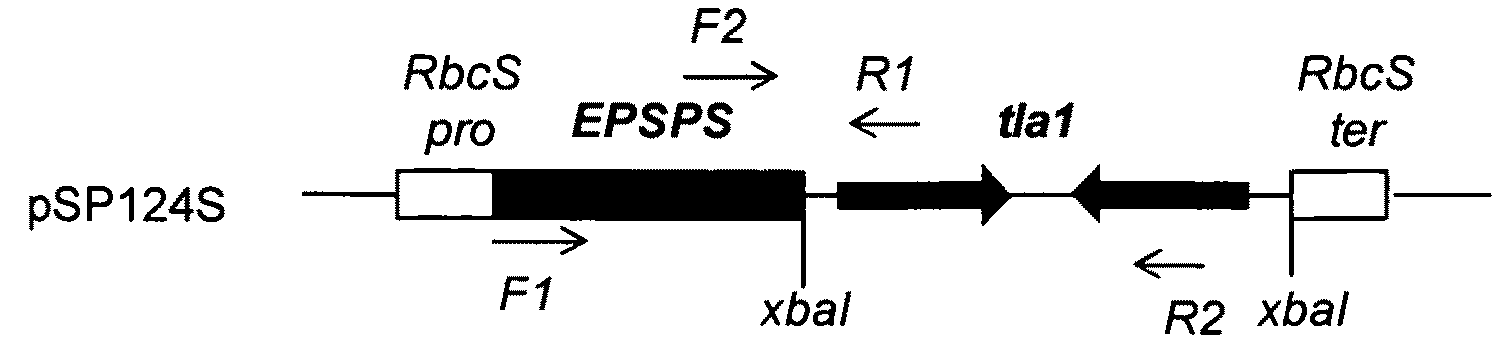
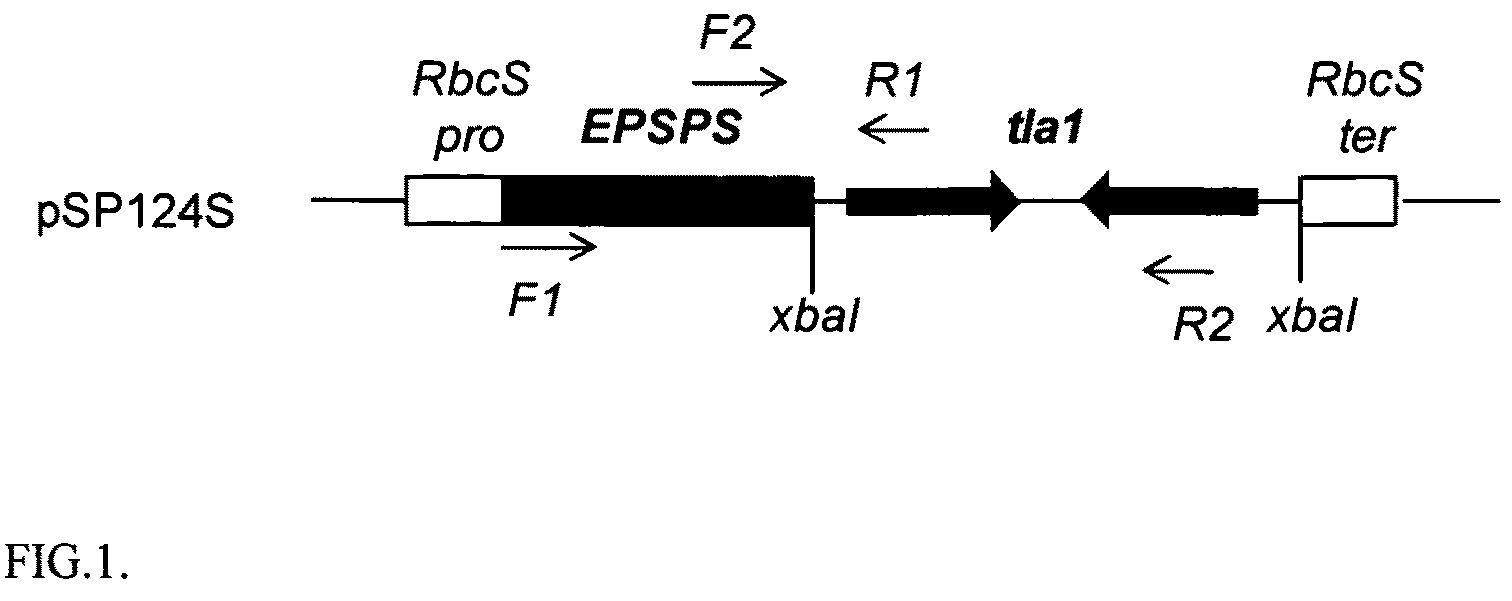
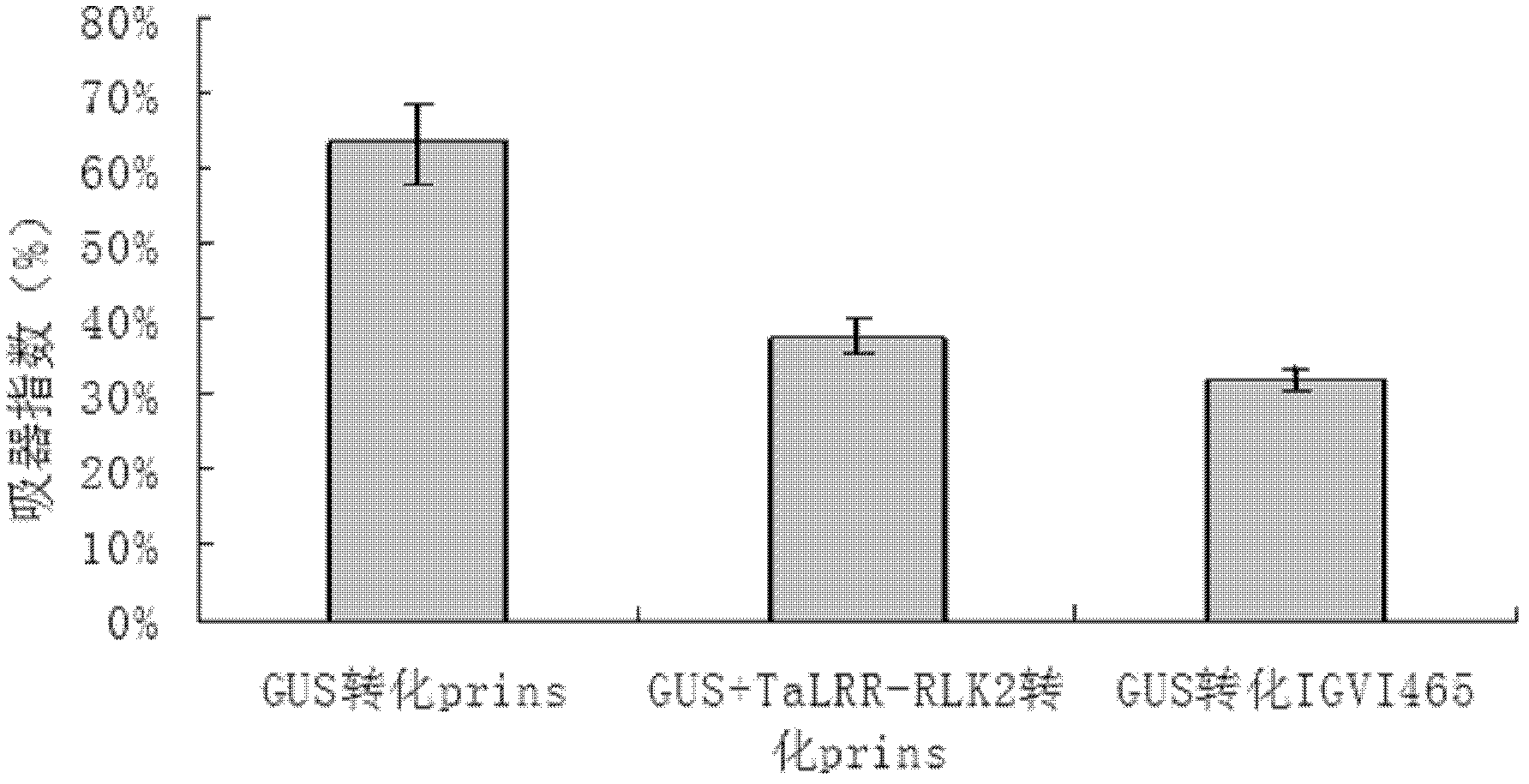Patents
Literature
259 results about "Introgression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Introgression, also known as introgressive hybridization, in genetics is the movement of a gene (gene flow) from one species into the gene pool of another by the repeated backcrossing of an interspecific hybrid with one of its parent species. Purposeful introgression is a long-term process; it may take many hybrid generations before the backcrossing occurs.
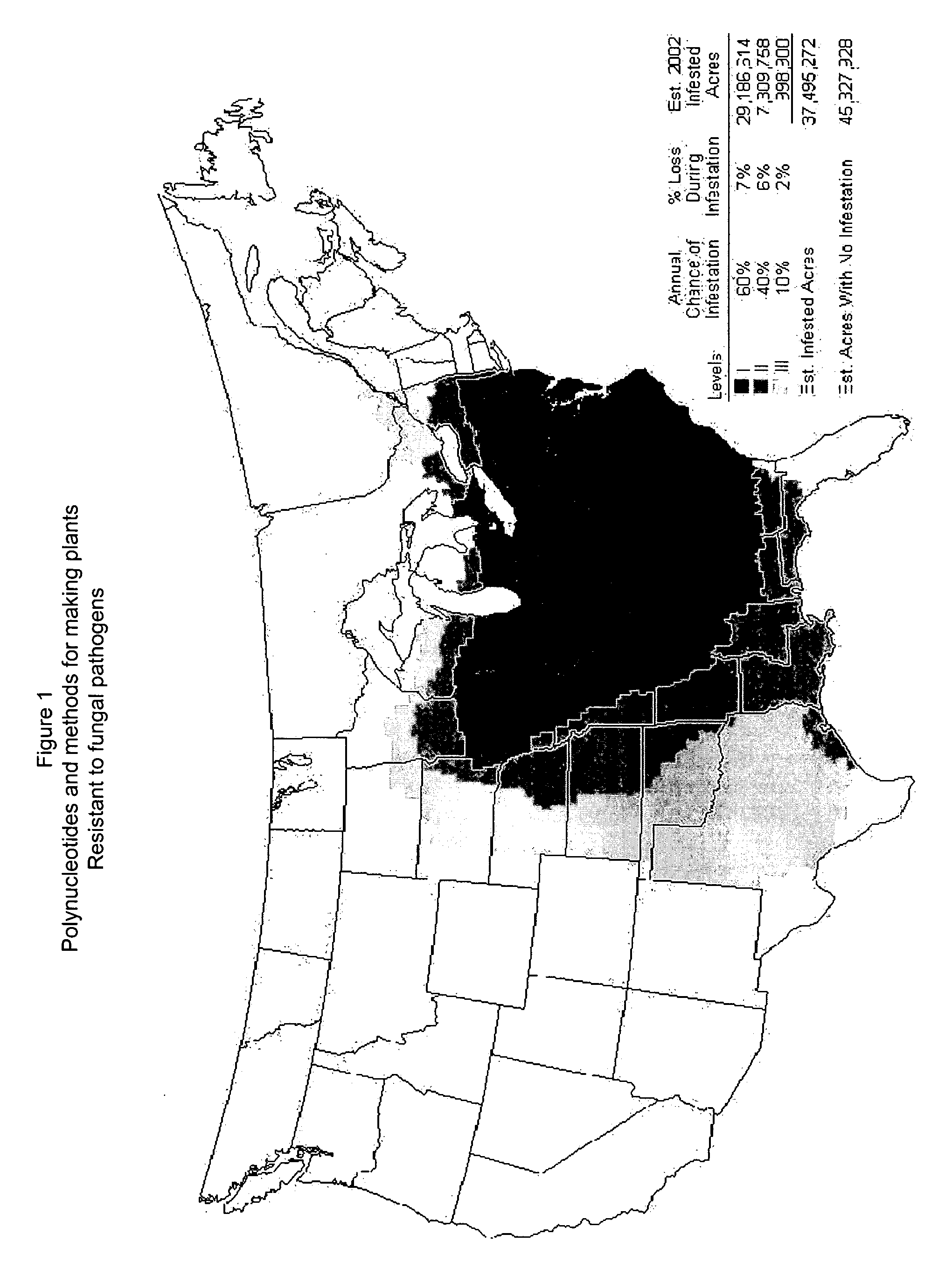
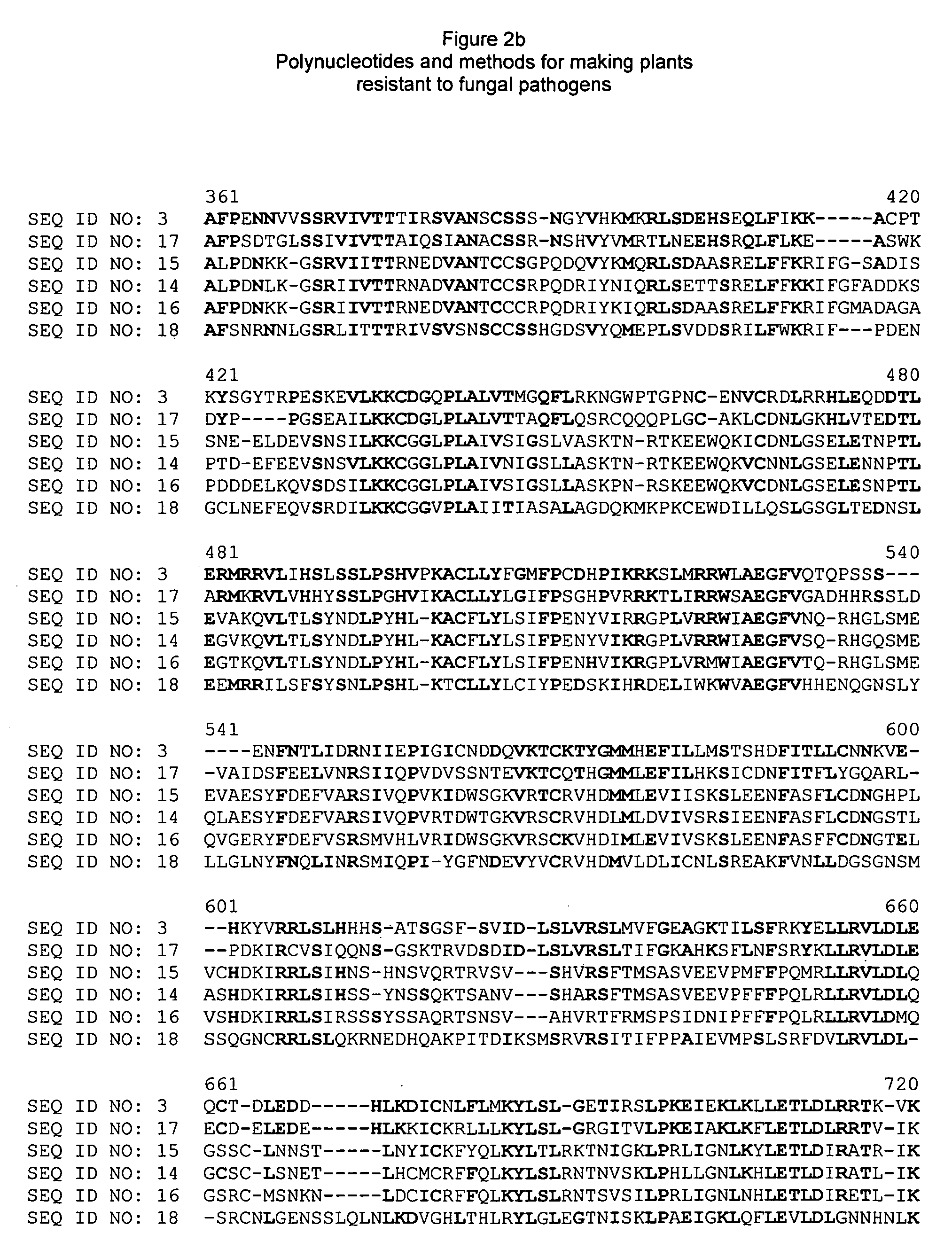
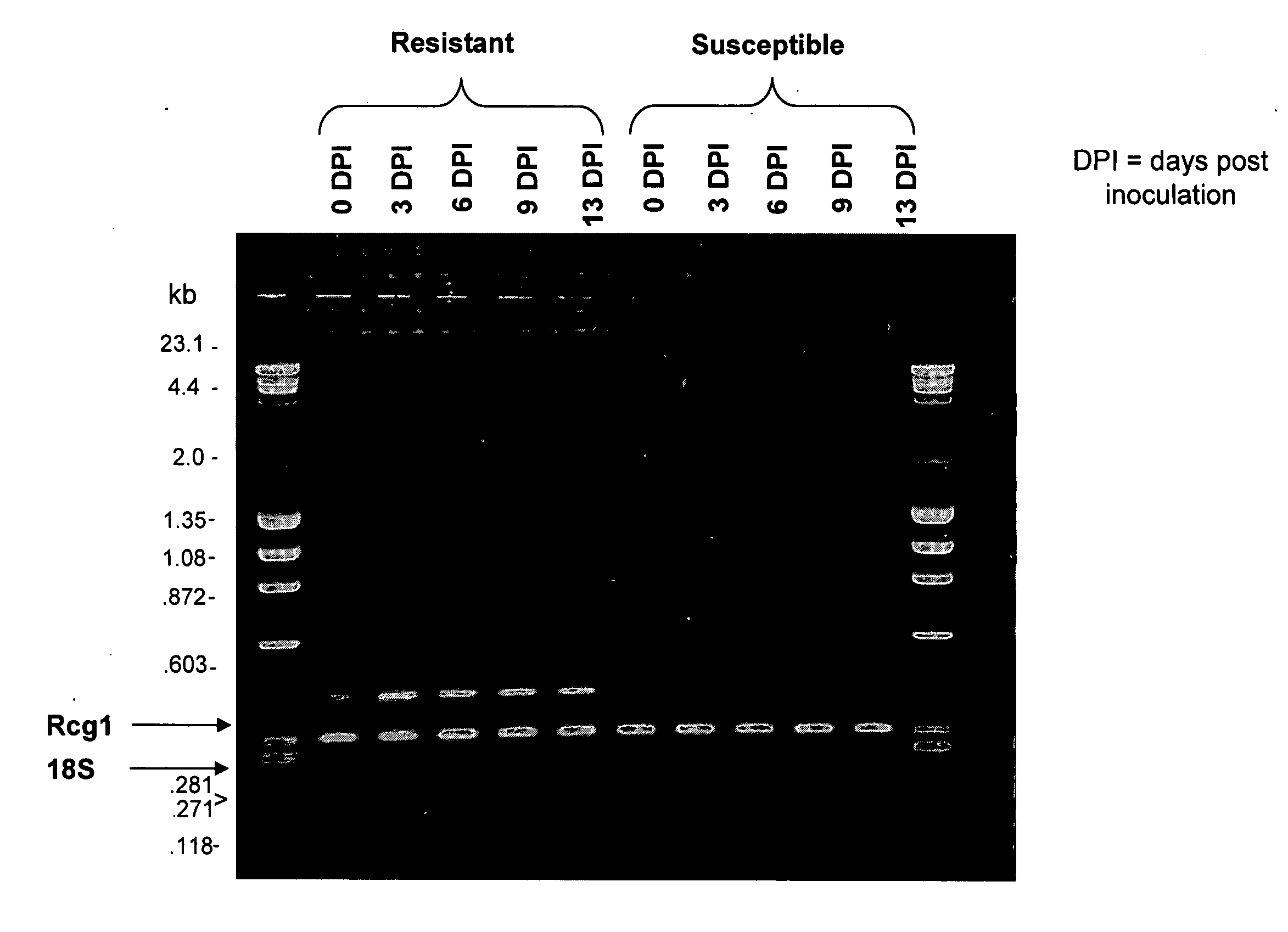
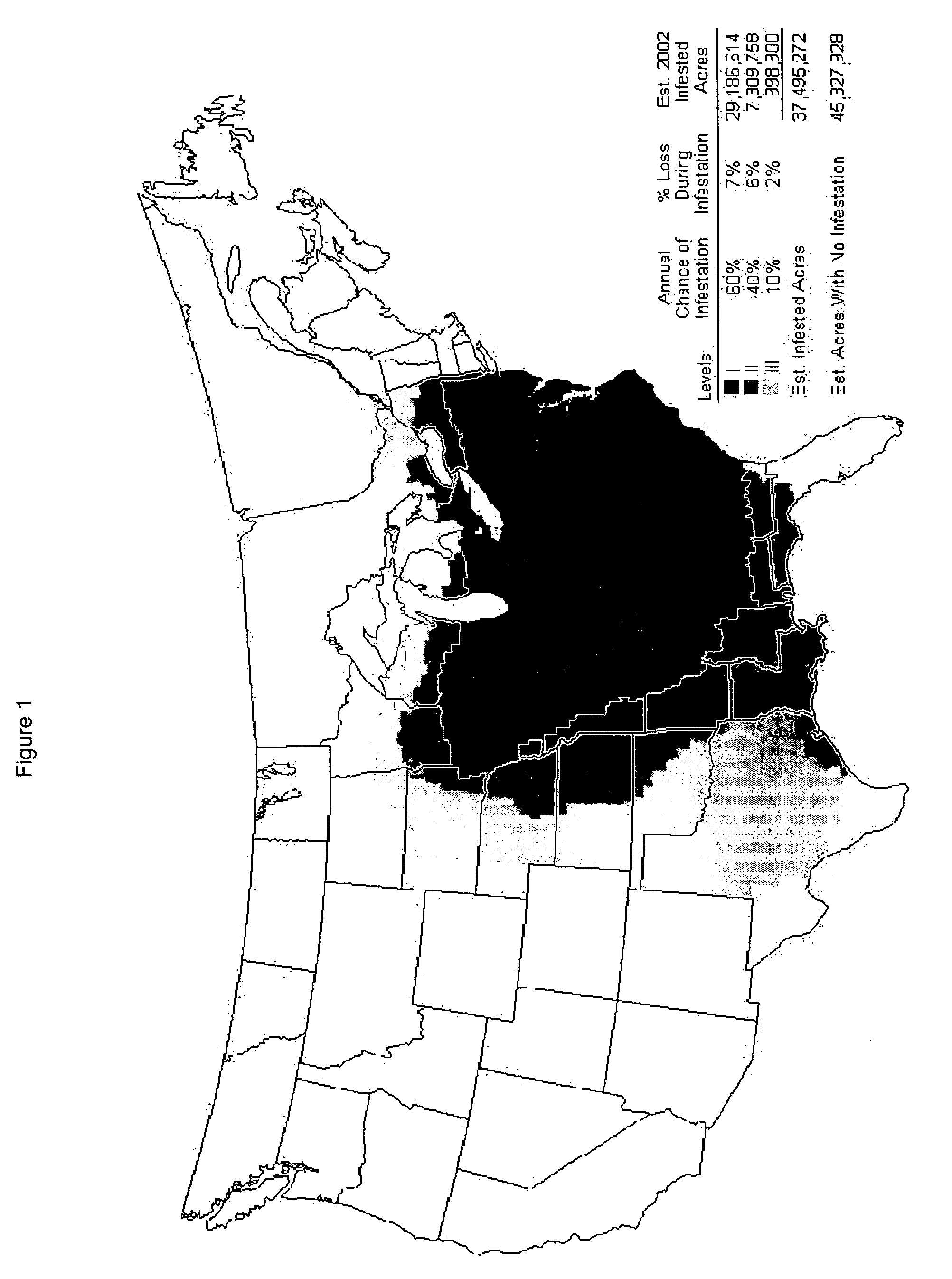
Polynucleotides and methods for making plants resistant to fungal pathogens
InactiveUS20060225152A1Microbiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesAnthriscus caucalisPolynucleotide
This invention relates to polynucleotide sequences encoding a gene that can confer resistance to the plant pathogen Colletotrichum, which causes anthracnose stalk rot, leaf blight and top dieback in corn and other cereals. It further relates to plants and seeds of plants carrying chimeric genes comprising said polynucleotide sequences, which enhance or confer resistance to the plant pathogen Colletotrichum, and processes of making said plants and seeds. The invention further presents sequences that can be used as molecular markers that in turn can be used to identify the region of interest in corn lines resulting from new crosses and to quickly and efficiently introgress the gene from corn lines carrying said gene into other corn lines that do not carry said gene, in order to make them resistant to Colletotrichum and resistant to stalk rot.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +2
Polynucleotides and methods for making plants resistant to fungal pathogens
InactiveUS20060223102A1Microbiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesAnthriscus caucalisPolynucleotide
This invention relates to polynucleotide sequences encoding a gene that can confer resistance to the plant pathogen Colletotrichum, which causes anthracnose stalk rot, leaf blight and top dieback in corn and other cereals. It further relates to plants and seeds of plants carrying chimeric genes comprising said polynucleotide sequences, which enhance or confer resistance to the plant pathogen Colletotrichum, and processes of making said plants and seeds. The invention further presents sequences that can be used as molecular markers that in turn can be used to identify the region of interest in corn lines resulting from new crosses and to quickly and efficiently introgress the gene from corn lines carrying said gene into other corn lines that do not carry said gene, in order to make them resistant to Colletotrichum and resistant to stalk rot.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +2
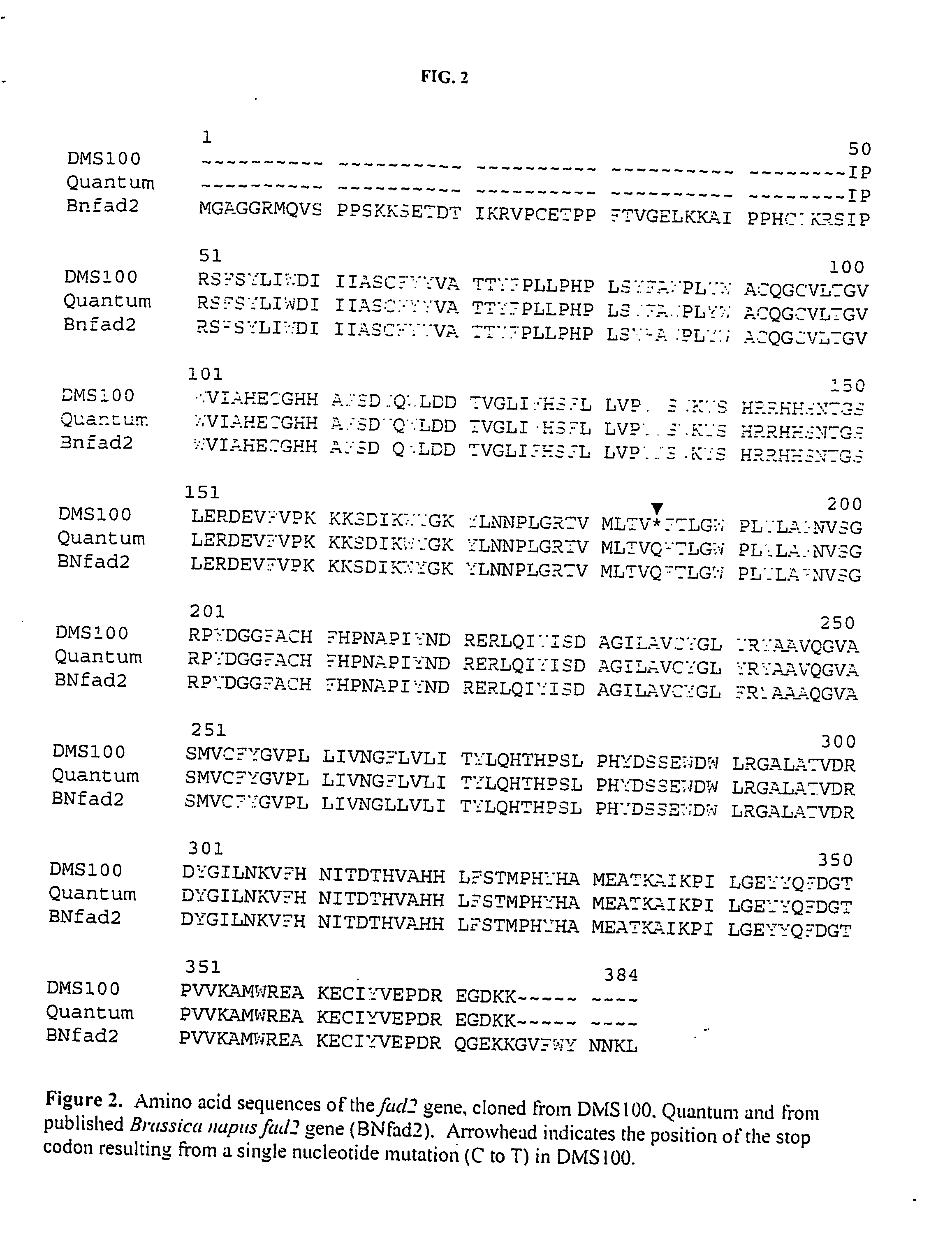
Altered fad2 and fad3 genes in brassica and the molecular marker-assisted detection thereof
ActiveUS20060248611A1Promote reproductionReliably and predictably introgressing traitSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementCrop speciesGene mutation
The present invention provides methods of marker assisted selection for high oleic / low linolenic traits in canola and in other oil seed crop species, as well as isolated nucleic acids for use as molecular markers in such methods. In particular, molecular markers and Brassica nucleic acid corresponding to fad2 and fad3 gene mutations are disclosed. The markers of the present invention are highly useful for the direct selection of desirable fad2 and fad3 alleles during marker-assisted trait introgression and breeding. In a one aspect of the embodiment, two single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers are provided which correspond to the alleles. Thus, the present invention advantageously permits one of skill in the art to breed for the molecular markers described herein, or derivatives thereof, rather than breeding for a high oleic / low linolenic phenotype.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Creation and transmission of megaloci
The current invention provides methods for creating a block of genetically linked transgenic traits or a megalocus that can be transmitted as a single genetic unit. The present invention further provides methods for trait introgression to other plants, varieties or species using the megaloci of the invention. Also provided are plants, seeds, and plant parts comprising the megaloci.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Peronospora resistance in spinacia oleracea
ActiveUS20130230635A1Easy to introduceConfer resistanceAnimal feeding stuffTissue culturePeronosporaSpinacea oleracea
The present invention relates to a spinach plant which may comprise a single dominant gene which confers resistance to Peronospora farinosa f. sp. spinaciae races Pfs1, Pfs2, Pfs3, Pfs4, Pfs5, Pfs6, Pfs9, Pfs11, Pfs12, Pfs13 and UA4410, wherein the gene is obtainable by introgression from a plant grown from seeds of which a representative sample was deposited with the NCIMB under NCIMB accession number 41857. The invention further relates to progeny of the plant, to propagation material therefore, such as seed, and to food products which may comprise the spinach leaves.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Soybean variety XB34D04
According to the invention, there is provided a novel soybean variety, designated XB34D04. This invention thus relates to the seeds of soybean variety XB34D04, to the plants of soybean XB34D04, to plant parts of soybean variety XB34D04 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing soybean variety XB34D04 with another soybean plant, using XB34D04 as either the male or the female parent. This invention also relates to methods for introgressing a transgenic or mutant trait into soybean variety XB34D04 and to the soybean plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to soybean varieties or breeding varieties and plant parts derived from soybean variety XB34D04, to methods for producing other soybean varieties or plant parts derived from soybean variety XB34D04 and to the soybean plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. This invention further relates to soybean seeds, plants, and plant parts produced by crossing the soybean variety XB34D04 with another soybean variety.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Transgenically preventing establishment and spread of transgenic algae in natural ecosystems
InactiveUS20090215179A1Improve productivityIncrease productionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPhylum CyanobacteriaAlgaenan
Genetic mechanisms for mitigating the effects of introgression of a genetically engineered genetic trait of cultivated algae or cyanobacteria to its wild type or to an undesirable, interbreeding related species. as well as preventing the establishment of the transgenic algae or cyanobacteria in natural ecosystems.
Owner:TRANSALGAE
Soybean variety XB43R04
According to the invention, there is provided a novel soybean variety, designated XB43R04. This invention thus relates to the seeds of soybean variety XB43R04, to the plants of soybean XB43R04, to plant parts of soybean variety XB43R04 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing soybean variety XB43R04 with another soybean plant, using XB43R04 as either the male or the female parent. This invention also relates to methods for introgressing a transgenic or mutant trait into soybean variety XB43R04 and to the soybean plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to soybean varieties or breeding varieties and plant parts derived from soybean variety XB43R04, to methods for producing other soybean varieties or plant parts derived from soybean variety XB43R04 and to the soybean plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. This invention further relates to soybean seeds, plants, and plant parts produced by crossing the soybean variety XB43R04 with another soybean variety.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Soybean variety XB04D04
InactiveUS6953877B2High yieldReduce stressPlant genotype modificationPlant cellsGenetically engineeredBotany
According to the invention, there is provided a novel soybean variety, designated XB04D04. This invention thus relates to the seeds of soybean variety XB04D04, to the plants of soybean XB04D04, to plant parts of soybean variety XB04D04 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing soybean variety XB04D04 with another soybean plant, using XB04D04 as either the male or the female parent. This invention also relates to methods for introgressing a transgenic or mutant trait into soybean variety XB04D04 and to the soybean plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to soybean varieties or breeding varieties and plant parts derived from soybean variety XB04D04, to methods for producing other soybean varieties or plant parts derived from soybean variety XB04D04 and to the soybean plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. This invention further relates to soybean seeds, plants, and plant parts produced by crossing the soybean variety XB04D04 with another soybean variety.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Soybean cultivar BA922834
ActiveUS7304217B1Modifying grain digestibilityModifying nutrient availabilityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSoybean cyst nematodeHeterodera
A soybean cultivar designated BA922834 with high yield potential, tolerance to Roundup™ herbicide, MG VI maturity, resistance to race 3 of soybean cyst nematode (Heterodera glycines), and resistance to frogeye leaf spot, further including the plants and seeds of the cultivar BA922834, methods for producing a soybean plant by crossing the cultivar BA922834 with itself or another soybean plant. The invention also relates to soybean cultivar BA922834 further comprising one or more single gene traits, and to methods of producing a soybean having such traits by introgression, transformation or mutagenesis. The invention also includes using the soybean cultivar BA922834 to produce other soybean cultivars, breeding lines, and progeny.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Soybean variety XB19U04
According to the invention, there is provided a novel soybean variety, designated XB19UO4. This invention thus relates to the seeds of soybean variety XB19UO4, to the plants of soybean XB19UO4, to plant parts of soybean variety XB19U04 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing soybean variety XB19U04 with another soybean plant, using XB19U04 as either the male or the female parent. This invention also relates to methods for introgressing a transgenic or mutant trait into soybean variety XB19UO4 and to the soybean plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to soybean varieties or breeding varieties and plant parts derived from soybean variety XB19UO4, to methods for producing other soybean varieties or plant parts derived from soybean variety XB19UO4 and to the soybean plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. This invention further relates to soybean seeds, plants, and plant parts produced by crossing the soybean variety XB19UO4 with another soybean variety.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
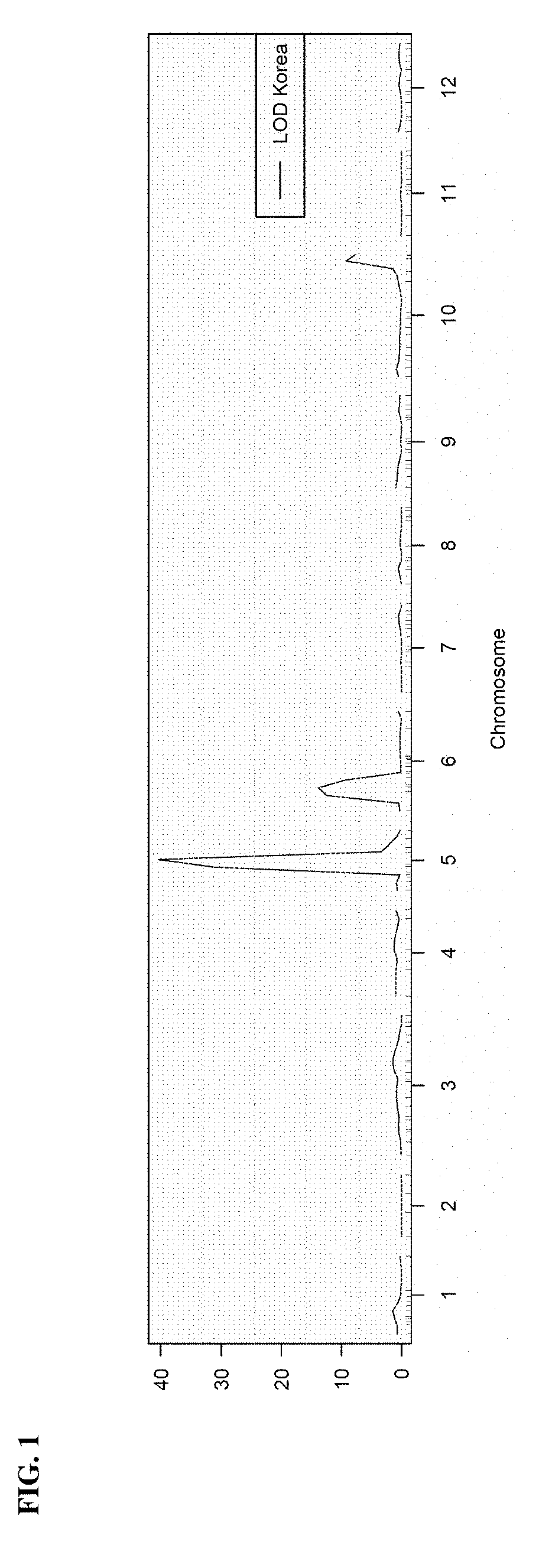
Resistance to gray leaf spot in maize
ActiveUS20100146657A1Microbiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationFungal diseaseDisease
The present invention is in the field of plant breeding and disease resistance. More specifically, the invention includes a method for breeding corn plants containing quantitative trait loci that are associated with resistance to gray leaf spot, a fungal disease associated with Cercospora spp. The invention further includes germplasm and the use of germplasm containing quantitative trait loci (QTL) conferring disease resistance for introgression into elite germplasm in a breeding program for resistance to gray leaf spot.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Inter-simple sequence repeat ISSR-SCAR marker specific to E-group chromosomes of agropyron elongatum
The invention discloses an inter-simple sequence repeat ISSR-SCAR marker specific to E-group chromosomes of agropyron elongatum. The invention provides a kit for detecting the E-group chromosomes of agropyron elongatum. The kit comprises the following primer pair: one primer in the primer pair is nucleotide shown in a sequence 3 of a sequence table, and the other primer in the primer pair is nucleotide shown in a sequence 4 of the sequence table. The E-group chromosomes of thinopyrum elongatum are the basic chromosome group forming the polyploid species of elytrigia and carry the genes beneficial to the genetic breeding of wheat, the detection of exogenous E chromatins in wheat is the key point for identifying recombination lines and introgression lines of the wheat, namely the agropyron elongatum, the work of screening and identifying a large number of filial generations is quite complicated, and tests prove that the ISSR-SCAR marker developed by the invention can lay a foundation for quickly and accurately identifying the E-group chromatins or chromosomes of exogenous agropyron elongatum under the genetic background of wheat.
Owner:HARBIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Soybean variety 95M80
According to the invention, there is provided a novel soybean variety, designated 95M80. This invention thus relates to the seeds of soybean variety 95M80, to the plants of soybean 95M80, to plant parts of soybean variety 95M80 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing soybean variety 95M80 with another soybean plant, using 95M80 as either the male or the female parent. This invention also relates to methods for introgressing a transgenic or mutant trait into soybean variety 95M80 and to the soybean plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to soybean varieties or breeding varieties and plant parts derived from soybean variety 95M80, to methods for producing other soybean varieties or plant parts derived from soybean variety 95M80 and to the soybean plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. This invention further relates to soybean seeds, plants, and plant parts produced by crossing the soybean variety 95M80 with another soybean variety.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Soybean variety XB35L04
According to the invention, there is provided a novel soybean variety, designated XB35L04. This invention thus relates to the seeds of soybean variety XB35L04, to the plants of soybean XB35L04, to plant parts of soybean variety XB35L04 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing soybean variety XB35L04 with another soybean plant, using XB35L04 as either the male or the female parent. This invention also relates to methods for introgressing a transgenic or mutant trait into soybean variety XB35L04 and to the soybean plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to soybean varieties or breeding varieties and plant parts derived from soybean variety XB35L04, to methods for producing other soybean varieties or plant parts derived from soybean variety XB35L04 and to the soybean plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. This invention further relates to soybean seeds, plants, and plant parts produced by crossing the soybean variety XB35L04 with another soybean variety.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Soybean variety 95M80
According to the invention, there is provided a novel soybean variety, designated 95M80. This invention thus relates to the seeds of soybean variety 95M80, to the plants of soybean 95M80, to plant parts of soybean variety 95M80 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing soybean variety 95M80 with another soybean plant, using 95M80 as either the male or the female parent. This invention also relates to methods for introgressing a transgenic or mutant trait into soybean variety 95M80 and to the soybean plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to soybean varieties or breeding varieties and plant parts derived from soybean variety 95M80, to methods for producing other soybean varieties or plant parts derived from soybean variety 95M80 and to the soybean plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. This invention further relates to soybean seeds, plants, and plant parts produced by crossing the soybean variety 95M80 with another soybean variety.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Soybean variety XB10L04
InactiveUS20040172708A1Reduce stressPlant genotype modificationPlant cellsGenetically engineeredSoya bean
According to the invention, there is provided a novel soybean variety, designated XB10L04. This invention thus relates to the seeds of soybean variety XB10L04, to the plants of soybean XB10L04, to plant parts of soybean variety XB10L04 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing soybean variety XB10L04 with another soybean plant, using XB10L04 as either the male or the female parent. This invention also relates to methods for introgressing a transgenic or mutant trait into soybean variety XB10L04 and to the soybean plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to soybean varieties or breeding varieties and plant parts derived from soybean variety XB10L04, to methods for producing other soybean varieties or plant parts derived from soybean variety XB10L04 and to the soybean plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. This invention further relates to soybean seeds, plants, and plant parts produced by crossing the soybean variety XB10L04 with another soybean variety.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Soybean variety XB48T04
According to the invention, there is provided a novel soybean variety, designated XB48T04. This invention thus relates to the seeds of soybean variety XB48T04, to the plants of soybean XB48T04, to plant parts of soybean variety XB48T04 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing soybean variety XB48T04 with another soybean plant, using XB48T04 as either the male or the female parent. This invention also relates to methods for introgressing a transgenic or mutant trait into soybean variety XB48T04 and to the soybean plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to soybean varieties or breeding varieties and plant parts derived from soybean variety XB48T04, to methods for producing other soybean varieties or plant parts derived from soybean variety XB48T04 and to the soybean plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. This invention further relates to soybean seeds, plants, and plant parts produced by crossing the soybean variety XB48T04 with another soybean variety.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Soybean variety XB11F04
According to the invention, there is provided a novel soybean variety, designated XB11F04. This invention thus relates to the seeds of soybean variety XB11F04, to the plants of soybean XB11F04, to plant parts of soybean variety XB11F04 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing soybean variety XB11F04 with another soybean plant, using XB11F04 as either the male or the female parent. This invention also relates to methods for introgressing a transgenic or mutant trait into soybean variety XB11F04 and to the soybean plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to soybean varieties or breeding varieties and plant parts derived from soybean variety XB11F04, to methods for producing other soybean varieties or plant parts derived from soybean variety XB11F04 and to the soybean plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. This invention further relates to soybean seeds, plants, and plant parts produced by crossing the soybean variety XB11F04 with another soybean variety.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
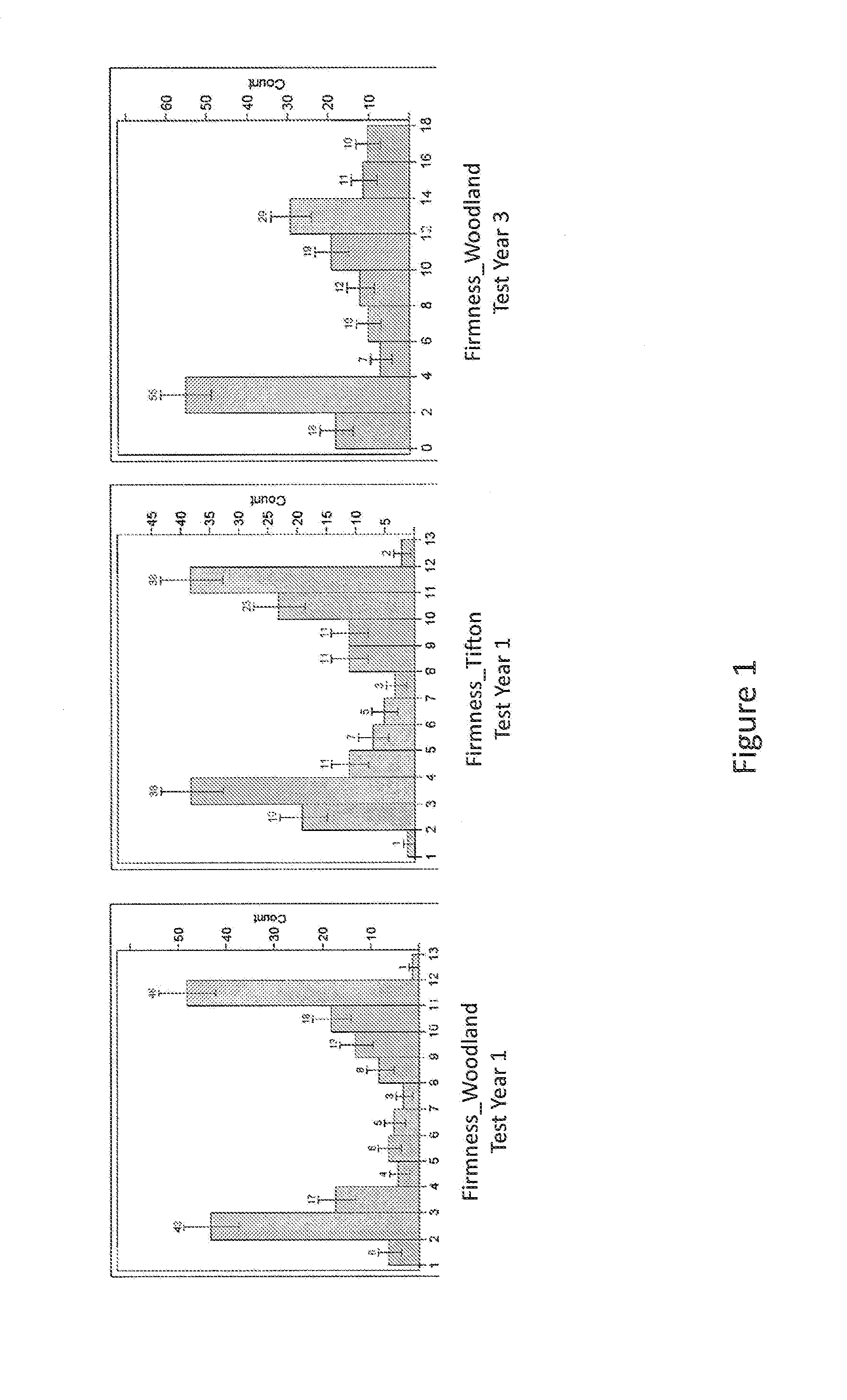
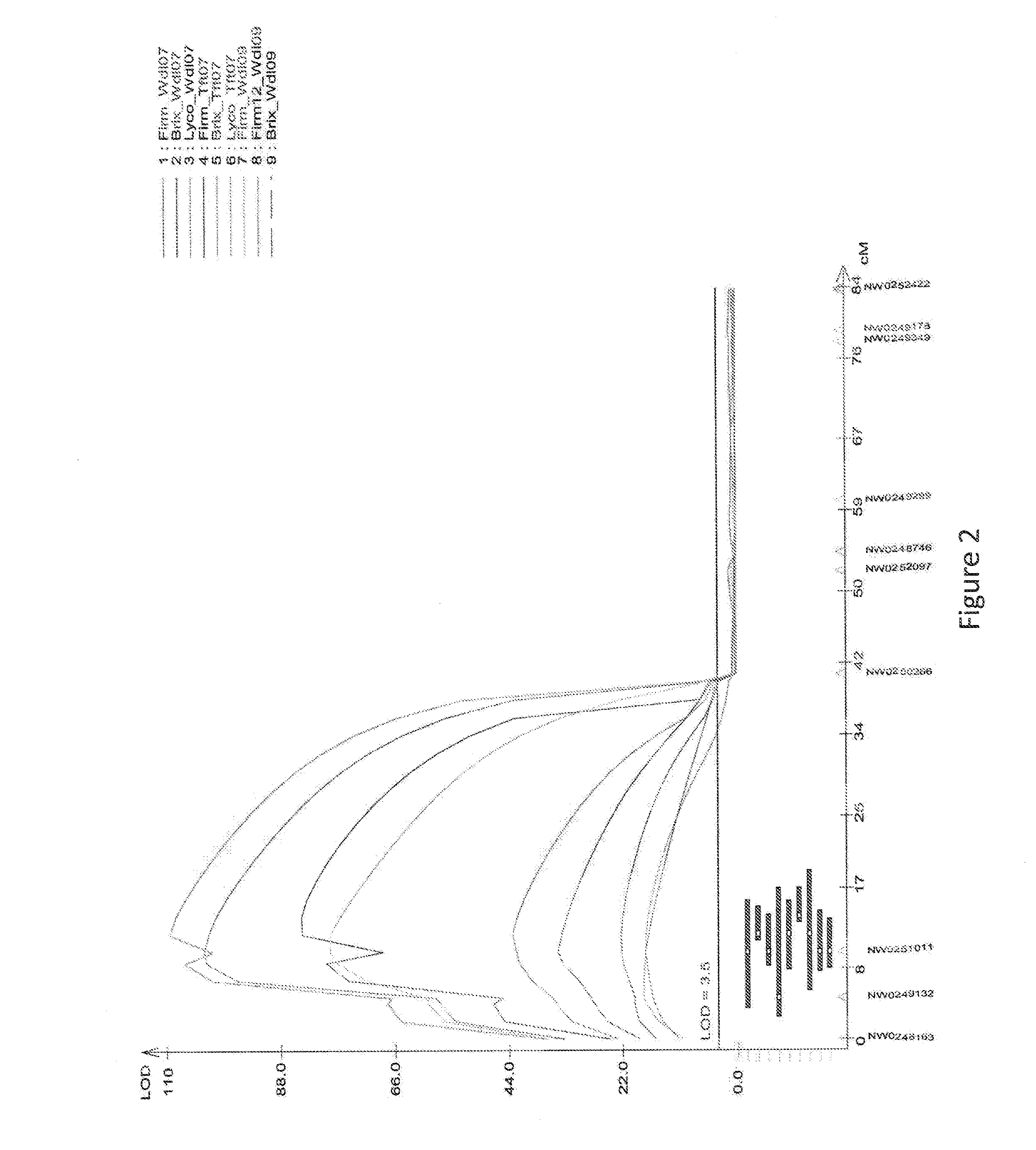
Methods and Compositions for Watermelon Firmness
The invention provides for unique watermelon plants with an ultra-firm flesh phenotype and their progeny. Such plants may comprise an introgressed QTL associated with an ultra-firm flesh phenotype. In certain aspects, compositions, including distinct polymorphic molecular markers, and methods for producing, breeding, identifying, selecting, and the like of plants or germplasm with an ultra-firm flesh phenotype are provided.
Owner:SEMINIS VEGETABLE SEEDS
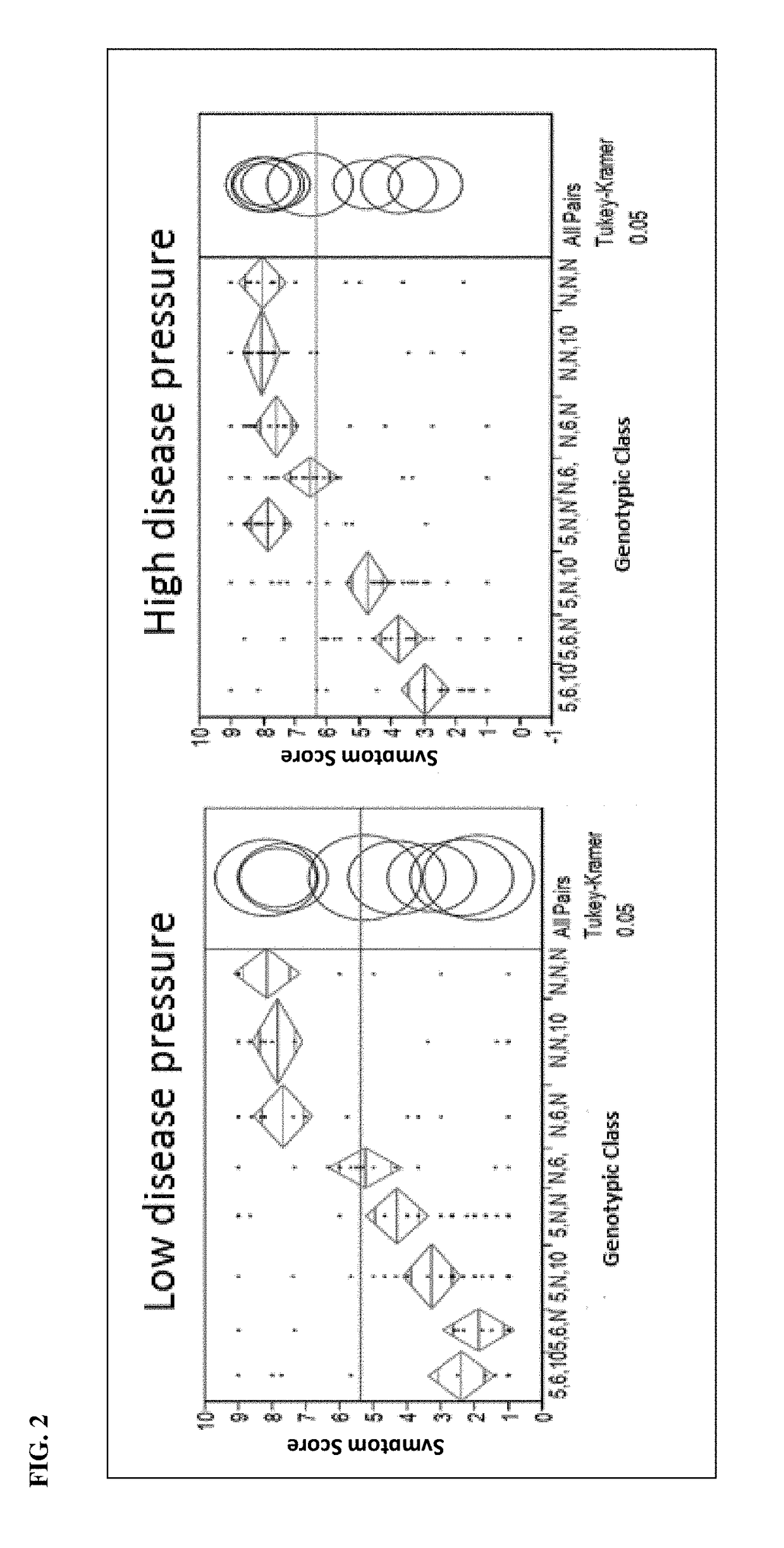
Pepper plants with improved disease resistance
ActiveUS20180171353A1Vector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationDiseaseGermplasm
The present disclosure provides pepper plants exhibiting resistance to Phytophthora capsici. Such plants may comprise novel introgressed chromosomal regions associated with disease resistance. In certain aspects, compositions, including novel polymorphic markers and methods for producing, breeding, identifying, and selecting plants or germplasm with a disease resistance phenotype are provided.
Owner:SEMINIS VEGETABLE SEEDS
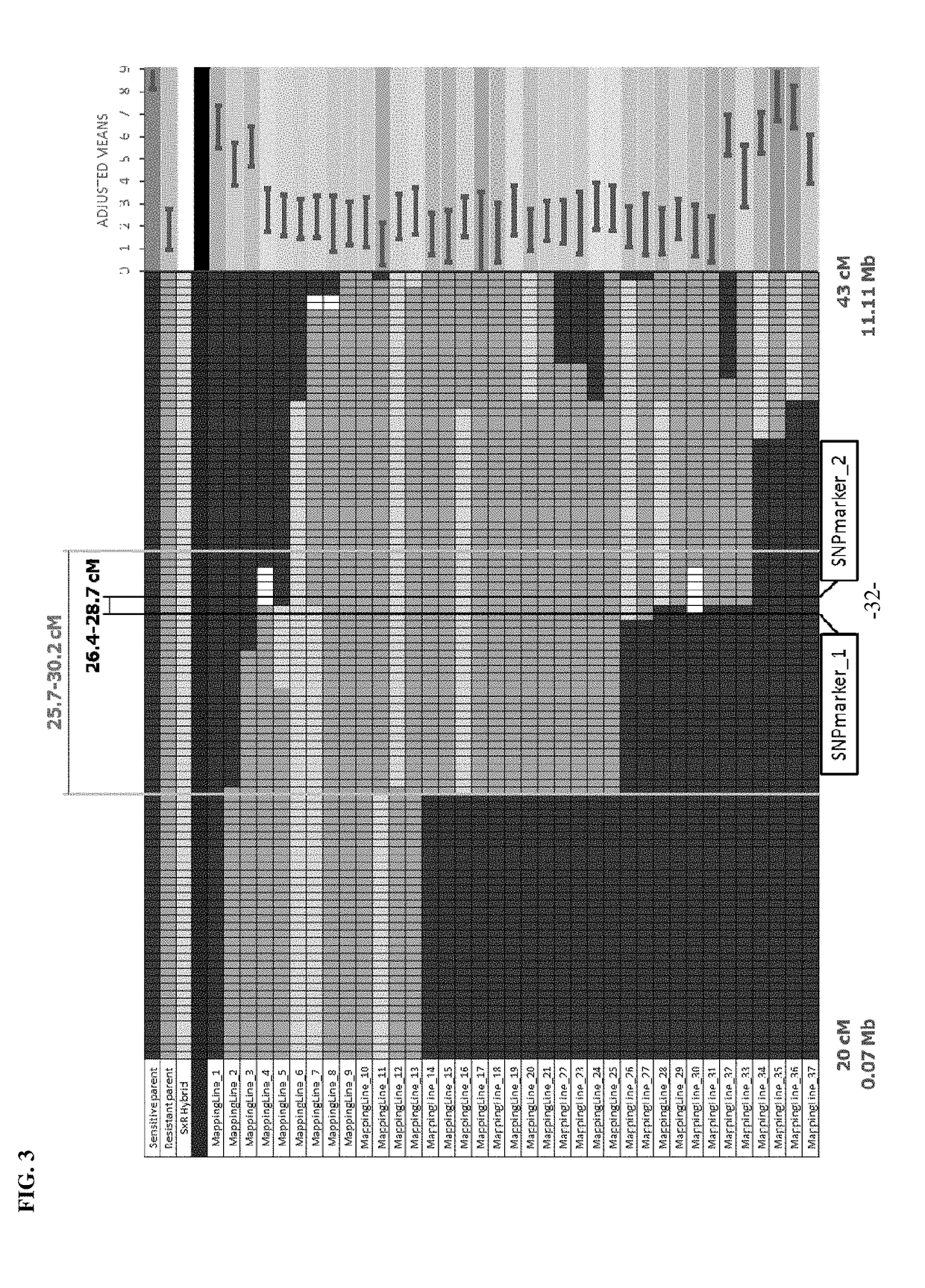
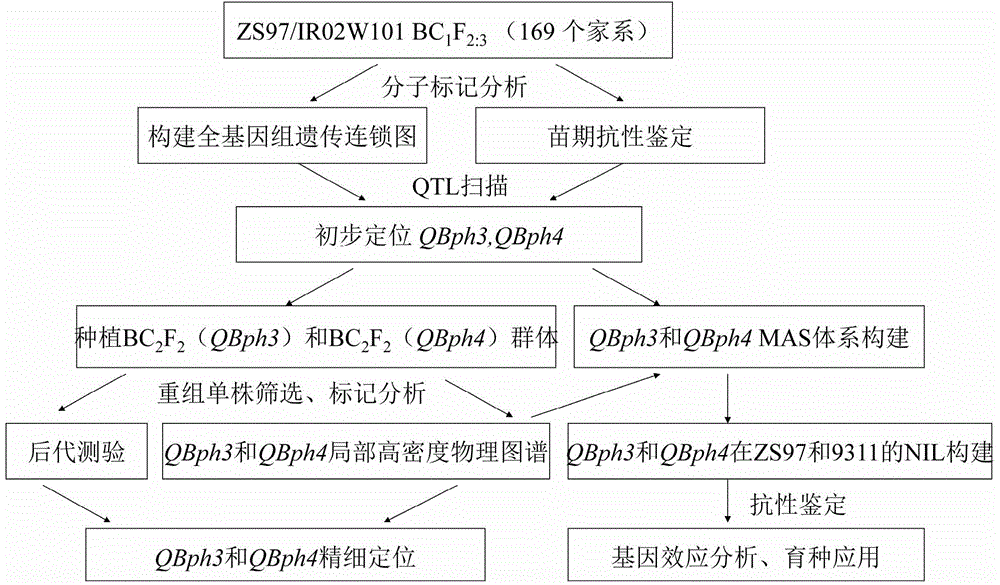
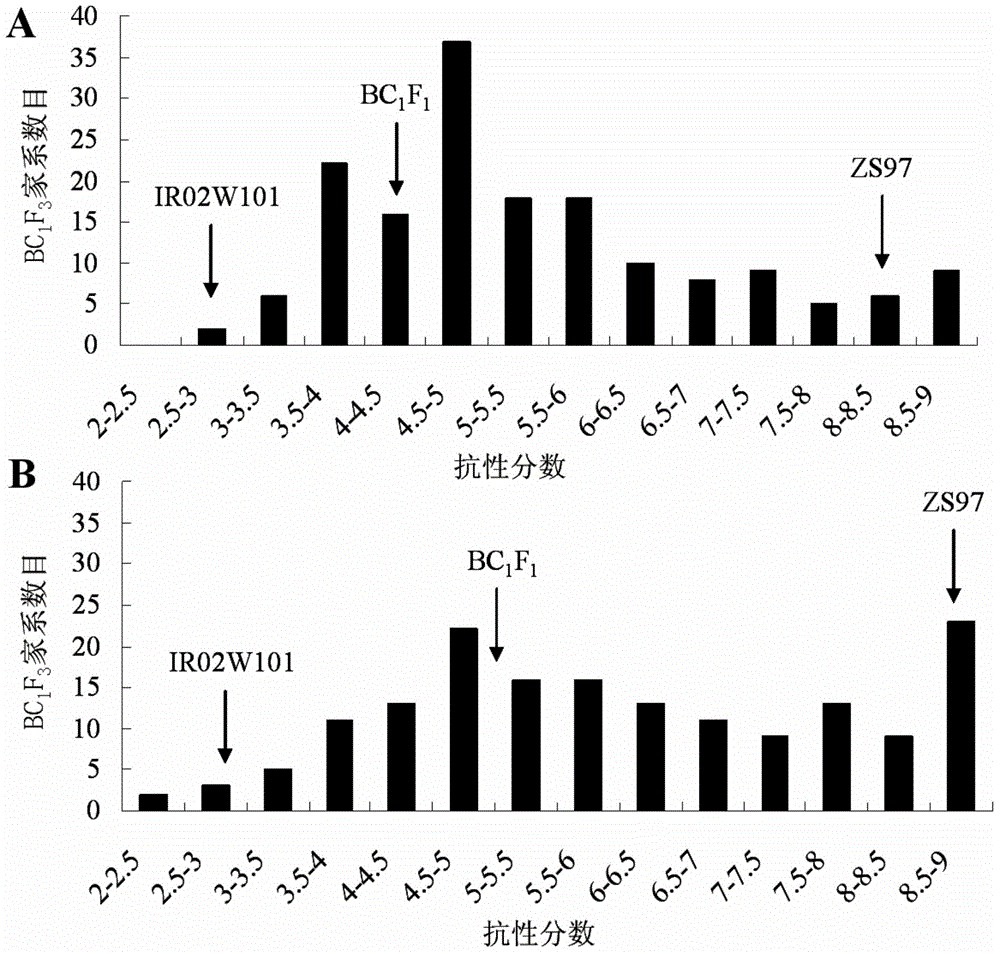
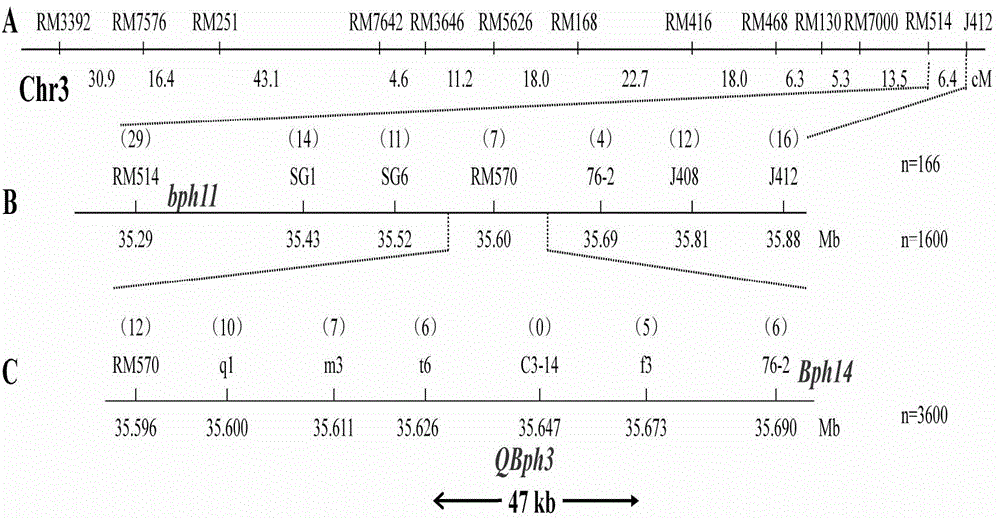
Molecular marker for rice brown planthopper-resistance QBph3 and QBph4 genes
InactiveCN105087553AImprove reliabilityEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceGenotype
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of a rice molecular marker, and in particular relates to a molecular marker for two rice brown planthopper-resistance major genes QBph3 and QBph4 which are simultaneously derived from a pest-resistance introgression line IR02W101. The molecular marker comprises the following steps: carrying out crossing, self-crossing and backcrossing on Zhenshan97, which is an herbivore-susceptible variety, and IR02W101 so as to obtain genotypes of various BC1F2 single plants; carrying out genetic linkage analysis in accordance with brown planthopper-resistance grades of various F2: 3 lines during seedling stage; precisely locating a resistance gene QBph3 of the IR02W101 between long-arm markers t6 and f3 of the 3rd chromosome so as to obtain a co-segregative marker c3-14 as well as closely linked markers q1 and m3; and precisely locating QBph4 between short-arm markers p17 and xc4-27 of the 4th chromosome so as to obtain closely linked markers p6, p9, c4-5, xc4-7, HJ16, J417 and IN156. The molecular marker disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively detecting whether the pest-resistance introgression line IR02W101 and derived varieties thereof contain the major gene site or not.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Soybean variety XB34D04
According to the invention, there is provided a novel soybean variety, designated XB34D04. This invention thus relates to the seeds of soybean variety XB34D04, to the plants of soybean XB34D04, to plant parts of soybean variety XB34D04 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing soybean variety XB34D04 with another soybean plant, using XB34D04 as either the male or the female parent. This invention also relates to methods for introgressing a transgenic or mutant trait into soybean variety XB34D04 and to the soybean plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to soybean varieties or breeding varieties and plant parts derived from soybean variety XB34D04, to methods for producing other soybean varieties or plant parts derived from soybean variety XB34D04 and to the soybean plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. This invention further relates to soybean seeds, plants, and plant parts produced by crossing the soybean variety XB34D04 with another soybean variety.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Soybean variety XB30E04
According to the invention, there is provided a novel soybean variety, designated XB30E04. This invention thus relates to the seeds of soybean variety XB30E04, to the plants of soybean XB30E04, to plant parts of soybean variety XB30E04 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing soybean variety XB30E04 with another soybean plant, using XB30E04 as either the male or the female parent. This invention also relates to methods for introgressing a transgenic or mutant trait into soybean variety XB30E04 and to the soybean plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to soybean varieties or breeding varieties and plant parts derived from soybean variety XB30E04, to methods for producing other soybean varieties or plant parts derived from soybean variety XB30E04 and to the soybean plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. This invention further relates to soybean seeds, plants, and plant parts produced by crossing the soybean variety XB30E04 with another soybean variety.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Soybean variety XB31U04
InactiveUS20040194167A1Reduce stressPlant genotype modificationPlant cellsGenetically engineeredSoya bean
According to the invention, there is provided a novel soybean variety, designated XB31U04. This invention thus relates to the seeds of soybean variety XB31U04, to the plants of soybean XB31U04, to plant parts of soybean variety XB31U04 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing soybean variety XB31U04 with another soybean plant, using XB31U04 as either the male or the female parent. This invention also relates to methods for introgressing a transgenic or mutant trait into soybean variety XB31U04 and to the soybean plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to soybean varieties or breeding varieties and plant parts derived from soybean variety XB31U04, to methods for producing other soybean varieties or plant parts derived from soybean variety XB31U04 and to the soybean plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. This invention further relates to soybean seeds, plants, and plant parts produced by crossing the soybean variety XB31U04 with another soybean variety.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
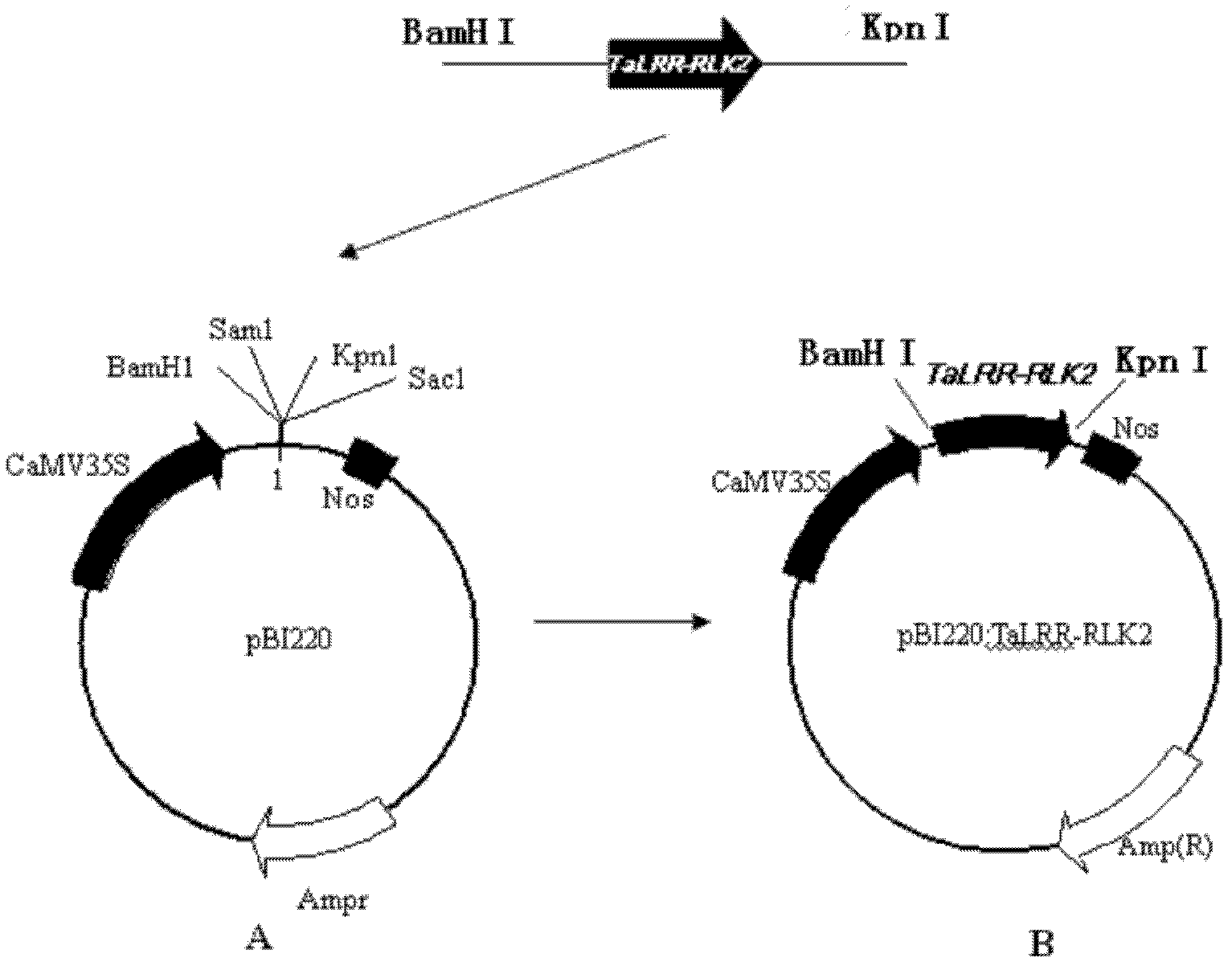
Receptor-like protein kinase gene, and expression vector and application thereof
ActiveCN102533812AIncrease resistancePowdery mildew resistantTransferasesFermentationBiotechnologyGene conversion
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and discloses a receptor-like protein kinase gene, and an expression vector and application thereof. The cDNA sequence of the receptor-like protein kinase gene TaLRR-RLK2 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and an ammonia acid sequence coded by the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The gene comes from a Triticum aestivum L. Prins-T. timopheevi Zhuk introgression line IGVI465, and is reported in wheat for the first time. The gene transforms susceptible wheat variety Prins through transient expression, and a result shows that the over-expression of the TaLRR-RLK2 can reduce the haustorium index of the Prins. Therefore, the TaLRR-RLK2 can be expected to be used for genetically engineered breeding, and can improve the powdery mildew resistance of wheat after the gene is transferred into a powdery mildew susceptible wheat variety.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Soybean variety XB27P04
InactiveUS20040205864A1Reduce stressLow pressureBryophytesPlant genotype modificationGenetically engineeredBotany
According to the invention, there is provided a novel soybean variety, designated XB27P04. This invention thus relates to the seeds of soybean variety XB27P04, to the plants of soybean XB27P04, to plant parts of soybean variety XB27P04 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing soybean variety XB27P04 with another soybean plant, using XB27P04 as either the male or the female parent. This invention also relates to methods for introgressing a transgenic or mutant trait into soybean variety XB27P04 and to the soybean plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to soybean varieties or breeding varieties and plant parts derived from soybean variety XB27P04, to methods for producing other soybean varieties or plant parts derived from soybean variety XB27P04 and to the soybean plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. This invention further relates to soybean seeds, plants, and plant parts produced by crossing the soybean variety XB27P04 with another soybean variety.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Soybean variety XB43R04
According to the invention, there is provided a novel soybean variety, designated XB43R04. This invention thus relates to the seeds of soybean variety XB43R04, to the plants of soybean XB43R04, to plant parts of soybean variety XB43R04 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing soybean variety XB43R04 with another soybean plant, using XB43R04 as either the male or the female parent. This invention also relates to methods for introgressing a transgenic or mutant trait into soybean variety XB43R04 and to the soybean plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to soybean varieties or breeding varieties and plant parts derived from soybean variety XB43R04, to methods for producing other soybean varieties or plant parts derived from soybean variety XB43R04 and to the soybean plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. This invention further relates to soybean seeds, plants, and plant parts produced by crossing the soybean variety XB43R04 with another soybean variety.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Soybean variety XB06H04
InactiveUS20040172696A1Reduce stressPlant genotype modificationPlant cellsGenetically engineeredSoya bean
According to the invention, there is provided a novel soybean variety, designated XB06H04. This invention thus relates to the seeds of soybean variety XB06H04, to the plants of soybean XB06H04, to plant parts of soybean variety XB06H04 and to methods for producing a soybean plant produced by crossing soybean variety XB06H04 with another soybean plant, using XB06H04 as either the male or the female parent. This invention also relates to methods for introgressing a transgenic or mutant trait into soybean variety XB06H04 and to the soybean plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to soybean varieties or breeding varieties and plant parts derived from soybean variety XB06H04, to methods for producing other soybean varieties or plant parts derived from soybean variety XB06R04 and to the soybean plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. This invention further relates to soybean seeds, plants, and plant parts produced by crossing the soybean variety XB06H04 with another soybean variety.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Soybean cultivar WW152201
ActiveUS7132594B1Modifying grain digestibilityModifying nutrient availabilityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationCultivarSingle gene
A soybean cultivar designated WW152201 with high yield potential and tolerance to Roundup™ herbicide, further including the plants and seeds of the cultivar WW152201, methods for producing a soybean plant by crossing the cultivar WW152201 with itself or another soybean plant. The invention also relates to soybean cultivar WW152201 further comprising one or more single gene traits, and to methods of producing a soybean having such traits by introgression, transformation or mutagenesis. The invention also includes using the soybean cultivar WW152201 to produce other soybean cultivars, breeding lines, and progeny.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com