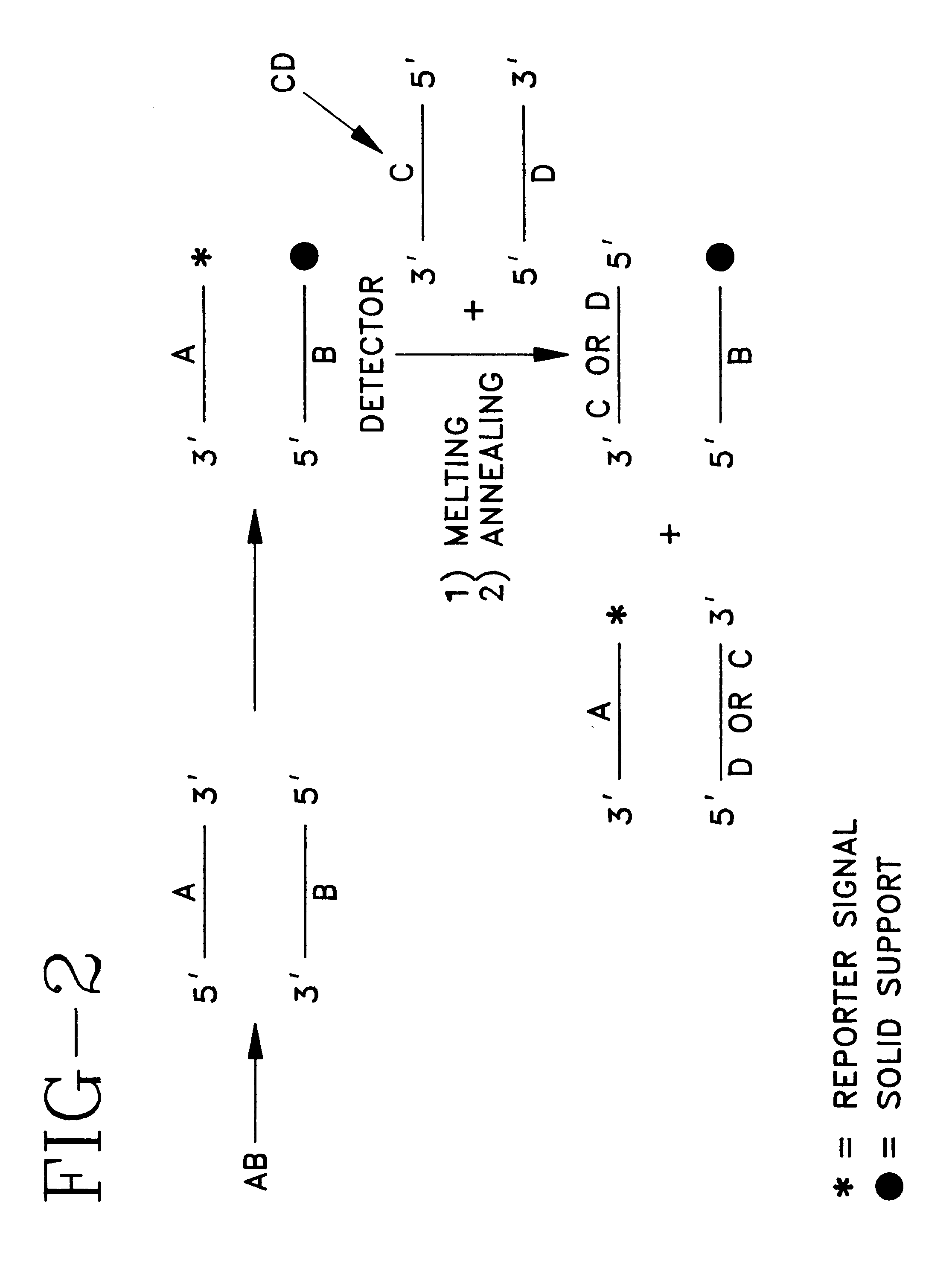
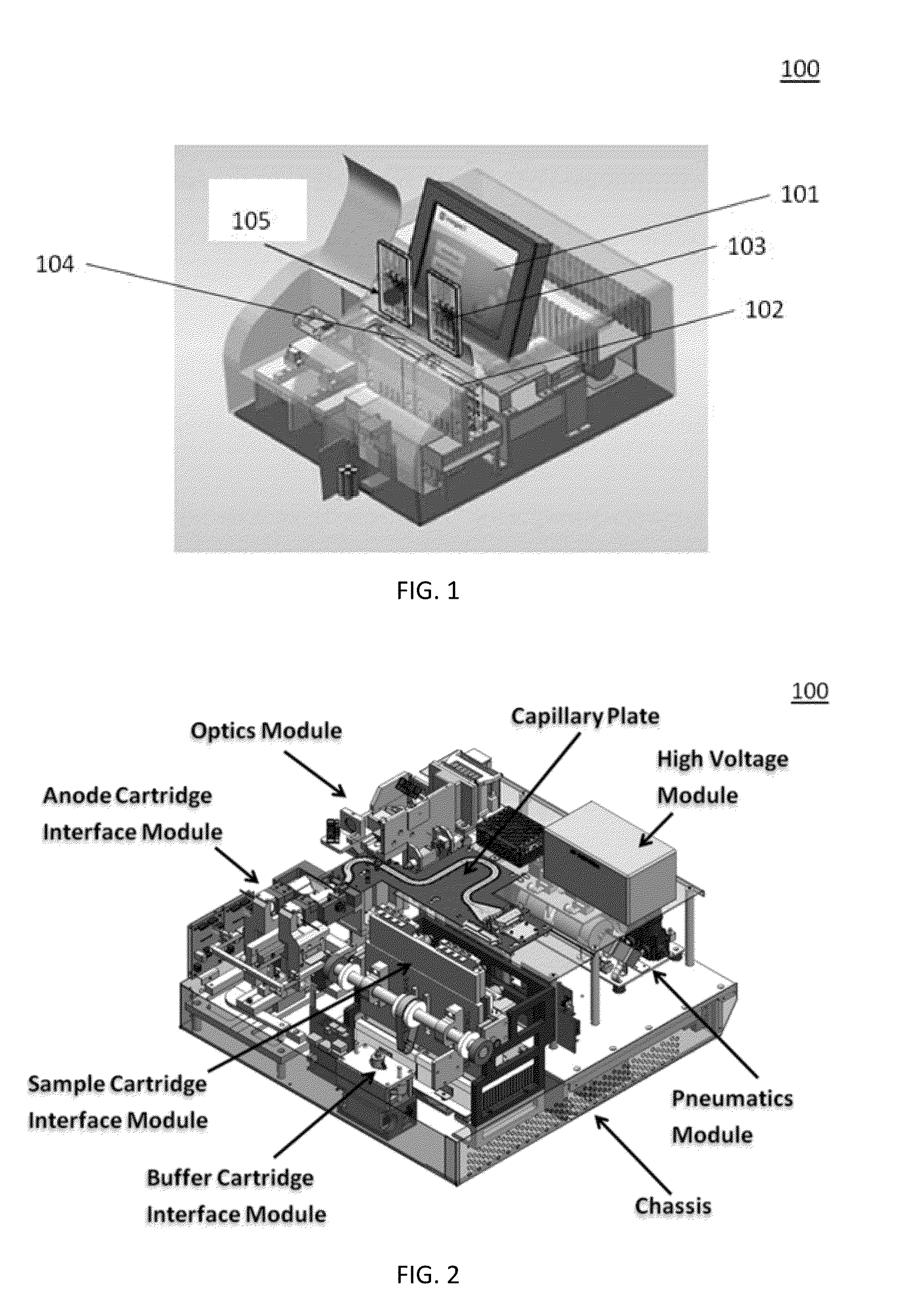
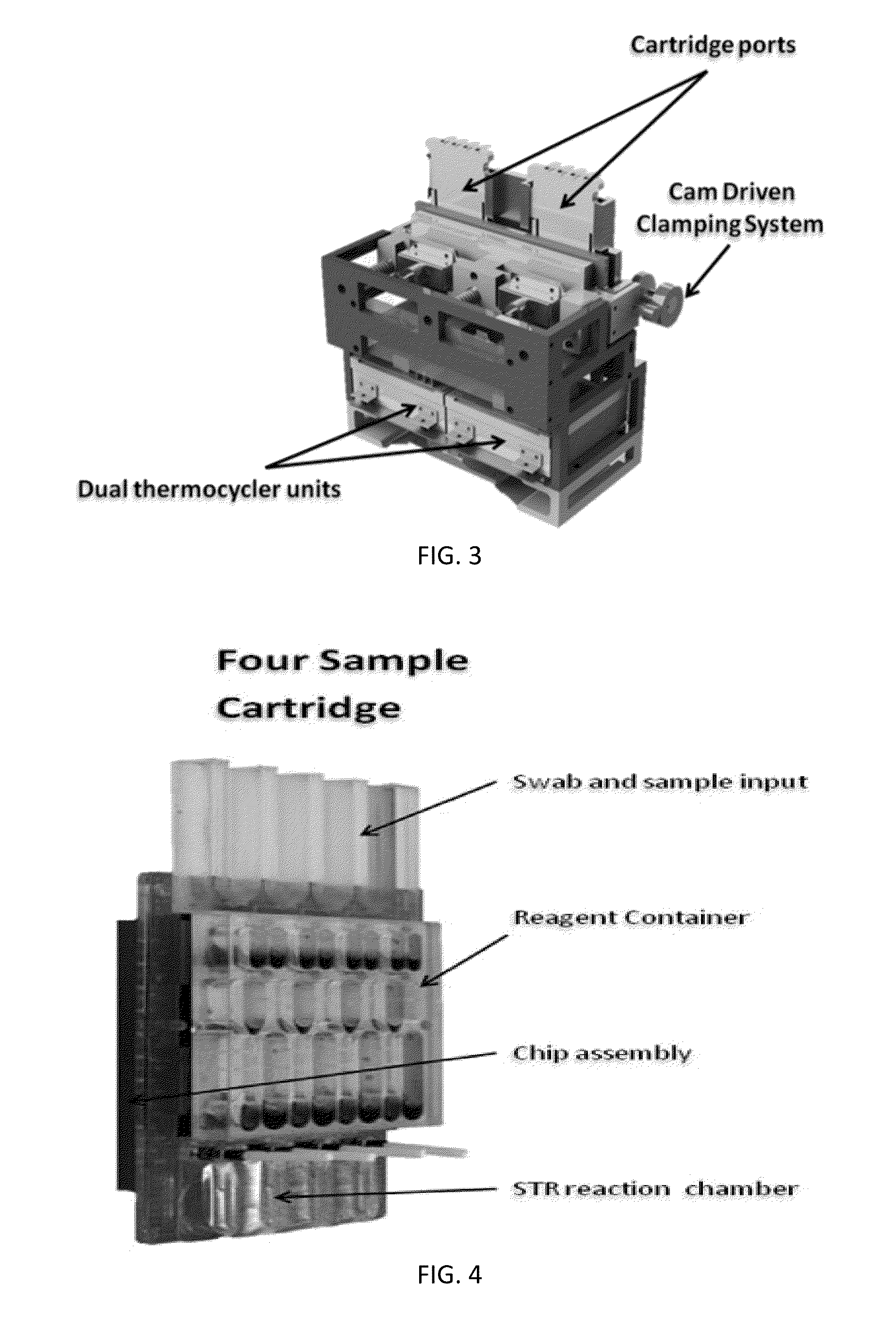
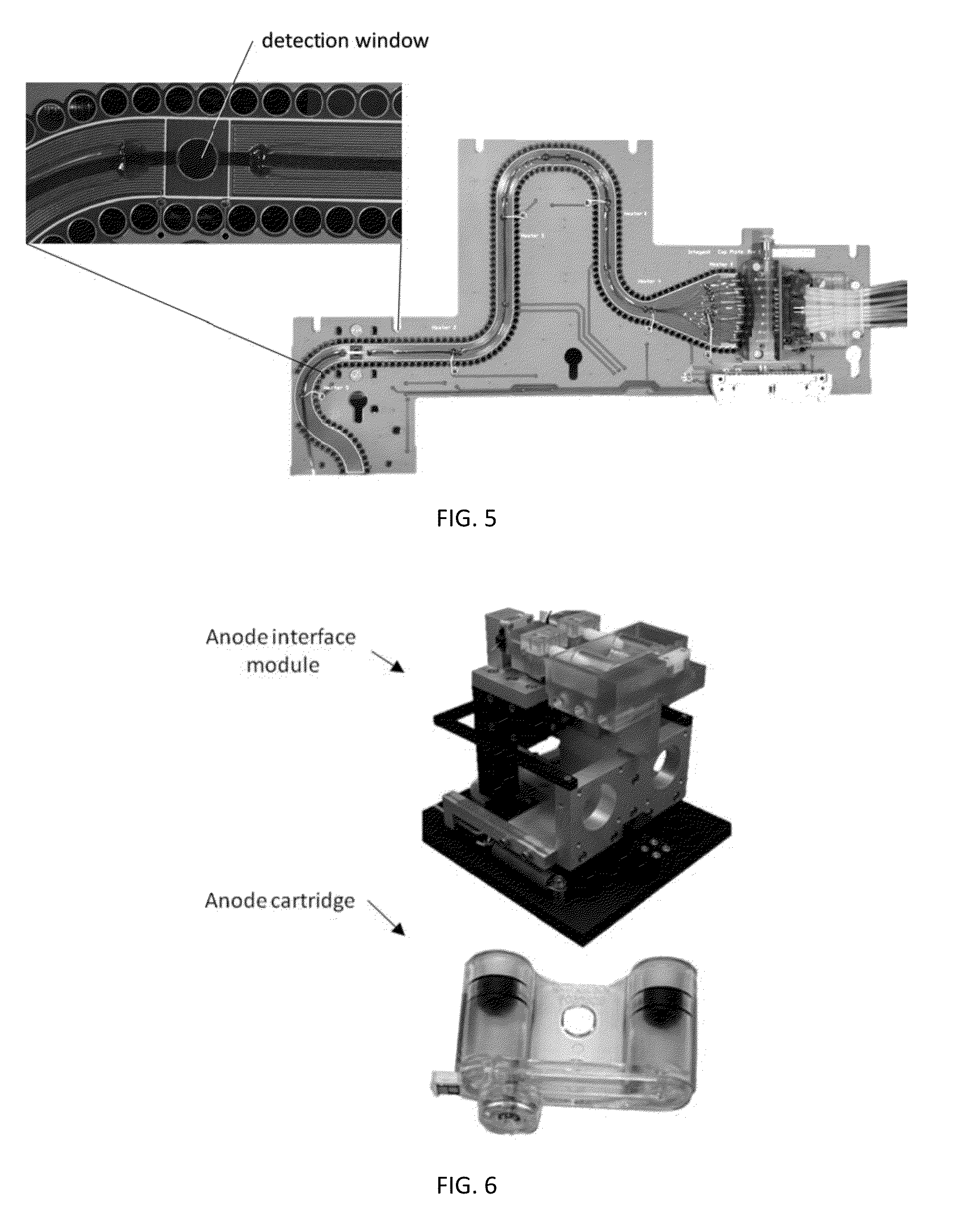
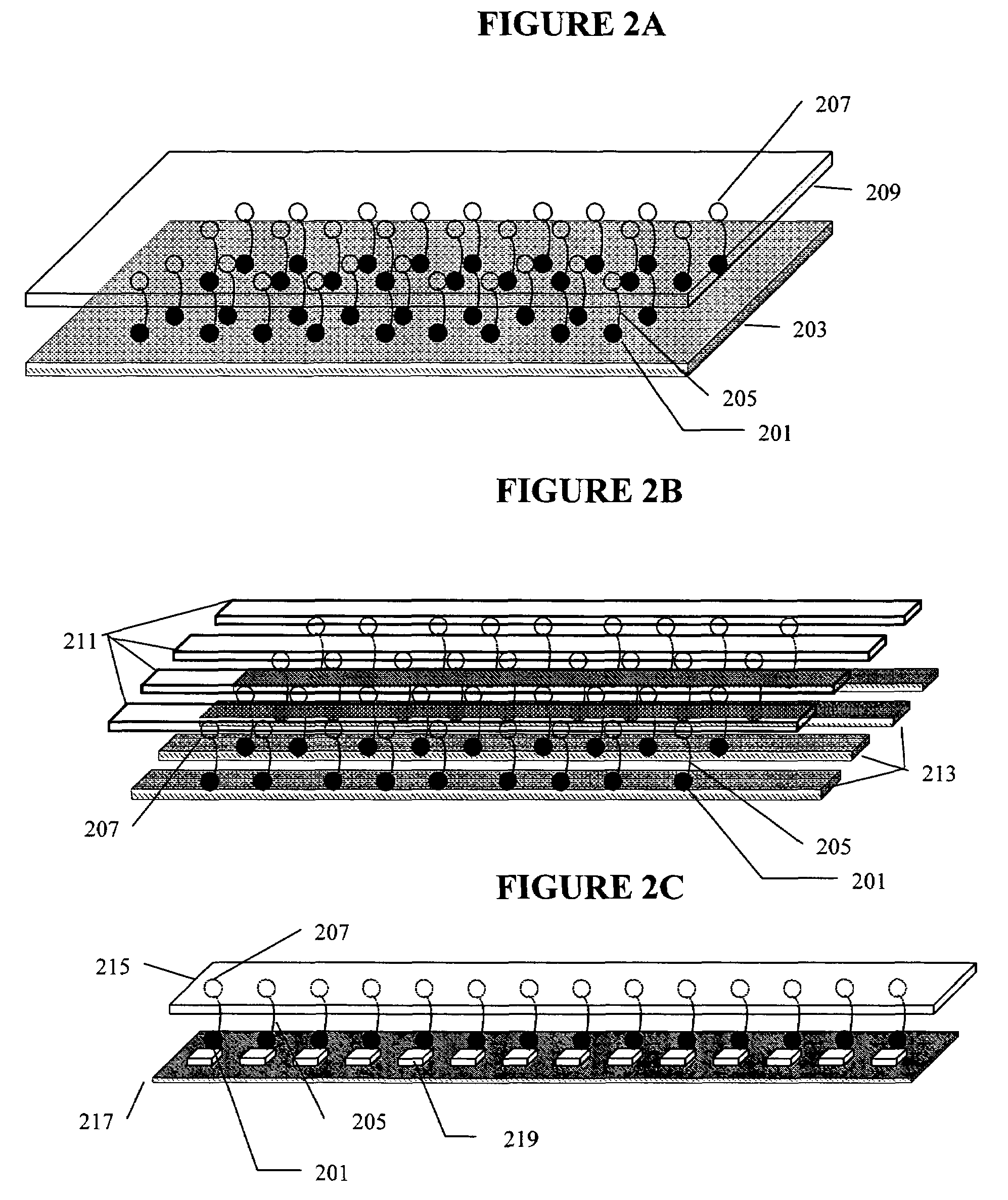
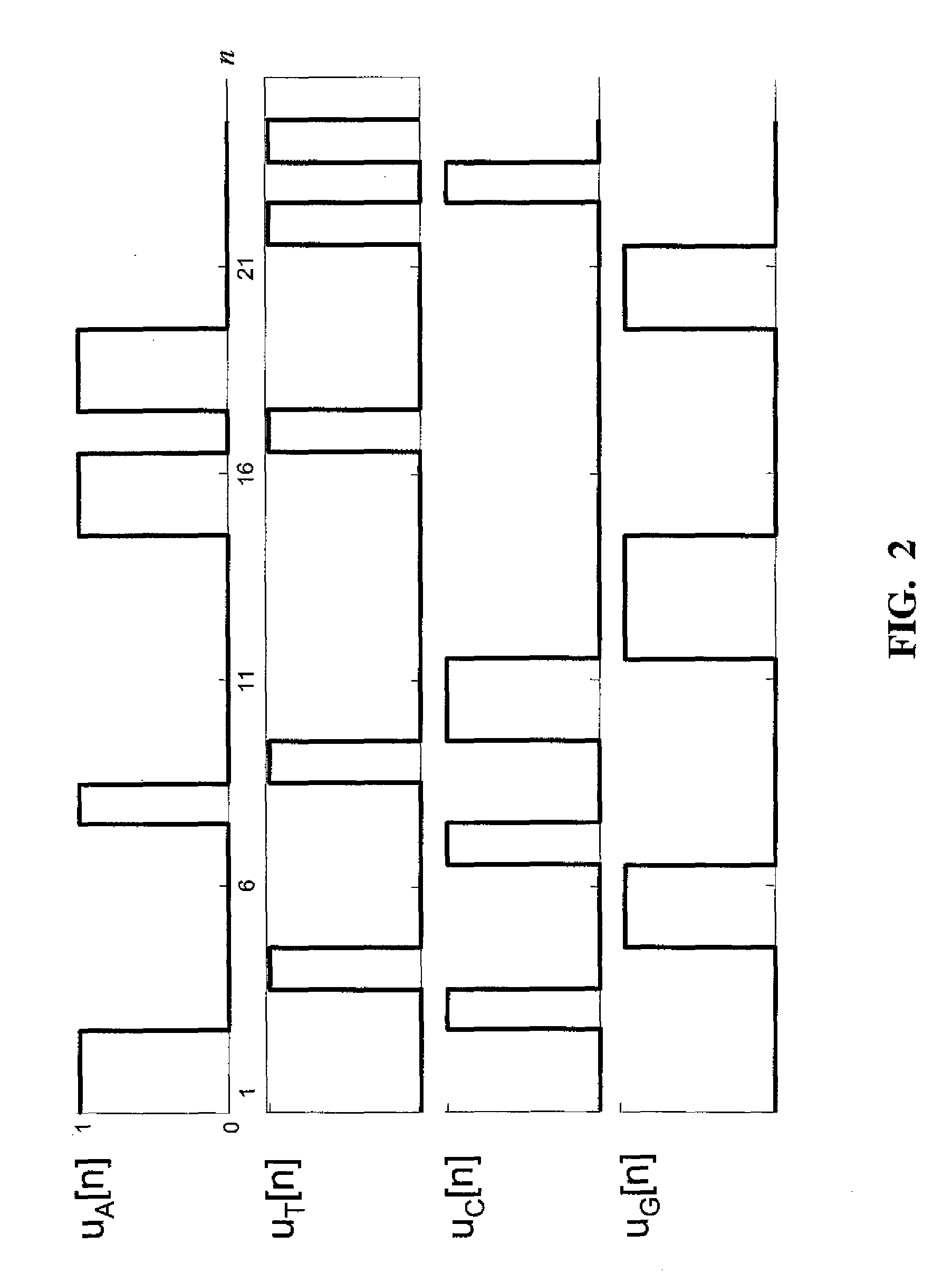
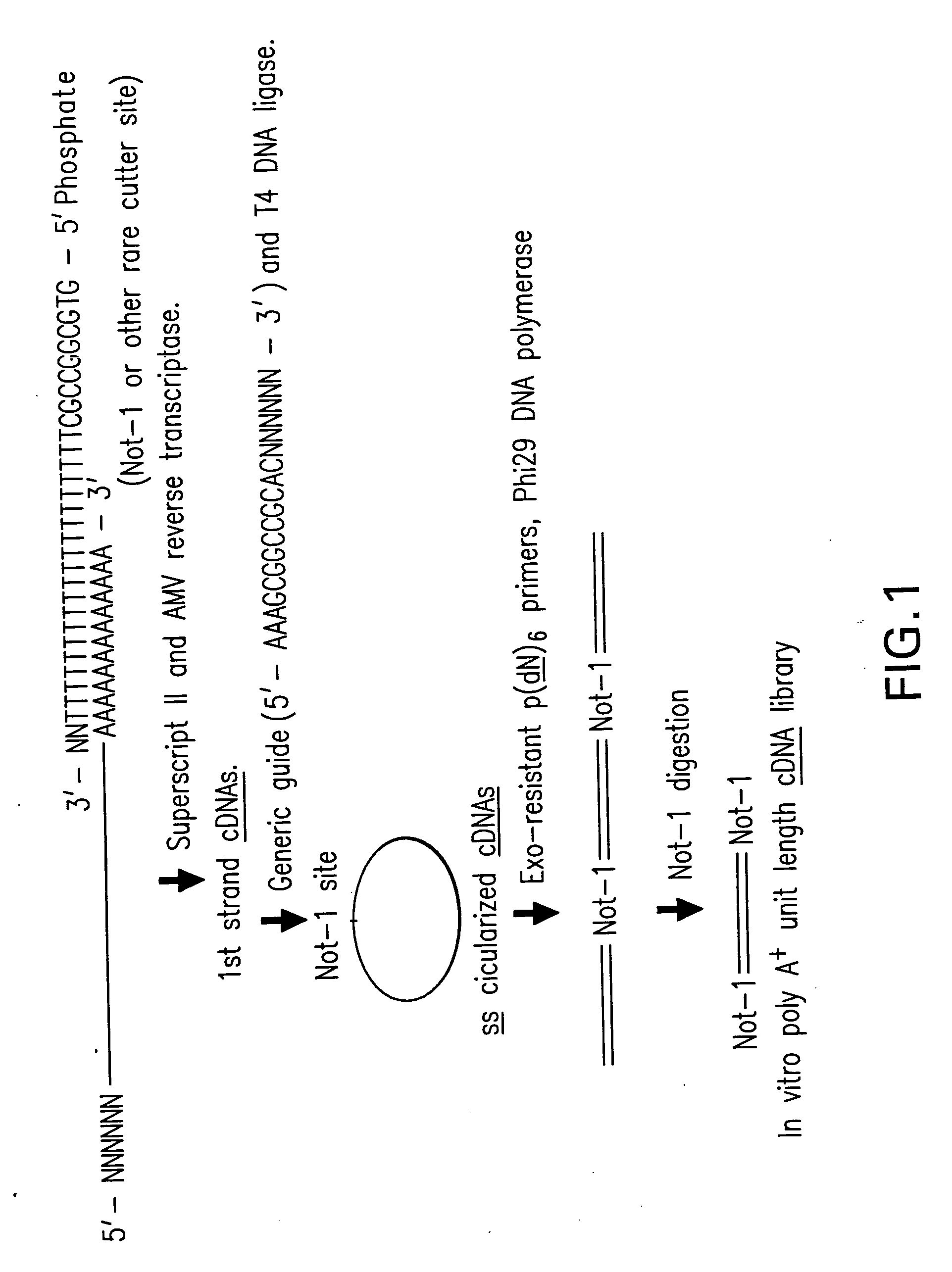
Patents
Literature
344 results about "Tandem repeat" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tandem repeats occur in DNA when a pattern of one or more nucleotides is repeated and the repetitions are directly adjacent to each other. Several protein domains also form tandem repeats within their amino acid primary structure, such as armadillo repeats. However, in proteins, perfect tandem repeats are unlikely in most in vivo proteins, and most known repeats are in proteins which have been designed.
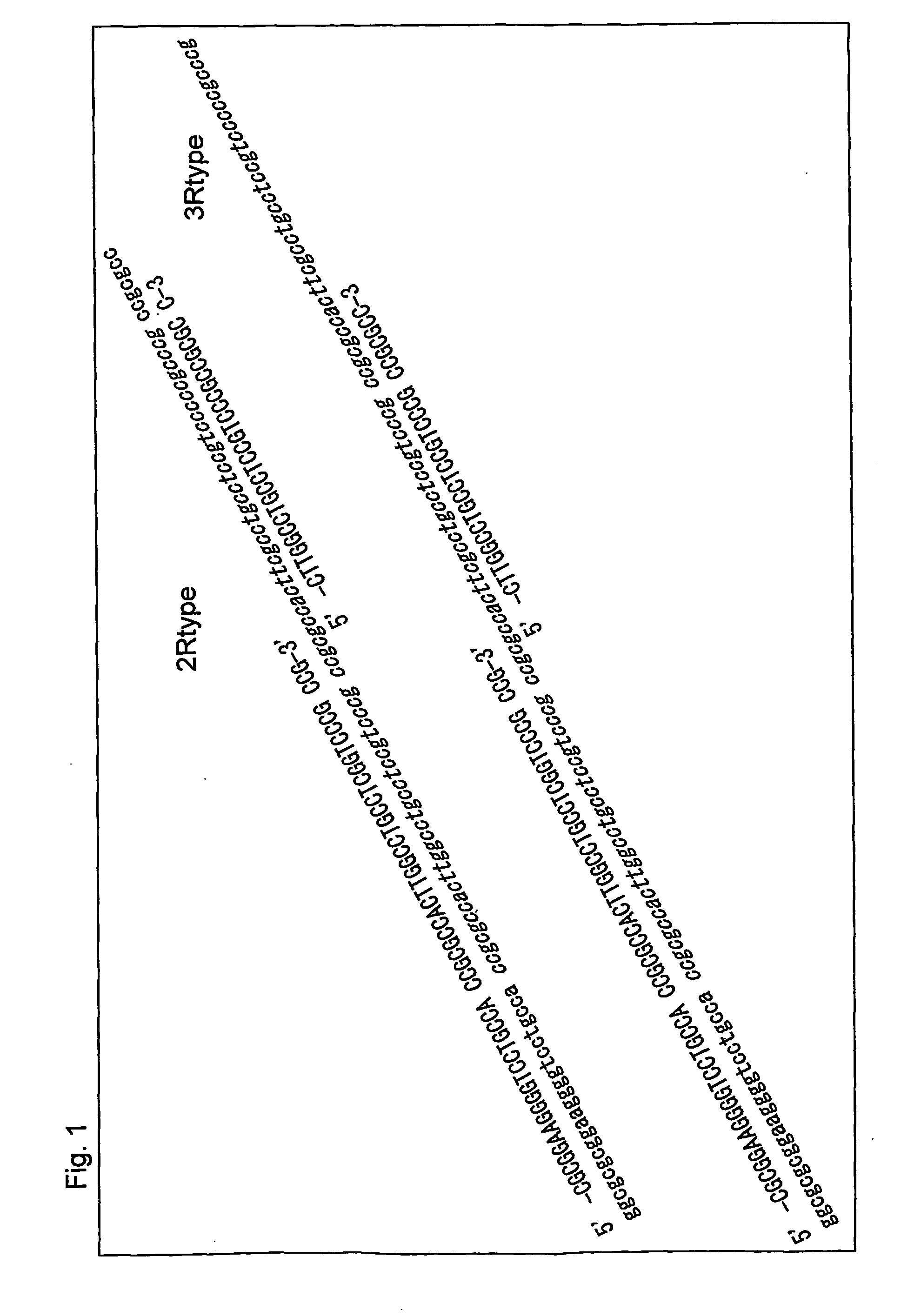
Oligonucleotides for genotyping thymidylate synthase gene
ActiveUS20070031829A1Sensitive and convenient detectionEasy to aimSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsGenomic DNA
Oligonucleotides for genotyping the thymidylate synthase gene are provided. The number of tandem repeats in the promoter region of the thymidylate synthase gene can be identified based on the hybridization of an oligonucleotide of the invention to the genomic DNA of a subject. Therefore, the genotype of the thymidylate synthase gene can be identified based on the number of tandem repeats. The genotype relates to the responsiveness of a subject towards an antitumor agent.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Multiplex amplification of short tandem repeat loci
InactiveUS6221598B1Quick checkFast analysisSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAlleleTandem repeat
The present invention is directed to the simultaneous amplification of multiple distinct genetic loci using PCR or other amplification systems to determine in one reaction the alleles of each locus contained within the multiplex.
Owner:PROMEGA
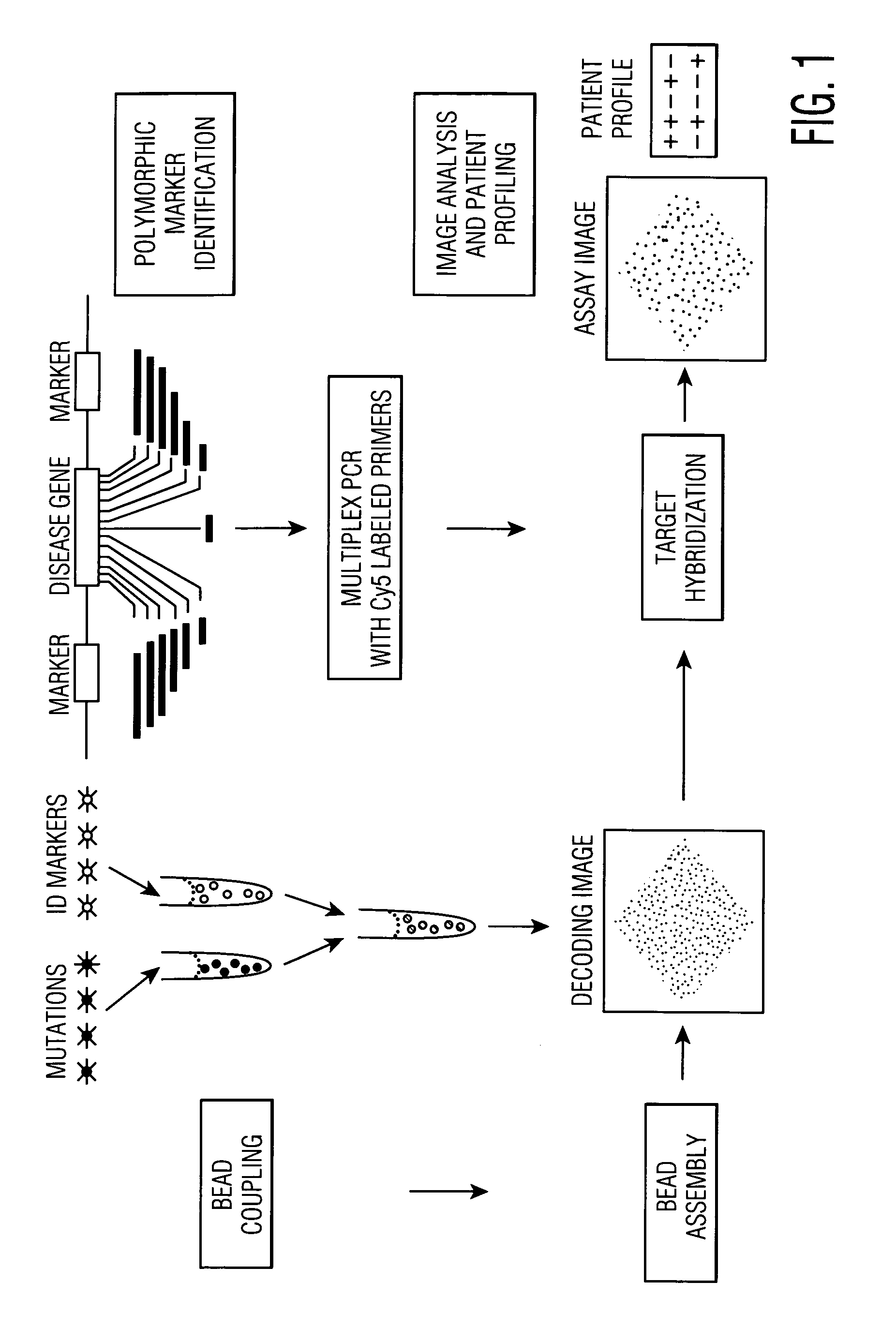
Genetic analysis and authentication
InactiveUS7157228B2Reduce morbidityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological bodyGenetic Screening (procedure)
This invention provides compositions and methods for genetic testing of an organism and for correlating the results of the genetic testing with a unique marker that unambiguously identifies the organism. The markers may be internal markers, such as for example single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), short tandem repeats (STRs), or other sites within a genomic locus. Alternatively, the markers may be external, such that they are separately added to the genetic sample before testing.
Owner:BIOARRAY SOLUTIONS
Detector for nucleic acid typing and methods of using the same
InactiveUS6238866B1Easy constructionSimple designSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteTyping
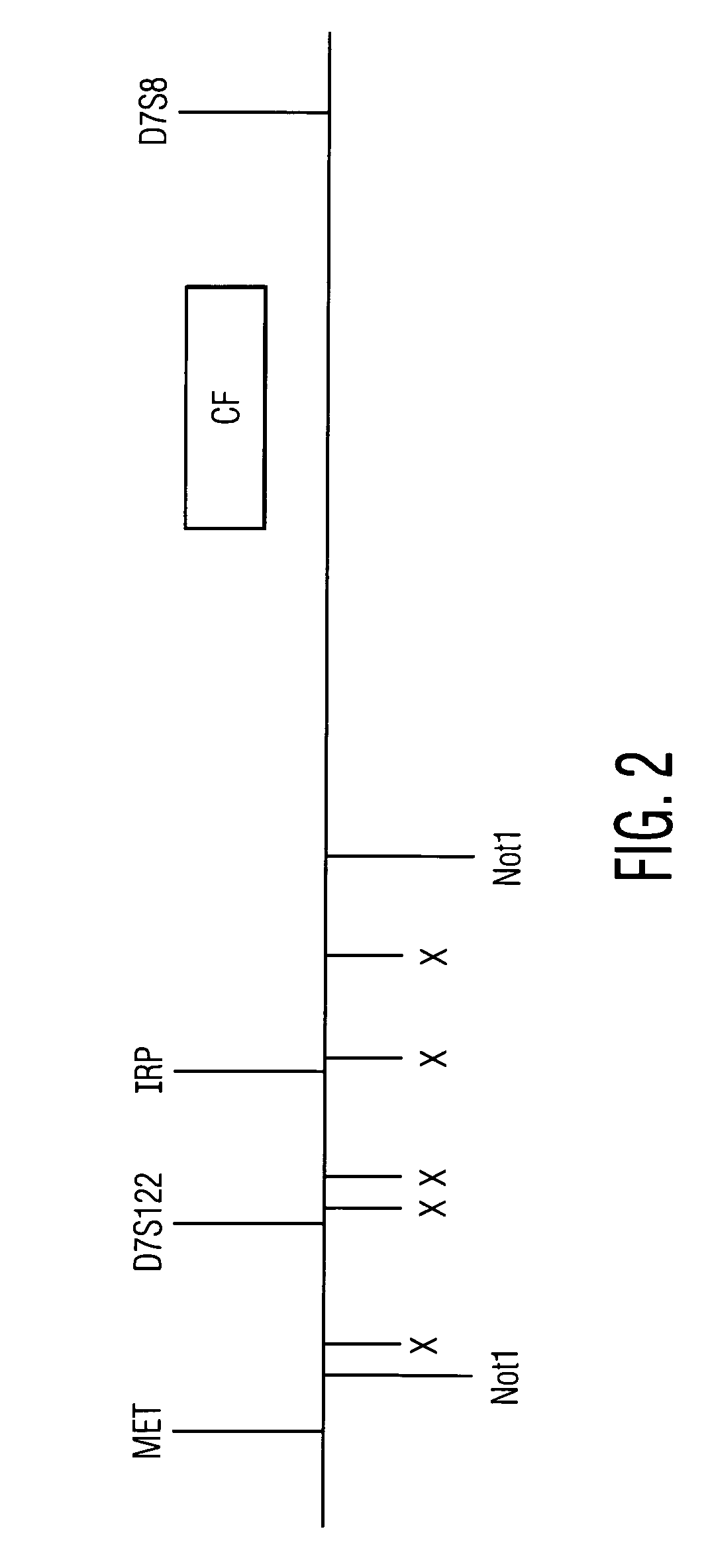
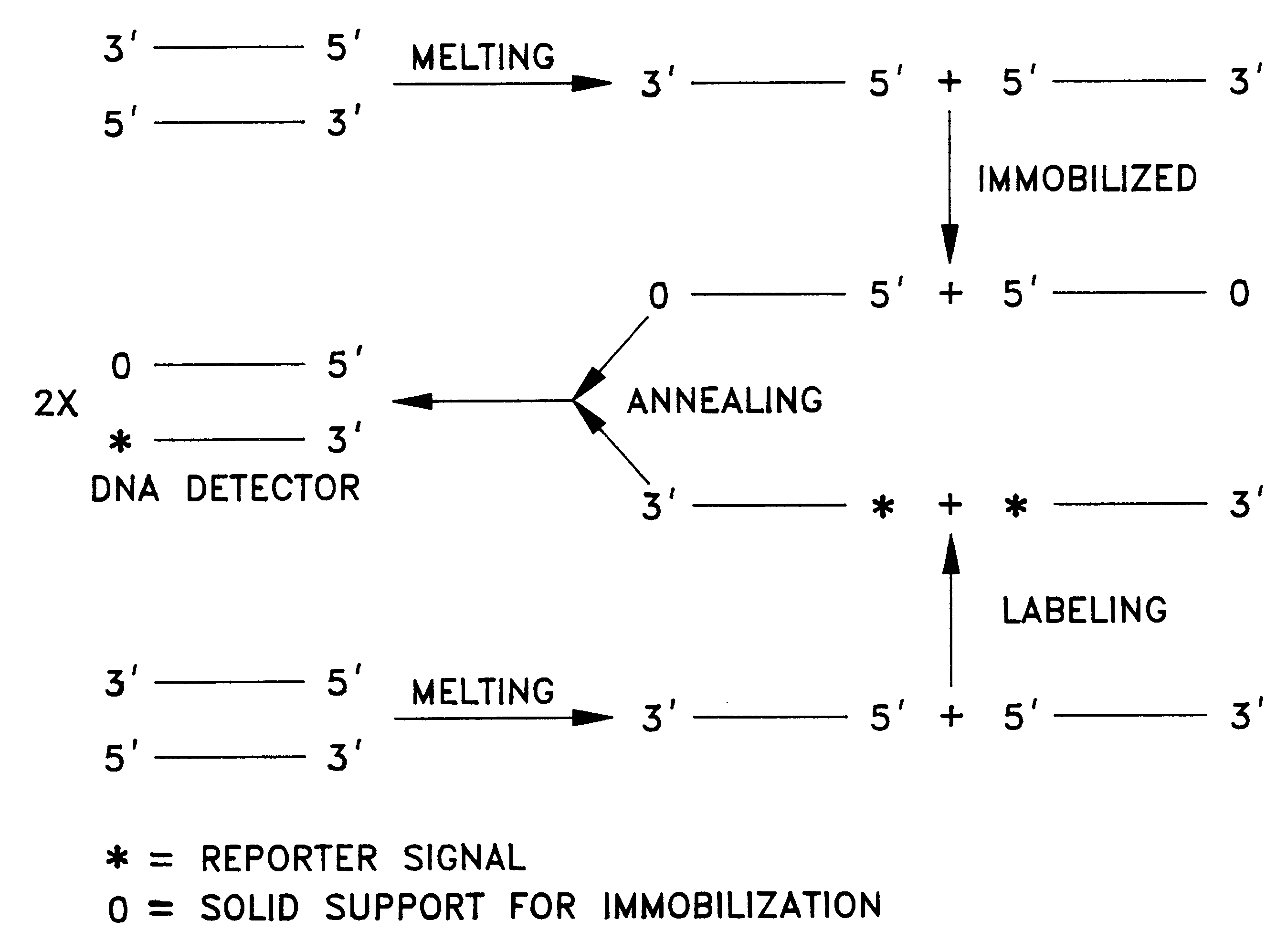
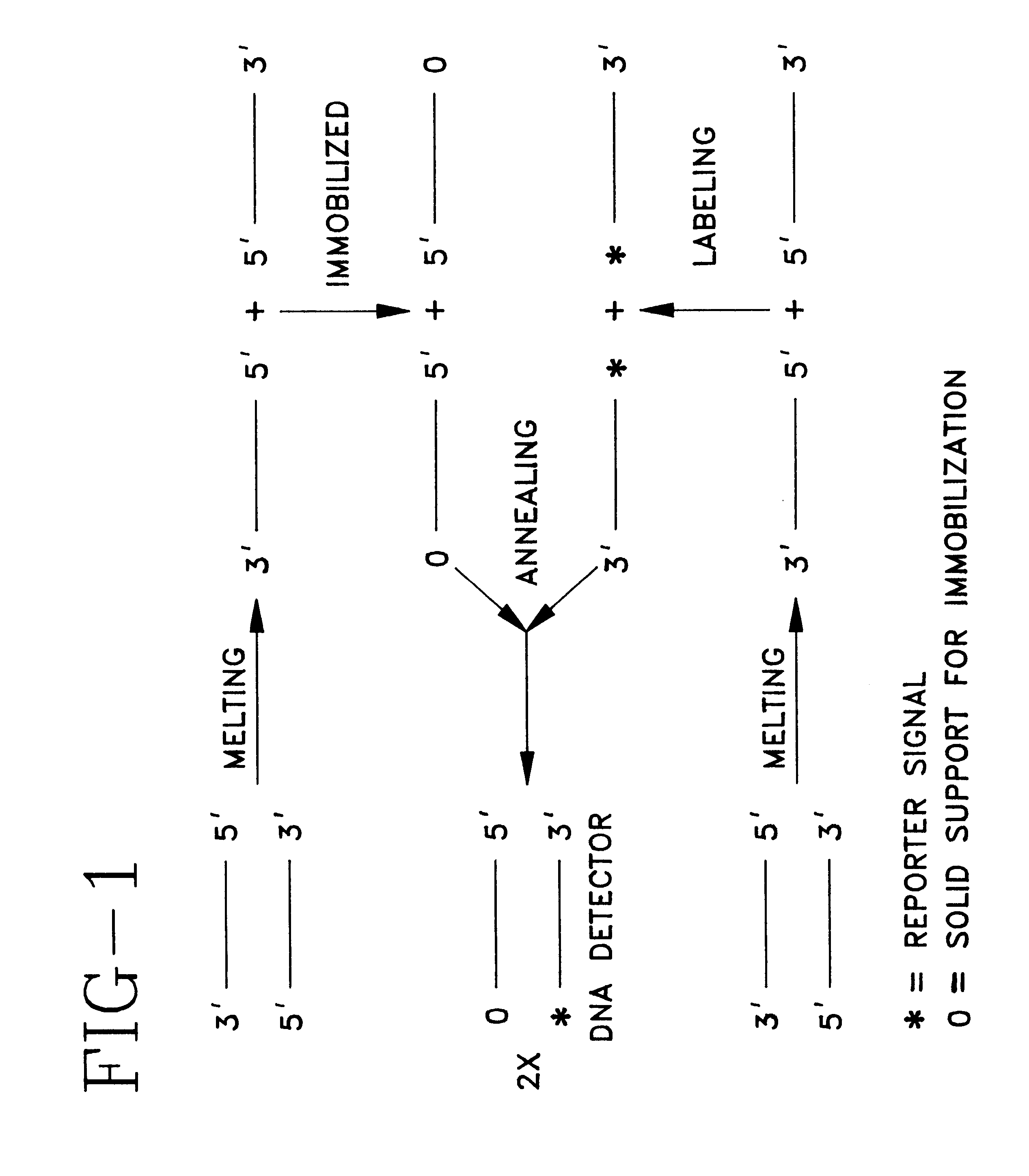
The present invention provides devices and methods for detecting or characterizing a nucleic acid analyte without requiring electrophoresis or the direct sequencing of analyte samples or analyte fragments. The device includes a panel or array of double stranded oligonucleotide probes immobilized on a solid support. each probe comprising a nucleotide sequence having a hypervariable number of tandem repeat sequences. Desirably, the specificity of the probes is varied with the location on the panel or array. One strand of each probe is preferably anchored at one terminus to a solid support and the opposite terminus of a second strand is not so anchored. The probes and / or the analyte are labeled by one or more reporter moieties, designed, for example, to allow for visual or instrument based detection of hybridization events.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
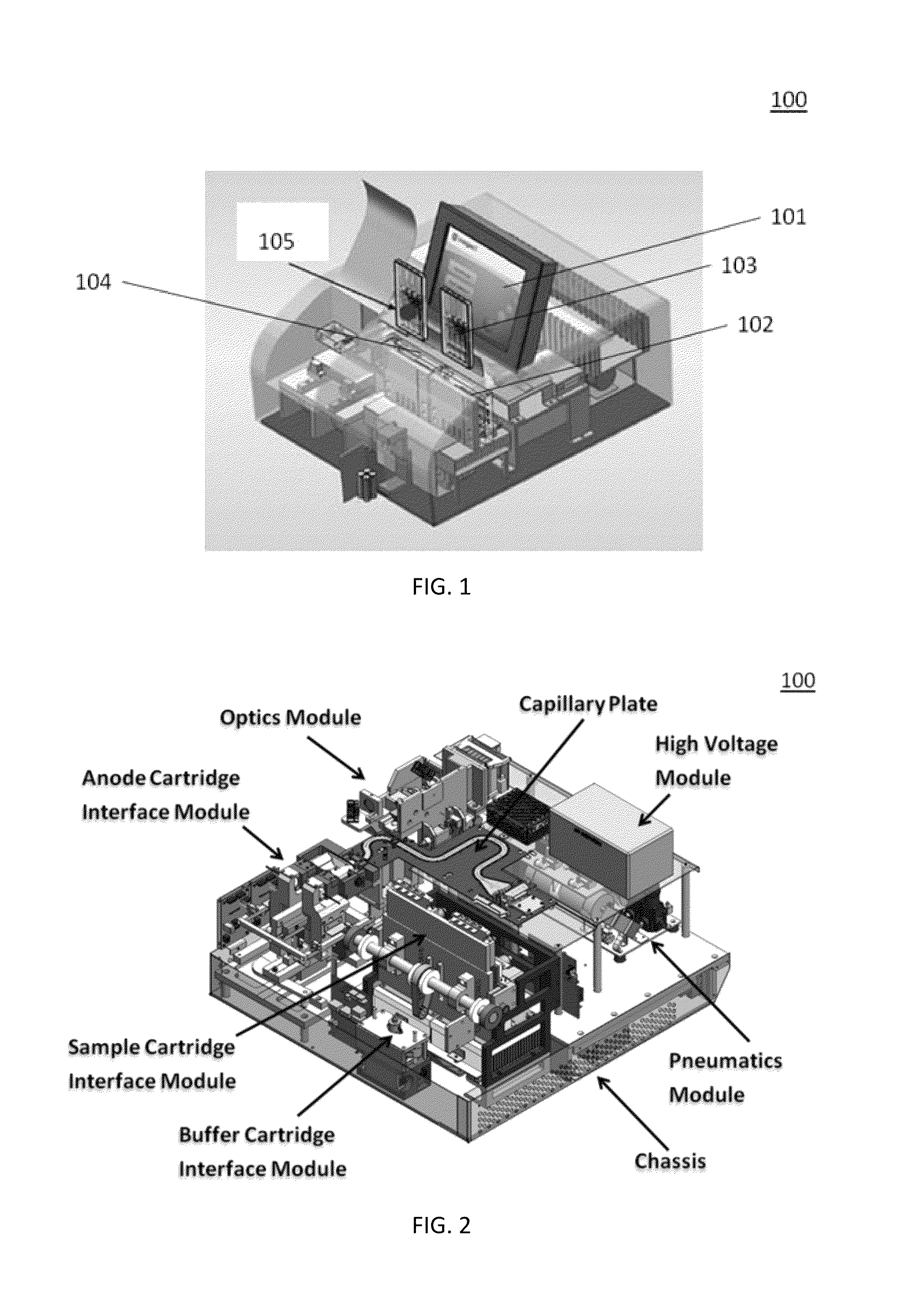
Sample Preparation, Processing and Analysis Systems
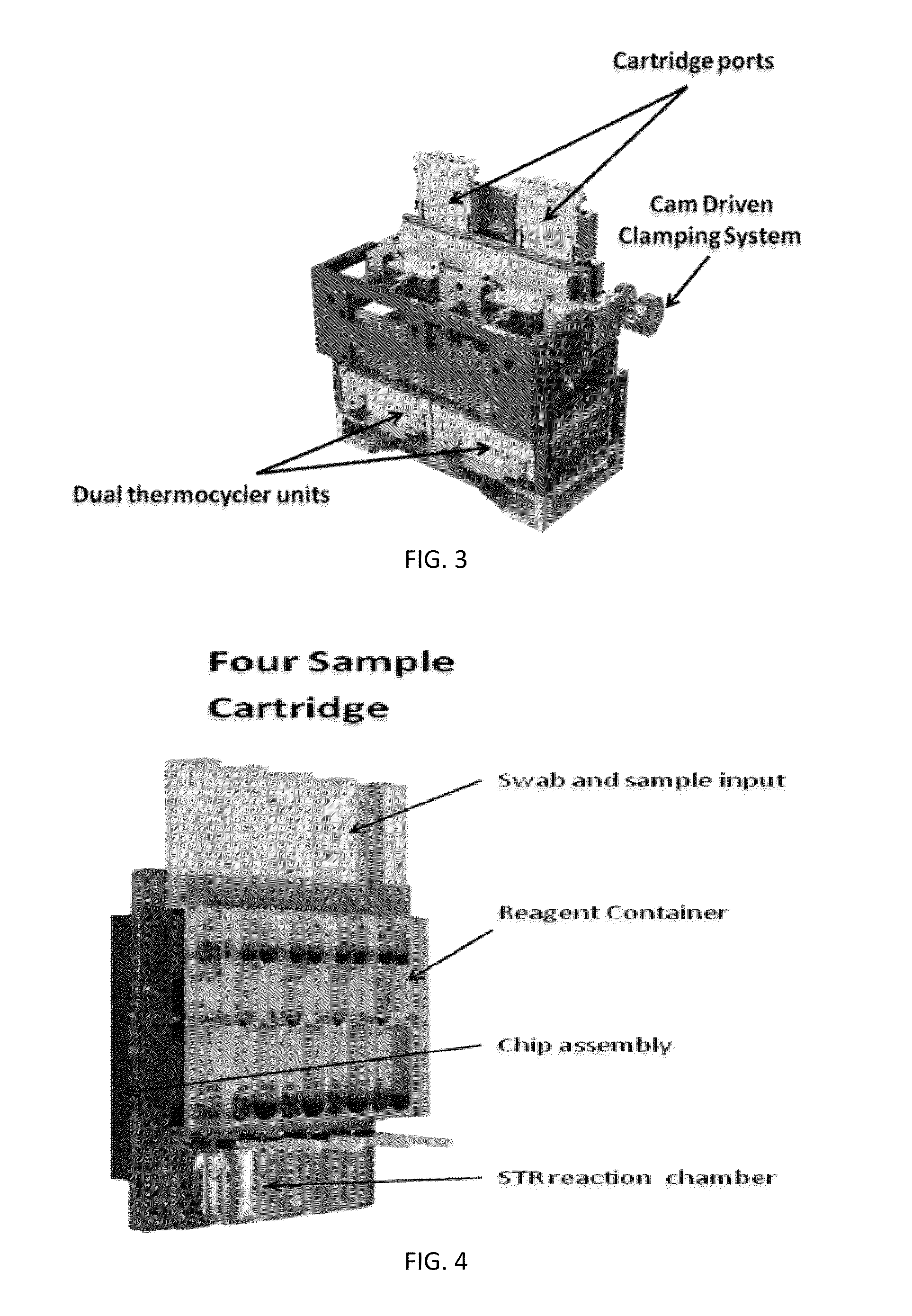
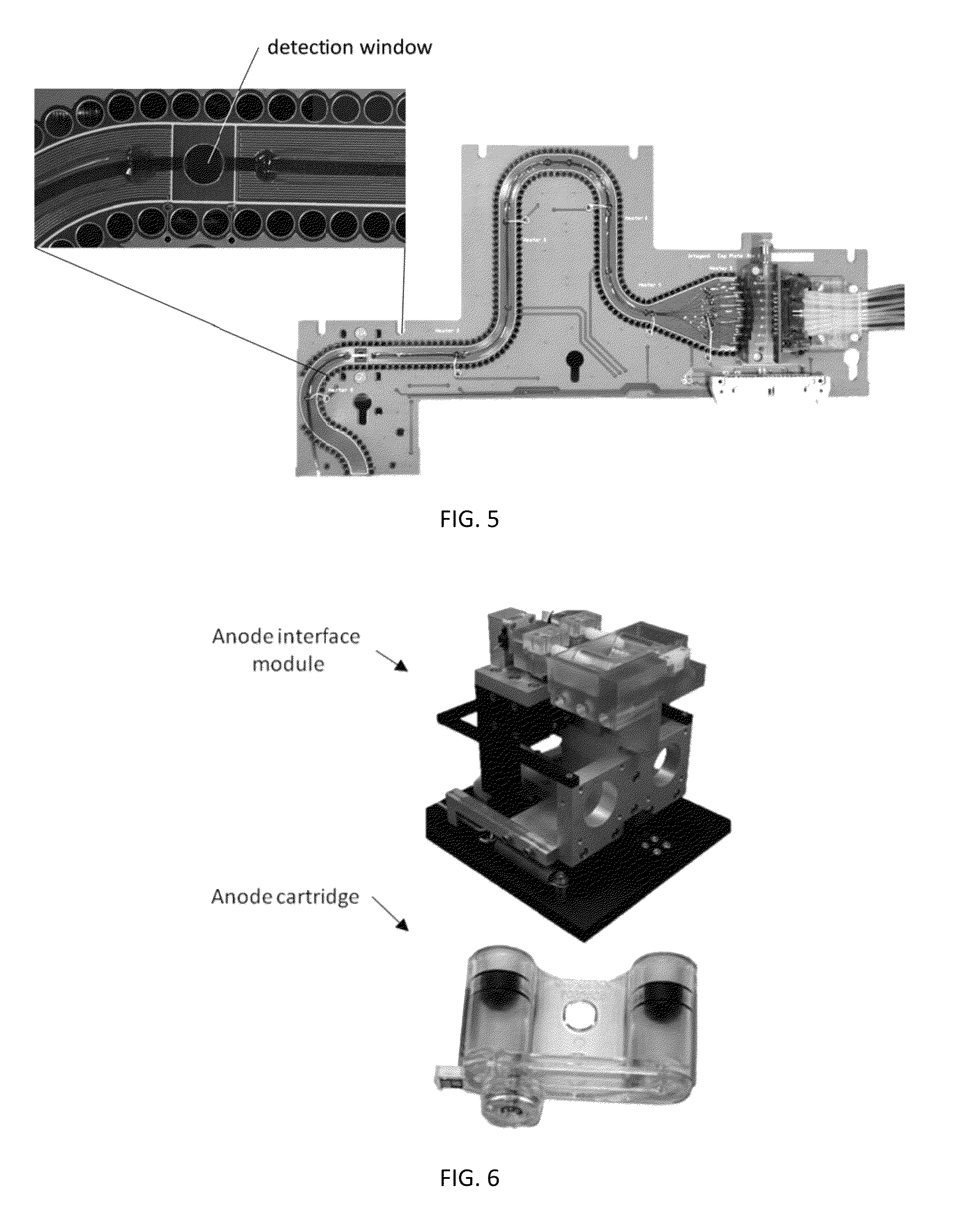
ActiveUS20130115607A1Small footprintFast timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenetic profileBioinformatics
This disclosure provides an integrated and automated sample-to-answer system that, starting from a sample comprising biological material, generates a genetic profile in less than two hours. In certain embodiments, the biological material is DNA and the genetic profile involves determining alleles at one or a plurality of loci (e.g., genetic loci) of a subject, for example, an STR (short tandem repeat) profile, for example as used in the CODIS system. The system can perform several operations, including (a) extraction and isolation of nucleic acid; (b) amplification of nucleotide sequences at selected loci (e.g., genetic loci); and (c) detection and analysis of amplification product. These operations can be carried out in a system that comprises several integrated modules, including an analyte preparation module; a detection and analysis module and a control module.
Owner:INTEGENX
Nano-PCR: methods and devices for nucleic acid amplification and detection
ActiveUS20060019274A1Significant improvementMaterial nanotechnologyHeating or cooling apparatusNucleic acid sequencingPcr method
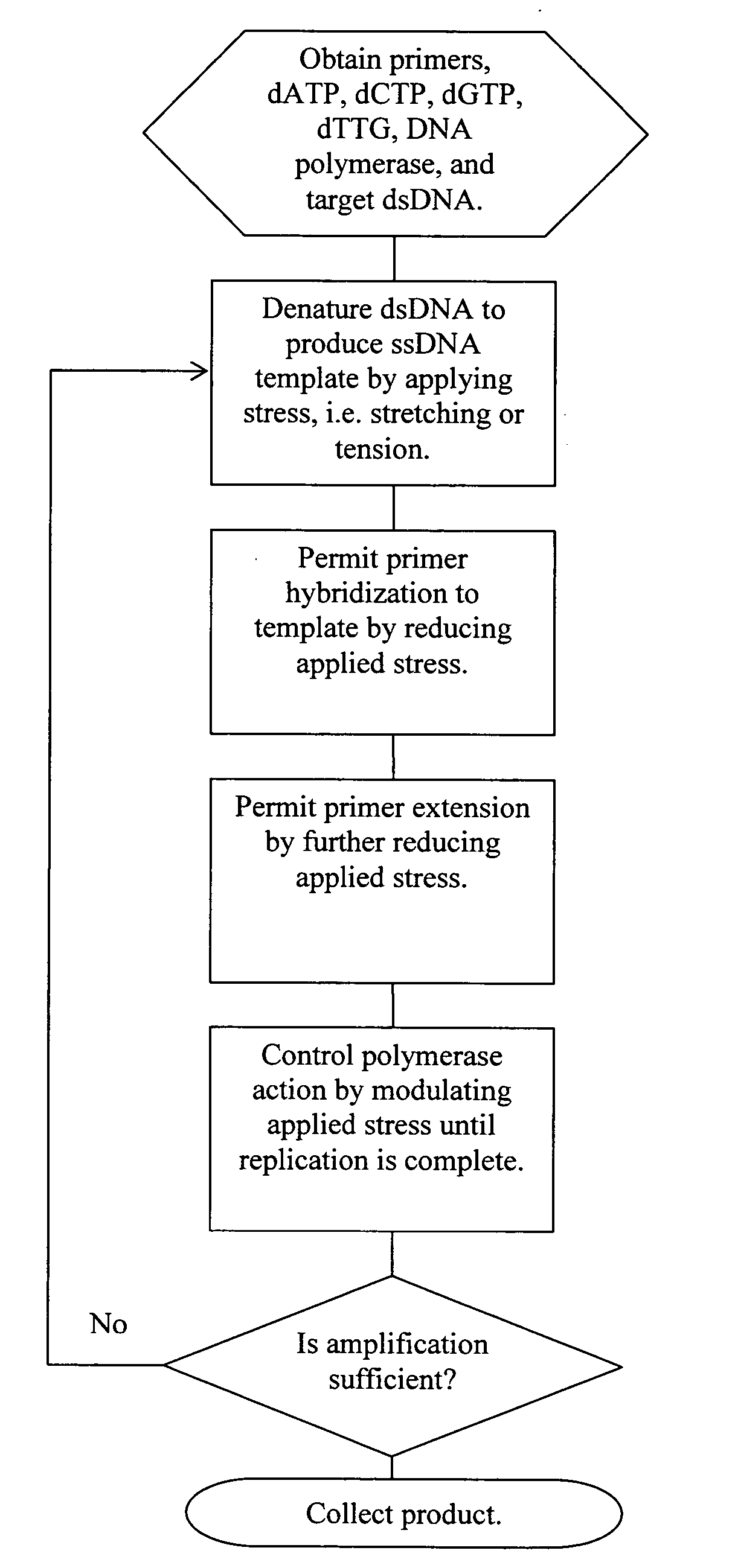
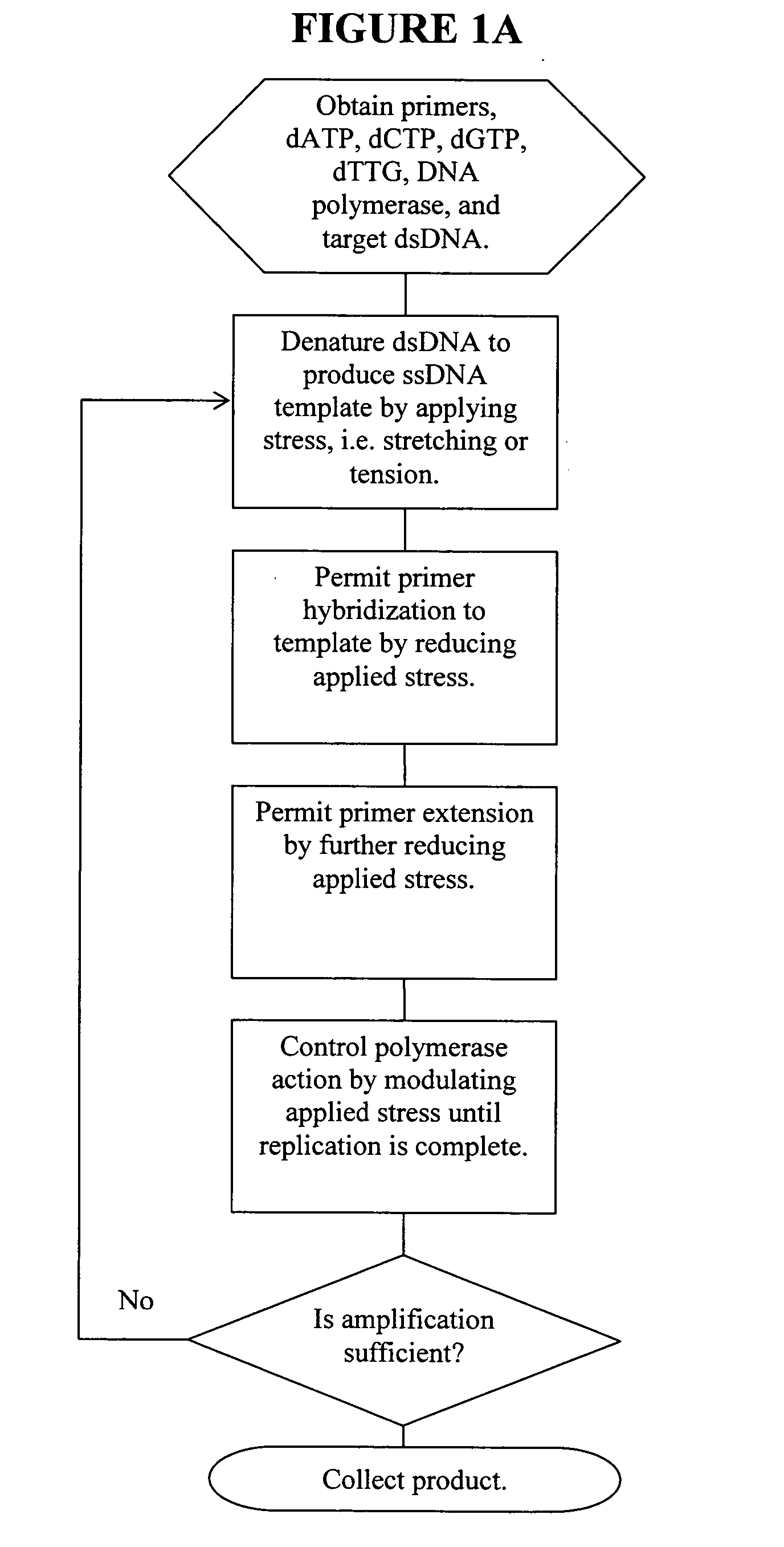
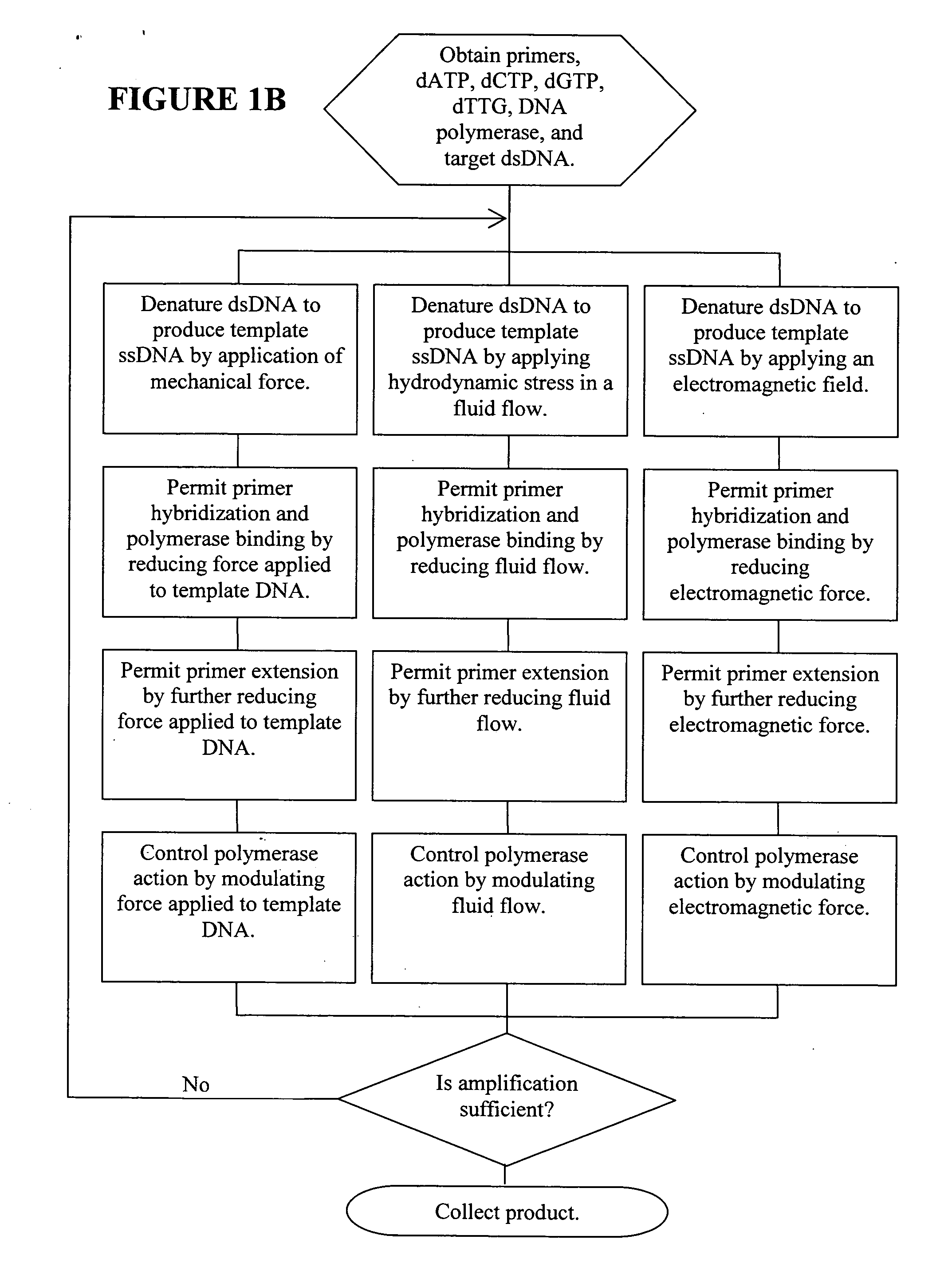
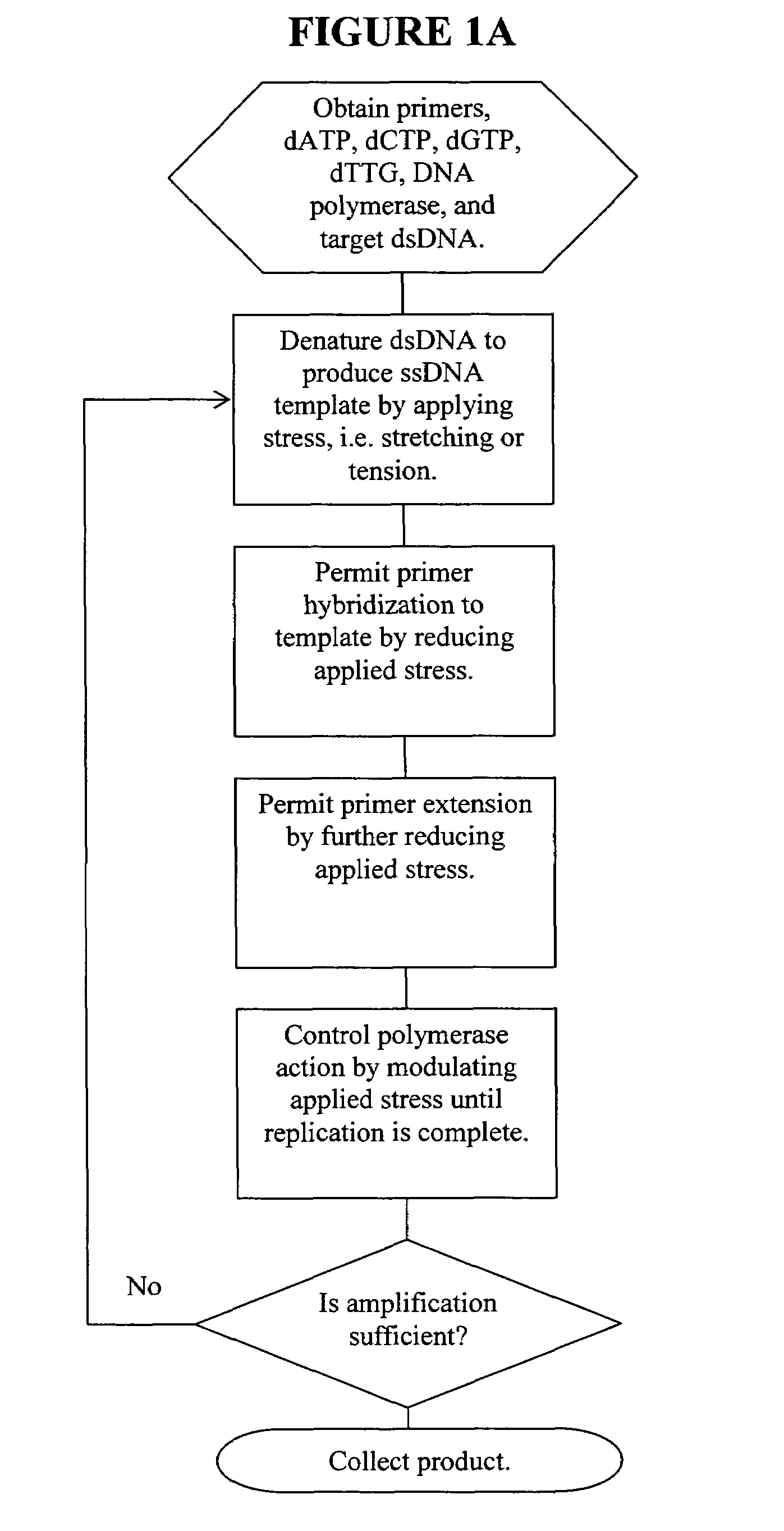
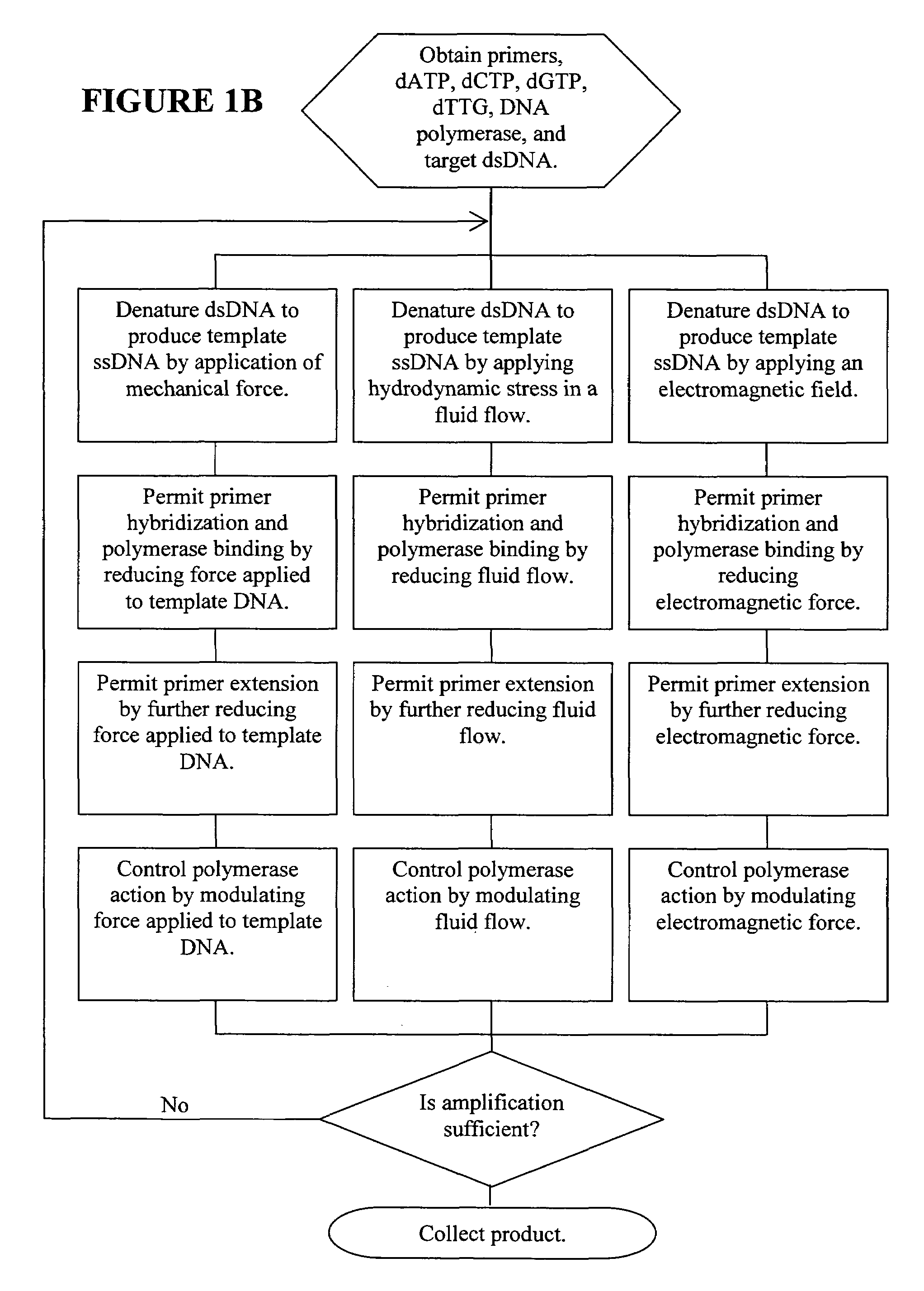
Methods, devices, and compositions are described that provide for amplification of nucleic acid sequences without reliance upon temperature cycling, thus freeing the methods from conventional benchtop thermal cycling devices. Denaturation of double stranded nucleic acids, primer annealing, and precision control over primer extension by polymerase can be accomplished by applying stress to a nucleic acid. These methods can provide one ore more benefits over conventional PCR methods including: precision control over the PCR process; generally improved fidelity; improved accuracy over problematic sequences such as GC-rich or tandem repeat regions; greater sequence length; increased reaction yield; reduced experimental time; greater efficiency; lower cost; greater portability; and, robustness to various environmental parameters, such as temperature, pH, and ionic strengths.
Owner:NANOBIOSYM INC
Detection and quantification of sample contamination in immune repertoire analysis
The invention is directed to methods for detecting and quantifying nucleic acid contamination in a tissue sample of an individual containing T cells and / or B cells, which is used for generating a sequence-based clonotype profile. In one aspect, the invention is implemented by measuring the presence and / or level of an endogenous or exogenous nucleic acid tag by which nucleic acid from an intended individual can be distinguished from that of unintended individuals. Endogenous tags include genetic identity markers, such as short tandem repeats, rare clonotypes or the like, and exogenous tags include sequence tags employed to determine clonotype sequences from sequence reads.
Owner:ADAPTIVE BIOTECH
Multiplex amplification of short tandem repeat loci
InactiveUS7008771B1Improve certaintyIncrease the number ofSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNATandem repeat
Methods and materials are disclosed for use in simultaneously amplifying at least thirteen loci of genomic DNA in a single multiplex reaction, as are methods and materials for use in the analysis of the products of such reactions. Included in the present invention are materials and methods for the simultaneous amplification of at least thirteen short tandem repeat loci, including specific materials and methods for the analysis of thirteen such loci specifically selected by the United States Federal Bureau of Investigation as core loci for use in the Combined DNA Index System (CODIS) database.
Owner:PROMEGA CORP
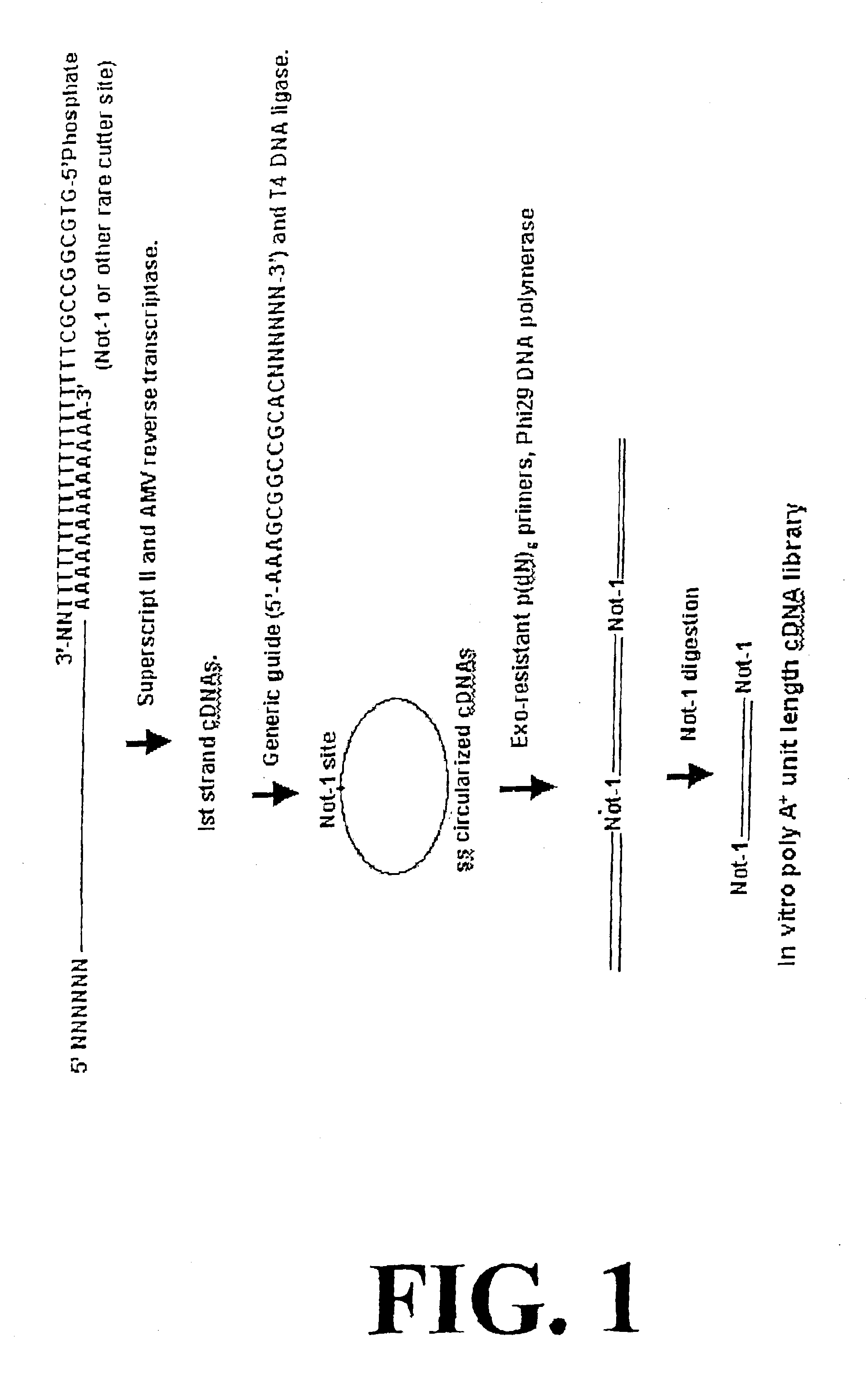
Rolling circle amplification of RNA
InactiveUS6977153B2Increase productionOptimization orderMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationTandem repeatDouble strand
Disclosed are compositions and methods for amplification of RNA molecules. The disclosed method involves synthesizing first strand cDNA molecules from RNA molecules, circularizing the first strand cDNA molecules and replicating the circularized first strand cDNA molecules using rolling circle replication. The method can be aided by the use of specialized primers for cDNA synthesis and specialized probes for circularizing the first strand cDNA molecules. The method can be used to replicate and amplify multiple RNA molecules, such as all RNA molecules in a sample or all mRNA molecules in a sample, or be used to replicate and amplify specific RNA molecules. Rolling circle replication of the circularized first strand cDNA molecules results in long DNA strands containing tandem repeats of the cDNA sequence. The tandem sequence DNA can be used directly (for detection of sequences, for example), further amplified, or used any other purpose. Double-stranded tandem sequence DNA can be used to produce unit lengths of the cDNA sequence. Tandem sequence DNA can also be transcribed to produce transcripts having sequence complementary to or matching the sequence of RNA molecules.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
Sample preparation, processing and analysis systems
ActiveUS8894946B2Small footprintFast timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusAnalyteAllele
This disclosure provides an integrated and automated sample-to-answer system that, starting from a sample comprising biological material, generates a genetic profile in less than two hours. In certain embodiments, the biological material is DNA and the genetic profile involves determining alleles at one or a plurality of loci (e.g., genetic loci) of a subject, for example, an STR (short tandem repeat) profile, for example as used in the CODIS system. The system can perform several operations, including (a) extraction and isolation of nucleic acid; (b) amplification of nucleotide sequences at selected loci (e.g., genetic loci); and (c) detection and analysis of amplification product. These operations can be carried out in a system that comprises several integrated modules, including an analyte preparation module; a detection and analysis module and a control module.
Owner:INTEGENX
Nano-PCR: methods and devices for nucleic acid amplification and detection
ActiveUS7494791B2Significant improvementMaterial nanotechnologyHeating or cooling apparatusNucleic acid sequencingPcr method
Methods, devices, and compositions are described that provide for amplification of nucleic acid sequences without reliance upon temperature cycling, thus freeing the methods from conventional benchtop thermal cycling devices. Denaturation of double stranded nucleic acids, primer annealing, and precision control over primer extension by polymerase can be accomplished by applying stress to a nucleic acid. These methods can provide one ore more benefits over conventional PCR methods including: precision control over the PCR process; generally improved fidelity; improved accuracy over problematic sequences such as GC-rich or tandem repeat regions; greater sequence length; increased reaction yield; reduced experimental time; greater efficiency; lower cost; greater portability; and, robustness to various environmental parameters, such as temperature, pH, and ionic strengths.
Owner:NANOBIOSYM INC
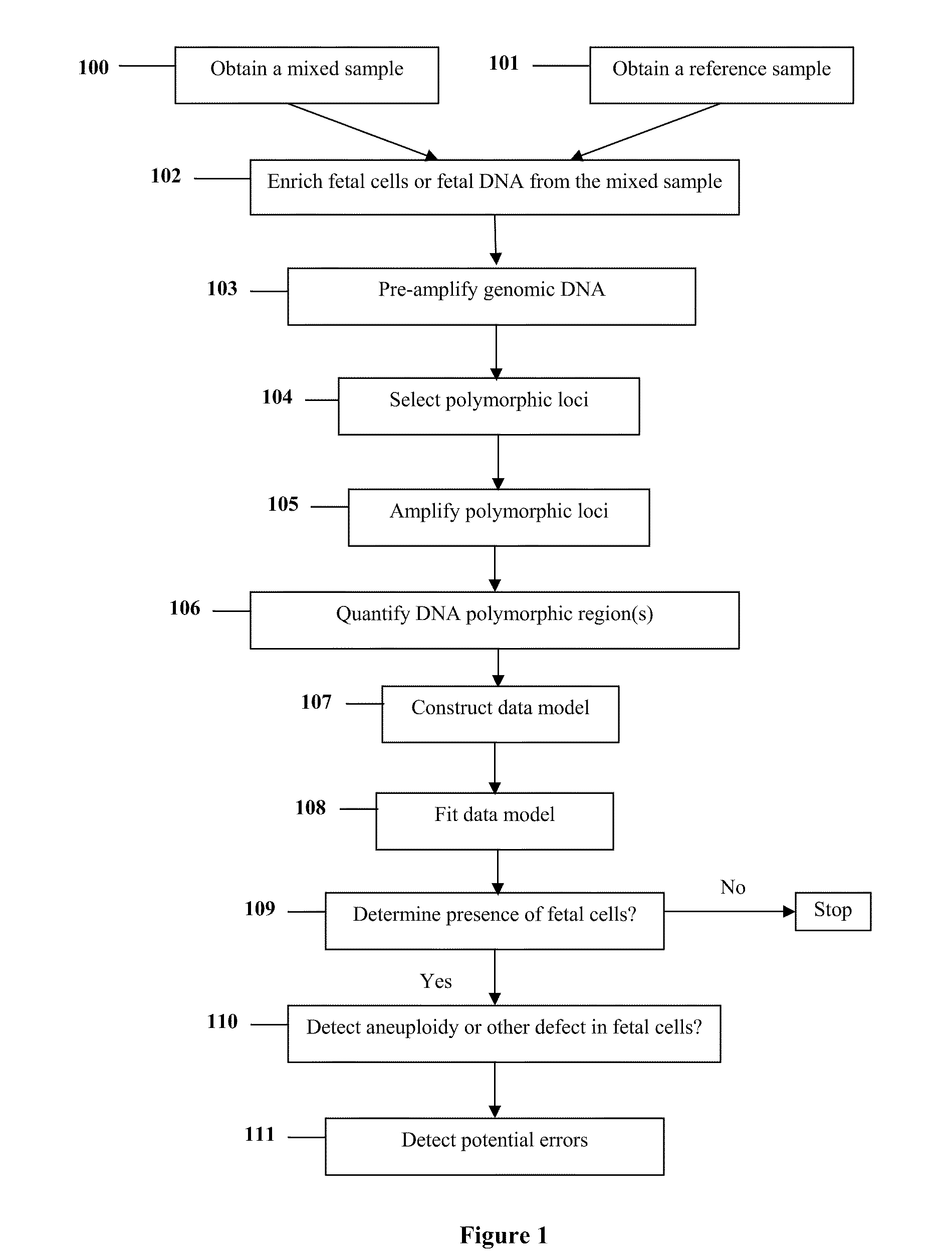
Diagnosis of fetal abnormalities using polymorphisms including short tandem repeats
InactiveUS20090280492A1Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationFetal abnormalityGenomic DNA
The present invention provides systems, apparatuses, and methods to detect the presence of fetal cells when mixed with a population of maternal cells in a sample and to test fetal abnormalities, i.e. aneuploidy. In addition, the present invention provides methods to determine when there are insufficient fetal cells for a determination and report a non-informative case. The present invention involves quantifying regions of genomic DNA from a mixed sample. More particularly the invention involves quantifying DNA polymorphisms from the mixed sample.
Owner:STOUGHTON ROLAND +2
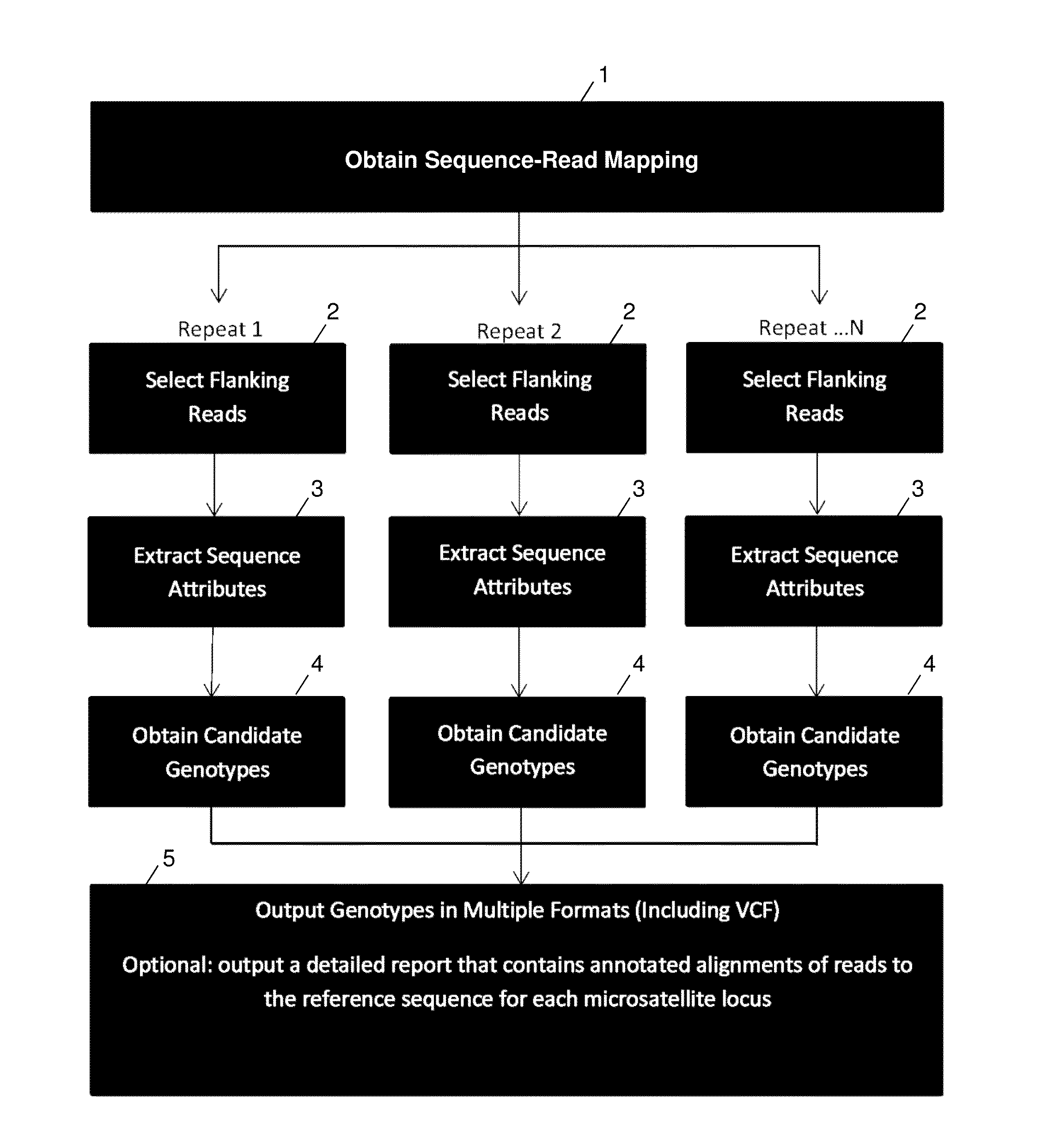
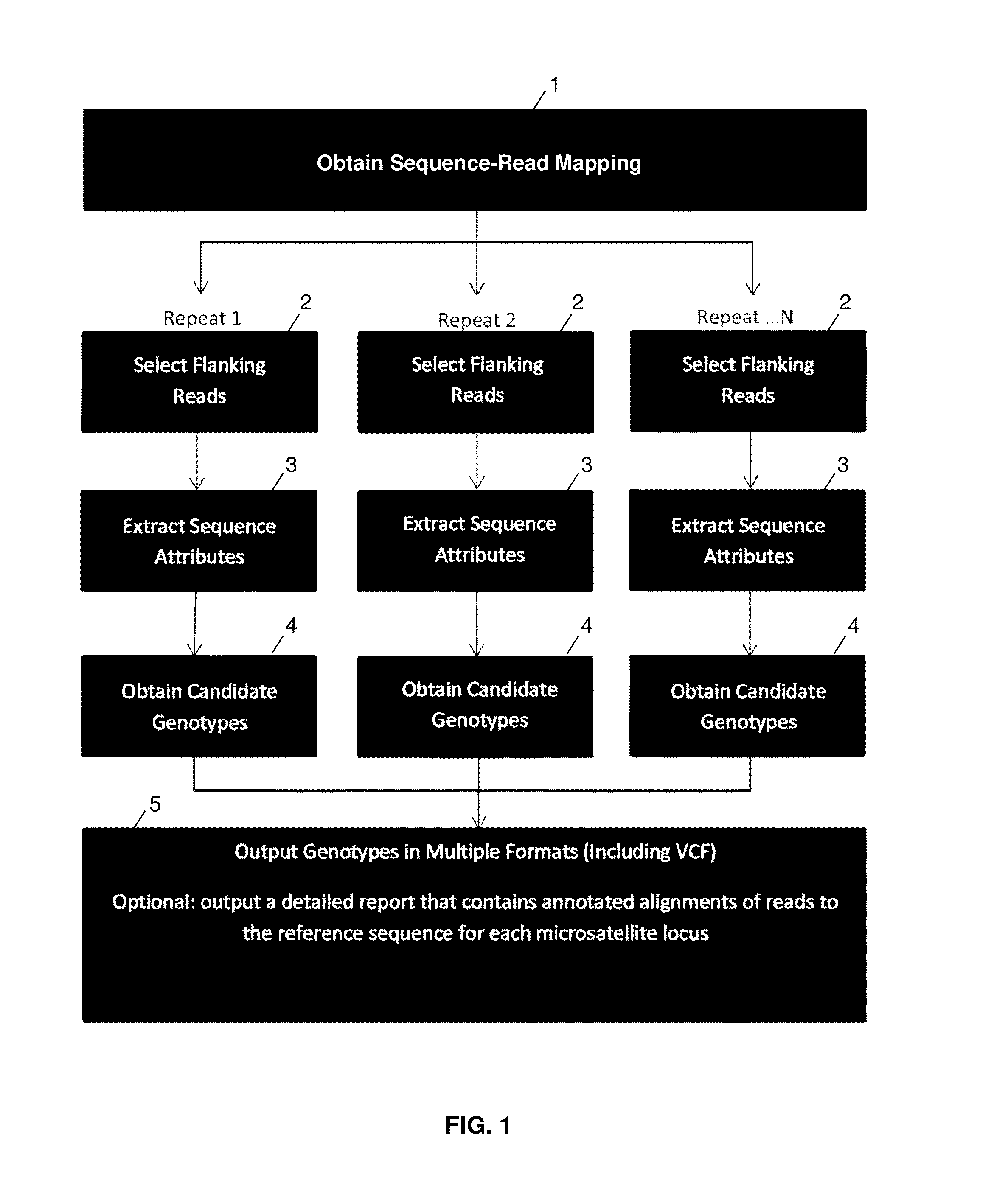
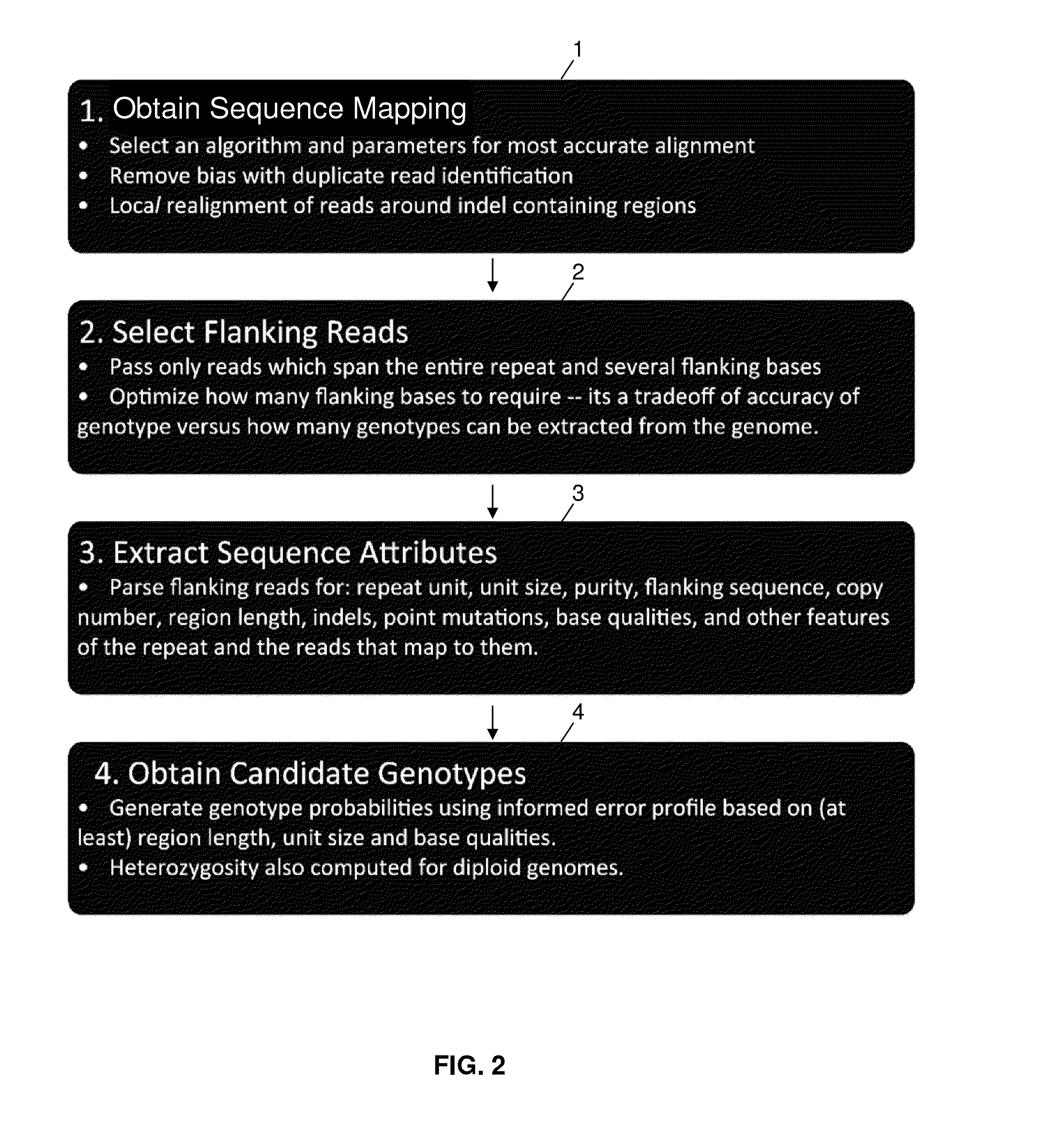
System and method for genotyping using informed error profiles
ActiveUS20140114582A1Minimal coverage dataAccurate genotypingProteomicsGenomicsModel selectionAlgorithm
A system and method for genotyping tandem repeats in sequencing data. The invention uses Bayesian model selection guided by an empirically-derived error model that incorporates properties of sequence reads and reference sequences to which they map.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
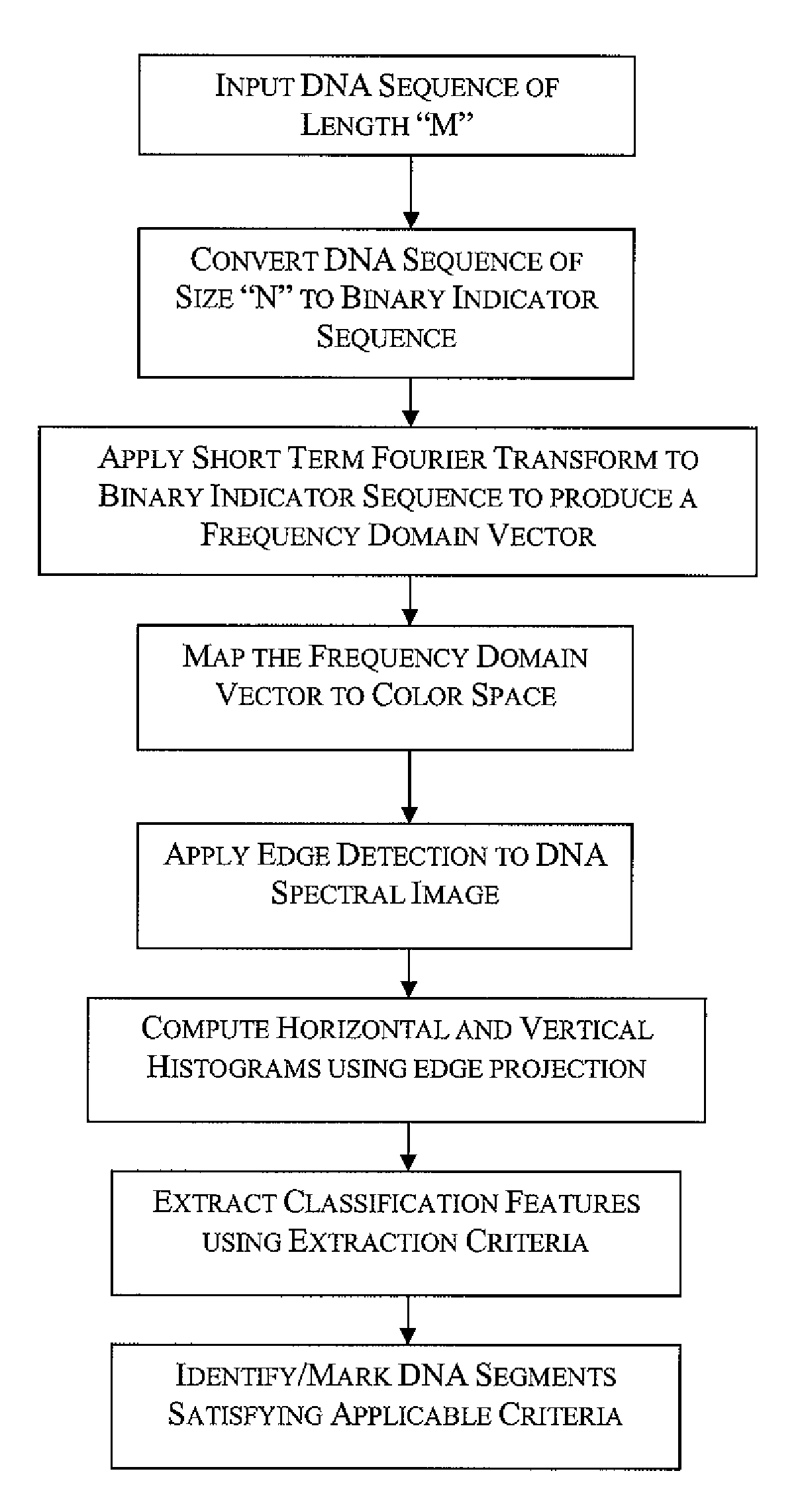
Methods and systems for identification of DNA patterns through spectral analysis
InactiveUS20090129647A1Improve visualizationHigh resolutionData visualisationBiostatisticsDNA PatternsCo-occurrence
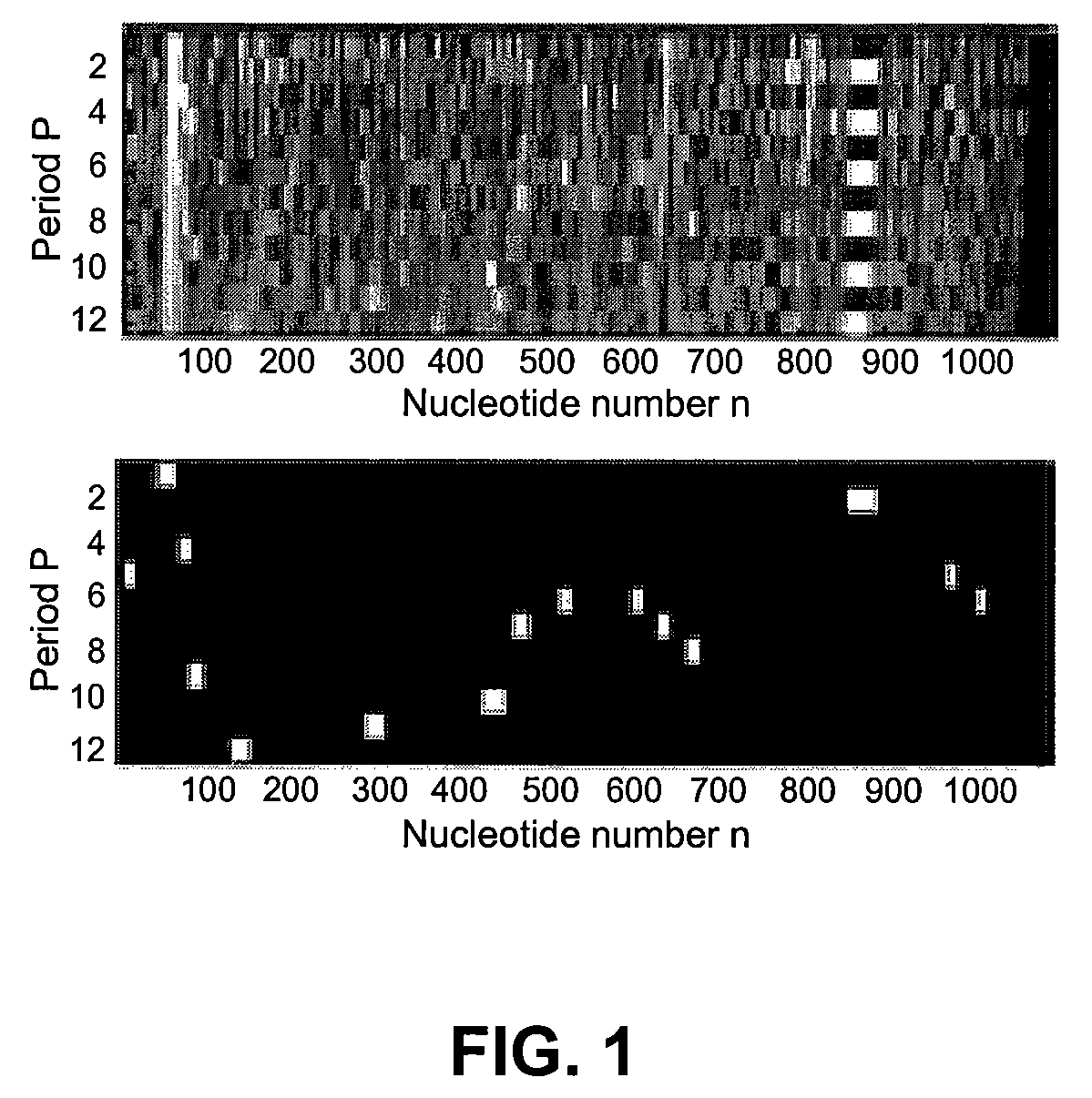
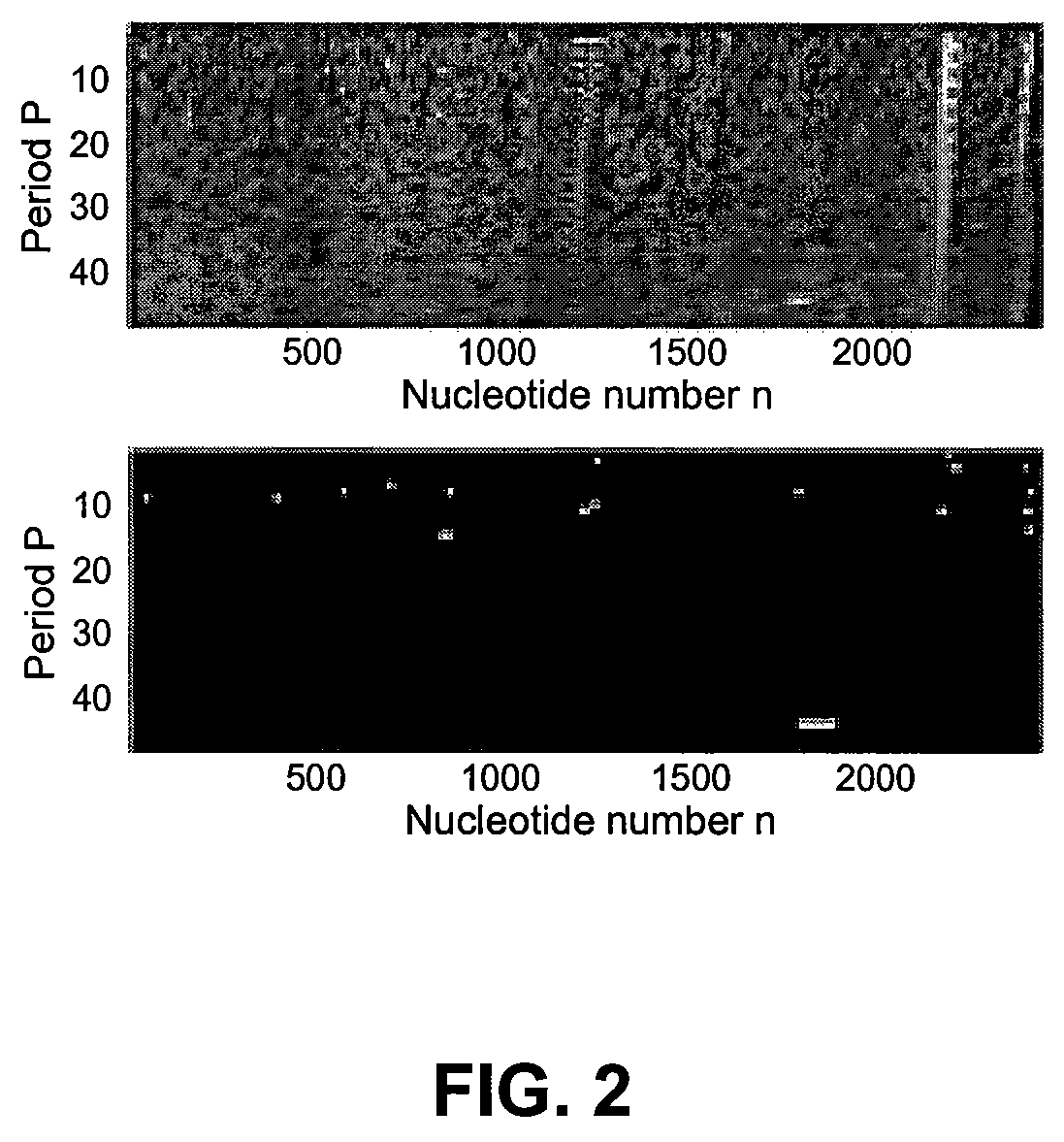
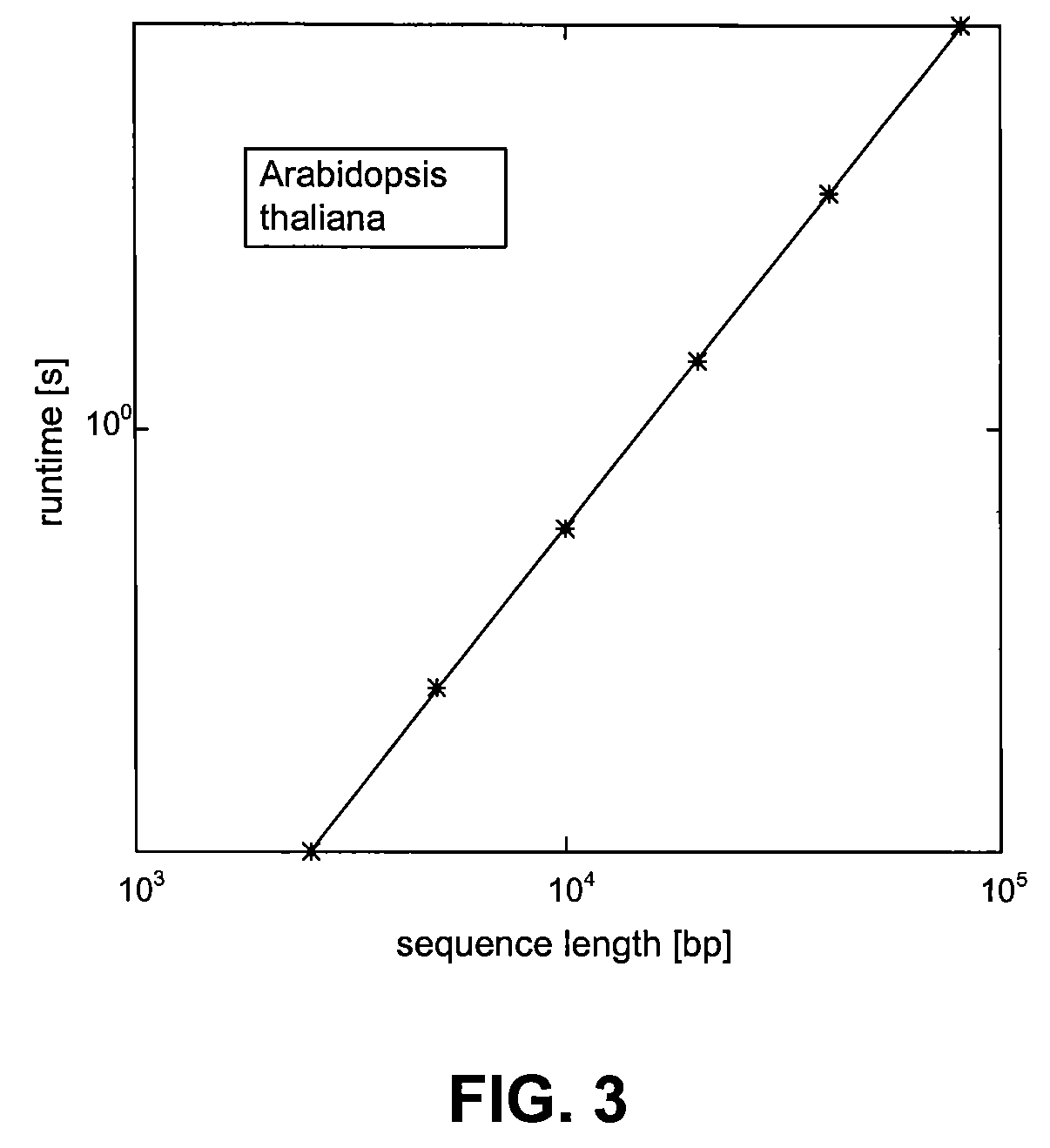
Spectrogram extraction from DNA sequence has been known since 2001. A DNA spectrogram is generated by applying Fourier transform to convert a symbolic DNA sequence consisting of letters A, T, C, G into a visual representation that highlights periodicities of co-occurrence of DNA patterns. Given a DNA sequence or whole genomes, with this method it is easy to generate a large number of spectrogram images. However, the difficult part is to elucidate where are the repetitive patterns and to associate a biological and clinical meaning to them. The present disclosure provides systems and methods that facilitate the location and / or identification of repetitive DNA patterns, such as CpG islands, Alu repeats, tandem repeats and various types of satellite repeats. These repetitive elements can be found within a chromosome, within a genome or across genomes of various species. The disclosed systems and methods apply image processing operators to find prominent features in the vertical and horizontal direction of the DNA spectrograms. Systems and methods for fast, full scale analysis of the derived images using supervised machine learning methods are also disclosed. The disclosed systems and methods for detecting and / or classifying repetitive DNA patterns include: (a) comparative histogram method, (b) feature selection and classification using support vector machines and genetic algorithms, and (c) generation of spectrovideo from a plurality of spectral images.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Rolling circle amplification of RNA
InactiveUS20060188893A1Optimization orderIncrease productionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDouble strandTandem repeat
Owner:KUMAR GYANENDRA +1
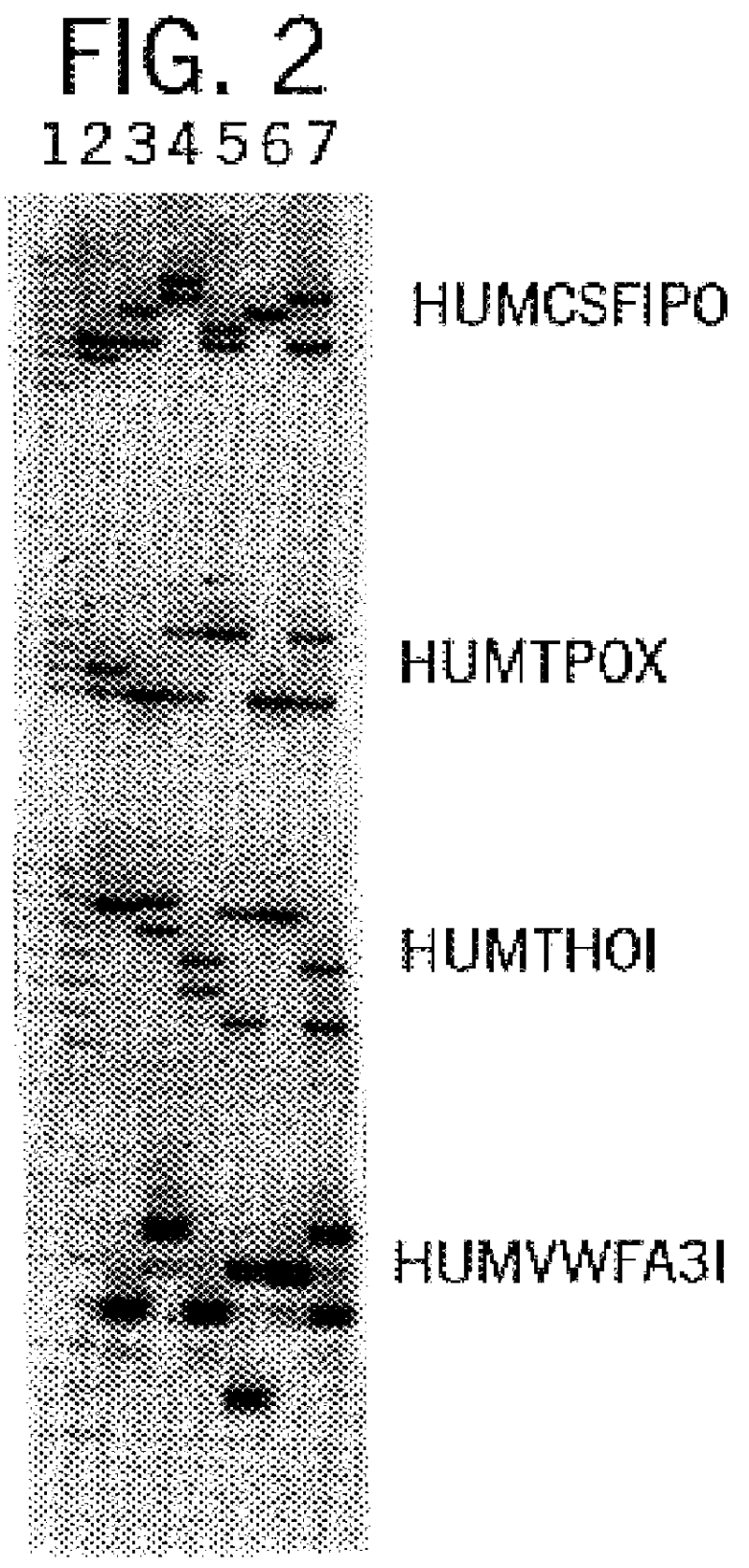
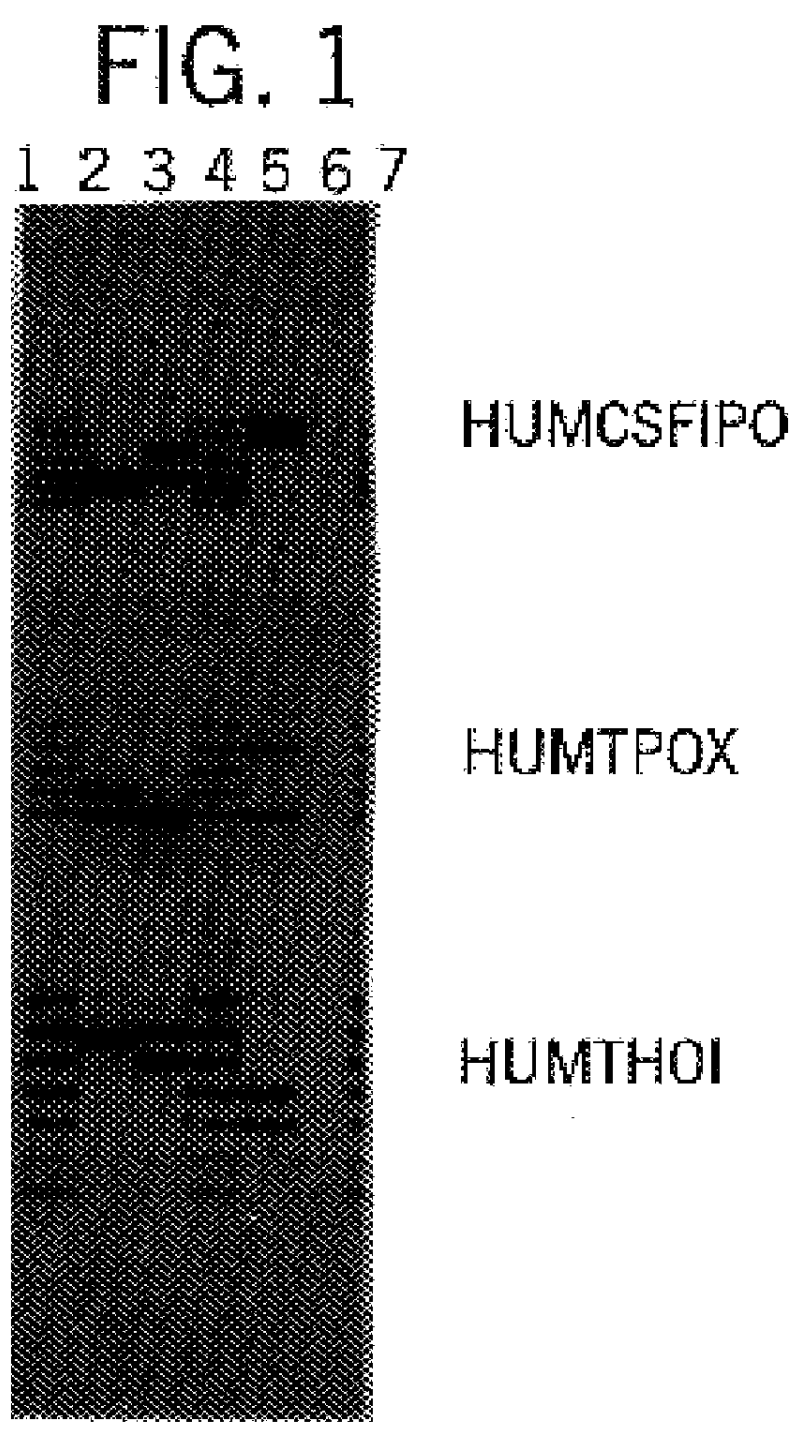
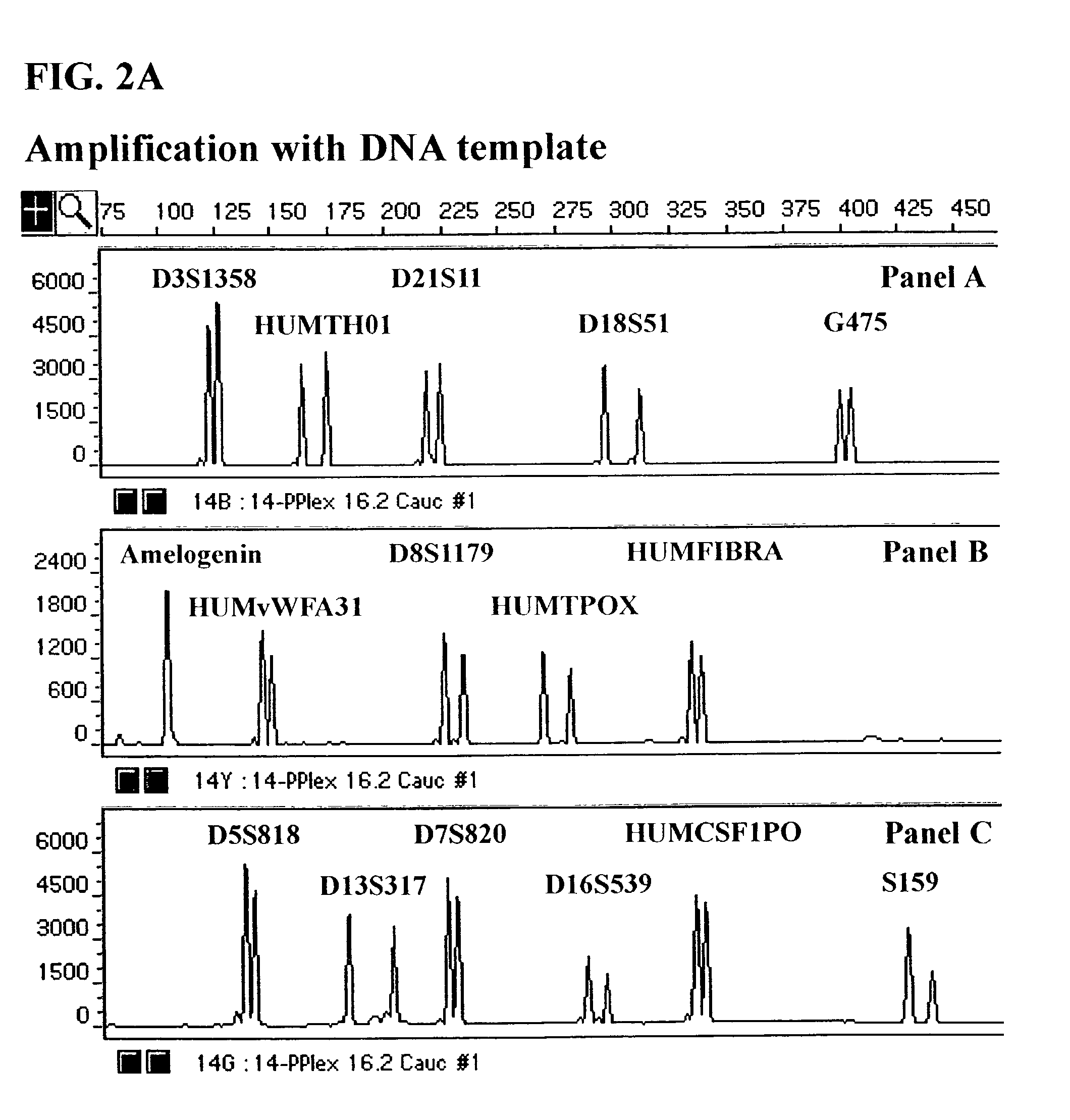
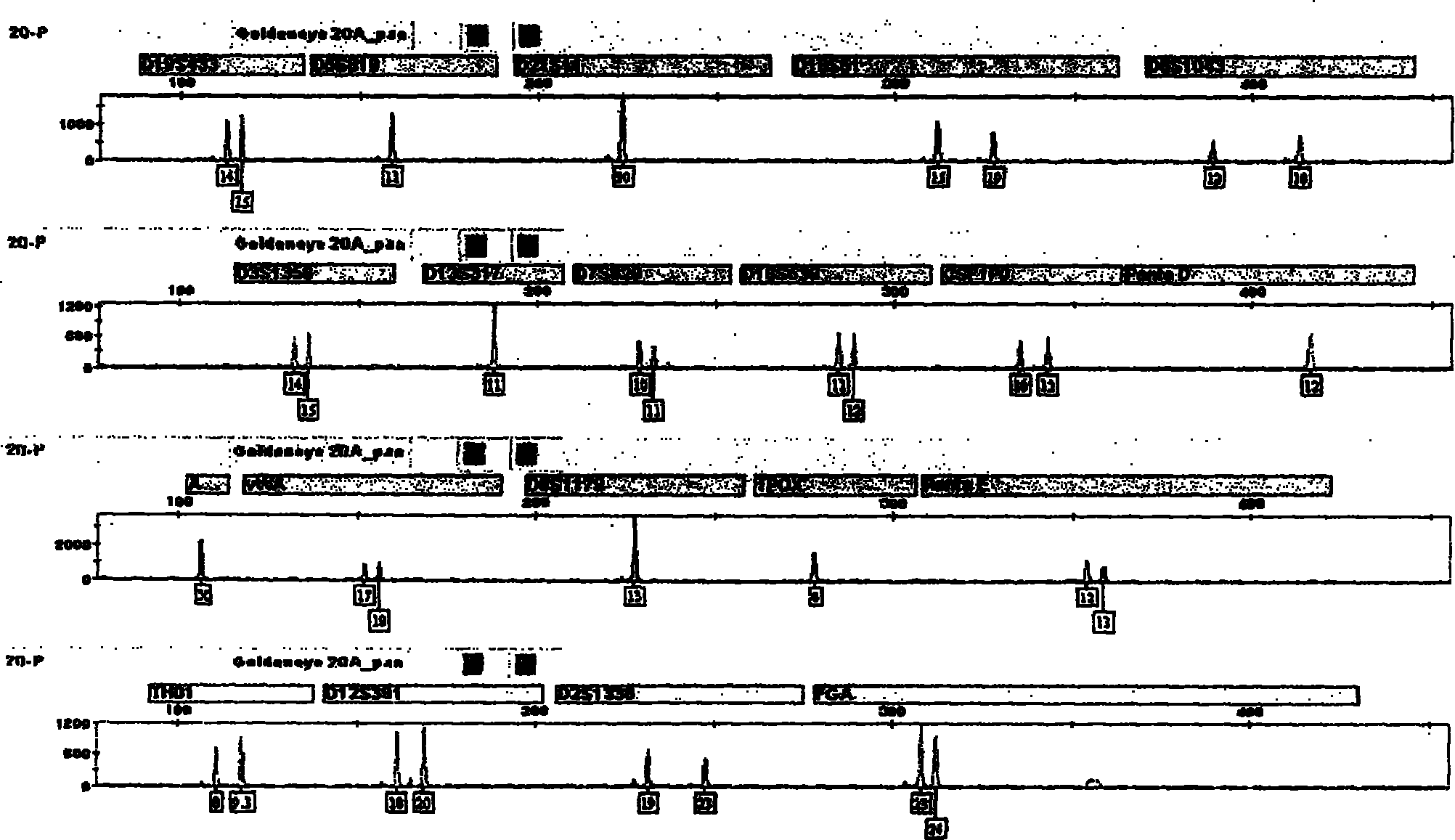
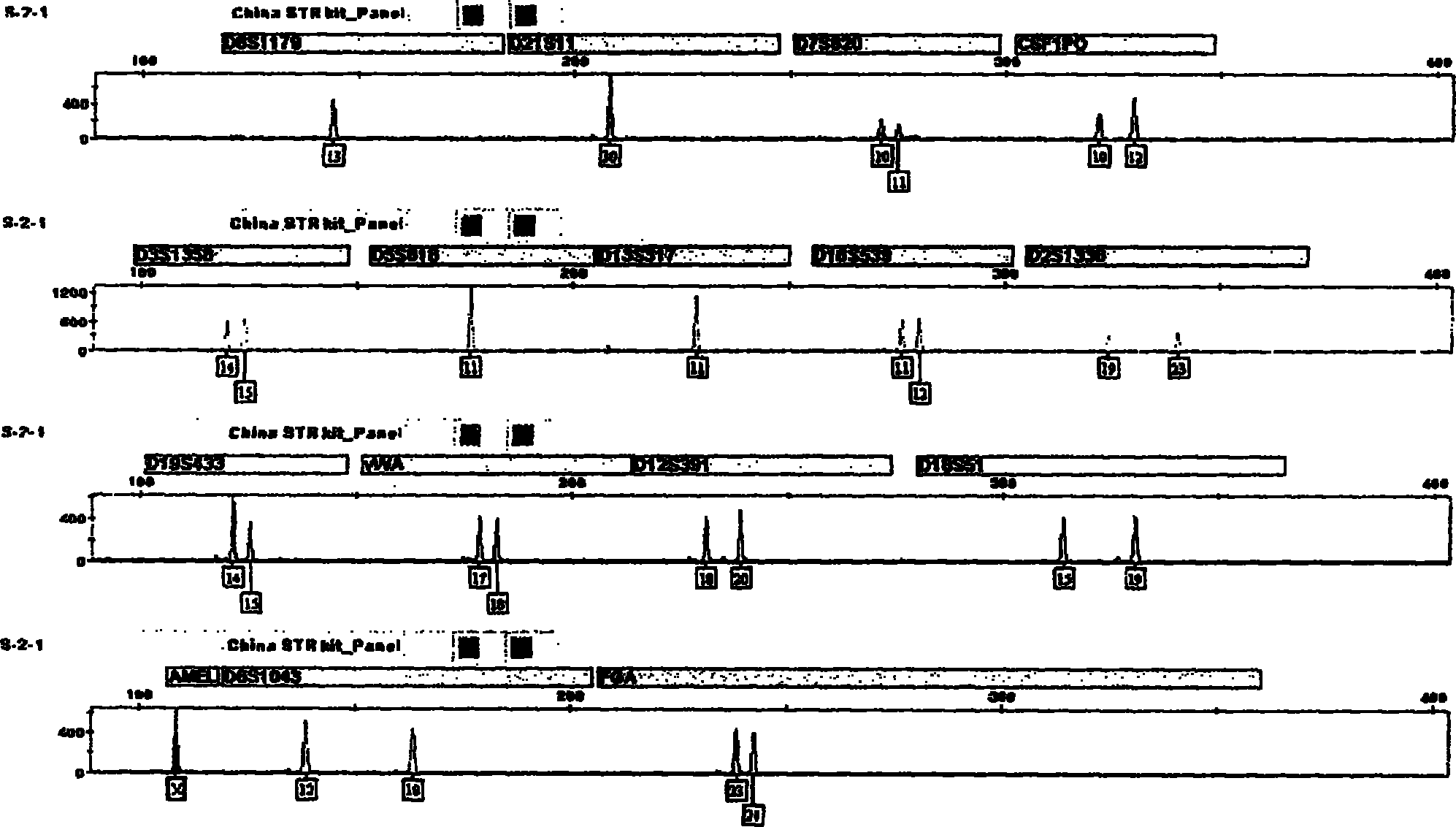
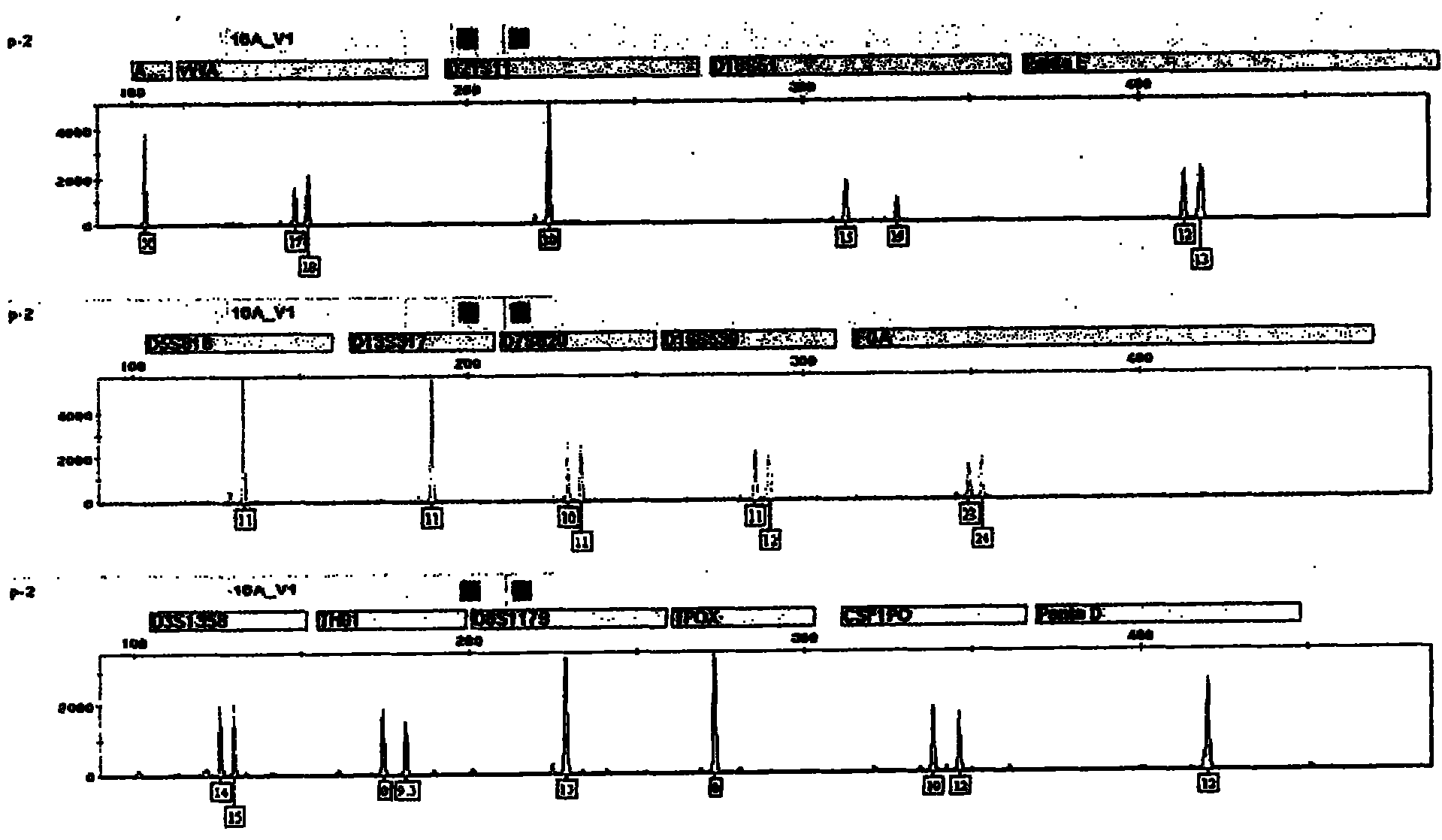
Compound amplification kit of 20 short tandem repeats
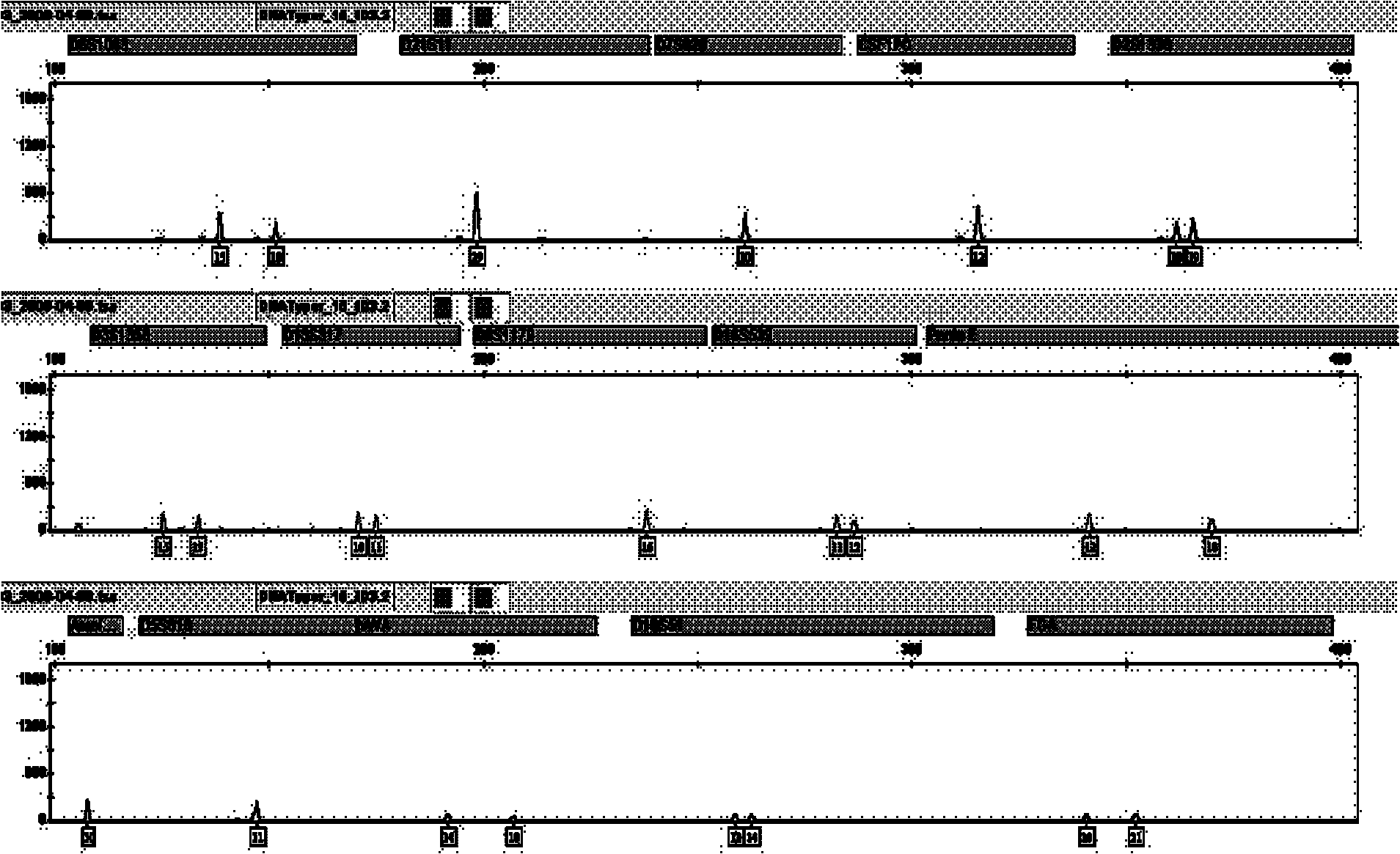
The invention relates to a compound amplification system for simultaneously analyzing a plurality of STR (short tandem repeat) loca, which is characterized by being used for carrying out compound amplification on 20 locas: Amelogenin, vWA, D21S11, D18S51, D5S818, D7S820, D13S317, D16S539, FGA, D2S1338, D19S433, D6S1043, D12S391, D8S1179, D3S1358, CSF1PO, Penta D, Penta E, TH01 and TPOX. The invention also relates to a method and a kit for simultaneously analyzing DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) samples and other applications of the loca.
Owner:BEIJING PEOPLESPOT TECH +1
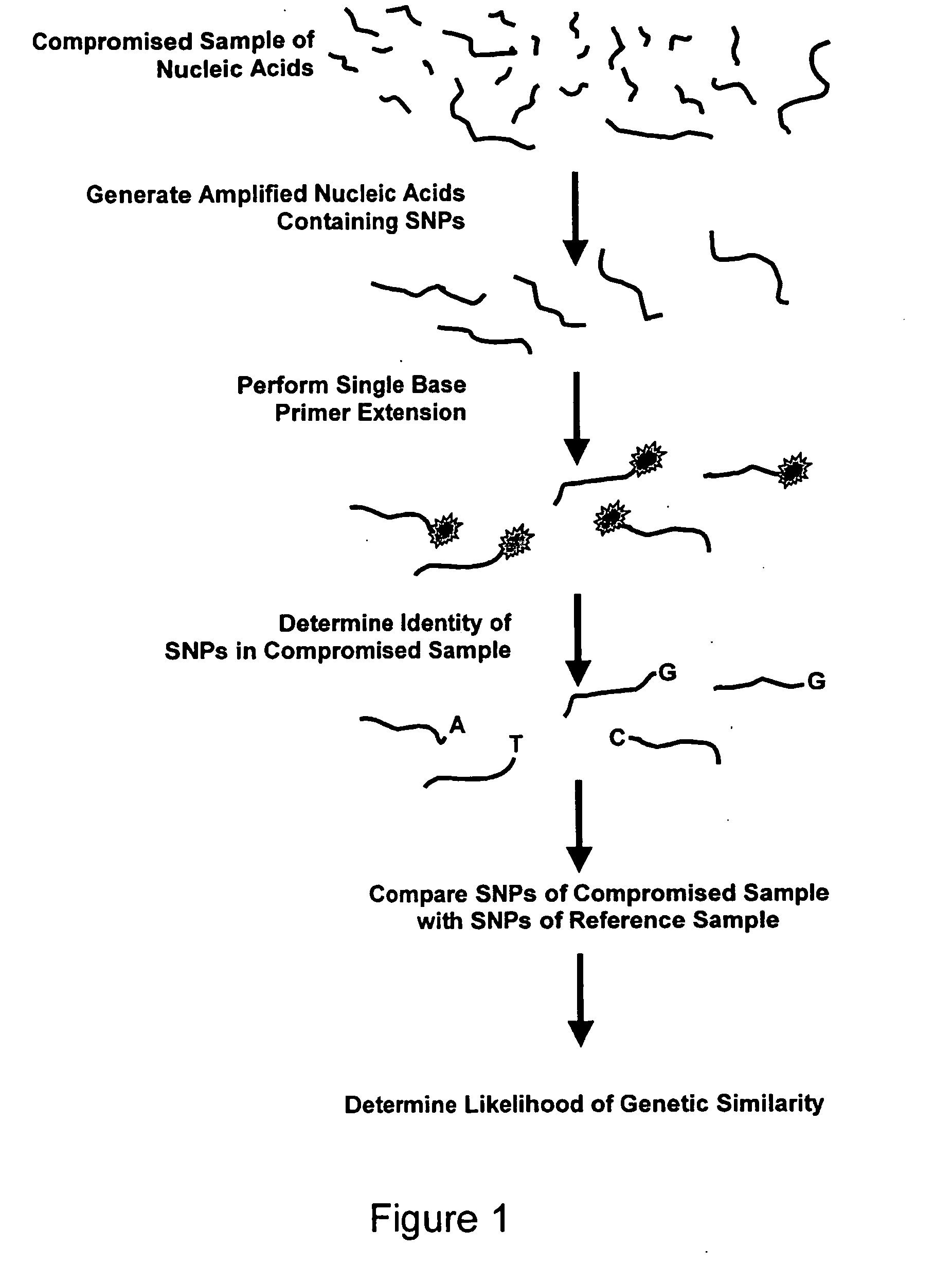
Methods and compositions for analyzing comprised sample using single nucleotide polymorphism panels
InactiveUS20060094010A1Used to determineMicrobiological testing/measurementTandem repeatNucleic acid
The present invention provides methods and compositions for analyzing compromised nucleic acid samples. The present invention also includes methods of selecting panels and panels of single nucleotide polymorphisms that are selected so as to be outside of tandem repeat regions, and are not genetically linked.
Owner:ORCHID CELLMARK INC
Nucleic acid size detection method
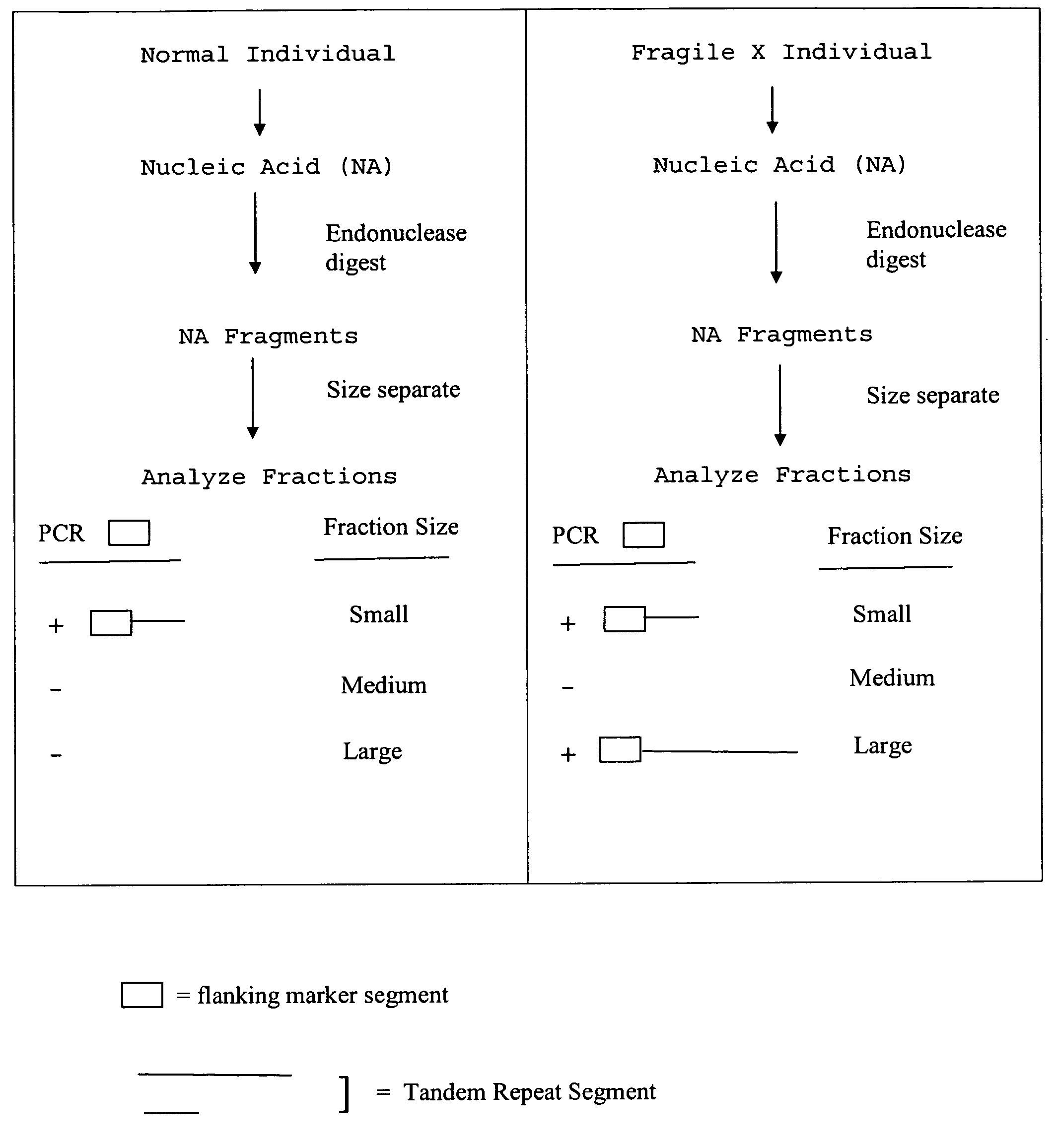
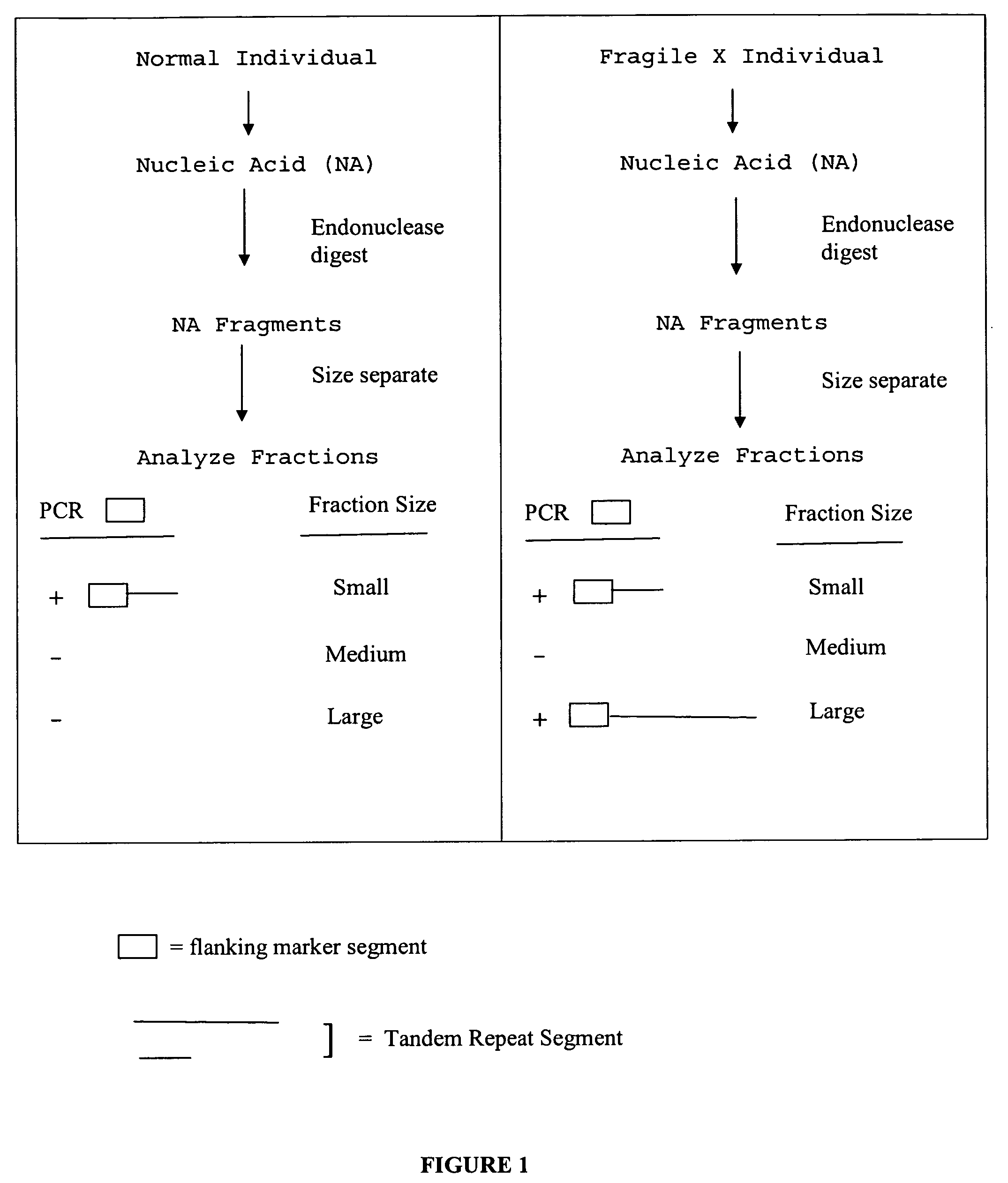
InactiveUS20080124709A1Finer of numberSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementFragile X chromosomeFractionation
The present invention provides methods of determining the size of a particular nucleic acid segment of interest in a sample of nucleic acids through fragmentation of DNA, size fractionation, an optional second fragmentation, and identification using a marker sequence. In particular aspects, an expansion or reduction of tandem repeat sequences can be detected. In further aspects, carriers and individuals afflicted with fragile X syndrome or other diseases associated with tandem repeats can be distinguished from normal individuals.
Owner:U S GENOMICS INC +1
Allelic ladders for short tandem repeat loci
Allelic ladders of short tandem repeat (STR) loci selected from the group consisting of D16S539, D7S820, D13S317, and D5S818; methods for their use in analyzing STR polymorphisms, and kits containing the allelic ladders are disclosed.
Owner:PROMEGA
Method for detecting cell proliferative disorders
InactiveUS6291163B1Fast and reliable and sensitive and non-invasive screeningHigh copy numberSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCervical tissuePolymerase L
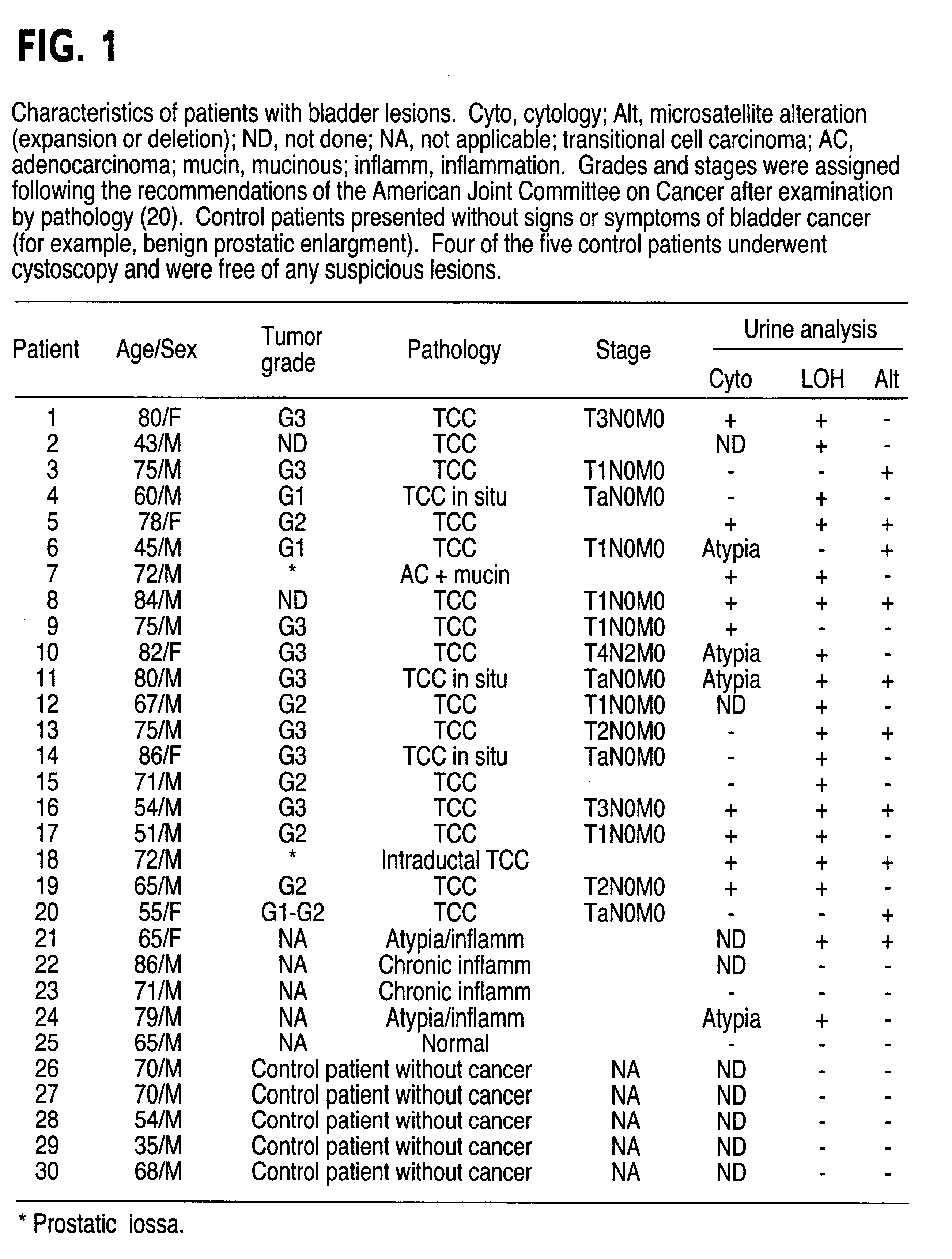
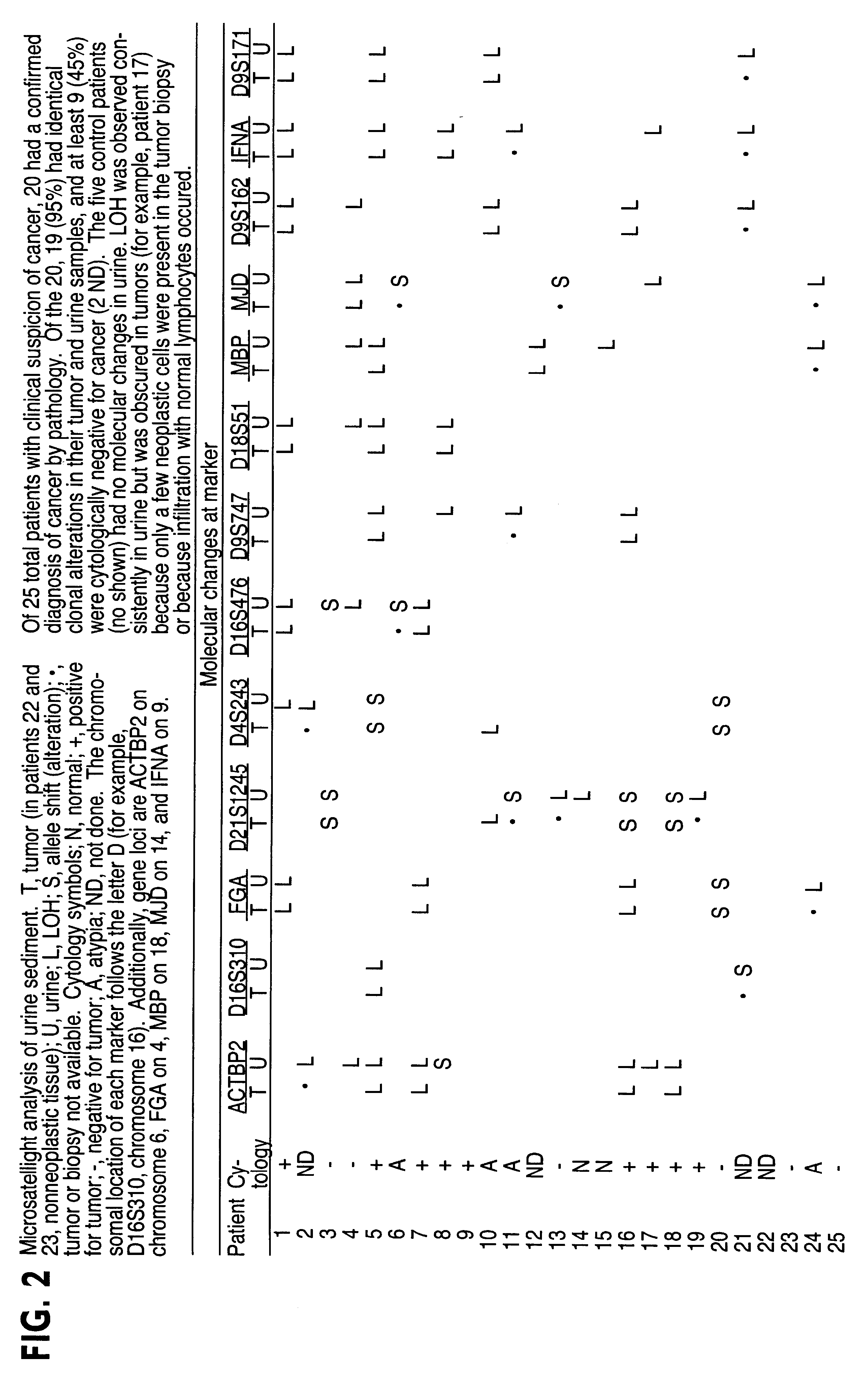
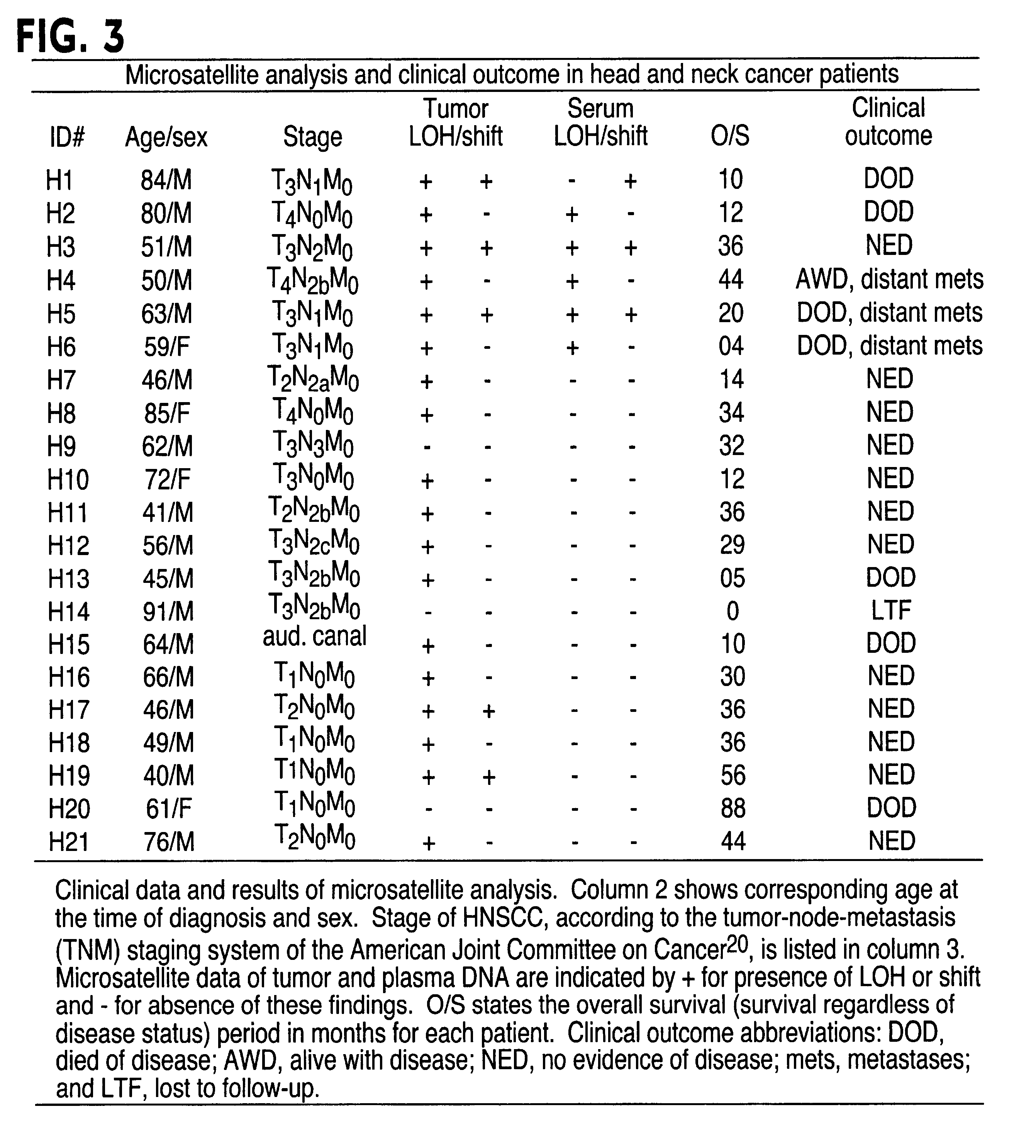
The present invention relates to the detection of a cell proliferative disorder associated with alterations of microsatellite DNA in a sample. The microsatellite DNA can be contained within any of a variety of samples, such as urine, sputum, bile, stool, cervical tissue, saliva, tears, or cerebral spinal fluid. The invention is a method to detect an allelic imbalance by assaying microsatellite DNA. Allelic imbalance is detected by observing an abnormality in an allele, such as an increase or decrease in microsatellite DNA which is at or corresponds to an allele. An increase can be detected as the appearance of a new allele. In practicing the invention, DNA amplification methods, particularly polymerase chain reactions, are useful for amplifying the DNA. DNA analysis methods can be used to detect such a decrease or increase. The invention is also a method to detect genetic instability of microsatellite DNA. Genetic instability is detected by observing an amplification or deletion of the small, tandem repeat DNA sequences in the microsatellite DNA which is at or corresponds to an allele. The invention is also a kit for practicing these methods.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method for extracting purified DNA from human exfoliative cells
InactiveCN102181434AMeet the extraction requirementsEasy to operateDNA preparationBiological cellLysis
The invention discloses a method for extracting purified DNA from human exfoliative cells. The method comprises the following steps: 1) pretreating: contacting the human exfoliative cells with pretreating lysate to remove the solid matters adhering to the biological cells to obtain coarse lysate; 2) nucleic acid adsorbing: mixing the coarse lysate obtained in the step 1) with lysis integrated liquid and magnetic bead suspension to form a solution system containing a magnetic nano microsphere-DNA compound and collecting the magnetic nano microsphere-DNA compound in the solution system; and 3) washing: washing the magnetic nano microsphere-DNA compound obtained in the step 2) with washing liquid I and washing liquid II respectively and then dissolving out the DNA with eluent. The efficiency of extracting DNA by the method can reach 90% and the extracted DNA can be applied to such downstream analysis operations as STR (short tandem repeat) multiplex amplification, DNA sequencing, DNA quantifying and the like.
Owner:INST OF FORENSIC SCI OF MIN OF PUBLIC SECURITY
Quaternionic algebra approach to DNA and RNA tandem repeat detection
InactiveUS20090164135A1High error rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsQuaternionNucleotide
A method of detecting and outputting tandem repeats in a sequence of symbols comprising a) mapping the symbols to quaternions; b) constructing a Quaternionic Periodicity Transform (QPT); c) computing the QPT of the sequence to determine the tandem repeats of the sequence; d) post-processing of the QPT; e) outputting a list of tandem repeats obtained from step d) to a computer's memory. In embodiments, the sequence of symbols is a sequence of letters representing nucleotides in a DNA or RNA sequence.
Owner:MITRE SPORTS INT LTD
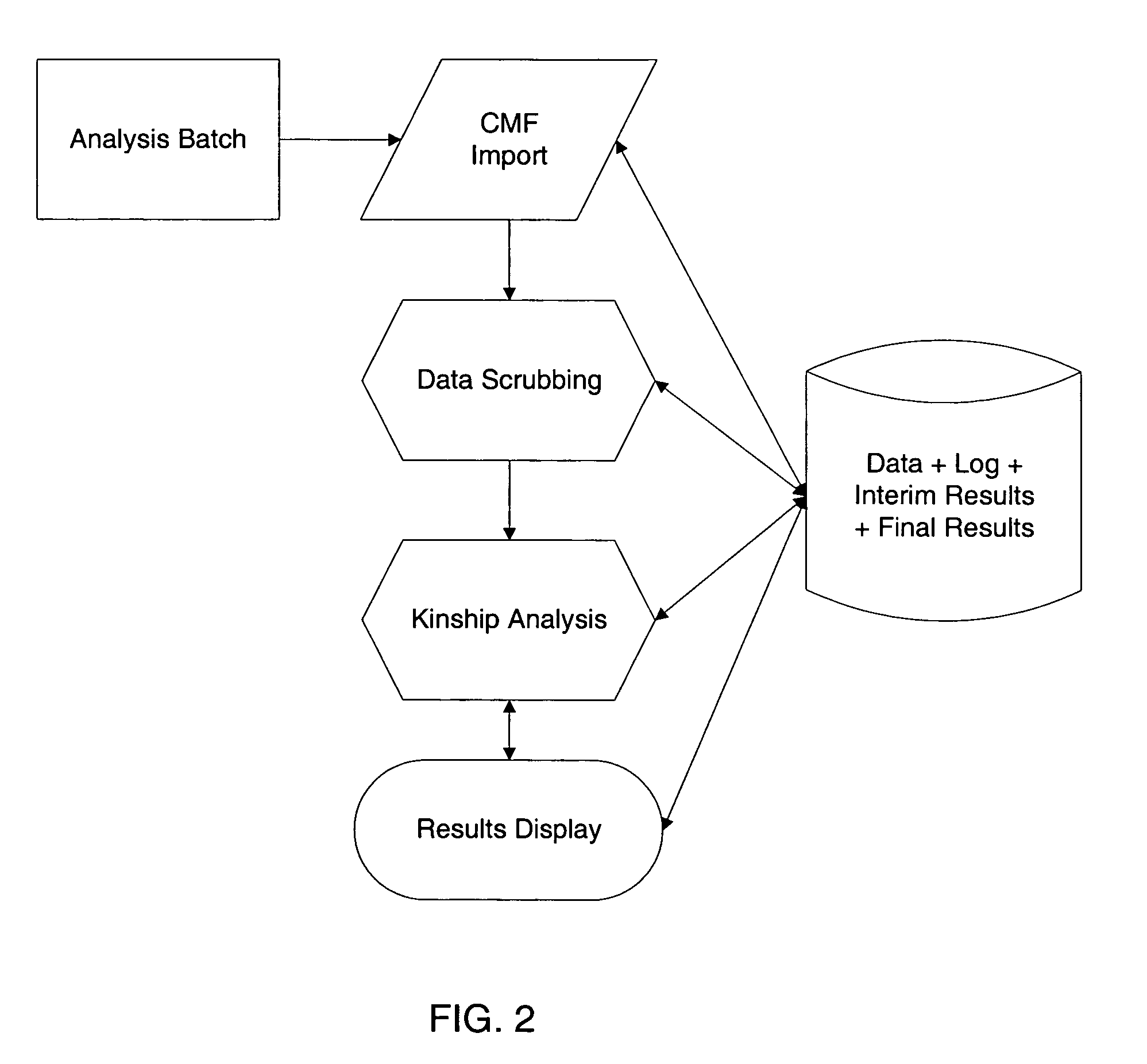
Kinship analysis program for missing persons and mass disaster
InactiveUS20050176031A1Easy to useProtect dataMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsData setMendelian inheritance
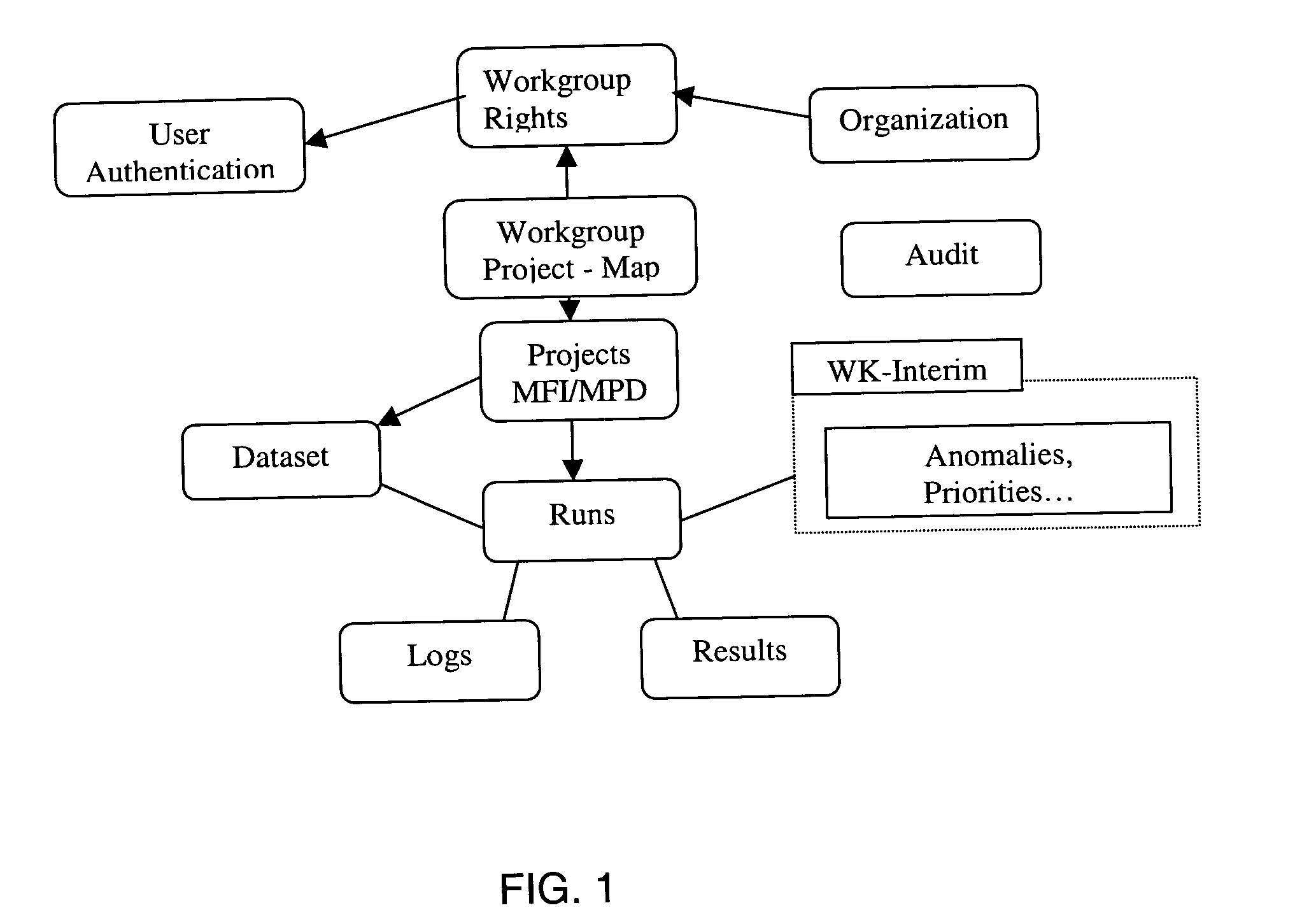
A kinship analysis program for missing persons and mass disasters for kinship and missing persons analyses. The inventive device includes consensusG, Kinship Indices, Matching, cross-checking, pedigree that performs the following: Extract a list of unique victims' genotypes from the remains or missing persons database, make perfect matches to personal effect, identify next-of-kin related to a victim, make matches through parentage trios, confirm consistency of family pedigrees, exclude nearly all fortuitous hits on the basis of the SM scoring performance of the entire family of the relative that triggered the fortuitous hit, make matches despite the known existence of errors in sample names and reported relationships, flag samples with inconsistent reported relationships, display matches in their context, so that “close-calls” are brought to the attention of the data reviewer. An algorithm which reduces very large collections of complete / partial STR (Short Tandem Repeats) genotypes derived from the remains down to a restricted number of consensus genotypes believed to reflect the many different victims. An algorithm which calculates Kinship Indices through a segregated score approach and likelihood ratio calculations through a linkage to the KinTest software. An algorithm which contrasts the consensus genotypes against the data set of genotypes from next-of-kin and personal effects for direct matches to personal effects, for evidence of genetic relatedness to kin through the Kinship Indices, or for successful production of a parentage trio with any two members of the next-of-kin cohort. An algorithm which cross-checks matches to parentage trios against other kinship scoring results between the victim and other members of the same family to confirm that the purported family structure is consistent with Mendelian inheritance rules. A schematic diagram describing the relationship of the relatives to a matched victim. A user interface that is accessible to a broader range of users.
Owner:SEARS CHRISTOPHER P +1
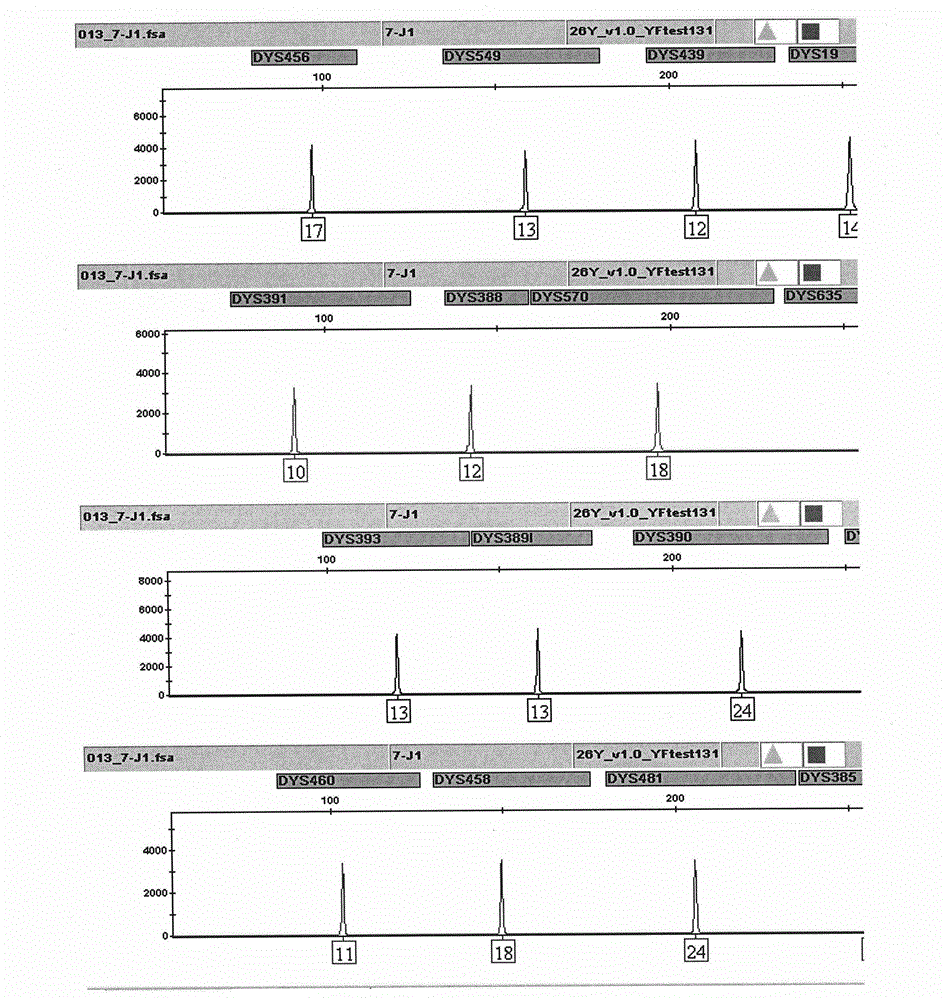
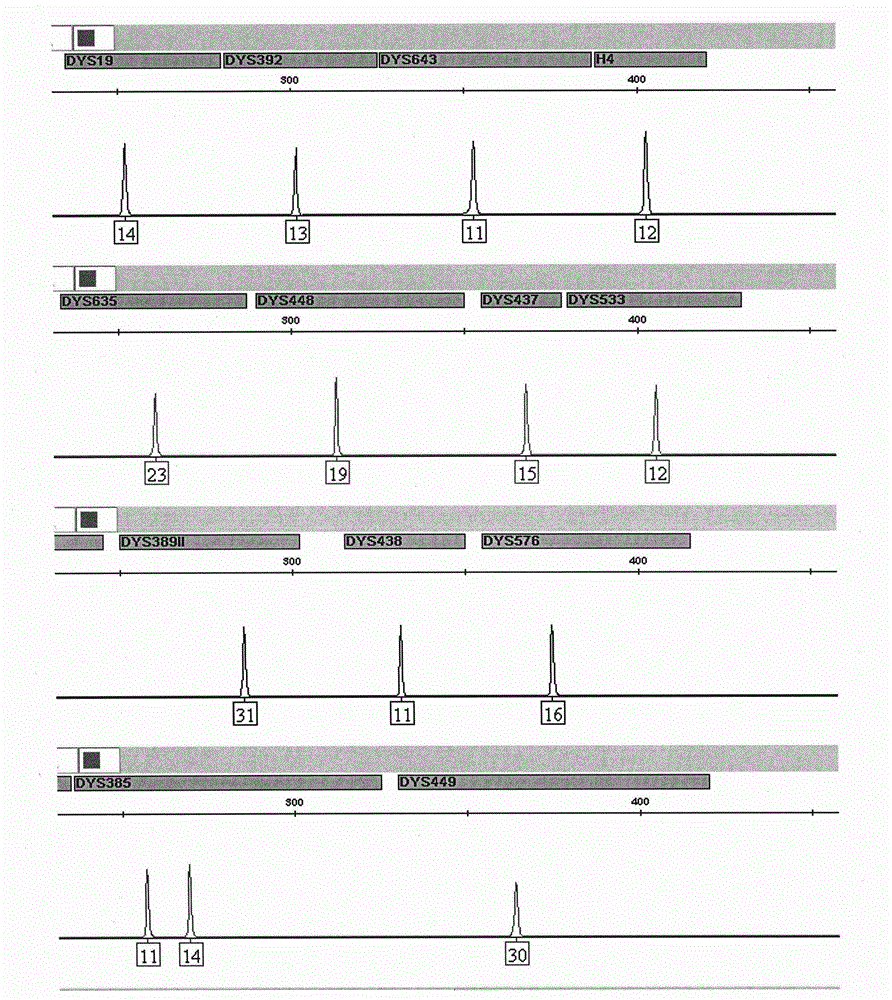
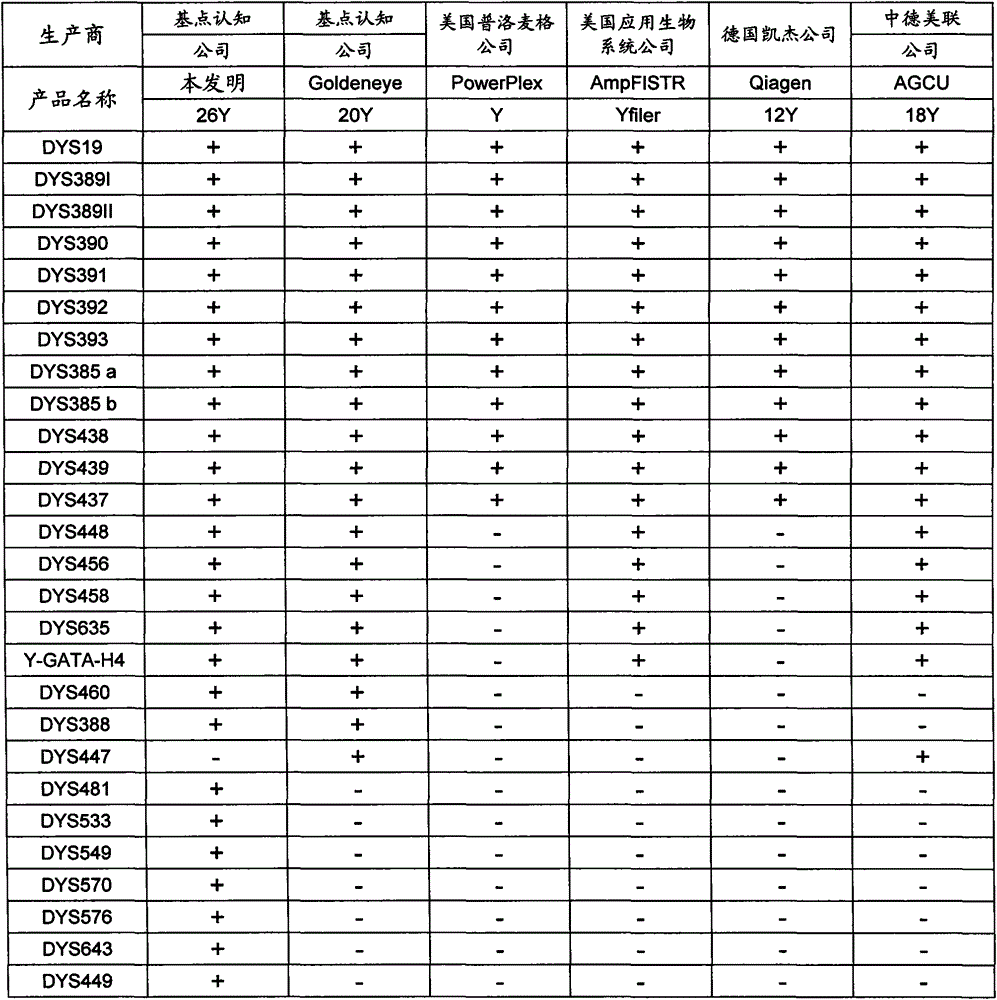
Composite amplification kit for 26 Y chromosome short tandem repeats
ActiveCN104017895AHigh individual recognition rateImprove compatibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAnalysis dnaTandem repeat
The invention relates to a composite amplification system for simultaneously analyzing multiple Y-STR loci. The composite amplification kit is characterized by compositely amplifying the following 26 Y chromosome loci: DYS19, DYS388, DYS389I, DYS389II, DYS390, DYS391, DYS392, DYS393, DYS385a, DYS385b, DYS437, DYS438, DYS439, DYS448, DYS456, DYS458, DYS635, DYS460, DYS481, DYS533, DYS549, DYS570, DYS576, DYS643, DYS449 and Y-GATA-H4. The invention also relates to a method and a kit for simultaneously analyzing DNA samples, and applications thereof.
Owner:BEIJING PEOPLESPOT TECH
Nucleic acid encoding receptor type protein kinase
InactiveUS6846630B2Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
To provide a nucleic acid encoding a receptor protein kinase, wherein the nucleic acid has tandem duplication in a nucleotide sequence of a juxtamembrane and is useful for diagnosis of leukemia; a polypeptide encoded by the nucleic acid; an antibody capable of specifically binding to a region encoded by the nucleic acid having tandem duplication occurring in a nucleotide sequence of a juxtamembrane; a nucleic acid capable of specifically binding to the nucleic acid having tandem duplication occurring in a nucleotide sequence of a juxtamembrane; a method for detection of the nucleic acid encoding a receptor protein kinase; and a kit therefor. A nucleic acid encoding a receptor protein kinase, wherein the nucleic acid has tandem duplication in a nucleotide sequence of a juxtamembrane; a polypeptide encoded by the nucleic acid; an antibody capable of specifically binding to the portion of the polypeptide; a nucleic acid capable of specifically binding to the nucleic acid; a method for detection of the nucleic acid; and a kit for detection.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
Methods and compositions for DNA profiling
Embodiments disclosed herein provide methods for constructing a DNA profile comprising: providing a nucleic acid sample, amplifying the nucleic acid sample with a plurality of primers that specifically hybridize to at least one target sequence comprising a SNP and at least one target sequence comprising a tandem repeat, and determining the genotypes of the at least one SNP and at least one tandem repeat in the amplification products, thereby constructing the DNA profile of the nucleic acid sample. Embodiments disclosed herein further provide a plurality of primers that specifically hybridize to at least one short target sequence and at least one long target sequence in a nucleic acid sample, wherein amplifying the nucleic acid sample using the plurality of primers in a single reaction results in a short amplification product and a long amplification product, wherein each of the plurality of primers comprises one or more tag sequences.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Application of high-pass DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequencing method on determination of short tandem repeat gene locus in human genome and method
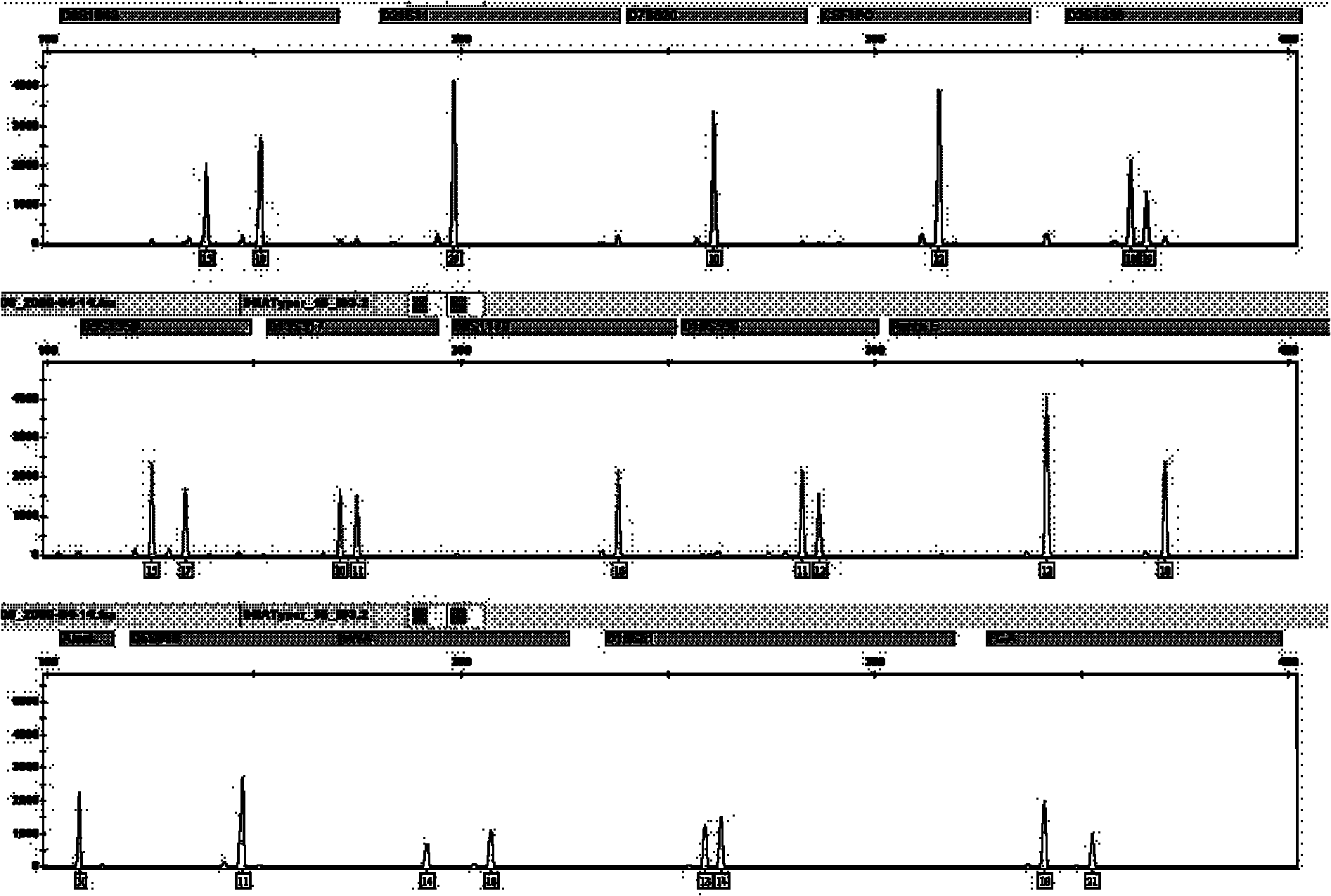
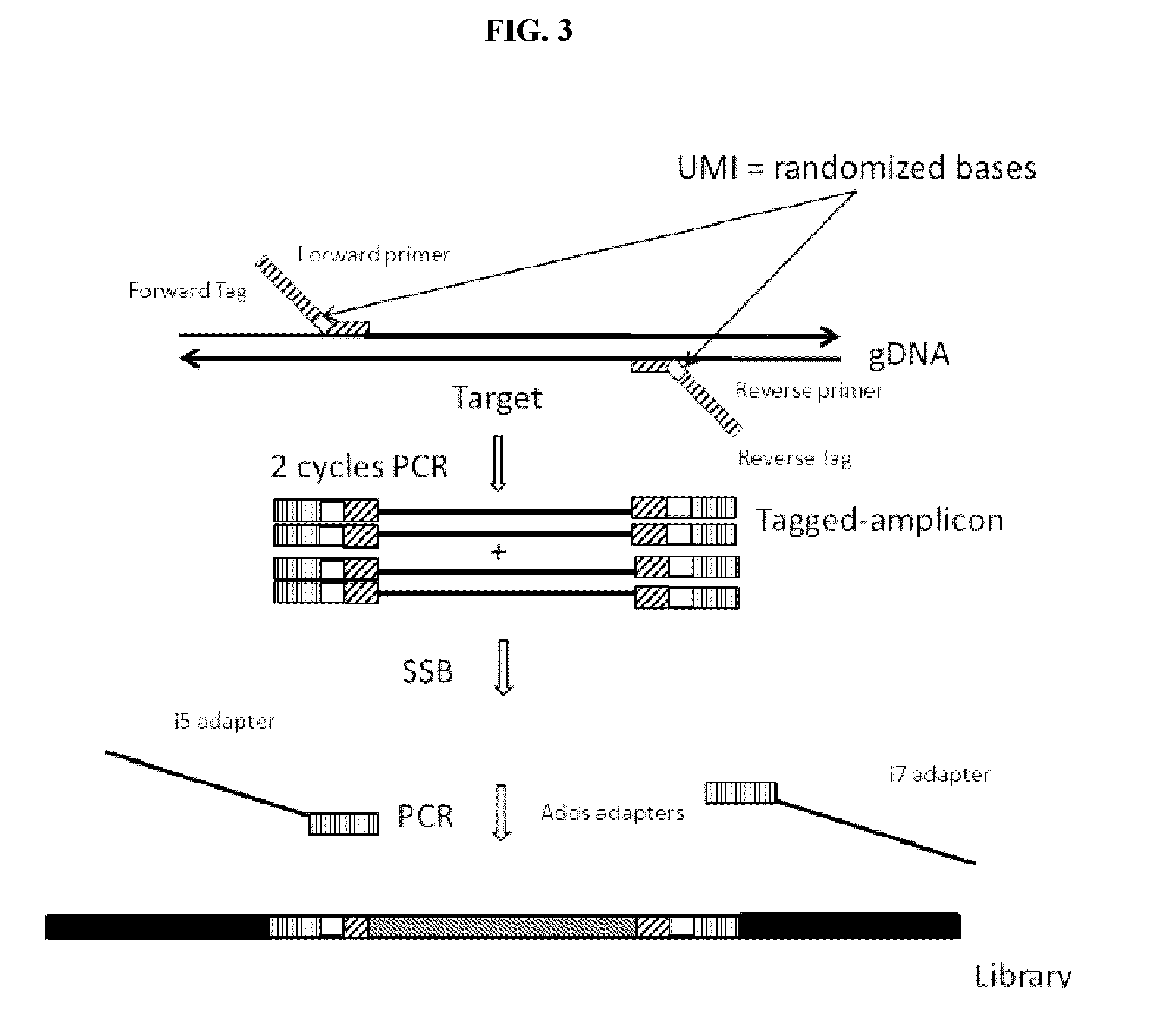
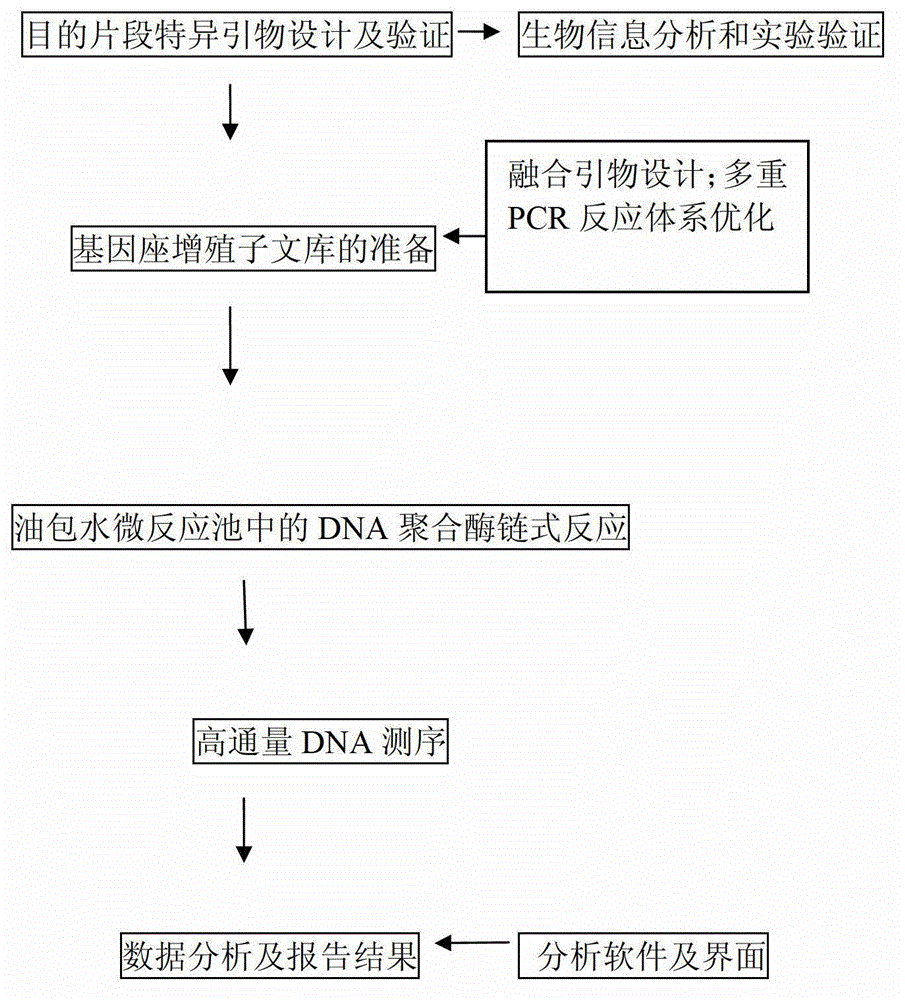
ActiveCN102943111AAccurate measurementSimultaneous sequencingMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman genomeTandem repeat
The invention discloses application of a high-pass DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequencing method on determination of a short tandem repeat gene locus in human genome and a method, belonging to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a multi-sample gene locus proliferation sublibrary; sequencing high-pass DNA; and analyzing data and reporting the result. According to the application and the method disclosed by the invention, the high-pass DNA sequencing technology is applied to determination of the human short tandem repeat (STR) gene locus for the first time and the resolving power and the sensitivity of the STR locus as individual human recognition are remarkably improved; and meanwhile, the detection pass of the STR is greatly improved.
Owner:IPE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Collagen-binding proteins from Enterococcal bacteria
InactiveUS20050180986A1Inhibit bindingBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaCell-Extracellular MatrixBinding site
A collagen-binding MSCRAMM entitled Ace from enterococcal bacteria is provided which was homologous to the ligand-binding region of Cna, the collagen-binding MSCRAMM from Staphylococcus aureus, and which can be utilized to inhibit adhesion of enterococcal bacteria to extracellular matrix proteins. The N-terminal region of Ace contained a region (residues 174-319), or A domain, contains several 47-residue tandem repeat units between the collagen-binding site and cell wall-associated regions. The Ace protein can be utilized in methods of preventing and / or treating enterococcal infection, and in addition, antibodies raised against Ace, or its A domain, can be used to effectively inhibit the adhesion of enterococcal cells to a collagen substrate.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY +1
Composite amplification system of 23 short tandem repeat sequences and a kit
ActiveCN103834732AImprove performanceIncrease independenceMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyDNA paternity testing
The invention relates to a composite amplification system of 23 short tandem repeat sequences and a kit, is used for detecting heredity mark gene of polymorphism in a mankind genome, and belongs to the biology technical field. The invention relates to a scheme that a plurality of short tandem repeat sequences are simultaneously amplified in a PCR system; a specific gene locus comprises 22 short tandem repeat sequences with high level heredity polymorphism and 1 gender determination locus; primers are respectively designed and a fluorophore is marked; the system has very high individual recognition rate and non-father elimination rate; the system and kit can be used for legal medical individual recognition, paternity tests, and colony genetics analysis, is high in accuracy, and good in sensitivity.
Owner:SUZHOU MICROREAD GENETICS
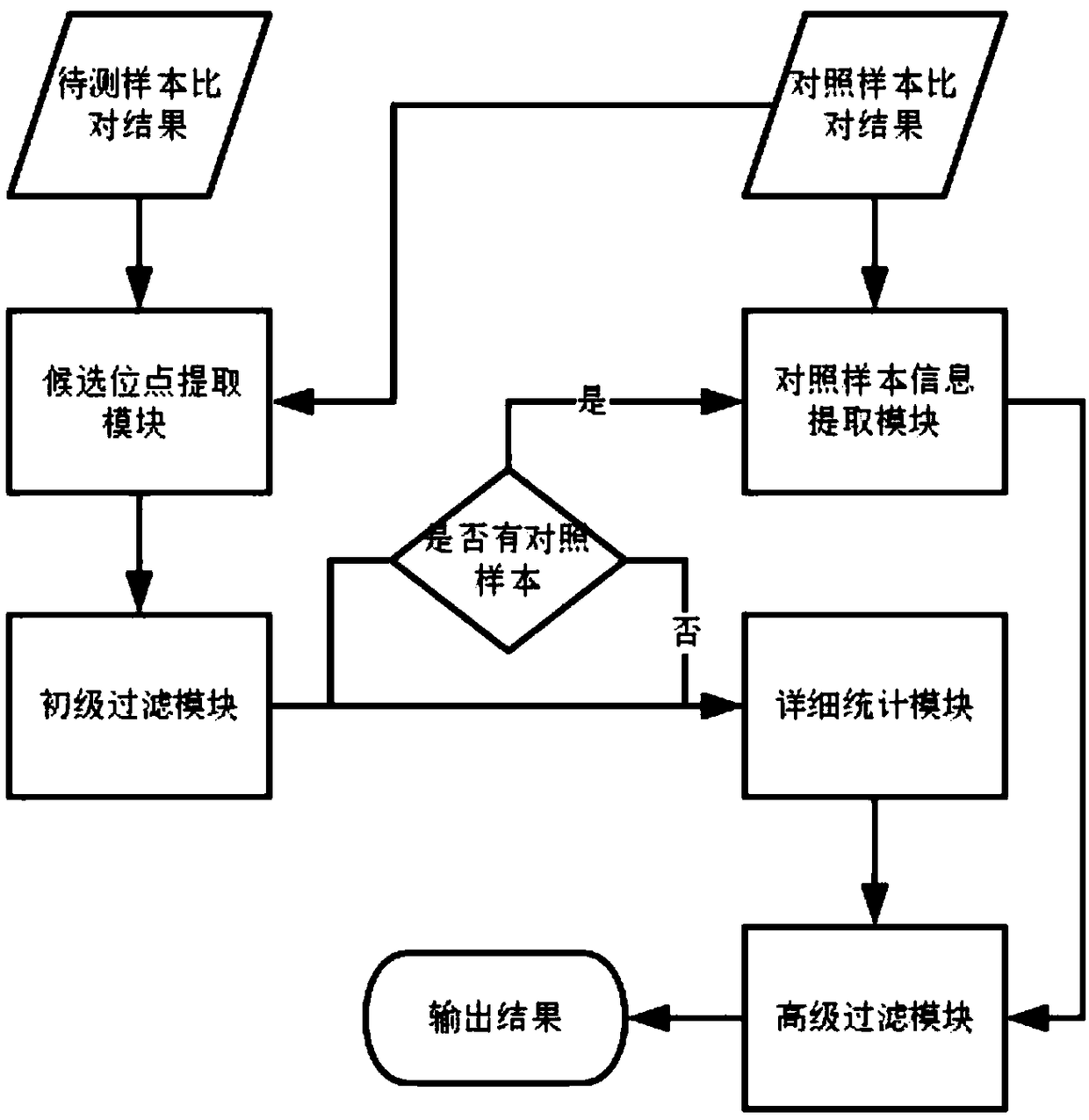
Method for detection of insertion deletion mutation based on second generation sequencing, device and storage medium
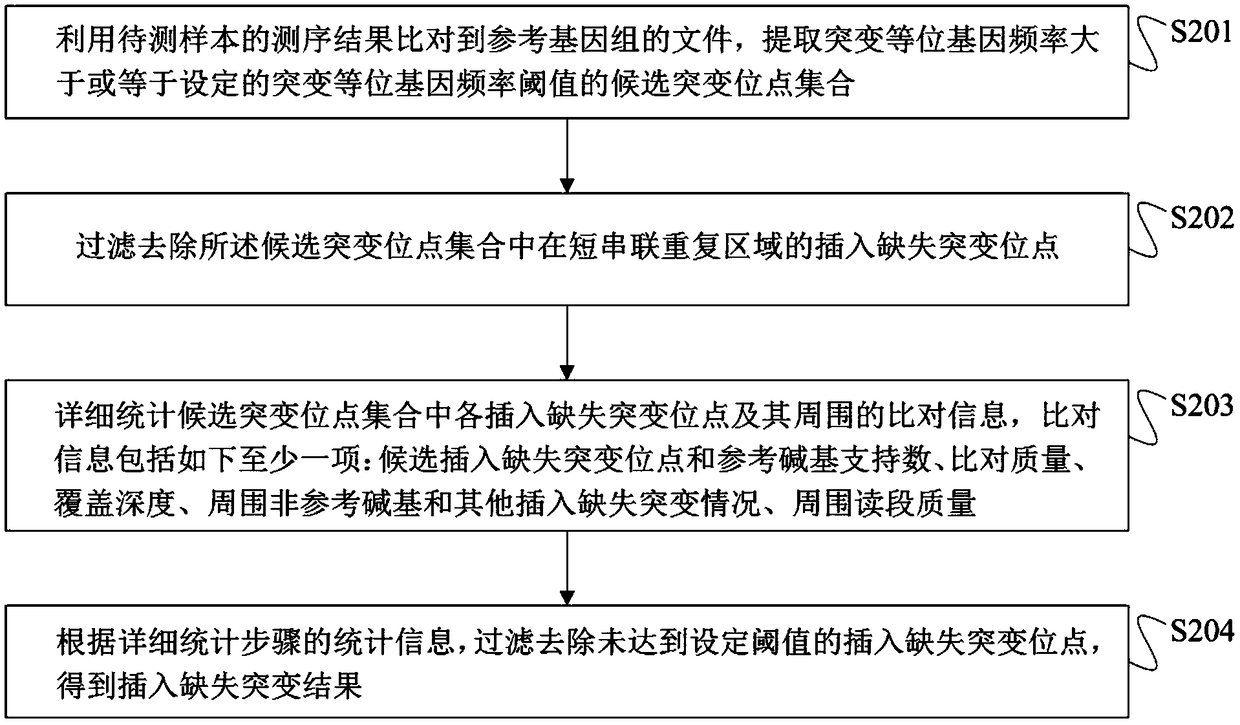
ActiveCN108690871AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsInsertion deletionAllele frequency
The present application discloses a method for detection of insertion deletion mutation based on second generation sequencing, a device and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps:comparing a sample to be tested with a file of a reference genome to extract a set of candidate mutation sites with mutation allele frequency being greater than or equal to a threshold; filtering to remove sites in a short tandem repeat region; making detail statistics of comparison information of the mutation sites and comparison information surrounding the mutation sites, wherein the comparisoninformation includes InDel site and reference base support number, comparison quality, coverage depth, surrounding non-reference base and other insertion deletion mutations, surrounding read quality;and filtering to remove sites that do not reach the set threshold according to statistical information to obtain mutation results. The method does not require partial assembly, and filters second-generation sequencing data in advance to quickly eliminate most of false positive results caused by the comparison, reduces detection running time and computing resources, improves detection efficiency, has strong sensitivity and specificity, and can quickly and accurately detect InDel mutations.
Owner:深圳裕策生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com