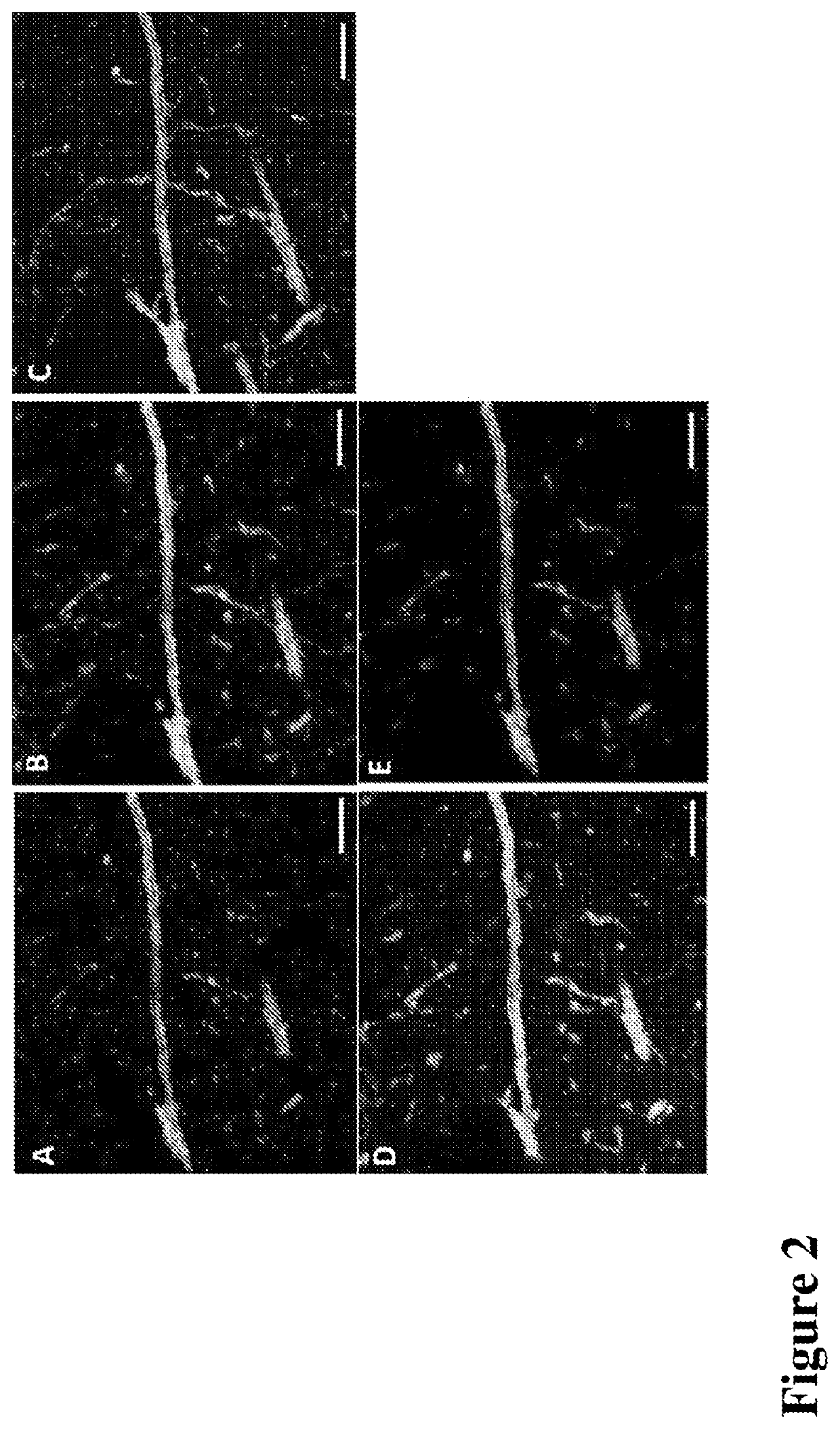
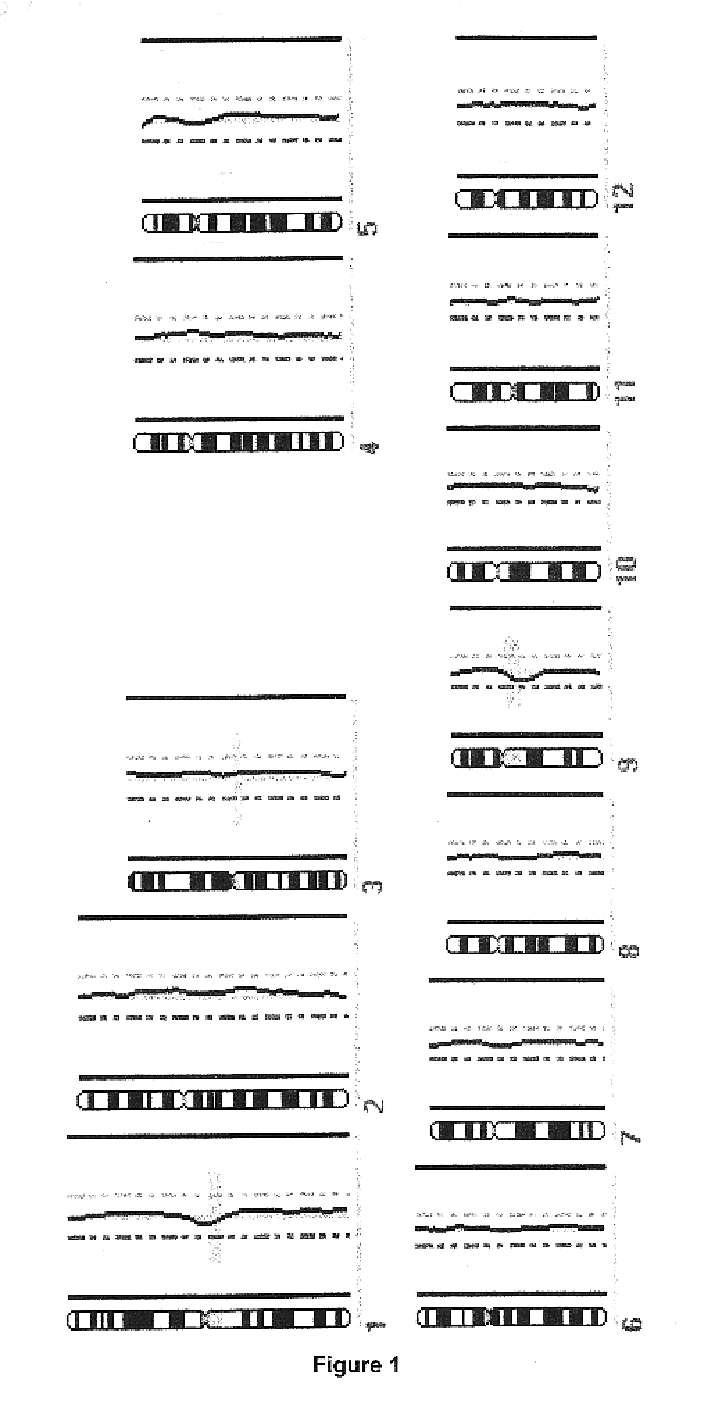
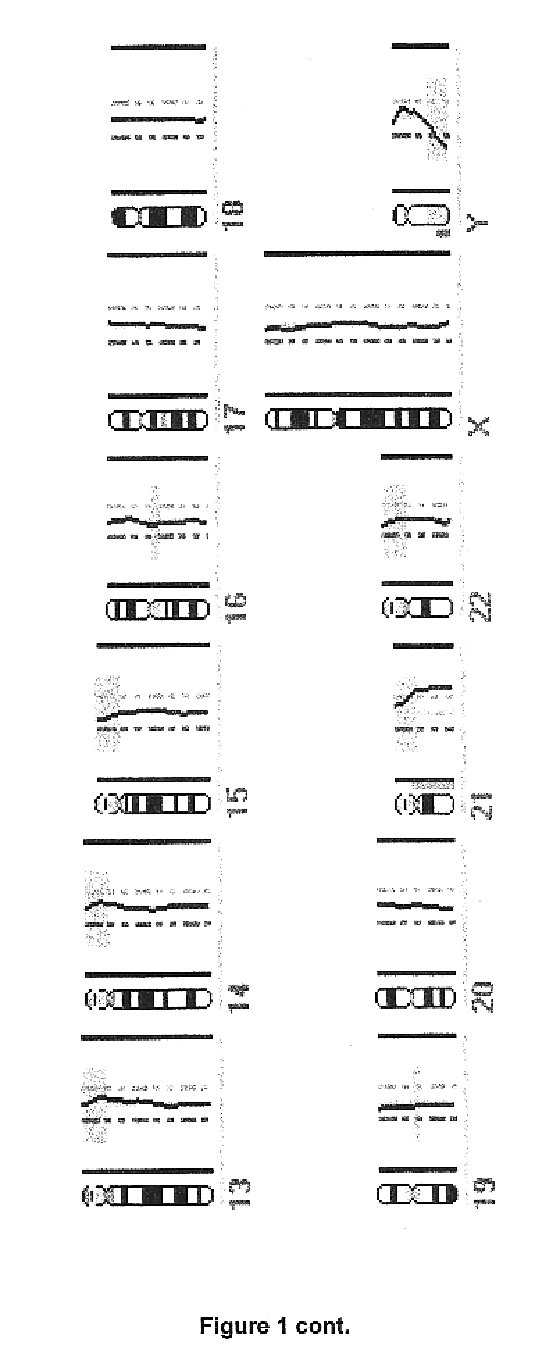
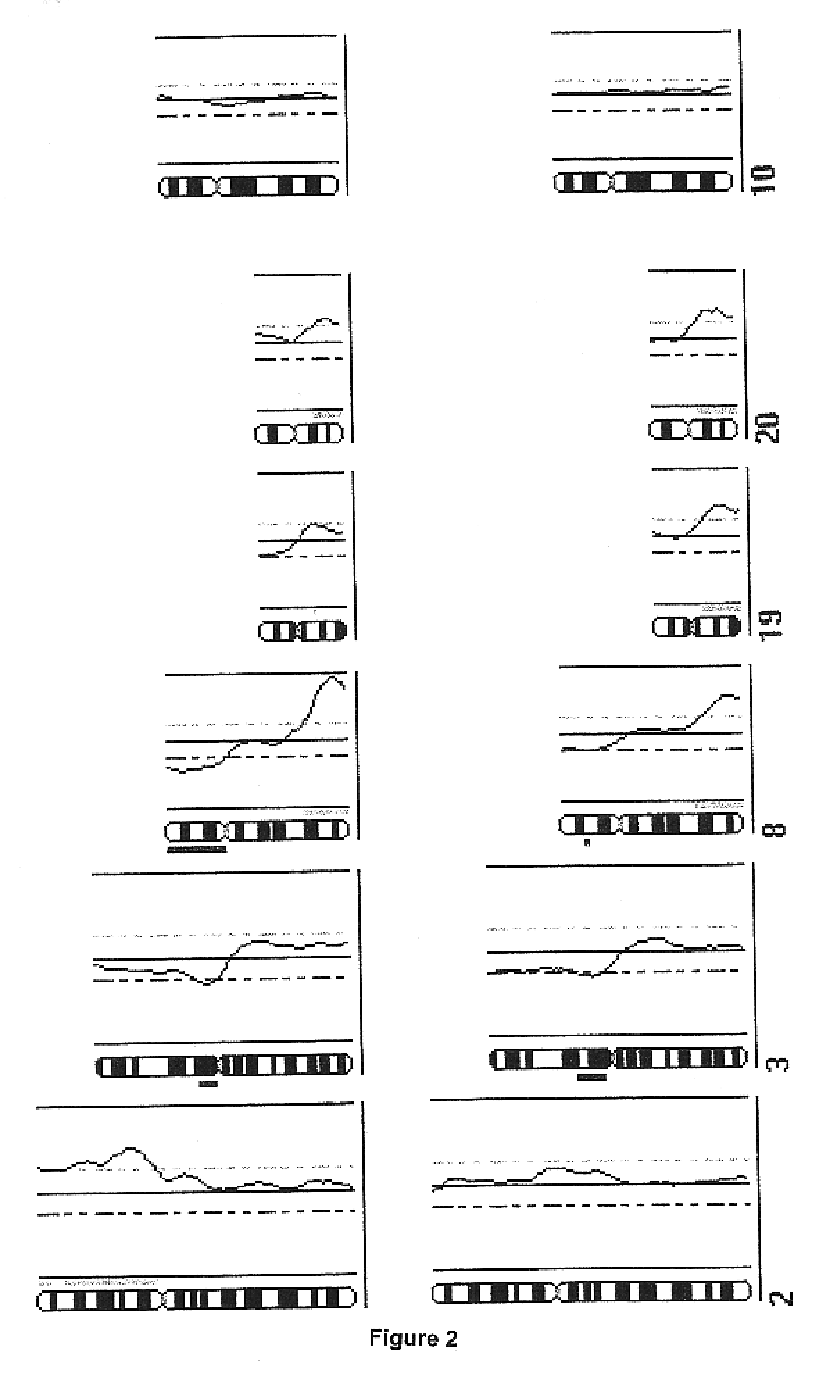
Patents
Literature
641 results about "In situ hybridization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In situ hybridization (ISH) is a type of hybridization that uses a labeled complementary DNA, RNA or modified nucleic acids strand (i.e., probe) to localize a specific DNA or RNA sequence in a portion or section of tissue (in situ) or if the tissue is small enough (e.g., plant seeds, Drosophila embryos), in the entire tissue (whole mount ISH), in cells, and in circulating tumor cells (CTCs). This is distinct from immunohistochemistry, which usually localizes proteins in tissue sections.
Nanoparticle conjugates
InactiveUS20060246524A1Easy to detectMaterial nanotechnologyPowder deliveryIn situ hybridisationOrganic chemistry
Conjugate compositions are disclosed that include a specific-binding moiety covalently coupled to a nanoparticle through a heterobifunctional polyalkyleneglycol linker. In one embodiment, a conjugates is provided that includes a specific-binding moiety and a fluorescent nanoparticle coupled by a heterobifunctional PEG linker. Fluorescent conjugates according to the disclosure can provide exceptionally intense and stable signals for immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization assays on tissue sections and cytology samples, and enable multiplexing of such assays.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Comparative genomic hybridization (CGH)
InactiveUS6335167B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingComparative genomic hybridization
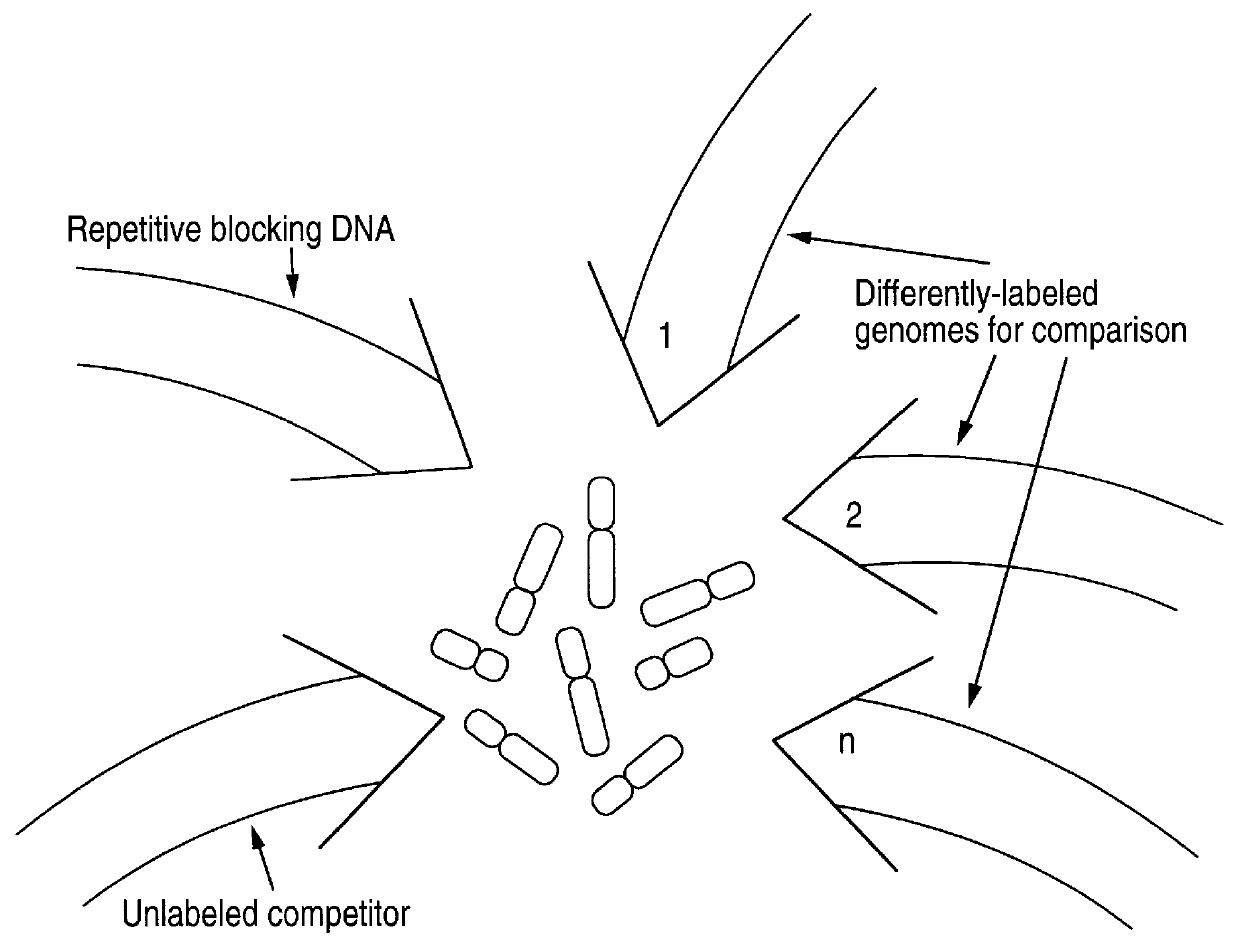
Disclosed are new methods comprising the use of in situ hybridization to detect abnormal nucleic acid sequence copy numbers in one or more genomes wherein repetitive sequences that bind to multiple loci in a reference chromosome spread are either substantially removed and / or their hybridization signals suppressed. The invention termed Comparative Genomic Hybridization (CGH) provides for methods of determining the relative number of copies of nucleic acid sequences in one or more subject genomes or portions thereof (for example, a tumor cell) as a function of the location of those sequences in a reference genome (for example, a normal human genome). The intensity(ies) of the signals from each labeled subject nucleic acid and / or the differences in the ratios between different signals from the labeled subject nucleic acid sequences are compared to determine the relative copy numbers of the nucleic acid sequences in the one or more subject genomes as a function of position along the reference chromosome spread. Amplifications, duplications and / or deletions in the subject genome(s) can be detected. Also provided is a method of determining the absolute copy numbers of substantially all RNA or DNA sequences in subject cell(s) or cell population(s).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for simultaneous detection of multiple fluorophores for in situ hybridization and multicolor chromosome painting and banding
InactiveUS6066459AImprove throughputShorten the timeRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryChromosome paintingFluorophore
A spectral imaging method for simultaneous detection of multiple fluorophores aimed at detecting and analyzing fluorescent in situ hybridizations employing numerous chromosome paints and / or loci specific probes each labeled with a different fluorophore or a combination of fluorophores for color karyotyping, and at multicolor chromosome banding, wherein each chromosome acquires a specifying banding pattern, which pattern is established using groups of chromosome fragments labeled with various fluorophore or combinations of fluorophores.
Owner:APPLIED SPECTRAL IMAGING
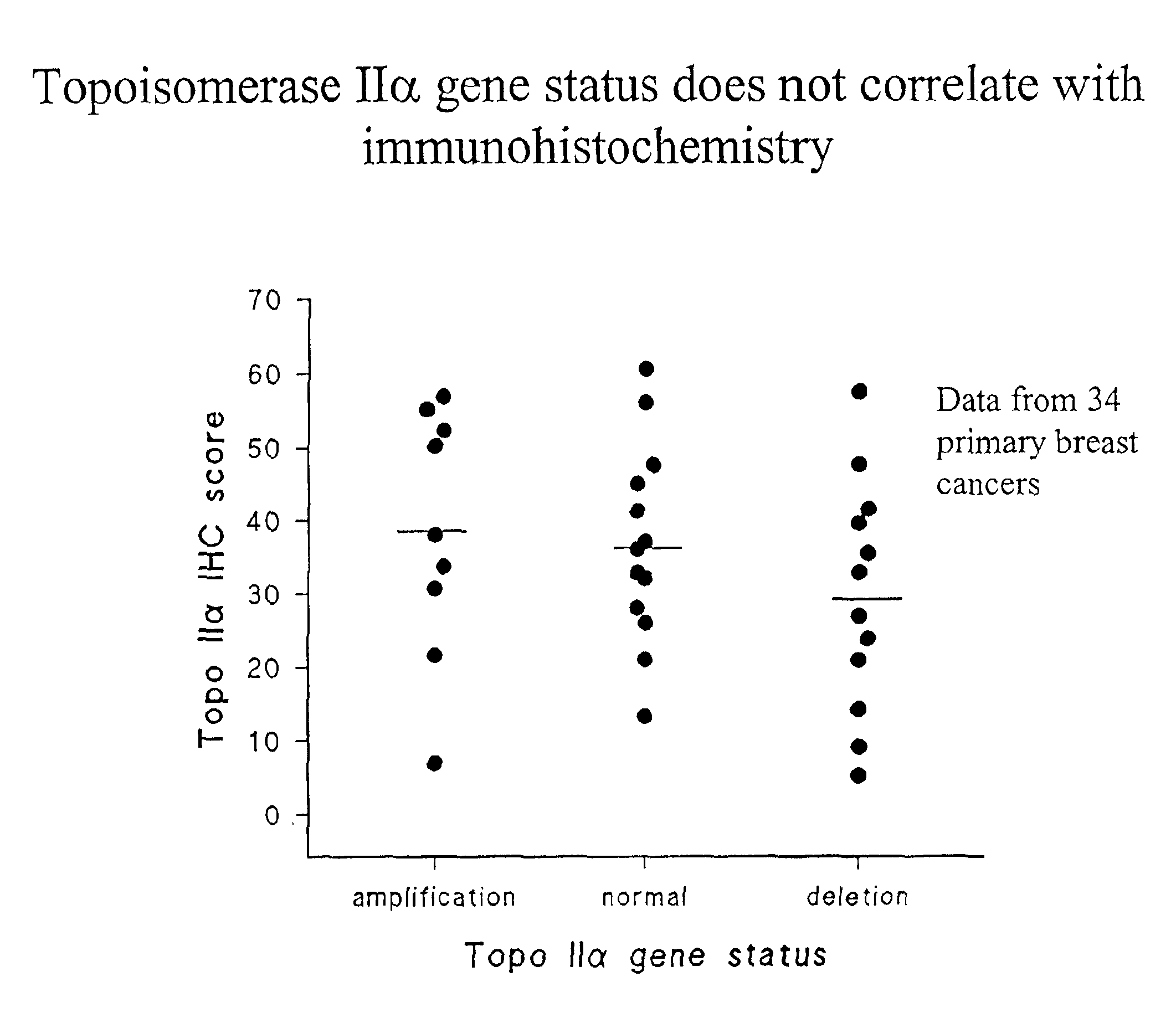
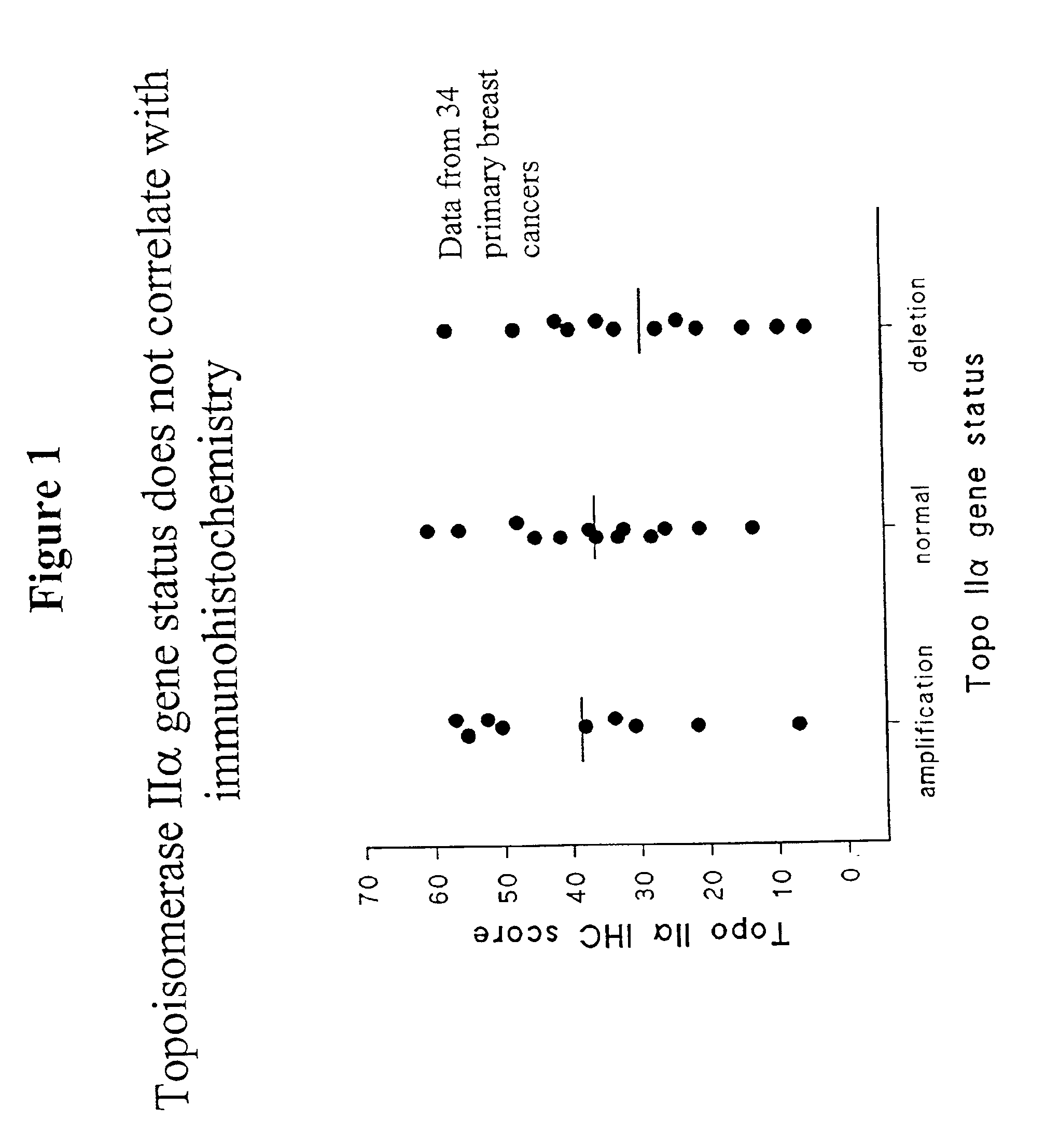
Identifying subjects suitable for topoisomerase II inhibitor treatment
InactiveUS6942970B2Suitable for treatmentSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA underwindingHybridization probe
The present invention provides methods for diagnosing and treating cancer, and in particular methods for determining the susceptibility of subjects suspected of having breast cancer (or known to have breast cancer) to treatment with topoisomerase II inhibitors. The present invention also provides in situ hybridization probes for specifically detecting topoIIα gene sequences.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Antibody conjugates
InactiveUS20060246523A1Easy to detectIntense stainingHybrid immunoglobulinsHydrolasesIn situ hybridisationAntibody conjugate
Antibody / signal-generating moiety conjugates are disclosed that include an antibody covalently linked to a signal-generating moiety through a heterobifunctional polyalkyleneglycol linker. The disclosed conjugates show exceptional signal-generation in immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization assays on tissue sections and cytology samples. In one embodiment, enzyme-metallographic detection of nucleic acid sequences with hapten-labeled probes can be accomplished using the disclosed conjugates as a primary antibody without amplification.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Methods and compositions for identifying a fetal cell
InactiveUS20100304978A1High expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCandidate Gene Association StudyTrophoblast
The present invention provides methods and compositions for specifically identifying a fetal cell. An initial screening of approximately 400 candidate genes by digital PCR in different fetal and adult tissues identified a subset of 24 gene markers specific for fetal nucleated RBC and trophoblasts. The specific expression of those genes was further evaluated and verified in more defined tissues and isolated cells through quantitative RT-PCR using custom Taqman probes specific for each gene. A subset of fetal cell specific markers (FCM) was tested and validated by RNA fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) in blood samples from non-pregnant women, and pre-termination and post-termination pregnant women. Applications of these gene markers include, but are not limited to, distinguishing a fetal cell from a maternal cell for fetal cell identification and genetic diagnosis, identifying circulating fetal cell types in maternal blood, purifying or enriching one or more fetal cells, and enumerating one or more fetal cells during fetal cell enrichment.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Gene detection assay for improving the likelihood of an effective response to a her2 antibody cancer therapy
InactiveUS20070166753A1Great likelihoodChoose accuratelyOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAbnormal tissue growthAssay
The invention provides a method for more effective treatment of patients susceptible to or diagnosed with tumors overexpressing HER2, as determined by a gene amplification assay, with a HER2 antibody. Such method comprises administering a cancer-treating dose of the HER2 antibody, preferably in addition to chemotherapeutic agents, to a subject in whose tumor cells her2 has been found to be amplified e.g., by fluorescent in situ hybridization.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Nanoscale Imaging of Proteins and Nucleic Acids via Expansion Microscopy
ActiveUS20170067096A1Use diversityMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationNew Approach to AppraisalBio-Specimen
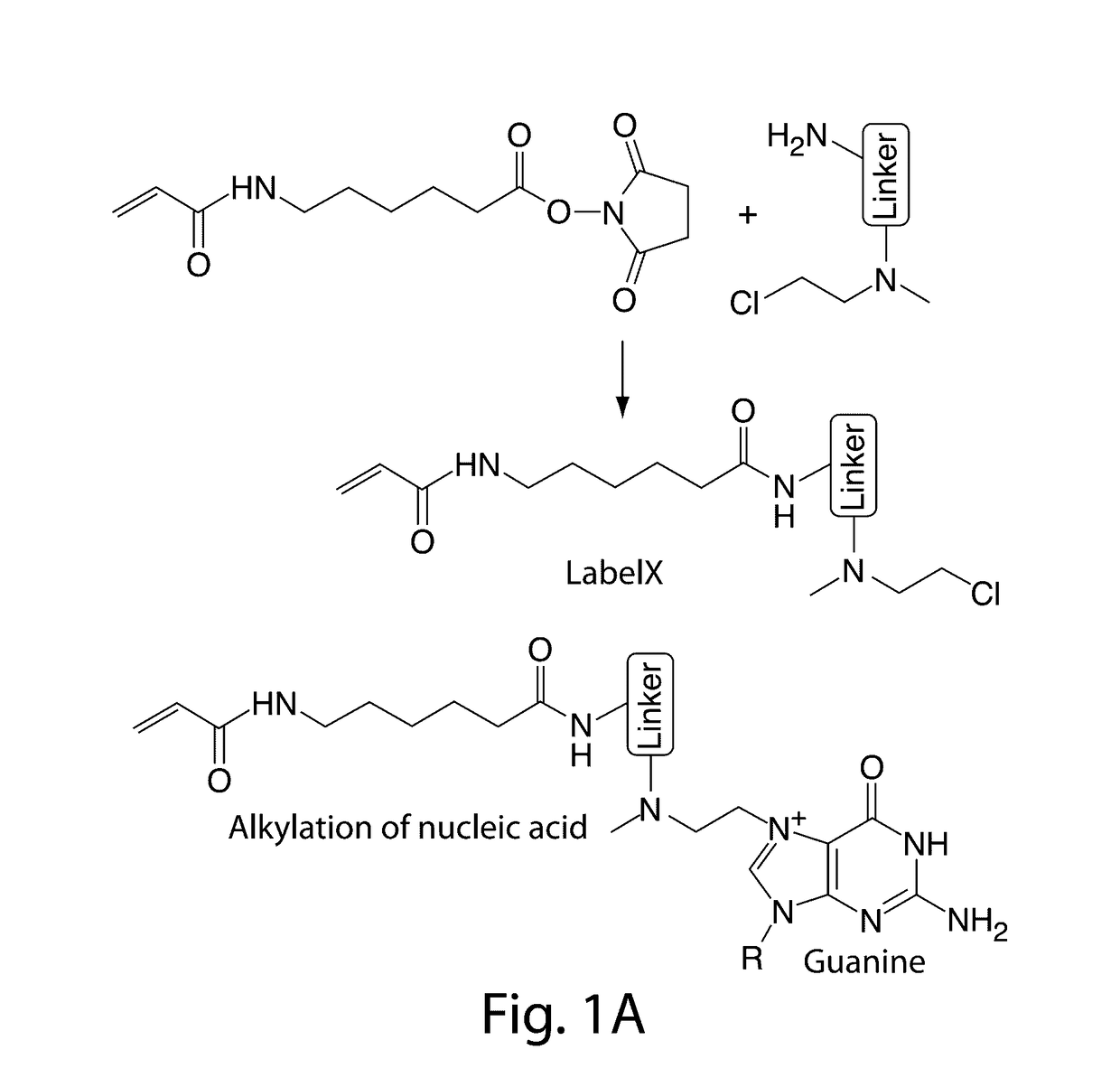
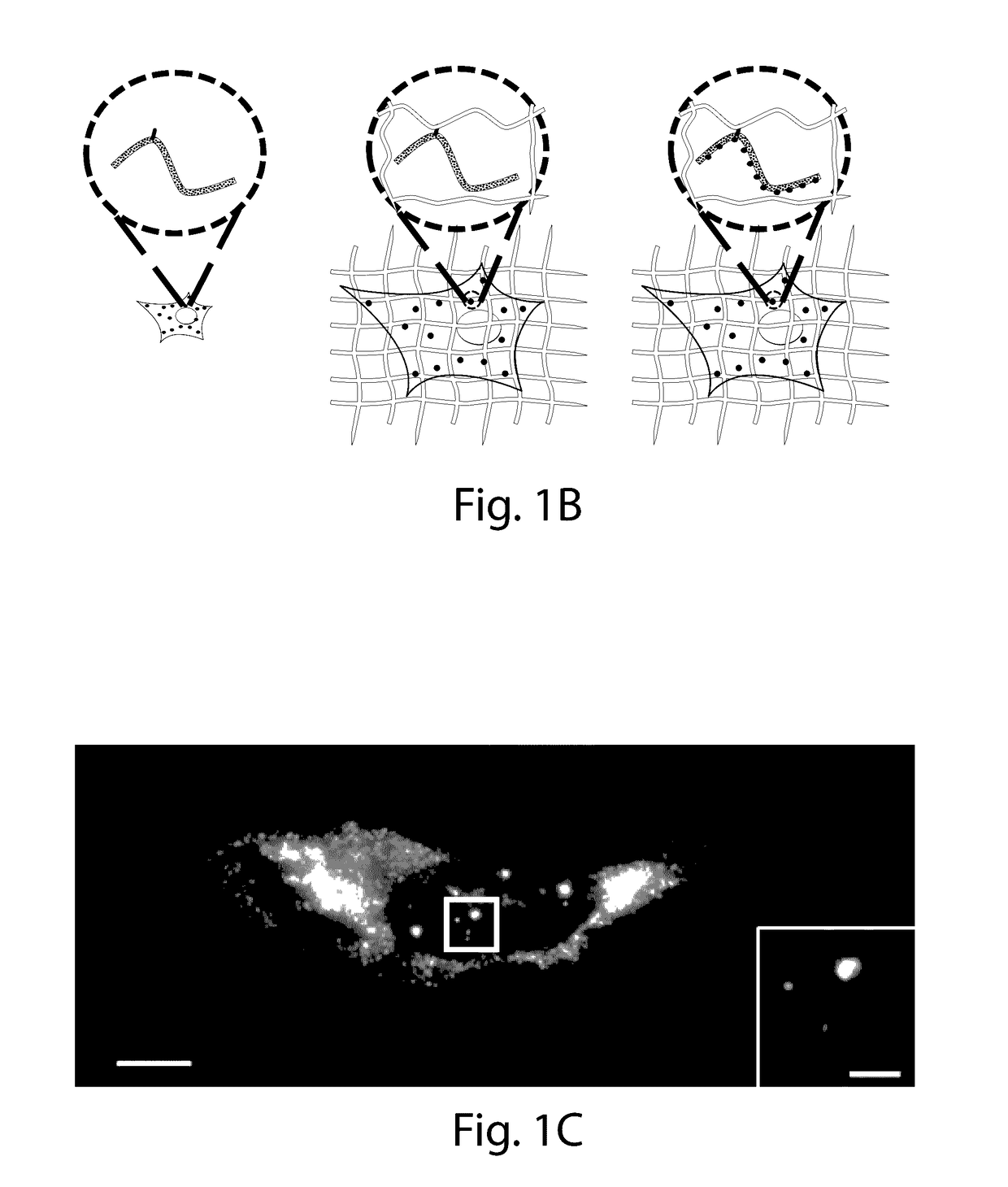
The invention enables in situ genomic and transcriptomic assessment of nucleic acids to be conducted in biological specimens that have been physically expanded. The invention leverages the techniques for expansion microscopy (ExM) to provide new methods for in situ genomic and transcriptomic assessment of nucleic in a new process referred to herein as “expansion fluorescent in situ hybridization” (ExFISH).
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
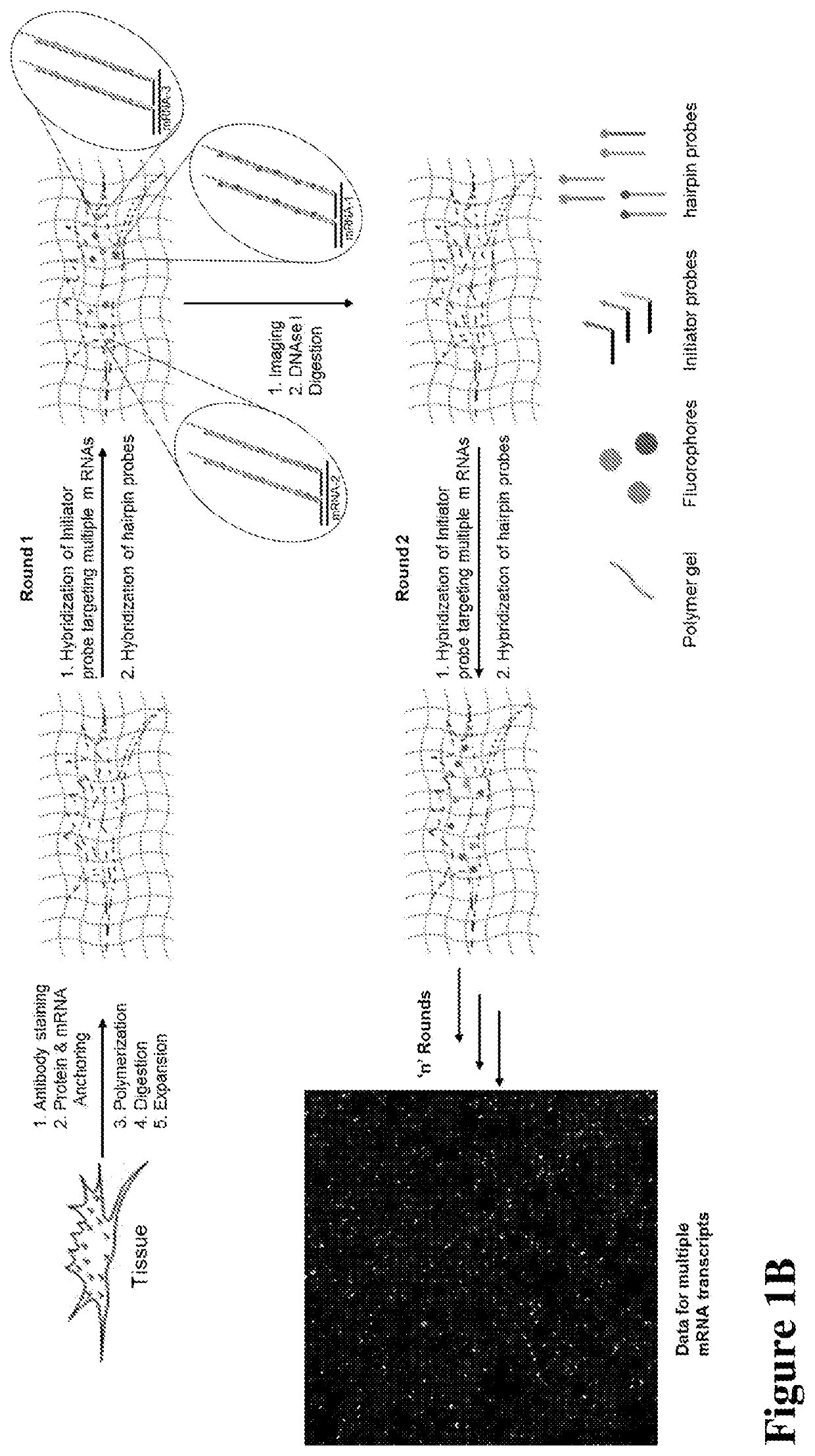
Multiplexed in situ hybridization of tissue sections for spatially resolved transcriptomics with expansion microscopy
This invention relates to imaging, such as by expansion microscopy, labelling, and analyzing biological samples, such as cells and tissues, as well as reagents and kits for doing so.
Owner:EXPANSION TECH
DNA amplification of a single cell
InactiveUS6673541B1Improve accuracyImprove comprehensive applicabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle-strand conformation polymorphismComparative genomic hybridization
The present invention relates to a novel method for the amplification of DNA, this method being particularly useful for the amplification of the DNA or the whole genome of a single cell, chromosomes or fragments thereof. Described is also the use of the method in DNA analysis for medical, forensic, diagnostic or scientific purposes, like comparative genomic hybridization (CGH)-, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)-, polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-, single strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP)-, DNA sequence-, "loss of heterozygosity" (LOH)-, fingerprint- and / or restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP)-analysis.
Owner:AMGEN RES (MUNICH) GMBH
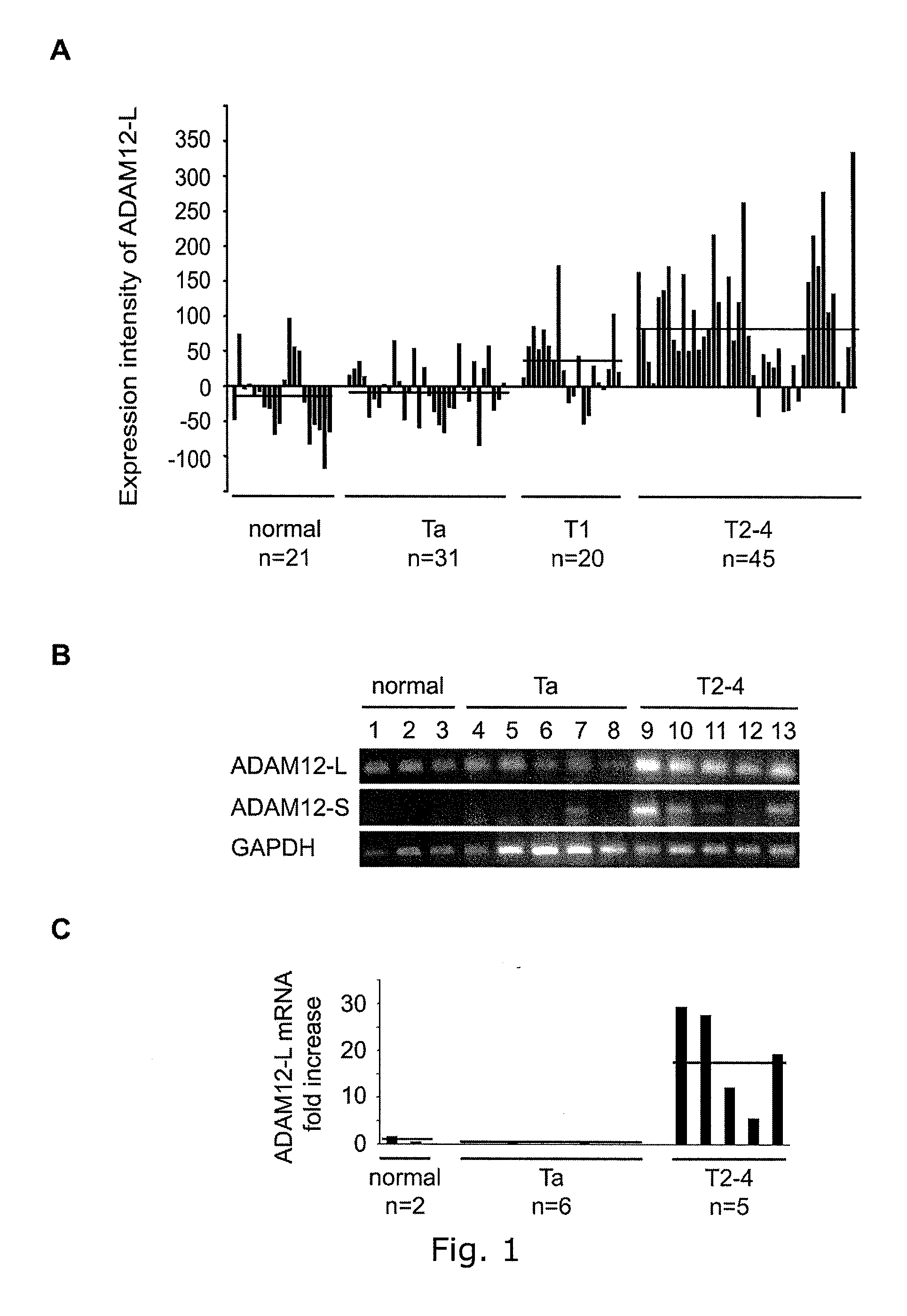
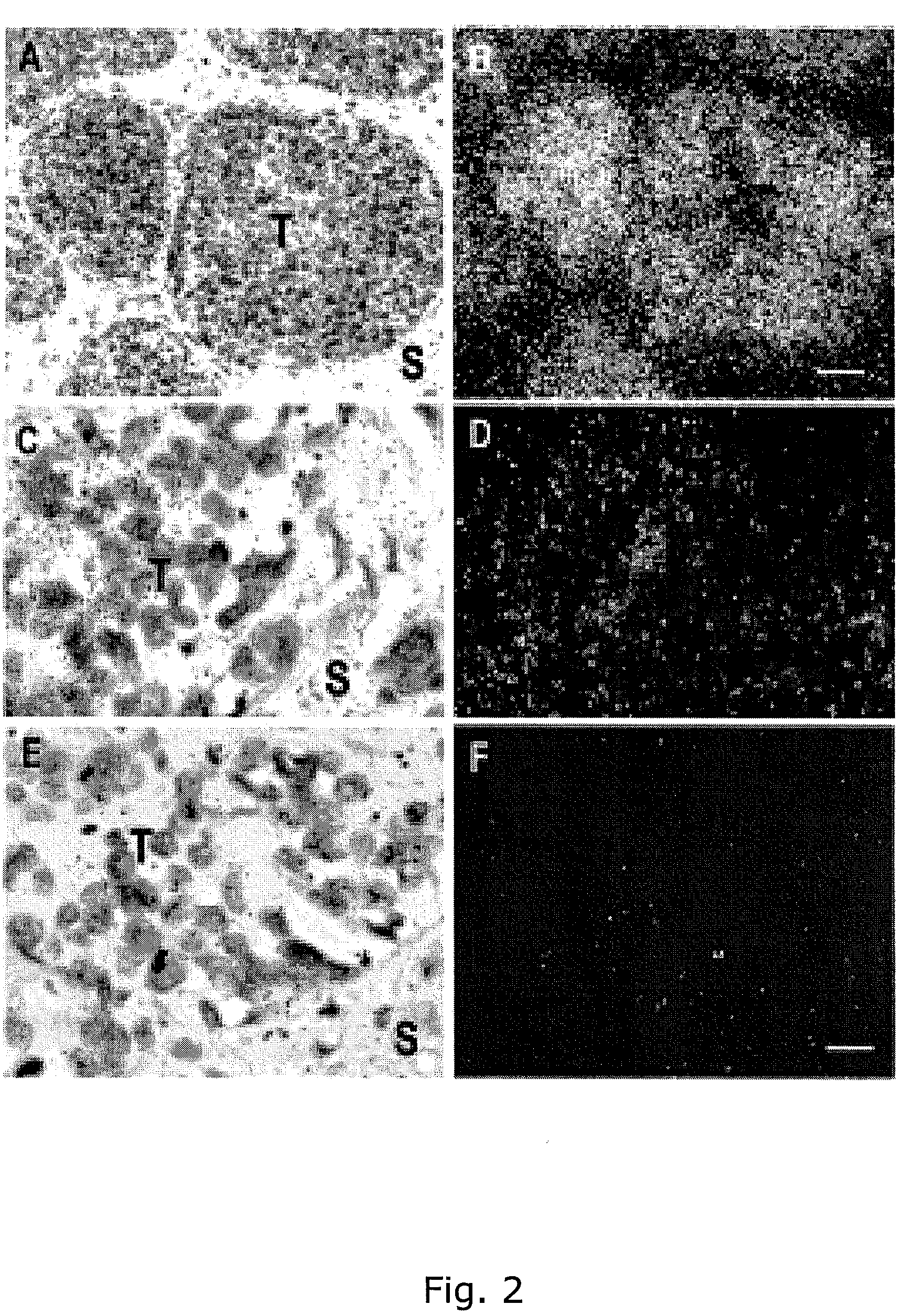
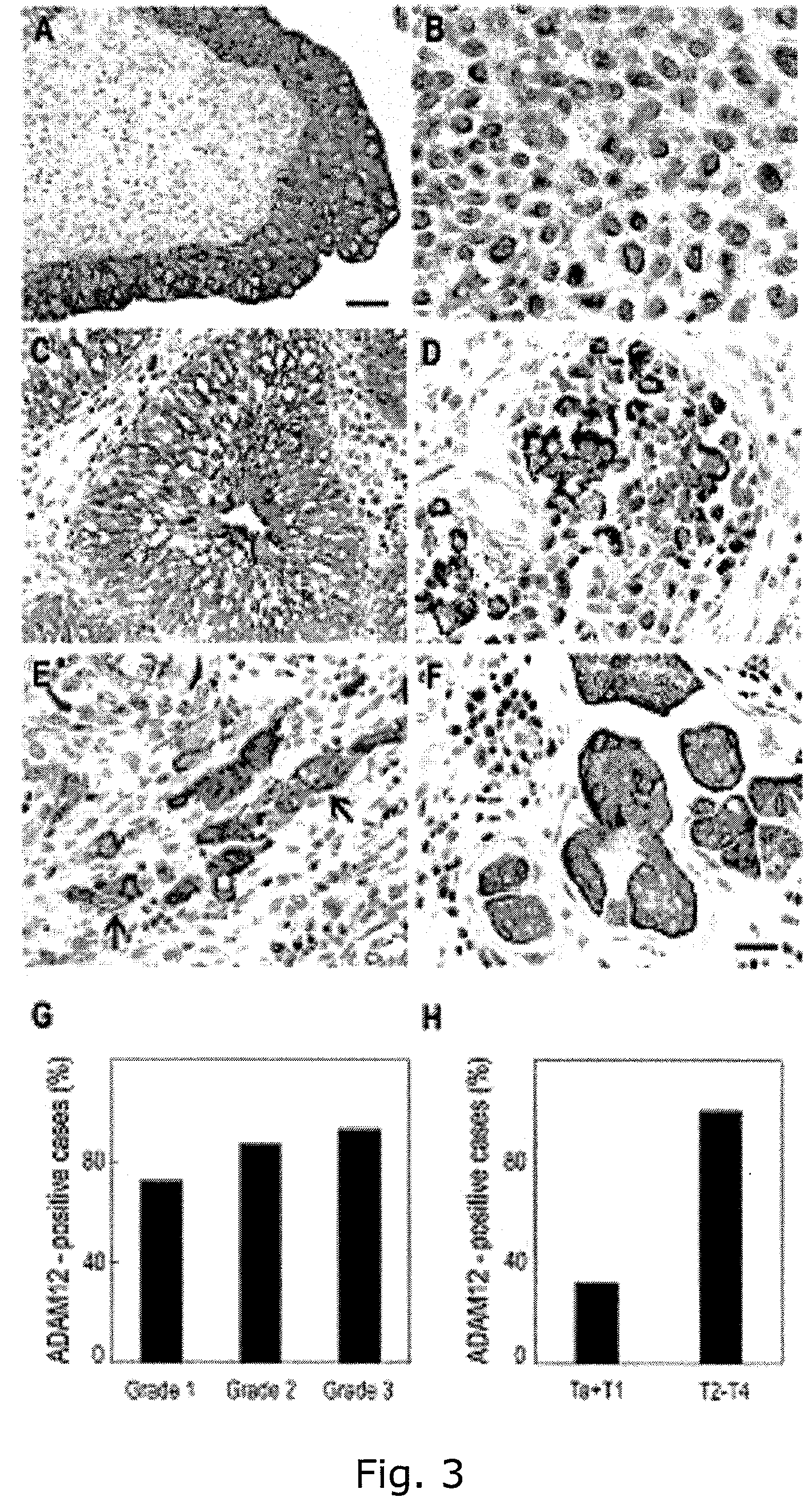
Adam12 as a biomarker for bladder cancer
InactiveUS20090029372A1Improve the level ofLower Level RequirementsMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisTissue ArraysAffymetrix genechip
The present inventors have shown that the gene and protein expression profiles of ADAM8, ADAM10 and ADAM12 in different grades and stages of bladder cancer.ADAM12 gene expression was evaluated in tumors from 96 patients with bladder cancer using a customized Affymetrix GeneChip. Gene expression in bladder cancer was validated using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), quantitative PCR, and in situ hybridization. Protein expression was evaluated by immunohistochemical staining on tissue arrays of bladder cancers.The presence and relative amount of ADAM12 in the urine of cancer patients were determined by Western blotting and densitometric measurements, respectively.Particularly ADAM12 mRNA expression was significantly upregulated in bladder cancer, as determined by microarray analysis, and the level of ADAM12 mRNA correlated with disease stage. ADAM12 protein expression correlated with tumor stage and grade. ADAM12 was present in higher levels in the urine from bladder cancer patients than in urine from healthy individuals. Significantly, following removal of tumor by surgery, in most bladder cancer cases examined the level of ADAM12 in the urine decreased and, upon recurrence of tumor, increased.
Owner:PHYSICIANS CHOICE LAB SERVICES +1
Frozen tissue microarray technology for analysis RNA, DNA, and proteins
InactiveUS6893837B2Withdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis dnaTissue Arrays
The invention disclosed herein improves upon existing tissue microarray technology by using frozen tissues embedded in tissue embedding compound as donor samples and arraying the specimens into a recipient block comprising tissue embedding compound. Tissue is not fixed prior to embedding, and sections from the array are evaluated without fixation or post-fixed according to the appropriate methodology used to analyze a specific gene at the DNA, RNA, and / or protein levels. Unlike paraffin tissue arrays which can be problematic for immunohistochemistry and for RNA in situ hybridization analyses, the disclosed methods allow optimal evaluation by each technique and uniform fixation across the array panel. The disclosed arrays work well for DNA, RNA, and protein analyses, and have significant qualitative and quantitative advantages over existing methods.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Ultra sensitive method for in situ detection of nucleic acids
ActiveUS8658361B2Exceptional specificity owningEasy to useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHigh signal intensityHigh intensity
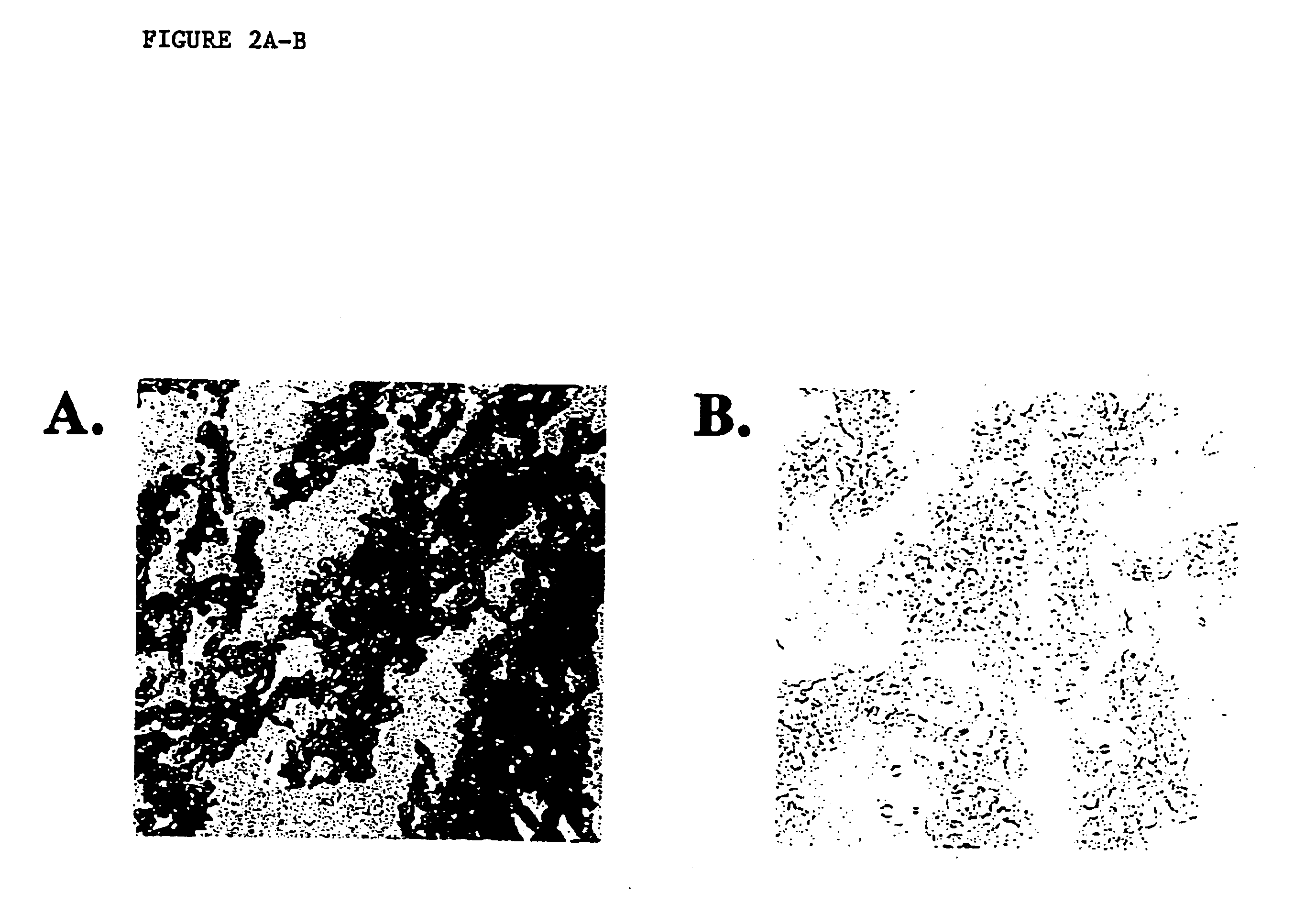
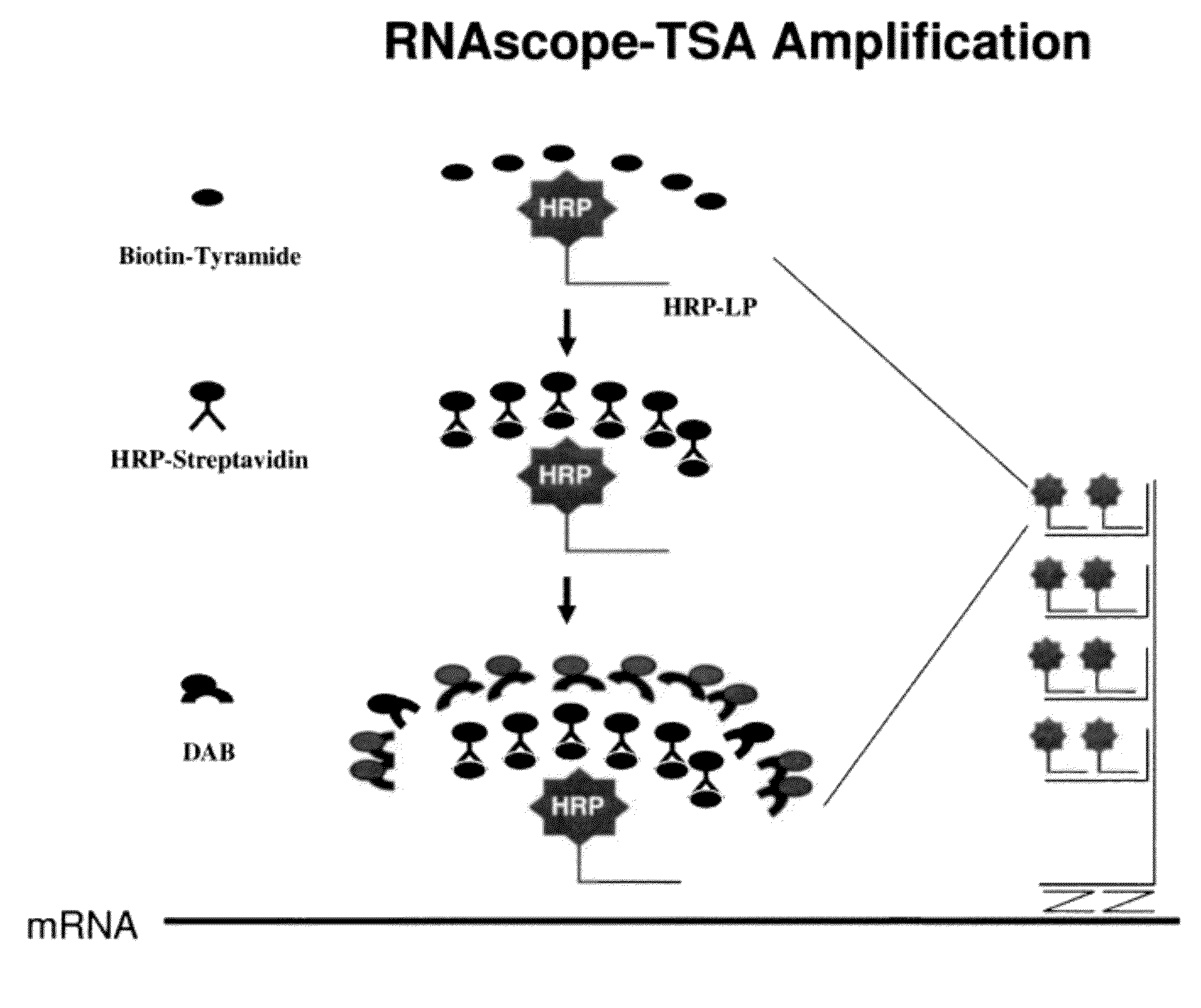
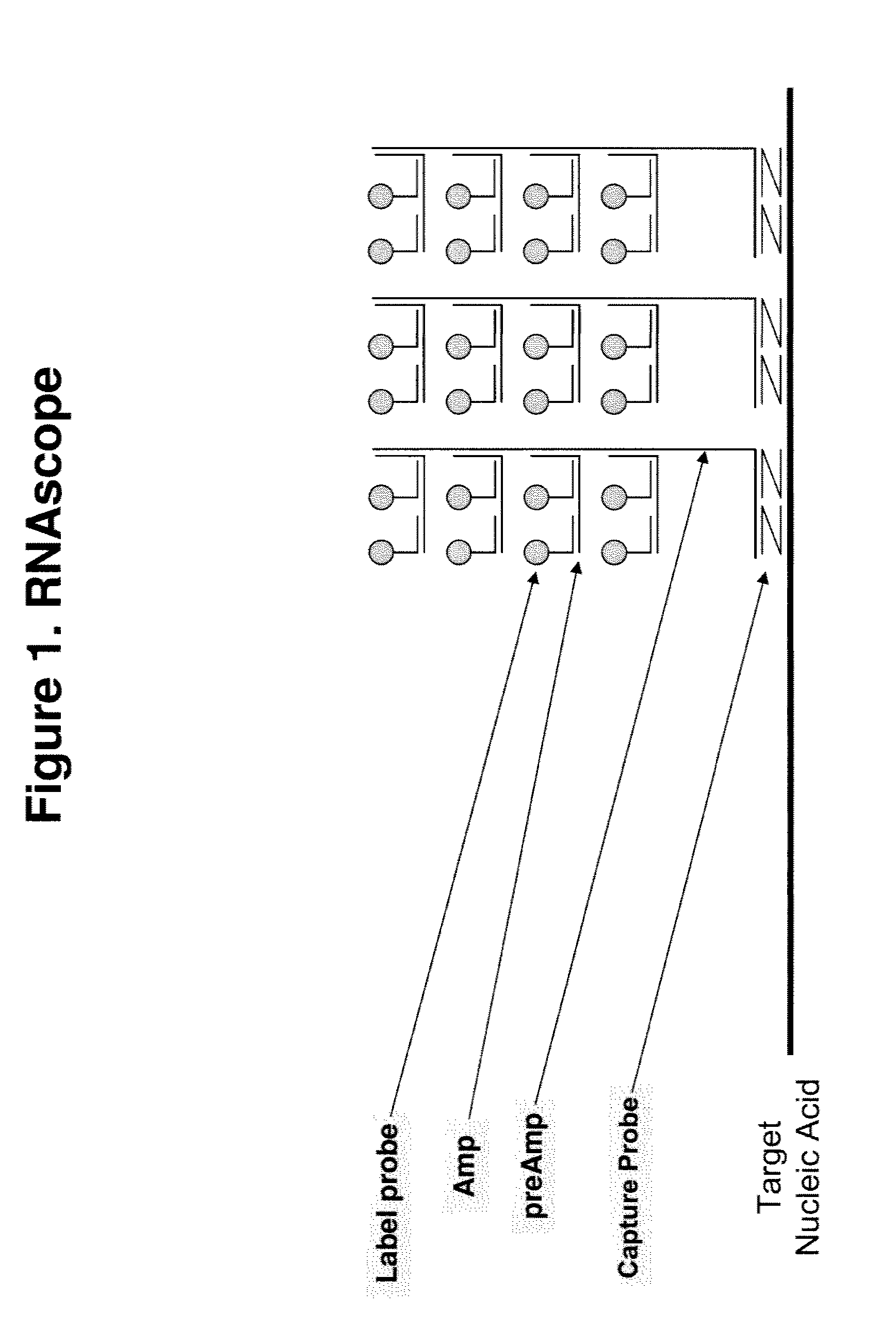
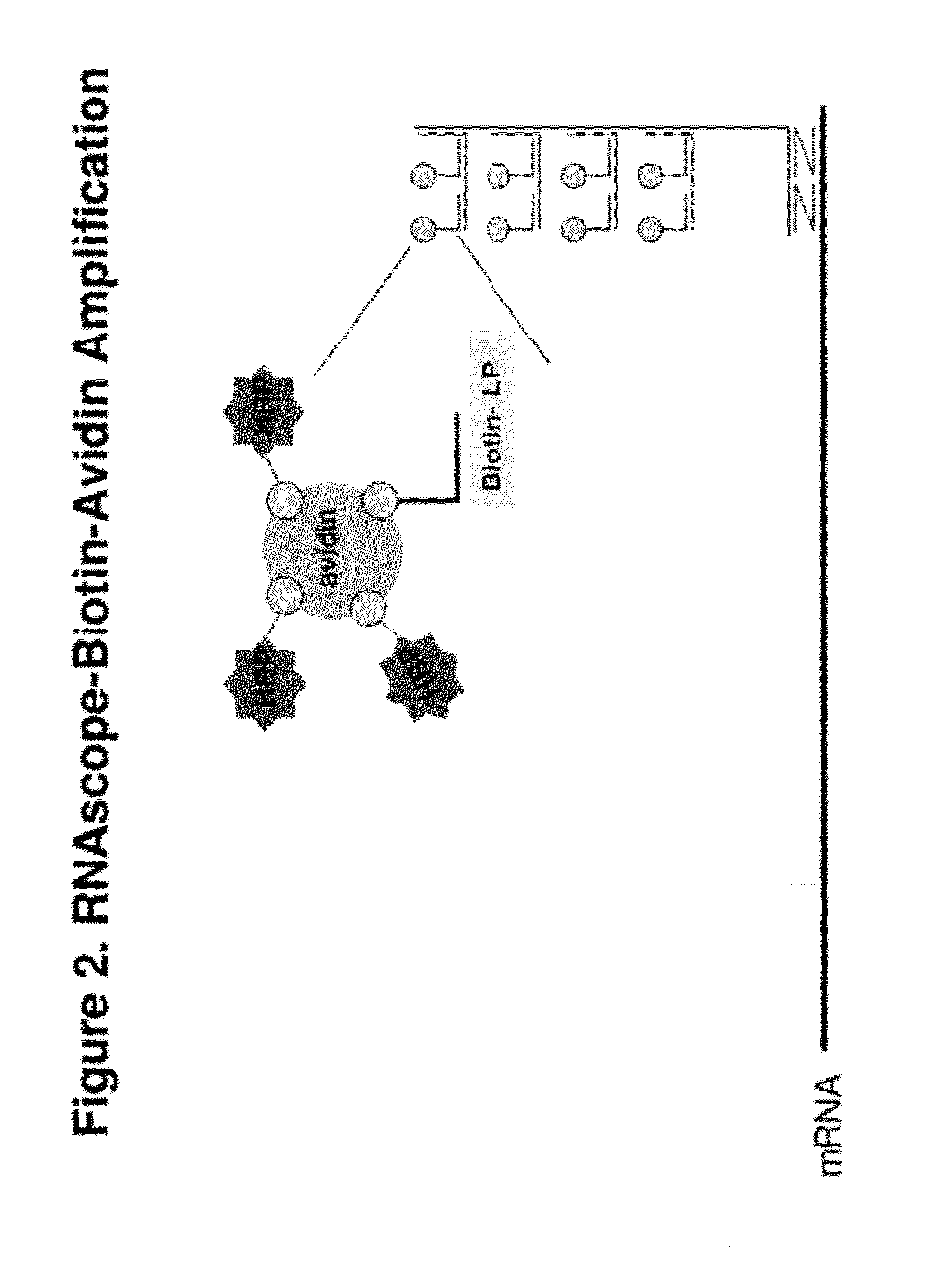
Disclosed is a method for in situ detection of one or more target nucleic acids based on a combination of an in situ hybridization (ISH) assay method and a general ISH signal amplification method. This new method produces high signal intensity and while keeps low background noise of signal amplification. The result can be consistently reproduced and the method can be easily adopted for routine clinic diagnostic use. Further, the invention relates to a kit, comprising the components of the ISH assay and a general ISH signal amplification assay, for sensitive detection of one or more target nucleic acids.
Owner:ADVANCED CELL DIAGNOSTICS INC
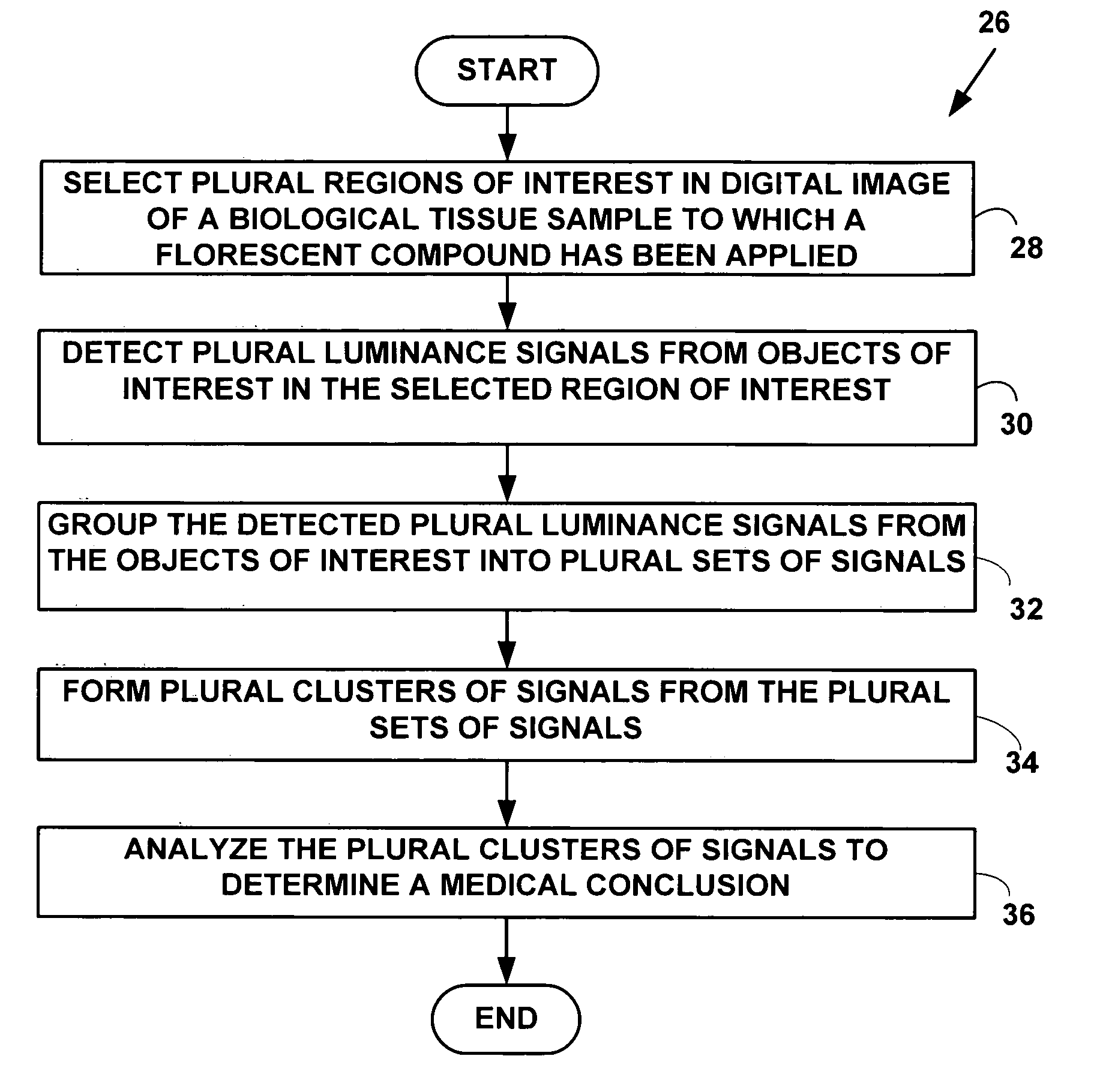
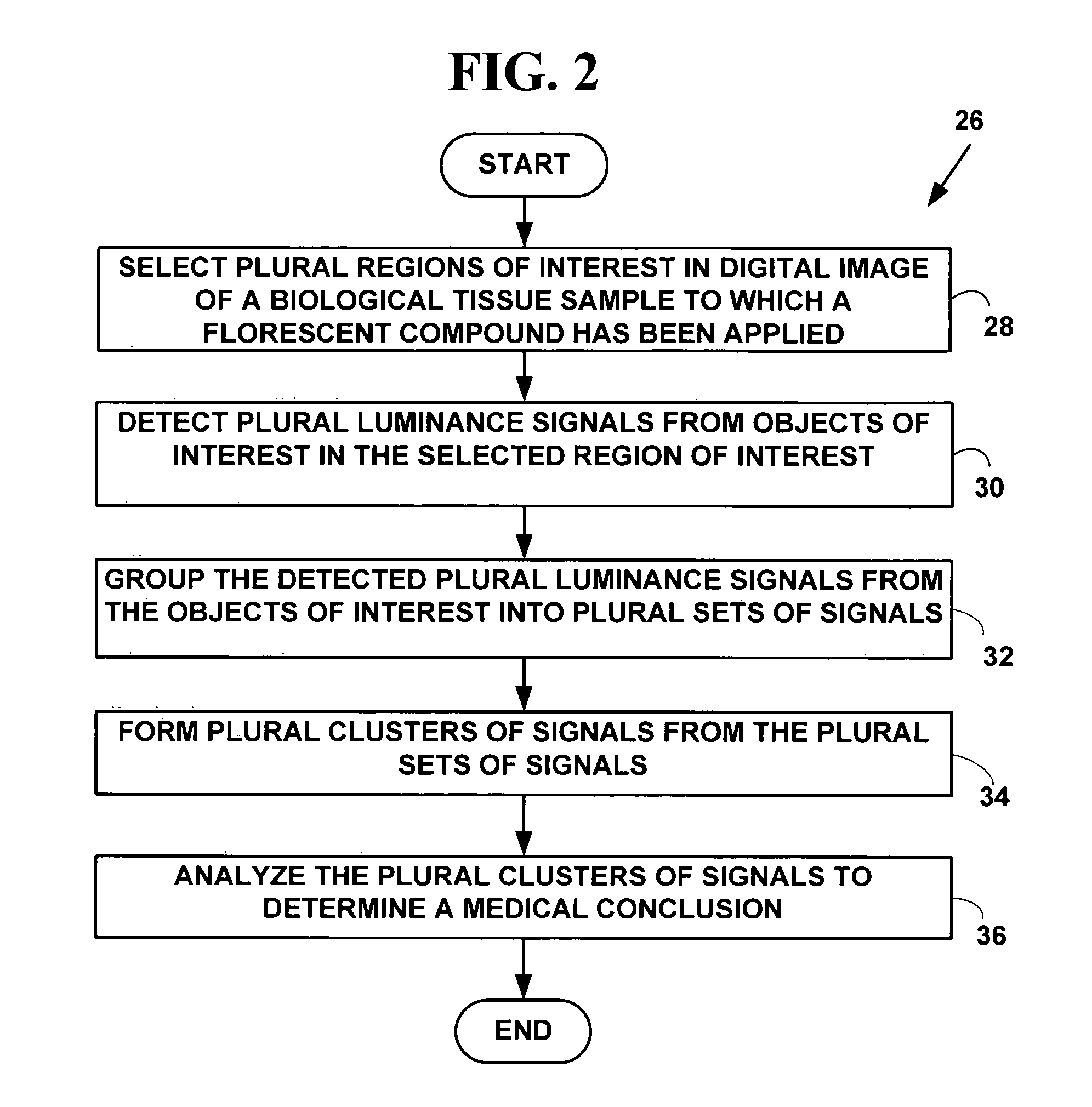
Method and system for digital image based flourescent in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis
A method and system for automated digital fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) image analysis. Luminance parameters from a digital image of a biological tissue sample to which a fluorescent compound (e.g., LSI-HER-2 / neu and CEP-17 dyes) have been applied are analyzed to determine plural regions of interest. Fluorescent color signals in the plural regions of interest including plural cell nuclei are identified, classified and grouped into plural groups. Each of the plural groups is validated based on pre-defined conditions. A medical diagnosis or prognosis or medical, life science or biotechnology experiment conclusion determined using a count of plural ratios of validated fluorescent color signals within each of the cell nuclei within the plural groups.
Owner:BIOIMAGENE
Automated immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization assay formulations
InactiveUS6855552B2Improve accessibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationIn situ hybridizationEtching
The present invention provides reagents for use in an automated environment for cell conditioning of biological samples wherein the cells or tissues are predisposed for access by reagent molecules for histochemical and cytochemical staining procedures. The components of the reagents are optimized to facilitate molecular access to cells and cell constituents within the biological sample. The present invention also provides reagents for use in an automated environment for removing or etching embedding media by exposing a biological sample to be stained in histochemical or cytochemical procedures without the dependence on organic solvents. The components of the reagents are optimized to facilitate removal or etching of the embedding media from the biological sample.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Blood test to monitor the genetic changes of progressive cancer using immunomagnetic enrichment and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH)
InactiveUS20080113350A1Accurate measurementEasy accessMicrobiological testing/measurementLymphatic SpreadGenetic Change
Amplification and overexpression of theHER-2 oncogene in breast cancer is felt to be stable over the course of disease and concordant between the primary tumor and metastases. Therefore, patients with HER-2 negative primary tumors will rarely receive anti-HER-2 antibody therapy. A very sensitive blood test is used to capture circulating tumor cells (CTC's) and evaluate their HER-2 gene status by FISH evaluation. The HER-2 status of the primary tumor and corresponding CTC's is used to assess the ratio of CTC's as a reliable surrogate marker. HER-2 expression of 10 CTC's is sufficient to make a definitive diagnosis of the HER-2 gene status for the whole population of CTC's in patients with recurrent breast cancer.
Owner:JANSSEN DIAGNOSTICS LLC
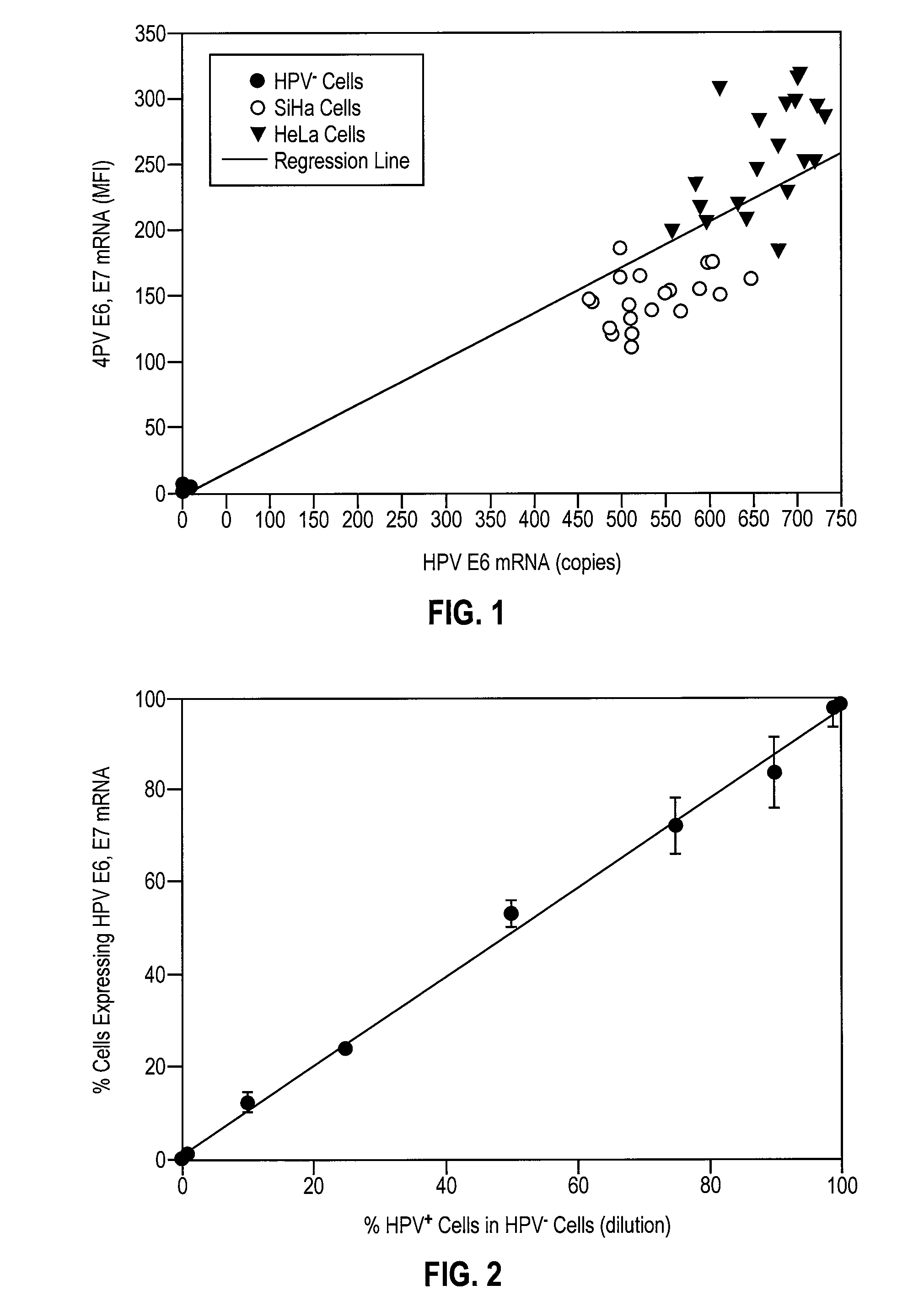
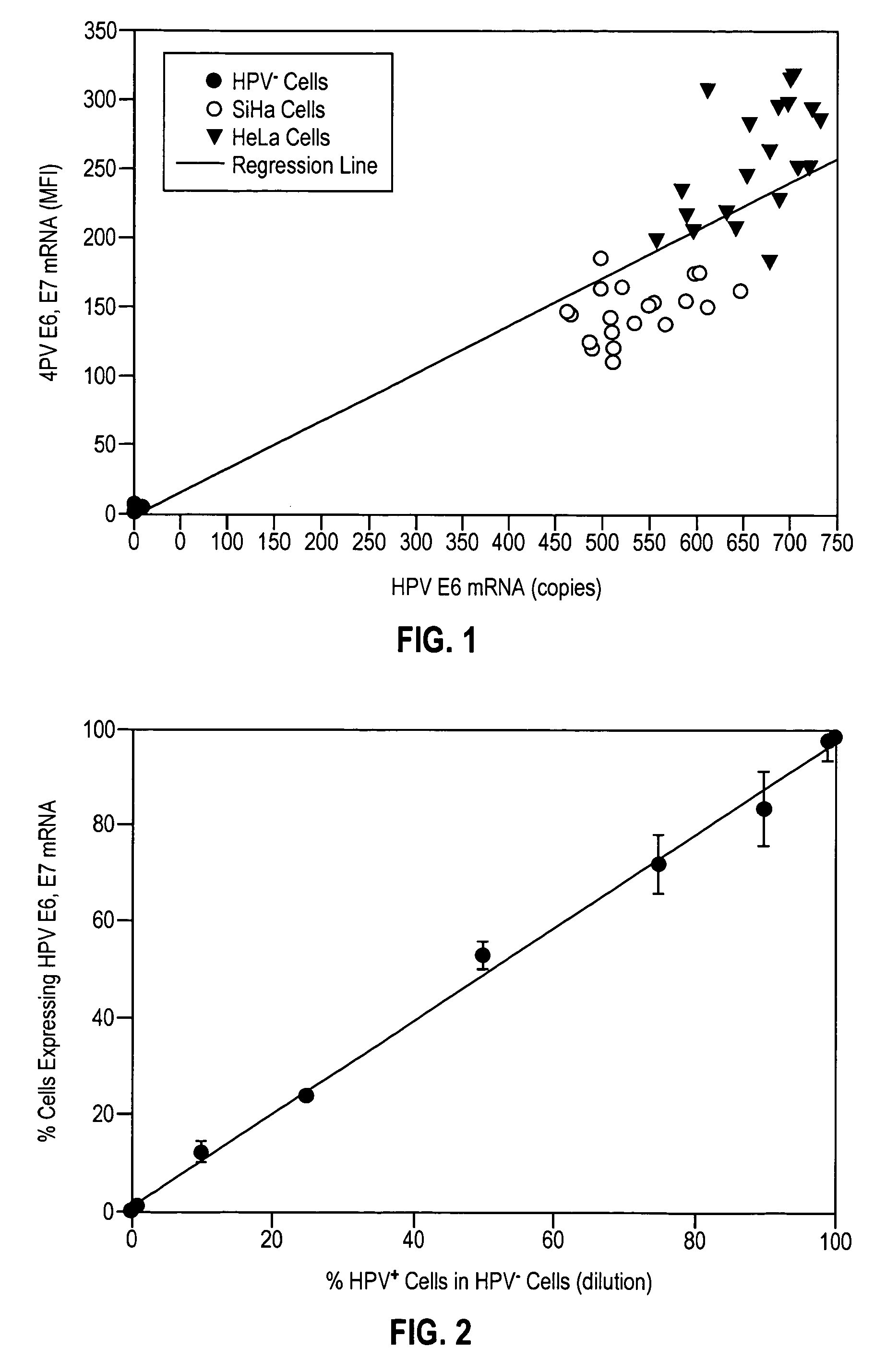
HPV E6, E7 mRNA assay and methods of use thereof
Provided is an HPV E6, E7 mRNA assay, referenced herein as the “In Cell HPV Assay,” that is capable of sensitive and specific detection of normal cervical cells undergoing malignant transformation as well as abnormal cervical cells with pre-malignant or malignant lesions. The In Cell HPV Assay identifies HPV E6, E7 mRNA via in situ hybridization with oligonucleotides specific for HPV E6, E7 mRNA and quantitates the HPV E6, E7 mRNA via flow cytometry. The In Cell HPV Assay can be carried out in less than three hours directly from liquid-based cervical (“LBC”) cytology specimens. The In Cell HPV Assay provides an efficient and highly sensitive alternative to the Pap smear for determining abnormal cervical cytology.
Owner:INCELLDX
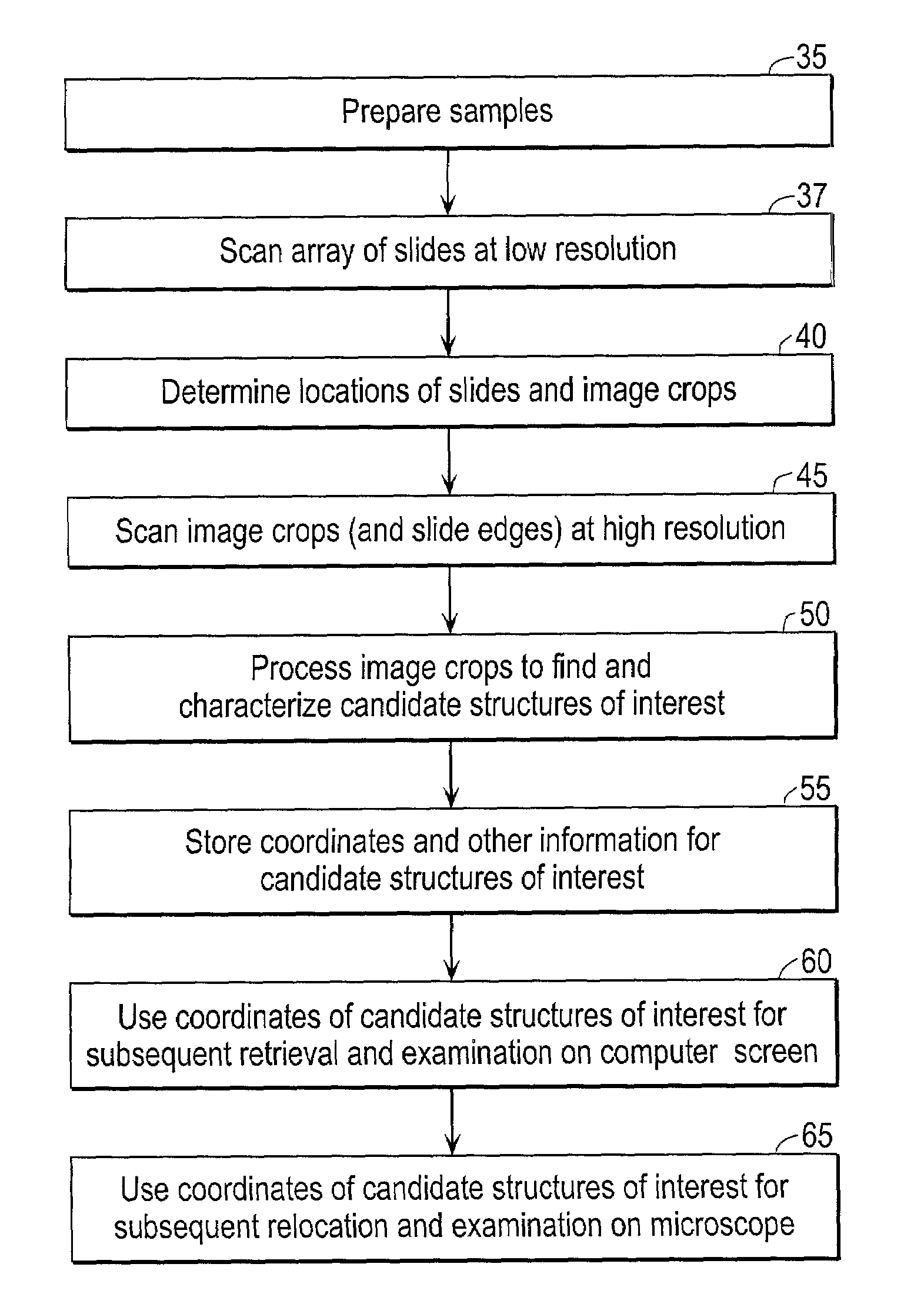
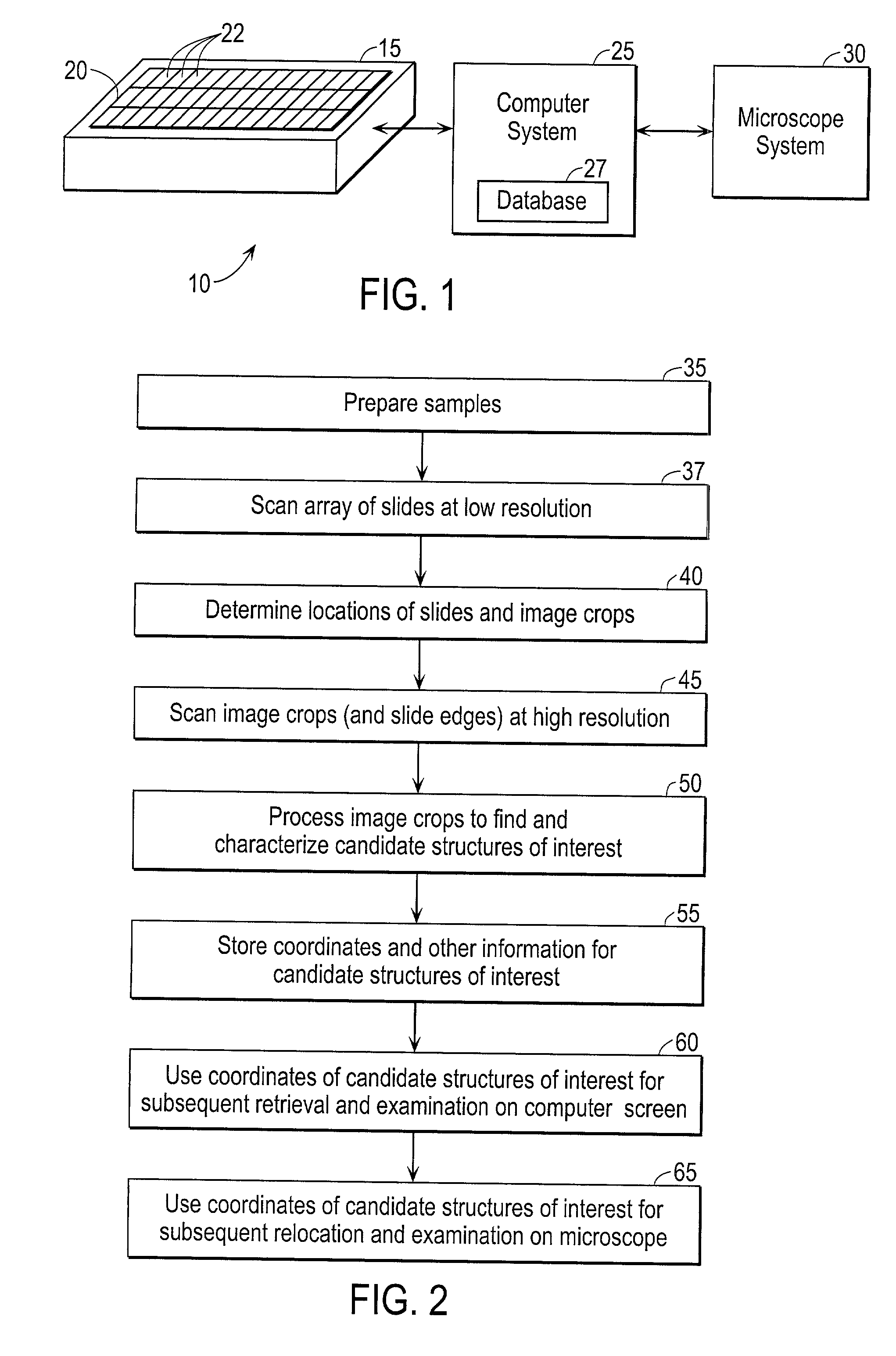
Automated scanning method for pathology samples
Scanning and analysis of cytology and histology samples uses a flatbed scanner to capture images of the structures of interest such as tumor cells in a manner that results in sufficient image resolution to allow for the analysis of such common pathology staining techniques as ICC (immunocytochemistry), IHC (immunohistochemistry) or in situ hybridization. Very large volumes of such material are scanned in order to identify cells or clusters of cells which are positive or warrant more detailed examination, and if analysis at higher resolution is necessary, information regarding these positive events is transferred to a secondary microscope, such as a conventional scanning microscope, to allow further analysis and review of the selected regions of the slide containing the sample.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
Gene detection assay for improving the likelhood of an effective response to an ErbB antagonist cancer therapy
InactiveUS20060228745A1Great likelihoodChoose accuratelyOrganic active ingredientsBiocideFhit geneTumor cells
The invention provides a method for more effective treatment of patients susceptible to or diagnosed with tumors overexpressing ErbB, as determined by a gene amplification assay, with an ErbB antagonist. Such method comprises administering a cancer-treating dose of the ErbB antagonist, preferably in addition to chemotherapeutic agents, to a subject in whose tumor cells ErbB has been found to be amplified e.g., by fluorescent in situ hybridization. ErbB antagonists described include an anti-HER2 antibody. Pharmaceutical packaging for providing the components for such treatment is also provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
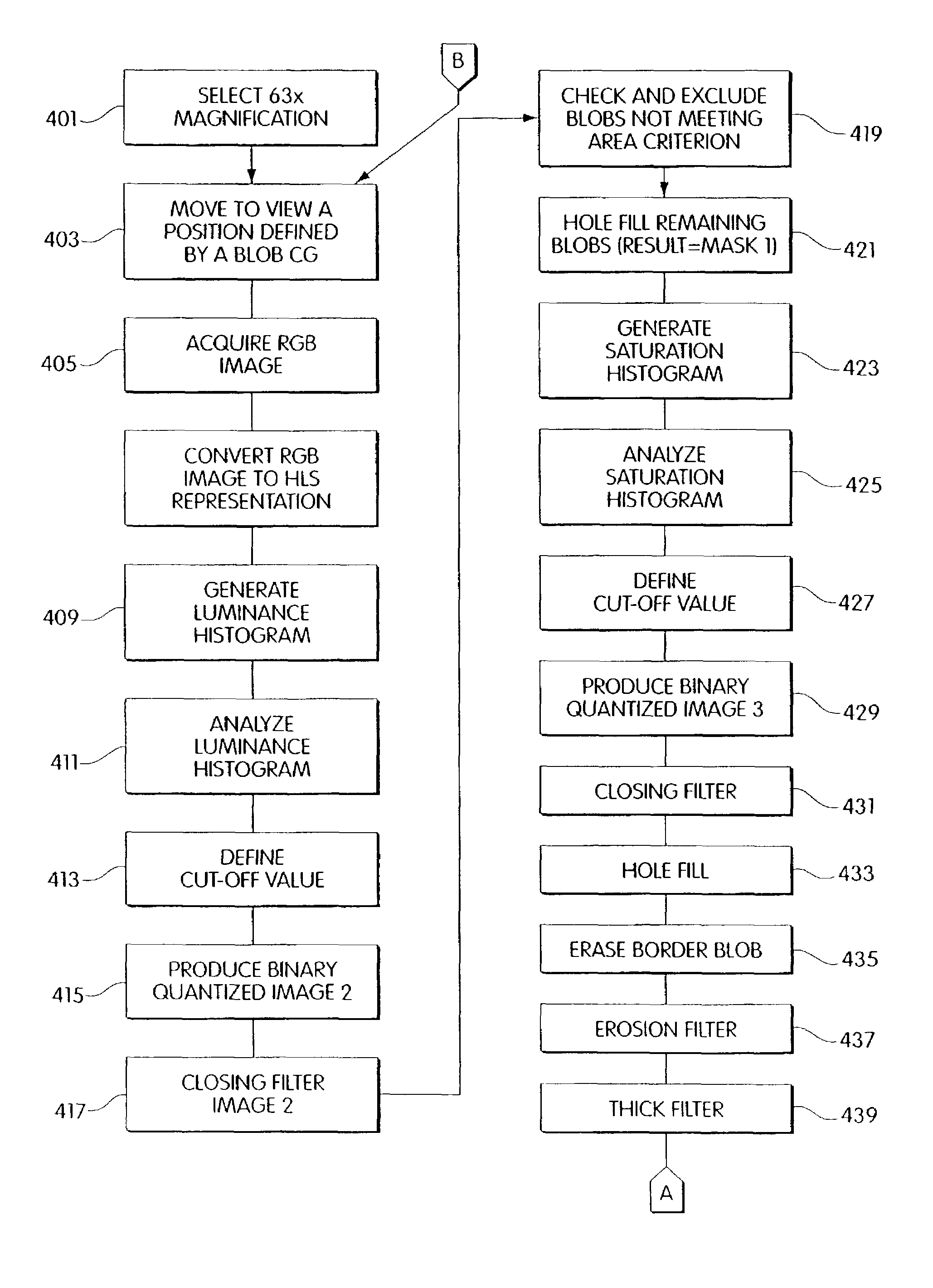
Method and apparatus for computer controlled cell based diagnosis
InactiveUS20060072805A1Minimize timePossible amount of timePreparing sample for investigationDisease diagnosisCancer cellRare cell
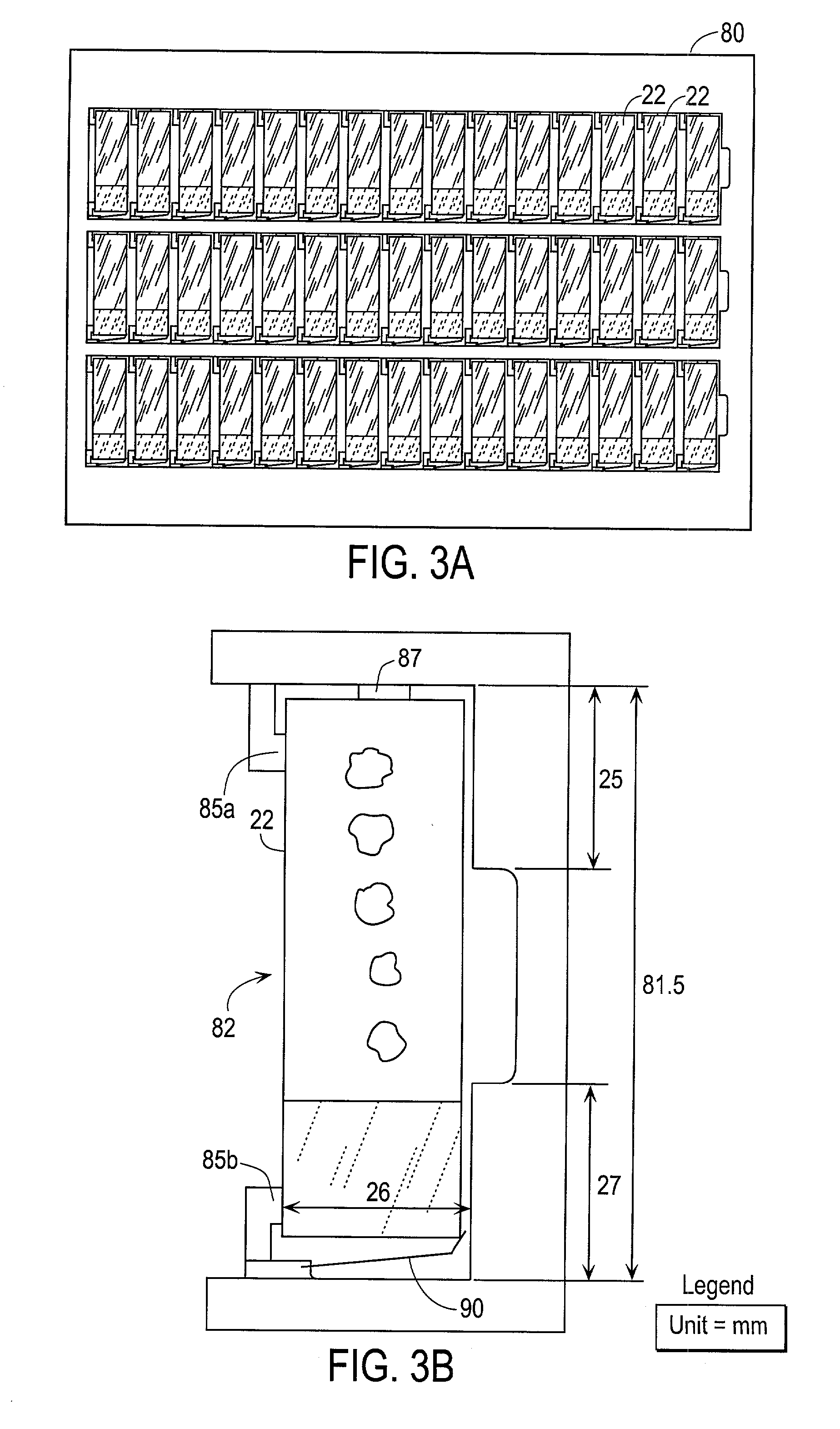
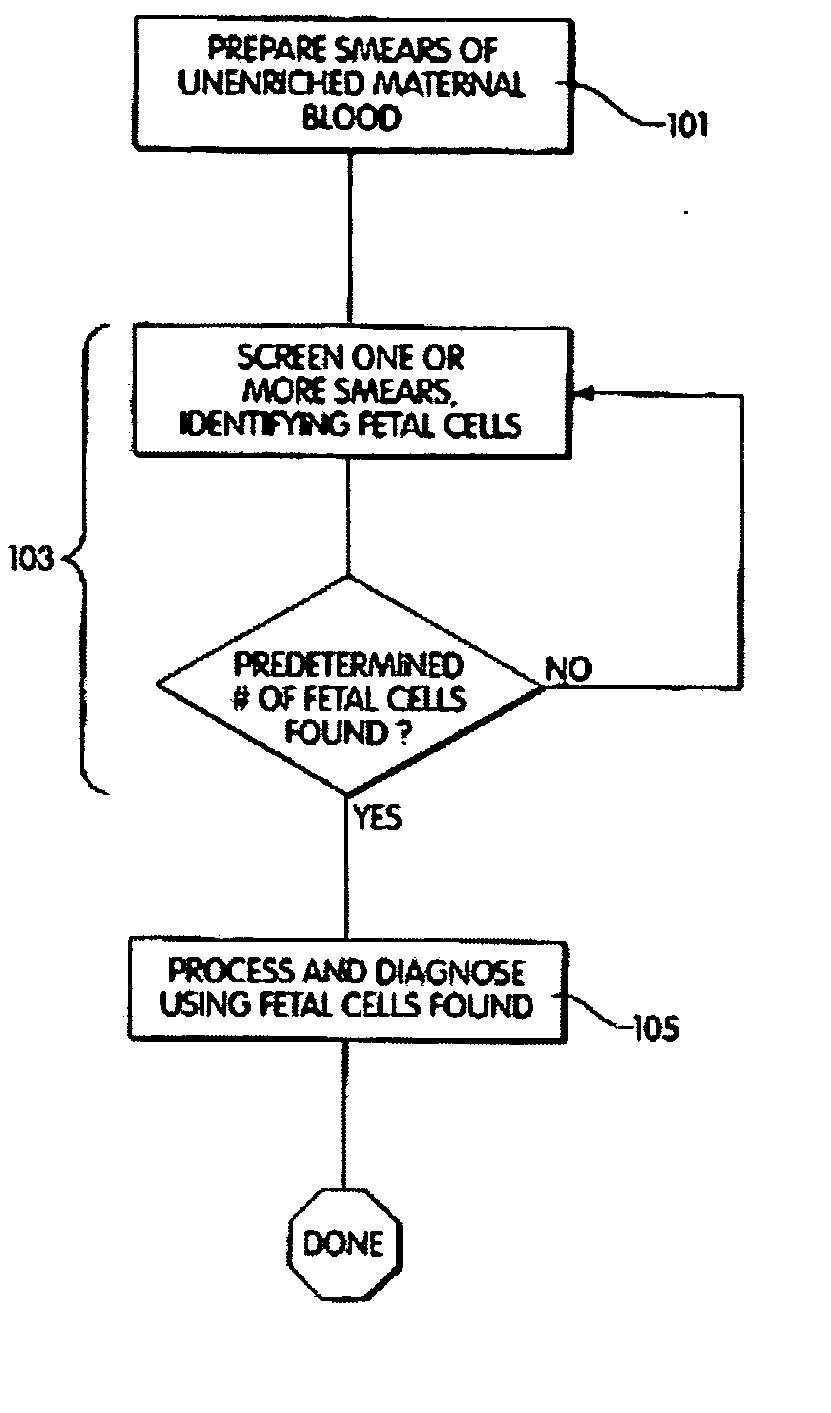
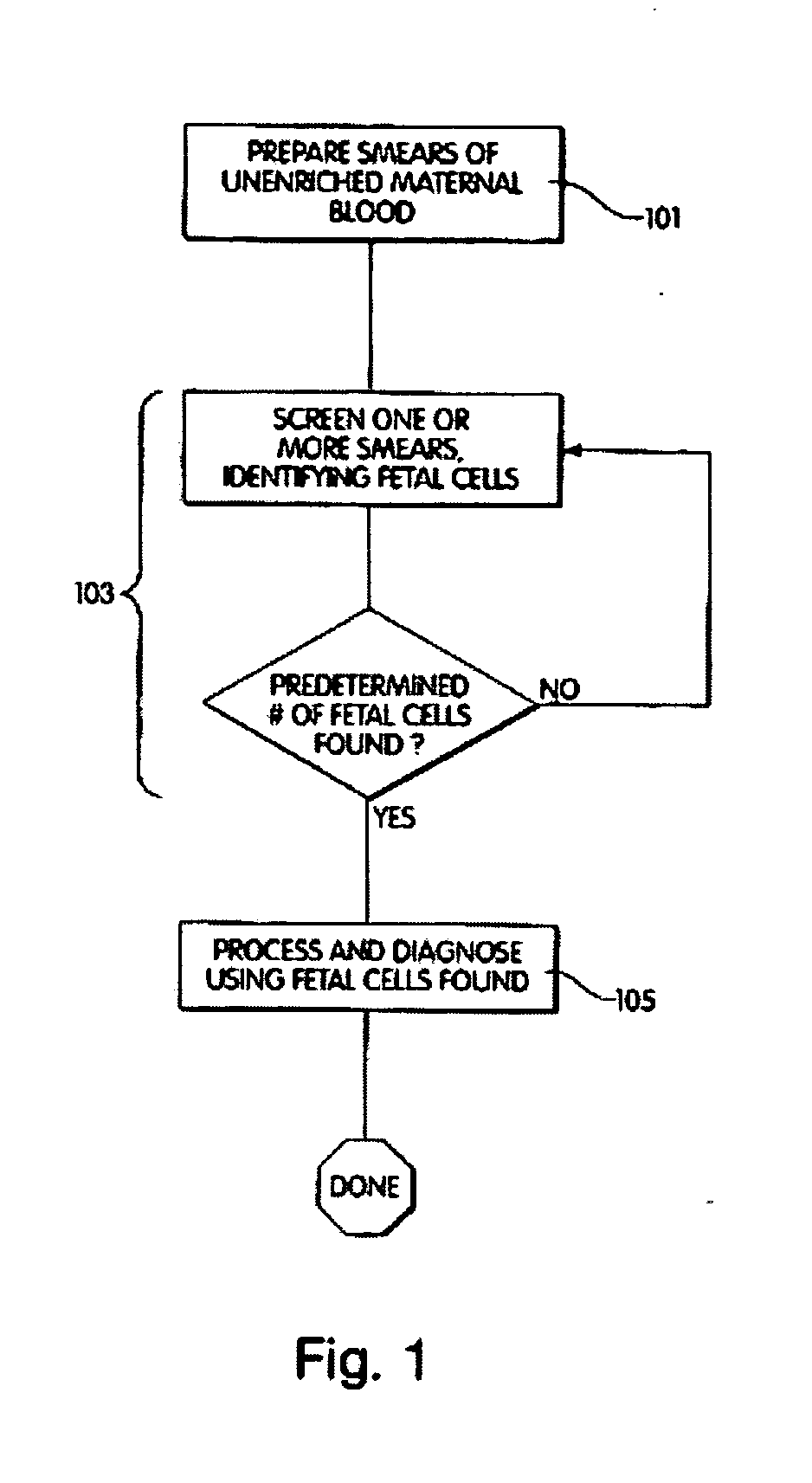
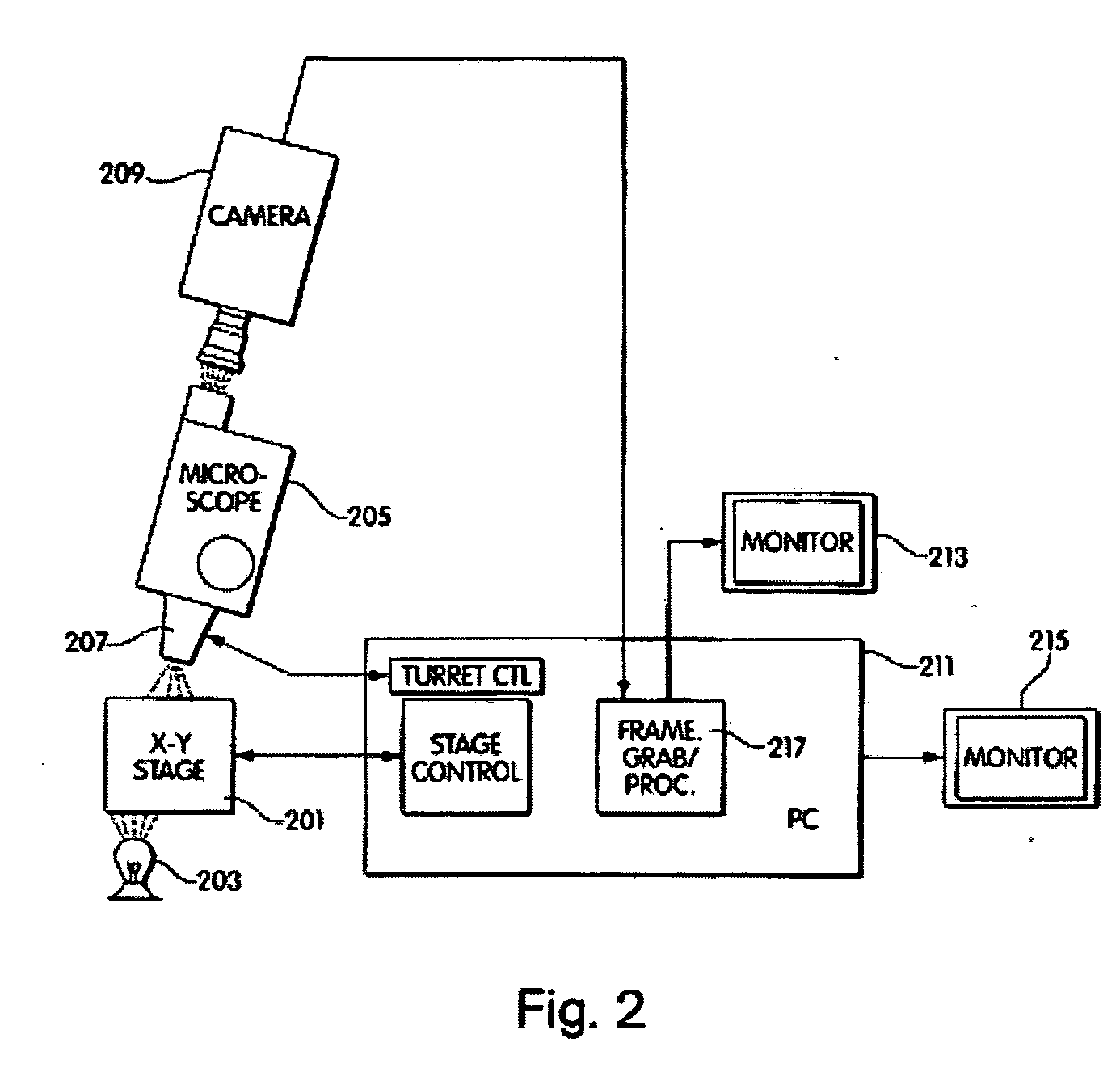
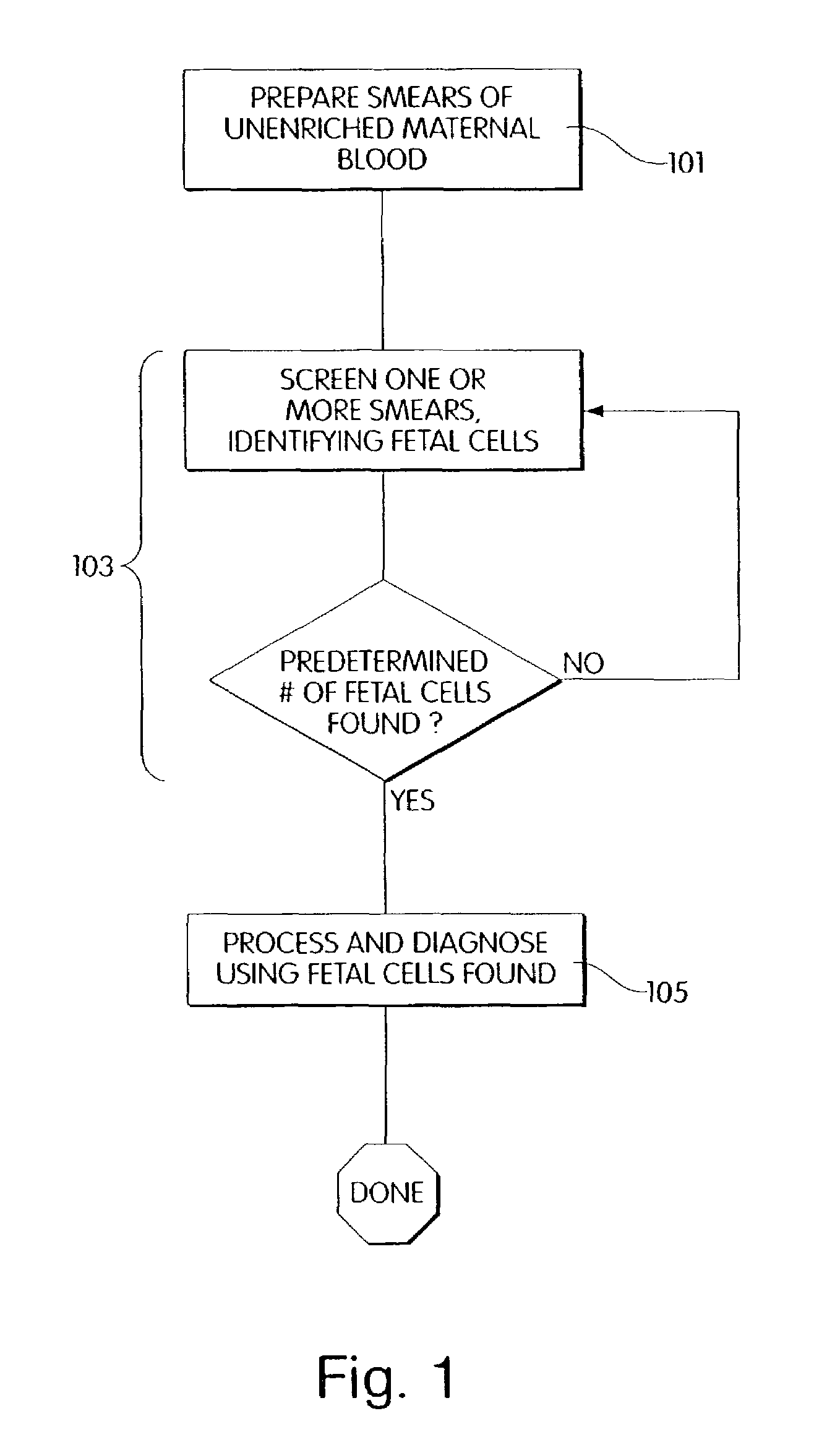
A computer controlled method for detecting and diagnosing a rare cell type in a tissue sample is provided, said method comprising treating the tissue sample such that it generates a first signal indicative of the presence at a location of a rare cell, detecting the first signal, treating the location at which the first signal is detected to generate a second signal indicative of a diagnostically useful cellular characteristic and detecting the second signal. The first signal can be morphological or a color present in a sought cell either before or after staining. The second signal can be generated by in situ PCR or PCR in situ hybridization. In one preferred embodiment, the rare cell type is a fetal cell in a maternal blood tissue sample, said sample consisting of a smear of unenriched maternal blood. In another embodiment, the method is used to diagnose or genotype cancer cells in a blood or tissue biopsy sample.
Owner:IKONISYS INC
Low temperature deparaffinization
InactiveUS20060252025A1Easy to explainImproving stainability and readabilityPreparing sample for investigationDead animal preservationCytochemistryBatch processing
Methods and apparatuses for gently removing embedding media from biological samples at temperatures below the embedding medium melting point with liquid composition using batch methods or automated instruments prior to immunohistochemical (IHC), in situ hybridization (ISH) or other special staining or histochemical or cytochemical manipulations.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Methods of detecting dna, RNA and protein in biological samples
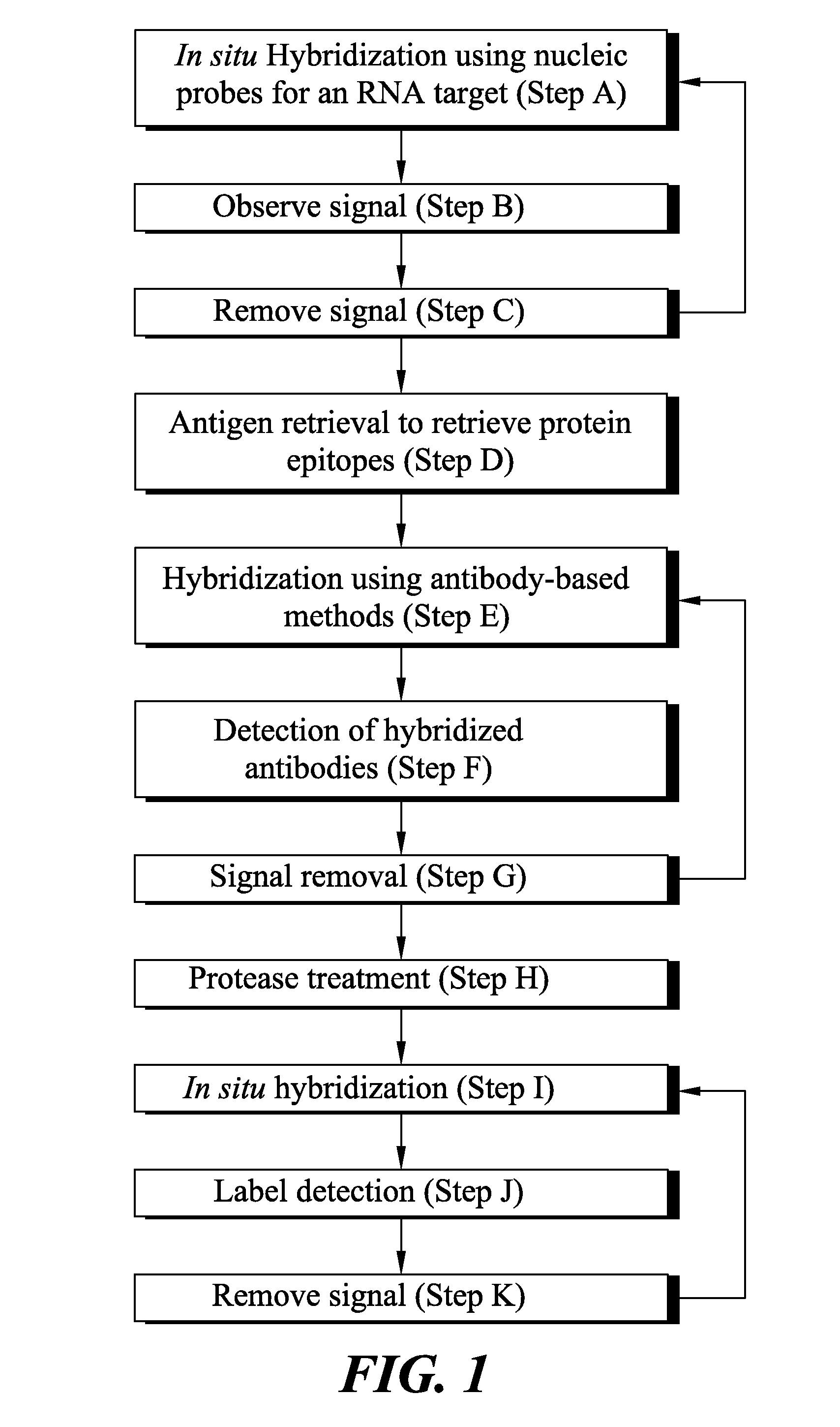
InactiveUS20140024024A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingIn situ hybridisationProteinase activity
Novel methods of probing multiple targets in a biological sample are provide whereby the targets are DNA, RNA and protein. The method comprises subjecting the sample to an in situ hybridization reaction using a labeled nucleic acid probe that binds an RNA target, observing a signal, and optionally removing the signal. The method further comprises an antigen retrieval protocol, observing a signal, removing the signal, and optionally applying a protease treatment to access the sample's DNA targets by subjecting the sample to an in situ hybridization reaction using a labeled nucleic acid probe, observing a signal from the labeled DNA targets, and optionally removing the signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Chlamys Farreri pathogeny rickettsia in situ hybridization detection method and its reagent kit
InactiveCN1769485AEfficient detectionAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementOligoribonucleotidesInfection rate
This invention relates to the original position cross checking method of a Hence Kong waters disease type Pamela Ci's body and its reagent box. This invention includes the following steps: composing the three oligoribonucleotides probes of the High Sim markings according to the special DNA list design of the Pamela Ci's body's 16S rDNA list in the bacteria taxonogy, this unusual probe crosses and combines with the Pamela Ci's body 16s rRNA of the Hence Kong waters slice up, and then enlarges signal through the antigen antibody reaction, and displays colour through enzyme reaction. This checking method can combine the pathogeny checking with its pathology together; it can analyze the infection rate and infection intension on the stylebook slice when effiently and correctly checking the Pamela Ci's body; and the checking result is sensitive and precisious; and the slice after being checked can be preserved perennially.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Antibody conjugates
ActiveUS20090176253A1Easy to detectHigh activityHydrolasesEnzyme stabilisationIn situ hybridisationAntibody conjugate
Antibody / signal-generating moiety conjugates are disclosed that include an antibody covalently linked to a signal-generating moiety through a heterobifunctional polyalkyleneglycol linker. The disclosed conjugates show exceptional signal-generation in immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization assays on tissue sections and cytology samples. In one embodiment, enzyme-metallographic detection of nucleic acid sequences with hapten-labeled probes can be accomplished using the disclosed conjugates as a primary antibody without amplification.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Method and apparatus for computer controlled cell based diagnosis
InactiveUS7346200B1Suitable for control and processingMinimize timePreparing sample for investigationDisease diagnosisCancer cellRare cell
A computer controlled method for detecting and diagnosing a rare cell type in a tissue sample is provided, said method comprising treating the tissue sample such that it generates a first signal indicative of the presence at a location of a rare cell, detecting the first signal, treating the location at which the first signal is detected to generate a second signal indicative of a diagnostically useful cellular characteristic and detecting the second signal. The first signal can be morphological or a color present in a sought cell either before or after staining. The second signal can be generated by in situ PCR or PCR in situ hybridization. In one preferred embodiment, the rare cell type is fetal cell in a maternal blood tissue sample, said sample consisting of a smear of unenriched maternal blood. In another embodiment, the method is used to diagnose or genotype cancer cells in a blood or tissue biopsy sample.
Owner:IKONISYS INC
Automated immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization assay formulations
InactiveUS20050118725A1Shorten the timeLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationCytochemistryOrganic solvent
The present invention provides reagents for use in an automated environment for cell conditioning of biological samples wherein the cells or tissues are predisposed for access by reagent molecules for histochemical and cytochemical staining procedures. The reagents comprise components optimized to faciliate molecular access to cells and cell constituents within the biological sample. The present invention also provides reagents for use in an automated environment for removing or etching embedding media by exposing a biological sample to be stained in histochemical or cytochemical procedures without the dependence on organic solvents. The reagents comprise components optimized to facilitate removal or etching of the embedding media from the biological sample.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Methods and compositions for the preparation and use of fixed-treated cell-lines and tissue in fluorescence in situ hybridization
InactiveUS6995020B2Easy to detectReduced autofluorescenceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical treatmentTreated cell
This invention relates to methods for the detection of one or more mRNA transcripts in paraffin-embedded tissue by “mRNA liberation in fixed-treated tissue or ‘MLIFTT’”. This method includes treating the tissue with ammonia-ethanol and sodium borohydride combined with pressure cooking of the tissue. The chemical treatments reduce the tissue autofluorescence and the physical treatments overcome the interference created by the fixation-induced chemical bonds. The methods of the present invention can be utilized to identify a plurality of mRNA transcripts in a microarray format.
Owner:AUREON LAB INC +2
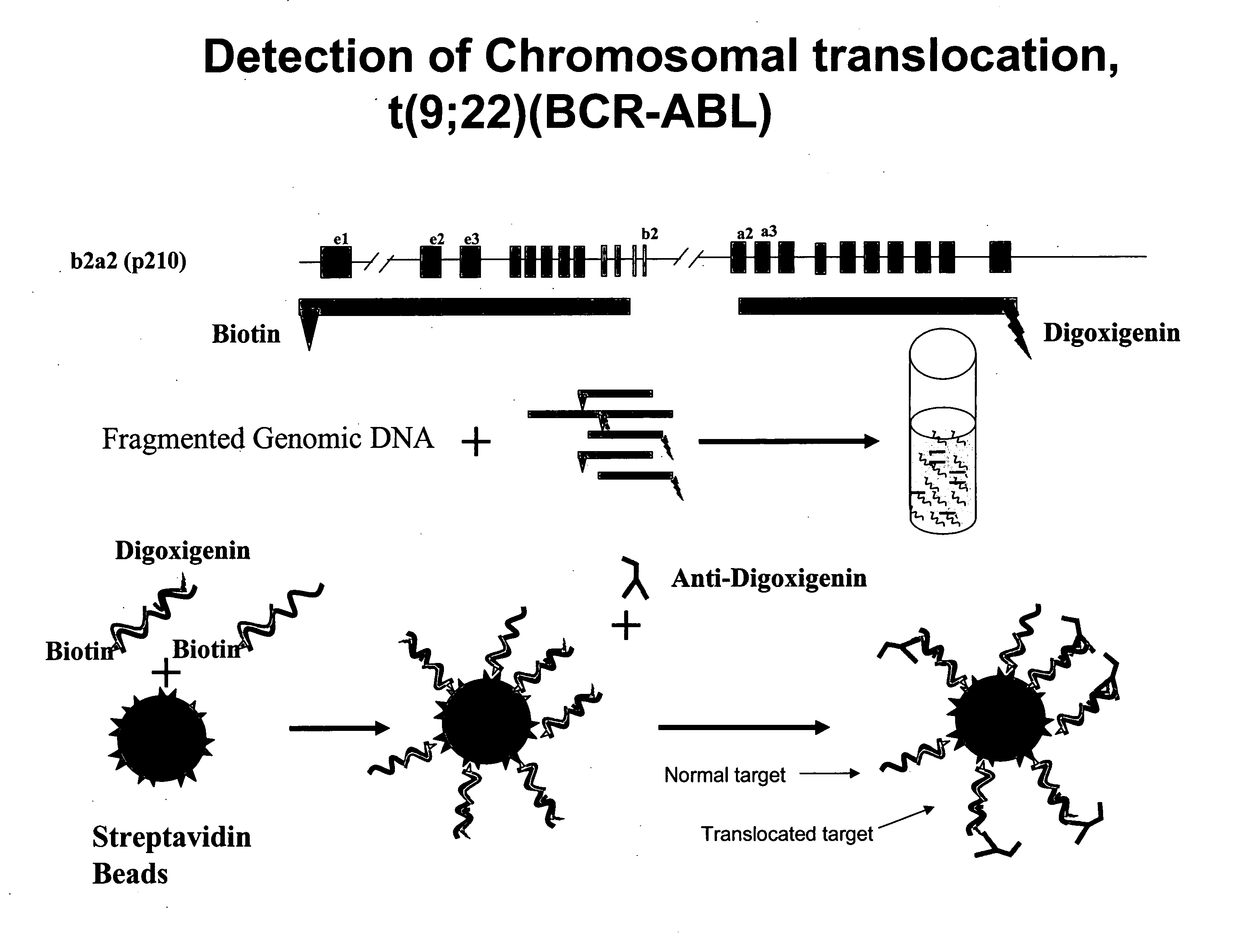
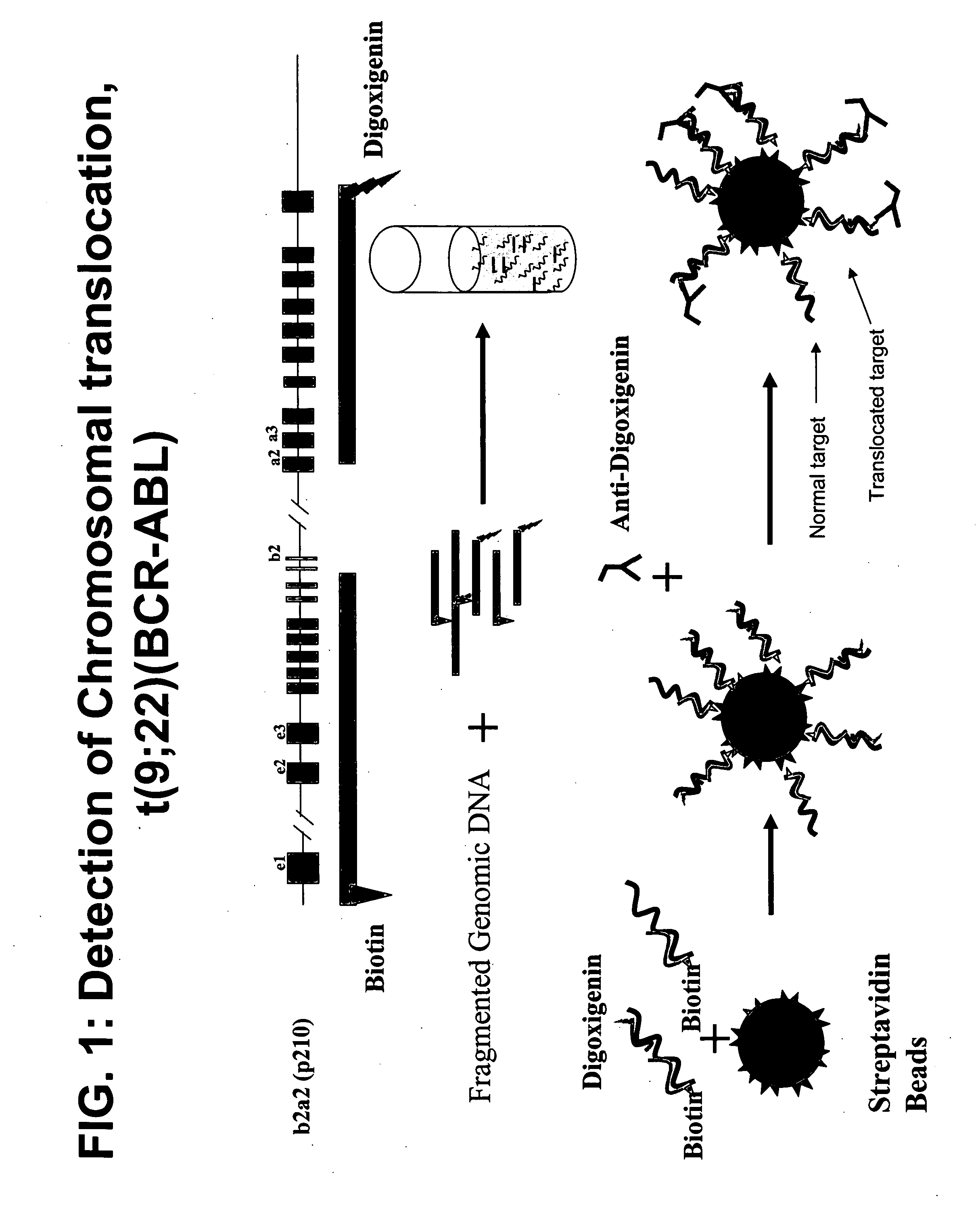
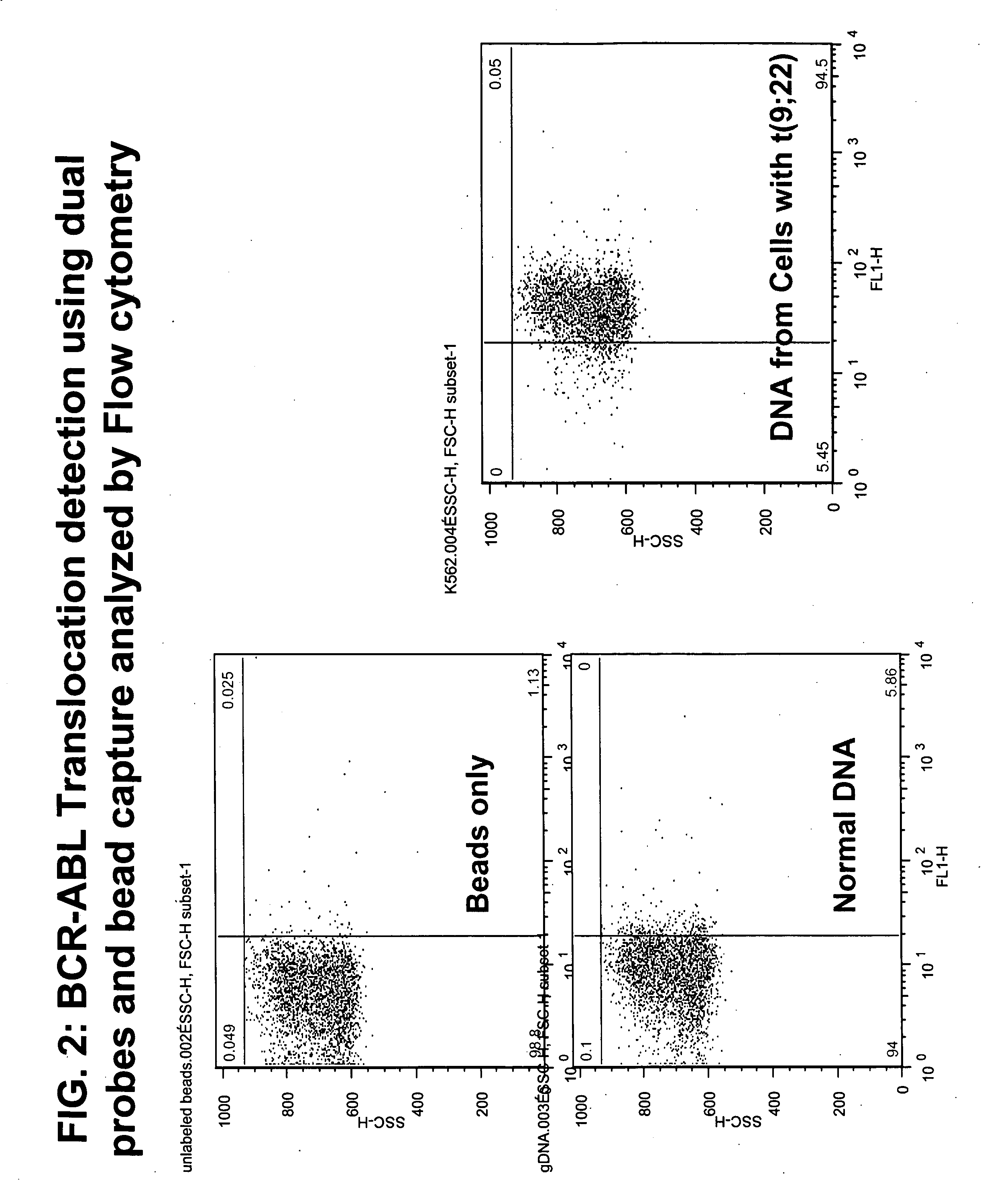
Non-in situ hybridization method for detecting chromosomal abnormalities
The present invention provides methods of detecting chromosomal or genetic abnormalities associated with various diseases or with predisposition to various diseases. In particular, the present invention provides advanced methods of performing DNA hybridization, capture, and detection on solid support. Invention methods are useful for the detection, diagnosis, predicting response to therapy, detecting minimal residual disease, prognosis, or monitoring of disease treatment or progression of particular disease conditions such as cell proliferative disorders
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
HPV E6, E7 mRNA assay and methods of use thereof
Provided is an HPV E6, E7 mRNA assay, referenced herein as the “In Cell HPV Assay,” that is capable of sensitive and specific detection of normal cervical cells undergoing malignant transformation as well as abnormal cervical cells with pre-malignant or malignant lesions. The In Cell HPV Assay identifies HPV E6, E7 mRNA via in situ hybridization with oligonucleotides specific for HPV E6, E7 mRNA and quantitates the HPV E6, E7 mRNA via flow cytometry. The In Cell HPV Assay can be carried out in less than three hours directly from liquid-based cervical (“LBC”) cytology specimens. The In Cell HPV Assay provides an efficient and highly sensitive alternative to the Pap smear for determining abnormal cervical cytology.
Owner:INCELLDX
Method of and composite for in situ fluorescent hybridization
InactiveUS6043039AMaximize denaturationReduce concentrationMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyHybridization probeSingle strand
A fluorescent in situ hybridization method including the steps of (a) obtaining a chromosome spread of a species; (b) preparing a hybridization composite containing a plurality of chromosomal paints each of the plurality of chromosomal paints being labeled with a different fluorophore-or-combination-of-fluorophores, such that an averaged specific activity of highly repetitive sequences in the hybridization composite substantially equals an averaged specific activity of unique sequences in the hybridization composite; (c) denaturing the hybridization composite and subjecting the hybridization composite to conditions for allowing at least a part of the highly repetitive sequences in the hybridization composite to reanneal while at least a part of the unique sequences in the hybridization composite remaining single stranded; (d) contacting under hybridization conditions the hybridization composite with the chromosome spread; (e) washing away excess of the hybridization composite; and (d) analyzing and presenting images of the now hybridized chromosome spread.
Owner:APPLIED SPECTRAL IMAGING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com