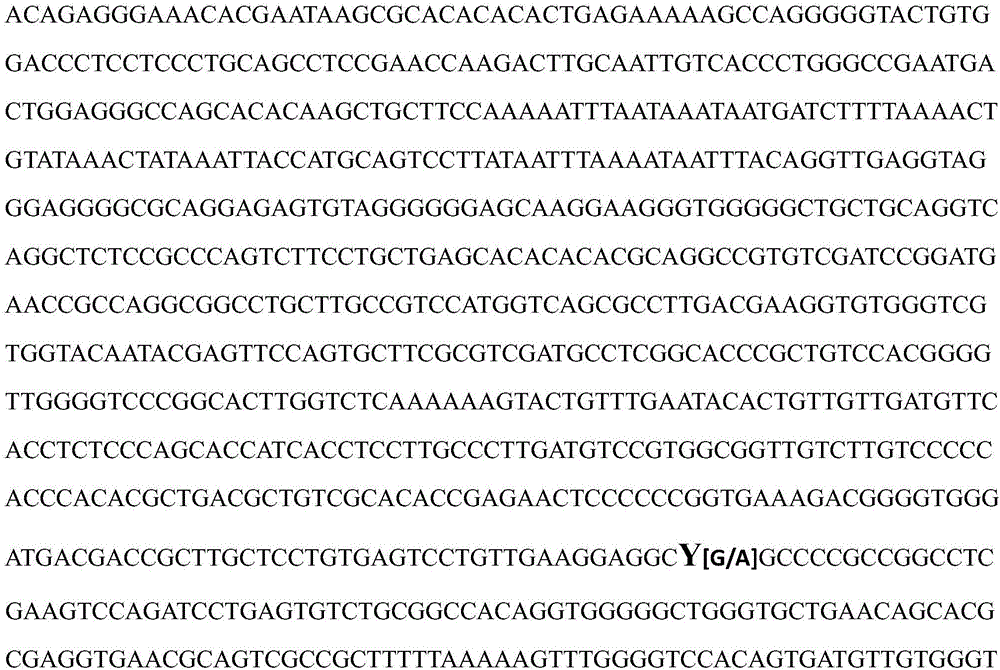Patents
Literature
74 results about "Gene bank" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gene banks are a type of biorepository which preserve genetic material. For plants, this could be by in vitro storage, freezing cuttings from the plant, or stocking the seeds (e.g. in a seedbank). For animals, this is the freezing of sperm and eggs in zoological freezers until further need. With corals, fragments are taken which are stored in water tanks under controlled conditions. Plant genetic material in a 'gene bank' is preserved at -196° Celsius in Liquid Nitrogen as mature seed (dry) or tissue (meristems).
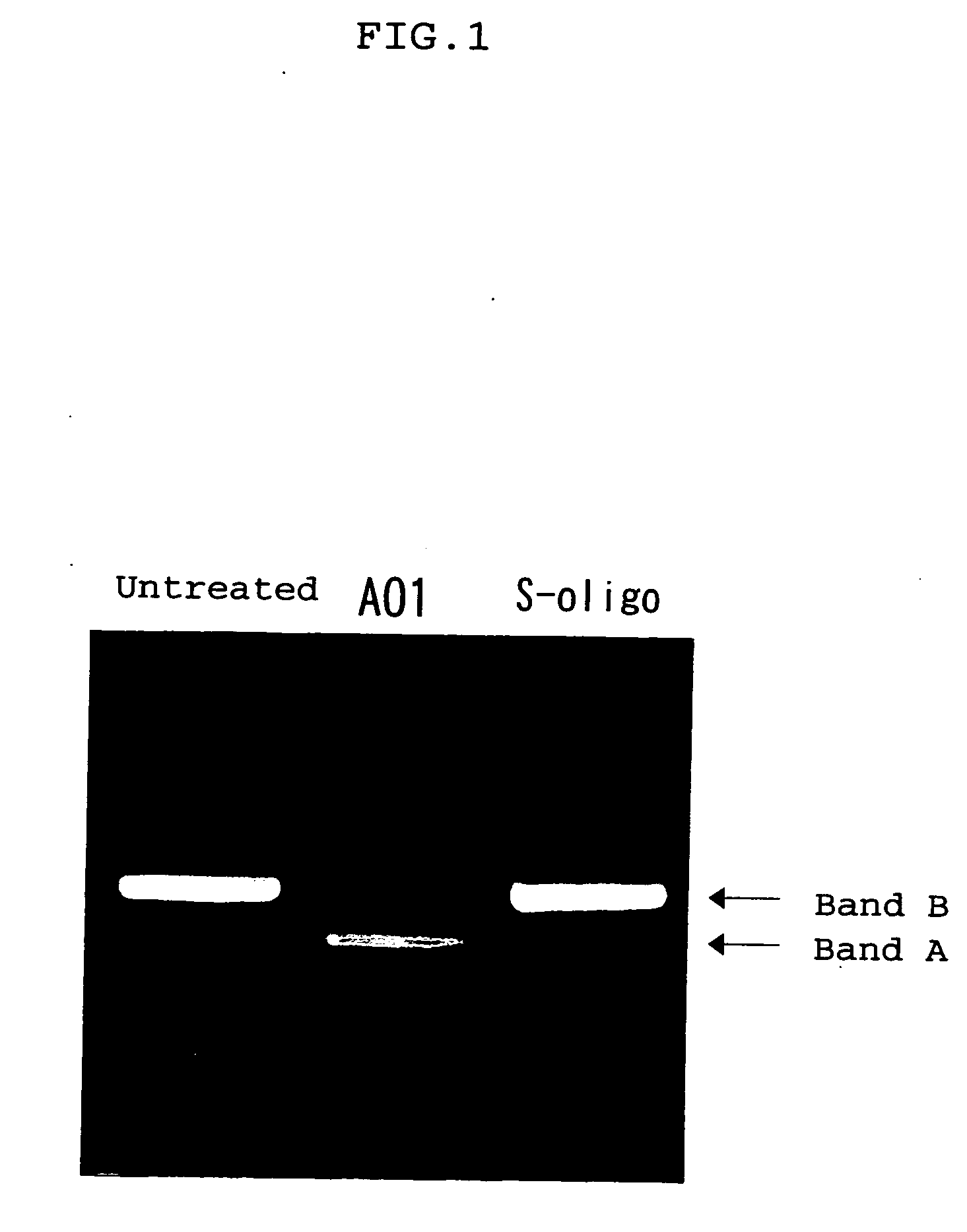
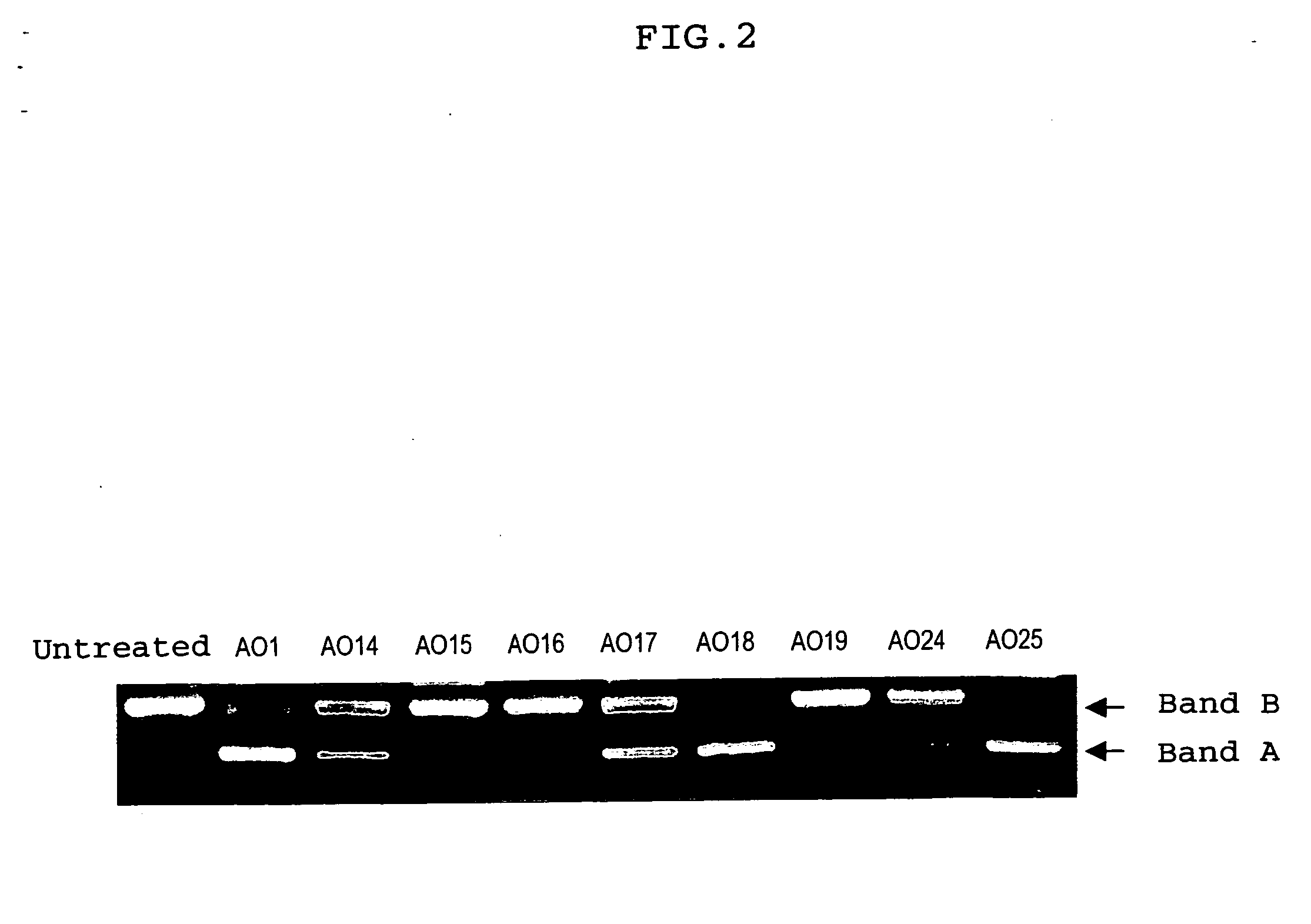
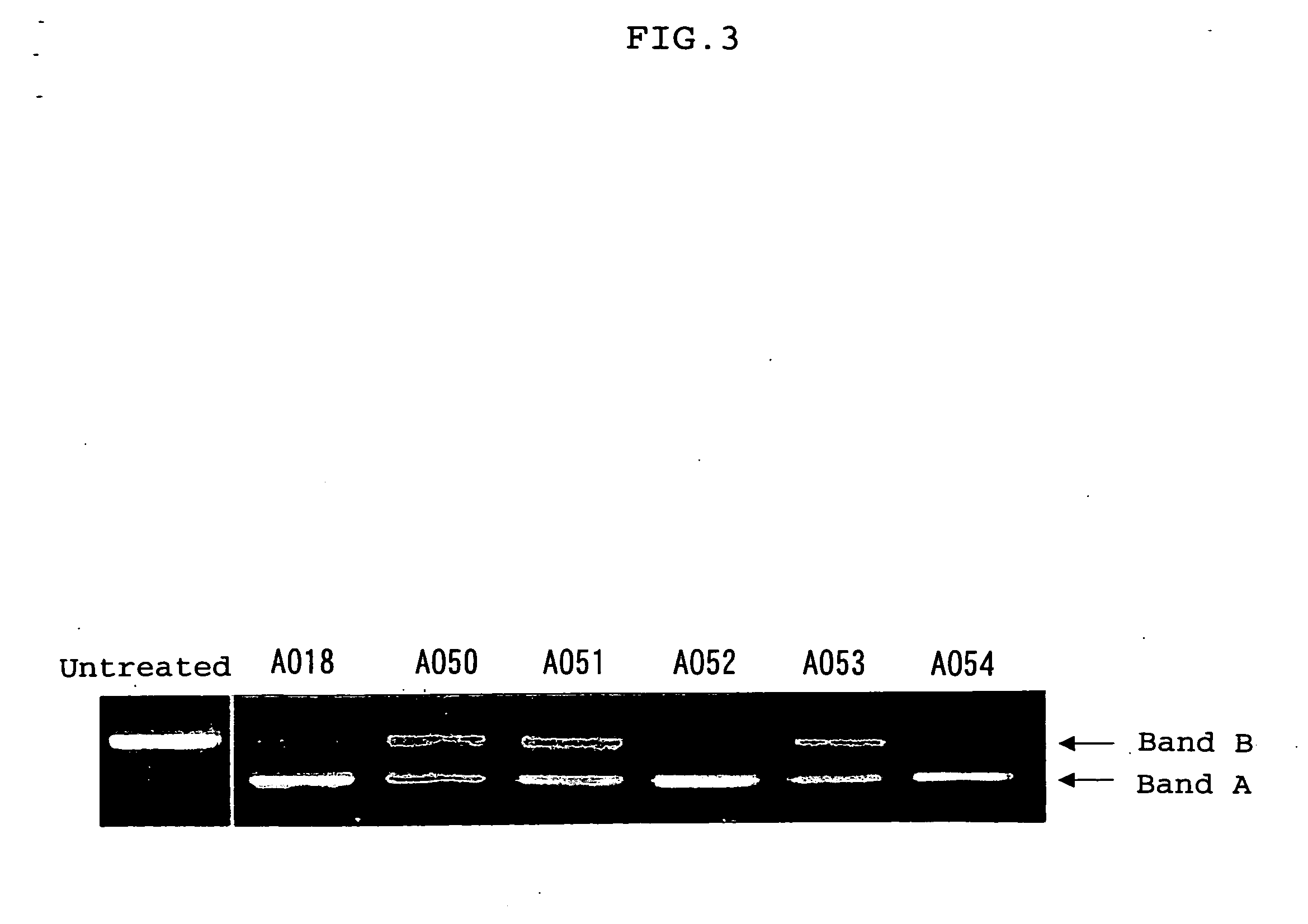
Ena nucleic acid drugs modifying splicing in mrna precursor
ActiveUS20070082861A1Efficient processImprove bindingSplicing alterationSugar derivativesGene bankDystrophin
Oligonucleotides having a nucleotide sequence complementary to nucleotide numbers such as 2571-2607, 2578-2592, 2571-2592, 2573-2592, 2578-2596, 2578-2601 or 2575-2592 of the dystrophin cDNA (Gene Bank accession No. NM_004006.1) and therapeutic agents for muscular dystrophy comprising such oligonucleotides.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
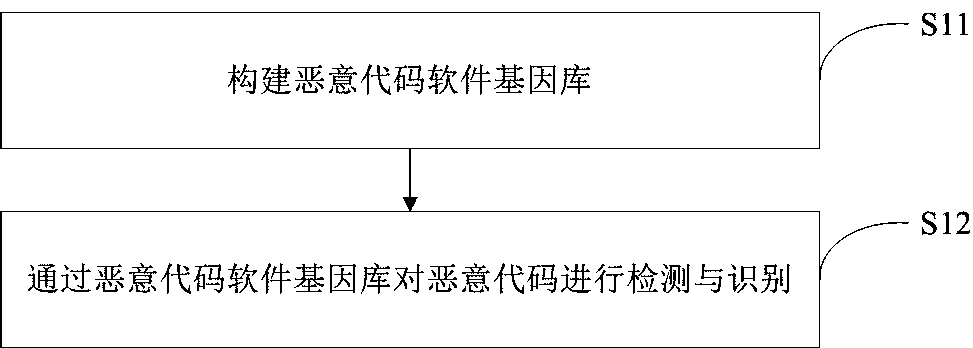
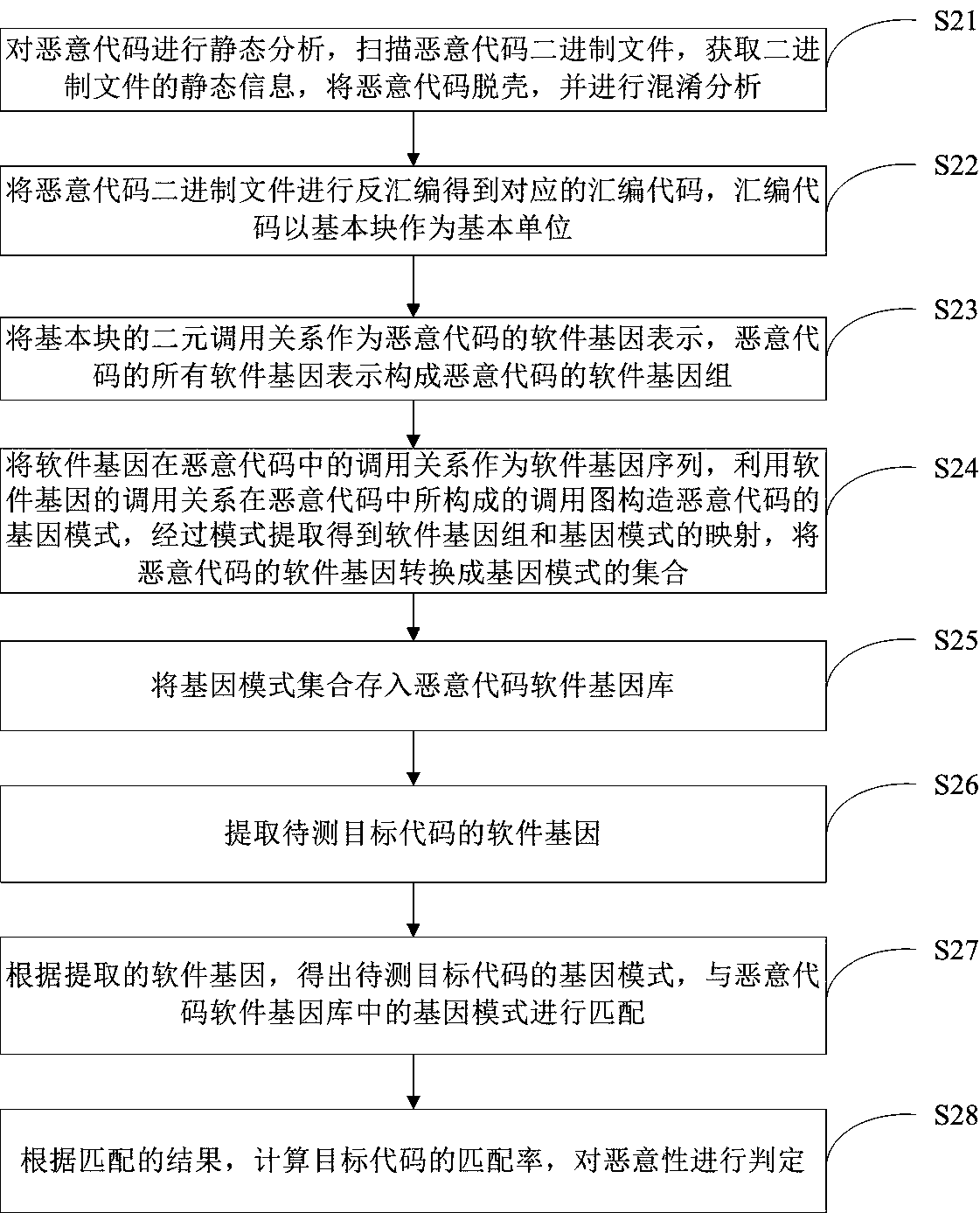
Malicious code detection and recognition method and device based on software genes
ActiveCN108171059AImprove detection accuracyReduce false alarm ratePlatform integrity maintainanceGene bankSoftware engineering
The invention relates to the field of malicious code analysis technology, in particular to a malicious code detection and recognition method and device based on software genes. According to the method, the software genes of malicious codes are defined and extracted, software genomes of the malicious codes are constructed, a gene mode based on graph structure expression is constructed for each malicious code according to software gene calling relations of different malicious codes, a malicious code software gene bank is established through learning of existing samples, and therefore a good detection accurate rate and a low false report rate are obtained. By coding different software genes, the software genes are combined into the software genomes, the software genomes are information sets of the malicious codes, the gene modes are expressed with a graph structure, overall characteristic information of the malicious codes can be represented, and the gene modes are material sets of the malicious codes. Through the malicious code detection and recognition method and device, the information property and the material property of the software genes are achieved at the same time, and genetic characteristics and mutation characteristics are well represented.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
Molecular marker of TrkA gene as sheep lambing number characteristic and application of molecular marker
ActiveCN105950638AImprove trait associationMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationEnzyme digestionAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the technical field of sheep molecular marker screening and application and relates to a molecular marker of TrkA gene as the sheep lambing number characteristic and application of the molecular marker. The molecular marker is cloned from the TrkA gene (Gene Bank ID: 101109763). The nucleotide sequence of the molecular marker is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, and C> exists in the positon of the 432 bit basic group of the shown sequence SEQ ID NO.1; T base substitution mutates, and the mutation causes SacII-RFLP enzyme digestion polymorphism. Related correlation analysis application is performed on Hu sheep and small-tailed Han sheep. A novel genetic marker resource is provided for marker assisted selection of the sheep lambing number characteristic.
Owner:甘肃羊如祥农业有限公司
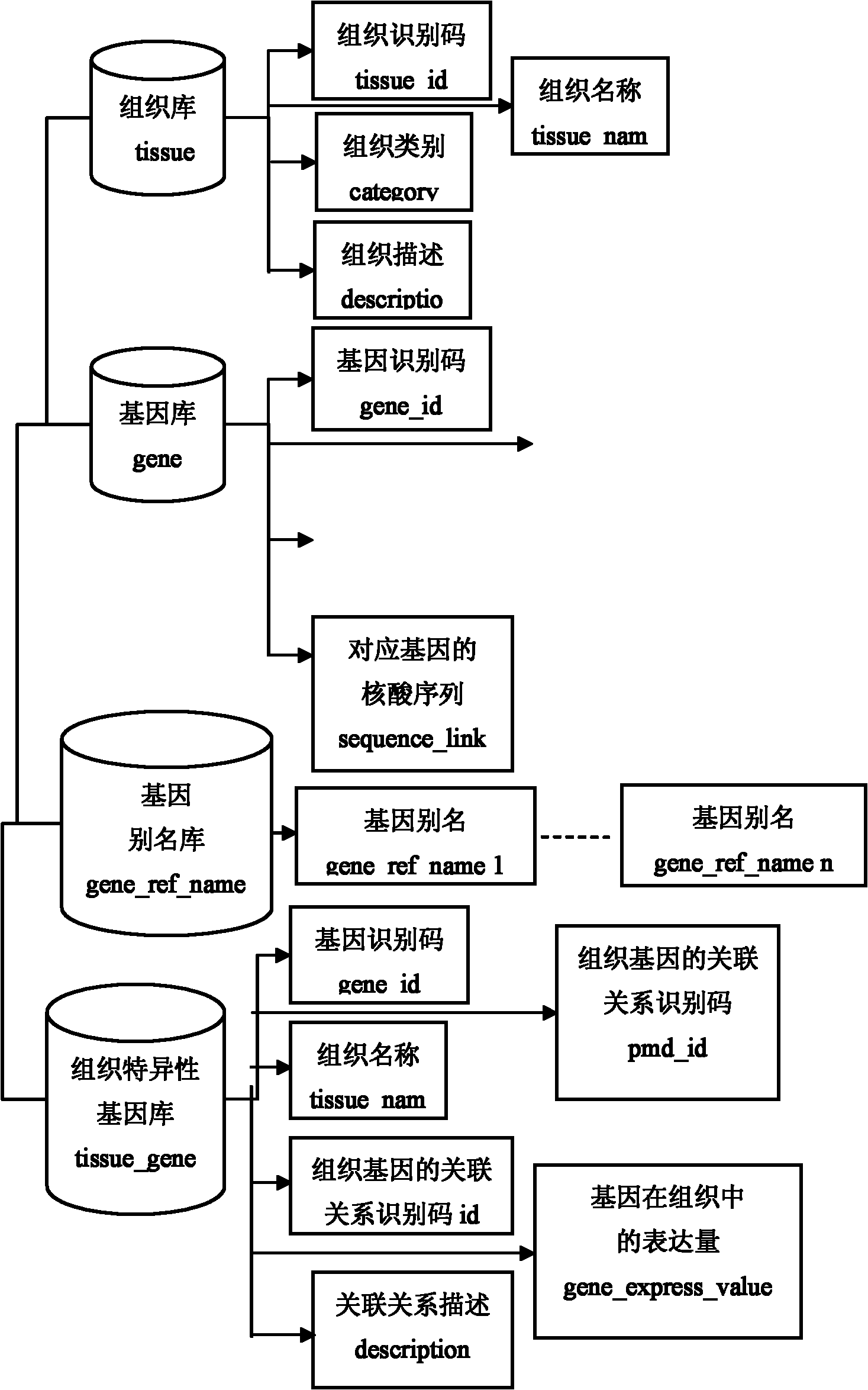
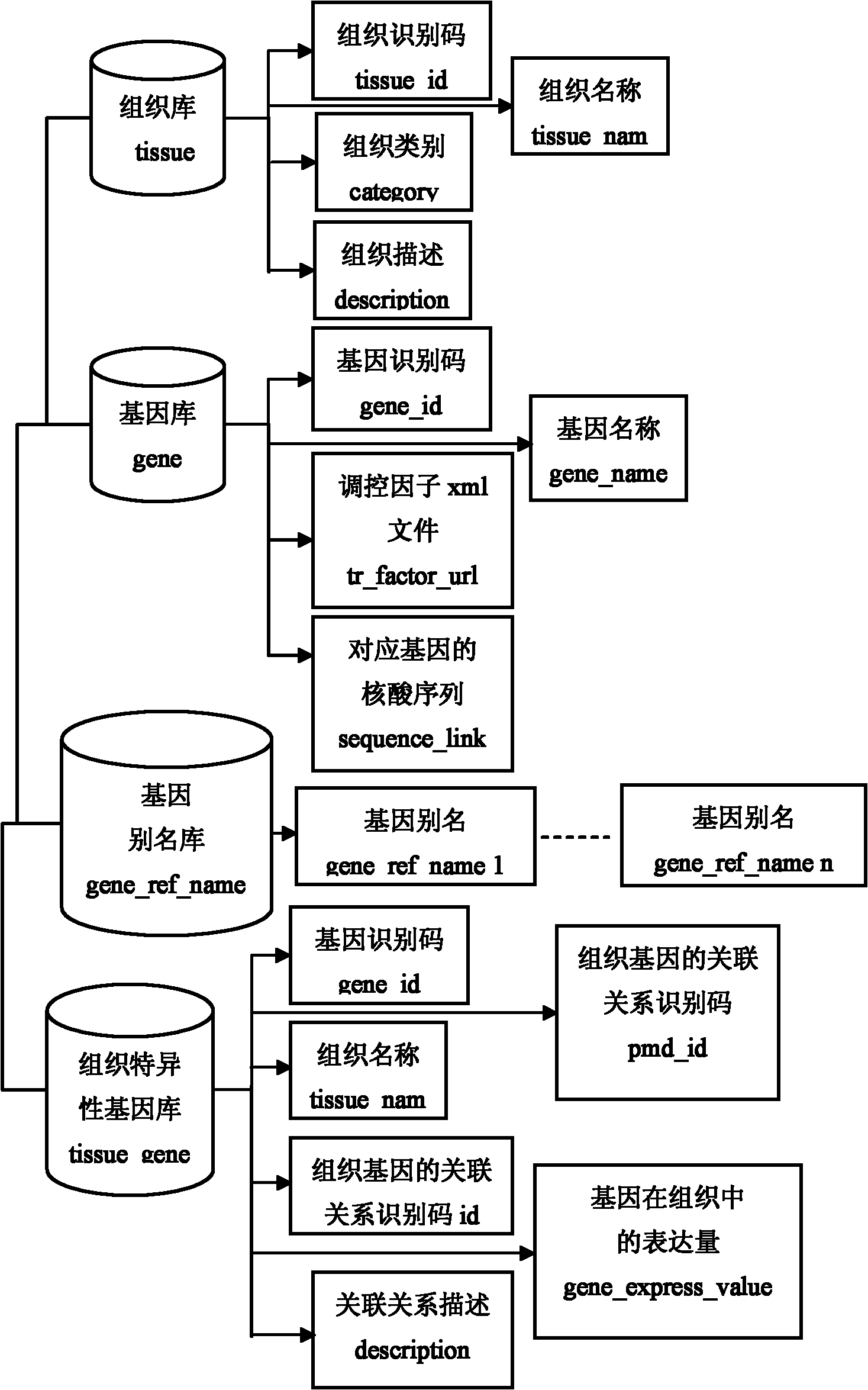
Tissue-specific gene and regulatory factor data storage method
InactiveCN101847181AEasy accessQuality improvementSpecial data processing applicationsResearch qualityGene bank
The invention discloses a tissue-specific gene and regulatory factor data storage method. In the method, data storage is realized by establishing a tissue-specific gene and regulatory factor database comprising a tissue bank, a gene bank, a gene reference name bank, a tissue-specific gene bank and the tissue bank of tissue-specific genes. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting the tissue-specific genes from a Pubmed bibliographic database in a literature mining form; adding extracted tissue information into the tissue bank; retrieving information about the genes in the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL), Genebank and NCBI by utilizing names of the genes, and adding the information into corresponding items of the gene bank; and generating regulatory factor XML files by utilizing the information of regulating the searching of the genes from Transfac, an Eukaryotic Promoter Database (EPD) and a compel database. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of bringing convenience to researchers utilizing modern computing technology to detect gene expression and regulate an inherent mechanism of network tissue specificity to acquire data on sequences of the tissue-specific genes and corresponding regulatory factors, fully utilizing tissue-specific gene analysis tools and improving research quality and efficiency.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
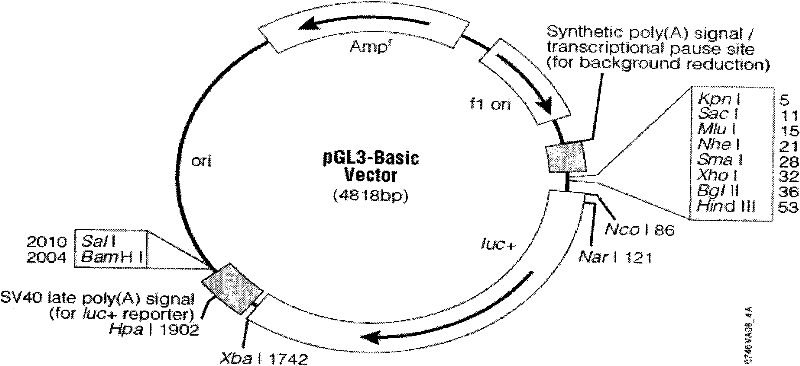
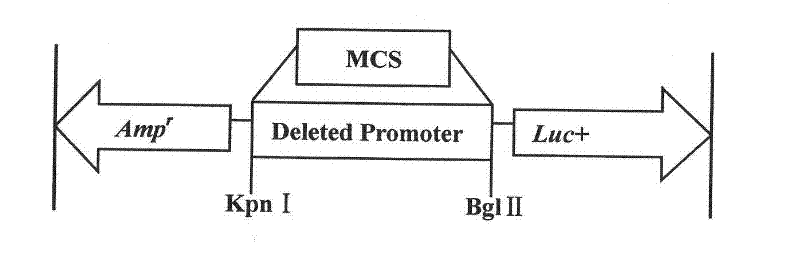
Clone and application of pig skeletal muscle specificity expression gene alpha-actin promoters
The invention belongs to the technical field of animal gene engineering and particularly relates to isolated identification and functional verification of different-length promoter regions of pig skeletal muscle specificity expression genes alpha-actin. Eight upstream different-length promoters of the skeletal muscle specificity expression genes alpha-actin (the Gene Bank accession number is 100154254) are cloned from the pig genome, and the nucleotide sequences of the promoters are respectively shown as SEQ ID No: 2 to SEQ ID No: 9. The results show that the region with the length being 249bp has independent promoting activity and muscle tissue specificity, the nucleotide sequence is shown as the SEQ ID No: 9 in a sequence table. The invention also discloses a method for obtaining eight different deletion promoter segments, a method for preparing corresponding recombinant expression vectors and an application of a dual-luciferase enzymatic activity detection system to the promoter activity analysis.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
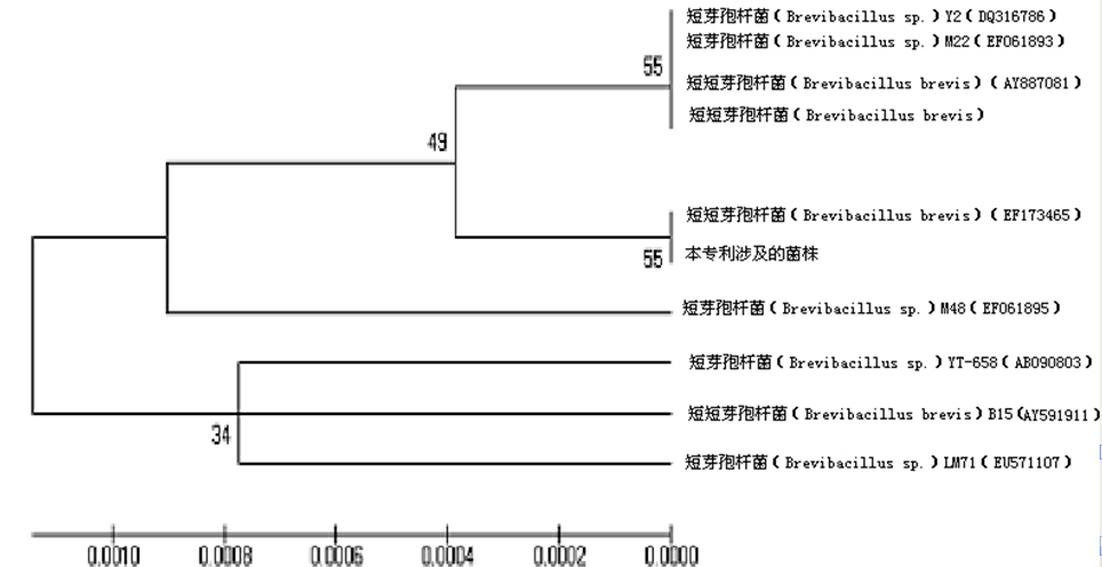
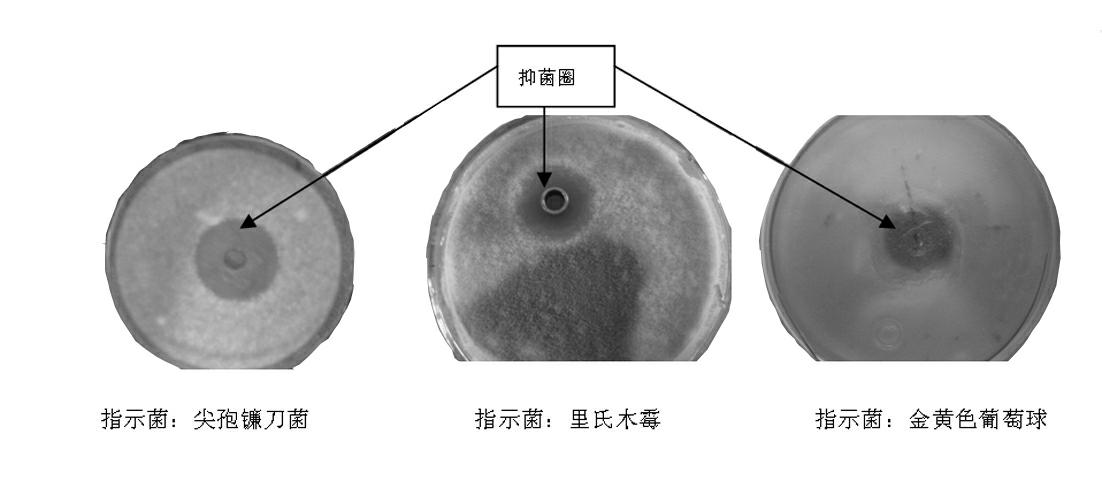
Brevibacillus brevis for preventing and treating plant fungus diseases and method for preparing biopesticide
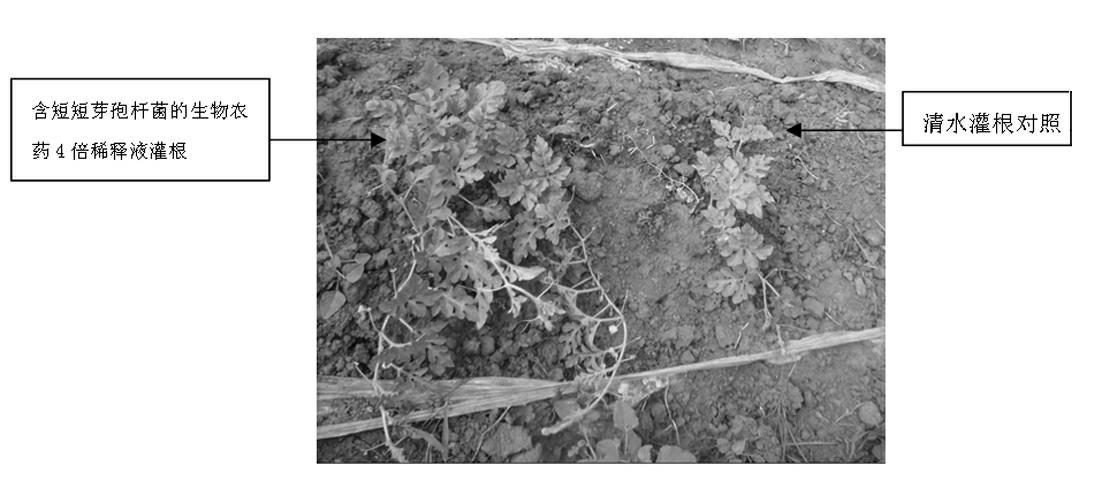
The invention relates to brevibacillus brevis for preventing and treating plant fungous diseases and application thereof. The brevibacillus brevis has a gene sequencing result of 1367bp, has an accession number of HQ585418 on a gene bank, is preserved in the China general microbiological culture collection center (CGMCC) and has a preservation number of CGMCC NO.4361. A method for preparing a brevibacillus brevis biopesticide for preventing and treating the plant fungous diseases comprises the following operation steps of: 1, preparing seed liquid; and 2, fermenting and preparing the brevibacillus brevis biopesticide. A field experiment proves that the brevibacillus brevis can obviously reduce the morbidity of cucurbit wilt, and thus, a strain disclosed by the invention can be effectively applied to prevention and treatment of cucurbit wilt and can be used for preparing the safe and high-efficiency biopesticide.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
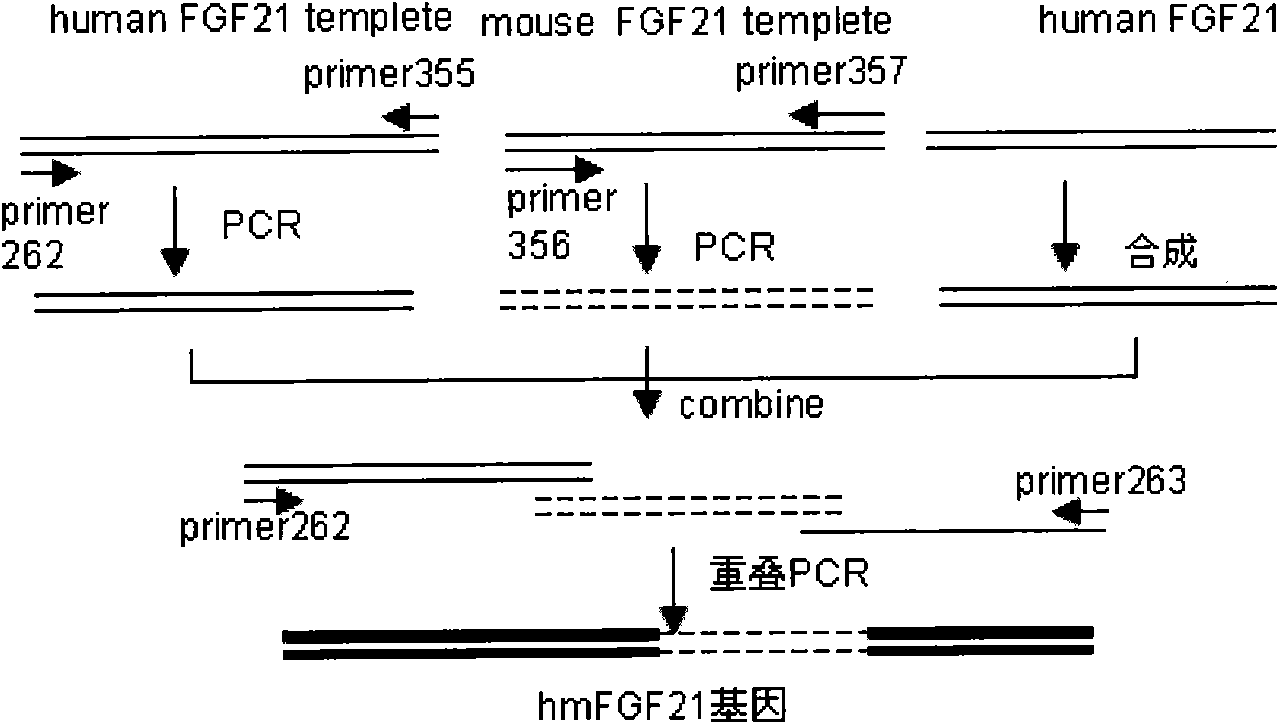
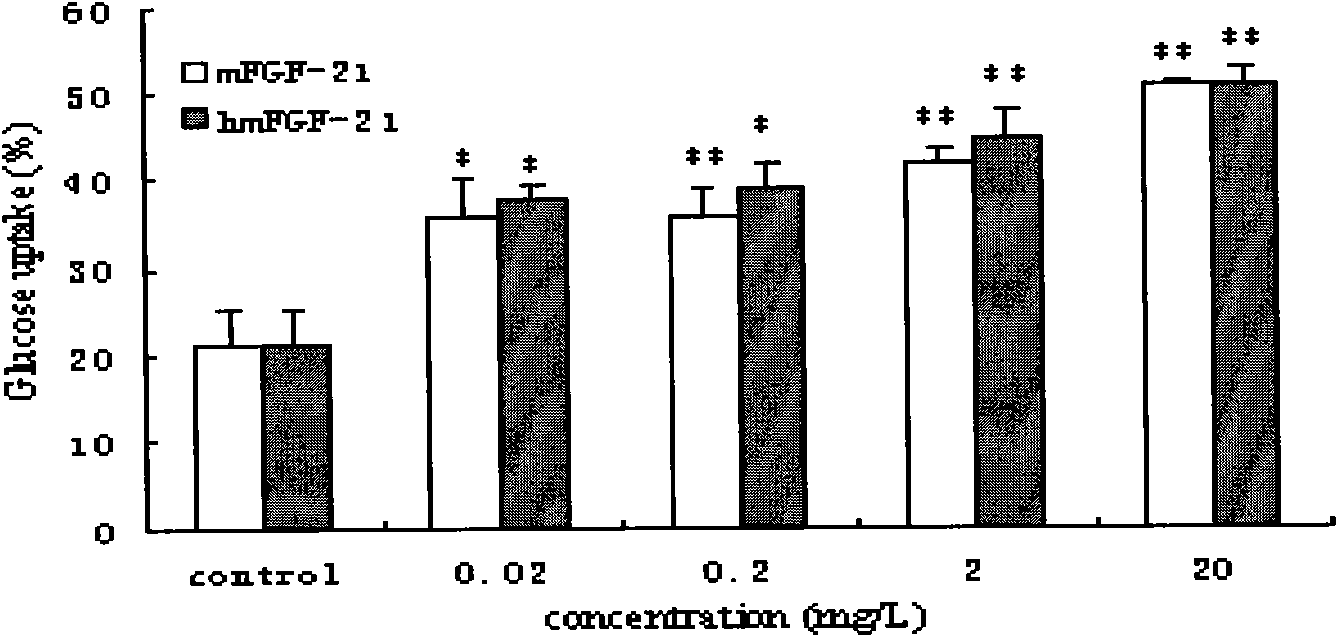
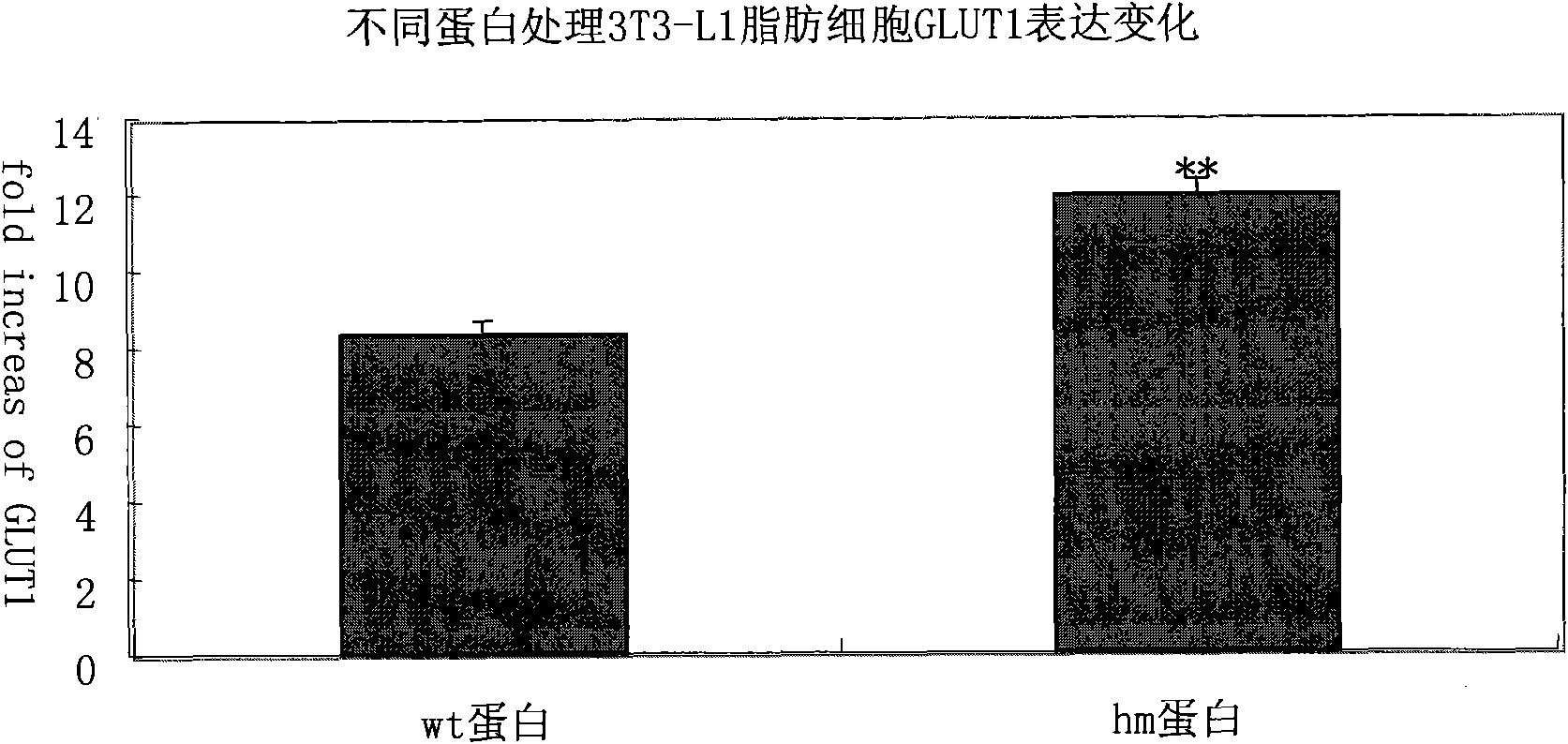
Mutated human-source fibroblast growth factor and application in treating endocrine diseases
The invention discloses a mutated human-source fibroblast growth factor and application in treating endocrine diseases. The amino acid sequence of the mutated human-source fibroblast growth factor-21 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2, and the coding genetic sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. In the invention, a human blood cell nucleic acid is used as a template, FGF-21 genes in a normal human body can be cloned by means of a natural gene bank in quantity, a natural human FGF-21 sample bank can be established, and the natural mutant of the FGF-21 can be obtained by a high-flux screening method. Zoological experiment results prove that the mutated FGF-21 can more effectively reduce the blood sugar level in an animal body, and the mutant has the advantages of quick response, long efficacy duration and the like in the aspect of reducing the blood sugar level. The mutated FGF-21 can be used as medicament for treating diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome or lipid metabolism disorder and other endocrine diseases.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
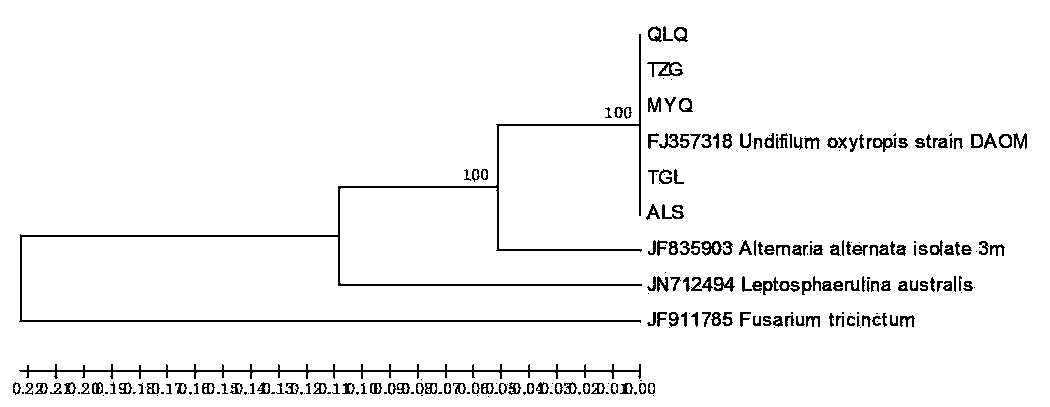
Method for directional separation and authentication of swainsonine fungal endophyte Undifilum oxytropis produced through oxytropis kansuensis
InactiveCN104031849ANot prone to mutationSimple separation methodFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyFungal endophyte
The invention relates to a method for directional separation and authentication of swainsonine fungal endophyte Undifilum oxytropis produced through oxytropis kansuensis. When the fungal endophyte Undifilum oxytropis is separated from oxytropis kansuensis, bacterial strains of other species can be inevitably separated, and therefore separation efficiency is affected. Stems and mature seeds of oxytropis kansuensis are sequentially cleaned through distilled water, ethanol, sterile water and sodium hypochlorite, tissue is sheared into small blocks and placed on a PDA flat plate, the flat plate is filled with CO2 and sealed by a fresh-keeping film, the tissue is cultured at indoor temperature under the illumination condition, after mycelia grow on incisions, the mycelia at the top ends are picked and transferred to a culture medium for purification, the mycelia are scraped, and then the bacterial strains are inoculated to a test tube slant for refrigeration; genome DNA of the separated bacterial strains is extracted, and sequence alignment is conducted in a Gene Bank. Only one fungus is separated from locoweed, interference of fungal endophyte of other species is reduced, the method is easy and convenient to implement and feasible, and in the storage process, the bacterial strains are not prone to mutation or activity of the bacterial strains is not reduced.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Rockfishes chitinase A gene, expression vector containing the same, recombinant strain and use thereof
The invention discloses a chitinase A gene of a grouper, an expression vector containing the gene, a recombinant and application of the gene to preparing fusion protein and additives of fish feed. A nucleotide sequence of the chitinase A gene of the grouper is expressed as SEQ ID NO:1, nucleotides in site 53 to 1,483 in the sequence code 456 amino acids, the nucleotide sequence is a sequence of mature peptide of the chitinase A gene of the grouper, and the amino acid sequence is expressed as SEQ ID NO:3. The chitinase A gene of the grouper not only enriches gene libraries of the grouper, but also provides novel research strategies for cultivation research for seeds of the grouper. The chitinase A gene of the grouper, the expression vector containing the gene, and the recombinant obtained after transformation can be used for preparing the fusion protein and the additives of the fish feed, can effectively promote growth of young fish, can improve immune function of the young fish at the same time, and have higher economic value.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for separating corn bacterial wilt pythium
InactiveCN102533568AEasy to manufactureEasy to operateFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGene bank
The invention relates to a method for separating corn bacterial wilt pythium and in particular relates to separation of corn bacterial wilt pythium by utilizing a separation culture medium. The method comprises the following steps of: designing and synthesizing primers, extracting DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of corn bacterial wilt pythium, amplifying and separating a target gene, separating the amplified final product, sequencing and identifying, and comparing in a gene bank to determine to be corn bacterial wilt pythium. According to the method for separating corn bacterial wilt pythium by utilizing the separation culture medium provided by the invention, the identification method is simple to operate, the identification result is rapid and accurate, and the method can be applied to practical production.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
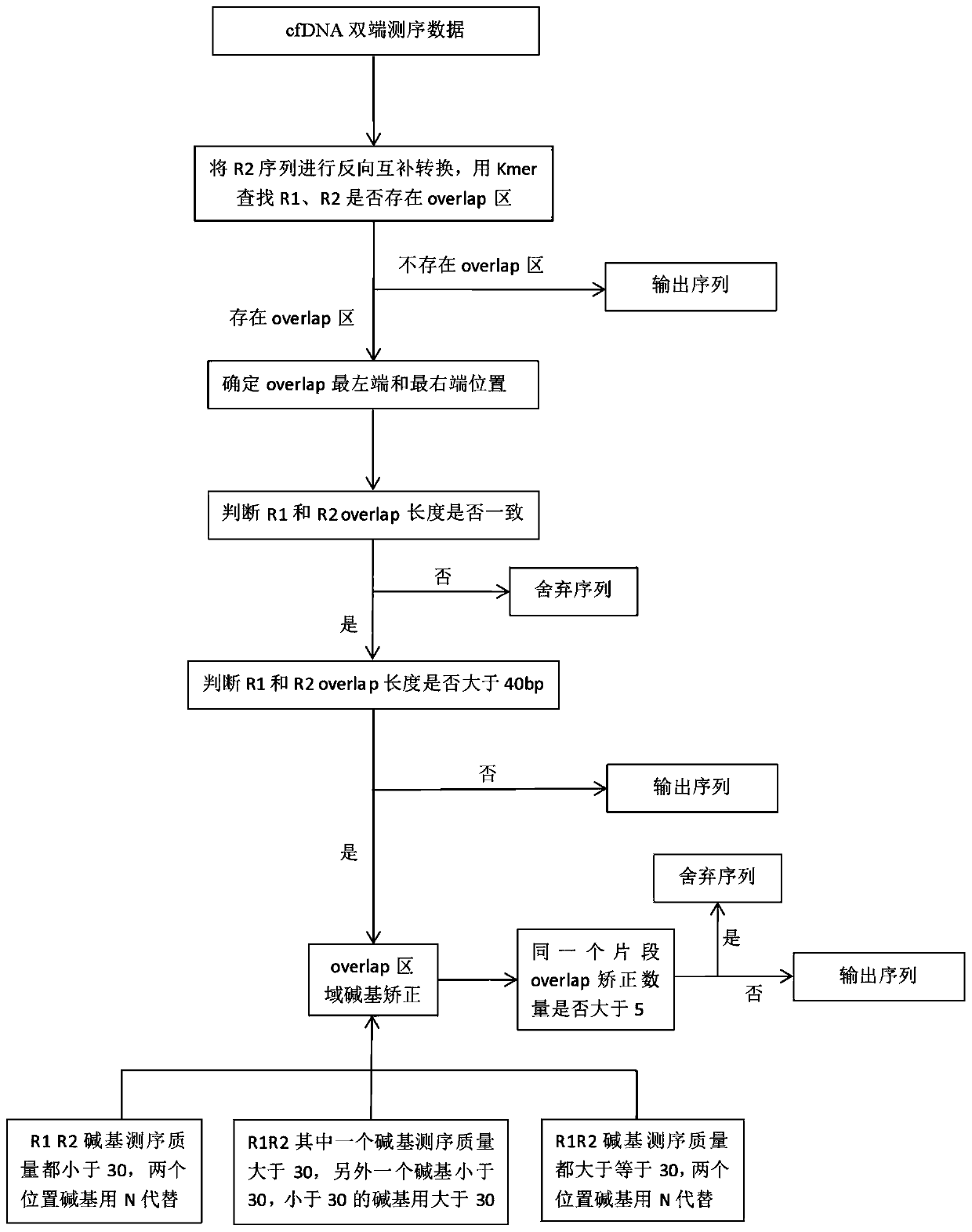
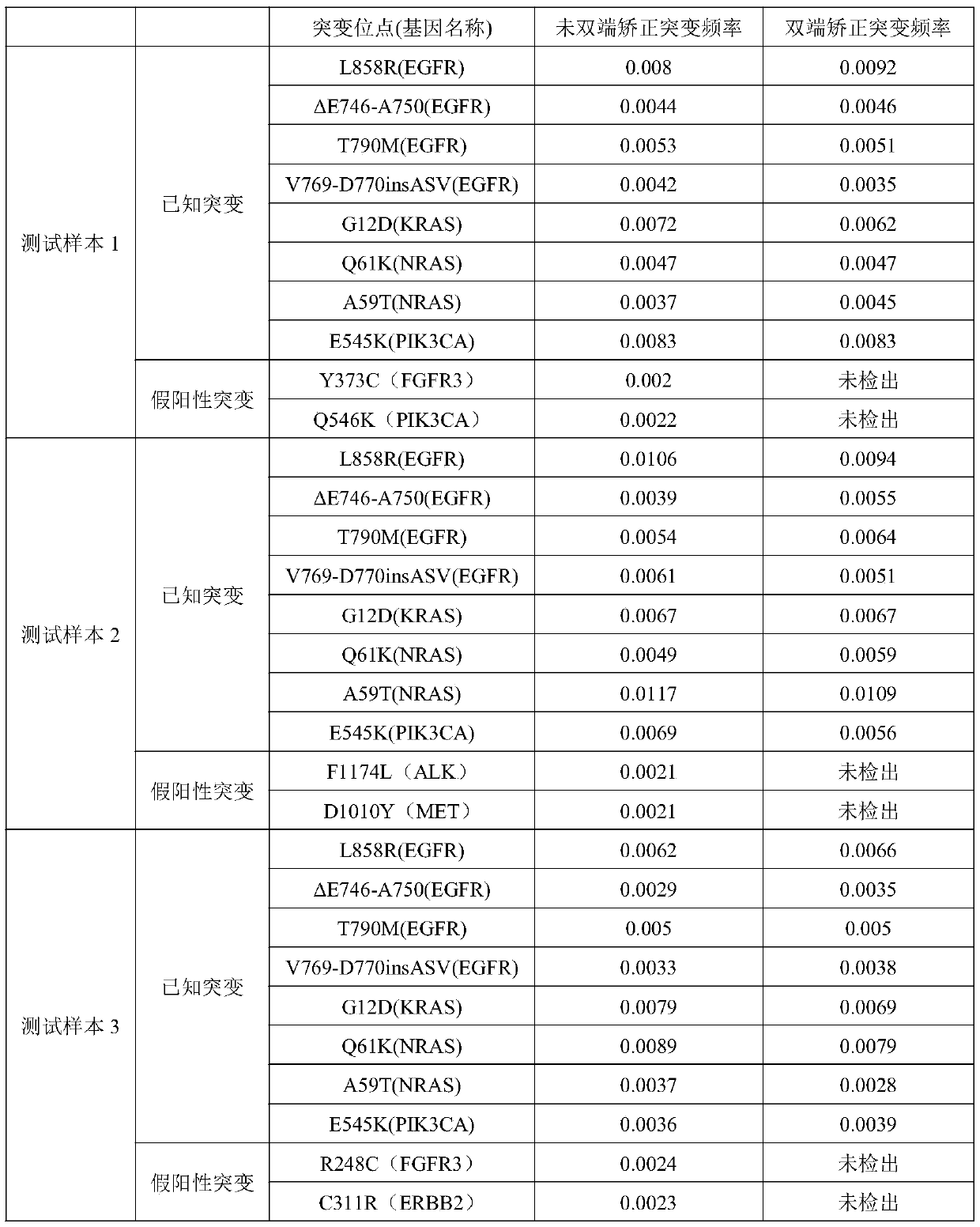
Method for dual-end correction of circulating tumor DNA sequencing data
PendingCN111321209AImprove accuracyReduce error rateMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGenes mutationGene bank
The invention discloses a method for dual-end correction of circulating tumor DNA sequencing data. The method comprises the steps of performing cfDNA extraction, performing targetted catching for establishing a gene bank, and performing sequencing; performing quality control on sequencing data; and performing dual-end correction on the sequencing data. A dual-end sequencing method is adopted, andtwo ends of the same DNA fragment are sequenced from the positive and negative directions. The ctDNA high-flux sequencing data is subjected to sequence overlap region alkali correction, because the dual-end sequencing overlap region sequence has concurrent characteristics, the sequencing error rate can be reduced, the ctDNA gene mutation detecting and analysing accuracy can be effectively improved, particularly low-enrichment gene mutation detection accuracy is improved, the false positive rate is reduced, and the application value of ctDNA detection to clinical treatment can be increased.
Owner:HANGZHOU HEYI GENE TECH
Establishment method of sinter gene bank and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of metallurgical chemical industry, and particularly relates to an establishment method of a sinter gene bank and application thereof. The establishment method of the sinter gene bank includes the following steps: 1) obtaining sinter samples with different composition information; 2) respectively obtaining sinter sample gene information of each sinter sample, wherein the sinter sample gene information includes microscopic information of the sinter sample, mesoscopic information of the sinter sample and macroscopic information of the sinter sample; and 3) establishing a database, which includes a correspondence relationship of composition information of each sinter sample and the sinter sample gene information corresponding to each sinter sample,to obtain the sinter gene bank. According to the method, intrinsic connections among composition, structures and performance of sinters can be established to facilitate better prediction and analysisof the performance of the sinters, and a vacancy of material gene databases can be compensated for.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for large-scale inducing plant gene mutation
InactiveCN1433675AMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyPlant genetic engineeringGossypium hirsutum
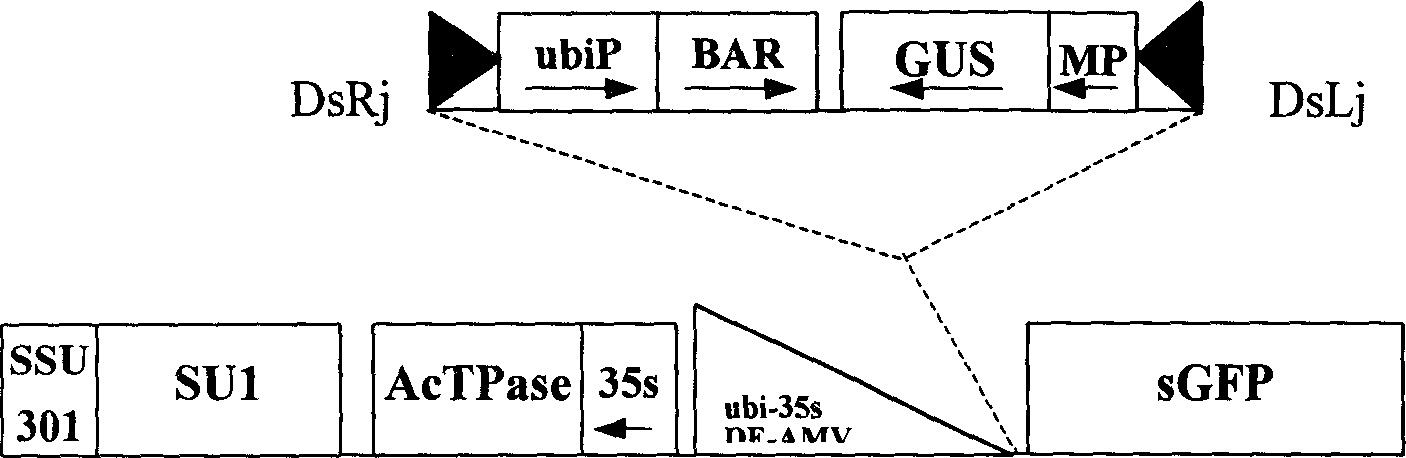
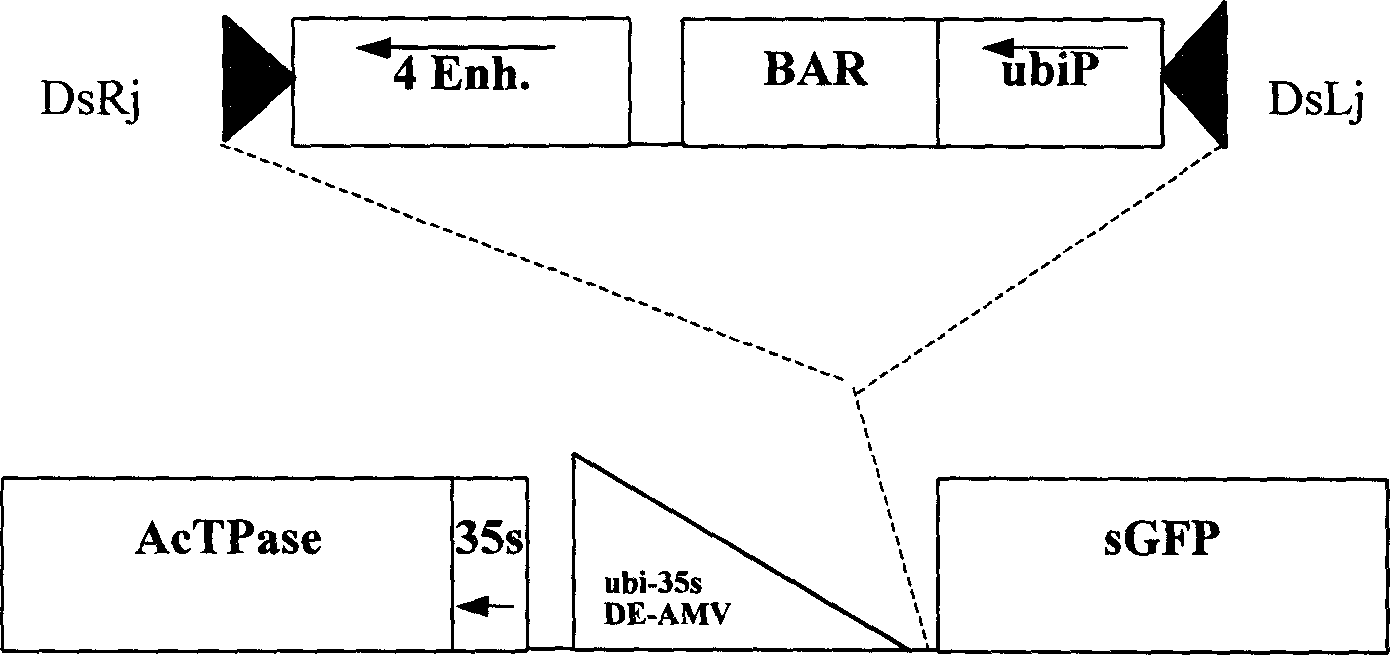
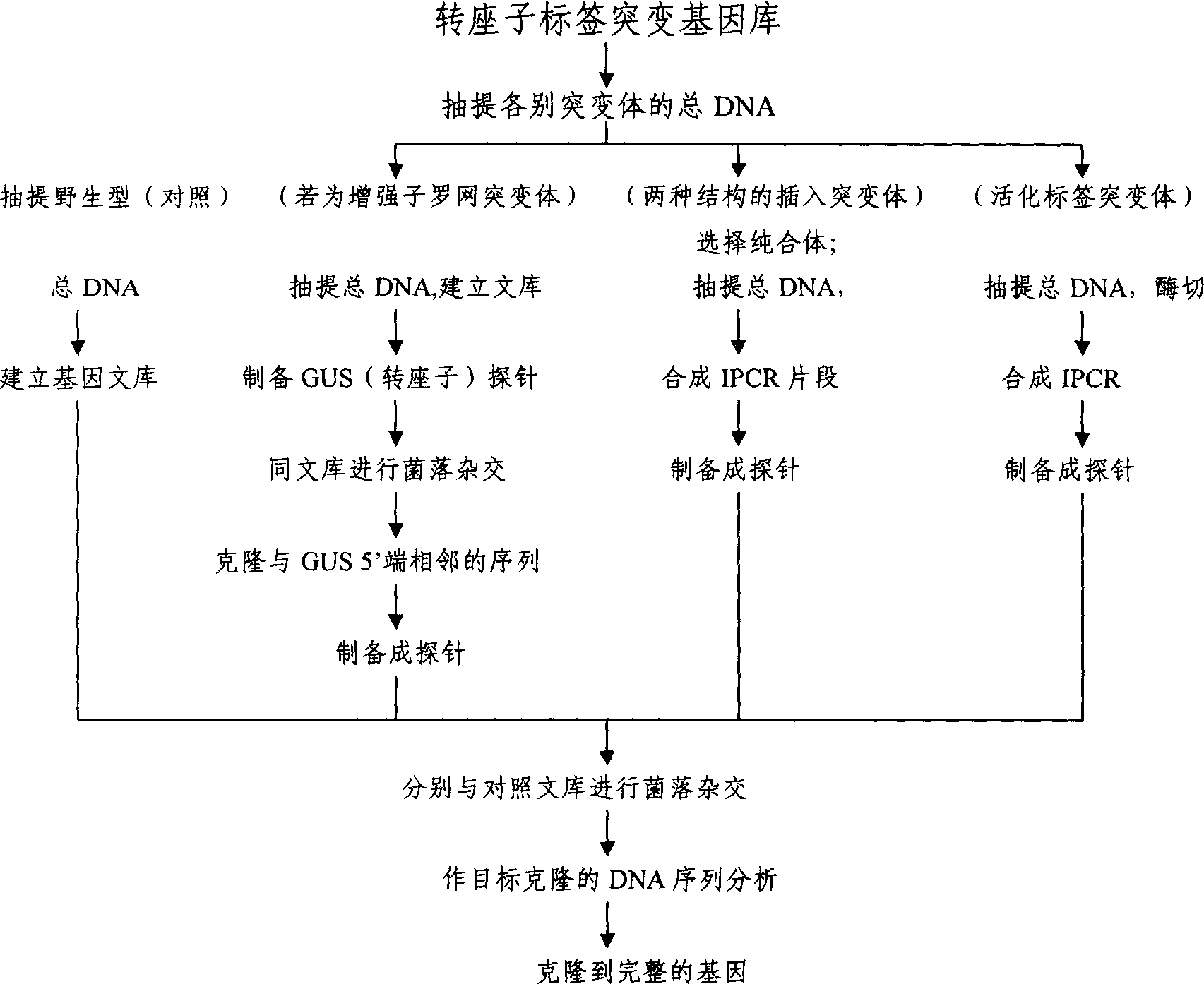
The present invention belongs to the field of plant gene engineering technology. It is characterized by that it utilzies agrobacterium mediated conversion method to introduce the artificially-constructed transposon label, i.e. enhancer net and transposition activatino label into plant, specially into the cultivated terrestrial cotton genome, and utilizes the random transposition of transposon andrandom induced gene mutation mechanism to find functional gene on a large scale and create a plant transposon label mutation gene bank containing lots of mutant genes including fixed and non-fixed transposons. Said mutation bank material can further find new functional gene of said crop by means of continuously planting, and the any mutant gene of the mutation bank can be cloned by adopting transposon label method.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for constructing Exendin-4 high-yielding engineering bacterial strain
The invention relates to the alteration of an Exendin-4 target gene and the construction of an expression vector, belonging to the field of genetic engineering. The method comprises the following steps: alternating 70 percent of codons of an original gene according to the amino acid sequence of the Exendin-4 in the gene bank and combining with the preference ranking of codons of colon bacillus so that the gene can be efficiently expressed in the colon bacillus; adding proper enzyme cutting sites and enterokinase sites to establish the proper expression vector; converting a recombined expression vector into different colon bacillus engineering bacteria; and selecting bacterial strains capable of efficiently expressing the Exendin-4.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
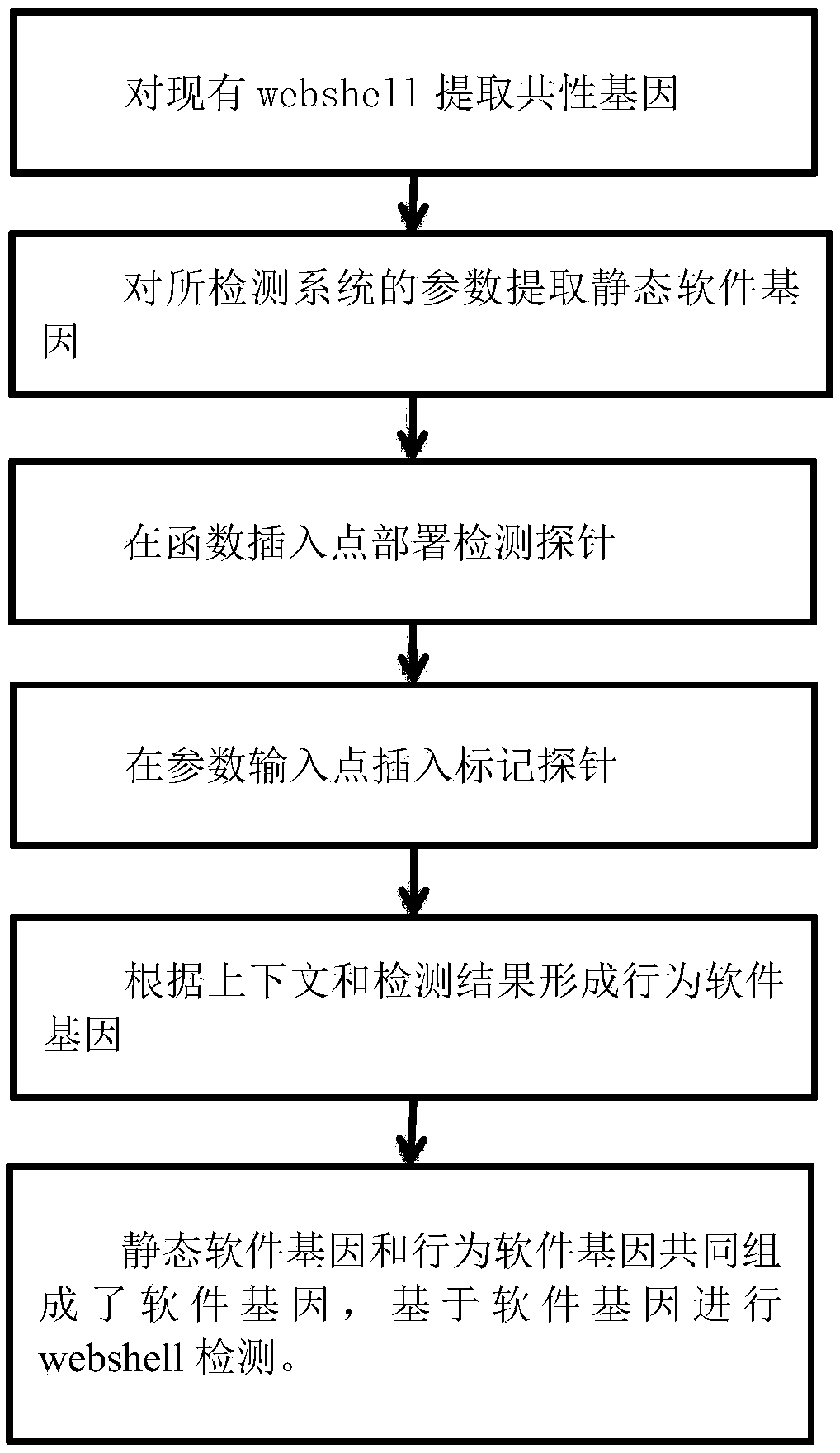
A method for extracting webshell software gene based on RASP for webshell detection
ActiveCN109240922AImprove extraction efficiencyImprove accuracySoftware testing/debuggingRaspGene bank
The invention discloses a method for extracting webshell software gene based on RASP technology, which can be used for webshell detection by deploying label probes and deploying detection probes to extract webshell software gene. The method includes extracting common software genes of webshell from existing webshell, Determining the parameter input point of the code of the system to be detected, extracting the input parameter, extracting the software gene and perfecting it as the static gene of the code of the system to be detected; Deploying RASP: determining the parameter input point of thesystem code to be detected, and marking the parameter input by inserting a marker probe; Determining a function insertion point of the system to be detected, and deploying a detection probe; Acquiringthe context of the code to be detected inserted into the detection probe, and forming a behavior gene of the code to be detected according to the detection result of the detection probe; comparing the software gene with webshell gene bank and virus trojan gene bank to determine whether it is webshell or not. The invention can improve the accuracy and efficiency of detecting webshell, and can be widely applied.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for cultivating polyploid dianthus caryophyllus germplasm
InactiveCN102217545AOvercome fertilityOvercoming activityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGermplasmCarnation
The invention discloses a method for cultivating polyploid dianthus caryophyllus germ plasm, which comprises the following steps: 2n gamete-containing diploid germplasm is cultivated which can be taken as a male parent to hybridize with a tetraploid female parent, the female parent is performed a castration and a bagging for 7 to 14 days during a full bloom stage, then an artificial pollination is performed, and the bag is removed and an ovary is taken off after pollinating for 15 - 45 days; the ovary is carried out a disinfection treatment and then cut off for taking off a white ovule, the ovule is performed an inoculation on an embryo culture medium for cultivating, the white ovule is grown to a black seed, a seed coat is cut off and a white embryo is taken off for continuous cultivating on a embryo culture medium, then a cultivation is conducted on a successive transfer culture medium for obtaining the polyploid dianthus caryophyllus germplasm. According to the invention, the diploid favorable gene and heterozygosity are successfully introduced in a tetraploid cultivation, which overcomes a problem of embryo abortion and greatly enriches a gene database of carnation genetic breeding, the invention is an effective approach of an objective trait introgression, and is beneficial to germplasmic introgression and gene flow of different ploidies, the hybridized progeny has more widely genetic variation and stable property as well.
Owner:FLOWER RES INST OF YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
System screening and clone identification method for heat shock protein genes of agasicles hygrophila
InactiveCN110106558AMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisKegg databaseFull length cdna
The invention relates to a system screening and clone identification method for heat shock protein genes of agasicles hygrophila and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The method comprises the steps that larvas of one to three ages, pupas of 2-6 days of age and imagoes which are subjected to eclosion in one day are taken, and the treatment samples above are collected and frozen for storage in liquid nitrogen; overall-length cDNA segment of mRNA is synthesized, an overall-length cDNA segment is screened, and cDNA gene banks different in capacity are established; the screened overall-length cDNA is subjected to secondary PCR amplification; the tail end of the overall-length cDNA is repaired; then secondary screening is conducted, and a testing gene bank is obtained; after the gene bank is established, the capacity of the gene banks is detected, after the gene bank quality detection result reaches the demand, on-computer sequencing is conducted, obtained non-redundant transcript sequences are compared with NR, Swissprot, GO, COG, KOG, Pfam and KEGG databases, annotation information of a transcript is obtained, all the heat shock protein genes are screened, EST sequence groups of each piece of heat shock protein are spliced and assembled, the most complete gene sequence is obtained, and finally according to the complete sequence, a primer is designed, and clone sequencing is conducted.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
Rice MeRING29 gene, coding protein, recombinant vector and application
ActiveCN111808870AImprove disease resistanceEasily damagedLigasesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyGene bank
The invention provides a rice MeRING29 gene, a coding protein, a recombinant vector and application, and relates to the technical field of genetic engineering. A full-length cDNA sequence of the YunnanOryza meyeriana Baill. MeRING29 gene is cloned for the first time, a plant disease resistance gene pool is enriched, and the rice MeRING29 gene has important value for further research on the rice disease resistance molecular mechanism and application thereof. The invention also provides a coding amino acid sequence of the MeRING29 gene and a recombinant vector containing the gene and application, and particularly relates to application in improving rice disease resistance. Rice plants transformed with the MeRING 29 gene have a significantly improved resistance to bacterial blight and rice blast.
Owner:云南省农业科学院生物技术与种质资源研究所
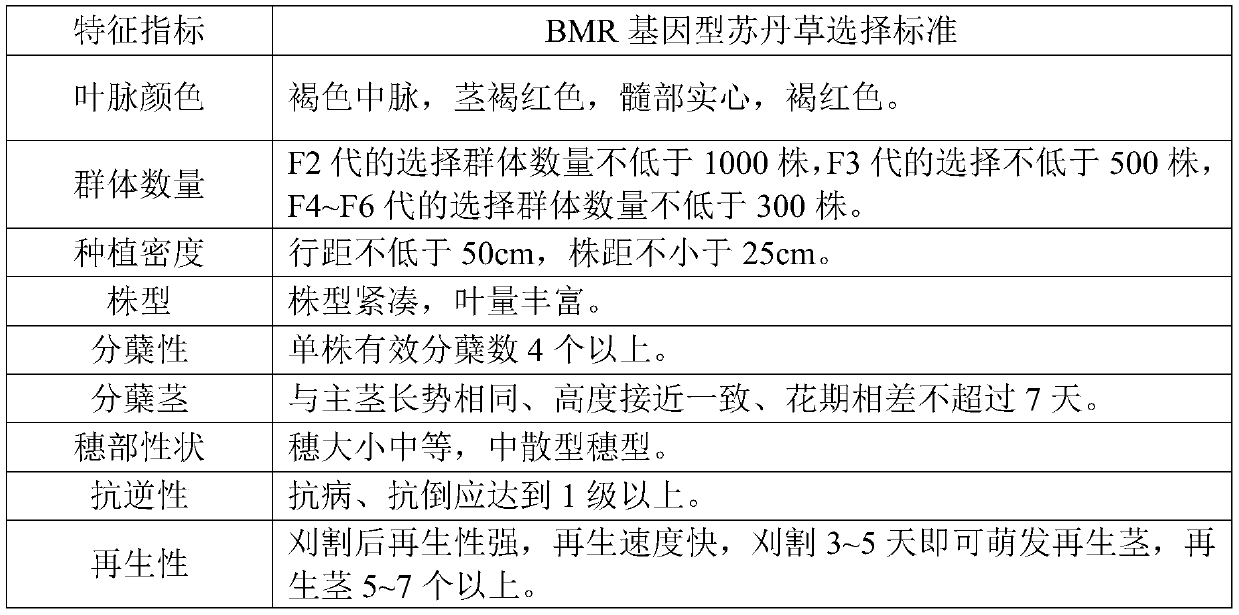
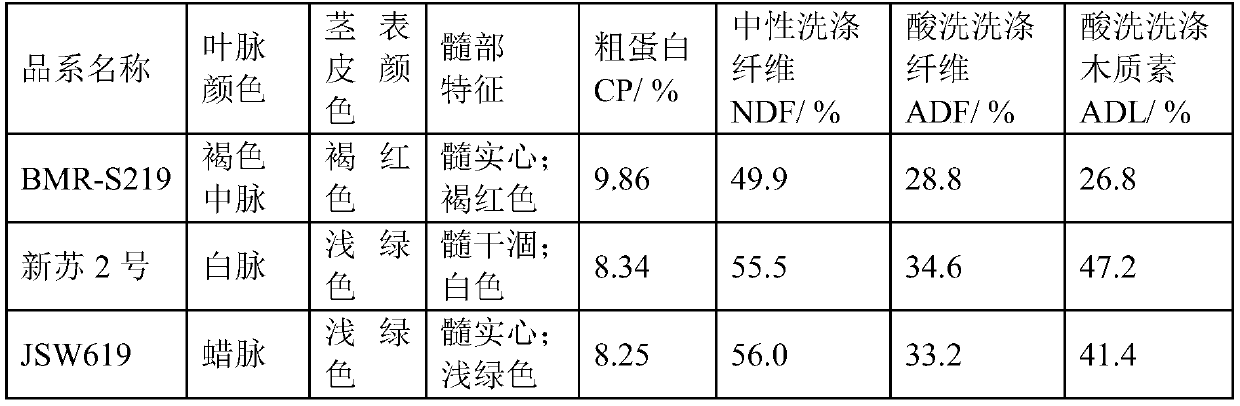
Hybridization and breeding method of BMR genotype sudangrass
PendingCN110679479AImprove feed qualityLow lignin contentPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyHybrid seed
The invention provides a hybridization and breeding method of BMR genotype sudangrass. The hybridization and breeding method of the BMR genotype sudangrass comprises the following steps: carrying outhybridization by taking the sudangrass as a male parent to obtain F0-generation hybrid seeds; planting the F0-generation hybrid seeds, selecting 8-10 true hybrids, and carrying out bagging and selfingto obtain F1-generation group mixed seeds; carrying out F2-F7 generation selection according to a pedigree method, wherein the selection standard is as follows: the midrib is brown, plants are compact, and the included angle between a tillering stem and a main stem is within 5 degrees; the tillering performance of a single plant is strong, and the number of effective tillers is more than 4; the tiller stem and the main stem have the same growth vigor and the same height, and the florescence difference is not more than 7 days; the size of panicles is moderate, and the panicle type is medium scattered; carrying out individual plant selfing with disease resistance and lodging resistance of more than 1 level; and finally obtaining the BMR genotype sudangrass through selection of six successive generations. The BMR genotype sudangrass bred by the invention enriches a sudangrass germplasm resource gene bank.
Owner:DRY LAND FARMING INST OF HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
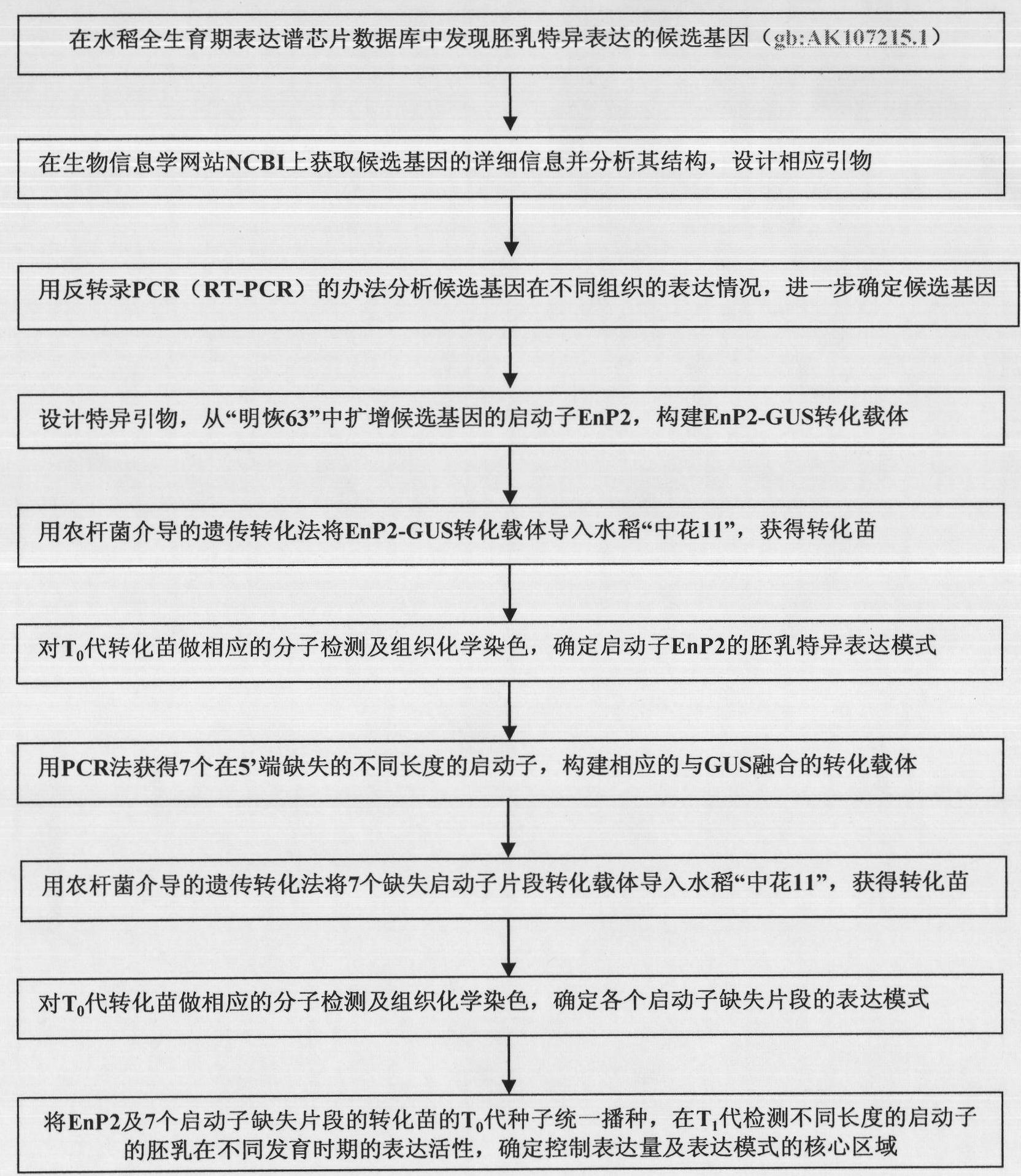
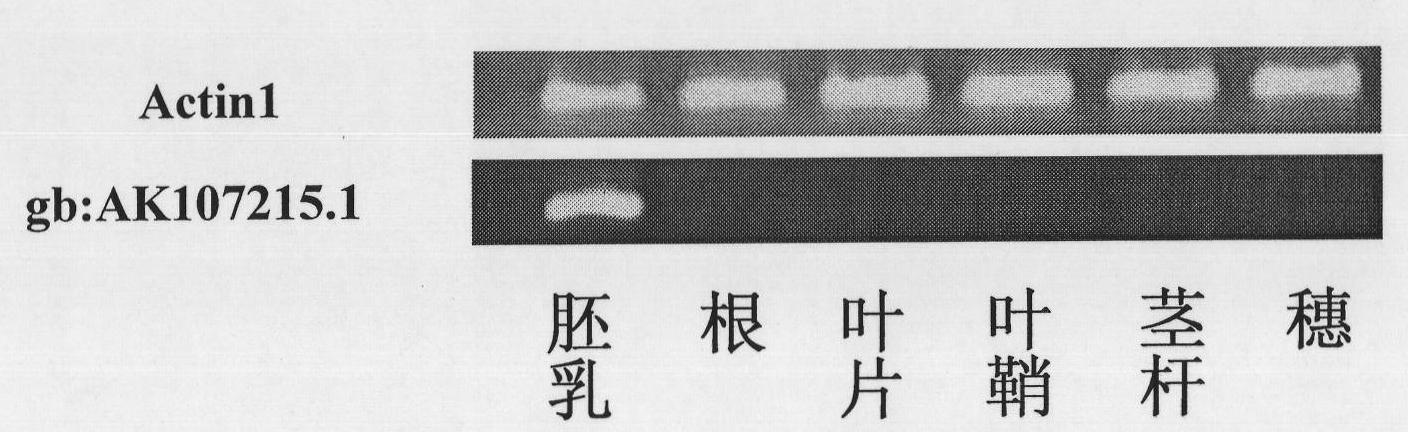
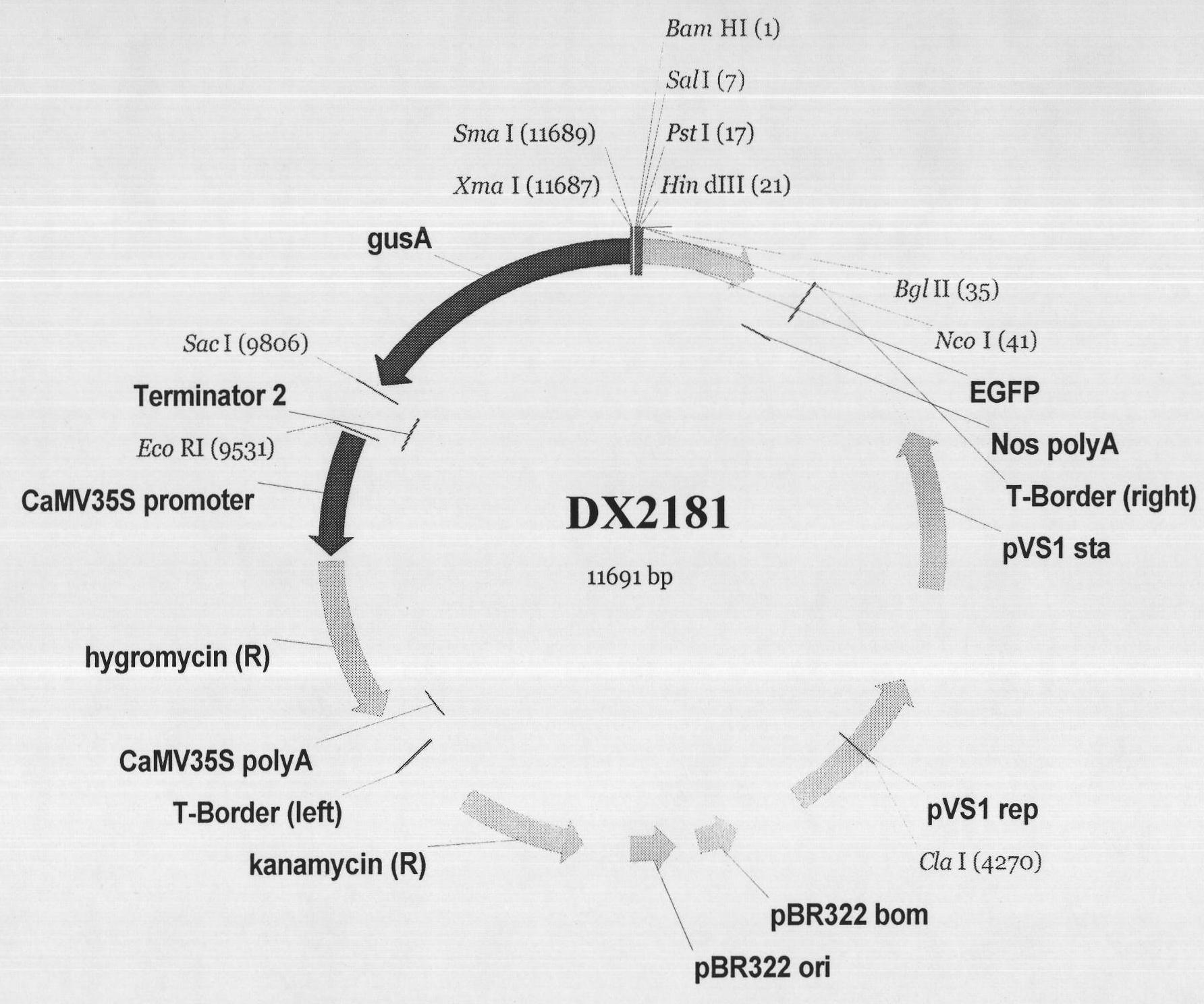
Separation clone and expression mode identification of promotor region of rice endosperm special expression gene
The invention belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering. Seven promotors with different lengths (EnP2, EnP2-967, EnP2-771, EnP2-591, EnP2-281, EnP2-186 and EnP2-155) at the upstream of the same endosperm special expression gene (GeneBank has an accession number gb: AK107215.1) are cloned in a rice gene bank, and nucleotide sequences thereof are shown in SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO:2, SEQ ID NO:3, SEQ ID NO:4, SEQ ID NO:5, SEQ ID NO: 6 and SEQ ID NO: 7. The promotors are expressed in endosperm of a transferred plant, and the expression is reduced with the growth of the endosperm; and the promotors are not expressed in other tissues, such as leaves, leaf sheaths, stems and straws, roots, flowers, glumes and endosperms. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the seven promotors and corresponding expression vectors, and application thereof guided into rice by using a transgenosis method mediated by bacillus.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
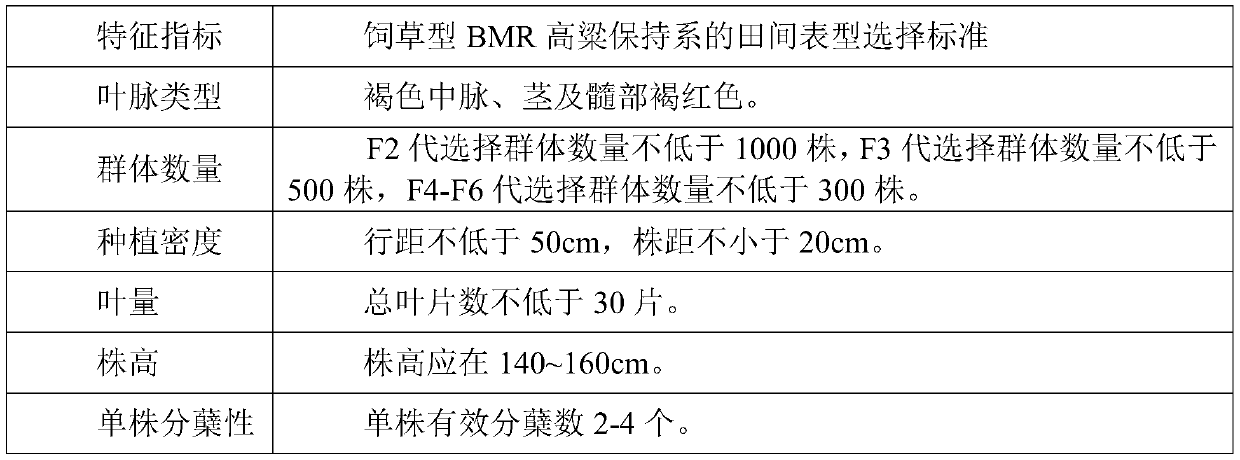
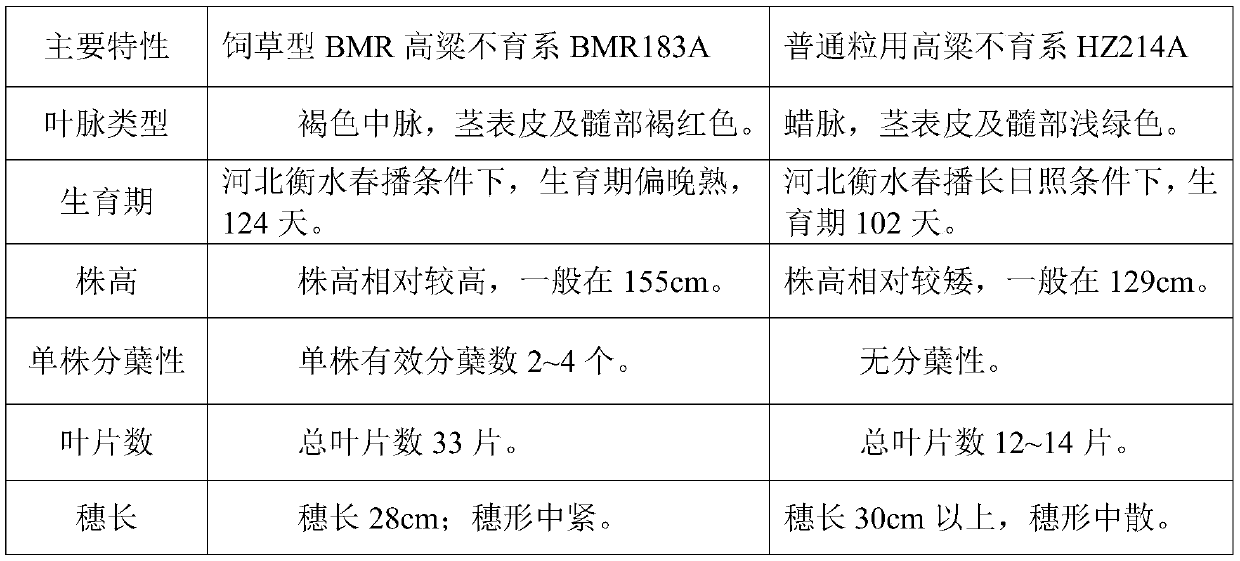
Breeding method of forage-type BMR sorghum sterile line
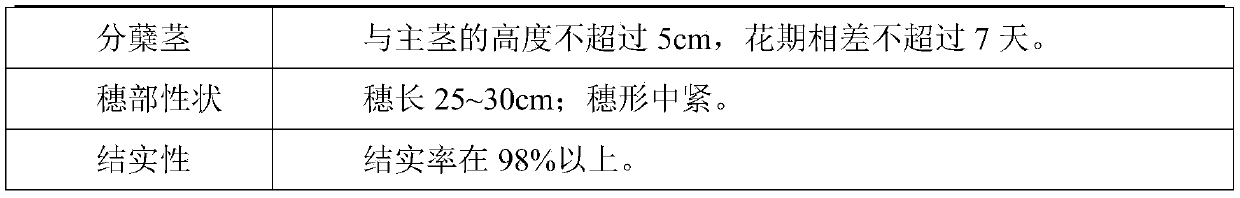
ActiveCN110679478AImprove feed qualityClarify parental selection criteriaPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyGene bank
The invention discloses a breeding method of a forage-type BMR sorghum sterile line and belongs to the technical field of forage variety breeding methods. The breeding method includes: taking a BMR genotype sorghum maintainer line as a female parent and a forage-type sorghum maintainer line with tillering performance as a male parent for hybridizing, and breeding to obtain a forage-type BMR sorghum maintainer line, wherein standards include that midribs are brown, plant height is 140-160cm, and total leaf number is not less than 30; the tillering performance is high, and single-plant effectivetillering number is 2-4; tillering stem and main stem height difference does not exceed 5cm, and flowering period difference does not exceed 7d; ear characters are good, and ear length is 25-30cm; ear shape is intermediately tight; fruiting rate is higher than 98%; performing backcross transformation with a common sorghum sterile line, and selecting completely sterile BMR single plants consistentwith the forage-type BMR sorghum maintainer line in agronomic character in backcross population to obtain the forage-type BMR sorghum sterile line. The forage-type BMR sorghum sterile line bred by the method enriches sorghum sterile line gene pools.
Owner:DRY LAND FARMING INST OF HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
NGF gene as molecular marker of sheep yeaning traits and application thereof
ActiveCN106256912AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMarker-assisted selectionNucleotide
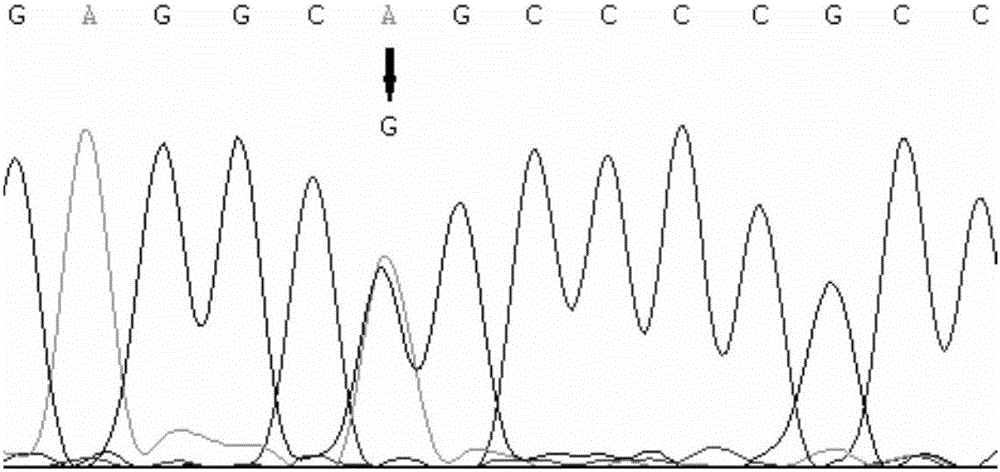
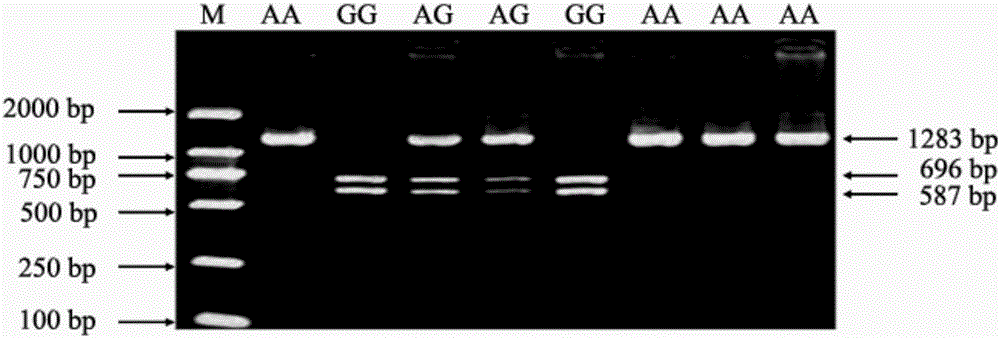
The invention belongs to the technical field of a livestock molecular marker, and more specifically relates to NGF gene as the molecular marker of sheep yeaning traits and an application thereof. The molecular marker is obtained by NGF gene (Gene Bank ID: 101104540) through cloning, a nucleotide sequence of the molecular marker is shown as a sequence table SEQ ID NO:1, a base mutation of G greater than A is existed at 689th bp of the sequence table SEQ ID NO:1, The SfiI-RFLP digestion polymorphism is generated due to mutation. In the sheep, the bit GG genotype sheep yeaning number is more than the AA genotype sheep yeaning number by 0.58. The invention also discloses a primer pair used for amplifying a NGF gene part DNA sequence and a molecule-labeled detection method, and provides novel labeling resource for marker auxiliary selection of the sheep yeaning traits.
Owner:甘肃润牧生物工程有限责任公司
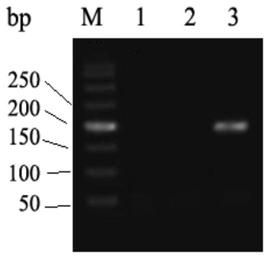
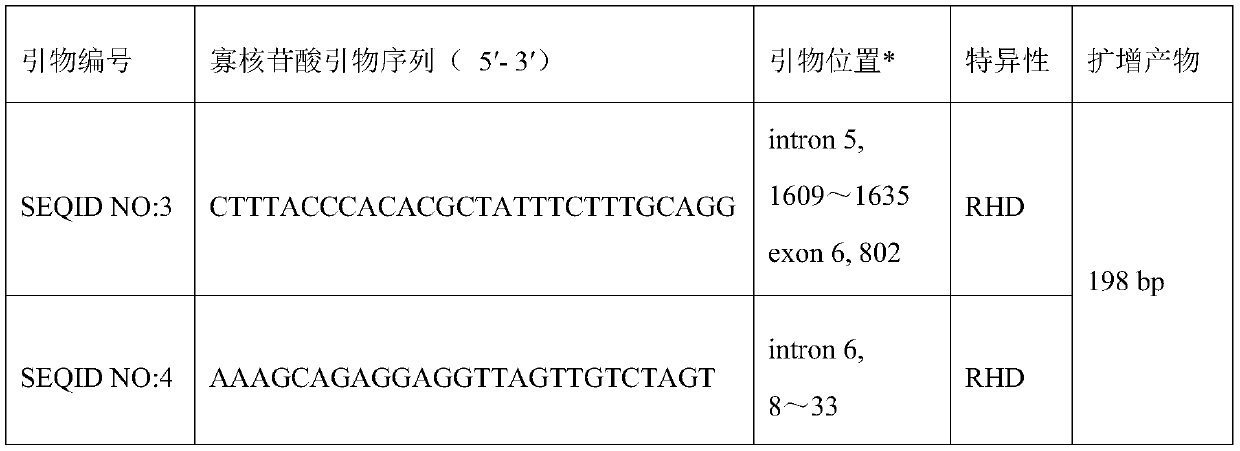
RHD-T268A mutant and detection thereof
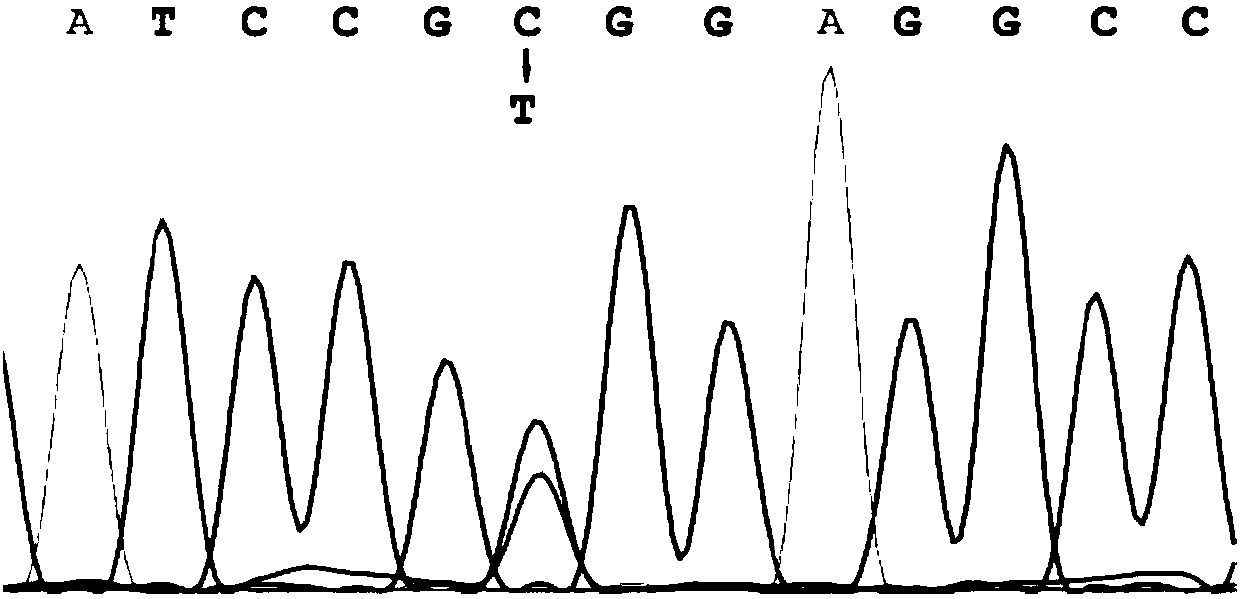
ActiveCN111304211AExtensive scientific research application valueMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGene bankRhD antigen
The invention discloses RhD blood group antigen RHD-T268A mutant RHD802A>G allele. A wild type RHD gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and a mutant type RHD gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. A specific primerused for detecting the RhD blood group antigen mutant is also disclosed; the upstream primer is shown as SEQ ID NO: 3, and the downstream primer is shown as SEQ ID NO: 4. Through the RHD-T268A mutantand detection thereof, highly sensitive and accurate detection of the presence of the mutant genes in gene banks can be achieved.
Owner:WUXI NO 5 PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Breeding method of photoperiod high-sensitive BMR sorghum sterile line
ActiveCN110679477AThe hybrid combination went wellCreate selection criteriaPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyGene bank
The invention discloses a breeding method of a photoperiod high-sensitive BMR sorghum sterile line, and belongs to the technical field of breeding methods of forage varieties. According to the breeding method, a BMR sorghum maintainer line serves as a female parent, photoperiod high-sensitive forage sorghum serves as a male parent, hybridization and combination of the female parent and the male parent are implemented in Sanya city, Hainan province, the photoperiod high-sensitive BMR sorghum maintainer line is bred by the aid of differences of long and short sunshine time, selection standards of the maintainer line include that non-heading or late-heading brown midrib single plants at a growth stage are selected under north spring sowing long sunshine conditions, heading brown midrib singleplants within 60 days are selected under short sunshine conditions in Sanya city, Hainan province, and continuous breeding of six generations is implemented to obtain the photoperiod high-sensitive BMR sorghum maintainer line. Backcross breeding of the maintainer line and a common sorghum sterile line is implemented, completely sterile brown midrib single plants with agronomic characters consistent with those of the photoperiod high-sensitive BMR sorghum maintainer line are selected in backcross population to obtain the photoperiod high-sensitive BMR sorghum maintainer line. According to themethod, a sorghum sterile line gene bank is enriched.
Owner:DRY LAND FARMING INST OF HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Redroot wild broad bean tissue culture rapid propagation new method
ActiveCN108834893ALong collection periodYield is not affectedHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGene bankShoot
The invention discloses a redroot wild broad bean tissue culture rapid propagation new method. The redroot wild broad bean tissue culture rapid propagation new method comprises the steps of selectingexplants, cleaning and disinfecting the explants, inducing multiple shoots, proliferating multiple shoots, rooting and the like. A tissue culture technology of redroot wild broad beans is explored; the ideal culture conditions of obtaining a sterile material, inducing the multiple shoots, proliferating the multiple shoots, rooting the multiple shoots and the like are determined; a tissue culture system of the redroot wild broad beans is successfully established finally; technical basis is laid for realizing protection and cultivation of redroot wild broad bean wild resources, demand on the seedlings and establishment of a gene bank; the problems of overdevelopment of the redroot wild broad bean wild resources, little medicine supply and scaleless planting are solved.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANTS YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
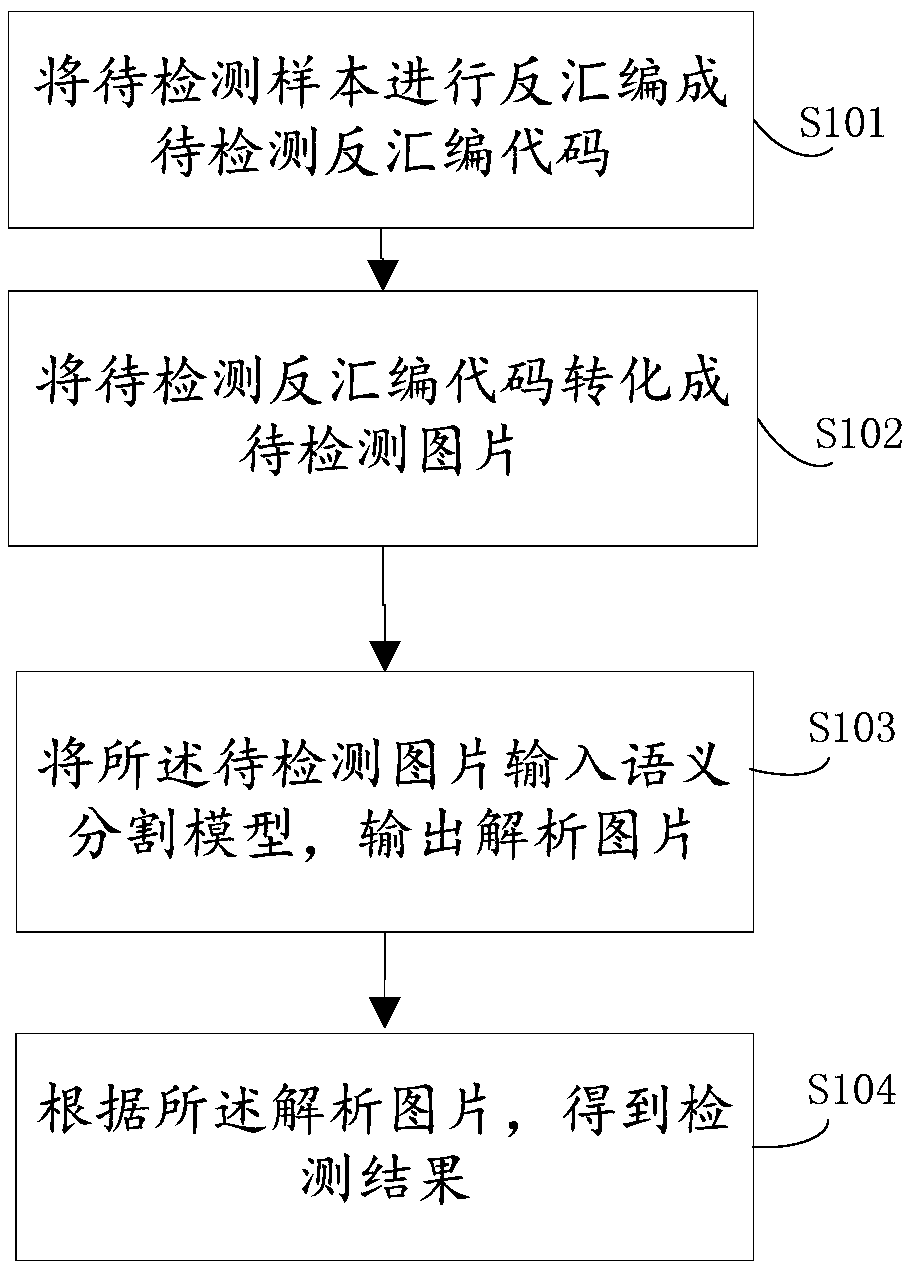
Rapid malware gene detection method and device based on semantic segmentation
ActiveCN109492396AImprove matching detection efficiencyImprove the accuracy of gene identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionPlatform integrity maintainanceFeature extractionGene bank
The invention provides a rapid malicious software gene detection method and device based on semantic segmentation, the matching detection efficiency of real-time samples can be greatly improved through a semantic segmentation model trained by a gene bank, and the trained semantic segmentation model does not need to carry the characteristics of the gene bank and even can be embedded into an offlinereal-time safety product; the gene recognition accuracy of malicious deformation can be improved through the automatic abstract feature extraction characteristic and the follow-up mature optimizationtechnology.
Owner:HANGZHOU ANHENG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
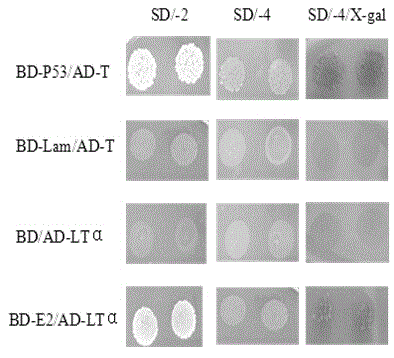
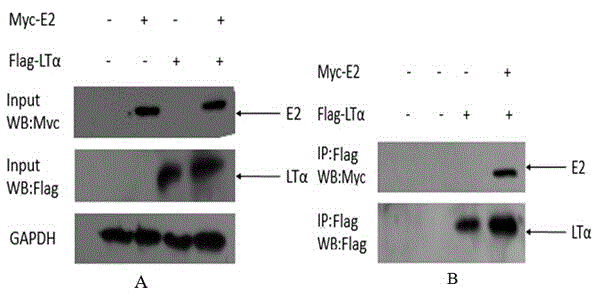
Human protein LT-alpha interacting with hepatitis g virus E2 protein
ActiveCN105085655AClear resultEasy to analyzeTumor necrosis factorFermentationCDNA libraryNucleotide
The invention discloses human protein LT-alpha interacting with hepatitis g virus E2 protein. An amino acid sequence of the human protein LT-alpha is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and a nucleotide sequence for coding genes of the human protein LT-alpha is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The human protein LT-alpha capable of achieving interaction with the hepatitis g virus E2 protein is obtained by screening a human T lymphocyte cDNA gene bank through a hepatitis g virus by utilizing a fourth-generation yeast two-hybrid method, and positive verification is performed on the interacting protein through a co-immunoprecipitation method. According to the human protein LT-alpha, a certain theoretical basis is provided for studying the action mechanism between the hepatitis g virus and an HIV-1 virus.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Seven synthesized shRNA (short hairpin ribonucleic acid) molecules for inhibiting expression of BMPR-1B (bone morphogenetic protein receptor-1B) genes
ActiveCN102433337AEnhanced inhibitory effectSignificant technological progressDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceWestern blot
The invention provides a synthesized shRNA molecule for inhibiting expression of BMPR-1B (bone morphogenetic protein receptor-1B) genes. According to sheep BMPR-1B genes (a NM_001009431.1 sequence) in a Gene Bank, a shRNA (short hairpin ribonucleic acid) molecule group interfering BMPR-1B gene transcription is designed by shRNA design software, 8 shRNA sequences aiming at different loca are screened from 34 designed shRNA molecules according to structures and positions and are synthesized; two synthesized complementary single-stranded shRNA molecules form double strands after being annealed and are connected to pLL3.7 slow virus interference vectors respectively to construct 8 slow virus interference RNA plasmids (pLL-BMPR-1B-shRNA), the interference RNA plasmids and BMPR-1B expression vectors produce toxin by a liposome transfection 293 T method, and 7 shRNA molecules which obviously inhibit the BMPR-1B genes are obtained after being detected and expressed by a fluorescence PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and a Western blot. The inhibition efficiency reaches more than 90 percent in an mRNA (messenger RNA) level, and the inhibition rate of BMPR-1B proteins reaches more than 80 percent.
Owner:新疆维吾尔自治区畜牧科学院中国-澳大利亚绵羊育种研究中心
Inkpad for anti-counterfeiting by using single nucleotide polymorphous biogenetic marker
InactiveCN101891986ALong durationPrevent decipheringMicrobiological testing/measurementInksGene bankNucleotide
The invention relates to an inkpad for anti-counterfeiting by using a single nucleotide polymorphous biogenetic marker. The inkpad comprises a common inkpad and is characterized by further comprising 0.1 to 10 weight percent of target gene segment PCR amplification product mixture and 0.001 to 0.1 weight percent of solution of a DNA enzyme inhibitor, wherein the target gene segment PCR amplification product is obtained by amplifying a SNP locus-containing gene segment. The inkpad amplifies part of segments from a complicated genome DNA by searching a sequence where the conventional known SNP locus is in a gene bank and by designing a gene segment of a specificity amplification individual of a primer and effectively prevents other people from decoding and counterfeiting. At the same time, the DNA is stable and can be stored for a long time, even for thousands of years.
Owner:叶欣
Preparation method and application of humanized neutralized anti-influenza NS1 genetic engineering antibody
The invention relates to a preparation method and an application of a humanized anti-influenza virus NS1 protein neutralized antibody. Antibodies capable of being combined with the antigenic specificities of influenza A viruses NS1 are directly screened from a human antibody gene bank through applying a gene engineering technology and a phage surface display technology so as to obtain and express antibody genes of the antibodies. The antibody is used for evaluating clinical medicaments for resisting the influenza A viruses and treating the influenza A viruses.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com