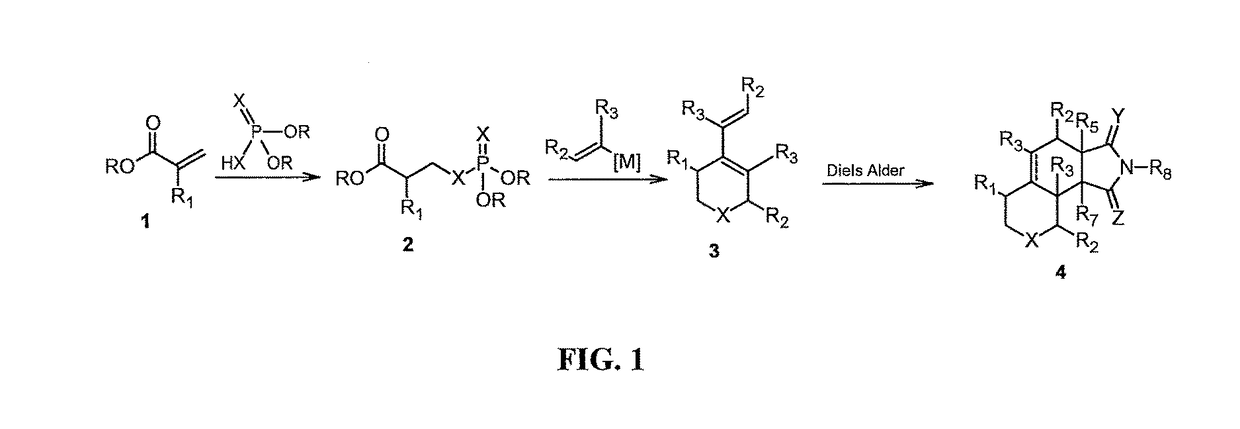
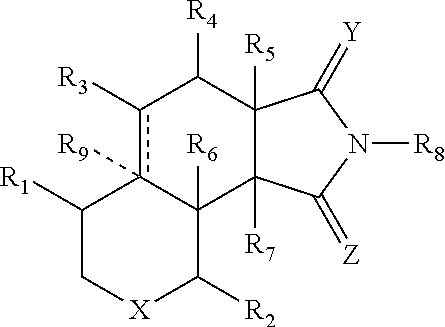
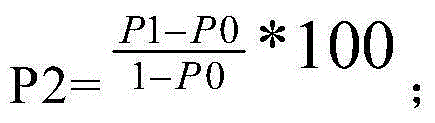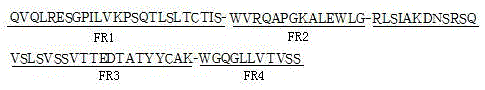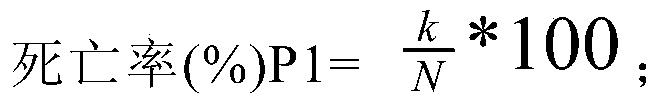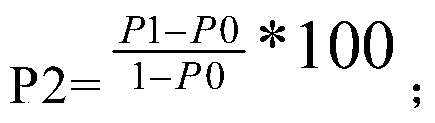Patents
Literature
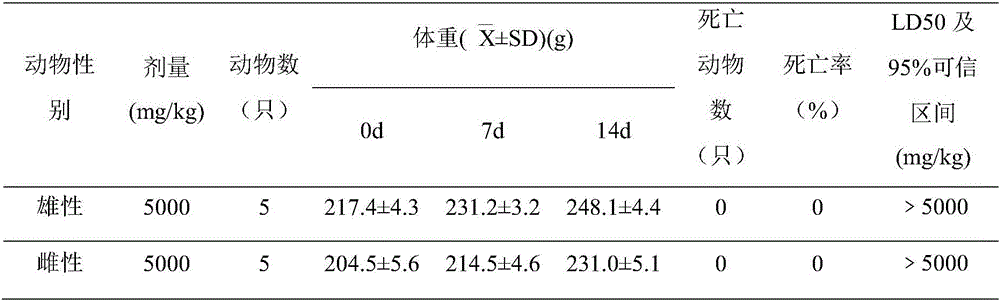
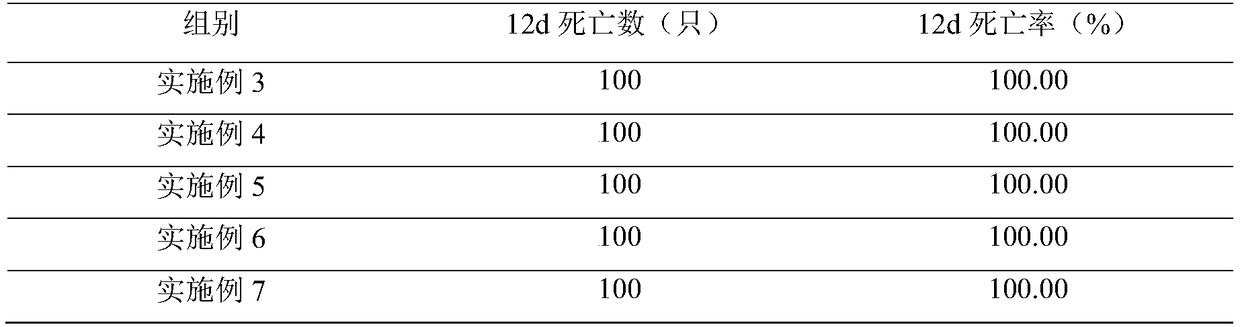
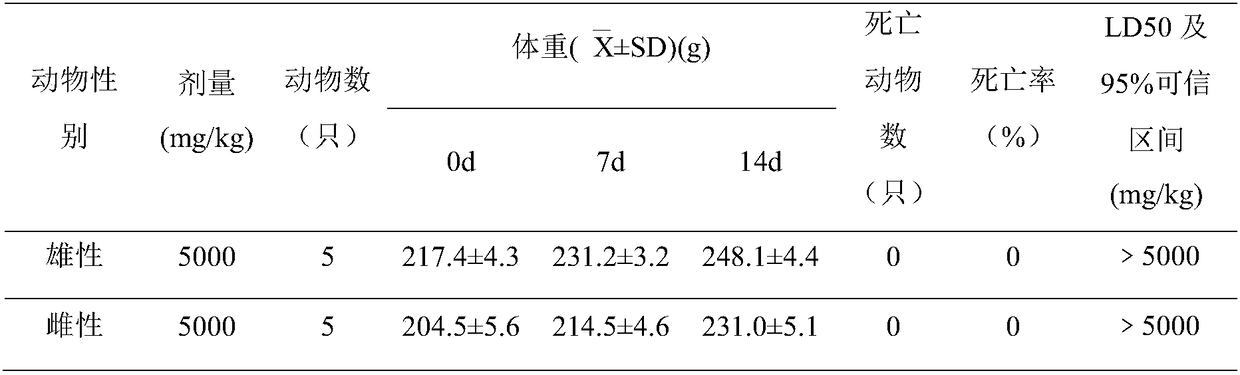
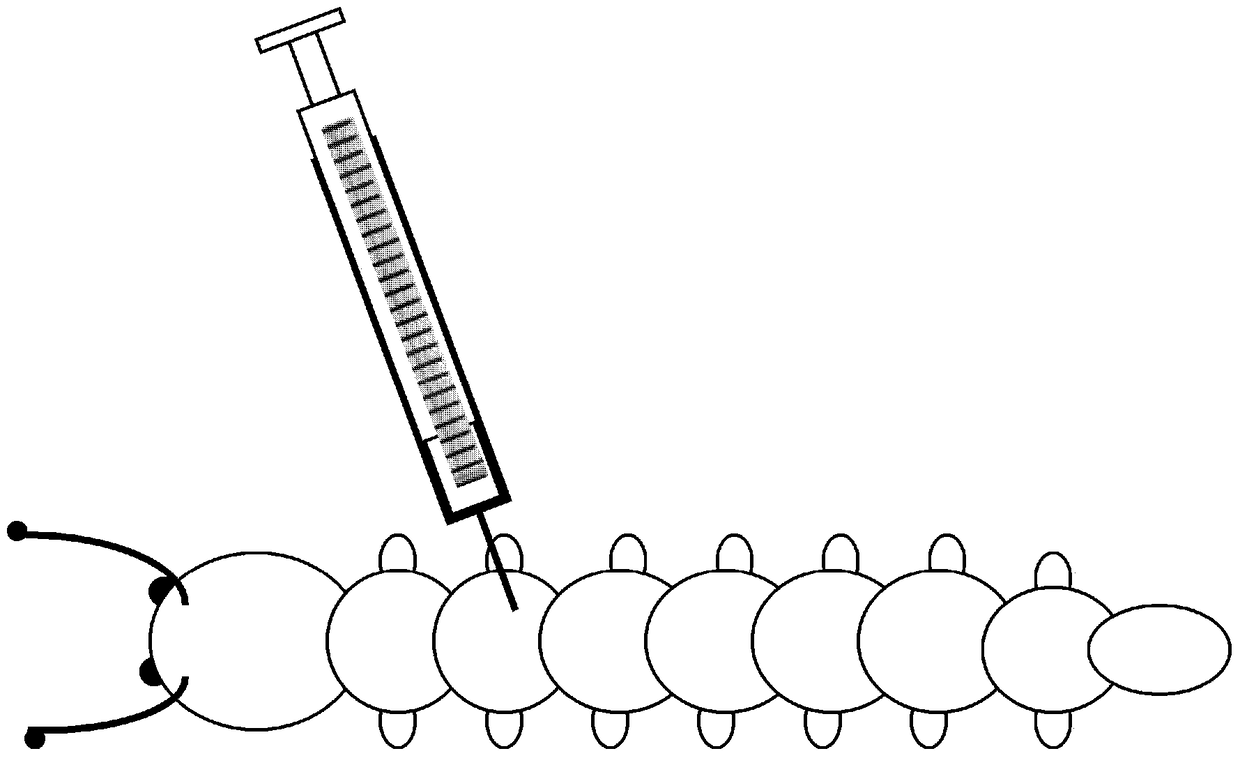
44 results about "Midgut" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The midgut is the portion of the embryo from which most of the intestines develop. After it bends around the superior mesenteric artery, it is called the "midgut loop". It comprises the portion of the alimentary canal from the end of the foregut at the opening of the bile duct to the hindgut, about two-thirds of the way through the transverse colon.
Direct PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) detection method of Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis pathogeny BmNPV
InactiveCN101886142AThe detection method is simpleEasy to scaleMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesDiseasePositive control
The invention discloses a direct PCR detection method of Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis pathogeny BmNPV, comprising the following steps of: firstly, treating the blood of infected Bombyx mori by ethanol precipitation to remove a PCR reaction inhibitor; designing the PCR primer of a polyhedrin gene according to the genome analysis of the Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis pathogeny BmNPV; carrying out PCR amplification on the polyhedrin gene, adding an anti-PCR reaction inhibitor BSA (Bull Serum Albumin) to a reaction system and simultaneously carrying out PCR reaction by the primer of a Bombyx mori chondriosome CO I gene to make positive control; respectively getting the blood of normal Bombyx mori and the inflected midguts of the Bombyx mori infected with white muscardine, green muscardine, a bacterial disease and a microsporidia disease and then carrying out PCR reaction specification analysis; and detecting the PCR reaction result by agar gel electrophoresis. The whole detection process has simple operation and can be completed only by 4 hours. The disease can be diagnosed at the early stage of BmNPV infection by adopting the direct PCR detection method to carry out periodical sampling detection so as to adopt a measure in time to prevent the disease from happening.
Owner:ANKANG UNIV
Method for extracting cockroach gathering pheromone, cockroach-killing gel bait and preparation method of cockroach-killing gel bait
The invention provides a method for extracting cockroach gathering pheromone. The method comprises the steps of feeding the cockroaches for 5-10 days, disecting midguts of the cockroaches, grinding and triturating the midgets together with feces of the cockroaches, adding 1.5-2.5 fold amounts of an organic solvent, carrying out extraction for 5-8 hours by virtue of a Soxhlet extraction method, and filtering, so as to obtain an extract. The invention further provides cockroach-killing gel bait. The cockroach-killing gel bait comprises the following components in parts by weight: 0.01-0.5 part of fipronil or a fipronil derivative, 0.05-0.5 part of the cockroach gathering pheromone, 5-30 parts of glucose syrup, 5-30 parts of sorbitol, 1-15 parts of butter, 1-15 parts of cooked flour, 1-10 parts of maltodextrin, 0.5-10 parts of azone, 0.3-2 parts of Carbopol 940, 0.3-2 parts of triethanolamine, 0.1-1.5 parts of sodium benzoate and 30-60 parts of jelly. The invention further provides a preparation method of the cockroach-killing gel bait.
Owner:武汉朗克环境科技有限公司
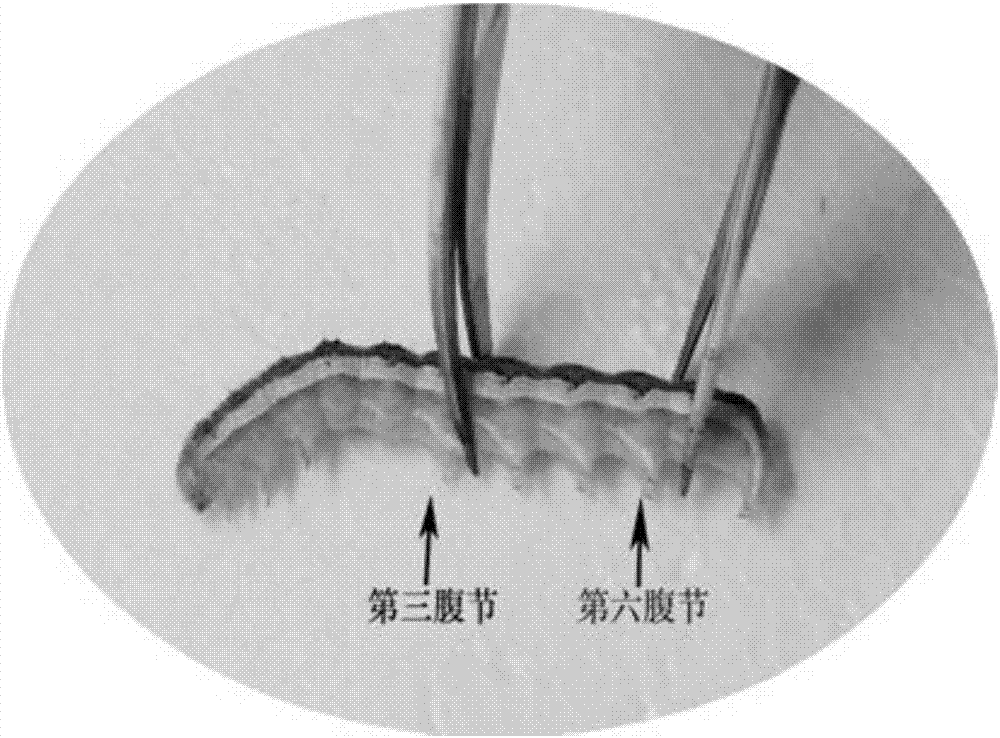
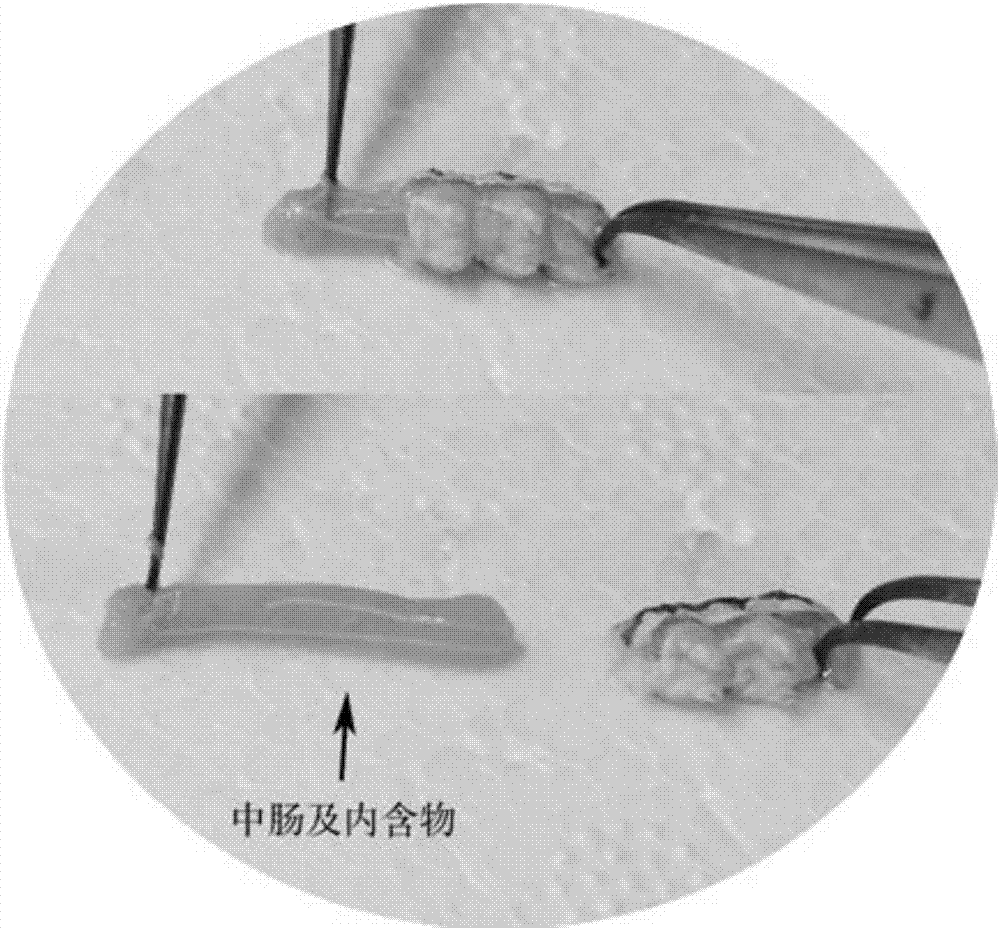
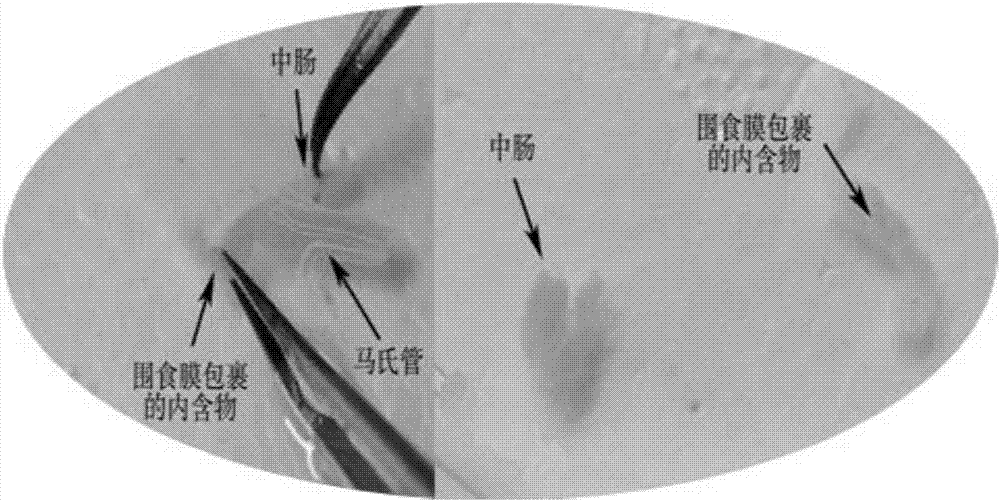
Rapid acquisition method of lepidopterous larvae midgut
The invention provides a rapid acquisition method of a lepidopterous larvae midgut. The rapid acquisition method of the lepidopterous larvae midgut belongs to the technical field of entomotomy, and comprises the steps of cutting off a third uromere to a sixth uromere of a lepidoptera insect with absent vital signs, pulling the midgut out from the cut-off uromeres, putting the midgut in normal saline, separating food debris encapsulated by a peritrophic membrane from the midgut, and washing, thus obtaining the lepidopterous larvae midgut. According to the method provided by the invention, the complete midgut tissue can be obtained, the whole operation process is short, the time can be saved by 50 percent compared with a traditional operation method, and the method is applicable to three-year-old and more than three-year-old lepidopterous larvae.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for large-scale quick separation of insect peritrophic membranes
InactiveCN103060261AFacilitate follow-up researchImprove efficiencyAnimal cellsMidgutMembrane organization
The invention discloses a method for large-scale quick separation of insect peritrophic membranes. The method can separate peritrophic membrane organizations from insect midgut in a short time, and then food residues therein are quickly cleaned, so that a large amount of purified peritrophic membrane organizations are obtained; the efficiency is improved by 16 times when compared with that of the general method; and the convenience is provided to the subsequent research of proteins in the peritrophic membranes.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
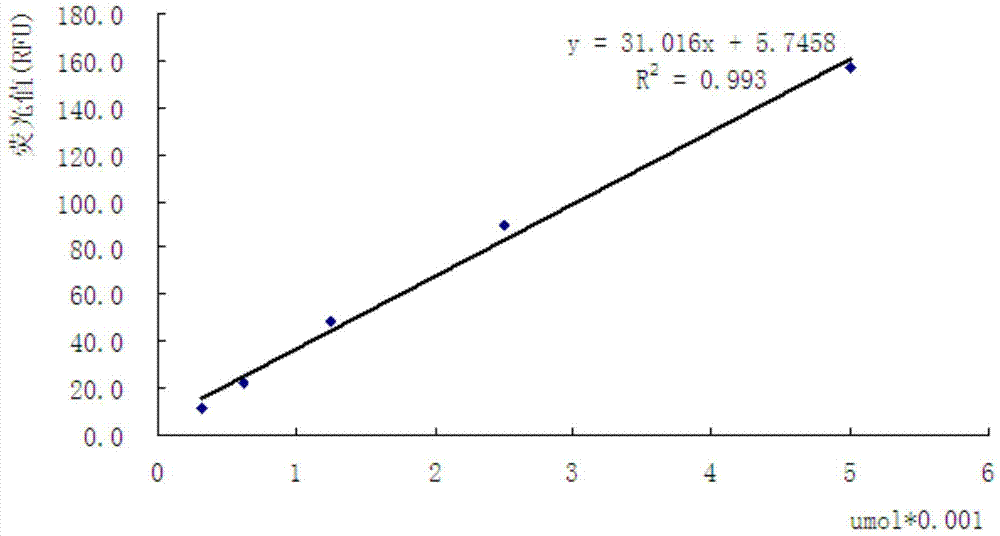
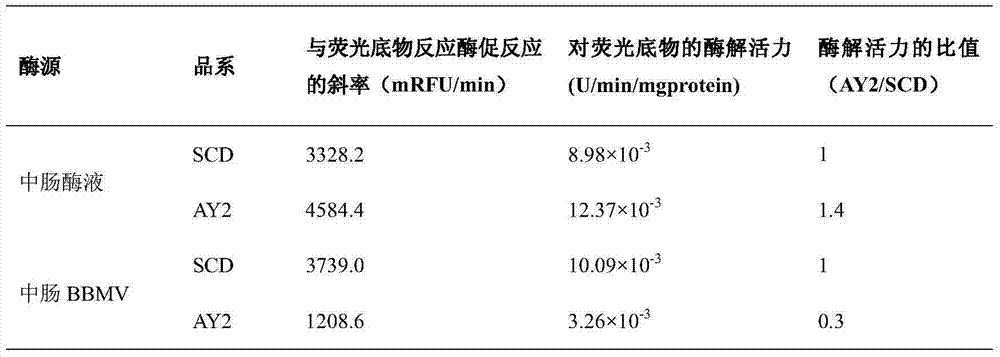
Fluorescent substrate for detecting activity of trypsin acting on Cry1A protoxin and application of fluorescent substrate
InactiveCN103923175AClear featuresClearly targetedMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacillus thuringiensisEnzymatic hydrolysis
The invention discloses a fluorescent substrate for detecting the activity of trypsin acting on Cry1A protoxin and an application of the fluorescent substrate. The fluorescent substrate consists of fluorescence quenching group-Gly-GLy-Glu-Arg-Ile-Glu-Thr-Gly-Glu-fluorescence group. The invention also discloses the application of the fluorescent polypeptide substrate R28 in detecting the activity of insect midgut trypsin which directly acts on activated bacillus thuringiensis Cry1A protoxin. Compared with a conventional protease detection method, the fluorescent substrate disclosed by the invention has definite specificity and pertinence for detecting the activity of the insect midgut trypsin which directly acts on the activated bacillus thuringiensis Cry1A protoxin and detecting the activity of the trypsin which only acts on the corresponding fluorescent substrate R28, and intense fluorescence signals are generated in an enzymatic hydrolysis reaction, so that the sensitivity of the detection is greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Prokaryotic expression method of cotton bollworm midgut serine protease gene
InactiveCN110079515AIncrease success rateAvoid in vitro activation stepsHydrolasesFermentationAgricultural scienceTotal rna
The invention discloses a prokaryotic expression method of cotton bollworm midgut serine protease gene. The prokaryotic expression method of cotton bollworm midgut serine protease gene comprises the following steps: extracting a total RNA from the midgut of a cotton bollworm larvae, and cloning cotton bollworm midgut protease gene segements; constructing a cotton bollworm midgut protease gene on aPet41 expression vector with His and Gst double tags; expressing, purifying, concentrating, removing the tag of and identifying the recombinant protein. The method directly expresses the mature peptide of cotton bollworm midgut serine protease, so as to avoid the in vitro activation step of zymogen after the expression of the zymogen, and improve the success rate of expressing the bioactive midgut serine protease.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Separation and in vitro culture method of midgut cells of insects
The invention provides a separation and in vitro culture method of midgut cells of insects. The separated midgut tissues are subjected to enzymolysis by using a Dispase II enzyme, and the obtained midgu cells are subjected to in vitro culture by using a TNM-FH culture medium added with a conditioned medium and fetal bovine serum. The separation method of midgut cells of insects is simple, effective and suitable for the in vitro culture of midgut cells of insects, midgut physiology and pathology research. Enzyme liquid for dissociating the midgut cells, suitable culture media for maintaining the in vitro condition of cells, serum concentration and additives are included; the survival rate of the just separated midgut cells can reach above 80%, the survival rate of cells can reach above 20% after 60 days of the in vitro culture, the midgut cells can be infected by nuclear polyhedrosis virus under the in vitro condition, the secretion capacity such as alkaline phosphatase is provided, and the foundation is laid for research of the midgut physiological function of insects.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Enteral nutrition preparation for balancing nutrition
ActiveCN107260996AImprove toleranceCause a burdenMetabolism disorderAntipyreticBiotechnologyLean meat
The invention provides an enteral nutrition preparation for balancing nutrition, which comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 245-255 parts of milk, 45-55 parts of rice water, 20-30 parts of tomato juice, 115-125 parts of rape juice, 10-15 parts of egg yellow, 45-55 parts of egg white, 10-15 parts of lean meat, 10-15 parts of chicken liver, 25-35 parts of farina, 3-7 parts of vegetable oil and 0.5-1.5 parts of salt. The enteral nutrition preparation can meet a demand of a functional dyspepsia patient, improves the tolerance of a gastrointestinal tract, effectively prevents and treats malnutrition, cannot generate an adverse effect on blood fat or blood glucose, cannot cause a burden on a liver or kidney function, has good safety, and can be applied by the patient for a long term.
Owner:BEIJING FRIENDSHIP HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Method for extracting, separating and identifying chilo suppressalis midgut stem cells
The invention relates to a method for extracting, separating and identifying chilo suppressalis midgut stem cells. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out enzymolysis on midgut cells by collagenase I so that the midgut cells fall off from the midgut wall, and then separating the stem cells and enteric cells by adopting a density gradient centrifugal process or a flow cytometry. By virtue of the method, high-purity chilo suppressalis midgut stem cells are efficiently obtained and can be applied to the subsequent stem cell function study.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A human-derived insecticidal gene and insecticidal peptide encoded thereby and application thereof
ActiveUS20170088633A1Reduce usageReduce security risksBiocideClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The present invention discloses a human-derived insecticidal gene and insecticidal peptide encoded by the same and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the human-derived insecticidal gene is as represented by SEQ ID NO.1. The amino acid sequence of the insecticidal peptide encoded by this gene is as represented by SEQ ID NO.2. The insecticidal peptide may be expressed through prokaryotic system. The primary culture has binding activity to Cnaphalocrocis medinalis midgut peritrophic membrane specific receptor BBMV. It is obtained without animal immunization and has a short production cycle and a small amino acid sequence. It is suitable for in vitro mass production and may lower the safety risks resulting from wide use of existing Bt toxins and even might substitute Bt to biologically control agricultural pests in the future. It has important scientific and practical significance to reducing the use of insecticides.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Targeted destruction of pests
InactiveUS7011835B1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansImmunoglobulins against plantsMidgutBacteriophage
The present invention is drawn to a safe, cost-effective, environmentally-friendly and ecologically-sound bioengineered pest eradication product and uses thereof. Immunological and genetic engineering techniques are used to generate monoclonal antibodies as well as viruses (phage) that display scFv heavy and / or light chain Ig fragments which exhibit high-avidity specific binding to cells of the microvilli of the midgut of imported fire ant queens. The specific monoclonal antibodies and phage displayed antibody Fab fragments are conjugated to a toxin for targeted delivery and destruction of imported fire ant queens, but not native species.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
Insecticide for green vegetables and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108208028AImprove photosynthesis efficiencyIncrease profitBiocidePlant growth regulatorsDiseaseCuticle
The invention discloses an insecticide for green vegetables. The insecticide is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 5 to 10 parts of abamectin, 40 to 60 parts of fermenting solution, 3 to 8 parts of surfactant, 2 to 10 parts of activator, and 0 to 6 parts of pure alkaline. The insecticide for the green vegetables has the beneficial effects that the limitation that the insecticide mainly enters into leaves via air pores in the leaves, hydrophilic small pores in cuticles of the leaves, and cytoplasm ectodesma of leaves is broken through, and the utilization rate is greatlyincreased; after an insect eats the leaves which absorb the insecticide, the active components in the insecticide directly act onto the corpus adiposum and midgut cell of insect larvae, and are quickly duplicated to cause the disease infection and death of the larvae; the pest population and injury can be effectively controlled by transversely infecting in the populations to cause epidemic diseases and longitudinally infecting to kill pupae and ova.
Owner:金华市铁骑士生物科技有限公司
Human-derived insect-resistant gene and anti-CRY1B toxin idiotype single-chain antibody encoded thereby and application thereof
ActiveUS9770038B2Reduce usageReduce security risksBiocideImmunoglobulins against bacteriaSingle-Chain AntibodiesNucleotide
Provided are a human-derived insect-resistant gene having a nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO.1, and an anti-Cry1B toxin idiotype single-chain antibody encoded by said human-derived insect-resistant gene and having an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO.2. The idiotype single-chain antibody is a β-type and has insecticidal activity, and after expression by the prokaryotic system, the primary culture thereof has binding activity to Cnaphalocrocis medinalis midgut peritrophic membrane specific receptor BBMV.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Tricyclic mosquitocides and methods of making and using thereof
Compounds that inhibit digestion in blood-ingesting pests are described herein. In one embodiment, the compounds described herein block entry of blood into the midgut and thereby inhibit digestion and nutrient processing. In another embodiment, the compounds described herein prevent pathogens contained in the blood meal from entering the midgut where they could cross the epithelial cell layer and infect the mosquito. The compounds can be administered to a population of blood-ingesting pests, such as mosquitos, directly or indirectly in an effective amount to prevent mosquitoes from transmitting diseases such as malaria, dengue fever, West Nile virus and lymphatic filariasis. Preferably, the compounds are lethal to blood-ingesting pests. The compounds can be combined with one or more excipients to prepare compositions.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
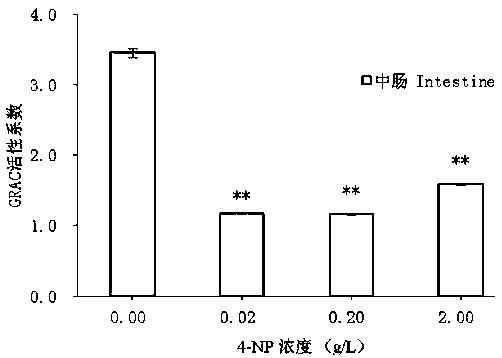
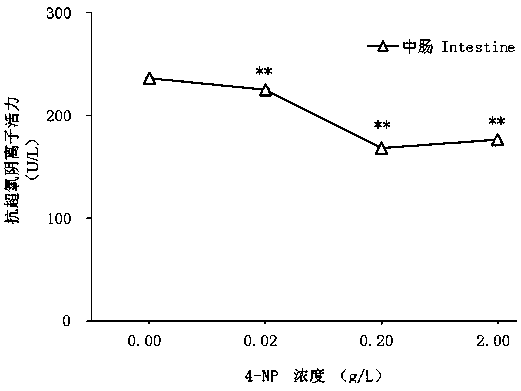
Test method of developmental toxicity of silkworms by environmental estrogen
ActiveCN109557319AFast detection methodThe detection method is simpleBiological testingSuperoxideGlutathione reductase activity
The invention discloses a test method of developmental toxicity of silkworms by environmental estrogen. The method includes following steps: firstly, injecting a test sample containing a series of concentrations to 5-age silkworm larvae through 2-hour starvation treatment by employing oral gavage; after 20 minutes, performing anatomy on the silkworms through gavage, and taking tissues and organs;determining the developmental toxicity of the silkworms by the test sample through comparison of toxic endpoints of an infected group and a control group, wherein the toxic endpoints comprise a glutathione reductase activity coefficient and an anti-superoxide anion free radical activity of midguts of the silkworms; and researching the influence of the environmental estrogen 4-nonylphenol on the development of the midguts of the silkworms in a larva stage to determine a dose-effect relation between the environmental estrogen and the developmental toxicity of the silkworms in the larva stage. Byemploying the technical scheme, multiple biological effect endpoints can be generated for the environmental estrogen nonylphenol, potential risks of the silkworms exposed in an estrogen environmentalconcentration level are evaluated, and the method is a relatively fast, simple and sensitive detection method.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for producing oil preparation of polyhedrosis virus in pine caterpillars character type
A kind of production method of pine caterpillar type polyhedrosis virus oil preparation, the viral polyhedron of susceptible pine caterpillar midgut is separated from worm body, and separates from other solid phase substances, then process and concentrate, add solvent ethylene glycol, The suspending agent sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate is prepared by mixing, stirring and grinding. Its pine caterpillar polyhedrosis virus has high purity, small particle size, and good suspension effect, which solves the problems of sedimentation and layering and blocking nozzles, thereby meeting the requirements of ultra-low volume spraying. The pine caterpillar polyhedrosis virus made according to this method Body virus oil agent, insecticidal rate of more than 92%, its production cost is low, does not pollute the environment, is safe for humans and animals, and has good economic and social benefits.
Owner:茂名市林业科学研究所 +1
Chilo suppressalis larva midgut cell line with high yield of baculovirus
InactiveCN105176911AContribute to researchImprove training effectAnimal cellsMicroorganism based processesBaculovirus expression vector systemMidgut
The invention discloses a cell line that is derived from an insect midgut tissue and is highly sensitive to baculovirus. The invention also discloses an establishment method of the cell line, and application of the cell line in baculovirus large-scale growth. The cell line can be used for replication of the virus, large-scale production of baculovirus insecticides, and construction of a baculovirus expression vector system to express protein with commercial or scientific value. Therefore, the chilo suppressalis larva midgut cell line has extremely high commercial and the scientific research value.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Simple method for rapidly screening substances effective to insects
The invention relates to a simple method for rapidly screening substances effective to insects. According to the method, the insects are taken as a target, candidate substances are applied to midguts of the insects, changes of the insects are observed, and the biological activity of the candidate substances for the insects is determined. The method is low in cost, good in repeatability and high in accuracy, special instruments are not required, and great convenience is provided for rapid, accurate and efficient screening of bioactive substances effective to the insects.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
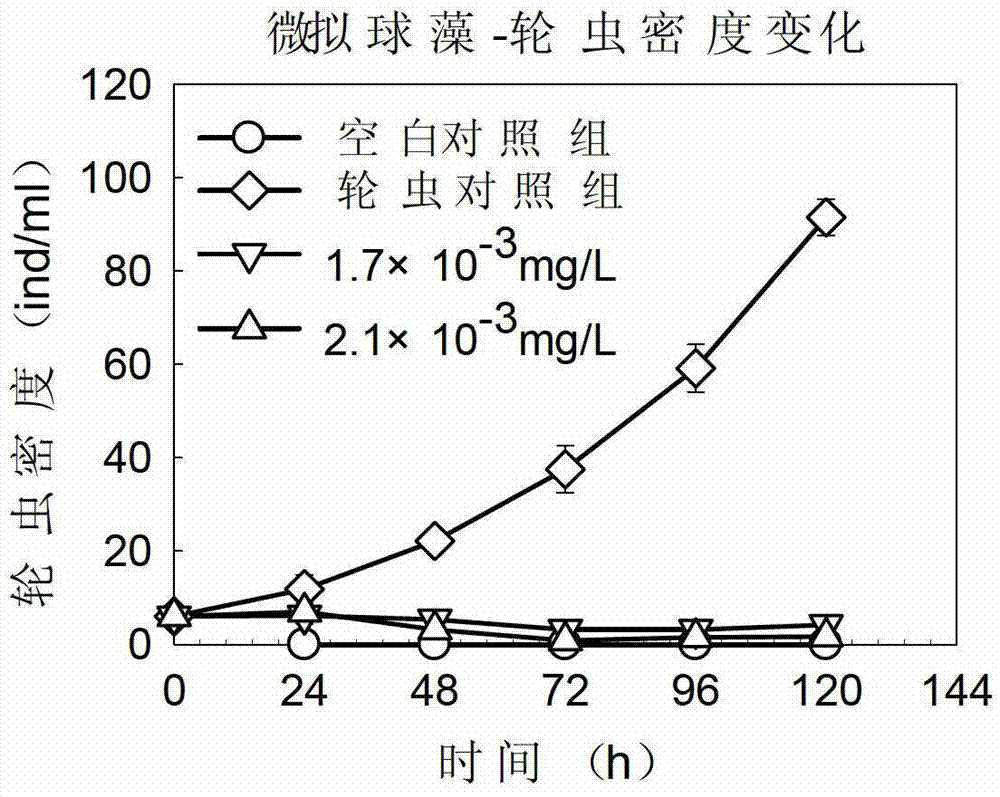
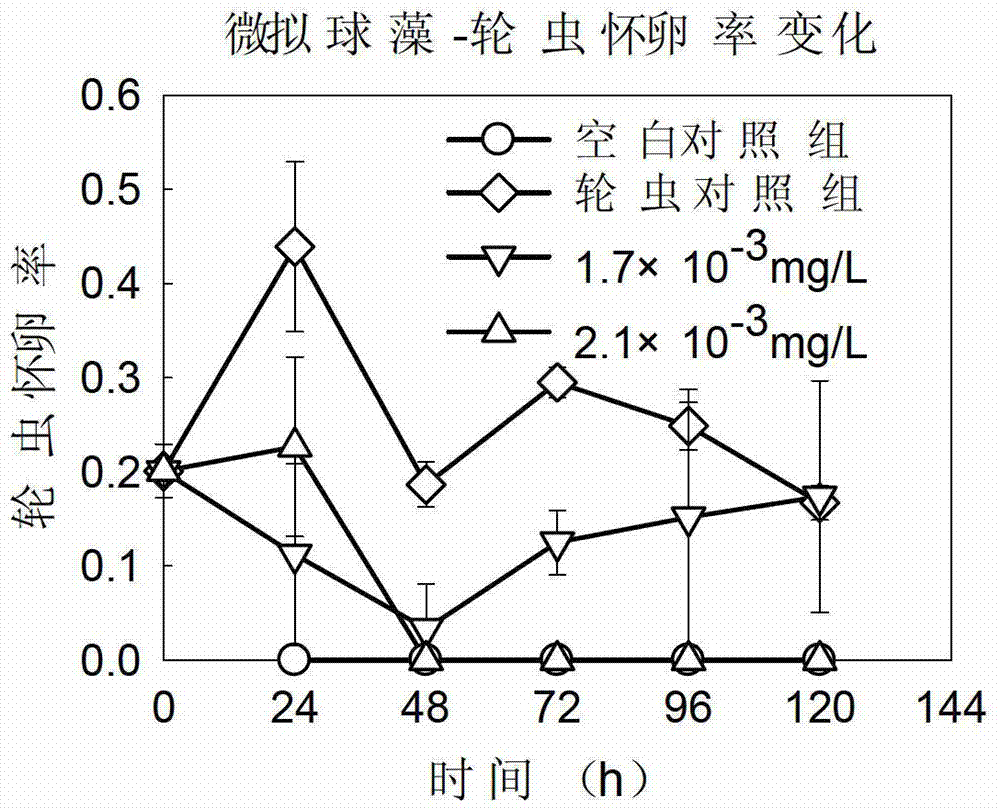
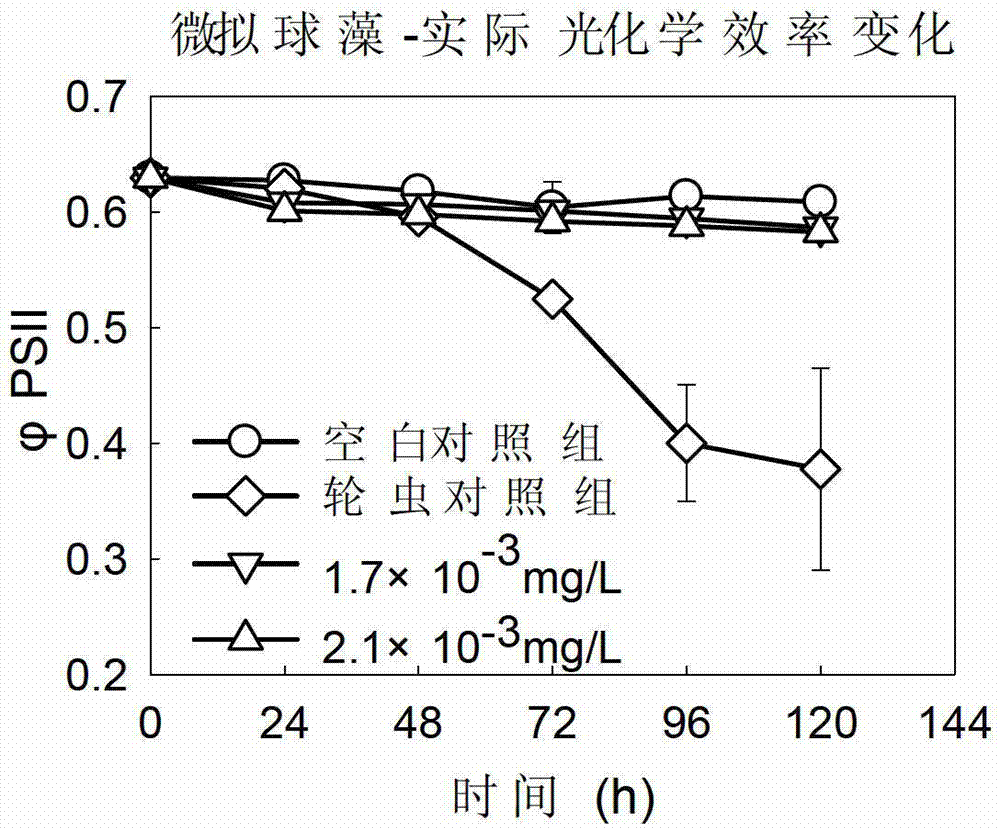
Application of tetracyclic triterpenoids in preparation of low-dosage rotifer insecticides
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and in particular relates to application of tetracyclic triterpenoids in preparation of low-dosage rotifer insecticides, and the tetracyclic triterpenoids are shown as the formula I. Based on the difference of basic biological characteristics of phytoplankton and zooplankton, on the basis of experiment, tissues and organs and submicroscopic organelles thereof are chosen as a main target for screening to obtain a plant-sourced drug which is capable of being rapidly degraded and low in toxicity, wherein the tissues and organs only exist in animal body, and not in microalgae, the plant-sourced drug can inhibit gustatory receptors of enemy organisms to cause food refusal reaction so as to act on midintestinal membrane system to seriously damage midintestinal cell structure, reduce the catalytic activity of pepsase and other digestive enzyme systems, influence digestion and absorption functions of the enemy organisms and eventually lead growth and developmental delay or even death. The technique method of the low-dosage rotifer insecticides has the characteristics of less drug use amount, safety, rapidness and effectiveness, and the low-dosage rotifer insecticides is specific on killing and inhibition of zooplankton (such as rotifers).
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Anthropogenic insect-resistant gene and Cry1C toxin idiotype single-chain antibody encoded thereby and application thereof
ActiveUS9745385B2Reduce usageReduce security risksBiocideImmunoglobulins against bacteriaSingle-Chain AntibodiesNucleotide
An anthropogenic insect-resistant gene having a nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO.1, and a Cry1C toxin idiotype single-chain antibody encoded by said anthropogenic insect-resistant gene and having an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO.2; the antibody is a β-type and has insecticidal activity, and after expression by the prokaryotic system, the primary culture thereof has binding activity to Cnaphalocrocis medinalis midgut peritrophic membrane specific receptor BBMV; the β-type Cry1C toxin idiotype single-chain antibody of the present invention is obtained without animal immunization, has a short preparation period and small amino acid sequence, and is suitable for large-scale in vitro production. The present invention is an entirely new insect-resistant gene resource, and has significant implications for decreasing the various safety risks associated with the widescale use of existing Bt toxins, substituting Bt toxins in the biocontrol of agricultural pests, and reducing the use of pesticides.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for isolated culture of intestinal epithelial cells of Takifugu obscurus and establishment of stress model
PendingCN114807012APollution suppressionCause damageCell dissociation methodsGastrointestinal cellsBiotechnologyOxidative stress
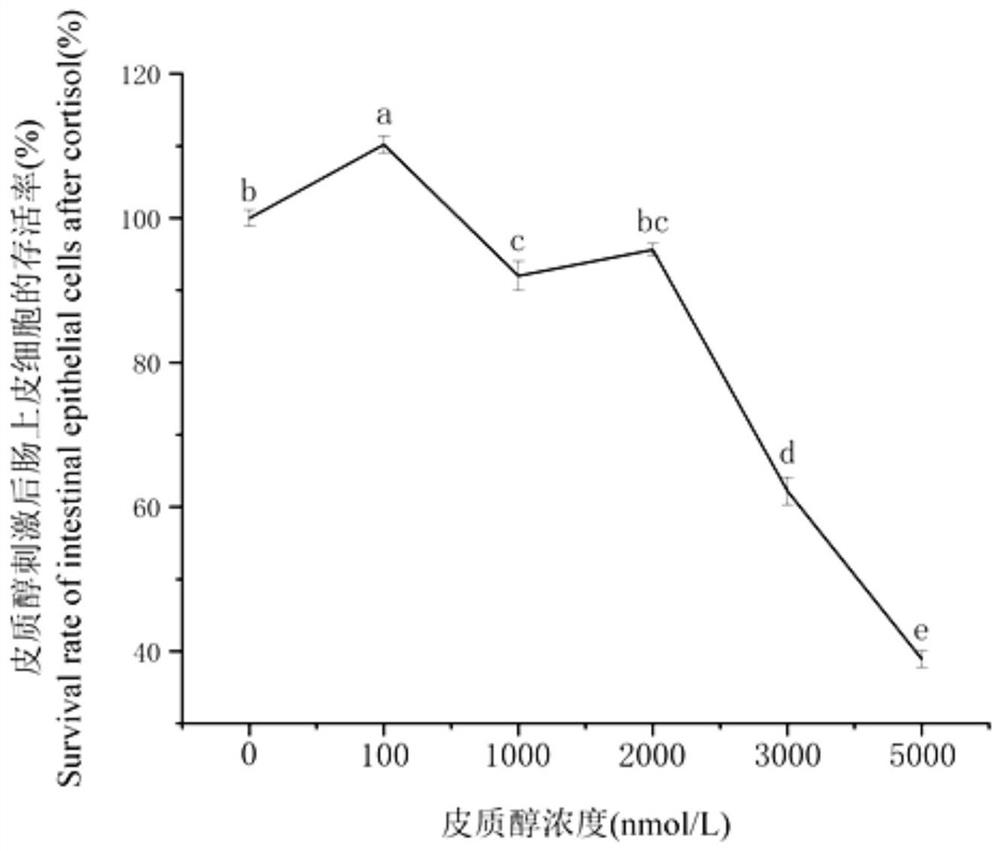
The invention discloses a method for isolated culture of intestinal epithelial cells of Takifugu obscurus and establishment of a stress model. According to the technical scheme, firstly, feed treated with antibiotics is fed in the takifugu obscurus breeding process; secondly, selecting the midgut part of the intestinal tract of takifugu obscurus; then, by optimizing a high-efficiency isolated culture technology of the Takifugu obscurus intestinal epithelial cells and cell primary culture conditions, the Takifugu obscurus intestinal epithelial cells which are relatively high in purity and good in growth are obtained; and finally, utilizing cortisol to stimulate intestinal epithelial cells of Takifugu obscurus so as to establish the oxidative stress model. The invention provides a powerful research material for application of fugu obscurus in research of developmental biology, immunology, toxicology, environment detection and the like.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Malaria vaccine
The present invention features immunogenic compositions based on pre-fertilization or post-fertilization antigens expressed in the circulating gametocytes in the peripheral blood of infected persons or on the malaria parastes' stages of development in the mosquito midgut including extracellular male and female gametes, fertilized zygote and ookinete. The invention also features methods to prevent the transmission of malaria using the immunogenic compositions of the invention.
Owner:US ARMY MEDICAL RES MATERIEL COMMAND USAMRMC +1
Method for large-scale quick separation of insect peritrophic membranes
The invention discloses a method for large-scale quick separation of insect peritrophic membranes. The method can separate peritrophic membrane organizations from insect midgut in a short time, and then food residues therein are quickly cleaned, so that a large amount of purified peritrophic membrane organizations are obtained; the efficiency is improved by 16 times when compared with that of the general method; and the convenience is provided to the subsequent research of proteins in the peritrophic membranes.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Bovine-derived reshaped antibody with insecticidal activity as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105131123AEfficiently obtainedImprove securityBiocideHybrid immunoglobulinsSingle-Chain AntibodiesMidgut
The invention determines the sequence of a bovine-derived reshaped antibody by predicating 8 FRs in heavy and light chain variable regions of a bovine-derived antibody through information biology and planting 6 CDRs of an anti-idiotypical single-chain antibody A12, and artificial synthesis is carried out to construct a bovine-derived reshaped antibody bovine-A12-PUC57 of the A12; a PIT2 carrier which is easily subjected to phage expression is replaced to obtain a bovine-derived reshaped antibody bovine-A12-PIT2. An ELISA analysis shows that the bovine-derived reshaped antibody bovine-A12-PIT2 has a certain combining capacity with plutella xylostella midgut BBMV; a biological activity test shows that the bovine-derived reshaped antibody has certain insecticidal activity. By utilizing a method of information biology predication and the artificial synthesis, the reshaped antibody (an insecticidal protein source) originated from animals can be rapidly and efficiently obtained. The possibility of utilizing genetically engineered antibody technologies to explore and develop novel and highly safe insecticidal protein resources provides a novel train of thought and direction for developing novel insecticidal proteins.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method of protecting plants by introducing a gene coded for a protein which enhances virus infection of host insects
InactiveUS6965059B1Readily apparentClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesNicotiana tabacumTrichoplusia
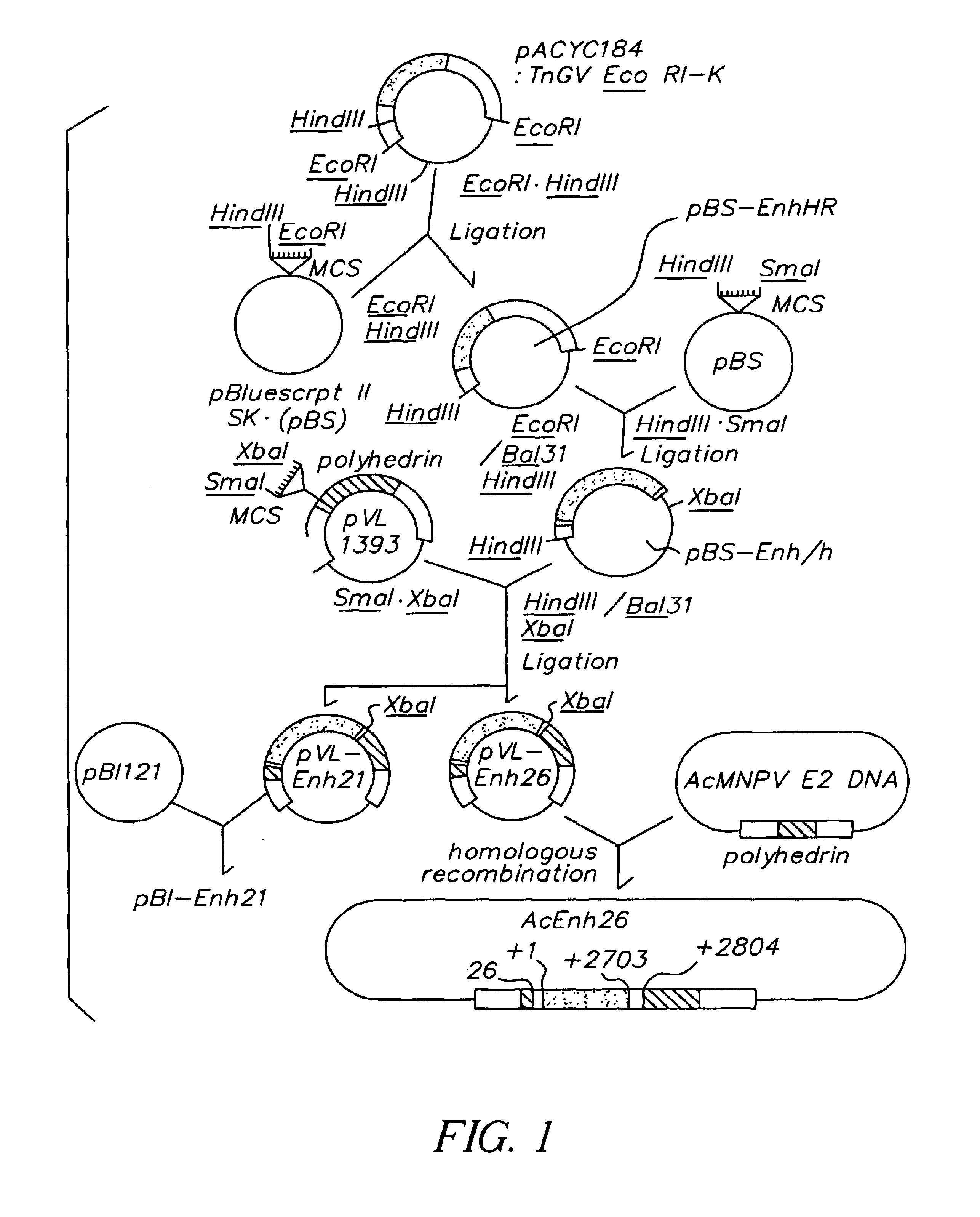
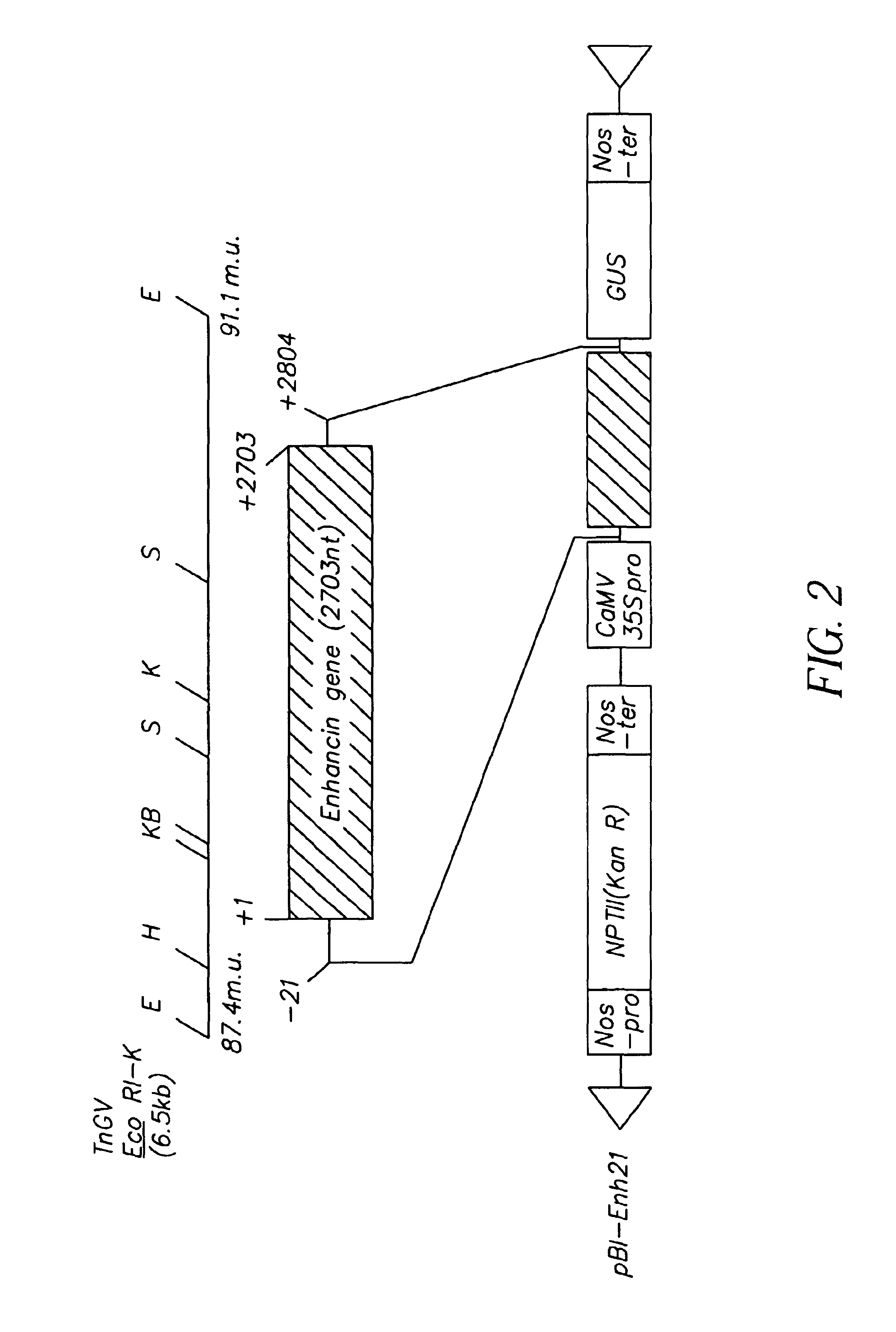
Recent advances of the research on synergistic effect of a mixed baculovirus infection demonstrated the presence of viral molecules enhancing the early event of infection. The enhancins from the Trichoplusia ni was identified to have such a function, i.e., disrupting the structural integrity of peritrophic membrane of midgut of T. ni larva. The enhancin gene was ligated downstream of the CaMV 355 promoter of a binary vector pBI121. With a drug resistant gene, the gene was introduced to a piece of tobacco leaf, from Nicotiana tobacum cv. Havana SR1. We screened 11 regenerated plants out of 37 by feeding tobacco powder mixed in artificial diet, to 3rd instar Pseudaletia separata larvae. The larval stage was usually delayed from 1 to 3 days in comparison of that of control larvae. The larvae did not pupate normally. The larvae showed irregular morphology of half larva and half pupae, suggesting a hormonal disturbance caused by the transgenic tobacco. The introduction of an enhancin gene into plants is an effective method of protecting them from insects due to the disruption of their normal life cycle.
Owner:BOYCE THOMPSON INST FOR PLANT RES
A method for extracting cockroach aggregation pheromone, a cockroach-killing gel bait and its preparation method
The invention provides a method for extracting cockroach gathering pheromone. The method comprises the steps of feeding the cockroaches for 5-10 days, disecting midguts of the cockroaches, grinding and triturating the midgets together with feces of the cockroaches, adding 1.5-2.5 fold amounts of an organic solvent, carrying out extraction for 5-8 hours by virtue of a Soxhlet extraction method, and filtering, so as to obtain an extract. The invention further provides cockroach-killing gel bait. The cockroach-killing gel bait comprises the following components in parts by weight: 0.01-0.5 part of fipronil or a fipronil derivative, 0.05-0.5 part of the cockroach gathering pheromone, 5-30 parts of glucose syrup, 5-30 parts of sorbitol, 1-15 parts of butter, 1-15 parts of cooked flour, 1-10 parts of maltodextrin, 0.5-10 parts of azone, 0.3-2 parts of Carbopol 940, 0.3-2 parts of triethanolamine, 0.1-1.5 parts of sodium benzoate and 30-60 parts of jelly. The invention further provides a preparation method of the cockroach-killing gel bait.
Owner:武汉朗克环境科技有限公司
An easy way to quickly screen substances effective against insects
The invention relates to a simple method for rapidly screening substances effective to insects. According to the method, the insects are taken as a target, candidate substances are applied to midguts of the insects, changes of the insects are observed, and the biological activity of the candidate substances for the insects is determined. The method is low in cost, good in repeatability and high in accuracy, special instruments are not required, and great convenience is provided for rapid, accurate and efficient screening of bioactive substances effective to the insects.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
A fluorescent substrate for detecting the activity of trypsin acting on cry1a protoxin and its application
InactiveCN103923175BClear featuresClearly targetedMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacillus thuringiensisEnzymatic hydrolysis
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
In vitro cultivation method for insect mesenteron cells
The invention discloses an in vitro cultivation method for insect mesenteron cells; the vitro cultivation method adds TNM-FH culture medium which contains conditional medium and fetal calf serum into the obtained mesenteron cells; the invention provides a simple and effective cultivation method for the insect mesenteron cells, which is suitable for in vitro cultivation of the insect mesenteron cells, and physiological and pathological research of mesenteron. The cultivation method comprises enzyme liquid used for dissociating mesenteron cells and suitable culture medium used for maintaining in vitro state of the cells, as well as serum concentration and additive, so that the survival rate of the mesenteron cells just separated is more than 80%, the survival rate of the cells after 60 d of in vitro cultivation is more than 20%; the mesenteron cells under in vitro state can be infected by karyotype polyhedral body virus, and is capable of secreting alkaline phosphatase; the in vitro cultivation method lays a foundation for researching physiological function of insect mesenteron.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com