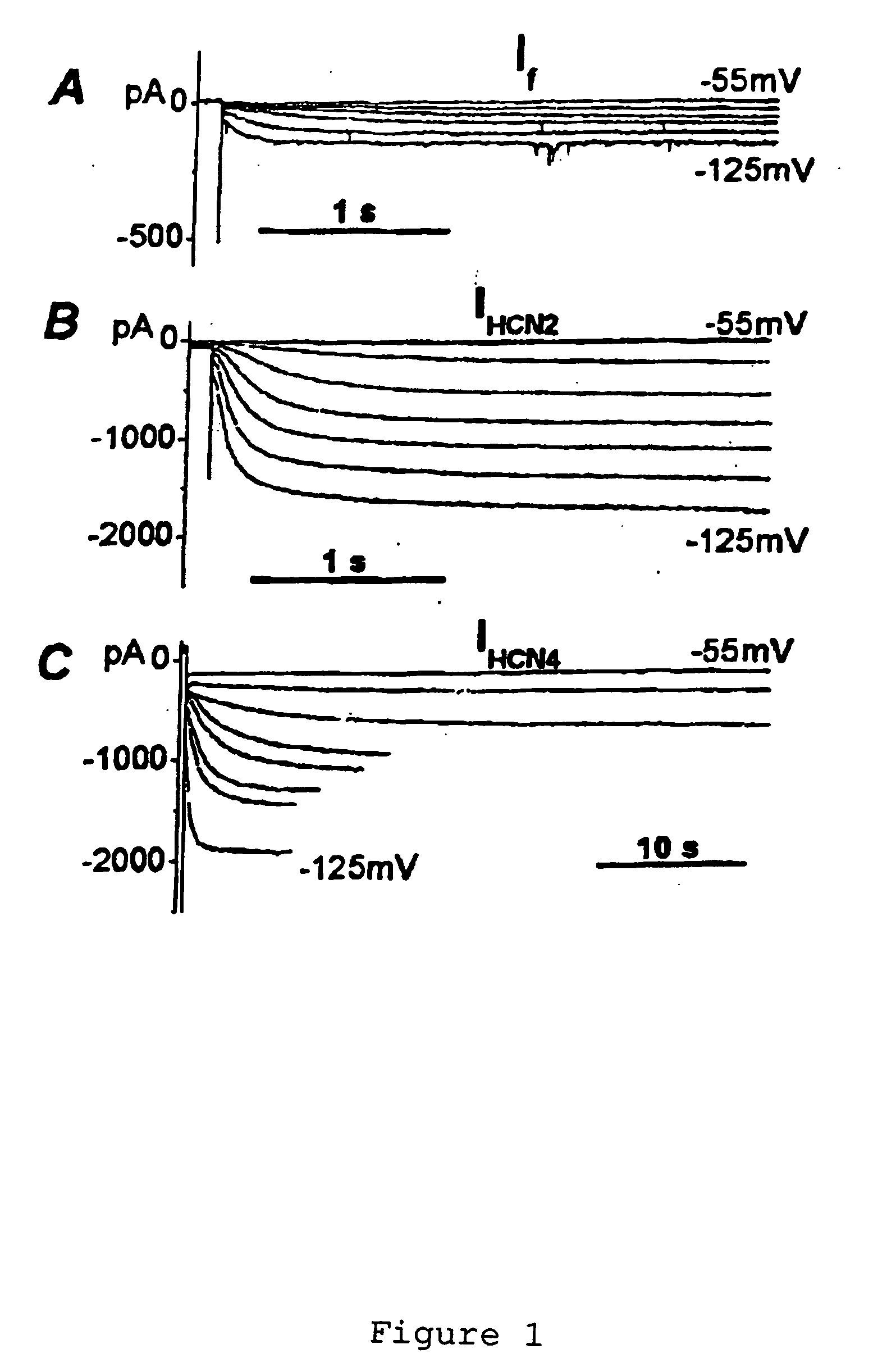
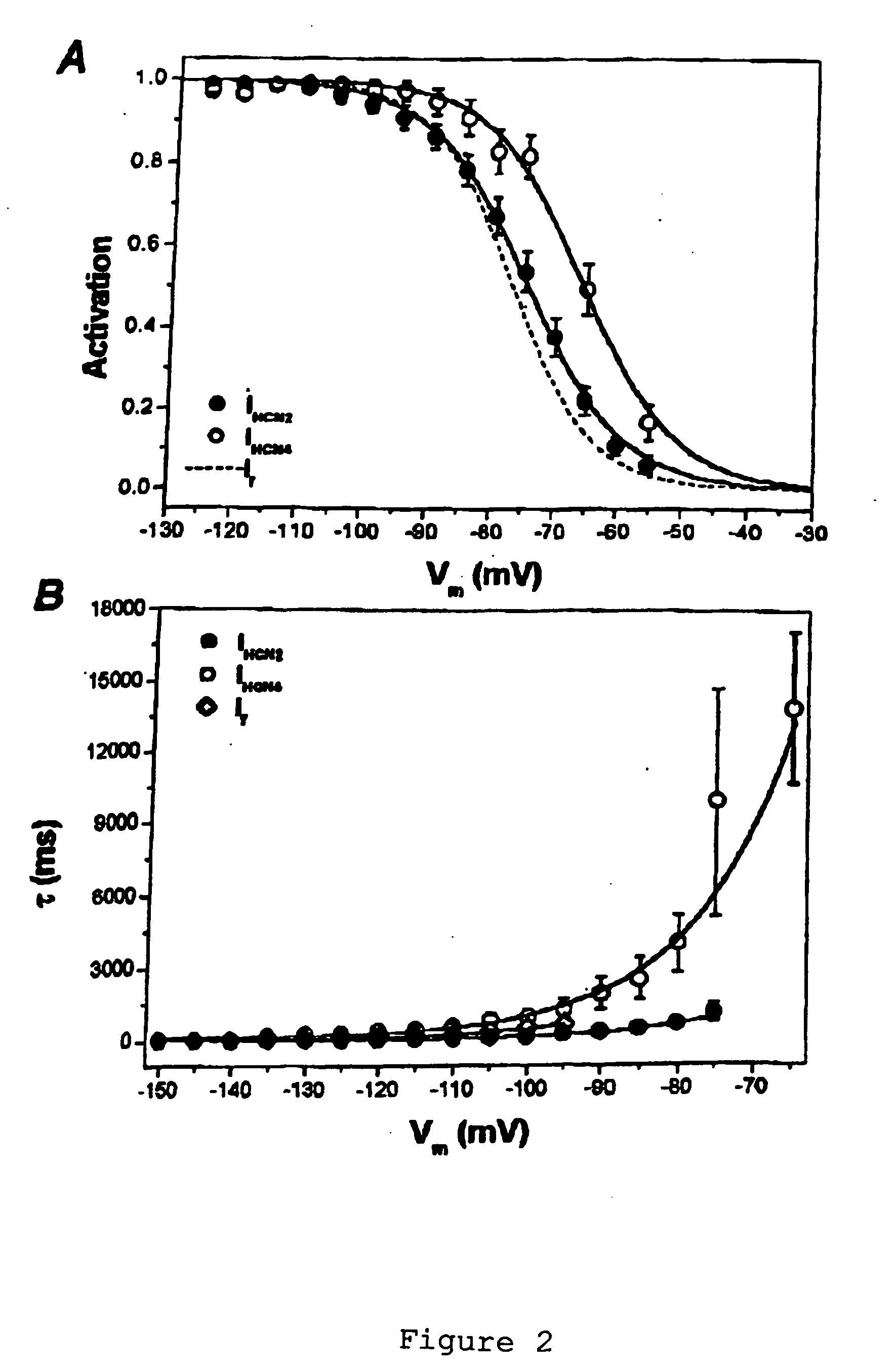
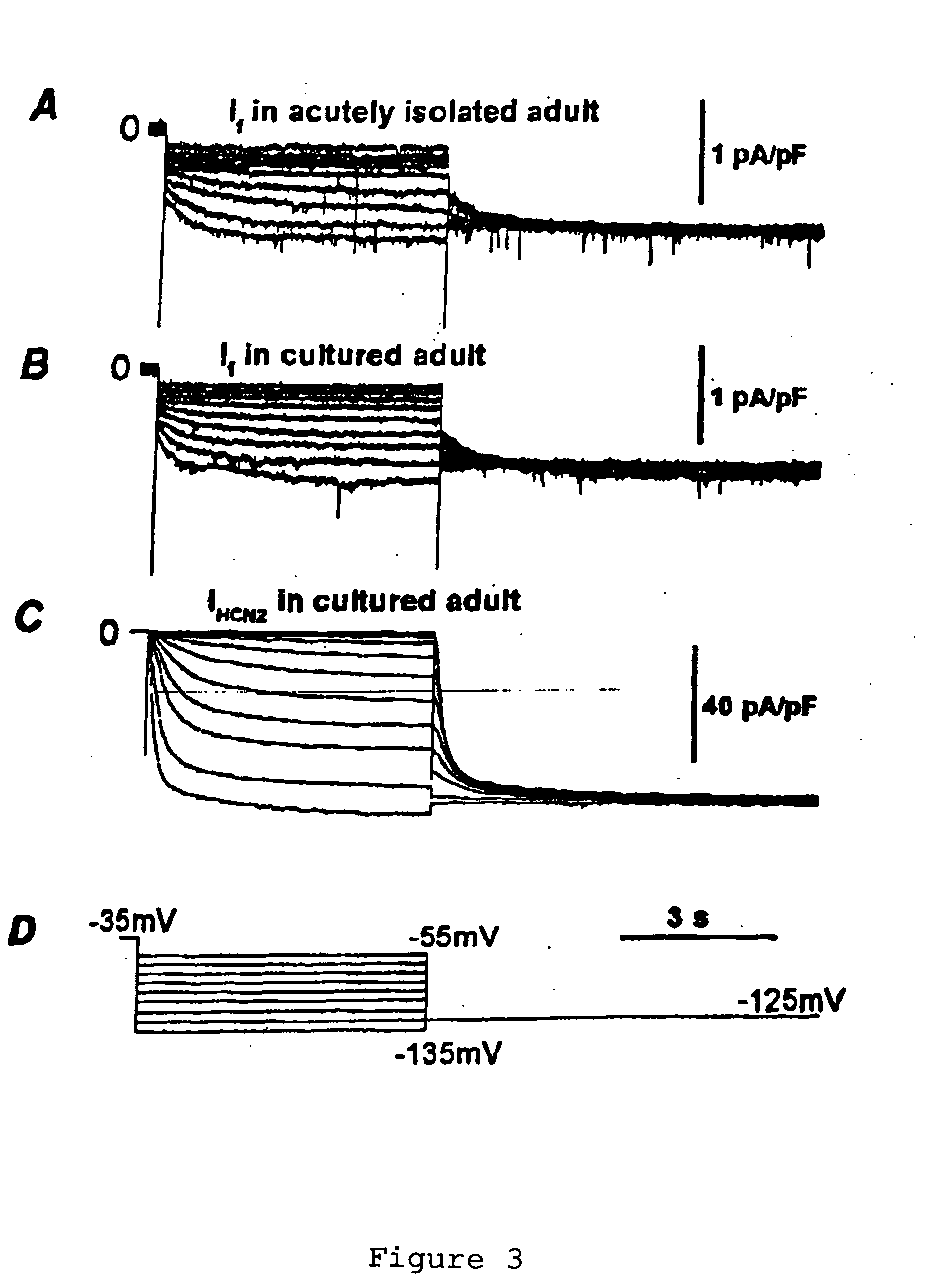
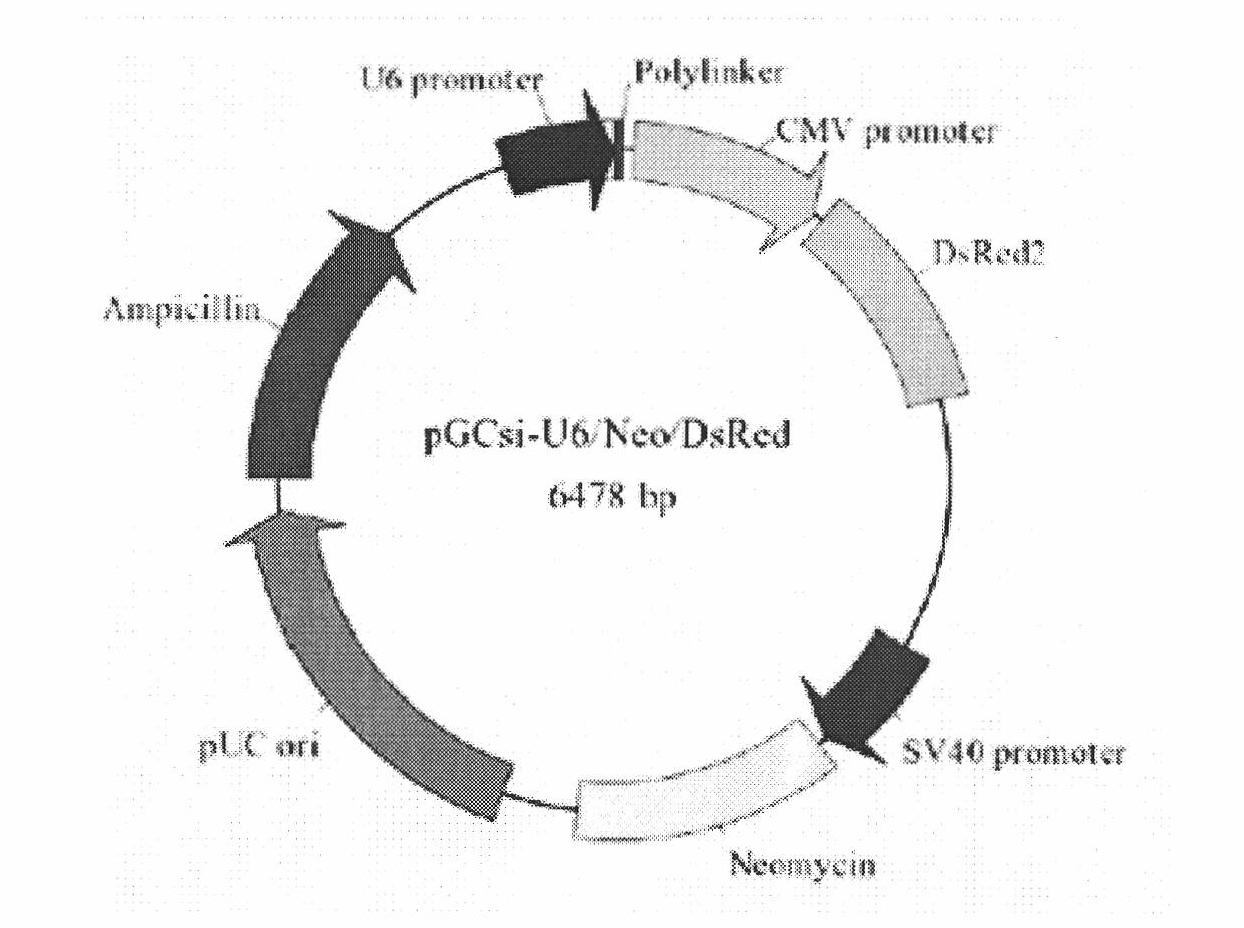
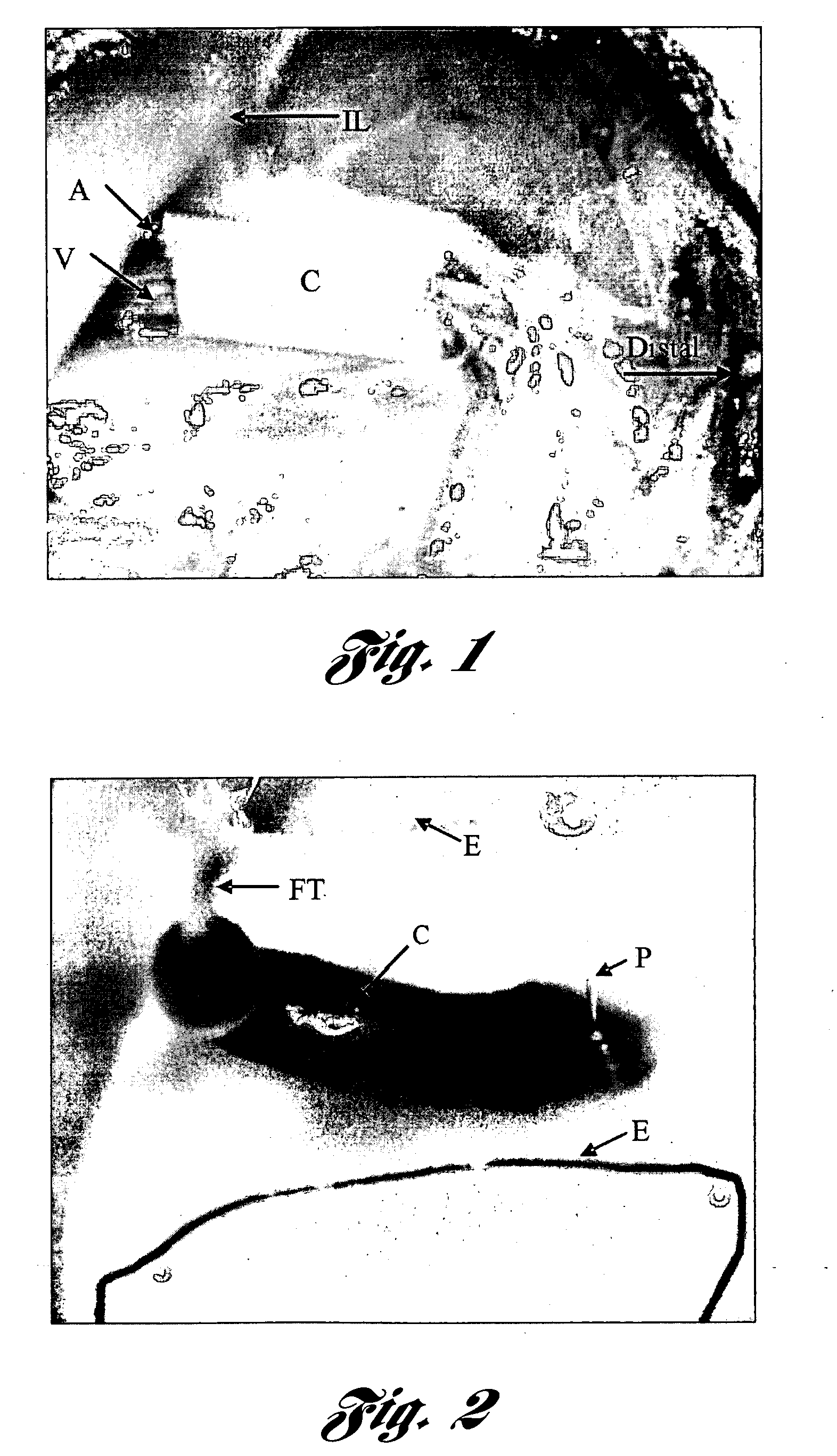
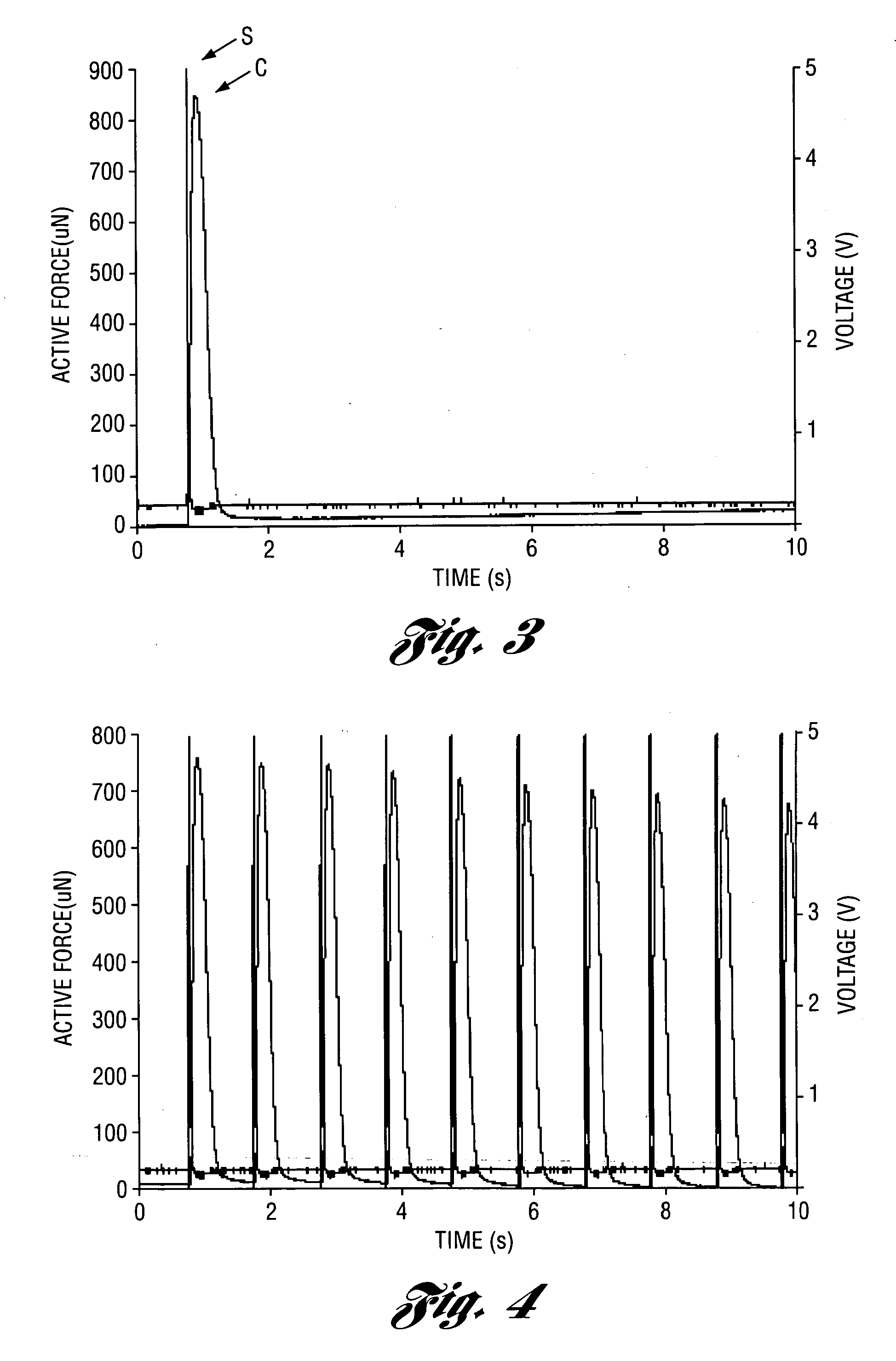
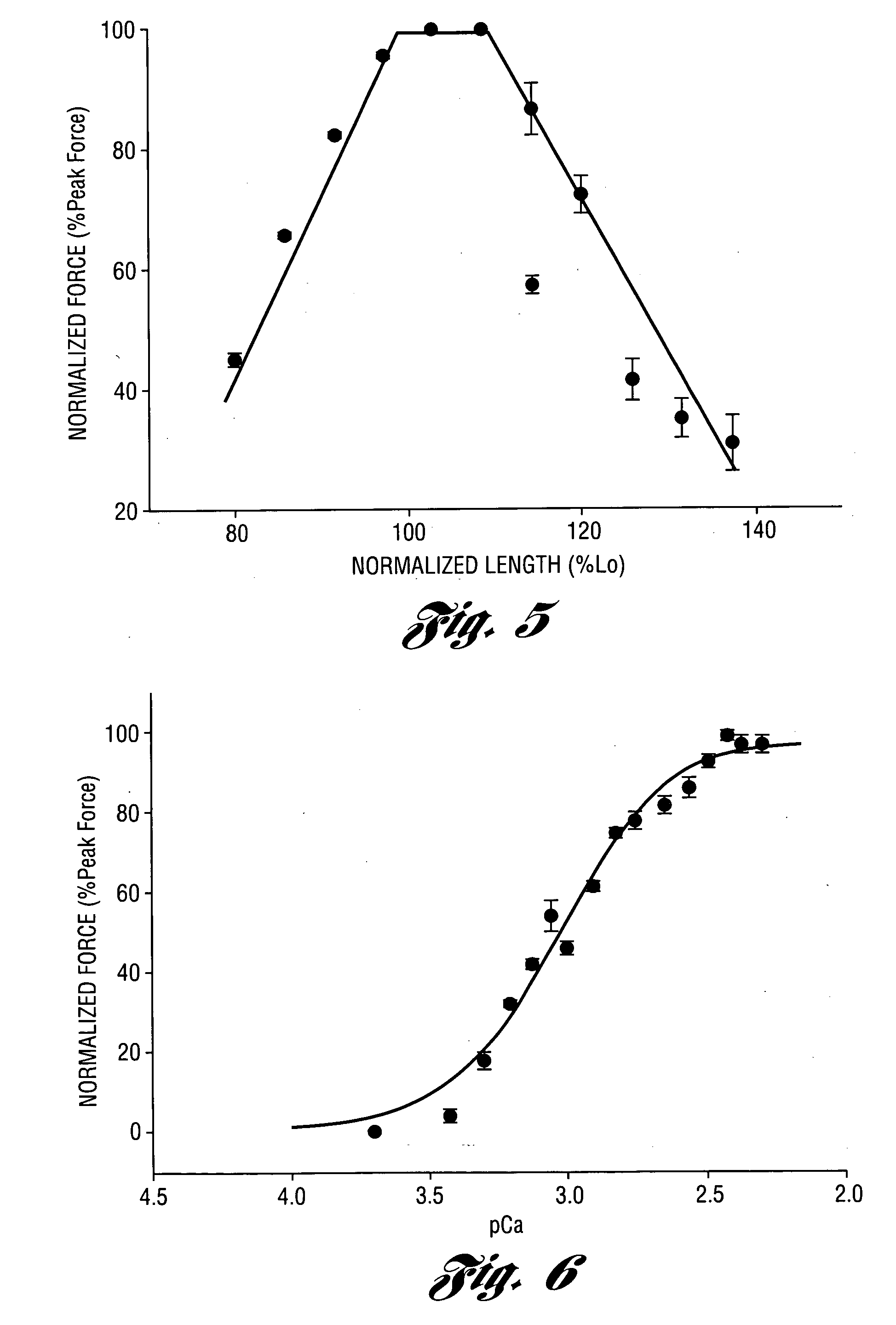
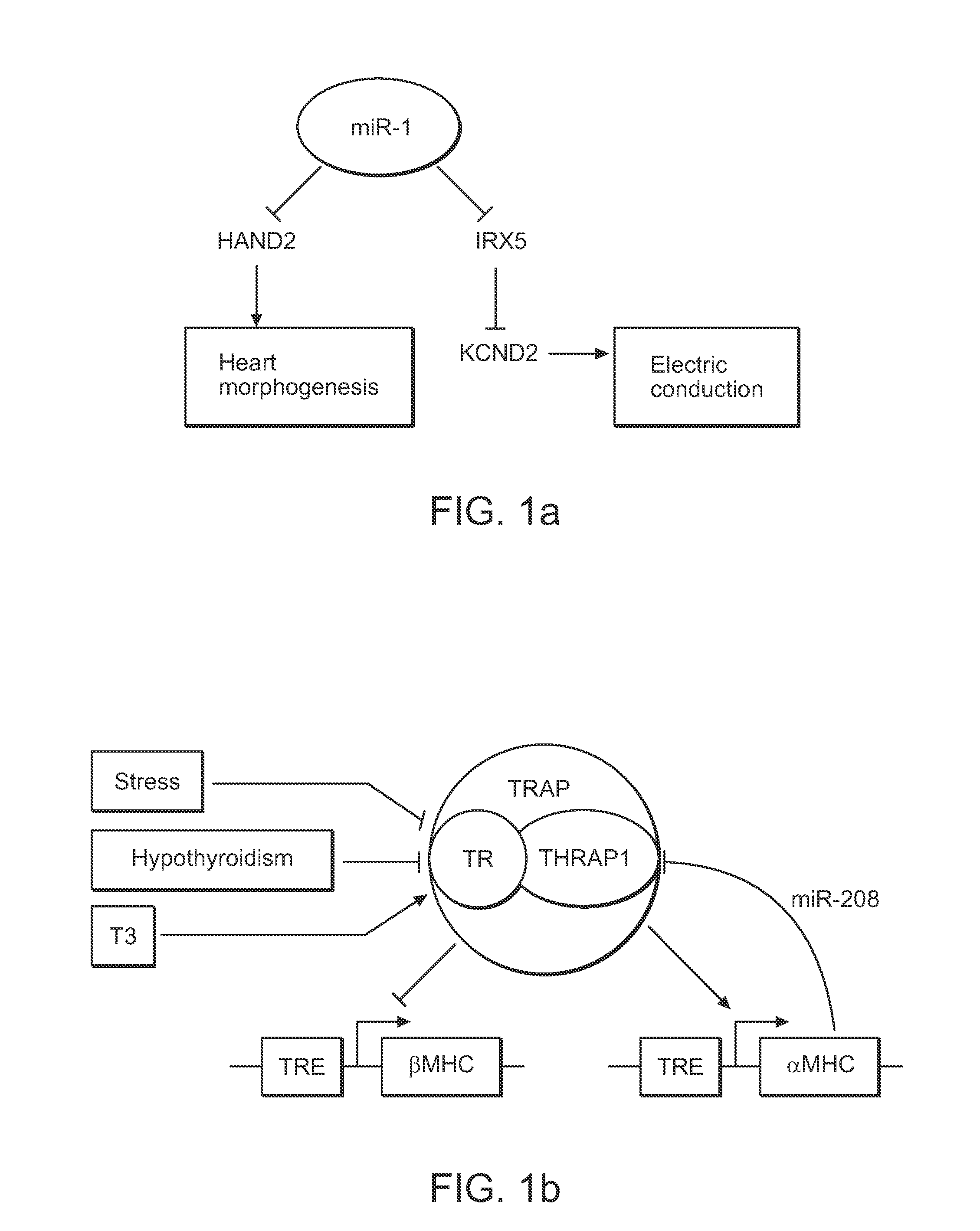
Patents
Literature
70 results about "Cardiac myocyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cardiac myocytes are the contractile cells of the heart and constitute the bulk of heart mass. There are differences between the myocytes of the ventricles, the atria, and the conduction system: ventricular myocytes are elongated cells and packed with myofibrils (the contractile apparatus) and mitochondria (for ATP production)....
Compositions comprising vascular and myocyte progenitor cells and methods of their use
InactiveUS20090148421A1Restoring structuralRestoring functional integrityBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsProgenitorCardiac progenitors
The invention provides compositions of adult cardiac vascular progenitor cells (VPCs) and adult cardiac myocyte progenitor cells (MPCs) useful for the treatment of various cardiac conditions. The invention also encompasses methods of generating a biological bypass, repairing damaged myocardium, and treating or preventing hypertensive cardiomyopathy and heart failure with the compositions of the invention. Methods of isolating the cardiac progenitor cells are also disclosed.
Owner:NEW YORK MEDICAL COLLEGE
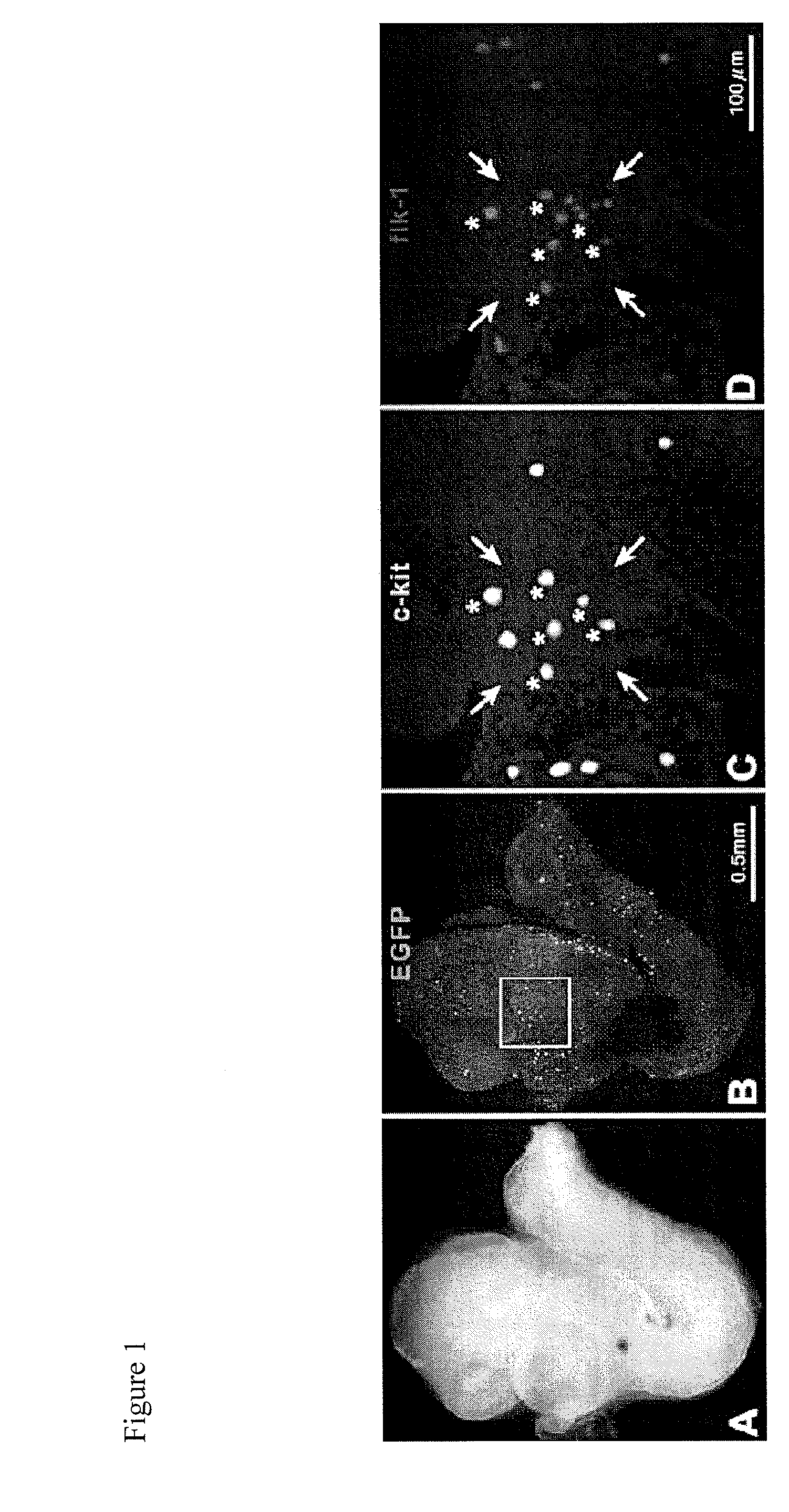
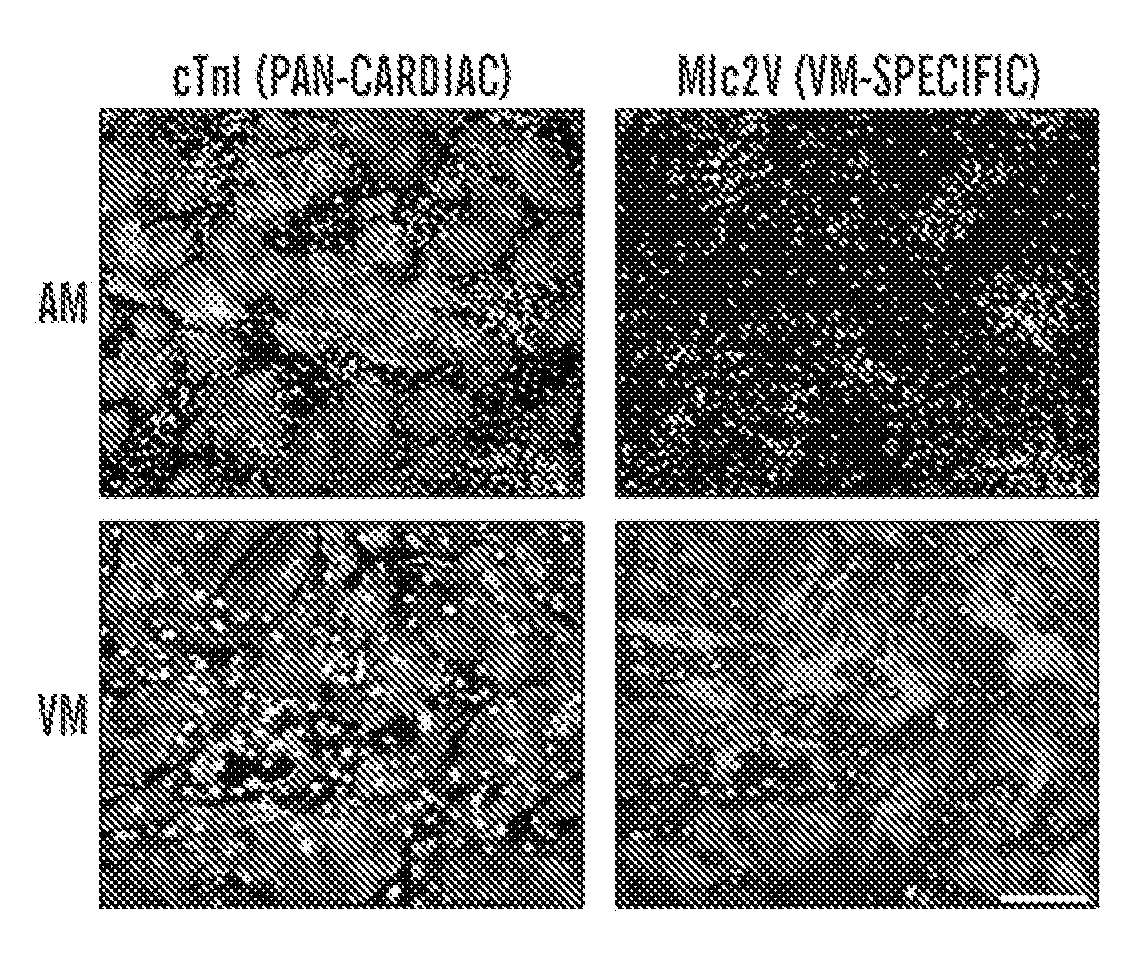
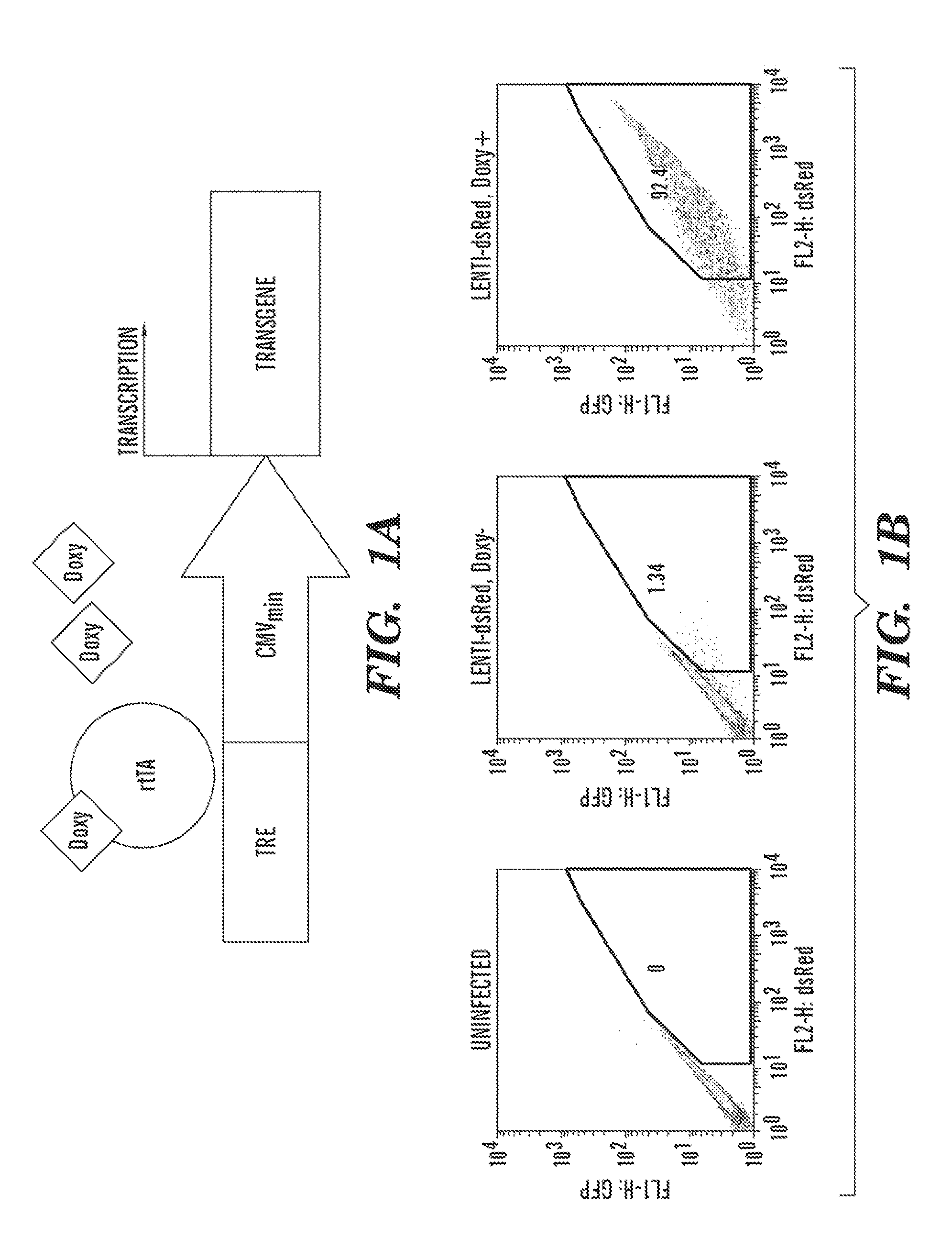
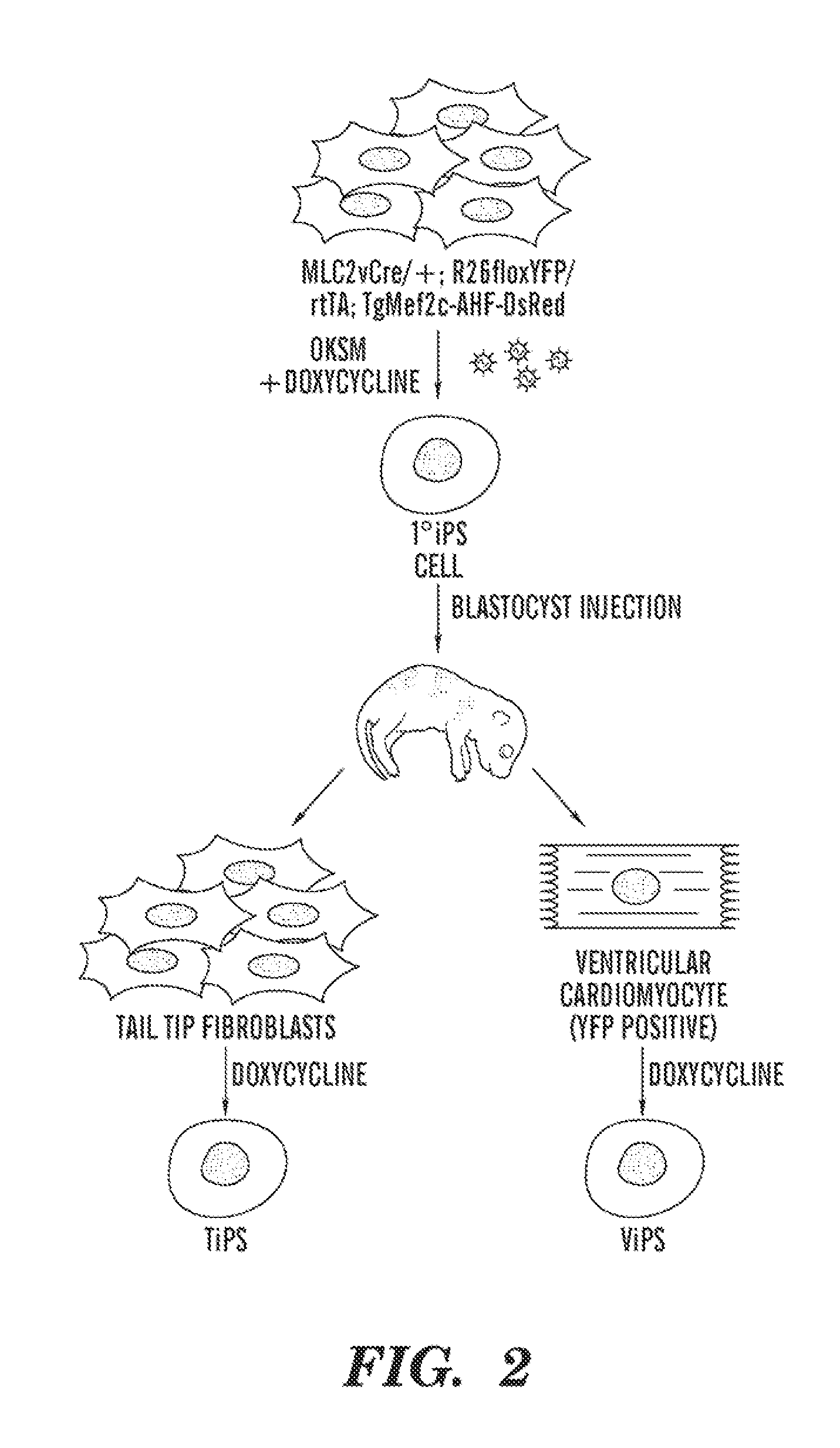
VENTRICULAR INDUCED PLURIPOTENT STEM (ViPS) CELLS FOR GENERATION OF AUTOLOGOUS VENTRICULAR CARDIOMYOCYTES AND USES THEREOF
InactiveUS20120009158A1More cardiomyogenicYieldBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsDiseaseCells heart
The present invention generally relates to methods and compositions to generate a secondary iPS (2iPS) cell to produce somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate. In some embodiments, the method relates to an increase in efficiency of differentiation and production of high yields of somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate produced from secondary iPS (2iPS) cells as compared to their differentiation from other pluripotent stem cell sources such as ES cells or primary iPS cells. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to compositions, methods and systems for reprogramming a first somatic cell into a primary iPS cell, where the primary iPS cell is then differentiated along a selected linage to produce a second somatic cell, which is then reprogrammed to a secondary iPS cell (2iPS) cell. The 2iPS cell has a high efficiency of differentiating into a cell of the same cell type as the second somatic cell, e.g., a somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate such as but not limited to a ventricular cardiomyocyte, a pancreatic β-cell or a hepatic cell. In some embodiments, the first somatic cell is a fibroblast, or a cardiac cell, but is not limited to cardiac fibroblast cells. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to compositions, methods and systems to produce ventricular cardiomyocytes from secondary induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC), where the iPSC are themselves generated from ventricular cardiomyocytes. The secondary iPS (2iPS) cell generated from ventricular cardiomyocytes have a higher cardiomyogenic potential and high cardiomyogenic yield as compared to primary iPSC, and are useful in drug discovery, disease modeling and cell-based therapy.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
High throughput biological heart rate monitor that is molecularly determined
InactiveUS20070042347A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsSystems design
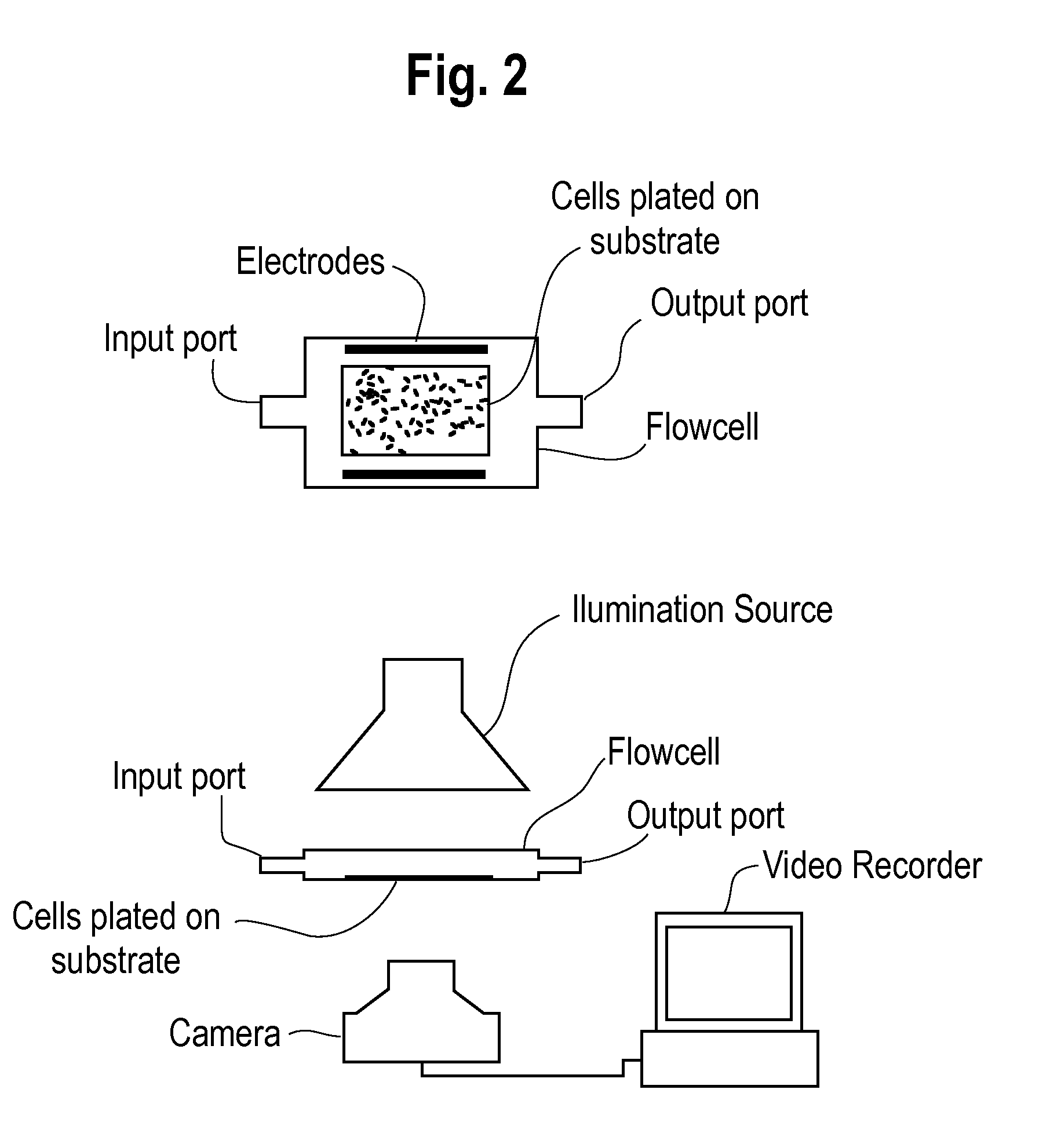
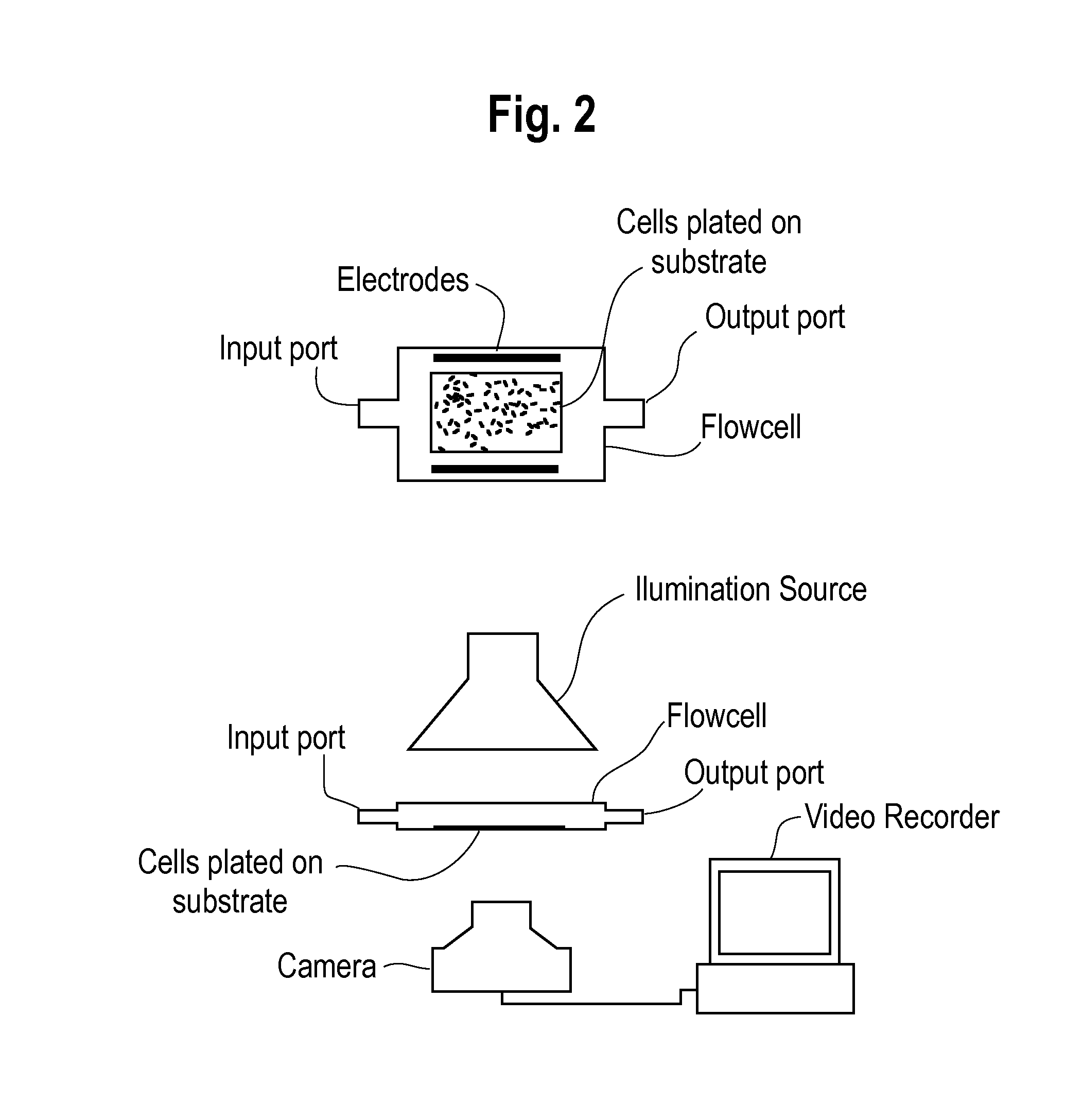
This invention provides for a chamber and system designed for use in assaying drug effects on heart rate. The chamber consists of a series of wells, each 3 mm by 3 mm in inner diameter. Cardiac myocytes disaggregated from neonatal animals are plated onto the bottom of each well and grown under standard tissue culture conditions. The chamber holds from 24-96 such wells. When drugs are to be assayed, the cells in each well are loaded with a calcium sensitive dye and the beating rate in each is monitored with a photodiode. Drug is added in graded concentrations to each well, and equilibrated and effects on rate are observed. This construct permits use of a cell based bioassay for the study of drugs or agents that may alter cardiac rate. This invention can be used in high throughput screening of drugs to evaluate / predict their effects on cardiac rate and rhythm. Further provided for by this invention is a A vector which comprises a compound which encode an ion channel.
Owner:ROSEN MICHAEL R +3
Construction and application of farnesyl pyrophosphoric acid synthetase RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) interference recombinant lentivirus vector
InactiveCN101805750AOvercoming No Commercial AntibodyOvercoming low transfection efficiencyMetabolism disorderGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseFhit gene
The invention provides the construction for a farnesyl pyrophosphoric acid synthetase RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) interference recombinant lentivirus vector, which comprises the following steps of: sieving the most effective target sequence of an FDS (farnesyl diphosphate synthase) gene RNAi (RNA interference) in a tool cell 293T cell, synthesizing the double-stranded DNA of the most effective target sequence, connecting to a pGCSIL-GFP vector and successfully constructing the recombinant vector through enzyme cutting, sequencing and identification. Researches indicate that the constructed RNA interference vector LV-sh-FDS can downwards modulate the expression of an FDS mRNA (Messenger RNA) level in a neonatal rat cardiac myocyte, simultaneously can downwards modulate the expression of myocardial hypertrophy markers such as cell areas and marker genes beta-MHC (Myosin Heavy Chain) and BNP (Brain Natriuretic Peptide), additionally can effectively inhabit the activity of RhoA while downwards modulating the FDS, can be applied in preparing medicaments for treating myocardial hypertrophy diseases and also can be applied in preparing medicaments for cholesterol metabolic control.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Use of human stem cells and/or factors they produce to promote adult mammalian cardiac repair through cardiomyocyte cell division
A method for treating a subject afflicted with a cardiac disorder, in vivo, comprising (i) producing a solution comprising media conditioned from the culture of cells, in vitro, and (ii) administering the solution of step (i) to the subject, thereby treating the cardiac disorder in the subject. Methods for determining whether an agent stimulates or inhibits myocyte proliferation.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
Adult Human Cardiac-Derived Progenitor Cells
The present invention is based, in part, on the discovery that cardiac progenitor cells are present in and can be isolated from adult human heart. Accordingly, a cell of the present invention comprises a human adult cardiac-derived progenitor cell capable of differentiating into a cardiac myocyte where said cell is isolated according to the expression of specific biomarkers, identified elsewhere herein. The present invention also includes methods of use of an adult cardiac-derived progenitor cell in the treatment of heart disease.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Compositions comprising vascular and myocyte progenitor cells and methods of their use
InactiveUS20100239538A9Restoring structural and functional integrityIncrease blood flowBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsProgenitorCardiac progenitors
The invention provides compositions of adult cardiac vascular progenitor cells (VPCs) and adult cardiac myocyte progenitor cells (MPCs) useful for the treatment of various cardiac conditions. The invention also encompasses methods of generating a biological bypass, repairing damaged myocardium, and treating or preventing hypertensive cardiomyopathy and heart failure with the compositions of the invention. Methods of isolating the cardiac progenitor cells are also disclosed.
Owner:NEW YORK MEDICAL COLLEGE
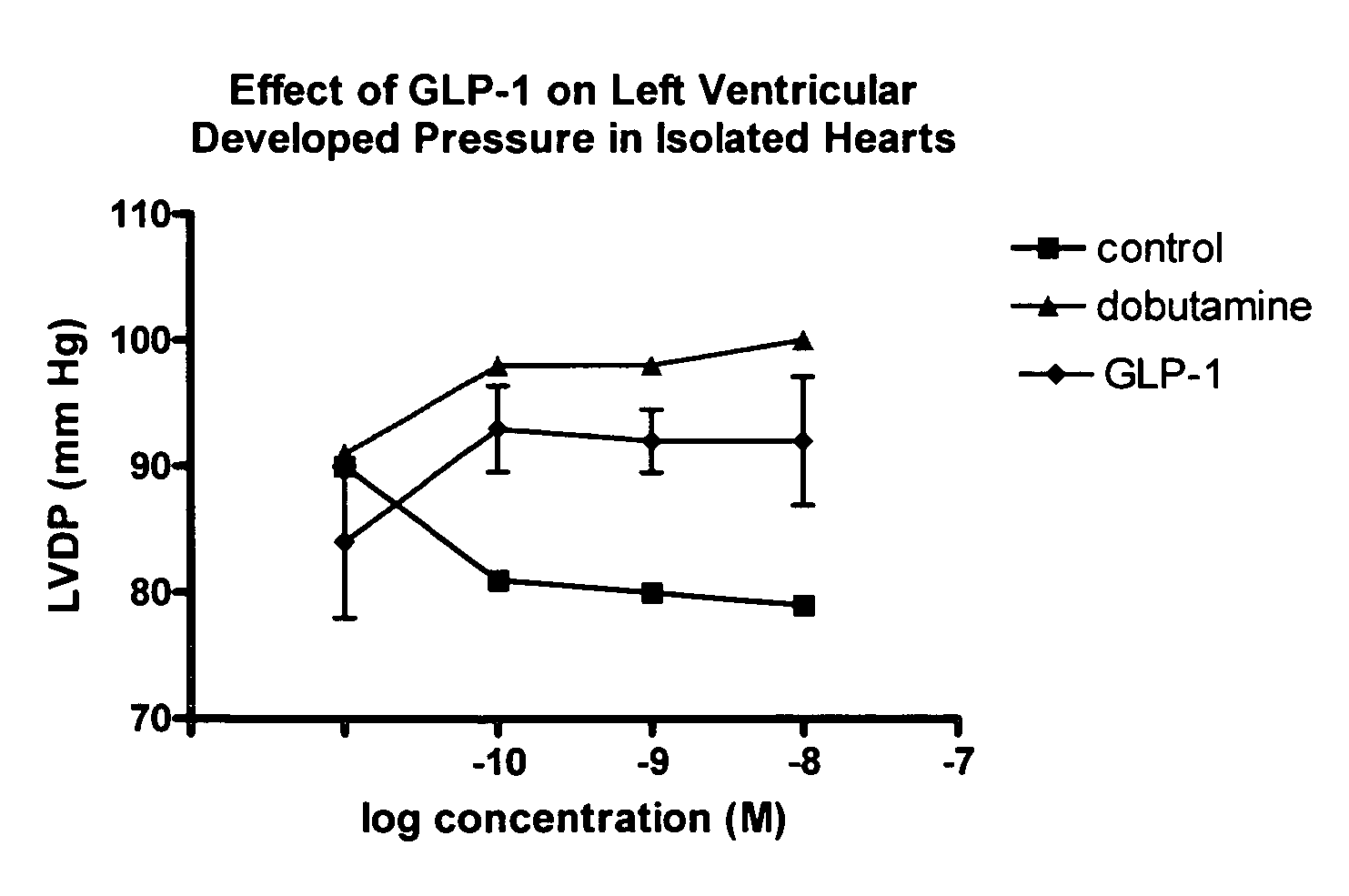
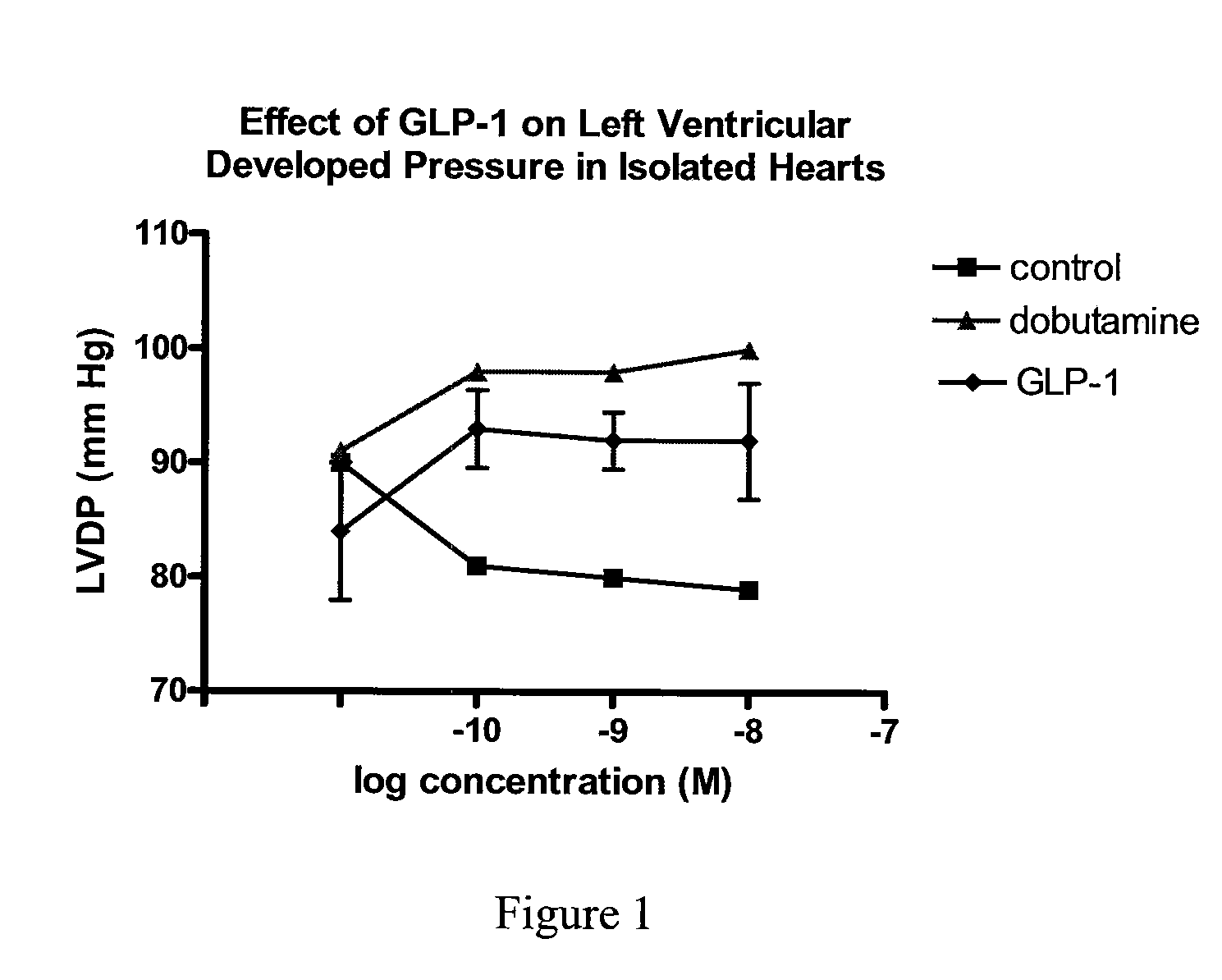
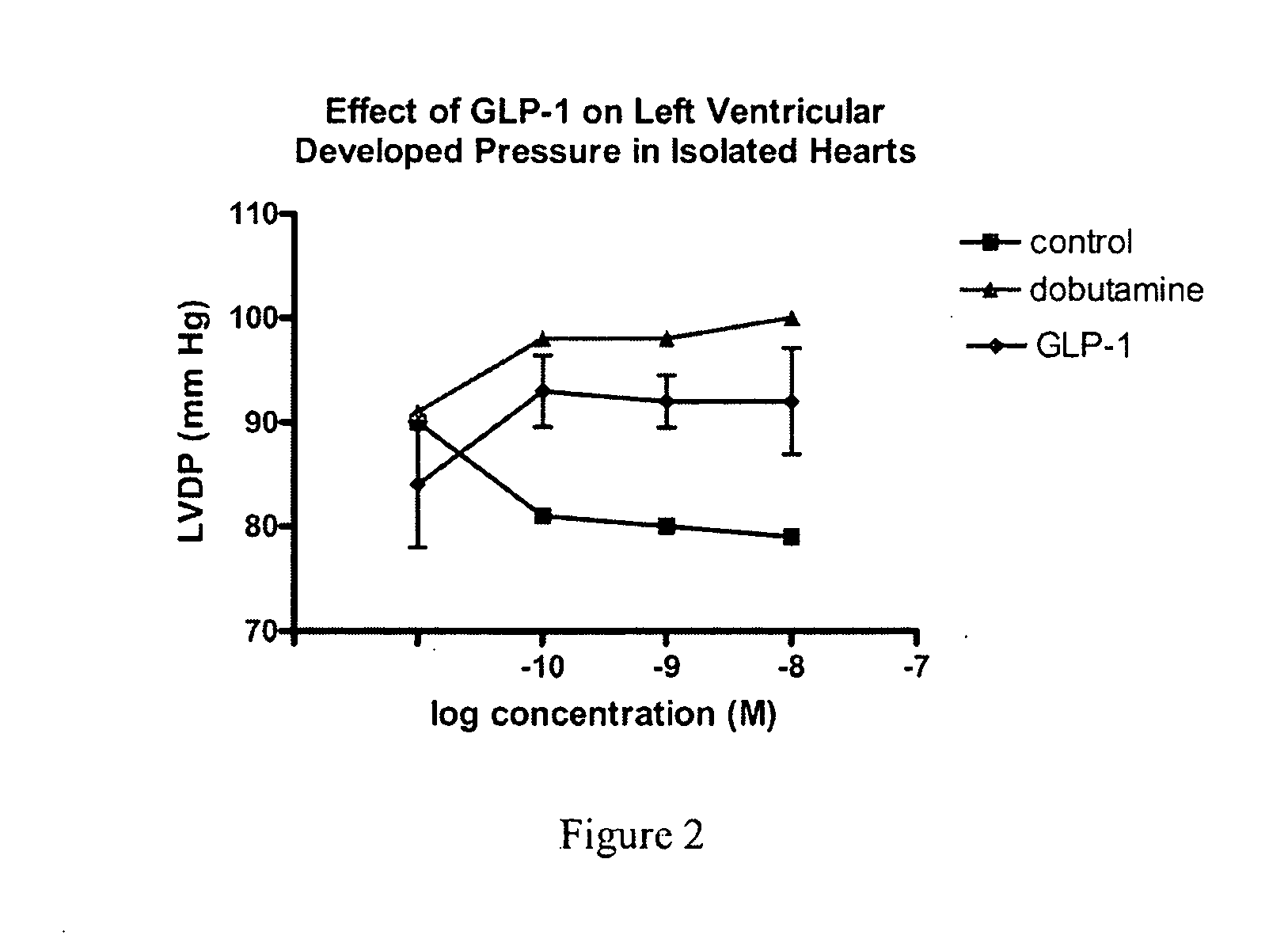
Use of GLP-1 and agonists thereof to prevent cardiac myocyte apoptosis
InactiveUS20070021336A1Prevent cardiac myocyte apoptosisImprove efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderApoptosisCardiac muscle
The present invention relates generally to the novel use of GLP-1, including analogs, and agonists, to prevent cardiac myocyte apoptosis. The present invention relates to methods for using GLP-1 for the treatment of conditions associated with cardiac myocyte apoptosis. The present invention further relates to improving the efficiency of cardiac myocytes and also to improving cardiac contractility.
Owner:AMYLIN PHARMA INC
99mTc-LABELED TRIPHENYLPHOSPHONIUM DERIVATIVE CONTRASTING AGENTS AND MOLECULAR PROBES FOR EARLY DETECTION AND IMAGING OF BREAST TUMORS
InactiveUS20090220419A1Radioactive preparation carriersPeptide preparation methodsHalf-lifeBreast fluid
99mTc-labeled triphenylphosphonium contrasting agents that target the mitochondria and are useful for early detection of breast tumors using scintimammographic imaging. 99mTc-Mito10-MAG3 possesses advantageous radiopharmaceutical properties. The uptake in the myocardium is reduced by one to two orders of magnitude compared to 99mTc-MIBI. 99mTc-Mito10-MAG3 exhibits fast blood clearance, with a blood half-life of less than 2 minutes in rats. A diminished myocardial uptake combined with a prompt reduction of cardiovascular blood pool signal to facilitate improved signal-to-background ratios.
Owner:LOPEZ MARCOS +3
Composition and method for clusterin-mediated stem cell therapy for treatment of atherosclerosis and heart failure
ActiveUS20060099194A1Reduce riskAvoid cell deathBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsOxysterolCytotoxicity
Methods and compositions are disclosed for inhibiting, deterring or preventing apoptosis of cardiac myocytes, transplanted stem cells, vascular stem cells, and vascular smooth muscle cells by means of expressing or synthesizing clusterin. Also disclosed are methods and compositions for producing recombinant clusterin, or its biologically active peptides, and for induction of clusterin-associated lipoproteins or enzymes for deterring or preventing inflammatory injury and apoptosis induced by oxLDL, oxysterols, cytokines, and Fas Ligand. Also disclosed is an induction method and composition for enhancing expression of ALDH and ALDH-associated enzymes or co-factors to prevent cytotoxicity or detoxification. Therapeutic methods providing new expression or overexpression of clusterin in vascular or cardiac tissue are expected to inhibit the formation of atherosclerotic lesions, stabilize existing atherosclerotic plaques, and repair failing or damaged cardiac tissue.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
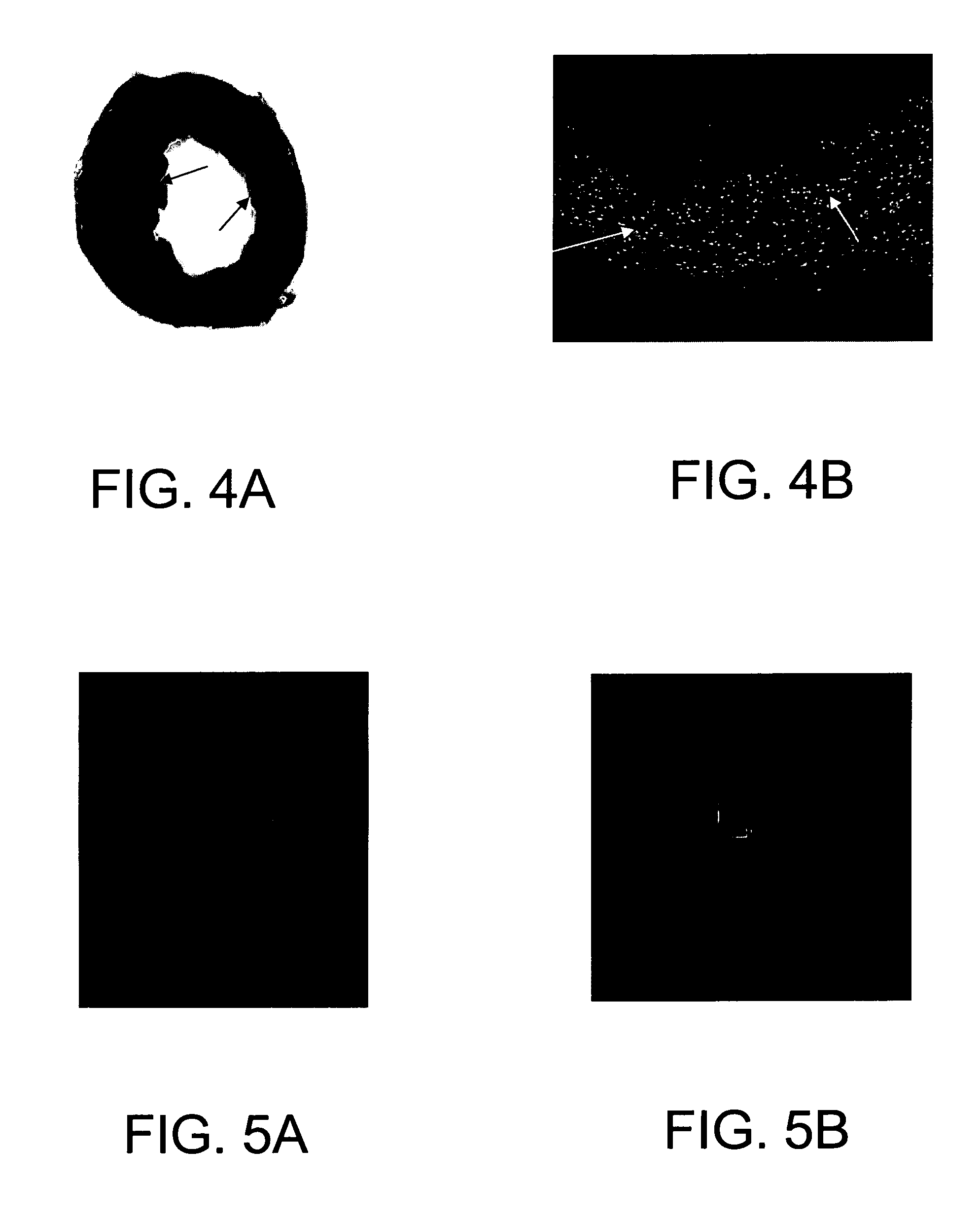
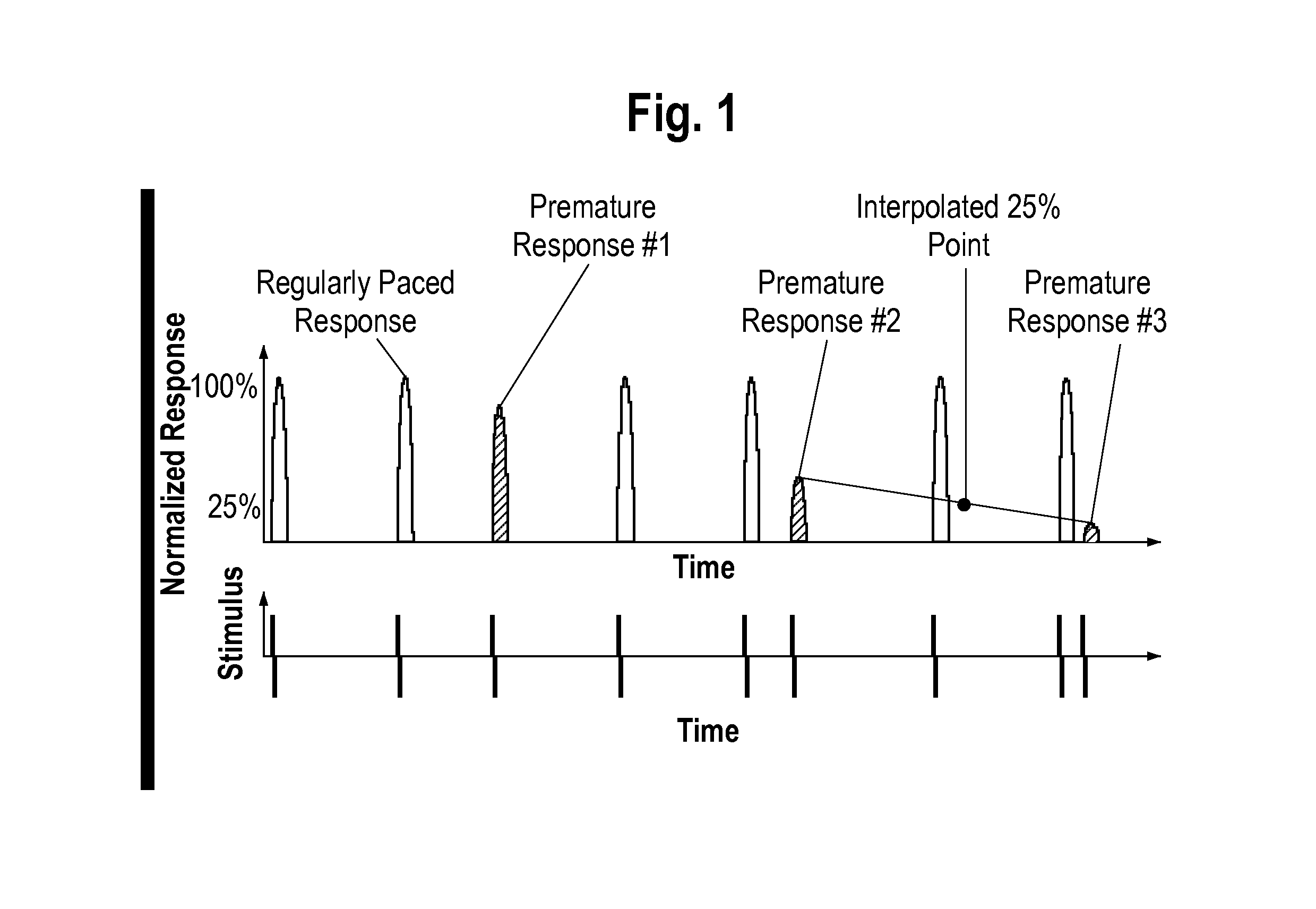
High throughput, optical method and system for determining the effect of a test substance on non-contiguous living cells
ActiveUS20120134570A1Rapidly and efficiently detecting, measuring, and/or verifying the effectsRapidly and efficiently selectedImage enhancementImage analysisCardiac repolarizationCardiac muscle
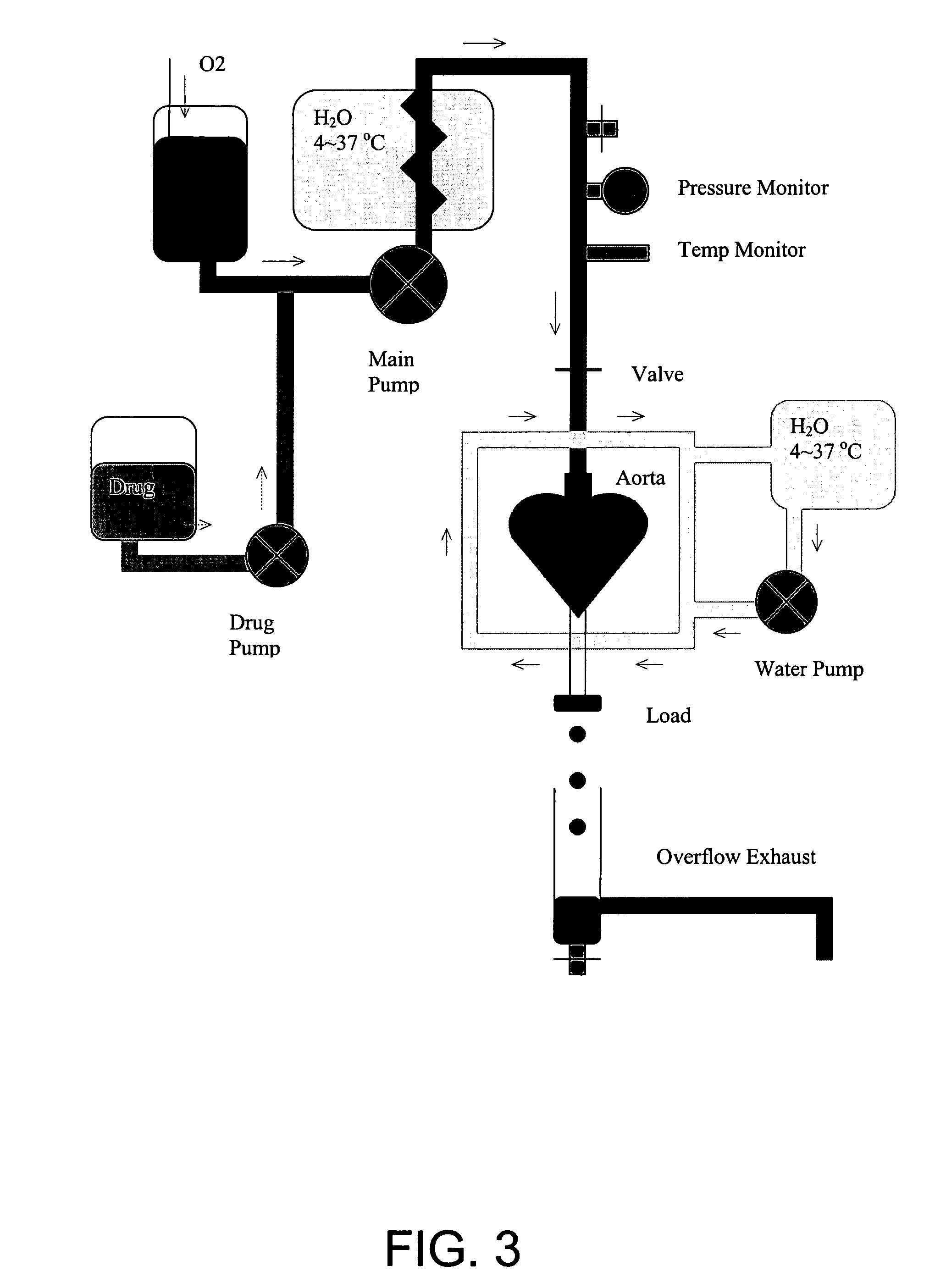
A rapid and efficient method and apparatus for detecting electrophysiologic, proarrhythmic, contractile, and other effects of substances such as compounds and drugs in native cellular cardiac preparations, the preparations representing an integrated cell-based pharmacologic response is disclosed. More specifically, a method to (1) rapidly and efficiently detect and verify the effects of chemicals, compounds and drugs on cardiac repolarization, contractility, and excitability using optically based techniques and customized simulation protocols, and (2) rapidly and efficiently screen and select compounds for electrophysiologic and proarrhythmic effects on cardiac myocytes is disclosed.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Use of glp-1 and agonists thereof to prevent cardiac myocyte apoptosis
InactiveUS20090264352A1Prevent cardiac myocyte apoptosisImprove efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderCardiac muscleApoptosis
The present invention relates generally to the novel use of GLP-1, including analogs, and agonists, to prevent cardiac myocyte apoptosis. The present invention relates to methods for using GLP-1 for the treatment of conditions associated with cardiac myocyte apoptosis. The present invention further relates to improving the efficiency of cardiac myocytes and also to improving cardiac contractility.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA PHARMA LP
Method for in-vitro separation and culture of goat male germ stem cells
InactiveCN101638633AHas the characteristics of ES cellsStrong shadingTissue cultureSeminiferous tubuleMatrigel
The invention discloses a method for in-vitro separation and culture of goat male germ stem cells. Spermatogonia are obtained from the testicular convolutedtubules of a male goat. A method for separating and purifying the goat male germ stem cells adopts 0.2% of gelatin and a Matrigel differential adherence combined cloning method to differentiate and separate un-adhered goat male germ stem cellsfrom other cells for adherence culture; and the culture of the separated goat male germ stem cells is MEF feeder-layer culture of feeder-layer-free culture. The separated goat male germ stem cells have ES cell characteristics and the potential of differentiation into nerve cells, cardiac myocytes and sperm sample cells.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
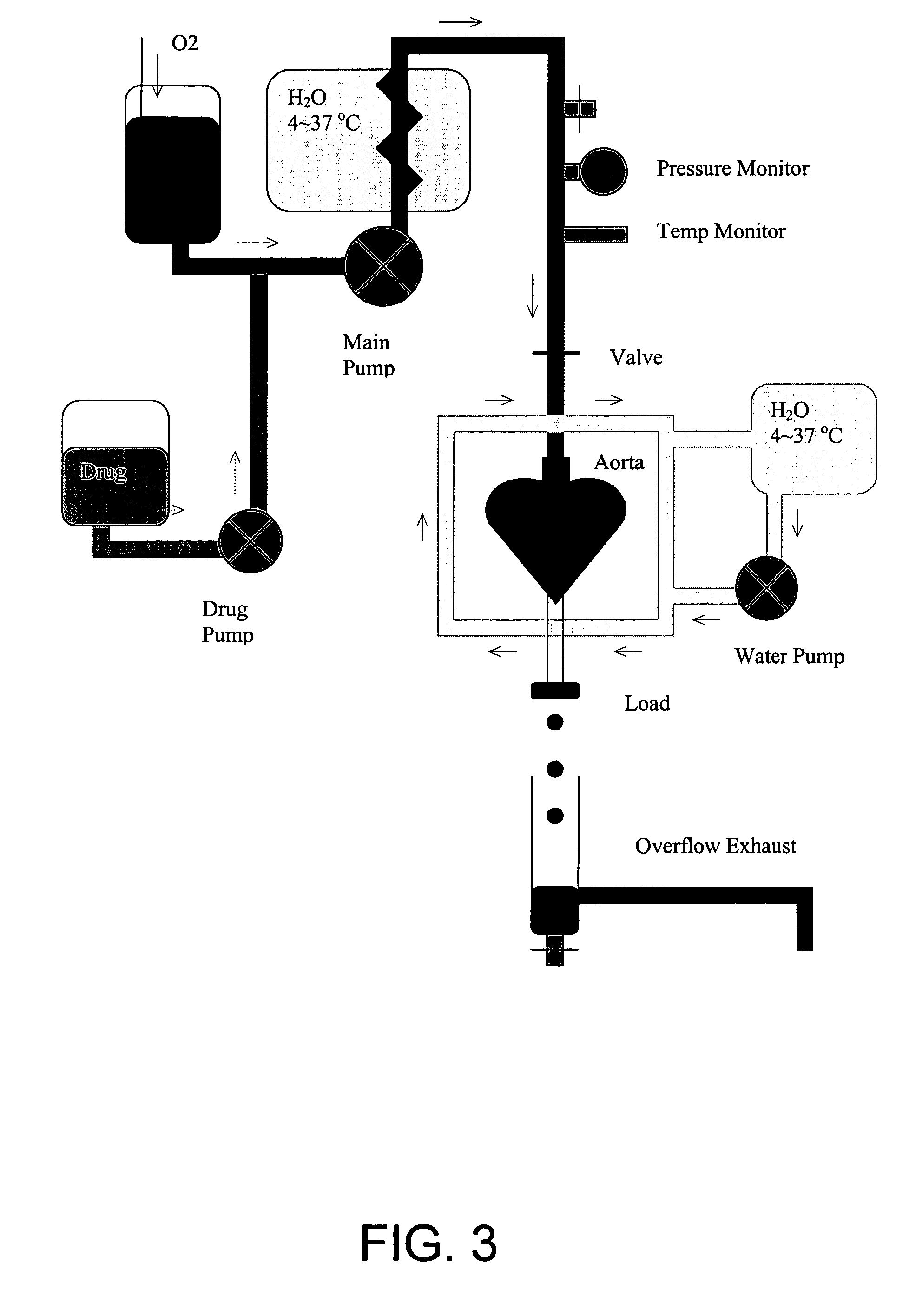
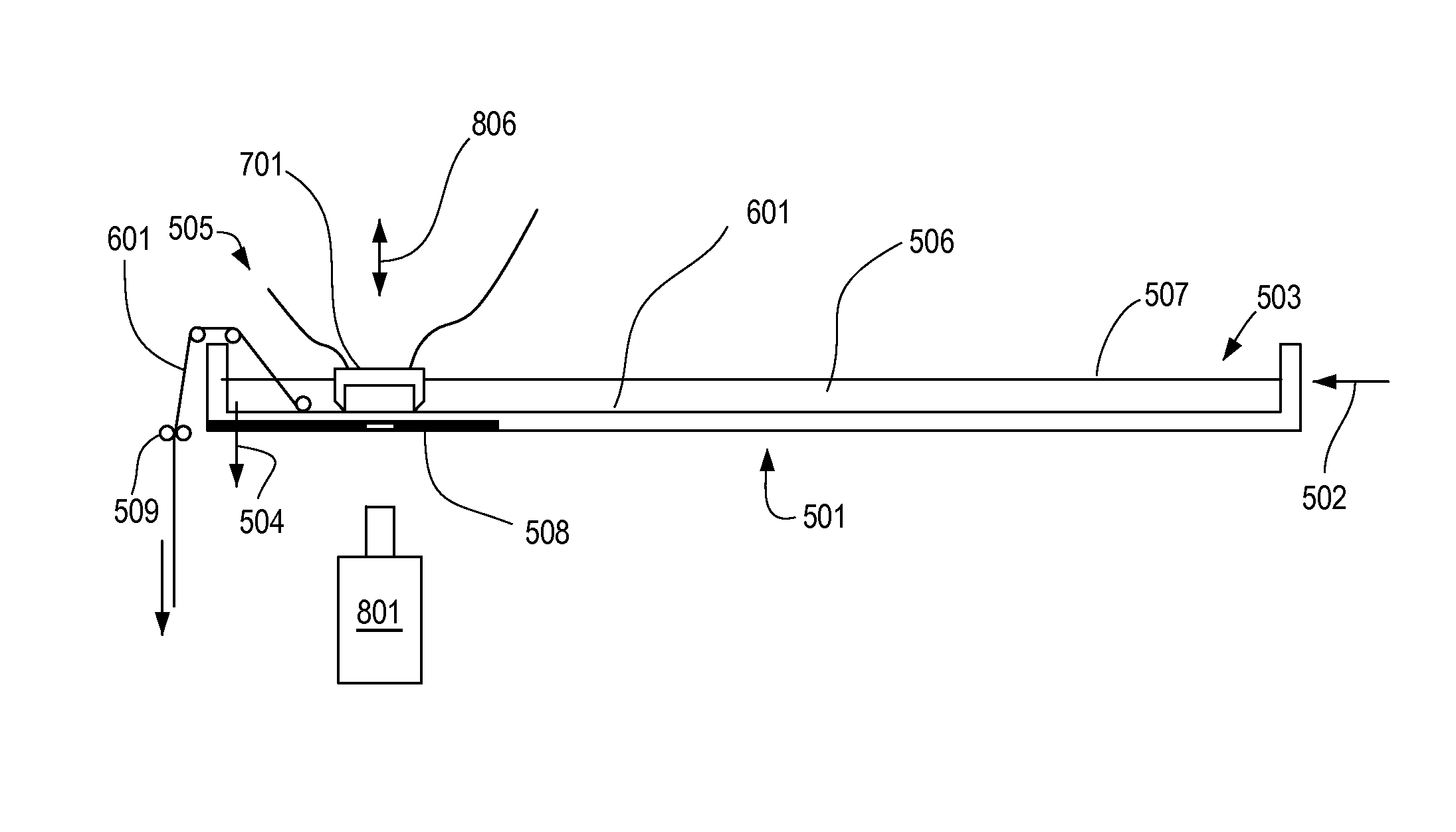
System and method for forming a cardiac tissue construct
InactiveUS20060141620A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCardiac muscleIn vivo
A system and method for forming a cardiac tissue construct includes a chamber and cardiac myocytes provided within the chamber. The chamber is arranged to at least partially surround an intact blood vessel in vivo to facilitate formation of the three-dimensional cardiac tissue construct within the chamber.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
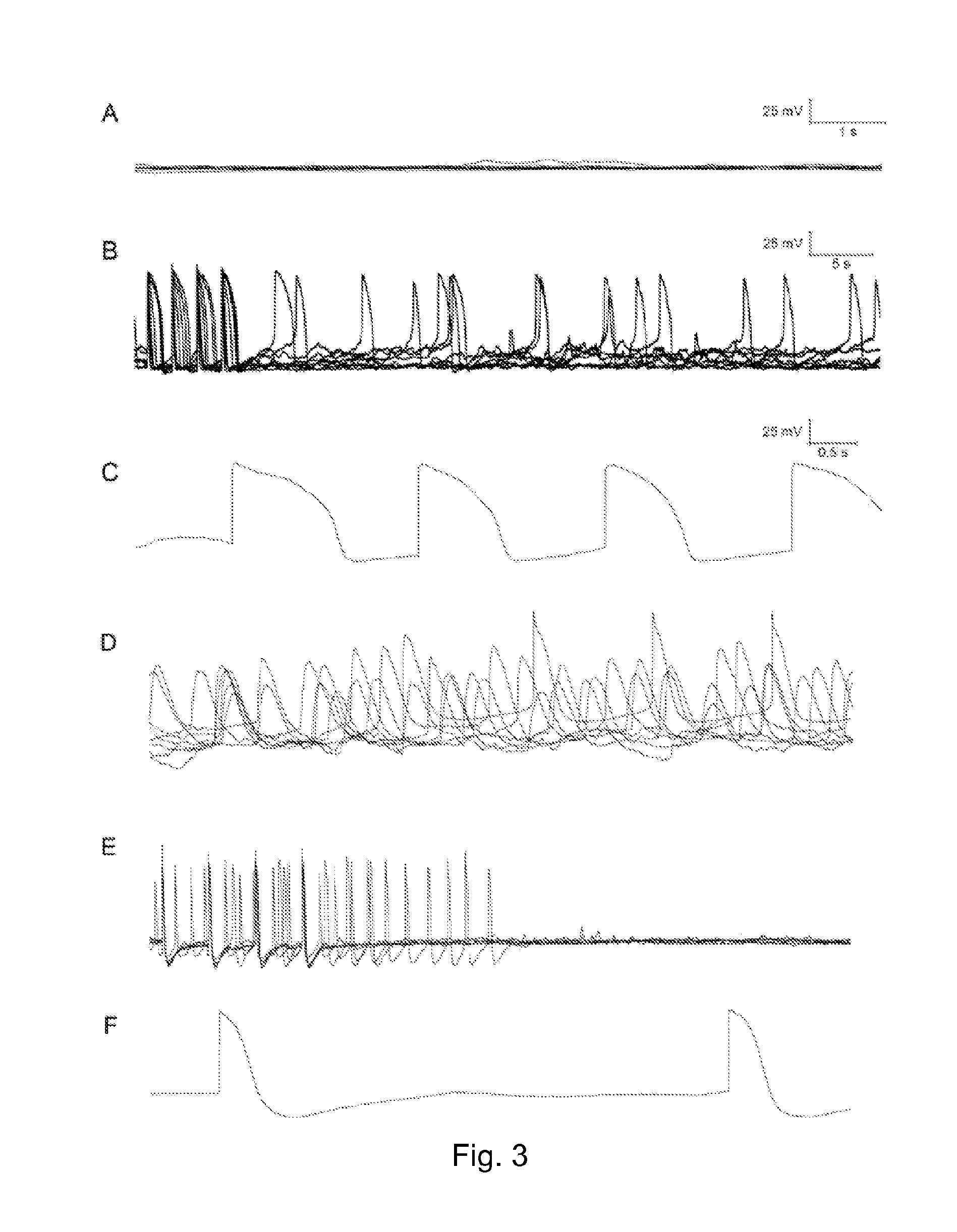
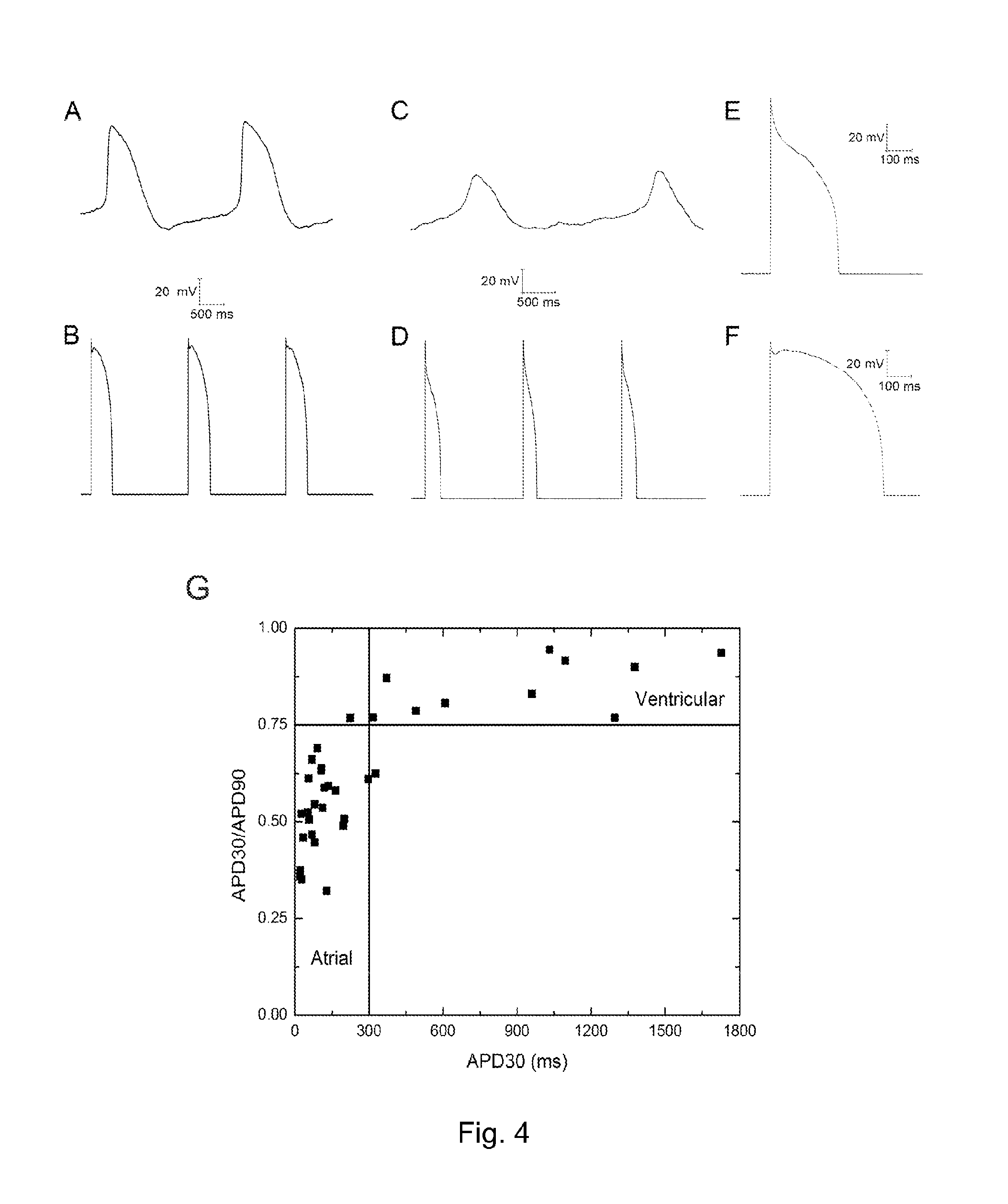
Direct Reprogramming of Cells to Cardiac Myocyte Fate
ActiveUS20140011281A1Promote conversionImprove efficiencyGenetically modified cellsSurgeryReprogrammingFibroblast
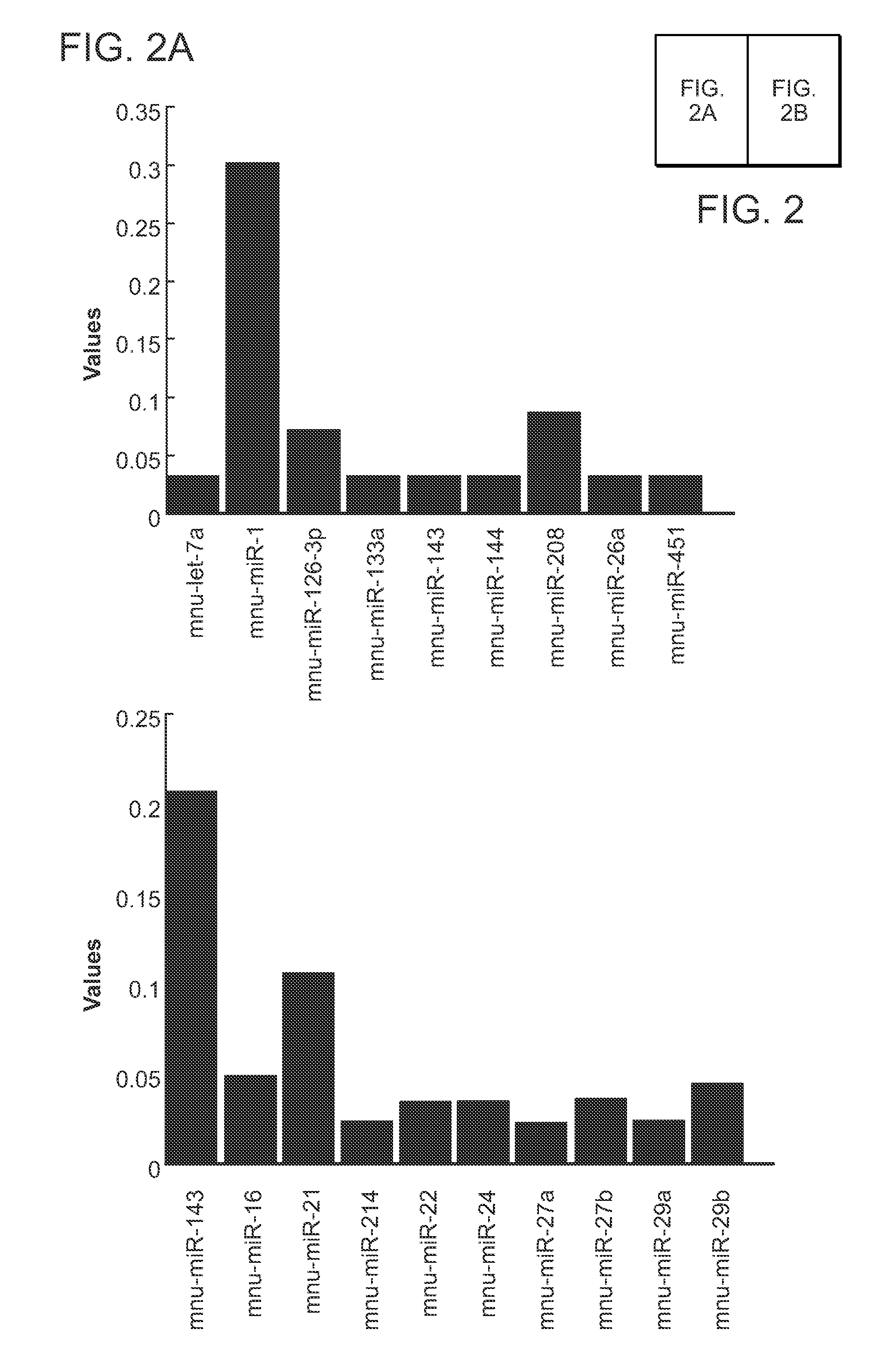
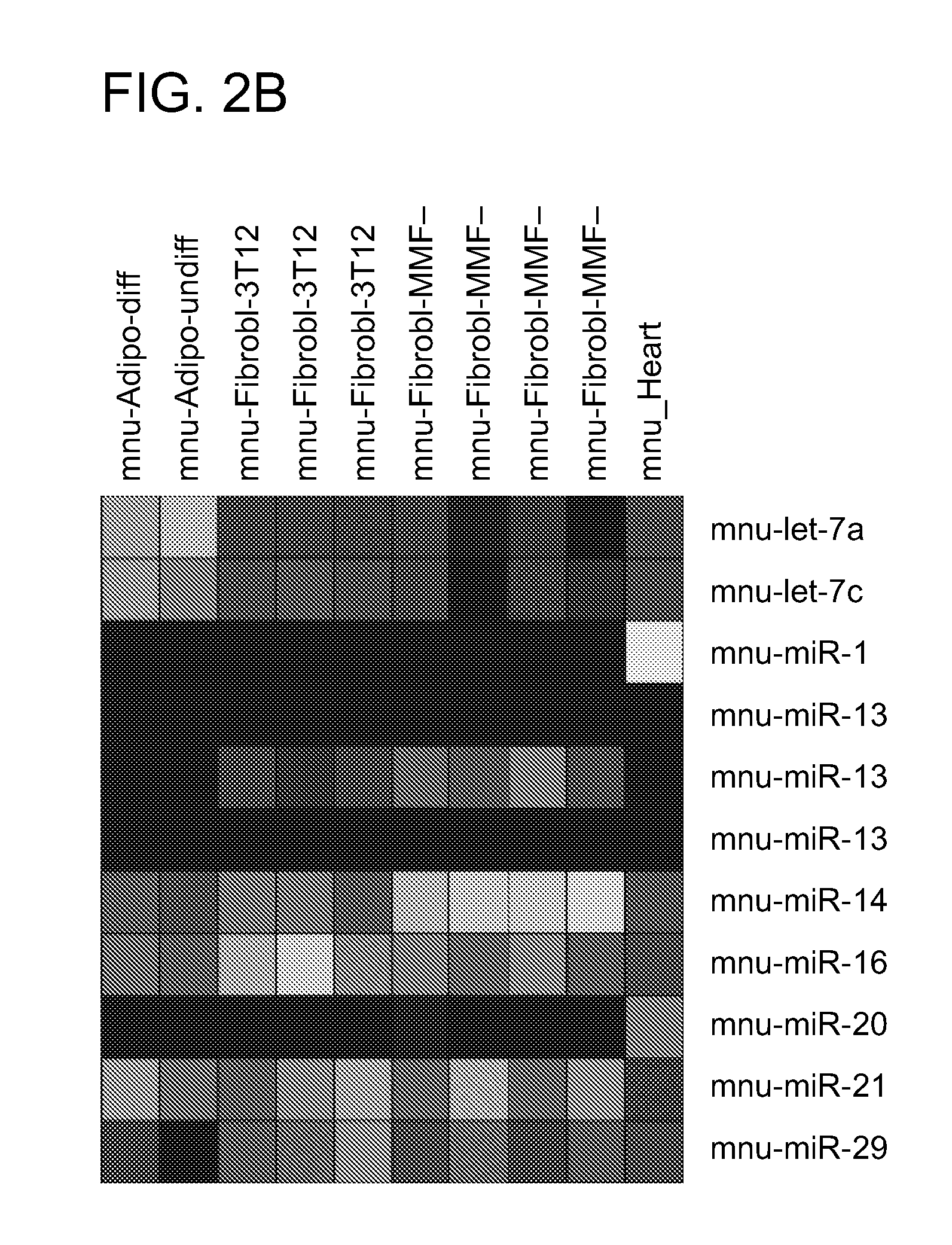
A method for promoting conversion of cells into cardiomyocytic tissue is carried out by contacting fibrotic tissue (e.g., scar tissue) with a microRNA oligonucleotide or combination of microRNA oligonucleotides. The methods lead to direct reprogramming of fibroblasts to cardiomyocytes or cardiomyoblasts.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Clusterin-mediated inhibition of apoptosis via stromal bone marrow cell delivery to a cardiac site
Methods and compositions are disclosed for inhibiting, deterring or preventing apoptosis of cardiac myocytes, transplanted stem cells, vascular stem cells, and vascular smooth muscle cells by means of expressing or synthesizing clusterin. Also disclosed are methods and compositions for producing recombinant clusterin, or its biologically active peptides, and for induction of clusterin-associated lipoproteins or enzymes for deterring or preventing inflammatory injury and apoptosis induced by oxLDL, oxysterols, cytokines, and Fas Ligand. Also disclosed is an induction method and composition for enhancing expression of ALDH and ALDH-associated enzymes or co-factors to prevent cytotoxicity or detoxification. Therapeutic methods providing new expression or overexpression of clusterin in vascular or cardiac tissue are expected to inhibit the formation of atherosclerotic lesions, stabilize existing atherosclerotic plaques, and repair failing or damaged cardiac tissue.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Cardiomyocytes and methods of producing and purifying cardiomyocytes
InactiveUS8153427B2Inhibition of differentiationSignal strengthMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture processNODALCardiac pacemaker electrode
The invention provides methods for producing a culture of cardiomyocytes and cultures of cardiomyocytes. Exemplary methods of producing and cultures of cardiomyocytes include a population of cells including cells having spontaneous and periodic electrical activity, and / or including nodal, sino-atrial or pacemaker cells; immature cardiomyocytes (cardiomyoblasts); mature contractile cardiomyocytes; or a mixed population of two or more of such cells.
Owner:NEOSTEM ONCOLOGY
Methods and compositions for preparing cardiomyocytes from stem cells and uses thereof
ActiveUS9273286B2Increase differentiationEffectively lead to differentiationBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementCardiac differentiationCardiac muscle
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Method for inducing mesenchymal stem cells to directionally differentiate into cardiac cells
The present invention provides a method for inducing amplified human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro to directionally differentiate into cardiac cells. According to the present invention, by using the biological characteristics of MSCs, human MSCs are isolated and enriched by the density gradient centrifugation method, and stem cells are amplified to obtain a large number of stem cells by using stem cell self-renewal and proliferation characteristics. The isolated stem cells are induced at a specific cultivation generation (3rd-7th generation, and 10th generation) by specific small molecule pyrimidine compounds and a specific concentration (100[mu]M). The in vitro induction directional differentiation scheme of the isolated stem cells has another feature of promoting cell proliferation and phenotype expression of cardiac myocytes by the use of bFGF. The method provides a supplementary source for injured cardiac myocytes, establishes a foundation for replacing clinical treatment of myocardial infarction and later period heart failure by stem cell transplantation, and has good prospects for clinical application.
Owner:北京清美联创干细胞科技有限公司
Methods and compositions for preparing cardiomyocytes from stem cells and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130209416A1Increase differentiationEffectively lead to differentiationBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementCardiac differentiationCardiac muscle
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Use of human stem cells and/or factors they produce to promote adult mammalian cardiac repair through cardiomyocyte cell division
InactiveUS20070072294A1RestoreLarge workGenetically modified cellsCell culture supports/coatingDiseaseMammal
A method for treating a subject afflicted with a cardiac disorder, in vivo, comprising (i) producing a solution comprising media conditioned from the culture of cells, in vitro, and (ii) administering the solution of step (i) to the subject, thereby treating the cardiac disorder in the subject. Methods for determining whether an agent stimulates or inhibits myocyte proliferation.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
Cardiac Conduction System Cells and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20070239136A1Expand the populationSugar derivativesGenetically modified cellsCardiac muscleCardiac conduction
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
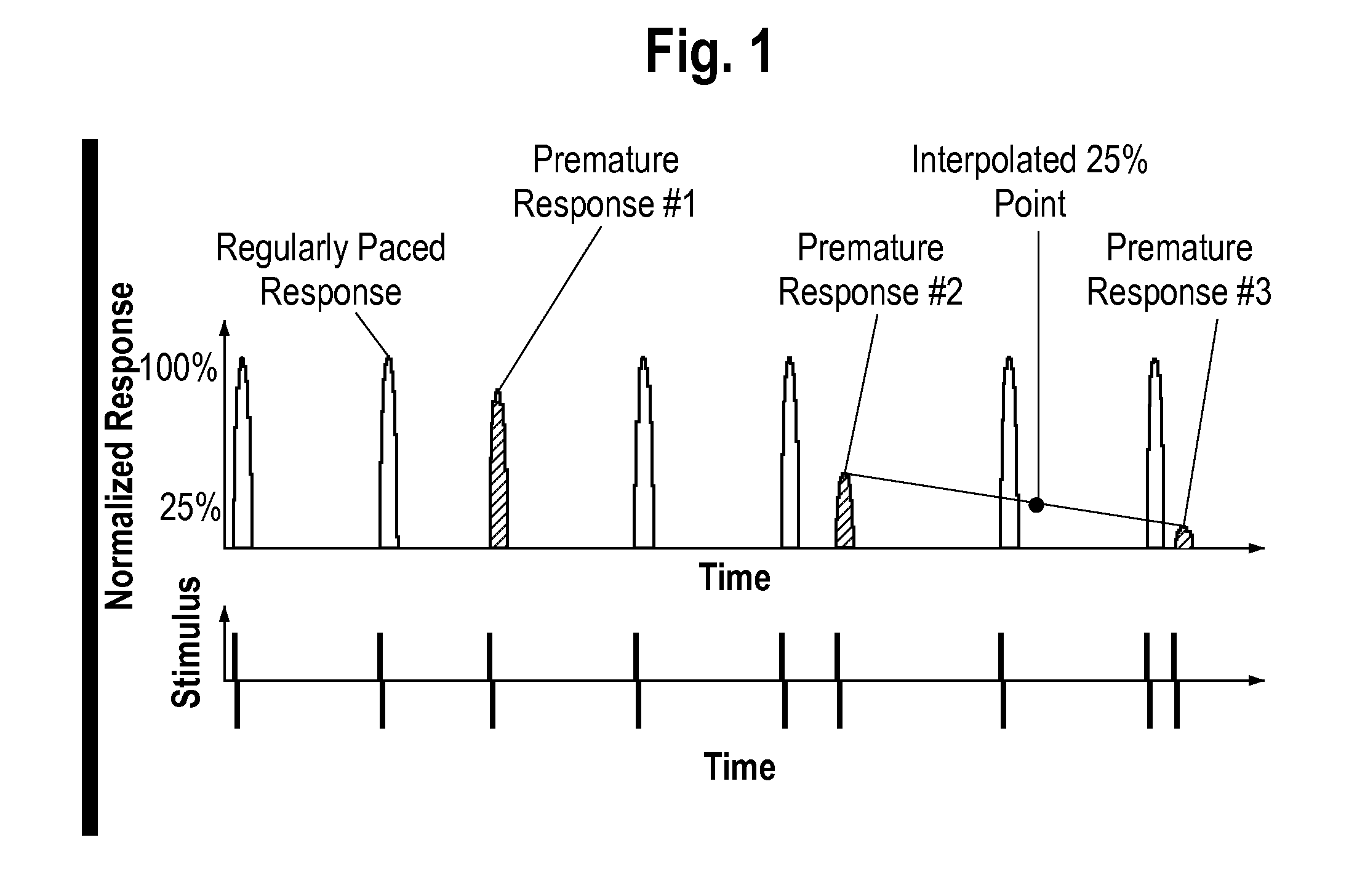
System and Method for Determining Quality of Stem Cell Derived Cardiac Myocytes
PendingUS20160203262A1High similarityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningCell basedCells heart
The present invention relates to a system and method for calculating a quality index of a differentiated cell. To calculate the quality index, the present invention measures a differentiated cell by at least one metric, calculates a strictly standardized mean difference between the differentiated cell and a targeted cell, and calculates a mean squared error versus the target cell to define a value that represents the total difference between the differentiated cell and targeted cell based on the at least one measured metric.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
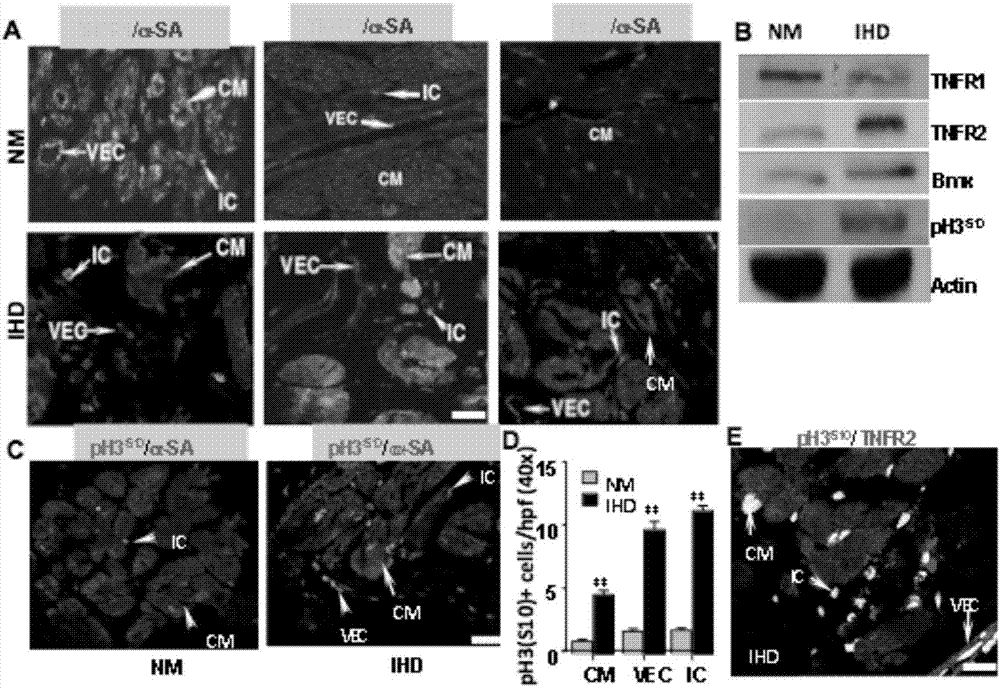
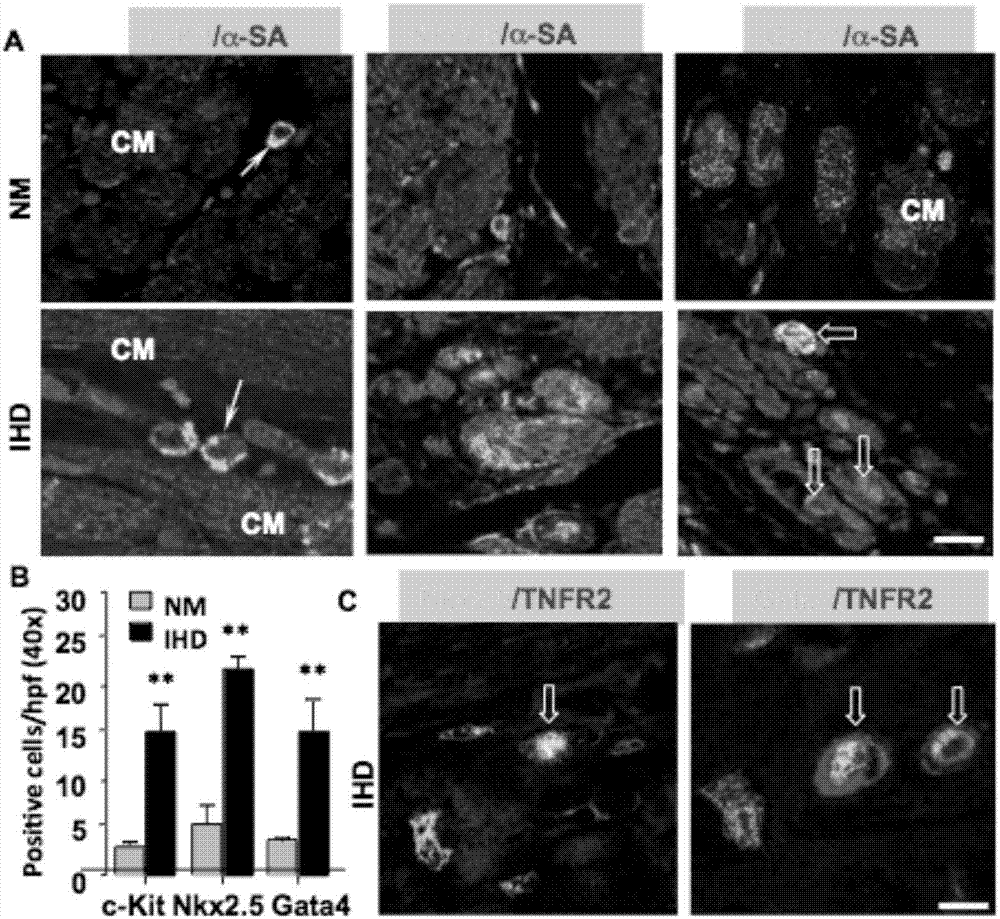
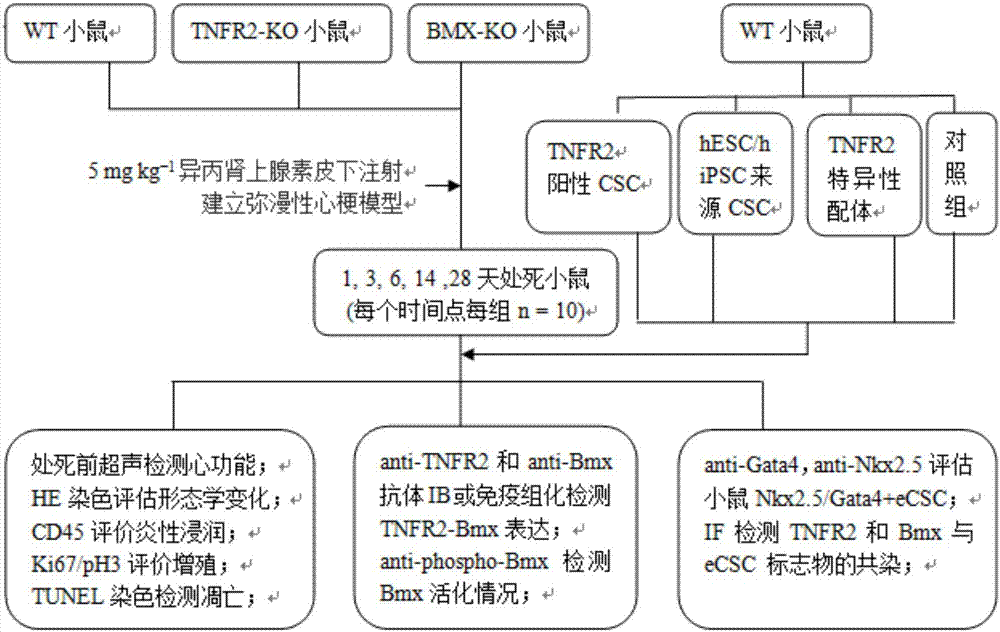
Application of TNFR2
InactiveCN107441491AHigh expressionHigh activityPeptide/protein ingredientsCardiovascular disorderDiseaseBiological activation
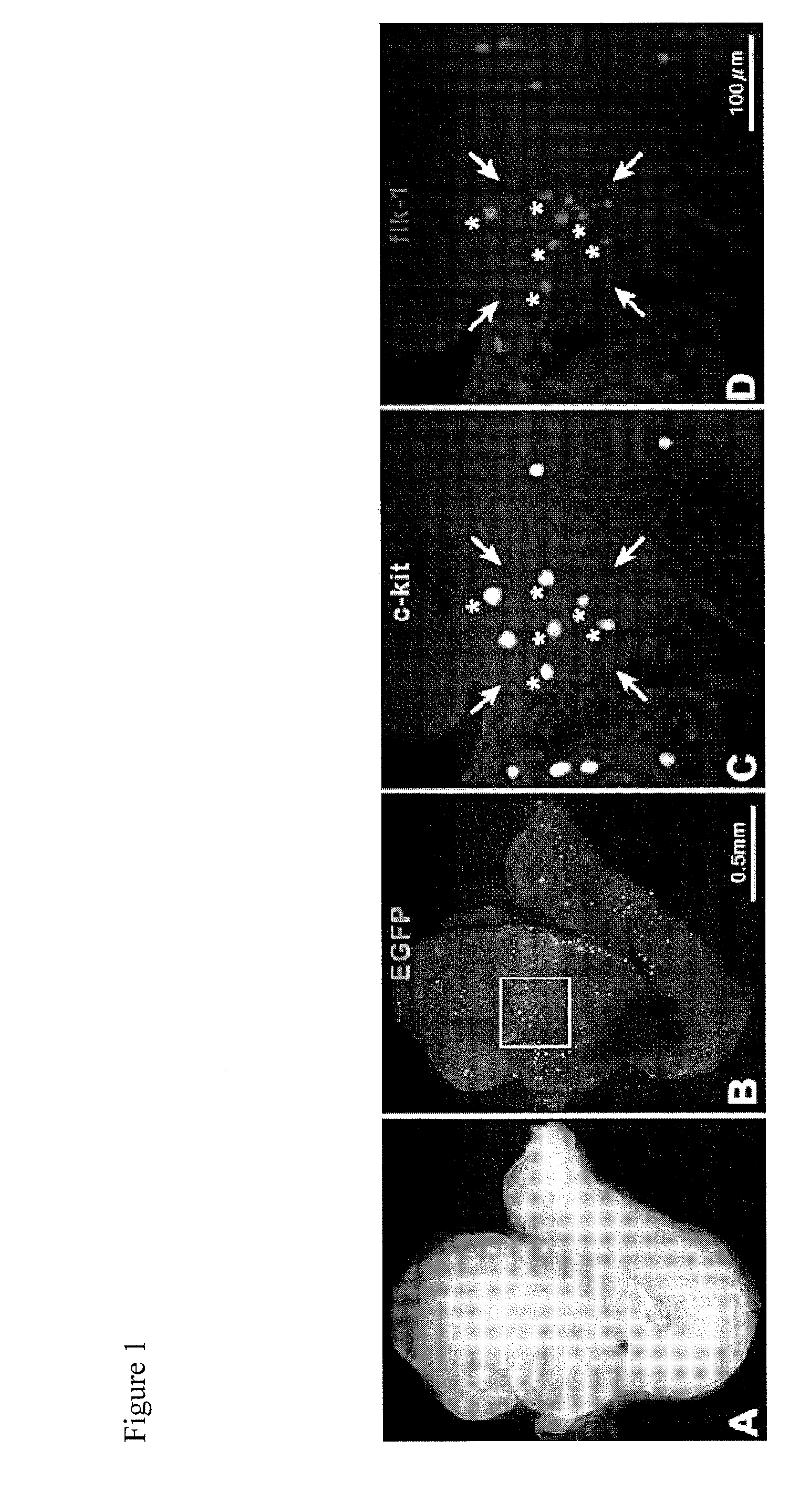
The invention discloses an application of a TNFR2 activating agent to preparing a drug for promoting activation, migration and survival of cardiac stem cells. The TNFR2 activating agent has the effect of promoting activation of the cardiac stem cells and cardiac repair. The activated TNFR2-Bmx can enhance expression and the activity of Nkx2.5+ / Gata4+, and mediate activation, migration and survival of c-Kit+ endogenous cardiac stem cells (eCSCs). In addition, the activation of the TNFR2 increases the differentiation of cardiac cells of a hESC / hiPSC source. The TNFR2 activating agent activates the TNFR2 through the specificity so that the TNFR2 is beneficial to repairing of myocardial infarction, and a new strategy can be provided for human heart disease treatment.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
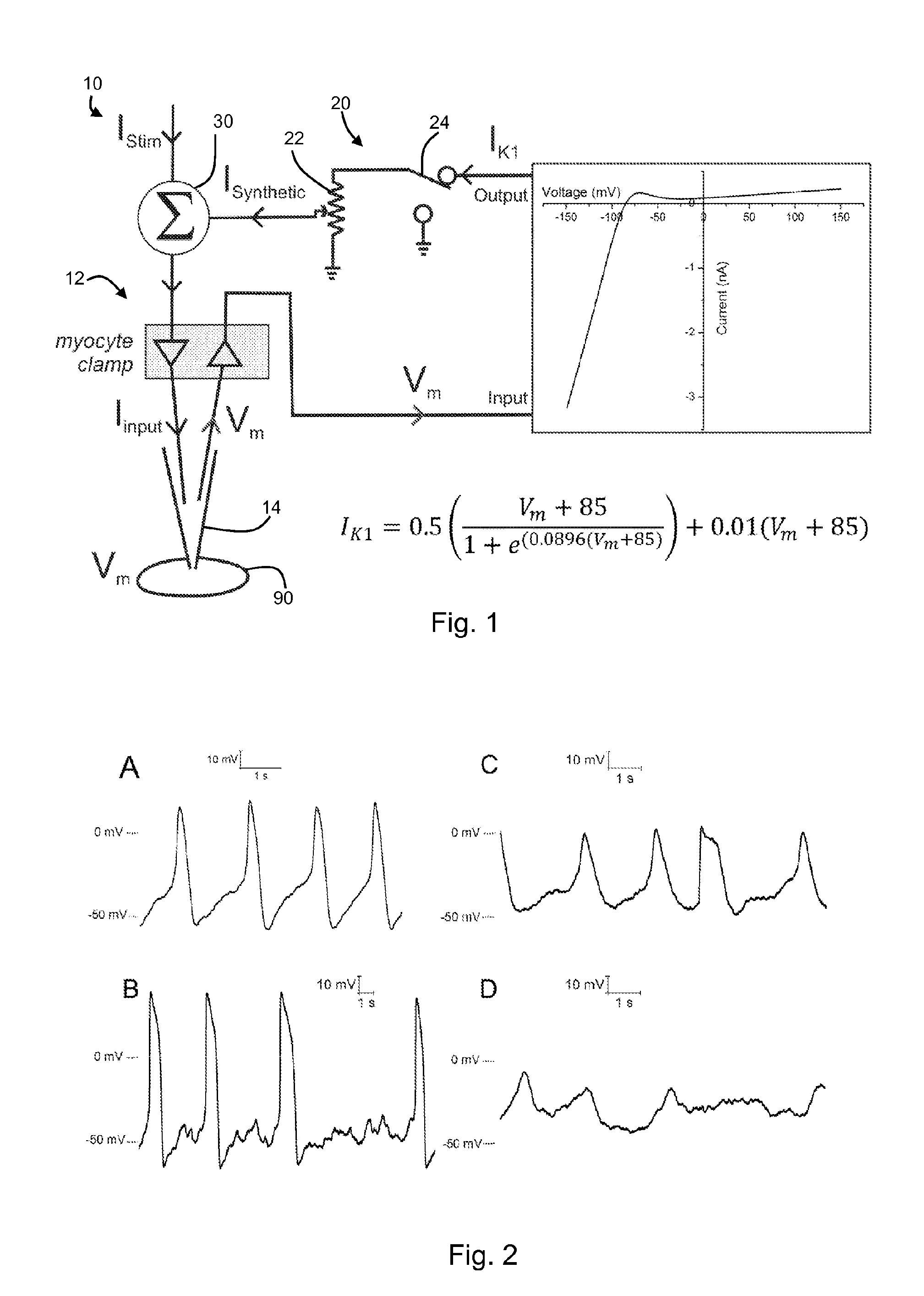
Electronic expression of the inward rectifier in cardiocytes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20160083715A1Affect characteristicBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCardiac muscleRest membrane potential
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Cardiac cell reprogramming with myocardin and ascl1
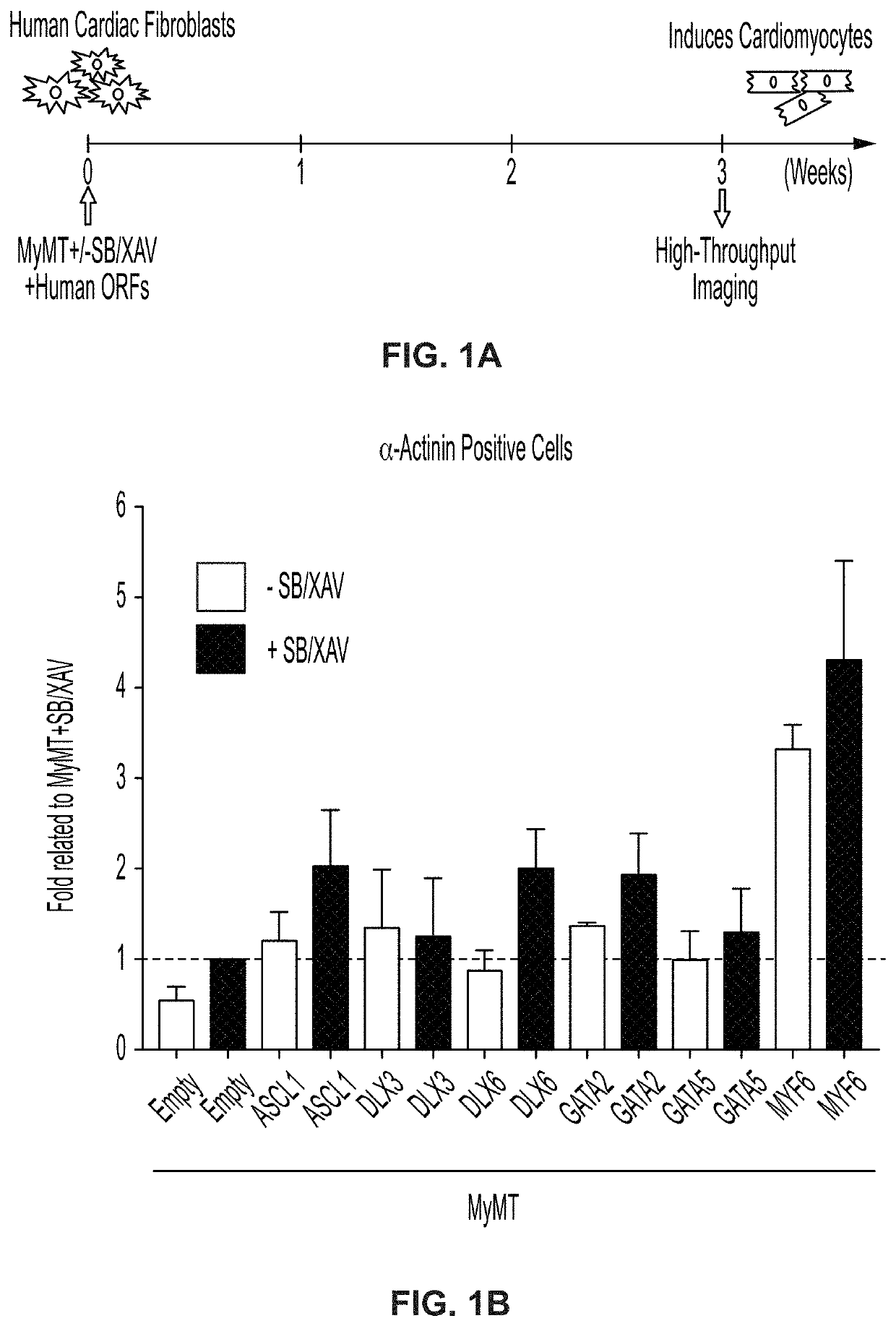
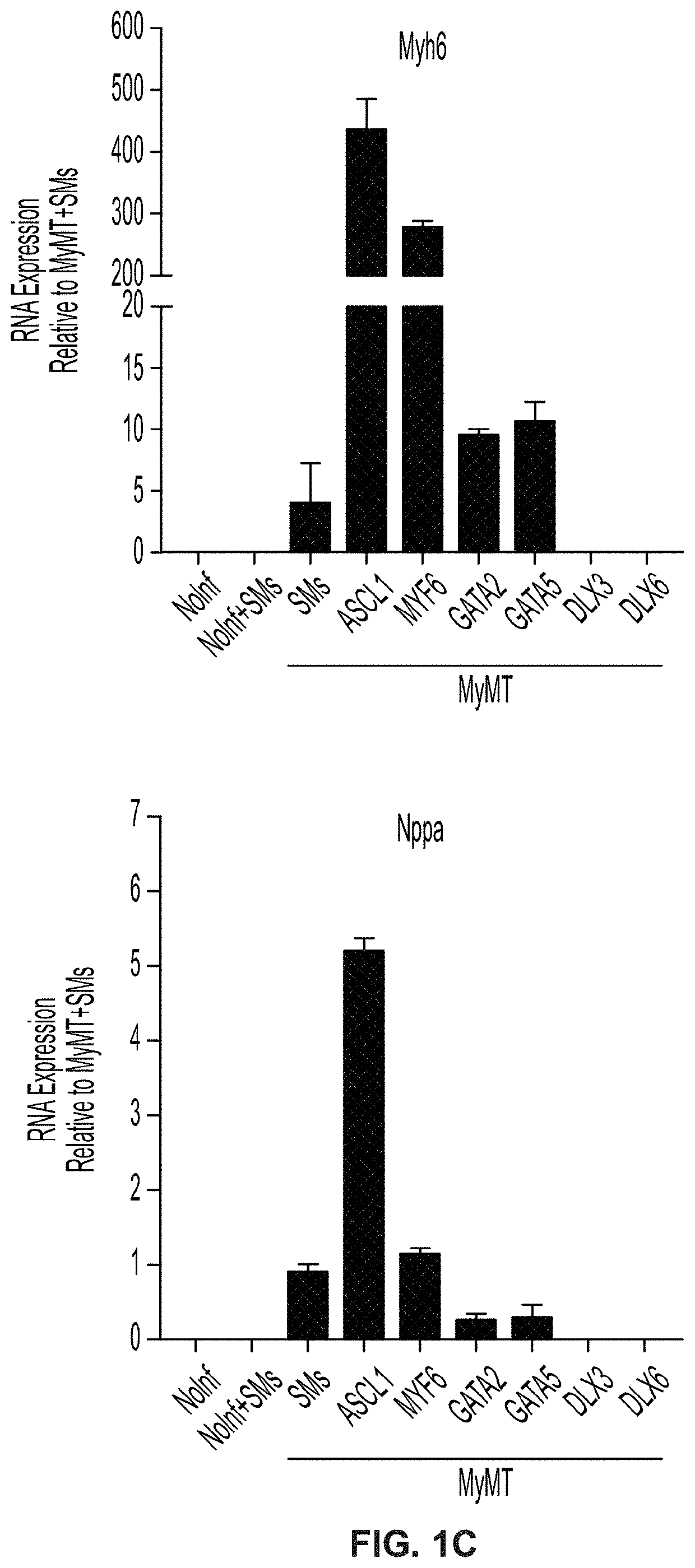
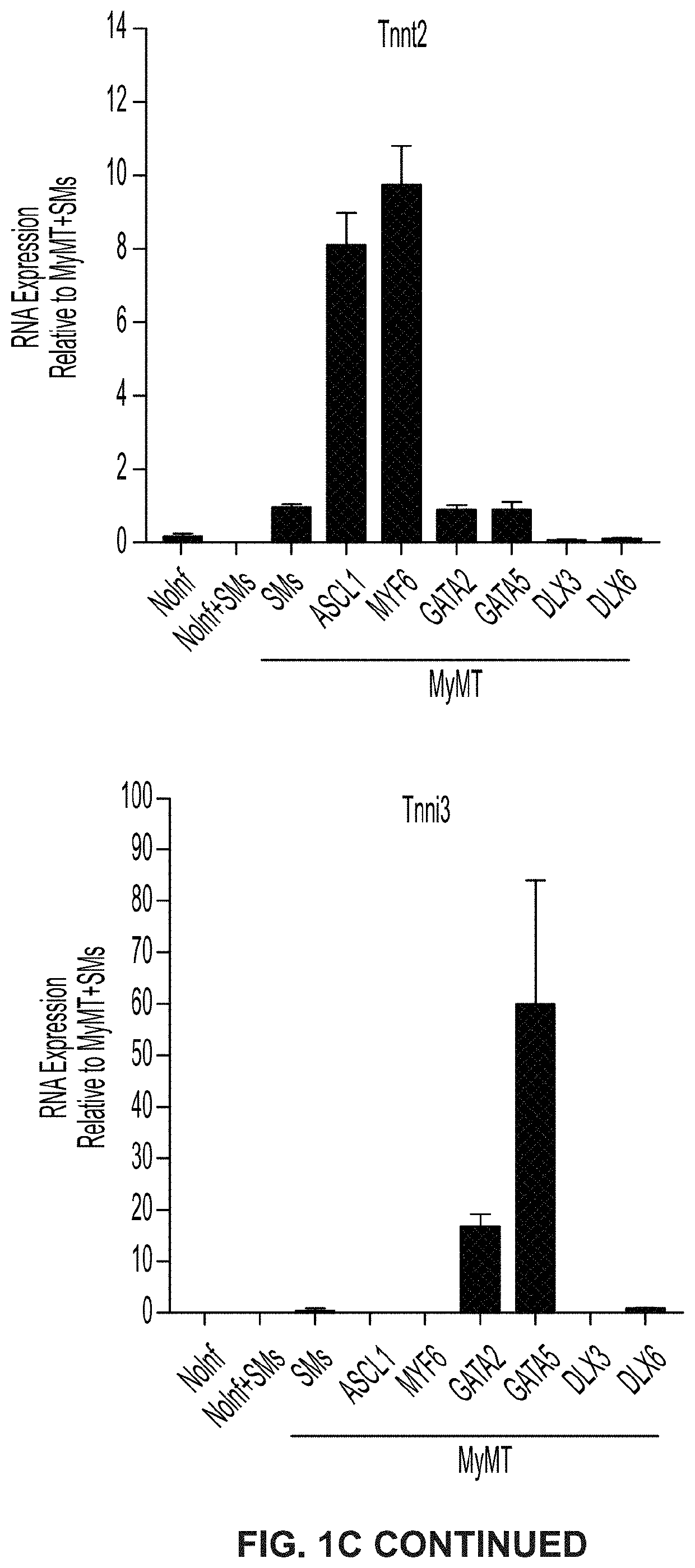
ActiveUS20210032659A1Improve effectivenessReserved functionVectorsPeptide/protein ingredientsHeart cellsASCL1
The present disclosure provides methods for generating induced cardiomyocytes and / or inducing a cardiomyocyte phenotype in cells in vivo or in vitro, such as by expression of ASCL1 or MYF6 and MYOCD. The present disclosure further provides gene-delivery vectors comprising one or more polynucleotides selected from ASCL1, MYF6, MYOCD, MEF2C, and TBX5. It further provides compositions comprising induced cardiomyocytes and provides methods of treating a heart condition, such as myocardial infarction. The disclosure also provides engineered myocardin proteins with an internal deletion, vectors encoding such engineered mycocardins, and methods of use thereof.
Owner:TENAYA THERAPEUTICS INC
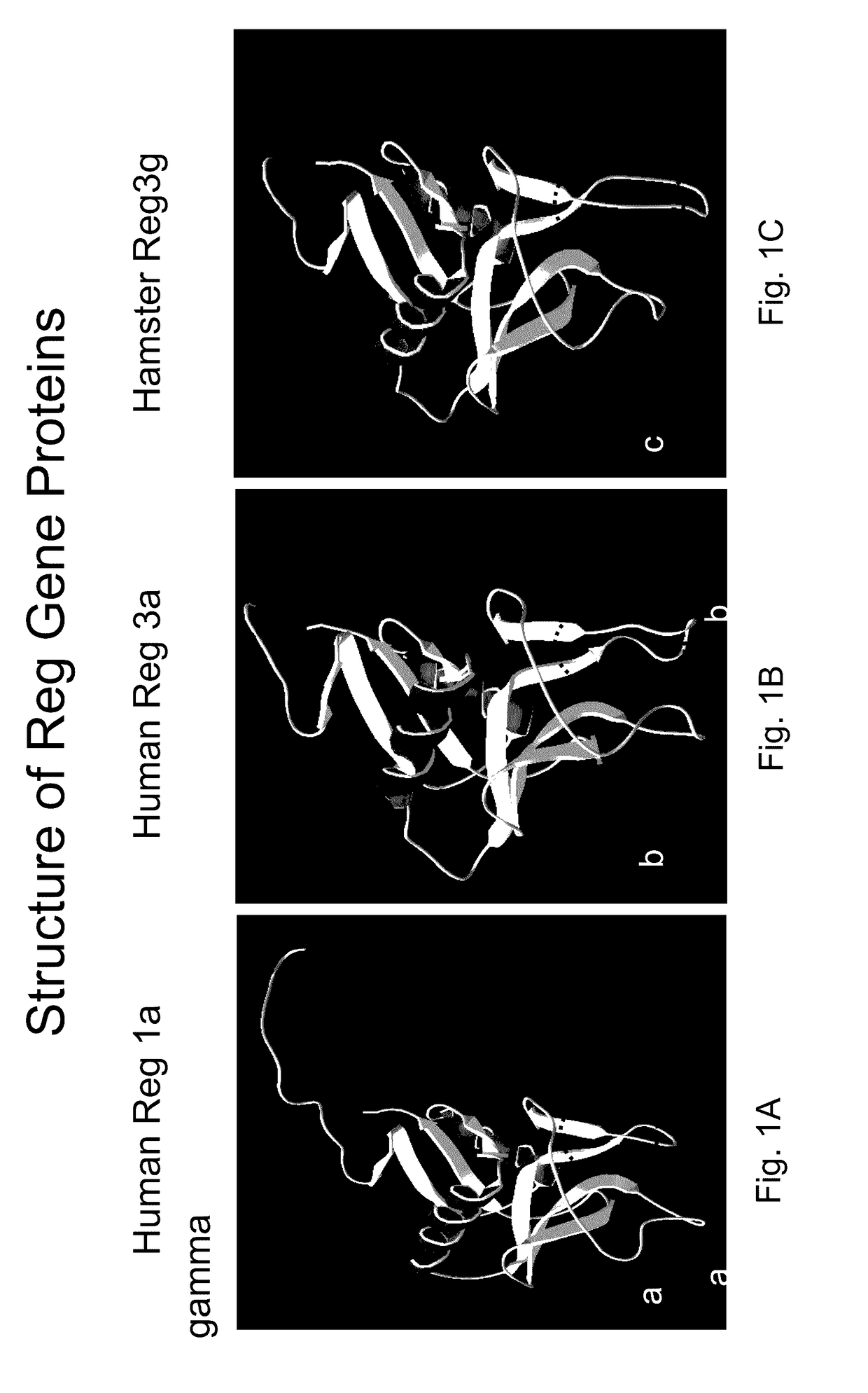
Generation of brain and spinal cord neurons, cardiac myocytes, renal nephrons and hepatocytes using reg peptides, peptidomimetics, small molecules and stimulatory antibodies to reg receptor
InactiveUS20170081375A1Improve solubilityImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsProgenitorNephron
Peptides that are bioactive regions and optimized bioactive regions of the human and mammalian Reg gene proteins and that are capable of generation of tissues such as brain, spinal cord, heart, liver, and kidney are described. In particular, 7-15-amino acid Reg peptides and optimized Reg peptides are disclosed which are capable of in vivo and ex vivo transformation of progenitor cells, progenitor tissue and stem cells into specialized cells and tissues, including functioning brain and spinal cord neurons, cardiac myocytes, liver hepatocytes and renal nephrons. Methods of in vivo and ex vivo transformation of progenitor cells into differentiated cells and tissues are also described.
Owner:LEVETAN CLARESA
High throughput, optical method and system for determining the effect of a test substance on non-contiguous living cells
ActiveUS9053352B2Rapidly and efficiently detecting, measuring, and/or verifying the effectsRapidly and efficiently selectedImage enhancementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCardiac repolarizationCardiac muscle
A rapid and efficient method and apparatus for detecting electrophysiologic, proarrhythmic, contractile, and other effects of substances such as compounds and drugs in native cellular cardiac preparations, the preparations representing an integrated cell-based pharmacologic response is disclosed. More specifically, a method to (1) rapidly and efficiently detect and verify the effects of chemicals, compounds and drugs on cardiac repolarization, contractility, and excitability using optically based techniques and customized simulation protocols, and (2) rapidly and efficiently screen and select compounds for electrophysiologic and proarrhythmic effects on cardiac myocytes is disclosed.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Direct reprogramming of cells to cardiac myocyte fate
ActiveUS9987309B2Promote conversionImprove efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsGenetically modified cellsReprogrammingFibroblast
A method for promoting conversion of cells into cardiomyocytic tissue is carried out by contacting fibrotic tissue (e.g., scar tissue) with a microRNA oligonucleotide or combination of microRNA oligonucleotides. The methods lead to direct reprogramming of fibroblasts to cardiomyocytes or cardiomyoblasts.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
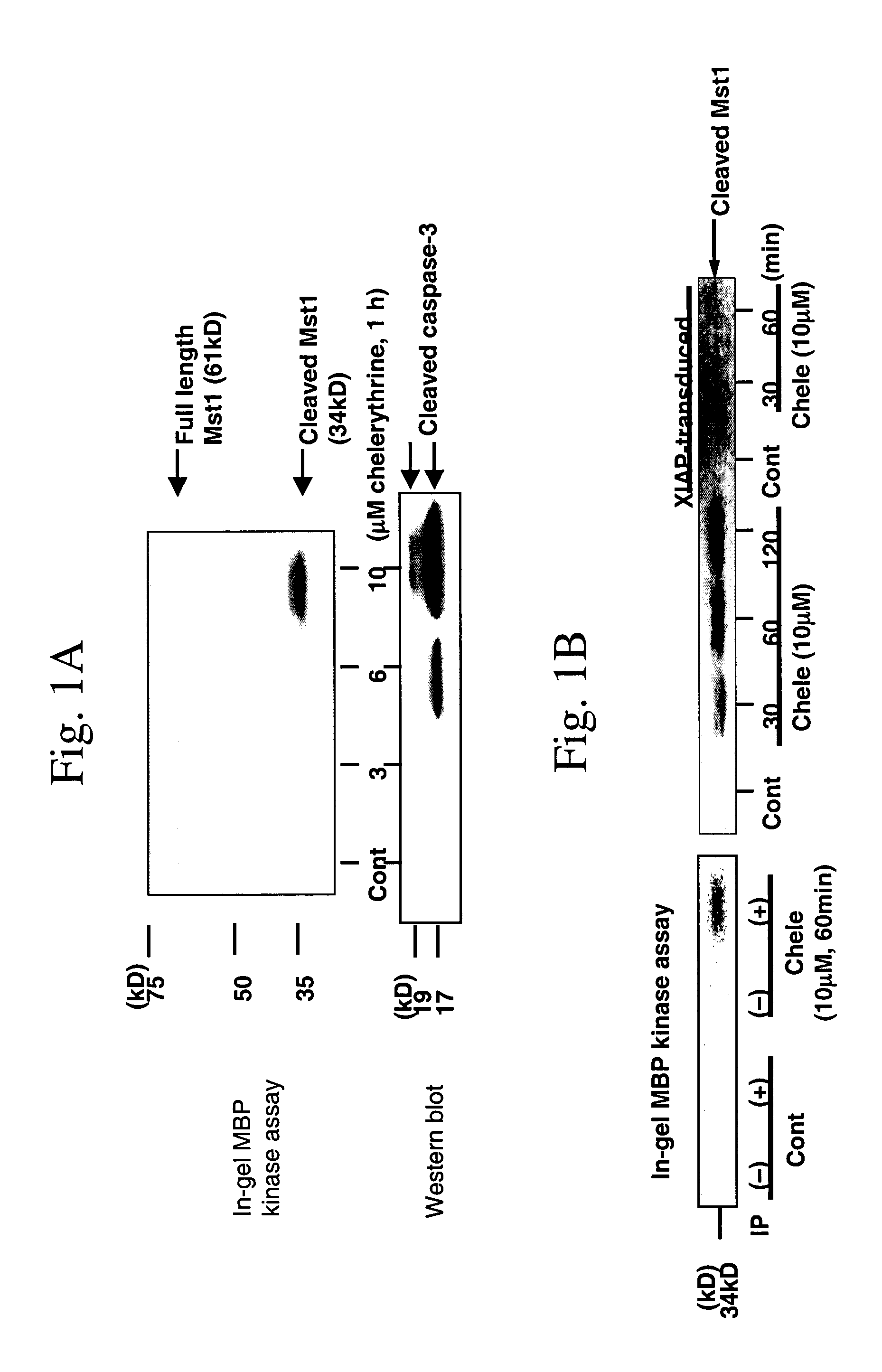
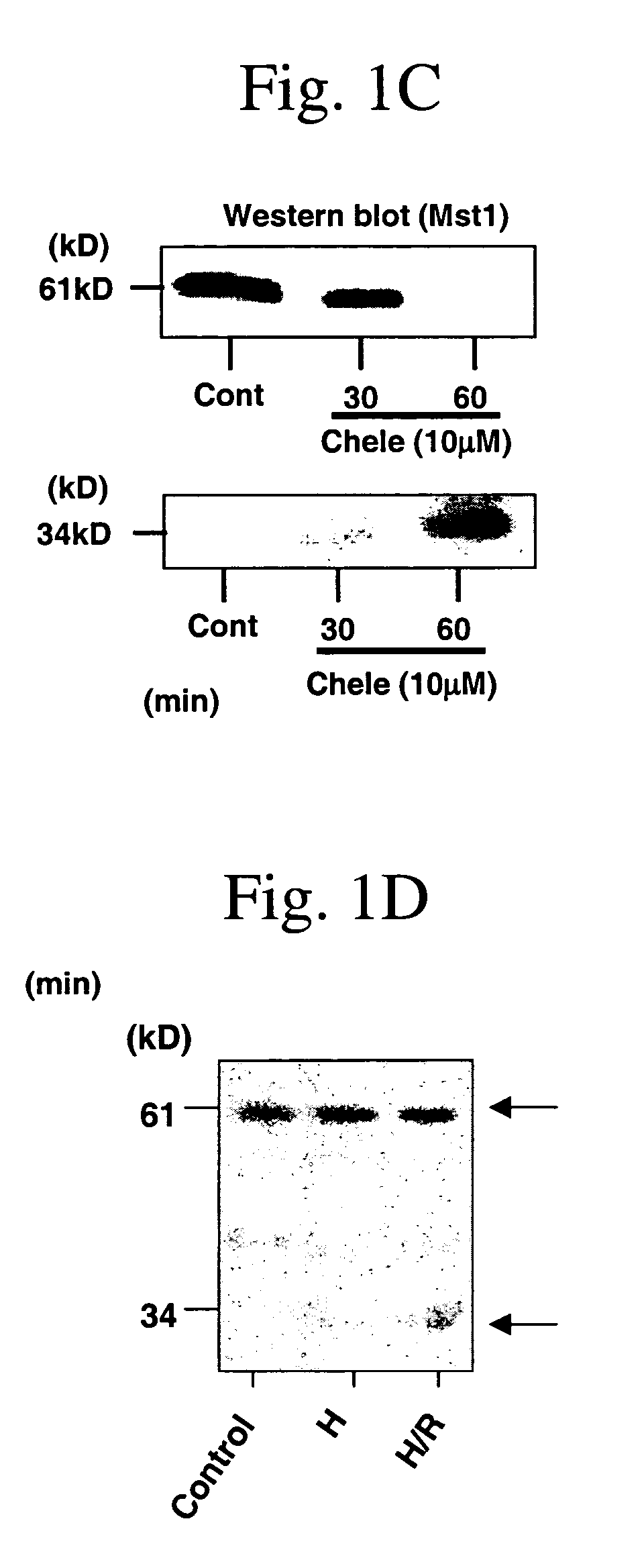
Mst1 modulation of apoptosis in cardiac tissue and modulators of Mst1 for treatment and prevention of cardiac disease
InactiveUS7160859B2Prevent myocardial infarctionNegative effectOrganic active ingredientsVirusesDiseaseMyopathy
The present invention relates to methods and agents for treatment, amelioration and prevention of cardiac disease, including cardiac myopathy, chronic heart failure and for management and reduction of cardiac myocyte death which may occur in response to ischemia / reperfusion or following myocardial infarction or other injury to the heart. The invention relates to methods for screening cardiotherapeutic compounds, including compounds which modulate cardiac myocyte apoptosis, particularly targeting Mst1 and the Mst1 pathway. The present invention further encompasses compounds identified by such screening methods and compositions comprising these compounds. The invention also provides methods for treatment, amelioration and prevention of cardiac disease comprising administering compounds or agents which modulate, particularly inhibit, Mst1 or the Mst1 kinase pathway, including administering a nucleic acid encoding an altered form of Mst1, particularly a dominant negative Mst1, which acts as an antagonist of Mst1.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com