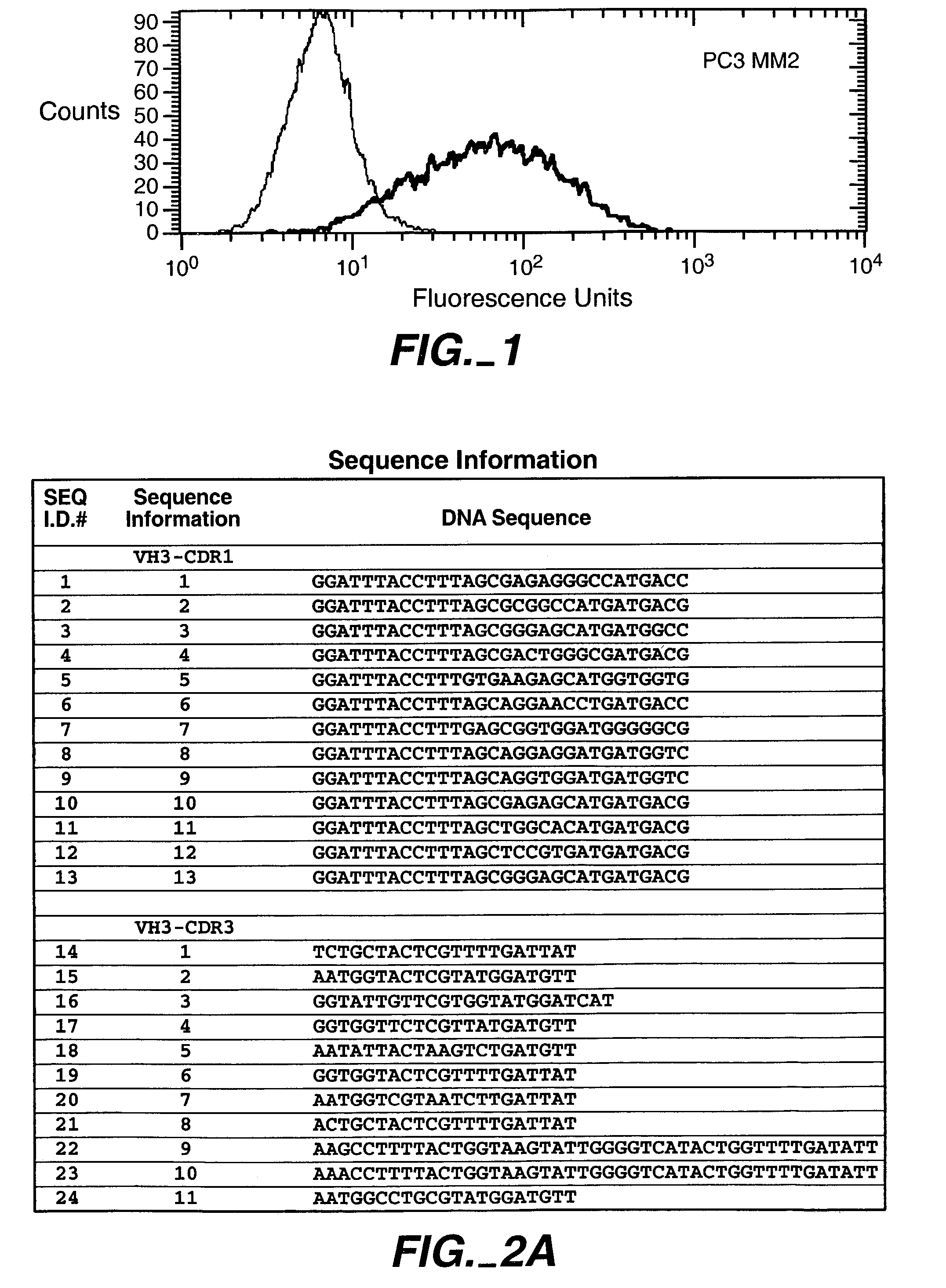
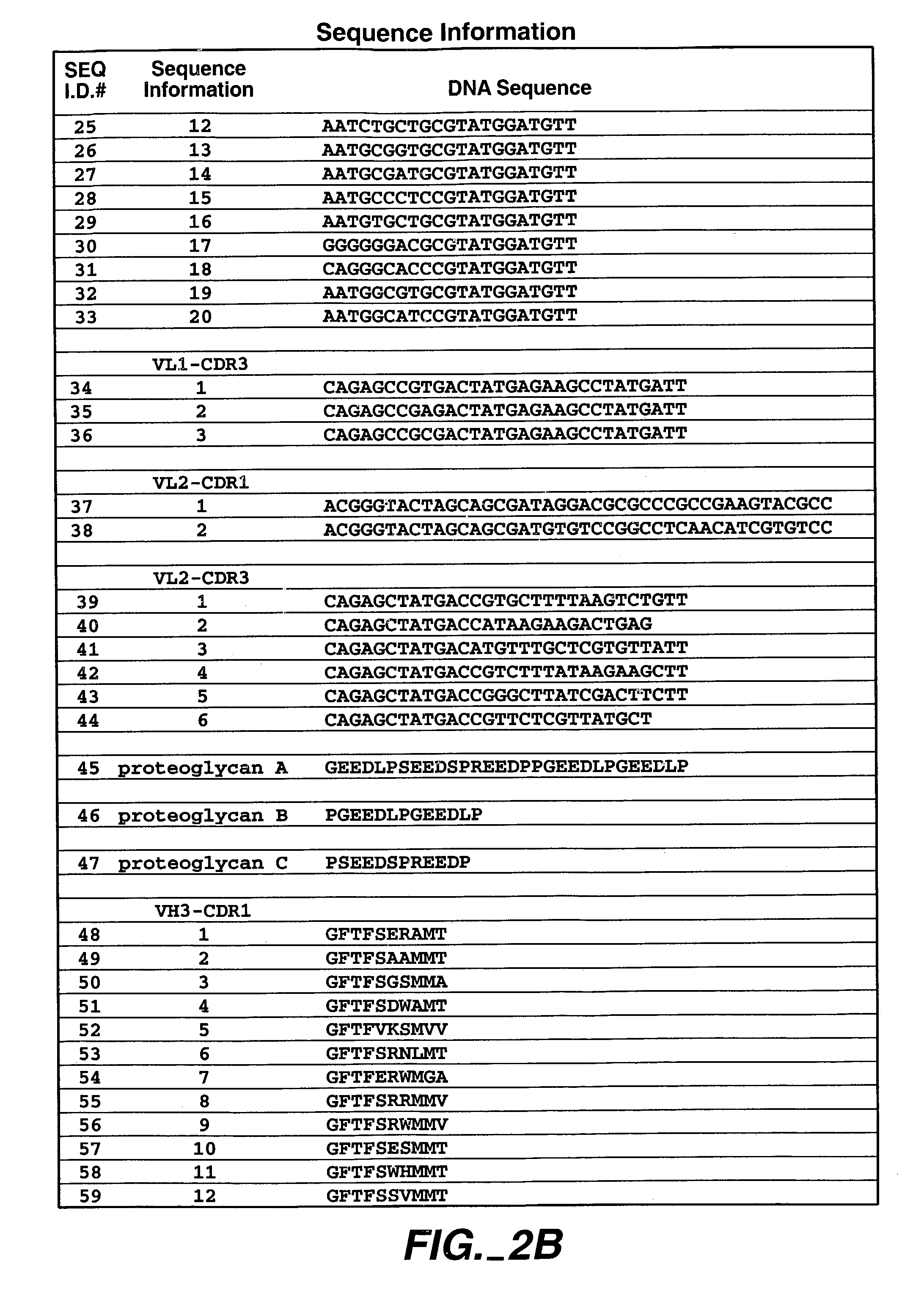
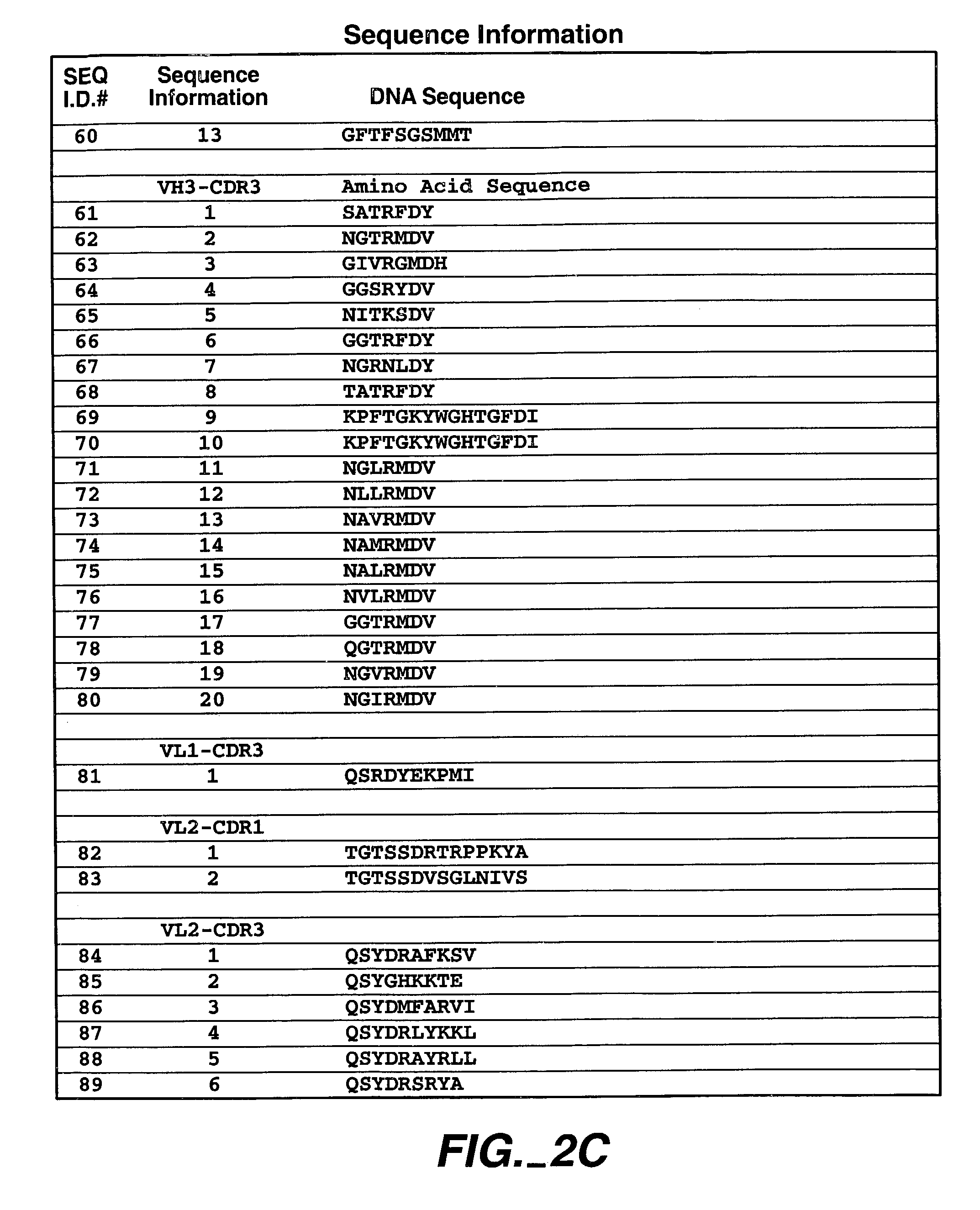
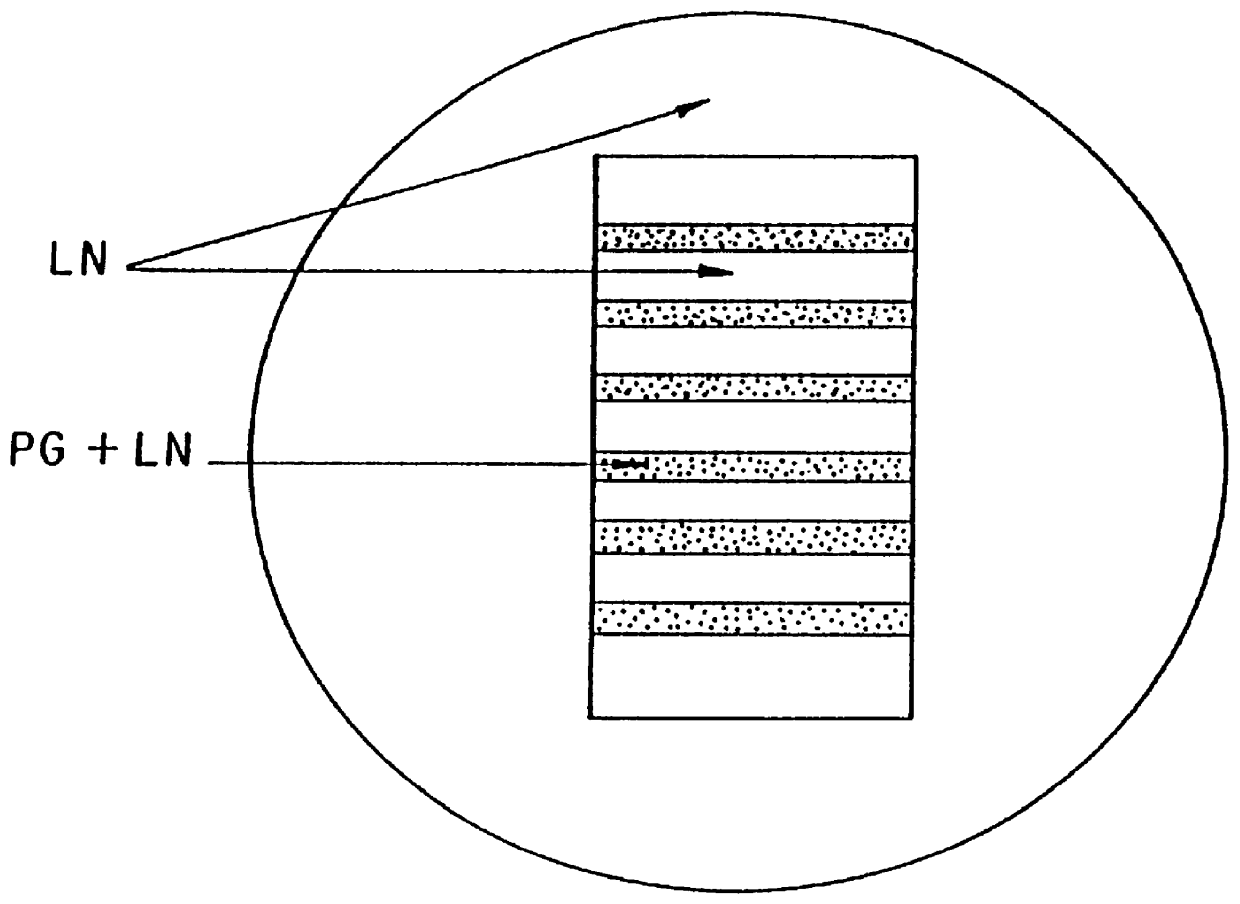
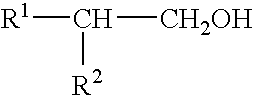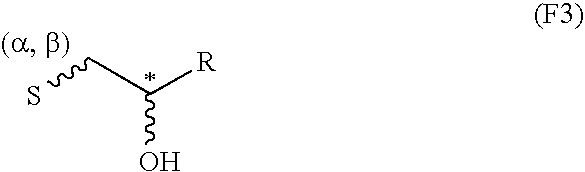Patents
Literature
389 results about "Proteoglycan" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
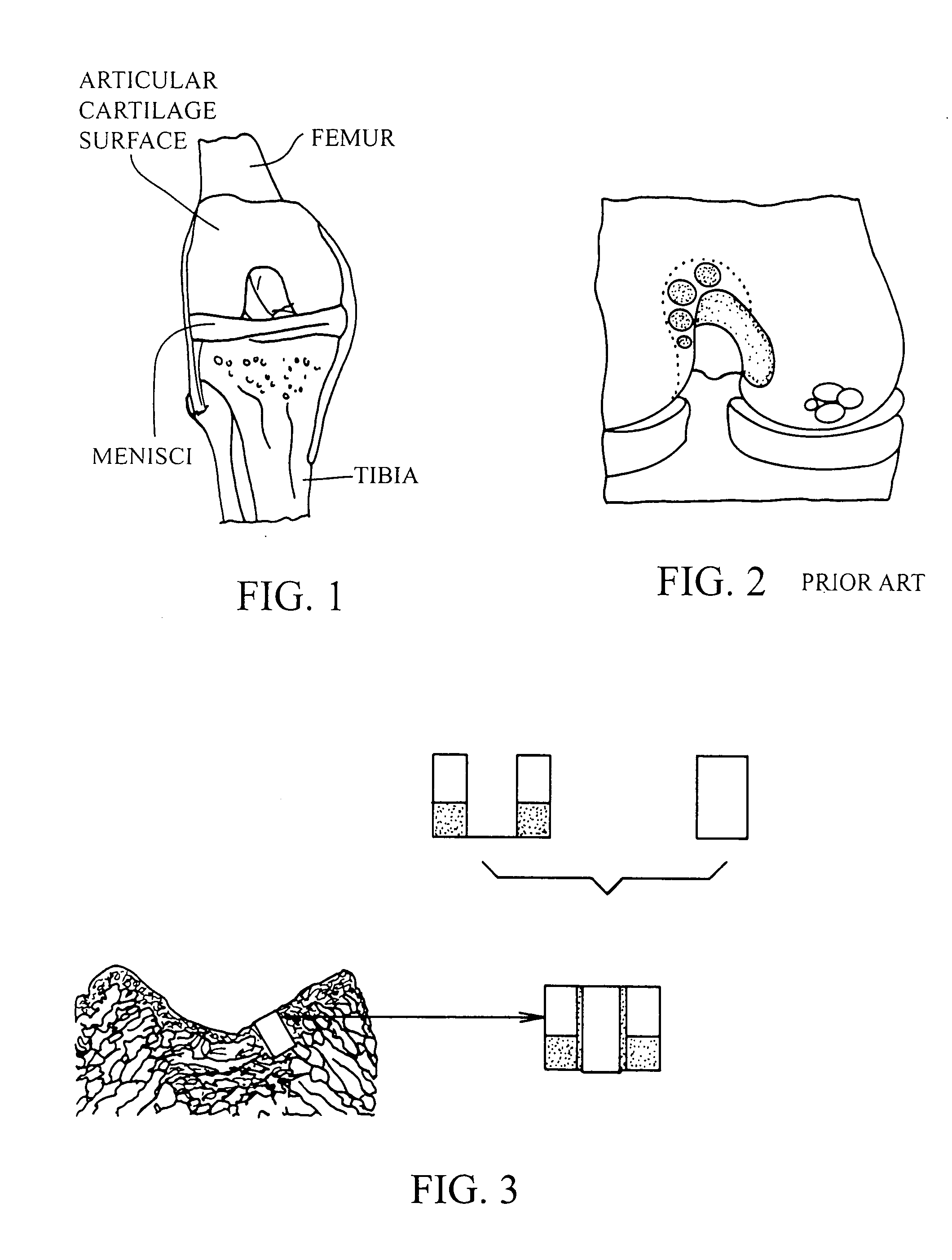
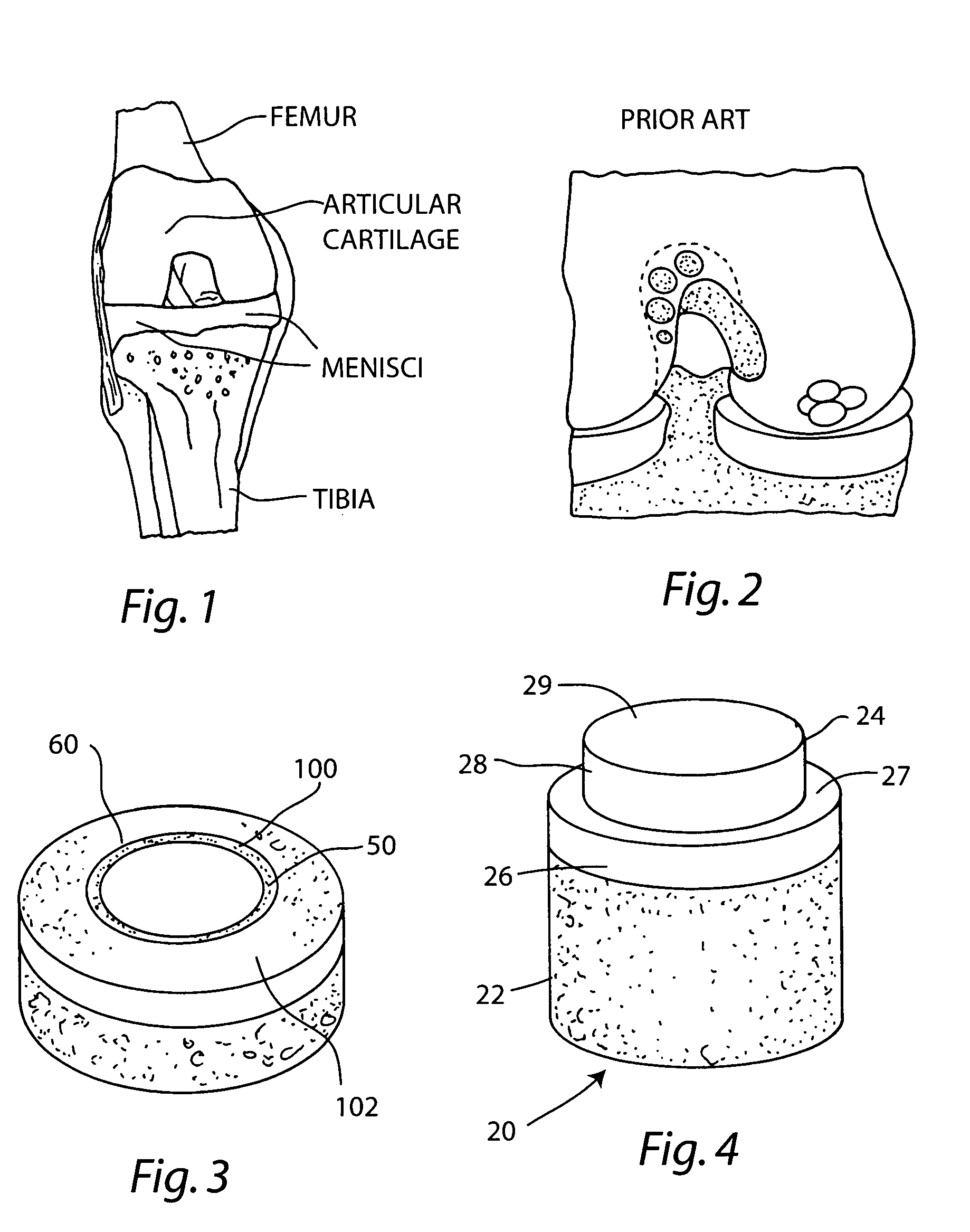
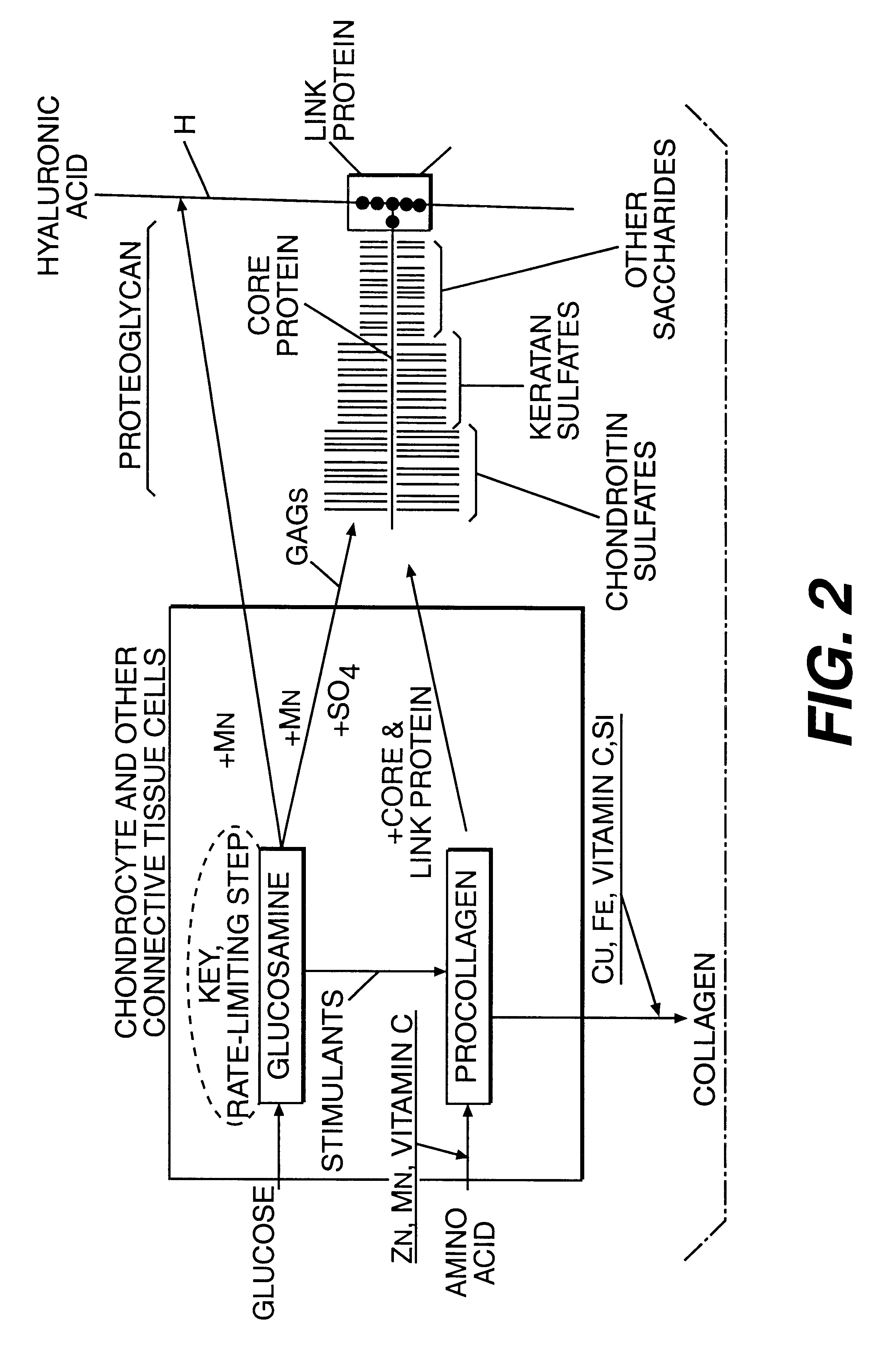
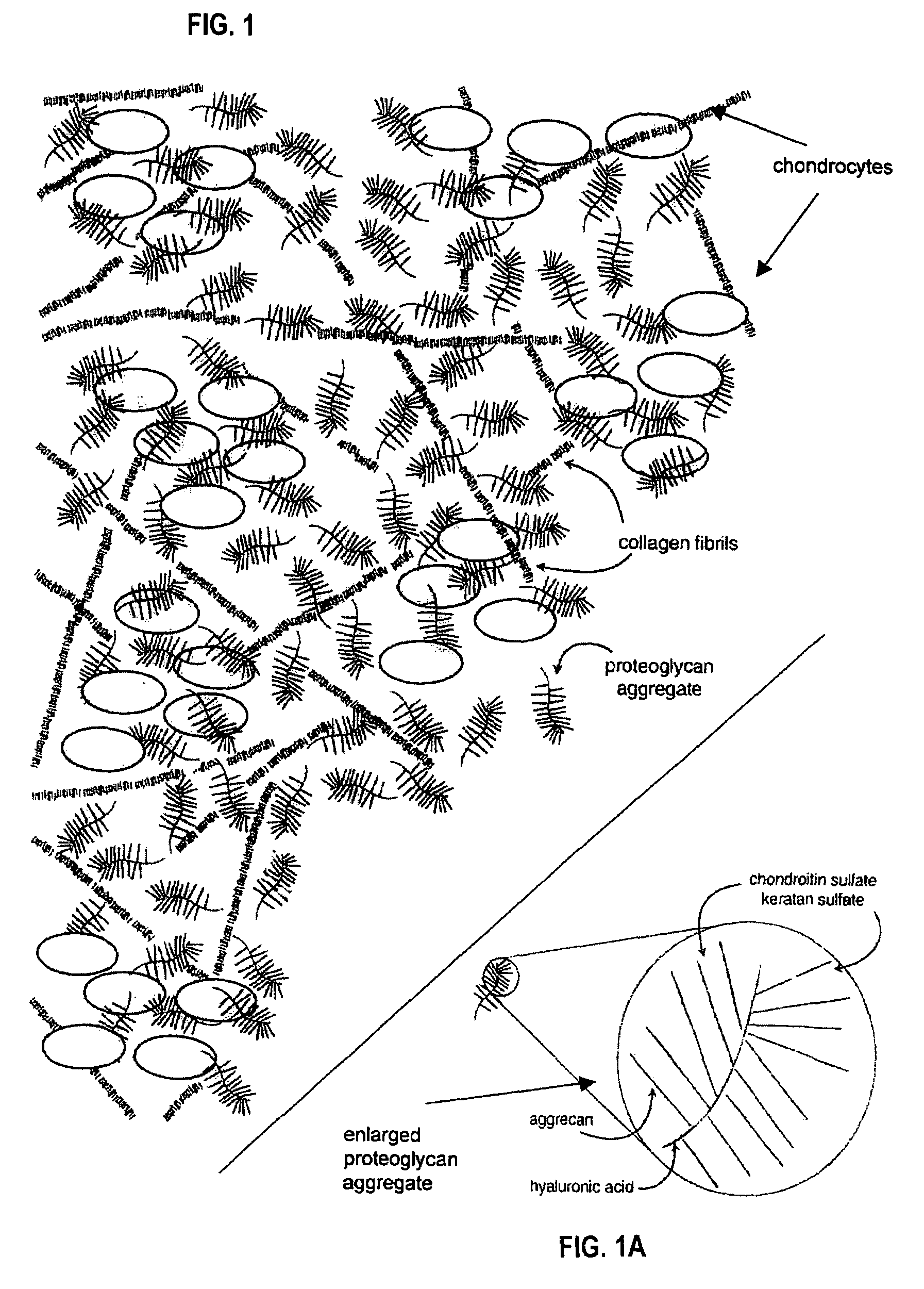
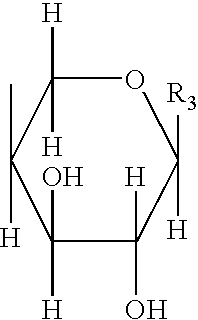
Proteoglycans are proteins that are heavily glycosylated. The basic proteoglycan unit consists of a "core protein" with one or more covalently attached glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chain(s). The point of attachment is a serine (Ser) residue to which the glycosaminoglycan is joined through a tetrasaccharide bridge (e.g. chondroitin sulfate-GlcA-Gal-Gal-Xyl-PROTEIN). The Ser residue is generally in the sequence -Ser-Gly-X-Gly- (where X can be any amino acid residue but proline), although not every protein with this sequence has an attached glycosaminoglycan. The chains are long, linear carbohydrate polymers that are negatively charged under physiological conditions due to the occurrence of sulfate and uronic acid groups. Proteoglycans occur in the connective tissue.
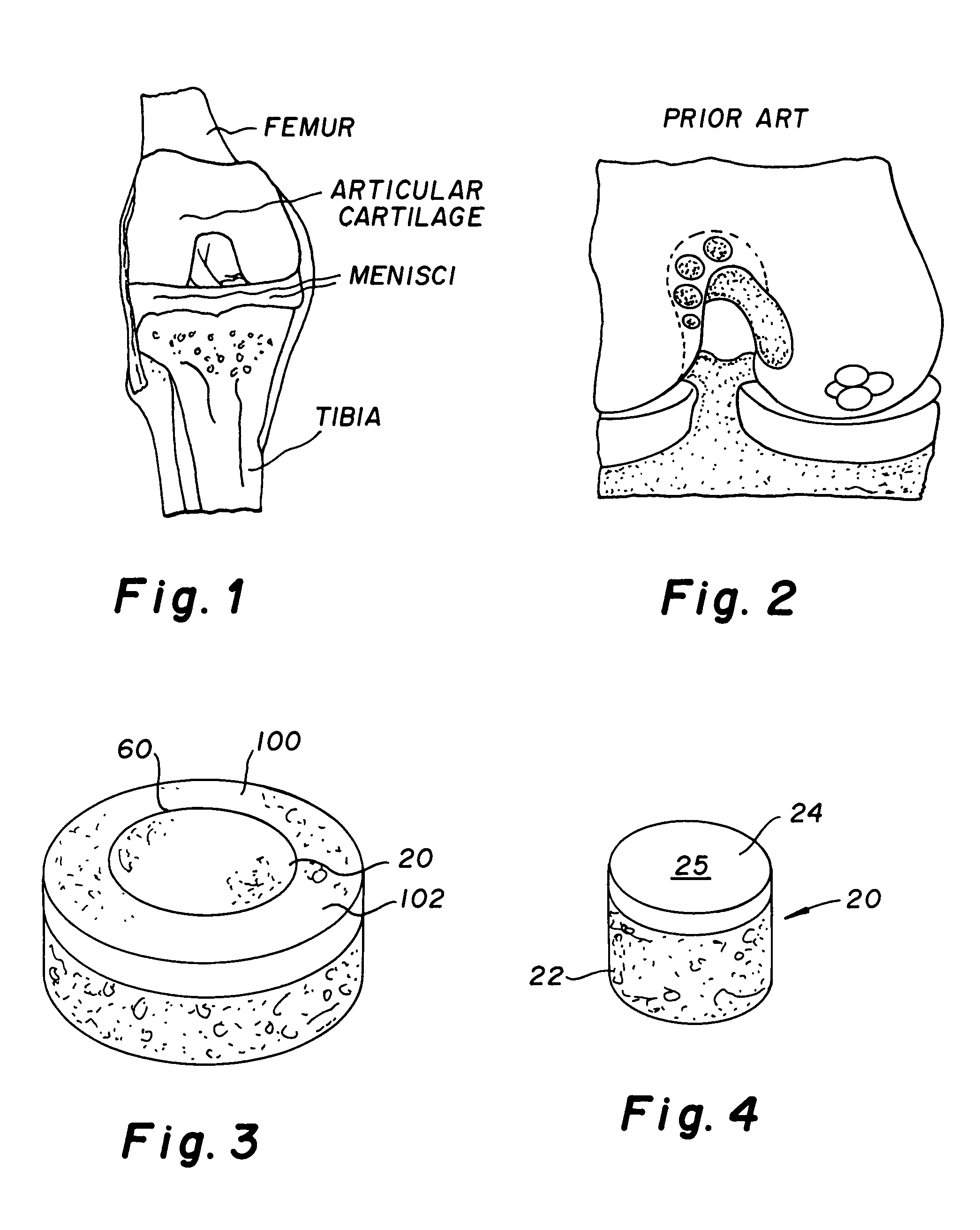
Cartilage implant plug with fibrin glue and method for implantation
InactiveUS20050064042A1Restores normal functionRelief painSurgical adhesivesPeptide/protein ingredientsThrombin activityChondral defect
The invention is directed toward a cartilage repair assembly comprising a shaped structure of subchondral bone with an integral overlying cartilage cap which is treated to remove cellular debris and proteoglycans and milled cartilage in a bioabsorbable carrier. The shaped structure is dimensioned to fit in a drilled bore in a cartilage defect area so that said shaped bone and cartilage cap when centered in the bore does not engage the side wall of the bore and is positioned from the side wall of the bone a distance ranging from 10 microns to 1000 microns and is surrounded by milled cartilage and a fibrin thrombin glue. A method for inserting the assembly into a cartilage defect area is disclosed.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Stem cells within gel microenvironments
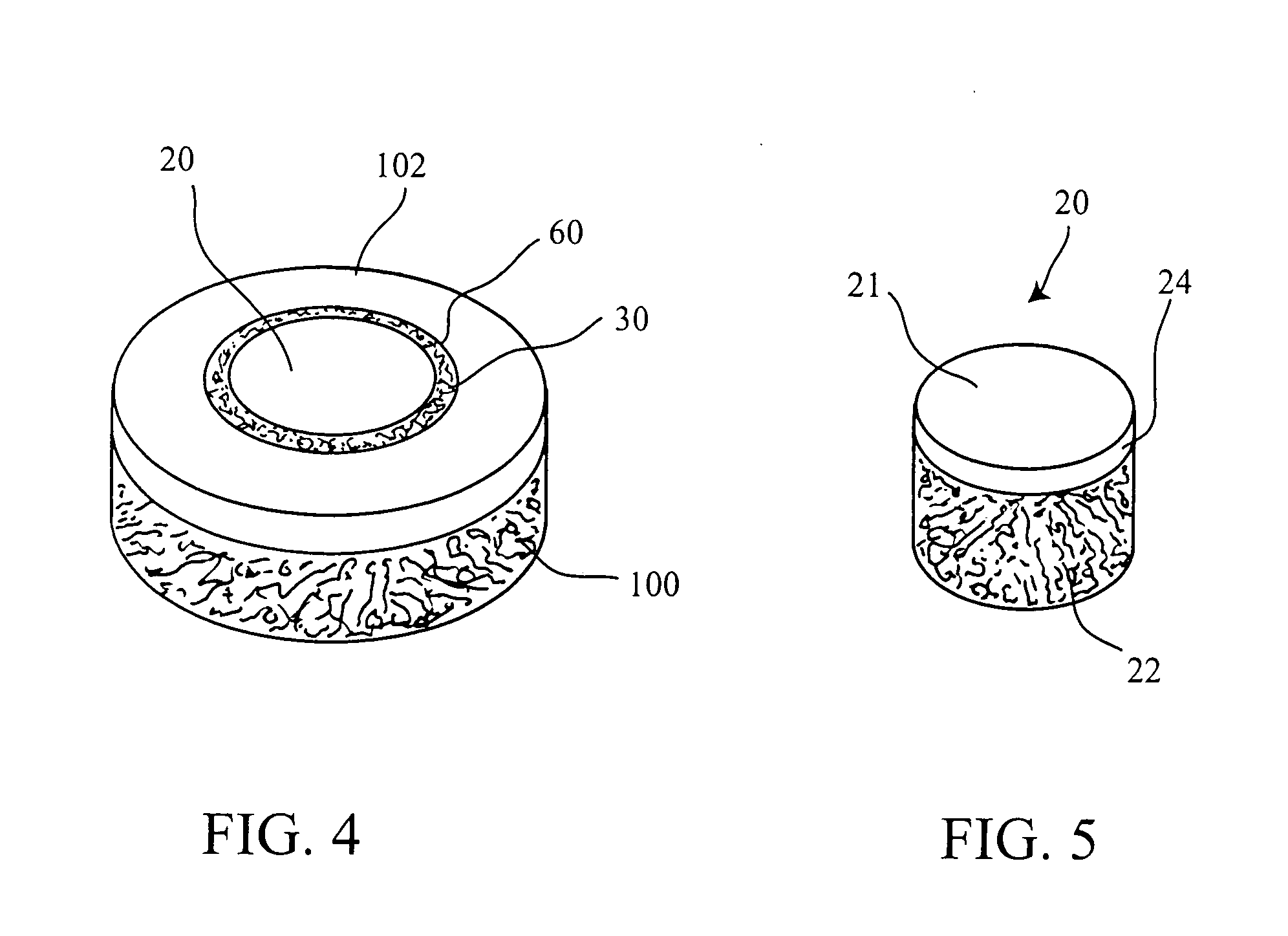
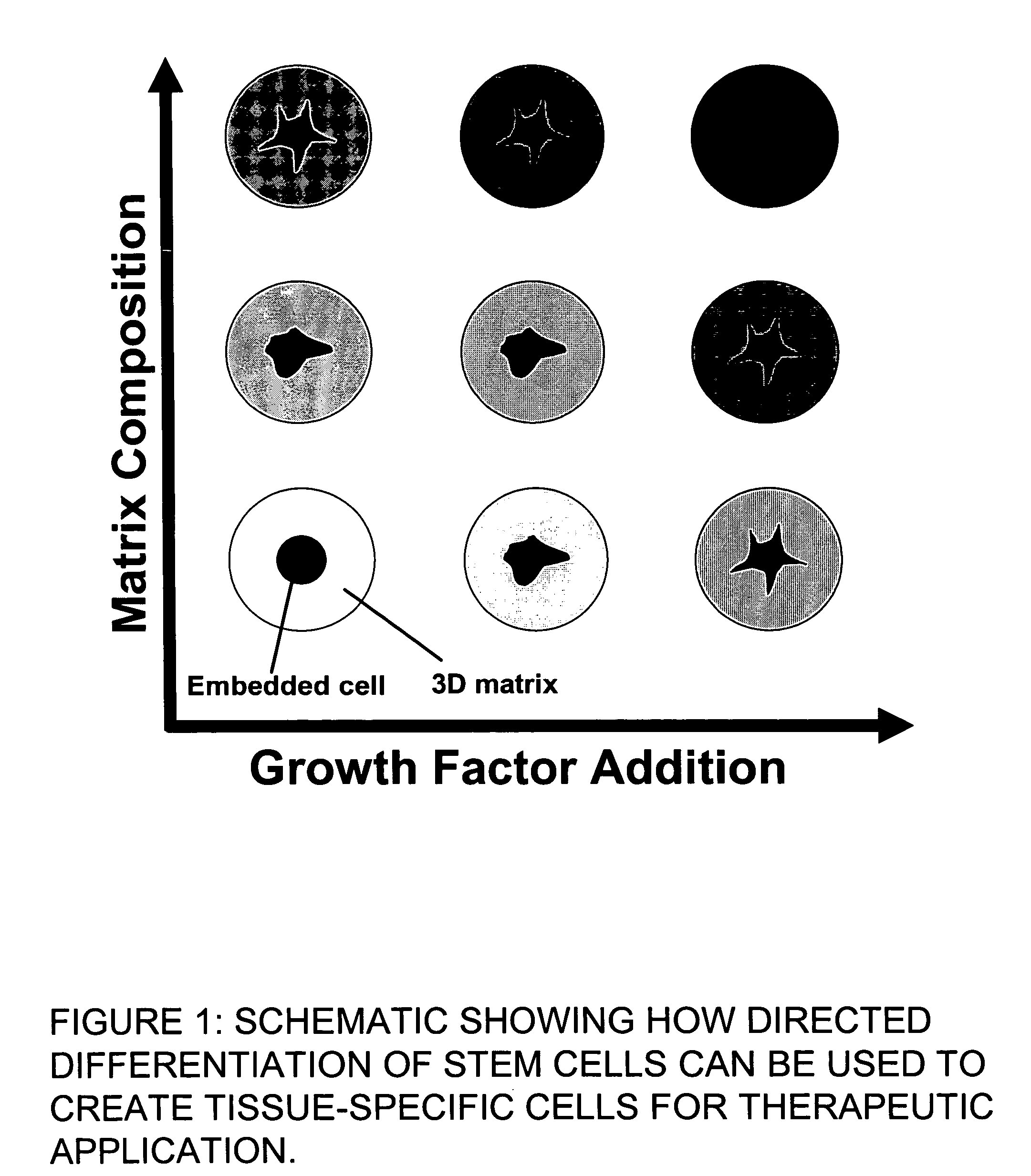
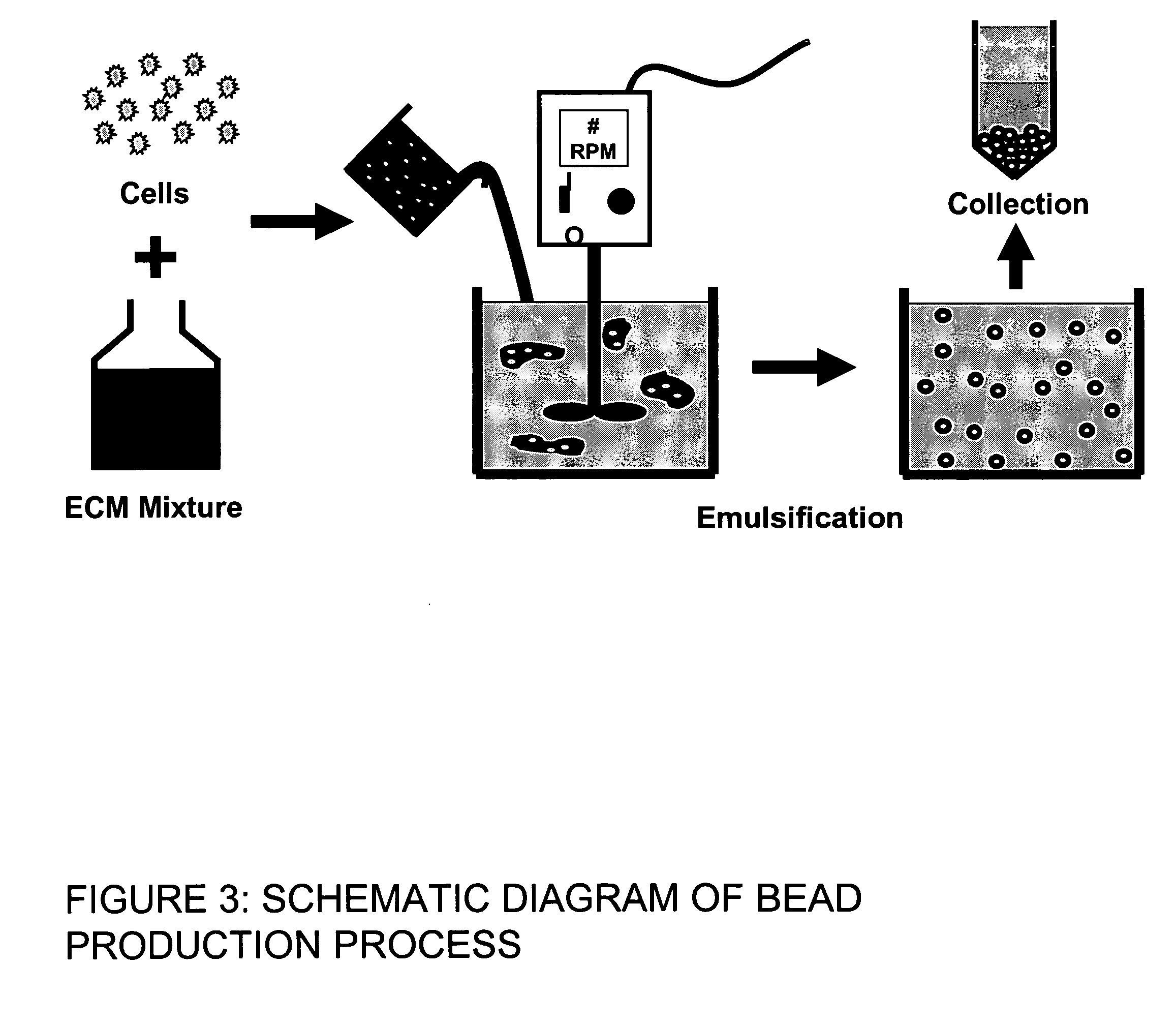
This invention provides a system to embed stem cells within three-dimensional (3D) hydrogel microenvironments consisting of naturally derived proteins, proteoglycans and / or polysaccharides. Pure matrices or combinations of materials can be used. The method involves suspending stem cells in solutions of the matrix components of interest, emulsifying these solutions in a hydrophobic phase, triggering gelation of the matrix components by changing the environmental conditions, and collection of the resulting hydrogel beads. The unique bead format of this invention has the advantage of allowing the use of small amounts of rare matrix proteins. Bead preparations can be concentrated into a paste for use as a cell delivery vehicle to damaged tissues, either directly after encapsulation or after a period of culture to promote stem cell differentiation. Defined 3D microenvironments can guide stem cell differentiation, and the resulting beads can be used directly as a cell delivery vehicle in various tissue repair applications.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Prion-free collagen and collagen-derived products and implants for multiple biomedical applications; methods of making thereof
InactiveUS6197935B1Preserve integrityPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsIn vivo biocompatibilityCollagen VI
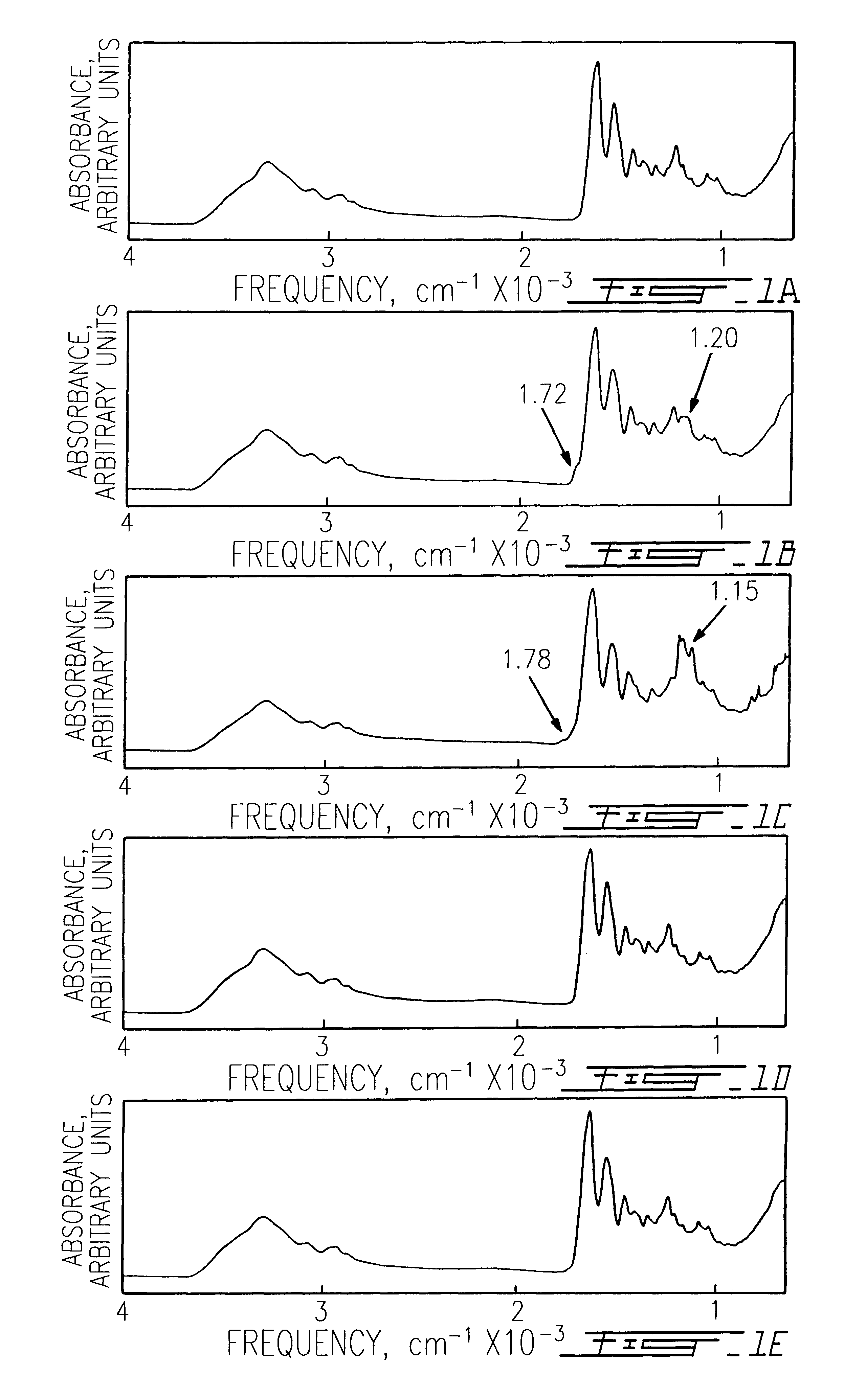
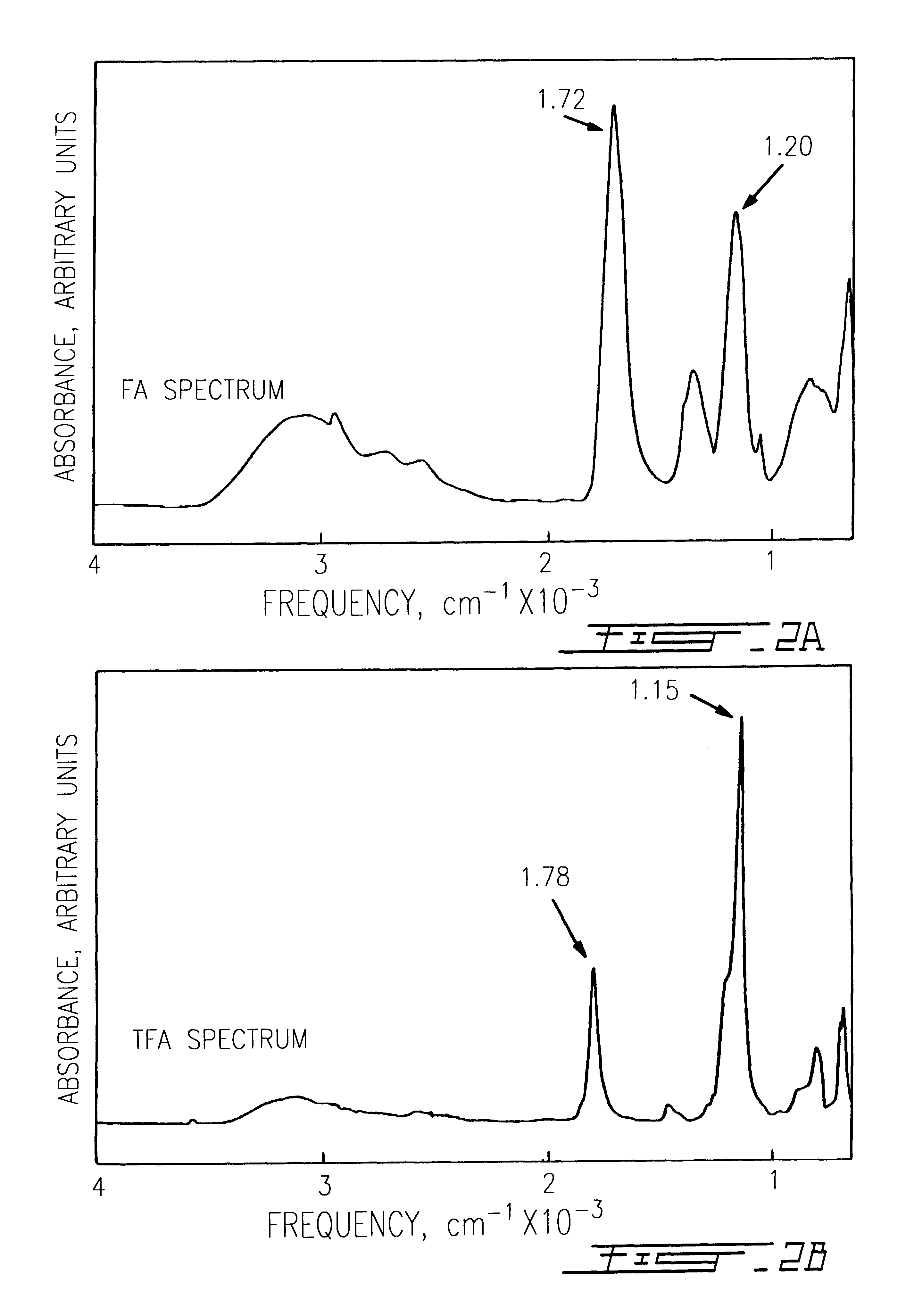
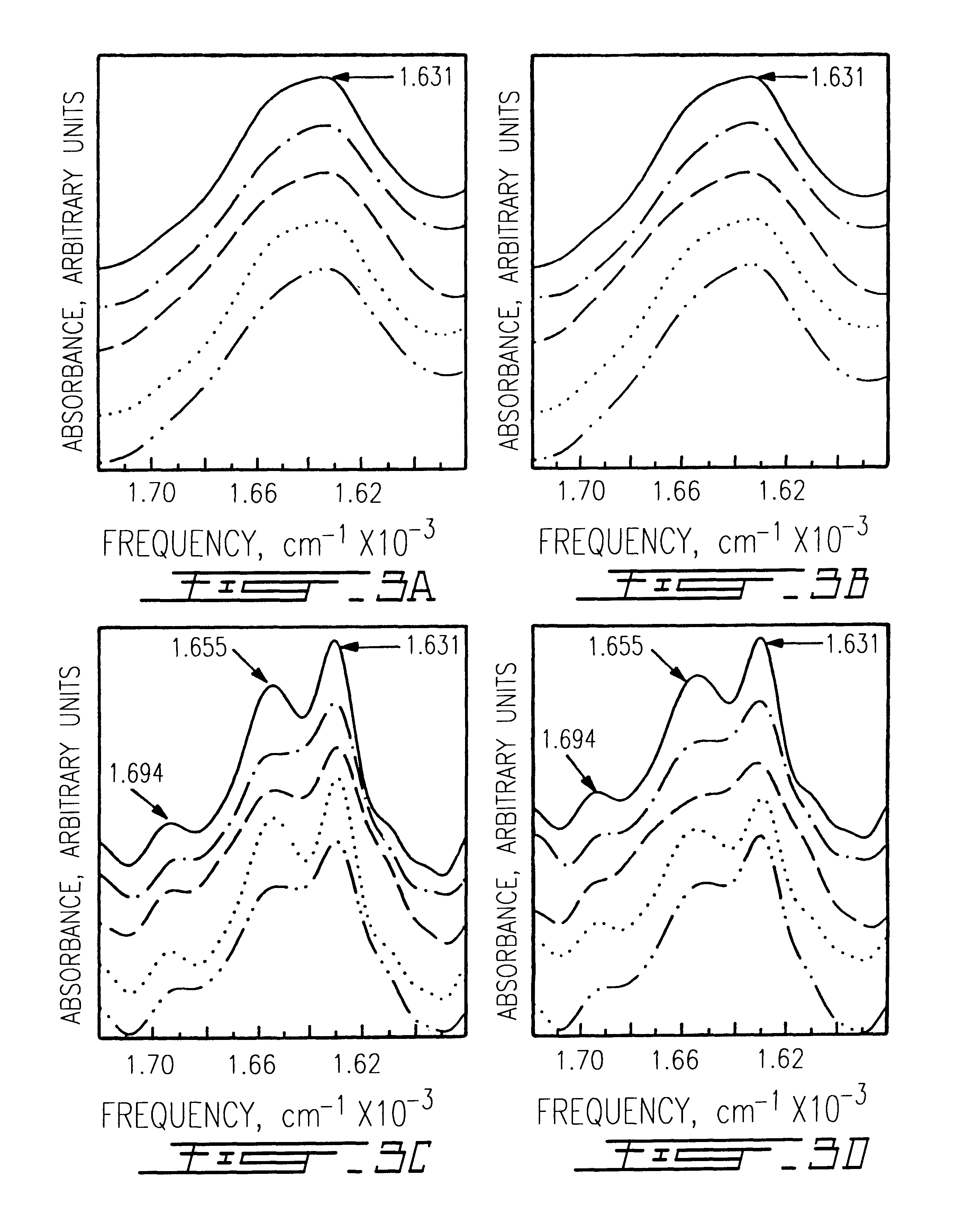
The use of collagen as a biomedical implant raises safety issues towards viruses and prions. The physicochemical changes and the in vitro and in vivo biocompatibility of collagen treated with heat, and by formic acid (FA), trifluoroacetic acid (TFA), tetrafluoroethanol (TFE) and hexafluoroiso-propanol (HFIP) were investigated. FA and TFA resulted in extensive depurination of nucleic acids while HFIP and TFE did so to a lesser degree. The molecules of FA, and most importantly of TFA, remained within collagen. Although these two acids induced modification in the secondary structure of collagen, resistance to collagenase was not affected and, in vitro, cell growth was not impaired. Severe dehydrothermal treatment, for example 110° C. for 1-3 days under high vacuum, also succeeded in removing completely nucleic acids. Since this treatment also leads to slight cross-linking, it could be advantageously used to eliminate prion and to stabilize gelatin products. Finally, prolonged treatment with TFA provides a transparent collagen, which transparency is further enhanced by adding glycosaminoglycans or proteoglycans, particularly hyaluronic acid. All the above treatments could offer a safe and biocompatible collagen-derived material for diverse biomedical uses, by providing a virus or prion-free product.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
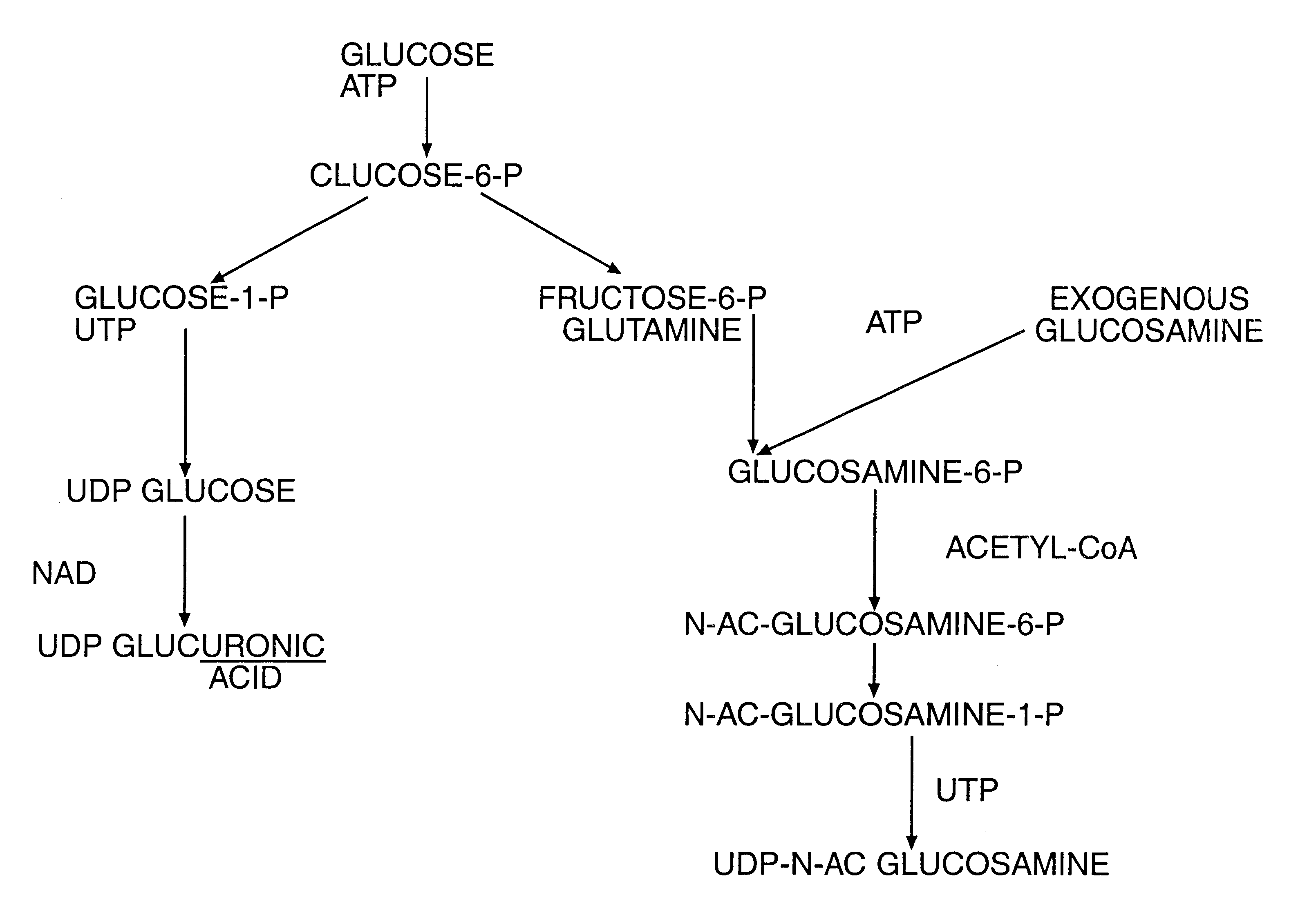
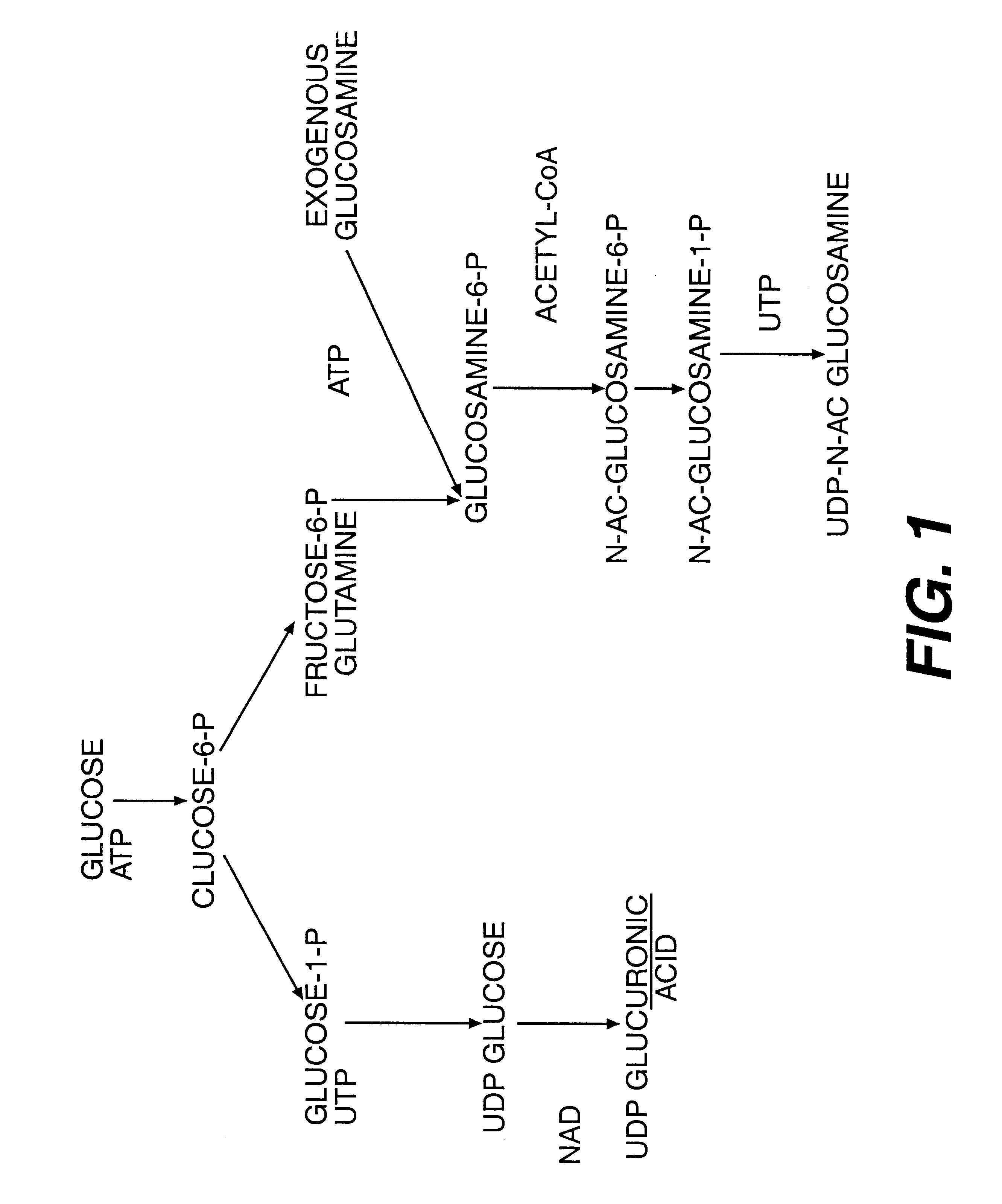
Methods for eliminating mannosylphosphorylation of glycans in the production of glycoproteins
The present invention relates to the elimination of mannosylphosphorylation on the glycans of glycoproteins in the yeast genus Pichia. The elimination of mannosylphosphorylated glycoproteins results from the disruption of the PNO1 gene and the newly isolated P. pastoris MNN4B gene. The present invention further relates to methods for producing modified glycan structures in host cells that are free of glycan mannosylphosphorylation.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Soluble Form of Carbonic Anhydrase IX (s-CA IX), Assays to Detect s-CA IX, CA IX's Coexpression with HER-2/neu/c-erbB-2, and CA IX-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies to Non-Immunodominant Epitopes
InactiveUS20080176258A1Improve efficiencyIncrease resourcesBiological material analysisDepsipeptidesImmunodominant EpitopesMonoclonal antibody
Disclosed herein among other MN / CA IX-related inventions are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, preferably monoclonal antibodies and immunoreactive fragments and engineered variants thereof. Subsets of the new antibodies are to either the proteoglycan-like (PG) domain or to the carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain of MN / CA IX, and methods are provided by which antibodies can be prepared to the other MN / CA IX domains. Such new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies, fragments and variants are useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer and precancer. Particularly preferred are the new monoclonal antibodies, fragments and variants that are specific for the non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, which antibodies are, among other uses, useful to detect soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, alone but preferably in combination with antibodies specific to the immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, for example, in a sandwich assay.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
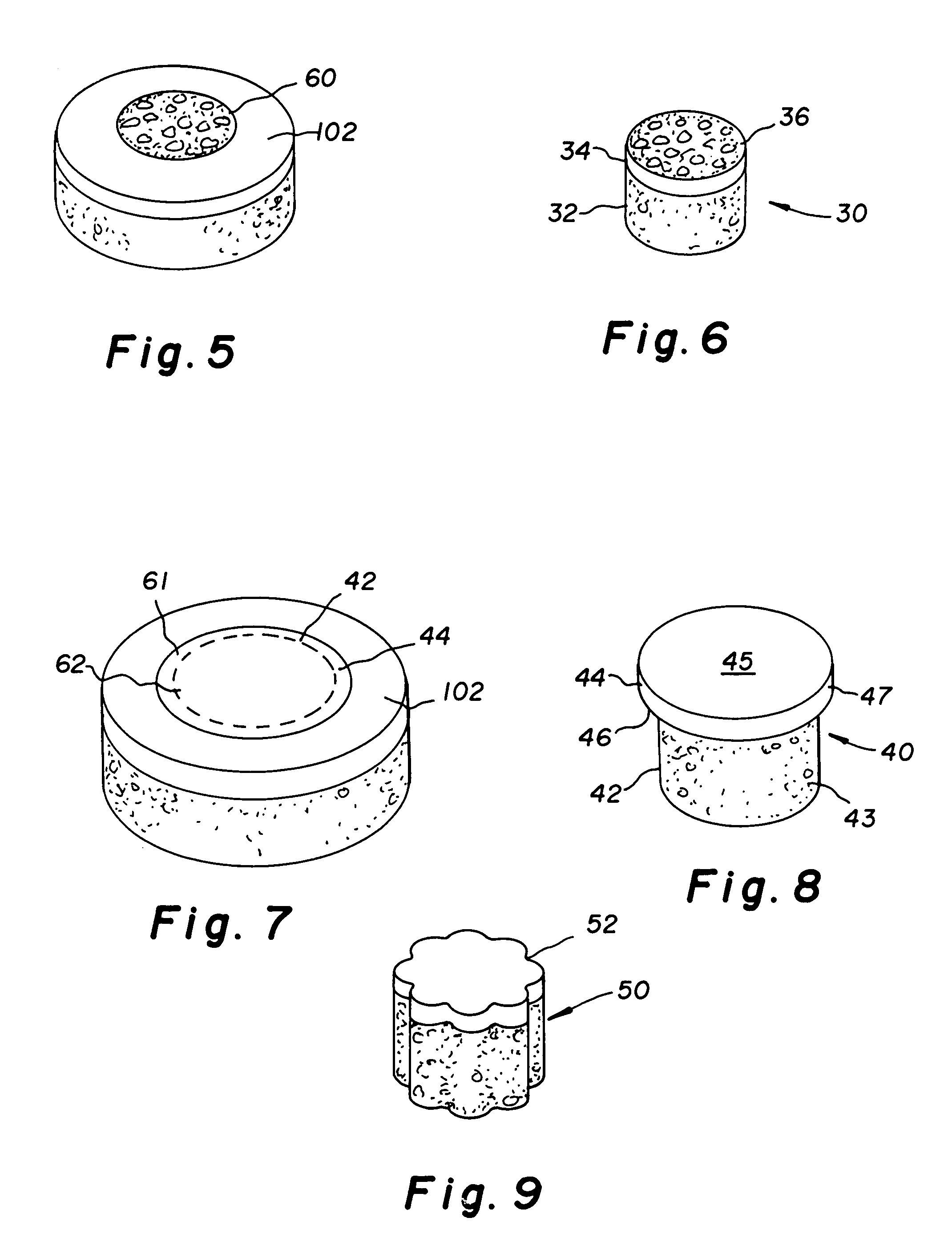
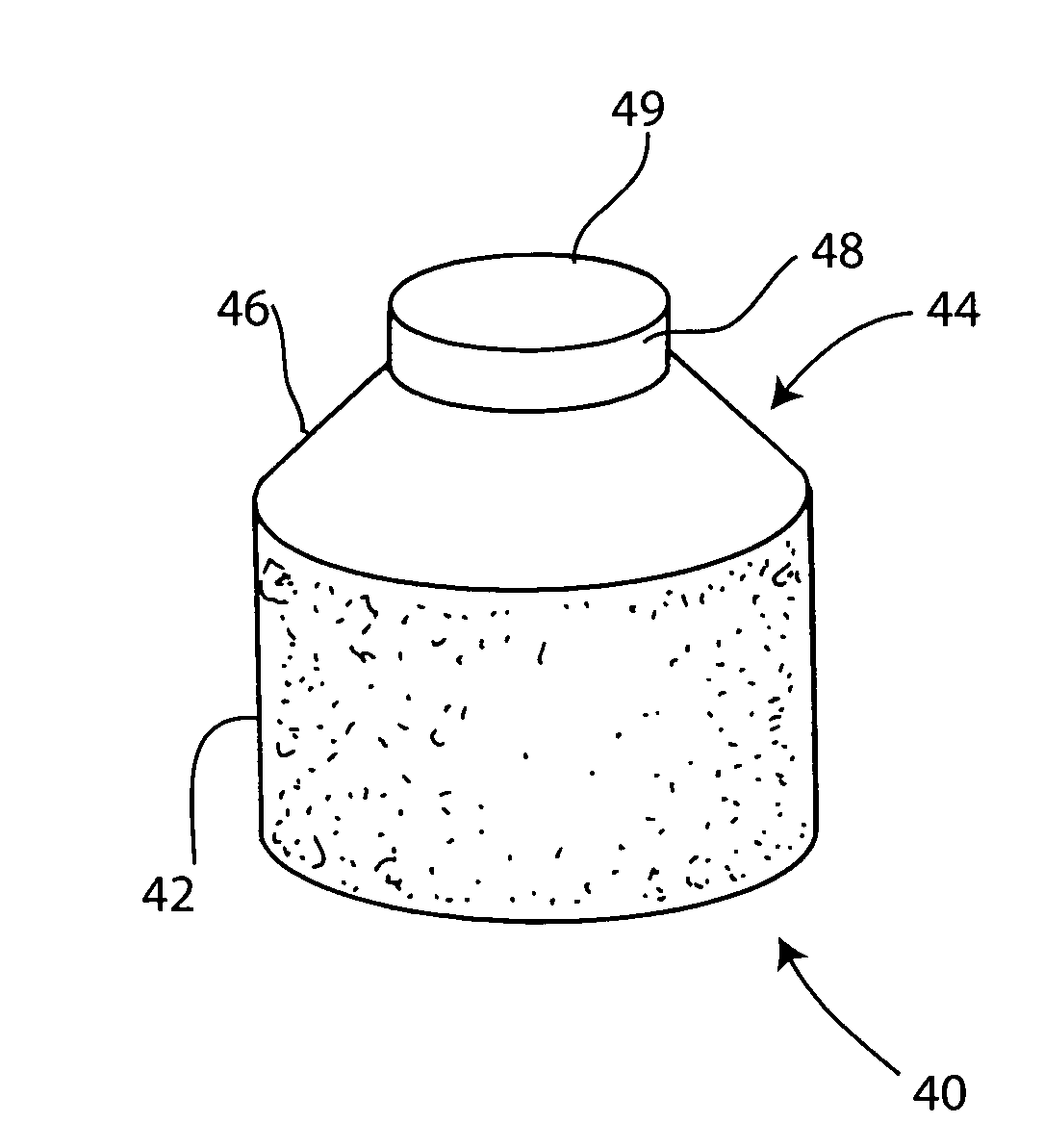
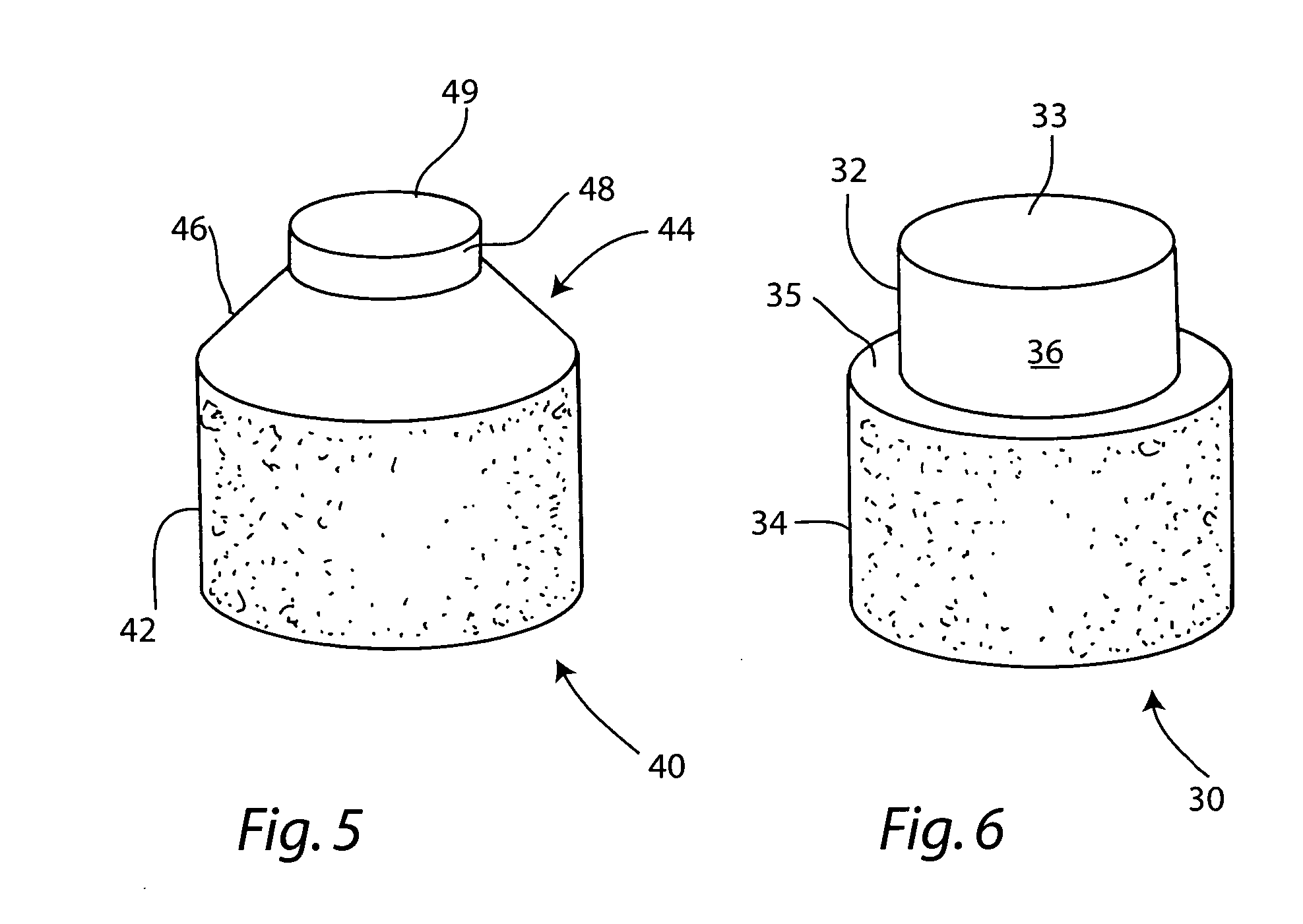
Cartilage allograft plug
InactiveUS7901457B2Promote migrationIncreased proliferationBone implantJoint implantsSubchondral boneInterference fit
The invention is directed toward a cartilage repair assembly comprising a shaped allograft structure of subchondral bone with an integral overlying cartilage cap which is treated to remove cellular debris and proteoglycans and milled allograft cartilage in a bioabsorbable carrier. The shaped structure is dimensioned to fit in a drilled bore in a cartilage defect area so that either the shaped bone or the cartilage cap engage the side wall of the drilled bore in an interference fit and is in contact with a milled cartilage and biocompatible carrier mixture allowing cell transfer throughout the defect area. A method for inserting the shaped allograft structure into a cartilage defect area is also disclosed.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
Cartilage allograft plug
InactiveUS7488348B2Guaranteed functionEasily placed in defect areaBone implantLigamentsInterference fitSubchondral bone
The invention is directed toward a cartilage repair assembly comprising a cylindrically shaped allograft structure of subchondral bone with an integral overlying smaller diameter cartilage cap which is treated to remove cellular debris and proteoglycans. The shaped structure is dimensioned to fit in a drilled bore in a cartilage defect area so that the subchondral bone of the structure engages the side wall of the bone portion of the drilled bore in an interference fit while the cartilage cap is spaced from cartilage portion of the side wall of the drilled bore forming a gap in which a milled cartilage and biocompatible carrier mixture is placed allowing cell transfer throughout the defect area. A method for inserting the shaped allograft structure into a cartilage defect area is also disclosed.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
Soluble Form of Carbonic Anhydrase IX (s-CA IX), Assays to Detect s-CA IX, CA IX's Coexpression with HER-2/neu/c-erbB-2, and CA IX-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies to Non-Immunodominant Epitopes
InactiveUS20080176310A1Improve efficiencyIncrease resourcesOxidoreductasesFermentationKilodaltonWestern blot
Disclosed herein is the discovery of a soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, such as, urine and serum. Said s-CA IX comprises the extracellular domain of CA IX or portions thereof. The predominant s-CA IX species is the extracellular domain comprising a proteoglycan-like (PG) domain and carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain, and having a molecular weight of about 50 / 54 kilodaltons (kd) upon Western blot. A smaller s-CA IX form of about 20 to about 30 kd comprising the CA domain or parts thereof, not linked to the PG domain, has also been found in body fluids. Diagnostic / prognostic methods for precancer and cancer that detect or detect and quantitate said s-CA IX in body fluids, are described. Also disclosed herein is the coexpression of CA IX and HER-2 / neu / c-erbB-2 that provides parallel, alternative and potentially synergistic diagnostic / prognostic and therapeutic strategies for precancer and cancer. Further disclosed are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, preferably monoclonal antibodies and immunoreactive fragments and engineered variants thereof. Such new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies, fragments and variants are useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer and precancer. Particularly preferred are the new monoclonal antibodies, fragments and variants that are specific for the non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, which antibodies are, among other uses, useful to detect soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, alone but preferably in combination with antibodies specific to the immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, for example, in a sandwich assay.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
Soluble Form of Carbonic Anhydrase IX (s-CA IX), Assays to Detect s-CA IX, CA IX's Coexpression with Her-2/neu/c-erbB-2, and CA IX-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies to Non-Immunodominant Epitopes
InactiveUS20080177046A1Good curative effectImprove efficiencyImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological material analysisKilodaltonWestern blot
Disclosed herein is the discovery of a soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, such as, urine and serum. Said s-CA IX comprises the extracellular domain of CA IX or portions thereof. The Predominant s-CA IX species is the extracellular domain comprising a proteoglycan-like (PG) domain and carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain, and having a molecular weight of about 50 / 54 kilodaltons (kd) upon Western blot. A smaller s-CA IX form of about 20 to about 30 kd comprising the CA domain or parts thereof, not linked to the PG domain, has also been found in body fluids. Diagnostic / prognostic methods for precancer and cancer that detect or detect and quantitate said s-CA IX in body fluids, are described. Also disclosed herein is the coexpression of CA IX and HER-2 / neu / c-erbB-2 that provides parallel, alternative and potentially synergistic diagnostic / prognostic and therapeutic strategies for precancer and cancer. Further disclosed are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, preferably monoclonal antibodies and immunoreactive fragments and engineered variants thereof. Such new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies, fragments and variants are useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer and precancer. Particularly preferred are the new monoclonal antibodies, fragments and variants that are specific for the non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, which antibodies are, among other uses, useful to detect soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, alone but preferably in combination with antibodies specific to the immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, for example, in a sandwich assay.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
Use Of A Mixture For The Production Of An Agent For Treating Defective Or Degenerated Cartilage In The Production Of Natural Cartilage Replacement In Vitro
InactiveUS20070275032A1Improve the lubrication effectImprove actionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsPhospholipidPerylene derivatives
A mixture of one or several substances from group A) lubricin, proteoglycan 4 (PRG4) and phosphollipid (SAPL); with one or several substances from group B) hyaluronic acid, glycosaminoglycan and derivatives of said substances; dissolved in a solvent, used for the production of an agent for treating defective or degenerated cartilage in vivo. Said mixture can also be used to produce natural cartilage replacement in vitro.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Cartilage allograft plug
ActiveUS20090069901A1Increase chondrocyte migrationIncreased proliferationBone implantJoint implantsSubchondral boneInterference fit
The invention is directed toward a cartilage repair assembly comprising a shaped allograft structure of subchondral bone with an integral overlying cartilage cap which is treated to remove cellular debris and proteoglycans and milled allograft cartilage in a bioabsorbable carrier. The shaped structure is dimensioned to fit in a drilled bore in a cartilage defect area so that either the shaped bone or the cartilage cap engage the side wall of the drilled bore in an interference fit and is in contact with a milled cartilage and biocompatible carrier mixture allowing cell transfer throughout the defect area. A method for inserting the shaped allograft structure into a cartilage defect area is also disclosed.
Owner:MUSCULOSKELETAL TRANSPLANT FOUND INC
Soluble form of carbonic anhydrase IX (S-CA IX), assays to detect s-CA IX, CA IX'S coexpression with HER-2/NEU/C-ERBB-2, and CA IX-specific monoclonal antibodies to non-immunodominant epitopes
InactiveUS7816493B2Good curative effectSugar derivativesBiological material analysisKilodaltonC erbb 2
Disclosed herein is the discovery of a soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) found in body fluids, such as, urine and serum. Soluble CA IX comprises the extracellular domain of CA IX or portions thereof. The predominant s-CA IX species is the extracellular domain comprising a proteoglycan-like (PG) domain and carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain, and having a molecular weight of about 50 / 54 kilodaltons. Diagnostic / prognostic methods for precancer / cancer that detect or detect and quantitate s-CA IX in body fluids, are described. Also disclosed is the coexpression of CA IX and HER-2 that provides potentially synergistic diagnostic / prognostic and therapeutic strategies for precancer / cancer. Further disclosed are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer / precancer. Preferred are new antibodies, specific for non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, useful to detect soluble CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, preferably in combination with antibodies specific to immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
Human antibodies that have MN binding and cell adhesion-neutralizing activity
The invention is composed of monoclonal human MN antibodies or MN antibody fragments that target the GEEDLP (SEQ ID NO: 118) repeat within the proteoglycan domain. The proteoglycan domain of the MN cell surface protein contains four of these identical GEEDLP (SEQ ID NO: 118) repeats. Binding to the desired epitope is verified by competition ELISA, where ELISA signal can be attenuated by co-incubation with a peptide containing this repeat (PGEEDLPGEEDLP (SEQ ID NO: 119)). This inhibition of binding can also be verified using Biacore assays, where binding of desired antibodies to immobilized MN or proteoglycan peptides can be inhibited by the peptide repeat. In addition to binding to the peptide repeat, human anti-MN antibodies can inhibit the cell adhesion of CGL-1 cells to MN coated plastic plates. Human anti-MN antibodies have been used to diagnose and quantify MN expression in cancer cells and tumors using FACS and immunohistochemical methods. An example is also provided where a human anti-MN IgG1 mediates tumor cell lysis though antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Therefore, these antibodies will be useful for the treatment of cancers in which MN is upregulated or can be useful for the diagnosis of cancers in which MN is upregulated.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Method for inhibition of bone growth by anionic polymers
InactiveUS6020326AInhibit bone growthPrevent invasionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCell invasionFibrosis
The present invention relates to the discovery that biocompatible anionic polymers can effectively inhibit fibrosis, scar formation, and surgical adhesions. The invention is predicated on the discovery that anionic polymers effectively inhibit invasion of cells associated with detrimental healing processes, and in particular, that the effectiveness of an anionic polymer at inhibiting cell invasion correlates with the anionic charge density of the polymer. Thus the present invention provides a large number of materials for use in methods of inhibiting fibrosis and fibroblast invasion. Anionic polymers for use in the invention include but are not limited to natural proteoglycans, and the glycosaminoglycan moieties of proteoglycans. Additionally, anionic carbohydrates and other anionic polymers may be used. The anionic polymers dextran sulfate and pentosan polysulfate are preferred. In a more preferred embodiment, dextran sulfate, in which the sulfur content is greater than about 10% by weight, may be used. In a more preferred embodiment, the average molecular weight is about 40,000 to 500,000 Daltons. The present invention provides compositions and methods to inhibit fibrosis and scarring associated with surgery. The invention further provides compositions and methods to inhibit glial cell invasion, detrimental bone growth and neurite outgrowth. In a preferred embodiment, the inhibitory compositions further comprise an adhesive protein.
Owner:TRIAD
Cosmetic compositions
A cosmetic composition comprising in a preblend; or in a the resting state prior to application to a keratinous surface, at least one peptide, at least one collagen containing compound, at least one penetration enhancer, at least one mucopolysaccharide, and at least one proteoglycan; wherein said ingredients are operable to associate in situ when the composition is applied to a keratinous surface and a method for plumping lips or skin by applying the composition.
Owner:REVLON CONSUMER PROD CORP
Anti-inflammatory compositions for treating multiple sclerosis
Compositions with synergistic anti-inflammatory effects in inflammatory diseases resulting from activation and consequent degranulation of mast cells and followed by secretion of inflammatory biochemicals from the activated mast cells, the compositions containg one or more of a flavone or flavonoid glycoside a heavily sulfated, non-bovine proteoglycan, an unrefined olive kernel extract that increases absorption of these compositions in various routes of administration, a hexosamine sulfate such as D-glucosamine sulfate, S-adenosylmethionine, a histamine-1 receptor antagonist, a histamine-3 receptor agonist, an antagonist of the actions of CRH, a long-chain unsaturated fatty acid, a phospholipid, Krill oil, a polyamine, glutiramer acetate and interferon. Certain of the present compositions are useful in protecting against the neuropathological components of multiple sclerosis and similar inflammatory neurological diseases.
Owner:THETA BIOMEDICAL CONSULTING & DEVMENT
Aminosugar and glycosaminoglycan composition for the treatment and repair of connective tissue
Owner:NUTRAMAX LABORATORIES INC
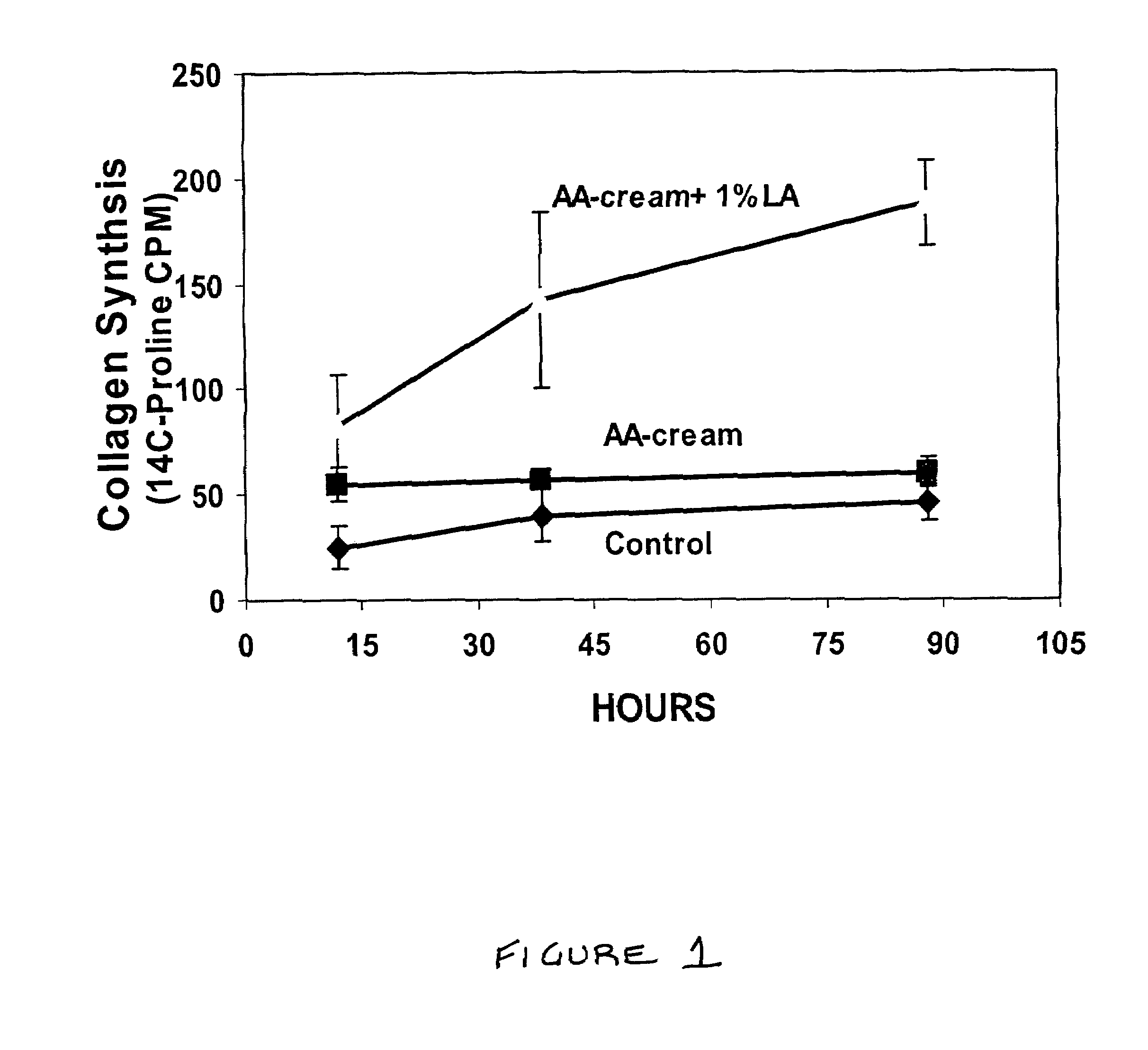
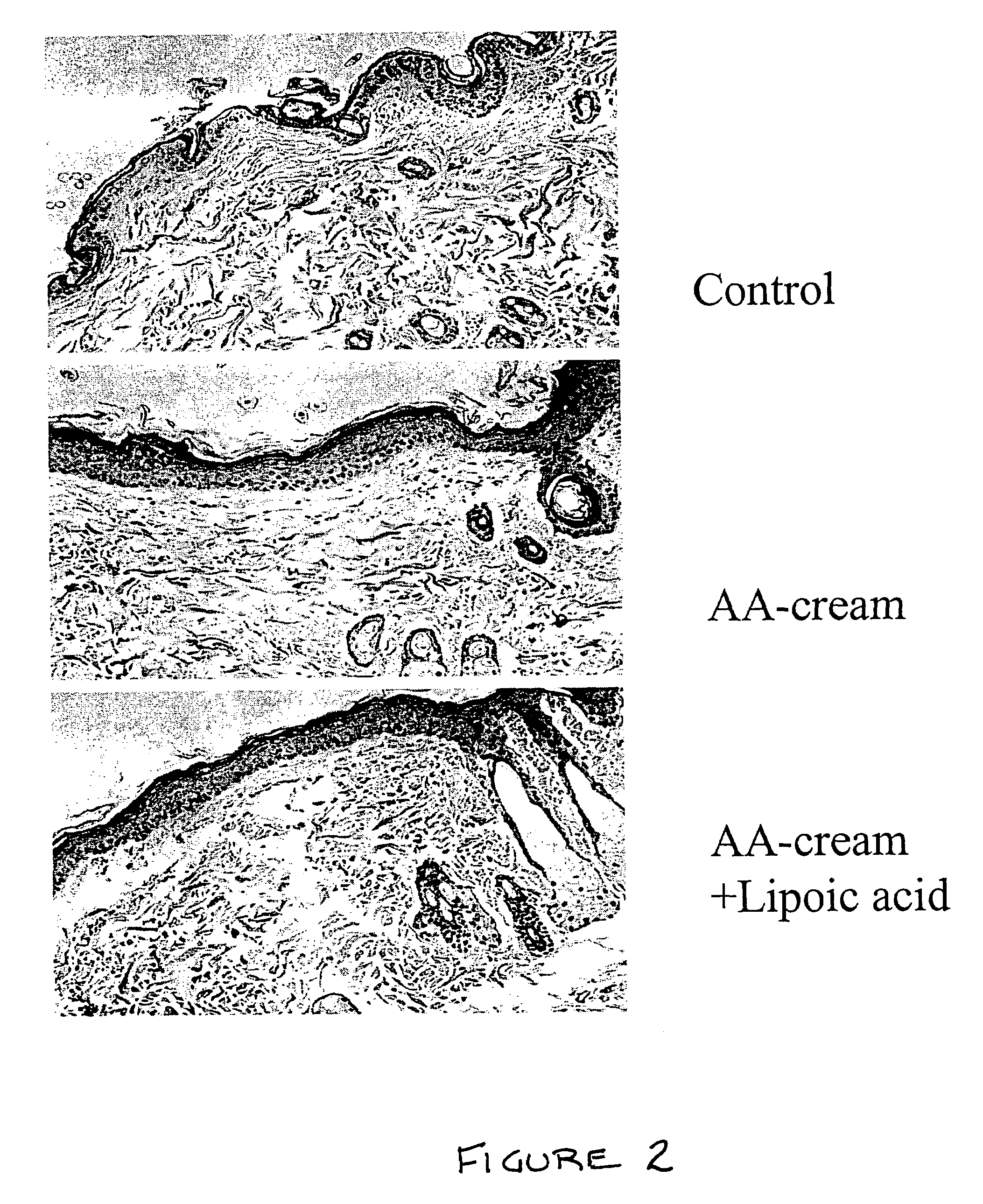
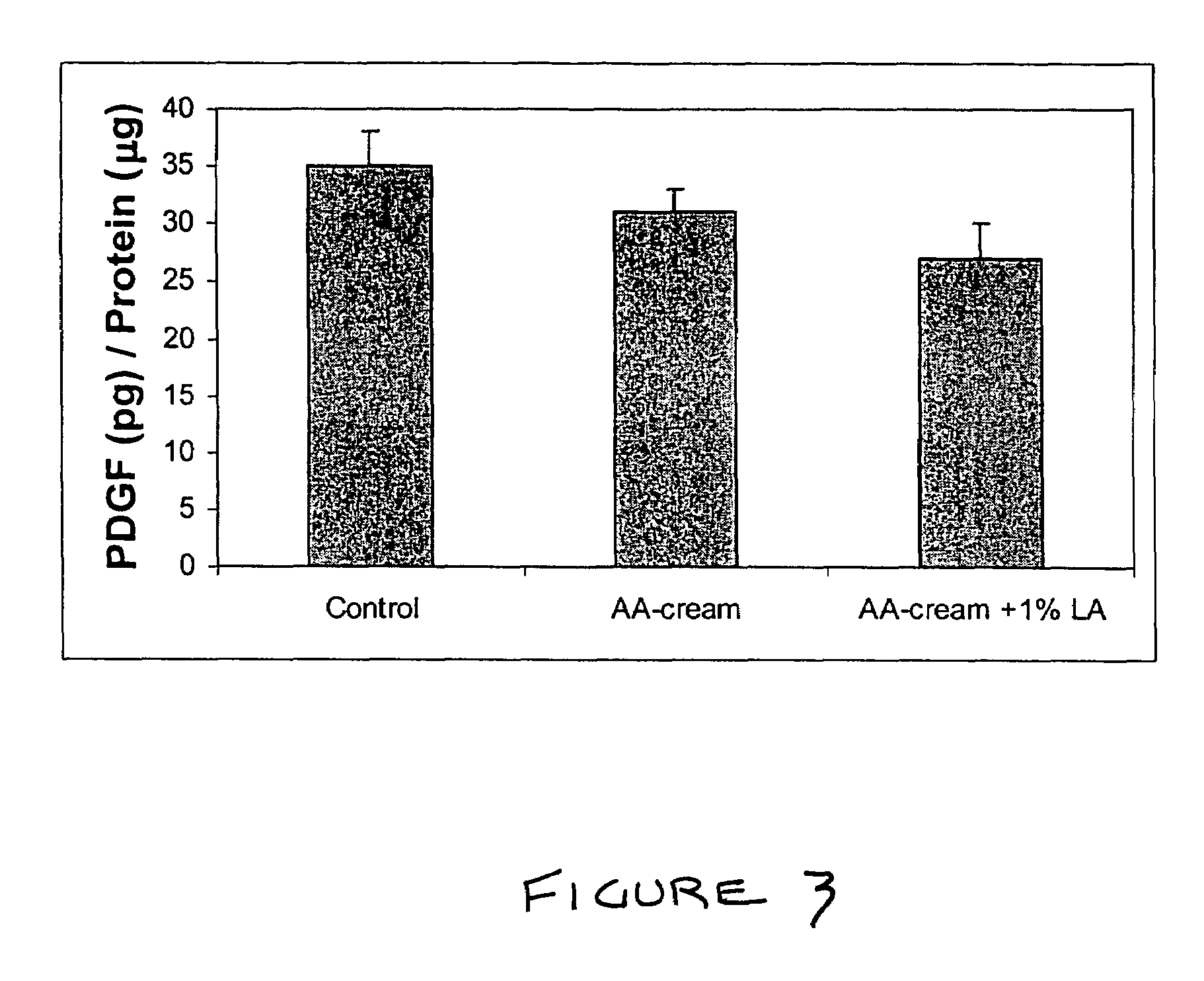
Methods and compositions for enhancing collagen and proteoglycan synthesis in the skin
ActiveUS7598291B2Increase synthesisSustainable hydrationBiocideCosmetic preparationsAdditive ingredientIsoflavones
A composition for application to the skin can stimulate the in vivo synthesis of collagen and proteoglycans and improve the appearance of the skin, increasing its elasticity and fullness. In general, a composition according to the present invention comprises: (1) an antioxidant compound in a quantity sufficient to enhance collagen synthesis in the skin; (2) an organic penetrant in which the antioxidant compound is soluble in a sufficient quantity that a concentration of the antioxidant compound sufficient to enhance collagen synthesis can be applied topically and penetrate the skin; (3) a mixture of essential amino acids; (4) a supplemental source of sulfur; and (5) a topical pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The antioxidant compound can be lipoic acid, a lipoic acid analogue or derivative, a bioflavonoid, a constituent of ginkgo, or an isoflavone. The organic penetrant is preferably benzyl alcohol. Other ingredients, such as esters of tocopherol and ascorbic acid, can be included.
Owner:NIMNI MARCEL +1
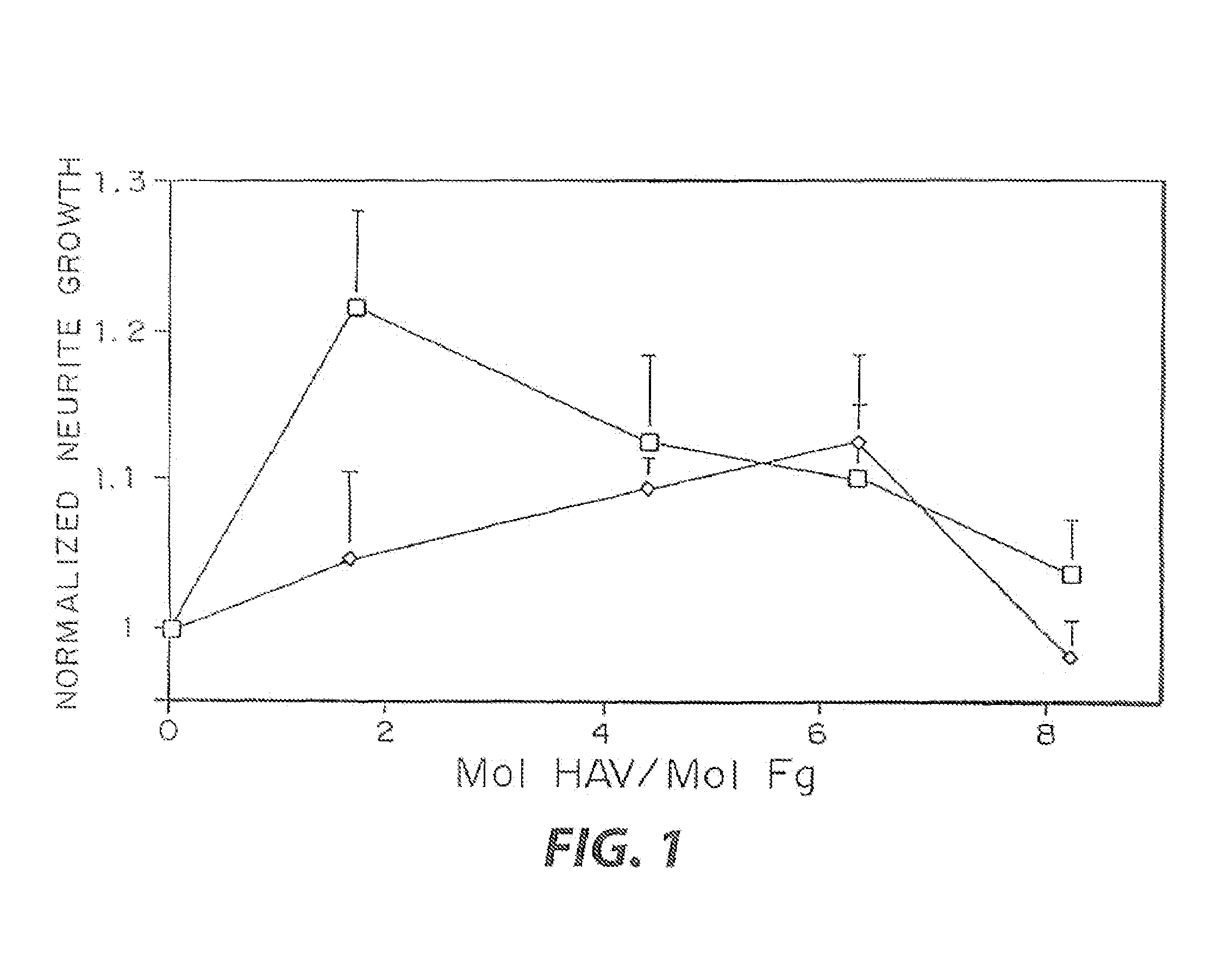
Enzyme-mediated modification of fibrin for tissue engineering: fibrin formulations with peptides
InactiveUS7241730B2Efficacious platformEnhanced andPeptide/protein ingredientsTransferasesCell Surface ProteinsADAMTS Proteins
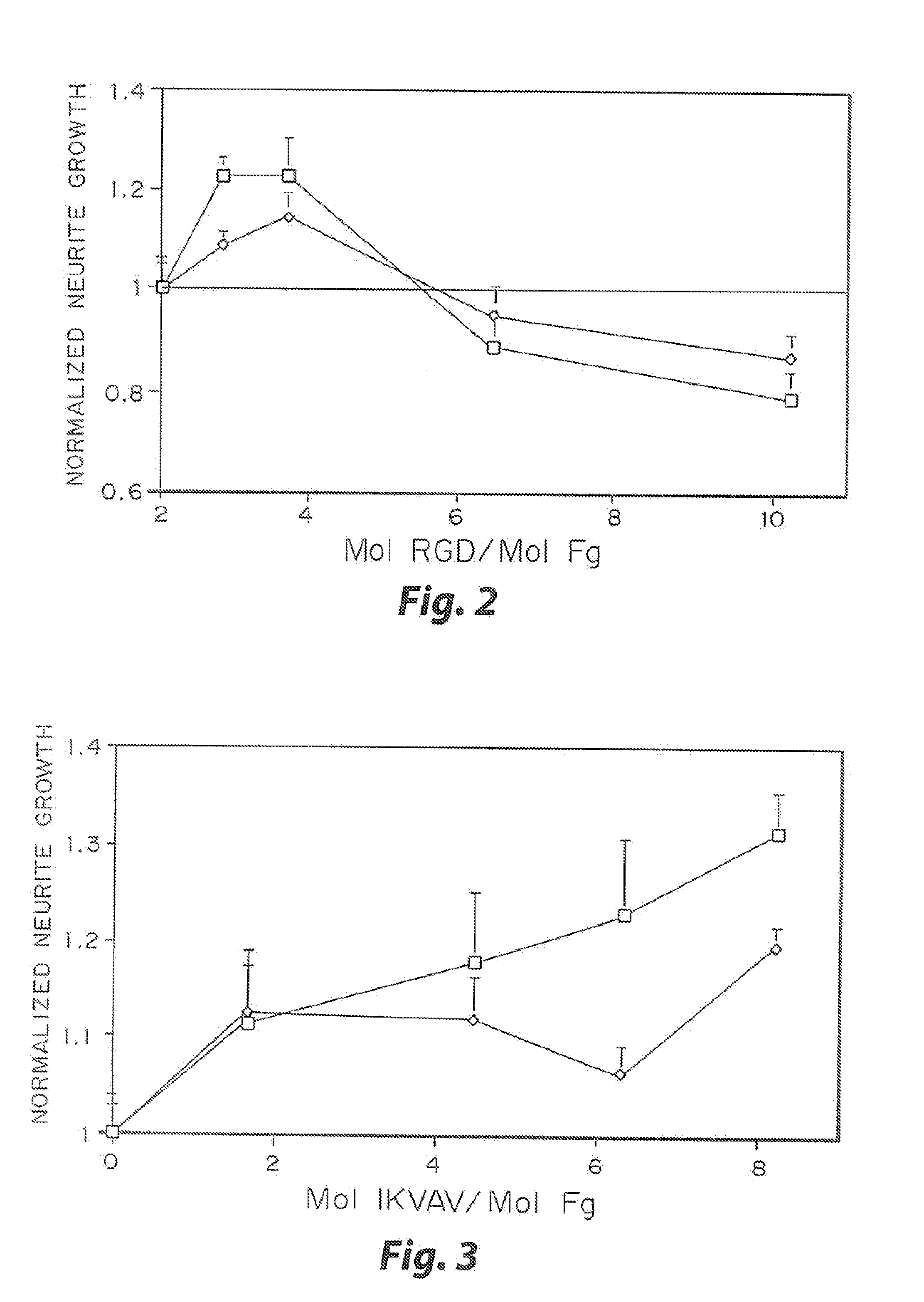
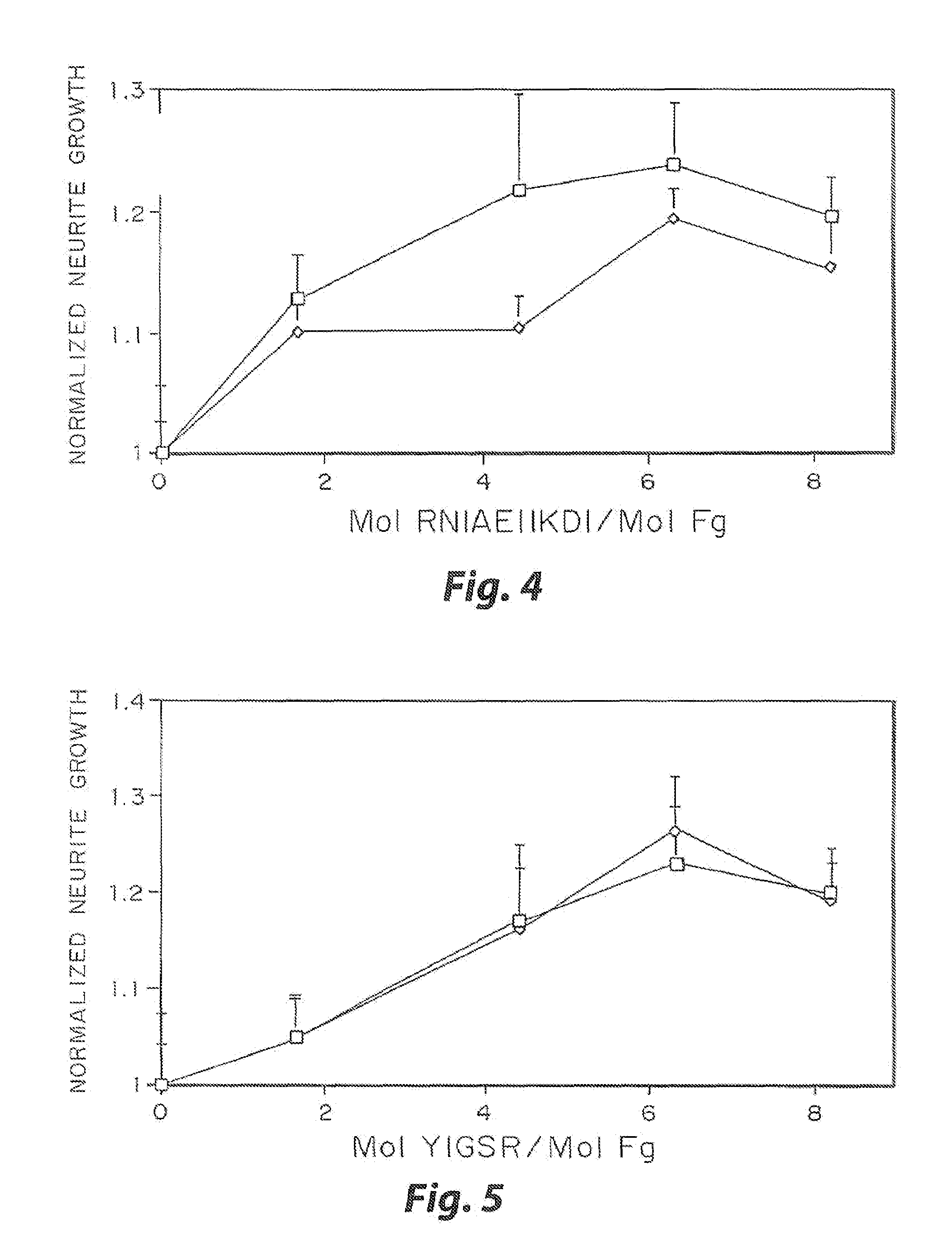
Heparin-binding regions of several proteins, such as neural cell adhesion molecule, fibronectin, laminin, midkine, and anti-thrombin III have been shown to promote neurite extension on two-dimensional surfaces. The effect of heparin-binding peptides on neurite extension through three-dimensional matrices was investigated by culturing embryonic chick dorsal root ganglia (DRG) within fibrin gels containing chemically attached heparin-binding peptide (HBP). The length of neurites within fibrin gels containing cross-linked HBP was increased by more than 70% over extension through fibrin gels containing no peptide. The HBP sequence of antithrombin III was incorporated into the fibrin gel as the C-terminal domain of a bidomian, chimeric peptide; the N-terminal second domain of this peptide contained the ∀2-plasmin inhibitor substrate for Factor XIIIa. Factor XIIIa, a transglutaminase, was used to chemically attach the HBP-containing chimeric peptide to the fibrin gels during polymerization. The amount of HBP cross-linked into the fibrin gels was determined, after degradation by plasmin using gel permeation chromatography, to be approximately 8 moles of peptide per mole fibrinogen. A peptide (HBP), where the cross-linking glutamine was replaced with glycine, showed no increase in extension in comparison with fibrin gels. The additional of heparin to the gel percursors resulted in no increase in neurite extension in comparison with fibrin gels. HBPs promote neurite extension by binding to cell surface proteoglycans on the DRG.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH +1
Cartilage implant plug with fibrin glue and method for implantation
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Methods and compositions for treating intervertebral disc degeneration
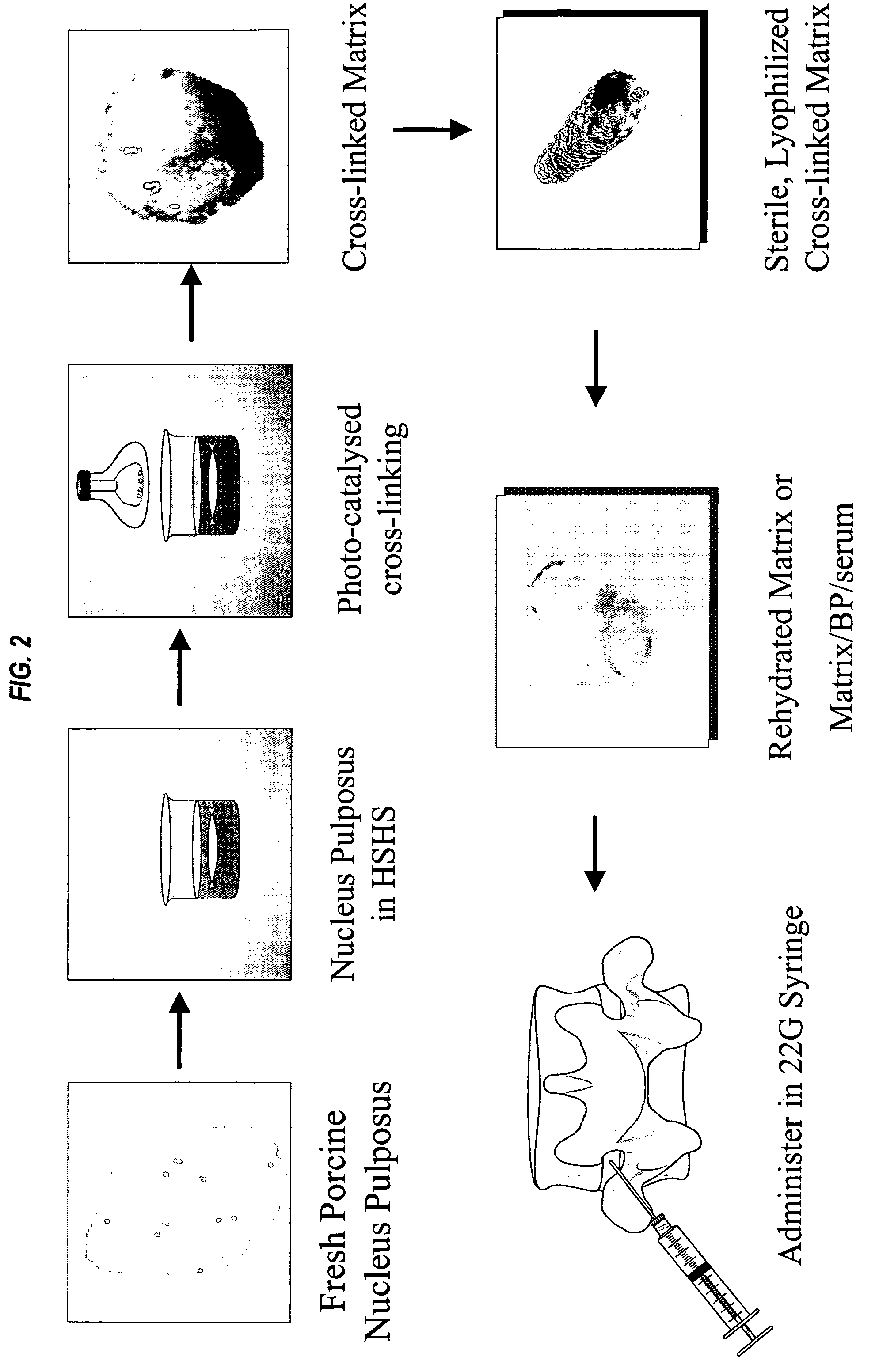
A fluid matrix comprising cross-linked remodelable collagen from a donor vertebrate animal is useful for regenerating hydrodynamic function in damaged intervertebral discs in vivo. The matrix may be injectable and may comprise cells and a plurality of purified cell growth factors. The matrix promotes cell growth and elaboration of proteoglycans to facilitate regeneration of native tissues. The collagen in the matrix may be cross-linked using photooxidative catalysis and visible light, and purified cell growth factors are preferably at least partly bone-derived.
Owner:ZIMMER ORTHOBIOLOGICS
Anti-inflammatory composition for treating pelvic endometriosis
InactiveUS20050220912A1Promote absorptionBiocideCarbohydrate active ingredientsDiseaseChondroitin Sulfate C
Compositions with synergistic anti-inflammatory effects in inflammatory diseases resulting from activation and consequent degranulation of mast cells and followed by secretion of inflammatory biomolecules from the activated mast cells, composed of a heavily sulfated, non-bovine proteoglycan such as shark cartilage chondroitin sulfate C, an unrefined olive kernel oil / extract that increases absorption of these compositions in various routes of administration, and one or more of a hexosamine sulfate such as D-glucosamine sulfate, a flavone such as quercetin, S-adenosylmethionine, a histamine-1 receptor antagonist, a histamine-3 receptor agonist, an antagonist of the actions of CRH, caffeine, and a polyamine.
Owner:THETA BIOMEDICAL CONSULTING & DEVMENT
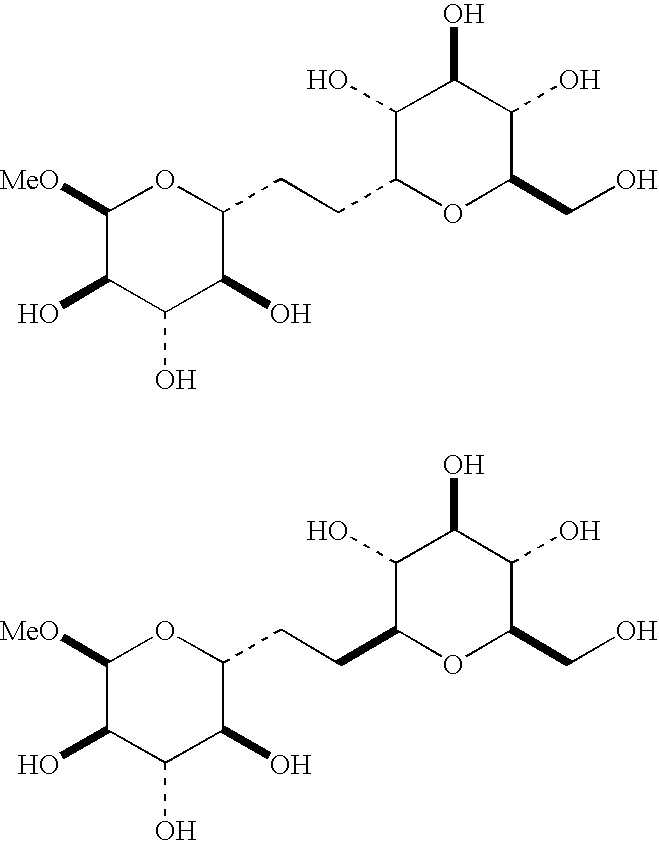
Novel C-glycosides, uses thereof
The present invention relates to novel C-glycoside compounds of given absolute configuration, to a process for synthesising them and to compositions containing them. The invention also relates to the cosmetic use of these C-glycoside compounds as agents to stimulate the synthesis of glycosaminoglycans containing a D-glucosamine and / or N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residue, advantageously hyaluronic acid, and / or of proteoglycans, advantageously proteoglycans containing hyaluronic acid, by fibroblasts and / or keratinocytes. The invention also relates to a cosmetic process for treating keratin materials using a composition containing at least one C-glycoside compound according to the invention.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Olive kernel composition containing absorption promoters, antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory agents
InactiveUS20070077317A1Promote absorptionBiocideAnimal repellantsCell membraneAntiinflammatory Effect
The claimed invention is composition comprising an organic extract of de-fleshed, purified, isolated olive kernels that contains one or more components that increase absorption of macromolecules such as proteoglycans across cell membranes, that have antioxidant properties, and that have anti-inflammatory effects in tissues.
Owner:THETA BIOMEDICAL CONSULTING & DEVMENT
Synergistic proteoglycan compositions for inflammatory conditions
Compositions with synergistic anti-inflammatory effect in inflammatory diseases resulting from activation and consequent degranulation of mast cell and followed by secretion of inflammatory biomolecules from the activated mast cells, composed of a heavily sulfated, non-bovine proteoglycan such as chondroitin sulfate C and one or more of a hexosamine sulfate such as D-glucosamine sulfate, a flavone such as quercetin, a special organic extra virgin kernel seed olive oil, S-adenosylmethionine and diphenhydramine.
Owner:THETA BIOMEDICAL CONSULTING & DEVMENT
Collagen peptide beverage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110692879AHigh densityBoost Density (Amount)Food ingredient functionsProtein compositionEngineering
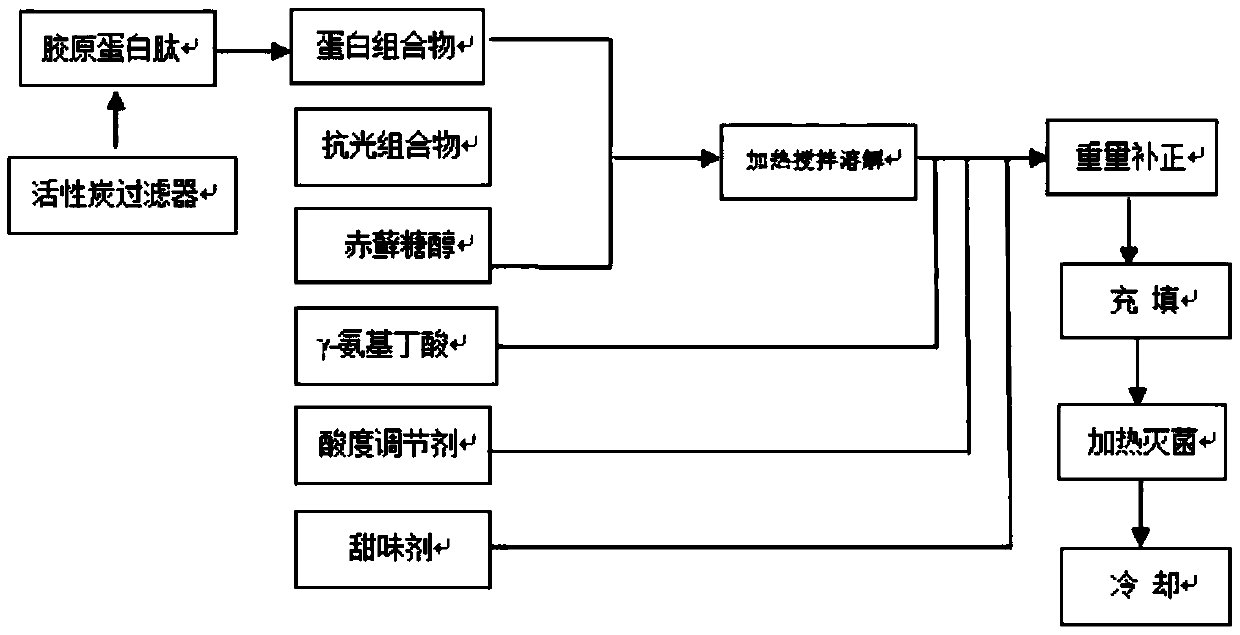
The invention relates to the field of beverages, in particular to a collagen peptide beverage and a preparation method thereof. The collagen peptide beverage comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight of 10-50 parts of a protein composition, 1-5 parts of a lightproof composition, 0.005-0.05 part of gamma-aminobutyric acid, 0.1-0.2 part of an acidity adjusting agent, 1-10 parts of erythritol, 0.05-0.1 part of a sweetening agent and 20-90 parts of water. The preparation method of the collagen peptide beverage comprises the following steps of (1) performing pretreatment: firstly, weighing fish collagen peptide powder in a certain proportion according to a formula, adding purified water, performing dissolving to obtain liquid, adding the liquid in a filter containing activated carbon, and adjusting the temperature to 60+ / -8 DEG C; (2) performing blending: adding proteoglycan and elastin to the fish collagen peptide obtained in the step 1, to obtain a protein composition, so as to obtain a material 1; (3) performing mixing, heating and stirring for dissolving; and (4) performing cooling to room temperature to obtain the collagen peptide beverage. The collagen peptide beverage disclosed by the invention can enter deeply the dermis layer to enable the dermis layer of the skin to achieve the best state, and nutrients of the dermis layer achieve a skin layer through a basal layer.
Owner:浙江英树生物科技有限公司
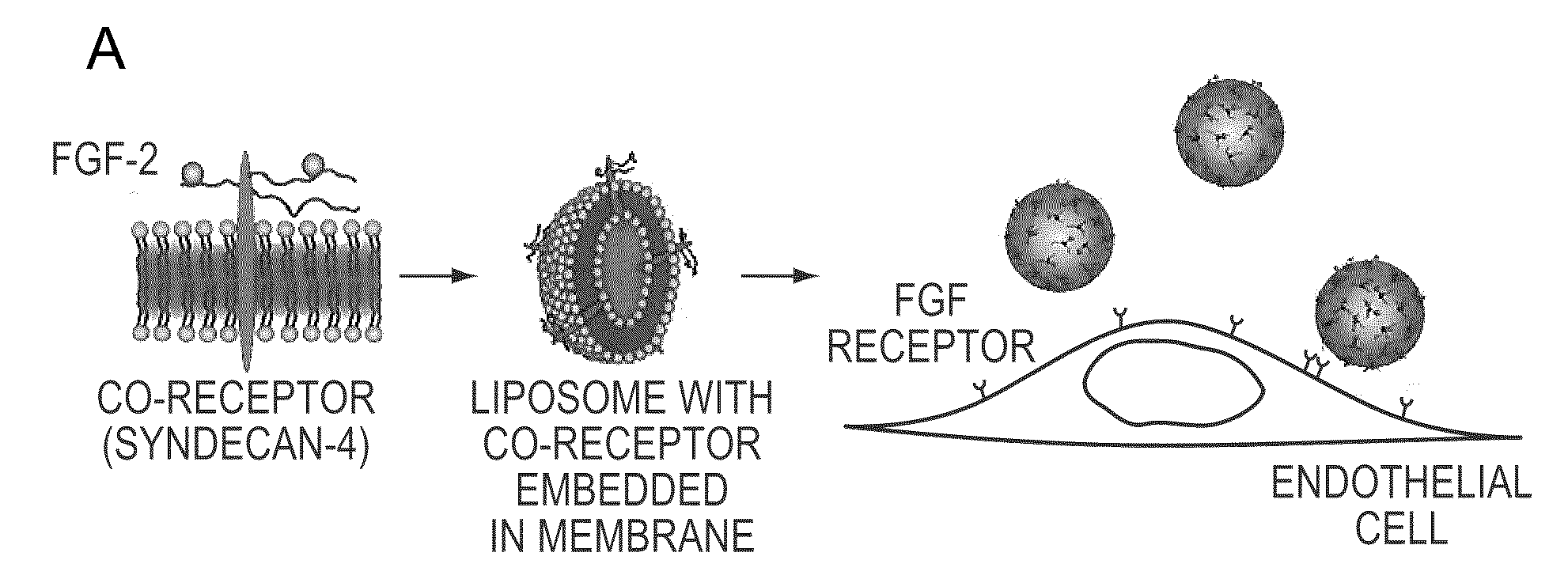
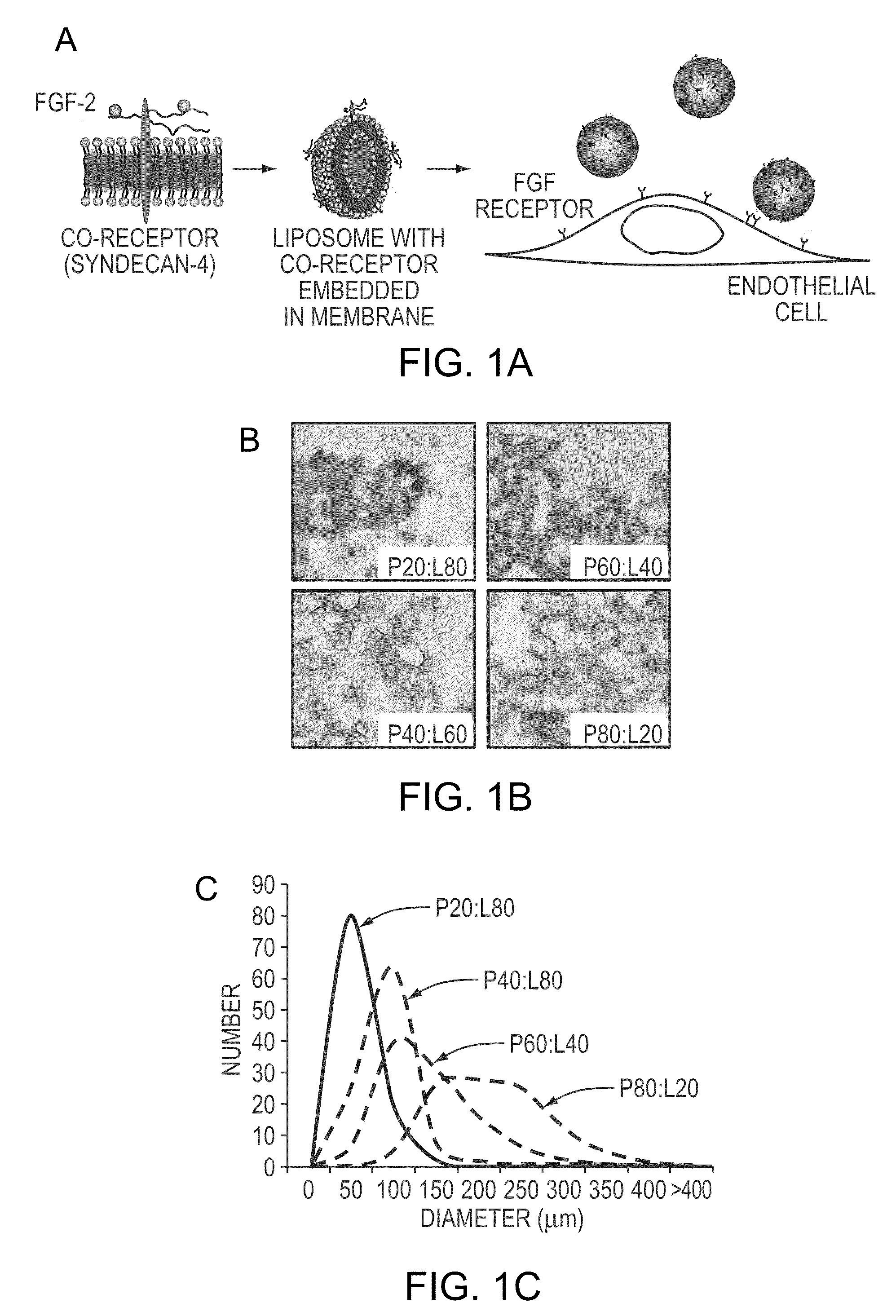
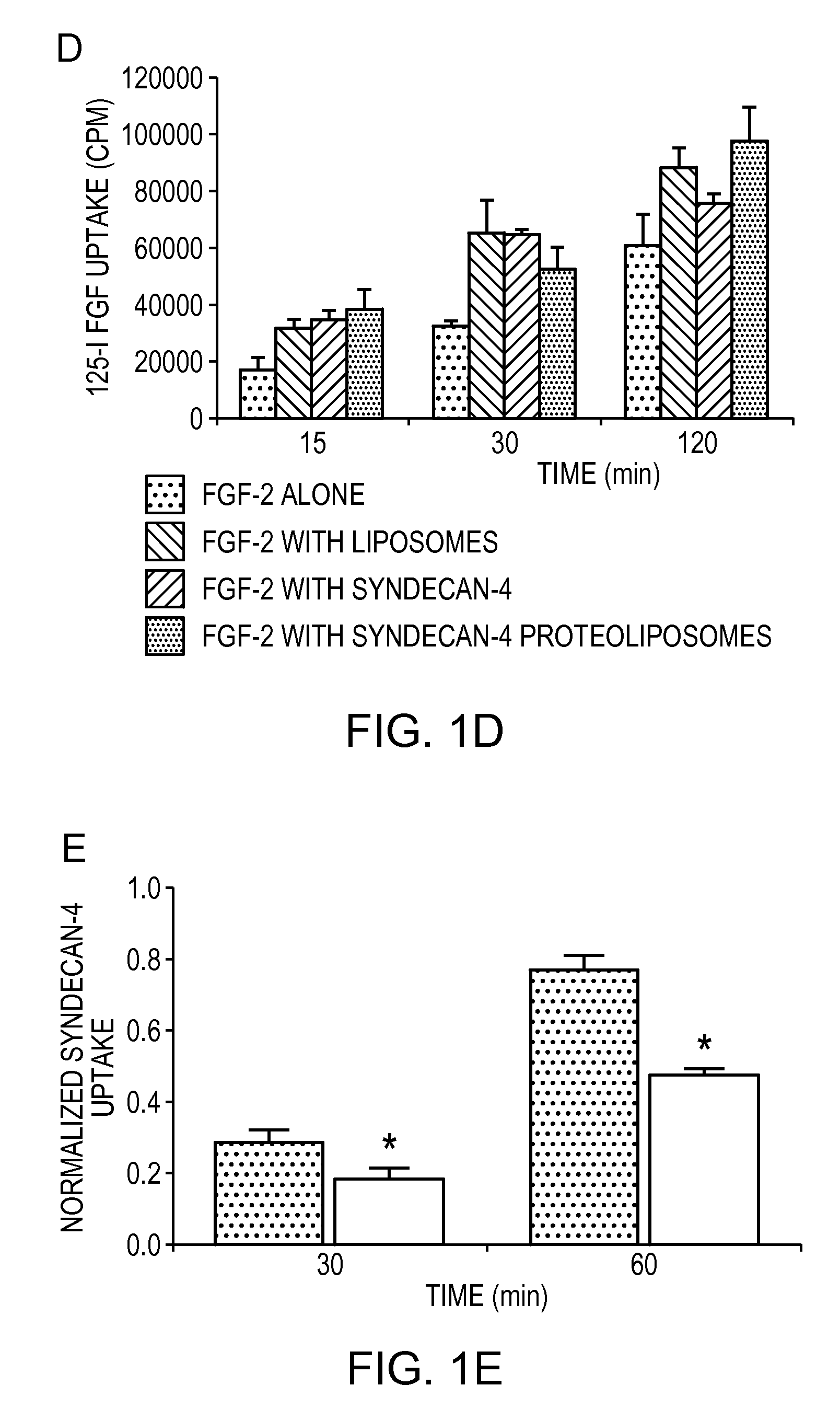
Simultaneous Delivery of Receptors and/or Co-Receptors for Growth Factor Stability and Activity
InactiveUS20090220588A1Reduce capacityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsFactor iiCo delivery
The compositions and methods of the present invention relate to the co-delivery of a molecule and a polypeptide to cells to improve the therapeutic efficacy of the molecules. In one embodiment of the invention, the invention may improve delivery of growth factors by co-delivering these growth factors with their receptors and co-receptors, such as syndecans. Co-delivery of growth factors with syndecans, for example, may protect growth factors from proteolysis, enhance their activity, and target the growth factors to the cell surface to facilitate growth factor signaling. This novel approach to growth factor therapy could be extended to other systems and growth factors enabling the enhancement of multiple signaling pathways to achieve a desired therapeutic outcome.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
C-glycoside compounds for stimulating the synthesis of glycosaminoglycans
C-glycoside compounds are suited for stimulating the synthesis of glycosaminoglycans containing a D-glucosamine and / or N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residue, advantageously hyaluronic acid, and / or proteoglycans, advantageously proteoglycans containing hyaluronic acid, by fibroblasts and / or keratinocytes.
Owner:LOREAL SA
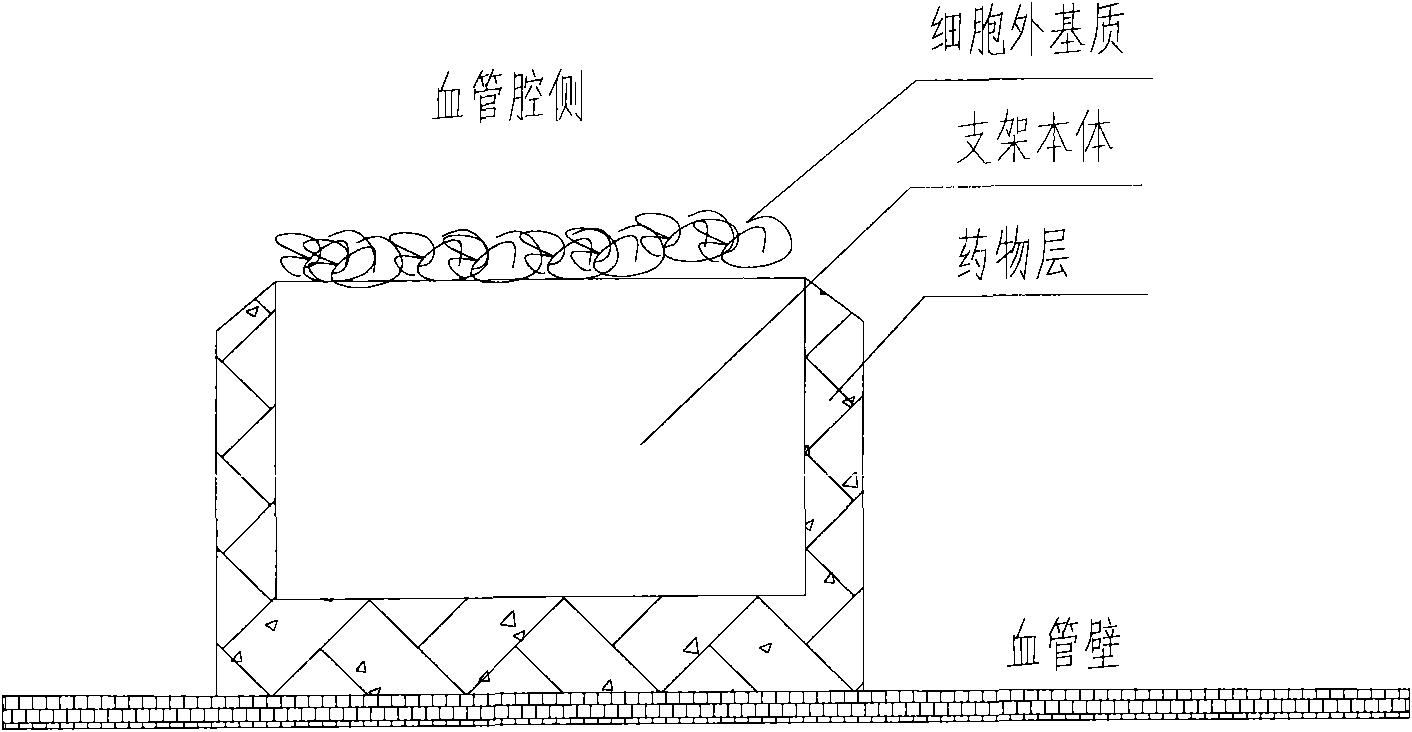
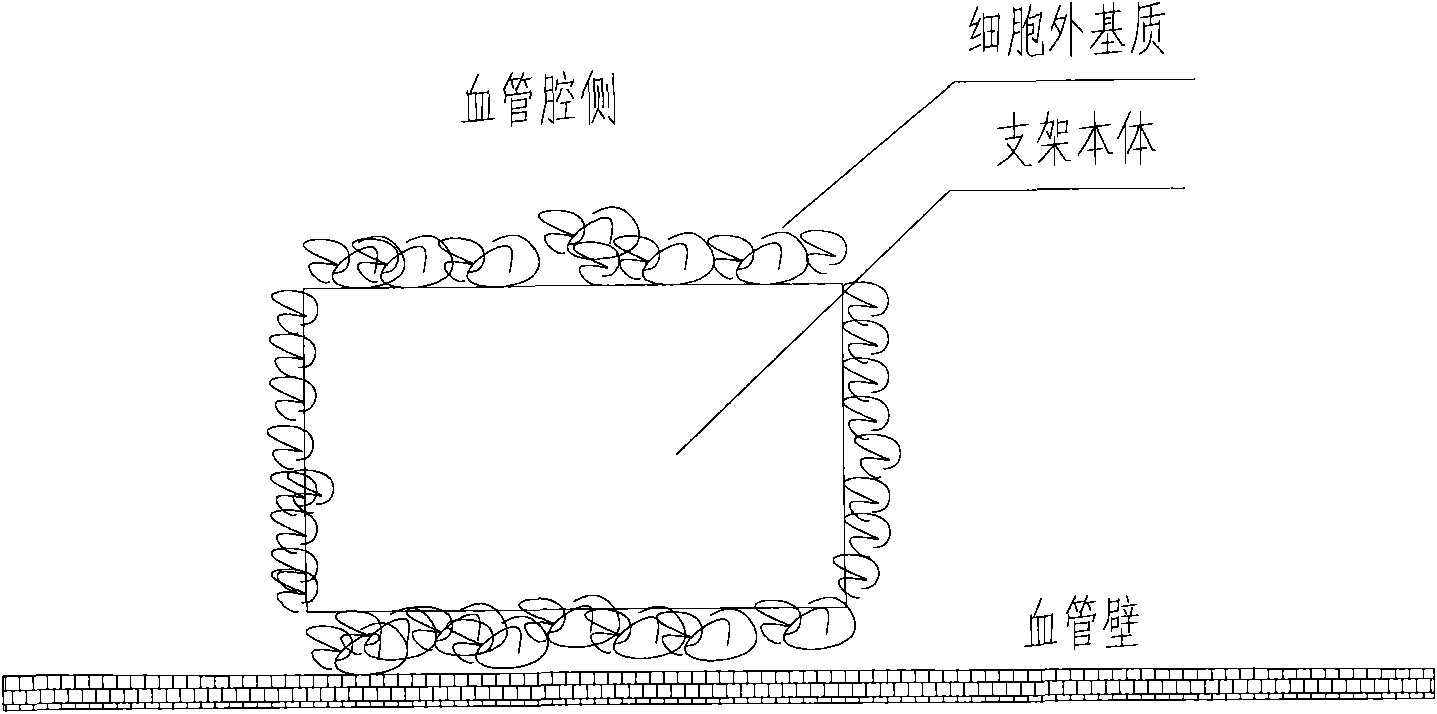
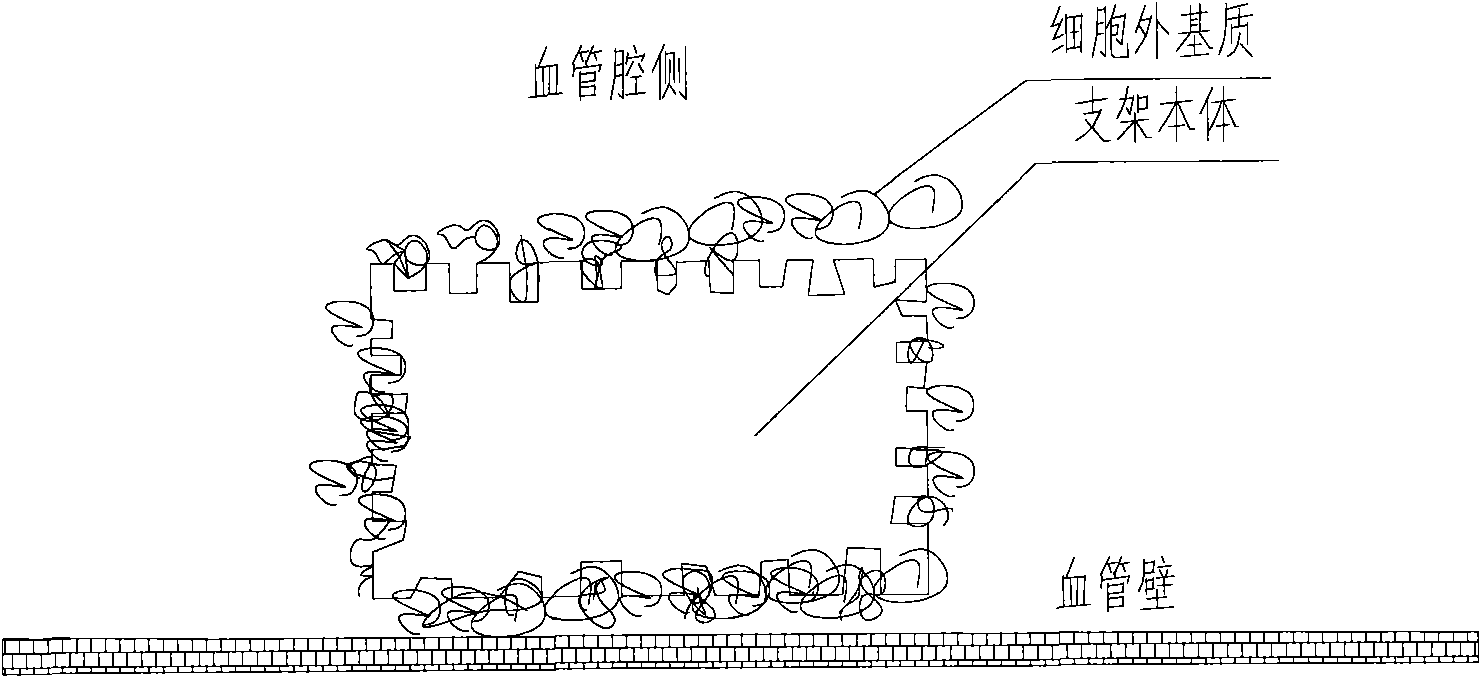
A medical equipment carrying extracellular matrix and its production method
ActiveCN101548916APromote endothelializationReduce restenosis rateStentsHeart valvesSide effectCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention relates to a kind of medical equipment carrying extracellular matrix and its production method. It includes the medical equipment body and the layer of extracellular matrix coating on the surface of the medical equipment body. The described extracellular matrix is collagen, laminin, non-collagenous glycoprotein, GAG and proteoglycan, elastin, and one or multiple endothelial cell extracellular matrixes obtained through cell treatment from the cultured endothelial cells. For the described medical equipment in the invention, the extracellular matrix on the body surface can withstand the wash of blood and other body fluids and advance the vascular endothelialization through slow release; if working together with the drug, it can not only reduce the restenosis rate, but also speed up the surface endothelialization to improve treatment; the preparation method of the invention is simple and may have no carrier. It uses the electrostatic and / or micropore adsorption principle to coat the extracellular matrix directly on the body surface, thus it can prevent the side effects such as the inflammation brought by the carrier.
Owner:LEPU MEDICAL TECH (BEIJING) CO LTD
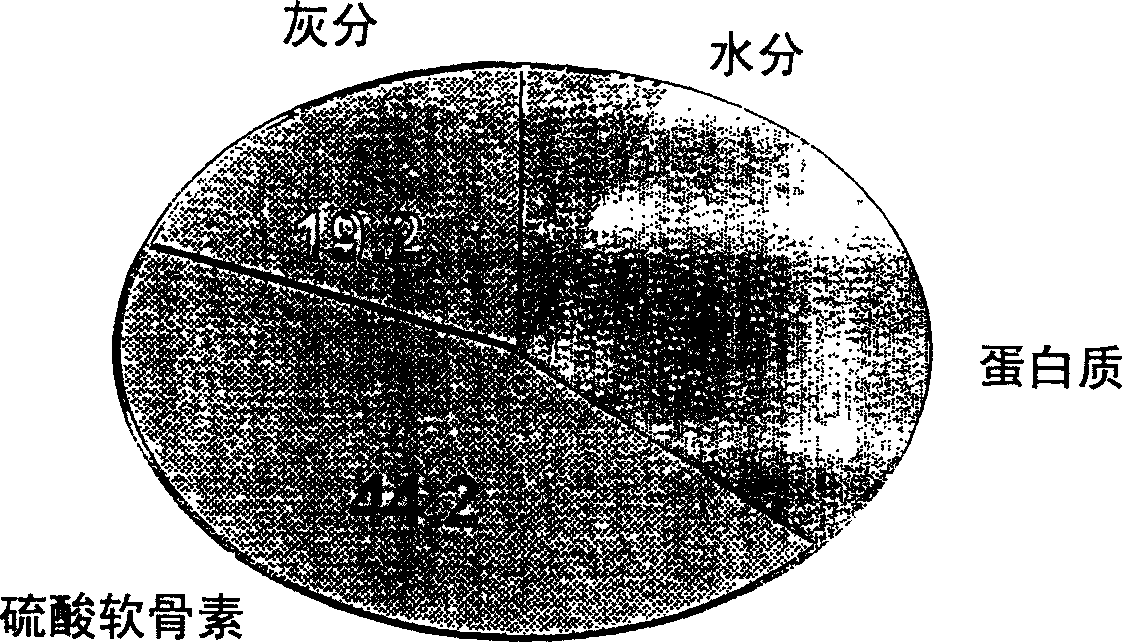
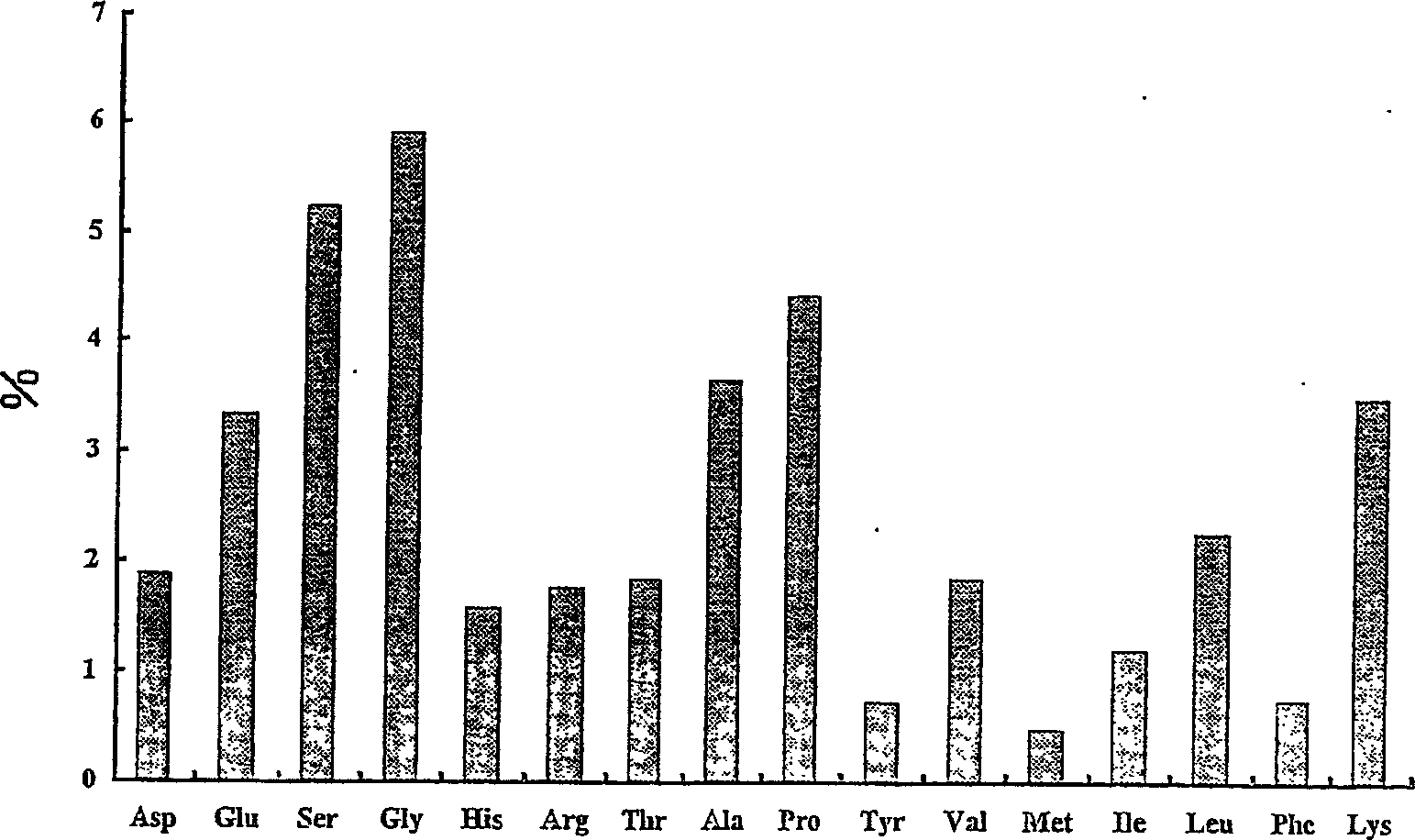
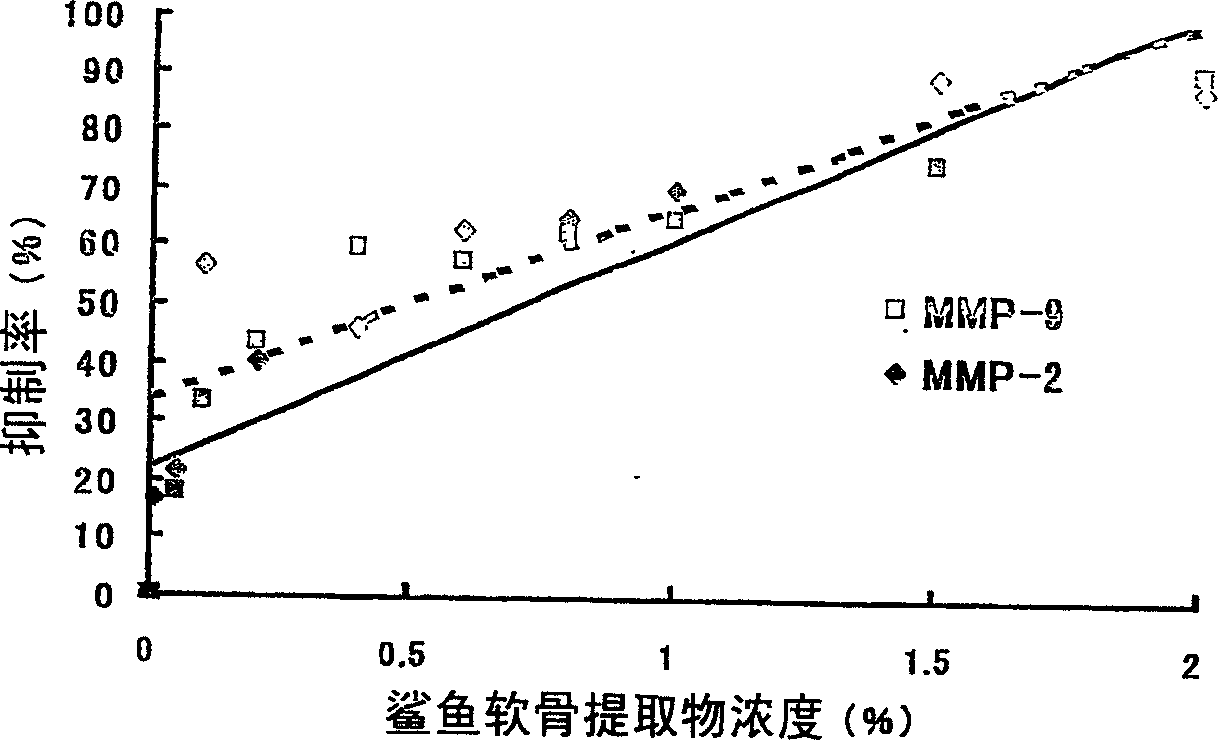
Proteoglycan isolated from cartilaginous fish and process for producing the same
InactiveCN1761686AThe mechanism of action is clearSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAlcoholMechanism of action
It is intended to provide a cartilage extract which exerts its effect even in the case of taking in a small amount and shows a definite function mechanism of the effect. Namely, isolated proteoglycan which originates in a water extract of the cartilage of a cartilaginous fish and the main component of which has a molecular weight of 500 kDa or higher; a composition containing this proteoglycan; a medicinal composition containing the proteoglycan as the active ingredient; and a process for producing the proteoglycan which comprises the step of grinding the cartilage of a cartilaginous fish into pieces of an average diameter of 100 mum or less, the step of adding water to the ground matter and extracting water-soluble components therefrom, the step of separating the aqueous phase containing the water-soluble components, and the step of adding an alcohol to the aqueous phase and obtaining the precipitate.
Owner:HOSOKAWA MICRON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com