Patents
Literature
120 results about "Cervical tissue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
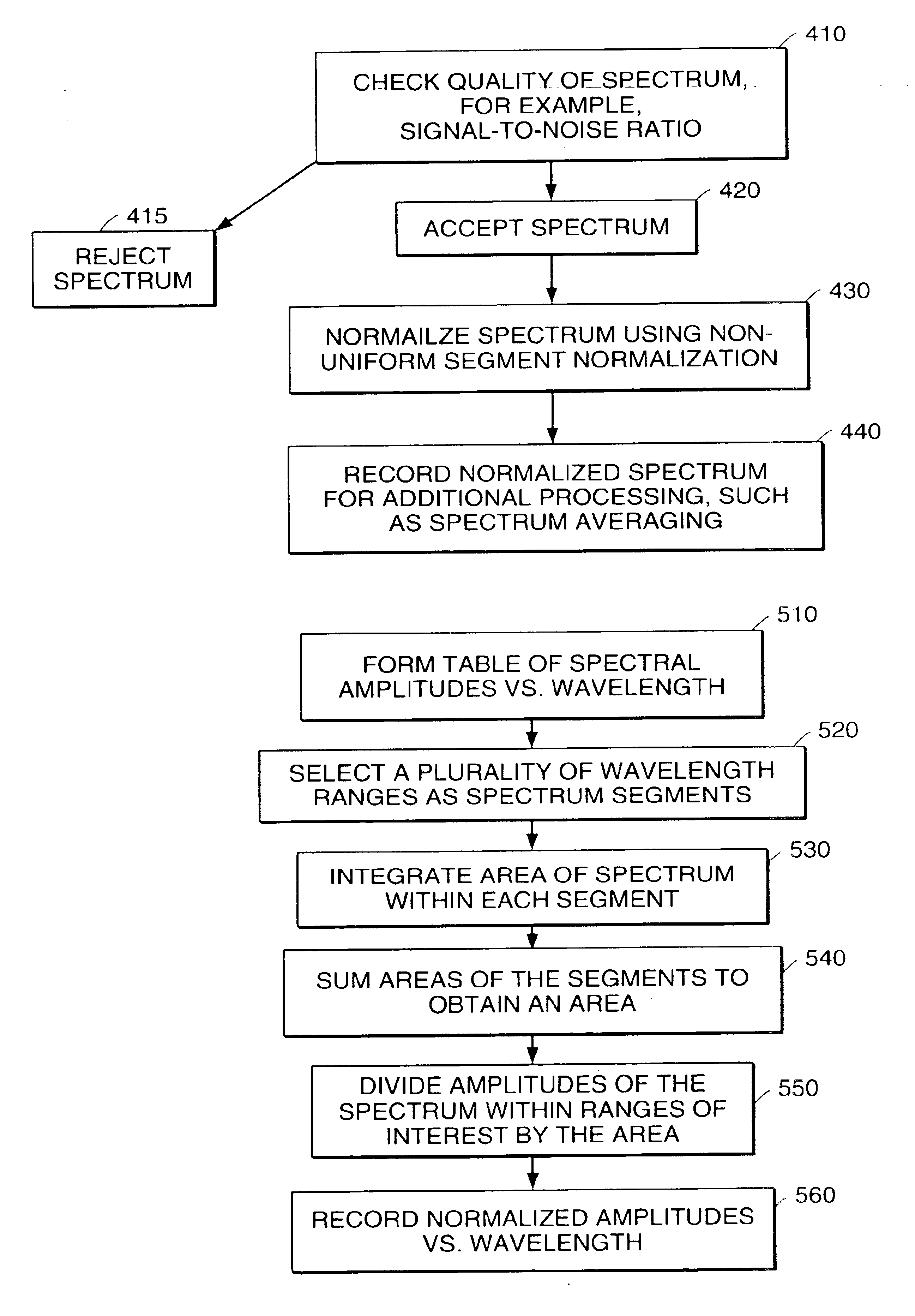
Spectral data classification of samples
A system and method for classifying tissue by application of discriminant analysis to spectral data. Spectra are recorded as amplitudes at a series of discrete wavelengths. Pluralities of reference spectra are recorded for specimens having known conditions. The reference spectra are subjected to discriminant analysis to determine wavelength regions of interest for the analysis. A plurality of amplitudes are selected for the analysis, and are plotted in an N-dimensional space. For each plurality of reference spectra corresponding to a specific known condition, a characteristic point is determined and plotted, the characteristic point representative of the known condition. A test spectrum is recorded from a test specimen, and the plurality of amplitudes corresponding in wavelength to the wavelength regions of interest are selected. A characteristic point in N-dimensional space is determined for the test spectrum. The distance of the characteristic point of the test spectrum from each of the plurality of characteristic points representative of known conditions is determined. The test specimen is assigned the condition corresponding to the characteristic point of a plurality of reference spectra, based on a distance relationship with at least two distances, provided that at least one distance is less than a pre-determined maximum distance. In some embodiments, the test specimen can comprise human cervical tissue, and the known conditions can include normal health, metaplasia, CIN I and CIN II / III.
Owner:LUMA IMAGING CORP
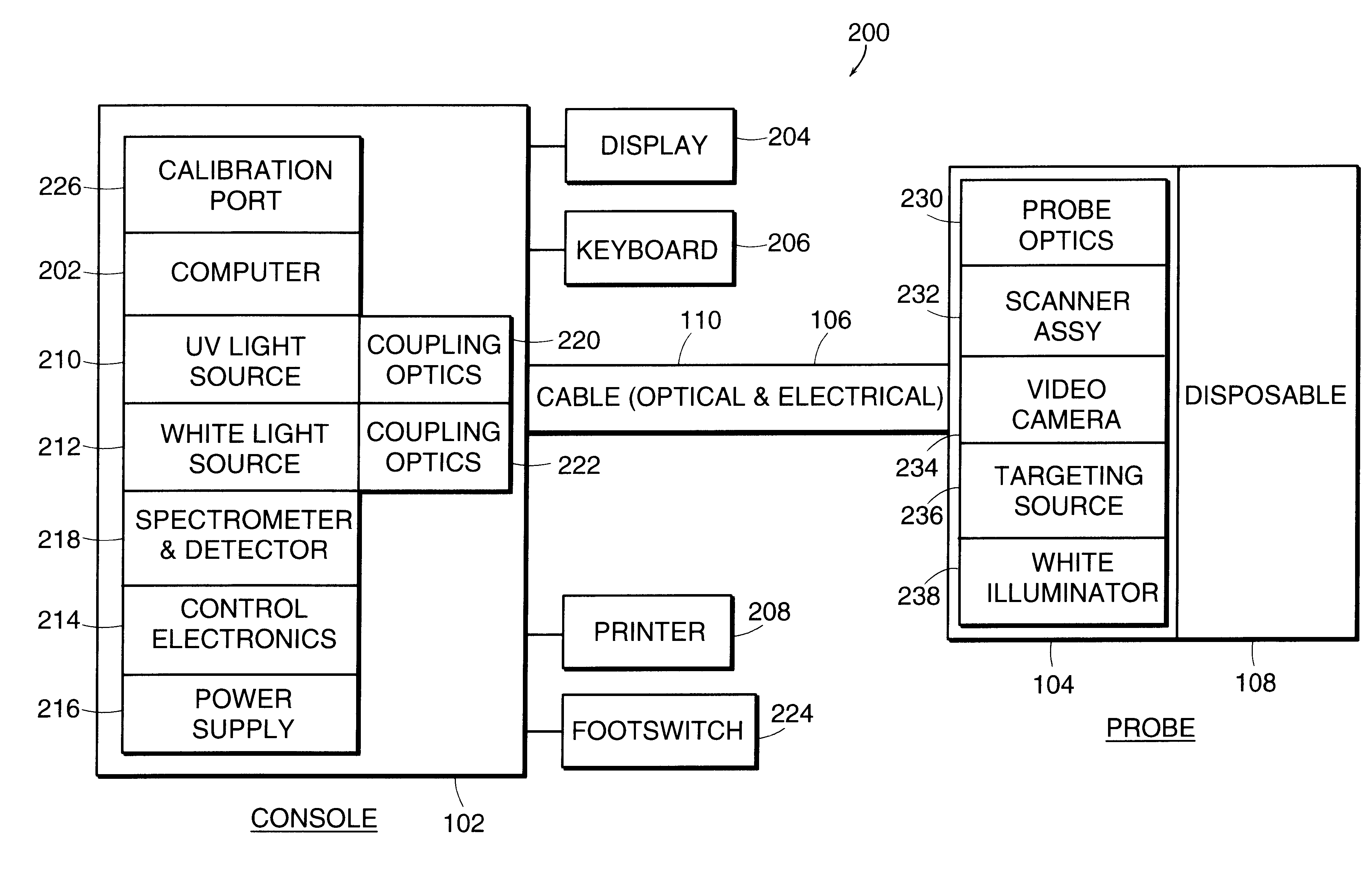
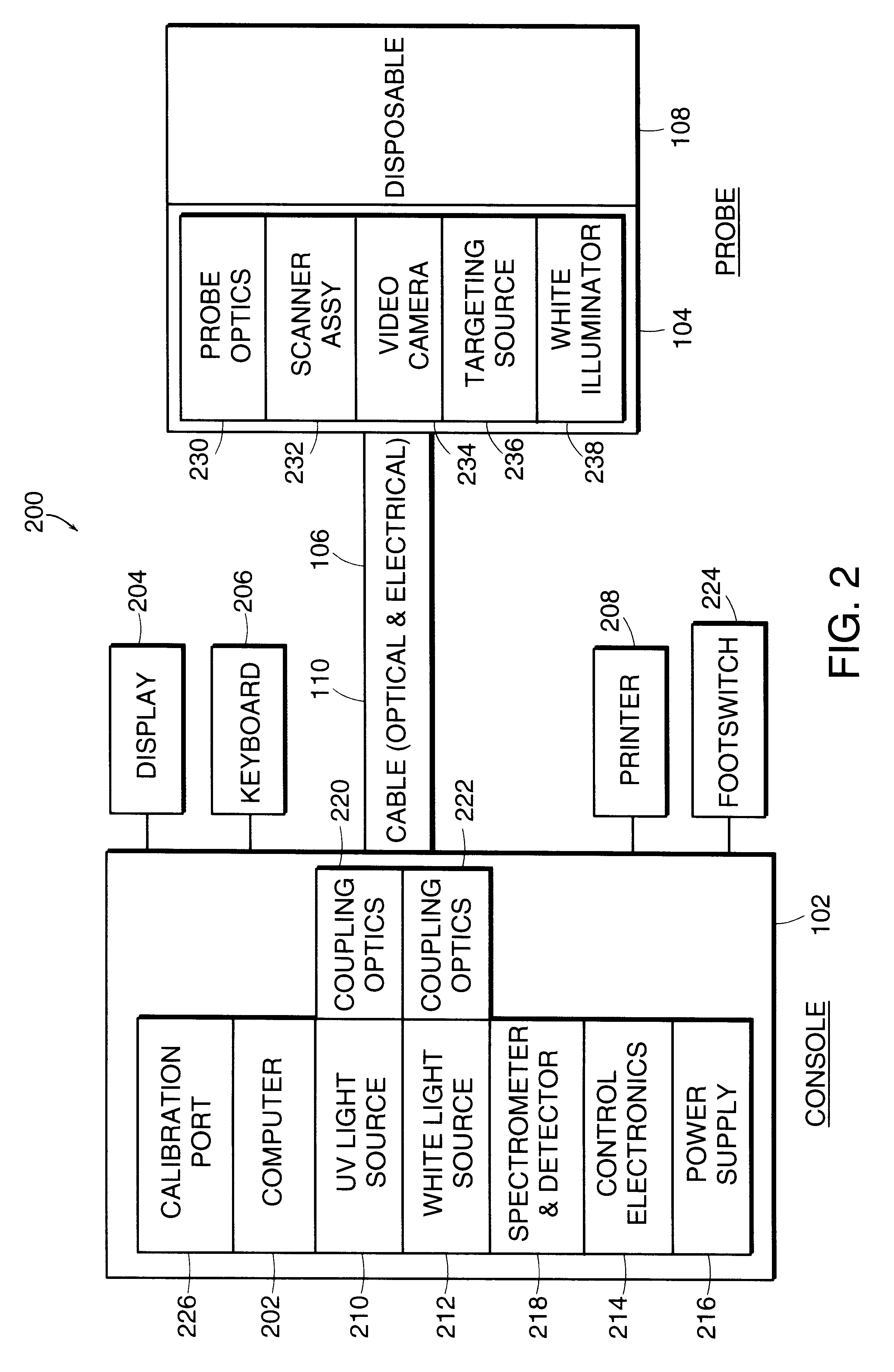
Medical diagnostic instrument with highly efficient, tunable light emitting diode light source
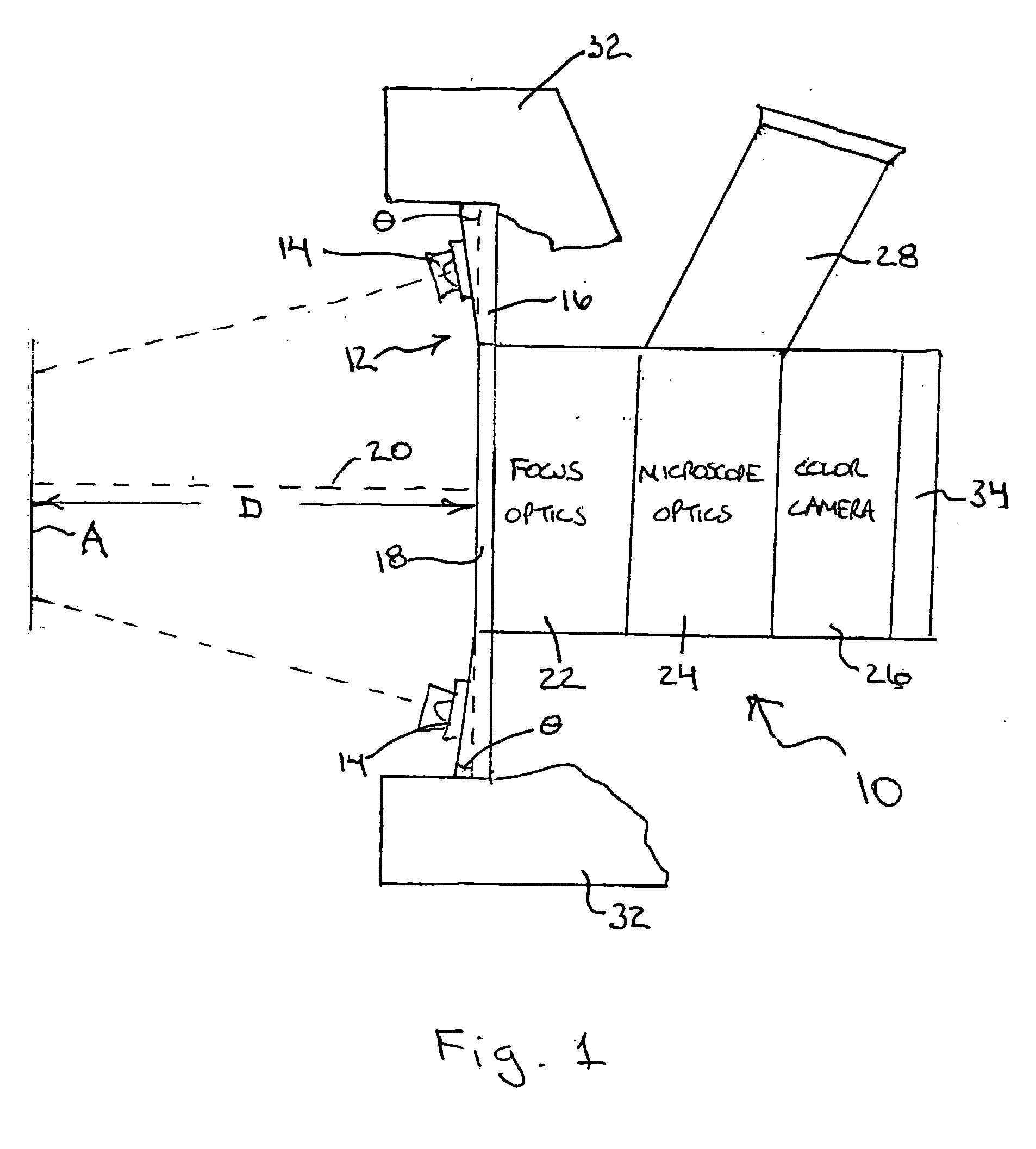
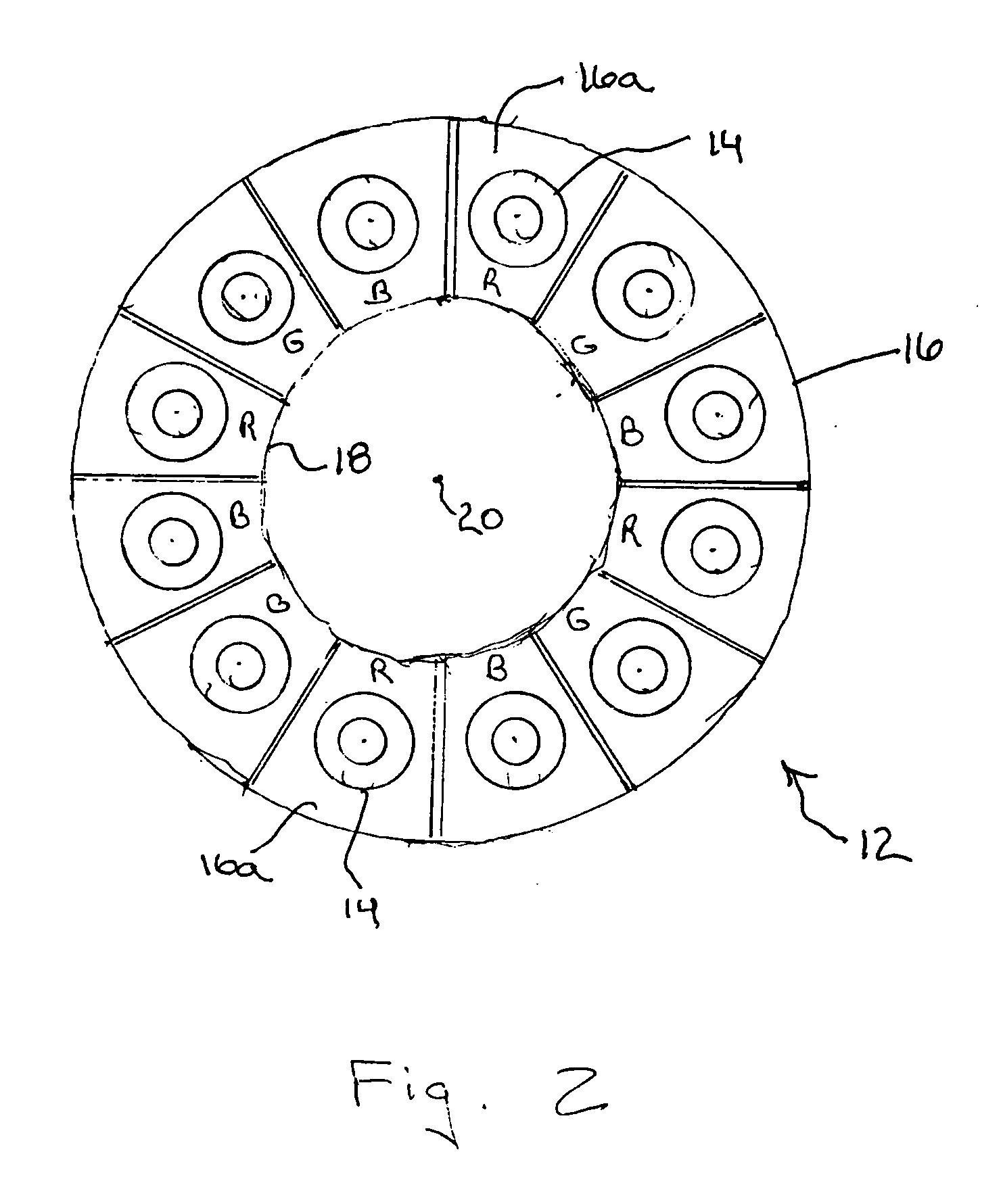
InactiveUS20060215406A1High strengthImprove evenlyNon-electric lightingLighting support devicesCervical tissueHigh intensity light
A medical diagnostic instrument, such as a colposcope for examining cervical tissue, includes a light source comprising an annular array of high intensity light emitting diodes (LEDs). The LED array includes a central access opening which provides viewing access for the colposcope optical components to the illumination site. The array includes a plurality of sets of LEDs, with each set including a red, blue and green emitting LED. The intensities of the red, blue and green LEDs, respectively, are controllable with a controller to continuously vary or tune the spectral characteristics of the illumination from the light source. Selected color mixes can be stored in a memory for later retrieval.
Owner:ADVANCED ILLUMINATION
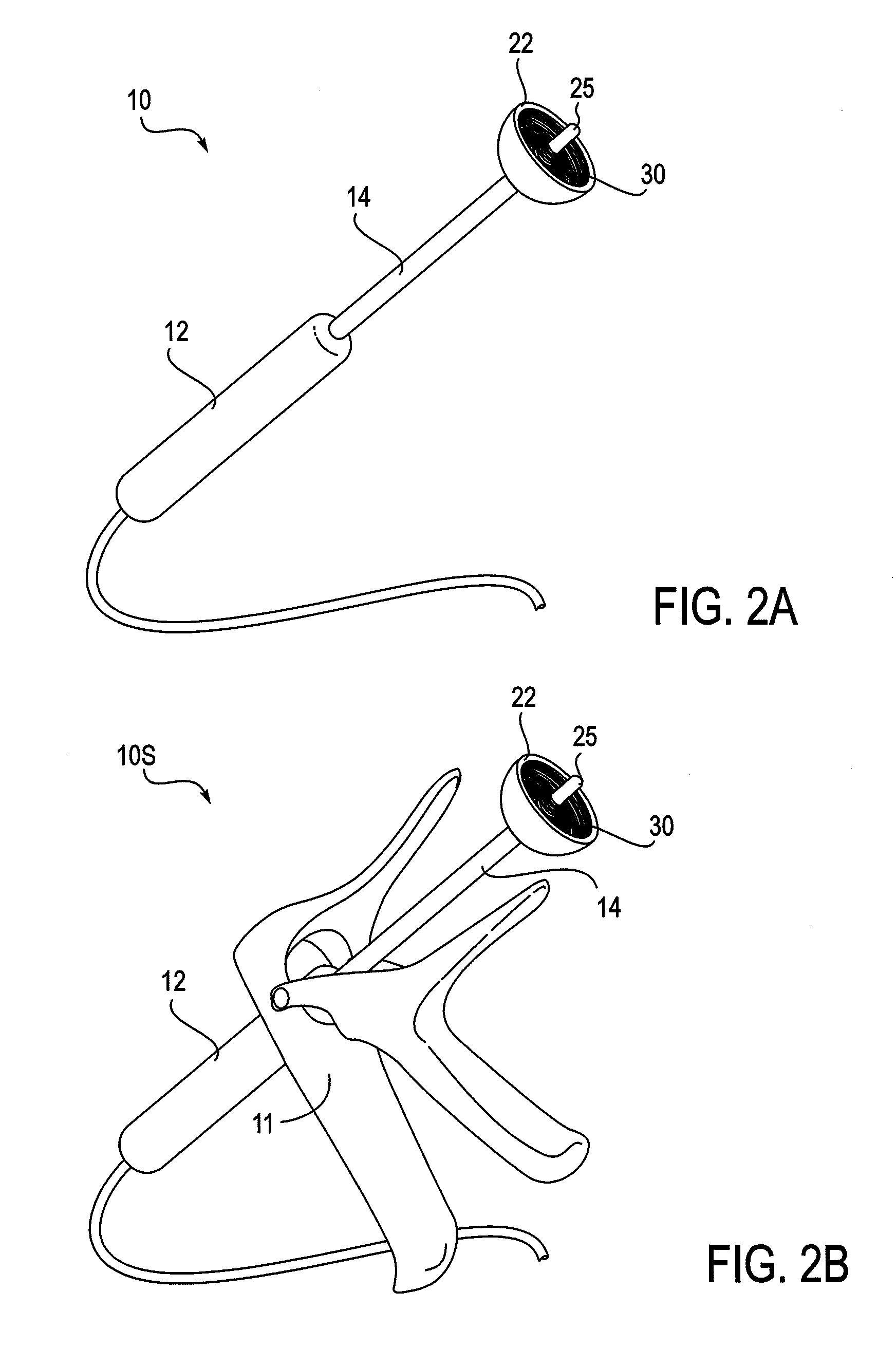
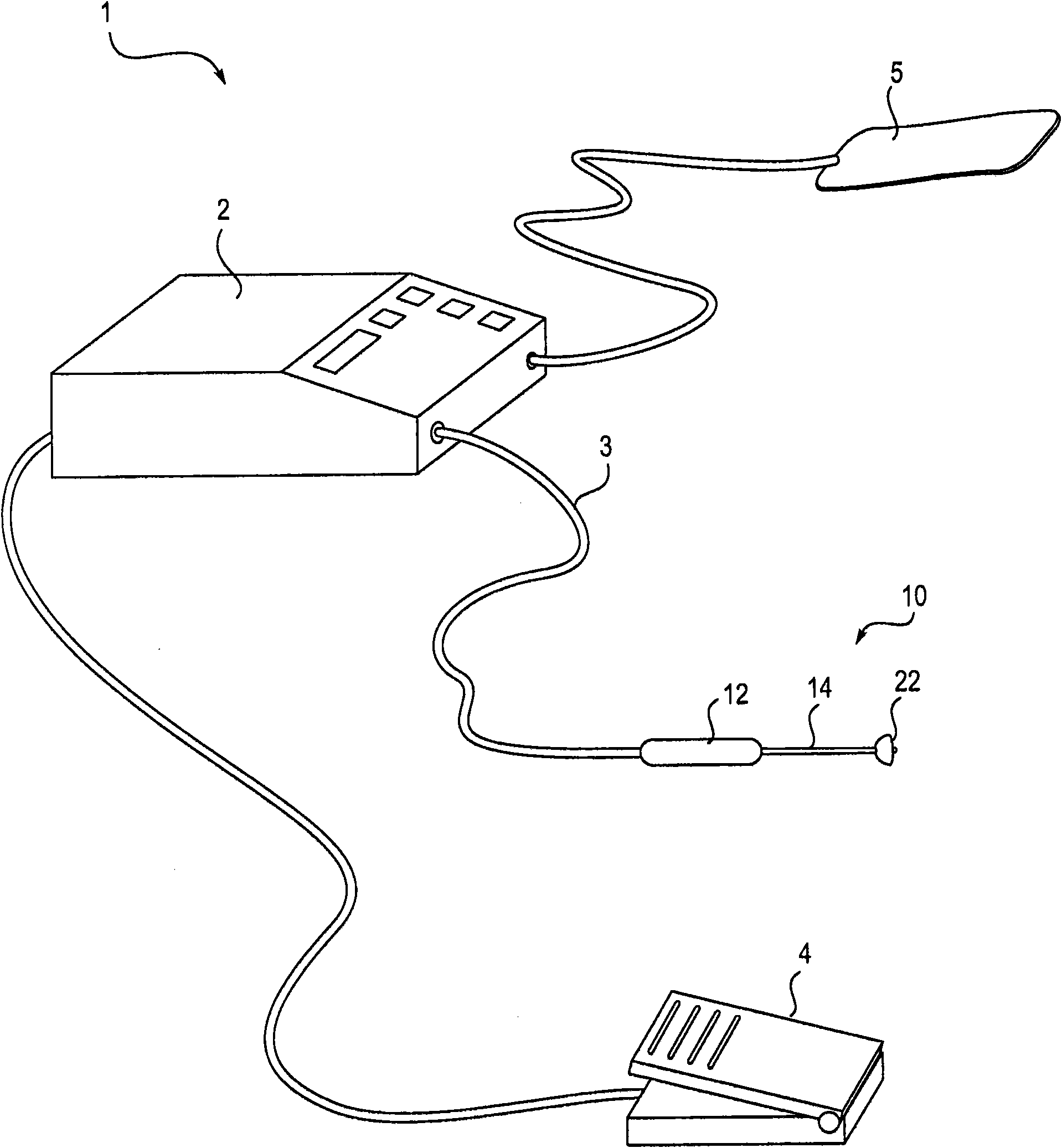
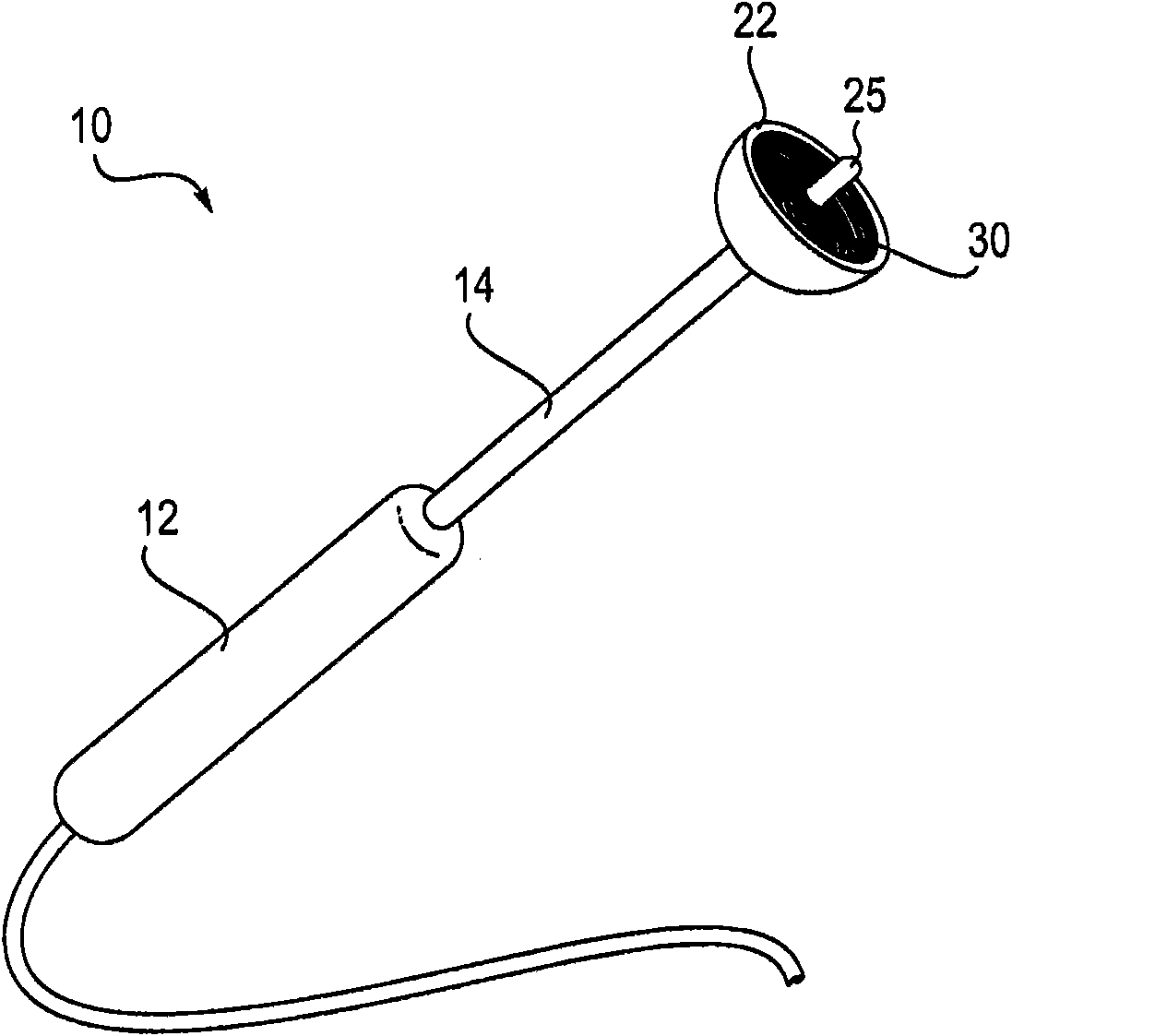
System and method for ablational treatment of uterine cervical neoplasia
InactiveUS20090318914A1Effective contactAvoid insufficient lengthSurgical furnitureDiagnosticsCervical tissueVagina
The invention provides a system, devices, and methods for ablating abnormal epithelial tissue of the uterine cervix. Embodiments of an ablation device include an operative head with a support surface adapted to conformably engage and therapeutically contact the cervix, and an energy delivery element on the support surface. The energy delivery element is configured to deliver energy, such as RF energy, to the tissue in a manner that controls the surface area and depth of ablation. The device may further include a shaft and a handle to support the ablation device, and may further include a speculum to facilitate access to the cervix. A system to support the operation of the ablation device includes a generator to deliver energy to the energy delivery element. Embodiments of a method for ablating abnormal cervical tissue include inserting an ablation device intravaginally to contact the cervix, aligning an energy delivery element support surface conformably against a region of the cervix with abnormal tissue, and ablating the tissue.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
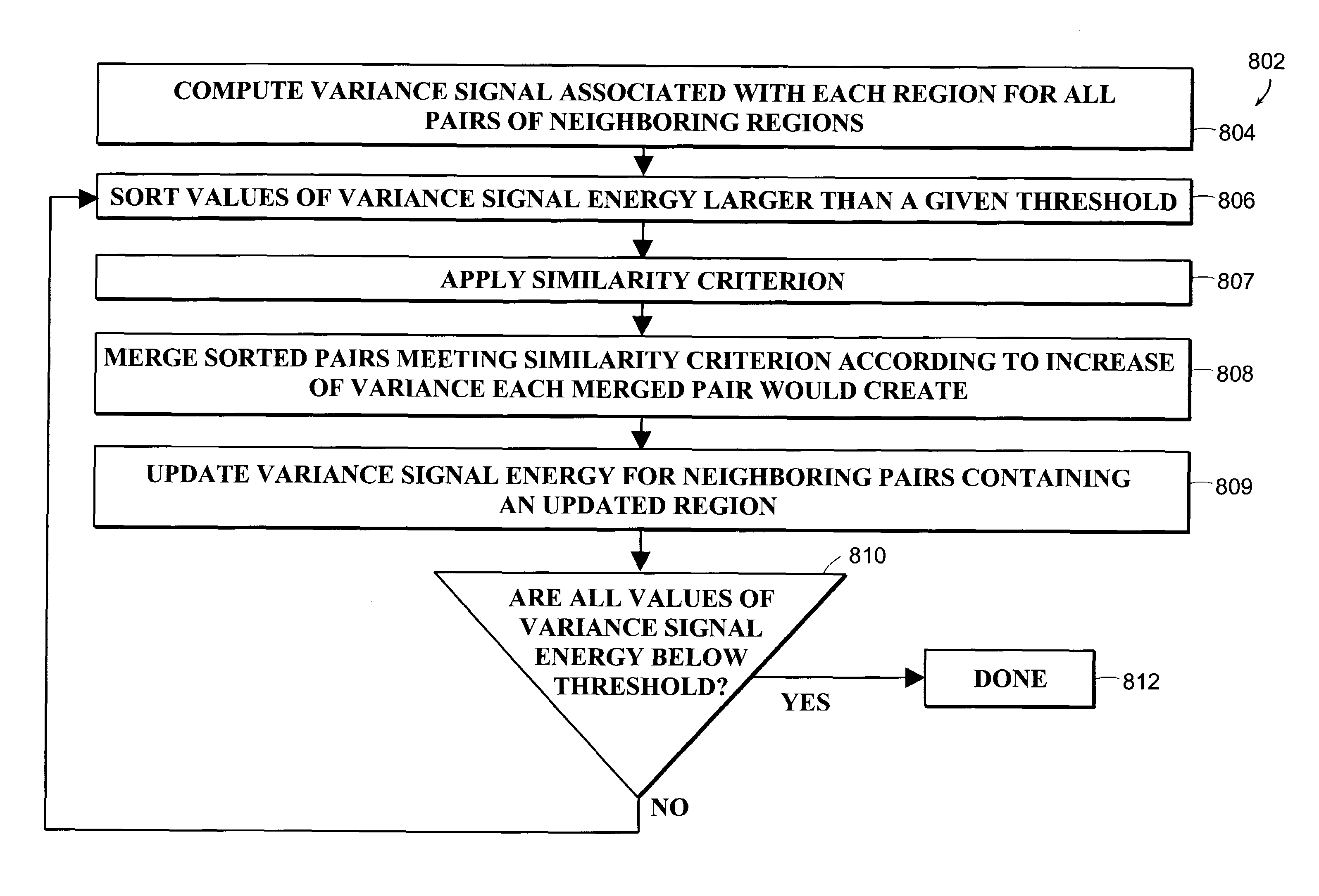
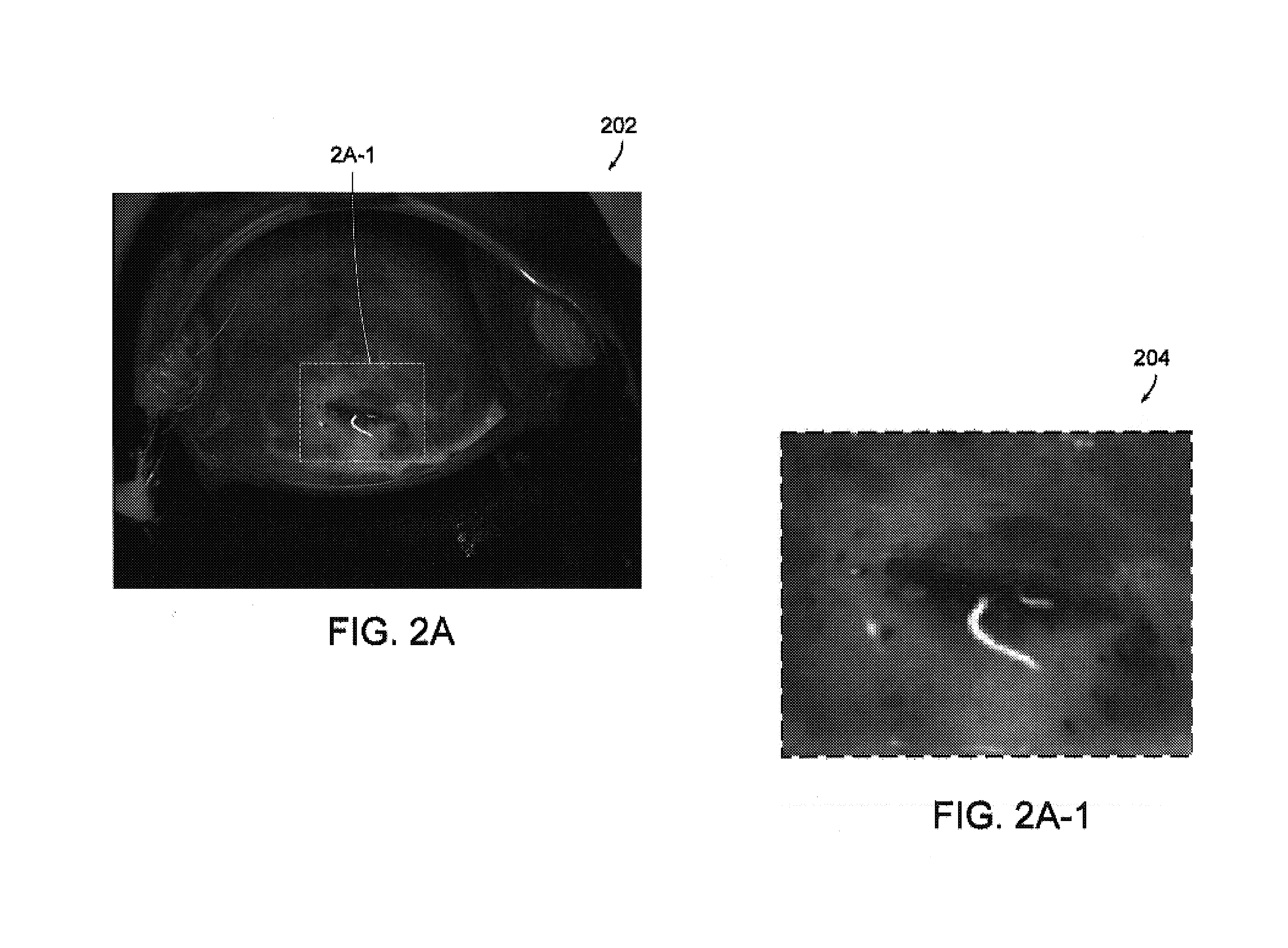
Image processing using measures of similarity
The invention provides methods of relating a plurality of images based on measures of similarity. The methods of the invention are useful in the segmentation of a sequence of colposcopic images of tissue, for example. The methods may be applied in the determination of tissue characteristics in acetowhitening testing of cervical tissue, for example.
Owner:LUMA IMAGING CORP
Systems and methods for a pregnancy monitoring device
InactiveUS20080171950A1Less invasiveLess intrusiveMedical devicesSensorsElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
Systems and methods are provided for characterizing electrical activity of a patient for making a pregnancy-related diagnosis. The system includes a wearable device for measuring an electrical impedance of a cervical tissue of the patient based on a signal applied to the cervical surface by the device. The system also includes a transmitter coupled to the wearable device for transmitting the measured electrical impedance of the cervical tissue to an analysis system for making a pregnancy-related diagnosis based on the impedance data.
Owner:GENISENT INT
Method and invention for the treatment of diseases and disorders of the cervix
A method and device for delivering therapeutic agents to the cervix. The method utilizes a diaphragm with an electrically conductive surface that is placed atraumatically over the outer surface and inner os of the mammalian (animal or human) cervix. The agent is delivered to the diaphragm after which the conductive surface of the diaphragm may be charged by a power source to deliver a electrophoretic field to force the agent deep into cervical tissue and cells. The diaphragm may be used with or without the aid of external or internal leads. A unique intrauterine lead designed in this patent may also be used with the diaphragm to enhance delivery of therapeutic agents.
Owner:WU ALLAN
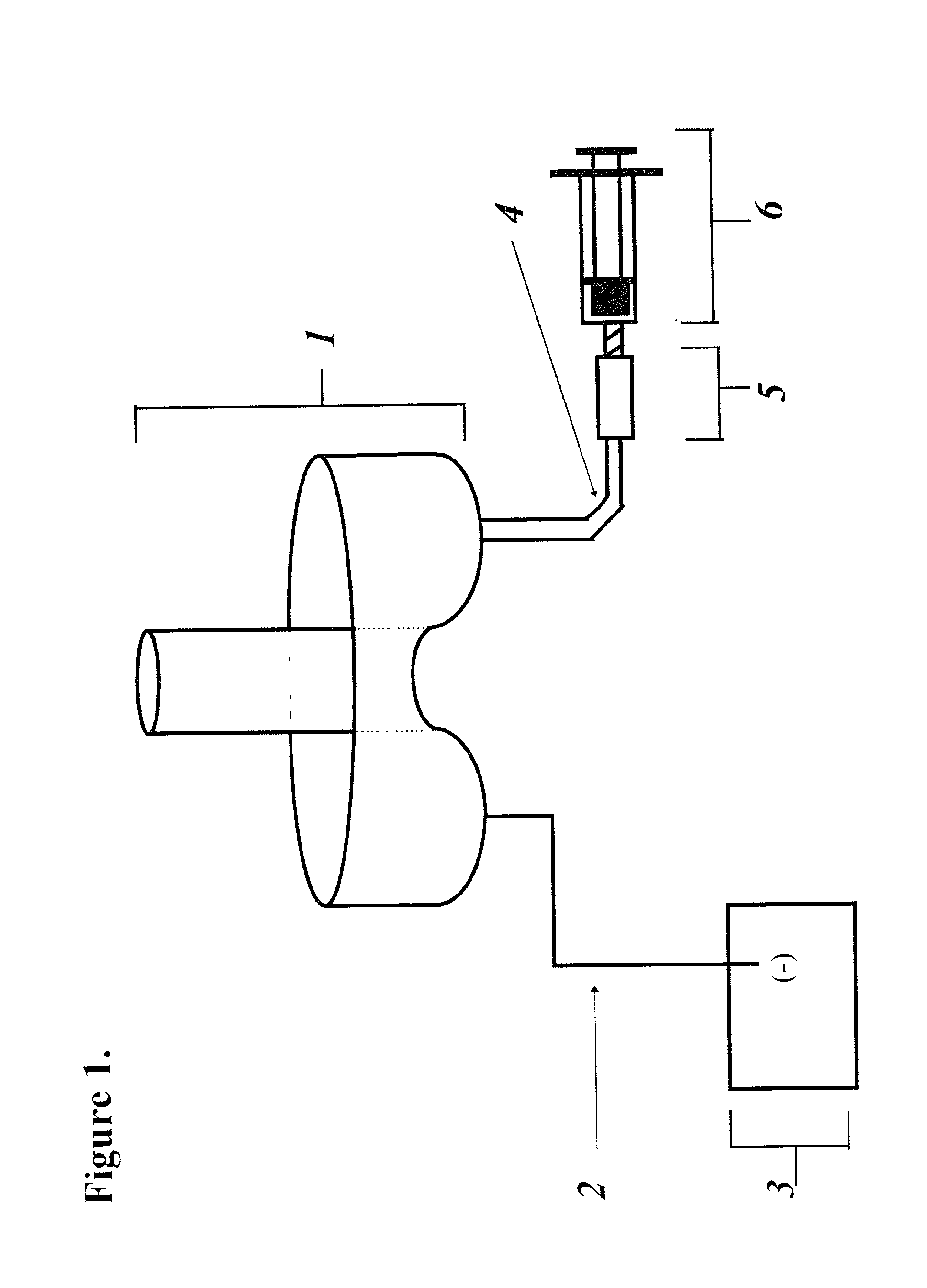
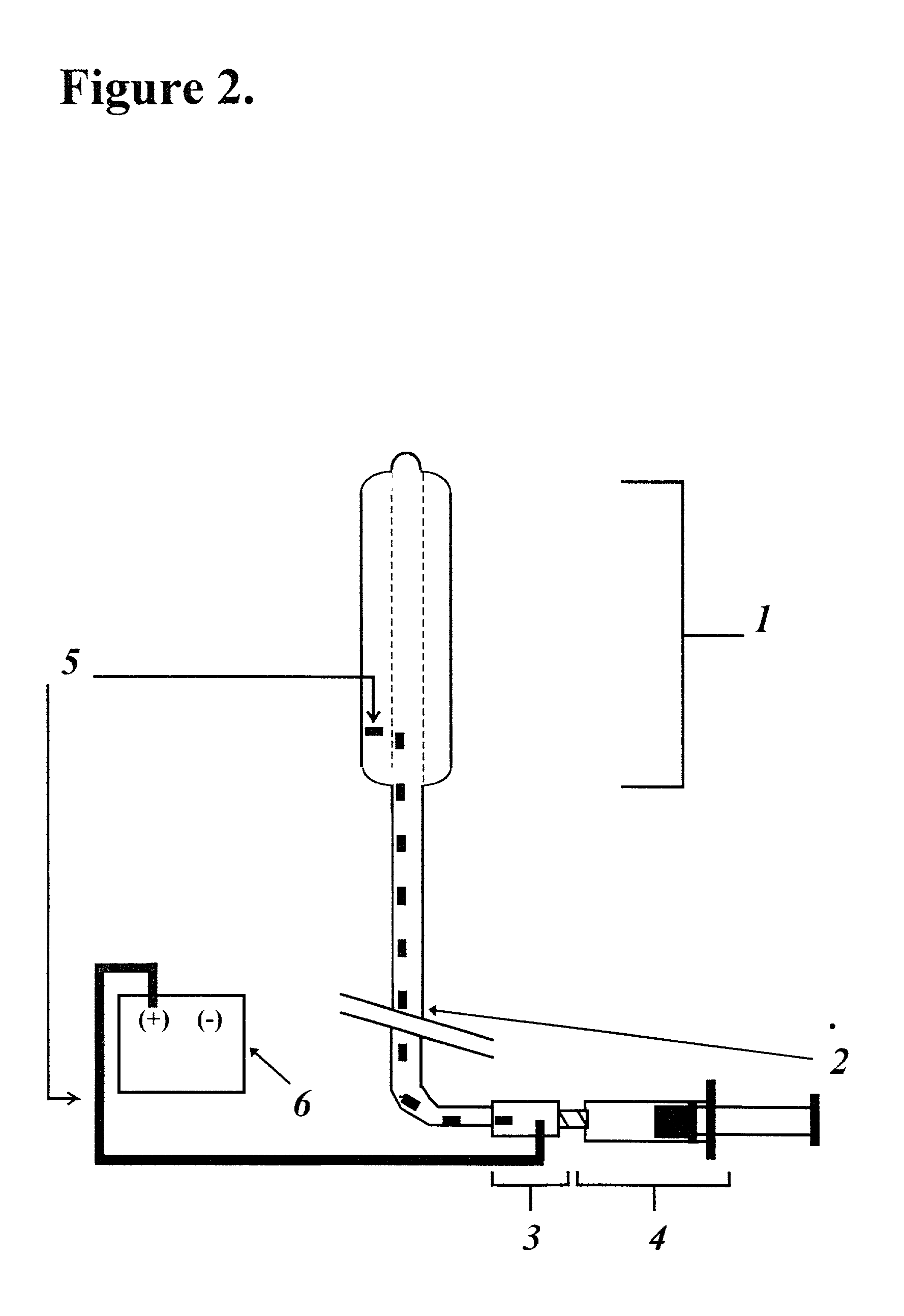
System for normalizing spectra
InactiveUS6839661B2Overcome disadvantagesAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsFrequency spectrumCervical tissue
A method and system for normalizing optical spectra using a non-uniform segment normalization. A spectrum is obtained and is represented as a function of wavelength as an amplitude at each of a plurality of wavelengths. At least one segment of the spectrum is selected, each selected segment being bounded by an upper wavelength and a lower wavelength. A normalization factor is computed as the sum of the areas for each of the selected segments. The spectrum is normalized by dividing at least one amplitude of the spectrum by the normalization factor. Segments can be selected with different wavelength ranges, that is, segments can be non-uniform. Test specimens can be categorized based on an analysis of normalized spectra. In particular, the specimen to be tested can be human cervical tissue, and the state of health of the tissue can be determined.
Owner:LUMA IMAGING CORP
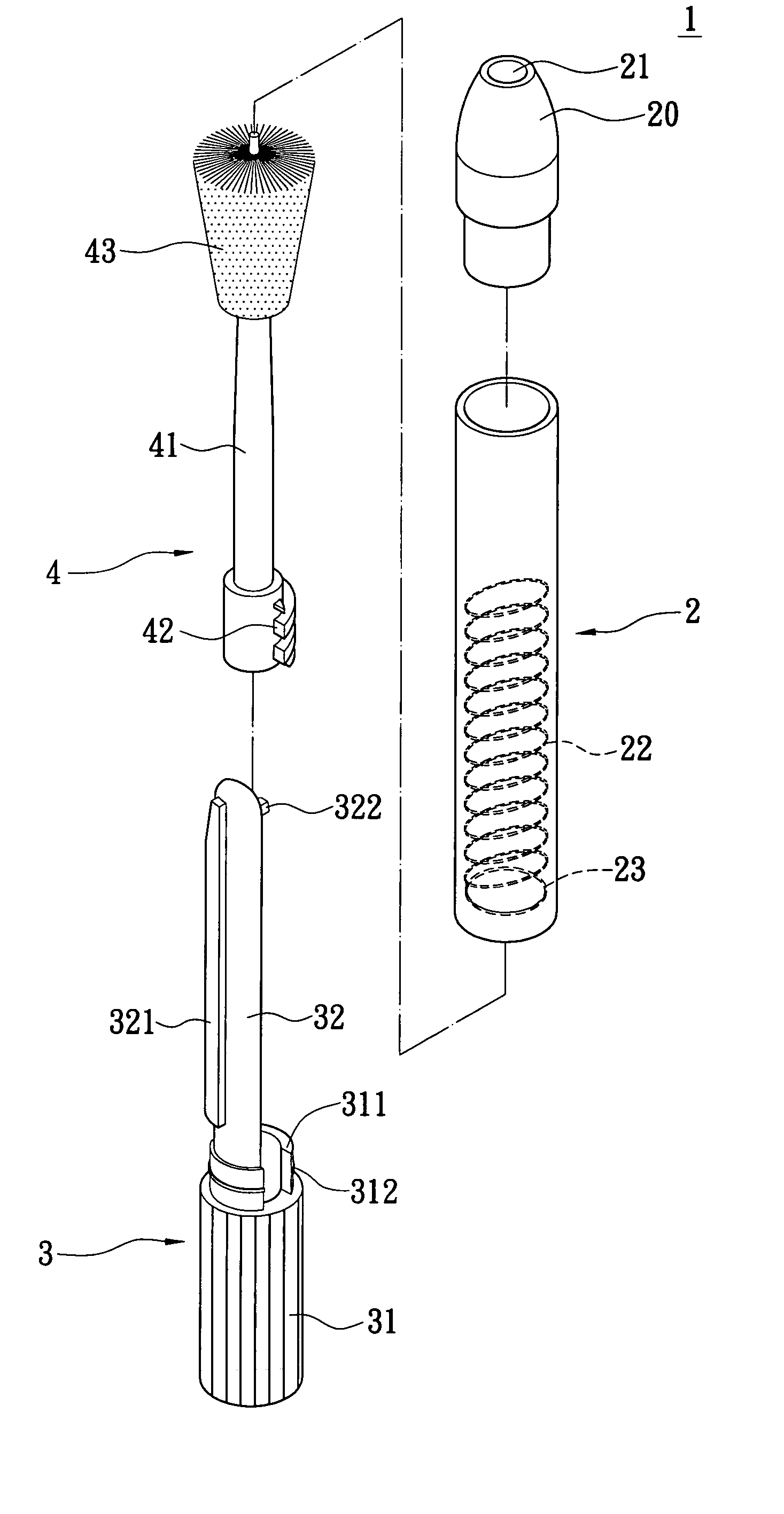
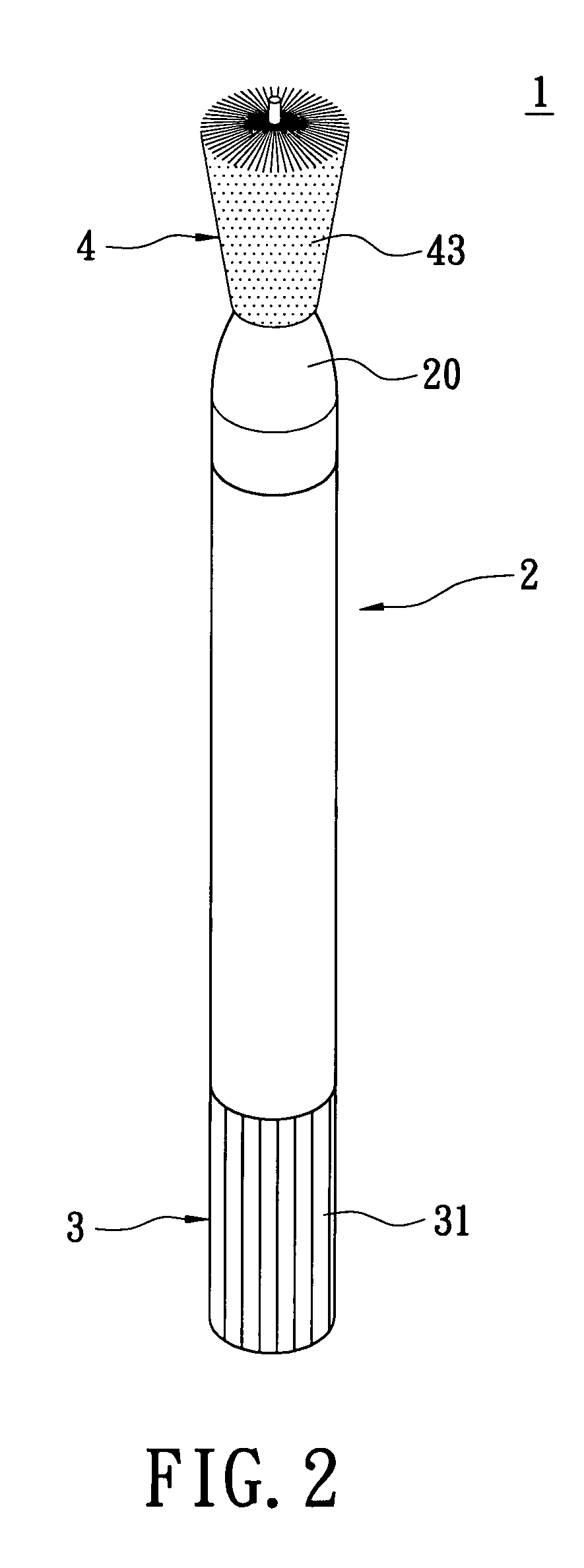
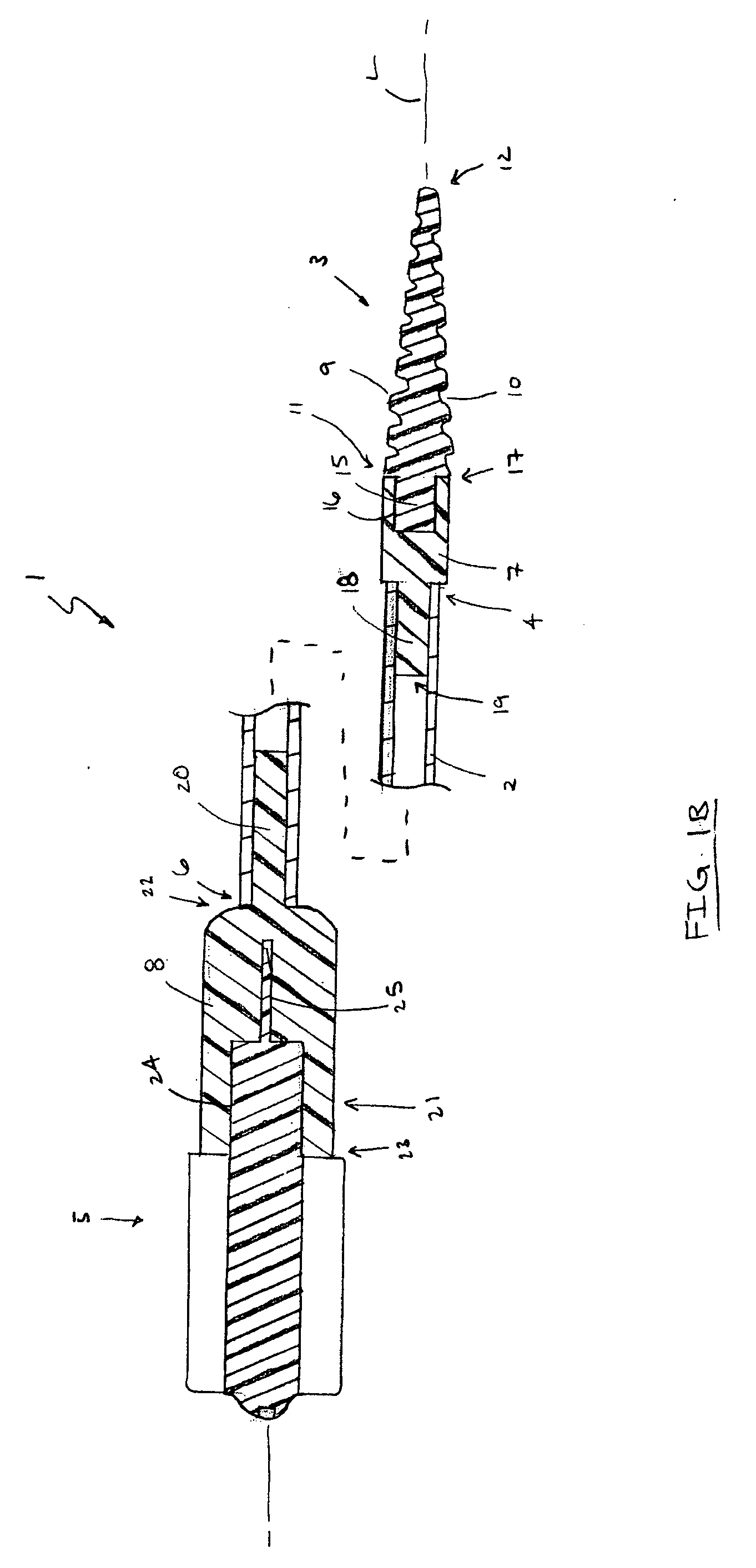
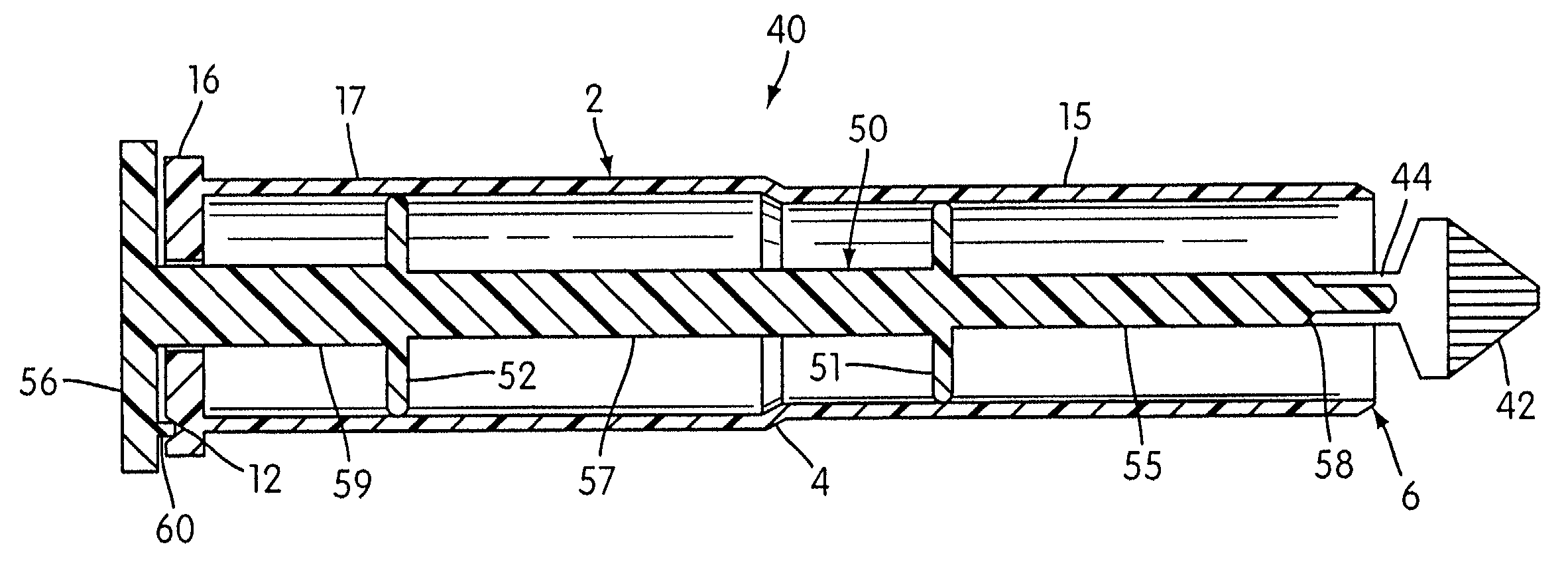
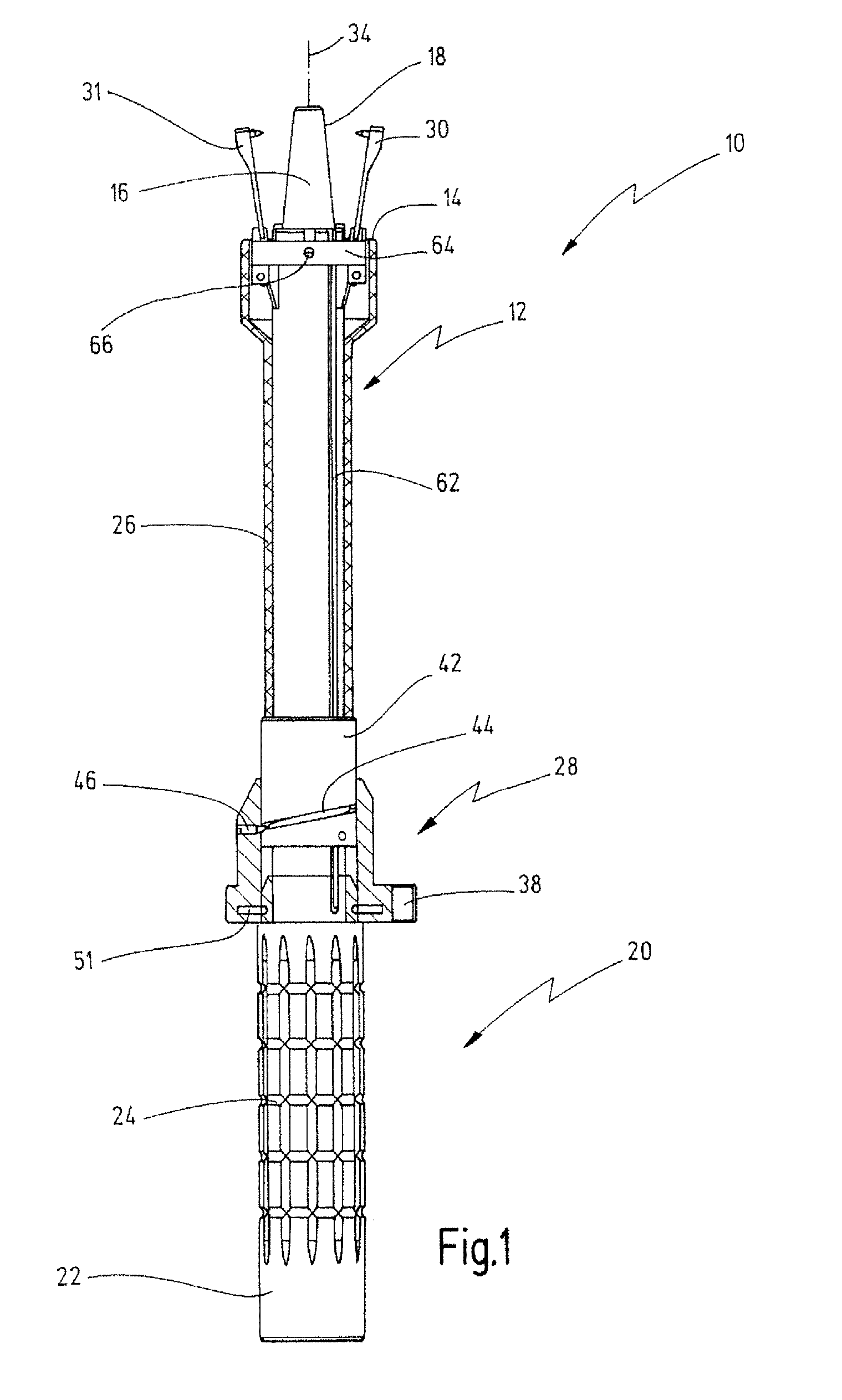
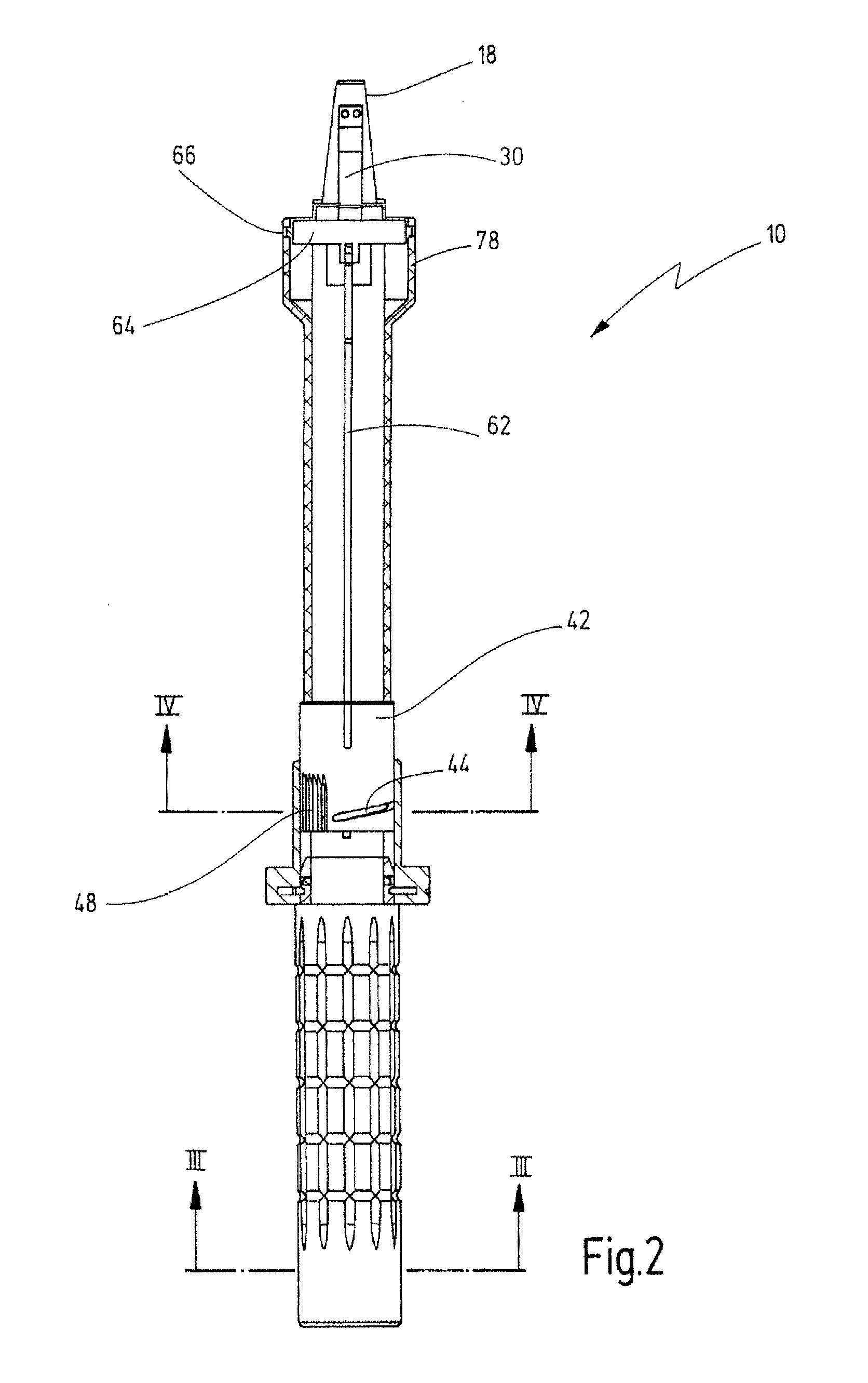
Cervical tissue sampling device
InactiveUS20050277846A1Easy to operateSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsCervical tissueScrew thread
A cervical tissue sampling device includes an exterior tube, a hold and an interior shaft. The exterior tube has an opening formed on a tapered end thereof and an internal screw thread arranged therein. The hold includes an operation base and a propelling plate connecting the operation base upwardly, wherein the propelling plate is sleeved on by the exterior tube. The interior shaft is adjacent to the propelling plate, arranged above the operation base and received in the exterior tube. The interior shaft includes a projective screw thread portion disposed on an end thereof, and a fluff portion arranged on an opposite end thereof. The projective screw thread portion abuts against and is pushed by the propelling plate to move upwards due to a match for the projective screw thread portion and the internal screw thread, so as to expose the fluff portion outside the exterior tube via the opening.
Owner:CHOU CHUN SHAN
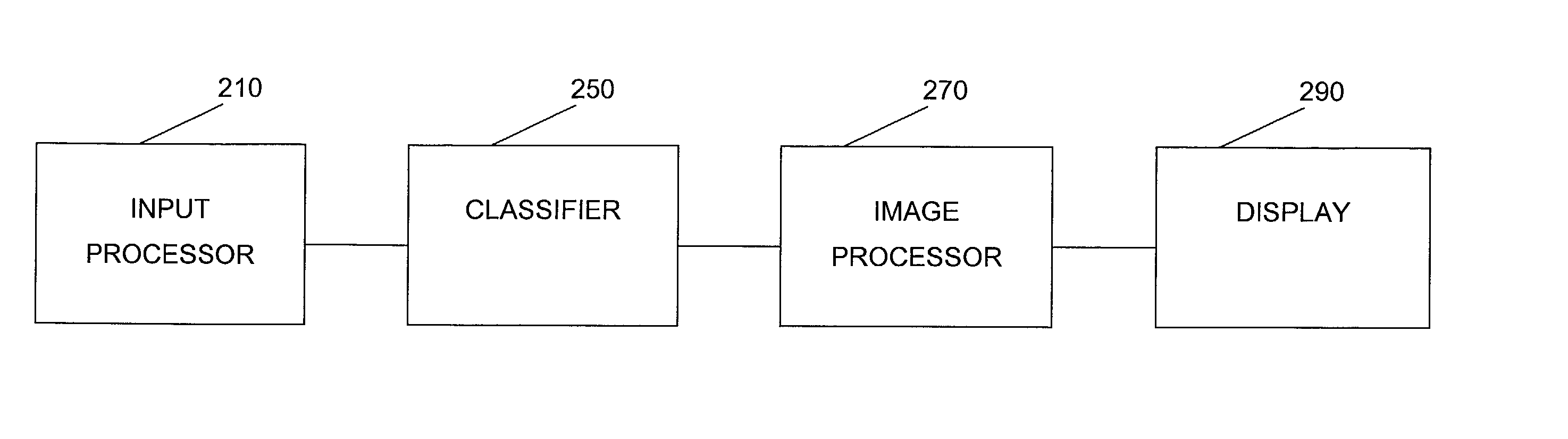
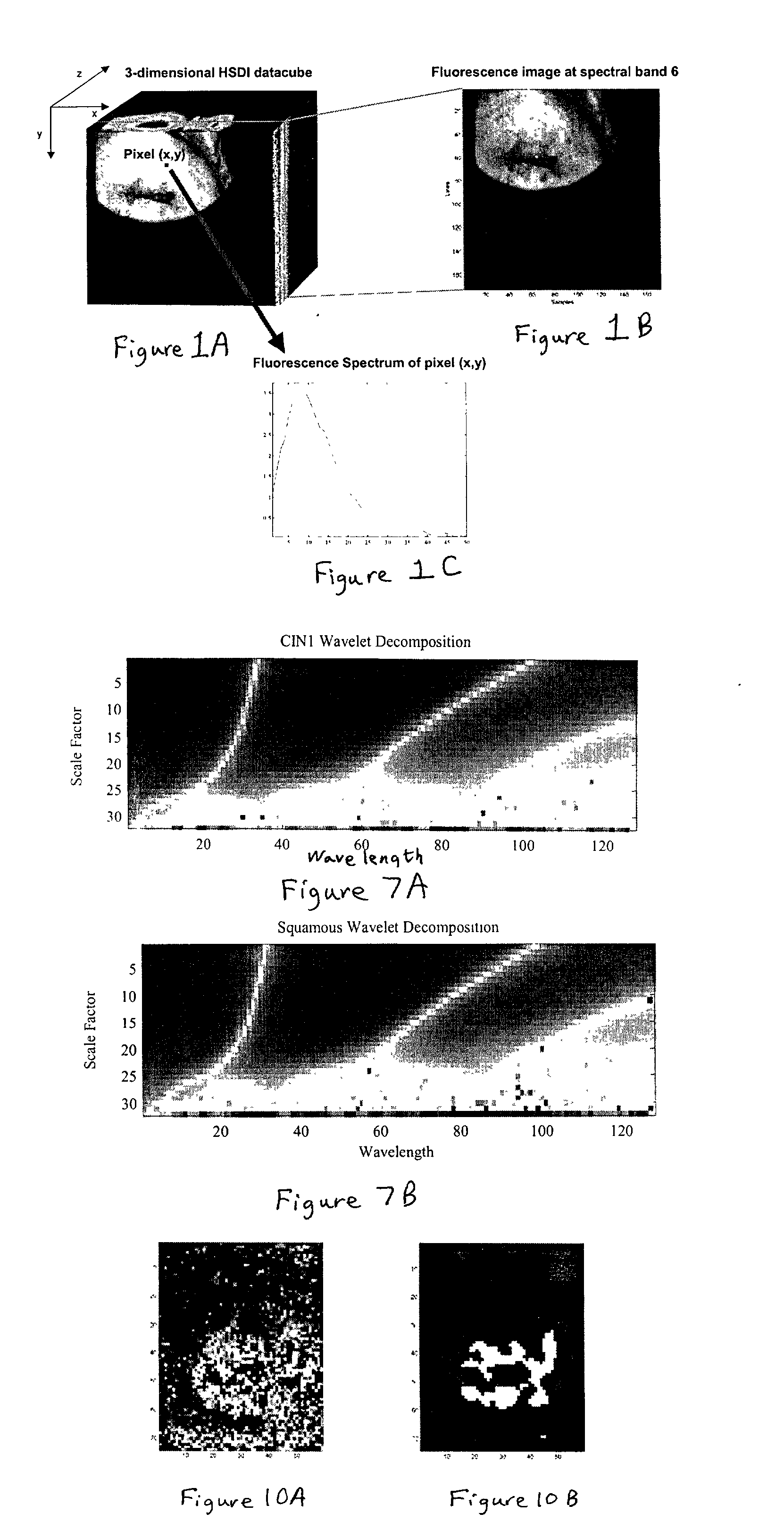
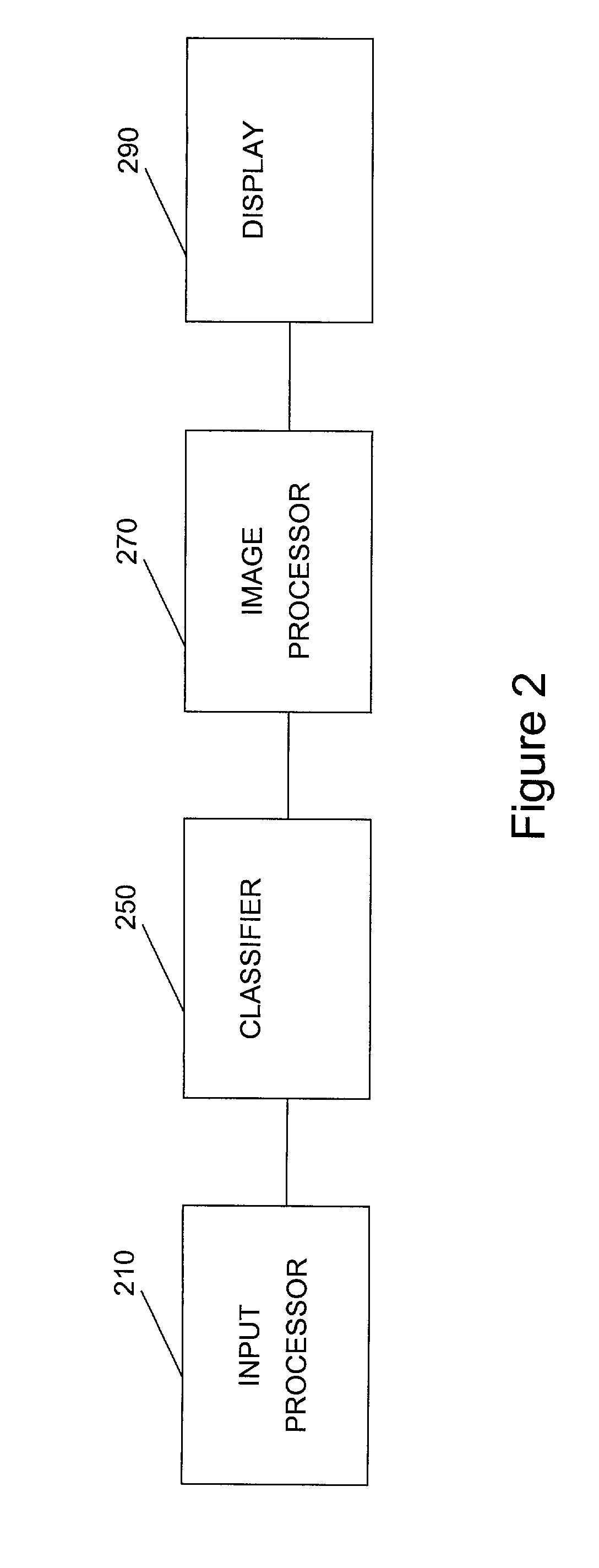
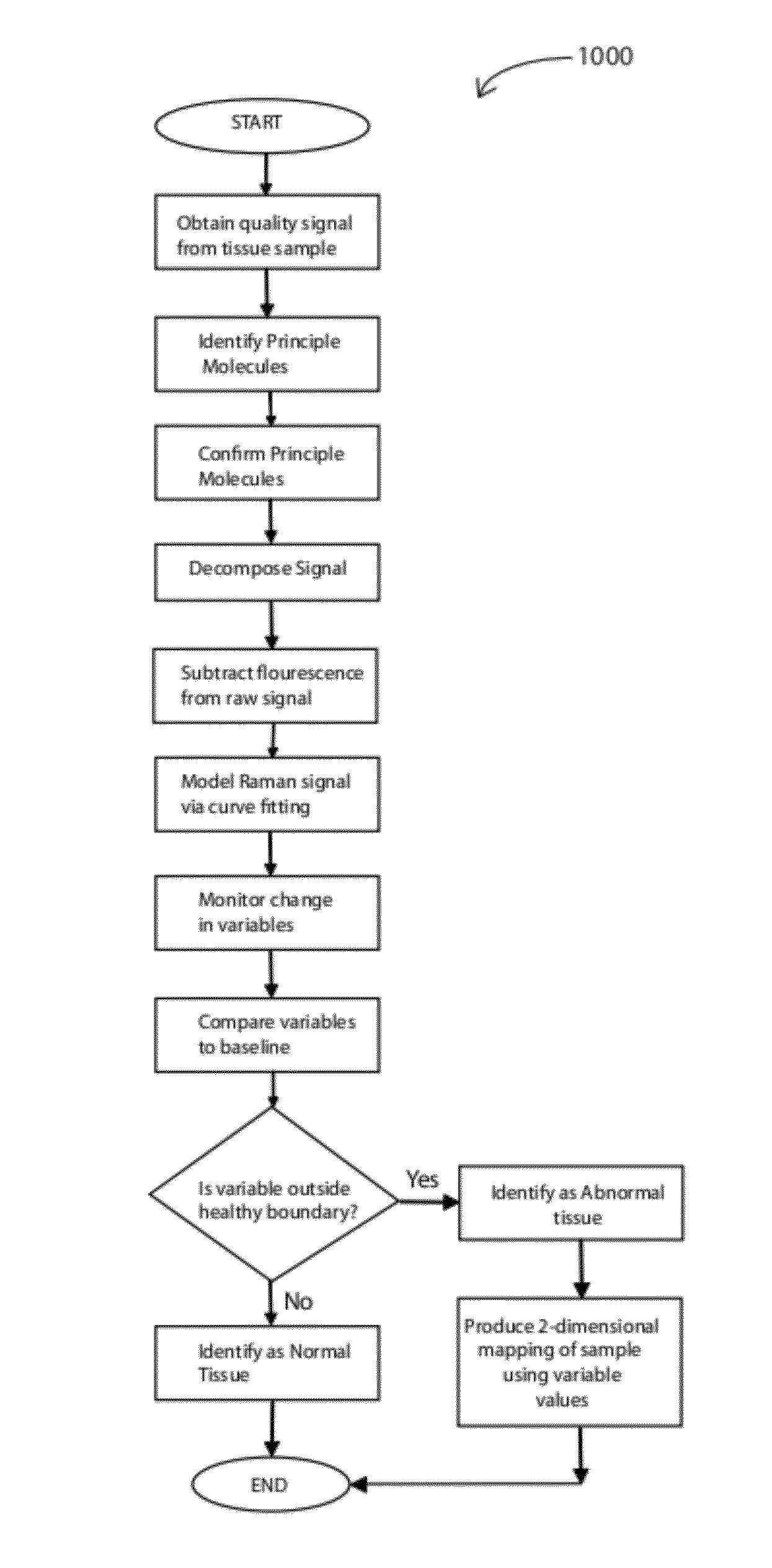
Method and apparatus for generating two-dimensional images of cervical tissue from three-dimensional hyperspectral cubes
A method and apparatus for generating a two dimensional image of a cervix from a three dimensional hyperspectral data cube includes an input processor constructed to normalize fluorescence spectral signals collected from the hyperspectral data cube. The input processor may be further constructed to extract pixel data from the spectral signals where the pixel data is indicative of cervical tissue classification. The input processor may be further configured to compress the extracted pixel data. A classifier is provided to assign a tissue classification to the pixel data. A two dimensional image of the cervix is generated by an image processor from the compressed data, the two dimensional image including color-coded regions representing specific tissue classifications of the cervix.
Owner:PARKER MARY F +2
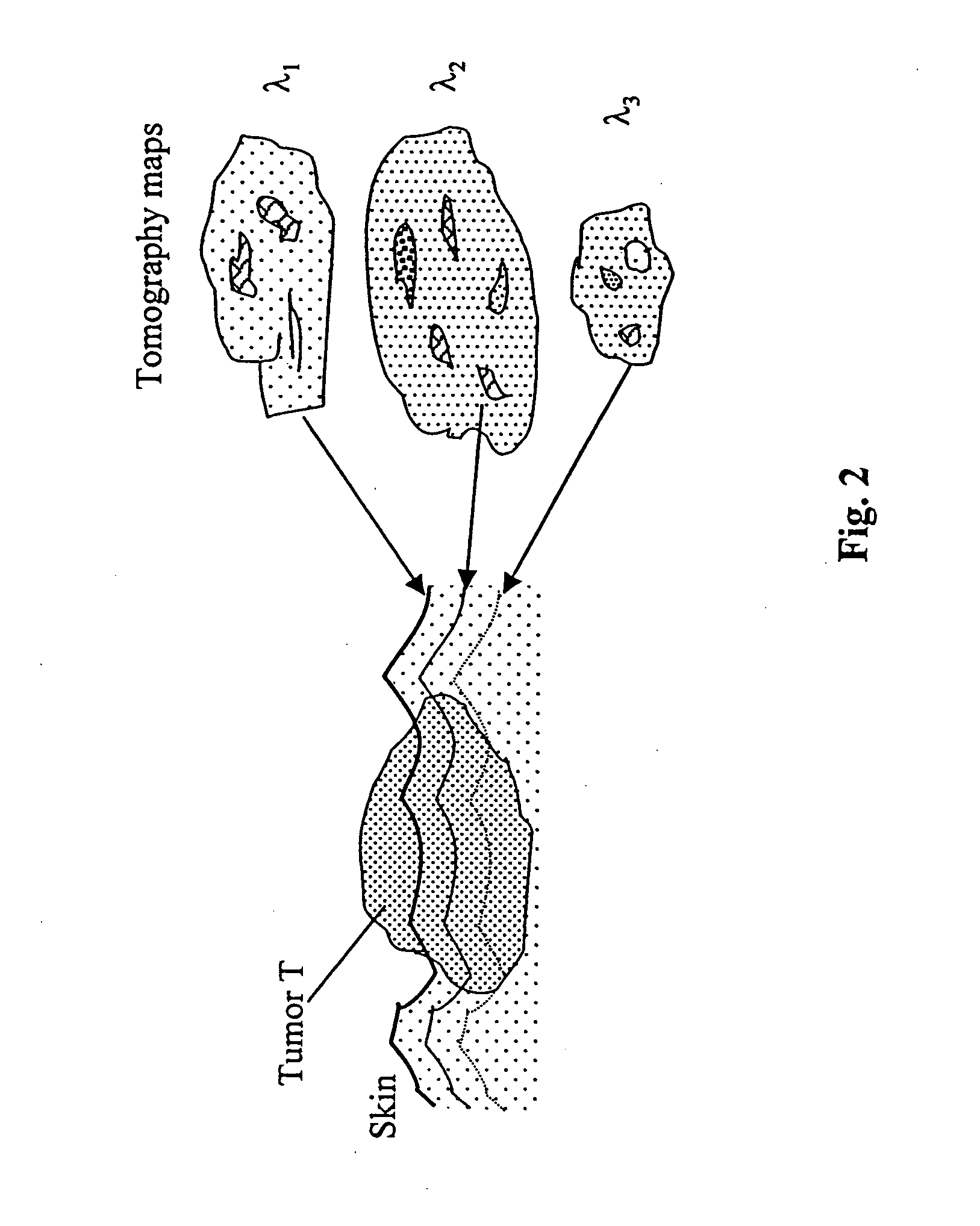
Optical methods and systems for rapid screening of the cervix
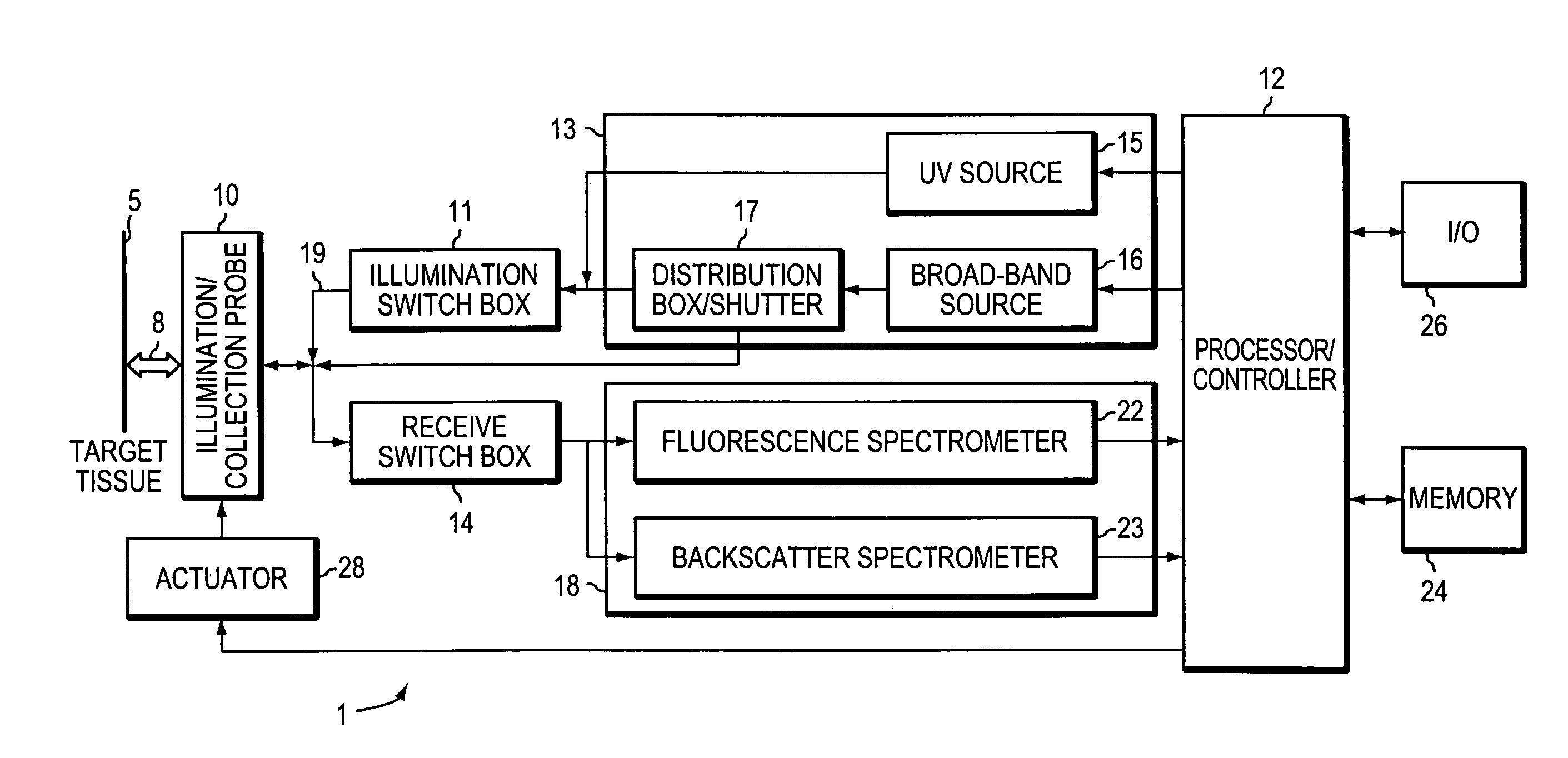
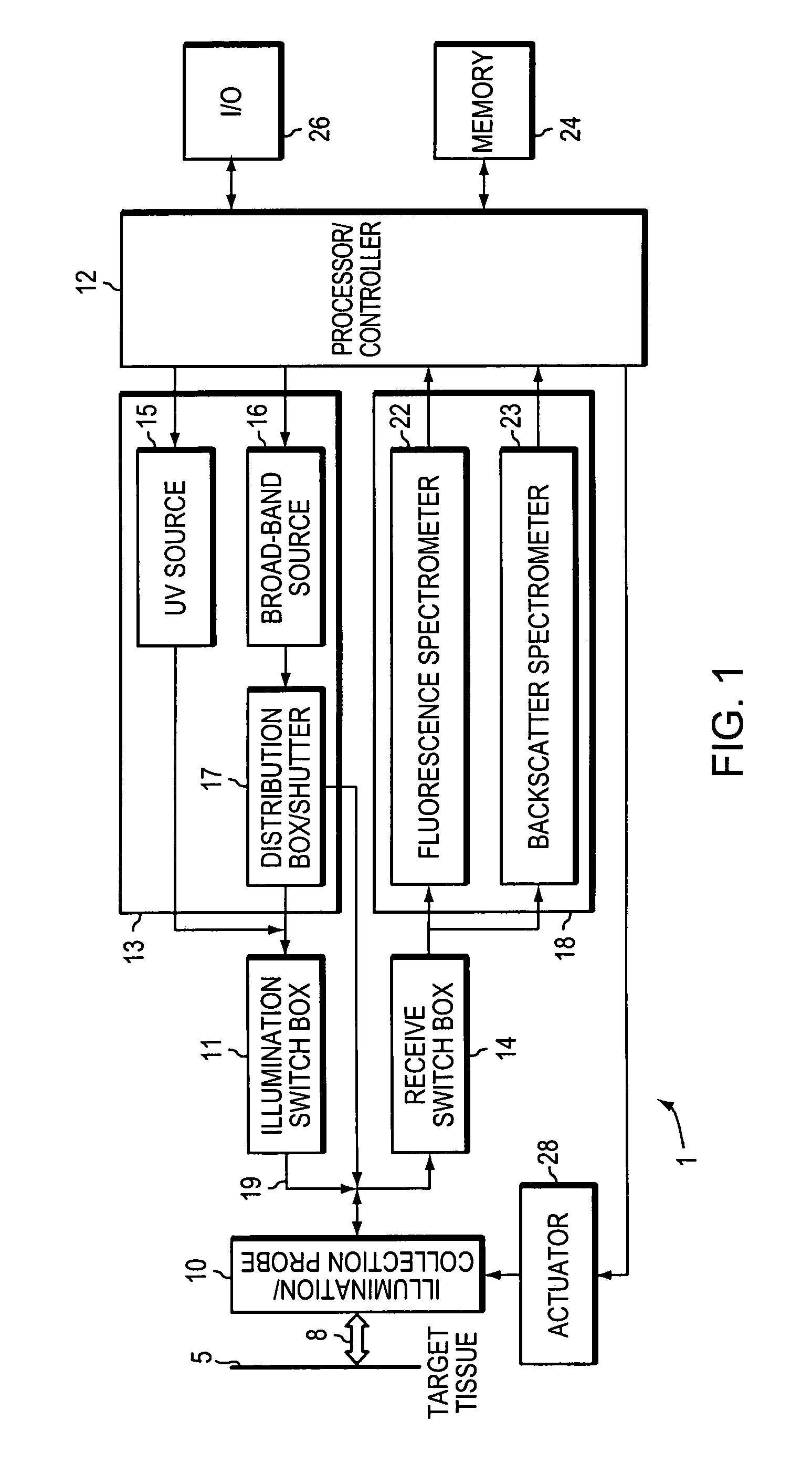
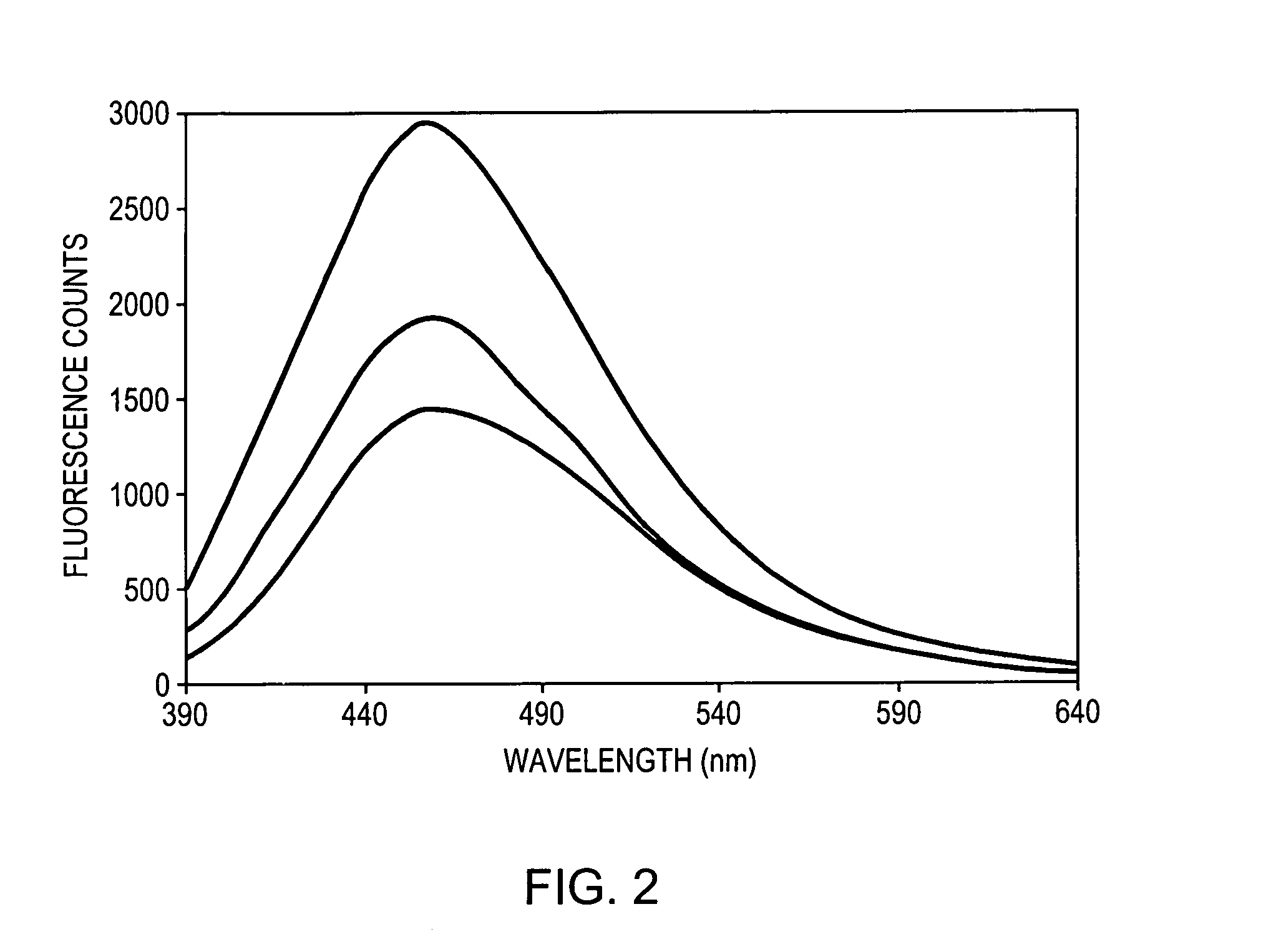
InactiveUS7127282B2Eliminate the problemDiagnostics using spectroscopySurgeryCervical tissueData set
A method and a system is provided for discriminating between healthy cervical tissue and pathologic cervical tissue based on the fluorescence response of the tissue to laser excitation (LIF) and the backscatter response to illumination by white light (in the spectral range of 360 to 750 nm). Combining LIF and white light responses, as well as evaluating a spatial correlation between proximate cervical tissue sites in conjunction with a statistically significant “distance” algorithm, such as the Mahalanobis distance between data sets, can improve the discrimination between normal and abnormal tissue. The results may be displayed in the form of a map of the cervix representing the suspected pathology.
Owner:LUMA IMAGING CORP
Cervical tissue biopsy system and methods of use
InactiveUS20070093727A1Precise cuttingNot to damageSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsCervical tissueBiomedical engineering
A cervical tissue sampling system is provided that includes a tissue cutting device and a snare. The tissue cutting device features a conical tip coupled to an elongated body and having a tapered helical cutting edge that defines a tissue receiving channel. The snare includes an elongated body, an adjustable wire loop and a stopper, the stopper arranged to lock the wire loop with a desired degree of tension around the cervix to assist in positioning the tissue cutting device.
Owner:FEMSUITE
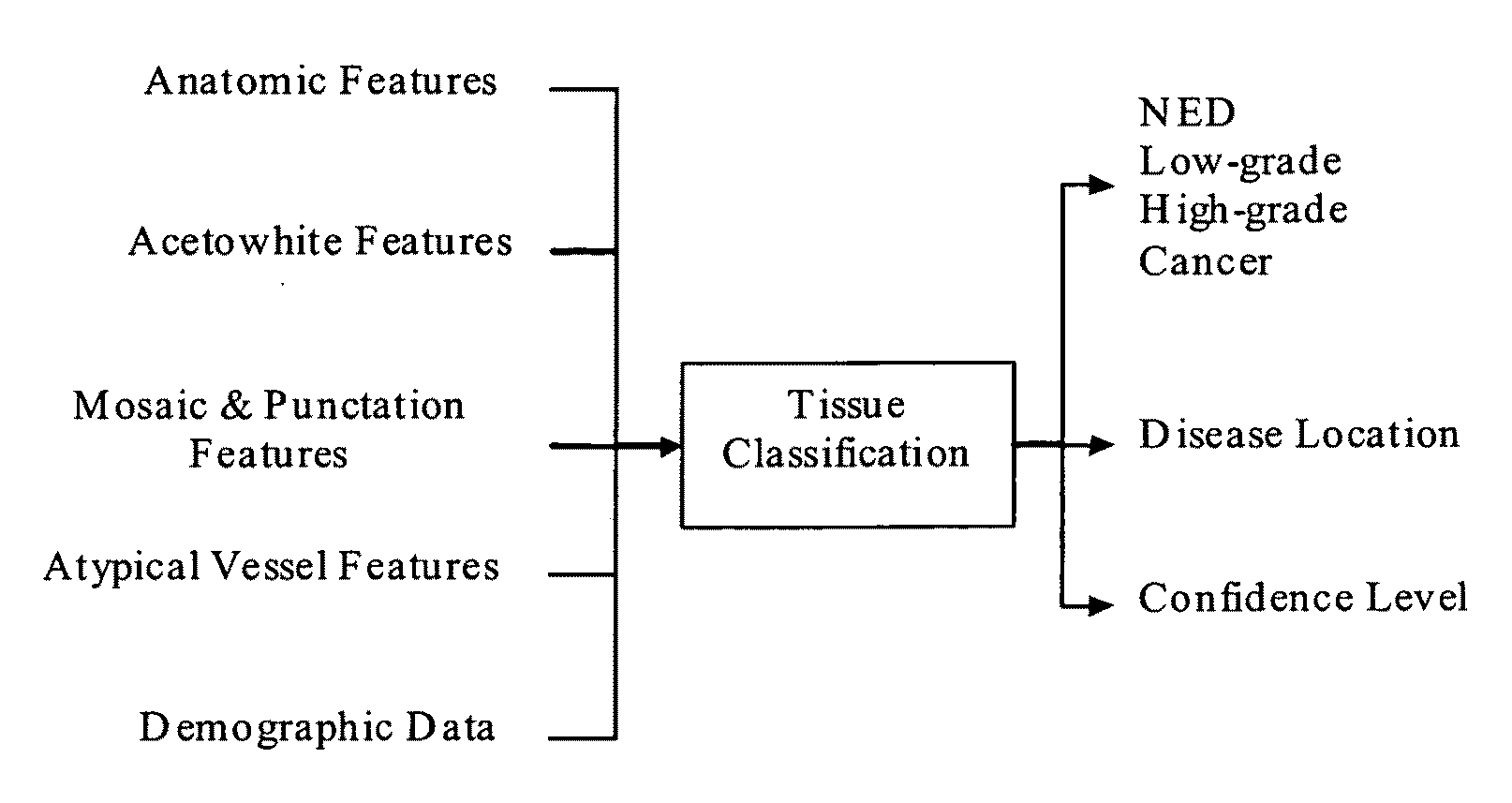
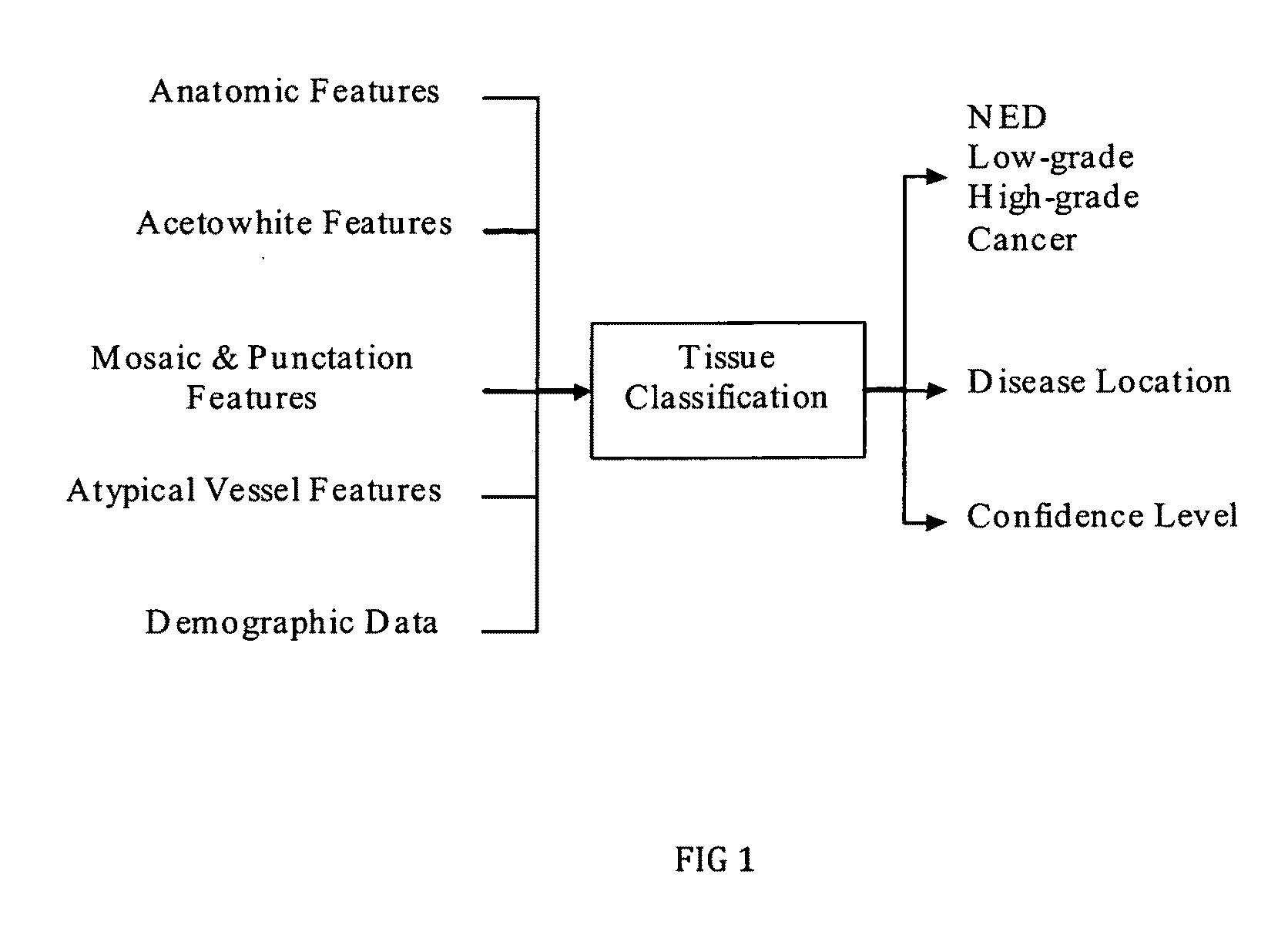
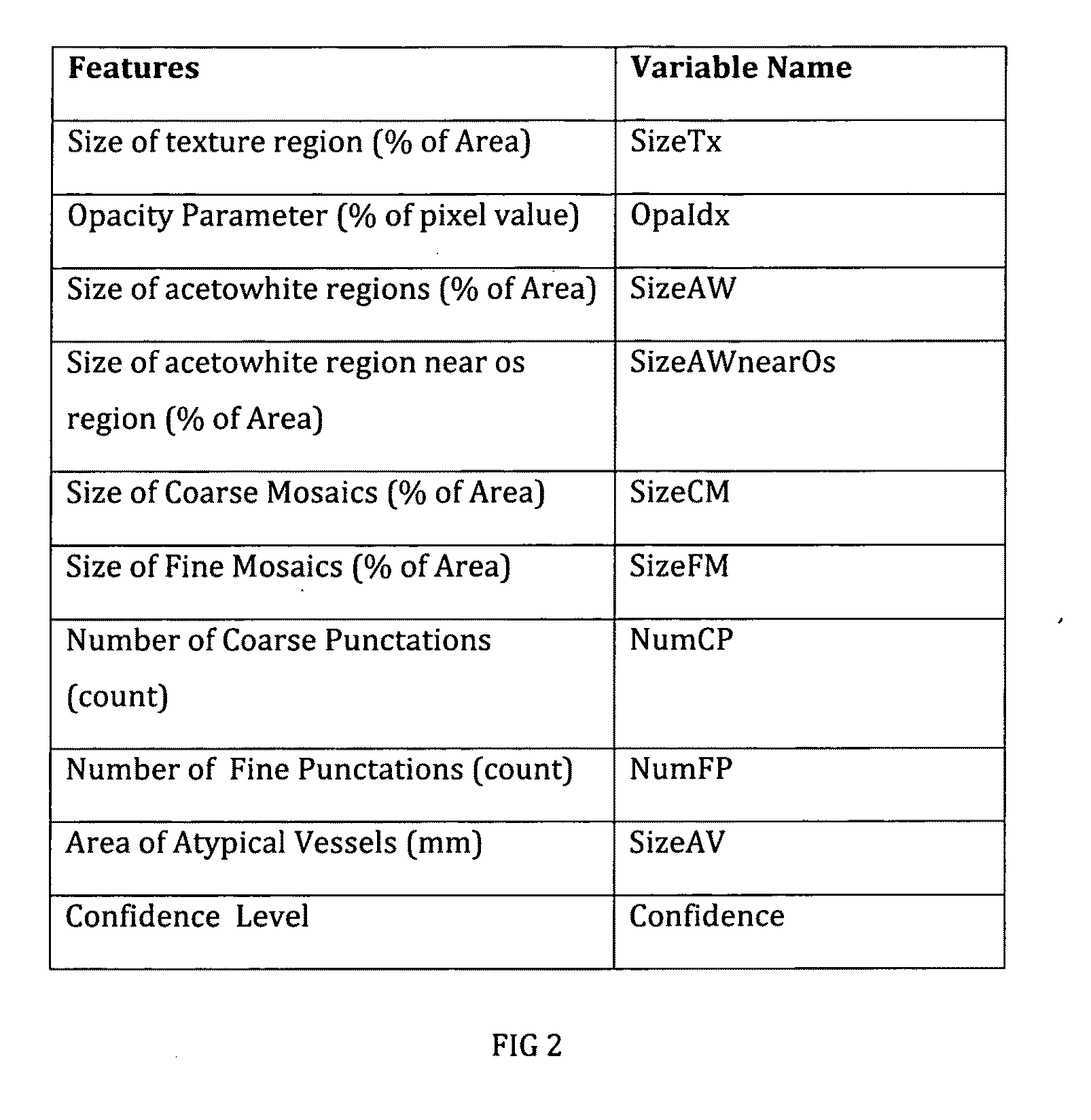
Methods for tissue classification in cervical imagery
A rule-based unsupervised process for classifying cervical tissue by serially applying classifiers selected from the group that consists of determining size of texture region, opacity parameter, size of acetowhite regions, number of coarse and fine punctations, size of coarse and fine mosaics, size of atypical blood vessels and demographic data, so that the cervical tissue can be classified into no evidence of disease, low-grade dysplasia, high-grade dysplasia or cancer.
Owner:CADES SCHUTTE A LIMITED LIABILITY LAW PARTNERSHIP
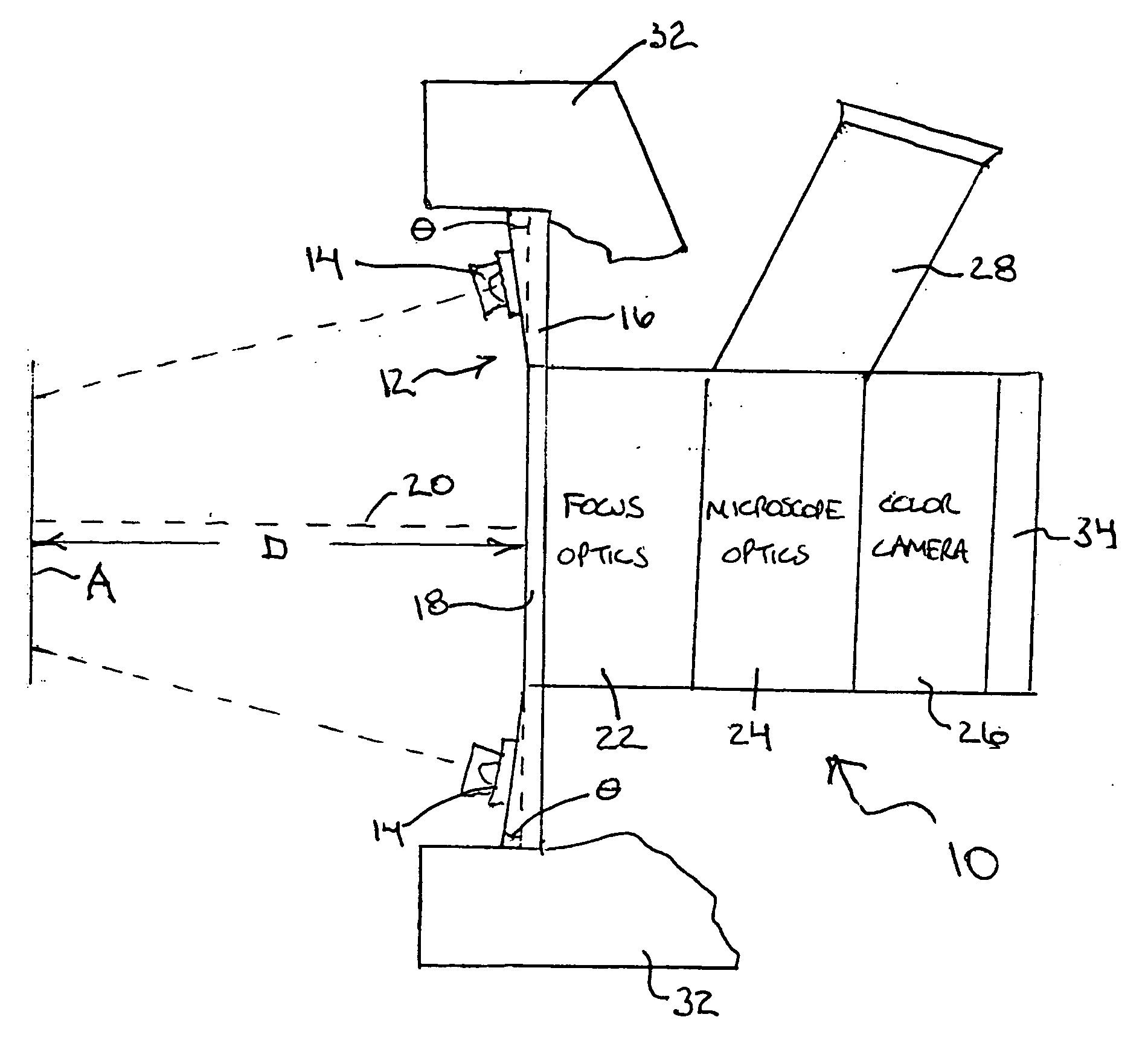
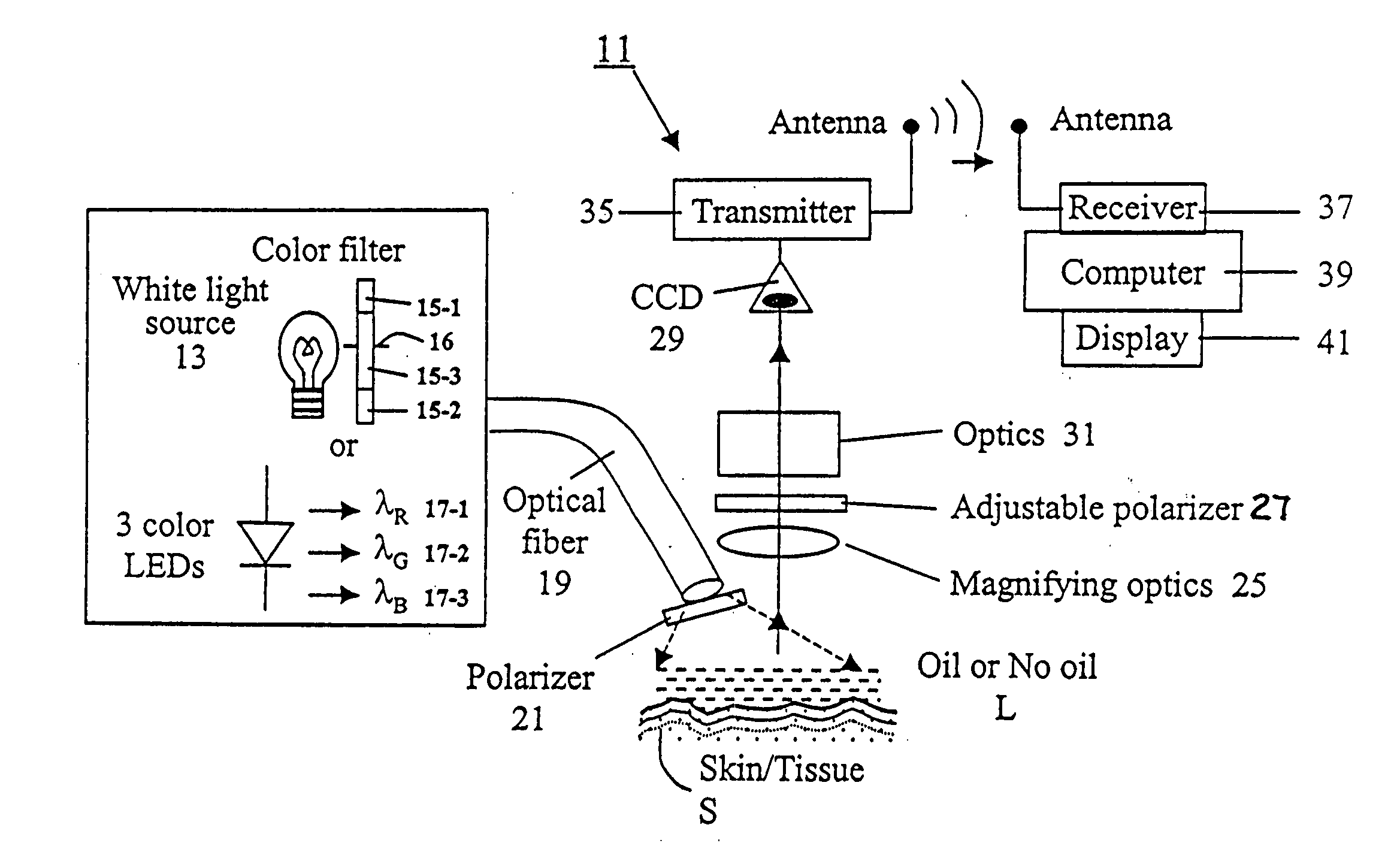
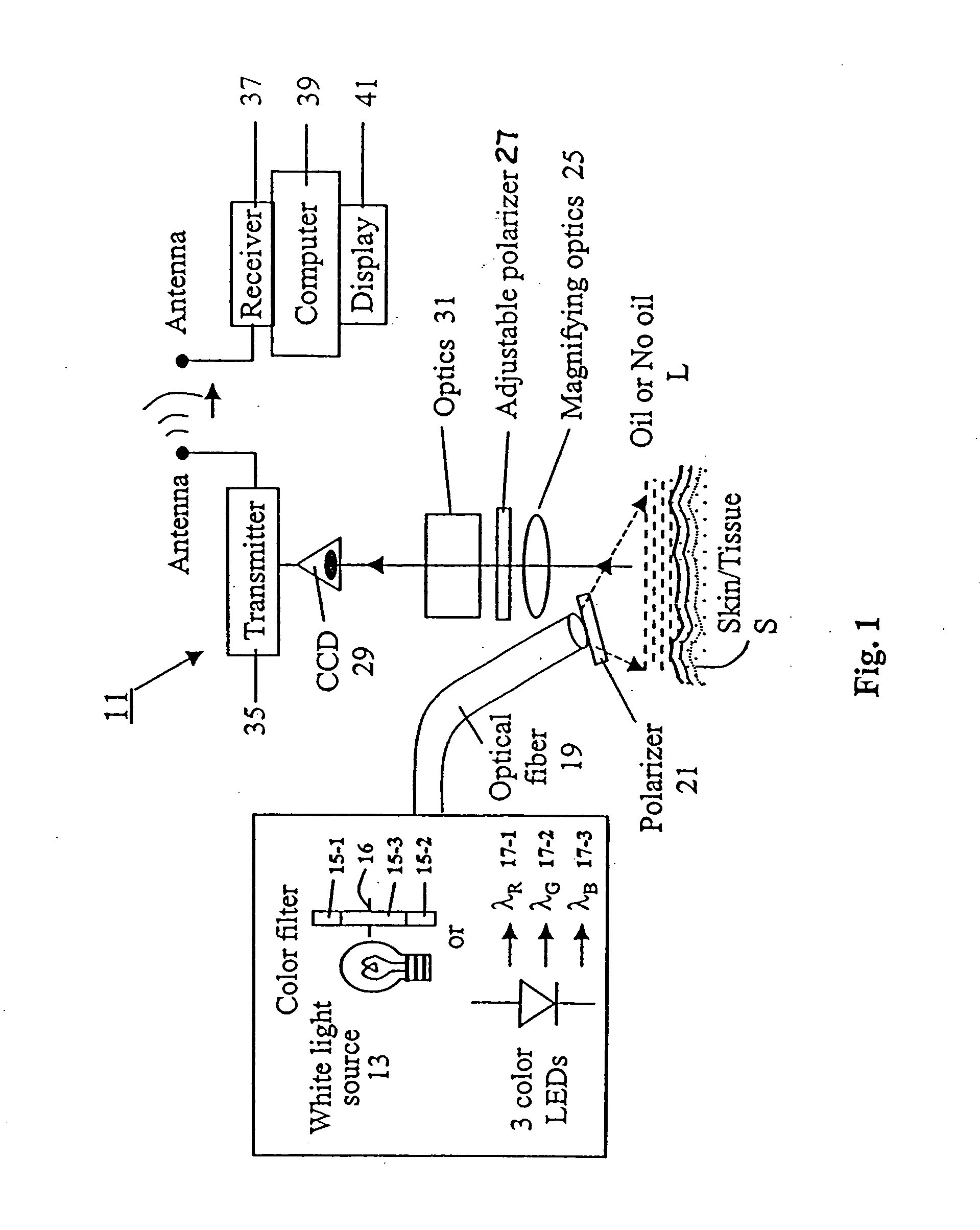
Spectral polarizing tomographic dermatoscope
An apparatus for use in examining an object, such as skin, mucosa and cervical tissues for detecting cancer and precancerous conditions therein. In one embodiment, the apparatus includes a gun-shaped housing having a handle portion and a barrel portion. The front end of the barrel portion is open, and a glass cover is mounted therein. LED's are disposed within the handle portion. A manually-operable switch for controlling actuation of the LED's is accessible on the handle portion. An optical fiber is used to transmit light from the LED's through a first polarizer in the barrel portion and then through the glass cover to illuminate a desired object. Reflected light from the object is passed through a second polarizer, which is adjustably mounted in the barrel portion and which is preferably oriented to pass depolarized light emitted from an illuminated object, and is then imaged by optics onto a CCD detector. The detector is coupled to a wireless transmitter that transmits the output from the detector to a remotely located wireless receiver.
Owner:ALFANO ROBERT R +3
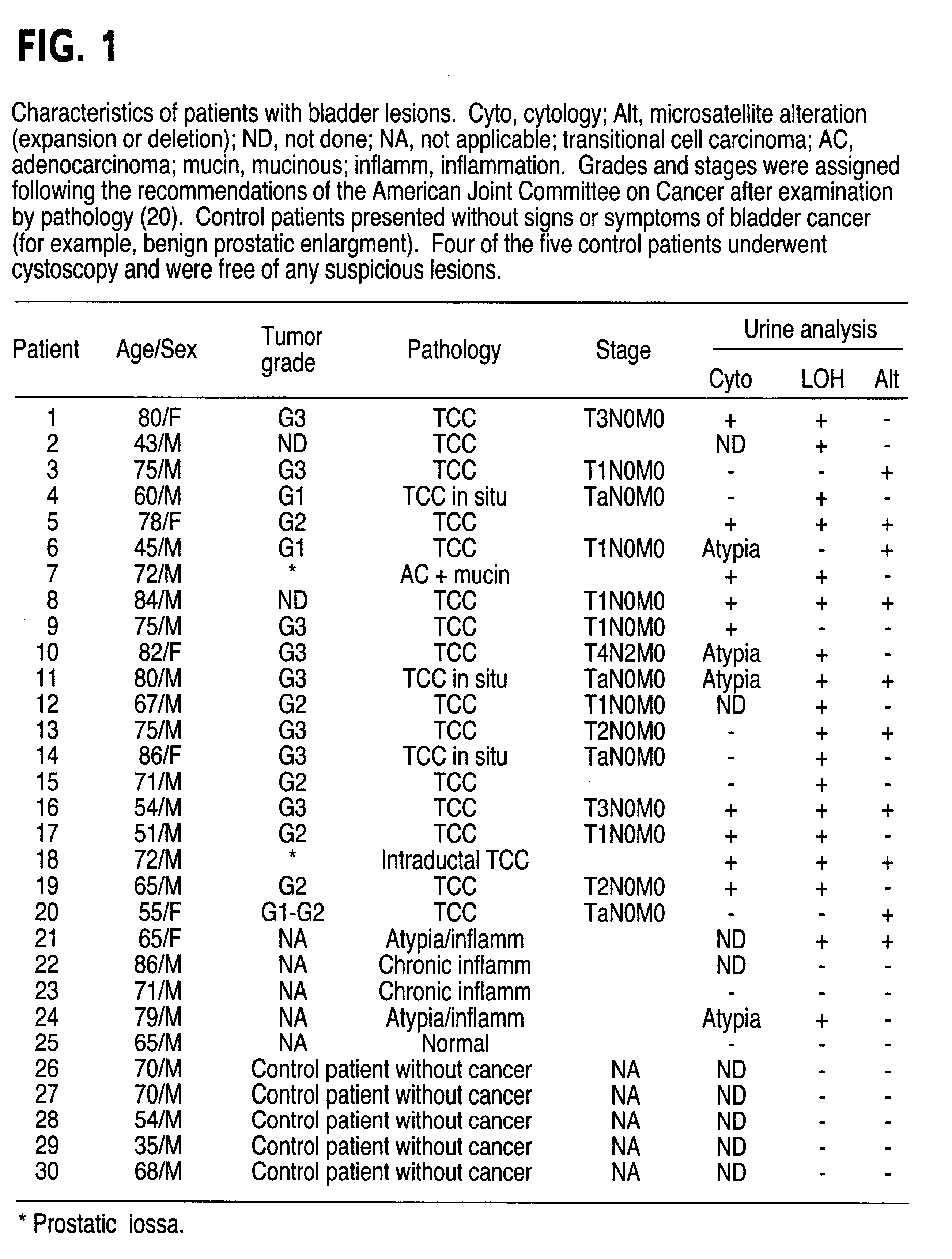
Method for detecting cell proliferative disorders
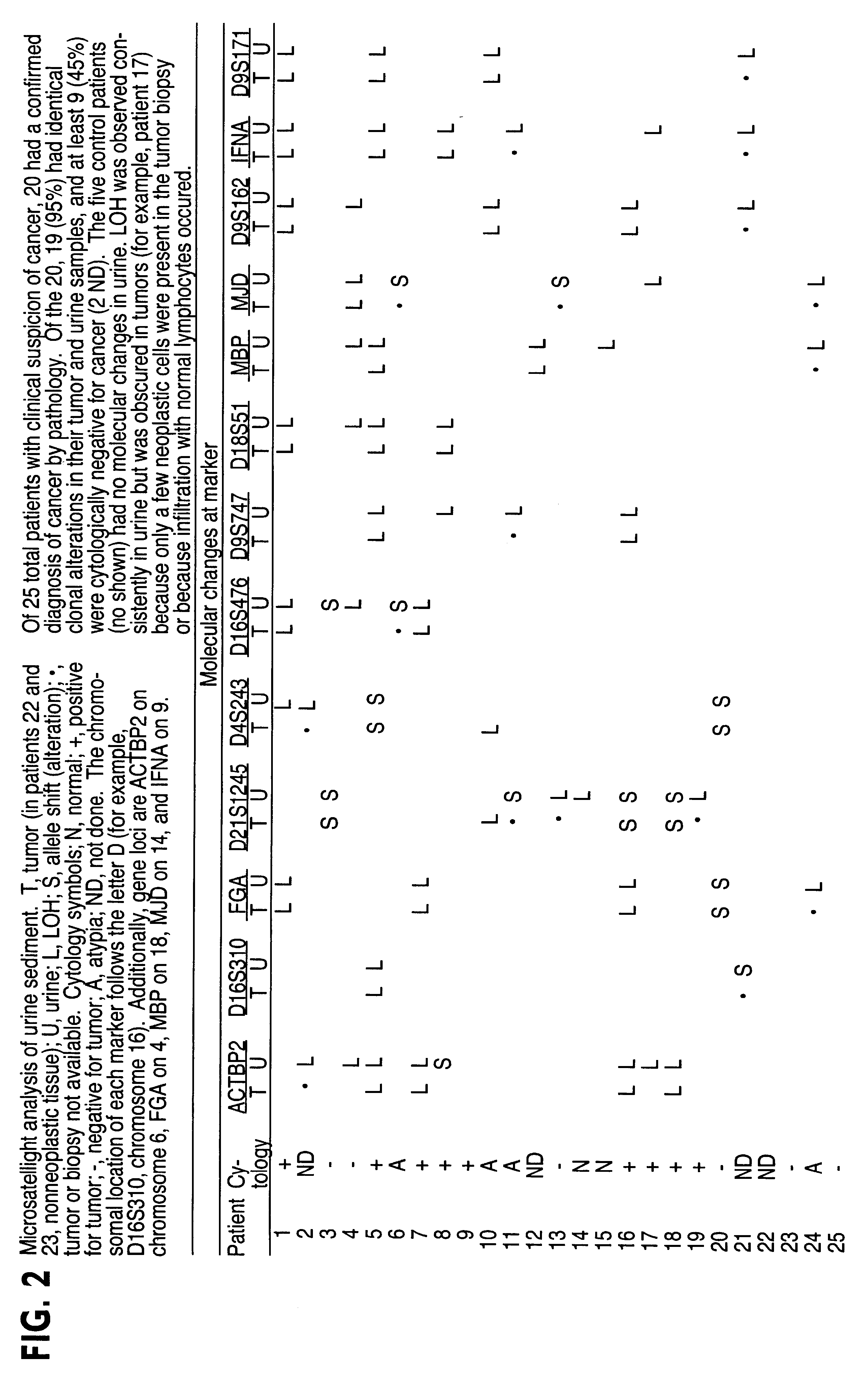
InactiveUS6291163B1Fast and reliable and sensitive and non-invasive screeningHigh copy numberSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCervical tissuePolymerase L
The present invention relates to the detection of a cell proliferative disorder associated with alterations of microsatellite DNA in a sample. The microsatellite DNA can be contained within any of a variety of samples, such as urine, sputum, bile, stool, cervical tissue, saliva, tears, or cerebral spinal fluid. The invention is a method to detect an allelic imbalance by assaying microsatellite DNA. Allelic imbalance is detected by observing an abnormality in an allele, such as an increase or decrease in microsatellite DNA which is at or corresponds to an allele. An increase can be detected as the appearance of a new allele. In practicing the invention, DNA amplification methods, particularly polymerase chain reactions, are useful for amplifying the DNA. DNA analysis methods can be used to detect such a decrease or increase. The invention is also a method to detect genetic instability of microsatellite DNA. Genetic instability is detected by observing an amplification or deletion of the small, tandem repeat DNA sequences in the microsatellite DNA which is at or corresponds to an allele. The invention is also a kit for practicing these methods.
Owner:THE JOHNS HOPKINS UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
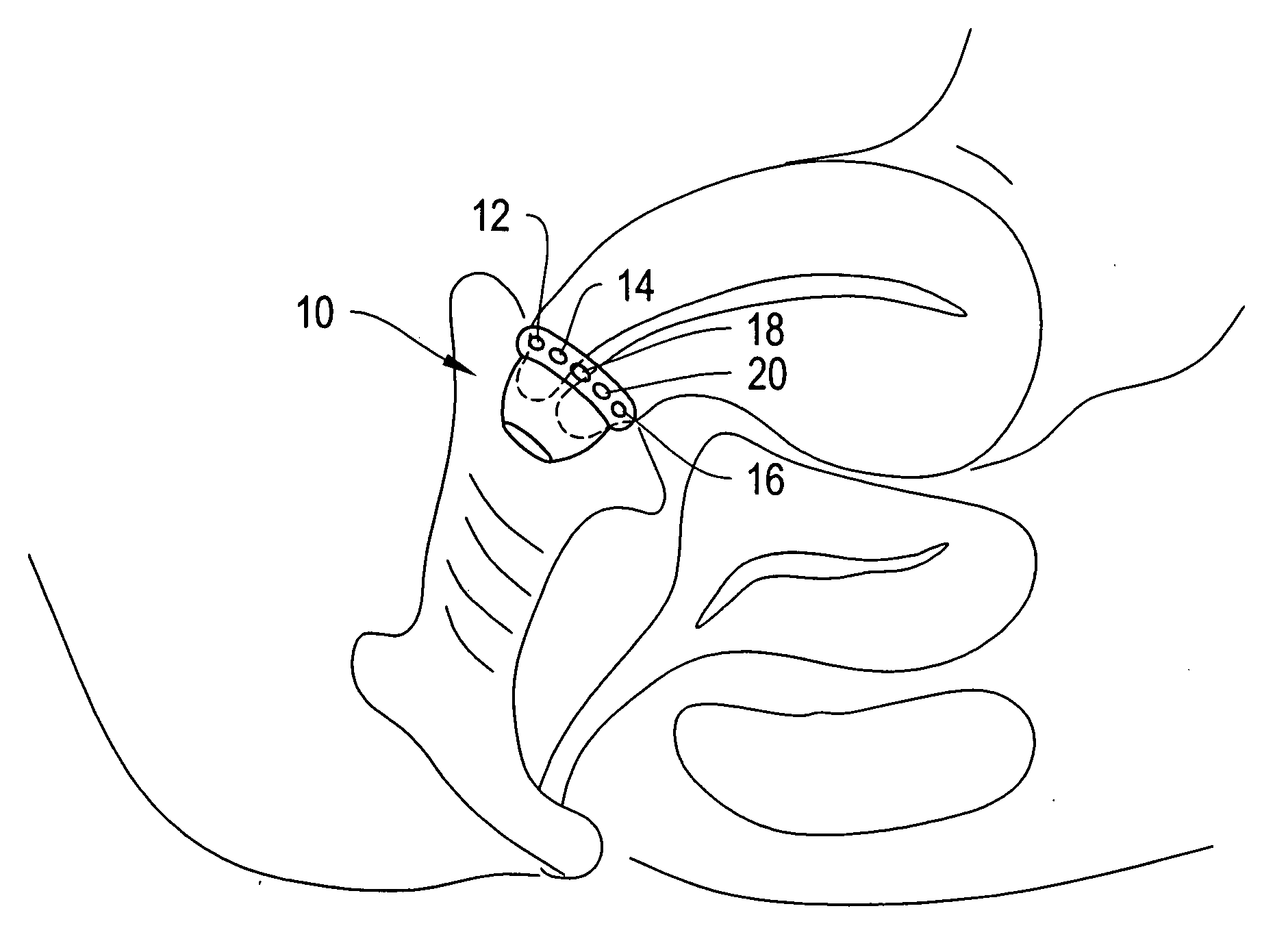
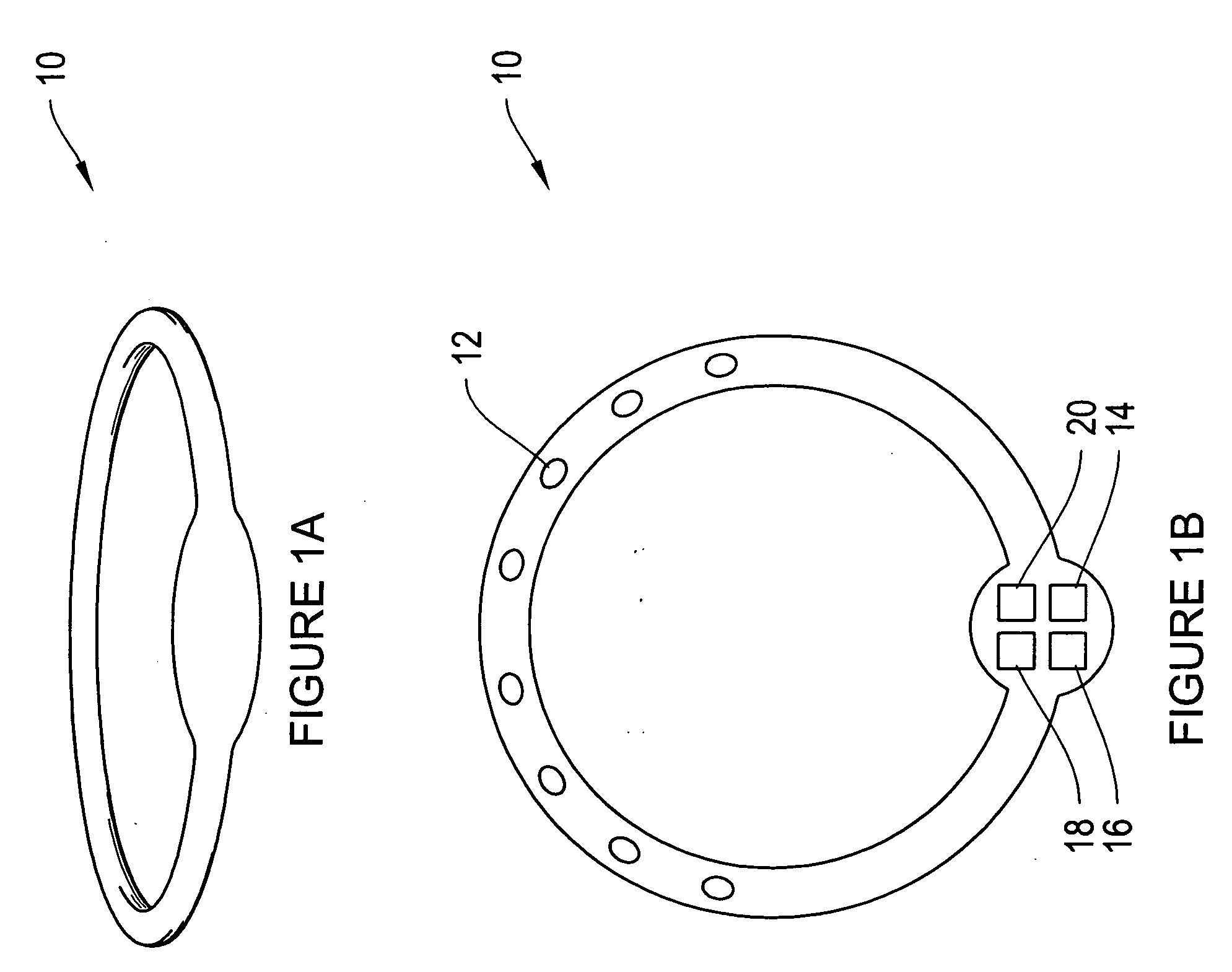
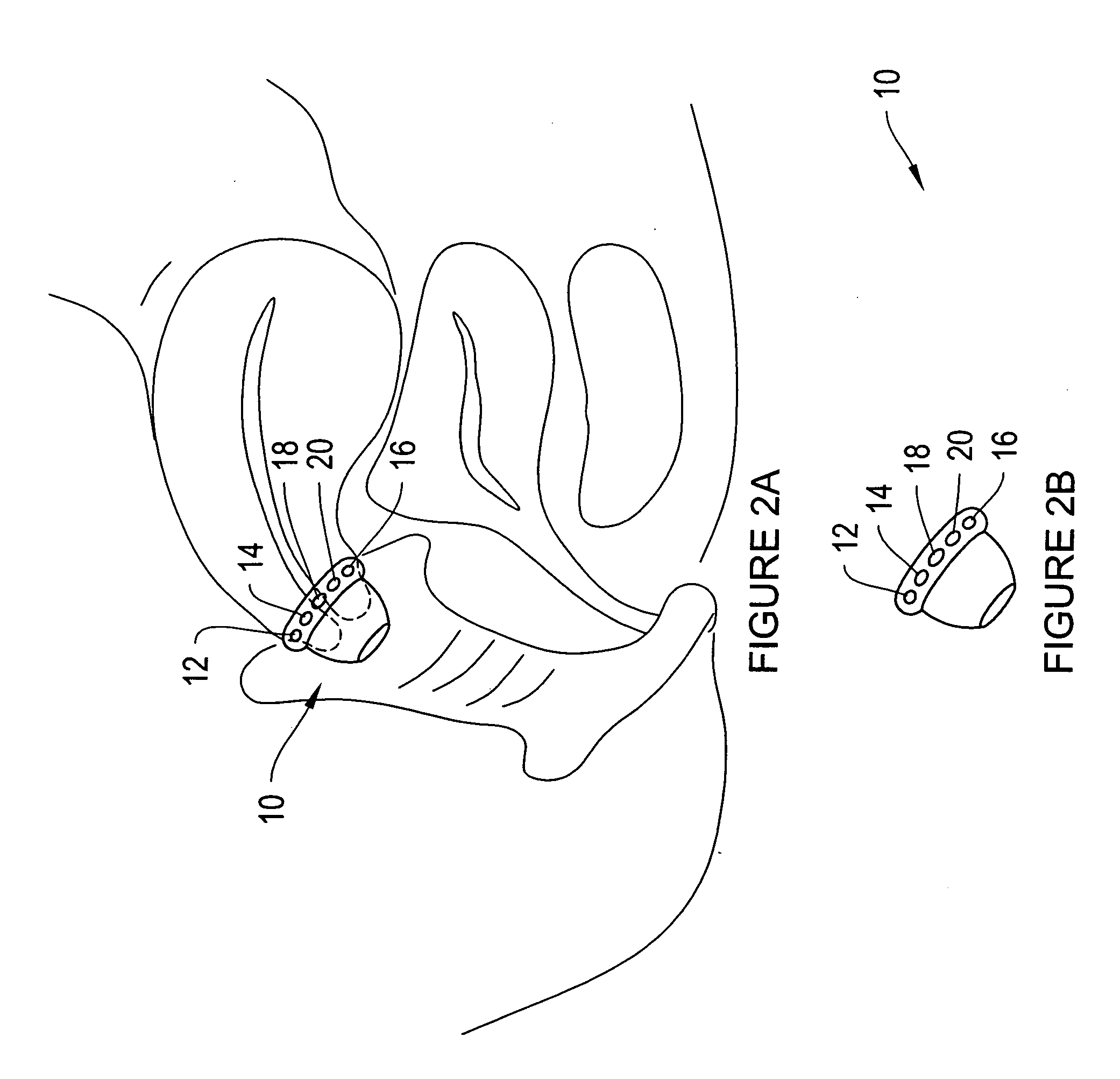
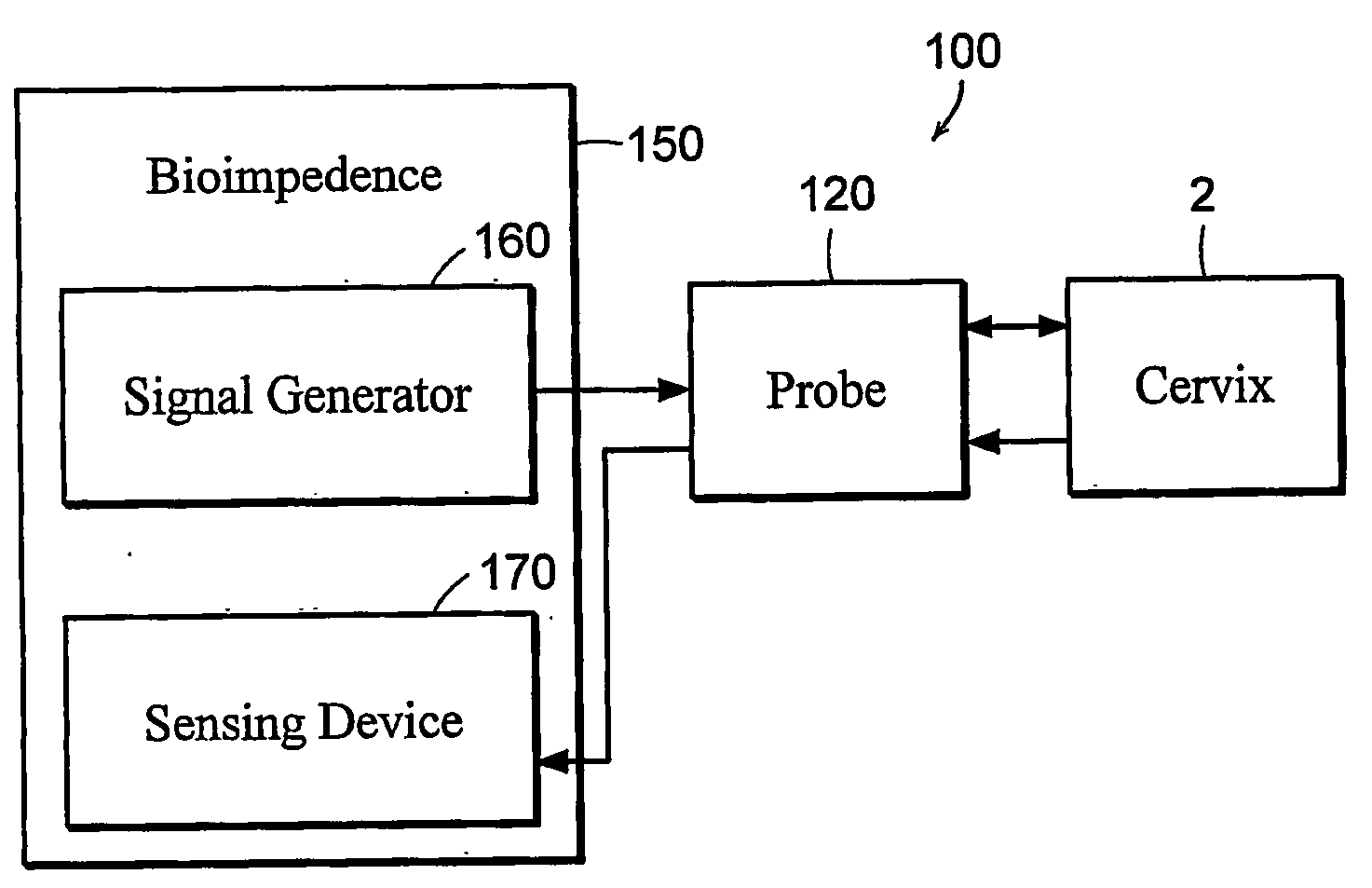
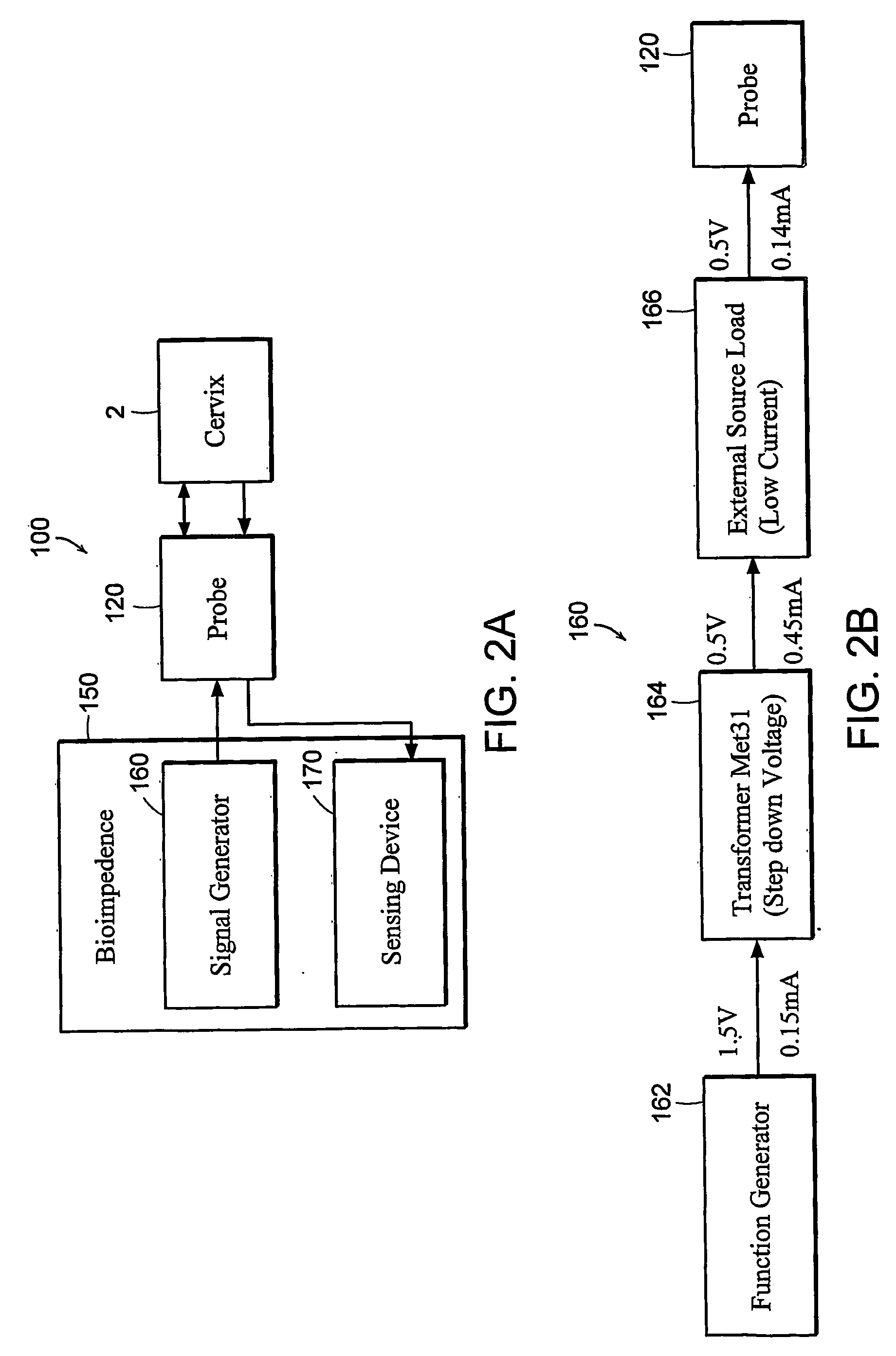
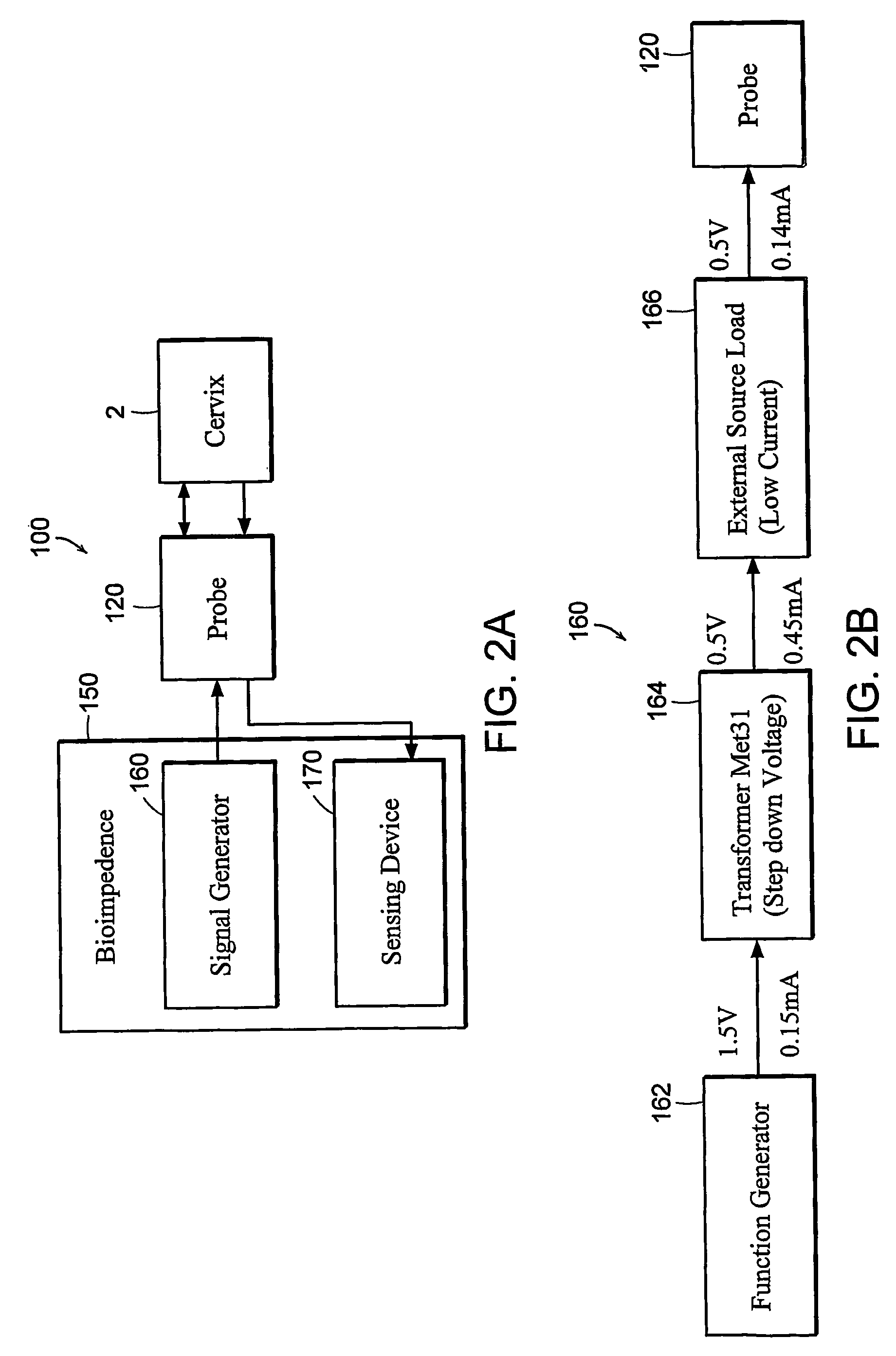
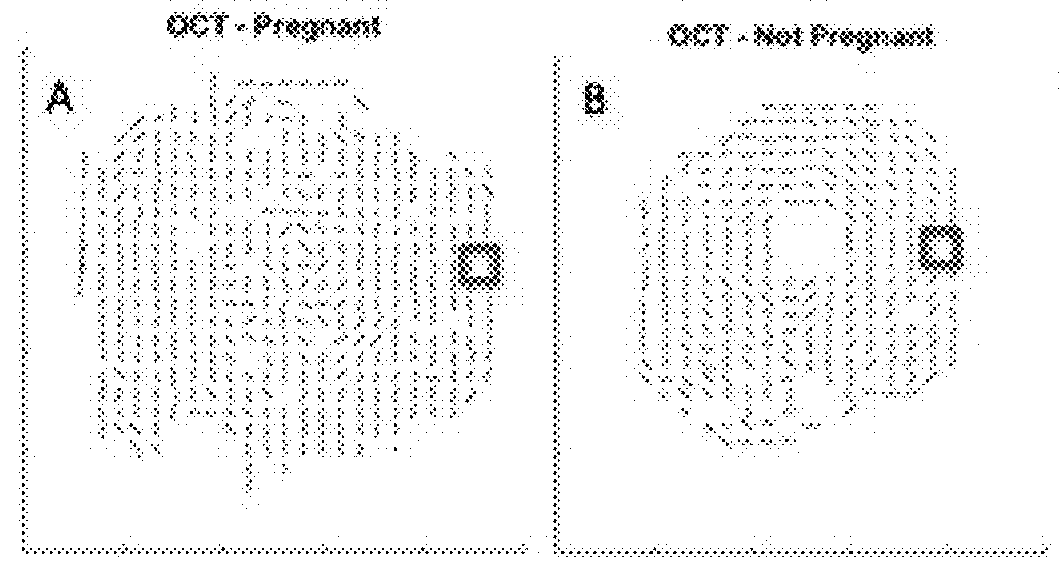
Devices, systems and methods for bioimpedance measurement of cervical tissue and methods for diagnosis and treatment of human cervix
Featured are apparatuses for measuring bioimpendence of tissues of the cervix, more specifically the mammalian cervix. Also featured are methods for examining the tissues of the cervix for clinical or diagnostic purposes such as during routine gynecological examinations to determine early onset of labor in pregnant patients or to assess such tissues for the presence of abnormalities such as cancerous lesions in both pregnant and non-pregnant women. Also featured are methods for treating onset of early or pre-term labor that embody such devices, apparatuses and methods of the present invention. Also featured are systems embodying such devices, apparatuses and / or methods, where such systems preferably are configured to provide diagnostic and / or clinical information to further assist the diagnostician or clinician in diagnosing and / or examining pregnant or non-pregnant patients.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Splice variants of human IL-23 receptor (IL-23R) mRNA and use of a delta 9 isoform in predicting inflammatory bowel diseases
ActiveUS20090311694A1Increased riskDecreased in levelSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCervical tissueCrohn's disease
There is disclosed the cloning and identification of human IL-23R splice variants caused by alternative splicing of the IL-23R mRNA in human. Alternative mRNA forms occur through skipping one, multiple full exons or partial exons, within the IL-23R gene. A total of twenty-five (25) different IL-23R transcripts were identified. A novel exon deletion (exon 9) isoform in the interleukin 23 receptor is disclosed, denoted as Δ9. The present application also describes a quantitative assay to measure different IL-23R isoform. Detection of Δ9 isoform of IL-23R is predominantly present in colon and cervical tissues. A decrease in Δ9 is observed in inflamed colon tissues in Crohn's patients. There is disclosed a method of predicting Crohn's disease by measuring Δ9 isoform of IL-23R.
Owner:MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC LAB
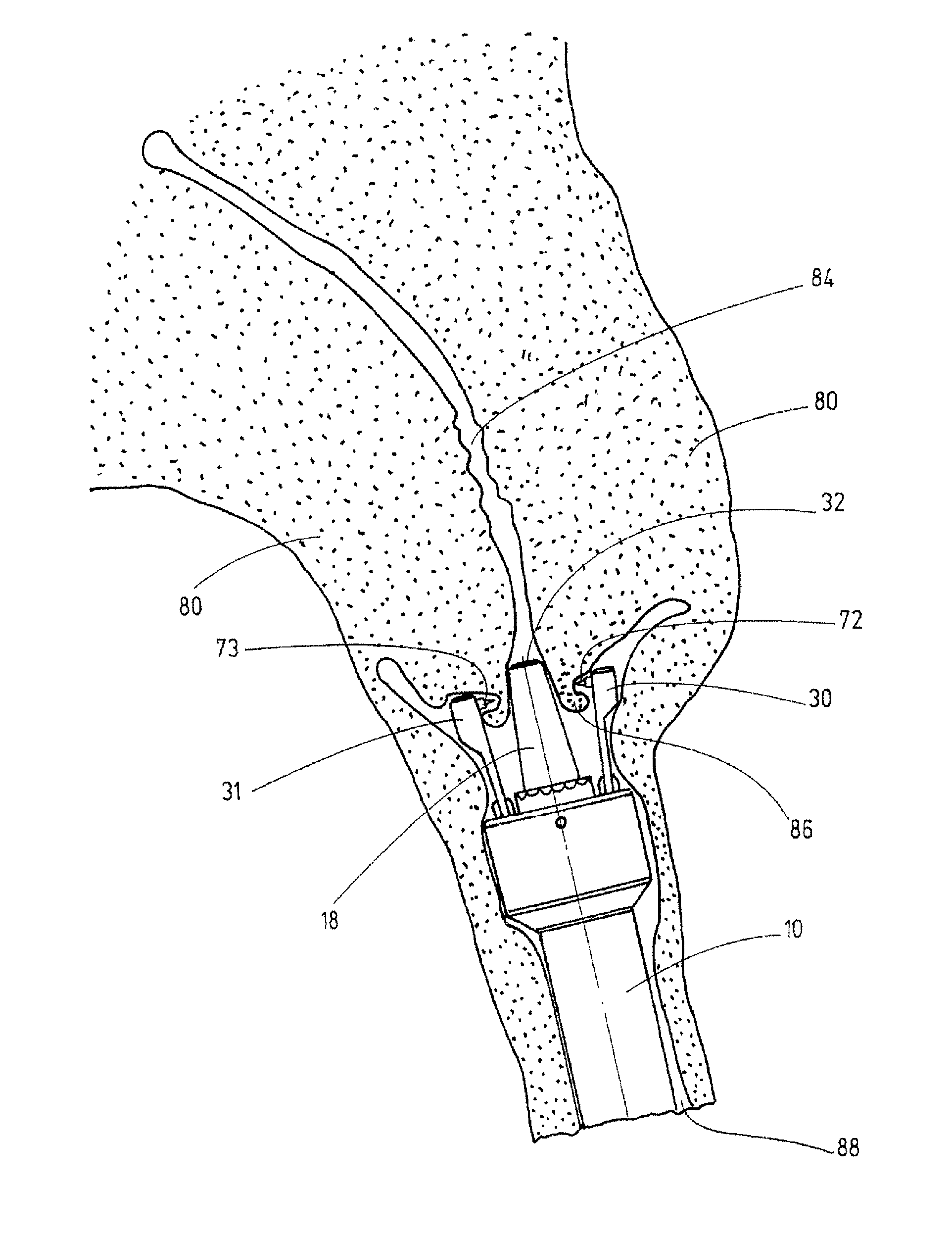
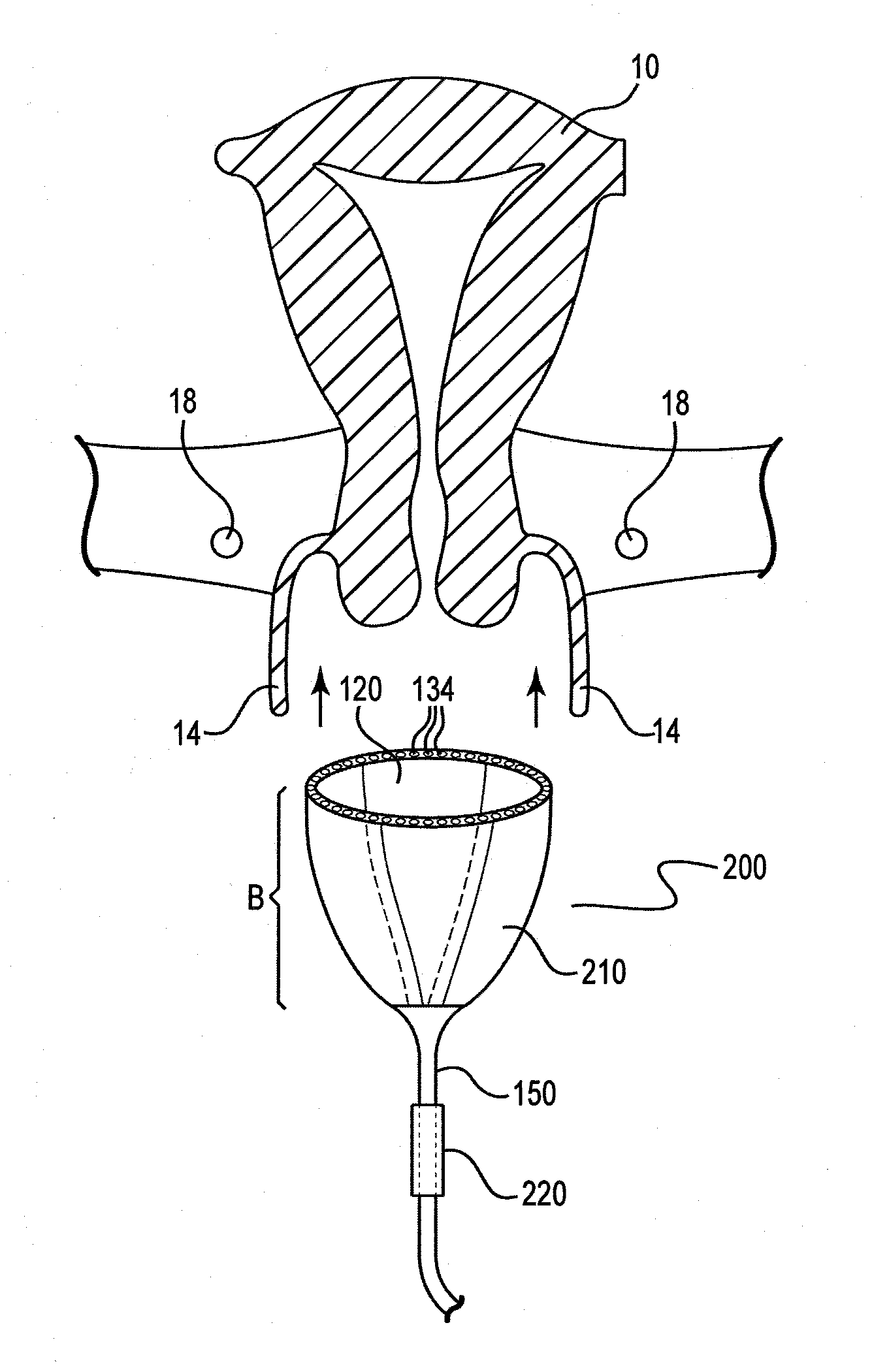
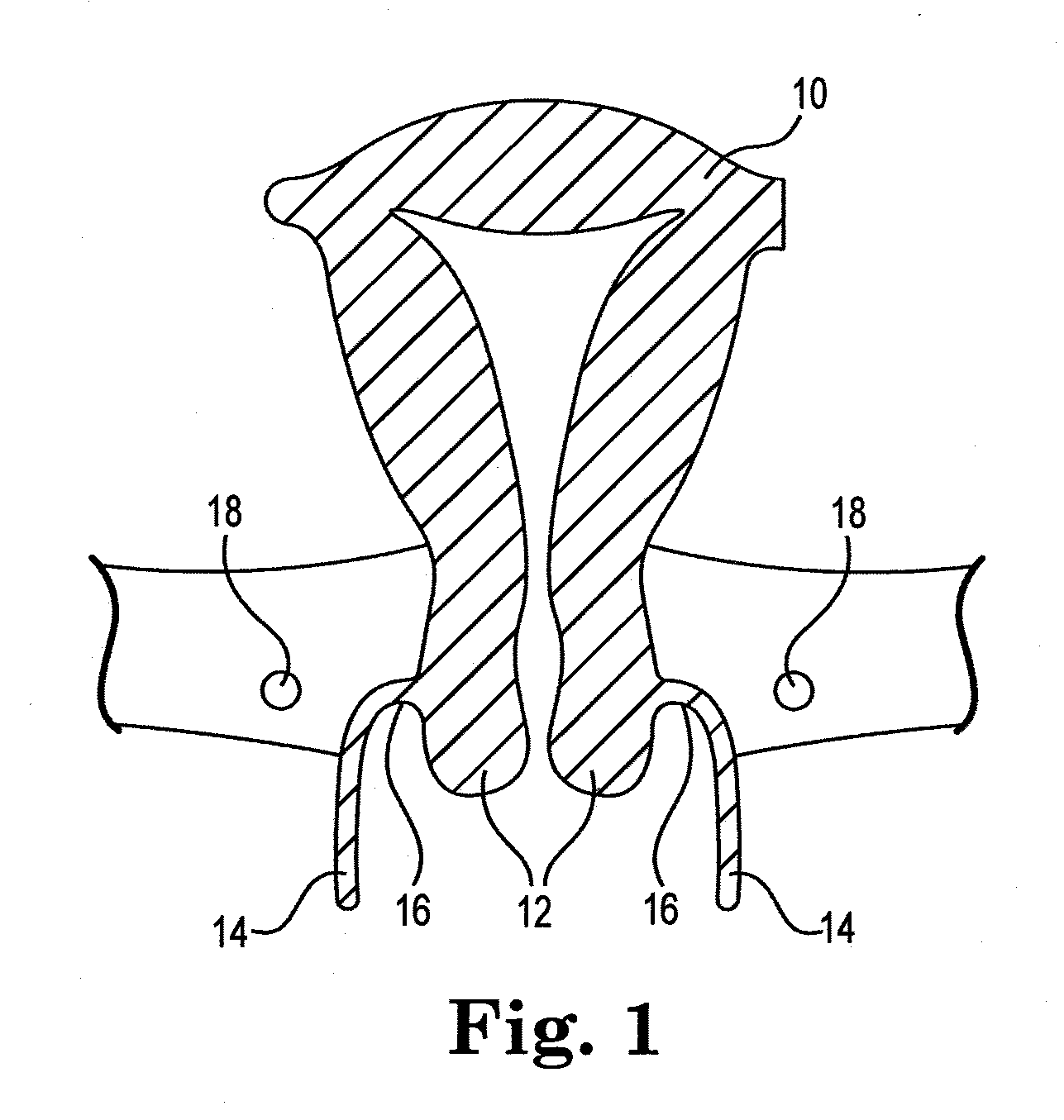
Cervical Seal
A thermal ablation device includes an elongated member sized and shaped for insertion into a uterus via a cervical opening. The elongated member defines a first lumen extending therethrough to a first distal opening which, when the apparatus is in an operative position, opens into the uterus and a seal positioned on the elongated member so that, when the elongated member is in the operative position, the seal engages cervical tissue around a circumference of the elongated member and prevent fluids introduced into the uterus via the first lumen from flowing therepast into the cervix. The seal includes a plurality of flexible members separated from one another along a length of the elongated member and projecting radially outward from an outer surface of the elongated member.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method for screening new internal reference molecules suitable for cervical tissue micro RNA real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR research
InactiveCN101818202AAvoid YieldAvoid quality problemsMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceCervical tissueFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for screening new internal reference molecules suitable for cervical tissue micro RNA real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR research. The method comprises the following technical steps: screening human Micro RNA probes by using a Micro RNA chip, and selecting Micro RNAs with constant normal tissue expression and high expression abundance of cervical cancer and cervix as candidate internal references; selecting a normal cervical epithelial tissue and a cancerous cervical tissue as clinical cervical tissue specimens respectively, and verifying the specimens by using fluorescence quantitative PCR; and analyzing data by using two special internal reference analysis software comprising geNorm software and Norm Finder so as to discover the internal reference molecules suitable for cervical tissue Micro RNA research. The internal reference molecules screened and verified by using the method of the invention can avoid possible differences of different cervical tissue specimens on the yield, quality and reverse transcription efficiency of the RNA, well correct and standardize the data for real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR detection, and improve the accuracy and the reliability of the search.
Owner:ATTACHED OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY OSPITAL MEDICALCOLLEGE ZHEJIANG UNIV
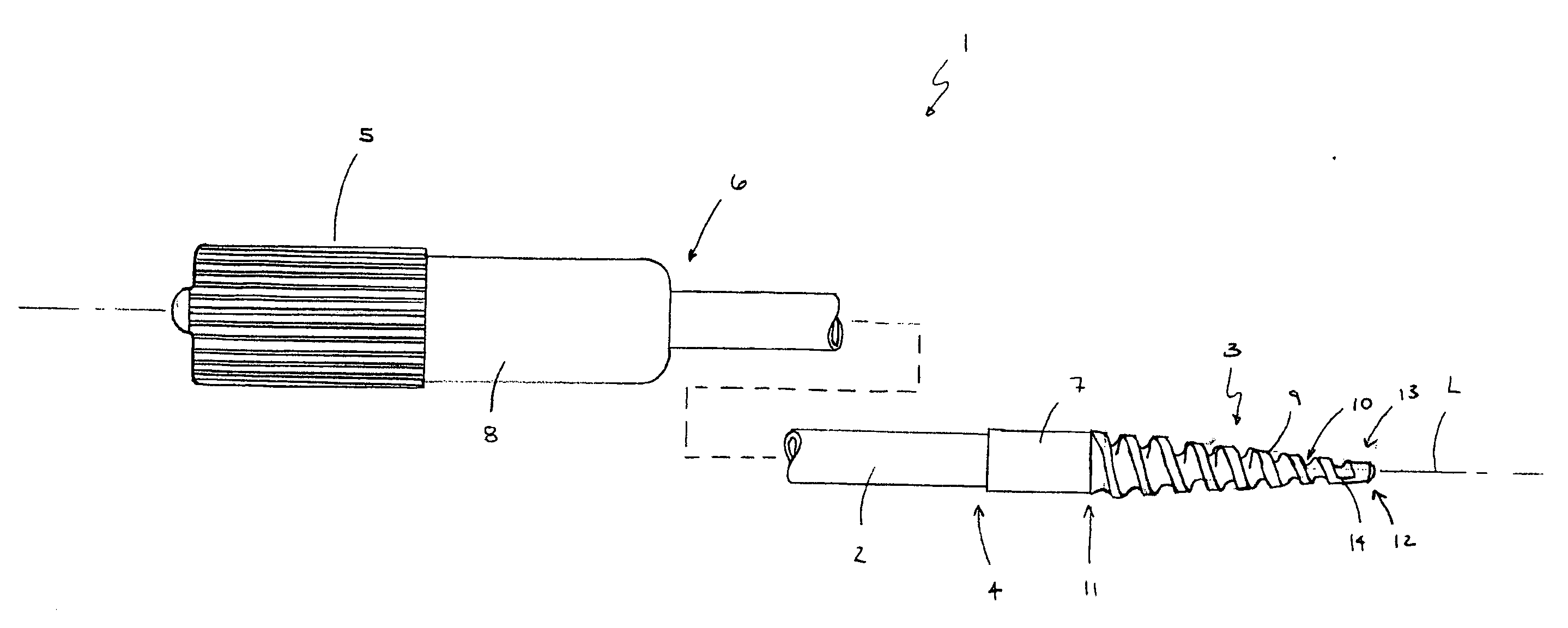
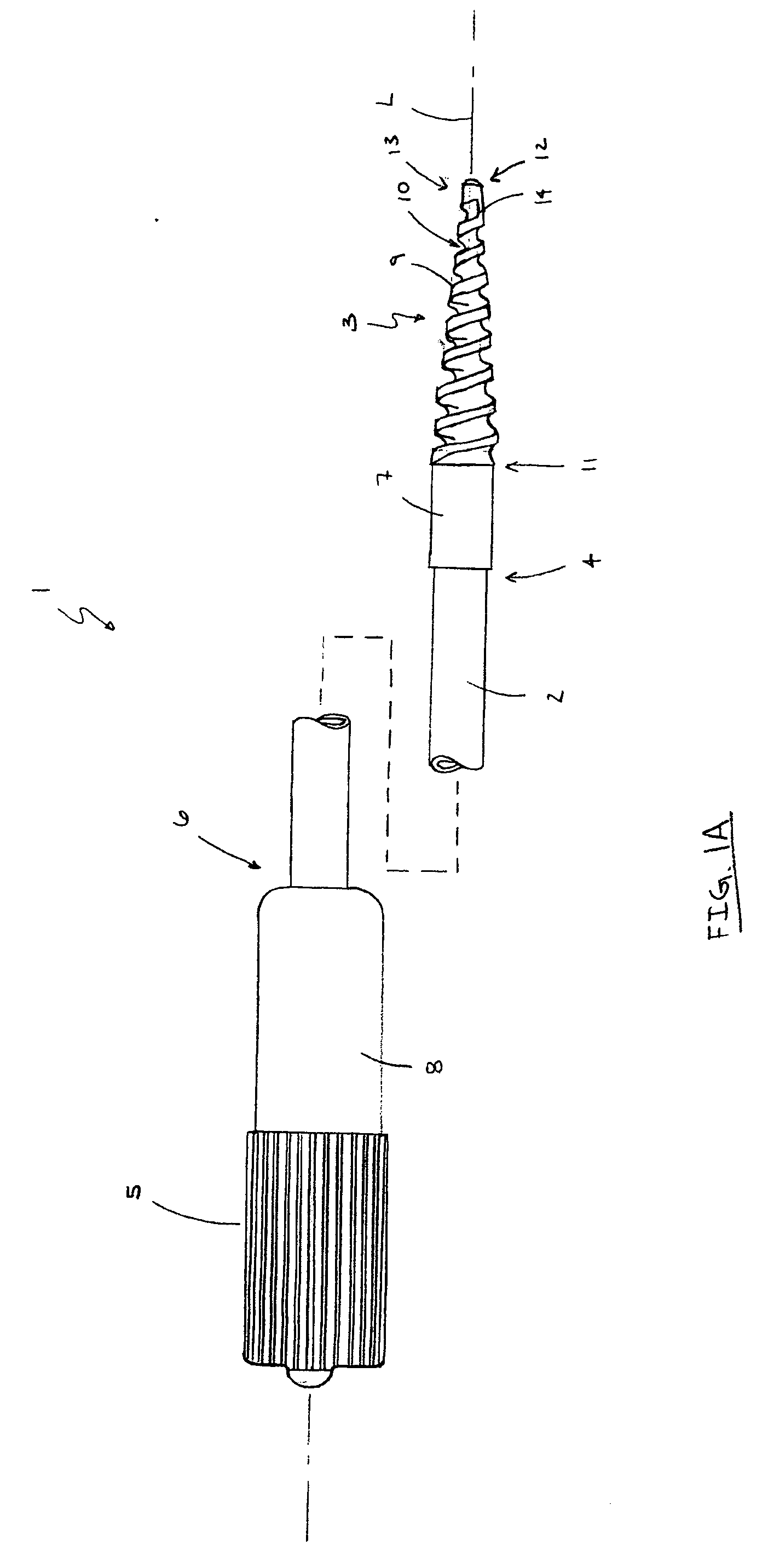
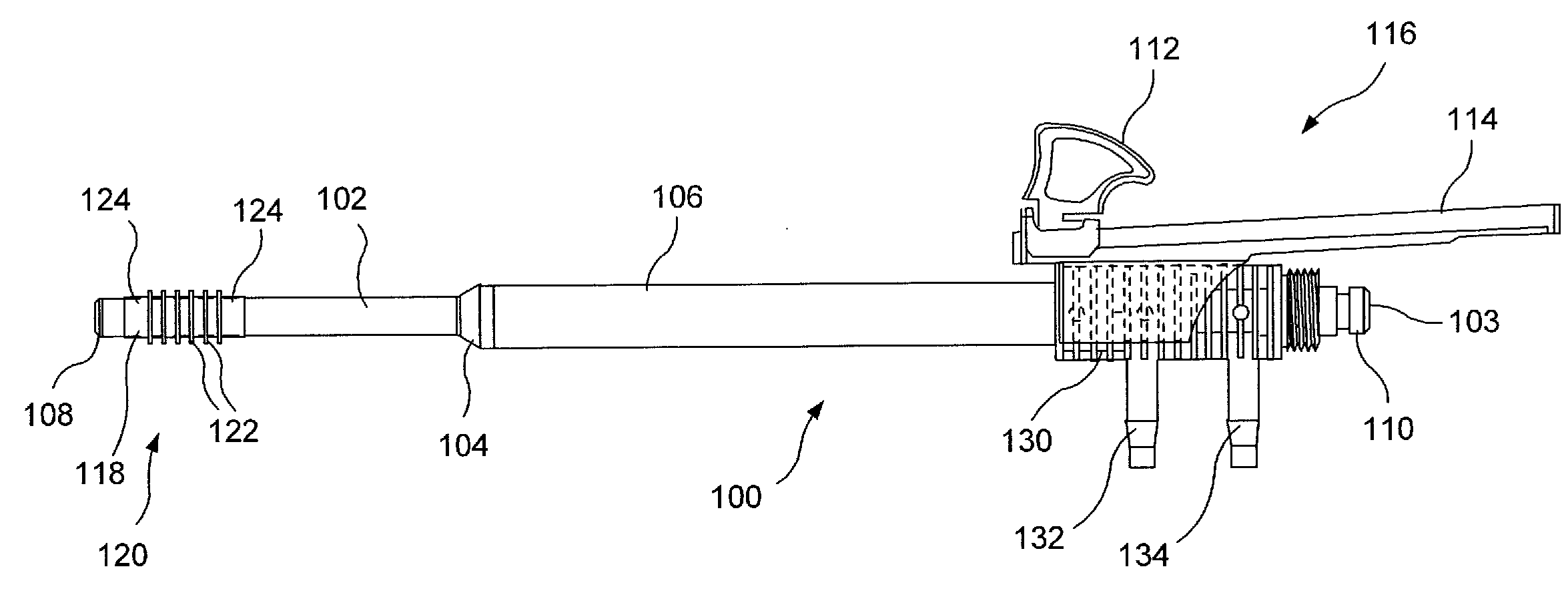
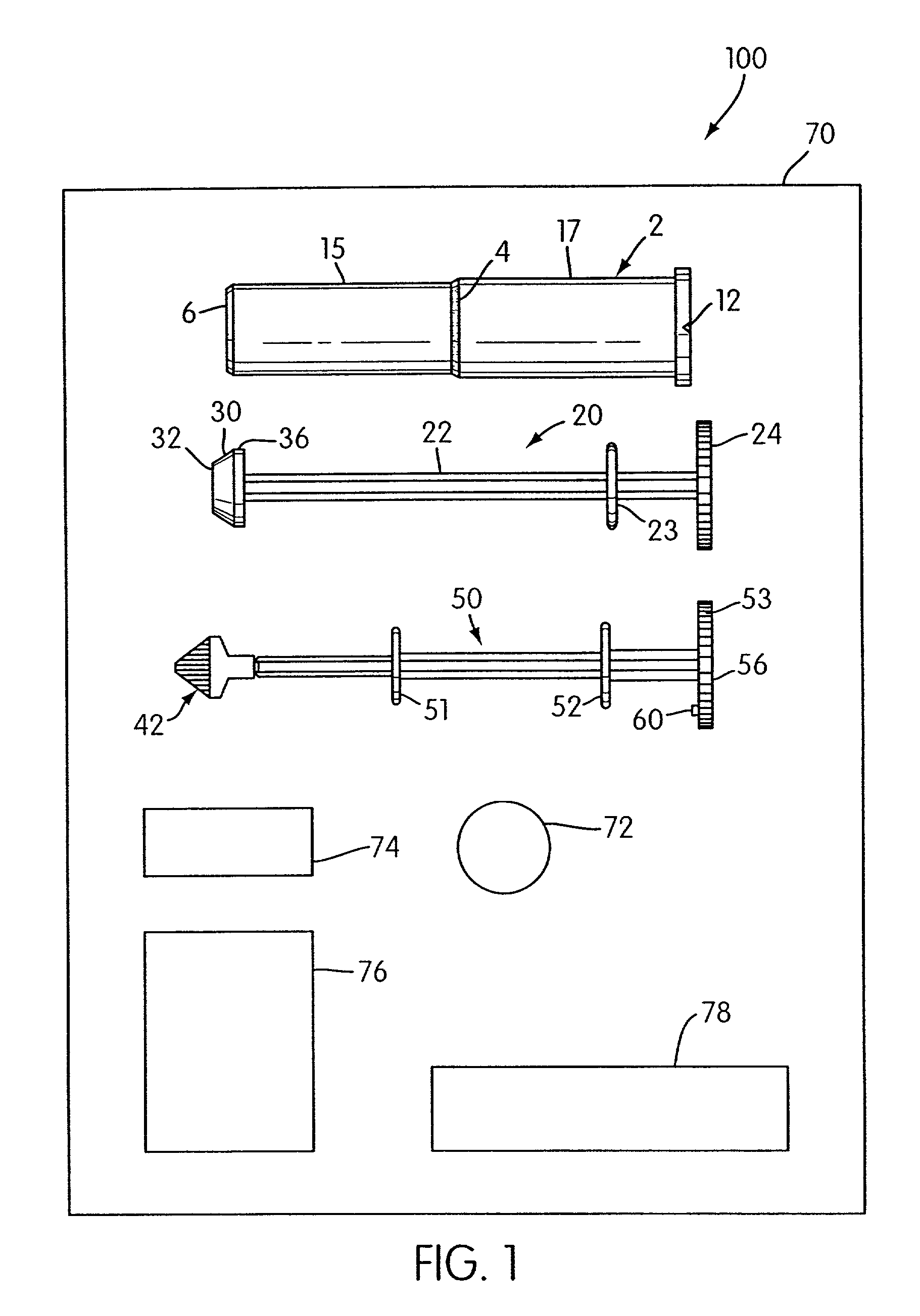
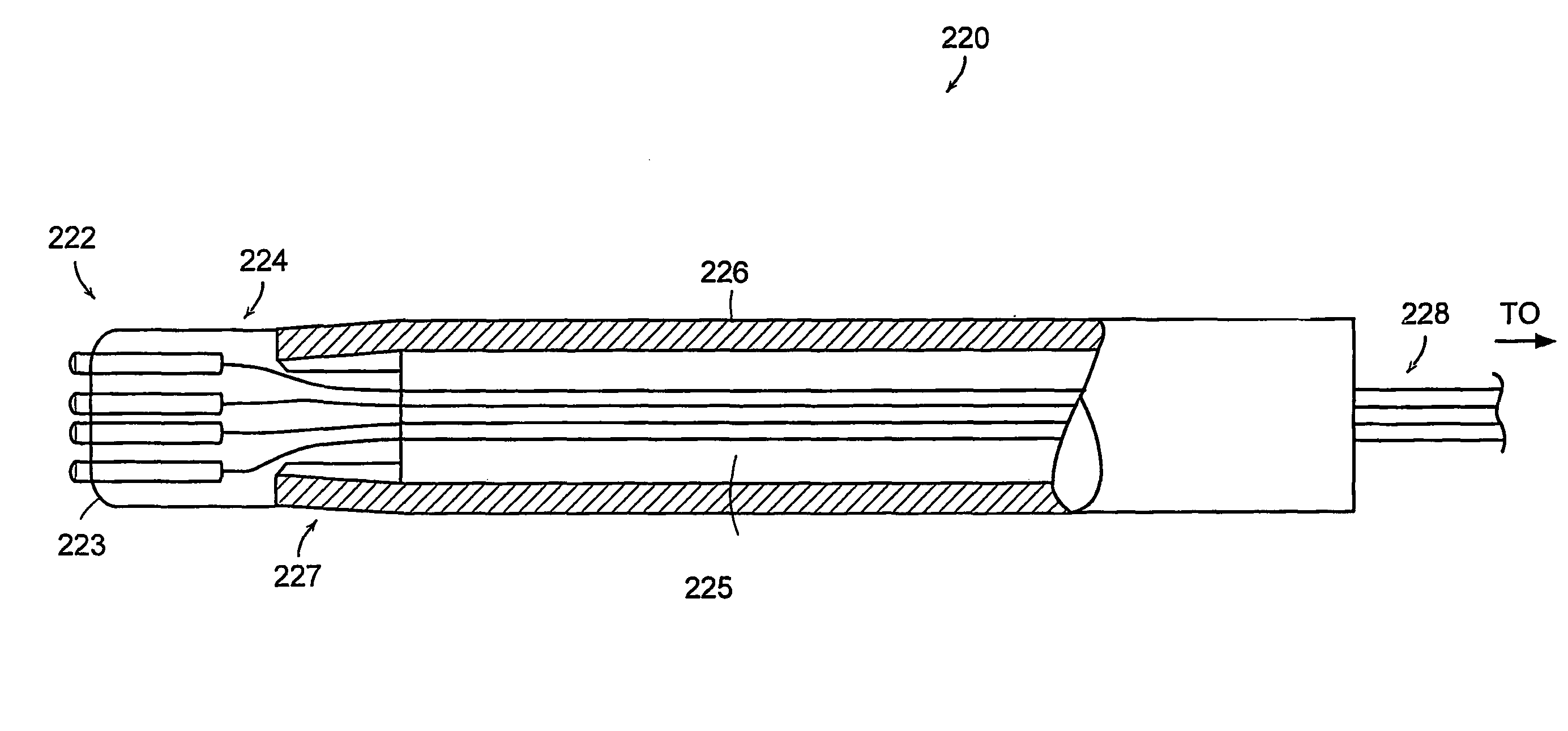
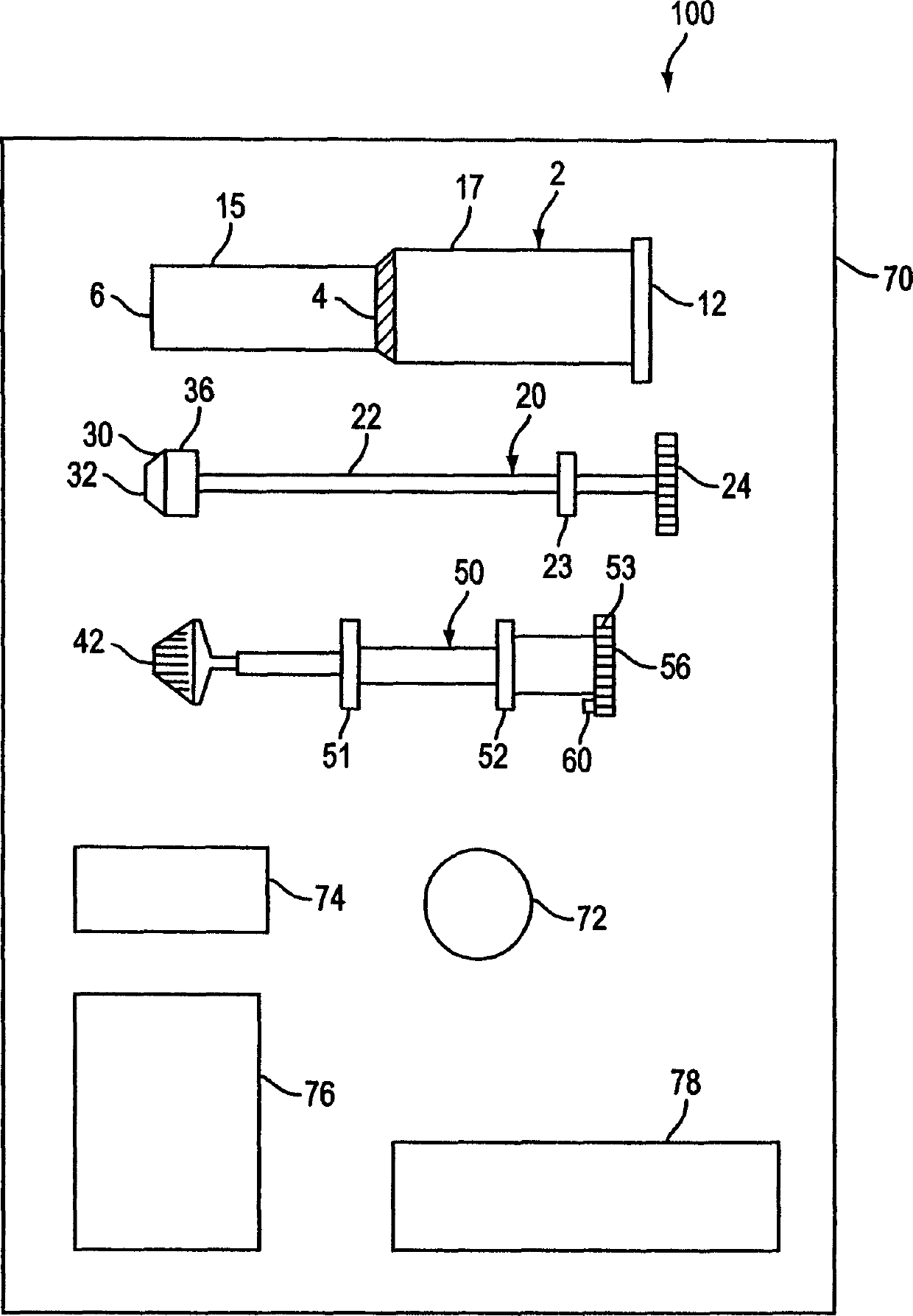
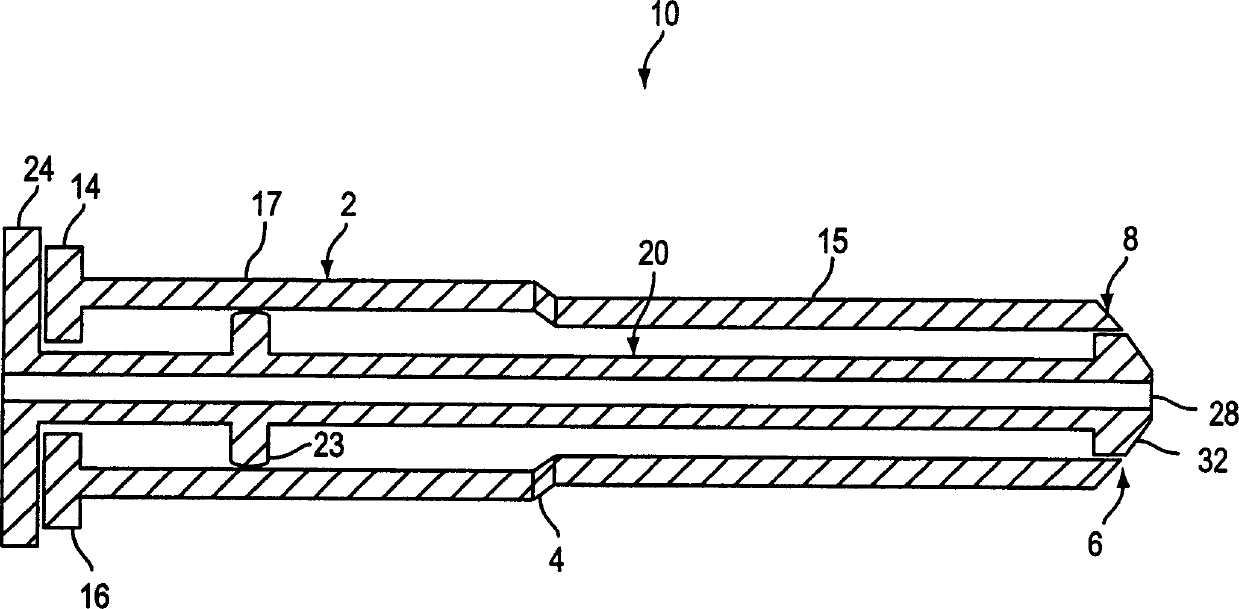
Method and apparatus for sampling cervical tissue
InactiveUS7087028B2Reduce painLess discomfortSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsCervical tissueInsertion depth
A cervical sampling system for collecting a cervical sample for using a Pap test. The cervical sampling system includes an insertion tube with an insertion position indicator, and an introduction guide member that guides the insertion tube into a vaginal cavity. The vaginal insertion tube includes an insertion depth indicator to allow the user to determine the appropriate depth to insert the tube. A cervical sampler is positioned within the vaginal insertion tube and extends into the vaginal cavity to collect samples. The insertion tube and cervical sampler include signaling members that cooperate to indicate to the user when the cervical sample has been rotated through a complete revolution. After the cervical sample has been collected, an ethanol based fixative is applied onto the collecting member before it is forwarded to a lab for slide preparation.
Owner:SOLOCELL +1
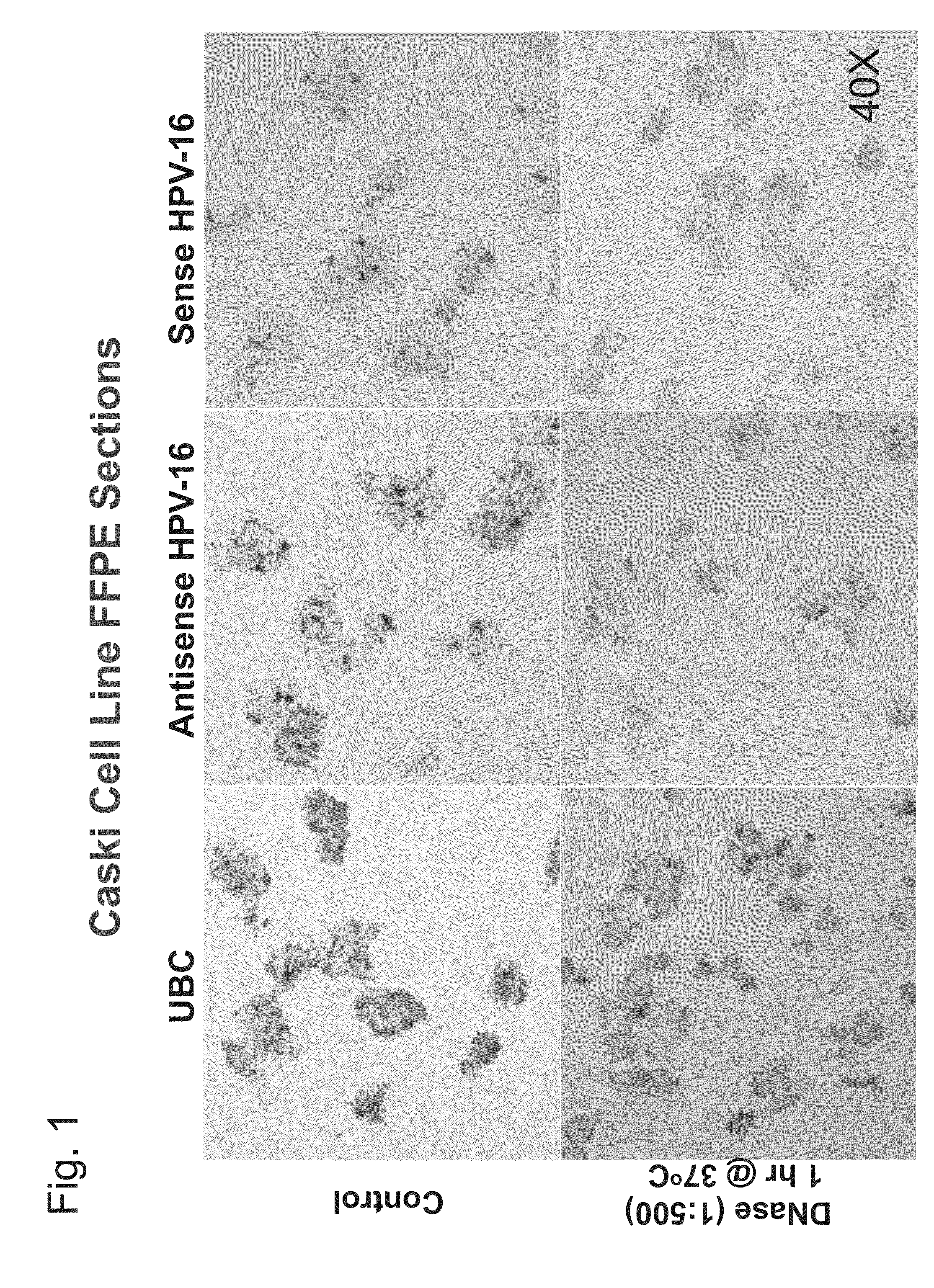
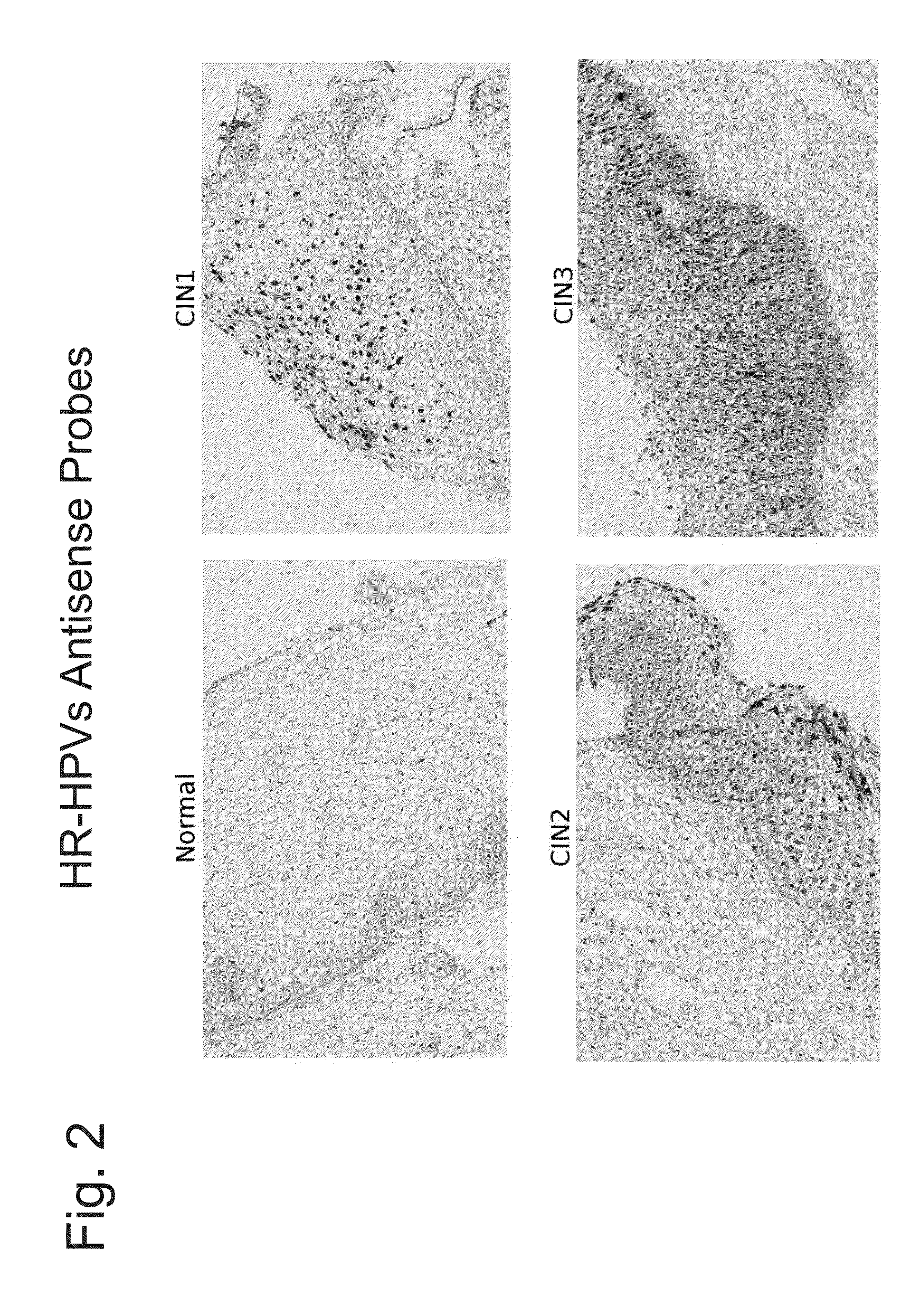
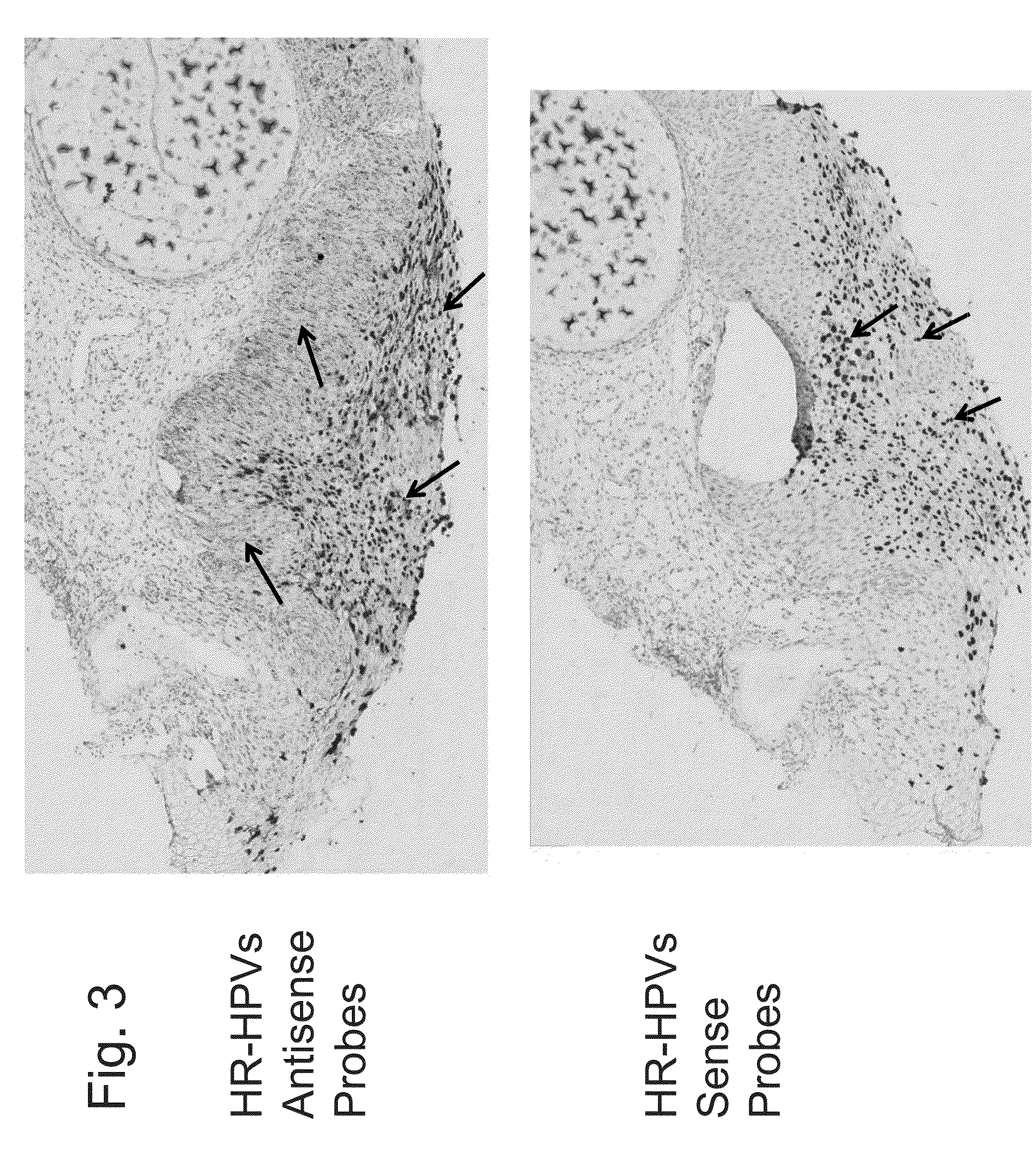
Differentiation between transient and persistent high-risk HPV infection by in situ hybridization
InactiveUS20140357509A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningIn situ hybridisationCervical tissue
The invention relates to methods of categorizing a cervical tissue or cytology sample by performing an in situ hybridization assay using an antisense E6 or E7 probe on a cervical tissue sample, wherein the antisense E6 or E7 probe can simultaneously detect HPV DNA and HPV RNA; detecting the presence of HPV nucleic acid; and categorizing the cervical tissue sample based on HPV nucleic acid expression.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL DIAGNOSTICS INC
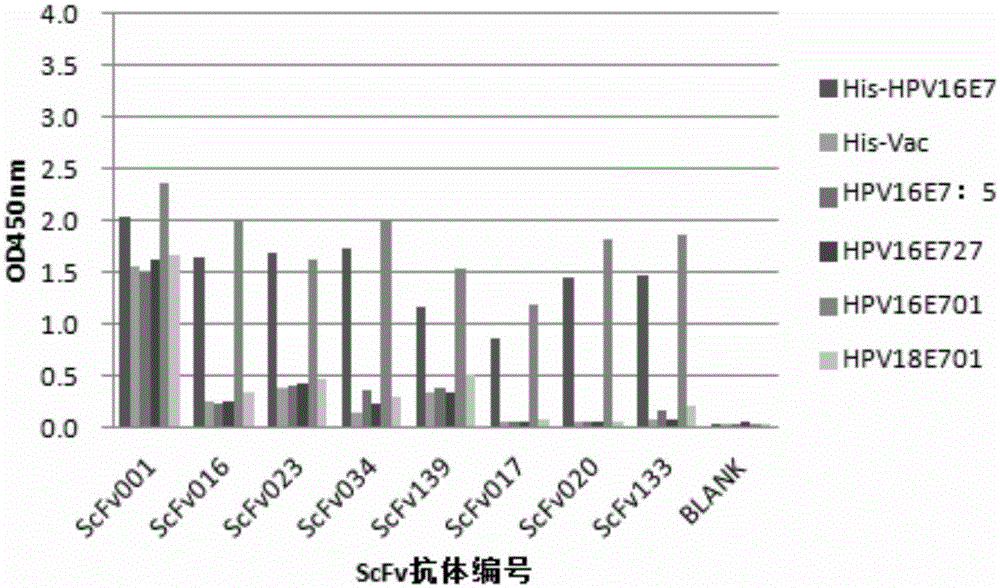
Monoclonal antibody for detection and classification of cervical cancer and application thereof
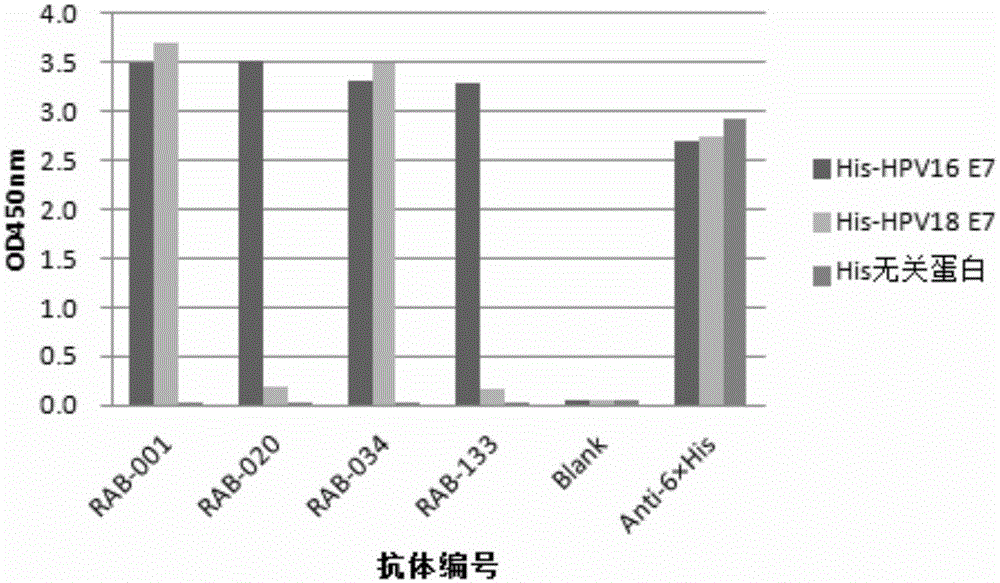
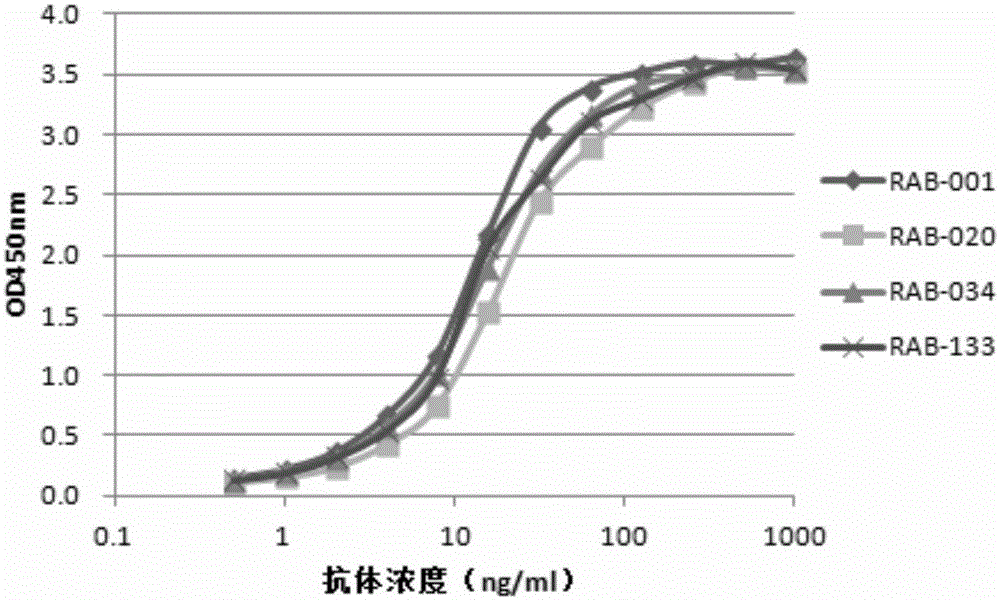
ActiveCN105131113AStrong specificityHigh affinityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsCervical lesionCervical tissue
The invention provides a monoclonal rabbit antibody for identifying HPV16 positive cervical tissues. The antibody can be used for specifically detecting a biomarker HPV16E7 protein in tissues including cervical cancer and cervical lesions, so that HPV persistent infection related cervical cancer tissues from abnormal or noncancerous cervical epithelial tissues, cervical cancer caused by high-risk HPV infection can be accurately diagnosed, and risk early-warning can be especially performed for whether early cervical lesions cancerate or not, so that the misdiagnosed rate of cervical lesions can be effectively reduced, and injuries and resource waste caused by over treatment for patients can be improved.
Owner:ATTOGEN BIOMEDICAL SUZHOU INC
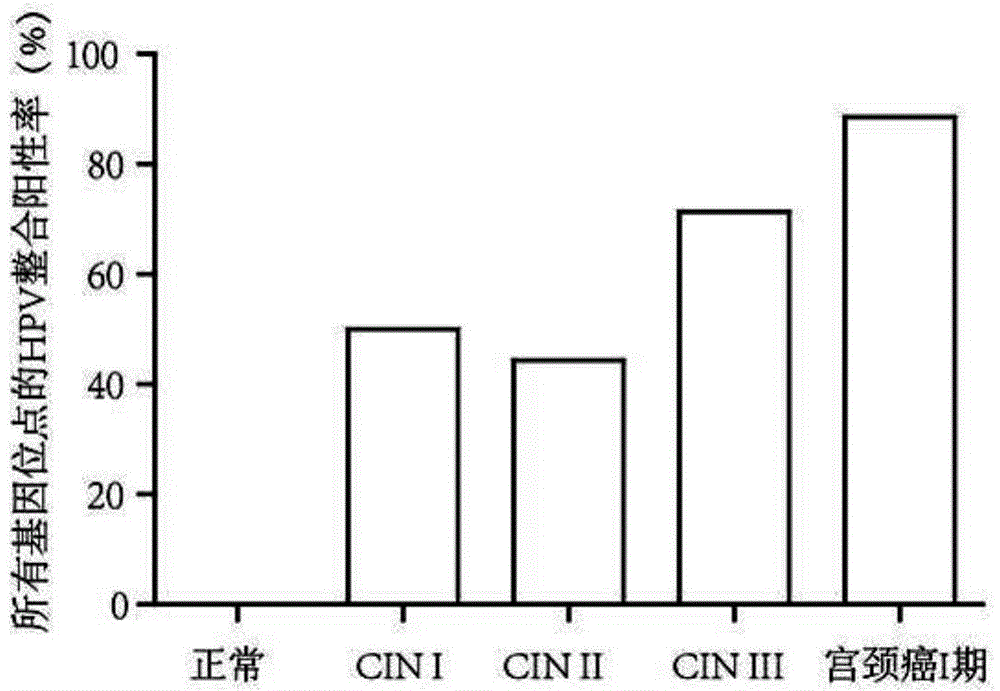
HPV-integrated gene sites related to occurrence of cervical carcinoma and application thereof
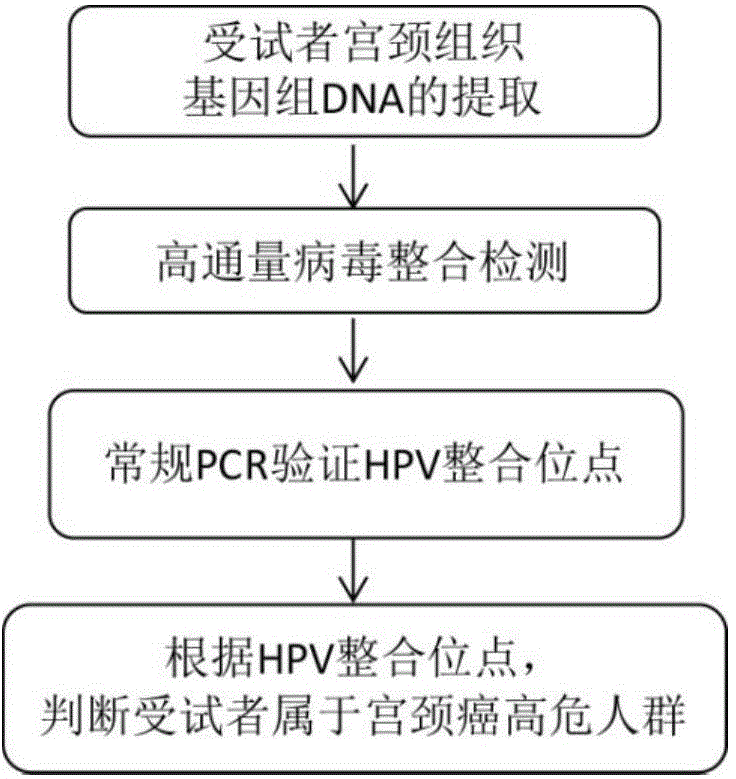
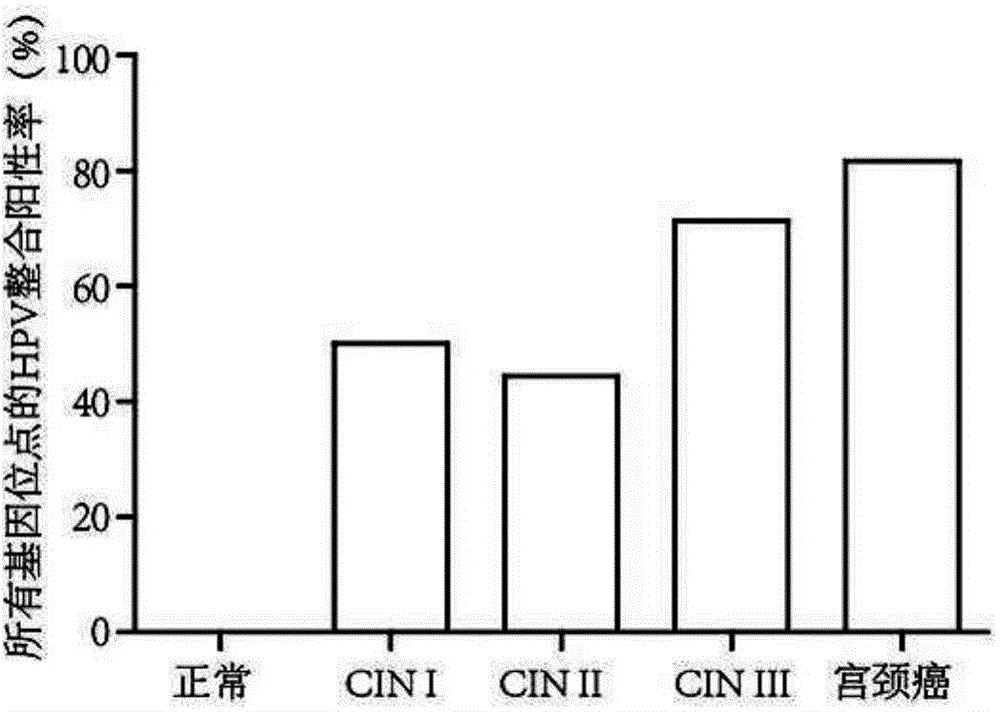
ActiveCN104830869AReduce false positive rateEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationHigh risk populationsCervical tissue
The invention relates to HPV-integrated gene sites related to occurrence of cervical carcinoma and a kit prepared based on the HPV-integrated gene sites related to occurrence of cervical carcinoma. Detection of high-risk populations of cervical carcinoma can be realized by extracting the DNA of cervical tissue of a subject, carrying out capturing and sequencing with a high flux virus, carrying out sequencing with PCR Sanger, detecting one or more arbitrary sites in the HPV-integrated gene sites in the DNA of the cervical tissue of the subject and calculating integration frequency. The kit prepared based on the HPV-integrated gene sites and used for detecting the high-risk populations of cervical carcinoma has the characteristics of accurate detection results, high sensitivity, etc.
Owner:武汉凯德维斯医学检验实验室有限公司
Devices, systems and methods for bioimpedance measurement of cervical tissue and methods for diagnosis and treatment of human cervix
Featured are apparatuses for measuring bioimpendence of tissues of the cervix, more specifically the mammalian cervix. Also featured are methods for examining the tissues of the cervix for clinical or diagnostic purposes such as during routine gynecological examinations to determine early onset of labor in pregnant patients or to assess such tissues for the presence of abnormalities such as cancerous lesions in both pregnant and non-pregnant women. Also featured are methods for treating onset of early or pre-term labor that embody such devices, apparatuses and methods of the present invention. Also featured are systems embodying such devices, apparatuses and / or methods, where such systems preferably are configured to provide diagnostic and / or clinical information to further assist the diagnostician or clinician in diagnosing and / or examining pregnant or non-pregnant patients.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
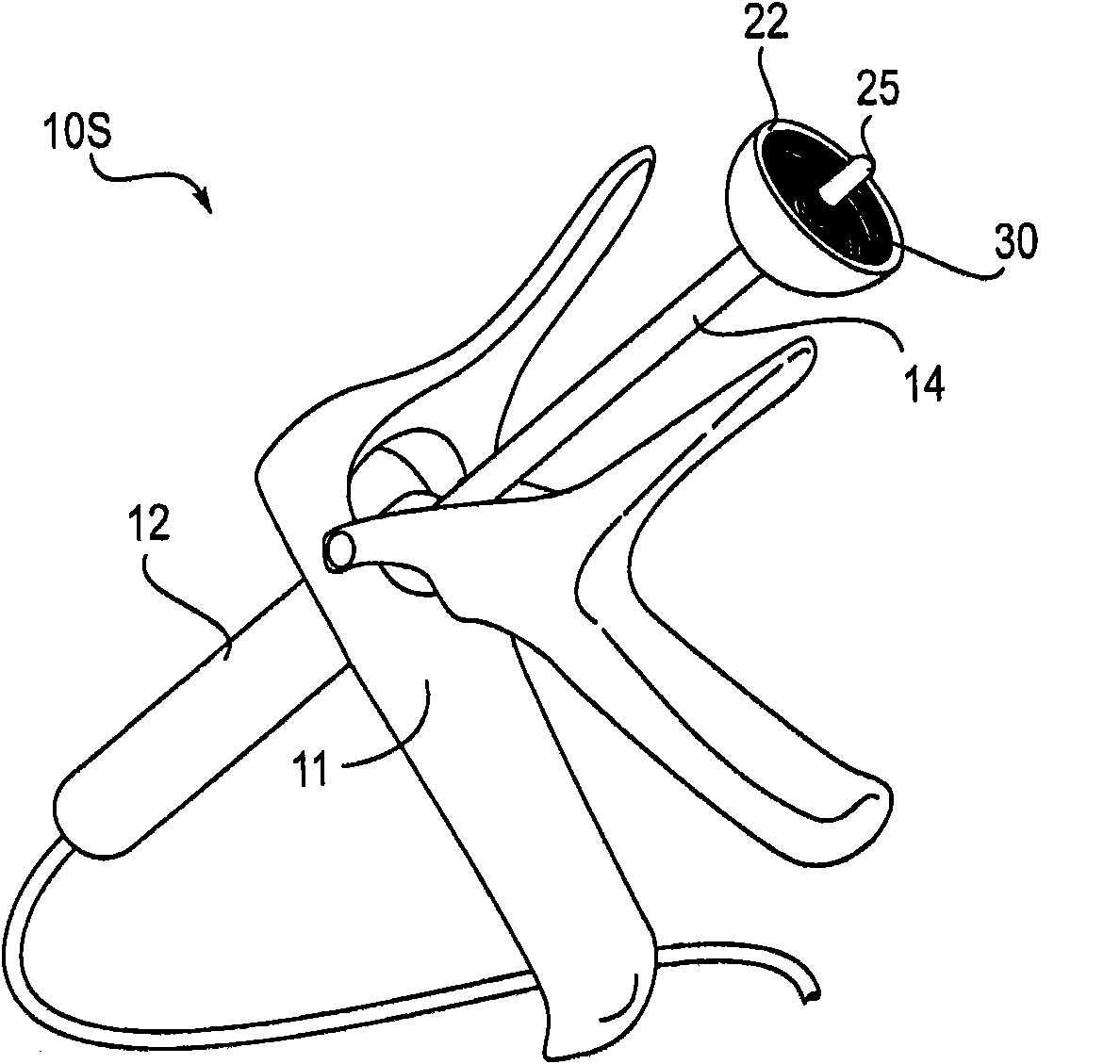
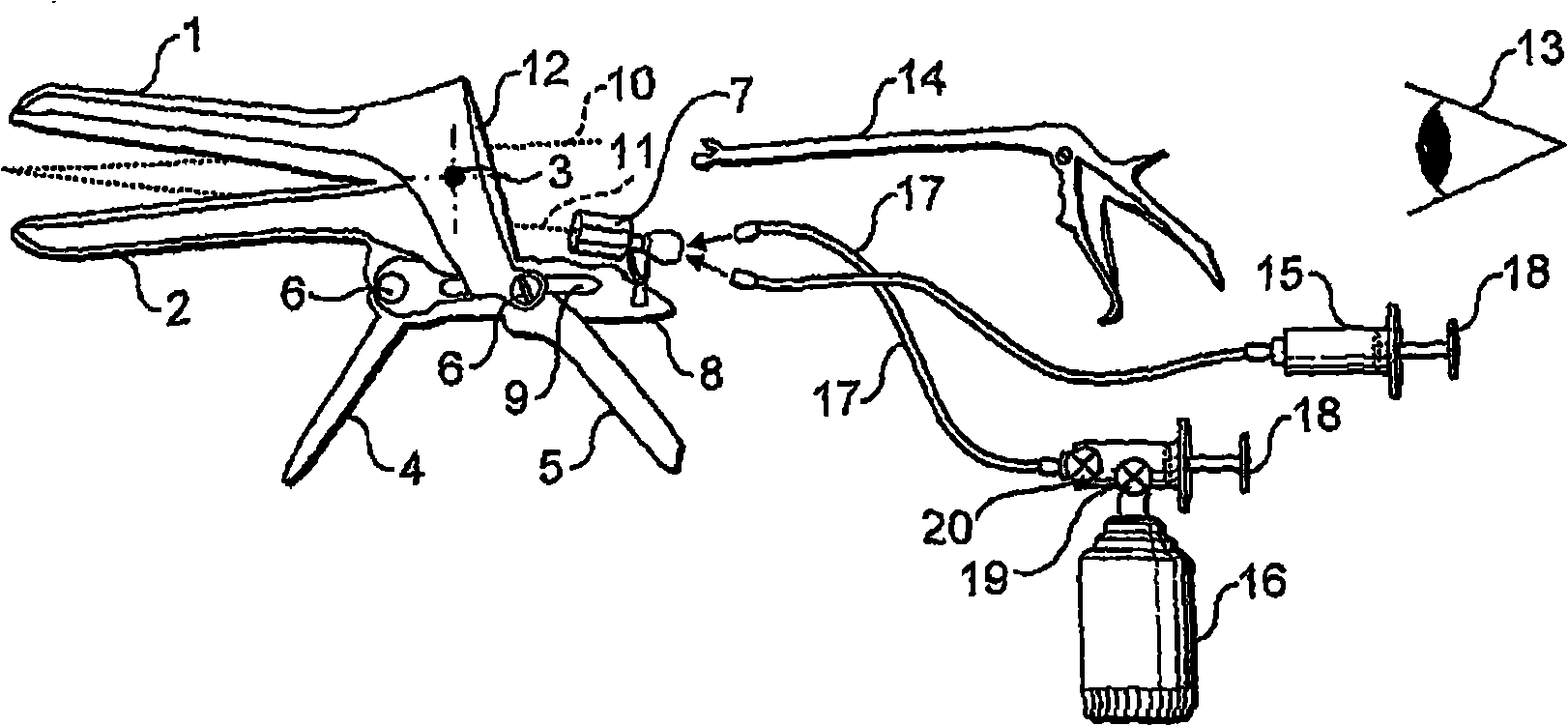
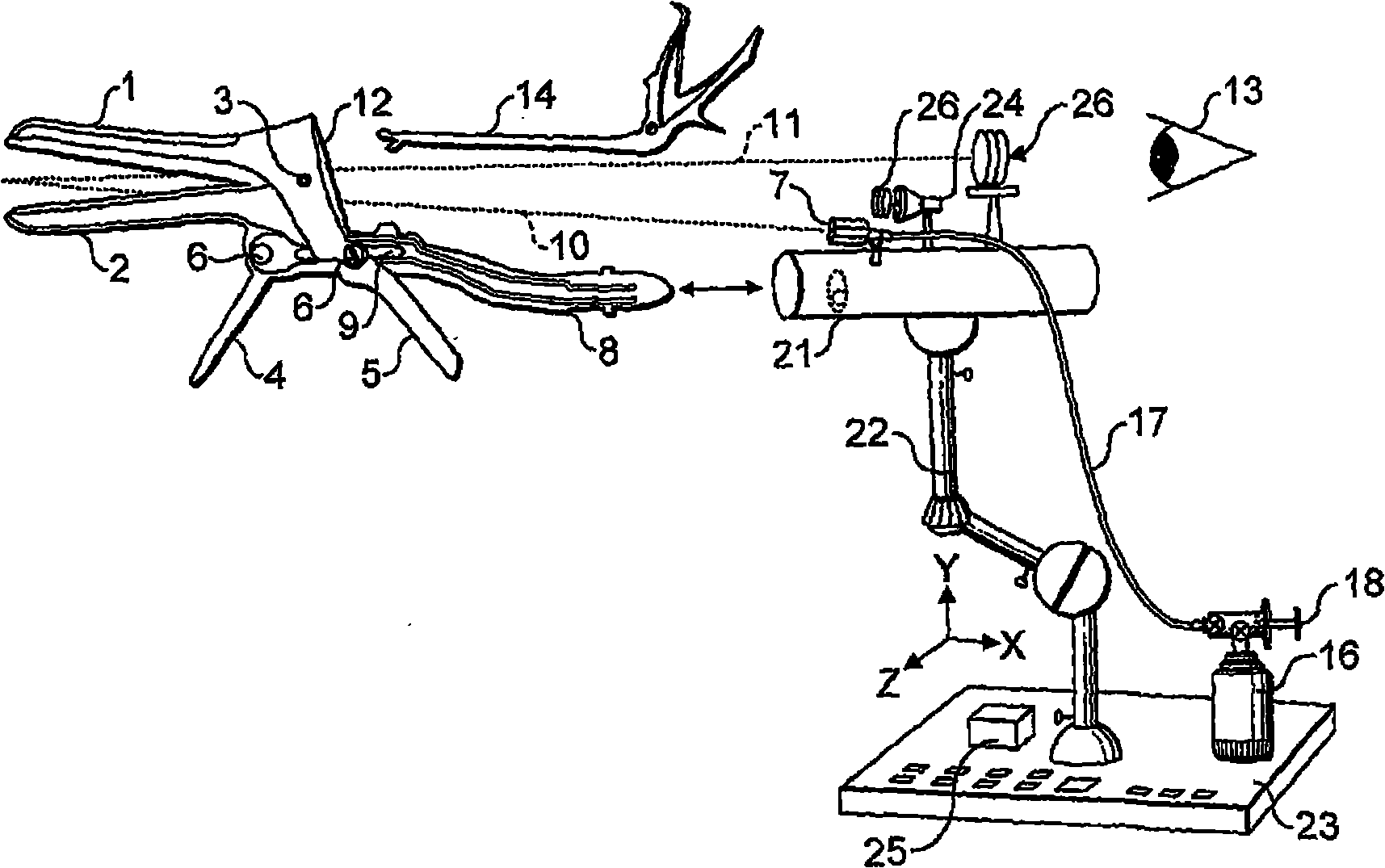
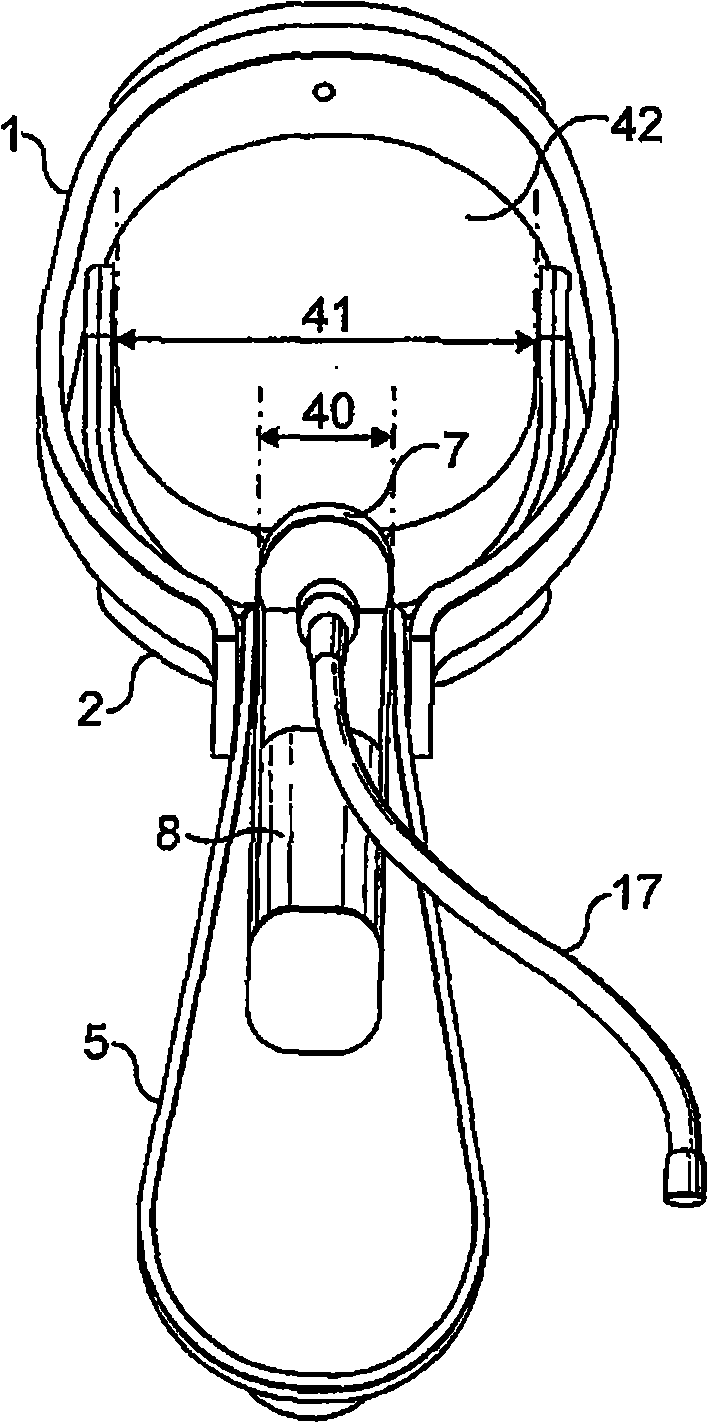
Device for performing examinations and surgical interventions on the uterus
A device serves for performing examination and surgical intervention on the uterus. The device comprises an approximate rod-shaped body and an extension piece protruding from a distal end of said body. Said extension piece can be introduced in a cervical canal of an uterus. At least one adjustable jaw part for fixing of a cervical tissue between said extension piece and said jaw part is provided. An operating device serves for operating said adjustable jaw part. Said operating device is arranged on said rod-shaped body in such a way that a hand of an operator gripping said body can operate said operating device.
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG
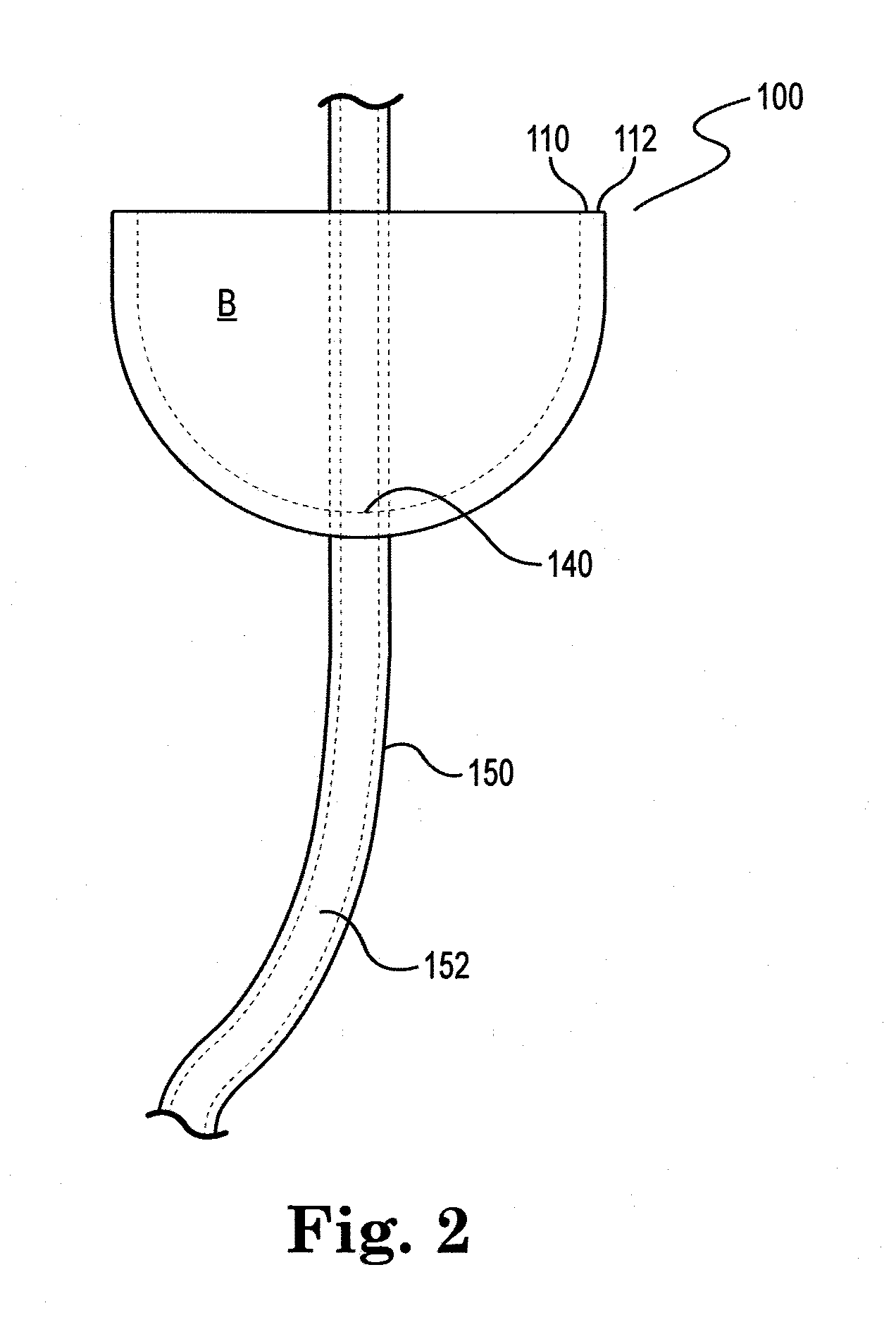
Device and method for illumination of vaginal fornix with ureter location, isolation and protection during hysterectomy procedure
InactiveUS20130131459A1Quickly and accurately identifyingProvide protectionEndoscopesCatheterCervical tissueIncision Site
The present invention comprises devices and methods that, in certain embodiments, provide a lighted cup, ring or cap that comprises a customizable size and fit, for use in hysterectomy procedures, whereby the ring or cup engages the vaginal fornix and is covered by the vaginal cervical tissue. The lighting allows the surgeon to visualize the location of the lighted cup, ring or cap, thereby quickly and accurately identifying the incision site while providing protection of the associated vasculature and the ureters.
Owner:LEXION MEDICAL LLC
System and method for ablational treatment of uterine cervical neoplasia
The invention provides a system, devices, and methods for ablating abnormal epithelial tissue of the uterine cervix. Embodiments of an ablation device include an operative head with a support surface adapted to conformably engage and therapeutically contact the cervix, and an energy delivery element on the support surface. The energy delivery element is configured to deliver energy, such as RF energy, to the tissue in a manner that controls the surface area and depth of ablation. The device may further include a shaft and a handle to support the ablation device, and may further include a speculum to facilitate access to the cervix. A system to support the operation of the ablation device includes a generator to deliver energy to the energy delivery element. Embodiments of a method for ablating abnormal cervical tissue include inserting an ablation device intravaginally to contact the cervix, aligning an energy delivery element support surface conformably against a region of the cervix with abnormal tissue, and ablating the tissue.
Owner:COVIDIEN CHINA MEDICAL DEVICES TECH
Improved method and apparatus for sampling cervical tissue
InactiveCN1440255ALess discomfortRelieve painSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsCervical tissueGynecology
A cervical sampling system for collecting a cervical sample for a Pap test. The cervical sampling system includes an insertion tube (2) and an introduction guide member (20) that guides the insertion tube (2) into a vaginal cavity. The vaginal insertion tube (2) includes an insertion depth indicator (12) to allow the user to determine the appropriate depth to insert the tube (2). A cervical sampler (50) is positioned within the vaginal insertion tube (2) and extends into the vaginal cavity to collect samples. The insertion tube (2) and cervical sampler (50) include signalling members which cooperate to indicate to the user when the cervical sample (50) has been rotated through a complete revolution.
Owner:R & G MEDICAL & DEV
Vaginal speculum arrangement
ActiveCN101277641AReduce sensitivityReduced characteristicsEndoscopesVaginoscopesCervical tissueColposcopy
A vaginal speculum arrangement includes a blade system for opening the vagina having a first blade (1) and a second blade (2) physically separable from one another, and an injection mechanism for dispensing a diagnostic marker onto the surface of the examined tissue having an injection probe (7). The direction of application of the diagnostic marker by the injection probe is not influenced by separation of the first and second blades and thus the injection probe (7) allows for a substantially homogeneous application of the diagnostic marker on a desired area in the examined vaginal or cervical tissue, irrespective of the degree of separation of the blades (1,2). The probe may be a nozzle generating a desirable injection pattern. The probe may be affixed to an extension rod, which may be mechanically coupled with the speculum blades. Optical, electronic imaging means, illumination means and treatment tools may be mounted onto the extension rod, which rod may be reversibly attached to mechanical positioning systems or to imaging devices used in colposcopy. The speculum arrangement may be used as a tool for diagnostic and screening examinations and for the treatment of cervical and vaginal neoplasias.
Owner:DYSIS MEDICAL
Optical imaging for preterm birth assessment
ActiveUS20180271430A1Quick snapEffective toolDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPreterm BirthsCervical tissue
Methods, apparatuses, and systems for measuring collagen organization in the cervix, assessing the health of a woman's cervix (including a pregnant woman's cervix), characterizing the composition and structure of cervical tissue, and measuring preterm labor risk are provided. Polarization sensitive techniques and properties of cervical tissue, including birefringence, can be used. A method can include acquiring in vivo images of cervical tissue, applying Mueller matrix (MM) polarimetry (including 4×4 Mueller matrix polarimetry), and determining one or more parameters of the cervical tissue using the Mueller matrix (MM) polarimetry. The in vivo images can be analyzed and various parameters that characterize the cervical tissue can be determined. Graphs and maps of the cervical tissue can be generated for use as care provider tools.
Owner:FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
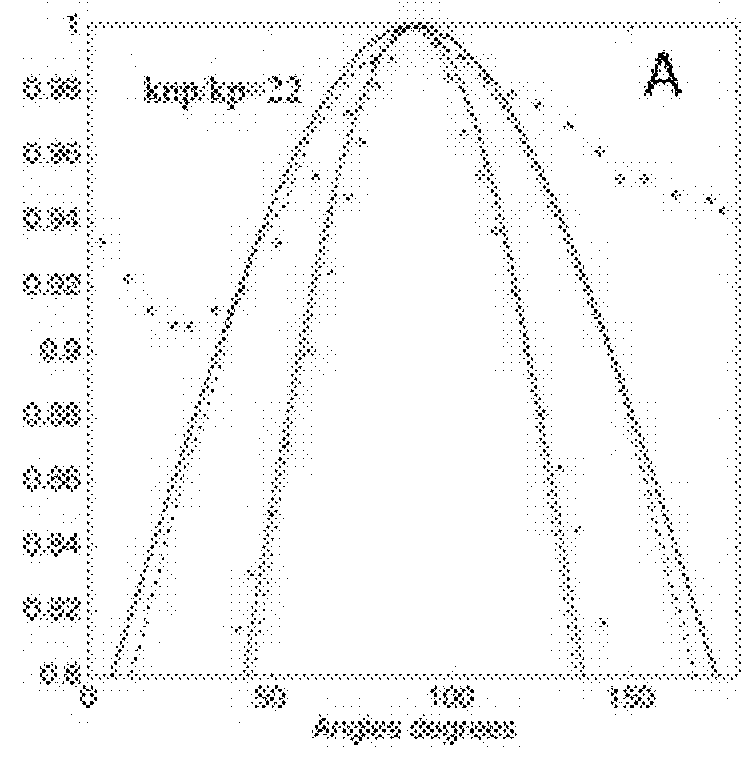
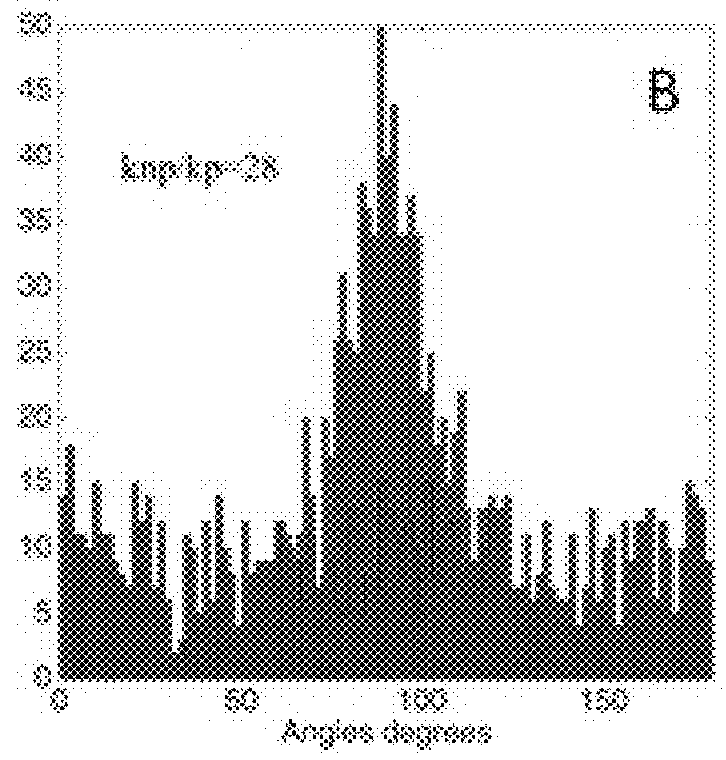
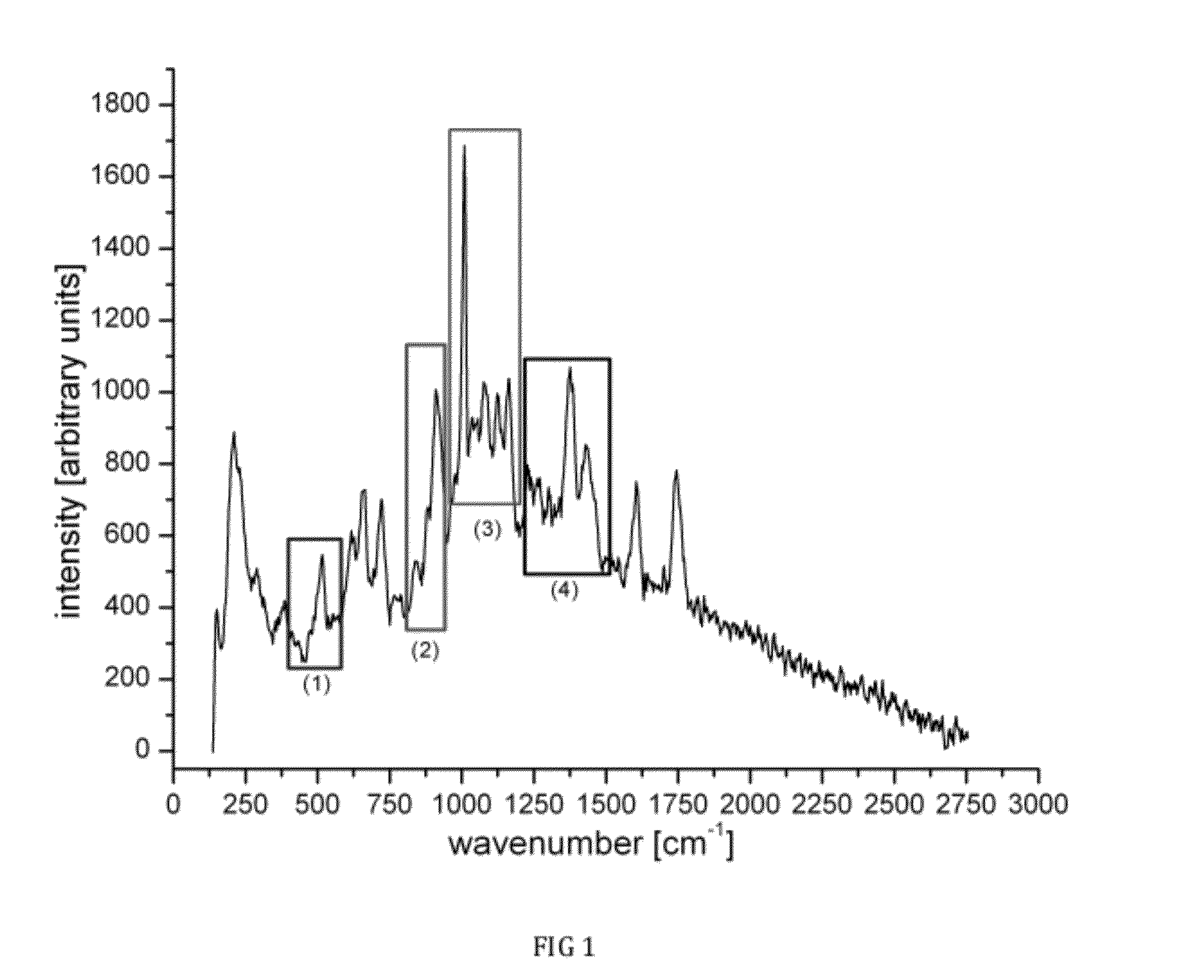
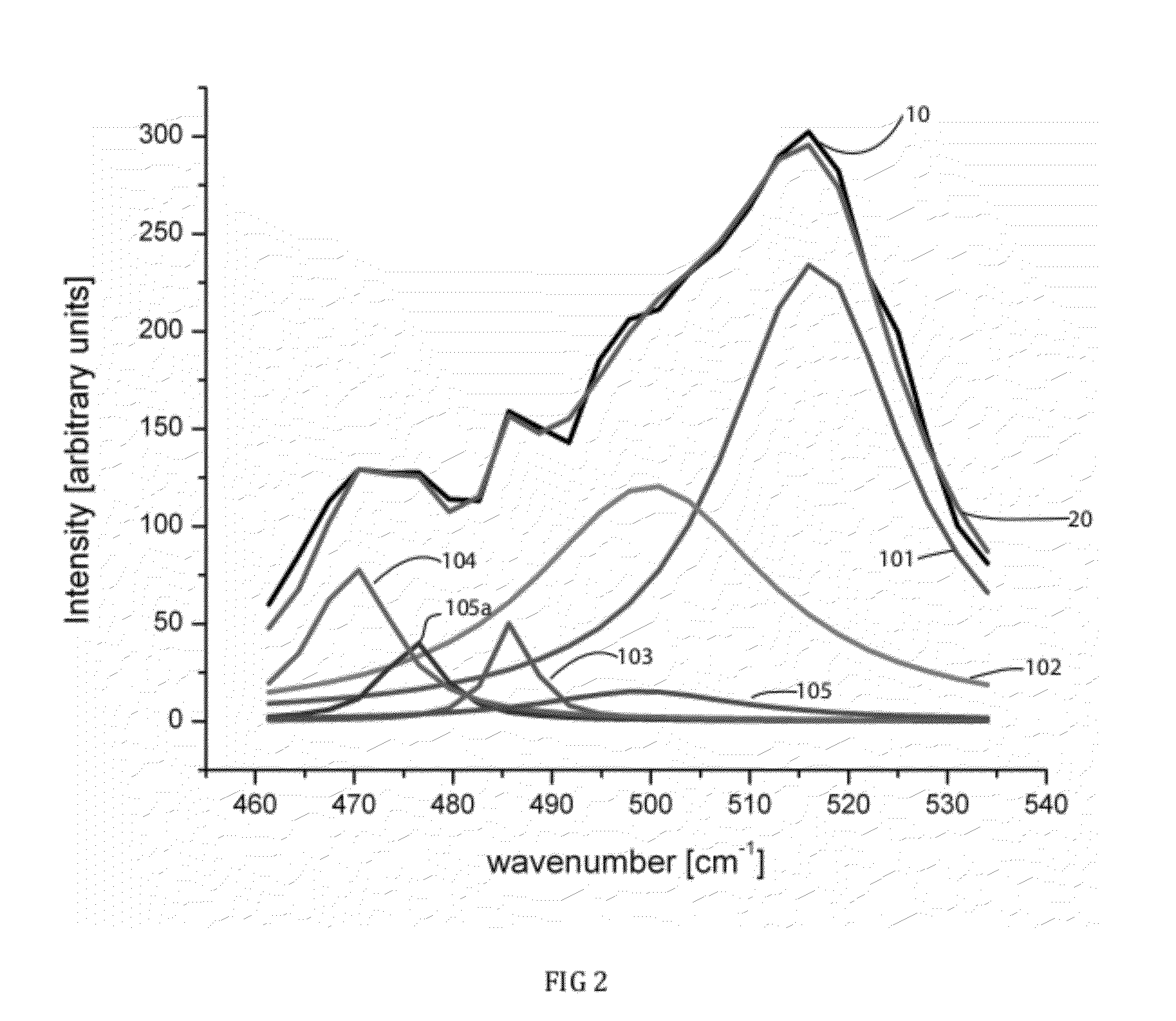
Raman spectral analysis for disease detection and monitoring
A system and method for Raman spectral analysis for diagnostic purposes to identify the disease state of biological tissue. The sampled tissue can be any human or animal tissue, including but not limited to prostate, breast, cervical tissue, etc. Raman spectroscopy is used to provide Raman bands which are decomposed and their chemical fingerprints identified after mathematical modeling. The method enables identification of chemical compounds in the tissue being diagnosed. Comparison with reference samples permits inferences concerning the presence or absence of disease, the stage of disease, and / or the response of disease to treatment. The method provides sufficient information about the chemical composition of the tissue to differentiate between normal and abnormal states, and may also reveal the locations of abnormalities. The method may also be used to monitor the treatment of a subject and / or the response of disease to drugs or other treatments.
Owner:VUKELIC SINISA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com