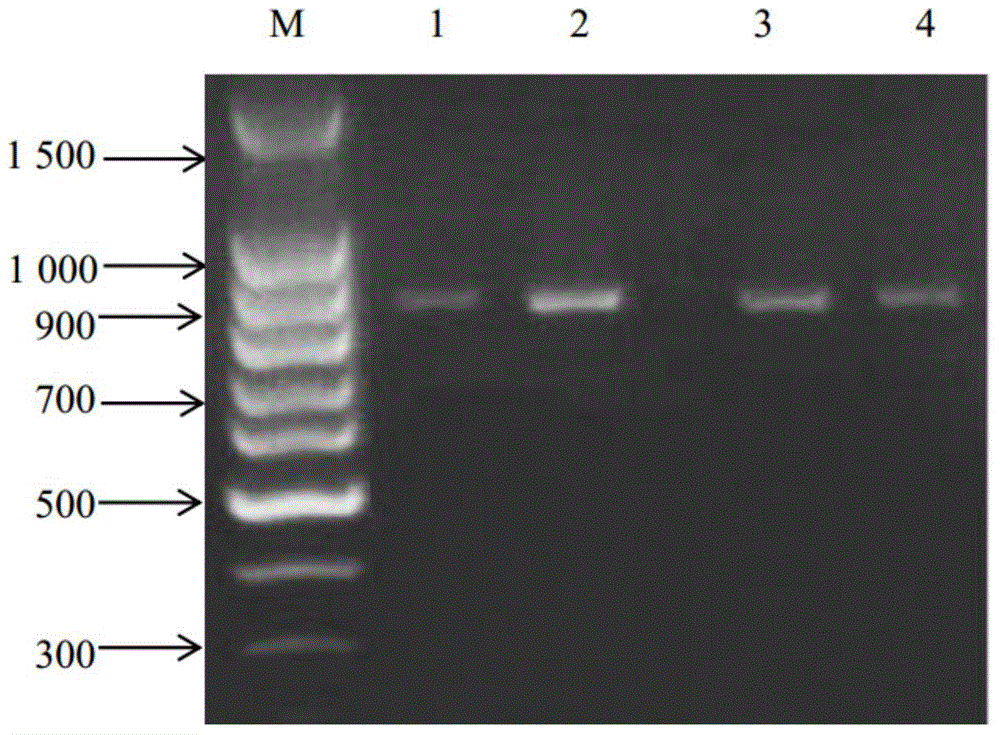
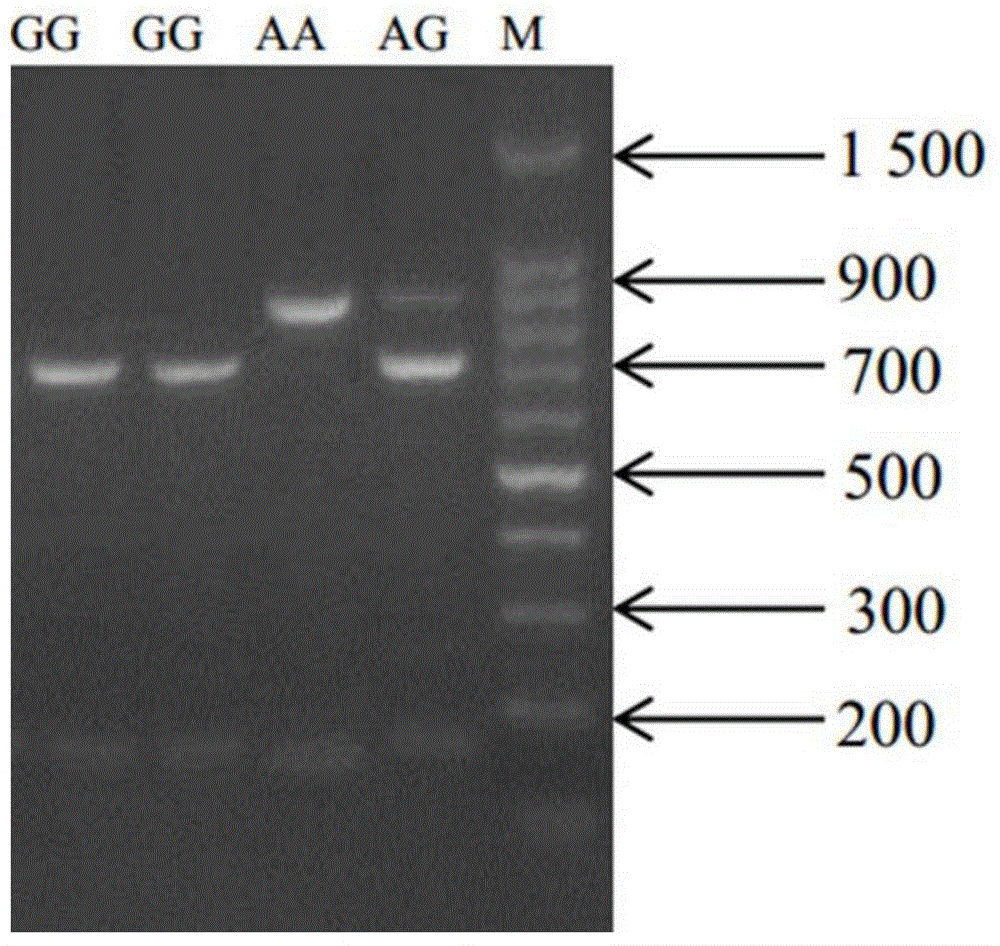
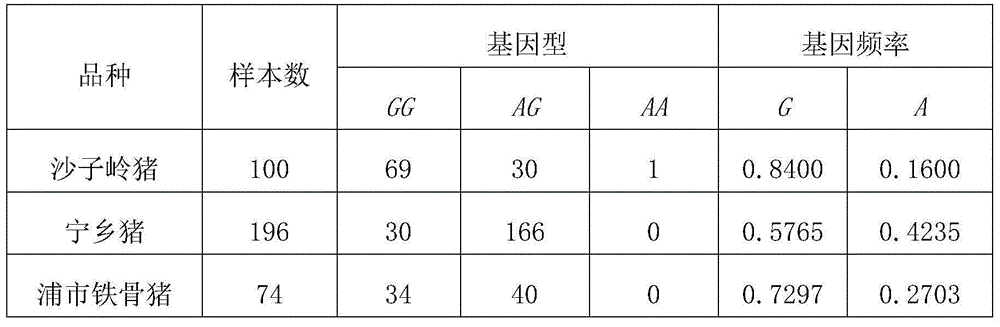
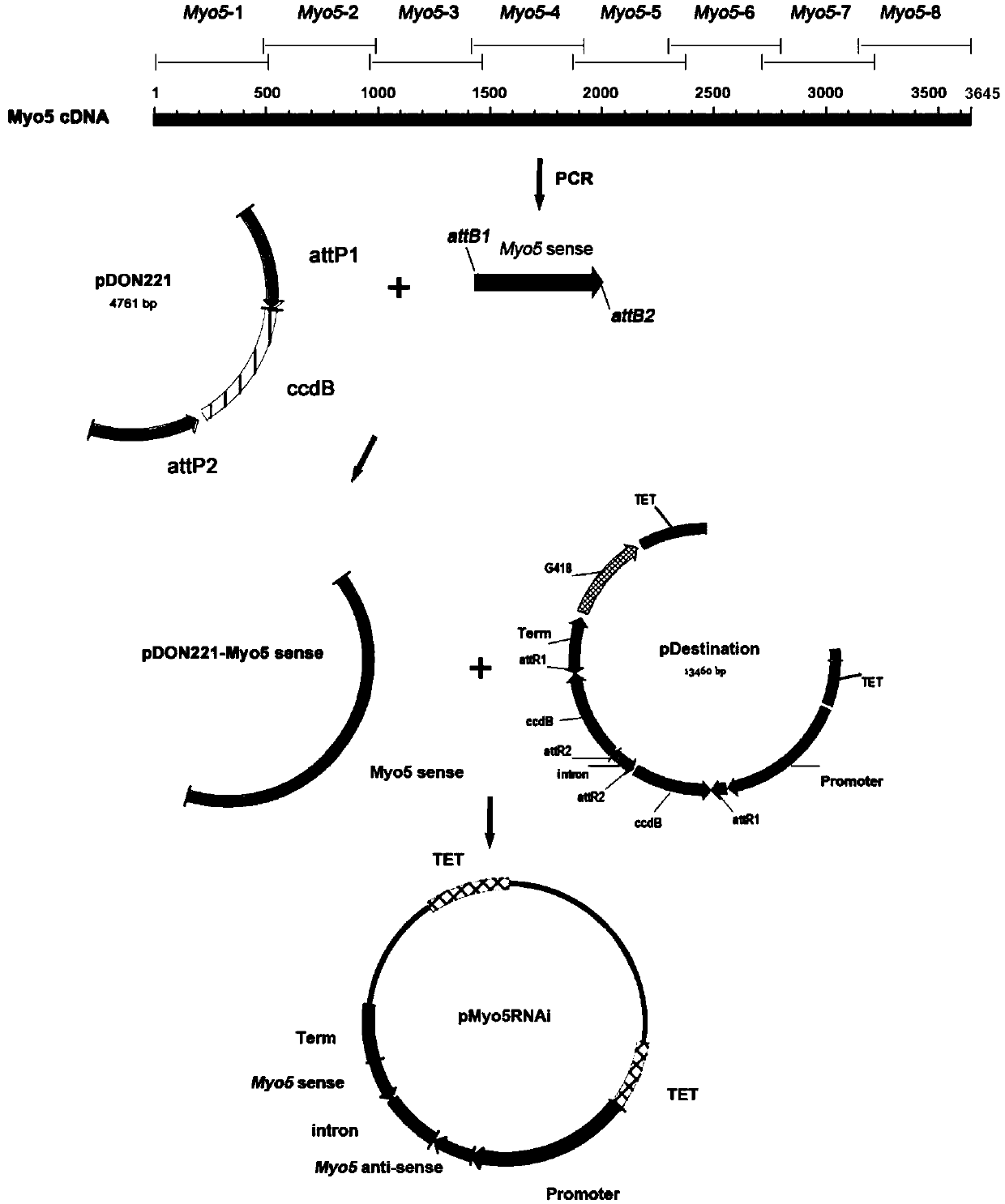
Patents
Literature
143 results about "Myosin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Myosins (/ˈmaɪəsɪn, -oʊ-/) are a superfamily of motor proteins best known for their roles in muscle contraction and in a wide range of other motility processes in eukaryotes. They are ATP-dependent and responsible for actin-based motility. The term was originally used to describe a group of similar ATPases found in the cells of both striated muscle tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Following the discovery by Pollard and Korn (1973) of enzymes with myosin-like function in Acanthamoeba castellanii, a global range of divergent myosin genes have been discovered throughout the realm of eukaryotes.
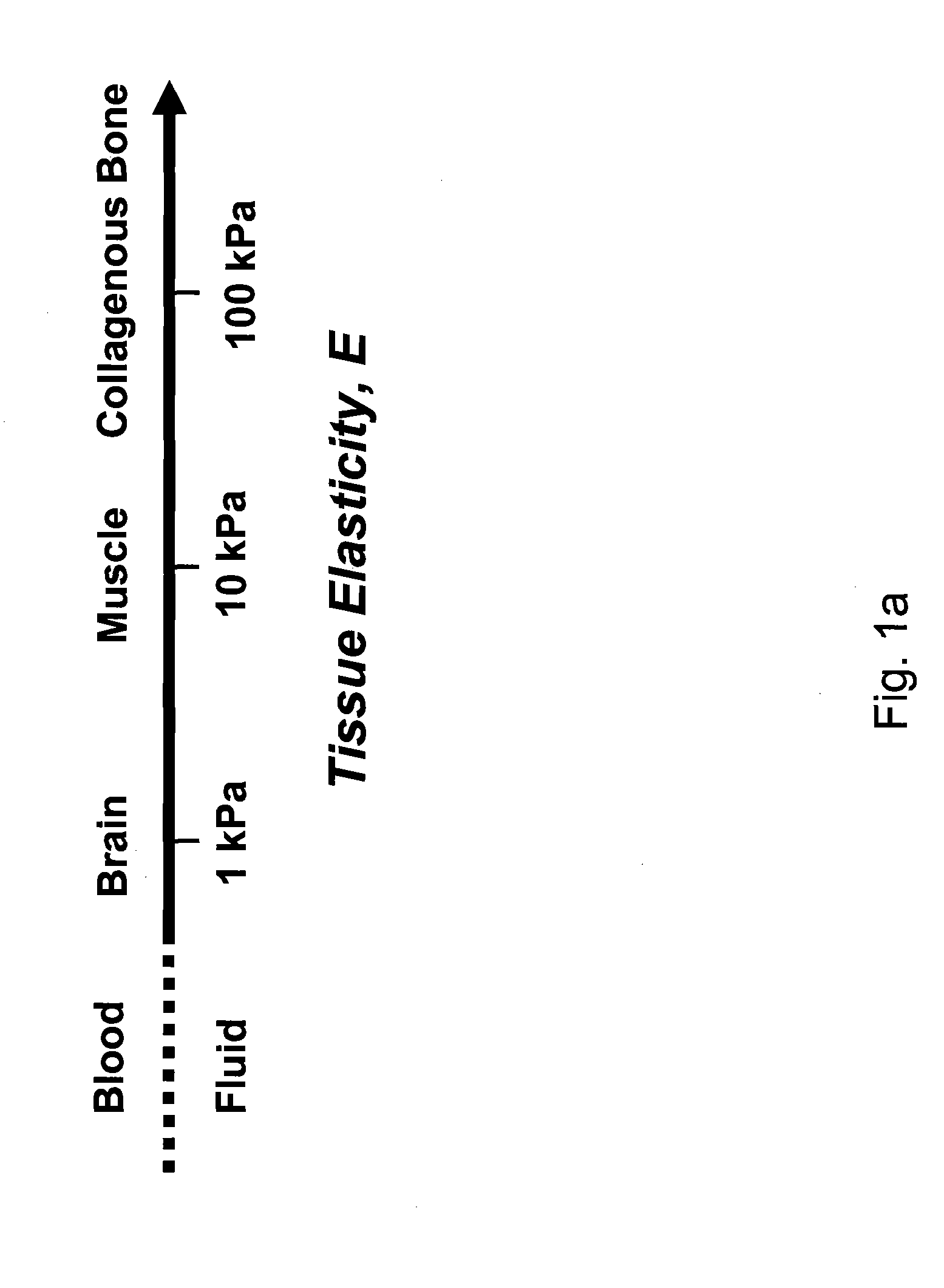
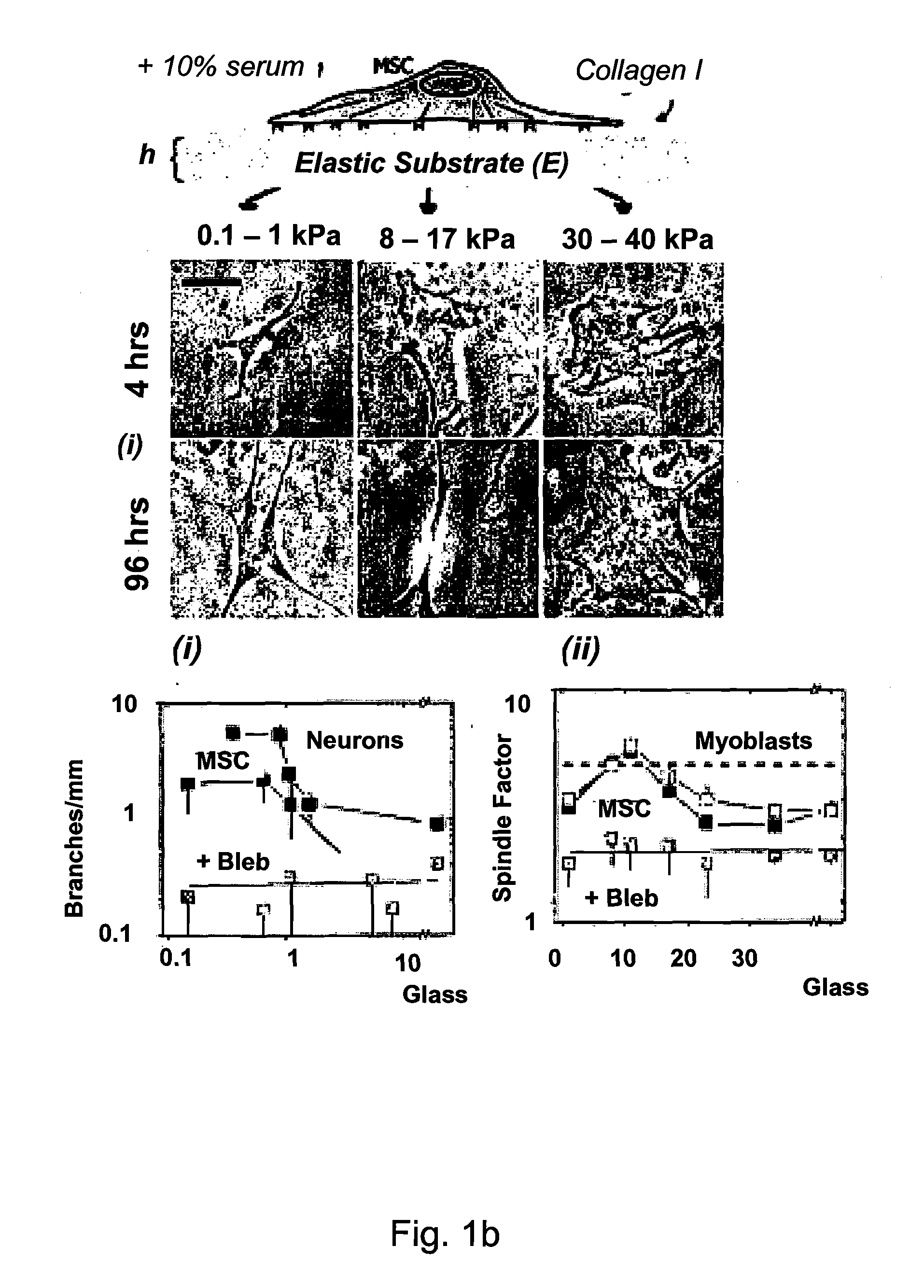
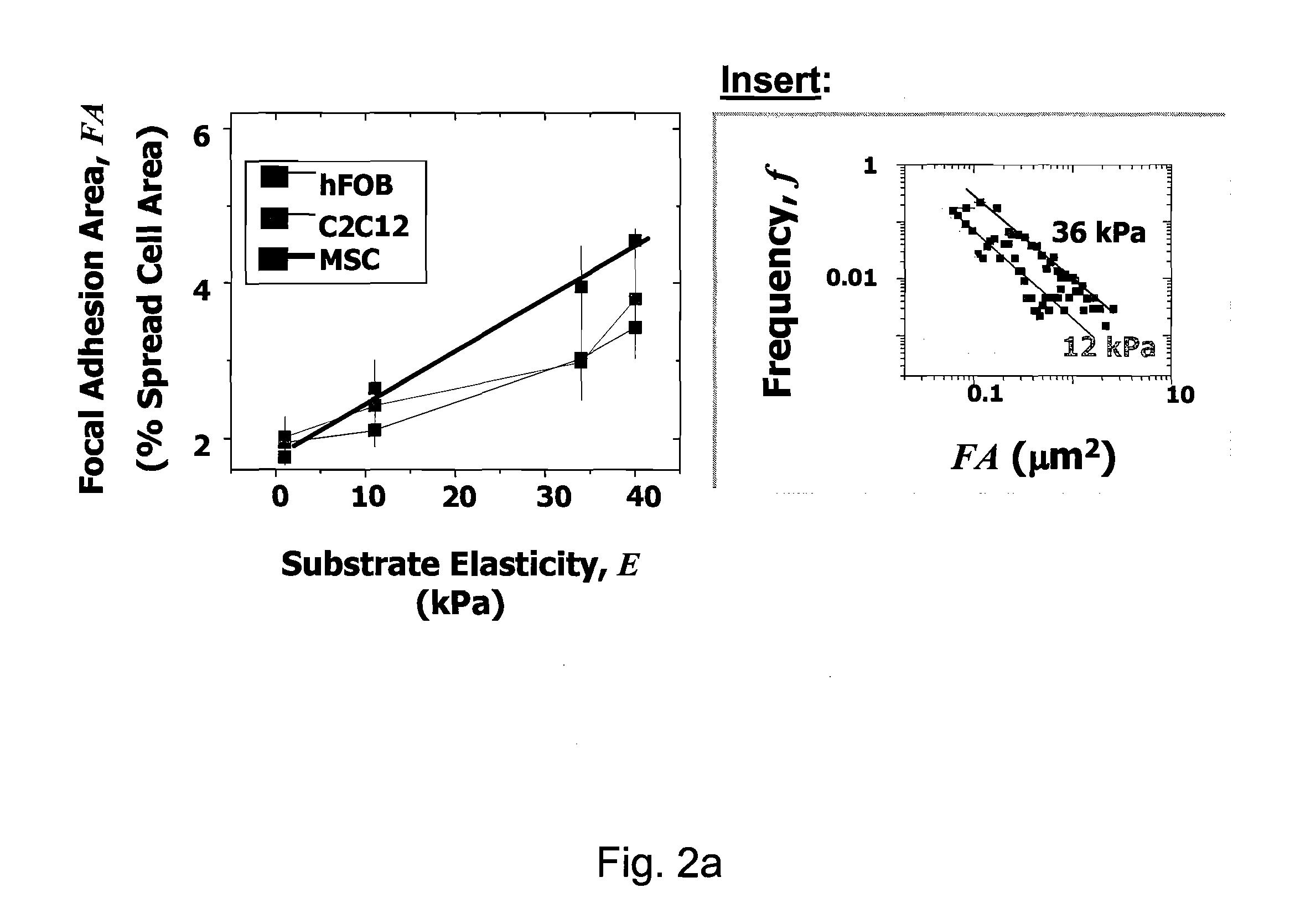
Regulating Stem Cell Differentiation By Controlling 2D and 3D Matrix Elasticity
InactiveUS20100015709A1Cell culture supports/coatingSkeletal/connective tissue cellsMyosinMesenchymal stem cell
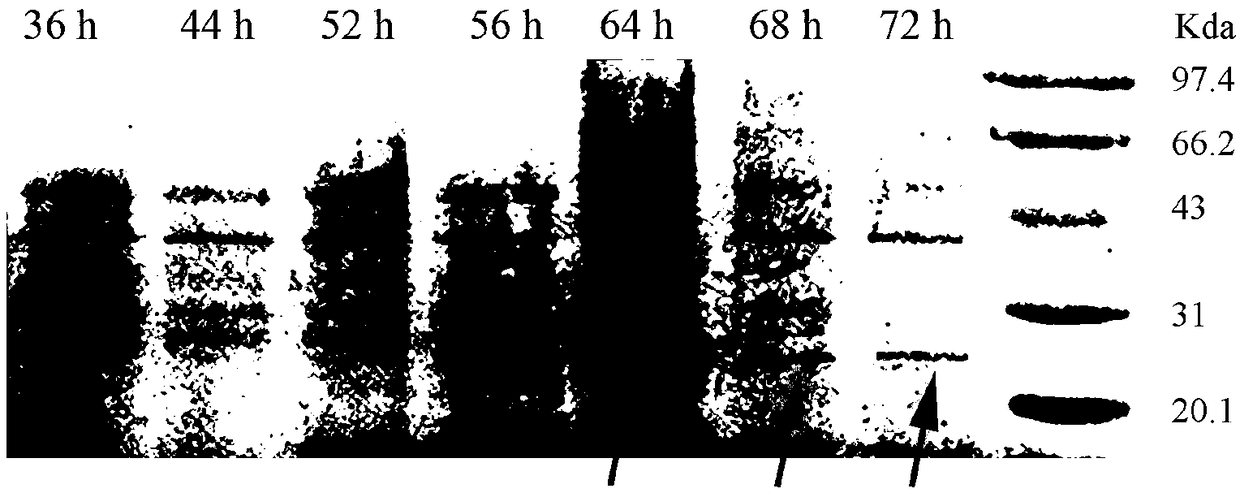
Provided are methods for the selection and regulation of the mechanical properties of 2D or 3D biocompatible substrates or tissue microenvironments as a technique to regulate in vitro differentiation, cell shape and / or lineage commitment of anchorage-dependent cells, such as mesenchymal stem cells into, e.g., neurogenic-, myogenic-, and osteogenic-type cells. Substrate mechanical properties include elasticity, tension, adhesion, and myosin-based contractile mechanisms. Inhibitors can be introduced to further regulate differentiation.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
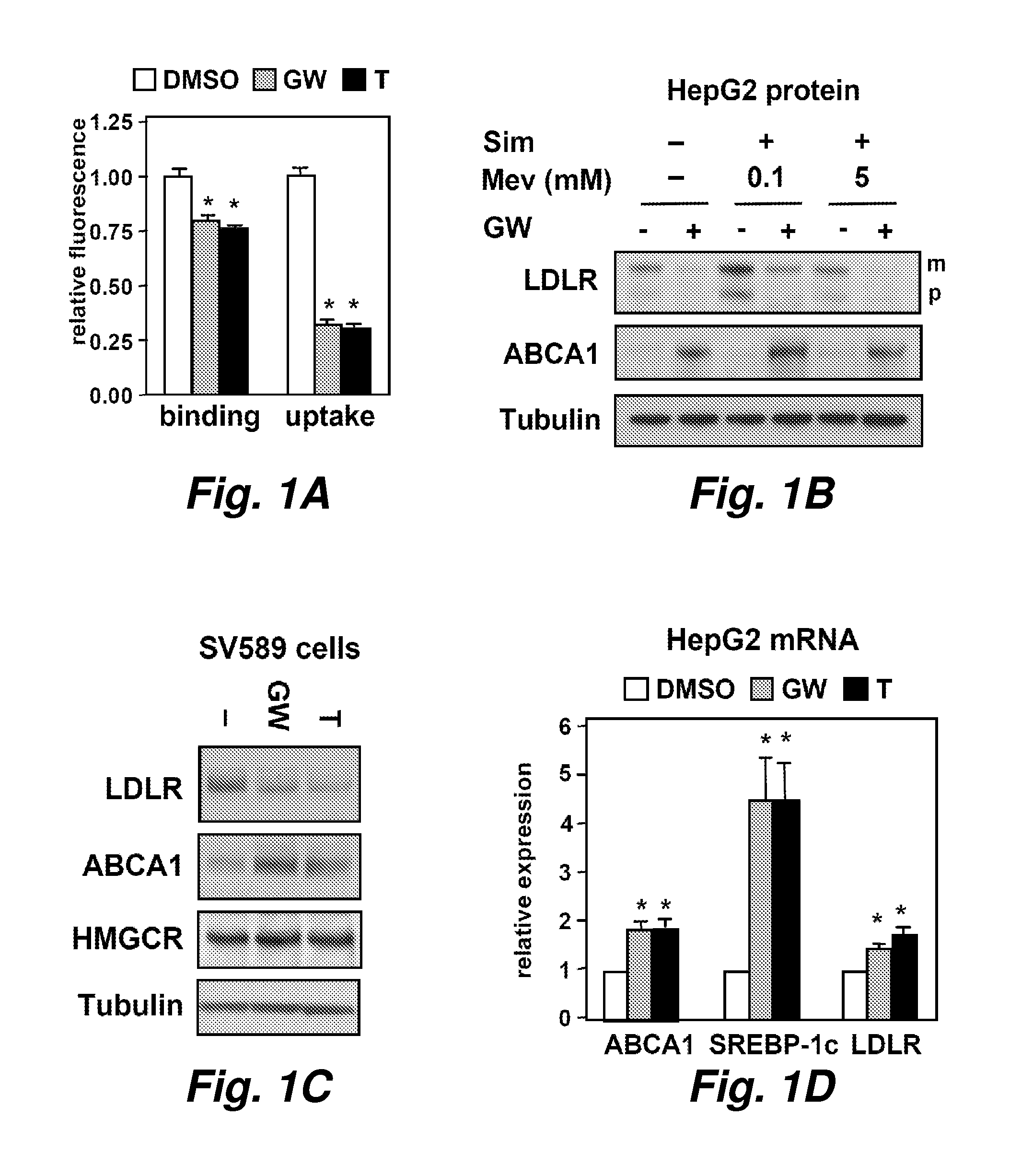
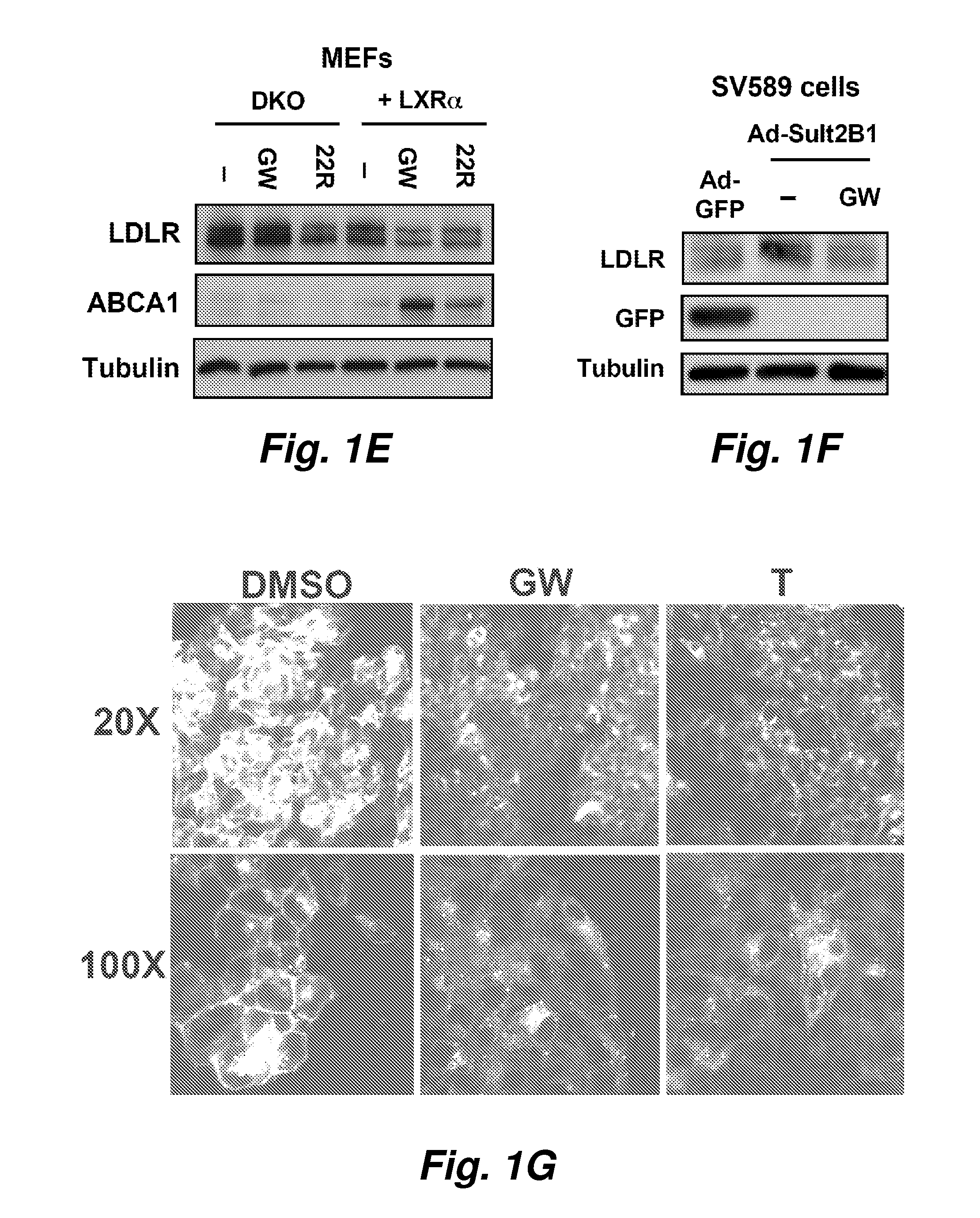
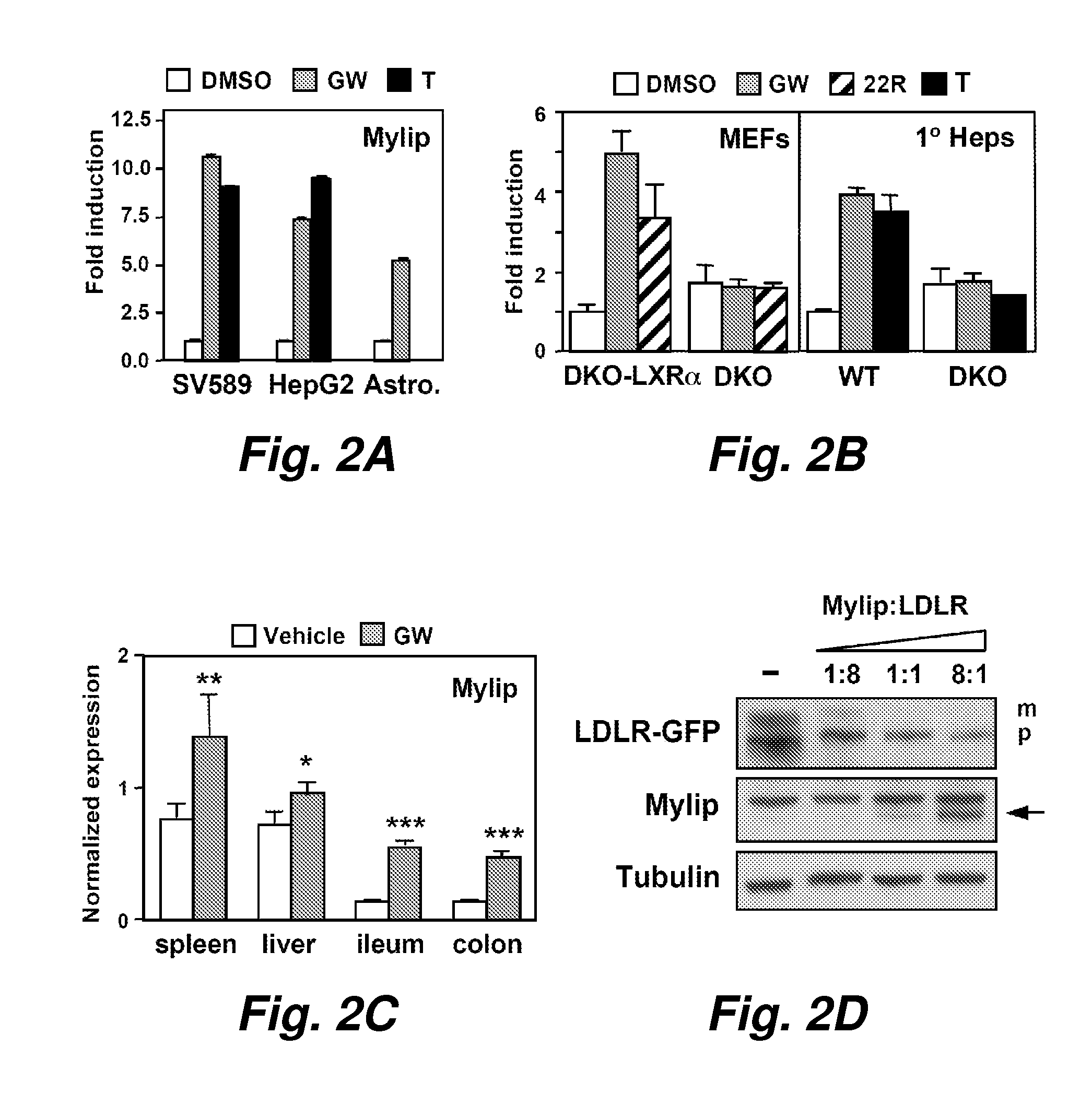
Targets for treatment of hypercholesterolemia
In certain embodiments this invention pertains to the discovery that inhibition of myosin light chain interacting protein (Mylip) can mitigate one or more symptoms of hypercholesterolemia. Methods of treating hypercholesterolemia and methods of screening for agents to treat hypercholesterolemia are provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
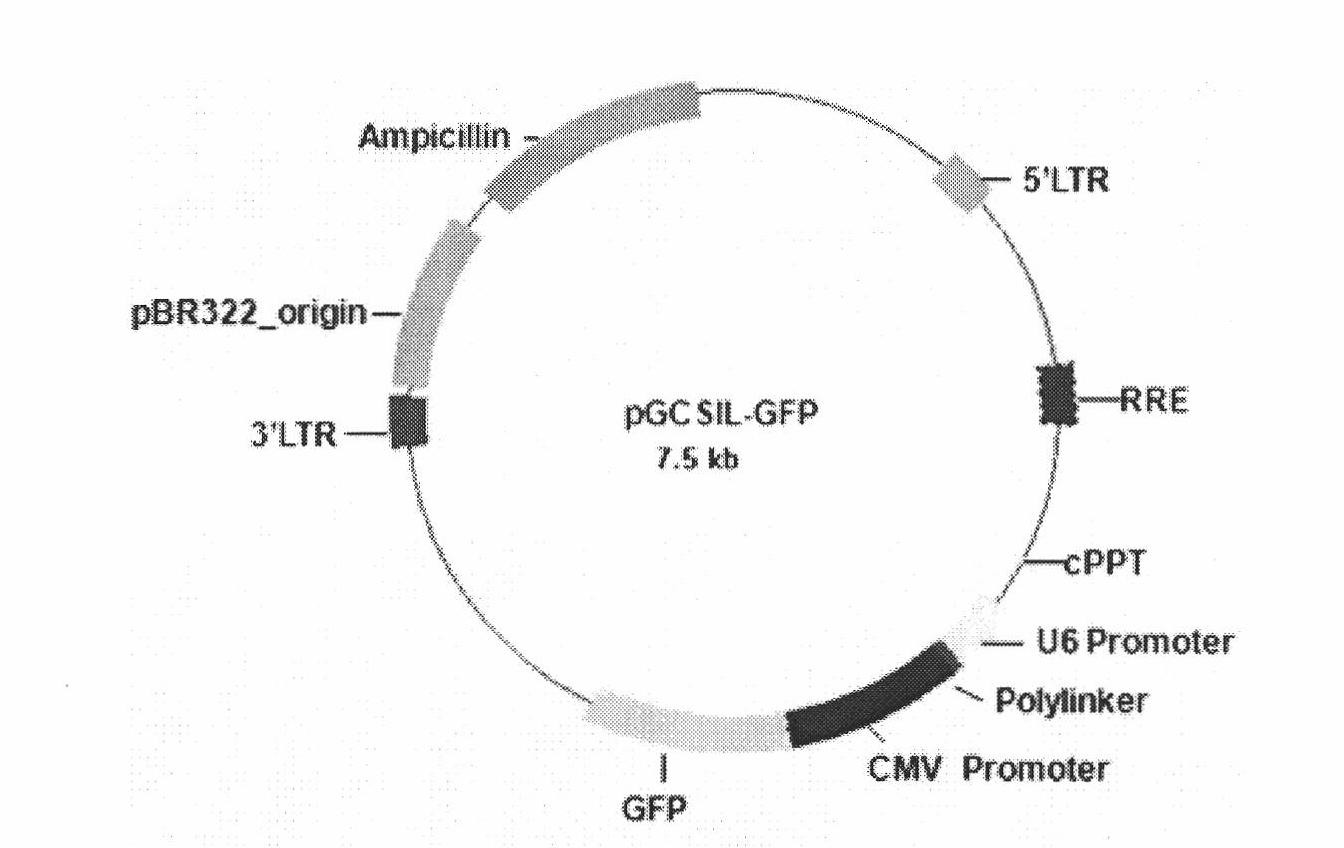
Construction and application of farnesyl pyrophosphoric acid synthetase RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) interference recombinant lentivirus vector
InactiveCN101805750AOvercoming No Commercial AntibodyOvercoming low transfection efficiencyMetabolism disorderGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseFhit gene
The invention provides the construction for a farnesyl pyrophosphoric acid synthetase RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) interference recombinant lentivirus vector, which comprises the following steps of: sieving the most effective target sequence of an FDS (farnesyl diphosphate synthase) gene RNAi (RNA interference) in a tool cell 293T cell, synthesizing the double-stranded DNA of the most effective target sequence, connecting to a pGCSIL-GFP vector and successfully constructing the recombinant vector through enzyme cutting, sequencing and identification. Researches indicate that the constructed RNA interference vector LV-sh-FDS can downwards modulate the expression of an FDS mRNA (Messenger RNA) level in a neonatal rat cardiac myocyte, simultaneously can downwards modulate the expression of myocardial hypertrophy markers such as cell areas and marker genes beta-MHC (Myosin Heavy Chain) and BNP (Brain Natriuretic Peptide), additionally can effectively inhabit the activity of RhoA while downwards modulating the FDS, can be applied in preparing medicaments for treating myocardial hypertrophy diseases and also can be applied in preparing medicaments for cholesterol metabolic control.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Blocking the migration or metastasis of cancer cells by affecting adhesion proteins and the uses of new compounds thereof
ActiveUS20100004190A1Growth inhibitionReduce adhesionBiocideSugar derivativesDiseaseLymphatic Spread
This invention provides methods, processes, compounds and compositions for modulating the gene expression and modulating the secretion, expression, or synthesis of adhesion proteins or their receptors to cure disease, wherein the modulating comprises positive and negative regulating; wherein comprises inhibiting cancer growth, wherein the adhesion proteins or receptors comprise fibronectin, integrins family, Myosin, vitronectin, collagen, laminin, Glycosylation cell surface proteins, polyglycans, cadherin, heparin, tenascin, CD 54, CAM, elastin and FAK; wherein the methods, processes, compounds and compositions are also for anti-angiogenesis; wherein the cancers comprise breast cancer, leukocyte cancer, liver cancer, ovarian cancer, bladder cancer, prostate cancer, skin cancer, bone cancer, brain cancer, leukemia cancer, lung cancer, colon cancer, CNS cancer, melanoma cancer, renal cancer or cervix cancer.
Owner:PACIFIC ARROW
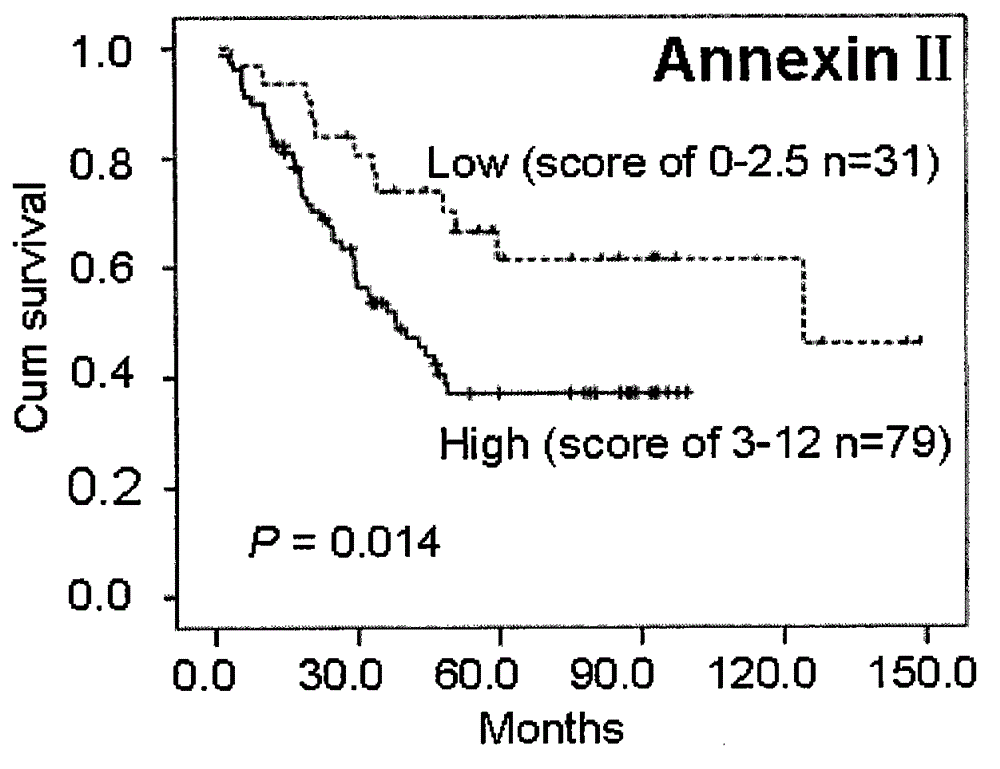
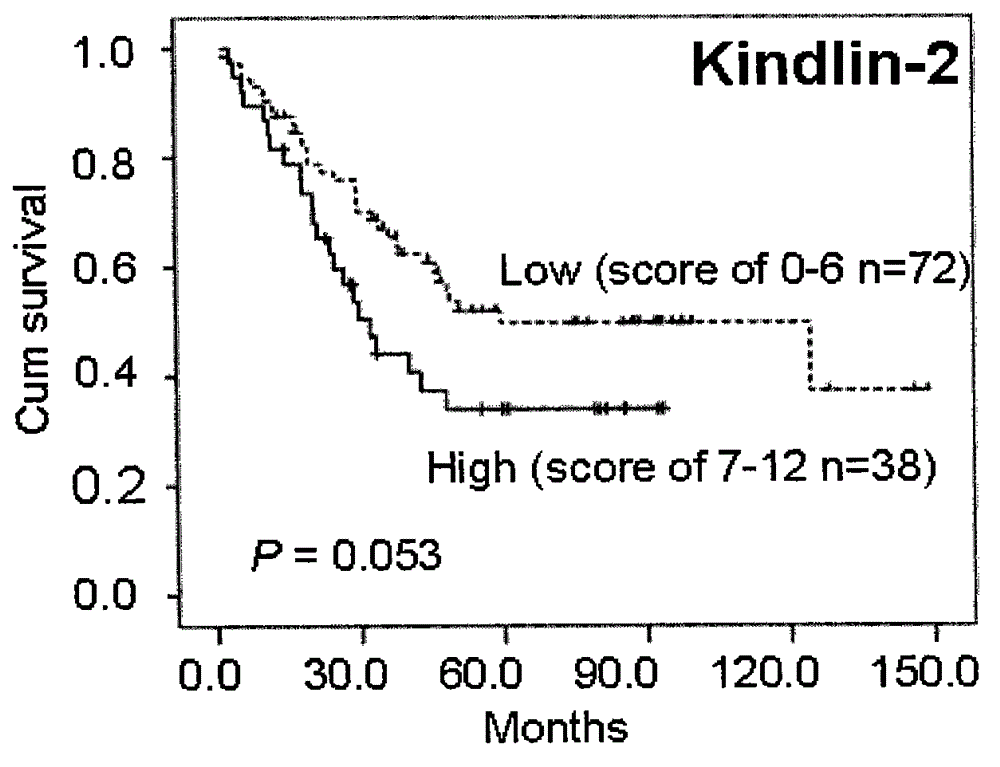
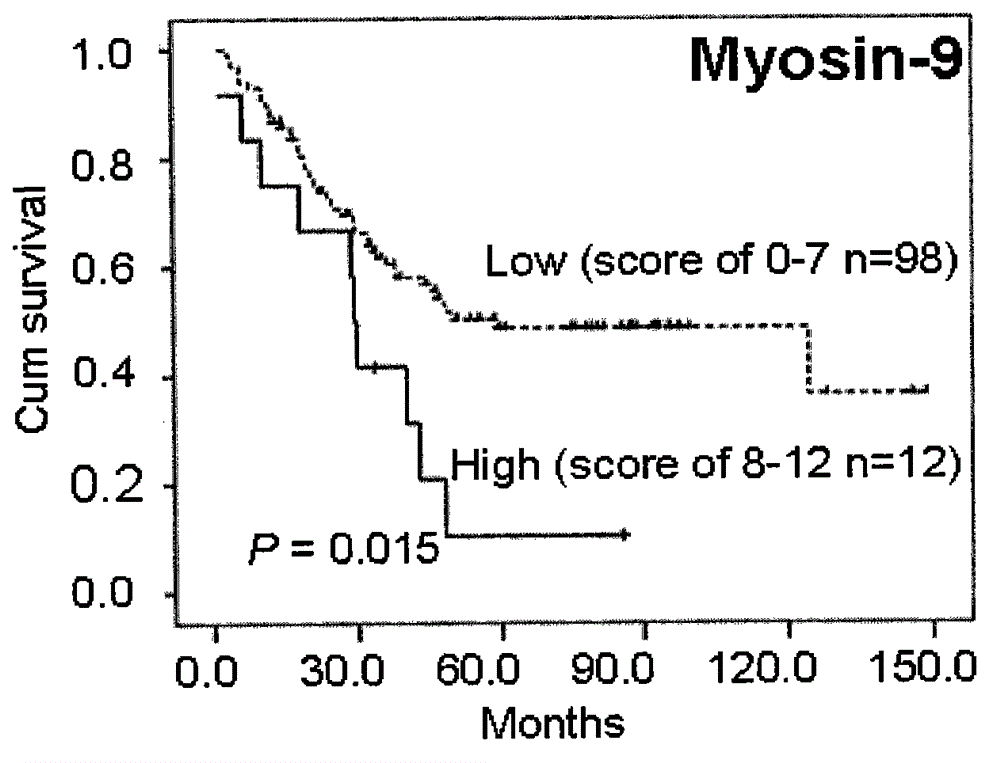
Kit integrating three proteins such as Kindlin-2, Myosin-9 and Annexin II for prognosis evaluation of patient suffering from esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
The invention aims to provide a reagent capable of detecting the expression condition of a target protein in a paraffin-embedded tissue, and particularly provides a kit used for evaluating the prognosis information of a patient suffering from the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. The kit comprises antibodies of the three target proteins, namely Annexin II, Kindlin-2 and Myosin-9, and further comprises goat serum, 0.01 M citrate repair liquid, 3% H2O2, a Polymer reinforcing agent, a Polymer, a DAB color reagent and a PBS solution. The kit can be used for evaluating the prognosis of the patient; compared with the international TNM staging, the kit is simpler and easier to use, and higher in both sensitivity and specificity, and is more suitable for the prognosis evaluation of Chinese suffering from the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV MEDICAL COLLEGE
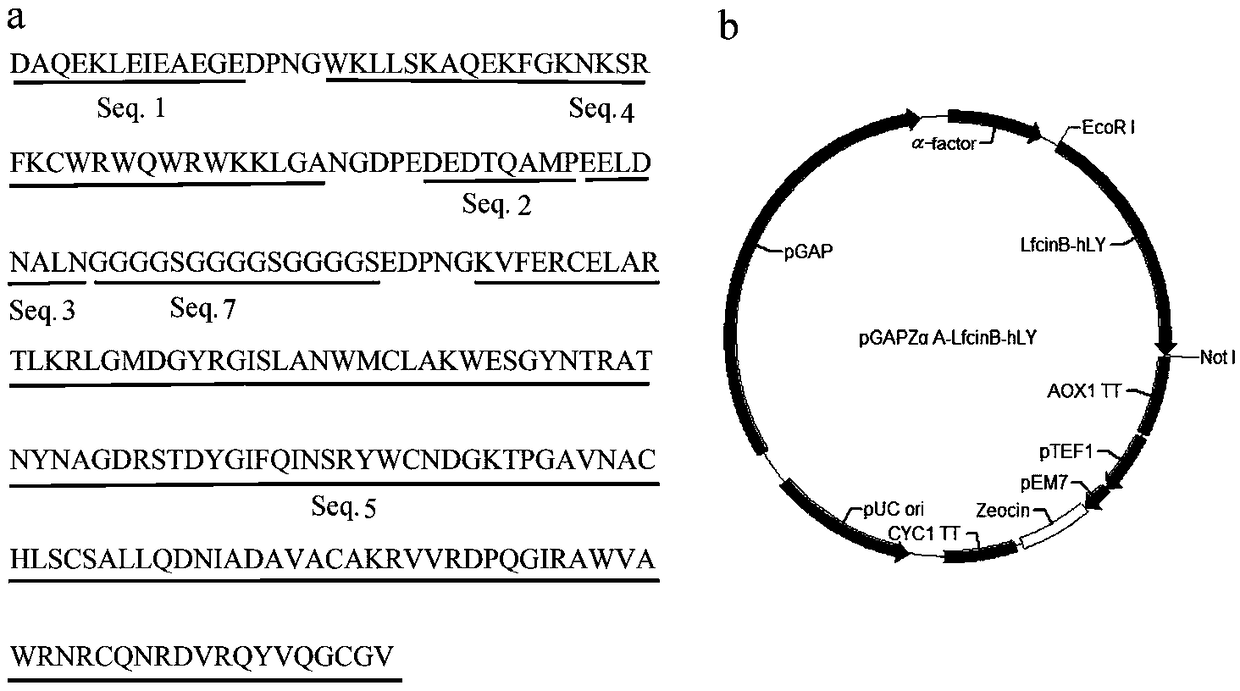
Bovine lactoferricin-human lysozyme fused protein, gene and application thereof
ActiveCN108794635AHas antibacterial activityHigh antibacterial activityTransferrinsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsEscherichia coliFhit gene
The invention discloses bovine lactoferricin-human lysozyme fused protein. The bovine lactoferricin-human lysozyme fused protein is characterized by comprising porcine myofibrillar protein antioxidative peptide, bovine lactoferricin, hen egg white protein antioxidative peptide, porcine muscle myosin antioxidative peptide, flexible peptide and human lysozyme which are connected in series. Through anionic antioxidative peptide derived from fusion expression animals, the positive charge of antimicrobial peptide is neutralized, and inhibition to host bacteria by antimicrobial peptide is reduced; antioxidative peptide is beneficial to the improvement of storage stability of the antimicrobial peptide, the antibacterial activity to escherichia coli (ATCC 25922) by the fused protein is only reduced by 7.7 percent after the fused protein is laid for 20d at 4 DEG C, and the loss of activity to the escherichia coli (ATCC 25922) by the fused protein is only reduced by 15.4 after the fused proteinis laid for 30d.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Myosin inhibitor, as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of medicinal chemistry, in particular to a myosin inhibitor, as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The invention provides a compound or pharmacologically acceptable salt, an isomer, a prodrug, a polymorphic substance or a solvate thereof. A chemical structural formula of the compound is as shown in a formula I. Compared with other similar medicines in the prior art, the compound or the pharmacologically acceptable salt, the isomer, the prodrug, the polymorphic substance or the solvate thereof provided by the invention have better activity and a more ideal pharmacokinetics characteristic.
Owner:SHANGHAI XIANXING PHARM CO LTD
Process for preparing antioxidative peptide and antifreeze peptide through enzymatic hydrolysis of salmon collagens
InactiveCN108118077ADifferent biological activitiesLow costConnective tissue peptidesHydrolasesOxygen radical absorbance capacityFiltration
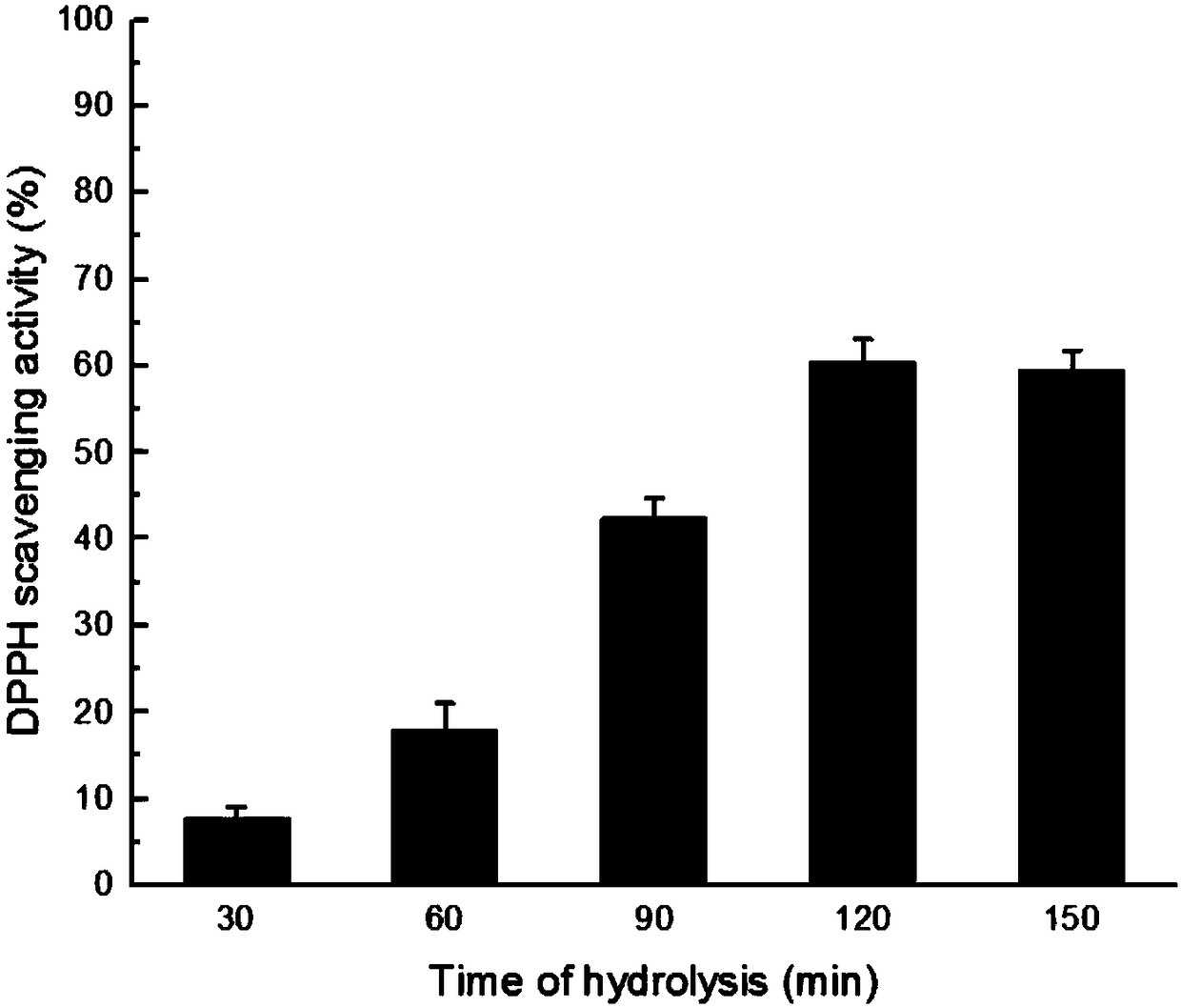
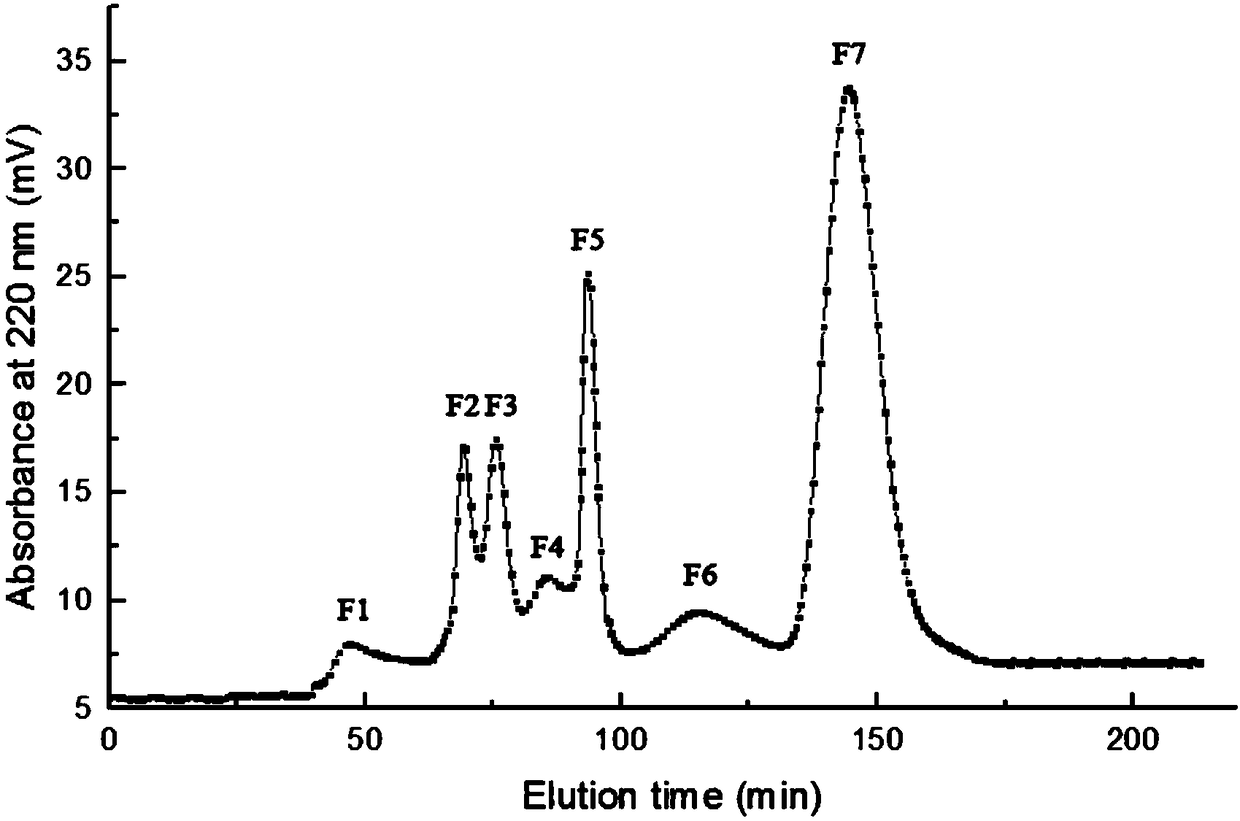
The invention discloses a process for simultaneously preparing an antioxidative peptide and an antifreeze peptide through enzymolysis of collagens. The method comprises the following steps: extractingcollagens by taking salmon skin as a raw material, hydrolyzing the collagens into a short peptide solution by utilizing crude enzymes of extracellaluar protease obtained by fermentation of Vibrio sp.SQS2-3, performing centrifugal ultrafiltration by a 3000 Da ultrafiltration tube 4500*g for 45 minutes so as to obtain the antifreeze peptide with effects of protecting myosin and relieving decreaseof Ca<2+>-ATPase activity in multigelation, performing Sephadex LH-20 gel filtration chromatography to separate lower ultrafiltration components so as to obtain the antioxidative peptide which has effects of scavenging DPPH free radicals and hydroxyl radicals and a certain ability of inhibiting DNA oxidative damage and shows concentration-dependent antioxidant activity in oxygen radical absorptioncapacity detection. The LC-MS technology shows that the antioxidant component contains 19 polypeptides.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Novel meat paste product preparing method
InactiveCN105394610AIncrease elasticityImprove toughnessFood ingredient as clouding agentFood ingredient as gelling agentGellan gumMyosin
The invention discloses a novel meat paste product preparing method. The method comprises the steps of conducting pretreatment and meat paste preparation with one or more kinds of livestock meat as the raw material, then adding gel prepared from curdlan gum, sodium alga acid, gellan gum and carrageenan, and obtaining a novel meat paste product by means of glutamine transaminase. By adding multiple gel agents to form the gel which reacts with myosin and actomyosin to form a protein gelinite, the elasticity, tenacity and juiciness of the product are controlled, and then the novel elastic, tenacious and juicy meat paste product which tastes strong is produced.
Owner:SICHUAN RENCONGZHONG FOOD CO LTD
Blocking the migration or metastasis of cancer cells by affecting adhesion proteins and the uses of new compounds thereof
This invention provides methods, processes, compounds and compositions for modulating the gene expression and modulating the secretion, expression, or synthesis of adhesion proteins or their receptors to cure disease, wherein the modulating comprises positive and negative regulating; wherein comprises inhibiting cancer growth, wherein the adhesion proteins or receptors comprise fibronectin, integrins family, Myosin, vitronectin, collagen, laminin, Glycosylation cell surface proteins, polyglycans, cadherin, heparin, tenascin, CD 54, CAM, elastin and FAK; wherein the methods, processes, compounds and compositions are also for anti-angiogenesis; wherein the cancers comprise breast cancer, leukocyte cancer, liver cancer, ovarian cancer, bladder cancer, prostate cancer, skin cancer, bone cancer, brain cancer, leukemia cancer, lung cancer, colon cancer, CNS cancer, melanoma cancer, renal cancer or cervix cancer.
Owner:PACIFIC ARROW
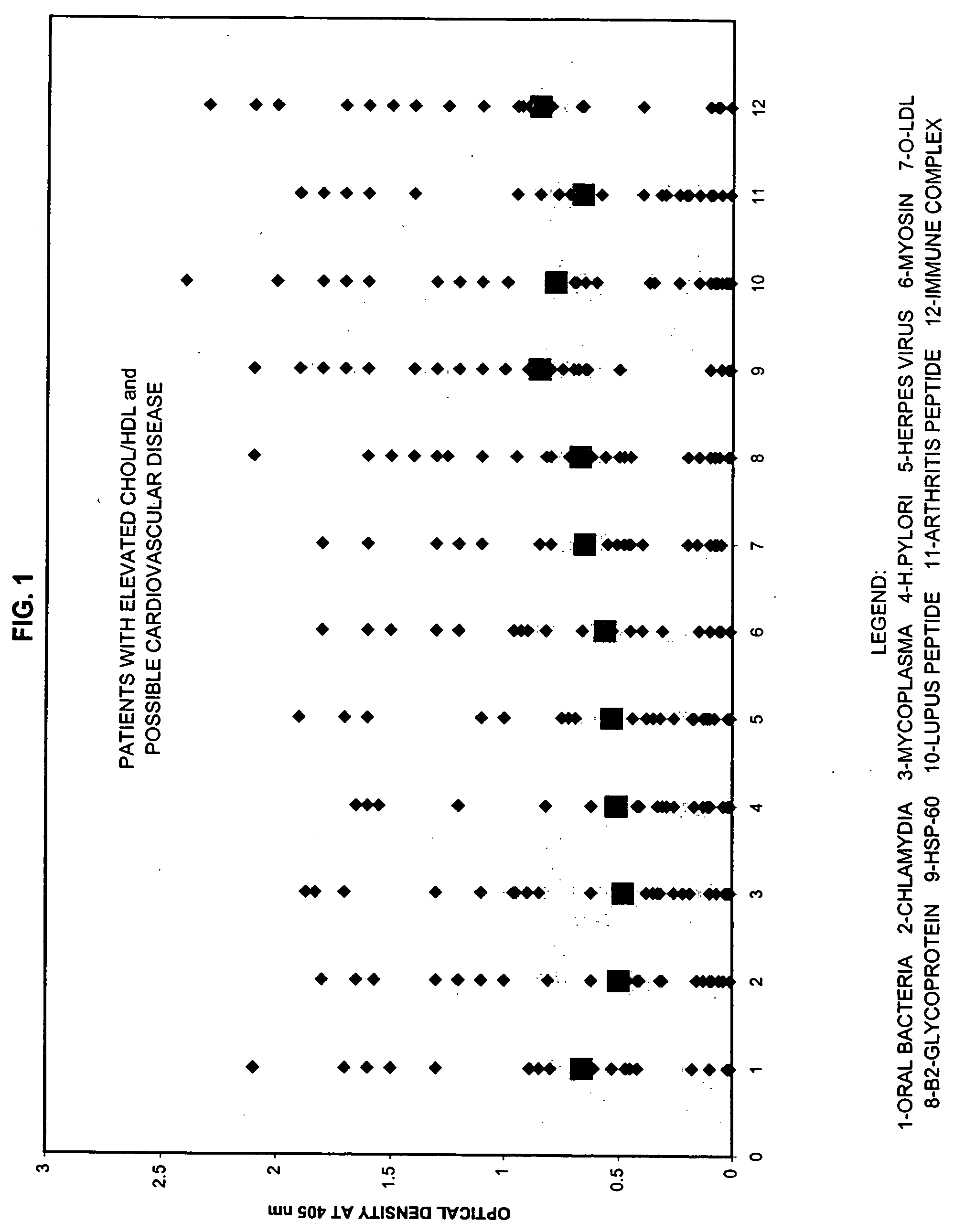
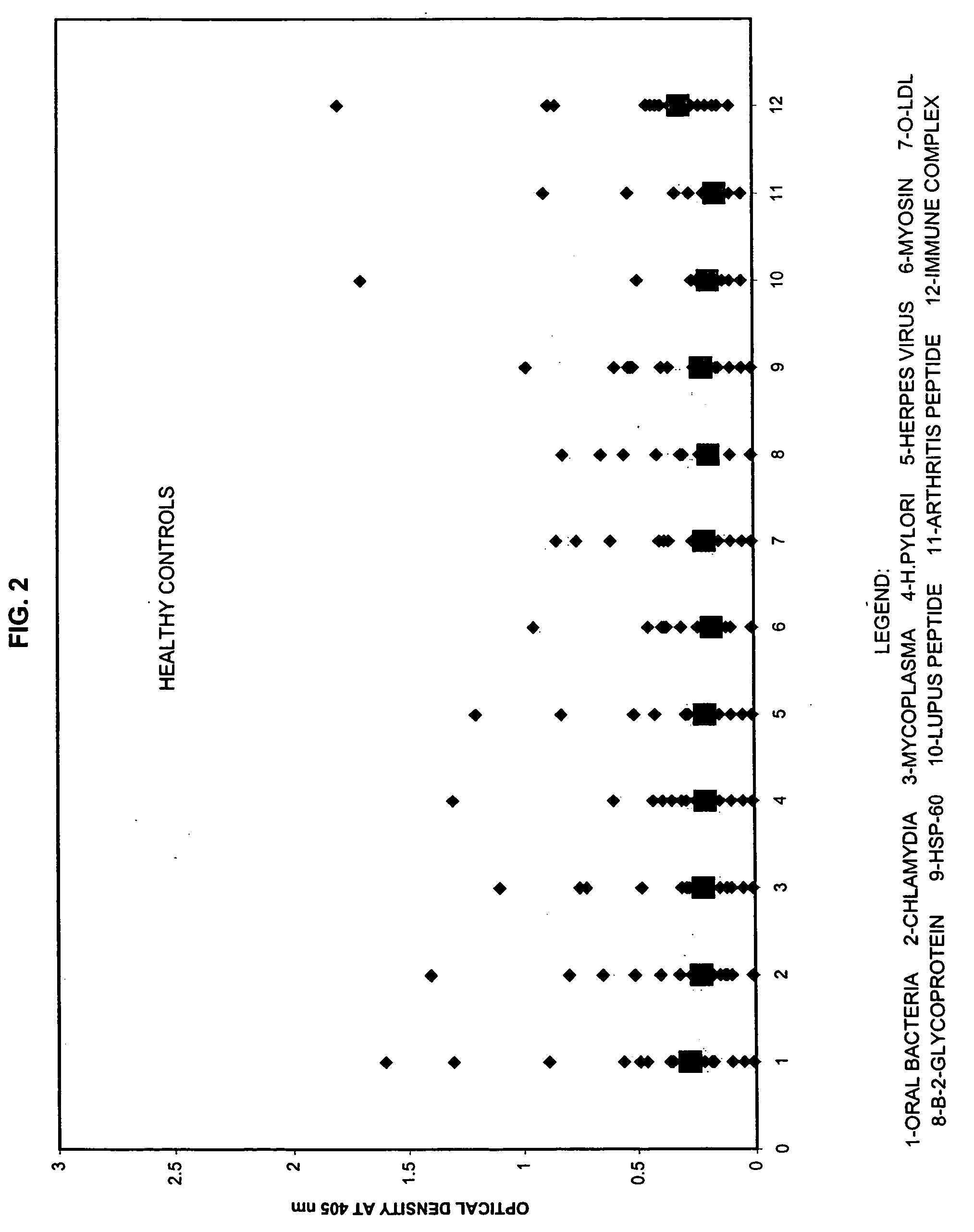
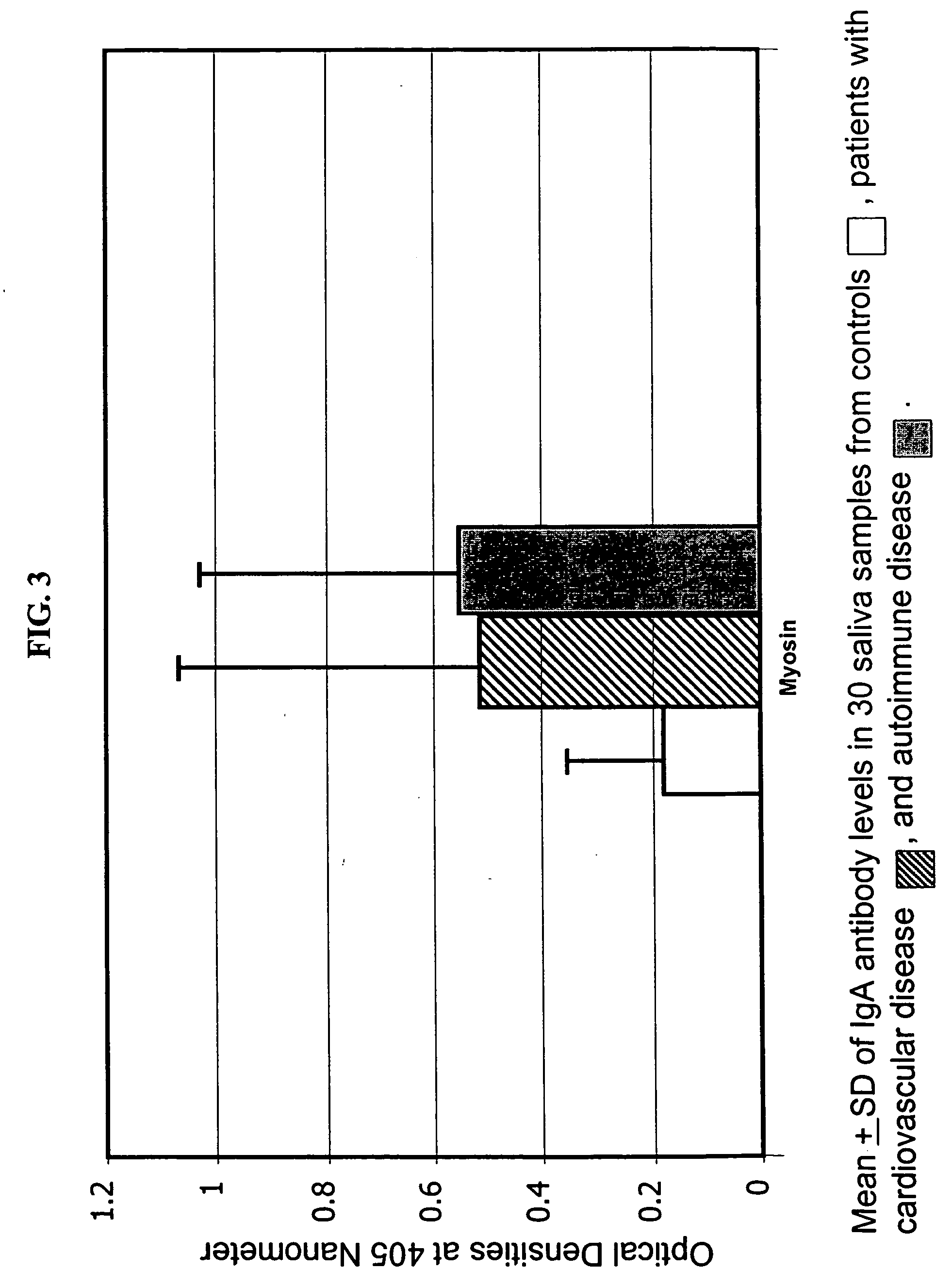
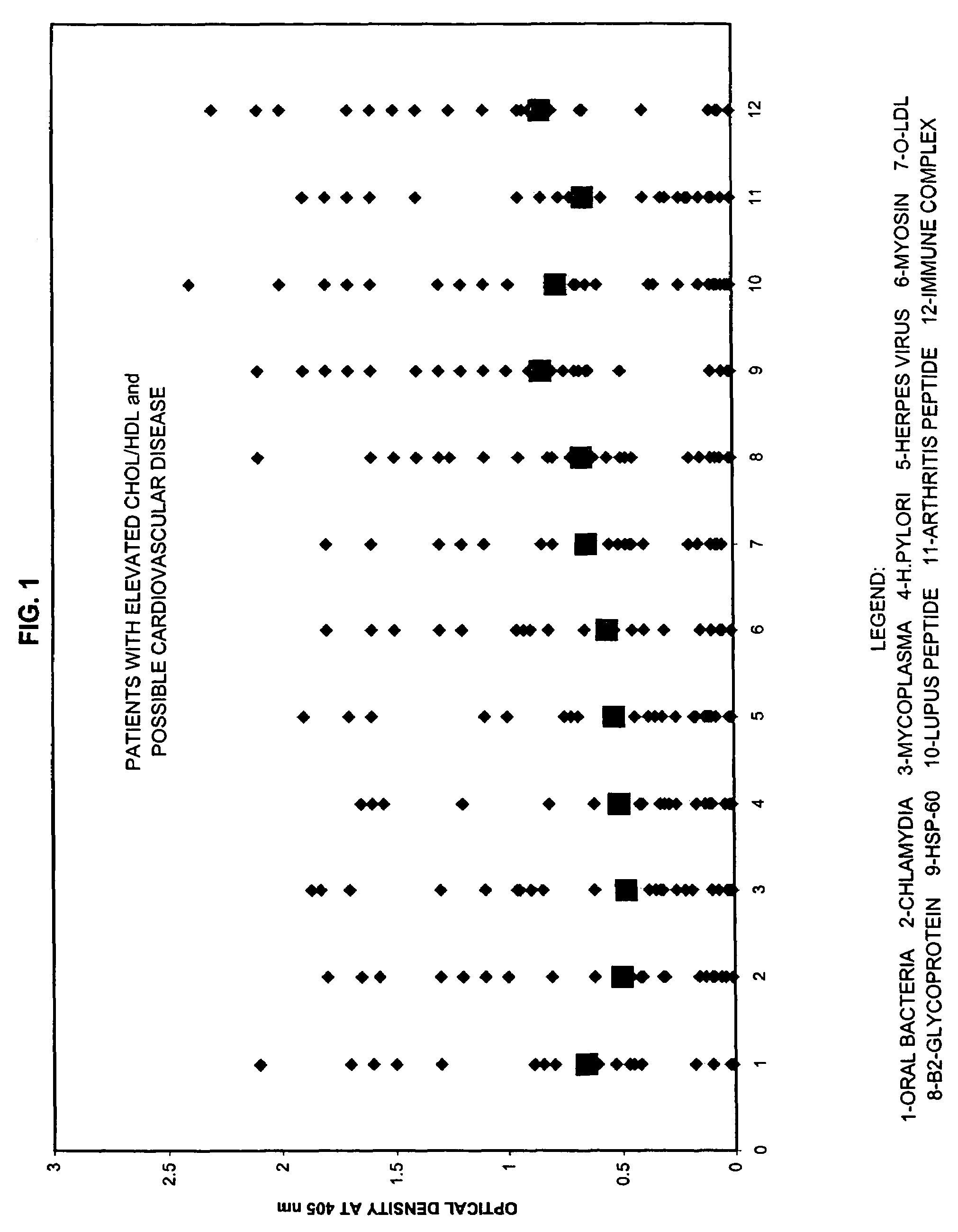
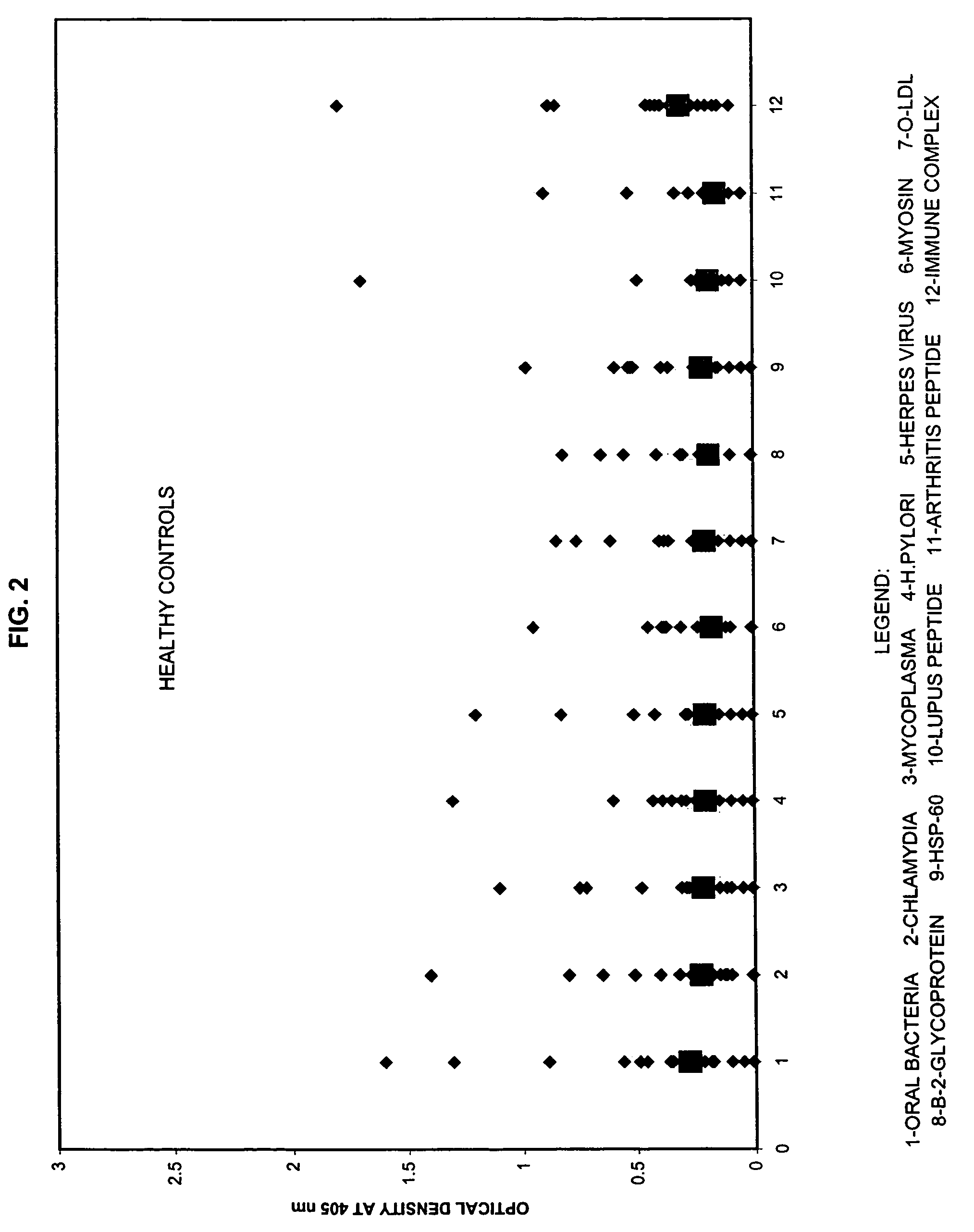
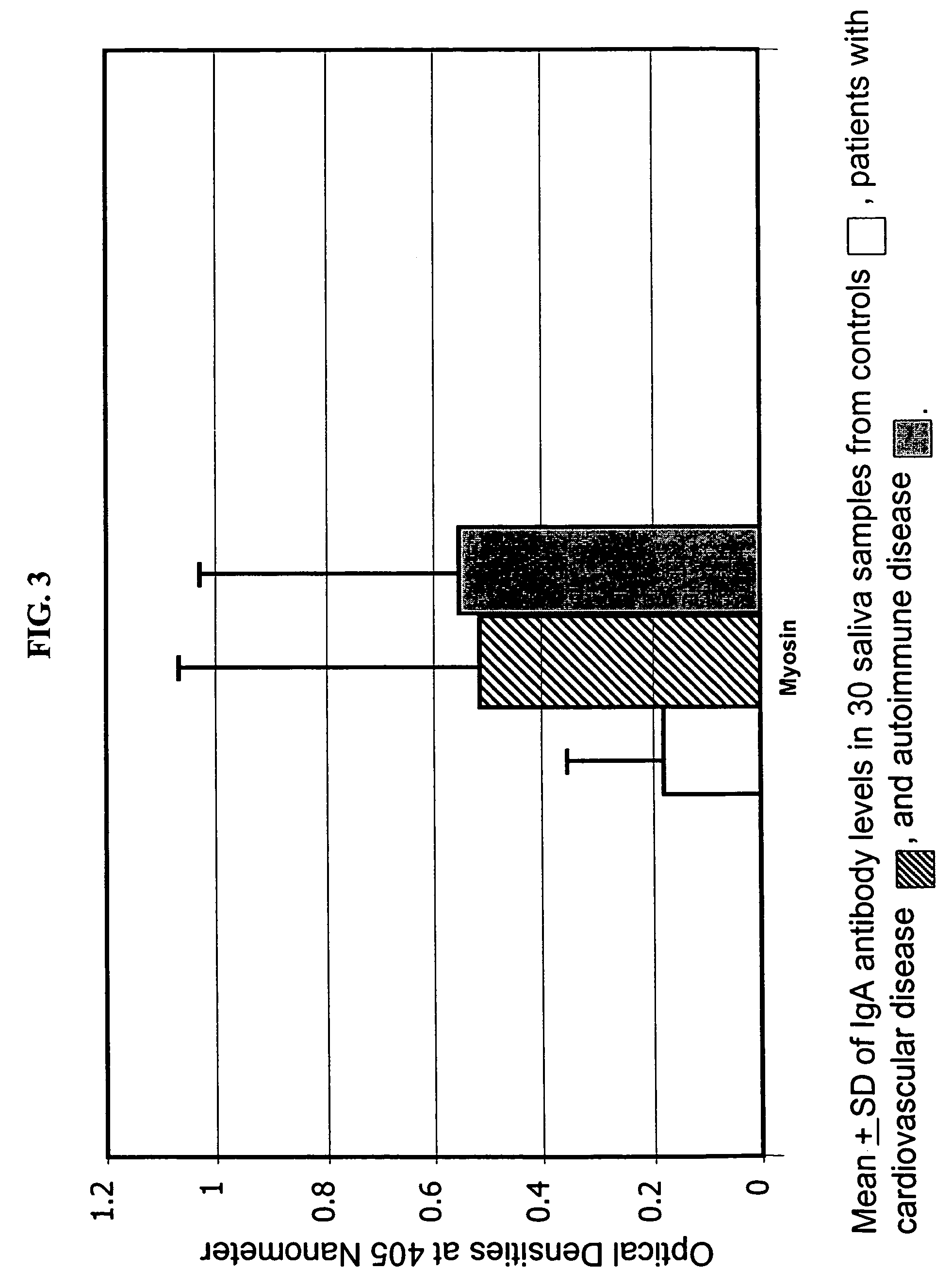
Saliva immunoassay for detection of antibodies for cardiovascular disease
InactiveUS20060094073A1OptimizationImprove the level ofDisease diagnosisBiological testingImmune complex depositionAntibody level
A method for diagnosing the likelihood and severity of cardiovascular disease in a patient is disclosed. The method determines the levels of antibodies against autoantigens, including myosin, oxidized LDL, β-2-glycoprotein, heat shock protein-60, platelet glycoprotein, and immune complexes. It then compares the results to normal levels to determine the likelihood and severity of cardiovascular disease.
Owner:IMMUNOSCI LAB
Saliva immunoassay for detection of antibodies for cardiovascular disease
A method for diagnosing the likelihood and severity of cardiovascular disease in a patient is disclosed. The method determines the levels of antibodies against autoantigens, including myosin, oxidized LDL, β-2-glycoprotein, heat shock protein-60, platelet glycoprotein, and immune complexes. It then compares the results to normal levels to determine the likelihood and severity of cardiovascular disease.
Owner:IMMUNOSCI LAB
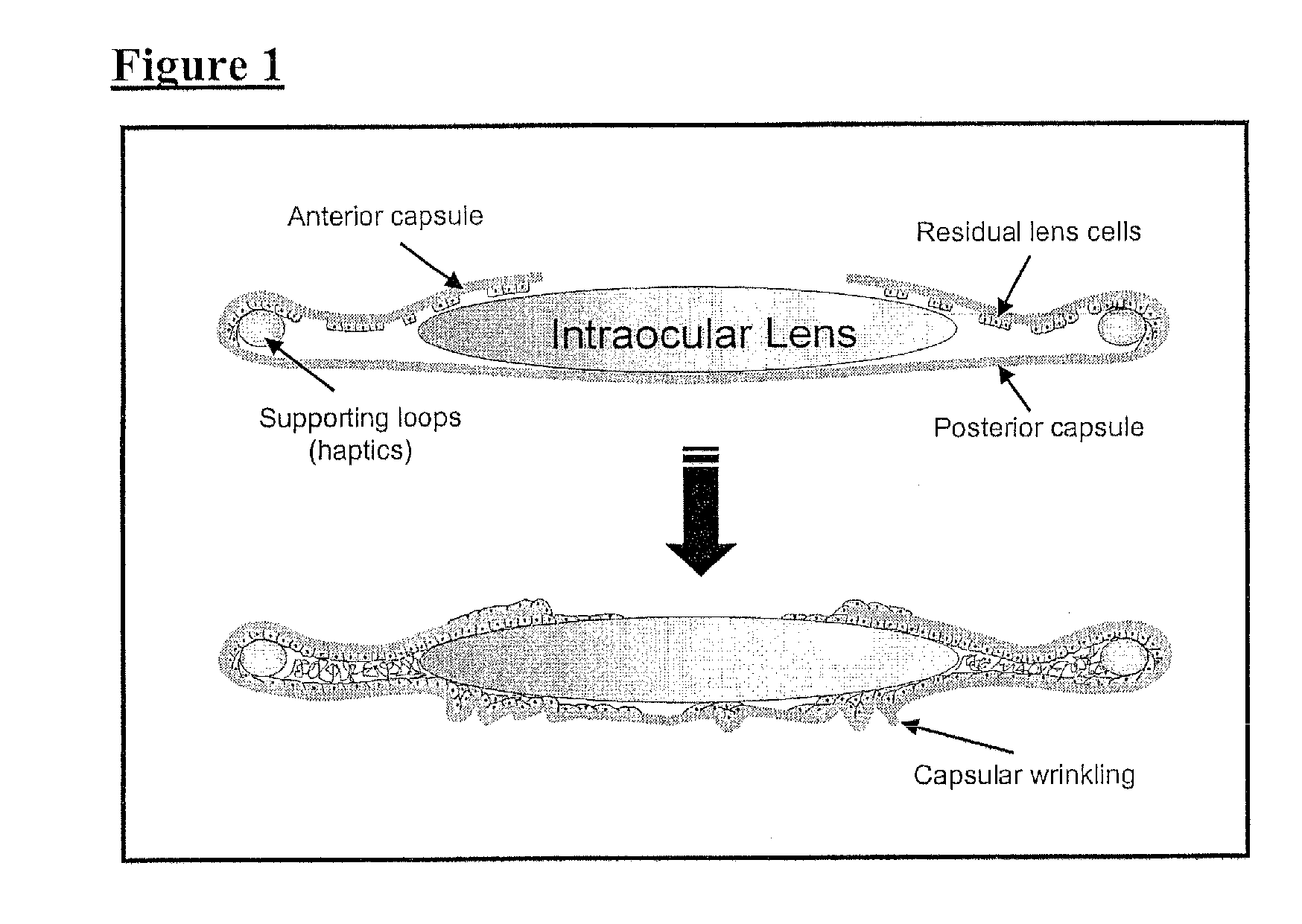
Treatment of fibrotic eye disorders
InactiveUS20110223177A1Slowly compositionAvoid rapid degradationBiocideSenses disorderMyosinPosterior capsule opacification
Inhibitors of myosin activity are used to treat or prevent a fibrotic disorder of the eye, for example posterior capsule opacification (PCO).
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF EAST ANGLIA
A kind of myosin ATP enzyme activity micro-assay method and its application
InactiveCN102288601AOrganic active ingredientsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMyosinAssay
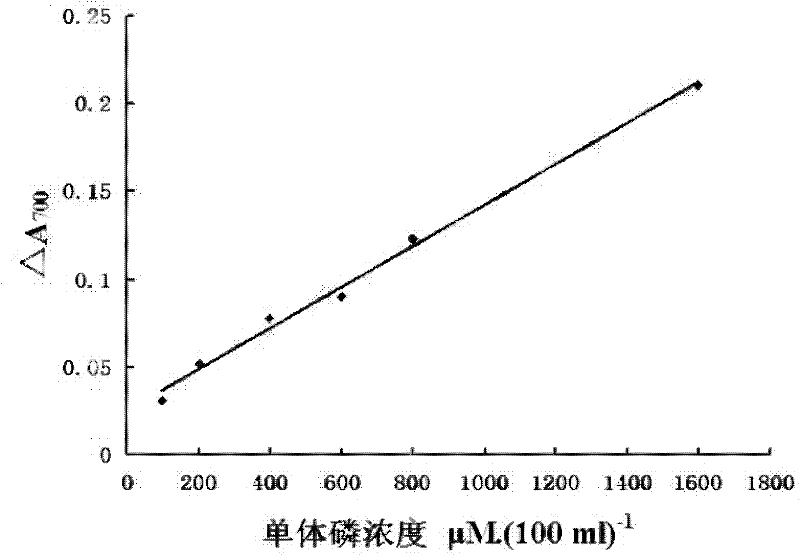
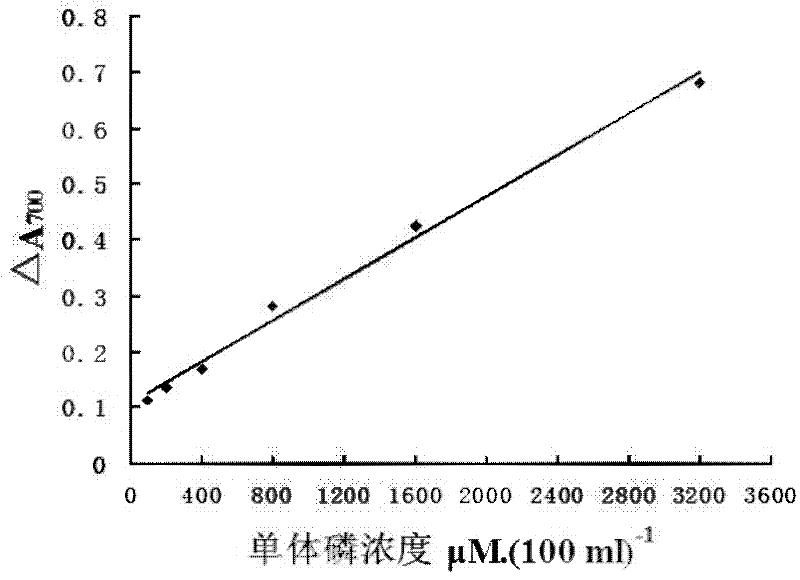
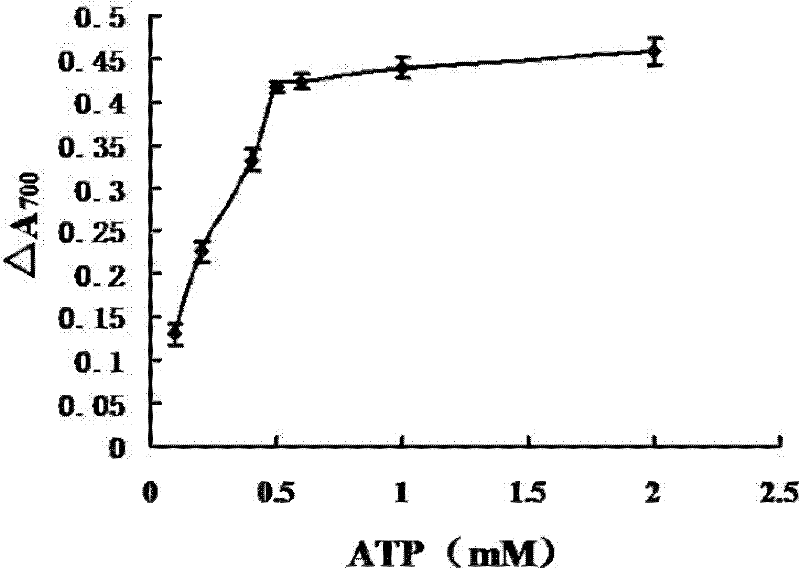
The invention relates to a method for the microdetermination of ATPase activity of myoglobulin, and the method is characterized in that based on the reaction method of a classic molybdenum blue method, the molar ratio of ATP (adenosine-triphosphate) to myoglobulin is controlled at 2000:1 and the molar ratio of ammonium molybdate to stannous chloride is controlled at 5.5:1. The determination method provided by the invention is simple, convenient, fast, high in response value and wide in linear range, and can be applied to the screening of inhibitors. The invention discloses an application of Ruscogenin in inhibiting the ATPase activity of the myoglobulin.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
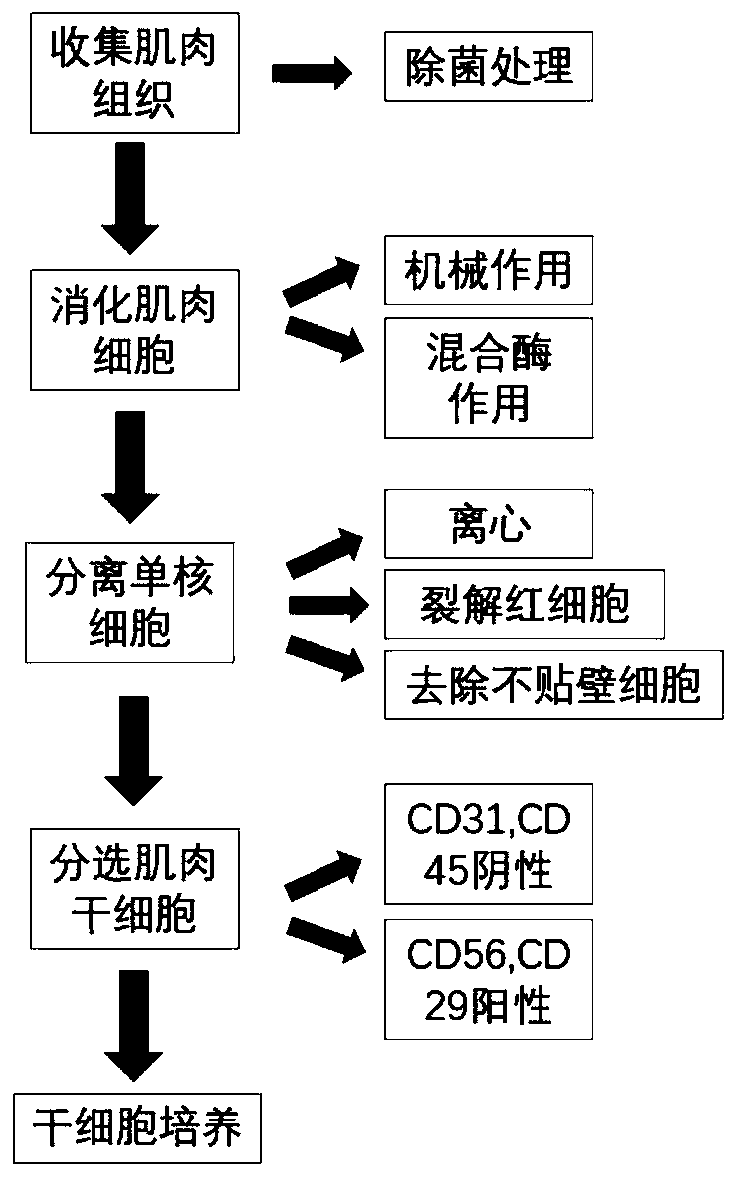
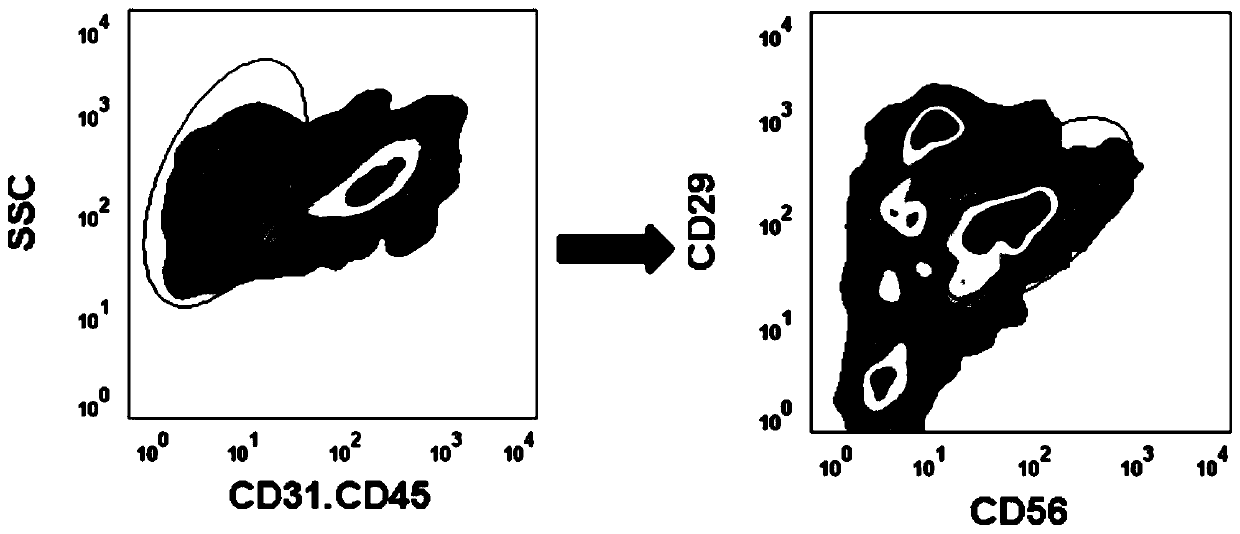
Separation and purification method of high-purity porcine muscle stem cells
InactiveCN110628708AHigh purityReduce usageCell dissociation methodsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsMyosinCultured meat
The invention relates to a separation and purification method of high-purity porcine muscle stem cells, for research and production of cultured meat. The separation and purification method disclosed by the invention comprises the steps of obtaining sterile muscular tissue, efficiently digesting the muscular tissue to obtain a large quantity of muscle mononuclear cells, and finally performing steaming cell sorting to obtain the high-purity porcine muscle stem cells. The invention further discloses a method for efficiently digesting the porcine muscular tissue. By the method, the digestion speedand the digestion intensity can be increased, and a large quantity of muscle mononuclear cells can be obtained. When the purification method disclosed by the invention is applied, the porcine musclestem cells of which the purity exceeds 92% (by PAX7) can be stably obtained. The porcine muscle stem cells obtained through separation have efficient disintegration efficiency, and MYOSIN expression quantity can reach 85%-90%. When the method disclosed by the invention is applied, a large quantity of seed cell sources can be provided for research and actual production of the cultured meat.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
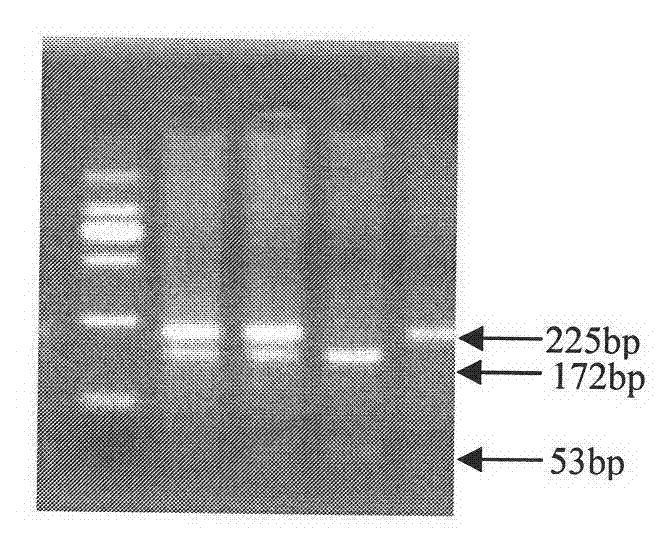
Genetic marker using pig MLC(myosin light chain)2 5' flanking promoter region SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) as pig carcass traits and application
The invention belongs to the technical field of pig molecular marker preparation and particularly relates to a genetic marker using pig MLC(myosin light chain)2 5' flanking promoter segments as pig carcass traits as well as a preparation method and application of the genetic marker. The genetic marker has the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO (sequencer identifier number):1 and SEQ ID NO:2 in a sequence table. One A / G mutation and one G / A mutation respectively exist at the 53bp part of the sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2, and the polymorphism of DraIII-RFLP is caused by the allele mutation. The genetic marker is used for carrying out pig carcass traits correlation analysis on large white pig and meishan pig F2 generations, and the transcriptional activity of promoters in different genotypes is detected. The invention also discloses a parting detection method of the genetic marker, and the novel genetic marker and the detection method are provided for the pig carcass traits molecular marker auxiliary selection.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
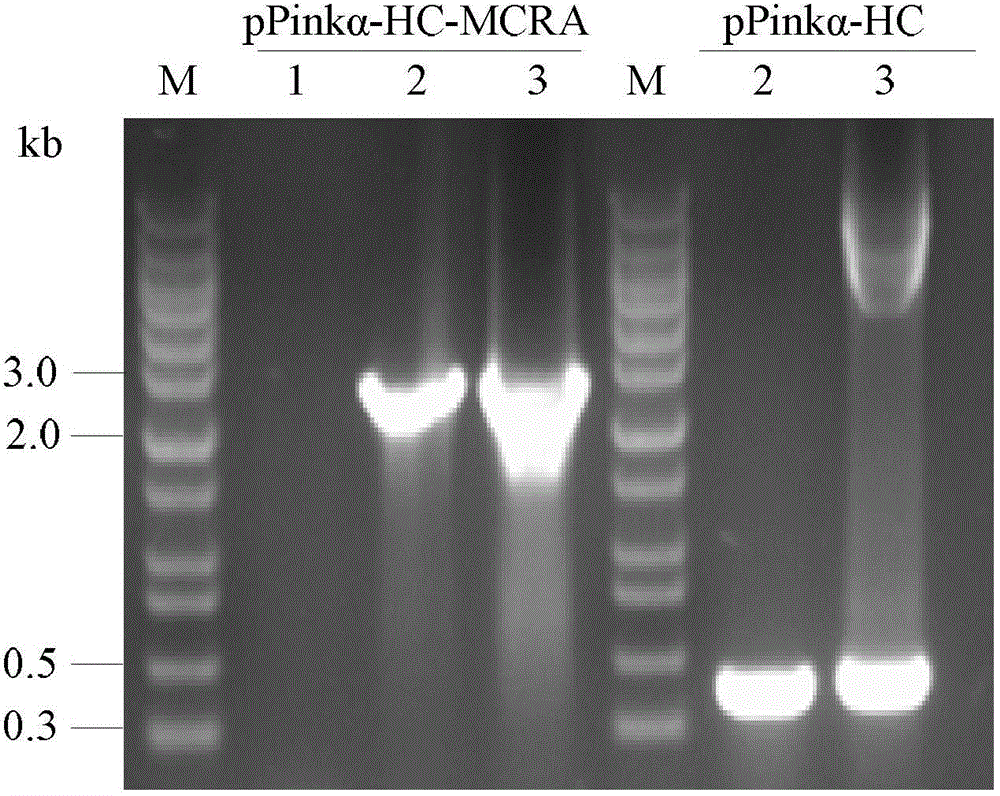
Method for heterologously expressing active membrane proteins by using Pichia pastoris expression system
InactiveCN102876708AAchieve active expressionAchieve positioningFungiMicroorganism based processesHeterologousMyosin
The invention discloses a method for heterologously expressing active membrane proteins by using a Pichia pastoris expression system. The invention relates to a method for expressing a myosin cross-reactive antigen (MCRA) of Bifidobacterium BB-12 in a recombinant mode and an expression host used in the method. The expression host is a PichiaPinkTM expression system transformed from pPink alpha-HC-MCRA plasmid. The invention also relates to application of an MCRA of Bifidobacterium BB-12 or an expression host in preparing conjugated linoleic acid.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
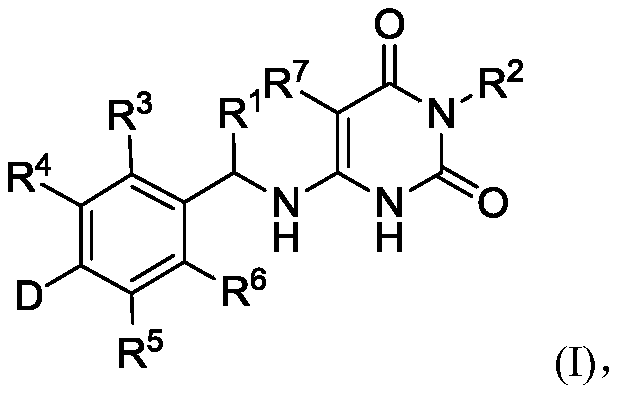
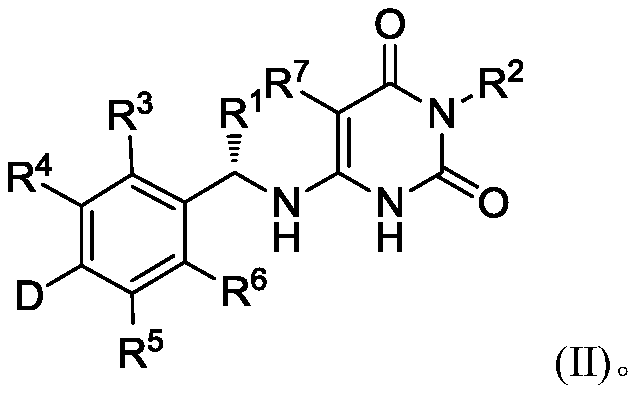
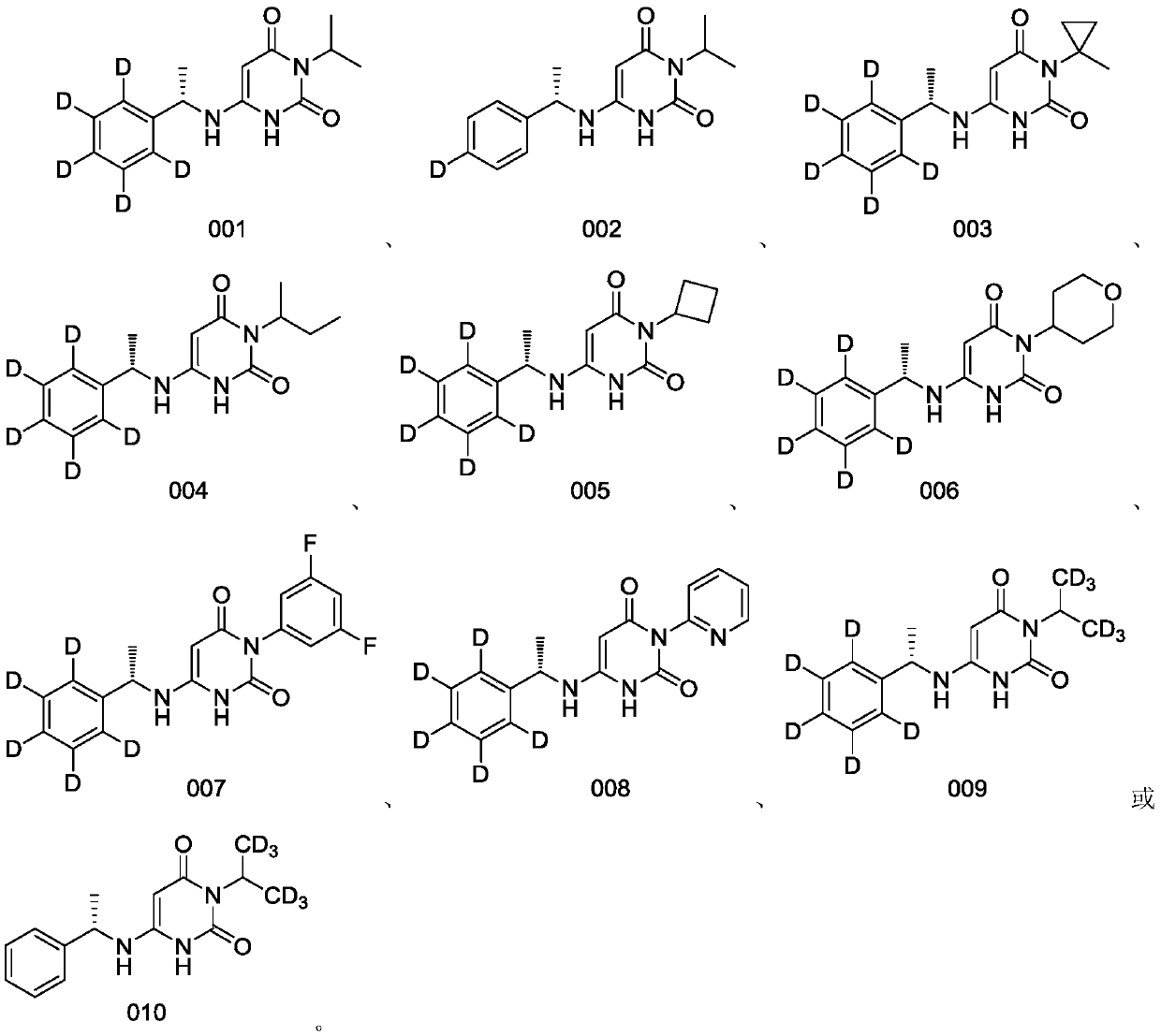
Deuterated benzylaminopyrimidine diketone derivative and application thereof
ActiveCN111116492AStable in natureImprove securityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryDiketoneMyosin
The invention discloses a deuterated benzylaminopyrimidine dione derivative and an application thereof, and a pharmaceutical composition containing the deuterated benzylaminopyrimidine dione derivative, and the deuterated benzylaminopyrimidine dione derivative and the pharmaceutical composition can be used for inhibiting the activity of myosin. The invention also relates to a method for preparingthe compound and the pharmaceutical composition, and an application of the compound and the pharmaceutical composition in treating hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and related heart diseases.
Owner:QINGDAO JIAO PHARMA TECH CO LTD
Method for purifying myoblast derived from bovine fetus skeletal muscle tissue
ActiveCN106350480AEasy to purifyCell dissociation methodsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsAnti plateletEagle
The invention discloses a method for purifying myoblast derived from bovine fetus skeletal muscle tissue. The method is characterized in that the material used by the method is the longissimus dorsi muscle tissue of a 3-month-old bovine fetus, and reagents used by the method are horse serum, anti-fast muscle myosin heavy chain antibodies, collagenase, fetal bovine serum, a low-sugar Dulbecco modified Eagle medium, a cell-sorting buffer solution and anti-platelet derived growth factor receptor alpha antibodies.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
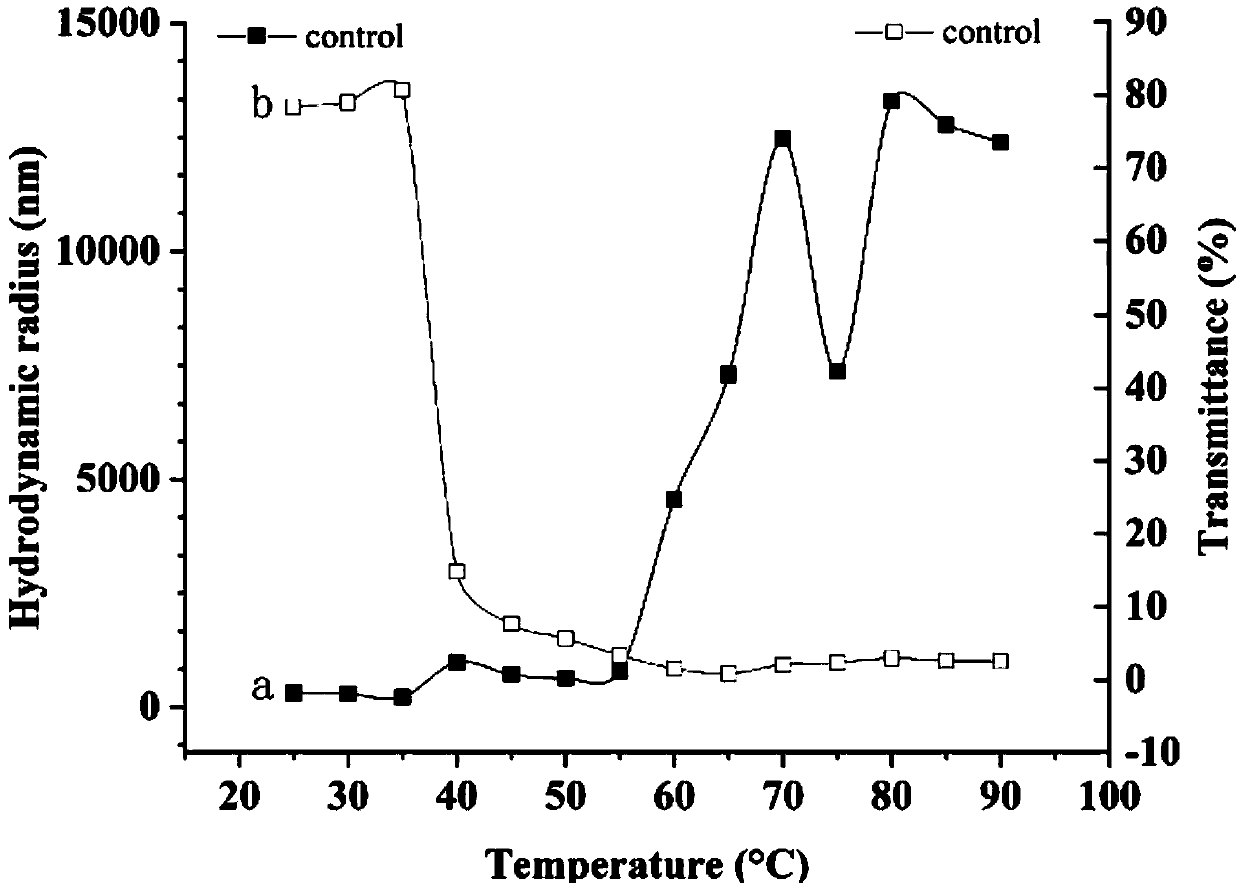
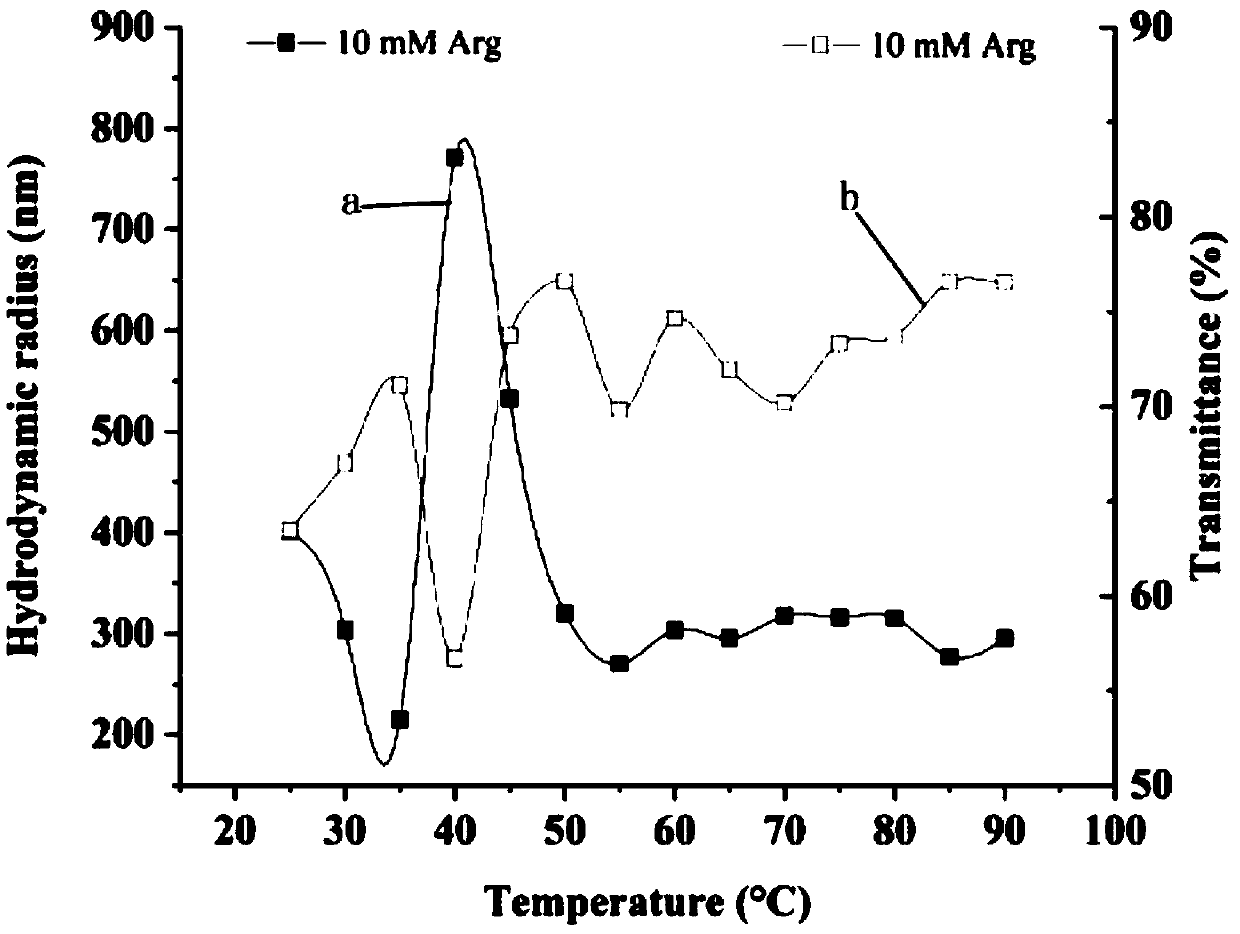
Method for maintaining liquid state of high concentration myosin at high temperature
InactiveCN109673811AImprove transmittanceRich and diverseProtein composition from fishAnimal proteins working-upHigh concentrationArginine
The invention relates to the technical field of quality improvement on aquatic products, in particular to a method for maintaining the liquid state of high concentration myosin at high temperature. The method comprises the following specific steps: firstly, selecting back fish flesh, cleaning and peeling; extracting to obtain a myosin solution, and determining the protein content as 10 to 20 mg / mL; adding arginine, lysine or histidine into the extracted myosin solution, wherein the final concentration is 10 to 100 mM; then carrying out two-stage heating, firstly heating at 40 DEG C for 60 minand then heating at 90 DEG C for 30 min, thus maintaining the liquid state of the high concentration myosin at high temperature. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple operation, high economic benefits and broad prospects; a foundation is laid for liquid fish protein products.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
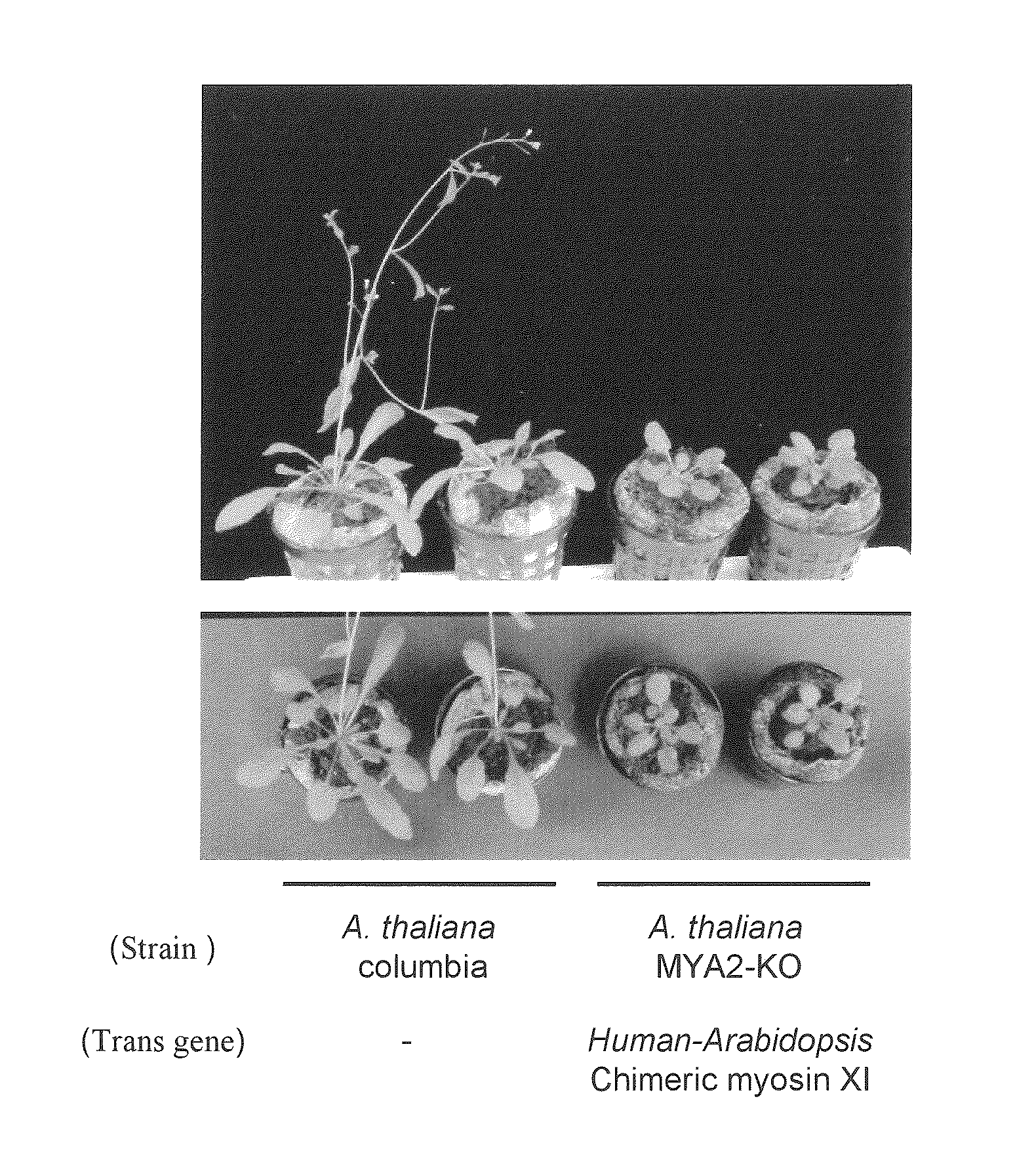
Plant with enhanced growth and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20130007915A1Improve scalabilityIncrease biomassClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesMyosinCoiled coil
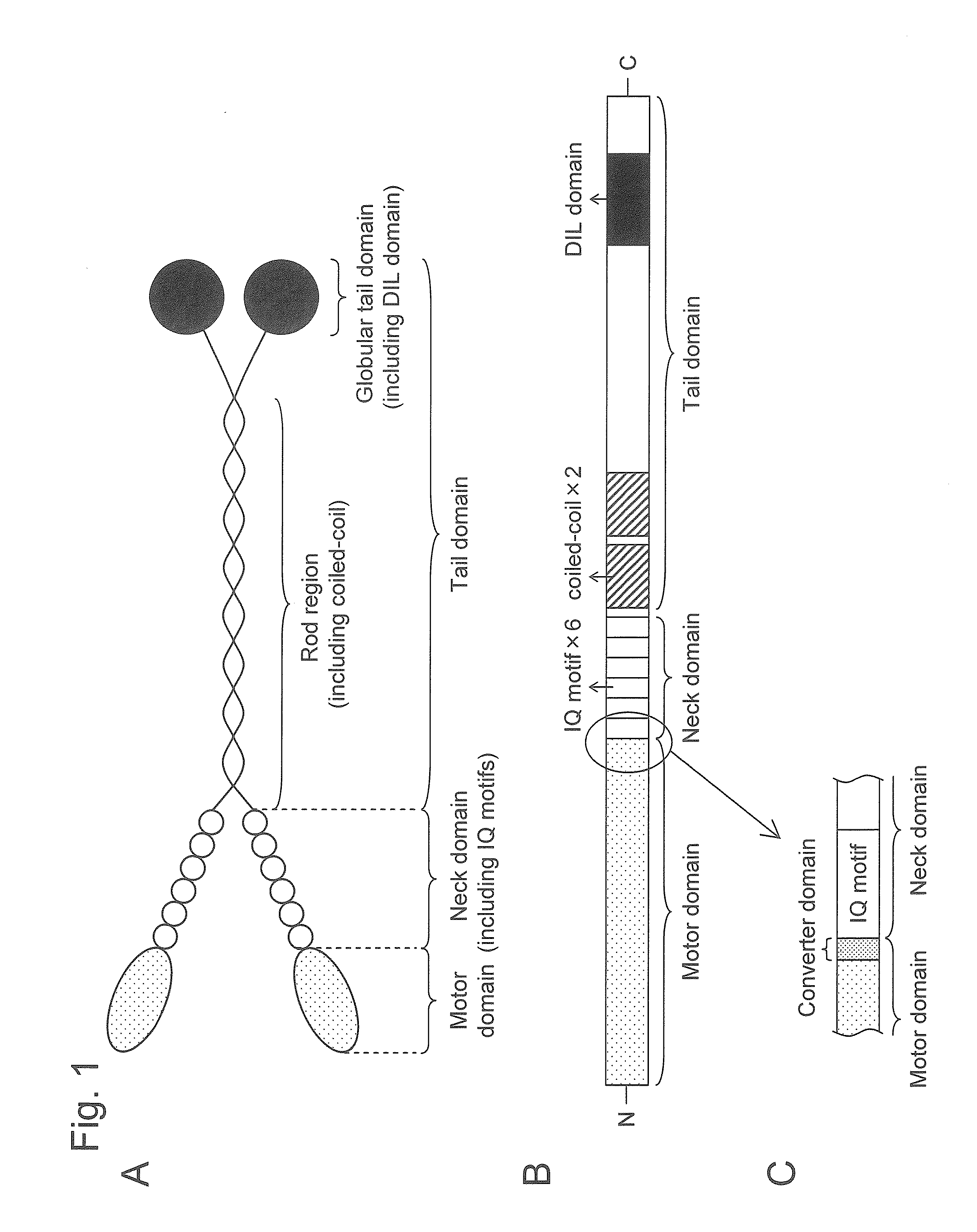
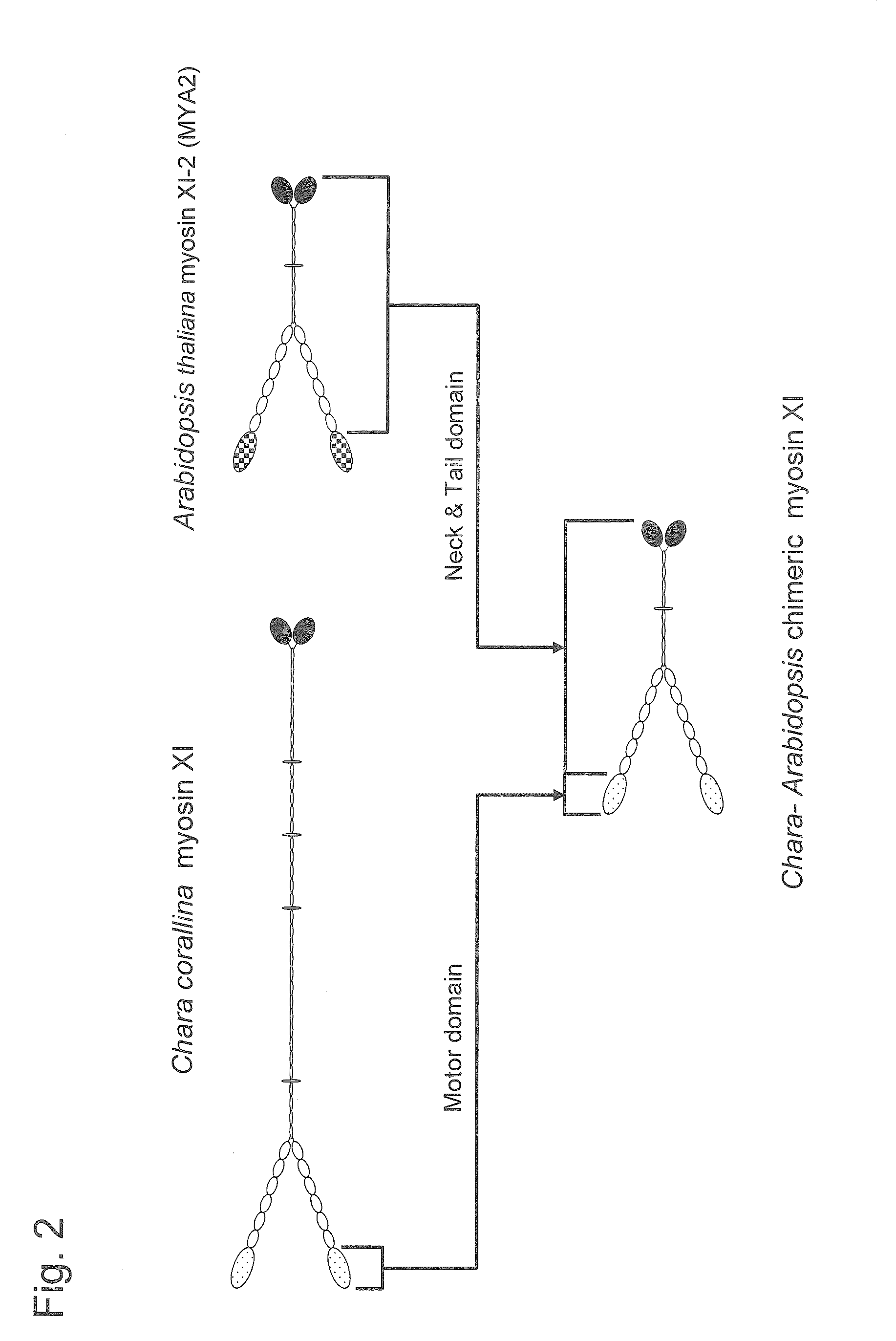
This invention provides a method for producing a plant with enhanced or suppressed growth through introduction of a mutated gene and a plant including such a mutated gene. This invention provides a method for producing a plant with enhanced growth or suppressed growth. Such method includes a step of introducing a gene encoding a chimeric myosin protein into a host plant so as to transform the host plant, wherein the chimeric myosin protein comprises: a neck domain, a coiled-coil domain, and a globular tail domain from a myosin protein involved in cytoplasmic streaming of a donor plant; and a motor domain from a myosin protein other than the myosin protein of the host plant, which has sliding velocity that is higher or lower, respectively, than that of the myosin protein involved in cytoplasmic streaming of the donor plant.
Owner:RIKEN
Soluble protein aggregation nanoparticle preparation method and application
ActiveCN108434099AEasy accessFull gatheringCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsWater bathsSolubility
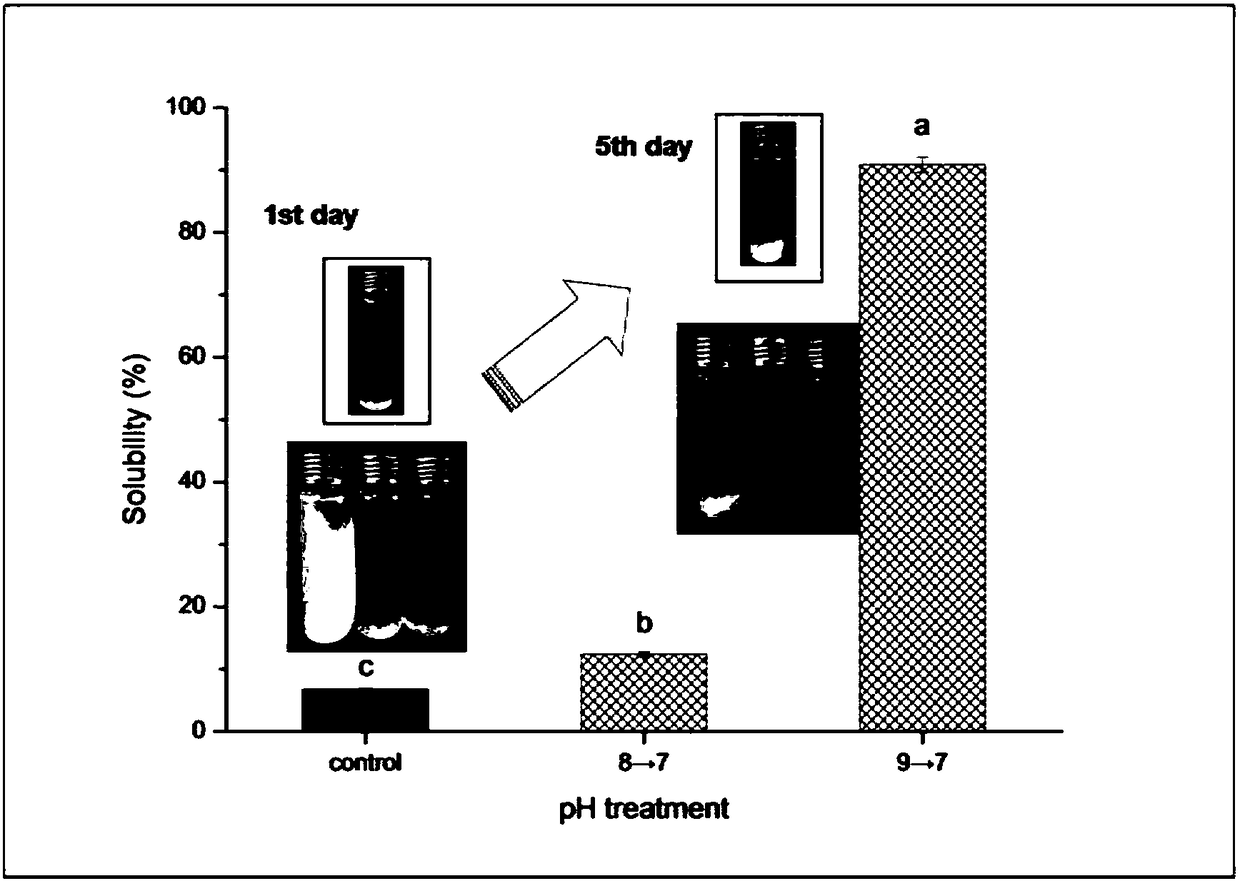
The invention discloses a soluble protein aggregation nanoparticle preparation method and application. The preparation method comprises the following steps that myosin is extracted; a myosin solutionis prepared; the pH of the solution is adjusted; water-bath heating is conducted; after cooling is conducted to reach the room temperature, the pH is set to be the original pH, and then soluble myosinaggregation nanoparticles can be obtained; meanwhile, by means of the obtained soluble myosin aggregation nanoparticles, soybean oil is emulsified, and the emulsification effect is better compared with a stable emulsion of ordinary myosin aggregates. The myosin aggregation nanoparticles obtained through the method are high in solubility, small in particle size, good in emulsifying property and applicable to industries of food, medicine, cosmetics and the like.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Compositions and methods for enhancing the therapeutic potential of stem cells
InactiveUS20160030482A1Reduce probabilityImprove angiogenesisOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseDamages tissue
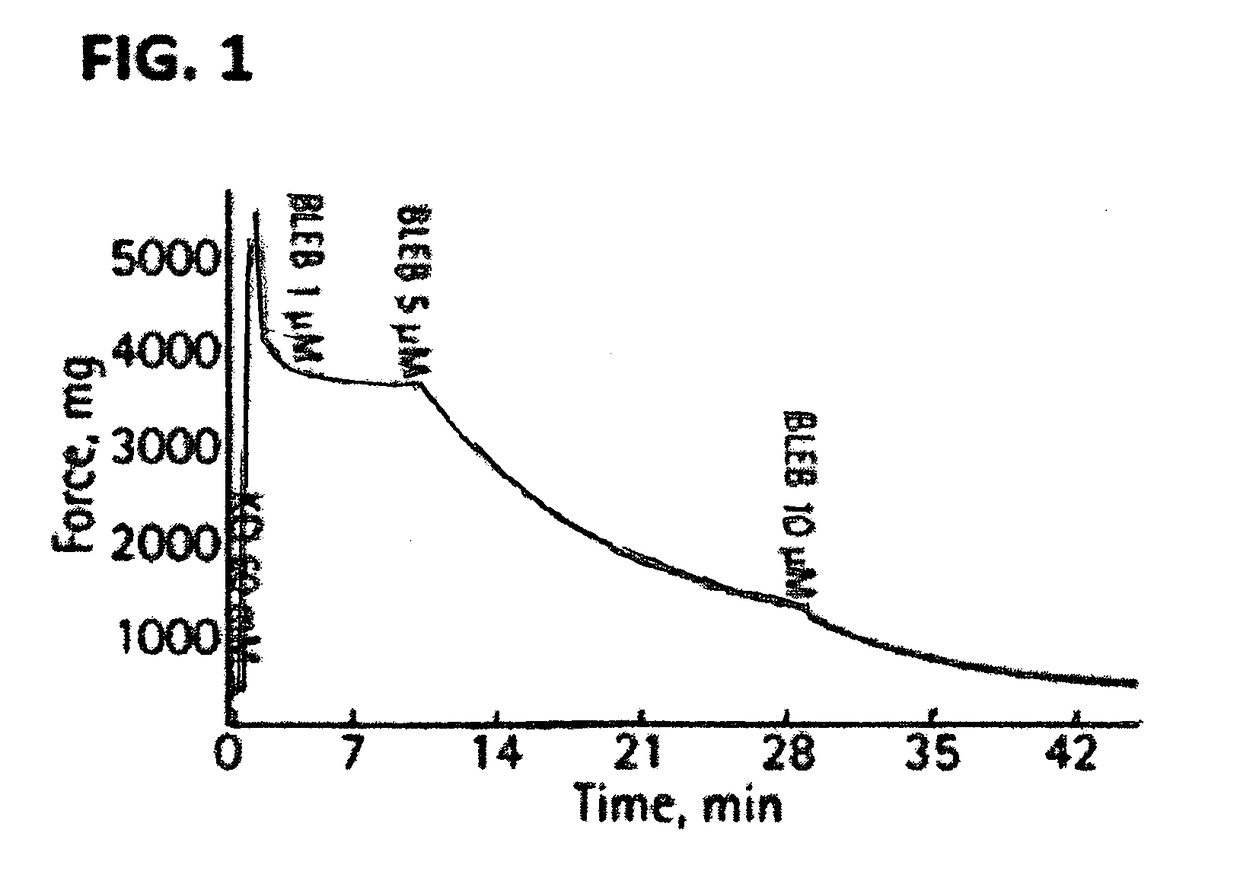
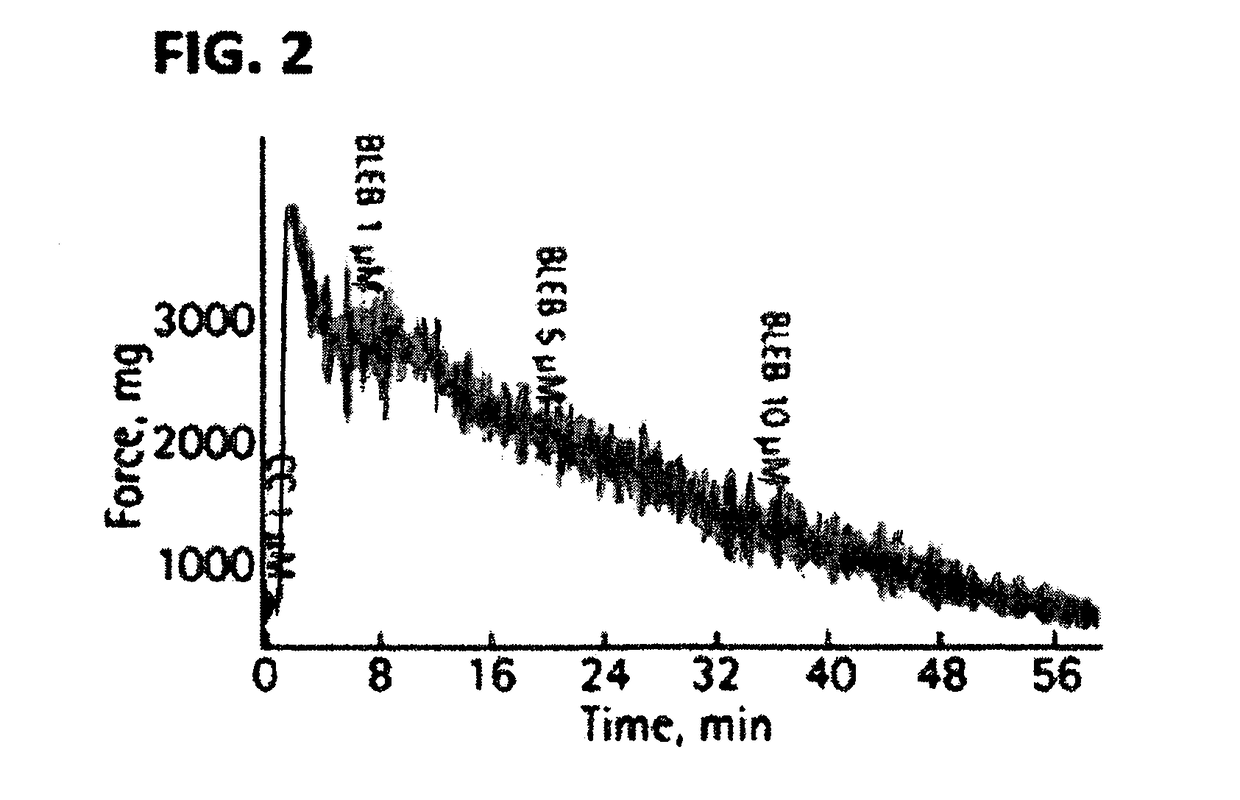
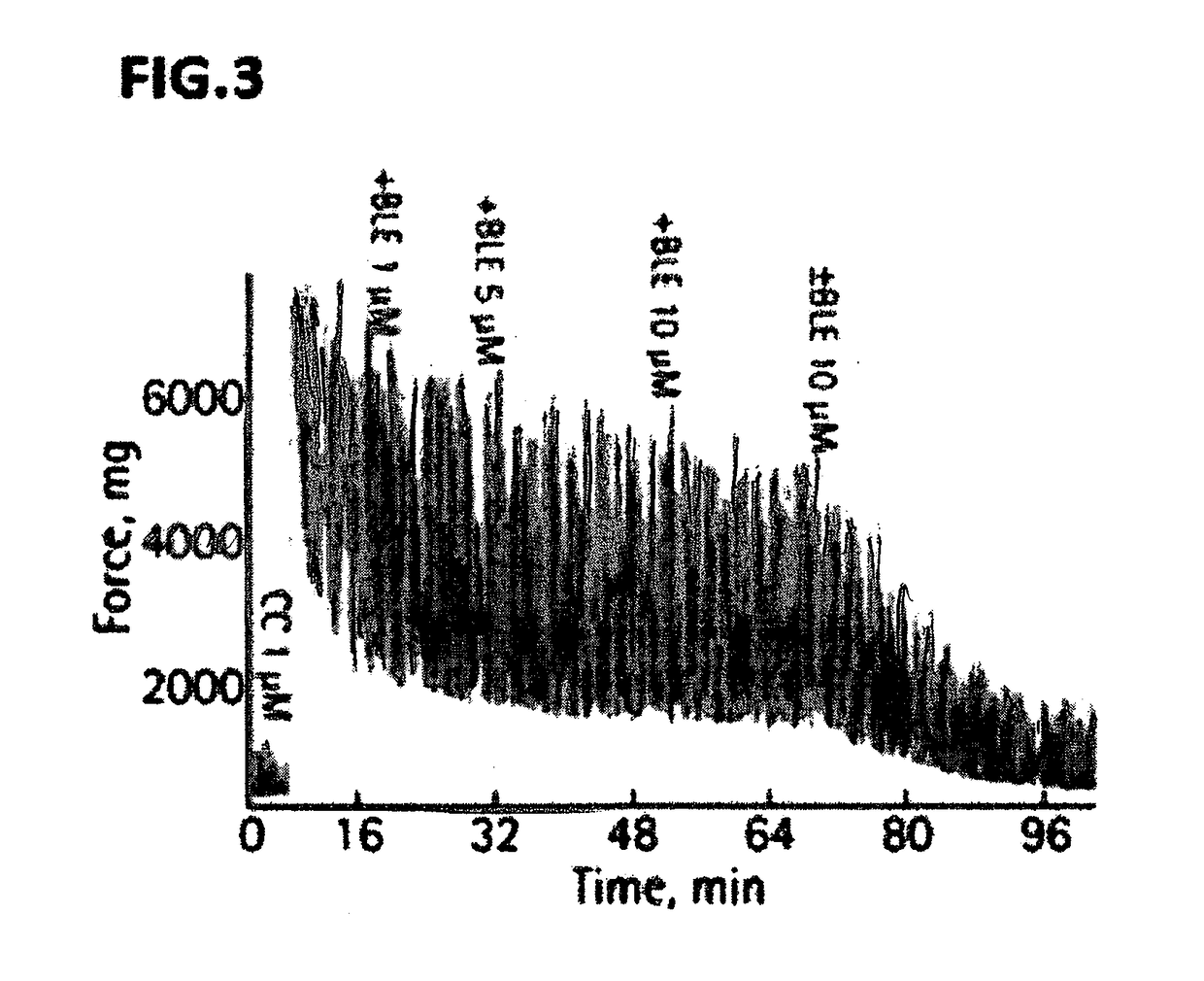
The invention encompasses compositions and method of treating a vascular disease such as peripheral artery disease, The methods involve—administering to a patient in need thereof, an effective amount of a composition comprising a population of cells such as mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and a non-muscle myosin 0 antagonist such as blebbistatin. Non-muscle myosin II antagonists are disclosed to surprisingly and dramatically accelerate MSC-triggered regeneration of damaged tissues arid unexpectedly and drastically reduce severe complications of stem cell treatment.
Owner:VAN DEN BOS CHRISTIAN
Dried salted yellow croaker myosin antibacterial peptide LCM13 and application thereof
ActiveCN113185596AInhibition of replication synthesisEnhanced inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyMyosin
The invention discloses a dried salted yellow croaker myosin antibacterial peptide LCM13. The amino acid sequence of the dried salted yellow croaker myosin antibacterial peptide LCM13 is VSIYKLTGAVMHYGNMKFK. The molecular weight of the antibacterial peptide is 2186 Da. The invention also discloses an application of the antibacterial peptide of the dried salted myosin of the yellow croaker, namely application in preventing or treating bacterial infection of algicidal vibrio, vibrio parahaemolyticus and the like. The invention lays a foundation for the subsequent further research of the salted yellow croaker myosin antibacterial peptide as a food preservative and the development of a feed additive for preventing fish diseases.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Molecular cloning and application of pork quality character related gene Myo6 (Myosin 6)
The invention belongs to the technical field of livestock molecular biology, and particularly relates to molecular cloning and application of pork quality character related gene Myo6 (Myosin 6). The molecular marker disclosed by the invention is obtained through cloning the Myo6 gene, and the sequence of the Myo6 molecular marker is described as SEQ ID NO: 1. The polymorphism of the Myo6 gene is as follows: a primer is designed by using the comparative genomics method according to the My06 gene sequence of human, the genome DNA of pigs is adopted as a template for amplification, SNP is screened by sequencing the amplified fragments, genotyping is carried out by using PCR-RFLP, a G / A base mutation at 709bp is discovered, and PCR-RFLP-Xba I polymorphism is caused. The molecular cloning and application of pork quality character related gene Myo6 provide a novel molecular marker for the assistant selection of pig markers.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
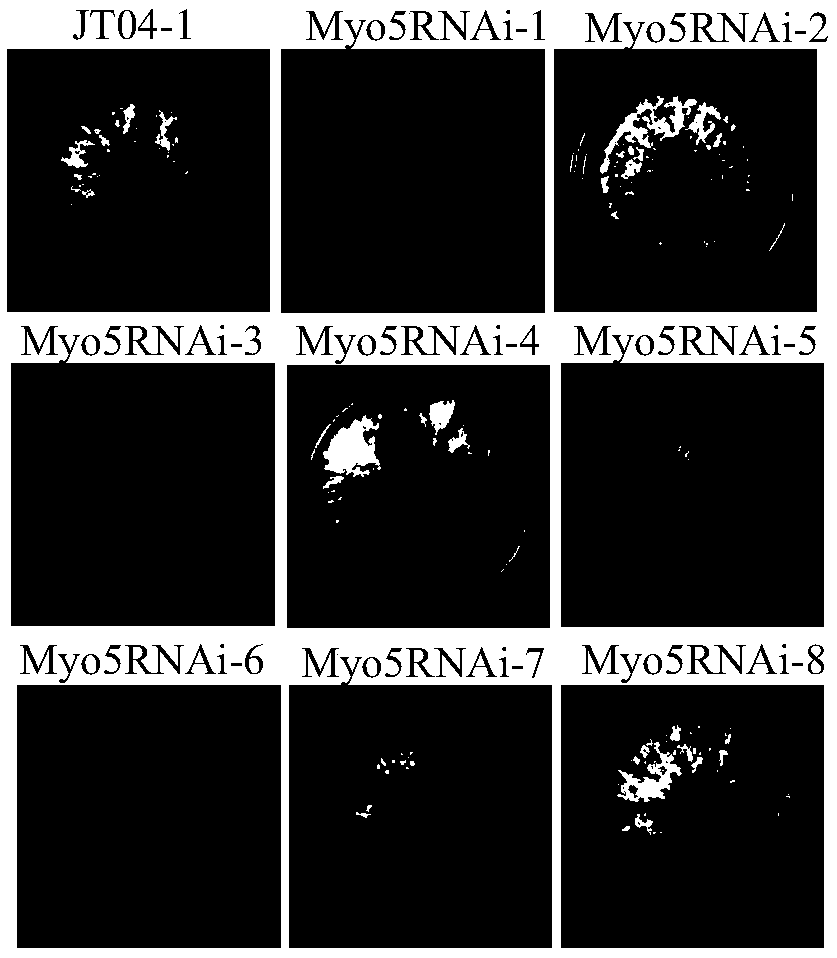
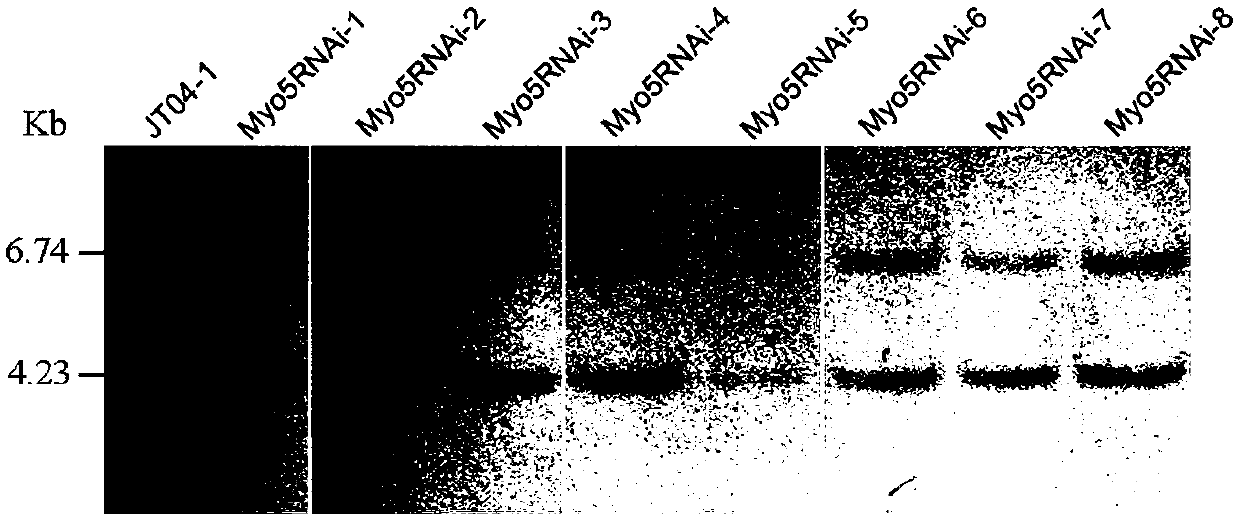
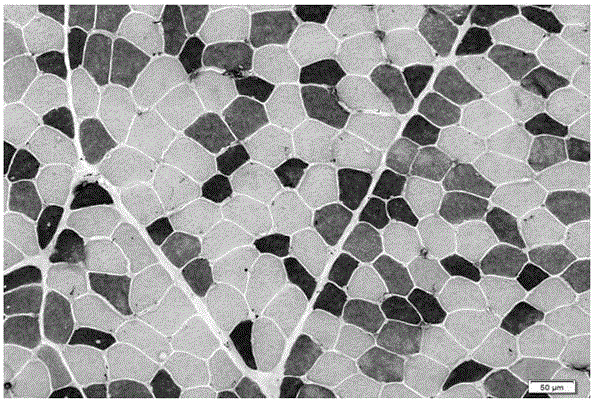
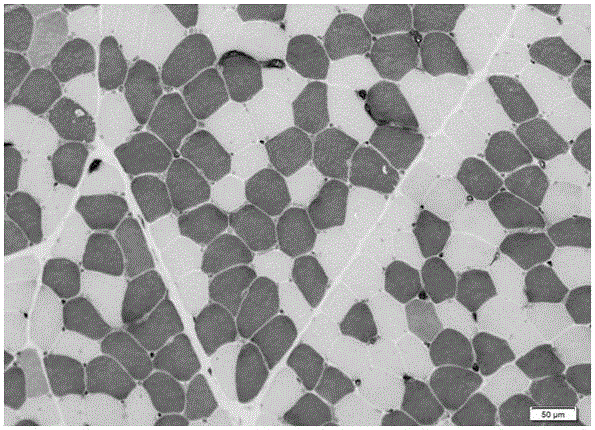
Myosin-5 and application of myosin-5 to cyanoacrylate drug resistance treatment
ActiveCN110540995AIncreased susceptibilityImprove disease resistanceDepsipeptidesFermentationMyosin IIADigestion
The invention provides application of a myosin-5 gene Myo5 segment to prevention and treatment of plant fungal diseases and / or enhancement of plant disease resistance. Myosin-5 gene is derived from fusarium graminearum, fusarium asiaticum, fussrium moniliforme, fusarium oxysporum, magnaporthe oryzae, botrytis cinerea, verticillium dahliae or sclerotinia sclerotiorum. The myosin-5 gene Myo5 segmentis siRNA of 15-30nt randomly generated after the combination of an Myo5dsRNA segment and a dsRNA segment or full-length or partial Myo5dsRNA is subjected to RNase digestion. The invention also provides an in vitro interference preparation containing the myosin-5 gene Myo5 segment. The myosin-5 gene Myo5 RNA interference technology has the green and safe outstanding advantages that the drug sensitivity of pathogenic fungi is improved, the drug resistance level is reduced, the pathogenicity is interfered, the disease resistance of plants is enhanced, and the specificity of plant diseases is prevented and treated.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Skeletal muscle tissue frozen section myosin adenosine triphosphatase dyeing kit
InactiveCN106771256ATimely treatmentGet timely treatmentDisease diagnosisBiological testingMyosinAdenosine triphosphatase
The invention provides a skeletal muscle tissue frozen section myosin adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) dyeing kit which comprises a CaCl2-containing buffer solution, an acetate buffer solution, a substrate incubation solution, 2wt% of cobalt chloride solution and 1wt% of ammonium sulfide solution. In the invention, a skeletal muscle tissue frozen section myosin adenosine triphosphatase dyeing kit is established, thus, the use is convenient, the working efficiency is improved, and the reporting period of a case is shortened; moreover, the reagent is saved, the cost is remarkably lowered, and a stable and satisfactory result is obtained.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
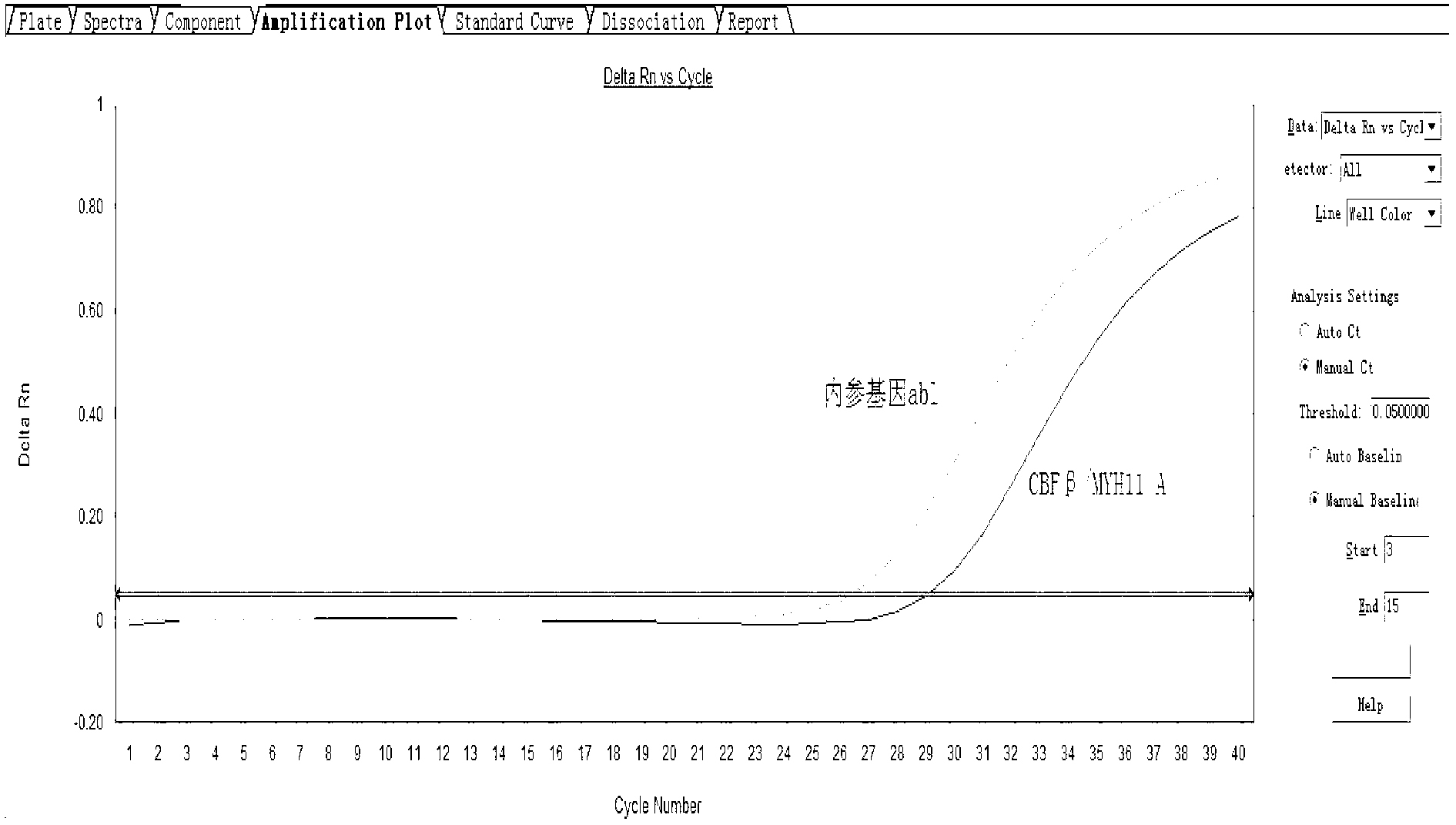
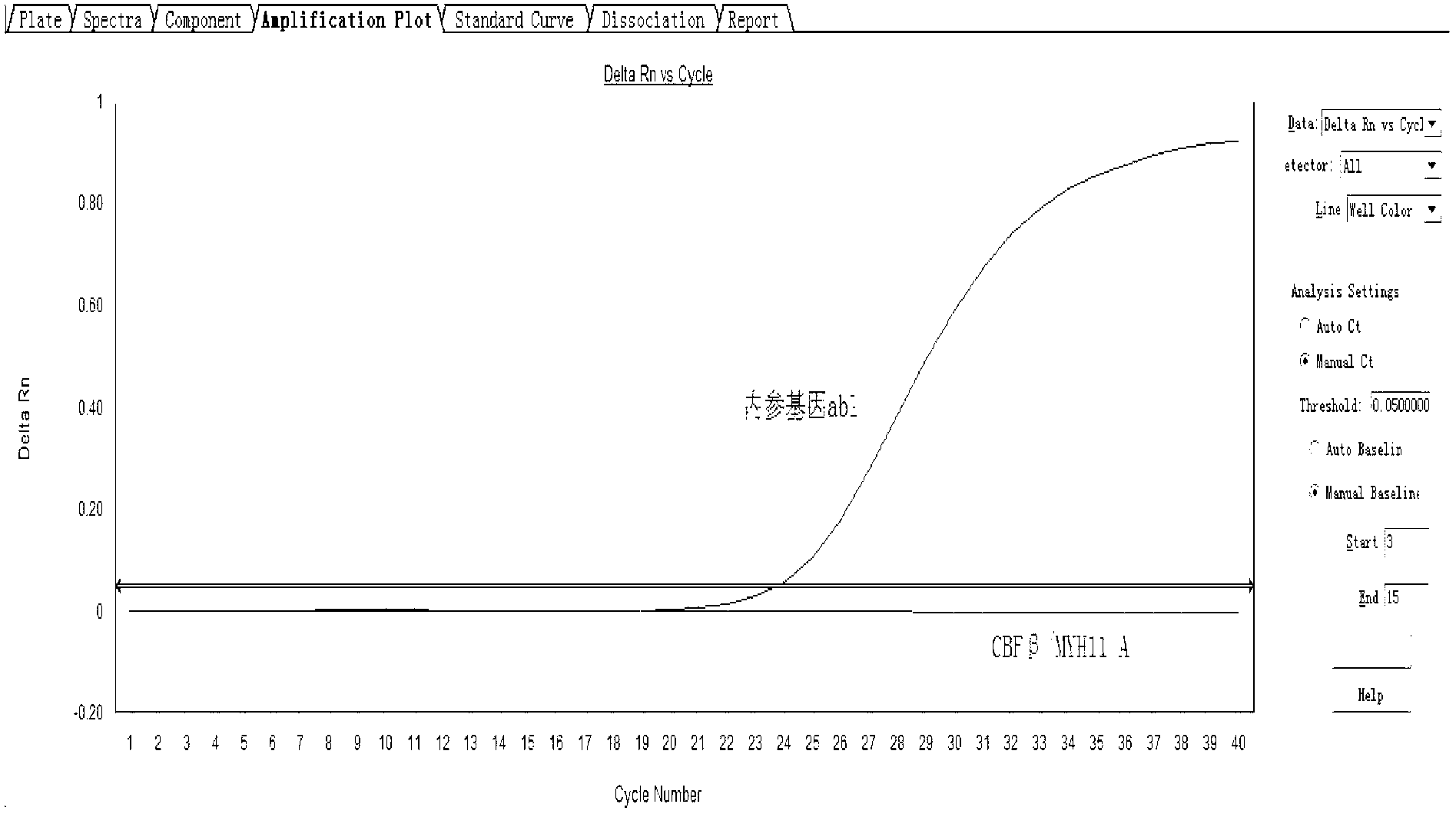
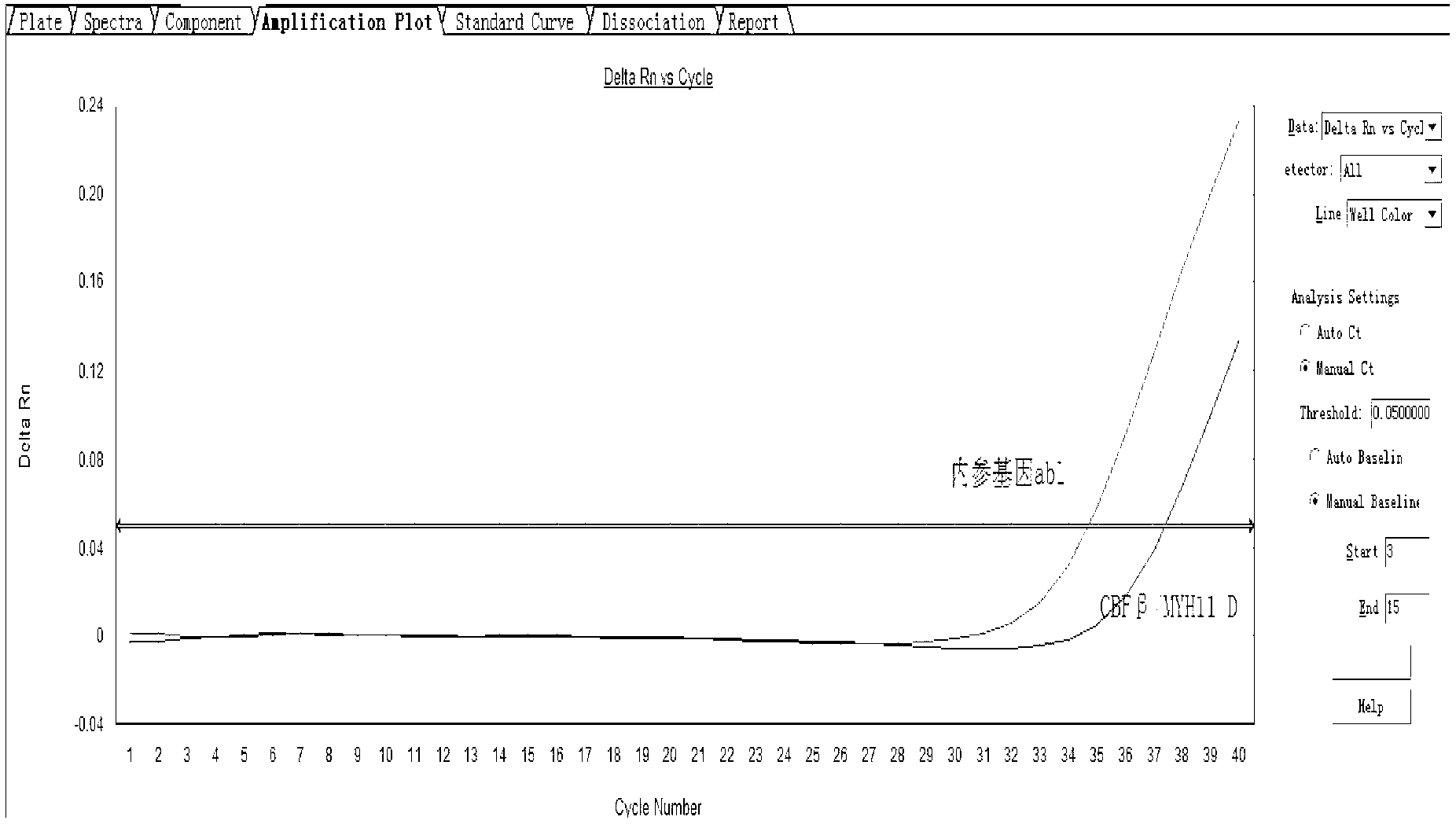
Assay kit for testing relative expression of core-binding factor (CBF) beta/myosin 11 fusion genes
InactiveCN102796818AHigh precisionStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceGene expression levelMyelocytic leukemia
The invention discloses an assay kit for testing the relative expression of core-binding factor (CBF) beta / myosin 11 fusion genes, and the kit comprises red blood cell lysis buffer, TRIzol, chloroform, absolute ethyl alcohol, ReverTraAceqPCRRTKit, testing system polymerase chain reaction (PCR) reaction solution, positive control substance and negative control substance, and is characterized in that the testing system PCR reaction solution comprises THUNDERBIRDqPCRMIX, primers of CBF beta / MYH11-F, CBF beta / MYH11-A-R, CBF beta / MYH11-D-R and CBF beta / MYH11-E-R for amplifying a target gene, probe of CBF beta / MYH11-Prob, primers of abl-F and abl-R for amplifying an internal control gene, and probe of abl-Probe. The assay kit can be used for testing the expression level of the CBF beta / myosin 11 fusion genes of a patient suffering from human acute myelognous leukemia (AML), so the test time can be effectively saved, and the test precision is improved.
Owner:南昌艾迪康医学检验实验室有限公司
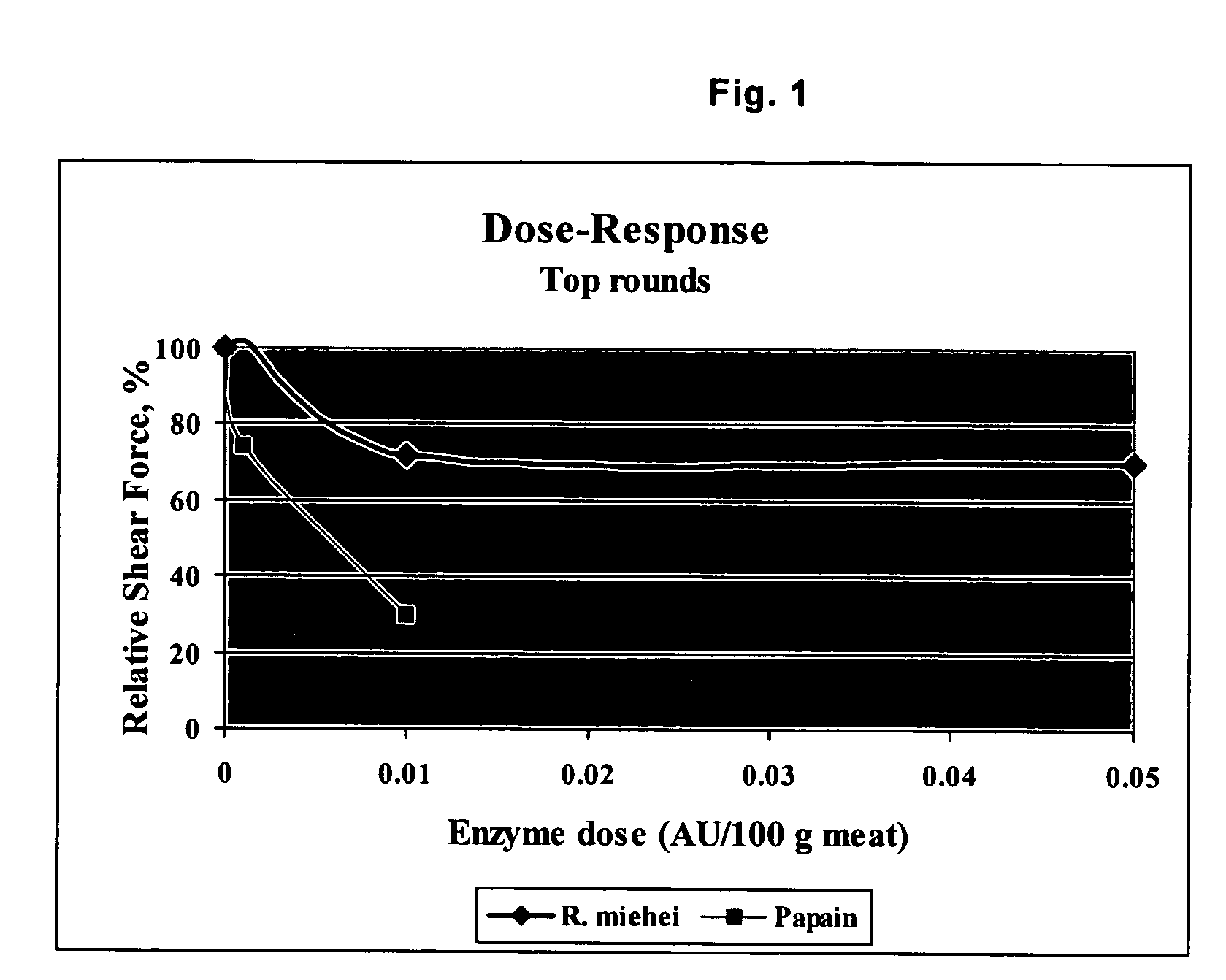
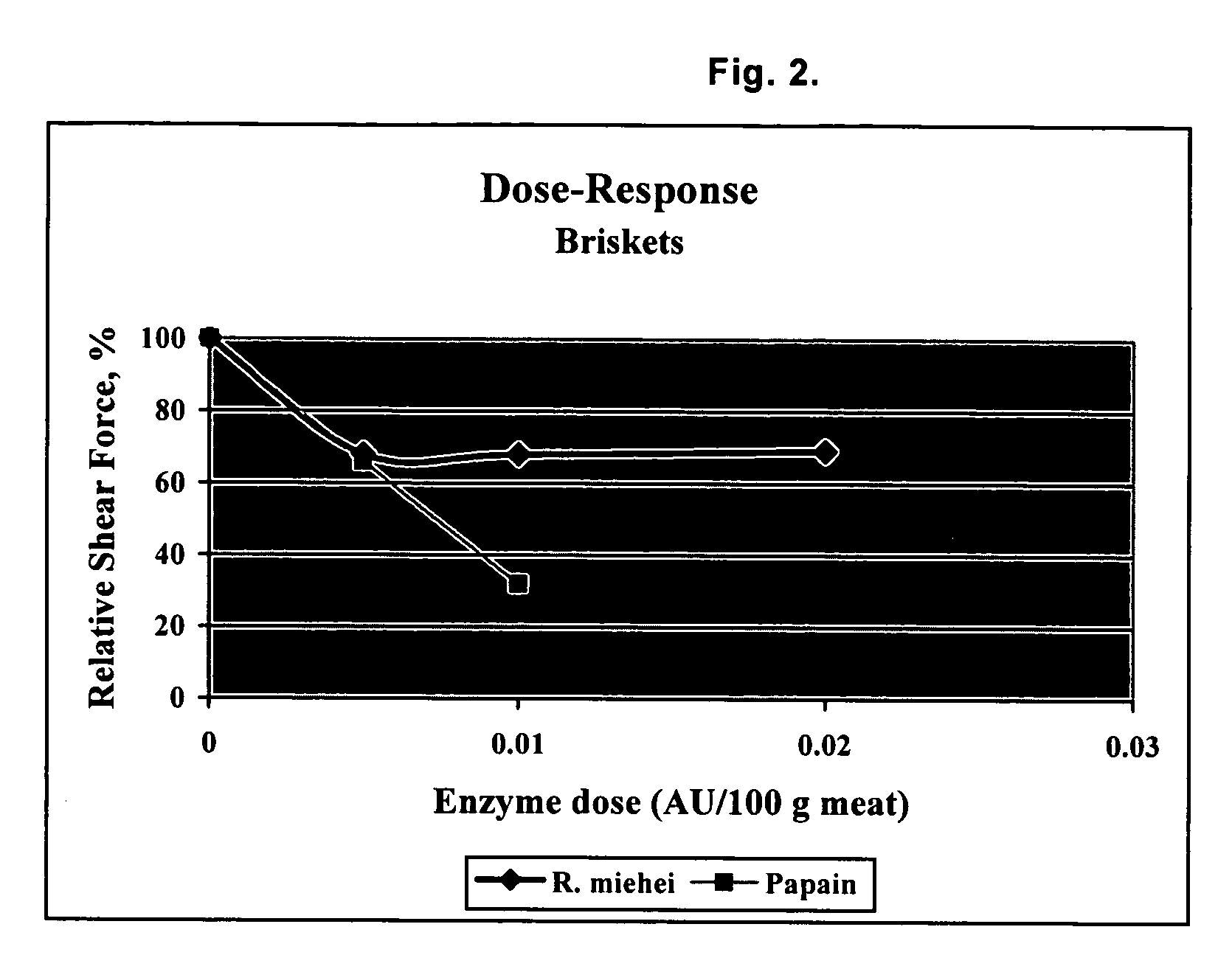
Compositions and methods for tenderizing meat
InactiveUS20050048166A1High activityMicrobiological testing/measurementFood preparationBiotechnologyMyosin
The present invention relates compositions and methods for meat tenderization by contacting meat with a protease that has higher activity on the meat proteins troponin and myosin as compared to the meat proteins actin and collagen. The present invention also relates to screening methods for identifying enzymes suitable for use in tenderizing meat.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com