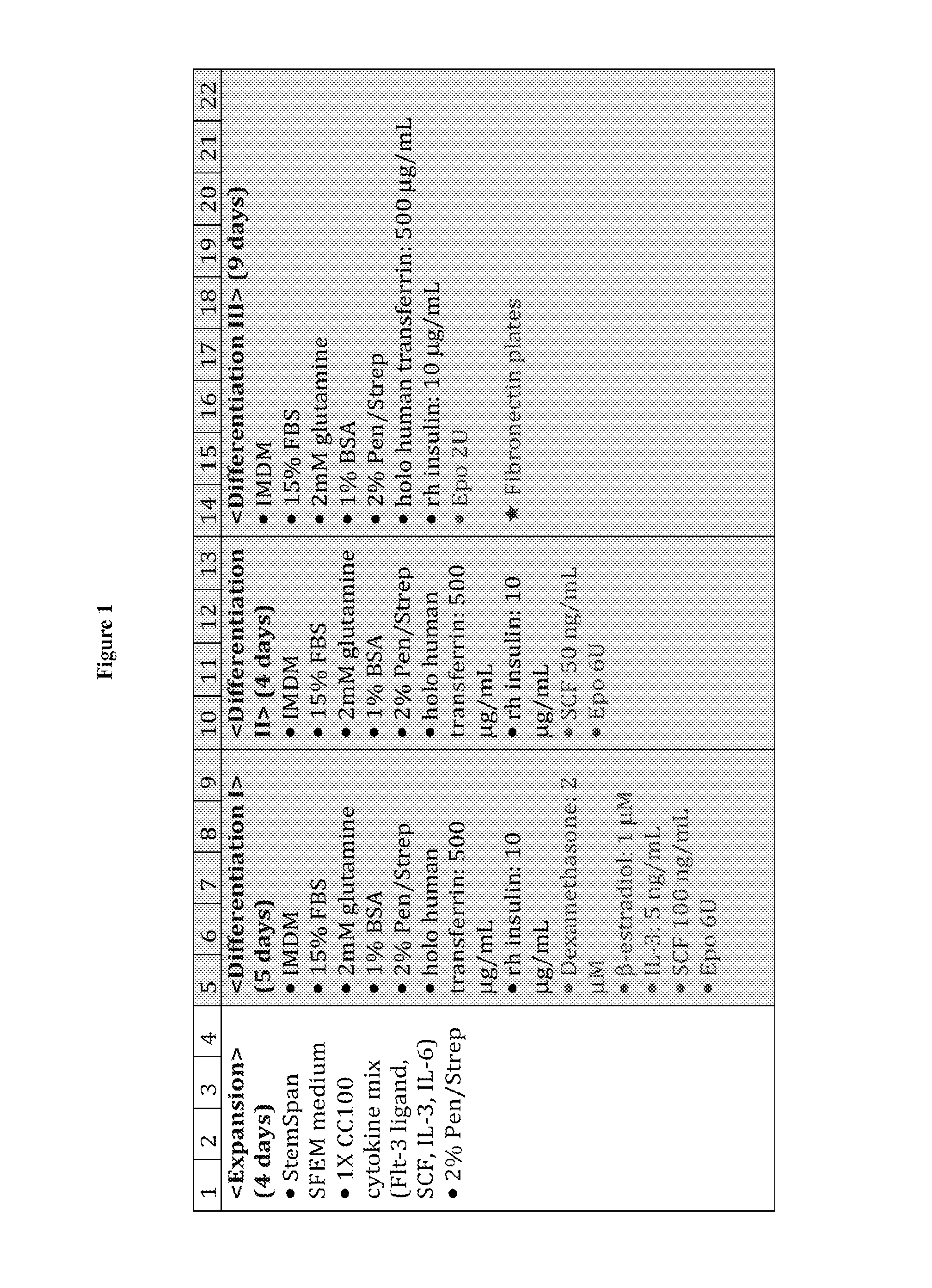
Methods for the in vitro production of enucleated red blood cells and the enucleated red blood cells thus prepared are provided. Such enucleated red blood cells may express a sortaggable surface protein, which allows for surface modification in the presence of a sortase. Also described herein are surface modified enucleated red blood cells, e.g., conjugated with an agent of interest such as a peptide, a detectable label, or a chemotherapeutic agent, and uses thereof in delivering the agent to a subject.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
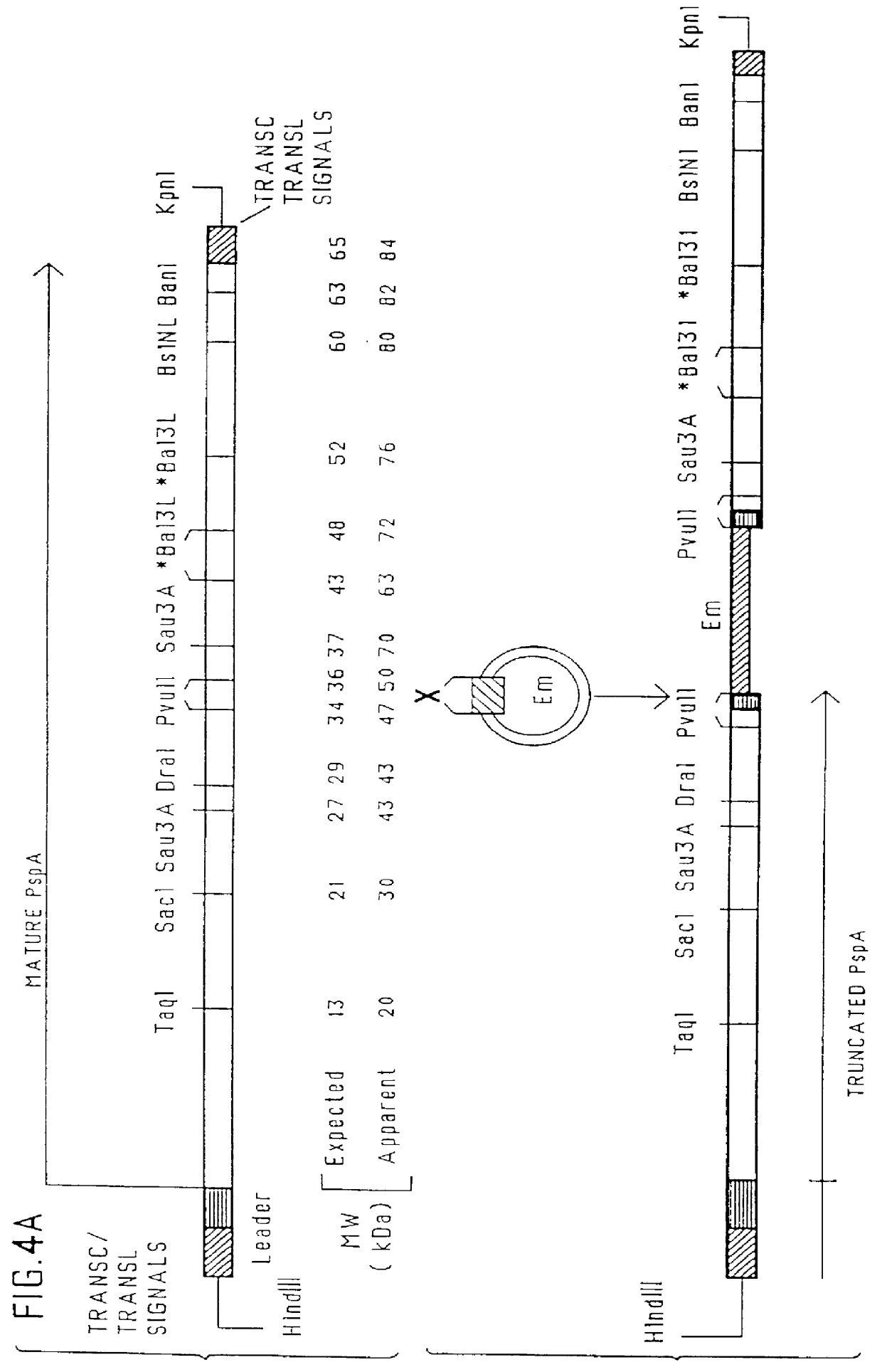
immunogenic compositions for mucosal administration of pneumococcal surface protein A (PspA)
InactiveUS6042838ALittle or no tropism for the GALTGood mucosal immunogenAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsCoccidiaPneumococcal surface protein A
Mucosal administration, particularly intranasally, of killed whole pneumococci, lysate of pneumococci and isolated and purified PspA, as well as immunogenic fragments thereof, particularly when administered with cholera toxin B subunit, provides protection in animals against pneumococcal colonization and systemic infection. The ability to elicit protection against pneumococcal colonization in a host prevents carriage among immunized individuals, which can lead to elimination of disease from the population as a whole.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA
Cytomegalovirus surface protein complex for use in vaccines and as a drug target
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Photosensitizing antibody-fluorophore conjugates
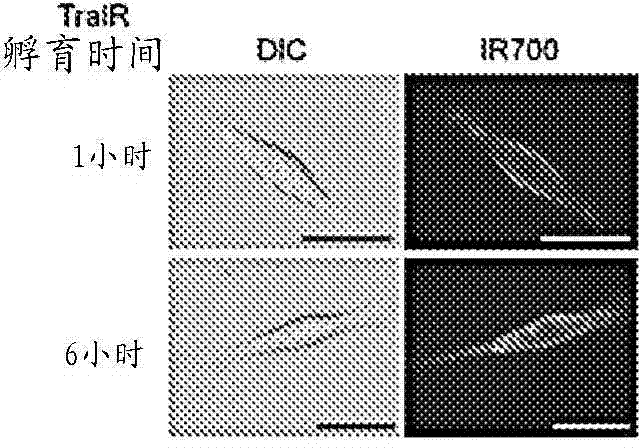
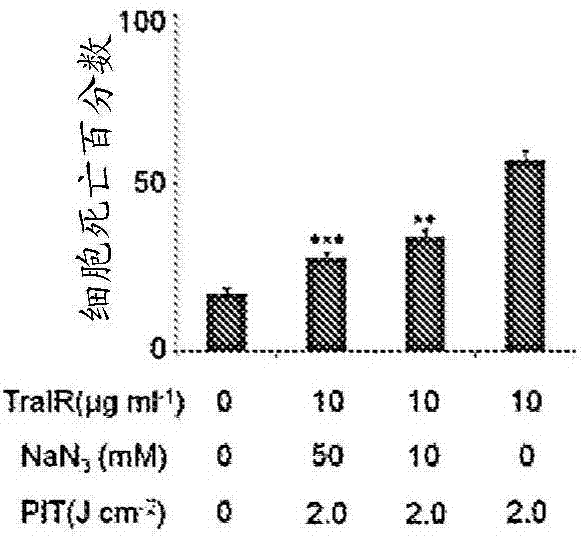
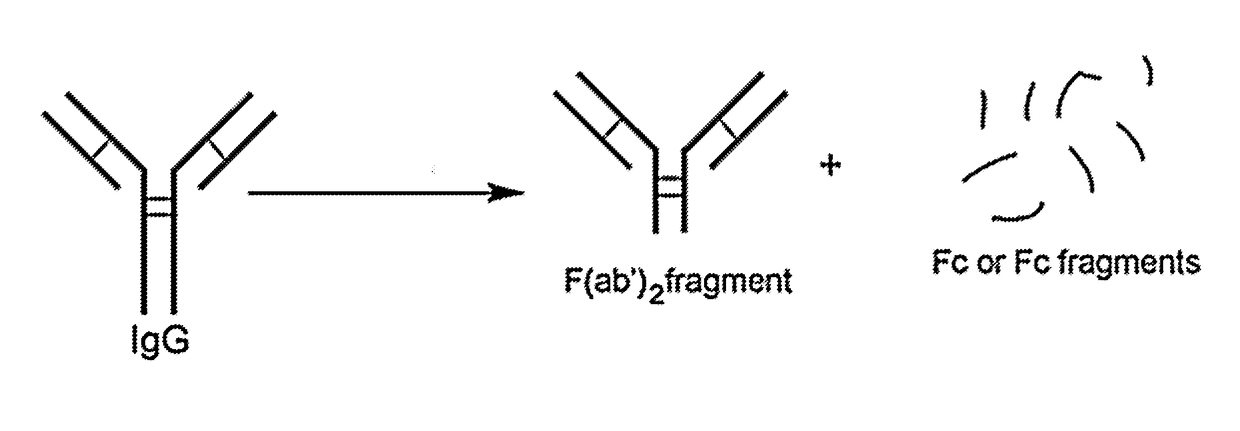
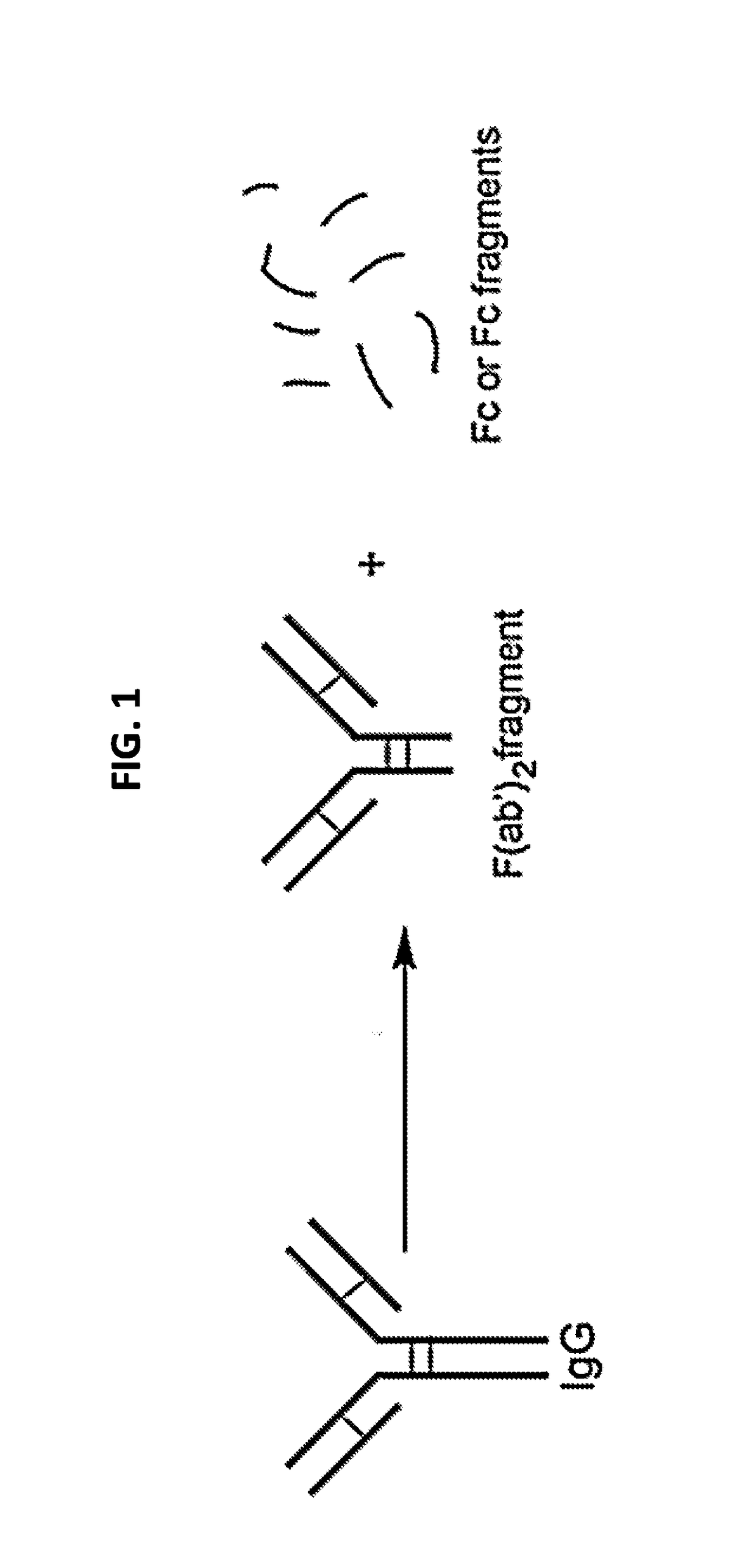
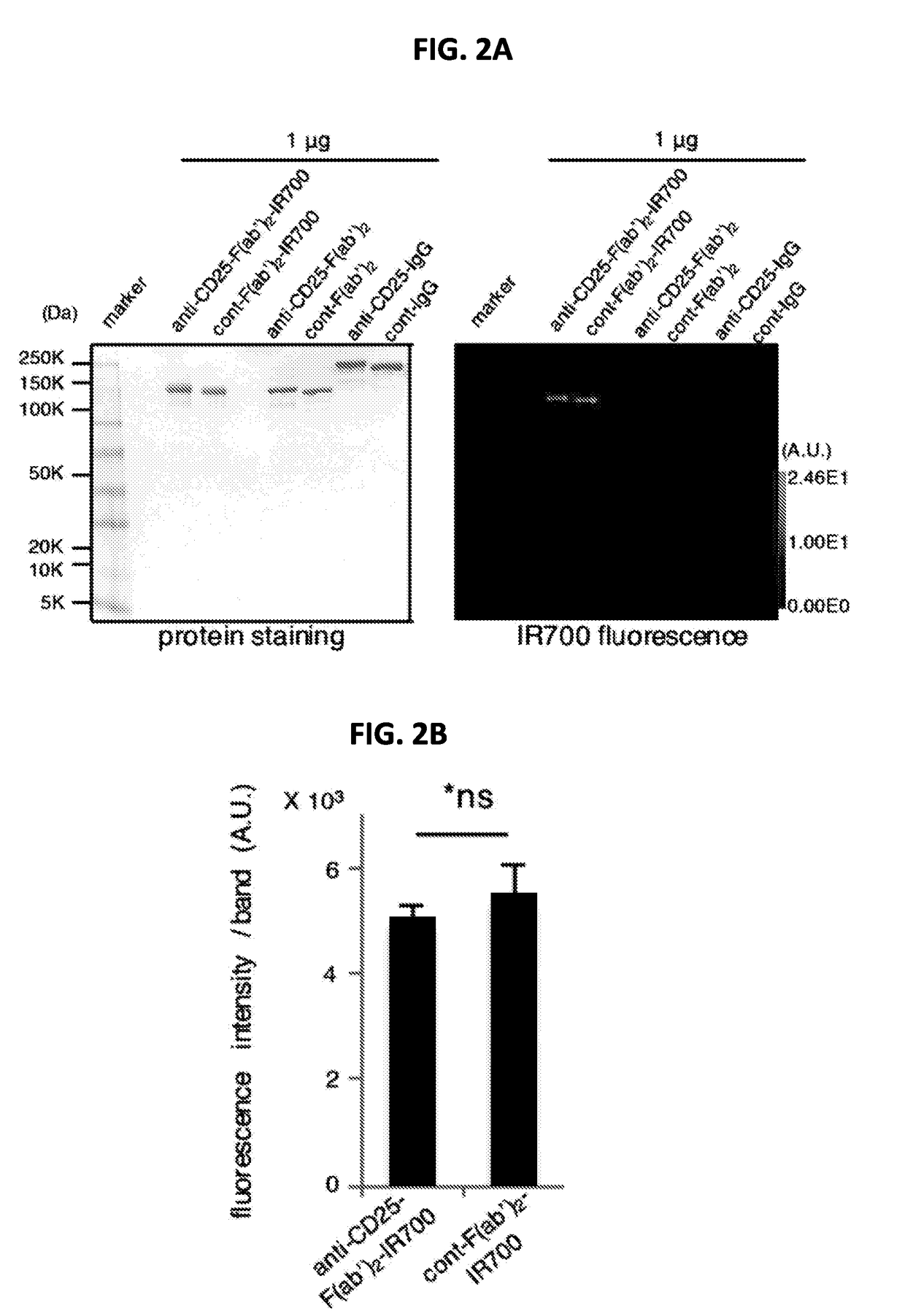
ActiveUS8524239B2Permit treatmentUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsCell Surface ProteinsFluorophore
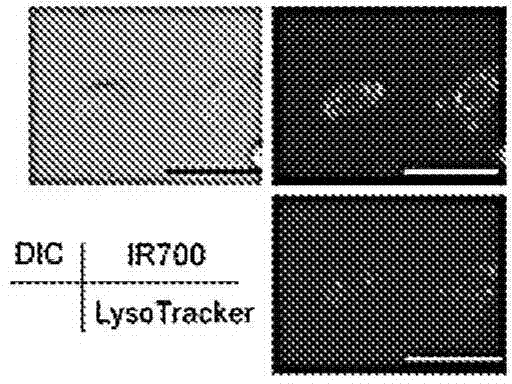
The present disclosure relates to compositions and methods of killing cells in vitro or in vivo. In particular examples, the method includes contacting a cell having a cell surface protein with a therapeutically effective amount of an antibody-IR700 molecule, wherein the antibody specifically binds to the cell surface protein. In particular examples the antibody recognizes a tumor-specific antigen on the surface of a tumor cell. The cell is subsequently irradiated, such as at a wavelength of 660 to 740 nm at a dose of at least 1 J cm−2, thereby killing the cell. Also provided are wearable devices that include an article of clothing, jewelry, or covering; and an NIR LED incorporated into the article, which can be used with the disclosed methods.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Methods and Compositions for Vaccination of Animals with Prrsv Antigens with Improved Immunogenicity
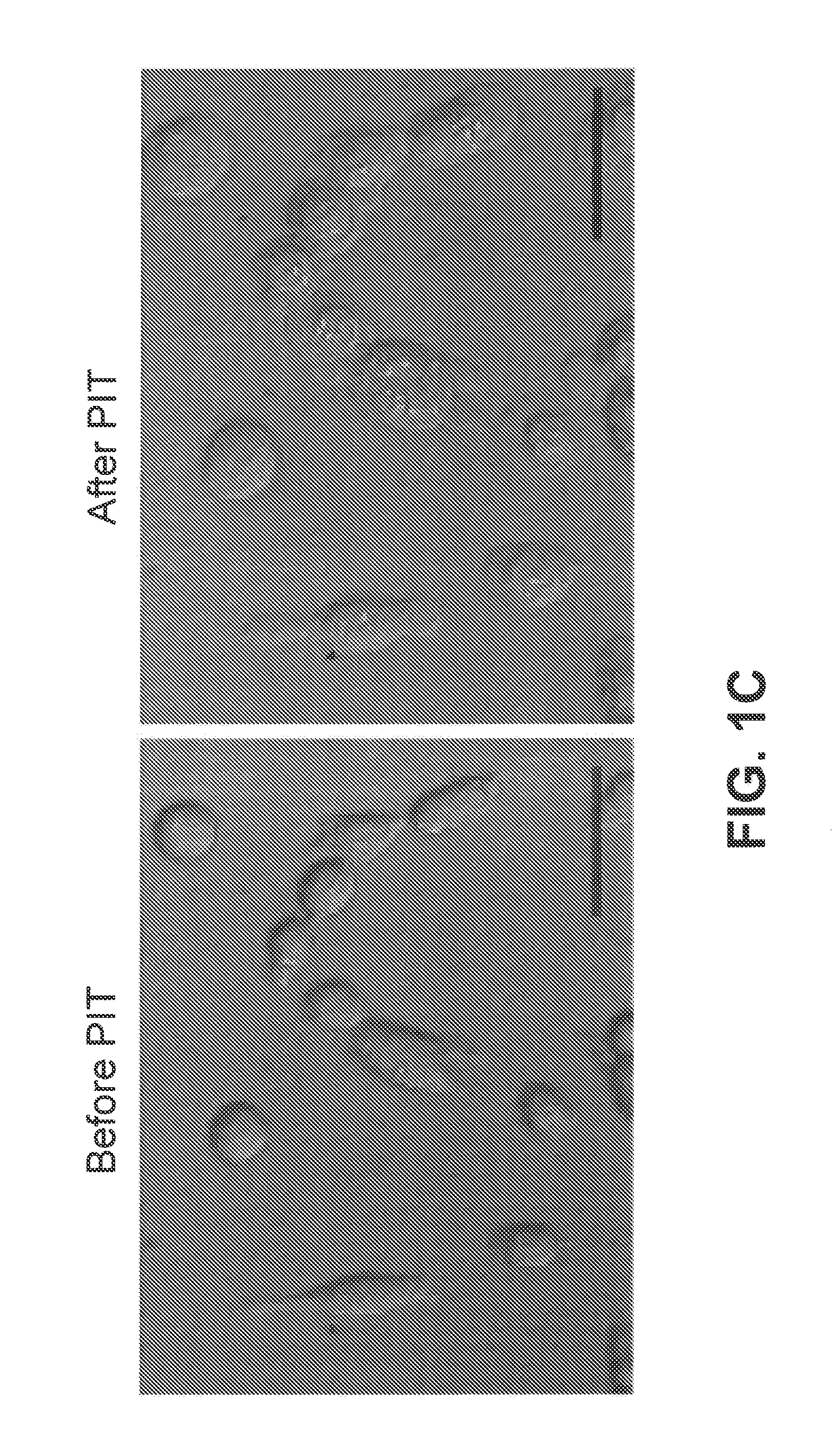
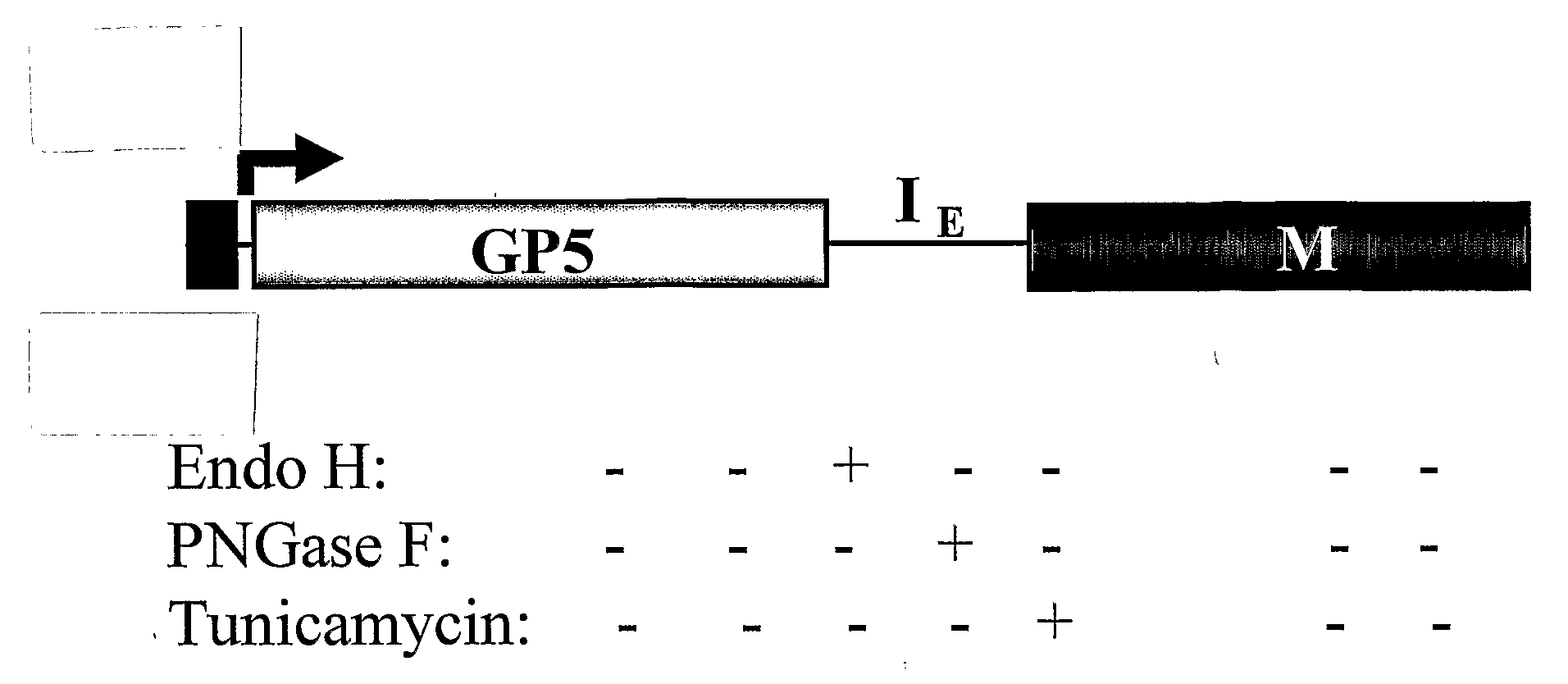
Pigs challenged with hypoglycosylated variants of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus (PRRSV) major surface protein GP5 exhibited increased production of PRRSV-neutralizing antibodies relative to the levels of neurtalizing antibodies produced by pigs immunized with wild type (wt) or glycosylated GP5. This invention provides for methods of obtaining improved immune responses in pigs to PRRSV, compositions useful for obtaining the improved immune responses as well as isolated polynucleotides that encode hypoglycosylated variants of PRRSV major surface protein GP5.
Owner:NUTECH VENTURES
Method for purification of viral vectors having proteins which bind sialic acid
ActiveUS7319002B2Method be rapidMethod is fastBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBinding siteViral vector
A method for isolating, from a mixture, a virus having a surface protein with a binding site for sialic acid is provided. The method involves contacting the mixture with mucin which has been linked to a solid support and washing the solid support to remove material from the mixture is non-specifically bound to the mucin-linked support. Thereafter, the specifically bound virus (e.g., AAV4 or AAV5) may be removed in a further washing step utilizing a concentrated slat or solution with low pH. Also described are pharmaceutical kits containing solid supports linked to mucin for use in isolating virus having a surface protein with a binding site for sialic acid, or detecting the presence of the virus in a biological sample.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
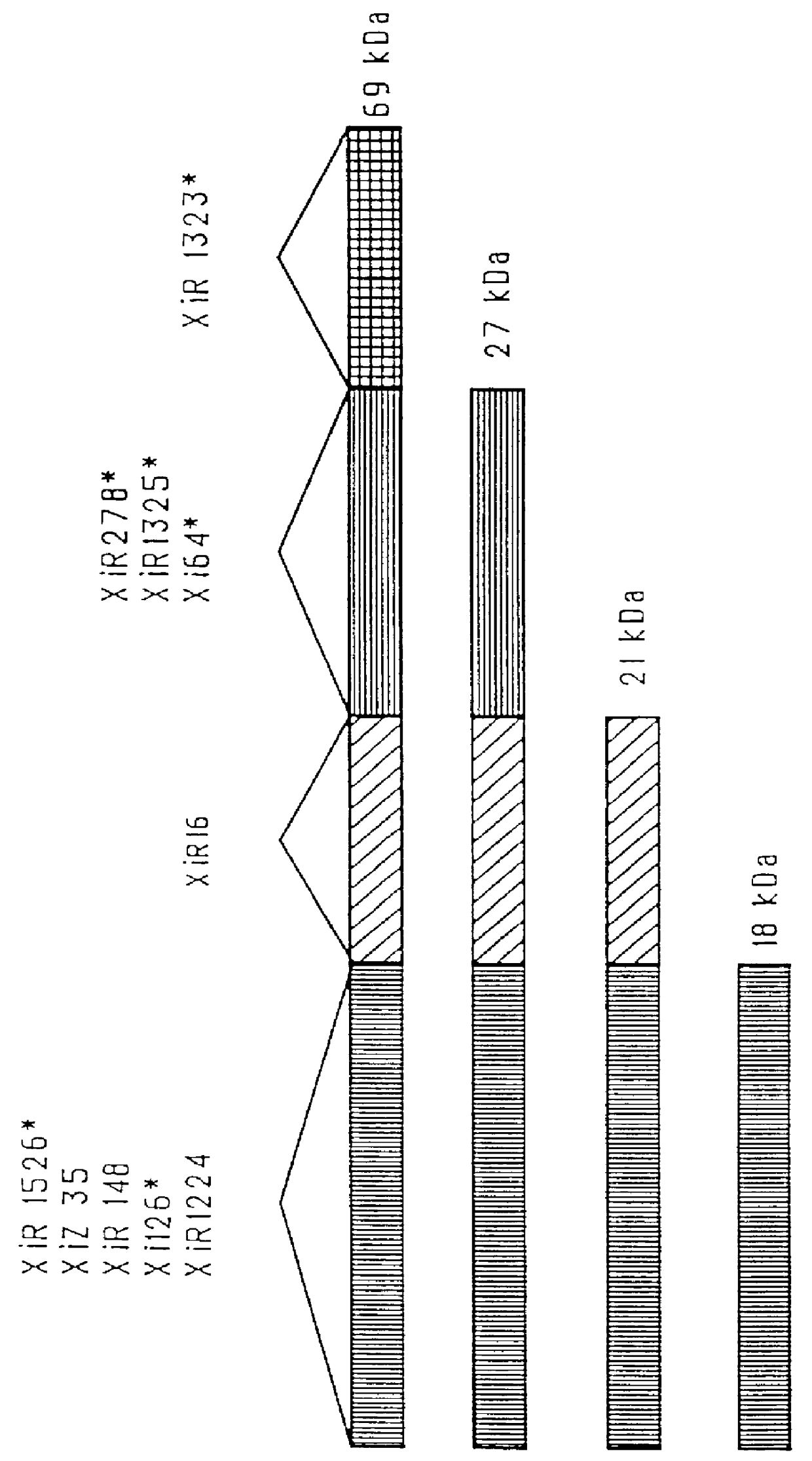
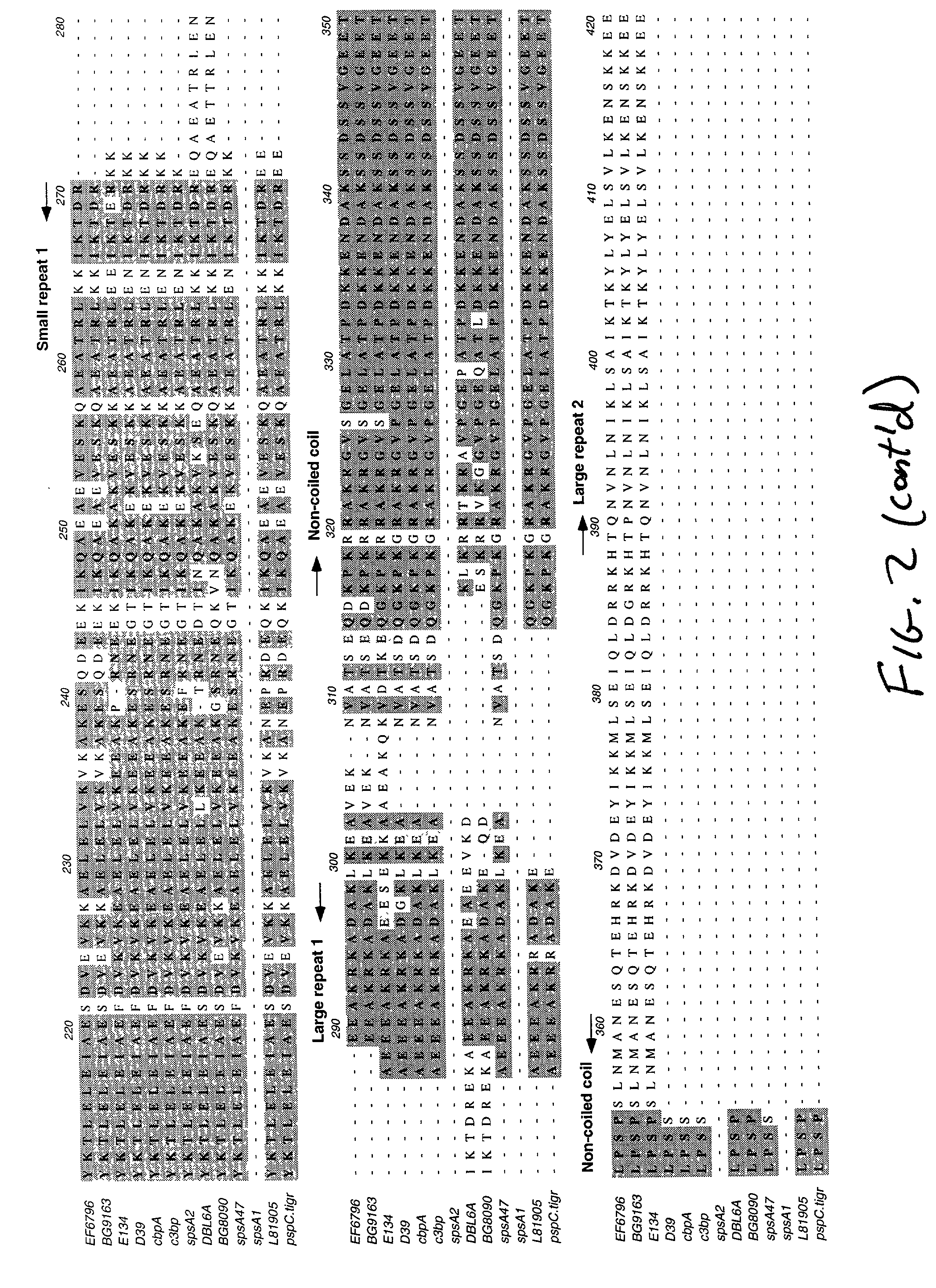
Pneumococcal surface proteins and uses thereof
InactiveUS6500613B1Improving immunogenicityLow production costAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsStreptococcus pneumoniaeCoccidia
The present invention relates to pneumococcal genes, portions thereof, expression products therefrom and uses of such genes, portions and products; especially to genes of Streptococcus pneumoniae, e.g., the gene encoding pneumococcal surface protein A (PspA), i.e., the pspA gene, the gene encoding pneumococcal surface protein A-like proteins, such as pspA-like genes, e.g., the gene encoding pneumococcal surface protein C (PspC), i.e., the pspC gene, portions of such genes, expression products therefrom, and the uses of such genes, portions thereof and expression products therefrom.
Owner:ALABAMA AT BIRMINGHAM UNIVERISTY OF
Bacterial polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine and preparation method thereof
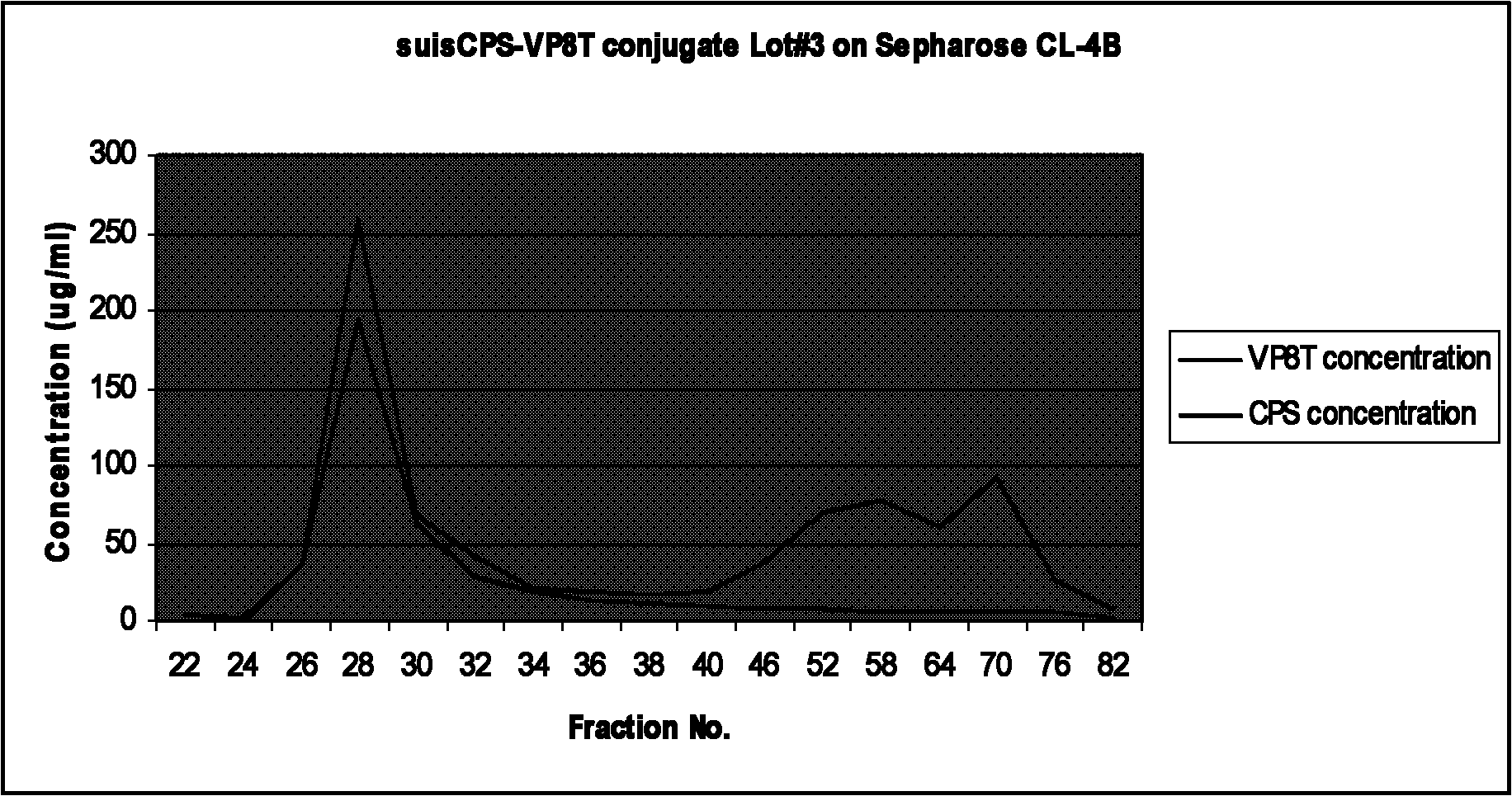
The invention relates to a bacterial polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccine with immunogenicity, in particular to a conjugate vaccine which is formed by connecting a recombinant rotavirus protein with a bacterial polysaccharide by using a covalent bond, a nucleotide sequence for coding the recombinant rotavirus protein, a recombinant expression system, a protein expressed by the recombinant expression system, a preparation method of the conjugate vaccine and a pneumococcus polysaccharide-recombinant rotavirus protein conjugate vaccine. The bacterial polysaccharide is connected with a recombinant rotavirus surface protein through a covalent bond. The recombinant rotavirus protein is selected from a partial or complete amino acid sequence of a P-gene rotavirus protein and a partial or complete amino acid sequence of a G-gene rotavirus protein.
Owner:普大生物科技(泰州)有限公司
Stabilized viral envelope proteins and uses thereof
This invention provides an isolated nucleic acid which comprises a nucleotide segment having a sequence encoding a viral envelope protein comprising a viral surface protein and a corresponding viral transmembrane protein wherein the viral envelope protein contains one or more mutations in amino acid sequence that enhance the stability of the complex formed between the viral surface protein and transmembrane protein. This invention also provides a viral envelope protein comprising a viral surface protein and a corresponding viral transmembrane protein wherein the viral envelope protein contains one or more mutations in amino acid sequence that enhance the stability of the complex formed between the viral surface protein and transmembrane protein. This invention further provides methods of treating HIV-1 infection.
Owner:PROGENICS PHARMA INC
Bacterial outer memberane vesicles
InactiveUS20060166344A1Good curative effectAvoid problemsAntibacterial agentsBacteriaImmunogenicityTreated cell
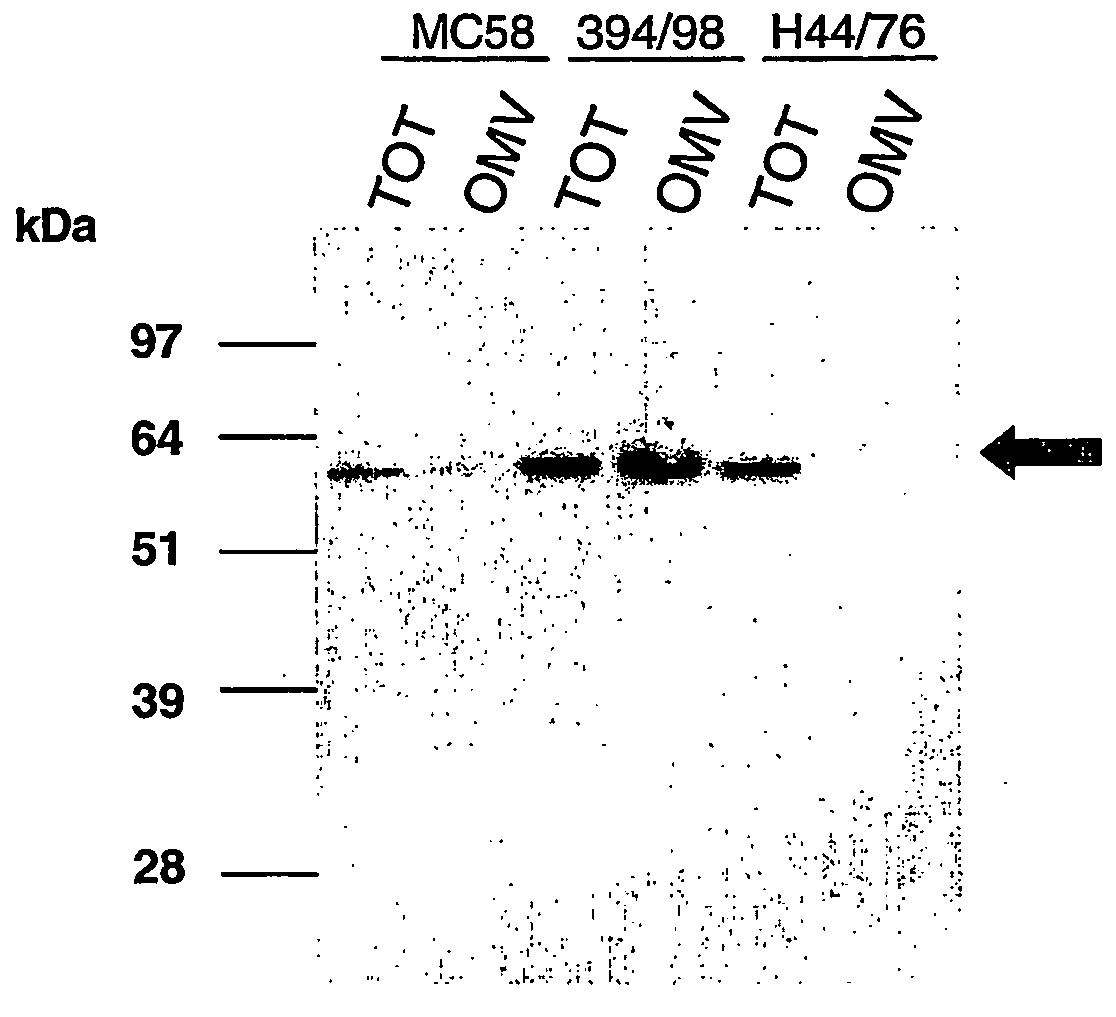
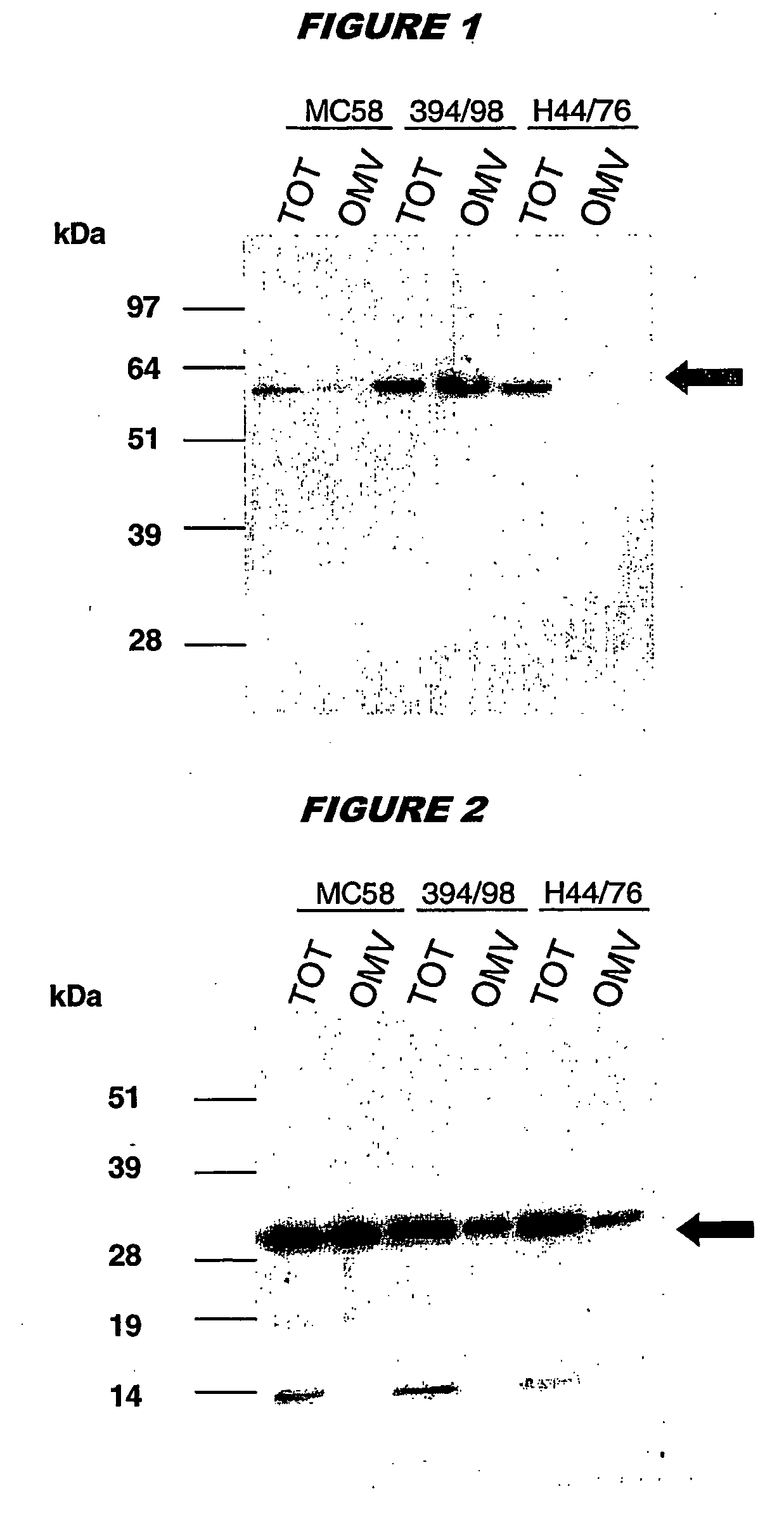
Existing methods of meningococcal OMV preparation involve the use of detergent during disruption of the bacterial membrane. According to the invention, membrane disruption is performed substantially in the absence of detergent. The resulting OMVs which retain important bacterial immunogenic components, particularly (i) the protective NspA surface protein, (ii) protein NMB2132 and (iii) protein NMB 1870. A Typical process involves the following steps: (a) treating bacterial cells in the substantial absence of detergent; (b) centrifuging the composition from step (a) to separate the outer membrane vesicles from treated cells and cell debris, and collecting the supernatant; (c) performing a high speed centrifugation of the supernatant from step (b) and collecting the outer membrane vesicles in a pellet; (d) re-dispersing the pellet from step (c) in a buffer; (e) performing a second high speed centrifugation in accordance with step (c), collecting the outer membrane vesicles in a pellet; (f) re-dispersing the pellet from step (e) in an aqueous medium.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
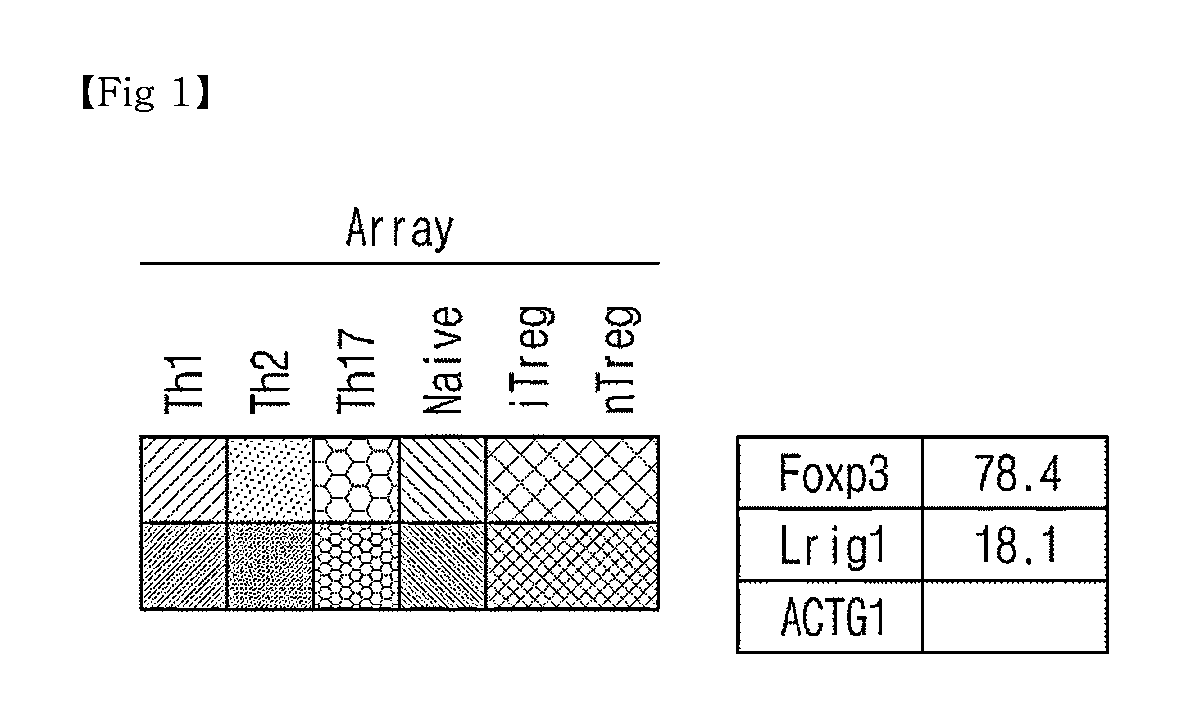
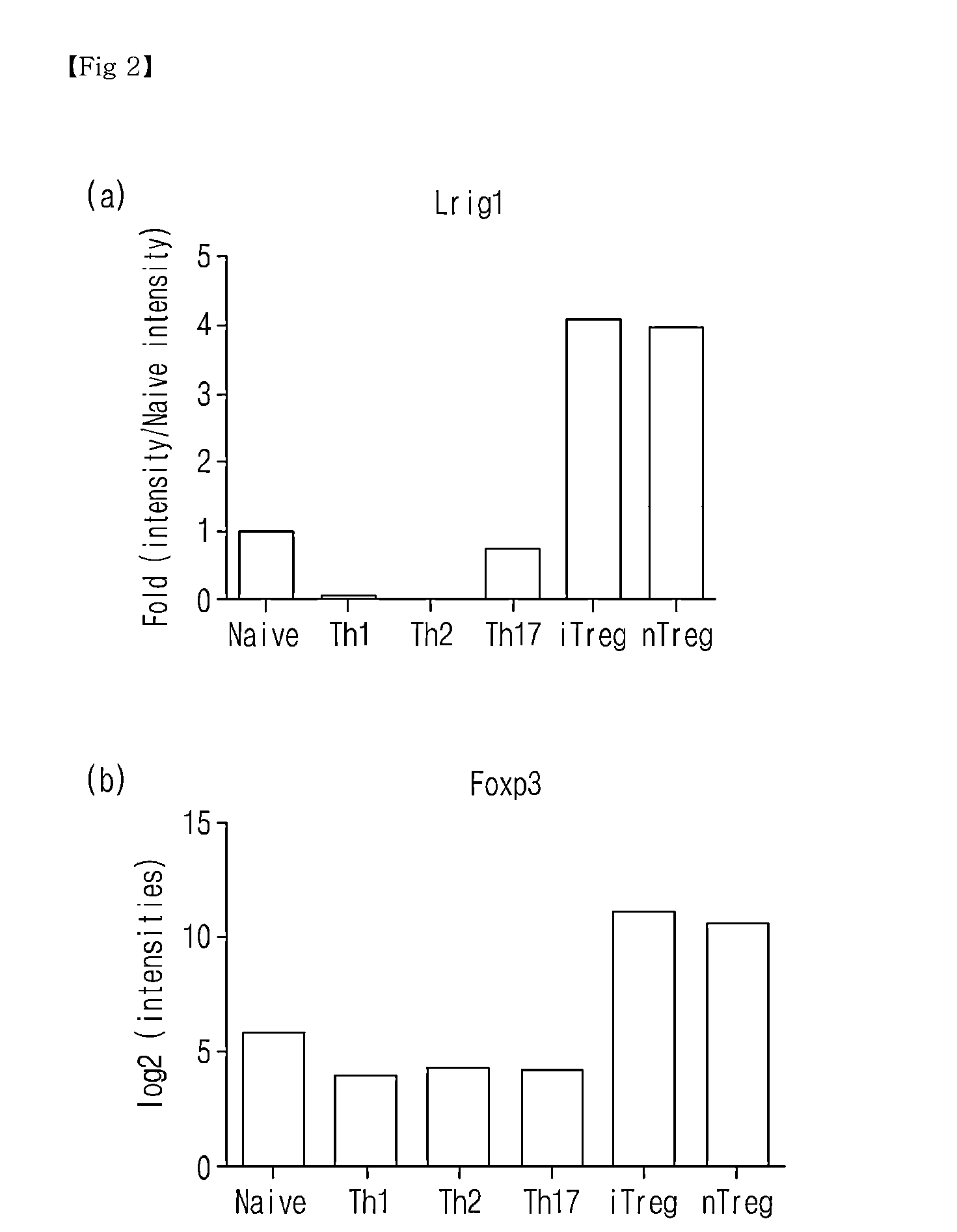
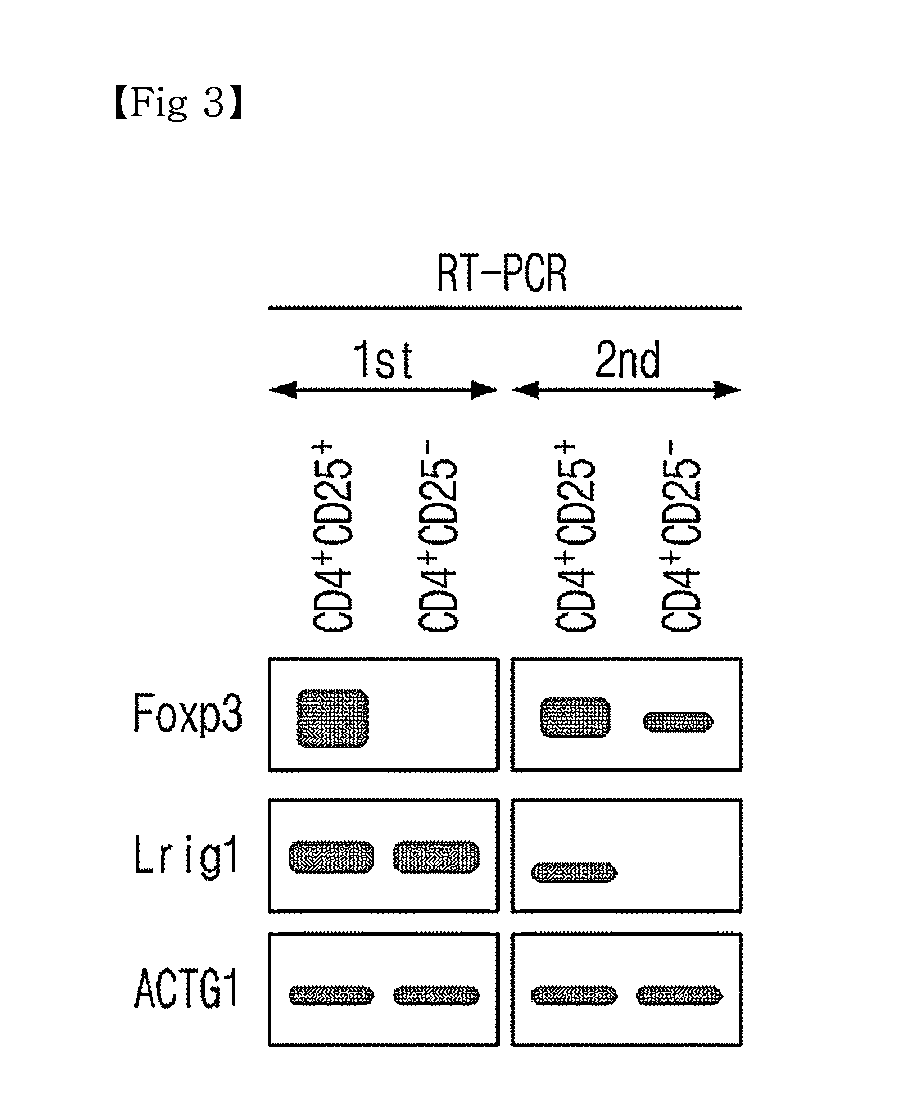
Novel Use of Regulatory T Cell-Specific Surface Protein LRIG-1
The present invention relates to a novel use of regulatory T cell-specific surface protein Lrig-1, and more specifically to an immunosuppressive agent comprising siRNA which inhibits the expression of surface protein Lrig-1. In addition, the invention relates to a method for screening an immunosuppressive agent which inhibits proteins of Lrig-1 or genes encoding the proteins. As a result, an immunosuppressive agent with low side effects and high specificity can be developed.
Owner:GOOD T CELLS INC
Modified surface antigen
Novel proteins that constitute modified forms of a Neisseria meningitidis surface antigen and encoding nucleic acids are provided. The modified surface proteins are characterized by having deletions of non-conserved amino acids, and thereby being capable of eliciting cross-protective immune responses against Neisseria meningitidis. The invention extends to the use of the modified surface antigens in diagnostics, in therapeutic and prophylactic vaccines and in the design and / or screening of medicaments. The modified surface antigens are particularly useful in vaccines which effectively immunize against a broader spectrum of N. meningitidis strains than would be expected from a corresponding wild-type surface antigen.
Owner:QUEENSLAND THE UNIV OF
Photosensitive antibody-phuorophore conjugates
InactiveCN103781495AAllow treatmentGarment special featuresEnergy modified materialsFluorescenceCell Surface Proteins
The present disclosure relates to compositions and methods of killing cells. In particular examples, the method includes contacting a cell having a cell surface protein with a therapeutically effective amount of an antibody-IR700 molecule, wherein the antibody specifically binds to the cell surface protein, such as a tumor-specific antigen on the surface of a tumor cell. The cell is subsequently irradiated, such as at a wavelength of 660 to 740 nm at a dose of at least 1 J cm<-2>. The cell is also contacted with one or more therapeutic agents (such as an anti-cancer agent), for example about 0 to 8 hours after irradiating the cell, thereby killing the cell. Also provided are methods of imaging cell killing in real time, using fluorescence lifetime imaging. Also provided are wearable devices that include an article of clothing, jewelry, or covering; and an NIR LED incorporated into the article, which can be used with the disclosed methods.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Methods for treating HIV infected subjects
InactiveUS20060099177A1Increase the number ofInhibit productionBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAccessory moleculeExogenous growth
Methods for inducing a population of T cells to proliferate by activating the population of T cells and stimulating an accessory molecule on the surface of the T cells with a ligand which binds the accessory molecule are described. T cell proliferation occurs in the absence of exogenous growth factors or accessory cells. T cell activation is accomplished by stimulating the T cell receptor (TCR) / CD3 complex or the CD2 surface protein. To induce proliferation of an activated population T cells, an accessory molecule on the surface of the T cells, such as CD28, is stimulated with a ligand which binds the accessory molecule. The T cell population expanded by the method of the invention can be genetically transduced and used for immunotherapy or can be used in methods of diagnosis.
Owner:GENETICS INST INC +2
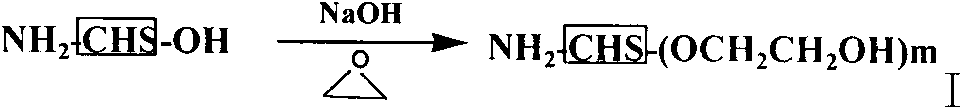
Sulfhydrylated amphipathic chitosan polymer carrier as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103143028APromote absorptionGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryBuccal administrationAmphiphilic chitosan
The invention relates to a sulfhydrylated amphipathic chitosan derivative carrier with biological adhesiveness. The derivatives are structured by respectively introducing hydrophilic groups, hydrophobic groups and groups containing sulfydryl. The derivative in an aqueous medium can be self-assembled to nano-micelle so as to load pharmaceutically active or pharmacologically active molecules. After the carrier reaches the mucosa of a living body, the sulfydryl groups can be bonded with surface protein of the mucosa through covalent bonds: disulfide bonds, so that the detaining and acting time of micelle on the surface of the mucosa is prolonged. In addition, the chitosan derivative further has the function of mutual effect in compact connection with cells and opening compact connection with cells of the mucosa. The auxiliary material can be used as the carrier of the pharmaceutically active or pharmacologically active molecules to be used for administration via oral administration, ocular administration, nasal mucosa administration and the like, so that medicine absorption is remarkably improved, and the bioavailability is improved. The carrier provided by the invention is simple in preparation method and manure in process, so that the carrier is suitable for large-scale continuous production.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
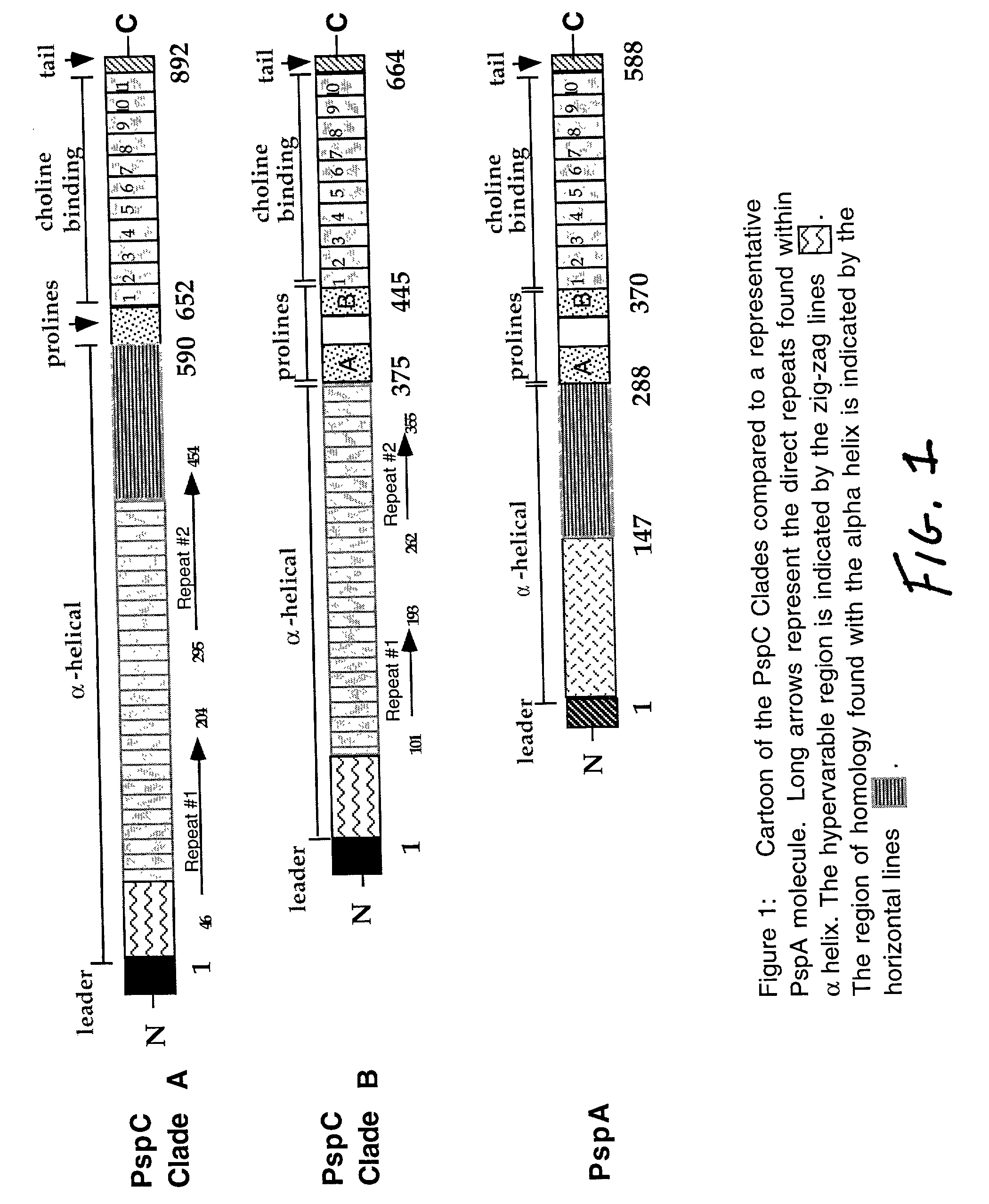
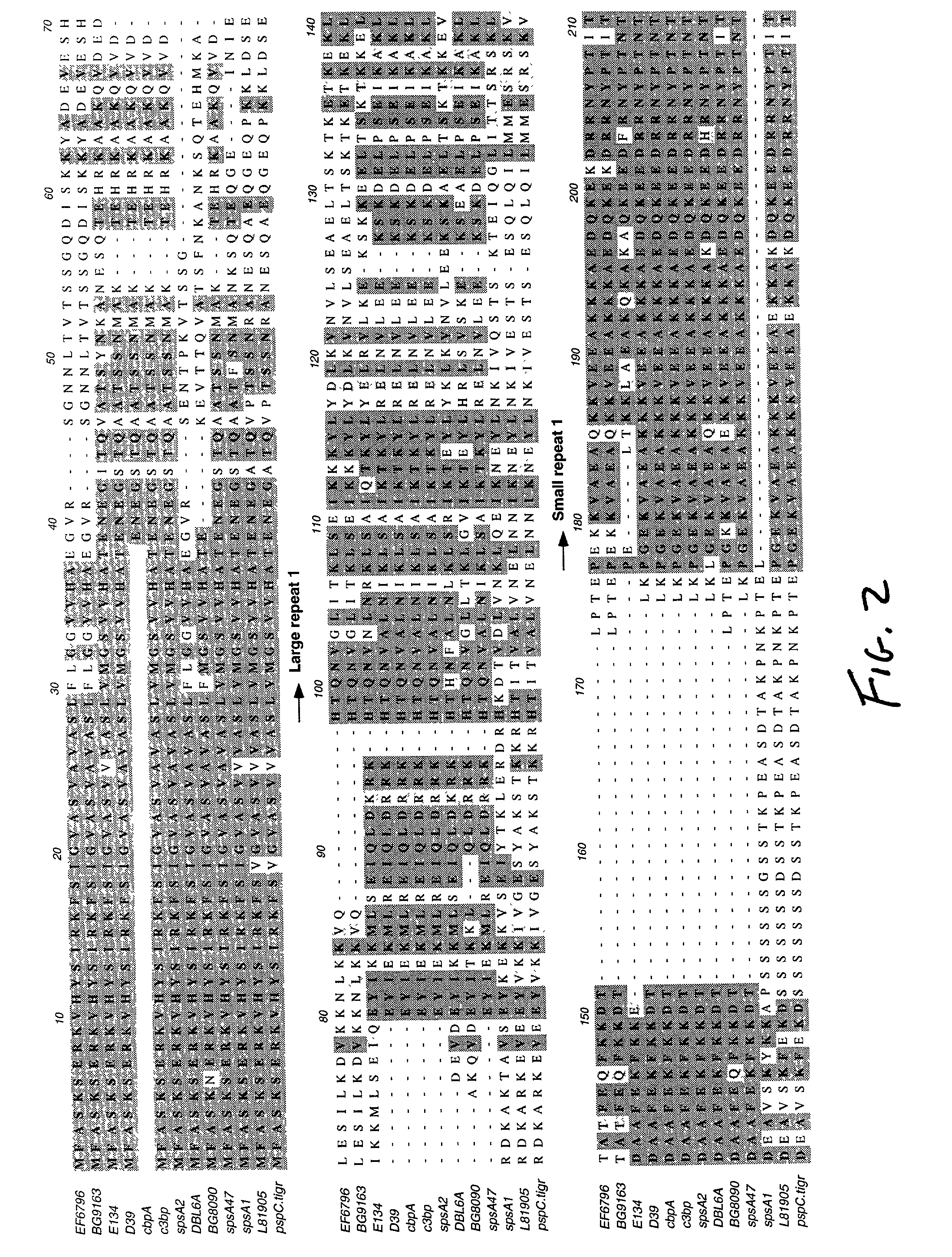
Pneumococcal surface protein c (PSPC), epitopic regions and strain selection thereof, and uses therefor
InactiveUS20030059438A1Improving immunogenicityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsEukaryotic plasmidsIn vivo
Disclosed and claimed are: epitopic regions of Pneumococcal Surface Protein C or "PspC", different clades of PspC, isolated and / or purified nucleic acid molecules such as DNA encoding a fragment or portion of PspC such as an epitopic region of PspC or at least one epitope of PspC, uses for such nucleic acid molecules, e.g., to detect the presence of PspC or of S. pneumoniae by detecting a nucleic acid molecule therefor in a sample such as by amplification and / or a polymerase chain reaction, vectors or plasmids which contain and / or express such nucleic acid molecles, e.g., in vitro or in vivo, immunological, immunogenic or vaccine compositions including at least one PspC and / or a portion thereof (such as at least one epitopic region of at least one PspC and / or at least one polypeptide encoding at least one epitope of at least one PspC), either alone or in further combination with at least one second pneumococcal antigen, such as at least one different PspC and / or a fragment thereof and / or at least one PspA and / or at least one epitopic region of at least one PspA and / or at least one polypeptide including at least one epitope of PspA. PspC or a fragment thereof, and thus a composition including PspC or a fragment thereof, can be administered by the same routes, and in approximately the same amounts, as PspA. Thus, the invention further provides methods for administering PspC or a fragment thereof, as well as uses of PspC or a fragment thereof to formulate such compositions.
Owner:ALABAMA AT BIRMINGHAM UNIVERISTY OF +1
Proteinase K resistant surface protein of neisseria meningitidis
A highly conserved, immunologically accessible antigen at the surface of Neisseria meningitidis organisms. Immunotherapeutic, prophylactic and diagnostic compositions and methods useful in the treatment, prevention an diagnosis of Neisseria meningitidis diseases. A proteinase K resistant Neisseria meningitidis surface protein having an apparent molecular weight of 22 kDa, the corresponding nucleotide and derived amino acid sequences (SEQ ID NO: 1, NO:3, NO:5 and NO:7: SEQ ID NO: 2, NO:4, NO:6, and NO:8), recombinant DNA methods for the production of the Neisseria meningitidis 22 kDA surface protein, and antibodies that bind to the Neisseria meningitidis 22 kDA surface protein.
Owner:ID BIOMEDICAL
Multivalent aptamer complexes
A compound of the formula A-B-C, is provided, wherein: A is a first nucleic acid that specifically binds to an extracellular surface protein expressed by a cell of interest, B is an alkyl linker; and C is a second nucleic acid that hybridizes to a complementary nucleic acid. In some embodiments, the first nucleic acid is an aptamer. In some embodiments, the nucleic acid comprises an active compound, particularly cytotoxic nucleotides such as poly-FdUMP. Compositions and methods of using such compounds for treating and / or detecting cancer are also described.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Near infrared photoimmunotherapy (nir-pit) of suppressor cells to treat cancer
ActiveUS20180236076A1Rapid and effective tumor killingReduce in quantityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthWhole body
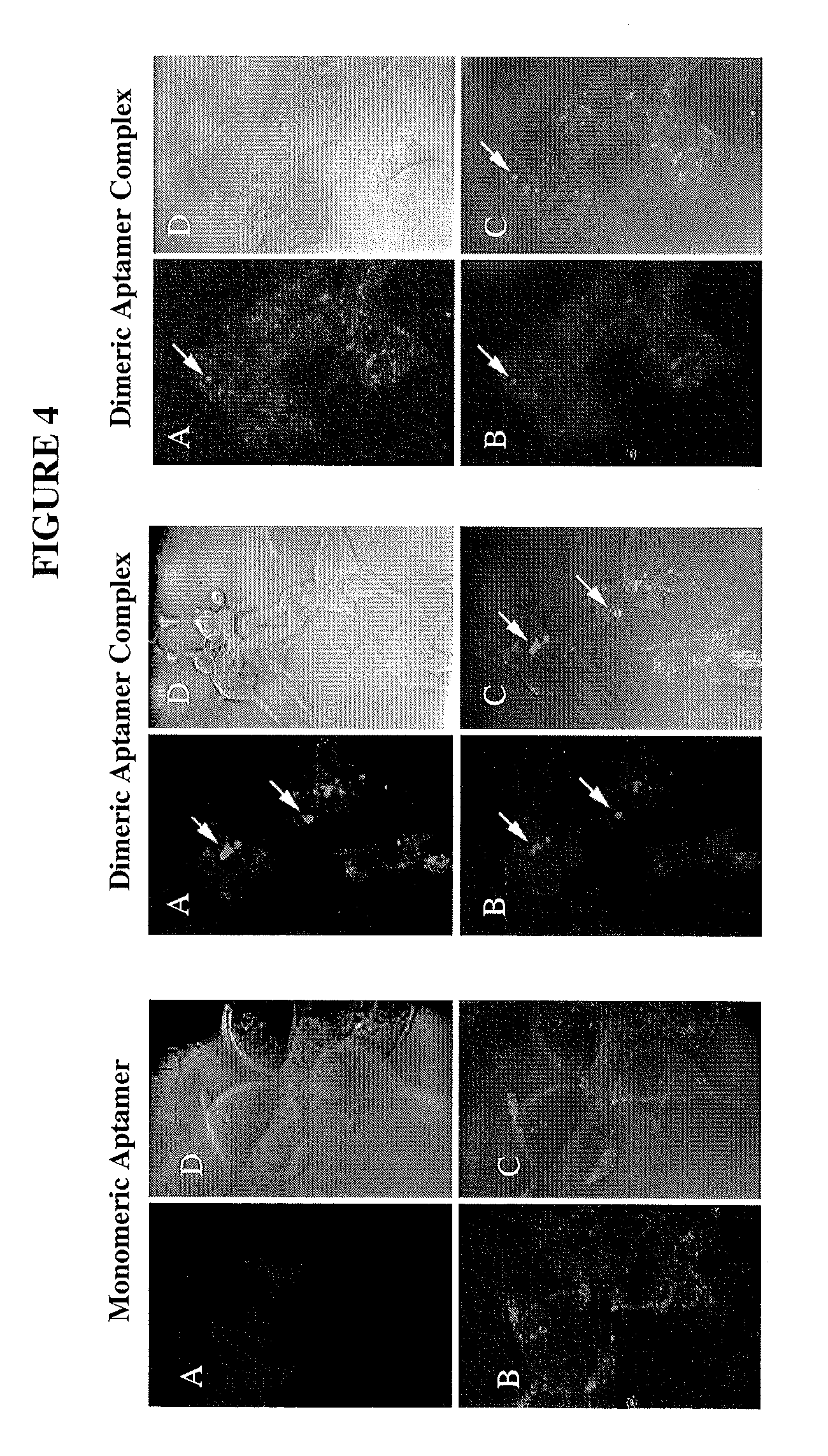
It is shown that CD25-targeted near-infrared photo-immunotherapy causes a unique, rapid and spatially selective depletion of Tregs leading to regression of the treated tumor and inducing systemic immunologic responses in untreated tumors. Based on these observations, provided are compositions and methods of killing immune suppressor cells, for example to treat cancer. Reducing the number of suppressor cells in a subject can remove suppression of effector T cells, for example, to treat cancer using the subject's own immune system. In particular examples, the method includes contacting suppressor cells having a suppressor cell surface protein with an antibody-IR700 molecule, wherein the antibody specifically binds to the suppressor cell surface protein, and in some examples the antibody does not have a functional Fc region. The cell is subsequently irradiated, such as at a wavelength of 660 to 740 nm, for example at a dose of at least 4 J cm−2.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Method of delivering therapeutic agents to site of tissue injury
A viral or non-viral vector particle having a modified viral surface protein wherein the viral surface protein is modified to include a targeting polypeptide including a binding region which binds to an extracellular matrix component. Such vector particles are useful in delivering genes encoding therapeutic agents to cells located at the site of an exposed extracellular matrix component.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com