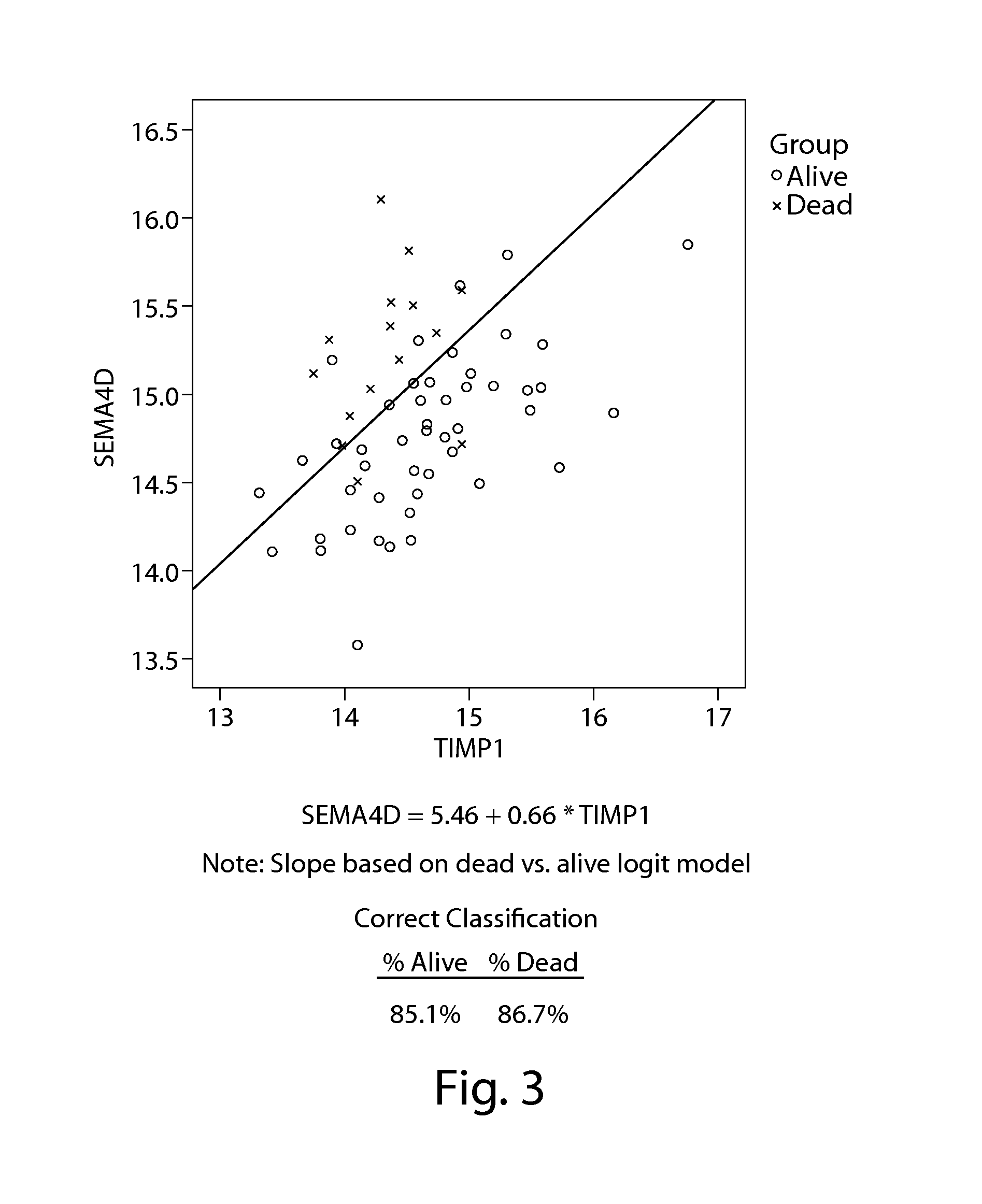
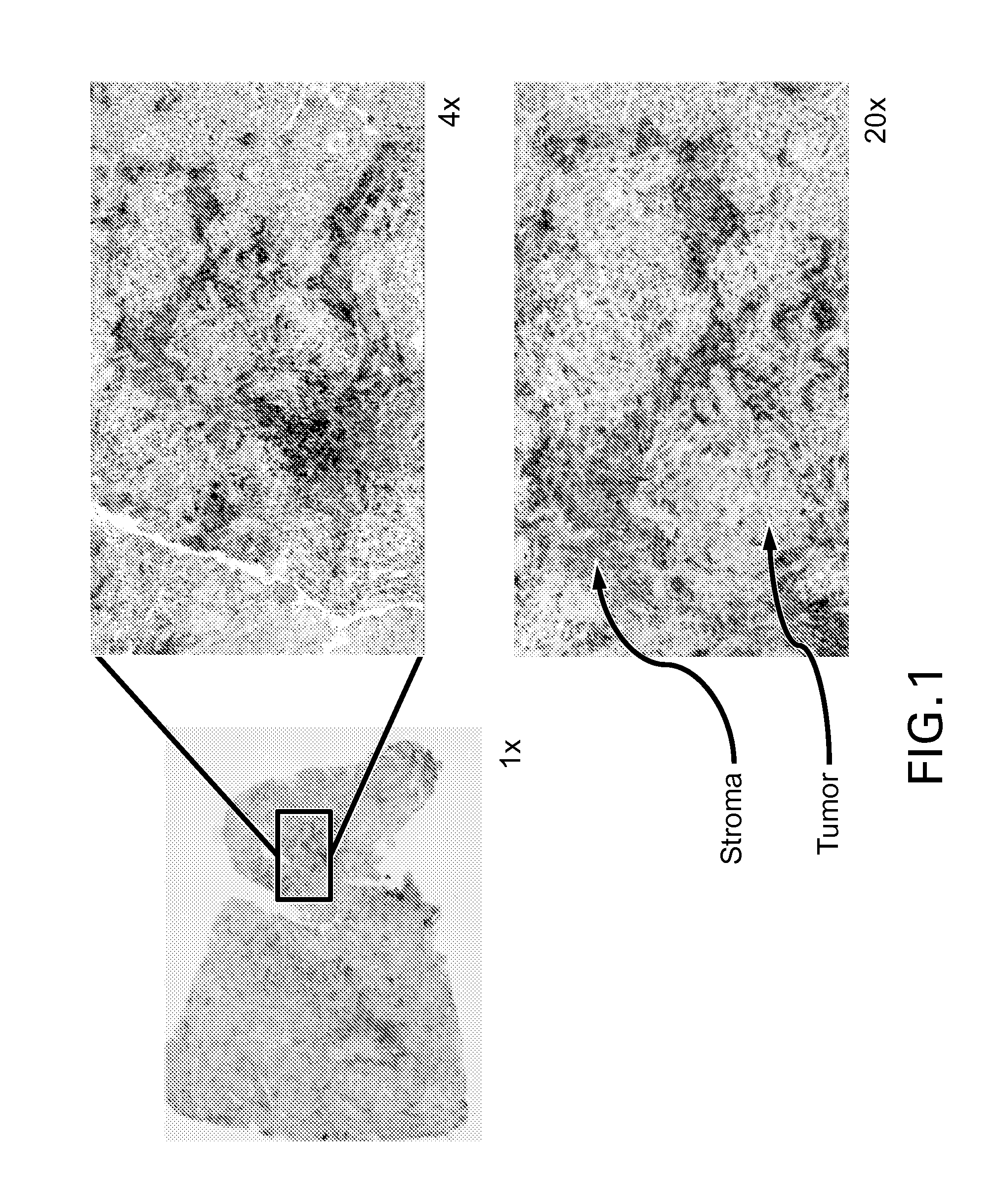
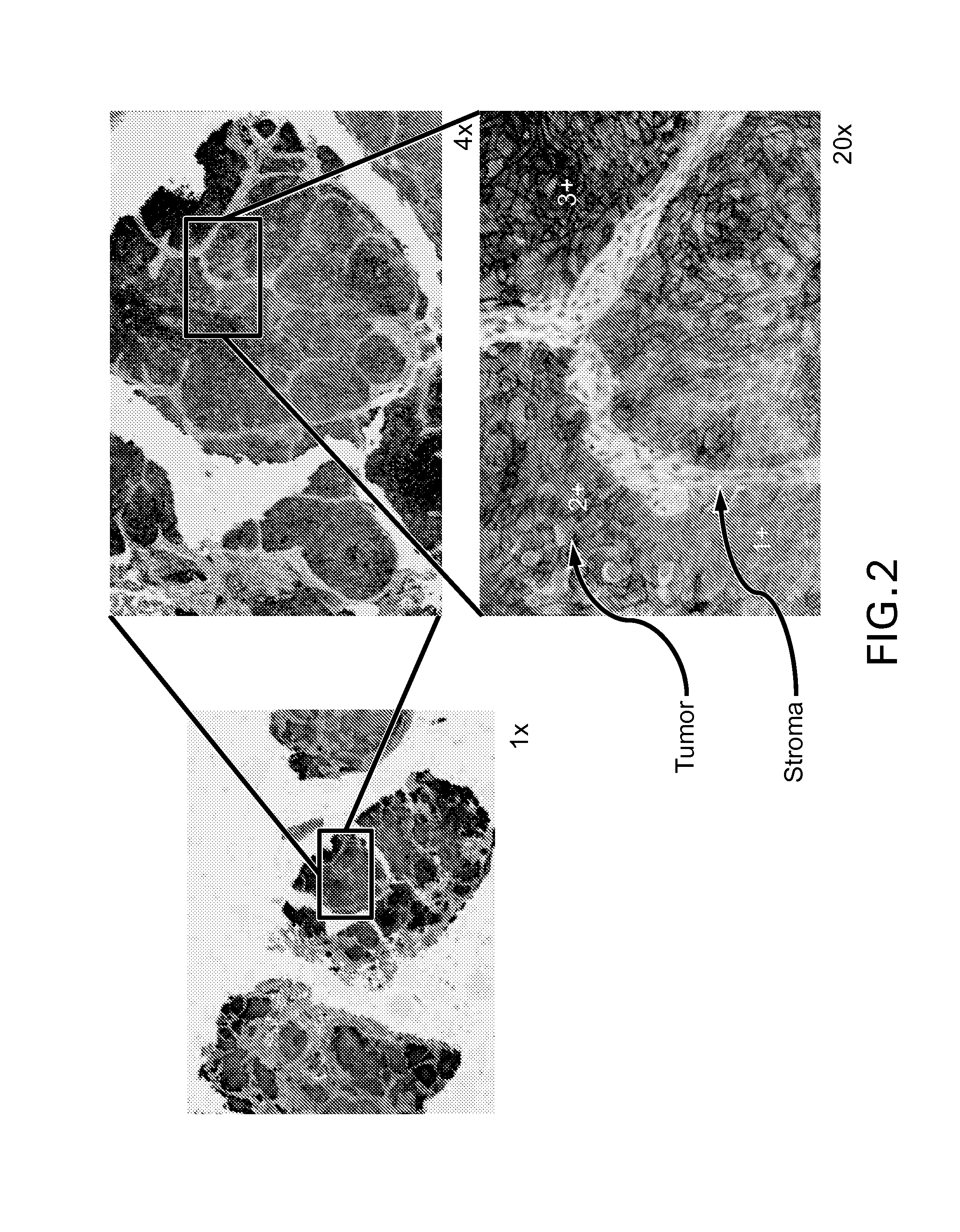
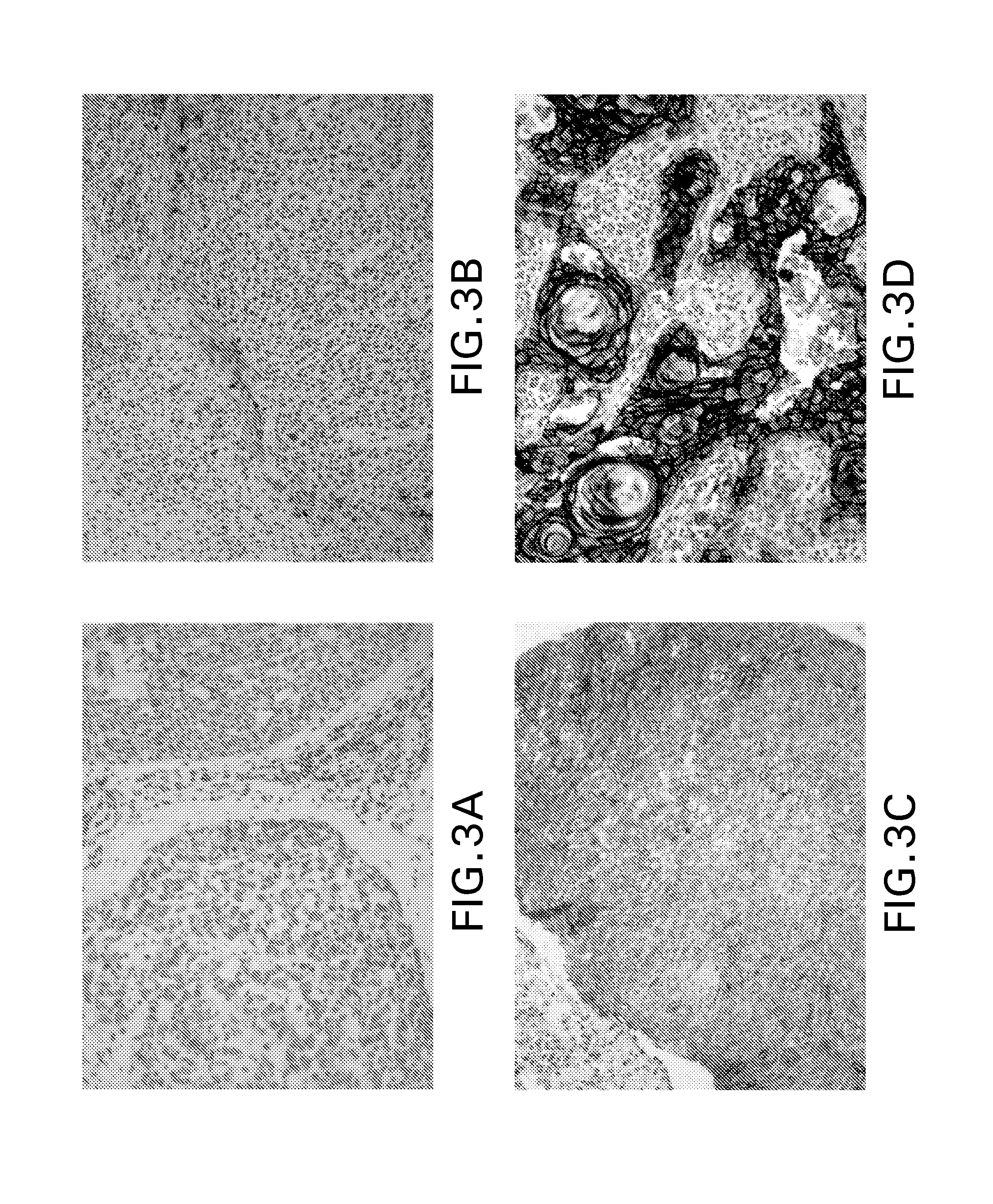
Patents
Literature
508 results about "Immunohistochemistry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the most common application of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. IHC takes its name from the roots "immuno", in reference to antibodies used in the procedure, and "histo", meaning tissue (compare to immunocytochemistry). Albert Coons conceptualized and first implemented the procedure in 1941.
Nanoparticle conjugates
InactiveUS20060246524A1Easy to detectMaterial nanotechnologyPowder deliveryIn situ hybridisationOrganic chemistry
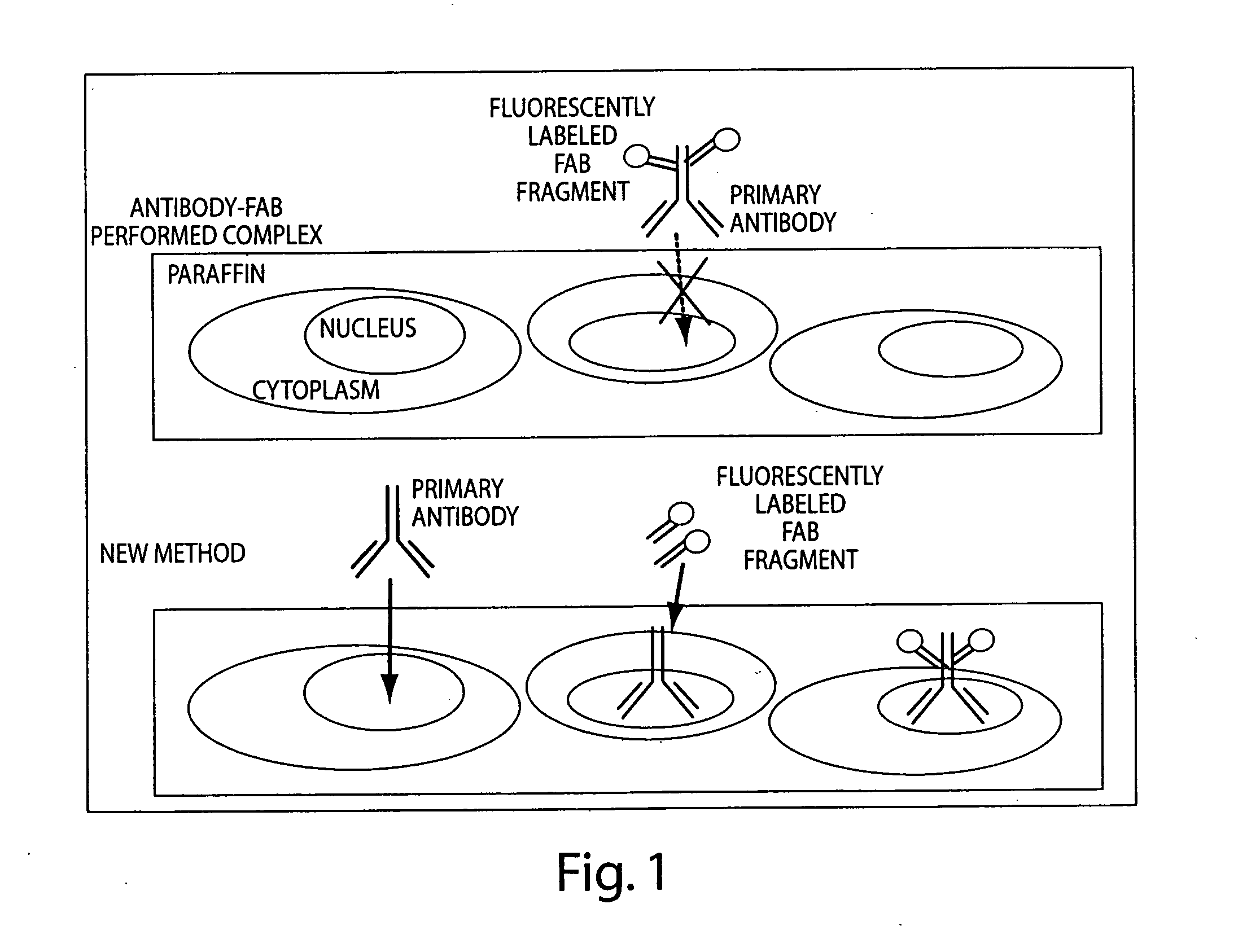
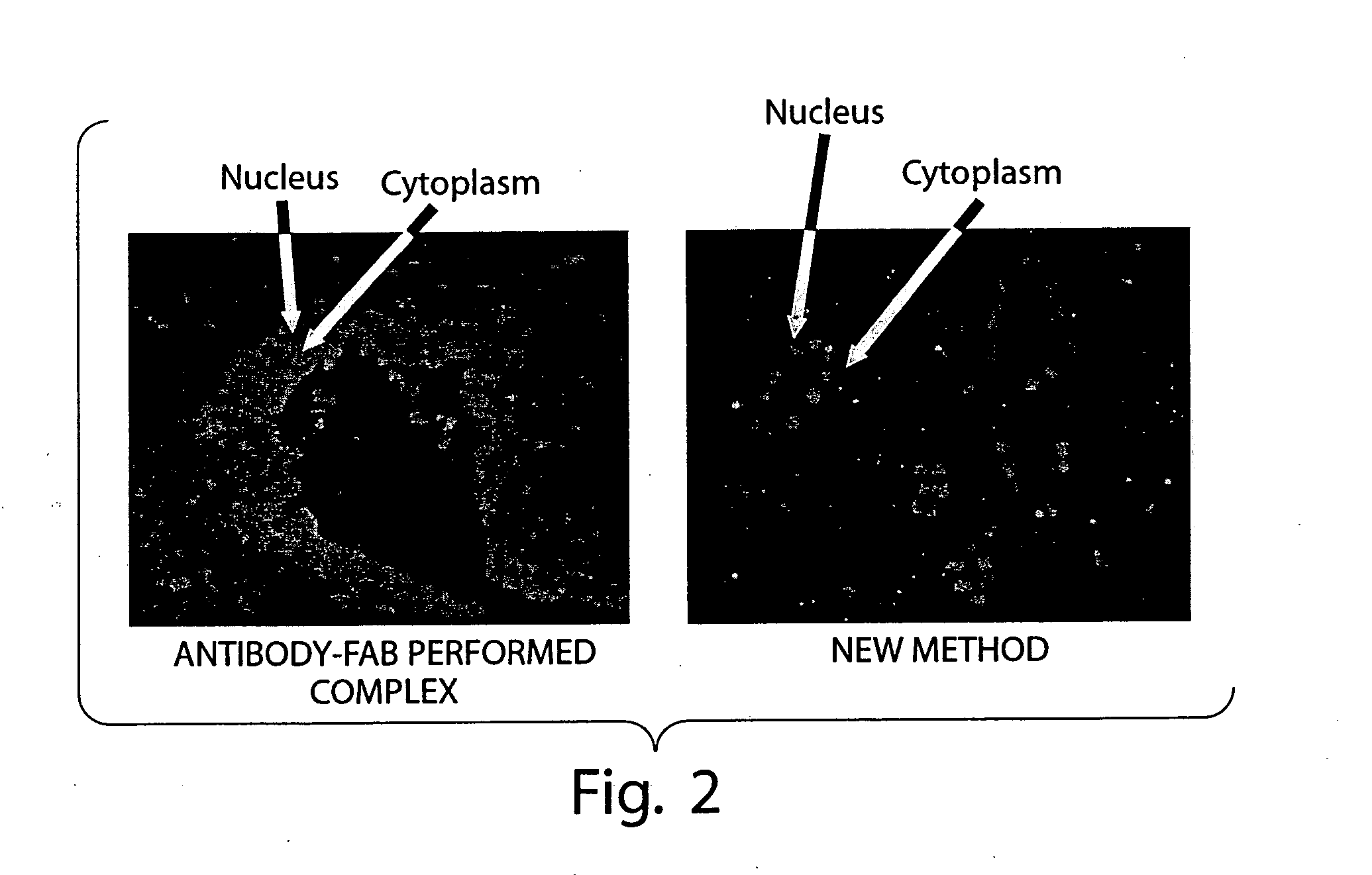
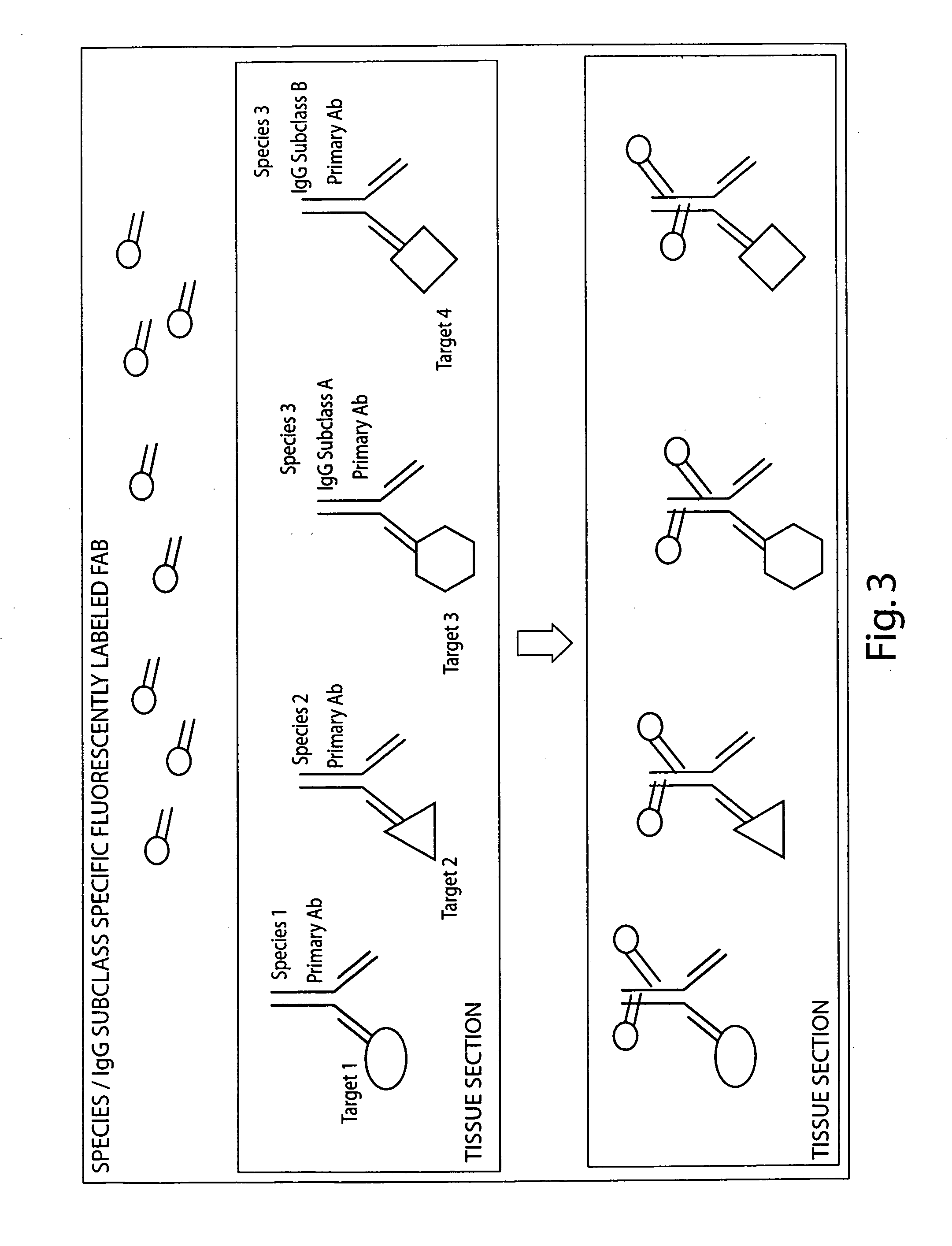
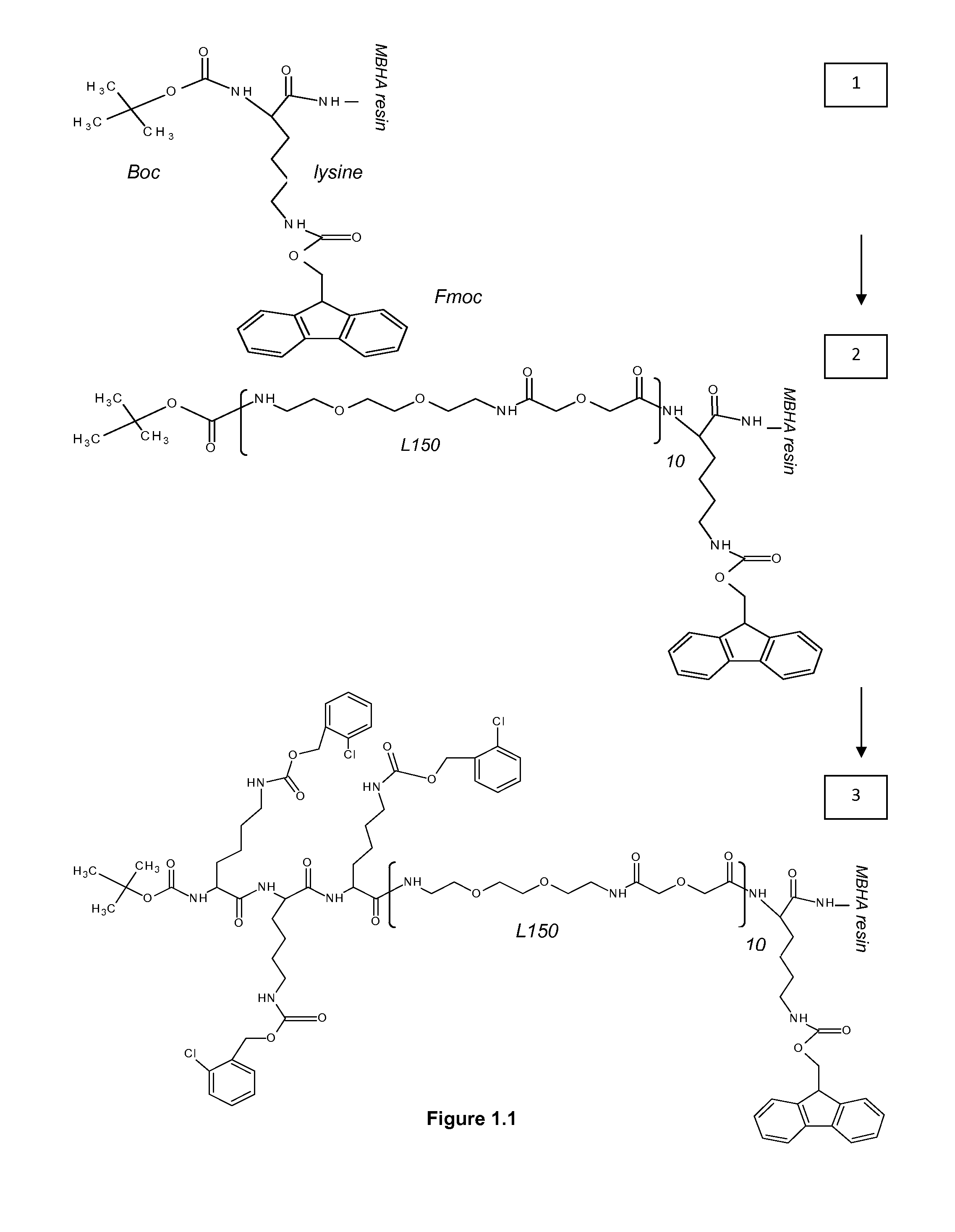
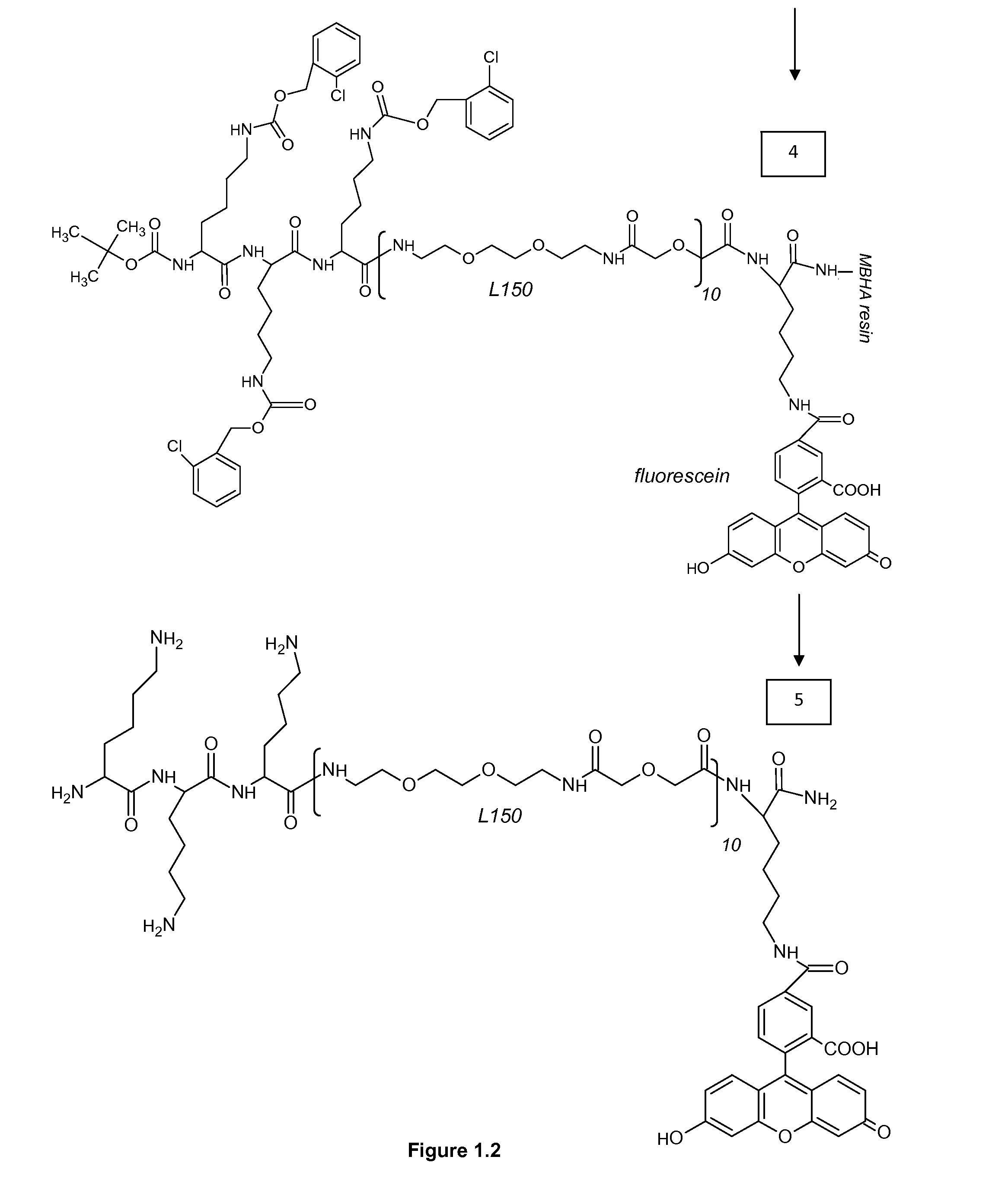
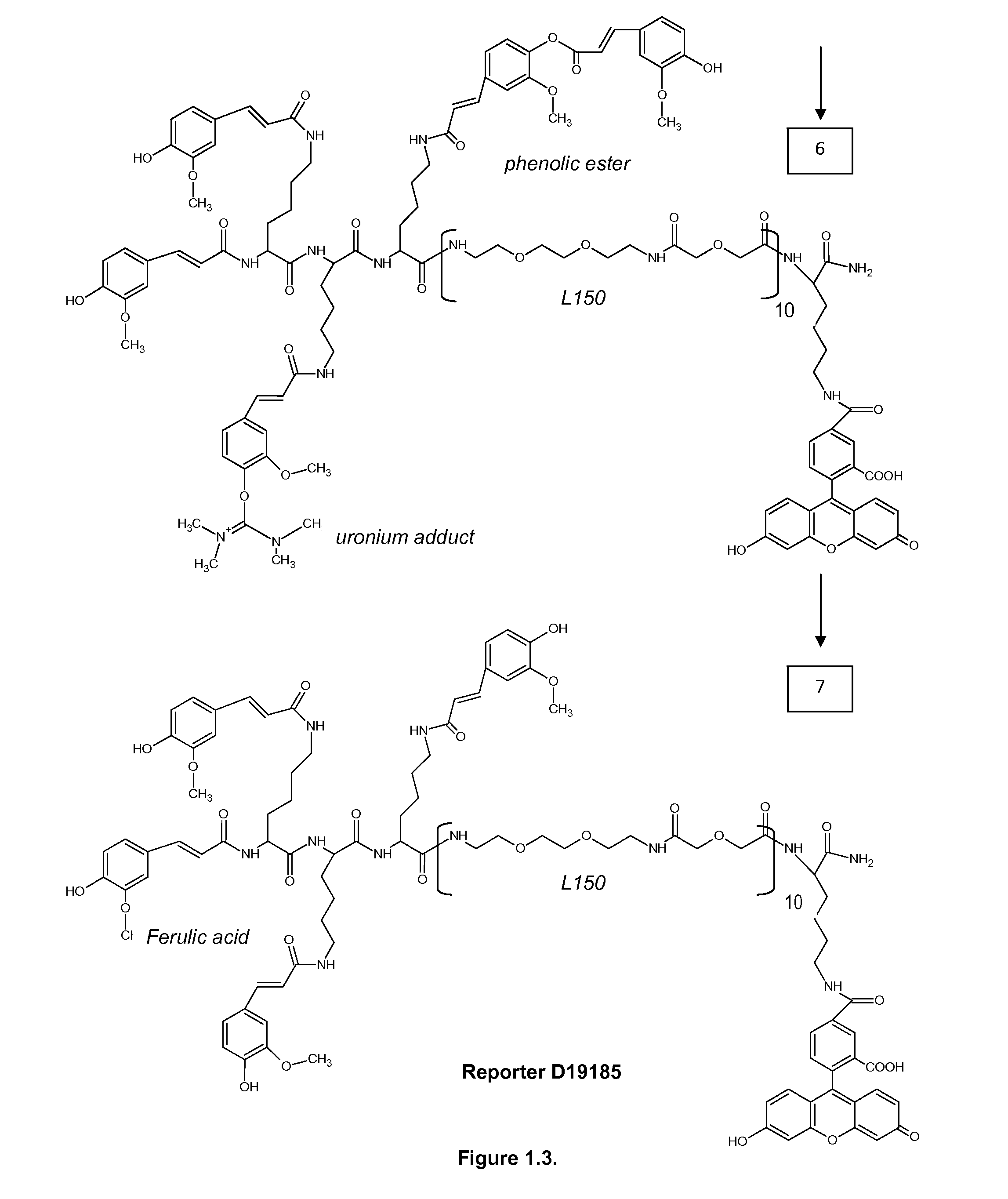
Conjugate compositions are disclosed that include a specific-binding moiety covalently coupled to a nanoparticle through a heterobifunctional polyalkyleneglycol linker. In one embodiment, a conjugates is provided that includes a specific-binding moiety and a fluorescent nanoparticle coupled by a heterobifunctional PEG linker. Fluorescent conjugates according to the disclosure can provide exceptionally intense and stable signals for immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization assays on tissue sections and cytology samples, and enable multiplexing of such assays.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
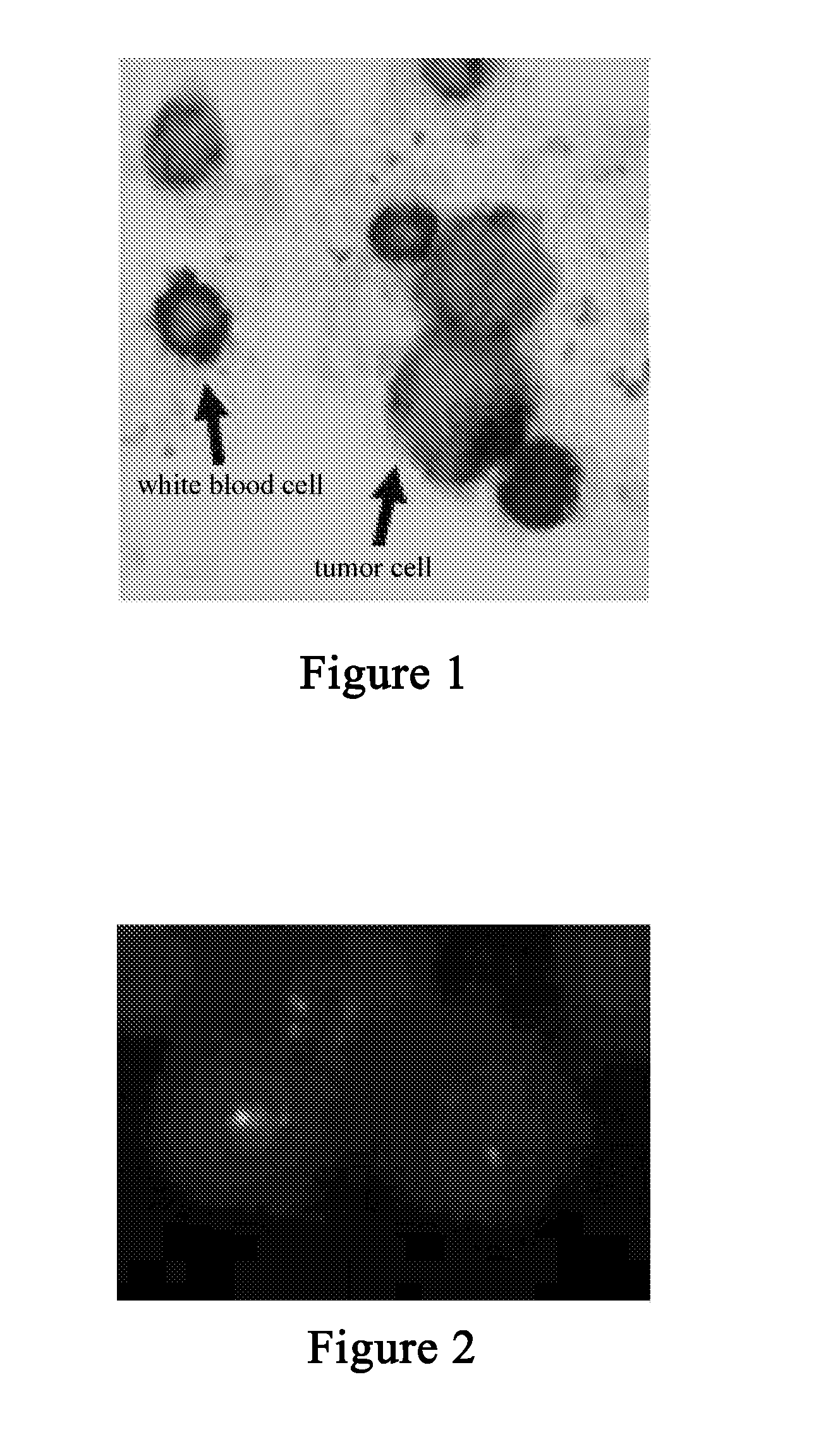
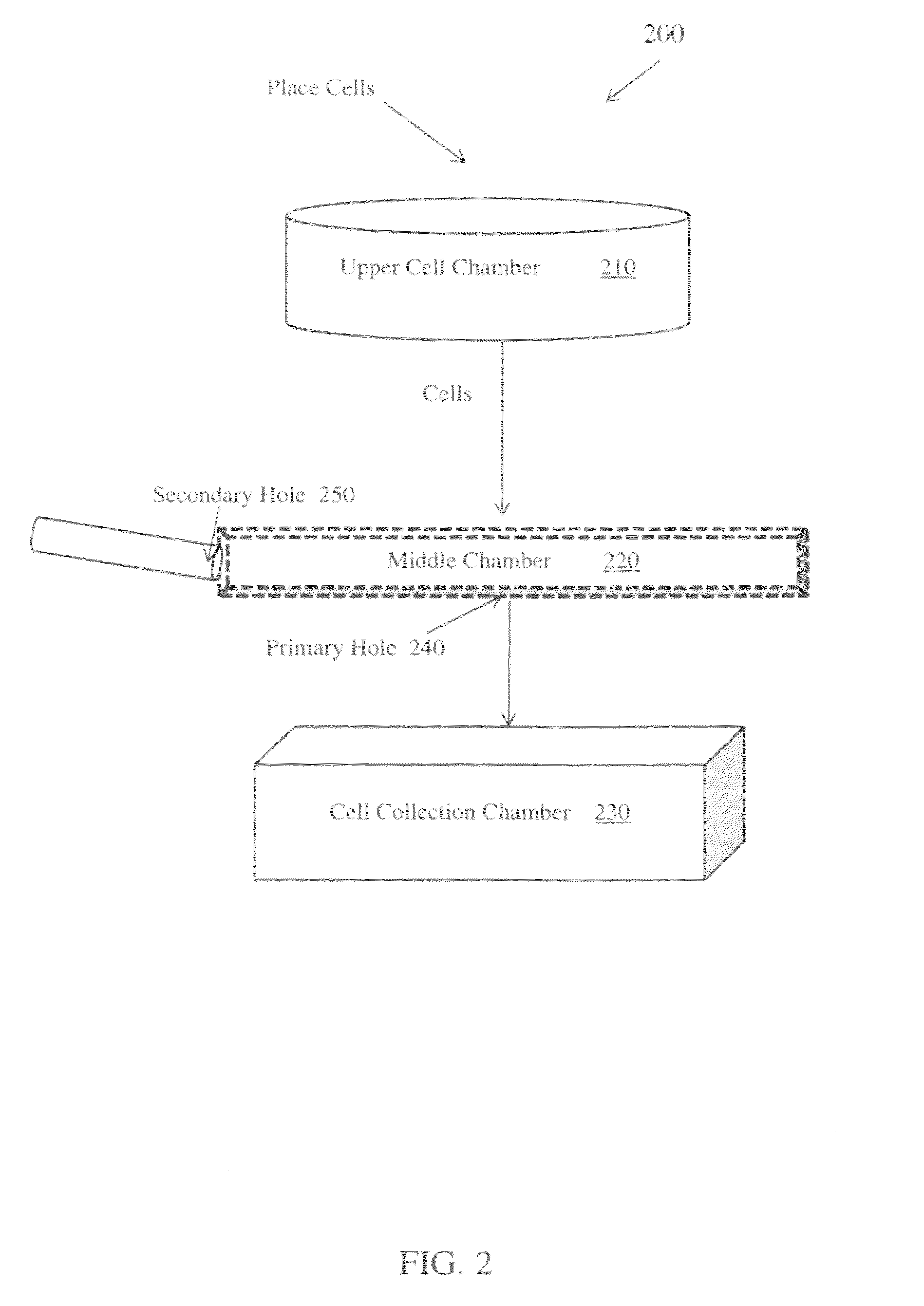
Methods and reagents for the rapid and efficient isolation of circulating cancer cells
InactiveUS7332288B2Efficient ConcentrationEasy to detectNanomagnetismMicrobiological testing/measurementCirculating cancer cellCell sensitivity
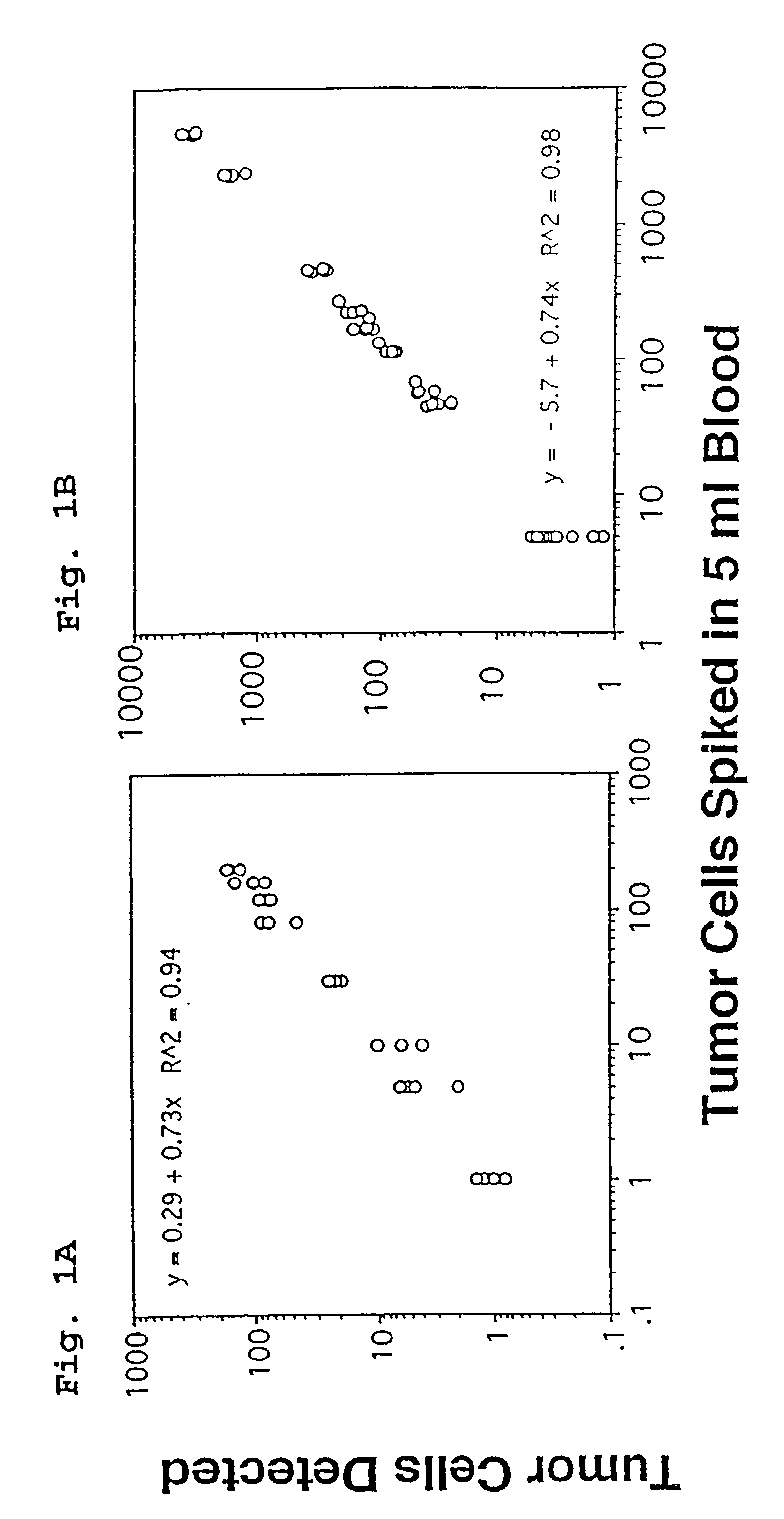
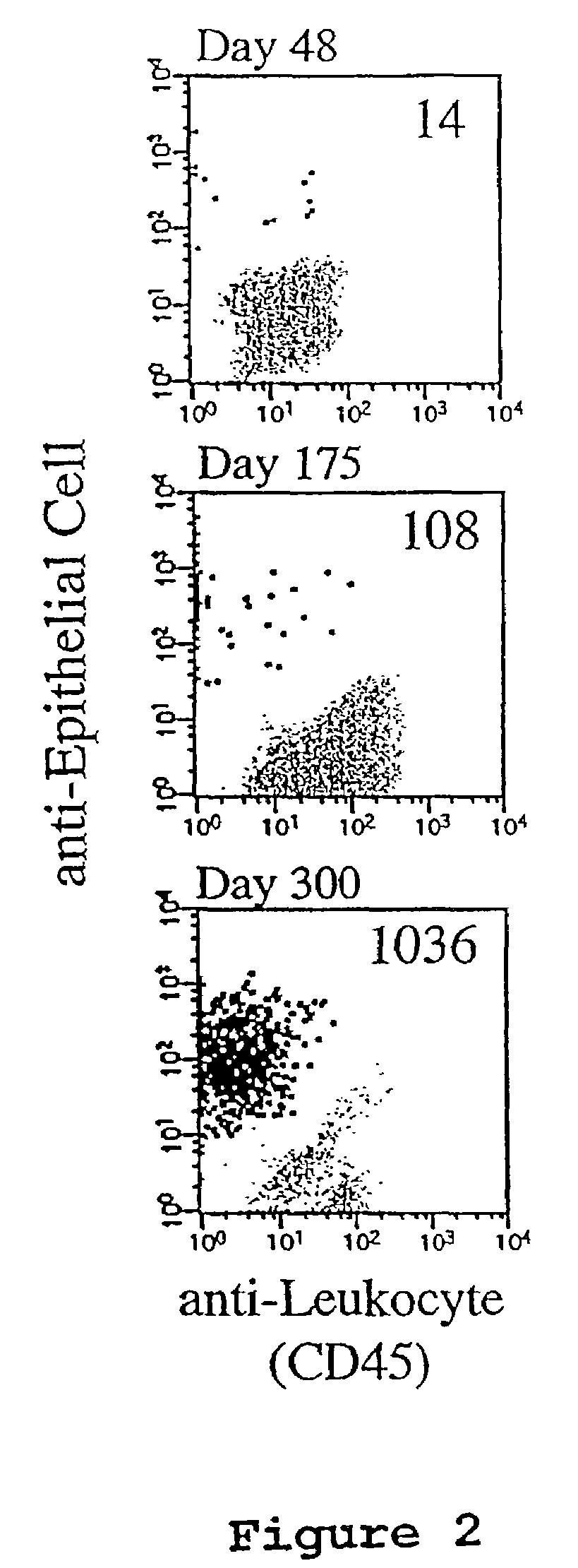
A highly sensitive assay is disclosed which combines immunomagnetic enrichment with multiparameter flow cytometric and immunocytochemical analysis to detect, enumerate and characterize carcinoma cells in the blood. The assay can detect one epithelial cell or less in 1 ml of blood and has a greater sensitivity than conventional PCR or immunohistochemistry by 1-2 orders of magnitude. In addition, the assay facilitates the biological characterization and staging of carcinoma cells.
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
Methods and systems for analyzing images of specimens processed by a programmable quantitative assay
ActiveUS20120163681A1Material analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionTissue sampleBioinformatics
Disclosed are methods and systems for analyzing images of specimens processed by a programmable quantitative assay or more specifically a robust programmable quantitative dot assay, PDQA, that enable specimens to be imaged and assessed across a wide variety of conditions and applications. Specific embodiments directed to immunohistochemical applications provide more quantitative methods of imaging and assessing biological samples including tissue samples.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
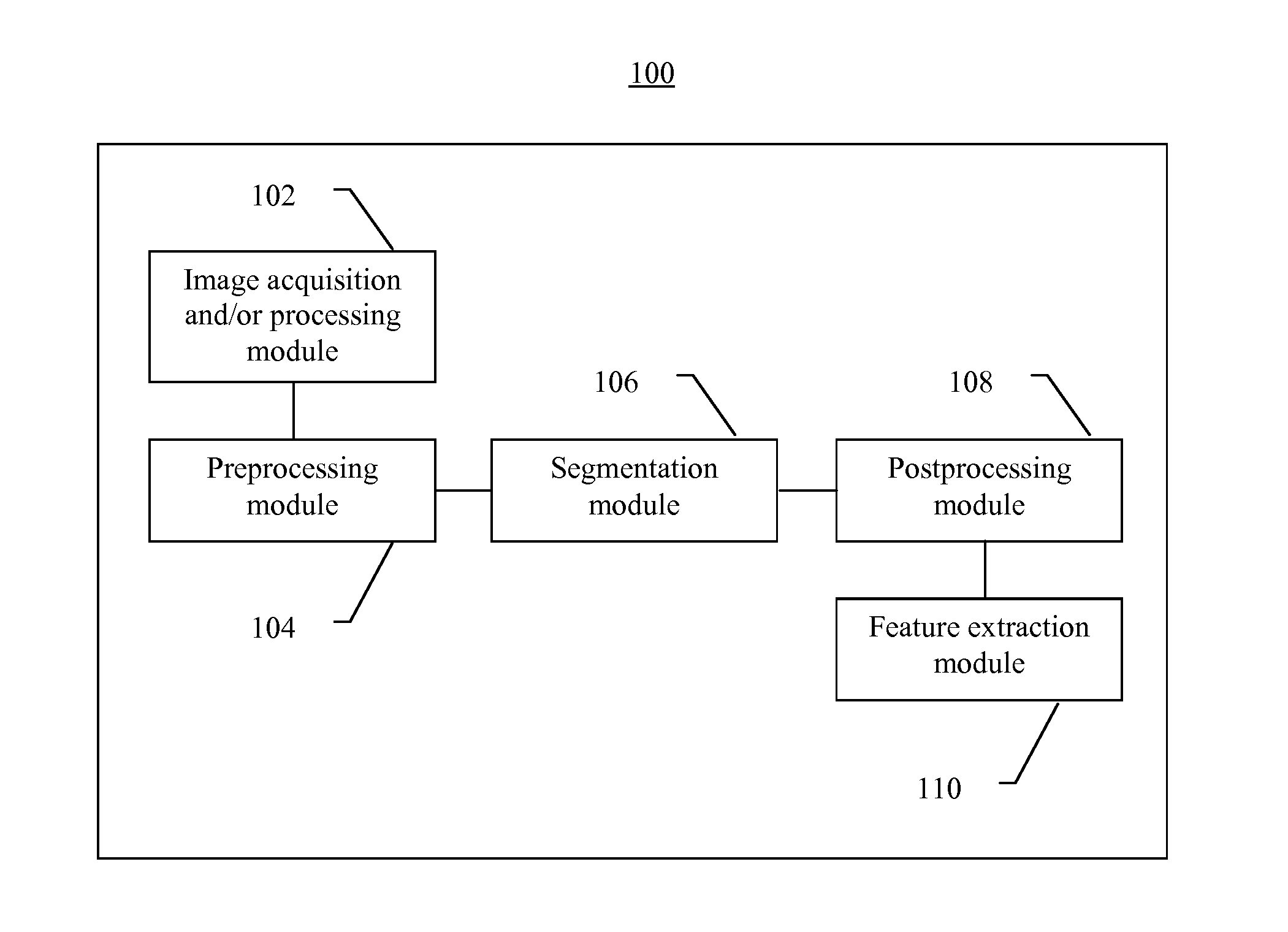
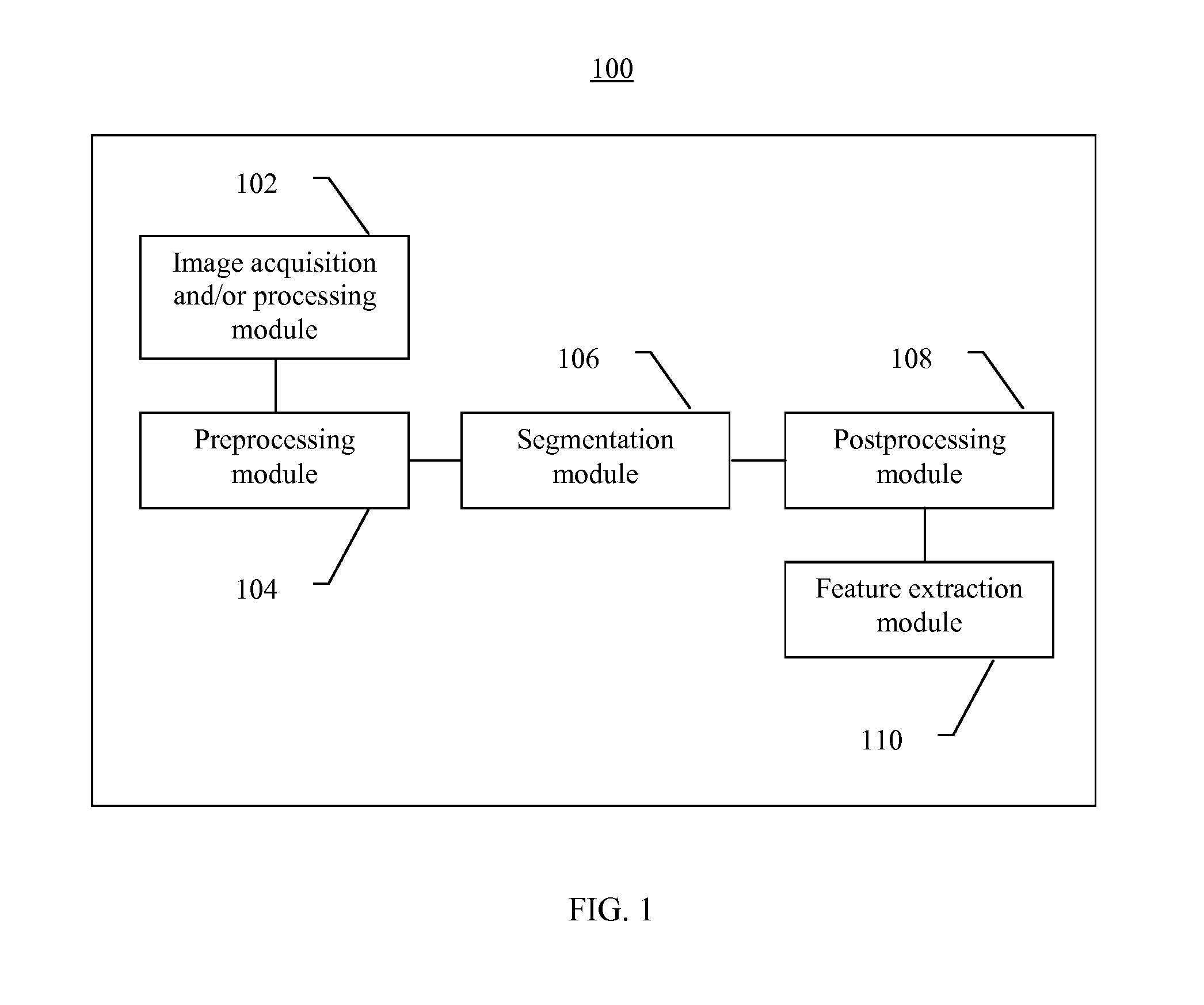
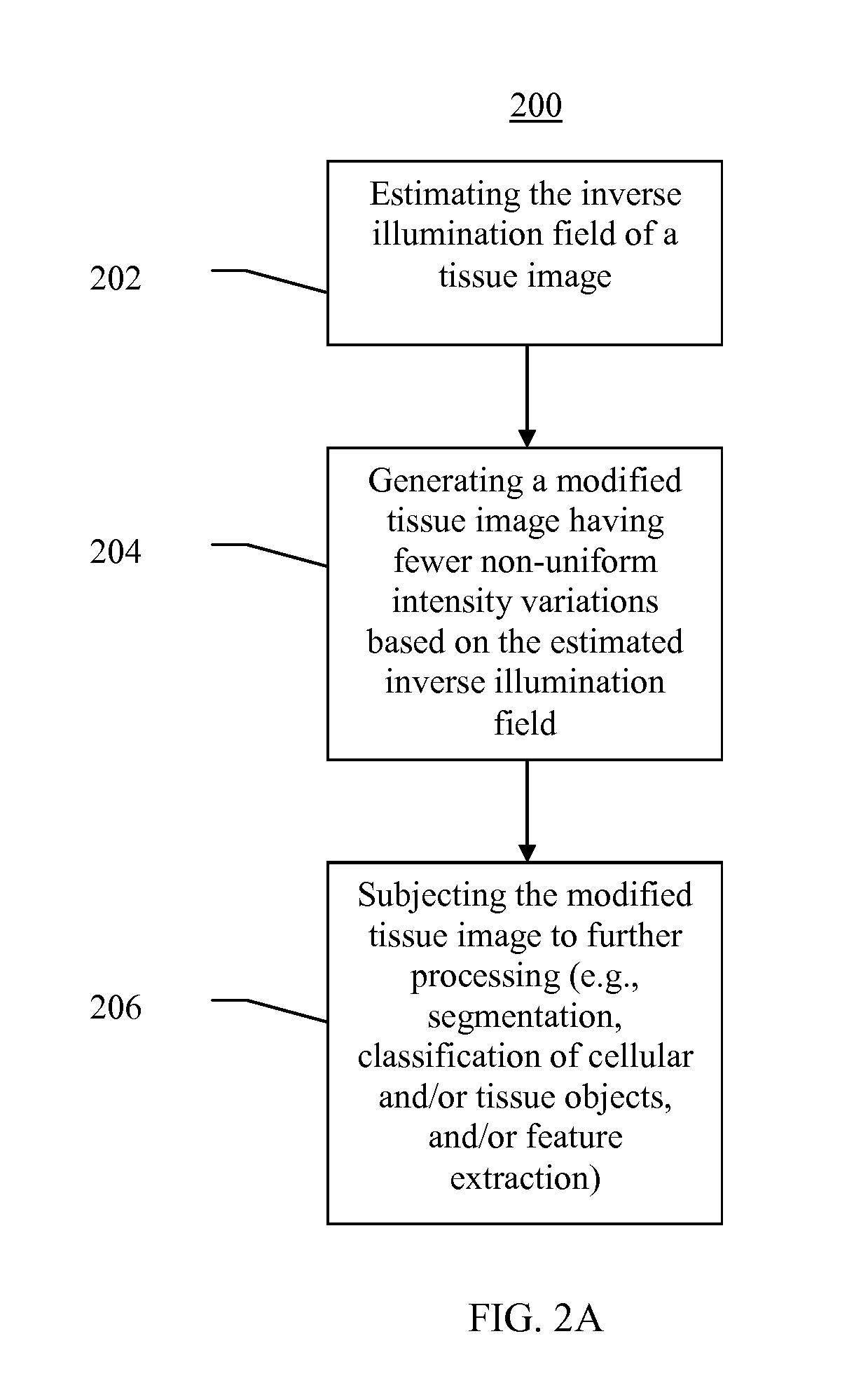
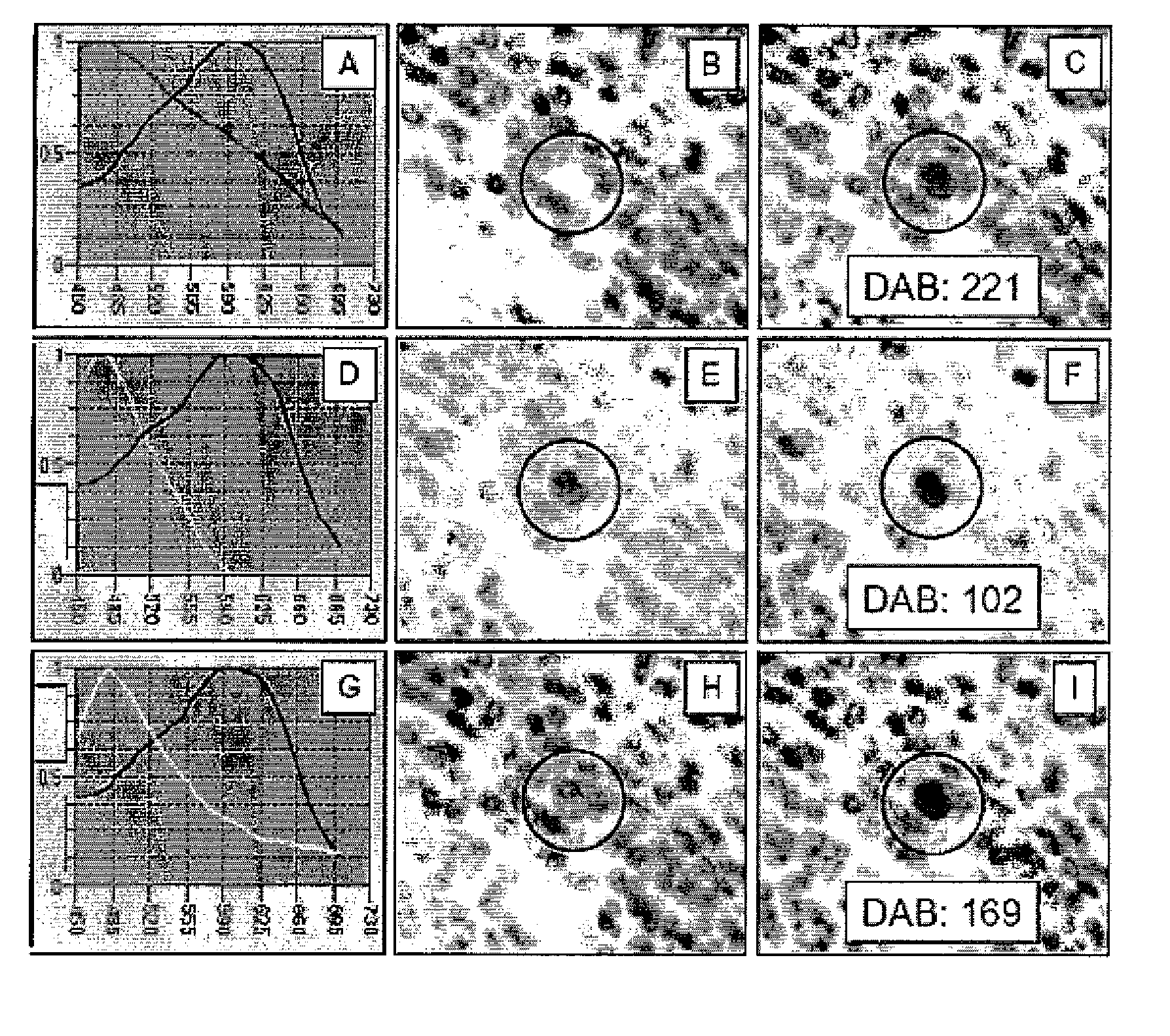
Systems and methods for segmentation and processing of tissue images and feature extraction from same for treating, diagnosing, or predicting medical conditions
ActiveUS20130230230A1Reduce non-uniform variationEliminate needImage enhancementImage analysisDiseaseFeature extraction
Apparatus, methods, and computer-readable media are provided for segmentation, processing (e.g., preprocessing and / or postprocessing), and / or feature extraction from tissue images such as, for example, images of nuclei and / or cytoplasm. Tissue images processed by various embodiments described herein may be generated by Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining, immunofluorescence (IF) detection, immunohistochemistry (IHC), similar and / or related staining processes, and / or other processes. Predictive features described herein may be provided for use in, for example, one or more predictive models for treating, diagnosing, and / or predicting the occurrence (e.g., recurrence) of one or more medical conditions such as, for example, cancer or other types of disease.
Owner:AUREON LAB INC +1
Quantifiable Internal Reference Standards for Immunohistochemistry and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20080038771A1Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationAntigenBiology
Methods for identifying Quantifiable Internal Reference Standards (QIRS) for immunohistochemistry (IHC). Also disclosed are methods for using QIRS to quantify test antigens in IHC.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Tissue analysis and kits therefor
InactiveUS20050100944A1Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationStainingFluorescence
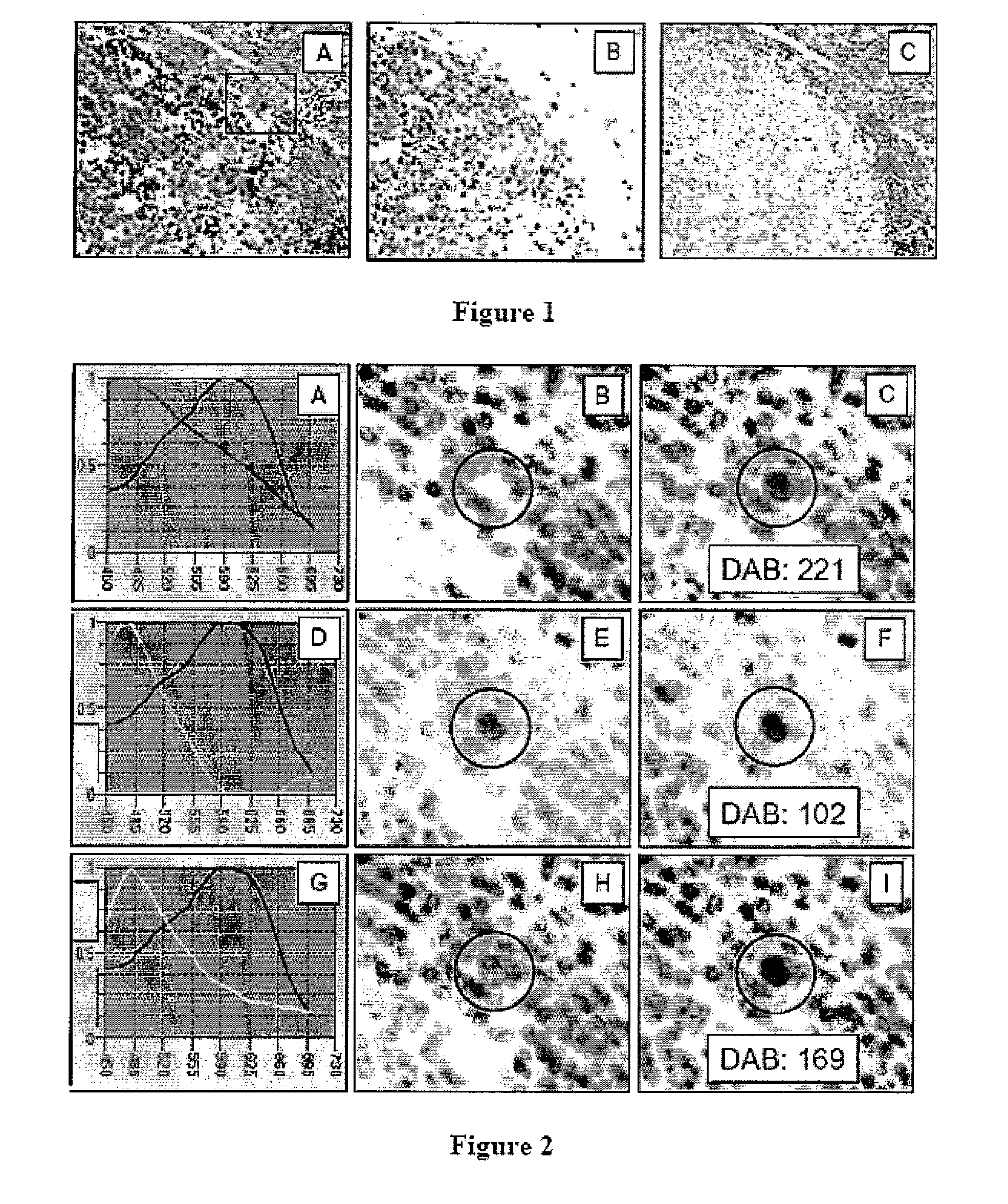
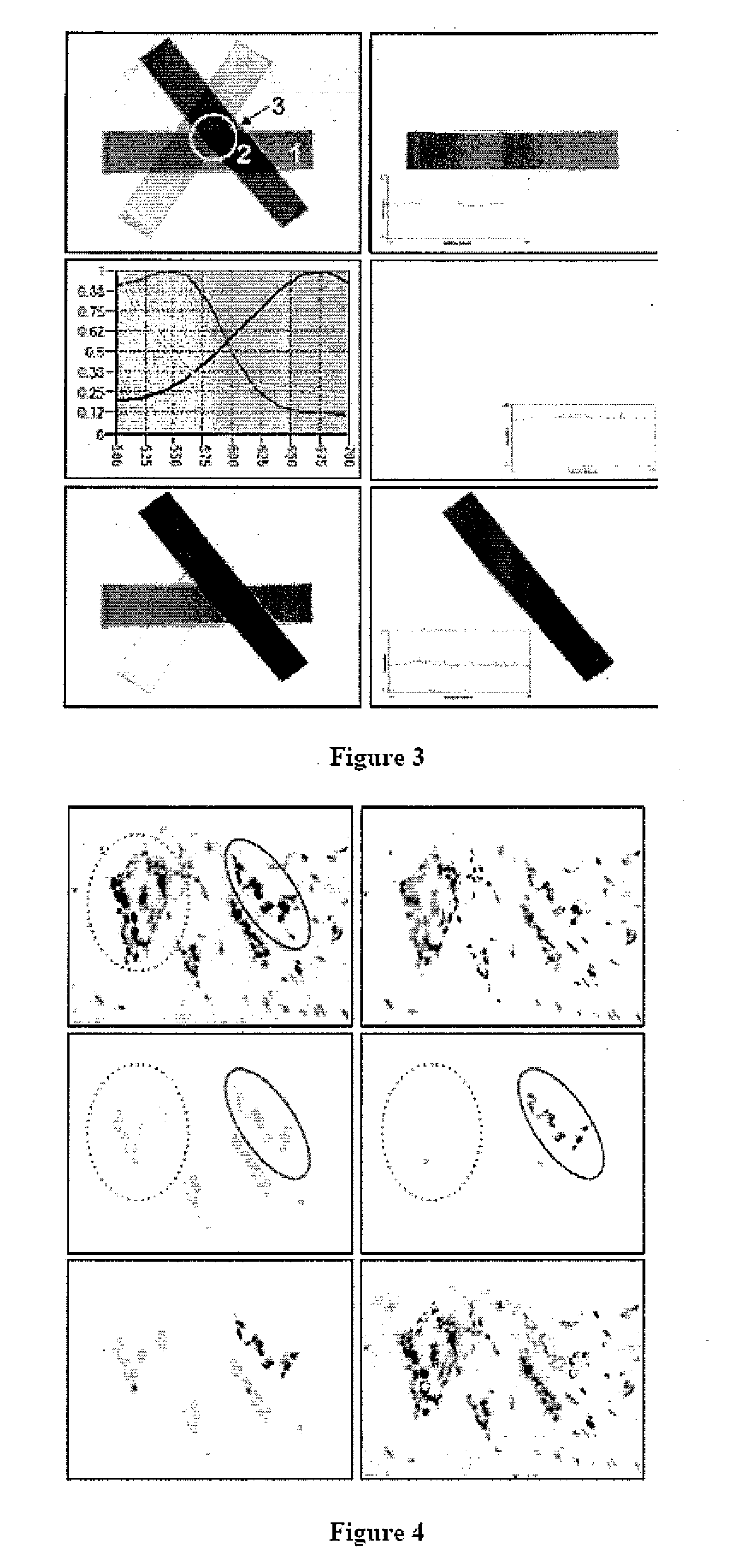
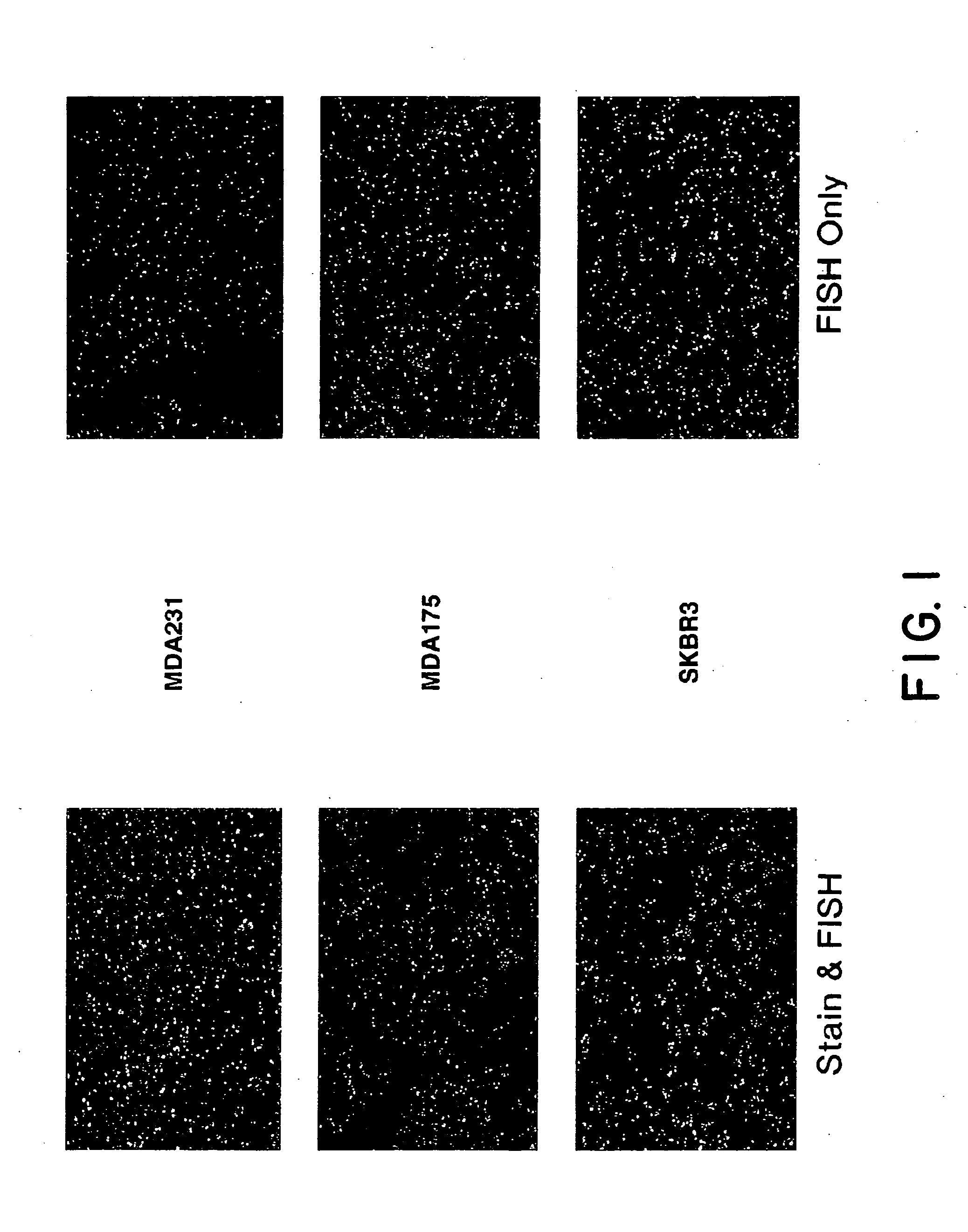
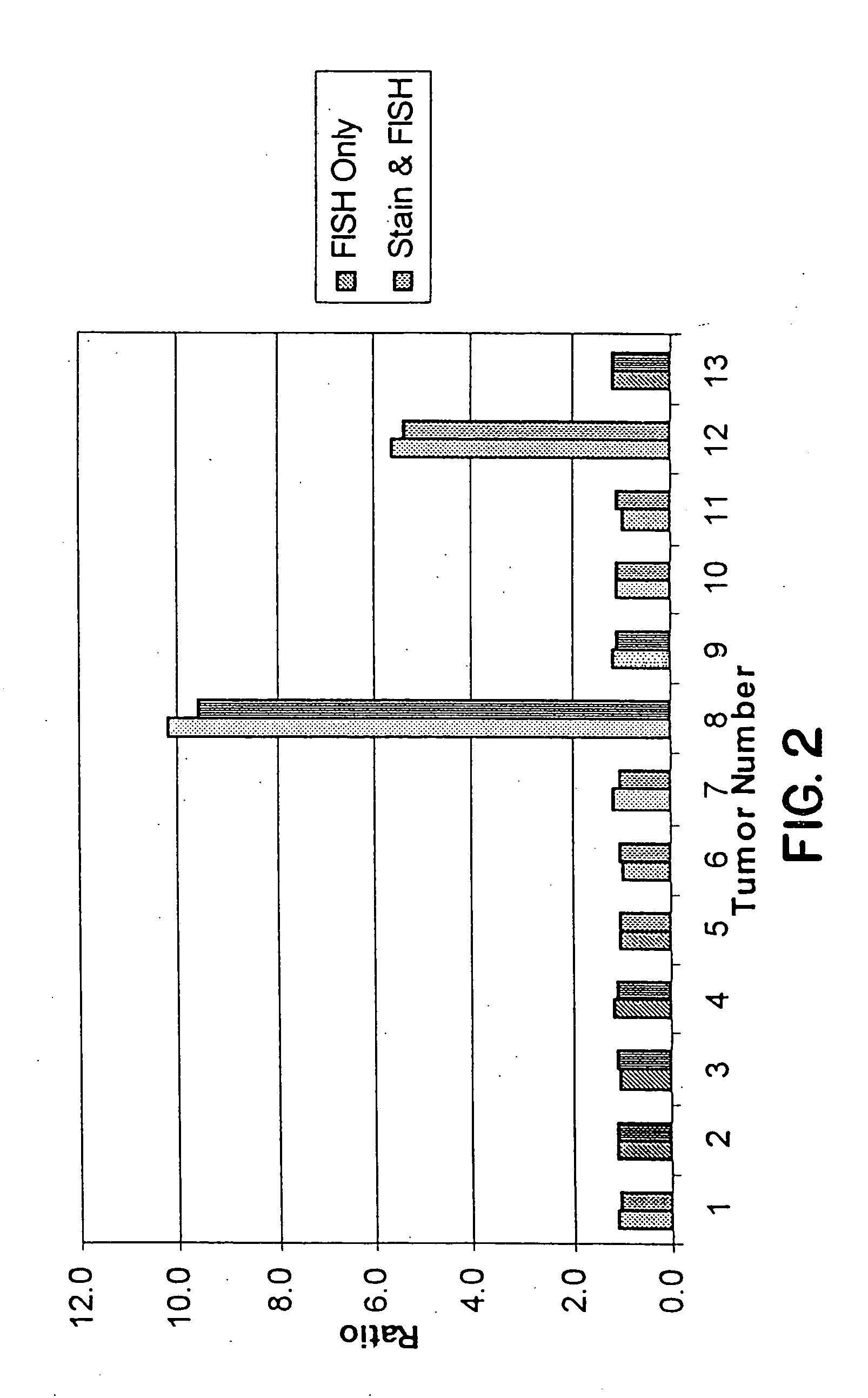
This invention relates to methods of analyzing a tissue sample from a subject. In particular, the invention combines morphological staining and / or immunohistochemistry (IHC) with fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) within the same section of a tissue sample. The analysis can be automated or manual. The invention also relates to kits for use in the above methods.
Owner:COHEN ROBERT L +3
Automated scanning method for pathology samples
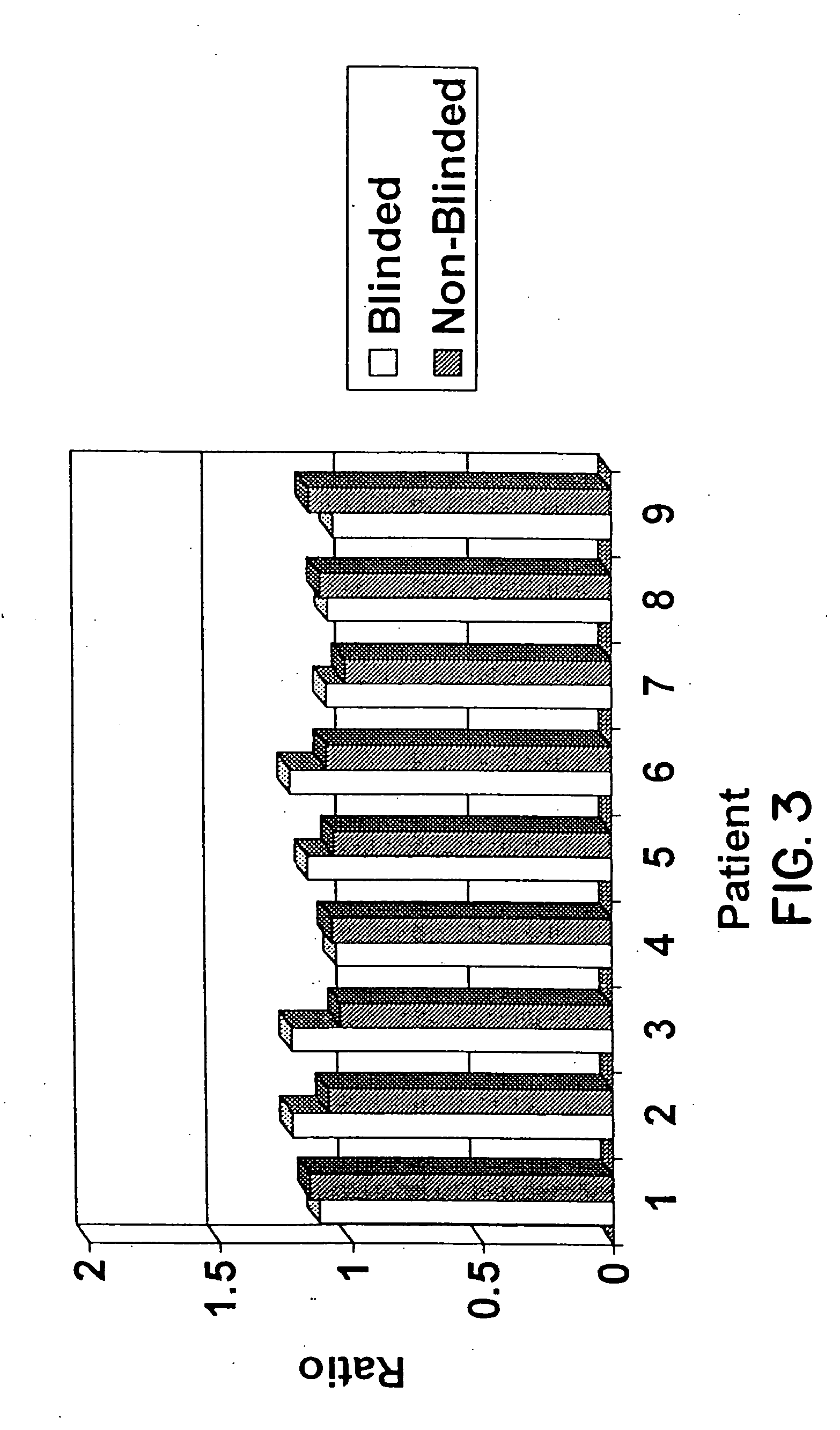
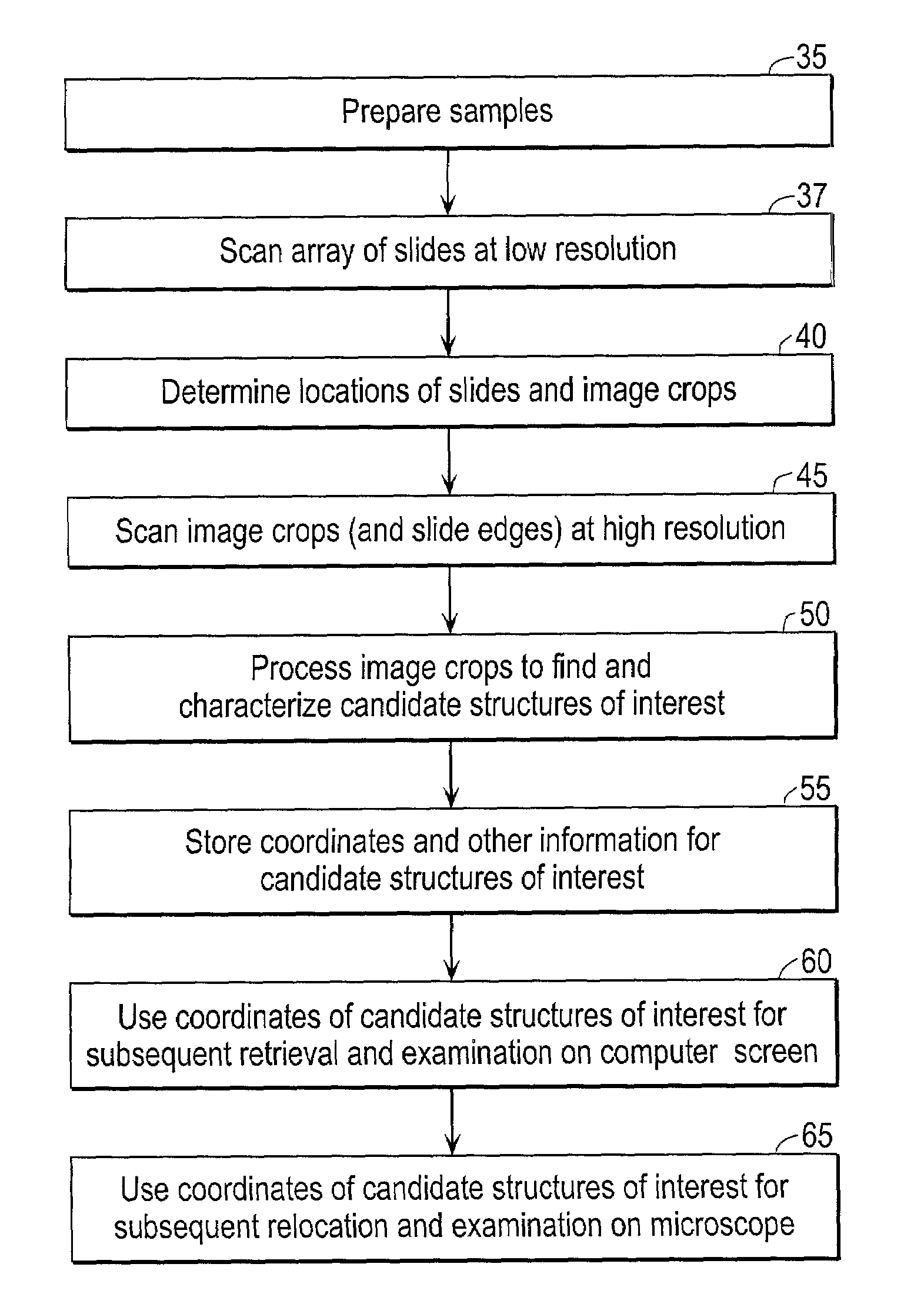
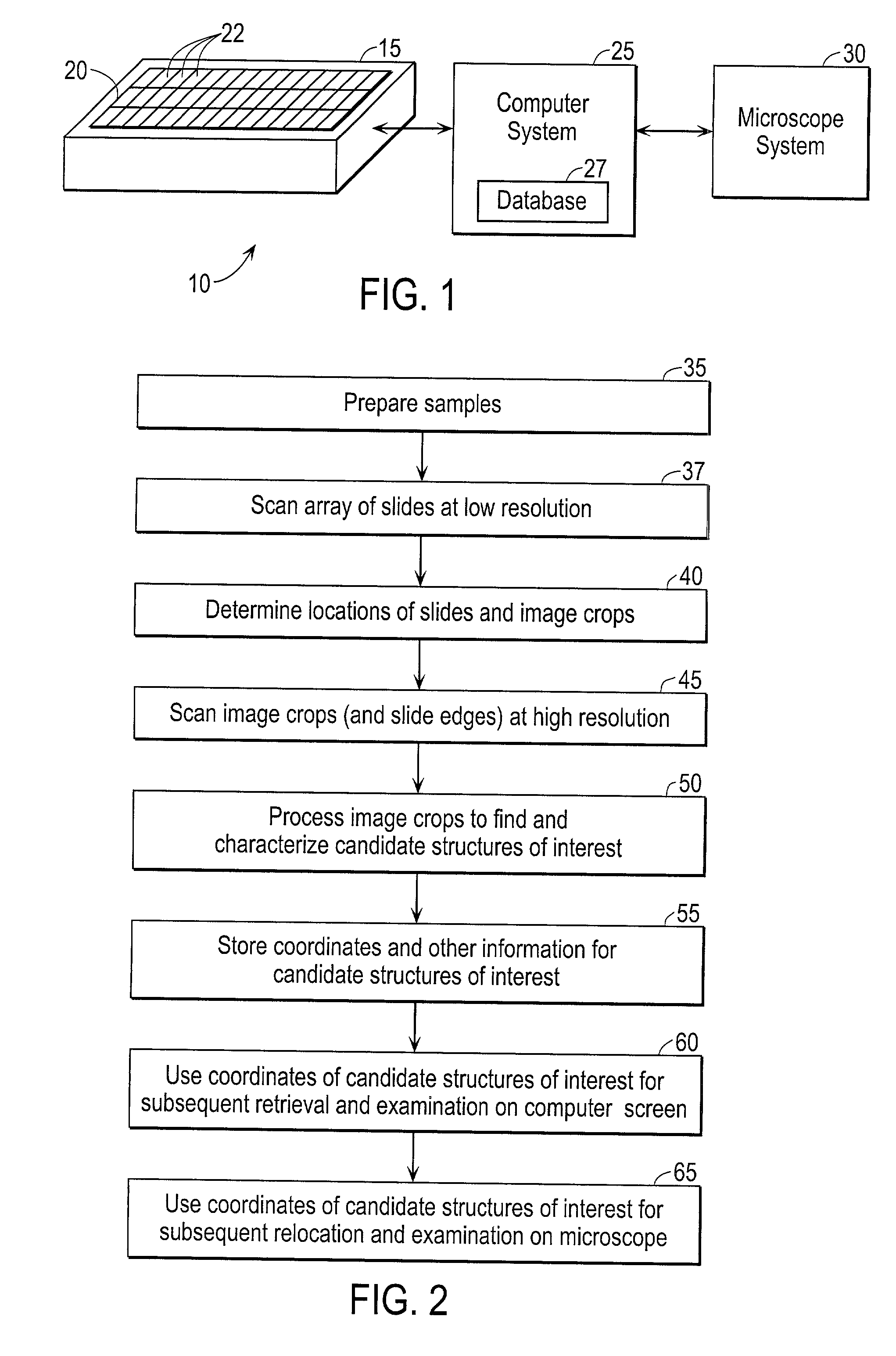
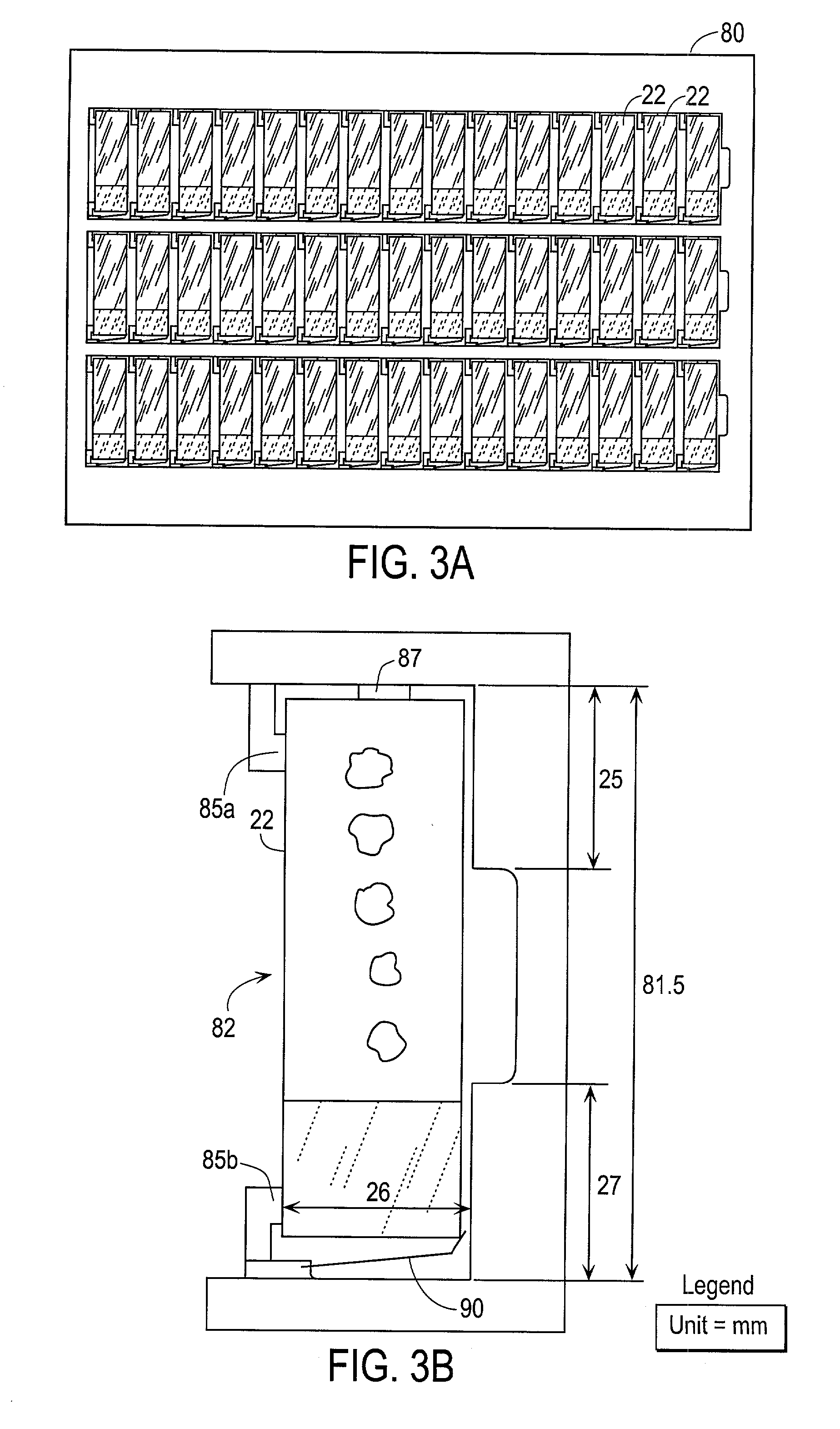
Scanning and analysis of cytology and histology samples uses a flatbed scanner to capture images of the structures of interest such as tumor cells in a manner that results in sufficient image resolution to allow for the analysis of such common pathology staining techniques as ICC (immunocytochemistry), IHC (immunohistochemistry) or in situ hybridization. Very large volumes of such material are scanned in order to identify cells or clusters of cells which are positive or warrant more detailed examination, and if analysis at higher resolution is necessary, information regarding these positive events is transferred to a secondary microscope, such as a conventional scanning microscope, to allow further analysis and review of the selected regions of the slide containing the sample.
Owner:LEICA BIOSYST IMAGING
Human antibodies that have MN binding and cell adhesion-neutralizing activity
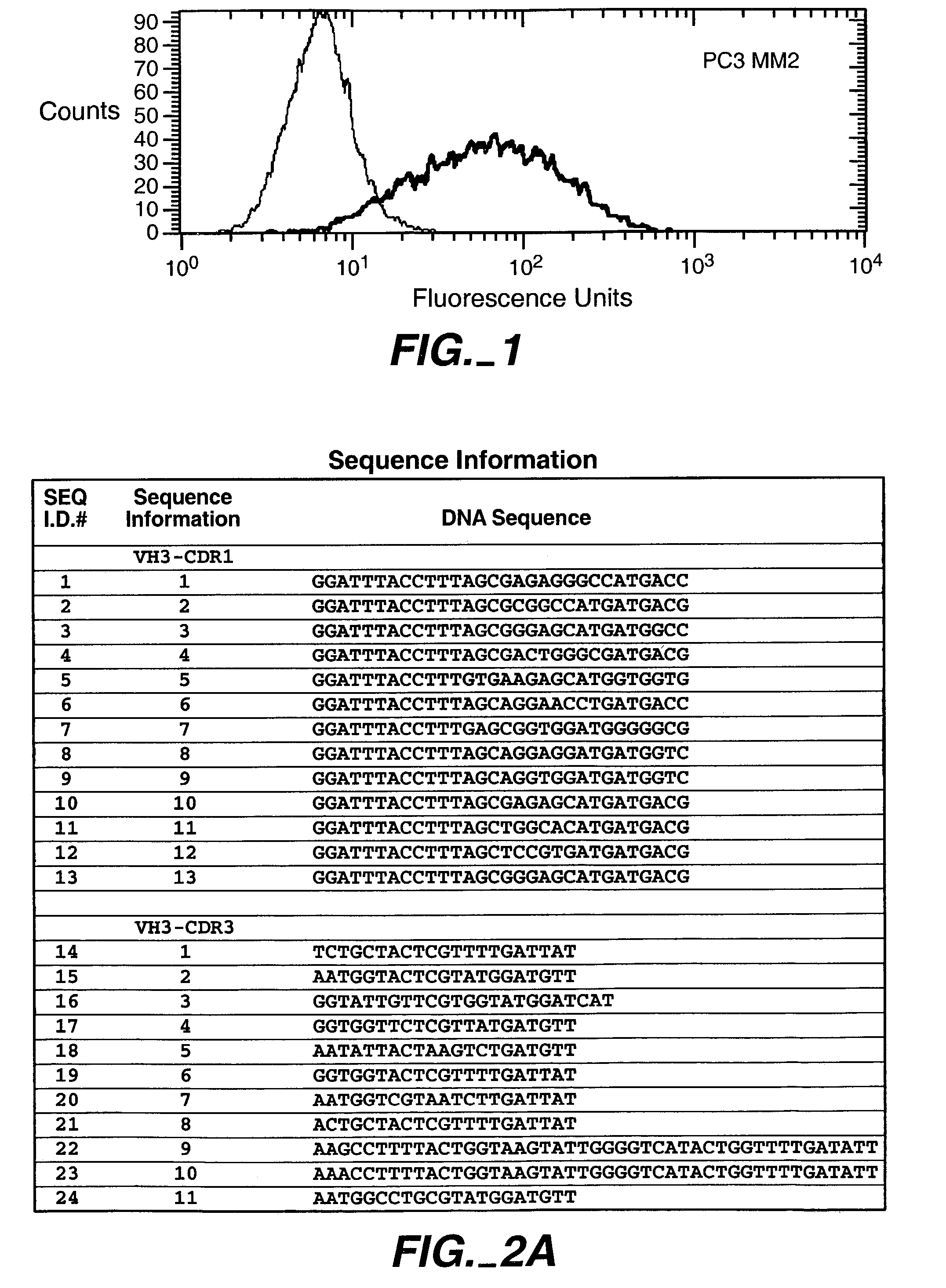
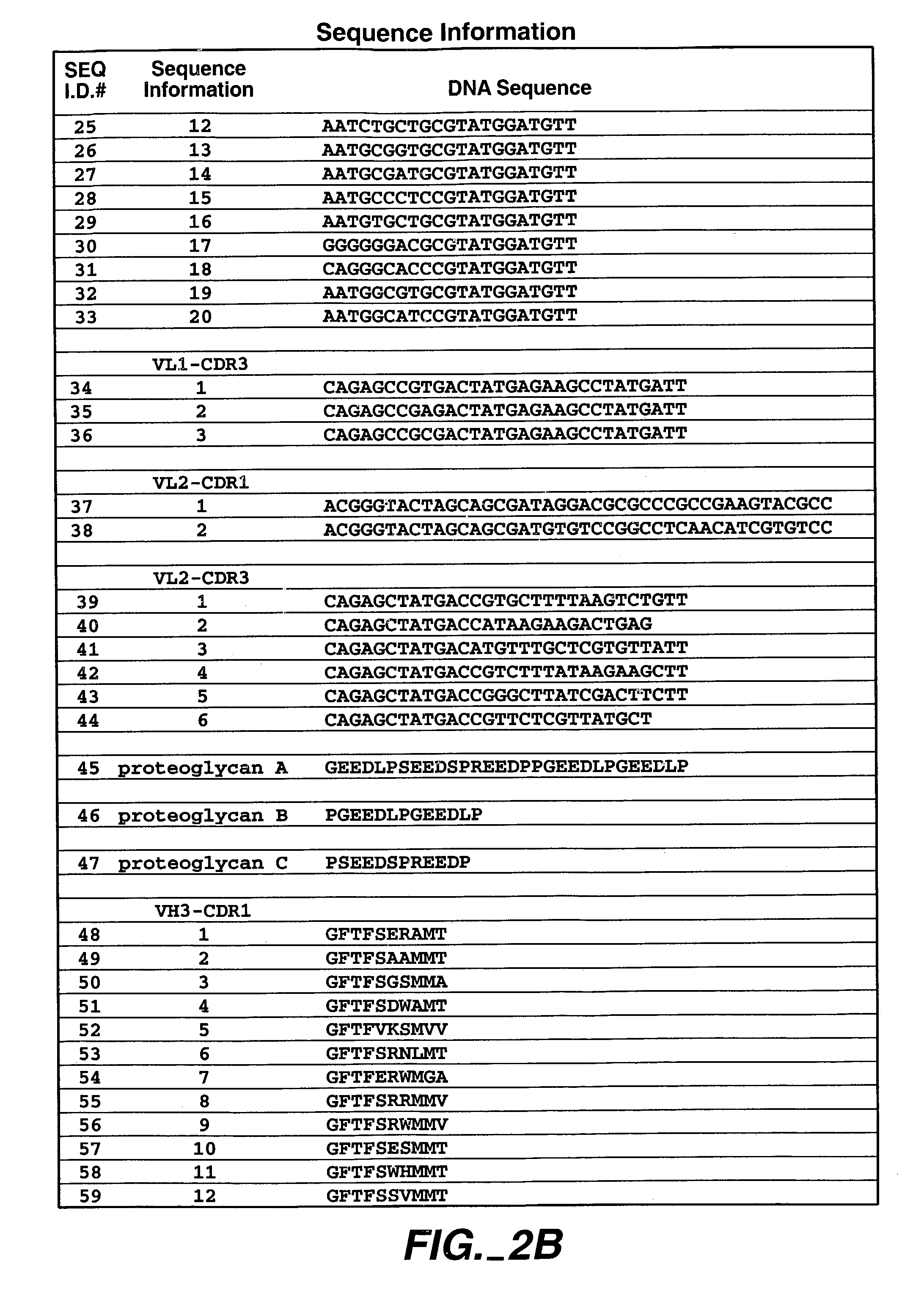
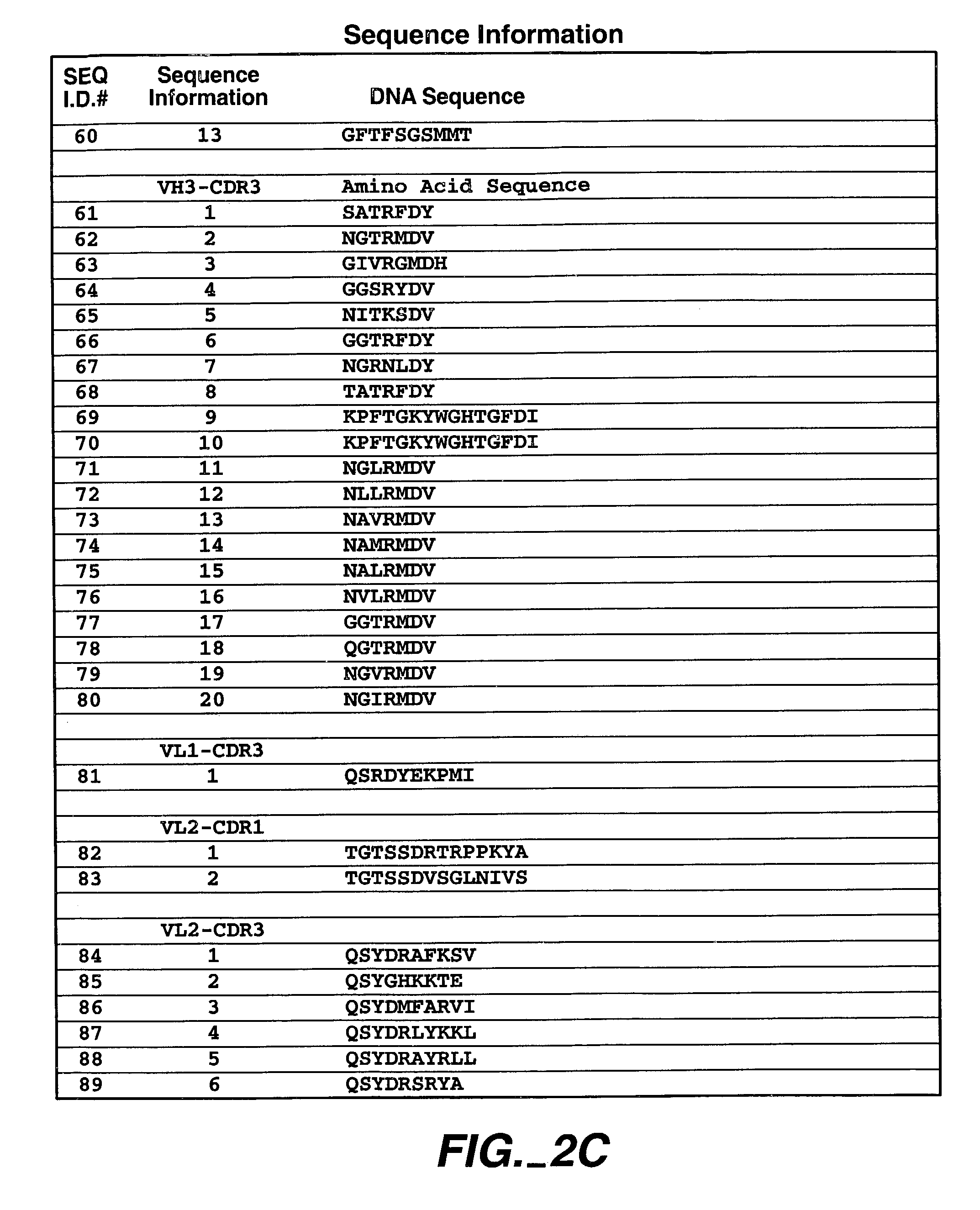
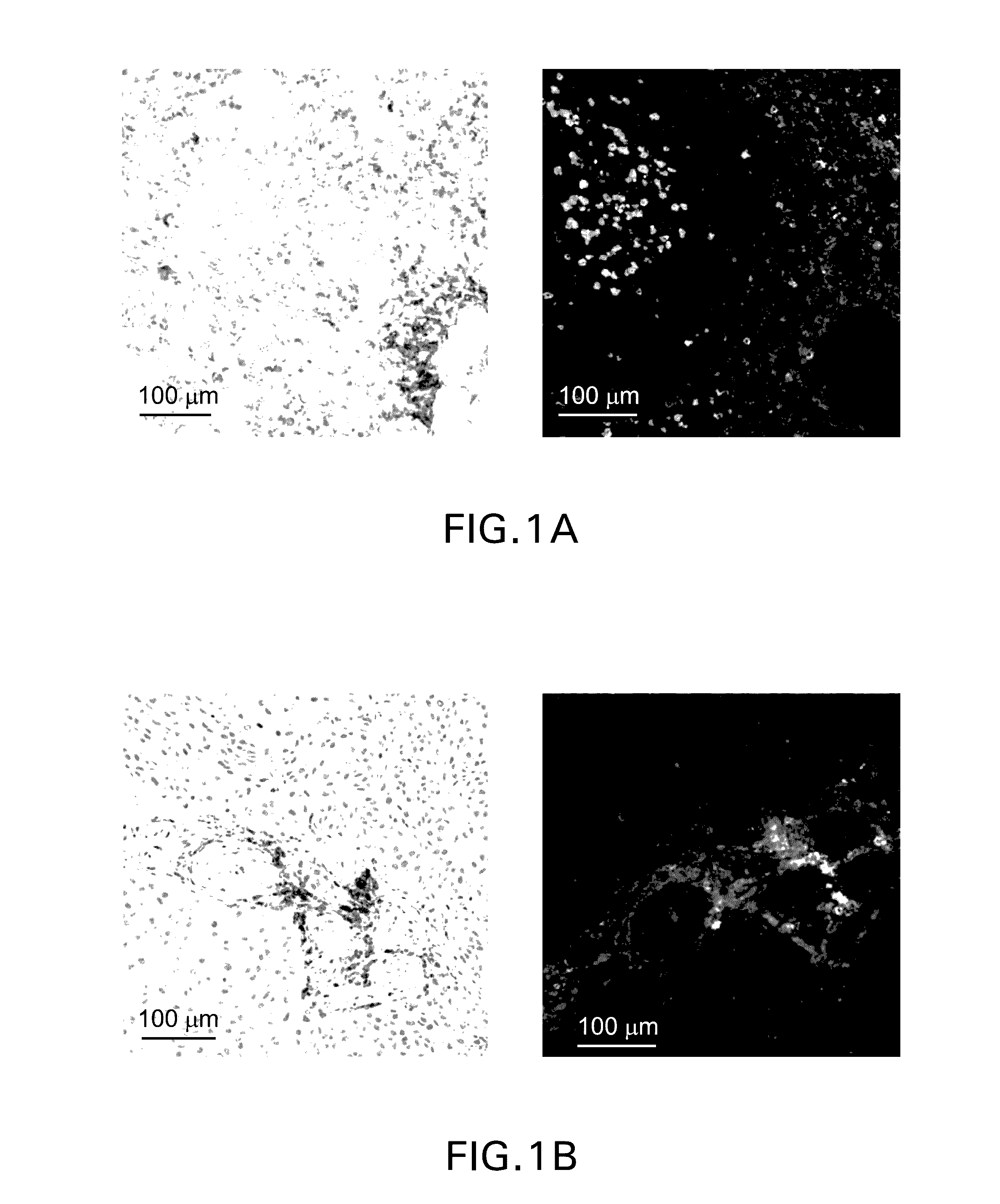
The invention is composed of monoclonal human MN antibodies or MN antibody fragments that target the GEEDLP (SEQ ID NO: 118) repeat within the proteoglycan domain. The proteoglycan domain of the MN cell surface protein contains four of these identical GEEDLP (SEQ ID NO: 118) repeats. Binding to the desired epitope is verified by competition ELISA, where ELISA signal can be attenuated by co-incubation with a peptide containing this repeat (PGEEDLPGEEDLP (SEQ ID NO: 119)). This inhibition of binding can also be verified using Biacore assays, where binding of desired antibodies to immobilized MN or proteoglycan peptides can be inhibited by the peptide repeat. In addition to binding to the peptide repeat, human anti-MN antibodies can inhibit the cell adhesion of CGL-1 cells to MN coated plastic plates. Human anti-MN antibodies have been used to diagnose and quantify MN expression in cancer cells and tumors using FACS and immunohistochemical methods. An example is also provided where a human anti-MN IgG1 mediates tumor cell lysis though antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Therefore, these antibodies will be useful for the treatment of cancers in which MN is upregulated or can be useful for the diagnosis of cancers in which MN is upregulated.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Immunohistochemical proximity assay for pd-1 positive cells and pd-ligand positive cells in tumor tissue
ActiveUS20160305947A1Easy to detectEasy to quantifyImage enhancementMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesTumor SampleWilms' tumor
The present disclosure describes an IHC assay for detecting and quantifying spatially proximal pairs of PD-1-expressing cells (PD-1+ cells) and PD-Ligand-expressing cells (PD-L+ cells) in tumor tissue, and the use of the assay to generate proximity biomarkers that are predictive of which cancer patients are most likely to benefit from treatment with a PD-1 antagonist. The disclosure also provides methods for testing tumor samples for the proximity biomarkers, as well as methods for treating subjects with a PD-1 antagonist based on the test results.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Antibody conjugates
ActiveUS8658389B2Easy to detectHigh activityHydrolasesChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAntibody conjugateNucleic acid sequencing
Antibody / signal-generating moiety conjugates are disclosed that include an antibody covalently linked to a signal-generating moiety through a heterobifunctional polyalkyleneglycol linker. The disclosed conjugates show exceptional signal-generation in immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization assays on tissue sections and cytology samples. In one embodiment, enzyme-metallographic detection of nucleic acid sequences with hapten-labeled probes can be accomplished using the disclosed conjugates as a primary antibody without amplification.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Multiplex in situ immunohistochemical analysis
ActiveUS20070154958A1Chemiluminescene/bioluminescencePreparing sample for investigationAntigenTissue sample
A method of in situ immunohistochemical analysis of a biological sample is provided. The method allows for the multiplex and simultaneous detection of multiple antigens, including multiple nuclear antigens, in a tissue sample.
Owner:DAVID SANS +2
Methods and Systems for Efficient Automatic Slide Staining in Immunohistochemistry Sample Processing
ActiveUS20110151504A1Improve productivityEffectiveBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProcess engineeringHandling system
Automated sample processing systems may include onboard efficient high-speed mixing of at least two components with an automatic vertical force fluidic turbulent component mixer of which a mixed component may be aspirated and high-speed dispensed in a mixing vial. Other aspects may include single sweep applying a multi-treatment cleaning cycle to at least one slide. A multi-treatment cleaning cycle may include a washing treatment and a drying treatment. In yet other aspects the present invention may include an automated recovery sample processing system with the capability of detecting at least one immediate condition of a fortuitously terminated automatic sample processing run and perhaps even an automatic terminated sample processing run reconstruction calculator.
Owner:BIOCARE MEDICAL
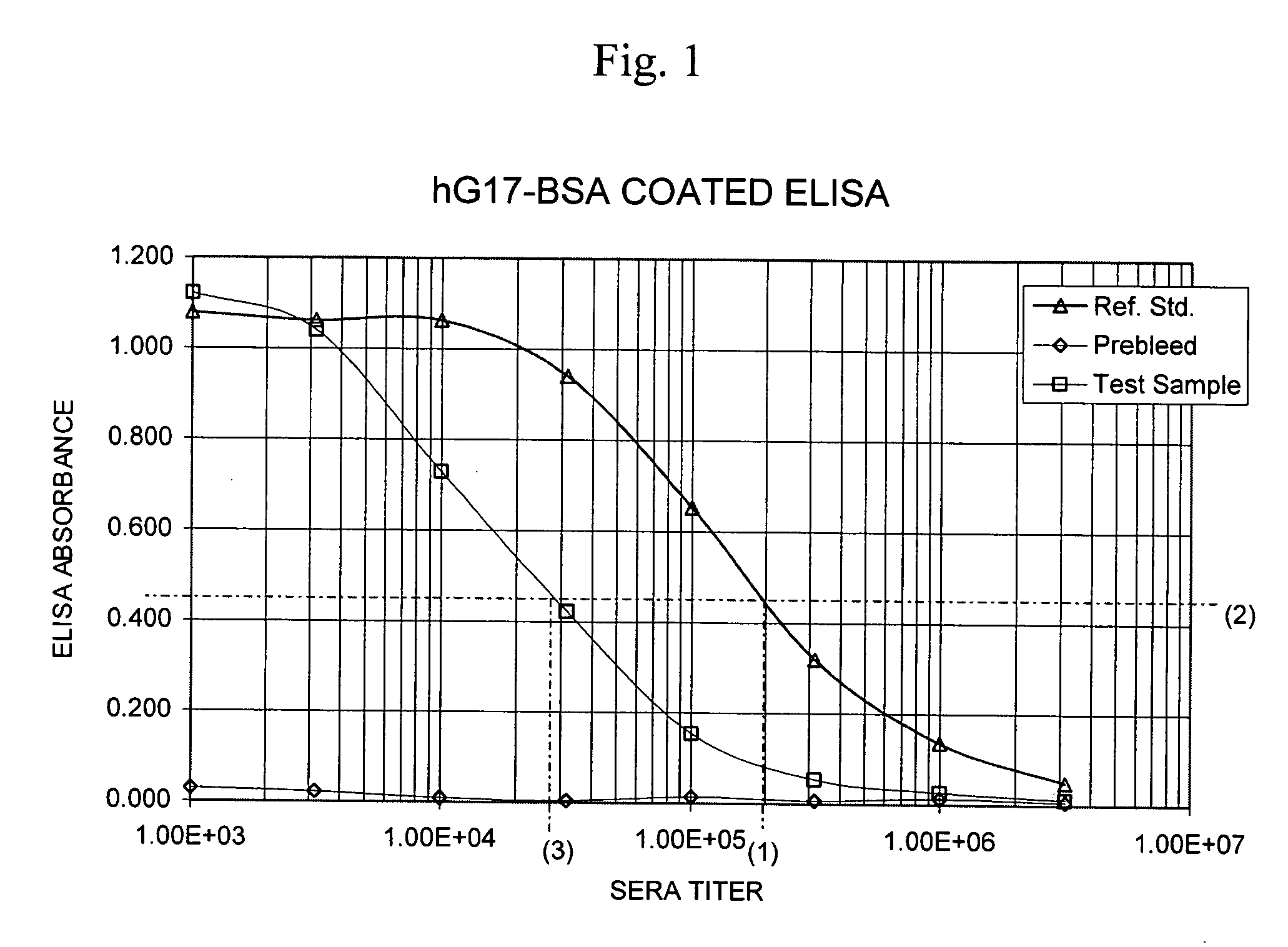
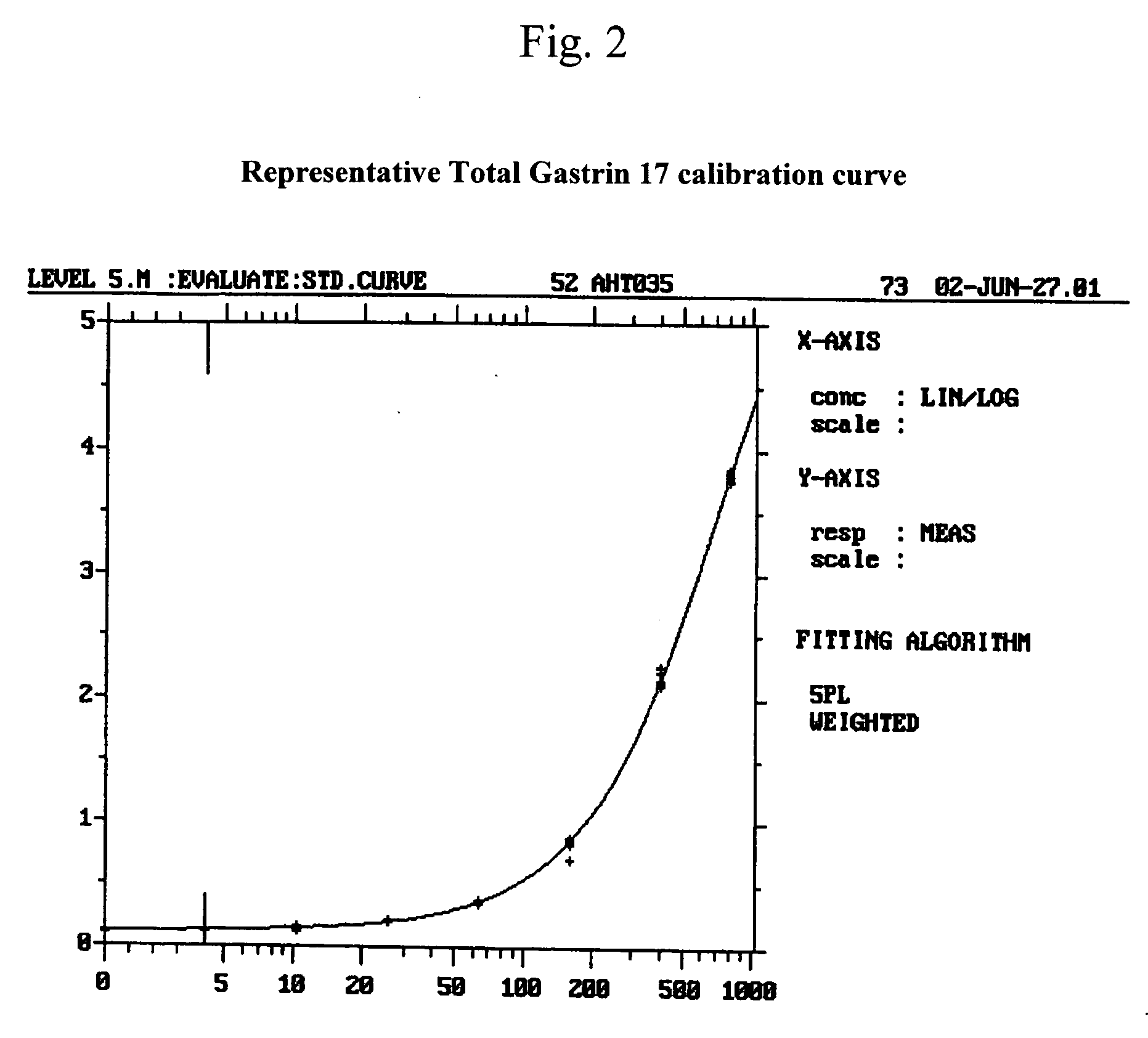
Monoclonal antibodies to gastrin hormone
InactiveUS20060020119A1Microbiological testing/measurementDigestive systemImmunofluorometric AssaysGlycine extended gastrin
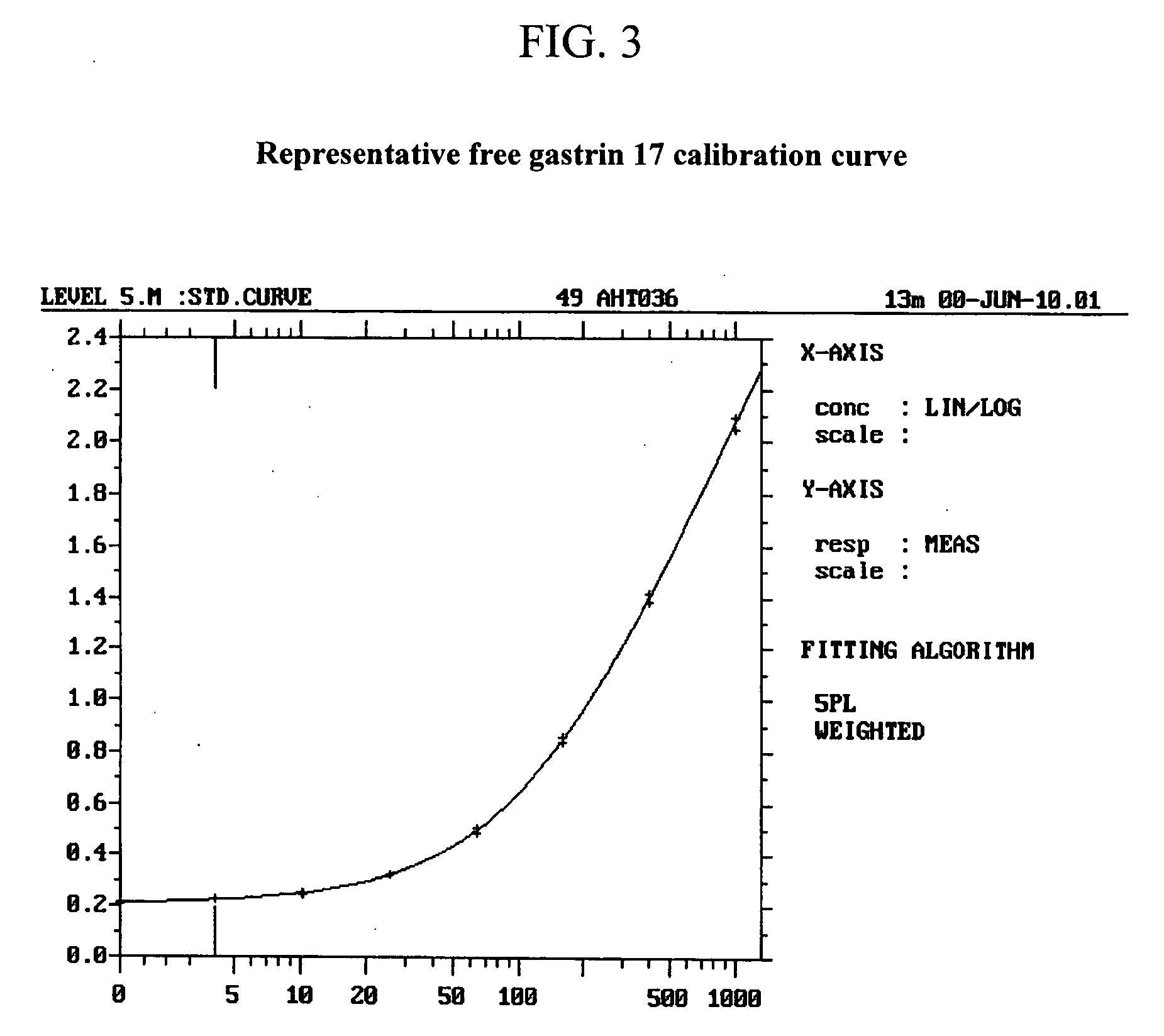
The present invention provides monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) selective for the N-termini and C-termini of the gastrin hormone forms, gastrin-17 (G17), glycine-extended gastrin-17 (G17-Gly), gastrin-34 (G34) and glycine-extended gastrin-34 (G34-Gly); and the hybridomas that produce these MAbs. Also provided are panels of MAbs useful for the detection and quantitation of gastrin-17 (G17), glycine-extended gastrin-17 (G17-Gly), gastrin-34 (G34) and glycine-extended gastrin-34 (G34-Gly). These assays are useful for monitoring a gastrin-mediated disease or condition, or for monitoring the progress of a course of therapy. The invention further provides solid phase assays including immunohistochemical (IHC) and immunofluorescence (IF) assays suitable for detection and visualization of gastrin species in solid samples, such as biopsy samples or tissue slices. Pharmaceutical compositions of the MAbs of the invention are also provided, along with methods of diagnosis, prevention and treatment of gastrin-mediated diseases or conditions. Methods of evaluating a gastrin hormone-blocking treatment are described. The course of a gastrin-mediated disease or condition may be monitored in a patient by means of assay methods provided.
Owner:CANCER ADVANCES INC
IMMUNONANOTHERAPEUTICS THAT PROVIDE IgG HUMORAL RESPONSE WITHOUT T-CELL ANTIGEN
ActiveUS20120087890A1Improve responseEffective amountSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibacterial agentsNanocarriersAntibody production
The present invention provides compositions and systems for delivery of nanocarriers to cells of the immune system. The invention provides synthetic nanocarriers capable of eliciting an immune system response in the form of antibody production, wherein the nanocarriers lack any T cell antigens. In some embodiments, the invention provides nanocarriers that comprise an immunofeature surface, which provides high avidity binding of the nanocarriers to antigen presenting cells. The invention provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising such nanocarriers. The present invention provides methods of designing, manufacturing maceutical compositions thereof.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +2
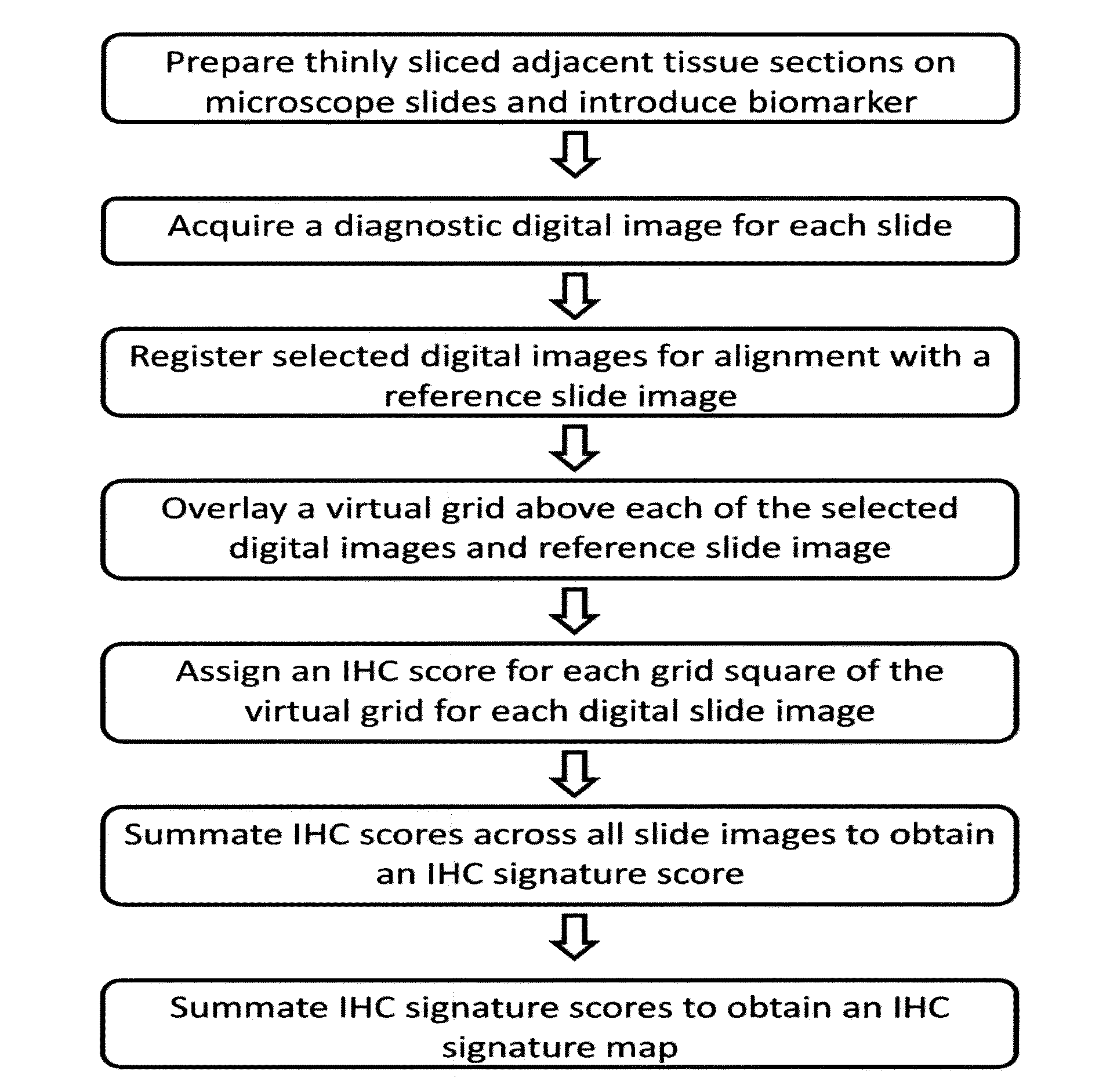
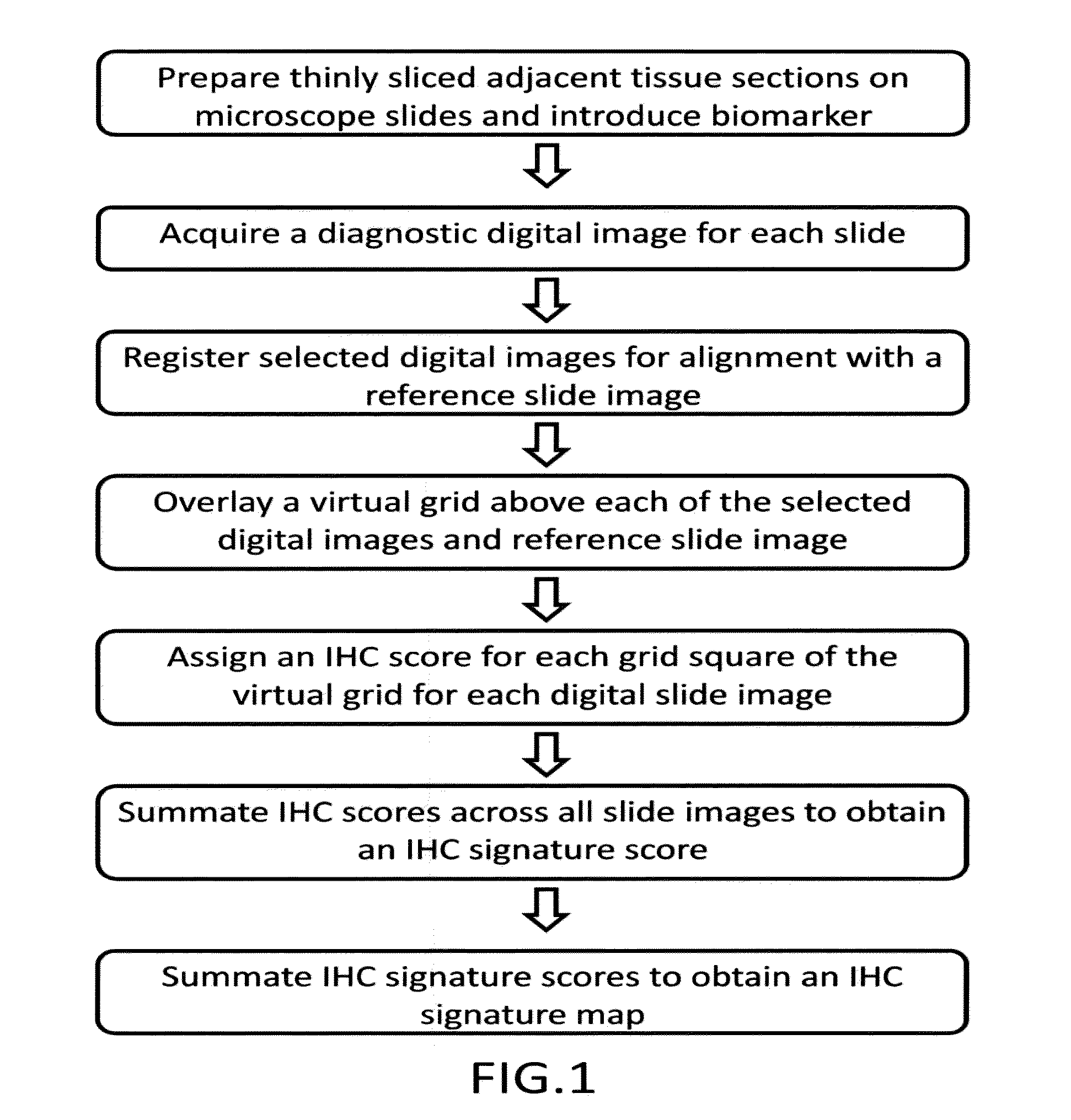
Computerized methods for tissue analysis using n-gene profiling
A computerized method for immunohistochemistry analysis of tissue utilizes digital images of multiple adjacent tissue sections aligned within a computerized software and processed with an algorithm to quantify a two-dimensional IHC signature score for each respective slide image. In various embodiments, the IHC score is performed over several adjacent sections and further processed to produce a three-dimensional IHC quantification referred to as an IHC signature map.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
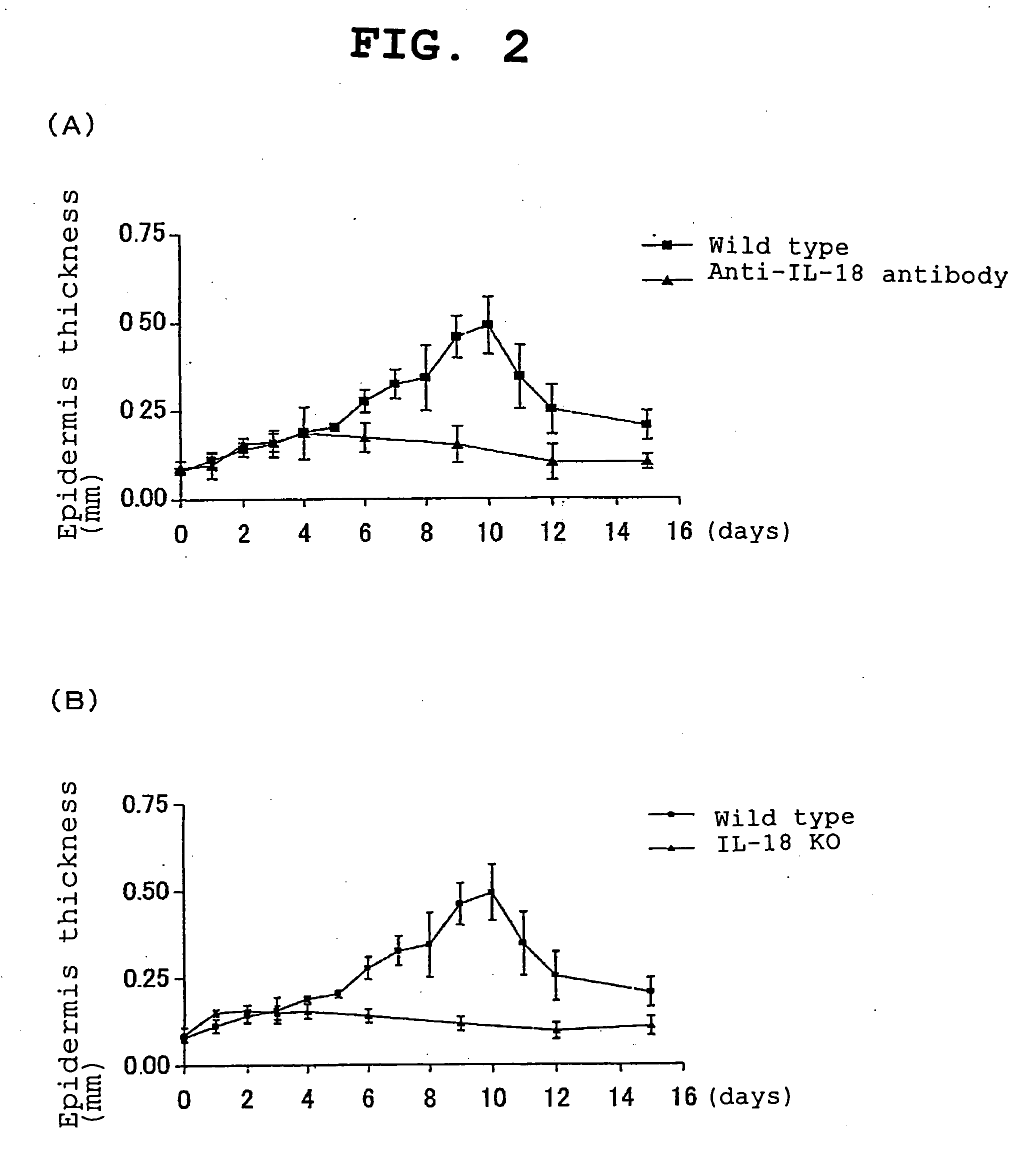
Il-18 Receptor Antagonist and Pharmaceutical Composition Containing the Antagonist
ActiveUS20080063644A1Inhibit functioningGuaranteed functionAntibacterial agentsNervous disorderΒ subunitAmino acid
Provided is an IL-18 receptor antibody usable for immunohistochemistry, which functions as an IL-18 receptor antagonist. Also provided is a pharmaceutical composition and method for preventing and / or treating an IL-18-dependent disorder, particularly skin thickening caused by ultraviolet, using the antibody. An antibody against the IL-18 receptor α subunit, which is characterized by binding specifically to a polypeptide consisting of the amino acid sequence shown by SEQ ID NO:1, or an antibody against the IL-18 receptor β subunit, which is characterized by binding specifically to a polypeptide consisting of the amino acid sequence shown by SEQ ID NO:2, is prepared.
Owner:SEKIYAMA ATSUO
Monoclonal Antibodies to Progastrin
The present invention provides progastrin-binding molecules specific for progastrin that do not bind gastrin-17(G17), gastrin-34(G34), glycine-extended gastrin-17(G17-Gly), or glycine-extended gastrin-34(G34-Gly). Further, the invention provides monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) selective for sequences at the N-terminus and the C-terminus of the gastrin precursor molecule, progastrin and the hybridomas that produce these MAbs. Also provided are panels of MAbs useful for the detection and quantitation of progastrin and gastrin hormone species in immuno-detection and quantitation assays. These assays are useful for diagnosing and monitoring a gastrin-promoted disease or condition, or for monitoring the progress of a course of therapy. The invention further provides solid phase assays including immunohistochemical (IHC) and immunofluorescence (IF) assays suitable for detection and visualization of gastrin species in solid samples, such as biopsy samples or tissue slices. The progastrin-binding molecules are useful therapeutically for passive immunization against progastrin in progastrin-promoted diseases or conditions. Also provided are surrogate reference standard (SRS) molecules that are peptide chains of from about 10 to about 35 amino acids, wherein the SRS molecule comprises at least two epitopes found in a protein of interest of greater than about 50 amino acids. Such SRS molecules are useful as standards in place of authentic proteins of interest.
Owner:CANCER ADVANCES INC
Integrated Method for Enriching and Detecting Rare Cells from Biological Body Fluid Sample
InactiveUS20110195413A1Good cell shapeHigh recovery rateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStainingSorbent
The present invention relates to an integrated method for enriching and detecting rare cells in biological body fluid sample. The enriching method comprises: (a) removing plasma protein by centrifugation; (b) optionally adding a red cell lysis solution to carry out red cell lysis so as to remove the red blood cells; (c) adding immunomicrospheres or immunoadsorbent to incubate; and (d) carrying out density centrifugation based on a special cell separation medium for separating the circulating rare cells, residual red blood cells after removing red blood cells and the white blood cells combined on the immunomicrospheres. The method for detecting the enriched rare cells according to the present invention comprises combining immunohistochemistry based staining with immunofluorescence, or bicolor, tricolor or multicolor staining based on immunohistochemistry, and observing and identifying by fluorescence or ordinary optical microscope or a scanner based on microscope principle. The novel and unique method for enriching and staining has been proved to have low cost and can rapidly, effectively and high specifically enrich and quantitatively detect the rare cells in blood.
Owner:CYTTEL BIOSCI BEIJING
Gene Expression Profiling for Predicting the Survivability of Prostate Cancer Subjects
A method is provided in various embodiments for determining a profile data set for predicting the survivability of a subject with prostate cancer based on a sample from the subject, wherein the sample provides a source of RNAs. The method includes using amplification under measurement conditions that are substantially repeatable for measuring the amount of RNA corresponding to at least 1 constituent from Table 1. Alternatively, the method uses electrophoresis or immunohistochemistry for measuring the mount of protein corresponding to at least 1 constituent from Table 20. The profile data set comprises the measure of each constituent.
Owner:GENOMIC HEALTH INC
Immunohistochemical assay for detecting expression of programmed death ligand 1 (pd-l1) in tumor tissue
InactiveUS20160084839A1Improve standardizationAntibody ingredientsDisease diagnosisProgrammed deathPD-L1
The present disclosure provides processes for describing and quantifying the expression of human programmed death ligand-1 (PD-L1) in tumor tissue sections as detected by immunohistochemical assay using an antibody that specifically binds to PD-L1. The results generated using these processes have a variety of experimental, diagnostic and prognostic applications.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Nanoparticle conjugates
InactiveUS20090181398A1Easy to detectMaterial nanotechnologyPowder deliveryOrganic chemistryFluorescent nanoparticles
Conjugate compositions are disclosed that include a specific-binding moiety covalently coupled to a nanoparticle through a heterobifunctional polyalkyleneglycol linker. In one embodiment, a conjugates is provided that includes a specific-binding moiety and a fluorescent nanoparticle coupled by a heterobifunctional PEG linker. Fluorescent conjugates according to the disclosure can provide exceptionally intense and stable signals for immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization assays on tissue sections and cytology samples, and enable multiplexing of such assays.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Method for chromogenic detection of two or more target molecules in a single sample
ActiveUS20110136130A1Low backgroundReduce and preventMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingSingle sampleTissue sample
The present invention provides a method and kit for detection of two or more target molecules in a single tissue sample, such as for gene and protein dual detection in a single tissue sample. Methods comprise treating a tissue sample with a first binding moiety that specifically binds a first target molecule. Methods further comprise treating the tissue sample with a solution containing a soluble electron-rich aromatic compound prior to or concomitantly with contacting the tissue sample with a hapten-labeled binding moiety and detecting a second target molecule. In one example, the first target molecule is a protein and the second is a nucleic acid sequence, the first target molecule being detected by immunohistochemistry and the second by in situ hybridization. The disclosed method reduces background due to non-specific binding of the hapten-labeled specific binding moiety to an insoluble electron rich compound deposited near the first target molecule.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Preparation method of brain tissue rapid freezing section
ActiveCN103674677ATo achieve the effect of quick freezingReduce formationPreparing sample for investigationAntigenPerfusion
The invention discloses a preparation method of a brain tissue rapid freezing section. According to the method, acetone is used as a freezing embedding medium and a liquid nitrogen intermediate medium, so that brain tissue can be rapidly frozen , and formation of ice crystals on the brain tissue can be effectively reduced; besides, factors affecting manufacturing quality, such as temperatures during material drawing and sectioning, fixing and soring conditions after sectioning and the like, of the freezing section are optimized, and the quality of the finally prepared section is further guaranteed. According to the brain tissue rapid freezing section obtained with the method, the freezing section which has stability and can well protect antigens and the enzyme activity is provided for further immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization tests on the brain tissue, and a pathological section meeting requirements is provided for future clinical diagnosis related to nervous system diseases and scientific researches. Particularly, molecular and biochemical index detection can be further performed on other tissue of a mouse which is not subjected to perfusion treatment in the scientific research.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Methods and compounds for detection of molecular targets
ActiveUS8435735B2Faster and more sensitive and precise detectionEasy to detectSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementIn situ hybridisationChemical compound
The present invention relates to methods and compounds for detection of molecular targets, such as biological or chemical molecules, or molecular structures, in samples using a host of experimental schemes for detecting and visualizing such targets, e.g. immunohistochemistry (IHC), in situ hybridization (ISH), ELISA, Southern, Northern, and Western blotting, etc.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Anti-silk fibroin polyclonal antibody and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104059131AStrong specificityHigh puritySerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansPolyclonal antibodiesBioinformatics
The invention relates to the technical field of biology and in particular discloses an anti-silk fibroin polyclonal antibody and a preparation method thereof. The anti-silk fibroin polyclonal antibody is produced by an animal under the condtion that polypeptide with an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1 is taken as an immunogen. The anti-silk fibroin polyclonal antibody has the characteristics of good specificity and high purity, can be specifically conjugated with silk fibroin and is widely applicable to immunohistochemistry, immunoblotting and in vitro immunoassay. The preparation method of the anti-silk fibroin polyclonal antibody is simple in operation and is applicable to preparation of a large quantity of anti-silk fibroin polyclonal antibodies.
Owner:SILK PLUG BEIJING BIOMEDICINE TECH
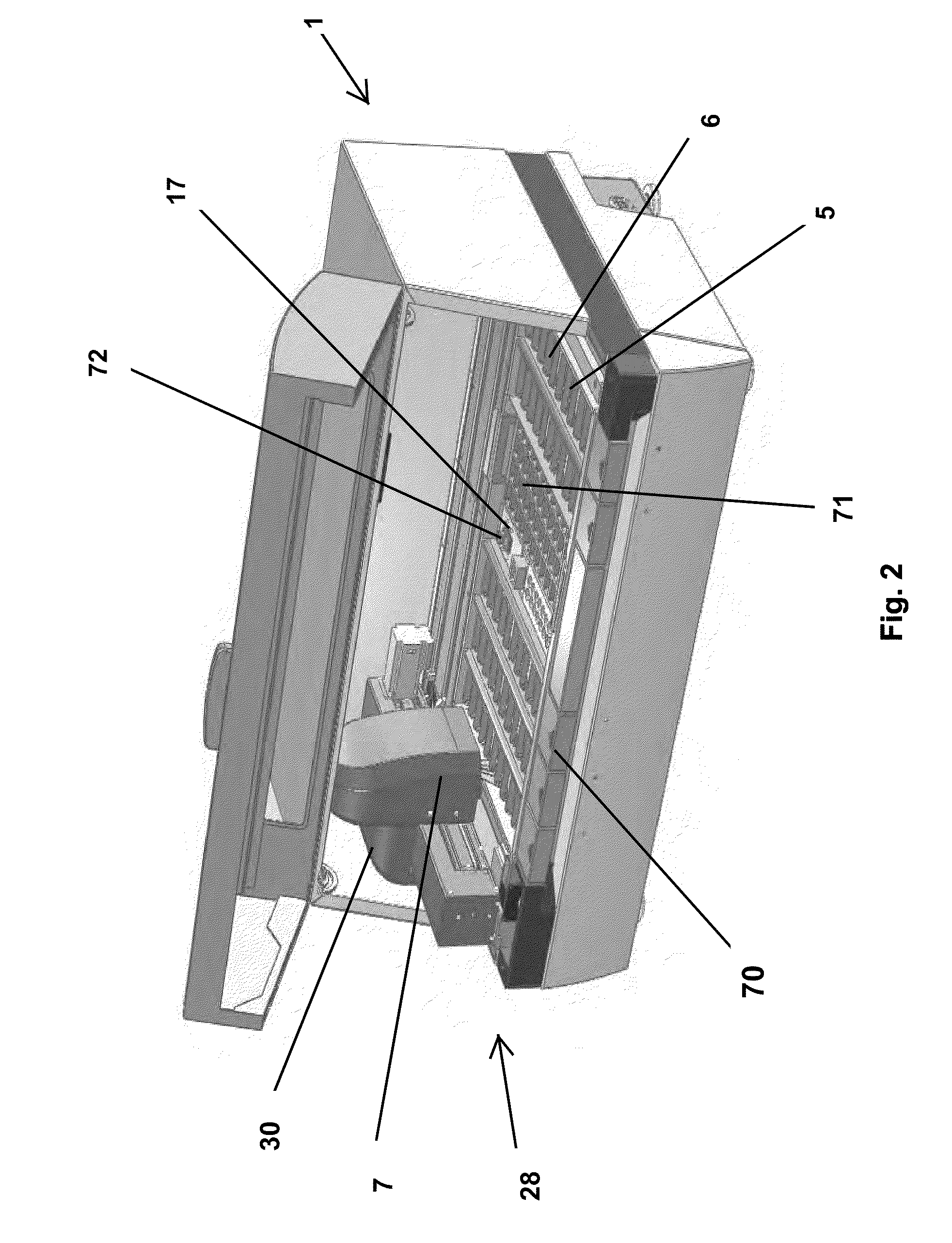
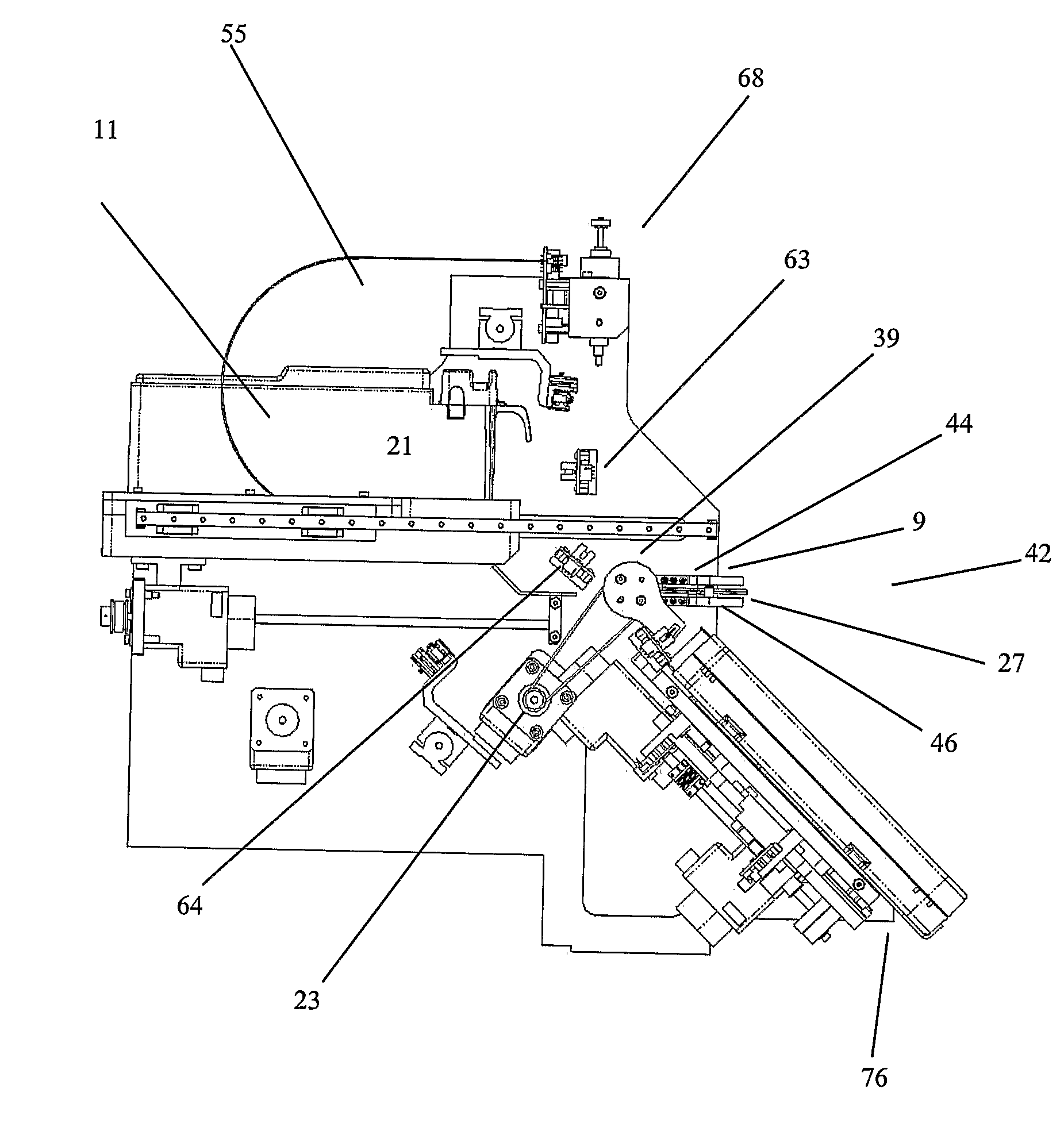
Parallel Processing Fluidic Method and Apparatus for Automated Rapid Immunohistochemistry
InactiveUS20080213804A1Easy to useShorten time for amountBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSurgical operationGuideline
A sample processing system that may be configured to achieve parallel or coincidental sample processing such as histochemical processing may involve a plurality of samples arranged for coincidental movement perhaps by use of angular microscopic slide movements to cause processing activity that may include repeated elimination and reapplication of a fluidic substance perhaps through the action of capillary motion in order to refresh a microenvironment adjacent to a sample such as a biopsy or other such sample. Snap in antibody and other substances may be included to ease operator actions and to permit location specific substance applications perhaps by including single container multiple chamber multiple fluidic substance magazines, linearly disposed multiple substance source, and primary antibody cartridges. Through refreshing of a microenvironment, depletion of the microenvironment is avoided and the time necessary for slide processing may be dramatically shortened from a more common 60 to 120 minutes to perhaps less than 15 minutes so as to permit use of such a system in an intraoperative or surgical environment such as recommended by the College of American Pathologists intraoperative guidelines or the like. Patients may thus avoid a need to be subjected to an additional surgical procedure when lab results become available to see if tumors or the like were fully removed in a prior procedure.
Owner:CELERUS DIAGNOSTICS
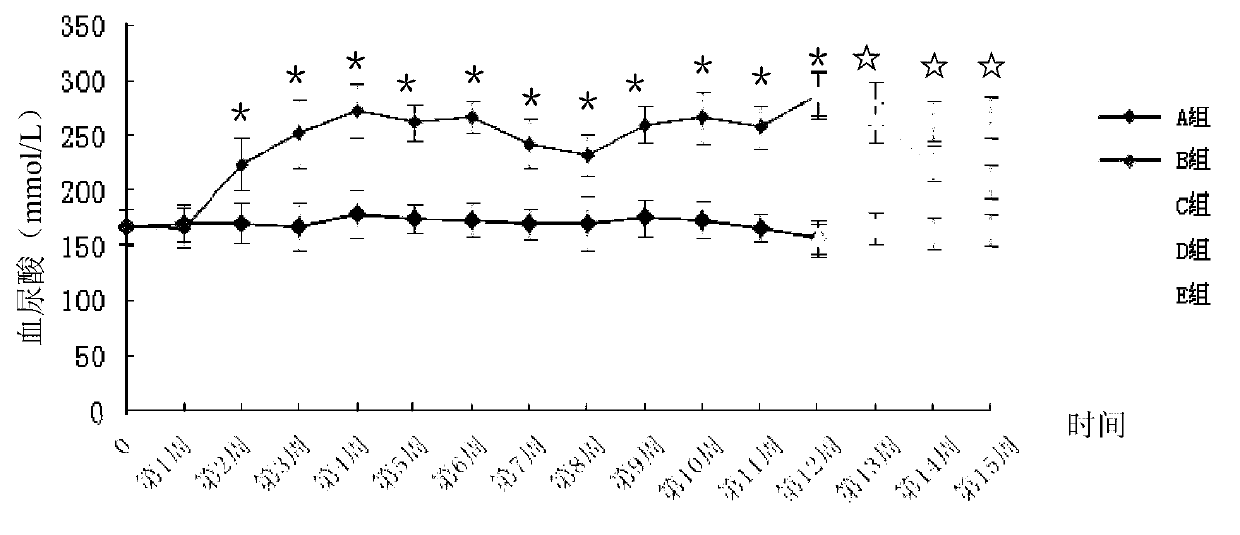
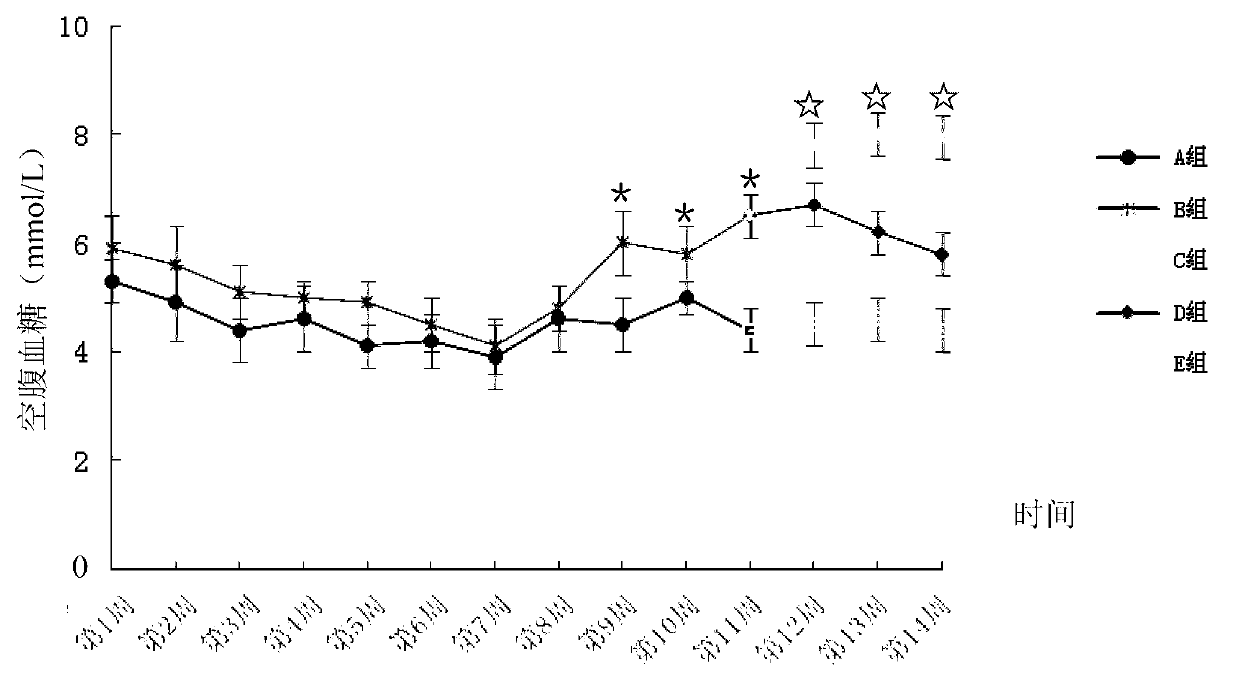
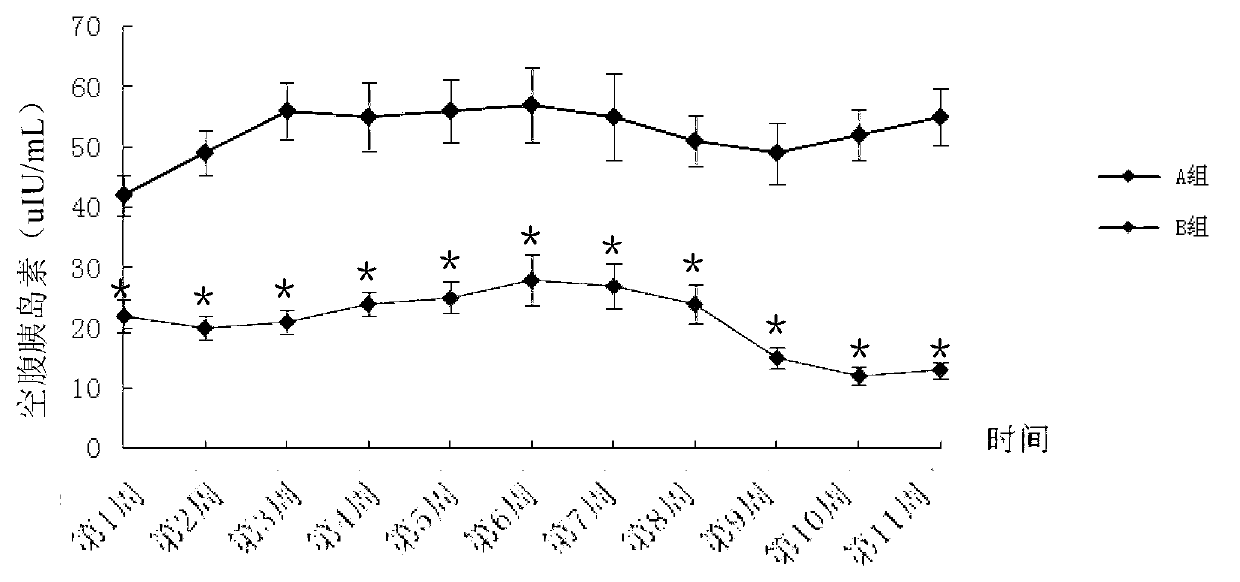
Method for building animal model with hyperuricemia-combined diabetes
The invention discloses a method for building an animal model with hyperuricemia-combined diabetes. The method comprises the following steps: 1) feeding an target animal with fodder containing 10% (by mass) of yeast powder; subjecting the target animal to a lavage with a 4% (by mass) adenine water solution according to the following dosage of 100 milligram of adenine per day per kilogram of body weight until the blood uric acid level of the target animal starts falling; 2) halving the dosage of the adenine water solution in step 1), subjecting the target animal to a subcutaneous injection with an oteracil potassium emulsion twice a day according to the following dosage of 100 milligram of oteracil potassium emulsion per day per kilogram of body weight until the target animal shows clinical symptoms of diabetes, and then obtaining the animal model with the hyperuricemia-combined diabetes. The method builds the animal model with the hyperuricemia-combined diabetes for the first time, the animal model has typical disease symptoms, the quantity index has statistical significance, and studies such as glucose clamp test and immunohistochemistry also prove that the modeling is successful. Therefore, the method for building the animal model with the hyperuricemia-combined diabetes is a reliable and practical technique.
Owner:李长贵
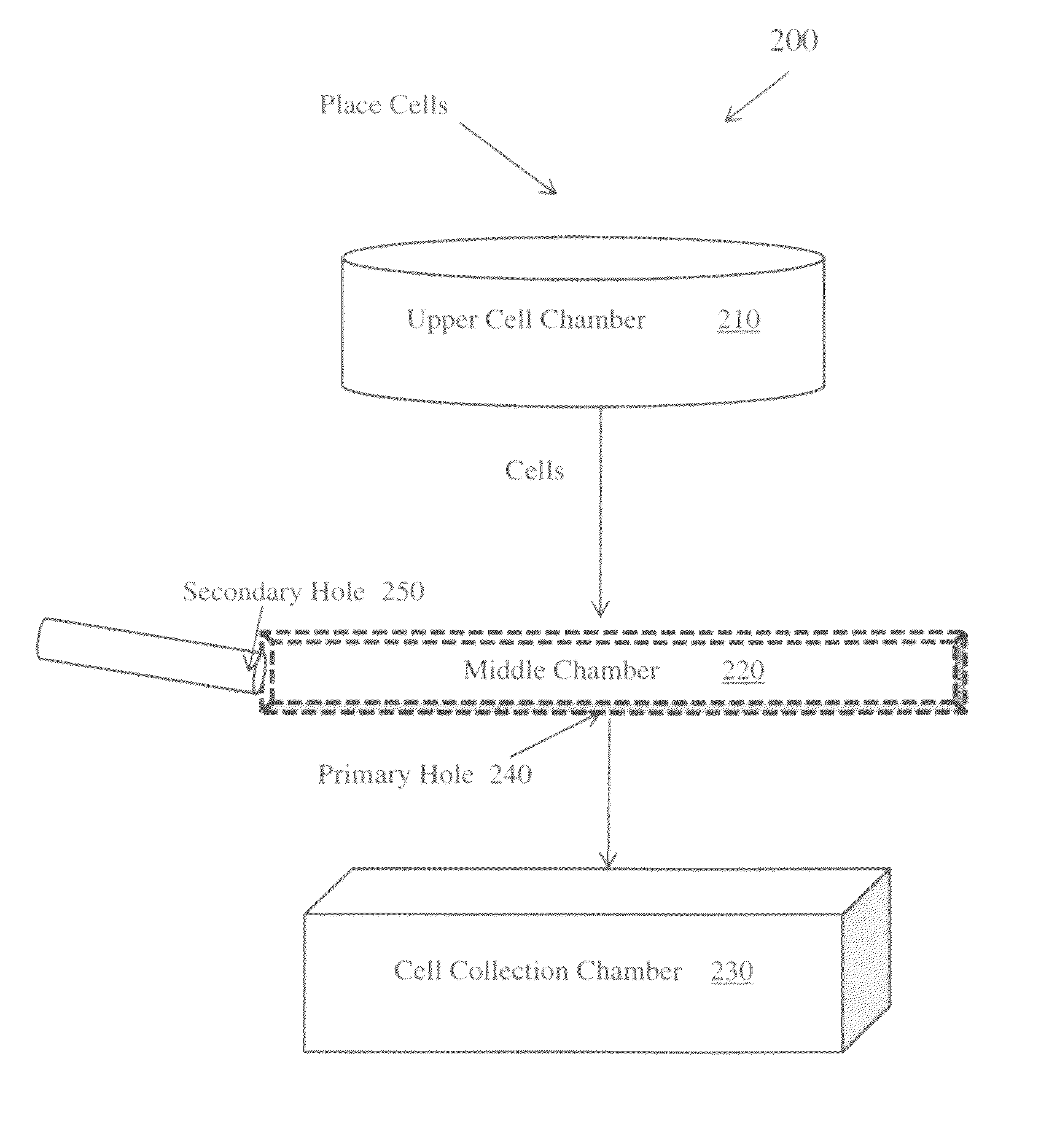
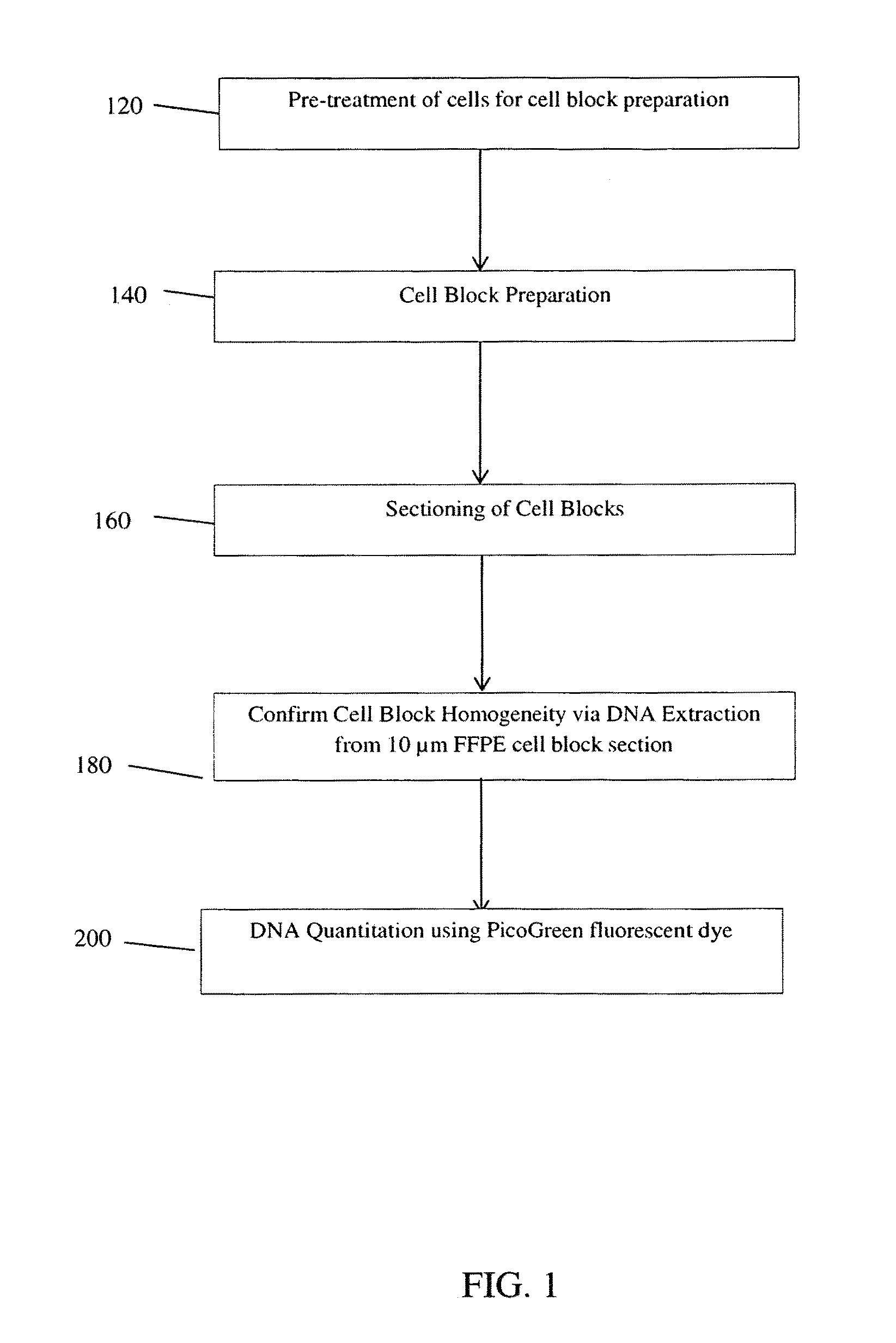
In vitro homogenous cell block, method of making and using
ActiveUS9395283B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPositive controlImaging analysis
An in vitro method of making a homogenous cell block for use as a positive control for biomarkers in immunohistochemistry experiments, such slide scanning and image analysis. The homogenous cell block is produced using a three layered vertical apparatus to create an evenly distributed suspension of FFPE cells, wherein the cells are mixed with 3% agarose while still rotating within the apparatus's middle layer. The injection of the cell mixture into a mold creates a homogeneous cell block where each cell, or ratio of different types of cells, is evenly distributed. The cell mixture within the cell block may comprise: a mixture of the same type of cell with different genetic modifications; a mixture of the same type of cell with different protein or nucleic acids expression; and a mixture of different types of cells with different genetic backgrounds, and / or different expression level of genes and / or proteins.
Owner:ALAMAK BIOSCI INC COMPANY
Method And Apparatus For Automated Rapid Immunohistochemistry
InactiveUS20080194034A1Reduce manufacturing costEasy to useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGuidelineMicroscopic scale
A sample processing system that may be configured to achieve parallel or coincidental sample processing such as histochemical processing may involve a plurality of samples arranged for coincidental movement perhaps by use of angular microscopic slide movements to cause processing activity that may include repeated elimination and reapplication of a fluidic substance perhaps through the action of capillary motion in order to refresh a microenvironment adjacent to a sample such as a biopsy or other such sample. Snap in antibody and other substances may be included to ease operator actions and to permit location specific substance applications perhaps by including single container multiple chamber multiple fluidic substance magazines, linearly disposed multiple substance source, and primary antibody cartridges. Through refreshing of a microenvironment, depletion of the microenvironment is avoided and the time necessary for slide processing may be dramatically shortened from a more common 60 to 120 minutes to perhaps less than 15 minutes so as to permit use of such a system in an intraoperative or surgical environment such as recommended by the College of American Pathologists intraoperative guidelines or the like. Patients may thus avoid a need to be subjected to an additional surgical procedure when lab results become available to see if tumors or the like were fully removed in a prior procedure.
Owner:CELERUS DIAGNOSTICS
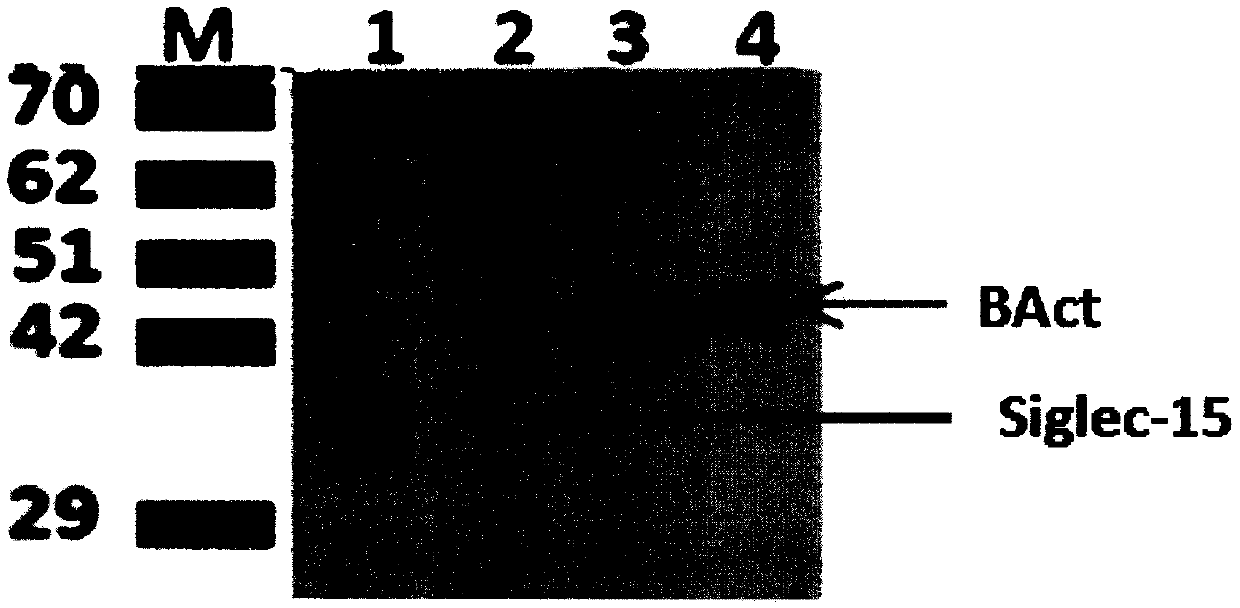
Preparation and application of mouse monoclonal antibody against human Siglec-15 protein
InactiveCN110386982AImprove featuresImprove reliabilityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsPD-L1Wilms' tumor
The invention discloses a mouse monoclonal antibody against a human Siglec-15 protein. The specificity is high, the performance is stable and the titer is high. The invention further relates to application of the monoclonal antibody to preparation of immunohistochemical detection tools for the Siglec-15 protein. According to the mouse monoclonal antibody against the human Siglec-15 protein, an immunohistochemistry method is used for detecting expression of Siglec-15 on the tumor cell surface for selection, the curative effect and the prognosis of therapeutic schedules of malignant tumors. Theinvention further relates to the application of the monoclonal antibody to preparation of antibody drugs for immunotherapy of the malignant tumors. The important application value is achieved. The adopted antibody drugs can be full-length or partial sections (Fab, F(ab)'2 or ScFv) of an Siglec-15 monoclonal antibody or combined use of the Siglec-15 monoclonal antibody and a PD-L1 monoclonal antibody. The malignant tumors mainly include colorectal cancer, endometrial cancer, thyroid cancer, bladder cancer, kidney cancer, lung cancer, liver cancer and the like.
Owner:广东三九脑科医院 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com