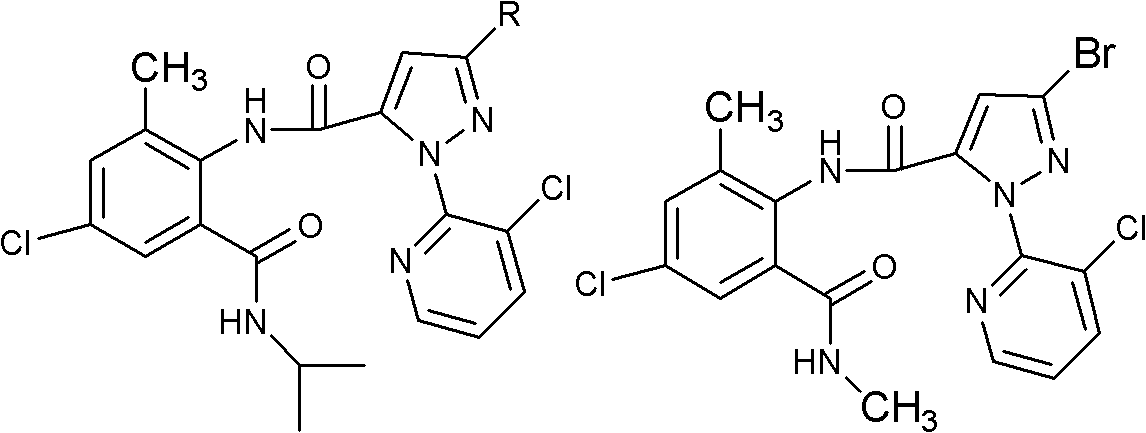
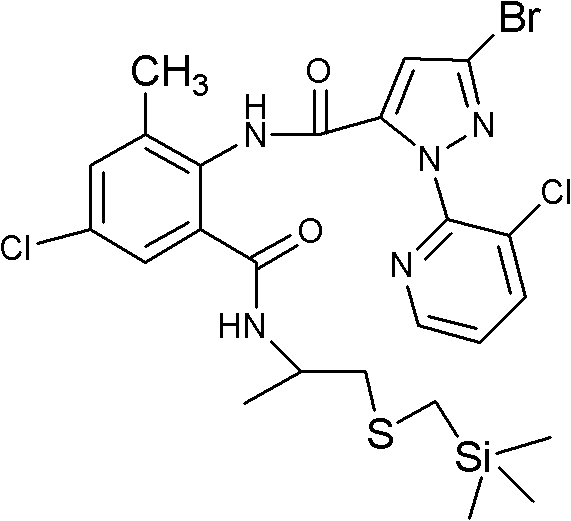
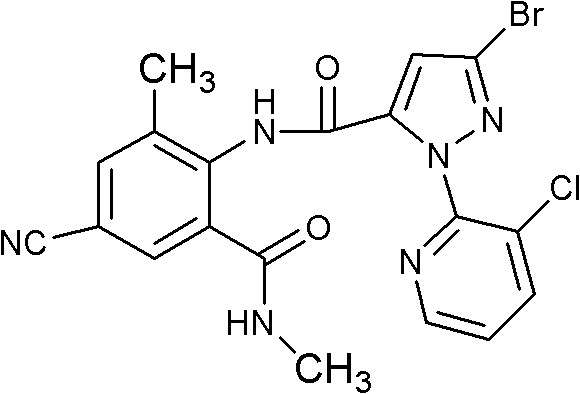
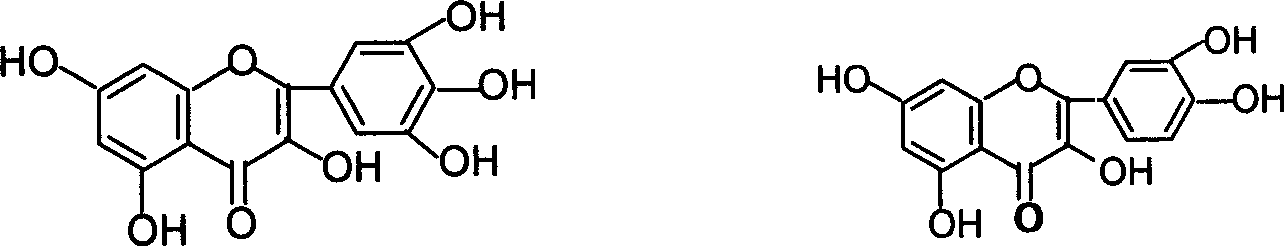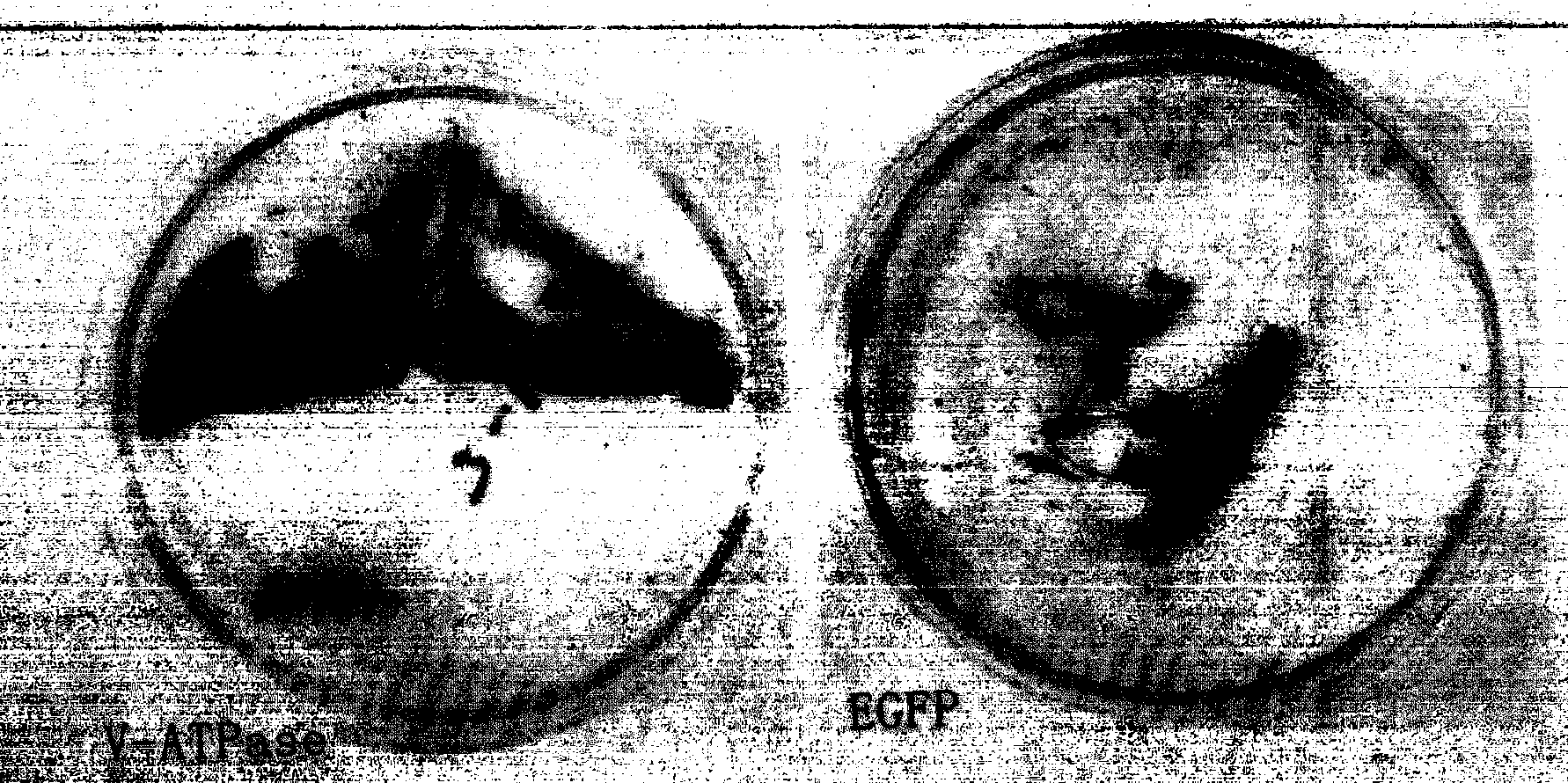Patents
Literature
265 results about "Gossypium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gossypium is a genus of flowering plants in the tribe Gossypieae of the mallow family, Malvaceae from which cotton is harvested. It is native to tropical and subtropical regions of the Old and New Worlds. There are about 50 Gossypium species, making it the largest genus in the tribe Gossypieae, and new species continue to be discovered. The name of the genus is derived from the Arabic word goz, which refers to a soft substance.
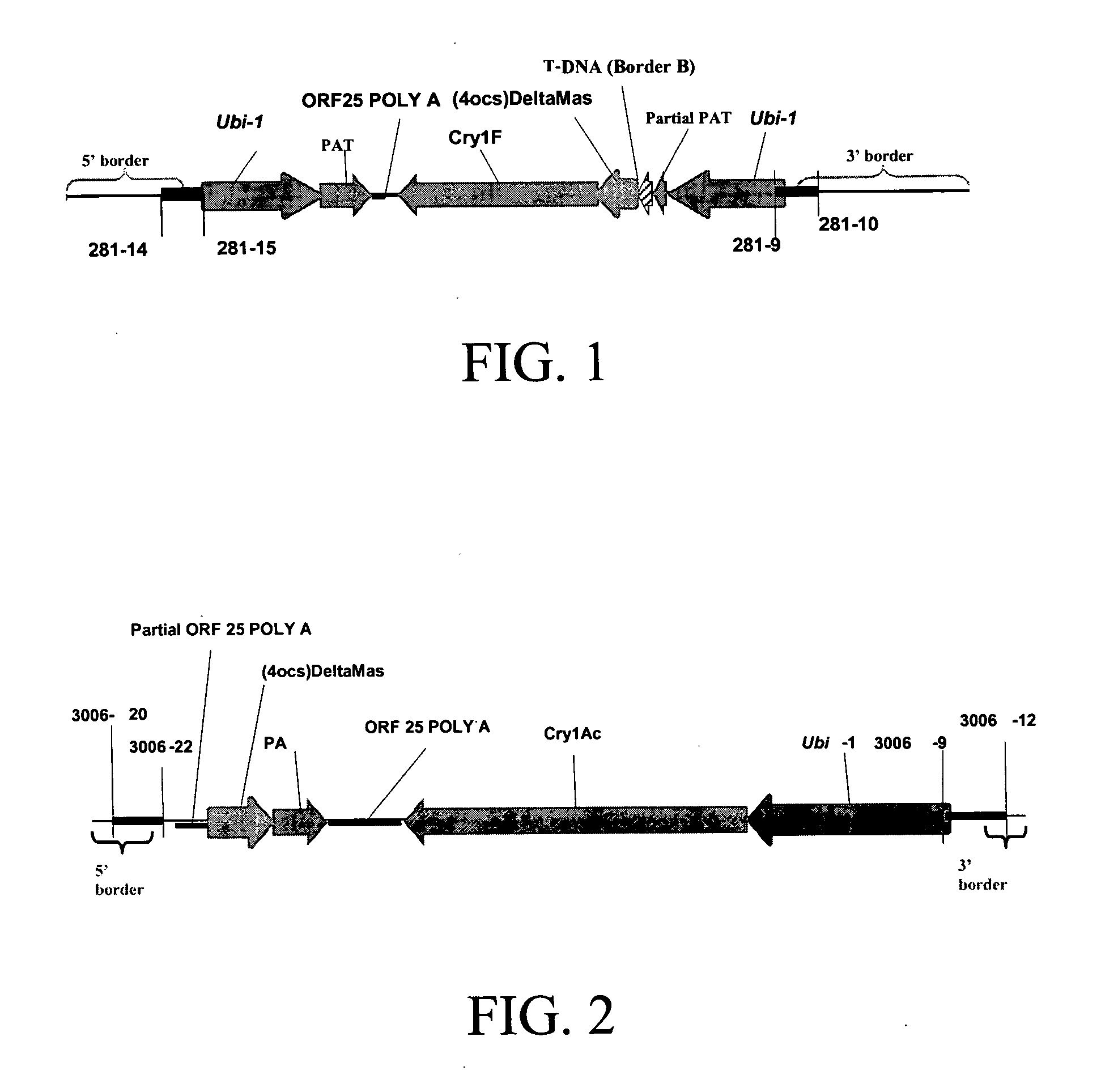
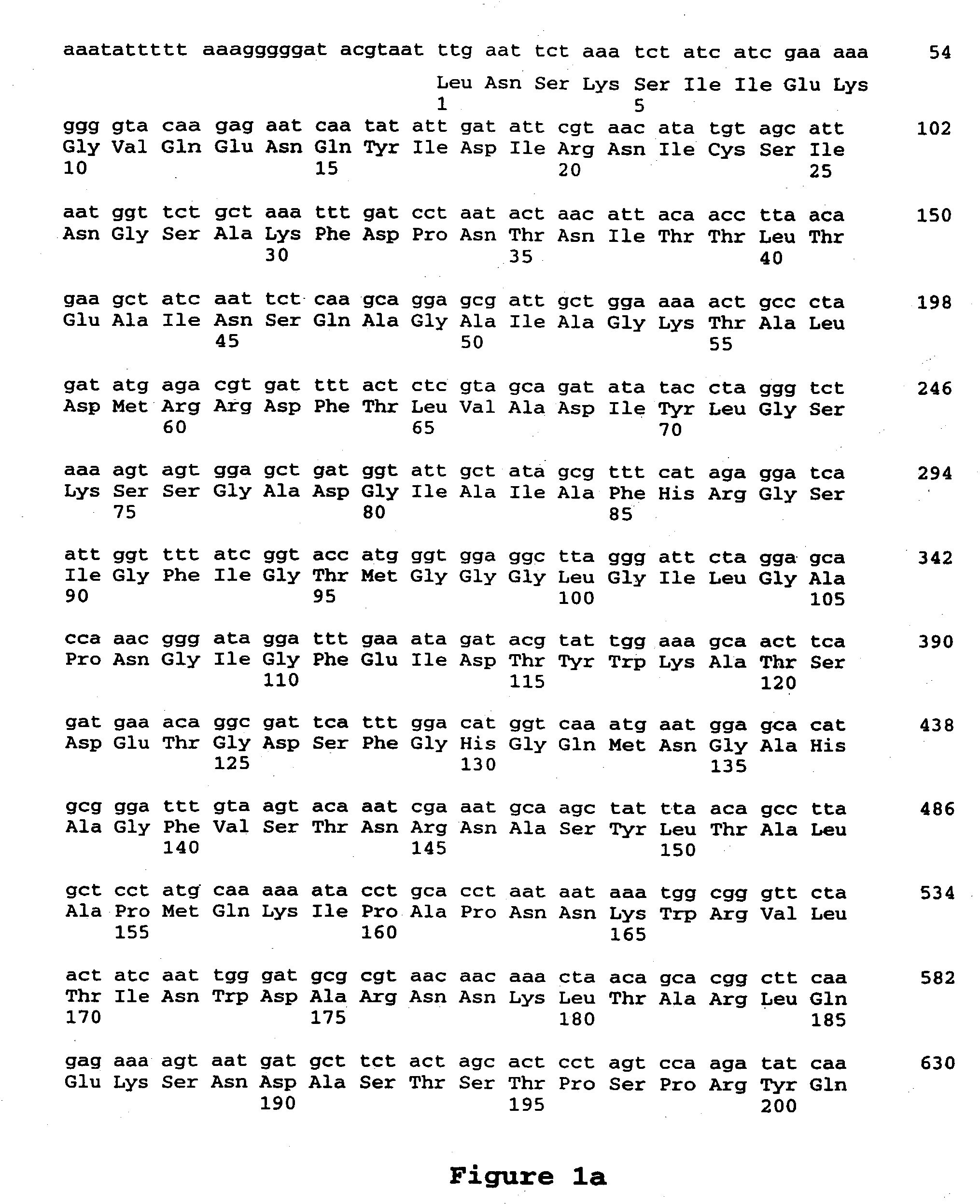
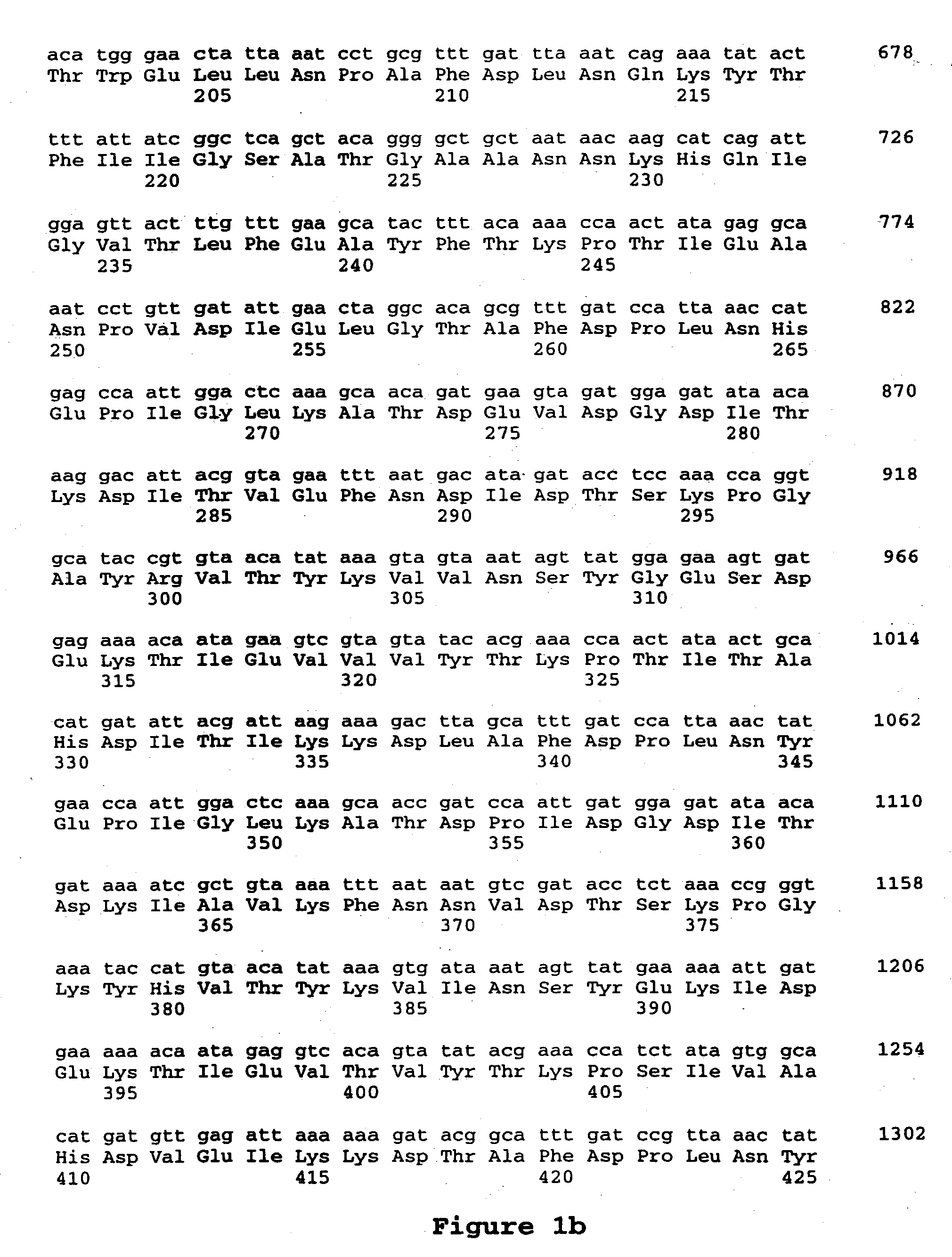
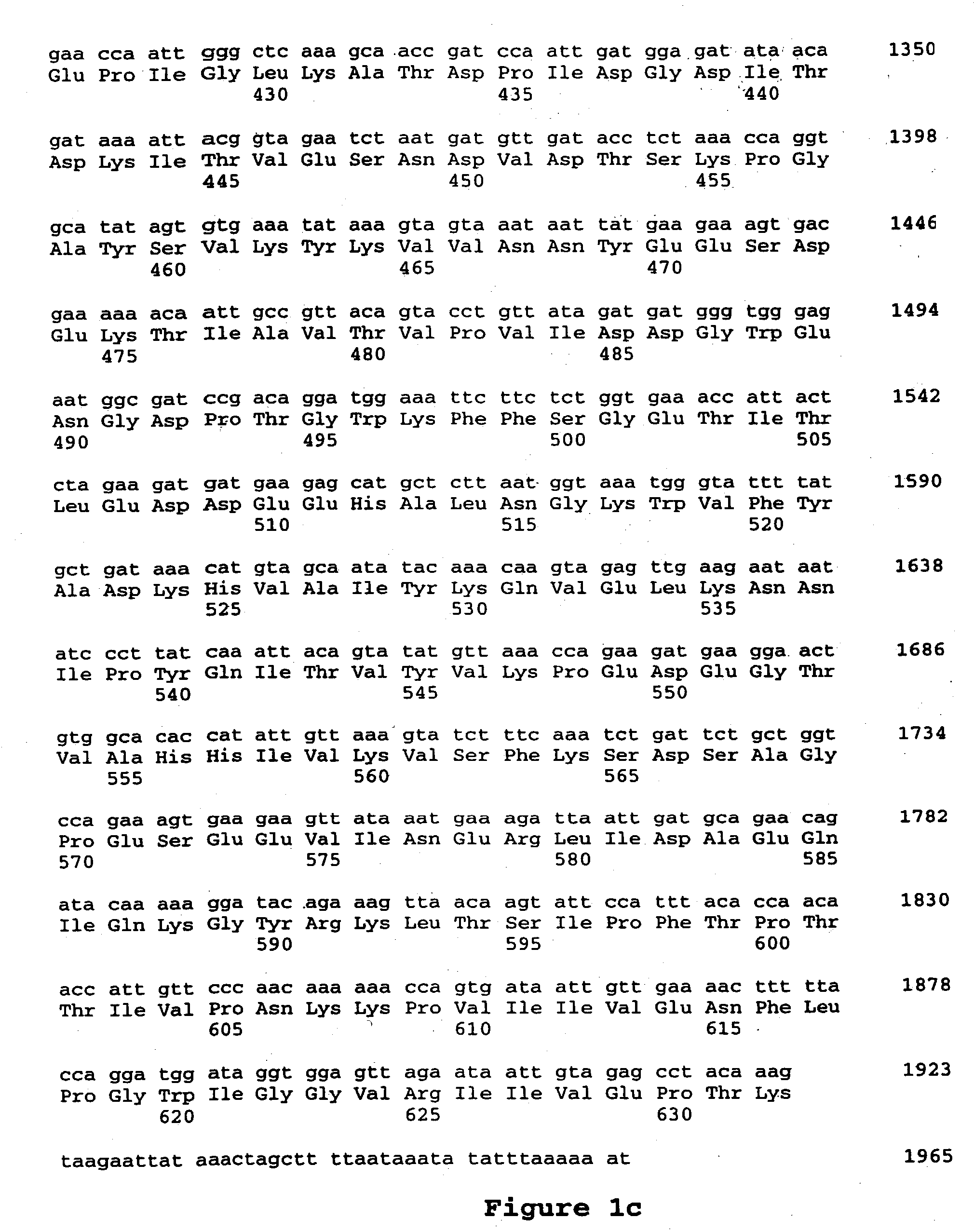
Cry1F and Cry1AC transgenic cotton lines and event-specific identification thereof
This invention relates to plant breeding and the protection of plants from insects. More specifically, this invention includes novel transformation events of cotton plants comprising one or more polynucleotide sequences, as described herein, inserted into specific site(s) within the genome of a cotton cell. In highly preferred embodiments, said polynucleotide sequences encode “stacked” Cry1F and Cry1Ac lepidopteran insect inhibitory proteins. However, the subject invention includes plants having single cry1F or cry1Ac events, as described herein. Additionally, the invention is related to cotton plants derived from that transformation event and to assays for detecting the presence of the event in a sample. More specifically, the present invention provides DNA and related assays for detecting the presence of certain insect-resistance events in cotton. The assays are based on the DNA sequences of recombinant constructs inserted into the cotton genome and of the genomic sequences flanking the insertion sites. These sequences are unique. Based on these insert and border sequences, event-specific primers were generated. PCR analysis demonstrated that these cotton lines can be identified in different cotton genotypes by analysis of the PCR amplicons generated with these event-specific primer sets. Thus, these and other related procedures can be used to uniquely identify these cotton lines. Kits and conditions useful in conducting the assays are also provided. These materials and methods can also be used to assist breeding programs to further develop traits in cotton.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Bollworm insect resistance management in transgenic plants
InactiveUS20090313717A1Prevent and delay resistance developmentPreventing and delaying insect resistance developmentClimate change adaptationGenetic engineeringHelicoverpaHelicoverpa zea
This invention relates to the use of a combination of different proteins insecticidal to Helicoverpa zea or Helicoverpa armigerain an insect resistance management process, wherein such proteins are: a) a Cry2A protein such as Cry2Aa, Cry2Ab, or Cry2Ae and b) a Cry1A, Cry1F or VIP3A protein, particularly wherein such proteins binds saturably to the insect midgut membrane of Helicoverpa zea or Helicoverpa armigera, as well as plants and seeds expressing such combination of proteins, which are used to delay or prevent the development of resistance in populations of such insect species.
Owner:BAYER BIOSCIENCE N V
Method for cultivating wood-rotting fungi
InactiveCN102415279AReduce dosageIncrease productionHorticultureFertilizer mixturesBiotechnologyGossypium
The invention discloses a method for cultivating wood-rotting fungi. The raw materials for cultivating the wood-rotting fungi comprise the following components of: 45-55 parts of cotton stalk crumb, 8-20 parts of fine sawdust, 8-20 parts of corncob, 5-20 parts of bran coat, 4-7 parts of bean dregs, 5-11 parts of pure chicken manure, 0.5-1.5 parts of phosphate fertilizer, 0.5-1.5 parts of plaster, 1-5 parts of lime and 8-20 parts of cotton seed hull. The raw materials in weigh ratio are cultivated to generate the wood-rotting fungi according to the steps of adding water in the raw materials and uniformly stirring, building pile and fermenting, producing an inoculation bacterial bag and generating mushroom. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the consumption of the cotton seed hull is reduced; and cotton straws are used to replace the cotton seed hulls and are simultaneously matched with the fine sawdust and the corncob to produce a cultivation raw material of the wood-rotting fungi. The method has the characteristics of ensuring quick material consumption by hypha during fingi fermentation, robust growth and white and density, compact produced fruiting body and rounding mushroom shape. According to the method, the labor and time are saved, the cost is reduced and the yield is increased.
Owner:河北省农业环境保护监测站
Methods for stable transformation of plants
InactiveUS6858777B2Improve conversion efficiencyImprove transformation efficiencyOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationAxillary budNicotiana tabacum
Multiple shoot structures are induced from plant tissues (e.g., shoot apices or axillary buds on an artificial medium) to produce multiple shoot cultures. These multi-shoot cultures are then transformed by known transformation methods. Plants are subsequently regenerated from the transformed cells. Crops that may be efficiently transformed by this method include plants normally recalcitrant to transformation such as sugar beet, sunflower, soybean, cotton, tobacco, tomato, peanuts, melons, watermelon, squash, Brassica, and pepper.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Fluoro methoxylpyrazole-containing o-formylaminobenzamide compound, synthesis method and application thereof
ActiveCN101967139AStrong noveltyBroad-spectrum insecticidal activityBiocideOrganic chemistrySynthesis methodsCotton bollworm
The invention discloses a fluoro methoxylpyrazole-containing o-formylaminobenzamide compound shown as a structural formula (I) or agriculturally suitable salts thereof, a synthesis method and application thereof. The fluoro methoxylpyrazole-containing o-formylaminobenzamide compound has the advantages of effectiveness, low toxicity, low cost and environmental safety and can be used for preventingand removing various pests in the fields of agriculture and horticulture or pests parasitized on animals. The fluoro methoxylpyrazole-containing o-formylaminobenzamide compound has very high activityon lepidopteran pests (plutella xylostella, spodoptera exigua and cotton bollworm), hemipteran pests (black peach aphid and aphis craccivora koch), homopteran pests (nilaparvata lugens), dipteran pests (liriomyza trifolii) and leaf beetle pests (phaedon conchleariae). Particularly, good effect on the lepidopteran pests, the hemipteran pests and the dipteran pests can be achieved under the condition of low dosage of the compound.
Owner:SINOCHEM LANTIAN +2
Total flavone extract of maniod eibish, its preparation and application
InactiveCN1994337ASignificant effect on the treatment of nephritisClear certaintySugar derivativesPill deliveryMedicineGlycoside formation
The invention relates to a hollyhock sunflower chromocor extractive, wherein it is characterized in that: the chromocor content is 50-90%; the chromocor comprises 1. 0-5. 0% meletin-3-acacia glycoside, 8-24. 0% hyperin, 7. 0-20.0% isoquercitrin, 5. 0-15. 0% meletin-3-glucosidase, 3. 0-10.0% cotton-3-glucosidase, 0.5-5. 0% gale element, 0.5-5. 0% cotton, and 2. 0-8. 0% meletin, etc. The inventive extractive can be used to prepare the drug that treats nephritis, with high reliability.
Owner:周亚球 +1
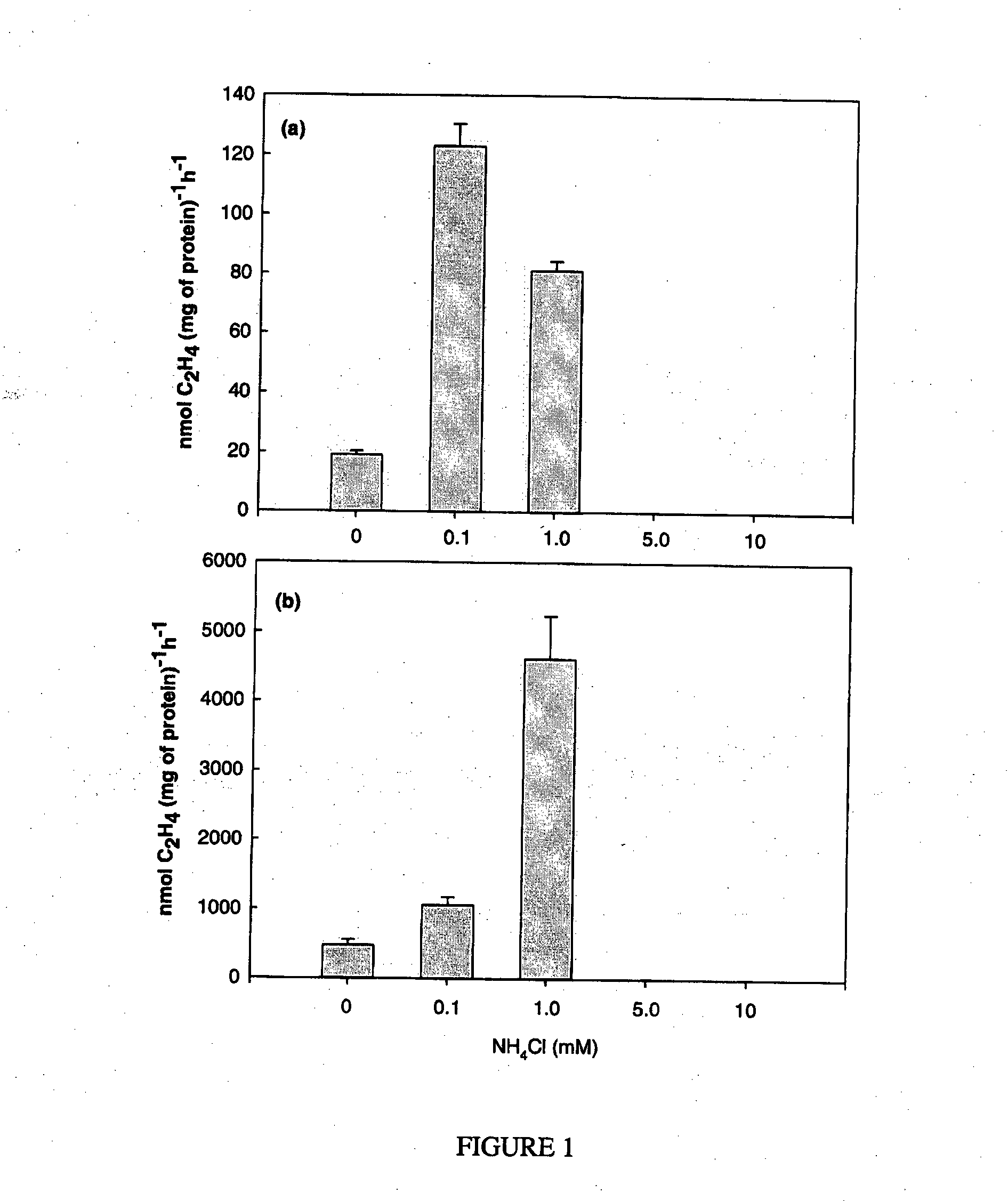
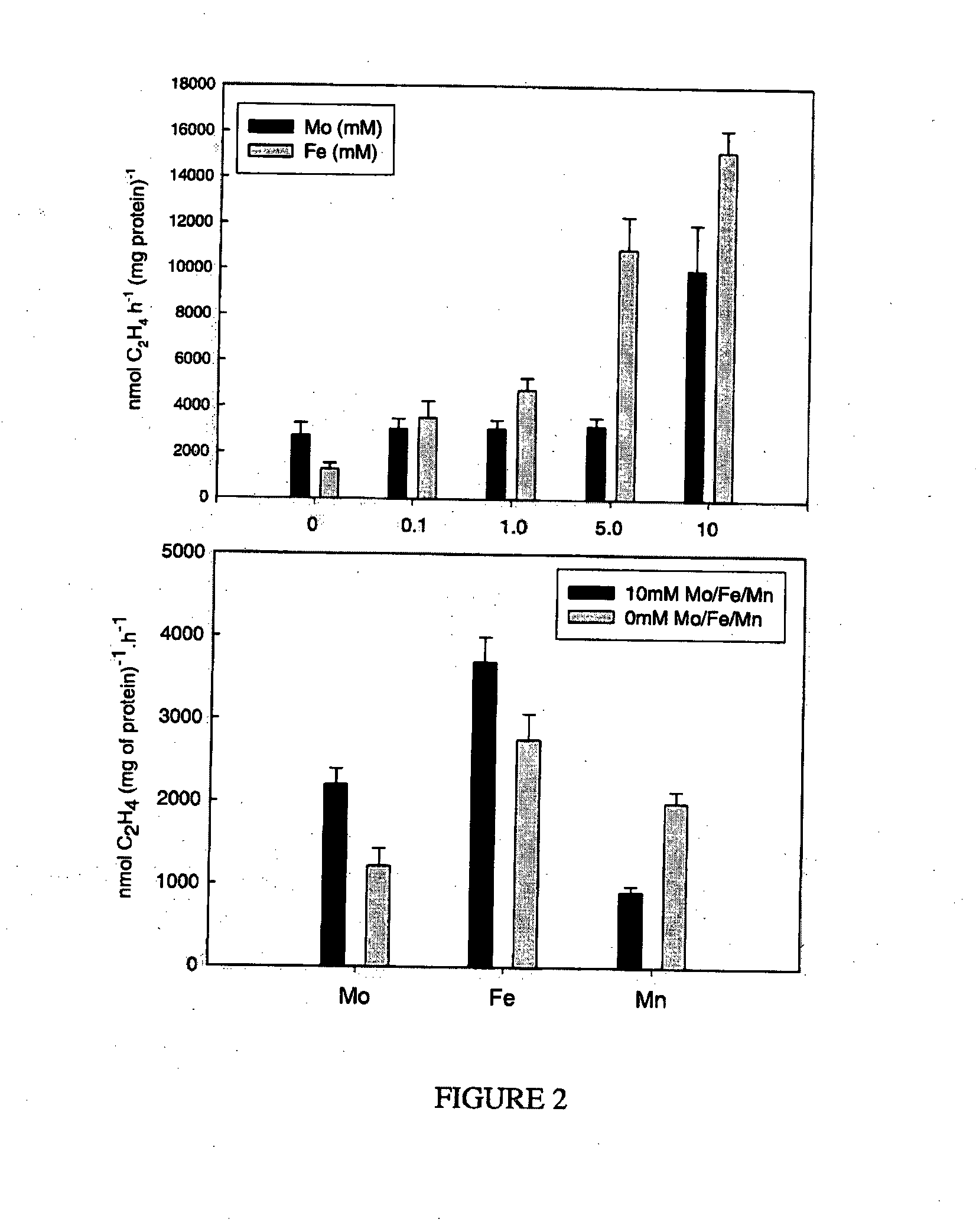
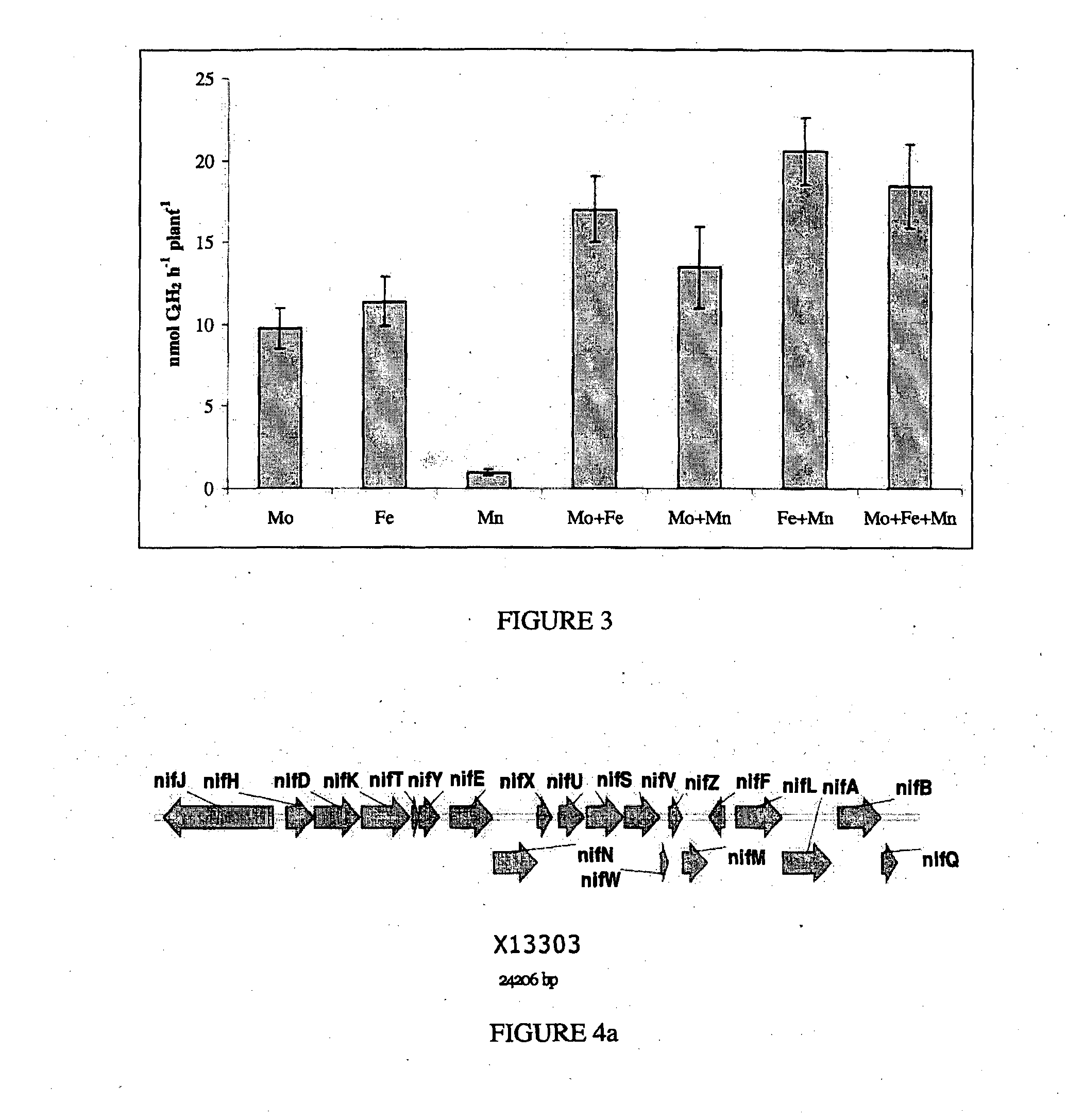
Nitrogen-fixing bacterial inoculant for improvement of crop productivity and reduction of nitrous oxide emission
The present invention relates to methods of reducing chemical fertilizer usage and greenhouse gas nitrous oxide emission and to methods of improving plant growth rate and seed productivity in agriculture through the application of a novel artificially manufactured formula containing a nitrogen-fixing bacterium that efficiently colonizes non-legume plants in aerial parts and the root system. The bacteria inocula and methods are particularly suitable for plants in the genera Jatropha, Sorghum, Gossypium, Elaeis, Ricinus, Oryza and Manihot.
Owner:TEMASEK LIFE SCIENCES LABORATORY
Polypeptide compositions toxic to anthonomus insects, and methods of use
A novel gene encoding a Coleopteran inhibitory Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal crystal protein is disclosed. The protein, tIC851, is insecticidally active and provides plant protection from at least cotton boll weevil, Anthomomus grandis, when applied to plants in an insecticidally effective composition.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Ganoderma lucidum potted landscape cultivation method
InactiveCN102318505AMeet training requirementsReliable growthHorticultureFertilizer mixturesAgricultural scienceGossypium
The invention provides a Ganoderma lucidum potted landscape cultivation method, which can solve the problem that the growth of Ganoderma lucidum fruit bodies is influenced because of insufficient nutrient compositions in substitute materials in the existing Ganoderma lucidum substitute material bag cultivation method, and can ensure the reliable growth of the Ganoderma lucidum fruit bodies at thesame time by controlling factors such as temperature, humidity, illumination and the like. The method comprises the following steps of medium preparation, medium bagging and sterilization, inoculation and mushroom development and fruit body culture management. The method is characterized in that cotton seed hulls are used as a culture medium which comprises 85 parts to 90 parts by weight of cotton seed hulls, 10 parts to 15 parts by weight of any one, any two or three of corn powder, wheat powder and soybean powder, and 1 part to 2 parts by weight of gypsum powder; or sawdust is used as the culture medium which comprises 90 parts to 92 parts by weight of sawdust, 8 parts to 10 parts by weight of any one, any two or three of corn powder, wheat powder and soybean powder and 1 part to 2 parts by weight of gypsum powder.
Owner:无锡飞凤生物科技有限公司
Bollworm insect resistance management in transgenic plants
InactiveCN102066566AClimate change adaptationVector-based foreign material introductionHelicoverpaGossypium
This invention relates to the use of a combination of different proteins insecticidal to Helicoverpa zeaor Helicoverpa armigeran an insect resistance management process, wherein such proteins are: a) a Cry2A protein such as Cry2Aa, Cry2Ab, or Cry2Ae and b) a Cry1A, Cry1F or VIP3A protein, particularly wherein such proteins binds saturably to the insect midgut membrane of Helicoverpa zeaor Helicoverpa armigera, as well as plants and seeds expressing such combination of proteins, which are used to delay or prevent the development of resistance in populations of such insect species.
Owner:BAYER BIOSCIENCE N V
Earlier-stage treatment method adopting cotton straw to prepare pleurotus edible mushroom cultivation raw material
InactiveCN102219574ABio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationFirewoodAgricultural science
The invention discloses an earlier-stage treatment method adopting cotton straw to prepare pleurotus edible mushroom cultivation raw material. The method comprises the step of fermenting the raw material including cotton and firewood powder dust to obtain an edible mushroom cultivation substrate. The core of the method is that fermentation treatment is conducted after the cotton straw is smashed to improve the physical and chemical properties of the cotton straw, so that the cotton straw becomes a main cultivation material suitable for edible mushroom cultivation. The species of mushroom suitable for the obtained cultivation substrate include oyster mushroom, pleurotus eryngii, pleurotus nebrodensis, pleurotus geesteranus, pleurotus cornucopiae and other pleurotus edible mushrooms.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Pest and glyphosate resistant expression vector, and plasmid and application thereof
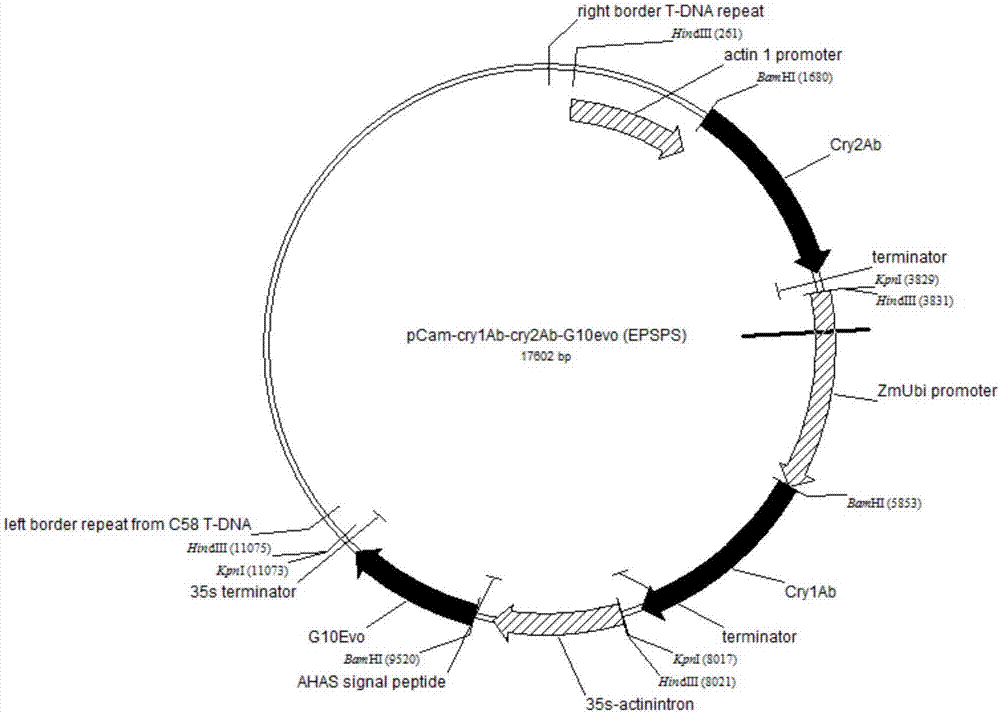
ActiveCN106916844ALower resistanceExpand insecticidal spectrumPlant peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceOrder Lepidoptera
The invention discloses a pest and glyphosate resistant expression vector, and a plasmid and an application thereof. The expression vector contains a pest-resistant gene cry1Ab, a pest-resistant gene cry2Ab and a glyphosate-resistant gene G10evo. The vector simultaneously expresses Cry1Ab, Cry2Ab and G10evo proteins, and transgenic crops obtained by transferring crops with the vector can simultaneously resist cotton bollworms, beet armyworms, corn borers, striped rice borer and other main lepidoptera pests of rice, corn and cotton, so the insecticidal spectrum is widened, the pest resistance is effectively delayed, the transgenic crops have glyphosate resistance, the transgenic crops with composite properties accord with the current development direction of transgenic crops, and demands of large-scale agricultural production are met.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Cotton breeding method
InactiveCN101707963ASimple Breeding MethodBroad Breeding PathwayPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAgricultural scienceGossypium
The invention relates to a cotton breeding method. In the method, a combination part of genetic variation generated by cotton graft is used as an explant for inducing to culture callus; the cultured callus is subjected to propagation, subculturing and differentiated culture to obtain cotton seedlings; and after hardening off, the cotton seedlings are grafted for transplantation or directly transplanted. The cotton breeding method has the advantages that: by utilizing graft to create genetic variation, the method not only improves plant quality, yield, stress resistance, and the like, but also obtains distant variation which cannot be obtained through sexual hybridization, and has simple operation, high seed selection efficiency and low cost; the method provides a novel cotton transgenic means and can transfer target gene to a breed to be improved to generate a variation type combining the merits of parental stock and cion parents; and the creation of genetic variation by utilizing graft can be taken as a supplementary means of general breeding and modern gene engineering breeding and is an important breeding means with broad prospects.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Agropolymer containing a carbohydrate and silica matrix from plants
InactiveUS6958232B2Improving water pollution controlReduce environmental pollutionSolid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationSilica matrixCajanus
The present invention relates to novel agropolymers, which comprise a carbohydrate and / or silica matrix substantially devoid of proteins, tannins and polyphenols and which comprise metal binding reactive sites. A method of producing the agropolymers is also disclosed wherein the agropolymers are derived from plant materials such as seed coats, seed covers, husks, or hulls of various agricultural crops. The agricultural crops typically used to produce the agropolymers include Oryza sativa, Panicum miliaceum, Setaria italica, Cajanus cajan, Vigna mungo, Vigna radiata, Triticum sp., Ricinus communis, Helianthus annus, Gossypium sp., and Arachis sp. The agropolymers of the present invention are capable of purifying aqueous solutions polluted or contaminated with metals and / or ions. Thus, the present invention also discloses a method whereby agropolymers are used in the purification of contaminated water and other aqueous solutions. The agropolymers disclosed herein are useful in several industrial applications including purifying polluted drinking water or ground water.
Owner:BIJAM BIOSCI
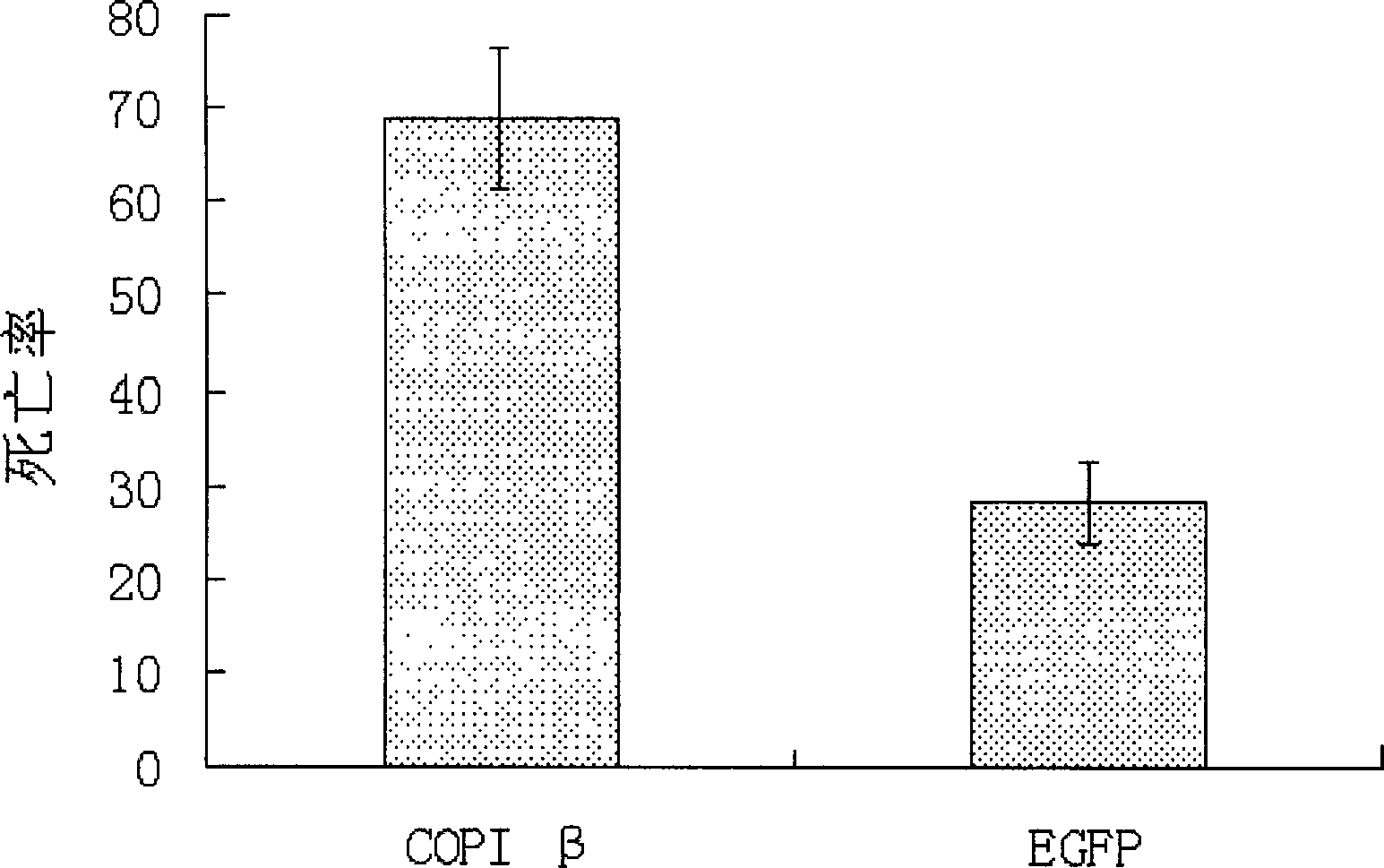
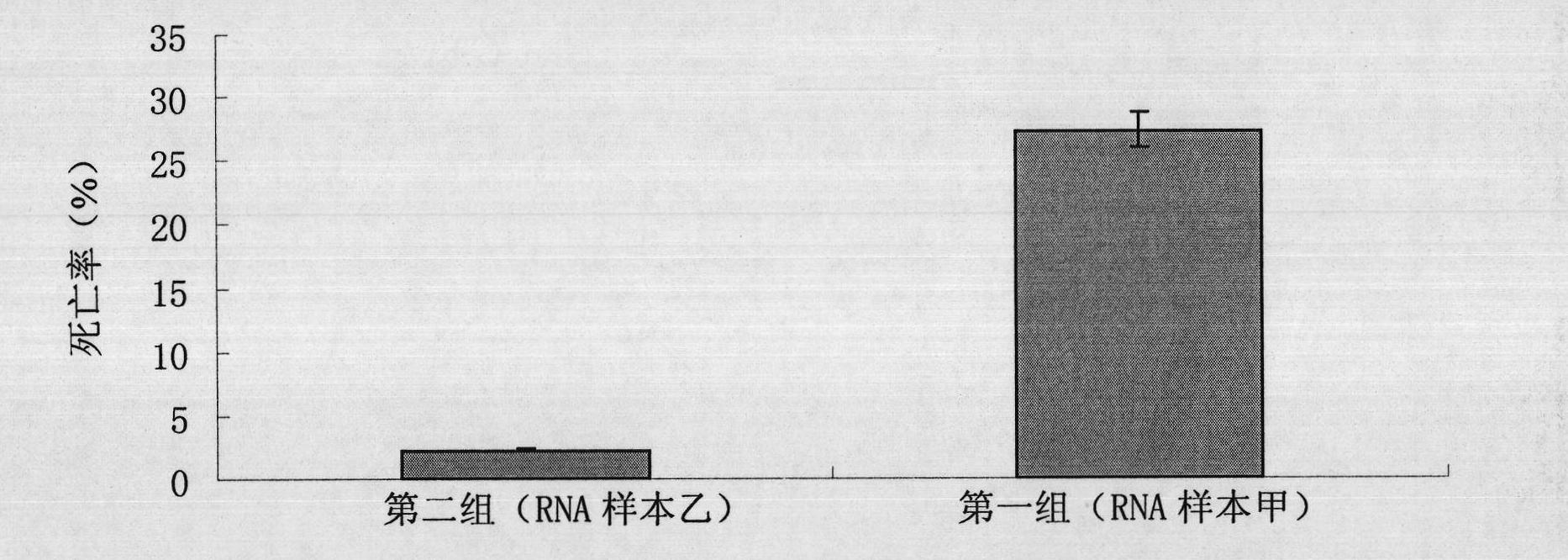
C DNA (Complementary Desoxvribose Nucleic Acid) of cotton bollworm COPI Beta gene and application of c DNA
InactiveCN103849625AReduced risk of developing resistanceReduce the risk of resistanceBiocideAnimal repellantsAgricultural scienceCotton bollworm
The invention discloses a c DNA (Complementary Desoxvribose Nucleic Acid) of a cotton bollworm COPI Beta gene and an application of the c DNA. A COPI Beta si (Small Interfering) RNA of a cotton bollworm is designed and synthesized, so that the expression of the COPI Beta gene is blocked after the COPI Beta si RNA is fed to the cotton bollworm, thus the death rate of the cotton bollworm is improved. Therefore, the biological prevention and control of the cotton bollworm is realized.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
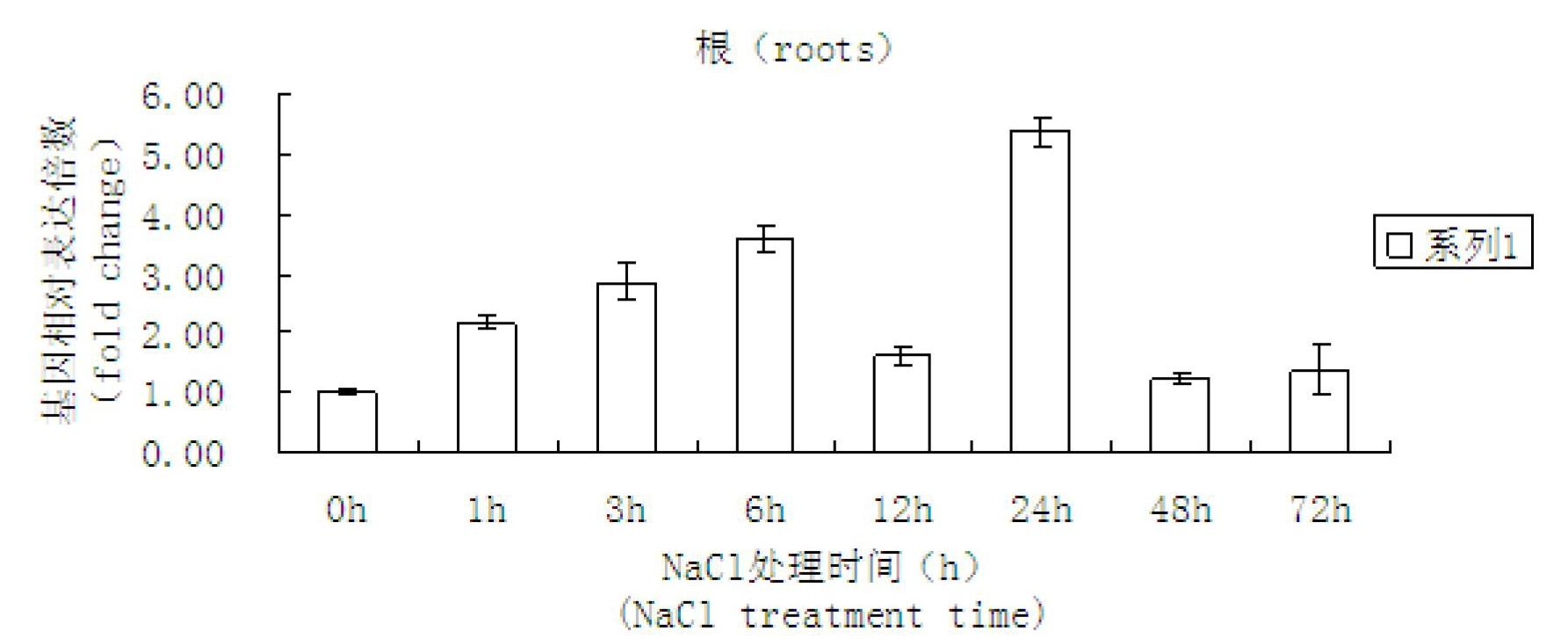
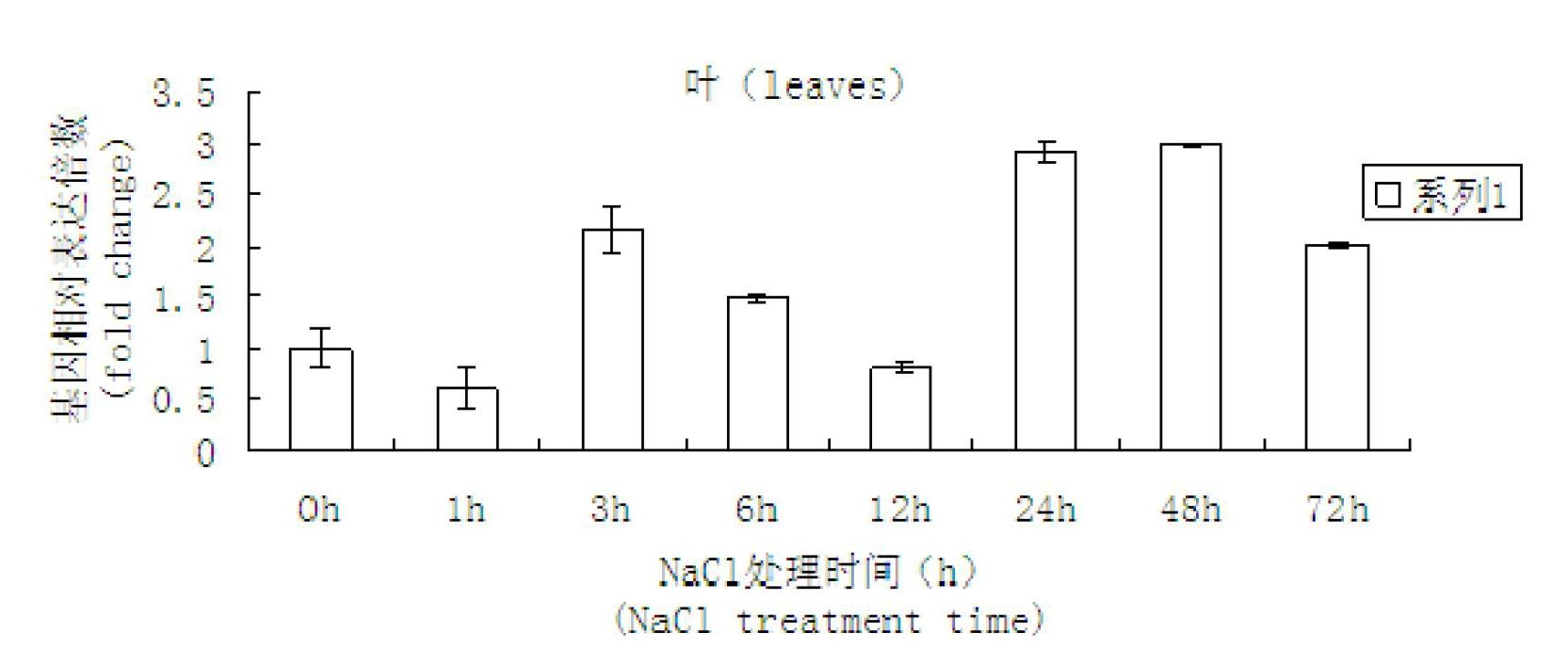
Cotton salt-tolerant gene GarCIPK for improving plant salt tolerance
The invention discloses a cotton salt-tolerant gene, i.e. Gossypium wild dry land cotton CIPK-like protein phosphokinase GarCIPK. The gene has the sequence of SEQ ID No.1 in a sequence list. A cotton stress tolerance related gene is separated by an electronic cloning and reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) technology, and function verification is performed by transferring gene into tobacco and shows that the salt tolerance of a transgenic plant is obviously improved.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Culture method for plant seedlings
InactiveCN102939890AEasy to fixFixed will not affectAgriculture gas emission reductionCultivating equipmentsNutritional deficiencyButt joint
The invention relates to a culture method for plant seedlings. The plant seedlings are cultured by a ventilated root division culture device, the side surfaces of two culture bowls of the device are in butt joint, a cover plate and a culture plate are arranged on the two culture bowls, culture holes are formed in the culture plate, and vent holes are formed in the two sides of the culture holes. The culture method comprises the followings steps: the plant seedlings of 3 days are taken and cultured in a Hoagland's nutrient solution with the concentration of 50 percent for 2 days then in a Hoagland's nutrient solution with the concentration of 100 percent for 12 days, the plant seedlings growing consistently are taken, the stems of the plant seedlings are wrapped by nutrient cotton and fixed in the culture holes of the culture plate, the roots of the plant seedlings are divided into a group A and a group B, the group A is put into the culture bowl containing the Hoagland's nutrient solution, and the group B is put into the culture bowl containing a nutritional deficiency nutrient solution; the pH values of the nutrient solutions are regulated to 6 at 8 o'clock in the morning and 15 o'clock in the afternoon; the nutrient solutions are changed every other three days; and after 4-12 days, the plant seedlings are taken out. The operation is simple, and the personal errors are reduced, so that the research result is more accurate, the culture time is saved, and the working efficiency is improved.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
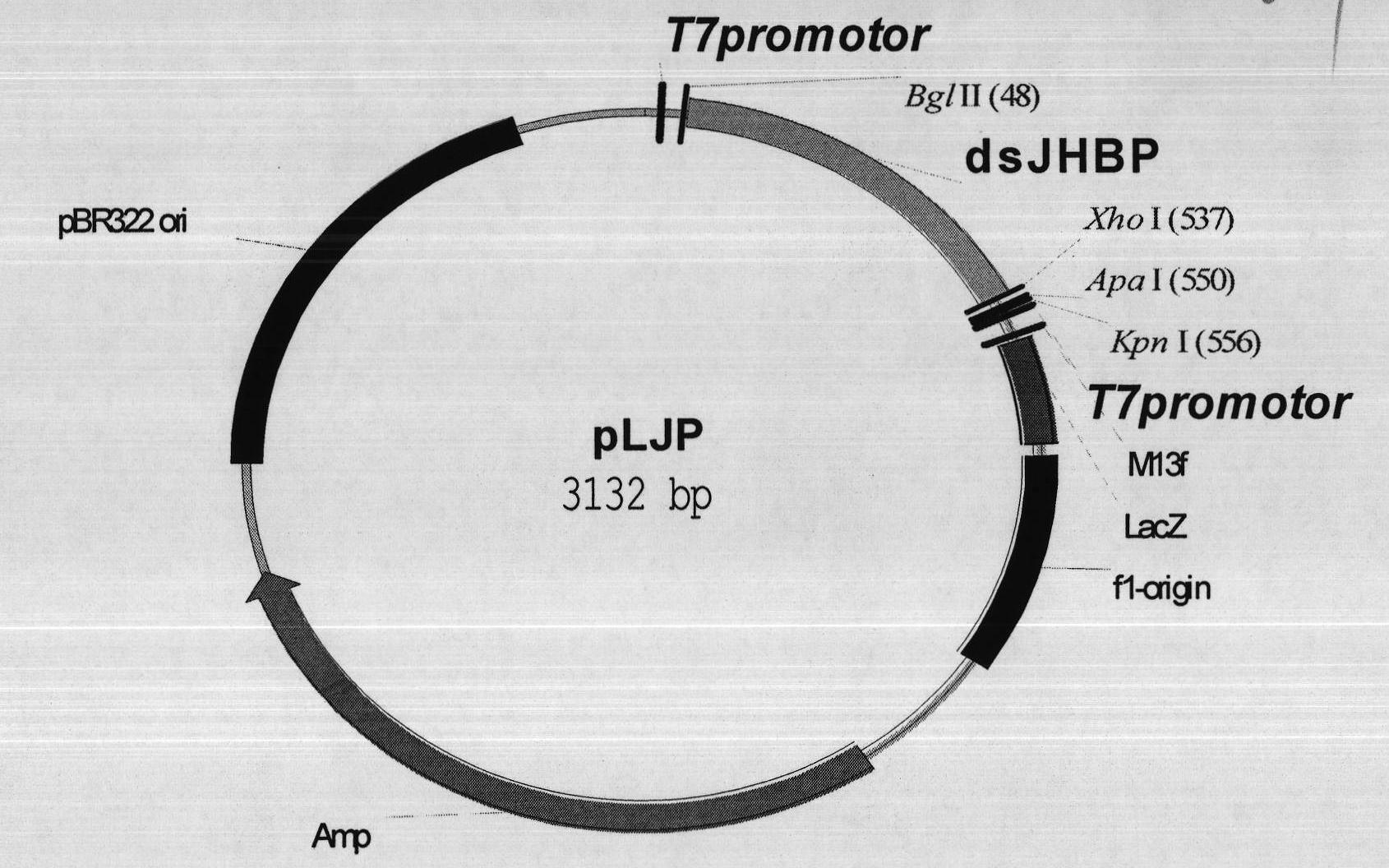
Helicoverpa armigera juvenile hormone binding protein (Ha-JHBP) and encoding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a helicoverpa armigera juvenile hormone binding protein (Ha-JHBP) and an encoding gene and application thereof. The helicoverpa armigera juvenile hormone binding protein provided by the invention is a protein shown as (a) or (b), wherein (a) is constituted by an amino acid sequence shown as a sequence 1 in a sequence table, and (b) is obtained by performing substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues on an amino acid residue sequence shown as a sequence 1, is relevant to helicoverpa armigera growth and is derived the sequence 1. The invention further provides an encoding gene of the protein and a functional fragment of the encoding gene. By establishing a dsRNA (double-stranded Ribonucleic Acid) plant expression vector in a way of taking a Ha-JHBP gene as a target gene and expressing a large quantity of dsRNAs of the Ha-JHBP in plants, the insect resistance of transgenic plants is enhanced. The Ha-JHBP has important application values in the fields of biological prevention and control of phytophagous insects, plant insect resistance gene engineering and molecular biology.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Artificial reconstruction synthetic pesticidal gene as well as encoding protein and use thereof
ActiveCN101255432AStrong resistancePromote activationClimate change adaptationDepsipeptidesNicotiana tabacumTransgene
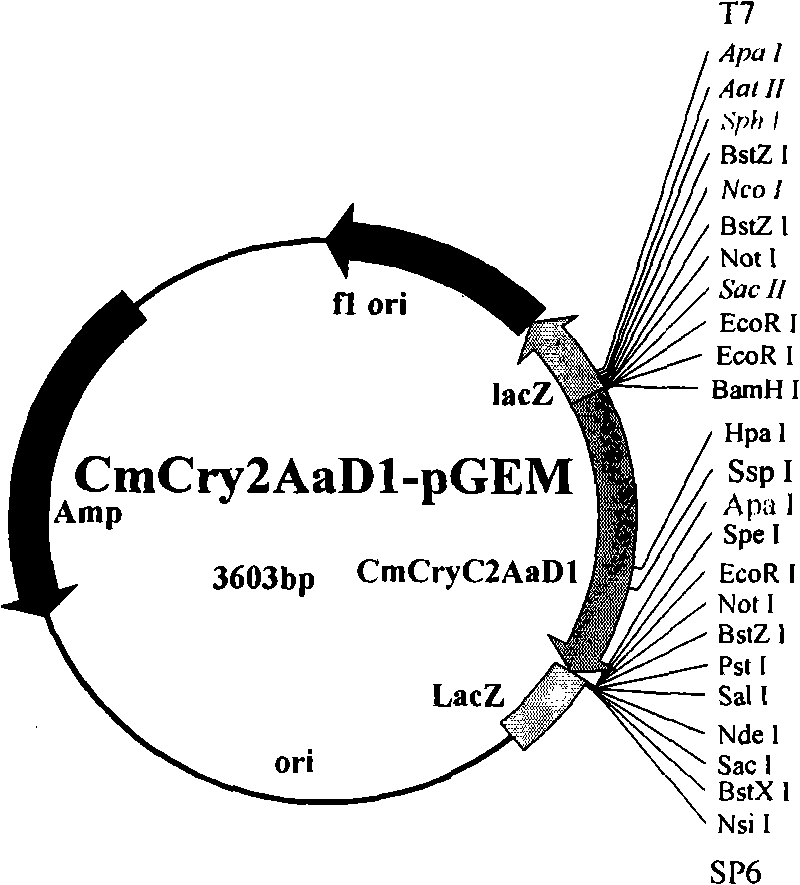
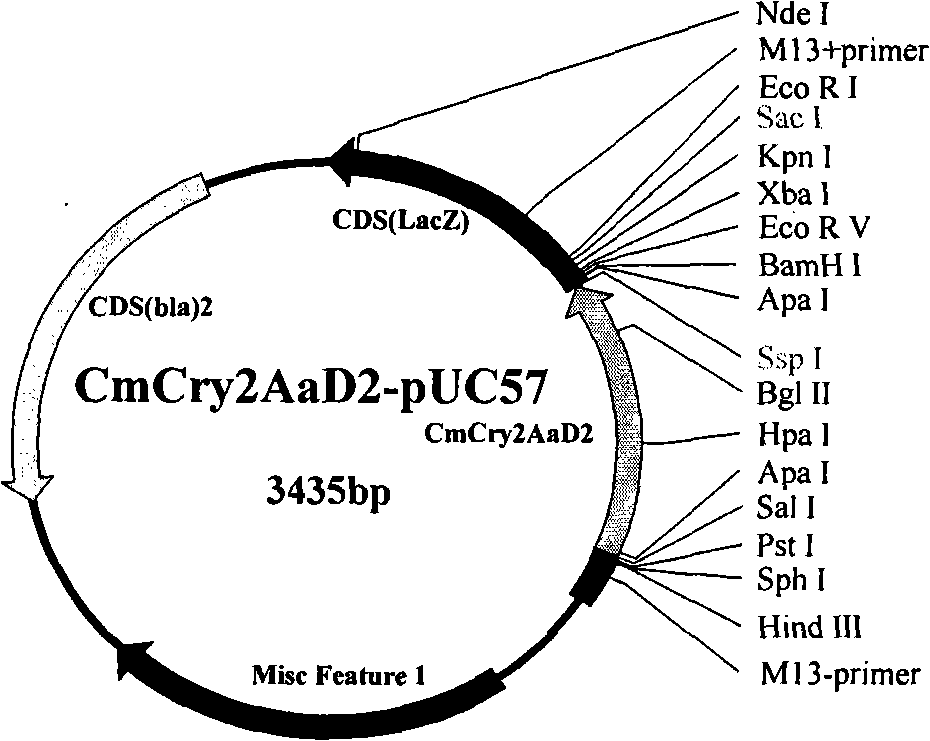
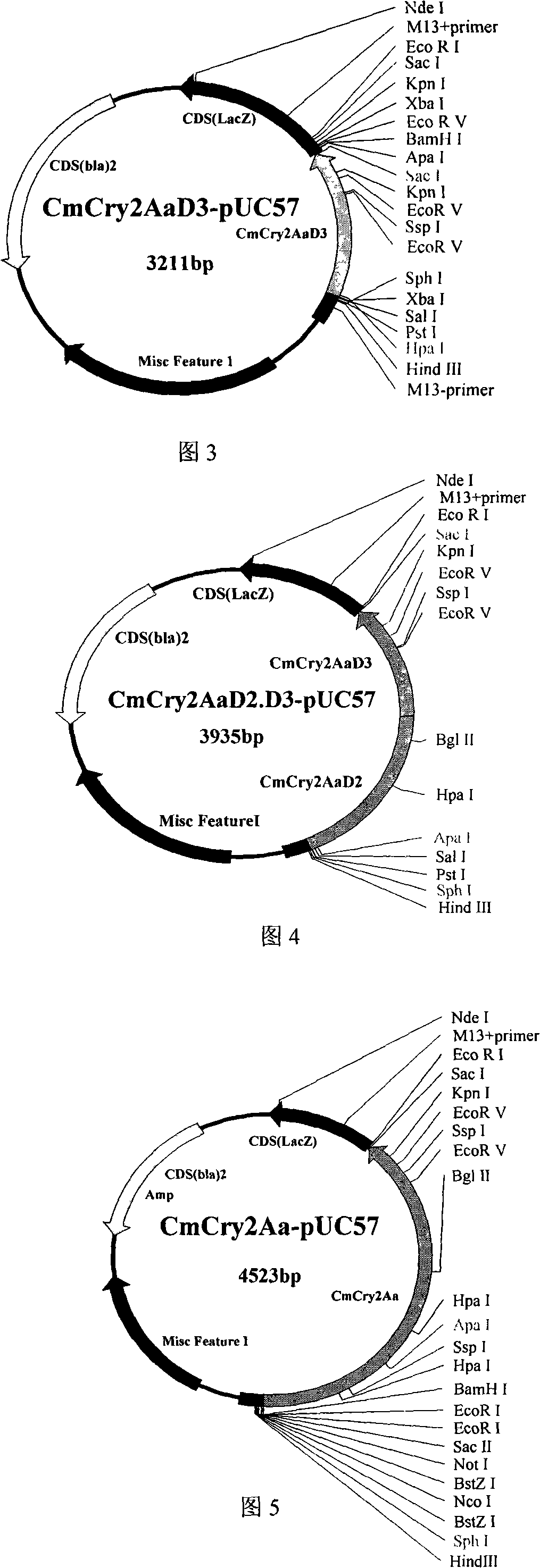
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering for plant, which provides an insect killing gene, encoded protein thereof and application of the same. The invention synthesizes CmCry2Aa insect killing protein gene by optimized codon design of cotton, and further obtains Cm1Cry2Aa insect killing protein gene which loses 29 amino acids at N terminal of the encoded protein, and constructs plant expression carrier respectively. Expert evidence of genetic modified tobacco indicates that CmCry2Aa and Cm1Cry2Aa insects killing gene has evident resistance to boll worm.
Owner:BIOCENTURY TRANSGENE CHINA
Straw mushroom nutrient
InactiveCN101891526AMeet growth and development needsBigBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationMushroomBran
The invention relates to a straw mushroom nutrient, which consists of the following components by weight percent: 35%-55% of cotton hull powder, 25%-45% of straw powder, 10%-16% of bran, 1.5%-2% of dry dairy manure, 0.5%-1% of bagasse, 0.5%-1% of lime, 0.5%-1% of gypsum, 1.5%-2% of wheat straw, 0.1%-0.3% of carbendazim, 0.1%-0.3% of calcium carbonate, 0.1%-0.3% of mold resisting liquid and 0.5%-0.8% of ammonium bicarbonate. The method for preparing the straw mushroom nutrient comprises the following steps: the cotton hull powder, the straw powder, the bran, the dry dairy manure, the bagasse and the wheat straw are taken according to a proportion, mixed together and poured into a pulverizer to be pulverized into a mixture with granules of about 80 meshes; the mixture is taken out; the lime, the plaster, the carbendazim, the calcium carbonate, the mold resisting liquid and the ammonium bicarbonate are added to the mixture based on a certain proportion; the new mixture is poured into a stirrer to be stirred for about 60 min and then taken; water is added to the stirred mixture at the ratio of 1:1.2-1.4 to evenly be stirred; and the stacked mixture is stacked to be fermented for 10-12h, therefore, the qualified straw mushroom nutrient is prepared.
Owner:时忠良
Biological assaying method for evaluating effect of transgene cotton on chrysopa pallens
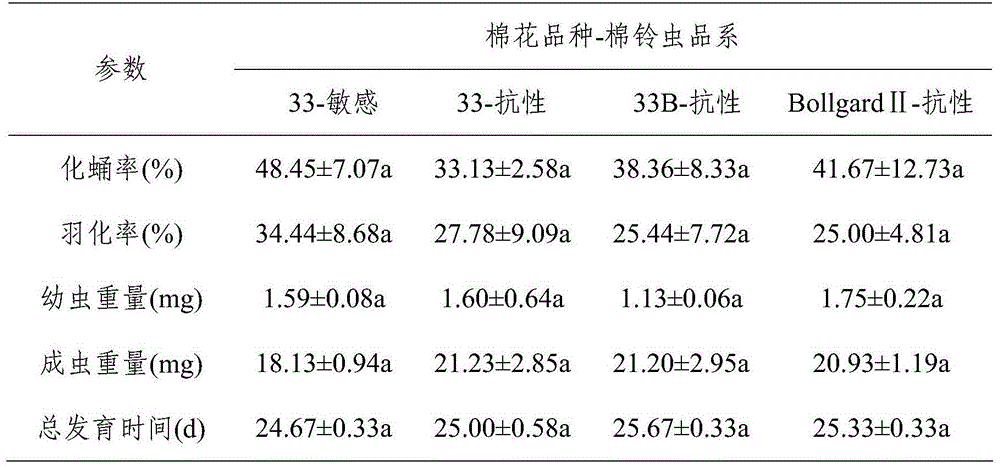
ActiveCN104133054AWide applicabilitySolve the preservation problemBiological testingChrysopa pallensHigh doses
The invention provides a biological assaying method for evaluating the effect of transgene cotton on chrysopa pallens. The method comprises the following steps: paving agar on the bottom of a culture dish; placing transgene cotton leaves on the surface of the agar, inoculating newly-hatched helicoverpa armigera larvae; feeding newly-hatched chrysopa pallens larvae for 1 to 3 days with pea aphid, then feeding the chrysopa pallens larvae with the helicoverpa armigera larvae which has been fed by the transgene cotton leaves for 1 to 3 days; observing the growth situation of the chrysopa pallens larvae since the first day when the chrysopa pallens larvae is fed with the helicoverpa armigera larvae until the chrysopa pallens larvae pupate and perform eclosion; setting a reference group; comparing the differences of the experiment group and the reference group on the indexes of pupation rate, eclosion rate, larva weight, imago weight, and total growth time, and analyzing the difference significance through variance analysis so as to evaluate the effect of transgene cotton on chrysopa pallens. The application range of the biological assaying method is wide. The effect of high dose protein in transgene plants on predators can be effectively measured by utilizing the nutrition relationship evaluation of transgene plant-pest-predator.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
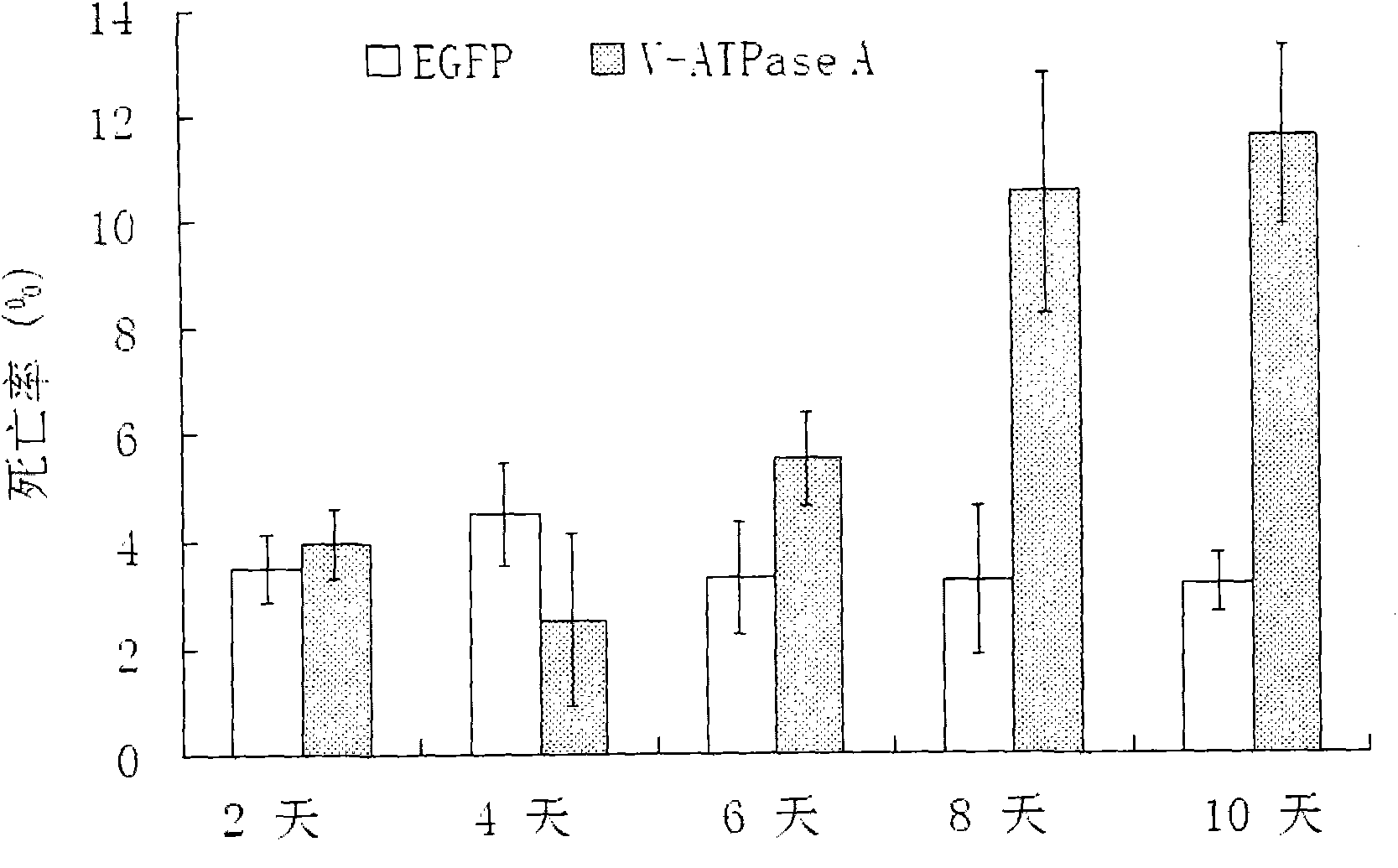
Helicoverpa armigera V-ATPase A gene cDNA and application thereof
InactiveCN104342448AWide range of hostsReduced risk of developing resistanceBiocideHydrolasesBiotechnologyGossypium
The invention discloses helicoverpa armigera V-ATPase A gene cDNA and application thereof. Helicoverpa armigera V-ATPase A siRNA is designed and synthesized, after helicoverpa armigera takes V-ATPase A siRNA in, expression of V-ATPase A gene is blocked, growth and metabolism of helicoverpa armigera are inhibited, the mortality is raised, and therefore helicoverpa armigera V-ATPase A gene cDNA is applicable to biological control of helicoverpa armigera.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
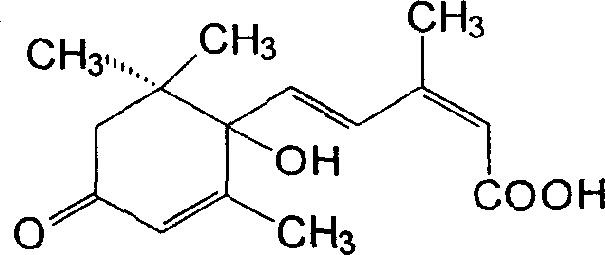
Seed coating agent for preventing cotton from fusarium / verticillium wilt
InactiveCN1698438AVerticillium wilt preventionIncrease productionBiocideAnimal repellantsDiseaseAgricultural science
The invention discloses a seed coating agent for resisting cotton pollenosis, whose essential components include natural abscisic acid and strong bacillus, the pesticide has prevention effect for cotton sprout damping-off disease, carbon anthrax and other mycosis.
Owner:江西华隆高科生物技术有限公司
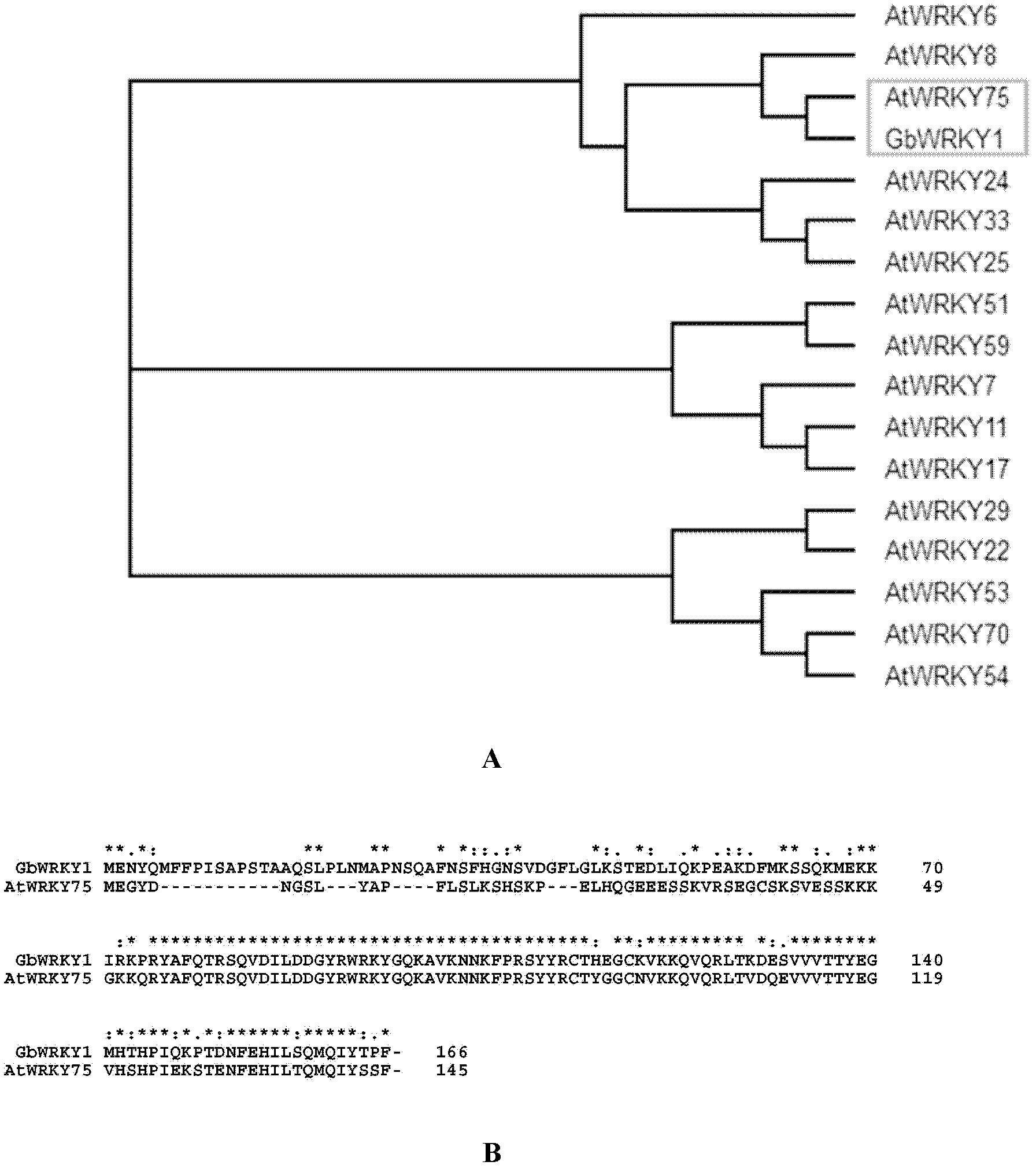
WRKY transcription factor of cotton and application of WRKY transcription factor
InactiveCN103173461AImprove stress resistanceAlleviate low phosphorus stress responsePlant peptidesFermentationPhosphate TransportersComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
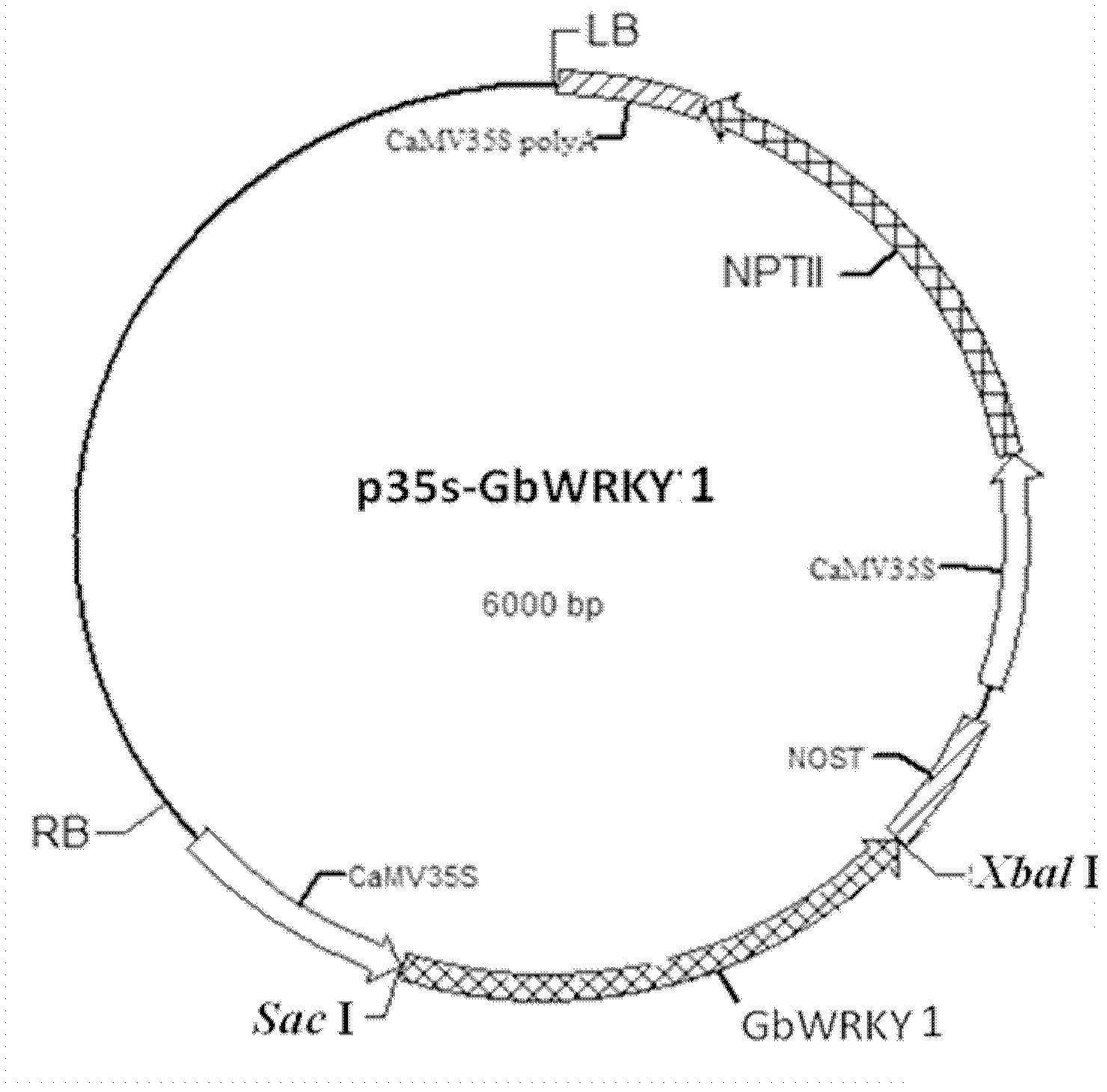
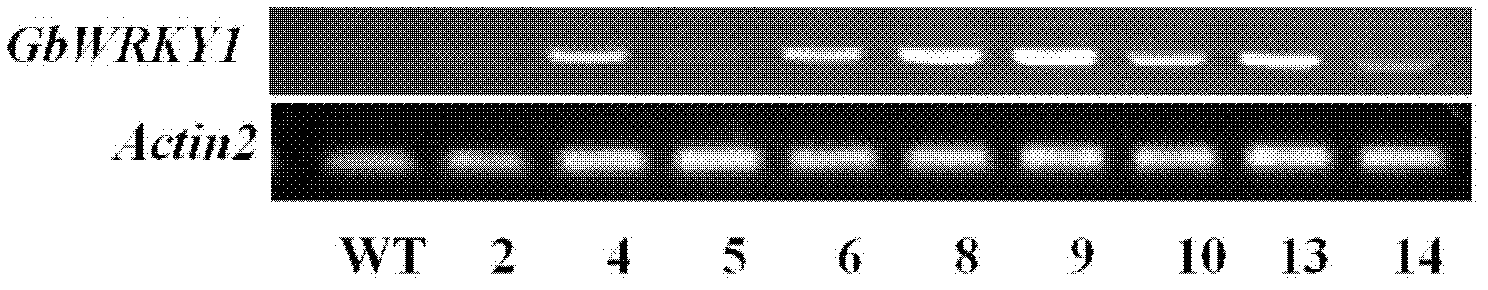
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and particularly relates to isolation and cloning, functional verification and application of an identified Gb-based WRKY1 factor in Sea Island cotton. The cDNA (Complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequence of an encoding gene of the Gb-based WRKY1 factor is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1; and the amino acid sequence of the encoding gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2. The invention also discloses a function of the gene (Gb WRKY1) for promoting the expression of the phosphate transporter; and the gene has the function of promoting the efficient utilization of arabidopsis thaliana phosphorus nutrition.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
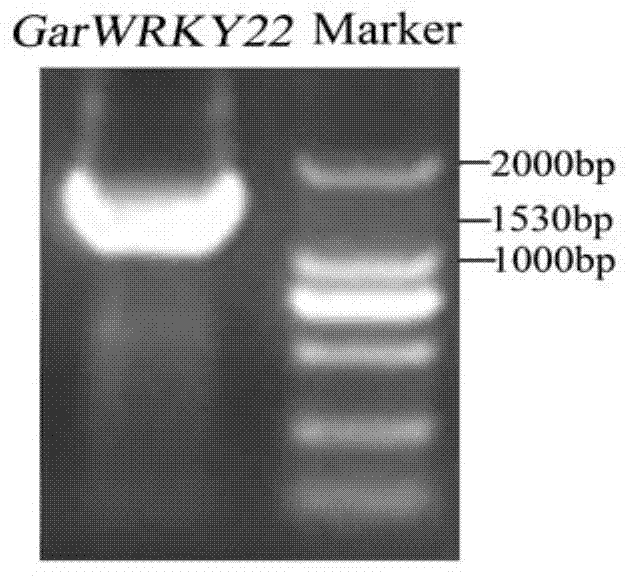
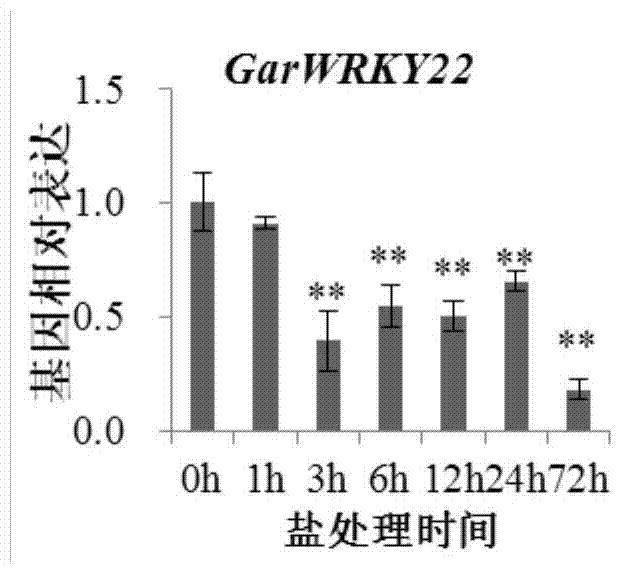
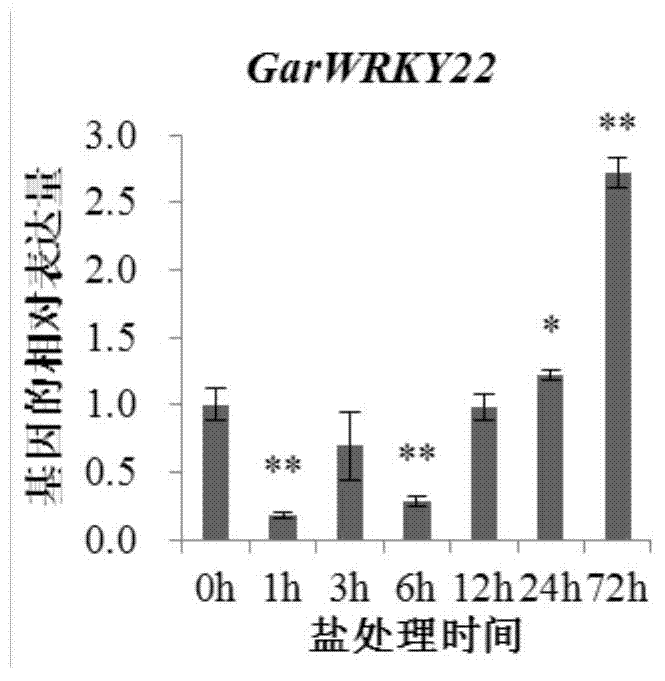
Cotton WRKY transcription factor GarWRKY22 for regulating salt tolerance of plants and application thereof
The invention discloses a transcription factor related to salt tolerance of cotton, namely gossypium wild species dry land cotton WRKY gene GarWRKY22 of which the sequence is disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2 in the sequence table. Electronic cloning and RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction) techniques are utilized to separate the protein GarWRKY22 related to salt tolerance of cotton. The functional verification by converting Arabidopsis thaliana proves that the transcription factor can regulate the salt tolerance. When the gene is overexpressed, the salt tolerance of the plants is obviously lowered.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Colored cotton ovule in vitro culture method
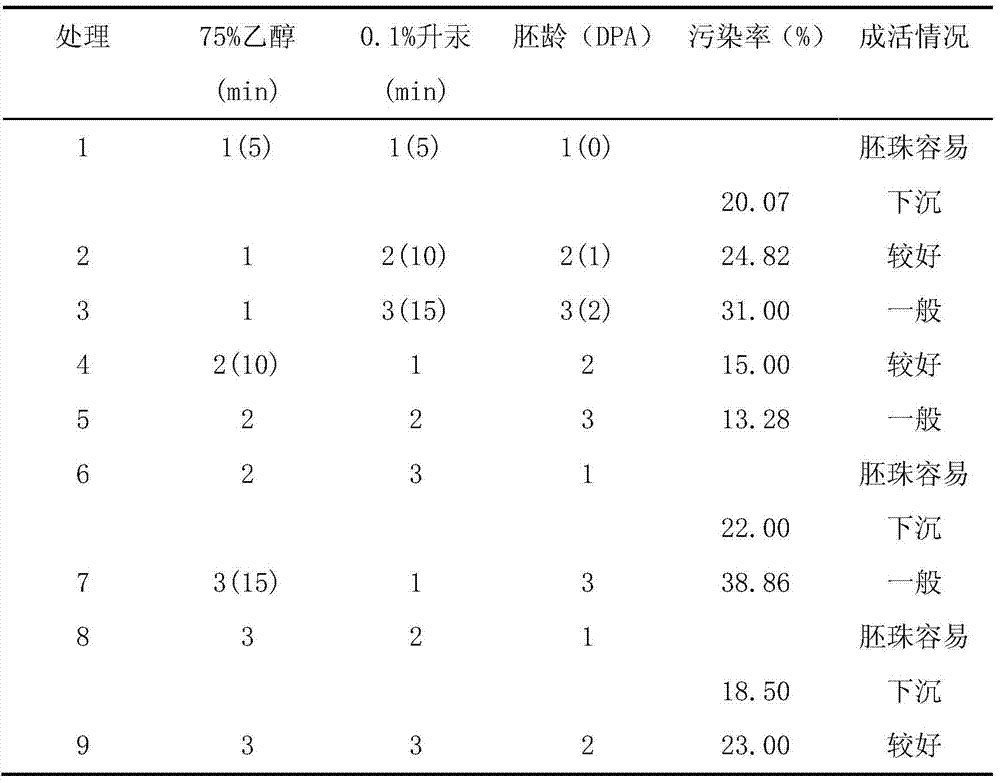
InactiveCN103931494AGuaranteed nutrition supplyKeep aliveHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureFiberContamination rate
The invention discloses a colored cotton ovule in vitro culture method, which comprises the steps of: collecting 0-2 days old young bolls of green cotton or brown cotton of the day, pulling off the corolla, stripping calyxes, and retaining flower stalks; washing the young bolls with distilled water twice, conducting disinfection with 75% alcohol for 5-15min under a sterile condition, then performing soaking with 0.1% mercury chloride for 5-15min, and conducting washing with sterile water 5-8 times, and stripping ovules; inoculating the ovules under a sterile condition into a BT medium containing hormone ZR, GA3 and IAA, inoculating 15-25 ovules of one ovary into each bottle, and carrying out dark culture for 30-40d at 30-32DEG C. Preferably, during inoculation of green cotton ovules, the hormone ratio wais GA31.0micromol / L+IAA5.0micromol / L+ZR2.5micromol / L, and during inoculation of brown cotton ovules, the hormone ratio is GA31.0micromol / L+IAA1.0micromol / L+ZR1.0micromol / L. The method provided by the invention can reduce the contamination rate, improve the survival rate, and promote cotton fiber growth and pigment synthesis.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
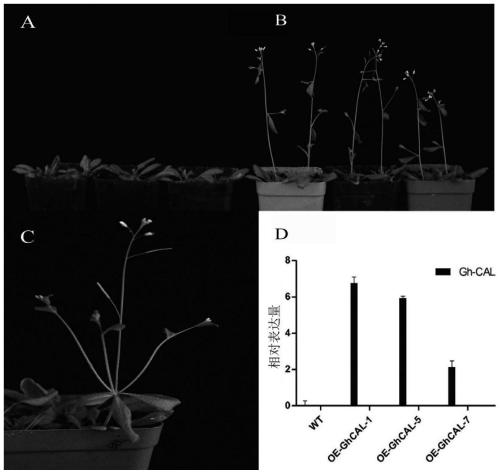
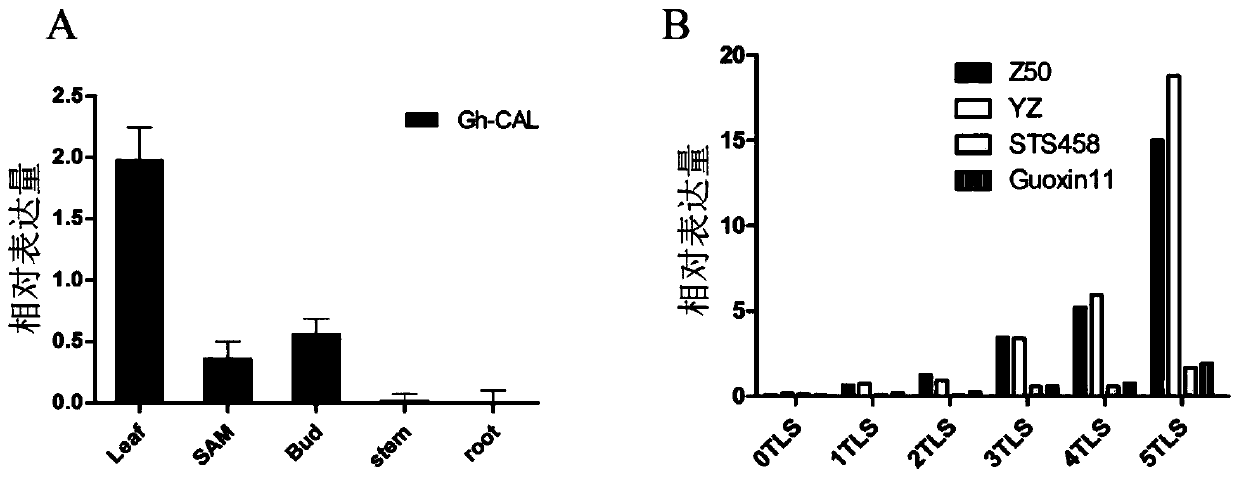
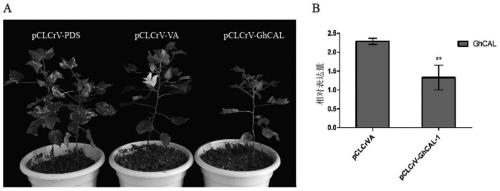
Application of cotton GhCAL-D07 gene in promotion of plant blooming
ActiveCN110117320AEarly floweringPromote floweringPlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural scienceNucleotide
The invention discloses application of a cotton GhCAL-D07 gene in promotion of plant blooming and belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering. The GhCAL-D07 gene comprises a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1 and can code a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2. According to the application, through a transgenic technology, an arabidopsis plant with the trans-GhCAL-D07 gene is obtained, so that blooming of the arabidopsis is obviously advanced. Furthermore, by silencing the GhCAL-D07 gene in cotton, it is proved through a result that the GhCAL-D07 gene has a key functionon promotion of cotton blooming. According to the application, beneficial gene resources are provided for cultivation of short-season cotton.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cultivating method for super early mature short season cotton
InactiveCN1586162AShortened reproductive periodIncrease productionPlant genotype modificationShootThird generation
The cultivation method of super early mature cotton includes selecting the cotton variety with genetically limited fruit bearing shoot or zero-type shoot in the 2-4 fruit bearing shoot positions; thrice spraying marketable mepiquat chloride of the amount of 1-1.5 g, 1.5-2 g and 2-3 g each mou in the full bud stage, the initial bloom stage and the full bloom stage separately. Compared with available similar variety, the present invention has growth period as short as 101 days, planting density up to 6000-12000 plants / mou and about 50 % raised cotton yield.
Owner:NAT RES CENT OF SEMI ARID AGRI ENG
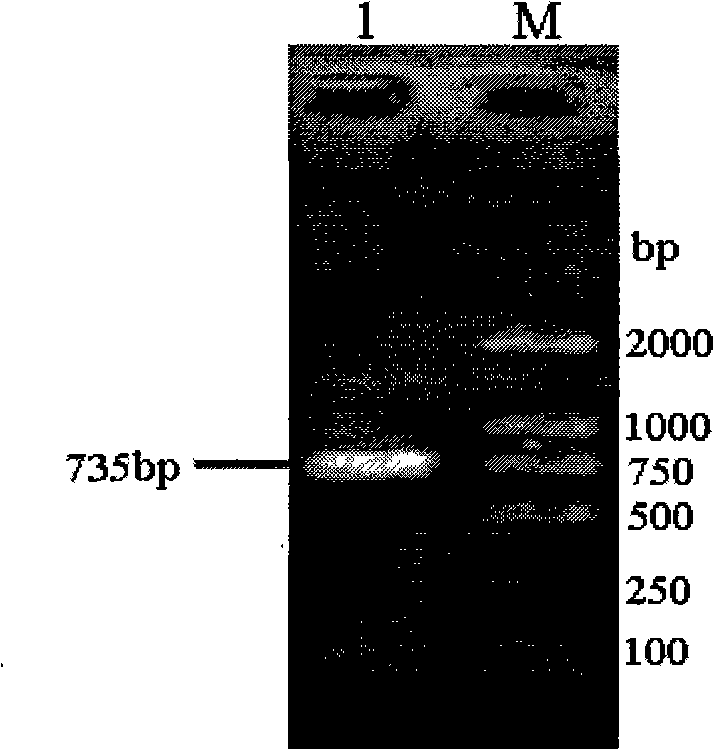
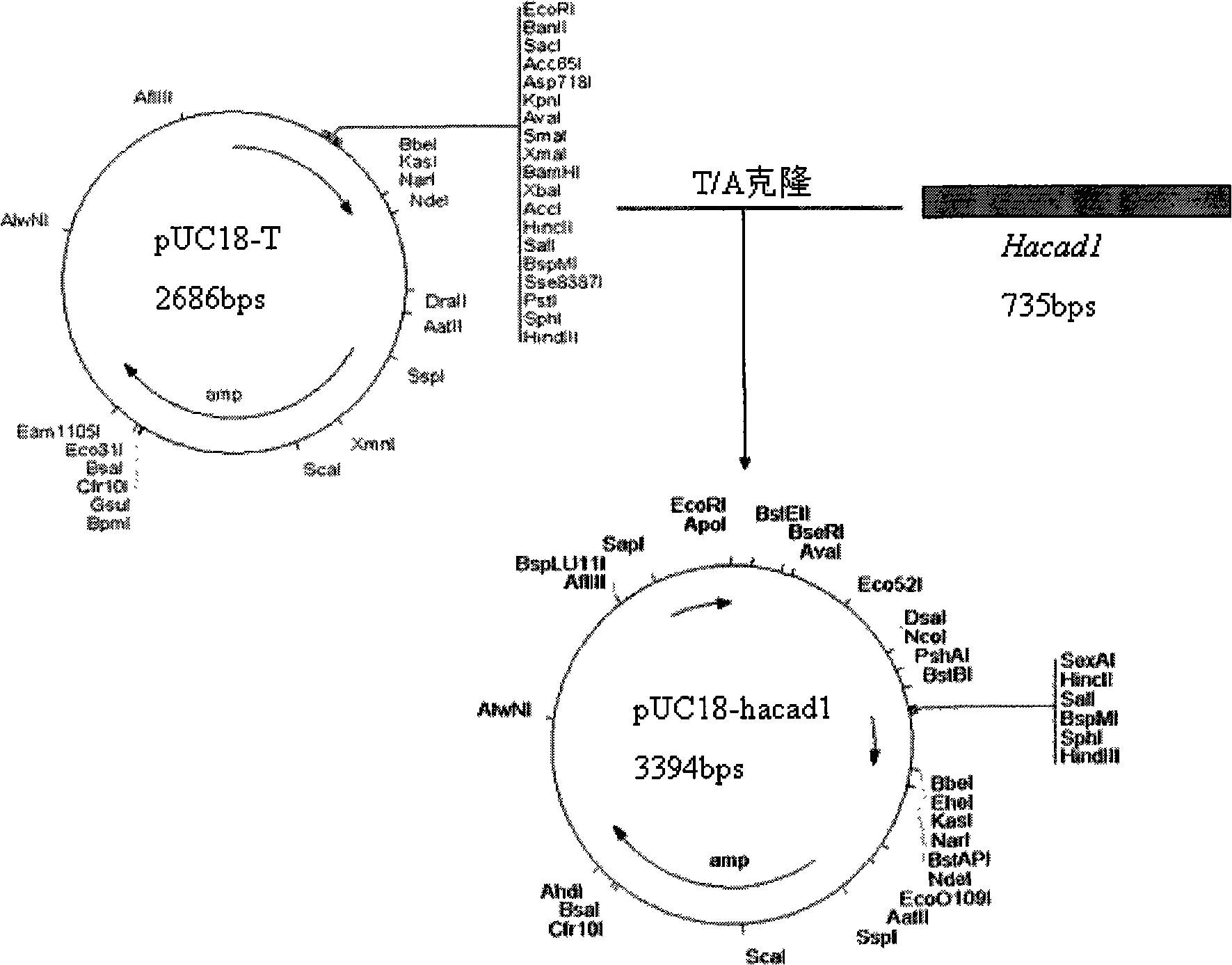
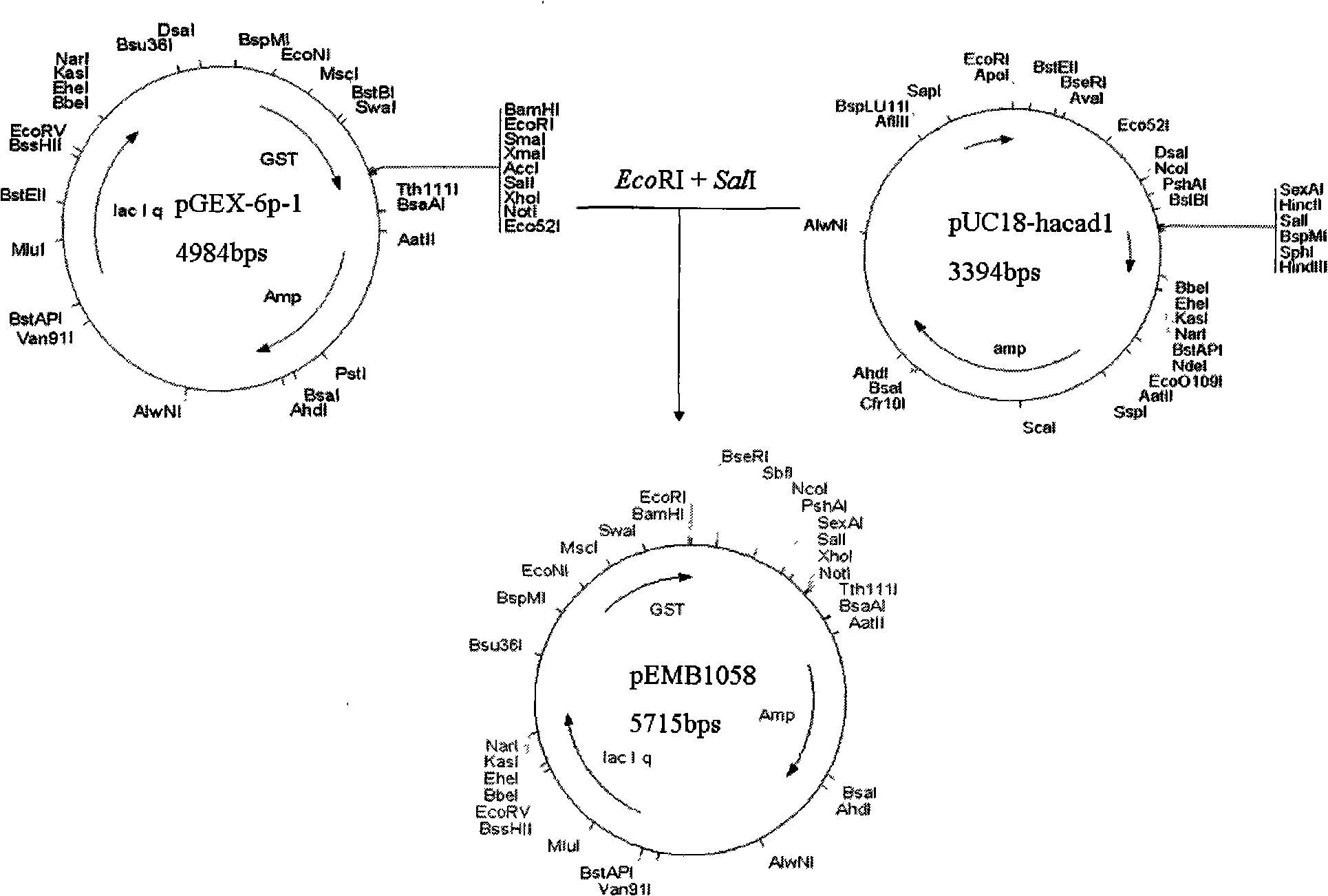
Cotton bollworm calcium mucoprotein gene fragment hacad1 with insect disinfestation building action and uses thereof
InactiveCN101492681AHigh insecticidal activityOvercoming or delaying the problem of drug resistanceBiocideBacteriaEscherichia coliOrder Lepidoptera
The invention relates to the technical field of agriculture microorganism genetic engineering, in particular to separation and cloning of a Helicoverpa armigera cadherin gene fragment hacad1and encoded polypeptide fragment HaCad1. By separation, the cadherin gene fragment hacad1 of 735bp is obtained from the midintestine of the Helicoverpa armigera, an encoded product thereof is the polypeptide fragment HaCad1 which can be combined with Bt toxin CrylAc10. Biological experiments indicate the polypeptide prepared in the invention has very strong enhancing insecticidal activity on insecticidal crystal protein CrylAc10 of lepidoptera insects. The invention also includes preparation and an application for recombinant Escherichia coli EMB1104 expressing the Helicoverpa armigera cadherin fragment HaCad1. The recombinant Escherichia coli EMB1104 is preserved in CCTCC, the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M209010.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
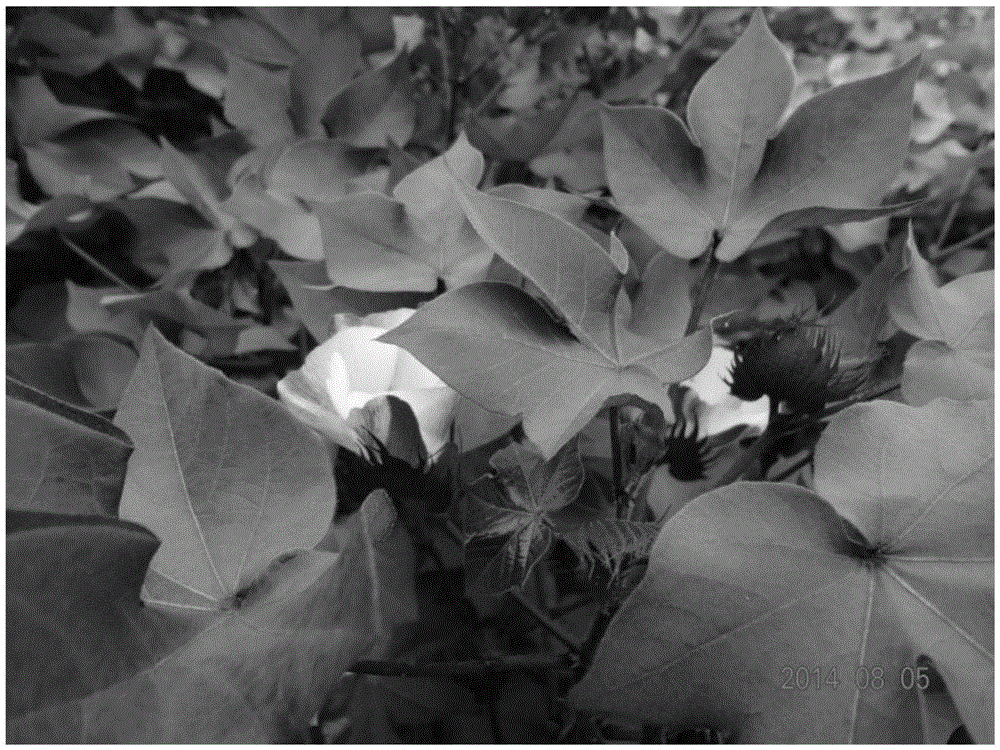
Ornamental cotton hybrid seed production method
InactiveCN105284602AGuaranteed purityShort breeding cyclePlant genotype modificationHybrid seedAgricultural science
The present invention provides an ornamental cotton hybrid seed production method, a short season cotton conventional material or a short season cotton HB safflower marked material is used for hybridization with upland cotton material T586, by hybridization breeding, stable lines carrying different traits are bred; the lines are transformed into sterile lines by use of an upland cotton cytoplasmic sterile line material as female parent and the bred stable lines carrying different traits respectively as male parent; the obtained sterile line carrying target trait is selected as female parent, sea island cotton sea 7124 or upland cotton HB is selected as male parent, hybridized combination is configured, and the generation F1 is ornamental cotton. The method can shorten the breeding cycle of the ornamental cotton, and broaden the ornamental cotton parental origin. The performances of the ornamental cotton in planting are: sterility, and only flowering without balling and opening of bolls, nutrient demand is relatively less, the cost of cultivation is reduced, and the purity of the ornamental cotton can be ensured because no seed is left for re cultivation.
Owner:SHANDONG COTTON RES CENT
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com