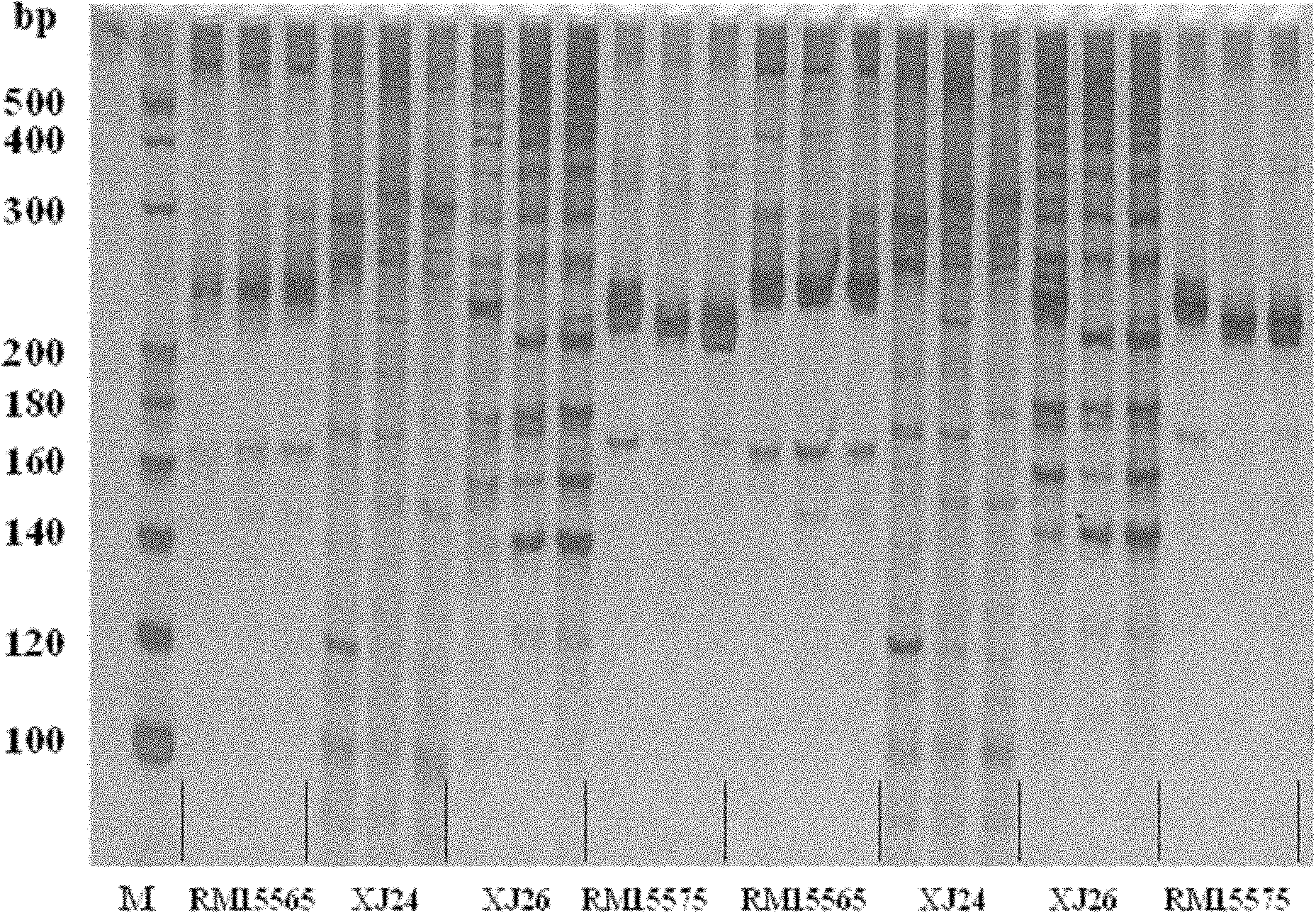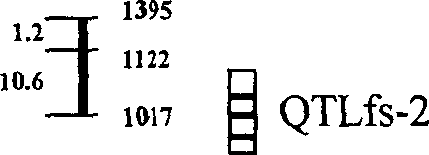Patents
Literature
226 results about "Major gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Major gene is a gene with pronounced phenotype expression, in contrast to modificator gene. Major gene characterizes common expression of oligogenic series, i.e. a small number of genes that determine the same trait.
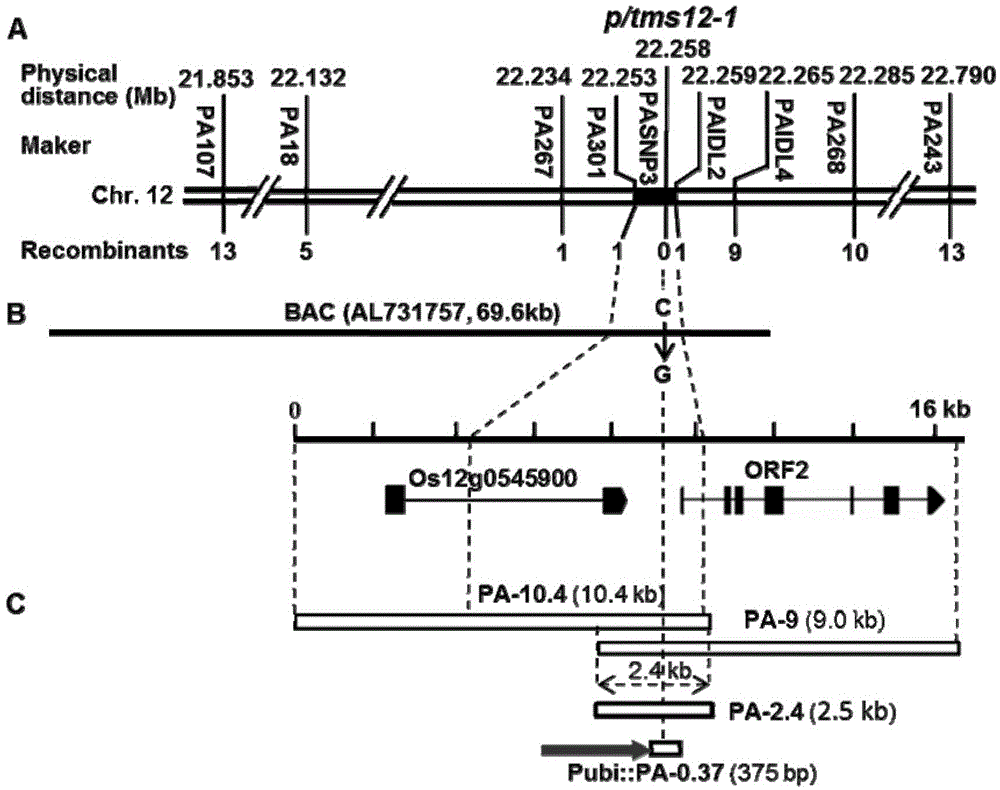
Method for obtaining temperature-sensitive sterile line by performing site-specific mutagenesis on P/TMS12-1 through CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats)/Cas9 system
ActiveCN104651392AAvoid possible risksAvoid damageVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsAgricultural scienceTransgenesis
The invention discloses a method for obtaining a temperature-sensitive sterile line by performing site-specific mutagenesis on P / TMS12-1 through a CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats) / Cas9 system. The method comprises the following steps: cloning and controlling a Pei'ai 64S temperature-sensitive sterile major gene P / TMS12-1 fragment; designing a target sequence according to the P / TMS12-1 sequence; constructing a pU3-gRNA carrier of the target-containing sequence fragment; constructing a pCRISPR / Cas9 carrier; obtaining a positive transgenic seedling by utilizing the pCRISPR / Cas9 carrier containing the target sequence fragment; screening a mutant plant from the positive transgenic seeding; performing subculture planting on the mutant plant to obtain the temperature-sensitive sterile line without transgenic components. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the CRISPR / Cas9 system is utilized to completely inactivate P / TMS12-1 non-coding RNA, and the temperature-sensitive sterile line without transgenic components is artificially cultivated. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being strong in purposiveness, small in genome damages and capable of avoiding transgenic interference.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for cultivating low-cadmium-accumulation indica rice variety
ActiveCN106544357AAvoid safety hazardsPrecise and controllable mutation sitesNucleic acid vectorPlant peptidesTransgenesisMutant
The invention discloses a method for cultivating a low-cadmium-accumulation indica rice variety. The method includes the steps of cloning part of the CDS sequence of OsNramp5 of an indica rice acceptor material; using a CRISPR / Cas9 system to select a target sequence according to an exon sequence; building pCRISPR / Cas9 recombinant vectors; leading the pCRISPR / Cas9 recombinant vectors into rice calluses to obtain transgene seedlings; screening transgene positive plants; obtaining mutant plants; and conducting seed propagation of the mutant plants, and separating afunction mutants containing no transgenic ingredients from plant progenies. By means of the method, the cadmium absorption major gene OsNramp5 of indica rice is directionally knocked out through the CRISPR / Cas9 technology, and the indica rice material containing no transgenic ingredients, having no significantly variant comprehensive agronomic characters and achieving a low cadmium content in rice is directionally cultivated. The method has the advantages that targeting is efficient, the breeding period is short, cost is low and practicality is high.
Owner:HUNAN HYBRID RICE RES CENT
Molecular mark method for rice variety anti-brownspot gene site
InactiveCN1896281AEasy to detectNot affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBrown planthopperGenotype
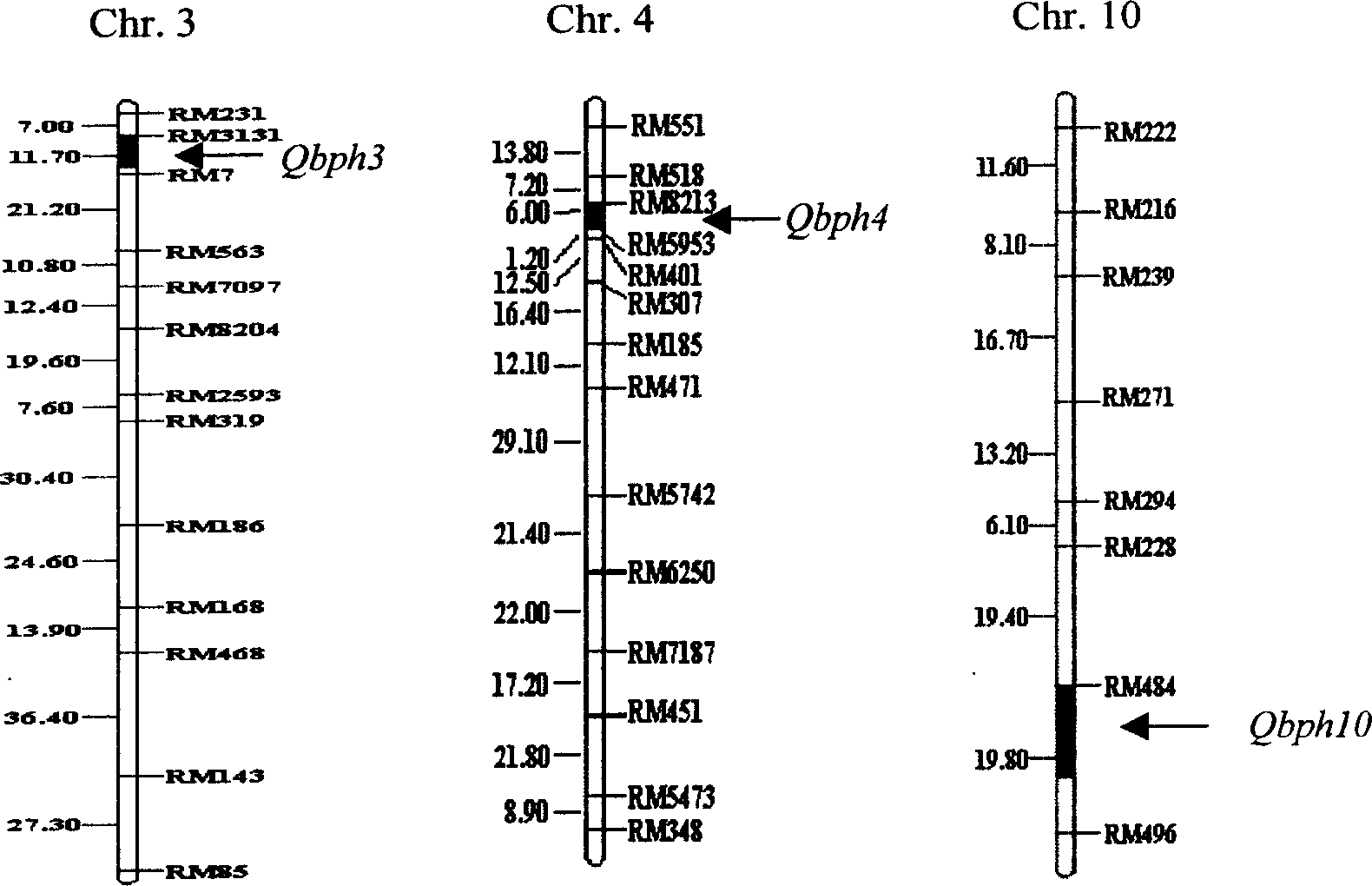
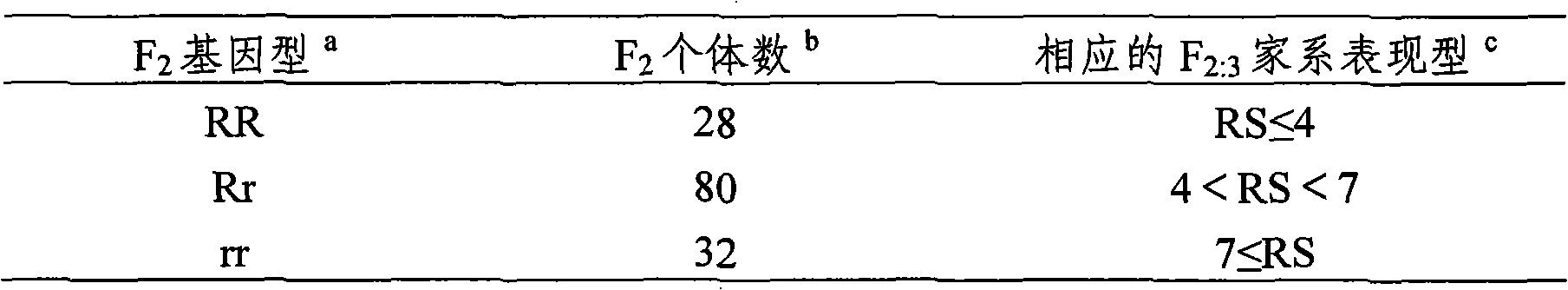
The present invention belongs to the molecular genetics field and relates to the molecular marker method of the major gene for brown planthopper resistance in the rice variety Rathu Heenati. Via genetic linkage analysis of the individual F2 plant genotype and the brown planthopper resistance level of each F2:3 family produced by hybridizing the insect-resistant variety Rathu Heenati with insect-susceptible variety 02428, the molecular markers RM8213 and RM5953 of the major gene loci Qbph4(Bph3) in the insect-resistant variety Rathu Heenati are obtained, the loci Qbph4(Bph3) is 3.6cM and 3.2cM distant from the markers RM8213 and RM5953 respectively. Detection of this major gene loci in Rathu Heenati and its derivatives via these molecular markers will increase the selection efficiency of brown plant hopper resistant rices.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
SSR markers lined with major gene of cotton fiber strength
InactiveCN101613761AImprove selection efficiencyGood effectMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationAgricultural scienceA-DNA
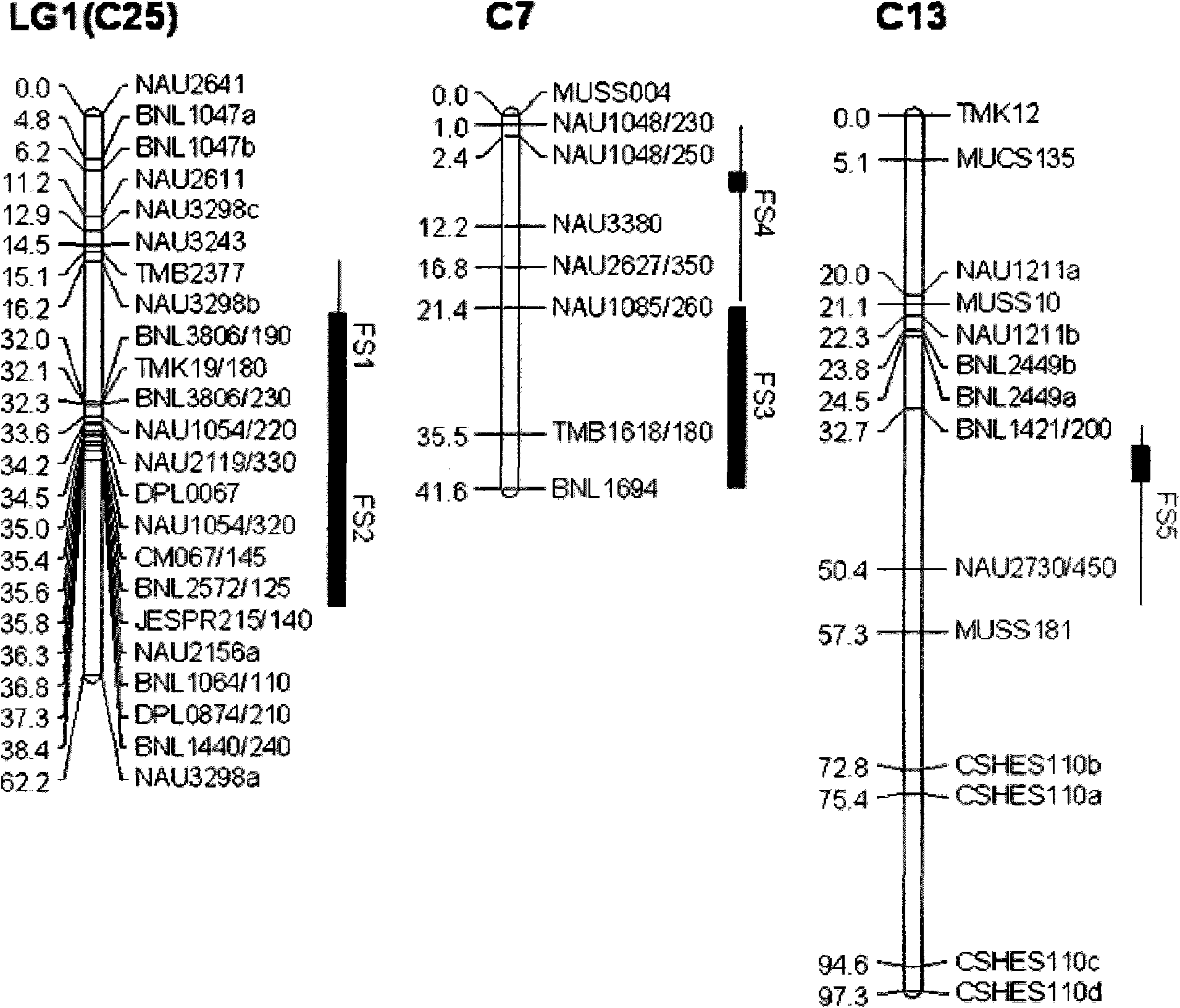
The invention discloser SSR markers lined with major genes of cotton fiber strength, which is obtained by the following steps: generating F2 and F2:3 populations by using a cotton search 41 line sGK9708 selected from cultivated varieties of gossypium hirsutum and a high quality line 0-153 of gossypium hirsutum as parents; allowing generation within the family of the F2:3 population to self cross till the F2:6 generation, performing within-family individual selection of the F2:6 generation once, and planting two generation till F6:8; performing polymorphism screening of the parents by using SSR primers and creating an RIL population linkage map; and performing the multi-environment major QTL screening of the cotton fiber strength to screen 6 QTLs of a cotton fiber strength character from line 0-153, wherein 5 QTLs are multi-environment stable QTLs and are FS1 linkage marker NAU2119330, FS2 linkage markers BNL2572125, BNL1064110 and DPL0874210, FS4 linkage markers are NAU1048250 and NAU2627350, and FS5 linkage markers BNL1421200 and NAU2730450. The SSR markers lined with the major genes of the cotton fiber strength are screen from high fiber quality materials and used as molecular markers to perform early auxiliary selection on a DNA level to improve the selection efficiency of the cotton fiber strength.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) site related to characters of plant root system and application thereof
ActiveCN103952402AGood characterMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyPlant roots
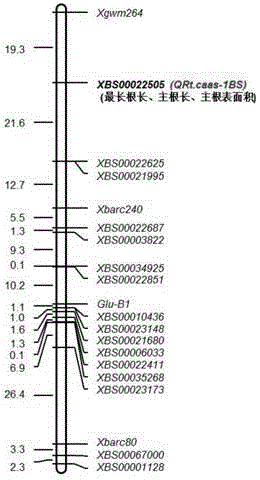
The invention discloses an SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) site relates to characters of a plant root system and application thereof. The SNP site related to the characters of the plant root system is a 55th nucleotide from a tail end 5' in SEQ ID No.4, and the 55th nucleotide is C and / or G; a DNA segment shown in SEQ ID No.4 is at a position 19.3cM on a wheat chromosome 1BS. The invention provides a new root system major gene site QRt.caas-1BS and an auxiliary excellent wheat root system screening SNP site; wheat with excellent root system characters can be screened by utilizing the SNP site, so that the SNP site plays an important role in wheat root system related breeding.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Glioma molecule typed gene group and application thereof
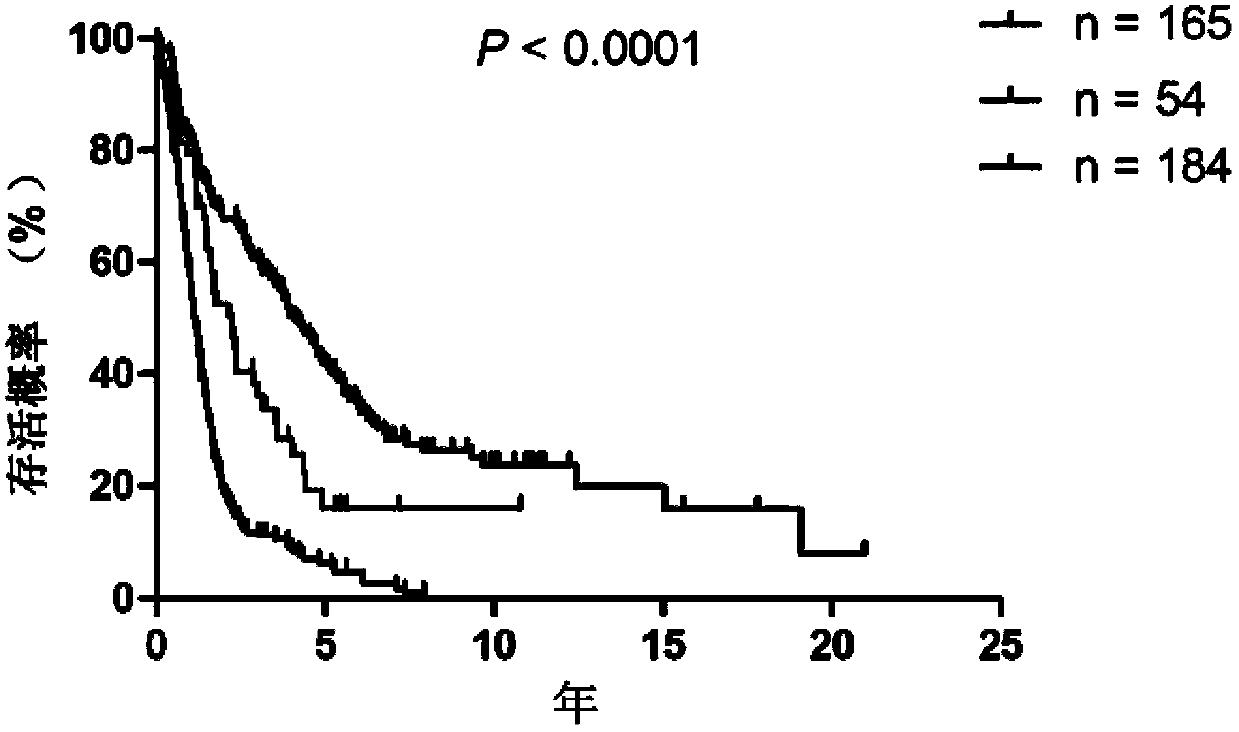
ActiveCN104178556AAccurately judge the prognostic survival timeOvercome limitationsMicrobiological testing/measurementMorphologic diagnosisWilms' tumor
Provided in the present invention is a set of gene groups for predicting or for the auxiliary prediction of the survival time prognosis of patients with neuroglioma, consisting of a PM gene group and an EM gene group with a total of 68 genes. A subtype marking gene group consisting of two major gene groups co-expressed with PDGFRA and EGFR can stably divide neuroglioma samples derived from different database sources into three specific subtypes, and can be applied to clinical diagnosis for neuroglioma and judging the survival time prognosis of patients with neuroglioma.
Owner:北京金岱生物科技有限公司
Cloning and application of major gene GS5 capable of controlling width and weight of rice grain
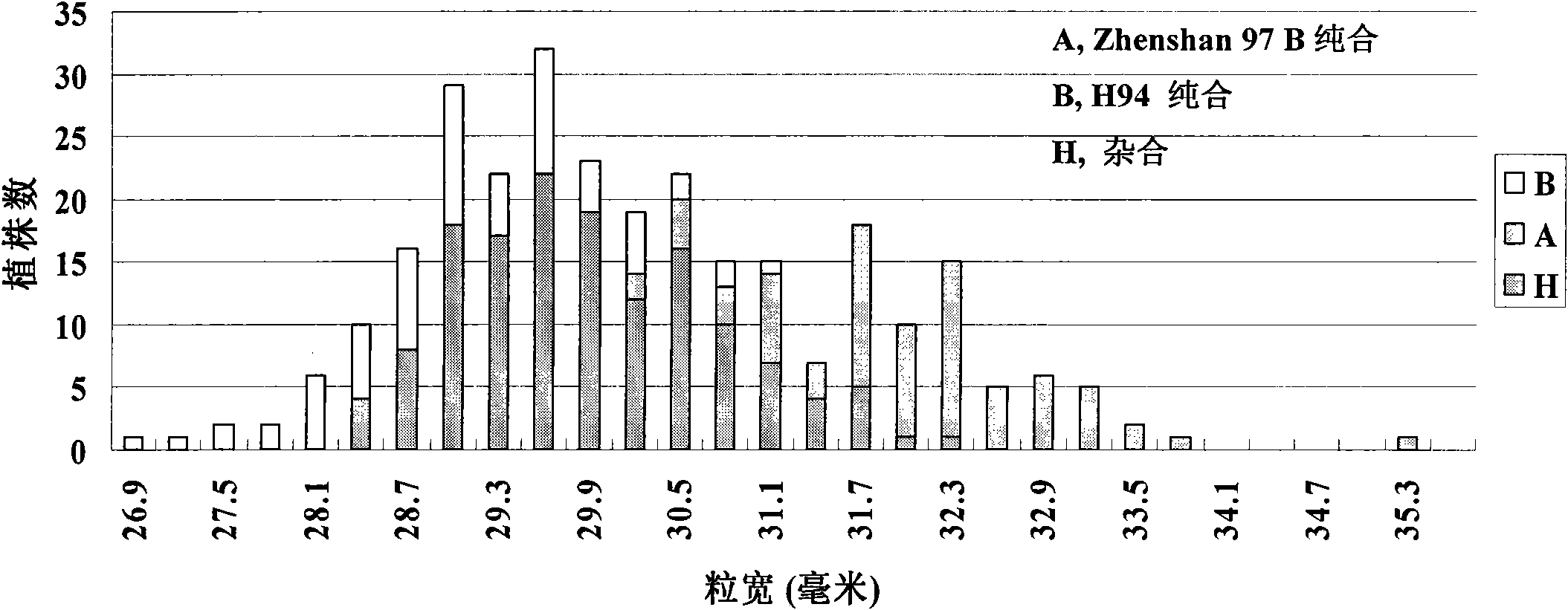
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering, disclosing a separated and cloned major gene GS5 capable of controlling the width and the weight of a rice grain and the DNA sequence of the allelic gene of the major gene GS5. The DNA sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 (Zhenshan 97B) and SEQ ID NO.3 (H94) and contains 10 exons. The amino acid sequence of the major gene and the amino acid sequence of the allelic gene are shown as SEQ ID NO.2 and SEQ ID NO.4. By using two large-grain rice varieties and two small-grain rice varieties for comparative sequencing, in an approximately 6.1kb range, 22 common base differences exist between the large-grain variety and the small-grain variety, wherein 18 mutations are in a promoter area, 4 mutations are in a code area and 5 amino acids are caused to be changed. By using a transgenic technology, GS5 transgenic rice plants are obtained and express that the width and the weight of the rice grain are obviously improved when being compared with the control width and the control weight of the rice grain. The character changes are quite coincident with the two genotype expressions of a Zhenshan 97 near-isogenic line and a GS5 near-isogenic line. The invention additionally discloses a method of near-isogenic line breeding, gene cloning and gene transfer and application thereof.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
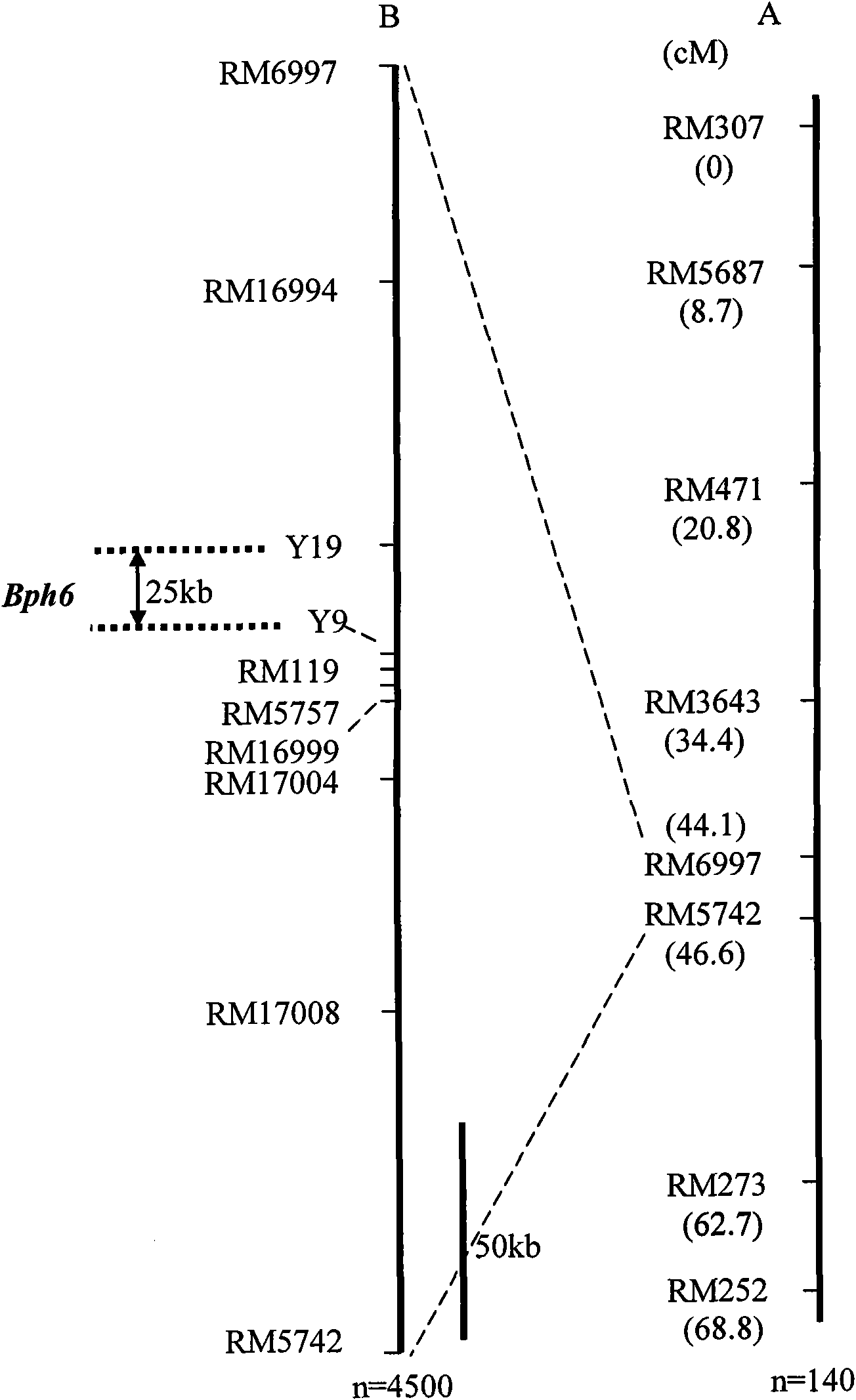
Molecular marker of major gene Bph6 resistant to brown planthopper and application thereof
InactiveCN101914531AQuick filterNot affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyBrown planthopper
The invention provides a molecular marker of major gene Bph6 resistant to brown planthopper and an application thereof. The invention can obtain a pest-resistant cultivar Swarnalata resistance gene Bph6 and position the resistance gene between molecular marker Y1 and molecular marker Y9 by hybridizing a rice pest-resistant cultivar Swarnalata with 9311 (female) to obtain the genetype of each F2 plant and performing genetic linkage analysis by combining resistance levels resistant to brown planthopper of each family of F2:3. The molecular marker linked with the resistance gene is one of RM16994, Y19, Y9, RM119, RM5757, RM16999, RM17004 and RM17008. The molecular marker in the invention can effectively detect whether the major gene locus exists in the pest-resistant cultivar Swarnalata and derived varieties (strains) thereof, thus greatly improving the selection efficiency of rice resistant to brown planthopper and obtaining brown planthopper resistant rice varieties containing Bph6 gene.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
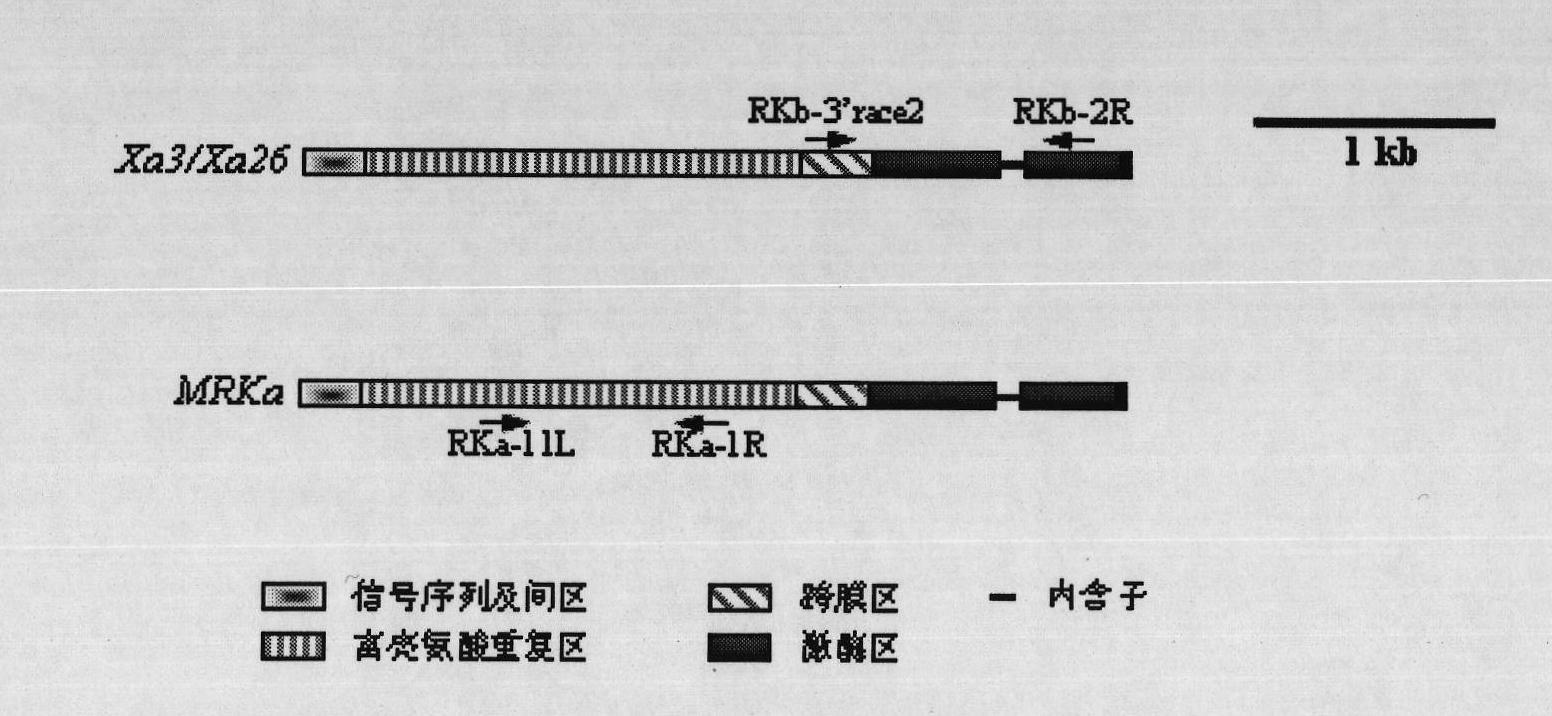
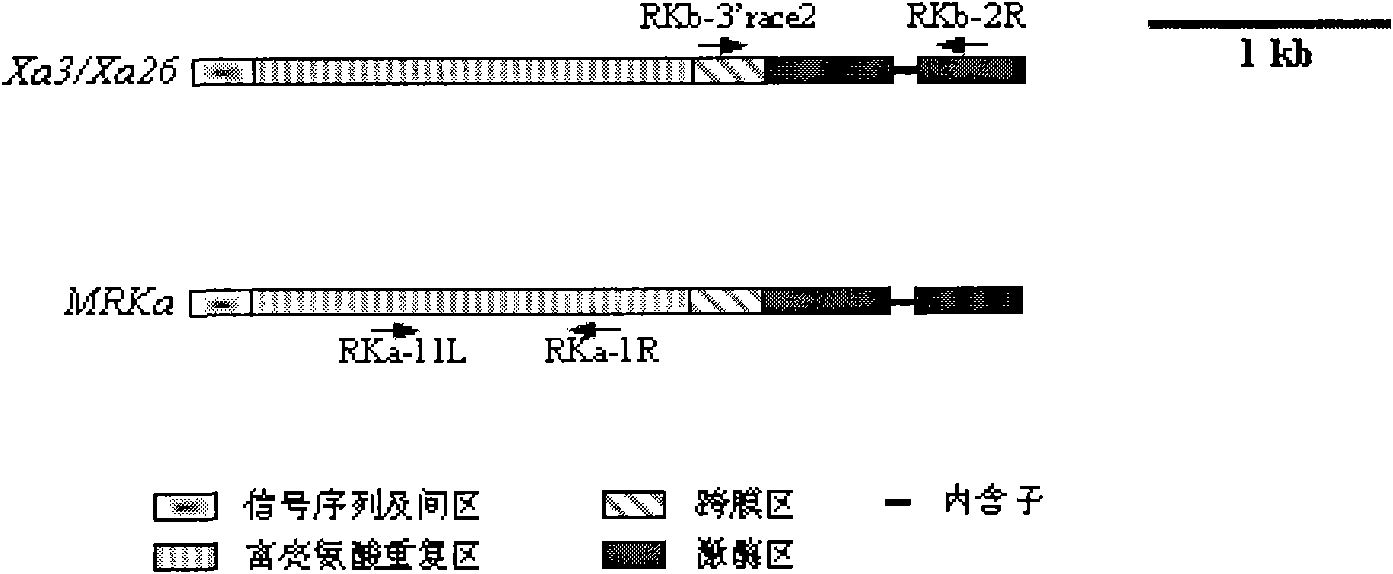
Oryza officinalis anti-Xanthomonas oryzae major gene Xa3/Xa26-2 and application for improving disease resistance of rice thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of the plant genetic engineering, in particular to the isolation and cloning and functional verification of the DNA fragment of oryza officinalis anti-Xanthomonas oryzae major gene Xa3 / Xa26-2. The Xa3 / Xa26-2 gene is used to code the leucine-rich protein kinase protein. The Xa3 / Xa26-2 gene ensures that rice can resist diseases caused by bacterial pathogen-Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. The DNA fragment and the regulatory sequence thereof are directly transferred in rice, and the resistance capability to Xanthomonas oryzae of the transgenic rice carrying Xa3 / Xa26-2 is significantly enhanced.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Gene marker of major gene Bph14 for resisting brown planthopper in rice and application thereof
InactiveCN103509791ANo genetic exchangeGood experimental repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerResistant genes
The invention relates to a gene marker of a major gene Bph14 for resisting brown planthopper in rice and application thereof. The gene marker Bph14-M1 of Bph14 has the following sequences of forward and reverse primers: a forward primer of (5'-3') AGCCACTTGGTGAACTTATT, and a reverse primer of (5'-3') GATTGACGATGAGGAGACTT. The application method includes 1) extracting rice genomic DNA; carrying out PCR amplification on the rice genomic DNA by using the forward and reverse primers; and carrying out electrophoresis detection on amplification products. The invention employs the marker to assist selection and can accurately transform the brown planthopper resistant gene Bph14 in B5 to a brown planthopper susceptible cultivar and greatly improve the breeding efficiency of brown planthopper resistant varieties.
Owner:江西省农业科学院水稻研究所
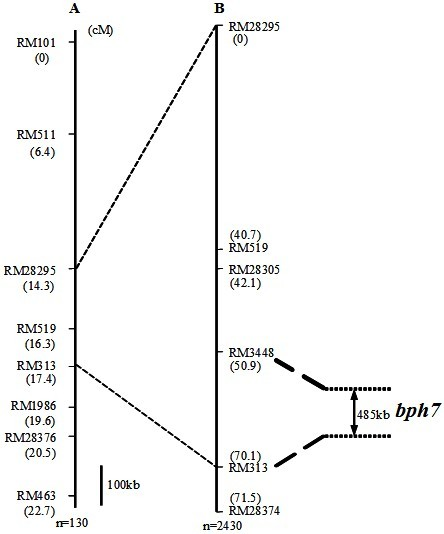
Molecular marker of brown planthopper-resistant major gene bph7 of rice and application thereof
ActiveCN102181440AQuick filterNot affectedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMajor geneInsect
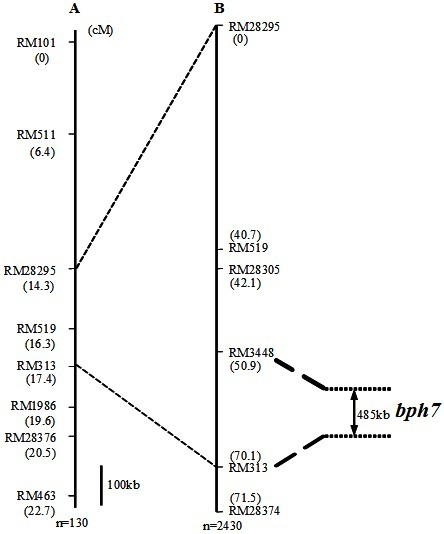
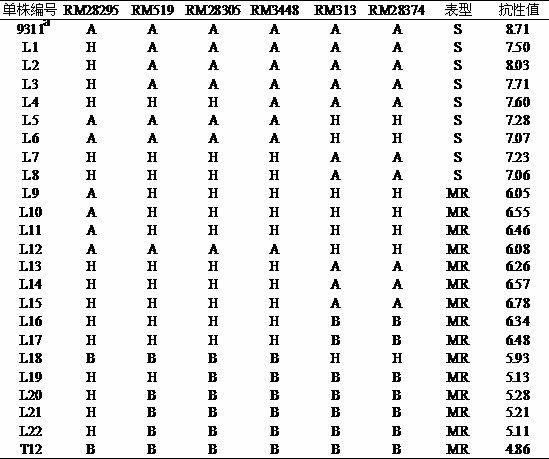
The invention provides a molecular marker of a brown planthopper-resistant major gene bph7 of rice and application thereof. The resistance gene bph7 of an insect-resistant variety T12 is obtained by performing genetic linkage analysis on genotypes of various F2 individual strains obtained by hybridizing the insect-resistant variety T12 (female parent) and an insect-susceptible variety 9311 (male parent) of the rice and brown planthopper resistance levels of various F2:3 families, and is positioned between a molecular marker RM3448 and a molecular marker RM313. Molecular markers, namely RM28295, RM519, RM28305 and RM28374 are also linked with the gene. The molecular marker can effectively detect whether the insect-resistant variety T12 and derived varieties (strains) thereof contain a siteof the major gene, so that the selection efficiency of brown planthopper-resistant rice is greatly improved, and a brown planthopper-resistant rice variety containing the bph7 gene is obtained.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Sudden cardiac death mutant gene detection kit
ActiveCN104561310AChange bad habitsAchieve the purpose of preventionMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh risk populationsCvd risk
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology and medical science, and in particularly relates to a sudden cardiac death mutant gene detection kit which is high in accuracy and good in predictability. The kit is used for performing polymorphism detection on 12 SNP sites of 8 major genes related to sudden cardiac death; three forward and reverse specific primers are respectively adopted for each SNP site by combining the characteristics of specific allelic gene PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and temperature gradient descent PCR; and the mutation of the 12 SNP sites can be simultaneously determined by virtue of program amplification of the temperature gradient descent PCR and agarose gel electrophoretic analysis. The detection kit provided by the invention is strong in specificity, high in detection rate, high in efficiency and low in cost, and can be used for screening high-risk population of sudden cardiac death, evaluating the risk degree of having the sudden cardiac death for a detected patient, and making clear pathogenic factors of patient sudden death from a gene level, thereby providing a new way of preventing, diagnosing and treating clinical sudden death.
Owner:谢怡
Molecular marker of anti-nilaparvata-lugens major gene Bph3 of rice
InactiveCN101956019AQuick checkQuick filterMicrobiological testing/measurementBrown planthopperGenotype
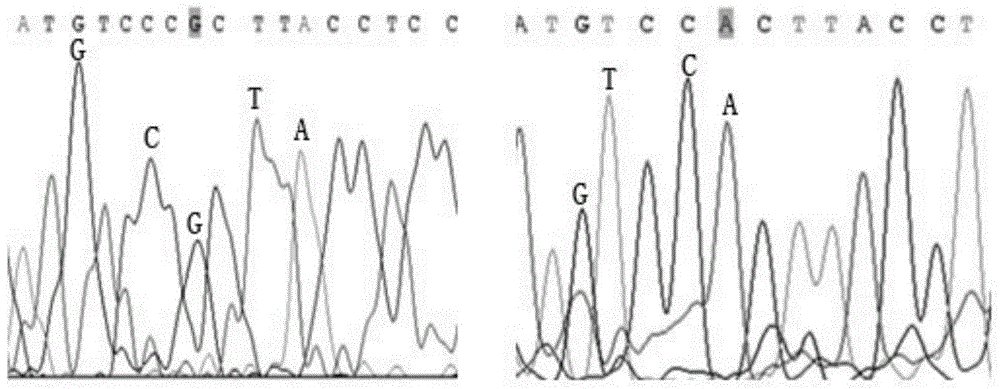
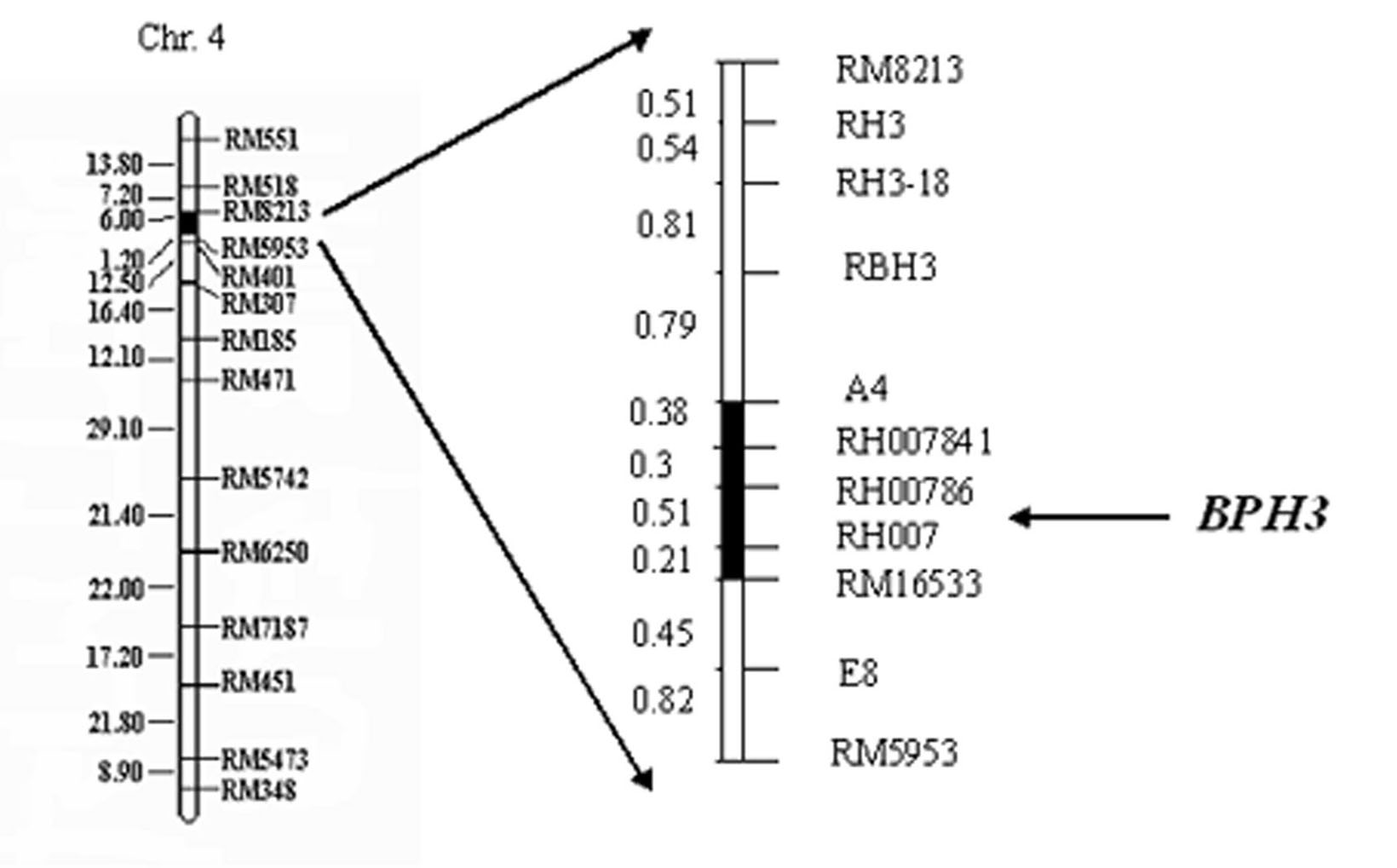
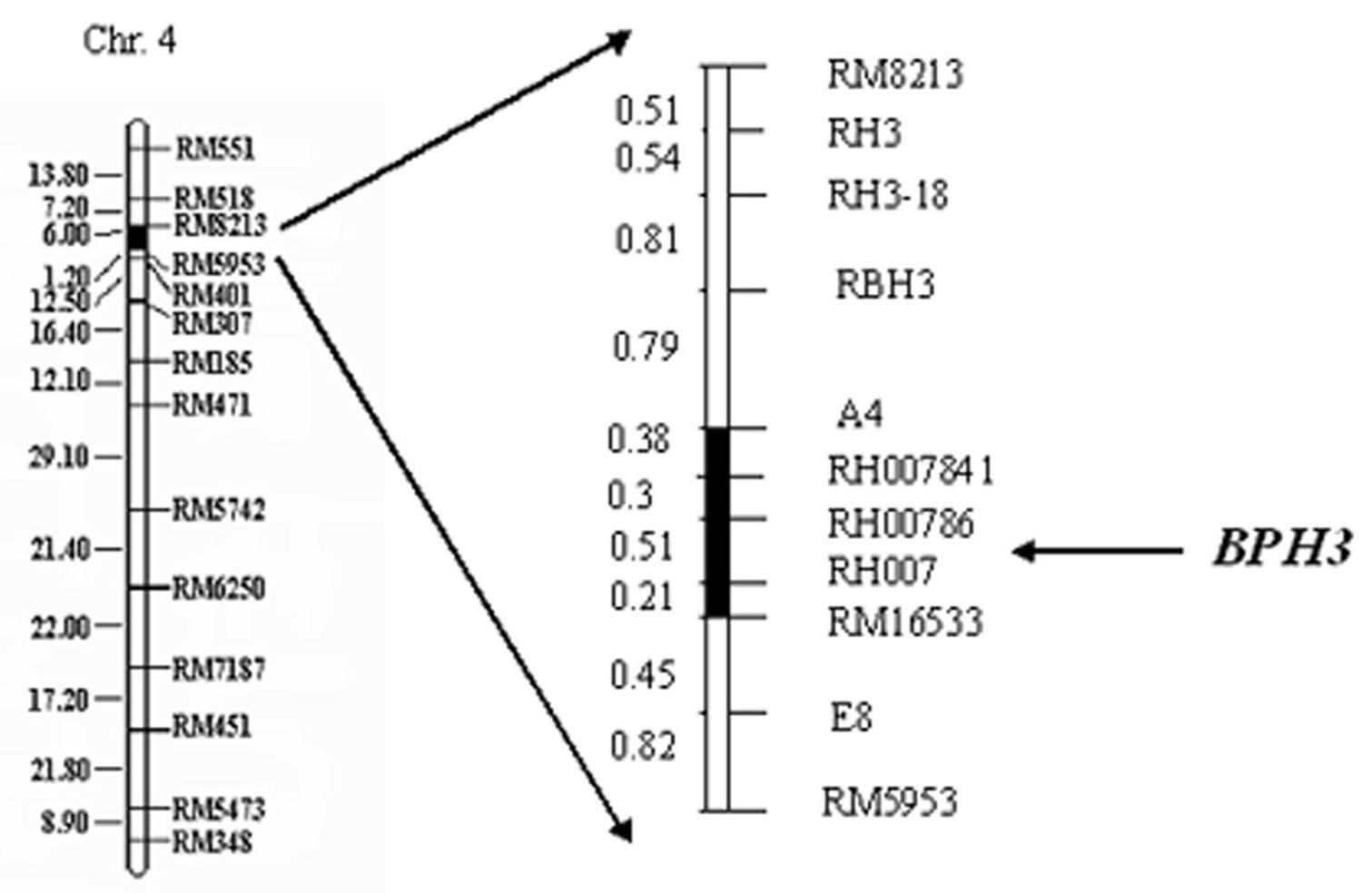
The invention relates to a molecular marker of an anti-nilaparvata-lugens major gene Bph3 of rice and belongs to the technical field of genetic breeding. A genetic linkage analysis is preformed on a genotype of each single plant of F2 obtained by crossing an rice anti-insect variety RathuHeenati (female) with an insect-susceptible variety 02428 (male) as well as on an anti-nilaparvata-lugens level of each family of F2: 3, thereby obtaining the anti-nilaparvata-lugens major gene Bph3 of the anti-insect variety RathuHeenati. The gene is positioned between the molecular marker A4 and the molecular marker RM16533; the selection efficiencies of three Indel markers RH784, RH786 and RH007 in the interval are around 97%. The molecular marker of the anti-nilaparvata-lugens major gene is used for detecting whether the major gene is contained in the anti-insect variety RathuHeenati as well as derived varieties thereof (family), thereby forecasting the anti-nilaparvata-lugens level; therefore, the selection efficiency of the anti-nilaparvata-lugens rice is improved greatly.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Molecular marker for rice brown planthopper-resistance QBph3 and QBph4 genes
InactiveCN105087553AImprove reliabilityEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceGenotype
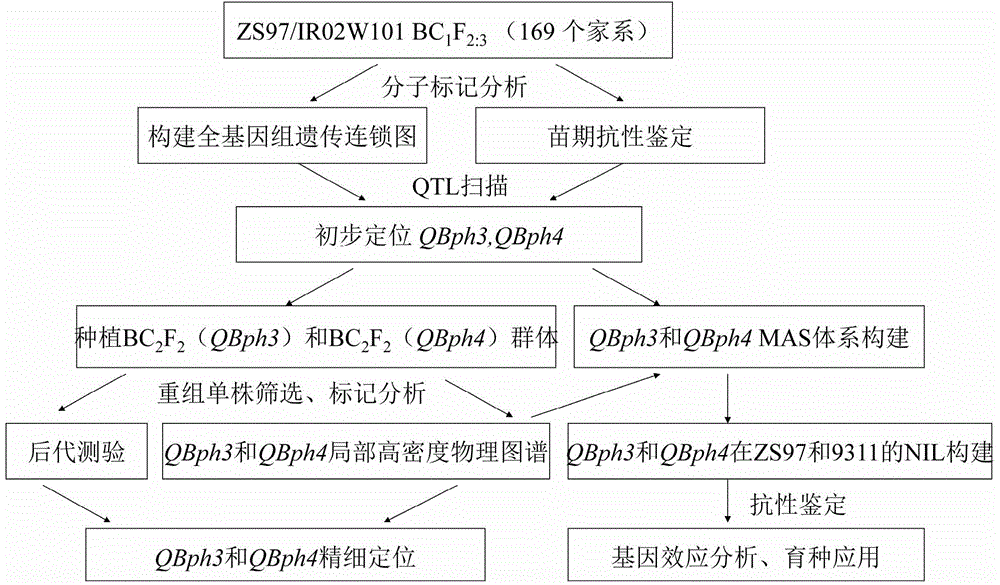
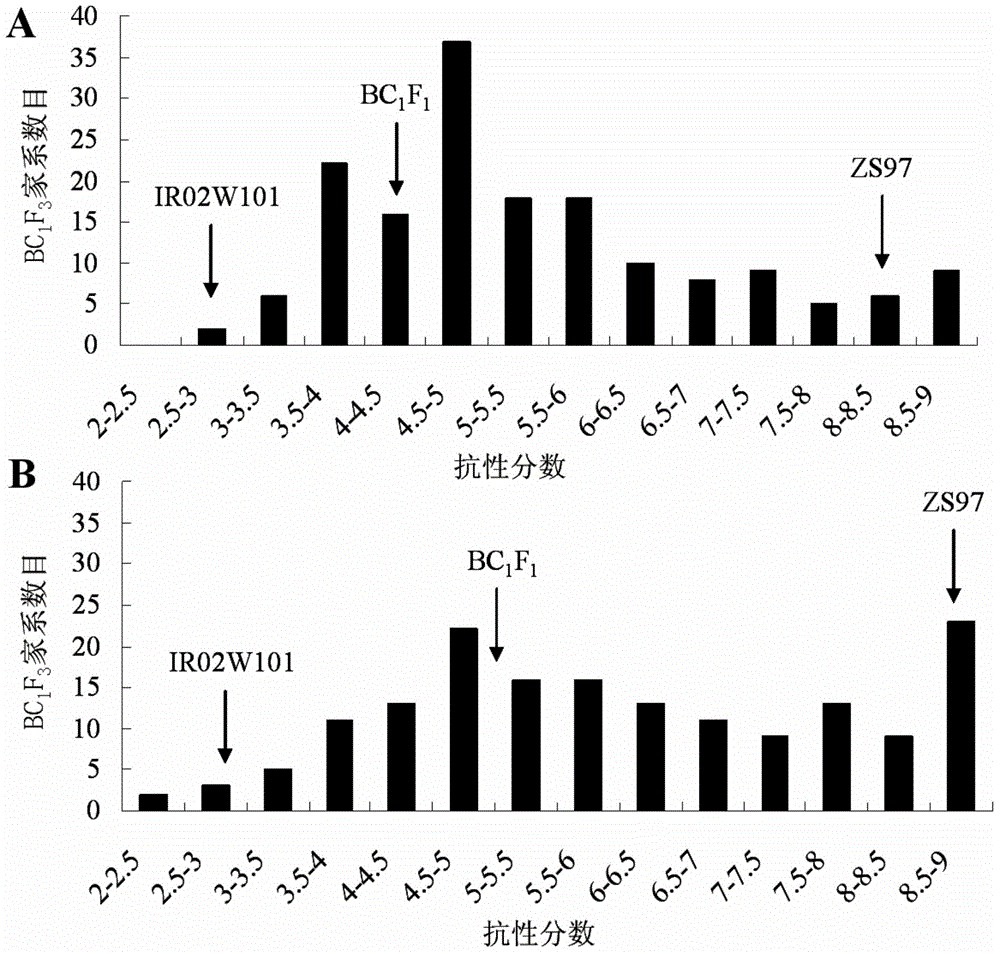
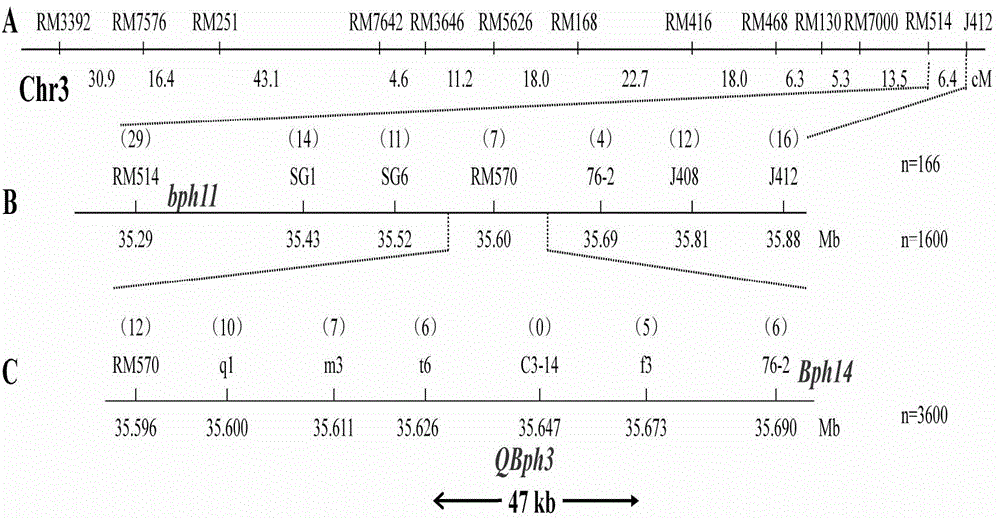
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of a rice molecular marker, and in particular relates to a molecular marker for two rice brown planthopper-resistance major genes QBph3 and QBph4 which are simultaneously derived from a pest-resistance introgression line IR02W101. The molecular marker comprises the following steps: carrying out crossing, self-crossing and backcrossing on Zhenshan97, which is an herbivore-susceptible variety, and IR02W101 so as to obtain genotypes of various BC1F2 single plants; carrying out genetic linkage analysis in accordance with brown planthopper-resistance grades of various F2: 3 lines during seedling stage; precisely locating a resistance gene QBph3 of the IR02W101 between long-arm markers t6 and f3 of the 3rd chromosome so as to obtain a co-segregative marker c3-14 as well as closely linked markers q1 and m3; and precisely locating QBph4 between short-arm markers p17 and xc4-27 of the 4th chromosome so as to obtain closely linked markers p6, p9, c4-5, xc4-7, HJ16, J417 and IN156. The molecular marker disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively detecting whether the pest-resistance introgression line IR02W101 and derived varieties thereof contain the major gene site or not.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Molecular marking method for major quantitative trait loci(QTL) for rice grain length
InactiveCN102154471AClear locationFine locationMicrobiological testing/measurementGermplasmRice grain
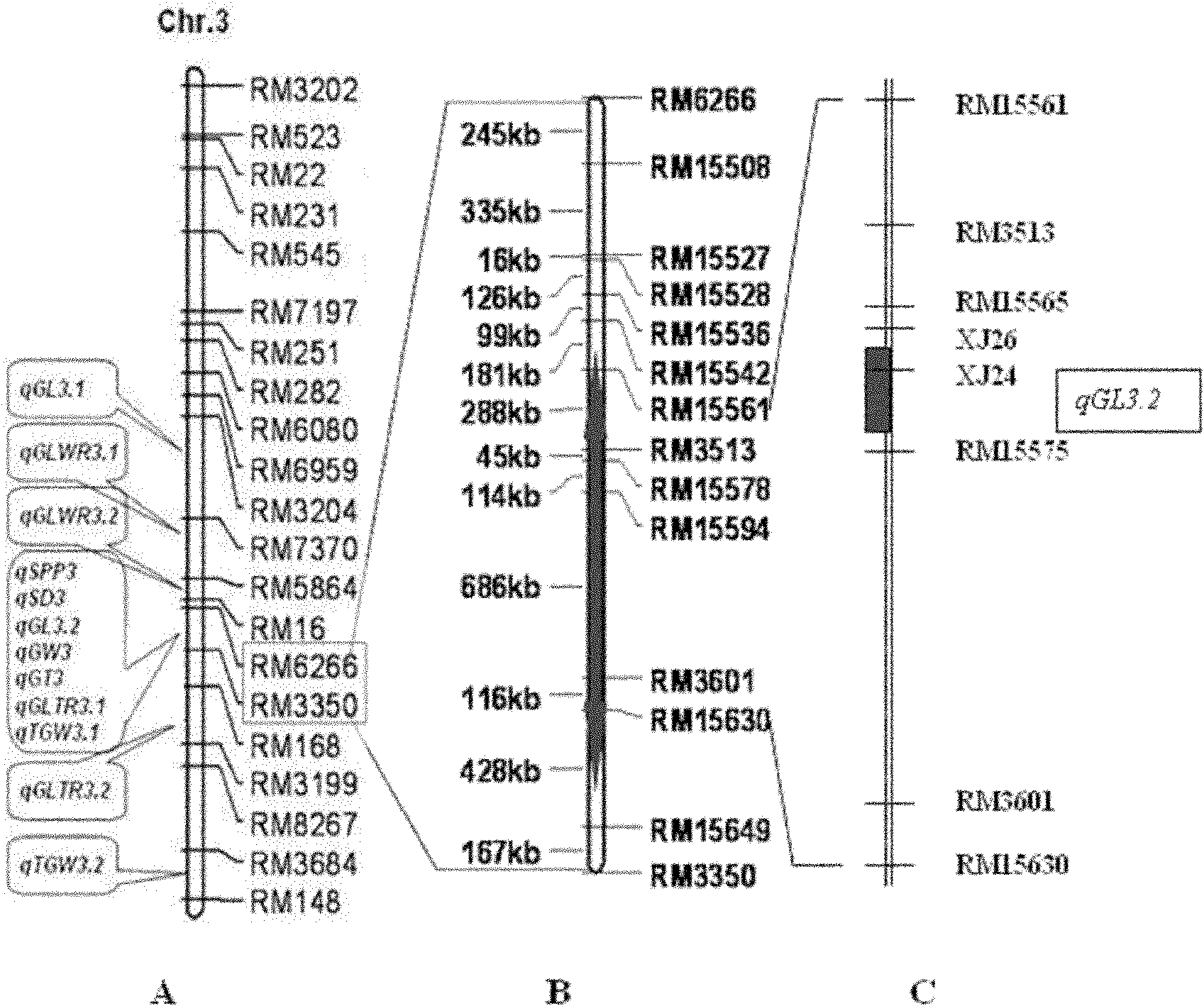
The invention belongs to the field of genetic breeding science and discloses a molecular marking method for a major quantitative trait loci (QTL) for rice grain length. In the method, Indel and simple sequence repeats (SSR) are used to mark one or more pairs of primers of XJ24 and XJ26 and RM15575 respectively to perform the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification of rice genome DNA, PCR amplification products undergo an electrophoretic test on 8 percent non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel, and if DNA fragments in corresponding size are generated through amplification, qGL 3.2 synergisticallelic mutant genes exist. When the large-grain germplasm of rice and breeding populations constructed by various parents of rice are detected by the grain length QTL qGL3.2 coseparated and closely interlocked molecular marking method, the major gene qGL 3.2 for controlling grain length and weight can be quickly imported, the selecting efficiency of the major gene qGL 3.2 is improved, and the method contributes to appearance improvement and high-yield breeding of rice.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Rice cold-resistant major gene identification method and special primer thereof
ActiveCN103866026AGood effectFast realization of screening and identification workMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyAssay
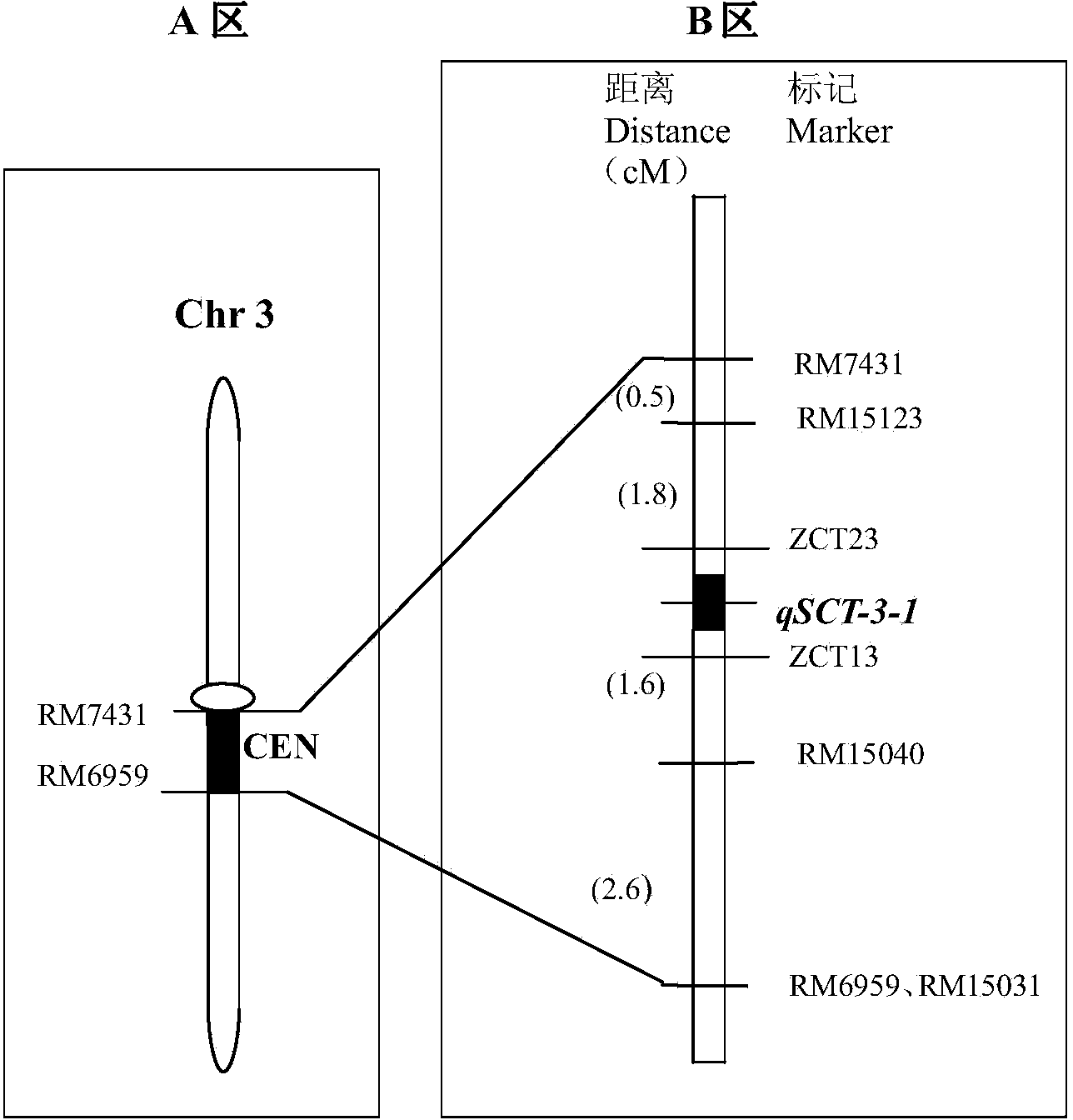
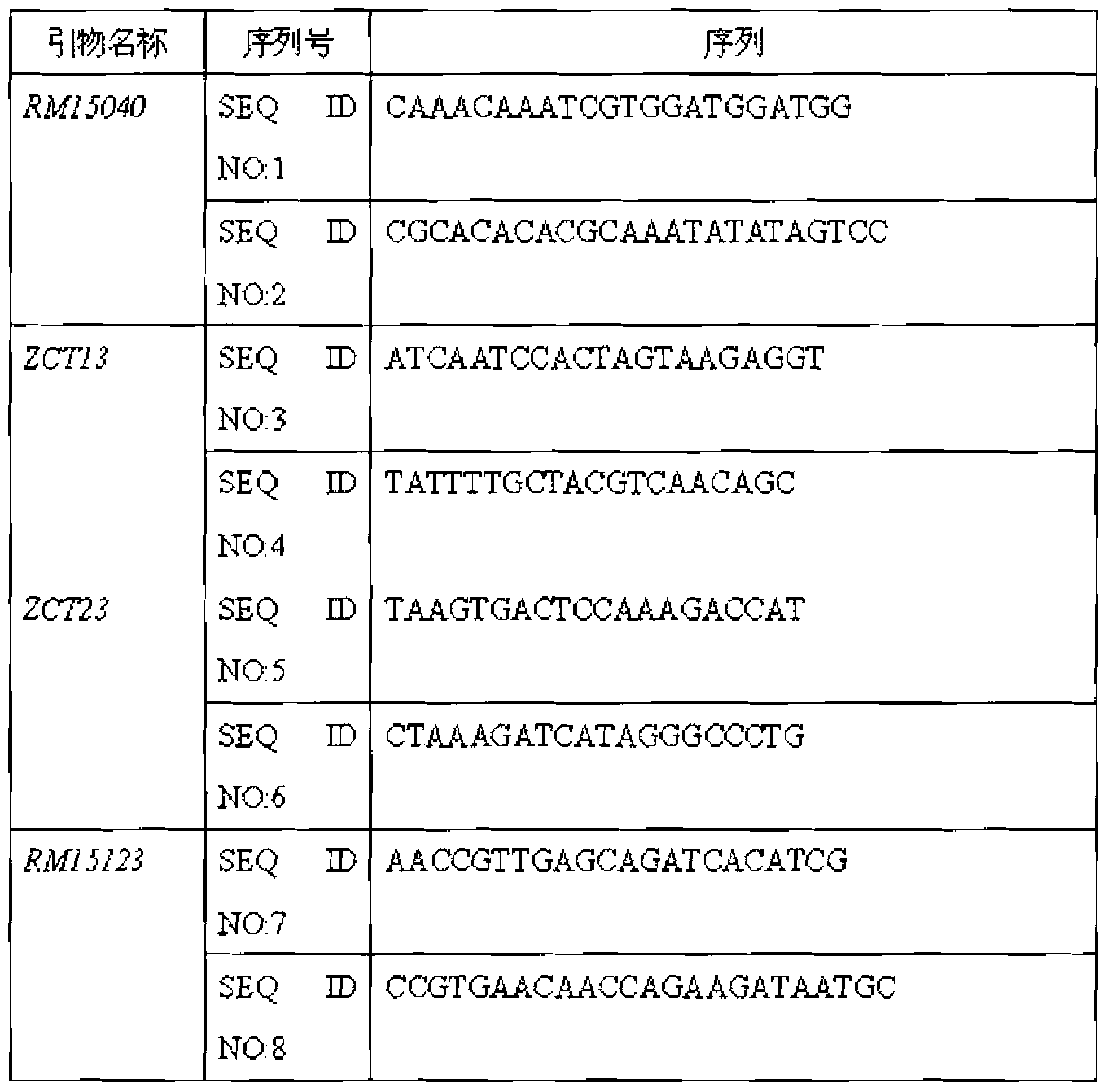
The invention relates to a rice seedling stage cold-resistant major gene and a special primer thereof. The rice cold-resistant major gene for the special primer comprises the following steps: by taking a rice genome DNA to be detected as a template, performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification by using any one labeled primer in a labeled primer RM15040, a labeled primer ZCT13, a labeled primer ZCT23 and a labeled primer RM15123, and performing gel electrophoresis assay on the PCR amplification product to obtain rice cold-resistant identification, wherein stripes with the size of 140-170bp or 230-270bp or 290-310bp or 380-400bp exist in the PCR amplification product, and the 3rd chromosome of the seedling stage rice contains cold-resistant major genes qCTS-3-1. According to the rice cold-resistant screening, the production cost can be saved, the selection efficiency is improved, the breeding cycle of rice varieties is shortened, and the errors of the detection result are reduced.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
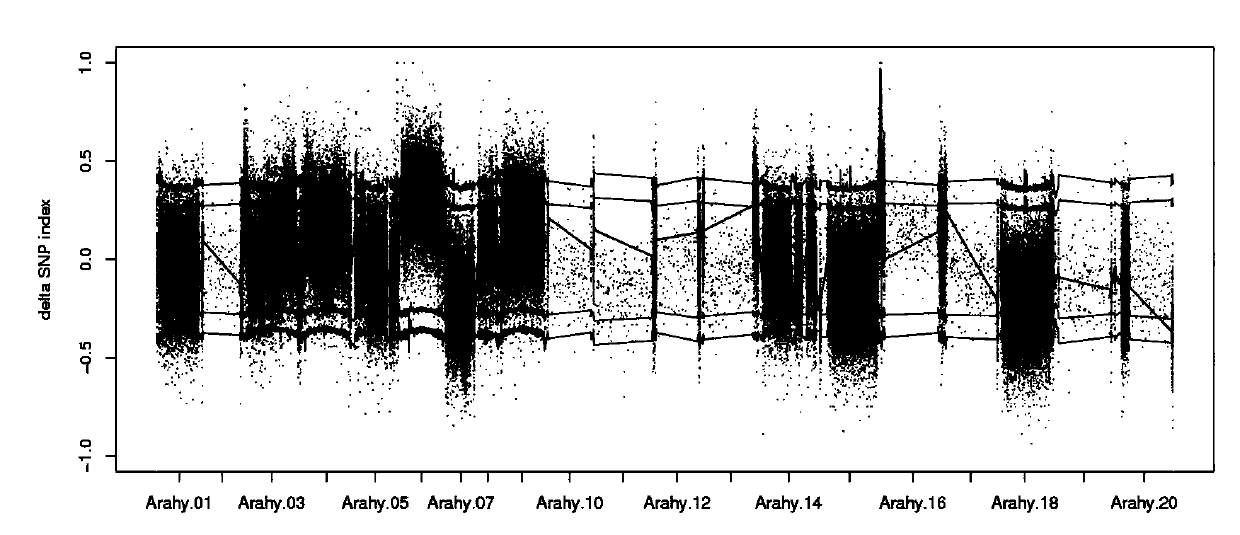
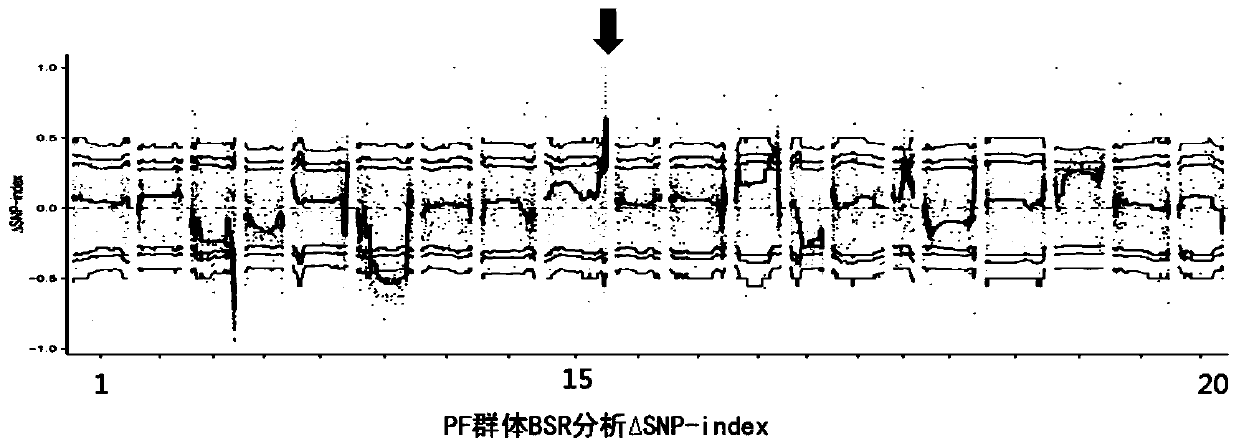
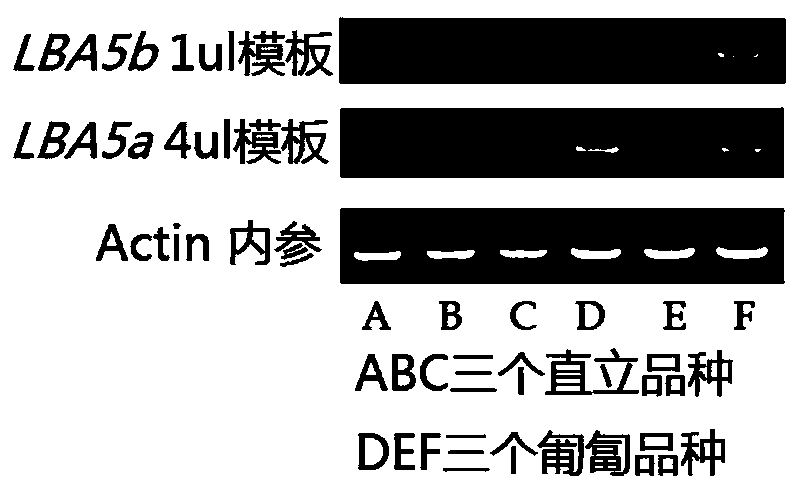
Gene LBA5 for regulating and controlling lateral branch angle, growth habit and plant type of peanut, and application thereof
ActiveCN110592102ARealize reasonable close plantingImprove yield per unit areaPlant peptidesFermentationMain stemHabit
The invention belongs to the technical field of biotechnology and genetic engineering, and provides a gene LBA5 for regulating and controlling a lateral branch angle, growth habit and plant type of apeanut, and application thereof. A major gene LBA5 for controlling the lateral branch angle, growth habit and plant type of the peanut is located and cloned in the peanut, and comprises two homologousgenes LBA5b and LBA5a and promoters thereof; genetic improvement of an included angle between a lateral branch and a main stem of the peanut can be achieved through selection of gene allelic variation via hybridization, backcross and the like; the functions or expression quantity of the gene in a creeping variety peanut can be regulated so that the included angle between the lateral branch and the main stem of the peanut is regulated; and thus, the two homologous genes LBA5b and LBA5a and the promoters thereof of the gene LBA5 can be applied to the genetic improvement and genetic engineeringimprovement of the lateral branch angle, growth habit and plant type of the peanut, even other crops.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Gene detection chip of OATP1B1 major gene mutation
ActiveCN101717816AAccurate detectionSensitive detectionNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh pressureMedicine use
The invention relates to a gene detection chip, in particular to a gene detection chip used for detecting common major gene mutation of organic anion transferred polypeptide 1B1 (OATP1B1 in short), which is closely related to reactiveness of medicines used for curing high blood pressure, malignant tumor, 2 type diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia. Through selecting 8 mutational sites and designing out corresponding probes, the invention realizes the detection on the mutational sites and is capable of providing information of the mutation sites, thereby providing foundation for medication guiding.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
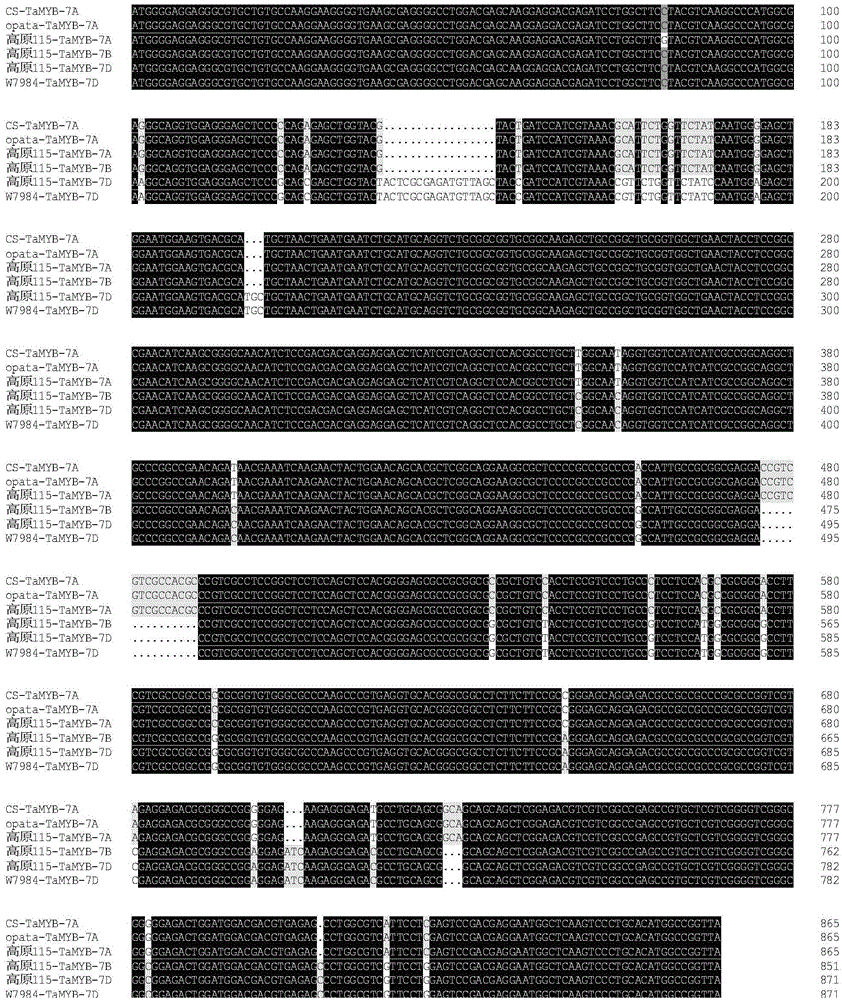
Novel wheat gene TaMYB7D capable of adjusting and controlling synthesis and metabolism of anthocyanin
InactiveCN104894142ARegulates transcriptional activityFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyPlant genetic engineering
The invention discloses a novel wheat gene TaMYB7D capable of adjusting and controlling the synthesis and the metabolism of anthocyanin, and belongs to the field of plant genetic engineering, wherein the novel wheat gene TaMYB7D is obtained through separation of the purple-grain wheat variety highland 115. The TaMYB7D is located on a wheat chromosome 7D, and a protein product subcell is located in a cell nucleus. A deduced amino acid sequence shows that TaMYB3 encodes an MYB transcription factor capable of adjusting and controlling the synthesis and the metabolism of anthocyanin. The expression quantity of the TaMYB7D in the coleoptiles of a purple wheat variety highland 115 grain can be increased under the induction of light. During transient expression, the TaMYB7D and the pericarpic cell of the highland 115 grain synthetize anthocyanin. Moreover, coseparation occurs between the color of the coleoptiles of the highland 115 grain and the expression of the TaMYB-7D, that is, the TaMYB7D has transcriptional activity used for adjusting and controlling the synthesis and the metabolism of anthocyanin, and is the major gene of the purple coleoptiles of the TaMYB7D highland 115 grain.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF SCI NORTHWEST HIGHLAND BIOLOGY INST
Structure and major gene locus Psr9 of pod shattering resistance character of rape and application thereof
InactiveCN102206635AClear locationIncrease costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationF1 generationDNA
The invention discloses a structure and a major gene locus Psr9 of a pod shattering resistance character of a rape and application thereof. A preparation method of the major gene locus Psr9 of the pod shattering resistance character of the rape comprises the following steps of: (a) hybridizing by utilizing a high-low pod shattering resistance assembly zy72360 of the rape and R1, and carrying out selfing on an F1 generation to generate an F2 generation segregation population; (b) extracting a parent zy72360 and R1, the leaf total DNA of the F1 generation and F2 generation segregation population; (c) collecting rape SSR (Simple Sequence Repeat) label public databases, autonomously developing an SSR label, and screening polymorphic primers by utilizing the parent zy72360; (d) establishing a genetic map through distributions inside the F2 generation segregation population, carrying out QTL (Quantitative Trait Loci) locus analysis by dint of pod shattering resistance index data, and obtaining the SSR label closely concatenated with a major gene of the pod shattering resistance character; and (e) observing the parent zy72360 and the structure of a mature pod of the F2 generation segregation population through a dissecting microscope, and measuring the combining area index of a carpel and a placenta frame. The invention has the advantages of enhanced selection efficiency, definite position of the pod shattering resistance major gene locus Psr9, convenience and fastness for detection, fast screening of a high pod shattering resistance strain used for the pod shattering resistance breeding of the rape, definite breeding selection target and cost saving.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
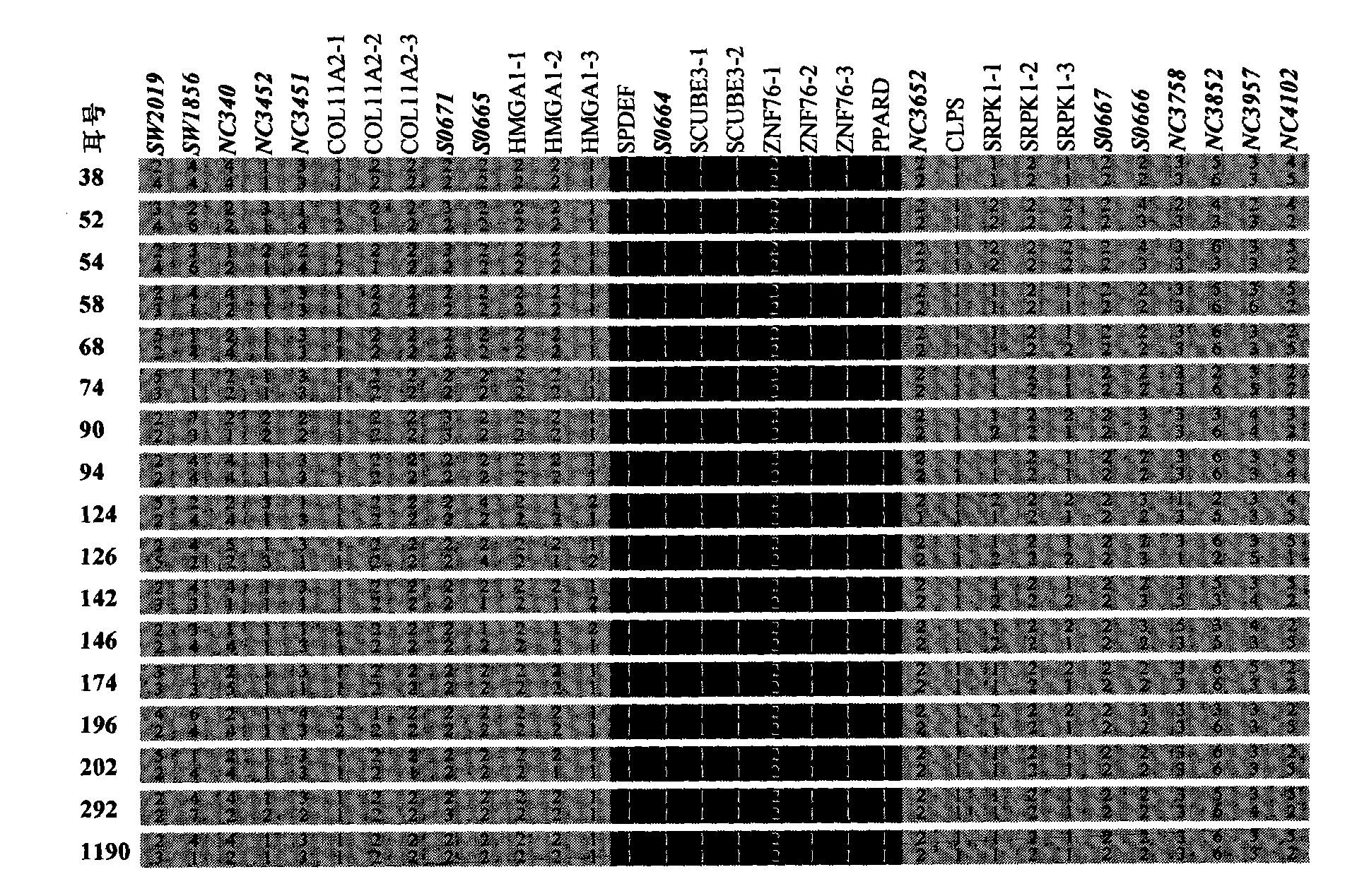
Identification method of PPARD major gene, establishment of molecular breeding method and application thereof
InactiveCN101805739AImprove the efficiency of breeding improvementTraits are genetically stableMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenotypeBiology
The invention relates to an identification method of PPARD major gene, establishment of a molecular breeding method and application in the genetic improvement of breeding pigs. In the invention, by adopting the white Duroc * Erhualian Intercross and the Chinese and exotic breeding pigs of distant population, the whole-genome scan and linkage mapping, the IBD fine mapping of the target region based on a high-density SNP mark and the selection effect analysis of the distant population are carried out, and then the major gene, i.e., PPARD for deciding the traits of pig ears, fat deposition, weight of pig head and carcass traits, and the mutation site of key cause, i.e., G32E are identified. The sites are detected by the modern molecular biotechnology; by adopting the gene-assisted selection method, the beneficial gene-typed individuals are selected for the breeding pigs, thereby the breeding improvement efficiency of the traits of pig ears, fat deposition, weight of pig head and carcass traits are remarkably improved. The invention further discloses an identification course of the gene and the cause mutation site and a method for breeding the traits of pig ears, fat deposition, weight of pig head and carcass traits by using the gene marker of the invention.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Molecular marker for QTL/major gene related to verticillium wilt resistance of cotton
ActiveCN104313016AStable detectionImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceVerticillium wilt
The invention discloses an SSR marker interlocked with verticillium wilt resistance QTL / major gene loci qDI-5-1, qDI-5-2, qDI-5-3, qDI-5-4 and qDI-5-5 of cotton. The qDI-5-1, the qDI-5-2, the qDI-5-3, the qDI-5-4 and the qDI-5-5 are all located on a chromosome C5. By utilizing the SSR marker interlocked with verticillium wilt resistance major gene loci of cotton to carry out assistant selection, breeding efficiency of verticillium wilt resistance of cotton can be improved.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
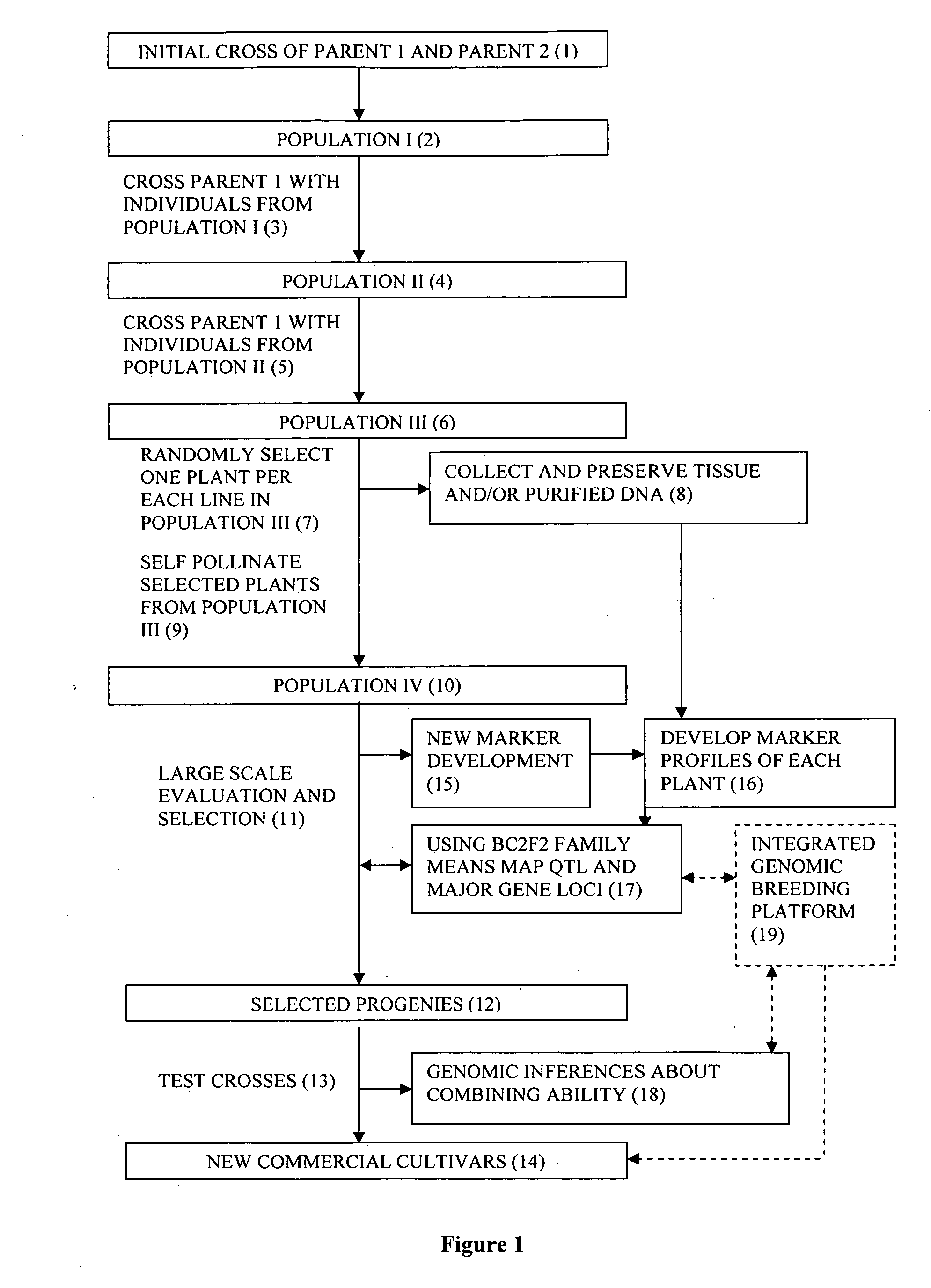
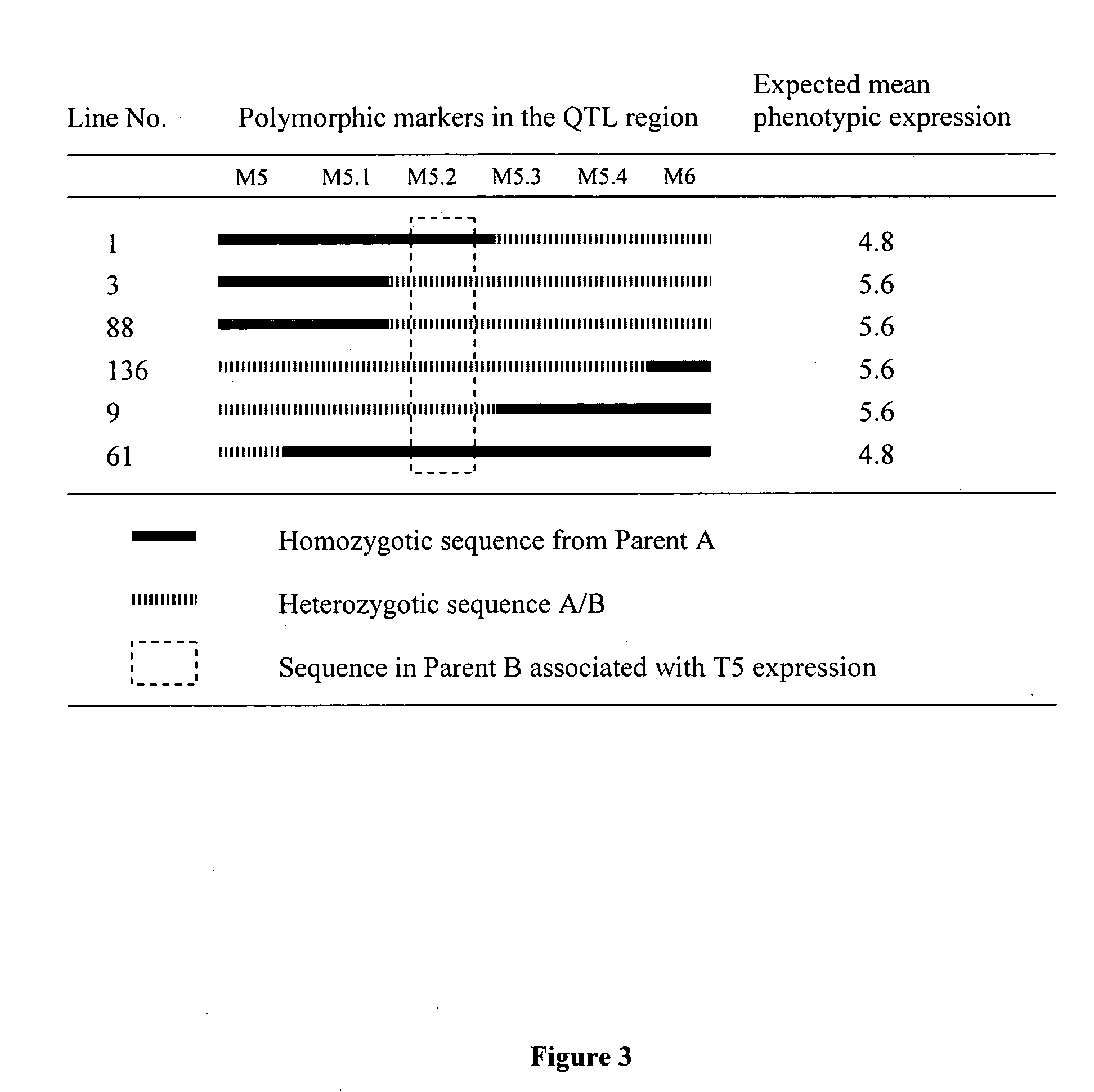
Integration of commercial plant breeding and genomic technologies
InactiveUS20080034450A1Flexible and economically sound integrationOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationPlant populationGenetic Materials
The invention relates to a method for integration of commercial breeding of plants and genomic methodology comprising the steps of: a) plant population development by crossing a Parent 1 and a Parent 2 to generate a Population I; b) crossing Parent 1 with individuals from Population I to generated a Population II; c) crossing Parent 1 with individuals from population II to generate a Population III; d) randomly selecting at least one plant per each line in Population III and collecting genetic material from the random plant; e) self pollinating selected plants from population III to generate a Population IV; f) evaluating and selecting plants of Population IV; and g) using selecting progeny plants of Population IV in test crosses for evaluating the potential to develop new commercial cultivars; where the genetic material in step d) is used to develop marker profiles of each plant to map QTL and major gene loci as part of the evaluation of plants in step f).
Owner:FRAMPTON ANNA J
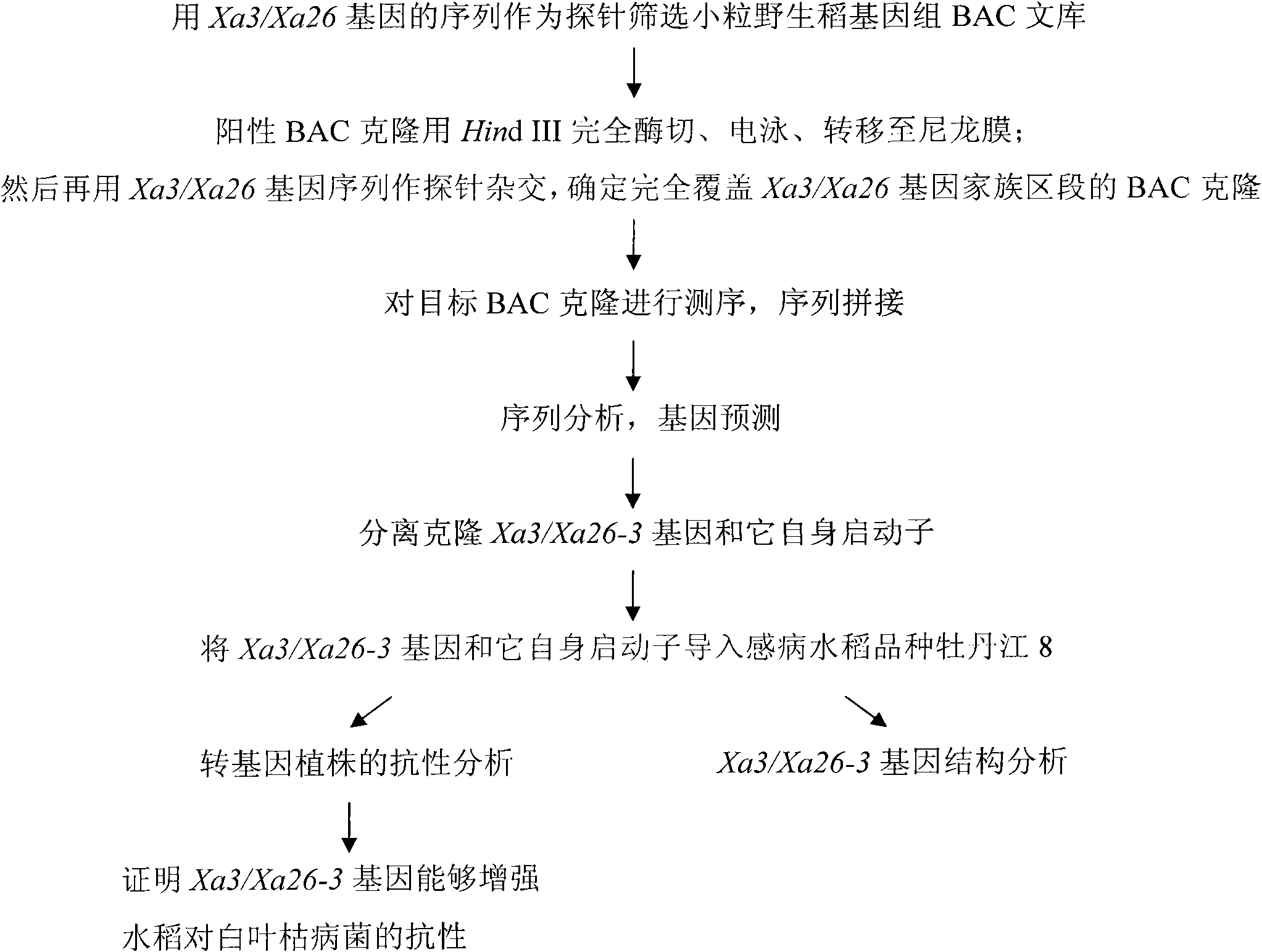
Oryza minuta bacterial blight-resisting major gene Xa3/Xa26-3 and application thereof in improving disease resistance of paddy rice
InactiveCN101880669AIncrease resistancePlant peptidesFermentationGenetically modified ricePlant disease
The invention relates to the technical field of plant gene engineering, more particularly to isolation and cloning as well as functional verification of DNA fragment containing Oryza minuta bacterial blight-resisting major gene Xa3 / Xa26-3. Xa3 / Xa26-3 codes leucine-rich protein kinase-type protein, which can enable paddy rice to resist the diseases caused by bacillary pathogenic bacteria-bacterial blight bacteria(Xanthomonas oryzae pv. Oryzae). The fragment and self-regulatory sequences thereof are directly transplanted into paddy rice, therefore, Xa3 / Xa26-3. Xa3 / Xa26-3-carrying transgenic rice is prominently strengthened in resisting bacterial blight.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Cotton high-strong fiber gene major gene site and moloecular labelling thereof
InactiveCN1528912AImprove selection efficiencyEasy to industrializeMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationFiberAgricultural science
The invention discloses major gene resistance locus and the molecular mark of cotton high intensity fiber, which is used auxiliary selection of molecular mark of cotton fiber intensity quickly. The major gene resistance locus QTLfs-2 has three SSR marks H H which connect with it, they are located by mark NAU / SSR / FS1130, NAU / SSR / FS2160, NAU / SSR / FS3160, and it can explain 16.9% phenotype variation in F2:3 of HS427-10xTM-1. Most of high intensity fibers have the same gene QTLfs-2, it has high application value. The expression is stable. It can enhance the fiber quality of cotton in our country and accelerates the industrialization of high intensity cotton seeds.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Efficient cell culture system for hepatitis c virus genotype 1a and 1b
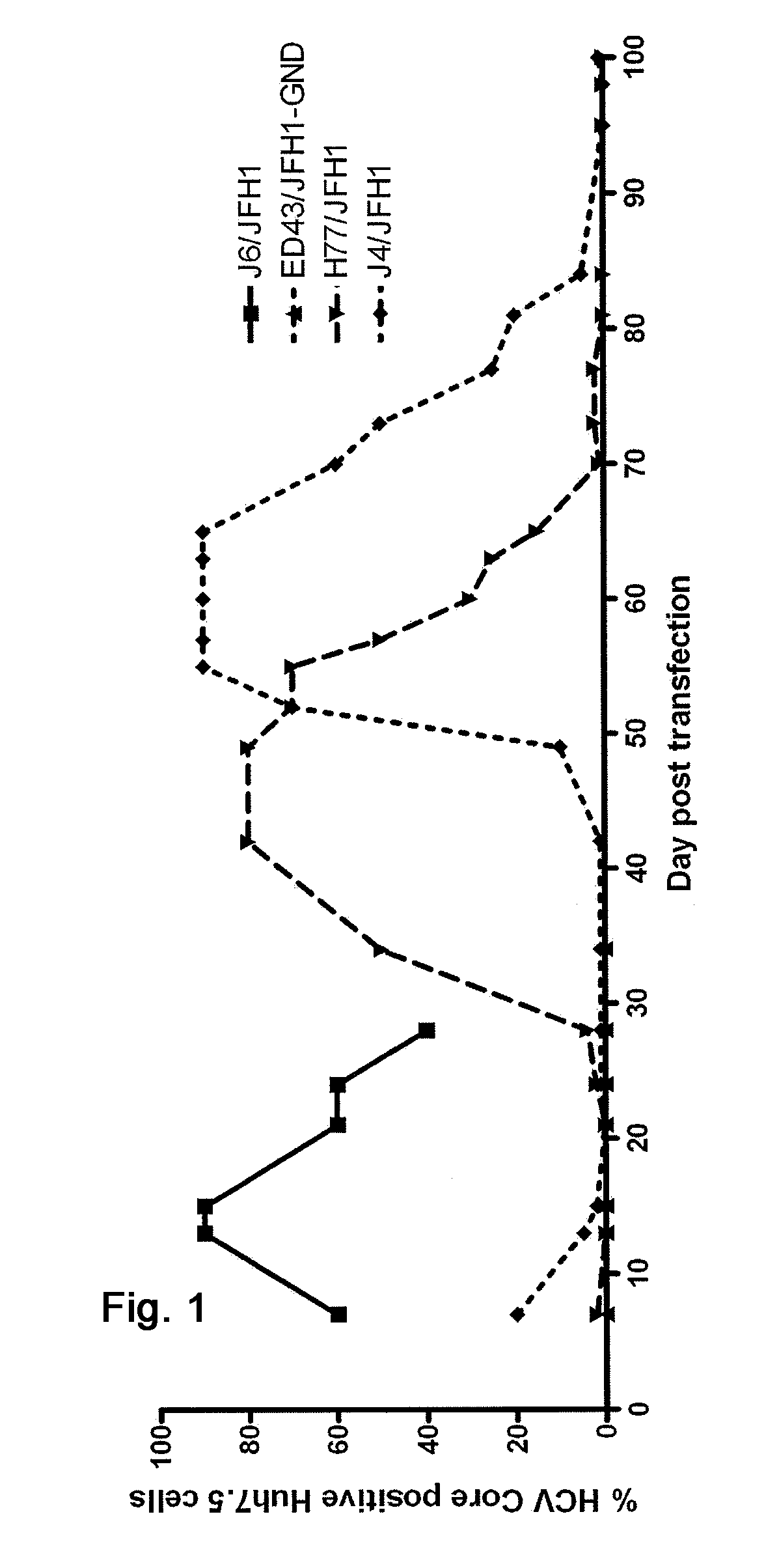
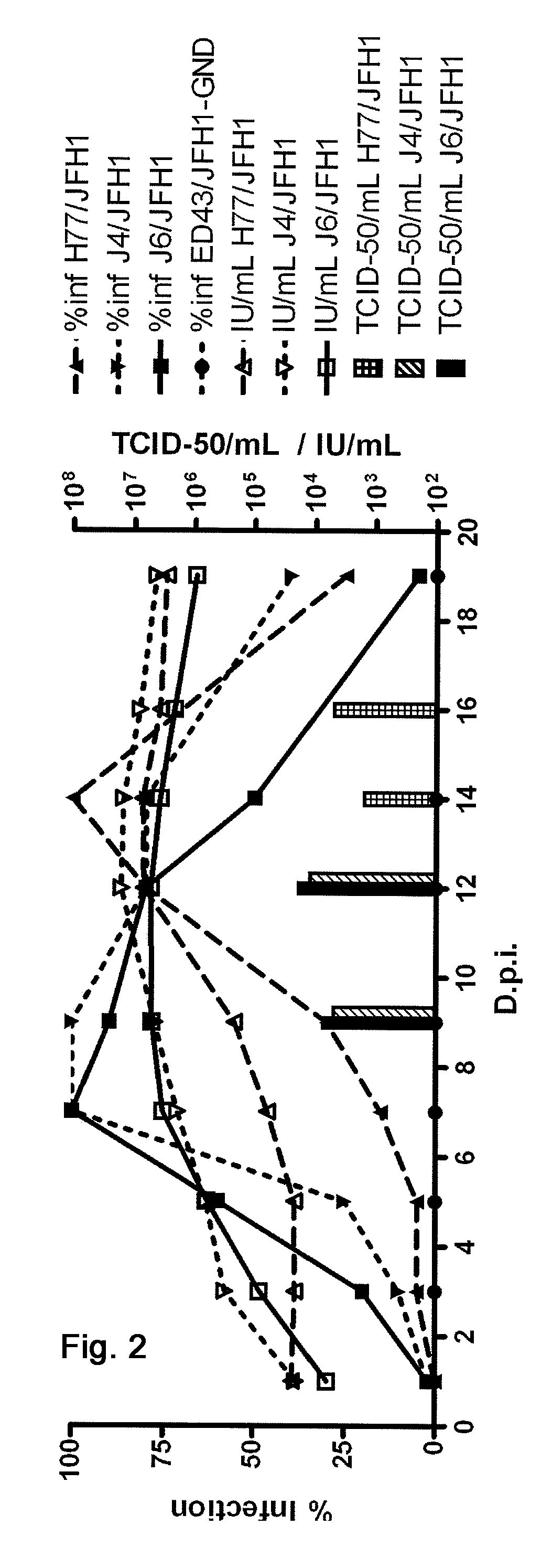
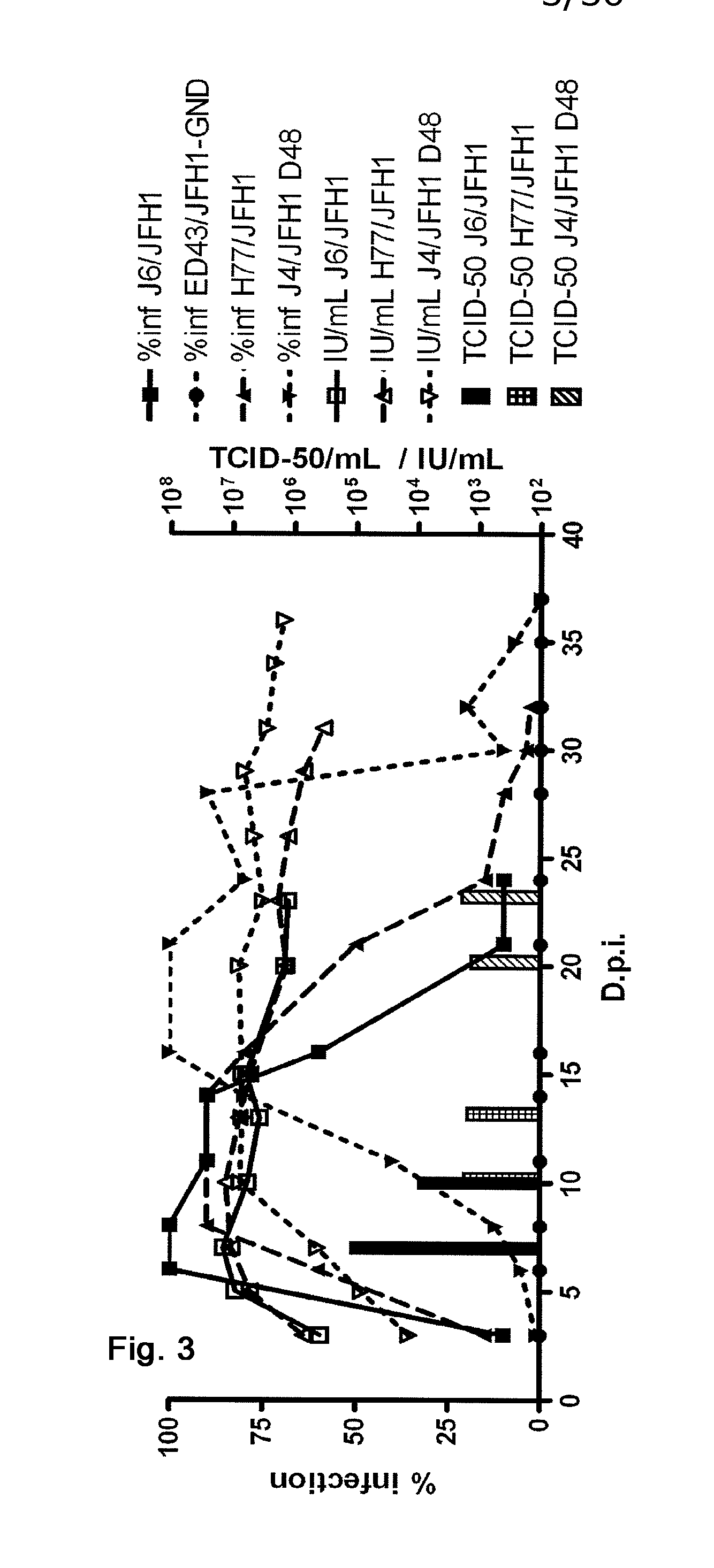
The present inventors developed hepatitis C virus 1a / 2a and 1b / 2a intergenotypic recombinants in which the JFH1 structural genes (Core, E1 and E2), p7 and NS2 were replaced by the corresponding genes of the genotype Ia reference strain H77C or TN or the corresponding genes of the genotype Ib reference strain J4. Sequence analysis of recovered 1a / 2a and 1b / 2a recombinants from 2 serial passages and subsequent reverse genetic studies revealed adaptive mutations in e.g. p7, NS2 and / or NS3. In addition, the inventors demonstrate the possibility of using adaptive mutations identified for one HCV isolate in generating efficient cell culture systems for other isolates by transfer of mutations across isolates, subtypes or major genotypes. Furthermore neutralization studies showed that viruses of e.g. genotype 1 were efficiently neutralized by genotype Ia, 4a and 5a serum, an effect that could be utilized e.g. in vaccine development and immunological prophylaxis. The inventors in addition demonstrate the use of the developed systems for screening of antiviral substances in vitro and functional studies of the virus, e.g. identification of receptors required for HCV entry
Owner:HVIDOVRE HOSPITAL
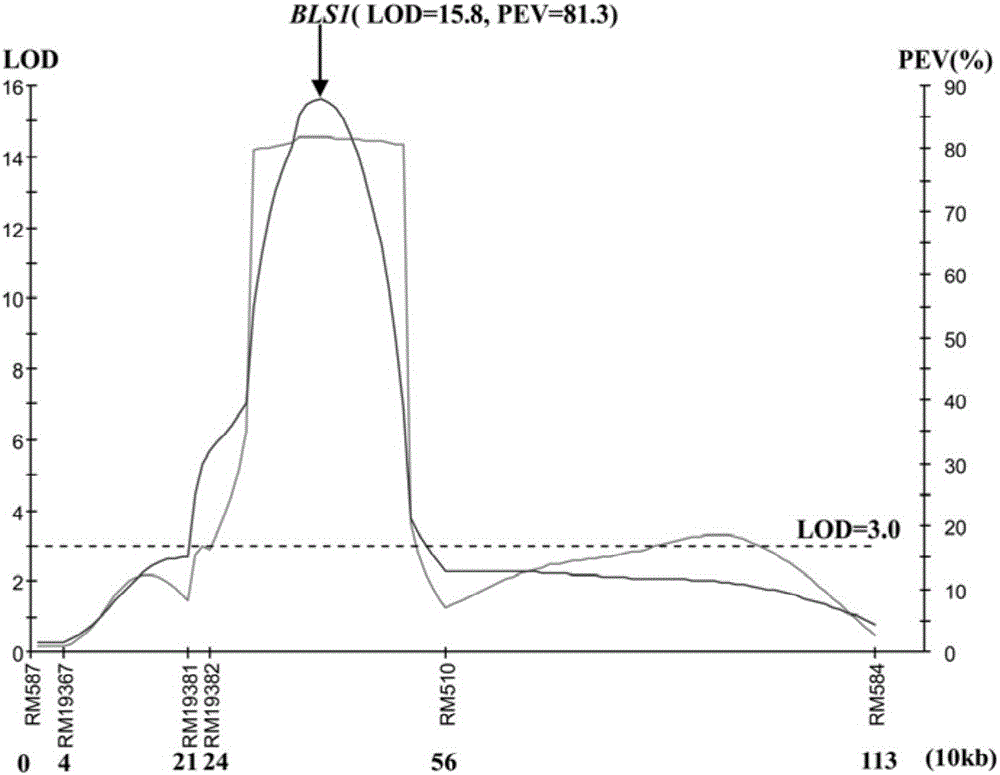
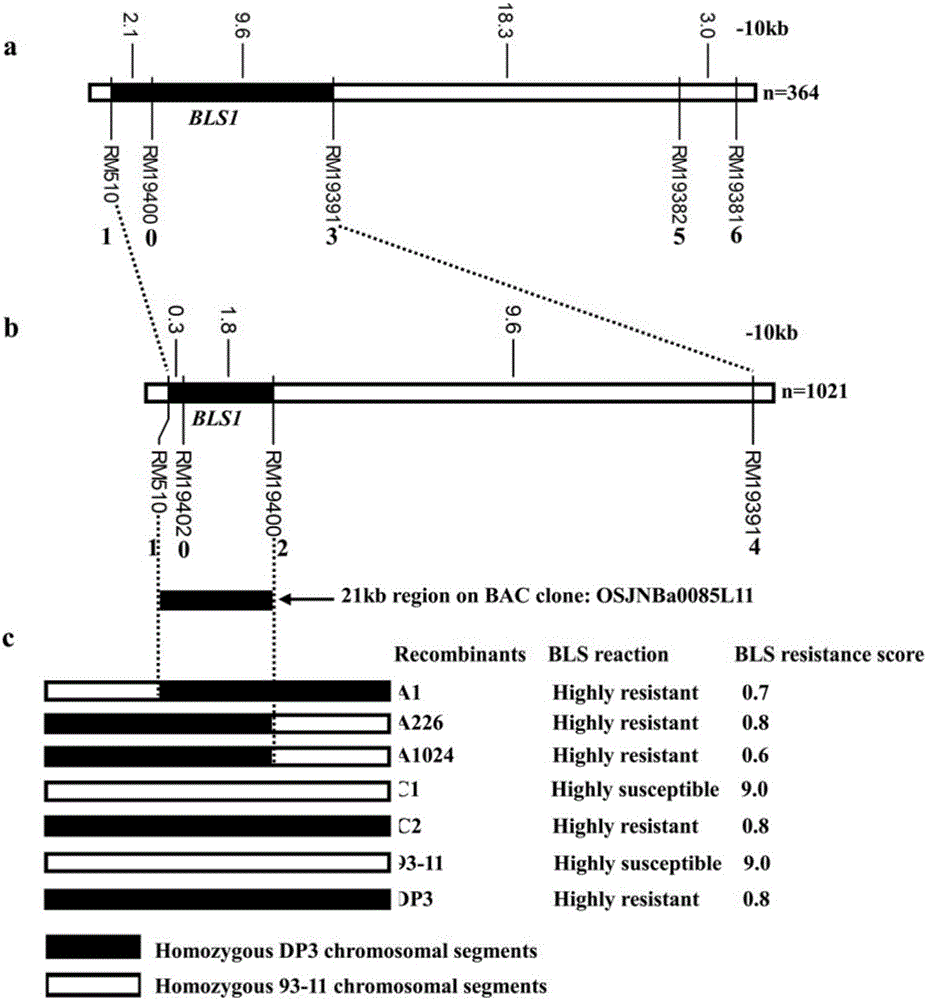
Molecular marker for bacterial stripe resisting major gene BLS1 locus of rice and application of molecular marker
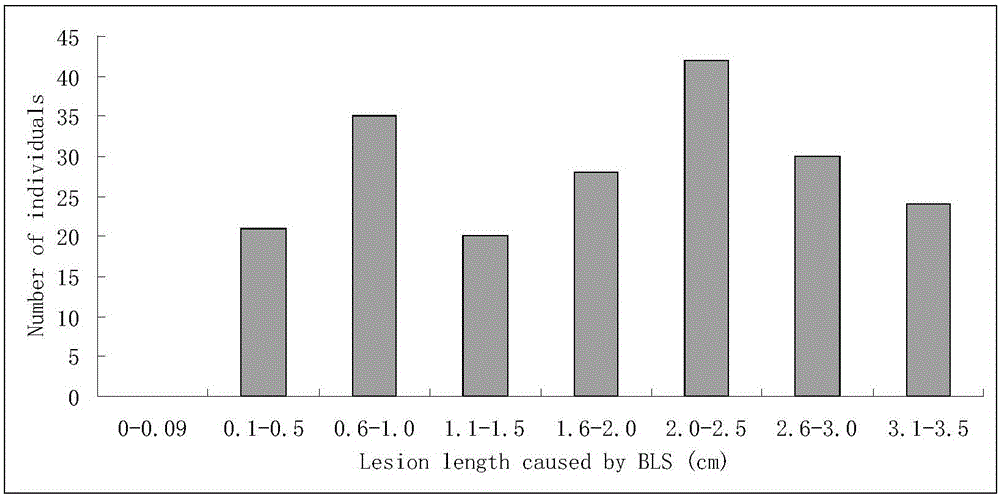
ActiveCN106011287AShorten the breeding cycleLow reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPopulationMajor gene
The invention discloses a molecular marker for a bacterial stripe resisting major gene BLS1 locus of rice and an application of the molecular marker. Specific steps for screening are as follows: (1) constructing a positioned segregation population, so as to obtain an approximate isogenic line F2 of the positioned segregation population; (2) extracting genomic DNA of rice leaves of each single strain of parents and a F2 population by adopting a CTAB method so as to carry out SSR molecular marker analysis; (3) preliminarily positioning a gene BLS1 in a region between RM19382 and RM510; (4) carrying out BLS1 close-linkage marking: carrying out detection and analysis after carrying out molecular marking by several kinds of marking primers, so as to position the BLS1 in a physical range, i.e., 21-kb between RM19400 and RM510. The molecular marker is applied to the selective breeding of bacterial stripe resisting rice varieties or the screening of resistant genetic resources. The molecular marker disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively detecting whether ordinary bacterial stripe resisting wild rice DP3 and derived varieties (lines) thereof contain the major gene locus or not, the efficiency of selection of bacterial stripe resisting rice is increased, and the bacterial stripe resisting rice varieties containing the gene BLS1 are obtained.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院水稻研究所
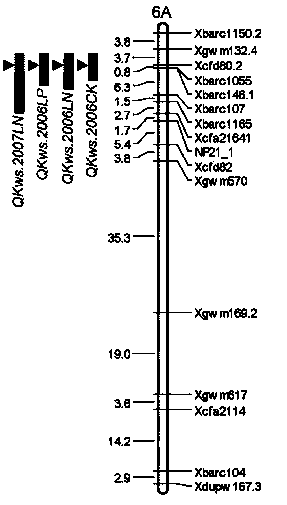
Molecular marker closely linked with major gene locus of grain weight of wheatear as well as acquiring method and application of molecular marker
InactiveCN103436533AQuick filterSpeed up the breeding processMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationBiotechnology3-deoxyribose
The invention discloses a molecular marker closely linked with a major gene locus of the grain weight of a wheatear. The DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) of a wheat variety Jing 411 is subjected to PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by using marker primers Xcfd80.2 and Xbarc146.1, and then, amplification products are electrophoretically separated on 8% polyacrylamide gel, so that the amplification products with the molecular weights of respectively 160bp and 142bp are obtained, i.e., the molecular marker of the major gene locus QKws.cas-6A of the grain weight of the wheatear is obtained. The molecular marker of the major gene locus of the grain weight of the wheatear, provided by the invention, can be used for detecting whether a wheat variety or strain contains the major gene locus QKws.cas-6A for increasing the grain weight of the wheatear, so that the wheat variety or strain with the gene locus is rapidly screened and used for breeding, and the breeding progress of the high-yield wheat variety can be greatly accelerated.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Molecular marker tightly interlocked with major gene locus of wheat spikelet number as well as obtaining method and application of molecular marker
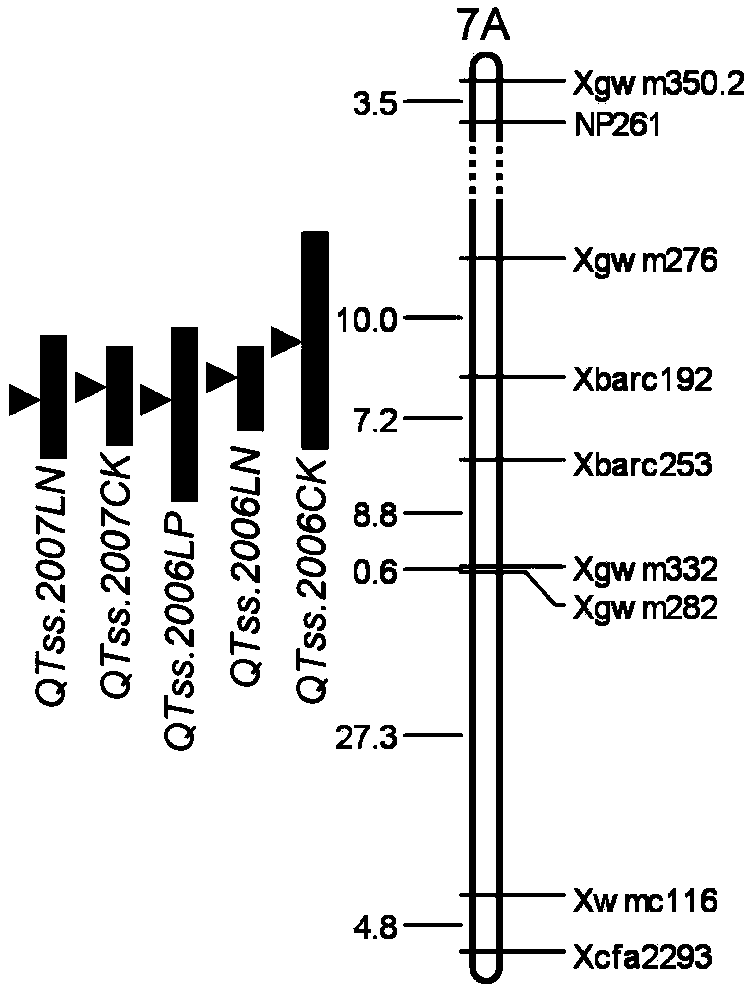
InactiveCN103451183AQuick filterSpeed up the breeding processMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationBiotechnology3-deoxyribose
The invention discloses a molecular marker tightly interlocked with a major gene locus of a wheat spikelet number. DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) of a wheat variety Jing411 is subjected to PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification by adopting labeled primers Xbarc192 and Xbarc253, amplification products are subjected to electrophoretic separation on 8 percent polyacrylamide gel, and the molecular weight of the obtained amplification products are respectively 200bp and 186bp, namely, the molecular marker of the major gene locus QTss.cas-7A of the wheat spikelet number. The molecular marker of the major gene locus of the wheat spikelet number, provided by the invention, can be used for detecting whether the major gene locus QTss.cas-7A for increasing the wheat spikelet number is contained in the wheat variety or strain so that the wheat variety or strain with the gene locus is rapidly screened for breeding, and thus the breeding progress of the wheat high-yield variety can be greatly increased.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
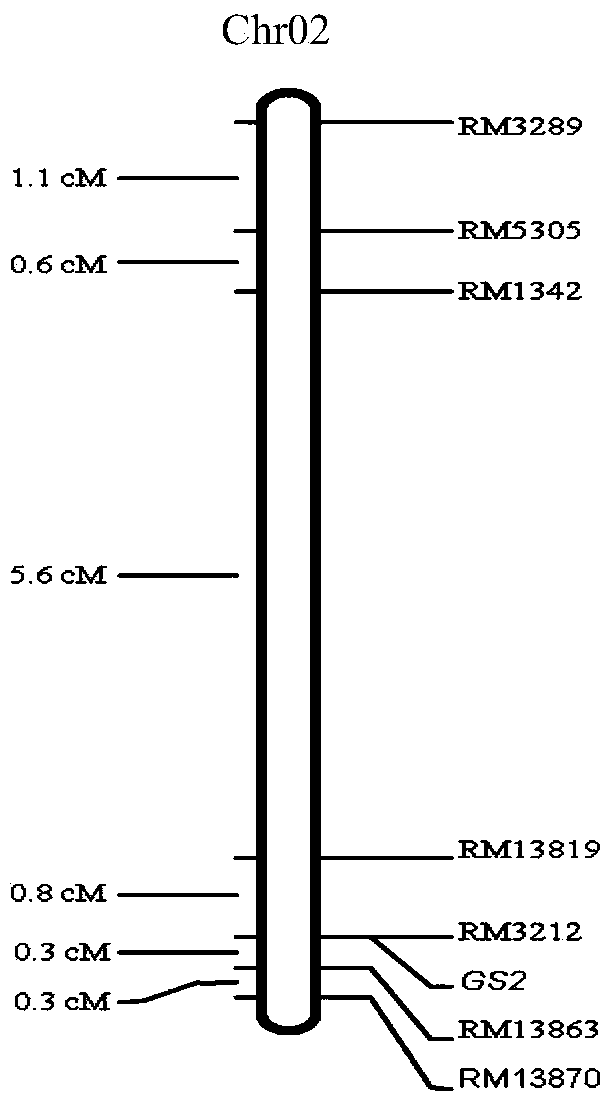
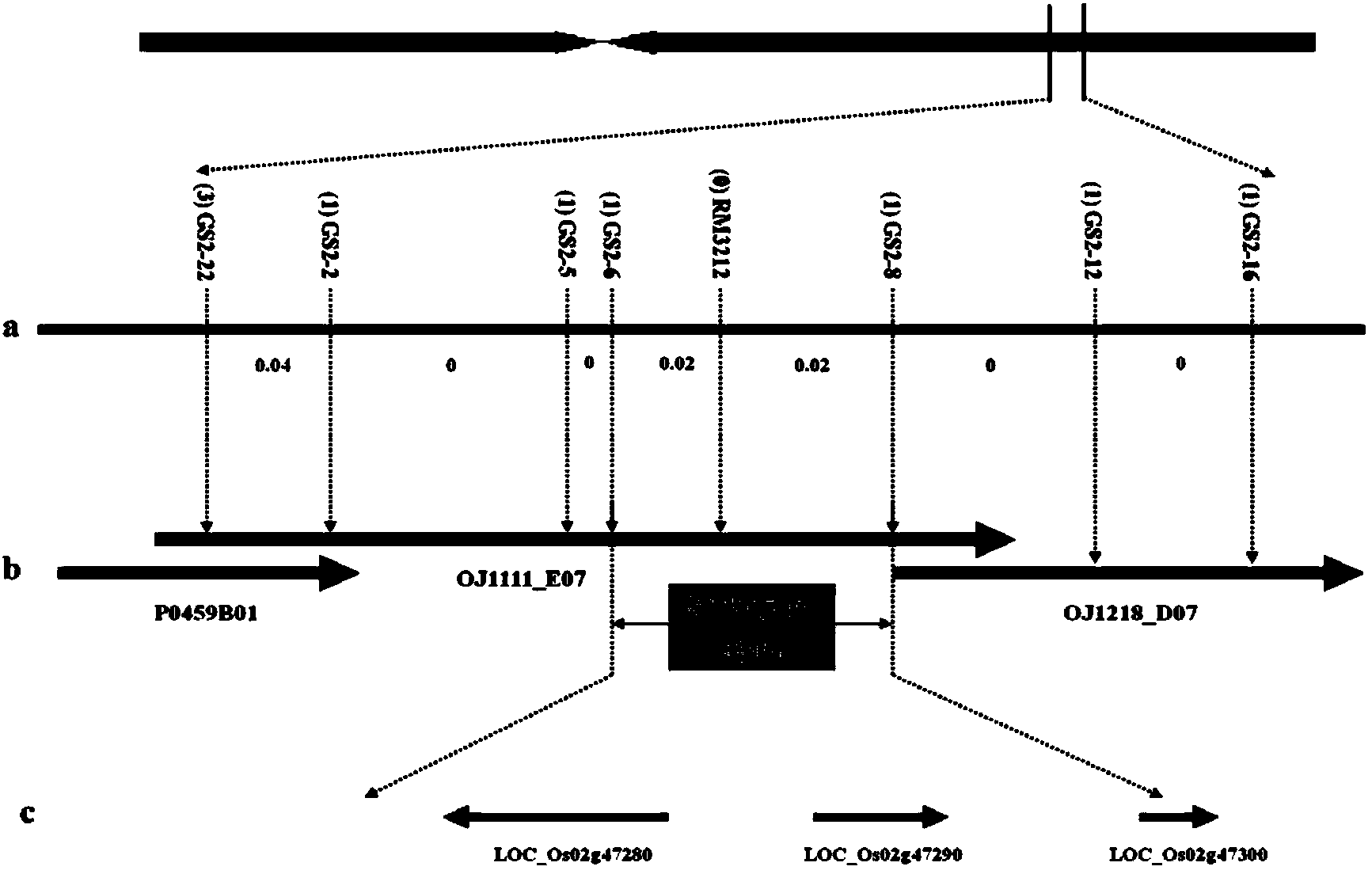
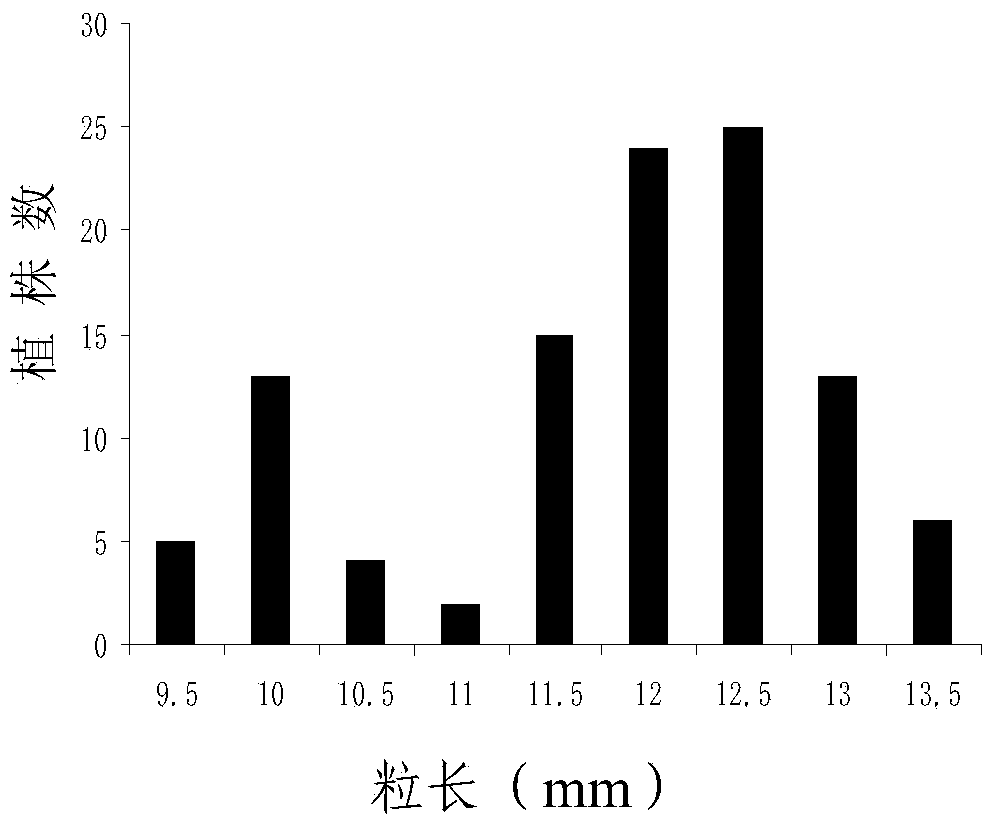
Molecular markers in close linkage with large grain gene GS2 of rice and application thereof
ActiveCN103409418AInhibition of grain width effectLittle or no grain width effectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceMolecular marker
The invention provides molecular markers in close linkage with a large grain gene GS2 of rice and an application of the molecular markers. Through a recombinant inbred line (RIL) advanced grain shape segregation population, the grain shape major gene GS2 is finely located on a second chromosome and within a range of 33.2kb from GS2-6 to GS2-8, so as to obtain a series of molecular markers in close linkage with GS2. The molecular markers include a common data base marker RM3212 and 22 self-developed InDel markers (from GS2-1 to GS2-22). The molecular markers can be used for effectively detecting the GS2 genetic locus and further improving the breeding efficiency of large grain varieties (or parents).
Owner:HUNAN HYBRID RICE RES CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com