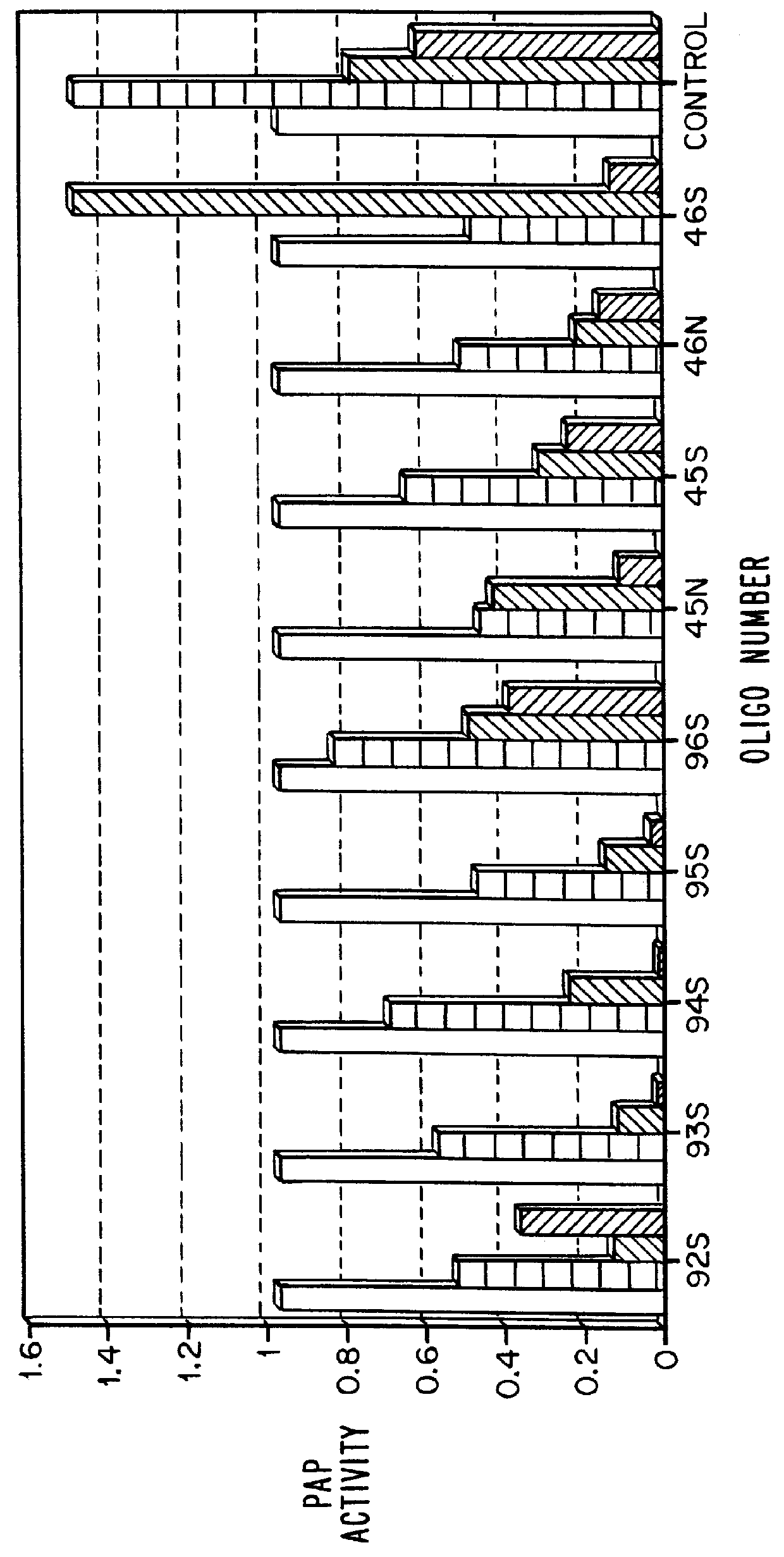
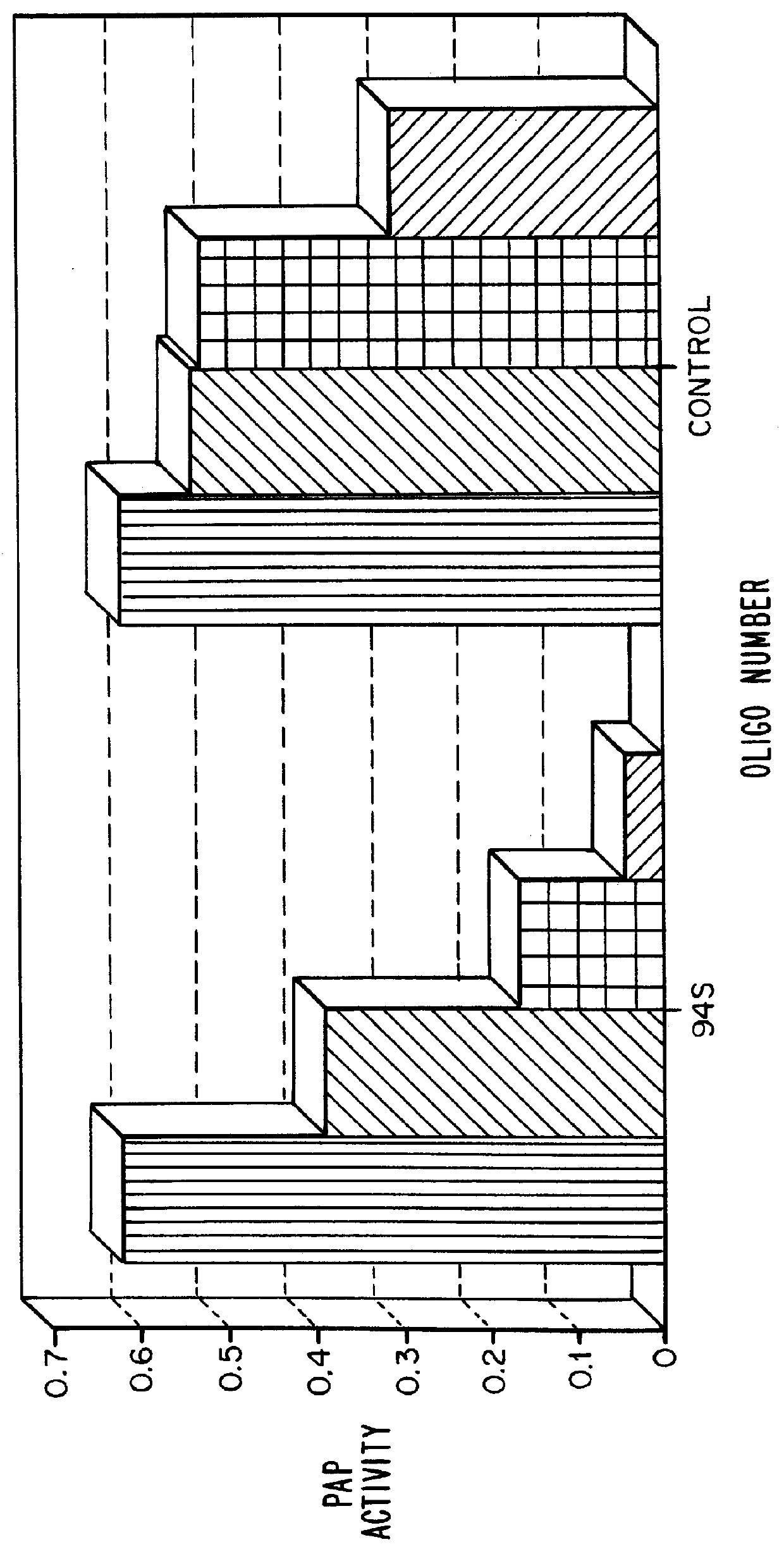
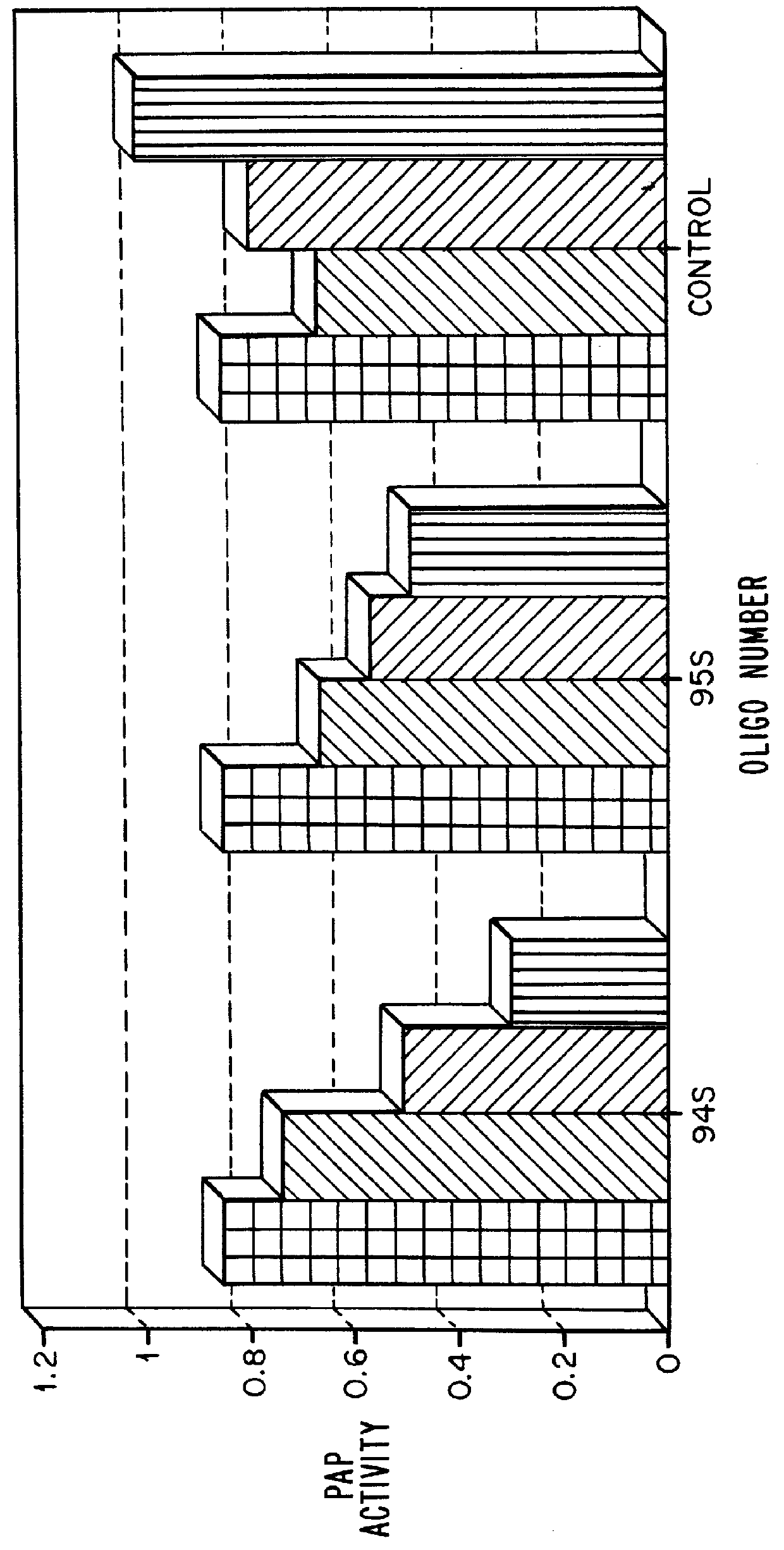
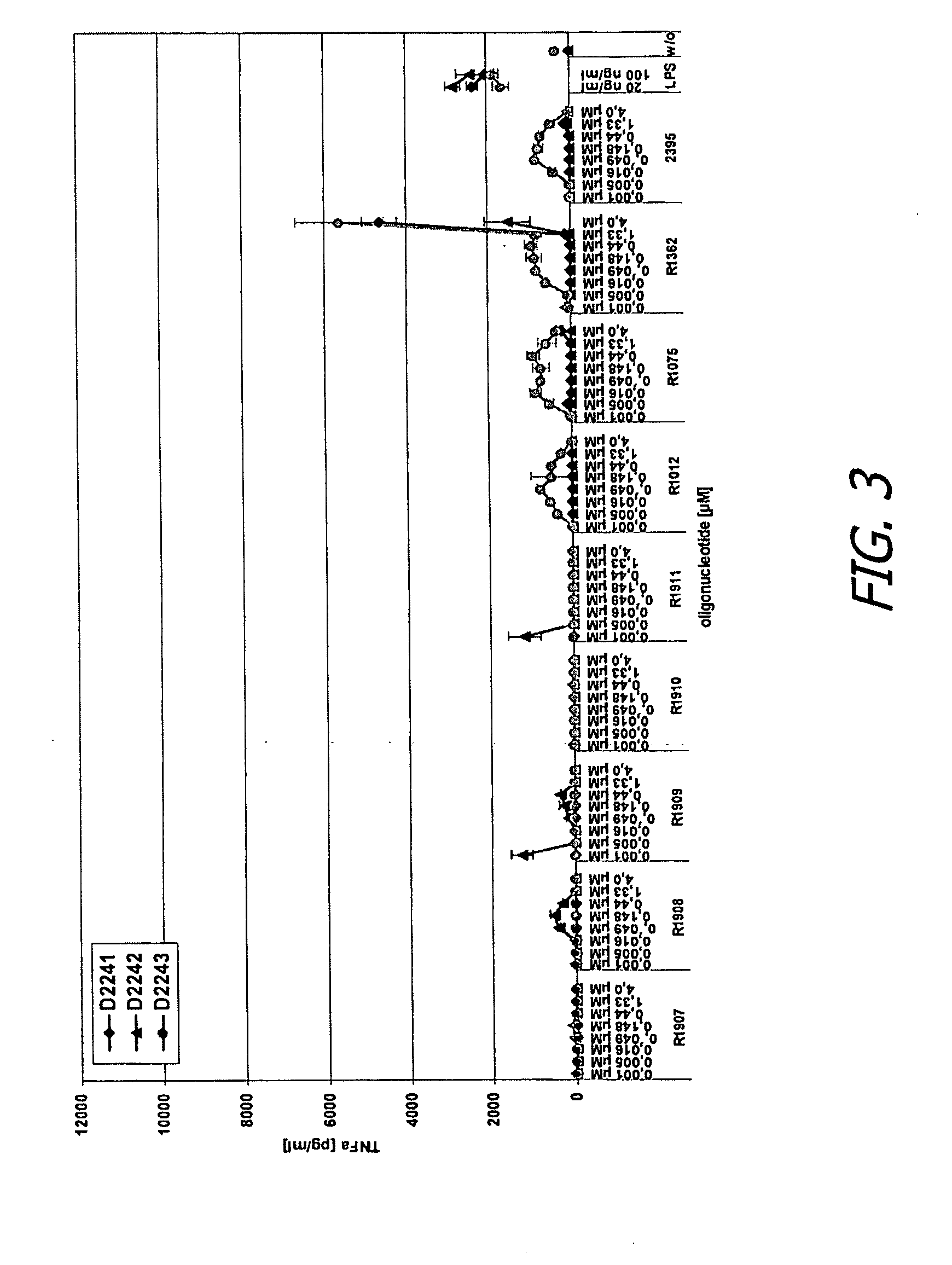
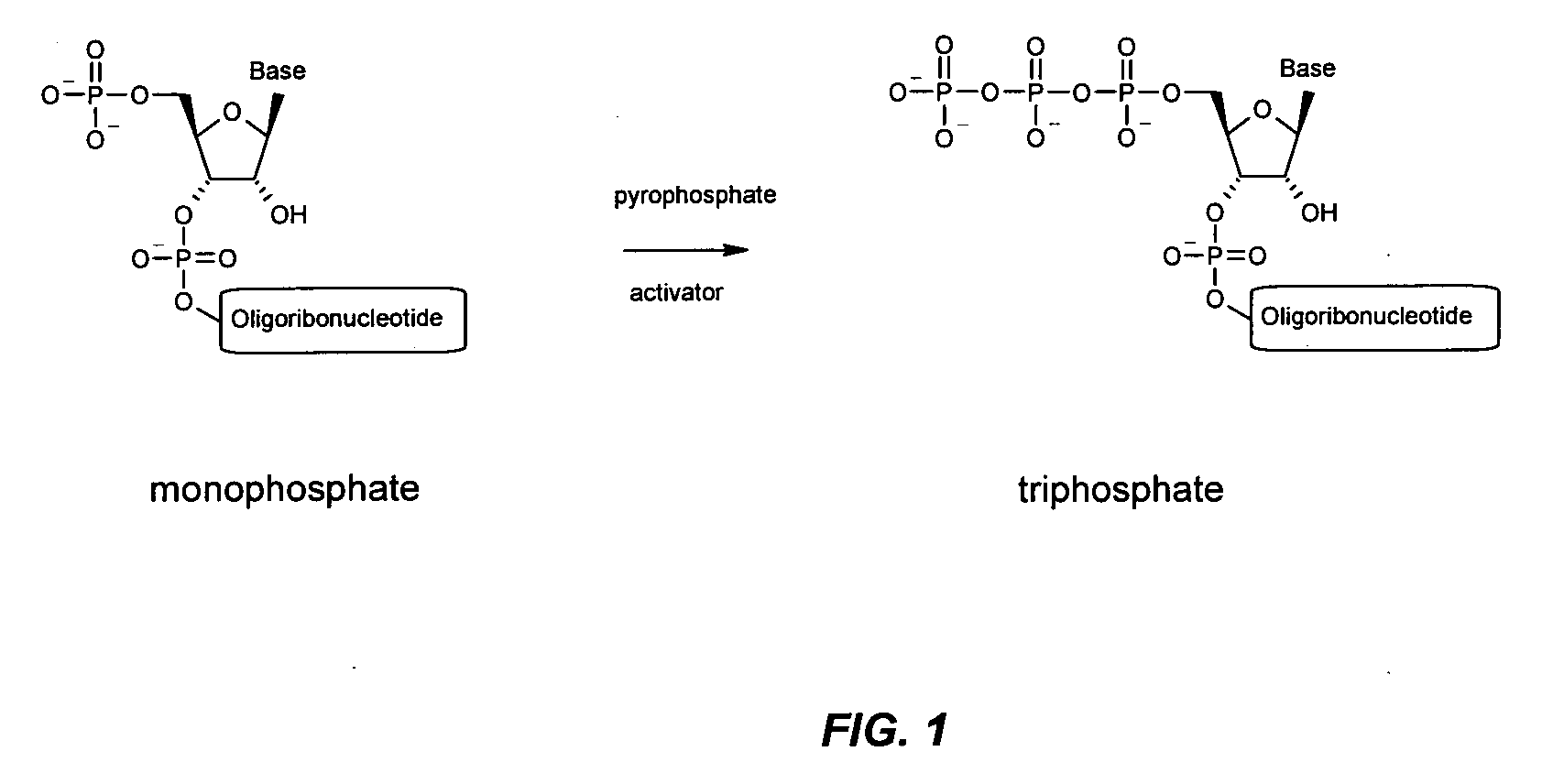
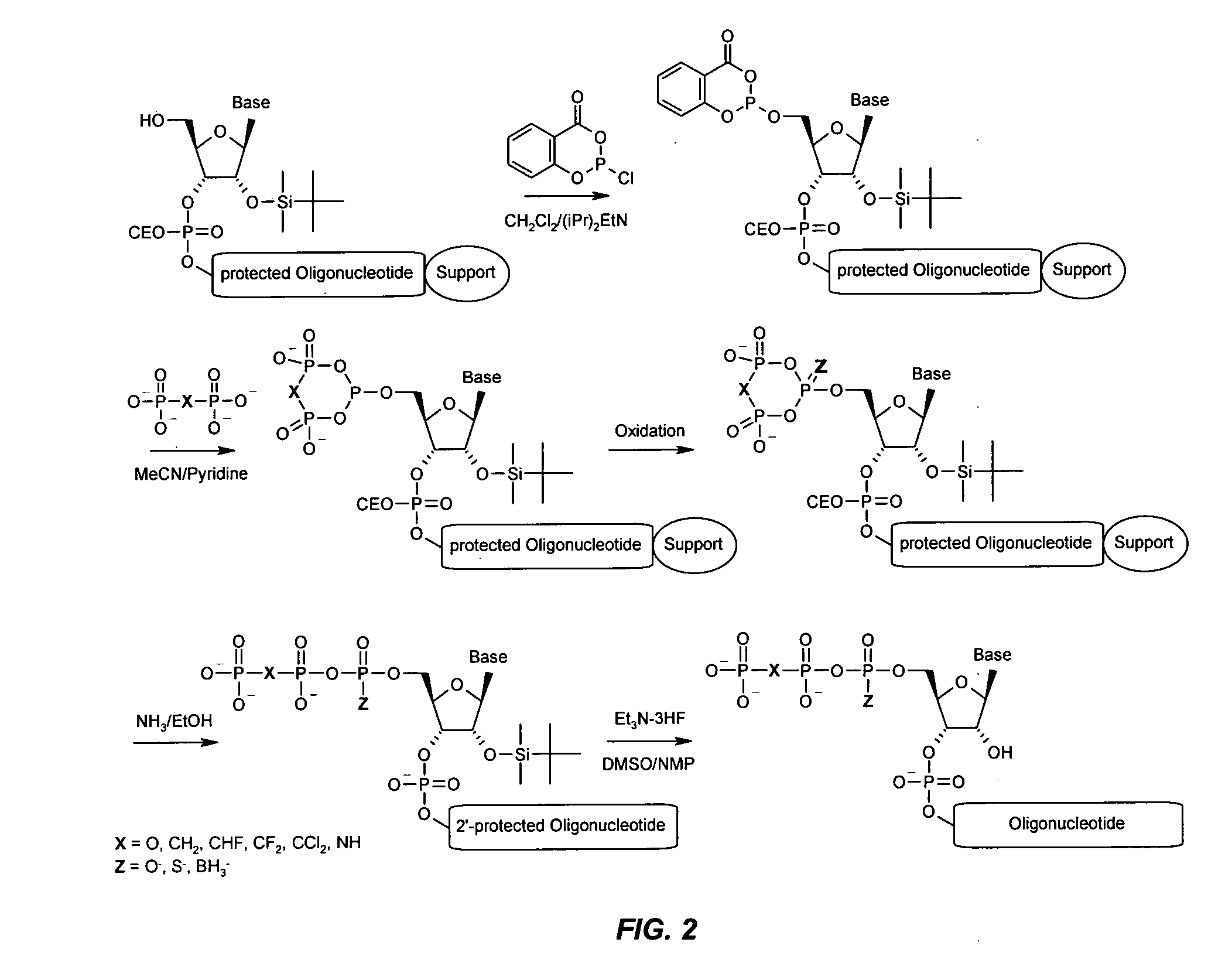
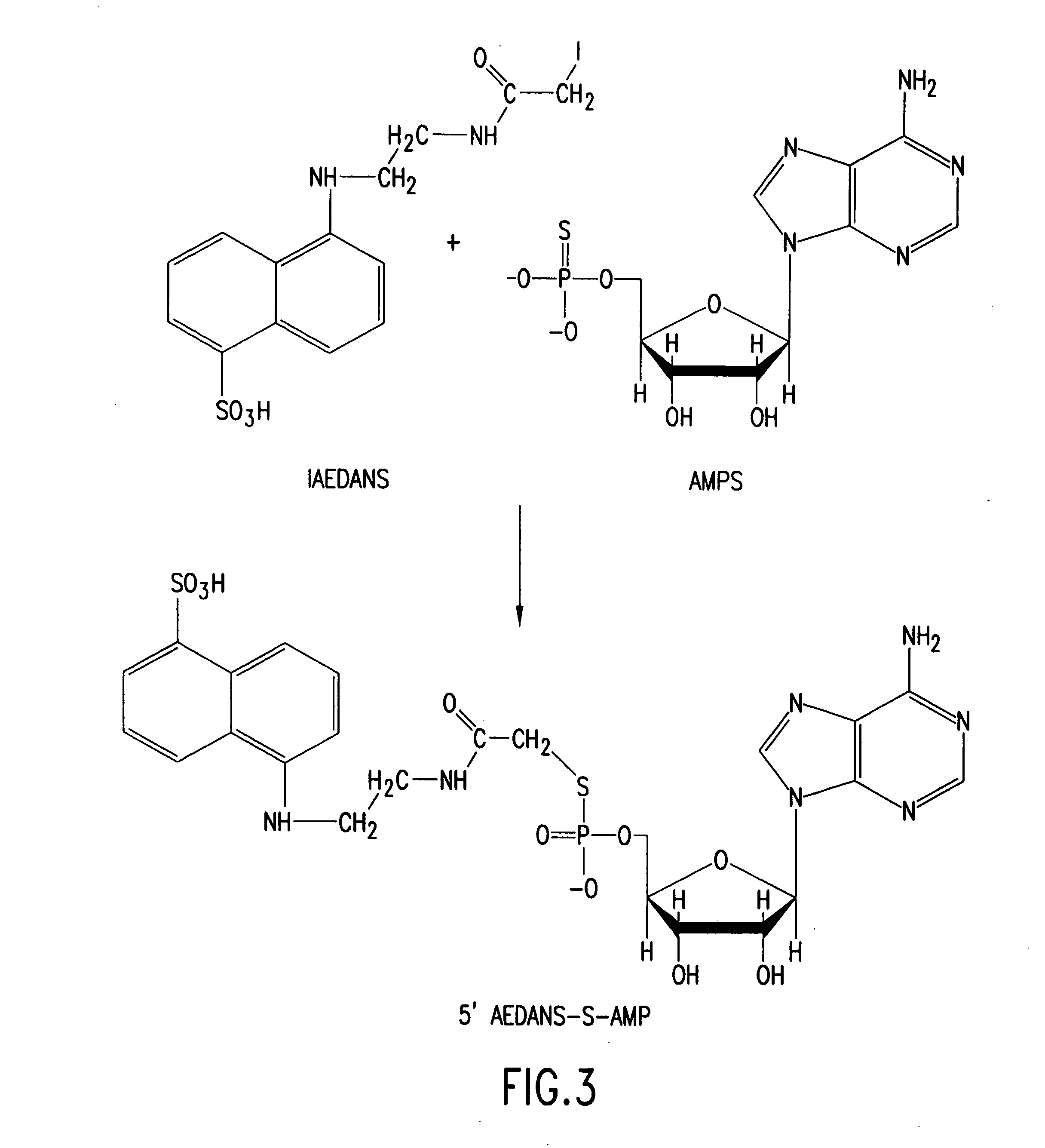
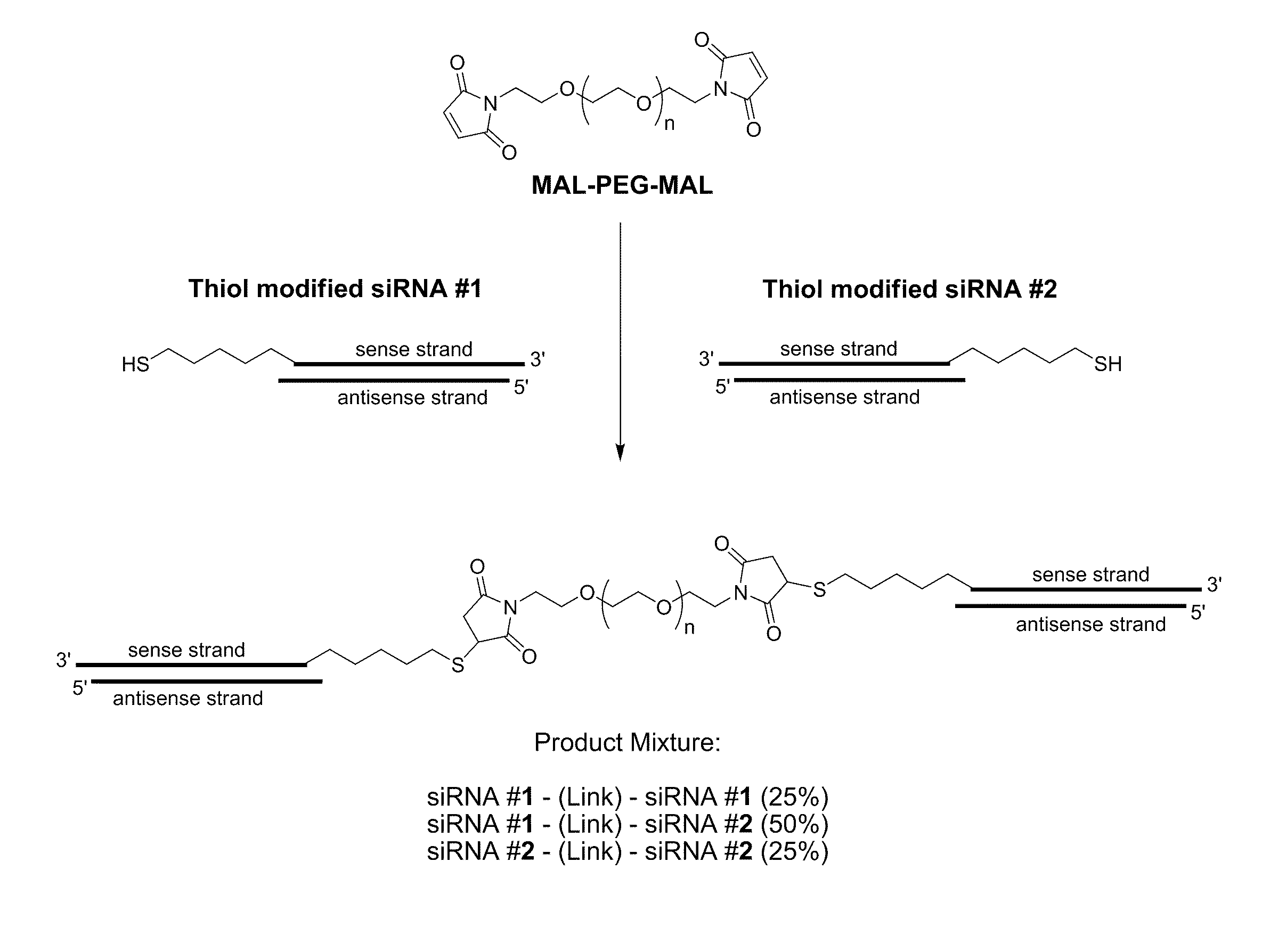
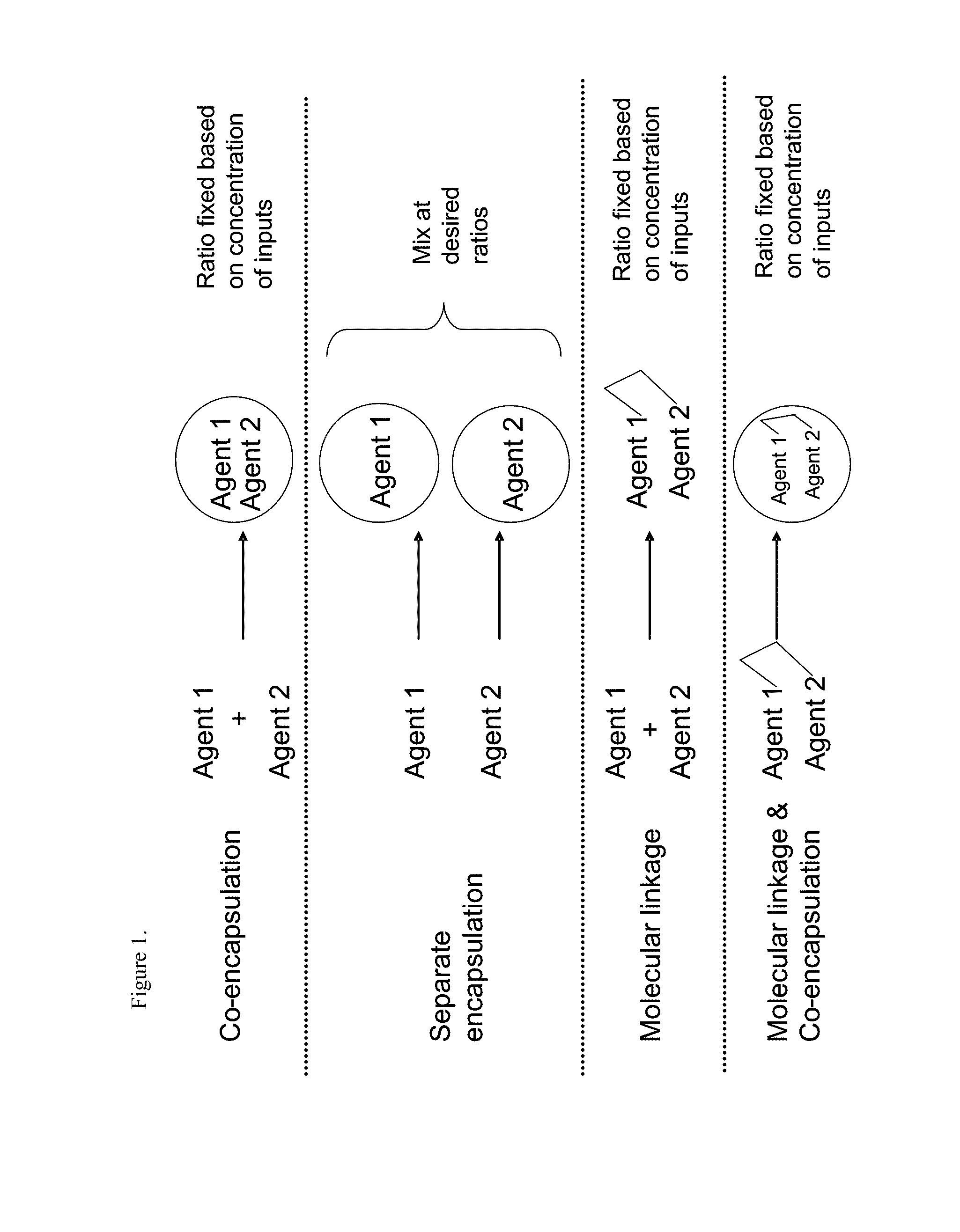
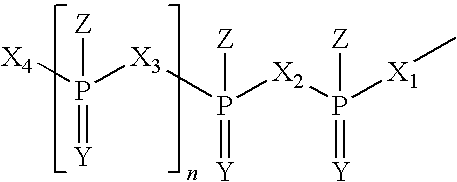Patents
Literature
69 results about "Oligoribonucleotides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
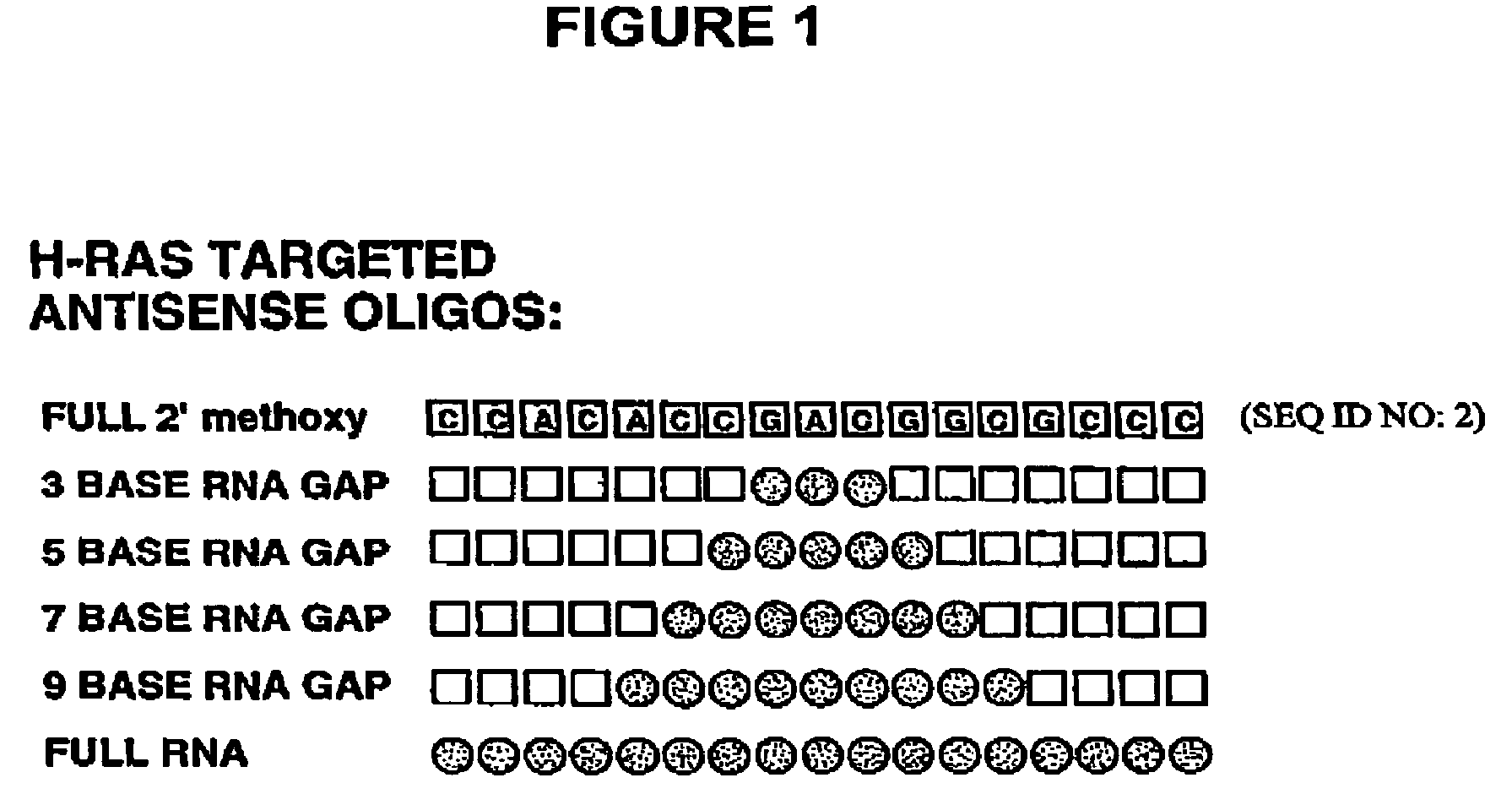
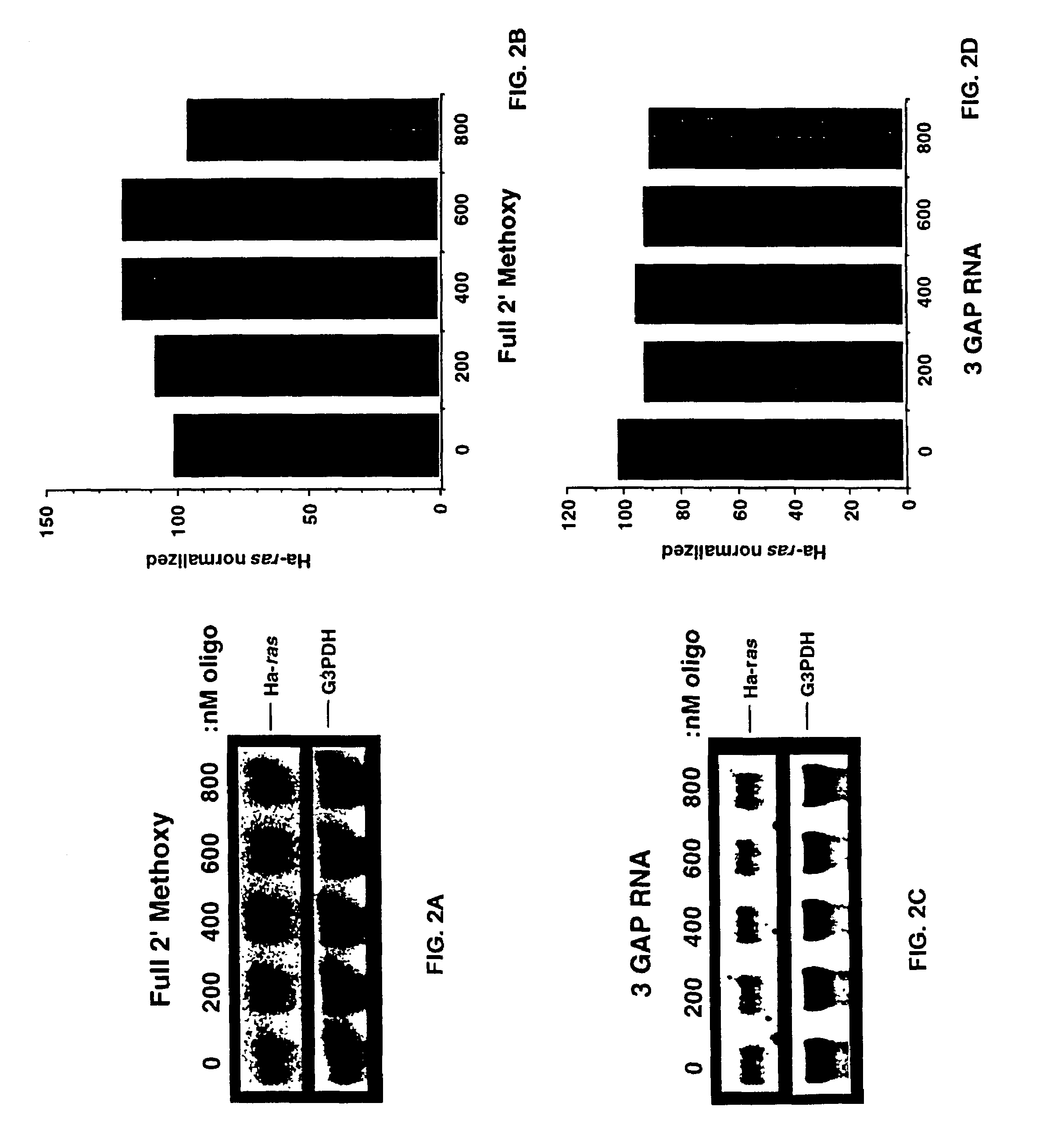
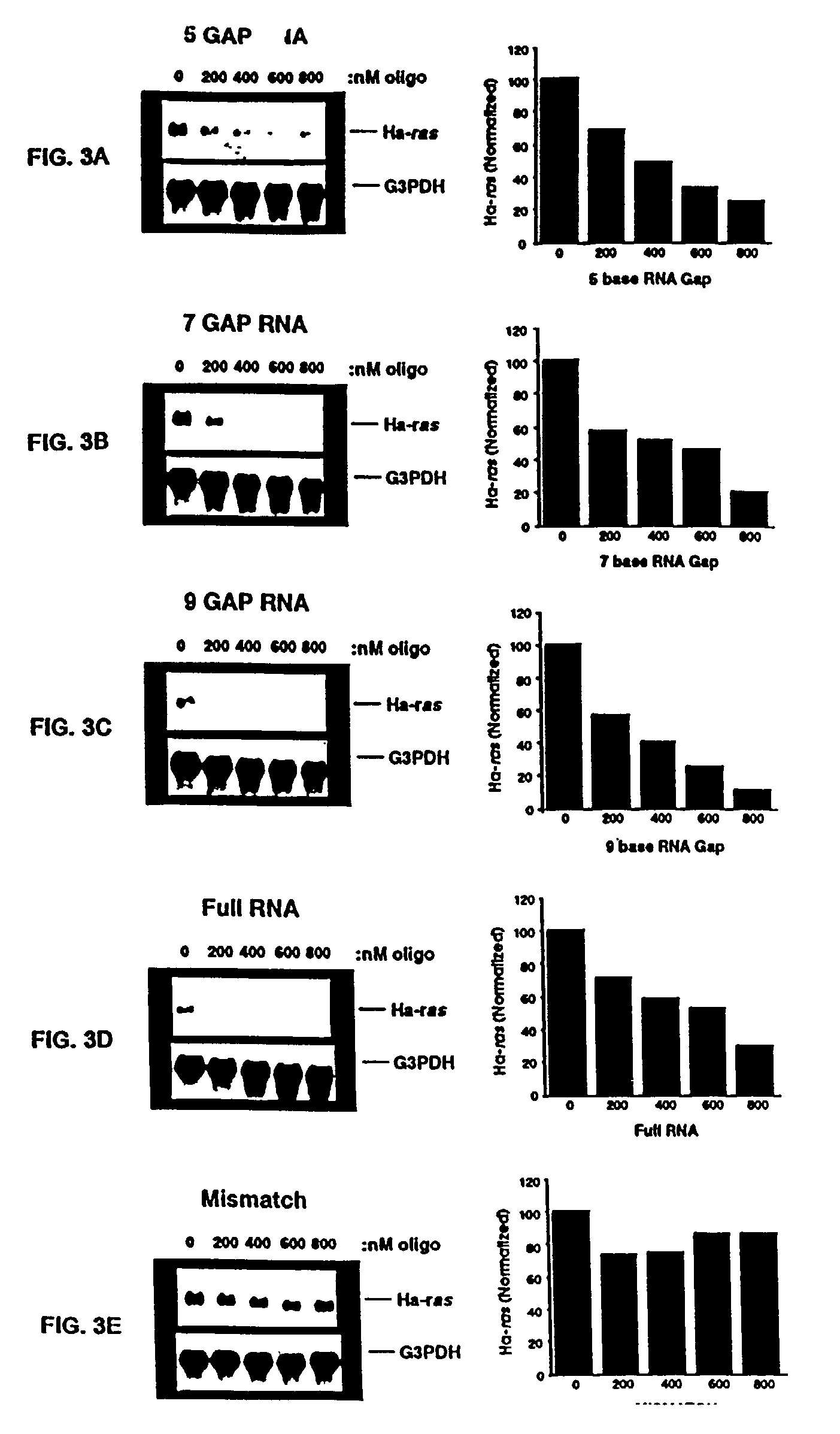
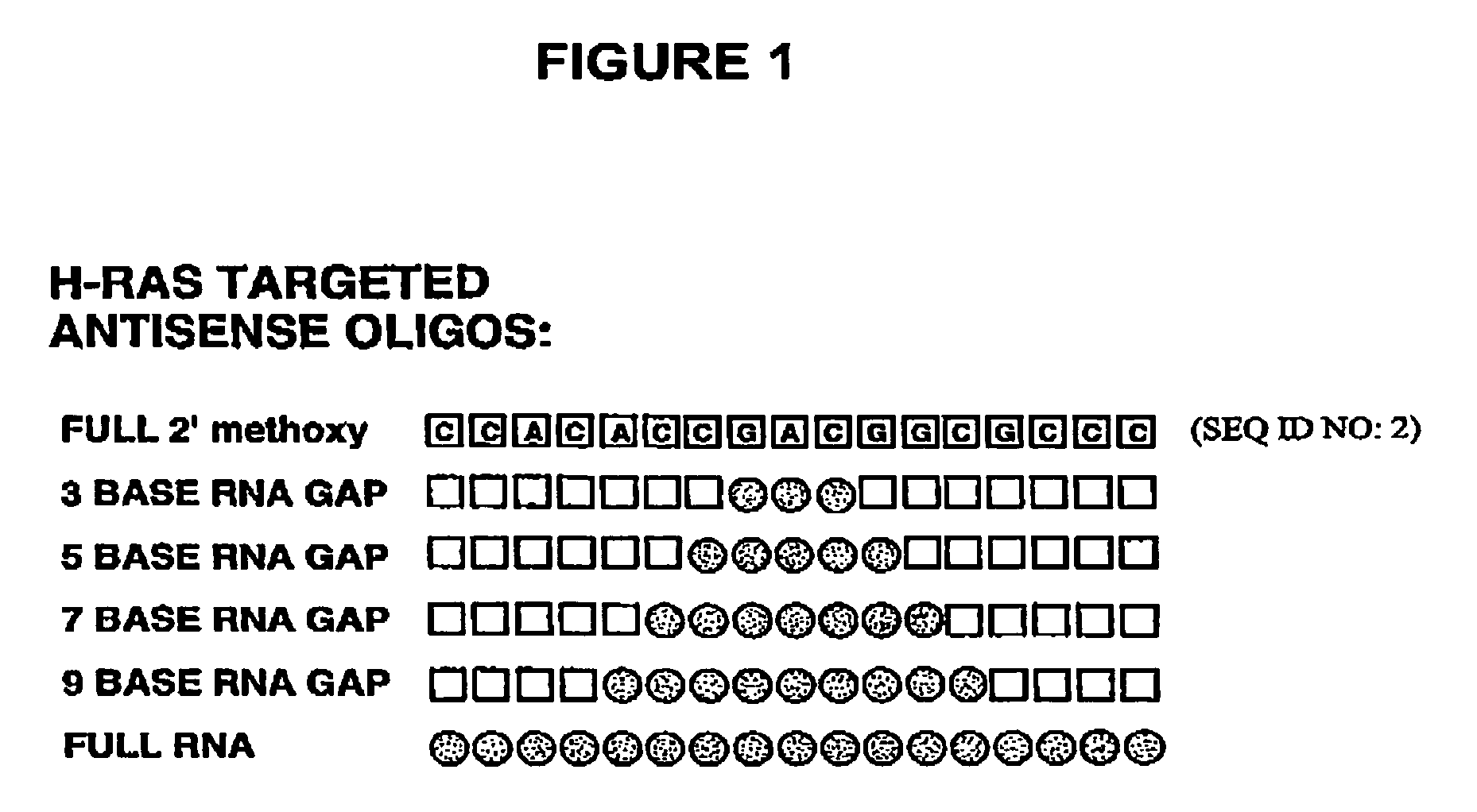
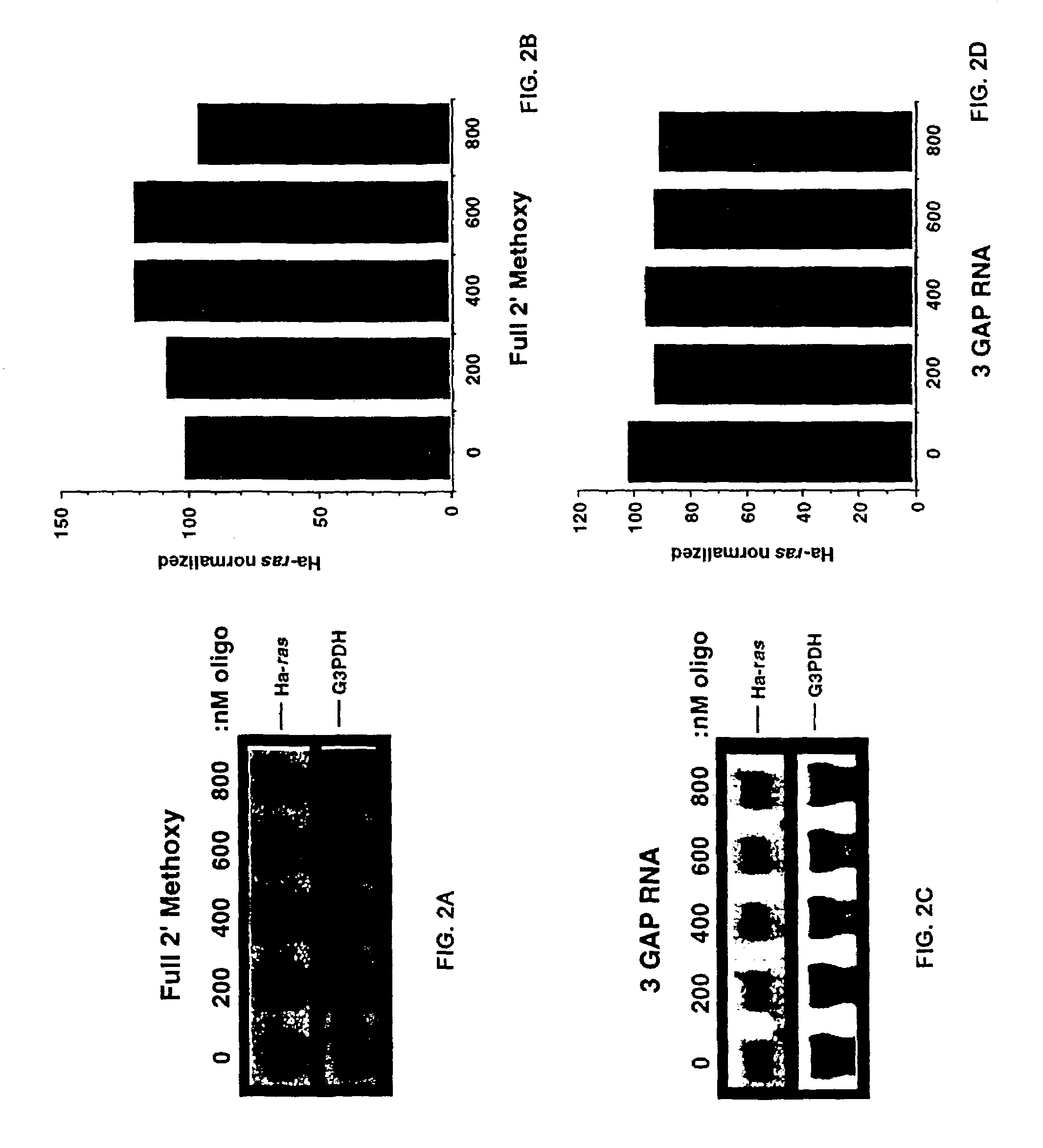
A group of ribonucleotides (up to 12) in which the phosphate residues of each ribonucleotide act as bridges in forming diester linkages between the ribose moieties.
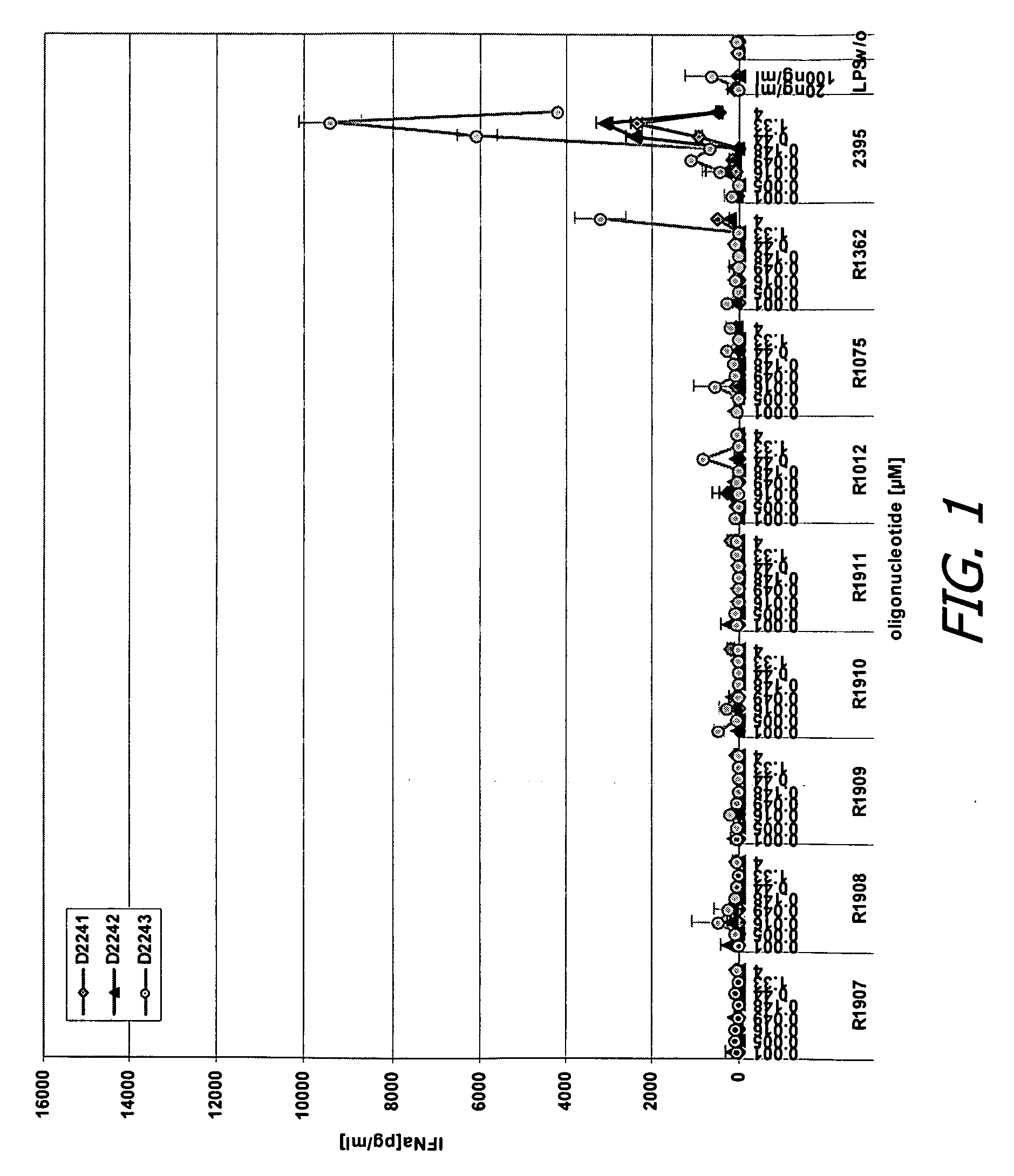
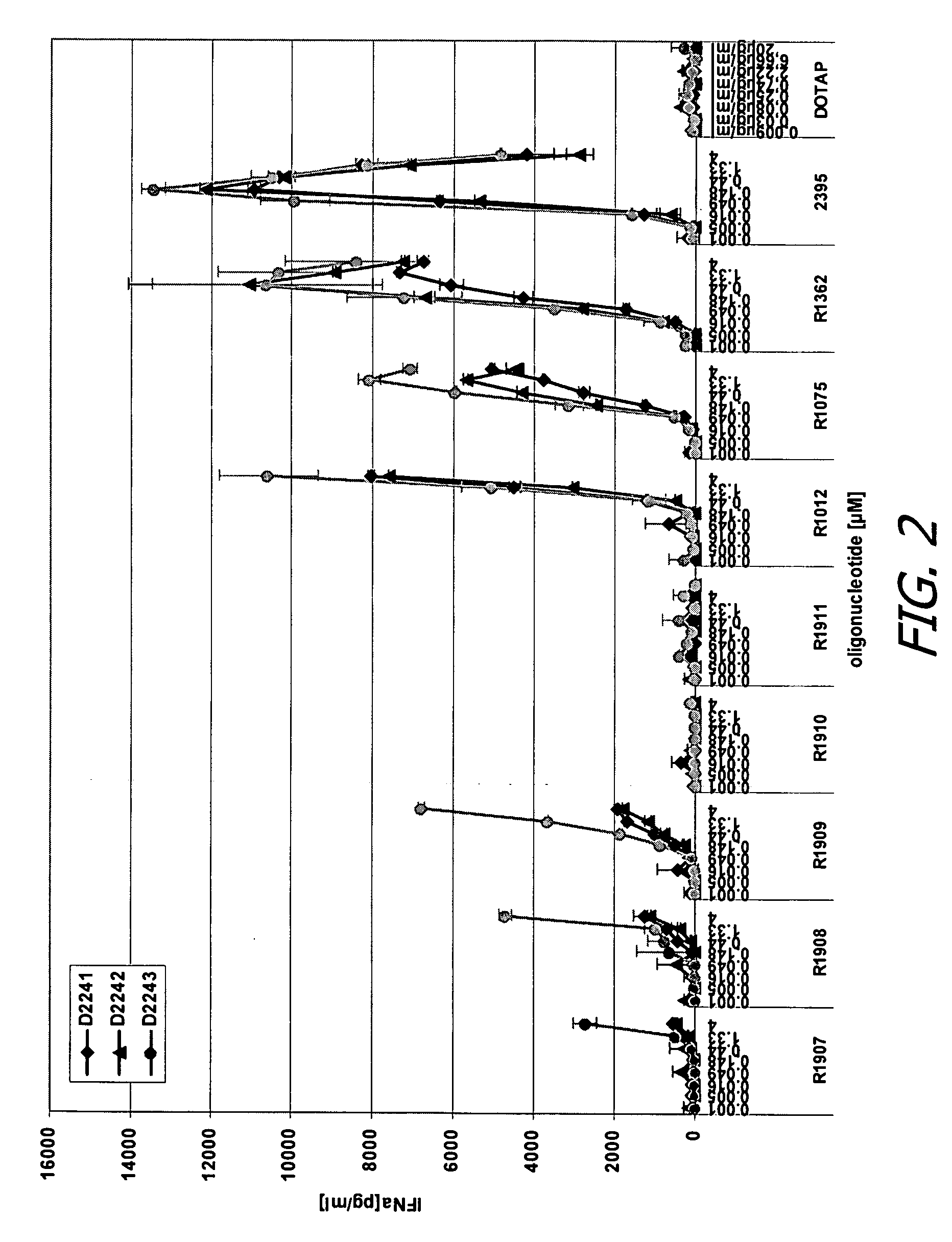
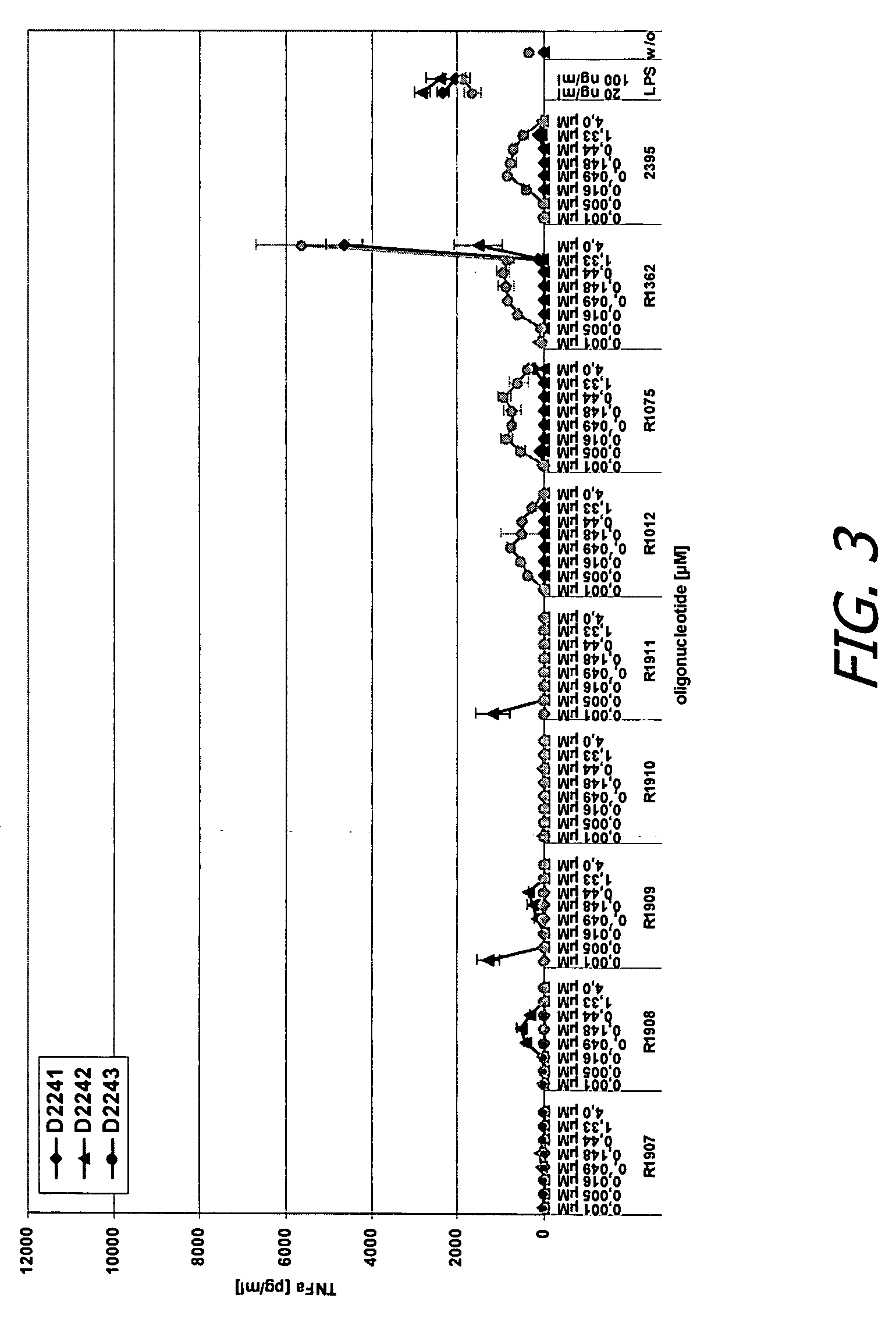
Modified oligoribonucleotide analogs with enhanced immunostimulatory activity
The invention provides immunostimulatory compositions and methods for their use. In particular, the immunostimulatory compositions of the invention include RNA-like polymers that incorporate an immunostimulatory sequence motif and at least one chemical modification to confer improved stability against nuclease degradation and improved activity. Specific modifications involving phosphate linkages, nucleotide analogs, and combinations thereof are provided. Compositions of the invention optionally include an antigen and can be used to stimulate an immune response. Also provided are compositions and methods useful for treating a subject having an infection, a cancer, an allergic condition, or asthma. Modified oligoribonucleotide analogs of the invention are believed to stimulate Toll-like receptors TLR7 and TLR8.
Owner:COLEY PHARMA GRP INC +1
Oligoribonucleotides and ribonucleases for cleaving RNA
InactiveUS7432250B2High affinityStrong specificityHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganismResearch purpose
Oligomeric compounds including oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides are provided that have subsequences of 2′-pentoribofuranosyl nucleosides that activate dsRNase. The oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides can include substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary nucleic acid strand as well as substituent groups for increasing nuclease resistance. The oligomeric compounds are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating the expression of a protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to oligonucleotide therapeutics. Also included in the invention are mammalian ribonucleases, i.e., enzymes that degrade RNA, and substrates for such ribonucleases. Such a ribonuclease is referred to herein as a dsRNase, wherein “ds” indicates the RNase's specificity for certain double-stranded RNA substrates. The artificial substrates for the dsRNases described herein are useful in preparing affinity matrices for purifying mammalian ribonuclease as well as non-degradative RNA-binding proteins.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Oligoribonucleotides and ribonucleases for cleaving RNA
InactiveUS7432249B2High affinityStrong specificityPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesADAMTS ProteinsOrganism
Oligomeric compounds including oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides are provided that have subsequences of 2′-pentoribofuranosyl nucleosides that activate dsRNase. The oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides can include substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary nucleic acid strand as well as substituent groups for increasing nuclease resistance. The oligomeric compounds are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating the expression of a protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to oligonucleotide therapeutics. Also included in the invention are mammalian ribonucleases, i.e., enzymes that degrade RNA, and substrates for such ribonucleases. Such a ribonuclease is referred to herein as a dsRNase, wherein “ds” indicates the RNase's specificity for certain double-stranded RNA substrates. The artificial substrates for the dsRNases described herein are useful in preparing affinity matrices for purifying mammalian ribonuclease as well as non-degradative RNA-binding proteins.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Oligoribonucleotides and ribonucleases for cleaving RNA
InactiveUS7629321B2High affinityStrong specificityHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsOrganismResearch purpose
Oligomeric compounds including oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides are provided that have subsequences of 2′-pentoribofuranosyl nucleosides that activate dsRNase. The oligoribonucleotides and oligoribonucleosides can include substituent groups for increasing binding affinity to complementary nucleic acid strand as well as substituent groups for increasing nuclease resistance. The oligomeric compounds are useful for diagnostics and other research purposes, for modulating the expression of a protein in organisms, and for the diagnosis, detection and treatment of other conditions susceptible to oligonucleotide therapeutics. Also included in the invention are mammalian ribonucleases, i.e., enzymes that degrade RNA, and substrates for such ribonucleases. Such a ribonuclease is referred to herein as a dsRNase, wherein “ds” indicates the RNase's specificity for certain double-stranded RNA substrates. The artificial substrates for the dsRNases described herein are useful in preparing affinity matrices for purifying mammalian ribonuclease as well as non-degradative RNA-binding proteins.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
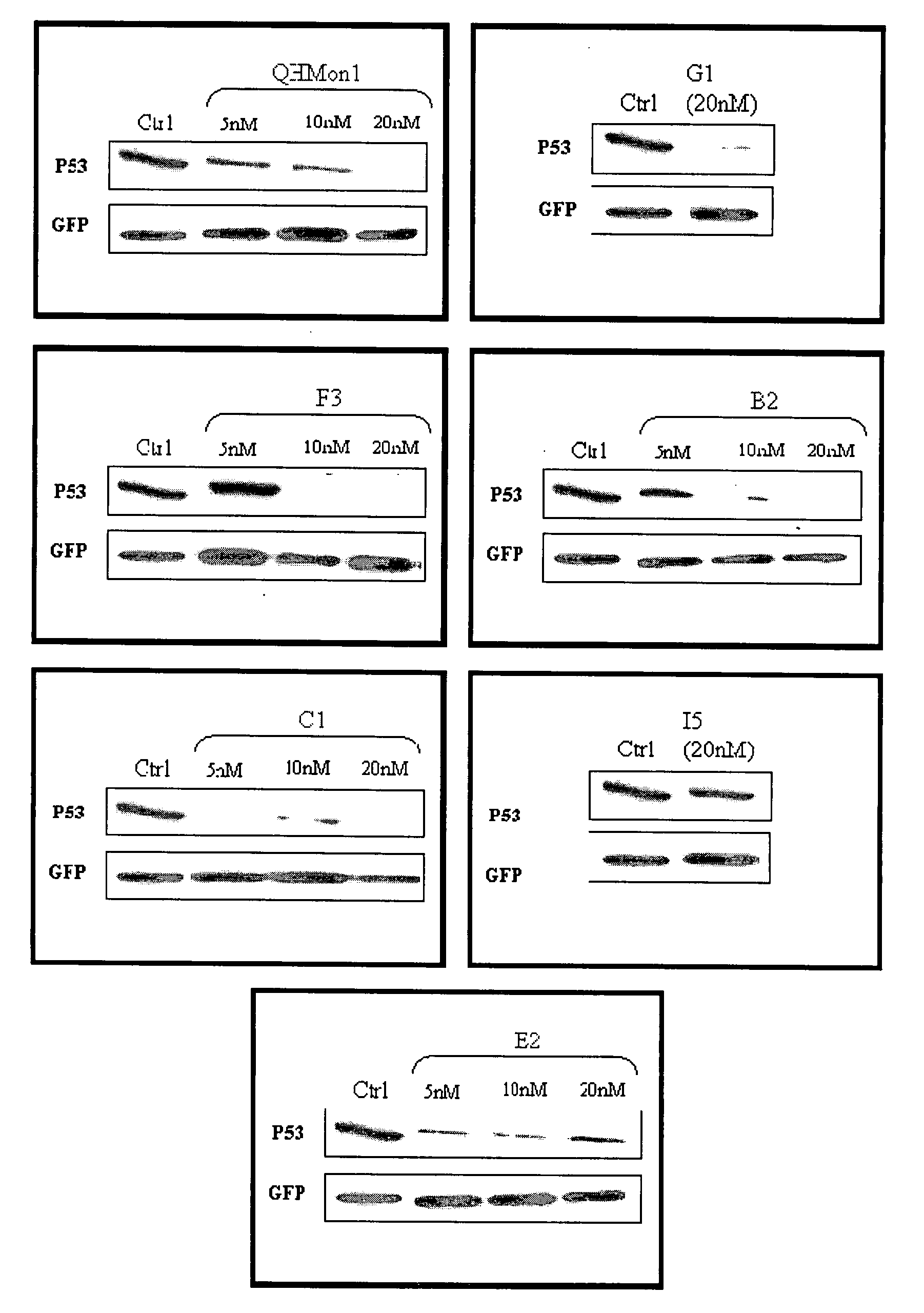
Oligoribonucleotides and methods of use thereof for treatment of alopecia, acute renal failure and other diseases
ActiveUS20060069056A1Increased riskImprove the level ofSenses disorderNervous disorderOligoribonucleotidesARF - Acute renal failure
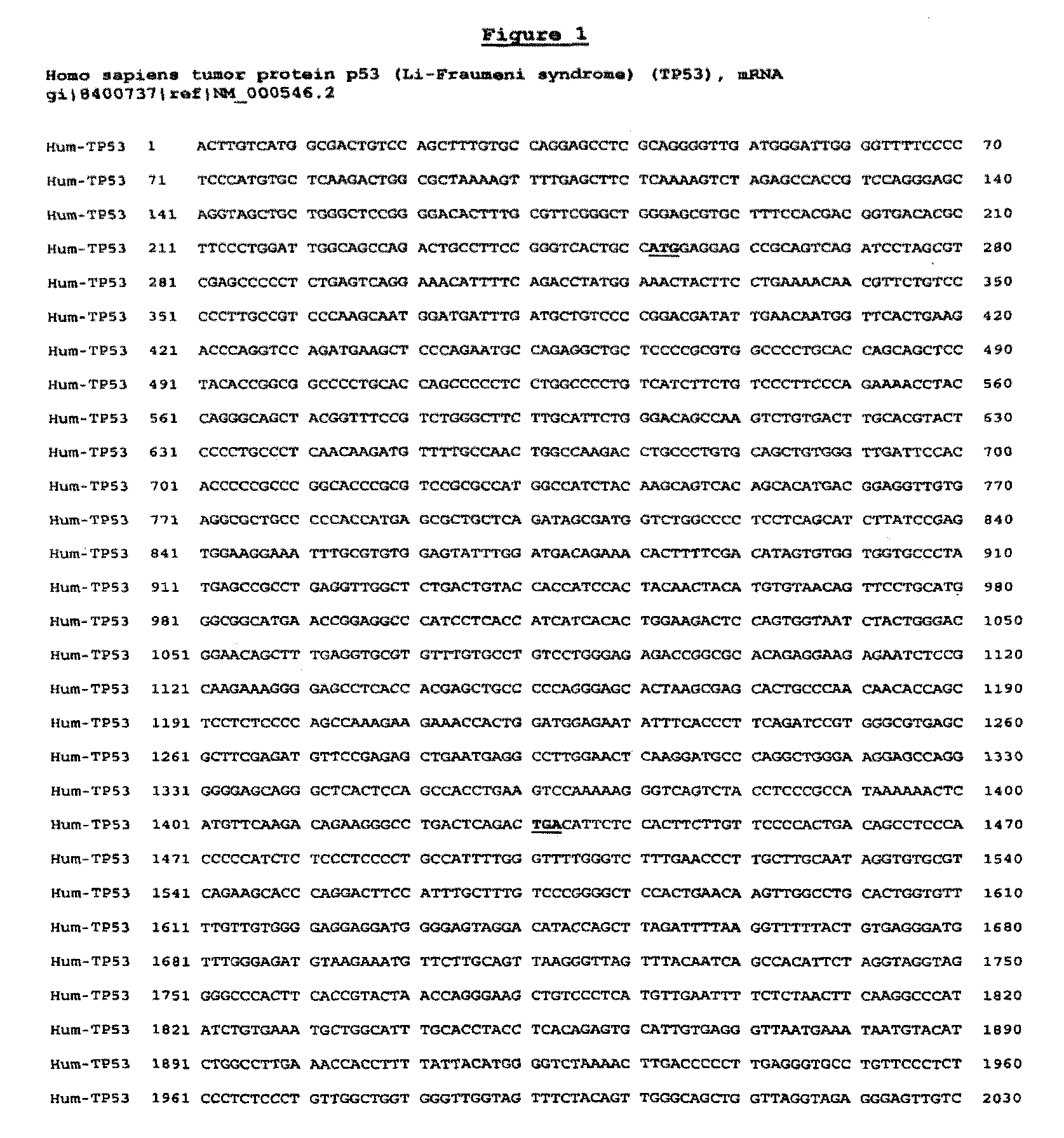
The invention relates to a double-stranded compound, preferably an oligoribonucleotide, which down-regulates the expression of a human p53 gene. The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the compound, or a vector capable of expressing the oligoribonucleotide compound, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention also contemplates a method of treating a patient suffering from alopecia or acute renal failure or other diseases comprising administering to the patient the pharmaceutical composition in a therapeutically effective dose so as to thereby treat the patient. The alopecia may be induced by chemotherapy or radiotherapy, and the patient may be suffering from cancer, in particular breast cancer.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
2'-O-alkylated oligoribonucleotides and phosphorothioate analogs complementary to portions of the HIV genome
InactiveUS6034233ARelieve symptomsSure easySugar derivativesVirus peptidesOligoribonucleotidesGenome
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
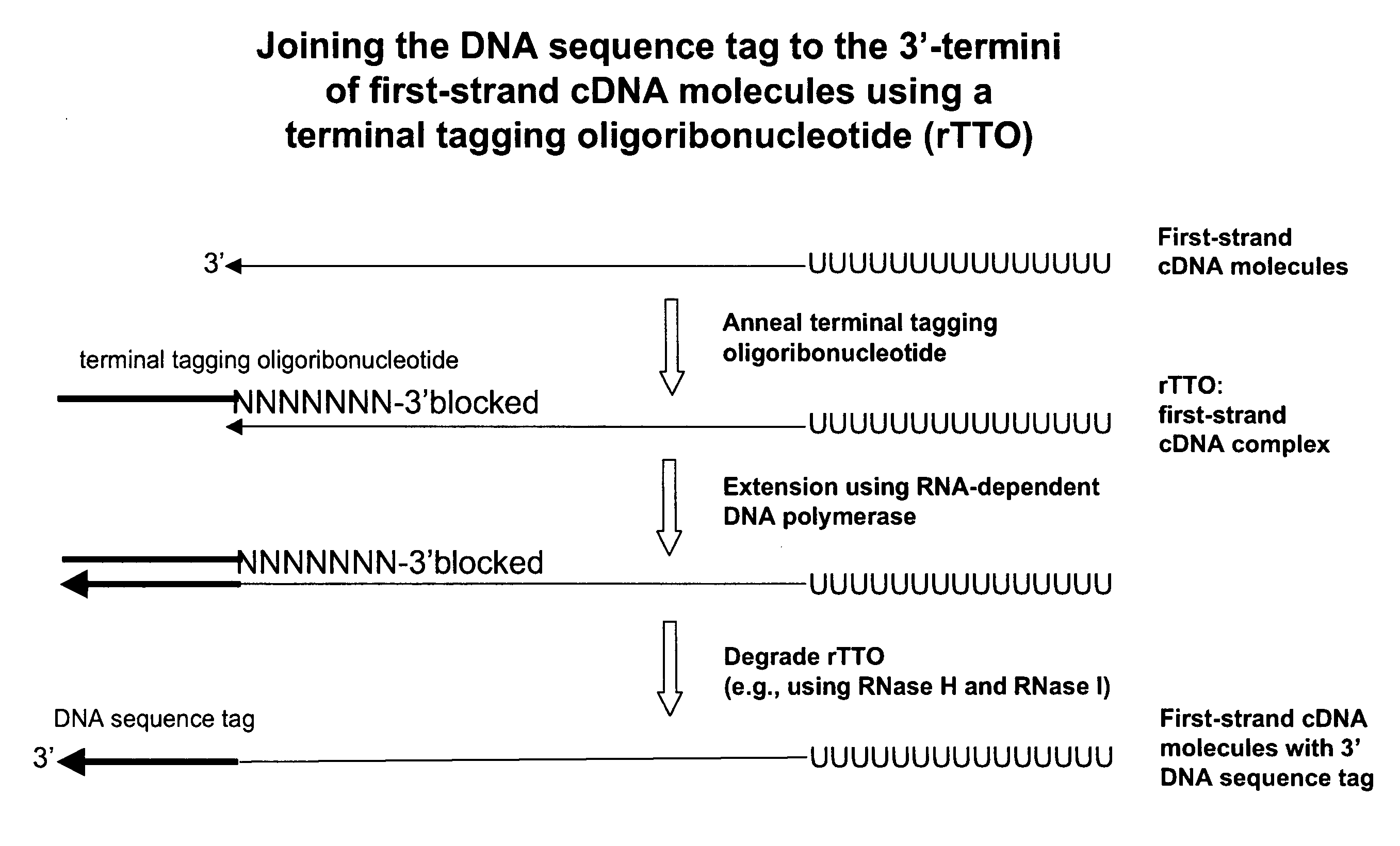
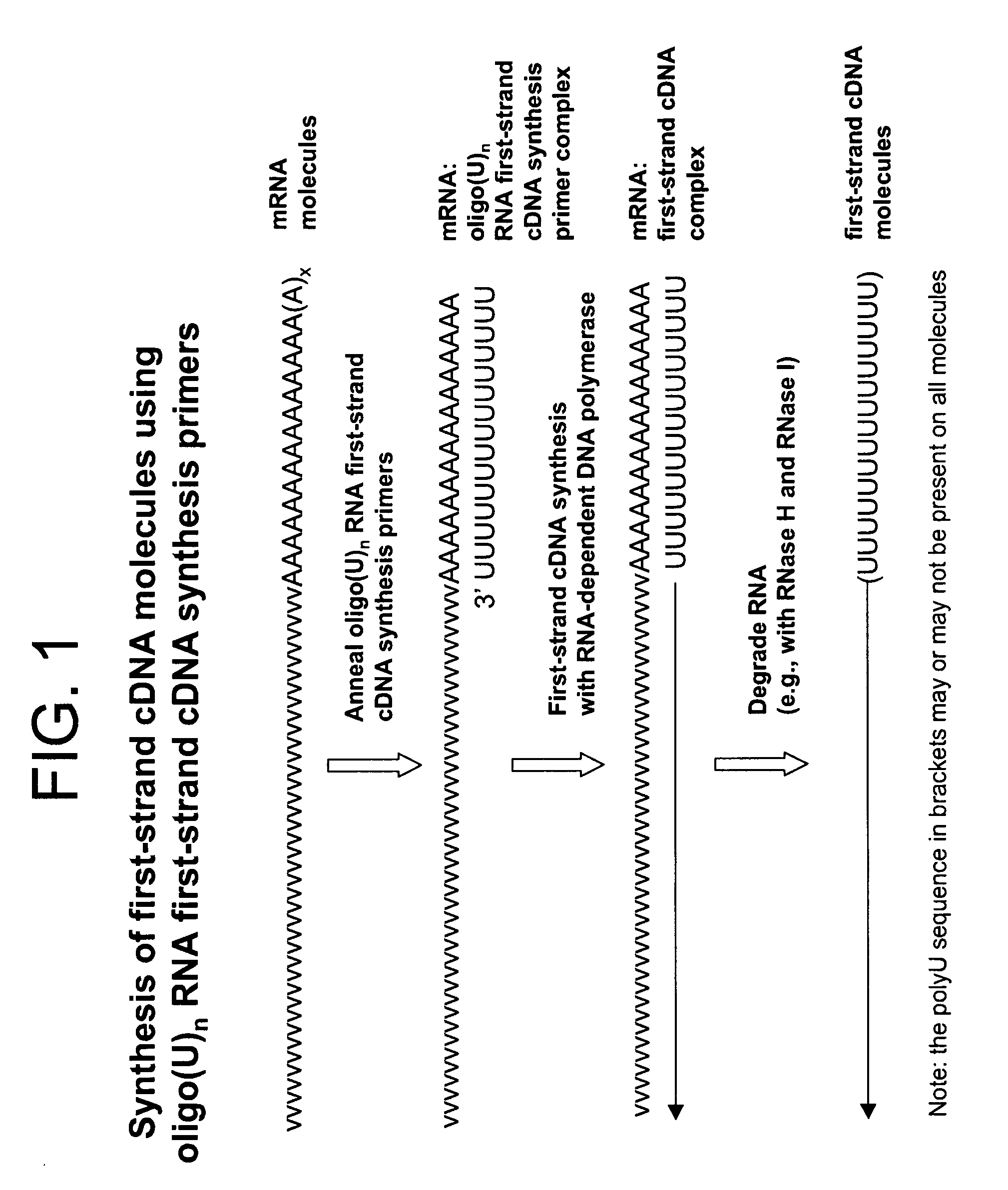
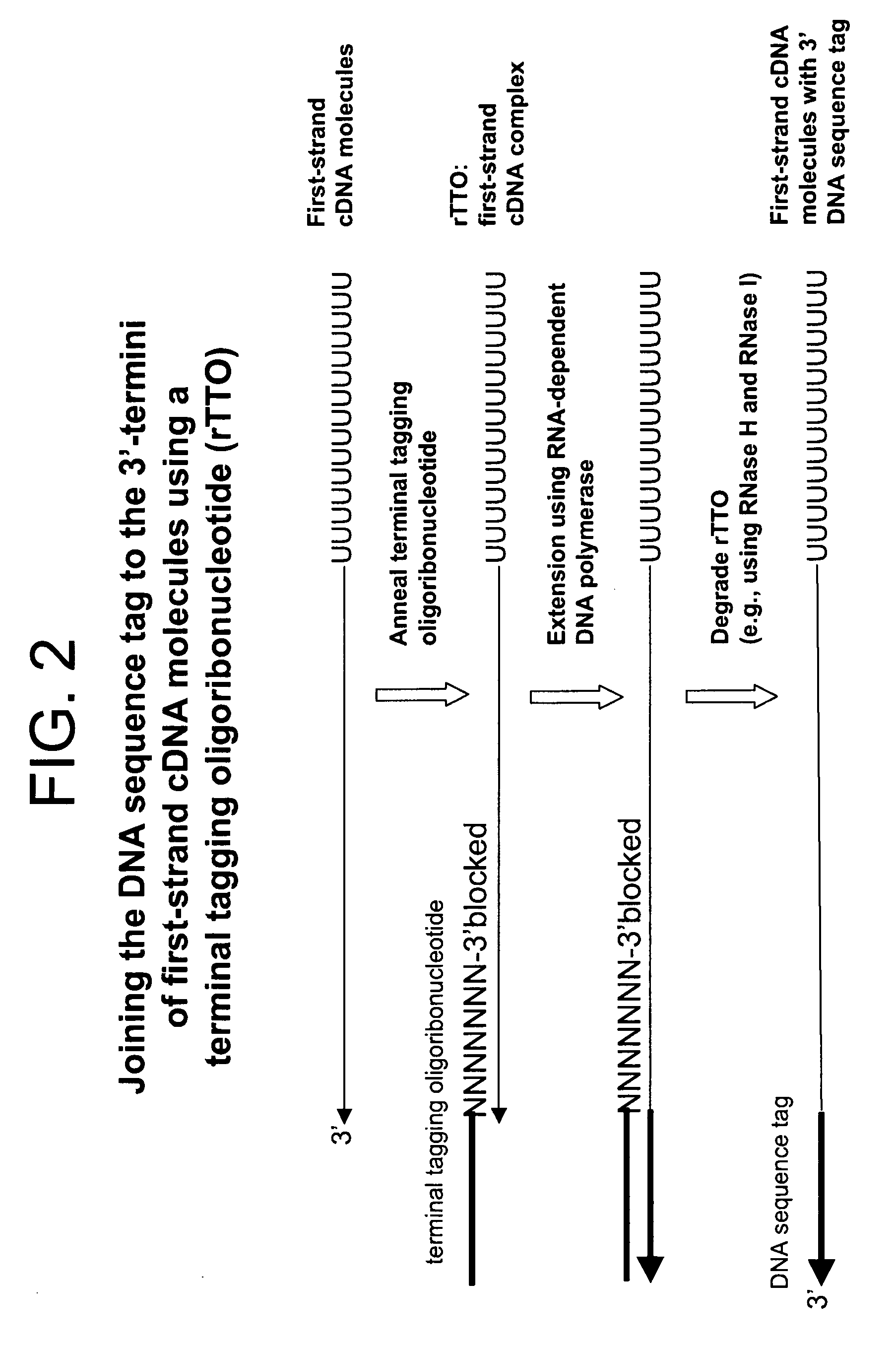
Synthesis of tagged nucleic acids
ActiveUS8039214B2Reduce in quantityGood removal effectMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesOligoribonucleotidesRibonucleotide synthesis
The present invention relates generally to methods, compositions and kits for synthesizing sense RNA molecules from one or more RNA molecules of interest in a sample. In exemplary embodiments, the methods use a terminal tagging oligoribonucleotide (rTTO) to join a DNA sequence tag to the 3′-termini of first-strand cDNA molecules. The use of an rTTO comprising ribonucleotides results in decreased oligonucleotide-derived background synthesis of RNA in the absence of sample RNA and, surprisingly and unexpectedly, also results in significantly increased yields of sense RNA molecules that exhibit sequences that are substantially identical to those of the RNA molecules of interest in the sample. The sense RNA molecules also have an RNA sequence tag on their 5′-termini that is useful for fixing the lengths of sense RNA molecules that are synthesized in a second or subsequent round.
Owner:CELLSCRIPT
Prevention and treatment of acute renal failure and other kidney diseases by inhibition of p53 by siRNA
InactiveUS20090105173A1Increased riskPrevent ototoxicitySugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseEprotirome
The invention relates to a double-stranded compound, preferably an oligoribonucleotide, which down-regulates the expression of a human p53 gene. The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the compound, or a vector capable of expressing the oligoribonucleotide compound, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention also contemplates a method of treating a patient suffering from acute renal failure or other kidney diseases comprising administering to the patient the pharmaceutical composition in a therapeutically effective dose so as to thereby treat the patient.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
Oligoribonucleotides and methods of use thereof for treatment of alopecia, acute renal failure and other diseases
ActiveUS20080287382A1Increased riskImprove the level ofOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderRadical radiotherapyDisease cause
The invention relates to a double-stranded compound, preferably an oligoribonucleotide, which down-regulates the expression of a human p53 gene. The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the compound, or a vector capable of expressing the oligoribonucleotide compound, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention also contemplates a method of treating a patient suffering from alopecia or acute renal failure or other diseases comprising administering to the patient the pharmaceutical composition in a therapeutically effective dose so as to thereby treat the patient. The alopecia may be induced by chemotherapy or radiotherapy, and the patient may be suffering from cancer, in particular breast cancer.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
Methods of treatment of acute renal failure
ActiveUS20090082291A1Increased riskImprove the level ofOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseOligoribonucleotides
The invention relates to a double-stranded compound, preferably an oligoribonucleotide, which down-regulates the expression of a human p53 gene. The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the compound, or a vector capable of expressing the oligoribonucleotide compound, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention also contemplates a method of treating a patient suffering from alopecia or acute renal failure or other diseases comprising administering to the patient the pharmaceutical composition in a therapeutically effective dose so as to thereby treat the patient. The alopecia may be induced by chemotherapy or radiotherapy, and the patient may be suffering from cancer, in particular breast cancer.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
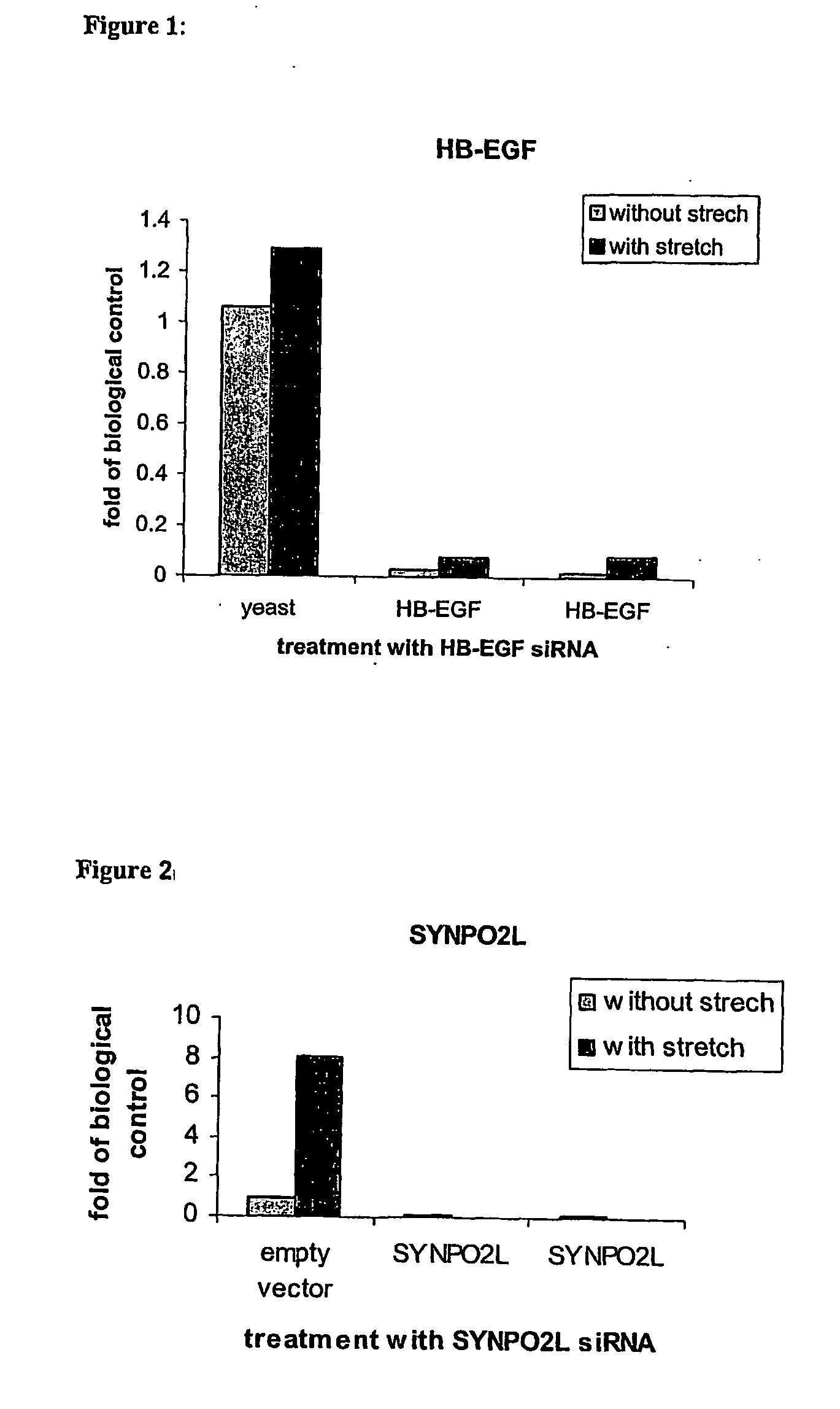
Oligoribonucleotides and Methods of use Thereof for Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease
InactiveUS20100035963A1Organic active ingredientsSugar derivativesOligoribonucleotidesVascular disease
The invention relates to a double-stranded compound, preferably an oligoribonucleotide, which down-regulates the expression of one or more cardiovascular-related gene. The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the compound, or a vector capable of expressing the oligoribonucleotide compound, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention also contemplates a method of treating a patient suffering from a cardiovascular disorder or other diseases comprising administering to the patient the pharmaceutical composition in a therapeutically effective dose so as to thereby treat the patient.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
Modified polynucleotides and uses thereof
InactiveUS6867290B2Improve stabilityReduce potential blockSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligoribonucleotidesPolyribonucleotides
Provided is a polynucleotide comprising mRNA, rRNA or viral RNA, comprising ribose rings that are covalently modified at the 2′-OH position. Further provided are methods for producing a double-stranded oligo- or polynucleotide from a template comprising an oligo- or polyribonucleotide, a proportion of the ribose rings of which are covalently modified at the 2′-OH position to bear a substituent which enables replication of the template by the nucleic acid polymerase. Also provided is use of a poly-nucleotide comprising mRNA, rRNA or viral RNA, a proportion of the ribose rings of which are covalently modified at the 2′-OH position, in a hybridisation reaction.
Owner:CYCLOPS GENOME SCI
Spinal muscular atrophy treatment via targeting smn2 catalytic core
ActiveUS20110269820A1Increase productionEasy to useOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationOligoribonucleotidesPrecursor mRNA
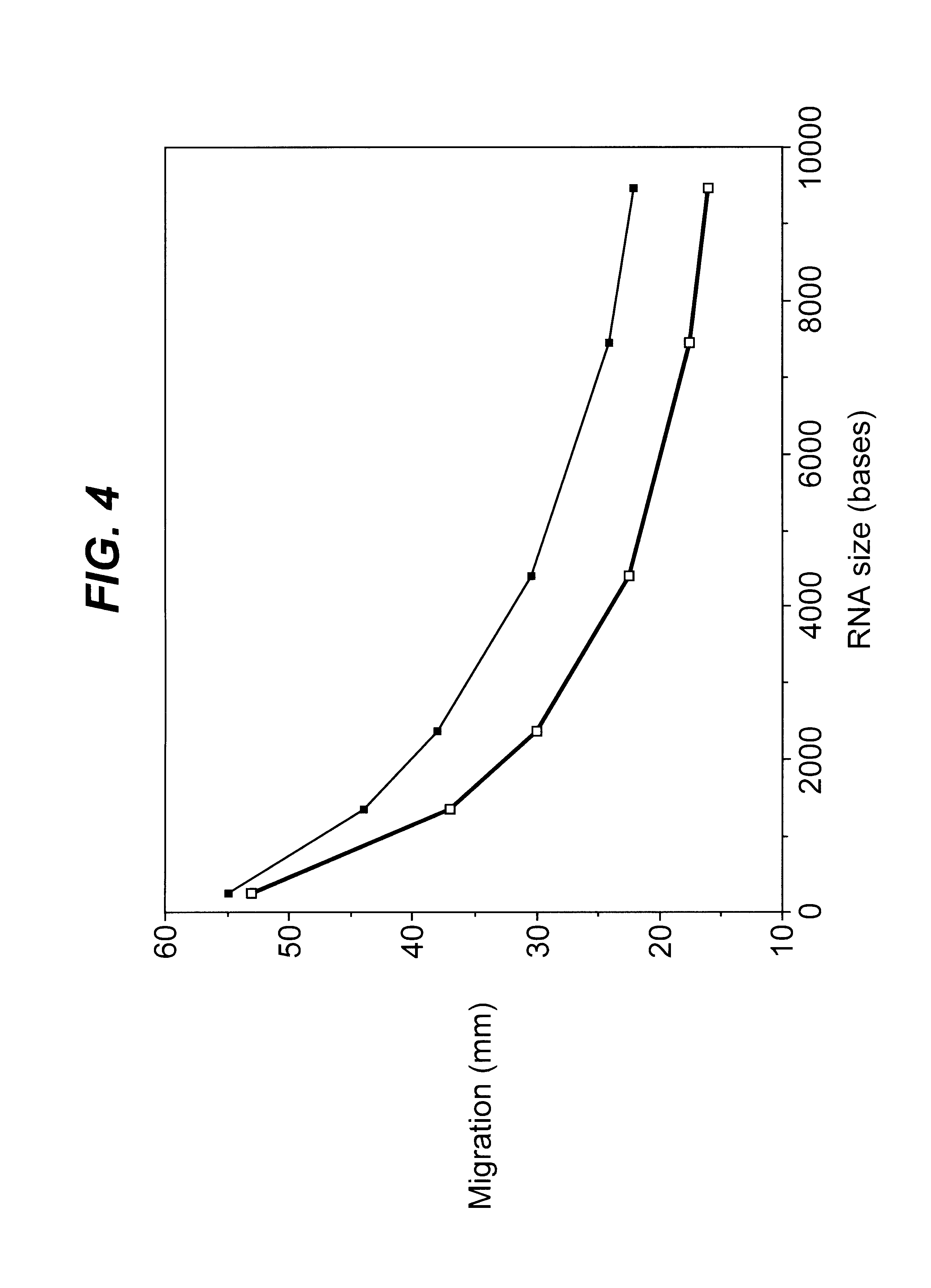
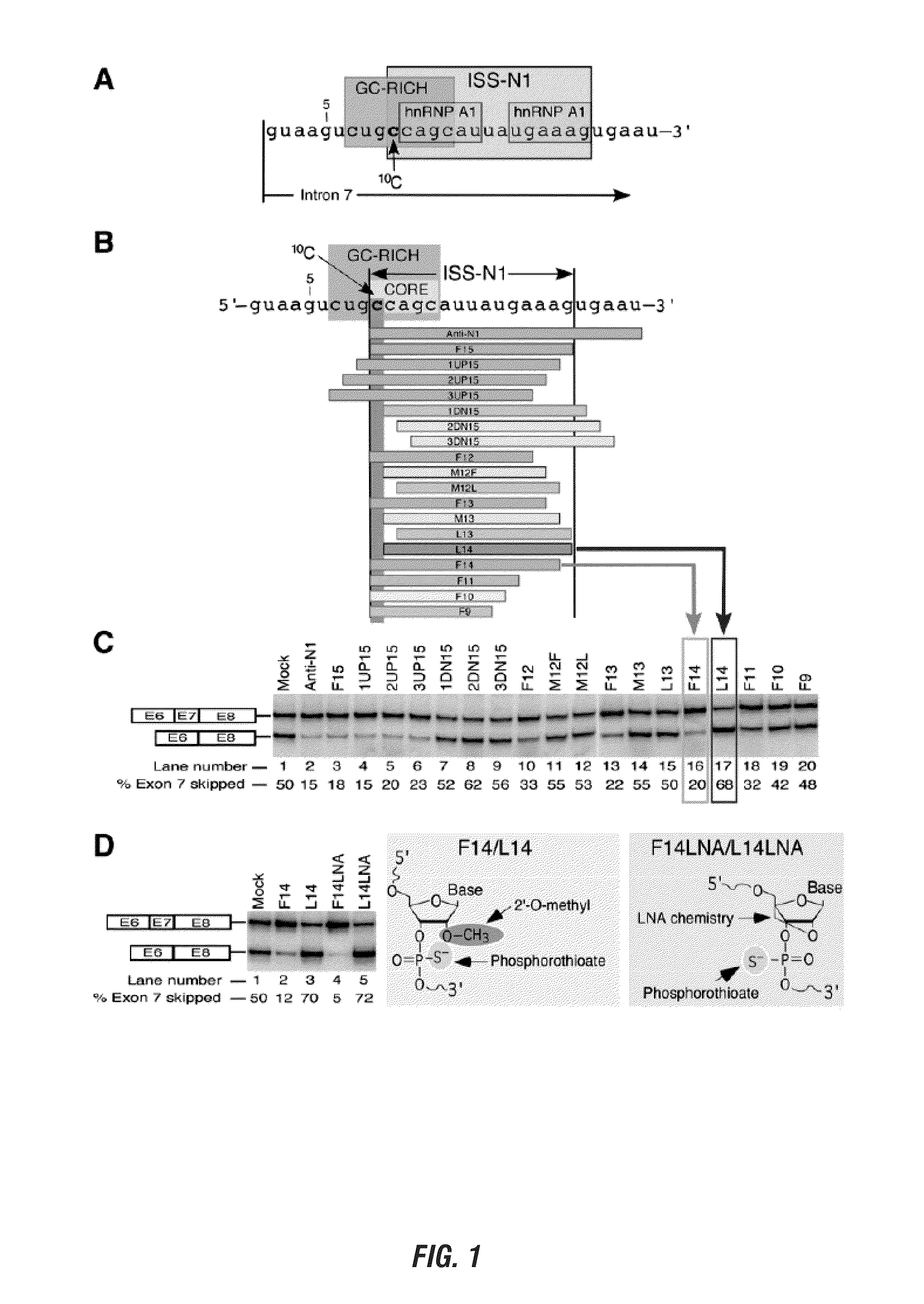
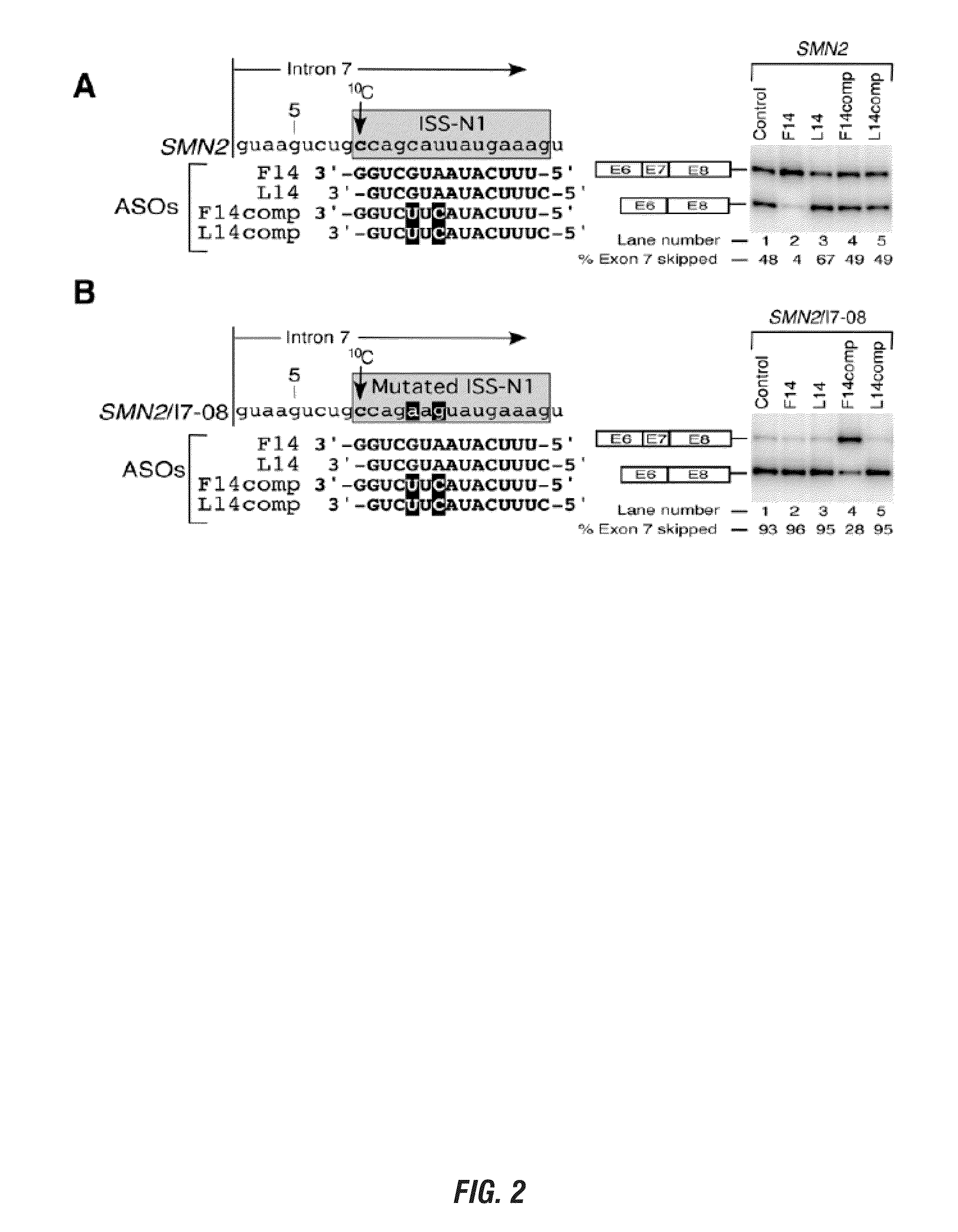
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for blocking the effect of the intronic inhibitory splicing region of intron 7 of the SMN2 gene. The compositions and methods of the instant invention include short oligonucleotide reagents (e.g., oligoribonucleotides) that effectively target sites in the SMN2 pre-mRNA, thereby modulating the splicing of SMN2 pre-mRNA to include exon 7 in the processed transcript. The short target regions are 8-mers and 5-mers and also include the identification of a single nucleotide base that is essential for initiating a long distance stearic inhibitory interactions as well as novel targets distant from intron 7 which block the intronic inhibitory splicing of the same. These short target regions and concomitant inhibitory blocking oligonucleotides are less expensive and easier to manufacture and are small enough to cross the blood brain barrier.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
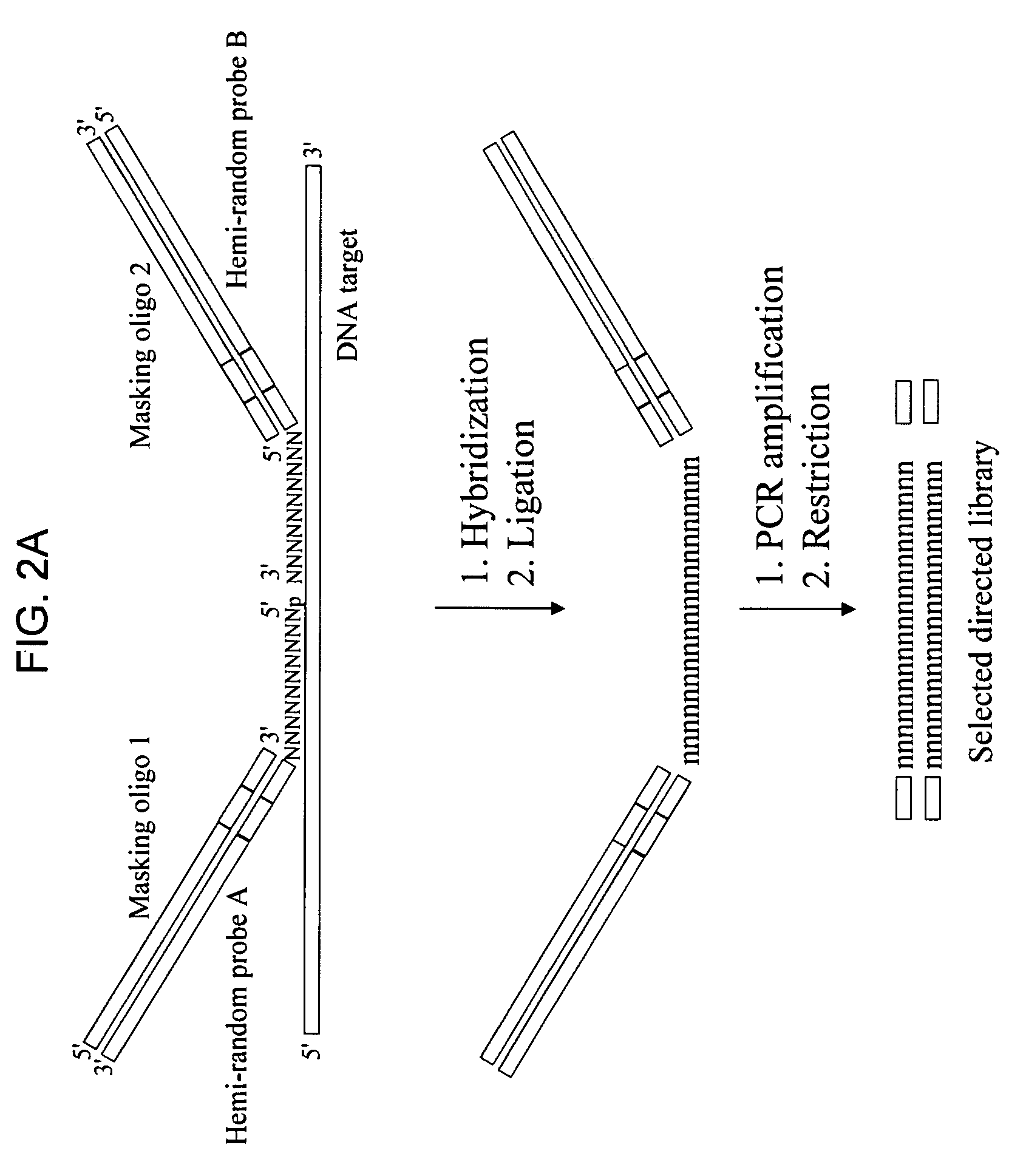
Methods of preparation of gene-specific oligonucleotide libraries and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060051789A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationOligoribonucleotidesRibonuclease
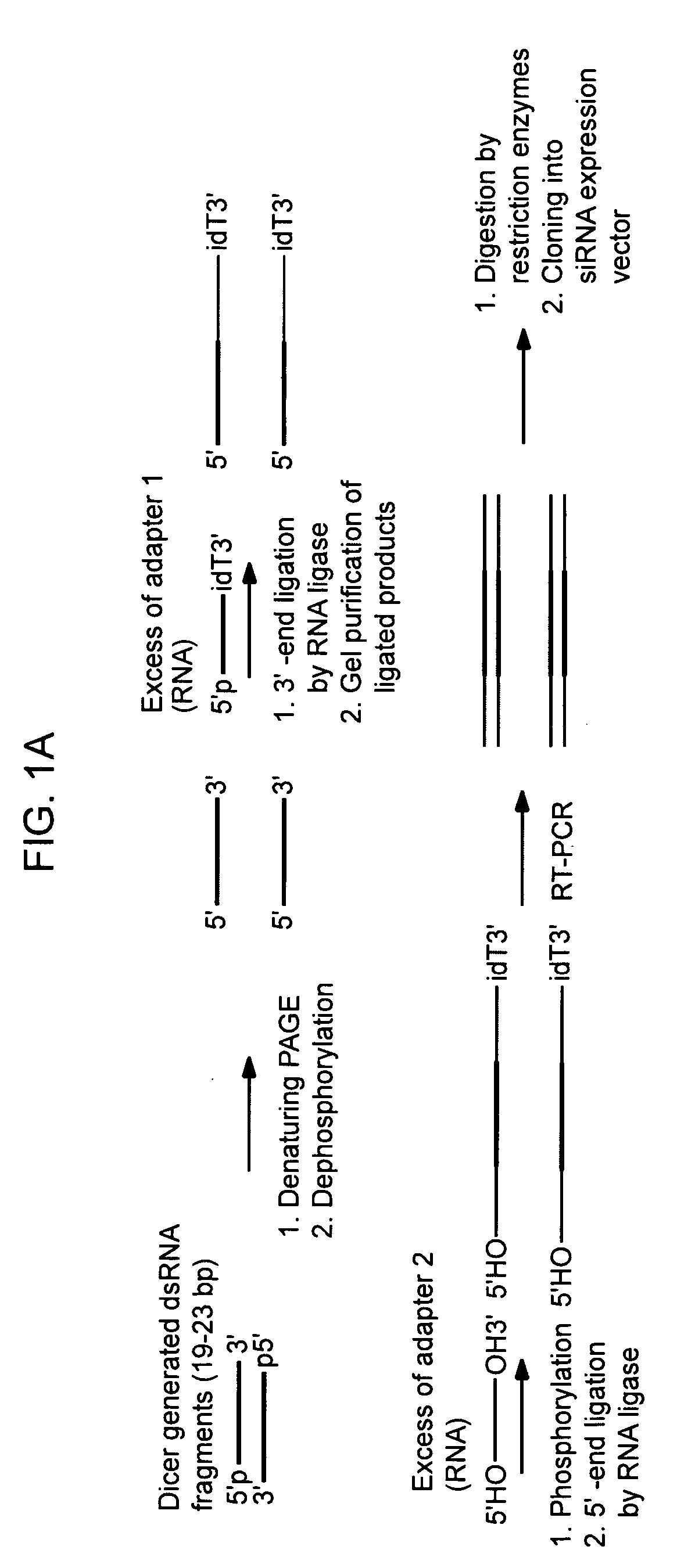
Methods of preparing gene-specific oligonucleotide libraries are disclosed. In one embodiment a double-stranded RNA corresponding to both sense and antisense strands of mRNA is digested by ribonuclease to produce short RNA fragments. In subsequent ligation steps, flanking oligoribonucleotides of defined sequences may be attached to the 3- and 5-ends of each fragment by RNA ligase (such as T4 RNA ligase). The products of ligation can be reverse transcribed and PCR amplified (RT-PCR) using the oligonucleotides attached to the gene-derived sequences as primer-binding sites. Various methods for incorporating libraries into expression vectors allowing expression of either siRNAs or shRNAs are also disclosed.
Owner:SOMAGENICS INC
Synthetic rna-based agonists of tlr7
The invention relates to the therapeutic use of novel stabilized oligoribonucleotides as immune modulatory agents for immune therapy applications. Specifically, the invention provides novel RNA-based oligoribonucleotides with improved nuclease and RNase stability and that selectively induce immune modulatory activity through TLR7.
Owner:IDERA PHARMA INC
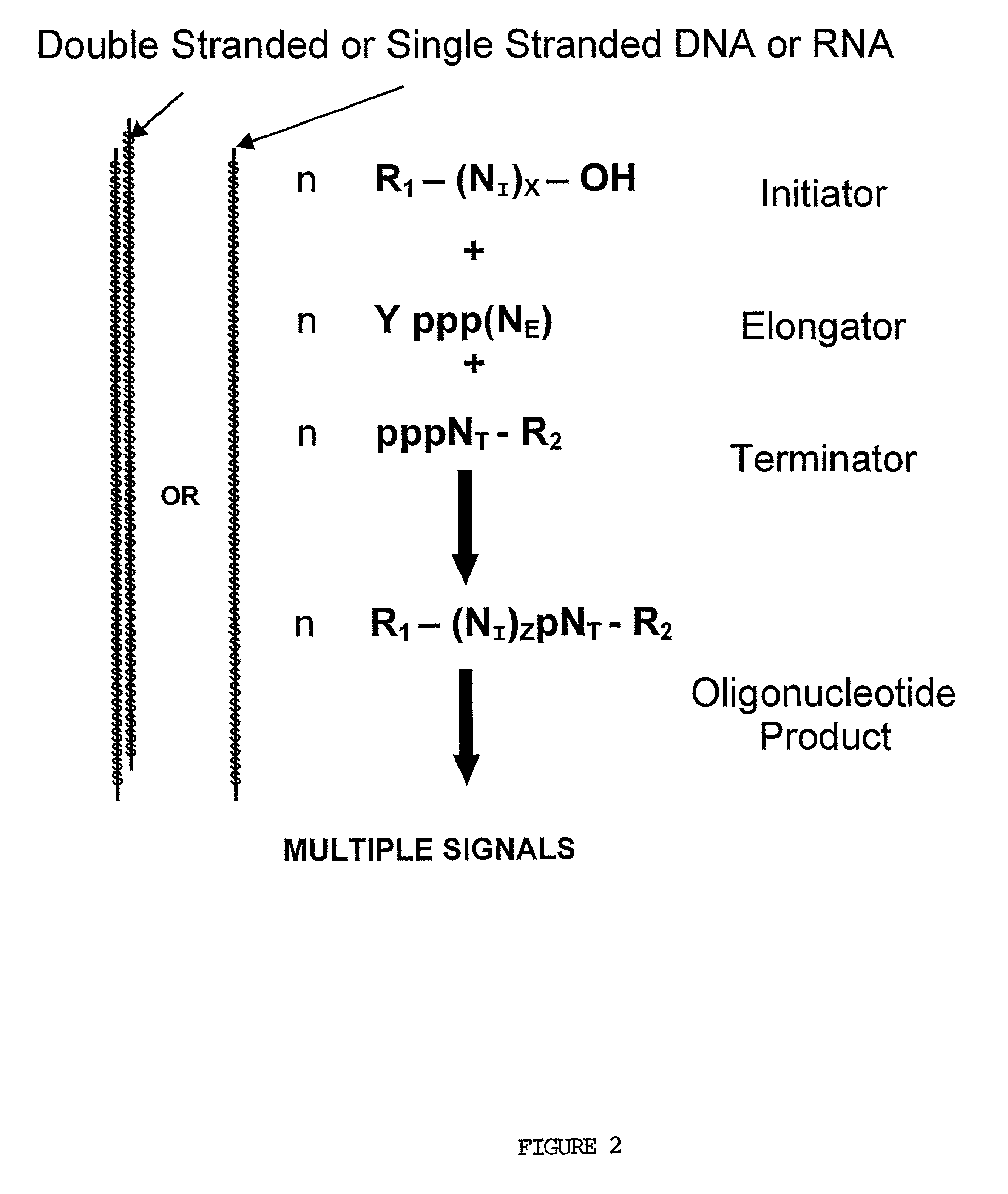
Molecular detection systems utilizing reiterative oligonucleotide synthesis
InactiveUS7045319B2Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationOligoribonucleotidesProtein target
Owner:RIBOMED BIOTECHNOLOGIES INC
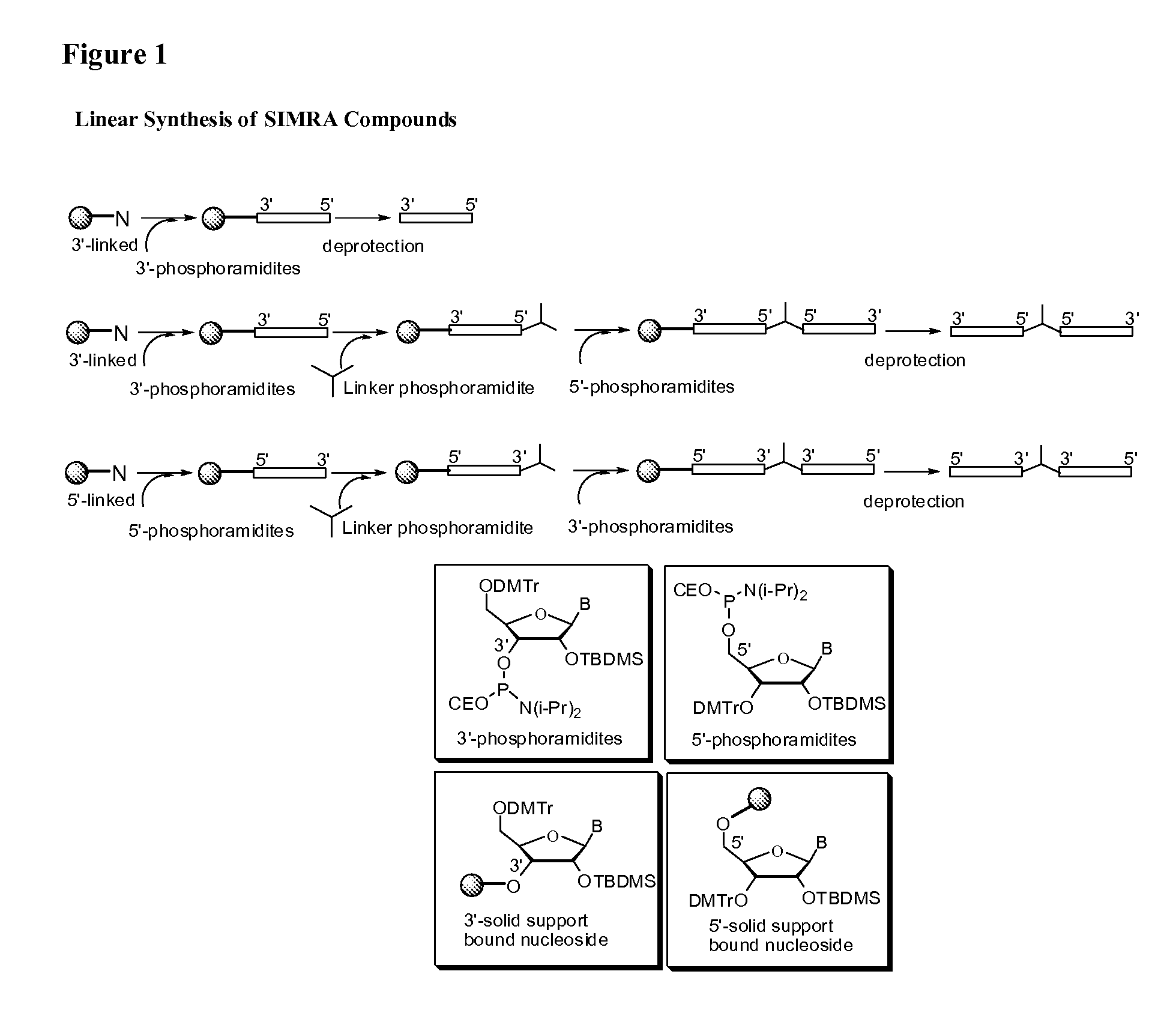
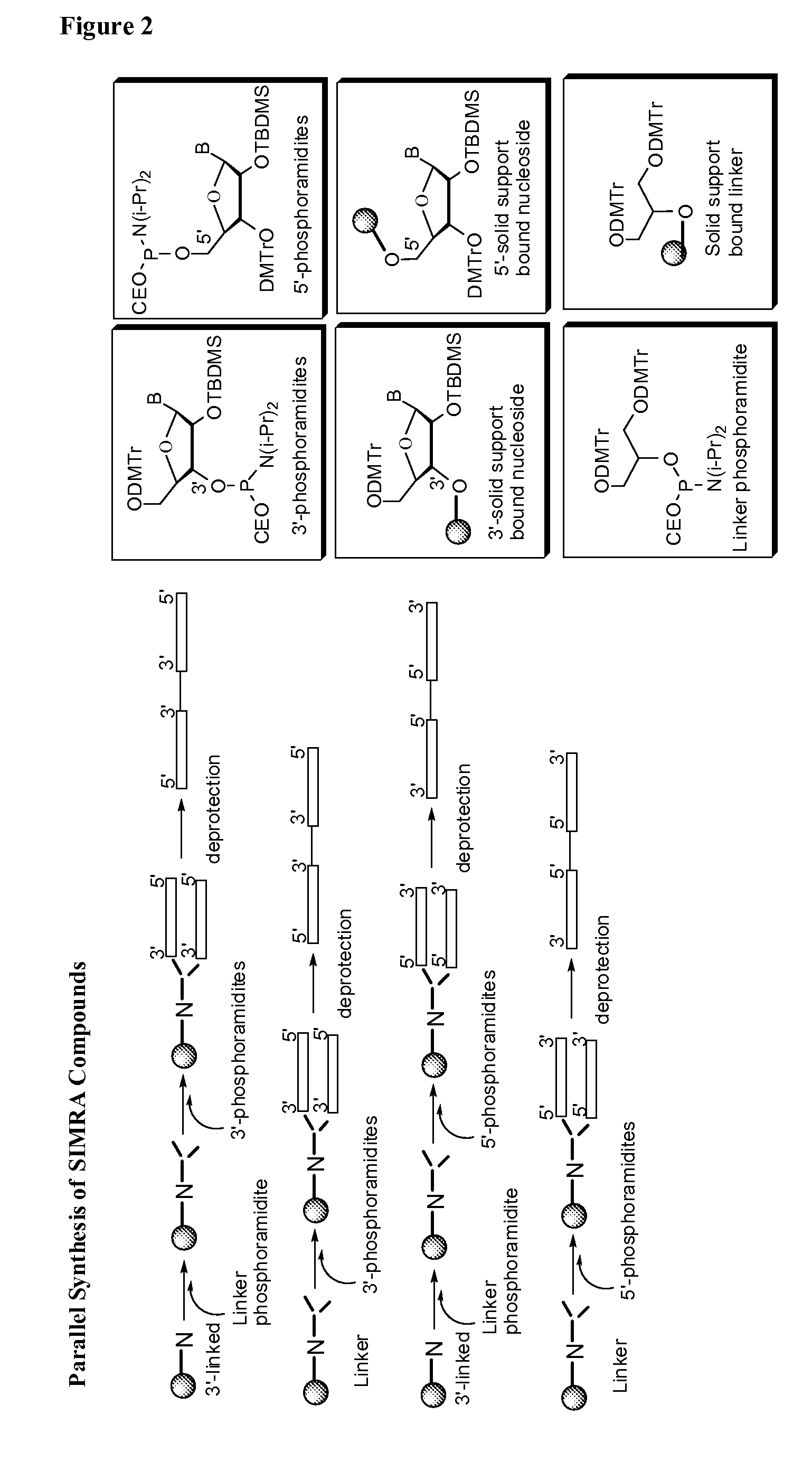
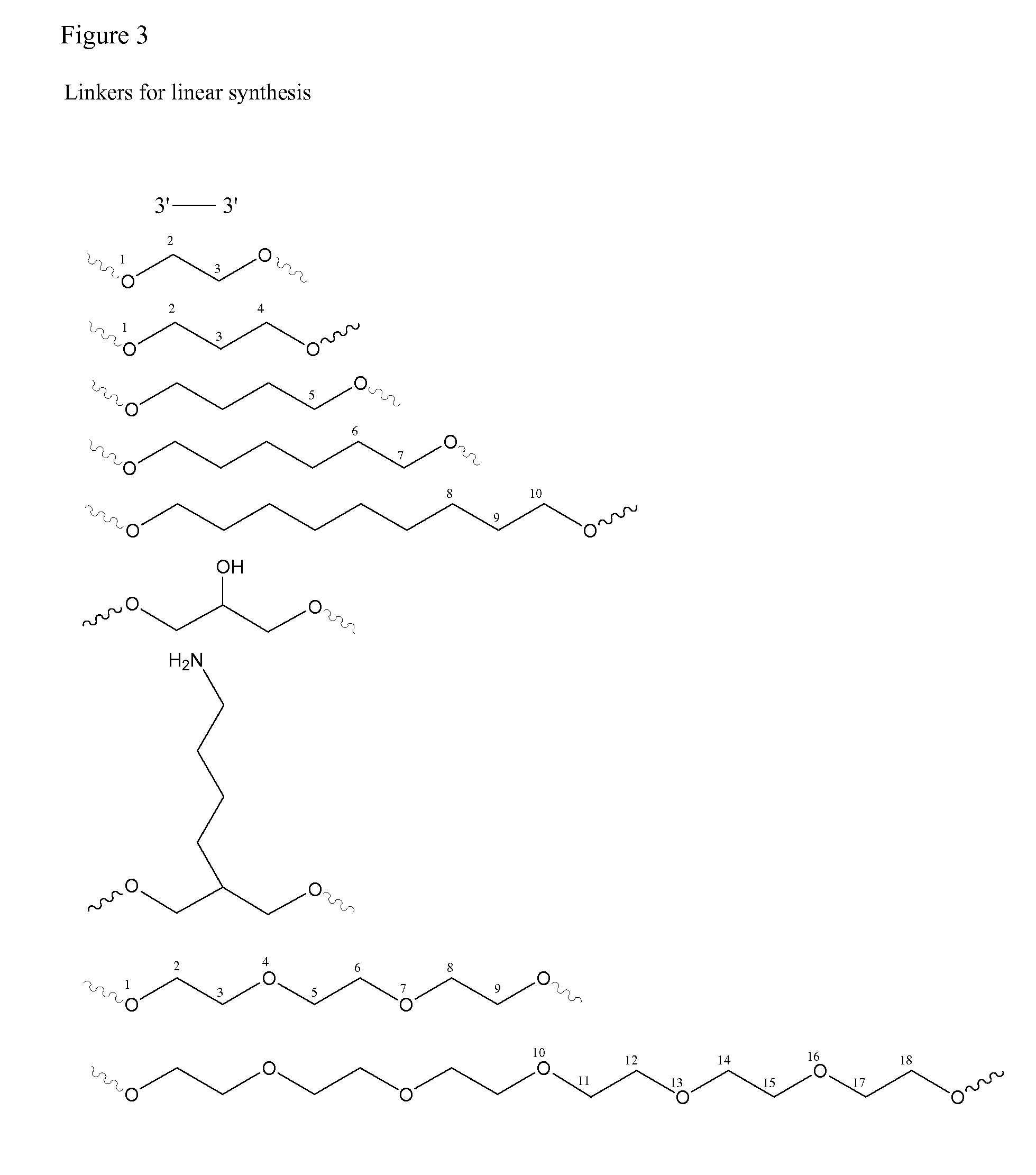
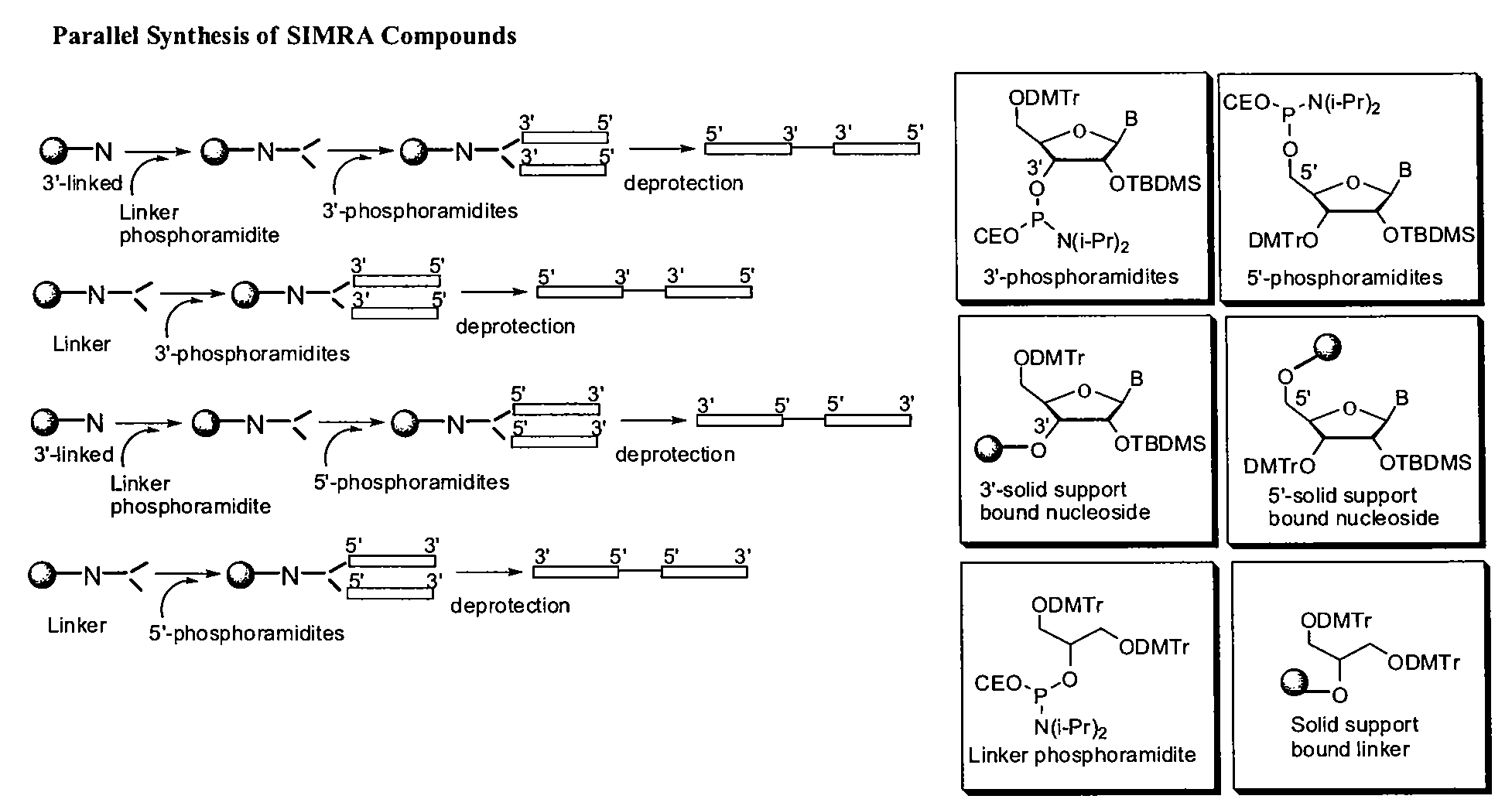
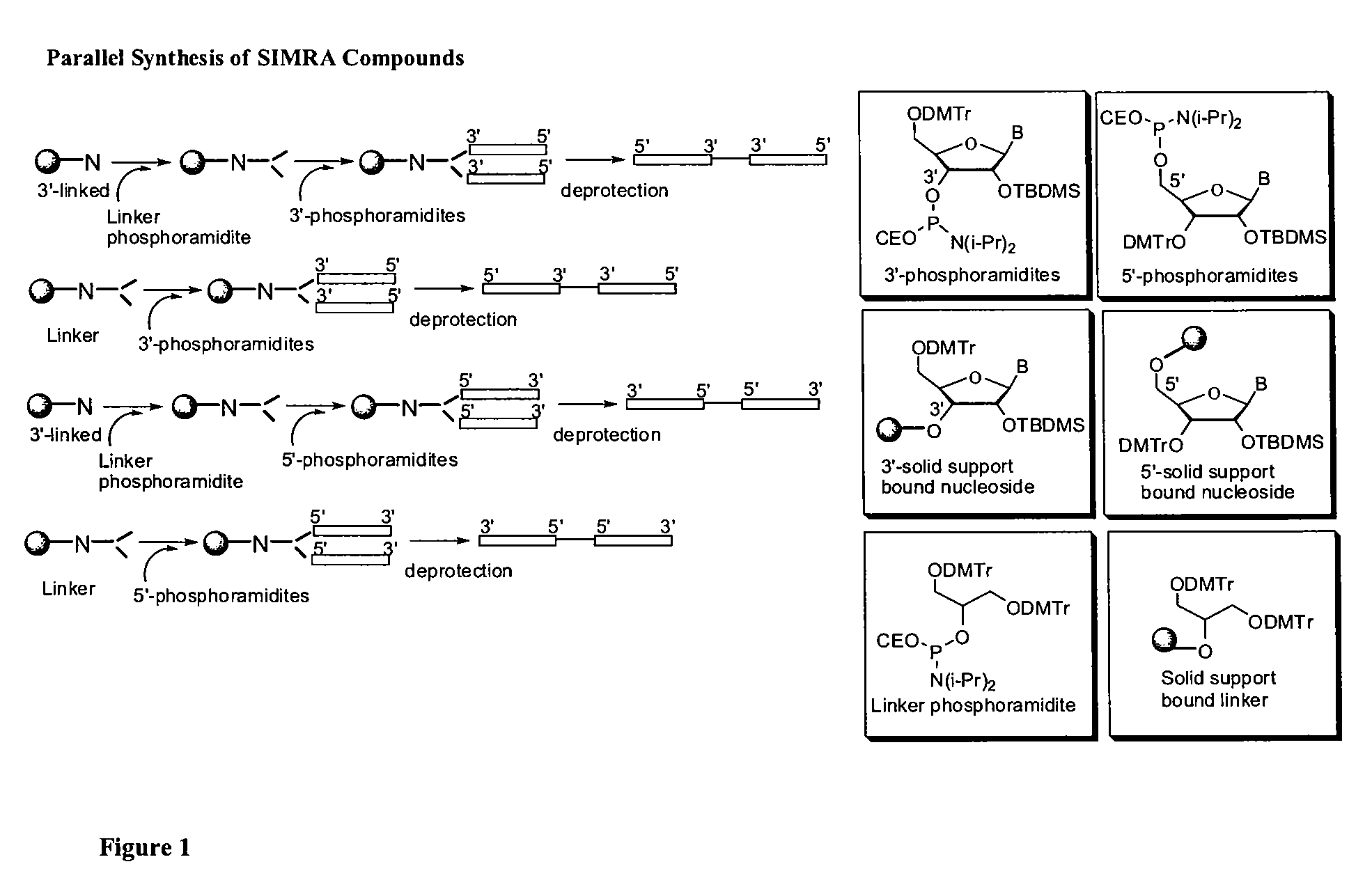
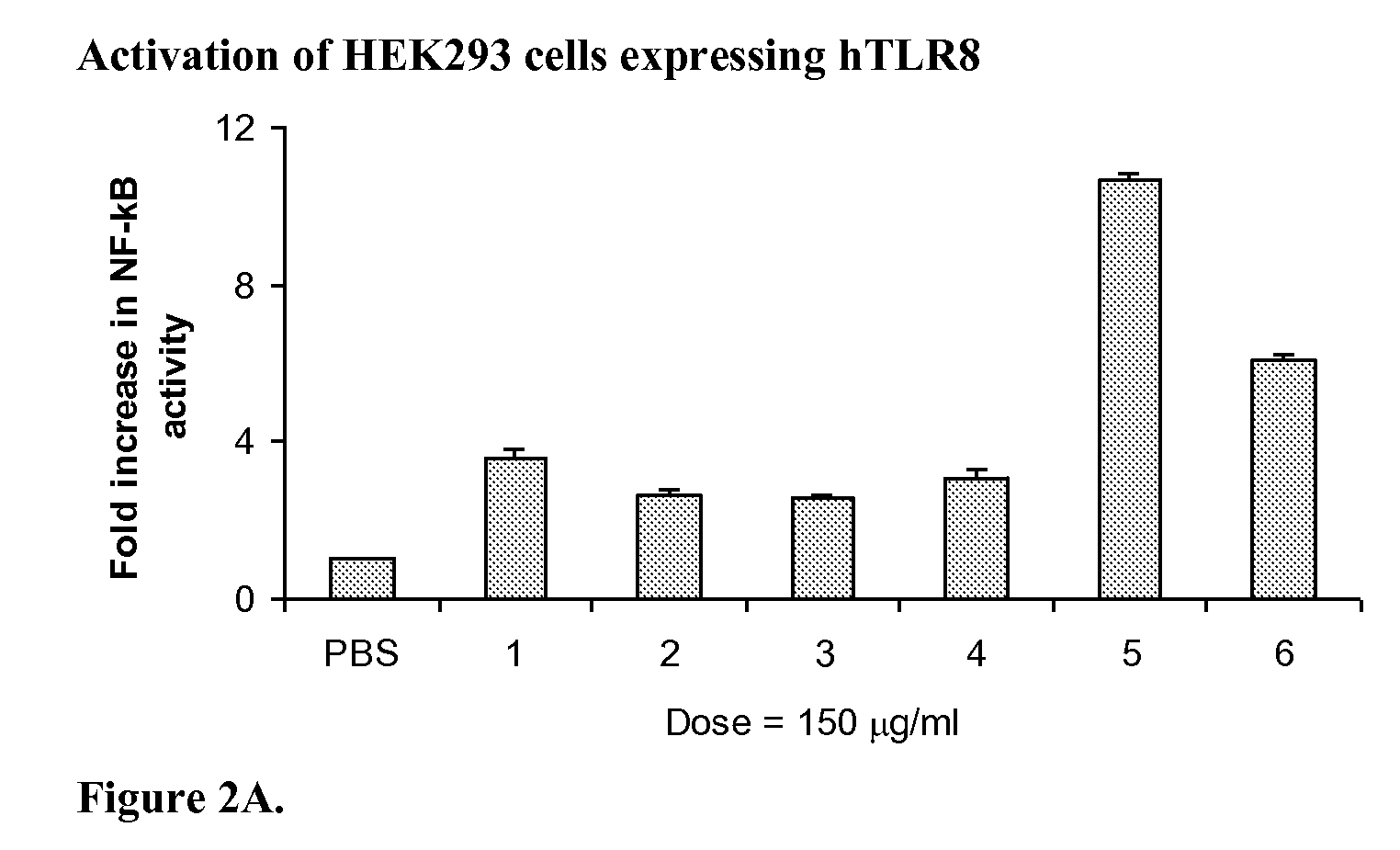
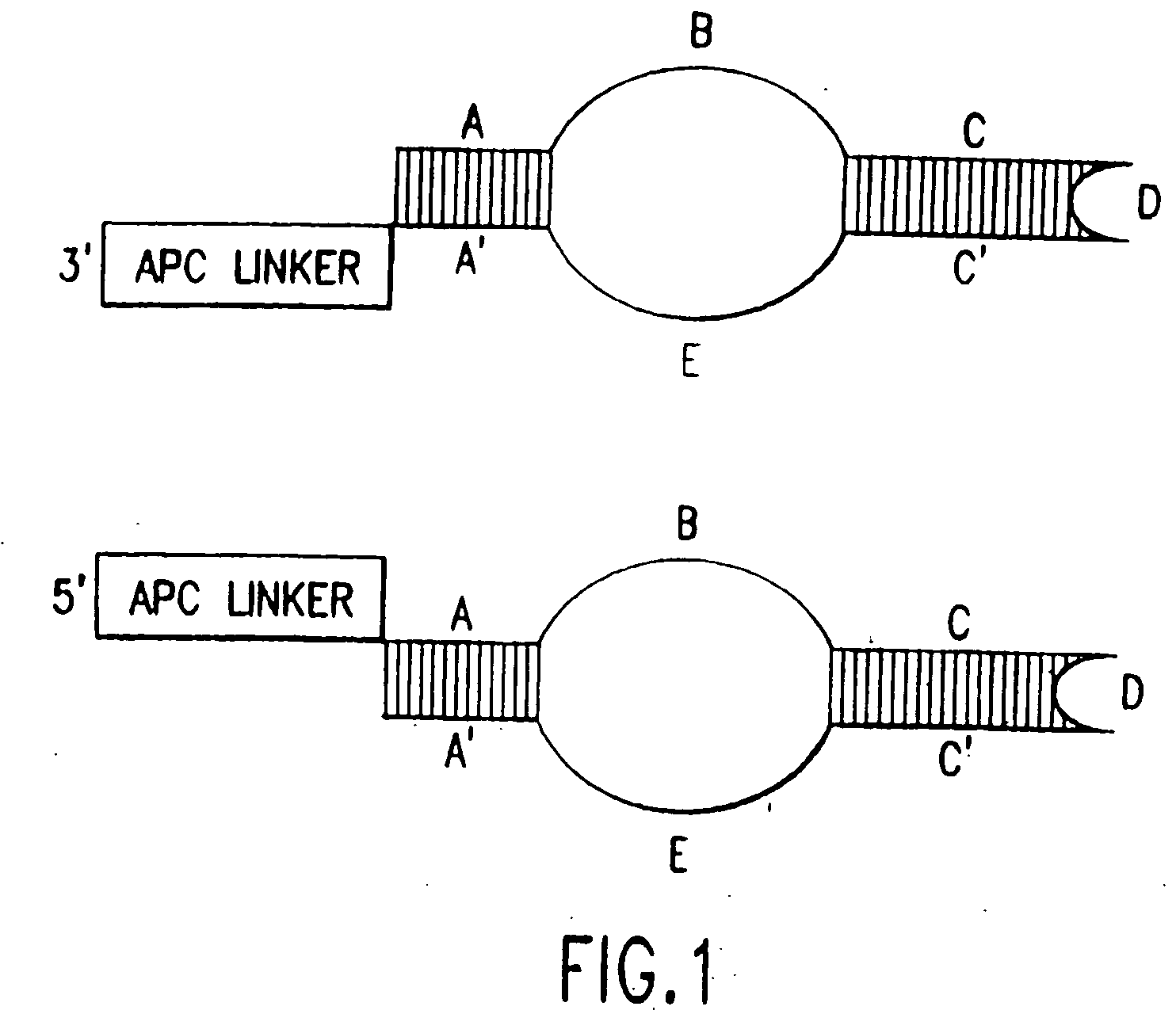
Stabilized immune modulatory RNA (SIMRA) compounds for tlr7 and tlr8
ActiveUS20080171712A1Improve stabilityImprove vaccination effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsOligoribonucleotidesTLR8
The invention relates to the therapeutic use of stabilized oligoribonucleotides as immune modulatory agents for immune therapy applications. Specifically, the invention provides RNA based oligoribonucleotides with improved nuclease and RNase stability and that have immune modulatory activity through TLR7 and / or TLR8.
Owner:IDERA PHARMA INC
Chlamys Farreri pathogeny rickettsia in situ hybridization detection method and its reagent kit
InactiveCN1769485AEfficient detectionAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementOligoribonucleotidesInfection rate
This invention relates to the original position cross checking method of a Hence Kong waters disease type Pamela Ci's body and its reagent box. This invention includes the following steps: composing the three oligoribonucleotides probes of the High Sim markings according to the special DNA list design of the Pamela Ci's body's 16S rDNA list in the bacteria taxonogy, this unusual probe crosses and combines with the Pamela Ci's body 16s rRNA of the Hence Kong waters slice up, and then enlarges signal through the antigen antibody reaction, and displays colour through enzyme reaction. This checking method can combine the pathogeny checking with its pathology together; it can analyze the infection rate and infection intension on the stylebook slice when effiently and correctly checking the Pamela Ci's body; and the checking result is sensitive and precisious; and the slice after being checked can be preserved perennially.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Process for the synthesis of oligonucleotides
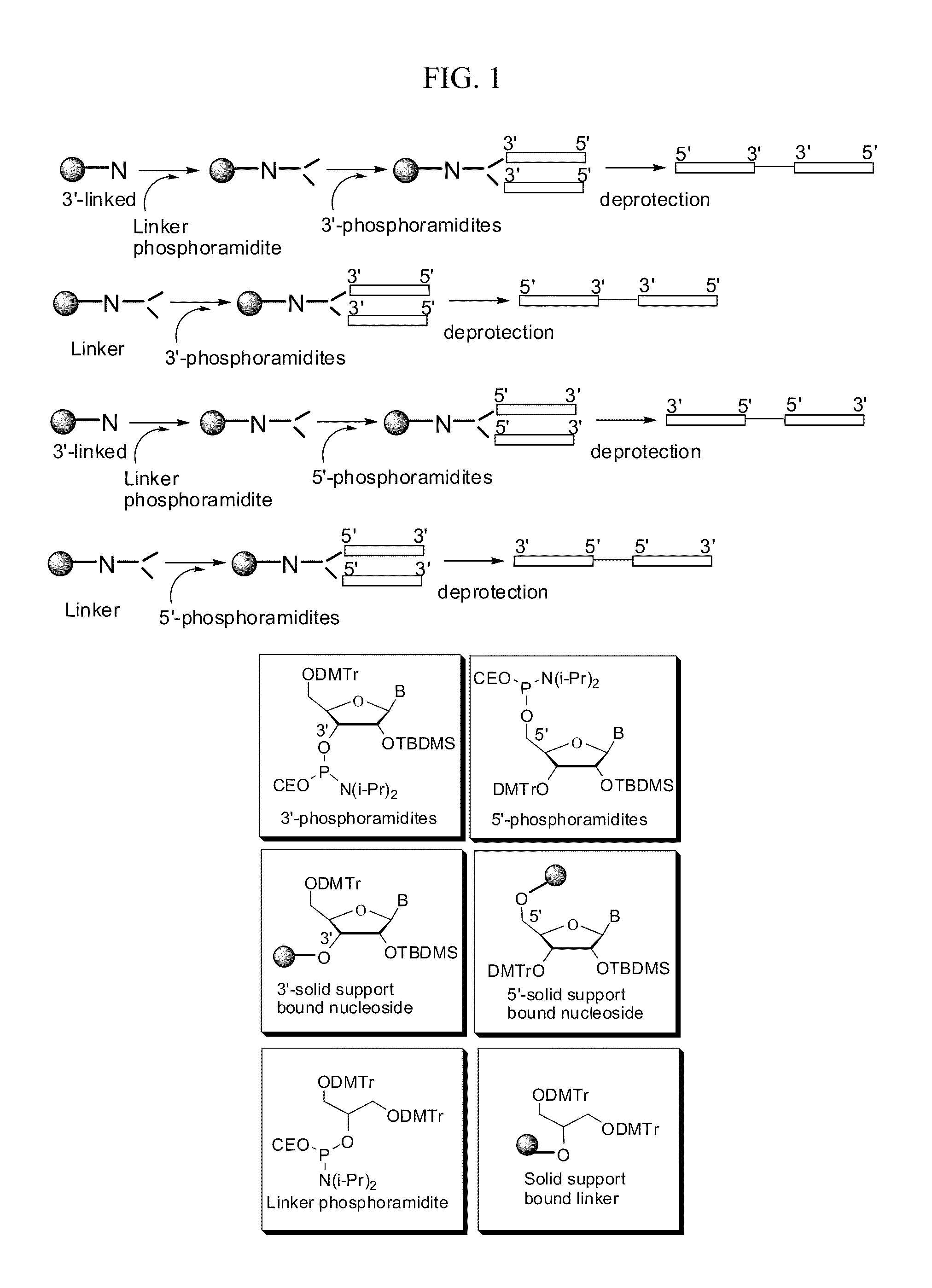
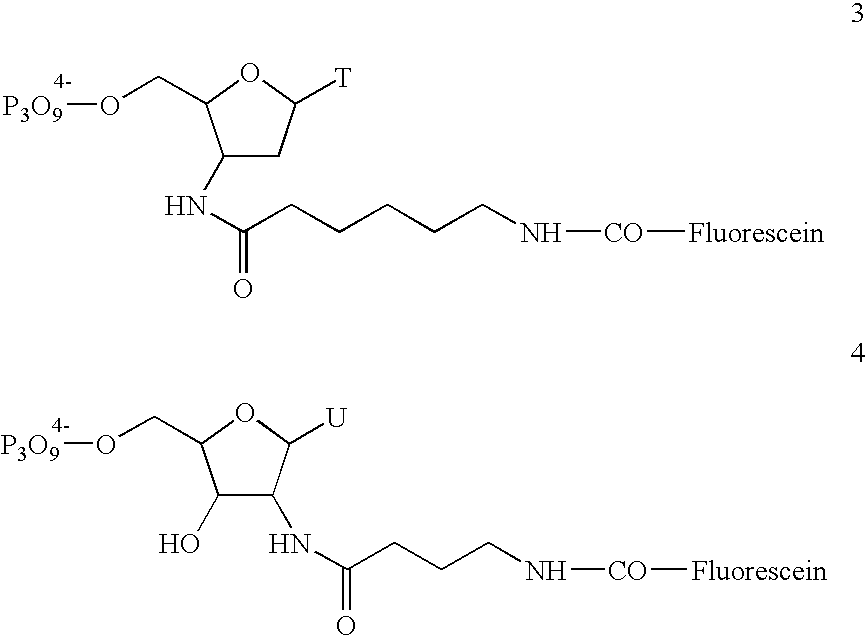
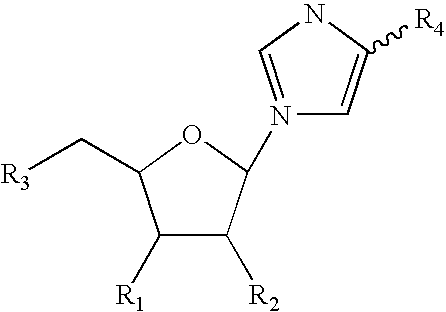
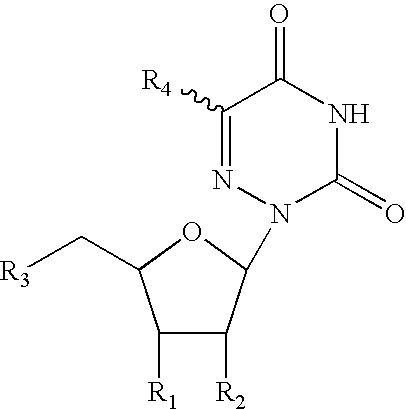
The present invention discloses novel methods for the synthesis of oligonucleotides with nucleoside phosphoramidites on solid supports. The methods comprise the stepwise chain assembly of oligonucleotides on supports with 5′-acyl phosphoramidites. The synthesis cycles consist of a front end deprotection step which is conducted with a solution of a primary amine or a phenolate, a phosphoramidite coupling step with a 5′-acyl nucleoside phosphoramidite in the presence of an activator, a phosphite oxidation step and an optional capping step. The novel methods improve the quality of synthetic oligonucleotides due to the irreversibility of the front end deprotection step, which prevents the formation of deletion sequences, and due to the avoidance of acidic reagents in the synthesis cycles, which prevent the formation of depurination side products. The invention further discloses novel nucleoside phosphoramidite compositions wherein the phosphoramidites carry acyl front end protective groups which are cleavable with primary amines or phenolates. The invention is applicable to the synthesis of oligodeoxyribonucleotides, oligoribonucleotides and oligonucleotides with modifications in their sugar or phosphate groups.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Prevention and treatment of acute renal failure and other kidney diseases by inhibition of p53 by siRNA
InactiveUS7910566B2Increased riskPrevent ototoxicitySugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseEprotirome
The invention relates to a double-stranded compound, preferably an oligoribonucleotide, which down-regulates the expression of a human p53 gene. The invention also relates to a pharmaceutical composition comprising the compound, or a vector capable of expressing the oligoribonucleotide compound, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention also contemplates a method of treating a patient suffering from acute renal failure or other kidney diseases comprising administering to the patient the pharmaceutical composition in a therapeutically effective dose so as to thereby treat the patient.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
Nucleic acid analysis techniques
InactiveUS20050191646A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnd labelingNucleoside triphosphate
The present invention provides a simplified method for identifying differences in nucleic acid abundances (e.g., expression levels) between two or more samples. The methods involve providing an array containing a large number (e.g. greater than 1,000) of arbitrarily selected different oligonucleotide probes where the sequence and location of each different probe is known. Nucleic acid samples (e.g. mRNA) from two or more samples are hybridized to the probe arrays and the pattern of hybridization is detected. Differences in the hybridization patterns between the samples indicates differences in expression of various genes between those samples. This invention also provides a method of end-labeling a nucleic acid. In one embodiment, the method involves providing a nucleic acid, providing a labeled oligonucleotide and then enzymatically ligating the oligonucleotide to the nucleic acid. Thus, for example, where the nucleic acid is an RNA, a labeled oligoribonucleotide can be ligated using an RNA ligase. In another embodiment, the end labeling can be accomplished by providing a nucleic acid, providing labeled nucleoside triphosphates, and attaching the nucleoside triphosphates to the nucleic acid using a terminal transferase.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Stabilized immune modulatory RNA (SIMRA) compounds
ActiveUS20090053205A1Exonuclease digestionOrganic active ingredientsActivity regulationOligoribonucleotidesTLR8
The invention relates to the therapeutic use of novel stabilized oligoribonucleotides as immune modulatory agents for immune therapy applications. Specifically, the invention provides novel RNA-based oligoribonucleotides with improved nuclease and RNase stability and that have immune modulatory activity through TLR7 and / or TLR8.
Owner:IDERA PHARMA INC
Compositions, methods and detection technologies for reiterative oligonucleotide synthesis
InactiveUS20050214796A1MicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementDendrimerOligoribonucleotides
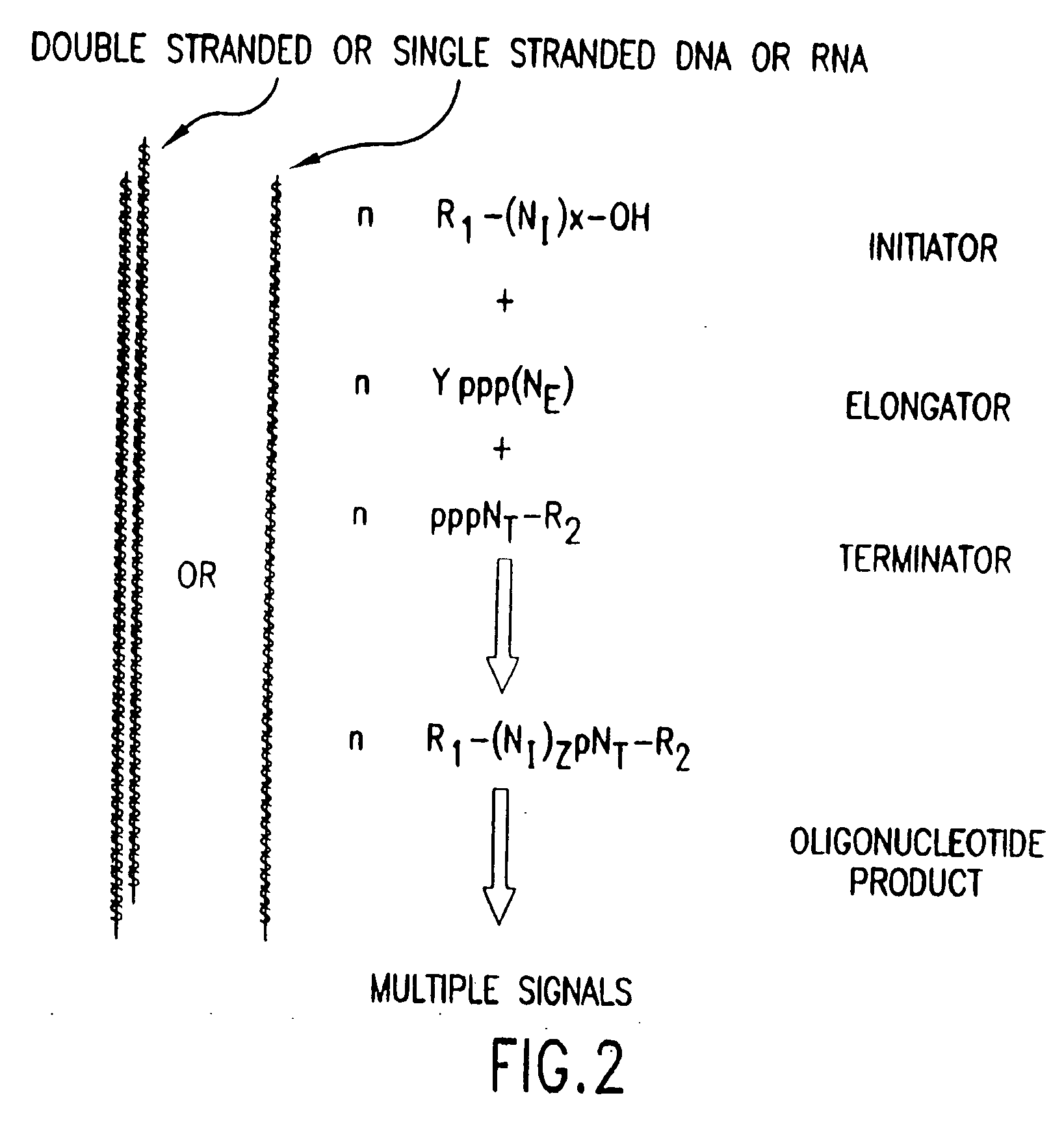
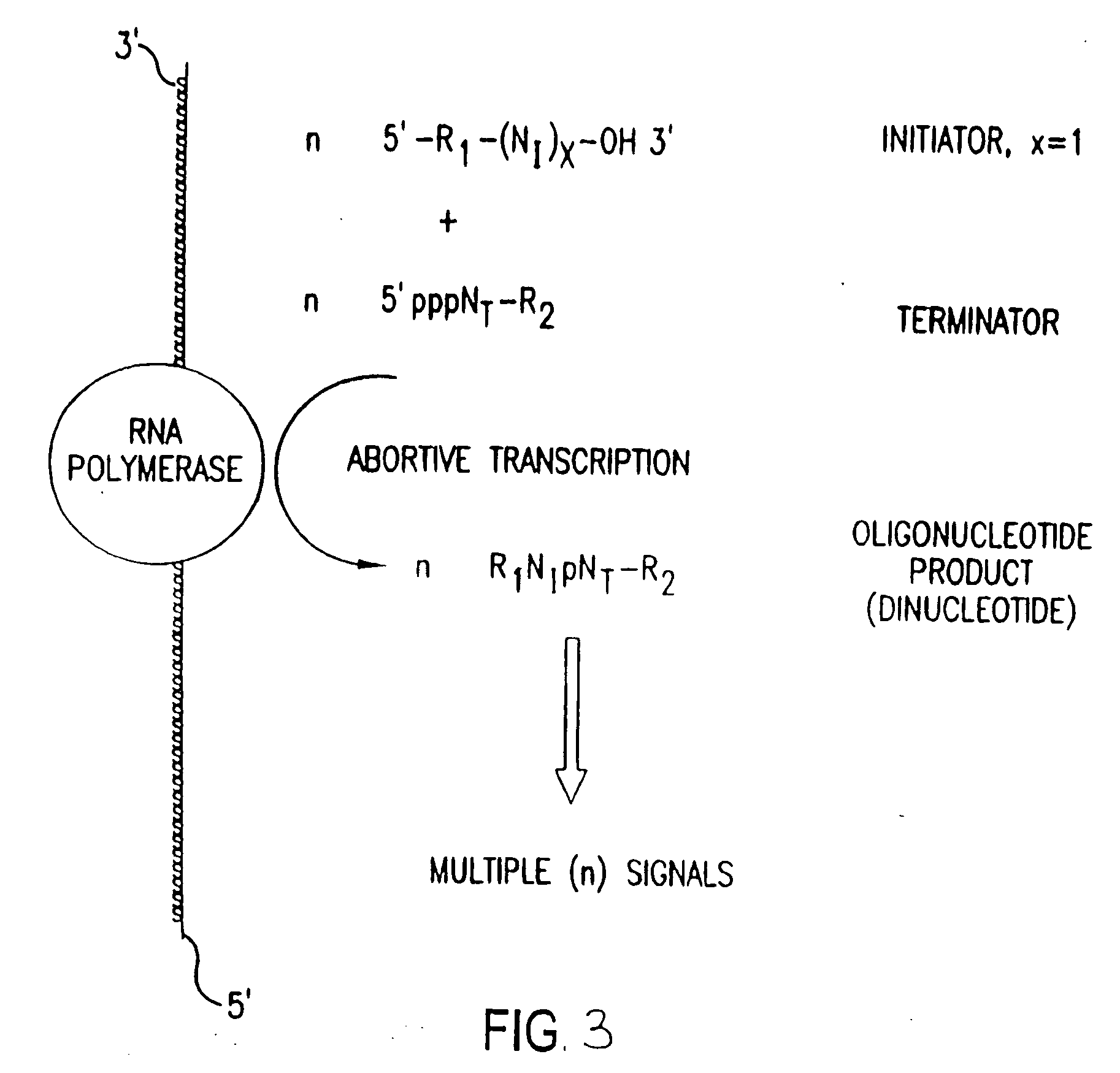
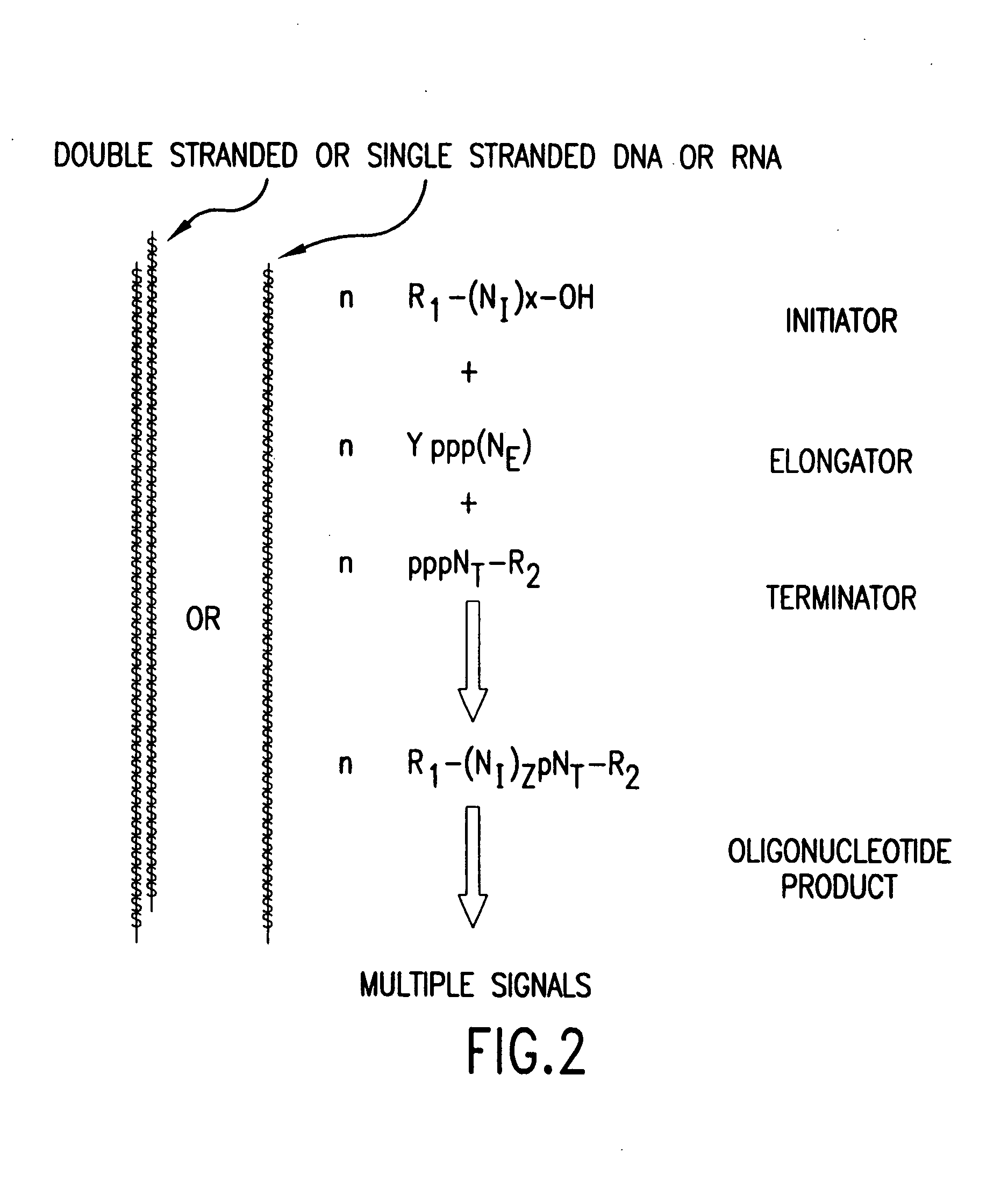
The present invention provides methods for detecting the presence of a molecule of interest by generating multiple detectable oligonucleotides through reiterative enzymatic oligonucleotide synthesis events on a polynucleotide sequence and detecting said products. The invention also provides for methods of multiplex abortive transcription. In a further aspect, the invention provides for the use of dendrimers containing abortive promoter cassettes. In one aspect, the invention provides for abortive promoter cassettes suitable for use in the present invention. In one aspect the products of abortive transcription are detected with the use of mass spectrometry. In another aspect, the invention provides a method for detecting a target protein, DNA or RNA by generating multiple detectable RNA oligoribonucleotides by abortive transcription that are detected, including by mass spectrometry.
Owner:RIBOMED BIOTECHNOLOGIES INC
Modified oligoribonucleotide analogs with enhanced immunostimulatory activity
The invention provides immunostimulatory compositions and methods for their use. In particular, the immunostimulatory compositions of the invention include RNA-like polymers that incorporate an immunostimulatory sequence motif and at least one chemical modification to confer improved stability against nuclease degradation and improved activity. Specific modifications involving phosphate linkages, nucleotide analogs, and combinations thereof are provided. Compositions of the invention optionally include an antigen and can be used to stimulate an immune response. Also provided are compositions and methods useful for treating a subject having an infection, a cancer, an to allergic condition, or asthma. Modified oligoribonucleotide analogs of the invention are believed to stimulate Toll-like receptors TLR7 and TLR8.
Owner:ZOTTIS BELGIUM
Immune Stimulatory Oligoribonucleotide Analogs Containing Modified Oligophosphate Moieties
InactiveUS20100260788A1Good chemical stabilityGood metabolic stabilityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsOligoribonucleotidesAdjuvant
Immunostimulatory oligoribonucleotides (ORN) featuring 5′-triphosphates and various 5′-triphosphate analogs are provided. Also provided are physiologically acceptable salts of the immunostimulatory ORN and pharmaceutical compositions containing the immunostimulatory ORN of the invention. ORN of the invention are useful as adjuvants and can be combined with an antigen to promote an antigen-specific immune response. ORN of the invention are also particularly useful for promoting a Th1-type immune response. Also provided are methods of use of the compounds and pharmaceutical compositions of the invention to enhance an immune response in a subject, as well to treat a number of conditions including cancer, infection, allergy, and asthma, and to vaccinate a subject against an antigen.
Owner:ADIUTIDE PHARMA
Nucleic acid analysis techniques
InactiveUS20050158772A1Easy and fast applicationBroaden applicationSugar derivativesOrganic chemistry methodsEnd labelingBiology
The present invention provides a simplified method for identifying differences in nucleic acid abundances (e.g., expression levels) between two or more samples. The methods involve providing an array containing a large number (e.g. greater than 1,000) of arbitrarily selected different oligonucleotide probes where the sequence and location of each different probe is known. Nucleic acid samples (e.g. mRNA) from two or more samples are hybridized to the probe arrays and the pattern of hybridization is detected. Differences in the hybridization patterns between the samples indicates differences in expression of various genes between those samples. This invention also provides a method of end-labeling a nucleic acid. In one embodiment, the method involves providing a nucleic acid, providing a labeled oligonucleotide and then enzymatically ligating the oligonucleotide to the nucleic acid. Thus, for example, where the nucleic acid is an RNA, a labeled oligoribonucleotide can be ligated using an RNA ligase. In another embodiment, the end labeling can be accomplished by providing a nucleic acid, providing labeled nucleoside triphosphates, and attaching the nucleoside triphosphates to the nucleic acid using a terminal transferase.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Molecular detection systems utilizing reiterative oligonucleotide synthesis
InactiveUS20050064414A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOligoribonucleotidesProtein target
The present invention provides methods for detecting the presence of a target molecule by generating multiple detectable oligonucleotides through reiterative enzymatic oligonucleotide synthesis events on a defined polynucleotide sequence. The methods generally comprise using a nucleoside, a mononucleotide, and oligonucleotide, or a polynucleotide, or analog thereof, to initiate synthesis of an oligonucleotide product that is substantially complementary to a target site on the defined polynucleotide sequence; optionally using nucleotides or nucleotide anologs as oligonucleotide chain elongators; using a chain terminator to terminate the polymerization reaction; and detecting multiple oligonucleotide products that have been synthesized by the polymerase. In one aspect, the invention provides a method for detecting a target protein, DNA or RNA by generating multiple detectable RNA oligoribonucleotides by abortive transcription.
Owner:RIBOMED BIOTECHNOLOGIES INC
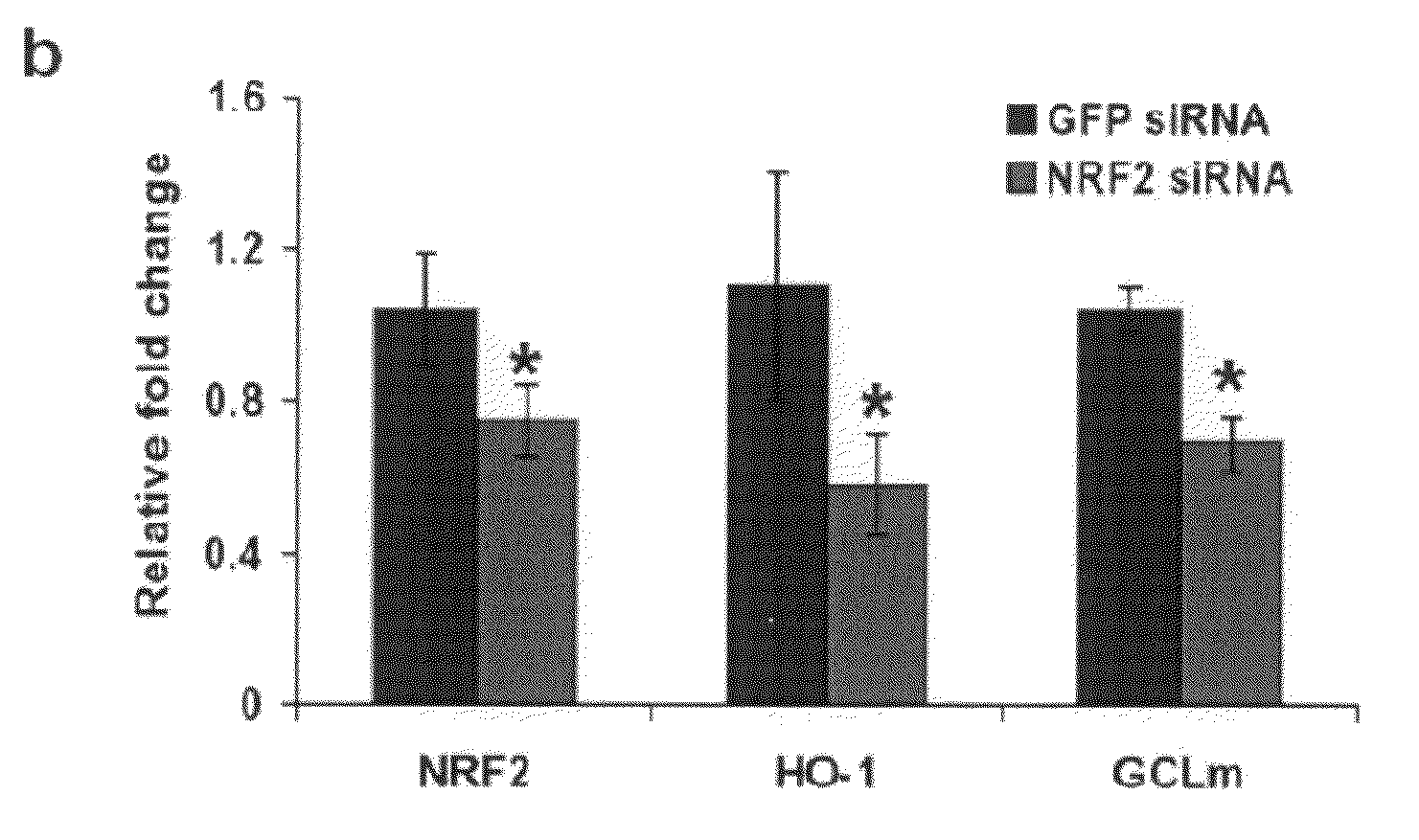
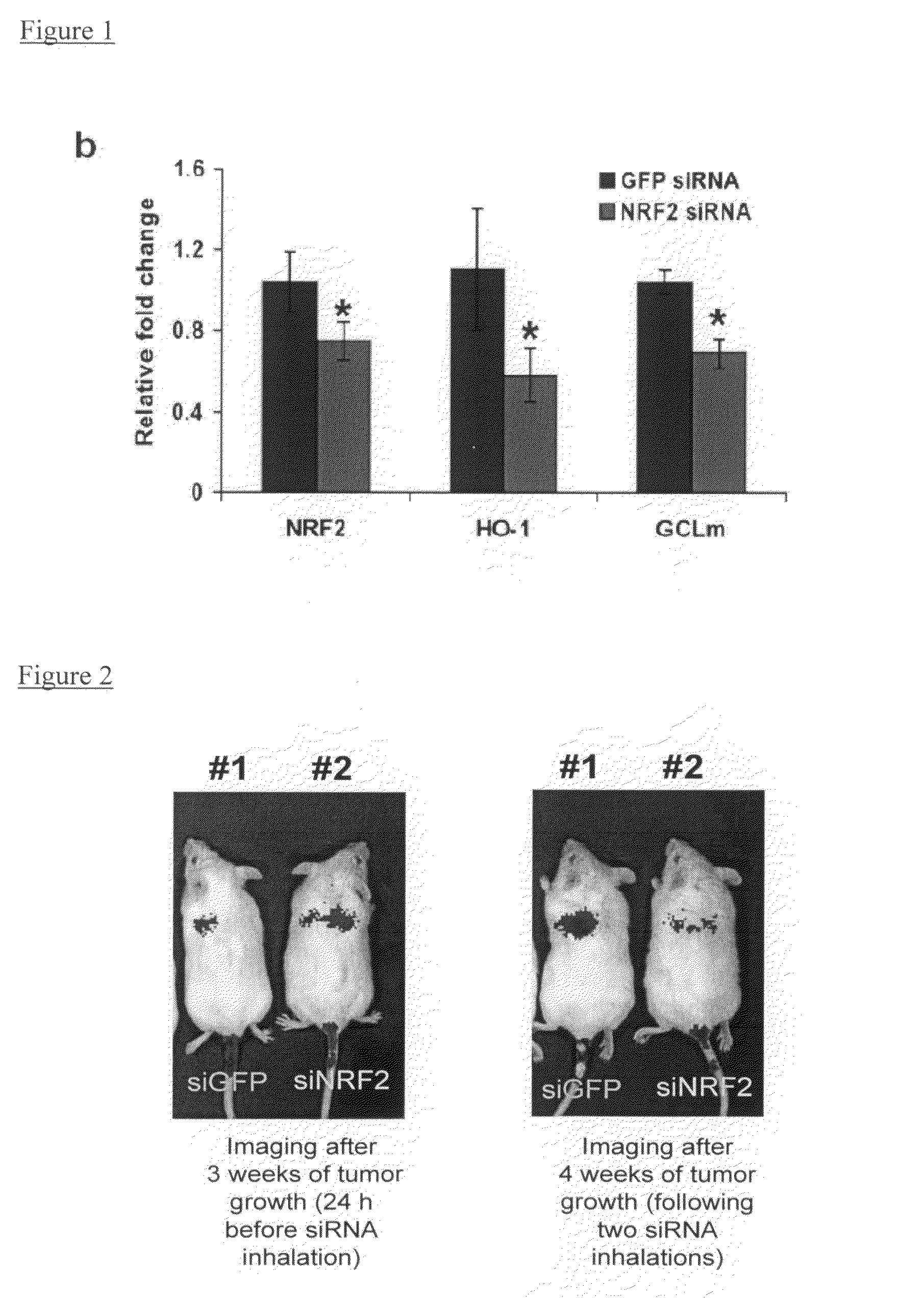
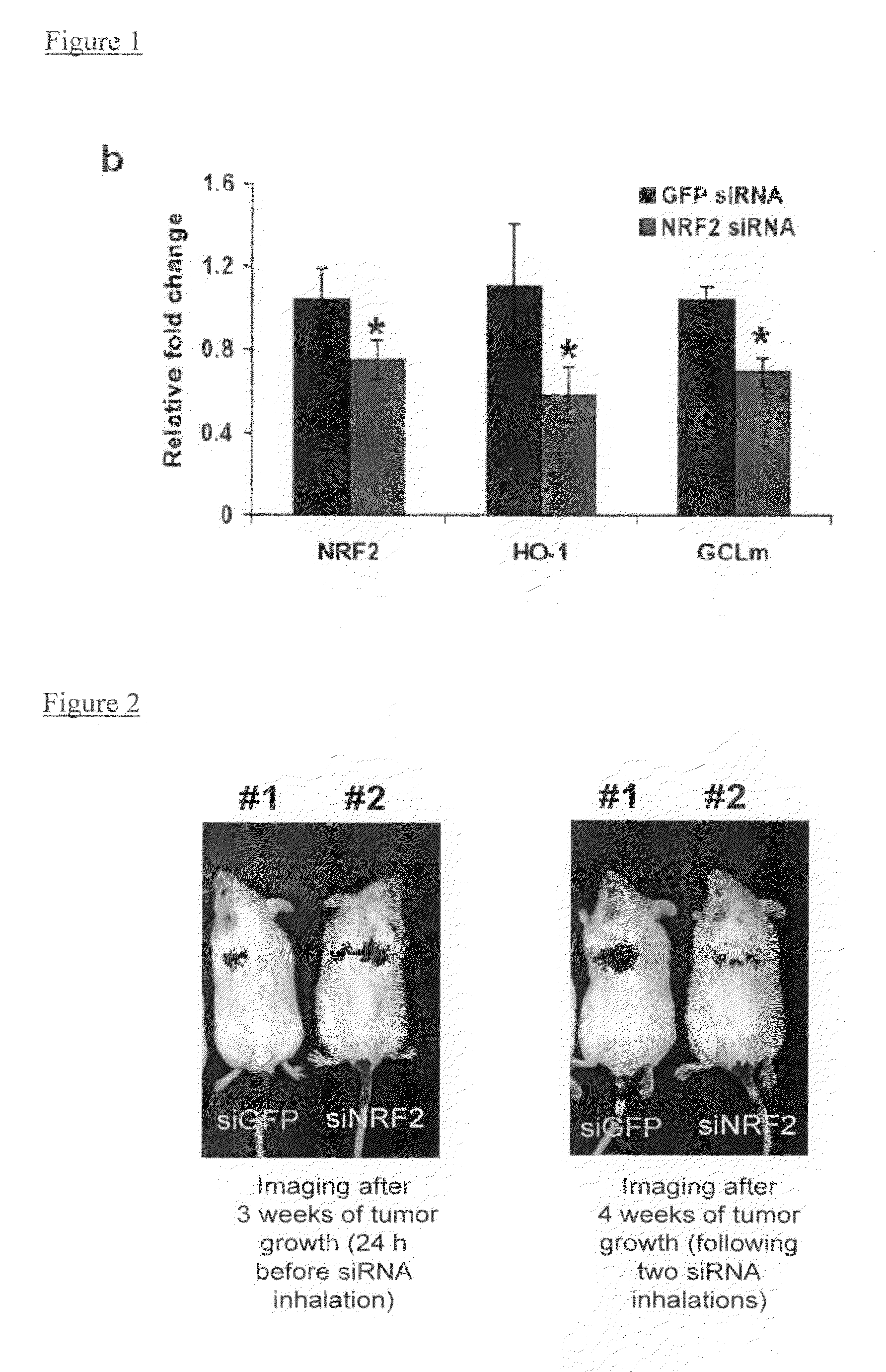
Oligoribonucleotide inhibitors of NRF2 and methods of use thereof for treatment of cancer
The invention provides novel double stranded oligoribonucleotides that inhibit the Nrf2 gene. The invention also provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising one or more such oligoribonucleotides, and a vector capable of expressing the oligoribonucleotide. The present invention also relates to methods and compositions for treating or preventing the incidence or severity of a cancerous disease, particularly various lung cancers.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
Oligoribonucleotide inhibitors of NRF2 and methods of use thereof for treatment of cancer
InactiveUS20090215864A1Increase concentrationOrganic active ingredientsHeavy metal active ingredientsDiseaseOligoribonucleotides
The invention provides novel double stranded oligoribonucleotides that inhibit the Nrf2 gene. The invention also provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising one or more such oligoribonucleotides, and a vector capable of expressing the oligoribonucleotide. The present invention also relates to methods and compositions for treating or preventing the incidence or severity of a cancerous disease, particularly various lung cancers.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
METHODS AND COMPOSITIONS FOR IMPROVED THERAPEUTIC EFFECTS WITH siRNA
InactiveUS20100330155A1Improve in vivo stabilityImprove efficacyOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesOligoribonucleotidesTherapeutic effect
The present invention relates to chemically modified, linked double-stranded (ds)RNA compositions comprising two or more double-stranded (ds) oligoribonucleotides linked by at least one linking moiety and methods of formulating and delivering such compositions to modulate gene expression through target-specific RNA co-interference (RNAco-i). The compositions of the invention may optionally comprise a conjugation or a complex with one or more small molecule drugs, protein therapeutics, or other dsRNA molecules. The present invention is directed at the methods of production for, methods of use of, and therapeutic utilities for RNAi co-interference therapy utilizing the compositions of the invention.
Owner:FLAGSHIP VENTURES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com