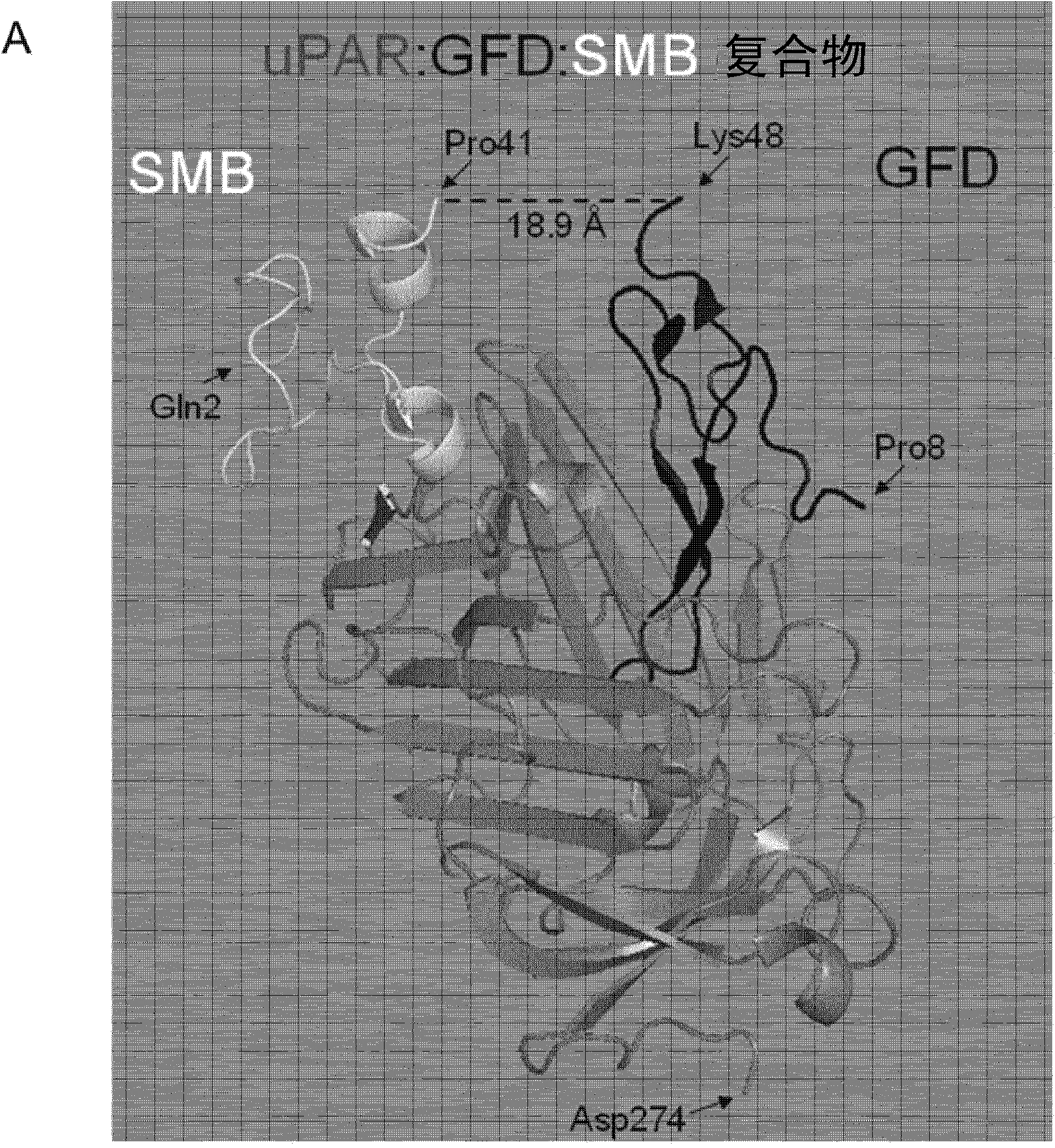Patents
Literature
56 results about "Extracellular protease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The extracellular proteases are a complex and heterogeneous superfamily of enzymes. They include metalloproteinases (matrix metalloproteinases, adamalysins, or pappalysins), serine proteases (elastase, coagulation factors, plasmin, tissue plasminogen activator, urokinase plasminogen activator), and the cysteine proteases (such cathepsins).
Plant extracts and dermatological uses thereof
InactiveUS20070122492A1Good for healthGood lookingBiocideCompound screeningMatrix metalloproteasesSkin lines
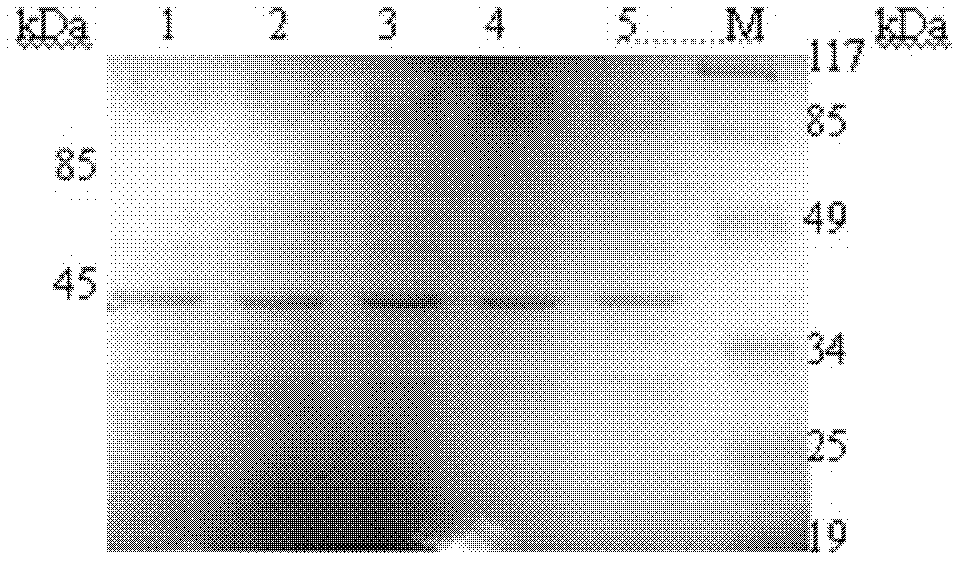
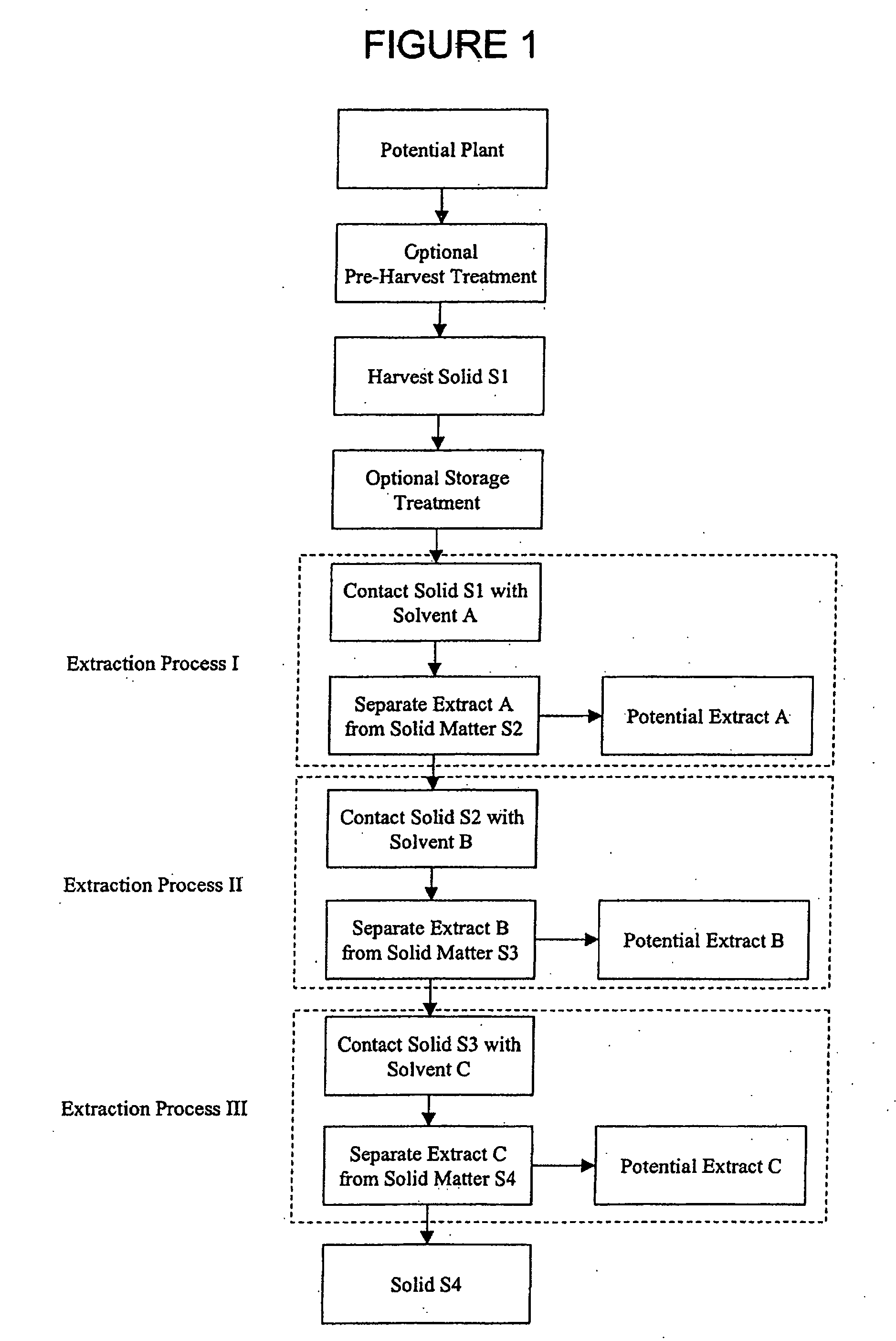
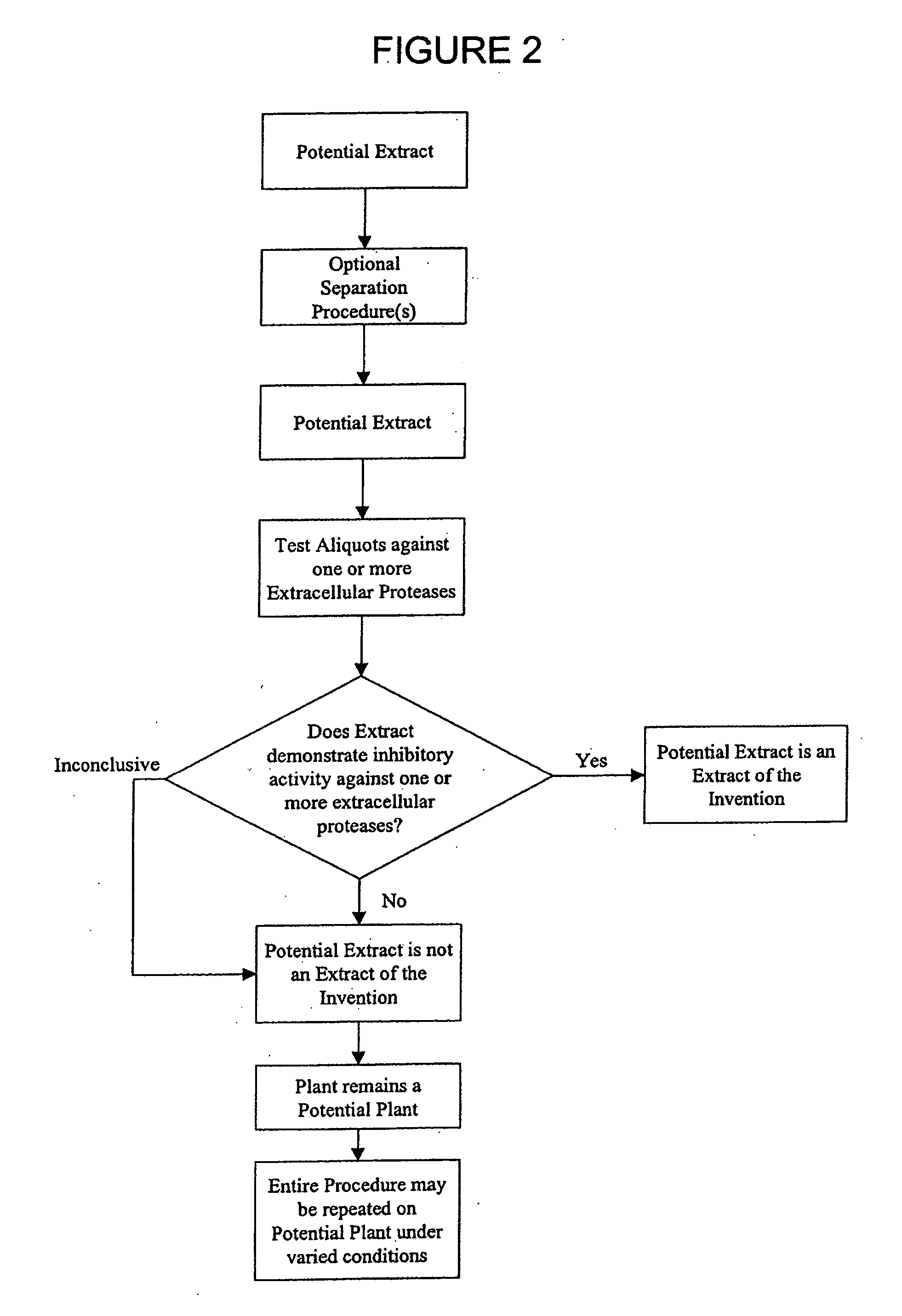
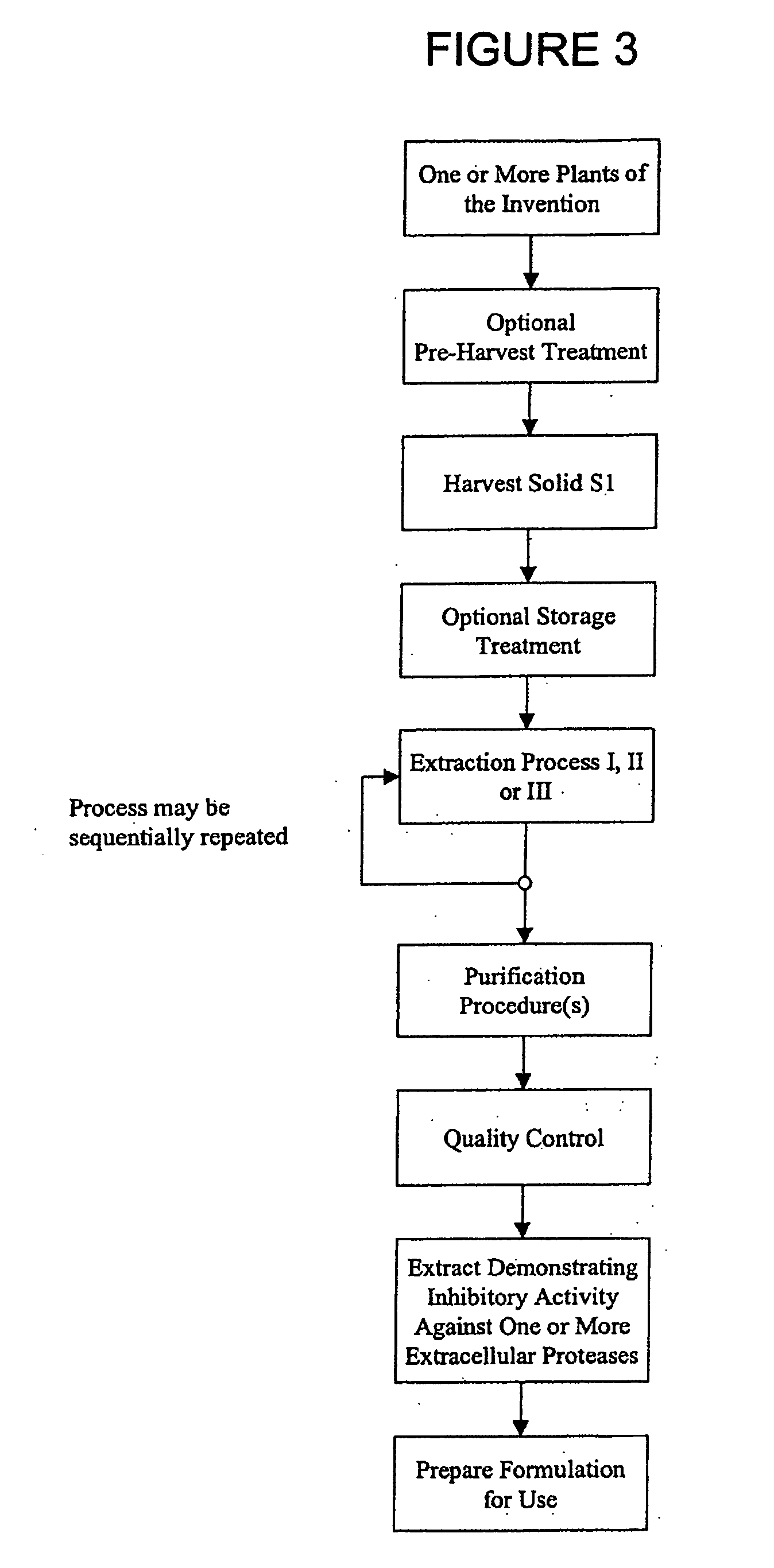
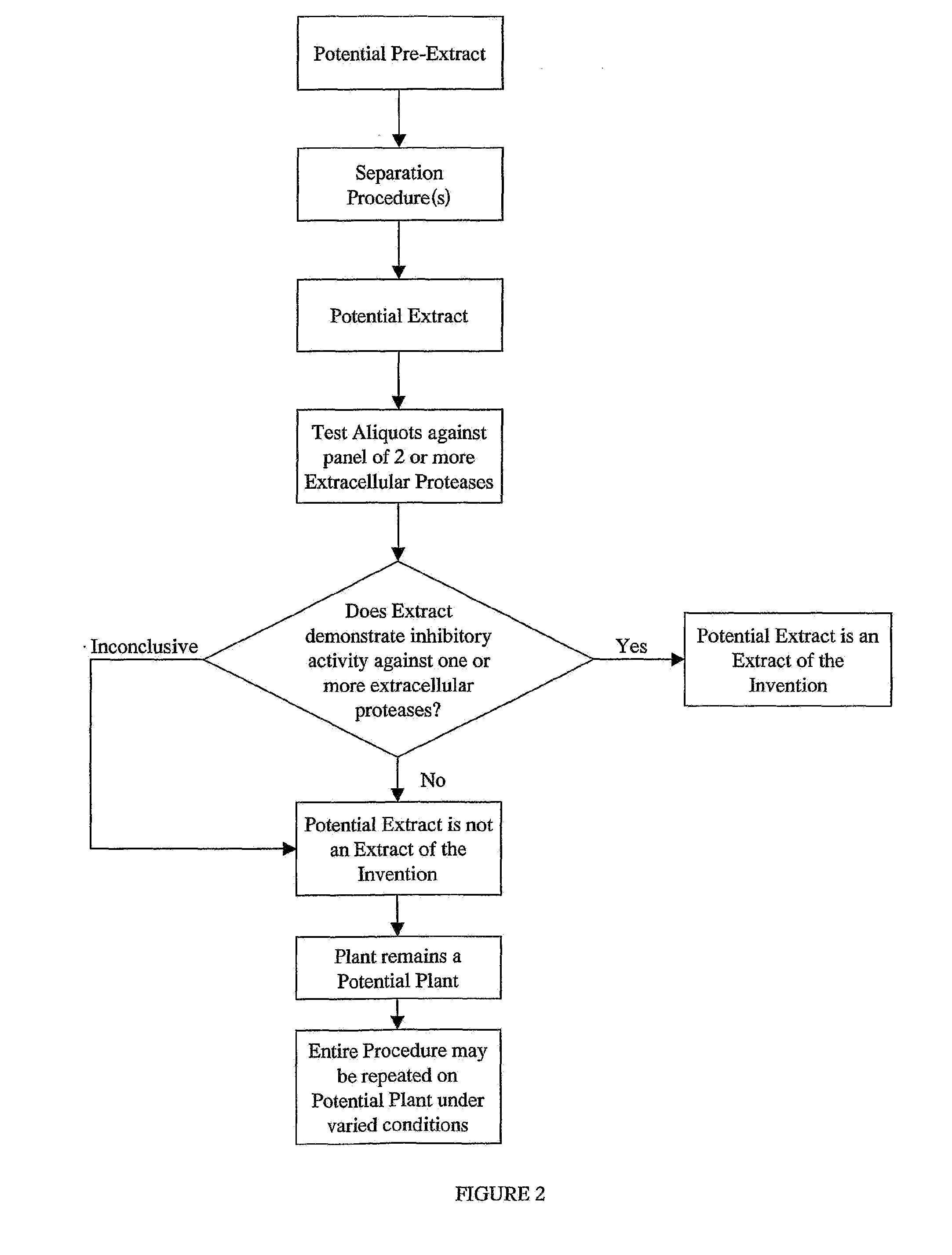
The present invention provides for plant extracts and dermatological formulations comprising one or more plant extracts that are capable of inhibiting one or more extracellular proteases selected from the group of: matrix metalloprotease-1 (MMP-1), matrix metalloprotease-2 (MMP-2), matrix metalloprotease-3 (MMP-3), matrix metalloprotease-9 (MMP-9) and human leukocyte elastase (HLE). The present invention further provides for a rapid method for screening plant extracts to identify those having the above activity that are suitable for incorporation into the dermatological formulations of the invention. The invention also provides for the use of the plant extracts as dermatological agents suitable for the treatment or prevention of various dermatological conditions, including wrinkling or sagging of the skin, irradiation induced skin and / or hair damage, deepening of skin lines, elastotic changes in the skin, as well as for the routine care of the skin, hair and / or nails.
Owner:BIOPHARMACOPAE DESIGN INT
Biocontrol bacteria strain preventing and curing plant disease
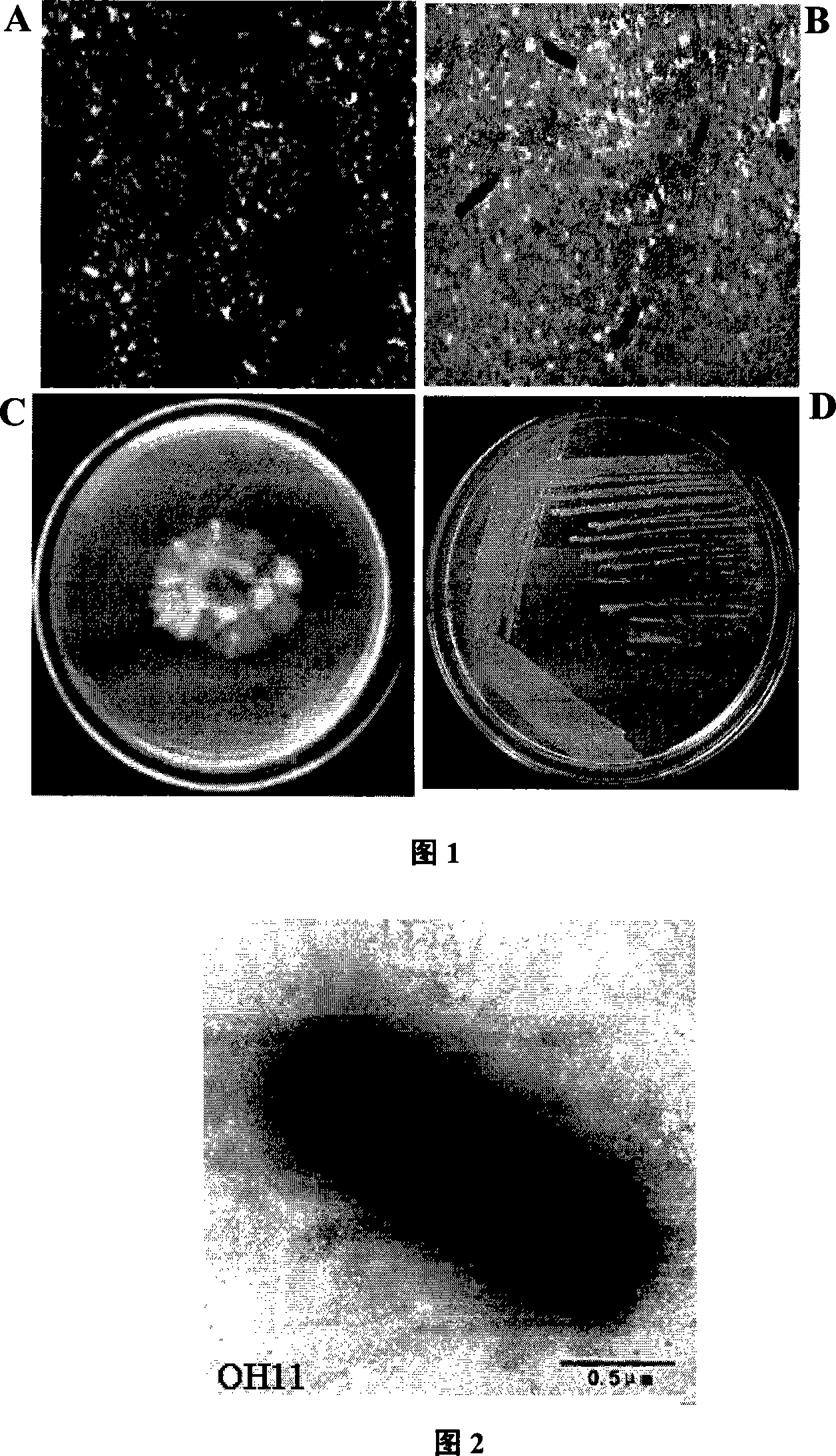
The invention provides a biocontrol bacterial strain for preventing and treating plant diseases and its bacterial agent, belonging to the field of biological control. The strains used are Gram-negative bacteria, identified as Lysobacter enzymogenes, and the strain code is OH11. Strain OH11 has no flagella but has slippage, can produce various extracellular hydrolytic enzymes including chitinase, β-1,3-glucanase and protease, and can effectively inhibit the growth of fungi and bacteria. The antibacterial zone diameters of strain OH11 against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Phytophthora capsici were both greater than 22.0 mm; the antagonism against potato ring rot was stronger, and the diameter of the inhibition zone reached 50 mm. The OH11 strain was inoculated into the seed tank, cultivated to the logarithmic growth phase, and the seed liquid was connected to the production tank for cultivation. The medium used in the production tank was the same as that of the seed tank. The liquid fermentation adopts aerobic submerged fermentation and fed-batch process, the dissolved oxygen is 15%-20%, the fermentation temperature is 30°C, the fermentation time is 72h, and the initial pH value is 7.5. After the fermentation is completed, the culture solution is taken out of the tank and directly packed into liquid dosage forms with plastic packaging barrels or packaging bottles, or subpackaged into solid dosage forms with peat adsorption packaging bags. The biocontrol strain OH11 can effectively control plant pathogenic fungi, bacteria, nematodes and other diseases, and the overall control effect is 50%-70%. In the greenhouse pot experiment, the control effects of OH11 on pepper blight and tomato bacterial wilt reached 83.6% and 86.4%, respectively. Strain OH11 has the characteristics of broad antibacterial spectrum, high activity, and environmental safety. In today's serious pesticide pollution, zymolysobacterium and its bacterial agent will be a good substitute.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Plant Extracts and Dermatological Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20110311661A1Good for healthGood lookingCompound screeningCosmetic preparationsRoutine careMedicine
Plant extracts and dermatological formulations comprising one or more plant extracts that are capable of inhibiting one or more extracellular proteases selected from the group of: matrix metalloprotease-1 (MMP-1), matrix metalloprotease-2 (MMP-2), matrix metalloprotease-3 (MMP-3), matrix metalloprotease-9 (MMP-9) and human leukocyte elastase (HLE). A rapid method for screening plant extracts to identify those having the above activity that are suitable for incorporation into the dermatological formulations of the invention. The use of the plant extracts as dermatological agents suitable for the treatment or prevention of various dermatological conditions, including wrinkling or sagging of the skin, irradiation induced skin and / or hair damage, deepening of skin lines, elastotic changes in the skin, as well as for the routine care of the skin, hair and / or nails.
Owner:LUCAS MEYER COSMETICS CANADA
Bacillus pumilus, probiotics preparation and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102586144AHigh activityBroad inhibitoryAntibacterial agentsBacteriaAmylaseAmylosucrase activity
The invention discloses bacillus pumilus, a probiotics preparation and a preparation method and application thereof. The Bacillus pumilus LV149 is preserved in China center for type culture collection (CCTCC) in Nov. 23th, 2011, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2011411. The bacillus pumilus LV149 has strong extracellular protease, lipase and amylase activities, has wide rejection capability to vibrio and has no hemolytic activity. The Bacillus pumilus LV149 serves as fermenting bacterial strains and is performed with solid fermentation, drying and smashing so as to prepare bacillus pumilus probiotics preparation which uses Bacillus pumilus LV149 as the active ingredients. The bacillus pumilus probiotics preparation can be added into prawn feeds for feeding prawns, so that growth of prawn intestinal pathogenic vibrio can be restrained, prawn vibriosis can be reduced, simultaneously prawn growth is promoted, fish bait coefficient is reduced, quality of commodity is improved, culture cycle is shortened, accordingly culture risk and culture cost are reduced, biological safety is high and the bacillus pumilus, the probiotics preparation and the preparation method and application thereof have wide application prospect in aquaculture.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Inhibitors of extracellular proteases
InactiveUS20110217753A1Minimize degradationImprove fractionationCosmetic preparationsOther chemical processesExtracellular proteinsProtein purification
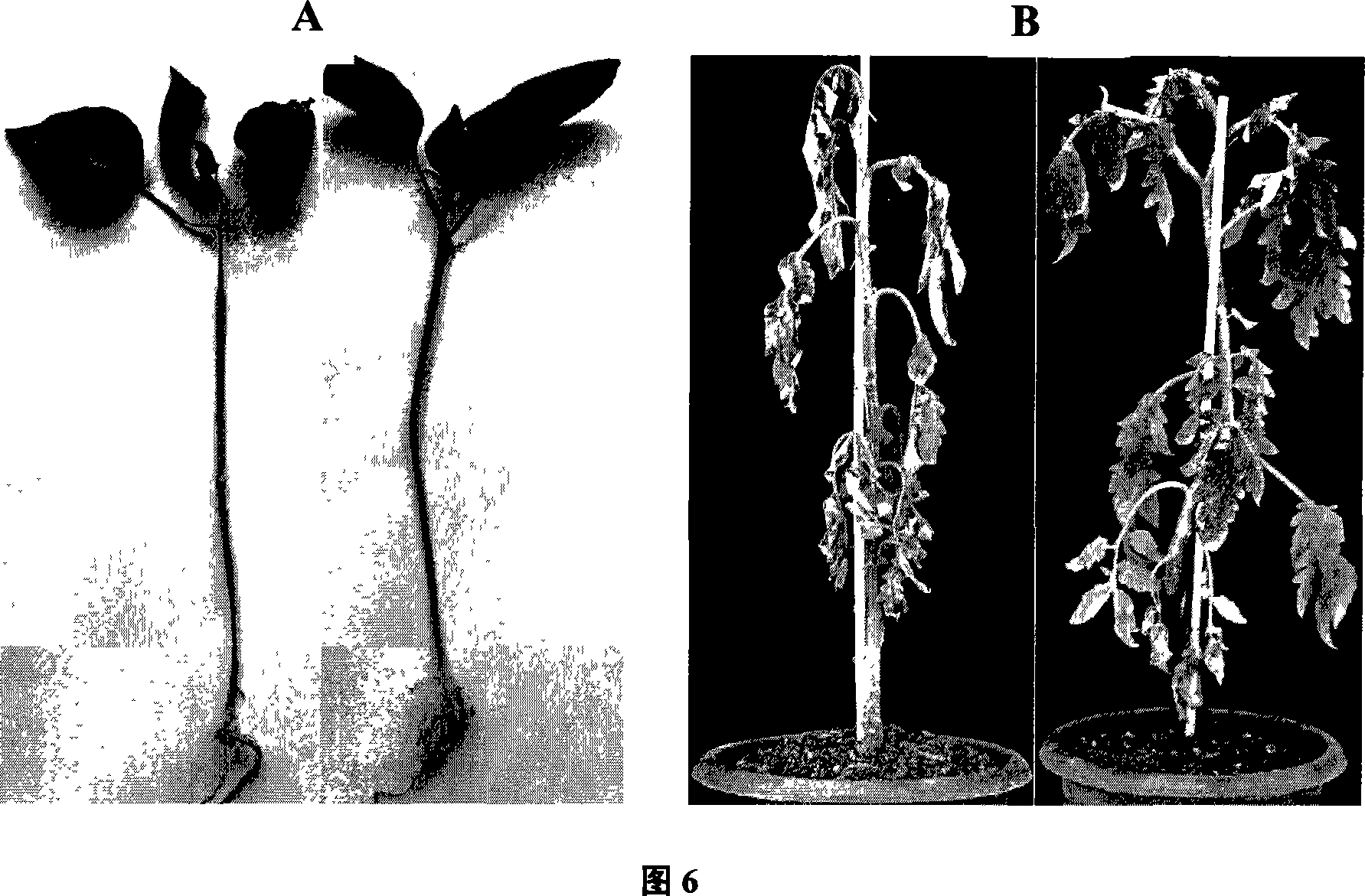
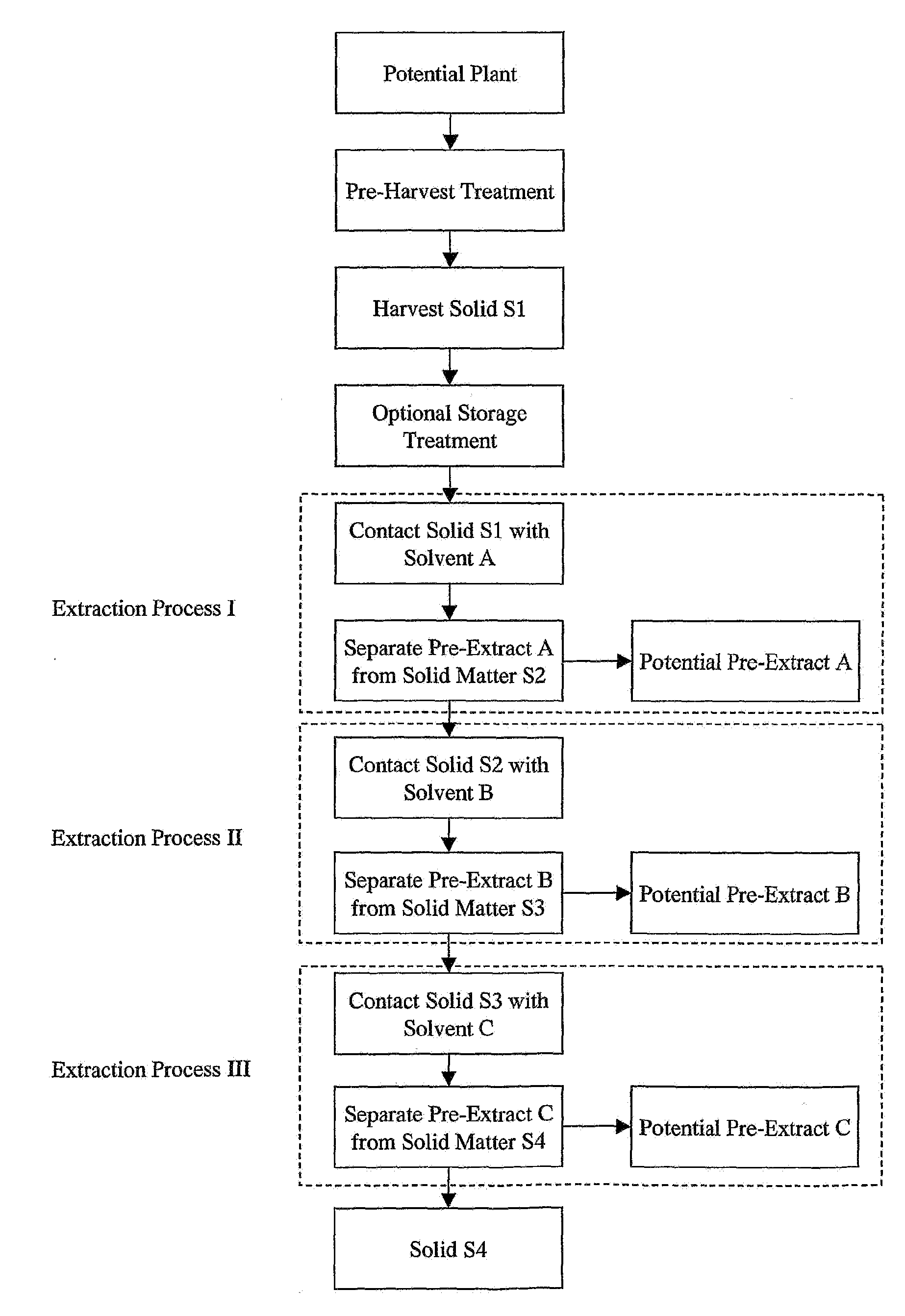
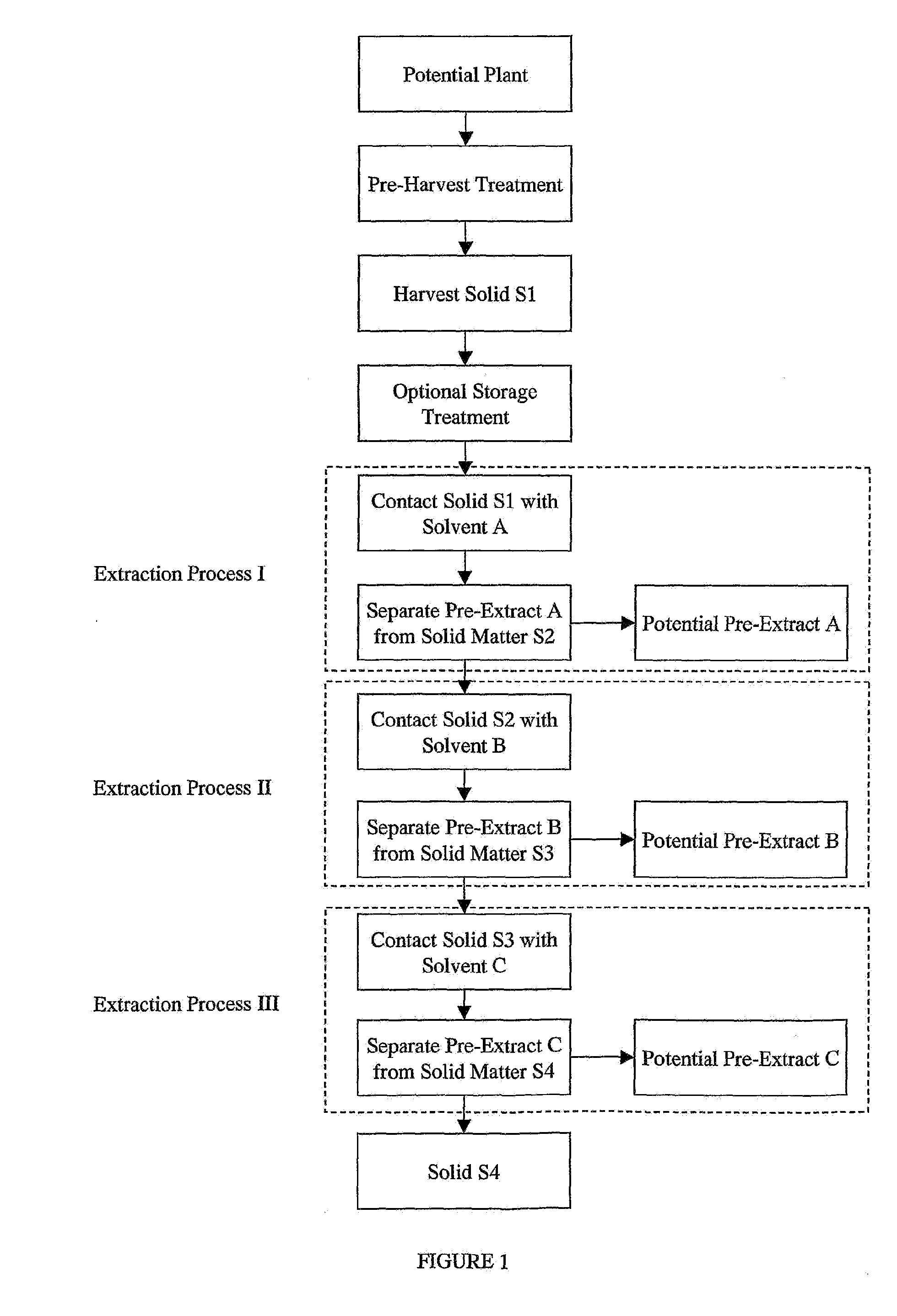
Provided is a plant derived extract including inhibitory activity against one or more extracellular proteases which degrade human tissue matrix. Moreover, the amount of inhibitory activity in an extract can be increased by stressing the plant prior to forming an extract. These extracts are each prepared by a process and demonstrate the ability to inhibit one or more extracellular proteases which degrade human tissue matrix. Libraries of extracts can be prepared from stressed and non-stressed plants, where each of the extracts demonstrate inhibitory activity against on or more extracellular protease inhibitors. Alternatively, semi-purified and purified inhibitory compounds can be isolated from the extracts. In one aspect, these extracts with inhibitory activity can be used during protein purification to minimize degradation due to extracellular proteases.
Owner:BIOPHARMACOPAE DESIGN INT
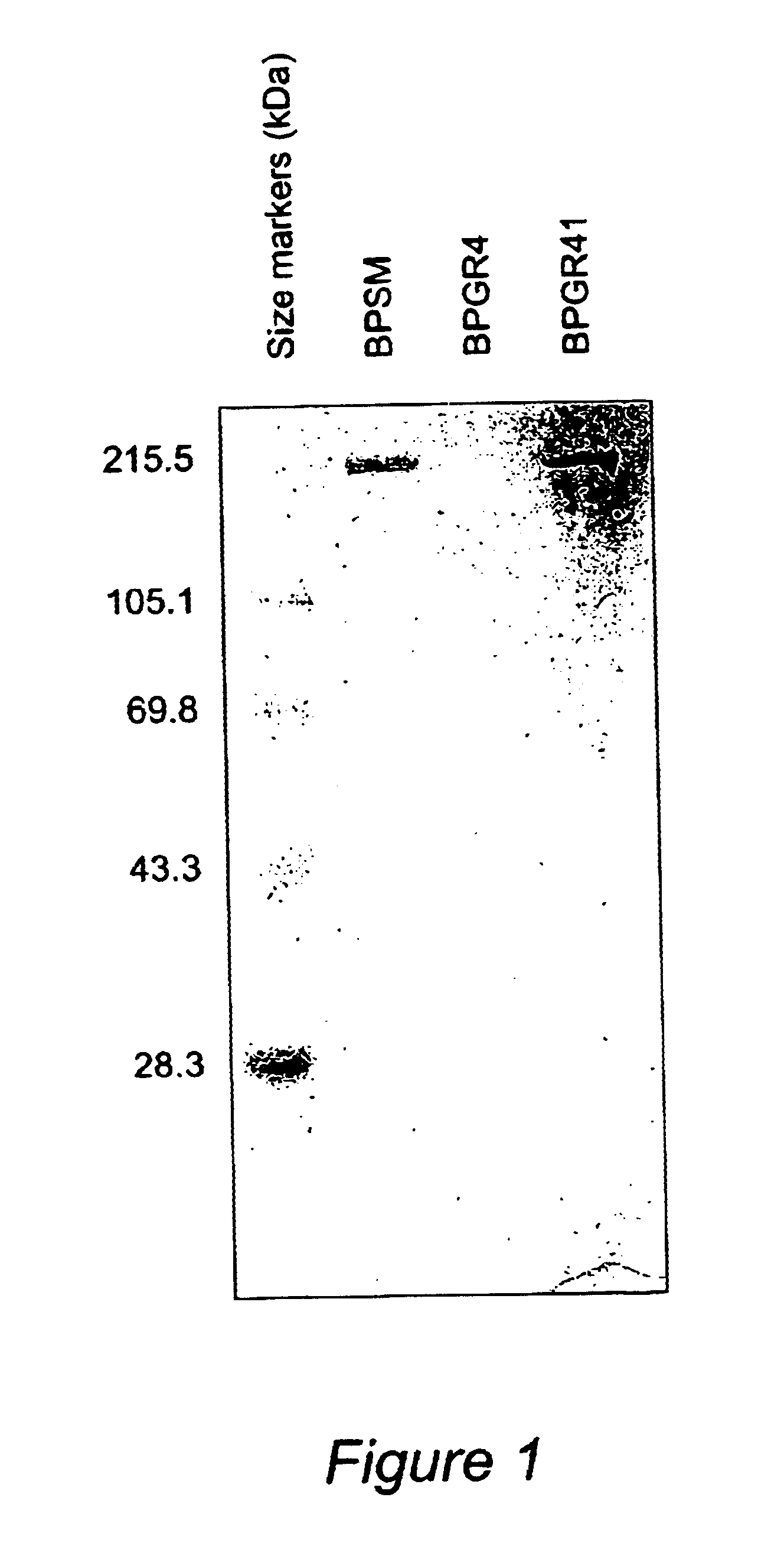
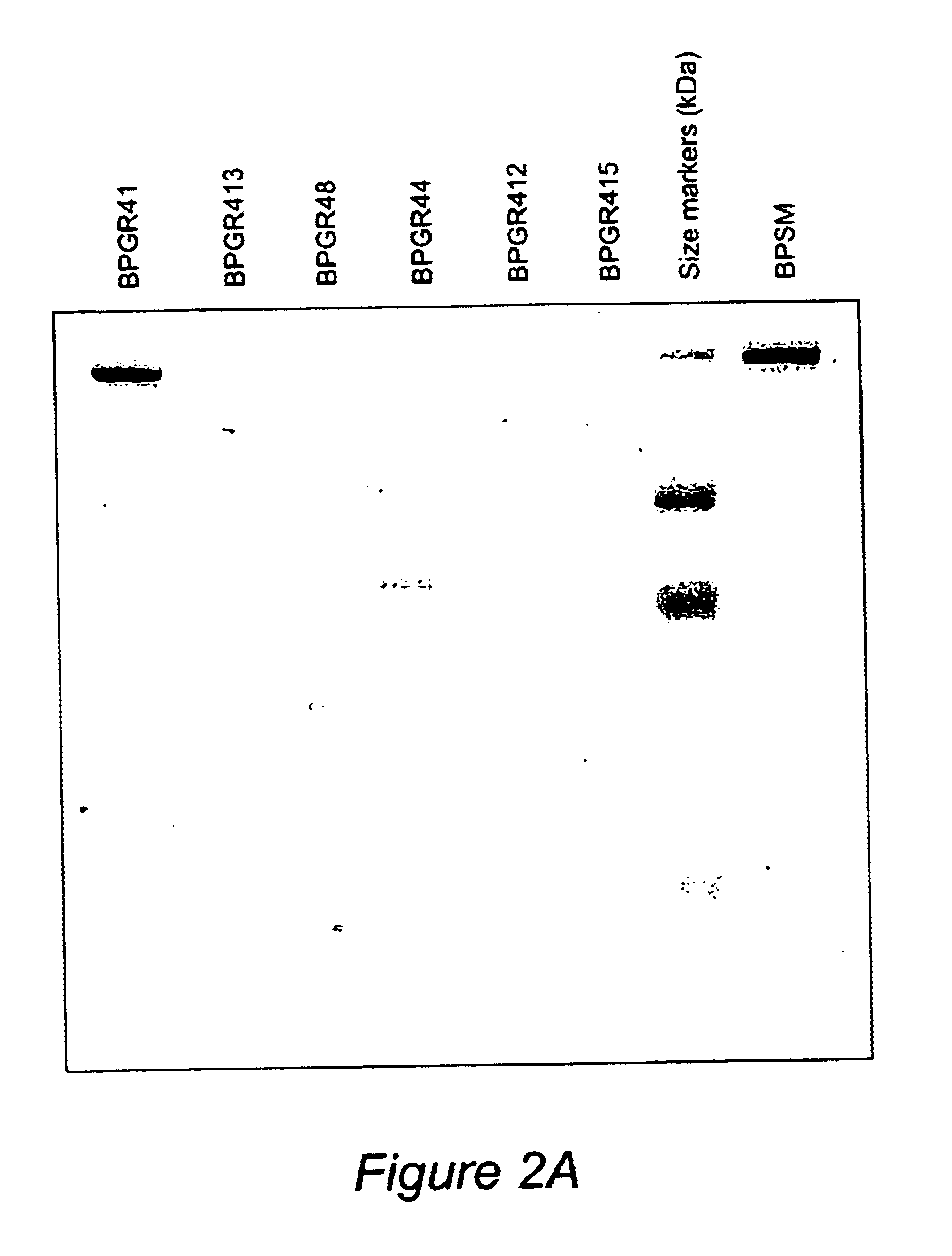
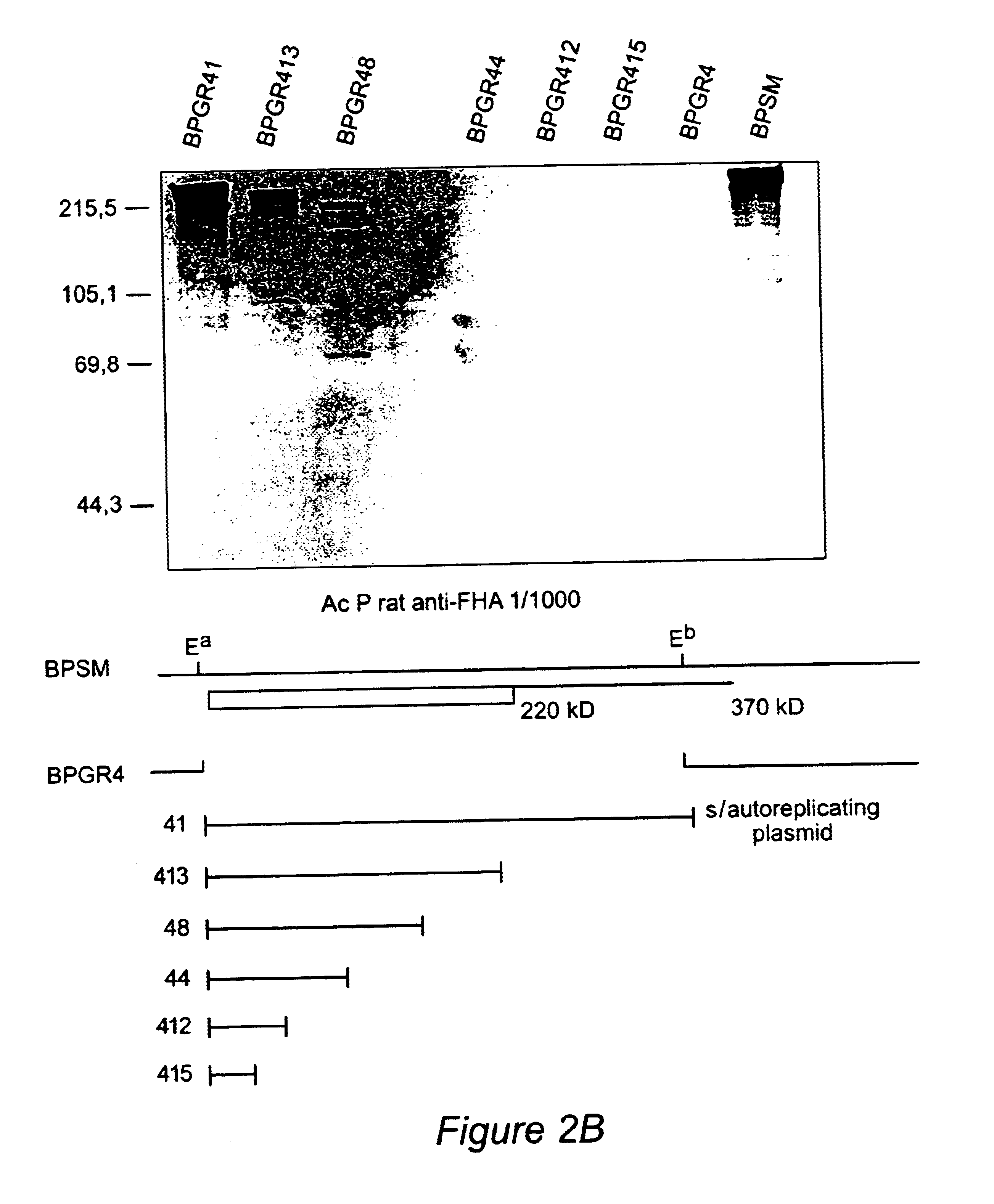
Recombinant proteins of filamentous haemagglutinin of bordetella, particularly bordetella pertussis, method for producing same, and uses thereof for producing foreign proteins of vaccinating active principles
InactiveUS6841358B1Easy to separateEasy to demonstrateBiocideBacterial antigen ingredientsHeterologousPolymerase L
A recombinant DNA containing a sequence (1) coding for a polypeptide heterologous to a filamentous haemagglutinin of Bordetella (Fha) fused within the reading frame to a sequence (2) located upstream from the first sequence. Sequence (2) codes for at least part of the Fha precursor, which part comprises at least the N-terminal region of a truncated mature Fha protein, which contains the interaction site of Fha and heparin and the secretion domain. This Fha protein is under the control of a promoter recognized by the cell polymerases of B. pertussis and is inserted into a B. pertussis cell culture, is expressed in the culture and excreted into the cell culture medium. The invention uses both the abilities of Bordetella and particularly B. pertussis to secrete or surface expose the heterologous polypeptide fused to the Fha portion corresponding to sequence (2), which does not appear to produce extracellular proteases, and the ease with which filamentous haemagglutinins can be isolated from other Bordetella proteins.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
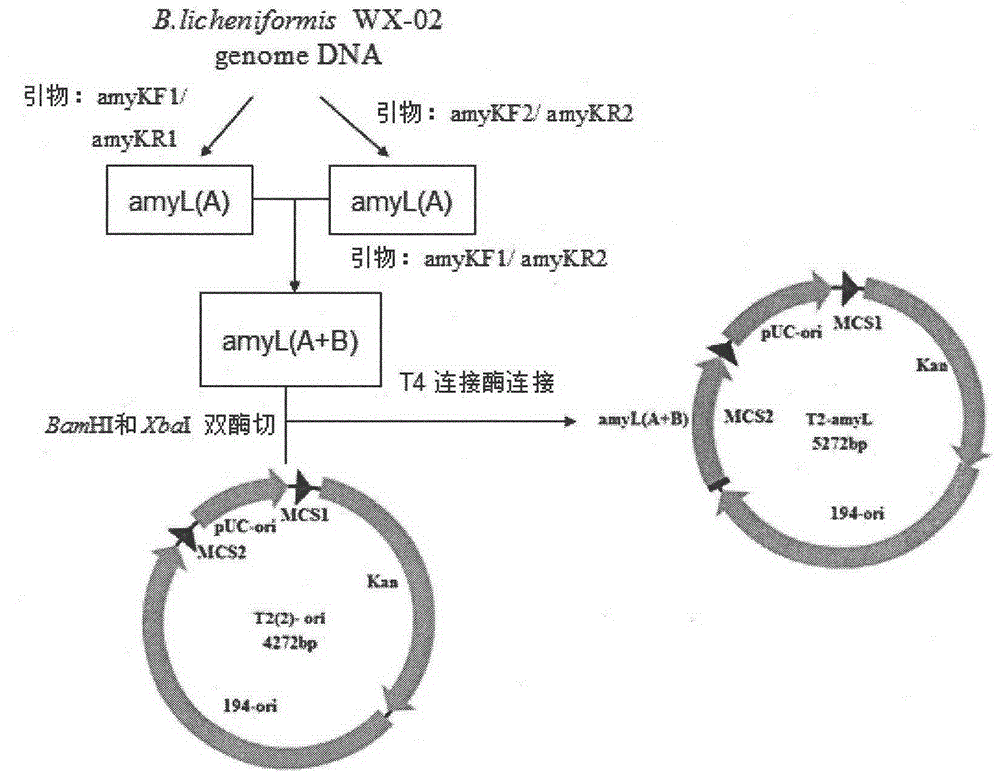
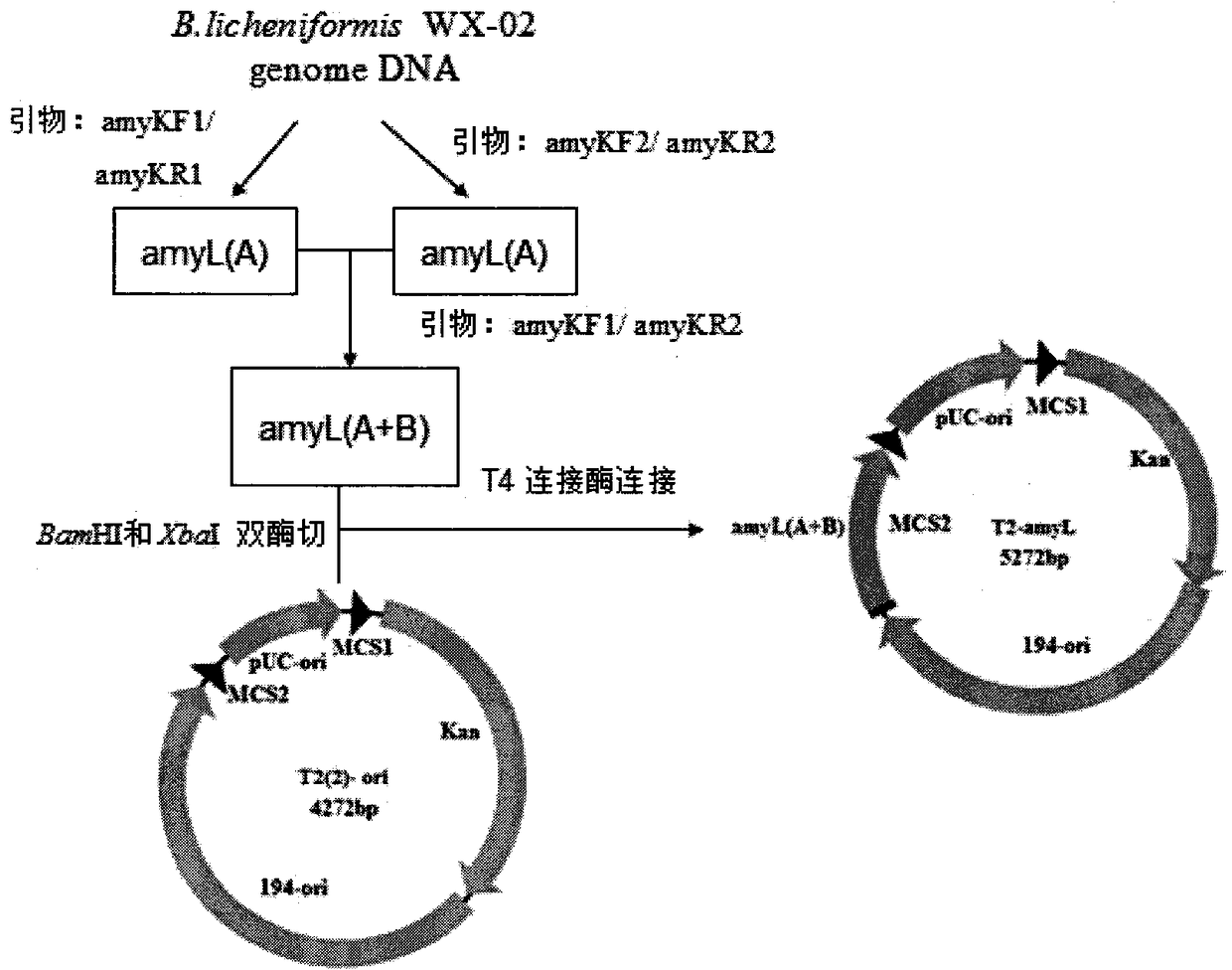
Bacillus licheniformis expression host
ActiveCN104630123AReduced activityIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaHydrolasesBacillus licheniformisProtein target
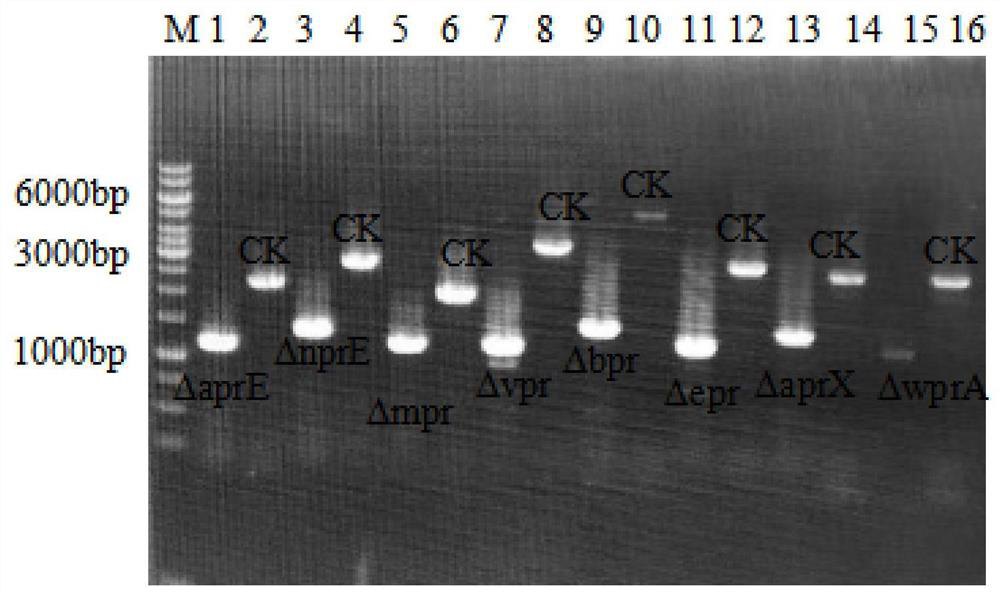
The invention discloses a bacillus licheniformis host bacterium BL10 with multiple gene deletion, the accession number of which is CCTCCNO:M2013400. The host bacterium derives from a bacillus licheniformis WX-02 which partially or completely has deletion of ten genes. The ten genes comprises eight protease genes (mpr encoding a metalloprotease; vpr encoding a serine protease; aprX encoding an intracellular serine protease; epr encoding a minimal extracellular protease; bpr encoding a bacillus peptidase F; wprA encoding a protease combined with cell walls; aprE encoding an extracellular alkaline serine protease; and bprA encoding a bacillus peptidase F) and two extracellular secretory protein genes (hag encoding flagellin; and amyL encoding alpha-amylase). The BL10 has completely no extracellular protease activity and can reduce the degradation effect of a protease on a target protein. When the target protein is expressed by the expression host, the expression level is higher, and the host bacterium benefits protein expression enhancement.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Application of trichoderma strains in preparation of biopesticide for preventing and controlling cucumber fusarium wilt
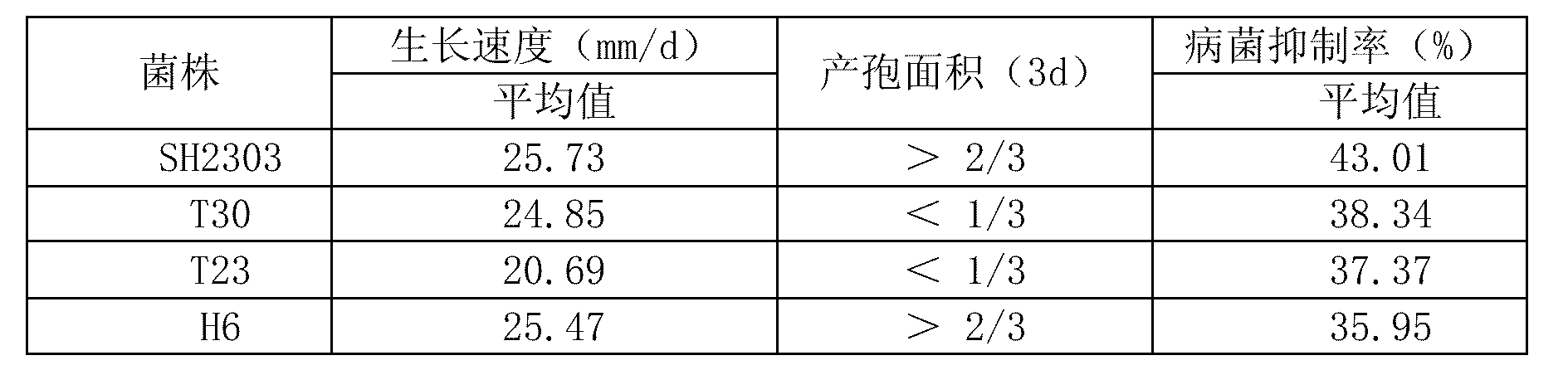
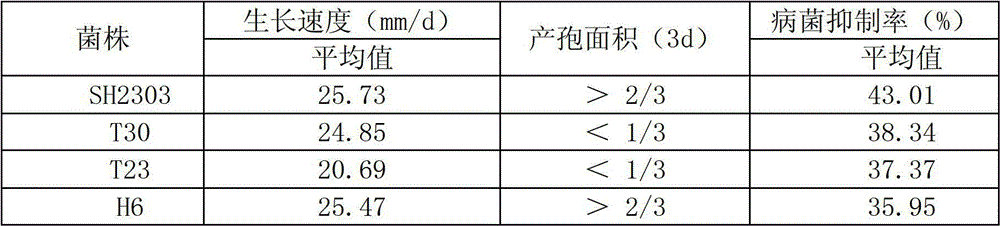
The invention relates to the application of trichoderma strains in preparation of biopesticide for preventing and controlling cucumber fusarium wilt. The trichoderma strains are Trichoderma harzianum SH2303CGMCC NO.4963. The main components for preventing and controlling the cucumber fusarium wilt are conidia of the Trichoderma harzianum SH2303; and the biopesticide can be seed coating agents or granules. The trichoderma strains in the application has high growth speed and high sporulation quantity; the confrontation pathogens inhibition rate in vitro reaches 43.01 percent; the inhibition rate of a non-volatile inhibitor to the cucumber fusarium wilt is 41.33 percent; the inhibition rate of a volatile inhibitor to the cucumber fusarium wilt is 11.49 percent; the chitinase activity is 3.9573U; the beta-1,3-glucanase enzyme activity is 0.5092U; the extracellular protease enzyme activity is 3.0678 U; the prevention effect aiming at the living bodies of the cucumber fusarium wilt is 71.43 percent; the overall proportion of the antibiosis secondary metabolites, having antagonism, in the strains is 30.28 percent; and the trichoderma strains can effectively prevent and treat the disease of the cucumber fusarium wilt.
Owner:侨昌生物科技(上海)有限公司
High-temperature-resistant protease, strain breeding method thereof and application method of high-temperature-resistant protease to enzymolysis
InactiveCN103981164AExtensive cleavage sitesLong storage timeFungiHydrolasesPichia pastorisSmall peptide
The invention relates to a high-temperature-resistant protease, a strain breeding method thereof and an application method of the high-temperature-resistant protease to enzymolysis. The high-temperature-resistant protease has activity and relatively high thermal stability at the temperature of 20-80 DEG C and is produced through pichia pastoris fermentation. Pichia pastoris which is used for fermenting to produce the high-temperature-resistant protease is classified and named as pichia pastoris MMpk-GS115. The strain breeding method comprises the steps of preparing engyodontium album, constructing a pichia pastoris expression vector, and the like. The application method of the high-temperature-resistant protease to enzymolysis comprises the following steps of firstly, preparing a crude high-temperature-resistant protease from the high-temperature-resistant protease; then, carrying out enzymolysis on an enzymolysis base material by using the crude high-temperature-resistant protease. The high-temperature-resistant protease has the advantages of capability of generating extracellular proteases, high enzymatic activity, short fermentation time and wide specificity of protease cutting sites; in addition, after being subjected to enzymolysis, vegetable proteins such as rice dregs, bean pulp, wine distiller grains, broussonetia papyrifera and the like and yeast cultures contain 10-50% of small peptides, can be improved in quality and increased in nutritional value and are easier to digest and absorb by animals.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Muricauda olearia and application thereof
ActiveCN103981140AReduce secretionReduce synthesisBiocideBacteriaVirulent characteristicsVirulence factor
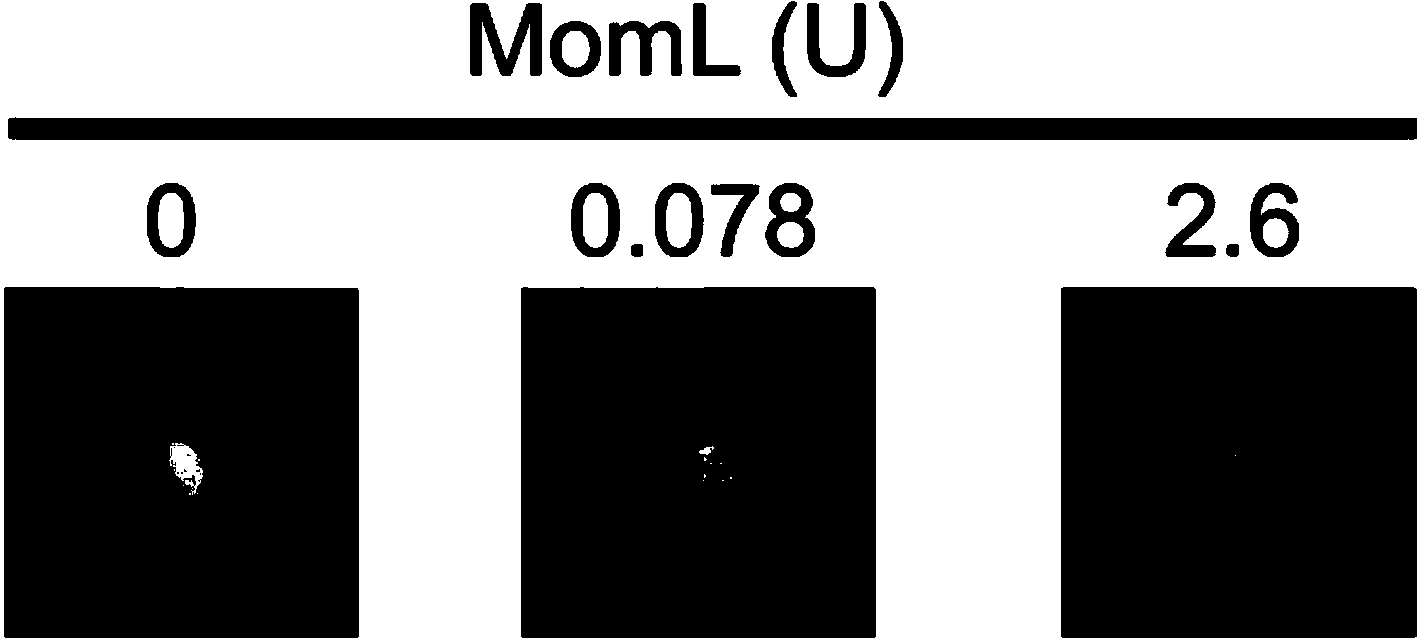
The invention provides Muricauda olearia. Muricauda oleariah is a quorum sensing quenching strain capable of inhibiting the secretion of pathogenic bacteria virulence factors, and the preservation number of Muricauda olearia LMM001 strain is CGMCC No. 8972. The invention also provides an AHL degrading enzyme MomL protein separated from the LMM001 strain, wherein the amino acid sequence of the MomL protein is SEQ ID NO: 1. The Muricauda olearia LMM001 strain disclosed by the invention can block the QS pathway of pathogenic bacteria by small molecule QS repressor, AHL lactonase MomL, AHL acyltransferase and other ways, and reduce the secretion of pathogenic bacteria virulence factors; the LMM001 strain has no toxic and side effects on zebrafish and can improve the resistance of zebrafish to the infection of Aeromonas hydrophila; AHL lactonase can greatly reduce the secretion of virulence factors such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa extracellular protease and pyocyanine and can reduce the synthesis of Chromobacterium violaceum and violacein.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Process for preparing antioxidative peptide and antifreeze peptide through enzymatic hydrolysis of salmon collagens
InactiveCN108118077ADifferent biological activitiesLow costConnective tissue peptidesHydrolasesOxygen radical absorbance capacityFiltration
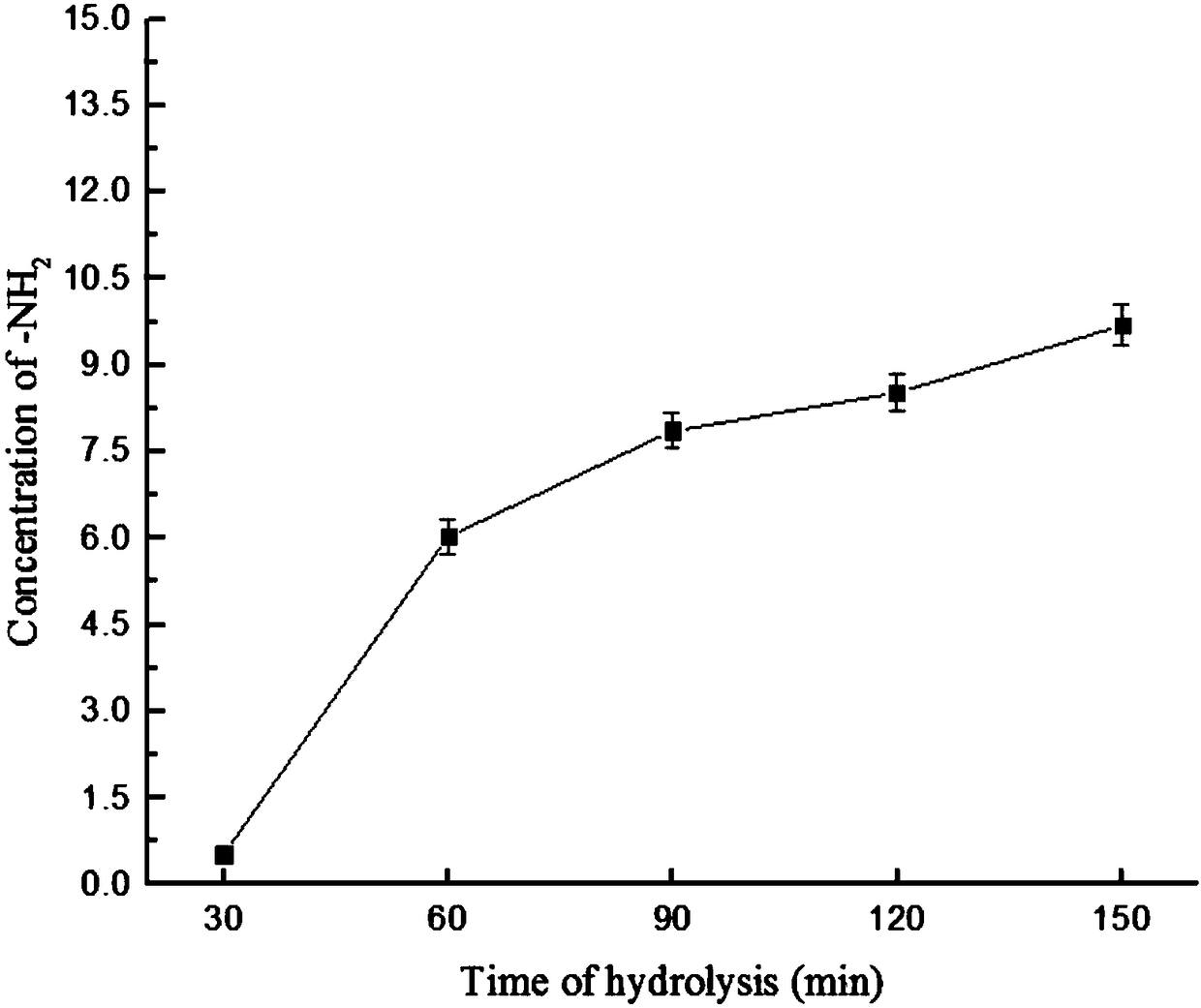
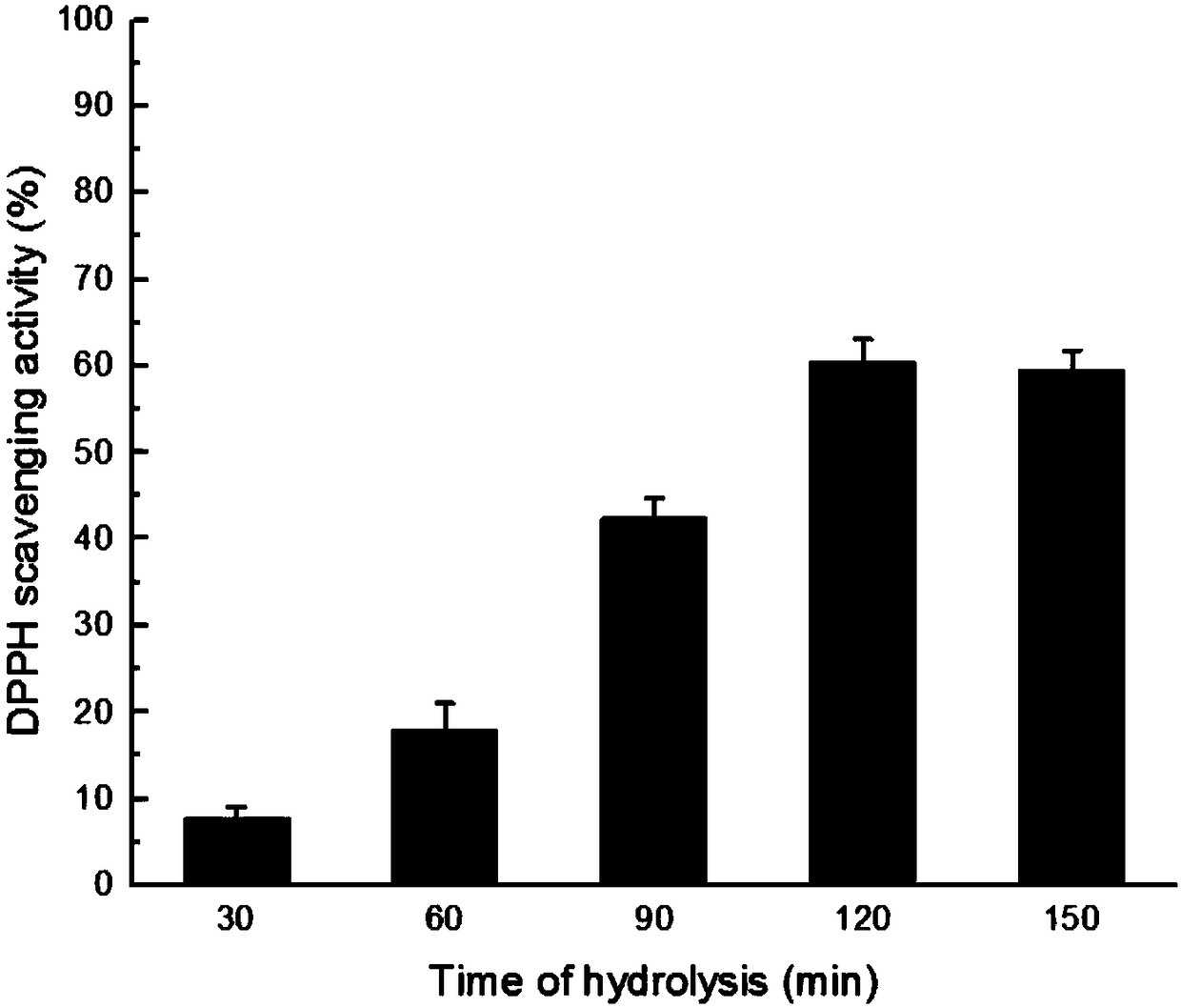
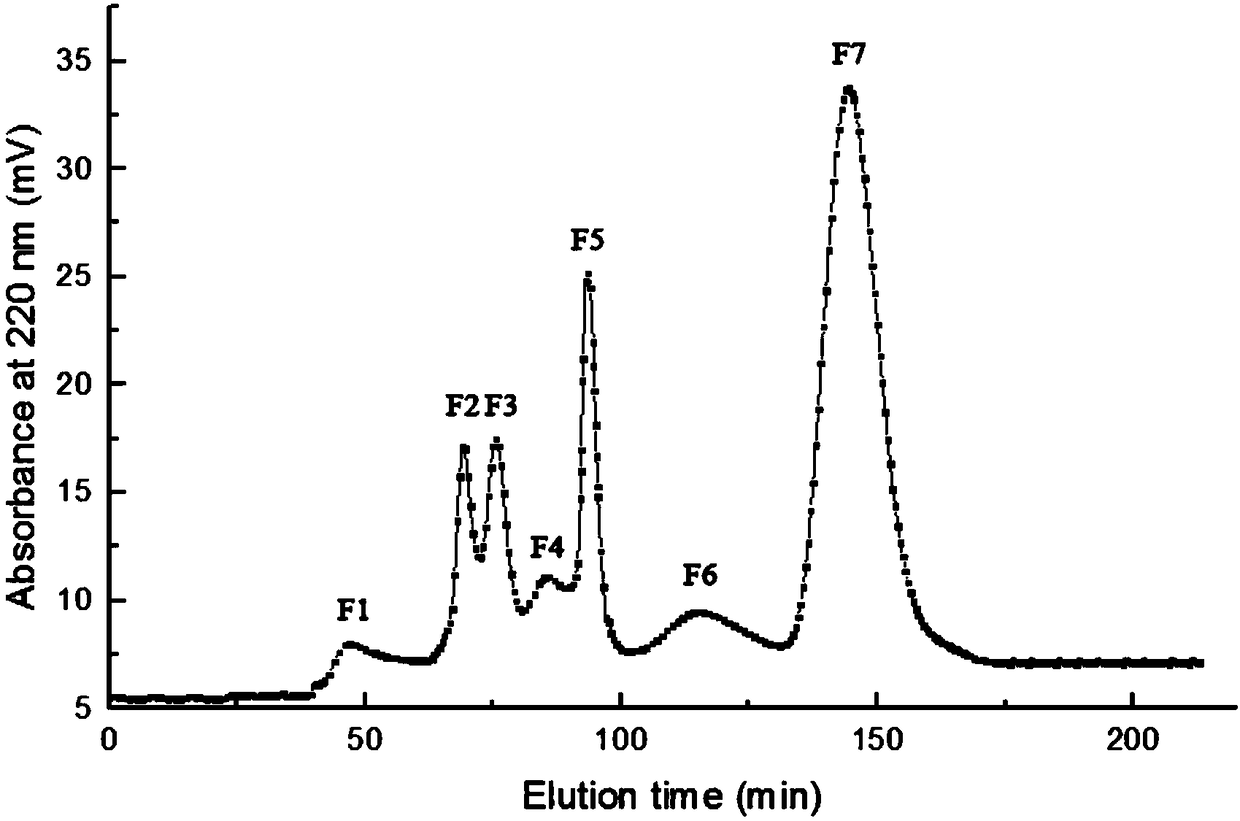
The invention discloses a process for simultaneously preparing an antioxidative peptide and an antifreeze peptide through enzymolysis of collagens. The method comprises the following steps: extractingcollagens by taking salmon skin as a raw material, hydrolyzing the collagens into a short peptide solution by utilizing crude enzymes of extracellaluar protease obtained by fermentation of Vibrio sp.SQS2-3, performing centrifugal ultrafiltration by a 3000 Da ultrafiltration tube 4500*g for 45 minutes so as to obtain the antifreeze peptide with effects of protecting myosin and relieving decreaseof Ca<2+>-ATPase activity in multigelation, performing Sephadex LH-20 gel filtration chromatography to separate lower ultrafiltration components so as to obtain the antioxidative peptide which has effects of scavenging DPPH free radicals and hydroxyl radicals and a certain ability of inhibiting DNA oxidative damage and shows concentration-dependent antioxidant activity in oxygen radical absorptioncapacity detection. The LC-MS technology shows that the antioxidant component contains 19 polypeptides.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
A kind of egg yolk antibody with high biological activity and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102276720AGood control effectEnsure safetyAntibacterial agentsEgg immunoglobulinsYolkBacterial disease
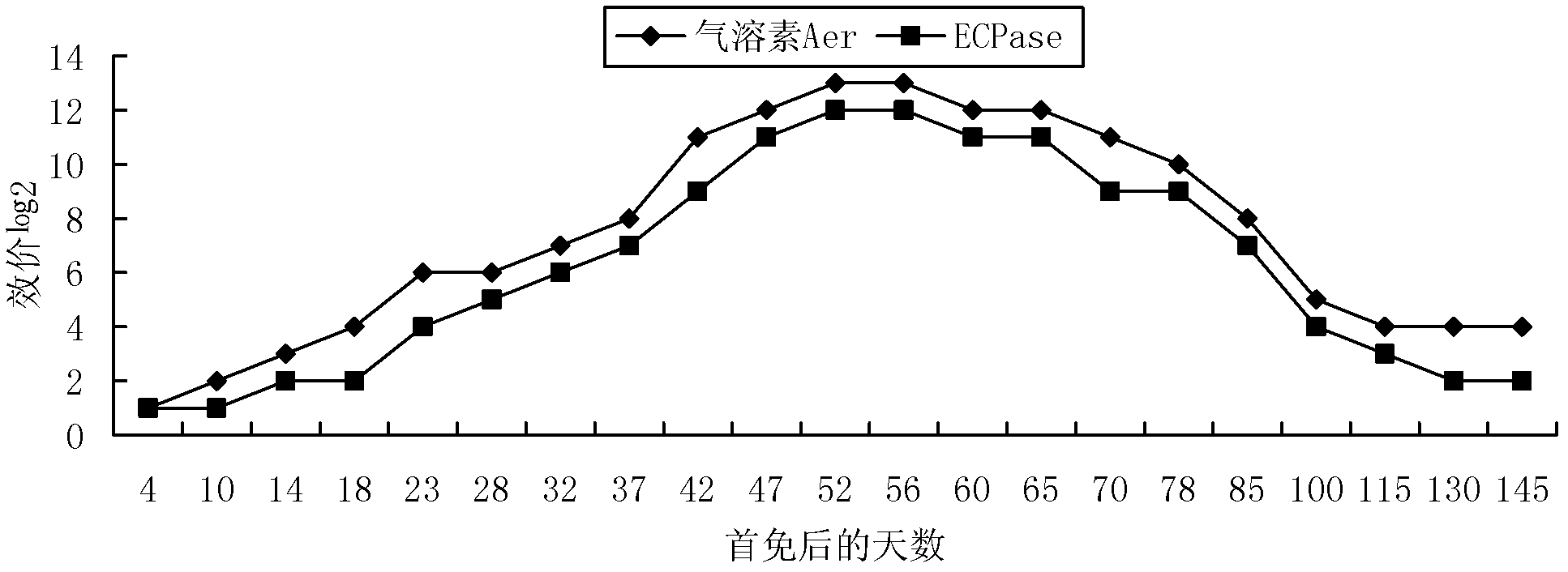
The invention discloses a highly biologically active yolk antibody and a preparation method thereof. The antibody in the present invention uses aerolysin and extracellular protease, the main pathogenic factors of pathogenic Aeromonas hydrophila, as immunogens respectively, and simultaneously immunizes laying hens with an appropriate immunization program to obtain highly immune eggs, and the titer can be as high as 1:212, the antibody was purified by octanoic acid-ammonium sulfate method and then spray-dried. The antibody titer obtained according to the invention is high, and can be used to control fish bacterial diseases, especially the immune protection effect on fish with hemorrhagic diseases can be as high as 90%. Moreover, the mass production of antibodies by this method is low in cost, labor-saving and workshop-saving, high in social benefits, and broad in prospects.
Owner:JIANGSU AGRI ANIMAL HUSBANDRY VOCATIONAL COLLEGE
Trichoderma strain for antagonizing cucumber fusarium wilt disease efficiently and application thereof
The invention relates to a trichoderma strain for antagonizing cucumber fusarium wilt disease efficiently and application thereof. The trichoderma strain is Trichoderma harzianum SH2303 CGMCC NO. 4963, and has the capacity of antagonizing cucumber fusarium wilt disease. The invention also relates to application of the strain to the preparation of pesticides for preventing and controlling cucumber fusarium wilt. The trichoderma strain is high in growing speed and large in spore-bearing quantity, the inhibition rate of in vitro on pathogenic bacteria is 43.01 percent, the inhibition rate of non-volatile inhibitors on cucumber fusarium wilt is 41.33 percent, the inhibition rate of volatile substances on cucumber fusarium wilt is 11.49 percent, the enzyme activity of chitin is 3.9573U, the enzyme activity of beta-1 and 3-glucanase is 0.5092U, the enzyme activity of extracellular protease is 3.0678U; and the in-vivo prevention effect of cucumber fusarium wilt is 71.43 percent, the total specific gravity of antibiotic secondary metabolites which achieve an antagonistic action in the strain accounts for 30.28 percent, and the cucumber fusarium wilt can be prevented and controlled effectively.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Bacillus subtilis with inactivated extracellular protease as well as construction method and application of bacillus subtilis
ActiveCN113957028AReduced activityReduce metabolic stressBacteriaStable introduction of DNANutritionTransformation efficiency
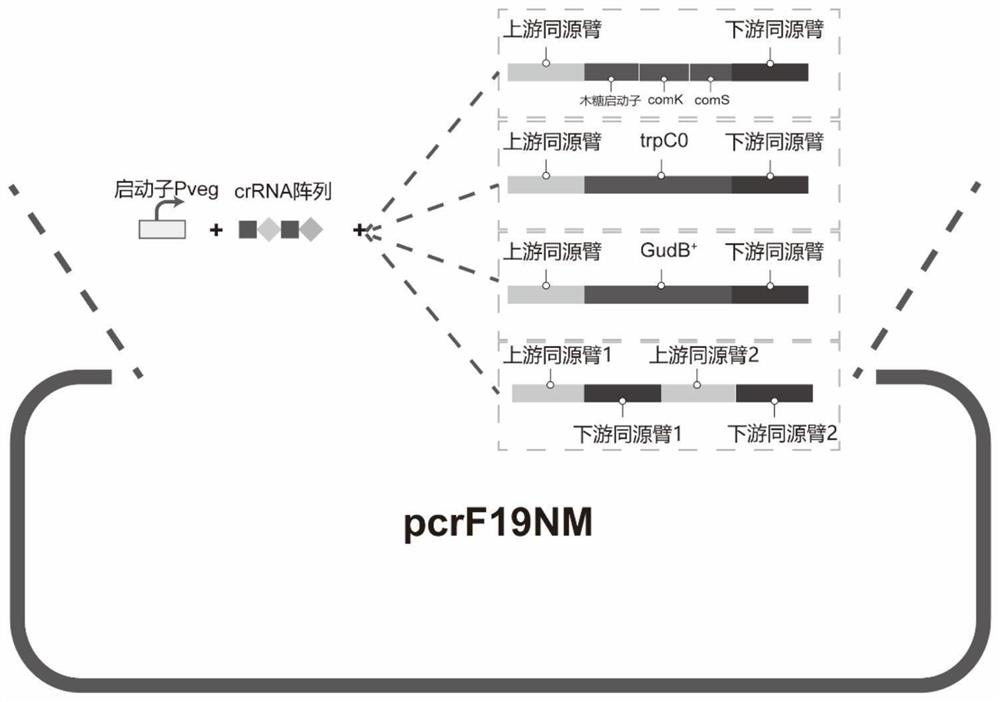
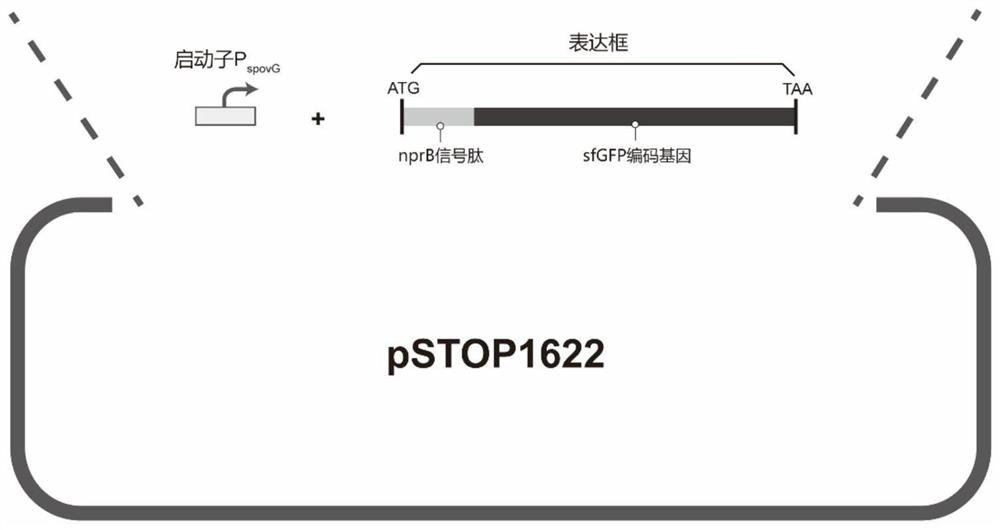
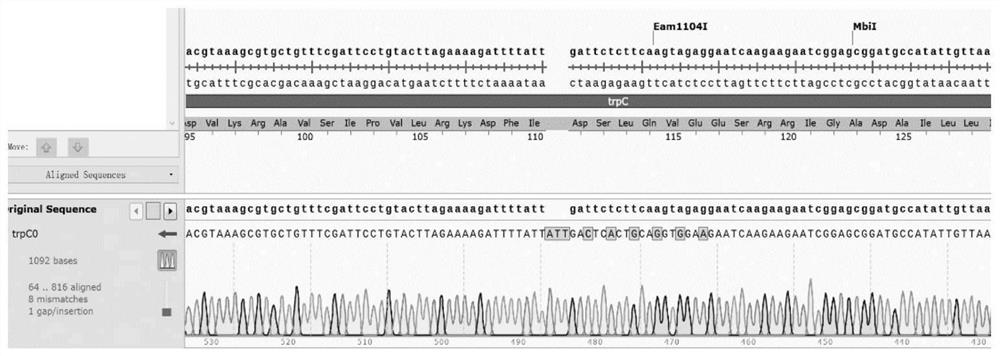
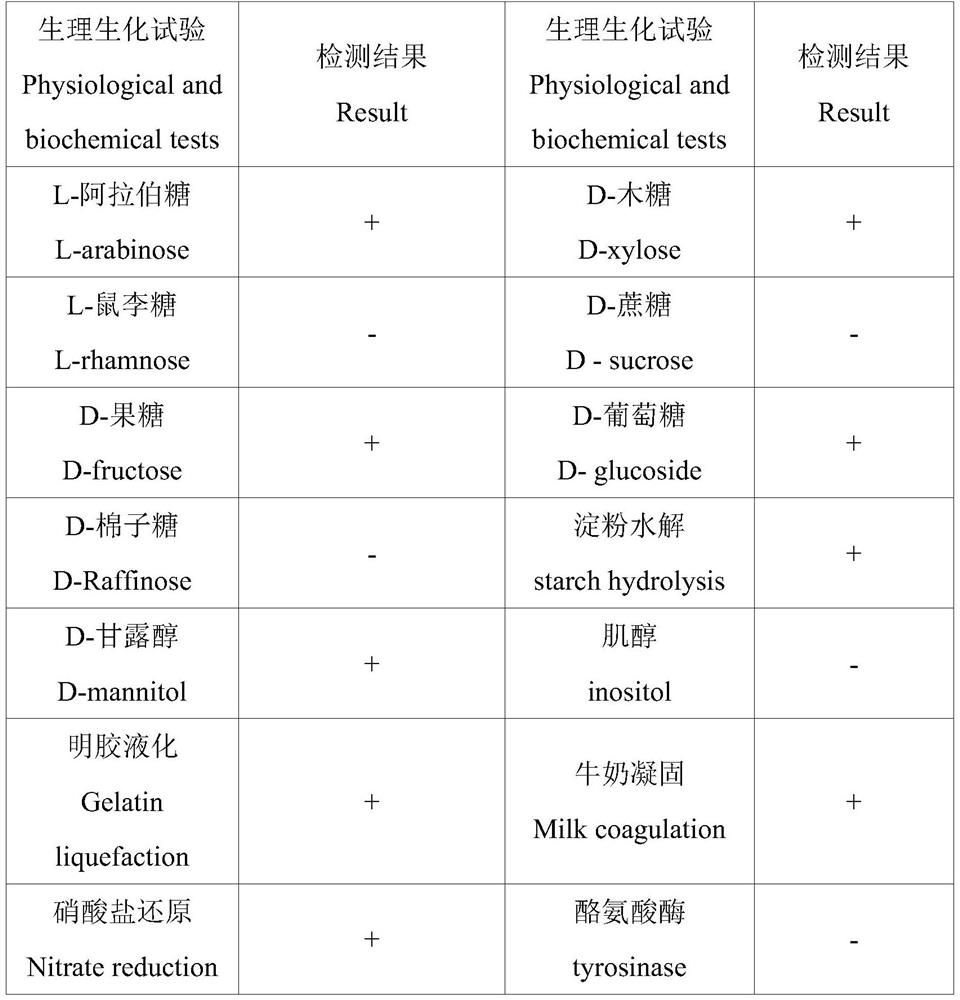
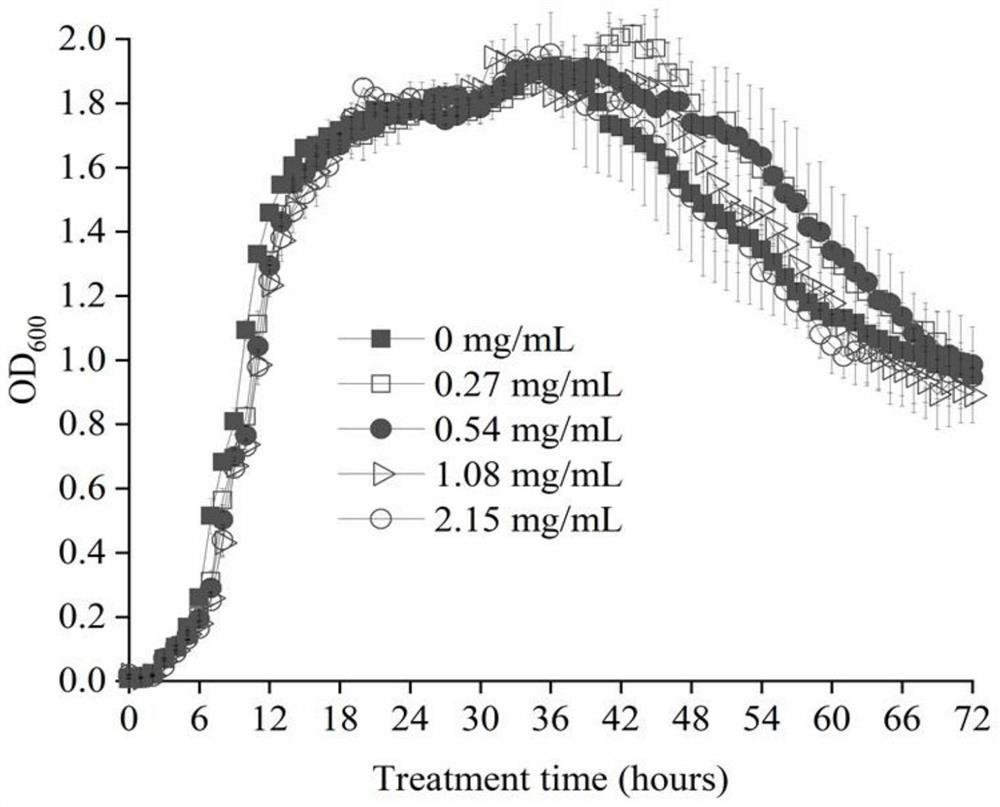
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis with inactivated extracellular protease as well as a construction method and application the bacillus subtilis. B.subtilis 168 is taken as an original strain, a transcription factor comK-comS gene controlled by a xylose inducible promoter PxylA is integrated on a genome by using a CRISPR / Cpf1 technology, so that the transformation efficiency of the bacillus subtilis is greatly improved; a trpC gene and a gudB gene are subjected to reverse mutation, so that tryptophan can be synthesized, and glutamic acid family amino acids can be effectively utilized; and besides, six extracellular protease genes are knocked out, so that the metabolic pressure of cells is reduced, and recombinant proteins can be effectively accumulated outside the cells. The content of extracellular sfGFP produced when a final engineering strain G601 is used for fermentation is 1.88 times of that of the B.subtilis 168, and the total content of intracellular and extracellular sfGFP is 1.94 times of that of the B.subtilis 168. An engineering bacterium constructed by the invention is simple and convenient to transform, has no nutritional deficiency, has better amino acid utilization capacity and low extracellular protease activity, can be widely applied to secretory expression of a recombinant protein, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Grape rhizosphere antagonistic growth-promoting Streptomyces F2 and application thereof
ActiveCN113789274APromote growthGood control effectPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBiotechnologyStreptomyces cavourensis
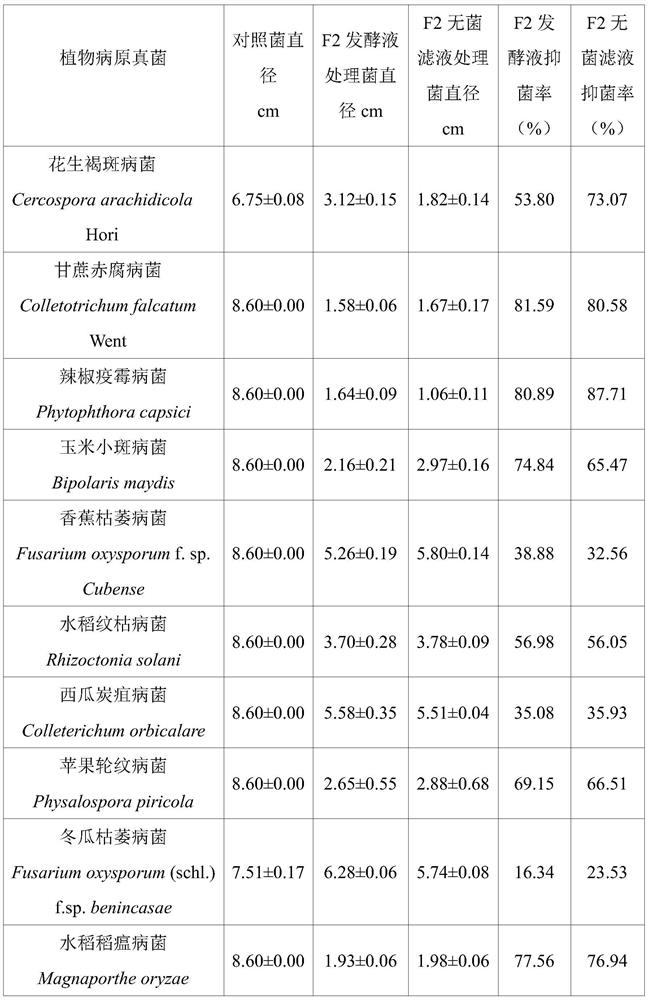
The invention discloses grape rhizosphere antagonistic growth-promoting Streptomyces F2 and application thereof. The Streptomyces F2 is Streptomyces cajeri, has a preservation number of GDMCC No: 61143 and is preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center on August 14, 2020, the address is Floor 5, Building 59, #100 Courtyard, Middle Xianlie Road, Guangzhou City, and the Streptomyces F2 is classified and named as Streptomyces sp. Fermentation liquor and sterile filtrate of the strain F2 have antagonistic effects on phytophthora capsici and other 10 phytopathogens, and the highest bacteriostasis rate reaches 80% or above, wherein the fermentation liquor and the sterile filtrate have excellent inhibitory effects on the phytophthora capsici, and the inhibition rates are 80.58% and 87.71% respectively. The strain F2 fermentation liquor has a control effect on phytophthora capsici mycelium blocks. The strain F2 fermentation liquor has control effect of 61.09% on phytophthora capsici sclertium. The strain F2 fermentation liquor has an obvious control effect on phytophthora capsici, and the highest control effect reaches 83.31%. The F2 has the effects of dissolving organic phosphorus and fixing nitrogen, and can secrete extracellular protease and produce IAA. The root irrigation treatment of the strain F2 fermentation liquor has a remarkable promotion effect on the growth of chilies. The Streptomyces F2 not only has a broad-spectrum antagonistic plant pathogenic bacterium effect, but also has a growth-promoting effect.
Owner:DONGGUAN AGRI SCI RES CENT
Application of citronellal in preparation of preparation for inhibiting toxicity and pathogenicity of pseudomonas aeruginosa
InactiveCN112219847AInhibitionInhibition of virulenceAntibacterial agentsBiocideChitinasePseudomonas
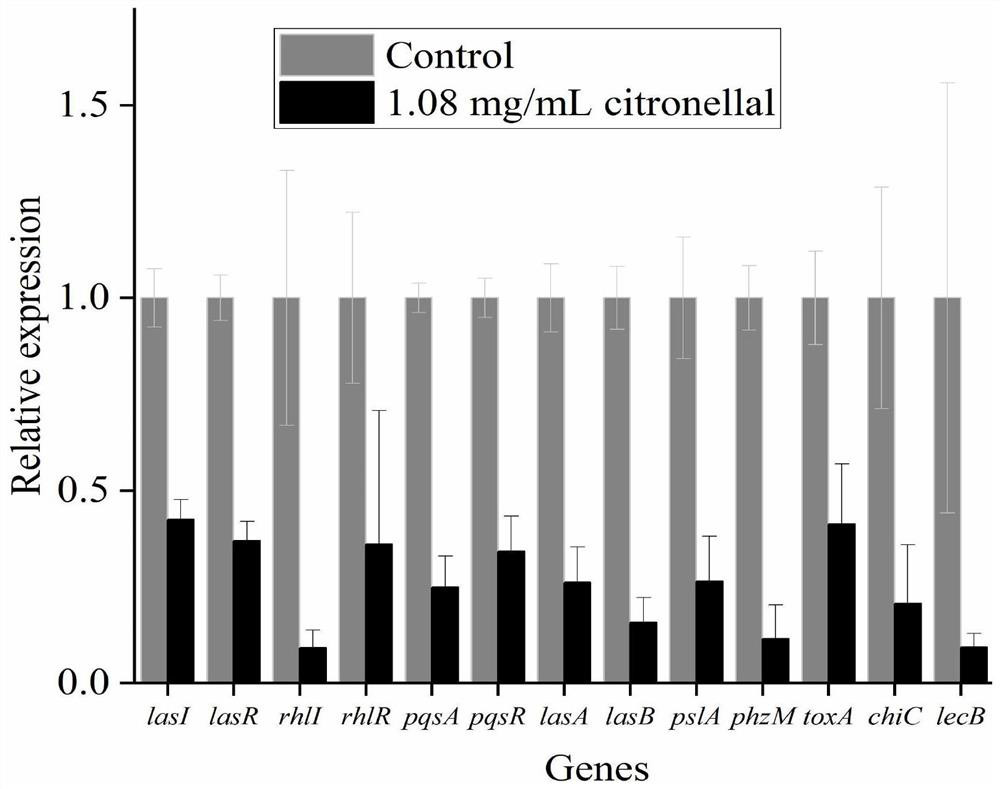
The invention discloses an application of citronellal in preparation of a preparation for inhibiting toxicity and pathogenicity of pseudomonas aeruginosa. What is found is that citronellal cannot inhibit growth of a pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 strain but can significantly inhibit las, rhl and pqs of three quorum sensing systems of the strain, and meanwhile generation of toxicity factors regulatedand controlled by the three quorum sensing systems is inhibited, and extracellular protease LasA, elastase LasB, pyocyanine, a biofilm, chitinase ChiC, exotoxin A and LecB and the like are included. Therefore, the strain can be used for inhibiting toxicity and pathogenicity of pseudomonas aeruginosa and reducing harm to infected hosts.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
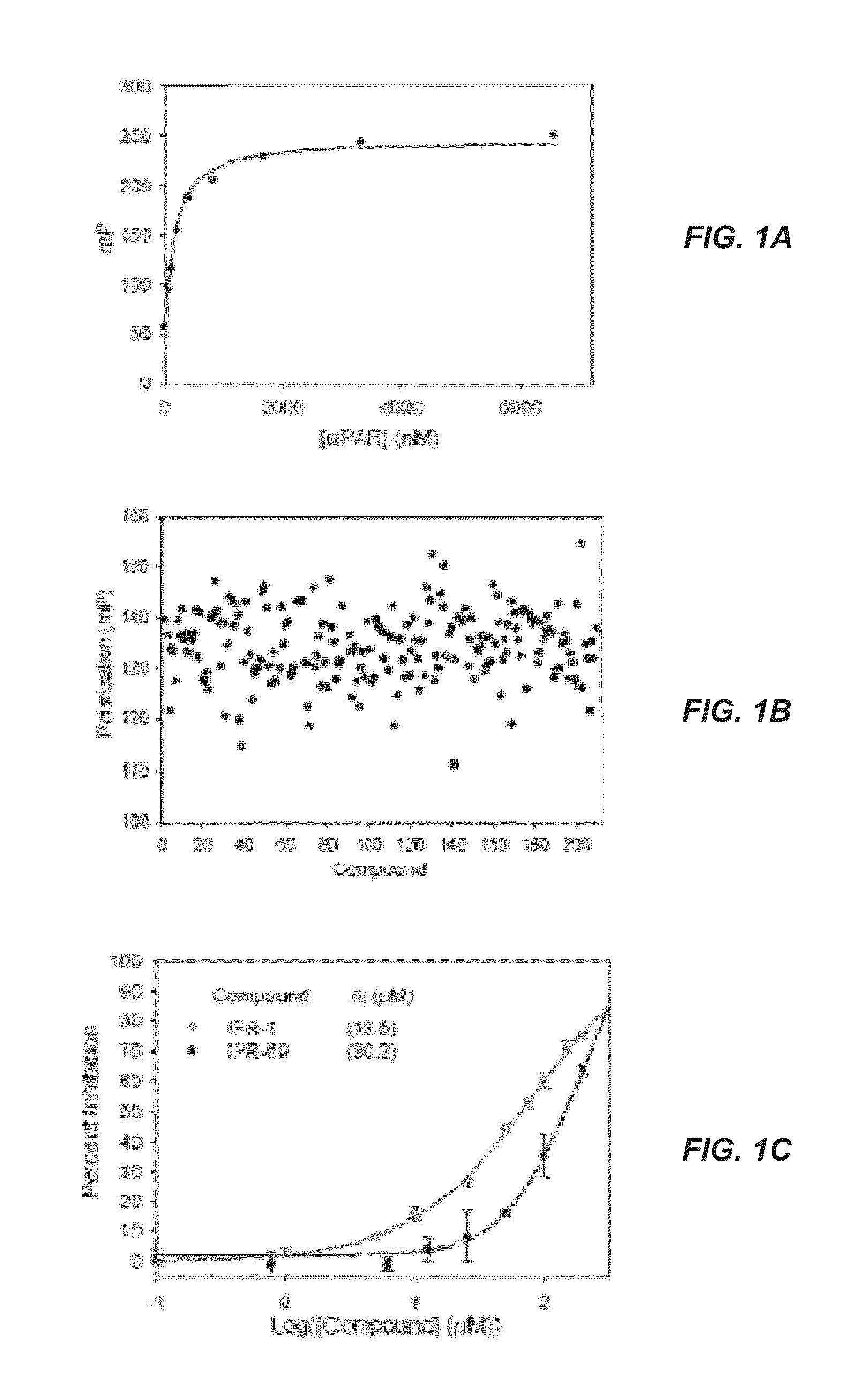
UPAR-antagonists and uses thereof
InactiveCN103391787AExcellent drug propertiesVarious clinical applicationsConnective tissue peptidesHydrolasesCell-Extracellular MatrixVitronectin
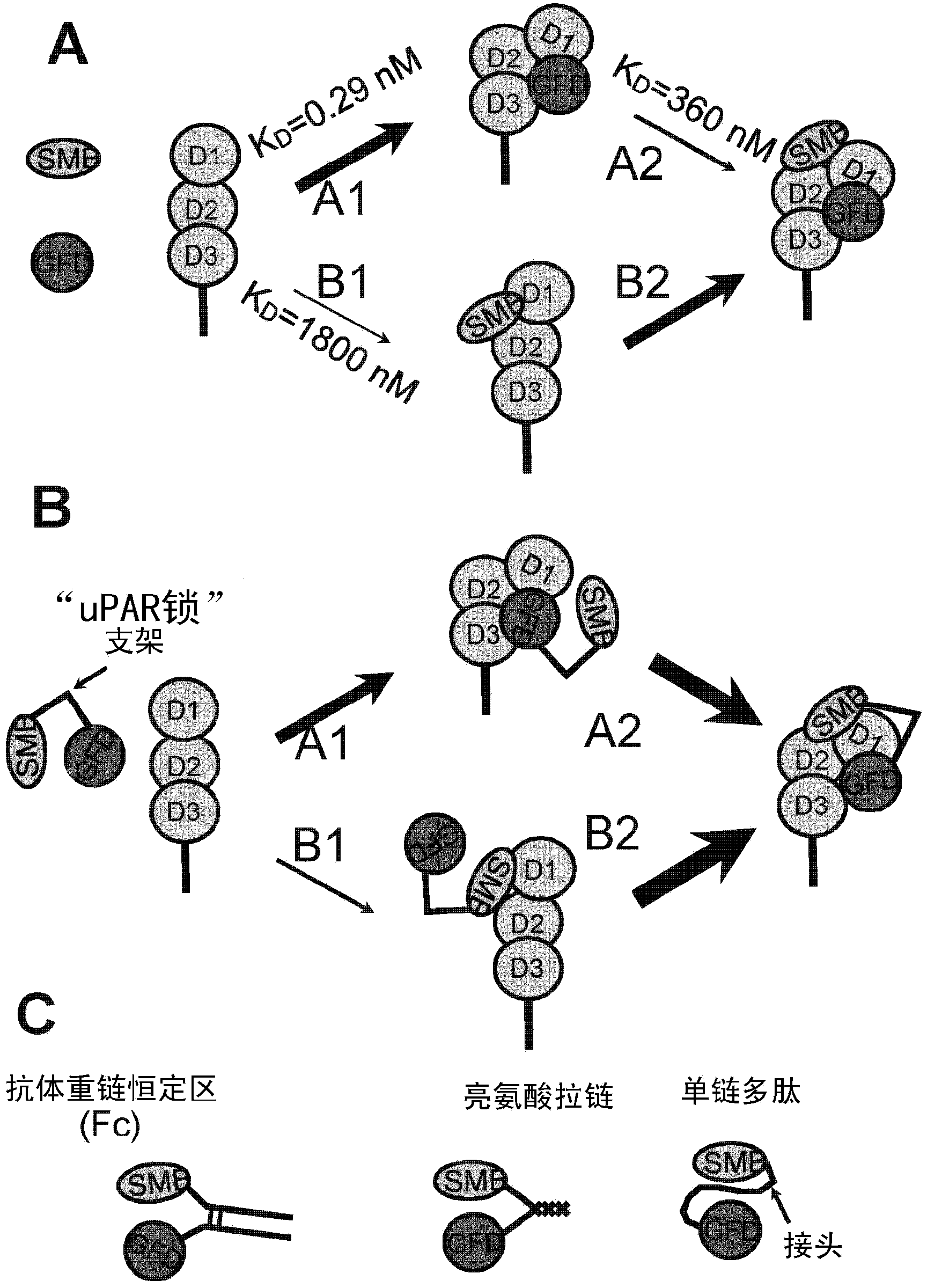
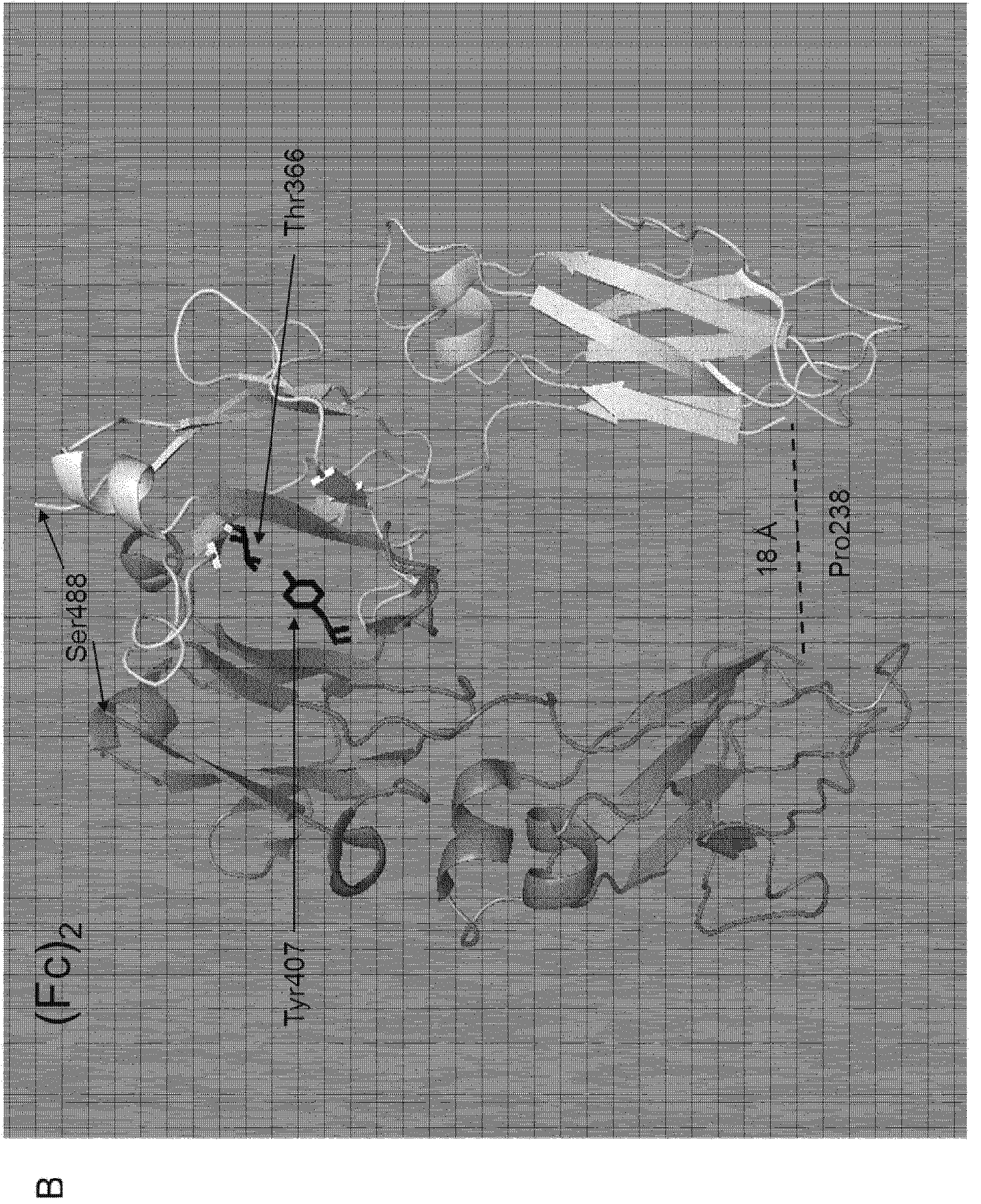
The invention relates to inhibitors of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR). The generated inhibitors are bivalent uPAR-ligands containing the receptor binding domains of the extracellular protease urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and of the extracellular matrix protein vitronectin (VN), in different configurations, linked by a scaffold. The present invention also refers to the above molecules for use as a medicament, in particular for treatment of cancer, and for diagnostic purposes.
Owner:IFOM FOND INST FIRC DI ONCOLOGIA MOLECOLARE
Chassis strain for producing alkaline protease as well as construction method and application of chassis strain
PendingCN113913357AReduce complexityReduce metabolic burdenBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideGenetic engineering
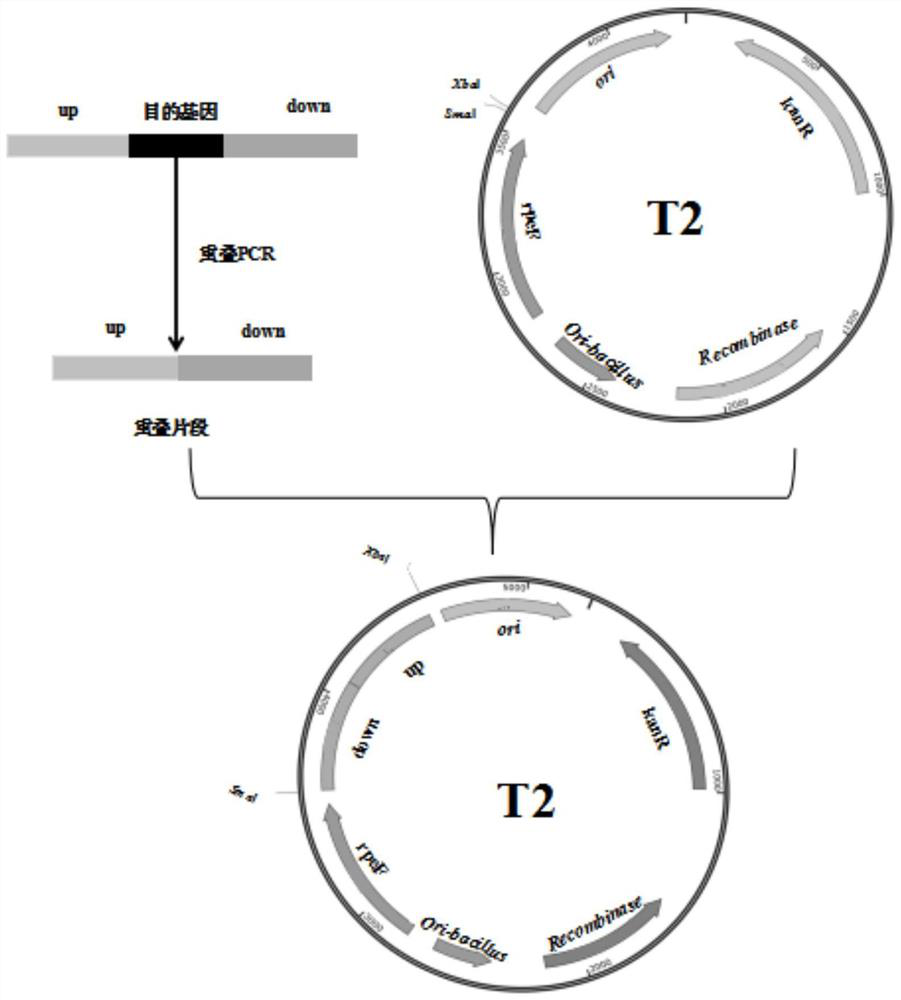
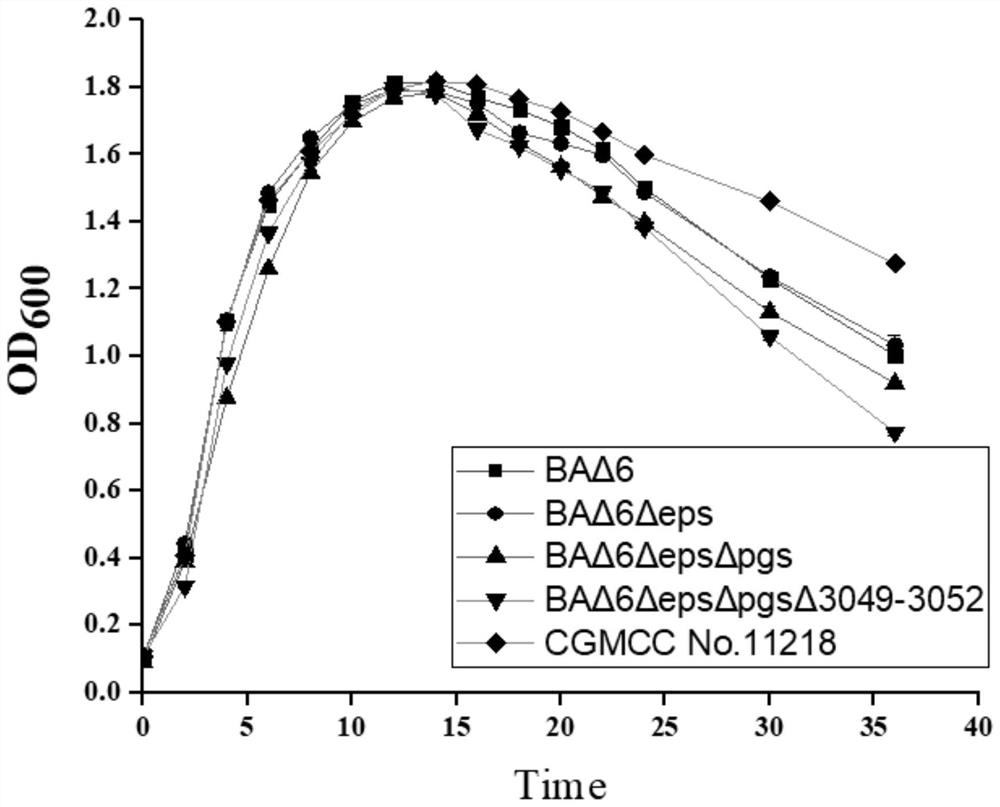
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and relates to breeding of industrial microorganisms, in particular to a chassis strain for producing alkaline protease as well as a construction method and application of the chassis strain. The invention provides a bacillus amyloliquefaciens gene engineering strain, which does not express six extracellular protease genes aprE, bpr, vpr, mpr, nprE and epr on a bacillus amyloliquefaciens genome, an extracellular polysaccharide gene cluster eps, a polyglutamic acid gene cluster pgs and a bacteriophage related gene with a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, and preferably, the bacillus amyloliquefaciens gene engineering strain also expresses an alkaline protease gene aprE in a heterologous overexpression manner. According to actual conditions in experiments and production, adverse factors influencing fermentation performance are analyzed, the chassis strain for producing alkaline protease at high yield is finally obtained through transformation and gene simplification of a genetic engineering host, and a new thought is provided for construction of the chassis strain for producing the alkaline protease at high yield.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Recombinant plasmid and subunit vaccine of extracellular protease recombinant protein of Aeromonas hydrophila prepared from same plasmid
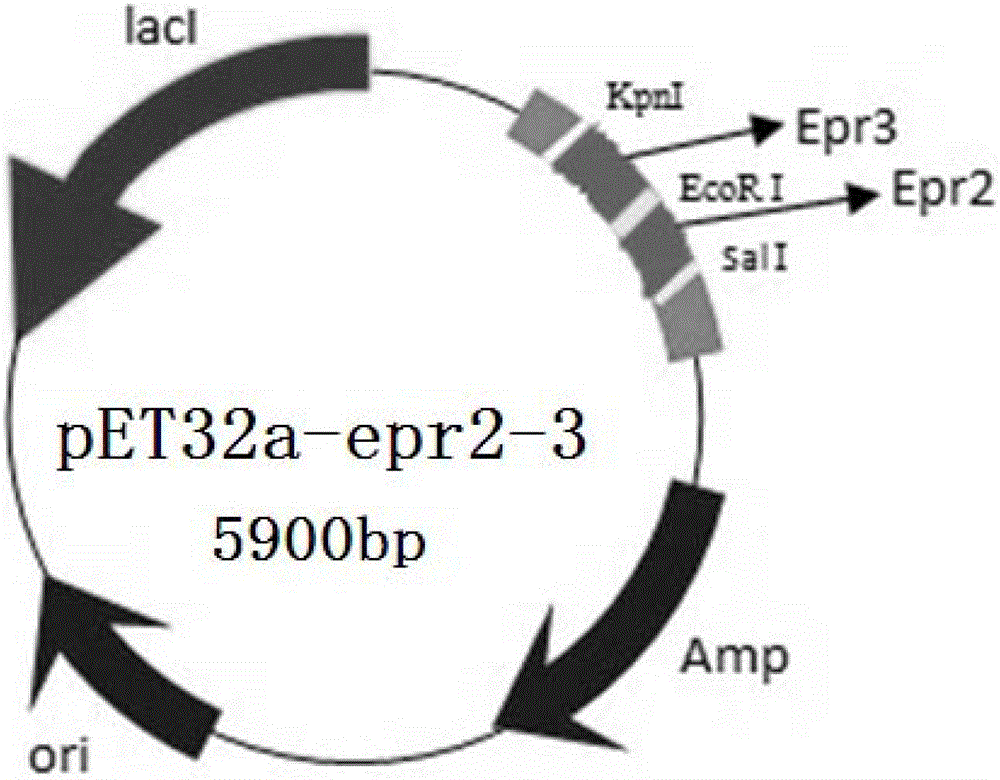
InactiveCN102719466ABreak through limitationsEasy Security EvaluationAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsEscherichia coliAdjuvant
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to a recombinant plasmid and a subunit vaccine of extracellular protease recombinant protein of Aeromonas hydrophila, the subunit vaccine being prepared therefrom the recombinant plasmid. The recombinant plasmid pET32a-epr2-3 uses pET32a as an original plasmid, an epr3 gene of the Aeromonas hydrophila is inserted between a restriction site KpnI and a restriction site EcoRI of the plasmid pET32a, and an epr2 gene of the Aeromonas hydrophila is inserted between the restriction site EcoRI and a restriction site SalI. The subunit vaccine of extracellular protease recombinant protein of Aeromonas hydrophila comprises a recombinant protein epr2-3 obtained by inducing an Escherichia coli transfected with the recombinant plasmid pET32a-epr2-3 to express and an adjuvant. Experiments show that the subunit vaccine is relatively high in security, simple in production technology, and undemanding in preservation and transportation conditions, can stimulate immune response of a body in all respects, and has a wide range of development and application prospects.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Expression box capable of efficiently achieving secretory expression of human FGF21 protein and application of expression box
ActiveCN109988802AImprove soluble expression and secretion capacityEase of industrial applicationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesProtein targetSecretory protein
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology and particularly relates to a method for efficiently expressing a recombinant human fibroblast growth factor 21 (rhFGF21) gene by using bacillus subtilis. Firstly, the method adjusts the transcription and translation efficiency of a target protein gene by adding different types of cistron sequences to the 5' end of the target protein gene so as to optimize the soluble expression level of the protein gene, and the method can be applied to the optimal expression of different types of heterologous protein; secondly, the method further optimizes disulfide bond related genes to construct a vector to promote the disulfide bond folding efficiency of rhFGF21, overexpresses a molecular chaperone system to construct a vector suitablefor the folding efficiency increasing of rhFGF21 protein, and knocks out various extracellular protease genes to construct a bacillus subtilis gene engineering strain for improving the extracellular stability of rhFGF21; and finally, the method provides a bacillus subtilis gene engineering strain with good application prospect and capable of achieving efficient secretory expression of the rhFGF21protein.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Thrombolytic enzyme gene, recombinant expression vector and recombinant bacteria comprising same and application
ActiveCN104928308AImprove solubilityHigh activityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyInclusion bodies
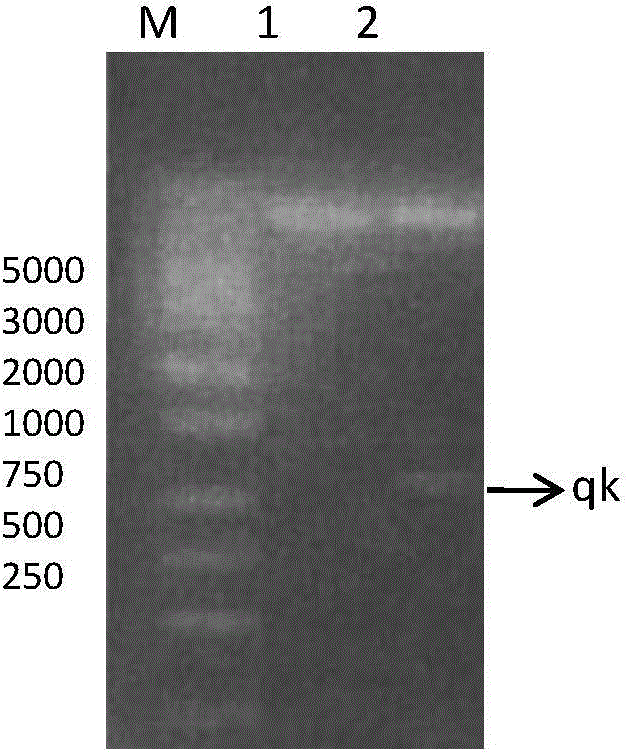
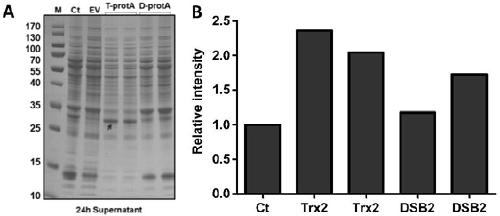
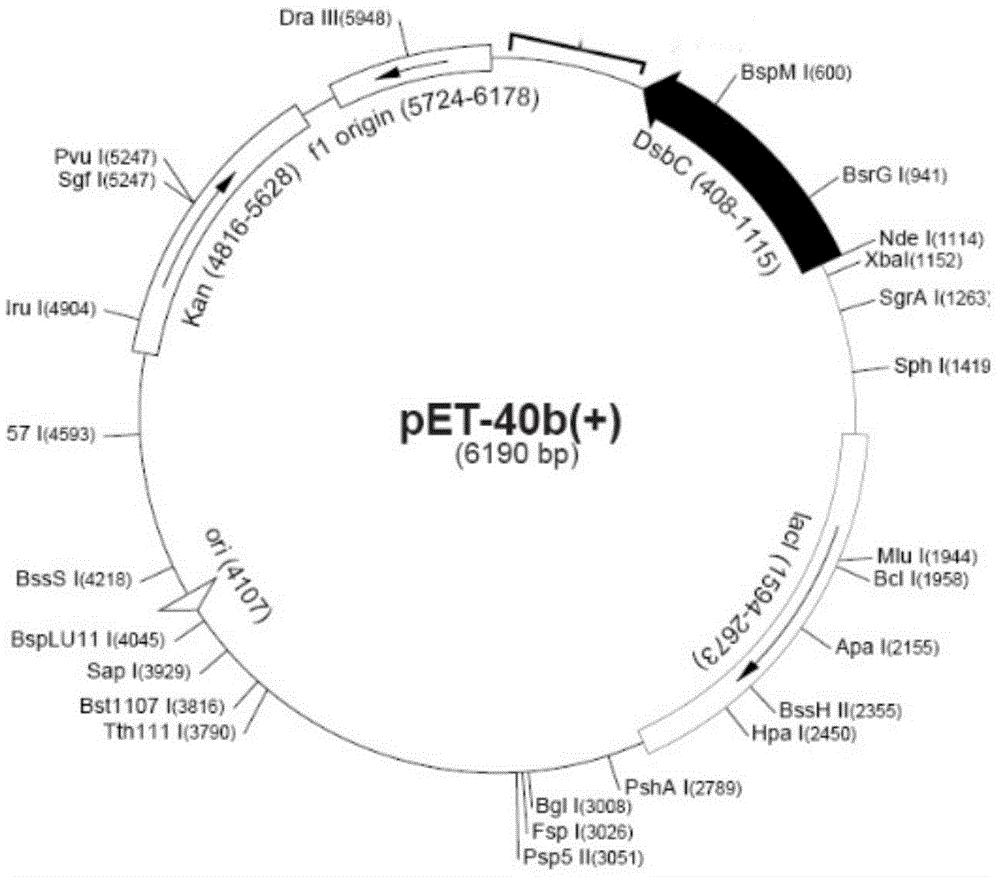
The invention discloses a thrombolytic enzyme gene, a recombinant expression vector and recombinant bacteria structured by the thrombolytic enzyme gene and application of the thrombolytic enzyme gene. A qk sequence obtained by optimization through the overlap extension of PCR (polymerase chain reaction) can be identified by an escherichia coli expression strain DE 3 better, meanwhile, the vector pET-40b for improving protein solubility is selected to be structured with the optimized qk so as to form the new recombinant expression vector and the recombinant bacteria for preparing expression proteins, functional extracellular proteases can be secreted into periplasm so as to improve solubility and activity of fusion proteins, and finally bacillus subtilis thrombolytic enzyme high in expression quantity and enzyme activity is obtained. The method does not include operations of solubilization of inclusion bodies and protein renaturation, so that cost is lowered, and better practicality is achieved.
Owner:湖北真福医药有限公司
Compounds and methods for treating cancer by inhibiting the urokinase receptor
Compounds and methods for treating or preventing cancer associated with binding to the urokinase receptor are provided. Biological processes affected by the compounds include cell migration, cell growth, cell adhesion, angiogenesis, cancer cell invasion, apoptosis, tumor formation, tumor progression, metastasis, degradation of the extracellular matrix, pericellular proteolysis, activation of plasminogen, changes in the levels of an extracellular protease, and changes in the levels of a VEGF receptor.
Owner:INDIANA UNIV RES & TECH CORP
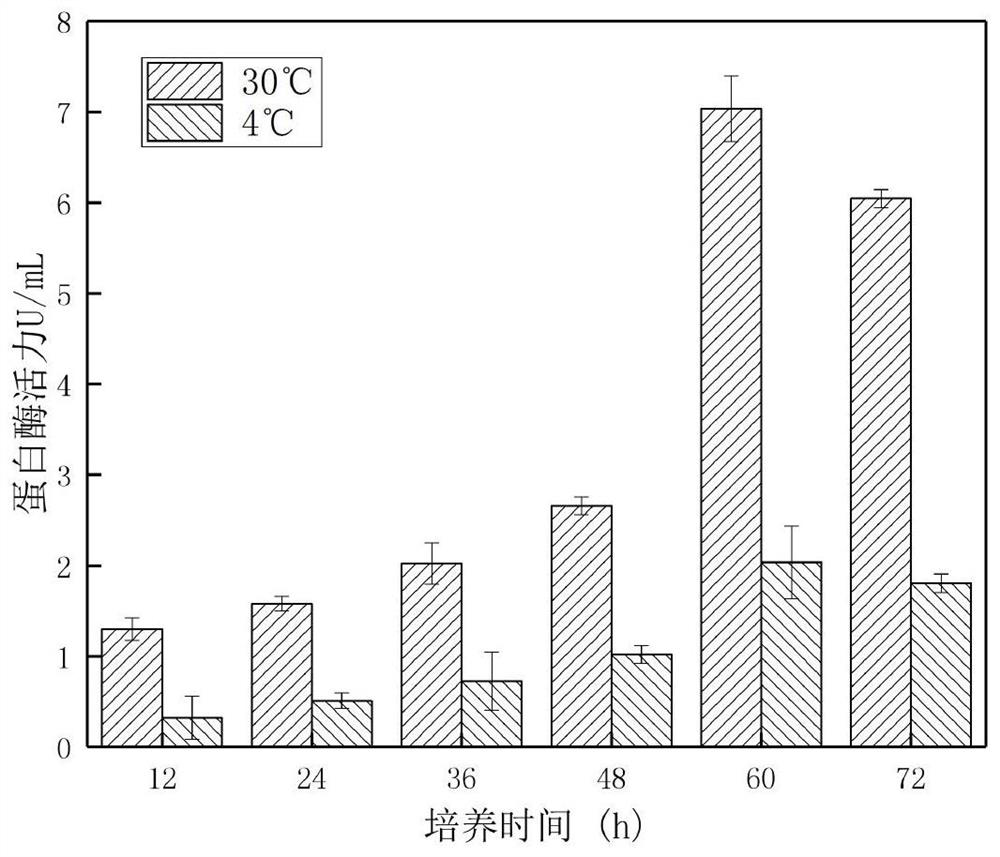
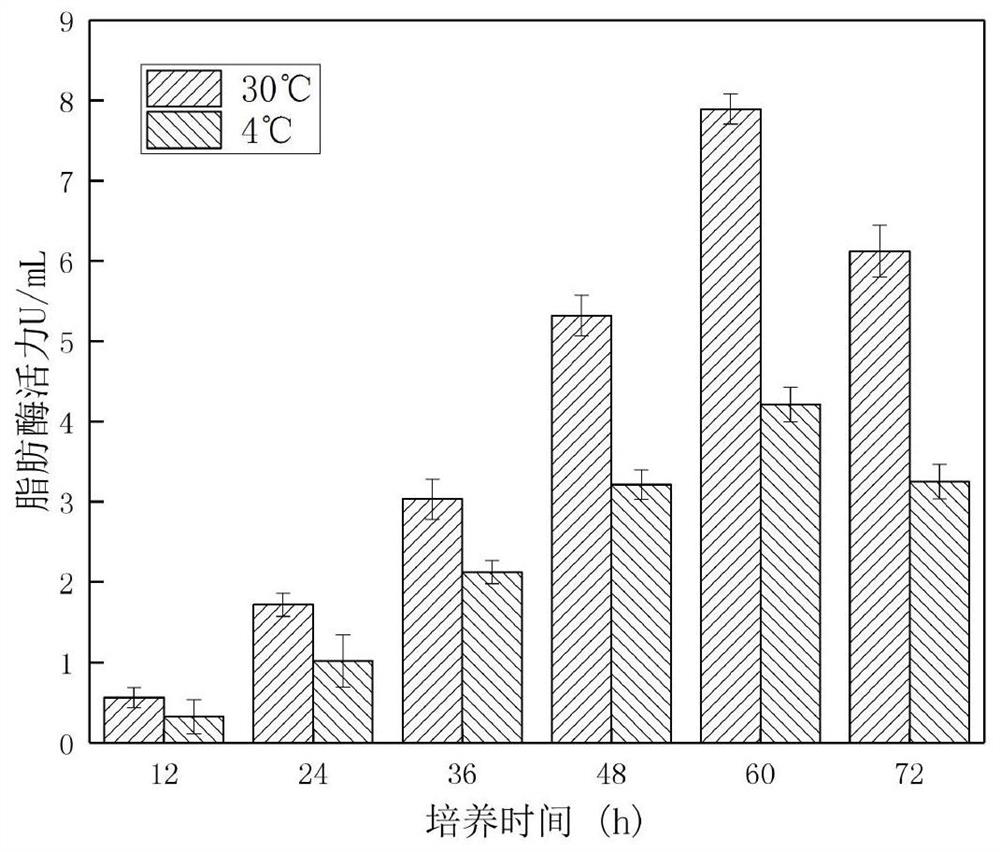
Milk sourced psychrophile and extracellular enzyme secreted by same
The invention discloses a milk sourced psychrophile and an extracellular enzyme secreted by the same, belongs to the field of milk product processing and aims to provide a milk sourced psychrophile with poorer heat resistance and the heat-resistant extracellular enzyme secreted by the milk sourced psychrophile. The milk sourced psychrophile is classified and named as a pseudomonas fluorescens W3 strain with the conservation number being CGMCC No.14540 and is conserved in CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) on August 21, 2017. The extracellular protease produced by the strain has the activity about 7.0-8.2 U / mL, the produced extracellular lipase has the activity about 6.8-7.5 U / mL, and the extracellular protease and lipase produced by the strain have certain heatresistance and have important characteristics of advantageous psychrophile in raw milk; and the strain comes from the raw milk and can be used for study of damage of the psychrophile to milk and a milk product and control methods.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
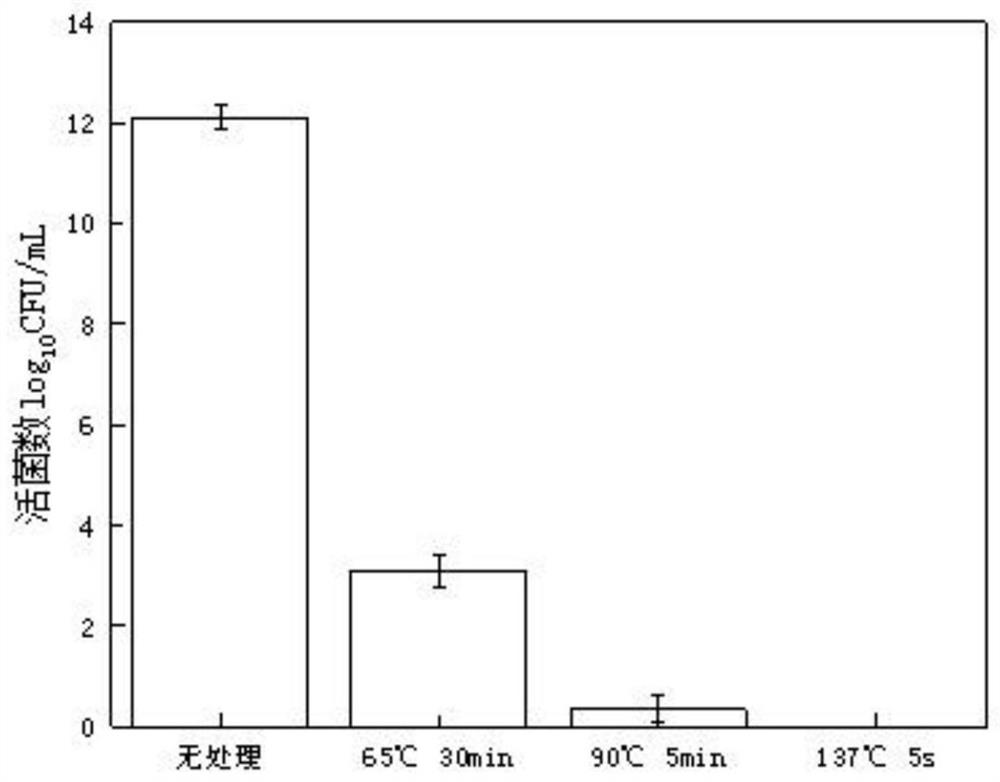
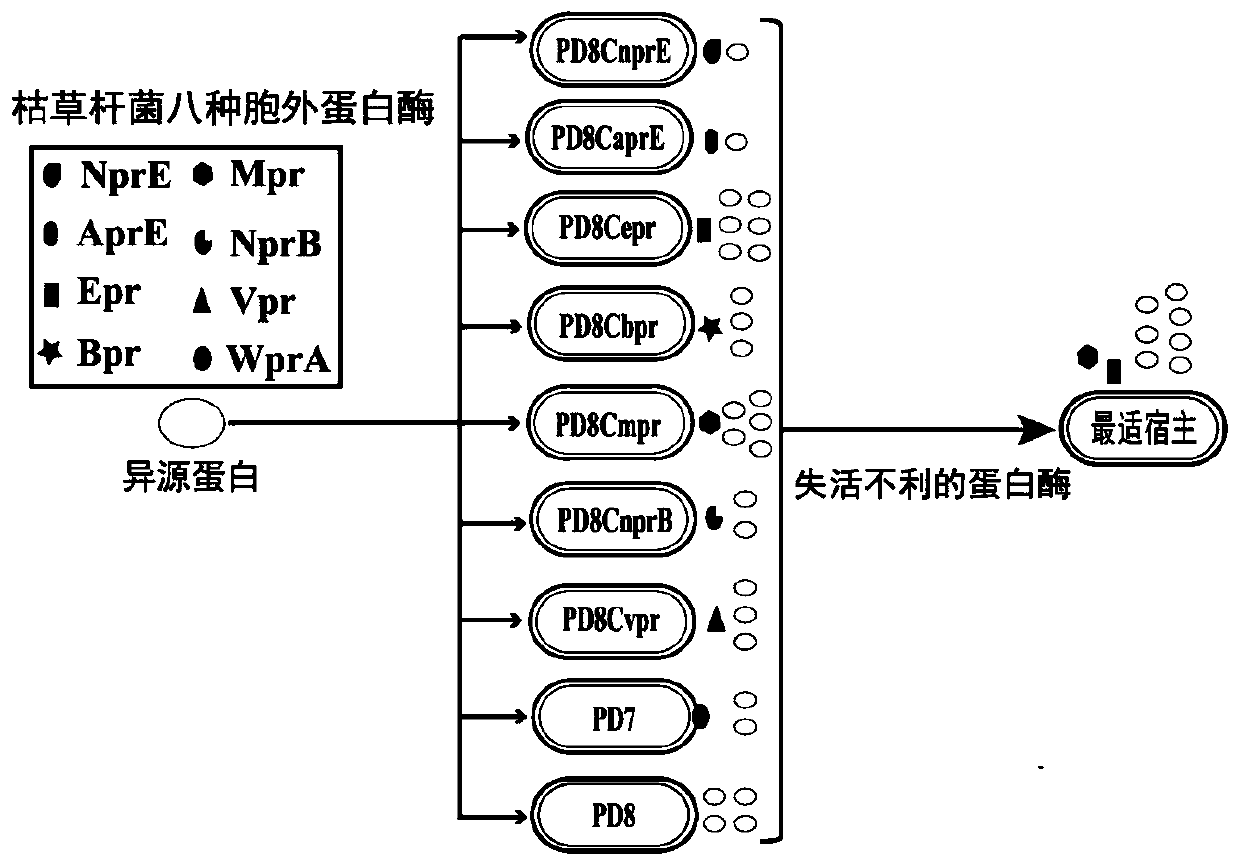
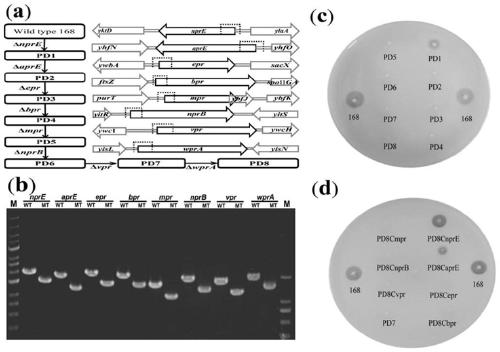
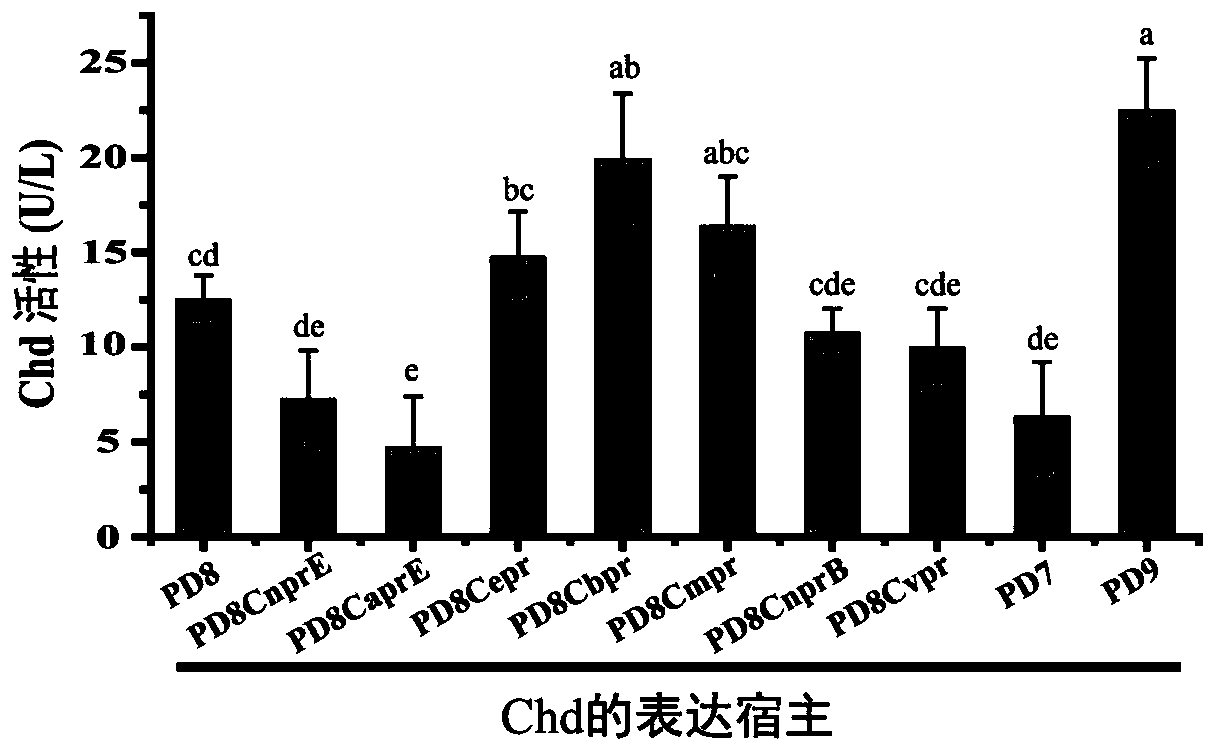
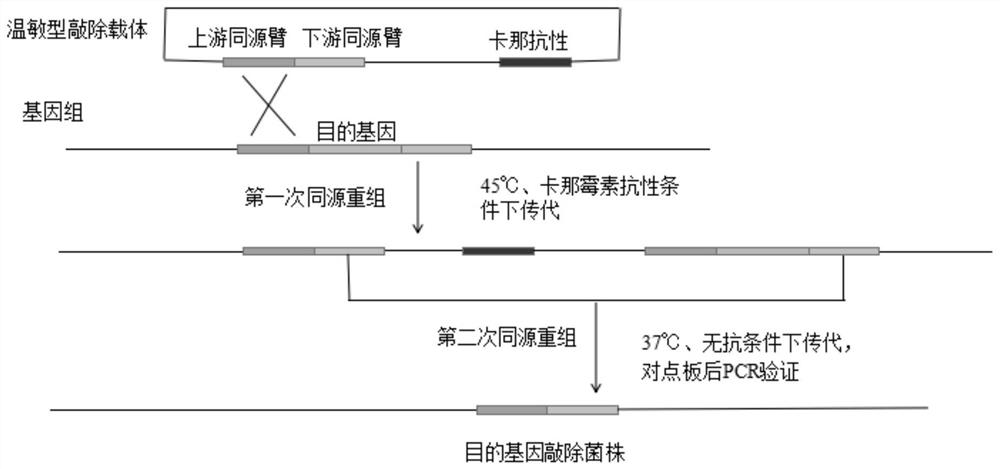
Method for cooperatively establishing optimal bacillus subtilis protease deletion expression host for target protein
The invention belongs to the technical field of biotechnology and discloses a method for cooperatively establishing a most proper bacillus subtilis protease deletion expression host for target protein. Each recombinant protein has a unique optimal protein deletion mutantion expression host, and an existing bacillus subtilis extracellular protease deletion expression host is poor in applicability and cannot meet the individuation demand. In this way, the method for cooperatively establishing the most proper extracellular protease deletion expression host for the recombinant protein is provided.According to the method, the influence of each extracellular protease of bacillus subtilis on target protein production can be accurately evaluated, the beneficial and harmful extracellular proteasesare determined, by inactivating harmful proteases and reserving beneficial proteases, the optimal host is obtained, and the yield of the target protein is increased maximally.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Engineering bacterium for producing heterologous alkaline protease and construction method thereof
ActiveCN112522173AHigh expressionPromote industrialized mass productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAmylaseHeterologous
The invention aims to provide a gene engineering bacterium capable of efficiently and stably producing heterologous alkaline protease through directional transformation of a gene engineering host. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens is used as the host, and firstly, eight extracellular proteases aprE, epr, mpr, vpr, nprE, bpr, wprA and aprX of the host are deleted to obtain an extracellular protease defecttype strain; alpha-amylase and an extracellular polysaccharide gene cluster eps of the host are also deleted; and high-copy plasmids expressing the heterologous alkaline protease are also introducedinto the host to obtain the gene engineering bacterium capable of efficiently producing the heterologous alkaline protease. In addition, the viscosity of the engineering bacterium in the fermentationprocess is greatly reduced, and the separation and purification of the product protease are facilitated.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Controlled release material for fouling organism-sensitive response anti-fouling agent and preparation method of controlled release material
ActiveCN107083095AImprove friendlinessExtend the antifouling periodBiocideAntifouling/underwater paintsCross-linkWater based
The invention relates to a controlled release material for a fouling organism-sensitive response anti-fouling agent and a preparation method of the controlled release material. The controlled release material contains a coated precursor and a cross-linking agent; a hyaluronic acid / poly L-lysine controlled release material of a nano thin-shell structure is prepared through alternating layer-by-layer self-assembly of hyaluronic acid and poly L-lysine; a poly-(allylamine hydrochloride) / poly L-glycine controlled release material of the nano thin-shell structure is prepared through alternating layer-by-layer self-assembly of poly-(allylamine hydrochloride) and poly L-glycine; and the cross-linking agent is prepared by compounding 1-(3-dimethylamino propyl)-3-ethylenediamine hydrochloride and N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide sodium salt. For a water-soluble anti-fouling agent, a fouling organism-sensitive response nano thin-shell is prepared from sodium carbonate as a template and the anti-fouling agent is loaded; and a water-based insoluble or micro-soluble antifouling agent is directly coated with a fouling organism-sensitive response controlled release material. The controlled release material is simple in process and friendly to environment; the target of adaptive regulation of release of the anti-fouling agent along with fouling organism attachment change in low and peak seasons is achieved on the basis of a special catalytic hydrolysis characteristic of fouling organism extracellular protease on the controlled release material; and the anti-fouling period of the paint is prolonged.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Preparation method and application of novel halophilic archaea extracellular protease
ActiveCN111705050AHigh research valueExcellent enzymatic propertiesHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionKanamycinGenetic engineering
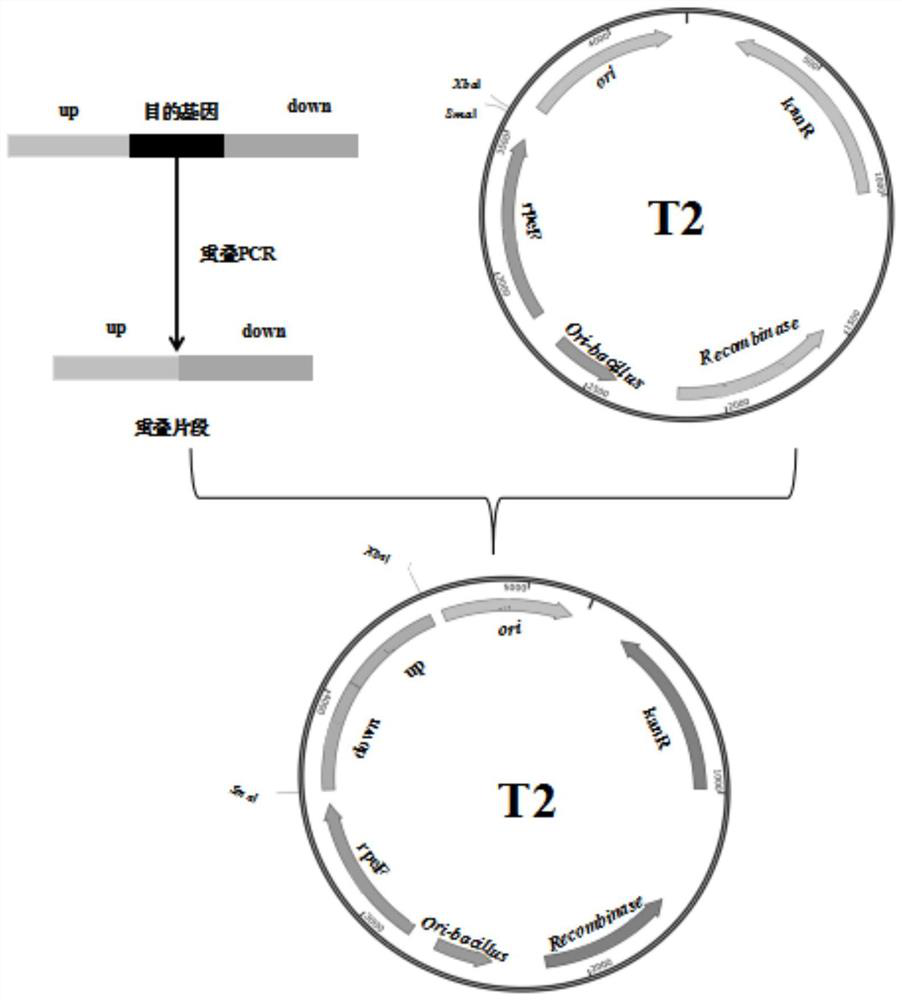
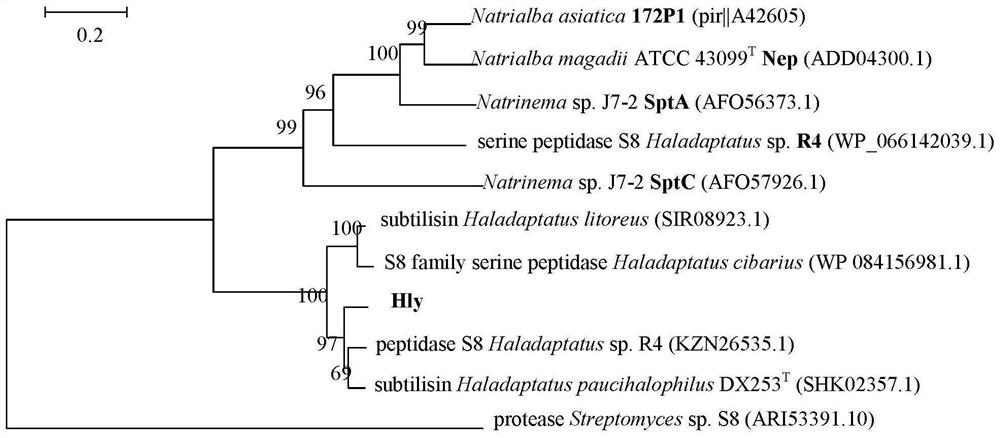
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and relates to a preparation method and application of novel halophilic archaea extracellular protease. The preparation method comprises thefollowing steps: firstly, obtaining a coding gene hly based on a genome of halophilic archaea DYF 46; connecting the hly to a vector by a molecular cloning technology to construct a recombinant plasmid; transforming the recombinant plasmid into a prokaryotic host, culturing the transformed recombinant host cells in an LB liquid culture medium containing kanamycin, centrifugally collecting thalli at low temperature after culture and inducible expression, resuspending in a cell lysis solution, ultrasonically crushing, centrifugally collecting supernatant for recombinant protein purification; andpurifying protein by nickel affinity chromatography, obtaining mature enzyme by a column renaturation method, and purifying by gel filtration chromatography to obtain high-purity Hly. The Hly obtained by the preparation method has excellent enzymatic characteristics, and can be applied to production and processing processes of complex and salt-containing degraded proteins such as detergents, wastewater treatment, pharmacy and environmental remediation.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
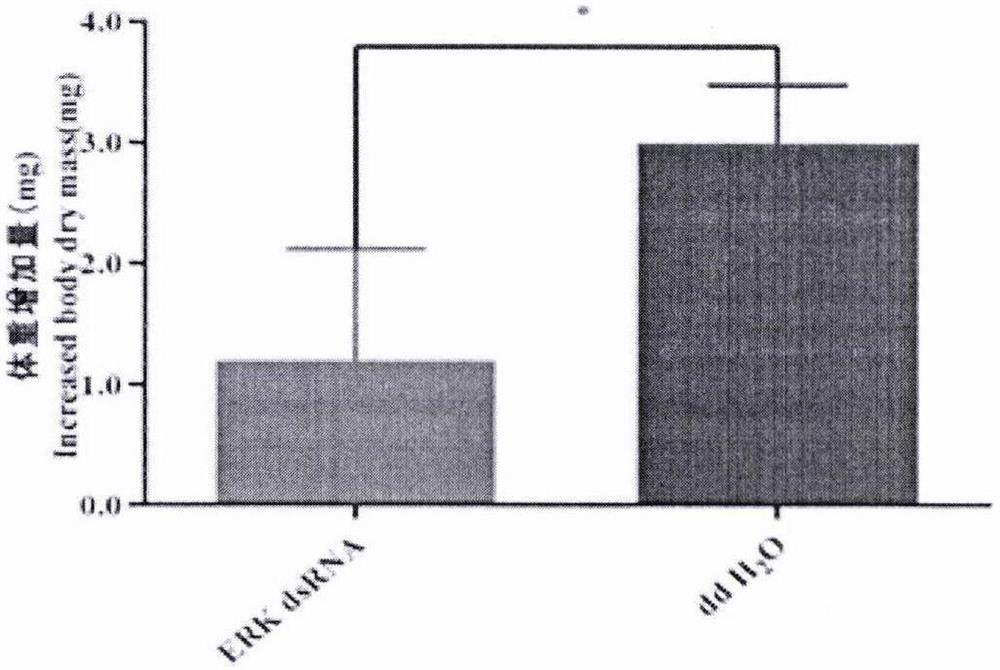
Oedaleus asiaticus extracellular regulated protein kinase (ERK) as well as encoding gene and application thereof
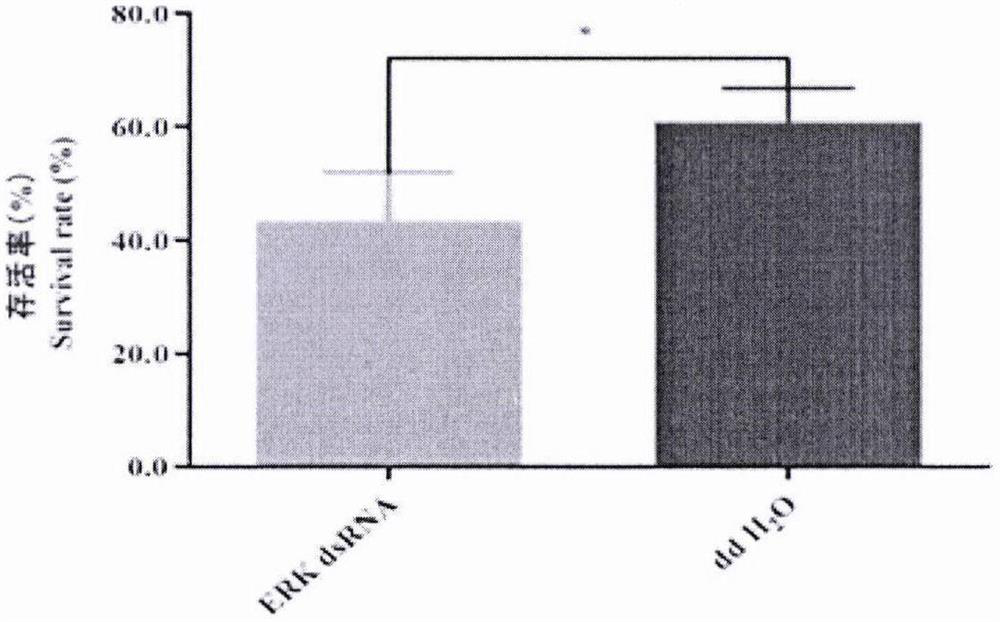
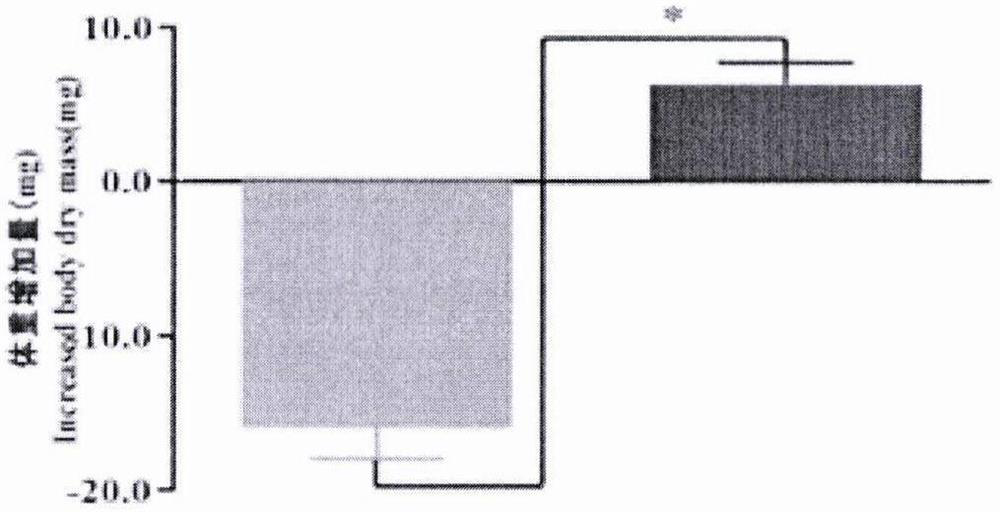
ActiveCN112226425AReduced survival rateReduced growth rateBiocideHydrolasesBiopesticideExtracellular protease
The invention discloses an oedaleus asiaticus extracellular regulated protein kinase (ERK) as well as an encoding gene and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: cloning the oedaleus asiaticus ERK gene from oedaleus asiaticus, designing primers for the oedaleus asiaticus ERK gene, synthesizing dsRNA for interfering with the oedaleus asiaticus ERK gene, and introducing the dsRNA into oedaleus asiaticus by an injection method to perform RNAi on the oedaleus asiaticus ERK gene. Results show that after dsRNA is injected into the oedaleus asiaticus, the survival rate, the growth rate, the weight and the overall expressive force are all remarkably reduced, and it is indicated that the oedaleus asiaticus ERK gene plays an important role in the insect growth and developmentprocess. A novel method is provided for molecular regulation of pests, and a theoretical basis is provided for deep understanding of the insect growth and development mechanism and creation of new biopesticide preparations.
Owner:宁夏中微泰克生物技术有限责任公司
Bacillus licheniformis expression host
ActiveCN104630123BReduced activityIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaHydrolasesBacillus licheniformisProtein target
The invention discloses a bacillus licheniformis host bacterium BL10 with multiple gene deletion, the accession number of which is CCTCCNO:M2013400. The host bacterium derives from a bacillus licheniformis WX-02 which partially or completely has deletion of ten genes. The ten genes comprises eight protease genes (mpr encoding a metalloprotease; vpr encoding a serine protease; aprX encoding an intracellular serine protease; epr encoding a minimal extracellular protease; bpr encoding a bacillus peptidase F; wprA encoding a protease combined with cell walls; aprE encoding an extracellular alkaline serine protease; and bprA encoding a bacillus peptidase F) and two extracellular secretory protein genes (hag encoding flagellin; and amyL encoding alpha-amylase). The BL10 has completely no extracellular protease activity and can reduce the degradation effect of a protease on a target protein. When the target protein is expressed by the expression host, the expression level is higher, and the host bacterium benefits protein expression enhancement.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Antifouling composition prepared from a pseudomonas pf-11 culture
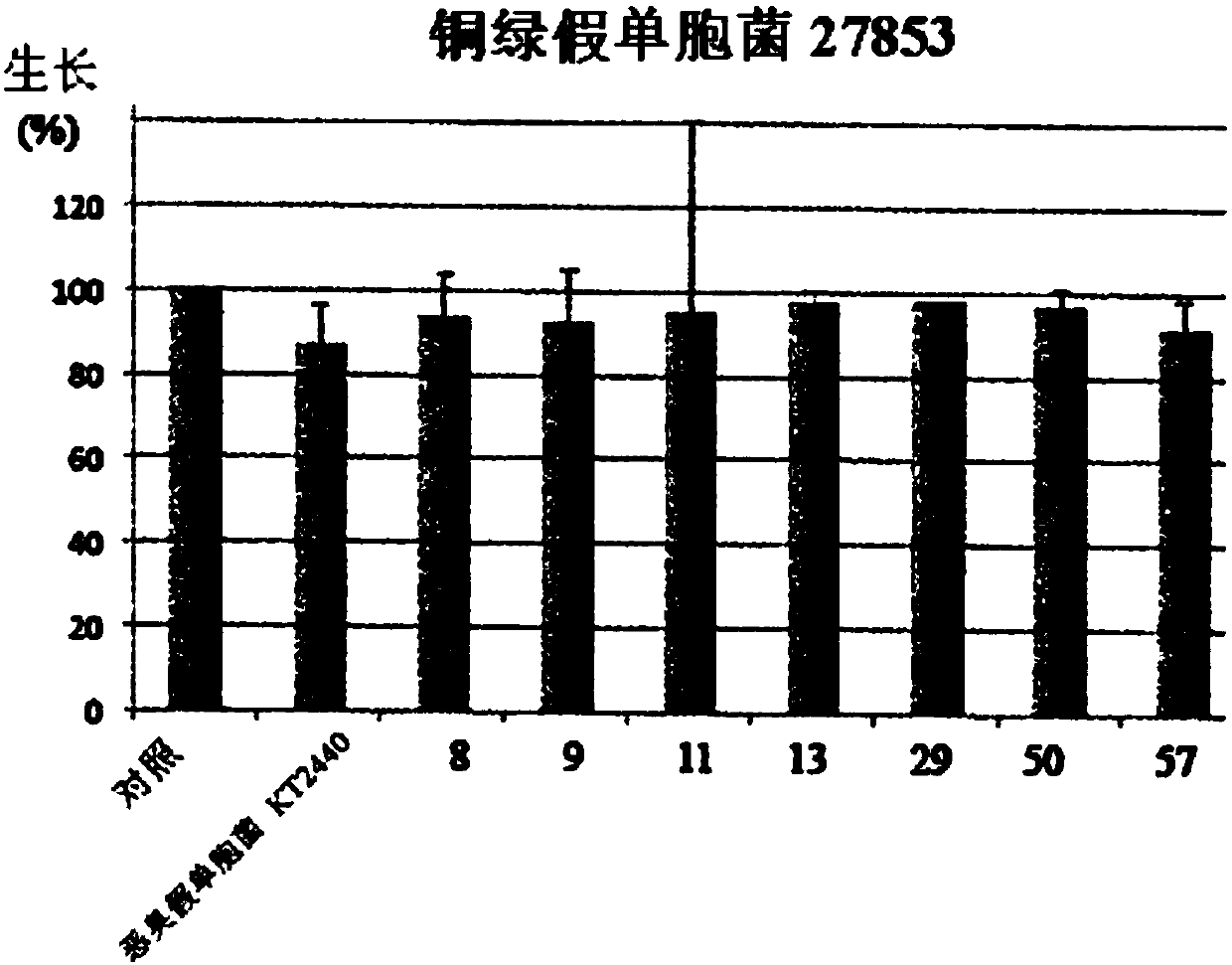
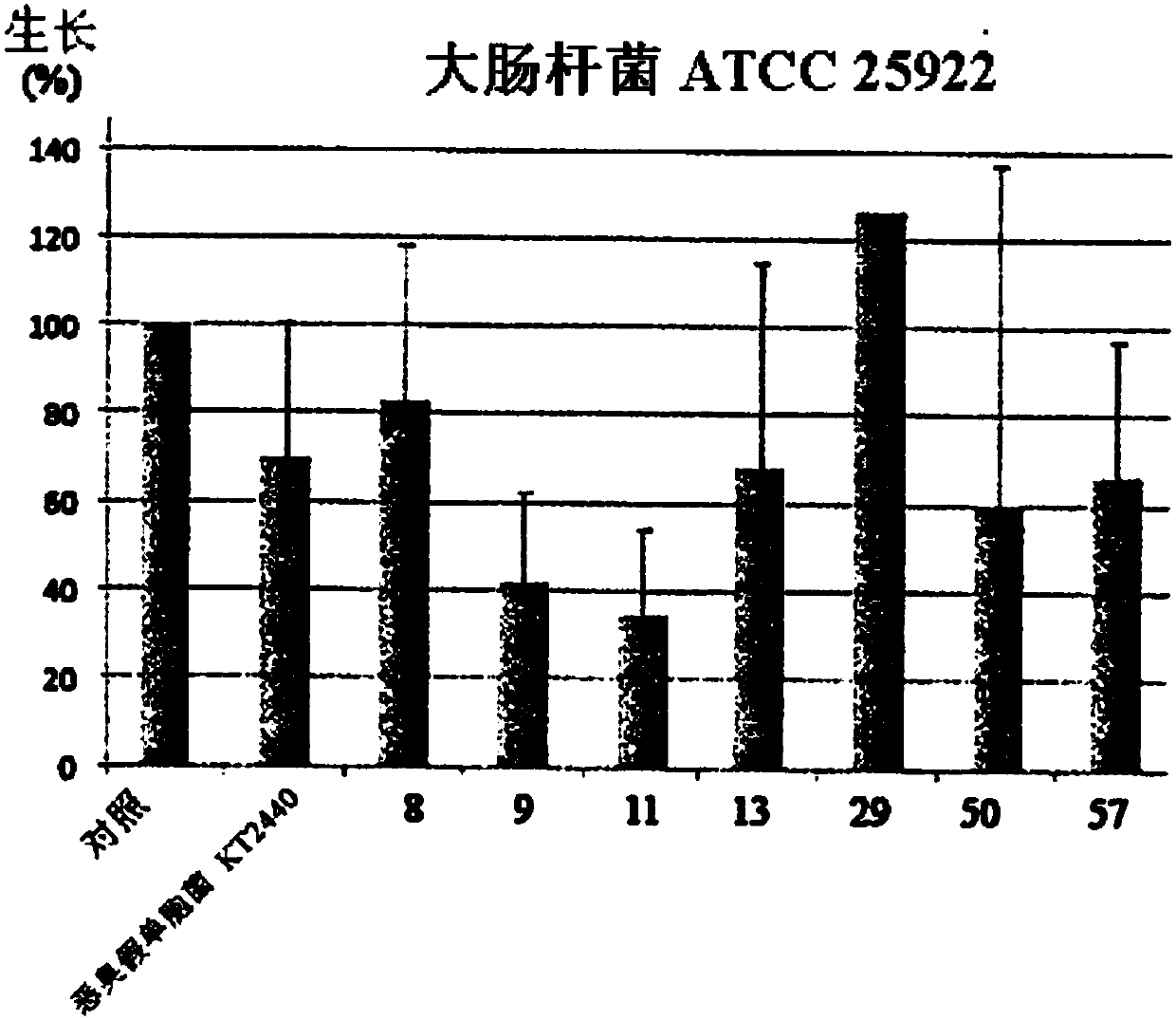
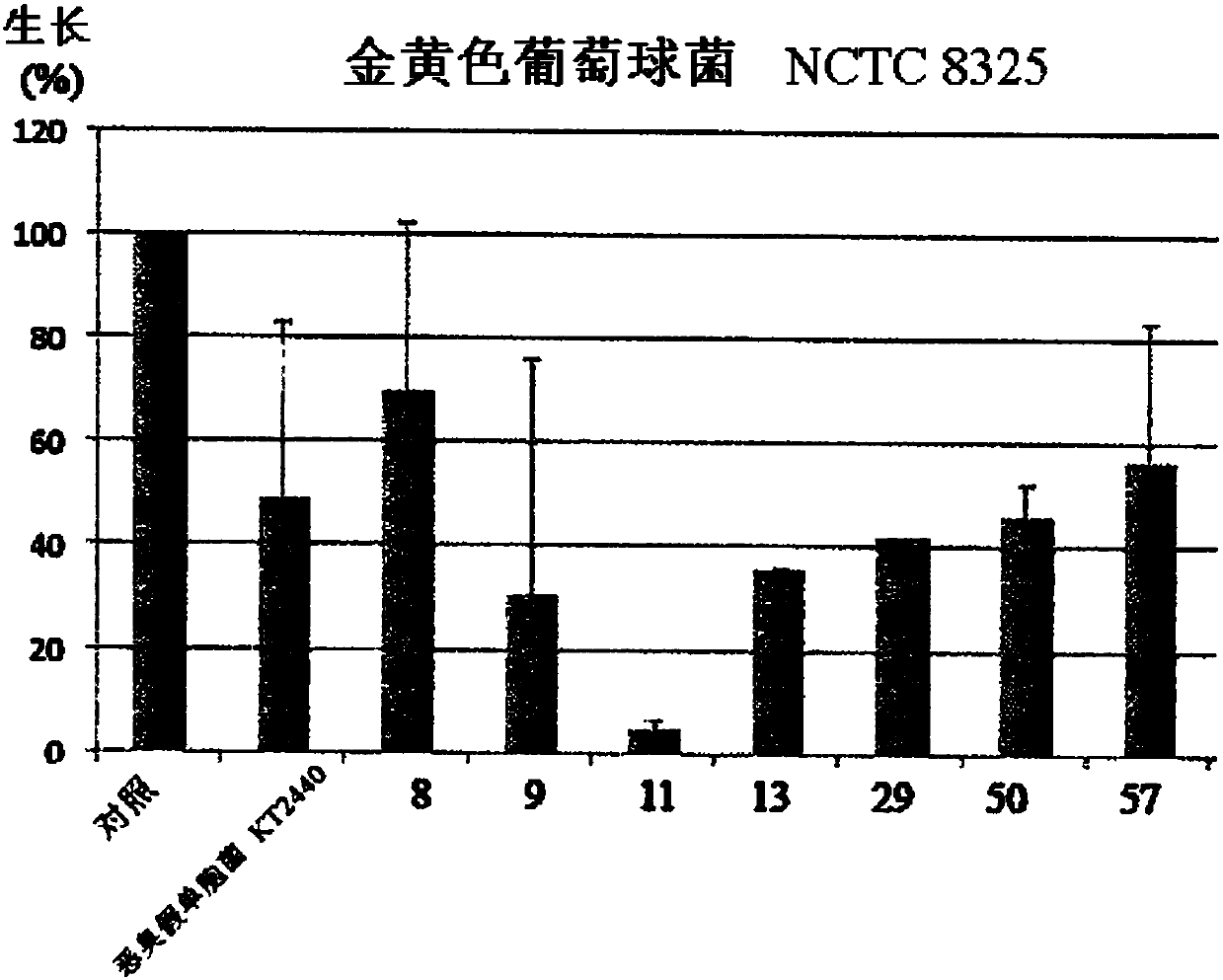
This invention concerns a method for preparing a bacterial supernatant comprising culturing a cell of Pseudomonas environmental strain PF-11; and recovering the supernatant. This invention also concerns a method for reducing the amount of a biofilm on a surface, reducing adhesion of at least one organism to a surface, or reducing microfouling or macrofouling on a surface comprising contacting thesurface with a supernatant, supernatant fraction, modified supernatant or modified supernatant fraction of Pseudomonas strain PF-11; or a composition comprising a supernatant, supernatant fraction, modified supernatant or modified supernatant fraction of Pseudomonas strain PF-11, and one or more acceptable carriers. This invention also concerns a method for killing or reducing the growth of a fungus or bacterial cell, or killing or inhibiting the development of an insect or marine copepod, comprising contacting the fungus, bacteria, insect or marine copepod with a supernatant, supernatant fraction, modified supernatant or modified supernatant fraction of a Pseudomonas strain PF-11 culture; or a composition comprising a supernatant, supernatant fraction, modified supernatant or modified supernatant fraction of a Pseudomonas strain PF-11 culture, and one or more acceptable carriers. This invention also concerns a substantially pure culture of Pseudomonas strain PF-11. This invention alsoconcerns a culture that is enriched in Pseudomonas strain PF-11. This invention also provides a method of identifying whether a bacterium is capable of producing one or more extracellular proteases capable of digesting a high molecular weight substrate.
Owner:BIOMIMETX SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com