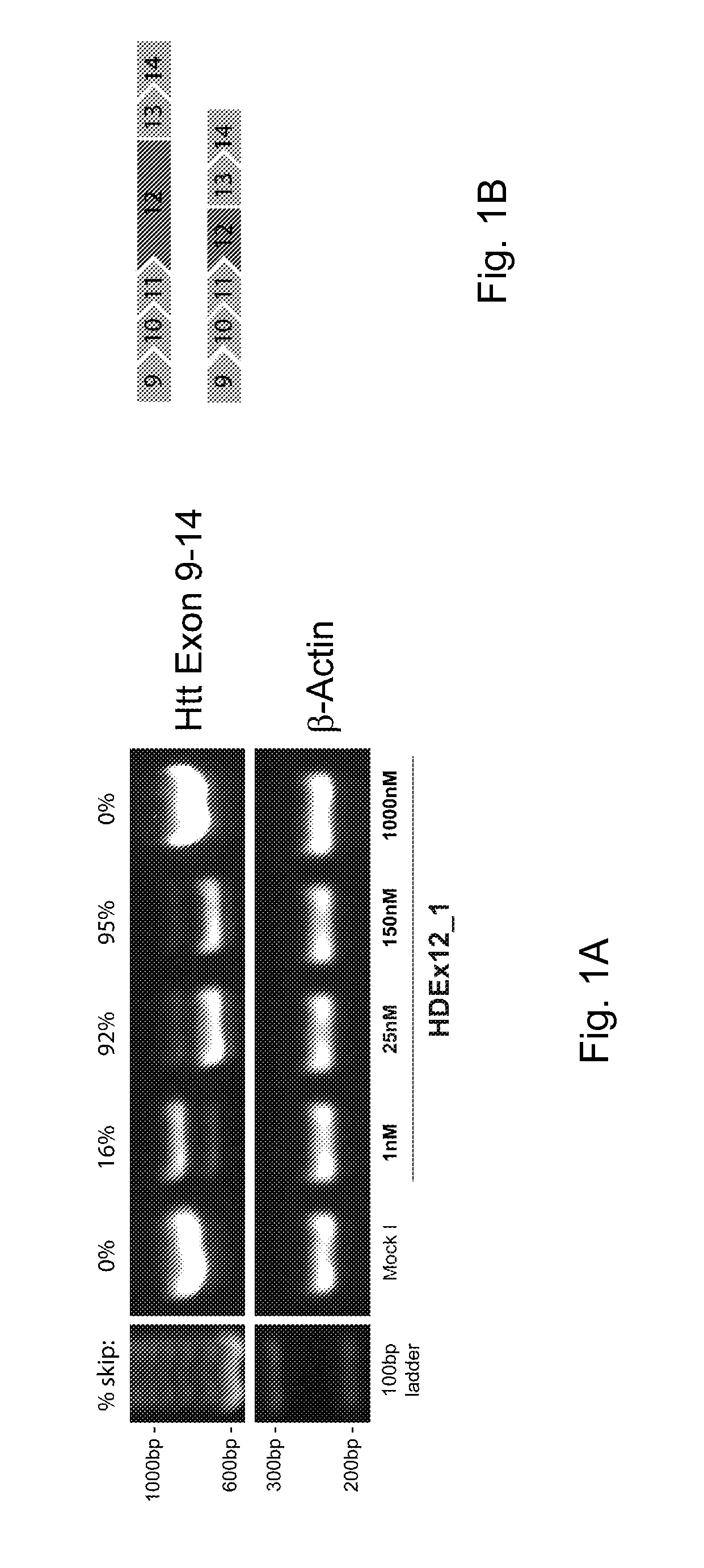
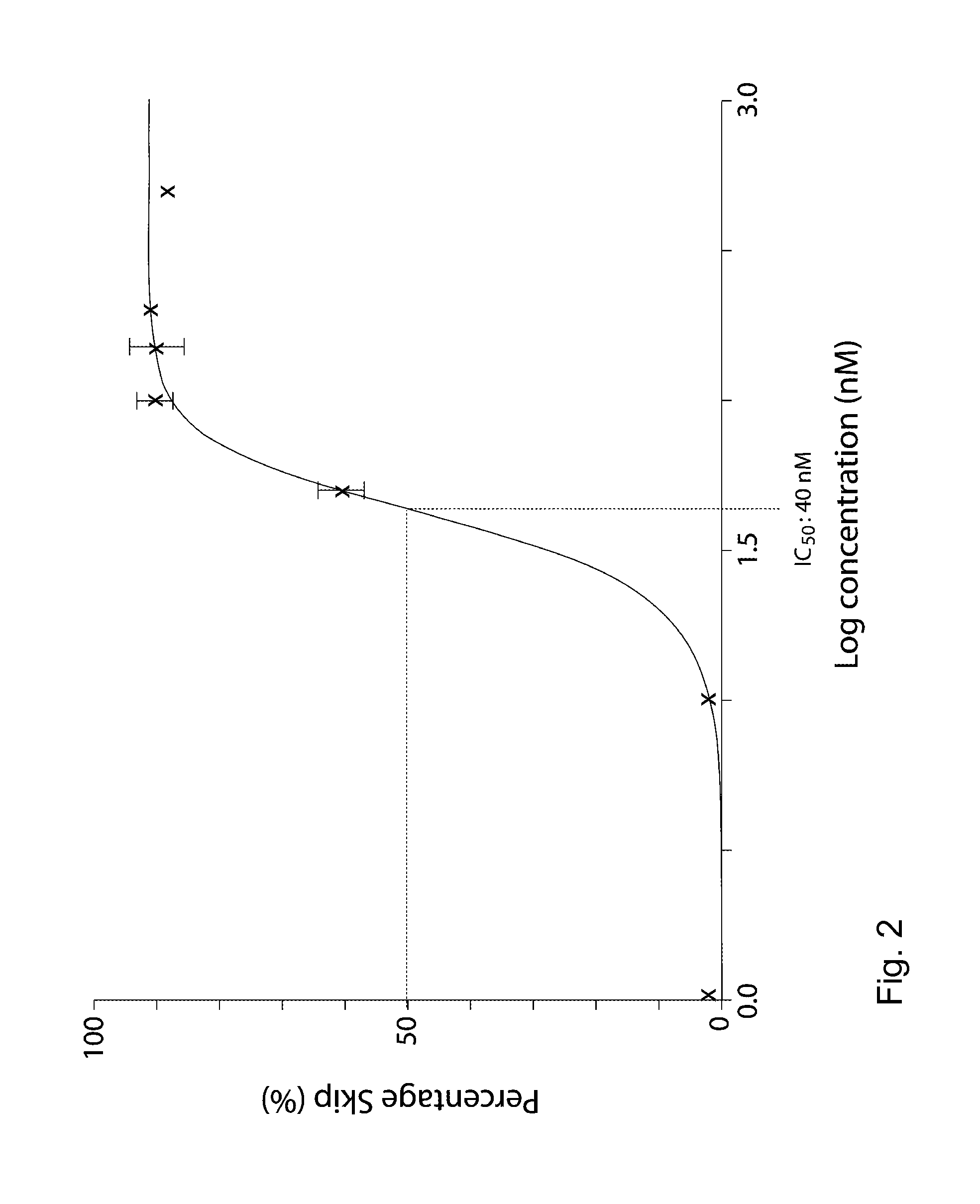
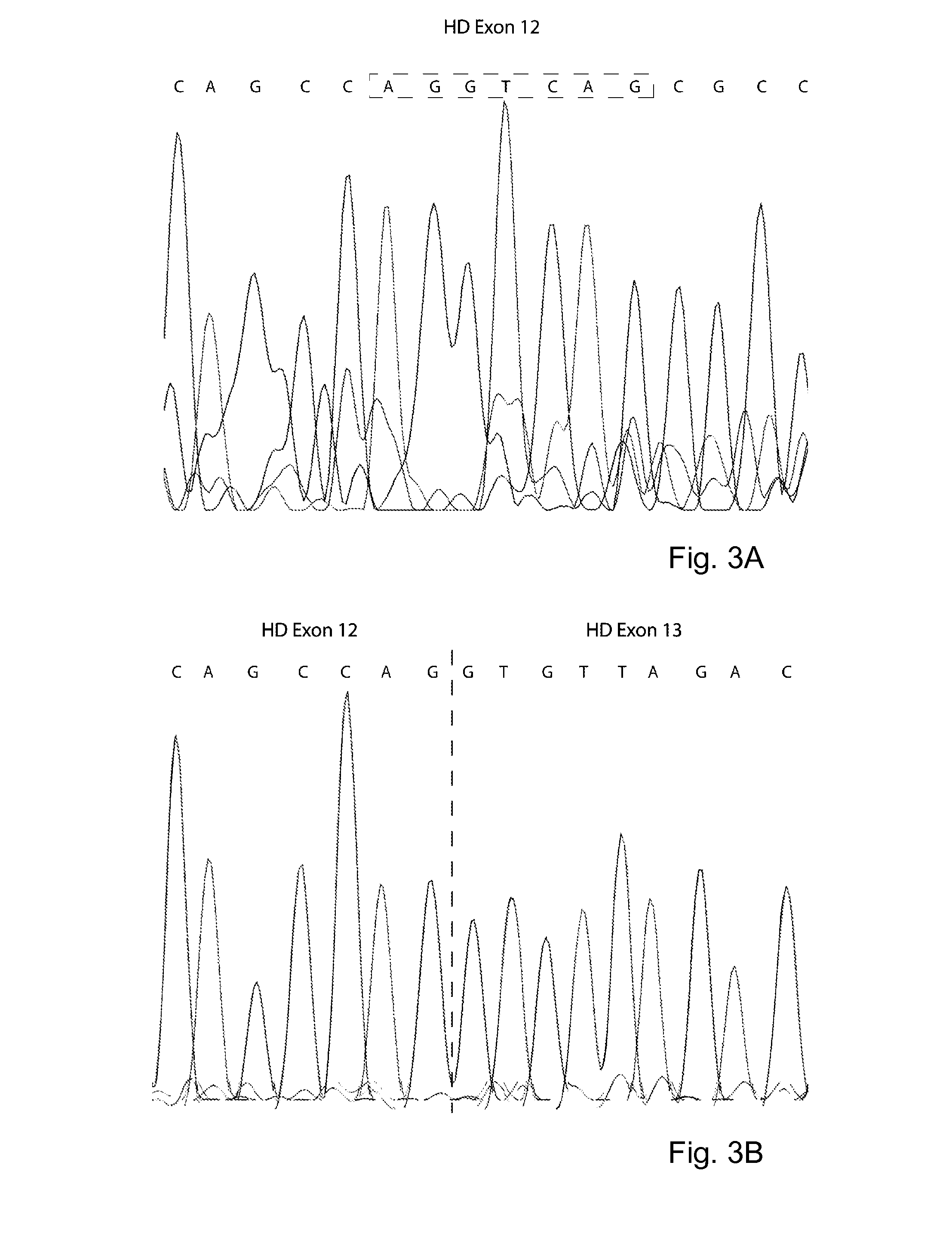
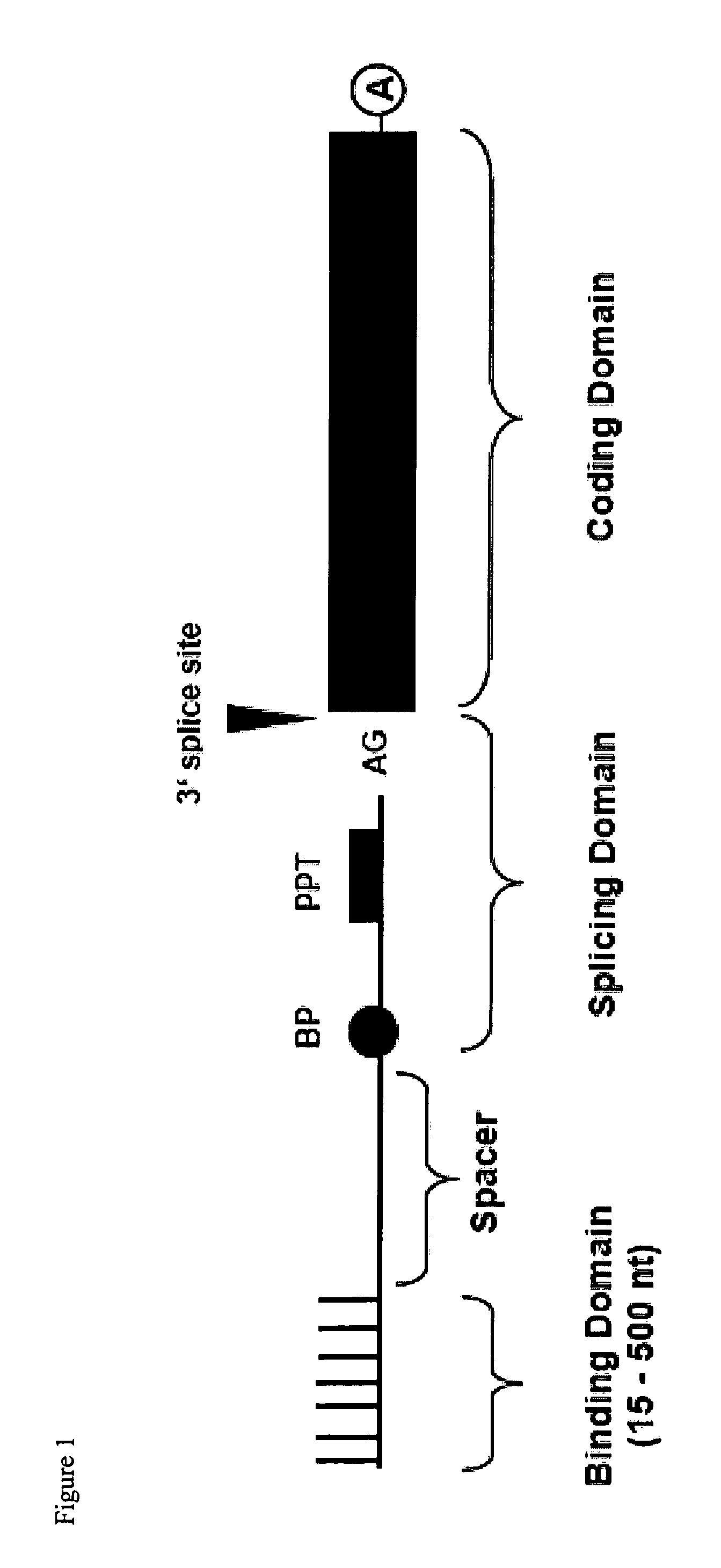
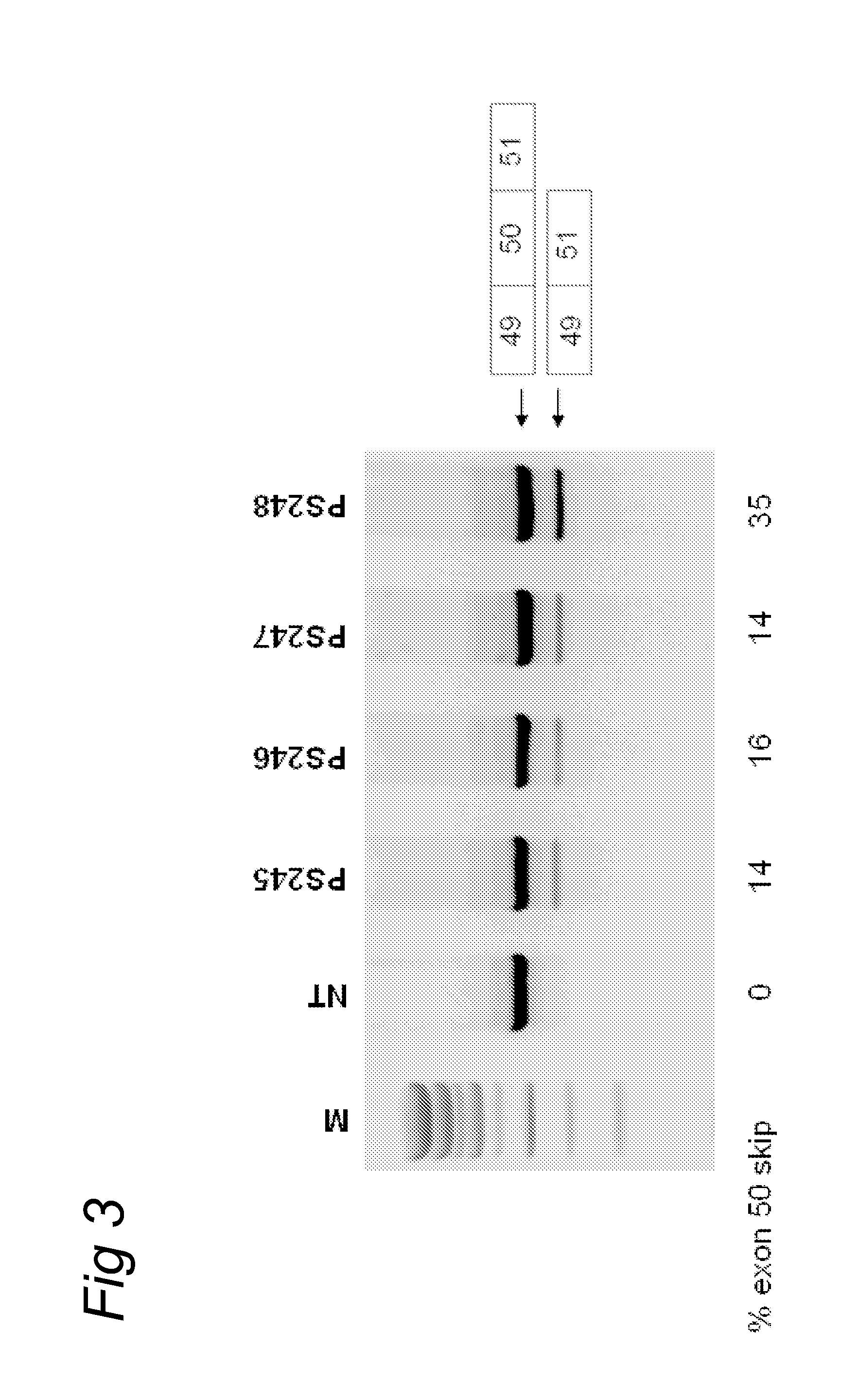Patents
Literature
93 results about "Precursor mRNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
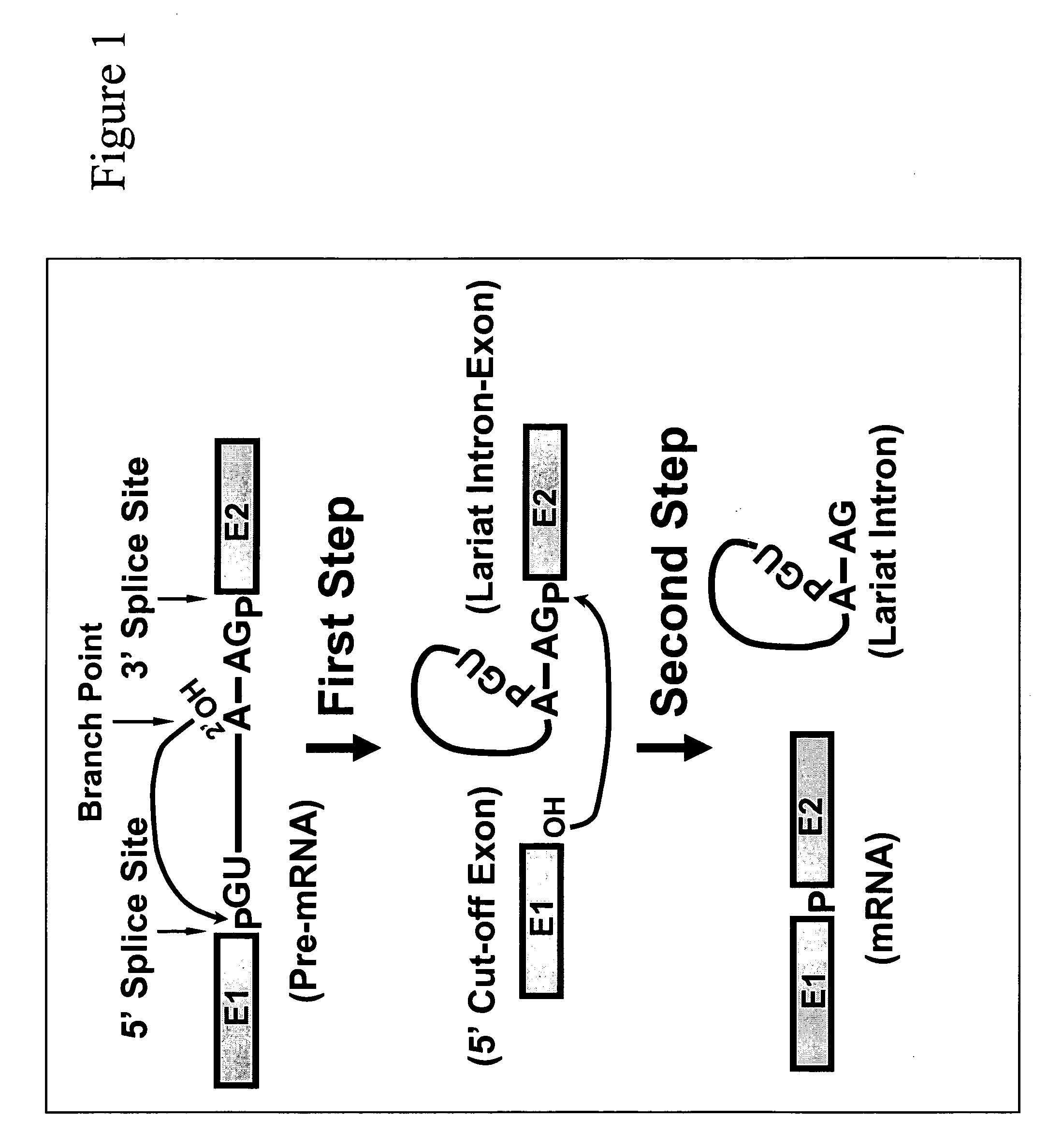
Precursor mRNA is an immature single strand of messenger ribonucleic acid. Pre-mRNA is synthesized from a DNA template in the cell nucleus by transcription. Pre-mRNA comprises the bulk of heterogeneous nuclear RNA. The term hnRNA is often used as a synonym for pre-mRNA, although, in the strict sense, hnRNA may include nuclear RNA transcripts that do not end up as cytoplasmic mRNA. Once pre-mRNA has been completely processed, it is termed "mature messenger RNA", "mature mRNA", or simply "mRNA".
Oligomers
ActiveUS20100168212A1High degreeOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesMuscular dystrophyOligomer
Molecules are provided for inducing or facilitating exon skipping in forming spliced mRNA products from pre-mRNA molecules in cells. The molecules may be provided directly as oligonucleotides or expression products of vectors that are administered to a subject. High rates of skipping can be achieved. High rates of skipping reduce the severity of a disease like Duchene Muscular Dystrophy so that the disease is more like Becker Muscular Dystrophy. This is a severe reduction in symptom severity and mortality.
Owner:ROYAL HOLLOWAY & BEDFORD NEW COLLEGE
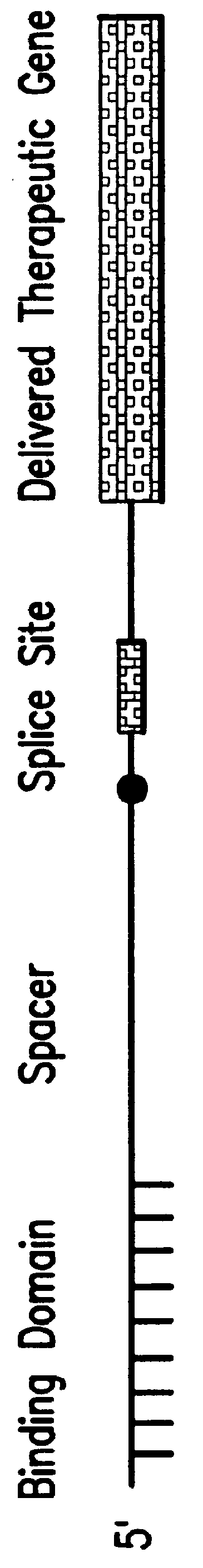
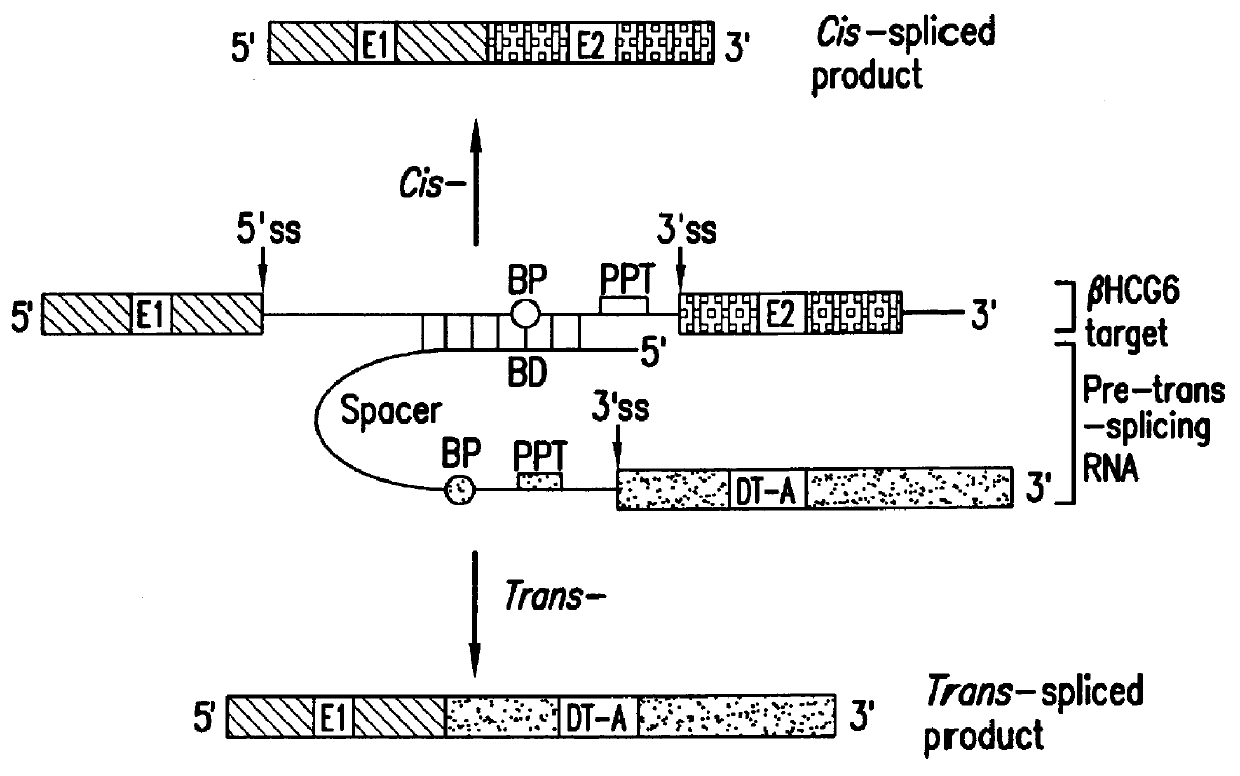
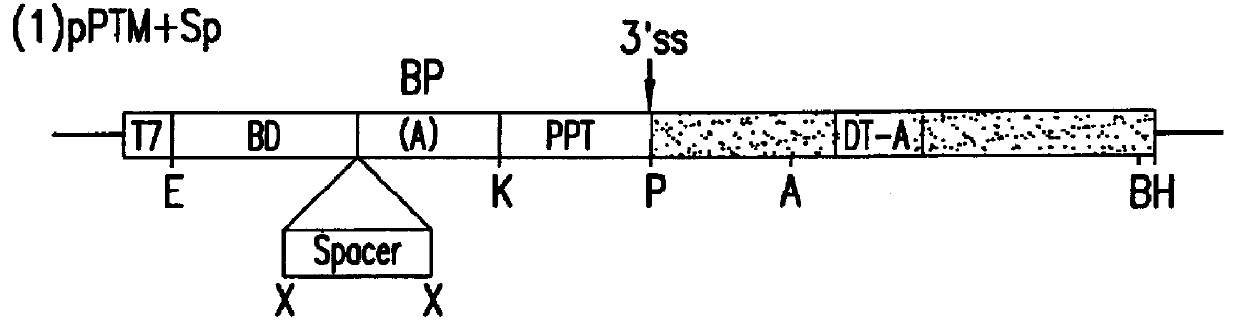
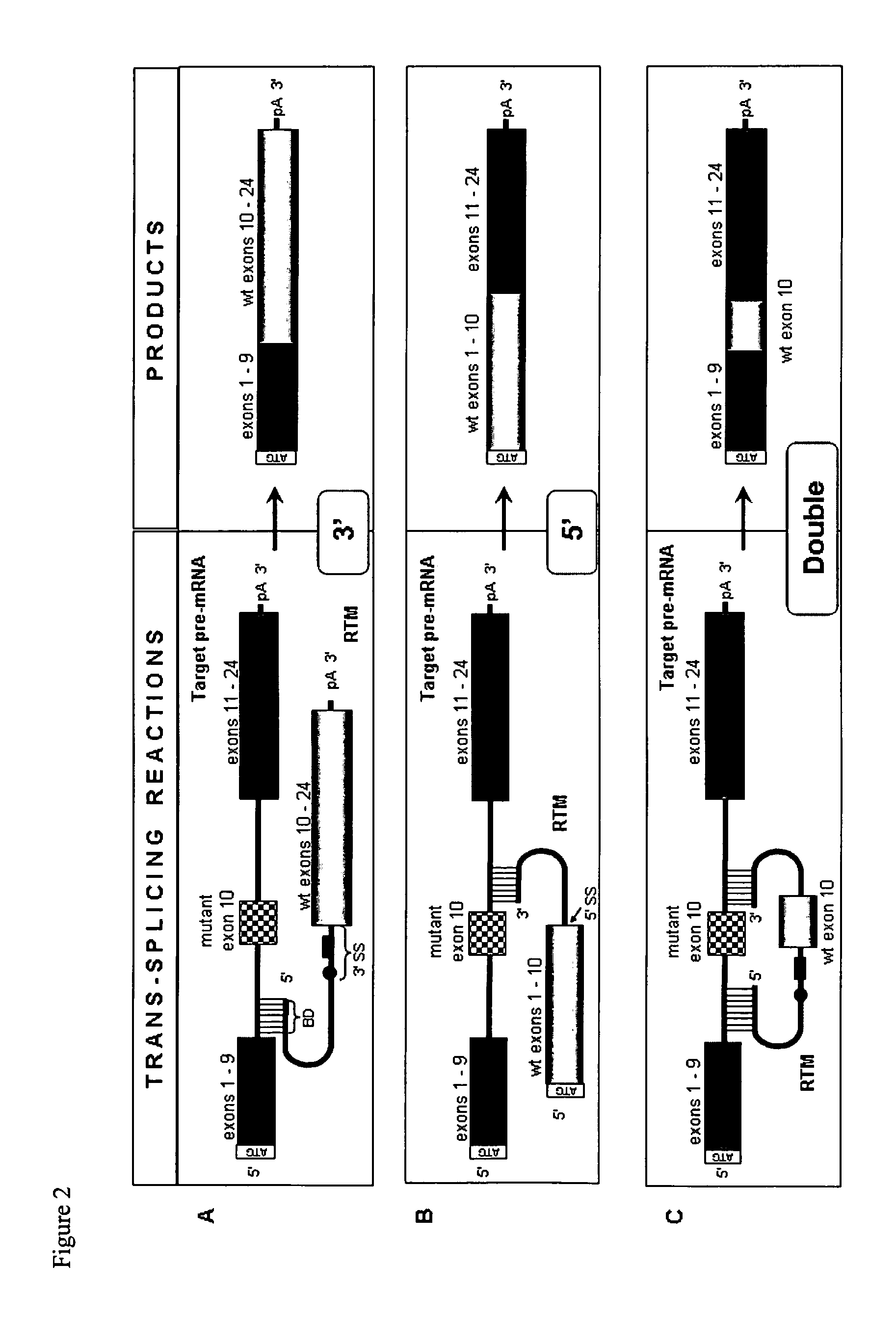
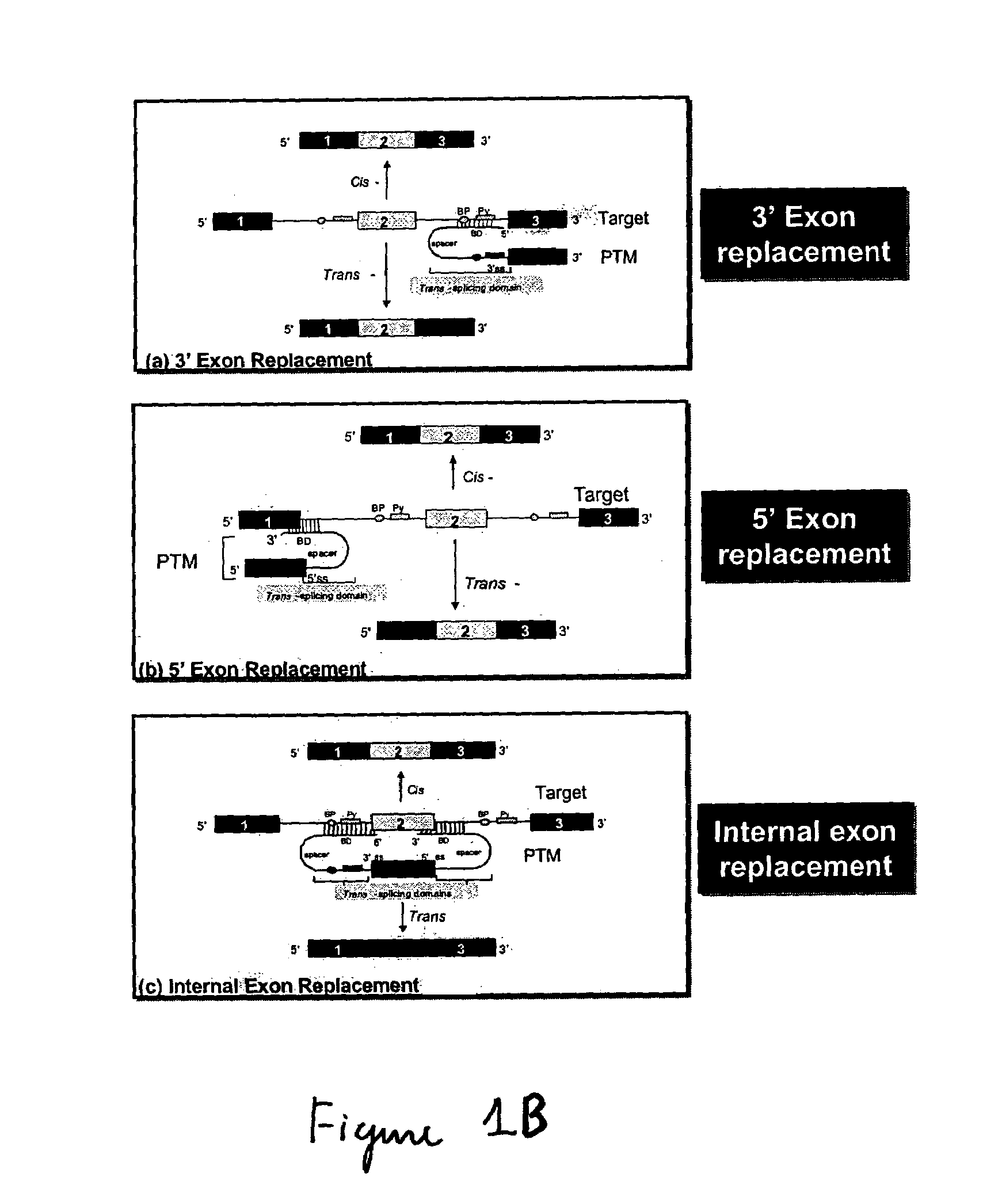
Methods and compositions for use in spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing
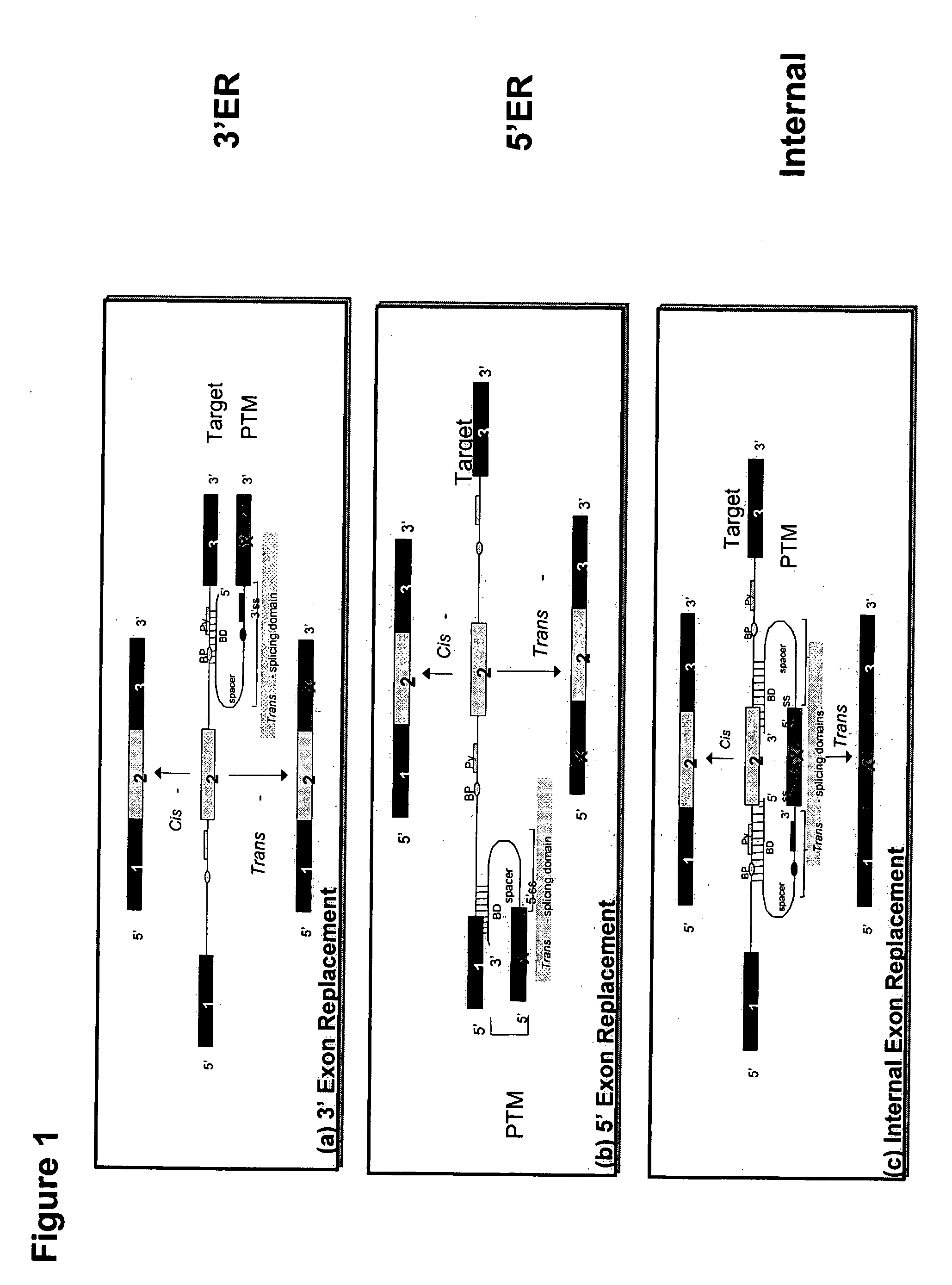
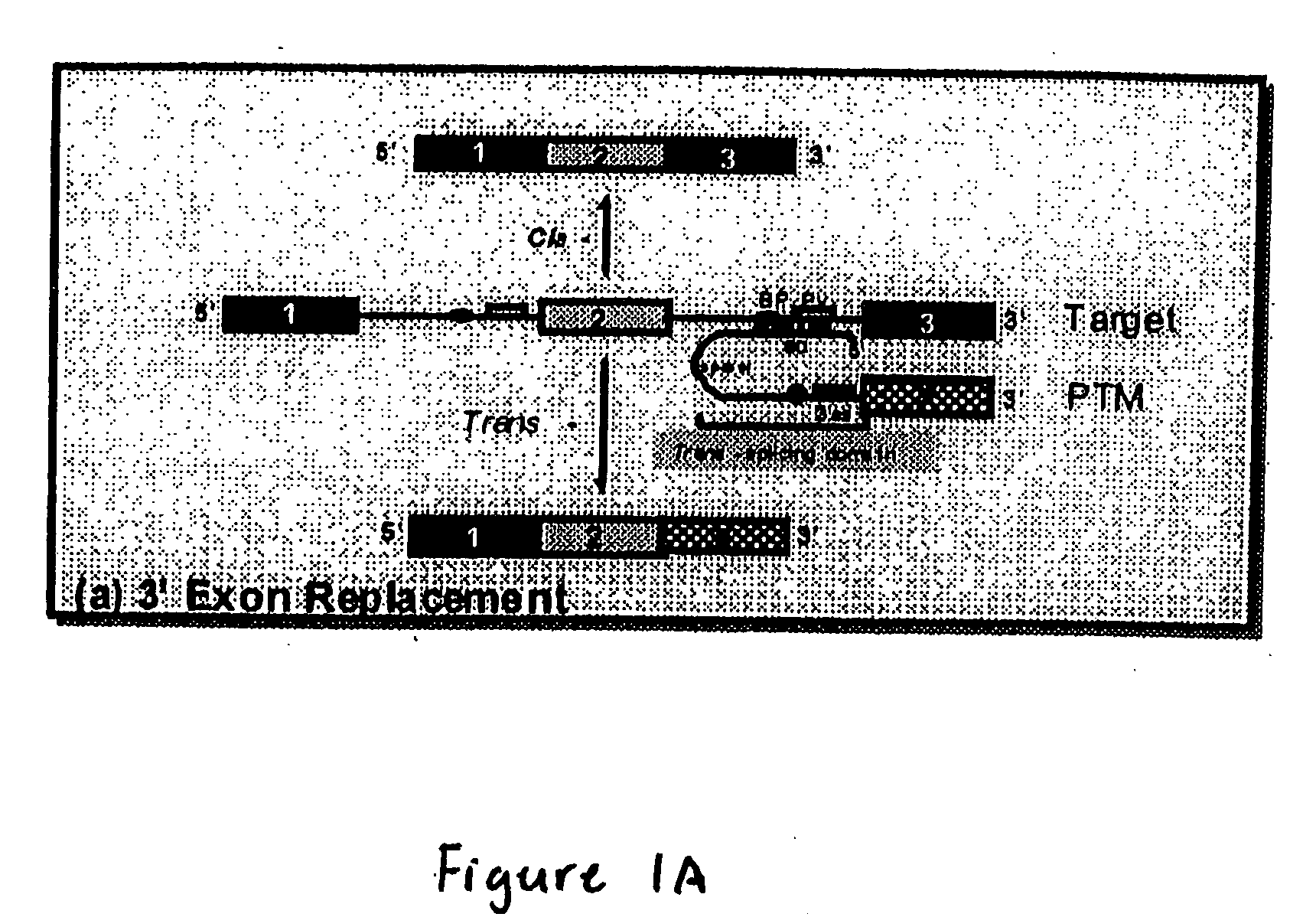
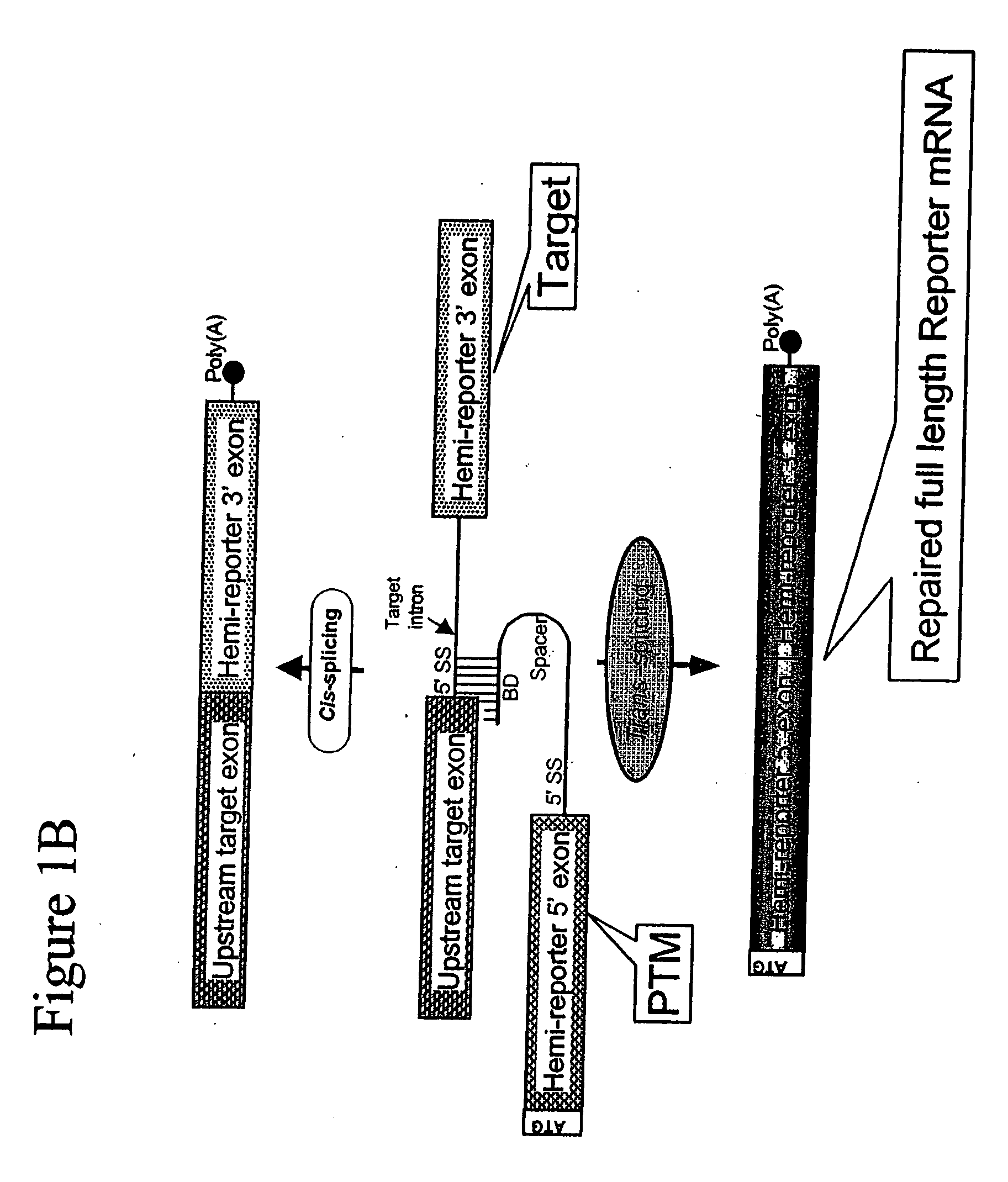
The molecules and methods of the present invention provide a means for in vivo production of a trans-spliced molecule in a selected subset of cells. The pre-trans-splicing molecules of the invention are substrates for a trans-splicing reaction between the pre-trans-splicing molecules and a pre-mRNA which is uniquely expressed in the specific target cells. The in vivo trans-splicing reaction provides a novel mRNA which is functional as mRNA or encodes a protein to be expressed in the target cells. The expression product of the mRNA is a protein of therapeutic value to the cell or host organism a toxin which causes killing of the specific cells or a novel protein not normally present in such cells. The invention further provides PTMs that have been genetically engineered for the identification of exon / intron boundaries of pre-mRNA molecules using an exon tagging method. The PTMs of the invention can also be designed to result in the production of chimeric RNA encoding for peptide affinity purification tags which can be used to purify and identify proteins expressed in a specific cell type.
Owner:INTRONN HLDG +1
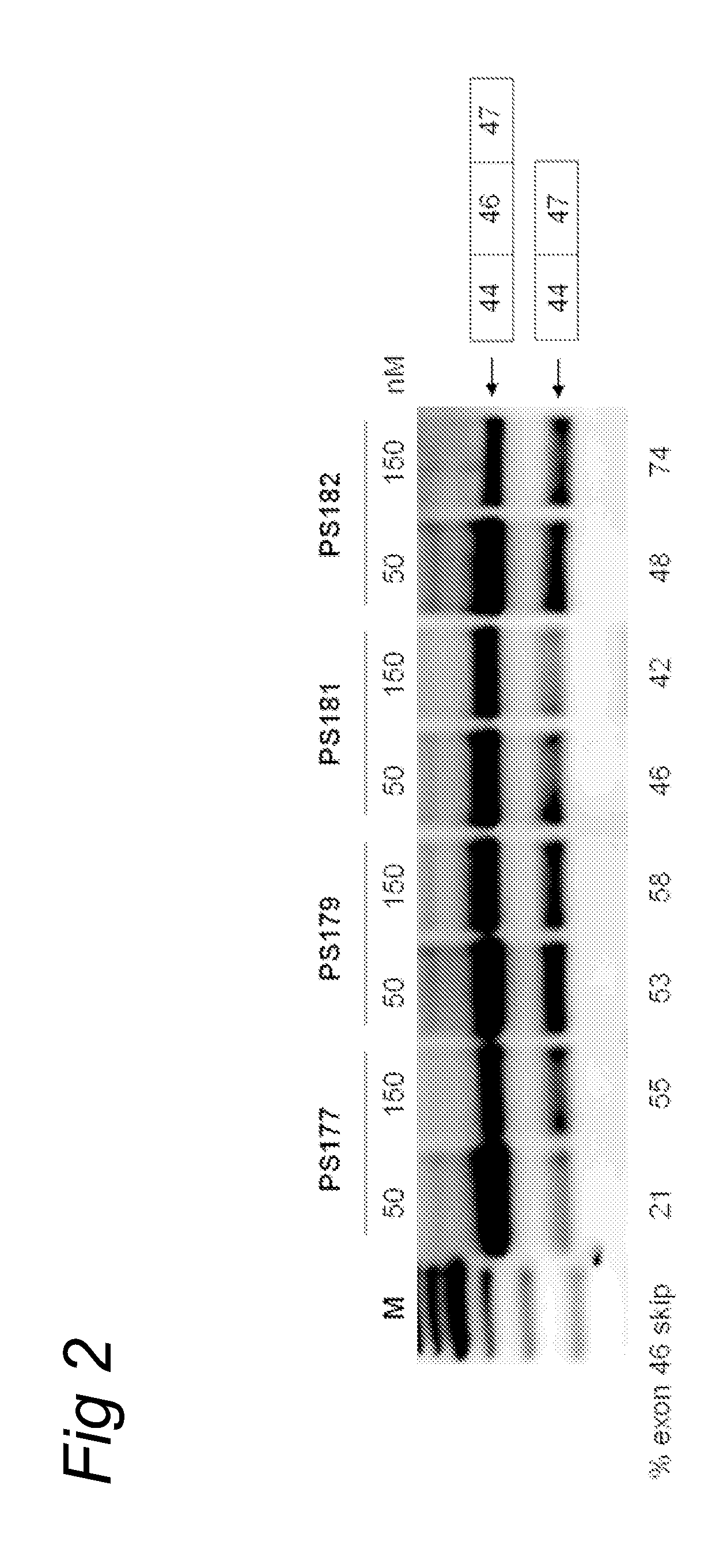
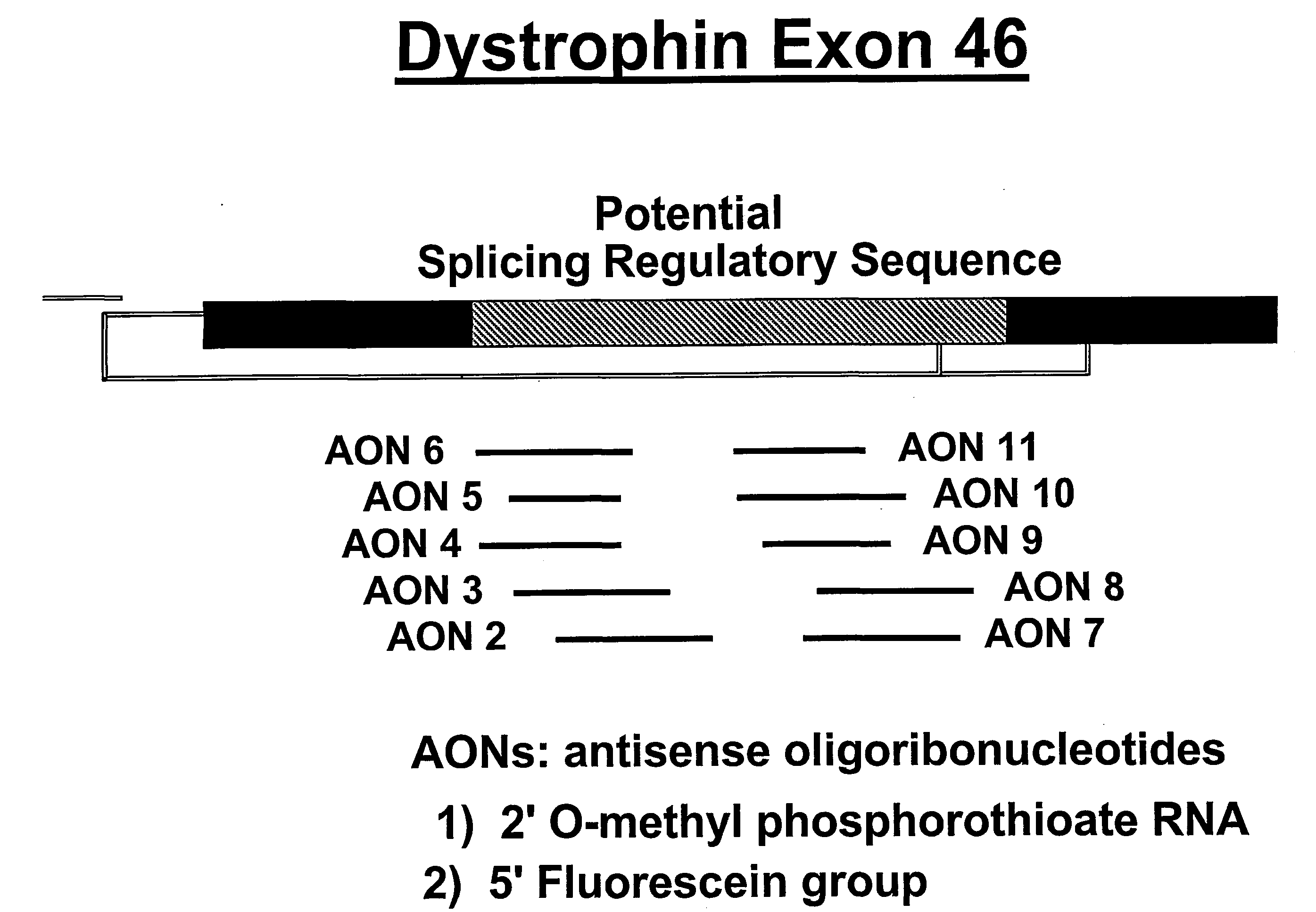
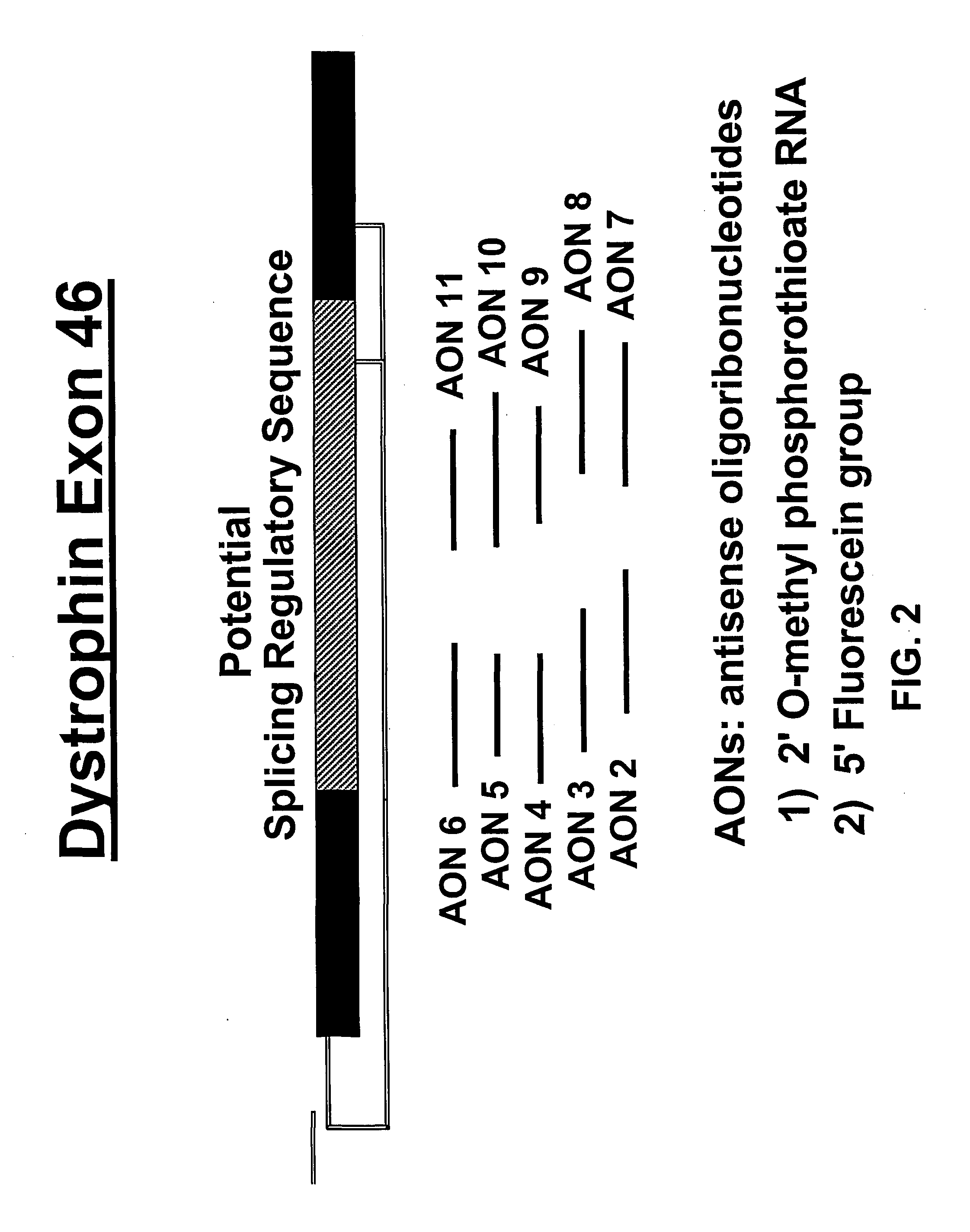
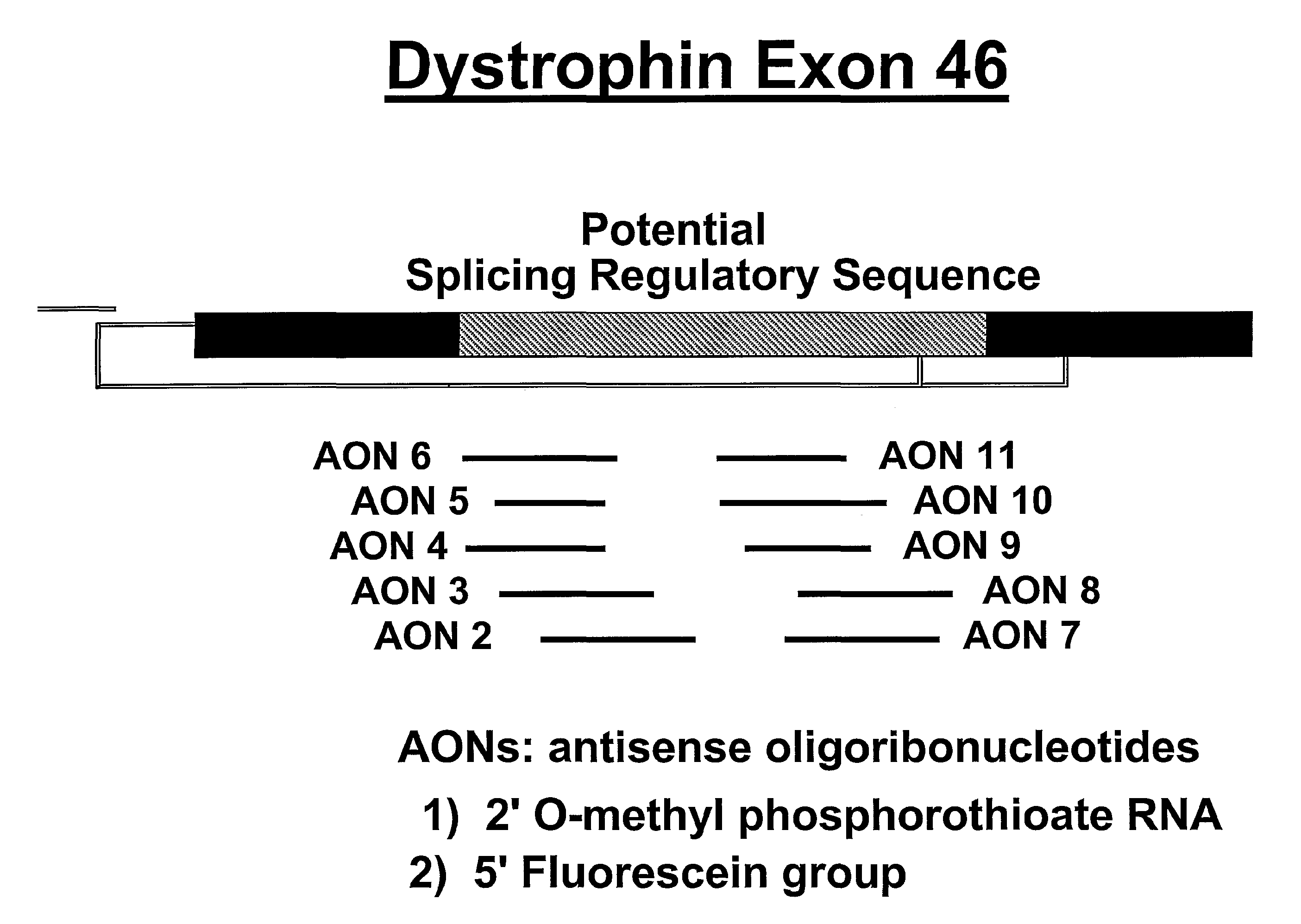
Induction of exon skipping in eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS7973015B2Efficiently maskedPotential for manipulationOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationPrecursor mRNARecognition sequence
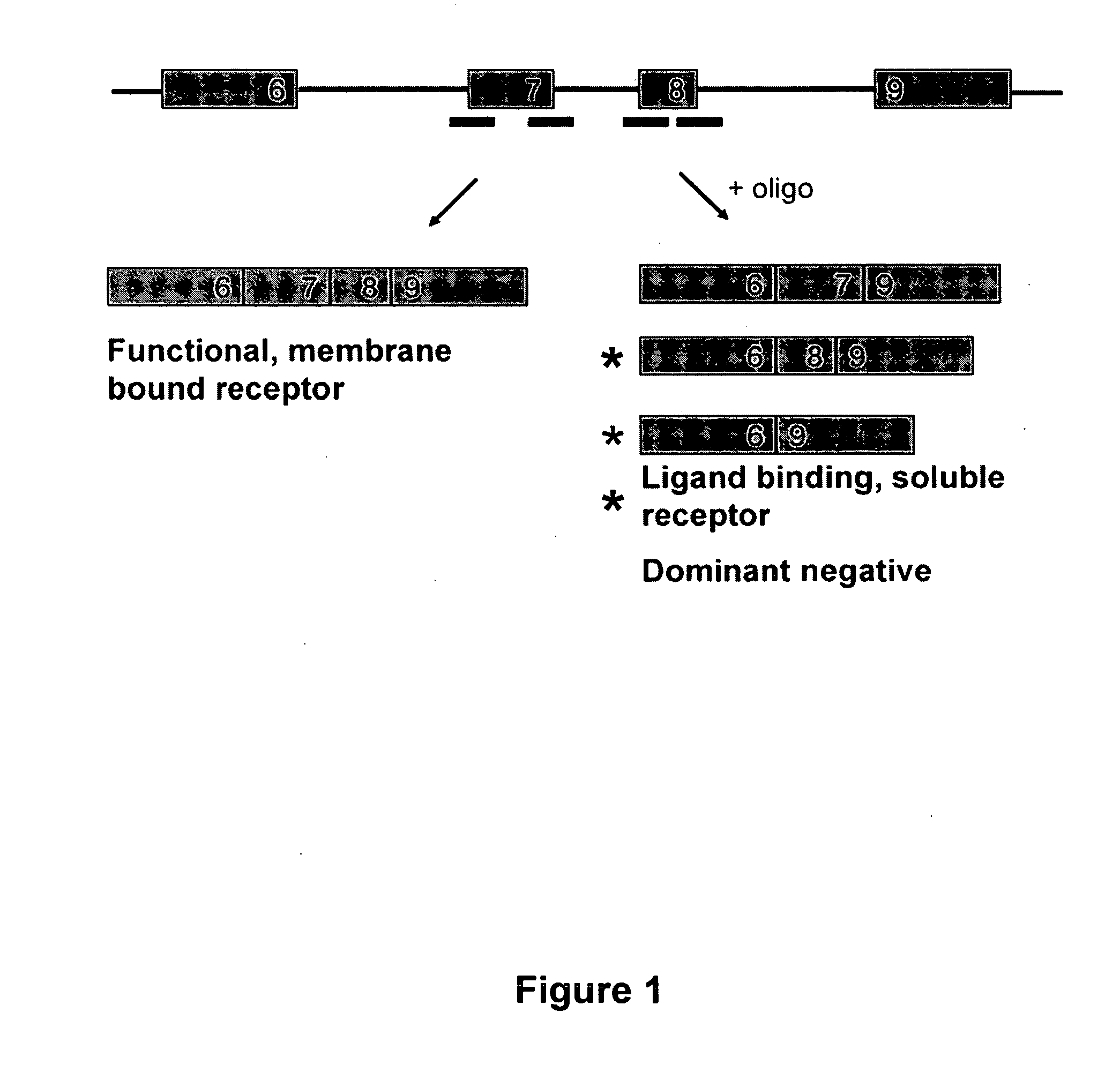
The present invention provides a method for at least in part decreasing the production of an aberrant protein in a cell, the cell comprising pre-mRNA comprising exons coding for the protein, by inducing so-called exon skipping in the cell. Exon-skipping results in mature MRNA that does not contain the skipped exon, which leads to an altered product of the exon codes for amino acids. Exon skipping is performed by providing a cell with an agent capable of specifically inhibiting an exon inclusion signal, for instance, an exon recognition sequence, of the exon. The exon inclusion signal can be interfered with by a nucleic acid comprising complementarity to a part of the exon. The nucleic acid, which is also herewith provided, can be used for the preparation of a medicament, for instance, for the treatment of an inherited disease.
Owner:LEIDEN ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS
Oligomers
Molecules are provided for inducing or facilitating exon skipping in forming spliced mRNA products from pre-mRNA molecules in cells. The molecules may be provided directly as oligonucleotides or expression products of vectors that are administered to a subject. High rates of skipping can be achieved. High rates of skipping reduce the severity of a disease like Duchene Muscular Dystrophy so that the disease is more like Becker Muscular Dystrophy. This is a severe reduction in symptom severity and mortality.
Owner:ROYAL HOLLOWAY & BEDFORD NEW COLLEGE
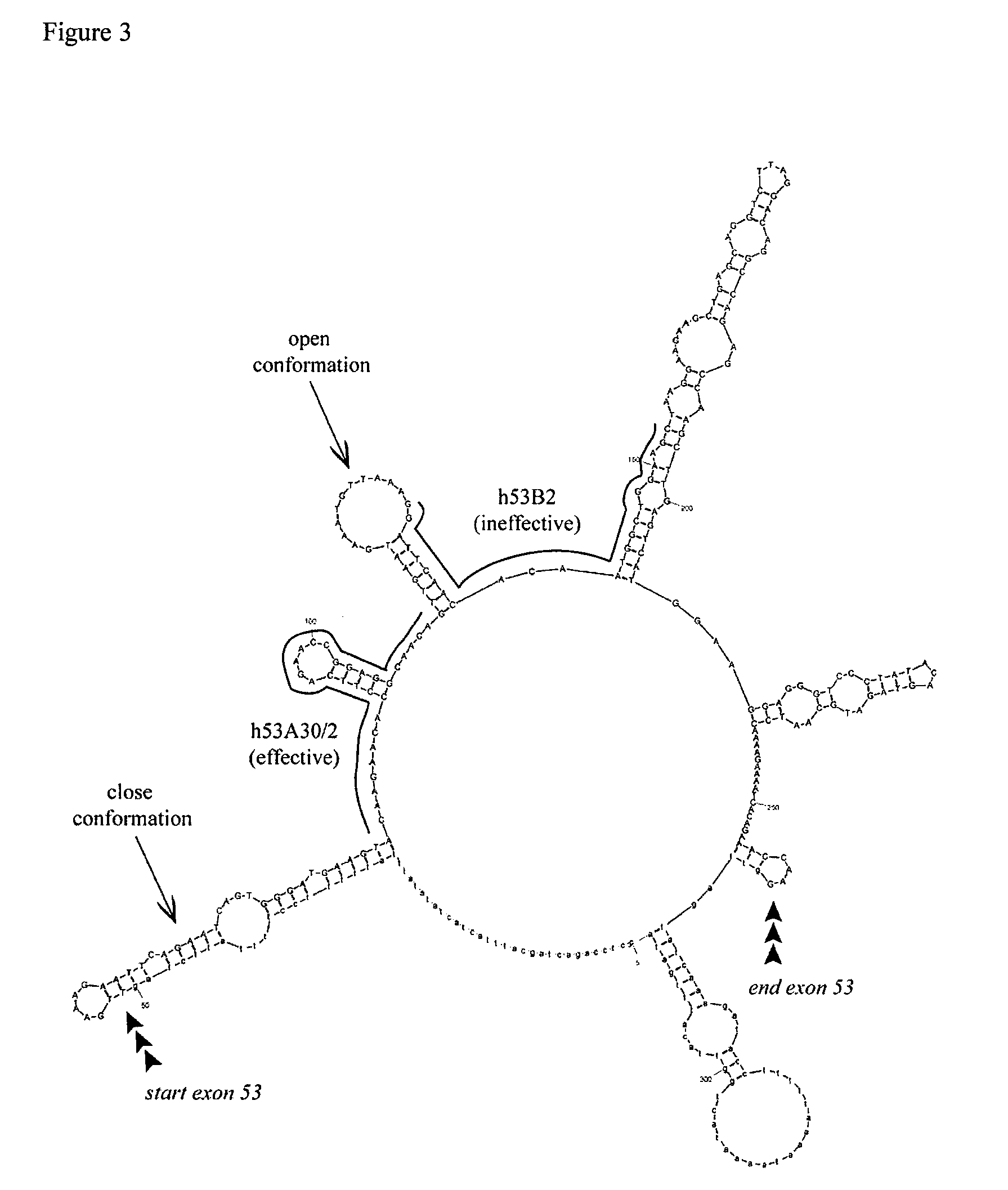
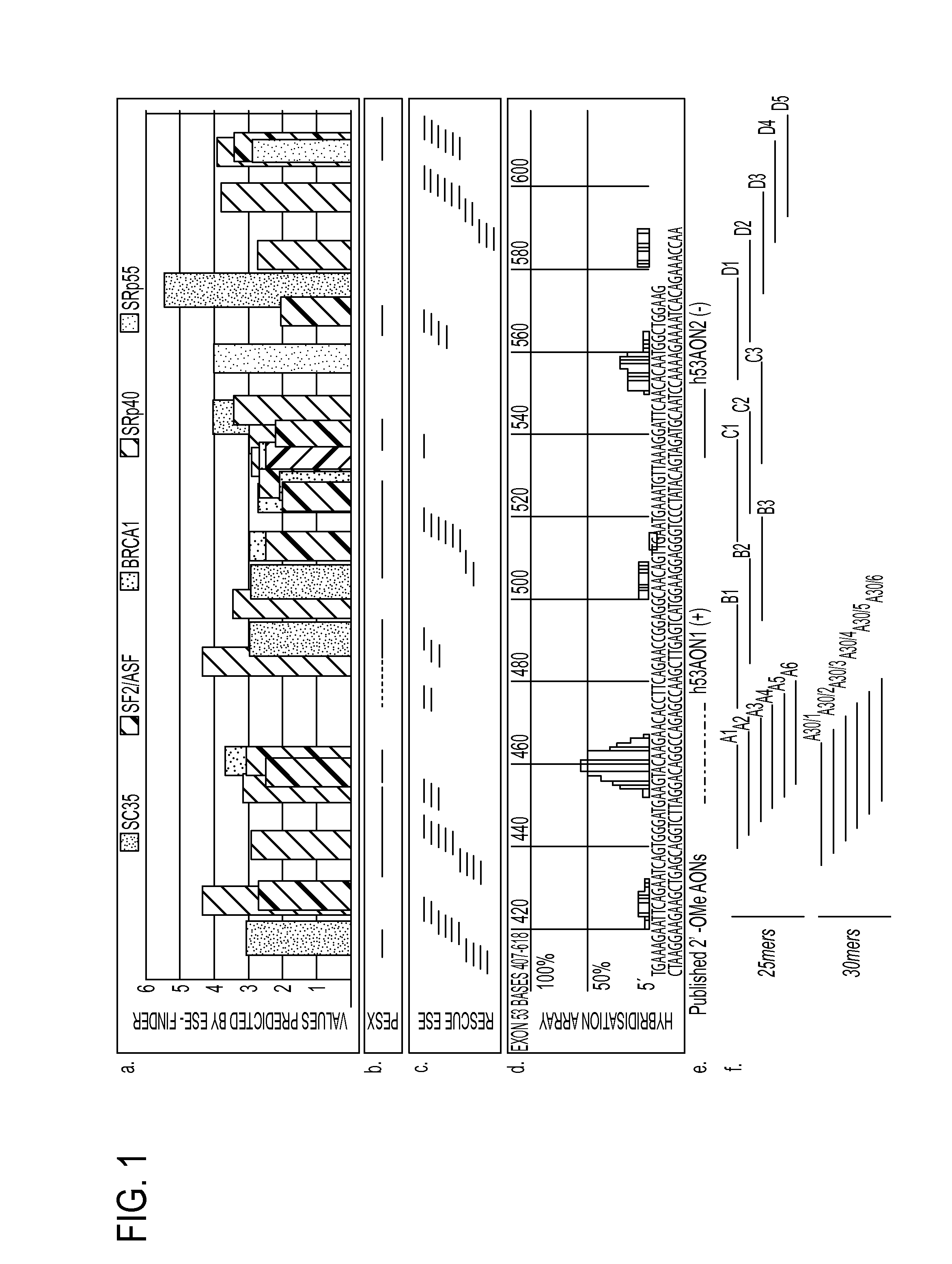
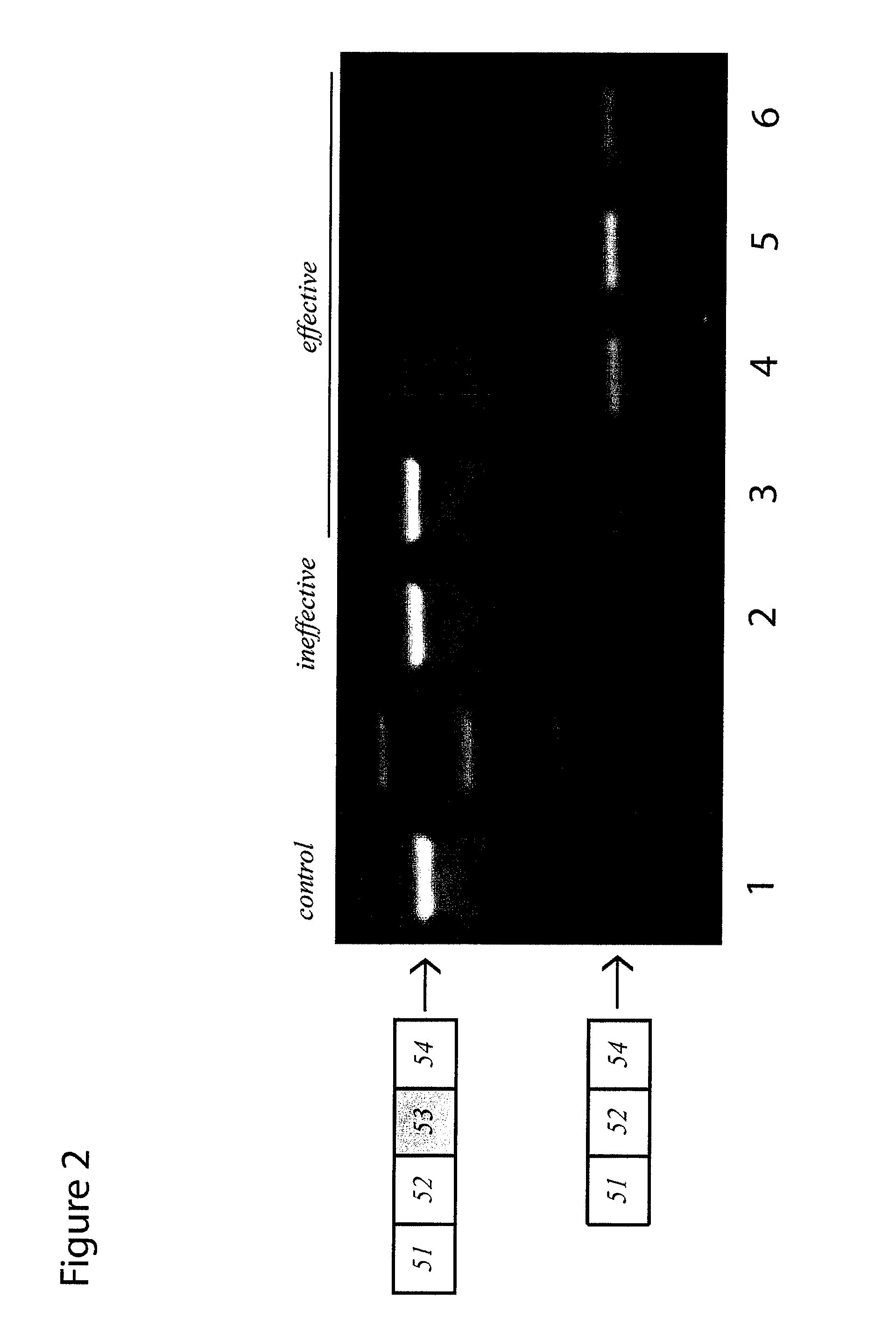
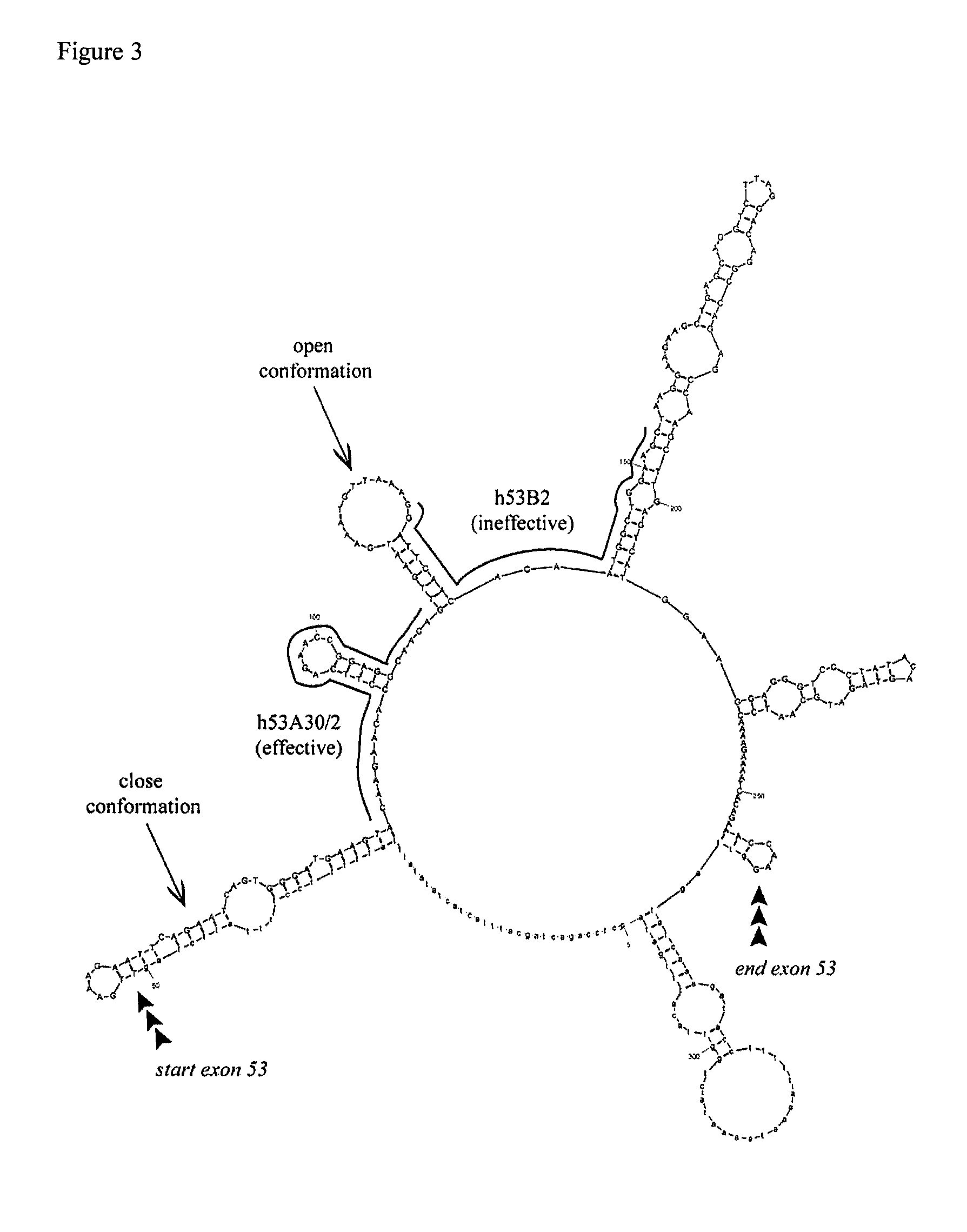
Modulation of exon recognition in pre-mRNA by interfering with the secondary RNA structure
InactiveUS20060099616A1Improves invasion efficiencyImprove efficiencySplicing alterationSugar derivativesPrecursor mRNAOligonucleotide
The invention provides a method for generating an oligonucleotide with which an exon may be skipped in a pre-mRNA and thus excluded from a produced mRNA thereof. Further provided are methods for altering the secondary structure of an mRNA to interfere with splicing processes and uses of the oligonucleotides and methods in the treatment of disease. Further provided are pharmaceutical compositions and methods and means for inducing skipping of several exons in a pre-mRNA.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
Correction of alpha-1-antitrypsin genetic defects using spliceosome mediated RNA trans splicing
InactiveUS20060234247A1Reduce lungReduce liver pathologySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseRNA Trans-Splicing
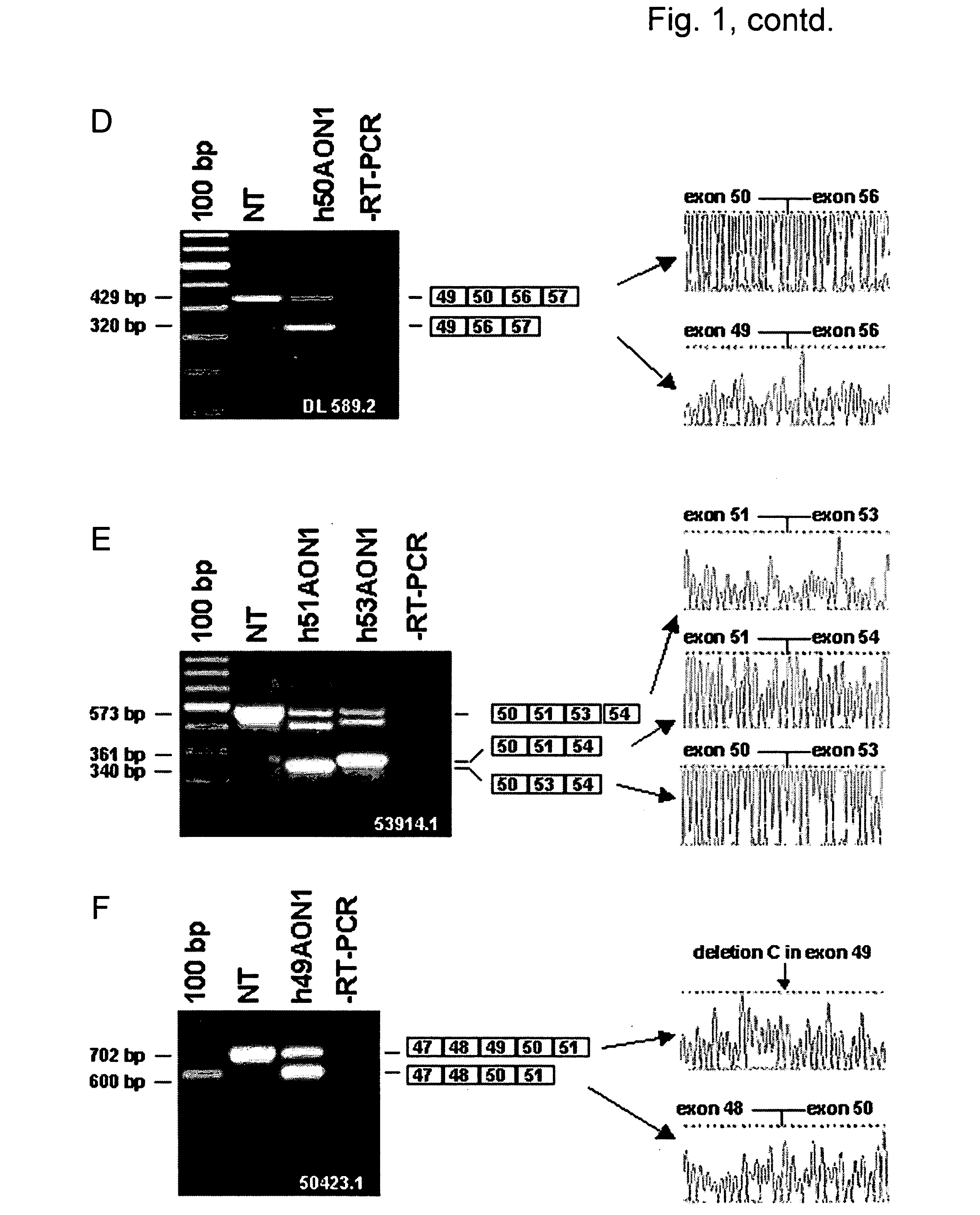
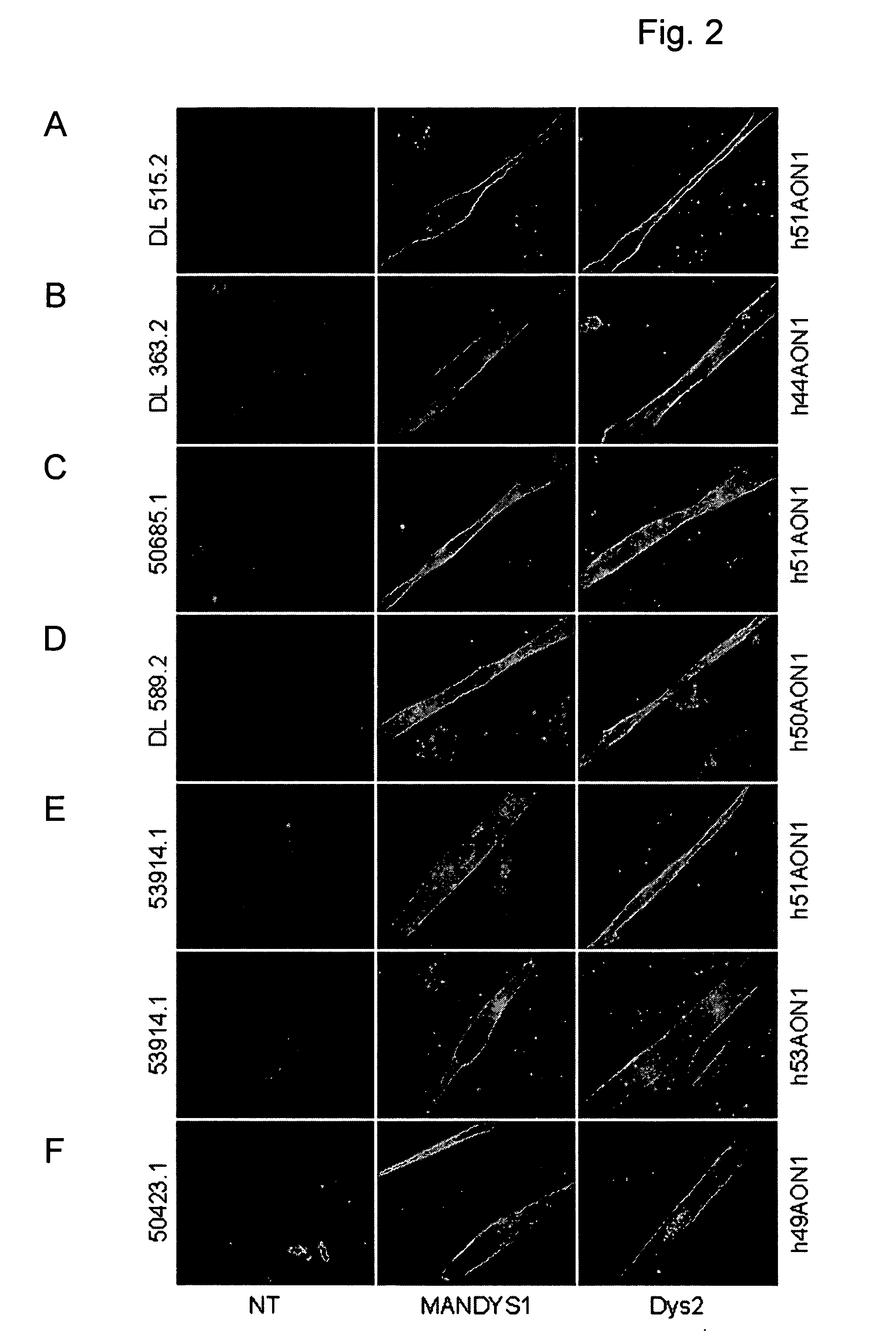
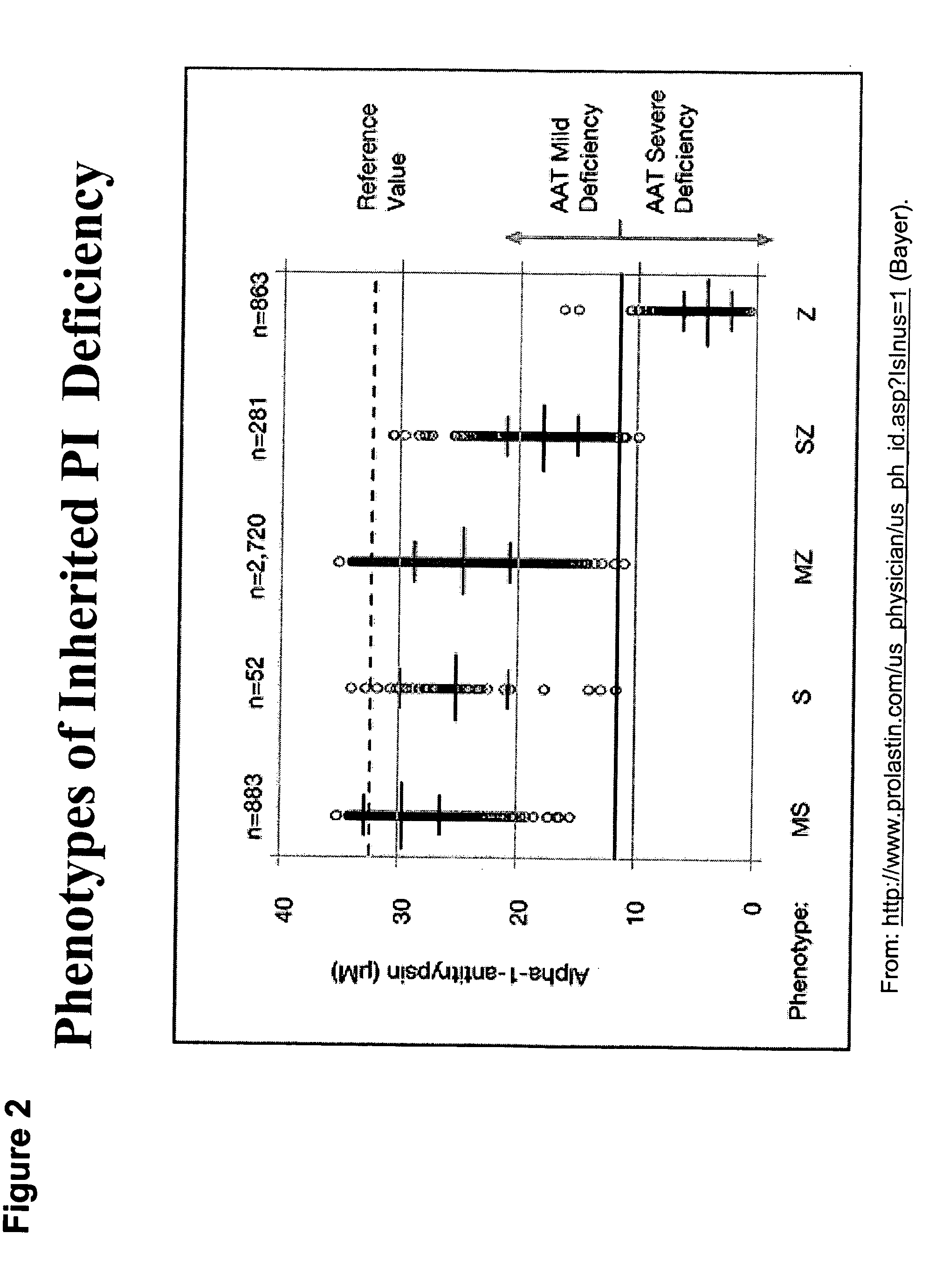
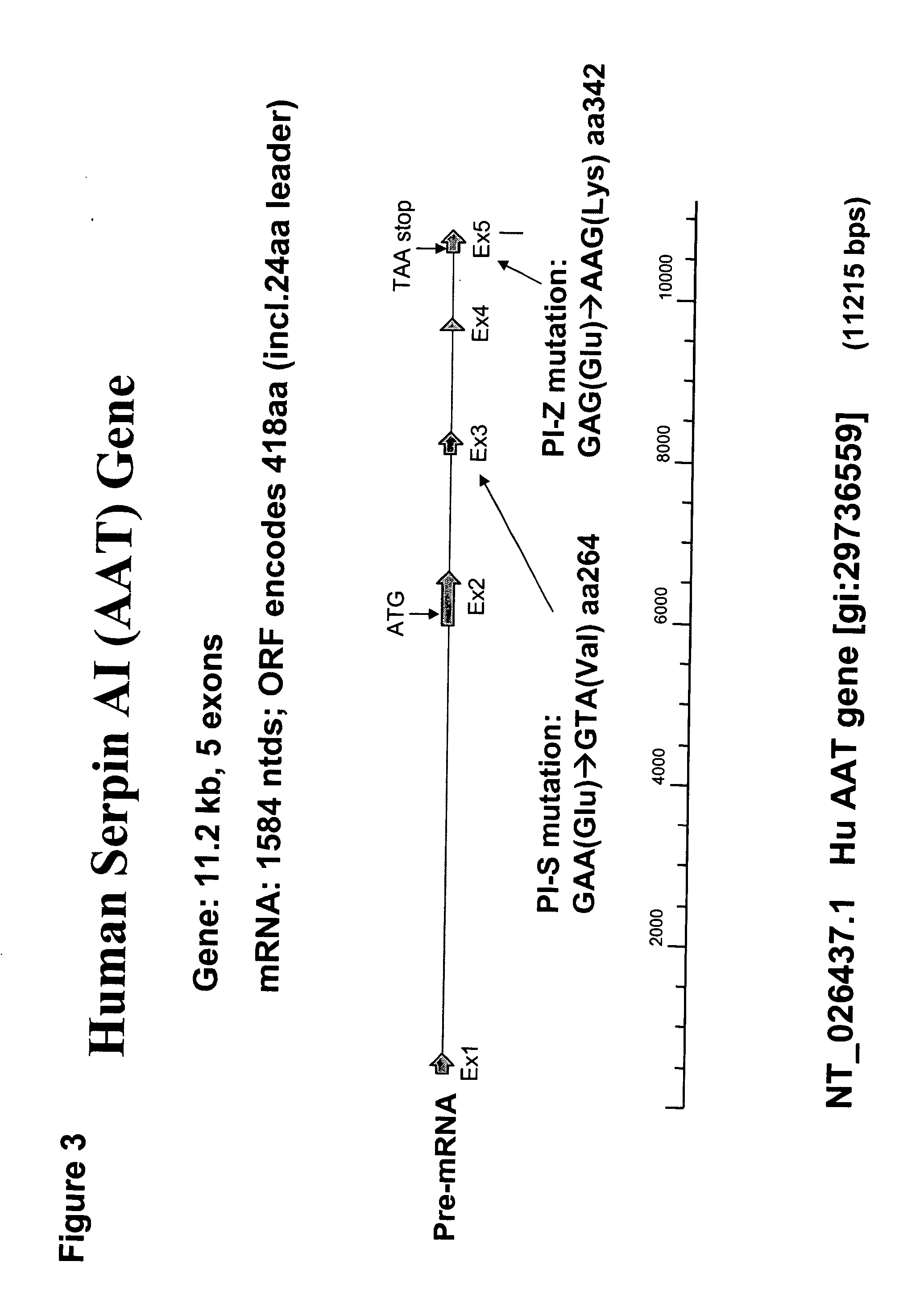
The present invention provides methods and compositions for generating novel nucleic acid molecules through targeted spliceosomal mediated RNA trans-splicing. The compositions of the invention include pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with a SERPINA1 target precursor messenger RNA molecule (target pre-mRNA) and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of a novel chimeric RNA molecule (chimeric RNA). In particular, the PTMs of the present invention include those genetically engineered to interact with SERPINA1 target pre-mRNA so as to result in correction of SERPINA1 genetic defects responsible for AAT deficiency. The PTMs of the invention may also comprise sequences that are processed out of the PTM to yield duplex siRNA molecules directed specifically to mutant SERPIN A1 mRNAs. Such duplexed siRNAs are designed to reduce the accumulation of toxic AAT protein in liver cells. The methods and compositions of the present invention can be used in gene therapy for correction of SERPINA1 disorders such as AAT deficiency.
Owner:VIRXSYS
Modulation of exon recognition in pre-mRNA by interfering with the secondary RNA structure
ActiveUS20060147952A1Lower Level RequirementsSevere phenotypeSplicing alterationSugar derivativesDiseasePrecursor mRNA
The invention provides a method for generating an oligonucleotide with which an exon may be skipped in a pre-mRNA and thus excluded from a produced mRNA thereof. Further provided are methods for altering the secondary structure of an mRNA to interfere with splicing processes and uses of the oligonucleotides and methods in the treatment of disease. Further provided are pharmaceutical compositions and methods and means for inducing skipping of several exons in a pre-mRNA.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
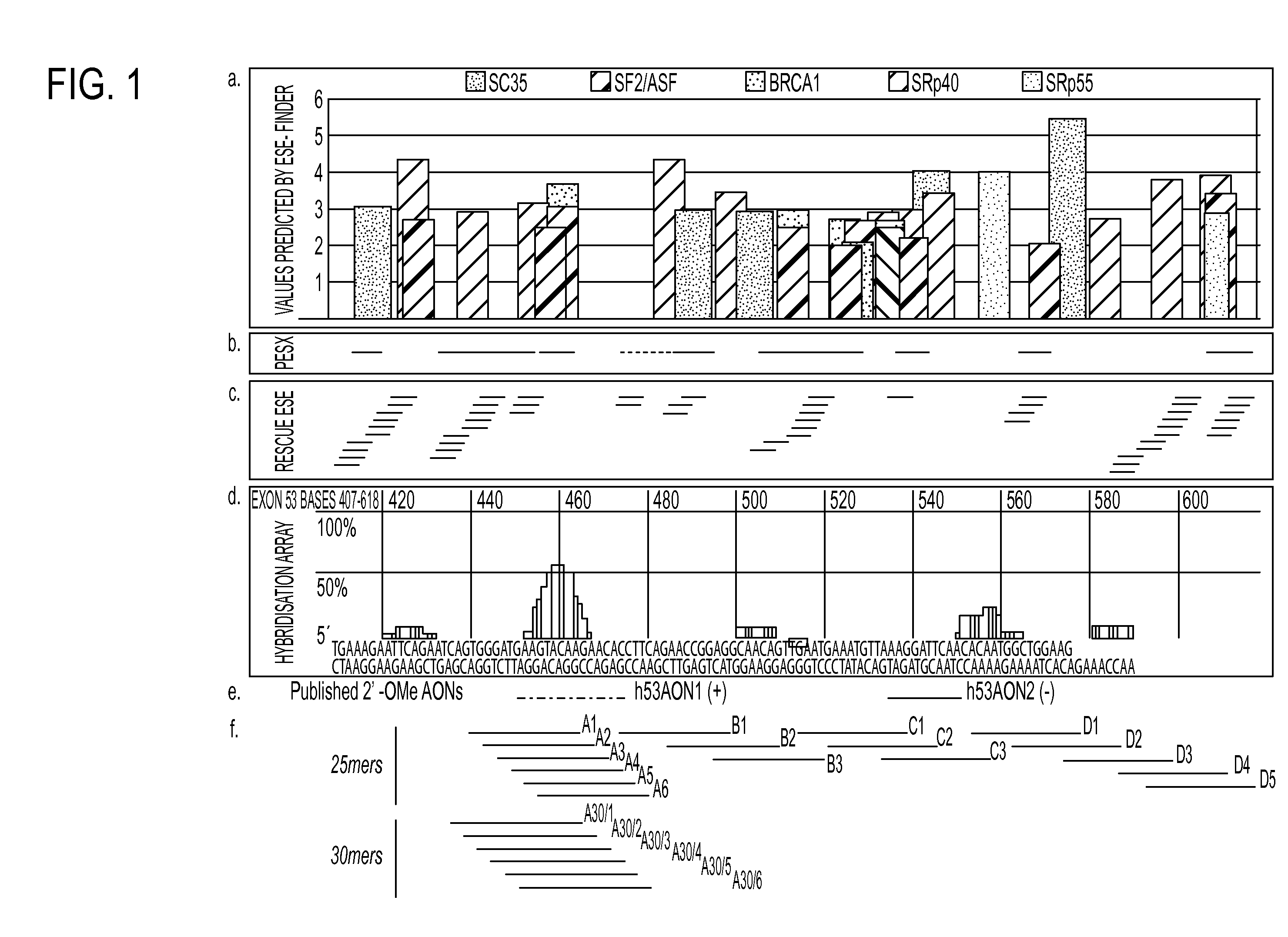
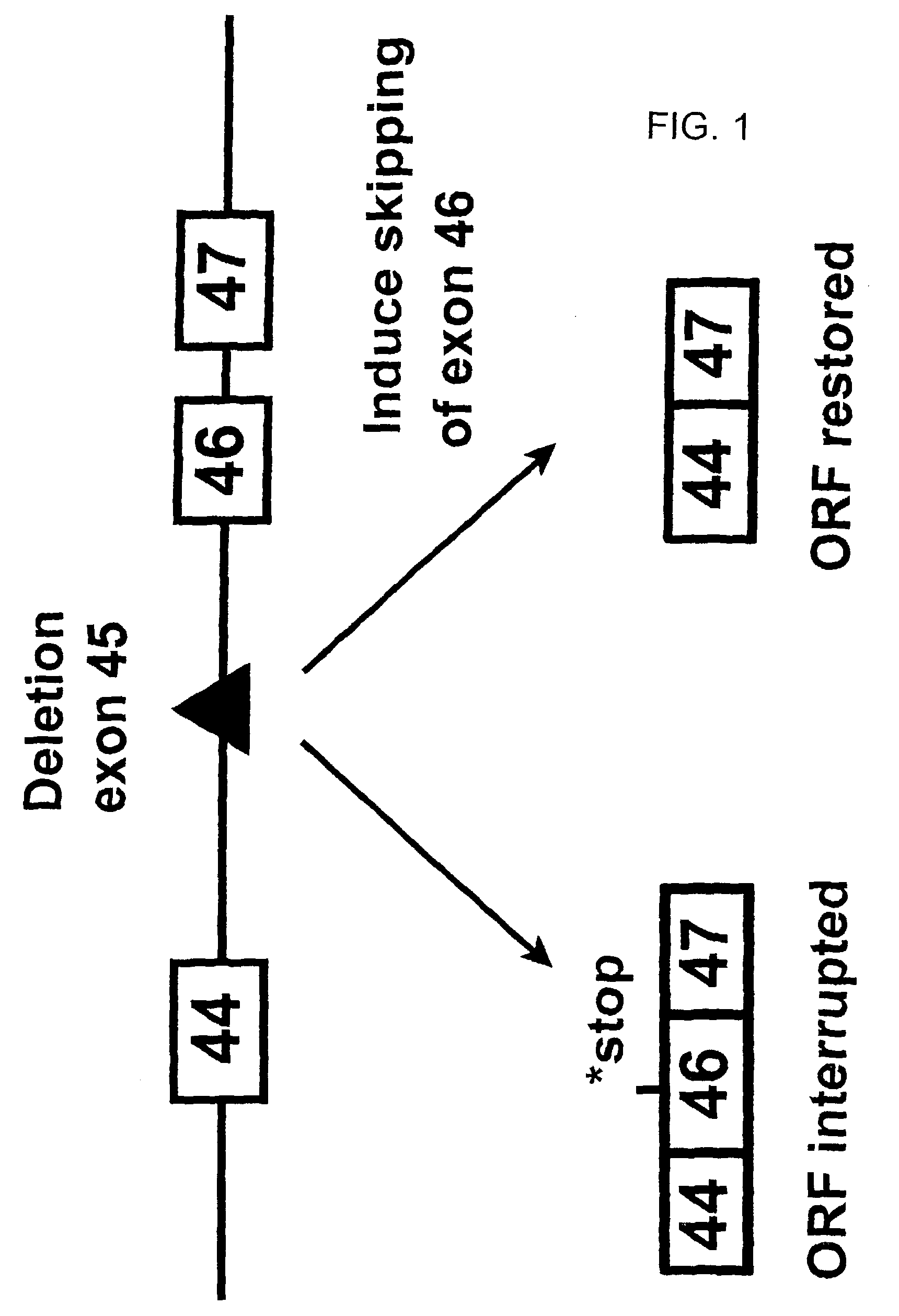
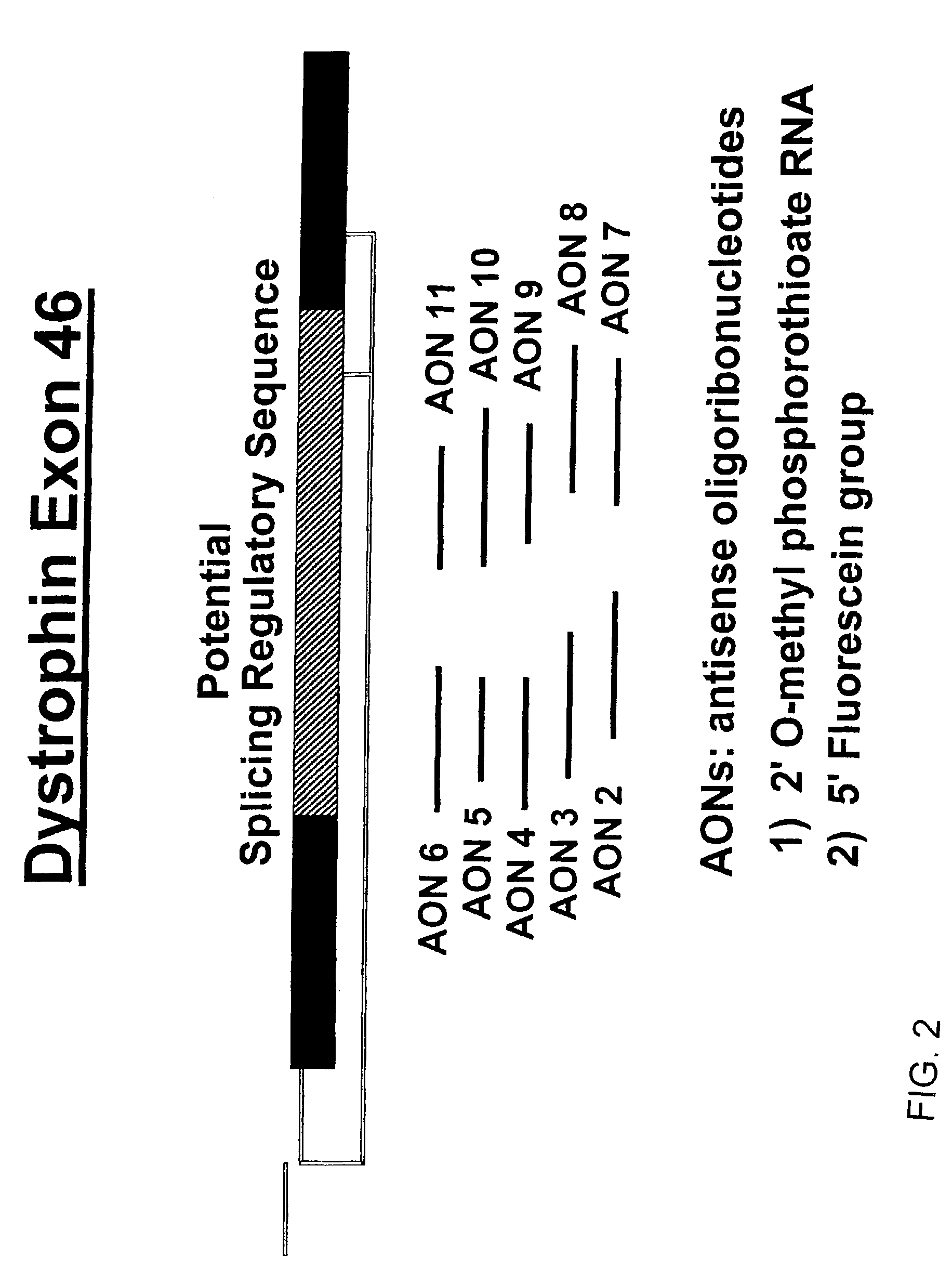
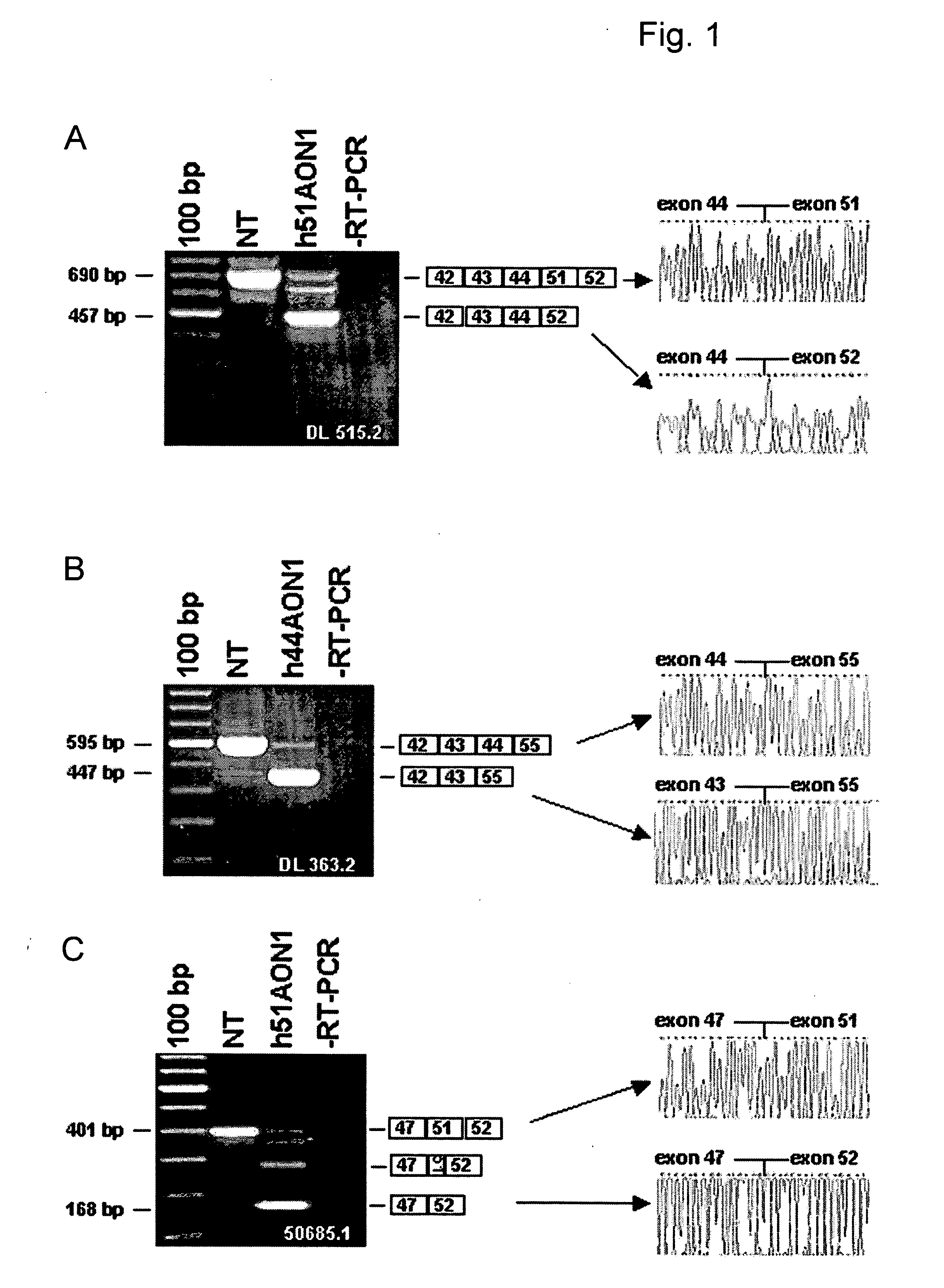
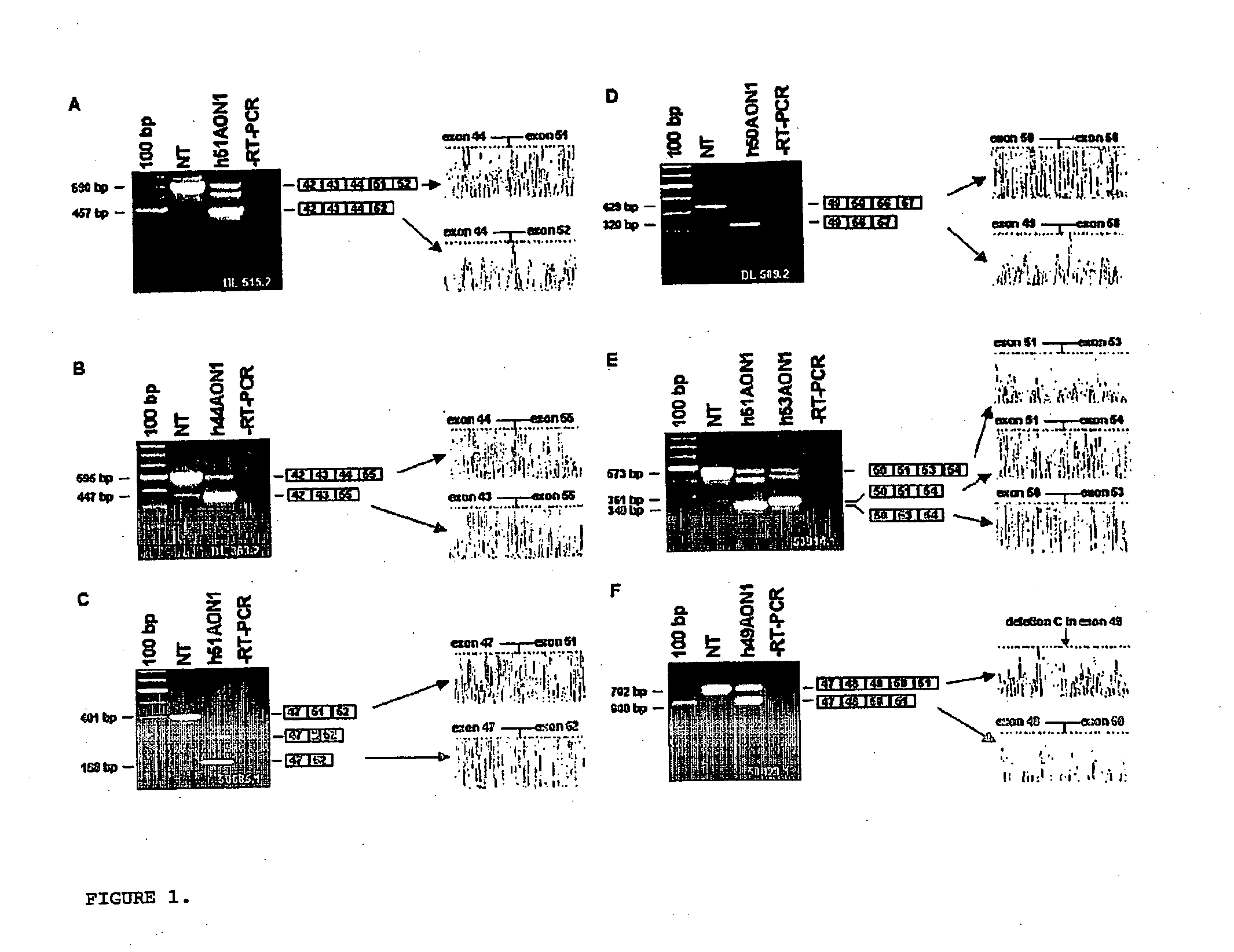
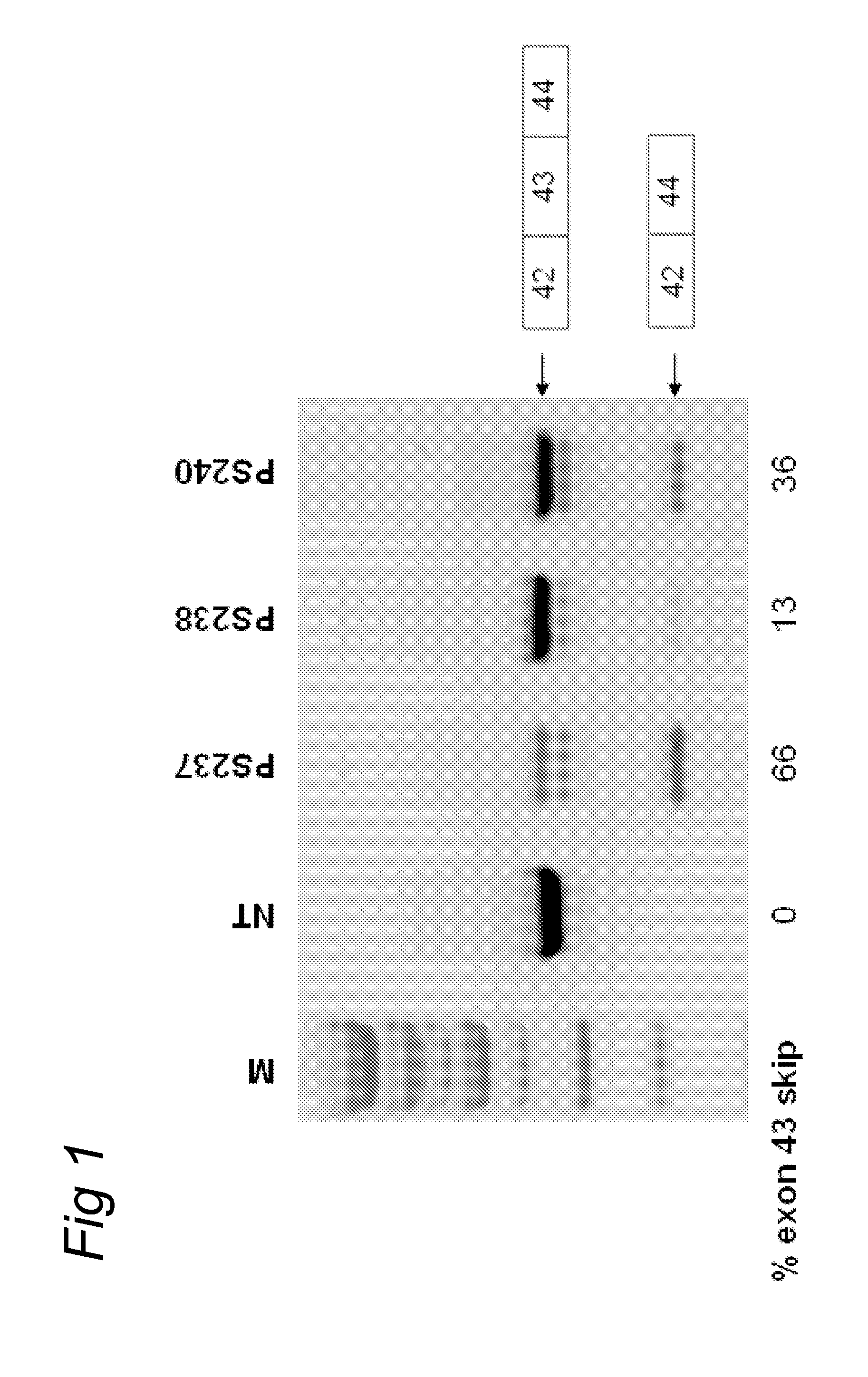
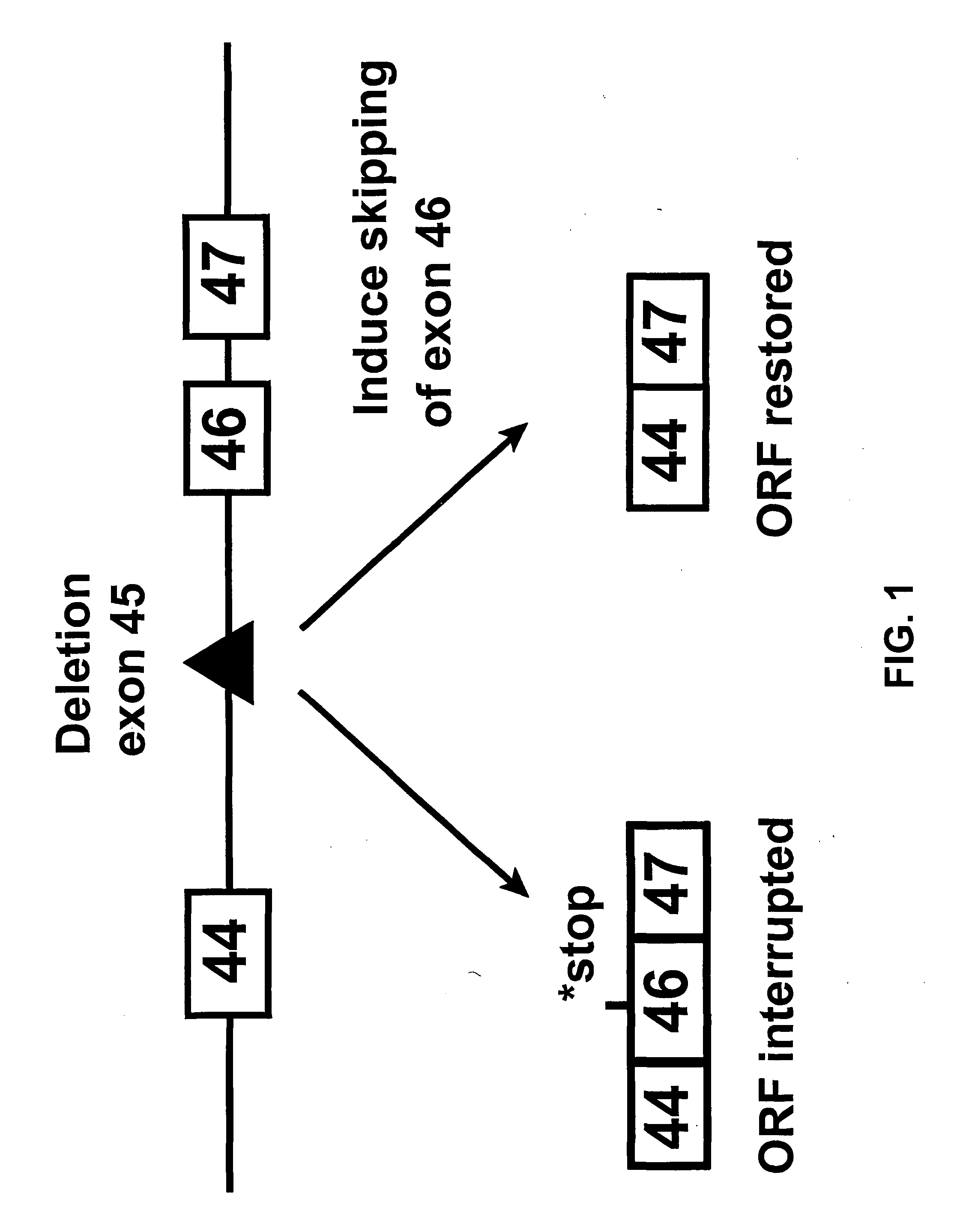
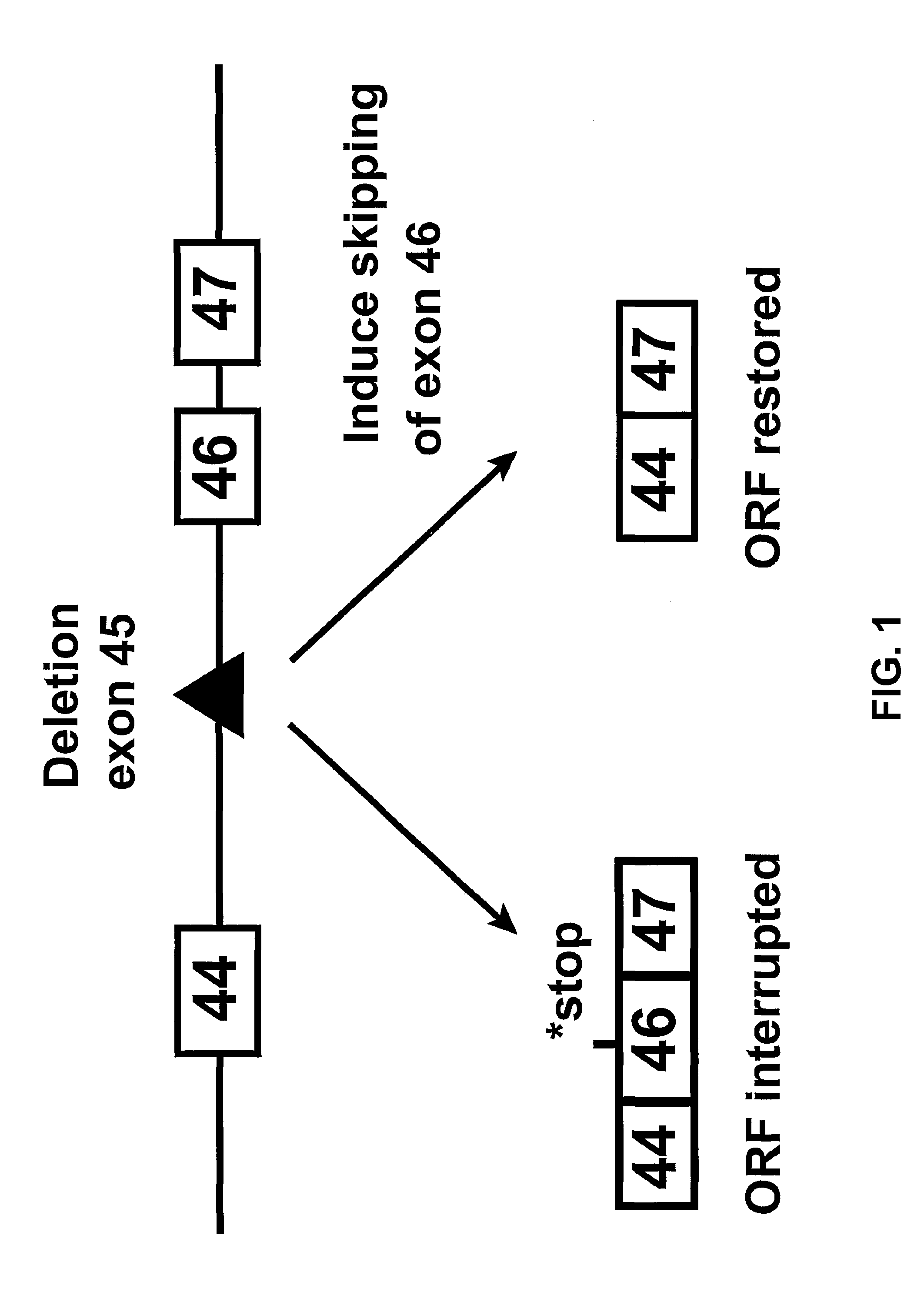
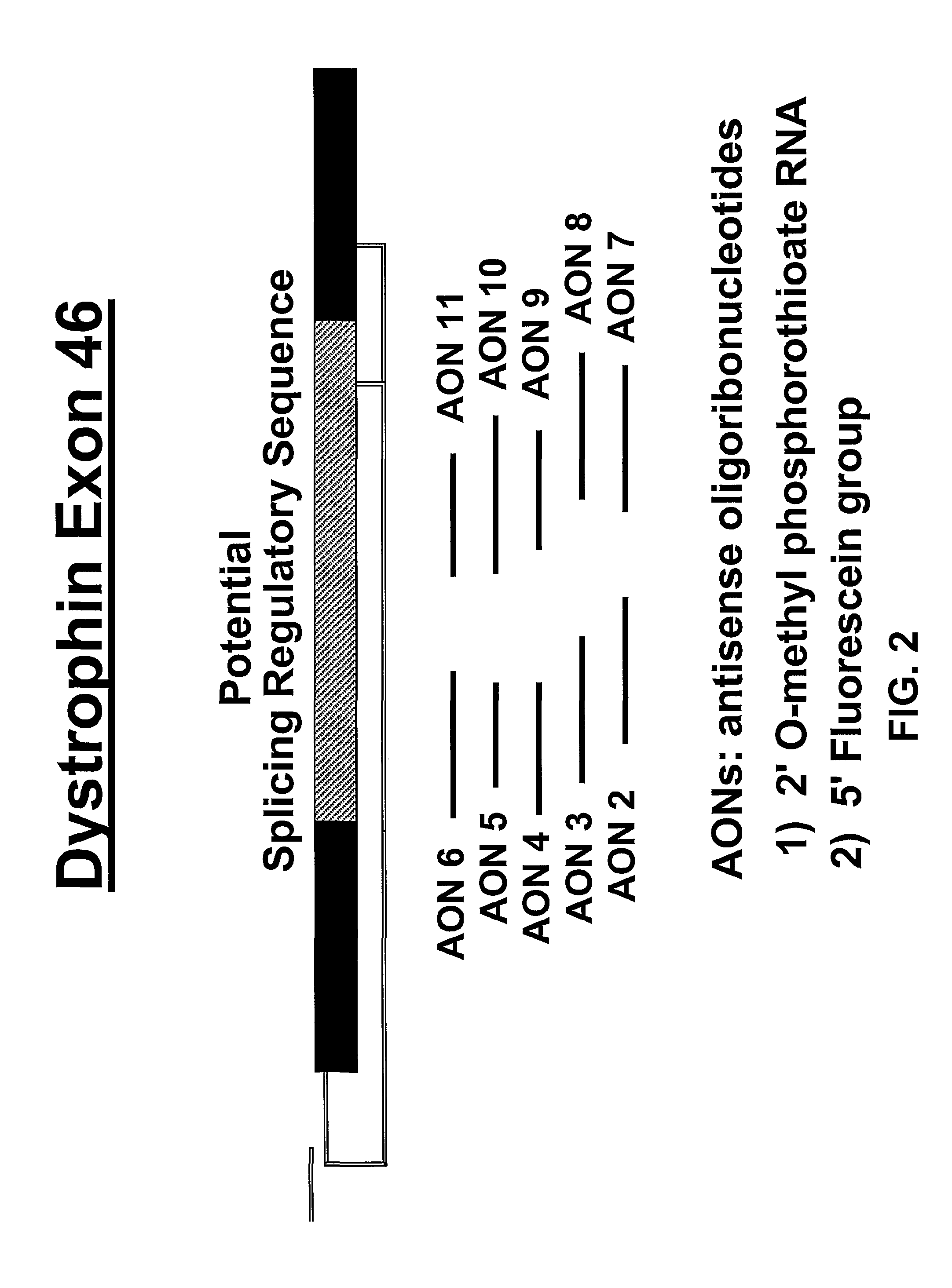
Methods and means for efficient skipping of at least one of the following exons of the human duchenne muscular dystrophy gene: 43, 46, 50-53
InactiveUS20110263682A1Improve featuresMany symptomOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationMedicinePrecursor mRNA
The invention relates a method wherein a molecule is used for inducing and / or promoting skipping of at least one of exon 43, exon 46, exons 50-53 of the DMD pre-mRNA in a patient, preferably in an isolated cell of a patient, the method comprising providing said cell and / or said patient with a molecule. The invention also relates to said molecule as such.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT +2
Induction of exon skipping in eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20090228998A1Efficiently maskedPotential for manipulationOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationPrecursor mRNARecognition sequence
The present invention provides a method for at least in part decreasing the production of an aberrant protein in a cell, the cell comprising pre-mRNA comprising exons coding for the protein, by inducing so-called exon skipping in the cell. Exon-skipping results in mature mRNA that does not contain the skipped exon, which leads to an altered product of the exon codes for amino acids. Exon skipping is performed by providing a cell with an agent capable of specifically inhibiting an exon inclusion signal, for instance, an exon recognition sequence, of the exon. The exon inclusion signal can be interfered with by a nucleic acid comprising complementarity to a part of the exon. The nucleic acid, which is also herewith provided, can be used for the preparation of a medicament, for instance, for the treatment of an inherited disease.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
Induction of exon skipping in eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20080209581A1Reduce productionReduce amountOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationPrecursor mRNARecognition sequence
Described is a method for at least in part decreasing the production of an aberrant protein in a cell, the cell comprising pre-mRNA comprising exons coding for the protein, by inducing so-called exon skipping in the cell. Exon-skipping results in mature mRNA that does not contain the skipped exon, which leads to an altered product of the exon codes for amino acids. Exon skipping is performed by providing a cell with an agent capable of specifically inhibiting an exon inclusion signal, for instance, an exon recognition sequence, of the exon. The exon inclusion signal can be interfered with by a nucleic acid comprising complementarity to a part of the exon. The nucleic acid, which is also herewith provided, can be used for the preparation of a medicament, for instance, for the treatment of an inherited disease.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
Targeted pre-mRNA/mRNA modification and gene regulation
ActiveUS20070141030A1Easy to identifyLarge productionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAdenosinePrecursor mRNA
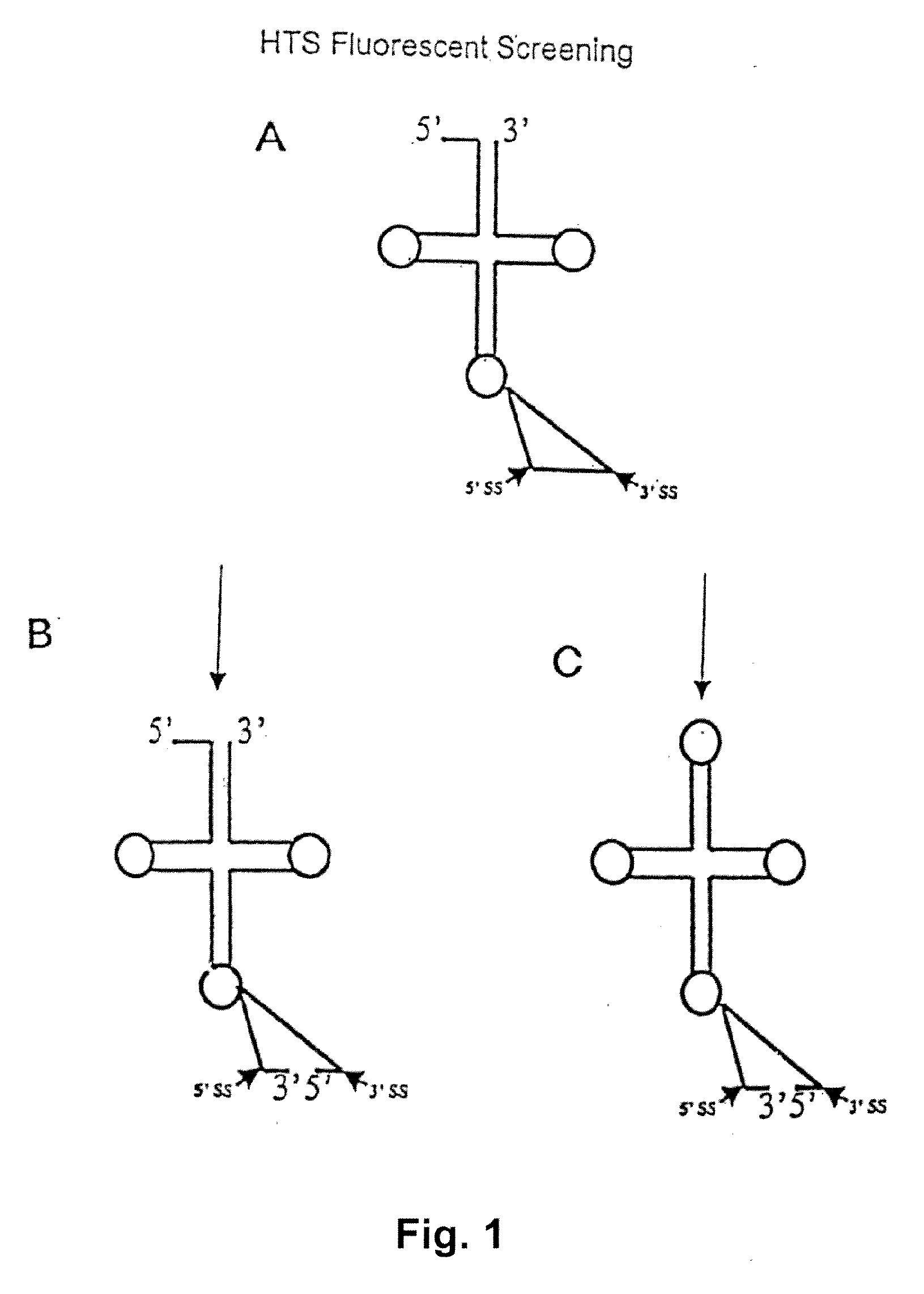
Methods for affecting mRNA expression or translation through the modification of pre-mRNA or mRNA transcripts are described. In one embodiment of the methods of the present invention, the branch point adenosine of a pre-mRNA transcript is 2′-O-methylated to block splicing and subsequent expression of the protein encoded by the transcript. In another embodiment, a uridine residue in a nonsense stop codon may be modified to pseudouridine, causing the translation machinery to read through the nonsense stop codon and translate a full length protein.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
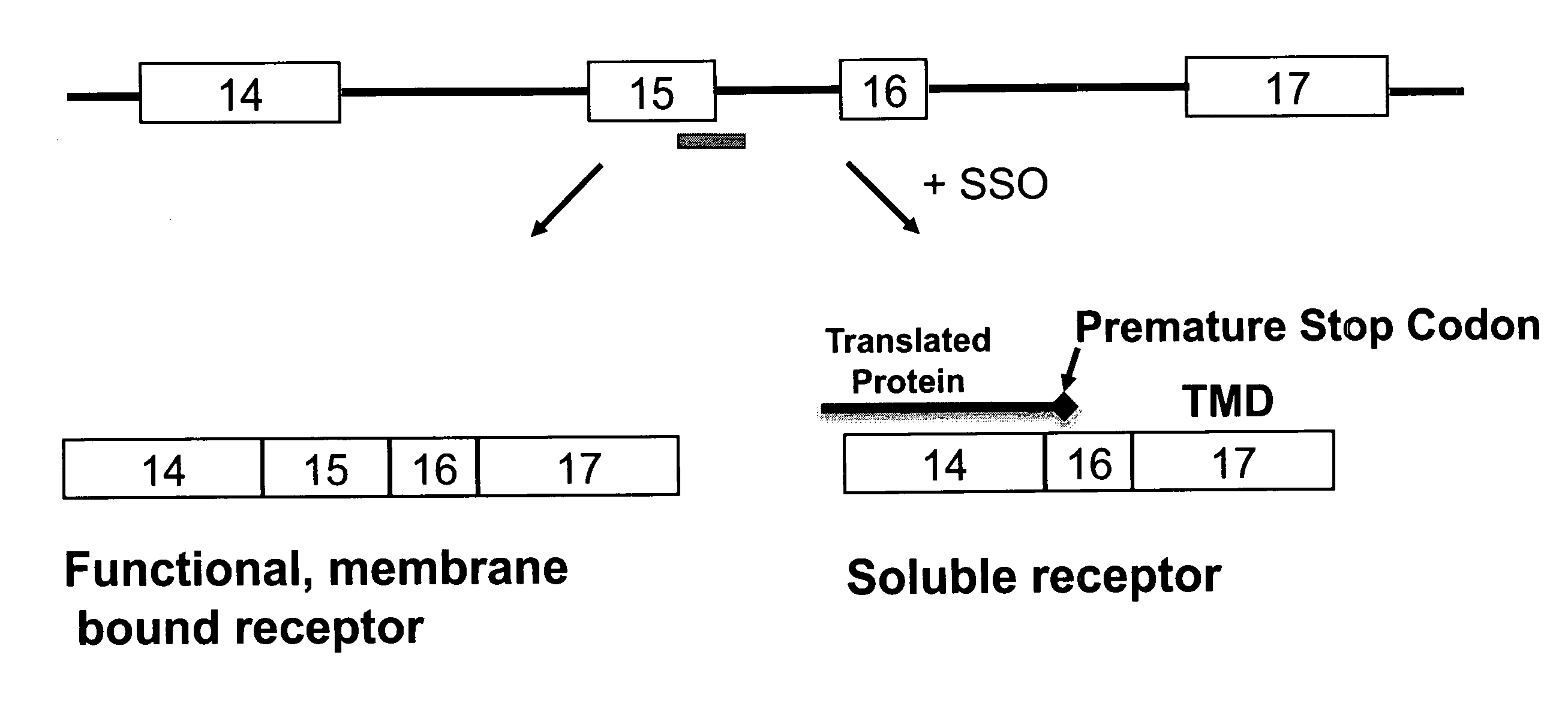
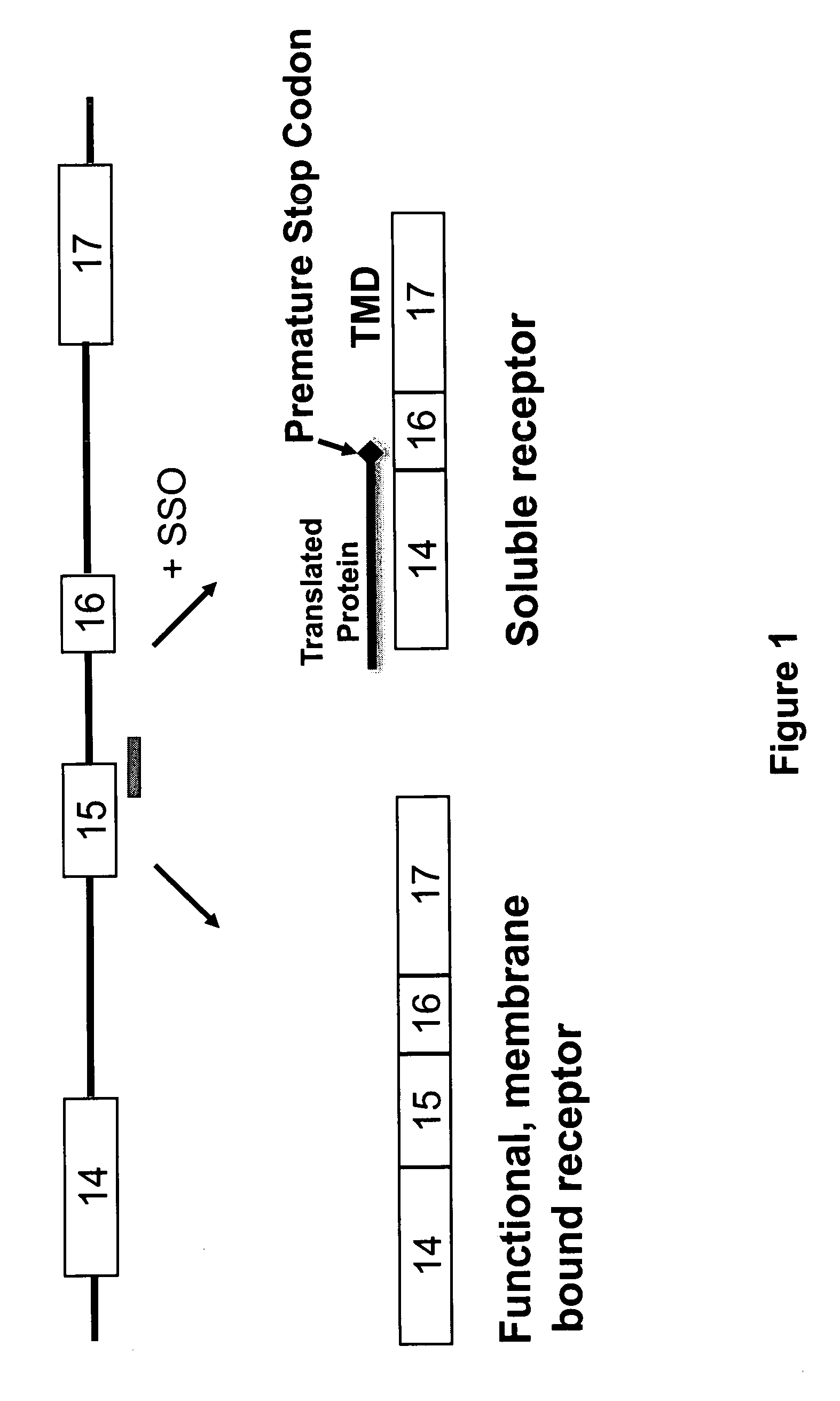
Splice switch oligomers for TNF superfamily receptors and their use in treatment of disease
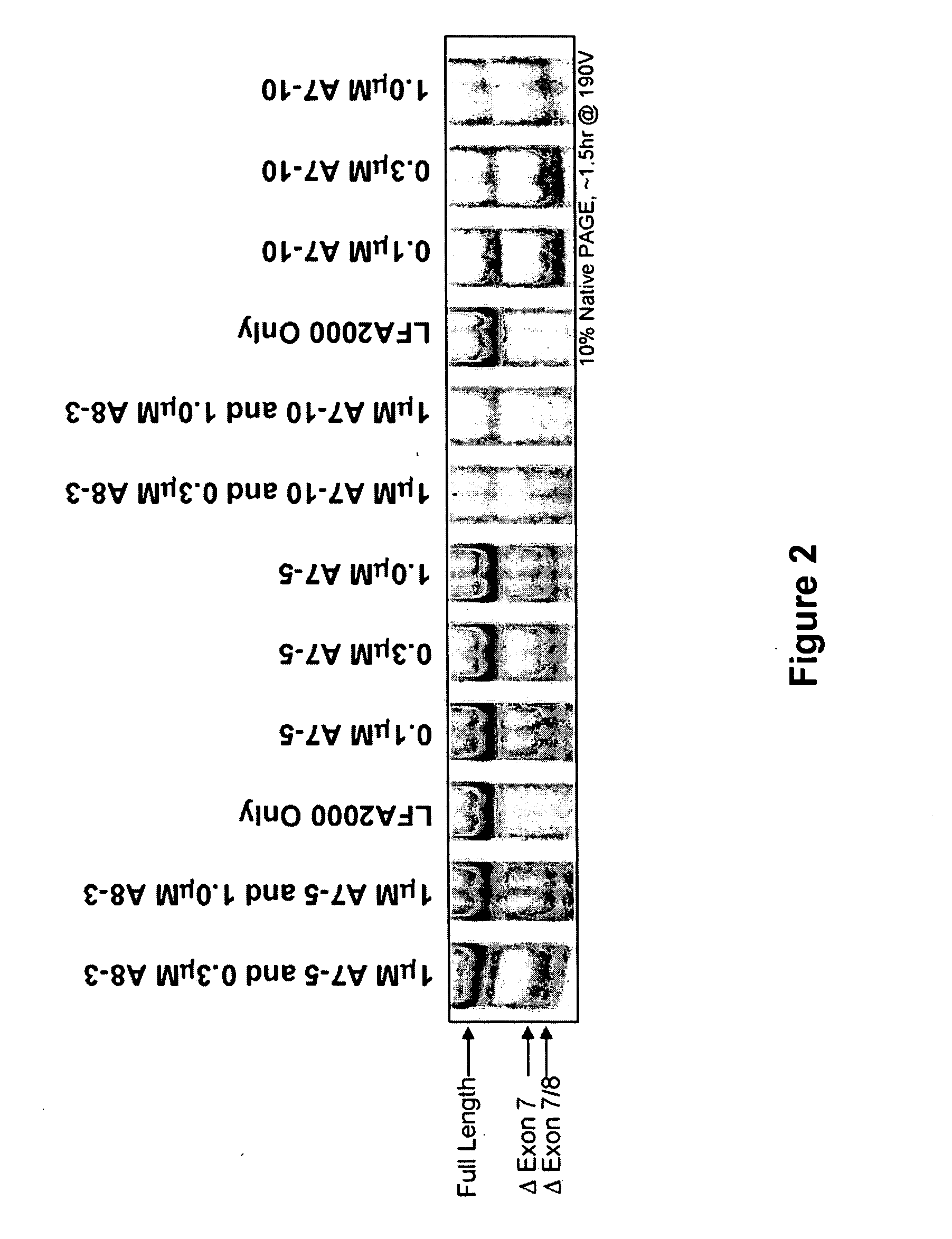
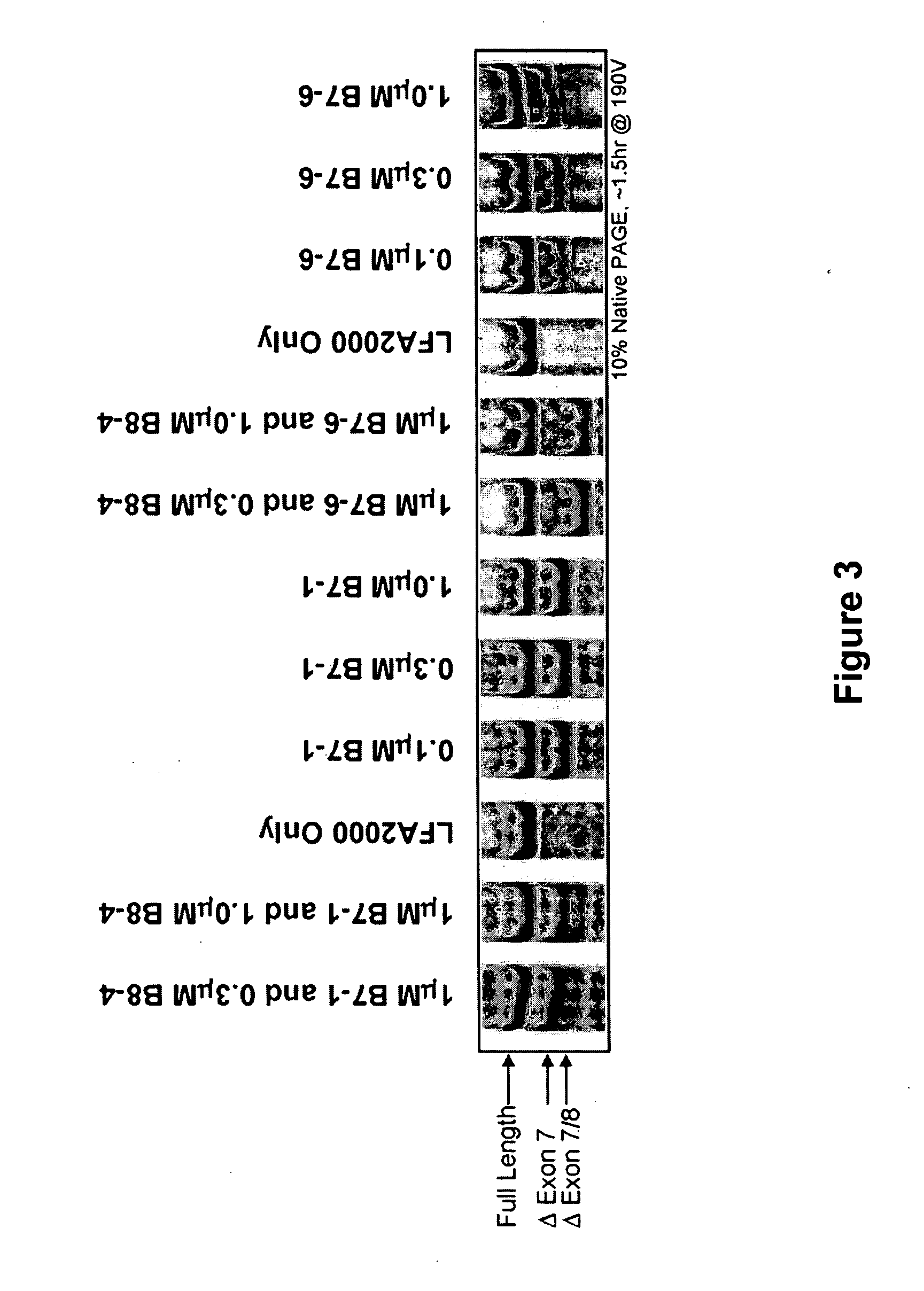
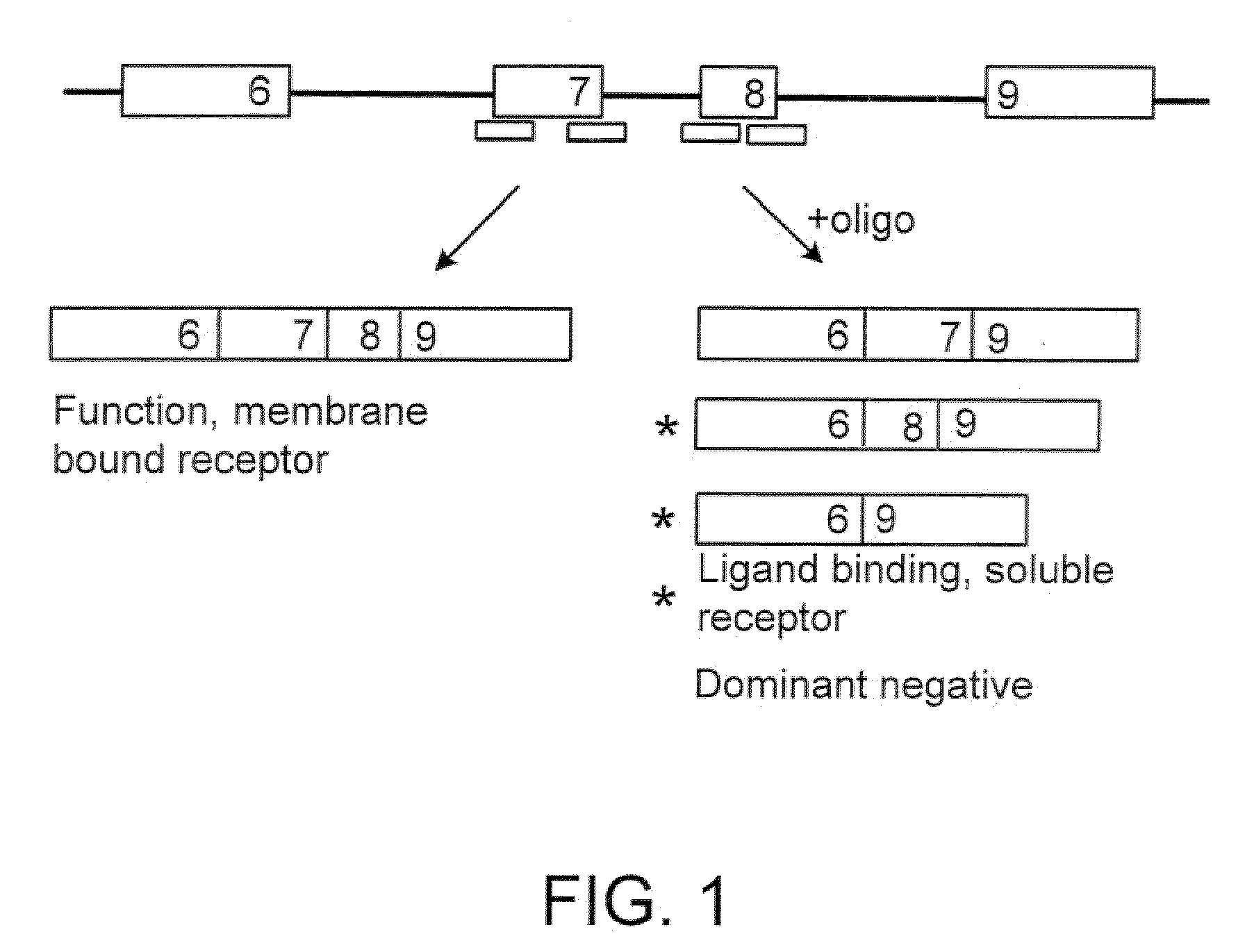
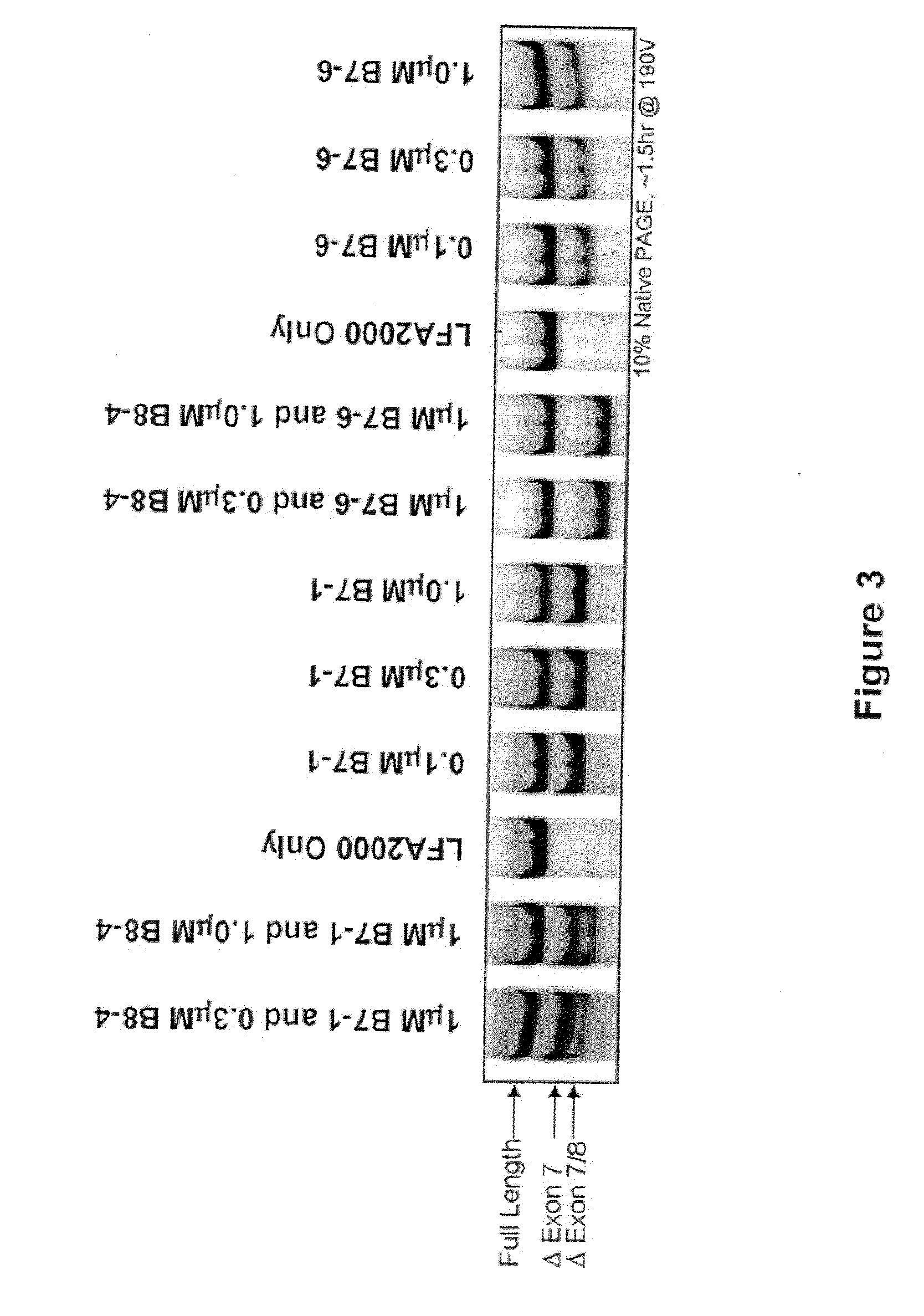
InactiveUS20070105807A1High expressionReduce expressionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSplice switchingPrecursor mRNA
Methods and compositions are disclosed for controlling expression of TNF receptors (TNFR1 and TNFR2) and of other receptors in the TNFR superfamily using compounds that modulate splicing of pre-mRNA encoding these receptors. More specifically these compounds cause the removal of the transmembrane domains of these receptors and produce soluble forms of the receptor which act as an antagonist to reduce TNF-α activity or activity of the relevant ligand. Reducing TNF-α activity provides a method of treating or ameliorating inflammatory diseases or conditions associated with TNF-α activity. Similarly, diseases associated with other ligands can be treated in like manner. In particular, the compounds of the invention are splice-splice switching oligomers (SSOs) which are small molecules that are stable in vivo, hybridize to the RNA in a sequence specific manner and, in conjunction with their target, are not degraded by RNAse H.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS +3
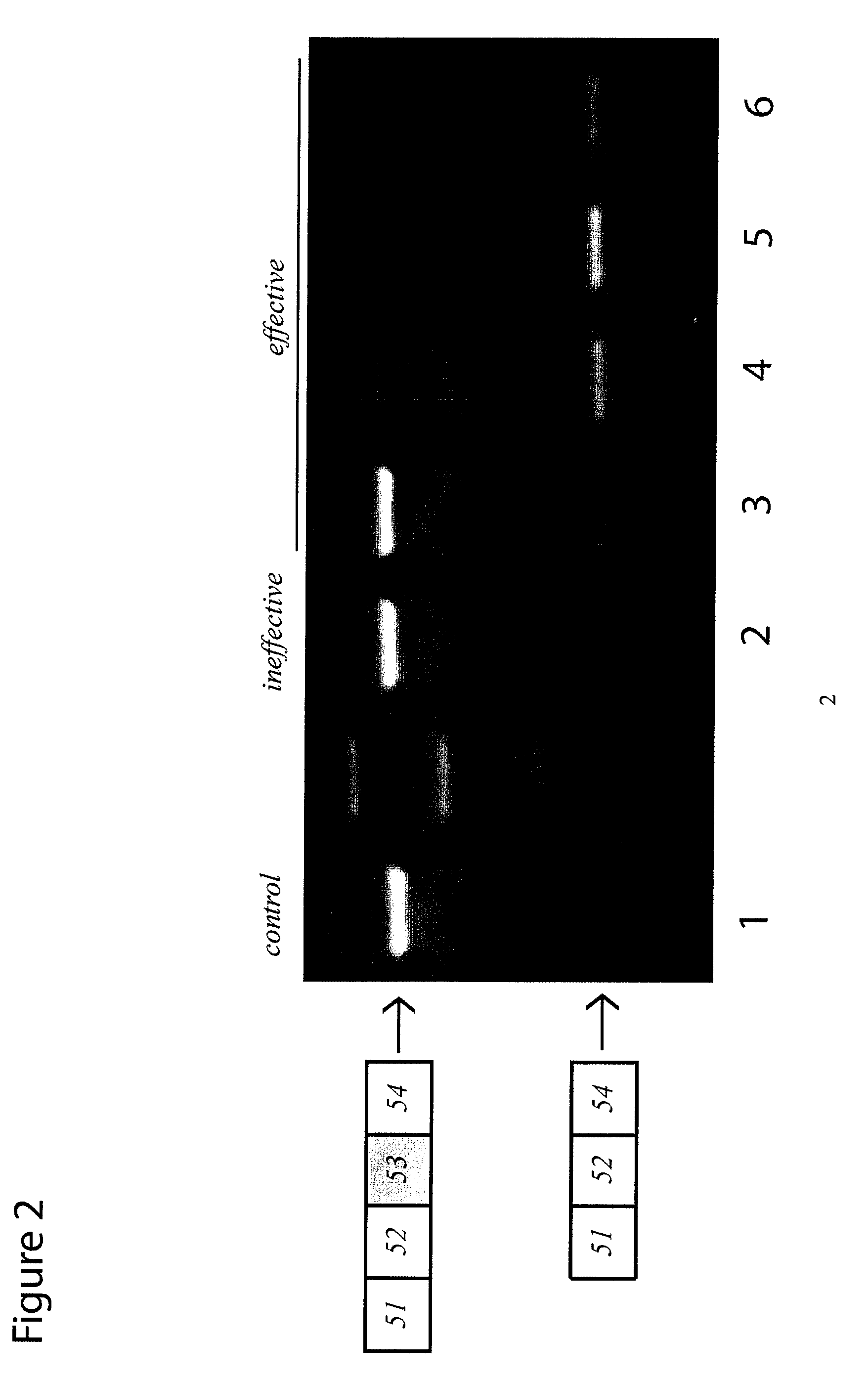
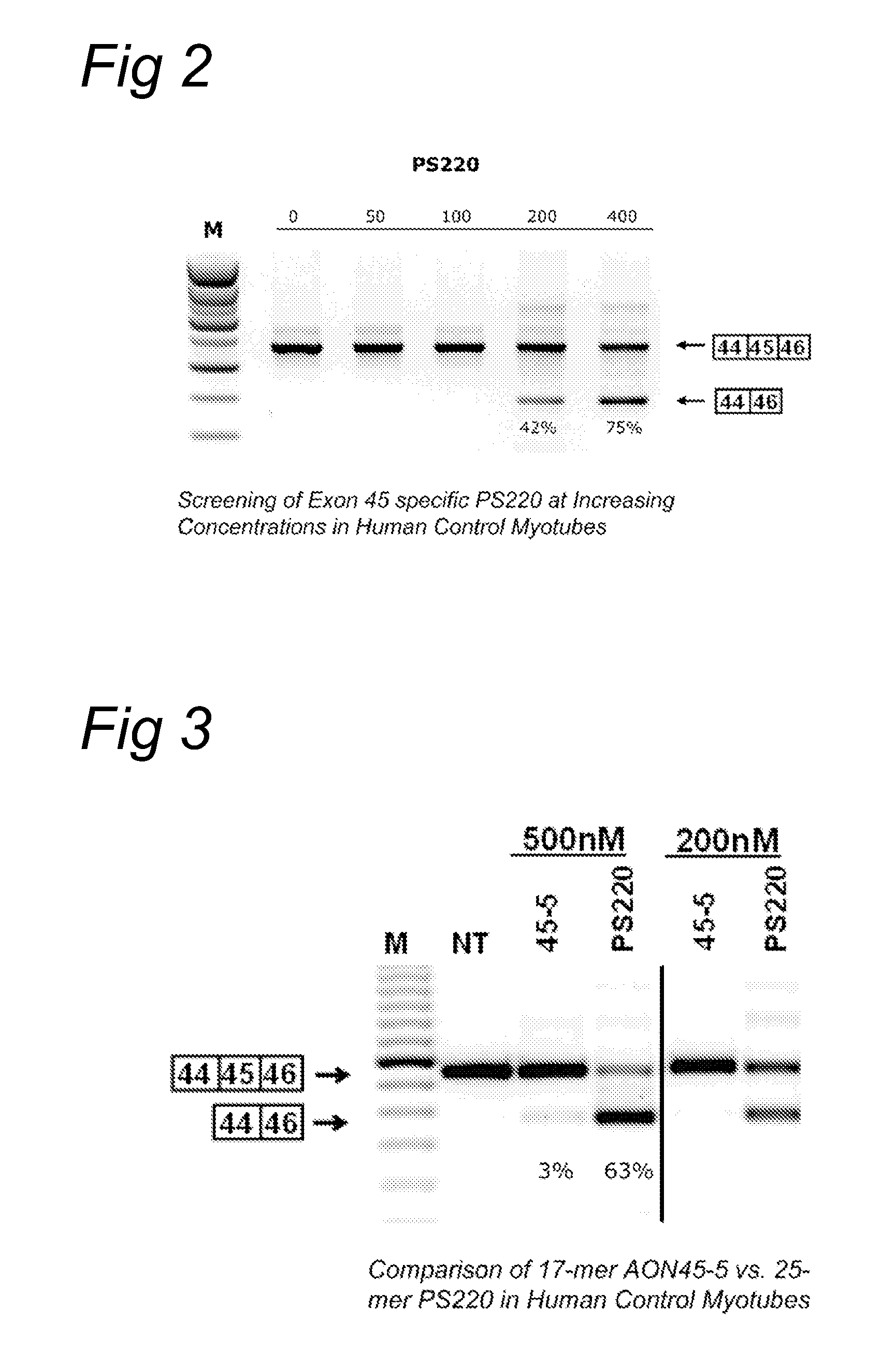
METHODS AND MEANS FOR EFFICIENT SKIPPING OF EXON 45 IN DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY PRE-mRNA
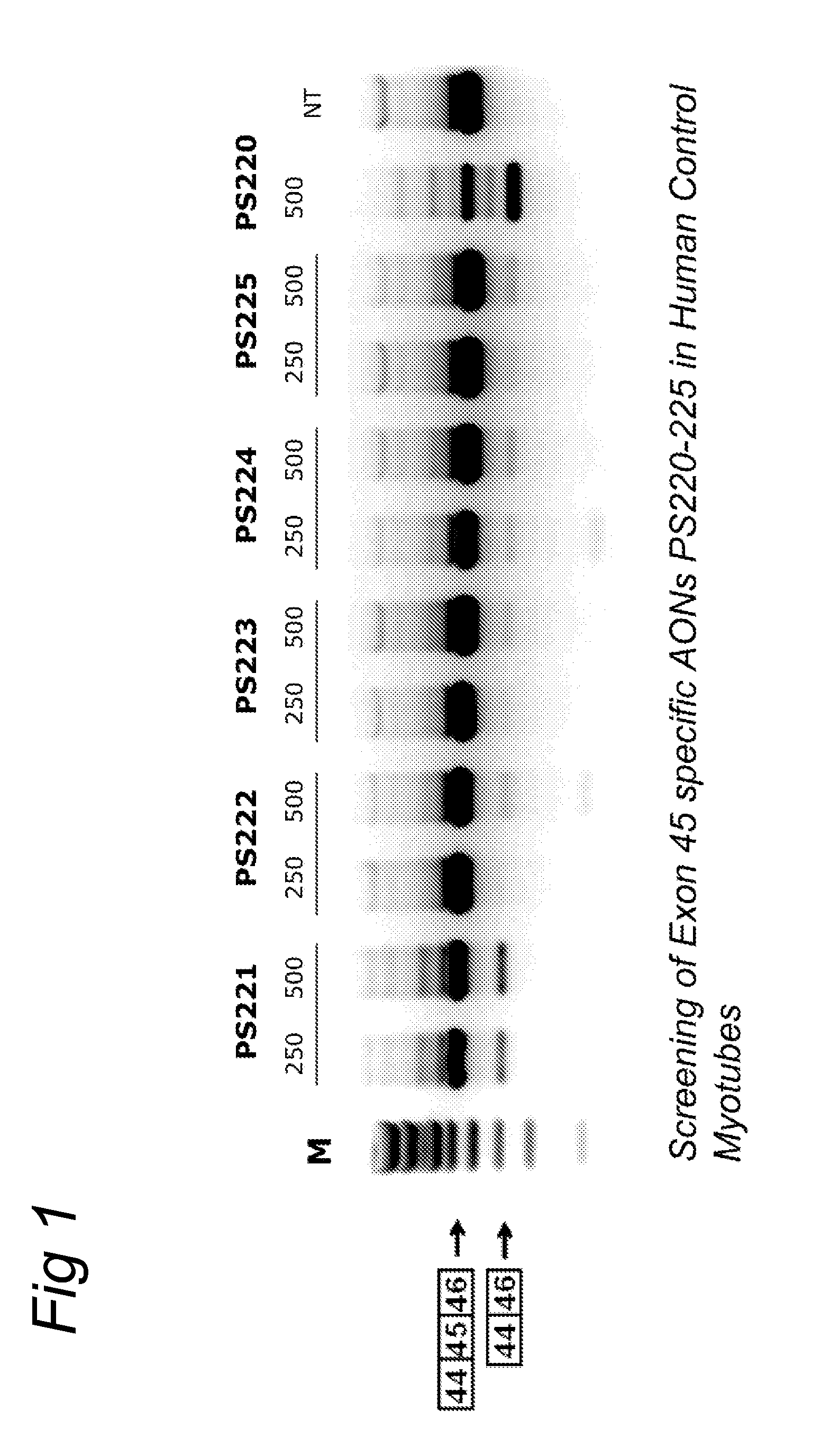
ActiveUS20120022134A1Reduced calcium uptake by muscle cellsReduce synthesisOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationNucleotidePrecursor mRNA
The invention relates to a method for inducing or promoting skipping of exon 45 of DMD pre-mRNA in a Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy patient, preferably in an isolated (muscle) cell, the method comprising providing said cell with a molecule that binds to a continuous stretch of at least 21 nucleotides within said exon. The invention further relates to such molecule used in said method.
Owner:BIOMARIN TECH BV +2
Identification of small molecules that facilitate therapeutic exon skipping
This invention relates, e.g., to a method for enhancing exon skipping in a pre-mRNA of interest, comprising contacting the pre-mRNA with an effective amount of a small molecule selected from the compounds shown in Table 1, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, hydrate, solvate, or isomer thereof, and, optionally, with an antisense oligonucleotide that is specific for a splicing sequence in the pre-mRNA Methods for treating Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) are disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Spinal muscular atrophy treatment via targeting smn2 catalytic core
ActiveUS20110269820A1Increase productionEasy to useOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationOligoribonucleotidesPrecursor mRNA
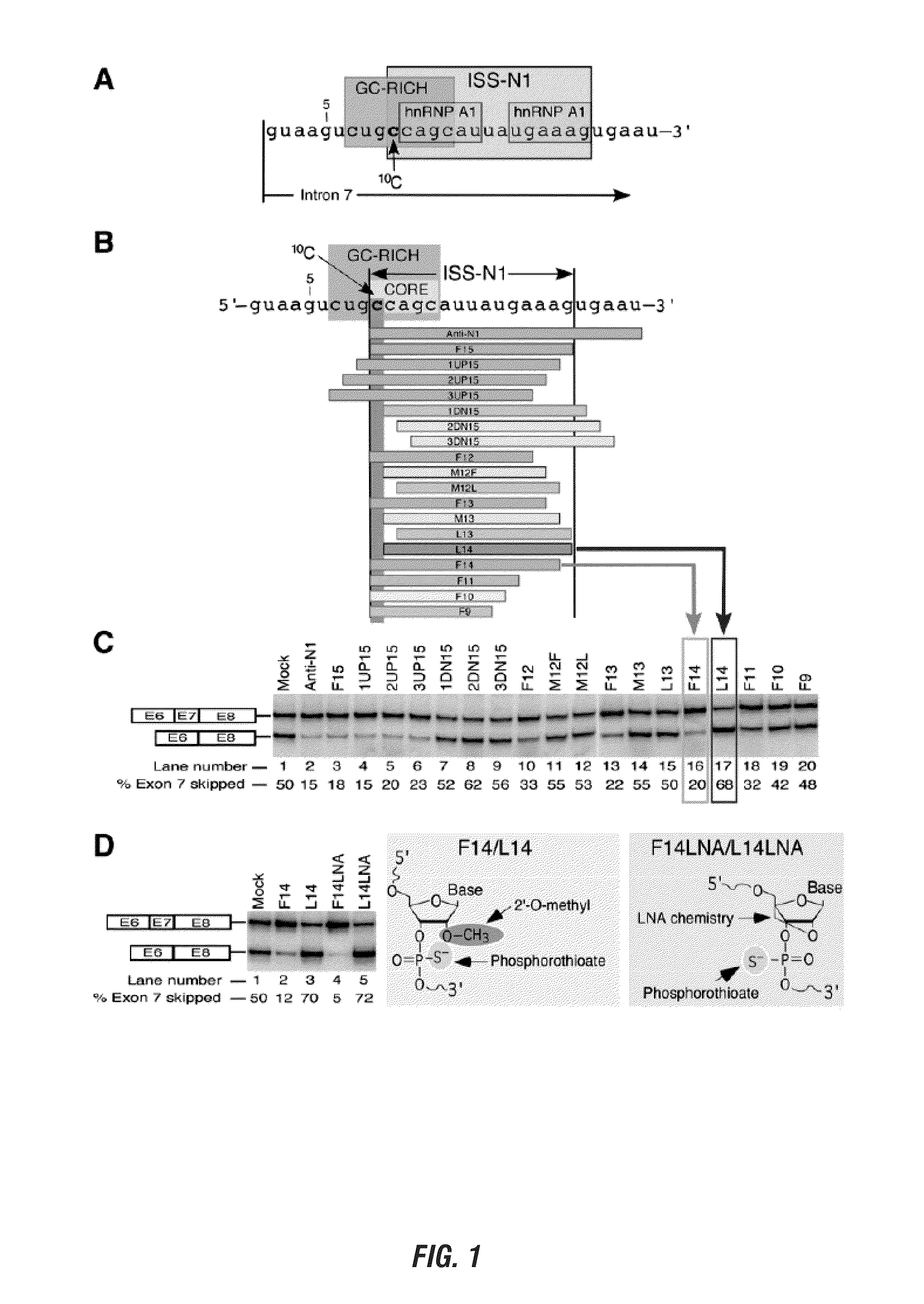
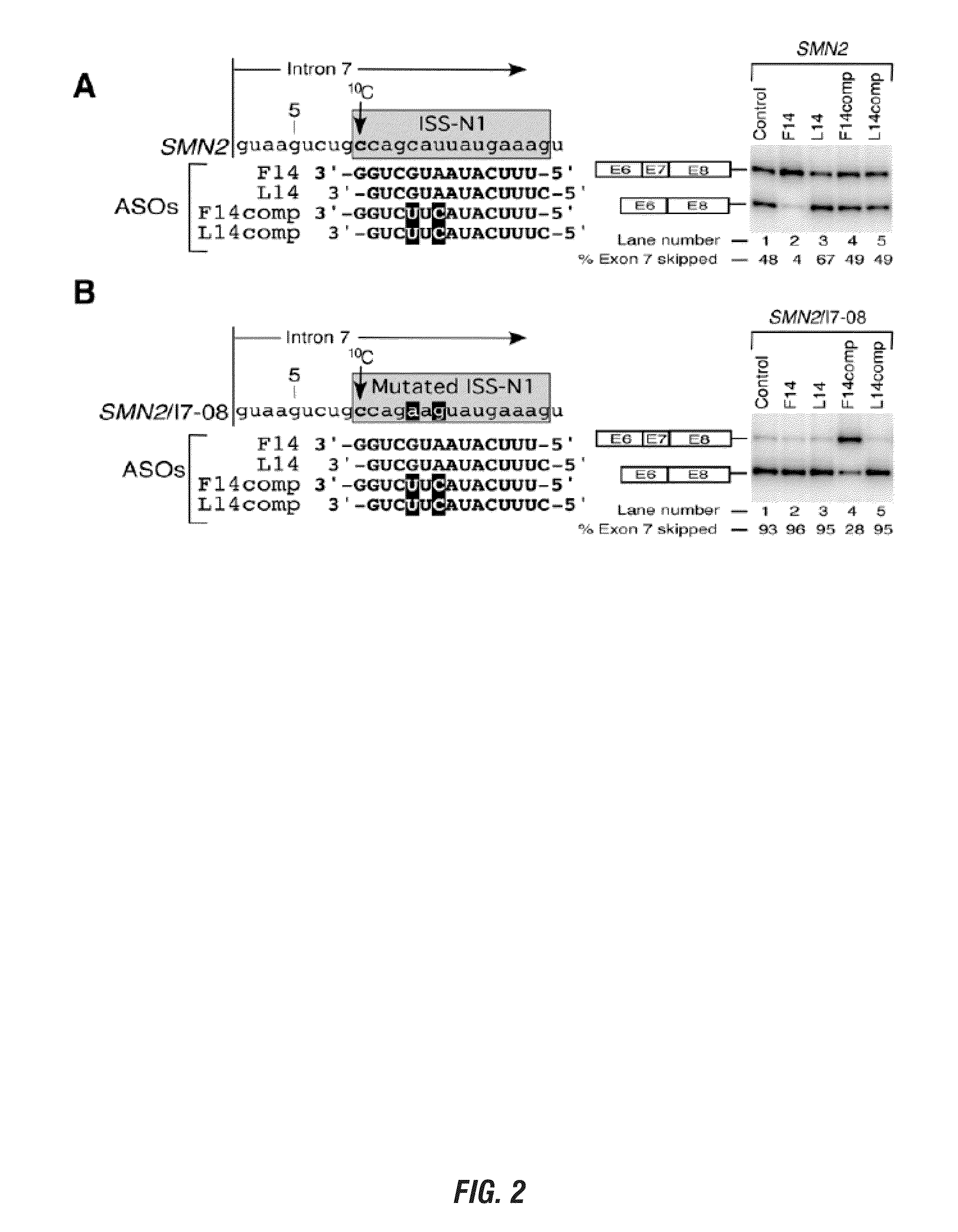
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for blocking the effect of the intronic inhibitory splicing region of intron 7 of the SMN2 gene. The compositions and methods of the instant invention include short oligonucleotide reagents (e.g., oligoribonucleotides) that effectively target sites in the SMN2 pre-mRNA, thereby modulating the splicing of SMN2 pre-mRNA to include exon 7 in the processed transcript. The short target regions are 8-mers and 5-mers and also include the identification of a single nucleotide base that is essential for initiating a long distance stearic inhibitory interactions as well as novel targets distant from intron 7 which block the intronic inhibitory splicing of the same. These short target regions and concomitant inhibitory blocking oligonucleotides are less expensive and easier to manufacture and are small enough to cross the blood brain barrier.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Splice Switching Oligomers for TNF Superfamily Receptors and their Use in Treatment of Disease
InactiveUS20090264353A1Reduce the amount requiredVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseSplice switching
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for preparing splice variants of TNFalpha receptor (TNFR) in vivo or in vitro, and the resulting TNFR protein variants. Such variants may be prepared by controlling the splicing of pre-mRNA molecules and regulating protein expression with splice switching oligonucleotides or splice switching oligomers (SSOs). The preferred SSOs according to the invention target exon 7 or 8 of TNFR1 (TNFRSF1A) or TNFR2 (TNFRSF1A) pre-mRNA, typically resulting in the production of TNFR variants which comprise a deletion in part or the entire exon 7 or 8 respectfully. SSOs targeting exon 7 are found to result in a soluble form of the TNFR, which has therapeutic benefit for treatment of inflammatory diseases. The SSO's are characterized in that they are substantially incapable or incapable of recruiting RNaseH.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS +1
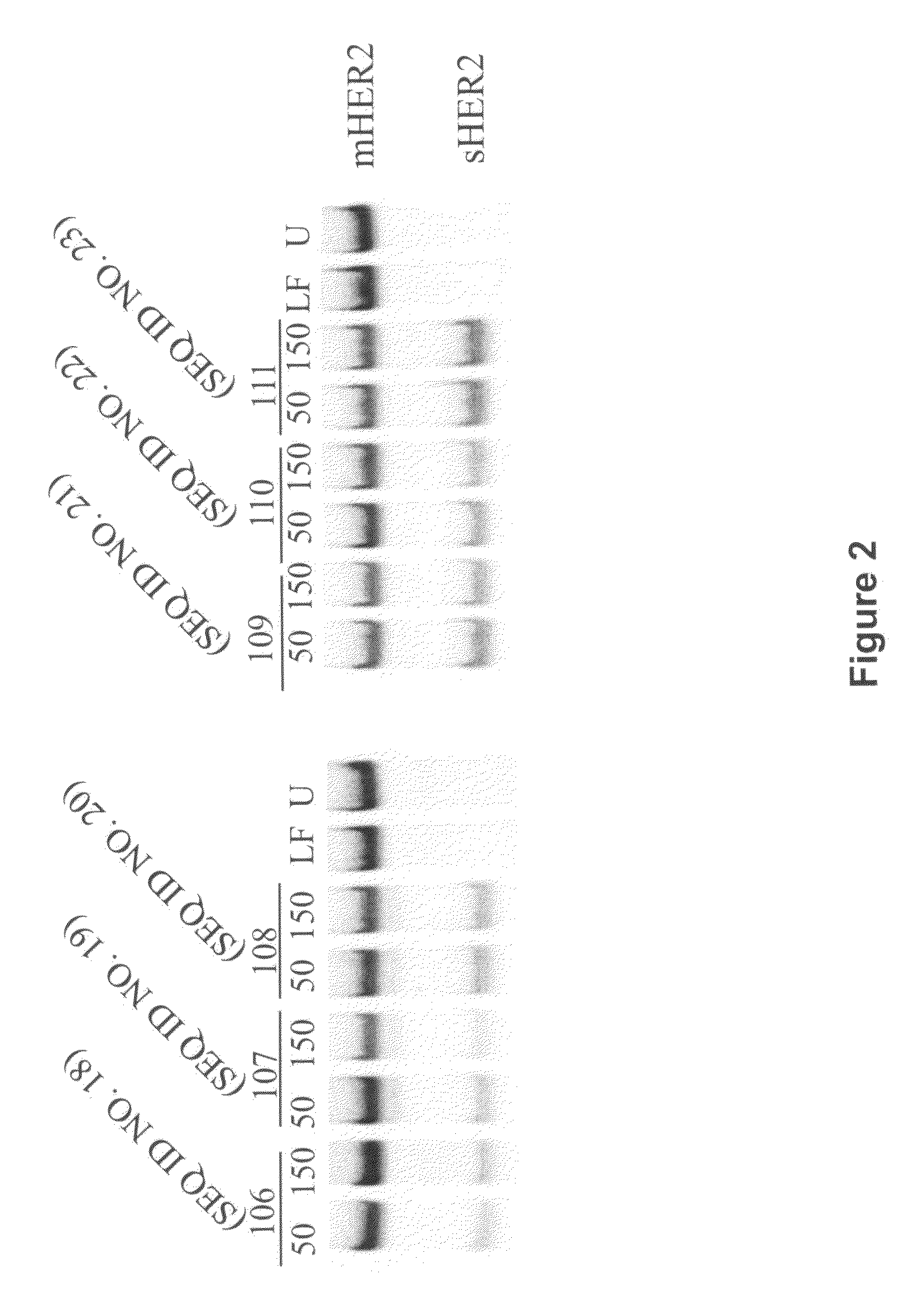
Soluble HER2 and HER3 splice variant proteins, splice-switching oligonucleotides, and their use in the treatment of disease
InactiveUS20090105139A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDiseaseSplice switching
Soluble epidermal growth factor receptors 2 and 3 (HER2 and HER3) splice variant proteins with HER2 and HER3 antagonist activity and anti-proliferative properties, as well as the corresponding nucleic acids, are provided for treatment of proliferative diseases, in particular cancer. Also provided are compositions and methods for inducing expression of these splice variants, including splice switching oligonucleotides that modulate splicing of pre-mRNA that codes for these receptors.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
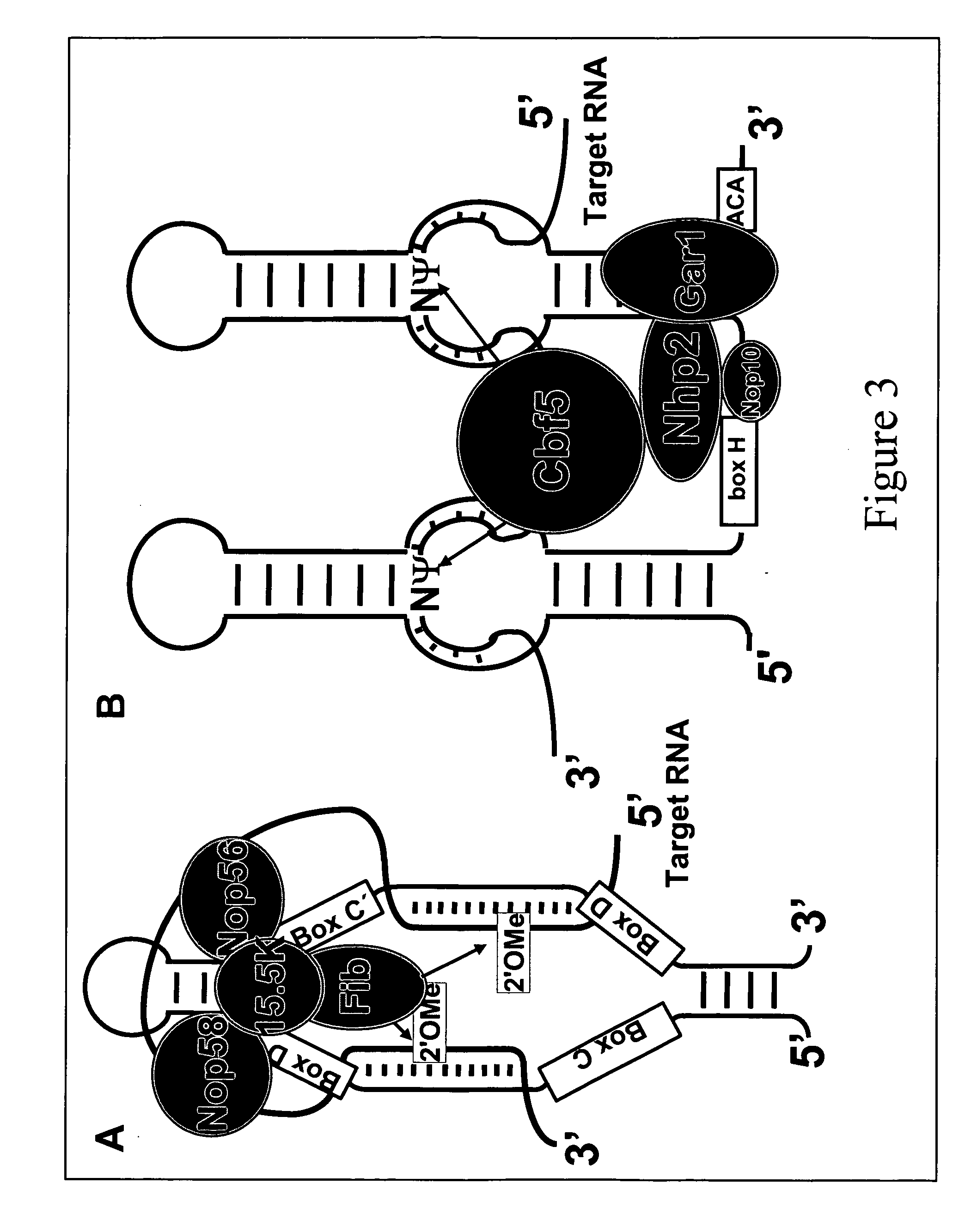
RNA processing protein complexes and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100136710A1Improve accuracyFidelity of of reducedSugar derivativesHydrolasesDiseaseProtein-protein complex
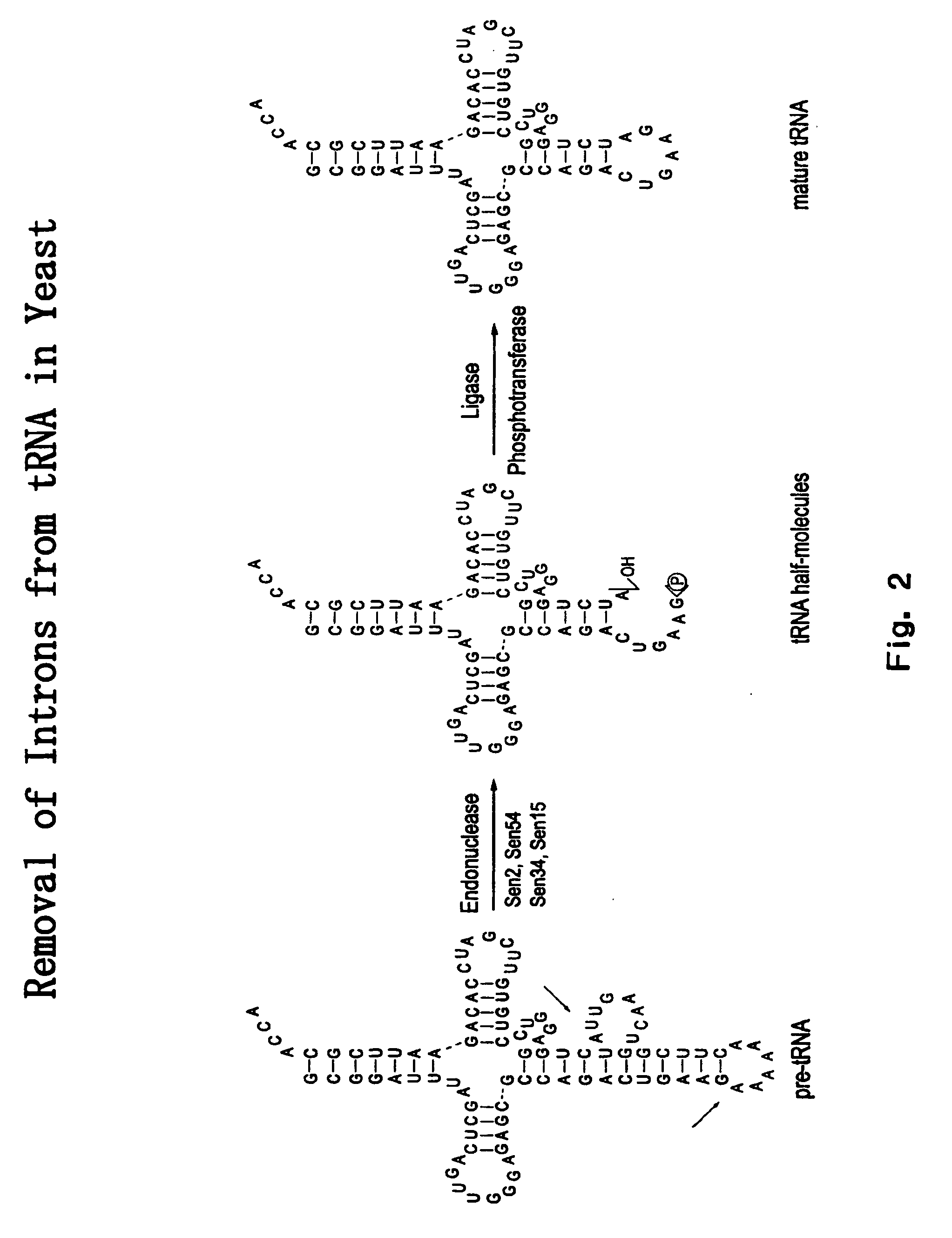
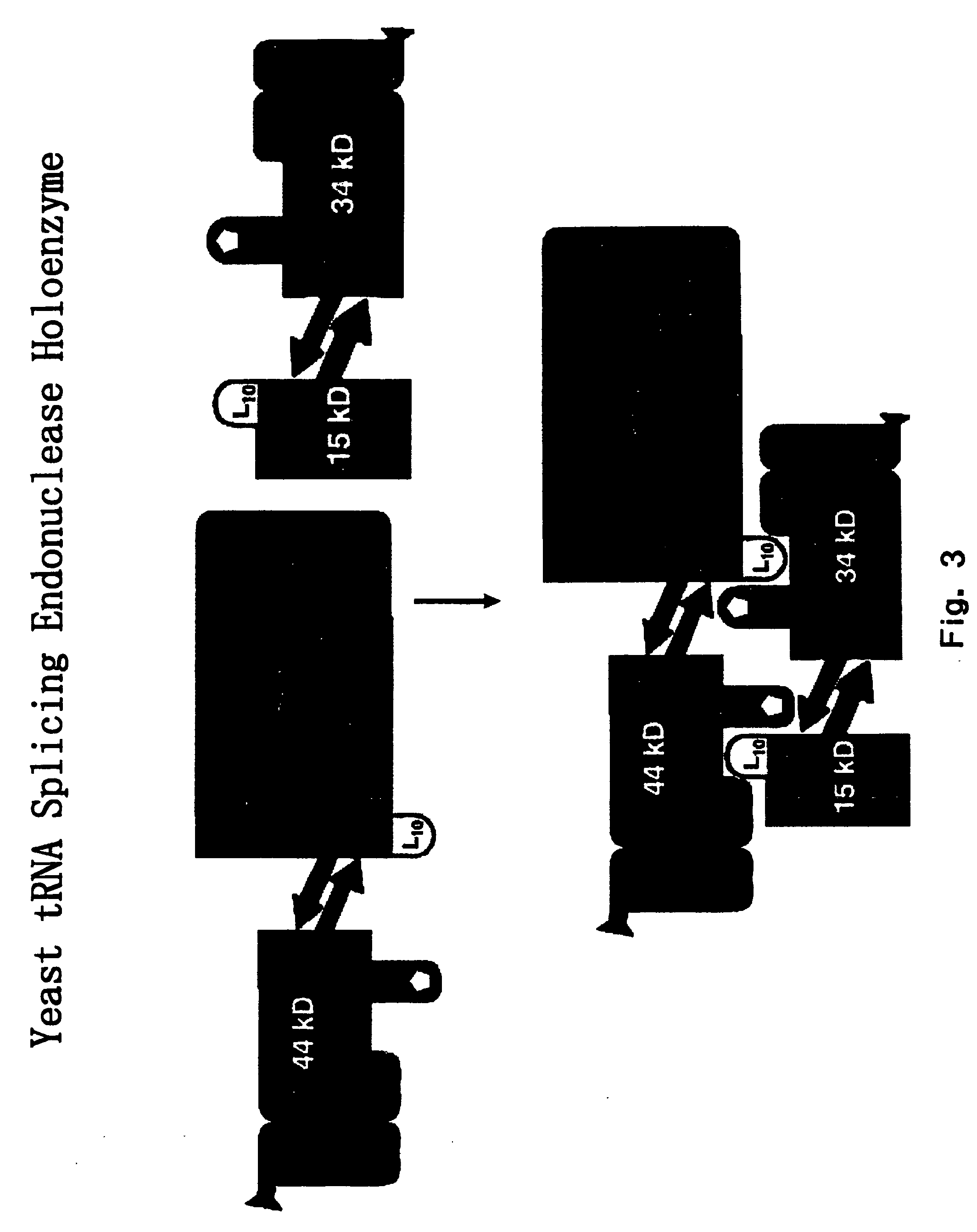
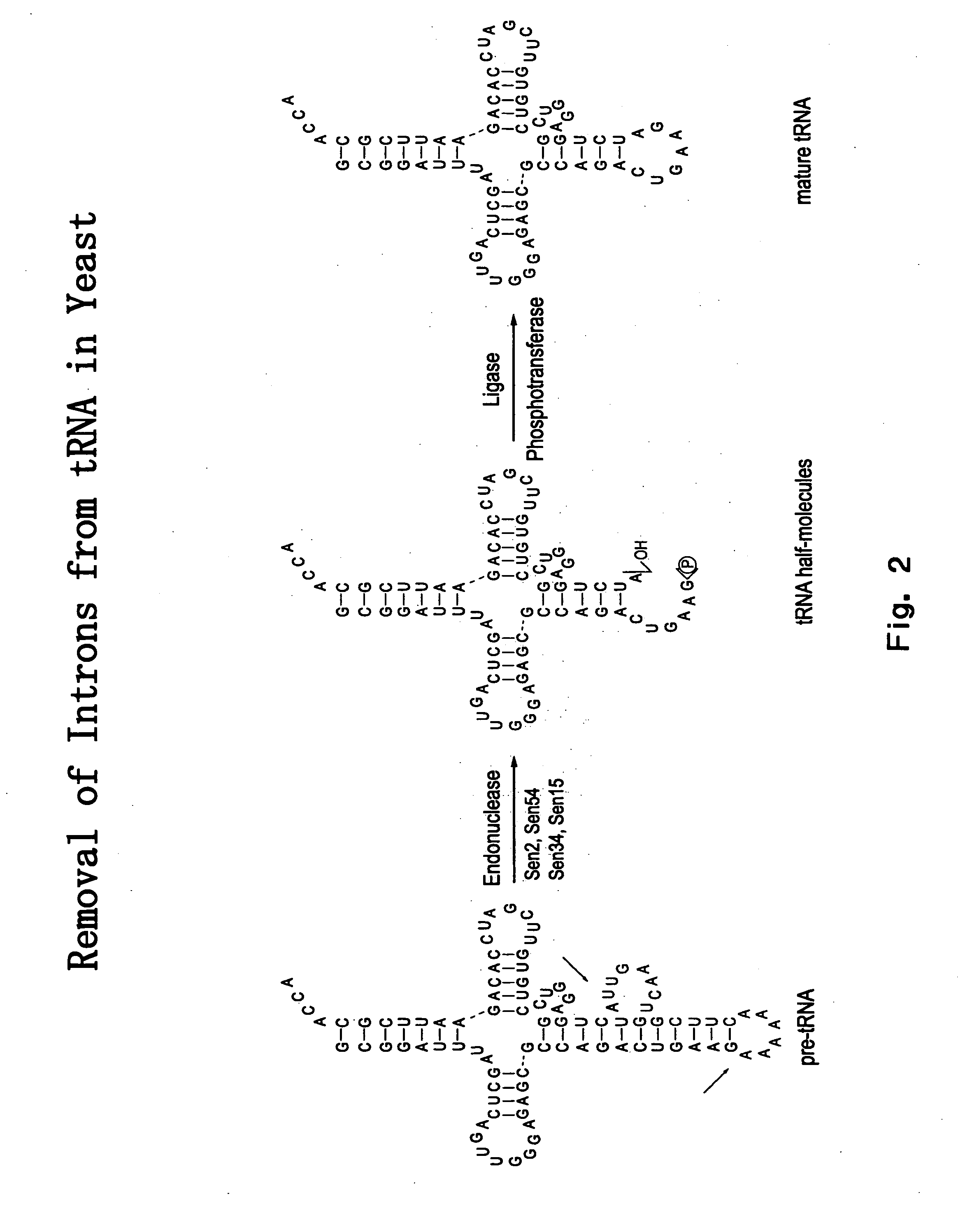
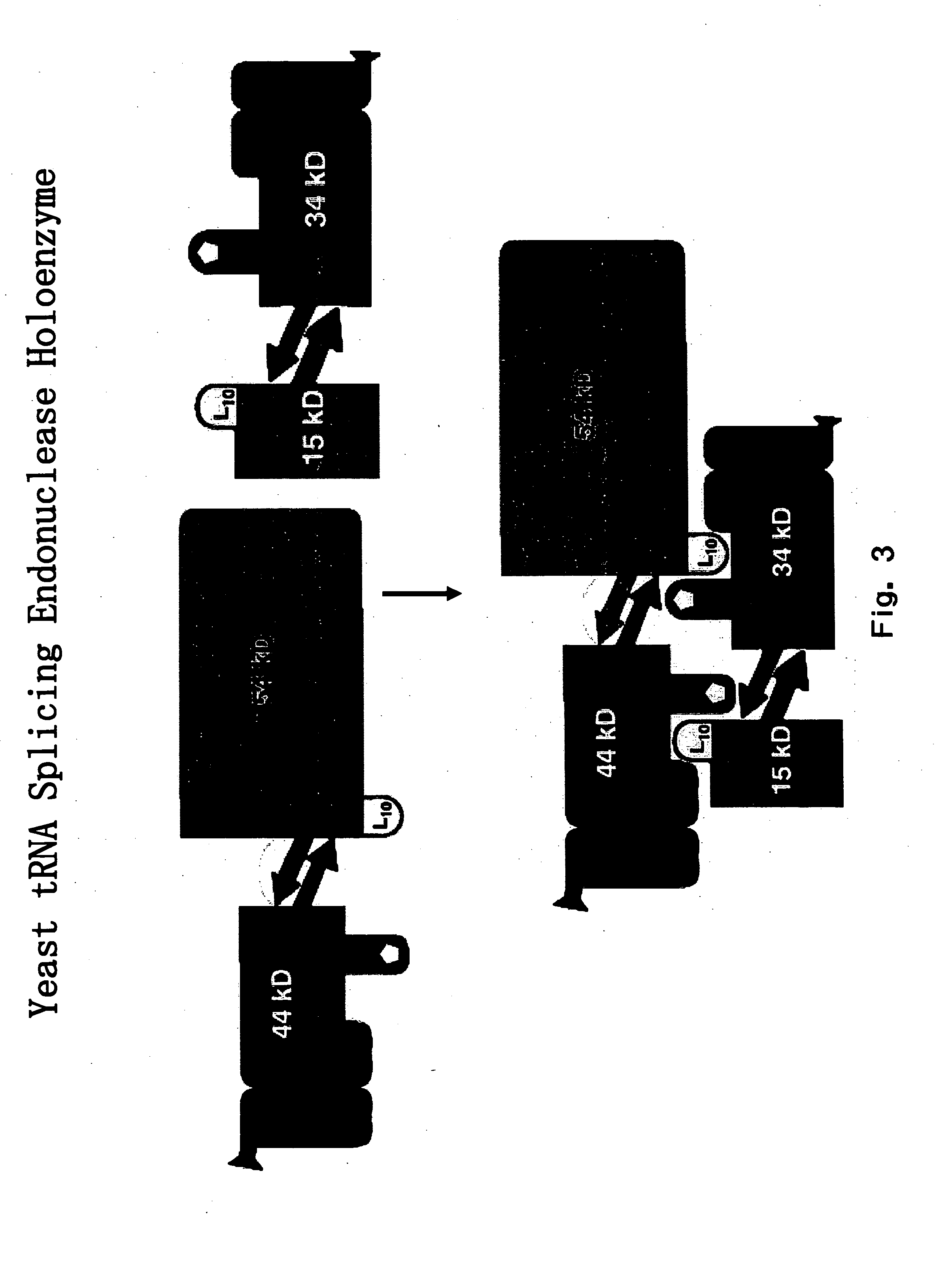
The invention provides human protein complexes with endonuclease activity. In particular, the invention provides human protein complexes with tRNA splicing endonuclease activity and / or 3′ end pre-mRNA endonuclease activity. The invention also provides a splice variant of human Sen2, namely human Sen2deltaEx8, and human protein complexes comprising human Sen2deltaEx8. The human Sen2deltaEx8 complexes have pre-tRNA cleavage activity and / or 3′ end pre-mRNA endonuclease activity. The invention also provides human protein complexes with pre-ribosomal RNA cleavage activity. The invention also provides antibodies that immunospecifically bind to a complex described herein or a component thereof, and methods of diagnosing, preventing, treating, managing or ameliorating a disorder utilizing such antibodies. The present invention also provides methods utilizing the complexes described herein, inter alia, in screening, diagnosis, and therapy. The invention further provides methods of preparing and purifying the complexes. The present invention further provides methods of identifying a compound that modulates the expression of a component of a complex described herein, the formation of a complex described herein or the activity of a complex described herein, and methods of preventing, treating, managing or ameliorating a disorder, such as a proliferative disorder, or a symptom thereof utilizing a compound identified in accordance with the methods.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods and compositions for treating a cell-proliferative disorder using CRE decoy oligomers, BCL-2 antisense oligomers, and hybrid oligomers thereof
InactiveUS20030176376A1Hinder and prevent bindingModulate transcriptional activitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAbnormal tissue growth
The present invention is directed to hybrid oligomers comprising a cyclic AMP response element (CRE) sequence and a sequence that hybridizes to a bcl-2 pre-mRNA or mRNA, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising such hybrids. The present invention is also directed to the use of CRE decoy oligomers, comprising a CRE consensus sequence, and bcl-2 antisense oligomers in combination therapies, and the use of bcl-2 / CRE hybrid oligomers, to treat or prevent cell-proliferative related disorders, including hyperplasias, cancers, tumors and carcinomas. In one embodiment, the invention relates to therapeutic protocols comprising the administration of a CRE decoy oligomer and a bcl-2 antisense oligomer for the treatment of cell-proliferative related disorders. In another embodiment, the invention relates to therapeutic protocols comprising the administration of a bcl-2 antisense / CRE decoy (bcl-2 / CRE) hybrid oligomer for the treatment of cell-proliferative related disorders.
Owner:GENTA INC
Oligomers
InactiveUS20130085139A1Improve securityLasting effectOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationMyostatinPrecursor mRNA
Certain disclosed oligomers induce exon skipping during processing of myostatin pre-mRNA. The oligomers may be in a vector or encoded by the vector. The vector is used for inducing exon skipping during processing of myostatin pre-mRNA. A therapeutically effective amount of the oligomer may be administered to a subject patient such that exon skipping during processing of myostatin pre-mRNA is induced. The administration to a subject may be used in order to increase or maintain muscle mass, or slowing degeneration of muscle mass in the subject. The administration to a subject may ameliorate muscle wasting conditions, such as muscular dystrophy. Examples of such muscular dystrophies which may be so treated include Becker's muscular dystrophy, congenital muscular dystrophy, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, distal muscular dystrophy, Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD), limb-girdle muscular dystrophy, myotonic muscular dystrophy, and oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy
Owner:ROYAL HOLLOWAY & BEDFORD NEW COLLEGE
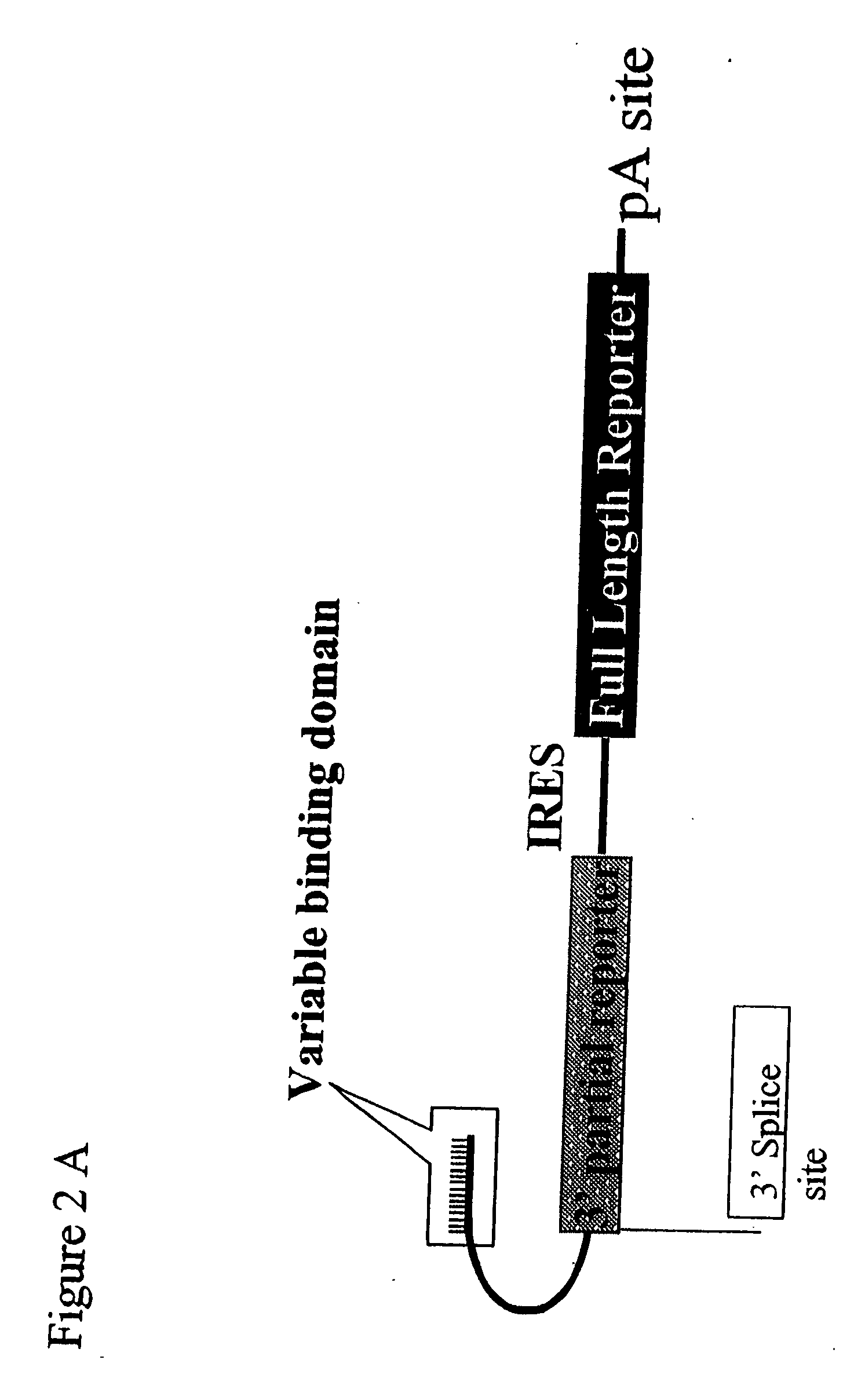
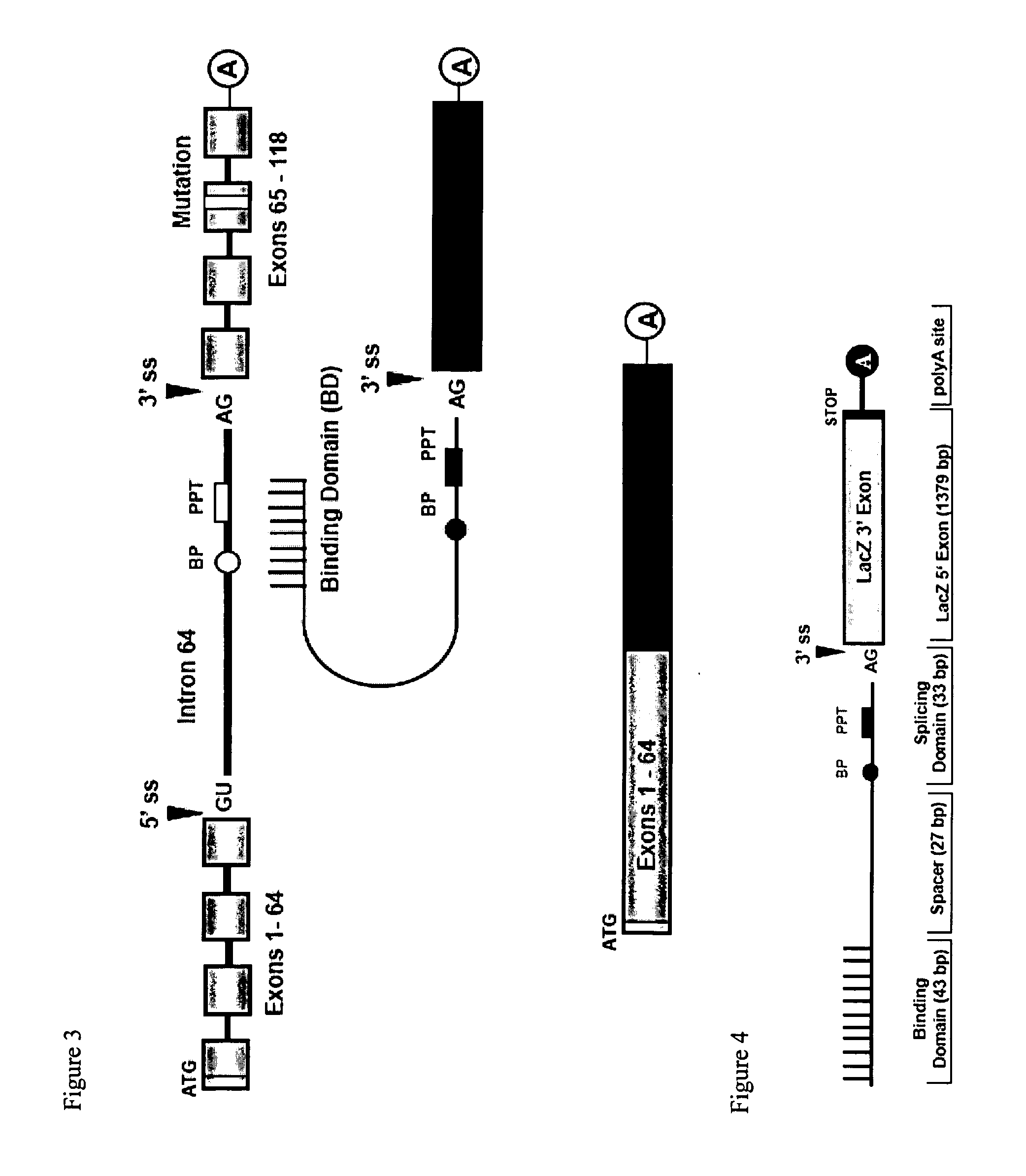
Screening method for identification of efficient pre-trans-splicing molecules
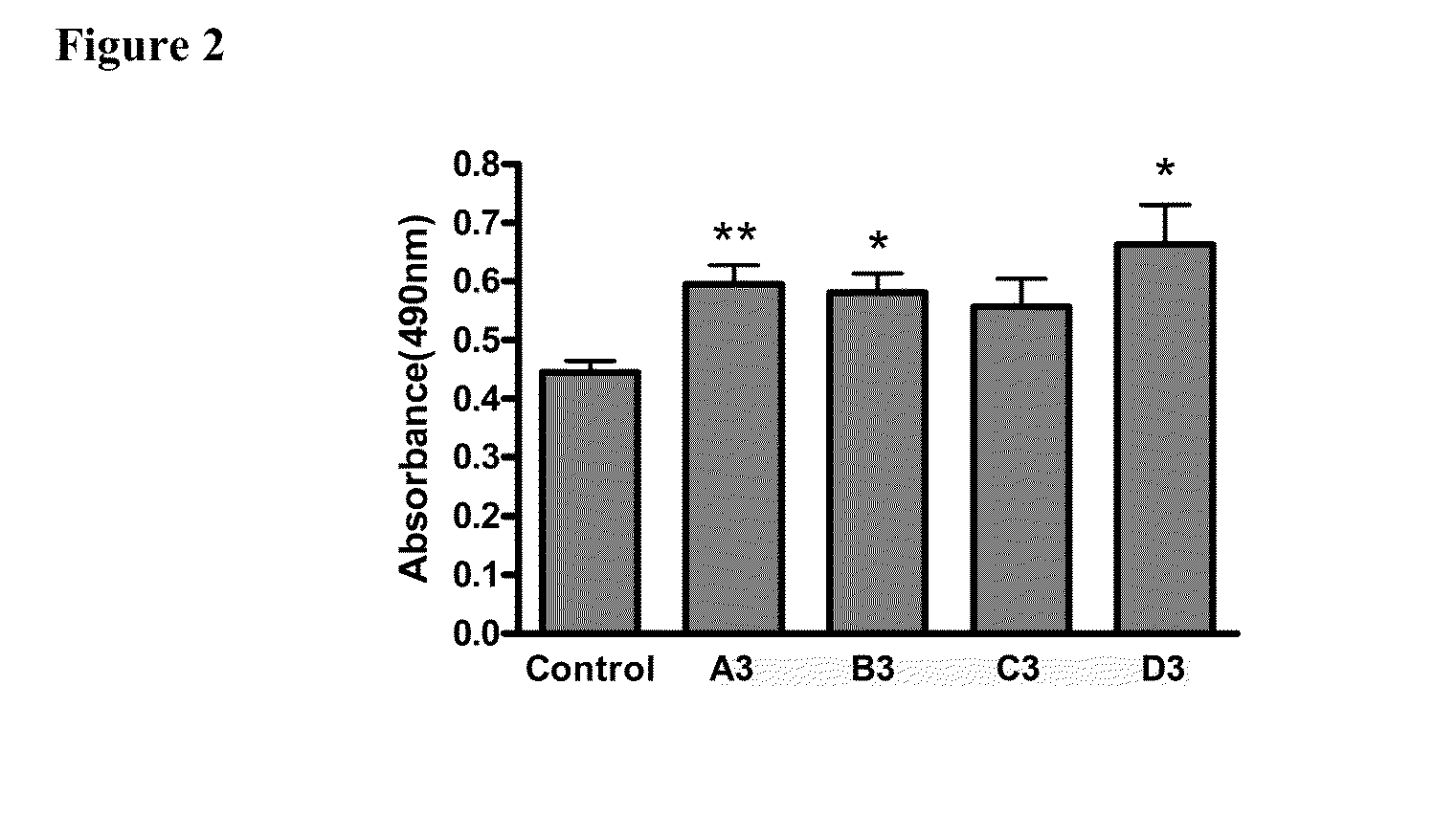
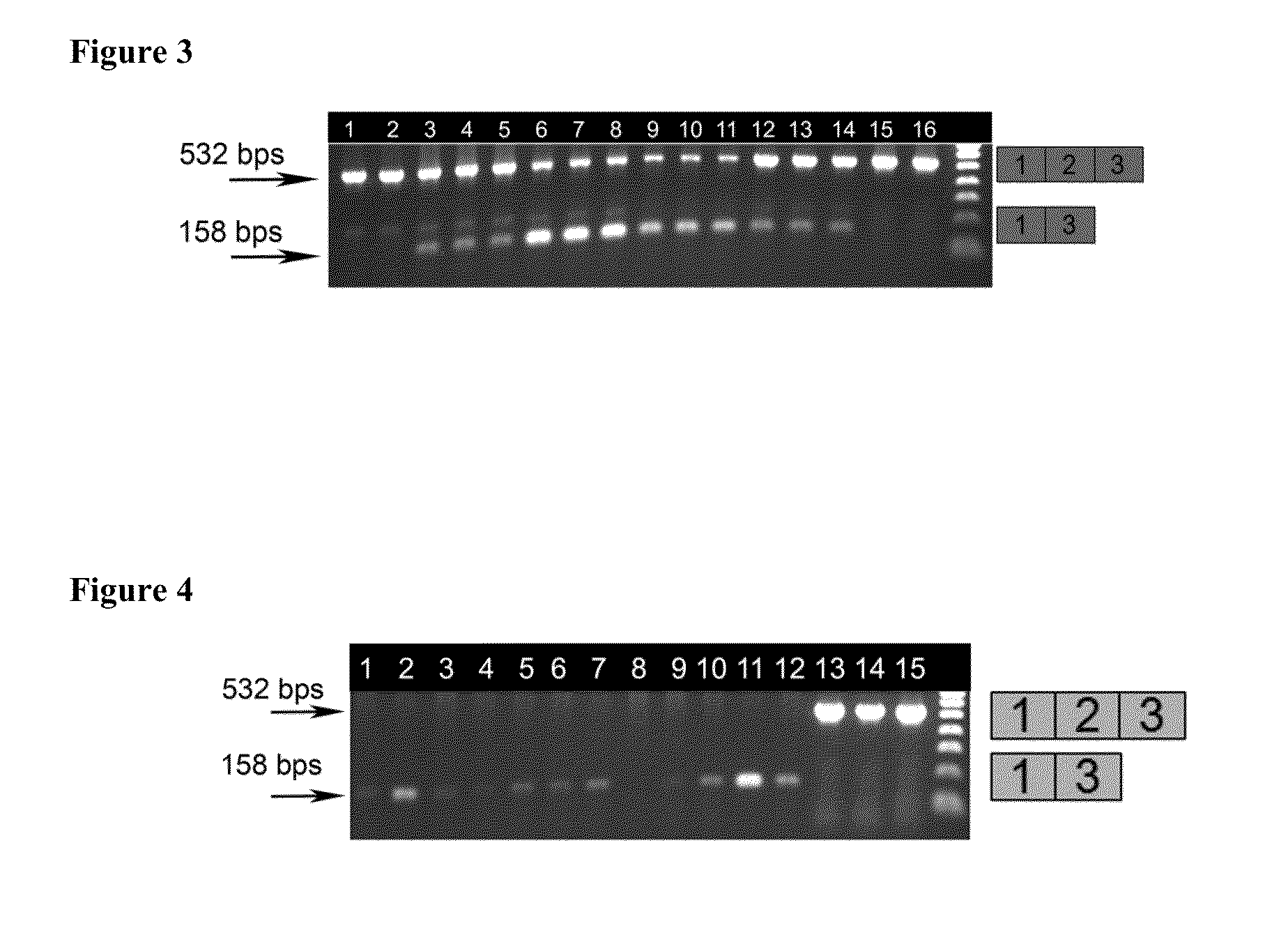
The present invention provides methods and compositions for rapid high capacity functional screening to identify optimal pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs). The compositions of the invention include PTM expression libraries capable of encoding candidate PTMs designed to interact with a target precursor messenger RNA molecule (target pre-mRNA) and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of a novel chimeric RNA molecule (chimeric RNA). The candidate PTMs of the invention encode a portion of a first reporter molecule and may encode one or more other reporter molecules, which can be used to select for cells expressing optimal PTMs (efficient and specific). The compositions of the invention also include cells that express a target pre-mRNA encoding the remaining portion of the first reporter molecule. The screening methods of the invention encompass (i) contacting a PTM expression library with cells expressing a target pre-mRNA under conditions in which a trans-splicing reaction will occur in the presence of an optimal PTM (expressed by the library vector) resulting in the formation of a chimeric repaired RNA molecule capable of encoding at least one reporter molecule; (ii) selecting for cells expressing the repaired reporter molecule wherein expression of the reporter molecule indicates the presence of an optimal PTM in the selected cell; and (iii) identifying the optimal PTM expressed in the selected cell(s). The additional reporter molecule(s) can be used to assess both specific and non-specific trans-splicing, as well direct PTM expression.
Owner:VIRXSYS
RNA processing protein complexes and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050053985A1High expressionInhibit and reduce expressionHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseasePrecursor mRNA
The invention provides human protein complexes with endonuclease activity. In particular, the invention provides human protein complexes with tRNA splicing endonuclease activity and / or 3' end pre-mRNA endonuclease activity. The invention also provides a splice variant of human Sen2, namely human Sen2deltaEx8, and human protein complexes comprising human Sen2deltaEx8. The human Sen2deltaEx8 complexes have pre-tRNA cleavage activity and / or 3' end pre-mRNA endonuclease activity. The invention also provides human protein complexes with pre-ribosomal RNA cleavage activity. The invention also provides antibodies that immunospecifically bind to a complex described herein or a component thereof, and methods of diagnosing, preventing, treating, managing or ameliorating a disorder utilizing such antibodies. The present invention also provides methods utilizing the complexes described herein, inter alia, in screening, diagnosis, and therapy. The invention further provides methods of preparing and purifying the complexes. The present invention further provides methods of identifying a compound that modulates the expression of a component of a complex described herein, the formation of a complex described herein or the activity of a complex described herein, and methods of preventing, treating, managing or ameliorating a disorder, such as a proliferative disorder, or a symptom thereof utilizing a compound identified in accordance with the methods.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods and compositions for treating a cell-proliferative disorder using CRE decoy oligomers, BCL-2 antisense oligomers, and hybrid oligomers thereof
InactiveUS7060690B2Hinder and prevent bindingModulate transcriptional activitySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAbnormal tissue growth
The present invention is directed to hybrid oligomers comprising a cyclic AMP response element (CRE) sequence and a sequence that hybridizes to a bcl-2 pre-mRNA or mRNA, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising such hybrids. The present invention is also directed to the use of CRE decoy oligomers, comprising a CRE consensus sequence, and bcl-2 antisense oligomers in combination therapies, and the use of bcl-2 / CRE hybrid oligomers, to treat or prevent cell-proliferative related disorders, including hyperplasias, cancers, tumors and carcinomas. In one embodiment, the invention relates to therapeutic protocols comprising the administration of a CRE decoy oligomer and a bcl-2 antisense oligomer for the treatment of cell-proliferative related disorders. In another embodiment, the invention relates to therapeutic protocols comprising the administration of a bcl-2 antisense / CRE decoy (bcl-2 / CRE) hybrid oligomer for the treatment of cell-proliferative related disorders.
Owner:GENTA INC
Antisense oligonucleotide directed removal of proteolytic cleavage sites, the hchwa-d mutation, and trinucleotide repeat expansions
InactiveUS20140039037A1Low toxicityMaintain levelSplicing alterationNervous disorderADAMTS ProteinsPrecursor mRNA
Described are methods for removing a proteolytic cleavage site, the HCHWA-D mutation or the amino acids encoded by a trinucleotide repeat expansion from a protein comprising providing a cell that expresses pre-mRNA encoding the protein with an anti-sense oligonucleotide that induces skipping of the exonic sequence that comprises the proteolytic cleavage site, HCHWA-D mutation or trinucleotide repeat expansion, respectively, the method further comprising allowing translation of mRNA produced from the pre-mRNA.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
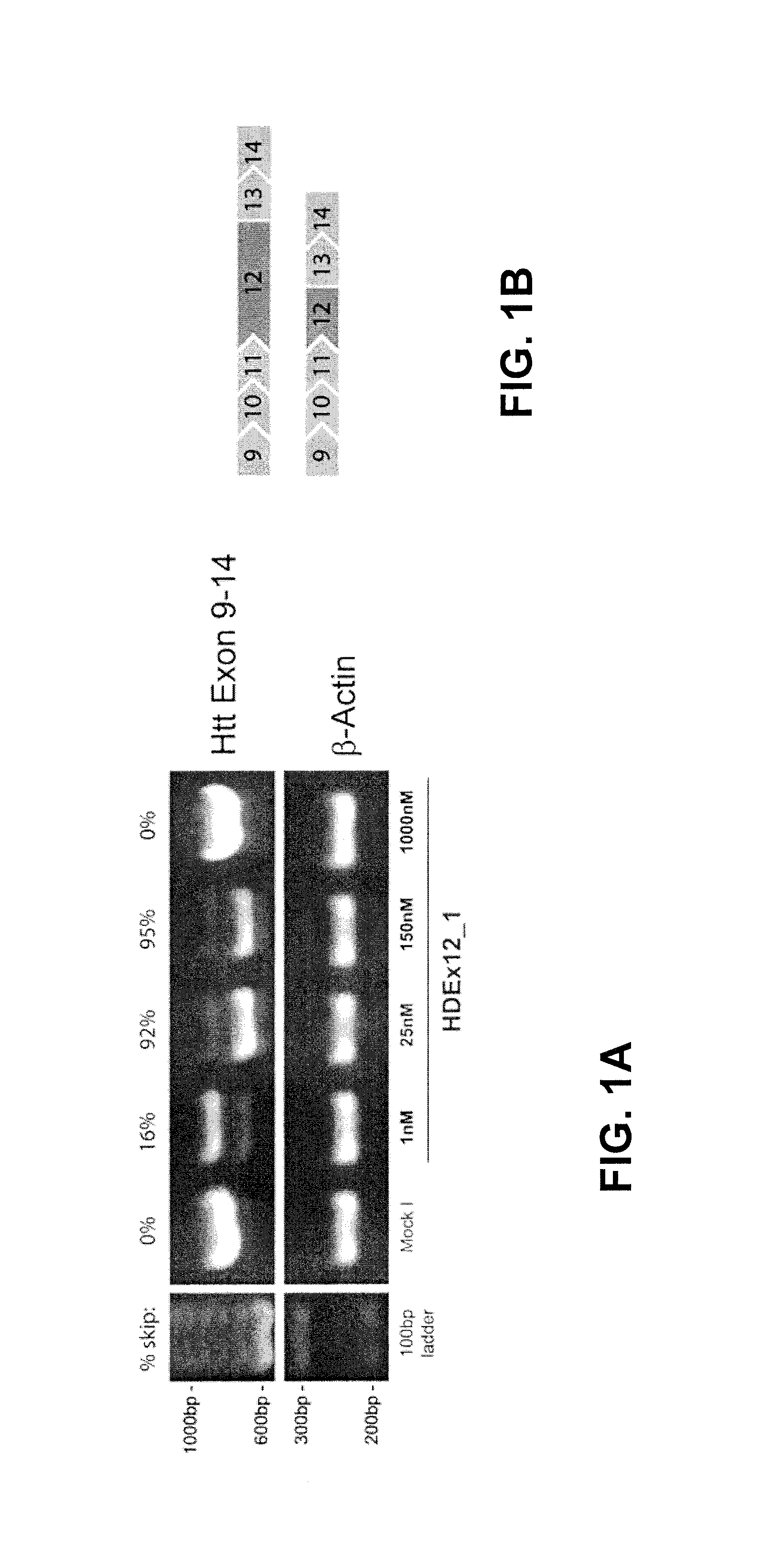
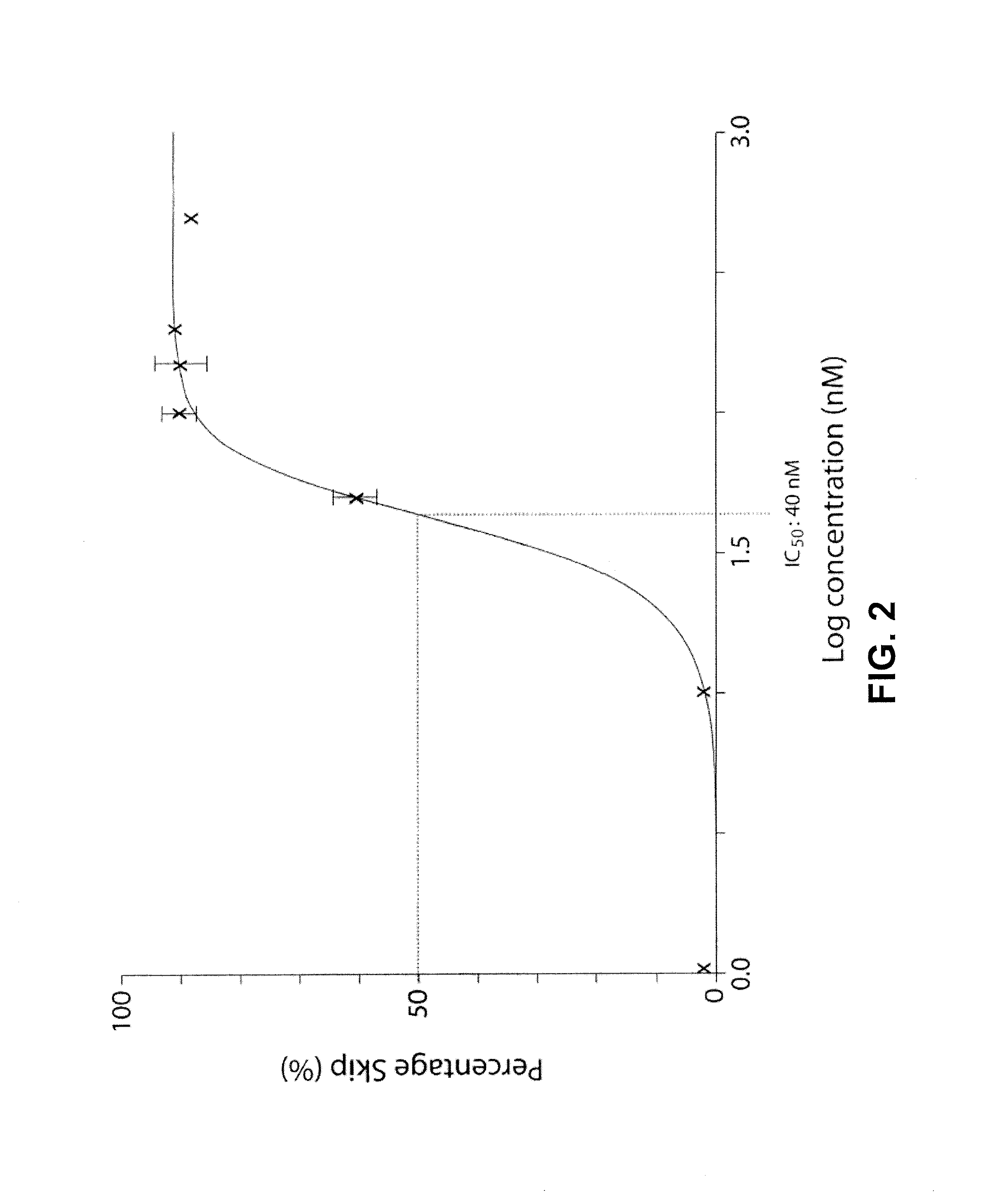
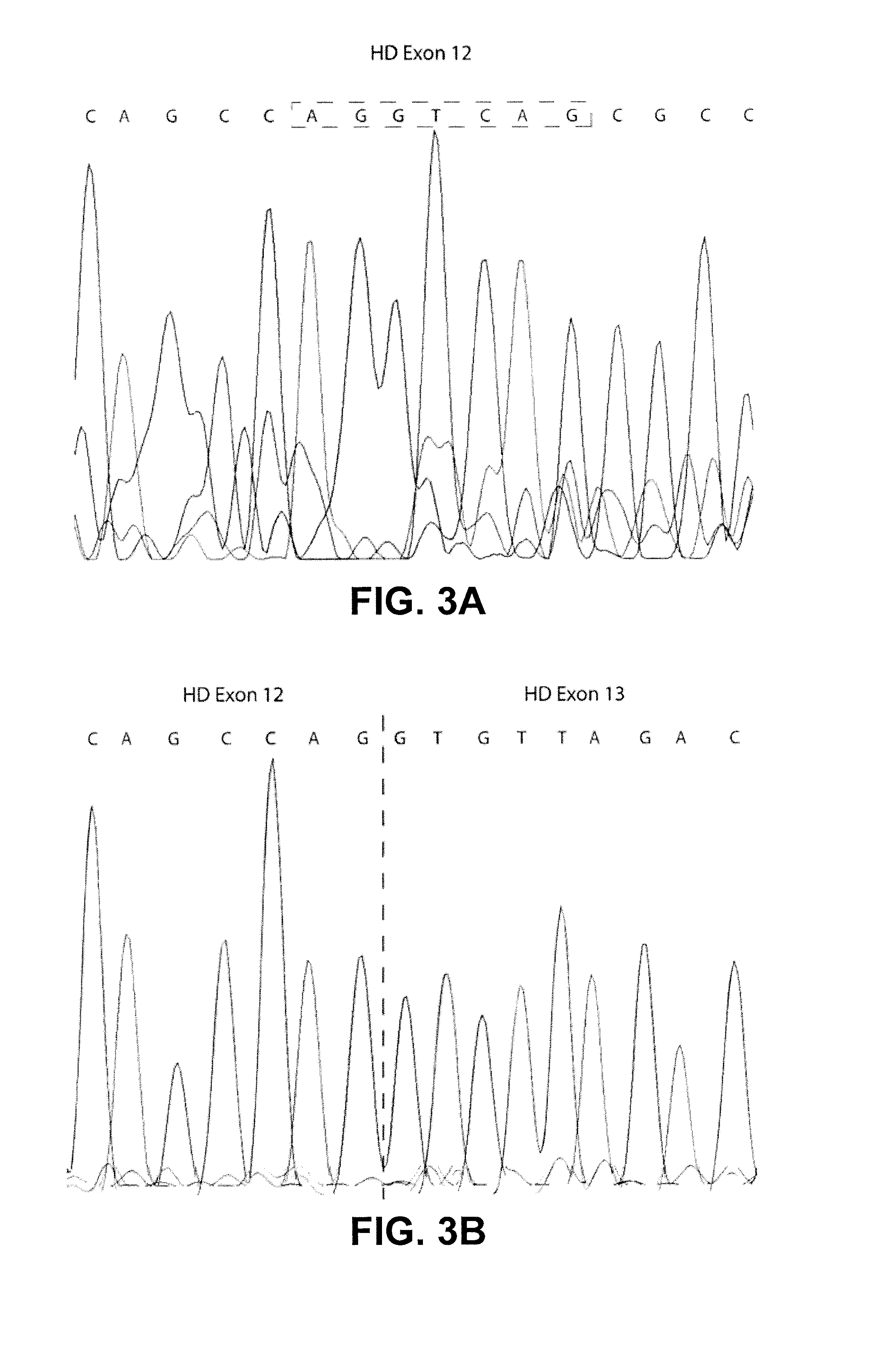
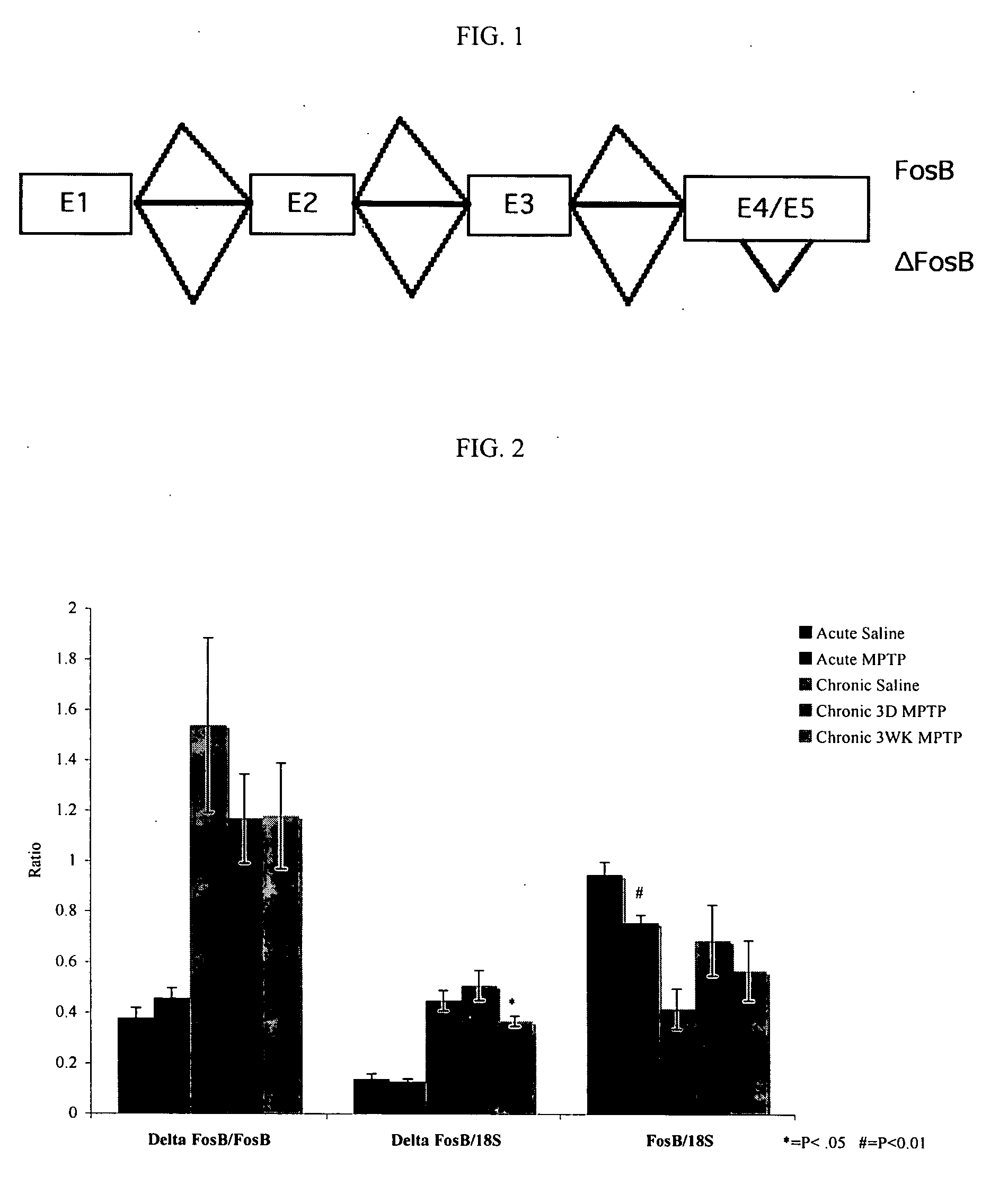
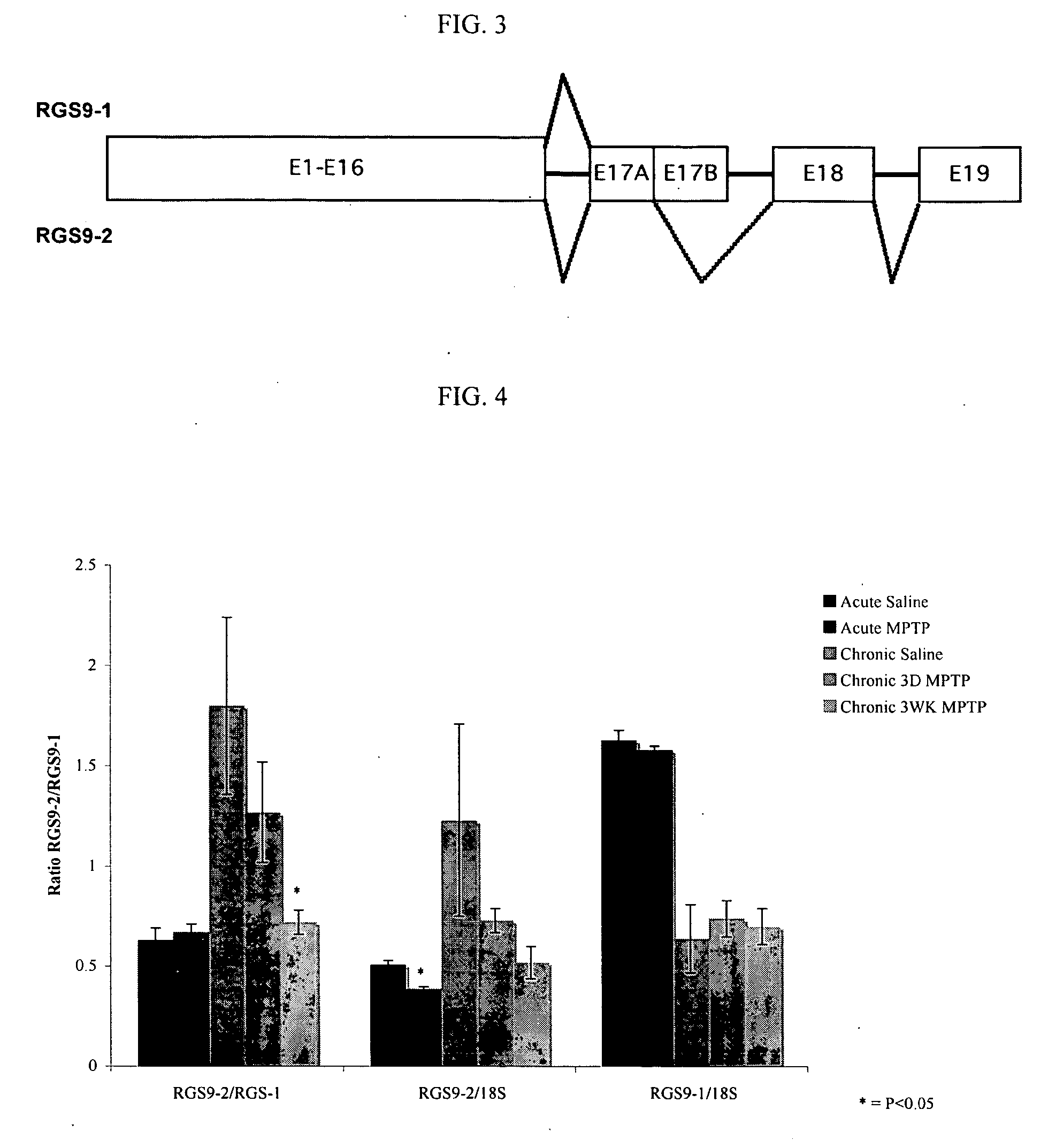
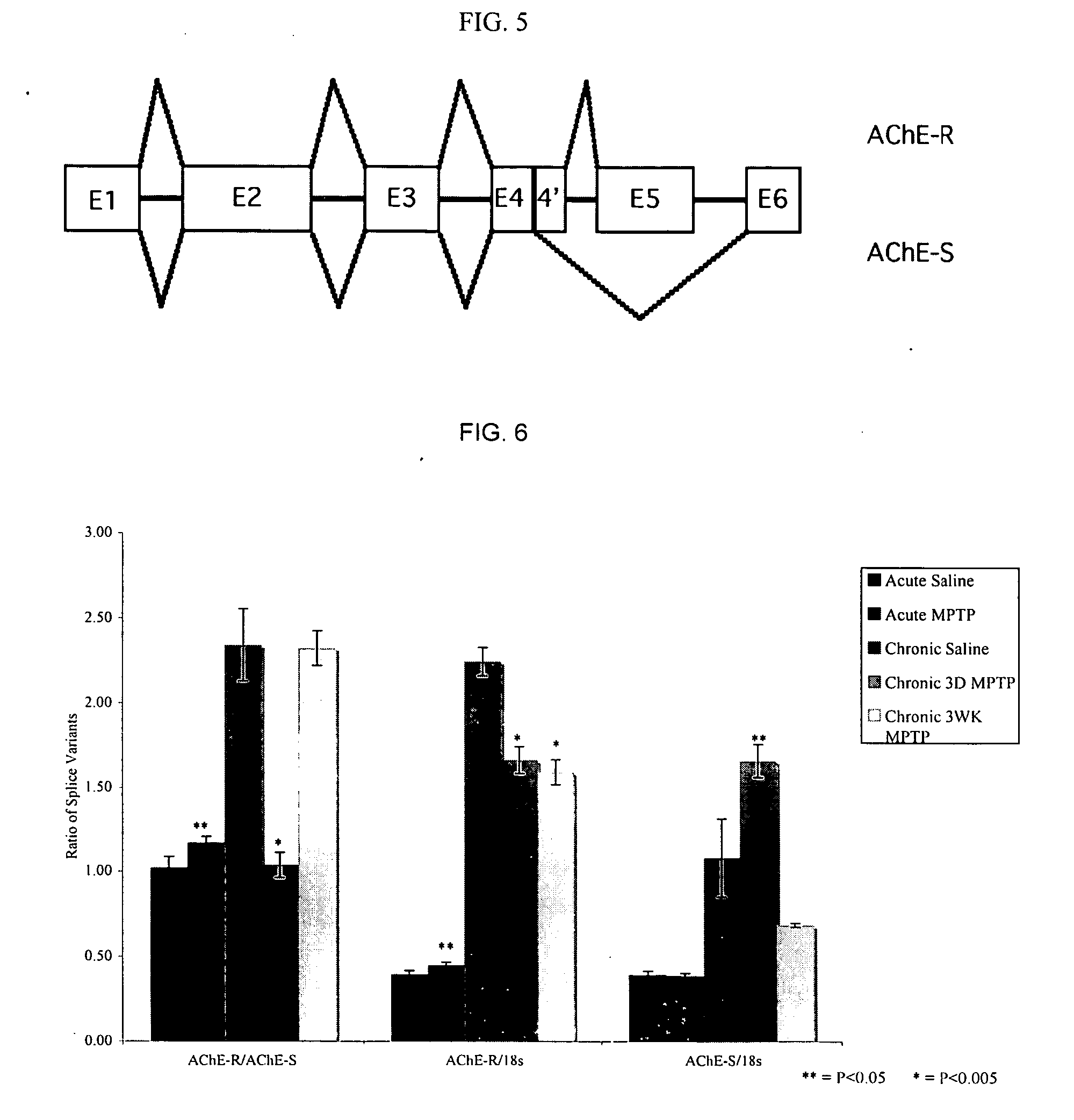
Splice variants of pre-mRNA transcripts as biomarkers in idiopathic neurodegenerative diseases
The present invention discloses a method to discover biomarkers indicative of an idiopathic neurodegenerative disease in a mammalian subject and biomarkers indicative of an idiopathic neurodegenerative disease in the mammalian subject. The biomarker comprises a splice variant mRNA of a precursor-messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) transcript of a gene in the mammalian subject wherein (a) the ratio of the amount of the splice variant mRNA to the amount of another splice variant mRNA of the same precursor-messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) transcript of the same gene is different in the mammalian subject having the neurodegenerative disease as compared to that of a control without the disease; or (b) the ratio of the amount of the splice variant mRNA to the amount of total 18S RNA is different in the mammalian subject having the neurodegenerative disease as compared to that of a control without the disease. The biomarkers can be used to diagnose neurodegenerative diseases in the subject.
Owner:ROSALIND FRANKLIN UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND SCIENCE
Methods to reprogram splice site selection in pre-messenger RNAs
InactiveUS20090186846A1Alter splice site useConvenient distanceSenses disorderNervous disorderBinding siteSplice Site SNP
The present invention relates to a method of modulating splice site selection, splicing and alternative, the method comprising the step of hybridizing an oligonucleotide-protein conjugate to a target pre-mRNA molecule in a cell or cell extract, wherein the oligonucleotide-protein conjugate comprises an oligonucleotide moiety which comprises at least two distinct sequence elements: (i) a nucleic acid sequence that is complementary to a specific region upstream of the splice site in the target pre-mRNA molecule; and (ii) an extension containing a protein binding site sequence element for covalently binding a protein; wherein the protein moiety comprises a protein capable of modulating splicing of the splice site upon binding with the protein binding site.
Owner:SOCPRA SCI SANTE & HUMAINES S E C
Identification of structurally similar small molecules that enhance therapeutic exon skipping
This invention relates, e.g., to a method for enhancing exon skipping in a pre-mRNA of interest, comprising contacting the pre-mRNA with an effective amount of a compound such as, for example, Perphenazine, Flupentixol DiHCl, Zuclopenthixol or Corynanthine HCl, or a compound which shares a similar 2-D structure and activity level with one of these compounds, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, hydrate, solvate, or isomer of the compound, and, optionally, with an antisense oligonucleotide that is specific for a splicing sequence in the pre-mRNA Methods for treating Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) are disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Antisense oligonucleotide directed removal of proteolytic cleavage sites from proteins
ActiveUS20130198877A1Improve the level ofLow toxicitySplicing alterationNervous disorderPrecursor mRNAProteolysis
Described are means and methods for removing a proteolytic cleavage site from a protein, the method comprising providing a cell that expresses pre-mRNA encoding the protein with an anti-sense oligonucleotide that induces skipping of the exonic sequence that encodes the proteolytic cleavage site, and allowing translation of mRNA produced from the pre-mRNA.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
Pre-MRNA trans-splicing molecule (RTM) molecules and their uses
The present invention relates to specific and markedly improved pre-mRNA trans-splicing molecule (RTM) molecules which are designed to correct specific genes expressed within cells to be targeted, and which are associated with epidermolysis bullosa, cystic fibrosis, pachyonychia congenital, and psoriasis or neurodermitis, as well as cancers of the skin. In particular, the RTMs of the present invention are genetically engineered to interact with a specific target pre-mRNA expressed in cells to be targeted so as to result in correction of genetic defects or reprogramming of gene expression responsible for a variety of different skin disorders.
Owner:BAUER JOHANN +1
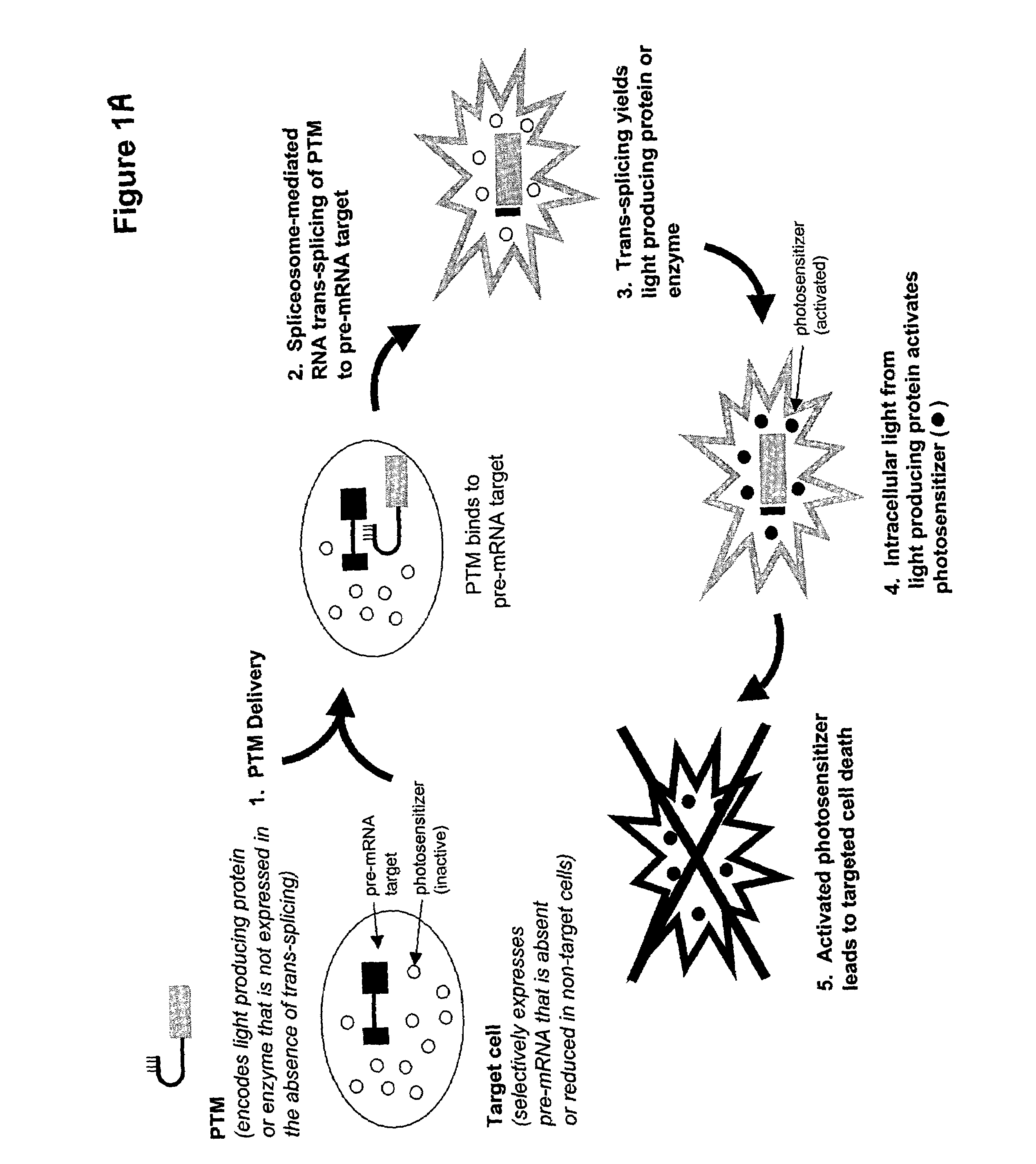
Trans-splicing mediated photodynamic therapy
The present invention provides methods and compositions for conferring selective death on cells expressing a specific target precursor messenger RNA (selective target pre-mRNA). The compositions of the invention include pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with a target precursor messenger RNA molecule (target pre-mRNA) expressed within a cell and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of a novel chimeric mRNA molecule (chimeric mRNA) capable of encoding a light producing protein or enzyme. Cell death is further mediated by the presence of a photosensitizer which upon photoactivation produces cytotoxicity.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES SEC GOVERNMENT OF UNITED STATES +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com