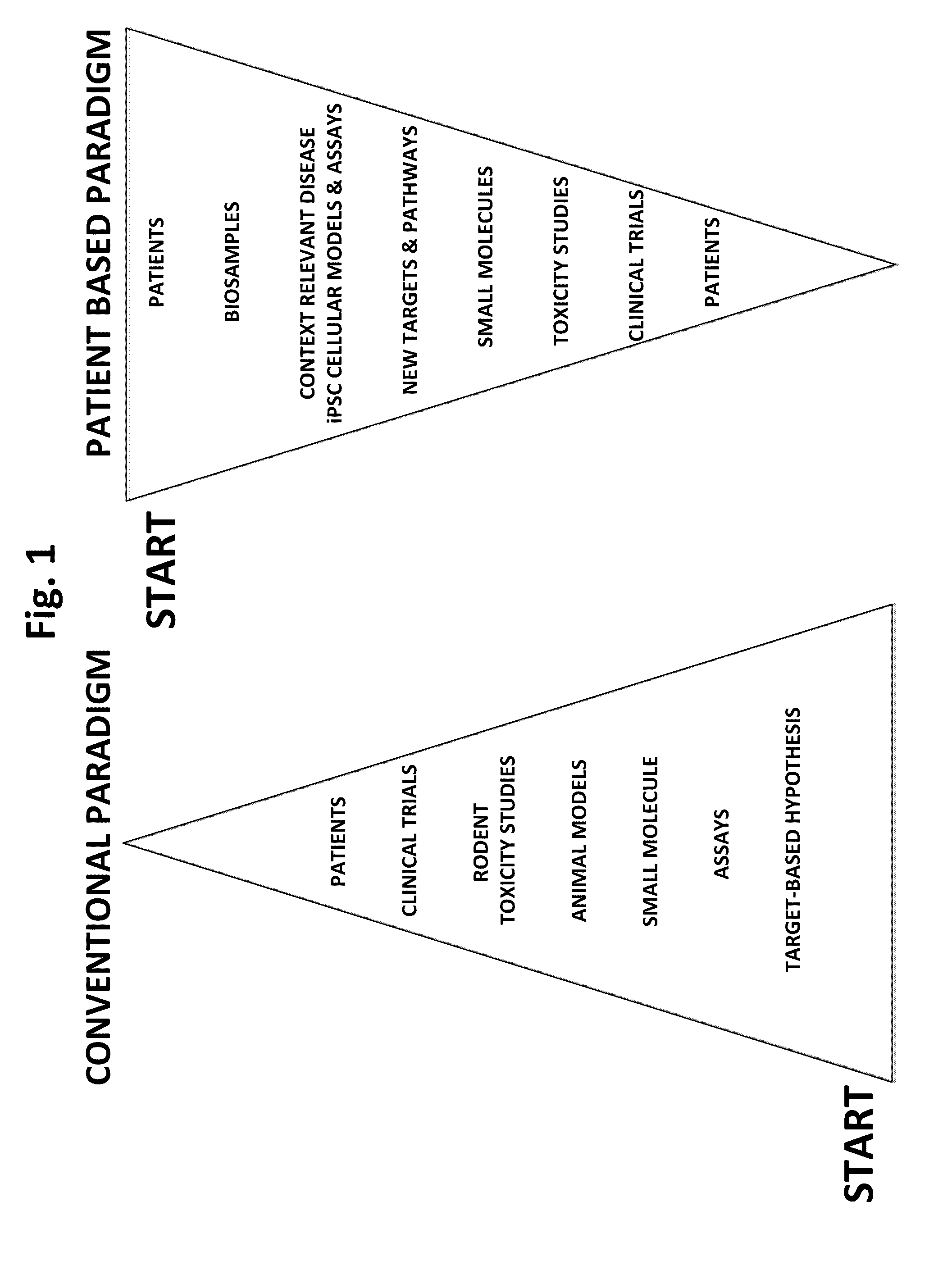
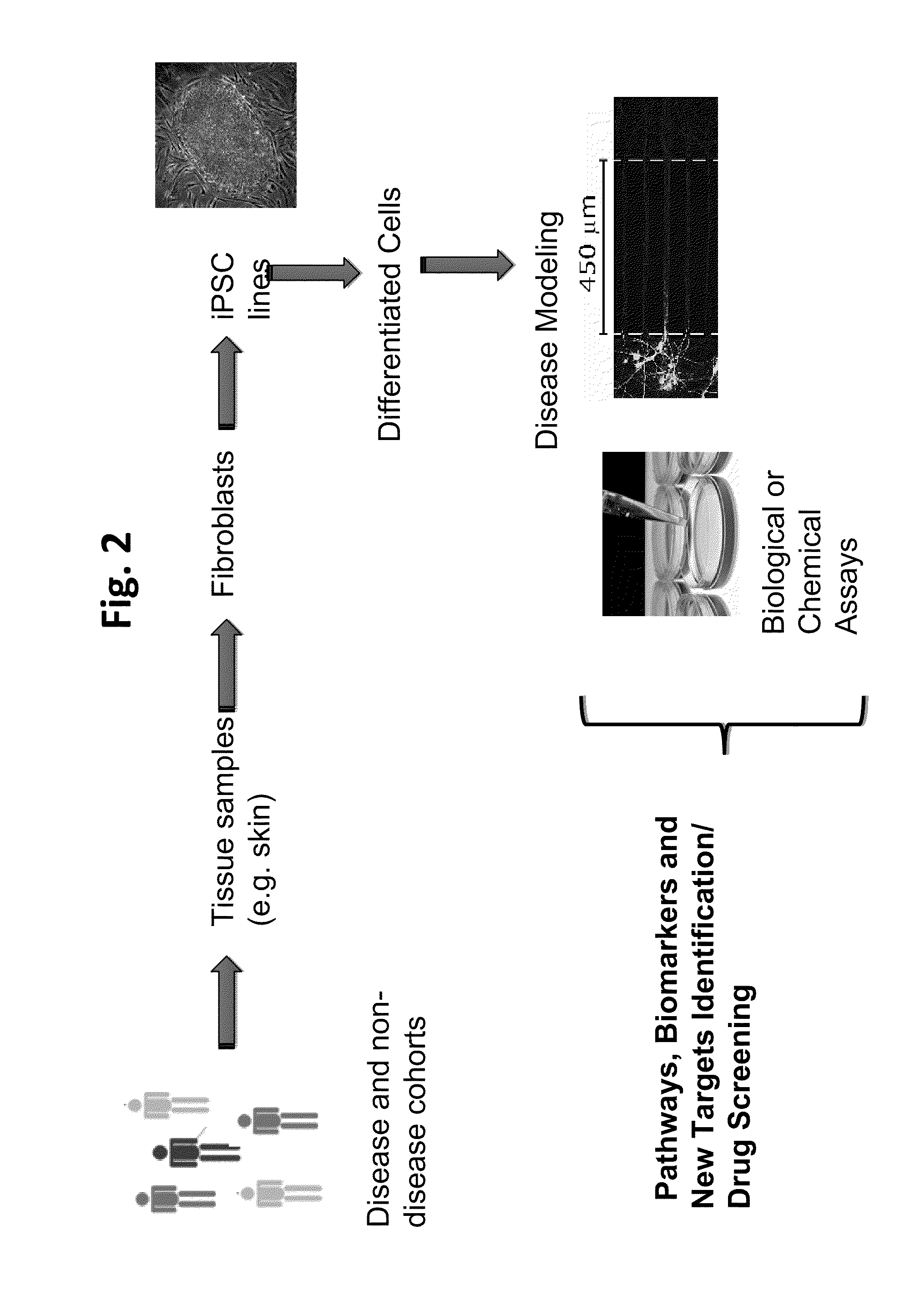
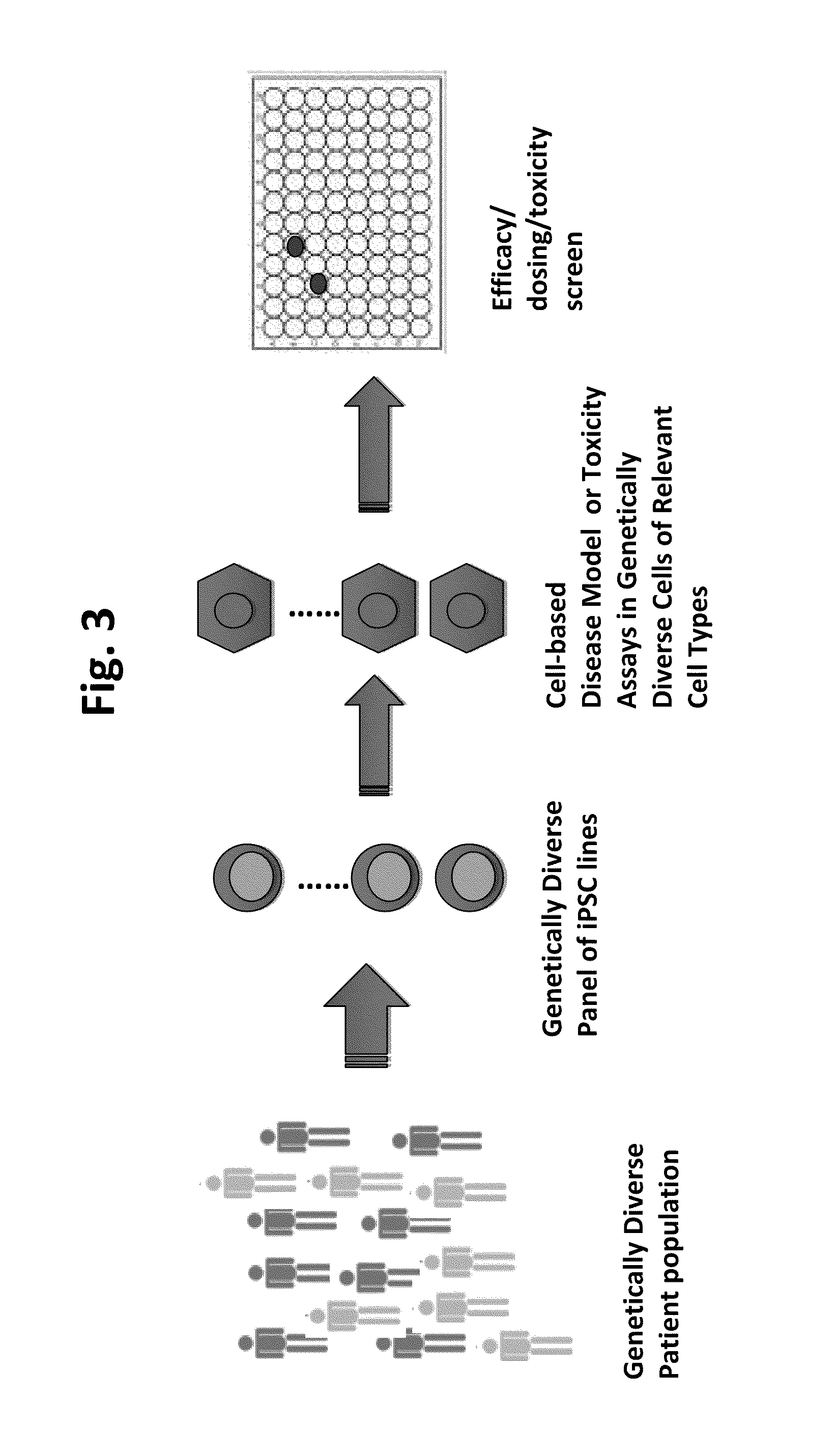
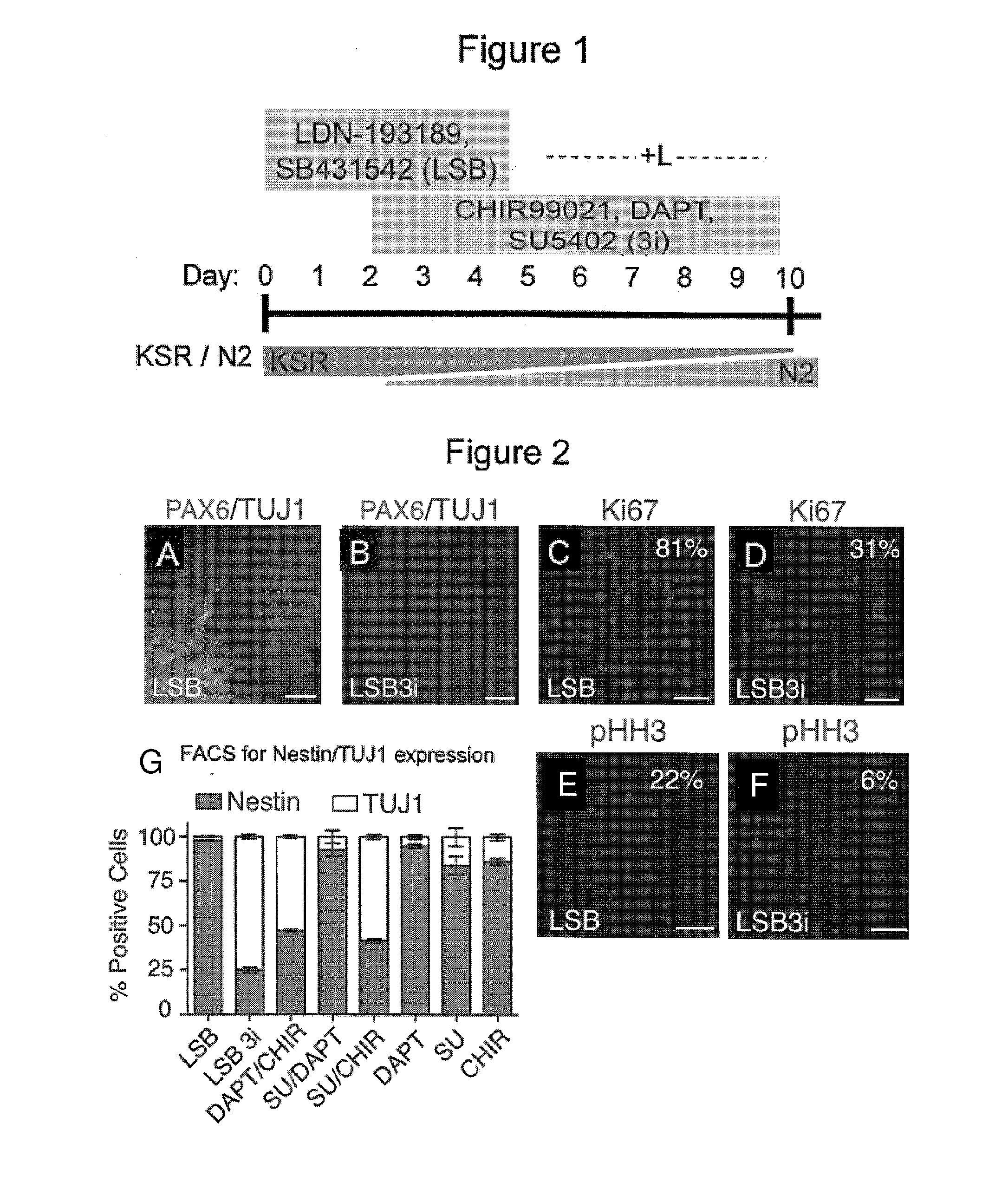
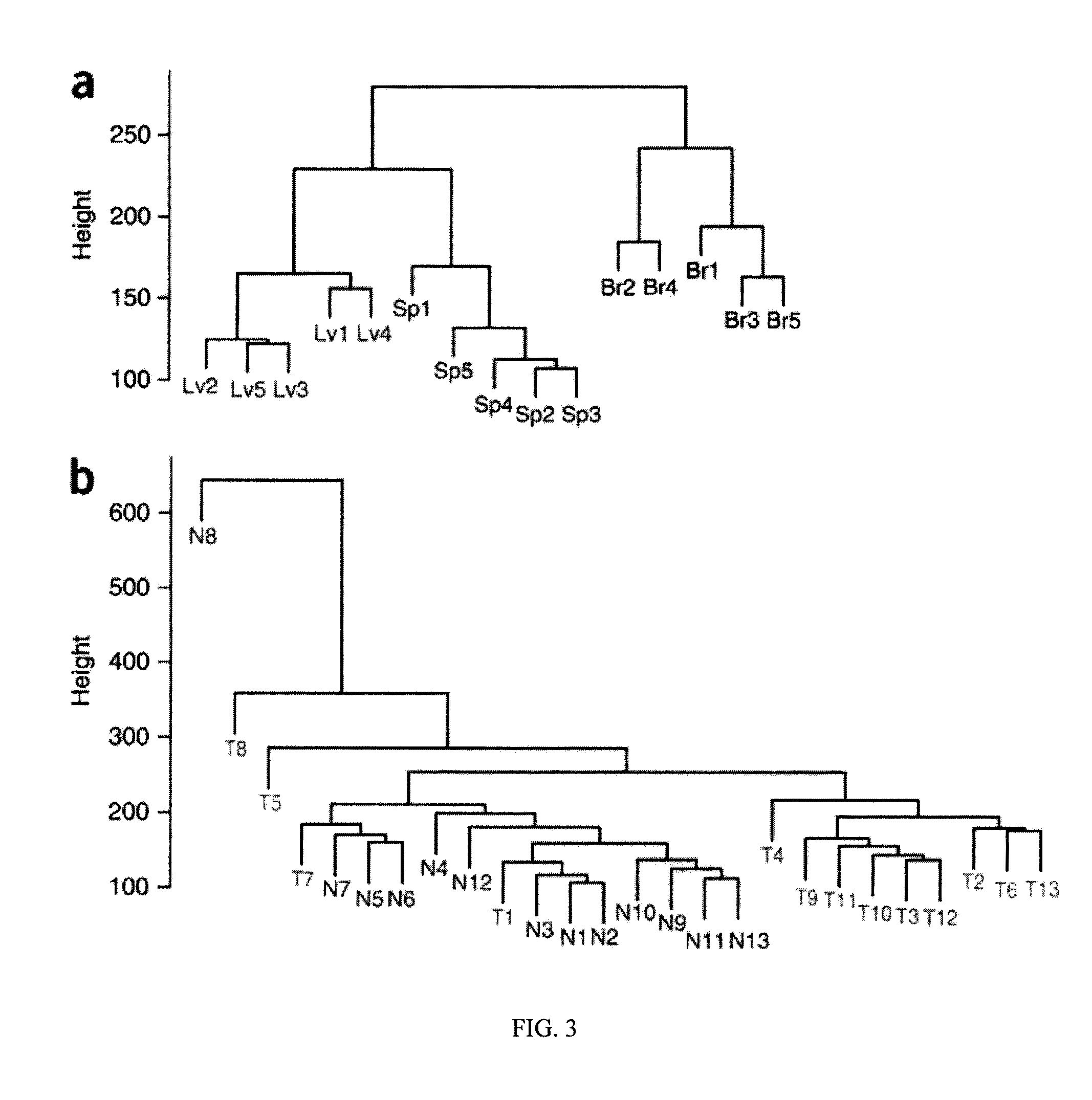
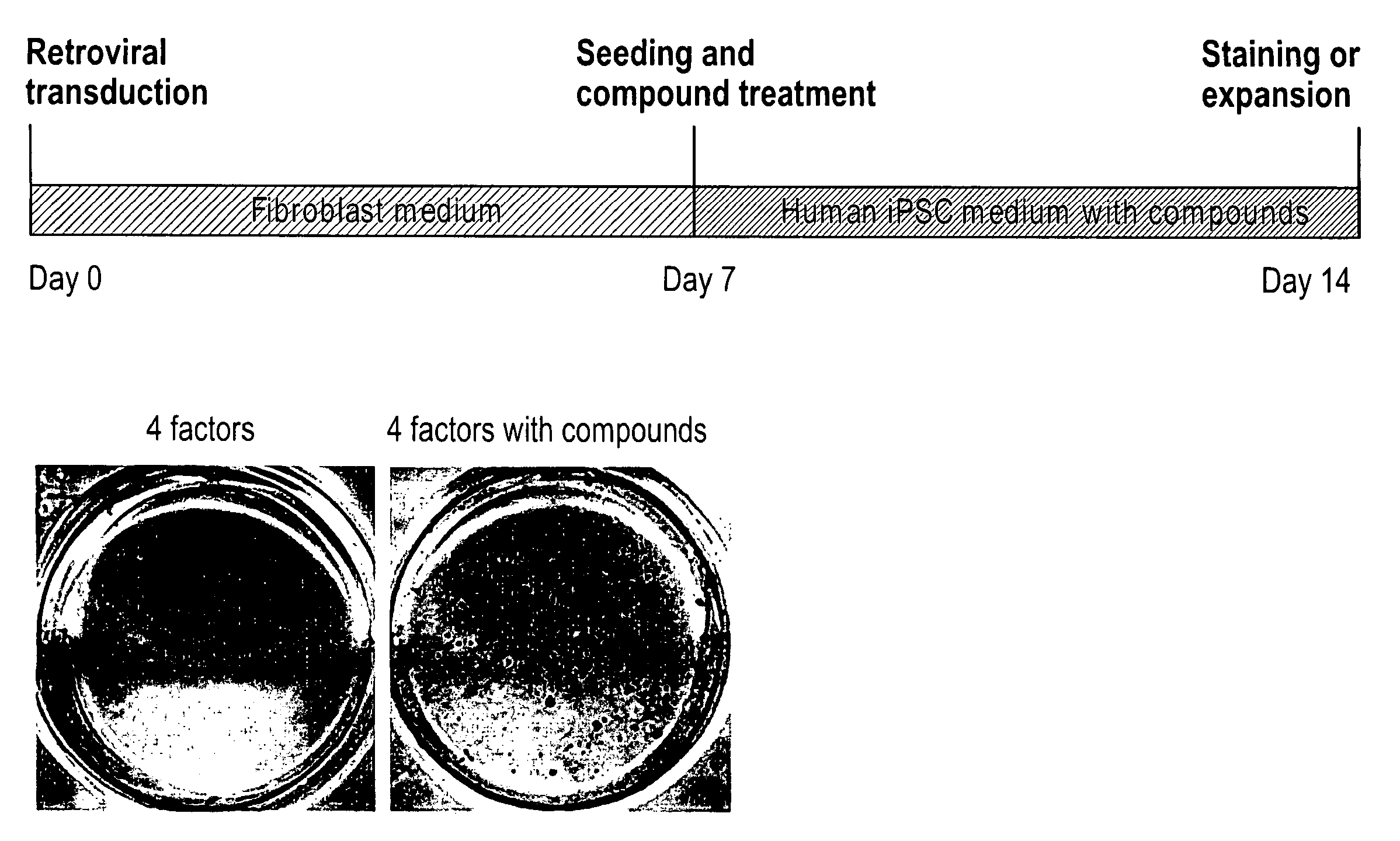
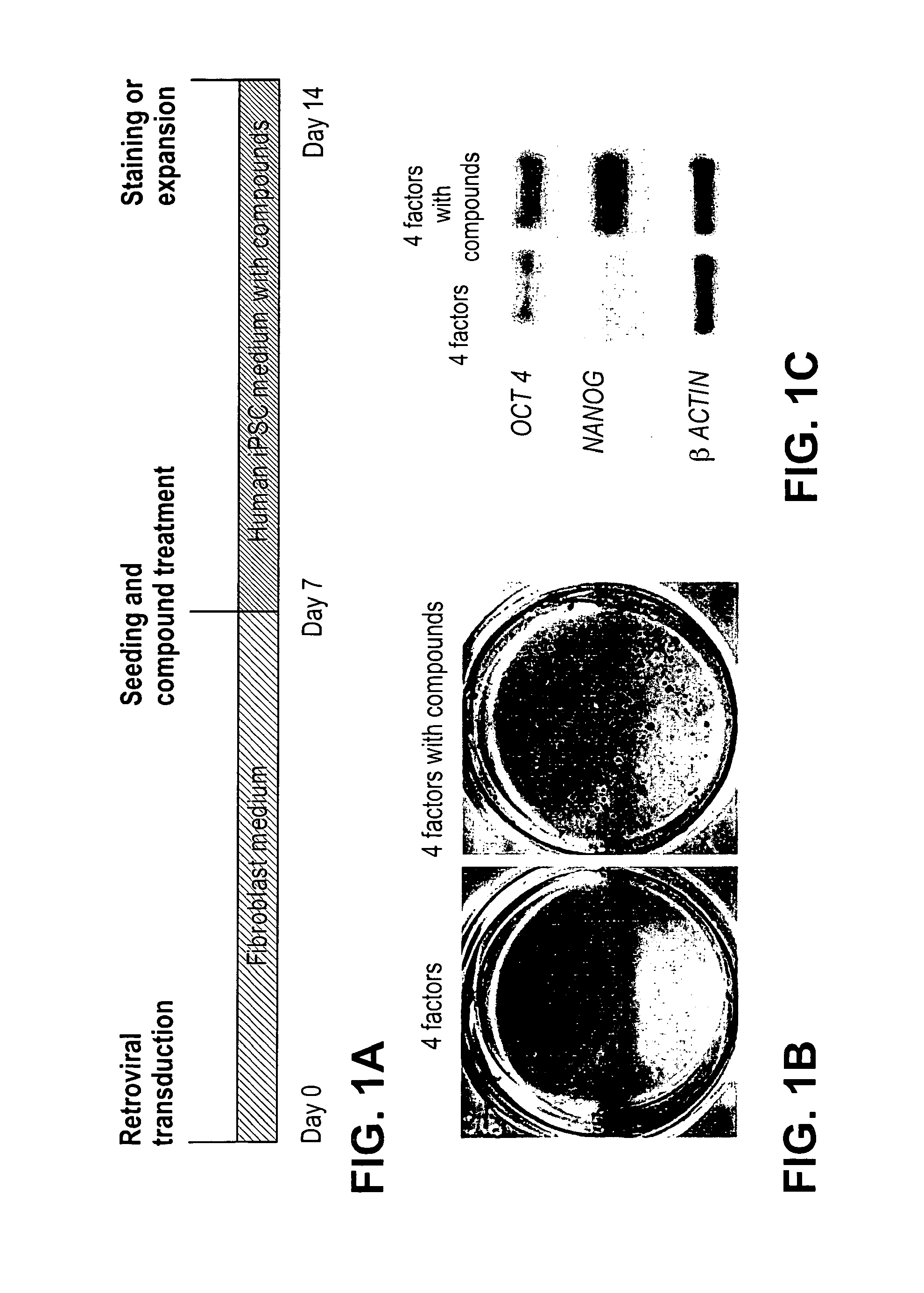
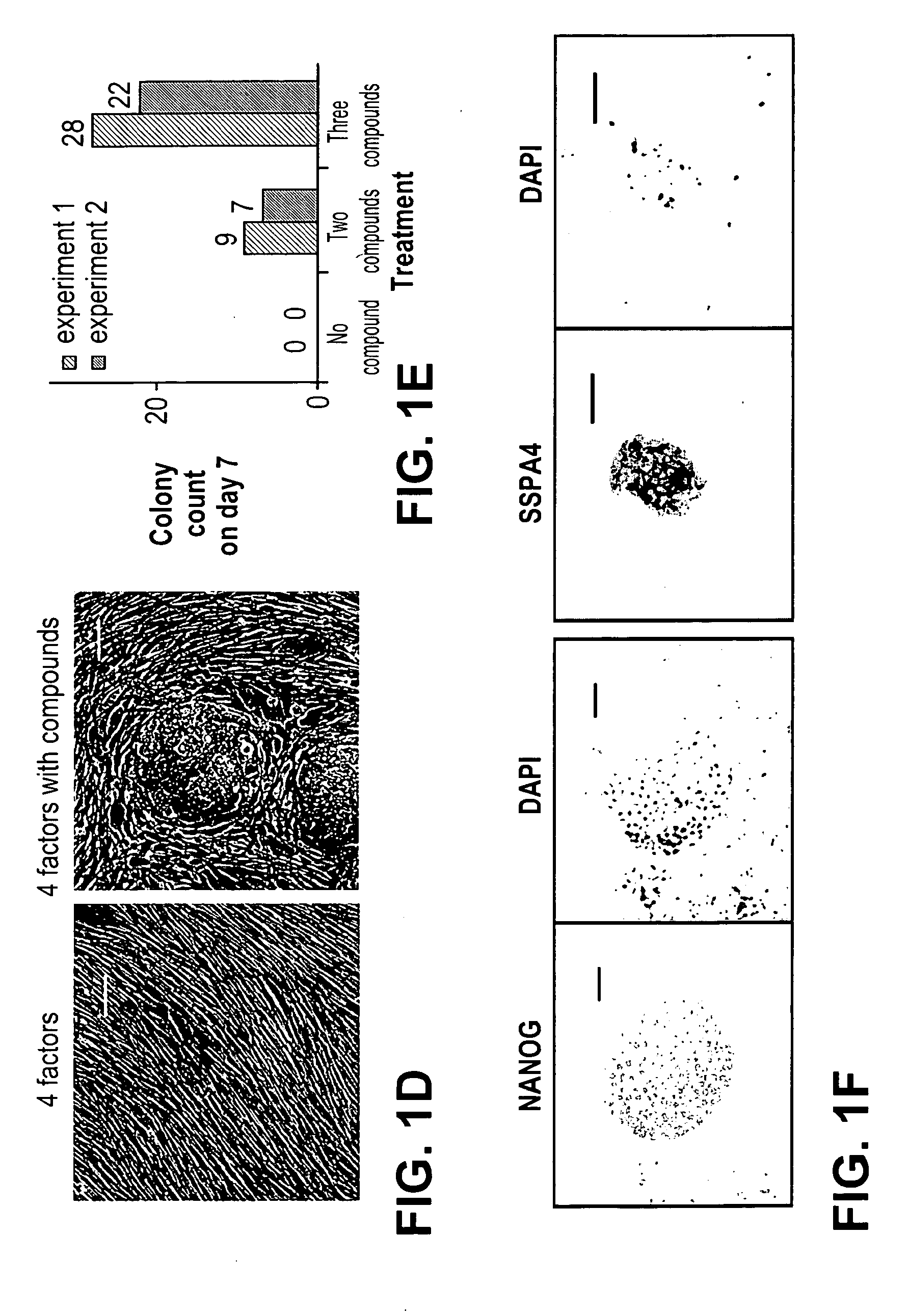
Patents
Literature
788 results about "Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
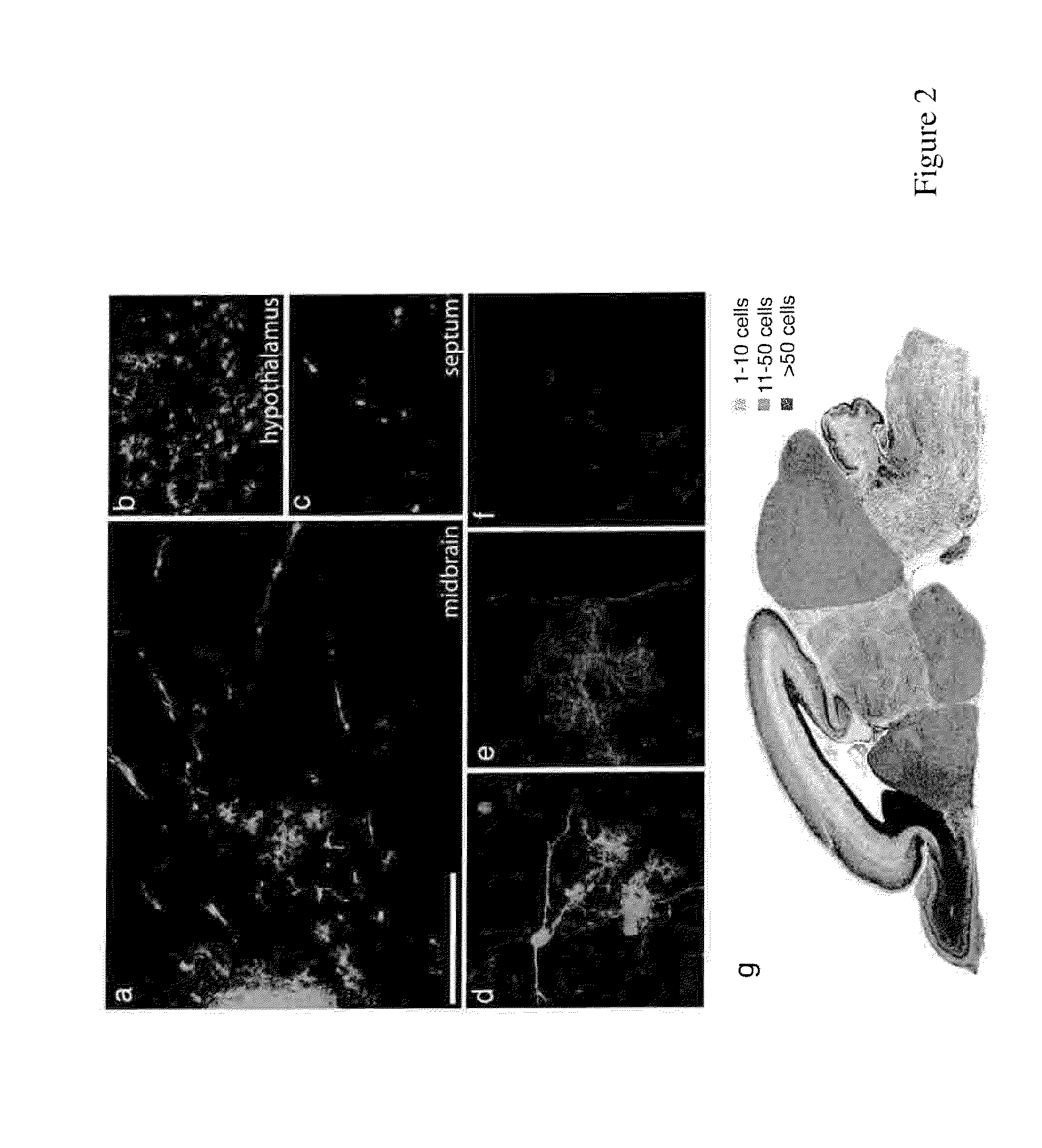
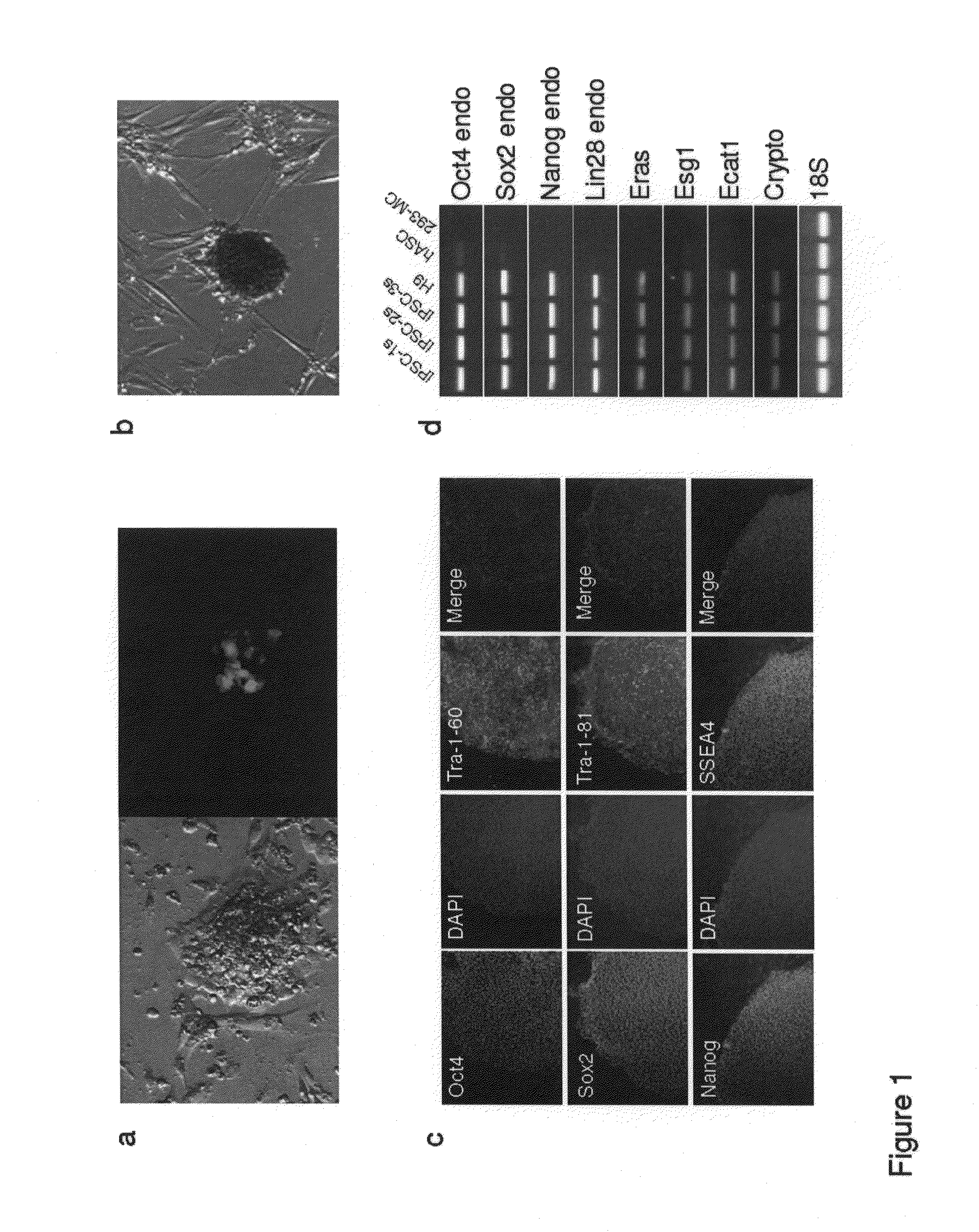
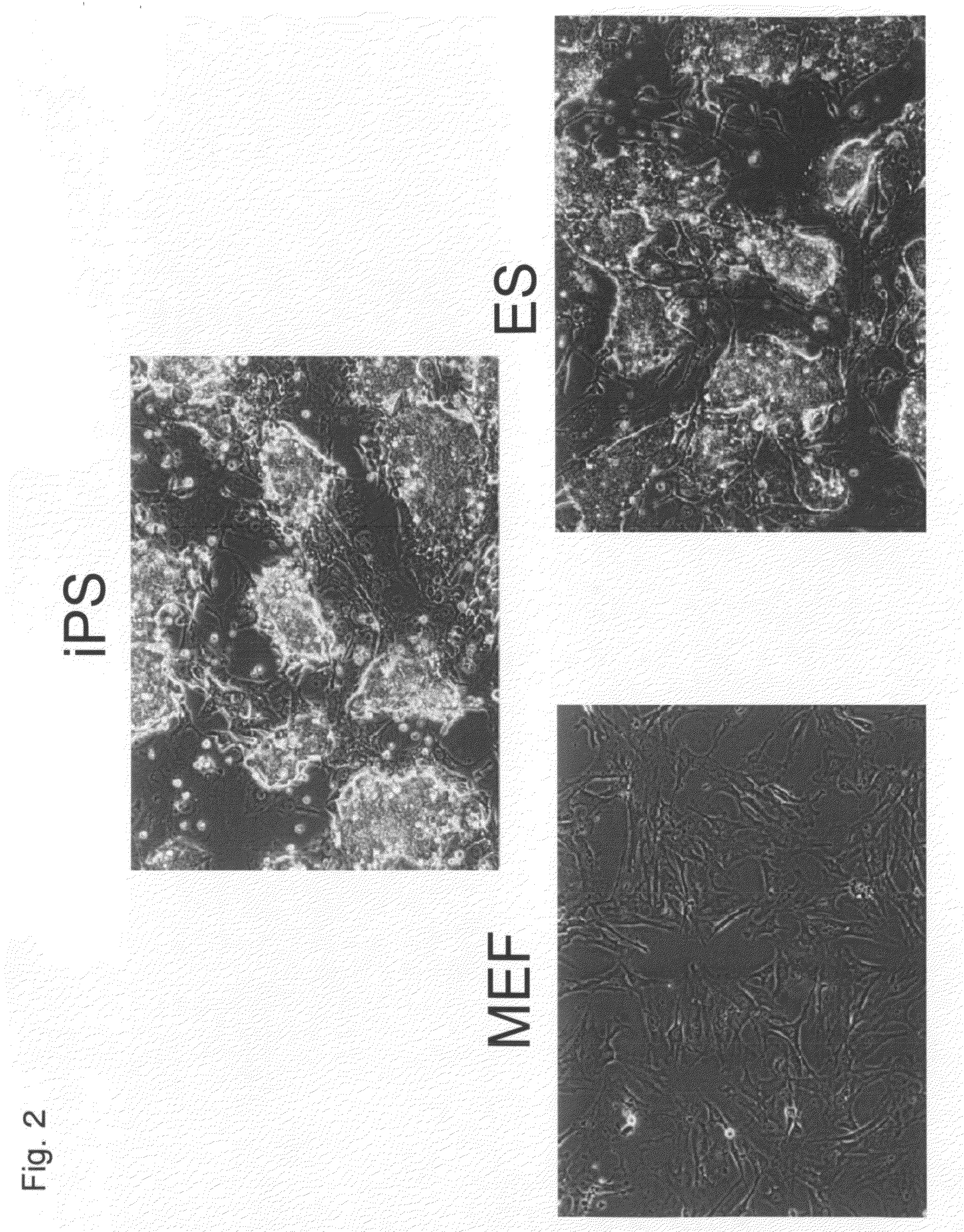
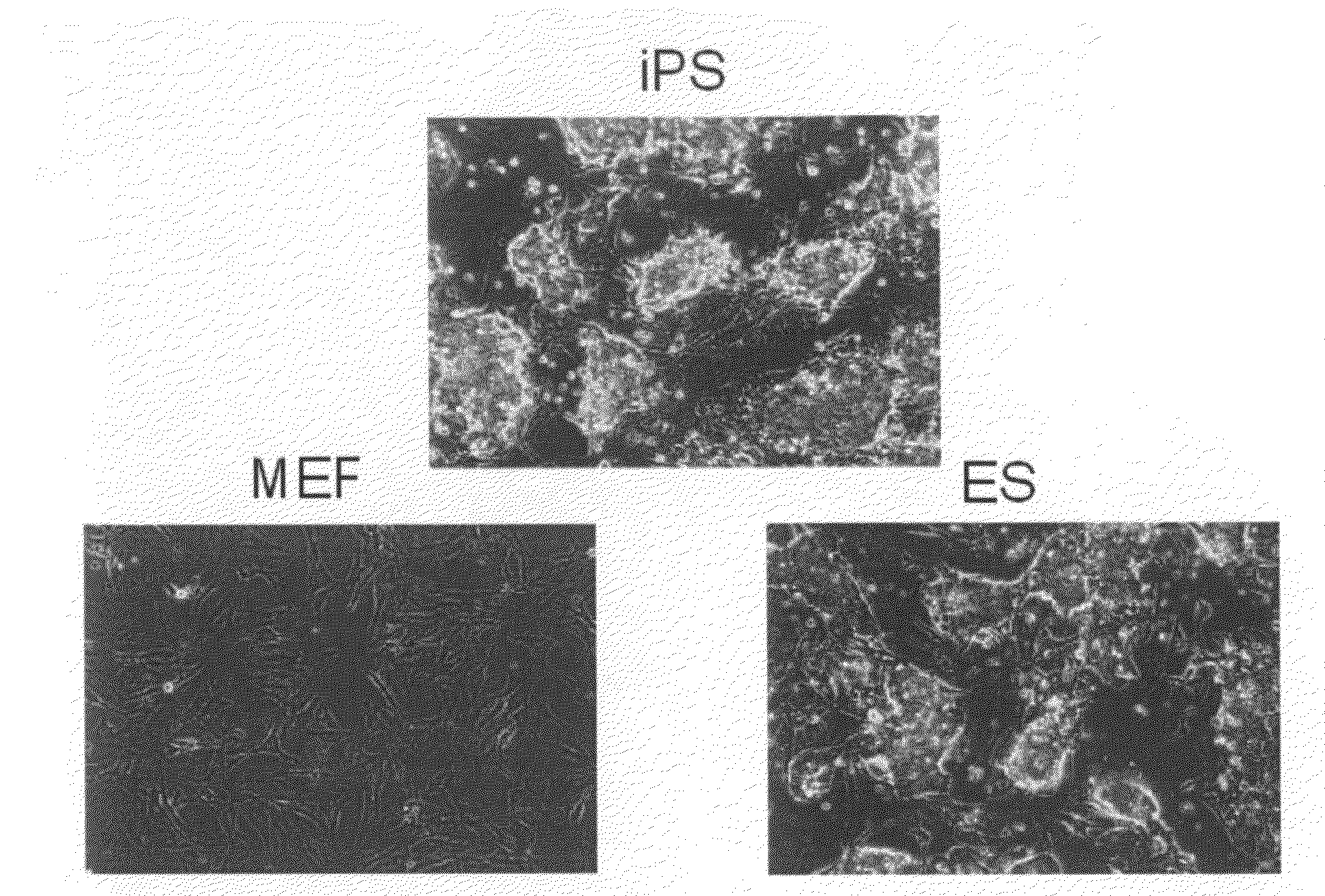
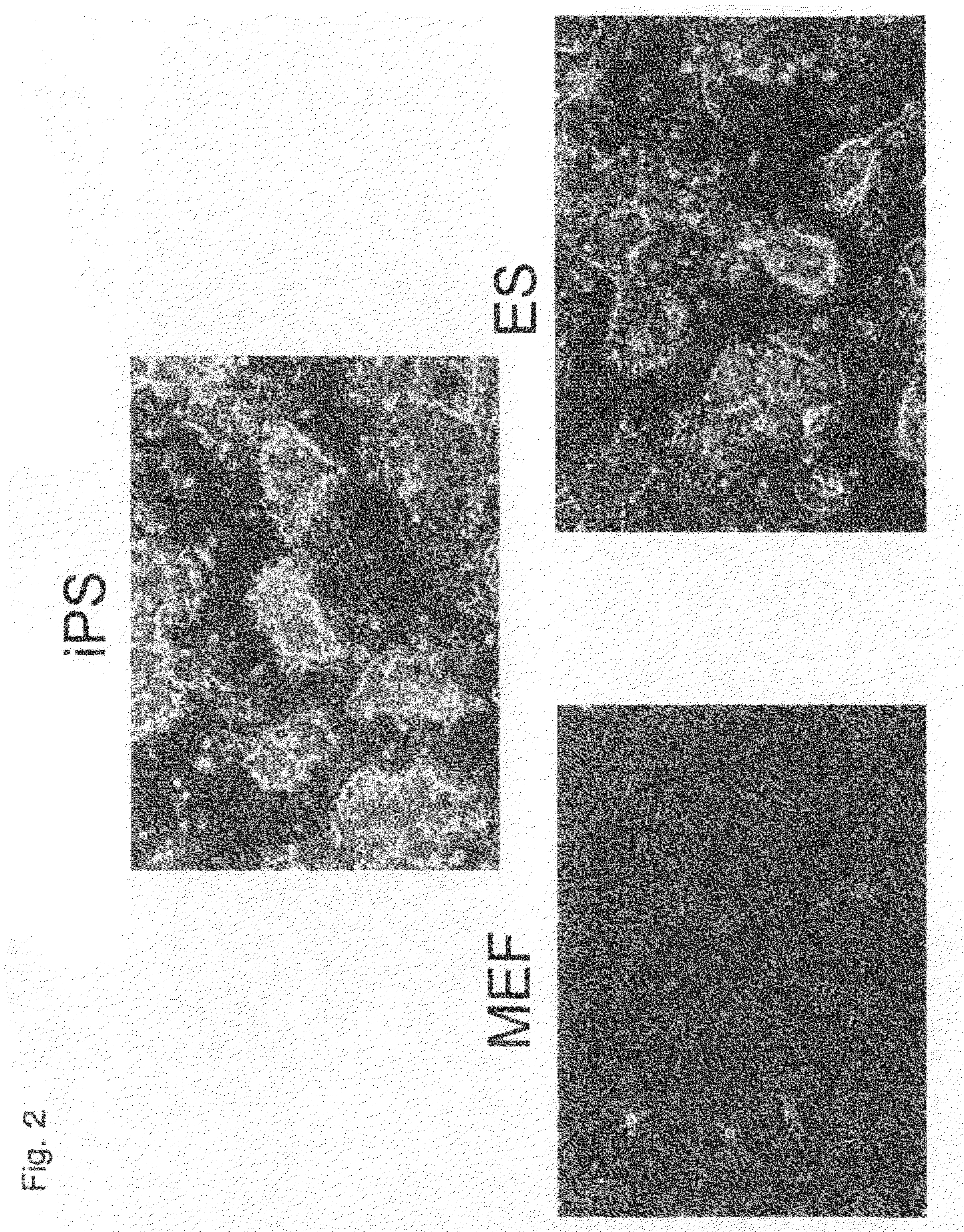
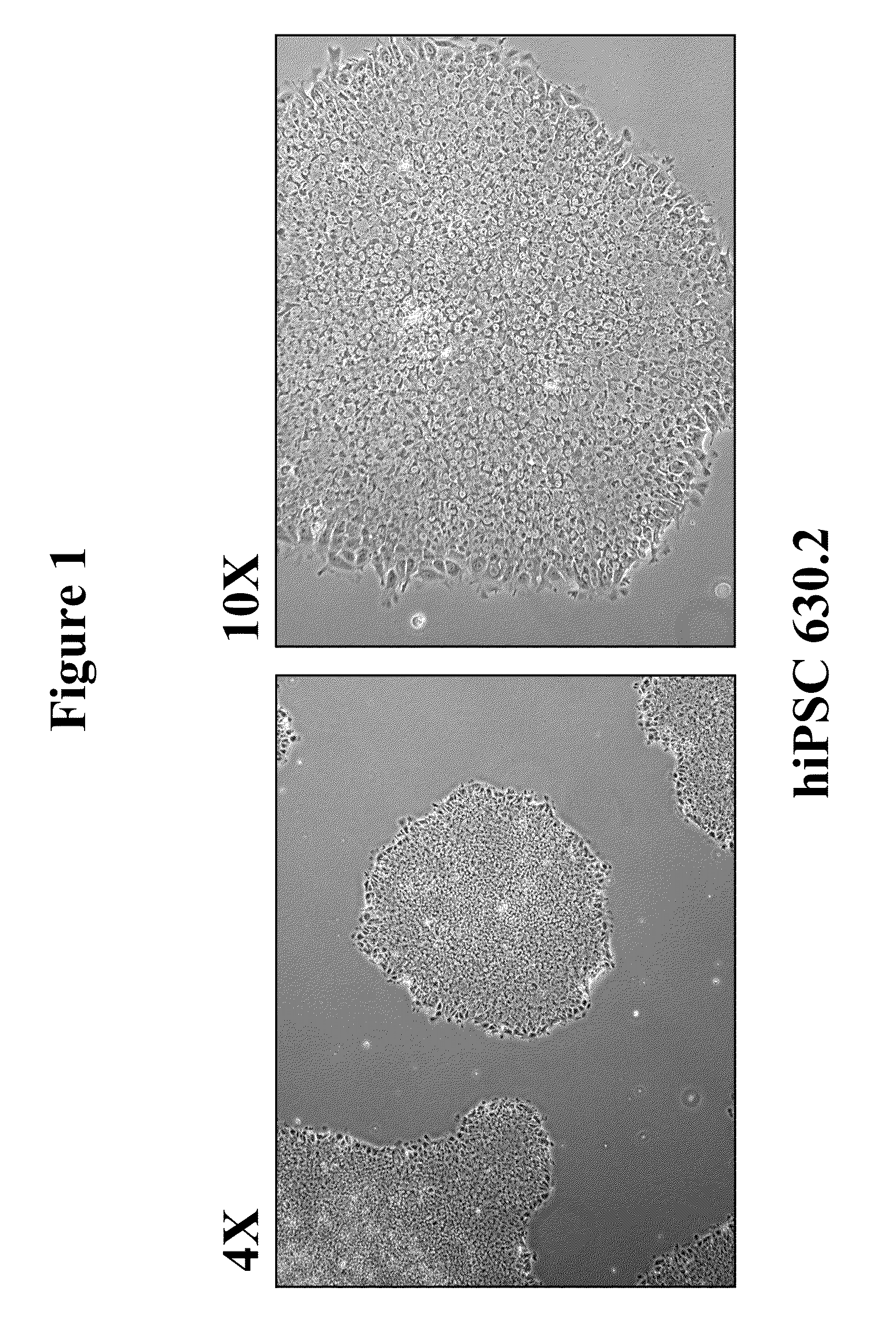
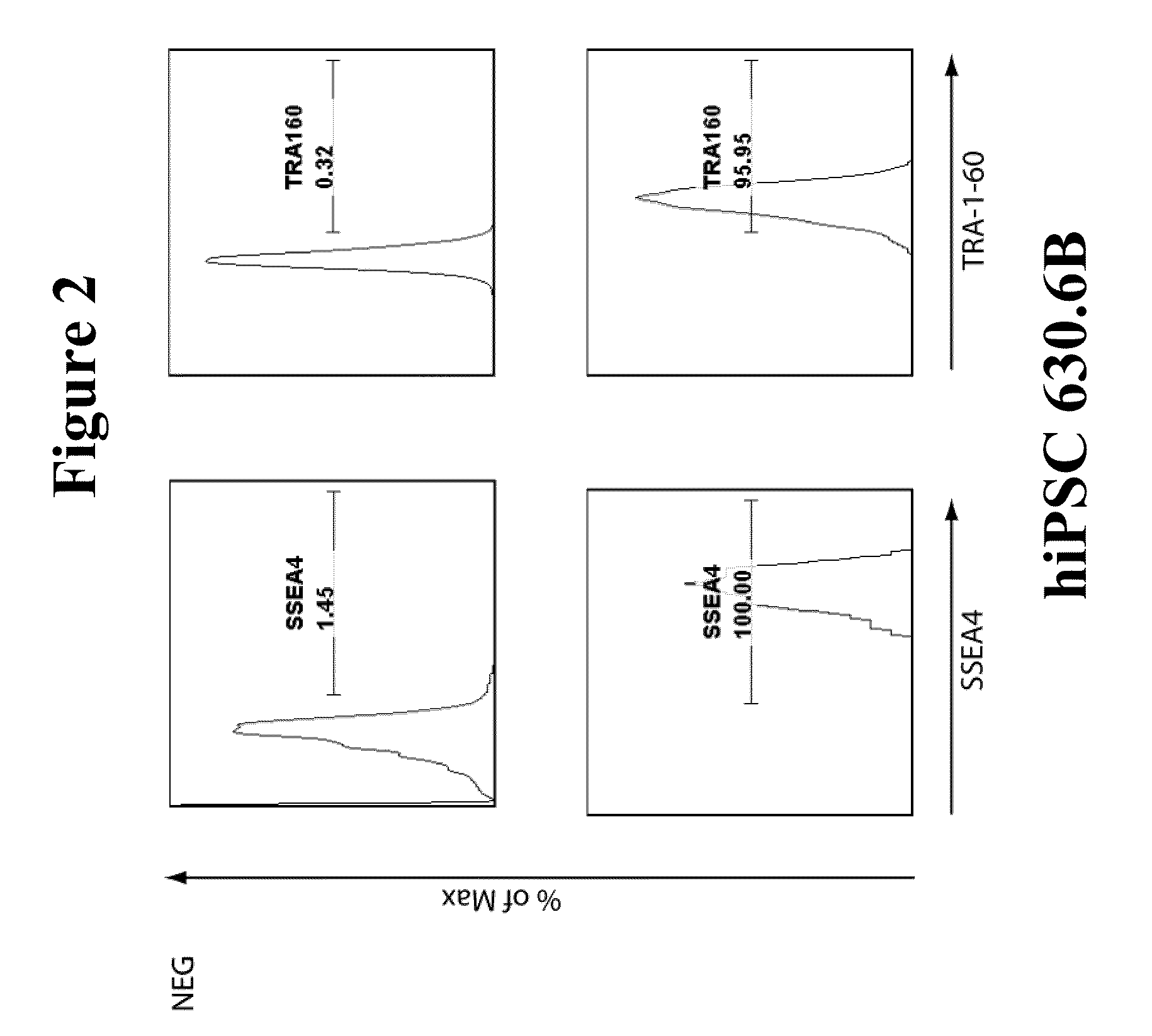
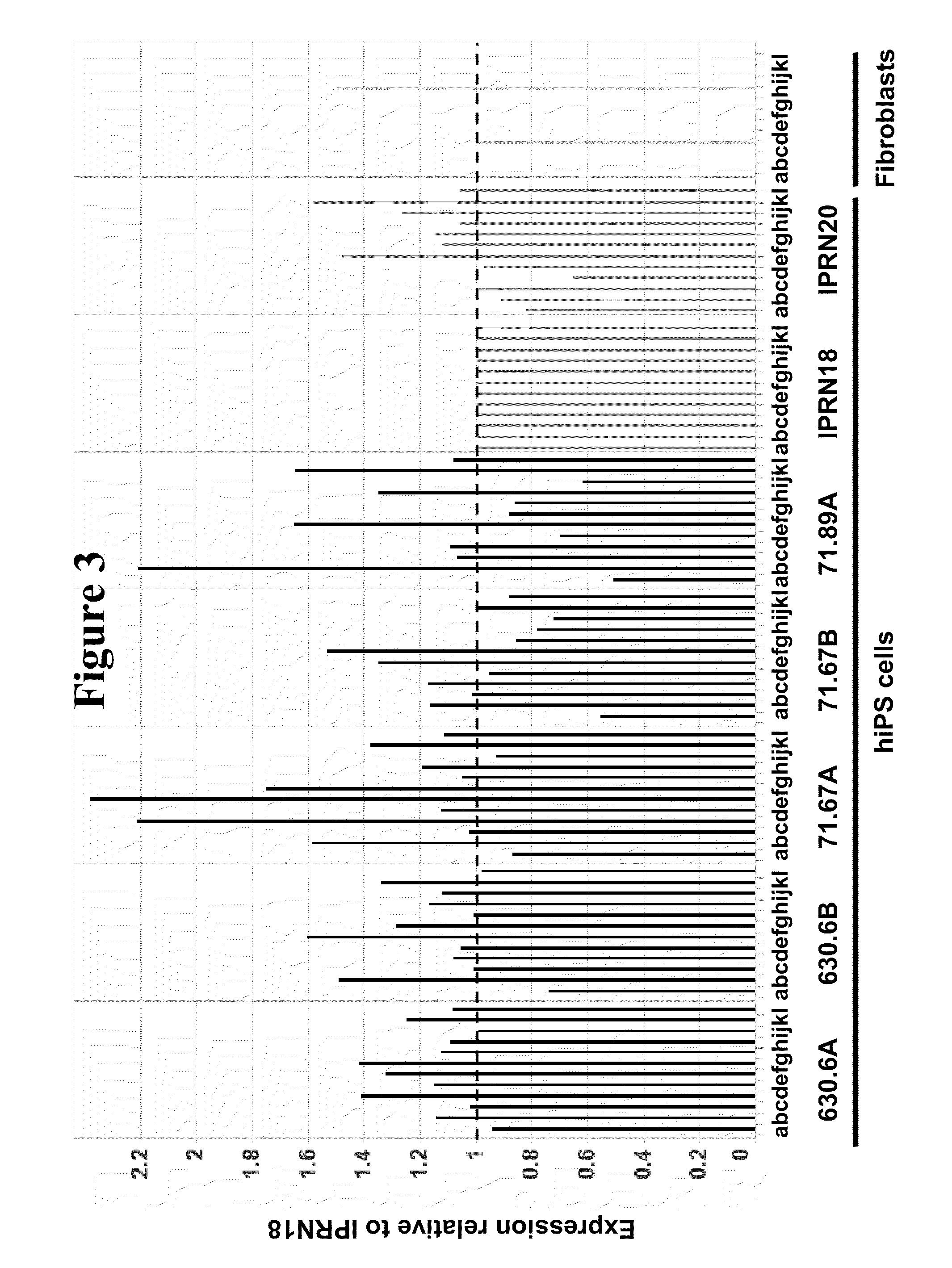
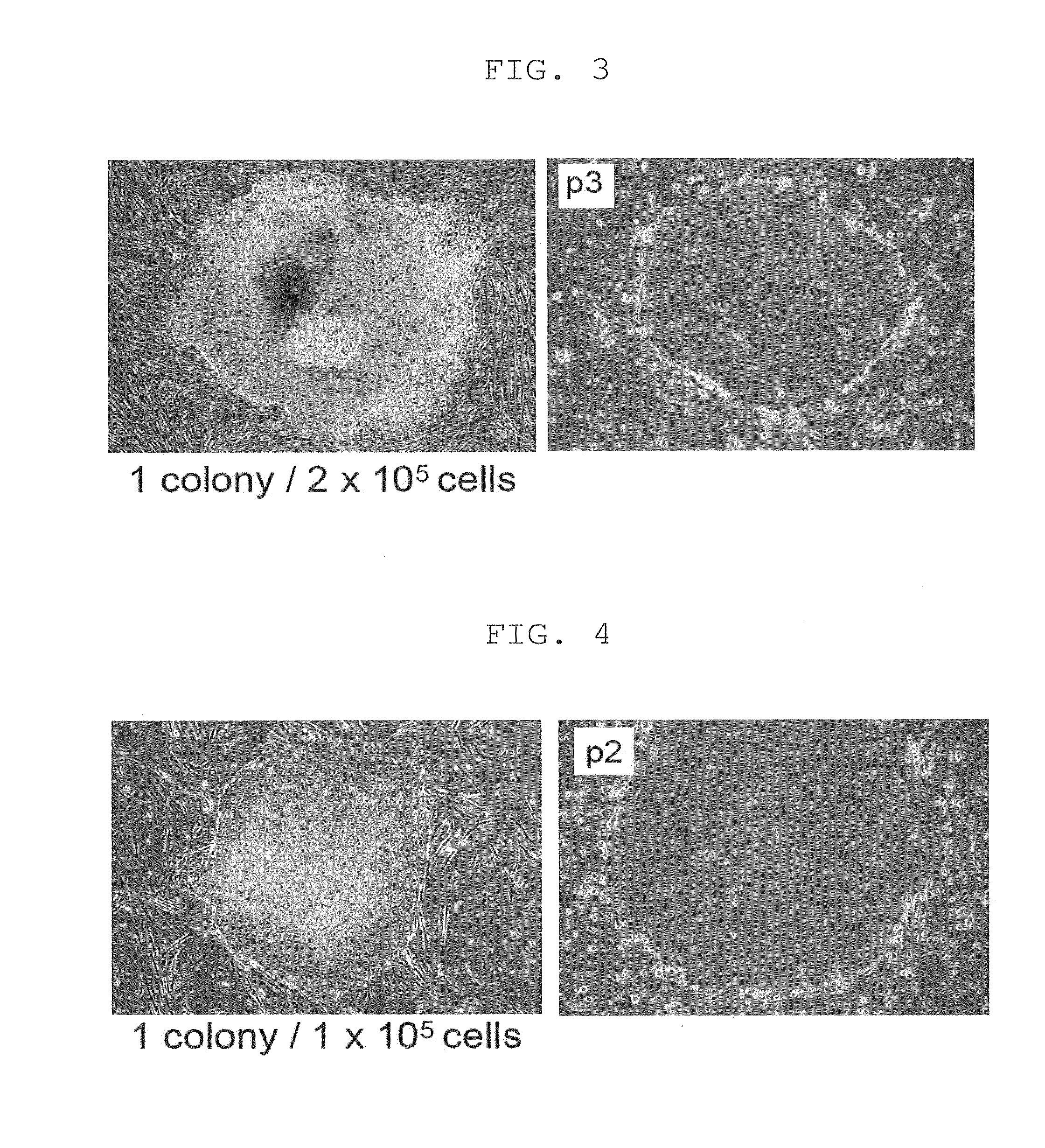
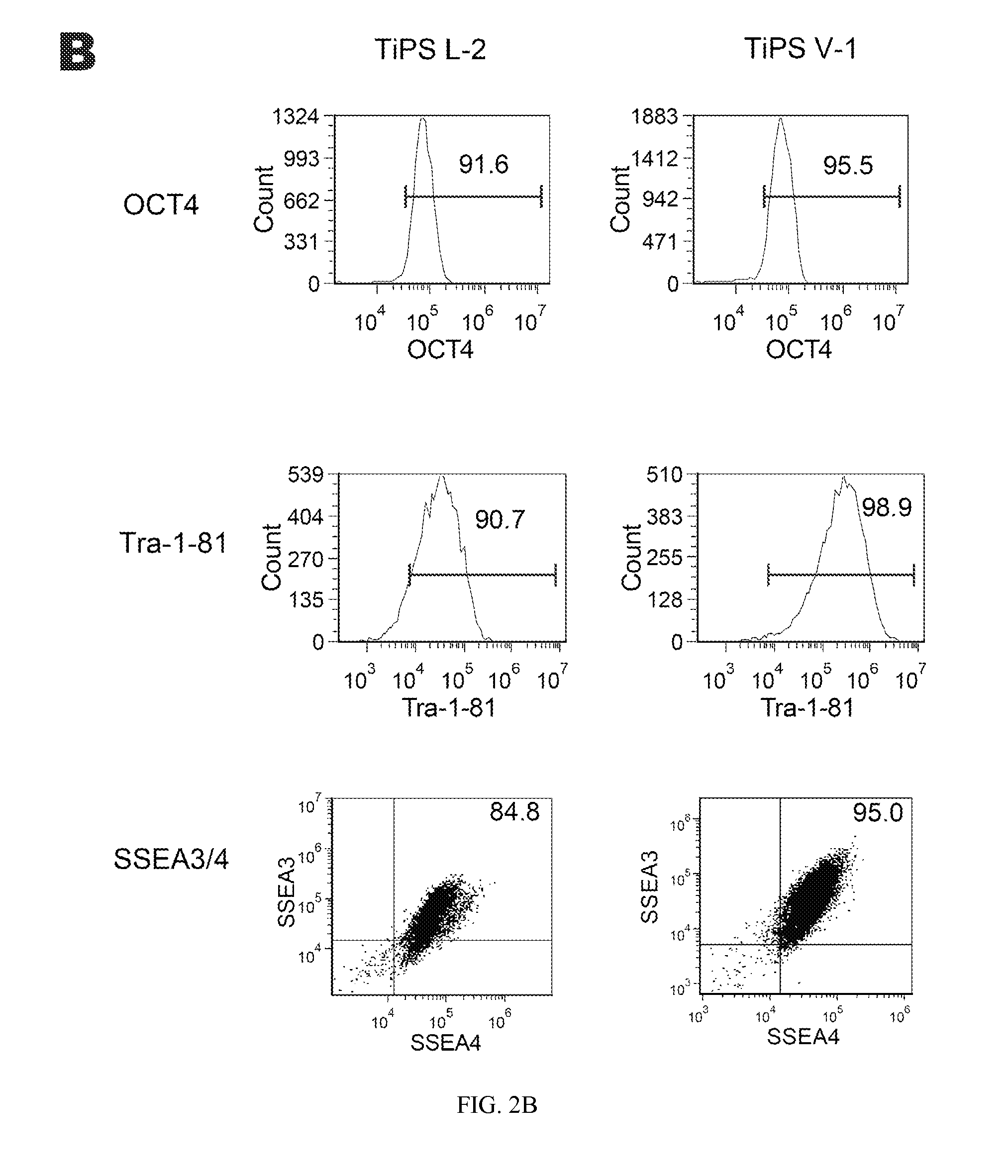
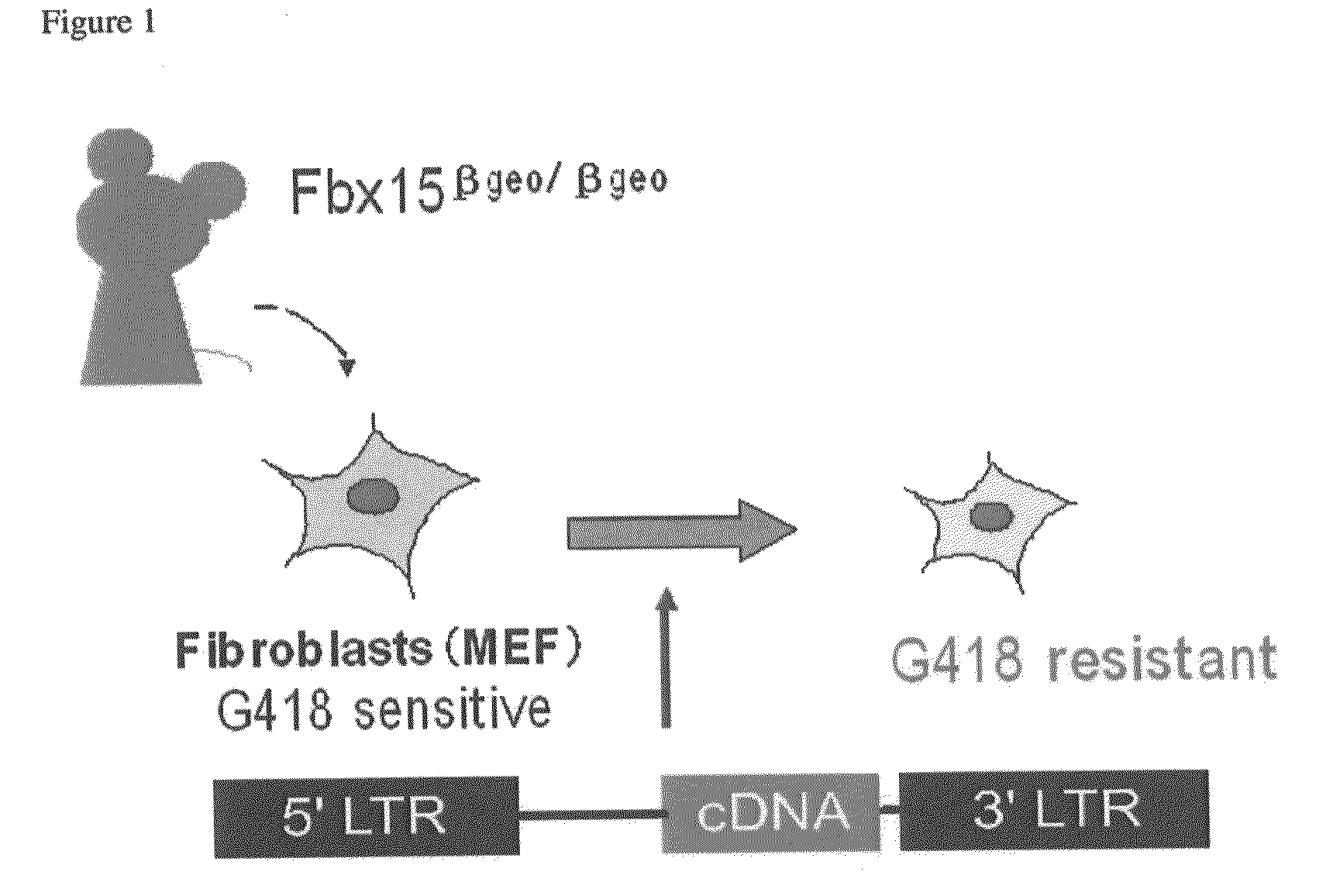
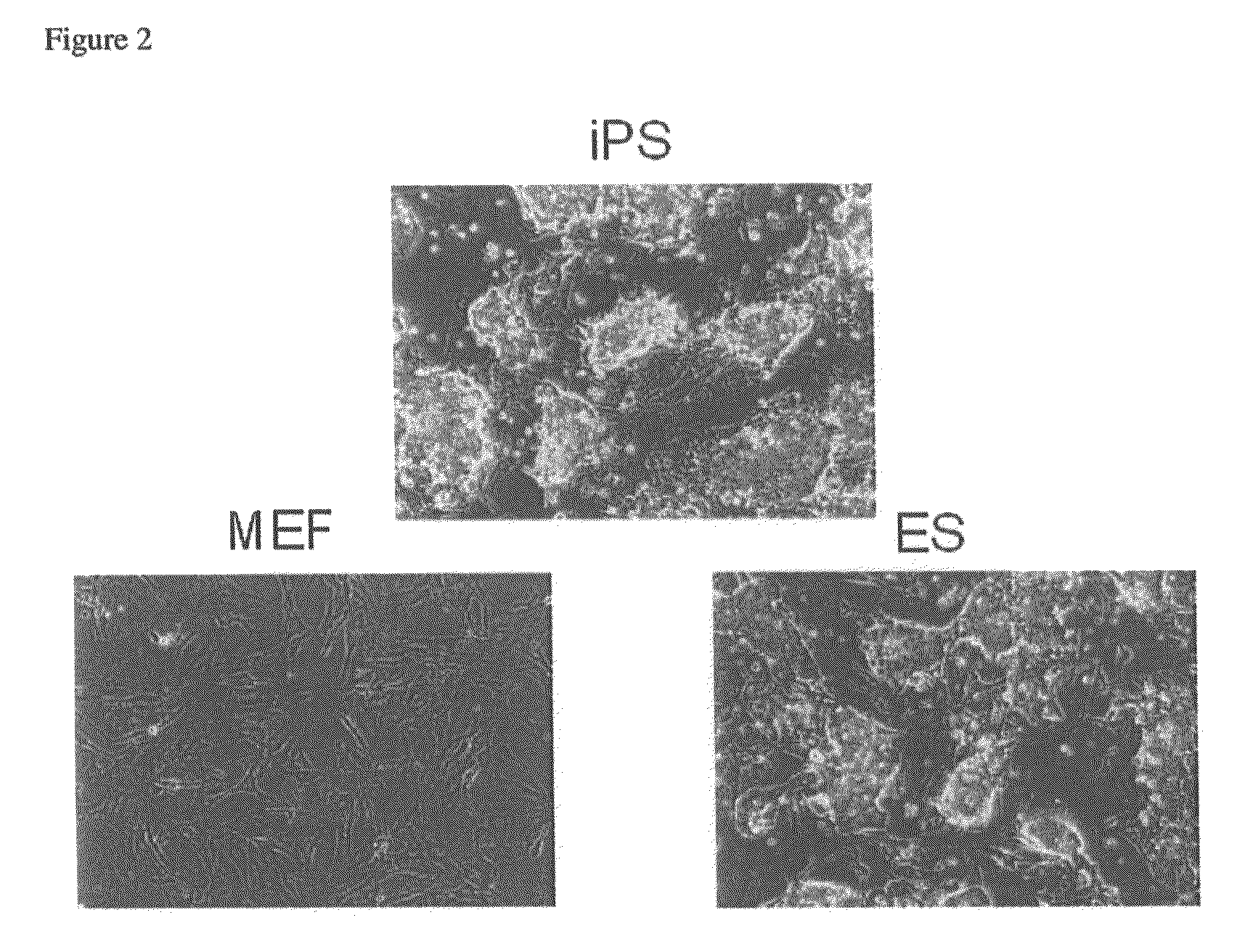
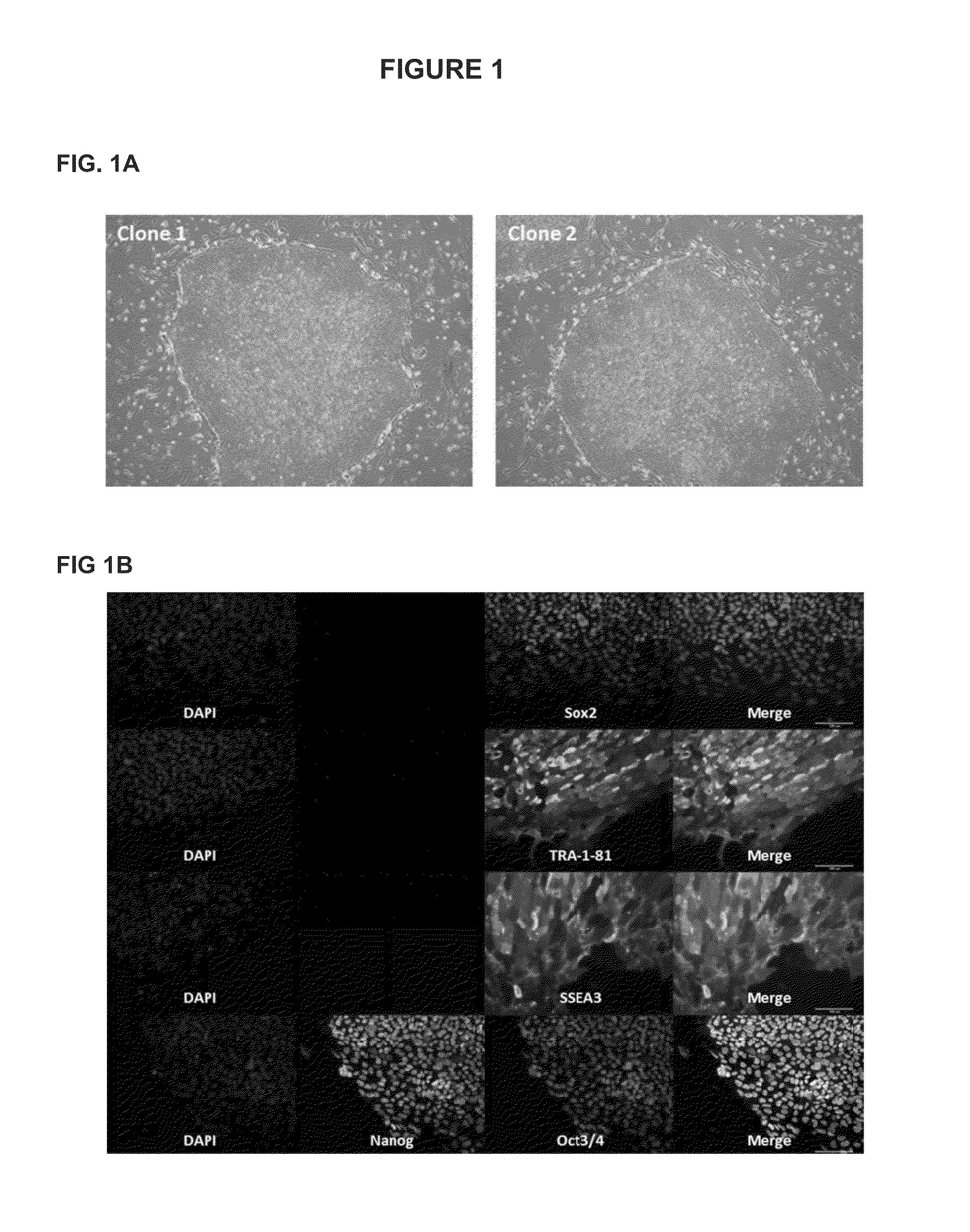
Human iPS cells colonies. The spindle-shaped cells in the background are mouse fibroblast cells. Only those cells comprising the center colony are human iPS cells. Induced pluripotent stem cells (also known as iPS cells or iPSCs) are a type of pluripotent stem cell that can be generated directly from adult cells.
Nuclear Reprogramming Factor
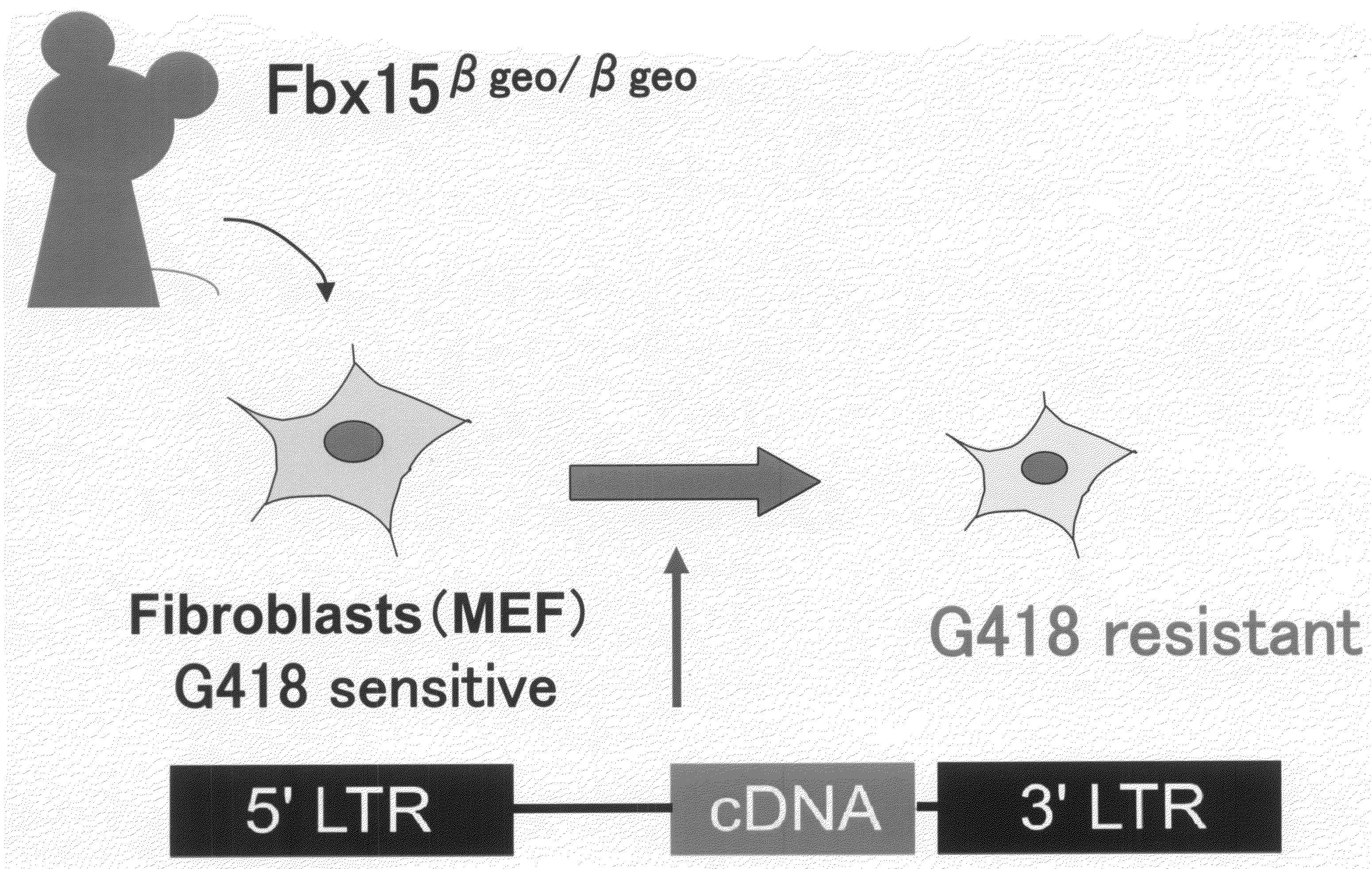
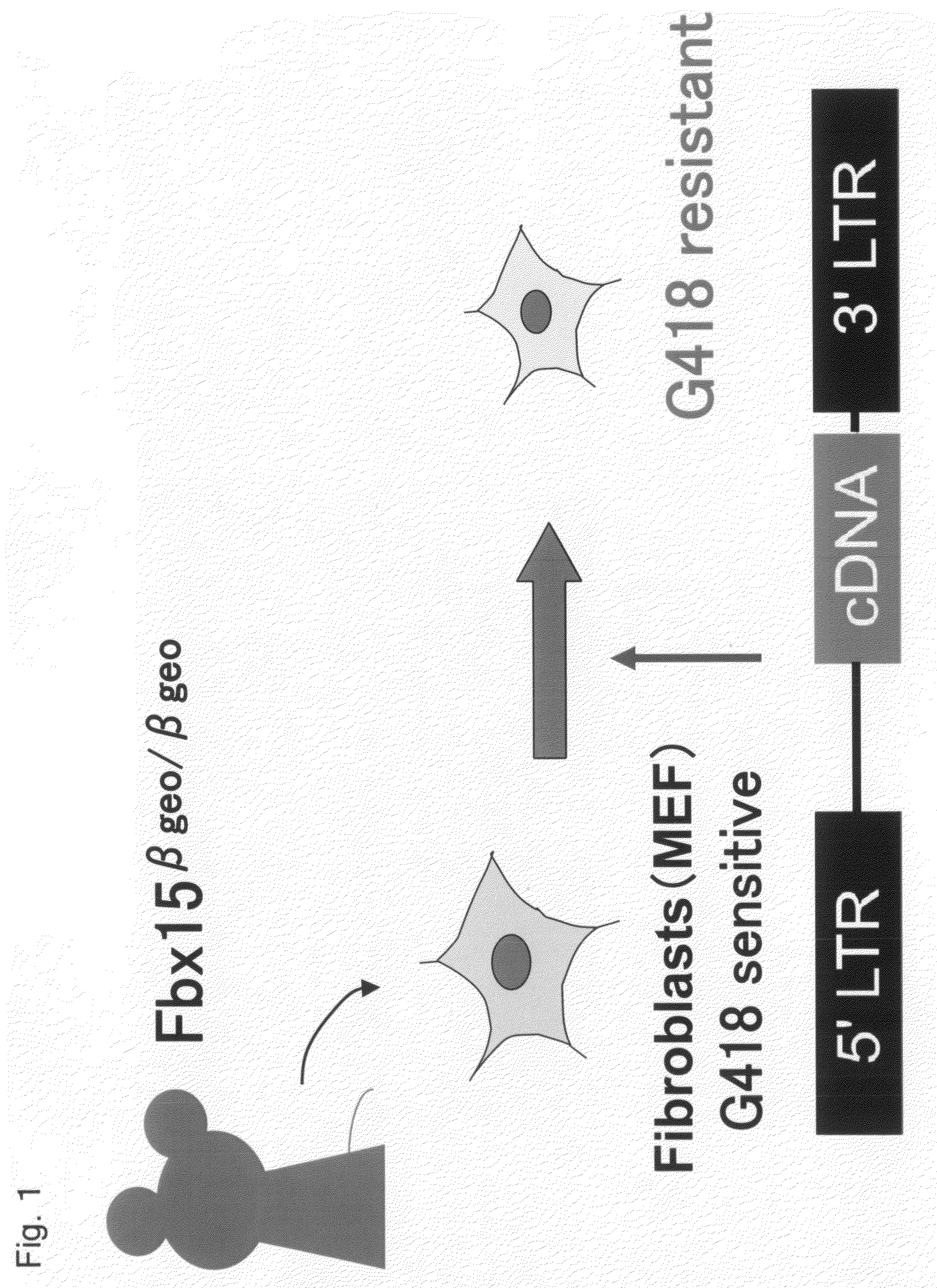
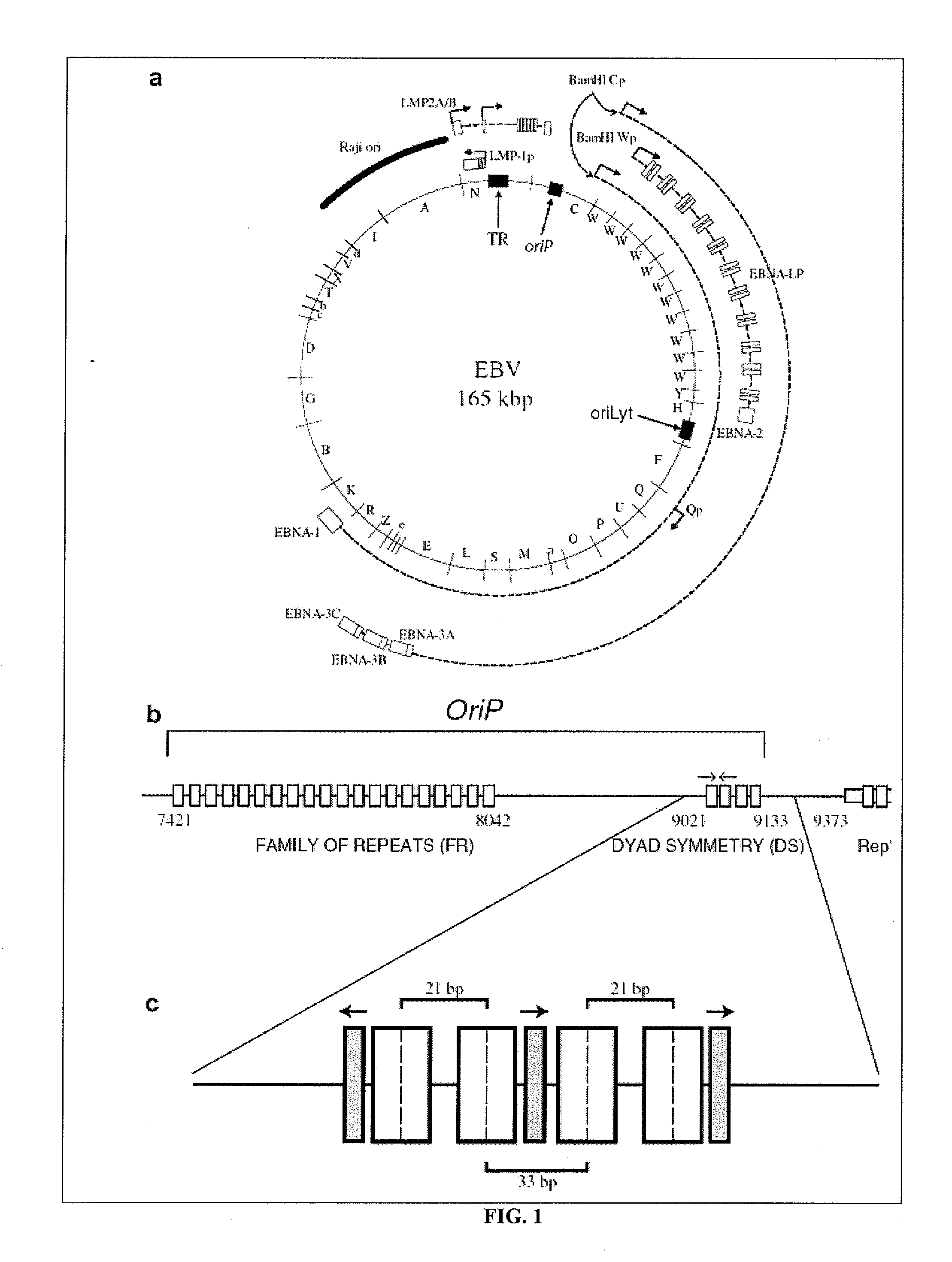
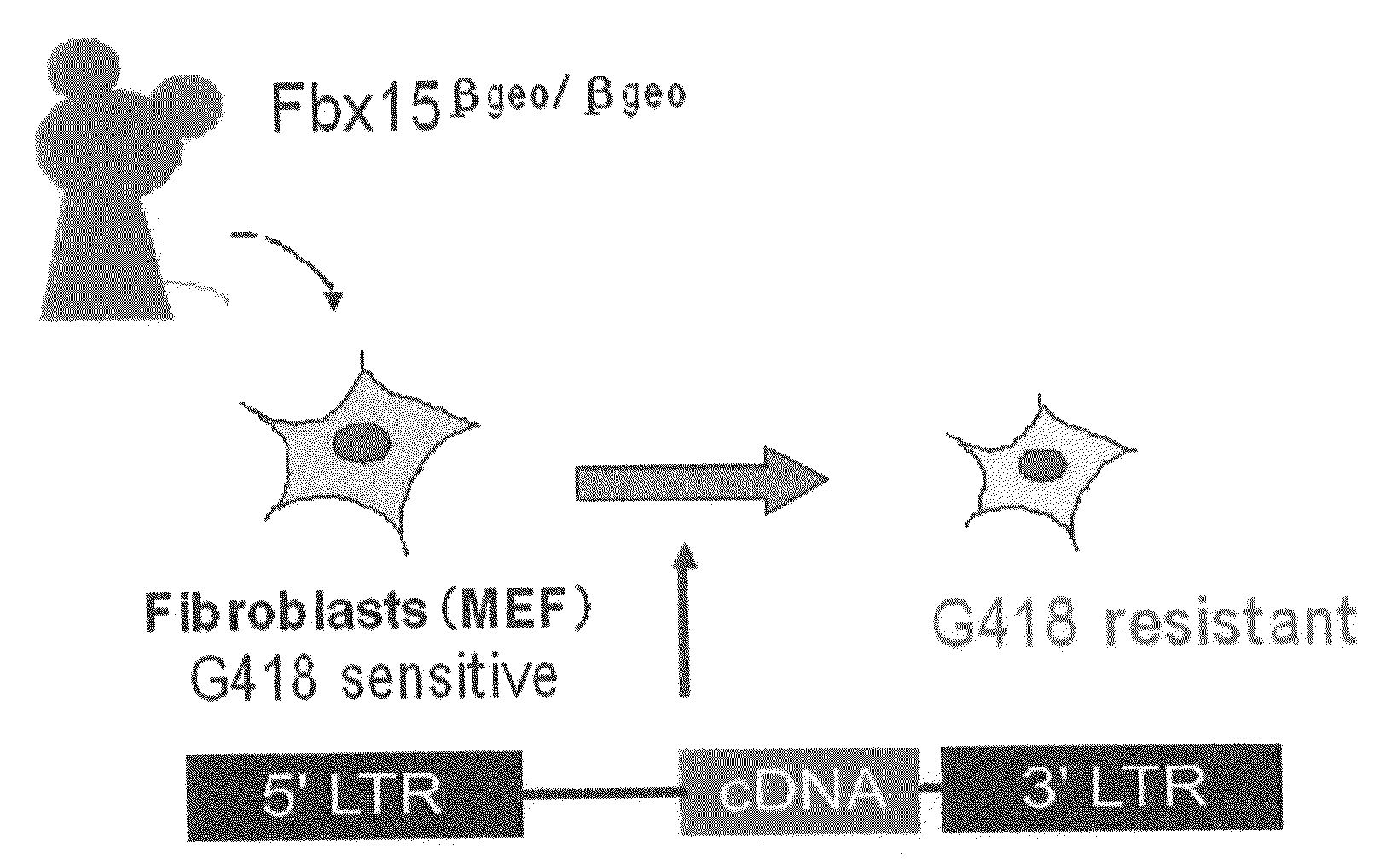
There is provided a nuclear reprogramming factor for a somatic cell, which comprises a gene product of each of the following three kinds of genes: an Oct family gene, a Klf family gene, and a Myc family gene, as a means for inducing reprogramming of a differentiated cell to conveniently and highly reproducibly establish an induced pluripotent stem cell having pluripotency and growth ability similar to those of ES cells without using embryo or ES cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Nuclear reprogramming factor and induced pluripotent stem cells
InactiveUS20090227032A1Easy to prepareEffective isolationGenetically modified cellsPeptidesNuclear reprogrammingCell therapy
The present invention relates to a nuclear reprogramming factor having an action of reprogramming a differentiated somatic cell to derive an induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell. The present invention also relates to the aforementioned iPS cells, methods of generating and maintaining iPS cells, and methods of using iPS cells, including screening and testing methods as well as methods of stem cell therapy. The present invention also relates to somatic cells derived by inducing differentiation of the aforementioned iPS cells.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Efficient method for nuclear reprogramming
ActiveUS20090246875A1Efficient preparationImprove efficiencyGenetically modified cellsCell culture active agentsHuman Induced Pluripotent Stem CellsBiology
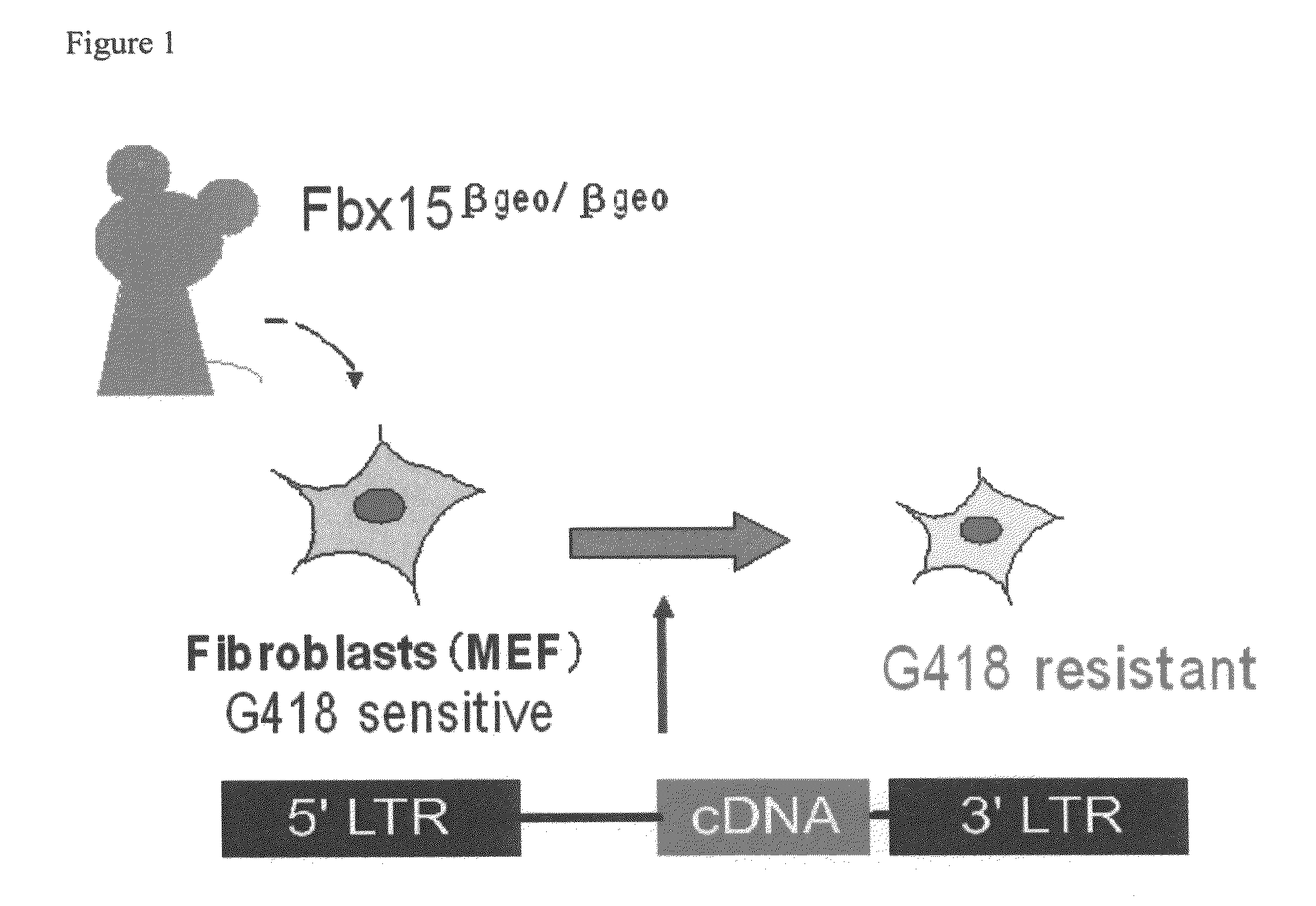
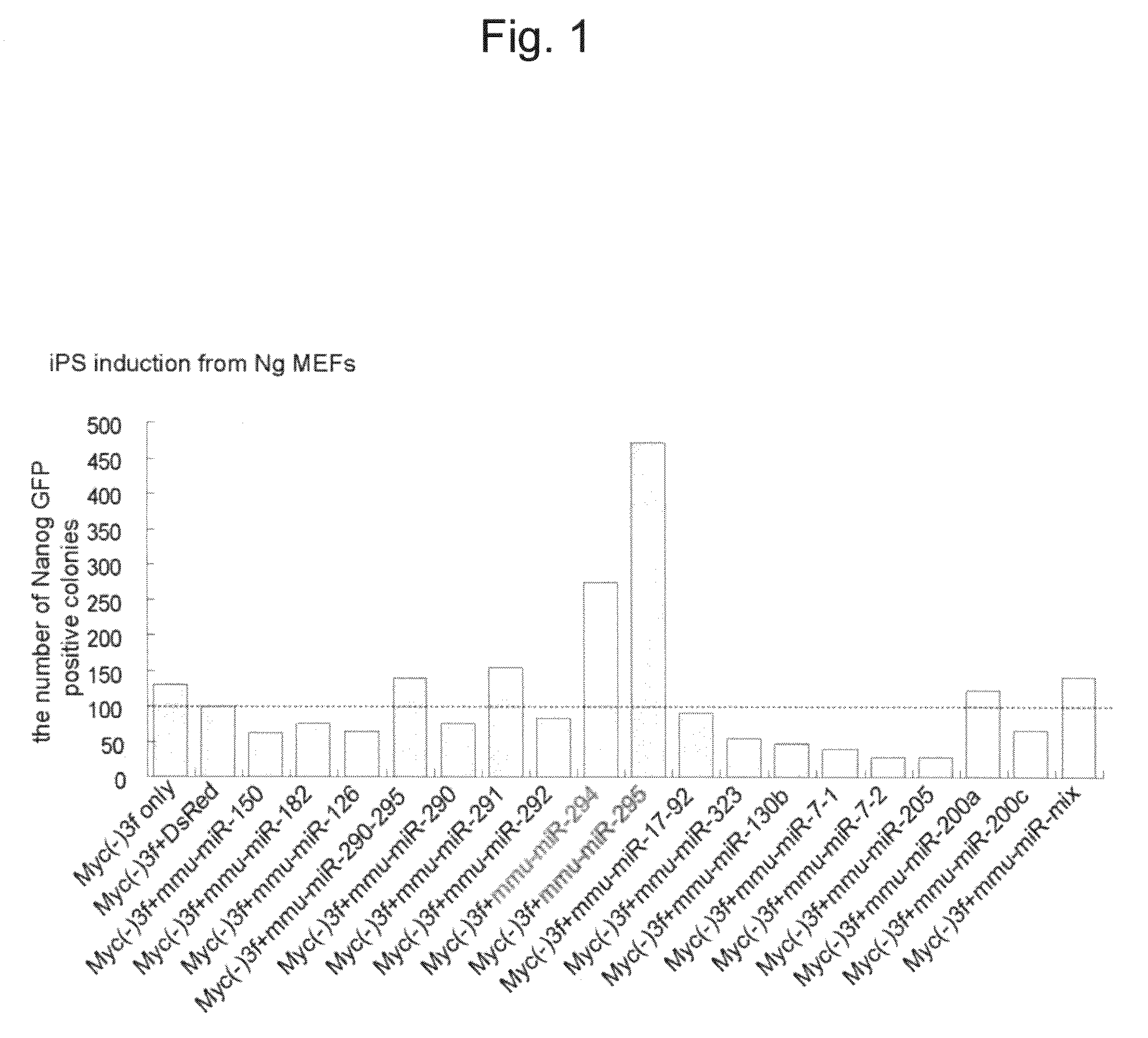
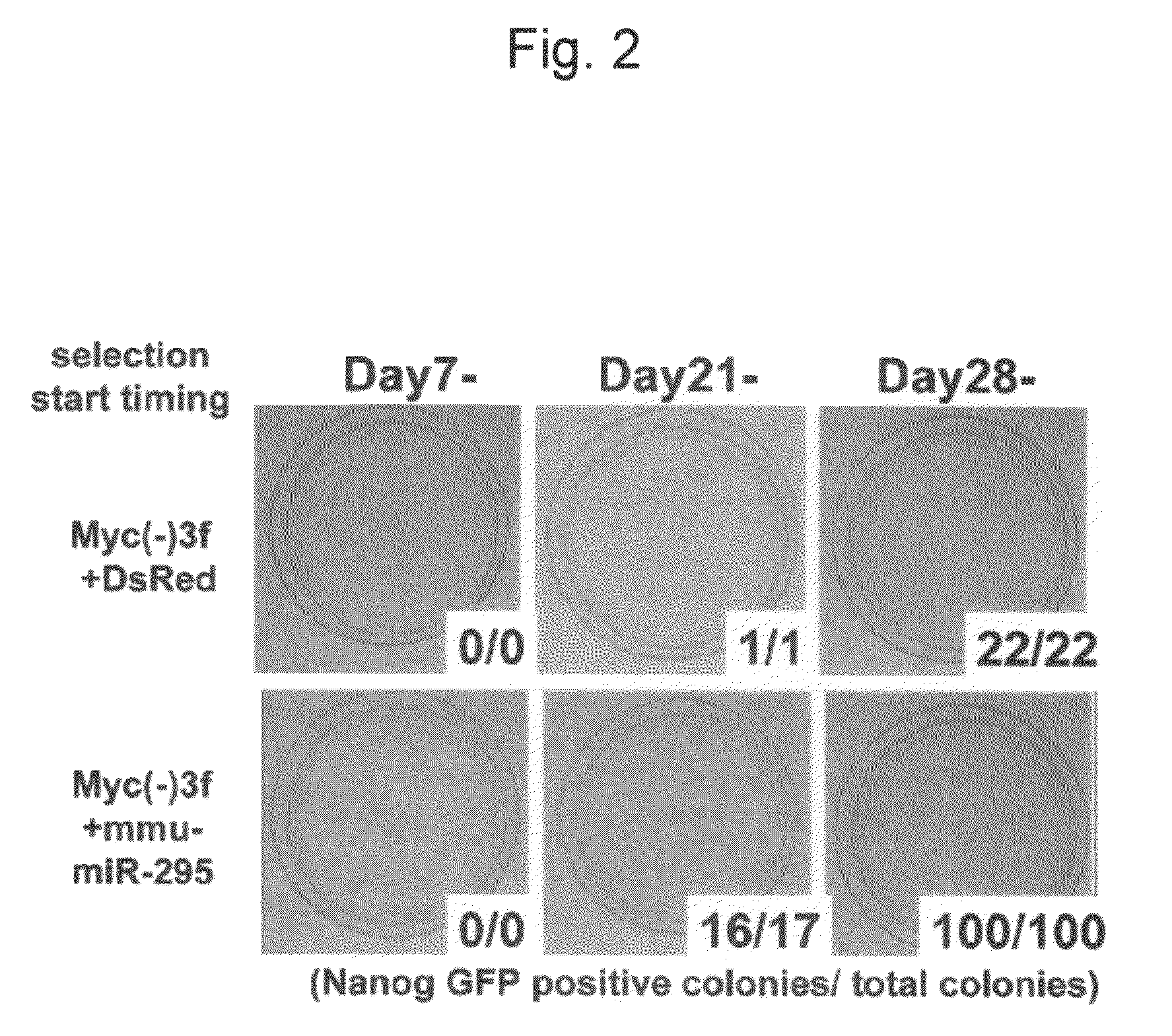
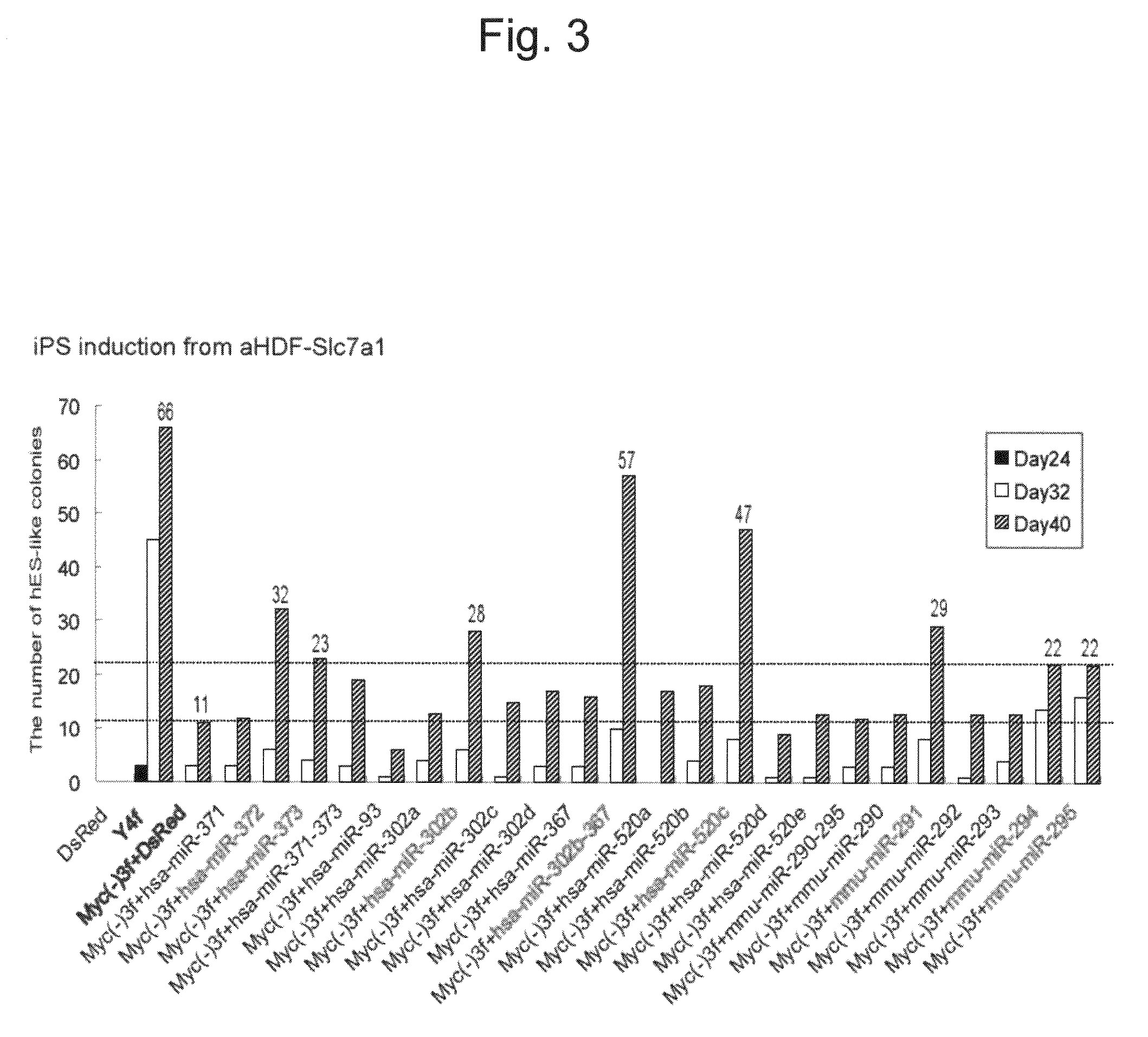
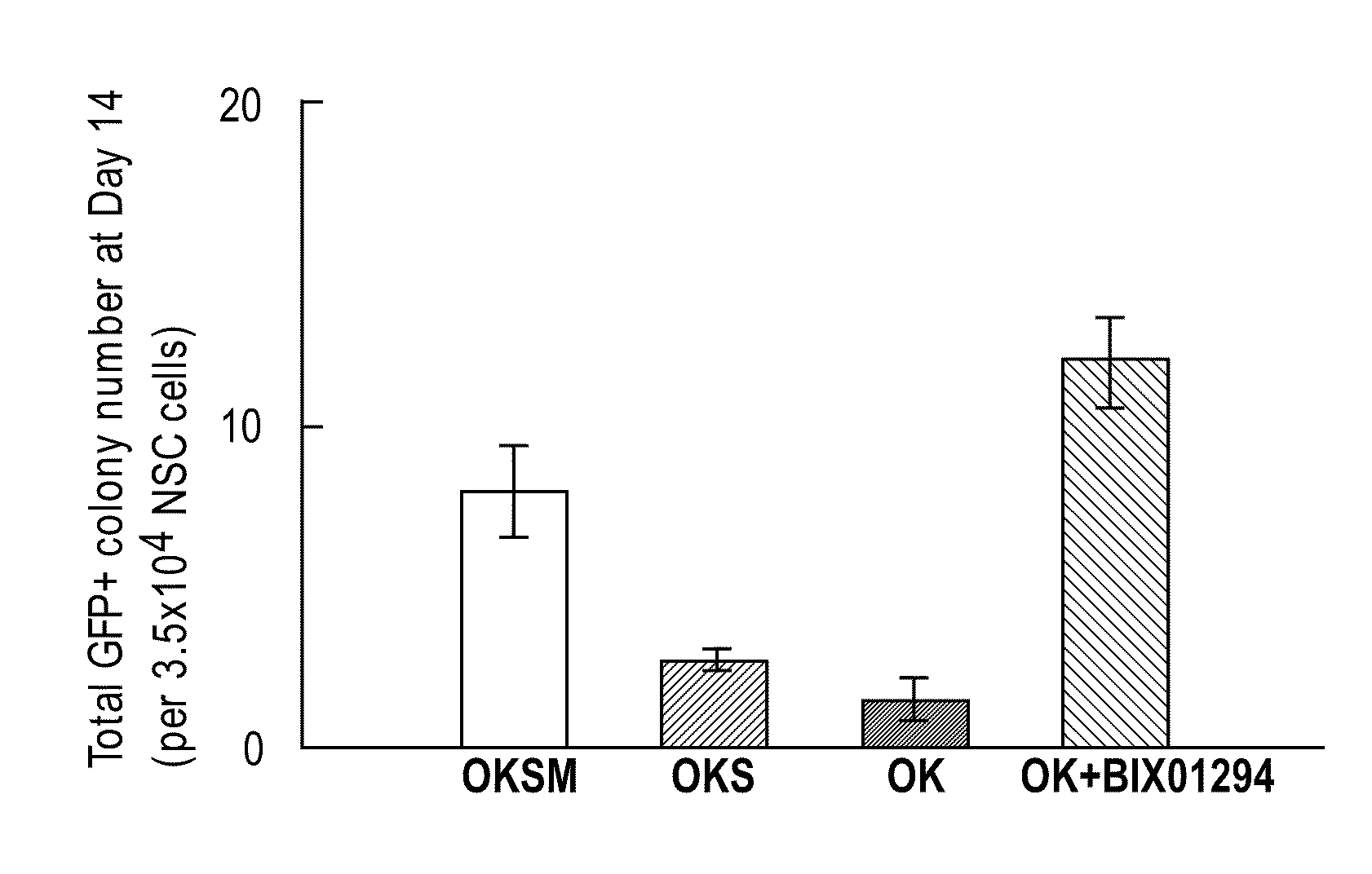
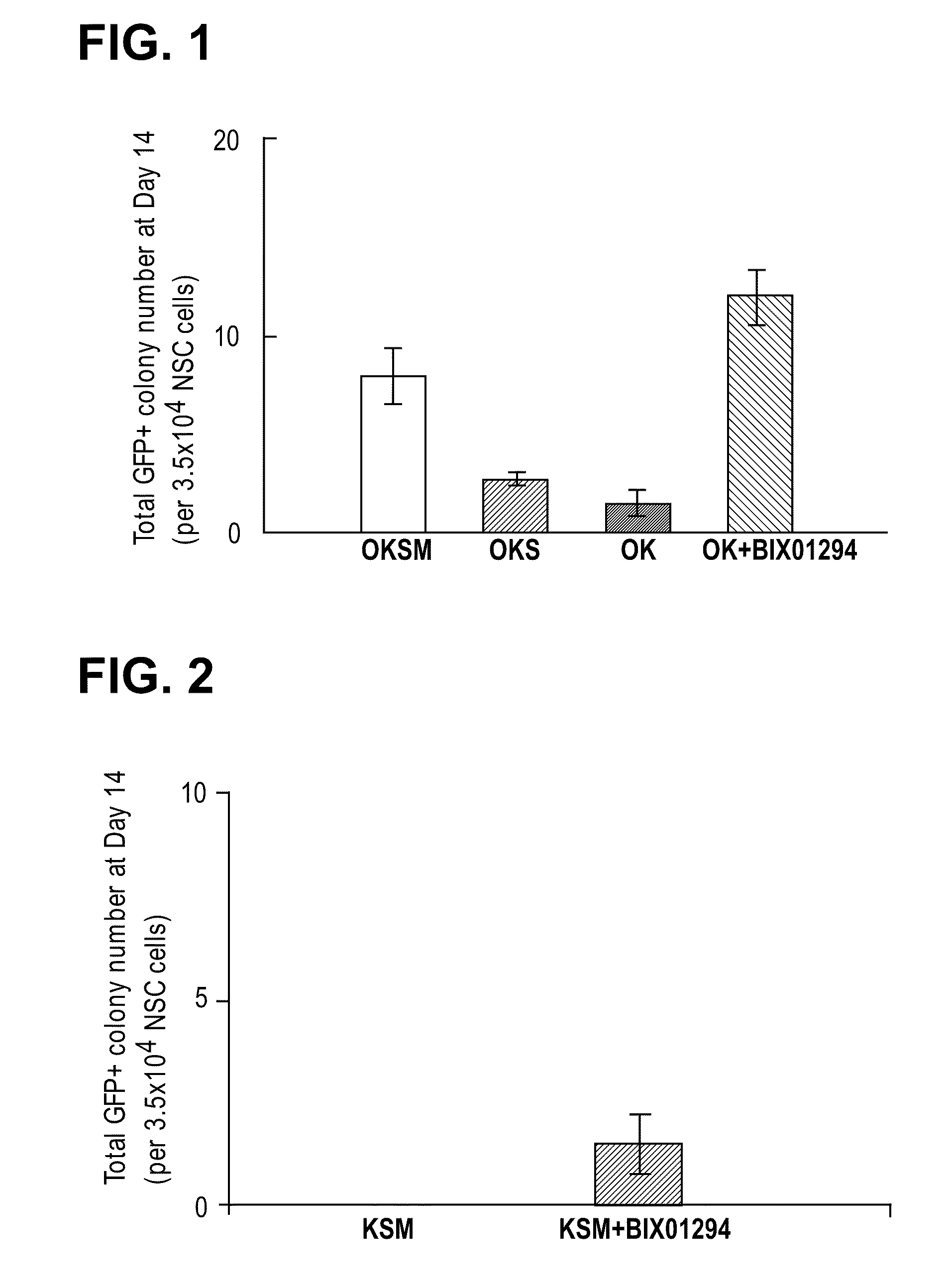
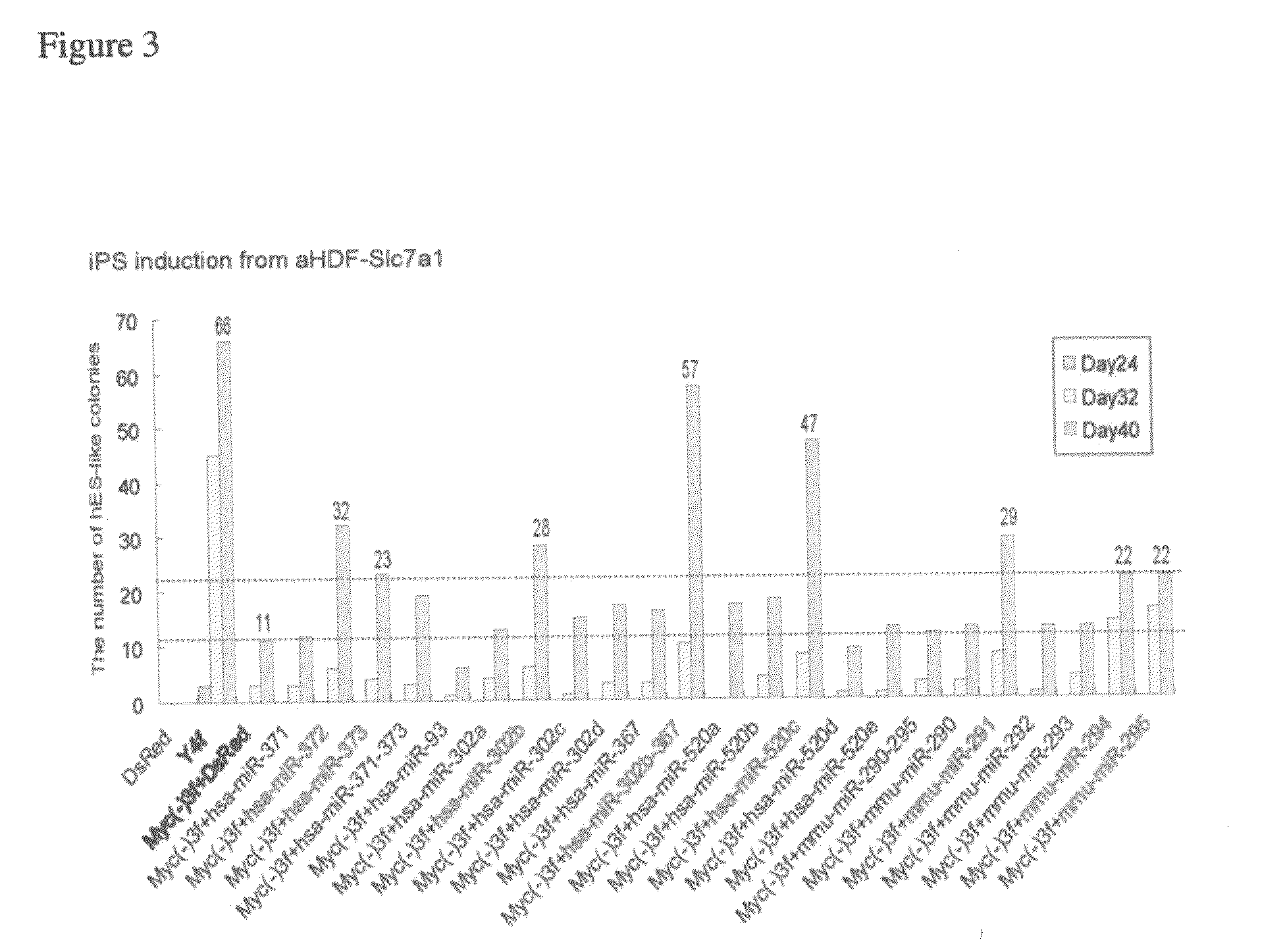
This relates to a method of preparing induced pluripotent stem cells, comprising a nuclear reprogramming step with a nuclear reprogramming factor in the presence of miRNA, wherein said miRNA has a property of providing a higher nuclear reprogramming efficiency in the presence of said miRNA than in the absence thereof.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Nuclear reprogramming factor
ActiveUS8048999B2Improve abilitiesPromote growthNervous disorderVirusesGene productNuclear reprogramming
There is provided a nuclear reprogramming factor for a somatic cell, which comprises a gene product of each of the following three kinds of genes: an Oct family gene, a Klf family gene, and a Myc family gene, as a means for inducing reprogramming of a differentiated cell to conveniently and highly reproducibly establish an induced pluripotent stem cell having pluripotency and growth ability similar to those of ES cells without using embryo or ES cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Methods for the production of ips cells using non-viral approach
ActiveUS20100003757A1Promote generationExpand the populationGenetically modified cellsVirus peptidesVector elementCell type
Methods and composition of induction of pluripotent stem cells and other desired cell types are disclosed. For example, in certain aspects methods for generating essentially vector-free induced pluripotent stem cells are described. Furthermore, the invention provides induced pluripotent stem cells and desired cell types essentially free of exogenous vector elements with the episomal expression vectors to express differentiation programming factors.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Chemical approaches for generation of induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20100267141A1Inhibiting methylationNervous disorderEpidermal cells/skin cellsMammalian cellHuman Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Efficient method for nuclear reprogramming
InactiveUS20100075421A1Efficient preparationImprove efficiencyGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsNuclear reprogrammingBiology
A method of preparing induced pluripotent stem cells, comprising a nuclear reprogramming step with a nuclear reprogramming factor in the presence of miRNA, wherein said miRNA has a property of providing a higher nuclear reprogramming efficiency in the presence of said miRNA than in the absence thereof.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Episomal reprogramming with chemicals
ActiveUS20110104125A1Easy to adaptHigh reprogramming efficiencyBiocideNervous disorderVector elementViral vector
Methods and composition of induction of pluripotent stem cells are disclosed. For example, in certain aspects methods for generating essentially vector-free induced pluripotent stem cells with cell signaling regulators are described. Furthermore, certain aspects of the invention provide novel compositions comprising induced pluripotent stem cells essentially free of exogenous retroviral vector elements in the presence of a medium comprising signaling inhibitors. In certain aspects, feeder-free episomal reprogramming methods may be provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Neural stem cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells
InactiveUS20100021437A1Preserve viabilityBiocideNervous disorderHuman Induced Pluripotent Stem CellsPopulation
Owner:MCLEAN HOSPITAL THE +1
Combined Chemical and Genetic Approaches for Generation of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Integration-free human induced pluripotent stem cells from blood
InactiveUS8048675B1Genetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsPluripotential stem cellOrigin of replication
Provided herein are methods for generating human induced pluripotent stem cells free from genomic integration of exogenous transgenes by transfecting into nucleated blood cells one or more DNA expression vectors (e.g., plasmid vectors) that do not contain a mammalian origin of replication, and encode and permit expression of one or more reprogramming factors (e.g., Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc). Also provided herein are the integration-free human induced pluripotent stem cells obtained by the methods described herein.
Owner:TRUE NORTH THERAPEUTICS
Automation augmentation and culture system of induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveCN102174395AEfficient conversionEfficient and fully automatedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsControl systemControl room
The invention relates to the technical field of cell automation augmentation and culture instrument, in particular relates to an automation augmentation and culture system of induced pluripotent stem cells, which comprises a cell automation augmentation and culture system, an operation room and a control system which are mutually connected, wherein, the cell automation augmentation and culture system comprises a culture box and a culture box control room connected with the culture box; the culture box comprises at least one culture device for fixing a culture container fixed block of a culture container, a culture container cover automatic opening and closing system, a culture container automatic popping and closing system, a digital temperature system and at least one sensor; the culture box control room comprises an air flow purification and induction system and a culture box digital power system; and the operation room comprises a bar code automatic entry system, an liquid automatic replace system and a cell on-line observing system. By utilizing the system provided by the invention, a somatic cell can be automatically induced into a pluripotent stem cell, and the system can be used for stem cell research and clinical stem cell treatment.
Owner:广东朗源生物科技有限公司
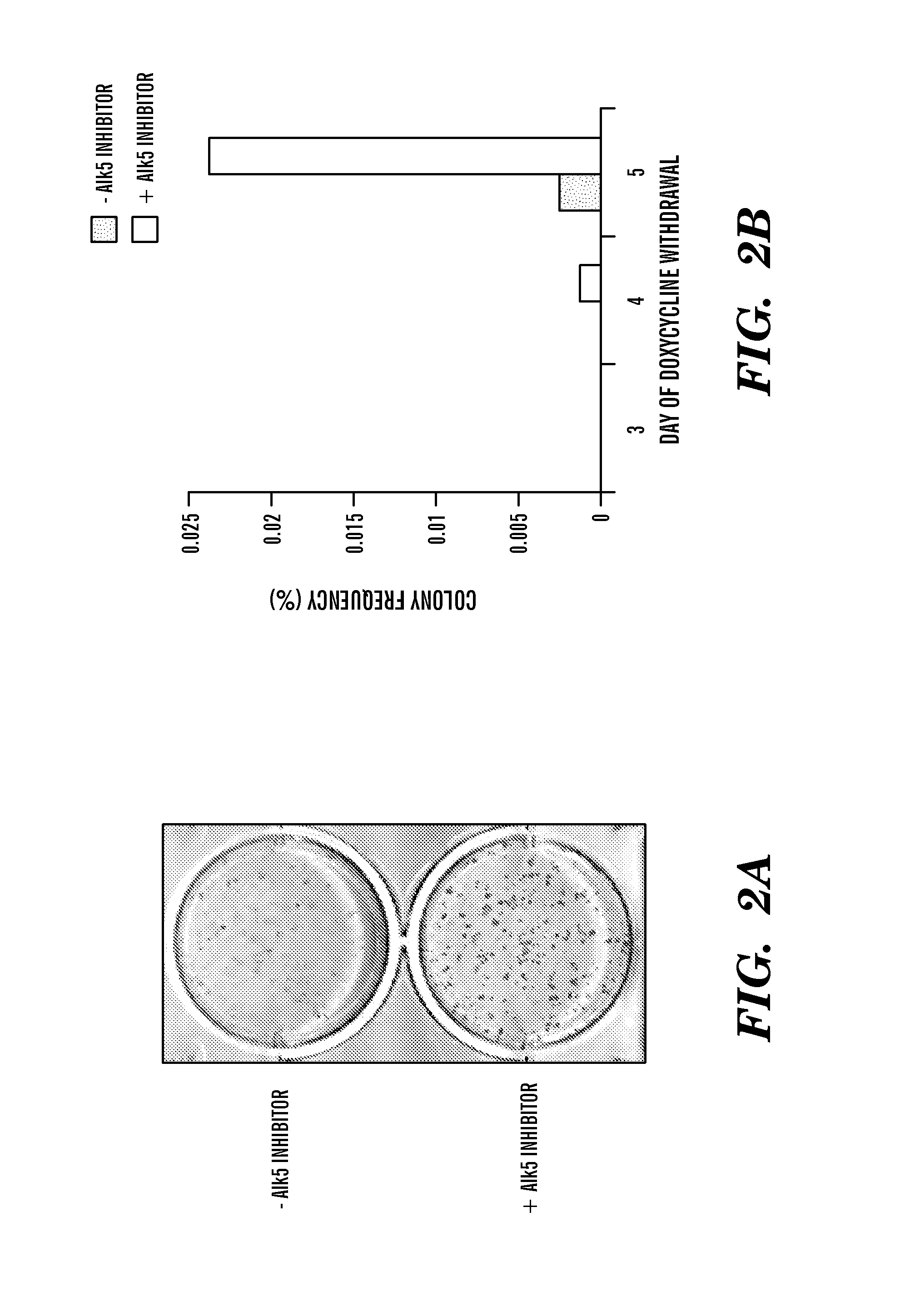
TGF-beta receptor inhibitors to enhance direct reprogramming
ActiveUS8298825B1Improve efficiencyIncrease ratingsGenetically modified cellsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsHuman Induced Pluripotent Stem CellsGene delivery
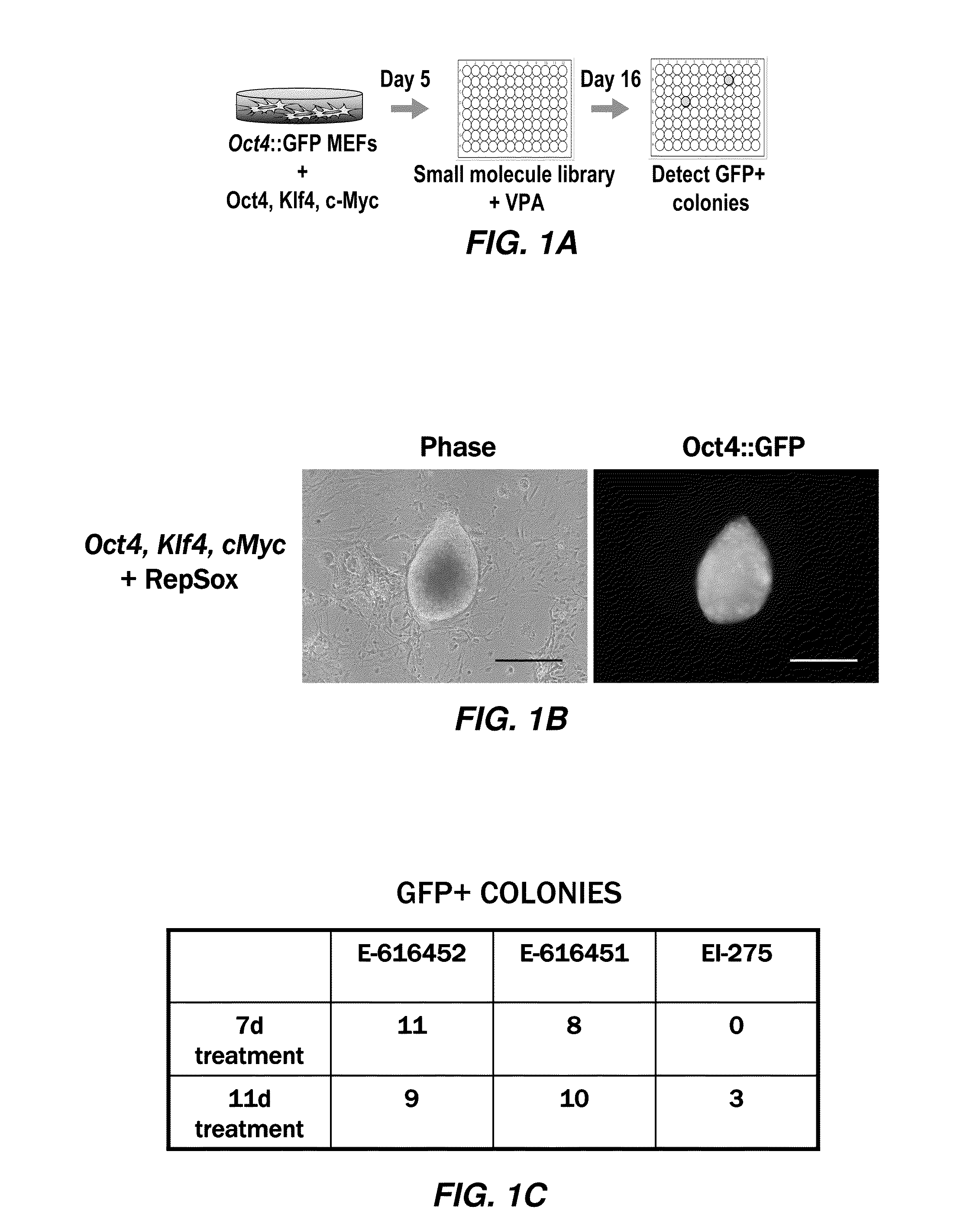
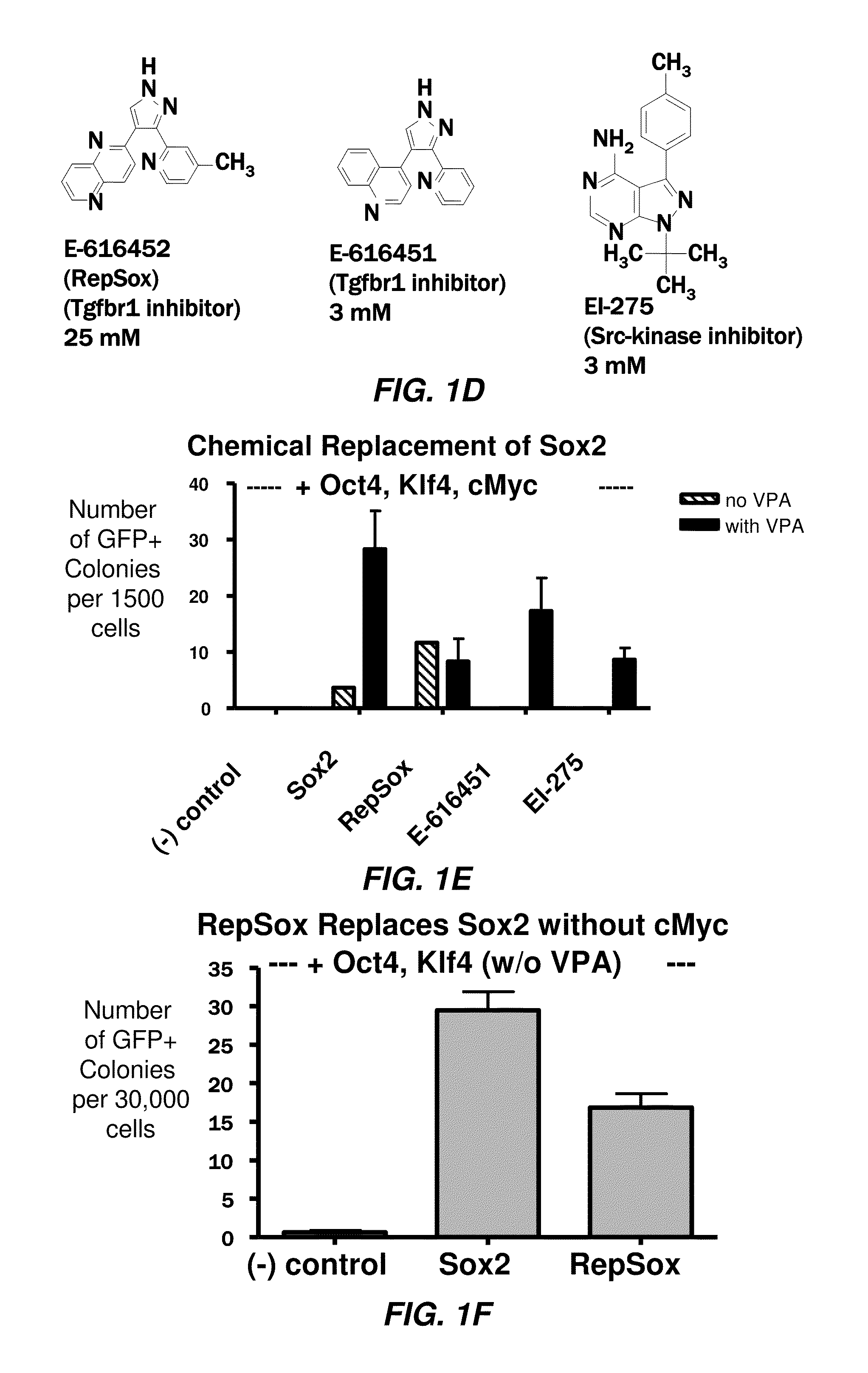
In general, iPS cells are produced by delivery of stem cell-associated genes into adult somatic cells (e.g., fibroblasts). Described herein are methods for enhancing the efficiency and rate of induced pluripotent stem cell production by treating somatic cells with a transforming growth factor-beta receptor (TGFβR) inhibitor. Also described herein are iPS cell compositions made according to the methods described herein and iPS cell compositions comprising an iPS cell in an admixture with a TGFβR inhibitor. Further described herein are kits for producing iPS cells using a TGFβR inhibitor.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Efficient induction of pluripotent stem cells using small molecule compounds
InactiveUS20120021519A1Effective treatmentArtificial cell constructsCell culture active agentsHuman Induced Pluripotent Stem CellsPopulation
The disclosure features a method of producing a reprogrammed cell (e.g. an induced pluripotent stem cell or an undifferentiated cell) from a differentiated (e.g. somatic) cell. In some embodiments, the methods includes contacting a differentiated (e.g. somatic cell) with a TGFBR1 inhibitor or anti-TGF-β-antibody to produce a reprogrammed cell (e.g. pluripotent stem cell or undifferentiated cell). Embodiments of the present invention relate to a reprogrammed cell and methods and compositions for producing a chemically produced reprogrammed cell or populations thereof.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Method of efficiently establishing induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20120196360A1Efficiently establishedImprove setup efficiencySugar derivativesGenetically modified cellsPlasmid VectorSomatic cell
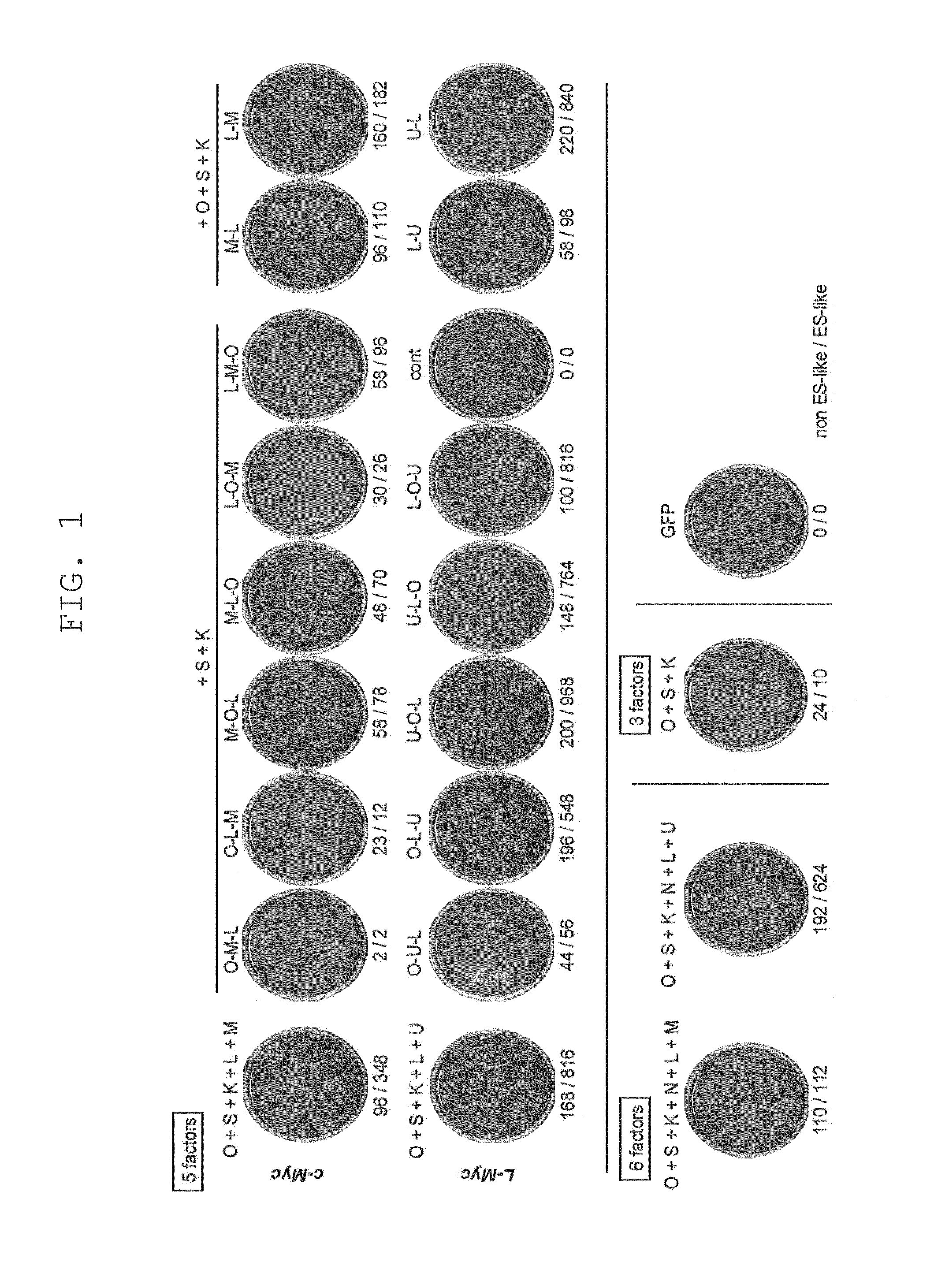
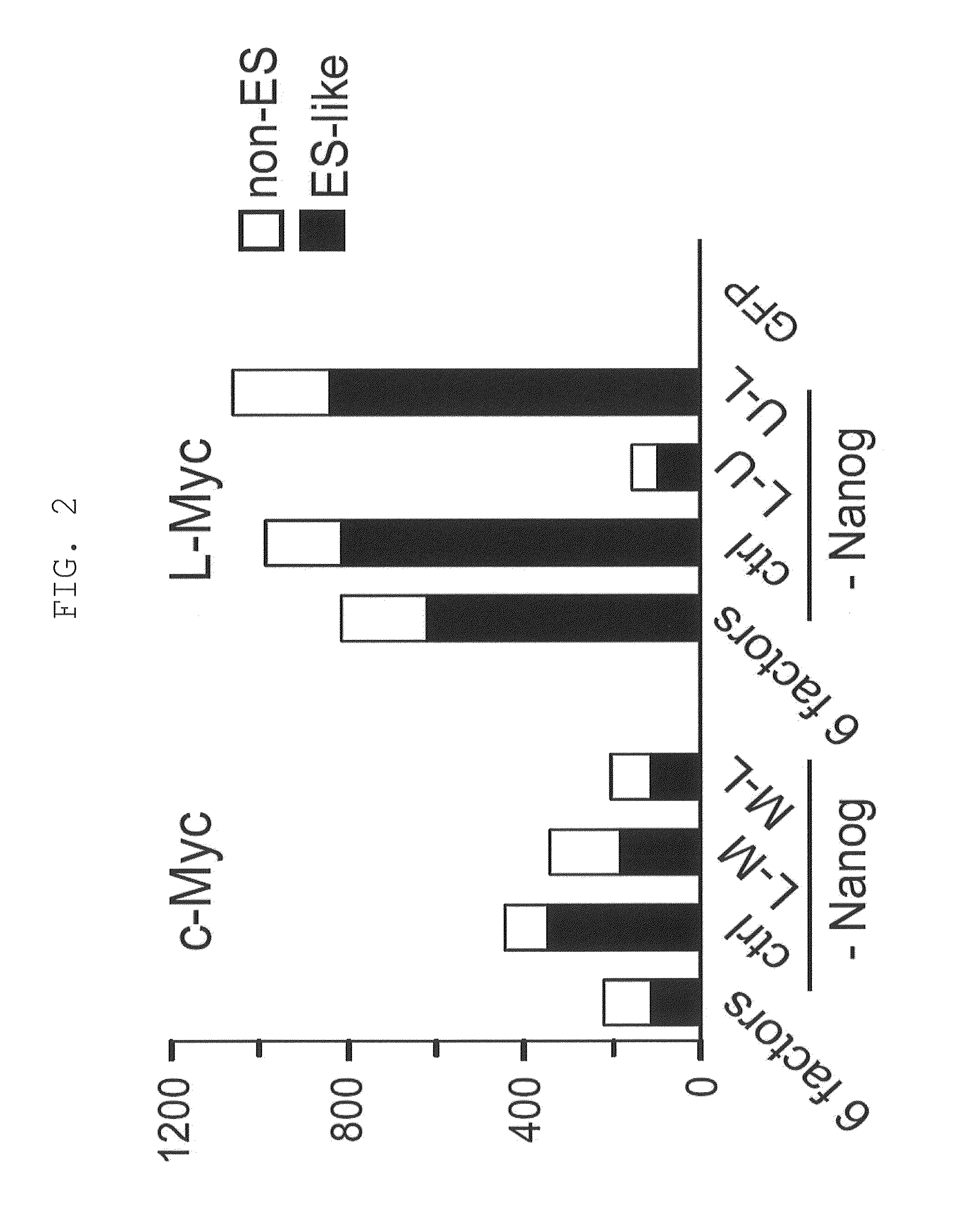
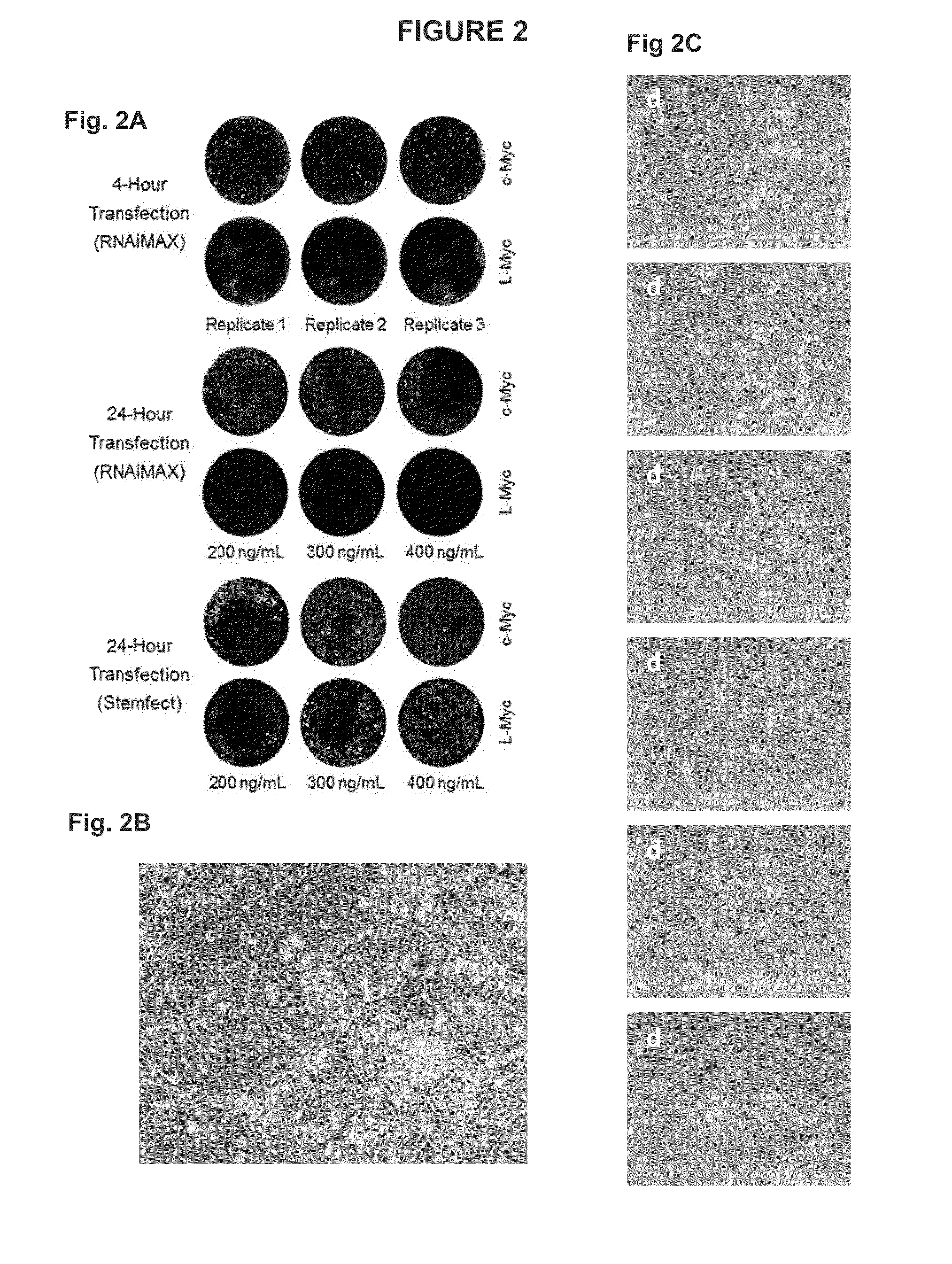
Provided is a method of producing an iPS cell, comprising bringing (a) Oct3 / 4 or a nucleic acid that encodes the same, (b) Klf4 or a nucleic acid that encodes the same, and (c) Sox2 or a nucleic acid that encodes the same, as well as (d1) L-Myc or a nucleic acid that encodes the same and / or (d2) a functional inhibitor of p53, into contact with a somatic cell. It is preferable that (a) a nucleic acid that encodes Oct3 / 4, (b) a nucleic acid that encodes Klf4, (c) a nucleic acid that encodes Sox2, (d1) a nucleic acid that encodes L-Myc and (e) a nucleic acid that encodes Lin28 or Lin28b be inserted into an episomal vector having loxP sequences placed in the same orientation on the 5′ and 3′ sides of a vector constituent essential for the replication of the vector, that (d2) a nucleic acid that encodes an shRNA against p53 be inserted into a vector ensuring transient expression (plasmid vector and the like), and that all these nucleic acids be transferred to a somatic cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Methods of cell-based technologies
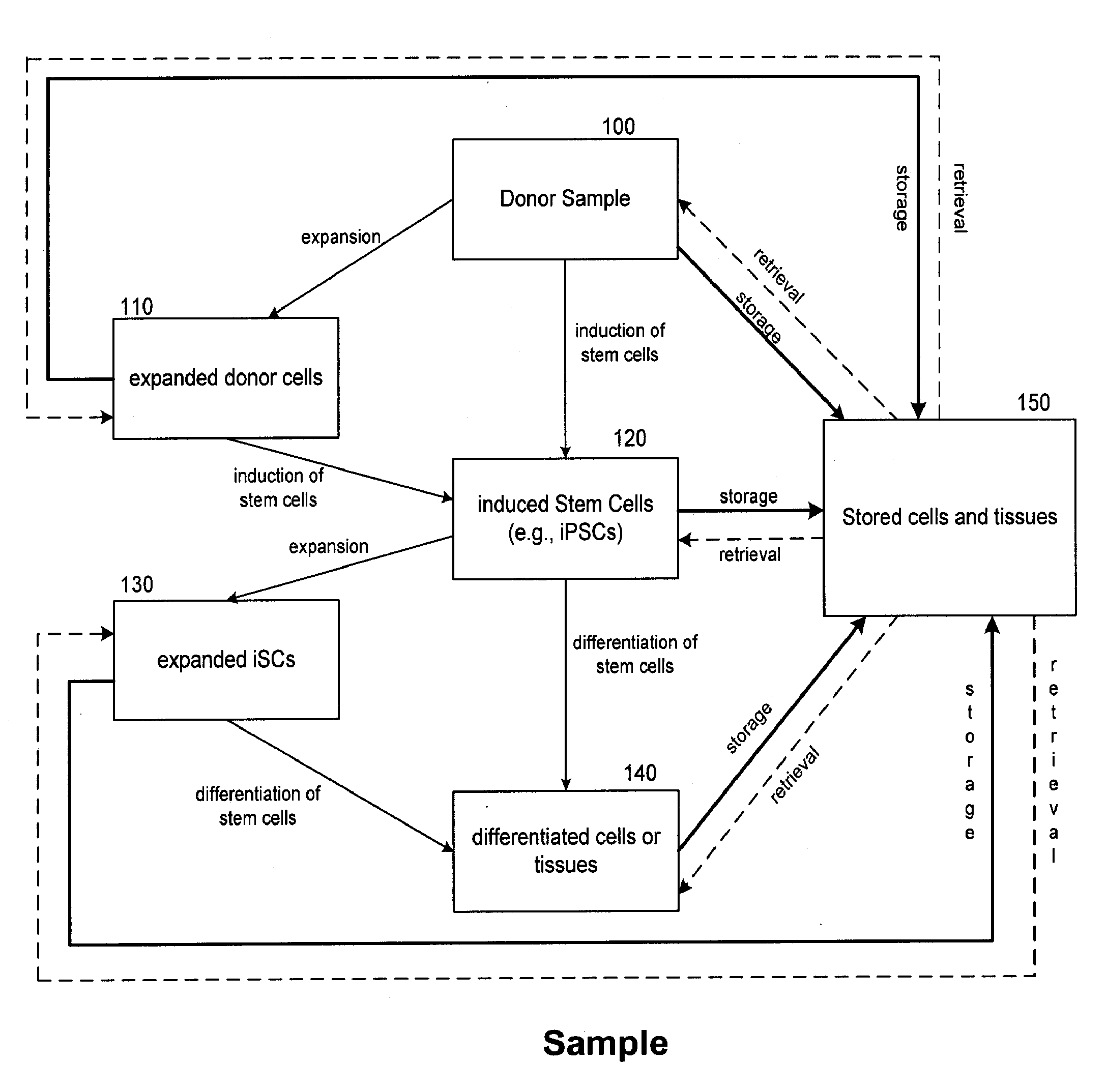
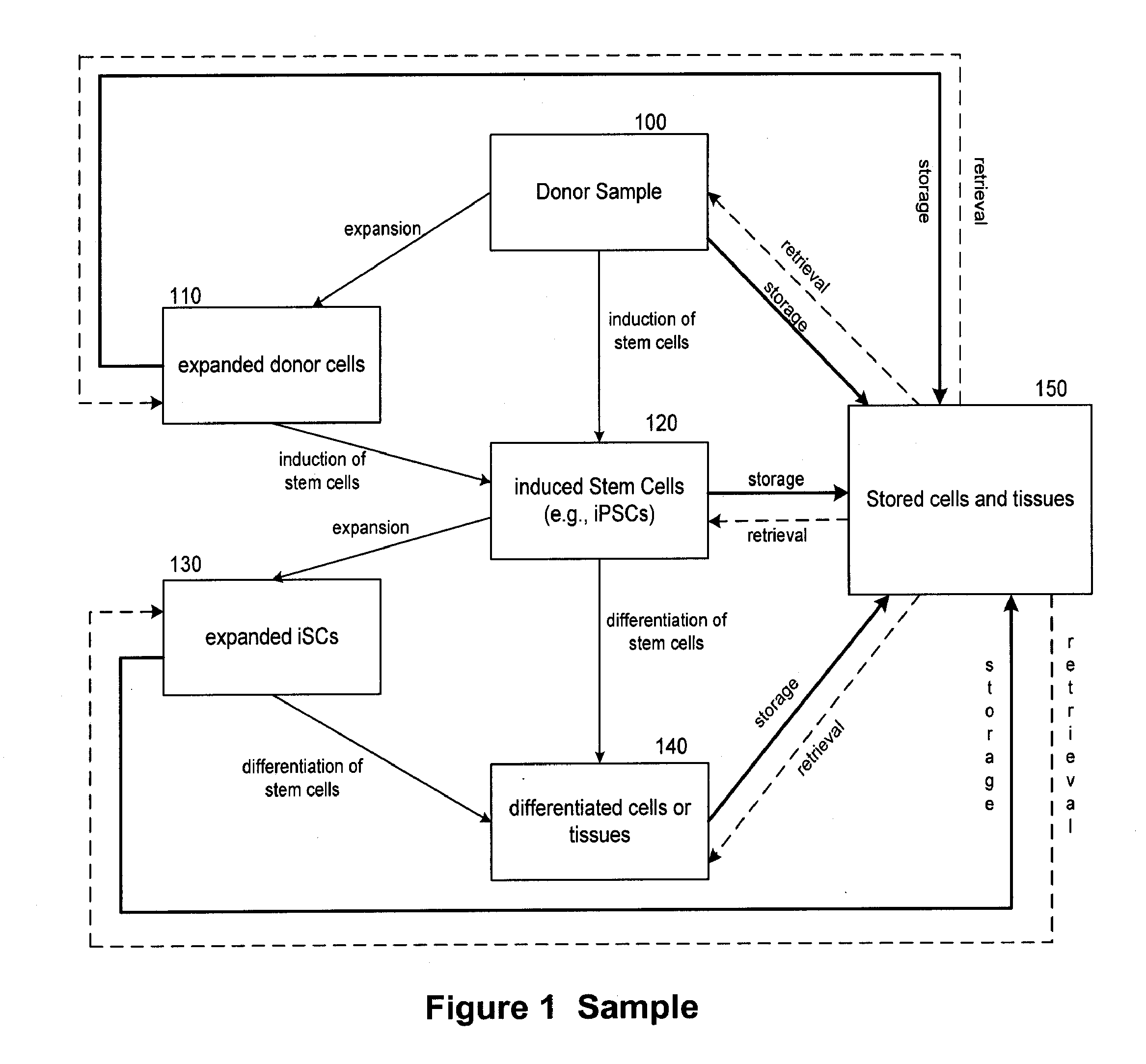
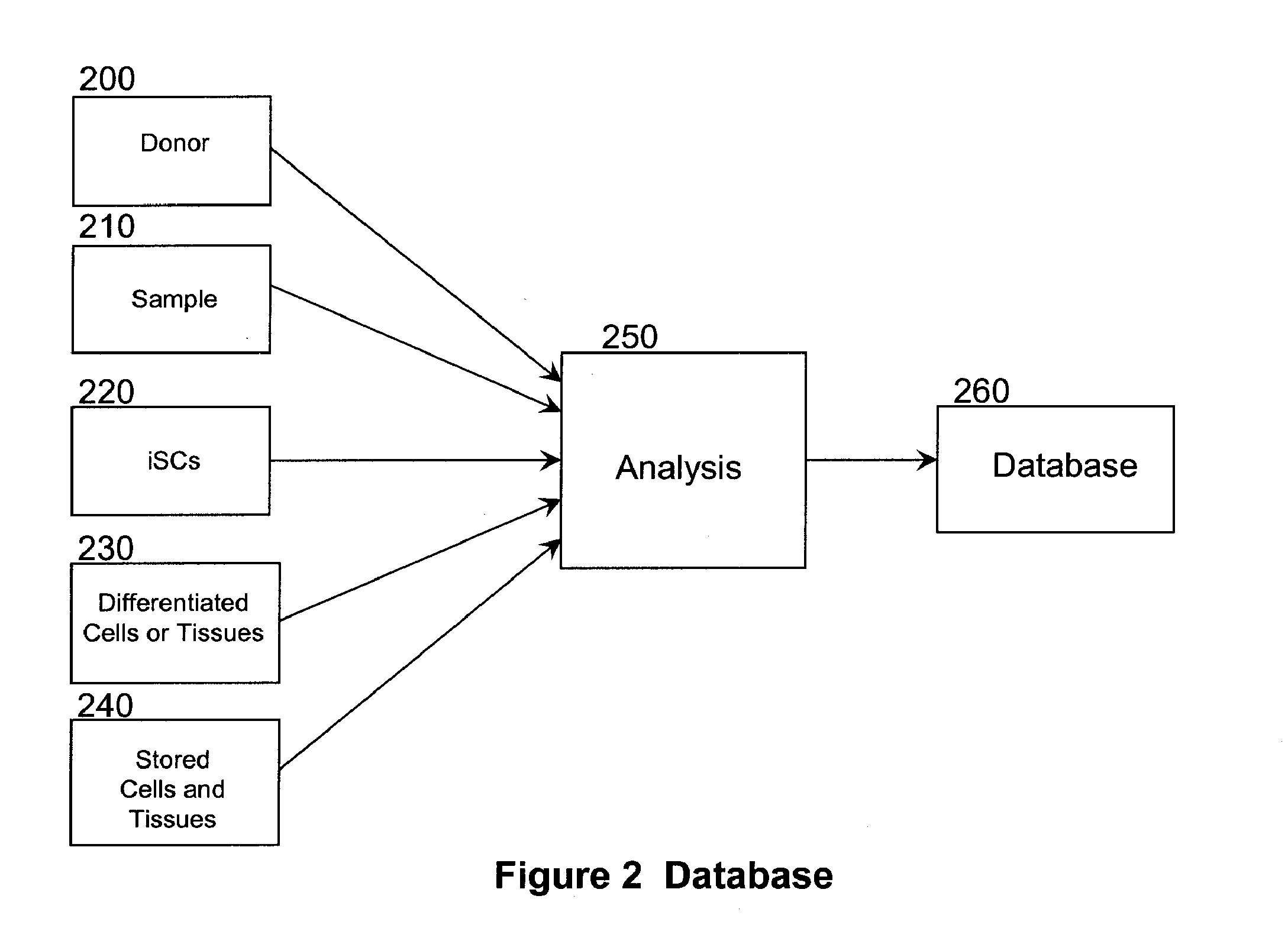
The present disclosure features methods relating to conducting a stem cell technology business such as a regenerative medicine business based on induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and cells differentiated from iPSCs. The present disclosure also provides a database of iPSC-derived cells and methods of using the database for tracking customers and samples, as well as methods for marketing and running the business.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
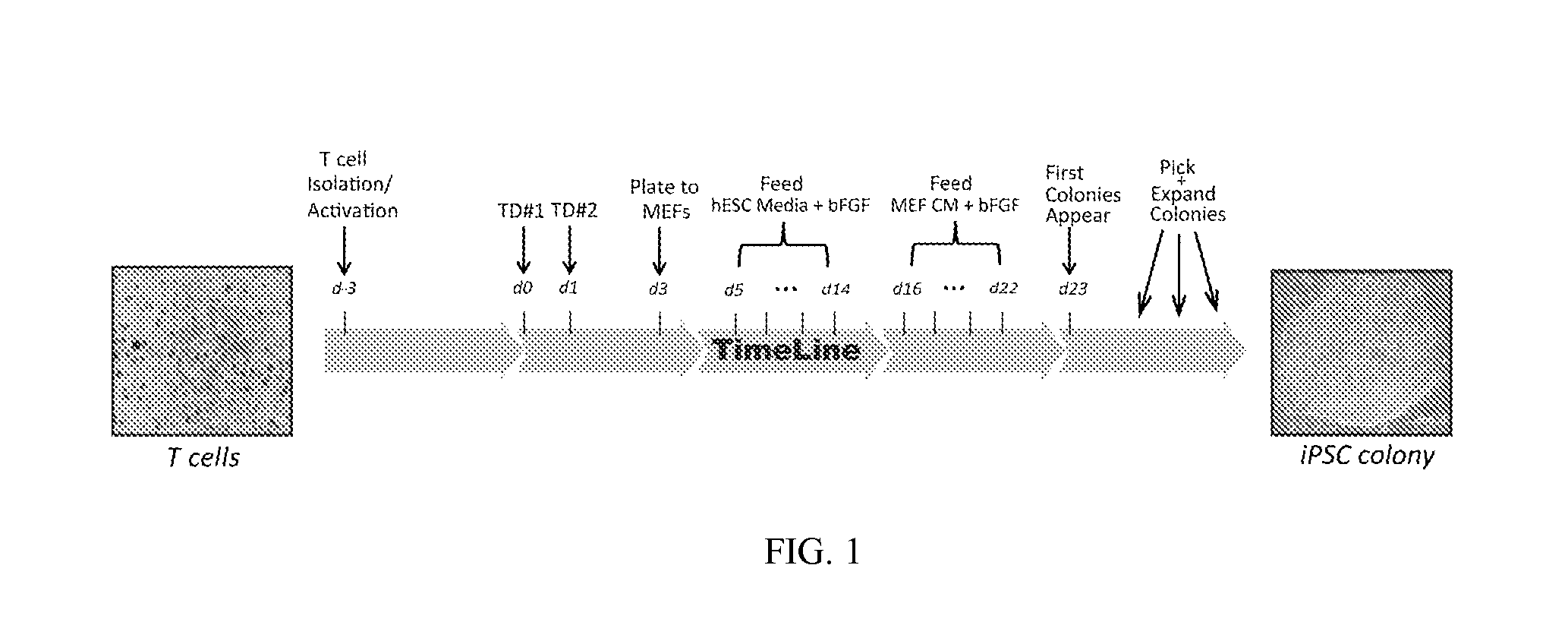
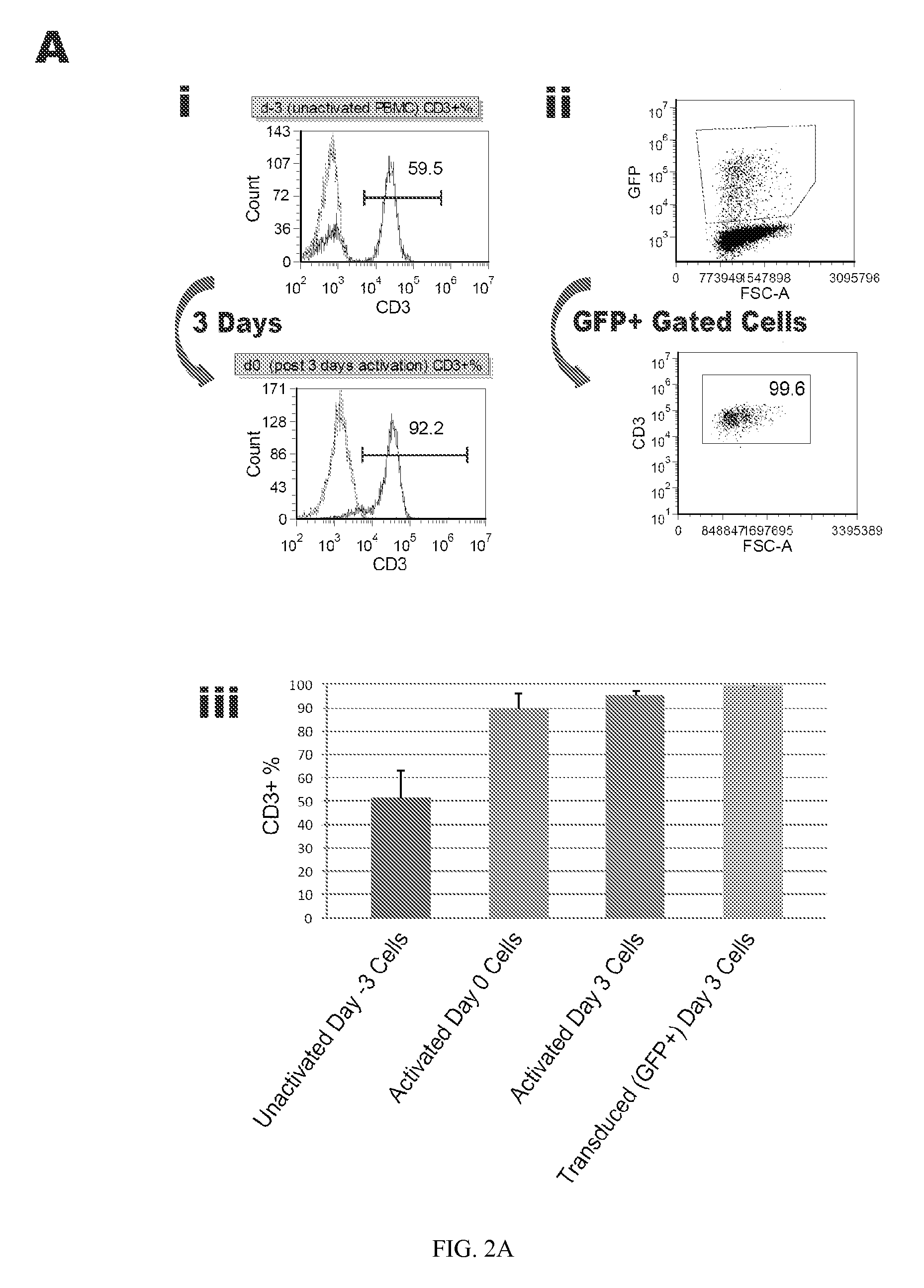
Reprogramming T cells and hematopoietic cells
ActiveUS8741648B2Increase capacityGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsProgenitorHematopoietic cell
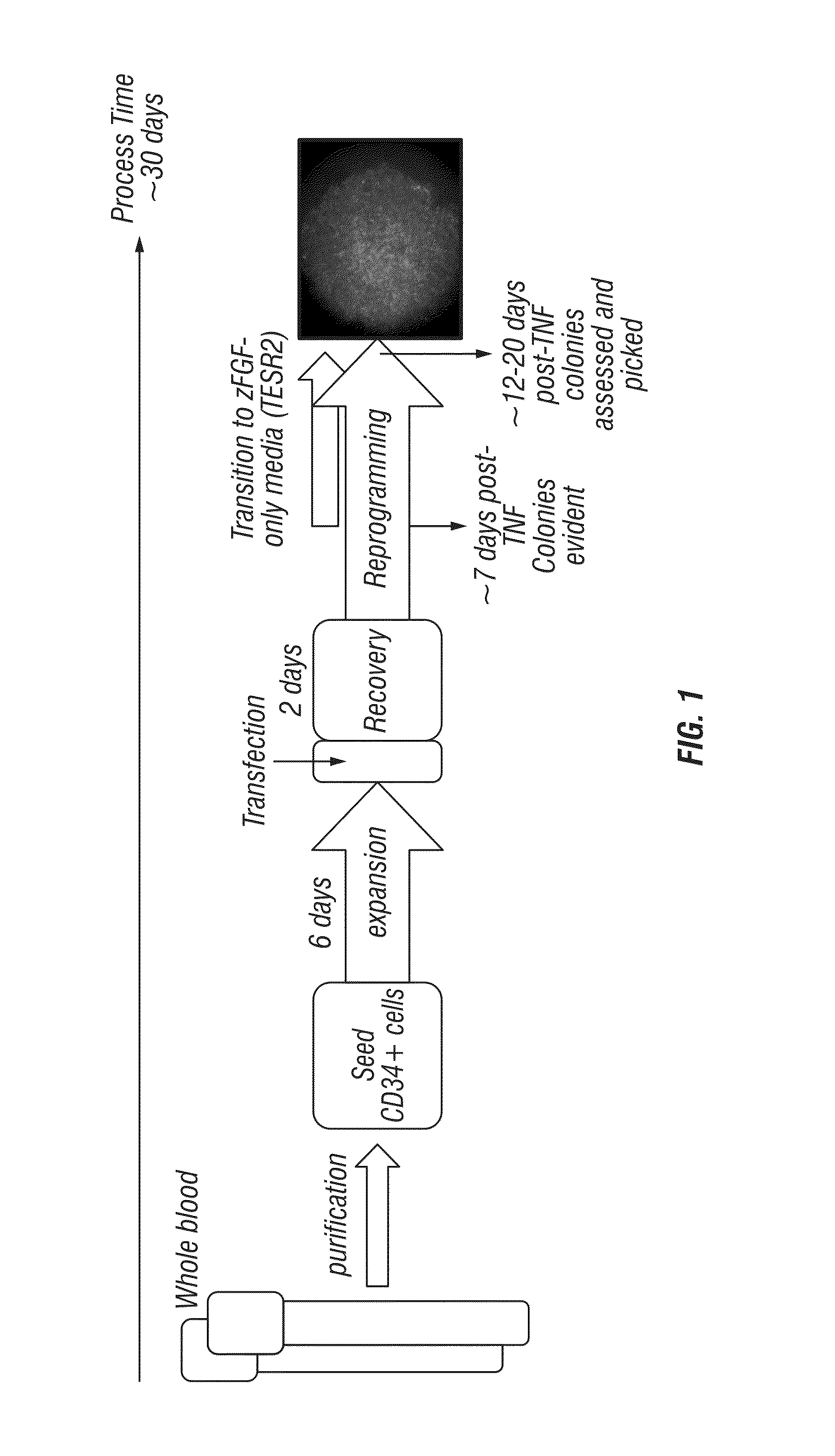
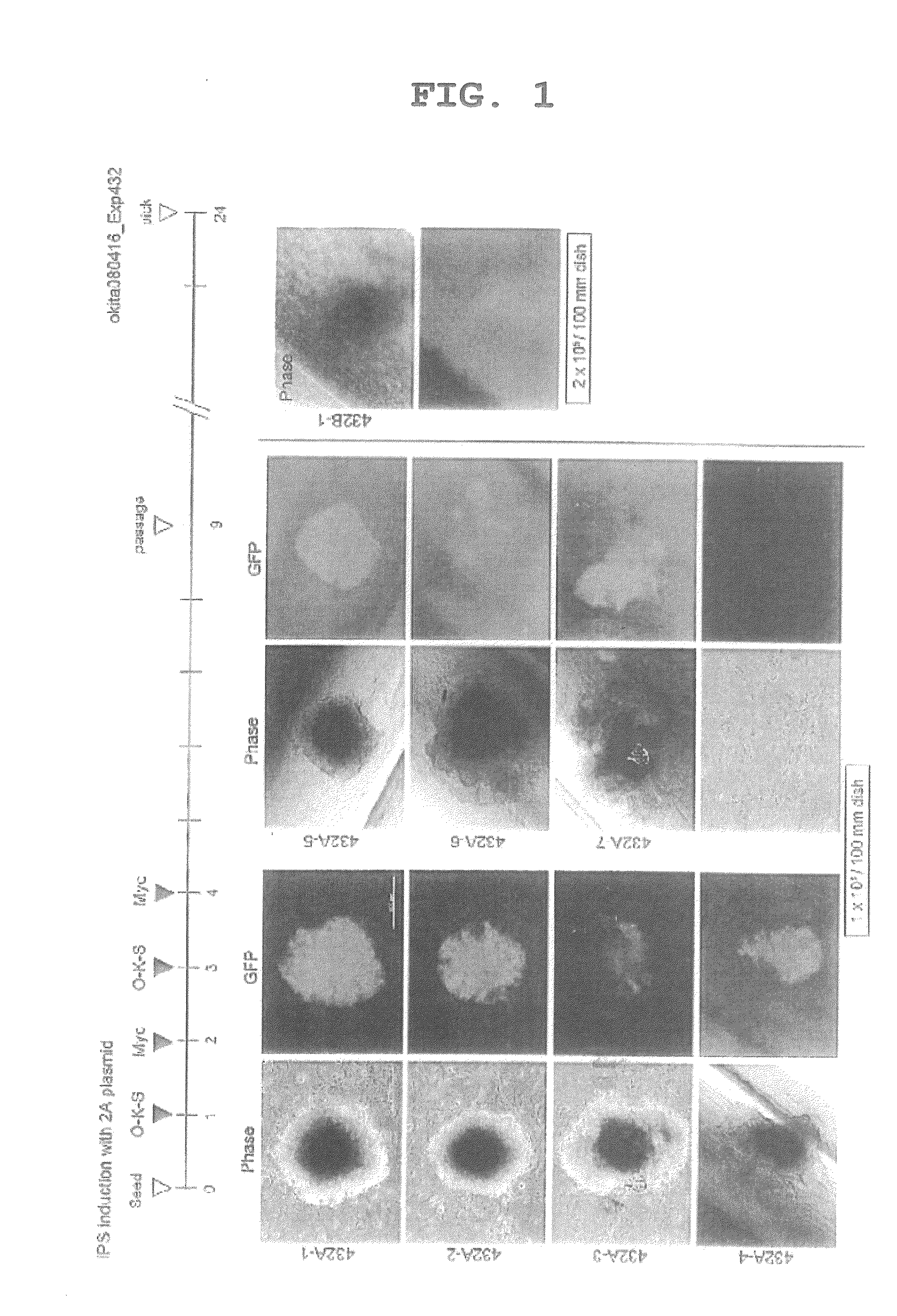
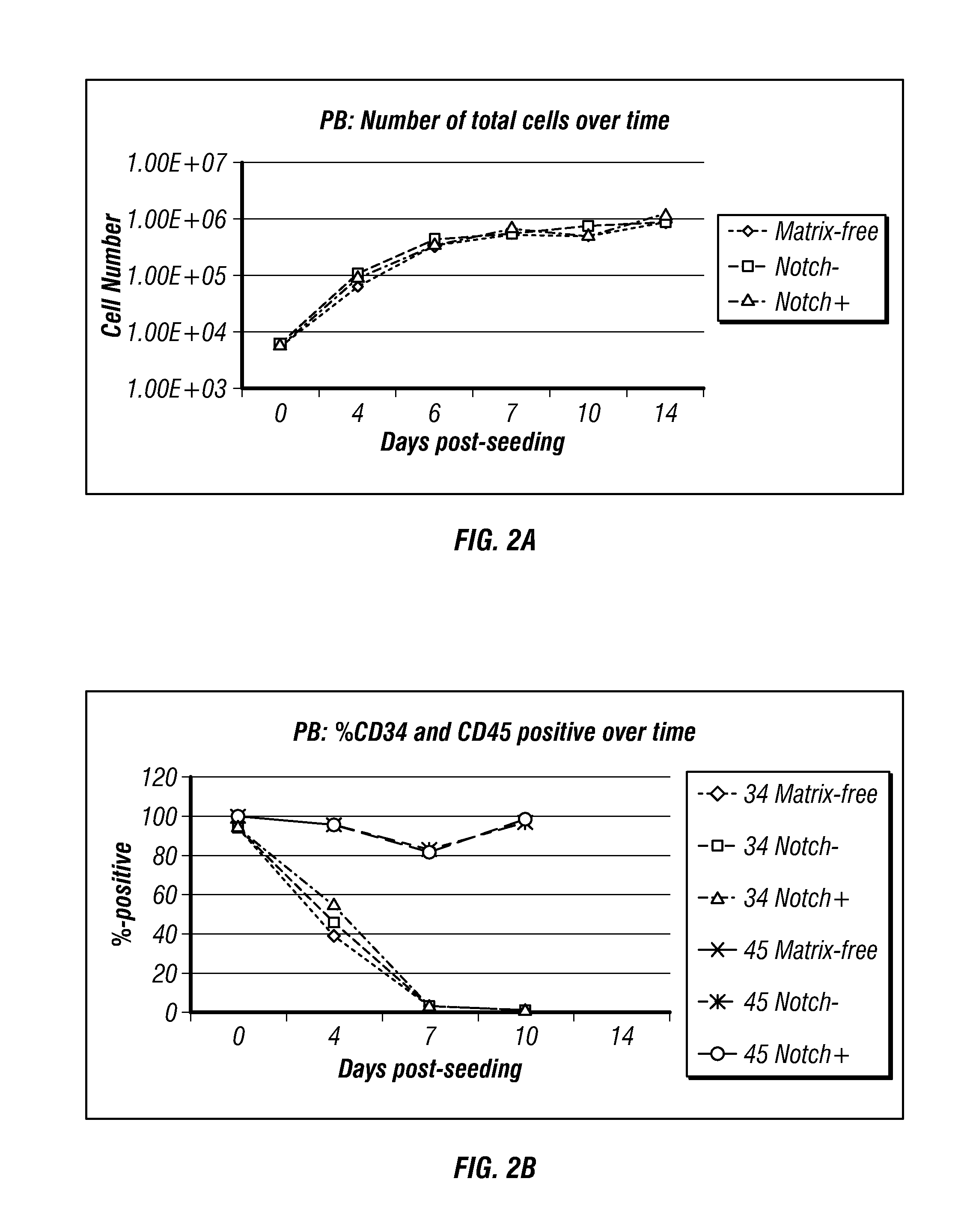
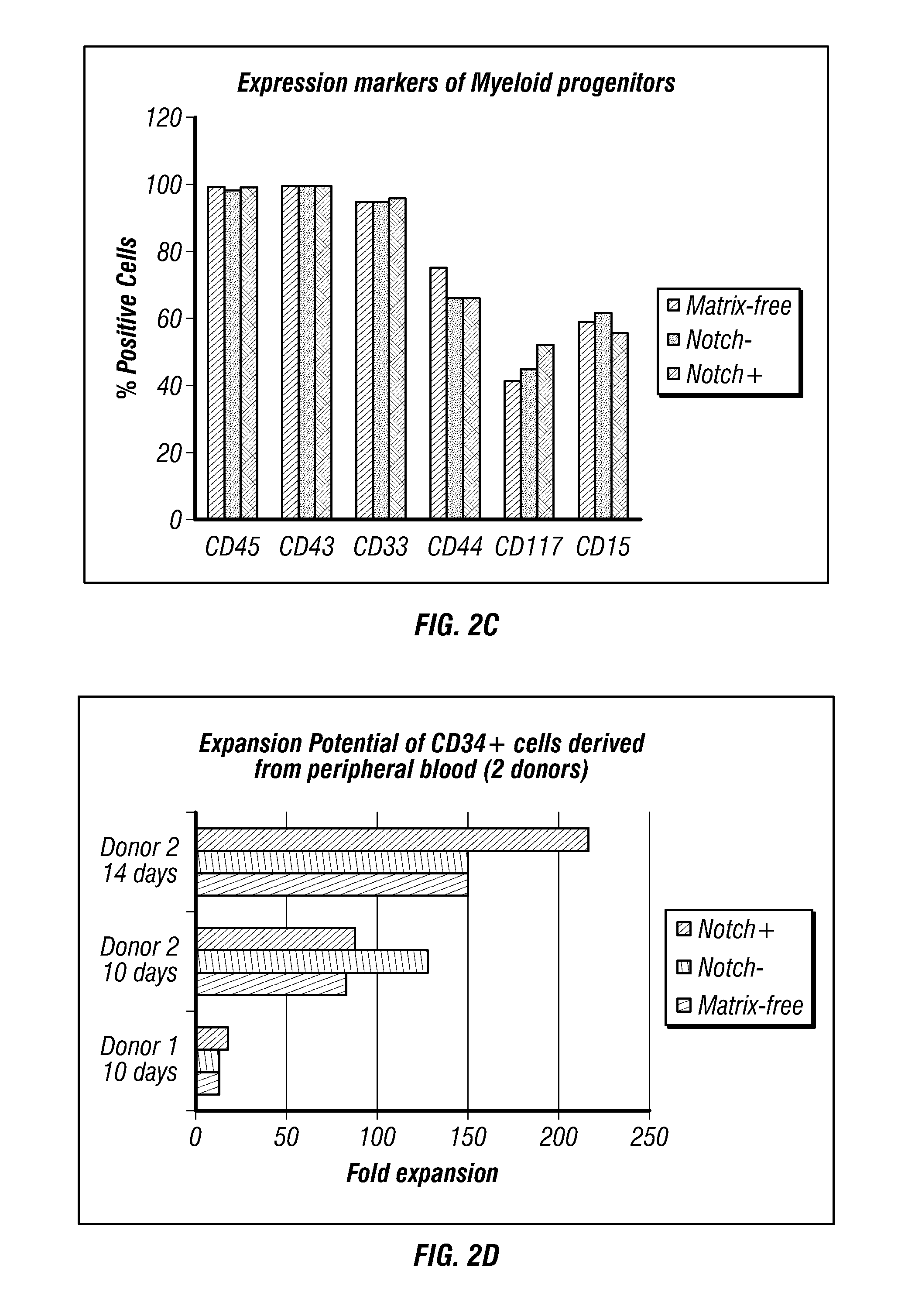
Methods and compositions relating to the production of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) are disclosed. For example, induced pluripotent stem cells may be generated from CD34+ hematopoietic cells, such as human CD34+ blood progenitor cells, or T cells. Various iPS cell lines are also provided. In certain embodiments, the invention provides novel induced pluripotent stem cells with a genome comprising genetic rearrangement of T cell receptors.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Nuclear reprogramming factor and induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20100062533A1Easy to prepareEffective isolationGenetically modified cellsPeptidesNuclear reprogrammingCell therapy
The present invention relates to a nuclear reprogramming factor having an action of reprogramming a differentiated somatic cell to derive an induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cell. The present invention also relates to the aforementioned iPS cells, methods of generating and maintaining iPS cells, and methods of using iPS cells, including screening and testing methods as well as methods of stem cell therapy. The present invention also relates to somatic cells derived by inducing differentiation of the aforementioned iPS cells.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Enhanced efficiency of induced pluripotent stem cell generation
Human somatic cells are reprogrammed to become induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) by the introduction of a minicircle DNA vector. Cells of interest include adipose stem cells.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Feeder-free derivation of human-induced pluripotent stem cells with synthetic messenger RNA
ActiveUS20130302295A1Improve efficiencyShorten the timeBiocideNervous disorderReprogrammingFibroblast
The present disclosure relates generally to novel methods and compositions for using engineered reprogramming factor(s) for the creation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) through a kinetically controlled process. Specifically, this disclosure relates to establishing combinations of reprogramming factors, including fusions between conventional reprogramming factors with transactivation domains, optimized for reprogramming various types of cells. More specifically, the exemplary methods disclosed herein can be used for creating induced pluripotent stem cells from various mammalian cell types, including human fibroblasts. Exemplary methods of feeder-free derivation of human induced pluripotent stem cells using synthetic messenger RNA are also disclosed.
Owner:ALLELE BIOTECH & PHARMA
Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from small volumes of peripheral blood
ActiveUS8691574B2Improve efficiencyLower the volumeGenetically modified cellsCulture processProgenitorReprogramming
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Feeder-free derivation of human-induced pluripotent stem cells with synthetic messenger RNA
ActiveUS20140349401A1Improve efficiencyShorten the timePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifGenetically modified cellsFeeder freeHuman Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
The present disclosure relates generally to novel methods and compositions for using engineered reprogramming factor(s) for the creation of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) through a kinetically controlled process. Specifically, this disclosure relates to establishing combinations of reprogramming factors, including fusions between conventional reprogramming factors with transactivation domains, optimized for reprogramming various types of cells. More specifically, the exemplary methods disclosed herein can be used for creating induced pluripotent stem cells from various mammalian cell types, including human fibroblasts. Exemplary methods of feeder-free derivation of human induced pluripotent stem cells using synthetic messenger RNA are also disclosed.
Owner:ALLELE BIOTECH & PHARMA
Method of nuclear reprogramming
InactiveUS20100279404A1Easy to useElectric discharge tubesGenetically modified cellsPlasmid VectorNuclear reprogramming
This invention provides a method of producing an induced pluripotent stem cell comprising the step of introducing at least one kind of non-viral expression vector (more preferably a plasmid vector) incorporating at least one gene that encodes a reprogramming factor into a somatic cell. An induced pluripotent stem cell wherein no exogenous genes induced is integrated into the cellular genome is also provided.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from small volumes of peripheral blood
ActiveUS20120009676A1Improve processing efficiencyLower the volumeGenetically modified cellsCulture processProgenitorReprogramming
Methods and compositions relating to the production of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) are disclosed. For example, induced pluripotent stem cells may be generated from peripheral blood cells, such as human blood progenitor cells, using episomal reprogramming and feeder-free or xeno-free conditions. In certain embodiments, the invention provides novel methods for improving overall reprogramming efficiency with low number of blood progenitor cells.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Methods and platforms for drug discovery
The present invention involves methods for identifying an agent that corrects a phenotype associated with a health condition or a predisposition for a health condition. The invention also involves methods for identifying a diagnostic cellular phenotype, determining the risk of a health condition in a subject, methods for reducing the risk of drug toxicity in a human subject, and methods for identifying a candidate gene that contributes to a human disease. The invention also discloses human induced pluripotent stem cell lines.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
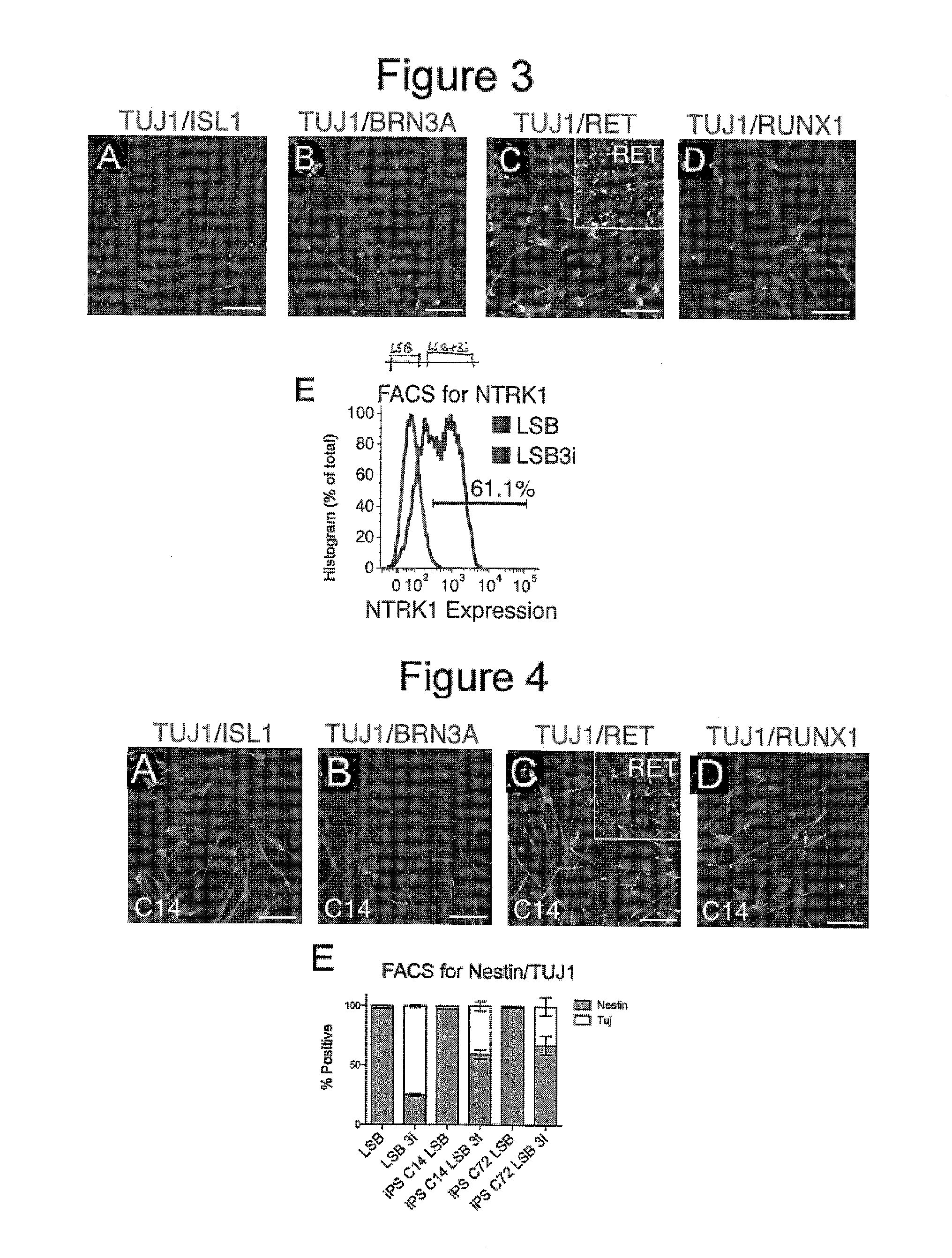
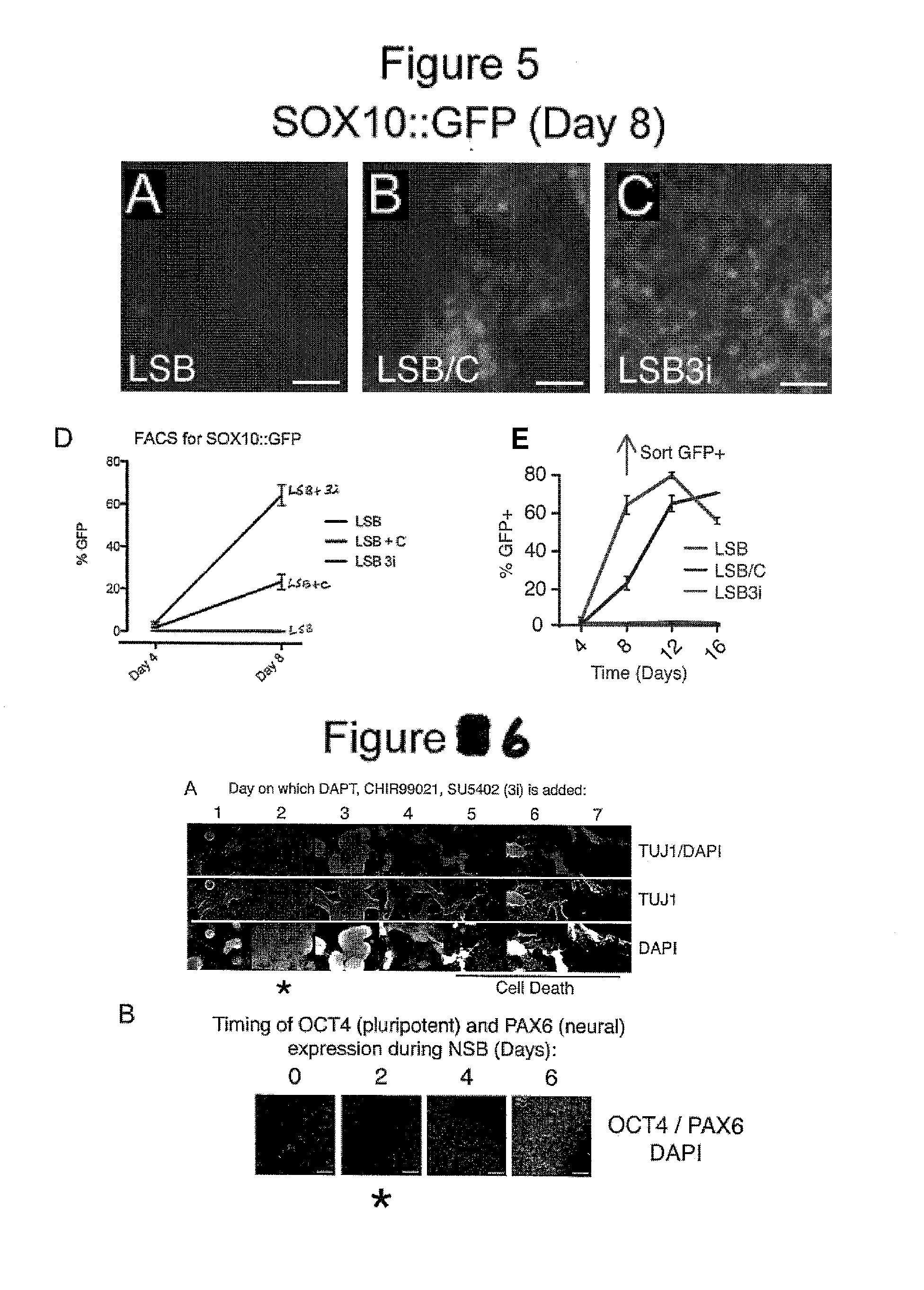
Method of nociceptor differentiation of human embryonic stem cells and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130183674A1Nervous disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementNervous systemLineage specific
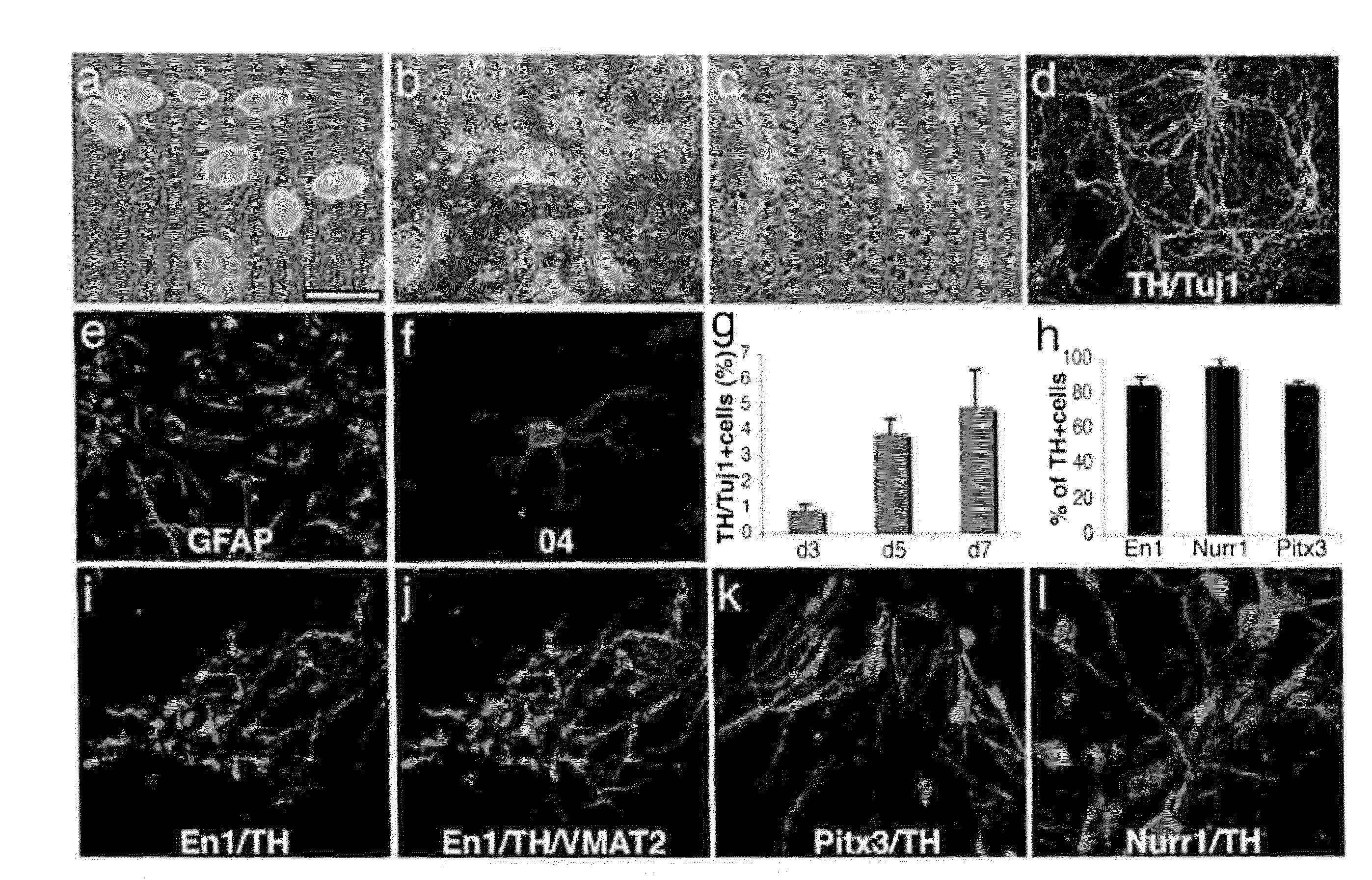
The present invention relates to the field of stem cell biology, in particular the linage specific differentiation of pluripotent or multipotent stem cells, which can include, but is not limited to, human embryonic stem cells (hESC), human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSC), somatic stem cells, cancer stem cells, or any other cell capable of lineage specific differentiation. Specifically described are methods to direct the lineage specific differentiation of hESC and / or hiPSC to nociceptors (i.e. nociceptor cells) using novel culture conditions. The nociceptors made using the methods of the present invention are further contemplated for various uses including, but limited to, use in in vitro drug discovery assays, pain research, and as a therapeutic to reverse disease of, or damage to, the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Further, compositions and methods are provided for producing melanocytes from human pluripotent stem cells for use in disease modeling.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
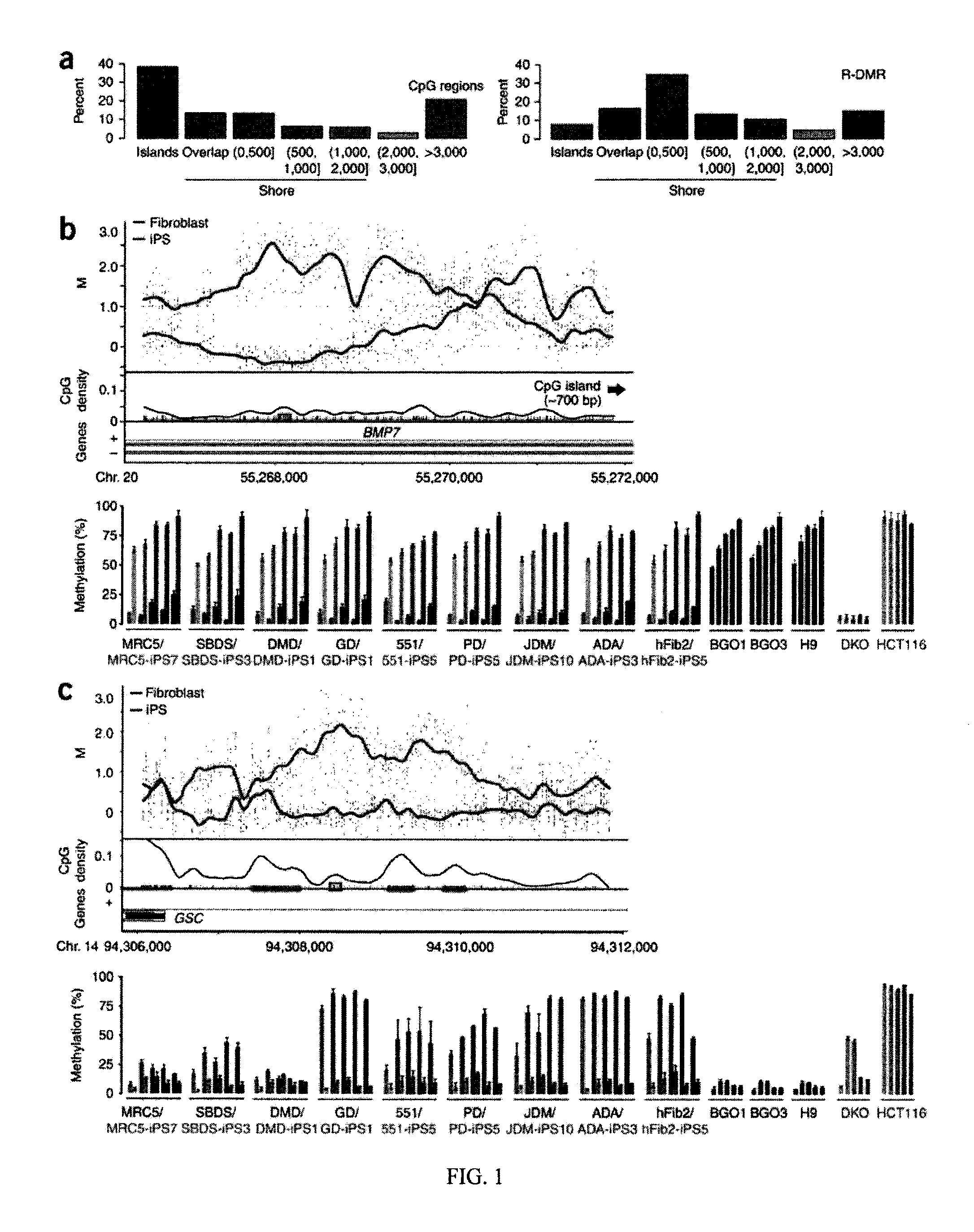
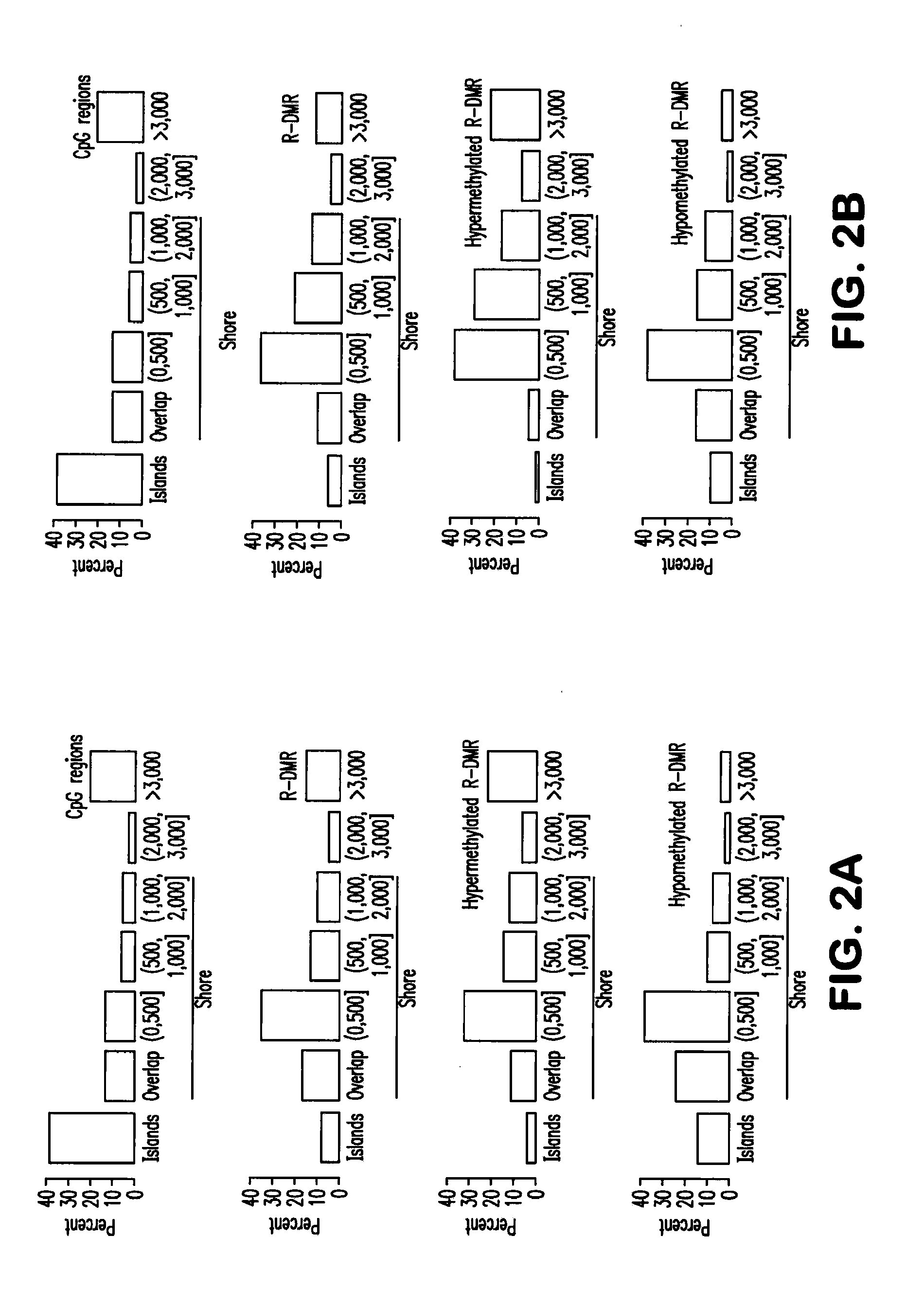
Differentially methylated regions of reprogrammed induced pluripotent stem cells, method and compositions thereof
InactiveUS20120164110A1Differentiation potentialReducing epigenetic memoryBiocideNucleotide librariesDifferentially methylated regionsDifferential Methylation
Provided herein are differentially methylated regions (DMRs) of reprogrammed iPS cells (R-DMRs) and methods of use thereof. The invention provides methods for detecting and analyzing alterations in the methylation status of DMRs in iPS cells, somatic cells and embryonic stem (ES) cells as well as methods for reprogramming somatic cells to generate an iPS cell.
Owner:FEINBERG ANDREW P +1
Induction of pluripotent cells
ActiveUS20120264218A1Improve efficiencyEfficient inductionOrganic chemistryGenetically modified cellsHuman bodyFibroblast
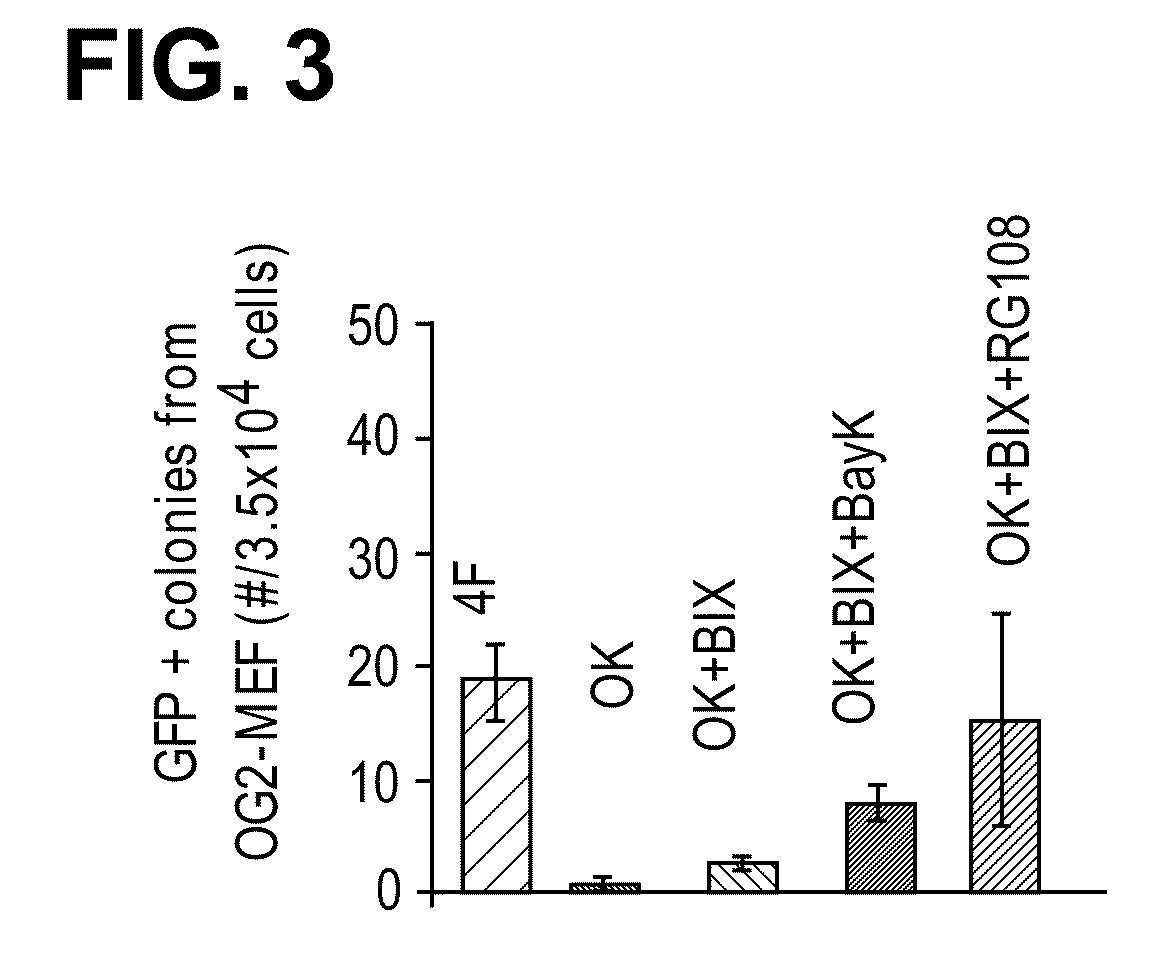
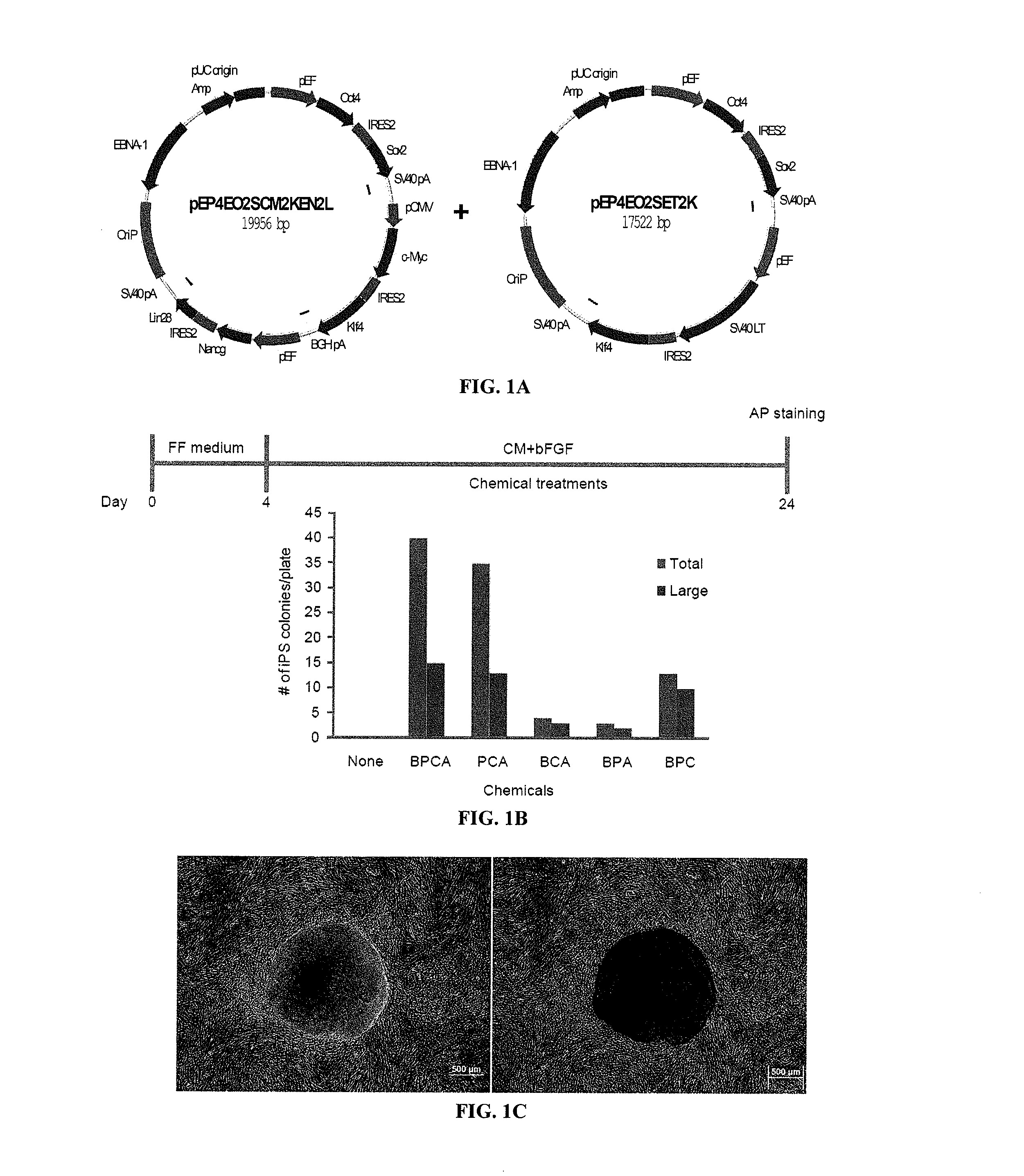
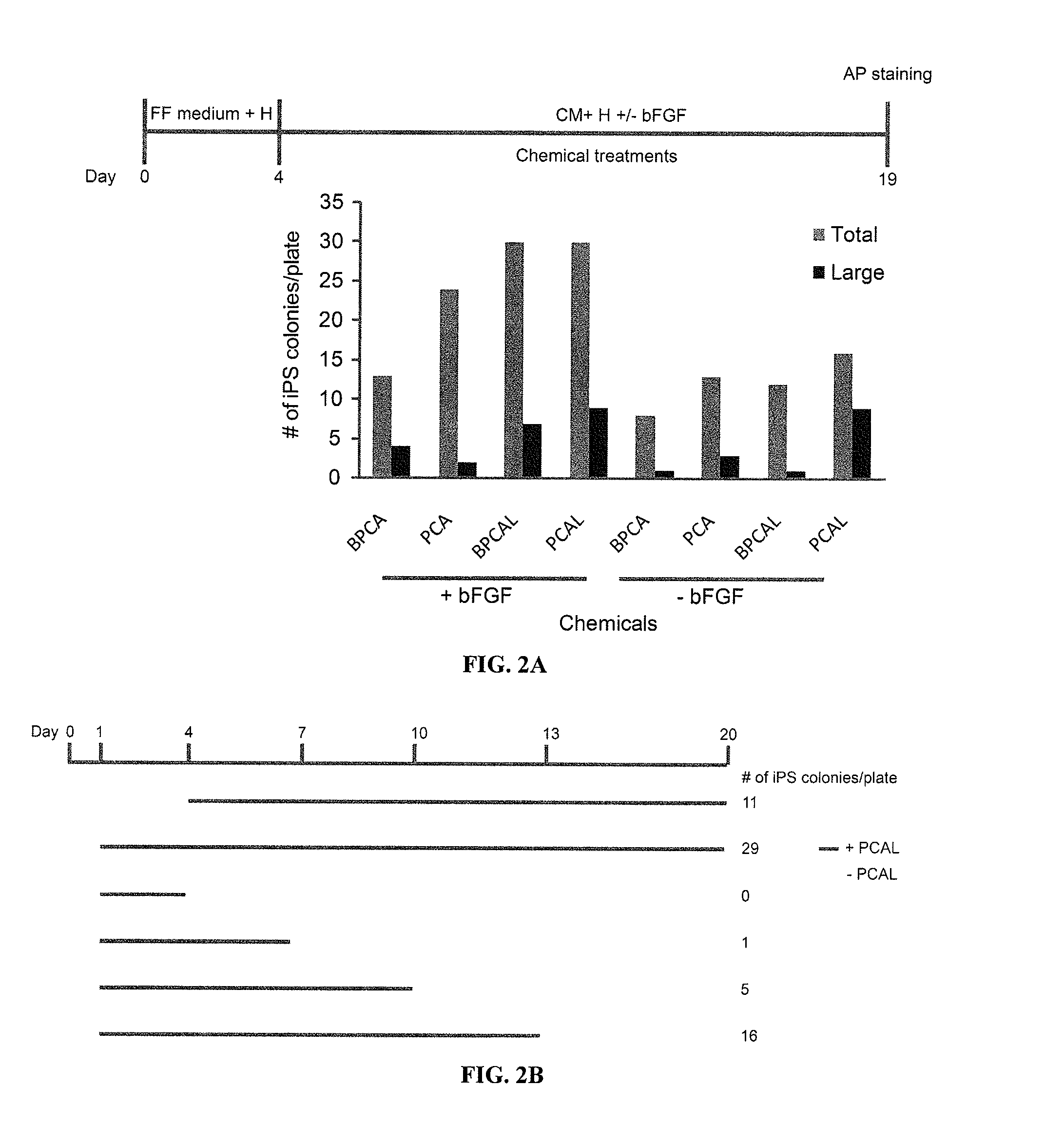
The slow kinetics and low efficiency of reprogramming methods to generate human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) impose major limitations on their utility in biomedical applications. Here we describe a chemical approach that dramatically improves (>200 fold) the efficiency of iPSC generation from human fibroblasts, within seven days of treatment. This will provide a basis for developing safer, more efficient, non-viral methods for reprogramming human somatic cells.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Method of efficiently establishing induced pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20110223669A1Improve setup efficiencyEfficient productionGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsNuclear reprogrammingBiology
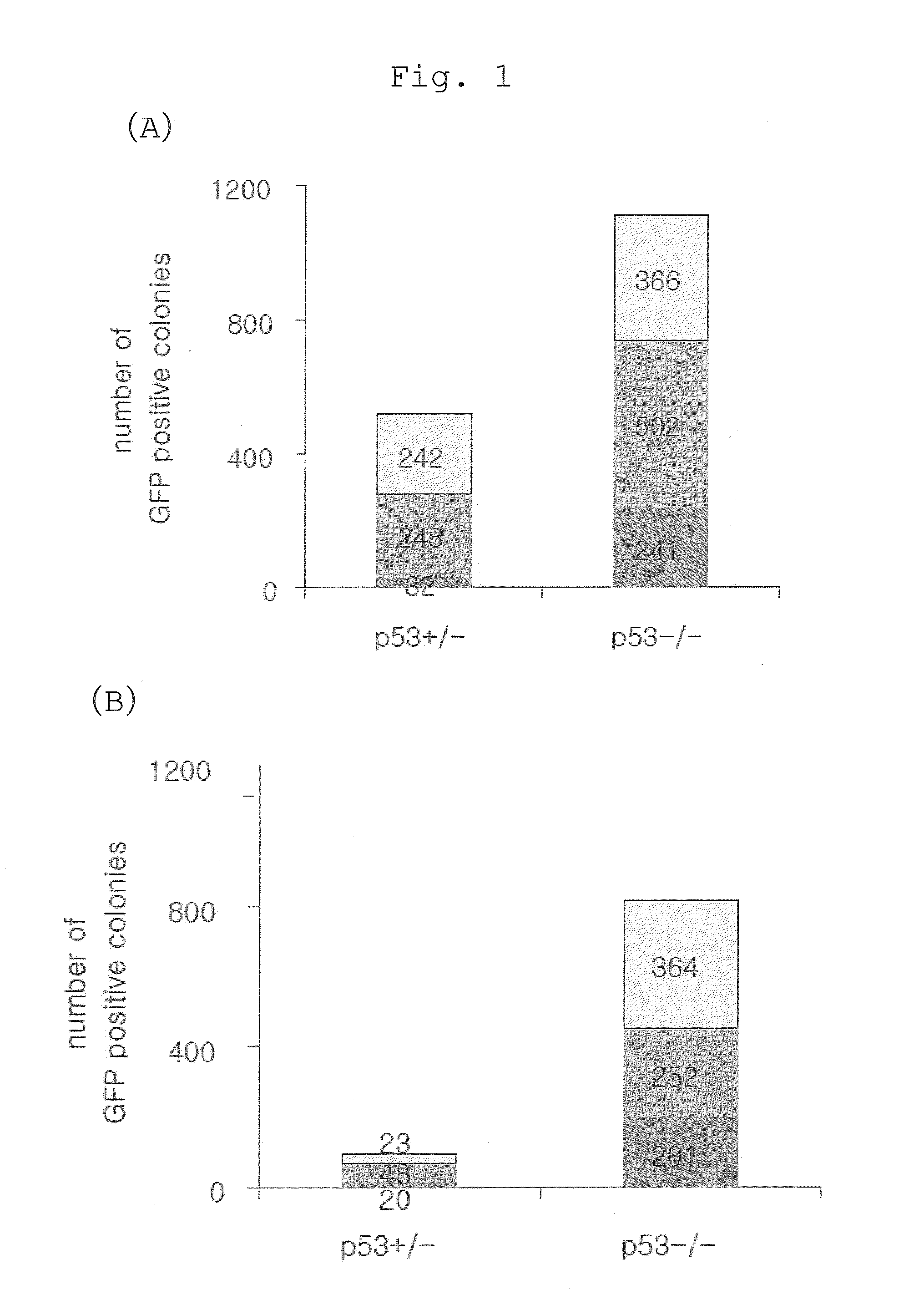
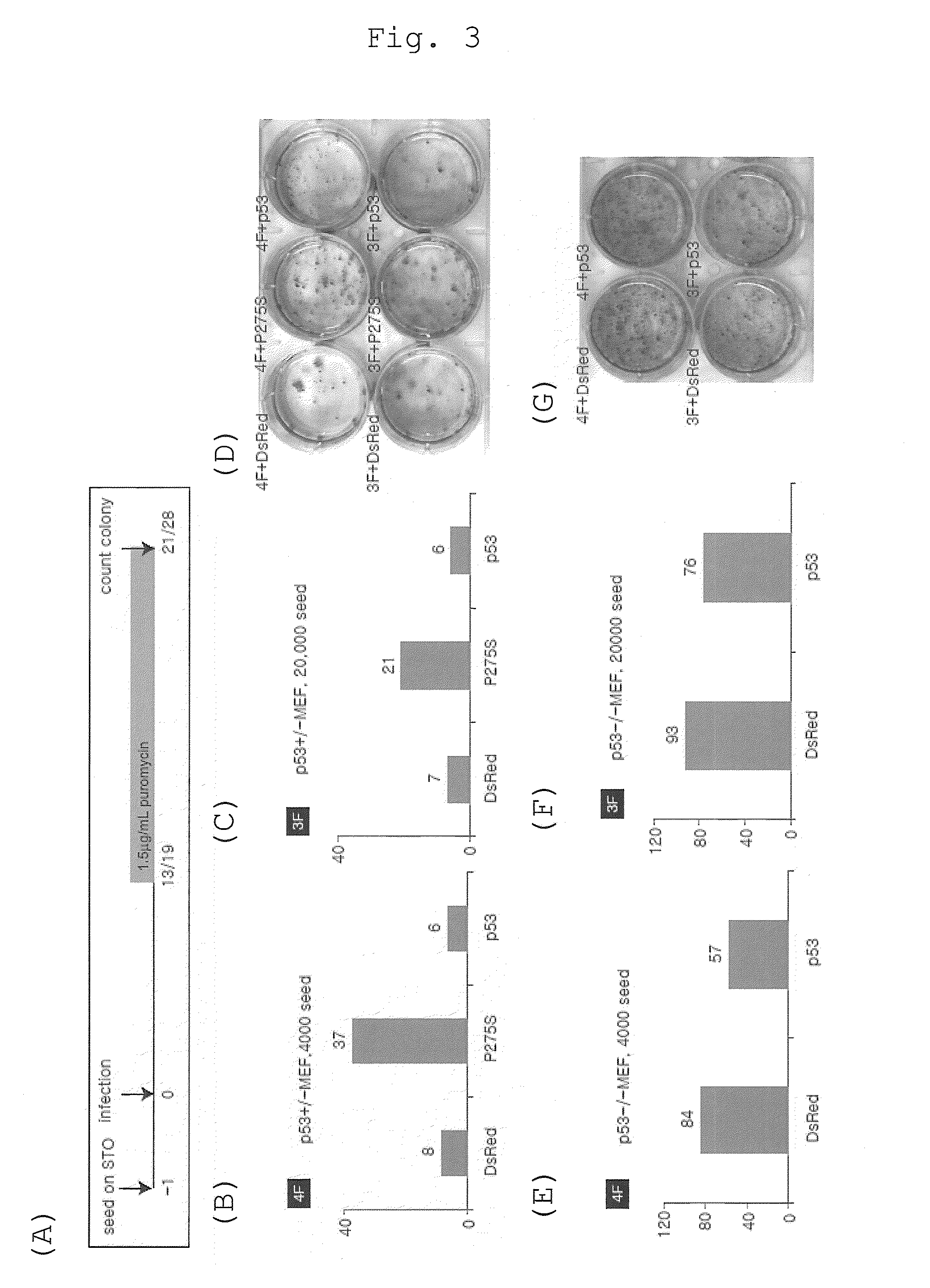
The present invention provides a method of improving the efficiency of establishment of induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, comprising inhibiting the p53 function in the step of somatic cell nuclear reprogramming. The inhibition of p53 function is achieved by bringing a substance selected from the group consisting of (1) chemical inhibitors of p53, (2) dominant negative mutants of p53 and nucleic acids that encode the same, (3) siRNAs and shRNAs against p53 and DNAs that encode the same, and (4) p53 pathway inhibitors, into contact with a somatic cell, and the like. The present invention also provides an agent for improving the efficiency of establishment of iPS cells, the agent comprising an inhibitor of p53 function, particularly (1) chemical inhibitors of p53, (2) dominant negative mutants of p53 and nucleic acids that encode the same, (3) siRNAs and shRNAs against p53 and DNAs that encode the same, and (4) p53 pathway inhibitors. The present invention further provides a method of producing an iPS cell, comprising bringing a nuclear reprogramming substance and an inhibitor of p53 function into contact with a somatic cell.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
Methods for producing induced pluripotent stem cells
InactiveUS20110306516A1Microbiological testing/measurementGenetically modified cellsFibroblastReprogramming
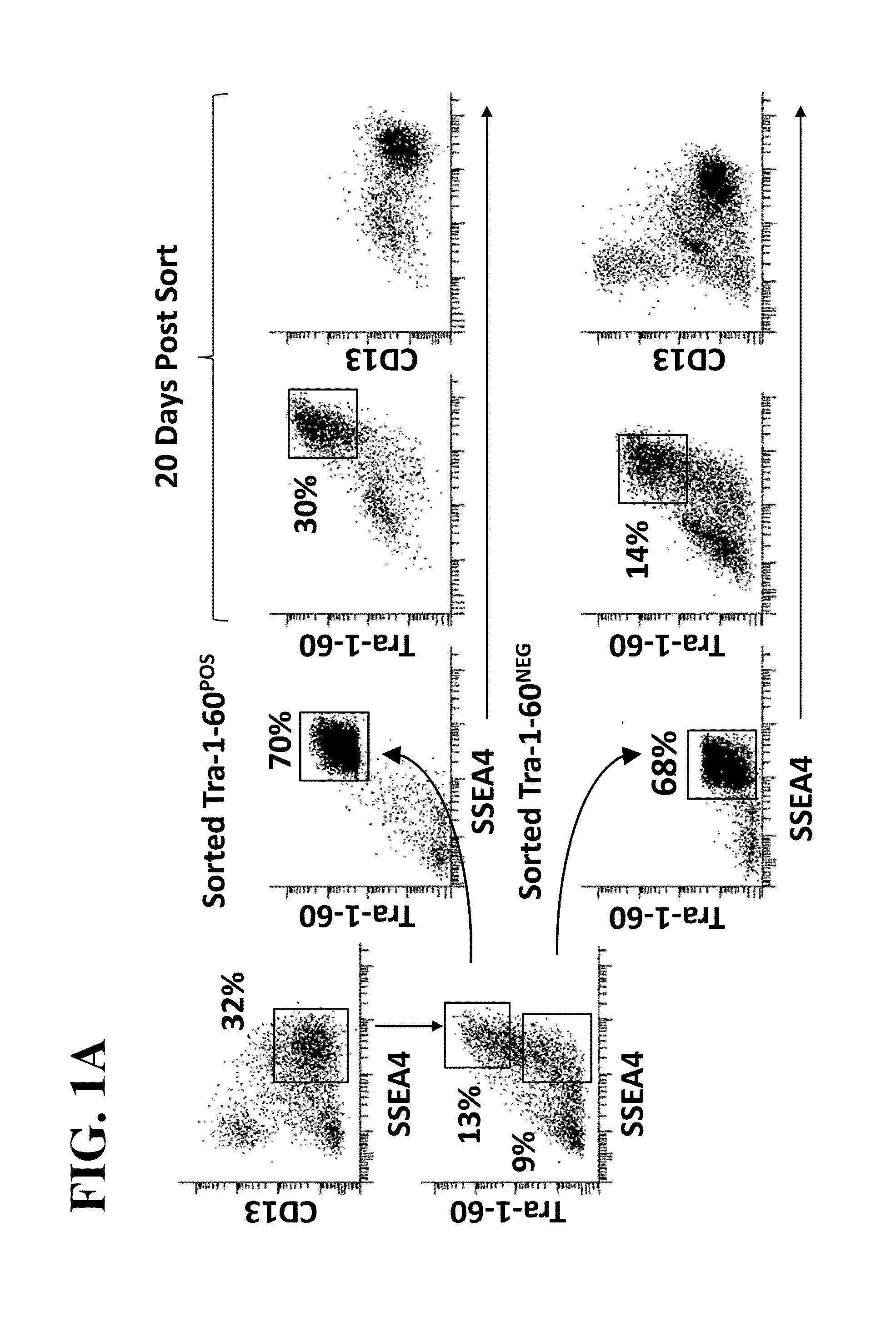
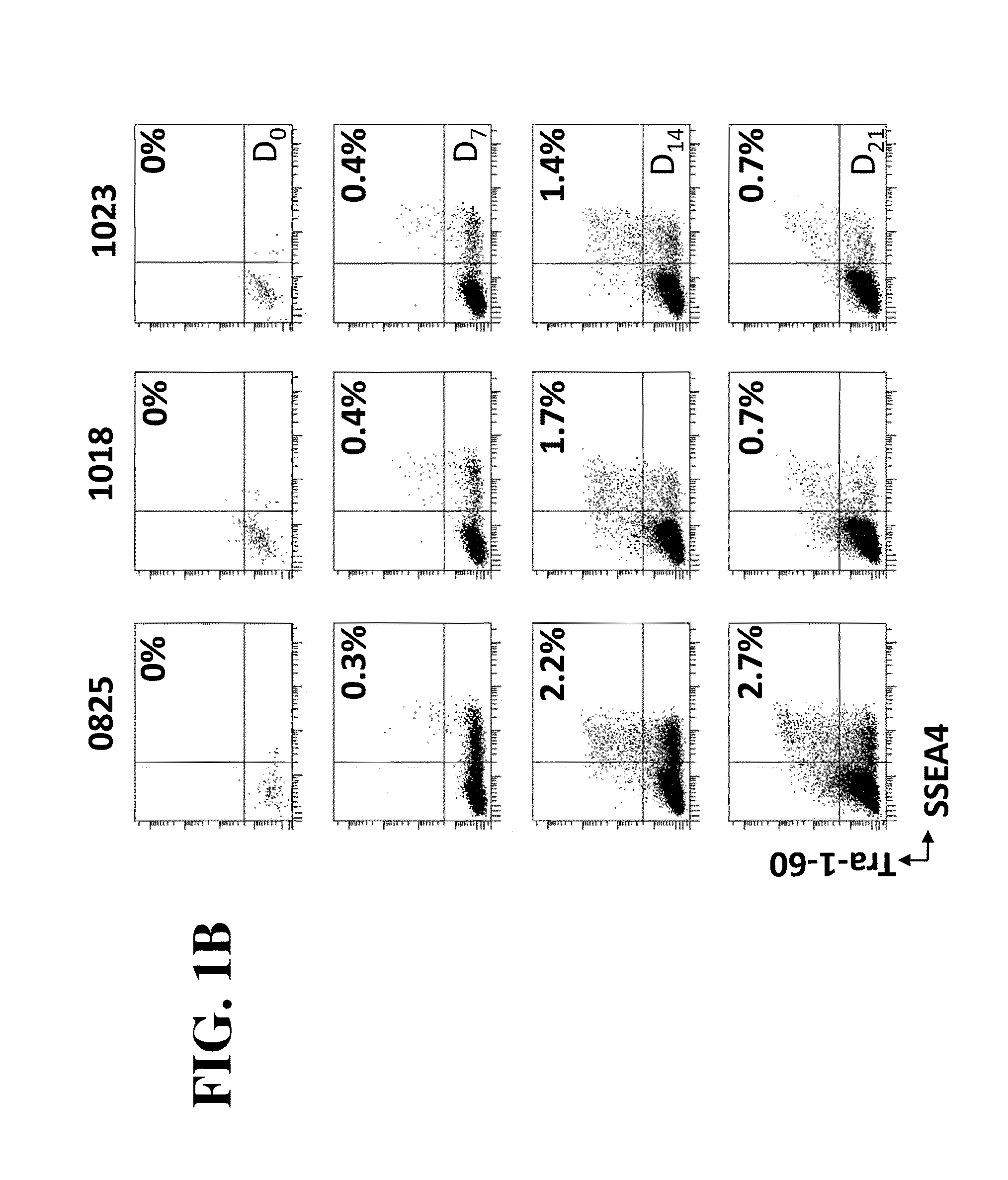
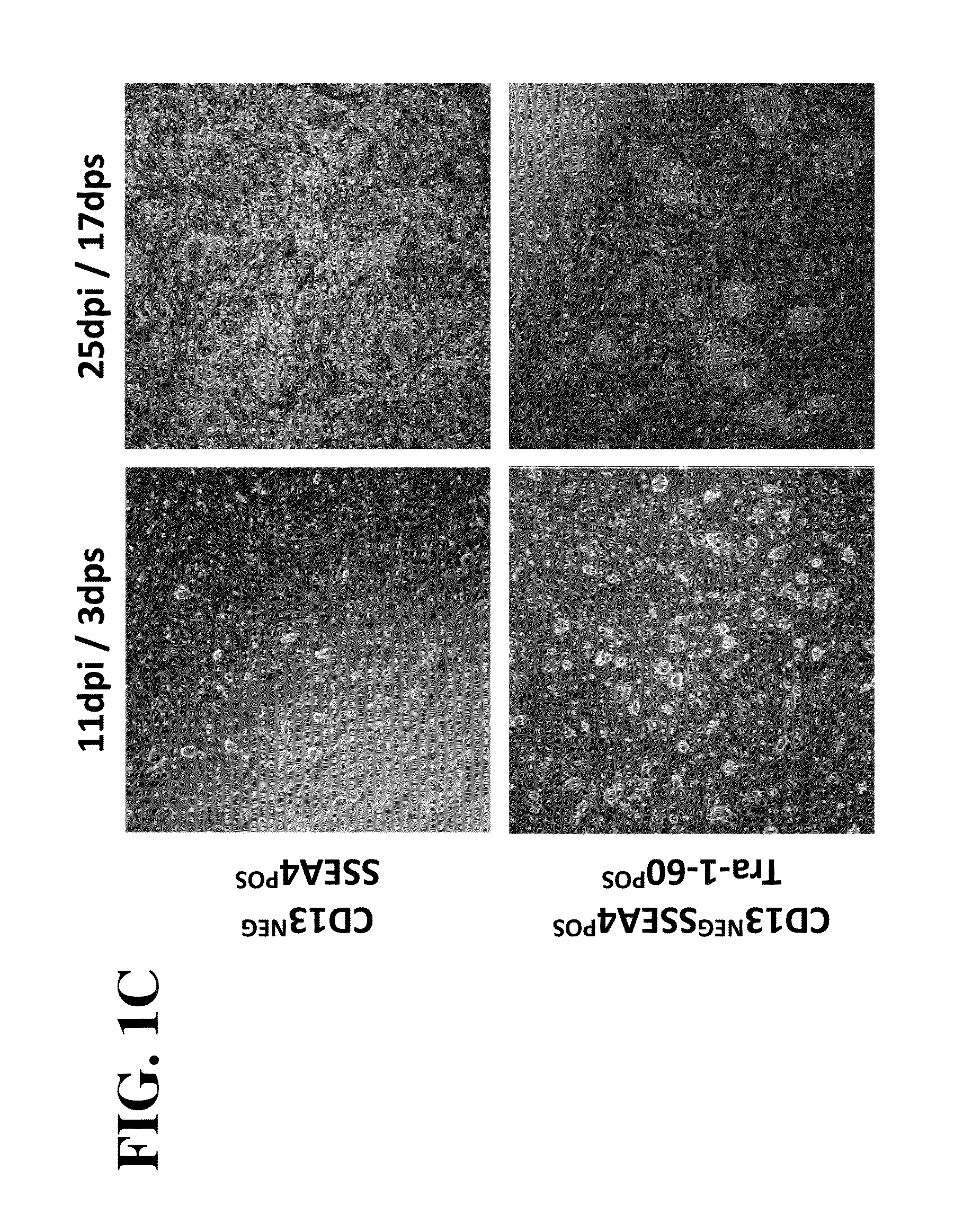
The invention provides improved methods for producing induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) from adult fibroblasts. The methods include contacting adult fibroblasts with a reprogramming composition suitable for reprogramming the adult fibroblasts to iPSC, under conditions effective for the reprogramming composition to penetrate the adult fibroblasts, followed by culturing the contacted fibroblasts for a time period sufficient for the cells to be reprogrammed. The cultured cells are then sorted to select cells based upon their expression of the cell membrane surface markers CD13NEG SSEA4POS Tra-1-60POS. iPSC colonies are then identified from the sorted cells.
Owner:NEW YORK STEM CELL FOUND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com