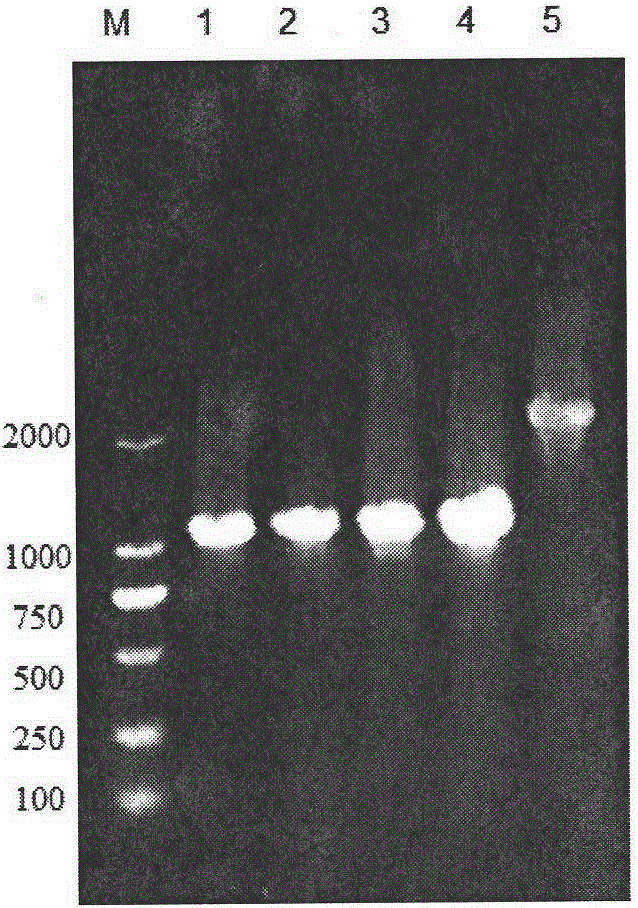
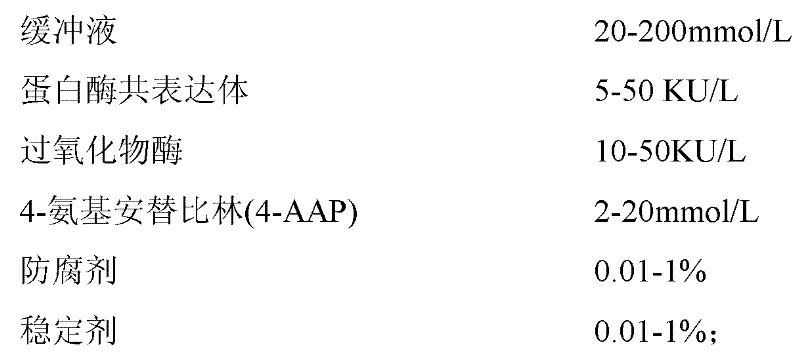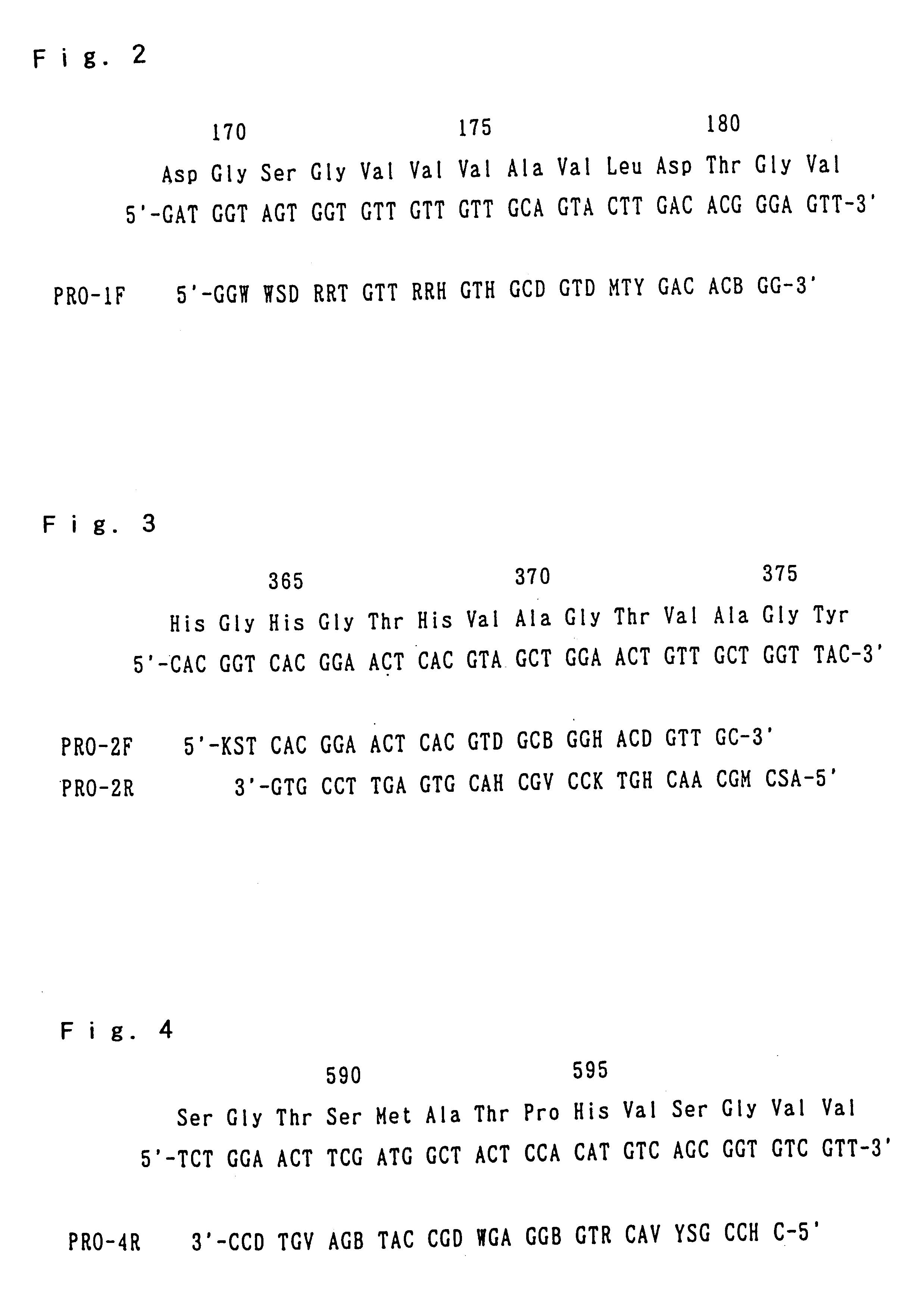Patents
Literature
136 results about "Protease Gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
This gene is located within a large protease gene cluster on chromosome 16. It belongs to the group-1 subfamily of serine proteases. The encoded protein is a secreted tryptic serine protease and is expressed mainly in the pancreas.
Nucleic acid arrays for monitoring expression profiles of drug target genes
InactiveUS20050221354A1Reagent cost per experimentRobust overall probe set signal valueBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDrug targetPolynucleotide
The present invention provides nucleic acid arrays and methods of using the same for detecting or monitoring expression profiles of drug target genes. Non-limiting examples of drug target genes include kinase genes, phosphatase genes, protease genes, G-protein coupled receptor genes, nuclear hormone receptor genes, and ion channel genes. The present invention also provides methods of using nucleic acid arrays for the identification or validation of drugs or drug targets. In one embodiment, a nucleic acid array of the present invention is concentrated with probes for drug target genes. These probes constitute a substantial portion of all of the polynucleotide probes that are stably attached to the nucleic acid array, and can hybridize under stringent or nucleic acid array hybridization conditions to the tiling sequences selected from Attachment C, or the complements thereof.
Owner:WYETH
EV71virus-like particles as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103255163AEfficient expressionGrow fastFungiSsRNA viruses positive-senseIon exchangeHigh pressure
Owner:BEIJING MINHAI BIOTECH +2
Recombinant bacillus subtilis and method for producing transglutaminase by utilizing recombinant bacillus substilis
InactiveCN102586167AReduce breakageSimplify the fermentation production processBacteriaTransferasesStreptoverticillium mobaraenseGlutaminase
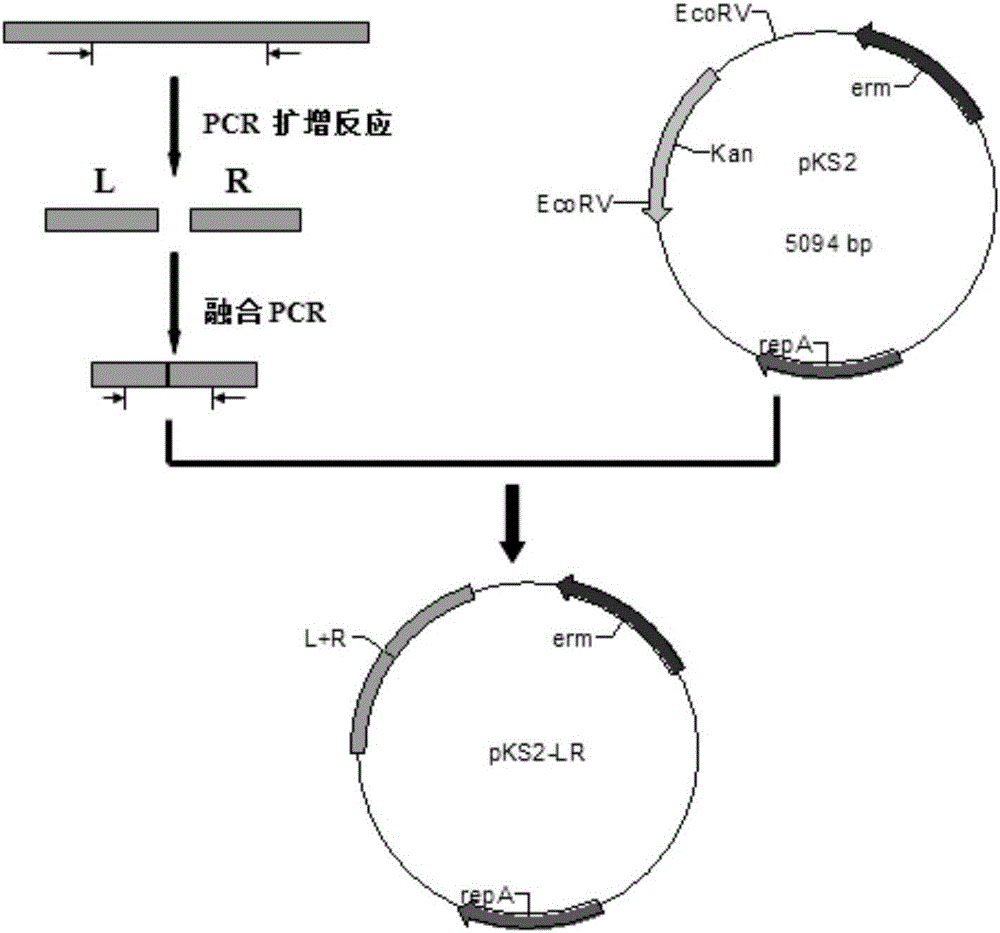
The invention discloses a recombinant bacillus subtilis and a method for producing transglutaminase by utilizing the recombinant bacillus substilis. The recombinant bacillus subtilis is obtained by the following steps of: (1) by virtue of fusion PCR (polymerase chain reaction), connecting a P43 promoter and a signal peptide gene with a subtilisin-like protease gene, and converting a fusion PCR amplification product into bacillus subtilis WB800 to obtain bacillus subtilis B.subtilis WB800S; and (2) carrying out PCR amplification on streptoverticillium mobaraense transglutaminase protogene, andthen converting amplification product into the bacillus subtilis B.subtilis WB800S to obtain bacillus subtilis B.subtilis WB800S / proMTG. The bacillus subtilis B.subtilis WB800S / proMTG is fermented and purified to obtain soluble transglutaminase. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the transglutaminase with biological activity can be directly obtained in supernatant of fermentation liquor, fussy processes of breaking cells and activating proenzyme after purification are eliminated, and a fermentation production process is simplified.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Method for detection of drug-selected mutations in the HIV protease gene
InactiveUS6803187B1Rapid and reliable detectionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAntiviral drugHIV protease gene
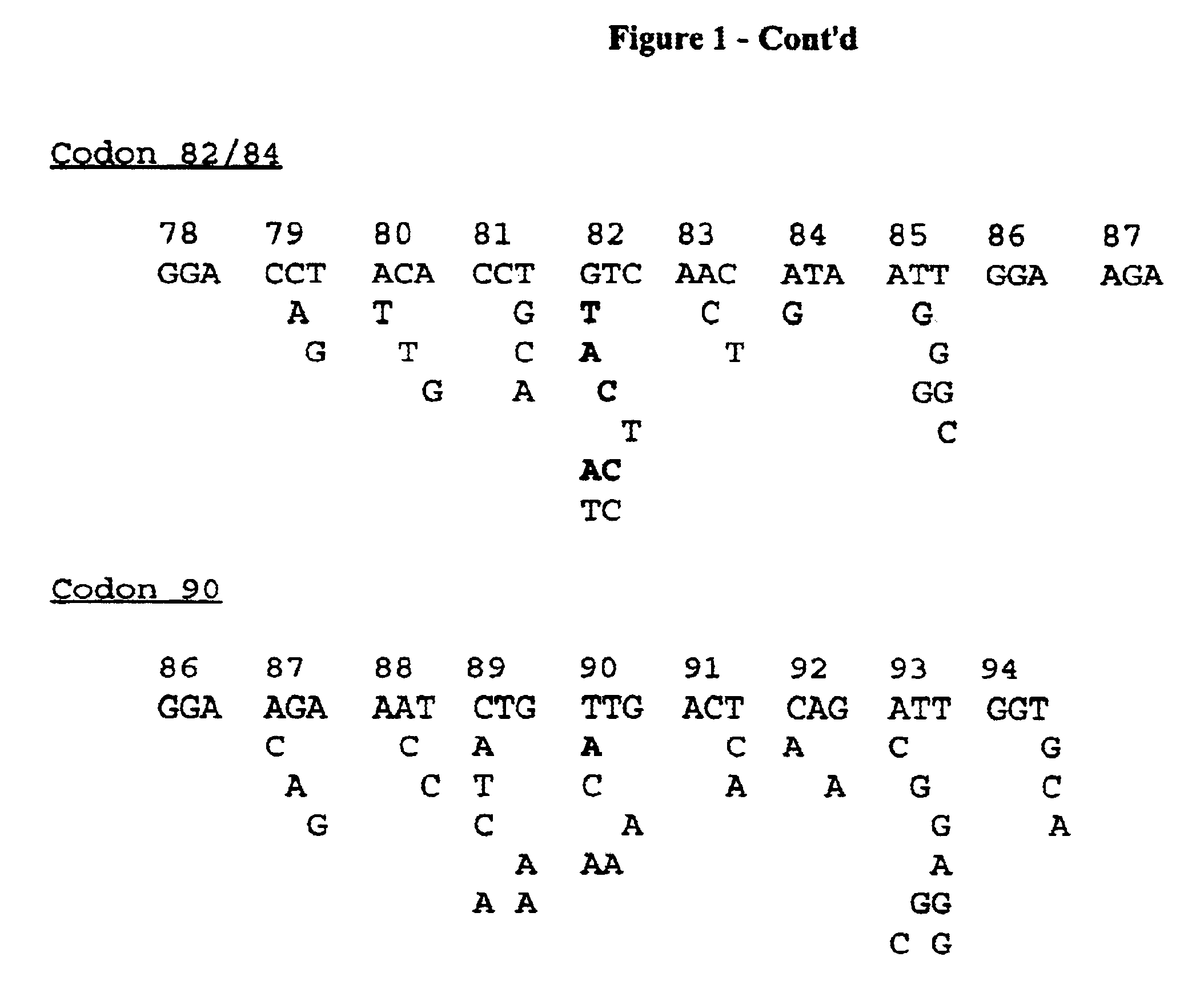
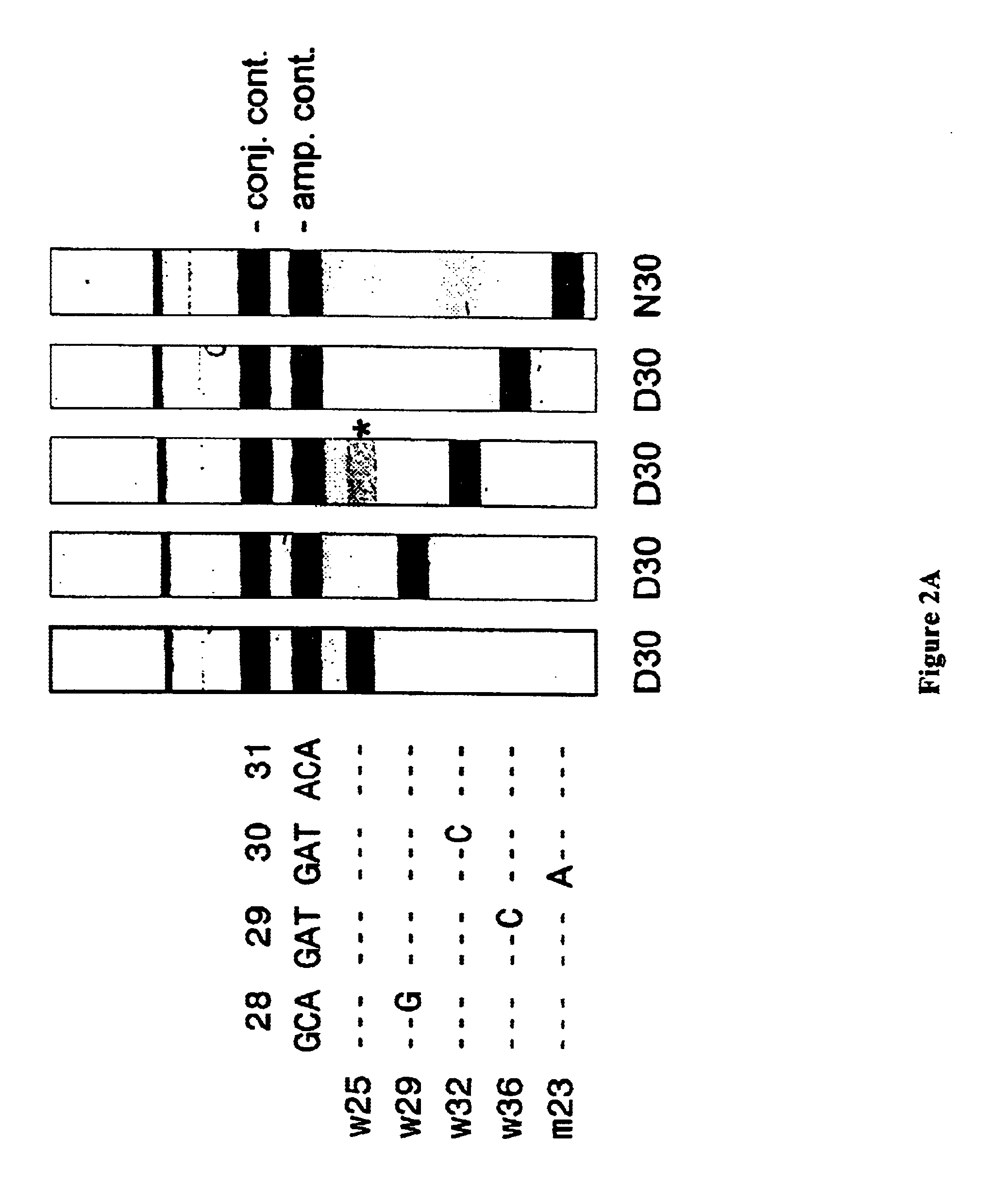
The present invention relates to a method for the rapid and reliable detection of drug-selected mutations in the HIV protease gene allowing the simultaneous charaterization of a range of codons involved in drug resistance using specific sets of probes optimized to function together in a reverse-hybridization assay. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method for determining the susceptibility to antiviral drugs of HIV viruses in a biological sample, with said method comprising: a) if need be, releasing, isolating or concentrating the polynucleic acids present in the sample; b) if need be amplifying the relevant part of the protease gene of HIV with at least one suitable primer pair; c) hybrydizing the polynucleic acids of step a) or b) with at least one of the following probes: probes specifically hybridizing to a target sequence comprising codon 30; probes specifically hybridizing to a target sequence comprising codon 46 and / or 48; probes specifically hybridizing to a target sequence comprising codon 50; probes specifically hybridizing to a target sequence comprising codon 54; probes specifically hybridizing to a target sequence comprising codon 82 and / or 84; probes specifically hybridizing to a target sequence comprising codon 90; or the complement of said probes; further characterized in that said probes specifically hybridize to any of the target sequences presented in FIG. (1), or the complement of said target sequences; d) inferring from the result of step c) whether or not a mutation giving rise to drug resistance is present in any of said target sequences.
Owner:INNOGENETICS NV
Bacillus licheniformis expression host
ActiveCN104630123AReduced activityIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaHydrolasesBacillus licheniformisProtein target
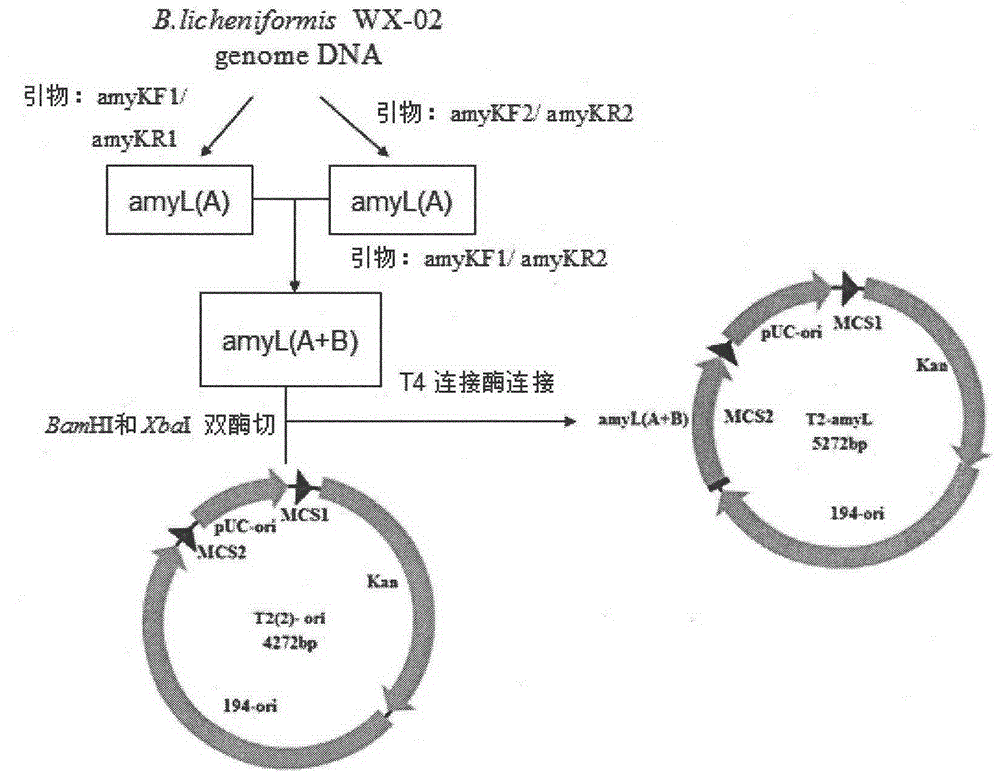
The invention discloses a bacillus licheniformis host bacterium BL10 with multiple gene deletion, the accession number of which is CCTCCNO:M2013400. The host bacterium derives from a bacillus licheniformis WX-02 which partially or completely has deletion of ten genes. The ten genes comprises eight protease genes (mpr encoding a metalloprotease; vpr encoding a serine protease; aprX encoding an intracellular serine protease; epr encoding a minimal extracellular protease; bpr encoding a bacillus peptidase F; wprA encoding a protease combined with cell walls; aprE encoding an extracellular alkaline serine protease; and bprA encoding a bacillus peptidase F) and two extracellular secretory protein genes (hag encoding flagellin; and amyL encoding alpha-amylase). The BL10 has completely no extracellular protease activity and can reduce the degradation effect of a protease on a target protein. When the target protein is expressed by the expression host, the expression level is higher, and the host bacterium benefits protein expression enhancement.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Filamentous fungi with inactivated protease genes for altered protein production
The invention relates to a filamentous fungal cell (e.g., Aspergillus sp.) comprising at least one inactivated protease gene chosen from apsB, a homolog of apsB, cpsA, a homolog cpsA, and combinations thereof. Nucleic acids and methods for making the inactivated mutant filamentous fungal cells are provided as well as methods for using the cells for the altered production of endogenous or heterologous proteins of interest.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
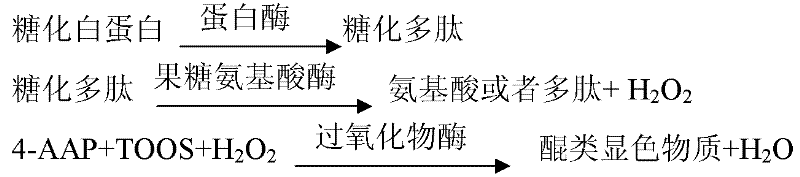
Human serum glycated albumin array kit
ActiveCN102565420AUnchanged vitalityStrong specificityBiological testingMethylanilineFructose lysine
The invention provides a human serum glycated albumin assay kit which comprises a reagent 1 and a reagent 2, wherein the reagent 1 comprises the following components: 20-200mmol / L of buffer solution, 5-50KU / L of protease co-expression vector, 10-50KU / L of peroxisome, 2-20mmol / L of 4-amino antipyrine, 0.01-1% of preservative and 0.01-1% of stabilizer, and the protease co-expression vector is obtained by cloning a protease gene and an ascorbic acid oxidase gene onto a same vector for performing co-expression; and the reagent 2 comprises the following components: 20-200mmol / L of buffer solution, 5-50U / mL of fructose lysine enzyme, 1-10mmol / L of N, N-bis(4-sulfobutyl ether)-3-methylaniline, 0.01-1% of preservative and 0.01-1% of stabilizer. The kit can remove the interferences of globulin and ascorbic acid in human serum and has good stability and low cost.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL SYSTEM BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
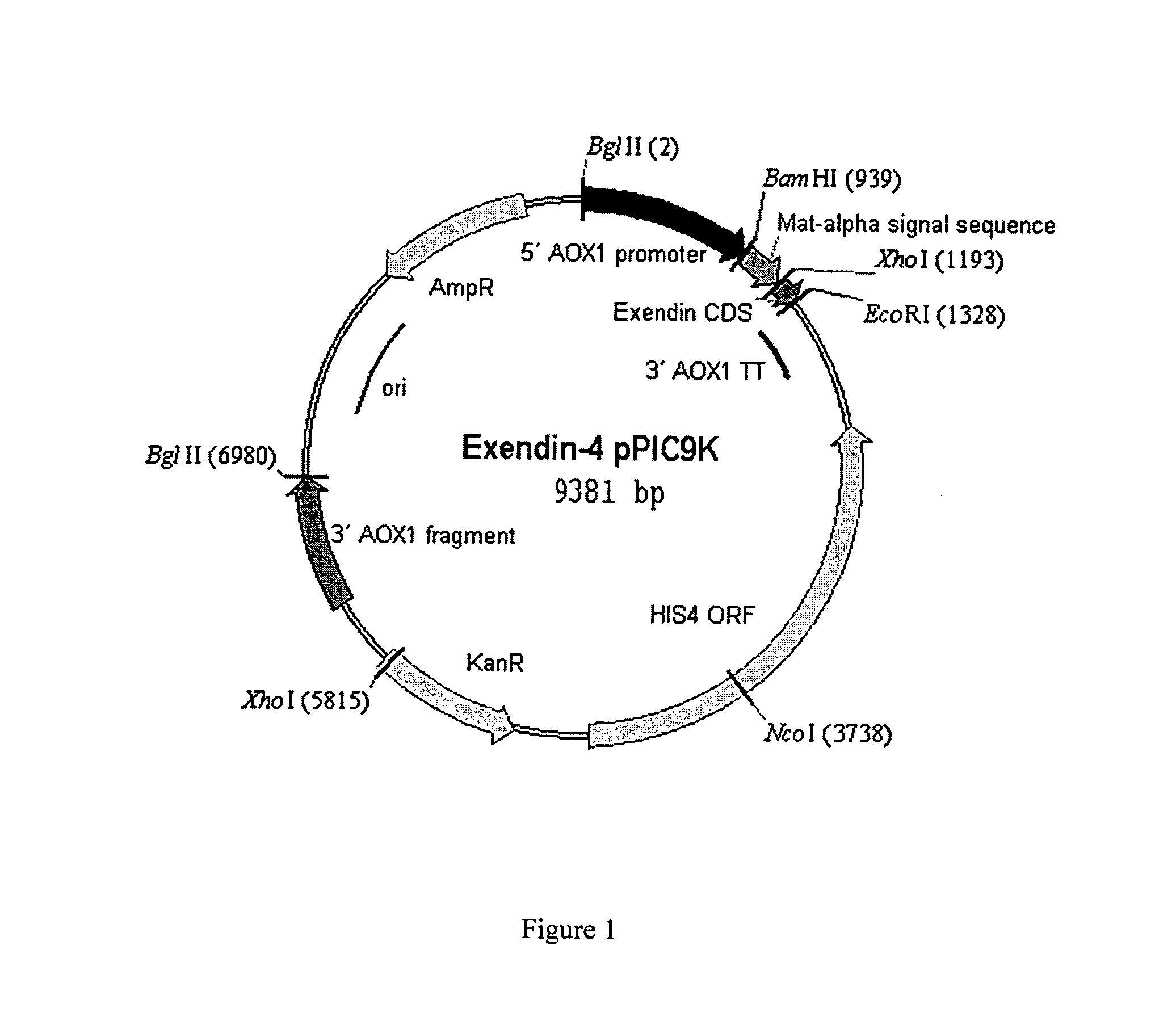
Method of producing biologically active polypeptide having insulinotropic activity
The present invention relates to a method of producing a biologically active polypeptide having insulinotropic activity, the method comprising steps of: (a) transforming a genetically modified host cell that has protease gene knockout, with a polynucleotide vector encoding the polypeptide; and (b) growing the transformed host cell to produce the biologically active polypeptide; and a method of producing a biologically active polypeptide having an N-terminal recognition site His-Gly with insulinotropic activity, the method comprising steps of: (a) transforming a genetically modified Pichia pastoris that has protease gene STE13 knockout, with a polynucleotide vector encoding the polypeptide; and (b) growing the transformed Pichia pastoris to produce the biologically active polypeptide.
Owner:BIOCON LTD
Low-temperature alkaline protease gene, engineering bacterium containing same, construction methods of low-temperature alkaline protease gene and engineering bacterium, and low-temperature alkaline pr
The invention relates to a low-temperature alkaline protease gene, an engineering bacterium containing same, construction methods of the low-temperature alkaline protease gene and the engineering bacterium, and low-temperature alkaline protease. The sequence of the low-temperature alkaline protease gene is described as SEQ ID No. 2, and the sequence characteristic is 810bp, nucleic acid, single chain, linearity and DNA. The engineering bacterium producing the low-temperature alkaline protease is transformed from a host bacterium bacillussubtilis WB600 and has the characteristic of producing the low-temperature alkaline protease. The construction method of the engineering bacterium comprises the following steps of: obtaining an objective gene, reconstructing the objective gene directionally, constructing an expression carrier and constructing and sieving the engineering bacterium containing the low-temperature alkaline protease gene. The sequence of the mature peptide basic group of the low-temperature alkaline protease is disclosed in SEQ ID No. 2, the optimum operative temperature is 30 DEG C, and the optimum operative pH is 11.0. The optimum temperature of the alkaline protease produced by the engineering bacterium is 30 DEG C, the optimum pH is 11.0, and the invention provides a theoretical basis for the low-temperature alkaline protease added and used in a detergent and has important economic benefit and social benefit.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Bacillus subtilis recombinant strain as well as preparation method and application thereof
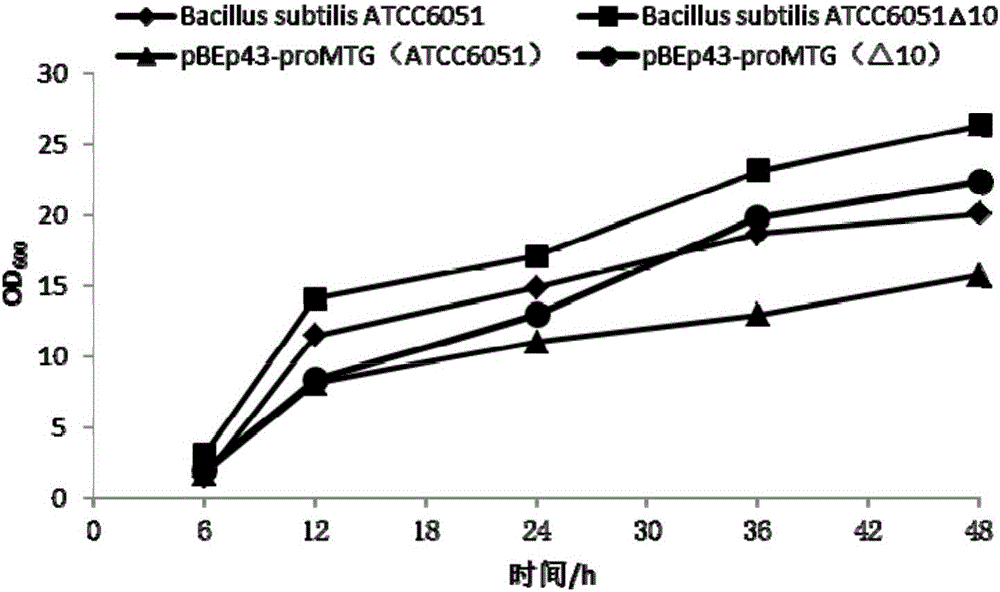
ActiveCN106085937AReduce the degree of degradationGrow fastBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyProteinase activity
The invention discloses a bacillus subtilis recombinant strain as well as a preparation method and application thereof and belongs to the field of a biological technology. The recombinant strain disclosed by the invention is obtained through knocking out or inactivating ten protease genes in bacillus subtilis; and the ten protease genes comprise: nprE, nprB, aprE, mpr, bpf, epr, vpr, wprA, spollAC and srfAC. The ten protease genes are knocked out through a homologous recombination method, the obtained bacillus subtilis recombinant strain is rapid in growth, and the expression amount of heterologous proteins is high. Therefore, the recombinant strain can be used as a host of efficient expression of the heterologous proteins.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Bacterial host strain
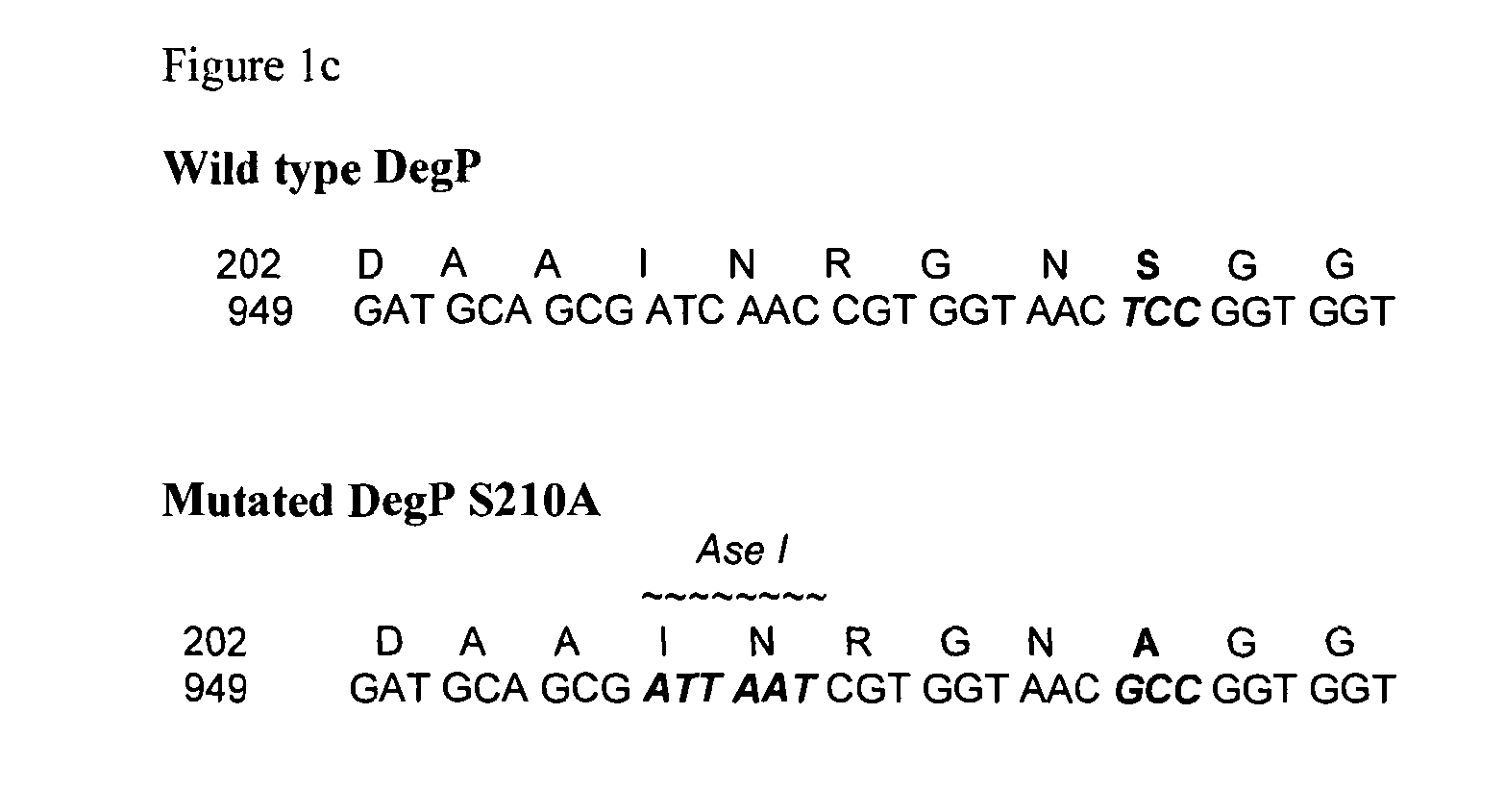
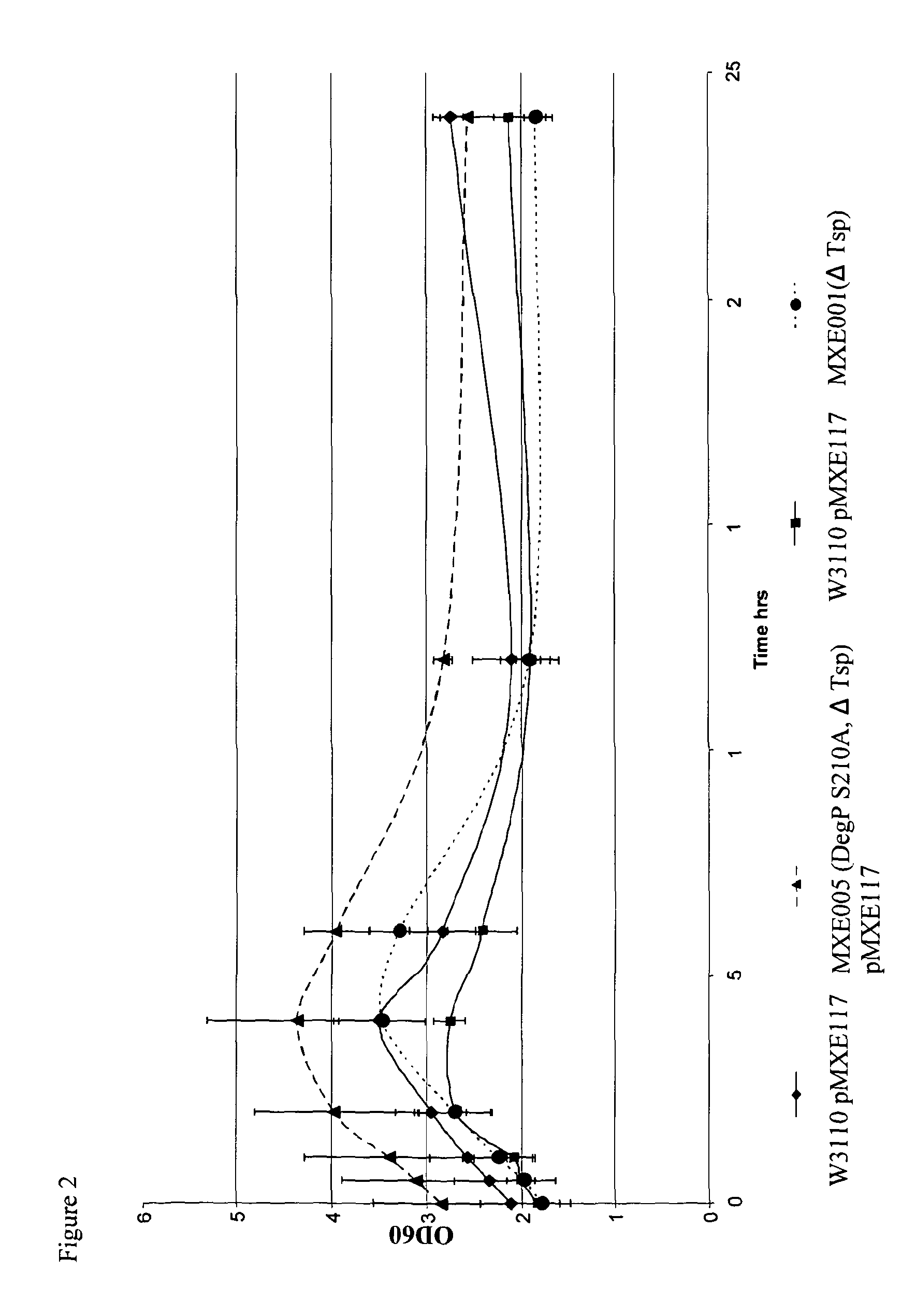
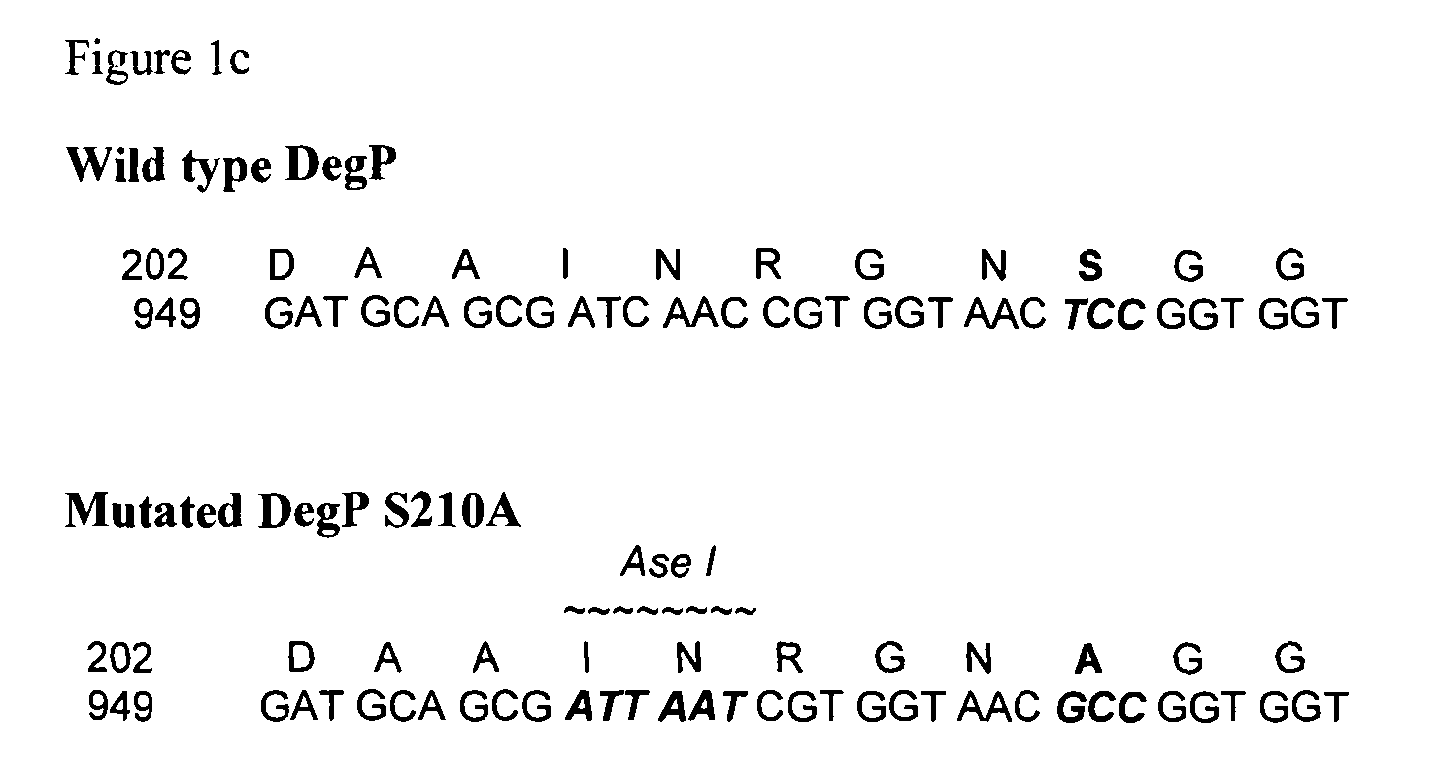
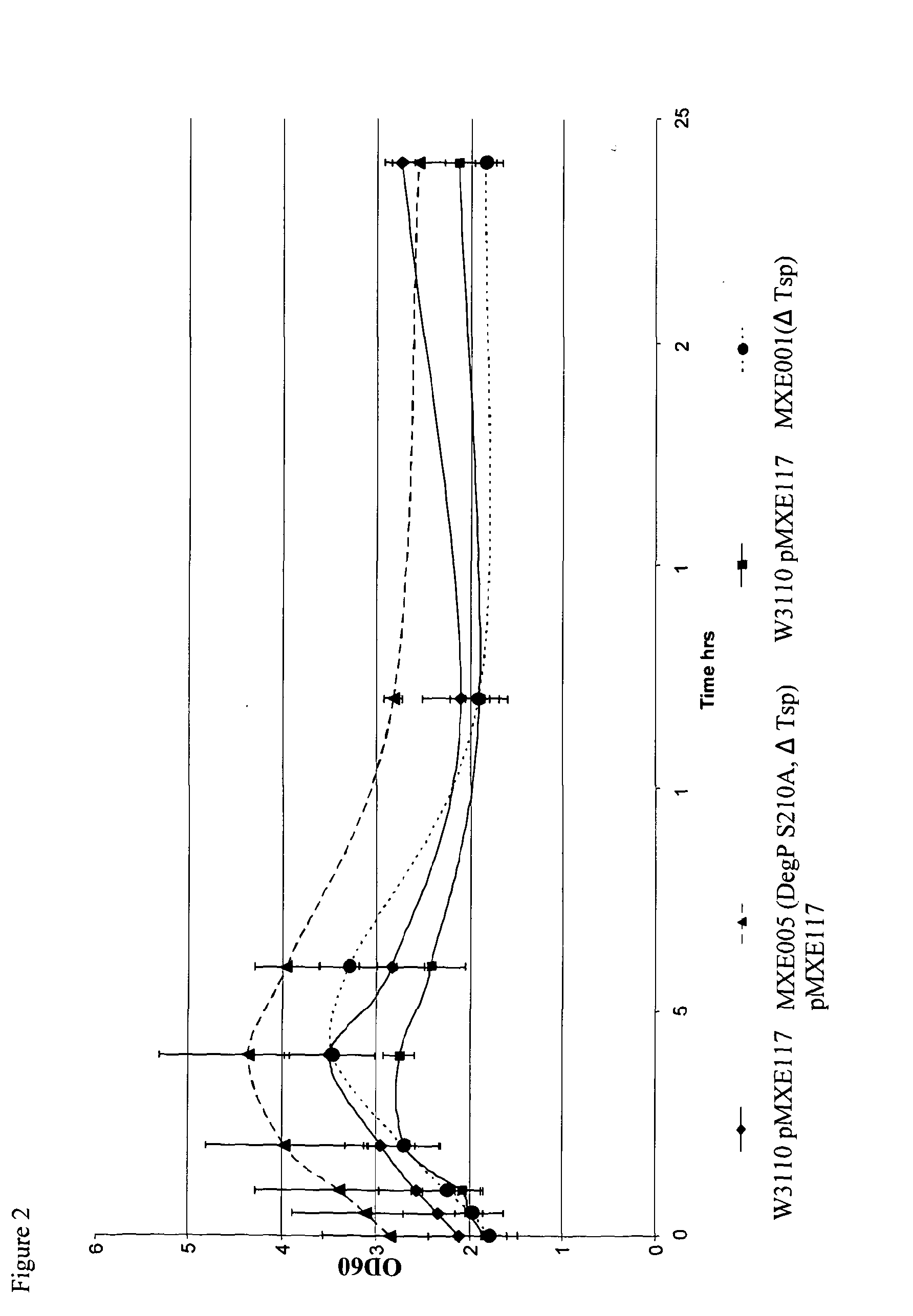
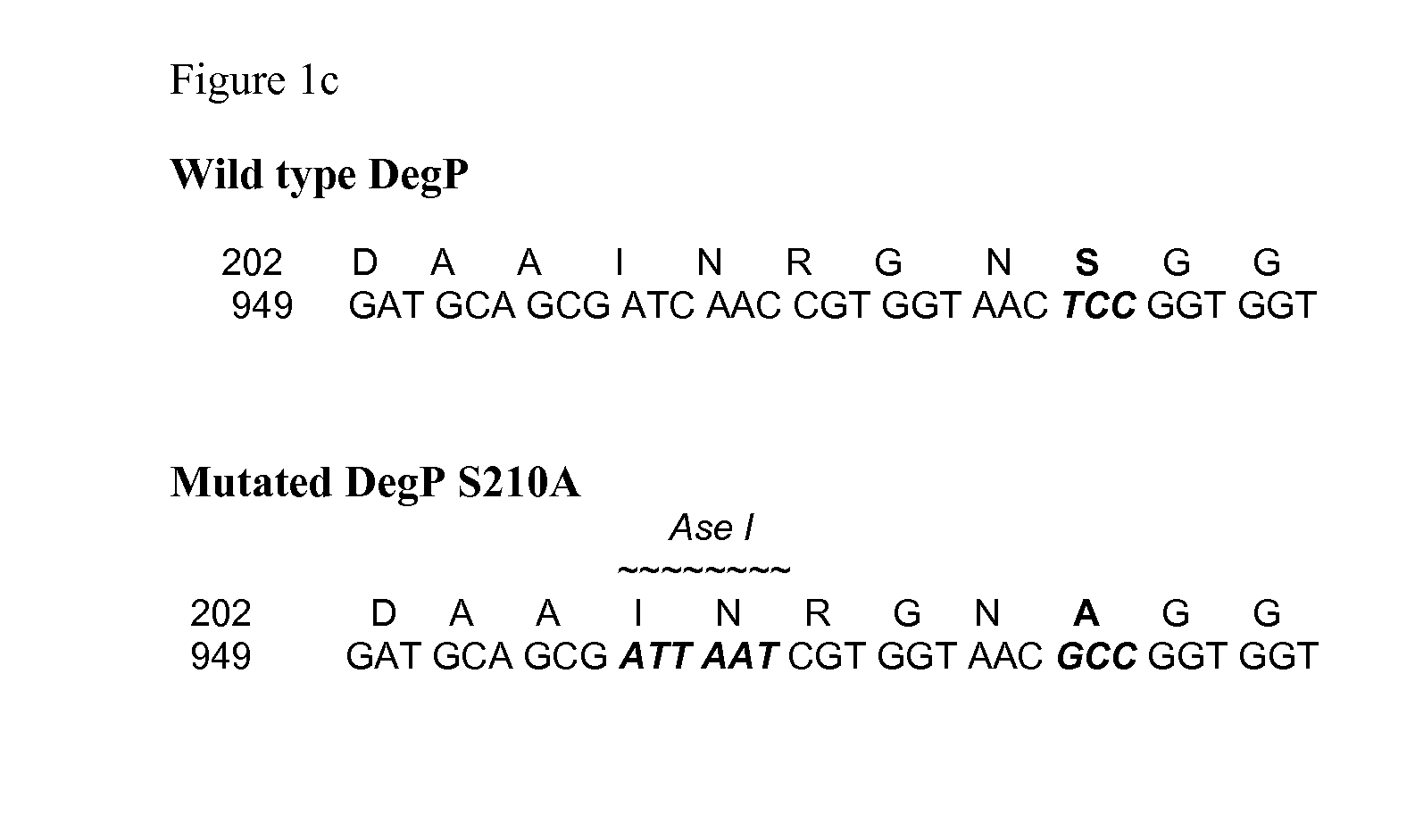
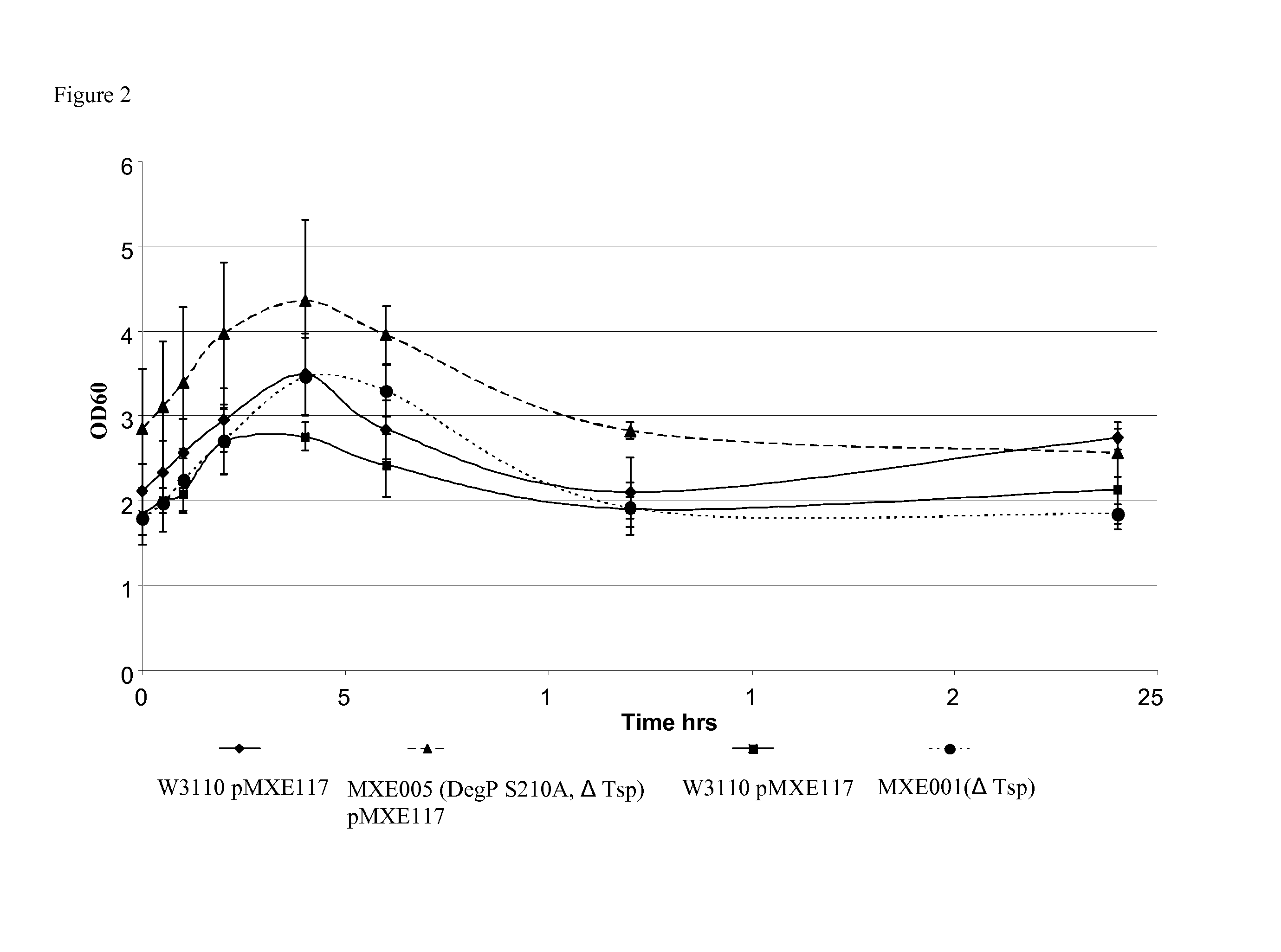
A recombinant gram-negative bacterial cell comprising one or more of the following mutated protease genes: a) a mutated Tsp gene, wherein the mutated Tsp gene encodes a Tsp protein having reduced protease activity or is a knockout mutated Tsp gene; b) a mutated ptr gene, wherein the mutated ptr gene encodes a Protease III protein having reduced protease activity or is a knockout mutated ptr gene; and c) a mutated DegP gene encoding a DegP protein having chaperone activity and reduced protease activity; wherein the cell is isogenic to a wild-type bacterial cell except for the mutated Tsp gene and / or mutated ptr gene and / or mutated DegP gene and optionally a polynucleotide sequence encoding a protein of interest.
Owner:UCB PHARMA SA
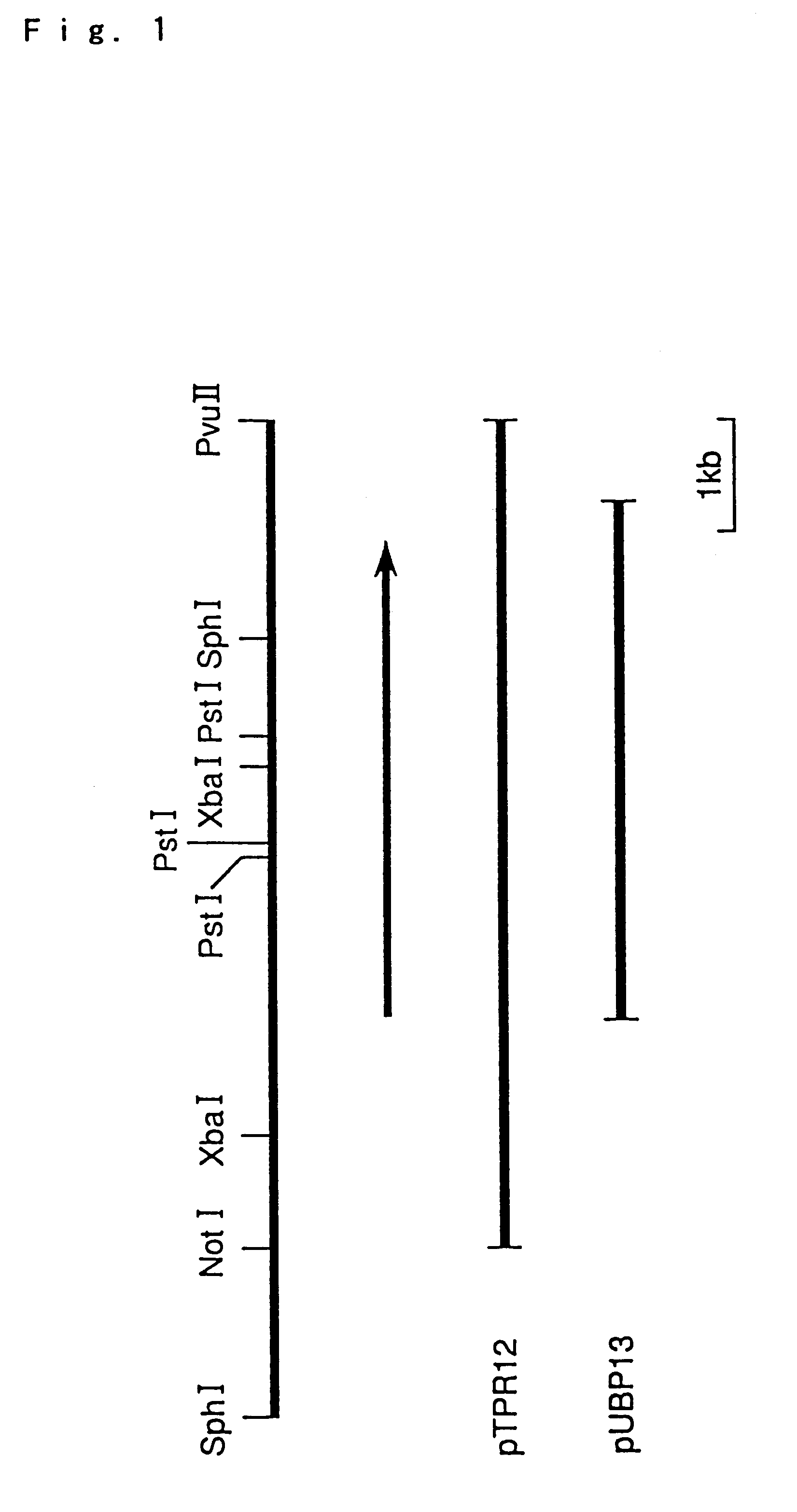
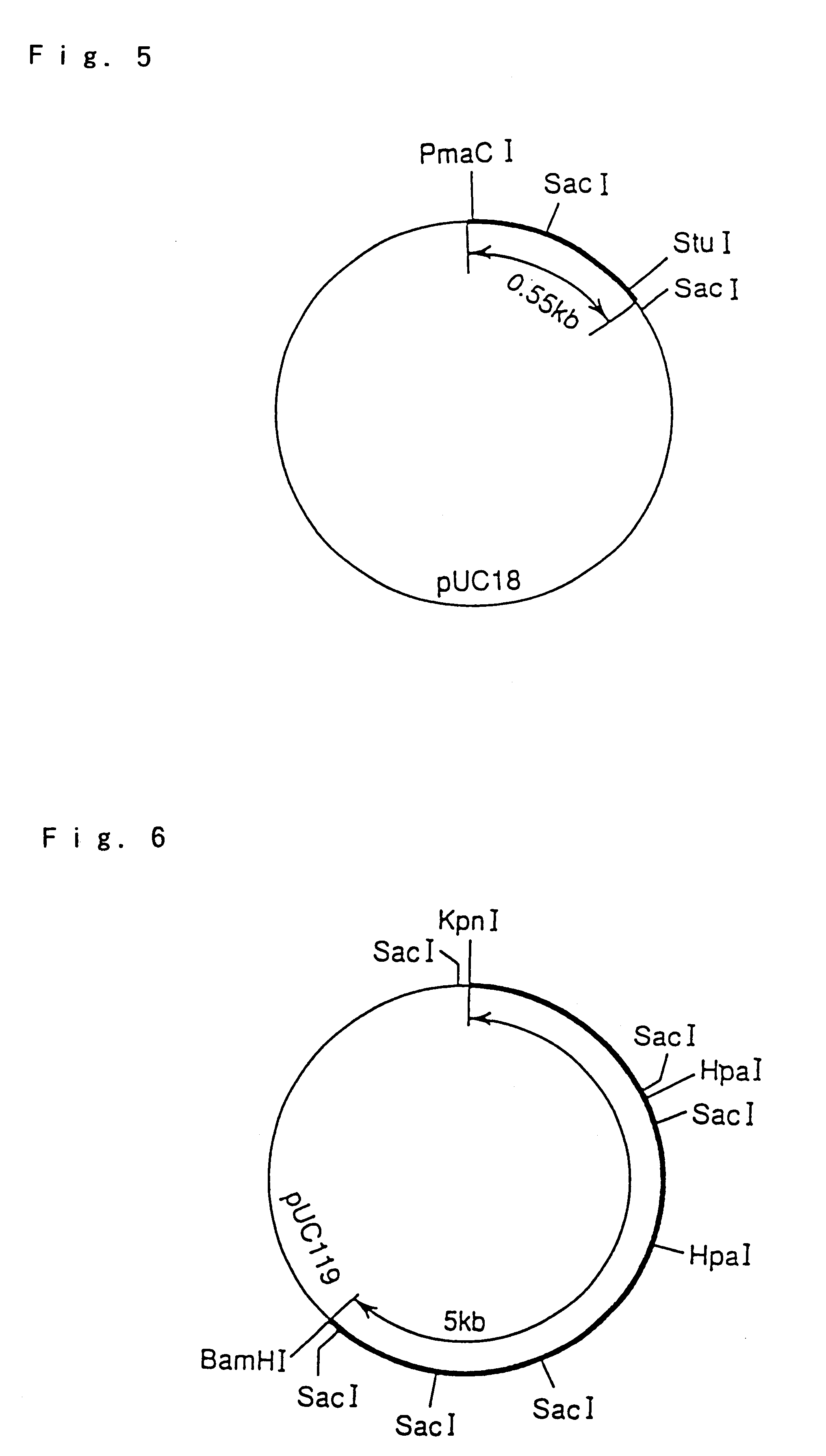
Hyperthermostable protease gene
There are provided hyperthermostable proteases having an amino acid sequences represented by SEQ ID NOs: 1, 3 and 5 of the Sequence Listing or functional equivalents thereof and hyperthermostable protease genes encoding those hyperthermostable protease. There is also disclosed a process for preparation of a hyperthermostable protease by culturing a transformant containing the gene.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
Ultrathermostable protease genes
InactiveUS6261822B1Reduced activitySubstantial decreaseBacteriaSugar derivativesProteinase activityFhit gene
There are provided hyperthermostable proteases having an amino acid sequences represented by SEQ ID Nos. 1, 3 and 5 of the Sequence Listing or functional equivalents thereof and hyperthermostable protease genes encoding those hyperthermostable protease. There is also disclosed a process for preparation of a hyperthermostable protease by culturing a transformant containing the gene.
Owner:TAKARA HOLDINGS
Bacterial host strain
ActiveUS20120258492A1Decrease protease activityDecreasing proteolysisBacteriaHydrolasesBacteroidesWild type
A recombinant gram-negative bacterial cell comprising one or more of the following mutated protease genes: a) a mutated Tsp gene, wherein the mutated Tsp gene encodes a Tsp protein having reduced protease activity or is a knockout mutated Tsp gene; b) a mutated ptr gene, wherein the mutated ptr gene encodes a Protease III protein having reduced protease activity or is a knockout mutated ptr gene; and c) a mutated DegP gene encoding a DegP protein having chaperone activity and reduced protease activity; wherein the cell is isogenic to a wild-type bacterial cell except for the mutated Tsp gene and / or mutated ptr gene and / or mutated DegP gene and optionally a polynucleotide sequence encoding a protein of interest.
Owner:UCB PHARMA SA
Cryophilous proteinase gene mcp01 and its prepn process
InactiveCN101045933AHigh catalytic efficiencyPromote degradationHydrolasesGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyProteinase activity
The present invention is one kind of cryophilous protease gene mcp01 and its preparation process, and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The cryophilous proteinase gene mcp01 has one genome DNA segment of 2676 bp containing one opened reading frame with 2508 nucleotides. The opened reading frame is the gene encoding protease MCP-01, and the protease MCP-01 gene mcp01 expressed cryophilous protease has optimal enzyme activity temperature of about 35 deg.c and optimal enzyme pH of 9.0. The present invention may be applied in low temperature preservation of meat, dairy product processing, detergent production, etc.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
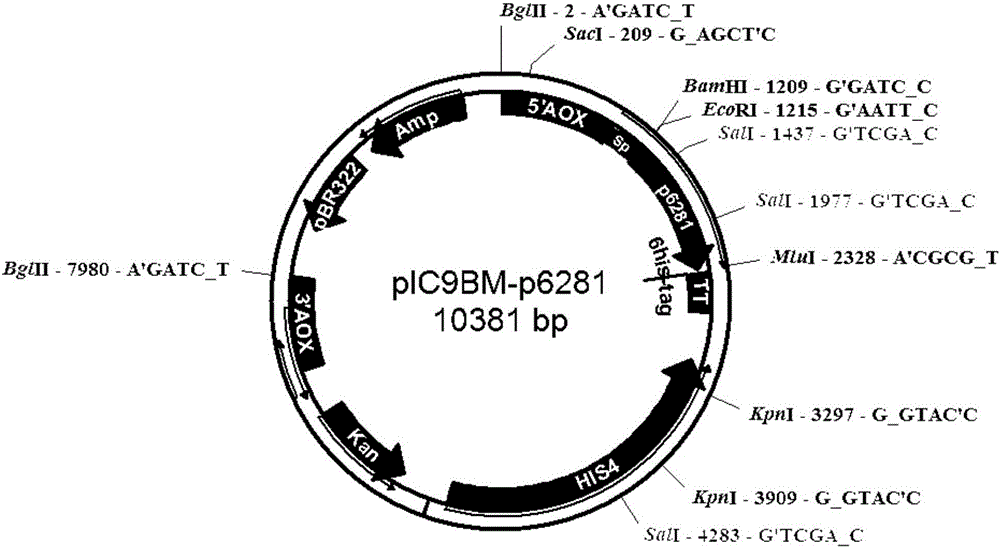
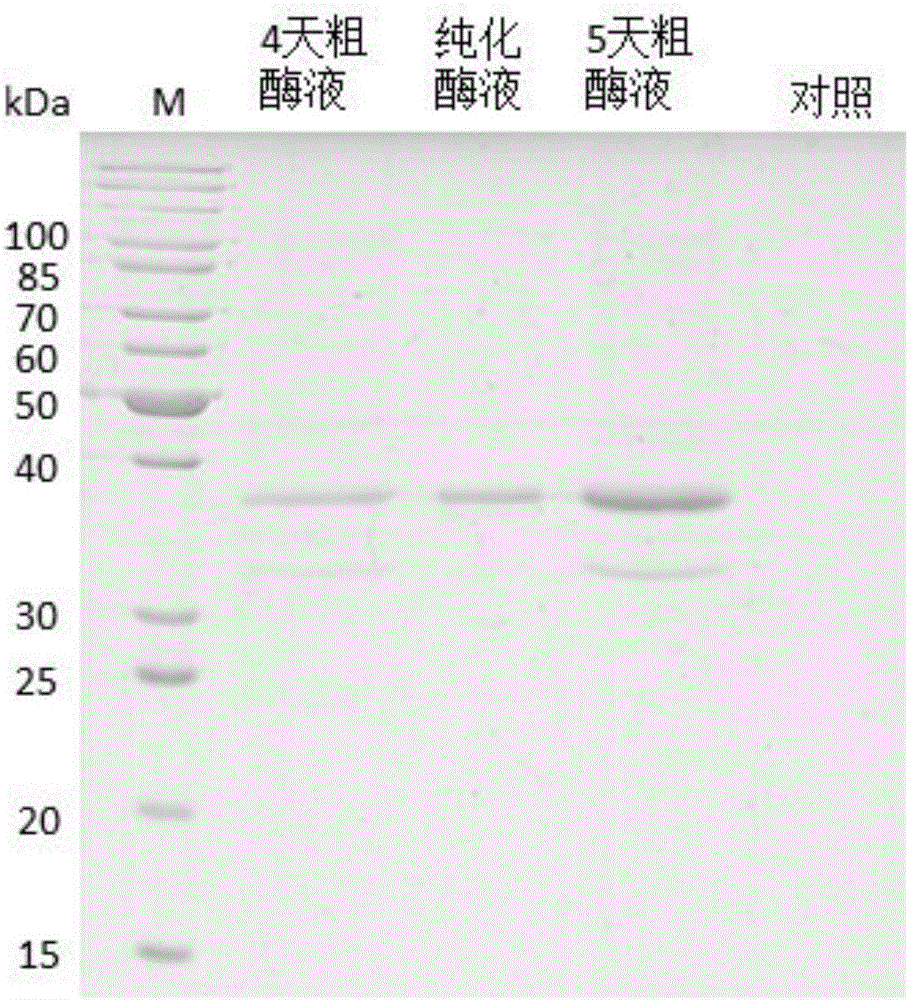
Method for heterologous expression and purification of trichoderma harzianum acidic protease P6281
ActiveCN106834336AIncrease enzyme activityIncrease productionHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisHeterologous
The invention discloses a method for heterologous expression and purification of trichoderma harzianum acidic protease P6281. Trichoderma harzianum RNA is extracted and is subjected to reverse transcription to obtain cDNA; an acidic protease gene is obtained by PCR and is inserted into an expression vector; a recombinant plasmid is electro-transformed and introduced into pichia pastoris GS115 and induced expression is performed; and then a relatively pure enzyme product is obtained by a nickel column affinity chromatography and molecular sieve chromatography. The trichoderma harzianum acidic protease P6281 is successfully expressed and purified for the first time; the method improves the yield of the P6281 protease; and the enzyme activity of the obtained acidic protease is much higher than that of conventional trichoderma acidic protease.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
EV71 virus-like particles and hand-foot-and-mouth disease vaccine prepared from EV71 virus-like particles
InactiveCN102154229ASuitable for industrial productionEasy to purifyInactivation/attenuationAntiviralsPichia pastorisSaccharum
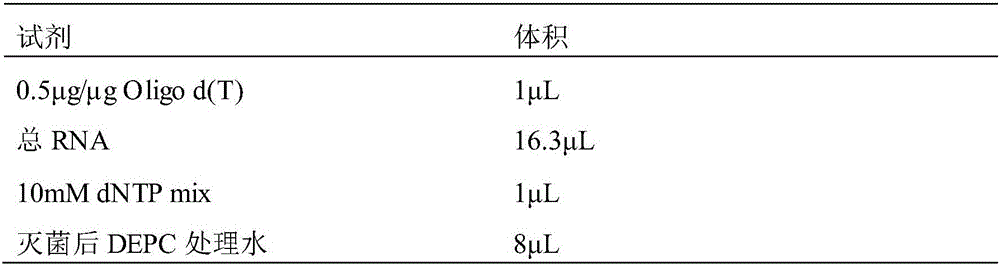
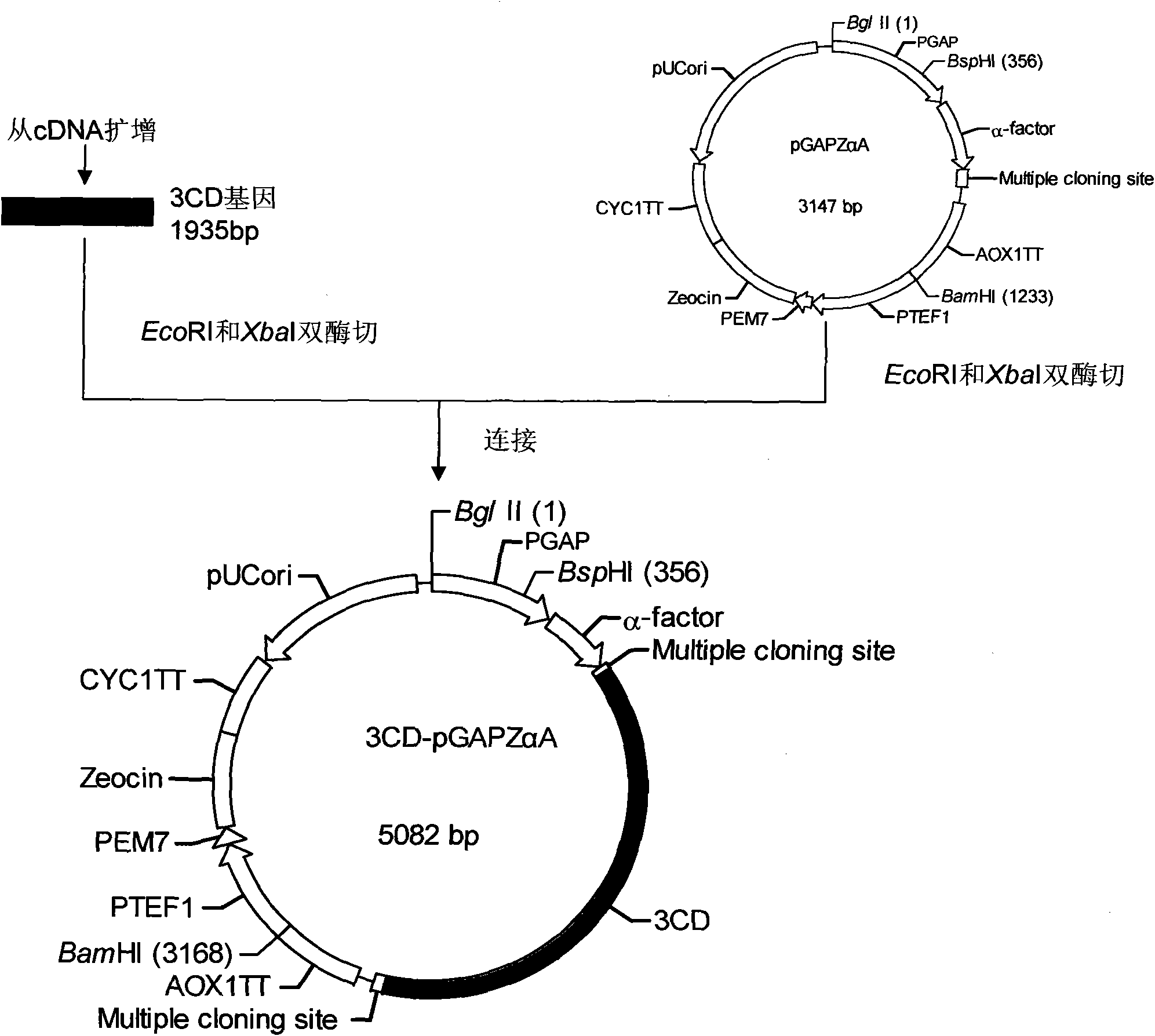
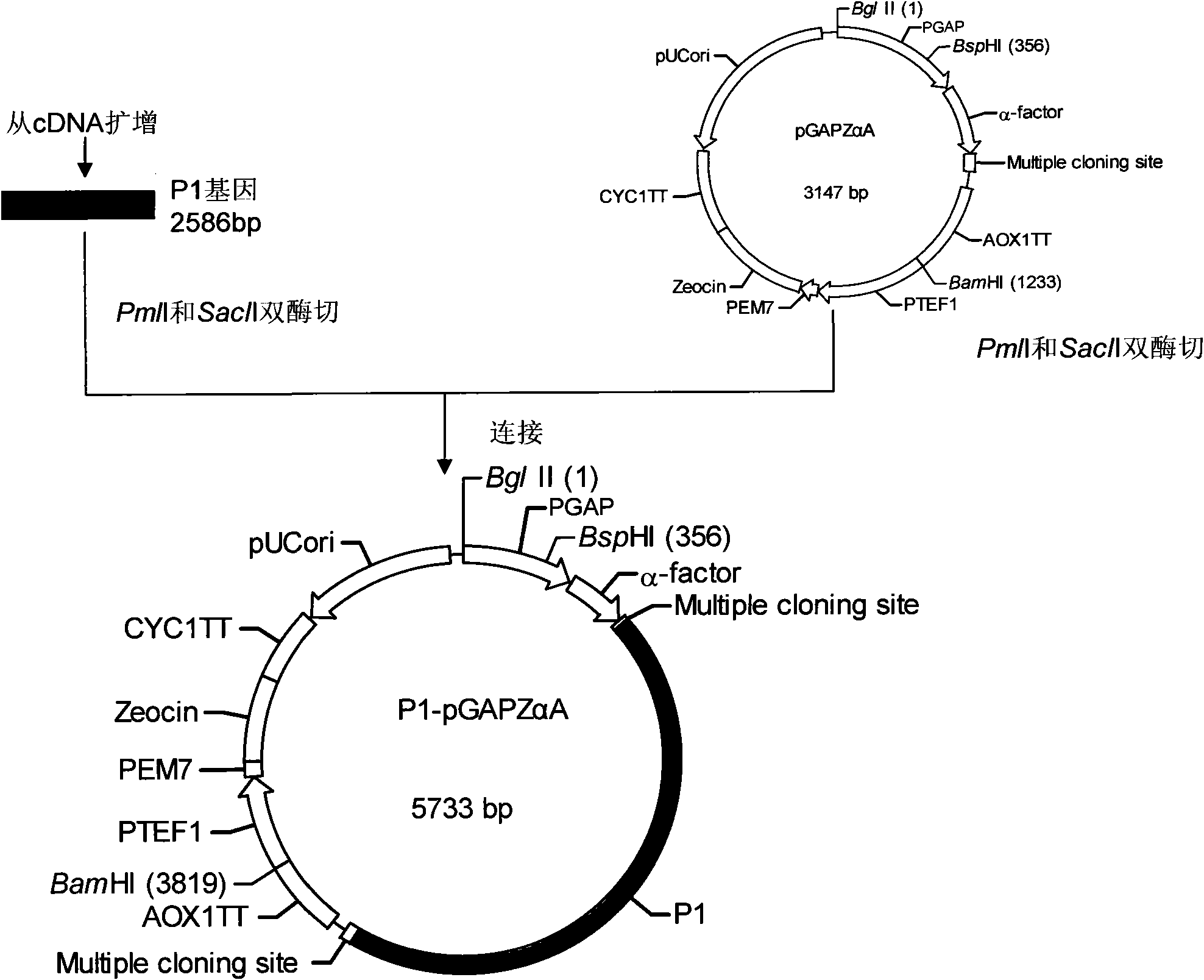
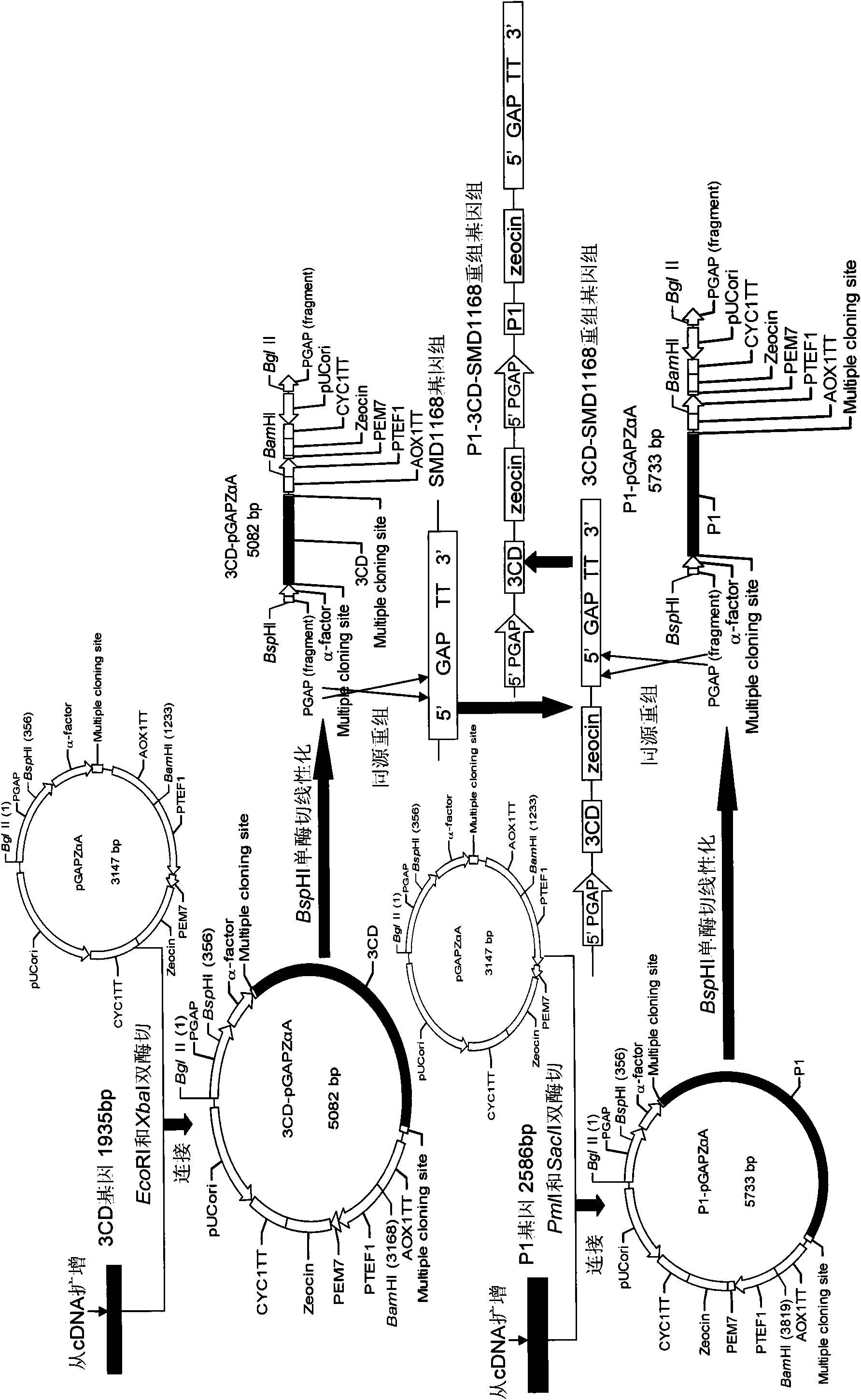
The invention relates to EV71 virus-like particles and hand-foot-and-mouth disease vaccine prepared from the EV71 virus-like particles. The EV71 virus-like particles are prepared according to the following steps: (1) constructing recombinant plasmid: respectively connecting pGAPZ alpha A plasmid with P1 protein gene of intestinal EV71 virus and 3CD protease gene to construct P1-pGAPZ alpha A and 3CD-pGAPZ alpha A recombinant plasmid; (2) transferring the recombinant plasmid to expression bacterial strains: sequentially transferring the recombinant plasmid to Pichia pastoris SMD1168 expression bacterial strains to obtain P1-pGAPZ alpha A-3CD-pGAPZ alpha A-SMD1168 recombinant expression strains; and (3) culturing thallus and purifying the EV71 virus-like particles: culturing the Pichia pastoris recombinant expression bacterial strains, centrifugalizing to separate supernate, and carrying out sucrose density gradient centrifugation on precipitation of the supernate after ultracentrifugation, thus obtaining the EV71 virus-like particles. In the invention, the EV71 virus-like particles are easy to obtain through thallus culture, have good stability, are easy to purify and suitable for preparing vaccine, and are convenient for industrial production.
Owner:张定梅 +3
Bacterial host strain
ActiveUS20150344840A1Reduced activityDecreasing proteolysisBacteriaHydrolasesBacteroidesMutated protein
A recombinant gram-negative bacterial cell comprising one or more of the following mutated protease genes: a) a mutated Tsp gene, wherein the mutated Tsp gene encodes a Tsp protein having reduced protease activity or is a knockout mutated Tsp gene; b) a mutated ptr gene, wherein the mutated ptr gene encodes a Protease III protein having reduced protease activity or is a knockout mutated ptr gene; and c) a mutated DegP gene encoding a DegP protein having chaperone activity and reduced protease activity; wherein the cell is isogenic to a wild-type bacterial cell except for the mutated Tsp gene and / or mutated ptr gene and / or mutated DegP gene and optionally a polynucleotide sequence encoding a protein of interest.
Owner:UCB PHARMA SA
Method for controlling domestic silkworm pupal stage growth
InactiveCN102250932ADevelopment does not affectAutomatic extension of the pupal stageFermentationGenetic engineeringAgricultural scienceF1 generation
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and specifically relates to a method of domestic silkworm transgene for controlling domestic silkworm pupal stage growth through UAS / GAL4 dual system. According to the method, piggyBAC transposon vector pigA3GFP is adopted as a base vector; through genetic engineering operation, GAL4 gene expressed transgenic domestic silkworm PDP-GAL4 system controlled by domestic silkworm cocoon protease gene promoter (PDP) is established; through genetic engineering operation, domestic silkworm baculovirus egt gene or charybdotoxin BmKIT3R gene expressed transgenic domestic silkworm UAS-egt or UAS-BmKIT3R system controlled by UAS promoter is established; the PDP-GAL4 system and the UAS-egt or UAS-BmKIT3R system are hybridized, such that larval stage growth of an F1 generation is normal, and pupal stage of the F1 generation is prolonged for 7 to 10 days. According to the invention, with an UAS / GAL4 dual system, the F1 generation silkworm pupal stage is prolonged by using domestic silkworm baculovirus egt gene or BmKIT3R gene. Flexibilities of silkworm cocoon purchasing and filature technology are improved. Therefore, the invention has important application value.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Organic solvent resisting proteinase high-yield bacterium, gene and application of the organic solvent resisting proteinase
The invention discloses a tolerance organic solvent protease high yield bacterial strain, protease gene and the protease application in organic phase catalysis peptides synthesis. The bacterial strain sorting naming is Pseudomonas aeruginosa PT121, preserving registration number is CCTCC M 208029, and is gram negative bacterial strain and various organic solvent which can resist certain concentration. The organic solvent-tolerance protease encode gene produced from the bacterium is separated and cloned by the invention which comprises nucleotide sequence showed as SEQ ID NO:1 and amino acid sequence showed as SEQ ID NO:2. The tolerance organic solvent protease has the habitude of high yield, high specific activity, strong solvent tolerance, wide acting pH range and high temperature resistant. The protease is provided with organic phase catalysis peptides synthesis etc. industry applications value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
HIV-1 virus protease inhibitor drug resistance mutation detection kit and method
InactiveCN103215348AHigh degree of integrationHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenes mutationMutation detection
The invention relates to an HIV-1 protease inhibitor drug resistance mutation detection method and a kit. Specifically, the invention also discloses a probe for detection of human immunodeficiency virus protease gene drug resistance mutation, and the probe includes a probe for detection of protease gene D30N mutation, a probe for detection of protease gene V32I mutation, a probe for detection of protease gene M46I and M46L mutation, a probe for detection of protease gene I47V and I47A mutation, a probe for detection of protease gene G48V mutation, a probe for detection of protease gene I50V mutation, a probe for detection of protease gene I54V mutation, a probe for detection of protease gene V82A, V82F, V82T and V82S mutation, a probe for detection of protease gene I84V mutation, a probe for detection of protease gene N88D mutation, and a probe for detection of protease gene L90M mutation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Ev71 virus-like particles and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveUS20160166675A1Easy to obtain high level expression strainHigh level expressionSsRNA viruses positive-senseBacteriaMolecular sieveMycelium
The present invention provides EV71 virus-like particles and a preparation method and application thereof. The method comprises: connecting a P1 protein gene and a 3CD protease gene of an EV71 virus with a PMV plasmid to construct a PMV-P1-3CD recombinant expression plasmid; then transforming a Hansenula polymorpha AU-0501 expression strain with the PMV-P1-3CD recombinant expression plasmid to obtain an AU-PMV-P1-3CD recombinant expression strain; fermenting and culturing the recombinant expression strain, and inducing the recombinant expression strain to express the EV71 virus-like particle protein with methanol; centrifuging and collecting mycelia for homogeneous breakage at a high pressure; and purifying the supernatant through ion-exchange chromatography, hydrophobic chromatography, and molecular sieve chromatography, so as to obtain EV71 virus-like particles.
Owner:BEIJING MINHAI BIOTECH
Protease gene obtained from paecilomyces cicadae and having function of degrading insect body wall and application
InactiveCN103233026AImprove insecticidal effectHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesBiologyAmino acid
The invention discloses protease gene obtained from paecilomyces cicadae and having a function of degrading an insect body wall, wherein the protease gene is shown in SEQ IN NO: 16; and a protease protein fragment which is obtained from the paecilomyces cicadae and has the function of degrading the insect body wall is provided, wherein the amino acid sequence of the protease is shown in SEQ IN NO: 17. By utilizing the protease gene disclosed by the invention and expressed by genes, the insect body wall can be degraded, and a new idea is provided and a new manner is created for the research on a novel, high-efficiency and safe pesticide.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SUB TROPICS CROP INST
Acid protease Bs2688 mutant K203E with improved thermal stability and gene and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural living things, and particularly relates to a fungal acid protease Bs2688 mutant and a gene and application thereof. An amino acid sequenceof the protease is as shown in SEQ ID No.3. The invention provides the novel protease gene, and the protease good in performance is produced by means of gene engineering, and can be applied to the industries of feed, food, medicines and the like.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
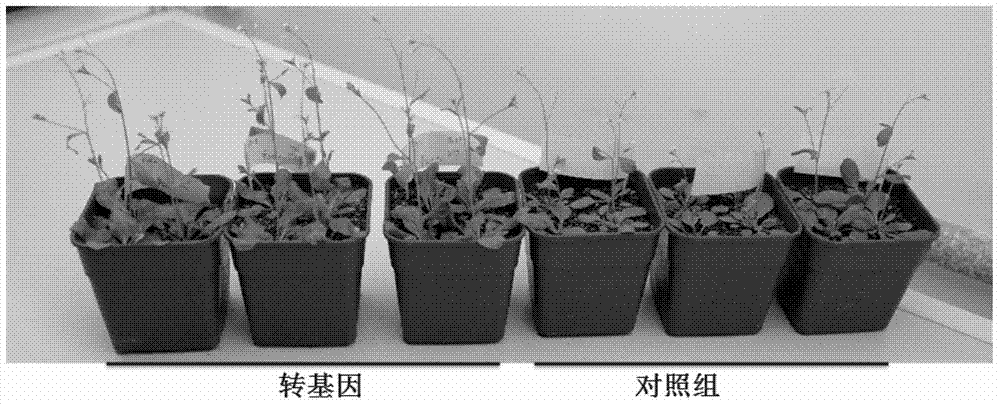
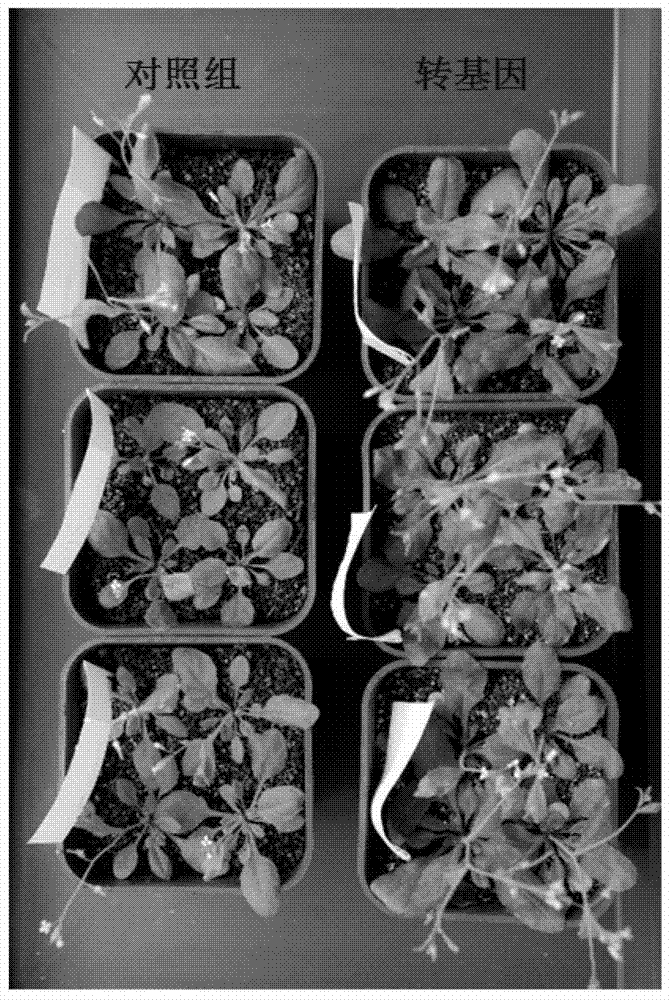
Method for promoting plant growth
The invention relates to a method for promoting plant growth. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a plant expression vector comprising FTO or other homologous demethylated protease gene; converting the plant expression vector into acceptor bacteria; converting the acceptor bacteria into target plants; culturing the obtained target plants, collecting and culturing the T0 generation seeds, screening positive plants from the seedlings; culturing the screened positive plants, after the growth of the seedlings, collecting the T1 generation seeds; culturing the T1 generation seeds, choosing positive plants from the seedlings; culturing the selected positive plants, after the growth of the seedlings, collecting the T2 generation seeds; culturing the T2 generation seeds, screening homozygous strain lines from the seedlings; and culturing the T1 generation seeds of the plants of the T2 generation homozygous strain lines so as to obtain the target plants. An exogenous gene that can modulate the RNA methylation modification of m6A in a cell is introduced into a plant through a transgene technology so as to modulate the m6A on the RNA of a plant in order to promote the plant growth.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
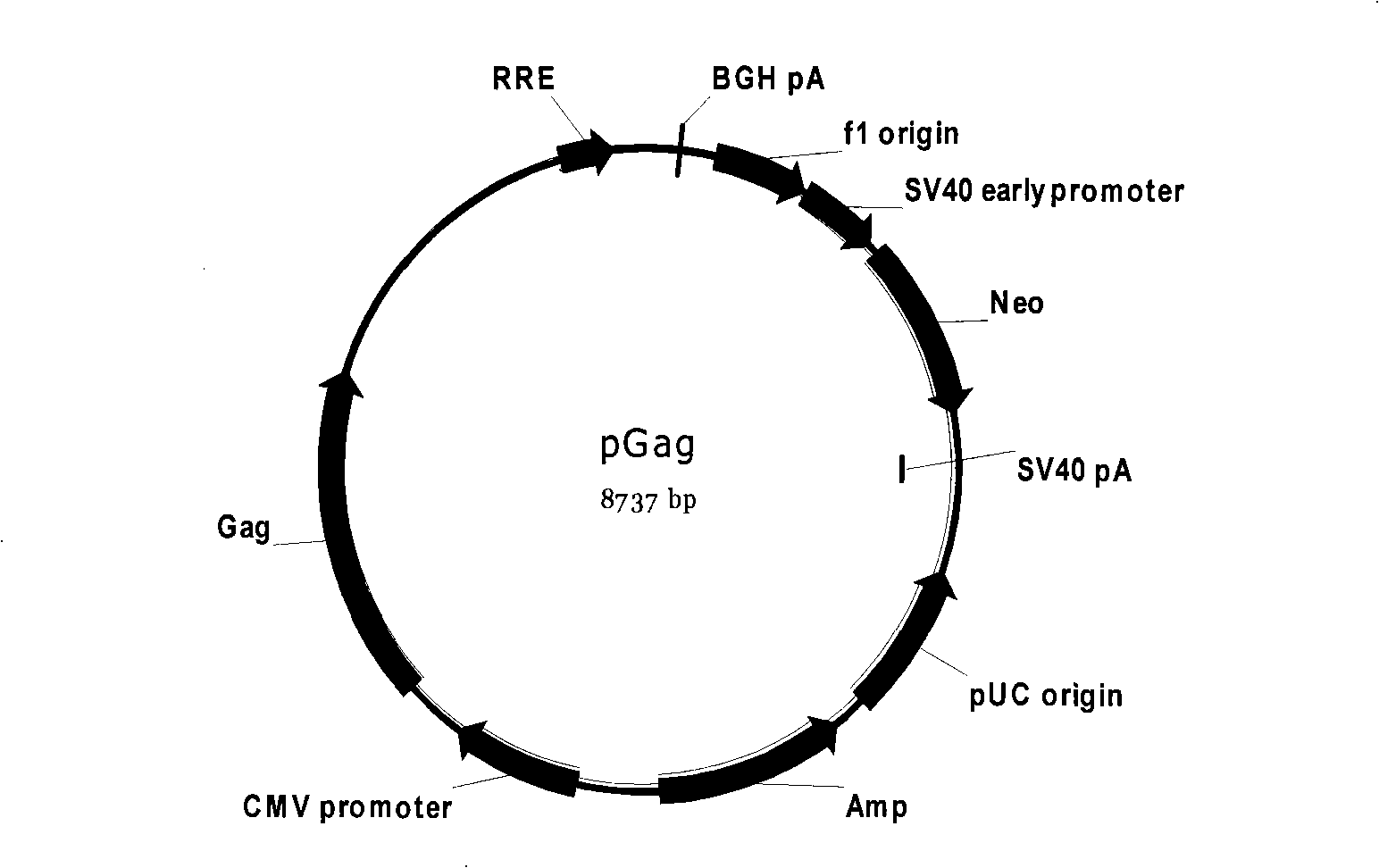
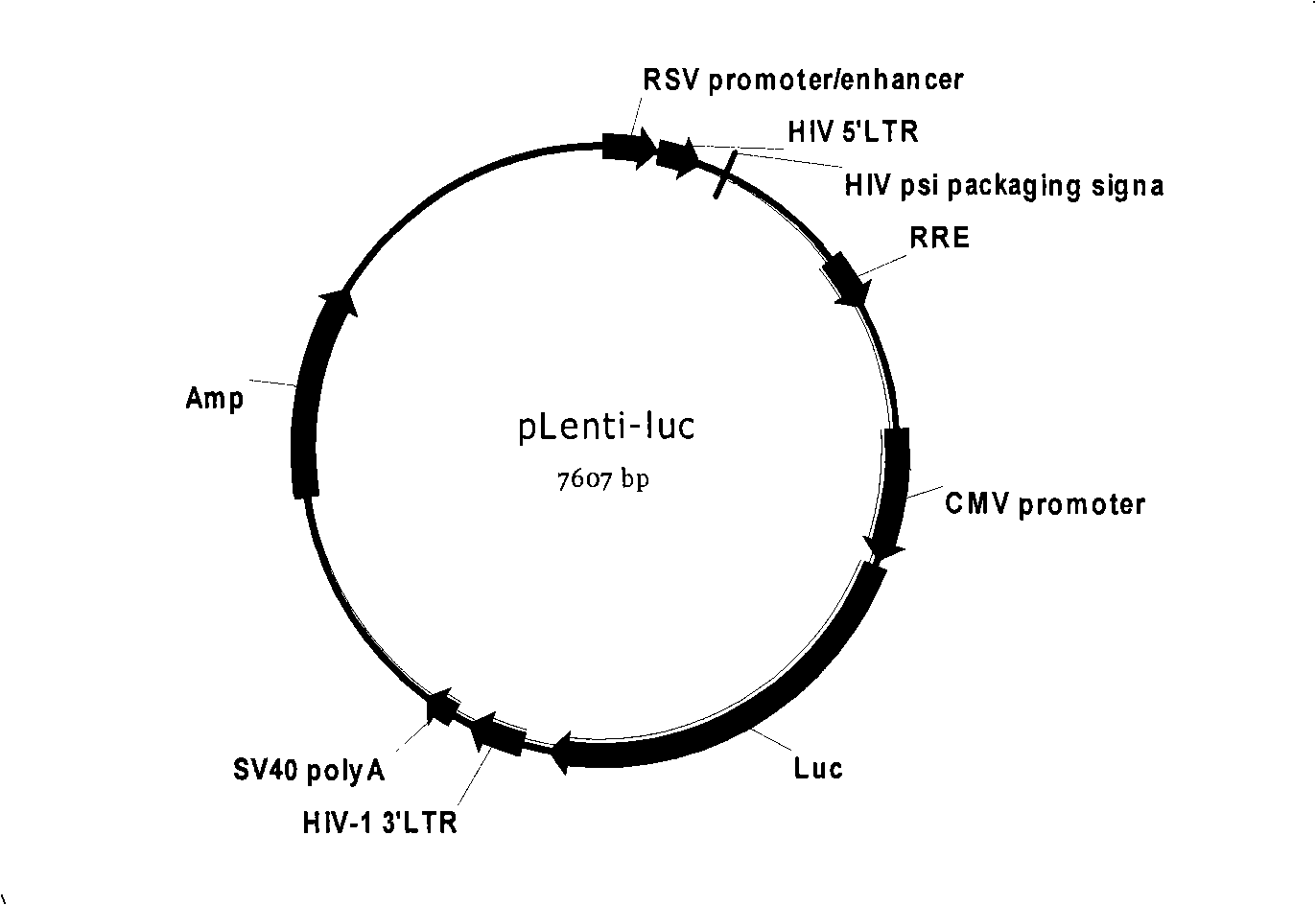
HIV stain drug-resistant phenotype analytical cell model and special pseudotype lentivirus therefor
InactiveCN101353667ARapid Phenotypic Resistance AnalysisSafety Phenotypic Resistance AnalysisMicrobiological testing/measurementViruses/bacteriophagesPhenotypic resistanceReverse transcriptase
The invention discloses a cell model of HIV strain phenotypic drug resistance analysis and special pseudotype slow virus thereof; the invention constructs plasmid for expressing Gag protein of HIV, recombinant slow-virus plasmid for expressing reporter gene and helper plasmid for expressing Rev protein of HIV; under the effect of the helper plasmid pVSV-G, the three plasmid and HIV reverse transcriptase and the gene fragment of protease which are amplified from strain can obtain the pseudotype slow virus of the HIV reverse transcriptase and protease gene containing strain. The pseudotype slow virus is used for infecting the cells of mammals, thus obtaining the strain phenotypic resistance cell model based on the reporter gene. The cell model of the invention can carry out phenotypic resistance analysis to the strain, the reporter gene leads the cell model to have super high sensitivity, and the cell model of HIV strain phenotypic drug resistance analysis is applicable to the phenotypic drug resistance analysis of HIV strain in Chinese population.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
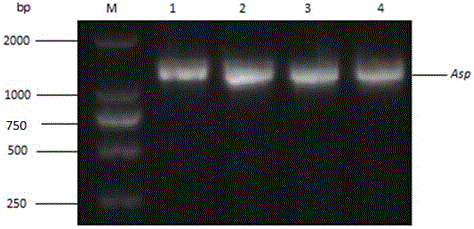
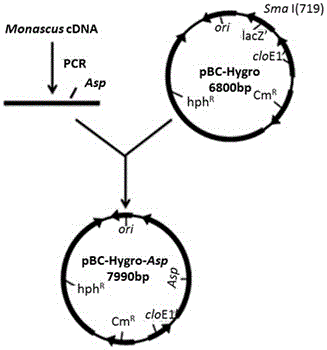
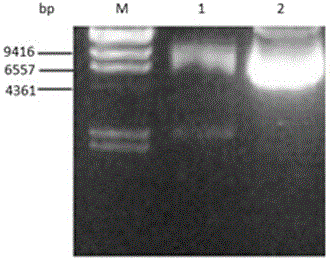
Method for constructing monascus strain capable of achieving high yield of acid protease
InactiveCN105039386AReduced activityHigh formulation costFungiMicroorganism based processesMonascus ruberWild type
The invention discloses a method for constructing a monascus strain capable of achieving high yield of acid protease. The method is characterized by firstly amplifying an Asp fragment of an acid protease gene in monascus from a monascus genome, then connecting the Asp fragment obtained through amplification to an empty vector to construct a recombinant expression vector of acid protease in monascus, transforming the recombinant expression vector of acid protease in monascus into agrobacterium tumefaciens to obtain recombinant agrobacterium tumefaciens and then guiding the recombinant agrobacterium tumefaciens into monascus by utilizing an agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated method, thus obtaining the monascus strain capable of achieving high yield of acid protease. The monascus transformant strain capable of achieving high yield of acid protease, which is obtained by a gene recombination method, has the characteristics of high-efficiency expression, accuracy in processing and genetic stability of the transformant and can achieve passage stability under non-selective pressure. The expression quantity of the acid protease gene in the monascus strain capable of achieving high yield of acid protease is 3.30 times the expression quantities of wild type genes, so that high yield of acid protease can be achieved.
Owner:LUZHOU LAOJIAO GRP CO LTD +2
Refractory metal prolease gene engineering bacterium and acquiring method therefor
The present invention discloses (pichia pastoris) CGMCC No1622, which can produce metal protease and a manufacturing method of obtaining the bacterial strain. Through designing a DNA primer, 1005 basic group is obtained by using PCR method and increasing from the total DNA of the Bacillus licheniformis XJT9503, and then cloned on the Pmd18-T carrier, after making a sequence analysis and measure to the obtained gene, the high temperature neutral protease gene is EMP, the snatch size is 942 basic group which expresses 314 aminophenol, and a Bacillus subtilis system is made use of validating and affirming the obtained gene. The present invention provides an effective way for making the extensive ferment and production and improving the output of enzyme.
Owner:THE INST OF MICROBIOLOGY XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
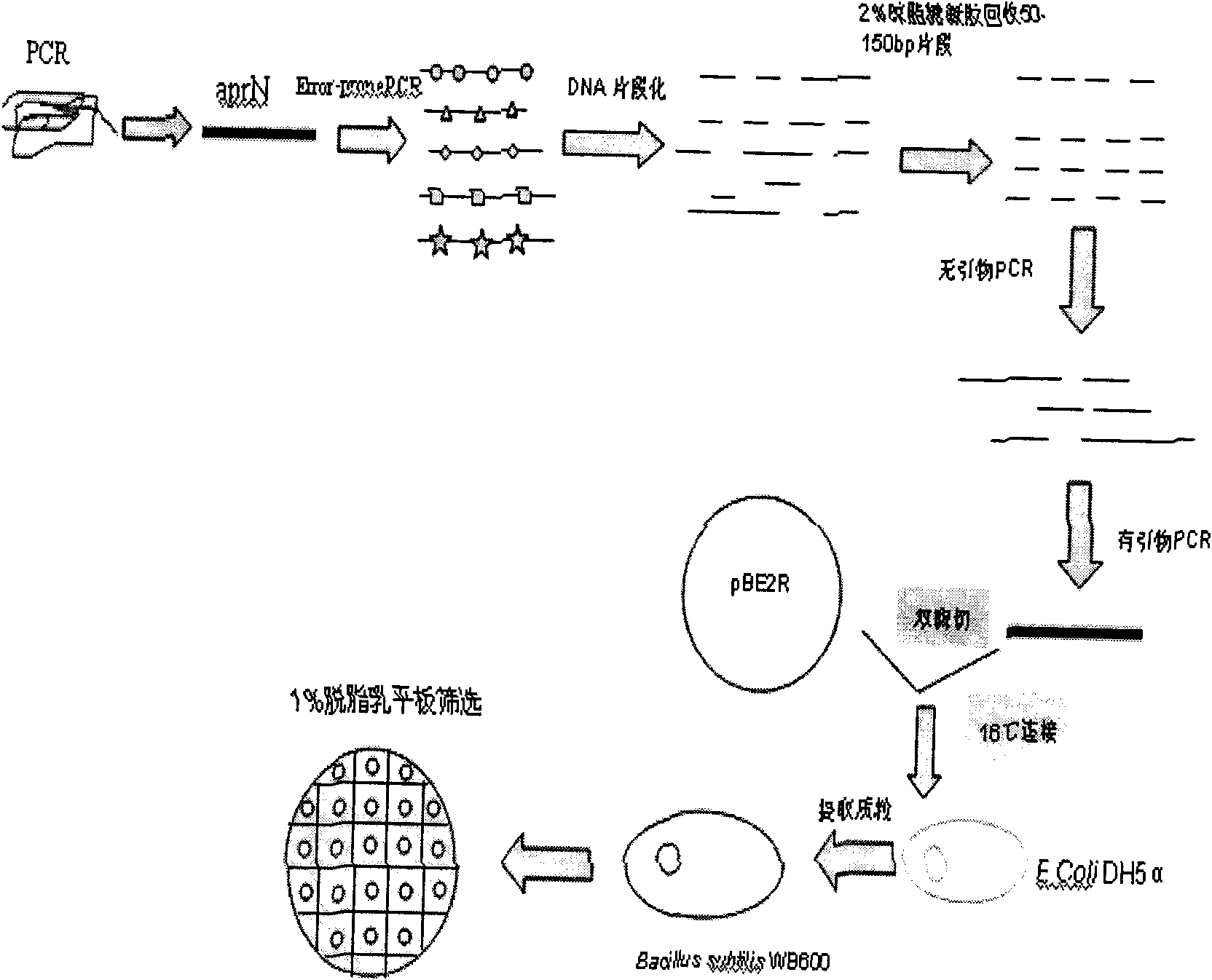
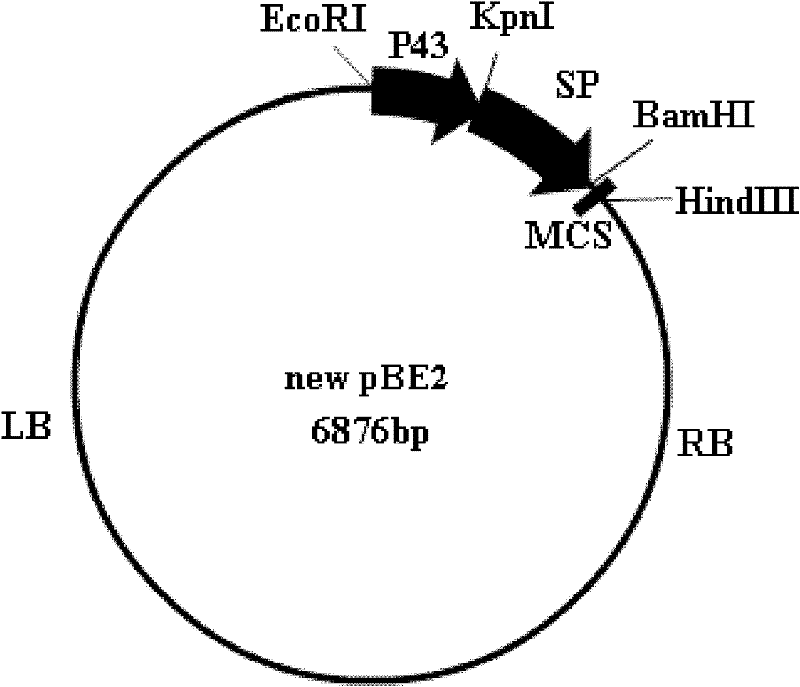
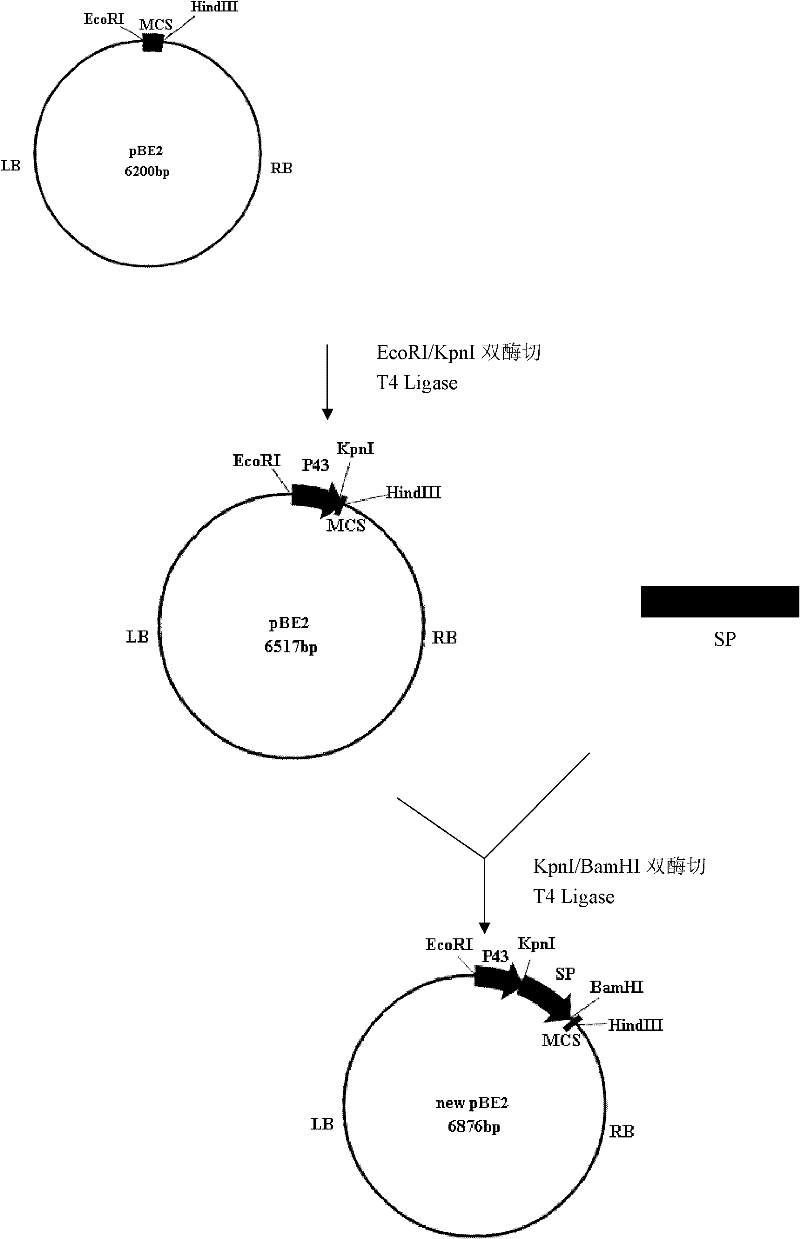
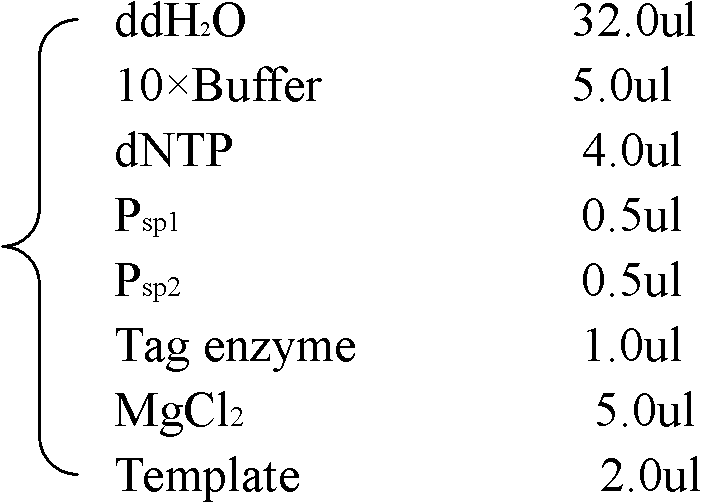
Multifunctional shuttle vector new pBE2, construction method thereof and method for constructing alkali protease mutation library by using same
InactiveCN102229942AImprove screening efficiencyReduce workloadMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliShuttle vector
The invention relates to a multifunctional shuttle vector new pBE2, a construction method thereof and a method for constructing an alkali protease mutation library by using the same. The main structure of the multifunctional shuttle vector is LB-P43-SP-MCS-RB. The construction method mainly comprises the following steps: connecting a big fragment of the pBE2 vector with a P43 strong promoter and the product of the amplification of surfactant protein (SP) and introducing a BamHI enzyme cutting site. The method for constructing the alkali protease mutation library mainly comprises: connecting a mature peptide fragment of an alkali protease gene of bacillus alcalophilus to the new pBE2, transferring into Escherichia coli to obtain a positive clone, transferring the positive clone into bacillus subtilis WB600 and performing several circles of high-flux screening. When the method for constructing the alkali protease mutation library, which is provided by the invention, is used, the pertinence to mutation of an alkali protease gene is increased, mutation is performed according to the mature peptide part of the alkali protease, and the workload required for oriented evolution study on the alkali protease is reduced greatly.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of low-temperature protease
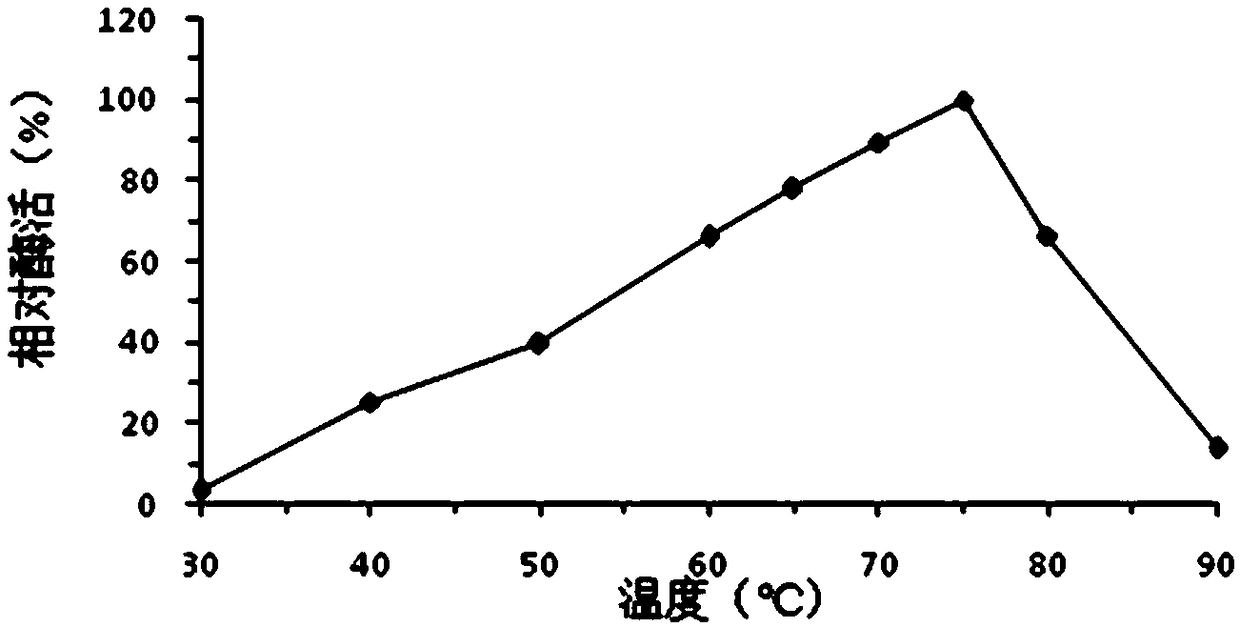
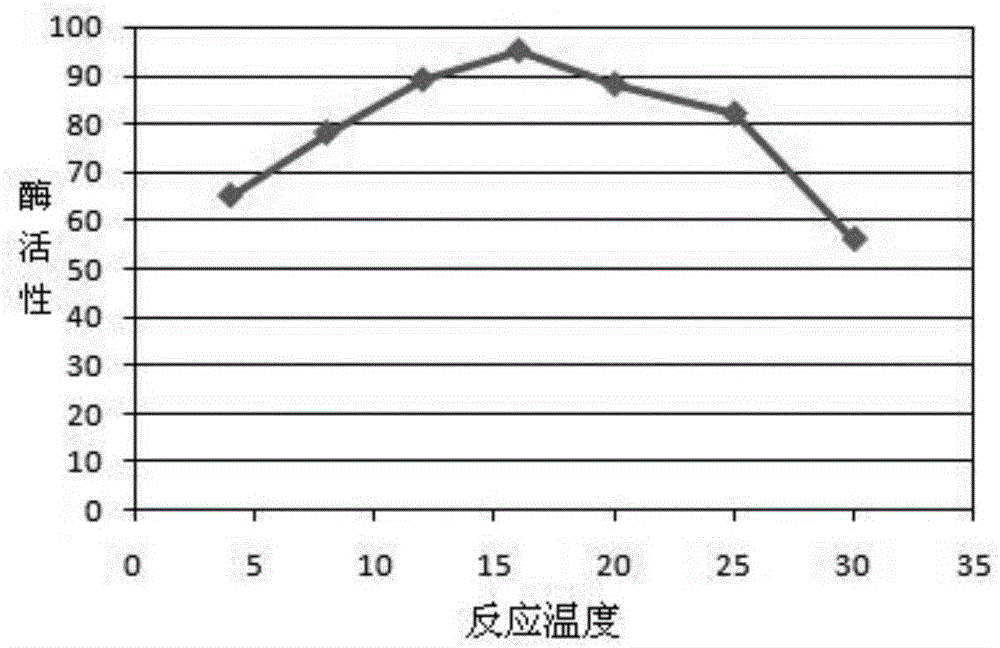
InactiveCN106636161AEnhance low temperature washing effectIncrease enzyme activityHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionColwellia psychrerythraeaChemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of low-temperature protease. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) designing and synthesizing a Colwellia psychrerythraea protease gene; 2) recombining and expressing Colwellia psychrerythraea protease; 3) performing affinity purification on the Colwellia psychrerythraea protease; 4) detecting the activity temperature dependency of the Colwellia psychrerythraea protease. The optimal temperature range of the enzymatic activity of the prepared low-temperature protease is 8 to 30 degrees; in the temperature range, various proteins can be dehydrated, so that the protease is very suitable for serving as protease of a cold water detergent.
Owner:SUZHOU KUANGSHI JUNCHI BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com