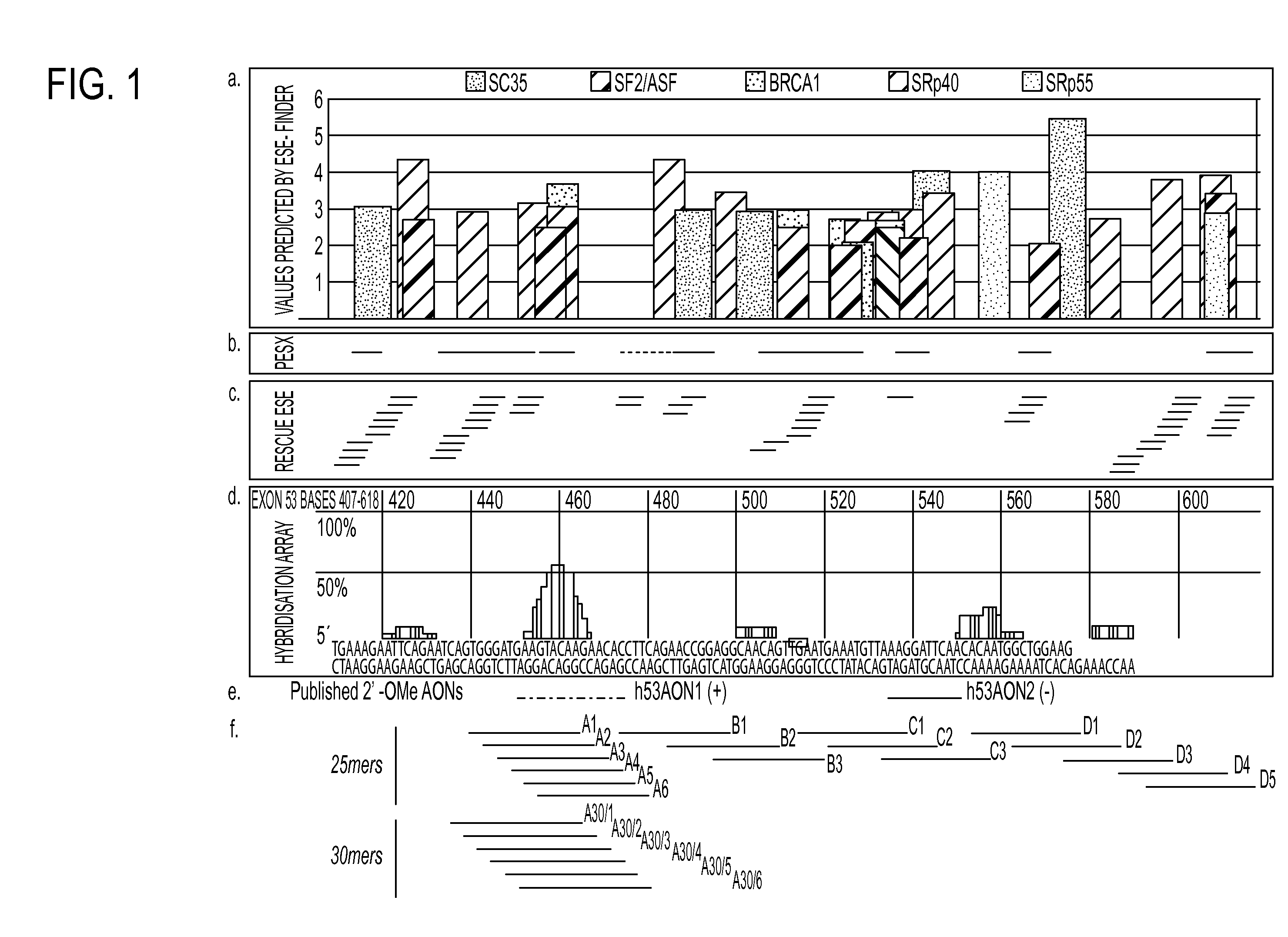
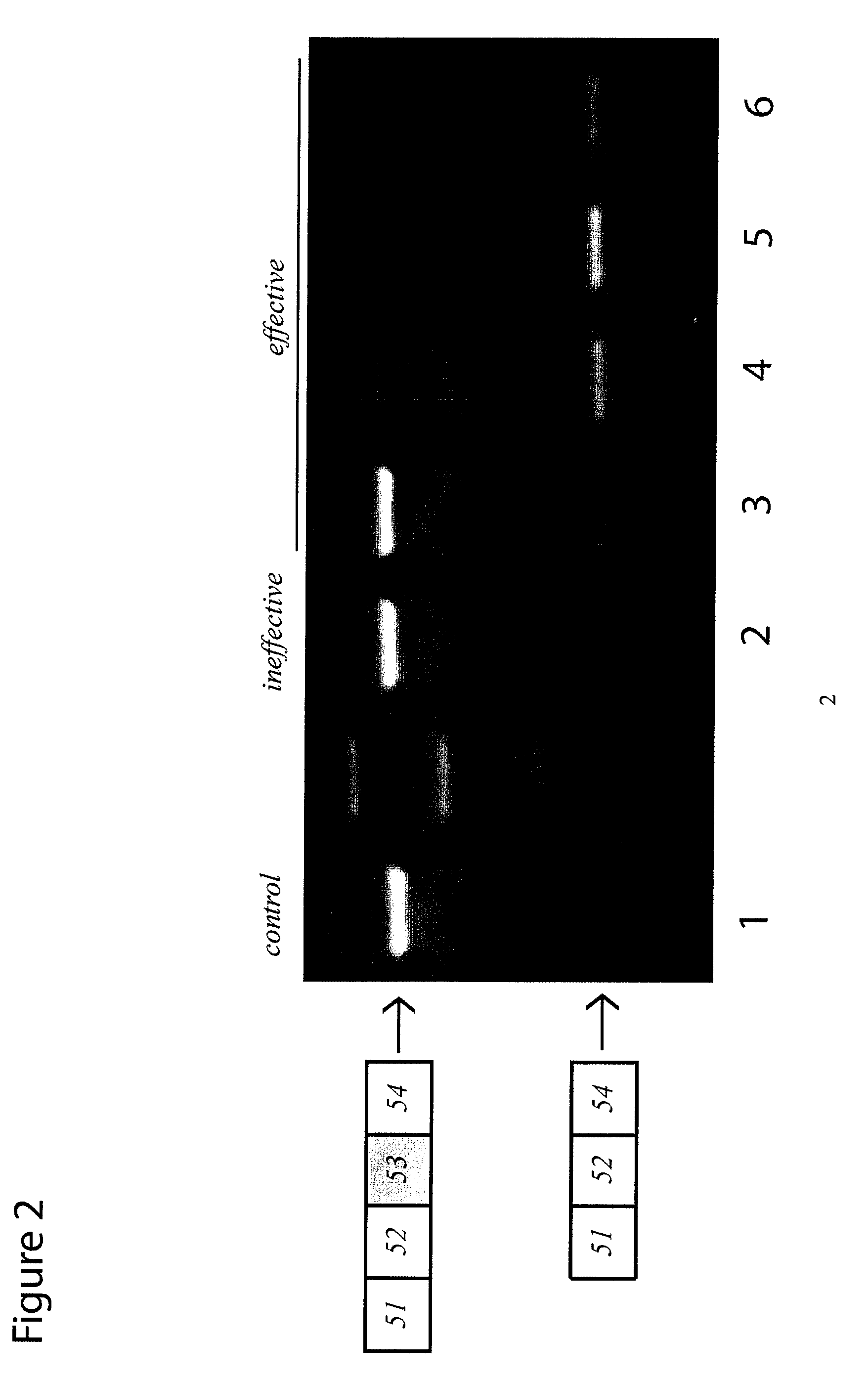
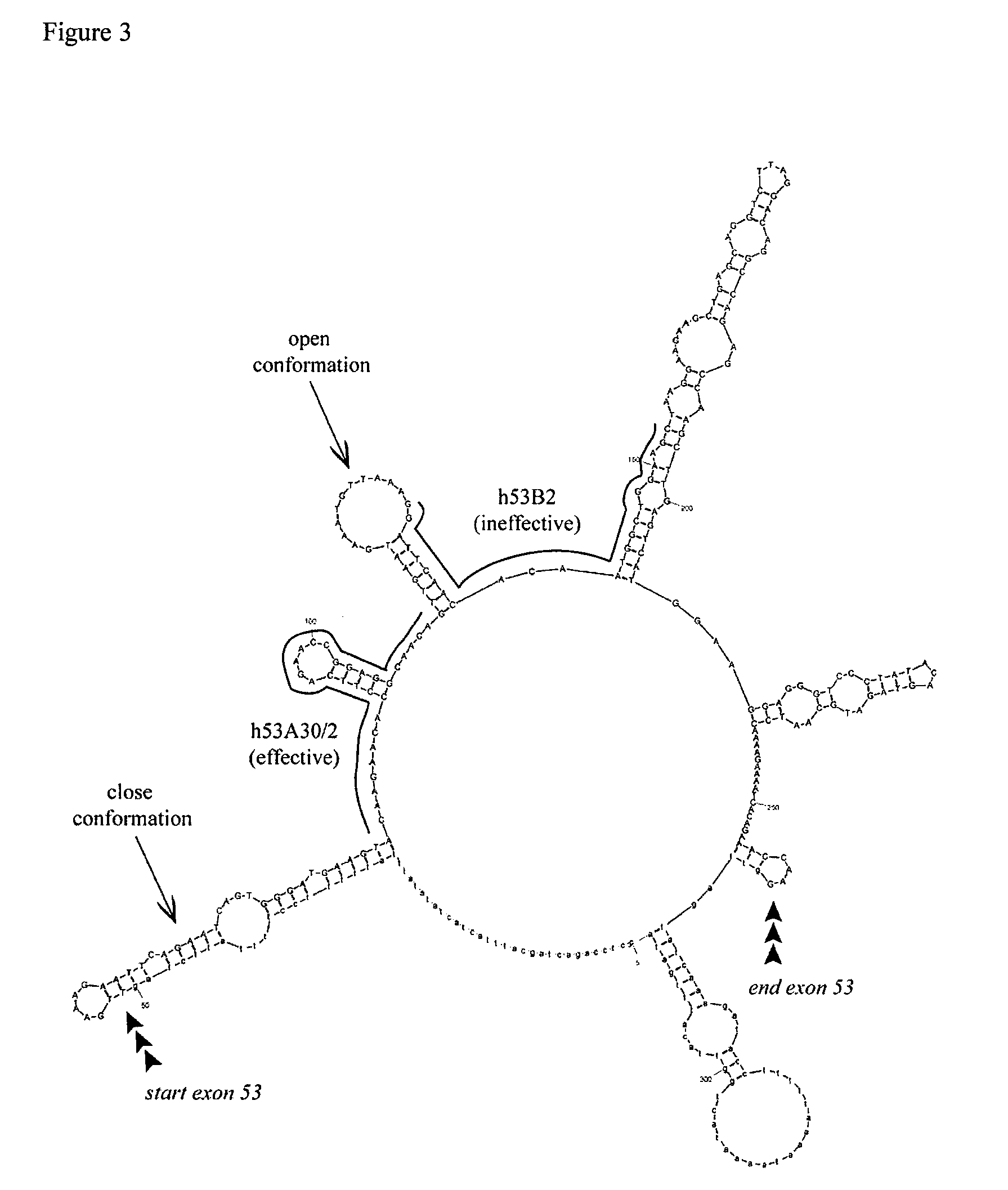
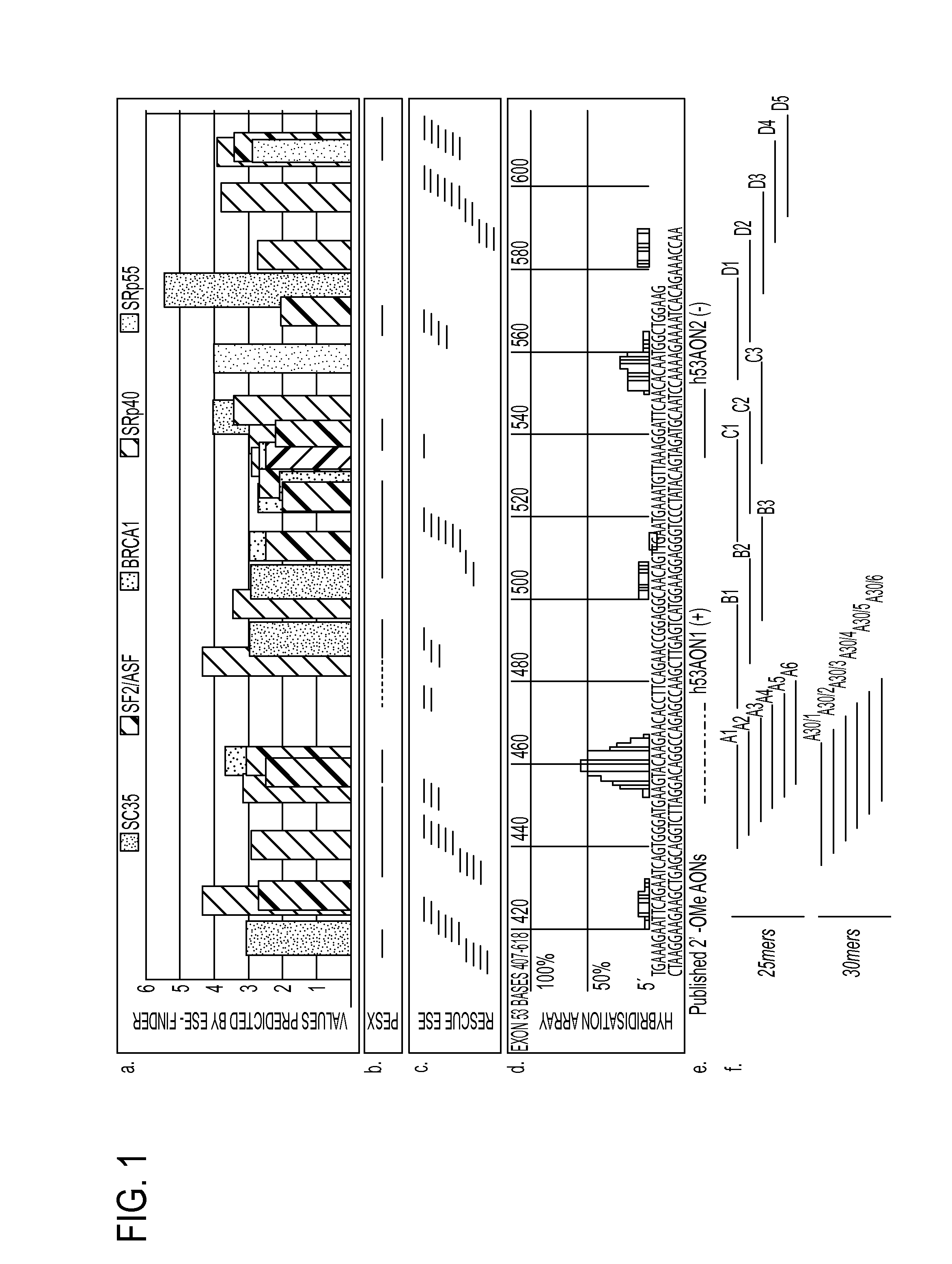
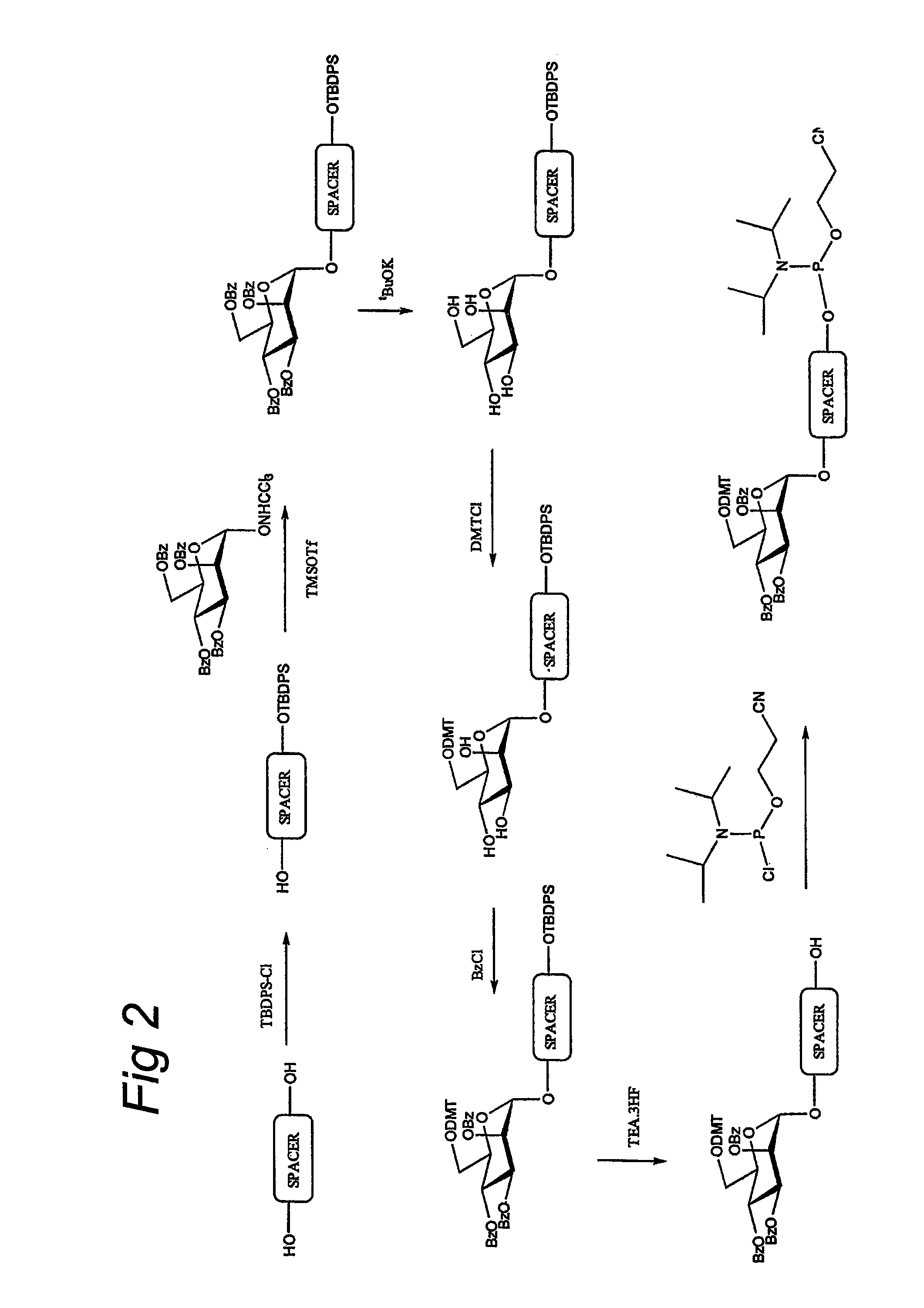
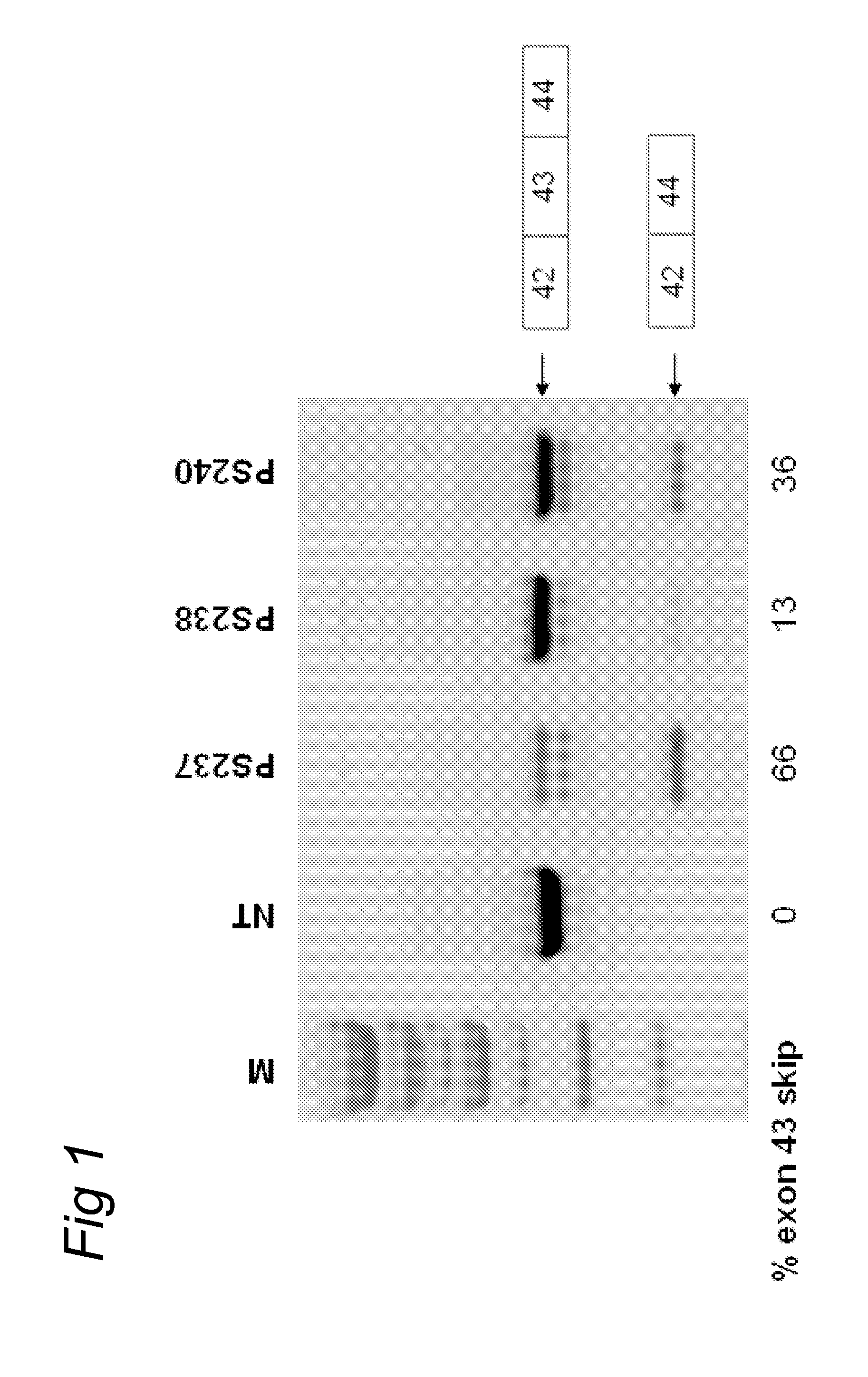
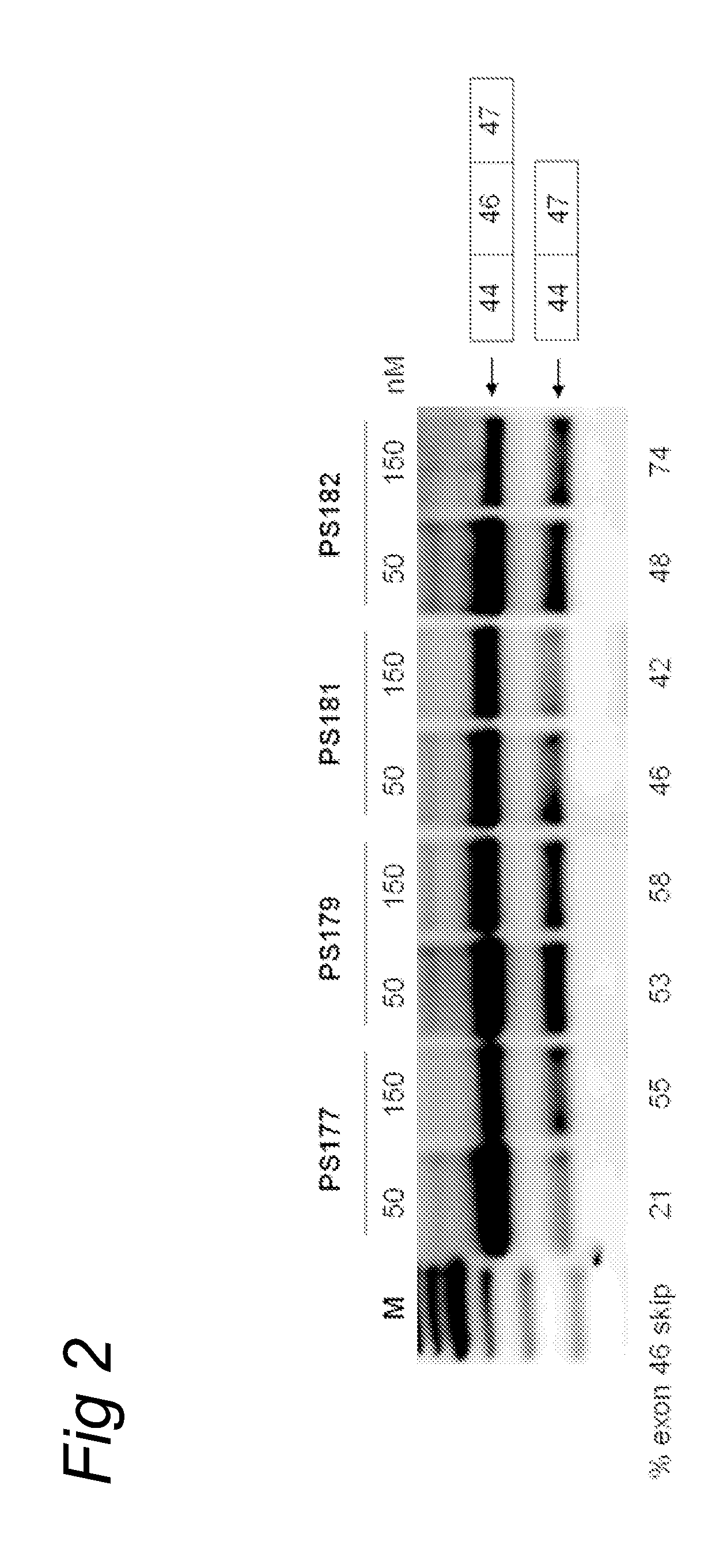
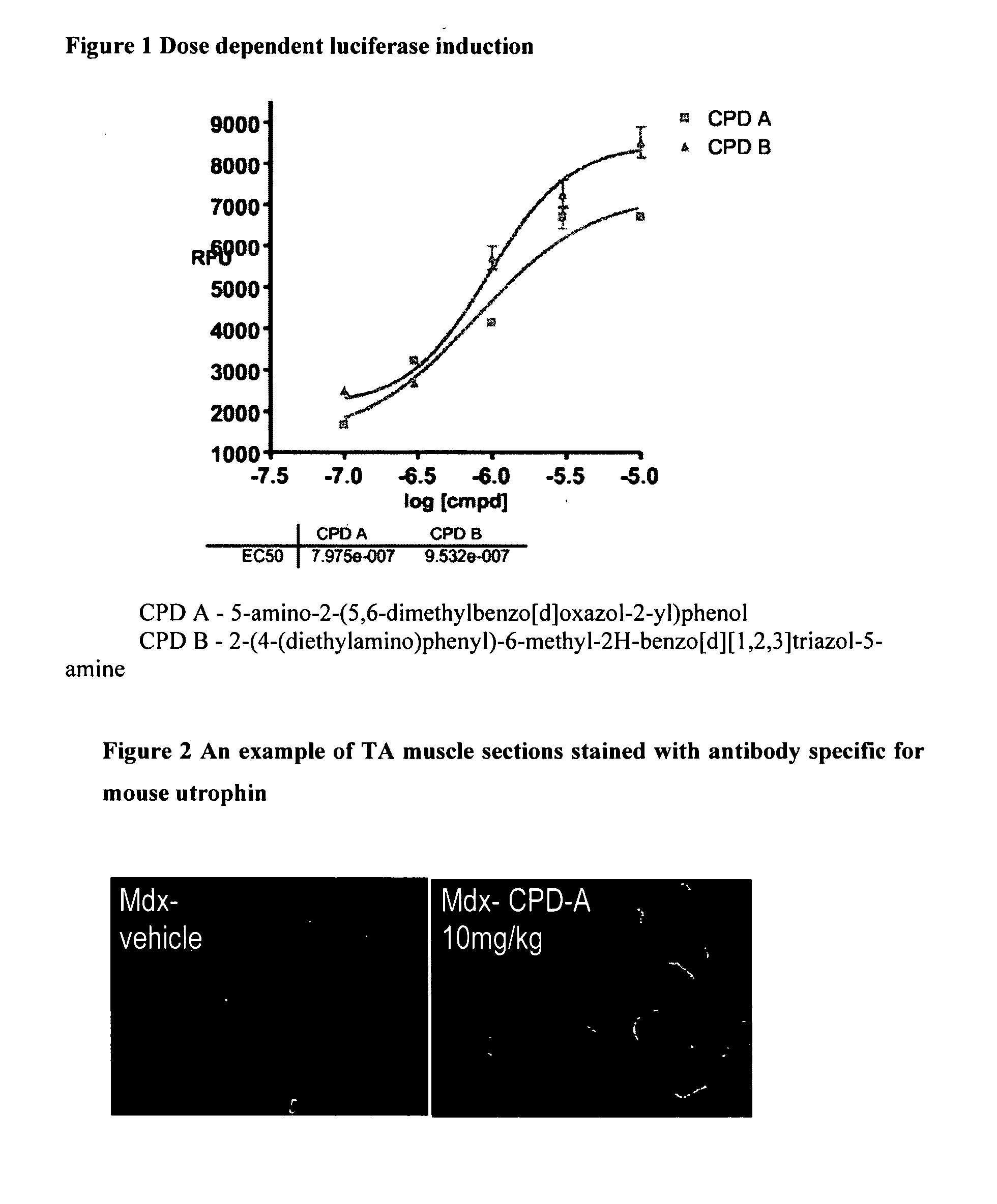
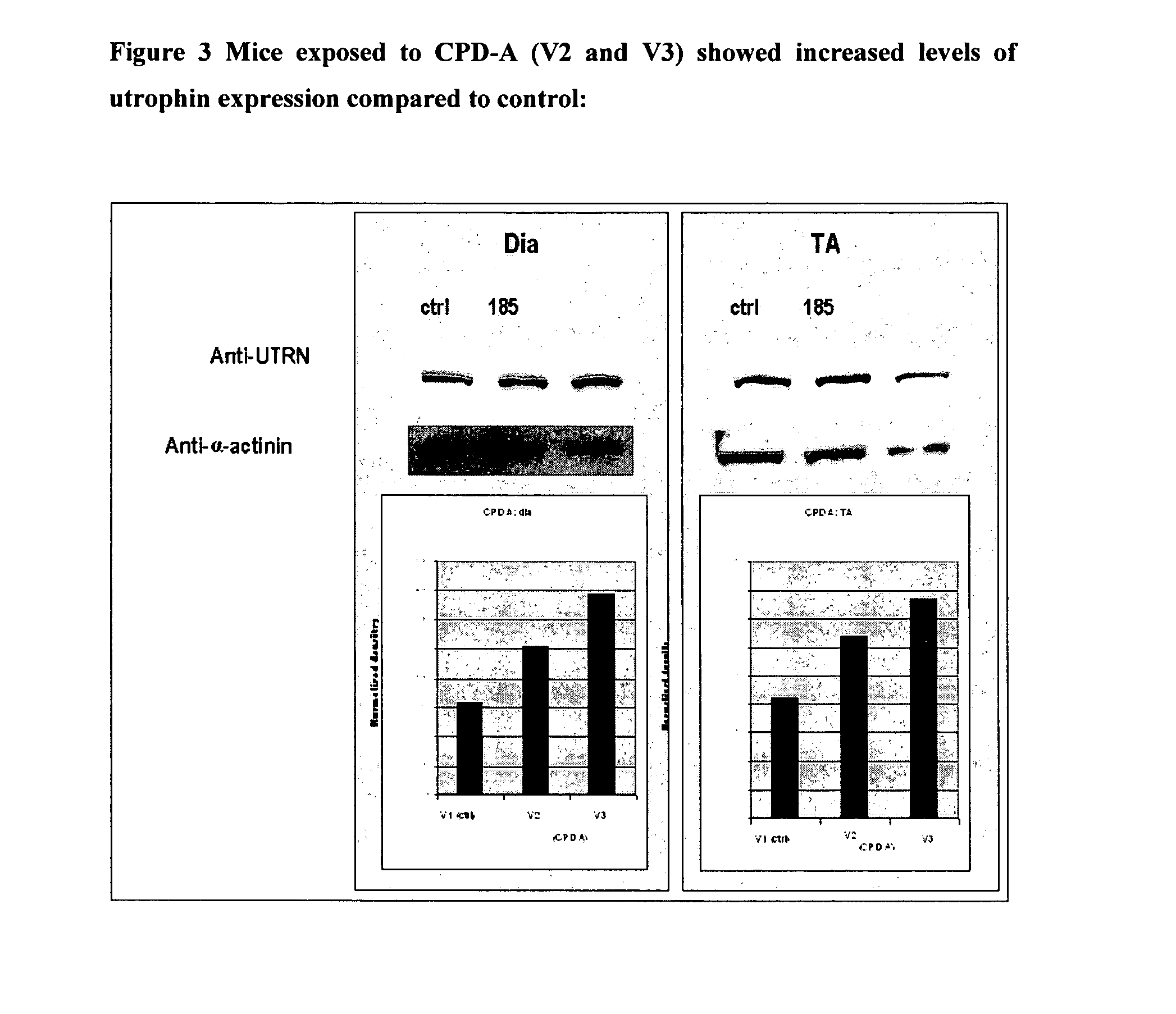
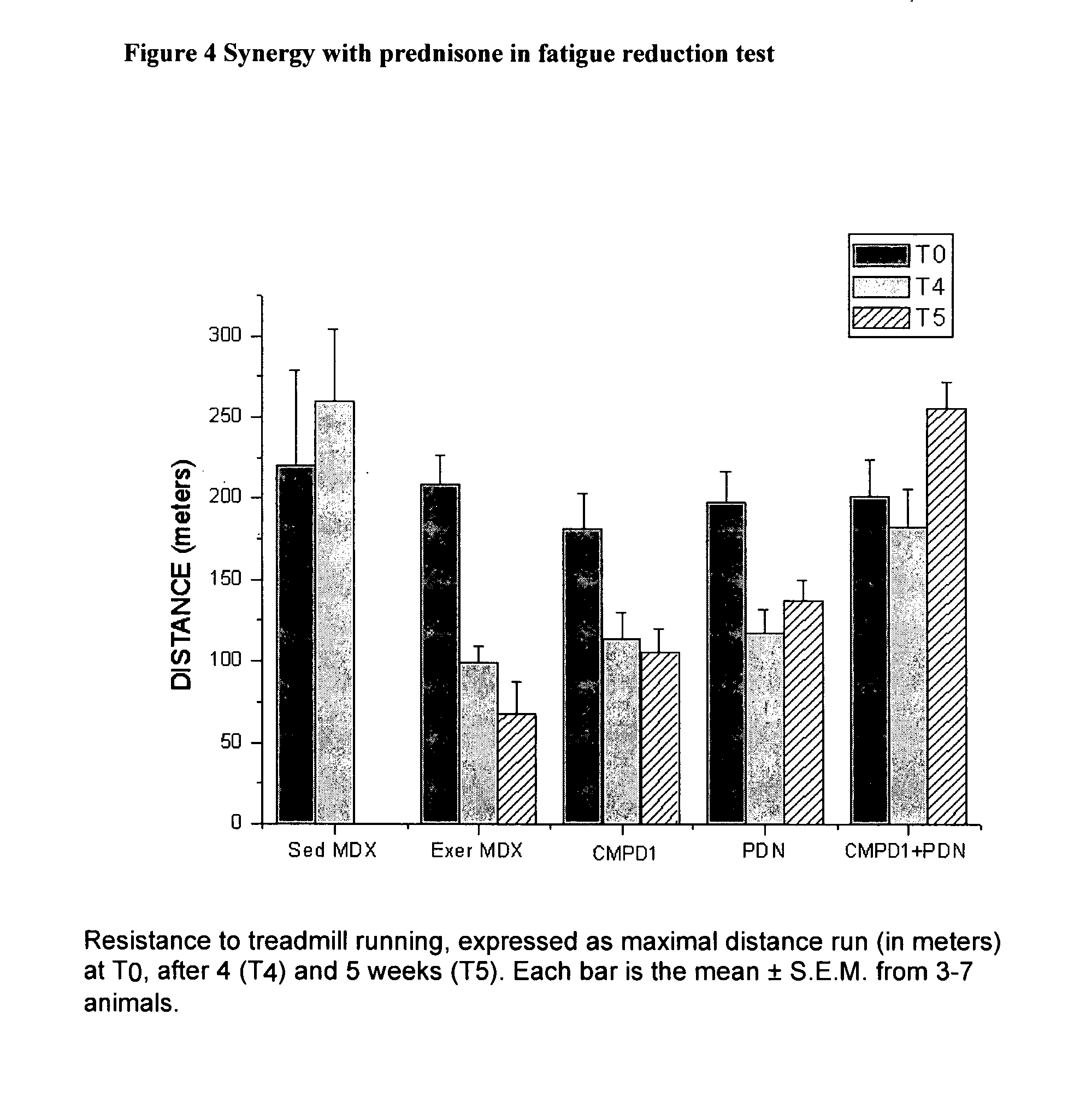
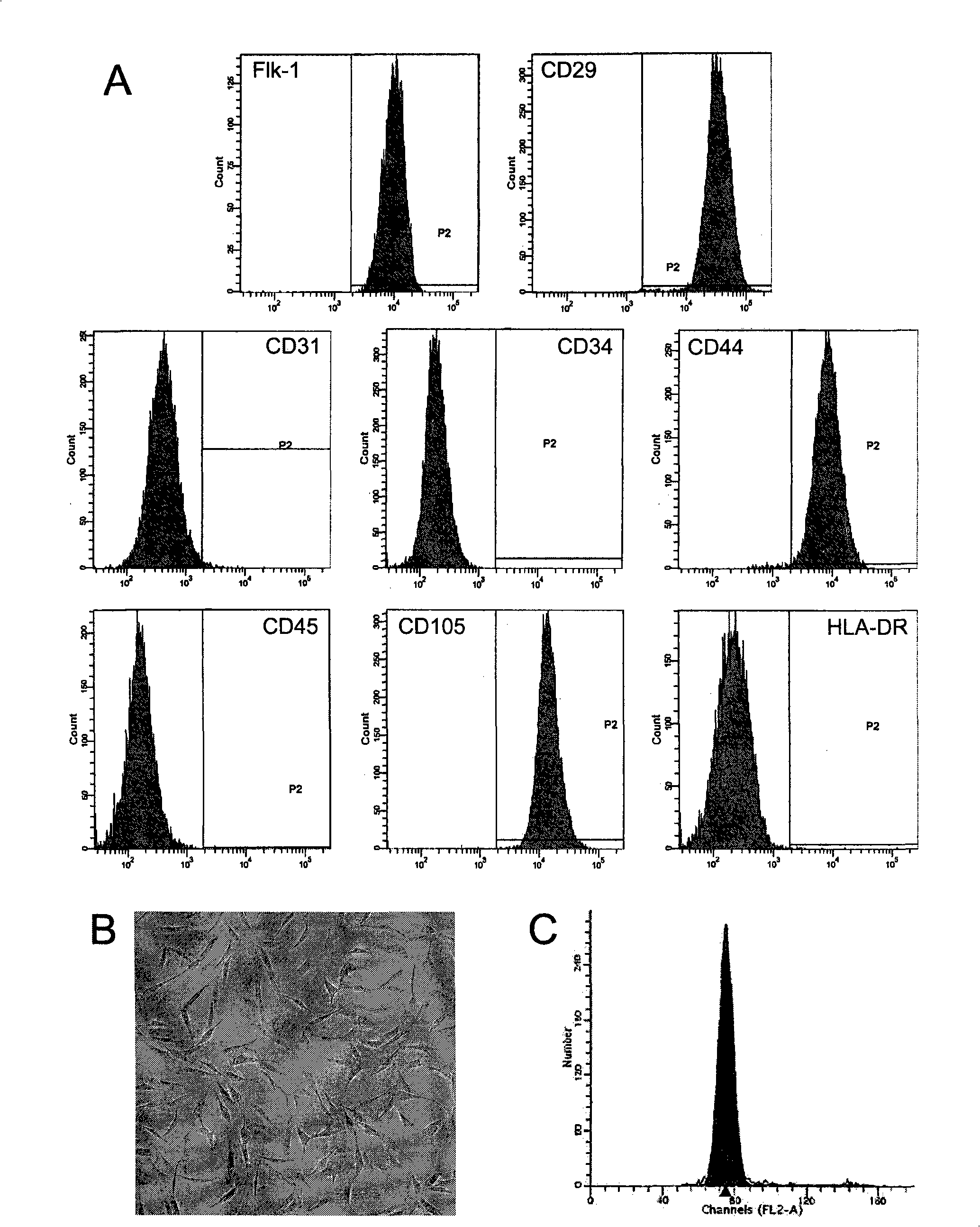
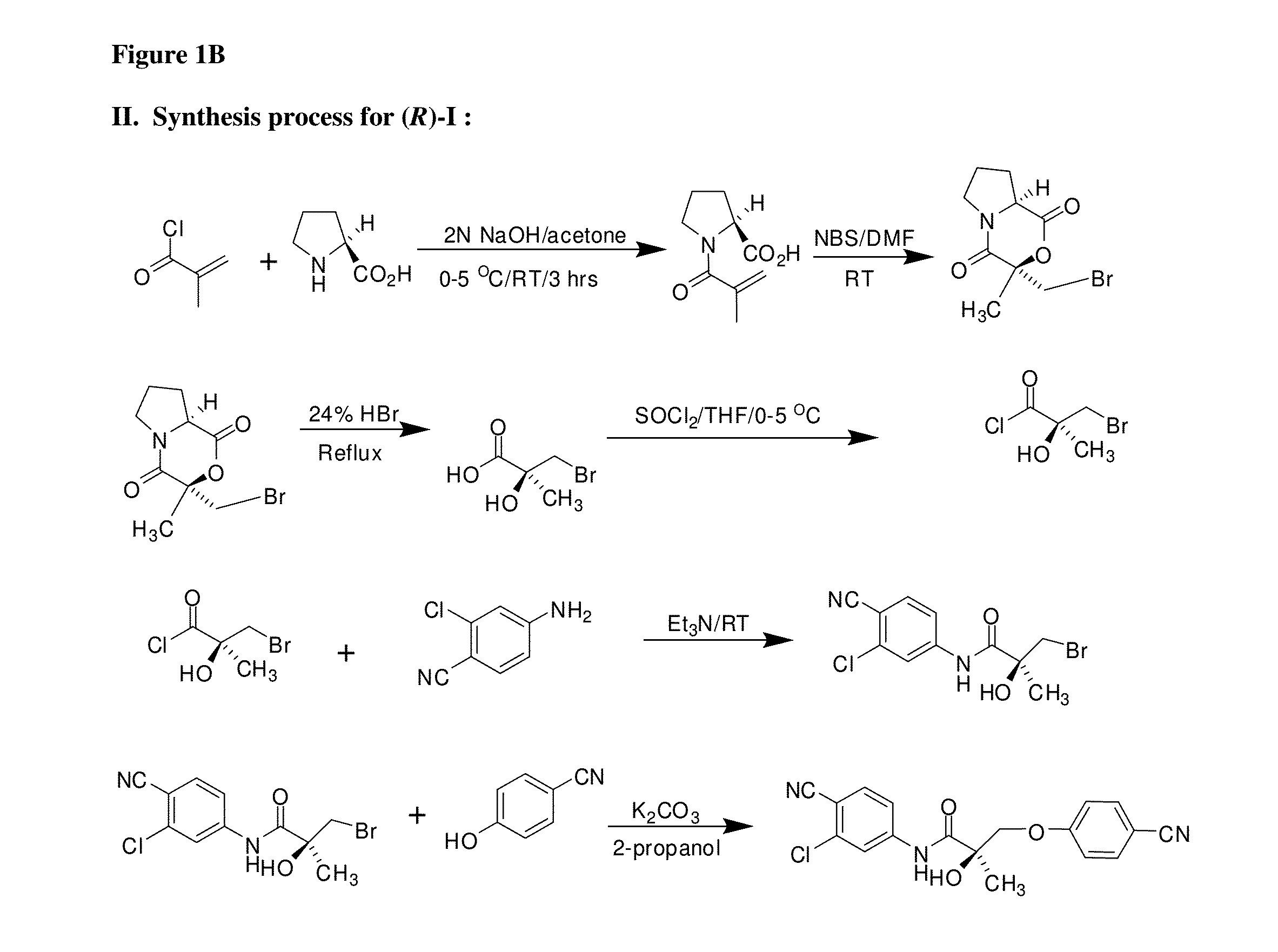
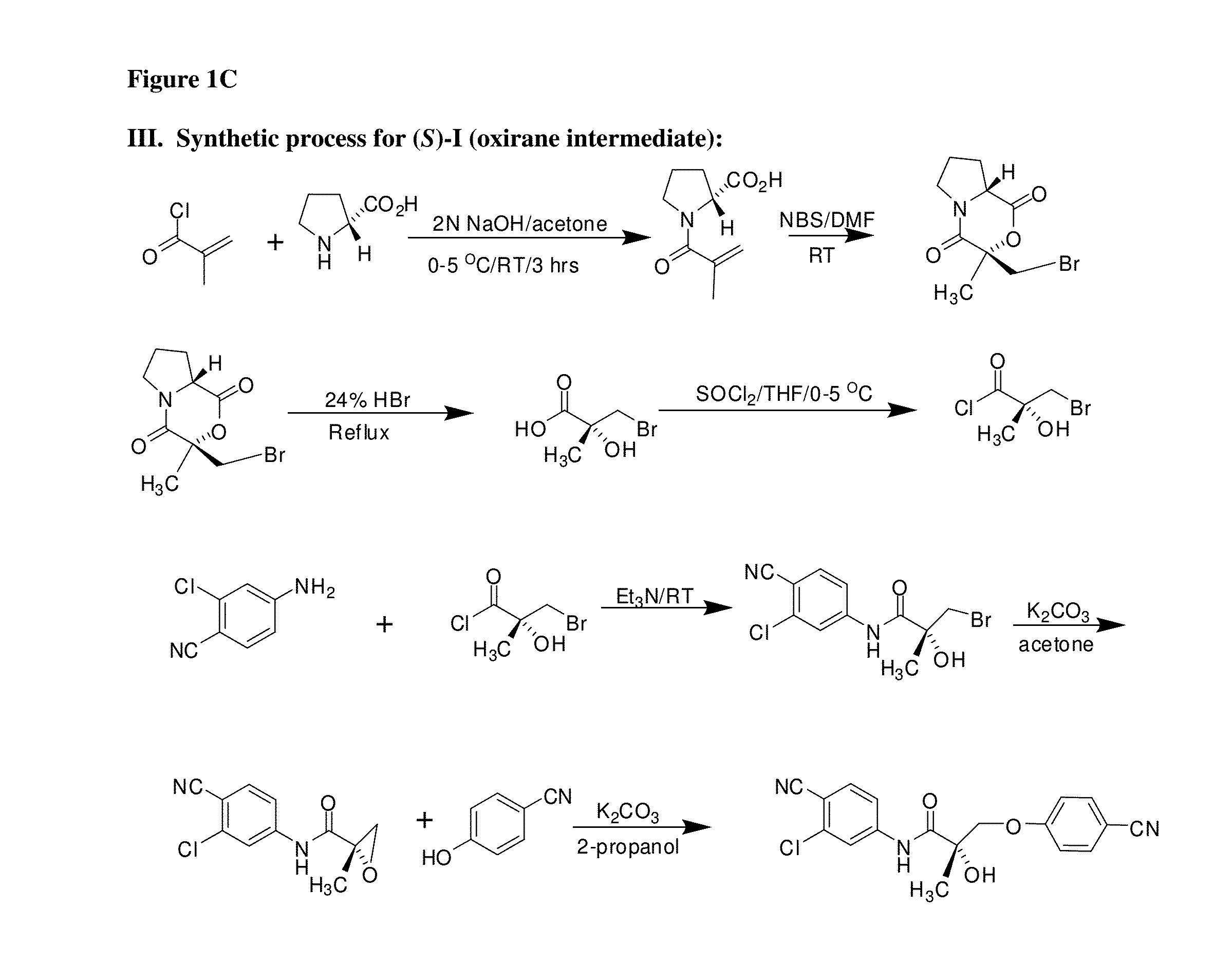
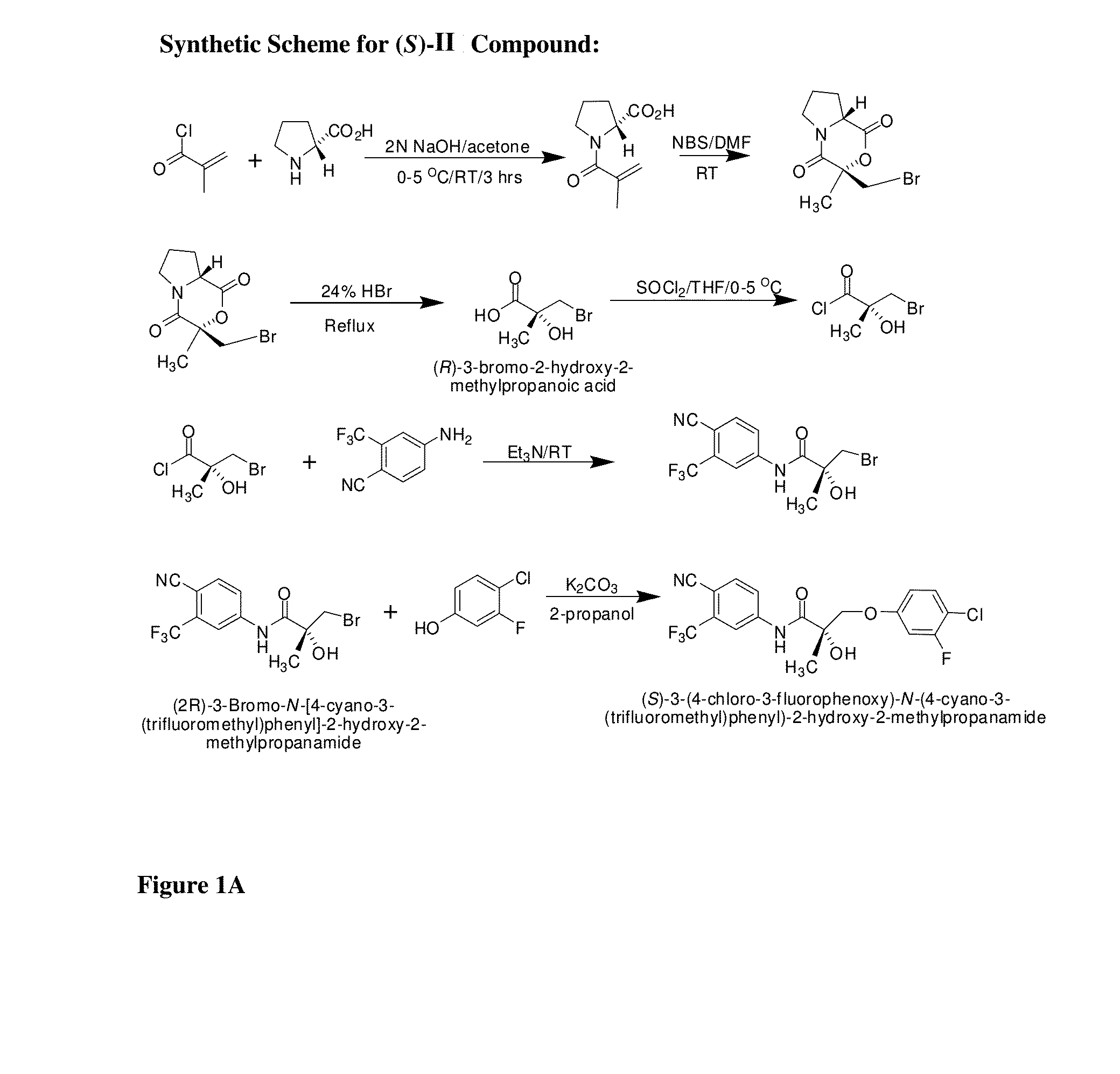
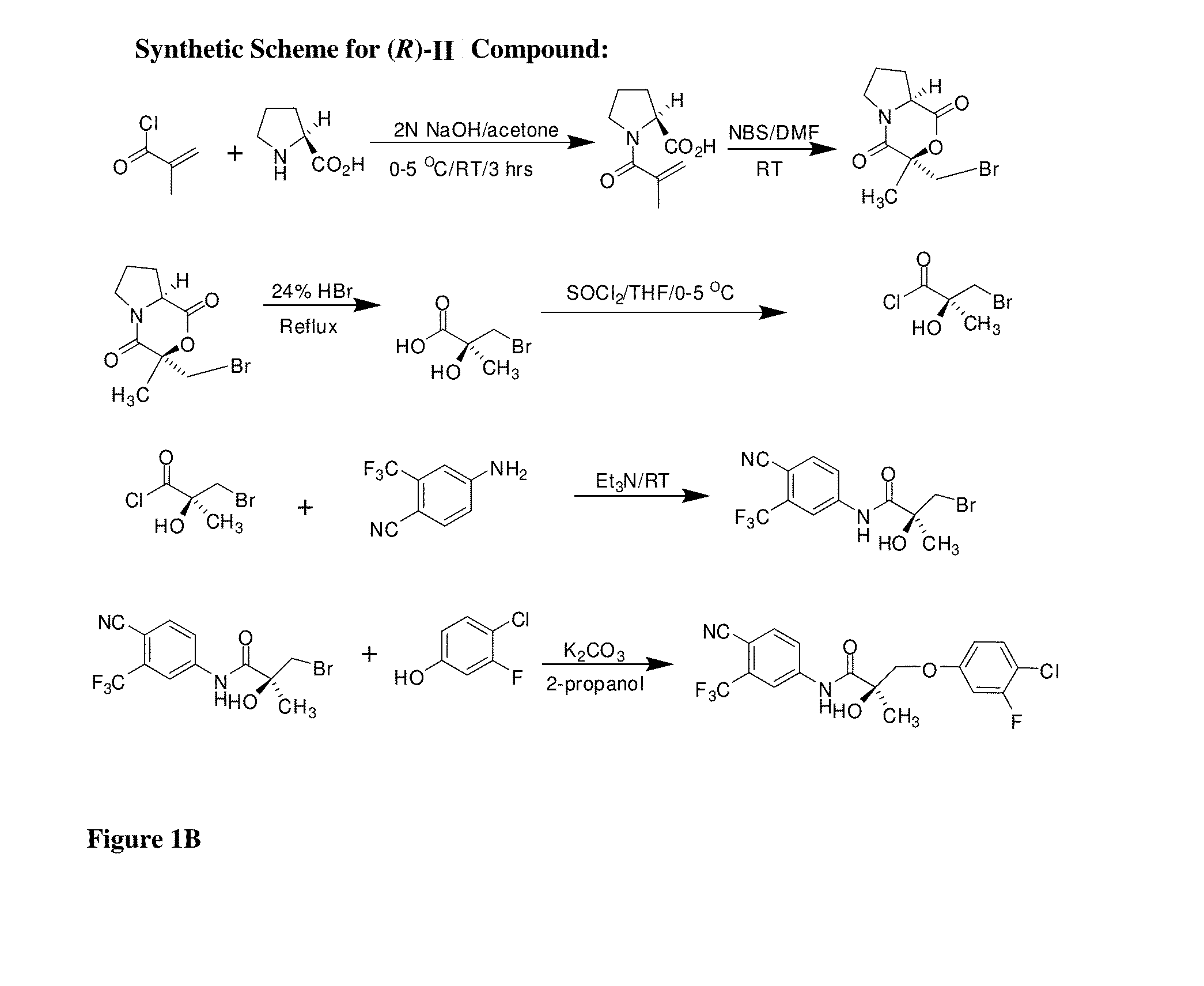
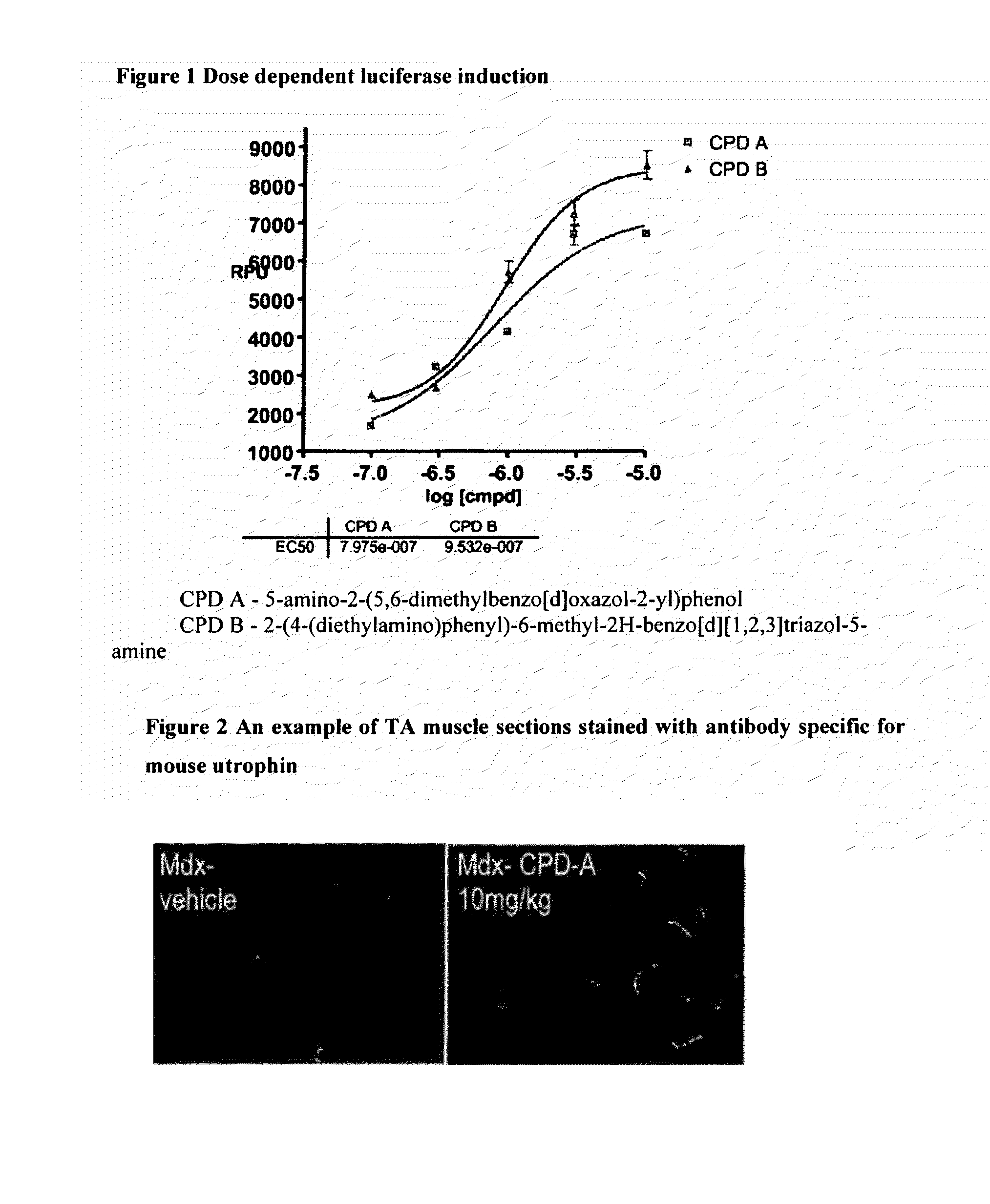
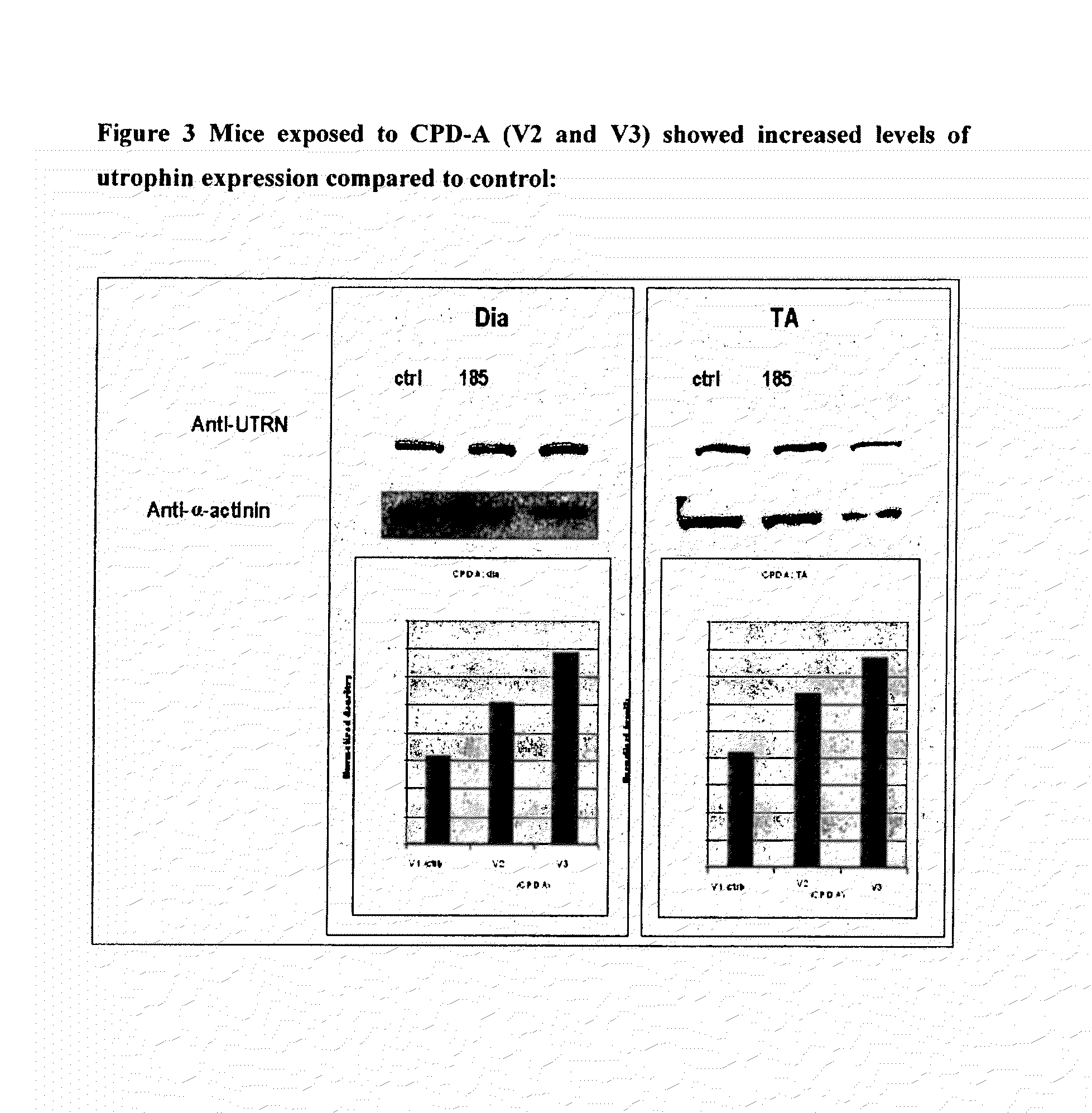
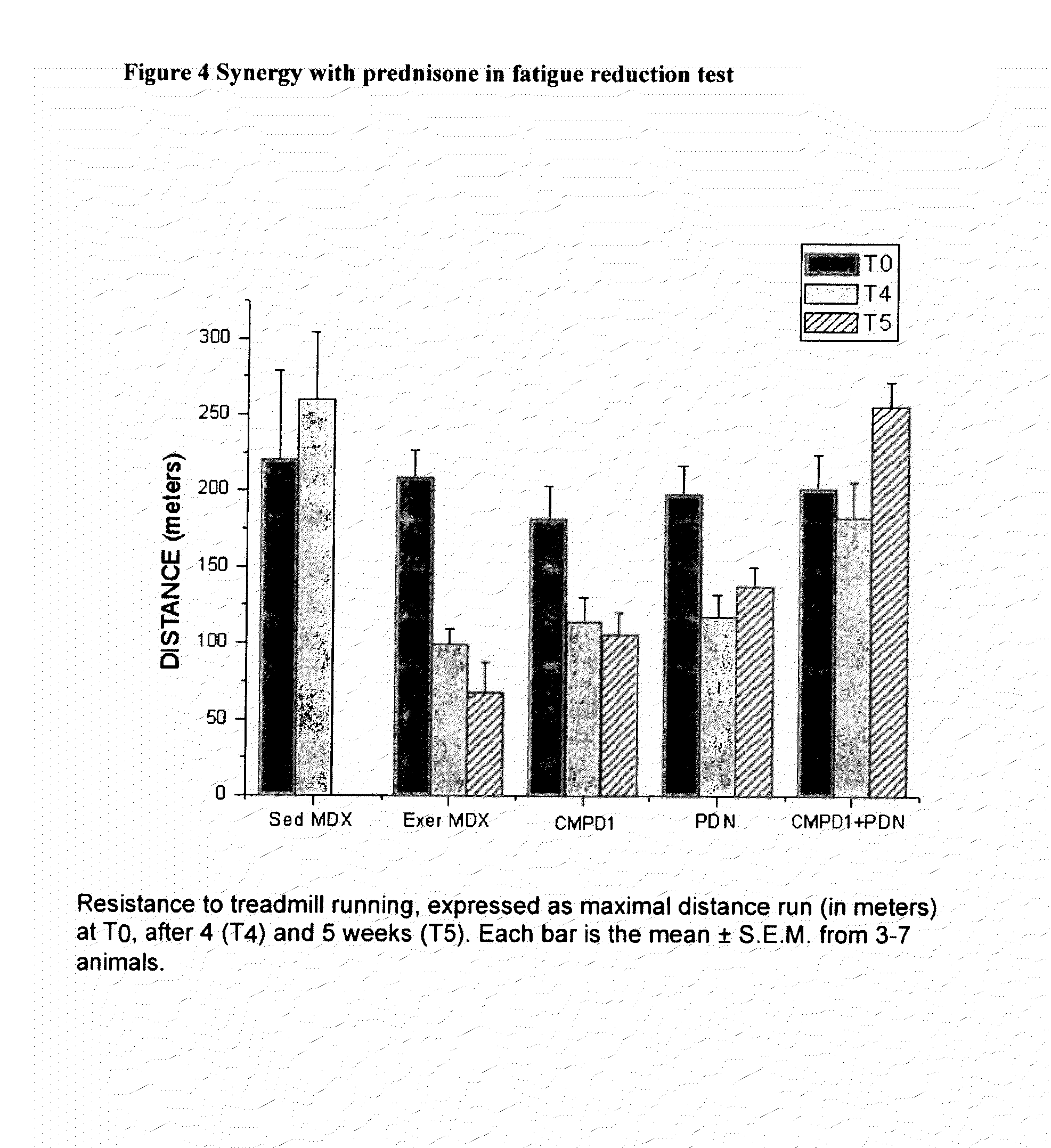
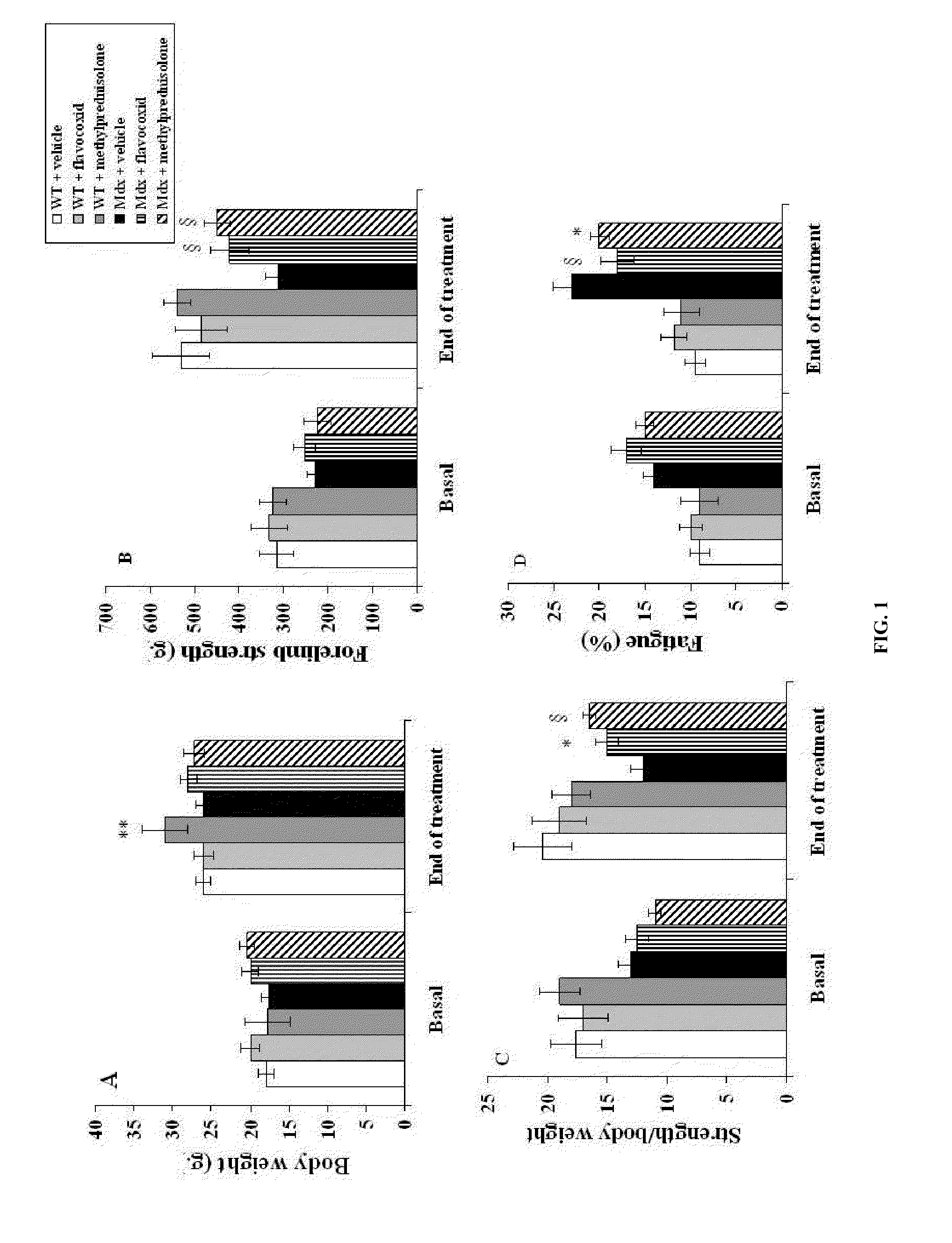
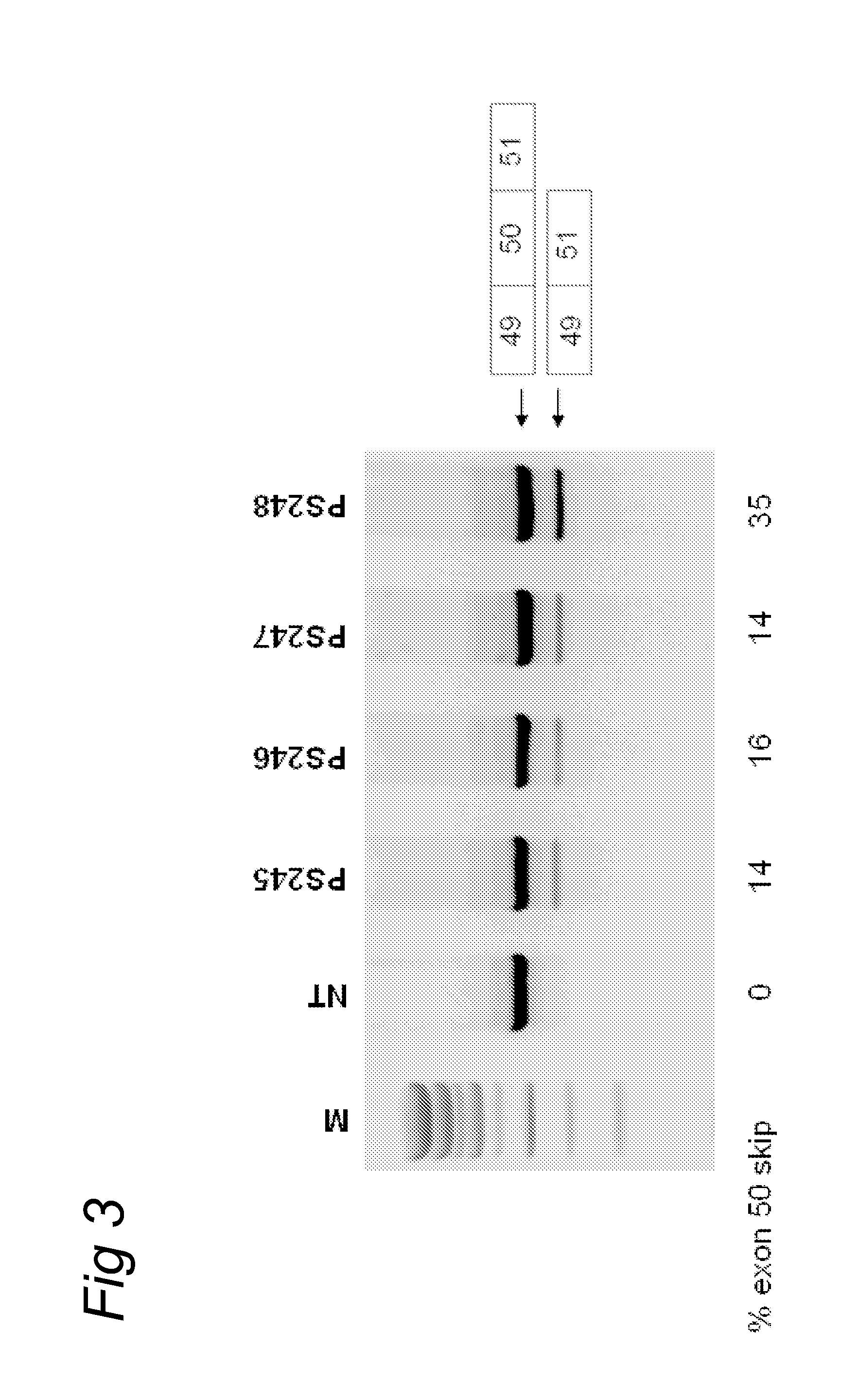Patents
Literature
93 results about "Duchenne's Muscular Dystrophy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Muscular dystrophies are a group of diseases that make muscles weaker and less flexible over time. Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is the most common type. It’s caused by flaws in the gene that controls how the body keeps muscles healthy.
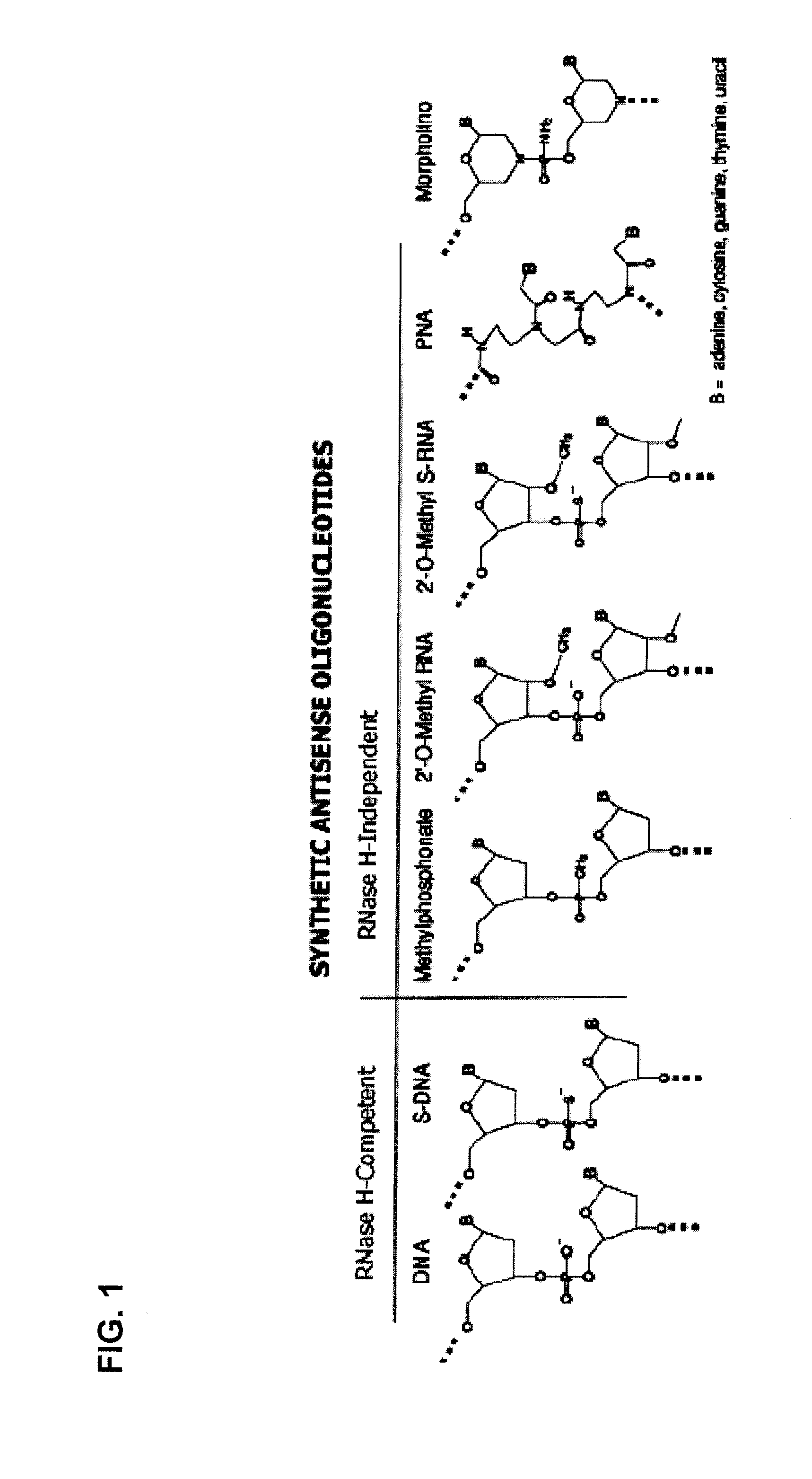
Oligomers
ActiveUS20100168212A1High degreeOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesMuscular dystrophyOligomer
Molecules are provided for inducing or facilitating exon skipping in forming spliced mRNA products from pre-mRNA molecules in cells. The molecules may be provided directly as oligonucleotides or expression products of vectors that are administered to a subject. High rates of skipping can be achieved. High rates of skipping reduce the severity of a disease like Duchene Muscular Dystrophy so that the disease is more like Becker Muscular Dystrophy. This is a severe reduction in symptom severity and mortality.
Owner:ROYAL HOLLOWAY & BEDFORD NEW COLLEGE
Oligomers
Molecules are provided for inducing or facilitating exon skipping in forming spliced mRNA products from pre-mRNA molecules in cells. The molecules may be provided directly as oligonucleotides or expression products of vectors that are administered to a subject. High rates of skipping can be achieved. High rates of skipping reduce the severity of a disease like Duchene Muscular Dystrophy so that the disease is more like Becker Muscular Dystrophy. This is a severe reduction in symptom severity and mortality.
Owner:ROYAL HOLLOWAY & BEDFORD NEW COLLEGE
Mannose-6-phosphate receptor mediated gene transfer into muscle cells
InactiveUS20120122801A1Organic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryGlycoside formationMannose 6-phosphate receptor
The invention relates to glycoside-compound conjugates for use in antisense strategies and / or gene therapy. The conjugates comprise a glycoside linked to a compound, in which the glycoside is a ligand capable of binding to a mannose-6-phosphate receptor of a muscle cell. For example the cells are muscle cells of a Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) patient and the conjugate comprises an antisense oligonucleotide which causes ex on skipping and induces or restores the synthesis of dystrophin or variants thereof.
Owner:PROSENSA THERAPEUTICS
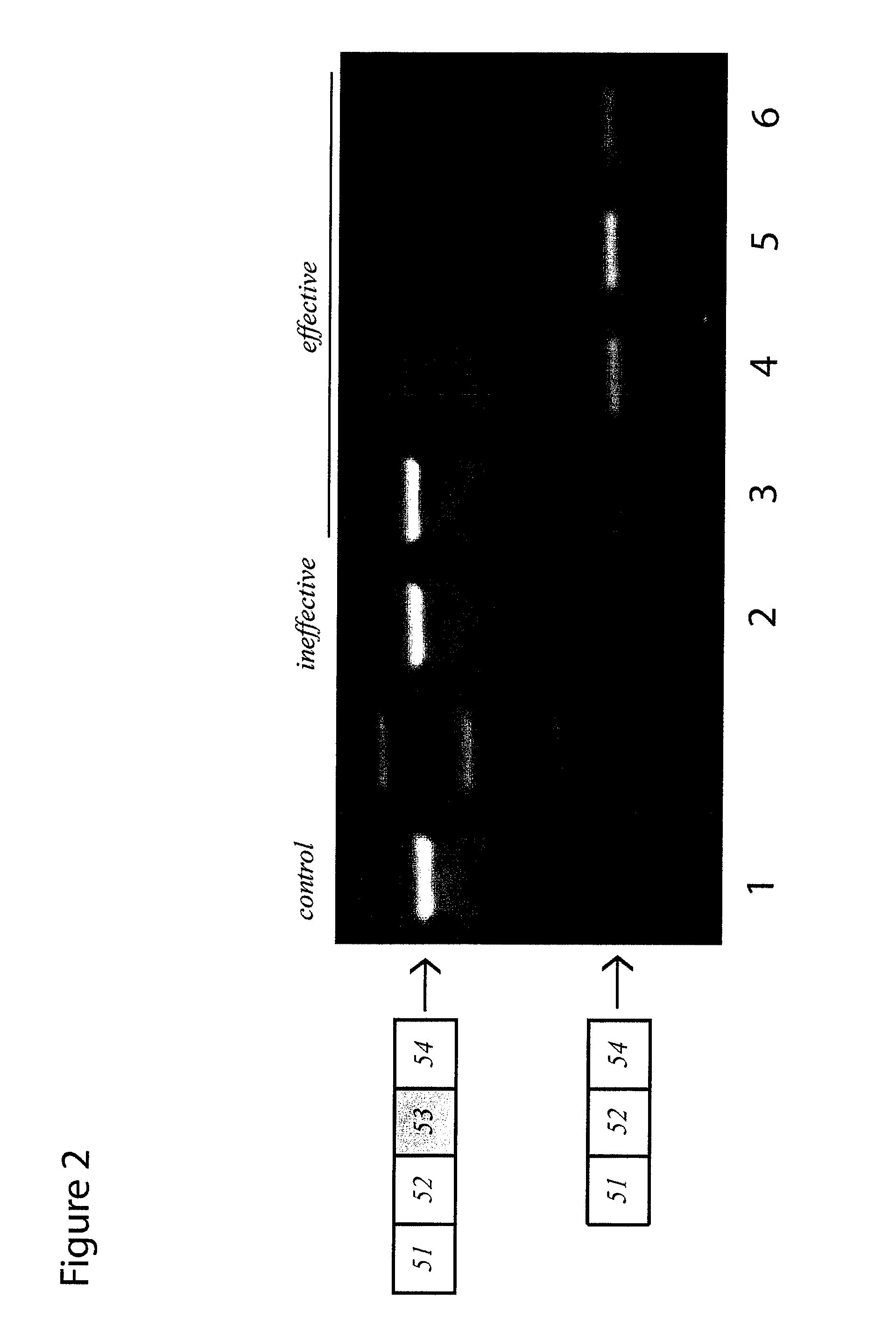
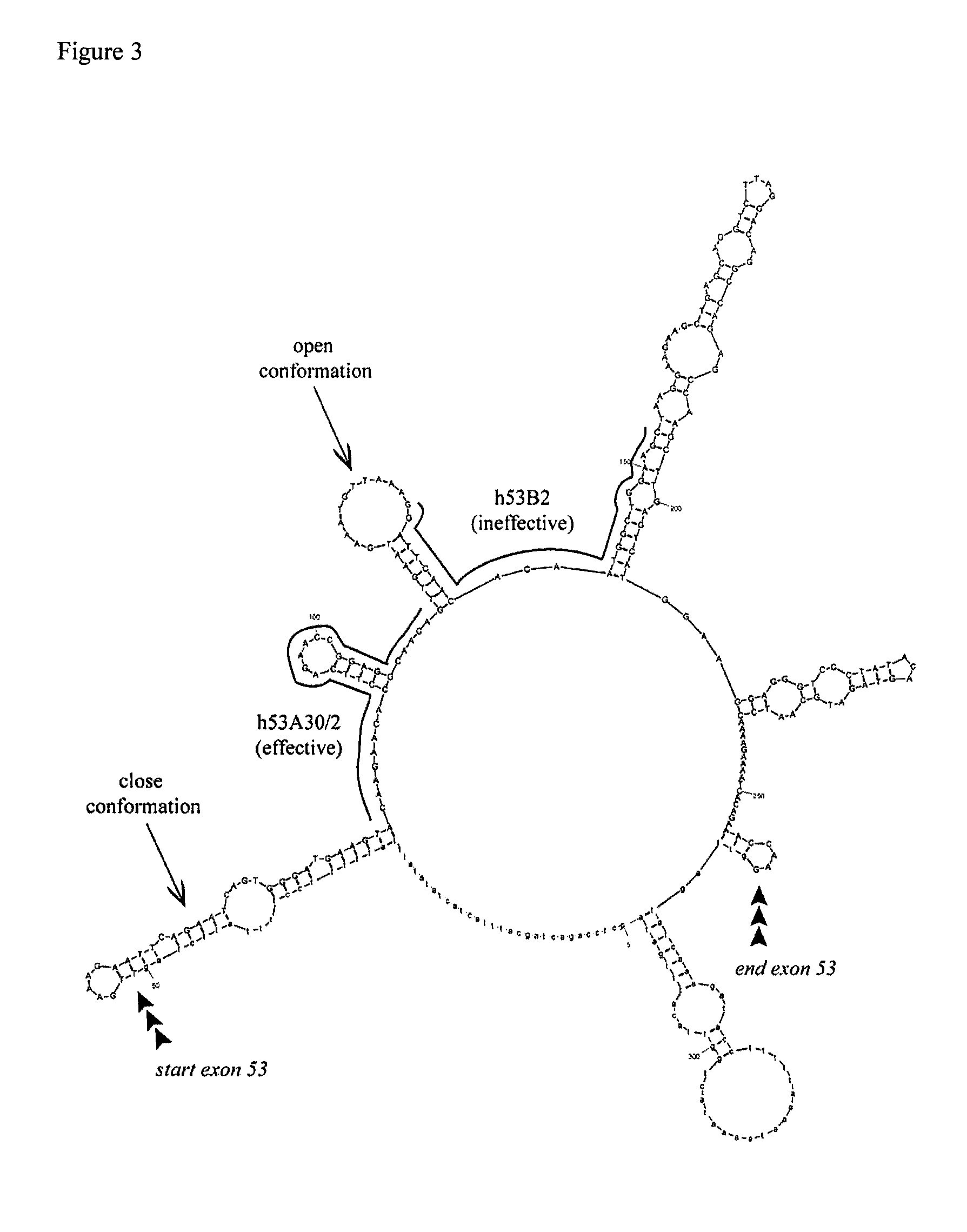
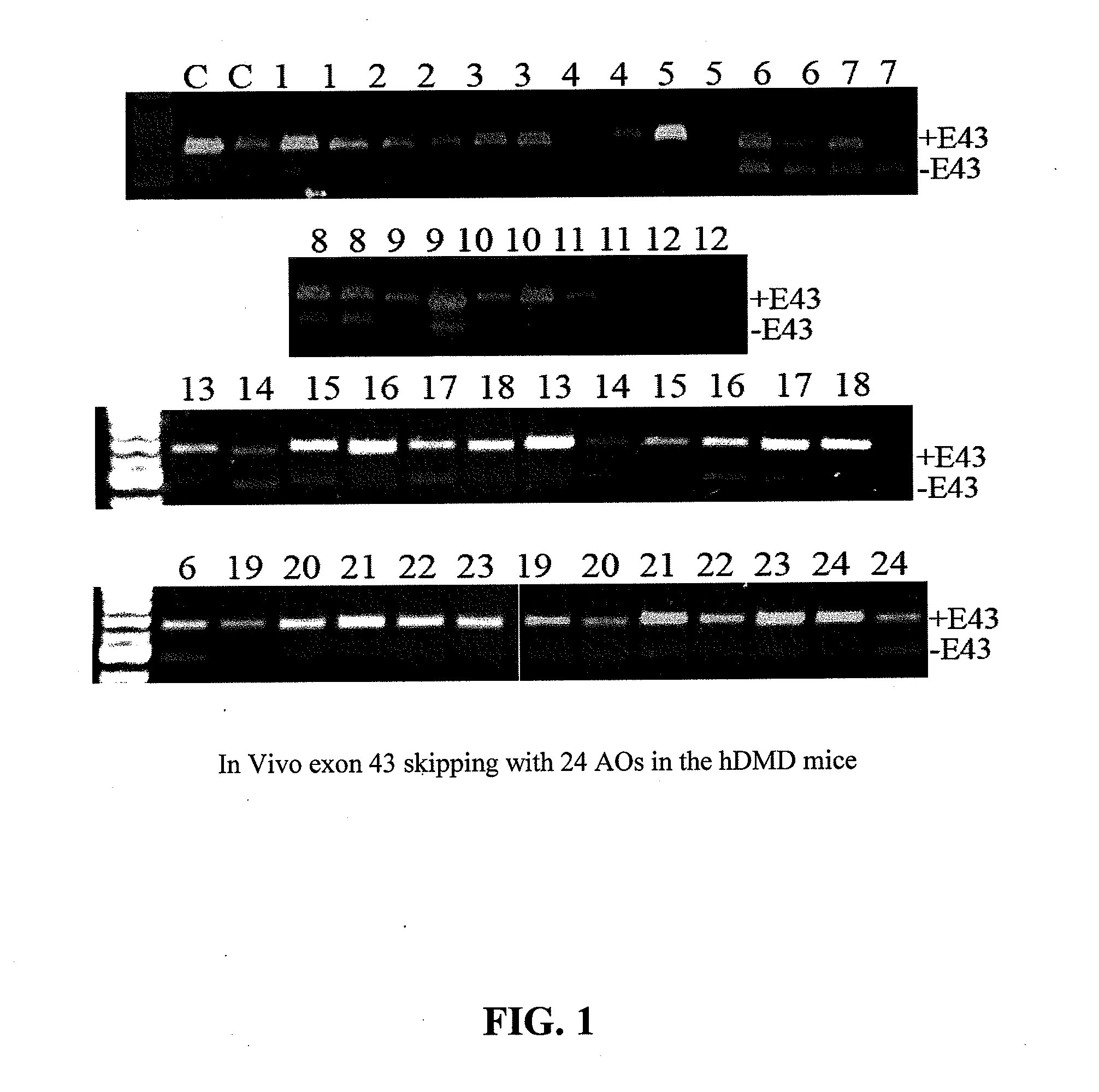
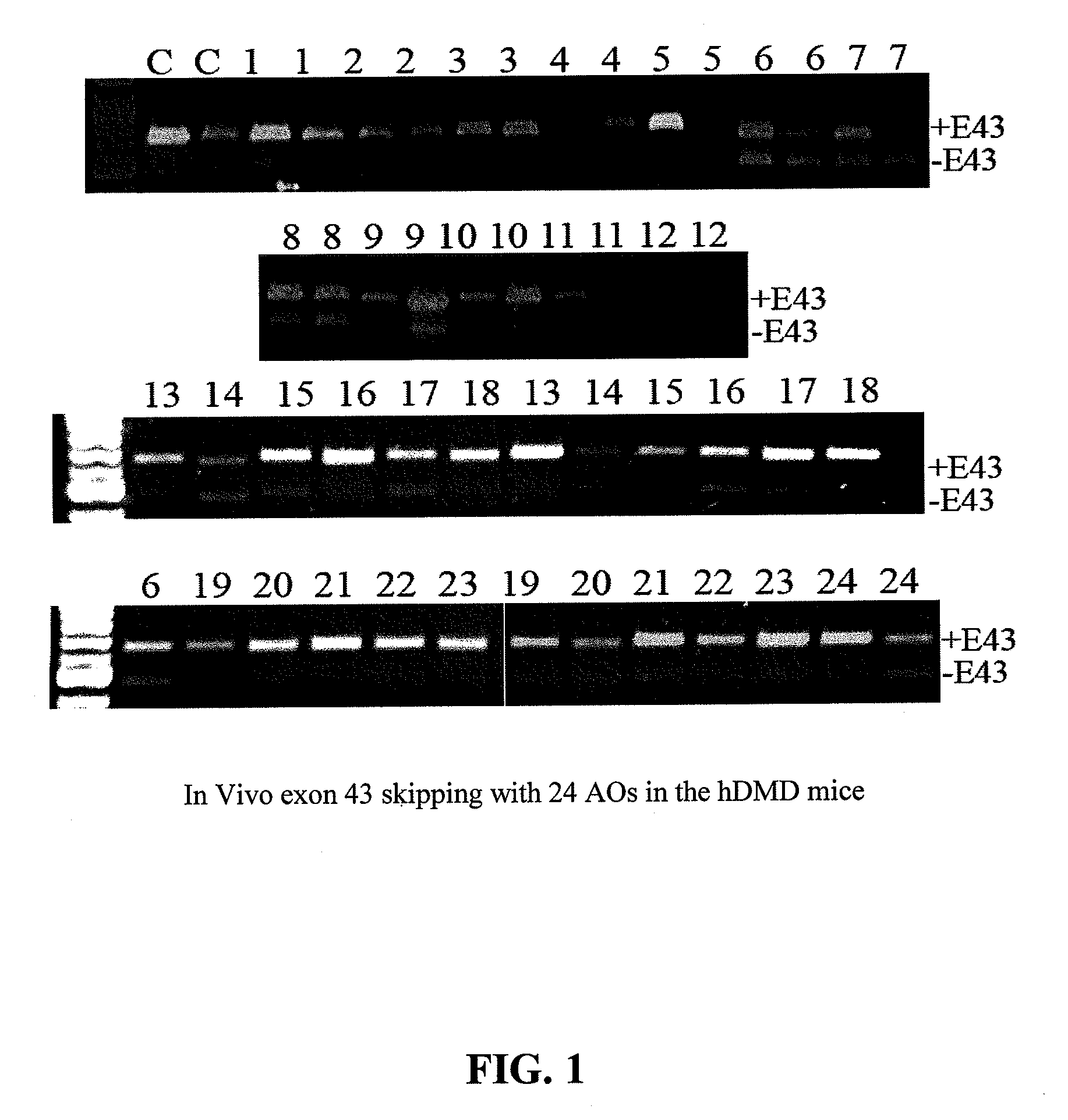
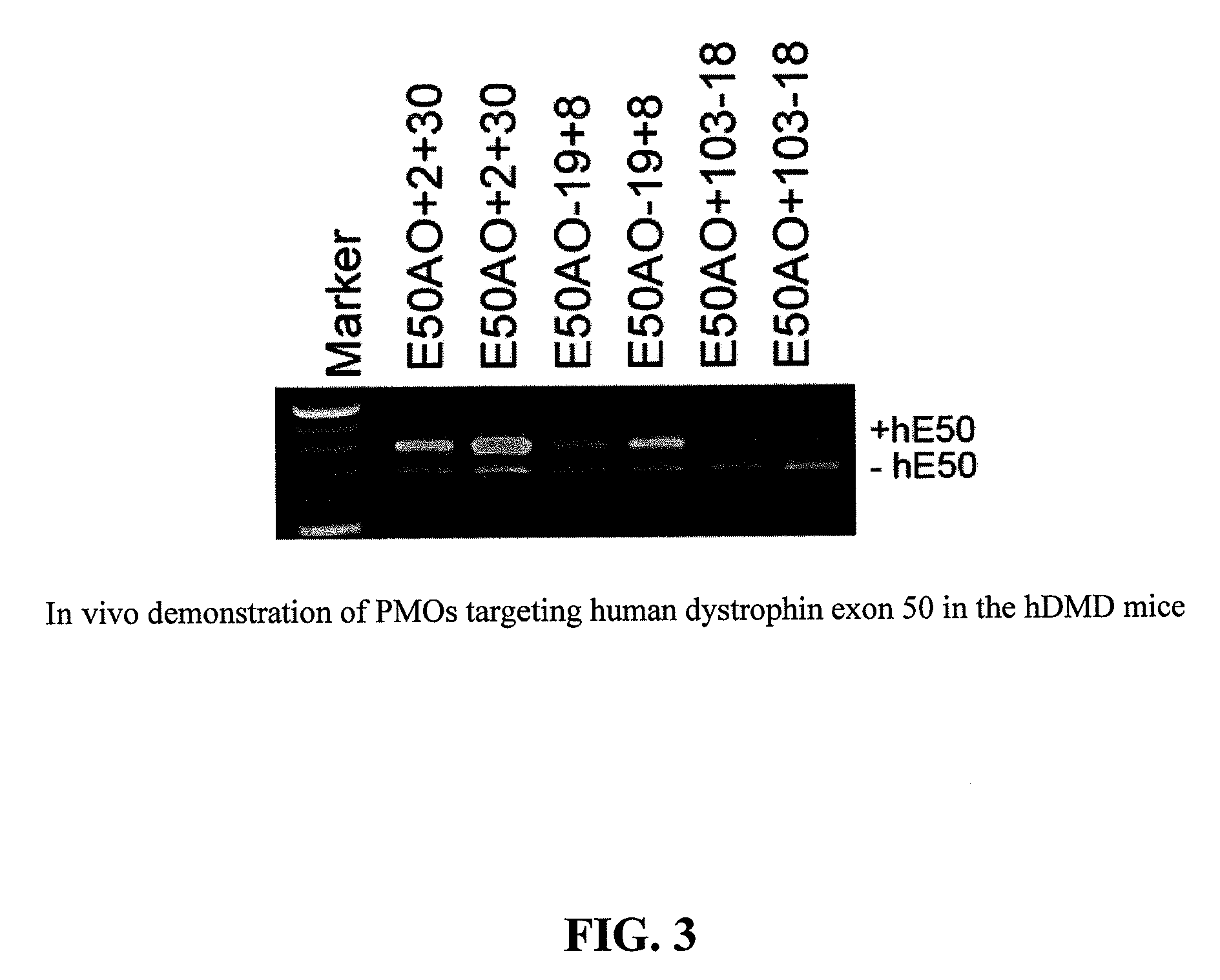
Methods and means for efficient skipping of at least one of the following exons of the human duchenne muscular dystrophy gene: 43, 46, 50-53
InactiveUS20110263682A1Improve featuresMany symptomOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationMedicinePrecursor mRNA
The invention relates a method wherein a molecule is used for inducing and / or promoting skipping of at least one of exon 43, exon 46, exons 50-53 of the DMD pre-mRNA in a patient, preferably in an isolated cell of a patient, the method comprising providing said cell and / or said patient with a molecule. The invention also relates to said molecule as such.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT +2
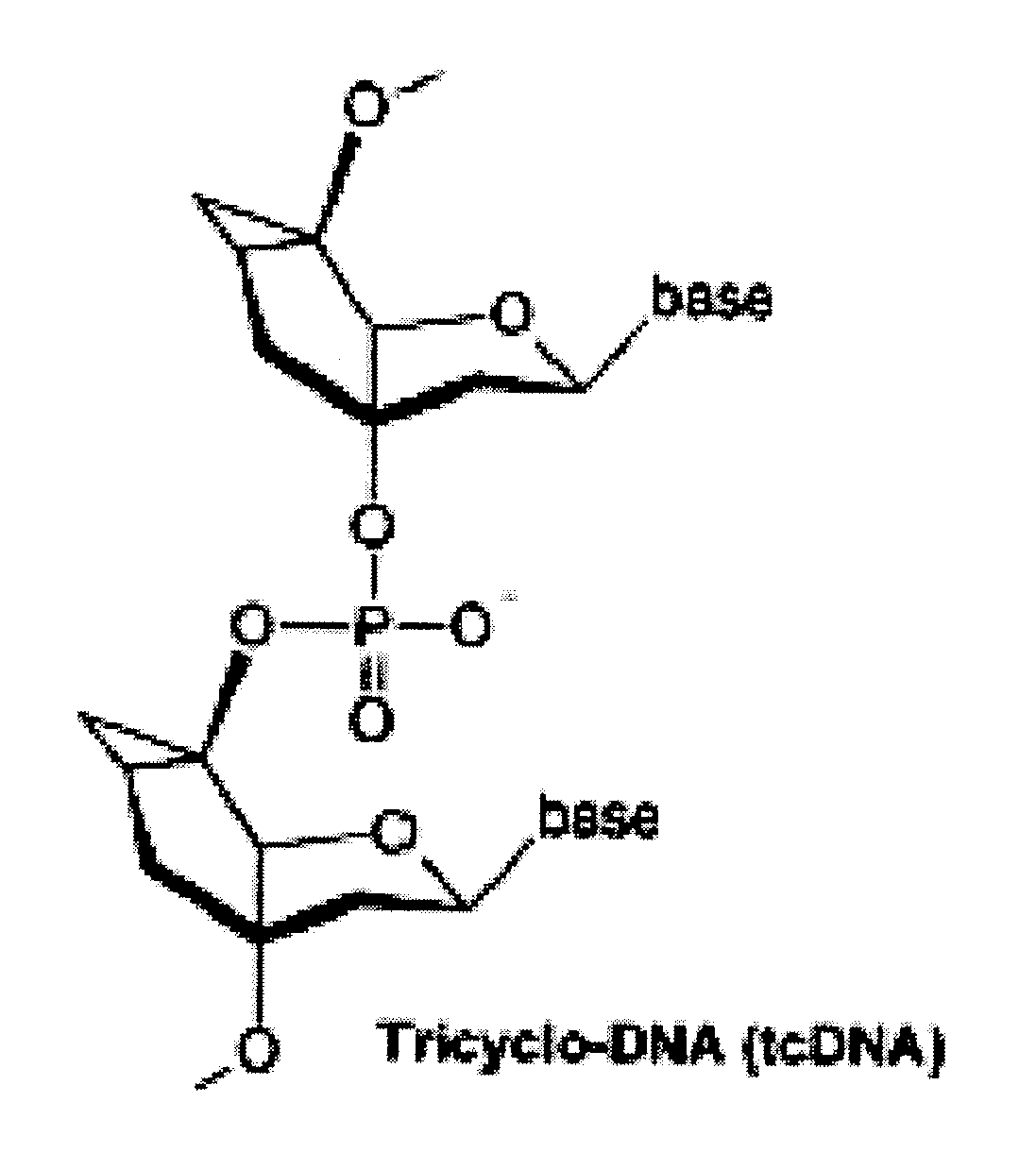
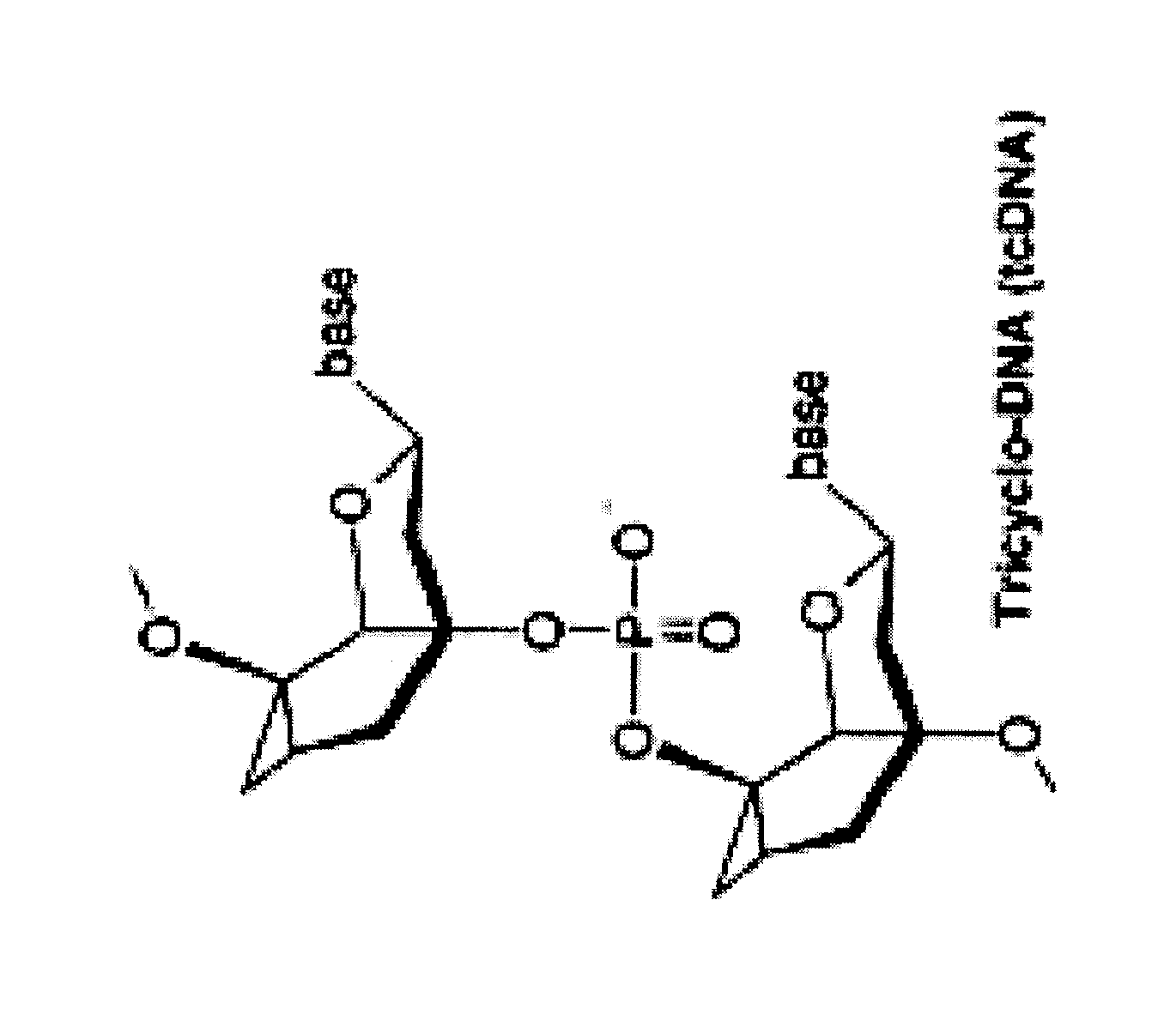
Tricyclo-dna antisense oligonucleotides, compositions, and methods for the treatment of disease
InactiveUS20120149756A1Find utilityFacilitates inclusionOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationDiseasePre mrna processing
Provided are tricyclo-DNA (tc-DNA) AON and methods employing tc-DNA AON for modifying splicing events that occur during pre-mRNA processing. Tricyclo-DNA (tc-DNA) AON are described that may be used to facilitate exon skipping or to mask intronic silencer sequences and / or terminal stem-loop sequences during pre-mRNA processing and to target RNase-mediated destruction of processed mRNA. Tc-DNA AON described herein may be used in methods for the treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy by skipping a mutated exon 23 or exon 51 within a dystrophin gene to restore functionality of a dystrophin protein; in methods for the treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy by masking an intronic silencing sequence and / or a terminal stem-loop sequence within an SMN2 gene to yield modified functional SMN2 protein, including an amino acid sequence encoded by exon 7, which is capable of at least partially complementing a non-functional SMN1 protein; and in methods for the treatment of Steinert's Myotonic Dystrophy by targeting the destruction of a mutated DM1 mRNA comprising 3′-terminal CUG repeats.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +4
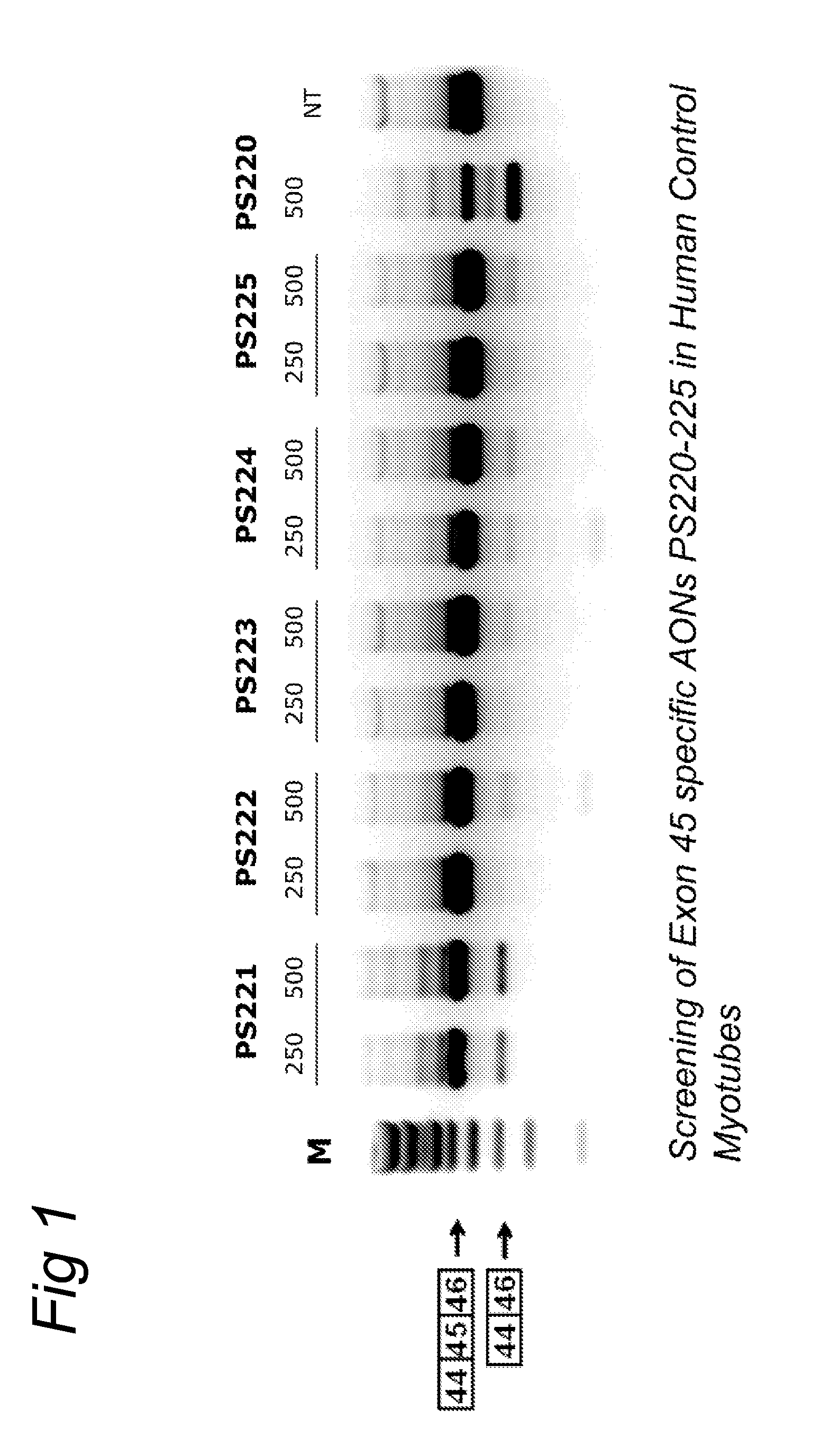
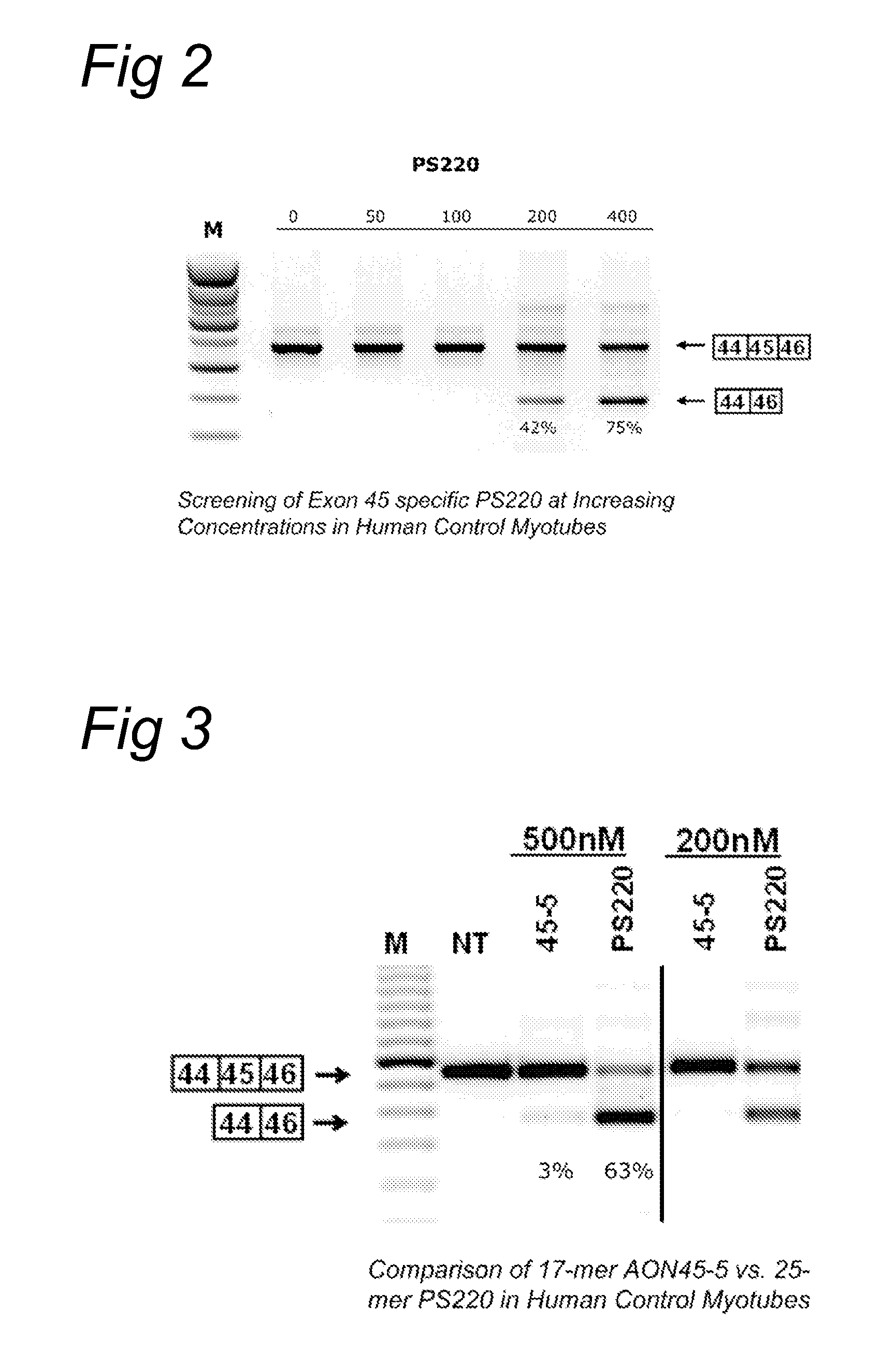
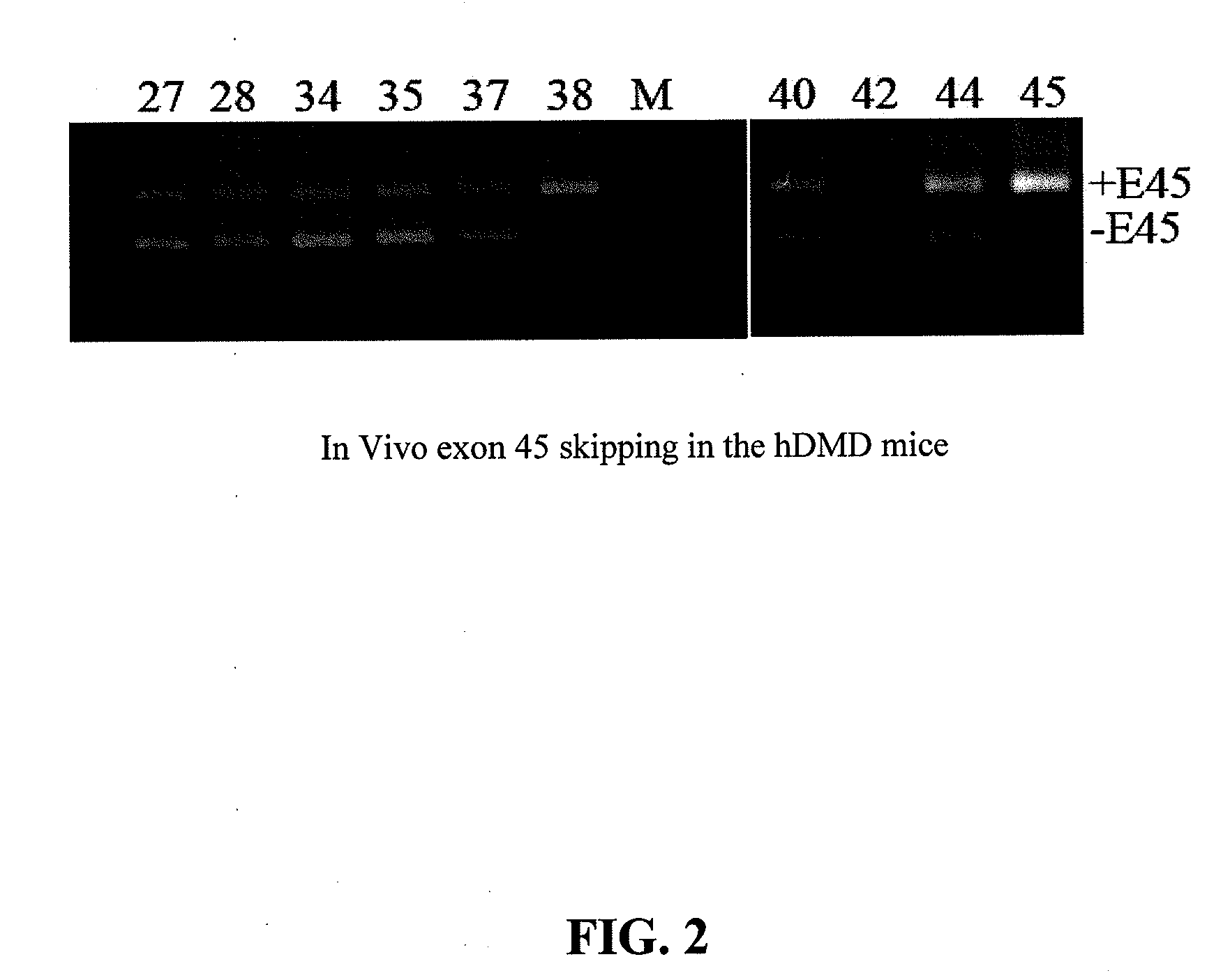
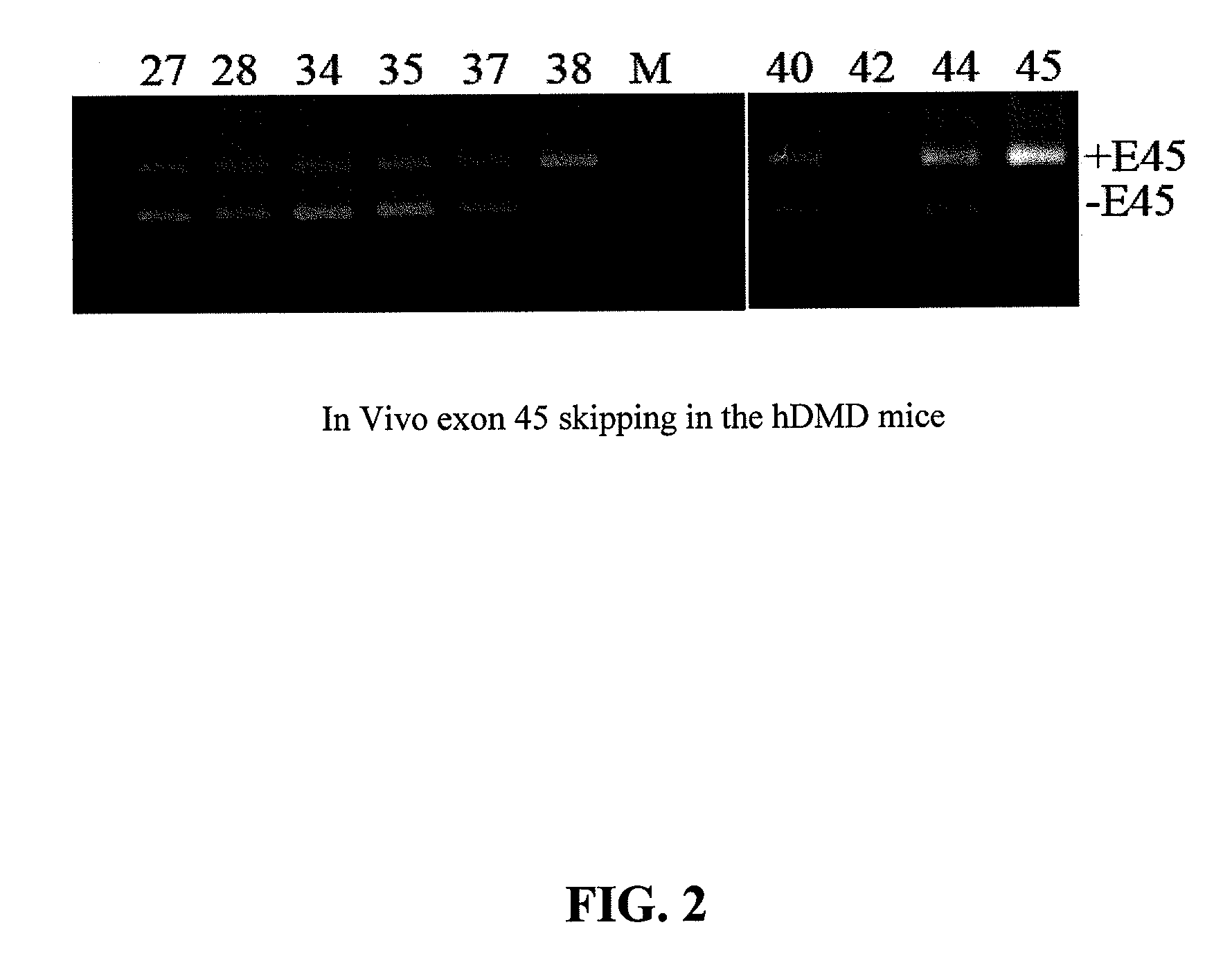
METHODS AND MEANS FOR EFFICIENT SKIPPING OF EXON 45 IN DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY PRE-mRNA
ActiveUS20120022134A1Reduced calcium uptake by muscle cellsReduce synthesisOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationNucleotidePrecursor mRNA
The invention relates to a method for inducing or promoting skipping of exon 45 of DMD pre-mRNA in a Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy patient, preferably in an isolated (muscle) cell, the method comprising providing said cell with a molecule that binds to a continuous stretch of at least 21 nucleotides within said exon. The invention further relates to such molecule used in said method.
Owner:BIOMARIN TECH BV +2
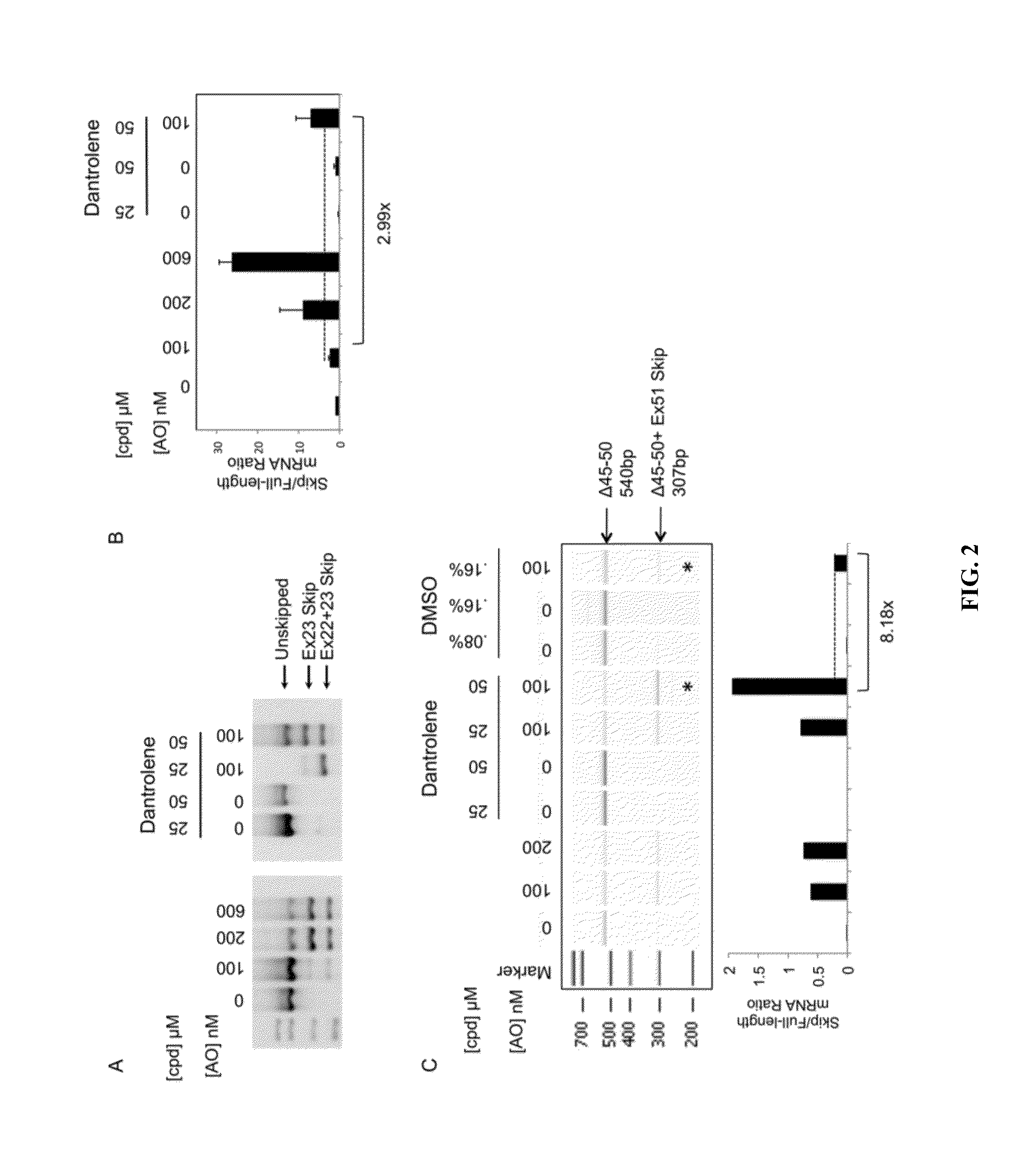
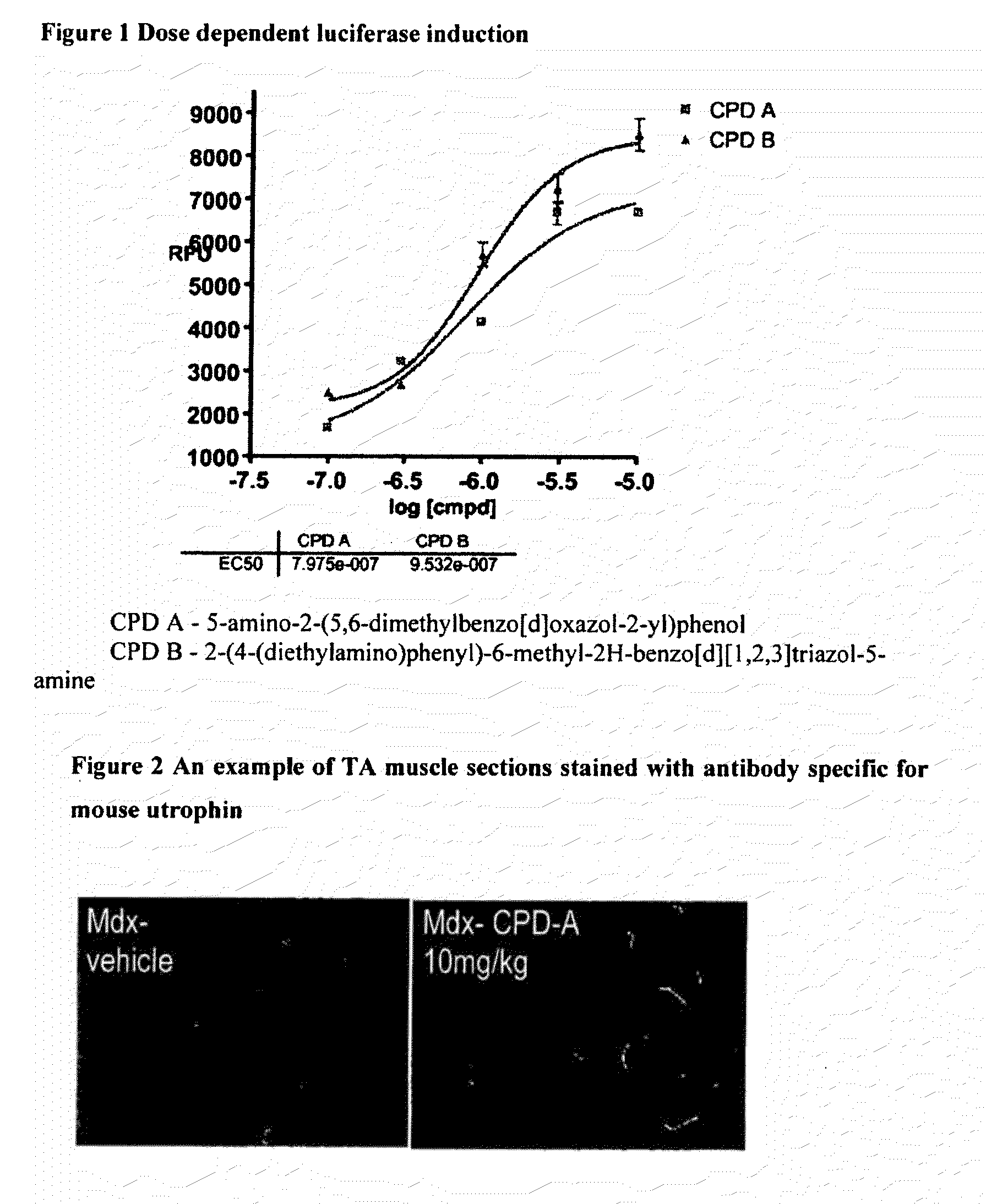
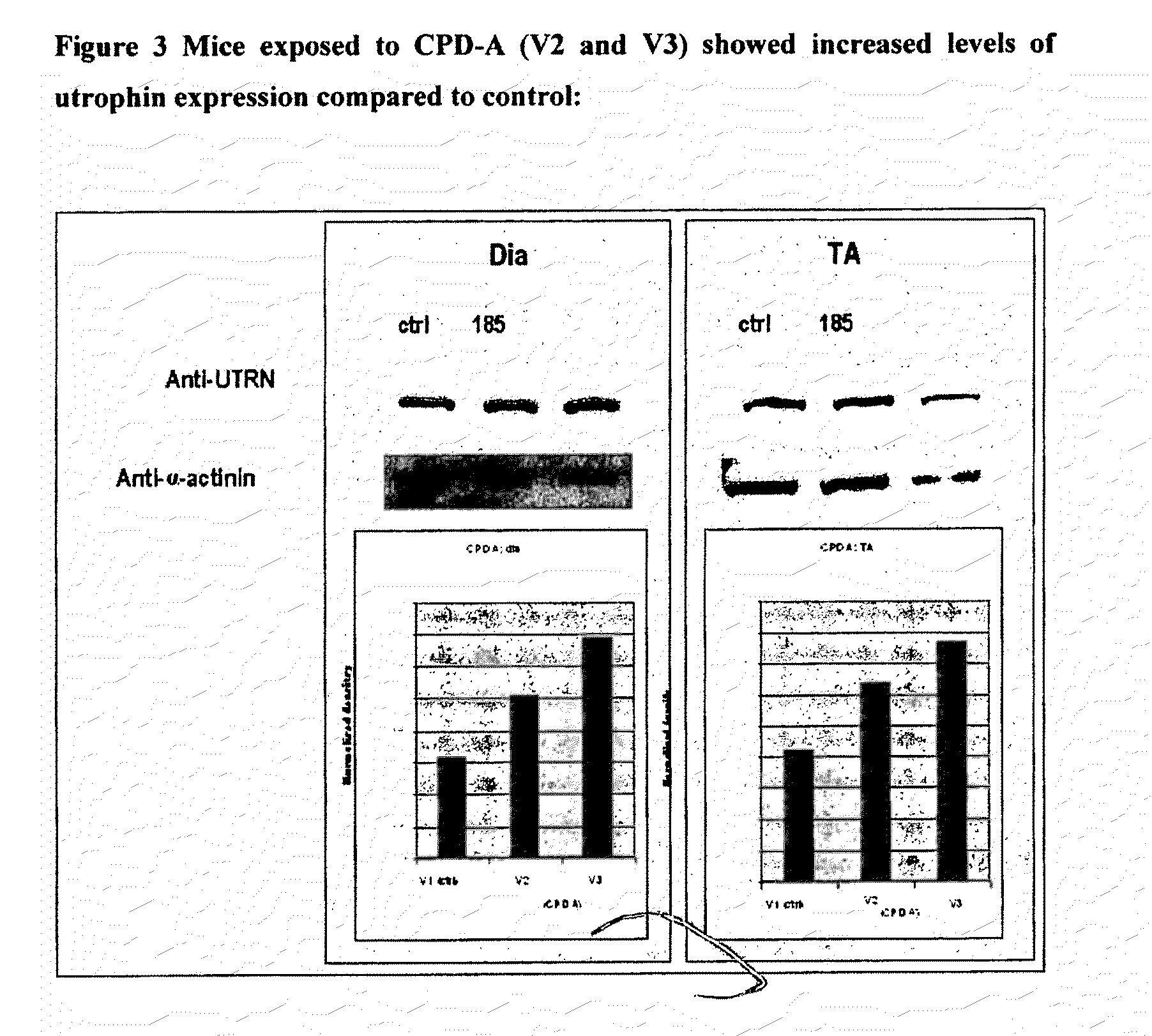
Identification of small molecules that facilitate therapeutic exon skipping
This invention relates, e.g., to a method for enhancing exon skipping in a pre-mRNA of interest, comprising contacting the pre-mRNA with an effective amount of a small molecule selected from the compounds shown in Table 1, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, hydrate, solvate, or isomer thereof, and, optionally, with an antisense oligonucleotide that is specific for a splicing sequence in the pre-mRNA Methods for treating Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) are disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
DNA sequences comprising dystrophin minigenes and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7001761B2Small sizeEfficient and stable correctionVirusesSugar derivativesPoly-A RNAPolyadenylation
The present invention provides a series of novel dystrophin minigenes that retain the essential biological functions. The expression of the dystrophin minigenes may be controlled by a regulatory element along with a small polyadenylation signal. The entire gene expression cassettes may be readily packaged into a viral vector, preferably an AAV vector. The present invention further defines the minimal functional domains of dystrophin and provides ways to optimize and create new versions of dystrophin minigenes. Finally, the present invention provides a method of treatment for Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) and Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD).
Owner:ASKLEPIOS BIOPHARMACEUTICAL INC
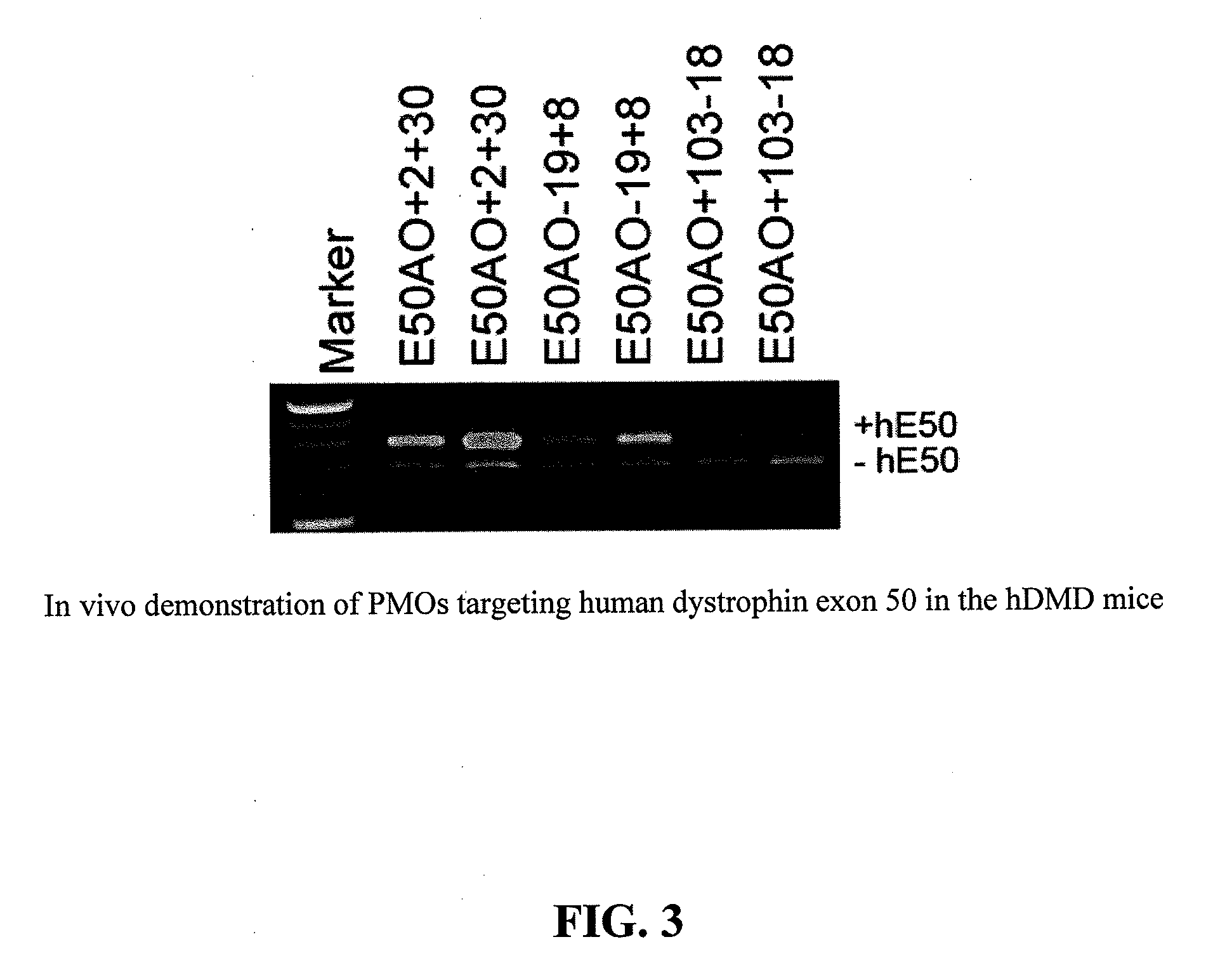
Antisense Oligonucleotides
ActiveUS20120202752A1Organic active ingredientsSplicing alterationDiseaseDuchenne's Muscular Dystrophy
Embodiments of the present invention are directed generally to antisense compounds and compositions for the treatment of muscular dystrophy, and in particular, Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). In one embodiment, the invention is directed to antisense oligonucleotide molecules, pharmaceutical compositions and formulations comprising antisense oligonucleotide molecules, and methods of treating muscular dystrophy related diseases and disorders wherein the antisense oligonucleotide molecules comprises a base sequence selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NO: 5-8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 24, 27, 28, 34, 35, 37, 40, 42, 44-46, 79, 97, 100, 101, and 116, and combinations thereof.
Owner:CHARLOTTE MECKLENBURG HOSPITAL AUTHORITY
Antisense oligonucleotides
Embodiments of the present invention are directed generally to antisense compounds and compositions for the treatment of muscular dystrophy, and in particular, Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). In one embodiment, the invention is directed to antisense oligonucleotide molecules, pharmaceutical compositions and formulations comprising antisense oligonucleotide molecules, and methods of treating muscular dystrophy related diseases and disorders wherein the antisense oligonucleotide molecules comprises a base sequence selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NO: 5-8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 24, 27, 28, 34, 35, 37, 40, 42, 44-46, 79, 97, 100, 101, and 116, and combinations thereof.
Owner:CHARLOTTE MECKLENBURG HOSPITAL AUTHORITY
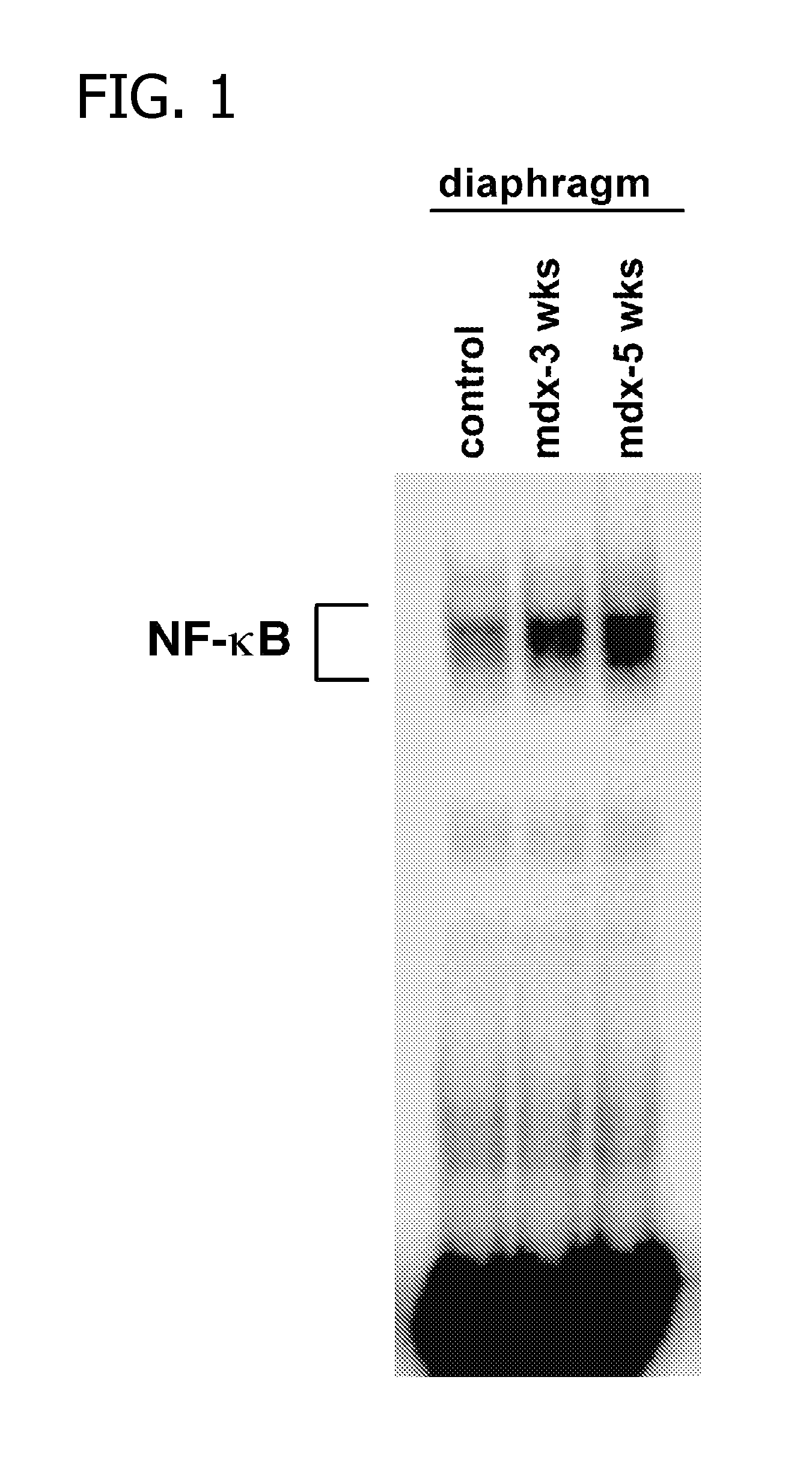
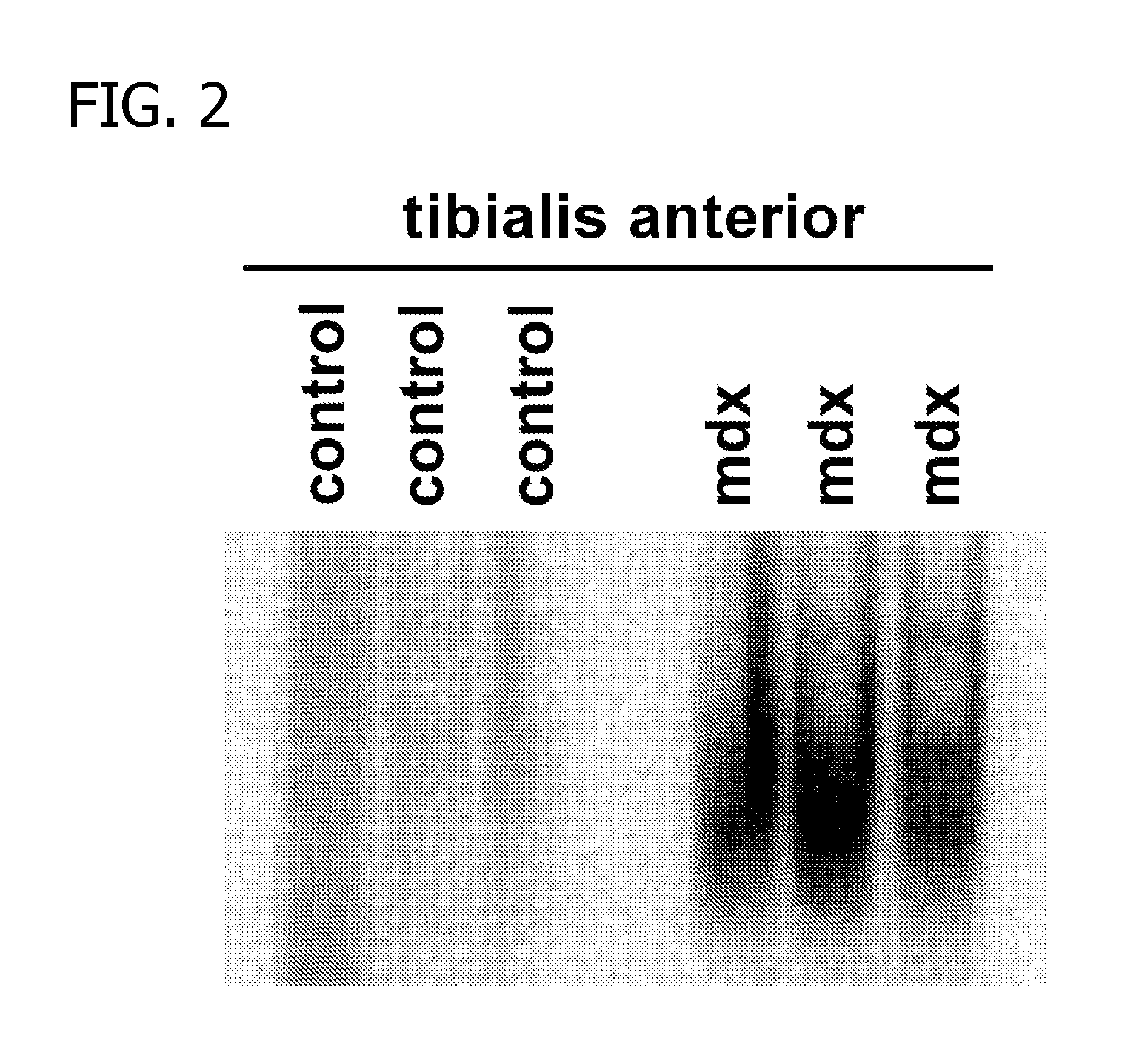
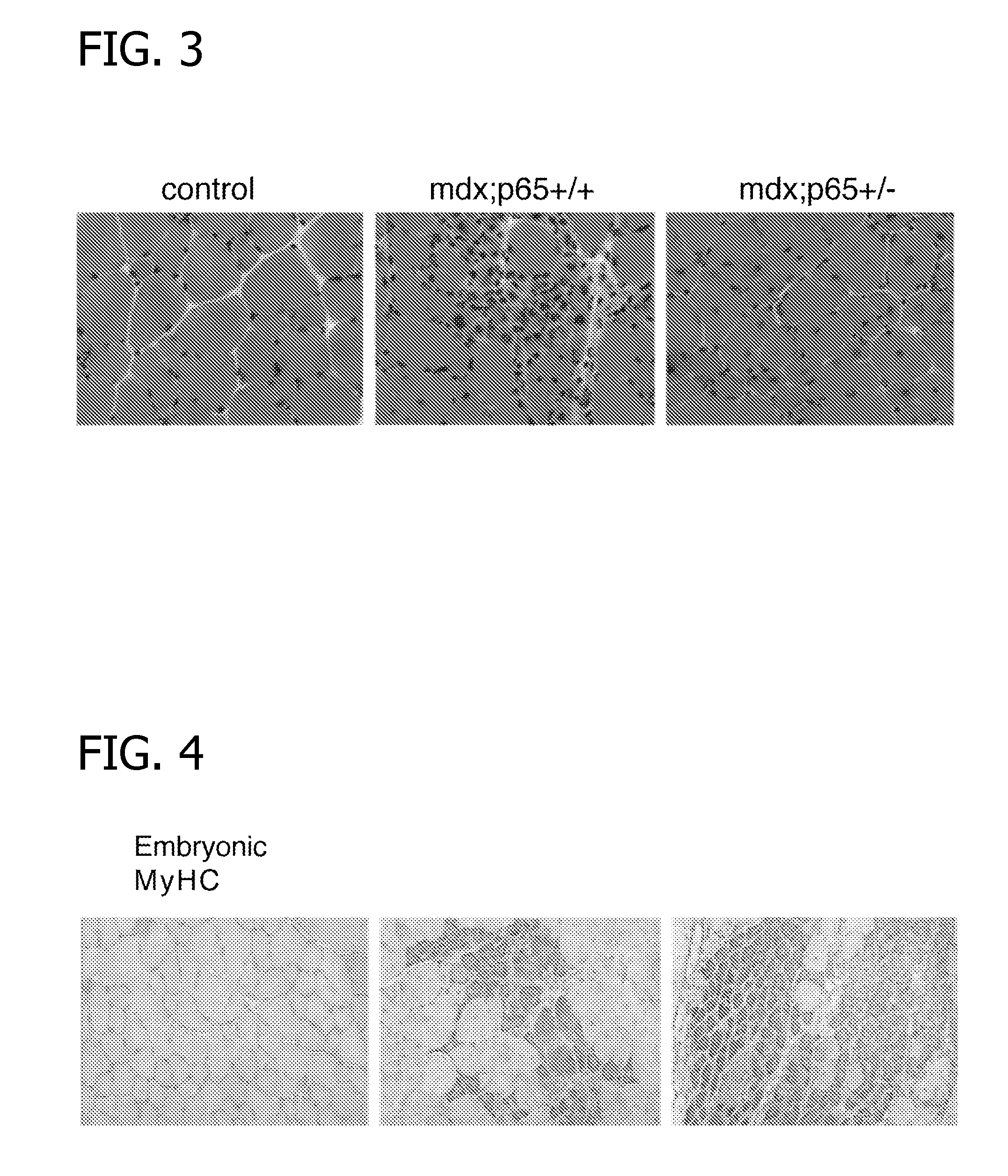
Methods of Treating Muscular Wasting Diseases Using NF-kB Activation Inhibitors
ActiveUS20070225315A1Inhibiting muscular wasting diseaseBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBiological activationDuchenne's Muscular Dystrophy
Methods for treating muscular wasting diseases such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy are disclosed. Specifically, the methods include administering to a subject in need of treatment for a muscular wasting disease, an NF-κB activation inhibitor capable of blocking the activation of NF-κB.
Owner:THERALOGICS
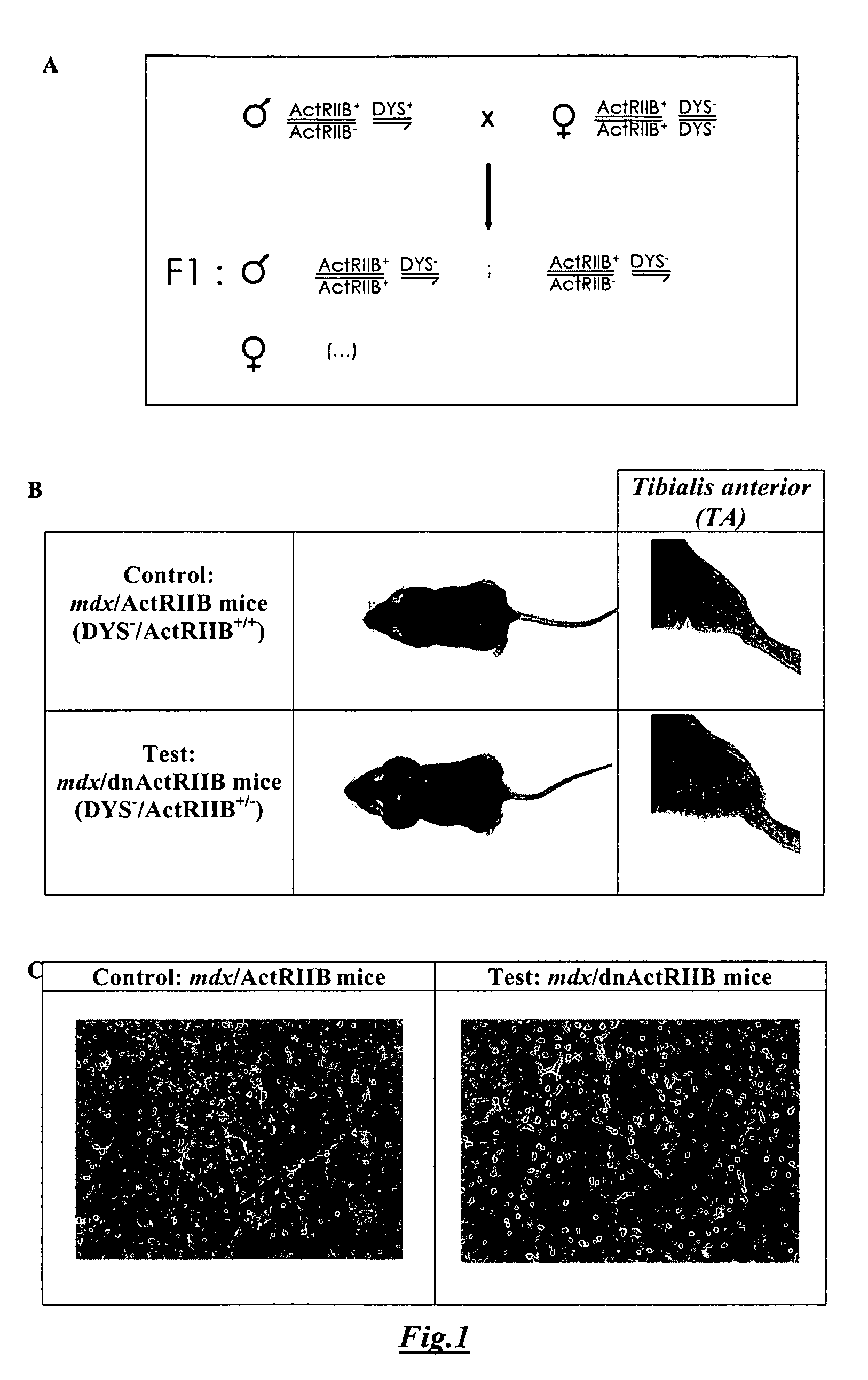
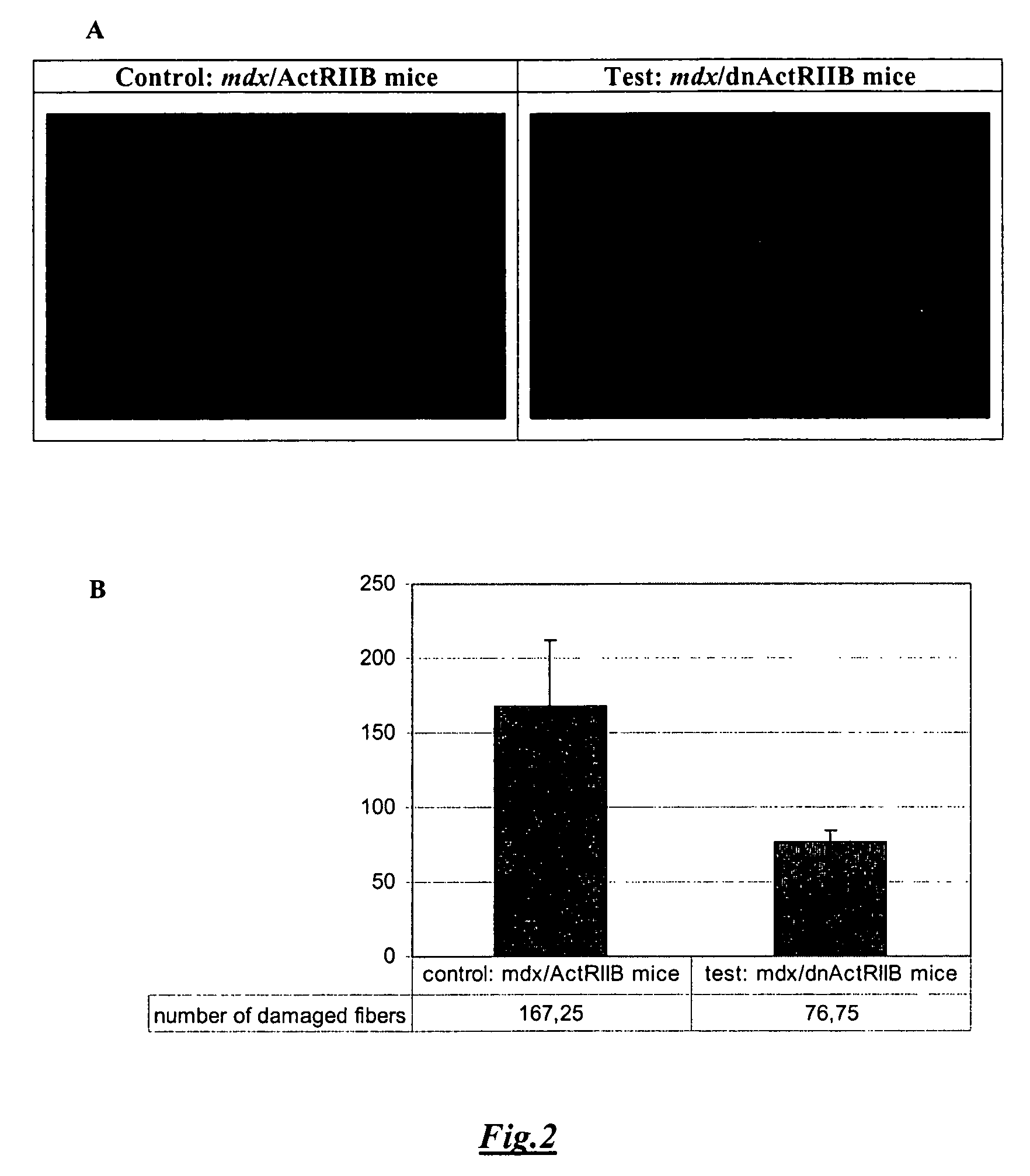
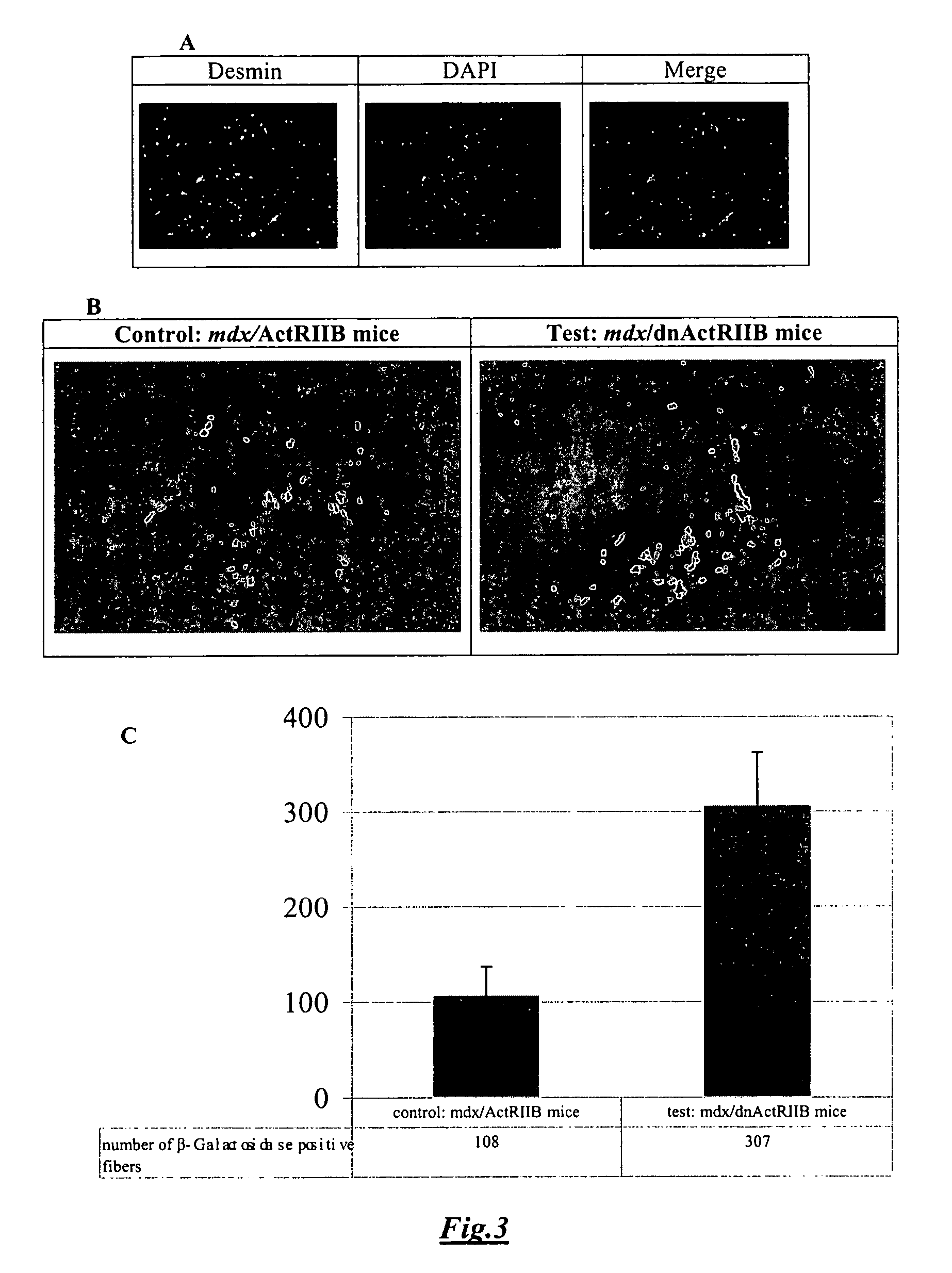
Treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy with myoblasts expressing dystrophin and treated to block myostatin signaling
InactiveUS7887793B2Increased proliferationQuality improvementBiocideAnimal repellantsMyostatinDisease
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
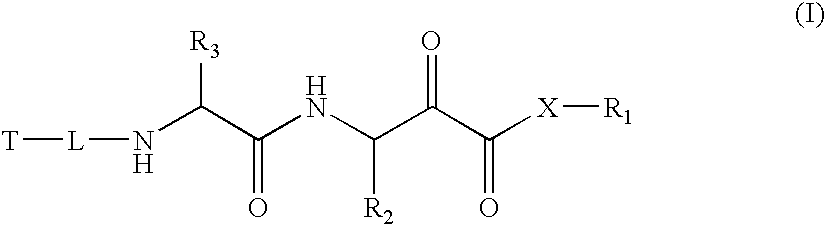
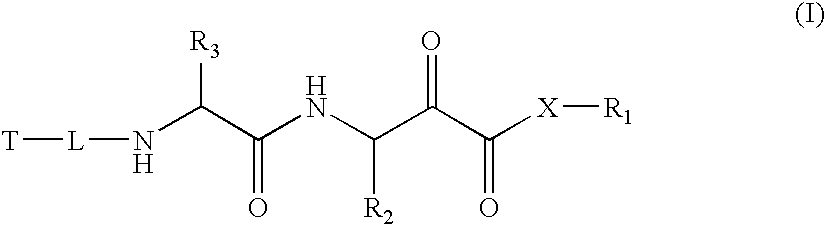
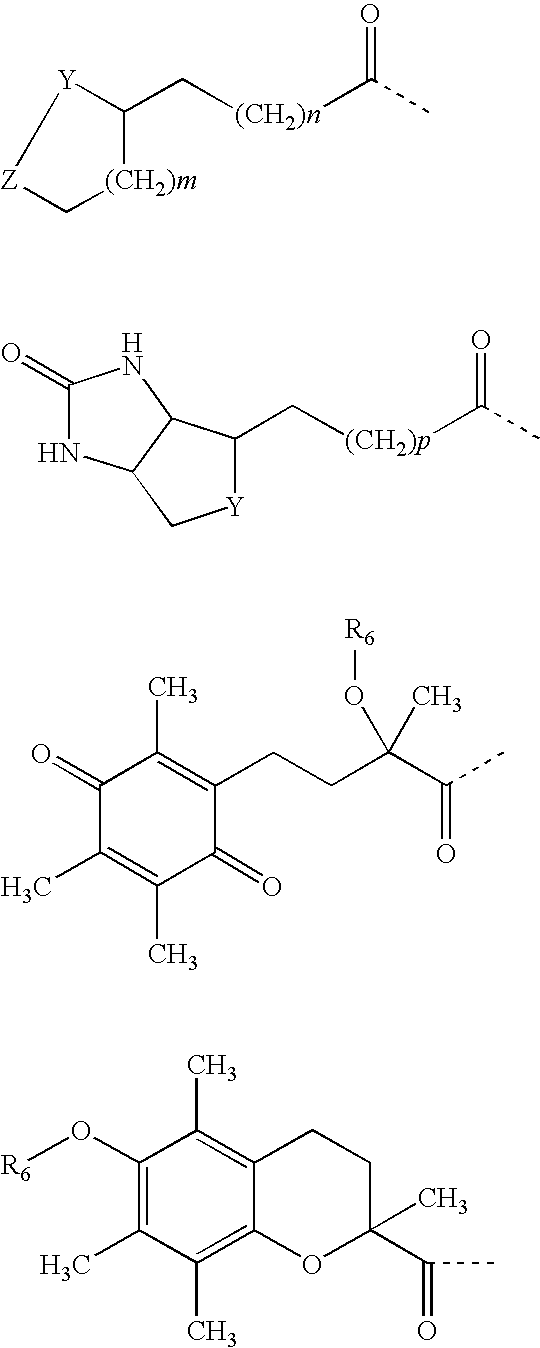
Drug Combinations for the Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
InactiveUS20110195932A1Patient compliance is goodHigh response rateBiocideMuscular disorderDuchenne's Muscular DystrophyCachexia
Combinations comprising (or consisting essentially of) one or more compounds of formula (1) with one or more ancillary agents, to processes for preparing the combinations, and to various therapeutic uses of the combinations. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions containing the combinations as well as a method of treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, Becker muscular dystrophy or cachexia using the combinations.
Owner:SUMMIT OXFORD
Method for isolated culture of human fat mesenchyma stem cell and special culture medium thereof
ActiveCN101314766AThe method of isolation and culture is simpleImprove efficiencySkeletal/connective tissue cellsAntigenMuscle injury
The invention discloses a method for separately culturing a human adipose mesenchymal stem cell and a dedicated culture medium thereof. The culture medium used for separately culturing the human adipose mesenchymal stem cell comprises an animal cell basic culture medium, fetal calf serum, an epidermal growth factor and a platelet-derived growth factor. The final concentration of the fetal calf serum is 1-200 mL / L, the final concentration of the epidermal growth factor is 1-100 ng / ml, and the final concentration of the platelet-derived growth factor is 1-100 ng / ml. The adipose mesenchymal stem cell of the invention has CD31-, CD34-, CD45- and HLA-DR-, as well as the phenotype of CD29+, CD44+, CD105+ and Flk-1+. The specificity cell surface marker and the relevant antihelion molecule of a skeletal muscle cell and a vascular endothelia cell can be expressed after inducement is performed in vitro. Muscle fiber, vascular endothelin and functional muscle satellite cells can be differentiated in a muscle injury model mouse body caused by medicine and the expression of dystrophin protein on the ducheme muscular dystrophy (DMD) model mouse (mdx) myolemma can be partially recovered, so as to release the pathological symptom of the model mouse.
Owner:微能生命科技集团有限公司
Compositions and methods for duchenne muscular dystrophy gene therapy
InactiveUS20150196670A1Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDuchenne's Muscular DystrophyFhit gene
The present invention relates to a gene therapy method for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, or DMD.
Owner:ASSOC FRE CONTRE LES MYOPATHIES
Microvesicle and stem cell compositions for therapeutic applications
PendingUS20180273906A1Production economyFacilitates lyophilization and preservationArtificial cell constructsMammal material medical ingredientsFibrosisDuchenne's Muscular Dystrophy
Provided herein are stem cell and exosome compositions having therapeutic utility to treat a variety of diseases and disorders, e.g., cardiovascular disease, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, and fibrotic disease.
Owner:IPS HEART
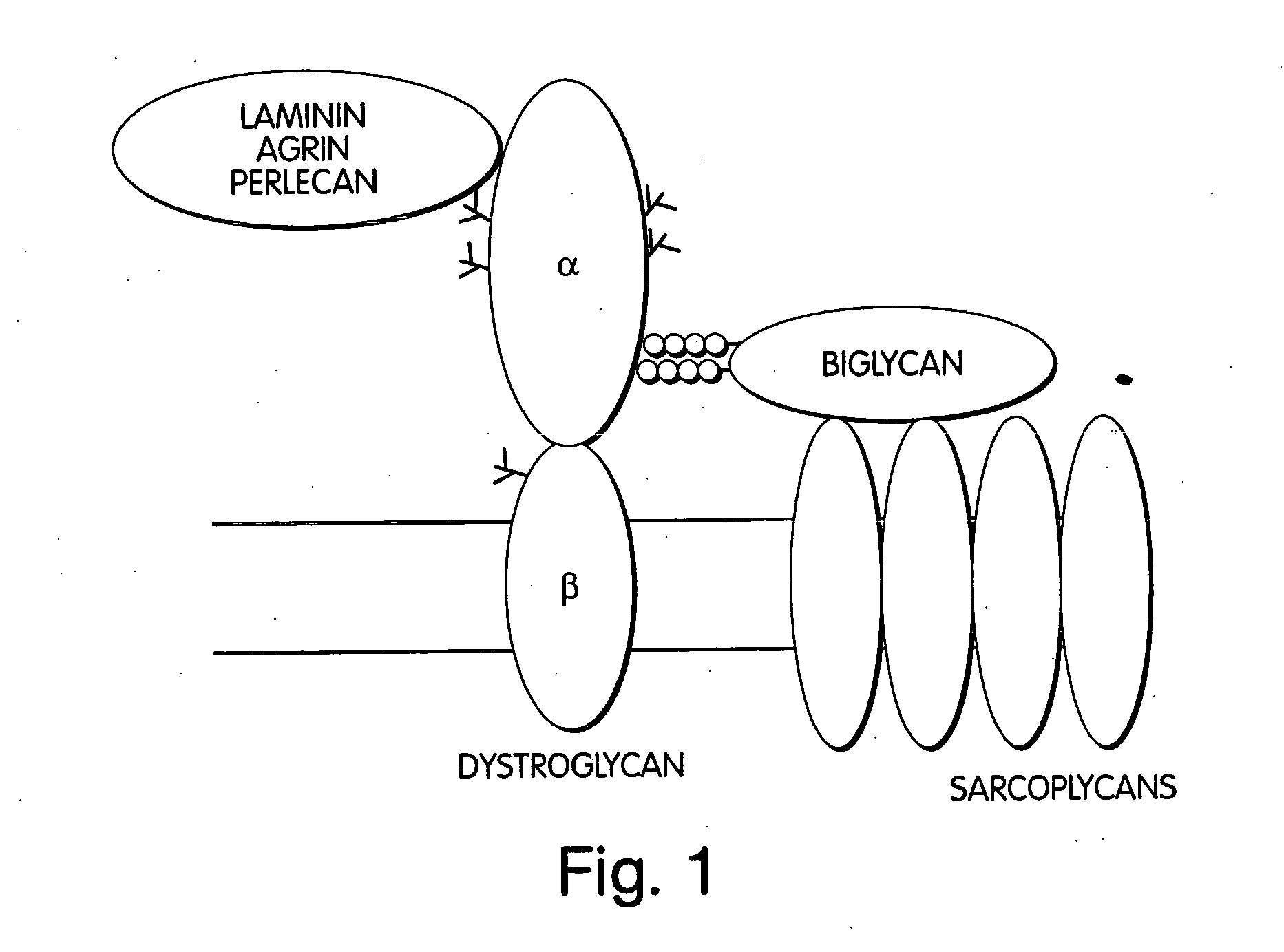
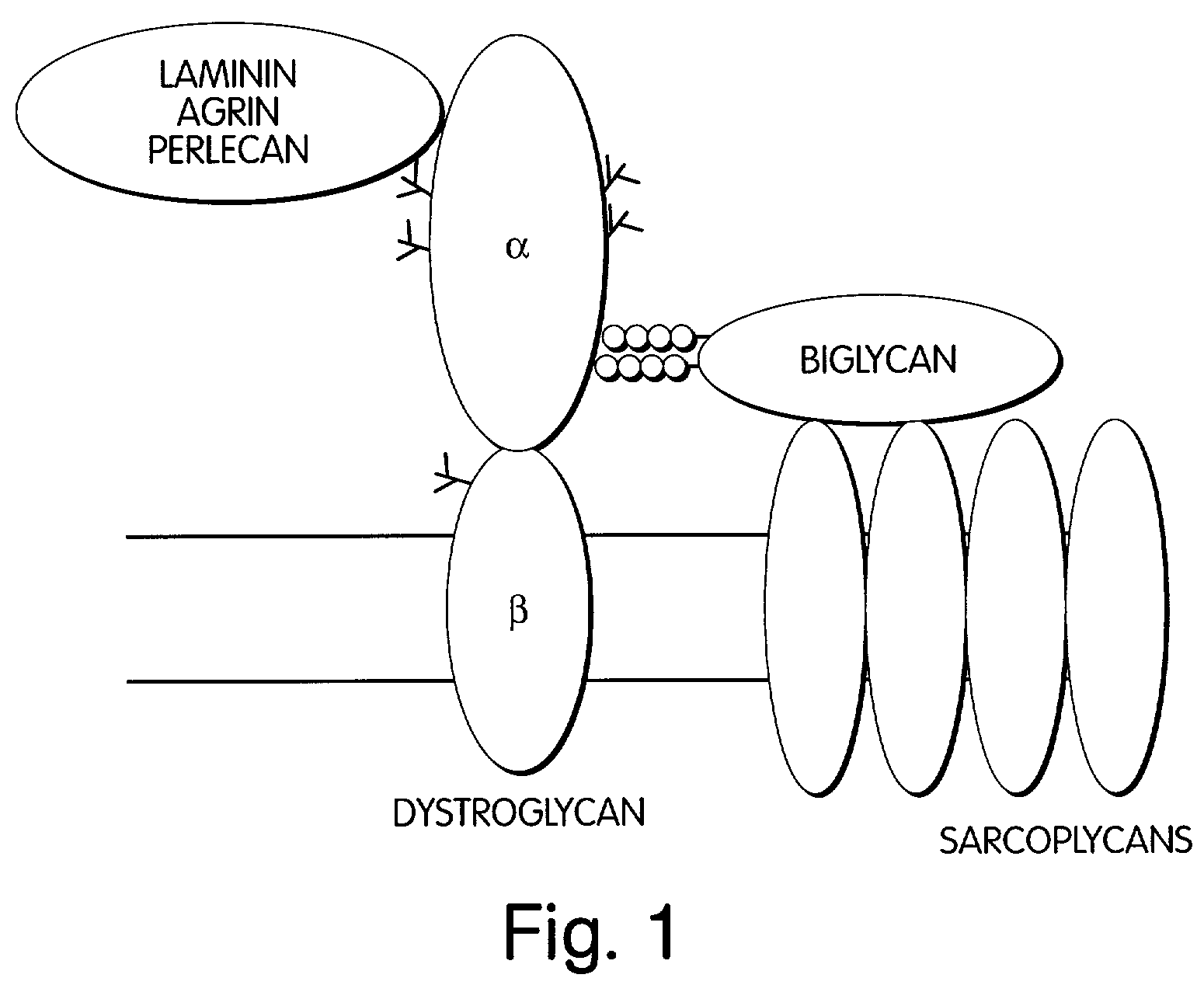
Biglycan and related therapeutics and methods of use
InactiveUS20050059580A1Less “ leaky ”Extend your lifeHormone peptidesSnake antigen ingredientsNervous systemBiglycan
The invention provides compositions and methods for treating, preventing, and diagnosing diseases or conditions associated with an abnormal level or activity of biglycan; disorders associated with an unstable cytoplasmic membrane, due, e.g., to an unstable dystrophin associated protein complex (DAPC); disorders associated with abnormal synapses or neuromuscular junctions, including those resulting from an abnormal MuSK activation or acetylcholine receptor (AChR) aggregation. Examples of diseases include muscular dystrophies, such as Duchenne's Muscular Dystrophy, Becker's Muscular Dystrophy, neuromuscular disorders and neurological disorders.
Owner:BROWN UNIV RES FOUND INC
Identification of structurally similar small molecules that enhance therapeutic exon skipping
This invention relates, e.g., to a method for enhancing exon skipping in a pre-mRNA of interest, comprising contacting the pre-mRNA with an effective amount of a compound such as, for example, Perphenazine, Flupentixol DiHCl, Zuclopenthixol or Corynanthine HCl, or a compound which shares a similar 2-D structure and activity level with one of these compounds, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, hydrate, solvate, or isomer of the compound, and, optionally, with an antisense oligonucleotide that is specific for a splicing sequence in the pre-mRNA Methods for treating Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) are disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Biglycan and related therapeutics and methods of use
The invention provides compositions and methods for treating, preventing, and diagnosing diseases or conditions associated with an abnormal level or activity of biglycan; disorders associated with an unstable cytoplasmic membrane, due, e.g., to an unstable dystrophin associated protein complex (DAPC); disorders associated with abnormal synapses or neuromuscular junctions, including those resulting from an abnormal MuSK activation or acetylcholine receptor (AChR) aggregation. Example of diseases include muscular dystrophies, such as Duchenne's Muscular Dystrophy, Becker's Muscular Dystrophy, neuromuscular disorders and neurological disorders.
Owner:BROWN UNIV RES FOUND INC
Alpha-keto carbonyl calpain inhibitors
InactiveUS20060258598A1Maintain good propertiesSenses disorderNervous disorderCathepsin HPercent Diameter Stenosis
The present invention relates to novel α-keto carbonyl calpain inhibitors for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases and neuromuscular diseases including Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy, Becker Muscular Dystrophy and other muscular dystrophies. Disuse atrophy and general muscle wasting can also be treated. Diseases of the eye, in particular cataract, can be treated as well. Generally all conditions where elevated levels of calpains are involved can be treated. The compounds of the invention may also inhibit other thiol proteases such as cathepsin B, cathepsin H, cathepsin L, papain or the like. Multicatalytic Protease (MCP) also known as proteasome may also be inhibited and the compounds can therefore be used to treat cell proliferative diseases such as cancer, psoriasis, and restenosis. The compounds of the present invention are also inhibitors of cell damage by oxidative stress through free radicals and can be used to treat mitochondrial disorders and neurodegenerative diseases, where elevated levels of oxidative stress are involved.
Owner:SANTHERA PHARMA SCHWEIZ
Substituted acylanilides and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20160089356A1Increasing lean massImprove physical functionBiocideOrganic chemistryDiseaseMedicine
This invention provides substituted acylanilide compounds and uses thereof in treating a variety of diseases or conditions in a subject, including, inter alia, a muscle wasting disease and / or disorder such as muscular dystrophies including Duchenne muscular dystrophy and Becker muscular dystrophy.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Sarms and method of use thereof
InactiveUS20160158185A1Increasing lean massImprove physical functionBiocideOrganic chemistryDiseaseDuchenne's Muscular Dystrophy
This invention is directed to substituted acylanilide compounds and uses thereof in treating a variety of diseases or conditions in a subject, including, inter alia, a muscle wasting disease and / or disorder such as Duchenne muscular dystrophy or Becker muscular dystrophy.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
Method of early detection of Duchenne muscular dystrophy and other neuromuscular disease
InactiveUS6875418B2Compounds screening/testingDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseaseDecreasing heart rate
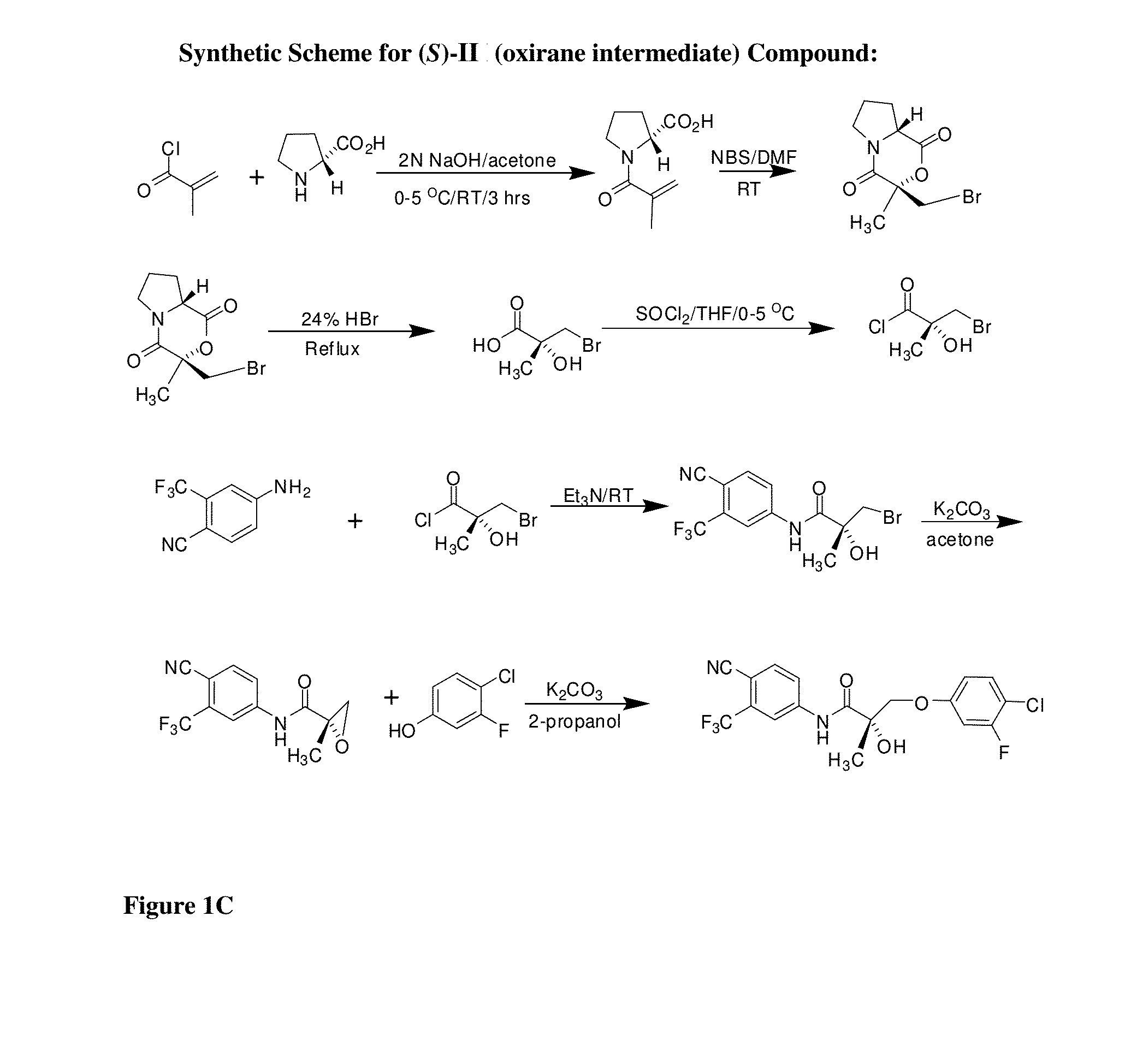
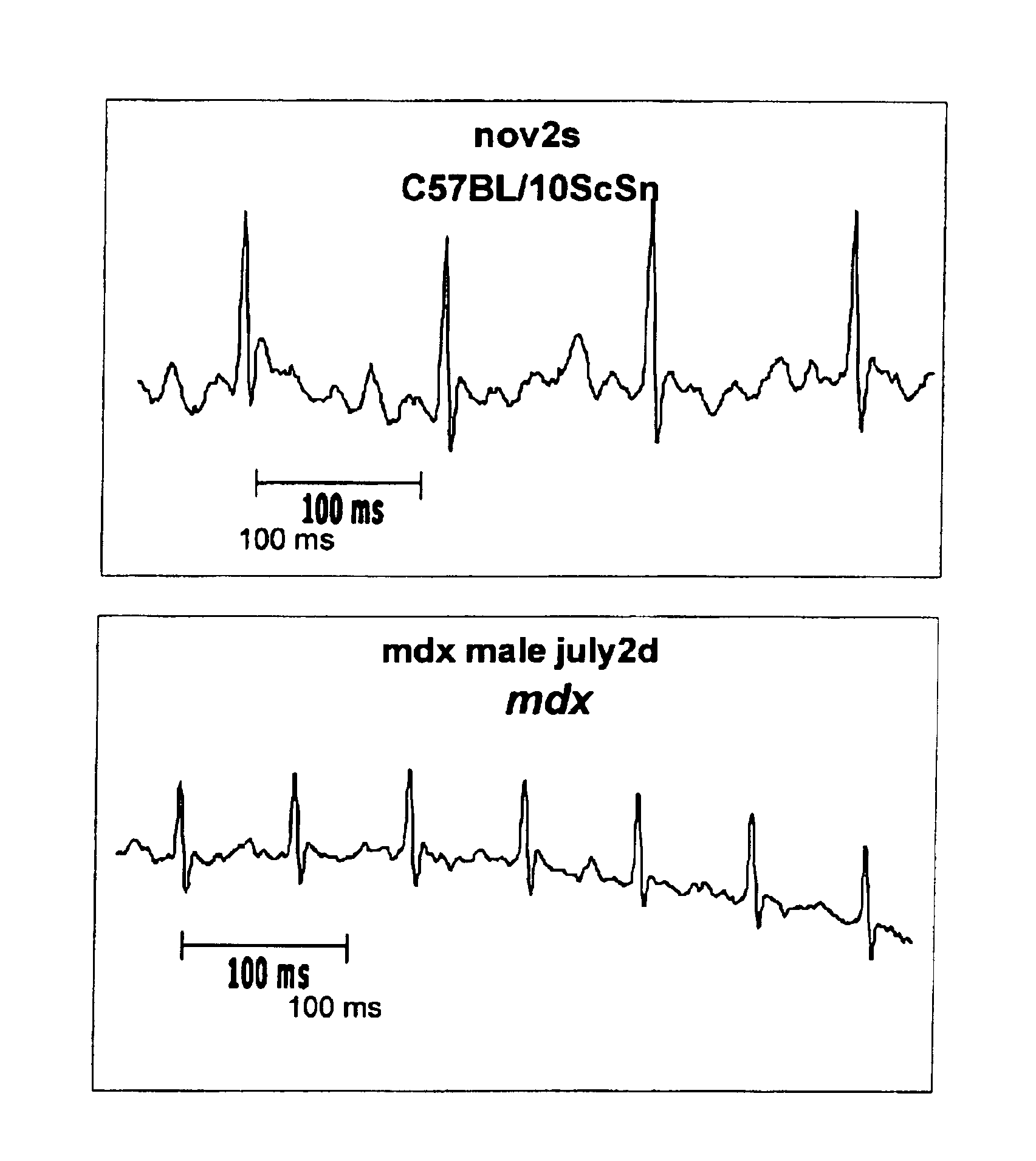
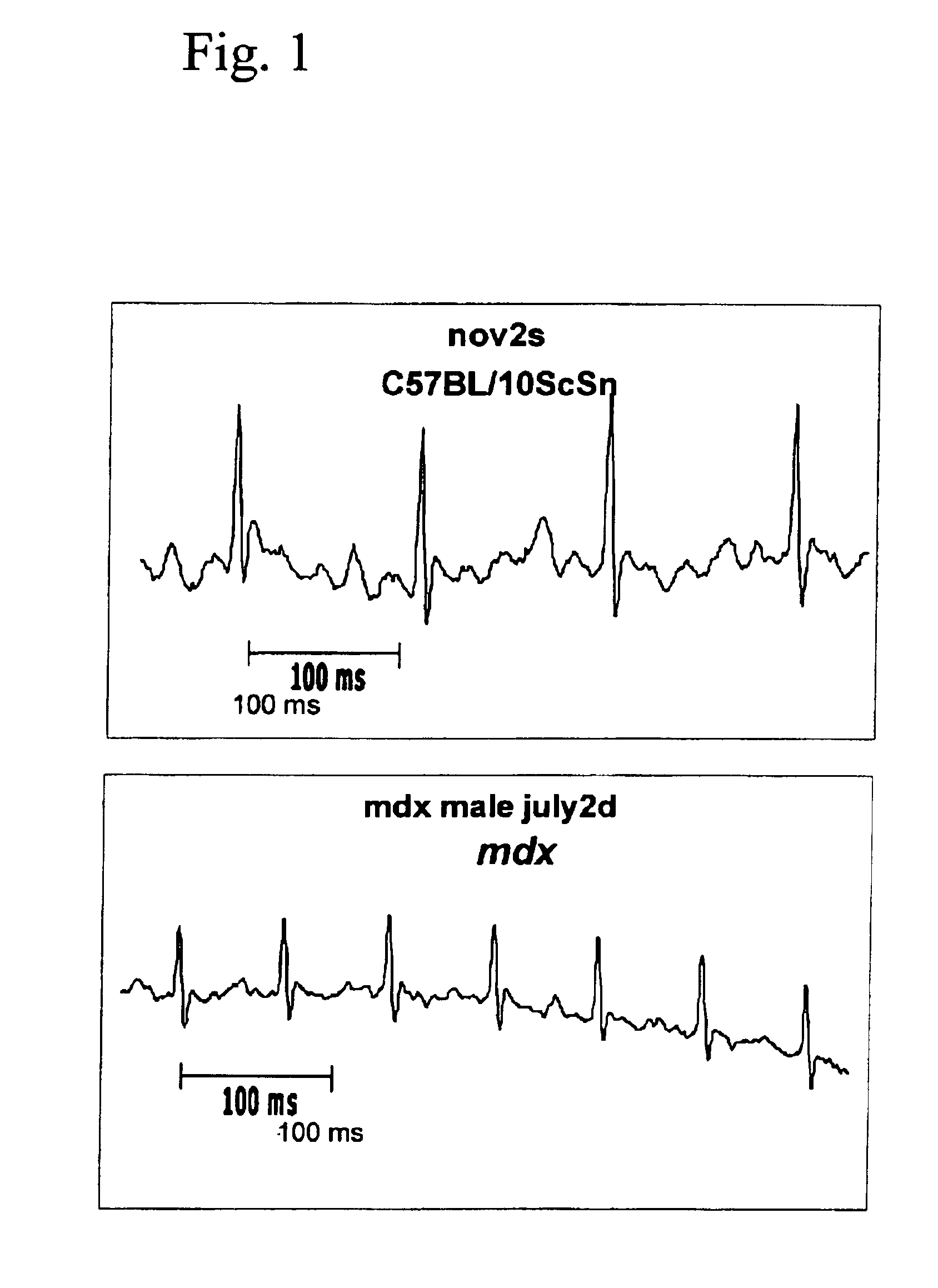
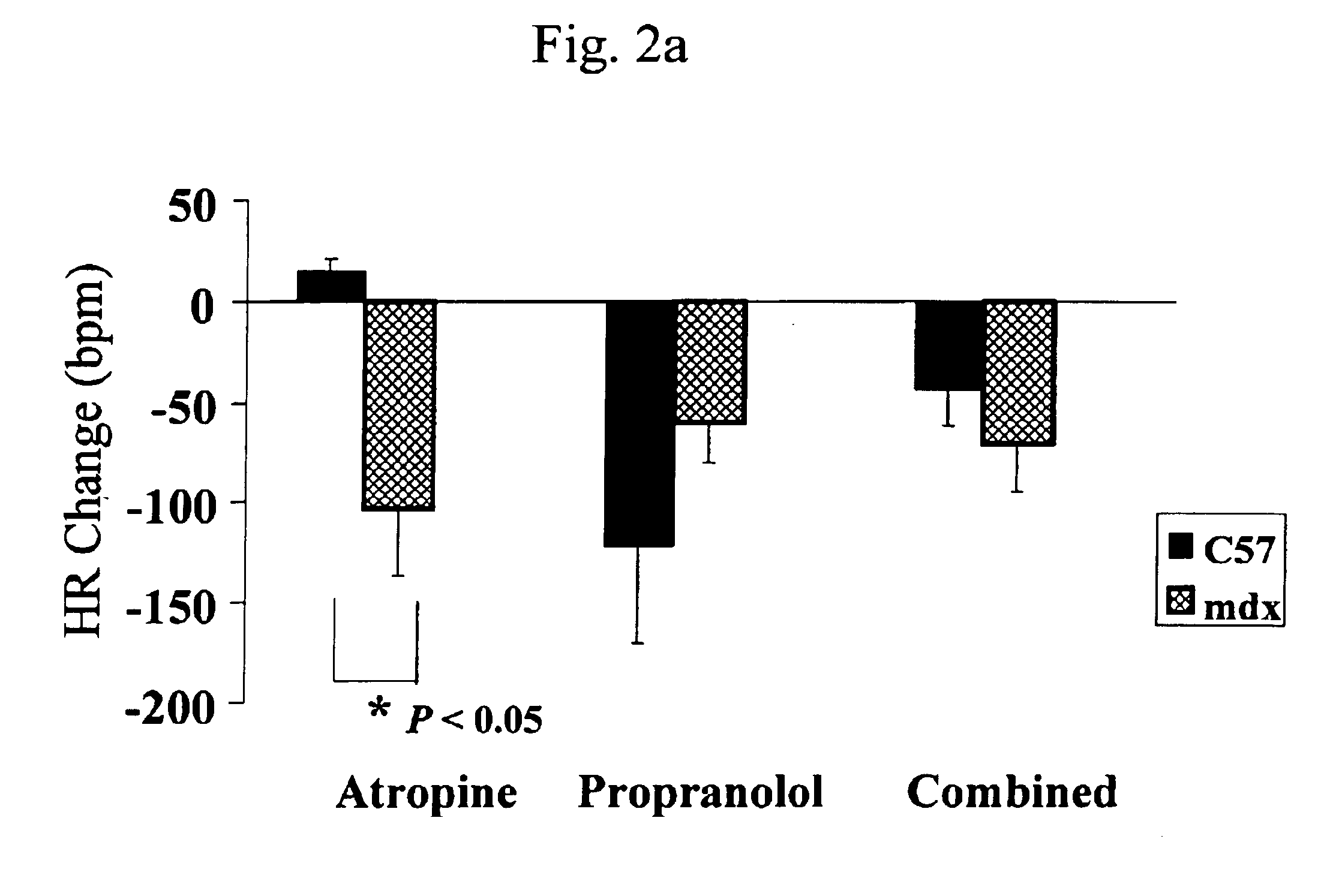
The mdx mouse is a model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. The present invention describes that mdx mice exhibited clinically relevant cardiac phenotypes. A non-invasive method of recording electrocardiograms (ECGs) was used to a study mdx mice (n=15) and control mice (n=15). The mdx mice had significant tachycardia, consistent with observations in patients with muscular dystrophy. Heart-rate was nearly 15% faster in mdx mice than control mice (P<0.01). ECGs revealed significant shortening of the rate-corrected QT interval duration (QTc) in mdx mice compared to control mice (P<0.05). PR interval duration were shorter at baseline in mdx compared to control mice (P<0.05). The muscarinic antagonist atropine significantly increased heart-rate and decreased PR interval duration in C57 mice. Paradoxically, atropine significantly decreased heart-rate and increased PR interval duration in all mdx mice. Pharmacological autonomic blockade and baroreflex sensitivity testing demonstrated an imbalance in autonomic nervous system modulation of heart-rate, with decreased parasympathetic activity and increased sympathetic activity in mdx mice. These electrocardiographic findings in dystrophin-deficient mice provide new bases for diagnosing, understanding, and treating patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Owner:MOUSE SPECIFICS
Drug combinations for the treatment of duchenne muscular dystrophy
Owner:SUMMIT OXFORD
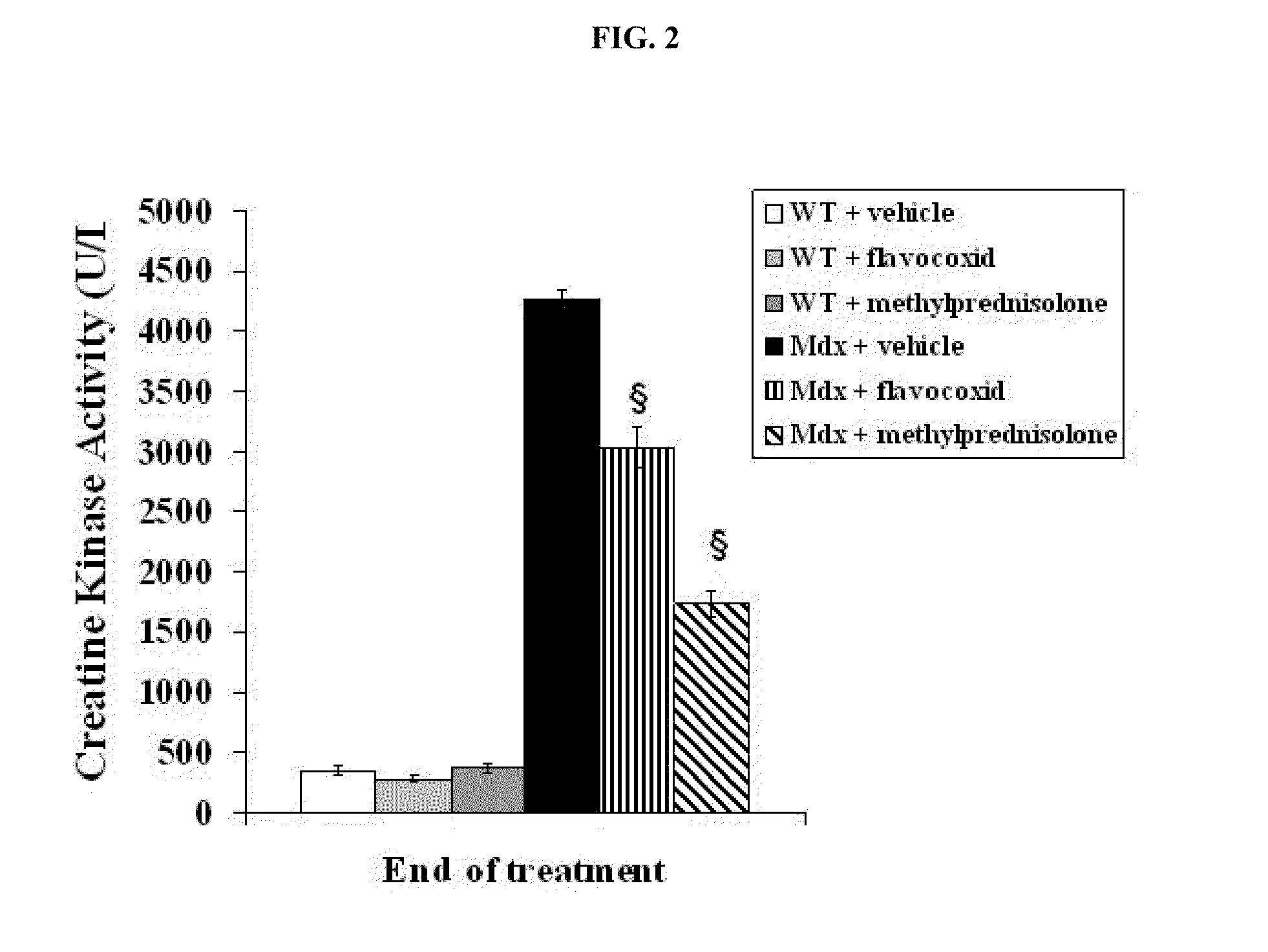
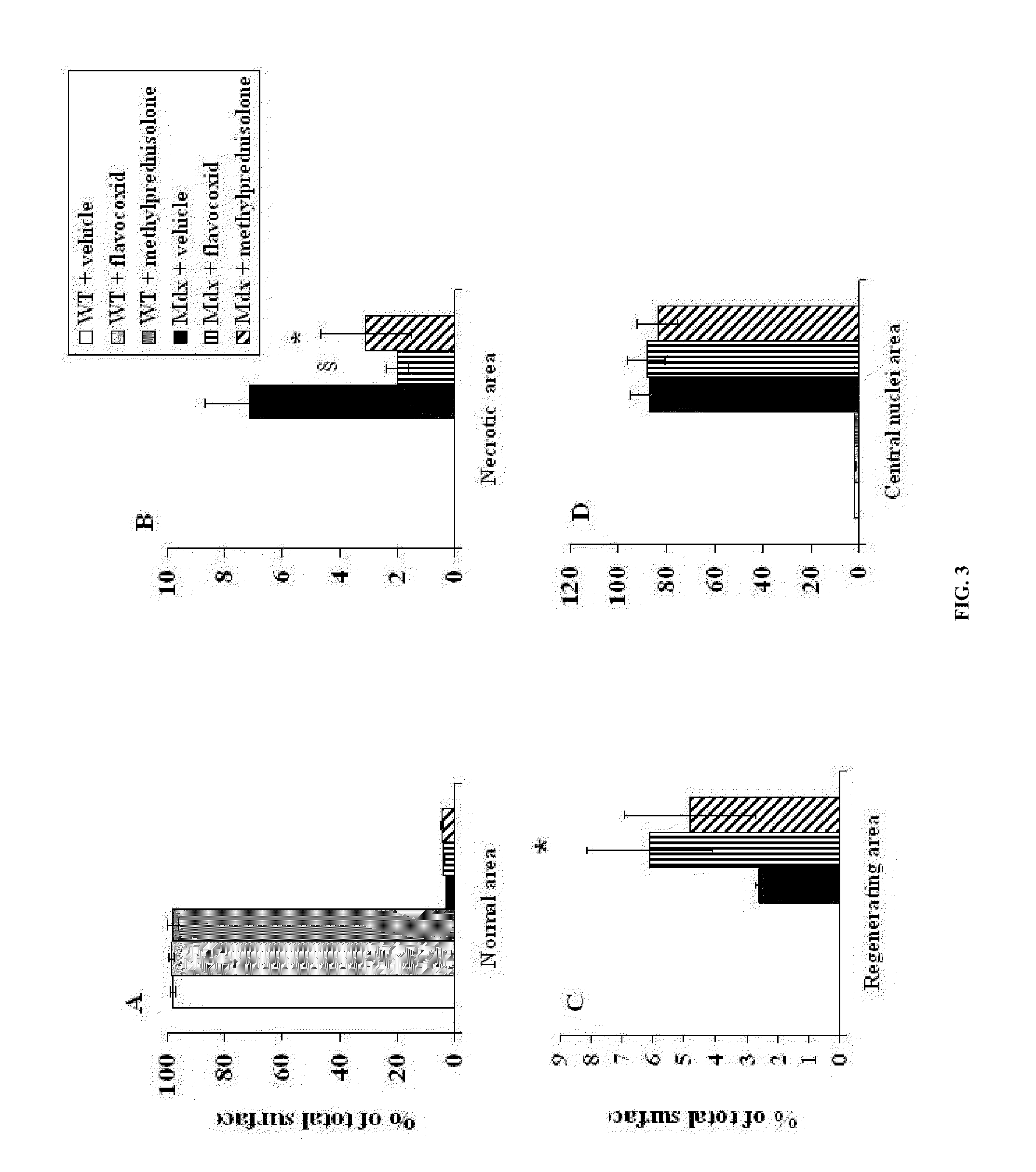
Methods of Treating Muscular Dystrophies
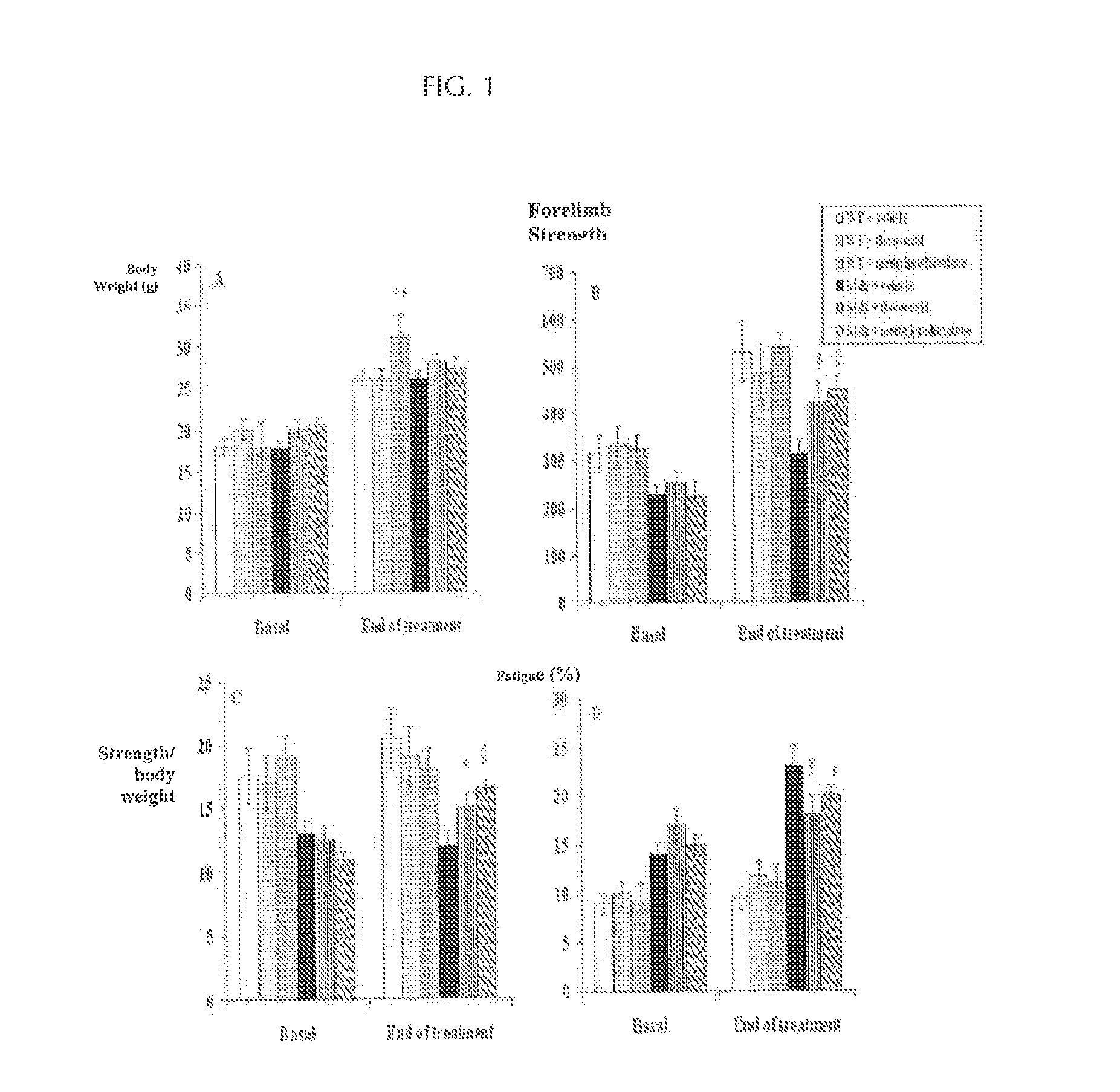
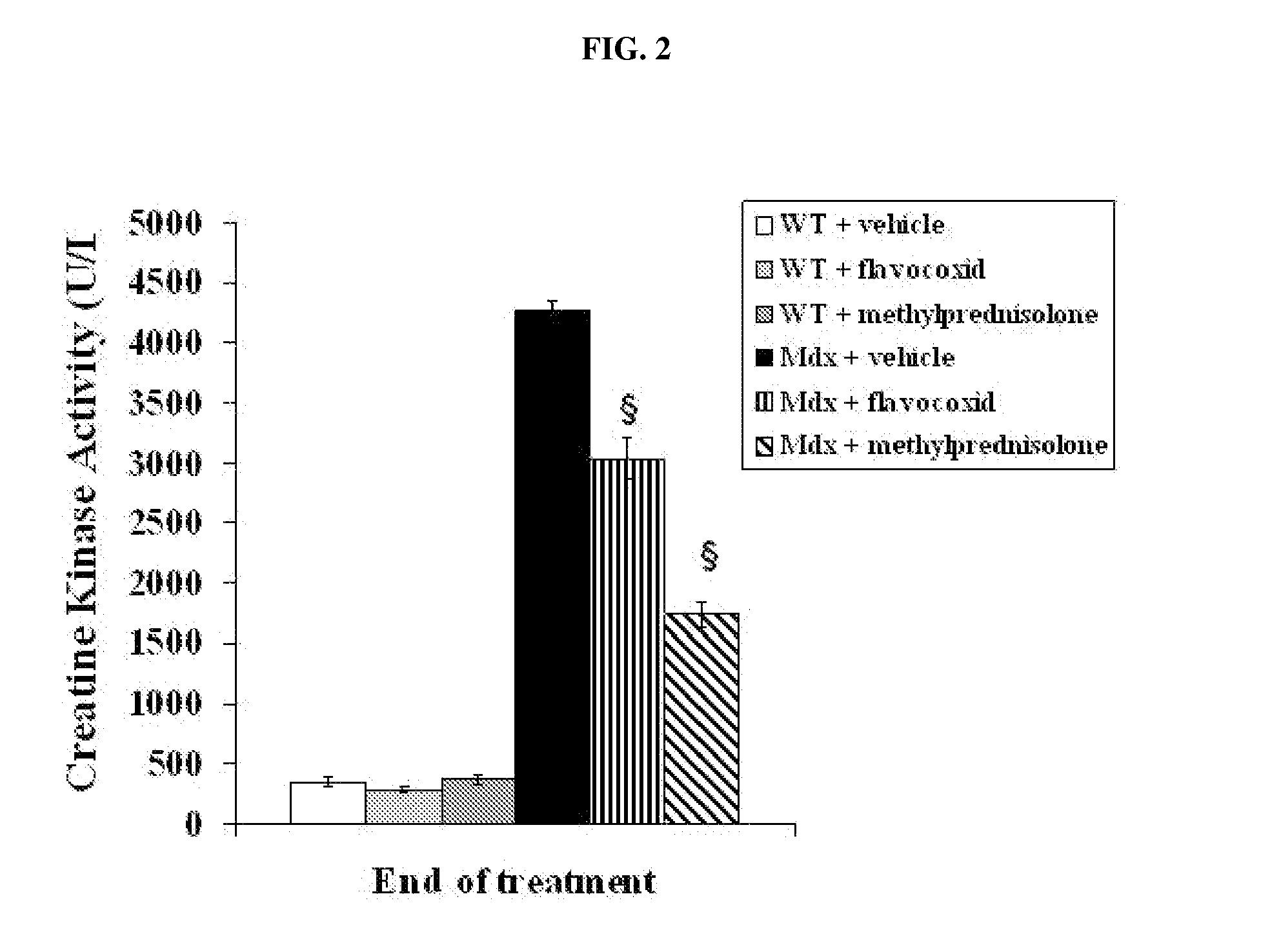
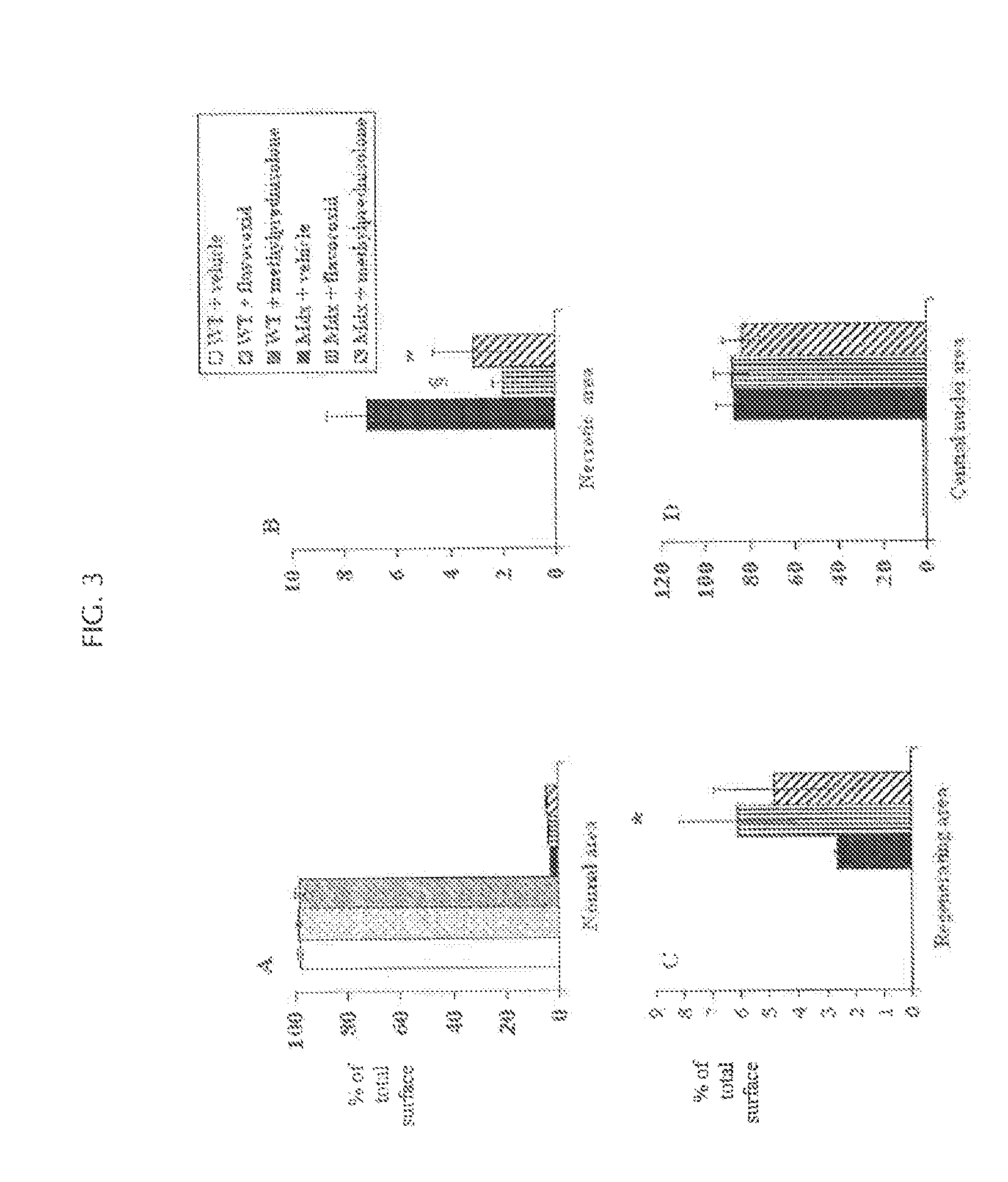
The invention relates to methods of treating Duchenne muscular dystrophy with flavonoids. The methods may include (a) providing a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of flavonoid, and (b) administering the composition to a human patient, wherein the flavonoid comprises an isoflav-4-one with at least one of the carbons located at positions 8, 7, 6, 5, 2, 2′, 3′, 4′, 5′, or 6′ modified by an alcohol group. Alternatively, the flavonoid may comprise (1) a flavan-3-ol with at least one of the carbons located at positions 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 2′, 3′, 4′, 5′, or 6′ modified by an alcohol group, or (2) a Free-B-Ring flavone with at least one of the carbons located at positions 8, 7, 6, 5 or 3 modified by an alcohol group and with at least one of the carbons located at positions 8, 7, 6, 5 or 3 modified by a glycoside group.
Owner:PRIMUS PHARM INC
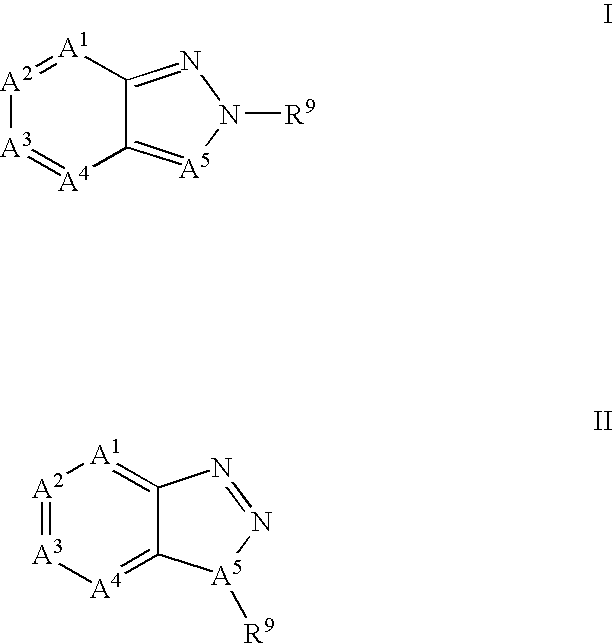
Drug Combinations for the Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Combinations comprising (or consisting essentially of) one or more compounds of the formula (I) or (II) with one or more ancillary compounds, to processes for preparing the combinations, and to various therapeutic uses of the combinations. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions containing the combinations as well as a method of treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, Becker muscular dystrophy or cachexia using the combinations.
Owner:BIOMARIN IGA
Methods of treating muscular dystrophies
The invention relates to methods of treating Duchenne muscular dystrophy with flavonoids. The methods may include (a) providing a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of flavonoid, and (b) administering the composition to a human patient, wherein the flavonoid comprises an isoflav-4-one with at least one of the carbons located at positions 8, 7, 6, 5, 2, 2′, 3′, 4′, 5′, or 6′ modified by an alcohol group. Alternatively, the flavonoid may comprise (1) a flavan-3-ol with at least one of the carbons located at positions 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 2′, 3′, 4′, 5′, or 6′ modified by an alcohol group, or (2) a Free-B-Ring flavone with at least one of the carbons located at positions 8, 7, 6, 5 or 3 modified by an alcohol group and with at least one of the carbons located at positions 8, 7, 6, 5 or 3 modified by a glycoside group.
Owner:PRIMUS PHARM INC
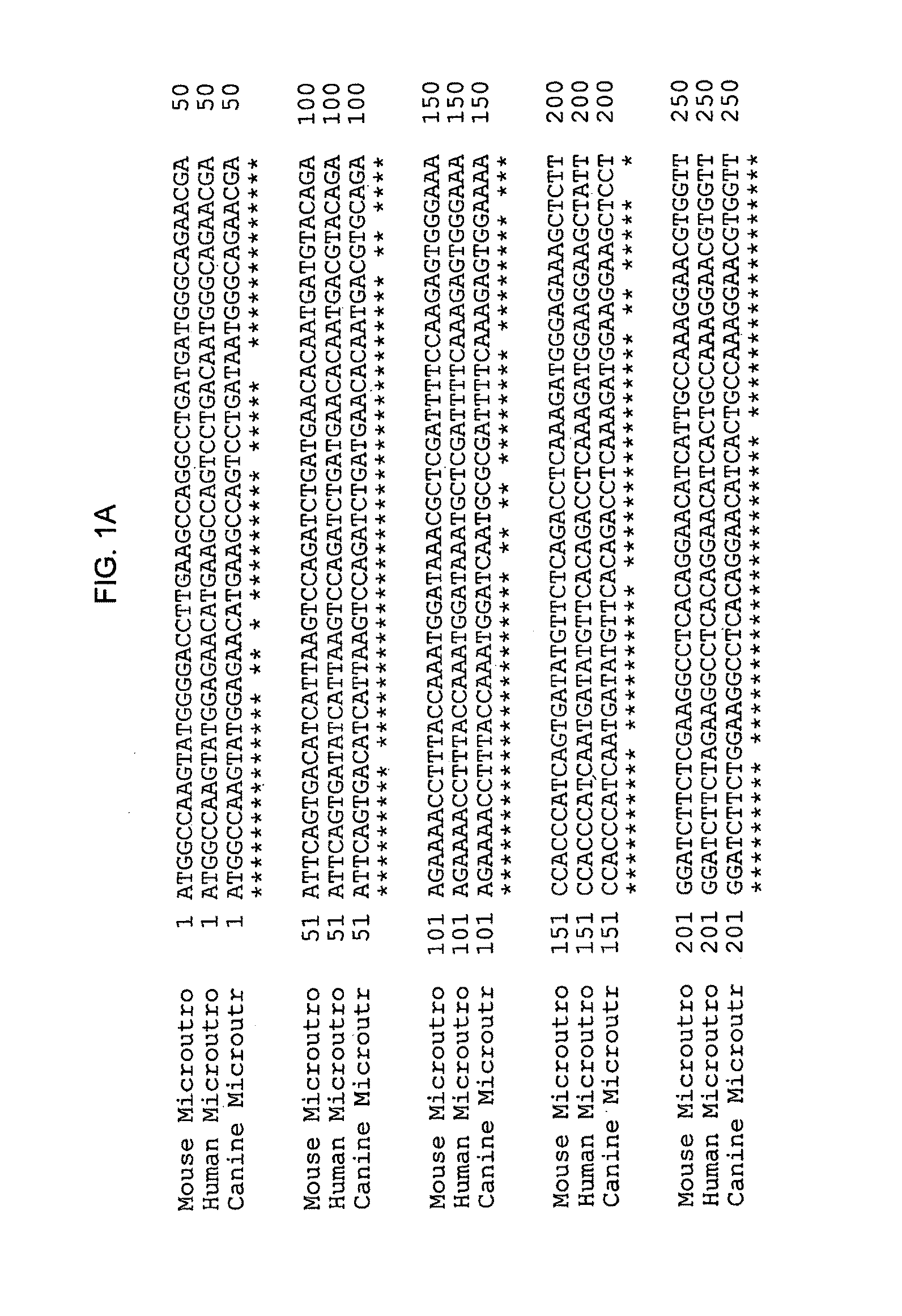
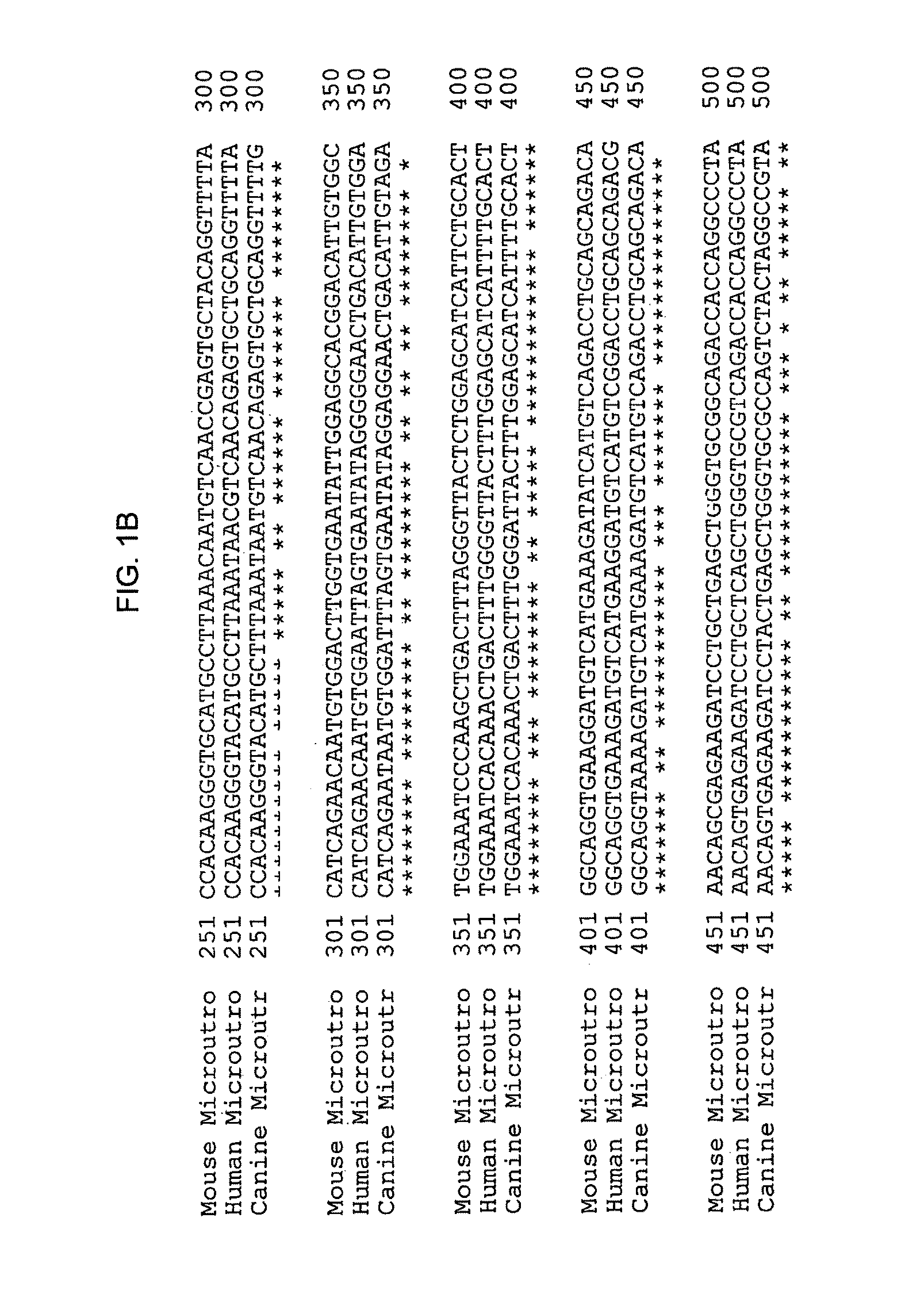
Microutrophin and uses thereof
A microutrophin containing a utrophin having internal deletions (relative to a native utrophin) in the hinge regions and a C-terminal deletion is provided. Also provided are vectors and compositions useful for delivering the microutrophin for the treatment of muscular disorders, including Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Sarms and method of use thereof
InactiveUS20170014370A1Increasing lean massOrganic chemistryAccessory food factorsDuchenne's Muscular DystrophyLung
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
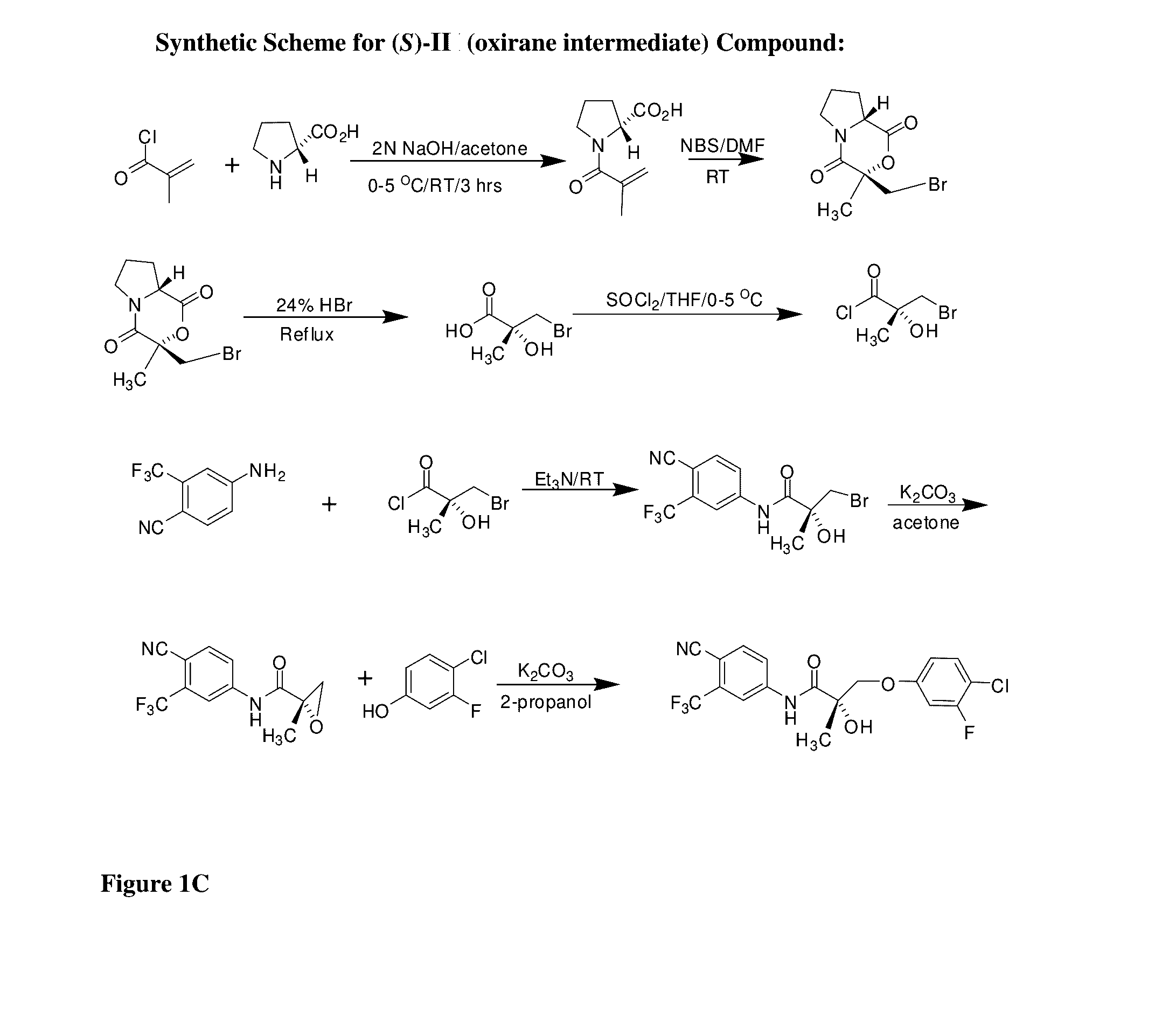
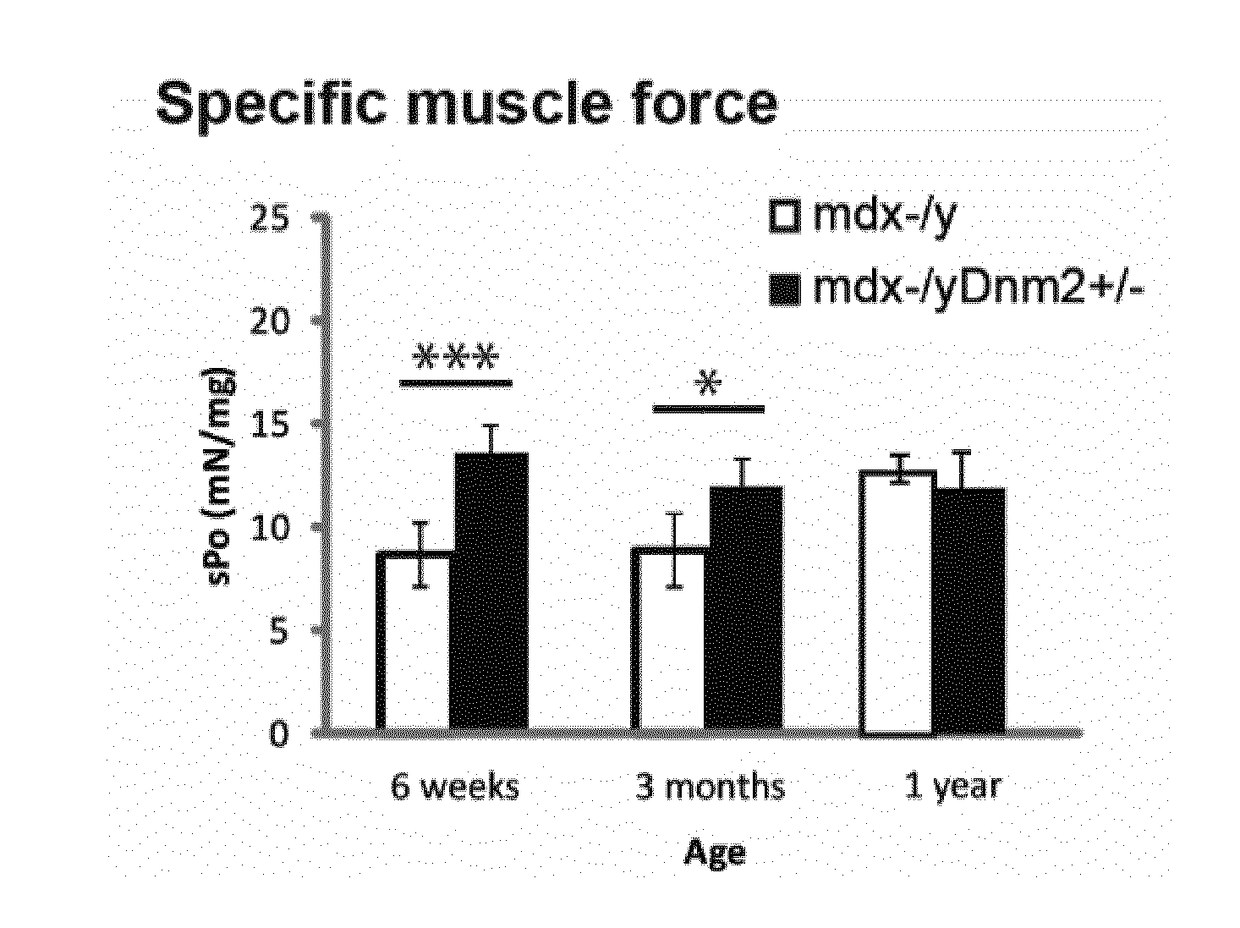
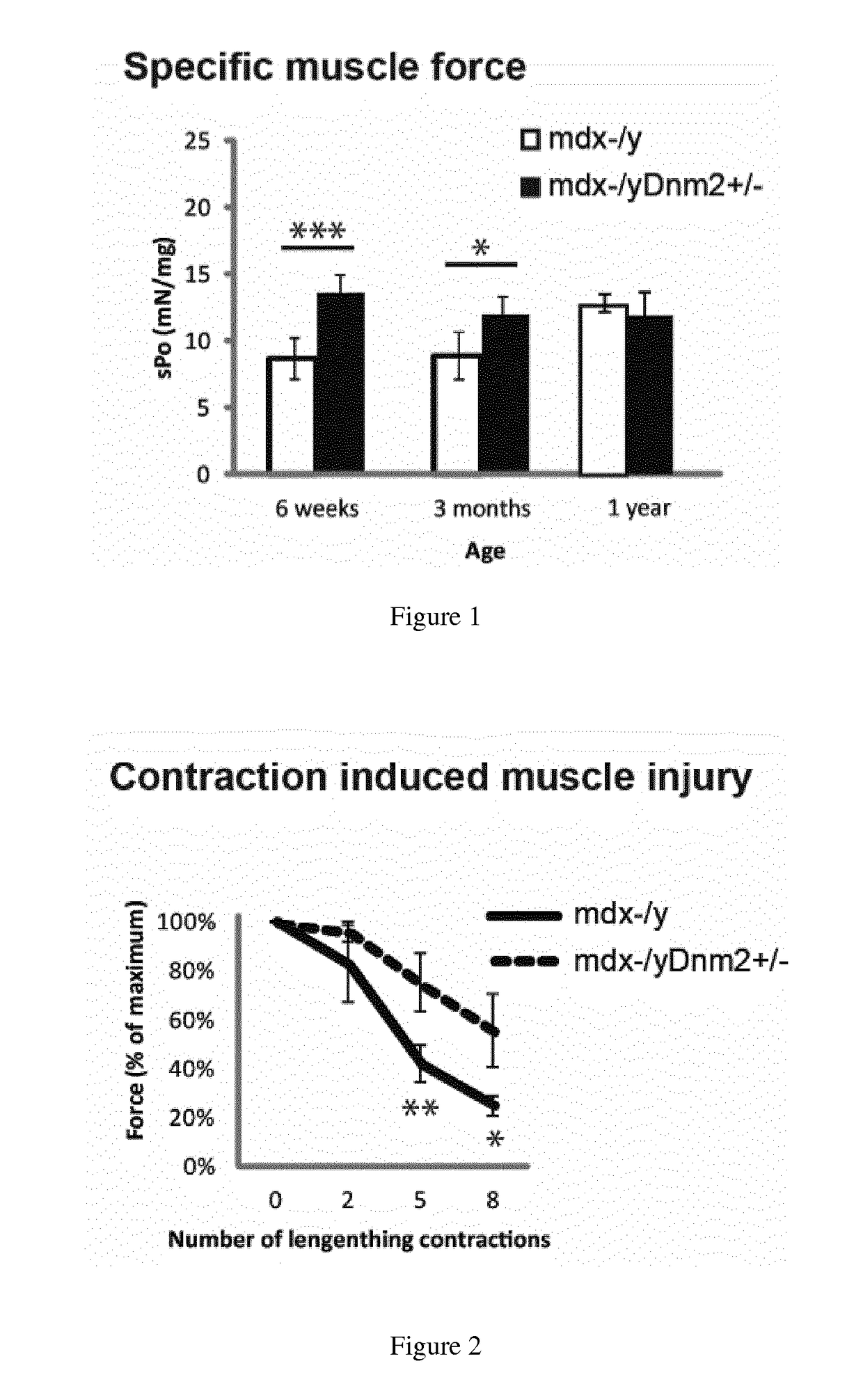
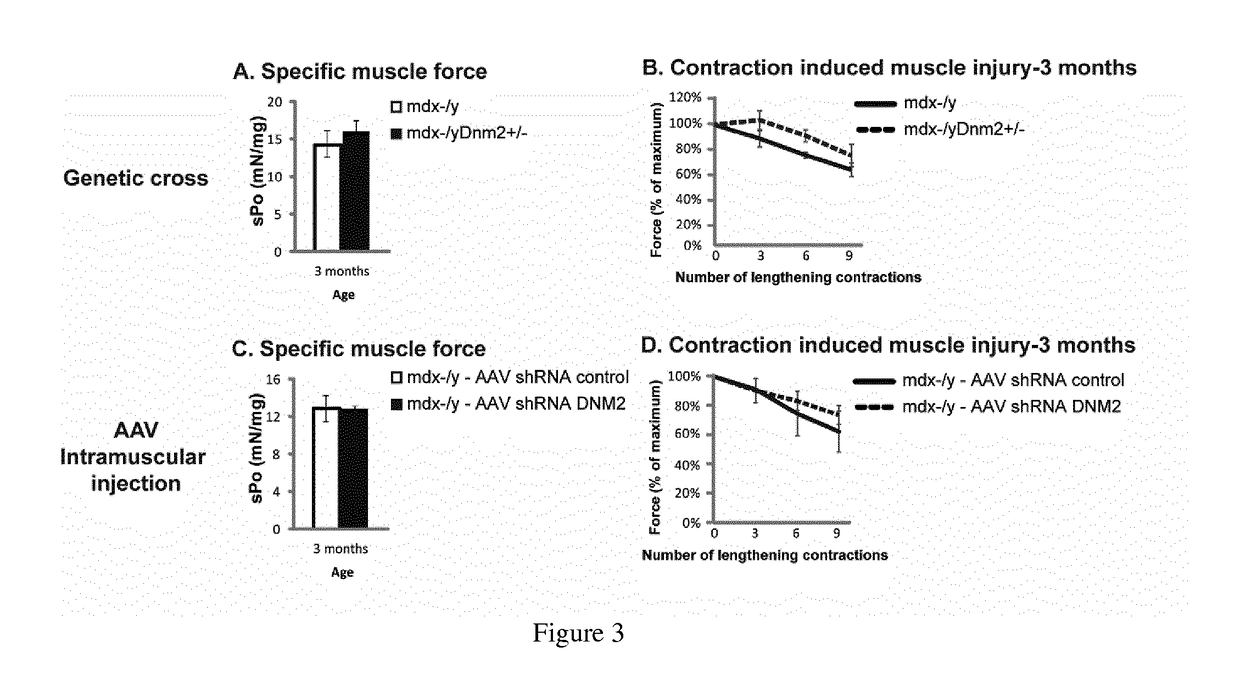
Dynamin 2 inhibitor for the treatment of duchenne's muscular dystrophy
ActiveUS20180142008A1HydrolasesImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDuchenne's Muscular DystrophyDynamin
The present disclosure relates to an inhibitor of Dynamin 2 or composition comprising the same for use in the treatment of Duchenne's muscular dystrophy.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF STRASBOURG +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com