Identification of small molecules that facilitate therapeutic exon skipping
a small molecule and exon skipping technology, applied in the field of identification of small molecules that facilitate the therapeutic exon skipping, can solve the problems of substantial side effects, progressive muscle function loss, and substantial impact on the practicality of chronic administration of expensive to produce oligonucleotides
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
Identification of Small Molecule Enhancers of Antisense Mediated Exon Skipping
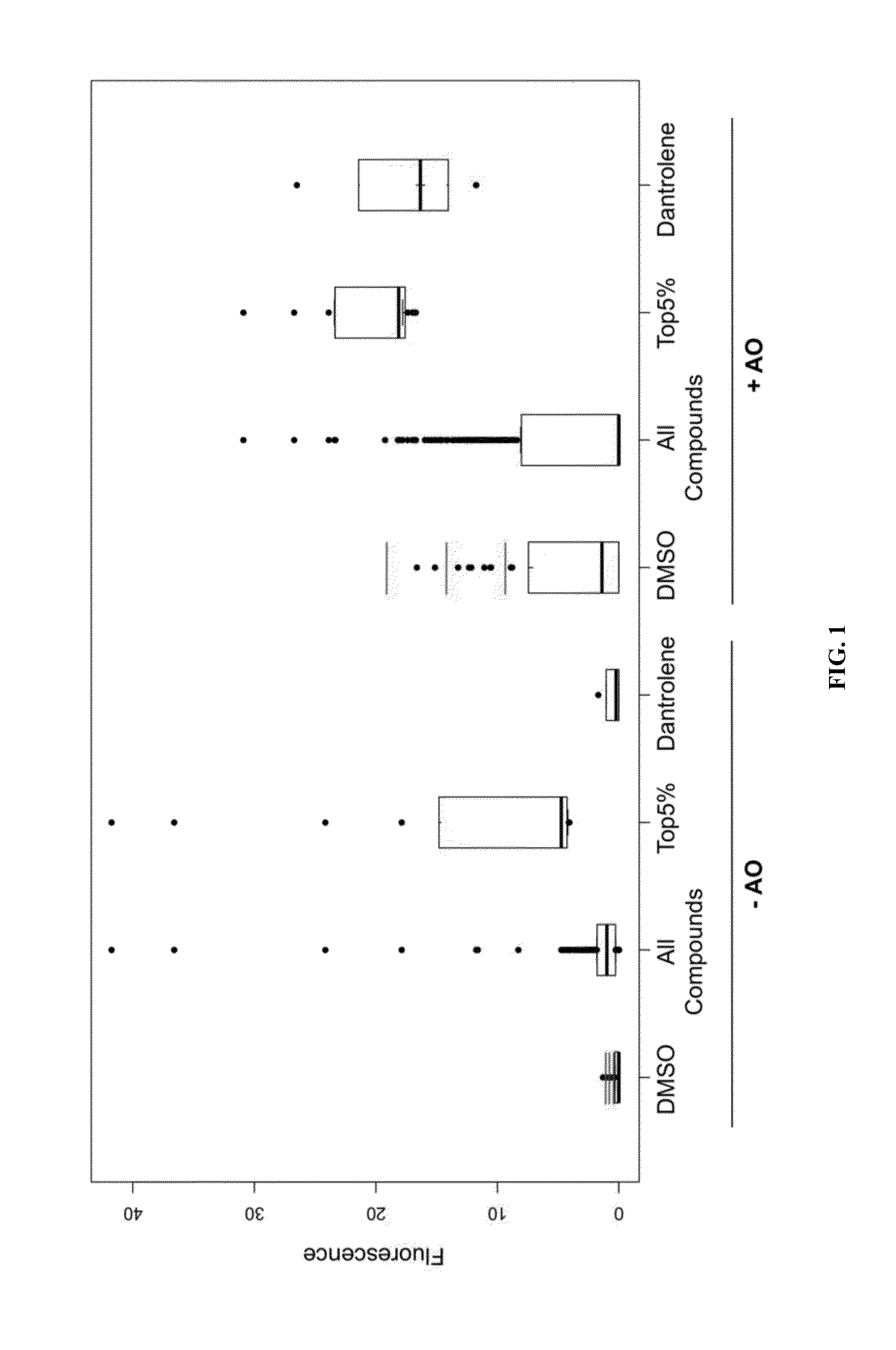
[0089]In this Example, we describe the implementation of a strategy to identify compounds that synergize with AO to promote exon skipping and the follow-up of a lead hit, dantrolene, in mutation repair of specific mouse and human models of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in vitro and in vivo. In contrast to prior screens aimed at identifying small molecules which impact exon skipping, our screen is unique at least because it relies on robust quantitation of a skipping reporter in the context of a muscle lineage cell in the presence and absence of suboptimal AO. These screens were performed using a mouse muscle cell line (C2C12) expressing a human DMD exon 50 GFP based reporter [18] selected to minimize experimental variation and sensitivity in the context of an automated and quantitative fluorescent scanning system.
[0090]The BioMol small molecule library (n=503) was screened at an effective concentration of 10...
example ii
Supplementary Studies
A. Materials and Methods
High-Throughput Screen and Secondary Screening in the Reporter Cell Line
[0103]A stable clone was generated from C2C12 cells transfected with a human exon 50 DMD GFP reporter (ex50GFP) that has been previously described [18]. Ex50GFP reporter myoblasts were seeded into uncoated 384 well plates and were incubated for 4 hours either with or without 300 nM of 2′-O-methyl phosphorothioate AON6 [5′ AACUUCCUCUUUAACAGAAAAGCAUAC 3′ (SEQ ID NO:1)] targeting the human exon 50 splice donor site. Cells were transfected with AON6 using the FUGENE (Roche) transfection reagent per manufacturer's instructions. Following AON6 incubation, each component of the BioMol library (n=503) was screened at 10 uM concentration with a final concentration of the DMSO carrier being 1%. Forty-eight hours later fluorescence was measured using the MicroXpress high content imager and analyzed using MetaXpress. Immediately preceding imaging, DNA was stained with Hoescht for...
example iii
Further Data
[0112]The experiments described in the figures as summarized below were carried out using methods described elsewhere herein, and / or by conventional methods that are well-known by those of skill in the art.
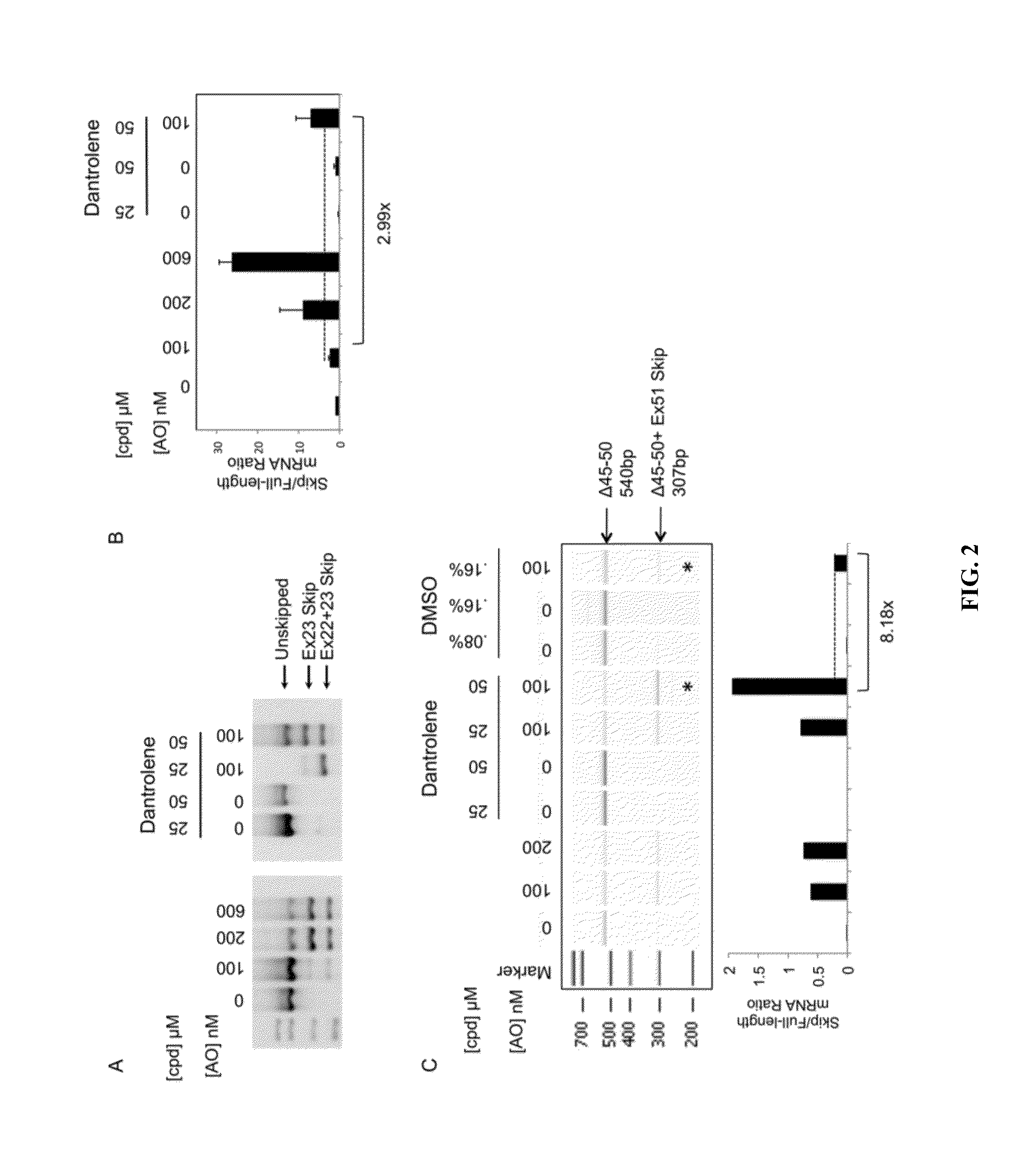
[0113]These experiments provide data showing, e.g., that 7 additional small molecule compounds can enhance exon skipping of the DMD gene of human myotube which are exon 51 skippable. See FIGS. 16, 17 and 18. It is noted that two of these molecules (Ryanodine and S107 (called a RYCAL) target the ryanodine receptor, which is also targeted by dantrolene. See FIGS. 19 and 20. Without wishing to be bound by any particular mechanism, it is suggested that this observation supports the conclusion that blocking the ryanodine receptor is one of the mechanisms of this effect.
[0114]Furthermore, additional confirmatory tests (titrations) are presented and functional testing of dantrolene is shown in a mouse system. FIG. 21 shows that low dose AO (exon 23 in mouse that repairs the m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com