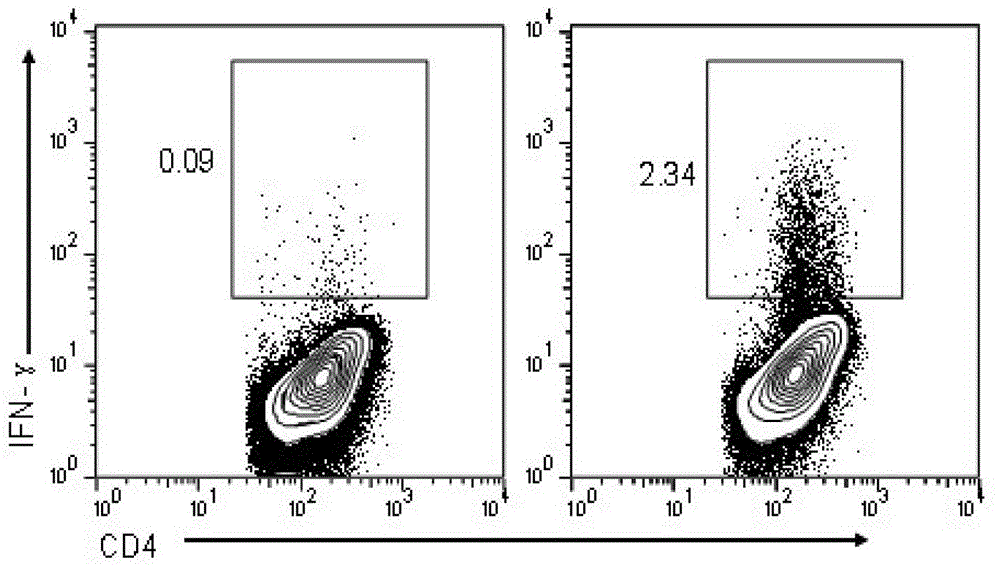
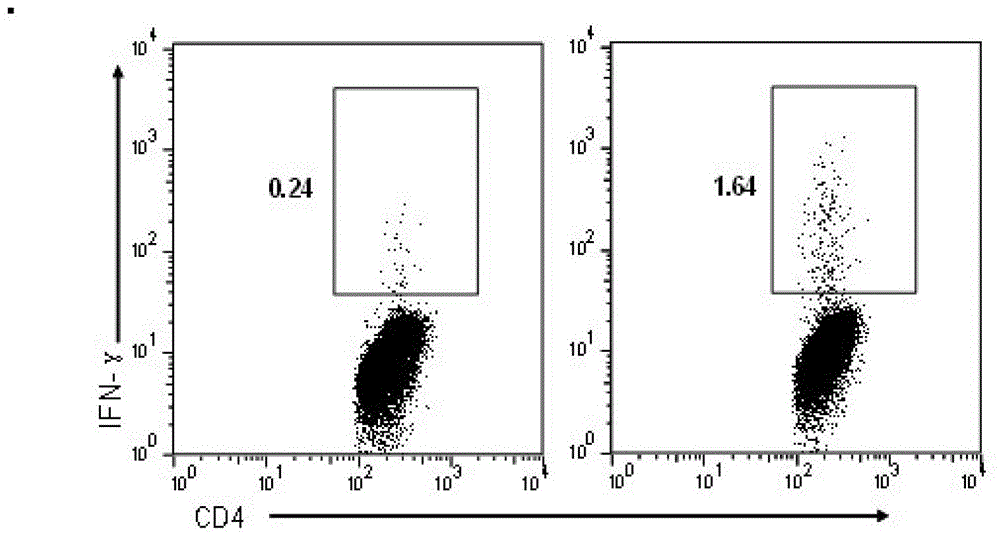
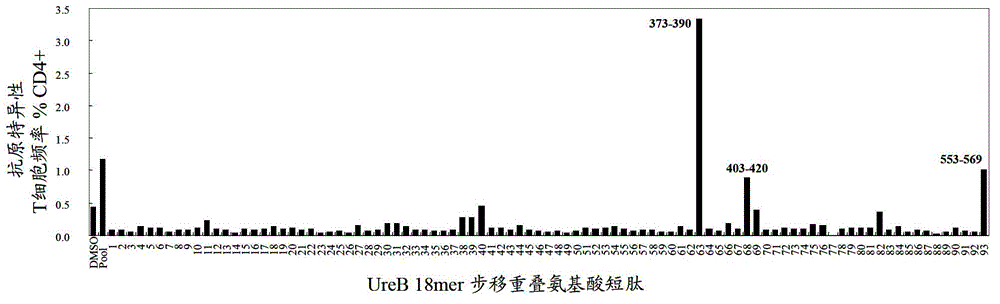
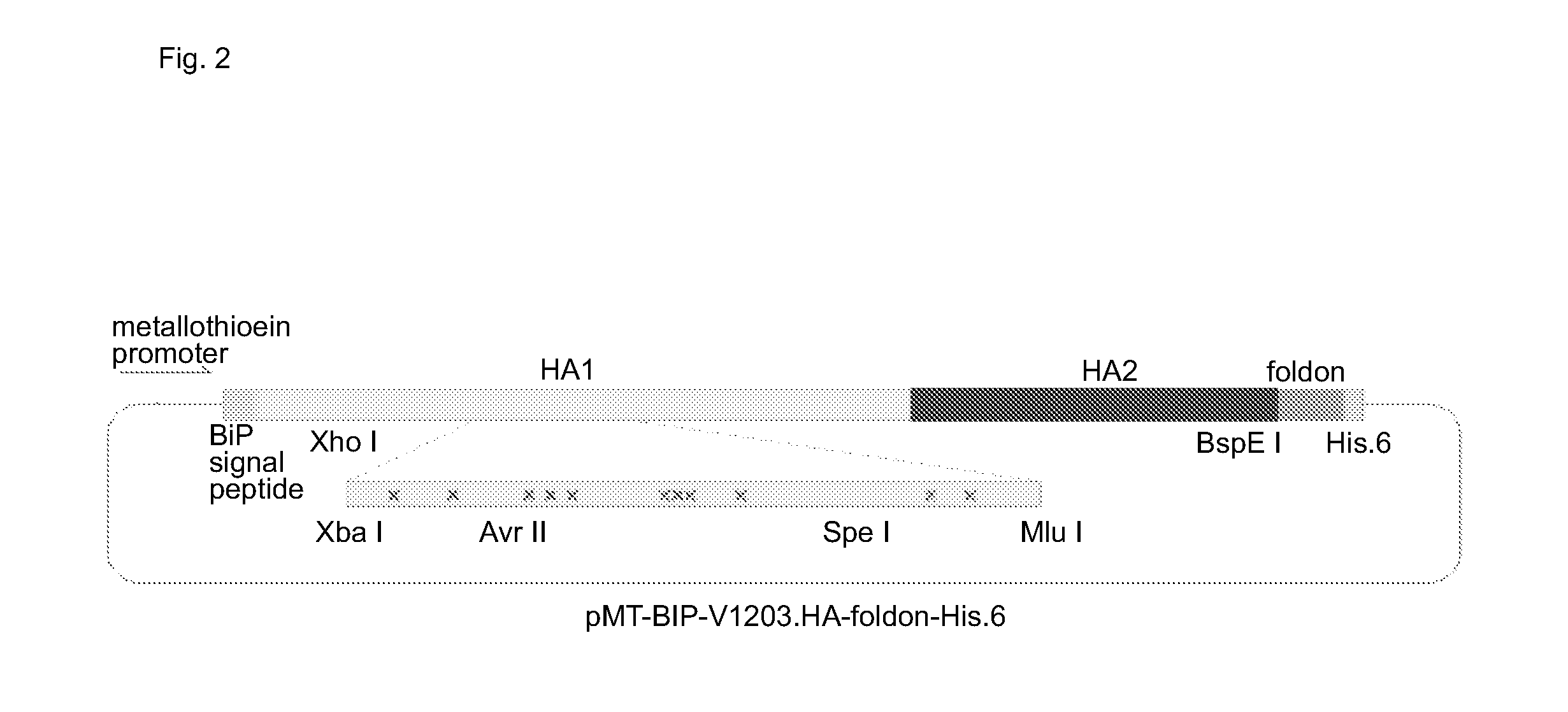
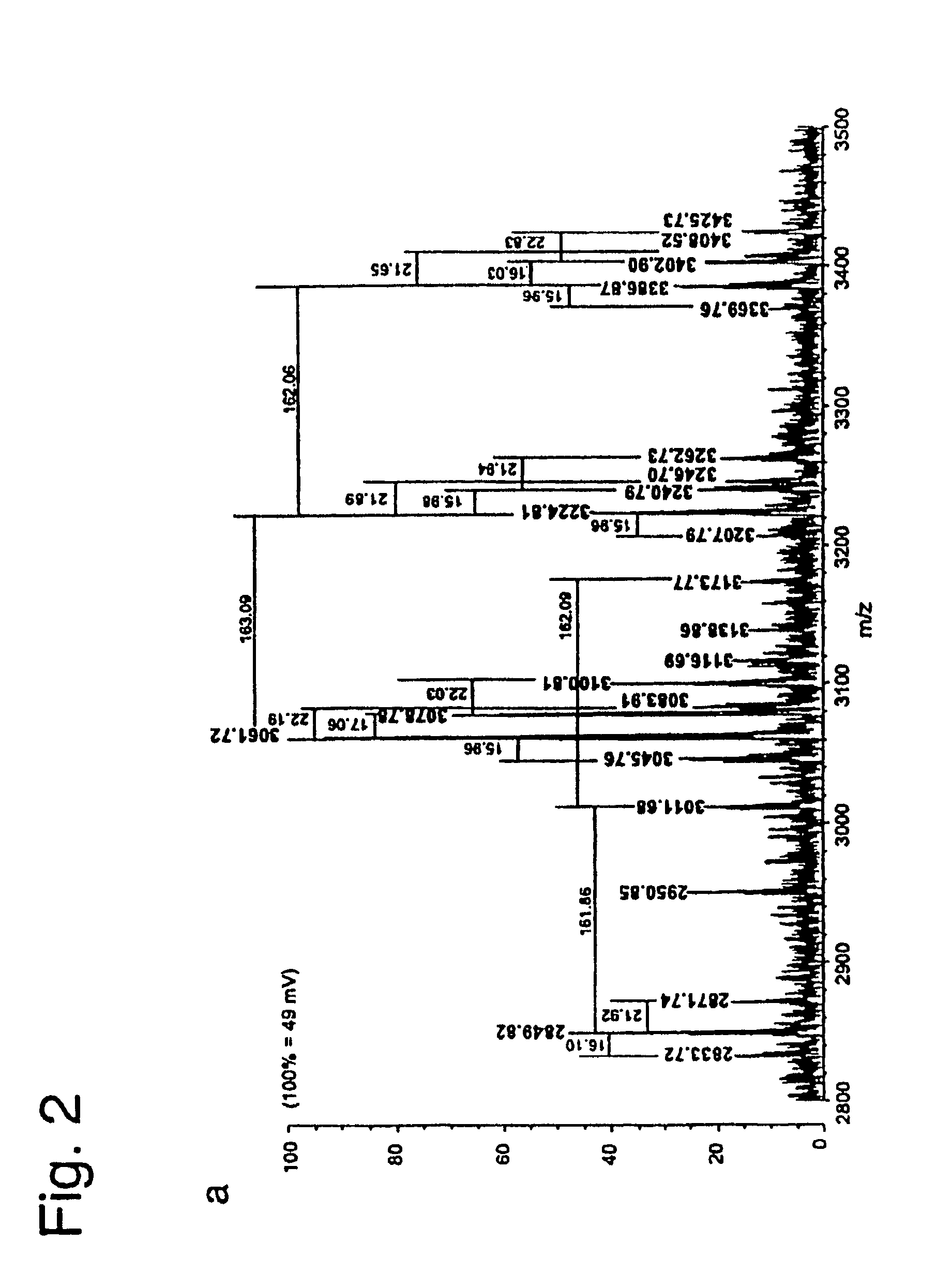
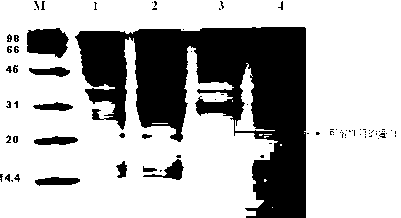Patents
Literature
40 results about "Immunodominant Epitopes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
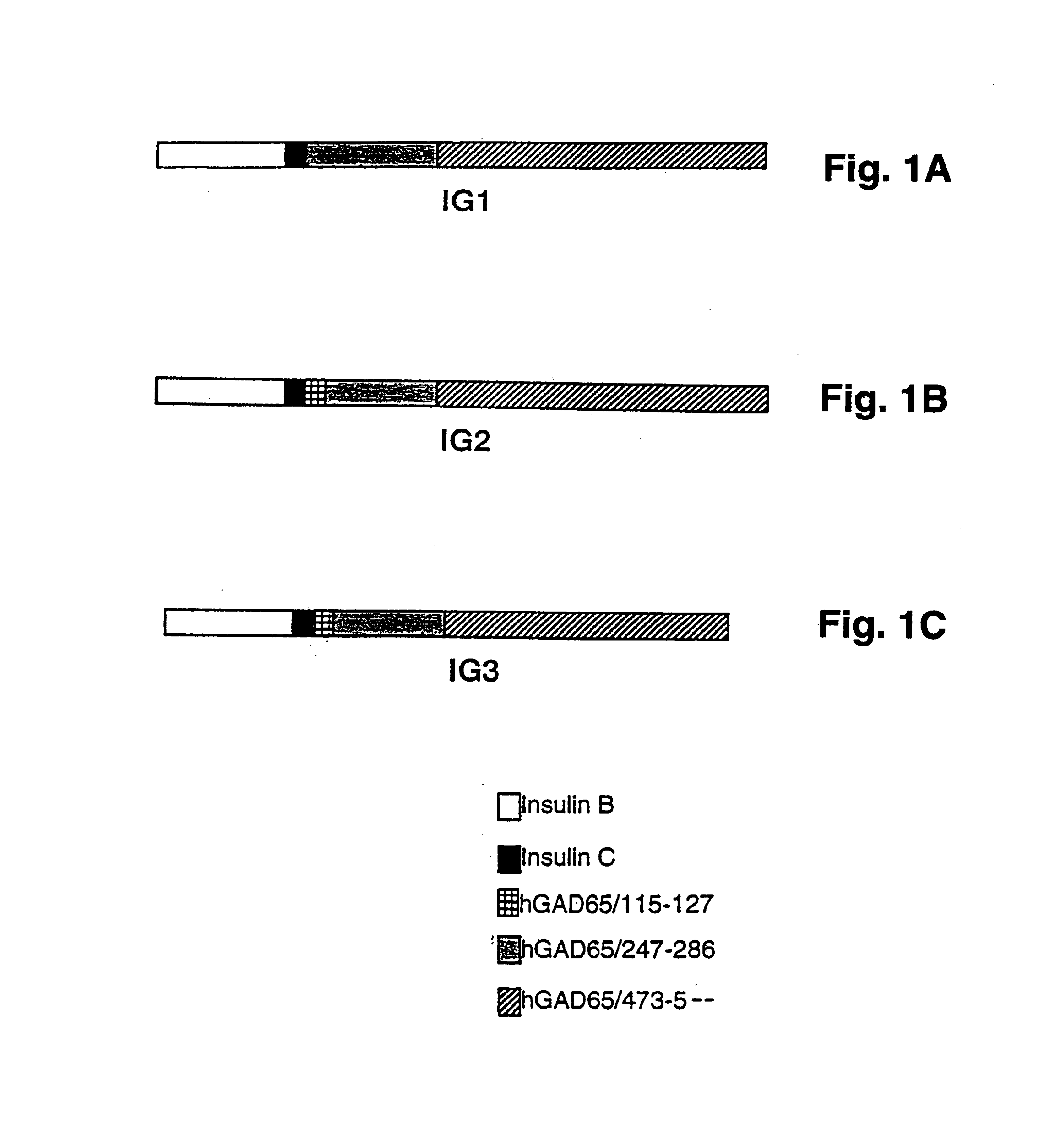
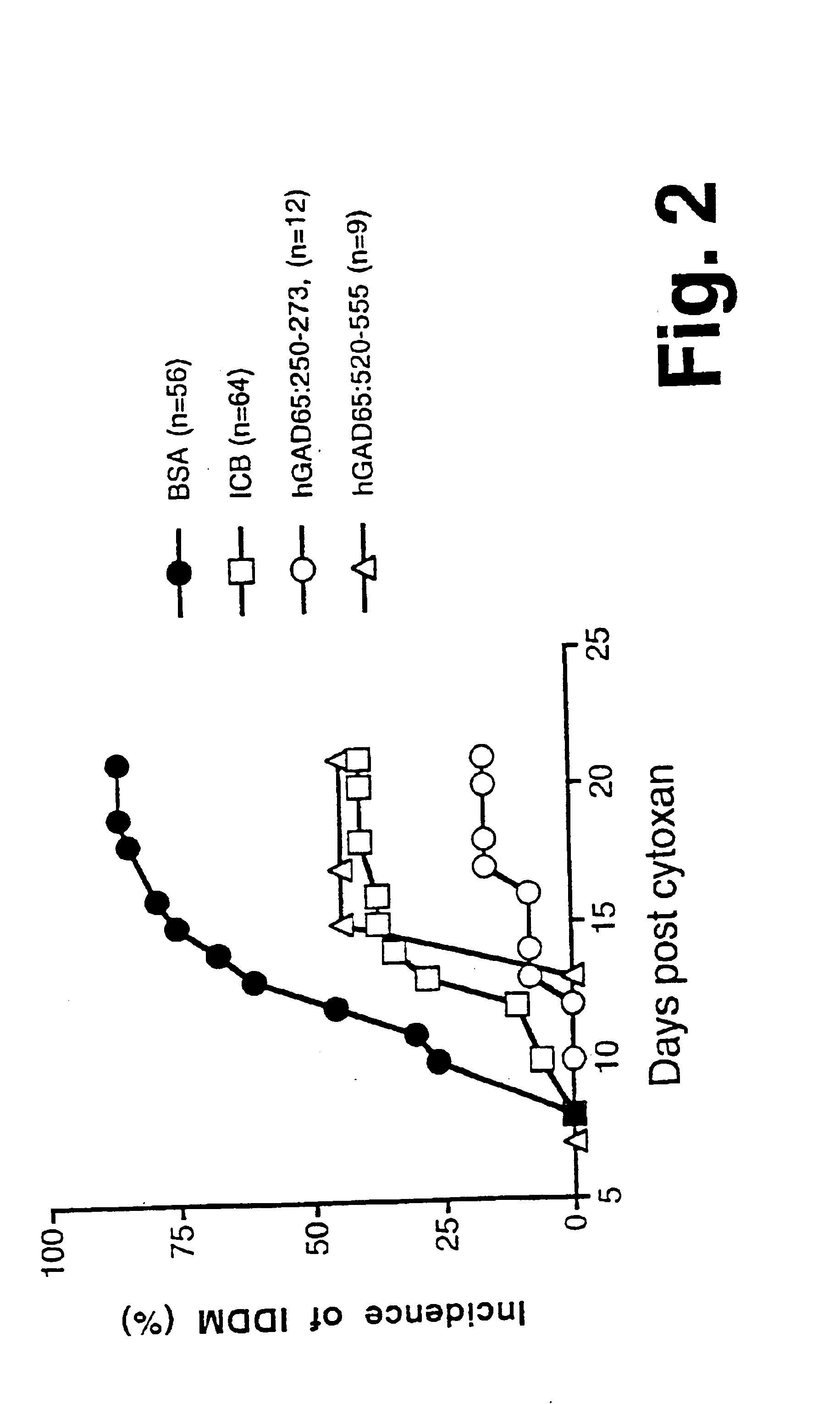
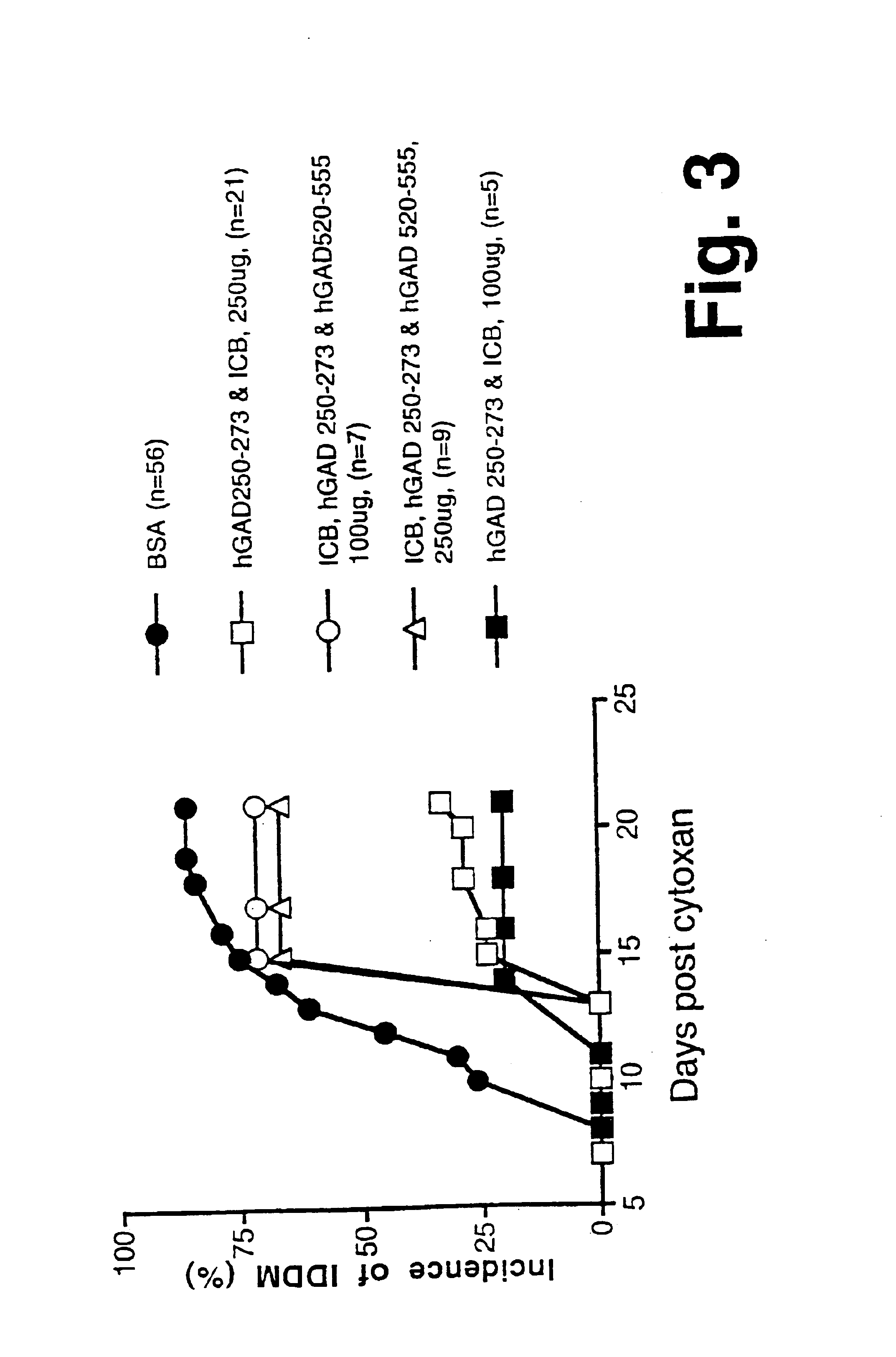
Chimeric proteins for diagnosis and treatment of diabetes
InactiveUS6982323B1Enhance the beneficial effectEasy diagnosisSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunodominant EpitopesPancreas
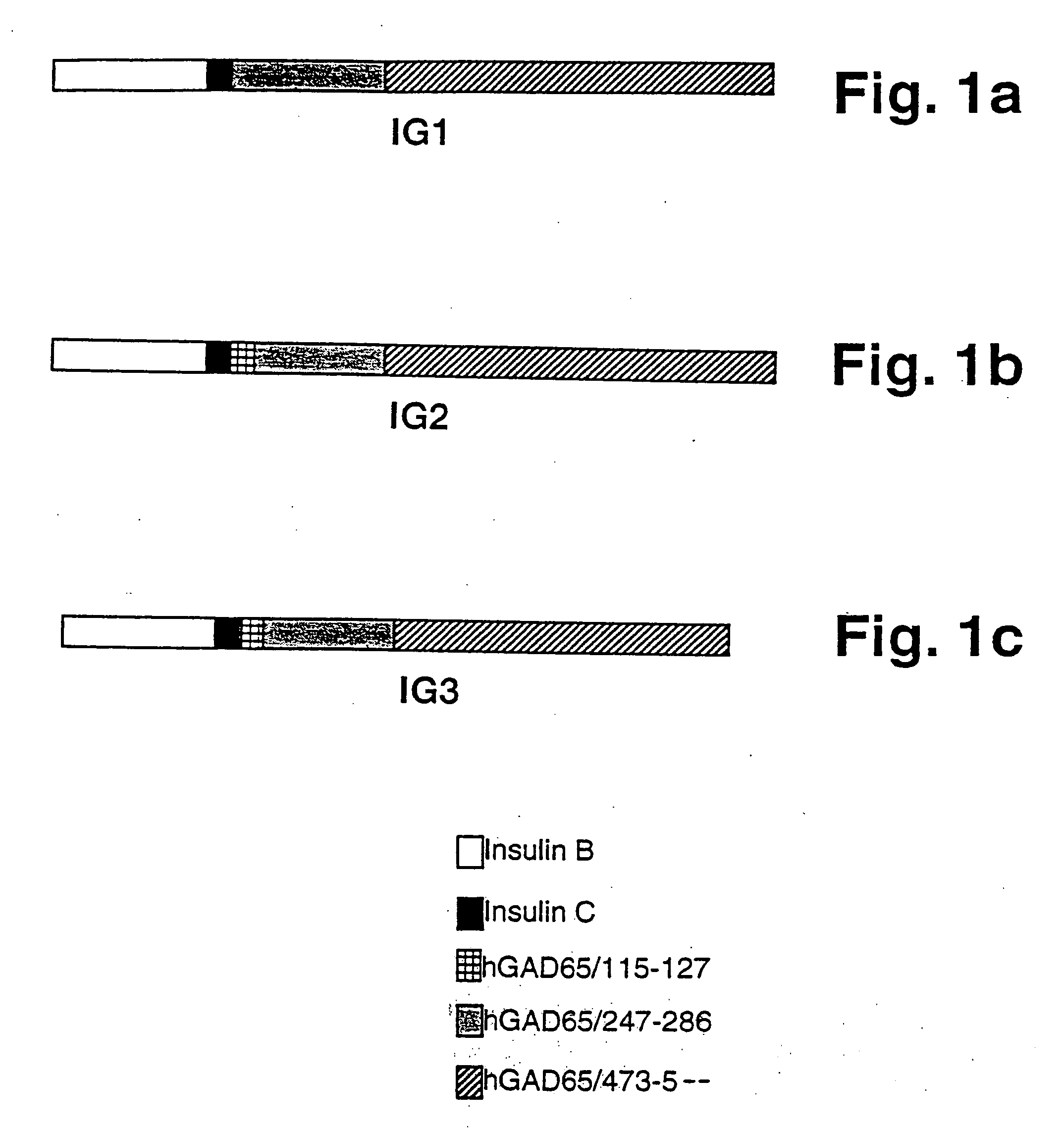
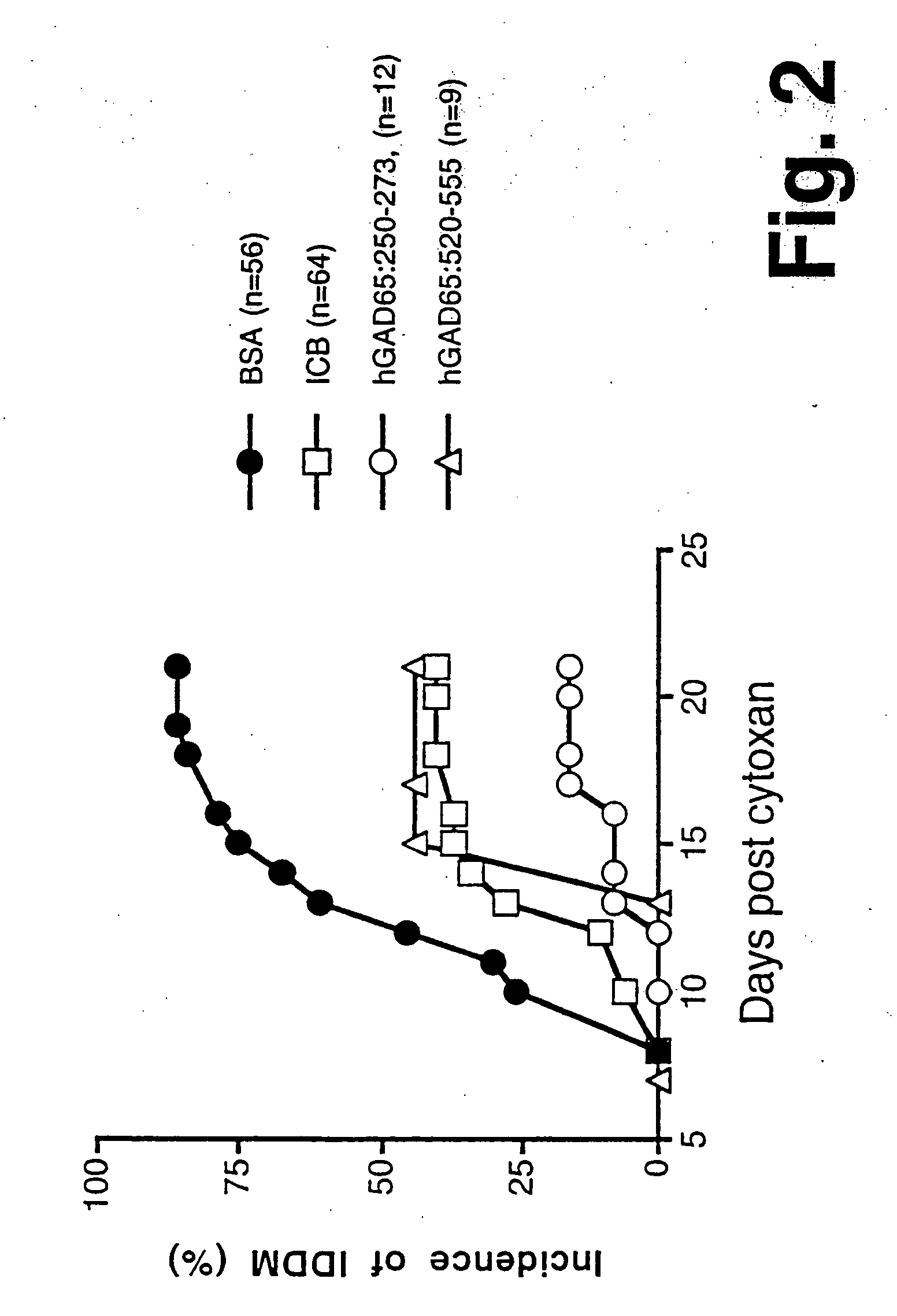
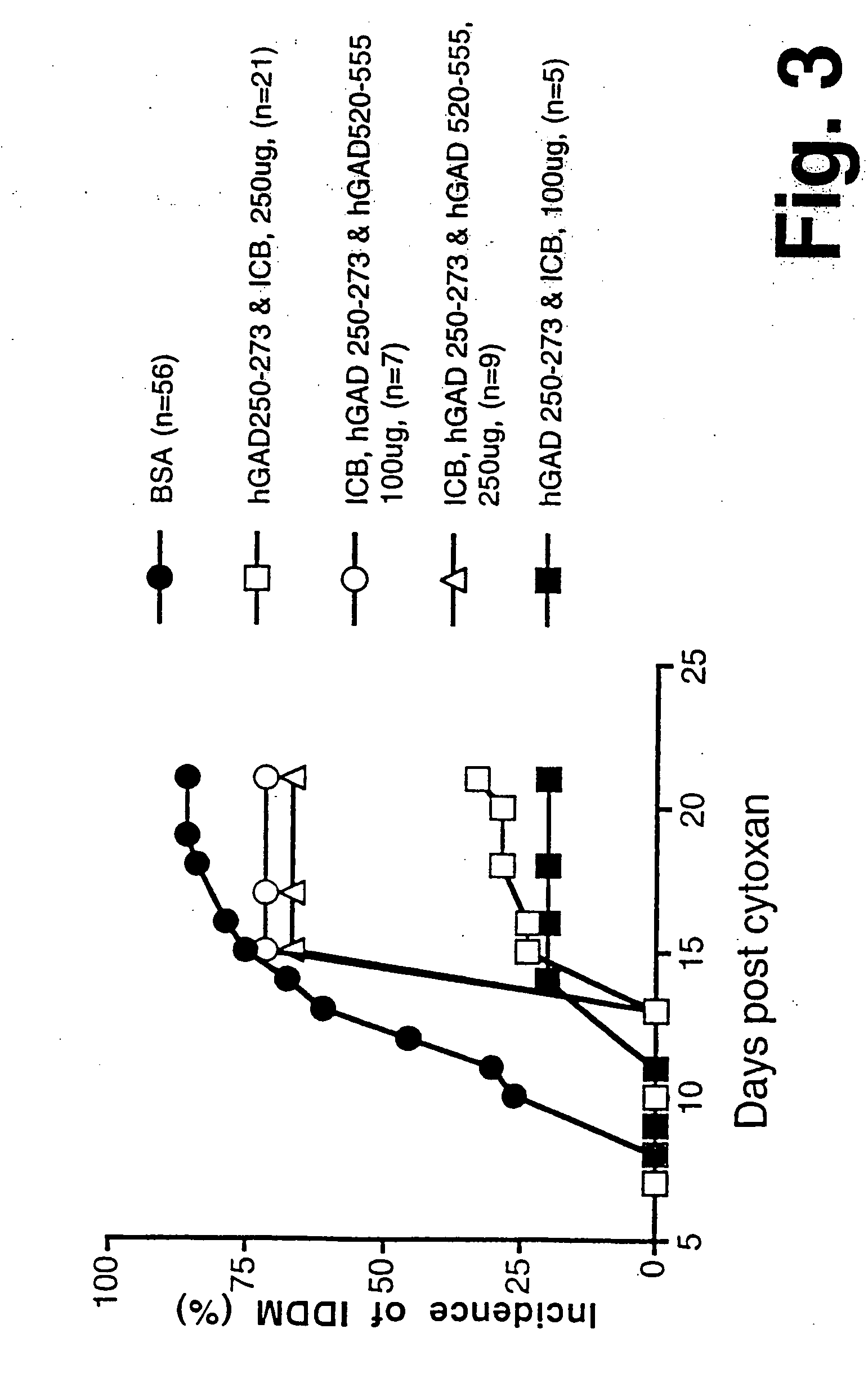
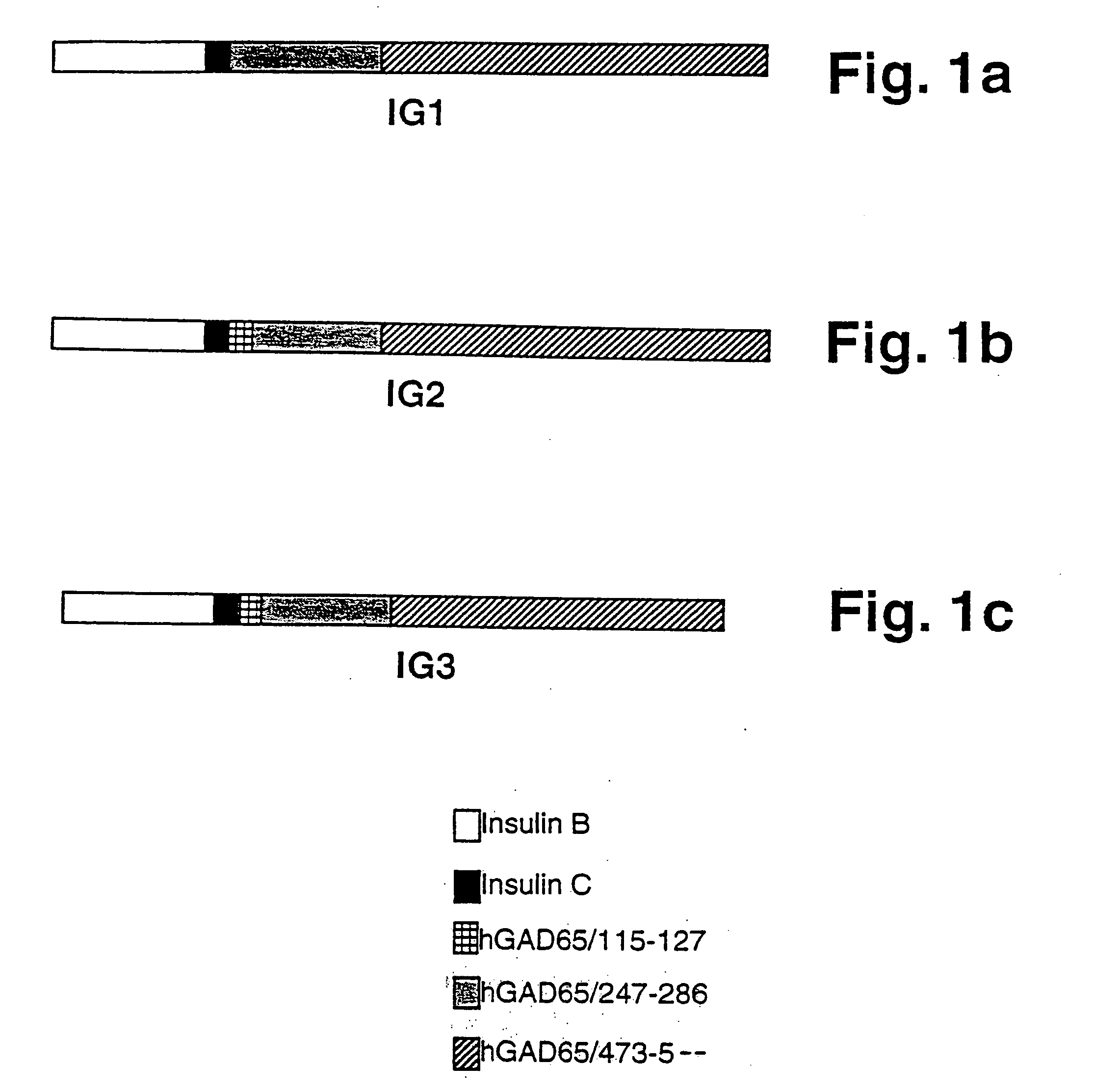
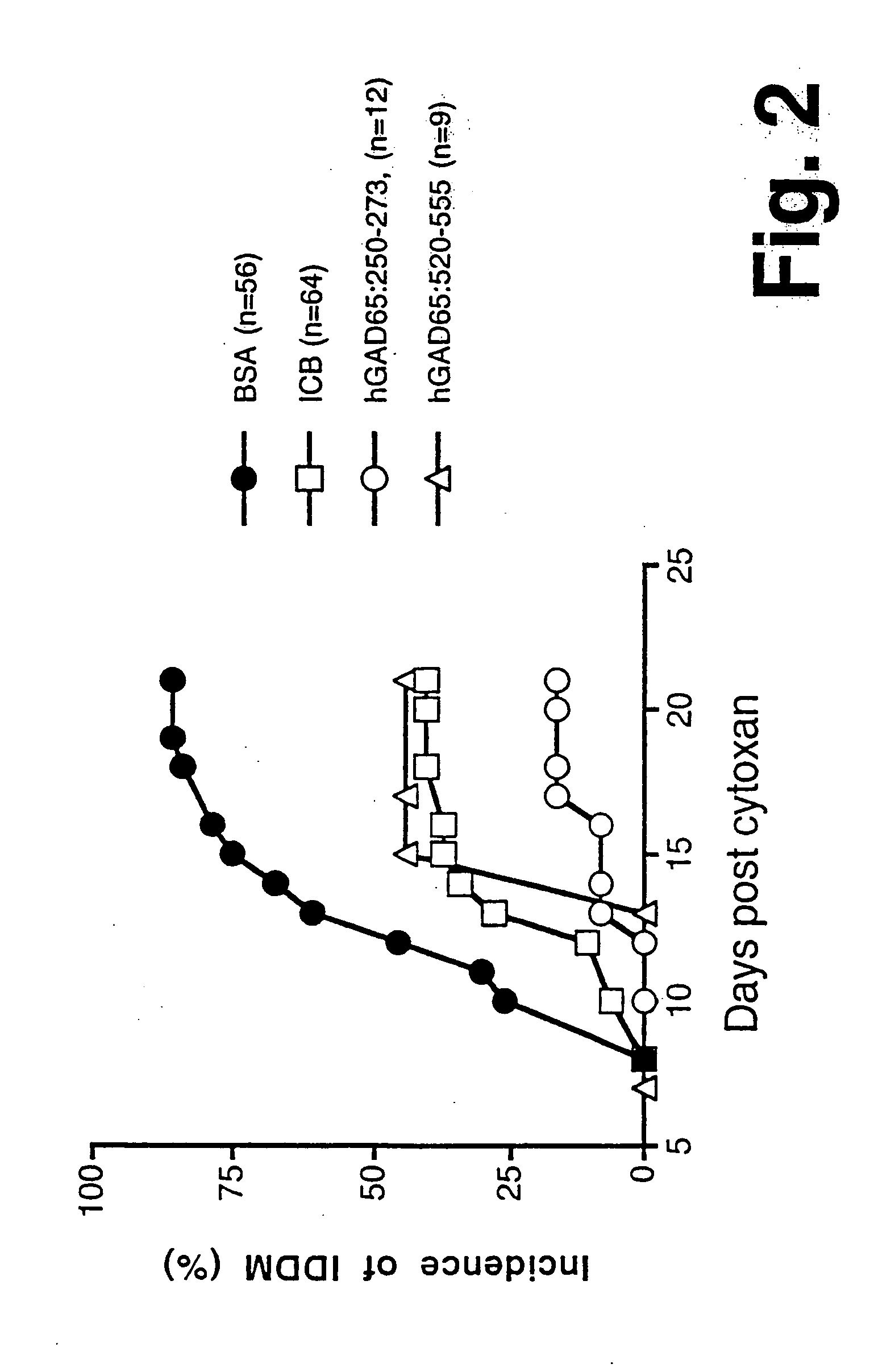
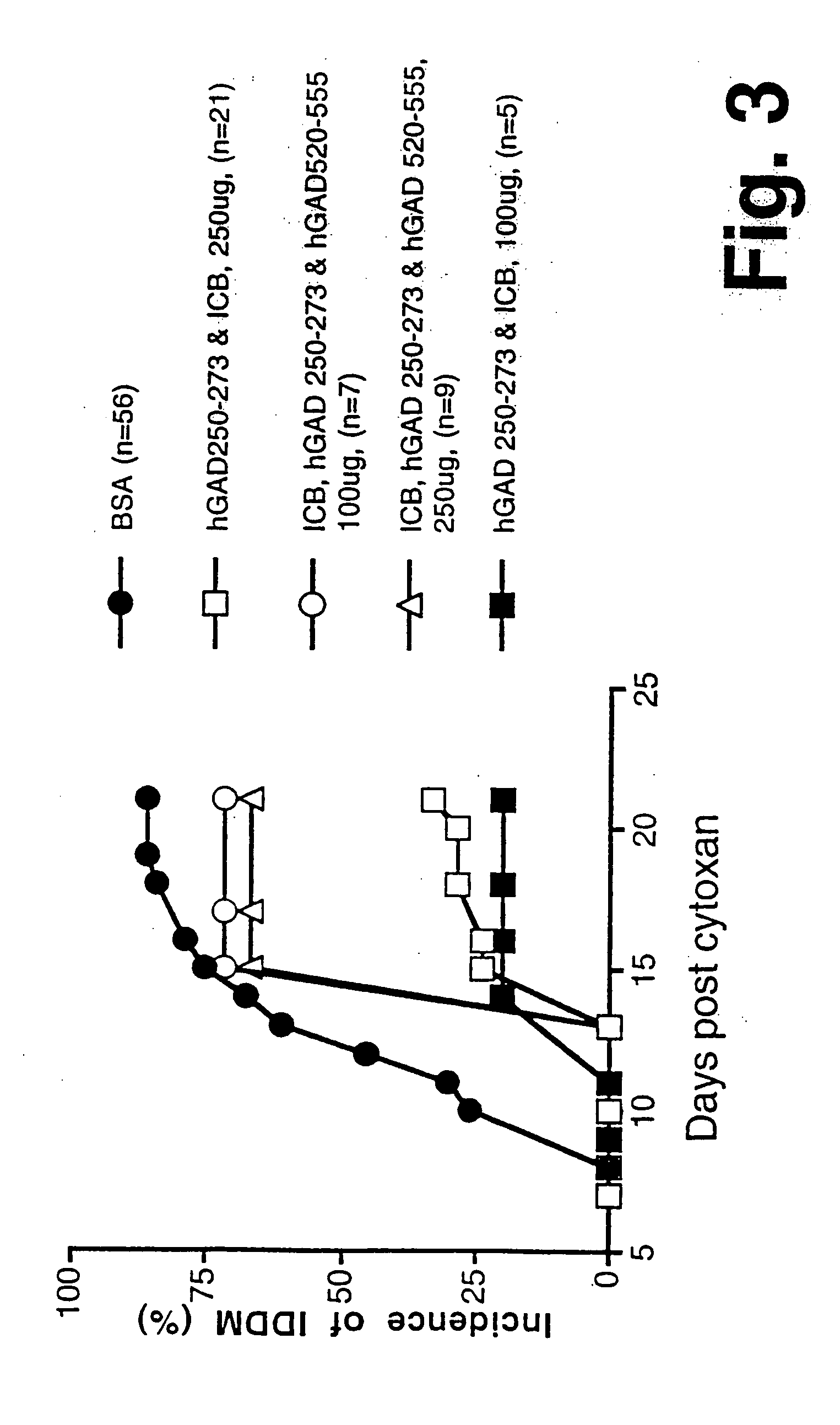
Novel chimeric fusion proteins comprising immunodominant epitopes of GAD and insulin are provided. Also provided are immunomodulatory methods for the use of such proteins for both the prevention and treatment of Type 1 diabetes mellitus. The chimeric fusion proteins of the invention are useful in predicting risk of onset of Type 1 diabetes, determining prognosis of Type 1 diabetes patients early in disease progression, and in evaluating patients for suitability as recipients of transplants of pancreatic cells or tissues. The administration of the proteins of the invention in accordance with the immunomodulatory methods of the invention results in beneficial effects on disease development and severity in patients suffering from or predicted to be at risk of developing Type 1 diabetes, as well as on the outcome of transplants of pancreatic cells or tissues in Type 1 diabetes patients.
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
Soluble Form of Carbonic Anhydrase IX (s-CA IX), Assays to Detect s-CA IX, CA IX's Coexpression with HER-2/neu/c-erbB-2, and CA IX-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies to Non-Immunodominant Epitopes
InactiveUS20080176258A1Improve efficiencyIncrease resourcesBiological material analysisDepsipeptidesImmunodominant EpitopesMonoclonal antibody
Disclosed herein among other MN / CA IX-related inventions are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, preferably monoclonal antibodies and immunoreactive fragments and engineered variants thereof. Subsets of the new antibodies are to either the proteoglycan-like (PG) domain or to the carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain of MN / CA IX, and methods are provided by which antibodies can be prepared to the other MN / CA IX domains. Such new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies, fragments and variants are useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer and precancer. Particularly preferred are the new monoclonal antibodies, fragments and variants that are specific for the non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, which antibodies are, among other uses, useful to detect soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, alone but preferably in combination with antibodies specific to the immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, for example, in a sandwich assay.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
Soluble Form of Carbonic Anhydrase IX (s-CA IX), Assays to Detect s-CA IX, CA IX's Coexpression with HER-2/neu/c-erbB-2, and CA IX-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies to Non-Immunodominant Epitopes
InactiveUS20080176310A1Improve efficiencyIncrease resourcesOxidoreductasesFermentationKilodaltonWestern blot
Disclosed herein is the discovery of a soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, such as, urine and serum. Said s-CA IX comprises the extracellular domain of CA IX or portions thereof. The predominant s-CA IX species is the extracellular domain comprising a proteoglycan-like (PG) domain and carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain, and having a molecular weight of about 50 / 54 kilodaltons (kd) upon Western blot. A smaller s-CA IX form of about 20 to about 30 kd comprising the CA domain or parts thereof, not linked to the PG domain, has also been found in body fluids. Diagnostic / prognostic methods for precancer and cancer that detect or detect and quantitate said s-CA IX in body fluids, are described. Also disclosed herein is the coexpression of CA IX and HER-2 / neu / c-erbB-2 that provides parallel, alternative and potentially synergistic diagnostic / prognostic and therapeutic strategies for precancer and cancer. Further disclosed are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, preferably monoclonal antibodies and immunoreactive fragments and engineered variants thereof. Such new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies, fragments and variants are useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer and precancer. Particularly preferred are the new monoclonal antibodies, fragments and variants that are specific for the non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, which antibodies are, among other uses, useful to detect soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, alone but preferably in combination with antibodies specific to the immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, for example, in a sandwich assay.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
Soluble Form of Carbonic Anhydrase IX (s-CA IX), Assays to Detect s-CA IX, CA IX's Coexpression with Her-2/neu/c-erbB-2, and CA IX-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies to Non-Immunodominant Epitopes
InactiveUS20080177046A1Good curative effectImprove efficiencyImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological material analysisKilodaltonWestern blot
Disclosed herein is the discovery of a soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, such as, urine and serum. Said s-CA IX comprises the extracellular domain of CA IX or portions thereof. The Predominant s-CA IX species is the extracellular domain comprising a proteoglycan-like (PG) domain and carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain, and having a molecular weight of about 50 / 54 kilodaltons (kd) upon Western blot. A smaller s-CA IX form of about 20 to about 30 kd comprising the CA domain or parts thereof, not linked to the PG domain, has also been found in body fluids. Diagnostic / prognostic methods for precancer and cancer that detect or detect and quantitate said s-CA IX in body fluids, are described. Also disclosed herein is the coexpression of CA IX and HER-2 / neu / c-erbB-2 that provides parallel, alternative and potentially synergistic diagnostic / prognostic and therapeutic strategies for precancer and cancer. Further disclosed are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, preferably monoclonal antibodies and immunoreactive fragments and engineered variants thereof. Such new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies, fragments and variants are useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer and precancer. Particularly preferred are the new monoclonal antibodies, fragments and variants that are specific for the non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, which antibodies are, among other uses, useful to detect soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, alone but preferably in combination with antibodies specific to the immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, for example, in a sandwich assay.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
Multiplex vaccine
The present invention provides antigen complexes comprising 15 or more, in some instances 15 to 100 or more, different antigens and / or compositions comprising the antigen complexes where the composition comprises 15 or more, in some instances 15 to 100 or more, different antigens. The invention also provides to methods of modulating immune responses through administration of the complexes to an individual and to methods of identifying immunodominant epitopes with use of the antigen complexes.
Owner:DENDRITHERAPEUTICS
Soluble form of carbonic anhydrase IX (S-CA IX), assays to detect s-CA IX, CA IX'S coexpression with HER-2/NEU/C-ERBB-2, and CA IX-specific monoclonal antibodies to non-immunodominant epitopes
InactiveUS7816493B2Good curative effectSugar derivativesBiological material analysisKilodaltonC erbb 2
Disclosed herein is the discovery of a soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) found in body fluids, such as, urine and serum. Soluble CA IX comprises the extracellular domain of CA IX or portions thereof. The predominant s-CA IX species is the extracellular domain comprising a proteoglycan-like (PG) domain and carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain, and having a molecular weight of about 50 / 54 kilodaltons. Diagnostic / prognostic methods for precancer / cancer that detect or detect and quantitate s-CA IX in body fluids, are described. Also disclosed is the coexpression of CA IX and HER-2 that provides potentially synergistic diagnostic / prognostic and therapeutic strategies for precancer / cancer. Further disclosed are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer / precancer. Preferred are new antibodies, specific for non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, useful to detect soluble CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, preferably in combination with antibodies specific to immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for designing vaccines against constantly mutating pathogens
InactiveUS20090162383A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic antibodyImmunodominant Epitopes
A unique method is disclosed for identifying and replacing surface amino acid residues of a protein antigen that reduces the antigenicity of the putative immunodominant epitopes of the antigen and makes all the accessible regions of the molecule essentially antigenically equivalent, so that the antibody response will be directed against more parts of the molecule and not mainly against the erstwhile immunodominant epitopes. The method will simultaneously change the antigenicity of the molecule and preserve its structure. The method is useful in the design of molecules useful for immunization, for example, as vaccines, or for the generation of therapeutic antibodies, against constantly mutating pathogens. It is also useful in the design of molecules useful for immunization against pathogens that had been intentionally mutated so as to render those pathogens able to infect erstwhile immune individuals.
Owner:PADLAN EDUARDO A
Expanding the T cell repertoire to include subdominant epitopes by vaccination with antigens delivered as protein fragments or peptide cocktails
A convenient way of inducing a broad recognition of dominant and subdominant responses to epitopes of any given antigen of importance for prophylaxis or treatment of a chronic disease is provided. The method involves by immunizing with pools of overlapping fragments (synthetic peptides, e.g., 10-30 mers with 2-20 aa overlap) of the desired antigen in appropriate adjuvants. The T cell repertoire is primed to include not only the immunodominant epitope recognized when the intact molecule is used for immunization and induced by the chronic infection itself, but induce a much broader and balanced response to a number of the subdominant epitopes as well. The vaccination with peptide mix induces a T-cell response that includes response to subdominant epitopes is important for protection against chronic disease that on their own induces a response focused only on immunodominant epitopes. The major advantage of the present invention is that it requires no prior knowledge of the precise localisation and identity of the subdominant epitopes and their recognition in a human population, but expands the T-cell repertoire and thereby the total number of epitopes recognized by specific T cells primed by vaccination from a few immunodominant epitopes to a multiple of epitopes.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
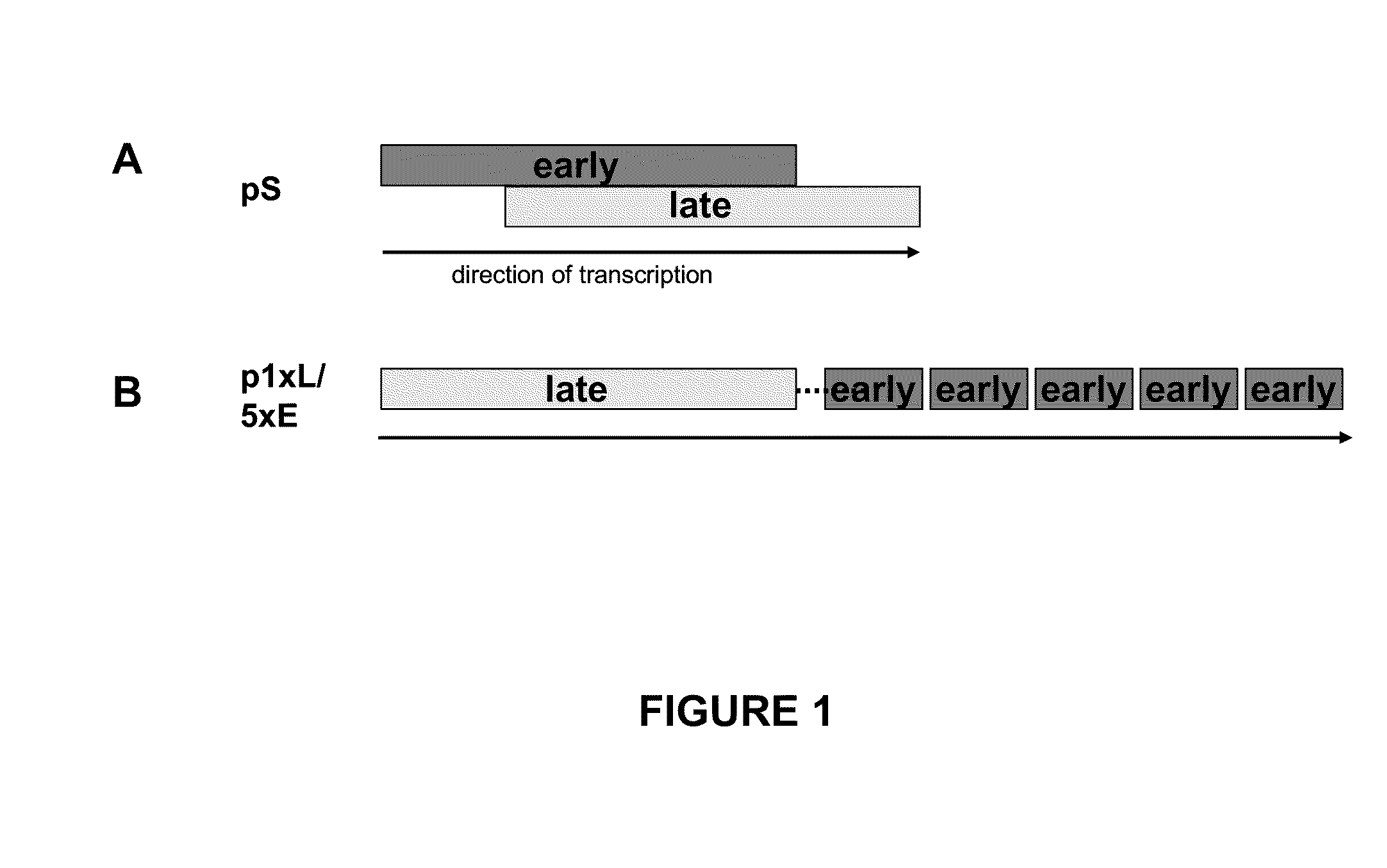
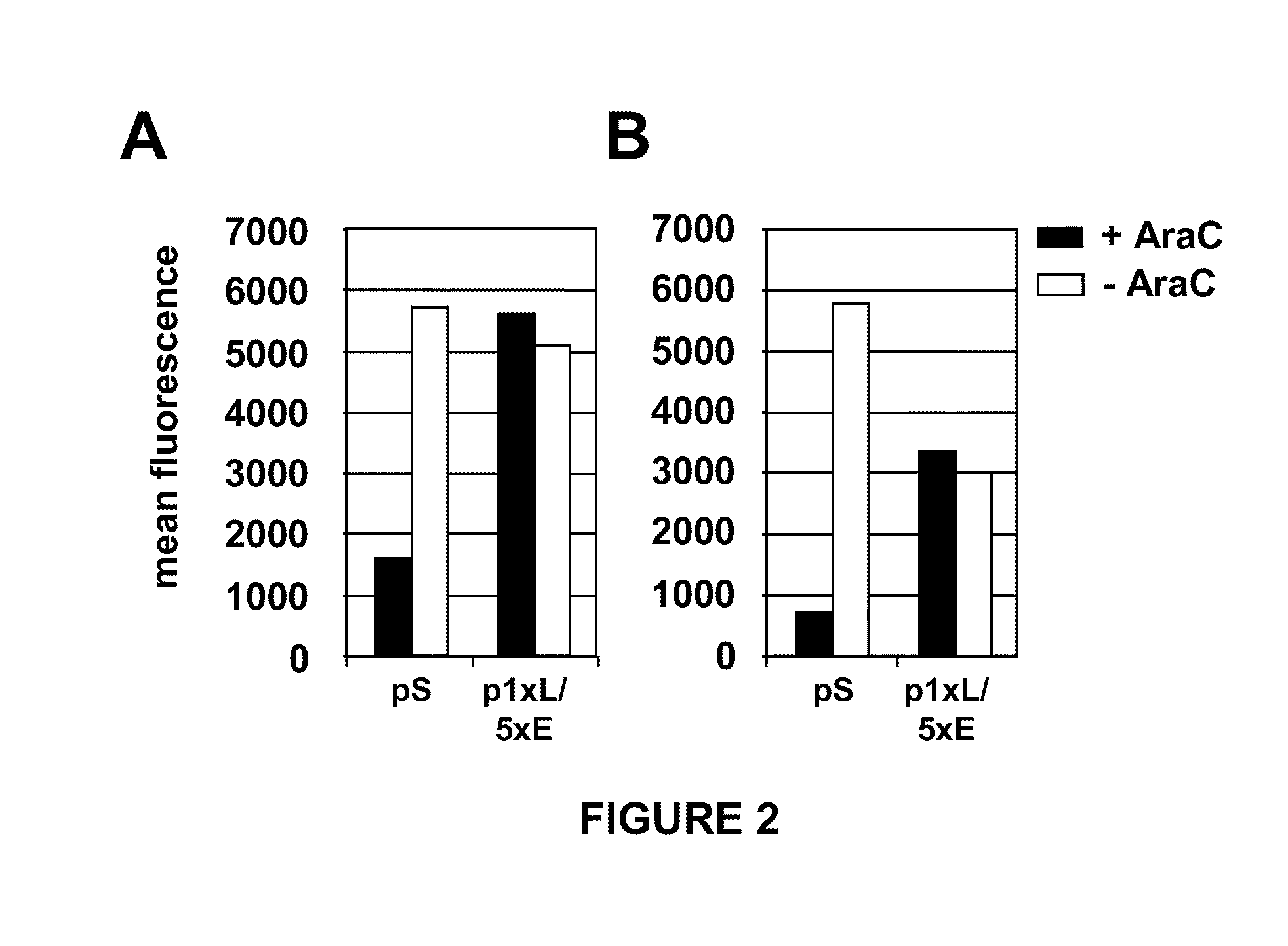
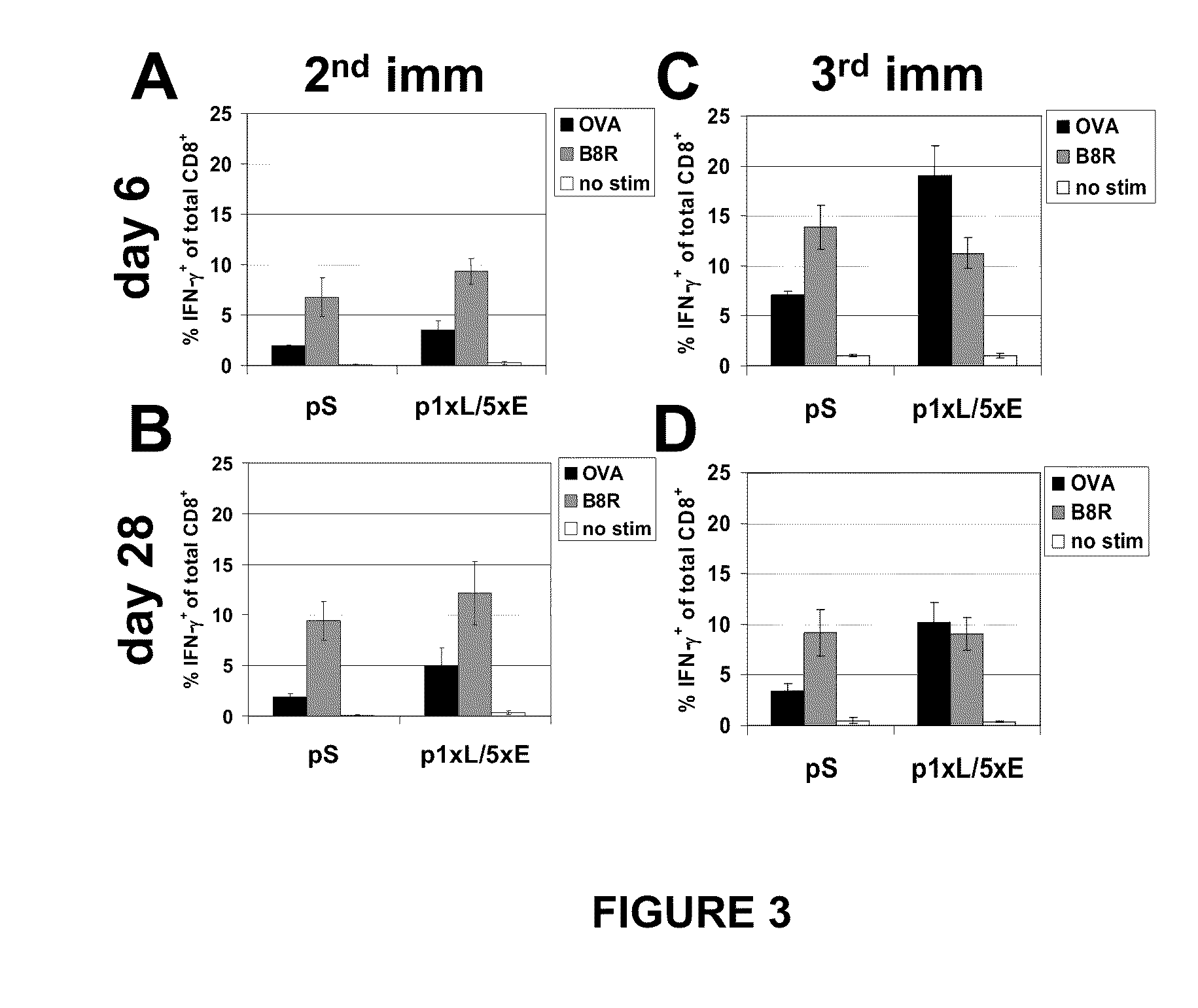
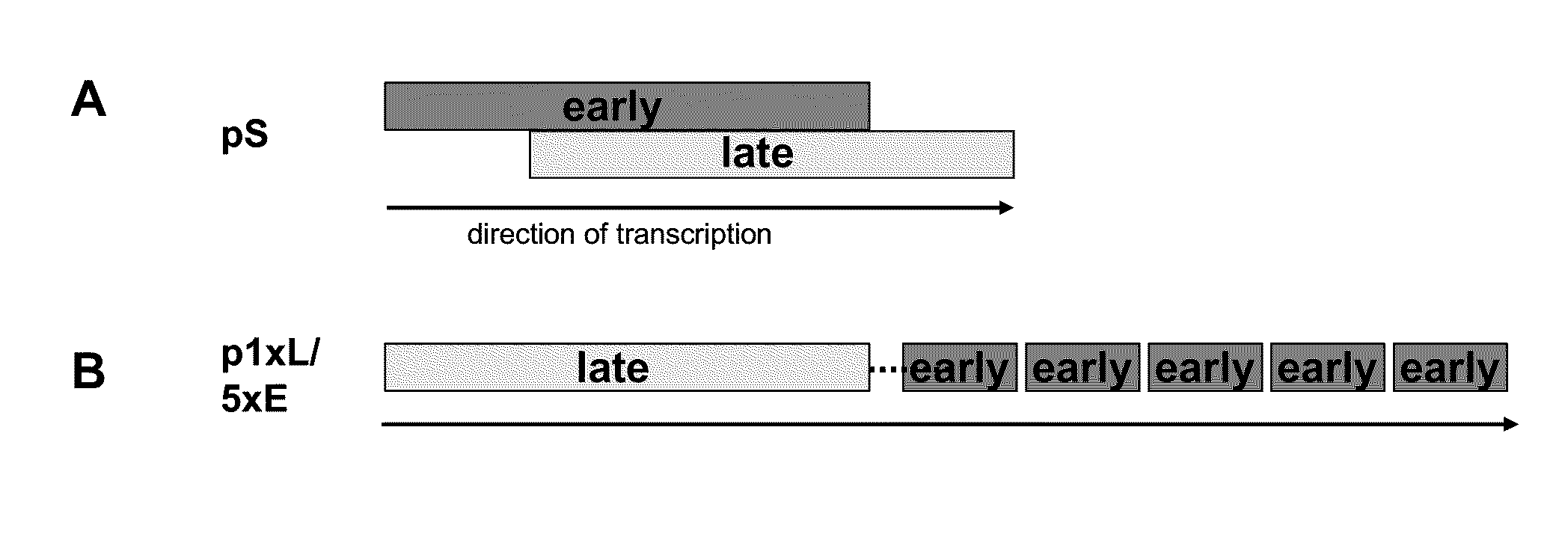
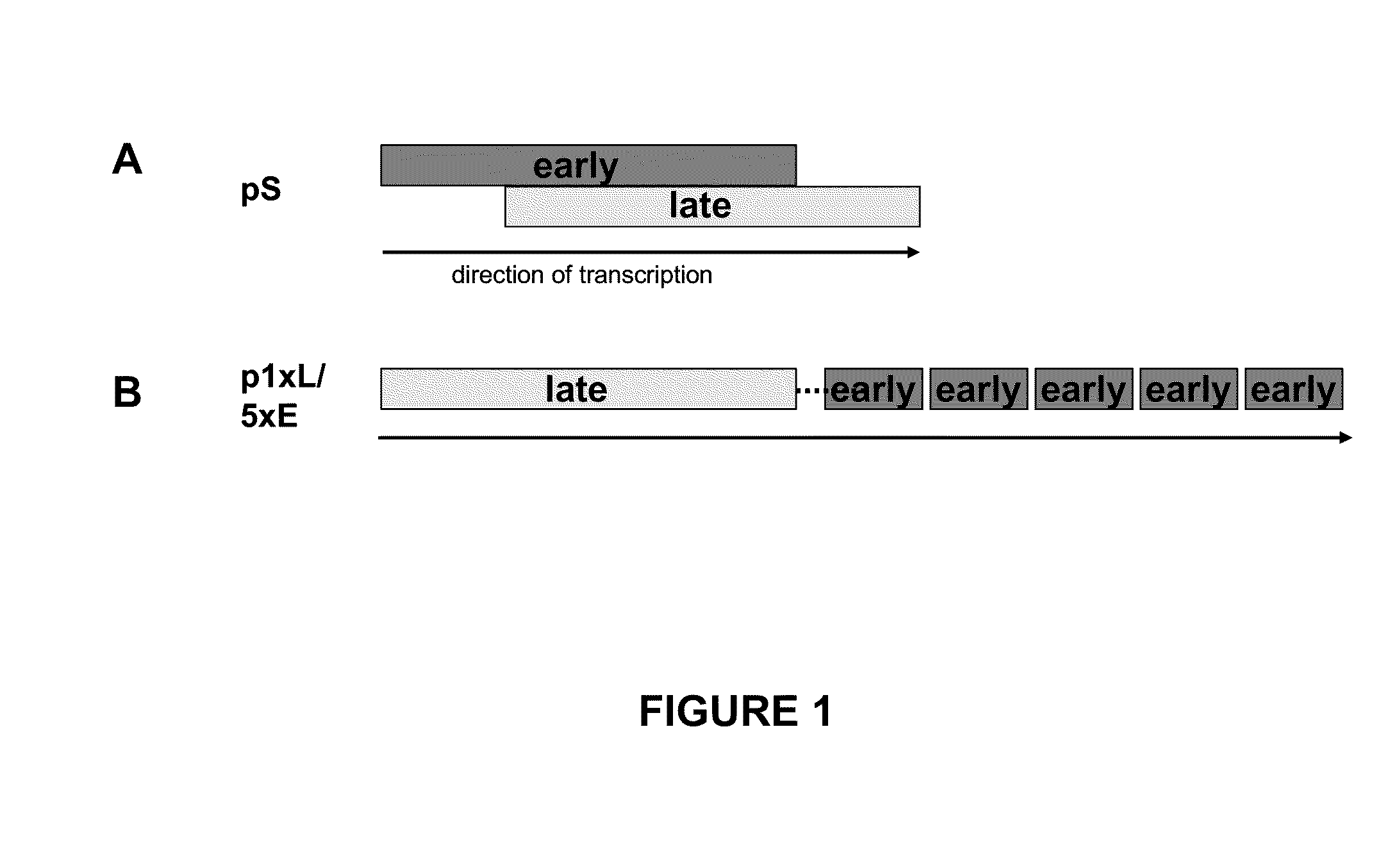
Optimized early-late promoter combined with repeated vaccination favors cytotoxic T cell response against recombinant antigen in MVA vaccines
The invention is drawn to compositions and methods for the induction of a strong CD8 T cell response to a specific antigen(s). The combination of an early / late hybrid promoter directing strongly enhanced early expression of a neoantigen with at least three immunization rounds resulted in a highly efficient neoantigen-specific CD8 T cell response. This combination reversed the immunodominance hierarchy and converted a moderately immunogenic and subdominant CD8 T cell epitope into the immunodominant epitope.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
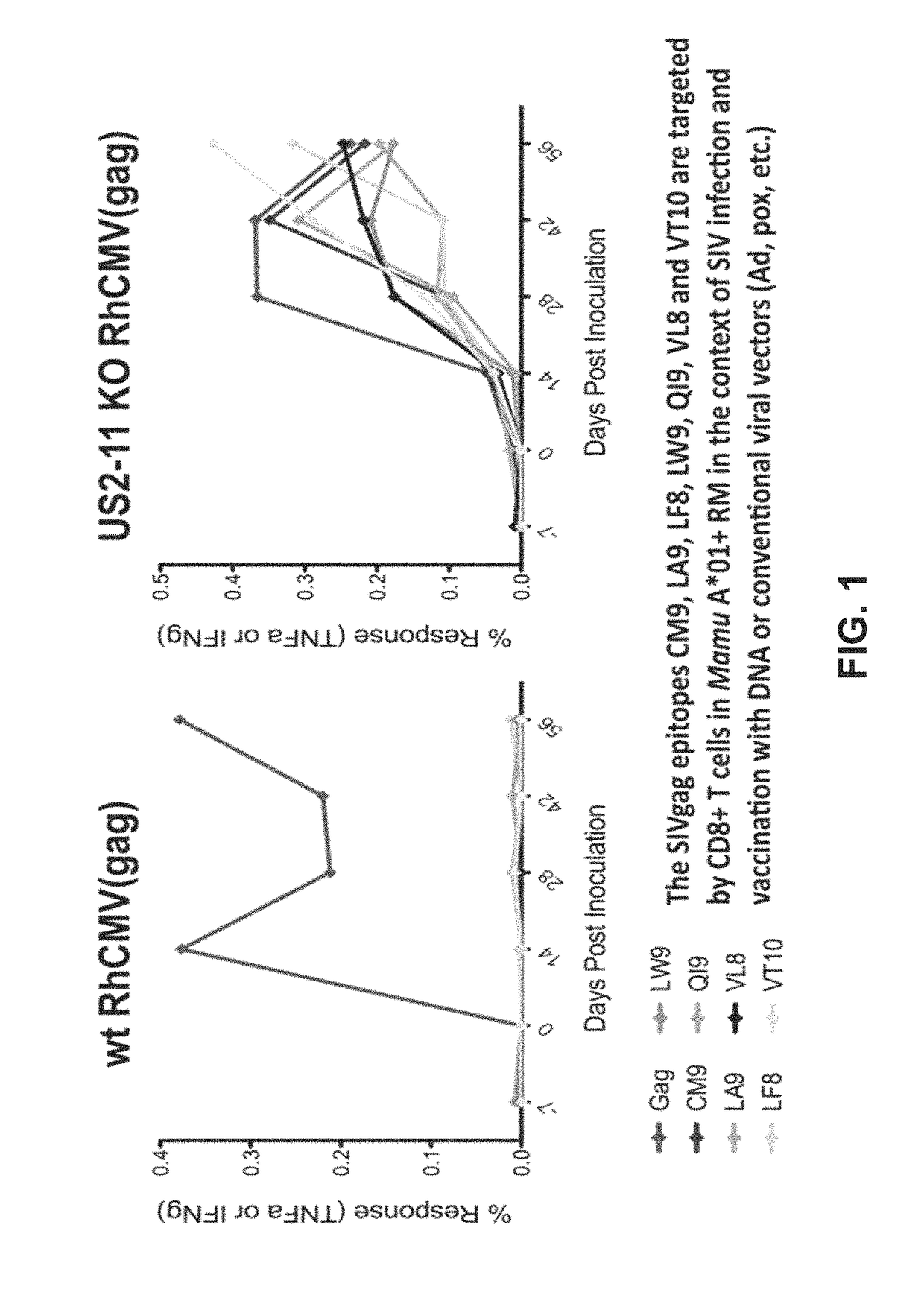
CMV glycoproteins and recombinant vectors
Disclosed herein are recombinant CMV vectors which may comprise a heterologous antigen that can repeatedly infect an organism while inducing a CD8+ T cell response to immunodominant epitopes of the heterologous antigen. The CMV vector may comprise a deleterious mutation in the US11 glycoprotein or a homolog thereof.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
Indirect ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) method for detecting PRRSV (porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus) antibody through tandem repeat expression of GP5 dominant antigen epitopes
InactiveCN103275193AVirus peptidesMicroorganism based processesPorcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virusEngineered genetic
The invention relates to an indirect ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) method for detecting a porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome antibody, which comprises the following steps: by using a pGEX-6p-1 prokaryotic expression vector, performing tandem repeat on two epitopes to improve the antigen activity of an expressed protein, thus constructing a gene engineering bacterium BLpGEX-6p-GP5 capable of realizing secretory expression of the GP5 protein dominant antigen epitopes, wherein one epitope is a linear conservative neutralizing epitope (epitope B) of a screened PRRSV (porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus) GP5 protein, which can be identified by a monoclonal antibody and can also be identified by porcine anti-PRRSV neutralizing serum, and the other epitope is a high-variability immunodominant epitope (A); and purifying and renaturing the expressed recombinant protein, and coating an ELISA plate, thus establishing the indirect ELISA method for detecting a PRRSV antibody to detect the PRRSV antibody level in porcine serum. Results show that the method has the characteristics of favorable repetitiveness and high specificity and can be used for PRRSV serological search.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
HIV composite multi-epitope DNA vaccine and application thereof
InactiveCN101579528AExtensive cross-reactivityShow feasibilityGenetic material ingredientsAntiviralsCtl epitopeVaccination
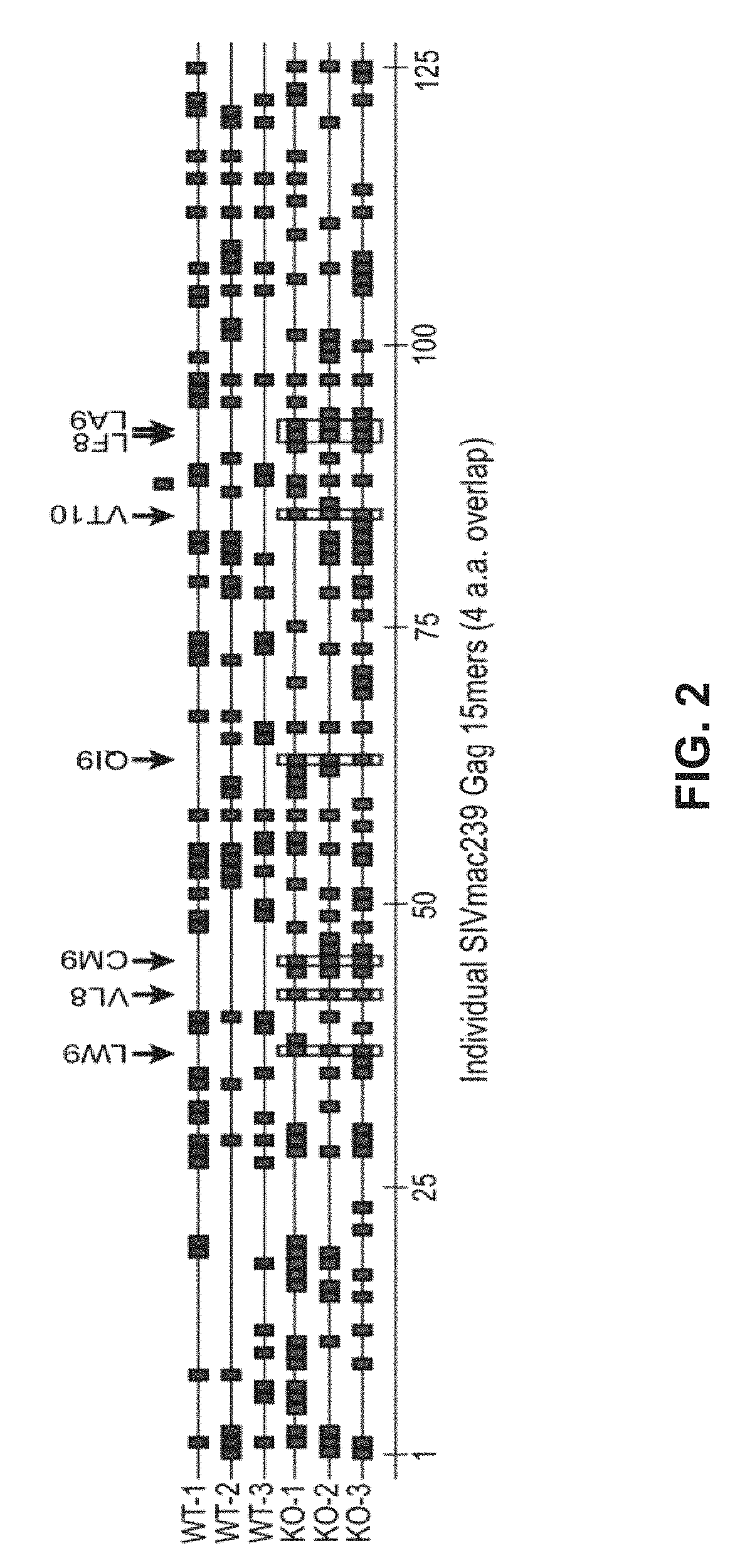
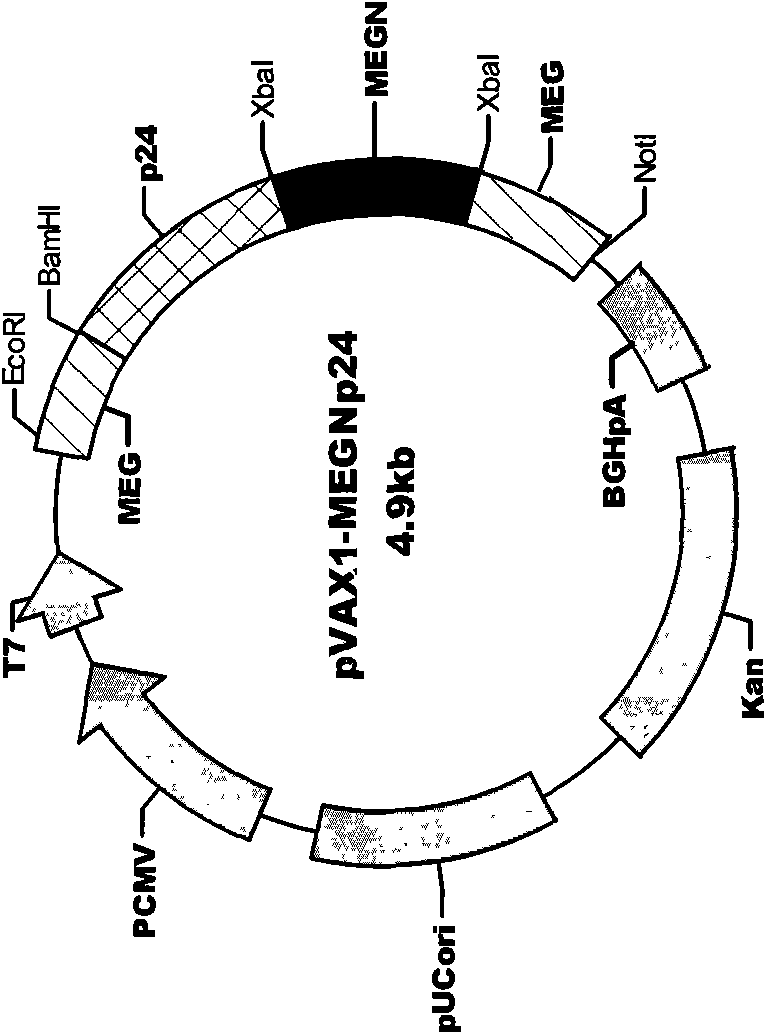
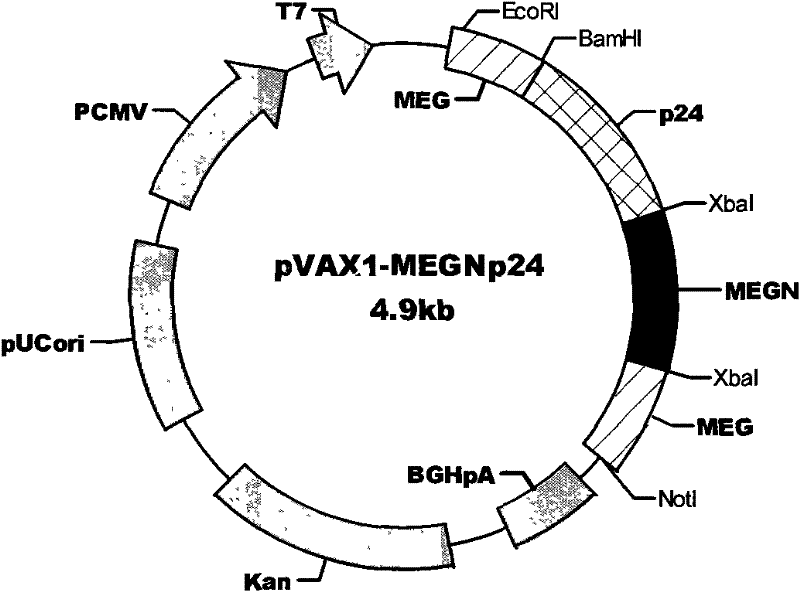
The invention discloses an HIV composite multi-epitope DNA vaccine which takes HIV-1 capsid protein p24 as a vector backbone molecule and ER signal peptide as a homing sequence, and contains twenty-six highly conservative immunodominant epitopes in an HIV genome; wherein, the HIV composite multi-epitope DNA vaccine comprises twenty-nine epitopes which are three neutralizing antibody epitopes, twenty-three CTL epitopes, one HIV-1 isolate common antibody epitope, one MHC nonrestrictive T helper lymphocyte epitope and one spasmotoxin B cell epitope. The vaccine can be used for vaccination of healthy people and immunization therapy of people who are infected by AIDS virus, thus having double effects of prevention and treatment.
Owner:MILITARY VETERINARY RES INST PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
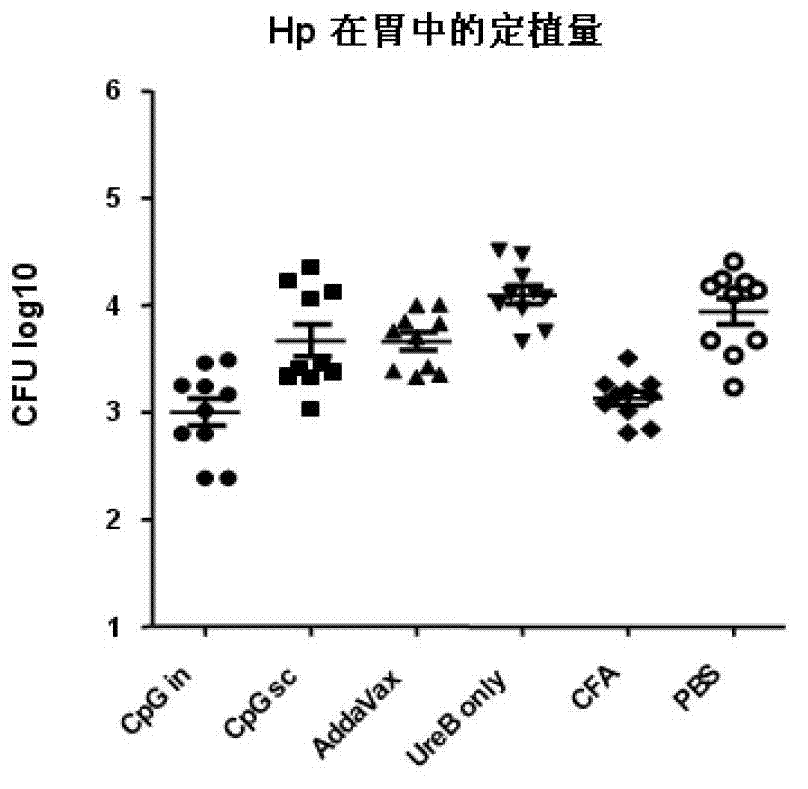
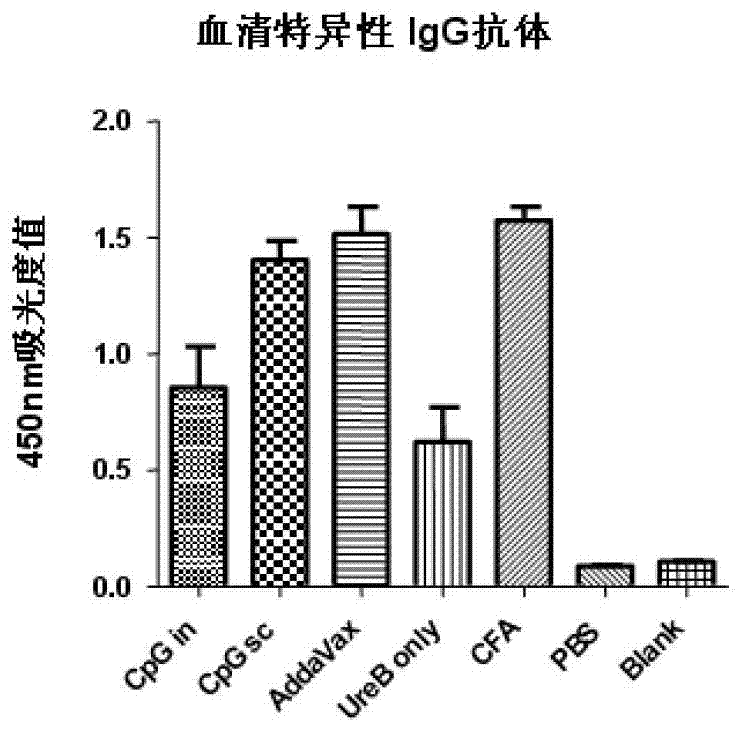
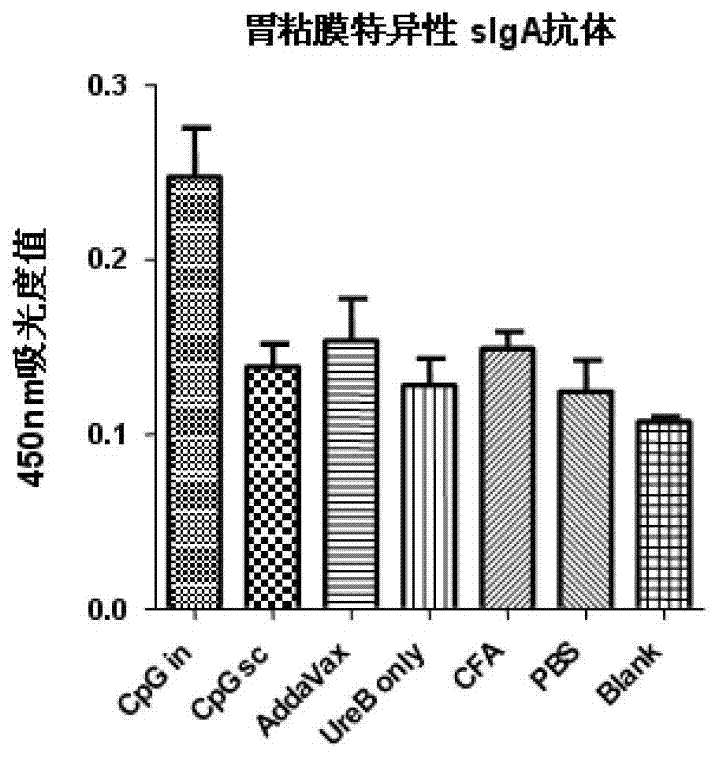
Helicobacter pylori antigen HLA restrictive immunodominance epitope peptide and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102746381AImproving immunogenicityReduce the risk of useAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsImmunodominant EpitopesImmunodominance
The invention relates to Helicobacter pylori antigen HLA restrictive immunodominance epitope peptide as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The dominance epitope peptide has the amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID NO:63, 74, 95 and 105. The invention also provides a preparation method of the epitope peptide, and further provides application of the epitope peptide to preparation for preventing or treating Helicobacter pylori infection.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
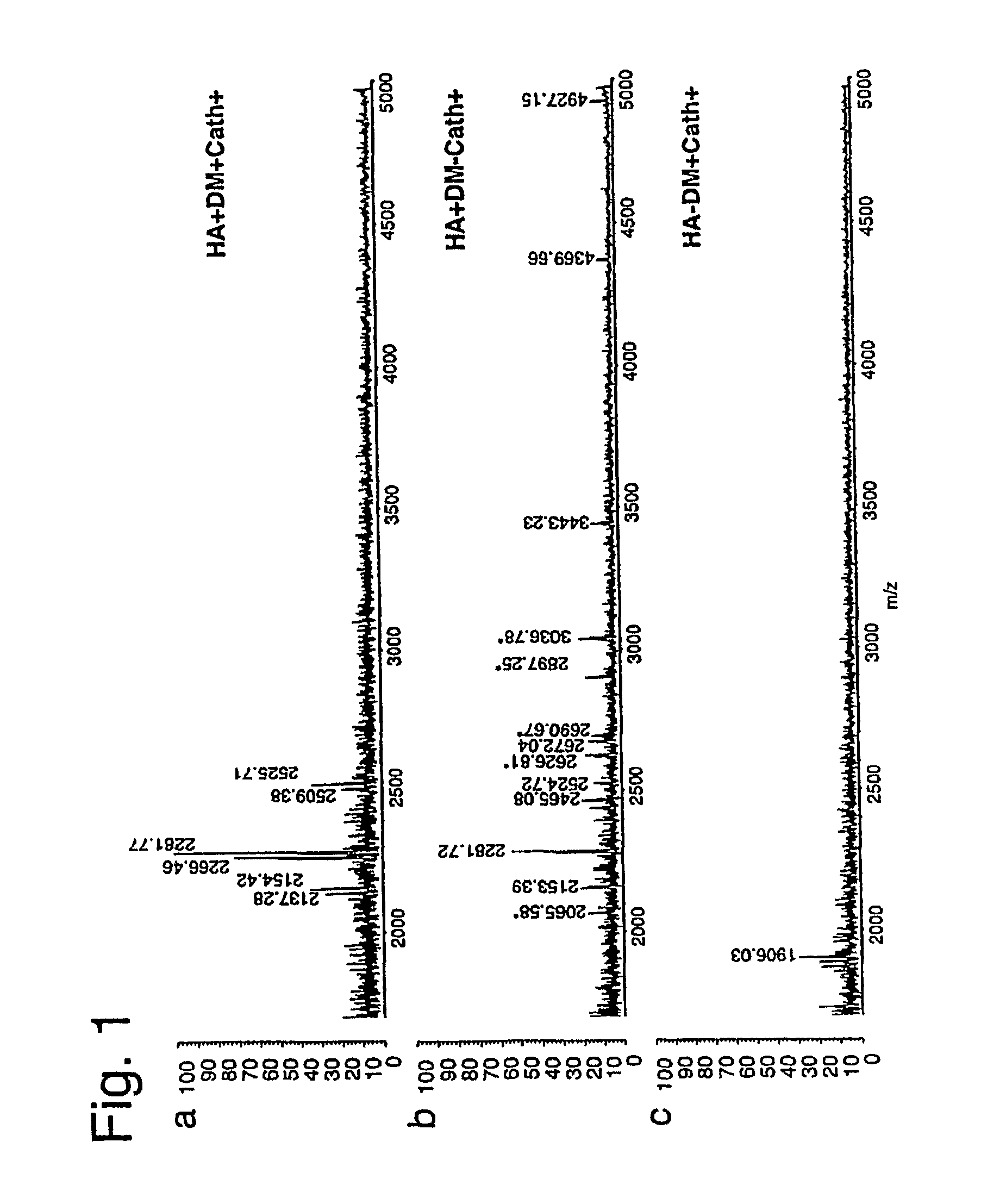
Vaccine antigens that direct immunity to conserved epitopes
ActiveUS20130315929A1Enhance immune responseLow antigenicitySsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsImmunodominant EpitopesVaccine antigen
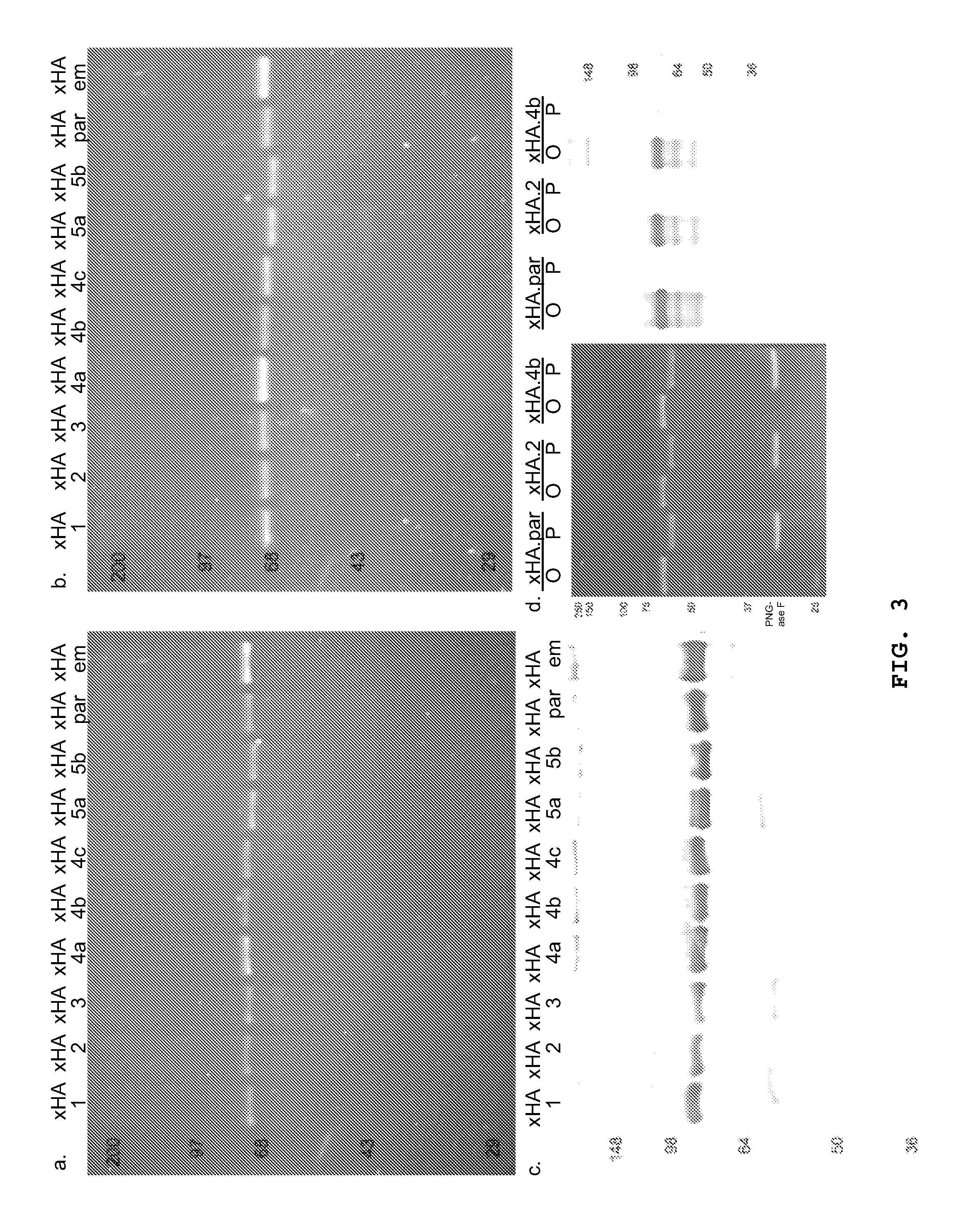
A method of identification and elimination of immunodominant epitopes to elicit a response to secondary epitopes, especially conserved structures, is described, and applied to influenza haemagglutinin (HA). Identification of the primary epitopes in (HA), and replacement of amino acids having high LODrps with corresponding low LODrps amino acids produces an HA molecule which induces antibody responses to conserved HA residues. Modified HA molecules induce a broadly neutralizing vaccine.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Hybridoma cell strain of monoclonal antibody resisting porcine delta coronavirus N protein epitope, antibody secreted by hybridoma cell strain and application of monoclonal antibody
PendingCN112899239AImprove hydrophilicityImprove bindingImmunoglobulins against virusesTissue cultureAntigen epitopeAntigen
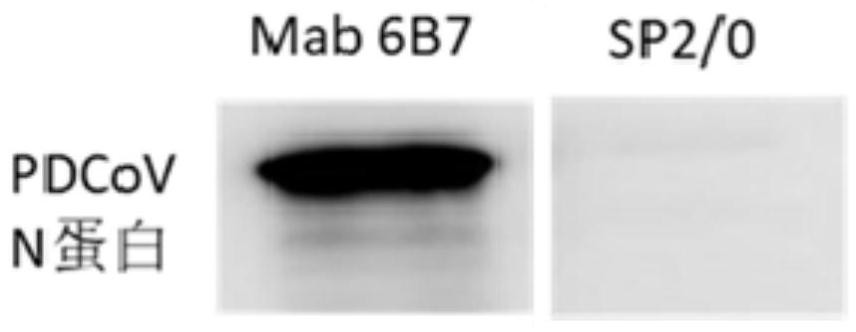
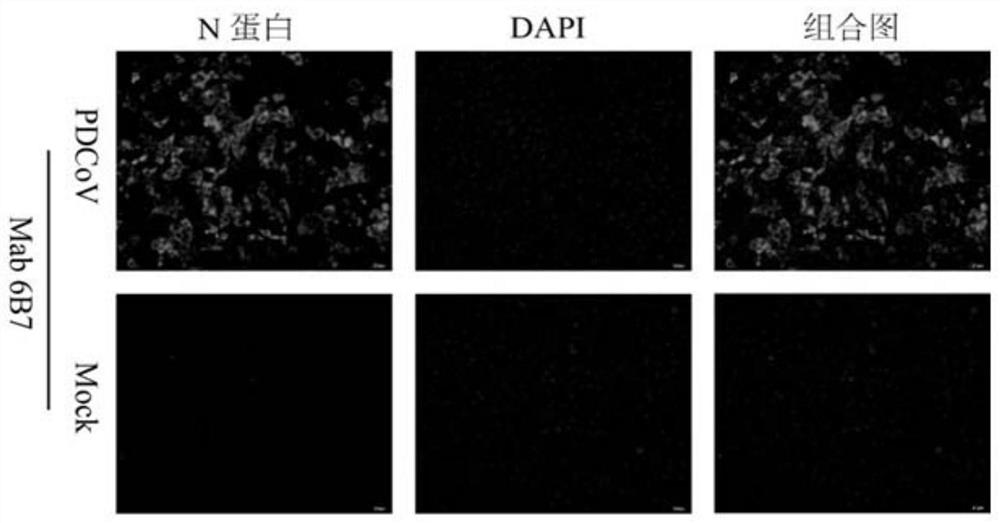
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to a hybridoma cell strain and an antibody secreted by the hybridoma cell strain, in particular to the hybridoma cell strain of a monoclonal antibody resisting porcine delta coronavirus (PDCoV) N protein epitope, the antibody secreted by the hybridoma cell strain and application of the monoclonal antibody. The amino acid sequence of the antigen epitope is 326-QDWEWDDA-333, the hybridoma cell strain is classified and named as hybridoma cell strain PDCoV-N-6B7, the preservation number is CCTCC NO: C202178, the preservation date is 2021.3. 26, and the preservation address is Wuhan University, Wuhan, China. The antigen epitope of the 6B7 monoclonal antibody is high in conservative property, is a linear epitope, belongs to an immunodominant epitope, and is beneficial to antibody combination in serum to be detected, so that establishment of a blocking ELISA kit by using the monoclonal antibody aiming at the epitope is more sensitive.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Modified TNF-alpha molecules, DNA encoding such and vaccines comprising such modified TNF-alpha and DNA
InactiveUS7118750B1Loss of receptor binding abilityLoss of cytotoxicityOrganic active ingredientsFungiImmunodominant EpitopesDna encoding
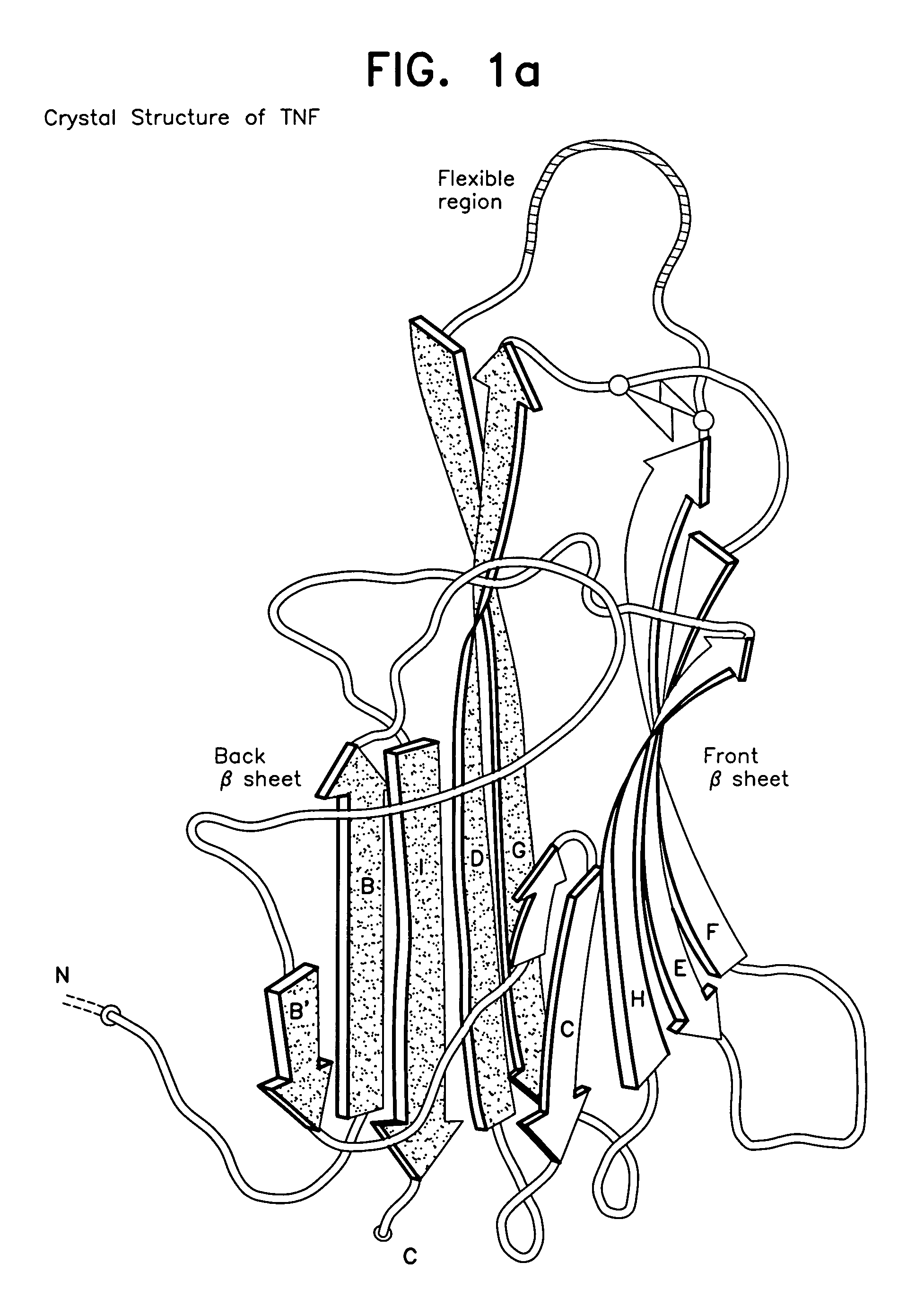
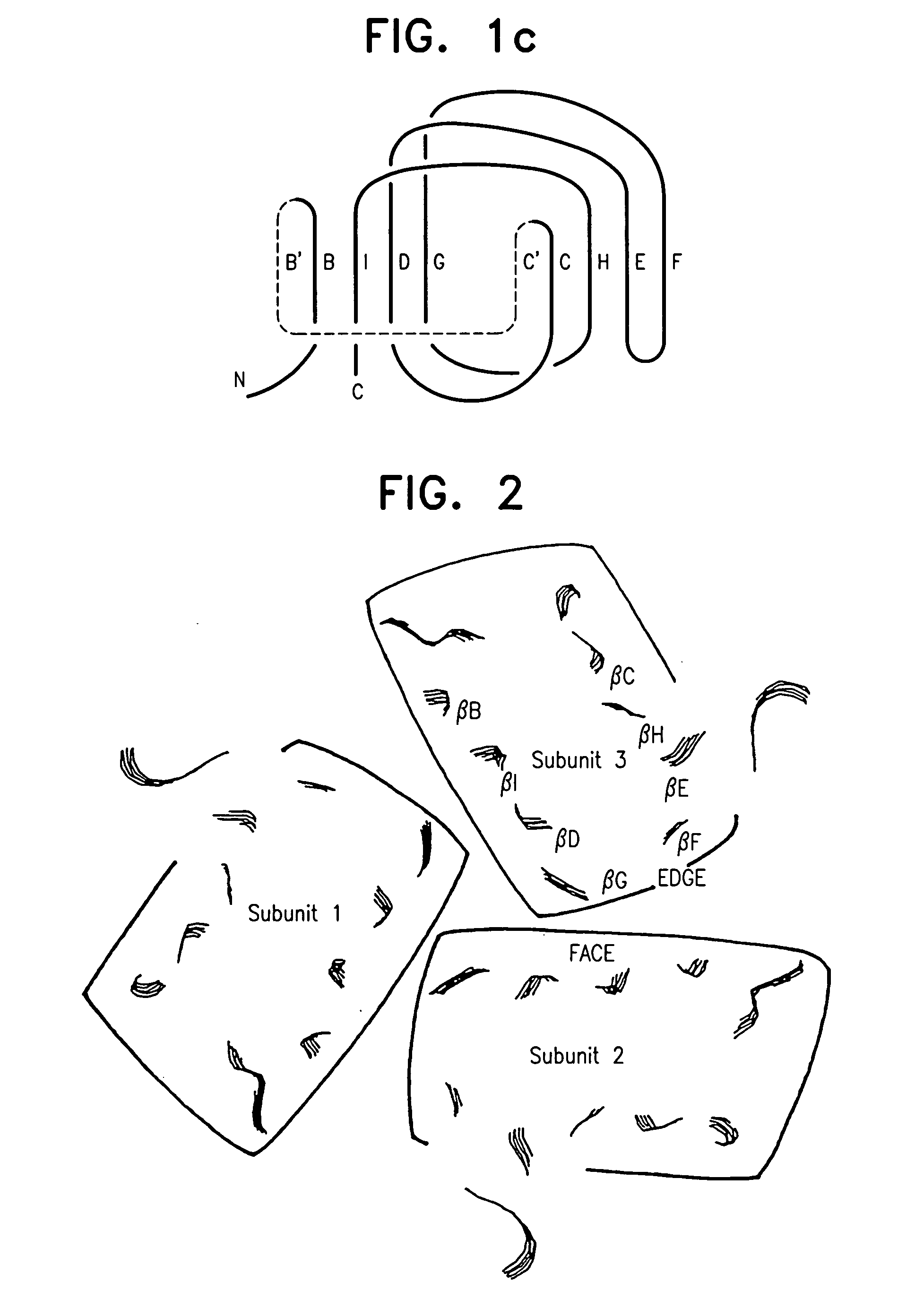
A modified human TNFα molecule is capable of raising neutralizing antibodies towards unmodified human TNFα following administration of the modified TNFα to a human host, wherein one or more peptide fragments of the human TNFα molecule has been substituted by one or more peptides containing immunodominant T cell epitopes or a truncated form of the molecule containing the immunodominant epitope and one or both flanking regions of the human TNFα-molecule containing at least one TNFα B cell epitope, wherein the substitution introduces a substantial change in the amino acid sequence of any one of the strands of the front β-sheet, in any one of the connecting loops, or in any one of the B′, I, or D strands of the back β-sheet.
Owner:PHARMEXA
Lyme disease vaccine
InactiveUS20110262475A1Broad protectionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunodominant EpitopesBorrelia garinii
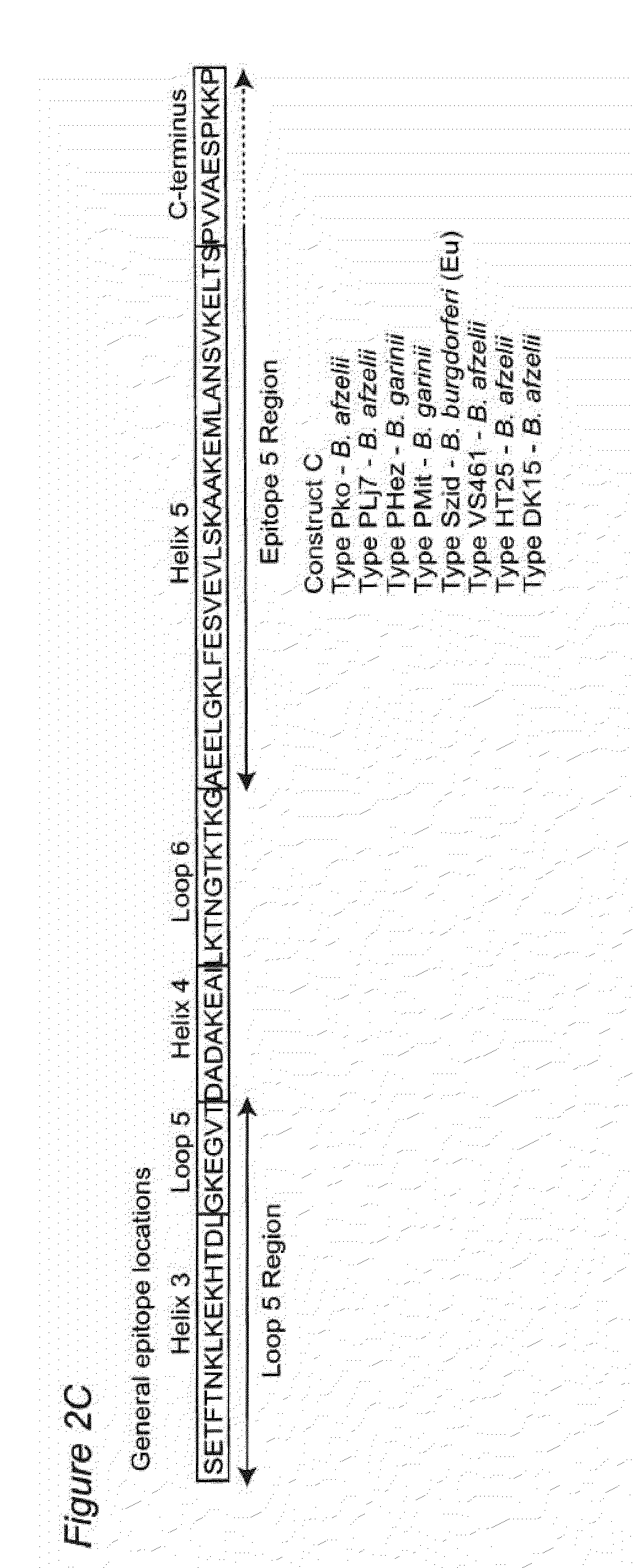
Antigenic polypeptides comprising linear immunodominant epitopes of Borrelia outer surface protein A (OspA) or Borrelia outer surface protein C (OspC) are useful as vaccines against Lyme disease, and as diagnostics for detecting Borrelia infections. The OspA and OspC antigenic polypeptides typically comprise a plurality of peptides representing epitope containing regions from multiple distinct phyletic groups. The antigenic polypeptides may also include epitopes from both Borrelia OspA and Borrelia OspC.
Owner:VIRGINIA COMMONWEALTH UNIV
Optimized early-late promoter combined with repeated vaccination favors cytotoxic t cell response against recombinant antigen in mva vaccines
ActiveUS20100233203A1Increasing early gene expressionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAntigenImmunodominant Epitopes
The invention is drawn to compositions and methods for the induction of a strong CD8 T cell response to a specific antigen(s). The combination of an early / late hybrid promoter directing strongly enhanced early expression of a neoantigen with at least three immunization rounds resulted in a highly efficient neoantigen-specific CD8 T cell response. This combination reversed the immunodominance hierarchy and converted a moderately immunogenic and subdominant CD8 T cell epitope into the immunodominant epitope.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
Soluble form of carbonic anhydrase IX (s-CA IX), assays to detect s-CA IX, CA IX's coexpression with HER-2/neu/c-erbB-2, and CA IX-specific monoclonal antibodies to non-immunodominant epitopes
InactiveUS7833728B2Good curative effectBiological material analysisDepsipeptidesKilodaltonWestern blot
Disclosed herein is the discovery of a soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, such as, urine and serum. Said s-CA IX comprises the extracellular domain of CA IX or portions thereof. The predominant s-CA IX species is the extracellular domain comprising a proteoglycan-like (PG) domain and carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain, and having a molecular weight of about 50 / 54 kilodaltons (kd) upon Western blot. A smaller s-CA IX form of about 20 to about 30 kd comprising the CA domain or parts thereof, not linked to the PG domain, has also been found in body fluids. Diagnostic / prognostic methods for precancer and cancer that detect or detect and quantitate said s-CA IX in body fluids, are described. Also disclosed herein is the coexpression of CA IX and HER-2 / neu / c-erbB-2 that provides parallel, alternative and potentially synergistic diagnostic / prognostic and therapeutic strategies for precancer and cancer. Further disclosed are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, preferably monoclonal antibodies and immunoreactive fragments and engineered variants thereof. Such new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies, fragments and variants are useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer and precancer. Particularly preferred are the new monoclonal antibodies, fragments and variants that are specific for the non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, which antibodies are, among other uses, useful to detect soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, alone but preferably in combination with antibodies specific to the immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, for example, in a sandwich assay.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
Helicobacter pylori immunodominance epitope peptide and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102924576AGood immune protectionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsImmunodominant EpitopesImmunodominance
The invention relates to helicobacter pylori immunodominance epitope peptide and a preparation method and the application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the dominance epitope peptide is shown as SEQ ID NO: 97, 100, 108 and 115. A preparation method and application of the dominance epitope peptide in prevention or treatment of helicobacter pylori infection are further provided.
Owner:中国人民解放军第三军医大学药学院
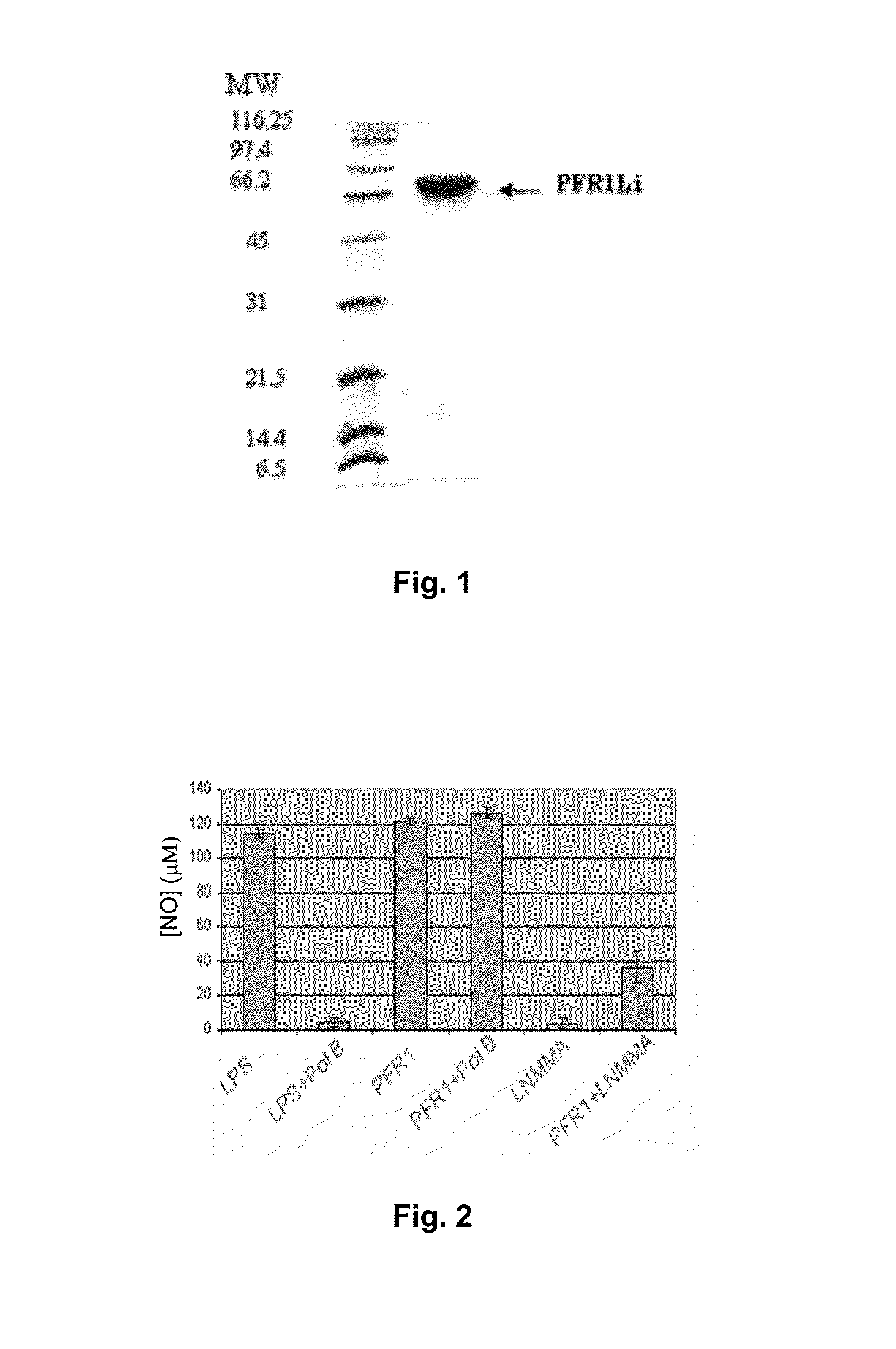
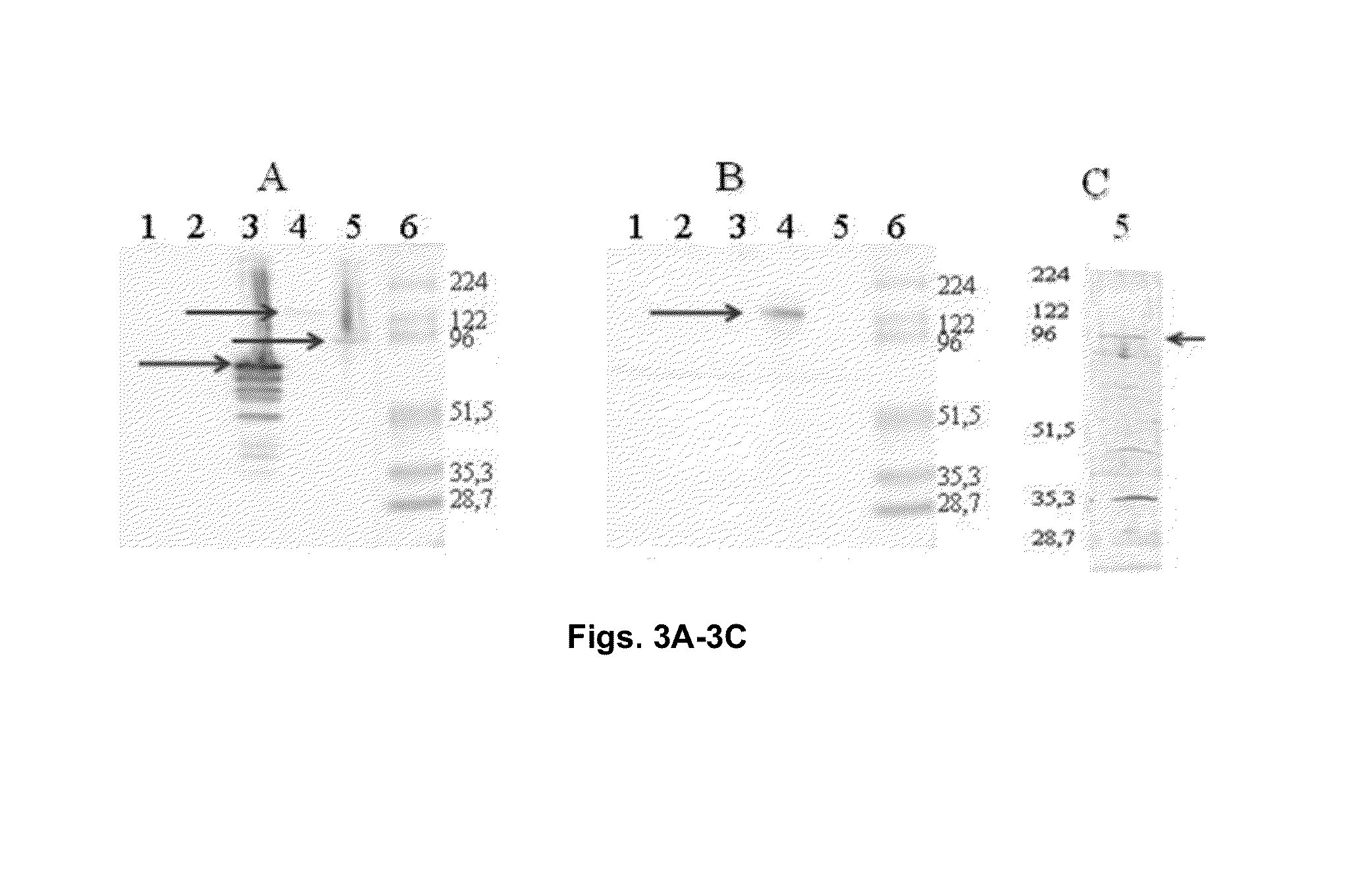
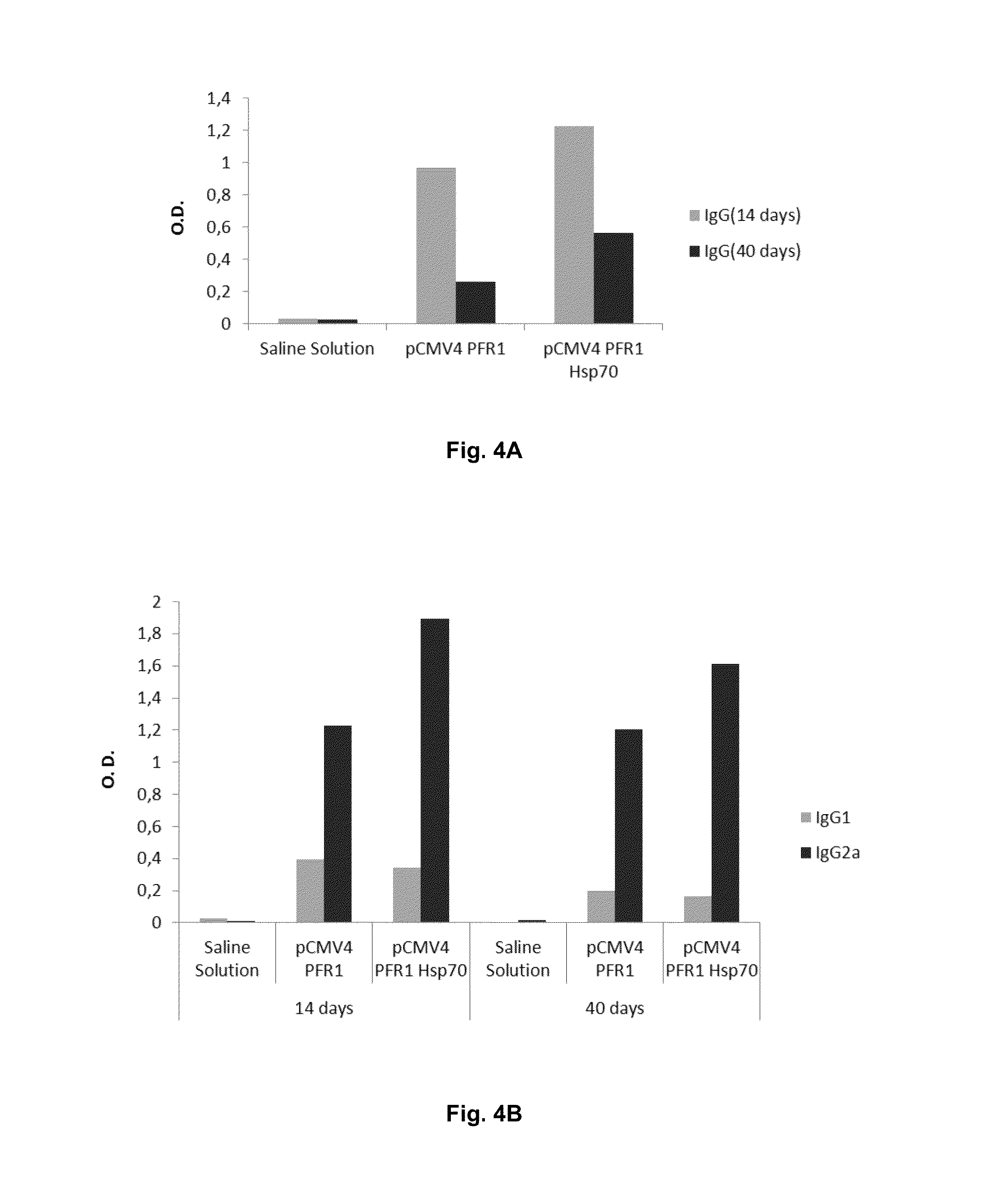
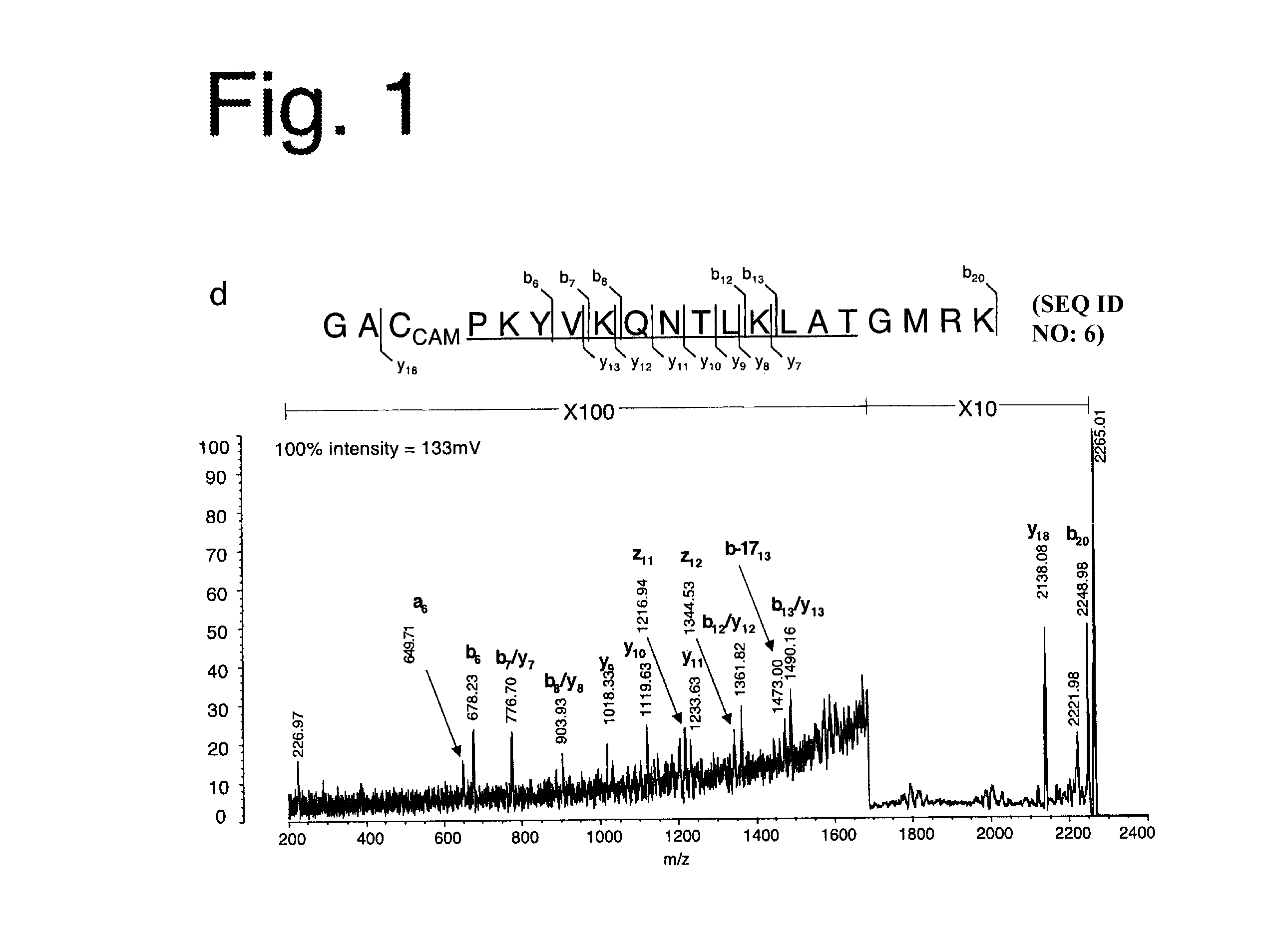
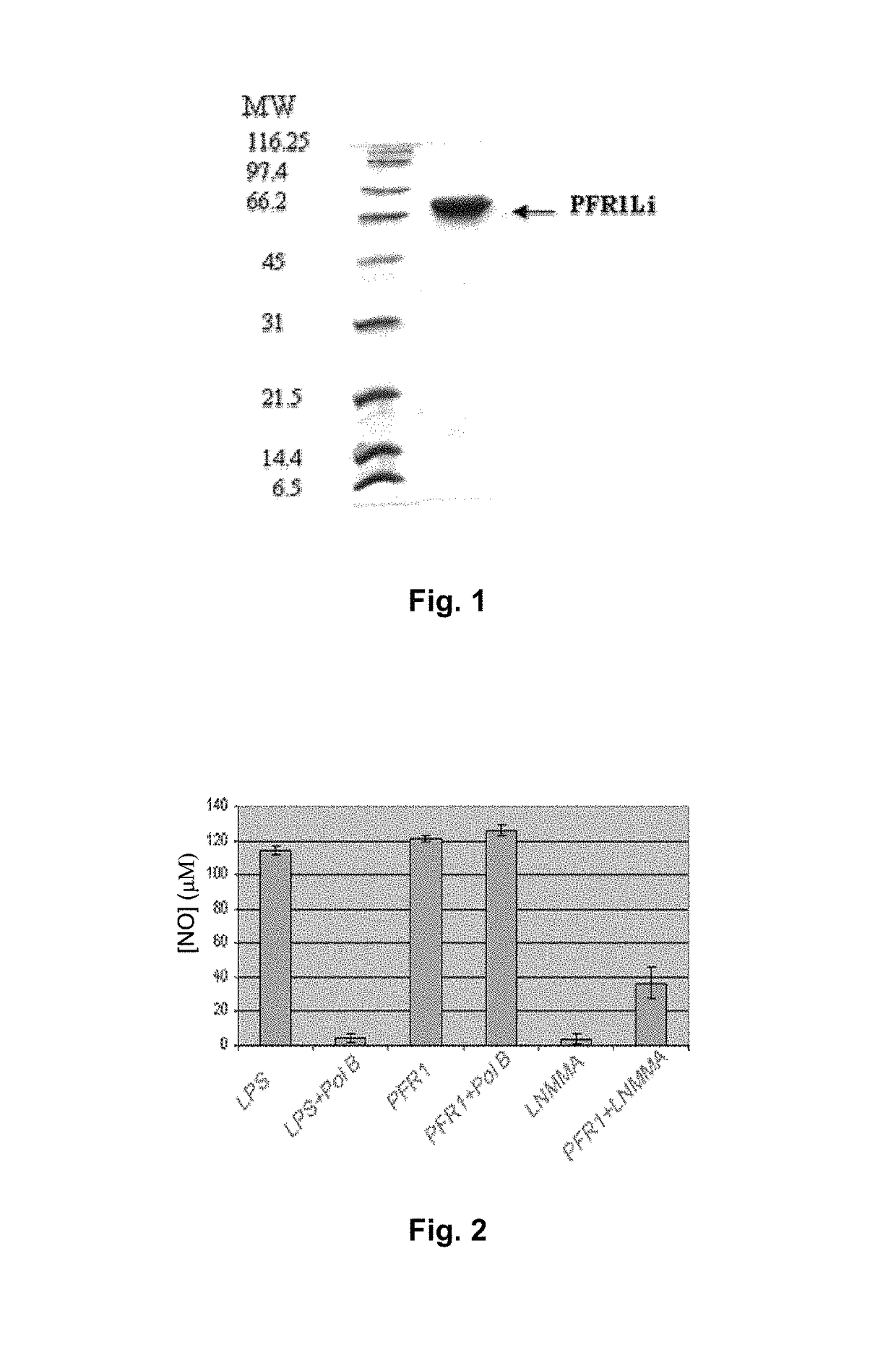
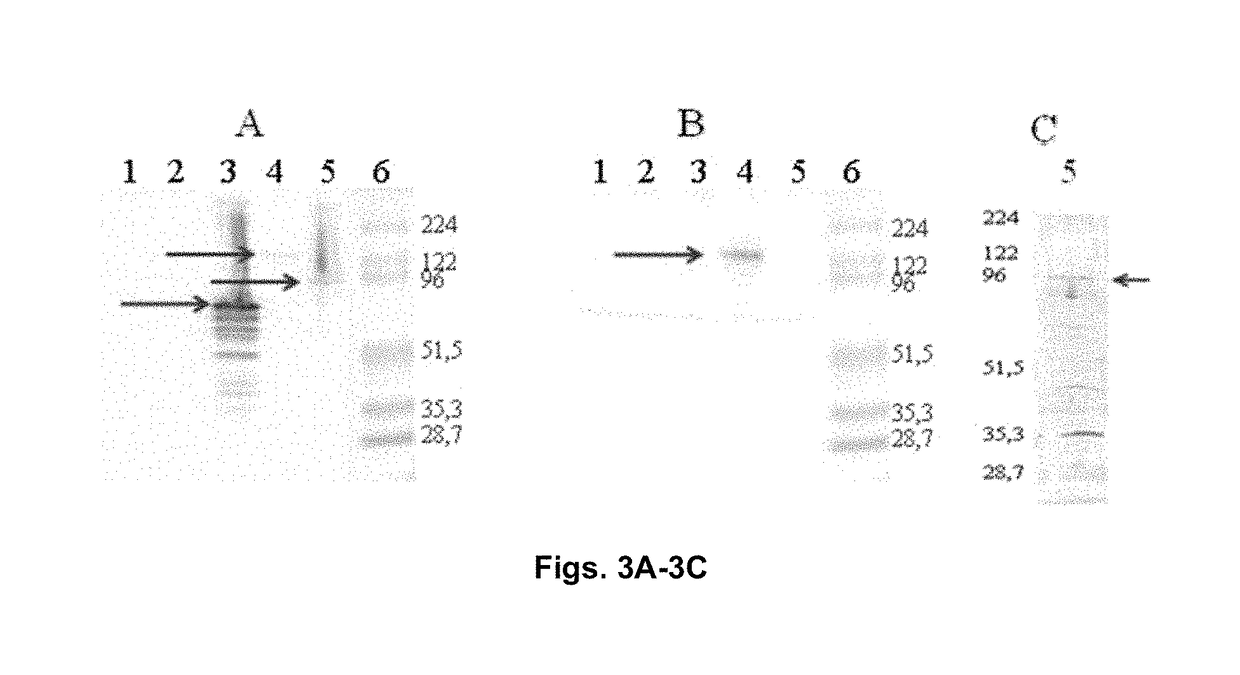
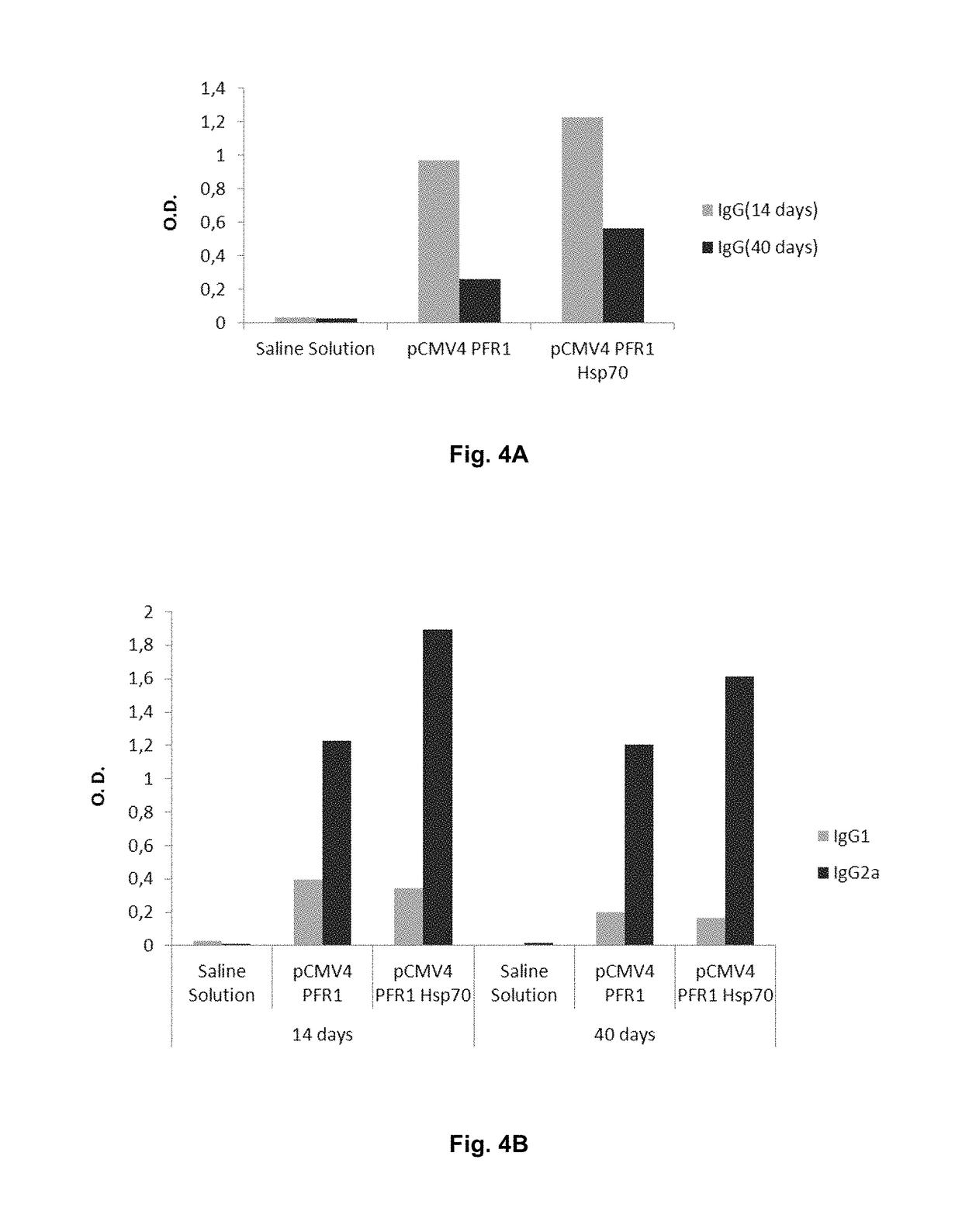
Chimeric molecule useful in immunotherapy for leishmaniasis, which includes a fragment of the pfr1 protein of leishmania infantum with specific immunodominant epitopes
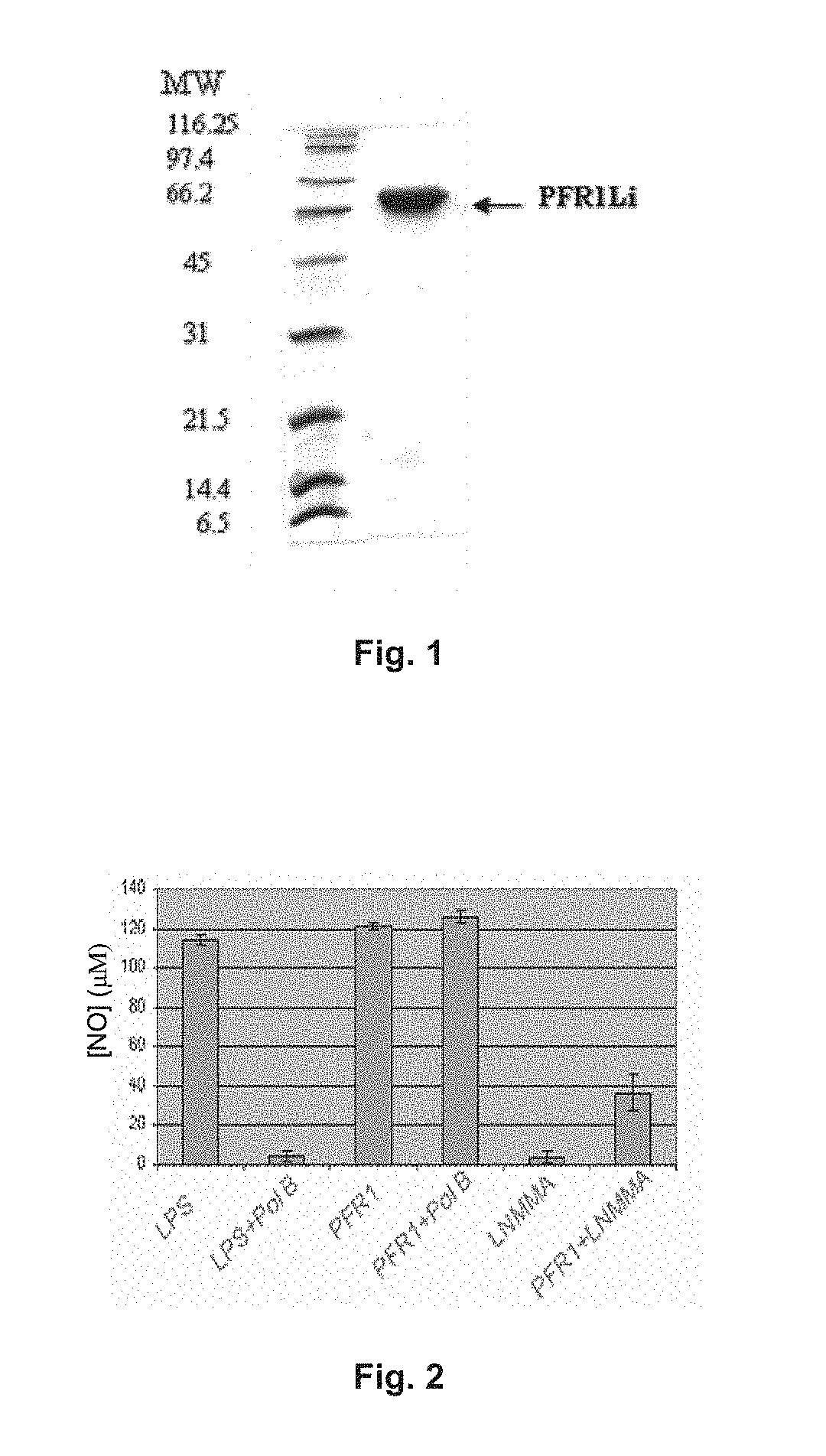
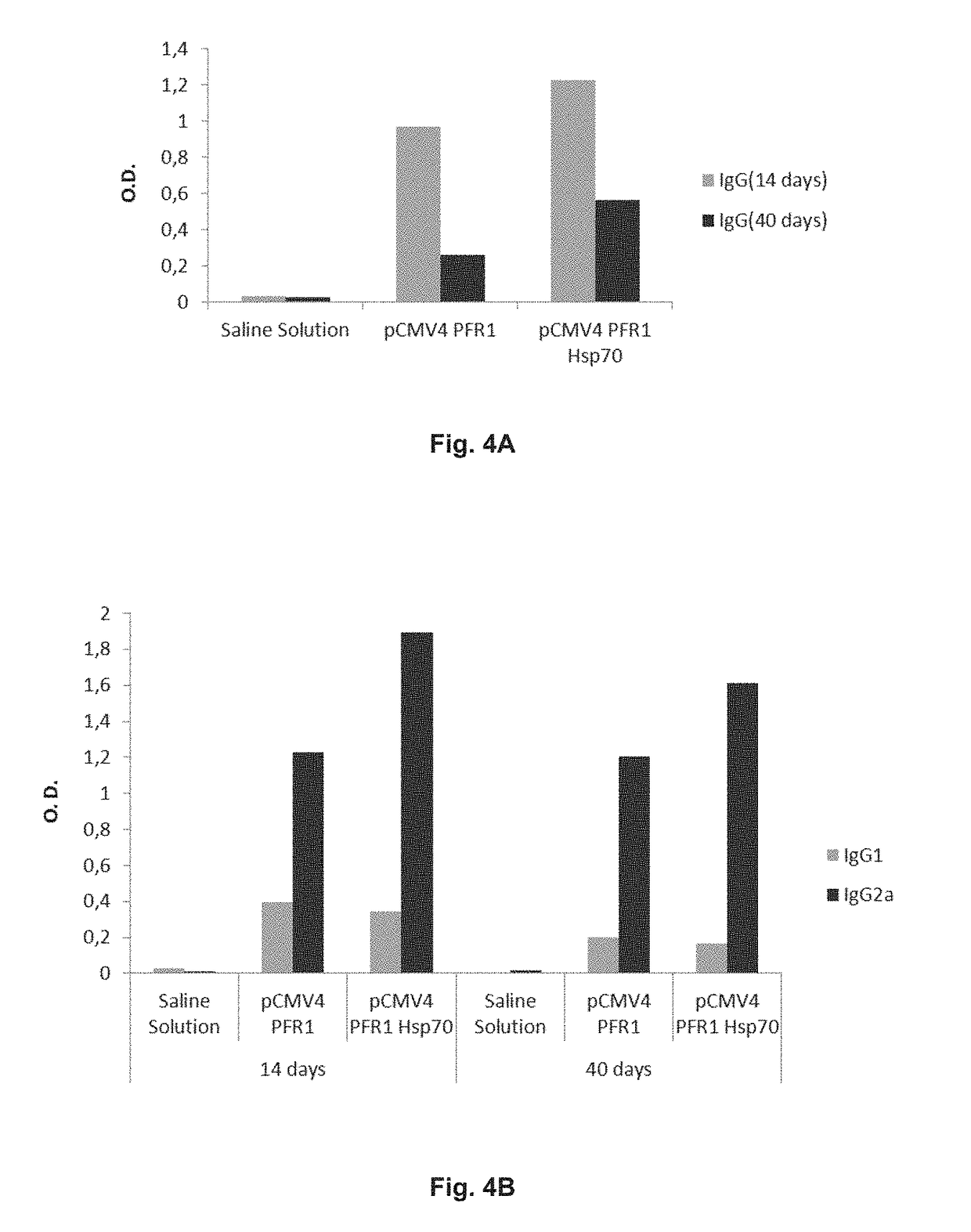
The present invention claims an isolated nucleotide sequence characterized by encoding the PFR1 protein of Leishmania infantum or a fragment thereof. This PFR1 protein or a fragment thereof comprises at least a selected immunodominant epitope between the following group: SEQ ID No: 1, SEQ ID No: 2, SEQ ID No: 3, SEQ ID No: 4, SEQ ID No: 5, SEQ ID No: 6, SEQ ID No: 7 and SEQ ID No: 8, where the immunodominant epitope is able to induce an antigen-specific T cell cytotoxic immune response in an animal, against the kinetoplastids causing the leishmaniasis disease. The immunodominant epitopes are cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activators and they present a high binding affinity for A2 type MHC Class I molecule.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC)
Method for identifying and validating dominant T helper cell epitopes using an HLA-DM-assisted class II binding assay
ActiveUS8916340B2SsRNA viruses negative-senseMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseImmunotherapeutic agent
Rational design of immunotherapeutics relies on clear knowledge of the immunodominant epitopes of antigens. Current methods for identifying kinetically stable peptide-MHC complexes are in many cases inadequate for a number of reasons. Disclosed herein is a reductionistic system incorporating known participants of MHC class II antigen processing in solution to generate peptide pools from antigens, including those for which no immunodominant epitope has yet been identified, that are highly enriched for proteolytic fragments containing their immunodominant epitopes. HLA-DM-mediated editing contributes significantly to immunodominance and is exploited in discovering immunodominant epitopes from novel or previously uncharacterized antigens, particularly antigens associated with pathogens, tumors or autoimmune diseases.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Helicobacter pylori antigen hla-restricted immunodominant epitope peptide and its application
ActiveCN102276697AImproving immunogenicityReduce the risk of useAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsImmunogenicityTGE VACCINE
The invention relates to a helicobacter pylori antigen HLA restricted immuno-dominant epitope peptide and an application thereof. The helicobacter pylori HpaA antigen immuno-dominant epitope polypeptide has amino acid sequences as shown in SEQ ID No:8, 22, 30 and 42. The polypeptide of the invention has high immunogenicity, and can initiate strong immune response. Additionally, the immuno-dominant epitope polypeptide does not contain unnecessary or even harmful parts, and thus application risk of vaccines prepared by the polypeptide is reduced. Superiority combination of the immuno-dominant epitope polypeptide with other vaccine components can be realized, which extends the width of immune response. Vaccines prepared by the immuno-dominant epitope polypeptide not only have prevention effect on helicobacter pylori infection, but also can be used as therapeutic vaccines.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Chimeric molecule useful in immunotherapy for leishmaniasis, which includes a fragment of the PFR1 protein of leishmania infantum with specific immunodominant epitopes
The present invention claims an isolated nucleotide sequence characterized by encoding the PFR1 protein of Leishmania infantum or a fragment thereof. This PFR1 protein or a fragment thereof comprises at least a selected immunodominant epitope between the following group: SEQ ID No: 1, SEQ ID No: 2, SEQ ID No: 3, SEQ ID No: 4, SEQ ID No: 5, SEQ ID No: 6, SEQ ID No: 7 and SEQ ID No: 8, where the immunodominant epitope is able to induce an antigen-specific T cell cytotoxic immune response in an animal, against the kinetoplastids causing the leishmaniasis disease. The immunodominant epitopes are cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activators and they present a high binding affinity for A2 type MHC Class I molecule.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC)
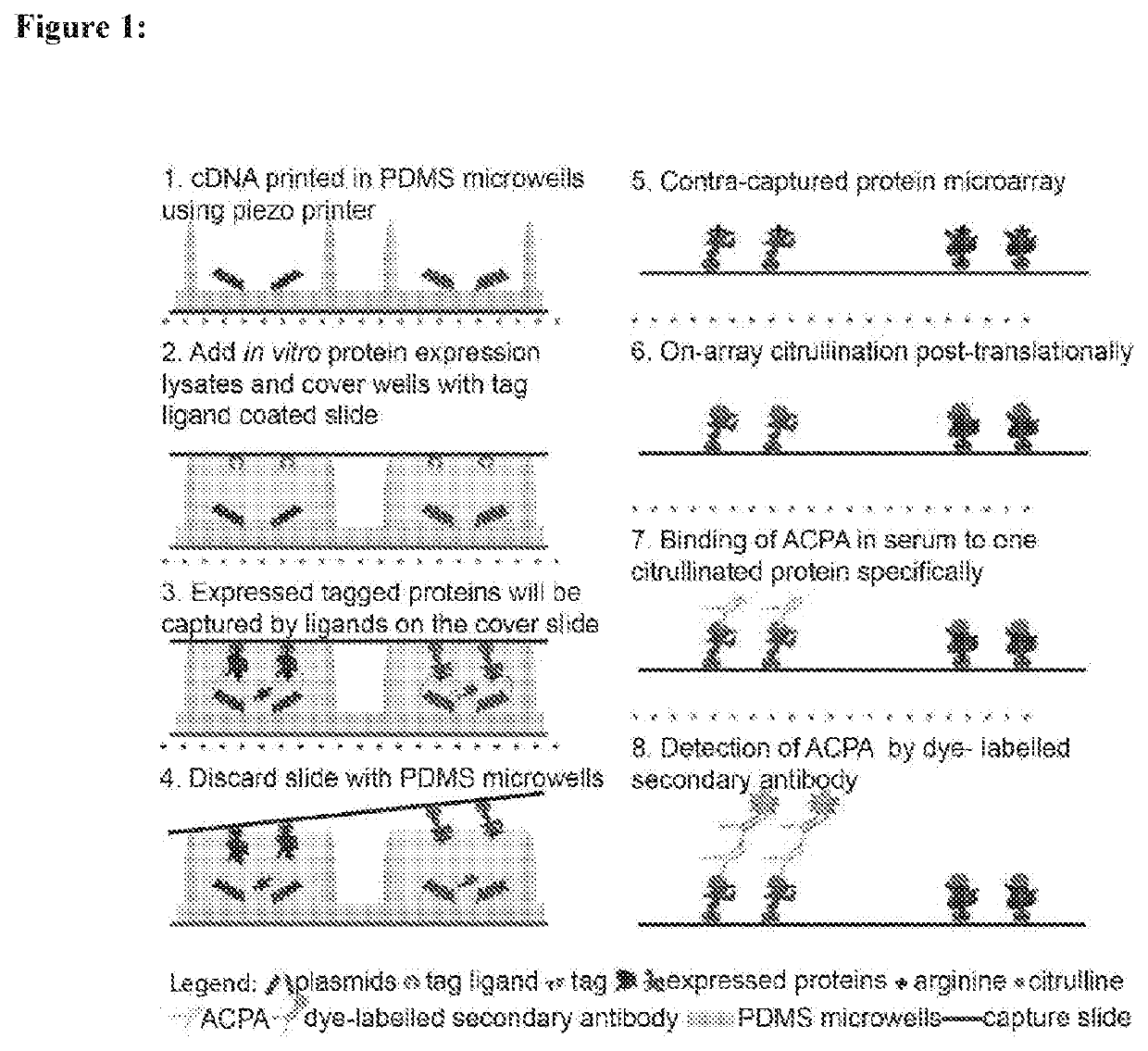
Identification and medical applications of Anti-citrullinated-protein antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis
PendingUS20200386754A1High prevalenceHydrolasesImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsInsulin-like growth factorPancreatic hormone
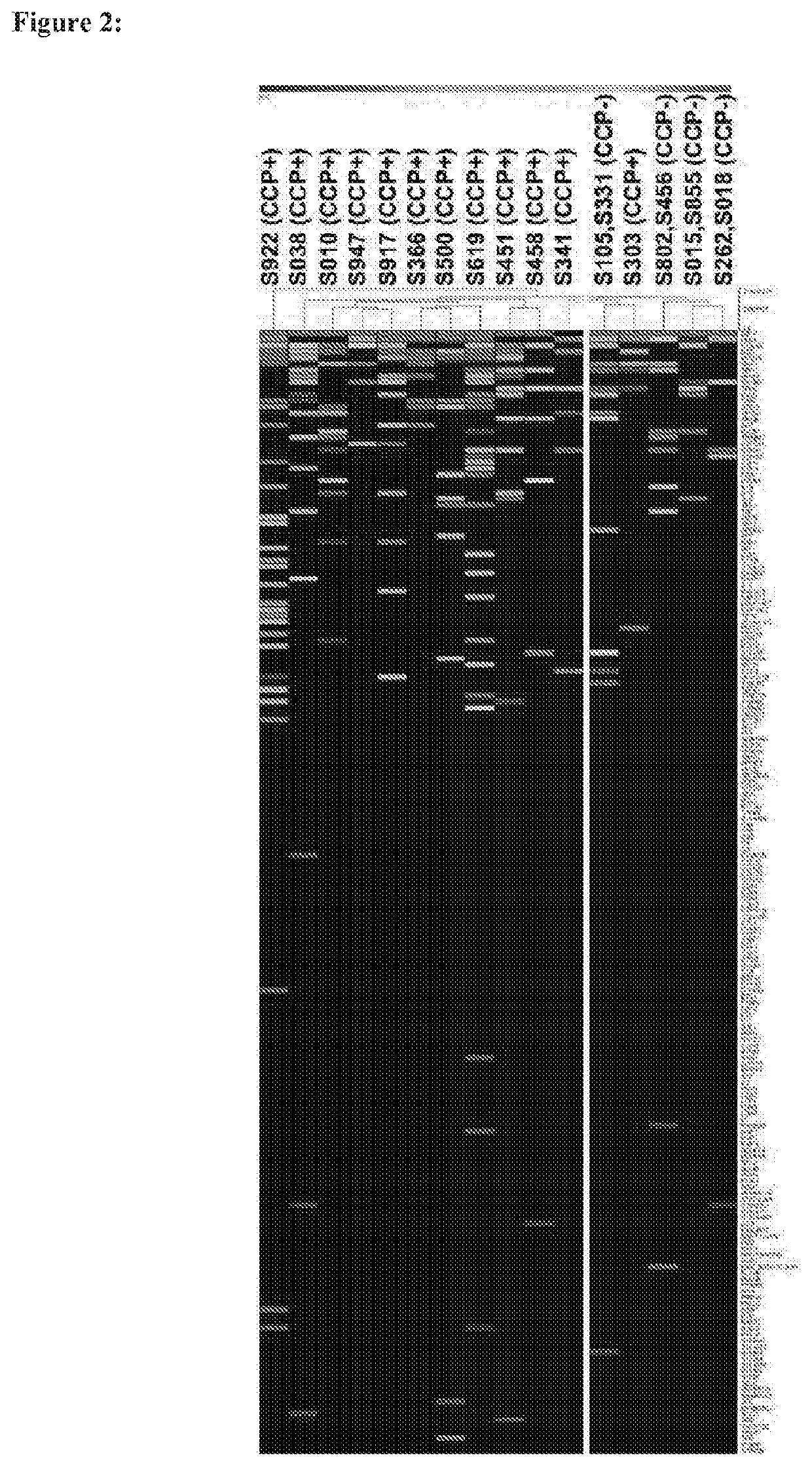
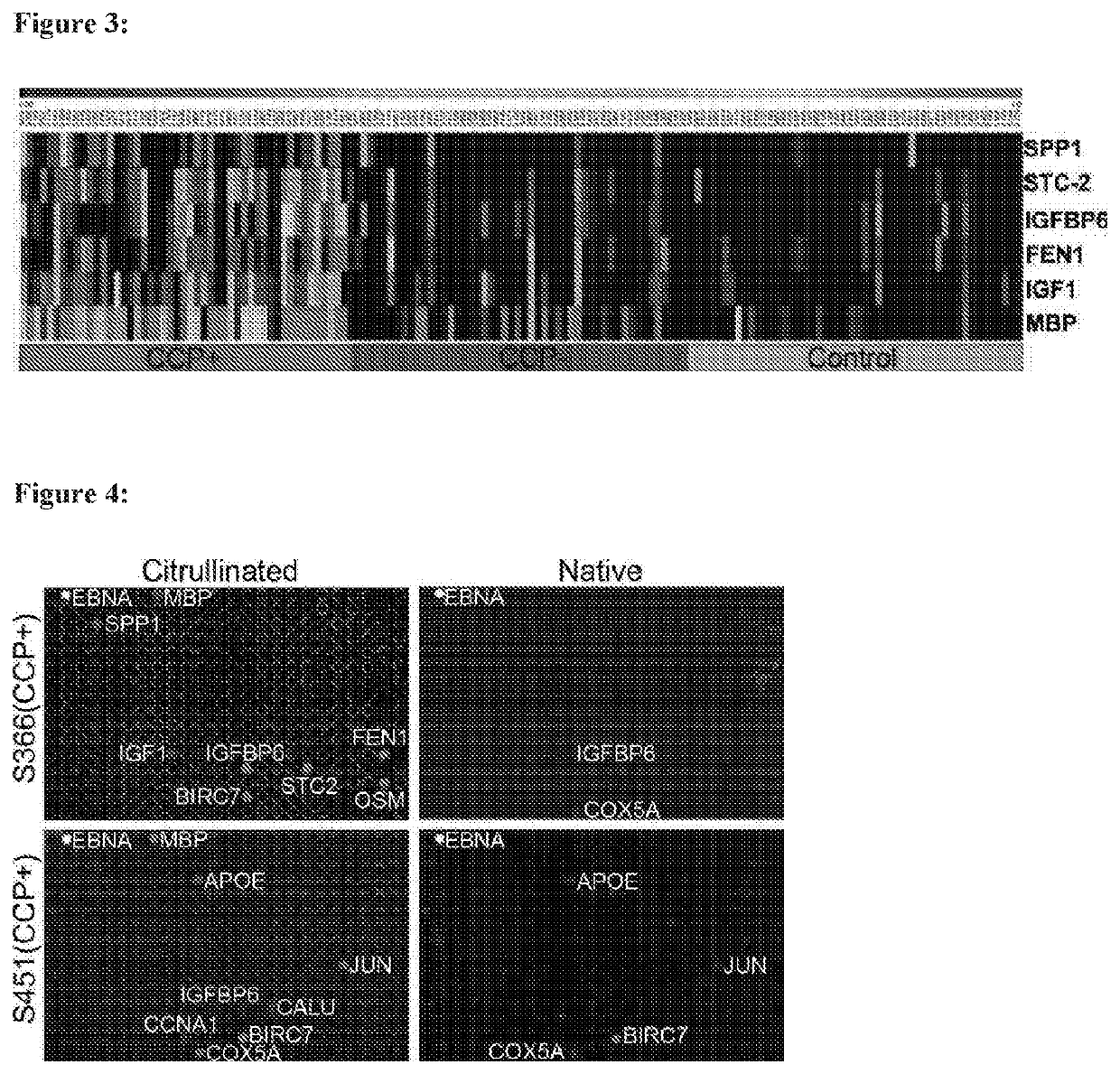
Compositions and methods for detection of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. Patient samples known or suspected of containing ACPAs were probed against citrullinated proteins, and antibody responses to 190 citrullinated proteins in 20 RA patients were investigated. Unique antibody reactivity patterns in both clinical anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide assay positive (CCP+) and negative (CCP−) RA patients were observed. At individual antigen levels, six novel antibody / antigen complexes were discovered and validated against specific citrullinated antigens (Myelin Basic Protein (MBP), osteopontin (SPP1), flap endonuclease (FEN1), insulin like growth factor binding protein 6 (IGFBP6), insulin like growth factor I (IGF1) and stanniocalcin-2 (STC2)) in RA patients. Identification of immune-dominant epitope(s) for citrullinated MBP was also performed. The identified biomarkers have high specificity, especially MBP.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Chimeric proteins for diagnosis and treatment of diabetes
InactiveUS20060052581A1Easy diagnosisEase of evaluationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunodominant EpitopesMedicine
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
Chimeric molecule useful in immunotherapy for leishmaniasis, which includes a fragment of the pfr1 protein of leishmania infantum with specific immunodominant epitopes
The present invention claims an isolated nucleotide sequence characterized by encoding the PFR1 protein of Leishmania infantum or a fragment thereof. This PFR1 protein or a fragment thereof comprises at least a selected immunodominant epitope between the following group: SEQ ID No: 1, SEQ ID No: 2, SEQ ID No: 3, SEQ ID No: 4, SEQ ID No: 5, SEQ ID No: 6, SEQ ID No: 7 and SEQ ID No: 8, where the immunodominant epitope is able to induce an antigen-specific T cell cytotoxic immune response in an animal, against the kinetoplastids causing the leishmaniasis disease. The immunodominant epitopes are cytotoxic T-lymphocyte activators and they present a high binding affinity for A2 type MHC Class I molecule.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC)
Chimeric proteins for diagnosis and treatment of diabetes
InactiveUS20060052580A1Easy diagnosisEase of evaluationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunodominant EpitopesPancreas
Novel chimeric fusion proteins comprising immunodominant epitopes of GAD and insulin are provided. Also provided are immunomodulatory methods for the use of such proteins for both the prevention and treatment of Type 1 diabetes mellitus. The chimeric fusion proteins of the invention are useful in predicting risk of onset of Type I diabetes, determining prognosis of Type 1 diabetes patients early in disease progression, and in evaluating patients for suitability as recipients of transplants of pancreatic cells or tissues. The administration of the proteins of the invention in accordance with the immunomodulatory methods of the invention results in beneficial effects on disease development and severity in patients suffering from or predicted to be at risk of developing Type 1 diabetes, as well as on the outcome of transplants of pancreatic cells or tissues in Type I diabetes patients.
Owner:ALEXION PHARMA INC
HIV composite multi-epitope DNA vaccine and application thereof
InactiveCN101579528BExtensive cross-reactivityShow feasibilityGenetic material ingredientsAntiviralsCtl epitopeVaccination
The invention discloses an HIV composite multi-epitope DNA vaccine which takes HIV-1 capsid protein p24 as a vector backbone molecule and ER signal peptide as a homing sequence, and contains twenty-six highly conservative immunodominant epitopes in an HIV genome; wherein, the HIV composite multi-epitope DNA vaccine comprises twenty-nine epitopes which are three neutralizing antibody epitopes, twenty-three CTL epitopes, one HIV-1 isolate common antibody epitope, one MHC nonrestrictive T helper lymphocyte epitope and one spasmotoxin B cell epitope. The vaccine can be used for vaccination of healthy people and immunization therapy of people who are infected by AIDS virus, thus having double effects of prevention and treatment.
Owner:MILITARY VETERINARY RES INST PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
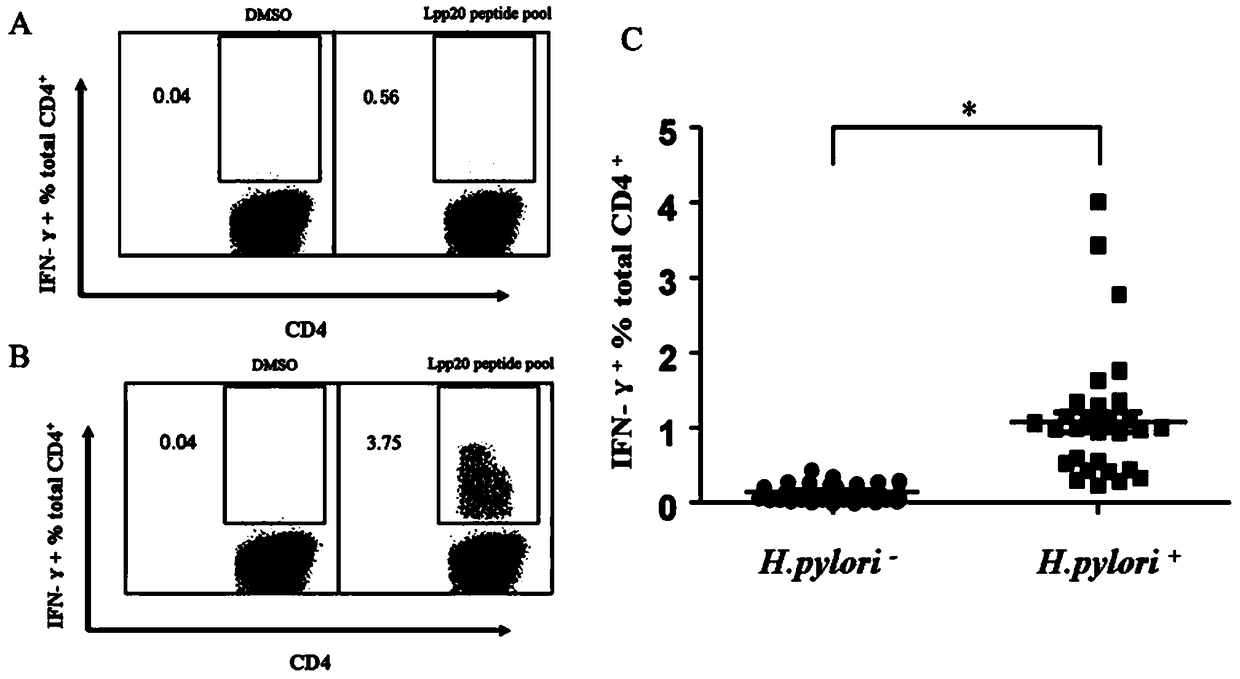
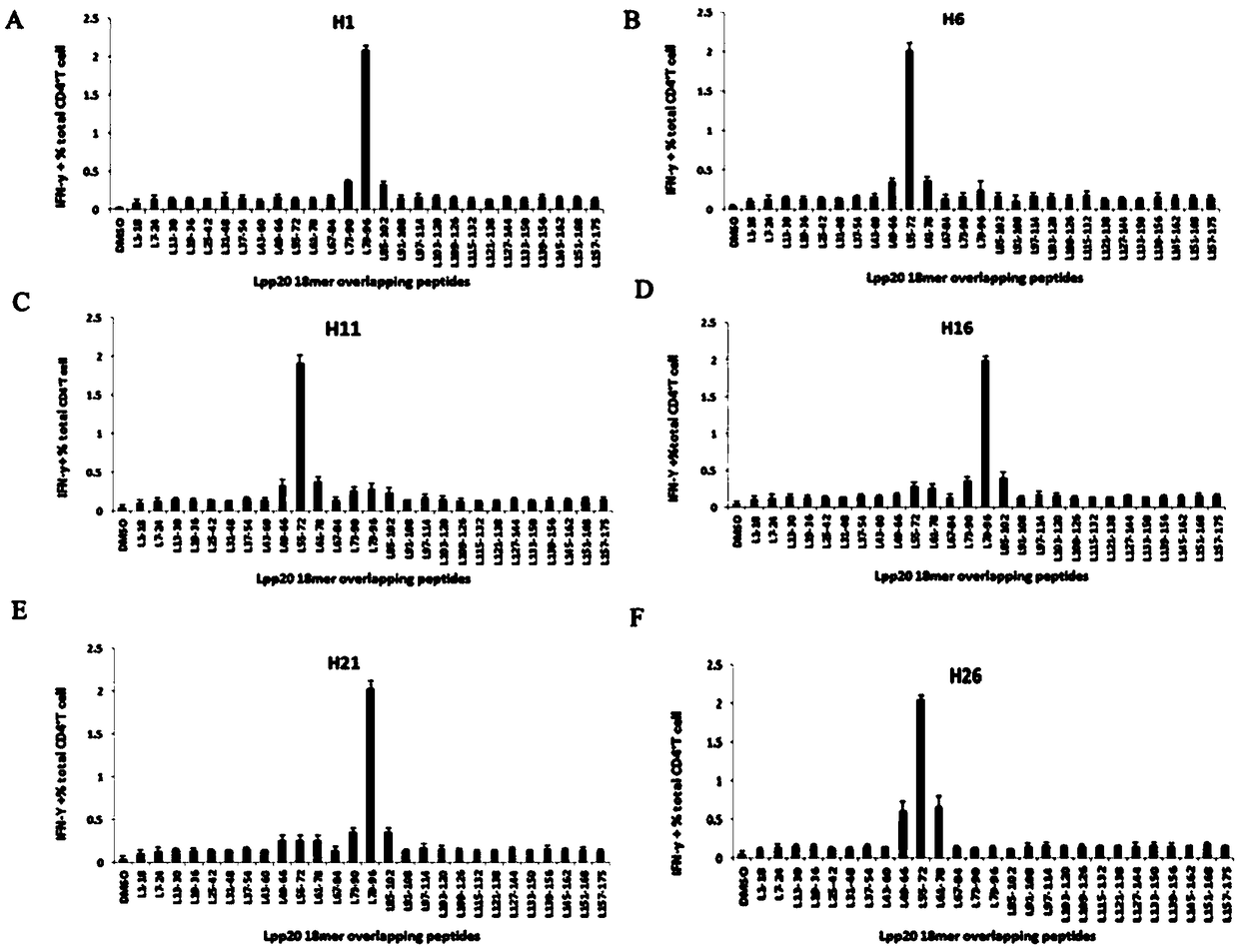
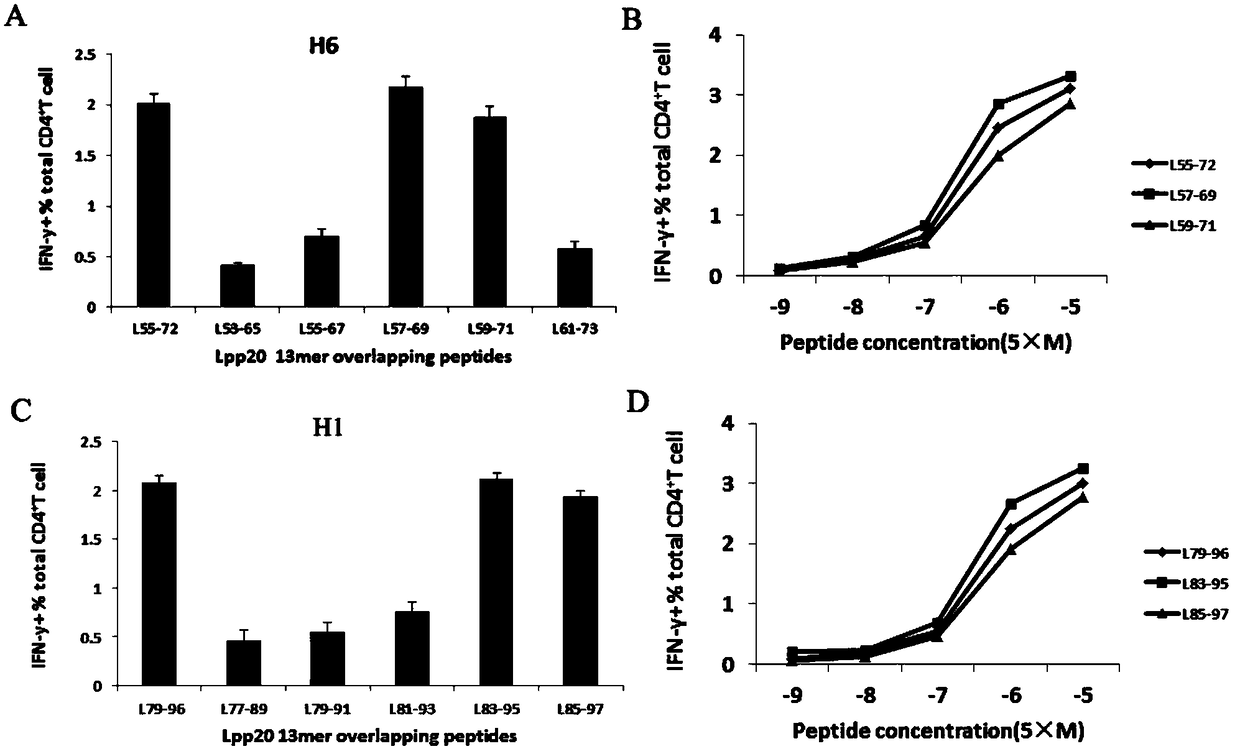
Helicobacter pylori immunodominant epitope peptide L79-96 and application of same
The invention relates to HLA-restricted CD4<+> T cell epitope immunodominant peptide and core peptide of Helicobacter pylori Lpp20, which have structures represented as the SEQ ID No.10 and SEQ ID No.30; the proper CD4<+> T cell epitopes (SEQ ID No.10 and SEQ ID No.30) in the invention are reliable and accurate; what is more, it can be evaluated that the identified epitope belongs to whether immunodominance or subdominance, which has advantages on design of epitope vaccines.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com