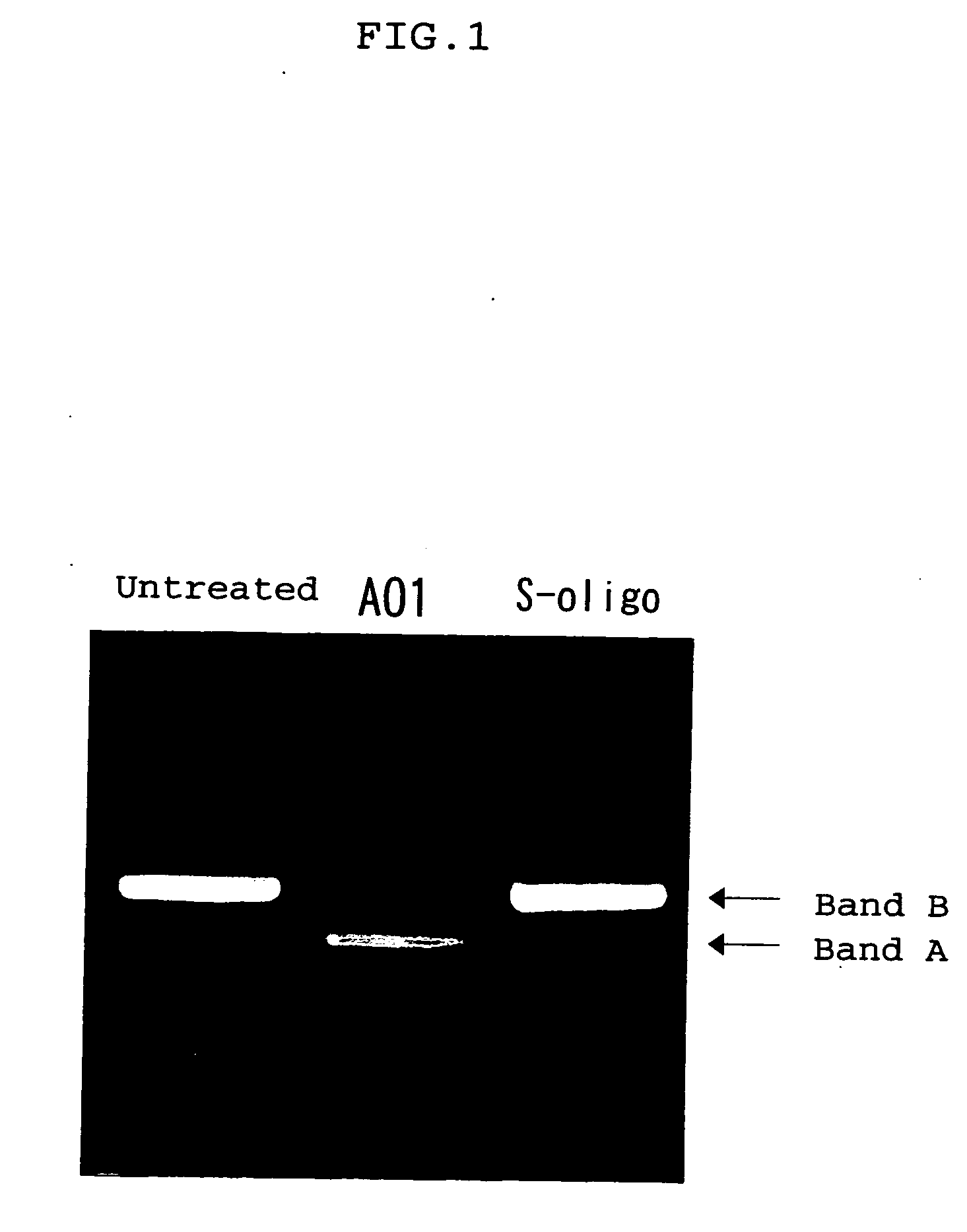
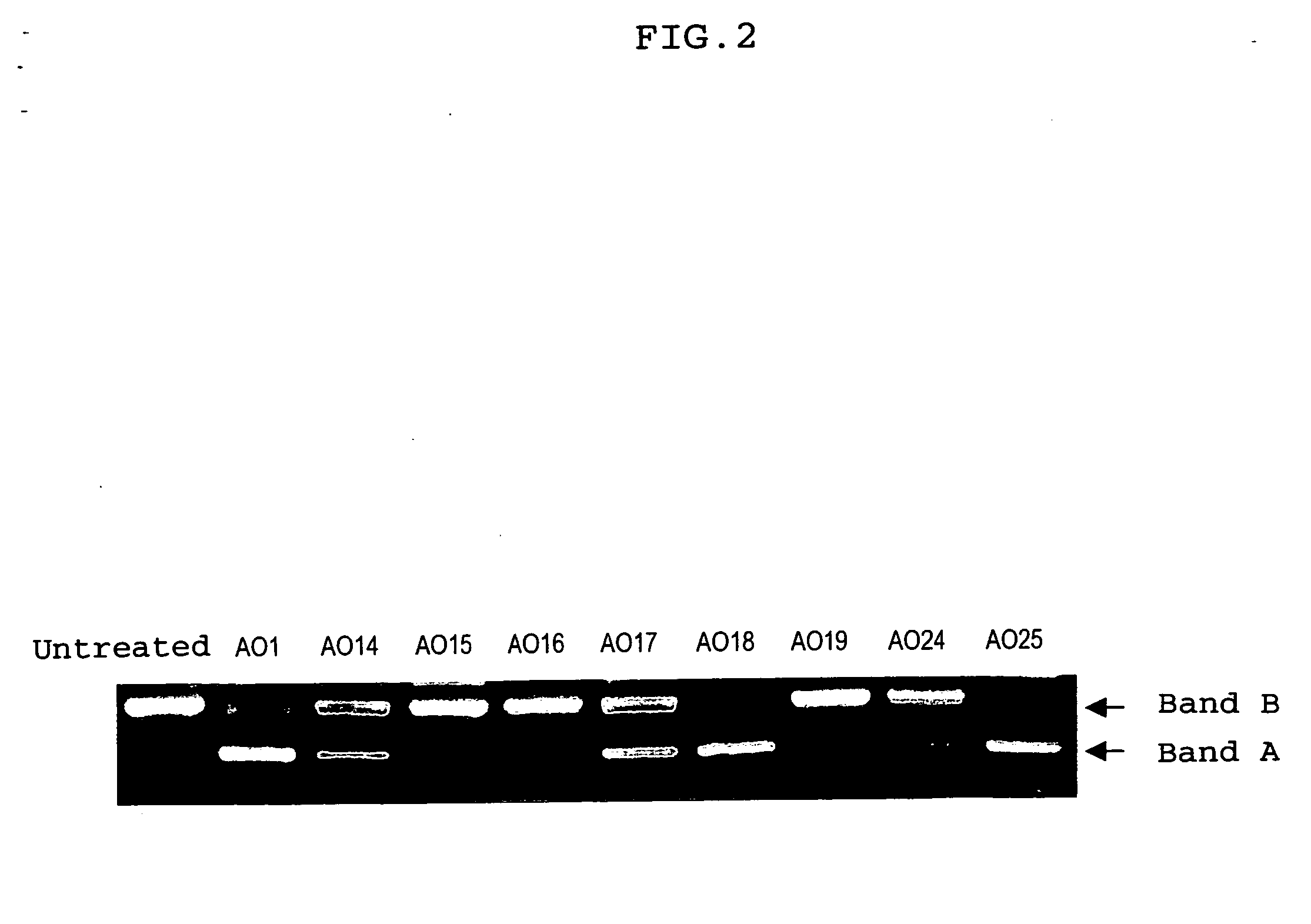
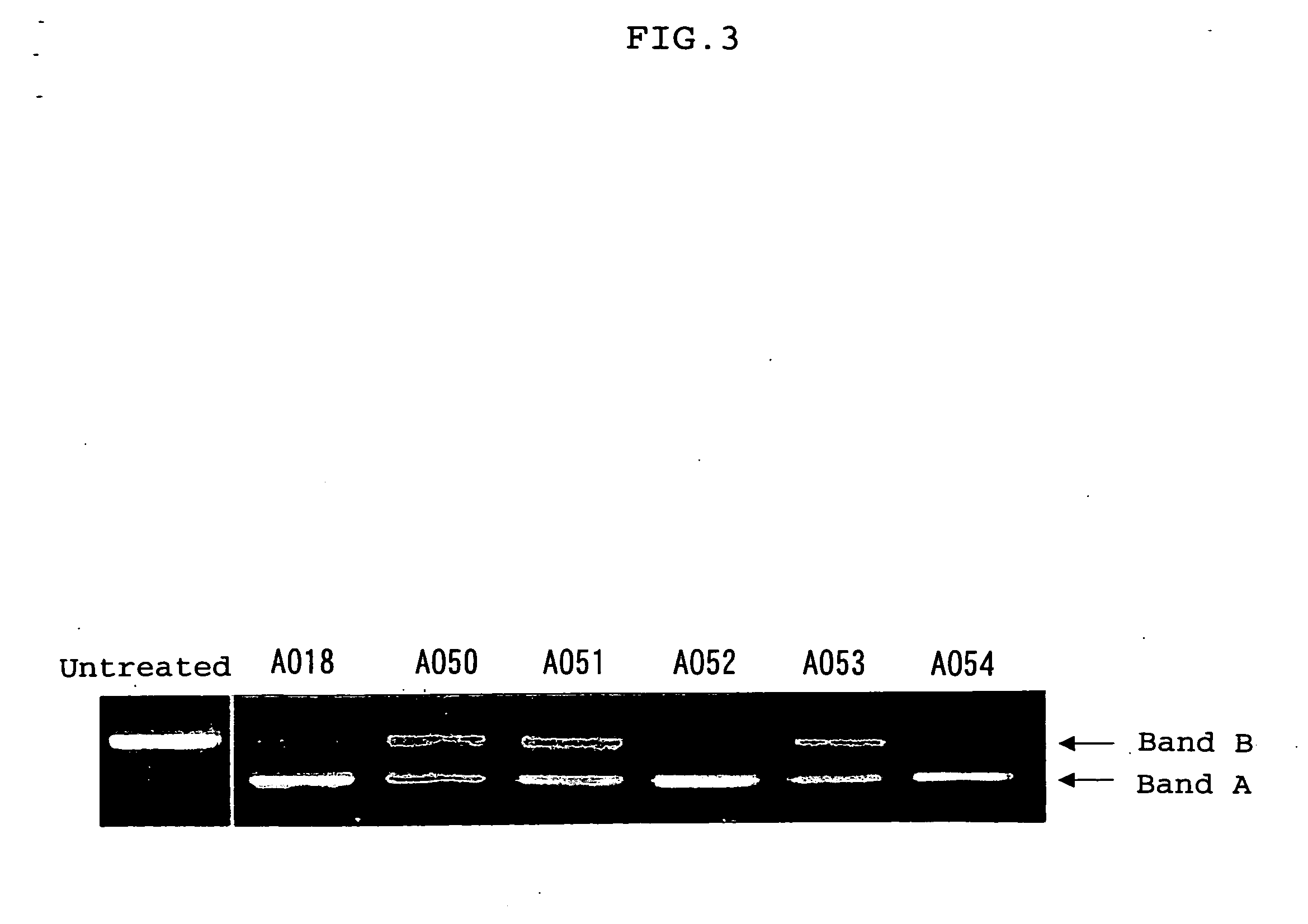
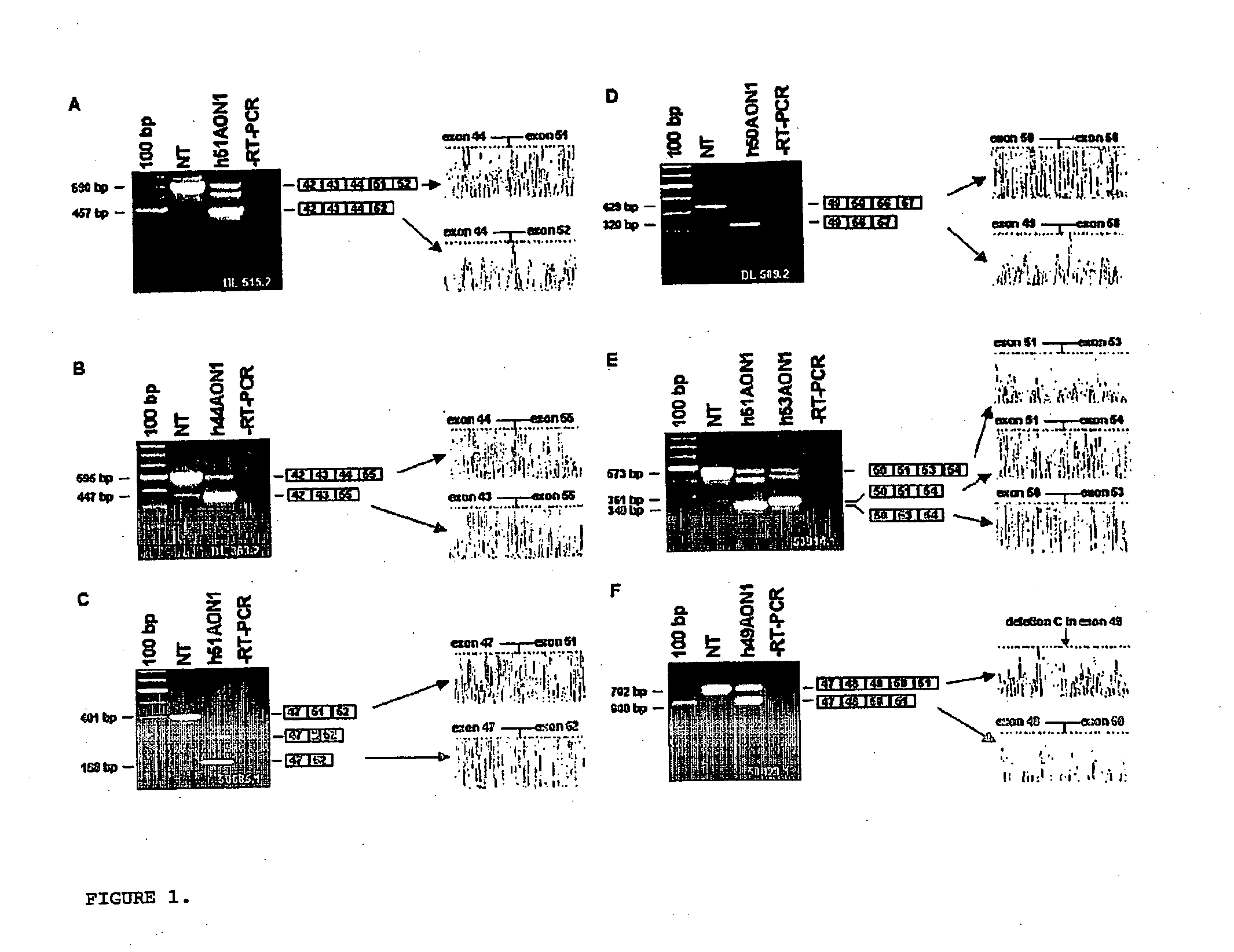
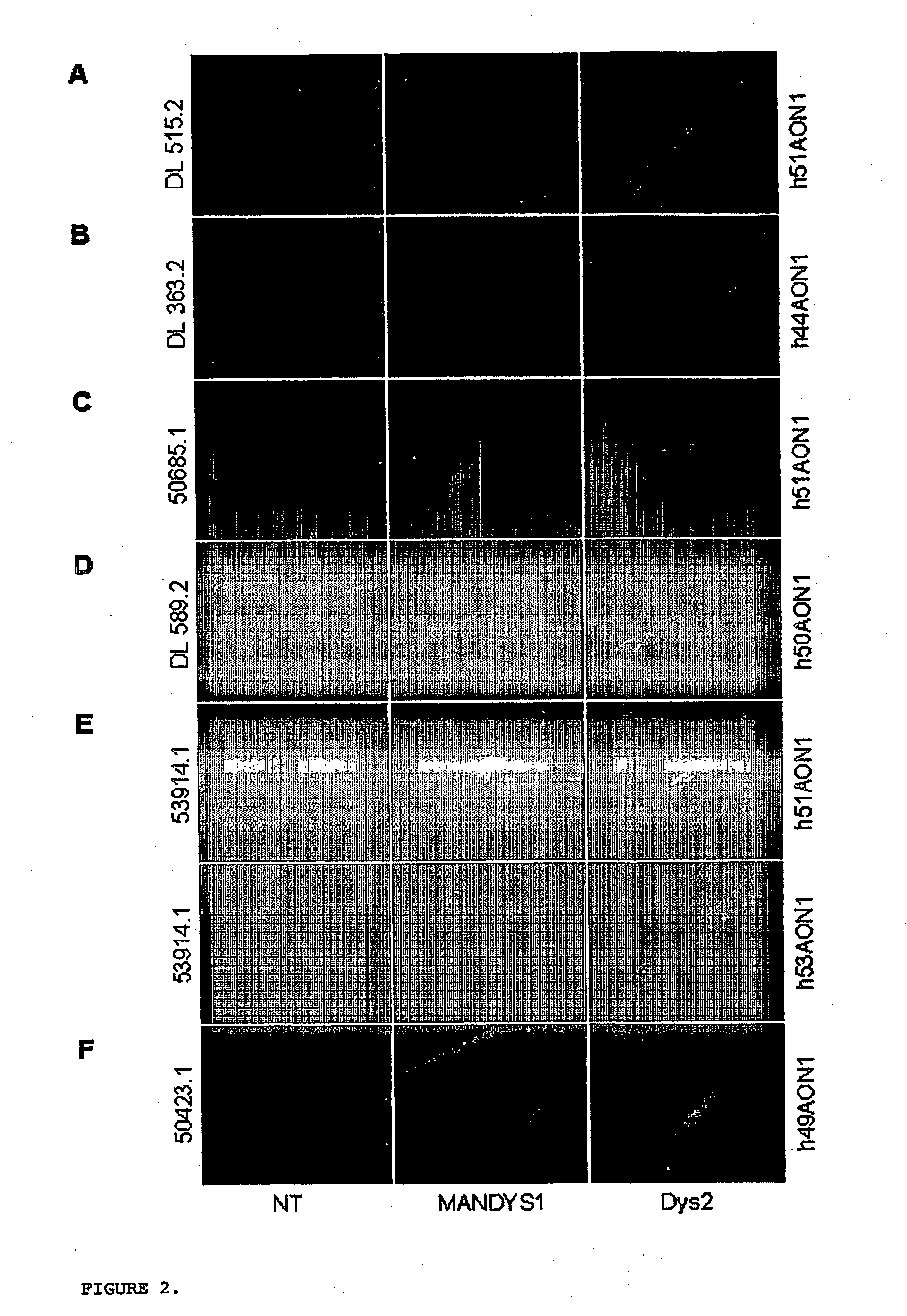
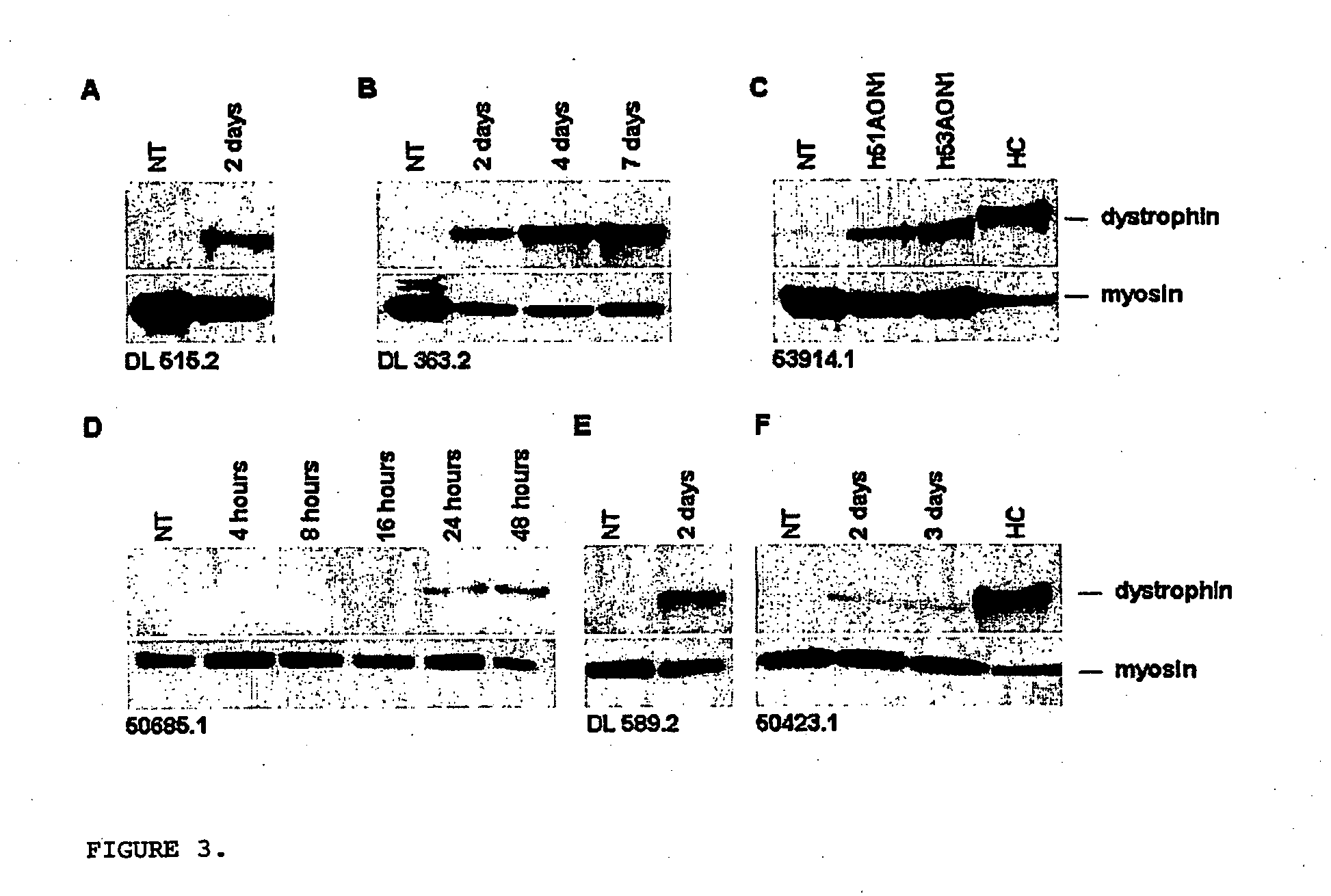
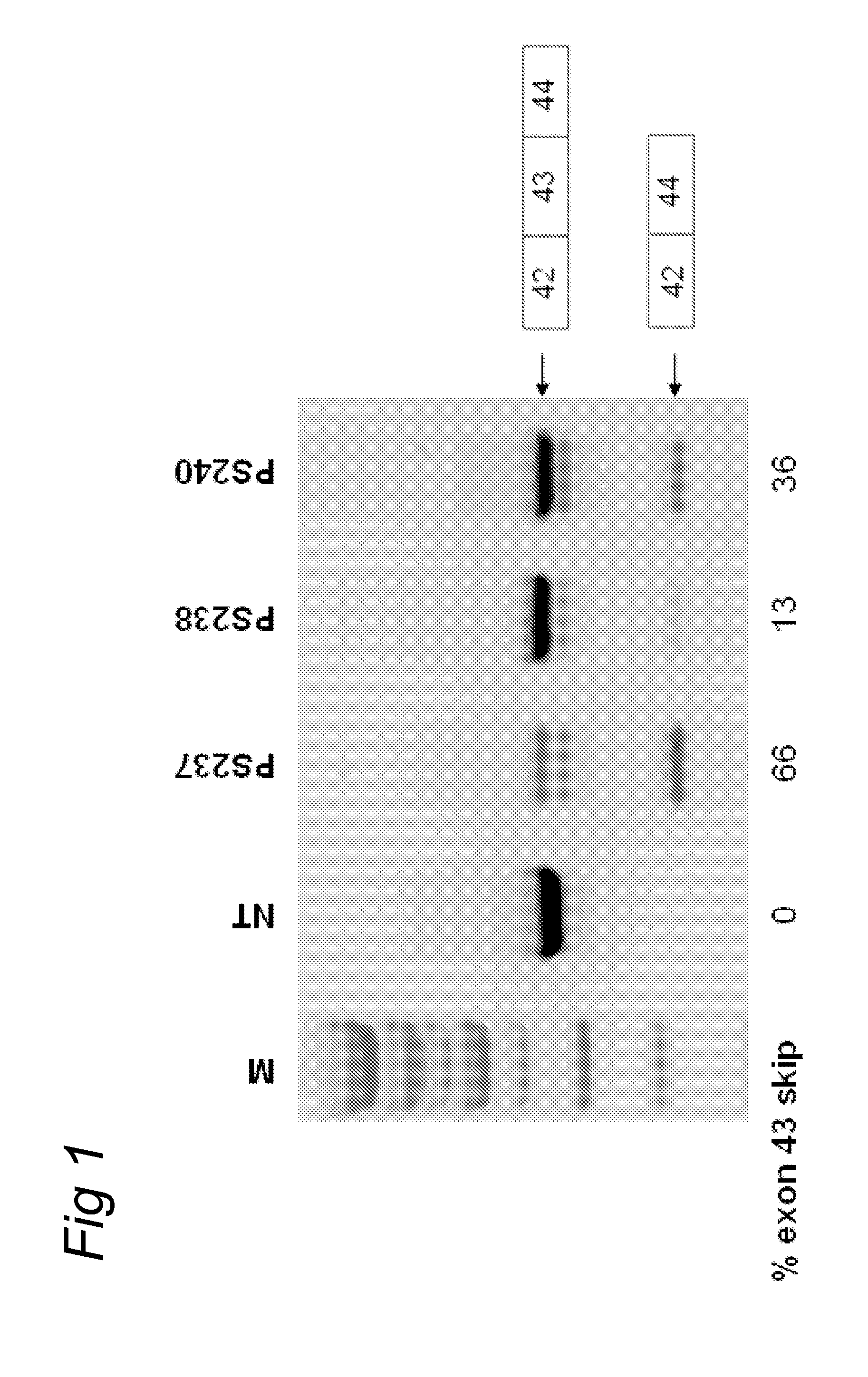
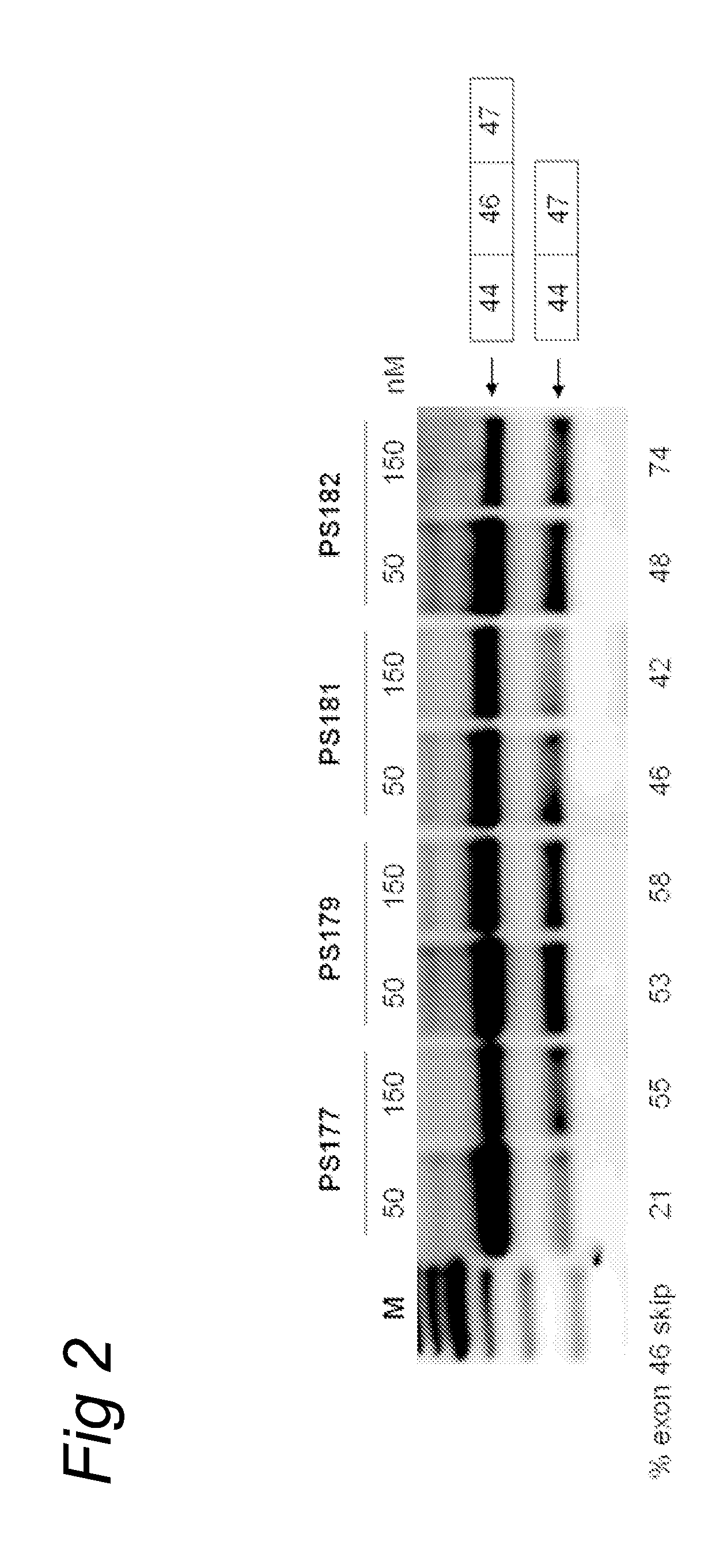
Patents
Literature
328results about "Splicing alteration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
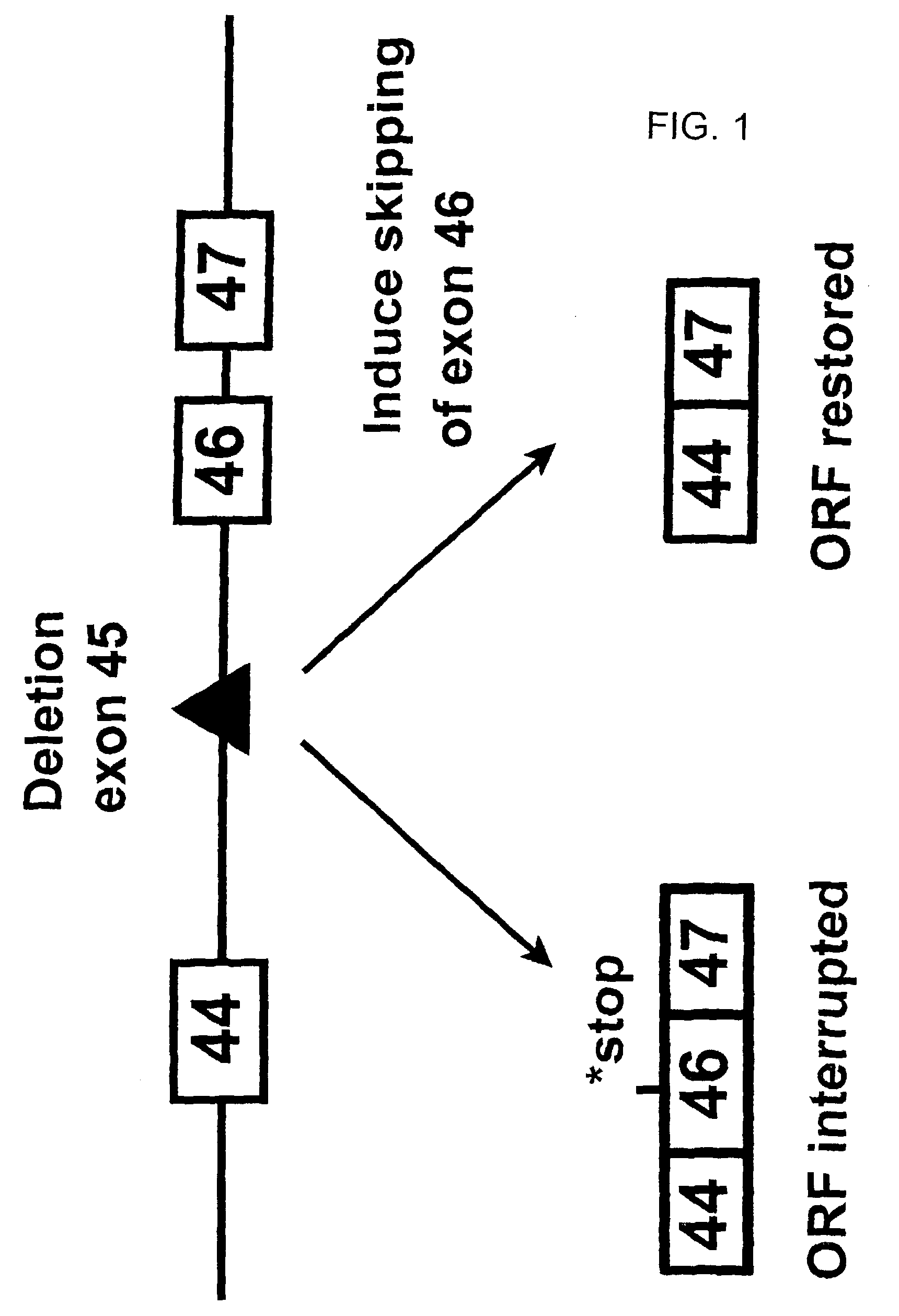
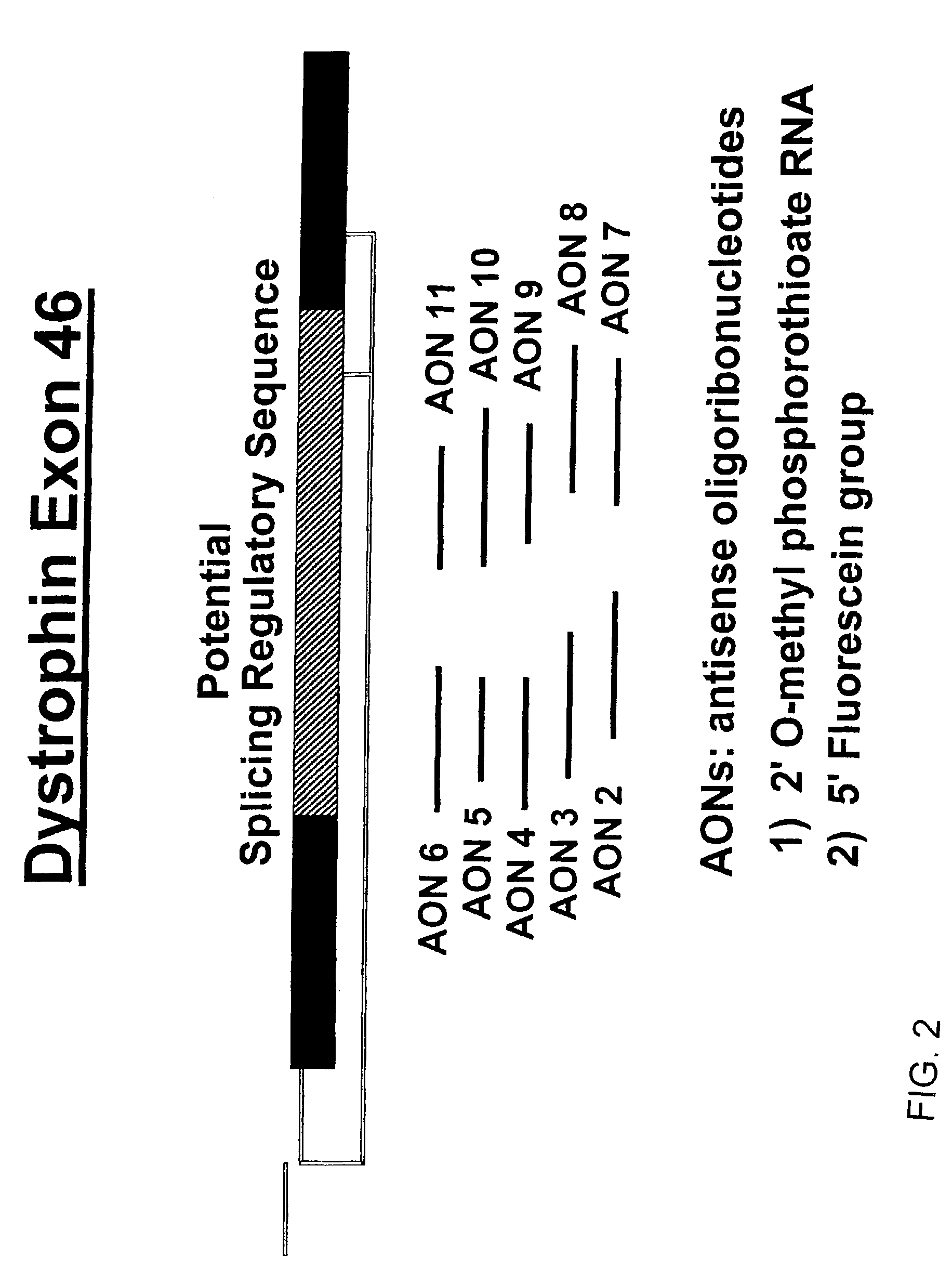
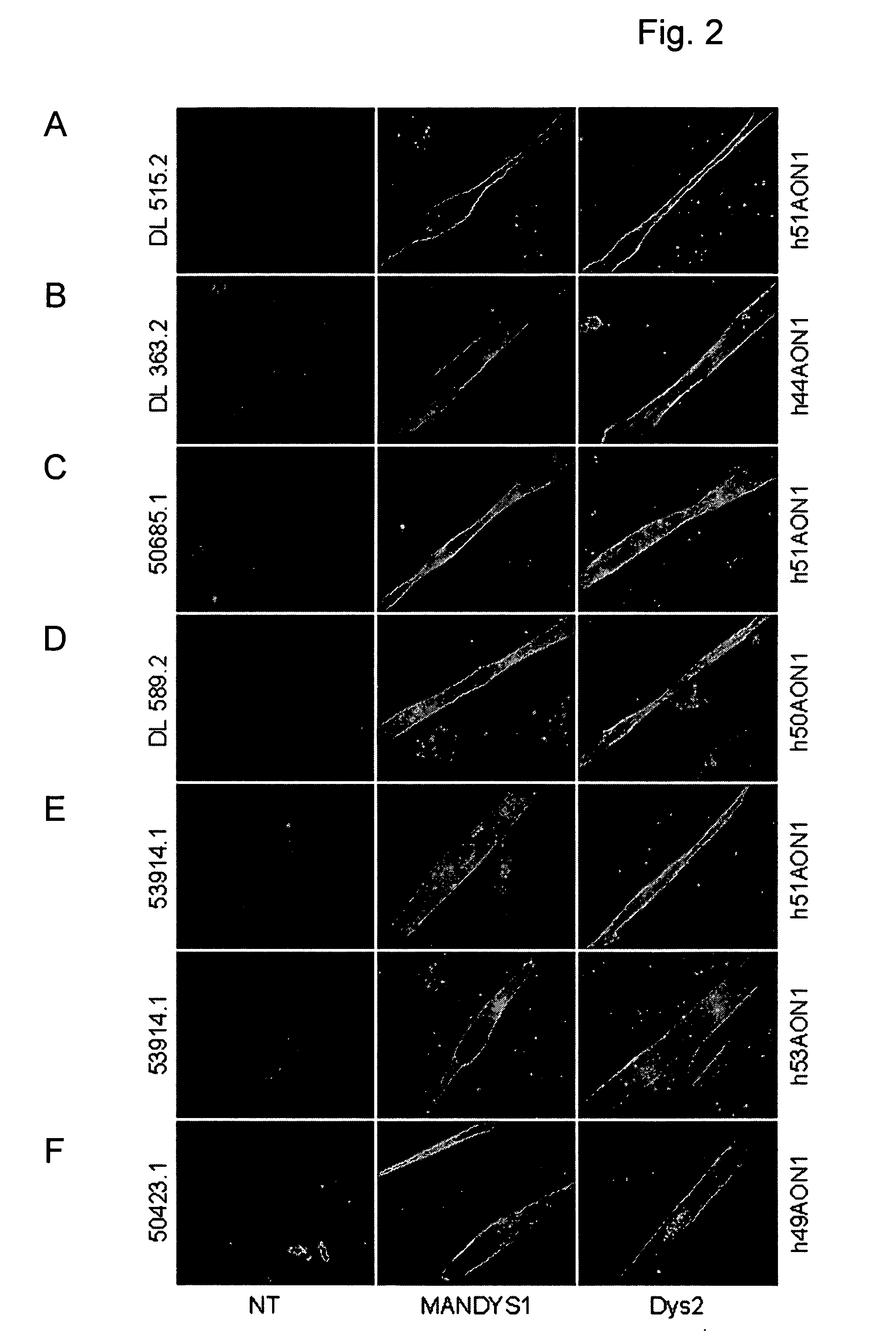
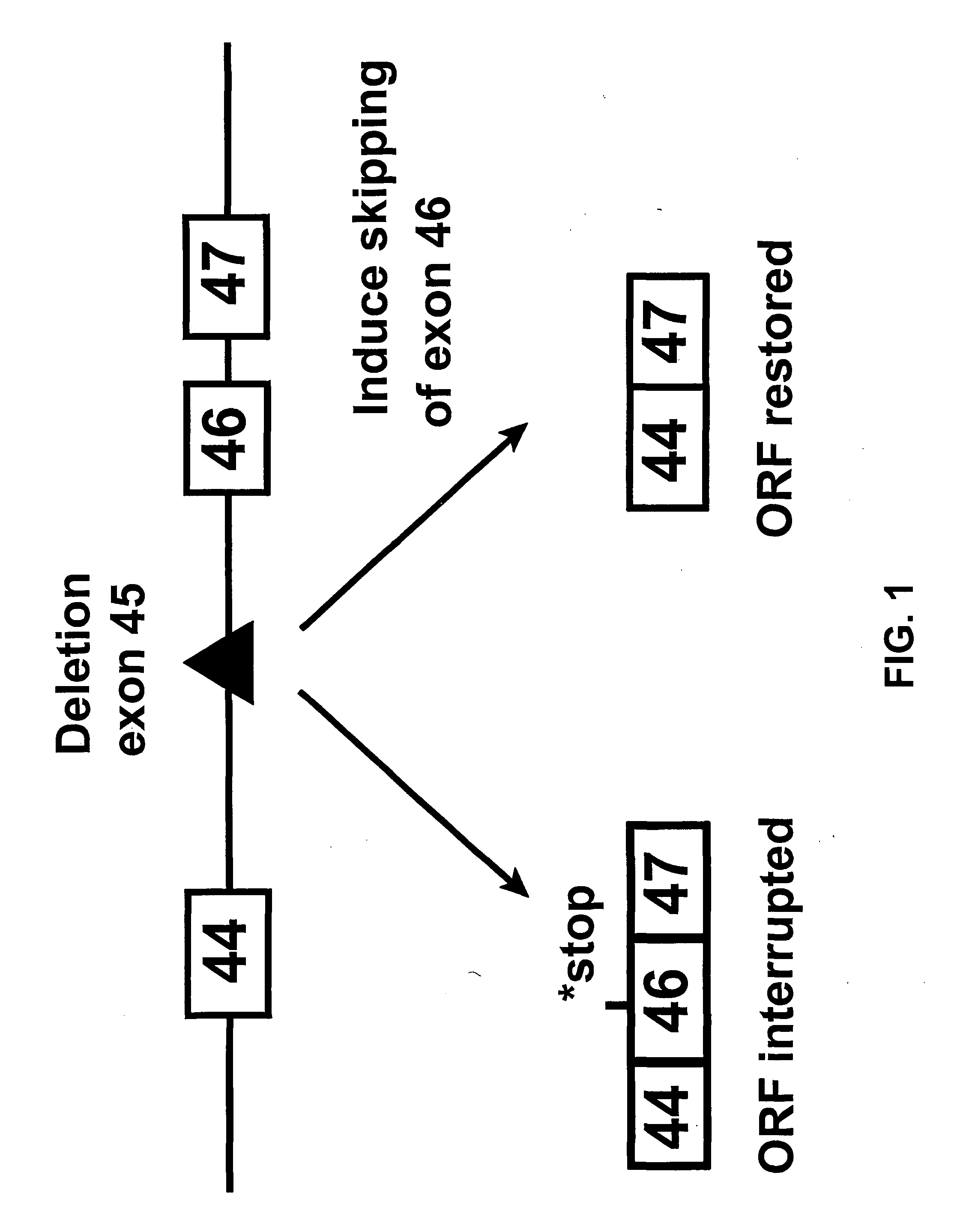
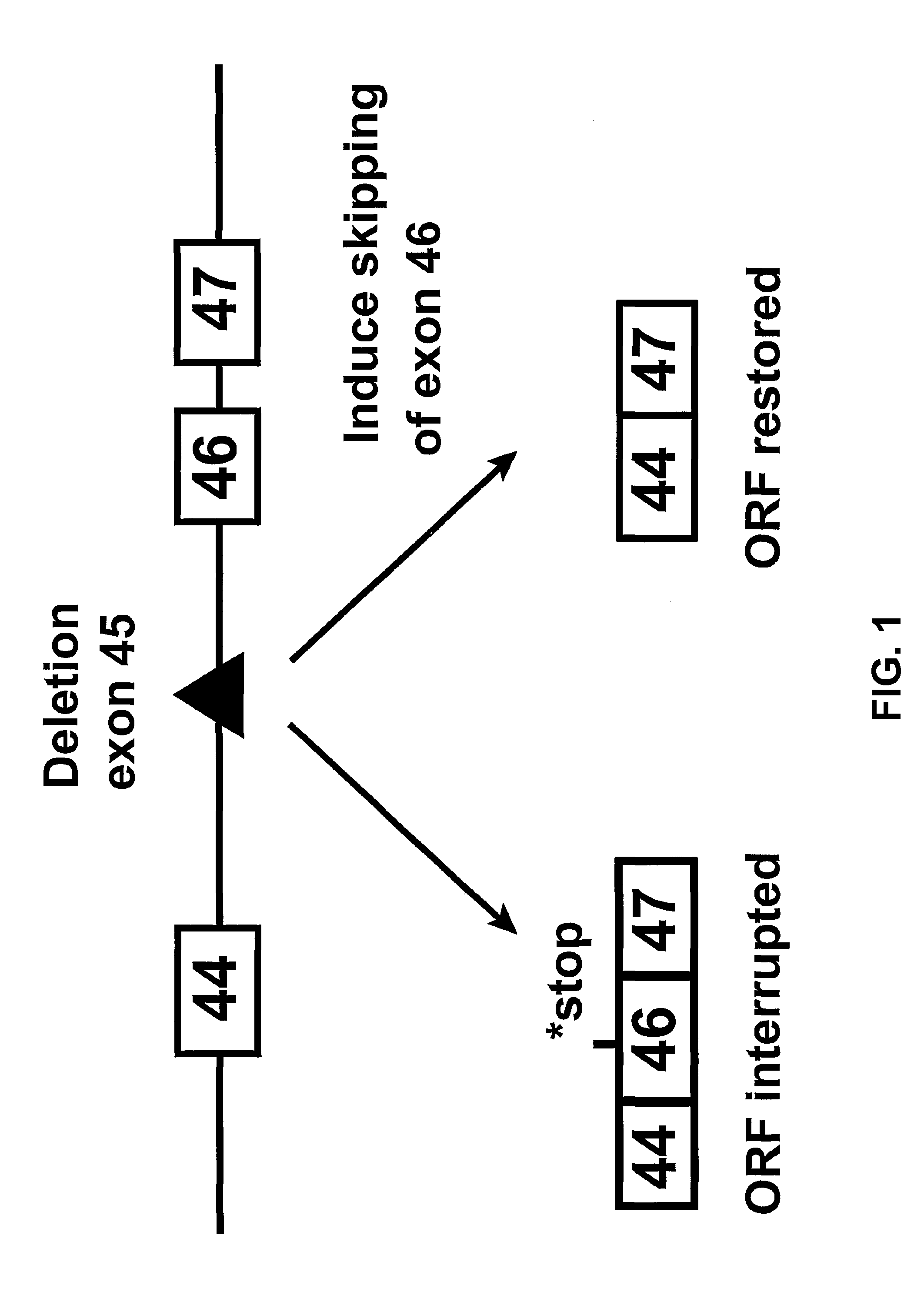
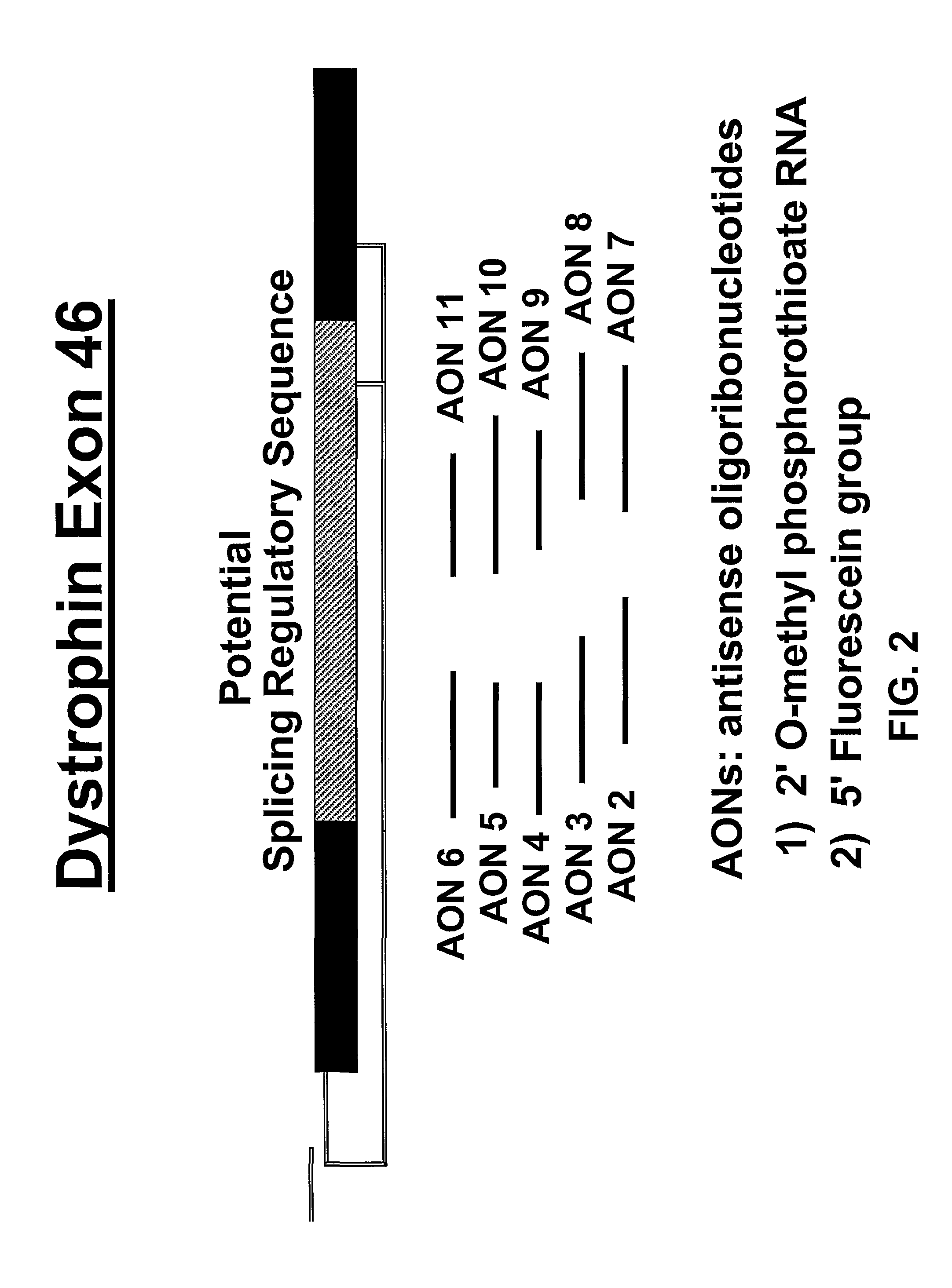
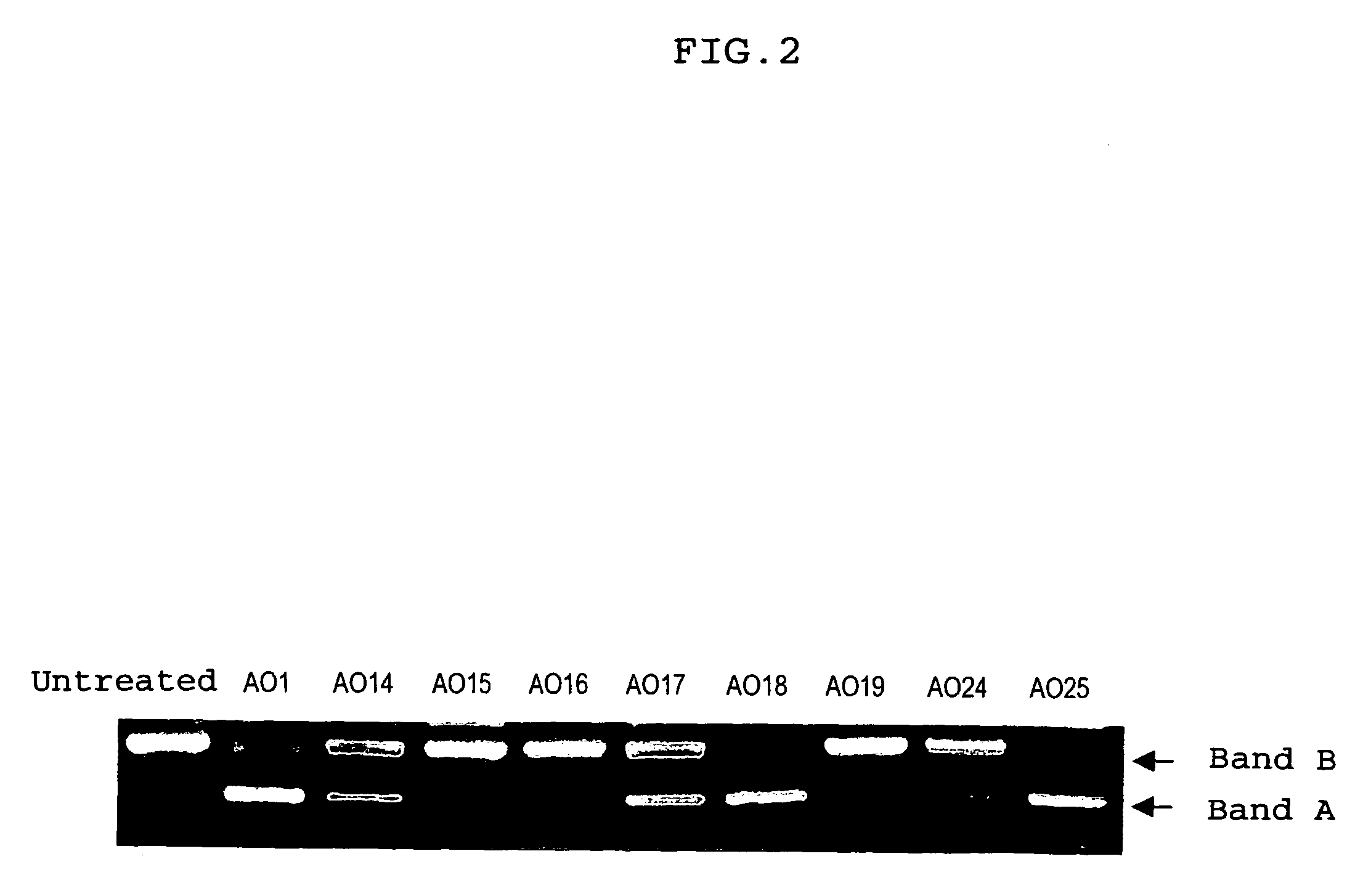
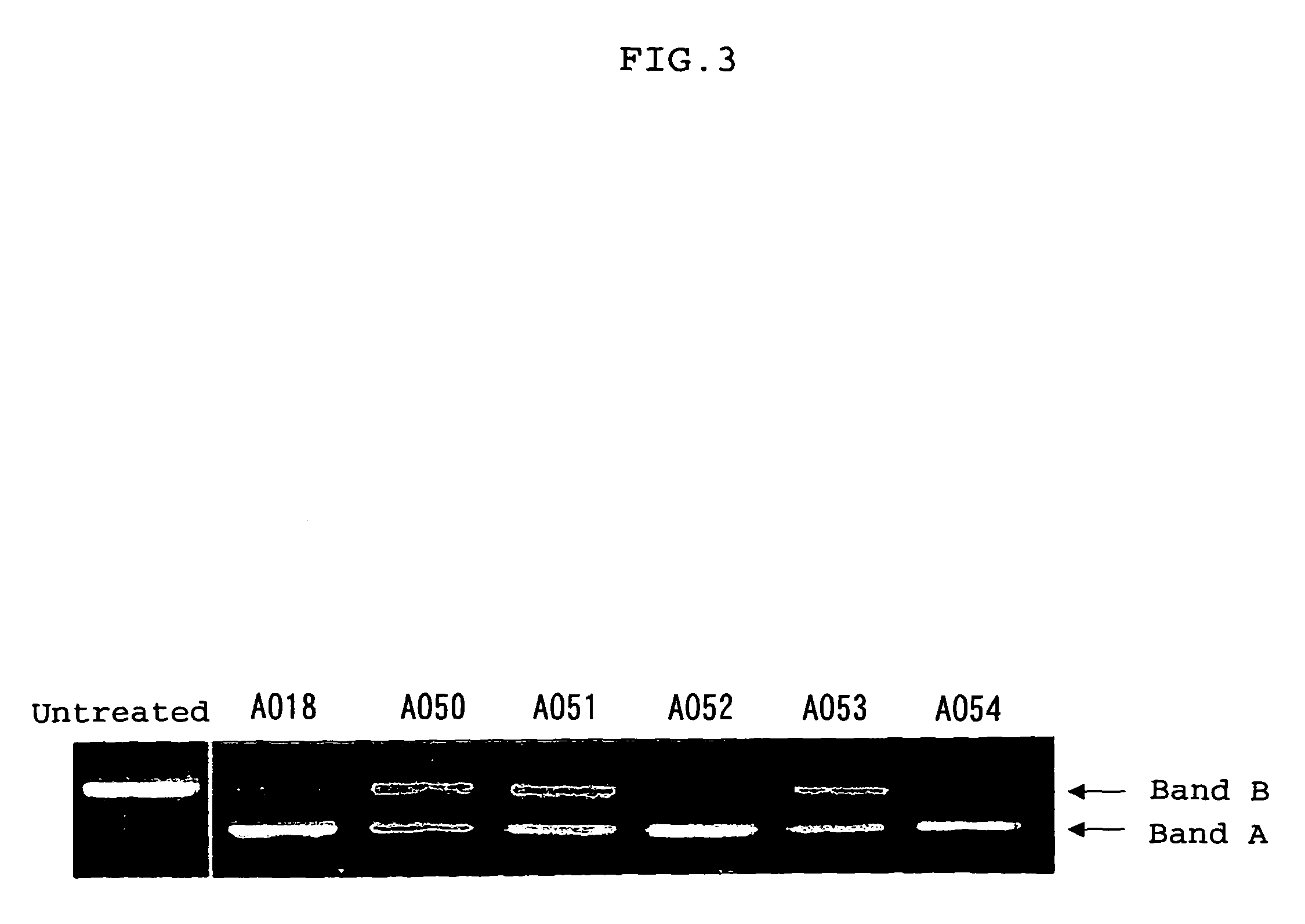
Induction of exon skipping in eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS7973015B2Efficiently maskedPotential for manipulationOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationPrecursor mRNARecognition sequence
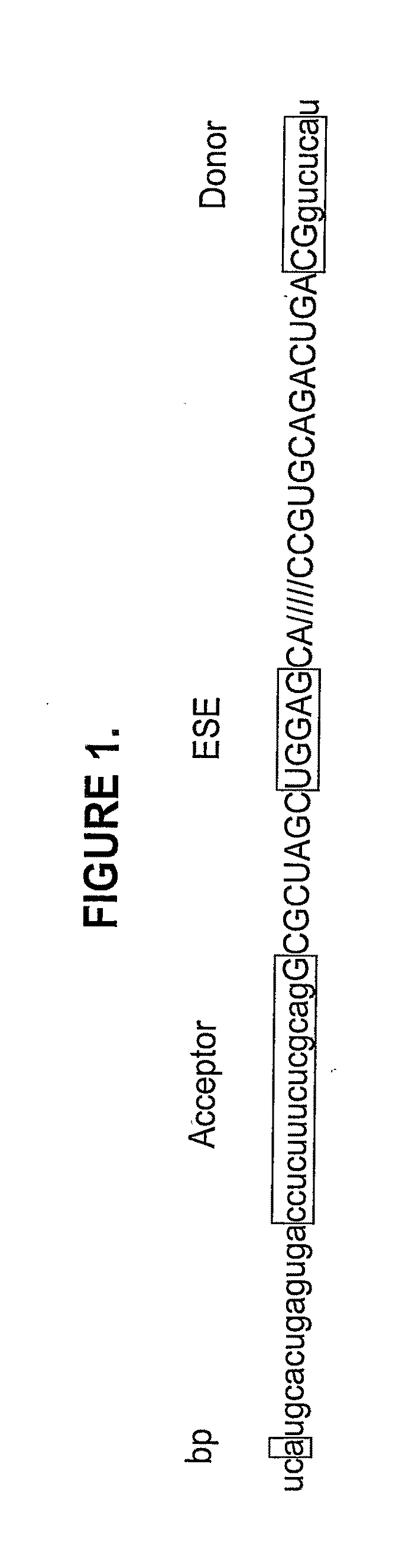
The present invention provides a method for at least in part decreasing the production of an aberrant protein in a cell, the cell comprising pre-mRNA comprising exons coding for the protein, by inducing so-called exon skipping in the cell. Exon-skipping results in mature MRNA that does not contain the skipped exon, which leads to an altered product of the exon codes for amino acids. Exon skipping is performed by providing a cell with an agent capable of specifically inhibiting an exon inclusion signal, for instance, an exon recognition sequence, of the exon. The exon inclusion signal can be interfered with by a nucleic acid comprising complementarity to a part of the exon. The nucleic acid, which is also herewith provided, can be used for the preparation of a medicament, for instance, for the treatment of an inherited disease.
Owner:LEIDEN ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS
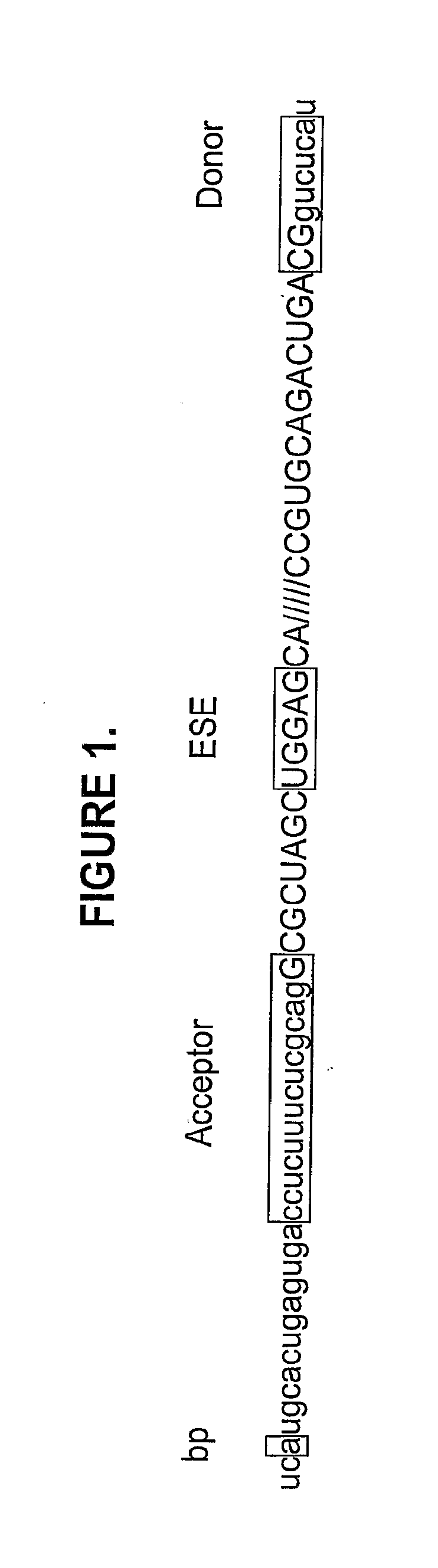
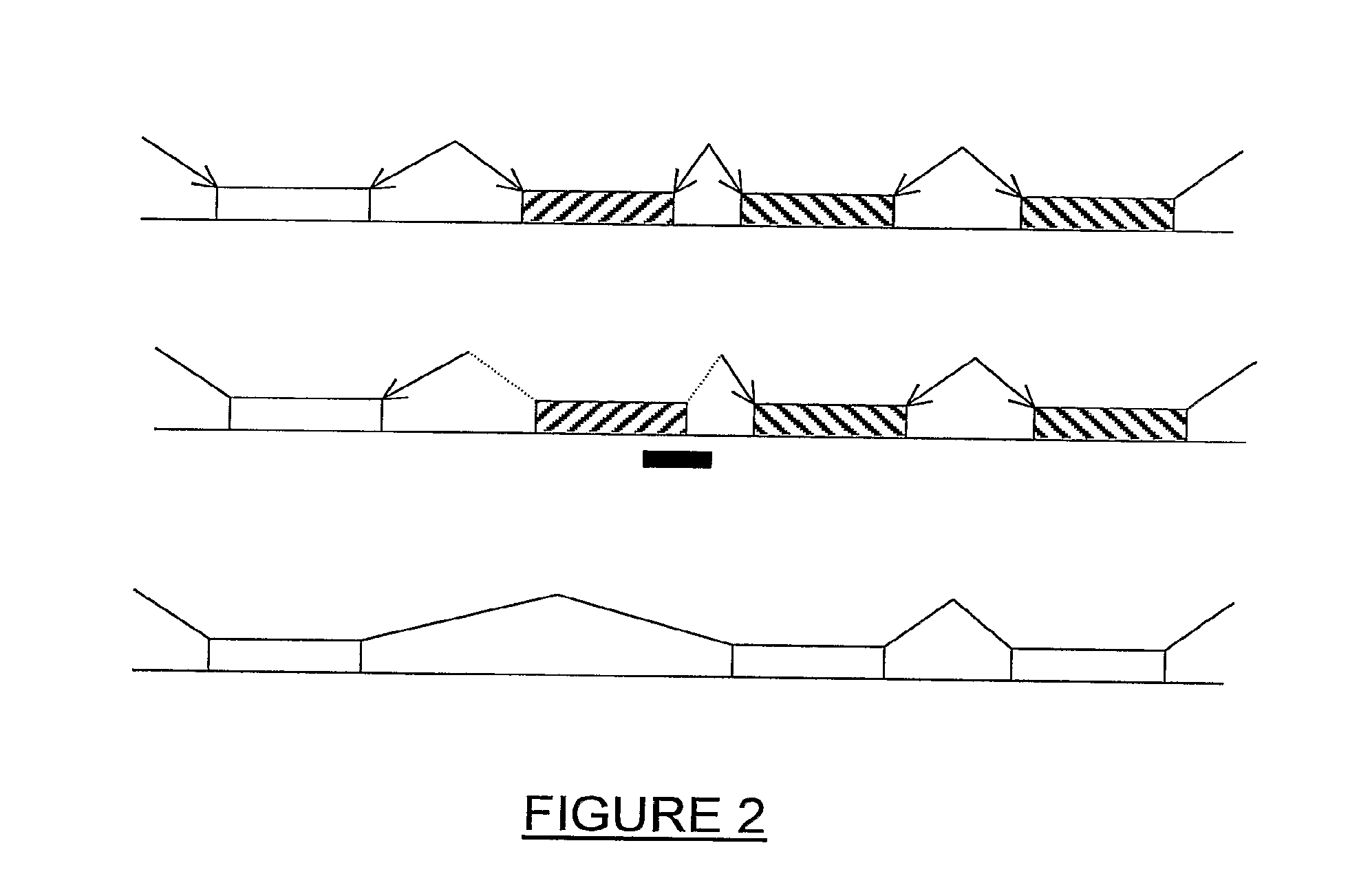
Modulation of exon recognition in pre-mRNA by interfering with the secondary RNA structure
InactiveUS20060099616A1Improves invasion efficiencyImprove efficiencySplicing alterationSugar derivativesPrecursor mRNAOligonucleotide
The invention provides a method for generating an oligonucleotide with which an exon may be skipped in a pre-mRNA and thus excluded from a produced mRNA thereof. Further provided are methods for altering the secondary structure of an mRNA to interfere with splicing processes and uses of the oligonucleotides and methods in the treatment of disease. Further provided are pharmaceutical compositions and methods and means for inducing skipping of several exons in a pre-mRNA.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
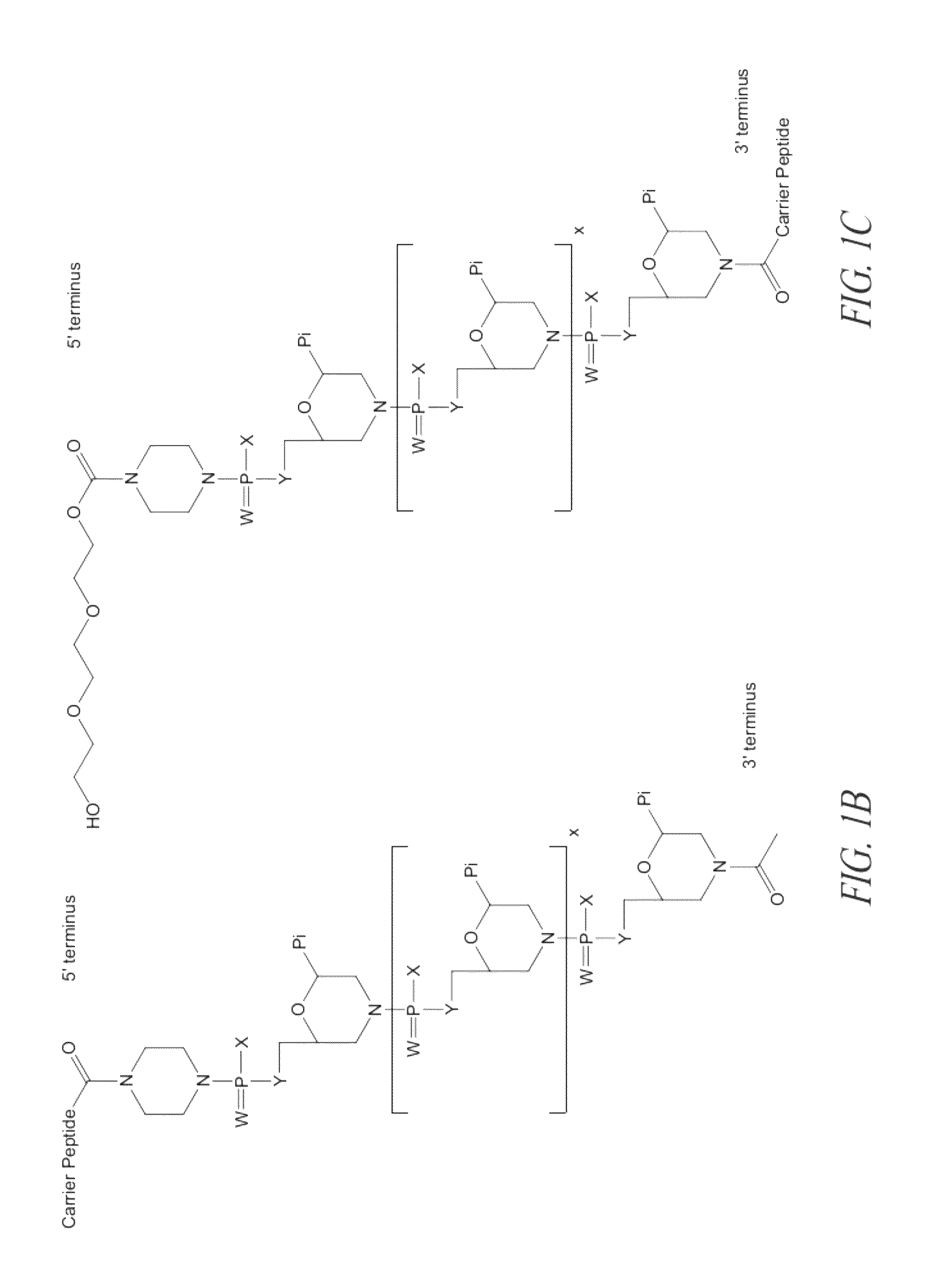
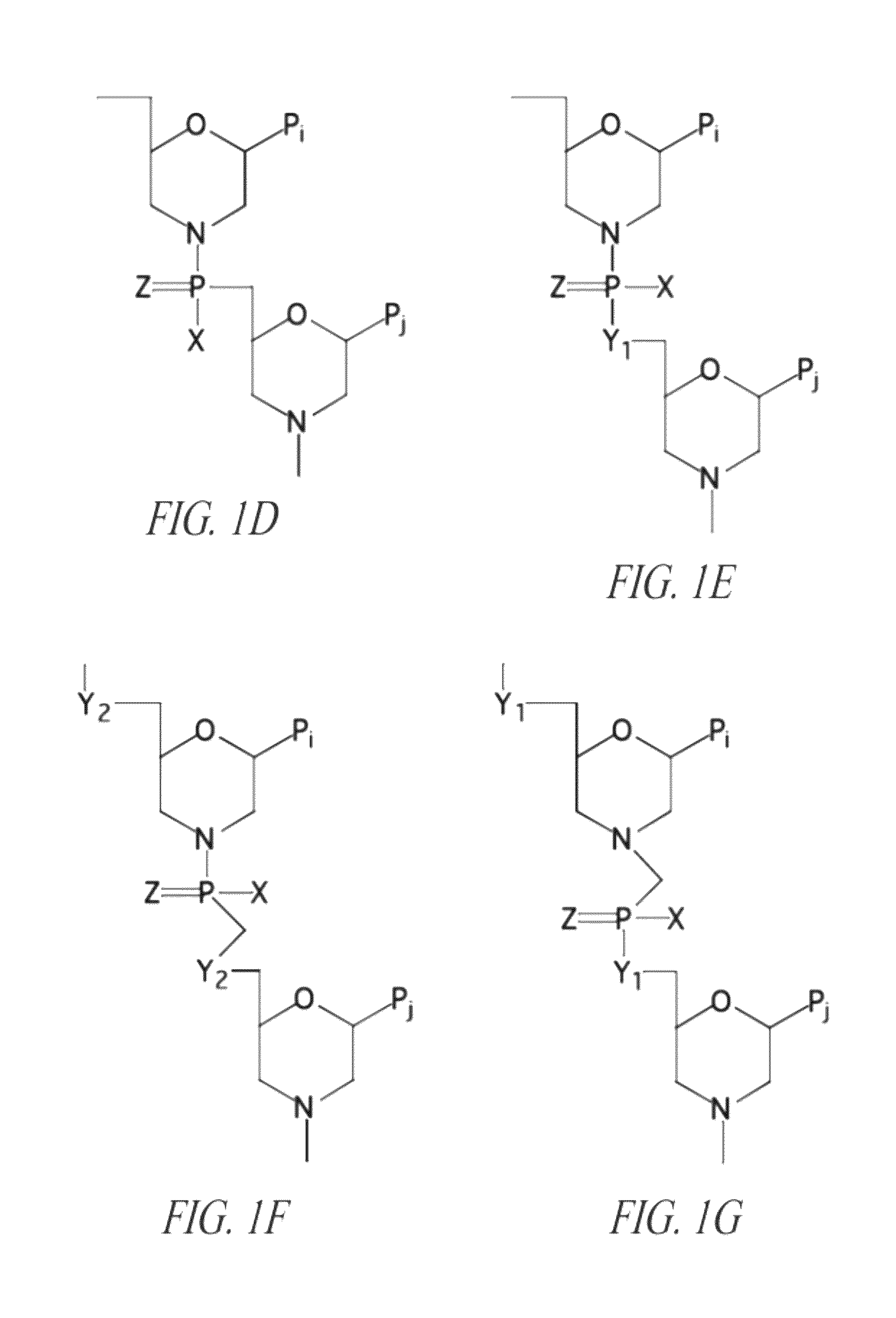
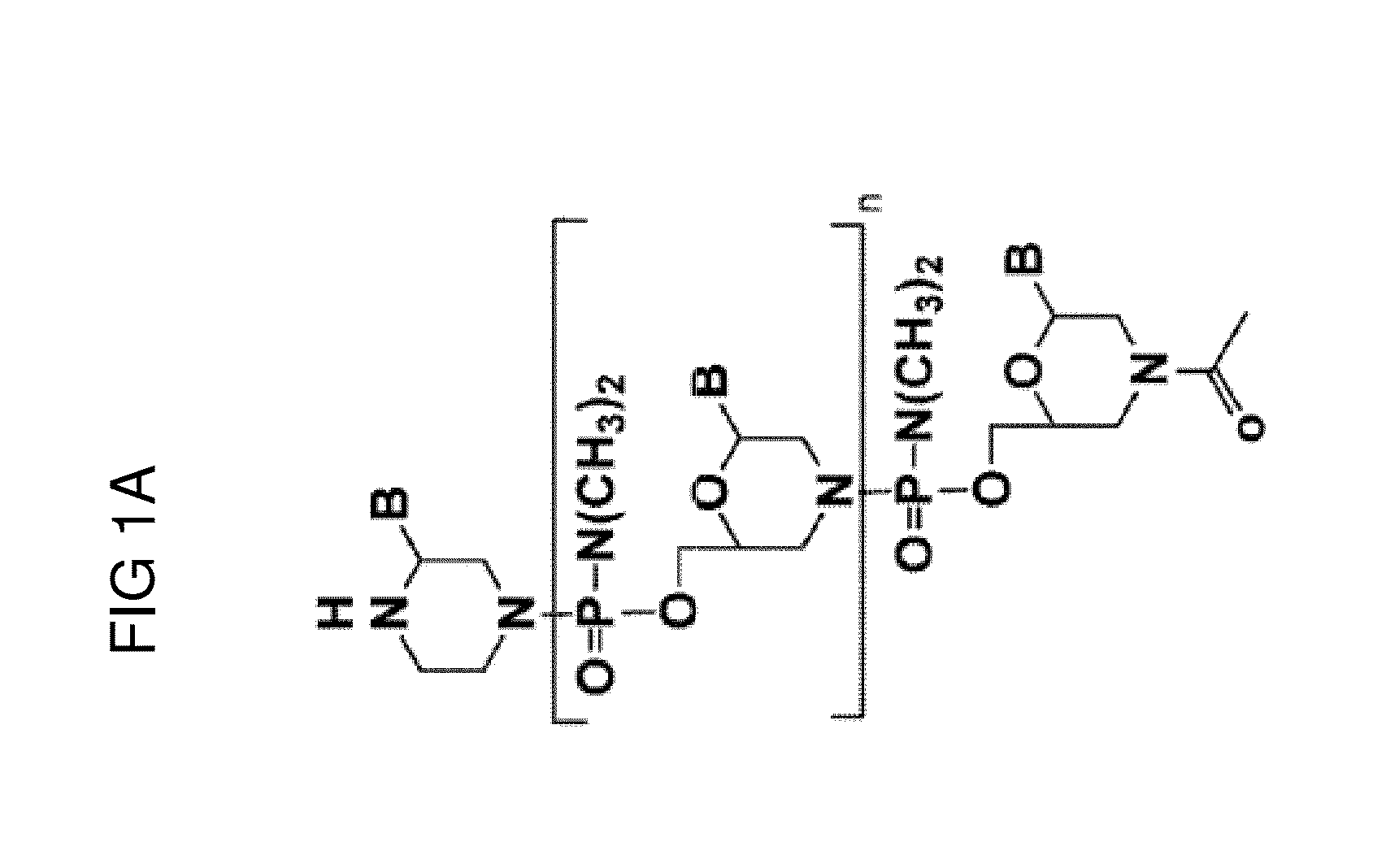
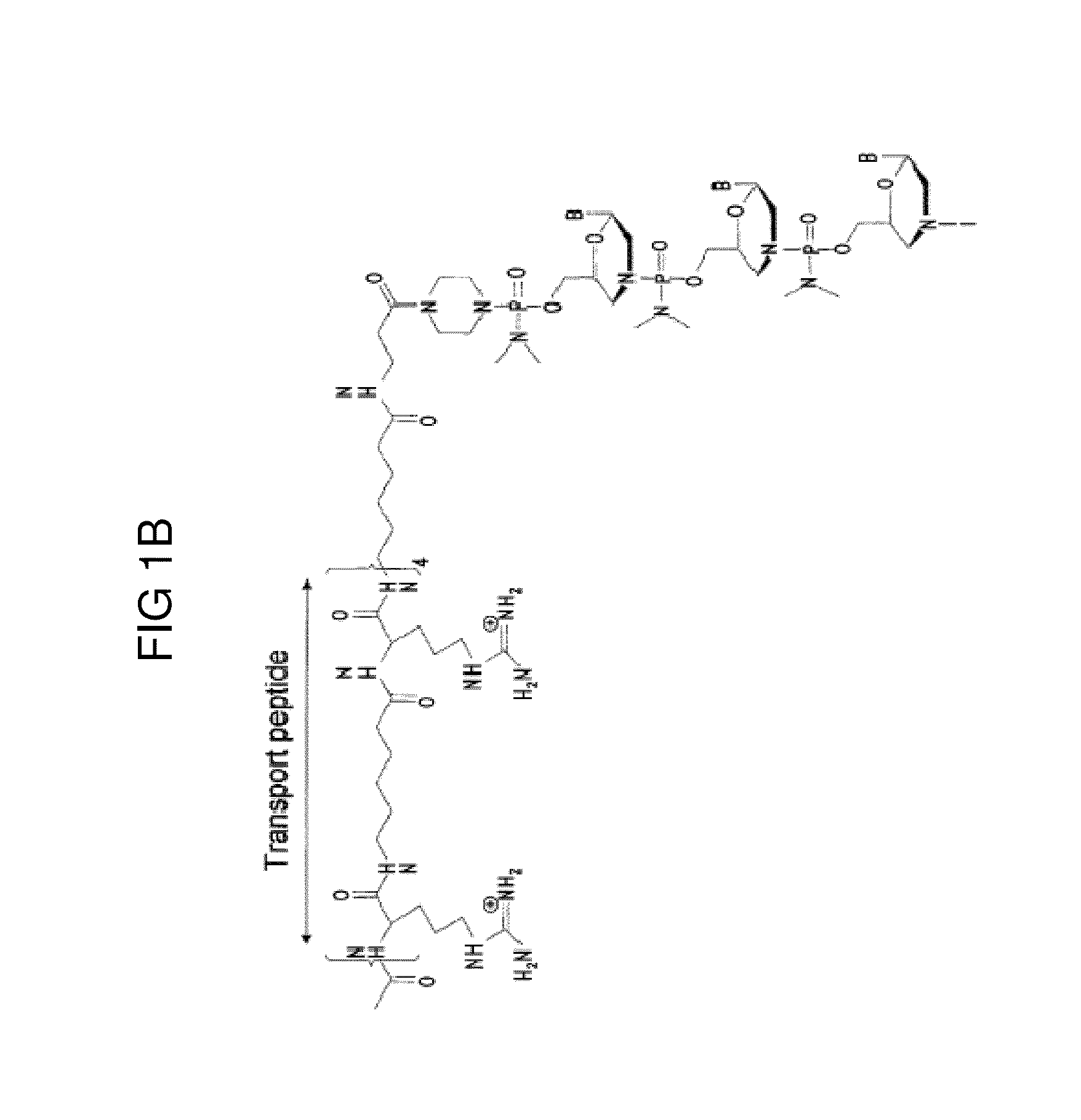
Peptide oligonucleotide conjugates
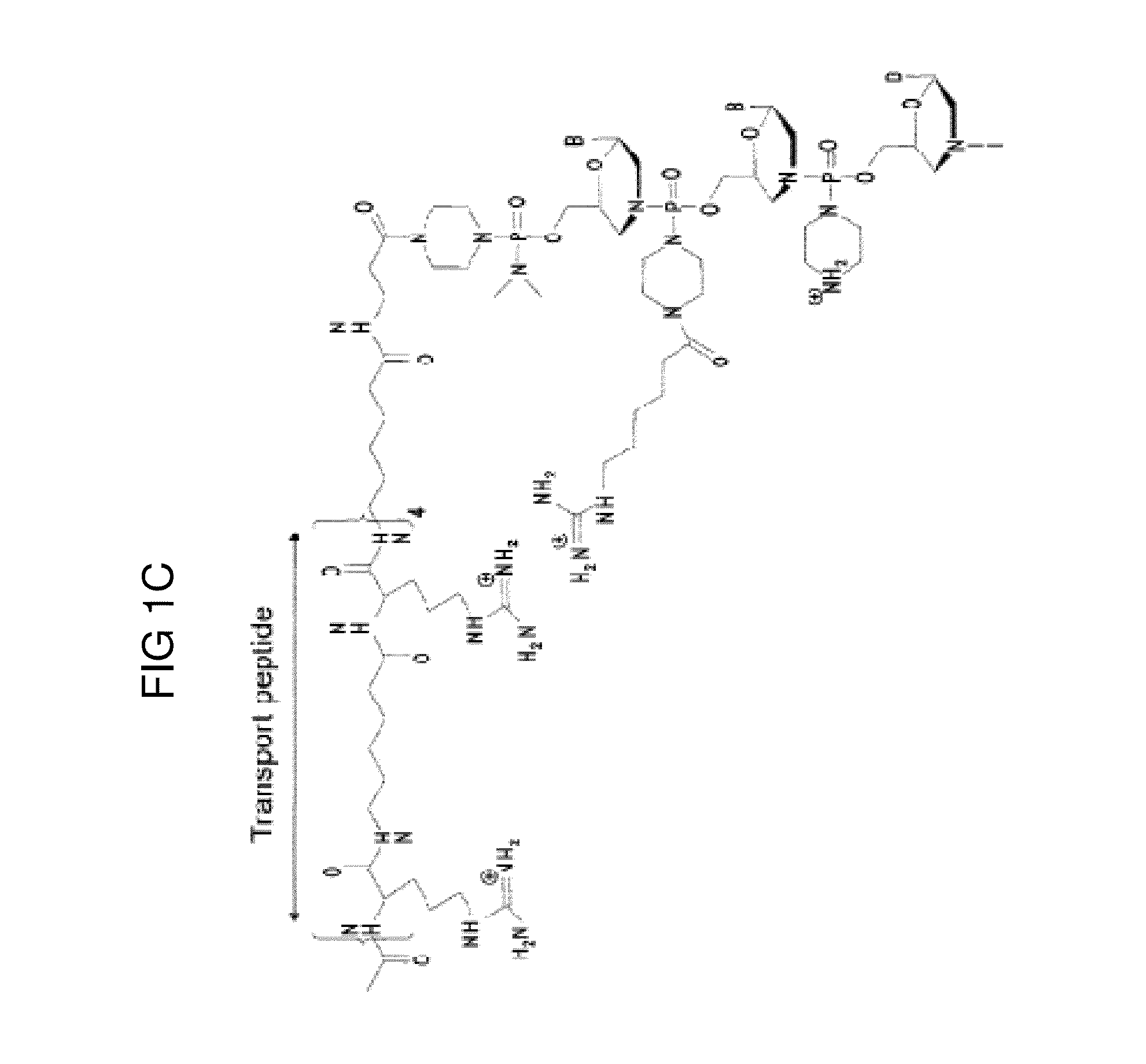
ActiveUS20120289457A1Easy to transportImprove propertiesAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseADAMTS Proteins
Oligonucleotide analogues conjugated to carrier peptides are provided. The disclosed compounds are useful for the treatment of various diseases, for example diseases where inhibition of protein expression or correction of aberrant mRNA splice products produces beneficial therapeutic effects.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Ena nucleic acid drugs modifying splicing in mrna precursor
ActiveUS20070082861A1Efficient processImprove bindingSplicing alterationSugar derivativesGene bankDystrophin
Oligonucleotides having a nucleotide sequence complementary to nucleotide numbers such as 2571-2607, 2578-2592, 2571-2592, 2573-2592, 2578-2596, 2578-2601 or 2575-2592 of the dystrophin cDNA (Gene Bank accession No. NM_004006.1) and therapeutic agents for muscular dystrophy comprising such oligonucleotides.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Modulation of exon recognition in pre-mRNA by interfering with the secondary RNA structure
ActiveUS20060147952A1Lower Level RequirementsSevere phenotypeSplicing alterationSugar derivativesDiseasePrecursor mRNA
The invention provides a method for generating an oligonucleotide with which an exon may be skipped in a pre-mRNA and thus excluded from a produced mRNA thereof. Further provided are methods for altering the secondary structure of an mRNA to interfere with splicing processes and uses of the oligonucleotides and methods in the treatment of disease. Further provided are pharmaceutical compositions and methods and means for inducing skipping of several exons in a pre-mRNA.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
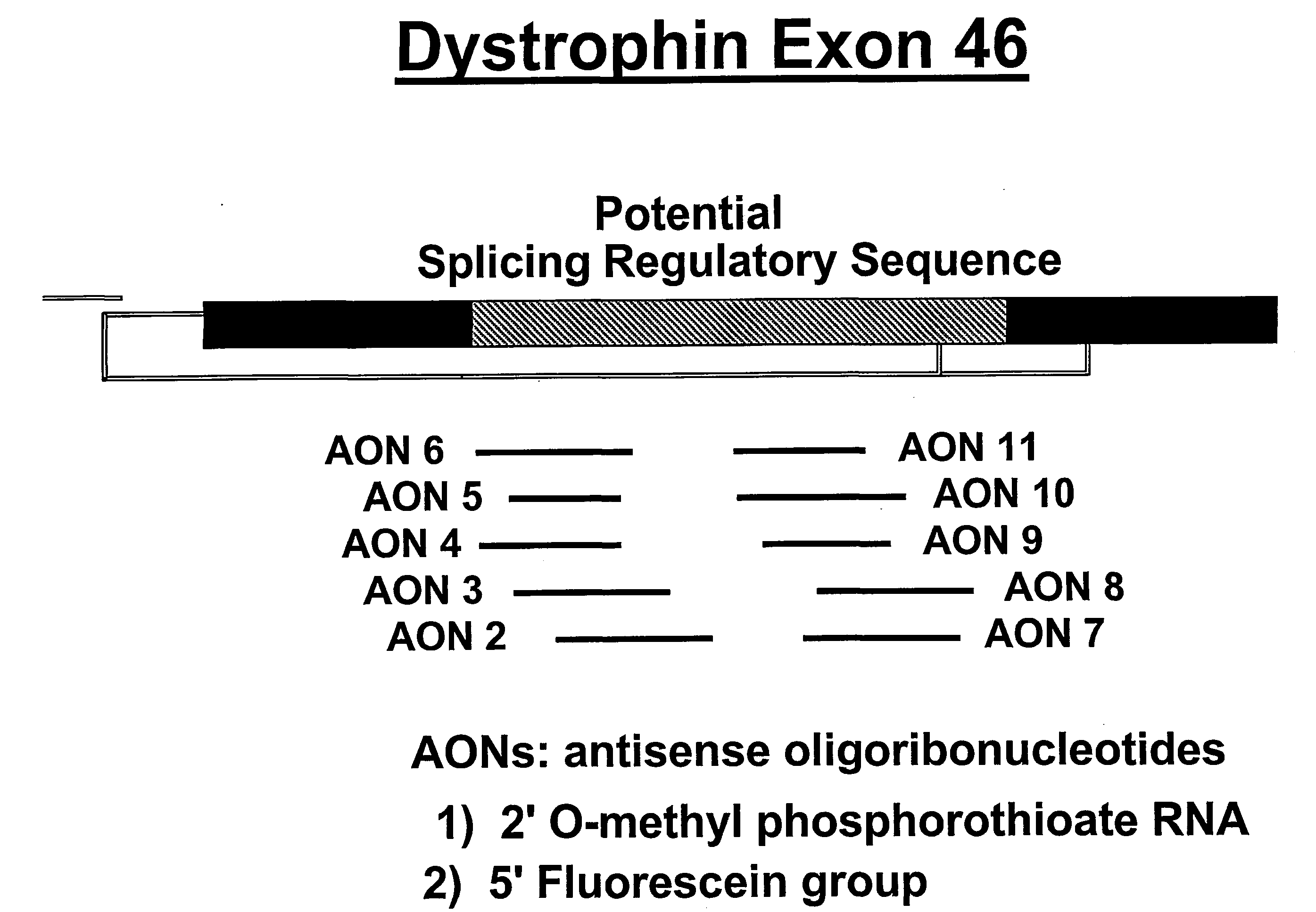
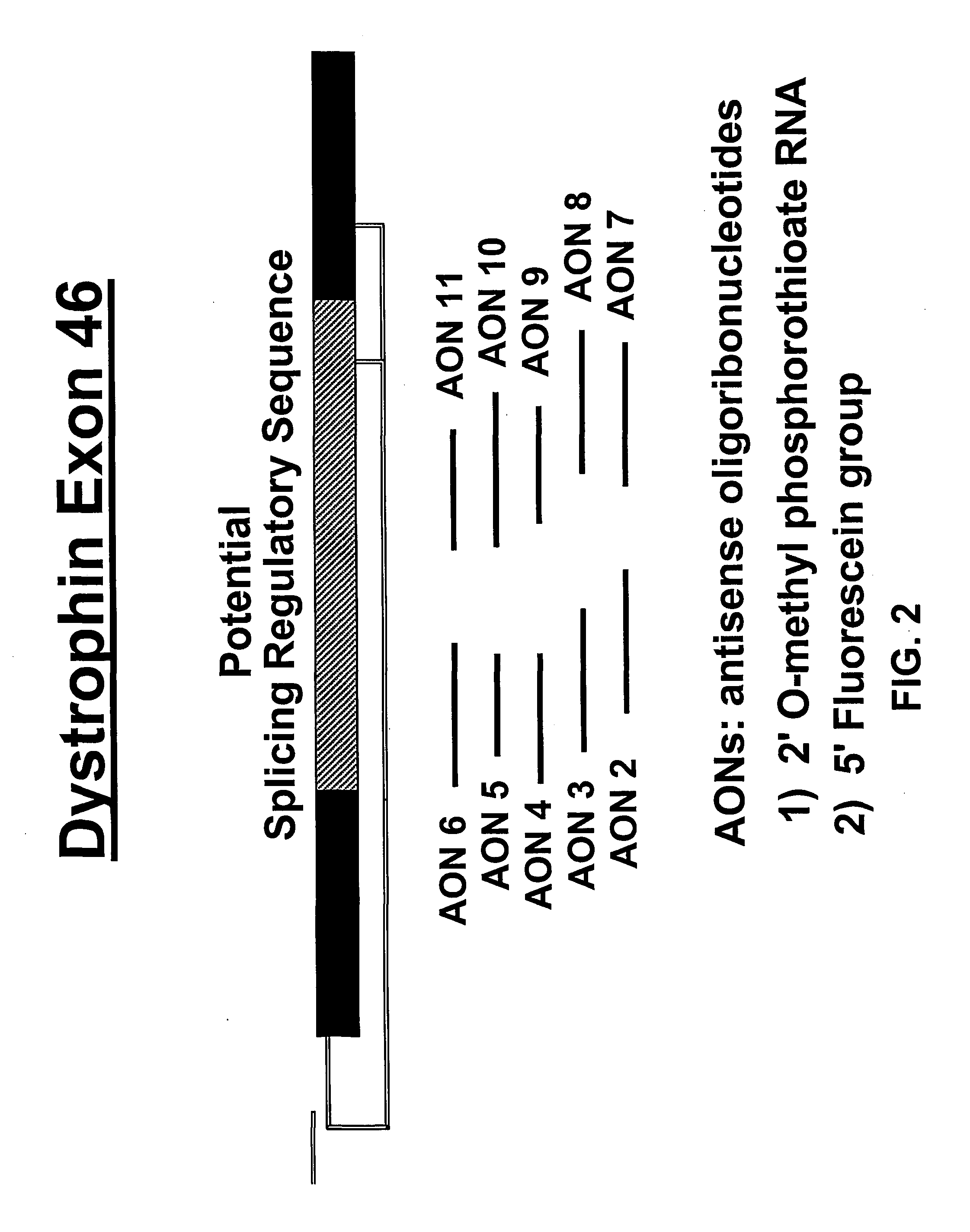
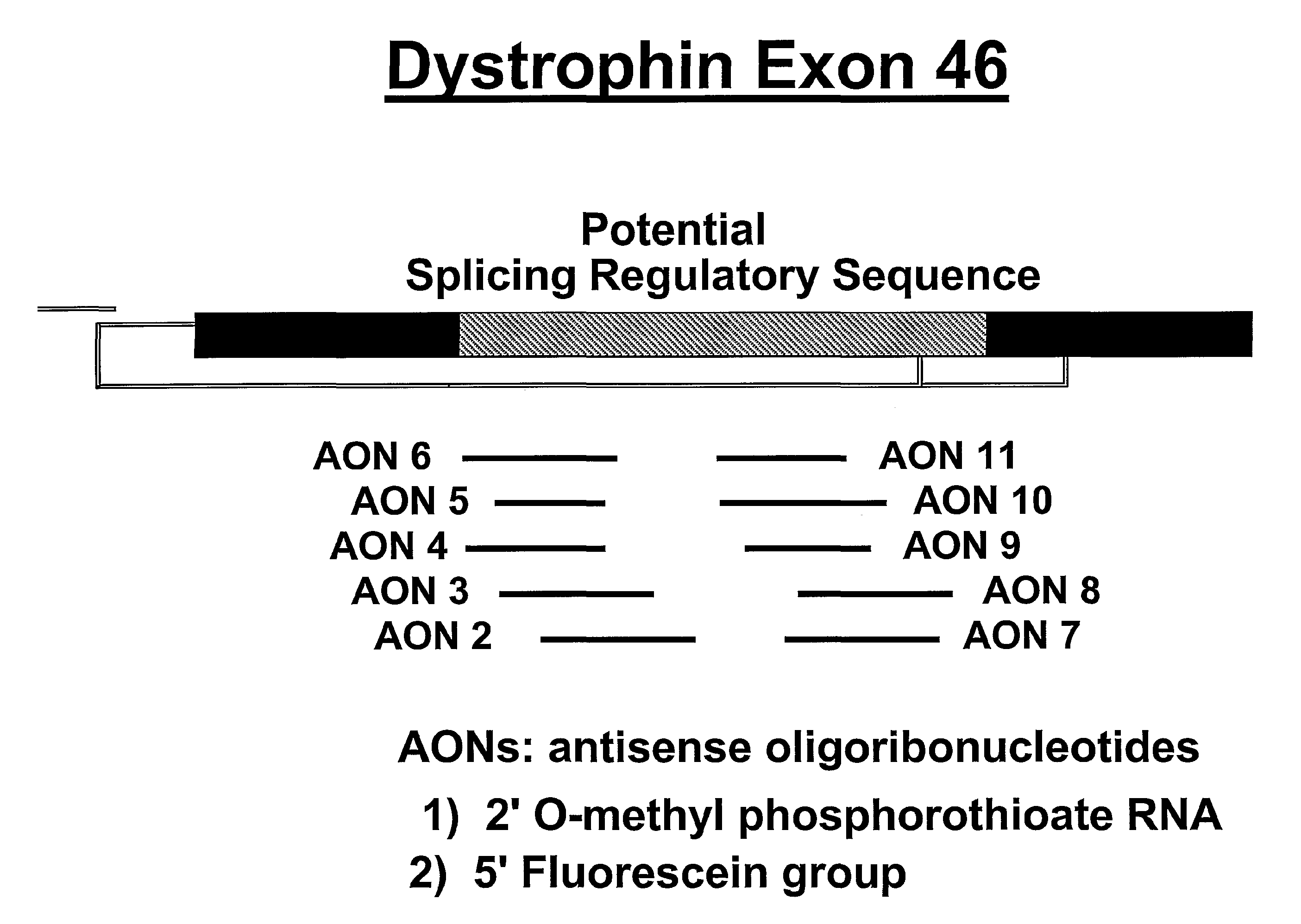
Methods and means for efficient skipping of at least one of the following exons of the human duchenne muscular dystrophy gene: 43, 46, 50-53
InactiveUS20110263682A1Improve featuresMany symptomOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationMedicinePrecursor mRNA
The invention relates a method wherein a molecule is used for inducing and / or promoting skipping of at least one of exon 43, exon 46, exons 50-53 of the DMD pre-mRNA in a patient, preferably in an isolated cell of a patient, the method comprising providing said cell and / or said patient with a molecule. The invention also relates to said molecule as such.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT +2
Compositions and methods for modulation of smn2 splicing in a subject
ActiveUS20120190728A1Increase inclusivenessOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationDiseasePharmaceutical drug
Disclosed herein are compounds, compositions and methods for modulating splicing of SMN2 mRNA in a subject. Also provided are uses of disclosed compounds and compositions in the manufacture of a medicament for treatment of diseases and disorders, including spinal muscular atrophy.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC +1
Antisense oligonucleotides for inducing exon skipping and methods of use thereof
An antisense molecule capable of binding to a selected target site to induce exon skipping in the dystrophin gene, as set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1 to 202.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA
Induction of exon skipping in eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20090228998A1Efficiently maskedPotential for manipulationOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationPrecursor mRNARecognition sequence
The present invention provides a method for at least in part decreasing the production of an aberrant protein in a cell, the cell comprising pre-mRNA comprising exons coding for the protein, by inducing so-called exon skipping in the cell. Exon-skipping results in mature mRNA that does not contain the skipped exon, which leads to an altered product of the exon codes for amino acids. Exon skipping is performed by providing a cell with an agent capable of specifically inhibiting an exon inclusion signal, for instance, an exon recognition sequence, of the exon. The exon inclusion signal can be interfered with by a nucleic acid comprising complementarity to a part of the exon. The nucleic acid, which is also herewith provided, can be used for the preparation of a medicament, for instance, for the treatment of an inherited disease.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
Induction of exon skipping in eukaryotic cells
InactiveUS20080209581A1Reduce productionReduce amountOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationPrecursor mRNARecognition sequence
Described is a method for at least in part decreasing the production of an aberrant protein in a cell, the cell comprising pre-mRNA comprising exons coding for the protein, by inducing so-called exon skipping in the cell. Exon-skipping results in mature mRNA that does not contain the skipped exon, which leads to an altered product of the exon codes for amino acids. Exon skipping is performed by providing a cell with an agent capable of specifically inhibiting an exon inclusion signal, for instance, an exon recognition sequence, of the exon. The exon inclusion signal can be interfered with by a nucleic acid comprising complementarity to a part of the exon. The nucleic acid, which is also herewith provided, can be used for the preparation of a medicament, for instance, for the treatment of an inherited disease.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
Antisense oligonucleotides for inducing exon skipping and methods of use thereof
An antisense molecule capable of binding to a selected target site to induce exon skipping in the dystrophin gene, as set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1 to 202.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA
ENA nucleic acid drugs modifying splicing in mRNA precursor
ActiveUS7902160B2Efficient processImprove bindingSplicing alterationSugar derivativesNucleotideDystrophin
Oligonucleotides having a nucleotide sequence complementary to nucleotide numbers such as 2571-2607, 2578-2592, 2571-2592, 2573-2592, 2578-2596, 2578-2601 or 2575-2592 of the dystrophin cDNA (Gene Bank accession No. NM_004006.1) and therapeutic agents for muscular dystrophy comprising such oligonucleotides.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Antisense oligonucleotides for inducing exon skipping and methods of use thereof
An antisense molecule capable of binding to a selected target site to induce exon skipping in the dystrophin gene, as set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1 to 202.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA
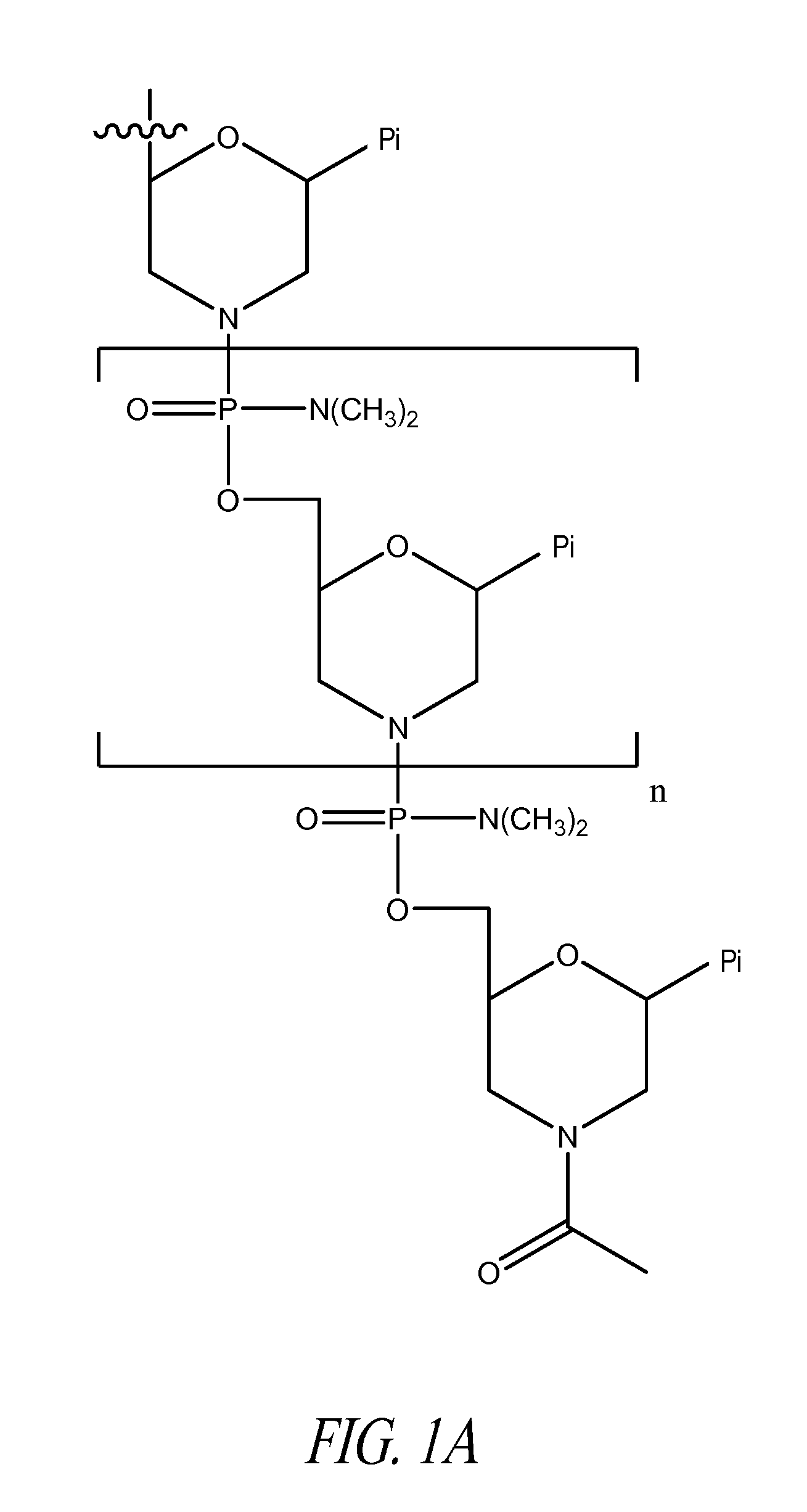
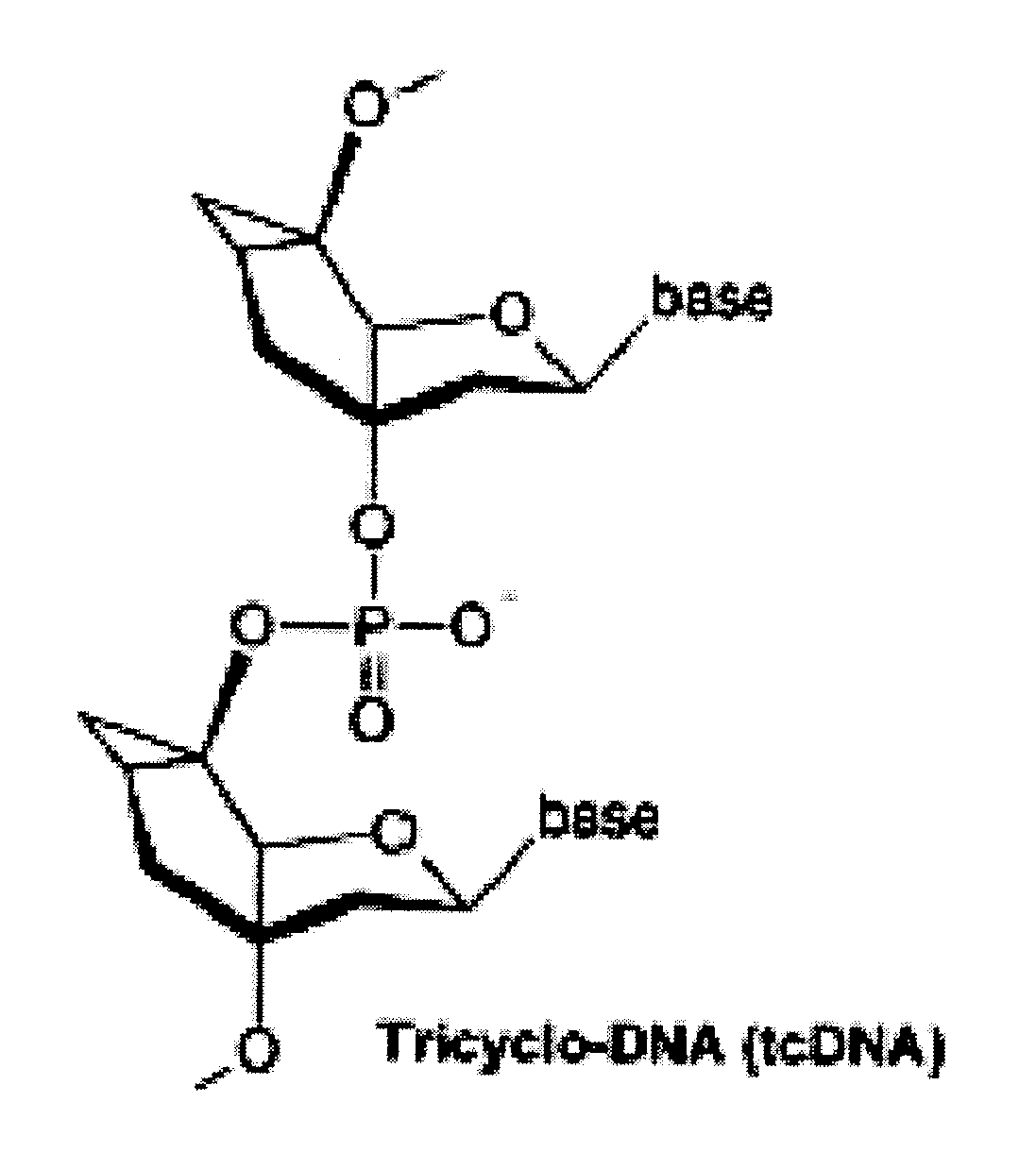
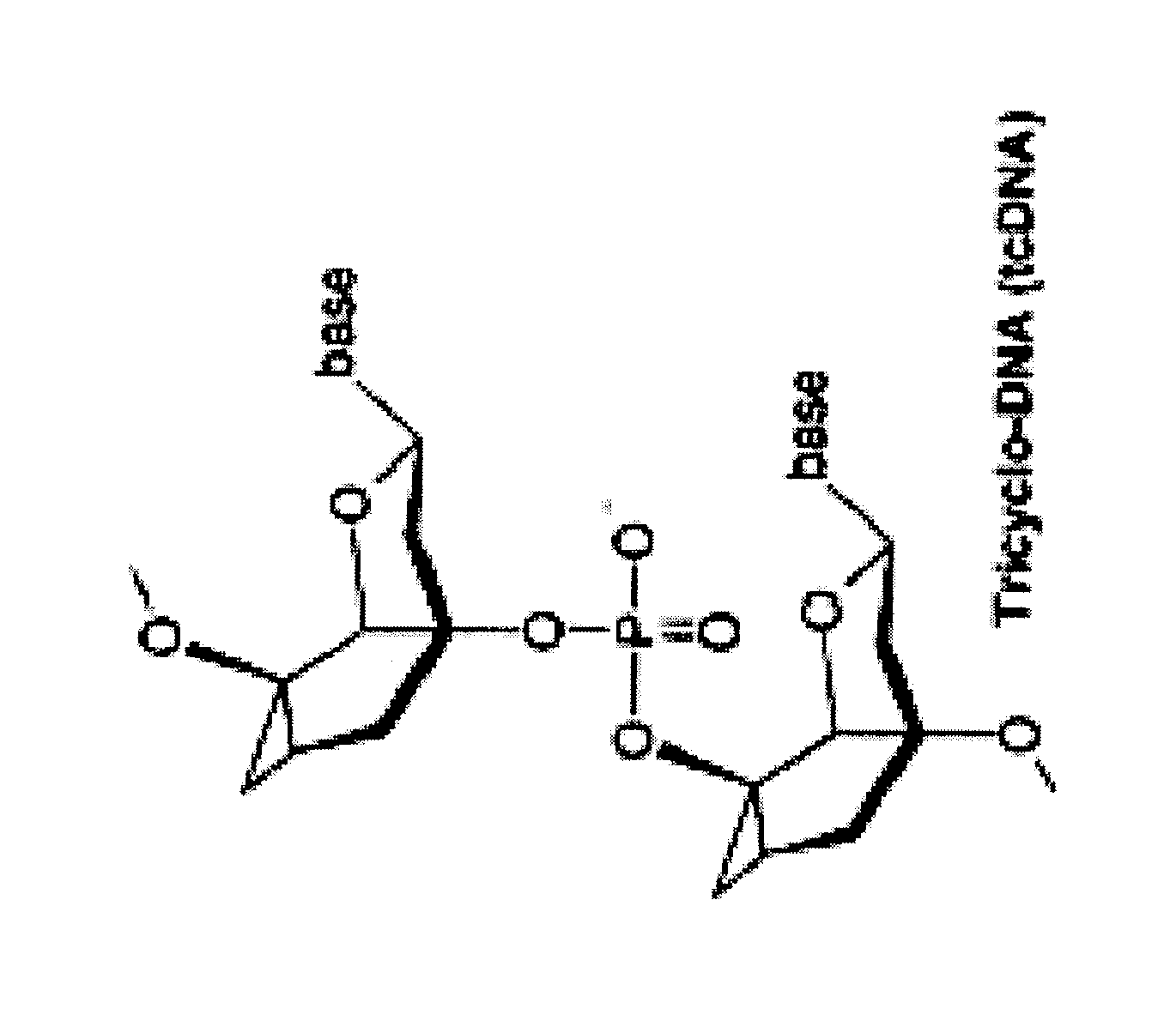
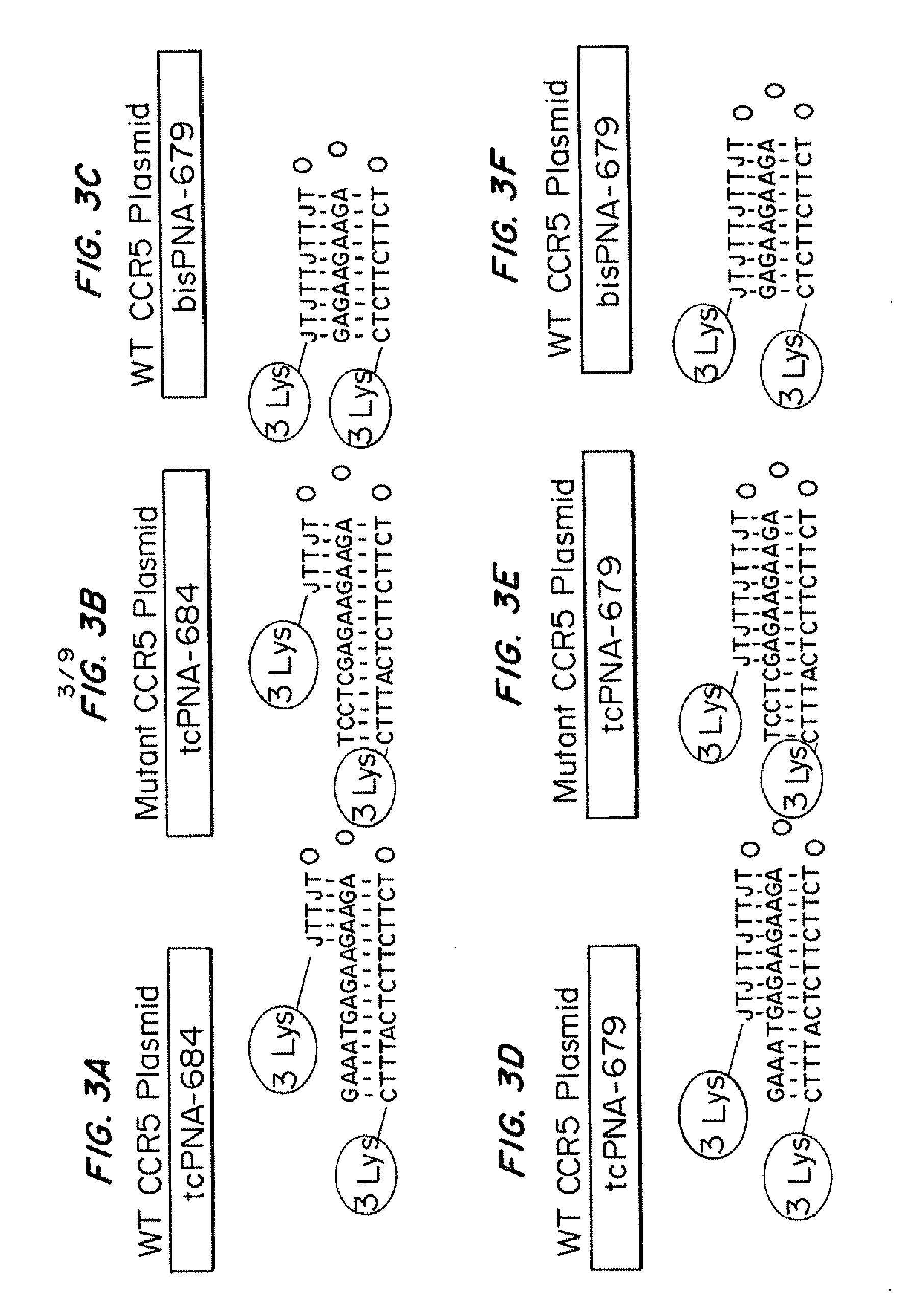
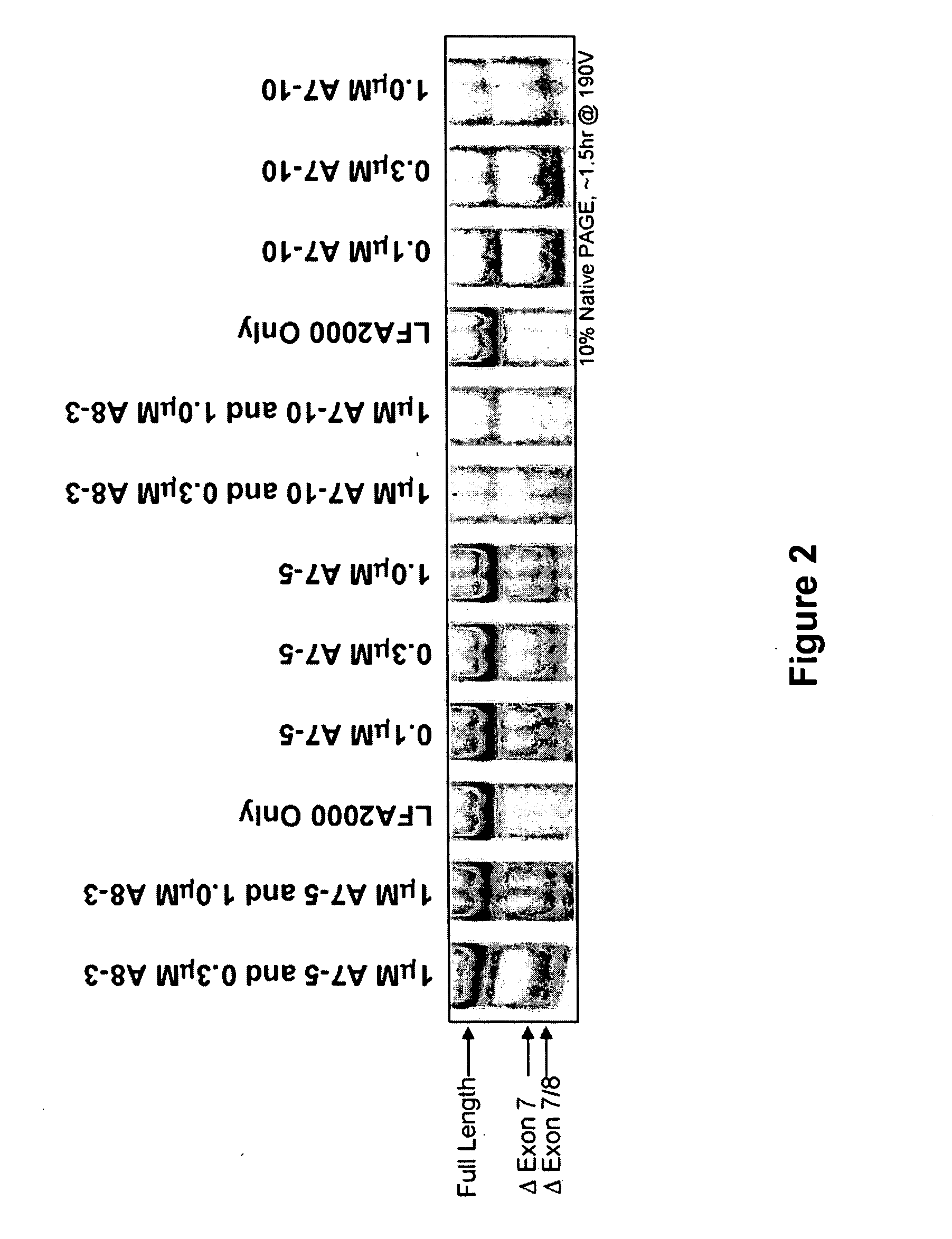
Tricyclo-dna antisense oligonucleotides, compositions, and methods for the treatment of disease
InactiveUS20120149756A1Find utilityFacilitates inclusionOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationDiseasePre mrna processing
Provided are tricyclo-DNA (tc-DNA) AON and methods employing tc-DNA AON for modifying splicing events that occur during pre-mRNA processing. Tricyclo-DNA (tc-DNA) AON are described that may be used to facilitate exon skipping or to mask intronic silencer sequences and / or terminal stem-loop sequences during pre-mRNA processing and to target RNase-mediated destruction of processed mRNA. Tc-DNA AON described herein may be used in methods for the treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy by skipping a mutated exon 23 or exon 51 within a dystrophin gene to restore functionality of a dystrophin protein; in methods for the treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy by masking an intronic silencing sequence and / or a terminal stem-loop sequence within an SMN2 gene to yield modified functional SMN2 protein, including an amino acid sequence encoded by exon 7, which is capable of at least partially complementing a non-functional SMN1 protein; and in methods for the treatment of Steinert's Myotonic Dystrophy by targeting the destruction of a mutated DM1 mRNA comprising 3′-terminal CUG repeats.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +4
Antisense nucleic acids
ActiveUS20130211062A1Improve efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationOligomerAntisense nucleic acid
The present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition which causes skipping of the 53rd exon in the human dystrophin gene with a high efficiency.The present invention provides an oligomer which efficiently enables to cause skipping of the 53rd exon in the human dystrophin gene.
Owner:NIPPON SHINYAKU CO LTD +1
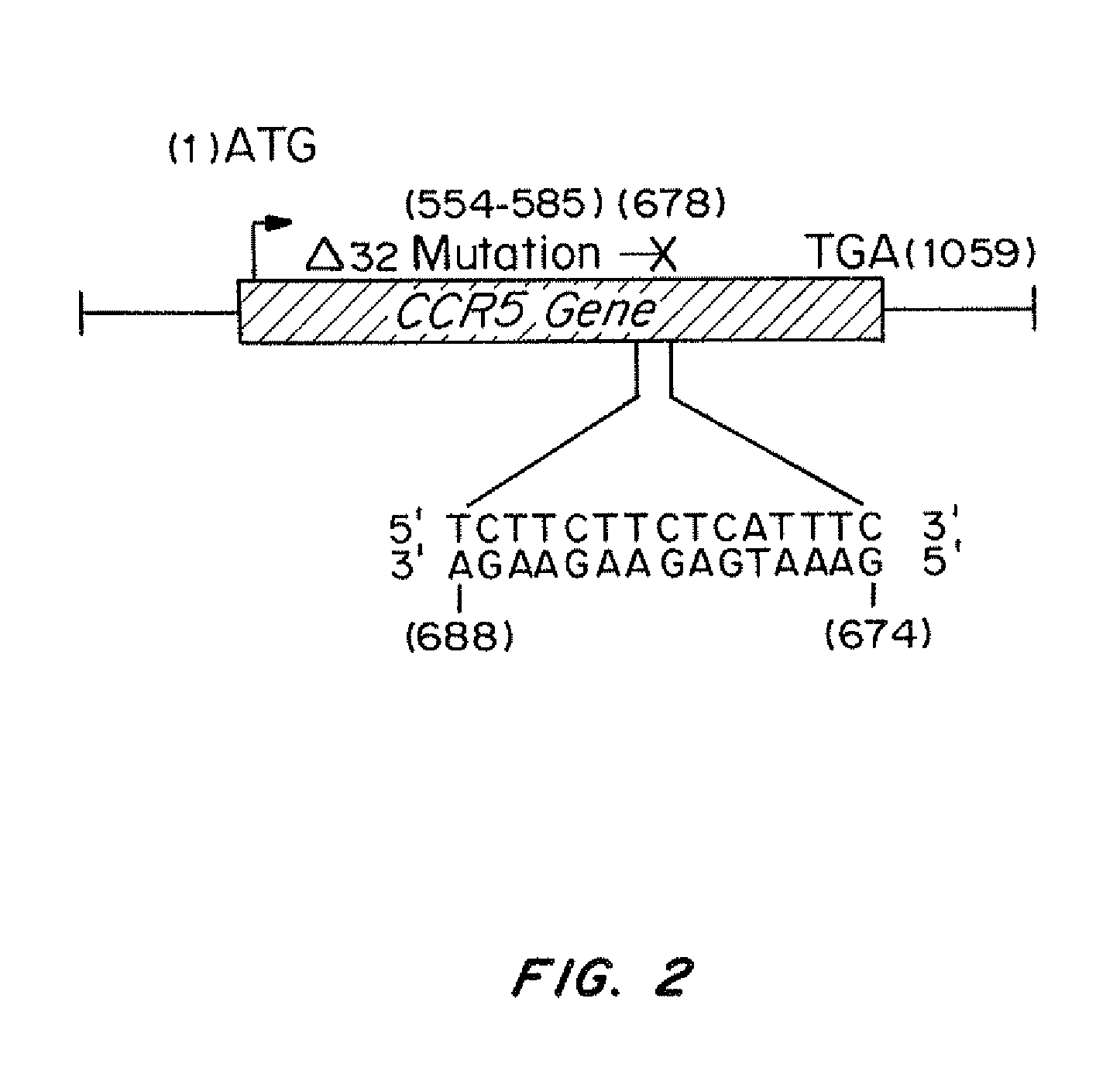
Compositions and methods for targeted inactivation of HIV cell surface receptors
InactiveUS20110262406A1Avoid infectionReduce viral loadBiocideOrganic active ingredientsImmunodeficiency virusTail
Compositions for targeted mutagenesis of cell surface receptors for HIV and methods of their use are provided herein. The compositions include triplex-forming molecules that displace the polypyrimidine strand of target duplex and form a triple-stranded structure and hybrid duplex in a sequence specific manner with the polypurine strand of the target duplex. The triplex-forming molecules include a mixed-sequence “tail” which increases the stringency of binding to the target duplex, improves the frequency of modification at the target site, and reduces the requirement for a polypurine:polypyrimidine stretch. Methods for using the triplex-forming molecules in combination with one or more donor oligonucleotides for targeted modification of sites within or adjacent to genes that encodes cell surface receptors for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) are also disclosed. Methods for ex vivo and in vivo prophylaxis and therapy of HIV infection using the disclosed compositions are also provided.
Owner:YALE UNIV
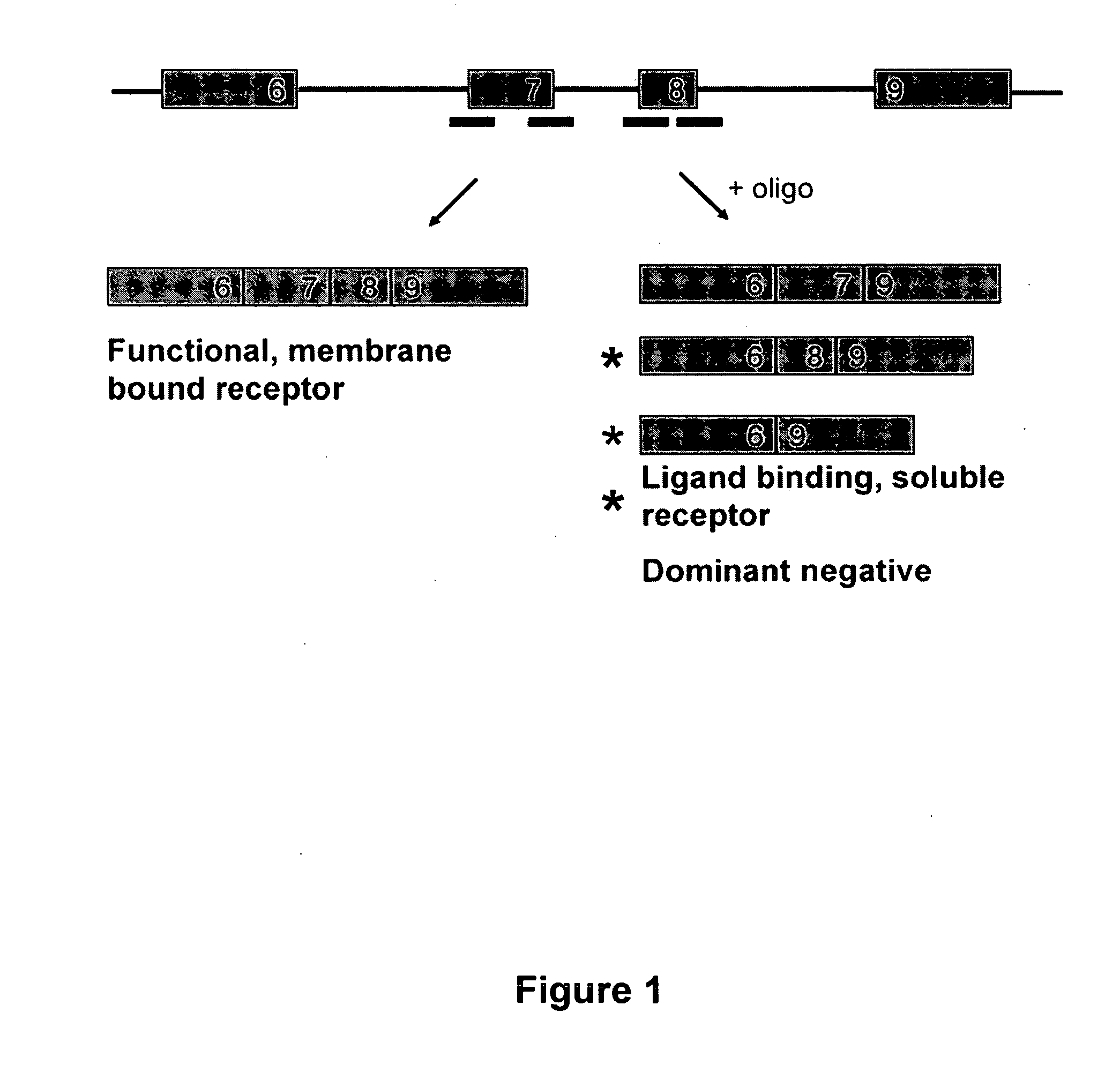
Splice switch oligomers for TNF superfamily receptors and their use in treatment of disease
InactiveUS20070105807A1High expressionReduce expressionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSplice switchingPrecursor mRNA
Methods and compositions are disclosed for controlling expression of TNF receptors (TNFR1 and TNFR2) and of other receptors in the TNFR superfamily using compounds that modulate splicing of pre-mRNA encoding these receptors. More specifically these compounds cause the removal of the transmembrane domains of these receptors and produce soluble forms of the receptor which act as an antagonist to reduce TNF-α activity or activity of the relevant ligand. Reducing TNF-α activity provides a method of treating or ameliorating inflammatory diseases or conditions associated with TNF-α activity. Similarly, diseases associated with other ligands can be treated in like manner. In particular, the compounds of the invention are splice-splice switching oligomers (SSOs) which are small molecules that are stable in vivo, hybridize to the RNA in a sequence specific manner and, in conjunction with their target, are not degraded by RNAse H.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS +3
METHODS AND MEANS FOR EFFICIENT SKIPPING OF EXON 45 IN DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY PRE-mRNA
ActiveUS20120022134A1Reduced calcium uptake by muscle cellsReduce synthesisOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationNucleotidePrecursor mRNA
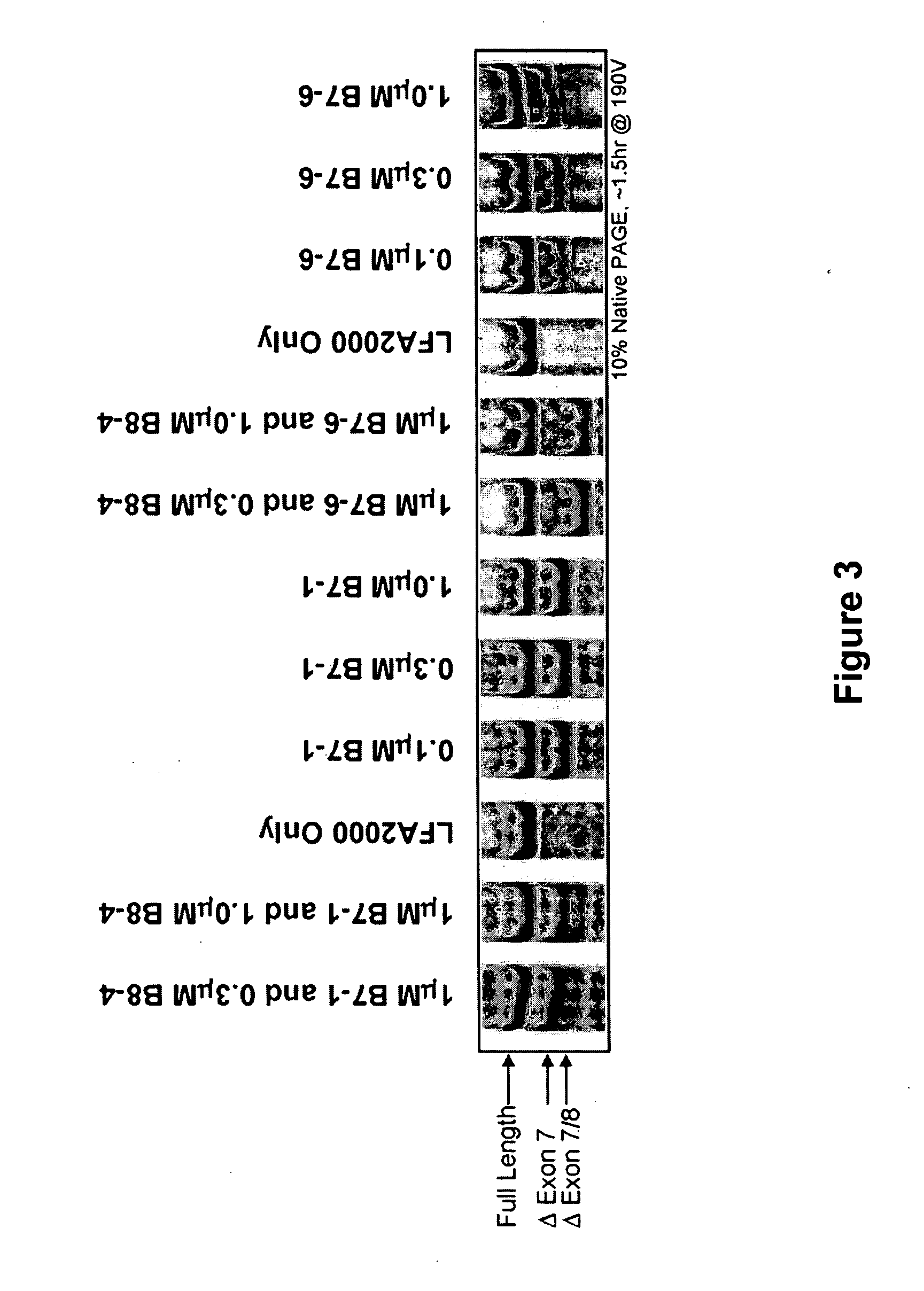
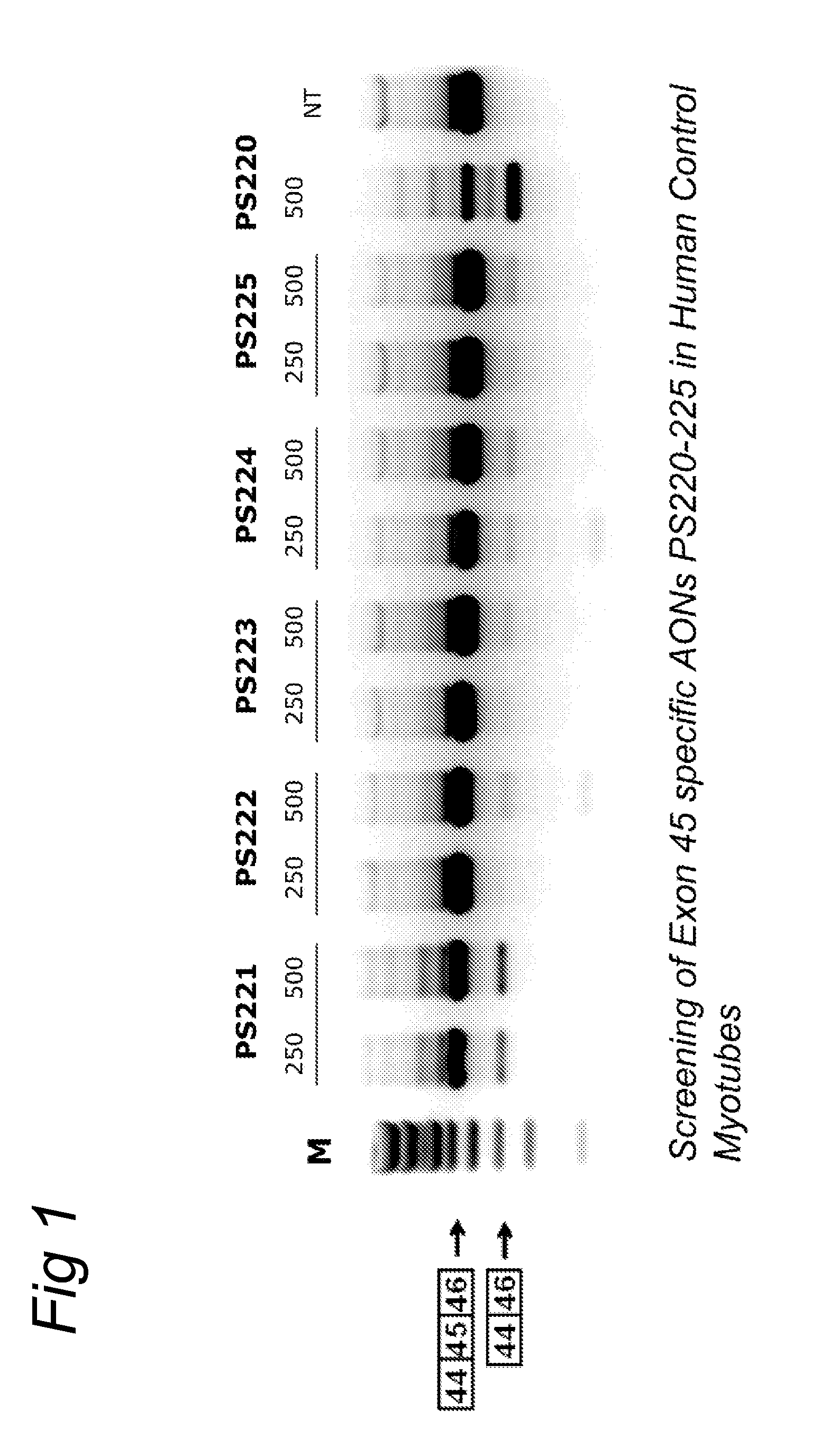
The invention relates to a method for inducing or promoting skipping of exon 45 of DMD pre-mRNA in a Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy patient, preferably in an isolated (muscle) cell, the method comprising providing said cell with a molecule that binds to a continuous stretch of at least 21 nucleotides within said exon. The invention further relates to such molecule used in said method.
Owner:BIOMARIN TECH BV +2
Identification of small molecules that facilitate therapeutic exon skipping
This invention relates, e.g., to a method for enhancing exon skipping in a pre-mRNA of interest, comprising contacting the pre-mRNA with an effective amount of a small molecule selected from the compounds shown in Table 1, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt, hydrate, solvate, or isomer thereof, and, optionally, with an antisense oligonucleotide that is specific for a splicing sequence in the pre-mRNA Methods for treating Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) are disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Antisense molecules and methods for treating pathologies
An antisense molecule capable of binding to a selected target site to induce exon skipping in the dystrophin gene, as set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1 to 59.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA
Antisense nucleic acids
ActiveUS20140343266A1Improve efficiencyExcellent skipping efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationAntisense nucleic acidGene
The present invention provides a pharmaceutical agent which causes skipping of the 55th, 45th, 50th or 44th exon in the human dystrophin gene with a high efficiency.The present invention provides an oligomer which efficiently enables to cause skipping of the 55th, 45th, 50th or 44th exon in the human dystrophin gene.
Owner:NIPPON SHINYAKU CO LTD +1
Compositions and methods for modulation of SMN2 splicing
Disclosed herein are compounds, compositions and methods for modulating splicing of SMN2 mRNA in a cell, tissue or animal. Also provided are uses of disclosed compounds and compositions in the manufacture of a medicament for treatment of diseases and disorders, including spinal muscular atrophy.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC +1
Antisense Oligonucleotides
ActiveUS20120202752A1Organic active ingredientsSplicing alterationDiseaseDuchenne's Muscular Dystrophy
Embodiments of the present invention are directed generally to antisense compounds and compositions for the treatment of muscular dystrophy, and in particular, Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). In one embodiment, the invention is directed to antisense oligonucleotide molecules, pharmaceutical compositions and formulations comprising antisense oligonucleotide molecules, and methods of treating muscular dystrophy related diseases and disorders wherein the antisense oligonucleotide molecules comprises a base sequence selected from the group consisting of SEQ ID NO: 5-8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 24, 27, 28, 34, 35, 37, 40, 42, 44-46, 79, 97, 100, 101, and 116, and combinations thereof.
Owner:CHARLOTTE MECKLENBURG HOSPITAL AUTHORITY
Oligonucleotide comprising an inosine for treating dmd
InactiveUS20120046342A1Avoid or decrease a potential multimerisation or aggregation of oligonucleotidesLow efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationInosineNucleotide
The invention provides an oligonucleotide comprising an inosine, and / or a nucleotide containing a base able to form a wobble base pair or a functional equivalent thereof, wherein the oligonucleotide, or a functional equivalent thereof, comprises a sequence which is complementary to at least part of a dystrophin pre-m RNA exon or at least part of a non-exon region of a dystrophin pre-m RNA said part being a contiguous stretch comprising at least 8 nucleotides. The invention further provides the use of said oligonucleotide for preventing or treating DMD or BMD.
Owner:BIOMARIN TECH BV
Compositions and methods for modulation of SMN2 splicing in a subject
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC +1
Spinal muscular atrophy treatment via targeting smn2 catalytic core
ActiveUS20110269820A1Increase productionEasy to useOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationOligoribonucleotidesPrecursor mRNA
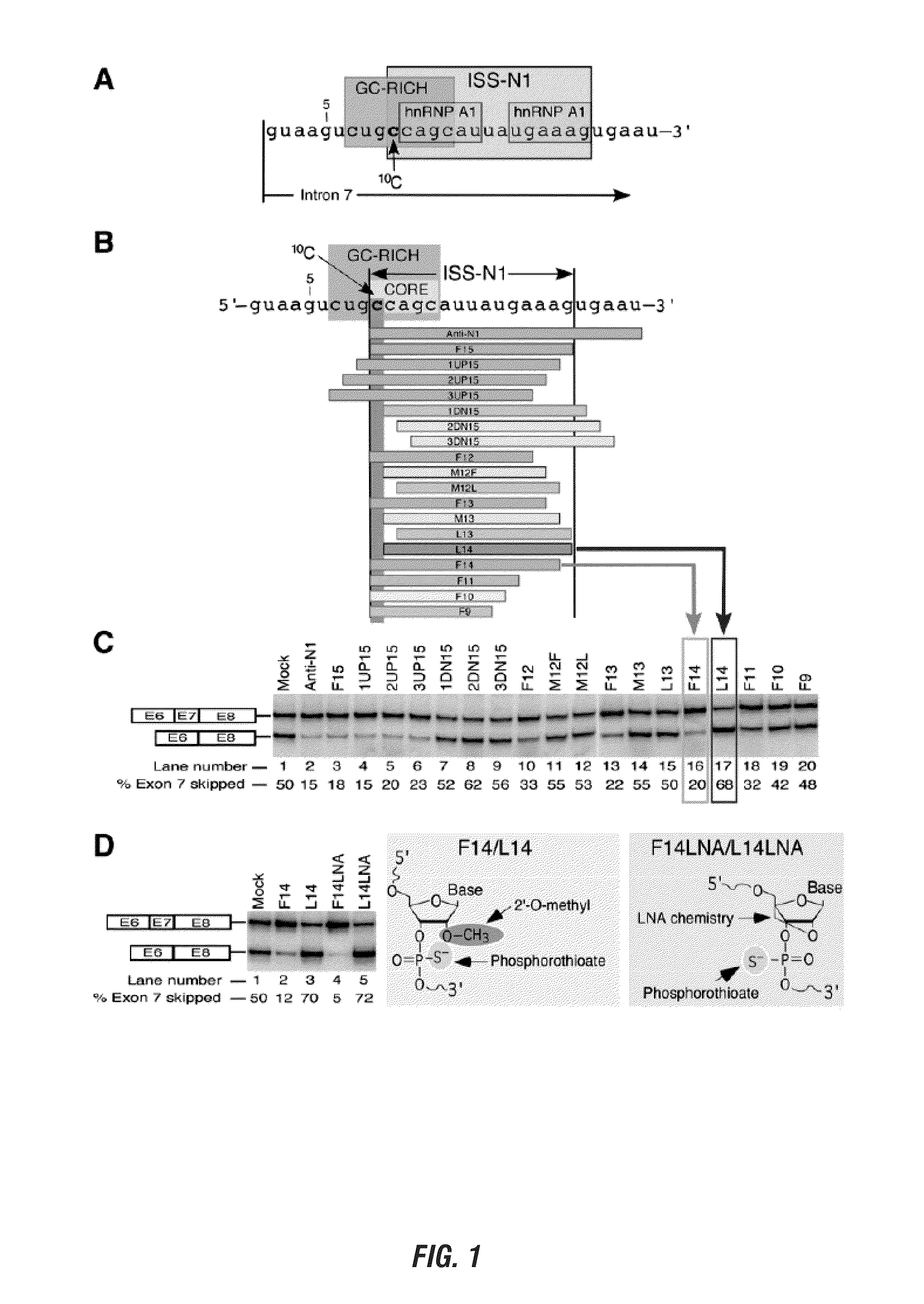
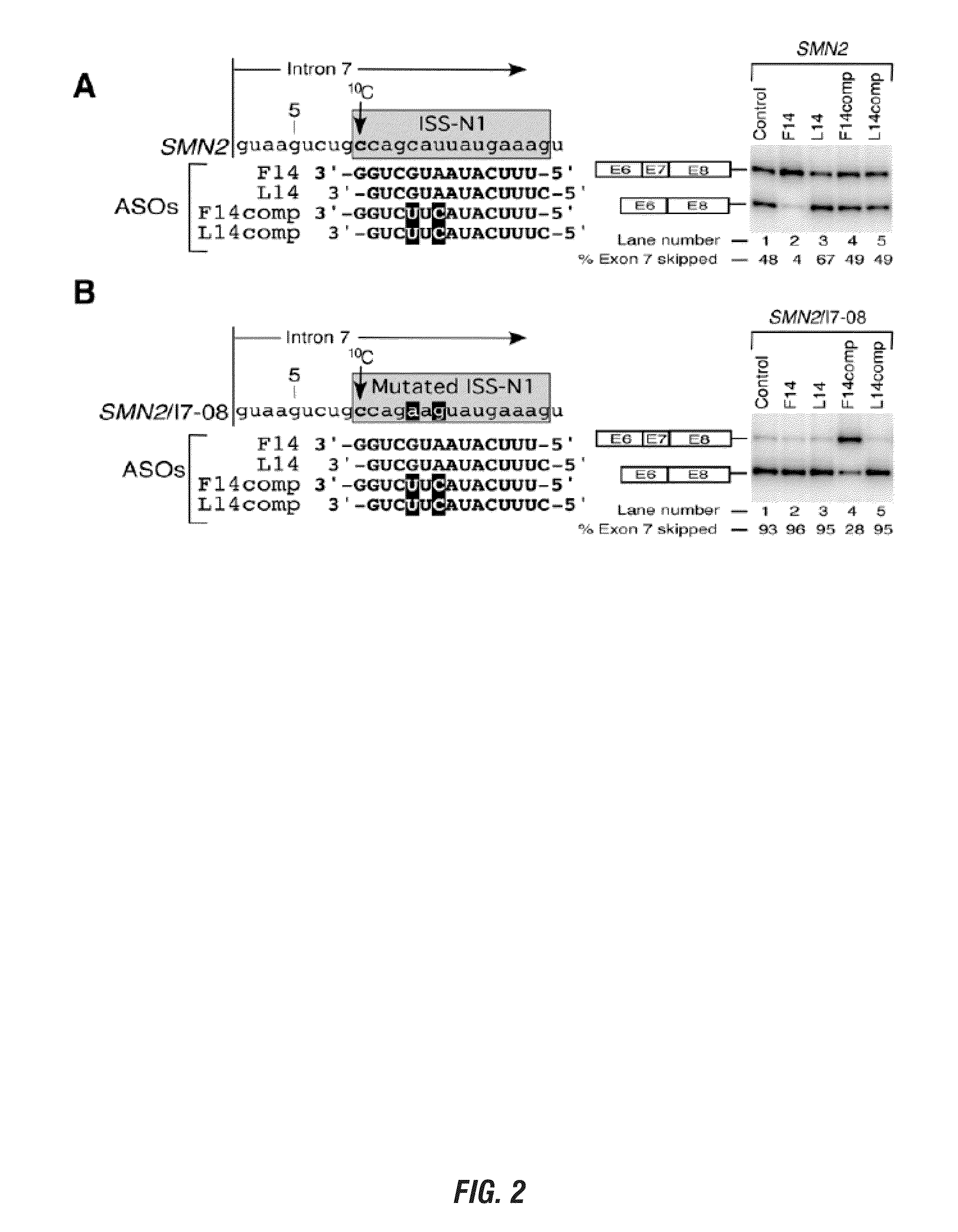
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for blocking the effect of the intronic inhibitory splicing region of intron 7 of the SMN2 gene. The compositions and methods of the instant invention include short oligonucleotide reagents (e.g., oligoribonucleotides) that effectively target sites in the SMN2 pre-mRNA, thereby modulating the splicing of SMN2 pre-mRNA to include exon 7 in the processed transcript. The short target regions are 8-mers and 5-mers and also include the identification of a single nucleotide base that is essential for initiating a long distance stearic inhibitory interactions as well as novel targets distant from intron 7 which block the intronic inhibitory splicing of the same. These short target regions and concomitant inhibitory blocking oligonucleotides are less expensive and easier to manufacture and are small enough to cross the blood brain barrier.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Splice-region antisense composition and method
Owner:AVI BIOPHARMA
Antisense molecules and methods for treating pathologies
ActiveUS20120270925A1Specific and efficient exon skippingOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationExon skippingCell biology
An antisense molecule capable of binding to a selected target site to induce exon skipping in the dystrophin gene, as set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1 to 59.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA
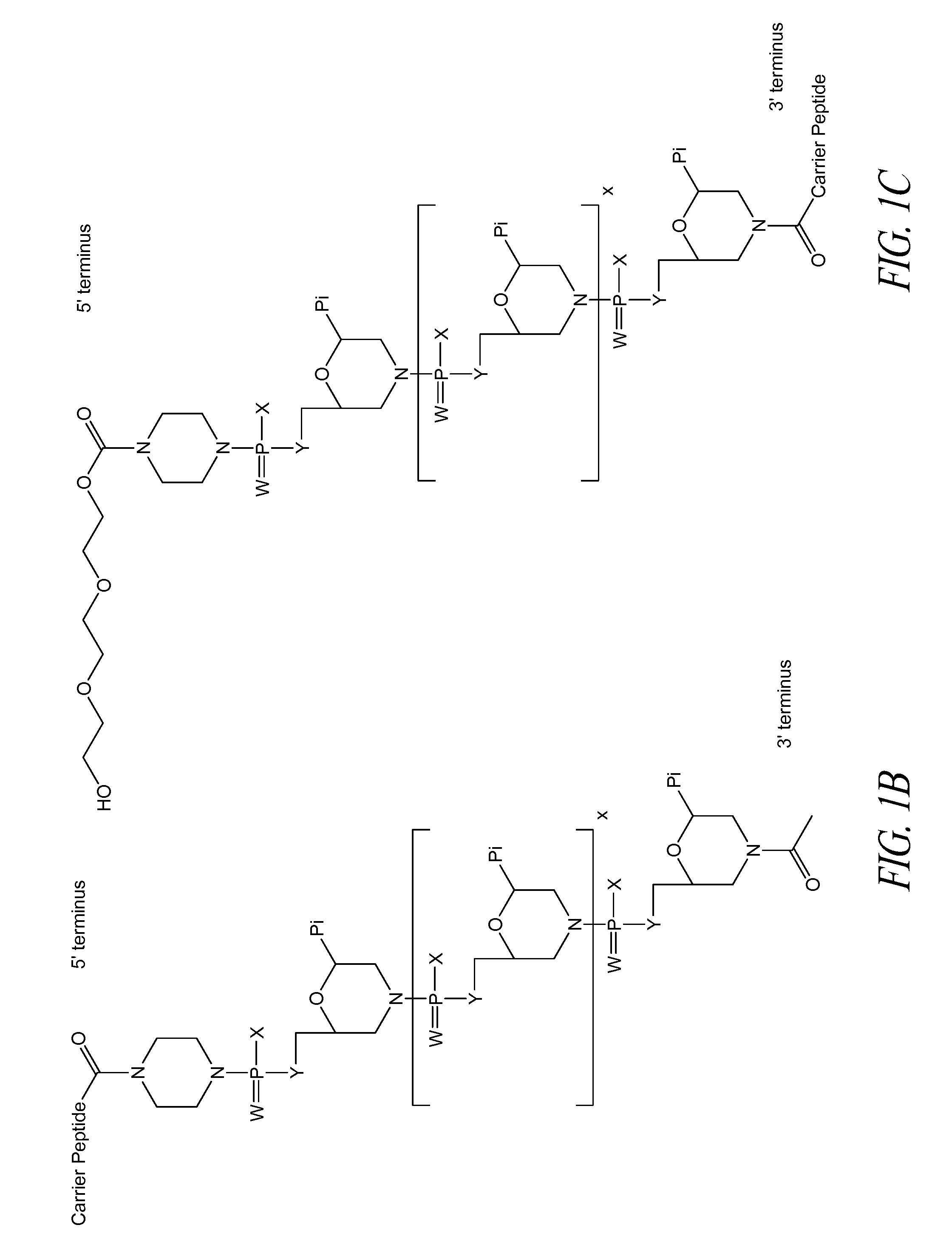
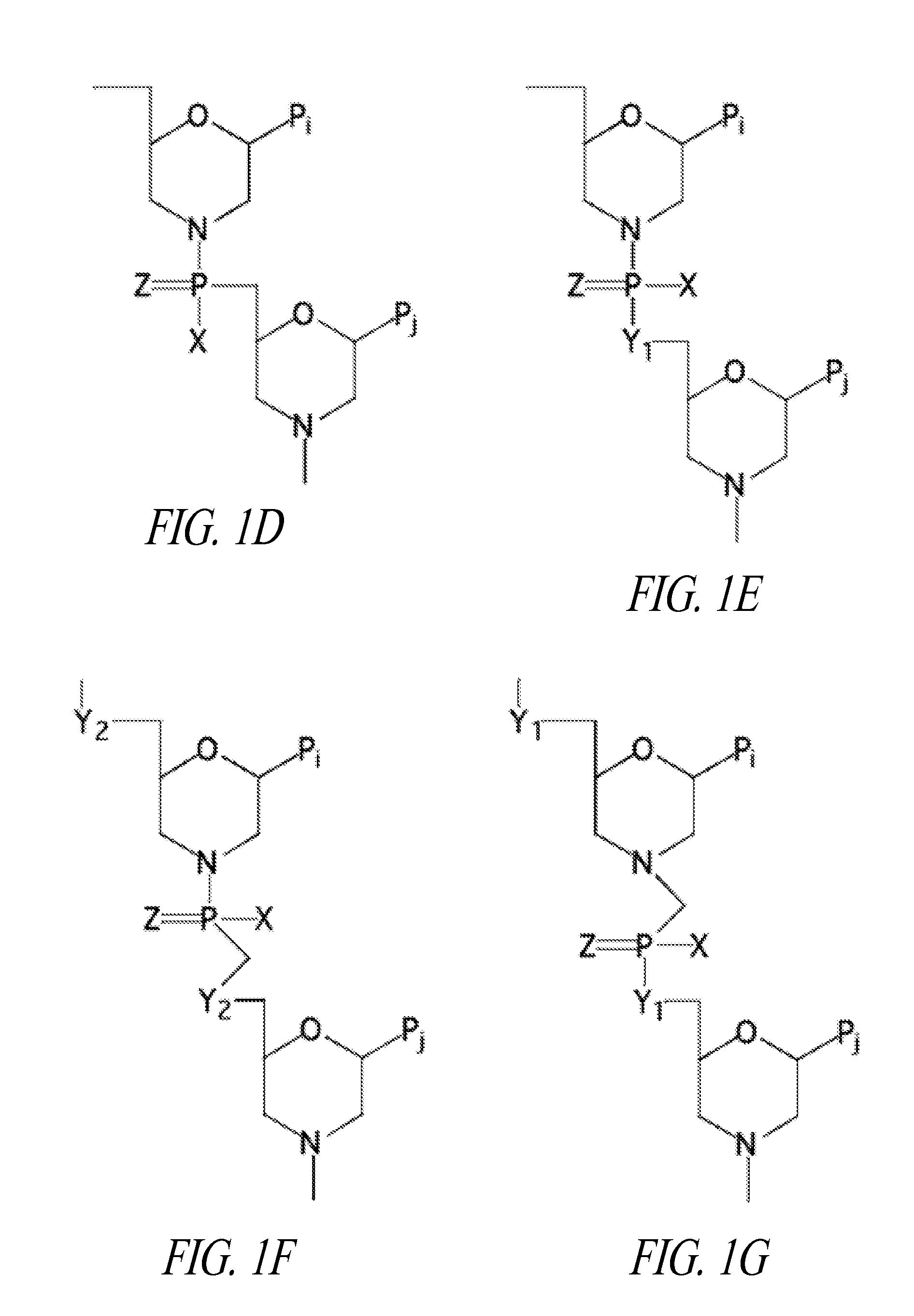
Peptide oligonucleotide conjugates
ActiveUS9161948B2Improve propertiesEfficient deliveryAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseTherapeutic effect
Oligonucleotide analogues conjugated to carrier peptides are provided. The disclosed compounds are useful for the treatment of various diseases, for example diseases where inhibition of protein expression or correction of aberrant mRNA splice products produces beneficial therapeutic effects.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Exon skipping compositions for treating muscular dystrophy
InactiveUS20140315977A1Enhance the activity, cellular distribution, or cellular uptake of the antisense oligonucleotideOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationDuchenne muscular dystrophyMuscular dystrophy
Antisense molecules capable of binding to a selected target site in the human dystrophin gene to induce exon 53 skipping are described.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com