Patents
Literature
161 results about "Two generation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
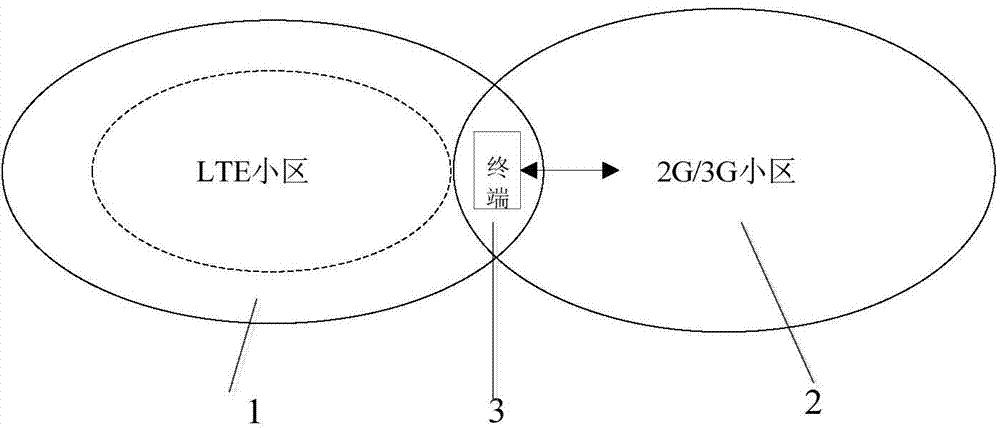
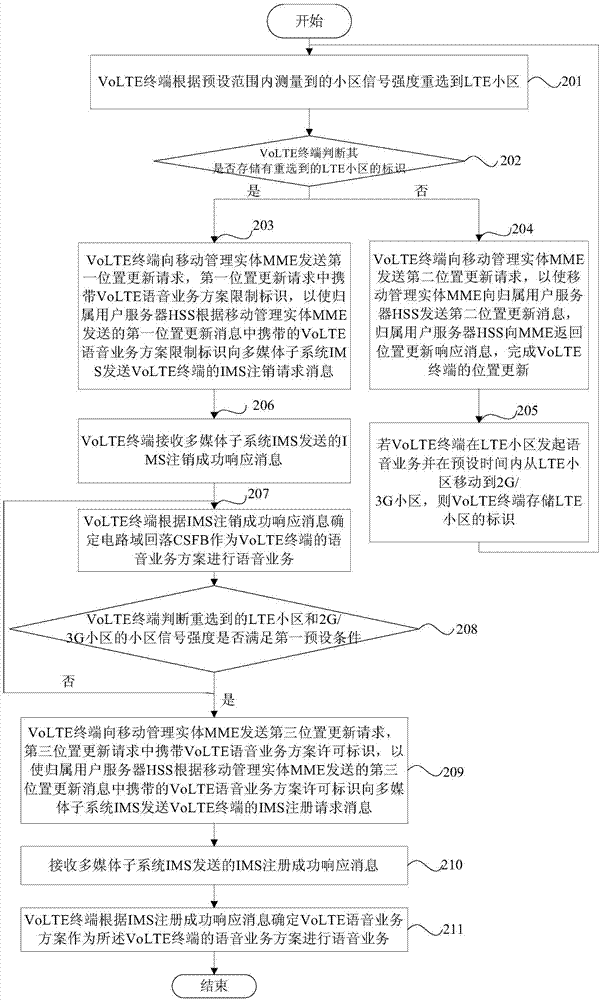
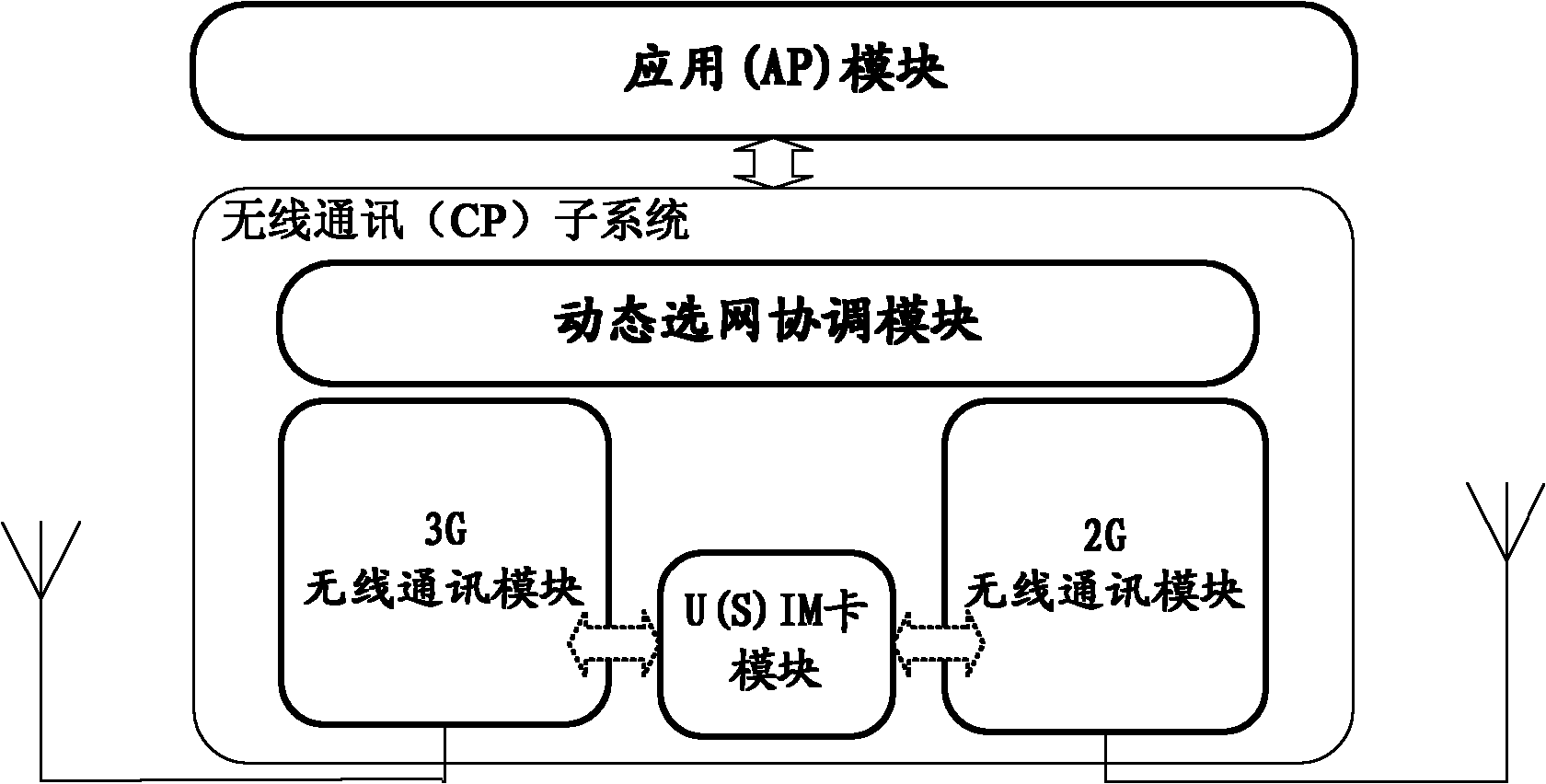
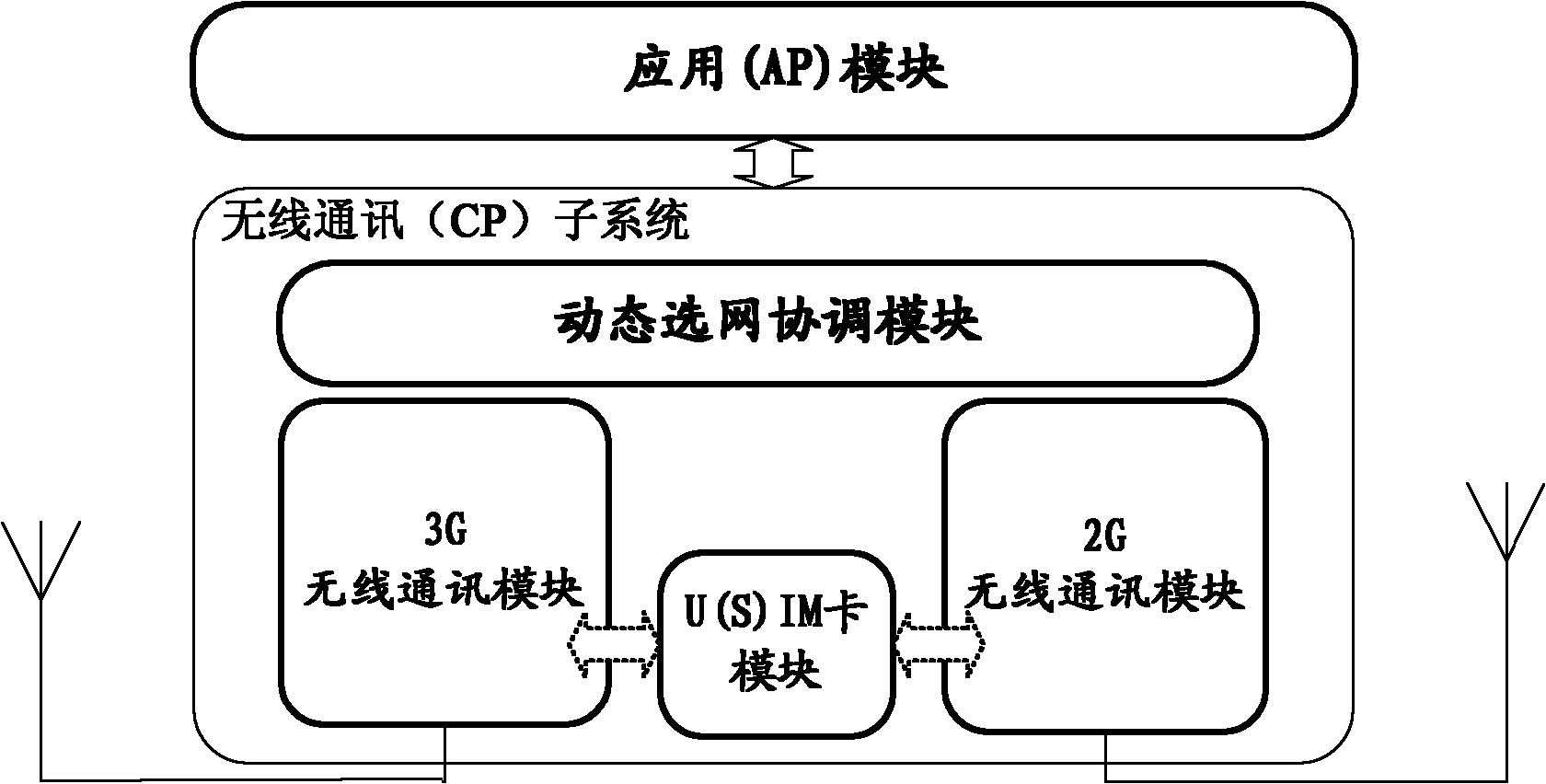
Determination method for voice service scheme of VoLTE (Voice over Long Term Evolution) terminal and VoLTE terminal
ActiveCN104507131AIncrease success rateImprove experienceWireless communicationSpeech soundCell identity
The invention provides a determination method for a voice service scheme of a VoLTE (Voice over Long Term Evolution) terminal and the VoLTE terminal. The method comprises the following steps: reselecting from a 2G / 3G (Two-Generation / Three-Generation) cell to an LTE cell by the VoLTE terminal according to cell signal intensity measured in a preset range; if a reselected LTE cell identity is stored at the VoLTE terminal, transmitting a first position updating request to a mobile management entity MME by the VoLTE terminal, wherein a VoLTE voice service scheme restriction identity is carried in the first position updating request, so an IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem) unregistration request message of the VoLTE terminal is transmitted to an IMS by a home subscriber server HSS according to the VoLTE voice service scheme restriction identity carried in a first position updating message; receiving, by the VoLTE terminal, an IMS unregistration success response message transmitted by the IMS; determining circuit switched fallback CSFB according to the IMS unregistration success response message to serve as the voice service scheme of the VoLTE terminal to perform the voice service.
Owner:CHINA UNITED NETWORK COMM GRP CO LTD
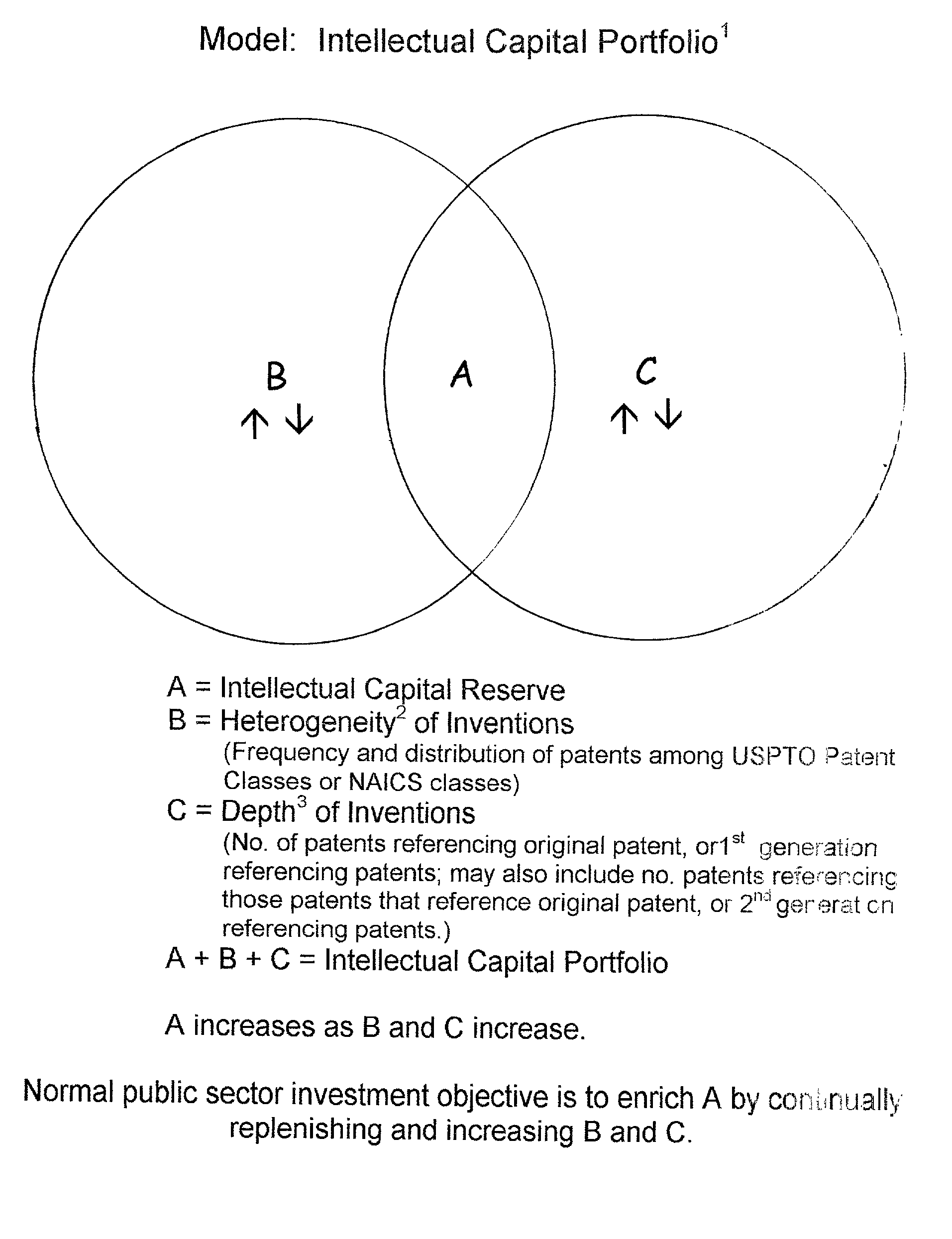
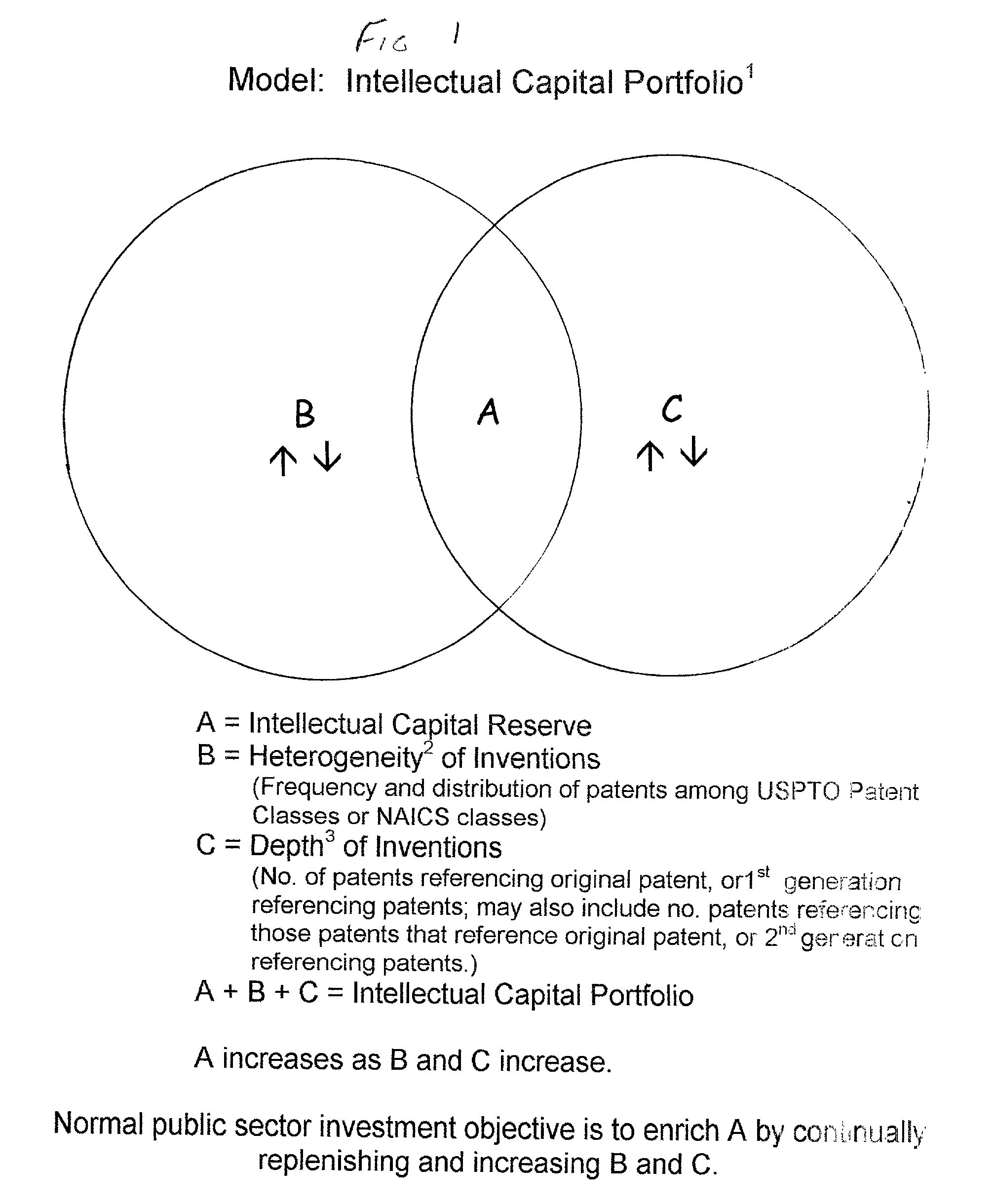
Method for evaluating a patent portfolio
A method for valuing large portfolios of publicly owned patents is disclosed. The method includes measuring the diversity and the depth of the portfolio's contents. Density or heterogeneity consists of calculating the ratio of the number of patents to the number of patented technology classes to which the patents have been assigned by the United States Patent and Trademark Office. The depth consists of the ratio of the number of patents with referencing an original patent as prior art through two generations of referencing patents. A base line for evaluation can be the utility patents awarded by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office for the period of 1976-2000 and over time as the heterogeneity and depth increase, the value of the portfolio increases.
Owner:KRAEMER SYLVIA K
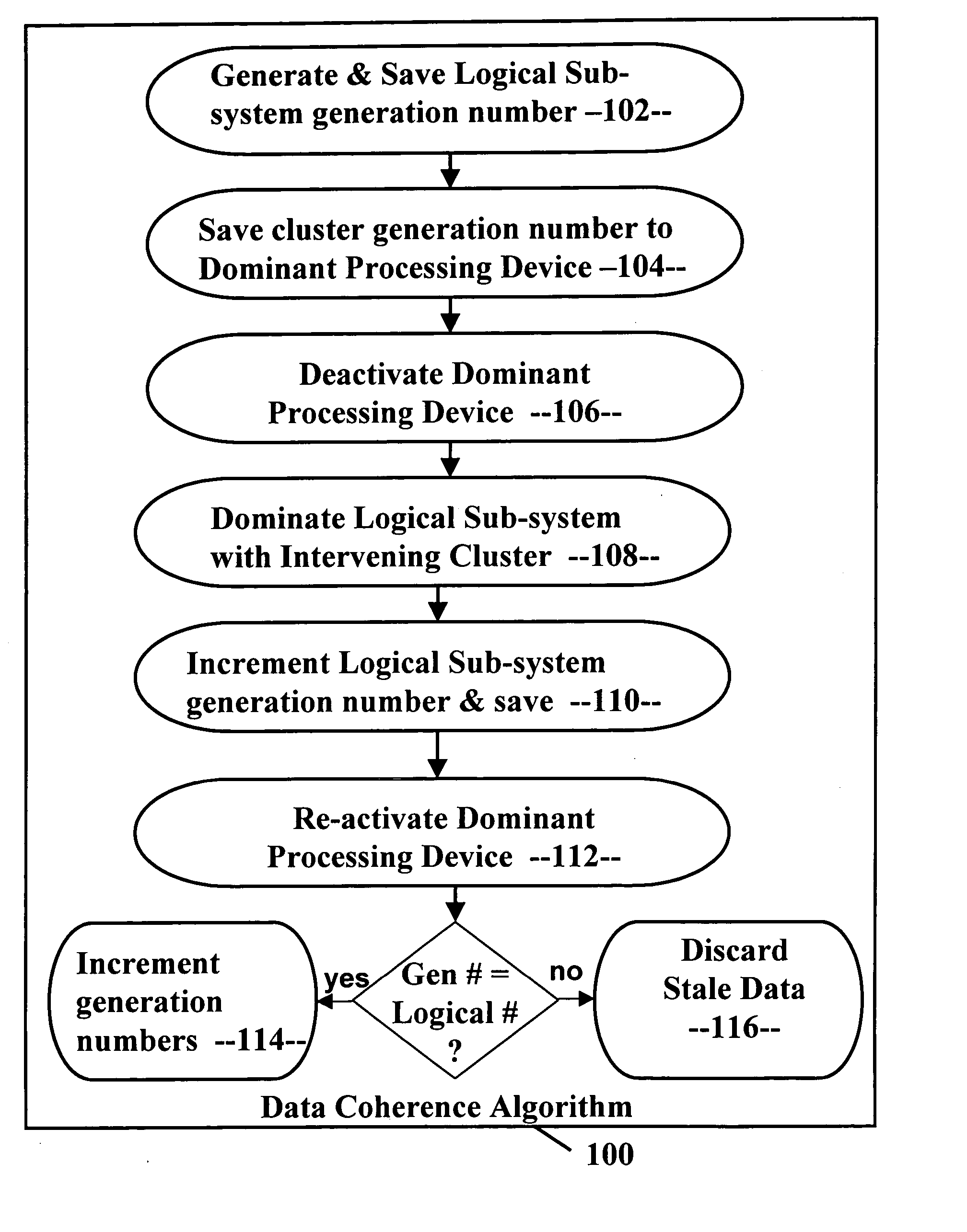
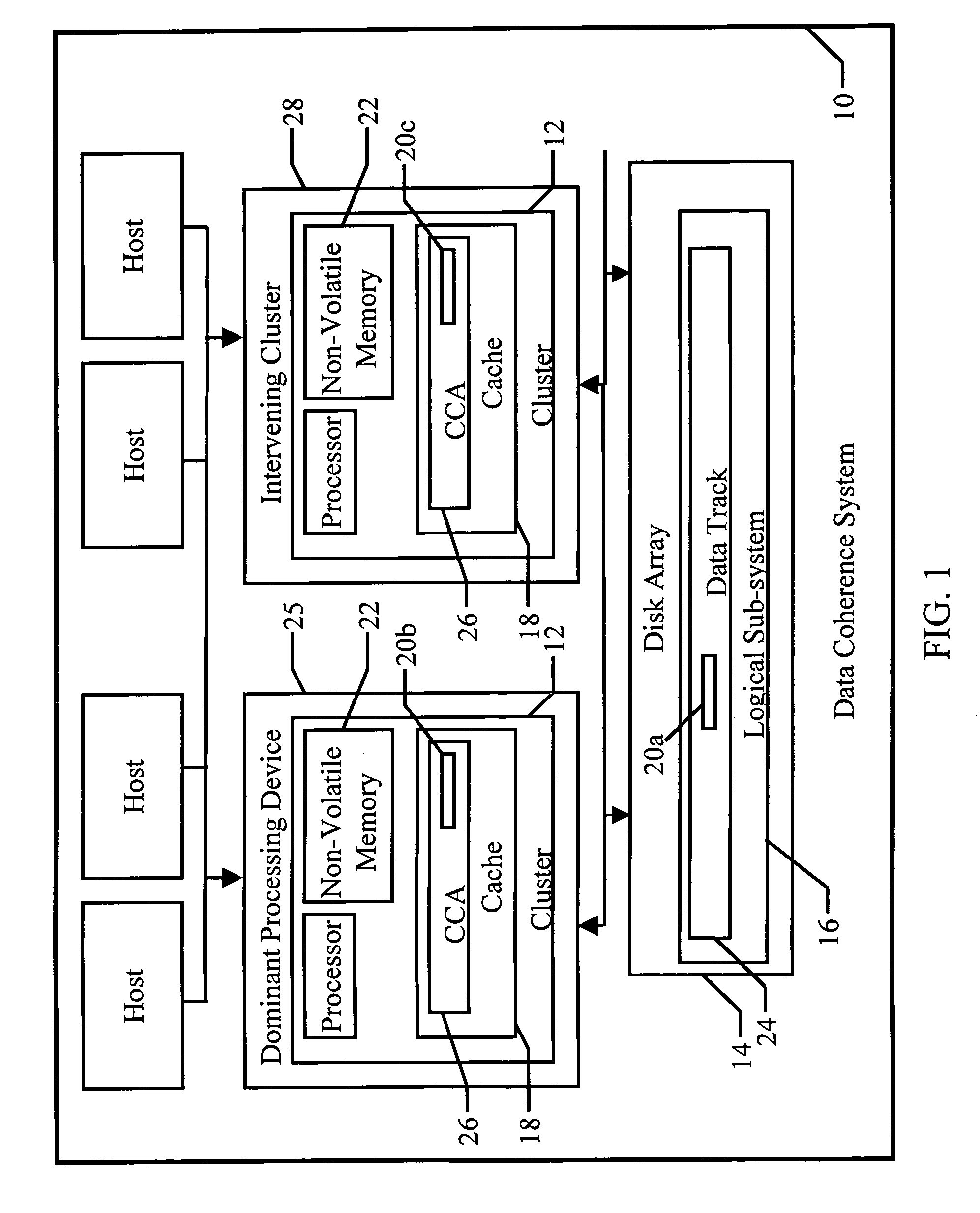
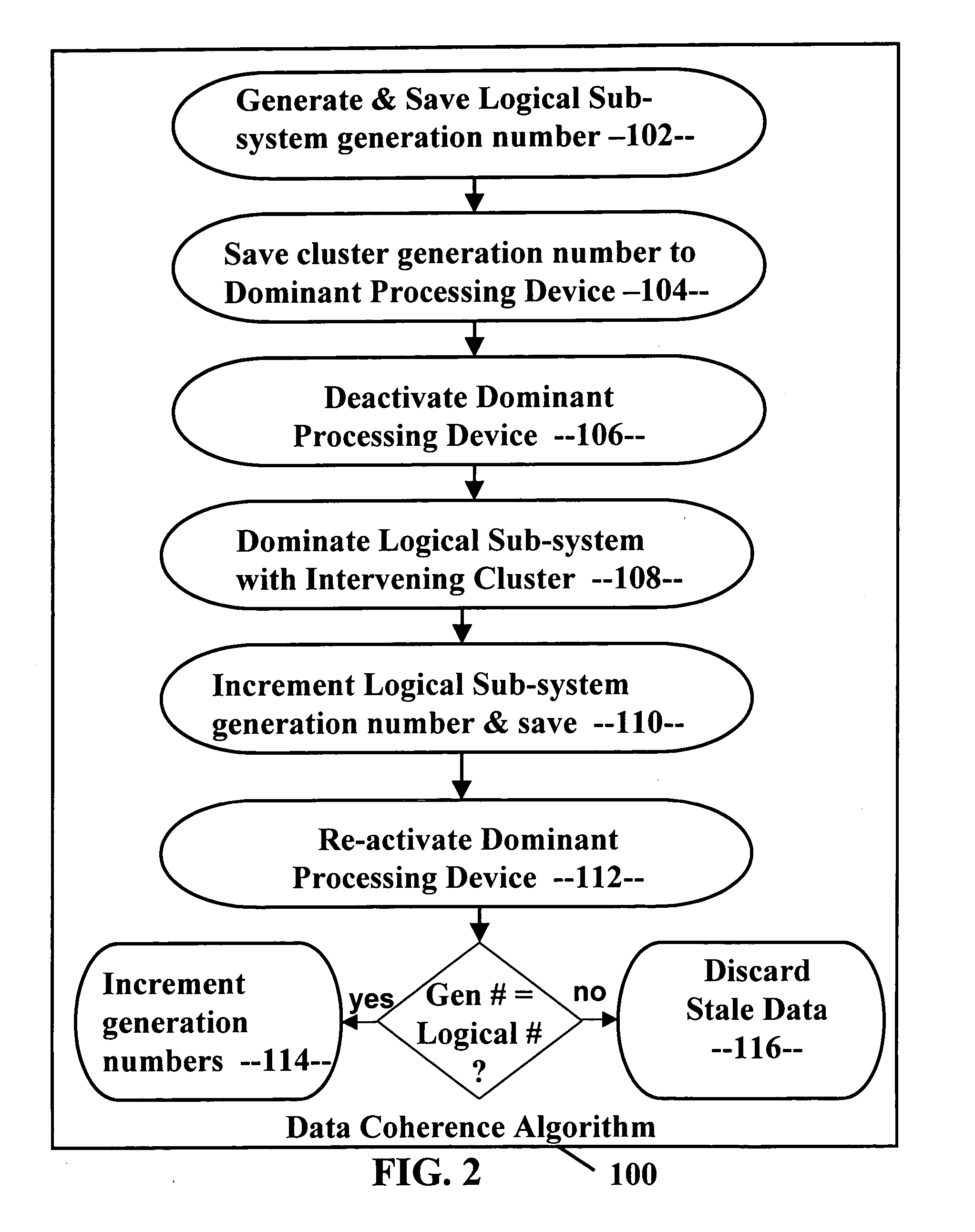
Data coherence system
A data coherence system includes a generation number written to a data track of a logical sub-system. The generation number is compared to a corresponding generation number in a processing device when it is initialized. If the two generations numbers are the same, the generation numbers are incremented and saved. If not, cache associated with the logical sub-system residing within the processing device is erased and the generation numbers are reset.
Owner:IBM CORP
SSR markers lined with major gene of cotton fiber strength
InactiveCN101613761AImprove selection efficiencyGood effectMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationAgricultural scienceA-DNA
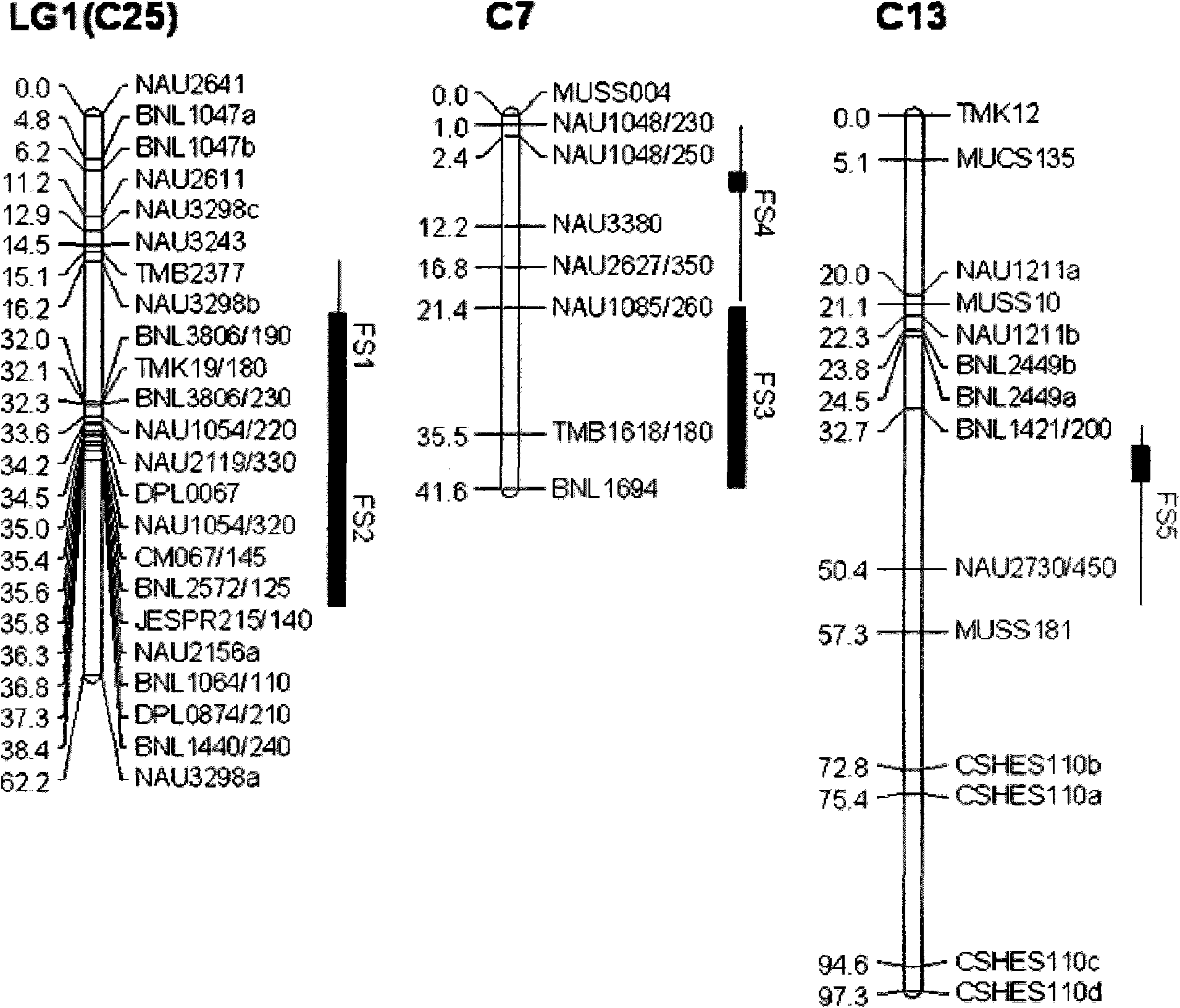
The invention discloser SSR markers lined with major genes of cotton fiber strength, which is obtained by the following steps: generating F2 and F2:3 populations by using a cotton search 41 line sGK9708 selected from cultivated varieties of gossypium hirsutum and a high quality line 0-153 of gossypium hirsutum as parents; allowing generation within the family of the F2:3 population to self cross till the F2:6 generation, performing within-family individual selection of the F2:6 generation once, and planting two generation till F6:8; performing polymorphism screening of the parents by using SSR primers and creating an RIL population linkage map; and performing the multi-environment major QTL screening of the cotton fiber strength to screen 6 QTLs of a cotton fiber strength character from line 0-153, wherein 5 QTLs are multi-environment stable QTLs and are FS1 linkage marker NAU2119330, FS2 linkage markers BNL2572125, BNL1064110 and DPL0874210, FS4 linkage markers are NAU1048250 and NAU2627350, and FS5 linkage markers BNL1421200 and NAU2730450. The SSR markers lined with the major genes of the cotton fiber strength are screen from high fiber quality materials and used as molecular markers to perform early auxiliary selection on a DNA level to improve the selection efficiency of the cotton fiber strength.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
High-density culture method for lactic acid bacteria
ActiveCN102191202ARaw materials are easy to getBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCulture mediums
The invention relates to a high-density culture method for lactic acid bacteria. The method comprises the following steps of: activating the lactic acid bacteria in a basic culture medium to obtain two generations; and inoculating the two generations according to the inoculation quantity of 1 percent to a fermentation culture medium to ferment at the temperature of between 35 and 38 DEG C for 20 to 24 hours so as to obtain high-density lactic acid bacteria fermenting liquid, wherein the fermentation culture medium consists of 0.5 to 1.5 percent of soy peptide, 3 to 5 percent of composite fruit and vegetable juice and the balance of raw milk. In the culture method, the raw materials of the fermentation culture medium are easy to obtain; other substances are not added in the culture process, so the method is simple and practicable; the viable bacterium number of the lactic acid bacteria in the fermenting liquid can reach 8.9*10<10> to 2.7*10<11> cfu / mL; and the lactic acid bacteria can serve as base materials of probiotic fermented milk and fermented milk beverage and can be directly used for producing other fermented milk products.
Owner:JUNLEBAO DAIRY GRP CO LTD
Breeding method of low-salt-resistant line of blue crab
ActiveCN102499130AStrong stress resistanceIncrease growth rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaLow salinityZoology
The invention provides a breeding method of a low-salt-resistant line of blue crab. The breeding method comprises the steps of: based on blue crab which is artificially bred for multiple years and has excellent growth characters as a base colony, subjecting young crab of 100 days old to low-salinity stress experiment, and carrying out two generations of low-salinity stress breeding to screen low-salt-resistant line of blue crab, wherein the screened core breeding colony can be used for production and application after passage propagation. According to the invention, a quick growth colony is selected as the base colony, and the low-salt-resistant stress-resistant characters are aggregated in the blue crab base colony through low-salt-resistant breeding, thus the cultured new line has strong stress resistance, and is suitable for breeding in low-salinity areas, and the growth rate and breeding survival rate are significantly increased; and the method is simple and convenient to operate, and is applicable to breeding of the low-salt-resistant line of blue crab.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
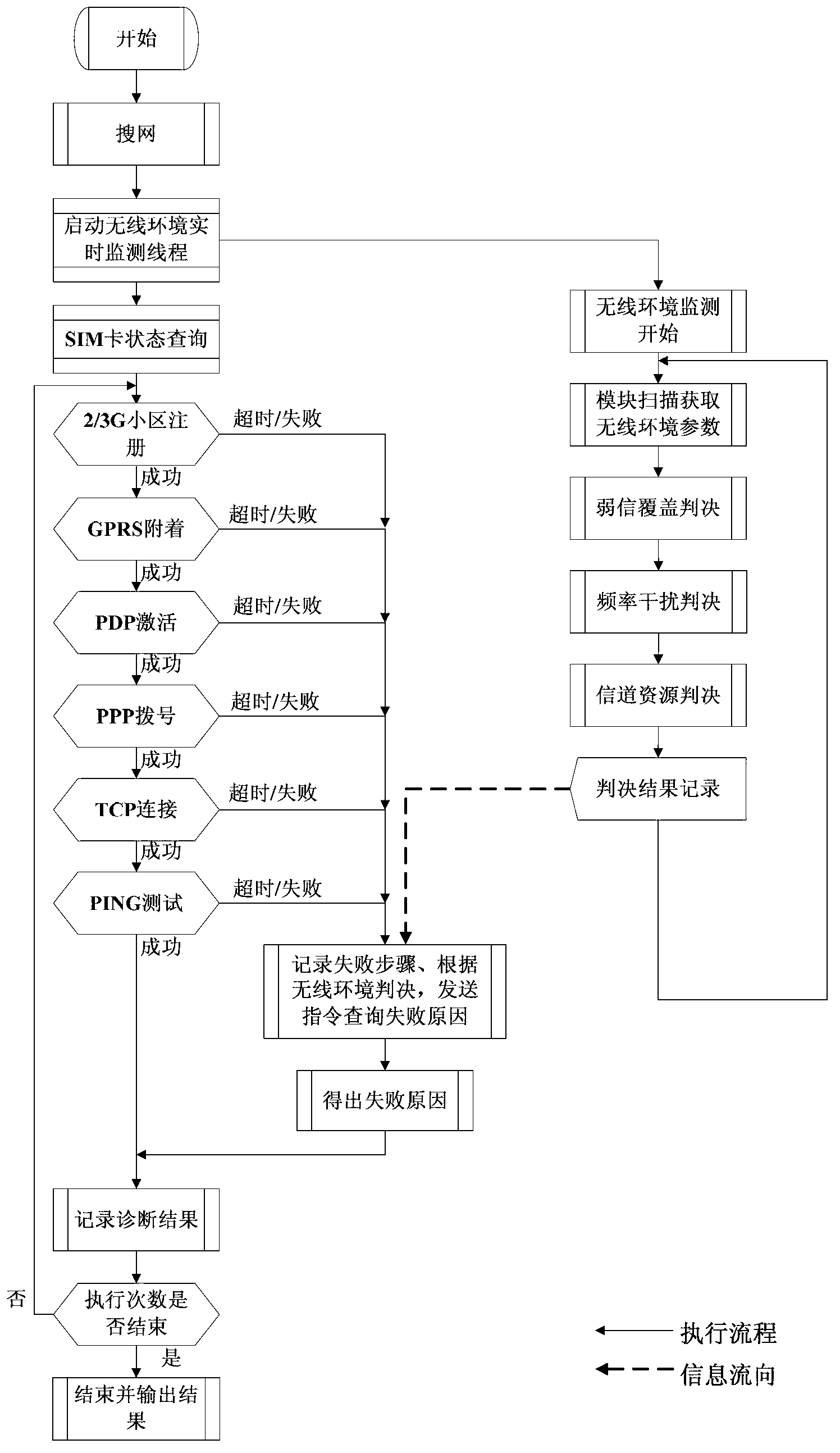
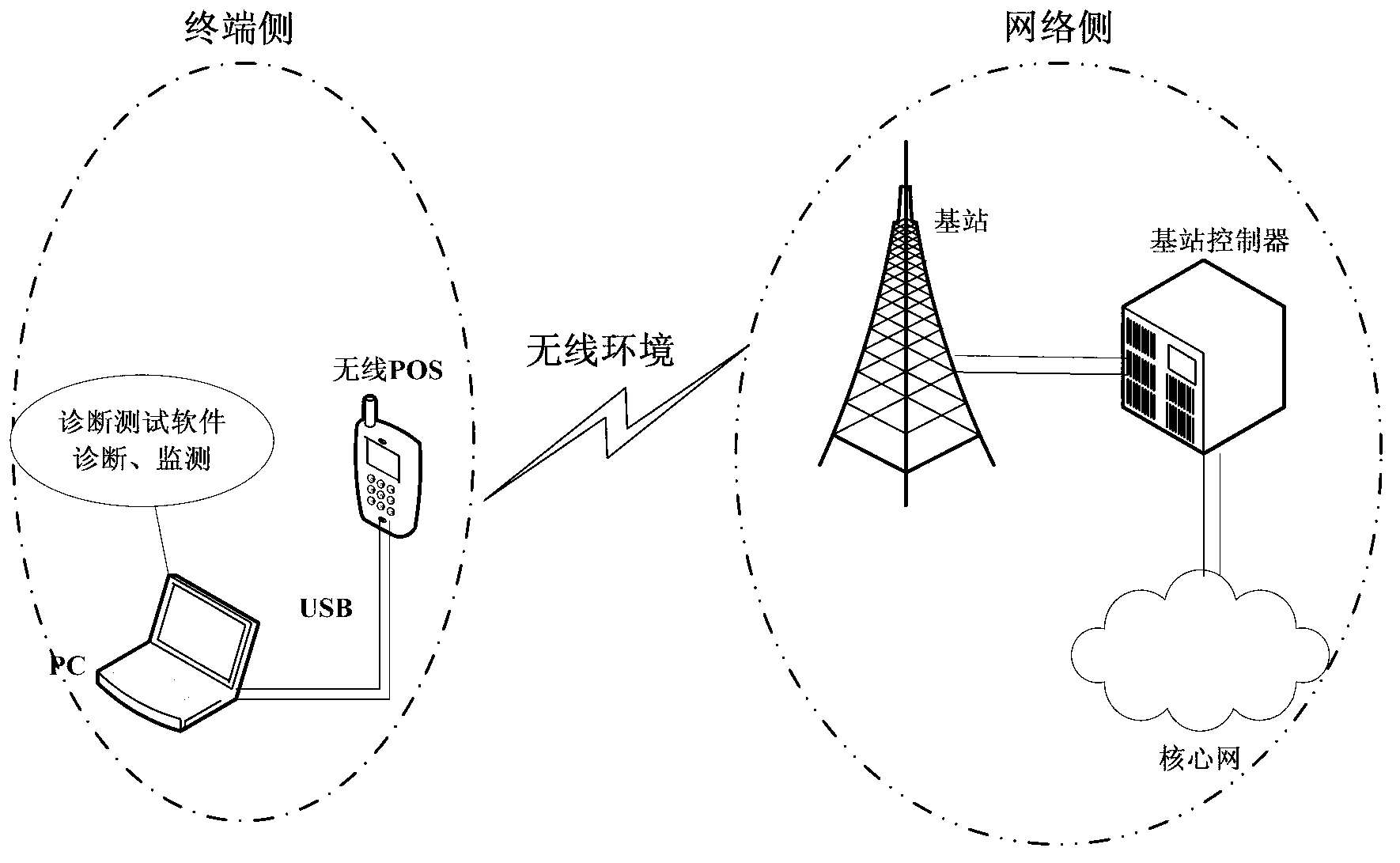
Two-generation/third-generation (2/3G) wireless module diagnosis test method and device
ActiveCN103179608AImplement diagnostic testsWireless communicationGeneral Packet Radio ServiceThird generation
Owner:FUJIAN LANDI COMML EQUIP CO LTD
Turbo decoding device and Turbo decoding method compatible with two generations of DVB-RCS
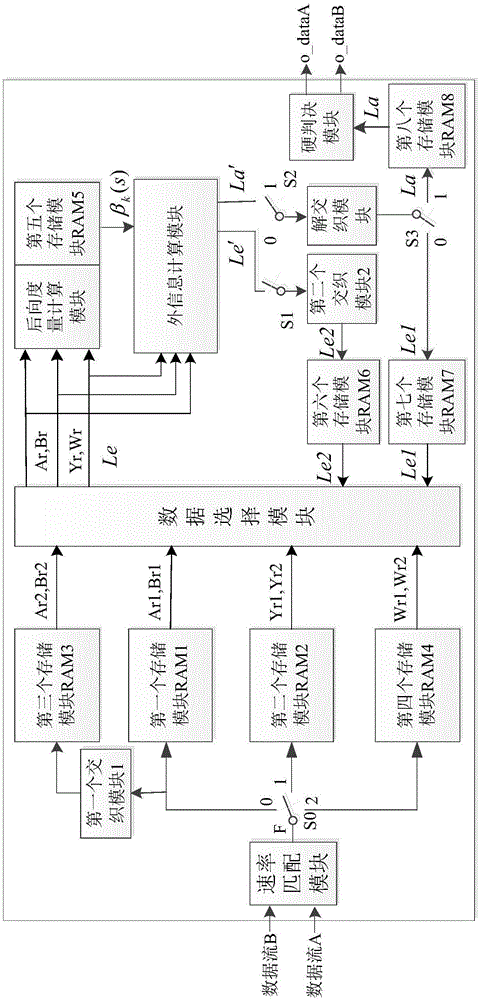
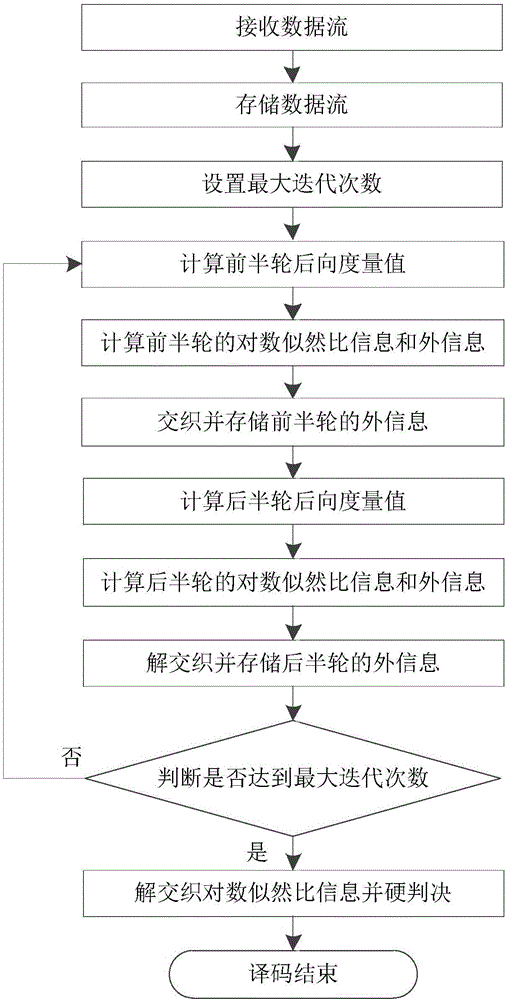
ActiveCN106253912AOvercome the disadvantage of excessive overheadReduce consumptionCode conversionError correction/detection by combining multiple code structuresComputer hardwareData selection
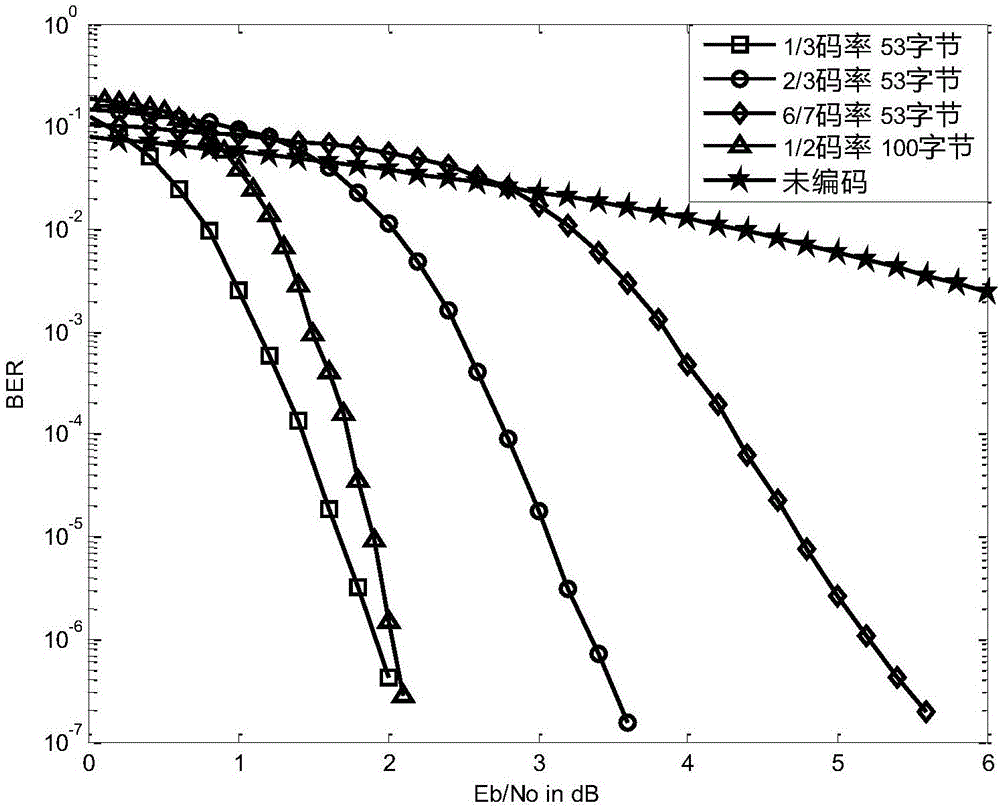
The invention discloses a Turbo decoding device and a Turbo decoding method compatible with two generations of DVB-RCS. The device comprises 16 modules, namely, a rate matching module, two interleaving modules, a de-interleaving module, eight storage modules, a data selection module, a backward measure calculation module, an external information calculation module, and a hard decision module. The method comprises the steps of receiving a data flow, storing an information flow, setting the maximum number of iterations, calculating the backward measure value of a front half wheel, calculating the logarithmic likelihood ratio information and external information of the front half wheel, storing the external information of the front half wheel, calculating the backward measure value of a back half wheel, calculating the logarithmic likelihood ratio information and external information of the back half wheel, storing the external information of the back half wheel, making a decoding termination decision, and making a hard decision. Turbo decoding compatible with two generations of standards is completed in one decoding device, and the consumption of hardware resources is reduced.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Mesenchymal stem cell nutrient solution
ActiveCN102703385AImprove securityFormulation ingredients determinedSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCulture fluidCell culture media
The invention provides a serum-free mesenchymal stem cell nutrient solution, which is simple in formula, low in cost and high in safety. The serum-free mesenchymal stem cell nutrient solution comprises a serum-free animal cell culture medium, a B27 serum-free additive, bFGFs (basic fibroblast growth factors) and EGFs (epidermal growth factors), wherein the nutrient solution also comprises fetuin and antibiotics. The nutrient solution does not contain animal serum, has higher safety and definite formula components, and is suitable for clinical treatment. Meanwhile, according to the serum-free mesenchymal stem cell nutrient solution, human fat stem cells can be normally attached to the surface of a culture vessel and grow, the antibiotics are added into the formula components, and the formula is simpler compared with that of the general serum-free nutrient solution. For the fat stem cells cultured according to the conventional formula, the cells began to differentiate and slowly grow after two generations. Compared with the fat stem cells cultured according to the conventional formula, the fat stem cells cultured according to the formula of the serum-free mesenchymal stem cell nutrient solution do not have the phenomena of differentiation and slow growth after being tested, so that the serum-free mesenchymal stem cell nutrient solution is extremely suitable for the growth of the fat stem cells and gum stem cells.
Owner:ASIA PACIFIC STEM CELL SCI
Breeding method of high-oleic-acid dormancy peanut variety
InactiveCN104542264AIncrease genetic diversityRich genetic variationPlant genotype modificationSingle plateHigh oleic acid
The invention discloses a breeding method of a high-oleic-acid dormancy peanut variety. The breeding method of the high-oleic-acid dormancy peanut variety comprises the following steps: hybridizing parents, namely taking dragonhead No.2 as a female parent and taking a high-oleic-acid dormancy peanut variety system P76 as a male parent; screening high oleic acid by using pressure, namely harvesting single plants of F2-F3 hybridized generations of seeds, carrying out detection on the content of the nondestructive oleic acid in all the seeds of the single plates commonly and carrying out two generations of screening; screening high dormancy by using pressure; testing the dormancy and testing the content of the nondestructive oleic acid; and obtaining the high-oleic-acid dormancy peanut variety. The bred peanut variety is high in content of oleic acid and high in dormancy; the problem that sprouts grow on the plants when harvesting the peanuts can be effectively solved.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Grifola high-yield cultivation technology
InactiveCN103493683AShorten the cultivation cycleSolve the technical problems of long artificial cultivation period and low yieldHorticulturePropaguleHigh yielding
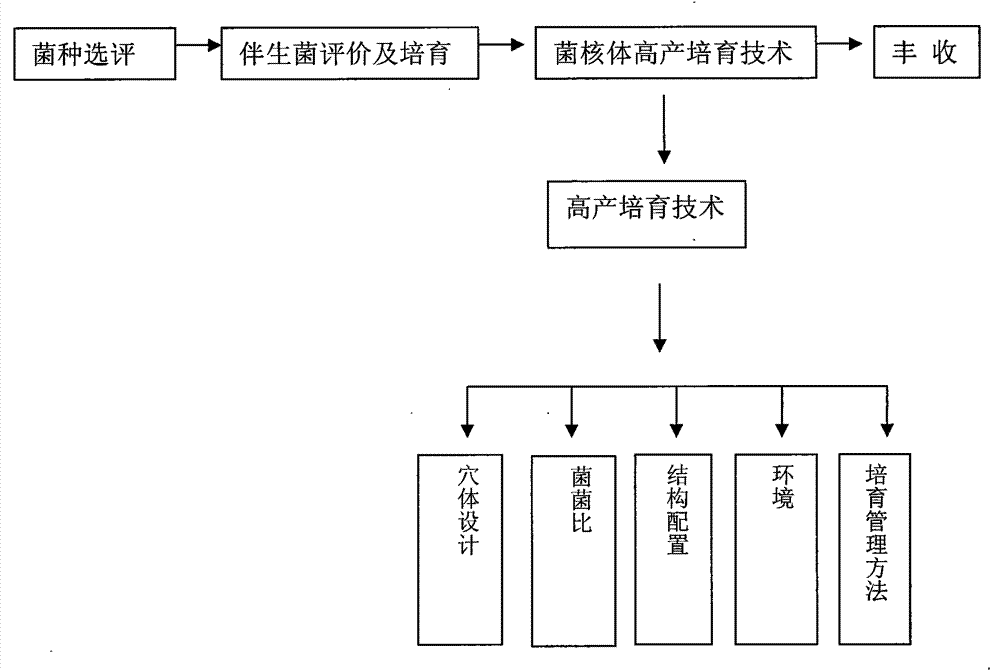
The invention discloses a grifola high-yield cultivation technology, and belongs to the technical field of cultivation. A method comprises the following steps: selecting and judging strains, selecting grifola wild funguses or propagules within two generations, evaluating and cultivating associated funguses, selecting robust and vigorous associated fungus strains to be cultivated, separating and purifying honey fungus strains from sclerotia, then conducting cultivation, and cultivating associated fungus sticks. According to the cultivation method, the scientific mode that the honey fungus strains and grifola 3+2 are arranged in an inclined mode is adopted, namely, the configuration structure that the three layers of honey fungus sticks are added on the two layers of the grifola strains is adopted, and the fungus stick plane inclined bodies are configurated in a staggered mode between layers. Cultivation ponding can shorten the grifola cultivation period by more than 2 years, the three-year period from planting to harvesting is reached, the high-yield effect that the output ratio is improved to be 1:10-15 is achieved, the production technology is stable, the grifola quality is high and safe, and the technical problems that the grifola artificial cultivation period is long, the production is unstable and the high-yield production can not be achieved for a long time are solved.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF TECH
Method for selectively breeding excellent strains of saline-alkaline tolerant tilapia
ActiveCN108207712AImprove salt and alkali resistanceSalt-alkali tolerance gene pool is goodClimate change adaptationAgricultural fishingNile tilapiaBase population
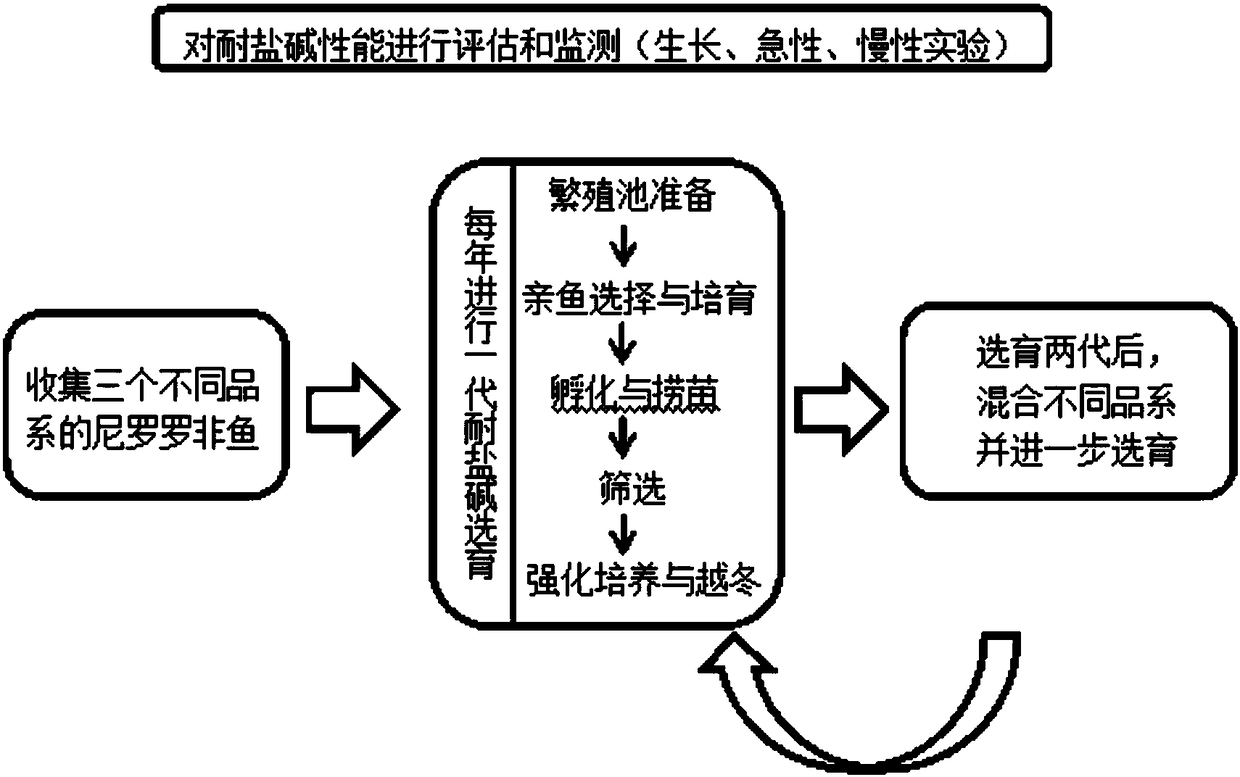
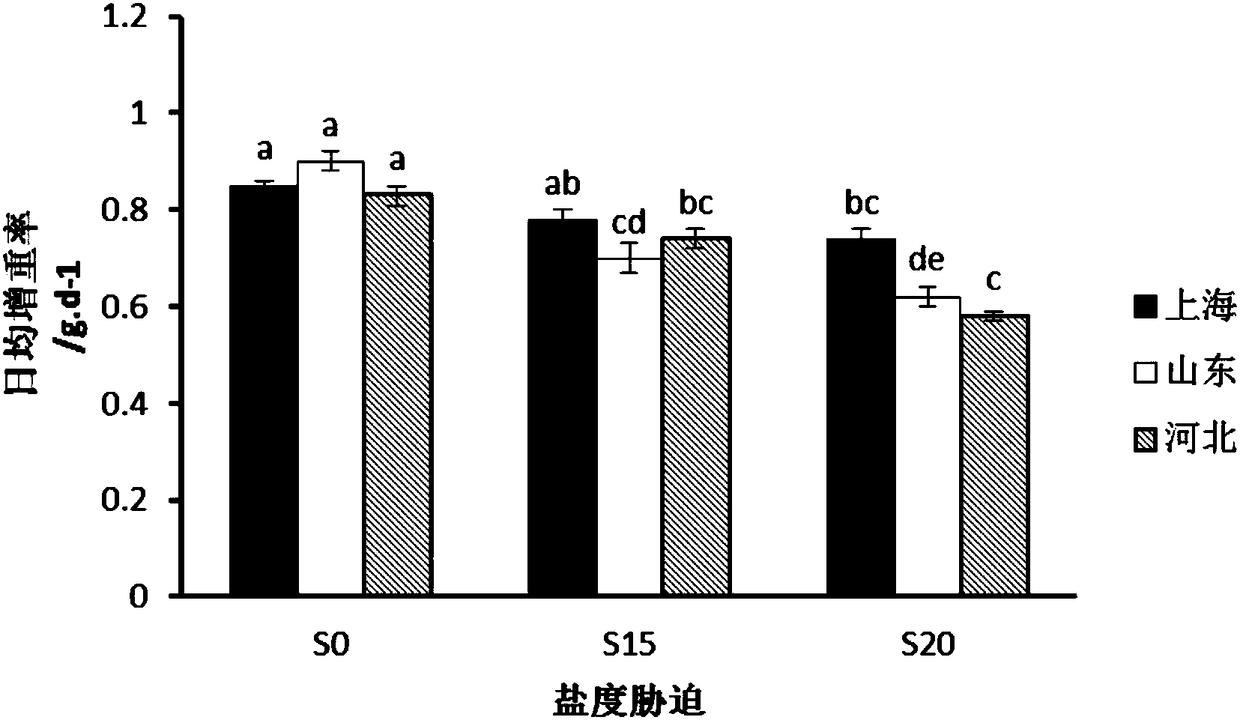
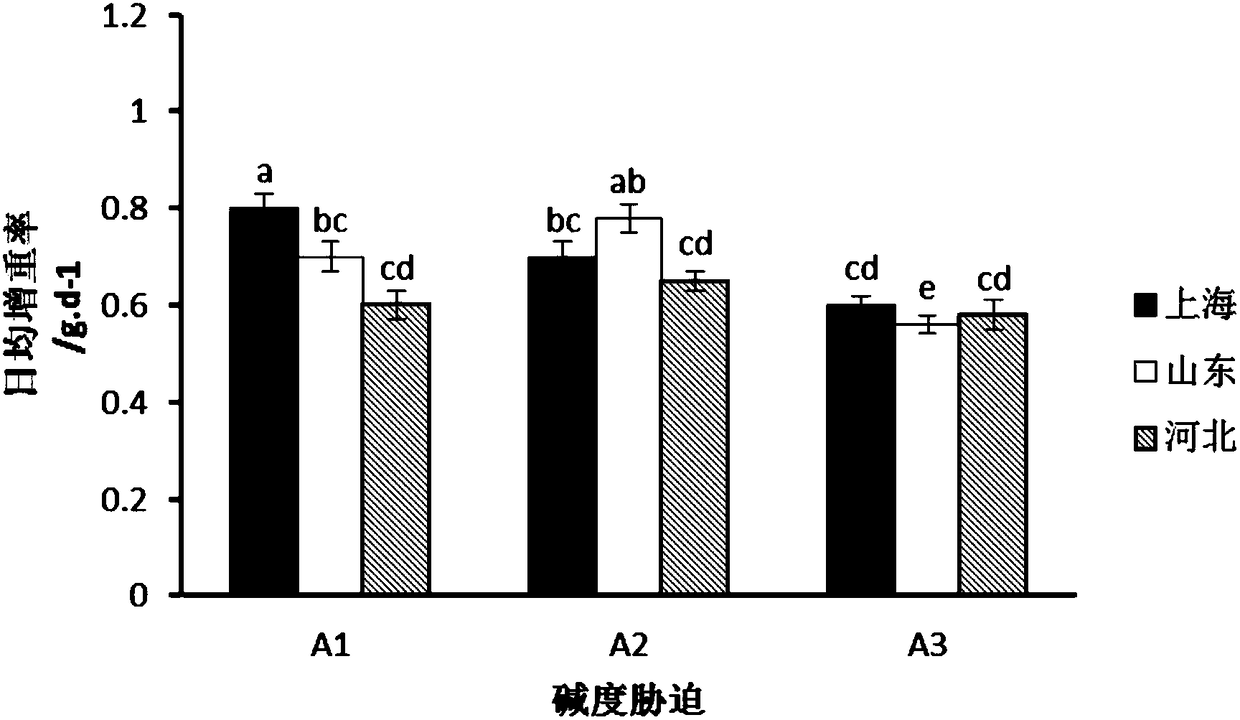
The invention discloses a method for selectively breeding excellent strains of saline-alkaline tolerant tilapia. The method includes steps of collecting at least three different strains of Nile tilapia to be used as selective breeding base population and evaluating the saline-alkaline tolerance; carrying out one-generation saline-alkaline tolerant selective breeding on the different strains of Nile tilapia in every year and continuously selectively breeding at least two generations; mixing the different strains of saline-alkaline tolerant Nile tilapia with obvious growth superiority with one another after saline-alkaline tolerant selective breeding is carried out on the different strains of saline-alkaline tolerant Nile tilapia, then carrying out saline-alkaline tolerant selective breedingon the different strains of saline-alkaline tolerant Nile tilapia and continuously selectively breeding at least four generations to obtain the saline-alkaline tolerant Nile tilapia of the excellentstrains. Saline-alkaline tolerant selective breeding procedures include reproduction pond preparing, parent tilapia selecting and rearing, fry hatching and fishing, screening and intensified culture and overwintering. The method has the advantages that the method is high in reliability, operability and efficiency; novel technical ways can be developed for selectively breeding stress-resistant varieties of fish, and the method has important significance and application value in popularization of rearing of stress-resistant improved varieties of cultured fish.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Molecular breeding method capable of improving length of cotton fibers by using gossypium barbadense chromosome segment introgression line
InactiveCN102229979ABreed fastEfficient cultivationMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationFiberAgricultural science
The invention discloses a molecular breeding method capable of improving length of cotton fibers by using gossypium barbadense chromosome segment introgression line, which is particularly used for crop (cotton) economical character oriented improvement and new variety bredding. An introgression line IL040-A4-1 of which the fiber length is increased obviously is screened out by cotton fiber detection of the gossypium barbadense chromosome segment introgression line. In the method, introgression line is used as a nonrecurrent parent, Xinluzao No.26, which is a variety promoted in cotton area in north of Xinjiang, is used as a recurrent parent are hybridized, hybridizing, two generations of back crossing and three generations of selfing are performed, molecular markers are also used to help to select cotton new lines with high fiber length. A high-quality and high-yield cotton new line named 'Nannong Haidao No.1' was bred by using the method.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method and system for predicting short-term power load of micro-grid of offshore oilfield group
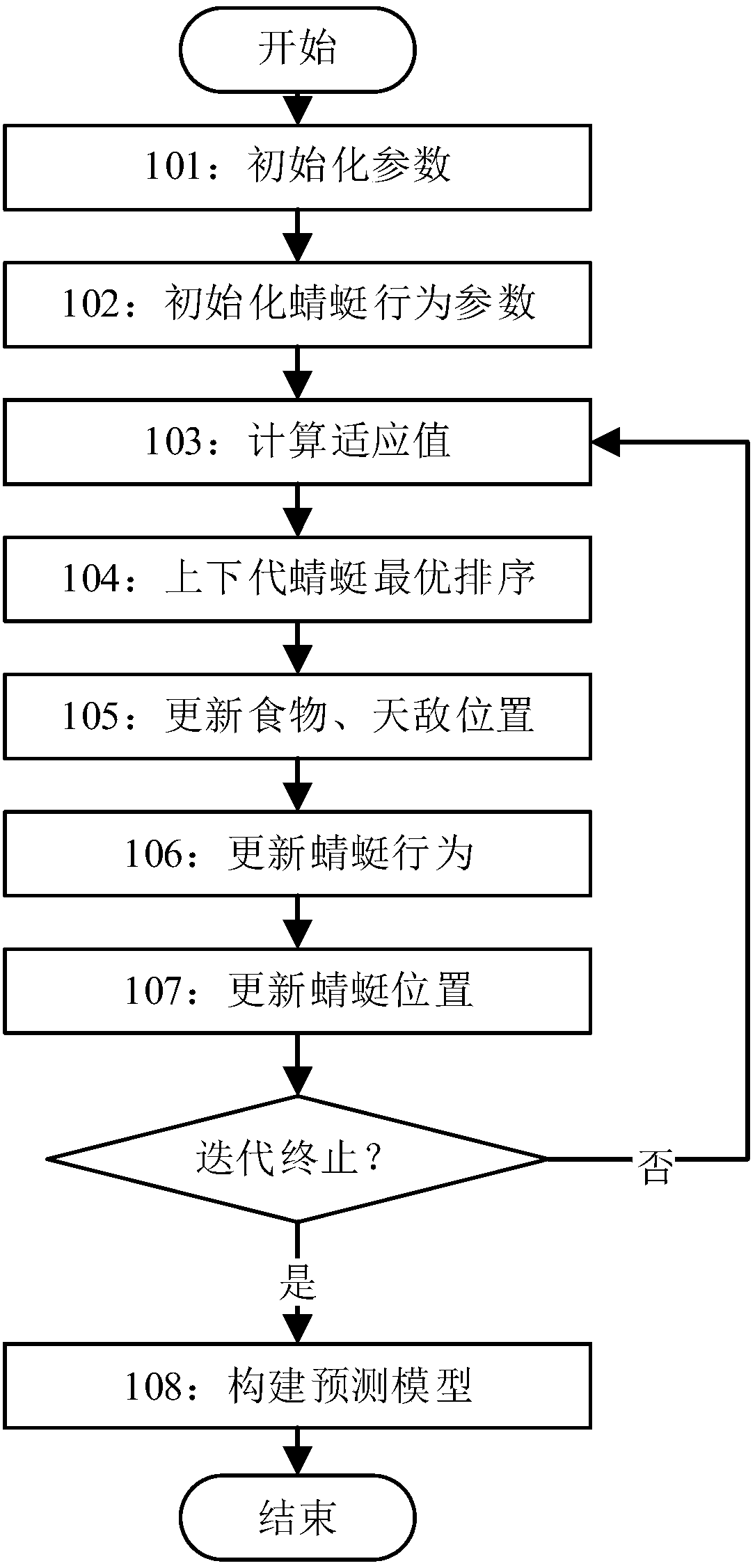
The invention discloses a method and system for predicting the short-term power load of a micro-grid of an offshore oilfield group. The global searching capacity is high, and the prediction precisionand calculation efficiency are higher. The method comprises the steps that respective upper and lower limit values of a penalty parameter C and a nuclear parameter sigma for a support vector machine (SVM) are set; the dimension of a position vector, the maximum iteration frequency and the number of dragonfly individuals of an improved dragonfly algorithm (IDA) are set; behavior parameters of the dragonfly individuals are initialized; current adaptive values of the dragonfly individuals in the IDA are calculated; two generations of the dragonfly individuals are sorted according to mapping, andthe corresponding maximum adaptive value is calculated and saved; the positions of food and natural enemies in the IDA are updated; behaviors of the dragonfly individuals in the IDA are updated; the positions of the dragonfly individuals in the IDA are updated; when the maximum iteration frequency is achieved, according to the positions of the dragonfly individuals corresponding to the saved maximum adaptive value, the penalty parameter C and the nuclear parameter sigma of the SVM are set, and a prediction module is established based on the SVM to predict the short-term power load of the micro-grid of the offshore oilfield group.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV +1
Fabrication method of high-temperature superconduction ReBCO cable structure applied to CICC
PendingCN110060815ASolve process problemsIncrease current carrying densitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesElectrical conductorHigh-temperature superconductivity
The invention discloses a fabrication method of high-temperature superconduction ReBCO cable structure applied to CICC. A ReBCO superconduction strip, a copper / aluminum filling tape, a copper wrappingtape and a spiral superconduction strip which are laminated form a circular superconduction line structure, the requirements of high critical current and high carrier density of a large-size magnet can be met, the superconduction ReBCO cable structure also has favorable mechanical characteristic, and the deformation demand such as bending during the manufacturing process of the magnet is satisfied; and more importantly, compared with an existing international ReBCO CICC superconduction cable design, the engineering critical current density is improved by 20% or above (for a small-size ReBCO CICC superconduction cable, the maximum improvement of the engineering critical current density can exceed that of current international researched superconduction cable by one time, so that the problem of cable twisting of the ReBCO superconduction strip during the application process of the CICC superconduction cable is solved, the cost of two-generation high-temperature superconductor in application of a large-size conductor is further reduced.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for inducing copepoda to produce diapause eggs
InactiveCN106577409AHarvest convenience methodImprove timelinessPisciculture and aquariaDiapauseDaphnia
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method and device for dual-mode dual-standby terminal to implement communications
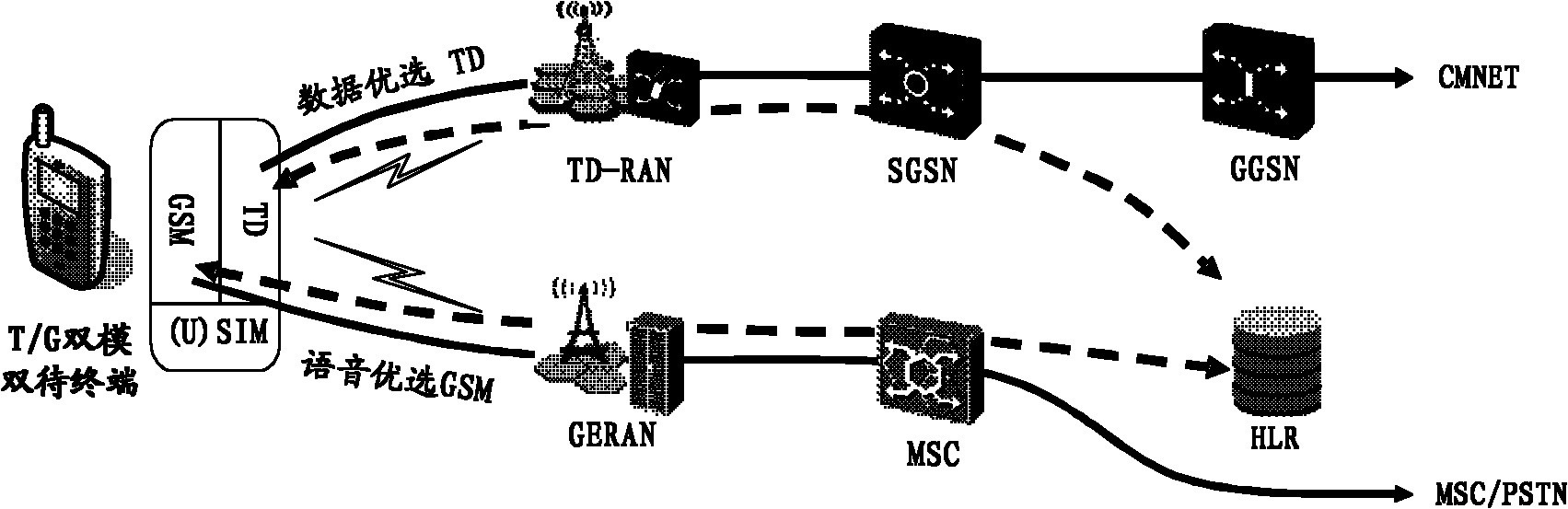
InactiveCN102149155AReduce the chance of switchingHigh level techniquesWireless communicationDual networkDual mode
The invention discloses a method and a device for a dual-mode dual-standby terminal to implement communications, wherein the method comprises the steps as follows: when a user of the dual-mode dual-standby terminal launches a packet service (PS), or a videophone service in a circuit service (CS), if a 3G (third-generation) network signal satisfies the condition of signal strengths, then the dual-mode dual-standby terminal selects a 3G network to implement communications; otherwise, the dual-mode dual-standby terminal selects a 2G (two-generation) network to implement communications; when the user of the dual-mode dual-standby terminal launches a CS service except the videophone service, and if the CS domain resources of the 2G network are saturated, then the dual-mode dual-standby terminal selects the 3G network to implement communications ; otherwise, the dual-mode dual-standby terminal selects the 2G network to implement communications. The invention can reduce and avoid the faults of a 2 / 3G dual-mode single-standby terminal like frequent network reselection, high power consumption, call drop, network fault caused by a `2 / 3G dual-mode switching` strategy, and improve the user experiences of the terminal.
Owner:ZTE CORP
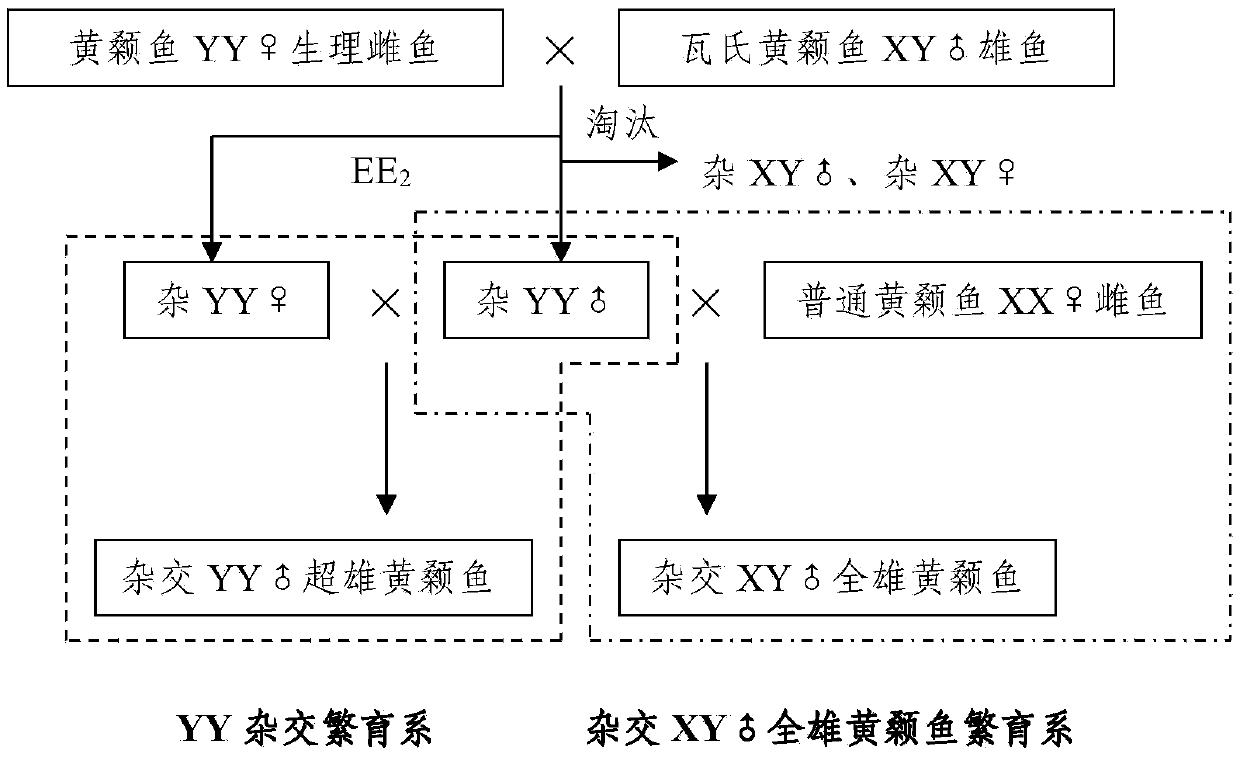
Method for quickly establishing cross-bred XY holandric pelteobagrus fulvidraco
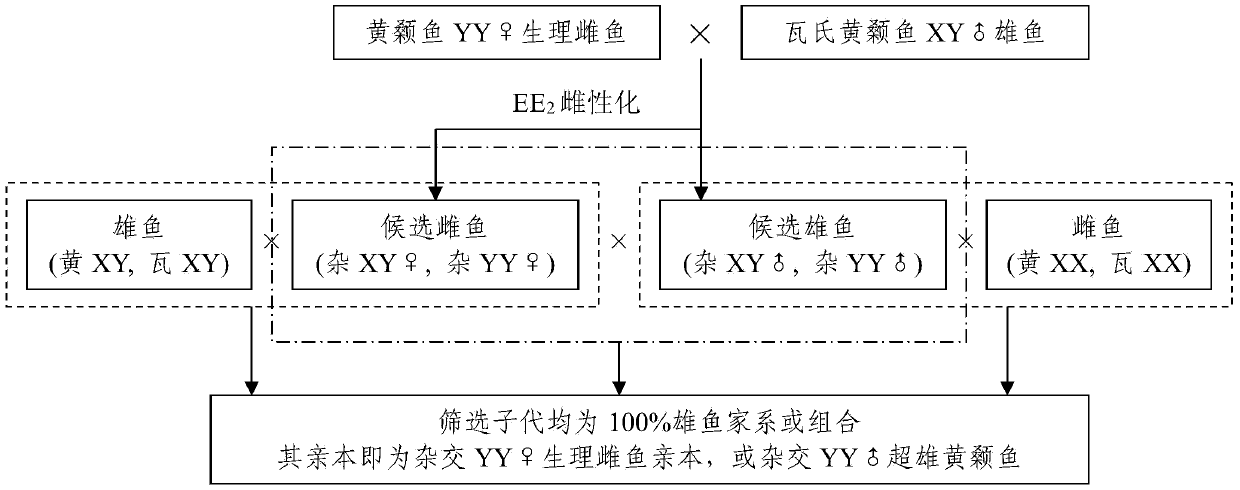
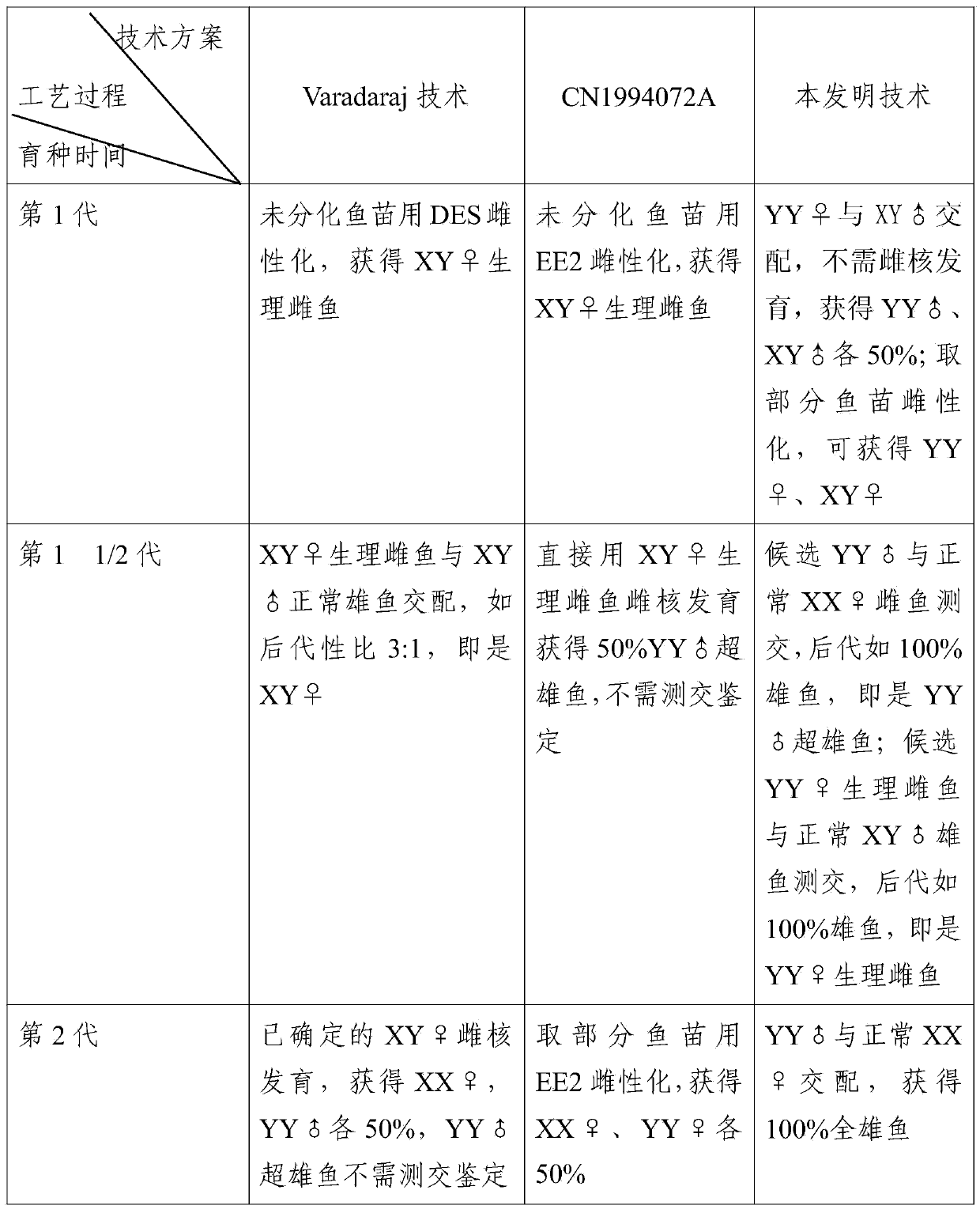
ActiveCN105360031AStable genetic traitsFast growthClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaEconomic benefitsFishery
The invention discloses a method for quickly establishing cross-bred XY holandric pelteobagrus fulvidraco. The method is characterized in that based on mating offspring of pelteobagrus fulvidraco YY physiological female fish and pelteobagrus vachelli XY male fish, cross-bred YY super-male fish is obtained by cultivation through a genetic method so as to mate with common pelteobagrus fulvidraco female fish to produce the XY holandric pelteobagrus fulvidraco. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the breeding period can be obviously shortened; compared with technologies such as Varadaraj and the like, two generations can be shortened; and compared with a method of continuously producing the holandric pelteobagrus fulvidraco by using sex reversal and gynogenesis, one generation can be shortened. Besides, the cross-bred holandric pelteobagrus fulvidraco obtained by the method disclosed by the invention is stable in genetic character, high in growth speed, large, and strong in adaptive capacity to the environment, has cross-breeding advantages and inherits advantages of the holandric fish, so that better breeding and economic benefits can be obtained.
Owner:武汉百瑞生物技术有限公司
High stigma exposure rate japonica rice sterile line selection and breeding technology
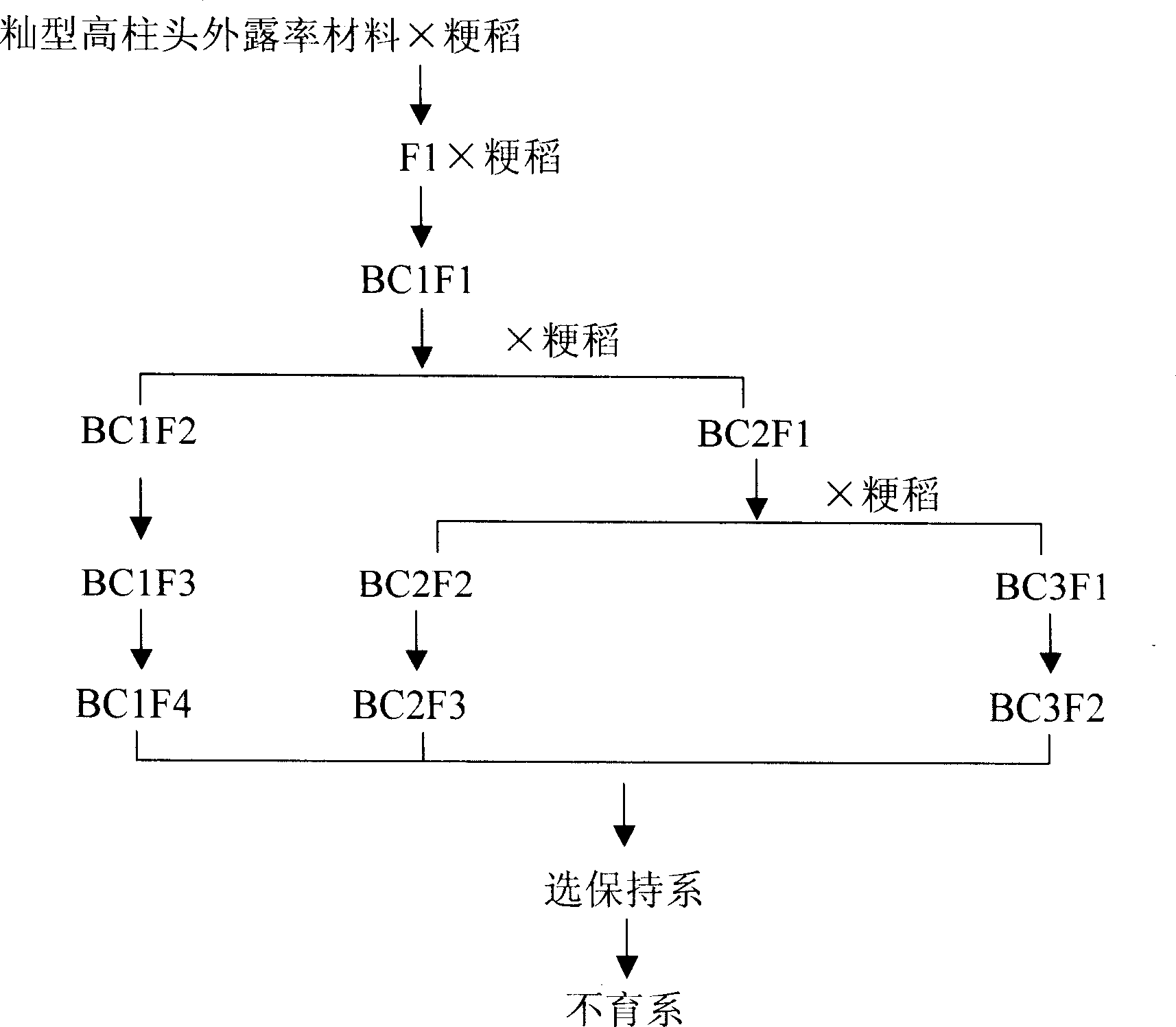
InactiveCN1843087AHigh rate of stigma exposureHigh rate of outcrossingPlant genotype modificationJaponica riceTwo generation
The invention relates to a method for breeding a sterile round-shaped rice with exposed high stigma, comprising the following steps: (1) crossing round-shaped rice with Shan rice and getting F1; (2) backcrossing the F1 with round-shaped rice to get BC1F1; (3) getting BC1F2 through BC1F1 with high exposed stigma rate auto-crossing and getting BC2F1 through backcrossing with round-shaped rice; (4) planting the BC1F1 in large group for two generations, auto-crossing and collecting together, getting BC3F1; (6) planting BC2F2 in large group, autocrossing and collecting together, getting BC2F3; (7) BC3F1 autocrossing, collecting together and getting BC3F2; (8) planting BC1F4, BC2F3 and BC3F2 in large group respectively, chossing strains and breeding sterile strain; (9) getting stable sterile strain through successive backcross with sterile strain for 4-5 generations. The invention can effectively increase the exposed stigma rate of round-shaped rice from 10-20% to above 60%, and thus increase the fruit-producing rate of the hybrid and increase the productivity.
Owner:辽宁省稻作研究所
Grape double cropping cultivation method
InactiveCN104126478AEasy to managePromote maturityCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsVitis viniferaCultivar
The invention discloses a grape double cropping cultivation method comprising the following steps: (1) fruiting mother branches are subjected to winter pruning; (2) first-crop fruits are managed with an existing regular cultivation management method, and first-crop fruit yield per mu is controlled at 1250-1500kg; (3) when the first-crop fruits are harvested, green branches with leaves are pruned in time, such that second-crop bloom is promoted, and second-crop fruits can be cultivated. According to the method provided by the invention, the green branches with leaves are pruned in time after the first-crop fruits are harvested, such that second-crop bloom is promoted and second-crop fruits can be formed. On the one hand, overlapping growth of the first-crop and second-crop fruits is avoided, such that interference between the growth of the first-crop and second-crop is prevented. Therefore, first-crop fruits coloring and mature can be promoted, and second-crop fruits management can be facilitated, such that production efficiency can be improved. One the other hand, with the cultivation method provided by the invention, because pruning and the promotion of second-crop blooming are performed in advance, a late-maturing variety can also be subjected to double-cropping cultivation with a mode that two generations are not in a single branch. Therefore, selections of grape double-cropping varieties are enriched.
Owner:广西特色作物研究院
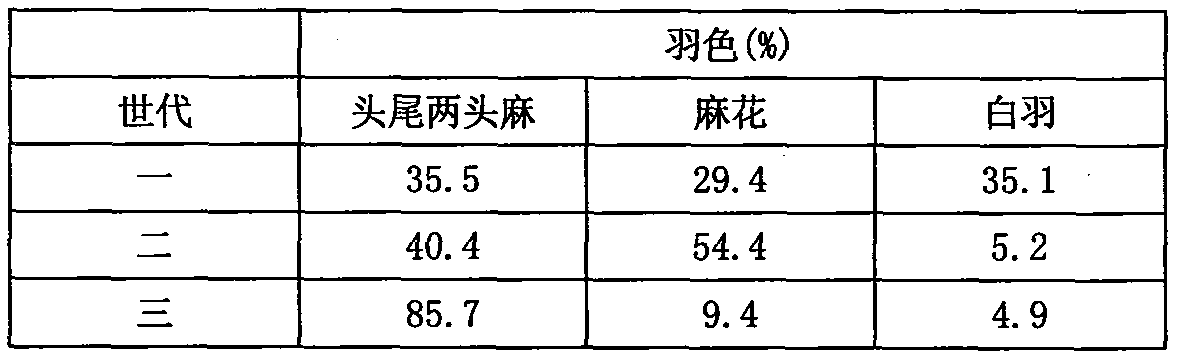
Method for breeding two-point-pattern lacy duck new breed
The invention relates to a method for breeding a two-point-pattern lacy duck new breed. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) selecting Sichuan lacy ducks as materials and inbreeding two generations, wherein the Sichuan lacy ducks are hybridized by white feather Tianfu meat male ducks and Sichuan local female sheldrakes; 2) hybridizing male ducks obtained in the step 1) with female cherry valley ducks to generate hybrid lacy ducks, performing appearance selection for three generations, and building the hybrid lacy duck F1 generation by the remained individuals; 3) performing early breeding on the hybrid lacy duck F1 generation by using a molecular marker of an MC1R gene; 4) performing family breeding on the obtained remained individuals and performing closed breeding to generate F2 generation; and 5) hybridizing the F2 generation individuals with Aobaixing Duck or Beijing ducks to generate the lacy ducks with a small amount of black feather on the heads and the tails. The method has the advantages that: hybrid combination is performed on the basis of natural group lacy ducks; and the meat duck new breed with consistent appearance and stable heritability are bred by the traditional breeding method and the modern molecular breeding method.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Selective breeding method for new variety of grain-saving green shank recessive white chickens
ActiveCN108220408AIndividual bigLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementAnimal husbandryMolecular breedingGenotype
The invention discloses a selective breeding method for a new variety of grain-saving green shank recessive white chickens and belongs to the technical field of molecular breeding. In the invention, by means of the molecular-assistant selection method, genotypes of chicken recessive white feather gene and sex-linked dwarf gene are identified, so that the genotypes can be quickly determined and thenew variety of grain-saving green shank recessive white chickens with genotype being cc / dwdw is produced. The method avoids complexness of test-cross selective breeding and reduces generation interval, and can breed the new variety of the grain-saving green shank recessive white chickens only after two generations, thus effectively reducing breeding cost. The grain-saving green shank recessive white chickens has small body size, consumes less feed, is low in basic metabolism and high in egg yield, has a delicious taste, is large in feeding density and high in feed conversion, can save cost, can be directly produced as commercial chicken and can be used in matching application.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF POULTRY SCI +1
Method for rapidly obtaining loose calluses of grapes and for long-term succeeding maintenance of grapes
InactiveCN102763593AImprove induction efficiencyQuality improvementHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureVitis viniferaTechnology research
The invention provides a method for rapidly obtaining loose calluses of grapes and for long-term succeeding maintenance of the grapes. The method sequentially comprises the following steps of: preparing sterile strains of the grapes; carrying out startup culture on the strains; preparing the loose calluses of the grapes to obtain the loose calluses of the grapes; grafting the obtained loose calluses of the grapes to a first culture medium to realize the succeeding maintenance of the grapes for at least two generations; and transferring the loose calluses of the grapes to a second culture medium to realize the succeeding maintenance of the grapes for one generation. The long-term succeeding maintenance of the loose calluses of the grapes can be implemented by repeatedly and alternately carrying out the steps, and the first culture medium and the second culture medium used in the succeeding maintenance process are both placed in a culturing room. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the obtained loose calluses of the grapes have the characteristics of high induction efficiency and high quality and can be subjected to long-term succeeding maintenance, thereby laying a good foundation for researches on the production of secondary metabolites through grape cell culturing, biological technology researches and the like.
Owner:INST OF AGRI ENG TECH FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Hybrid carp and pengze crucian carp hybrid breeding method
ActiveCN104161000AIncreased labor induction rateImprove fertilization rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaDiseaseCarp
The invention provides a hybrid carp and pengze crucian carp hybrid breeding method and belongs to the technical field of freshwater fish hybrid breeding. The hybrid carp and pengze crucian carp hybrid breeding method aims at solving the problem that no proper hybrid method exists in the prior art to prevent carp diseases in the northern area. The method includes the steps that a first filial generation is obtained by regarding a German mirror carp as a female parent and a jian carp as a male parent for hybridization, an irregular male carp with the high growth speed and a few large body surface scales serves as a male parent, a batch of plump female pengze crucian carps with more than 31 lateral line scales and high growth speed are optimized out through two-generation breeding to serve as a female parent, parent mature promotion and artificial propagation are carried out on the basis of optimizing and directive breeding of hybrid parents, hybrid carps coincident with the pengze crucian carp female parent in appearance can be obtained after distant hybridization is carried out, hybrid generation has no carp characters, and the hybrid carp and pengze crucian carp hybrid breeding method has the advantages of being high in growth speed and disease resistance, and is of great significance in improving unit yield, increasing breeding benefits, breeding new species and achieving large-scale fry rearing.
Owner:沈阳华泰渔业有限公司
Breeding method for maize inbred line
InactiveCN101790957AHigh combination abilityIncrease productionPlant genotype modificationDiseaseAgricultural science
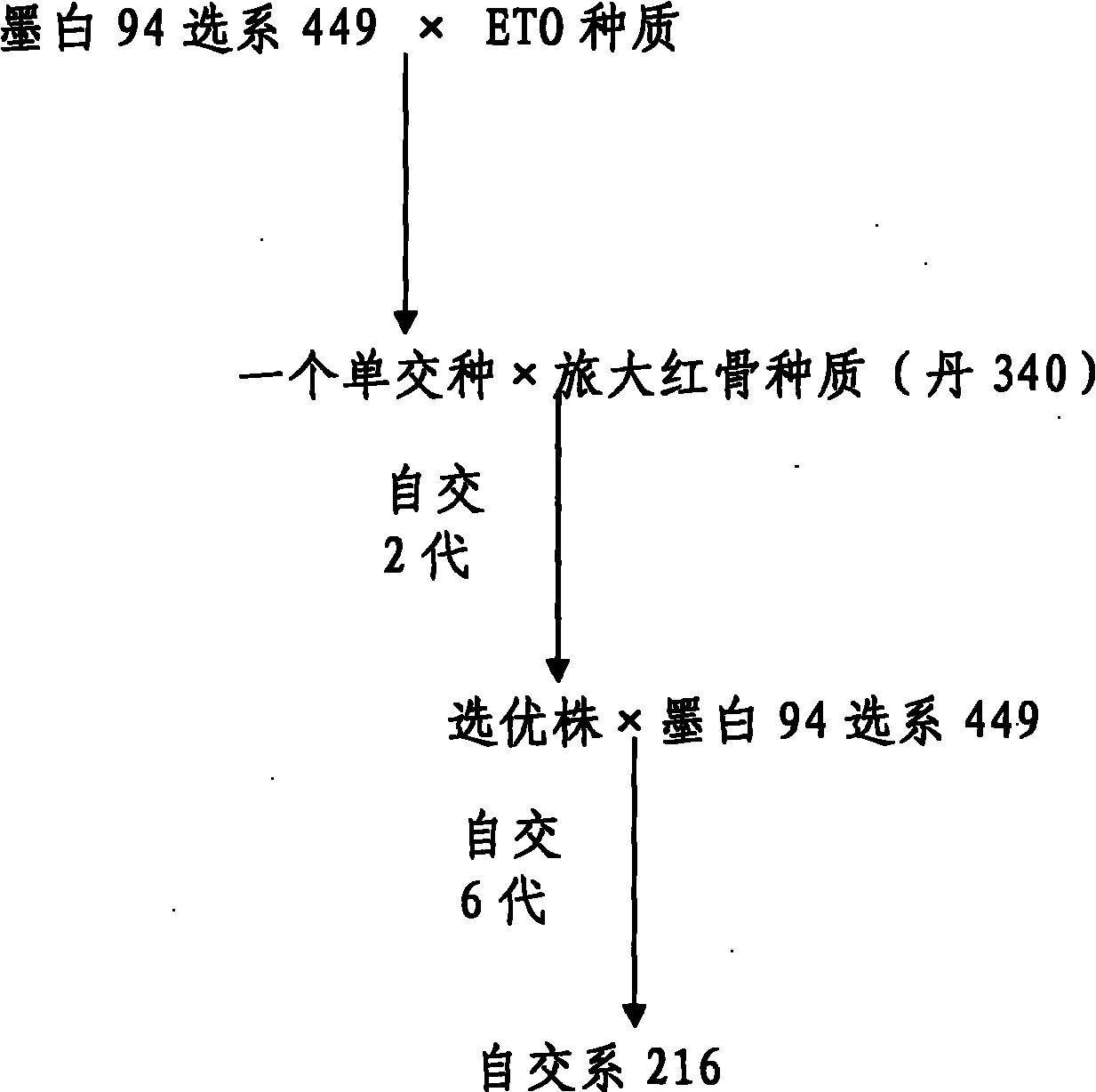
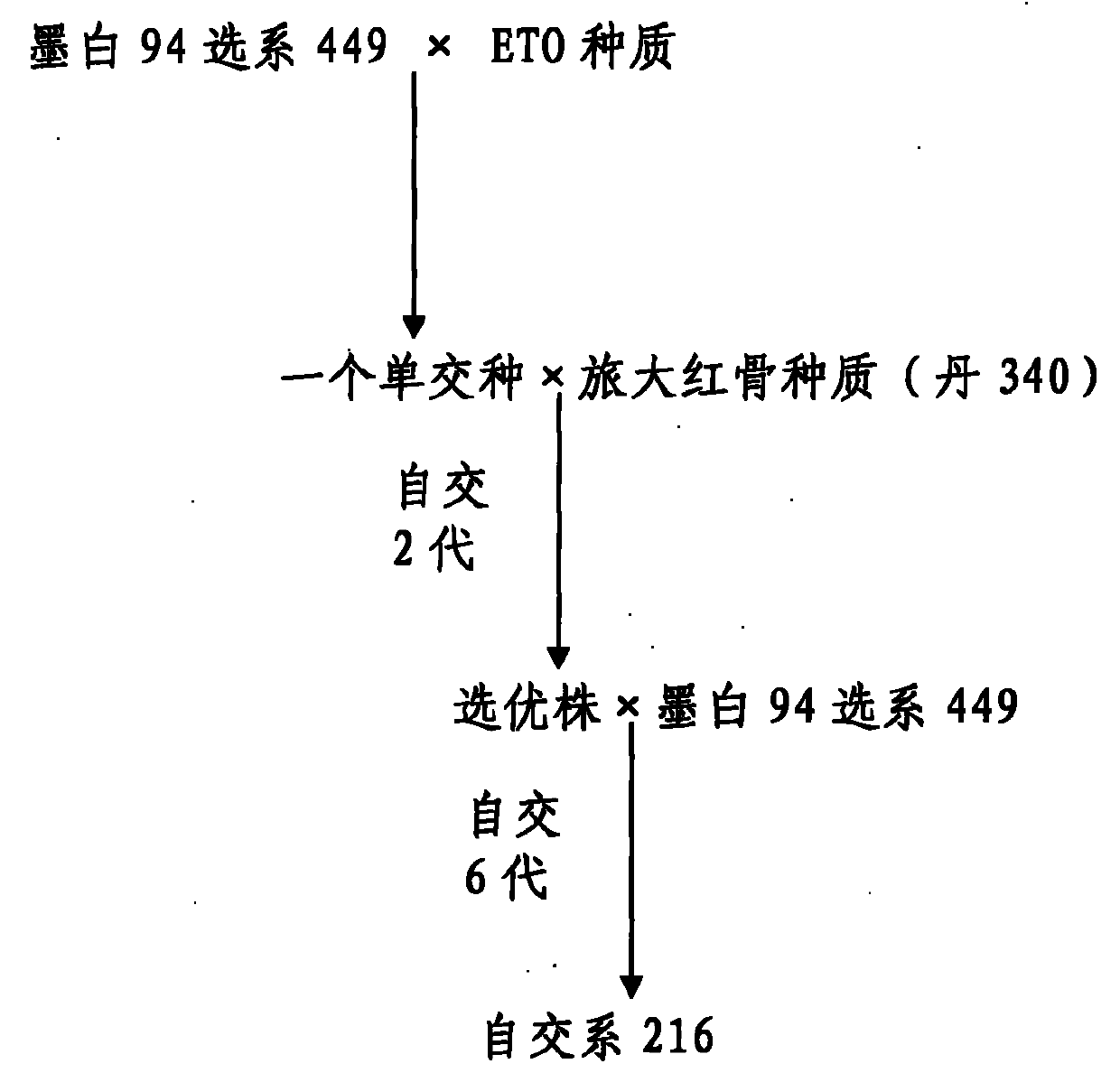
The invention relates to a preparation method for maize hybrids, belonging to the technical field of agricultural new species breeding. By taking MW94 line 449 as a female parent and ETO germ plasm as a male parent, a single hybrid is obtained through hybridization. By taking the single hybrid as a female parent and Luda red cob 340 as a male parent, a triple hybrid is obtained through hybridization. Superior plants are selected after two generations of continuous inbreeding. MW94 line 449 is used as a male parent for hybridization to obtain a base material. Then six generations of inbreeding are conducted to obtain an inbred line 216. The inbred line 216 of the invention has the advantages that a plurality of kinds of diseases such as gray speck can be resisted, the hereditary character is stable and the combining ability is strong, and is a superior inbred line for the preparation of maize hybrids.
Owner:贵州省毕节地区农业科学研究所
Method by adopting molecular marker-assisted backcross to improve gibberellic disease expansion resistance of wheat
InactiveCN102599047AShort breeding cycleLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationDiseaseGenotype
The invention discloses a method by adopting molecular marker-assisted backcross to improve gibberellic disease expansion resistance of wheat. A recombinant inbred line family carrying expansion-resistant quantitative trait loci (QTL) is adopted as a donor, a line which has excellent comprehensive character but is infected by gibberellic diseases is adopted as a receptor, and the donor is hybridized and backcrossed with the receptor. Two side markers which are closely interlocked with a target QTL are utilized for selecting a foreground in each backcross generation, 150 pairs of simple sequence repeats (SSR) markers which are distributed in an entire wheat genome are utilized for selecting a background respectively for a single plant carrying the target QTL, and the single plant with the highest background repeated rate is selected for the next generation of backcross. A near-isogenic line with the resistance being obviously improved and other characters being basically consistent with that of a recurrent parent is obtained after being continuously backcrossed for three generations and then being inbred for two generations. A target single plant can be obtained by extracting deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of seedling leaves of backcrossed generations and analyzing a marker genotype, so that the problems in phenotypic selection that the gibberellic disease resistance is susceptible to an environmental condition and a resistance phenotype can be determined only in a flowering period can be effectively solved; and meanwhile, the population size can be reduced, the breeding cost can be reduced, and the gibberellic disease expansion resistance of the wheat line can be rapidly and effectively improved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Breeding method for chilli pepper nuclear male sterile dual purpose line and nuclear substance male sterile recovery line
ActiveCN1820581ASolve the problem of few recovery sourcesHigh purityPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceHot peppers
The present invention relates to plant breeding technology, and is especially anther cultivation technological method of breeding unclear sterile dual purpose line and unclear substance sterile recovery line of capsicum. Extracorporeal anther cultivation technology is used in selective breeding of unclear sterile dual purpose line and unclear substance sterile recovery line of capsicum. That is, the dual purpose line is obtained through test cross of the fertile plant and sterile plant in contemporary anther cultivation offspring of dual purpose line hybrid, F1 selfing, test cross of similar fertile plant and sterile plant in the offspring lines and continuous two generation selection; and the recovery line is obtained through the test cross of the fertile plant and sterile plant in the contemporary anther cultivation offspring of three line hybrid with available sterile line, selectively breeding the F1 with fertility recovering rate of 100 % and stable fertility to obtain fertile plant as the corresponding recovering plant and final selfing.
Owner:北京市海淀区植物组织培养技术实验室
Rapid identification method of Chinese caterpillar fungus fertile bacterial strain
InactiveCN101353628AIncrease production costSolve fertility problemsFungiMicroorganism based processesLiquid mediumAscospore
The invention relates to a fast appraisal method of Cordyceps militaris fertile strains, which belongs to the edible fungus cultivation field. Single colonies which are sprouted by ascospore are selected, 100 single colonies are selected each time to be put under the constant temperature of 20 DEG C for culture for 16 days, with indoor natural lighting and the air humidity of 70 percent; strong strains with above 20 grass teeth, which grow uniformly, and have faint yellow colonies, golden yellow grass teeth, even growing trend, and no abnormalities are picked up, examined and confirmed by a microscope to obtain the fertile strain. The fertile strains are propagated and cultured for one time, the propagated strains are reproduced for 5 to 8 days by using a liquid media, and a mycelium pellet formed in the liquid becomes the strains for production. The method of the invention has short appraisal time and high accuracy. The time from the colony selection to the appraisal result only lasts for 20 days, more production cycles suitable for the two generation can be won for the Cordyceps militaris production, thereby further reducing the production cost, increasing the production speed, and improving the quality and the output of the Cordyceps militaris.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Stable soybean hundred-grain weight related QTL (quantitative trait loci) locus and close linkage mark satt281 thereof
InactiveCN103898105AIncrease production levelsQuick filterMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceQuantitative trait locus
The invention relates to a stable soybean hundred-grain weight related QTL (quantitative trait loci) locus and a close linkage mark satt281 thereof, which belong to the technical field of crop selective breeding. The locus is located on a linkage group of soybean C2, the close linkage mark is an SSR primer satt 281 and located on a position of 40.3cm on a public map, and the close linkage mark satt281 can be detected in two generations and two environments by adopting four different location methods (double-tail and single marking square difference analysis adopts the P which is less than or equal to 0.01 as the standard, and CI and MICIM adopt LOD which is more than or equal to 3 as the standard). The trait related QTL is located by adequately utilizing different methods, the hundred-grain weight QTL detection situations are compared in different environments and different generations, and the stable soybean hundred-grain weight QTL locus can be determined. The stable soybean hundred-grain weight related QTL can be used for improving the hundred-grain weight traits by utilizing the molecular mark auxiliary selection and map-based cloning, so that powerful technical support can be provided for the breeding and improvement of the soybean crops.
Owner:INST OF CEREAL & OIL CROPS HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Maize breeding method
InactiveCN103493727AImprove breeding efficiencyImprove accuracyPlant genotype modificationWide areaTemperate climate
The invention discloses a maize breeding method. Two maize inbred lines of different germ lines in a temperate zone and a tropic zone are selected and used as breeding materials and radiated; two generations are grown through selfing; target trait variation strains are selected and used as parent generations for hybridization; re-planting is conducted after single-corncob threshing, and an induction line is used for induction; haploid seeds are selected from harvested clusters to be doubled, wherein the haploid seeds have aleurone layers, the top ends of the haploid seeds are provided with violet marks, and plumule tips are not provided with violet marks; plants which are successfully doubled are subjected to selfing to harvest self-fruiting seeds; the self-fruiting seeds are planted, and head progeny rows meeting a breeding objective are selected for selfing to obtain a new maize inbred line; pollen of the new maize inbred line is used for test matching with test seeds; a test matching combination is planted, and a new maize variety is bred after field identification. The maize breeding method has the advantages that radiation is used for irradiating the seeds, the breeding cycle is shortened, the variety breeding rate is increased, the bred seeds are high in quality and suitable for being grown in wide areas, and the plants are proper in height, fast in growth, and resistant to drought and weeds.
Owner:山东连胜种业有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com