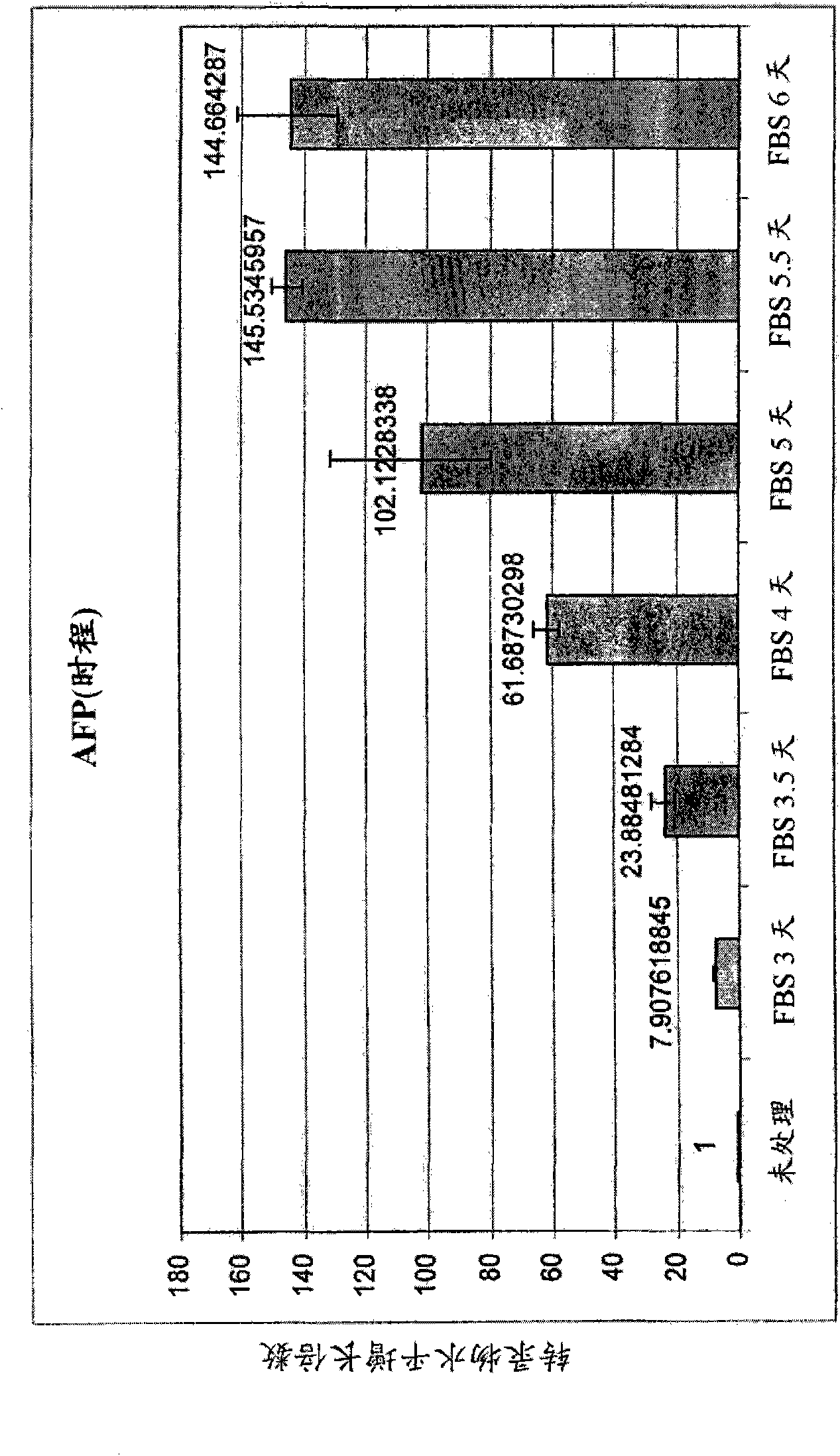
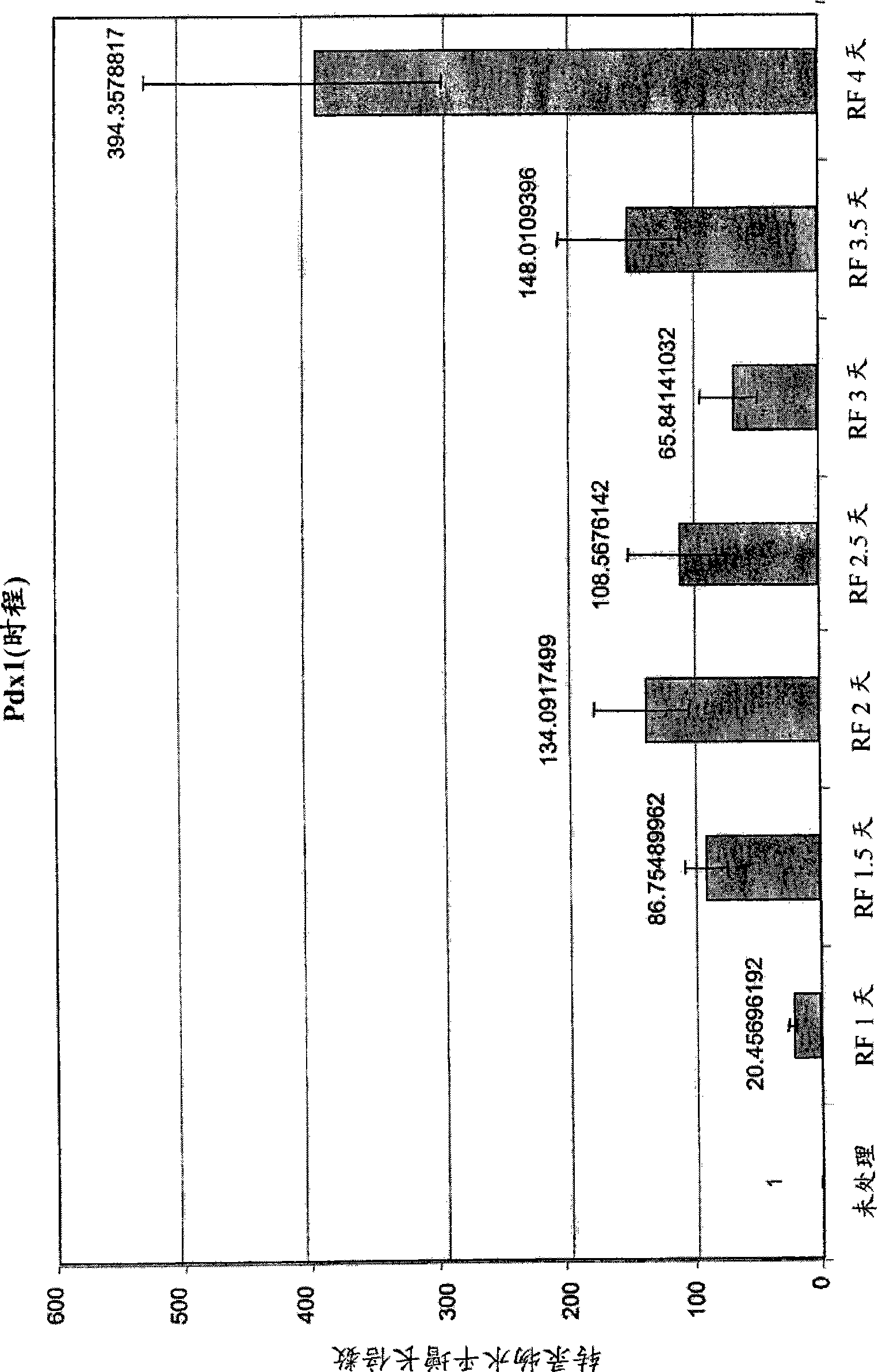
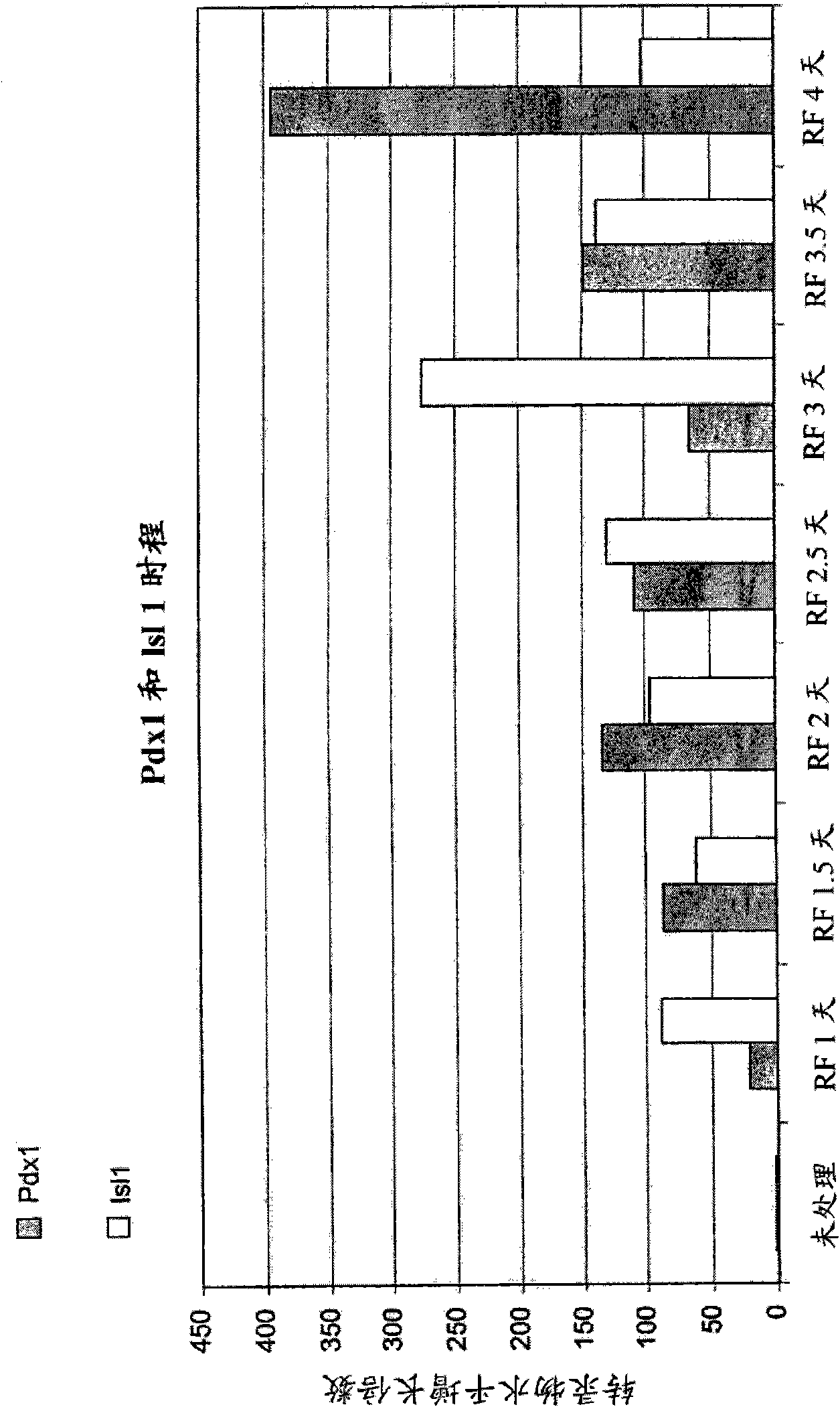
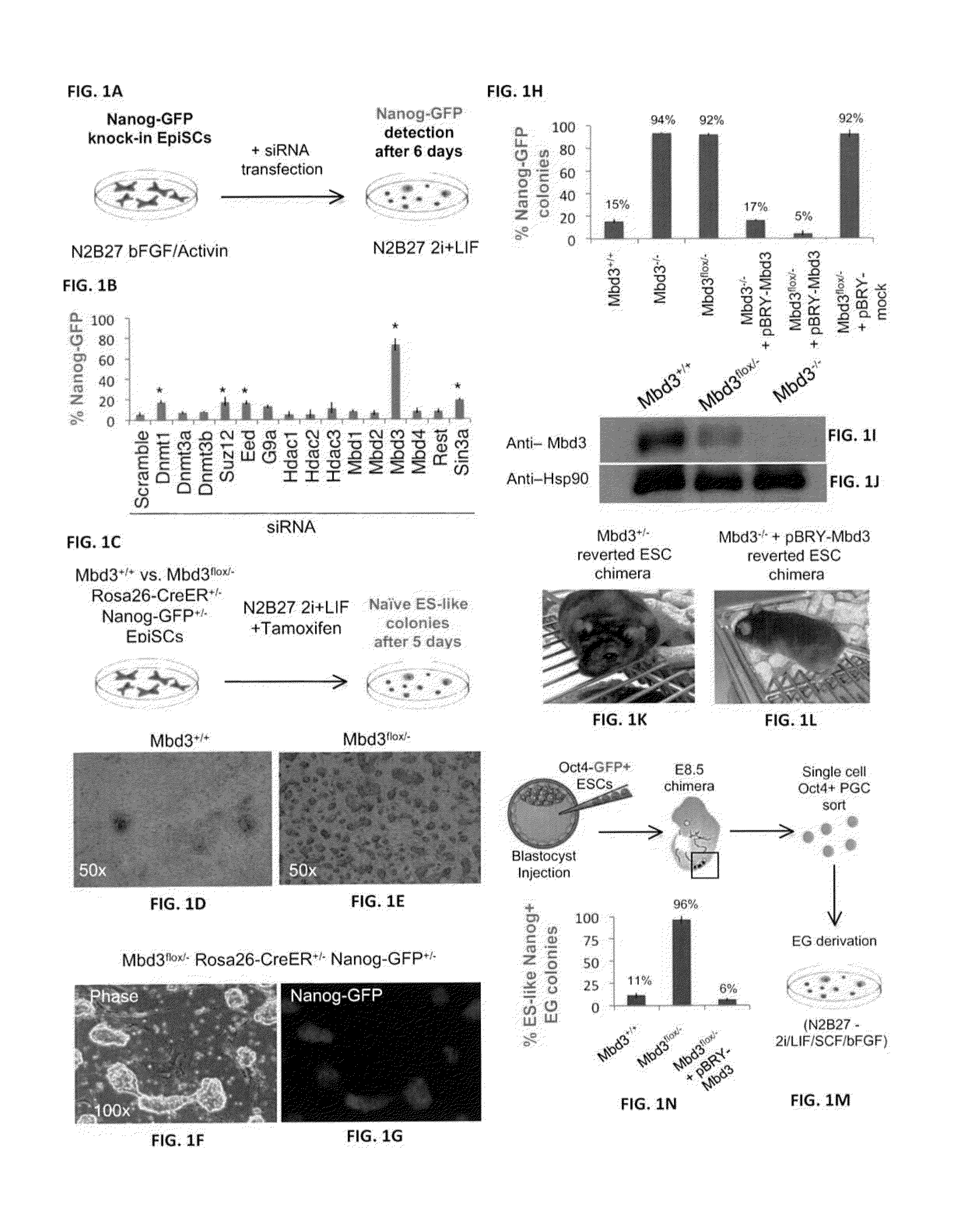
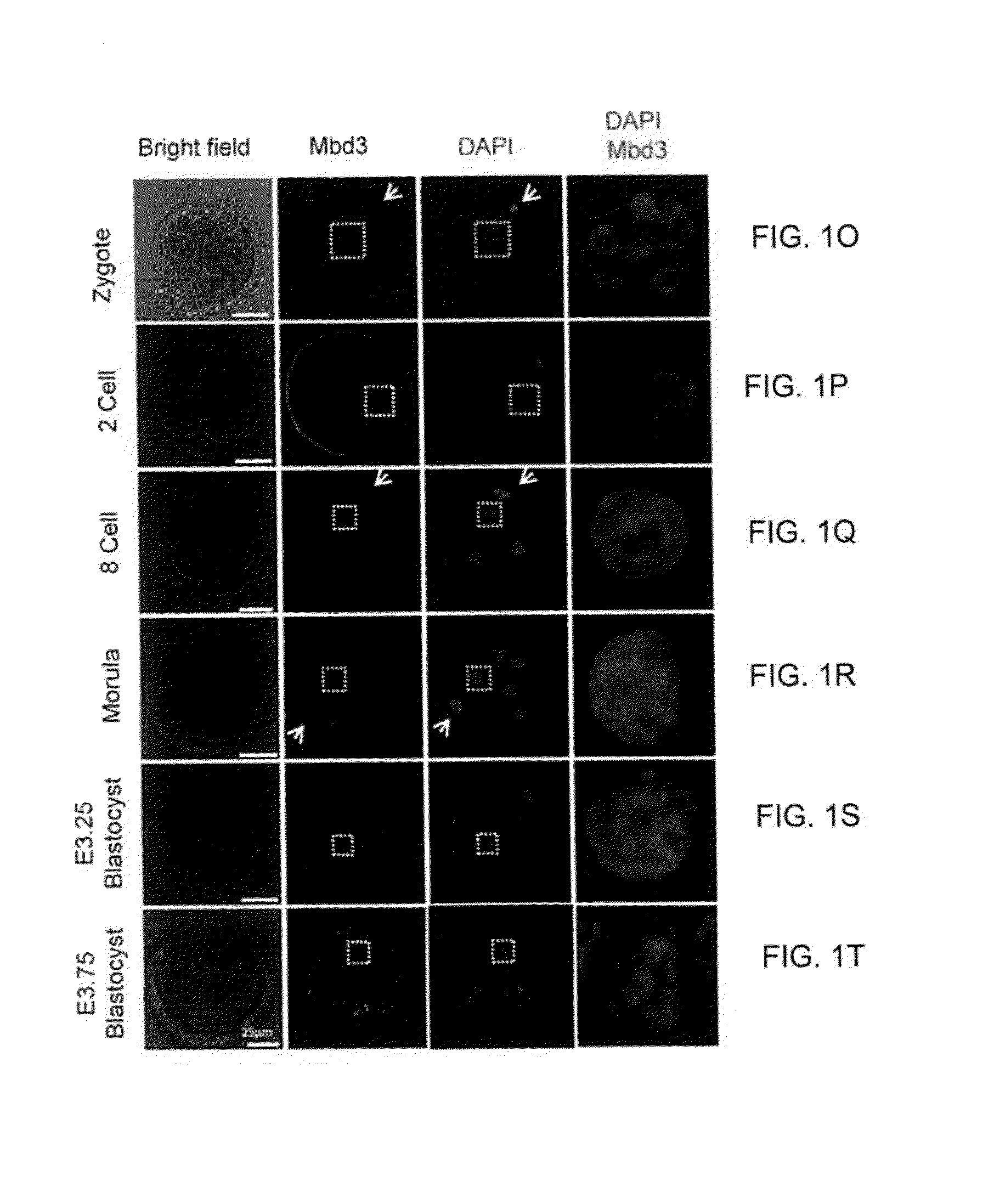
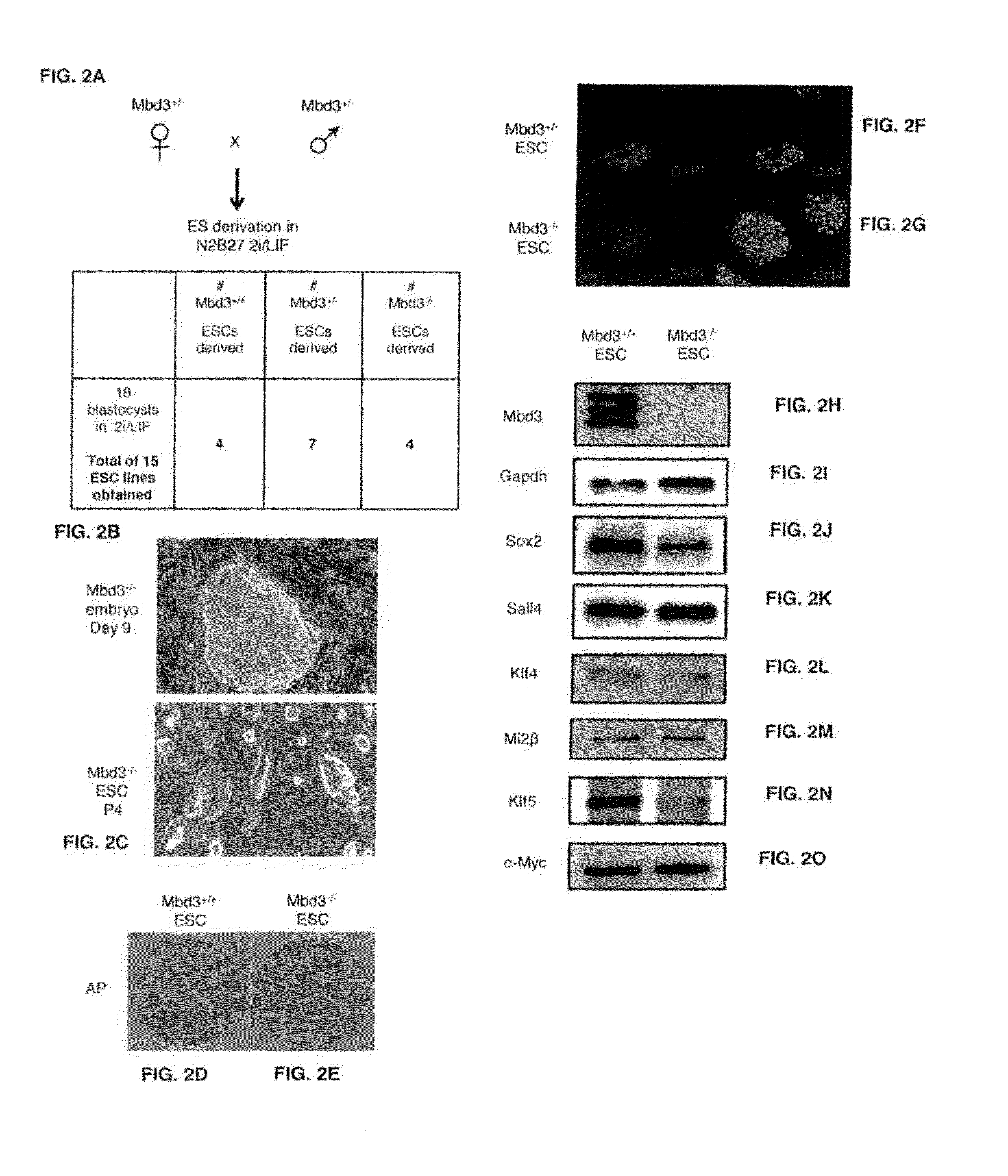
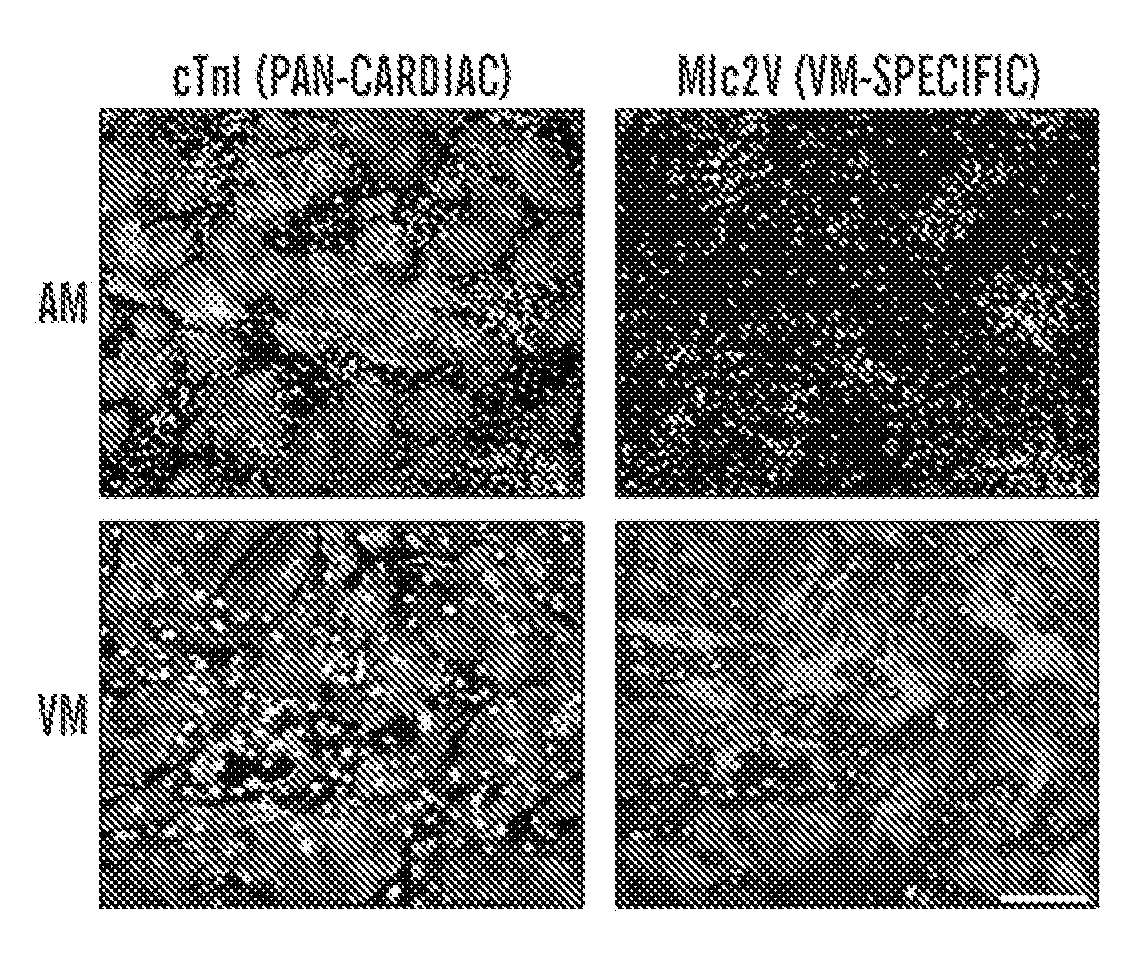
Patents
Literature
448 results about "Pluripotential stem cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chronic myeloid leukemia is a pluripotential stem cell disorder characterised by anemia, markedly elevated leucocyte count with shift to left in the myeloid series, basophilia, often thrombocytosis and splenomegaly.
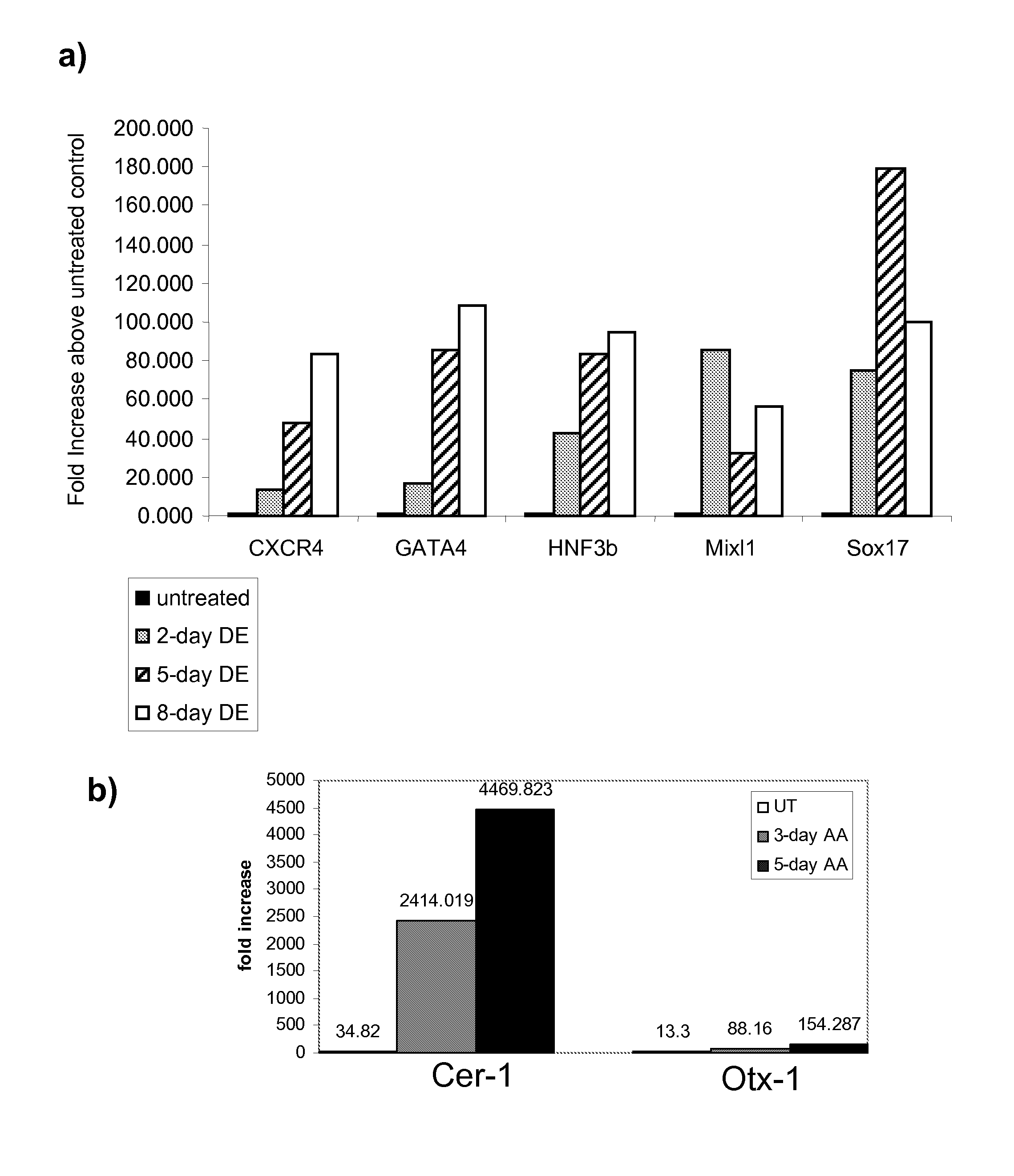
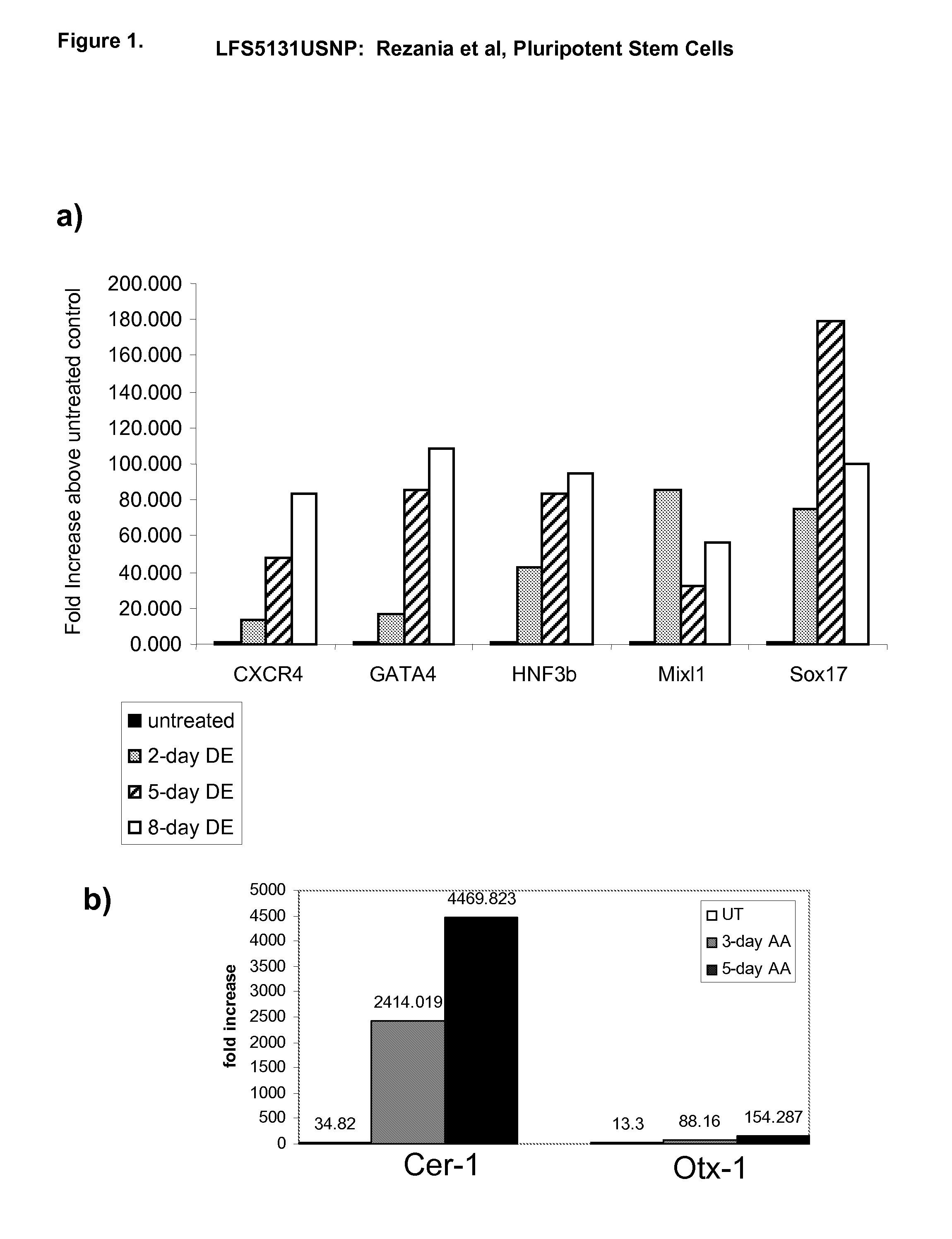
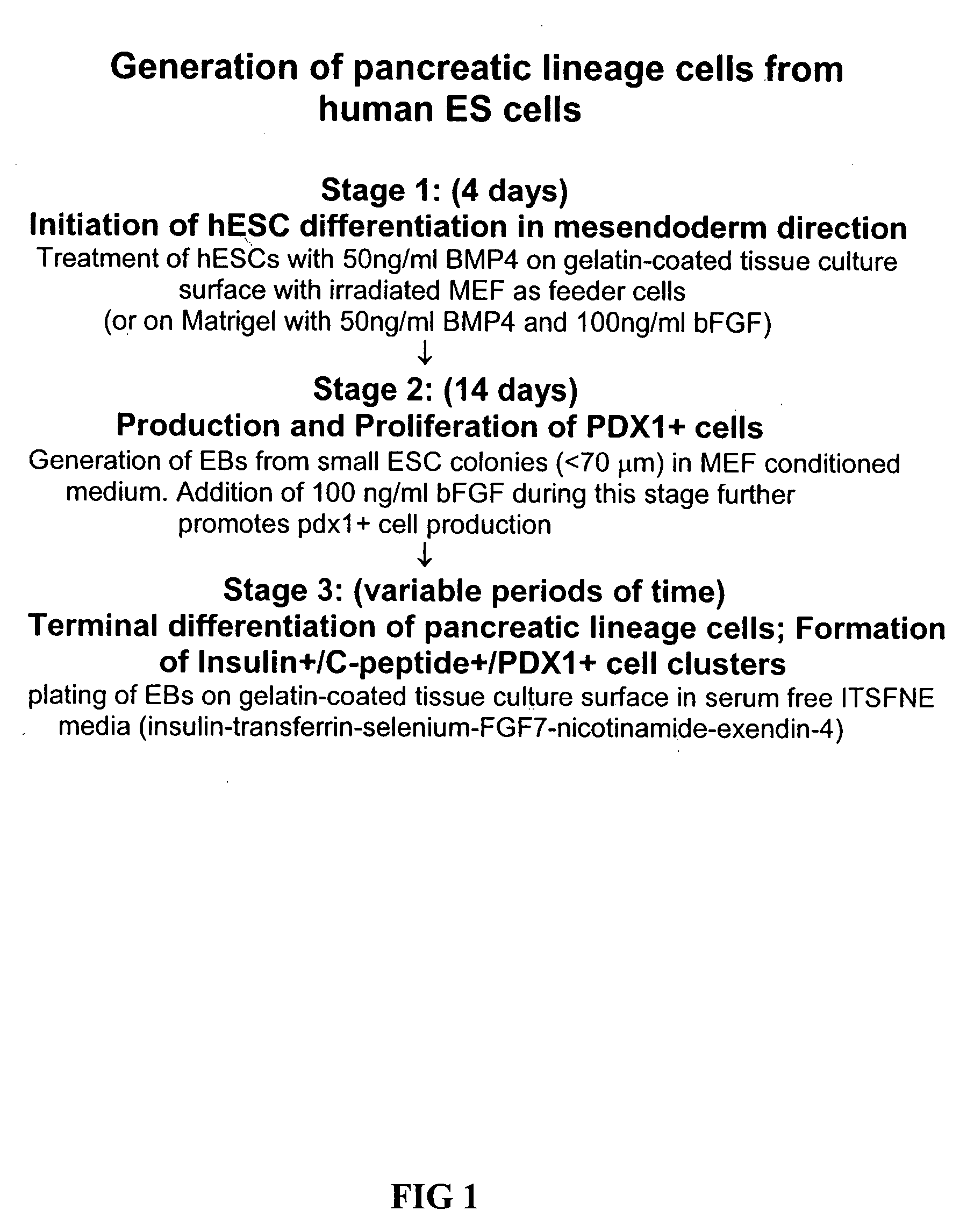
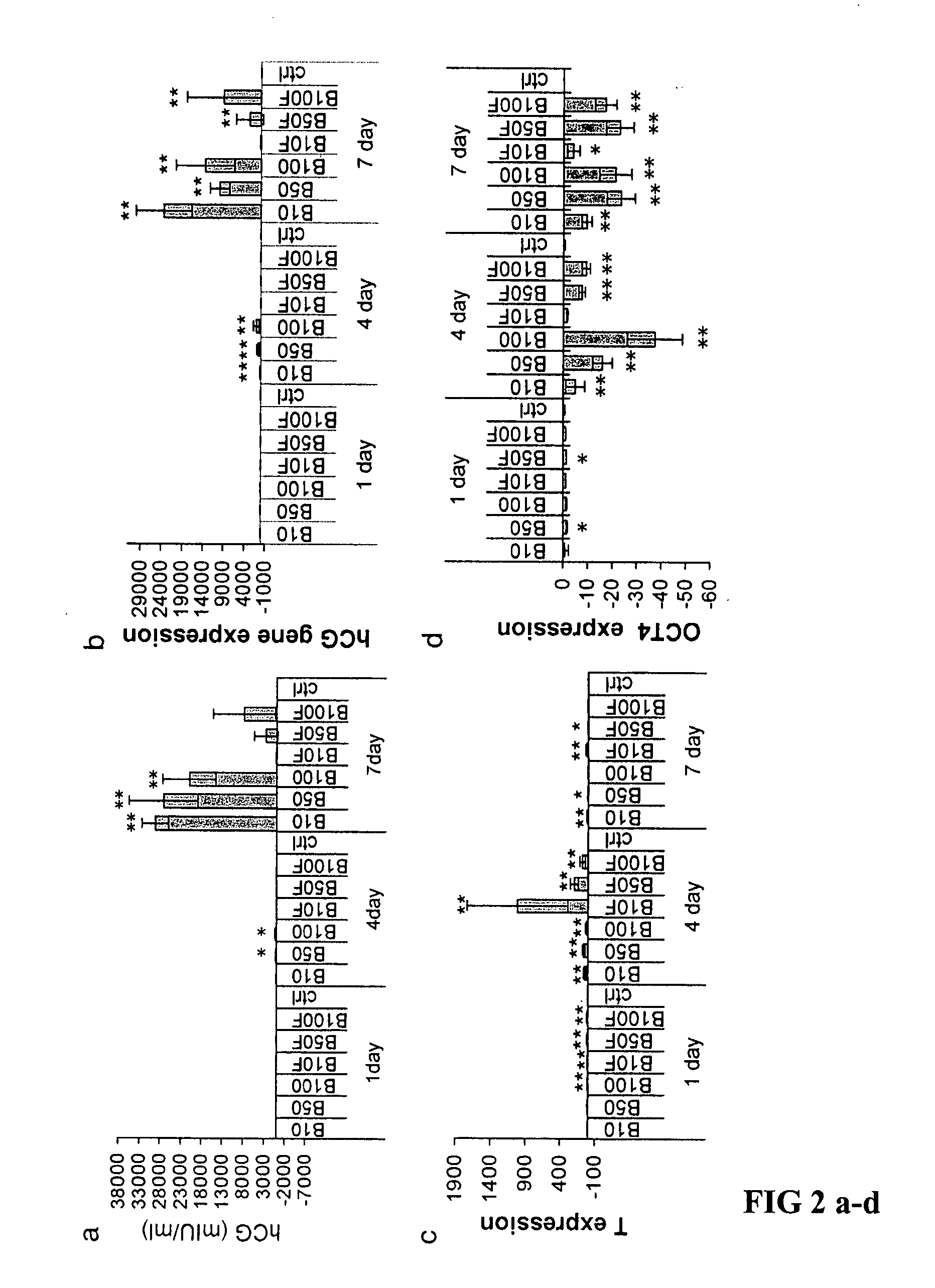
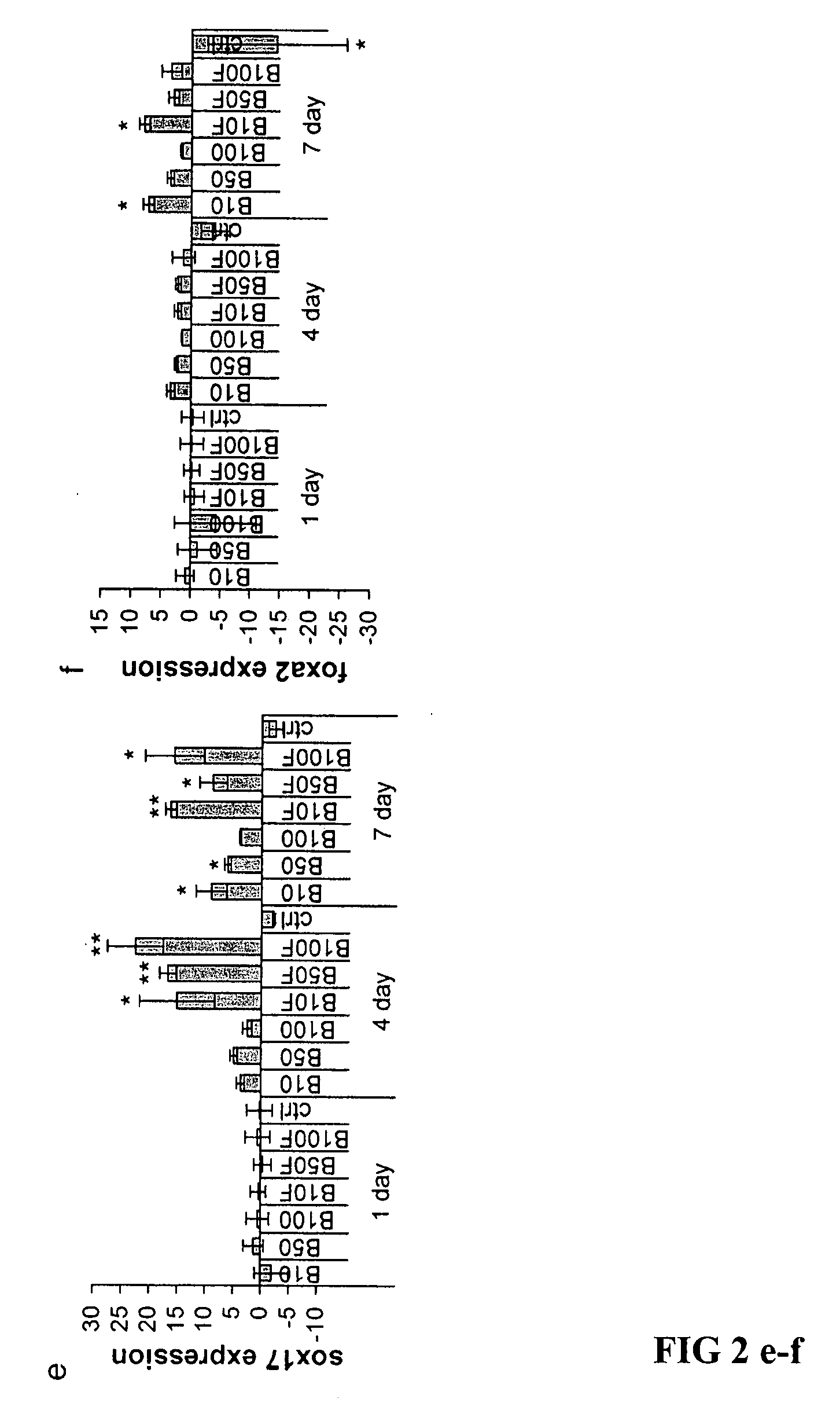
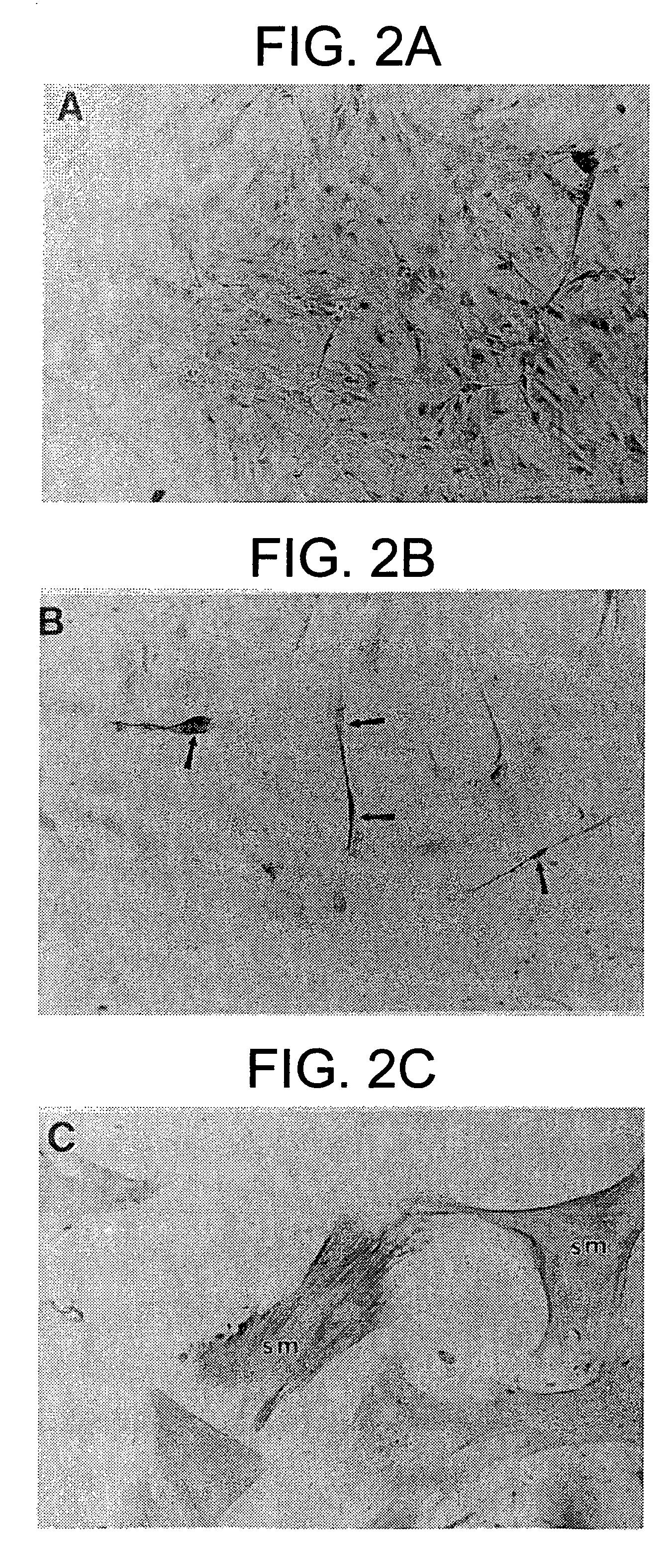
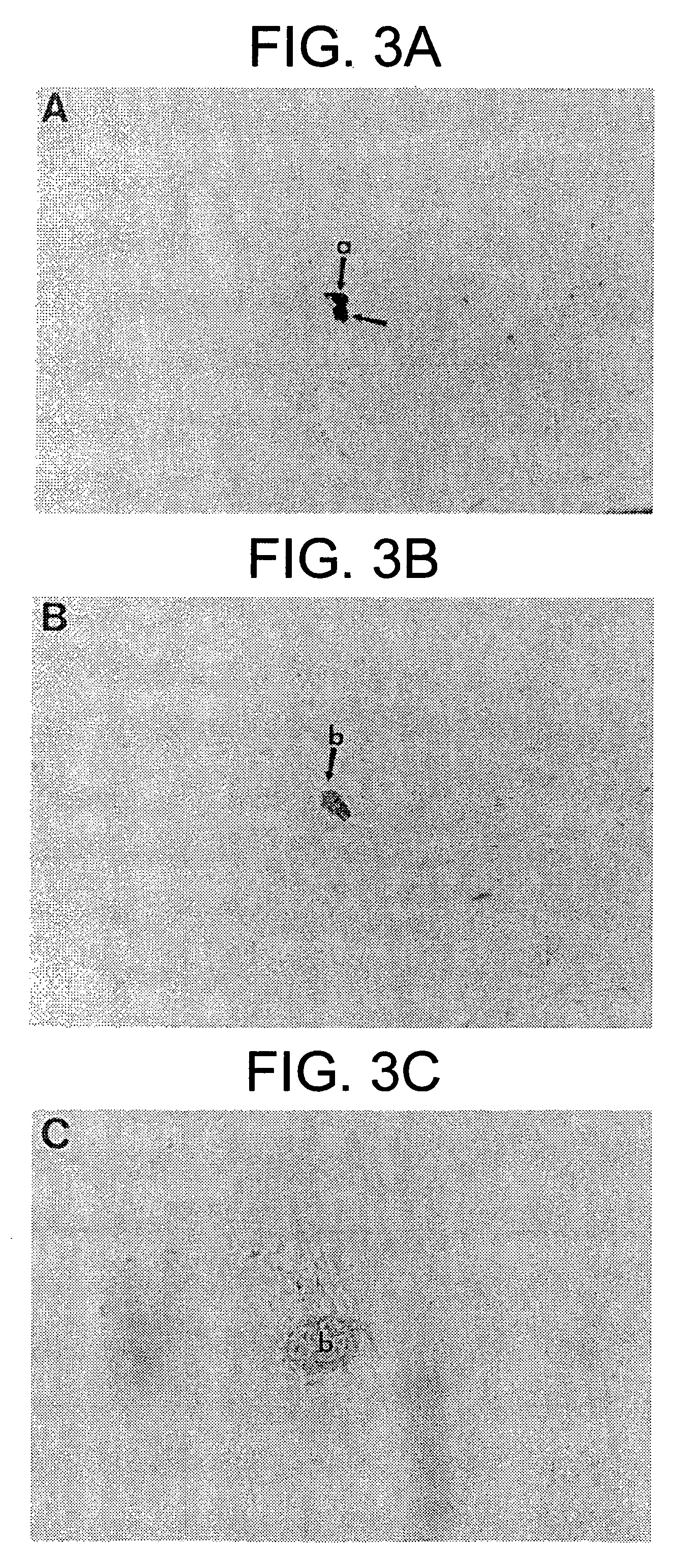
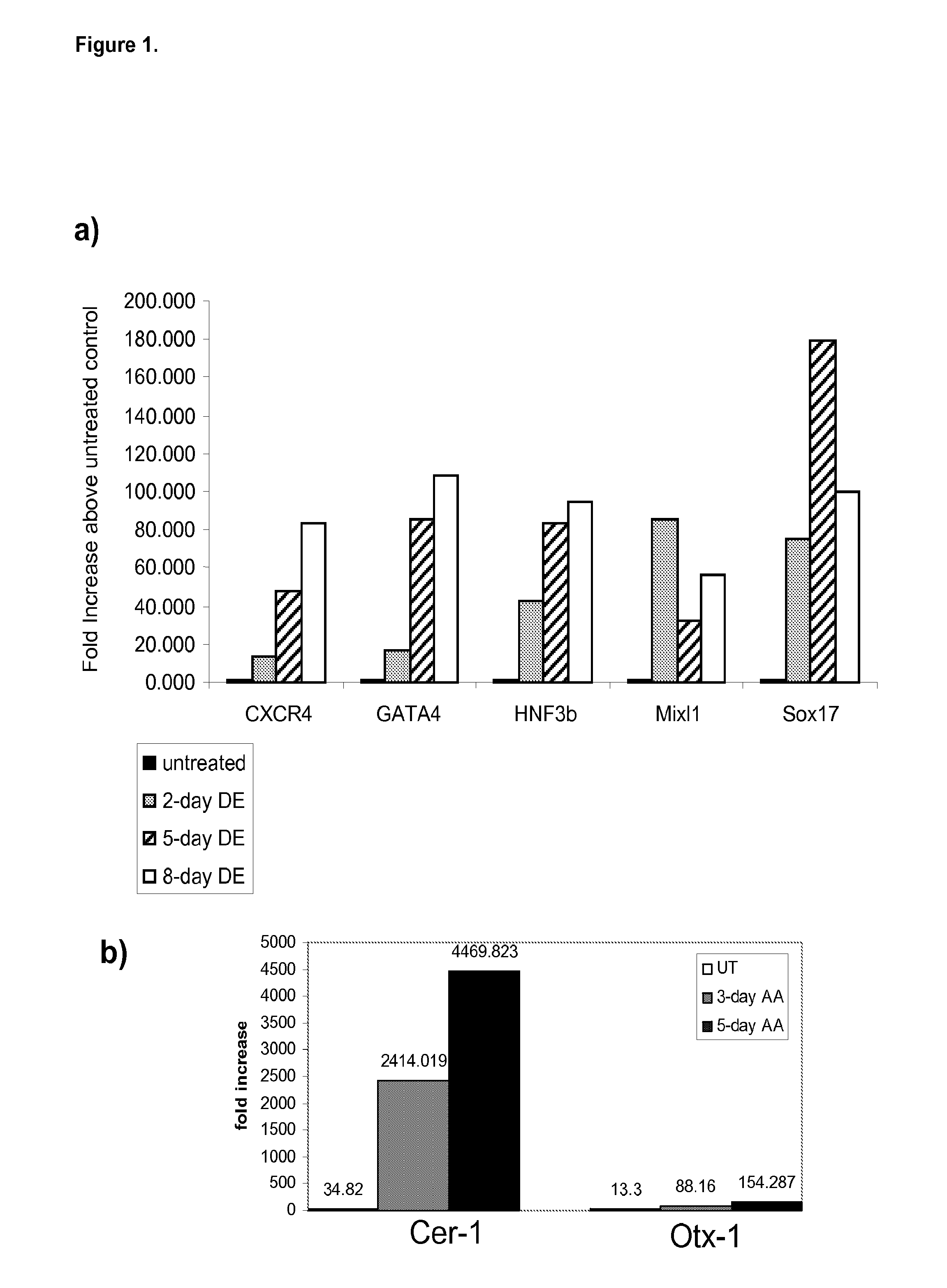
Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells
ActiveUS20070254359A1Inhibits Notch signalingPancreatic cellsArtificial cell constructsGerm layerPluripotential stem cell
The present invention provides methods to promote the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells. In particular, the present invention provides an improved method for the formation of pancreatic endoderm, pancreatic hormone expressing cells and pancreatic hormone secreting cells. The present invention also provides methods to promote the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells without the use of a feeder cell layer.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
Defined media for pluripotent stem cell culture
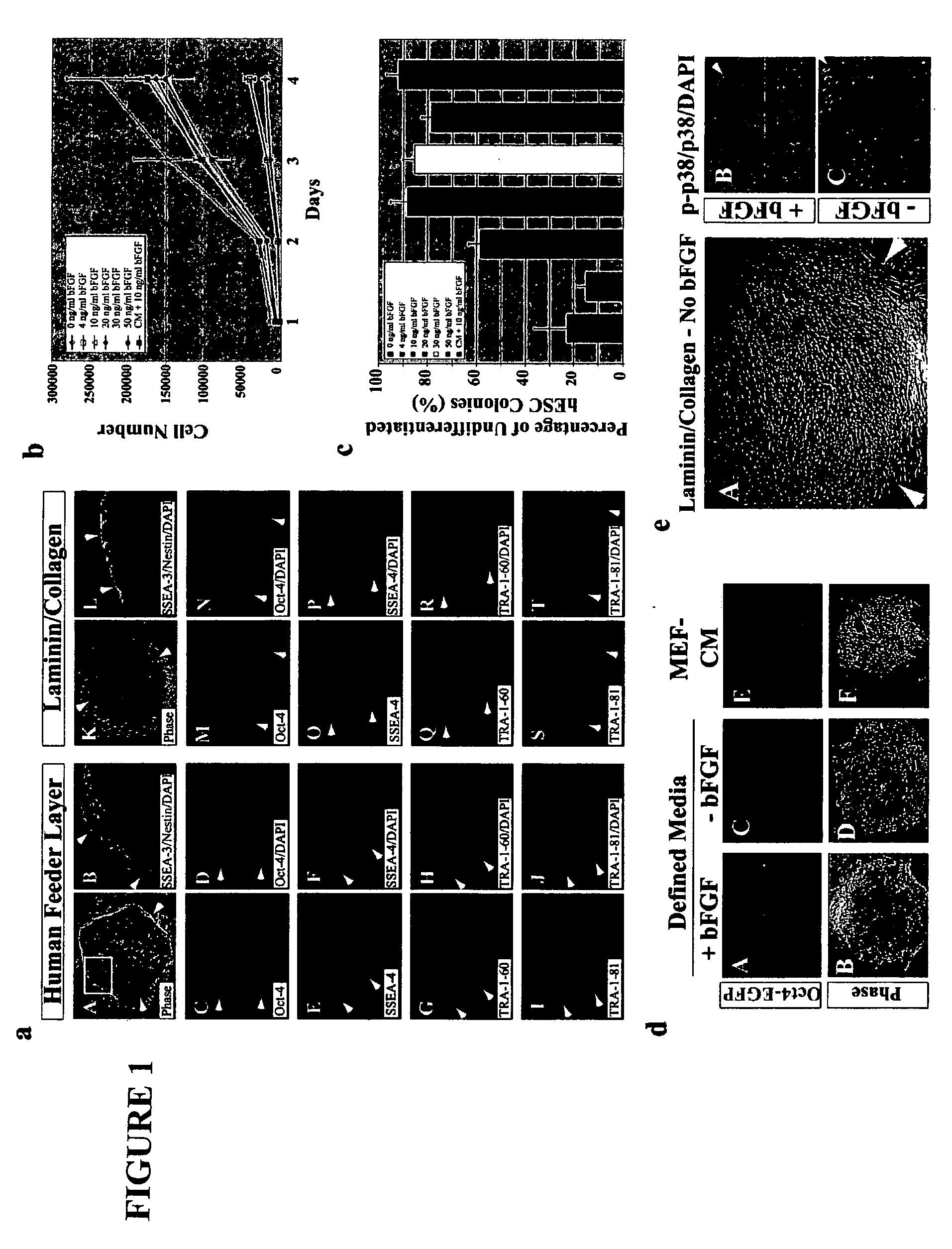
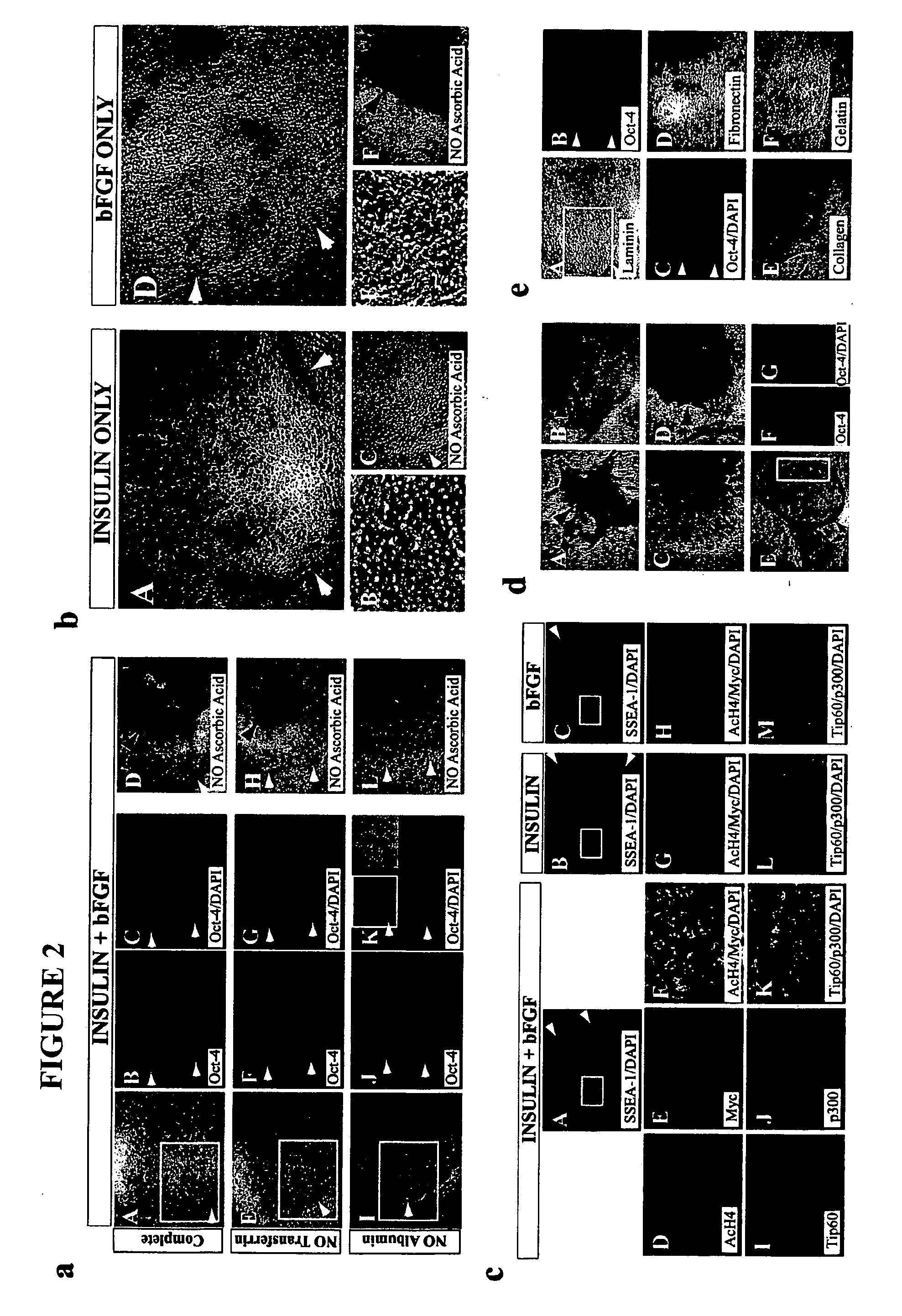
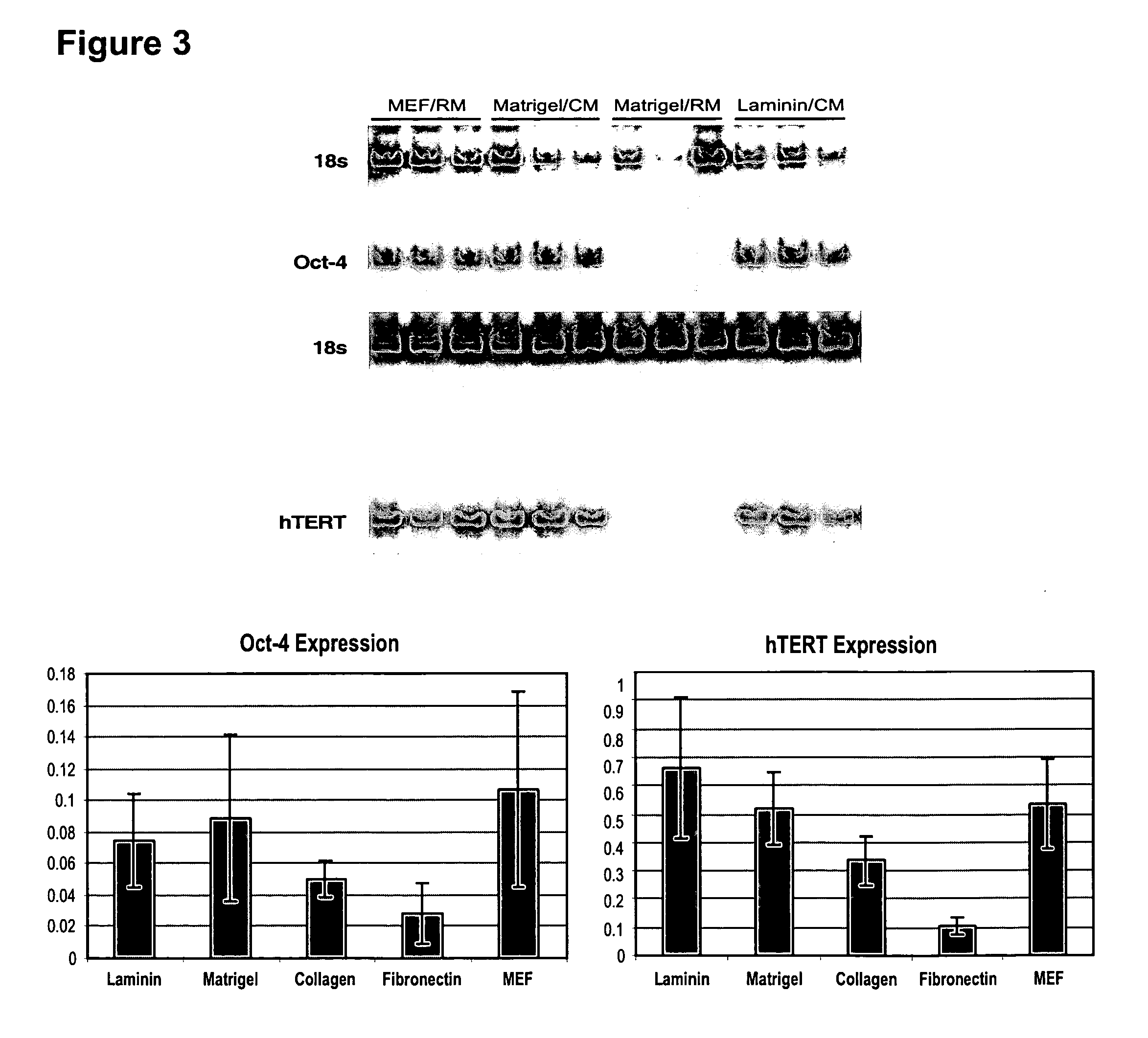
Stem cells, including mammalian, and particularly primate primordial stem cells (pPSCs) such as human embryonic stem cells (hESCs), hold great promise for restoring cell, tissue, and organ function. However, cultivation of stem cells, particularly undifferentiated hESCs, in serum-free, feeder-free, and conditioned-medium-free conditions remains crucial for large-scale, uniform production of pluripotent cells for cell-based therapies, as well as for controlling conditions for efficiently directing their lineage-specific differentiation. This instant invention is based on the discovery of the formulation of minimal essential components necessary for maintaining the long-term growth of pPSCs, particularly undifferentiated hESCs. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), insulin, ascorbic acid, and laminin were identified to be both sufficient and necessary for maintaining hESCs in a healthy self-renewing undifferentiated state capable of both prolonged propagation and then directed differentiation. Having discerned these minimal molecular requirements, conditions that would permit the substitution of poorly-characterized and unspecified biological additives and substrates were derived and optimized with entirely defined constituents, providing a “biologics”-free (i.e., animal-, feeder-, serum-, and conditioned-medium-free) system for the efficient long-term cultivation of pPSCs, particularly pluripotent hESCs. Such culture systems allow the derivation and large-scale production of stem cells such as pPSCs, particularly pluripotent hESCs, in optimal yet well-defined biologics-free culture conditions from which they can be efficiently directed towards a lineage-specific differentiated fate in vitro, and thus are important, for instance, in connection with clinical applications based on stem cell therapy and in drug discovery processes.
Owner:THE BURNHAM INST
Pluripotent stem cells derived without the use of embryos or fetal tissue
InactiveUS20030113910A1New breed animal cellsArtificial cell constructsPluripotential stem cellGerm layer
Owner:STEMA
Method of differentiating stem cells into cells of the endoderm and pancreatic lineage
InactiveUS20070259423A1Promote differentiationMass productionPancreatic cellsCulture processPluripotential stem cellGerm layer
Methods are described to more efficiently produce cells of the endoderm and pancreatic lineage from mammalian pluripotent stem cells. These methods provide a simple, reproducible culture protocol using defined media components to enable consistent, large-scale production of pancreatic cell types for research or therapeutic uses.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells, compositions, methods and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050255588A1Avoid developmentInhibit progressBone marrow stroma cellsGenetic material ingredientsGerm layerIn vivo
The present invention relates to pluripotent stem cells, particularly to pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells. The invention further relates to methods of purifying pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells and to compositions, cultures and clones thereof. The present invention also relates to a method of transplanting the pluripotent stem cells of the present invention in a mammalian host, such as human, comprising introducing the stem cells, into the host. The invention further relates to methods of in vivo administration of a protein or gene of interest comprising transfecting a pluripotent stem cell with a construct comprising DNA which encodes a protein of interest and then introducing the stem cell into the host where the protein or gene of interest is expressed. The present also relates to methods of producing mesodermal, endodermal or ectodermal lineage-committed cells by culturing or transplantation of the pluripotent stem cells of the present invention.
Owner:ABT HOLDING COMPANY
Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells
The present invention provides methods to promote the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells. In particular, the present invention provides an improved method for the formation of pancreatic endoderm, pancreatic hormone expressing cells and pancreatic hormone secreting cells. The present invention also provides methods to promote the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells without the use of a feeder cell layer.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
Protocols for making hepatocytes from embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050037493A1Promote cell differentiationCulture processDrug screeningGerm layerPluripotential stem cell
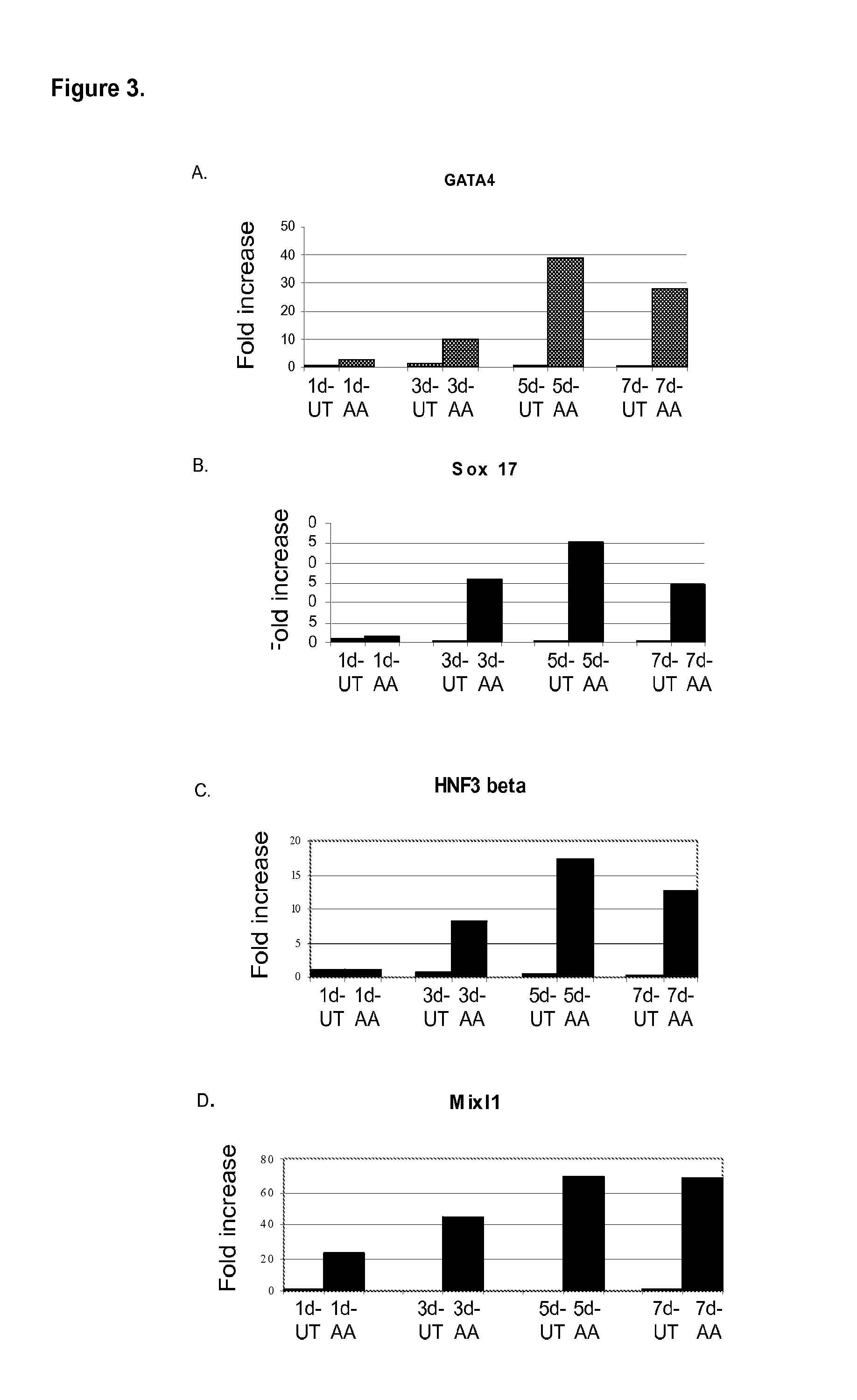
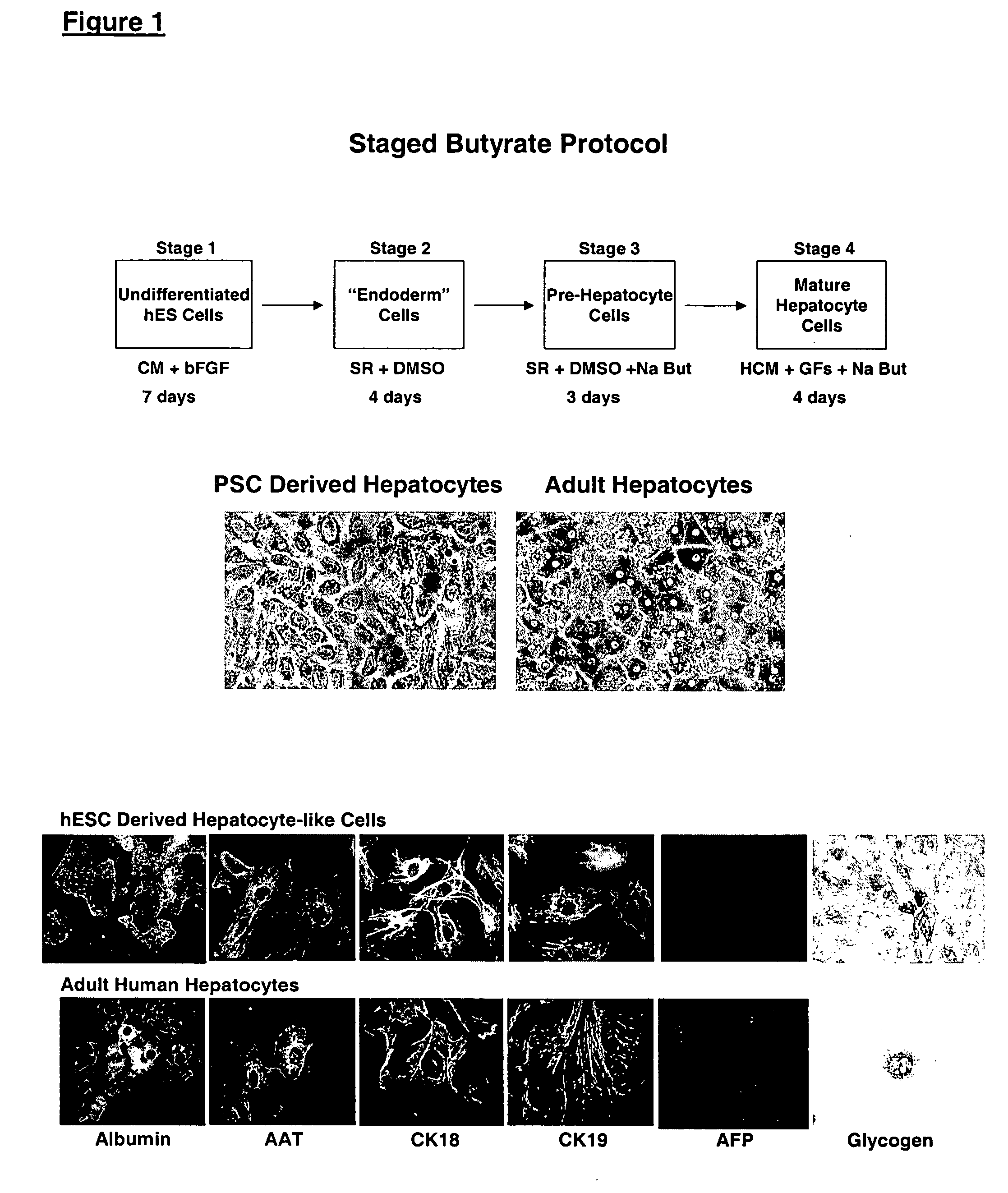
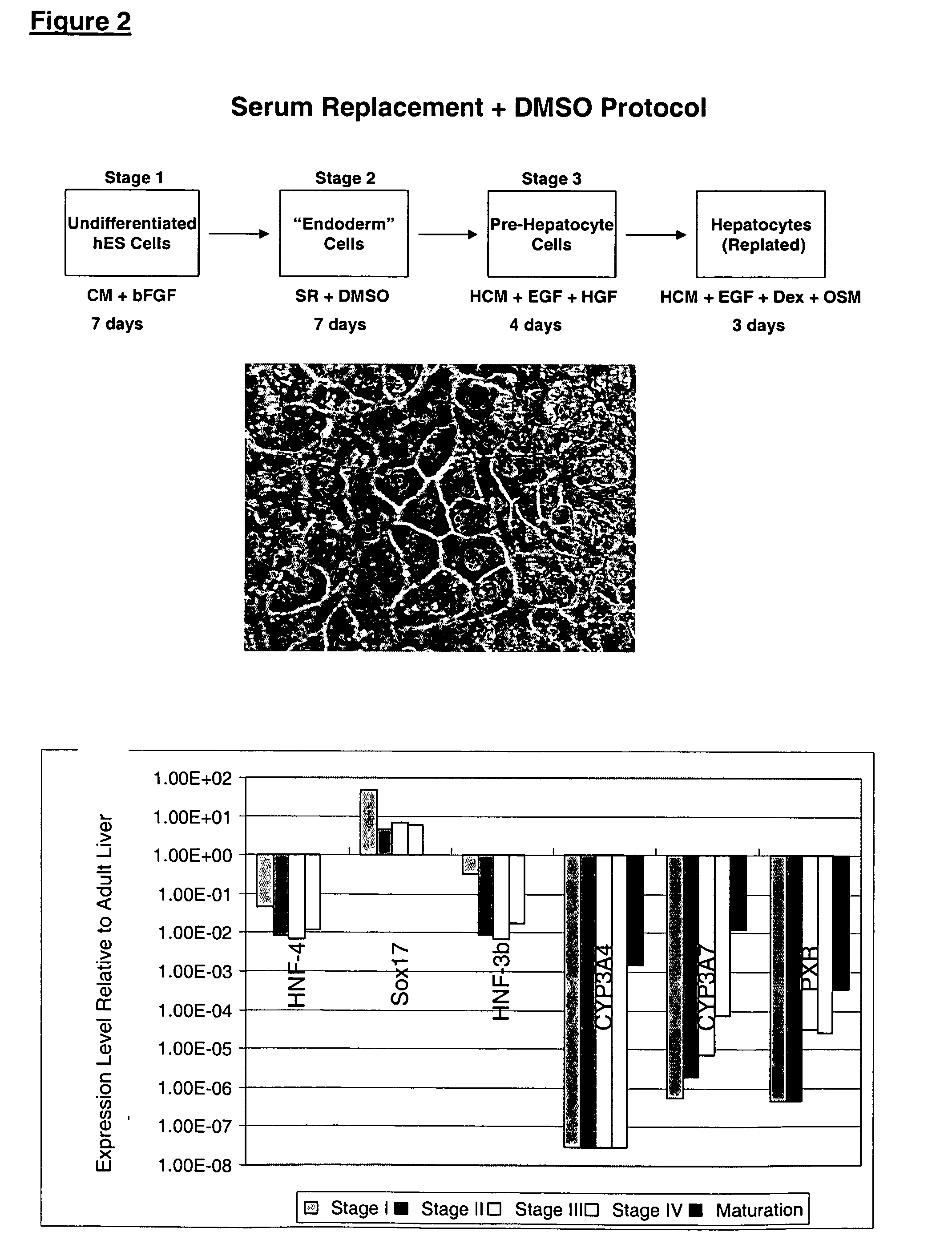
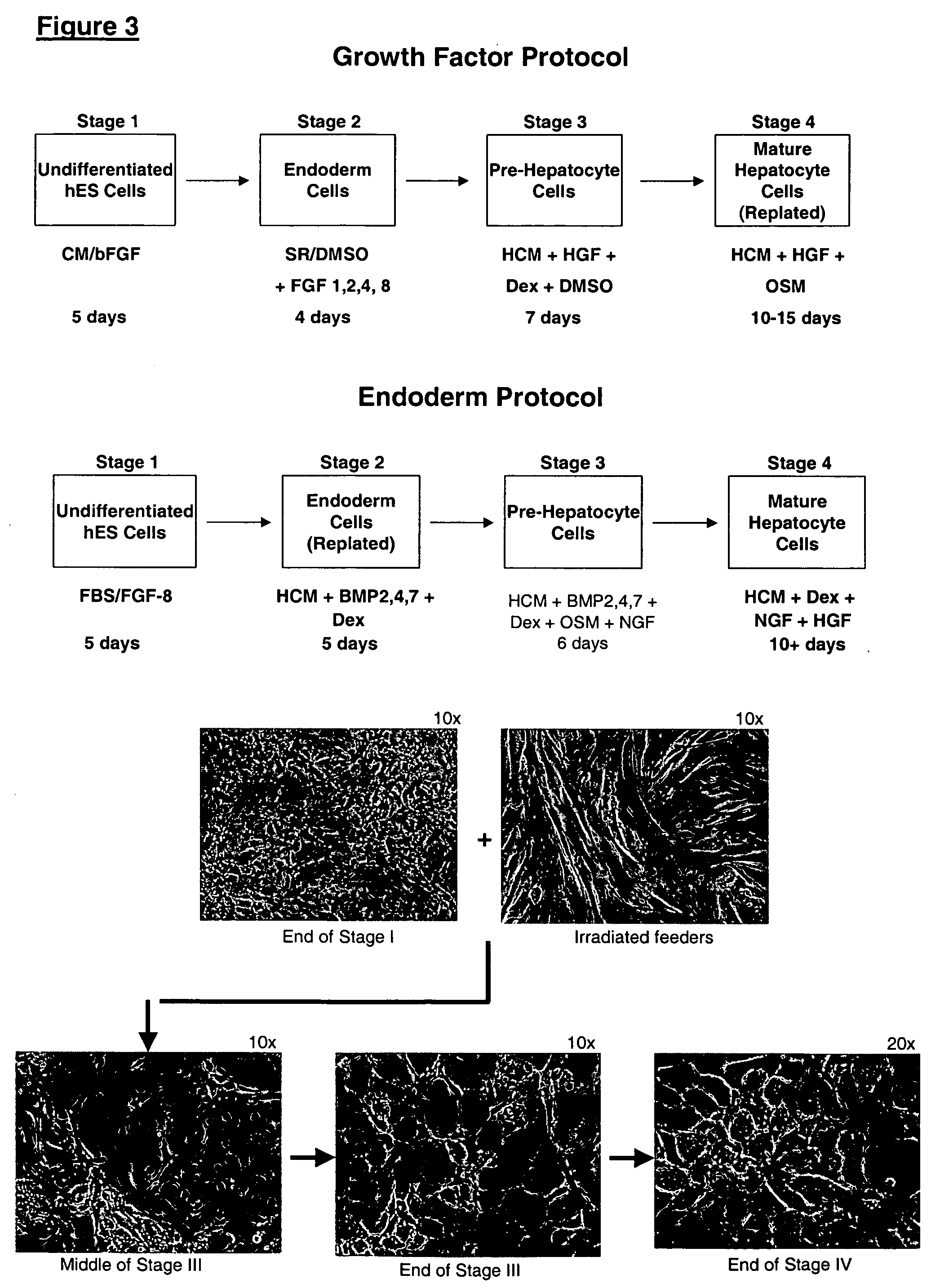
This disclosure provides a newly developed strategy and particular options for differentiating pluripotent stem cells into cells of the hepatocyte lineage. Many of the protocols are based on a strategy in which the cells are first differentiated into early germ layer cells, then into hepatocyte precursors, and then into mature cells. The cells obtained have morphological features and phenotypic markers characteristic of human adult hepatocytes. They also show evidence of cytochrome p450 enzyme activity, validating their utility for commercial applications such as drug screening, or use in the manufacture of medicaments and medical devices for clinical therapy.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
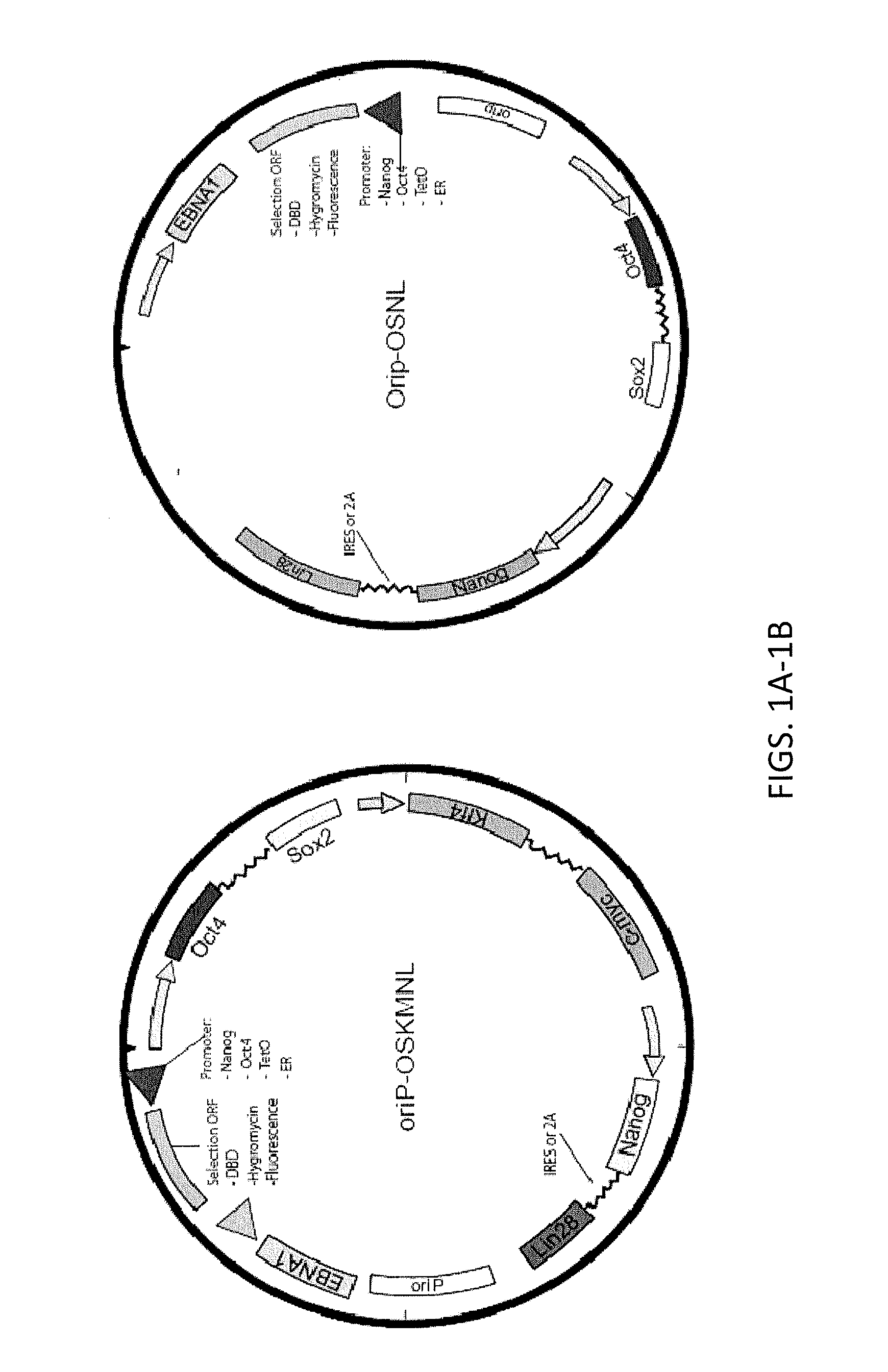
Integration-free human induced pluripotent stem cells from blood
InactiveUS8048675B1Genetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsPluripotential stem cellOrigin of replication
Provided herein are methods for generating human induced pluripotent stem cells free from genomic integration of exogenous transgenes by transfecting into nucleated blood cells one or more DNA expression vectors (e.g., plasmid vectors) that do not contain a mammalian origin of replication, and encode and permit expression of one or more reprogramming factors (e.g., Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc). Also provided herein are the integration-free human induced pluripotent stem cells obtained by the methods described herein.
Owner:TRUE NORTH THERAPEUTICS
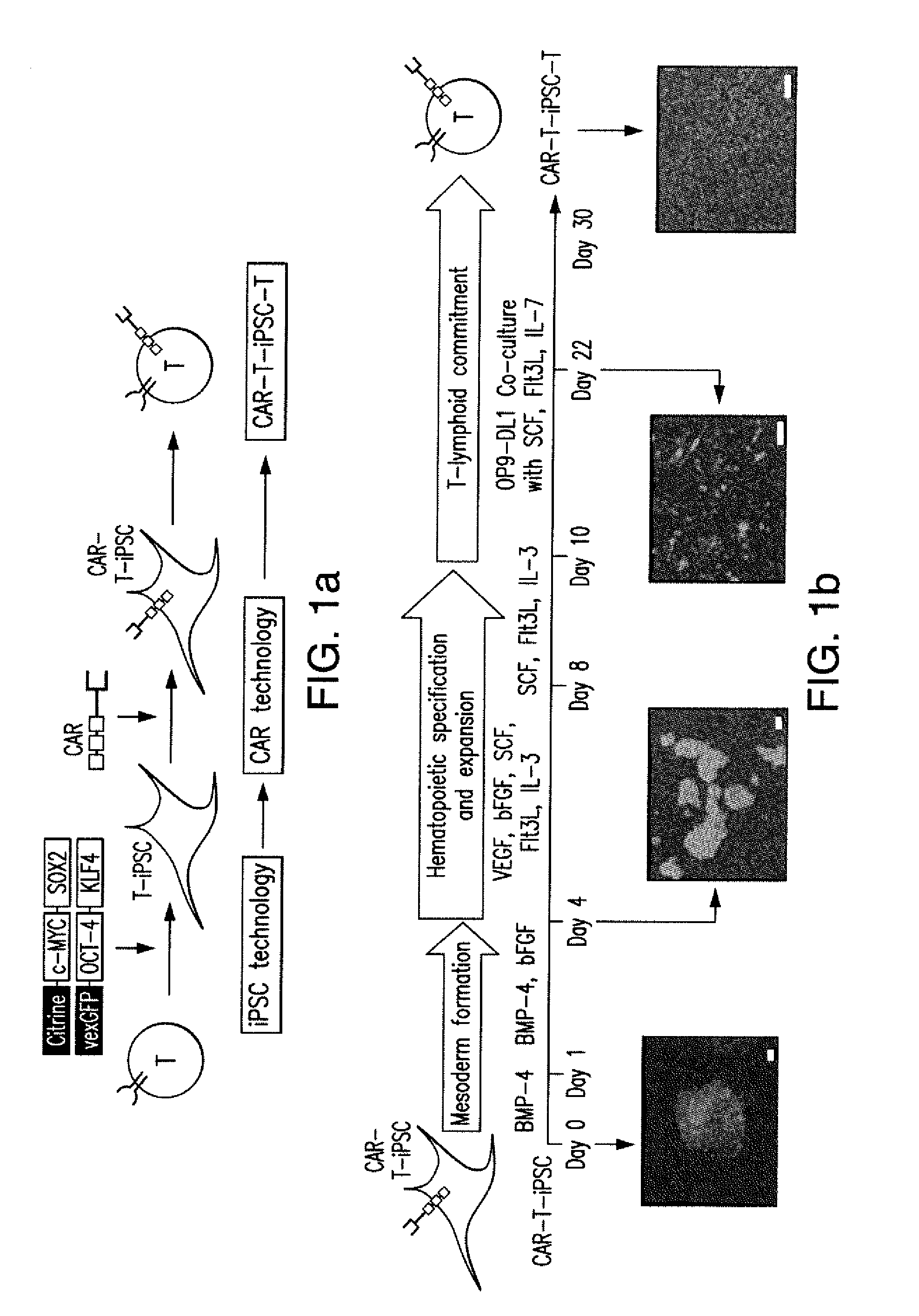
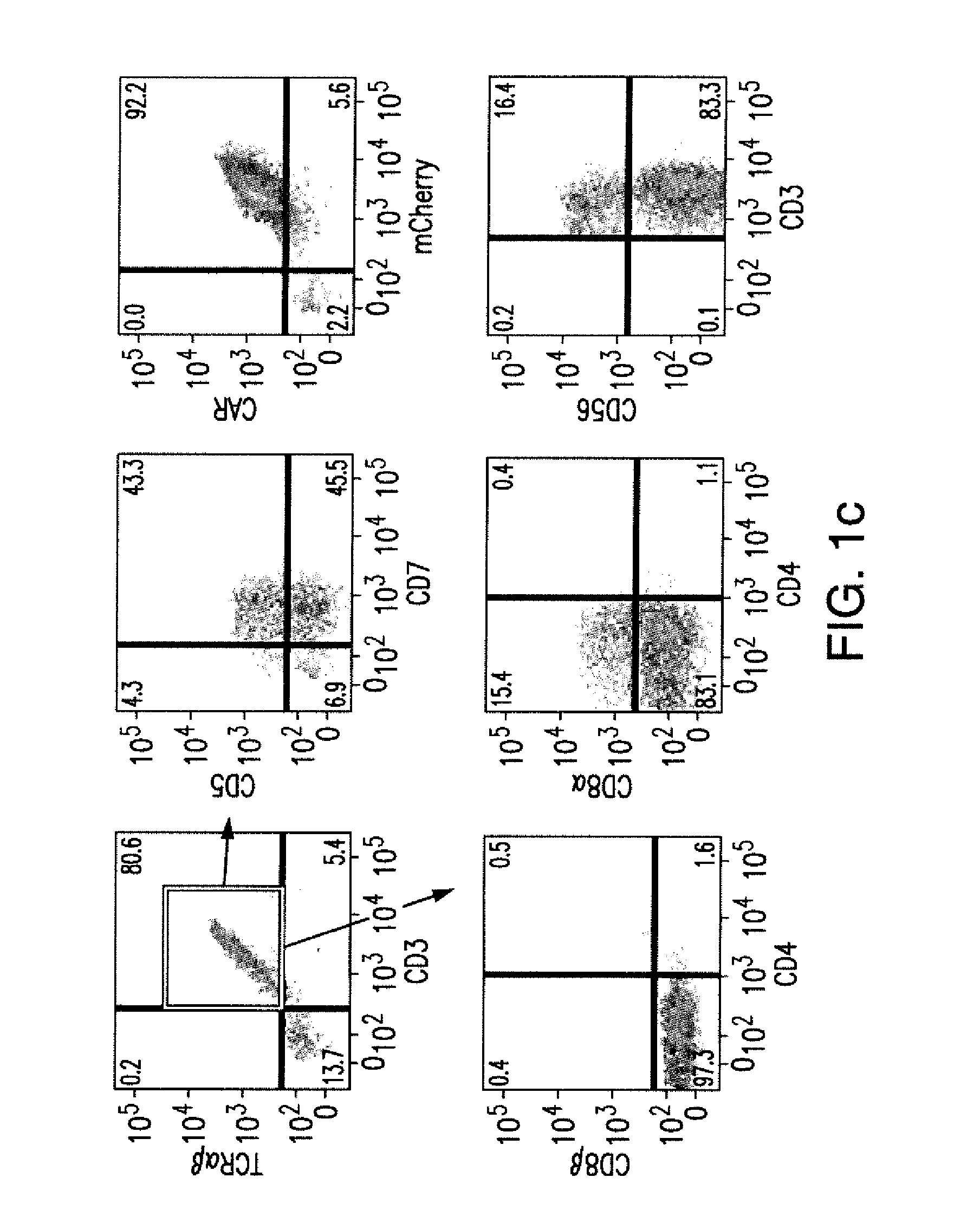
Effective generation of tumor-targeted t cells derived from pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20160009813A1Improve survivalGood antitumor activityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMammal material medical ingredientsAntigenPluripotential stem cell
The present invention relates to the field of adoptive immunotherapy. The invention provides methods for generating phenotypically defined, functional, and / or expandable T cells from pluripotent stem cells engineered through safe genetic modifications. The engineered cells may provide one or more of: 1) targeting a specific predetermined antigen expressed on the cell surface of a target cell in an HLA independent manner, 2) enhanced survival and functional potential 3) “off-the-shelf” T cells for administration to multiple recipients, eventually across immunogenic barriers, and / or 4) cytotoxic potential and anti-tumor activity.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT
Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells
ActiveUS20110151561A1High expressionPancreatic cellsEpidermal cells/skin cellsPluripotential stem cellIntracrine
The present invention provides methods to promote the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into insulin producing cells. In particular, the present invention provides a method to increase the expression of NGN3 and NKX6.1 in populations of cells expressing markers characteristic of the pancreatic endocrine lineage.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Pluripotent Stem Cells
InactiveUS20110104805A1Improve efficiencySkeletal/connective tissue cellsDrug compositionsPluripotential stem cellInduced pluripotent stem cell
The present invention provides methods to produce pluripotent stem cells from adult cells. In particular, the present invention provides methods to produce pluripotent stem cells from somatic cells without the use of a feeder-cell layer or an agent that increases efficiency of retroviral transfection.
Owner:CENTOCOR ORTHO BIOTECH
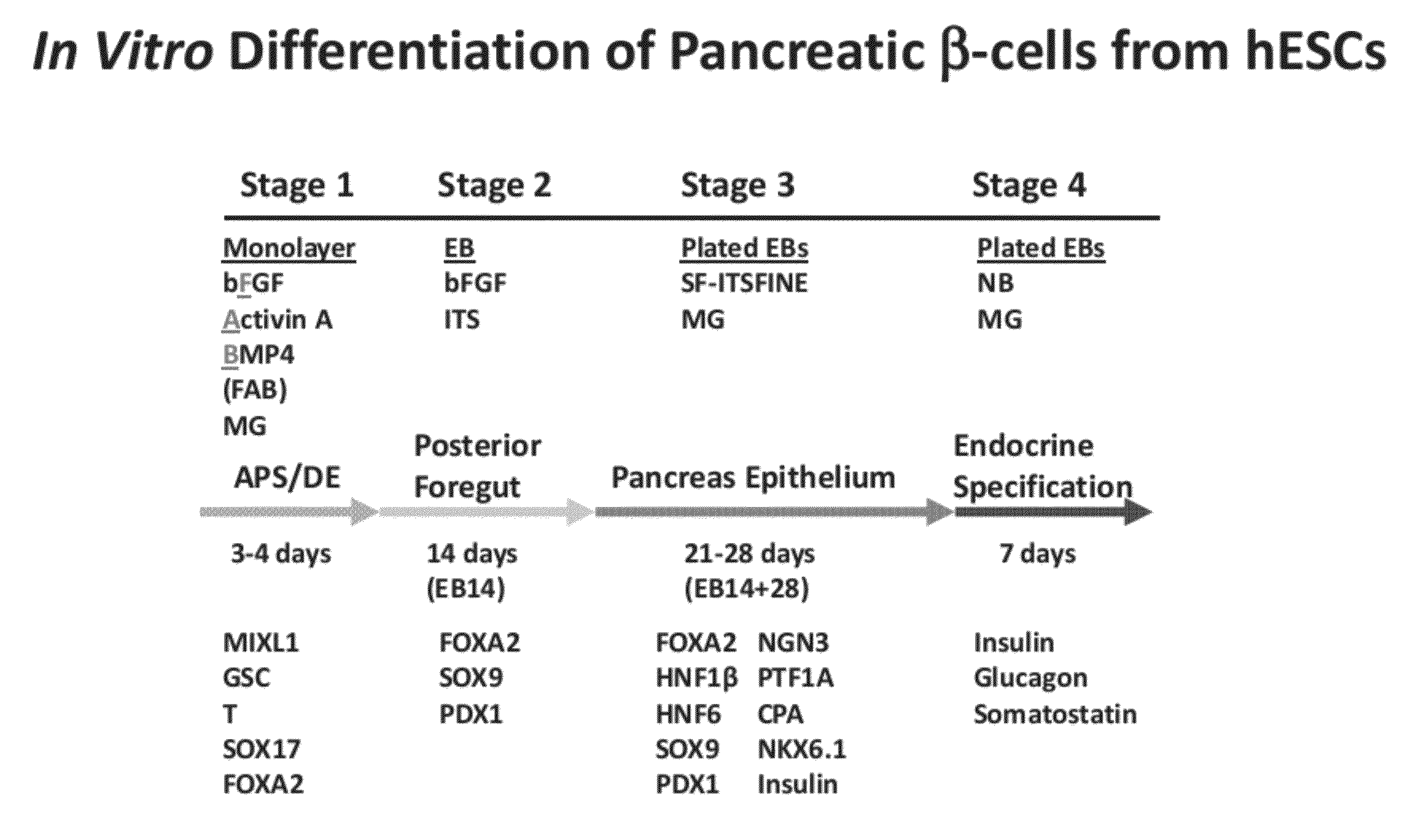
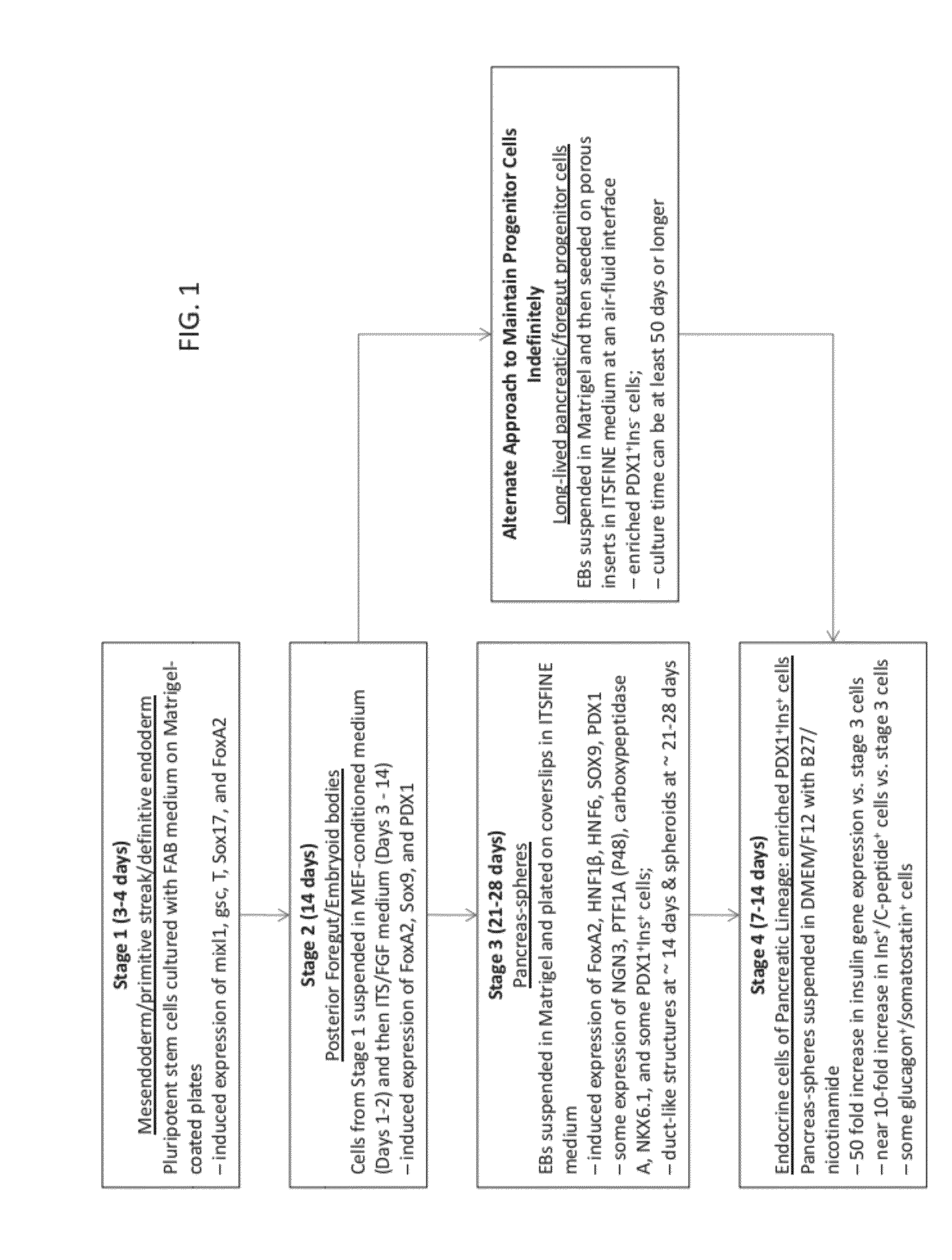
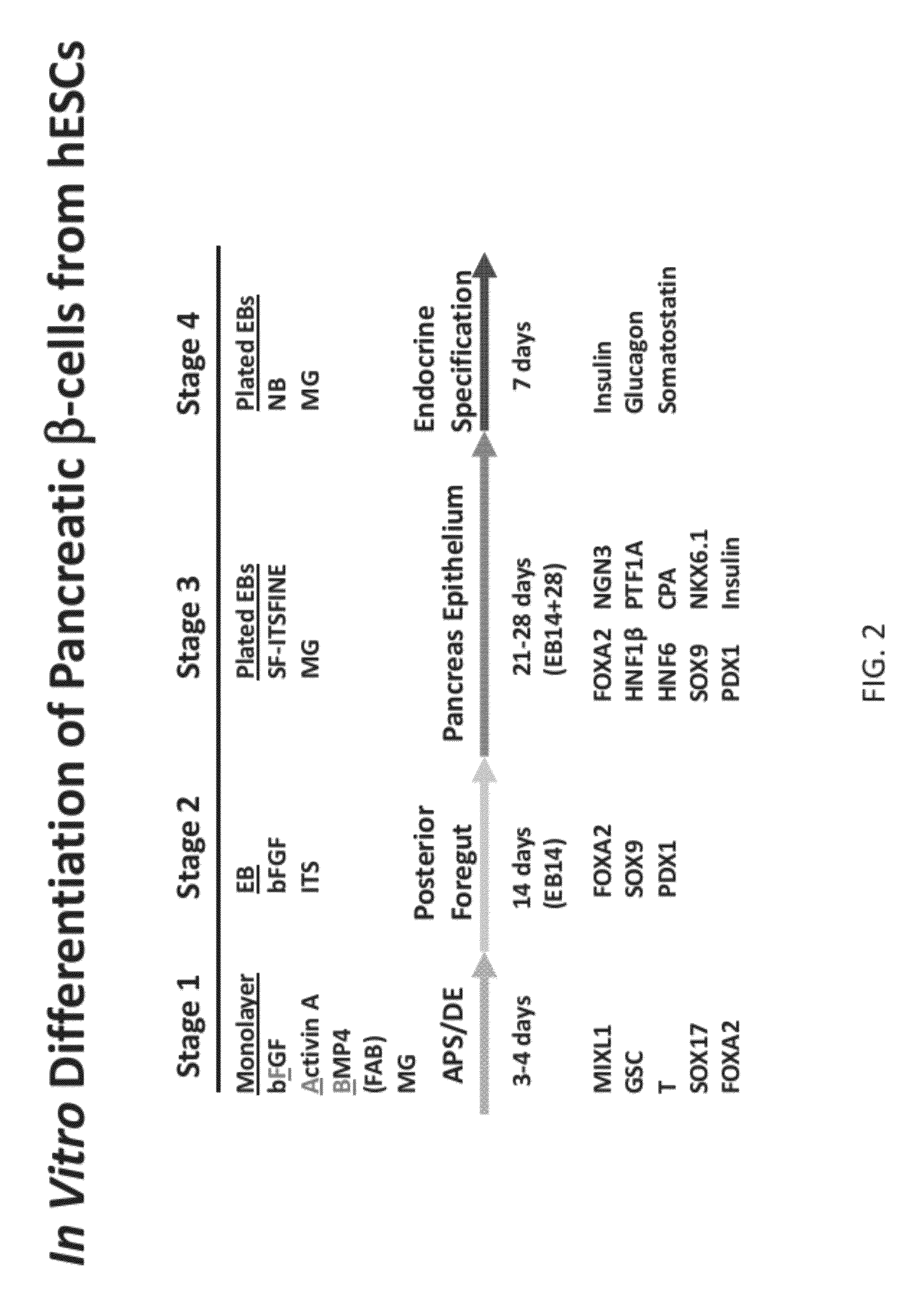
Methods and devices for differentiating pluripotent stem cells into cells of the pancreatic lineage
Methods and devices for culturing human pluripotent stem cells to produce cells of the pancreatic lineage are disclosed. The methods include steps of culturing the stem cells under conditions that induce the expression of mesendoderm / primitive streak and definitive endoderm markers in a chemically defined medium including an effective amount of i) fibroblast growth factor, ii) Activin A, and iii) bone morphogenetic protein. The methods further include the steps of culturing cells under conditions favoring the formation of at least one of intact embryoid bodies and pancreatic progenitor PDX1+ Ins− cells.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Pancreatic and liver endoderm cells and tissue by differentiation of definitive endoderm cells obtained from human embryonic stems
The invention relates to methods that allow for the efficient differentiation to form pancreatic endoderm cells from pluripotent stem cells such as human embryonic stem cells and definitive endoderm cells. The invention is directly applicable to the ultimate generation of pancreatic beta cells that could be used as part of a therapy to treat or even cure diabetes. Additionally, the present invention may be used to generate liver endoderm cells from human embryonic stem cells and definite endoderm cells as well. This invention relates to a method for generating definitive endoderm and pancreatic endoderm cells from stem cells, preferably human embryonic stem cells using defined media in the absence of feeder cells. A simply two step procedure to provide pancreatic endoderm cells from embryonic stem cells represents further embodiments of the present invention.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC
Pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells, compositions, methods and uses thereof
The present invention relates to pluripotent stem cells, particularly to pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells. The invention further relates to methods of purifying pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells and to compositions, cultures and clones thereof. The present invention also relates to a method of transplanting the pluripotent stem cells of the present invention in a mammalian host, such as human, comprising introducing the stem cells, into the host. The invention further relates to methods of in vivo administration of a protein or gene of interest comprising transfecting a pluripotent stem cell with a construct comprising DNA which encodes a protein of interest and then introducing the stem cell into the host where the protein or gene of interest is expressed. The present also relates to methods of producing mesodermal, endodermal or ectodermal lineage-committed cells by culturing or transplantation of the pluripotent stem cells of the present invention.
Owner:ABT HOLDING COMPANY
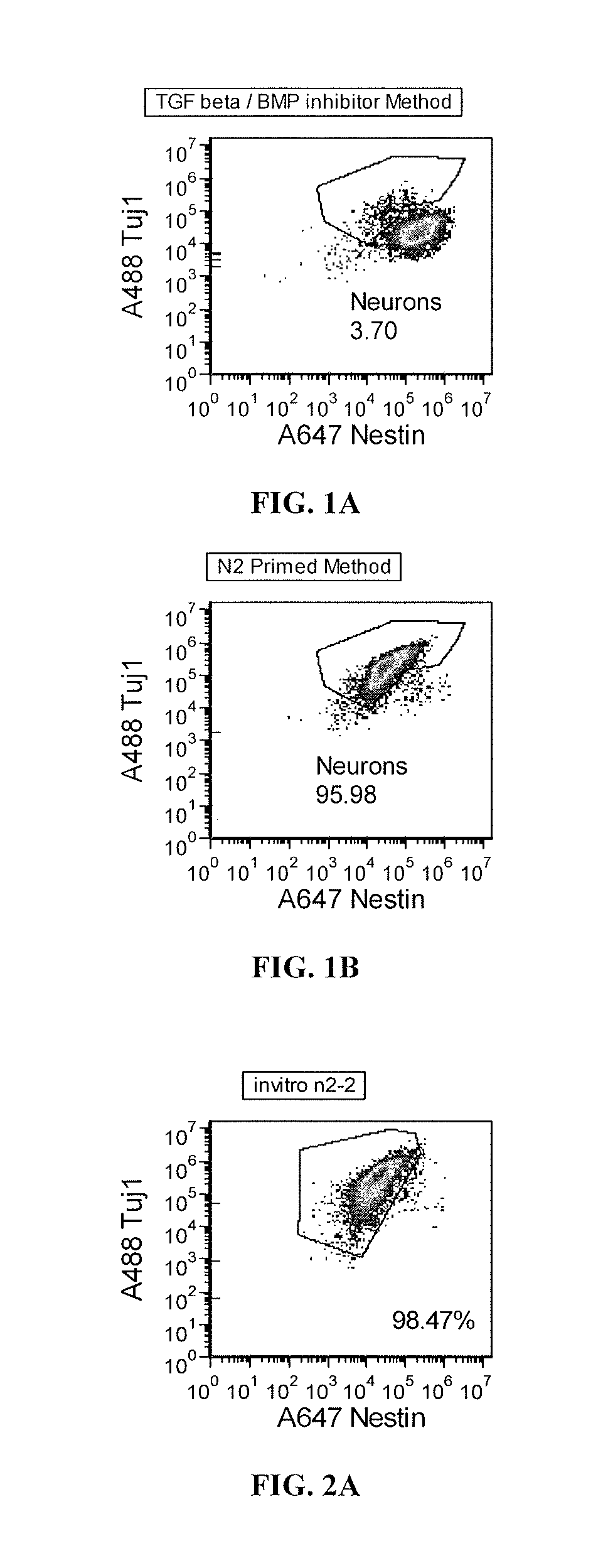
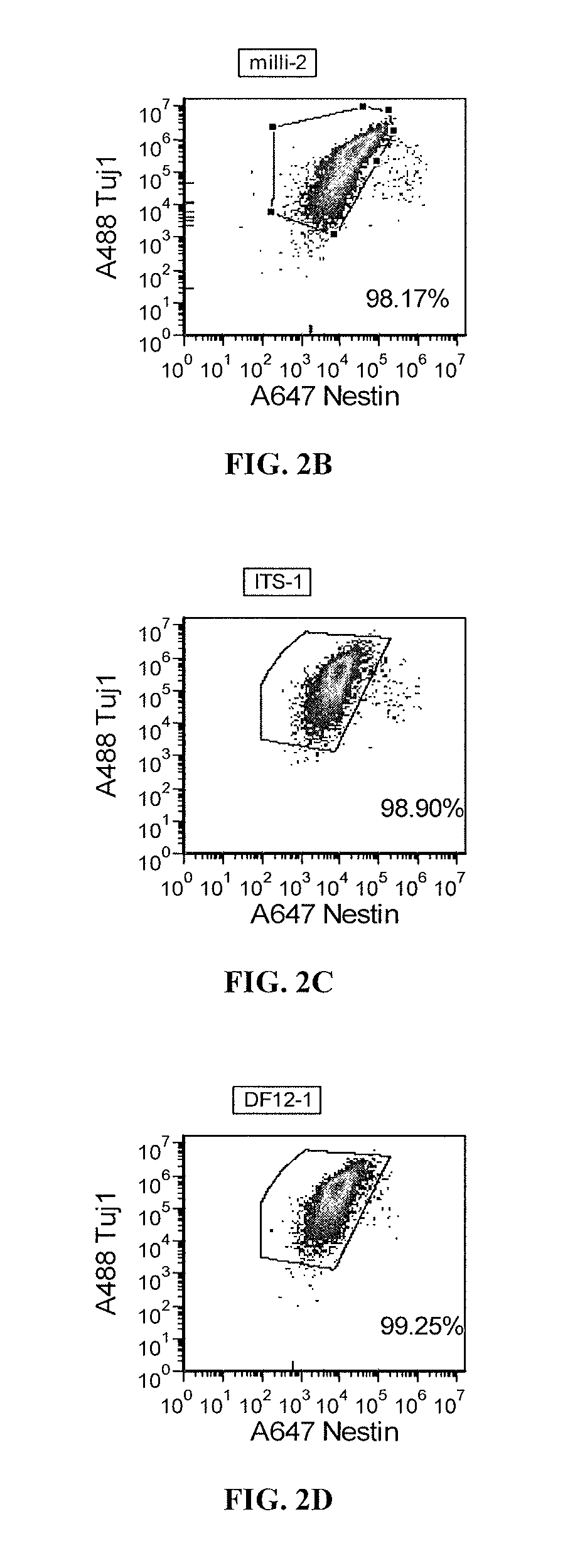
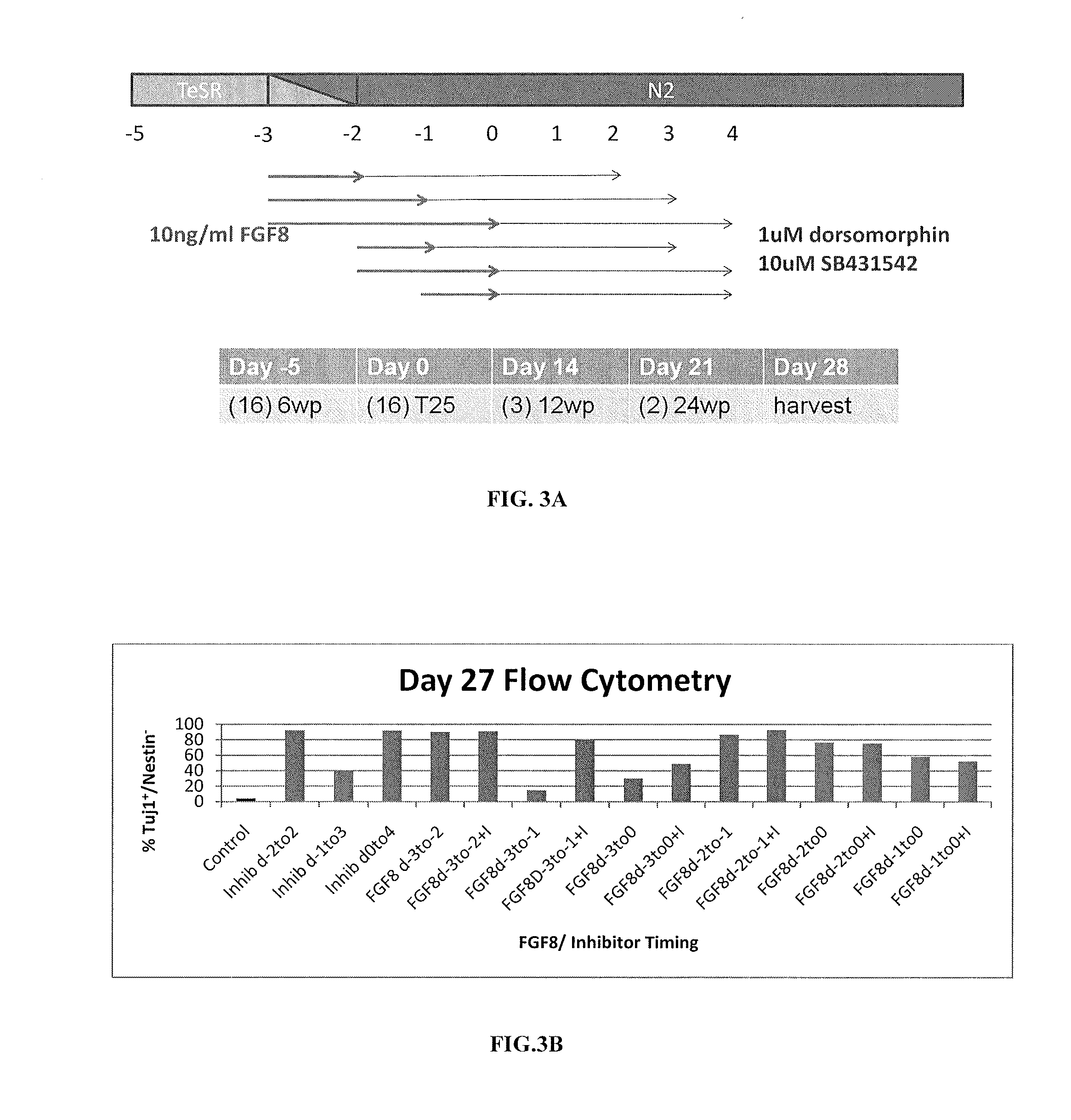
Priming of pluripotent stem cells for neural differentiation
ActiveUS20120276063A1Improve efficiencyMass productionBiocideSenses disorderPluripotential stem cellNeurulation
Methods and composition for differentiation of pluripotent stem cells are provided. For example, in certain aspects methods including priming stem cells for neural differentiation in a culture medium essentially free of growth factors such as FGF and TGFβ. As an advantage, the neural cells may be provided with improved consistency and purity.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Isolated naive pluripotent stem cells and methods of generating same
ActiveUS20140315301A1Increase generationArtificial cell constructsCell culture active agentsPhysiologyAllele
Provided is an isolated human naive pluripotent stem cell (PSC), wherein: (i) when the naive PSC is a female PSC, then said naive female PSC has two unmethylated alleles of an X-inactive specific transcript (XIST) gene; and (ii) when said naive PSC is a male PSC, then said naive male PSC has an unmethylated allele of said XIST gene. Also provided is a culture medium which comprises an ERK1 / 2 inhibitor, a GSK3beta inhibitor, a p38 inhibitor, a JNK inhibitor, a STAT3 activator and at least one agent selected from the group consisting of: bFGF, TGFbeta 1, a PKC inhibitor, a ROCK inhibitor and a NOTCH inhibitor; or at least agent selected from the group consisting of: a TGFR inhibitor, a FGFR inhibitor, a PKC inhibitor, a ROCK inhibitor and a NOTCH inhibitor.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
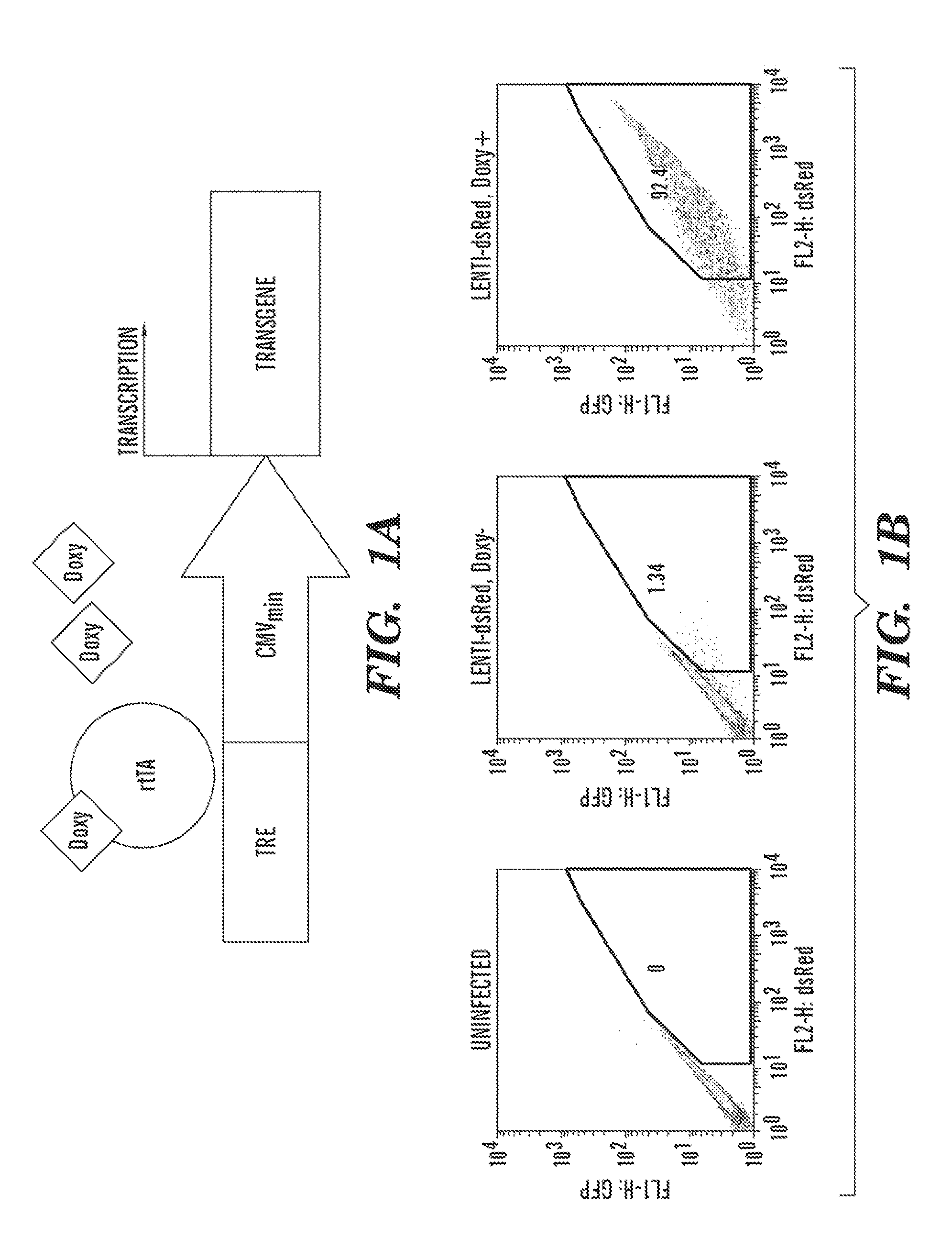
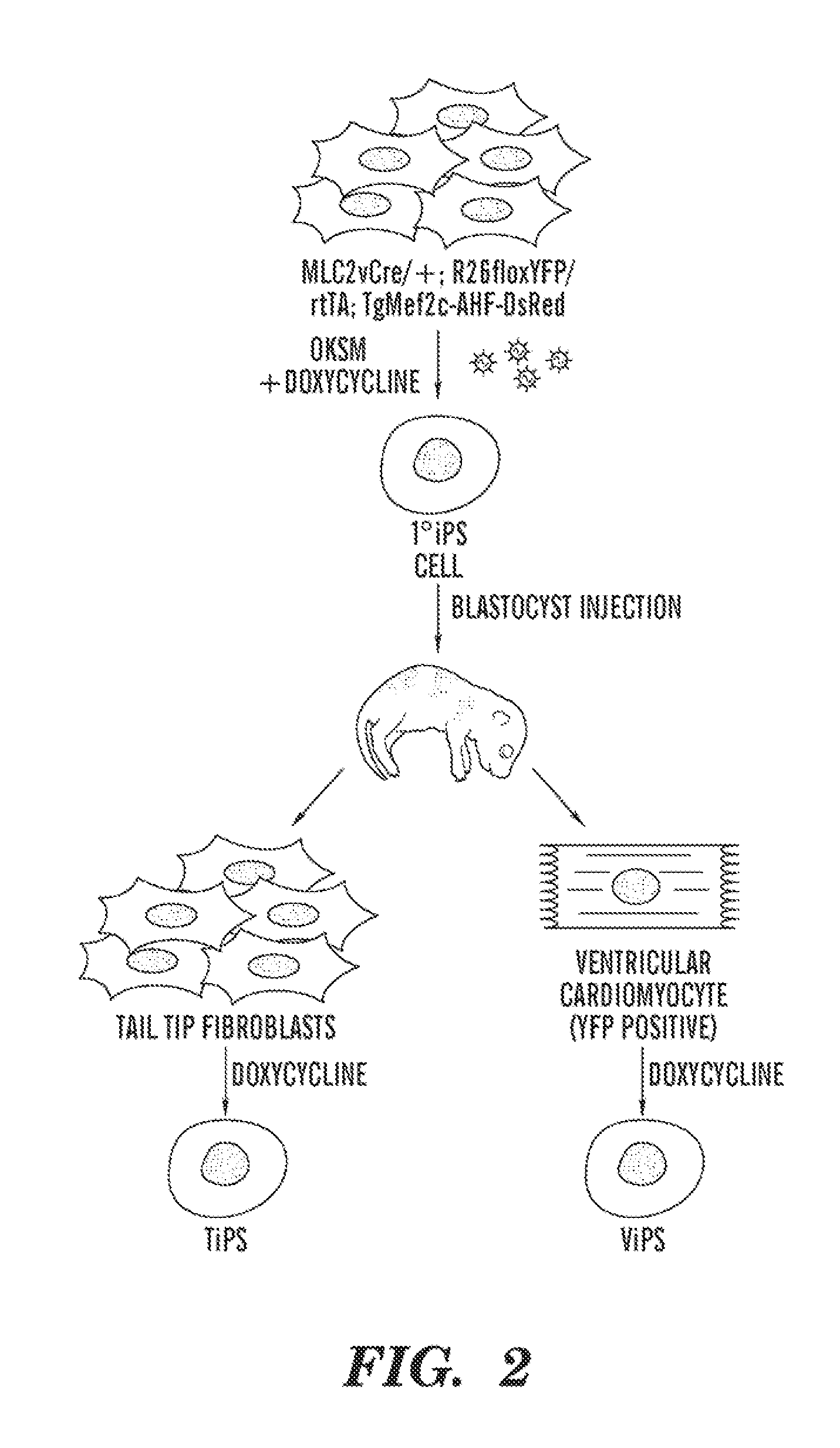
VENTRICULAR INDUCED PLURIPOTENT STEM (ViPS) CELLS FOR GENERATION OF AUTOLOGOUS VENTRICULAR CARDIOMYOCYTES AND USES THEREOF
InactiveUS20120009158A1More cardiomyogenicYieldBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsDiseaseCells heart
The present invention generally relates to methods and compositions to generate a secondary iPS (2iPS) cell to produce somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate. In some embodiments, the method relates to an increase in efficiency of differentiation and production of high yields of somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate produced from secondary iPS (2iPS) cells as compared to their differentiation from other pluripotent stem cell sources such as ES cells or primary iPS cells. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to compositions, methods and systems for reprogramming a first somatic cell into a primary iPS cell, where the primary iPS cell is then differentiated along a selected linage to produce a second somatic cell, which is then reprogrammed to a secondary iPS cell (2iPS) cell. The 2iPS cell has a high efficiency of differentiating into a cell of the same cell type as the second somatic cell, e.g., a somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate such as but not limited to a ventricular cardiomyocyte, a pancreatic β-cell or a hepatic cell. In some embodiments, the first somatic cell is a fibroblast, or a cardiac cell, but is not limited to cardiac fibroblast cells. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to compositions, methods and systems to produce ventricular cardiomyocytes from secondary induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC), where the iPSC are themselves generated from ventricular cardiomyocytes. The secondary iPS (2iPS) cell generated from ventricular cardiomyocytes have a higher cardiomyogenic potential and high cardiomyogenic yield as compared to primary iPSC, and are useful in drug discovery, disease modeling and cell-based therapy.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Cardiomyocyte production
ActiveUS20110097799A1Enhanced signalPromote differentiationCell dissociation methodsSugar derivativesCardiac muscleCulture mediums
Methods and composition for the production of cardiomyocytes from differentiation of pluripotent stem cells are provided. For example, in certain aspects methods including differentiating pluripotent stem cells in a large volume of suspension culture in the presence of ROCK inhibitors are described. In further aspects, methods for differentiation of stem cells into cardiomyocytes that overcome variability between different stem cell clones and different batch of culture medium are provided.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells, compositions, methods and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100239543A1Avoid developmentInhibit progressBiocideGenetic material ingredientsGerm layerPluripotential stem cell
The present invention relates to pluripotent stem cells, particularly to pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells. The invention further relates to methods of purifying pluripotent embryonic-like stem cells and to compositions, cultures and clones thereof. The present invention also relates to a method of transplanting the pluripotent stem cells of the present invention in a mammalian host, such as human, comprising introducing the stem cells, into the host. The invention further relates to methods of in vivo administration of a protein or gene of interest comprising transfecting a pluripotent stem cell with a construct comprising DNA which encodes a protein of interest and then introducing the stem cell into the host where the protein or gene of interest is expressed. The present also relates to methods of producing mesodermal, endodermal or ectodermal lineage-committed cells by culturing or transplantation of the pluripotent stem cells of the present invention.
Owner:YOUNG HENRY E +1
Culture of pluripotent autologous stem cells from oral mucosa
ActiveUS9534201B2Epidermal cells/skin cellsArtificial cell constructsPluripotential stem cellAdult Somatic Stem Cells
The present invention provides a new readily accessible source of adult somatic stem cells from the gastrointestinal tract in general and oral mucosa in particular, methods for isolating pluripotent stem cells from oral mucosa, cells derived therefrom and uses thereof.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Reprogramming immortalized b cells
ActiveUS20120058562A1High reprogramming efficiencySave stepsGenetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsLymphocyteB cell
Methods and composition for providing induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells are provided. For example, in certain aspects methods including reprogramming B lymphocytes transformed by episomal vectors such as Epstein-Barr virus-based vectors are described. Furthermore, the invention provides induced pluripotent stem cells essentially free of exogenous elements and having B cell immunoglobin variable region rearrangement.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
Compositions and methods for differentiating pluripotent stem cells into primitive blood cells and uses thereof
InactiveUS20130171110A1High expressionAccelerate self-renewalBiocideCulture processInduced pluripotent stem cellAntioxidant
Compositions and methods that employ various combinations of such factors as retinoic acid signaling inhibitors, antioxidants, BMP4, VEGF, prostaglandin E2 pathway stimulants, TPO, SCF, FLT-3, EPO, TGFβ1, p38 MAPK inhibitors, beta adrenergic receptor agonists, cell cycle inhibitors, RXR agonists, Cripto, and chromatin remodelers to drive differentiation of pluripotent stem cells towards primitive blood cells. Uses of such primitive blood cells are provided.
Owner:NUCLEUS BIOLOGICS LLC
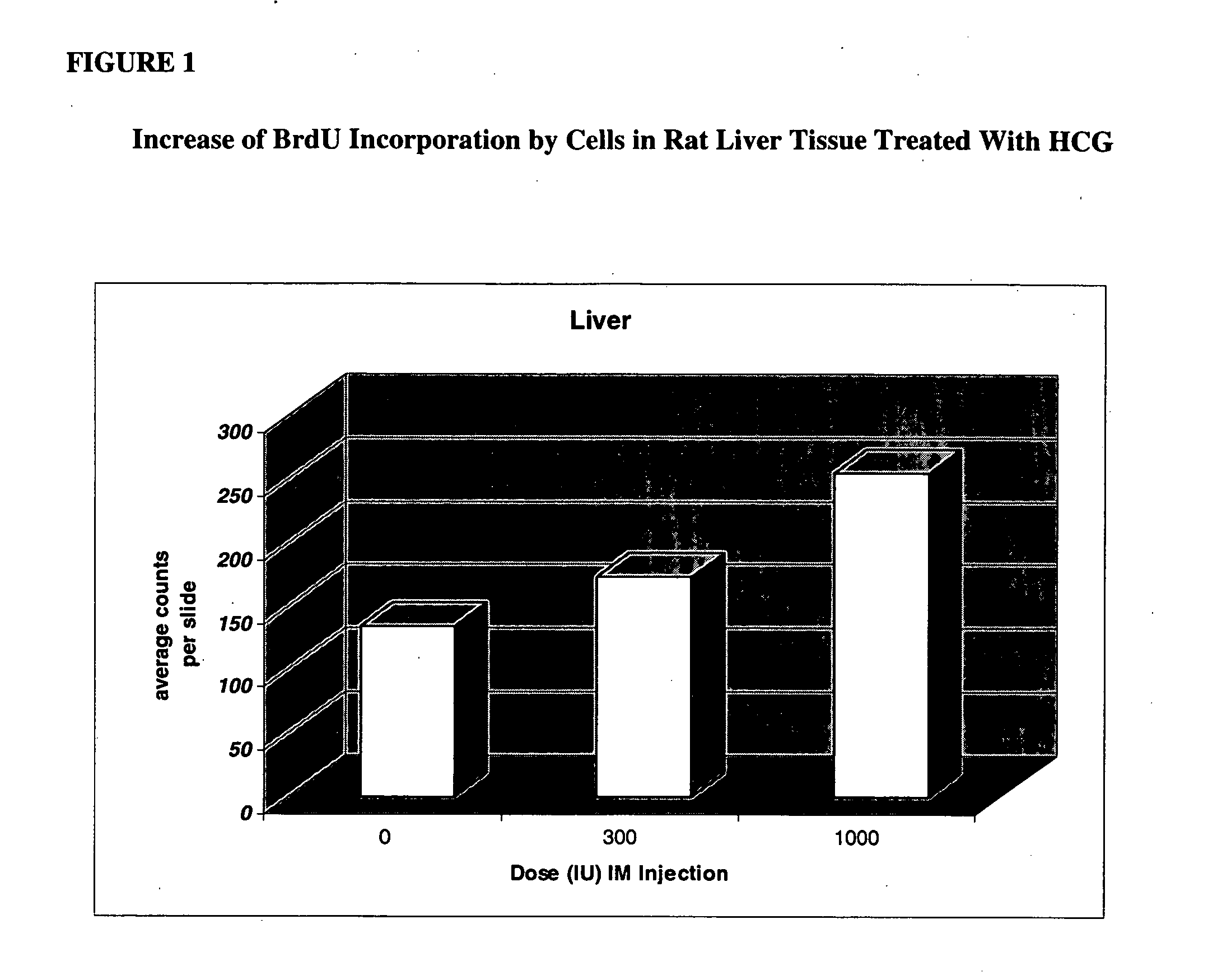
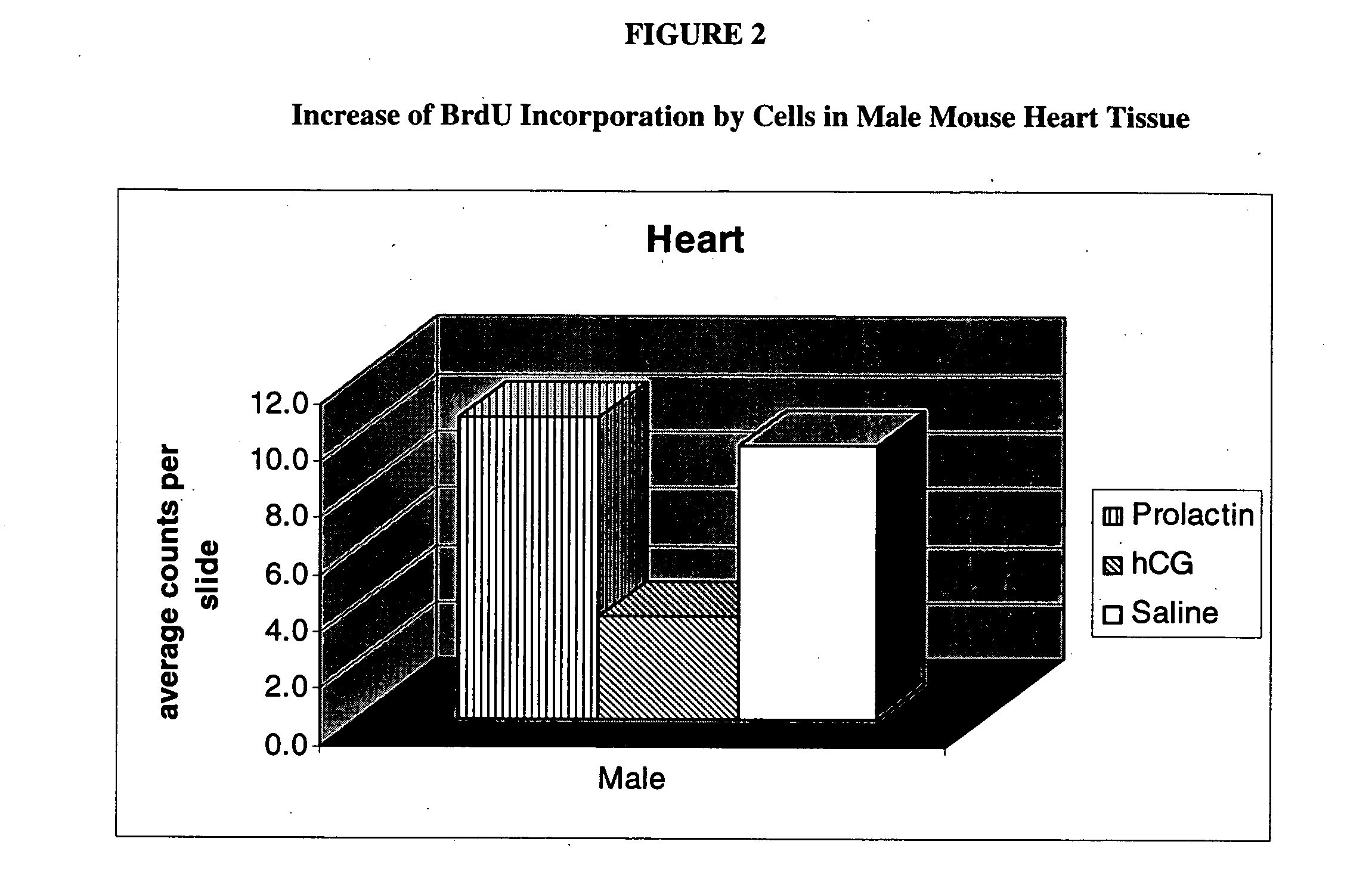
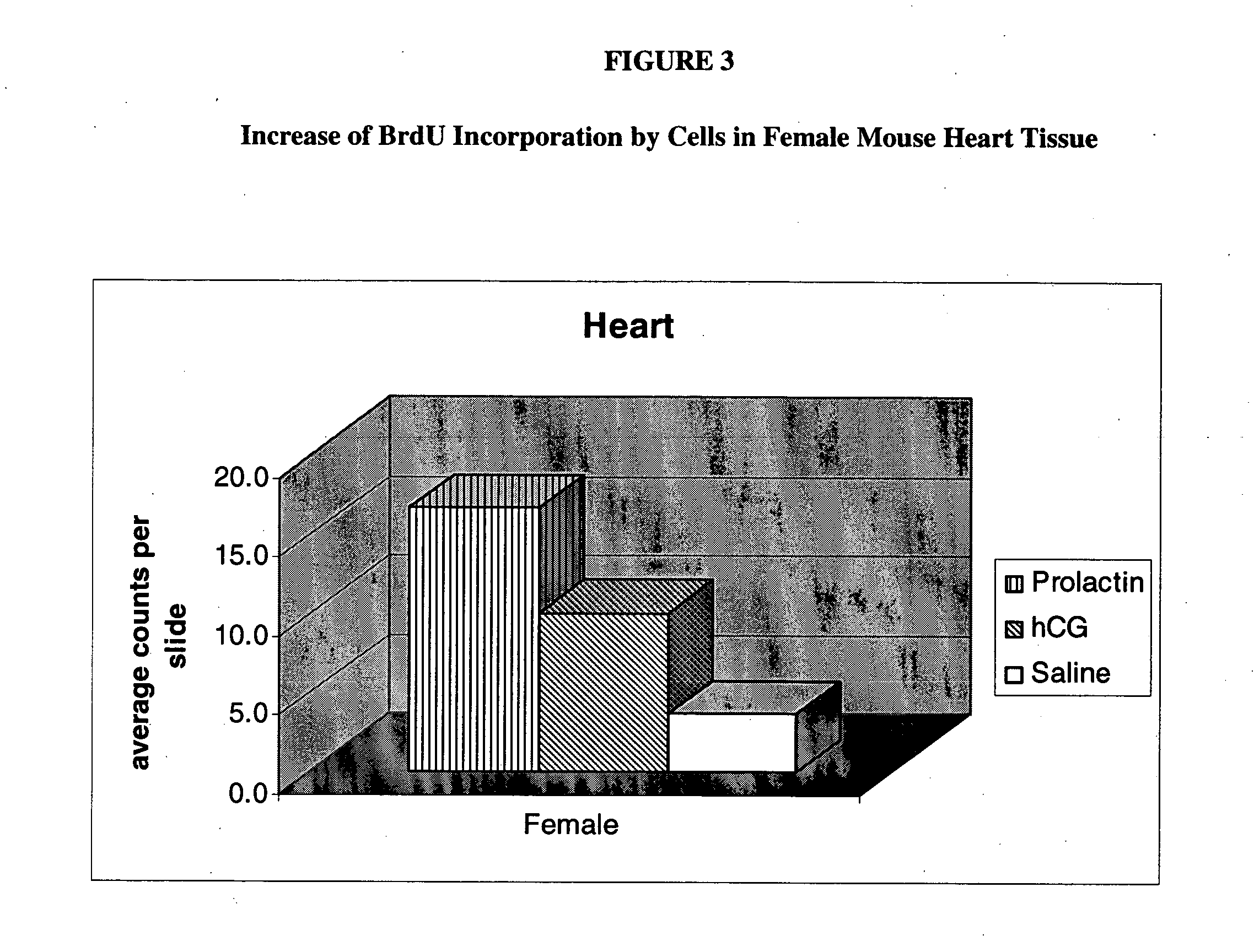
Stimulation of proliferation of pluripotential stem cells through administration of pregnancy associated compounds
The present invention provides for a method for stimulating the proliferation of pluripotential stem cells in a mammal comprising administration of pregnancy related compounds more particularly human chorionic gonadotropin, leutenizing hormone or prolactin. The present invention further provides for a method of treatment of tissues or organs experiencing cellular damage, injury or disease.
Owner:STEM CELL THERAPEUTICS
Functional oligodendrocytes derived from pluripotent stem cells and methods of making and using the same
ActiveUS20170183627A1Low costComparable myelination potentialNervous disorderNervous system cellsProgenitorInduced pluripotent stem cell
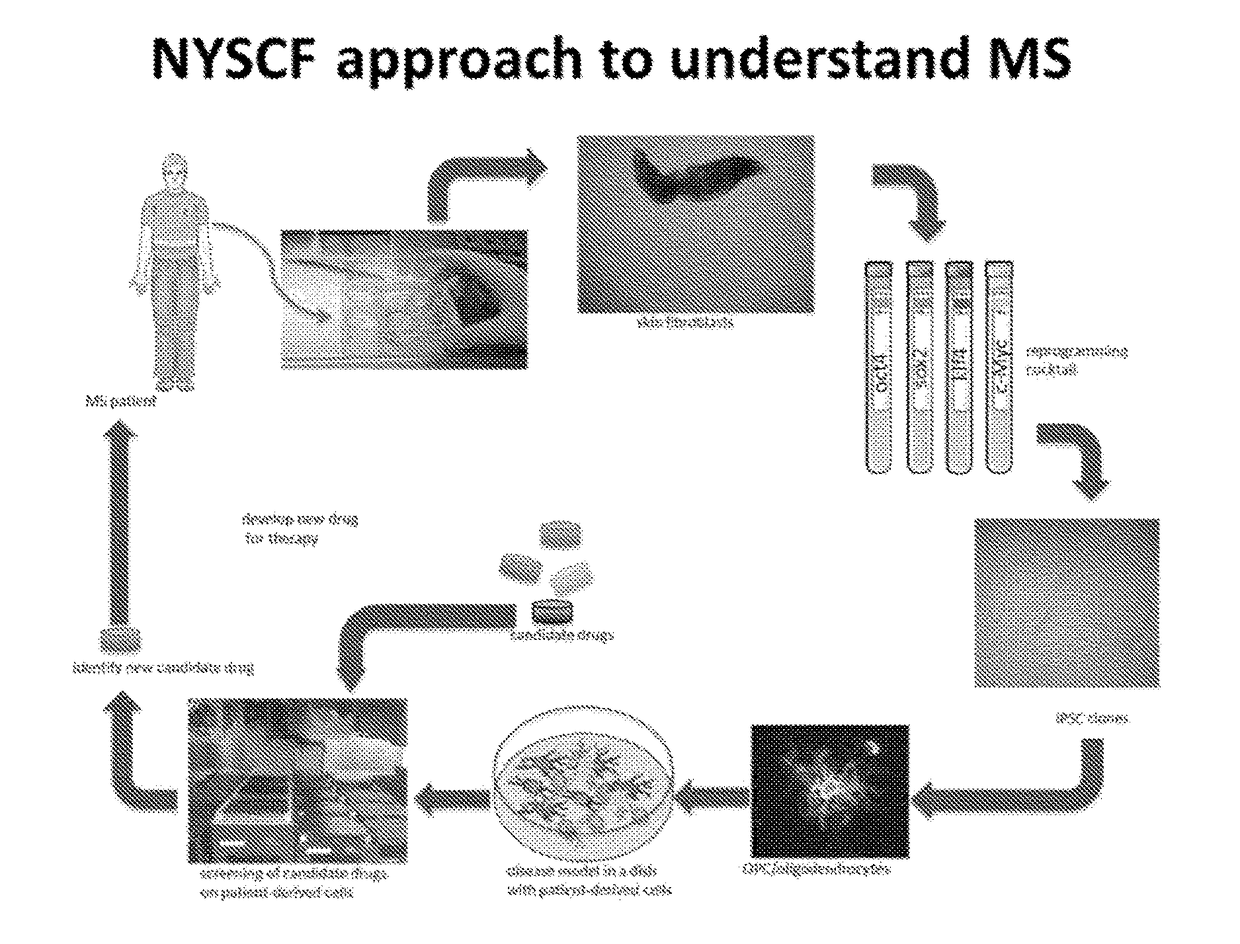
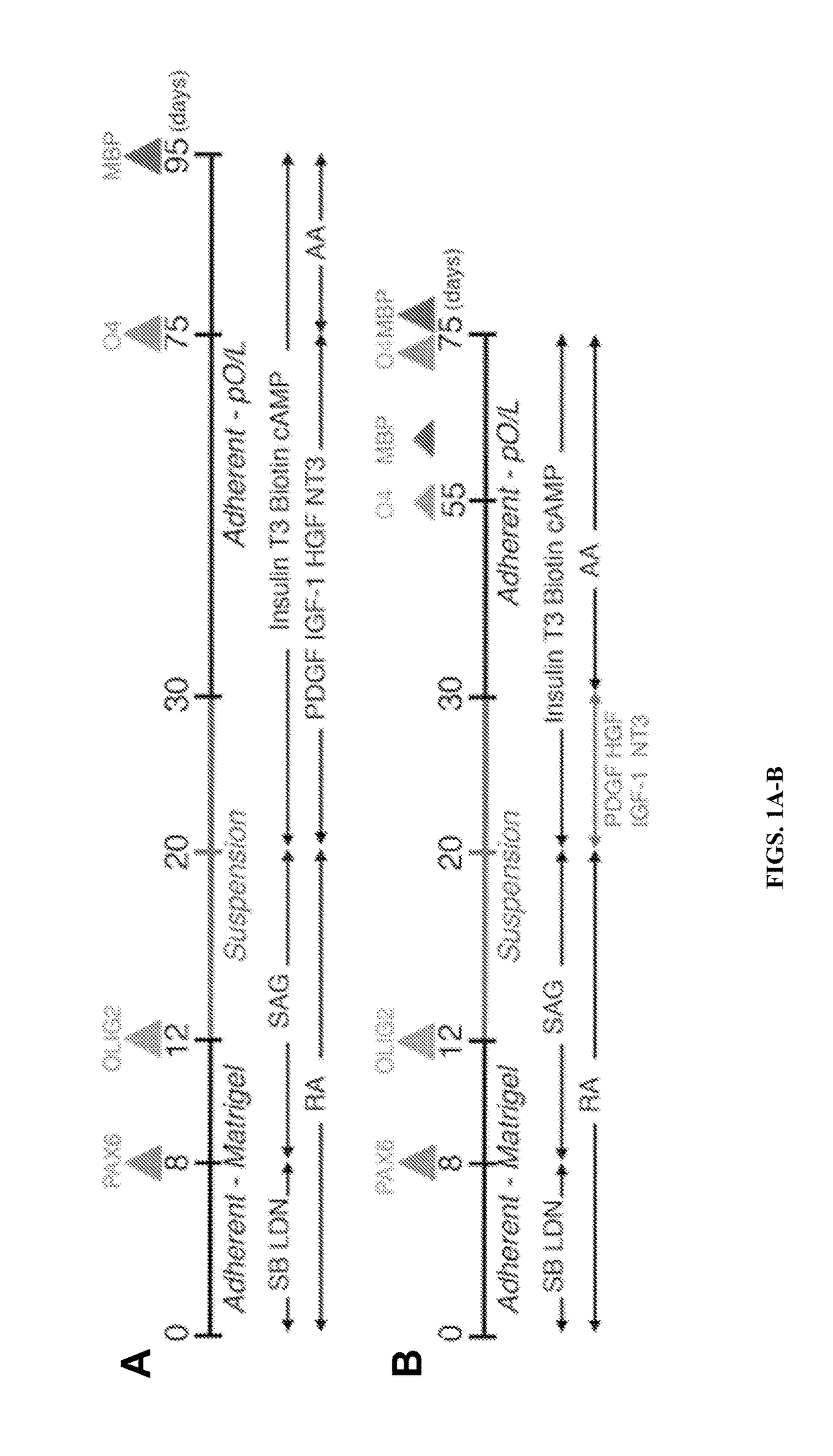
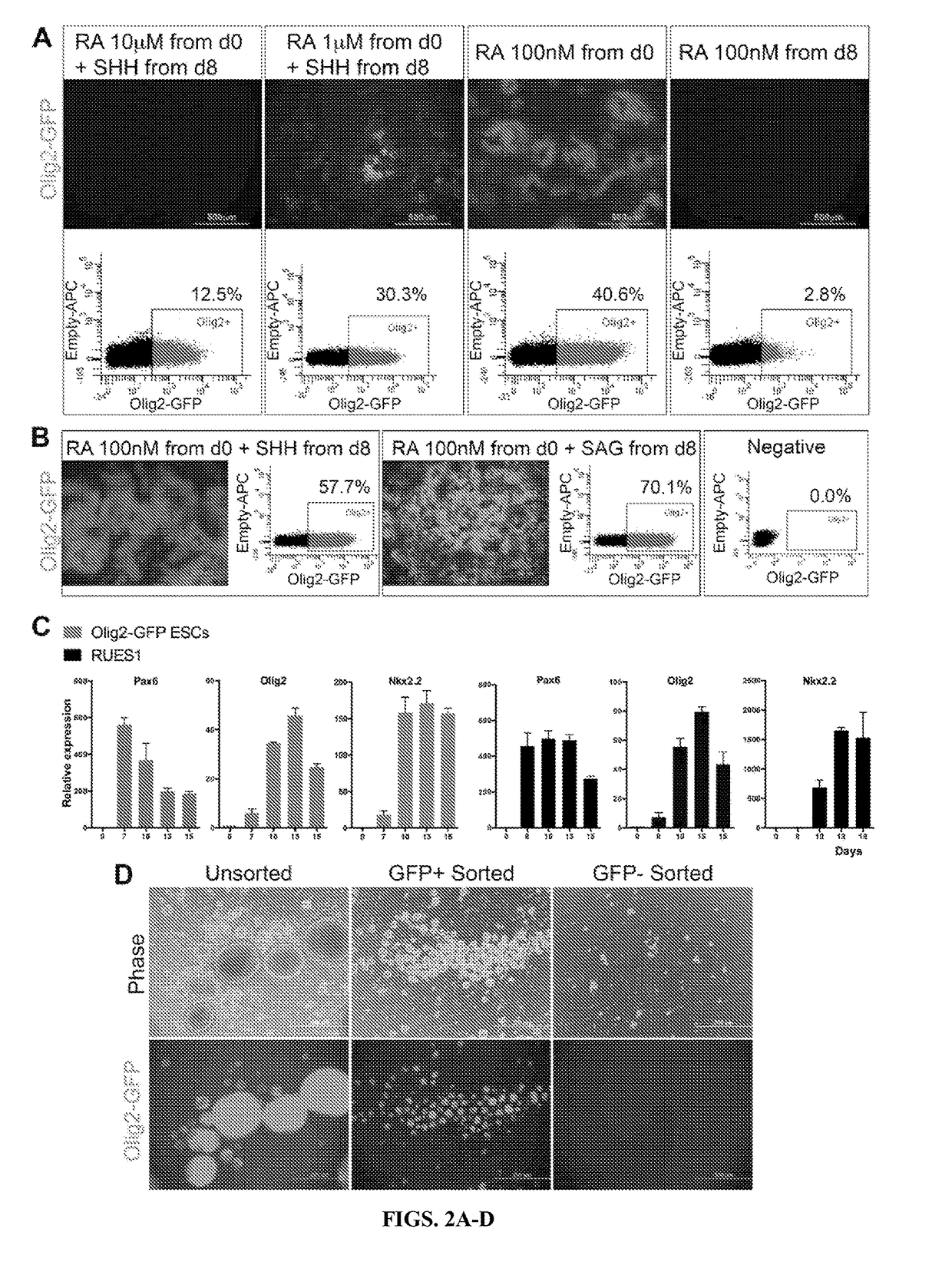
Described is the efficient and robust generation of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs) and oligodendrocytes from pluripotent stem cells (PSCs). The protocols provided recapitulate the major steps of oligodendrocyte differentiation, from neural stem cells to OLIG2+ progenitors, and then to 04+ OPCs, in a significantly shorter time than the 120-150 days required by previous protocols. Furthermore, 04+ OPCs are able to differentiate into MBP+ mature oligodendrocytes in vitro, and to myelinate axons in vivo when injected into immuno-compromised Shiverer mice, providing proof of concept that transplantation of PSC-derived cells for remyelination is technically feasible.
Owner:NEW YORK STEM CELL FOUND
Cardiomyocytes from induced pluripotent stem cells from patients and methods of use thereof
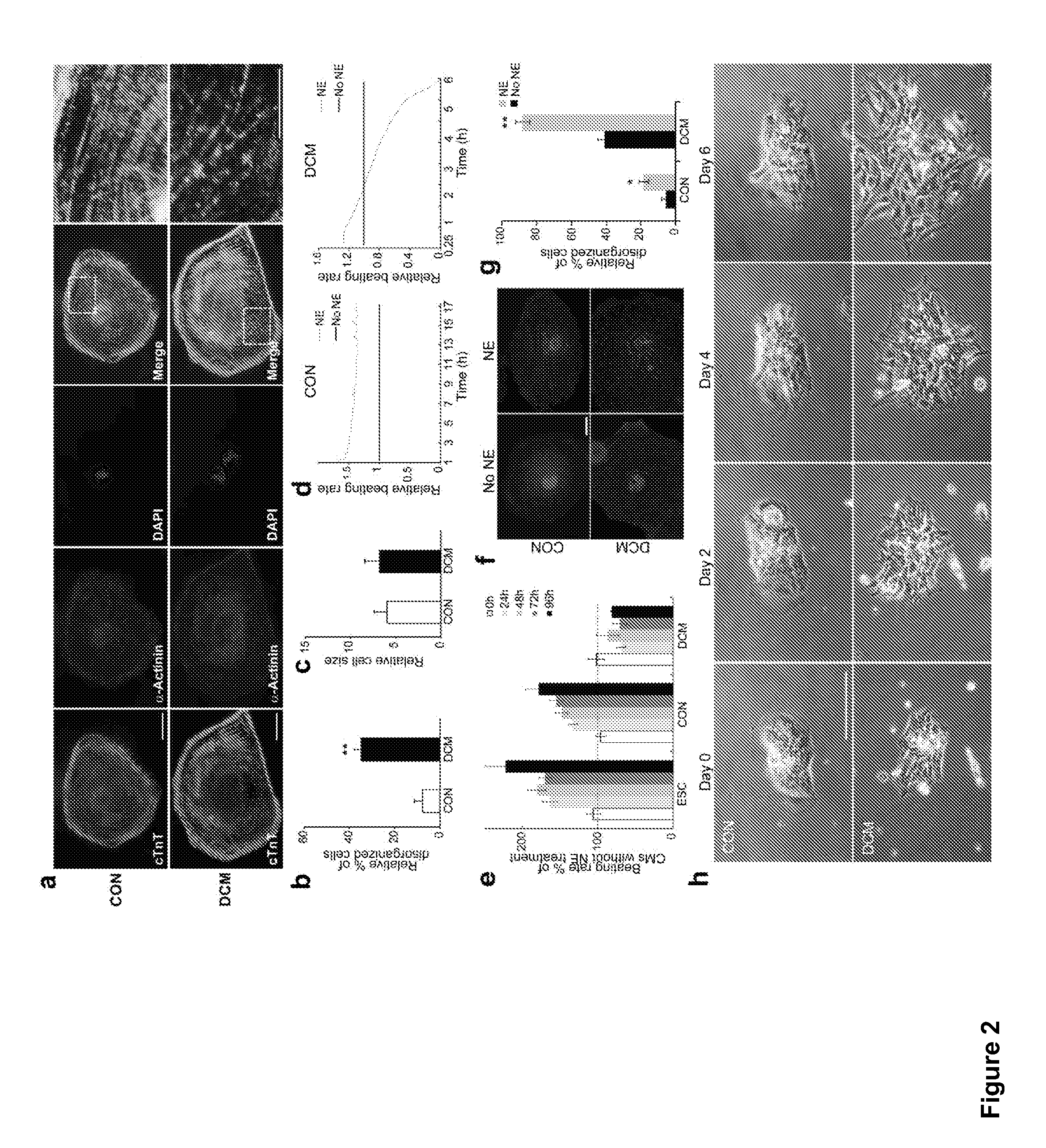
ActiveUS20130029866A1Abnormal sarcomeric α-actinin distributionReduce the probability of jumpingLibrary screeningDrug screeningPluripotential stem cellHuman body
Human somatic cells obtained from individuals with a genetic heart condition are reprogrammed to become induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells), and differentiated into cardiomyocytes for use in analysis, screening programs, and the like.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
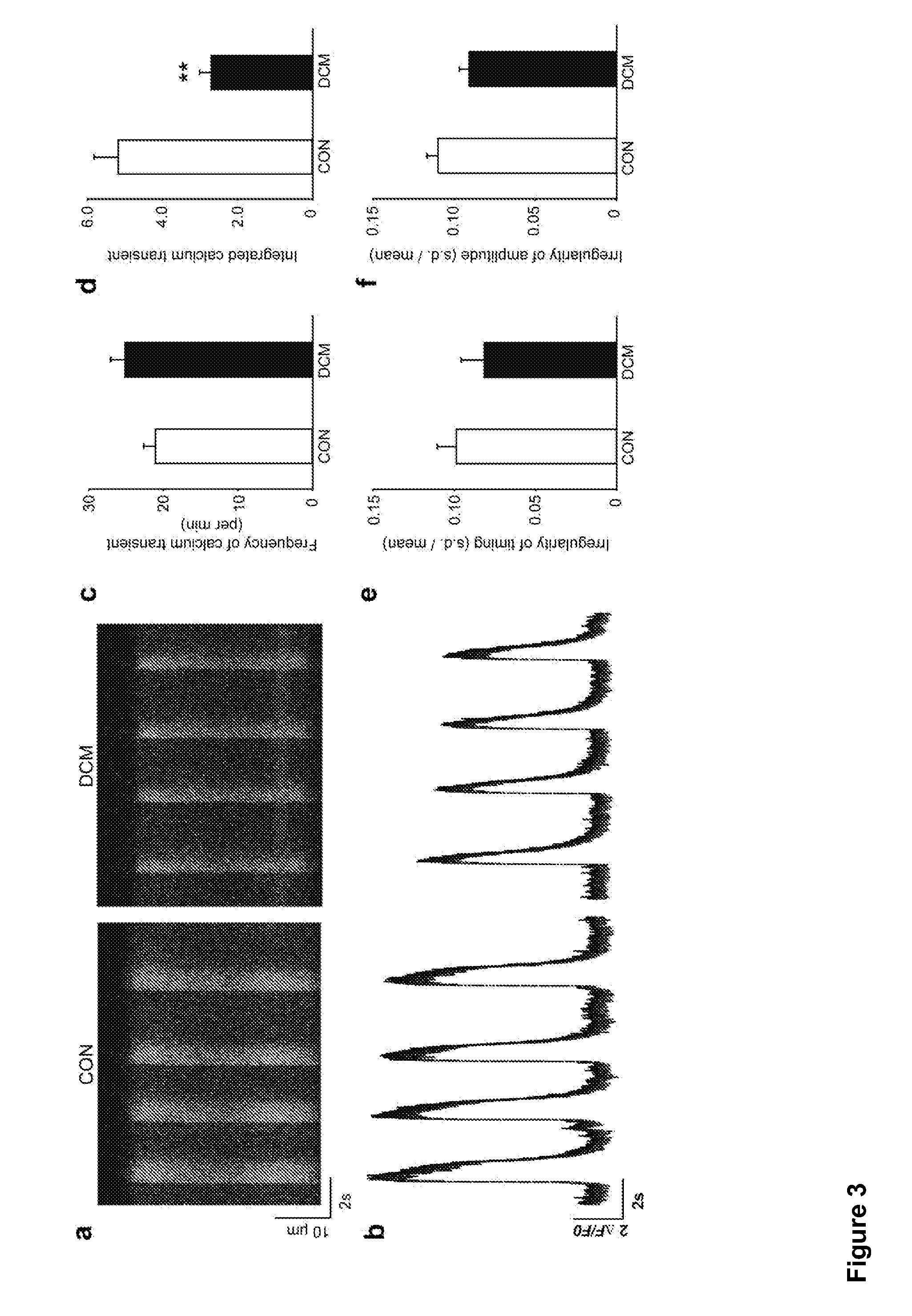
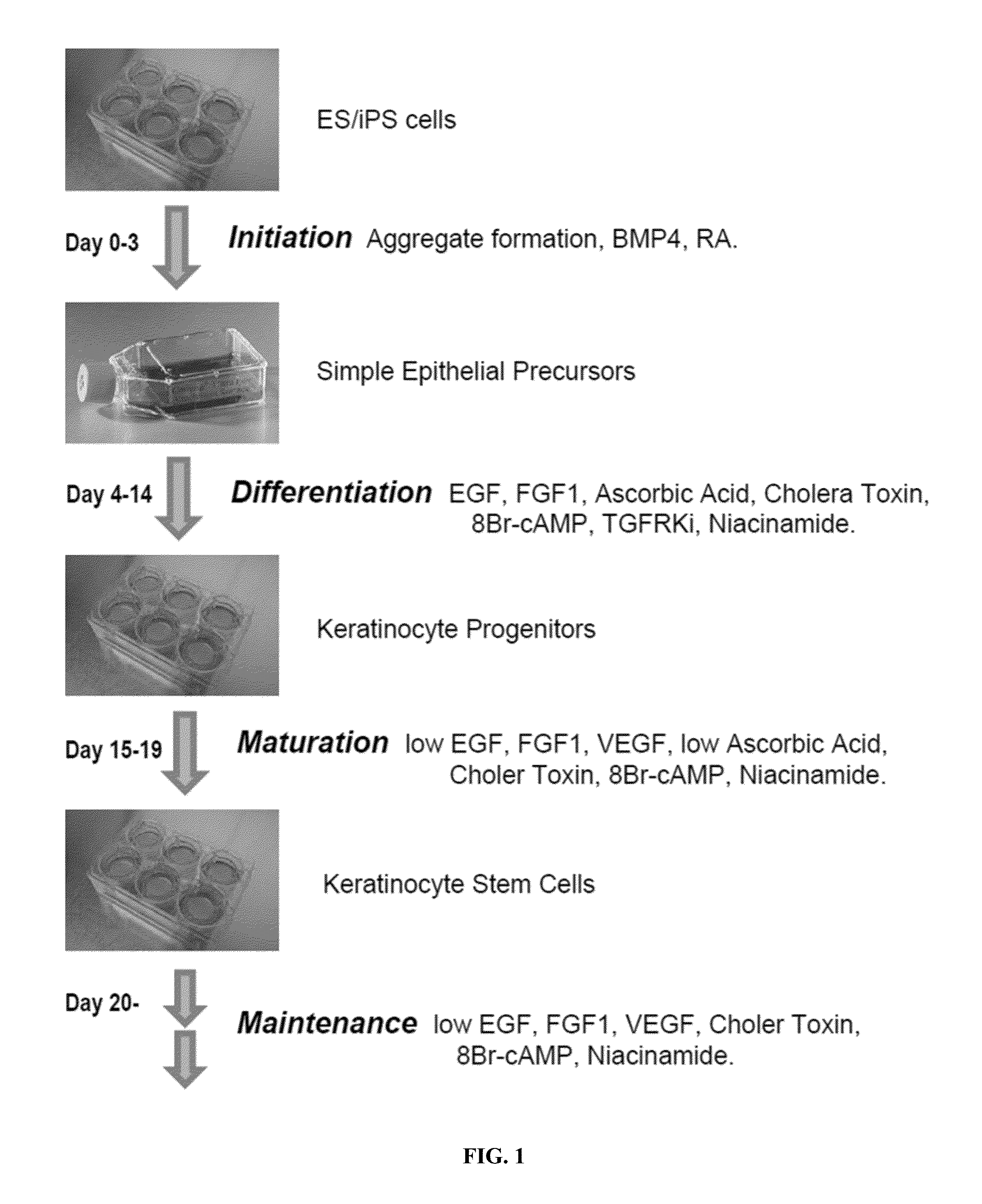
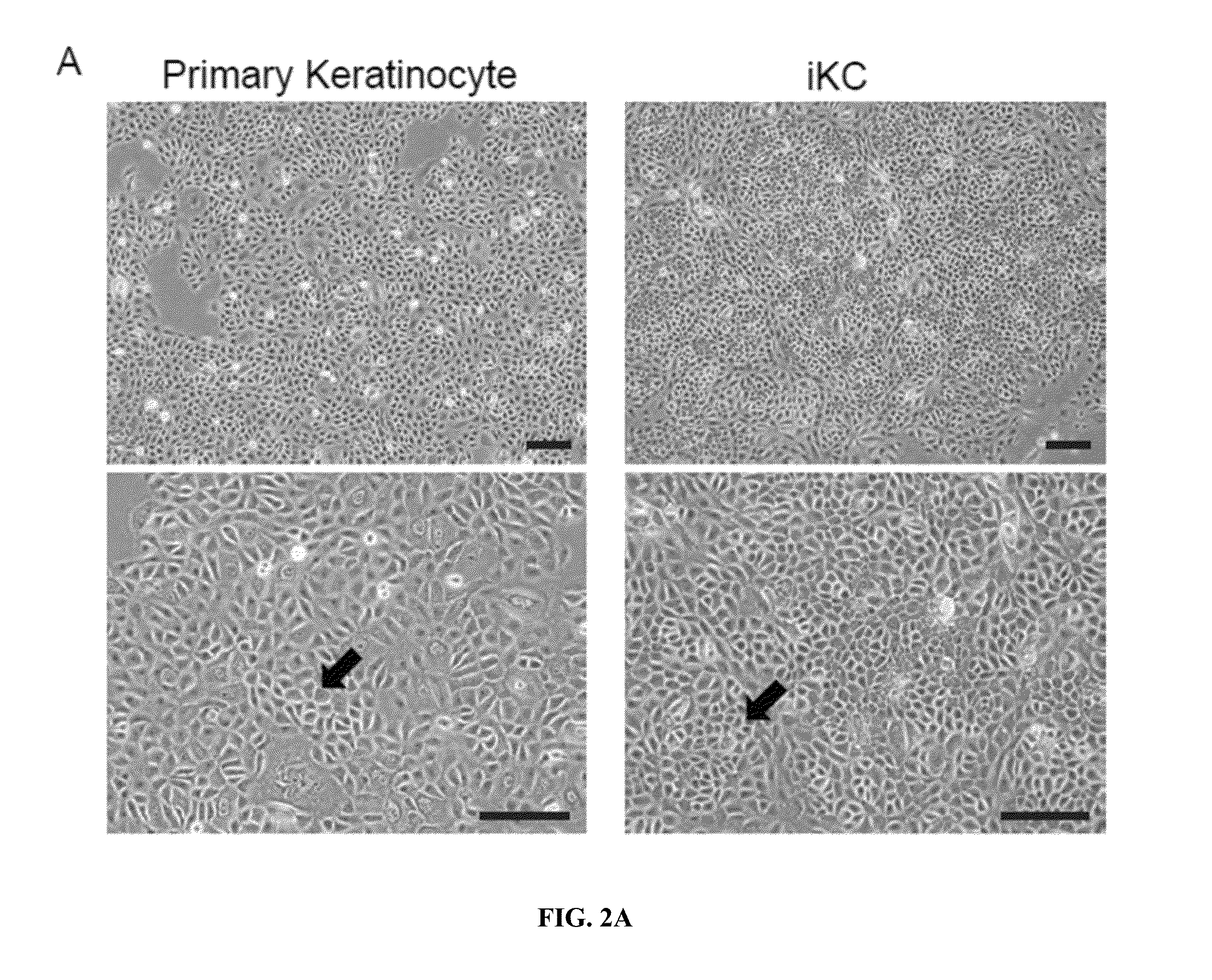
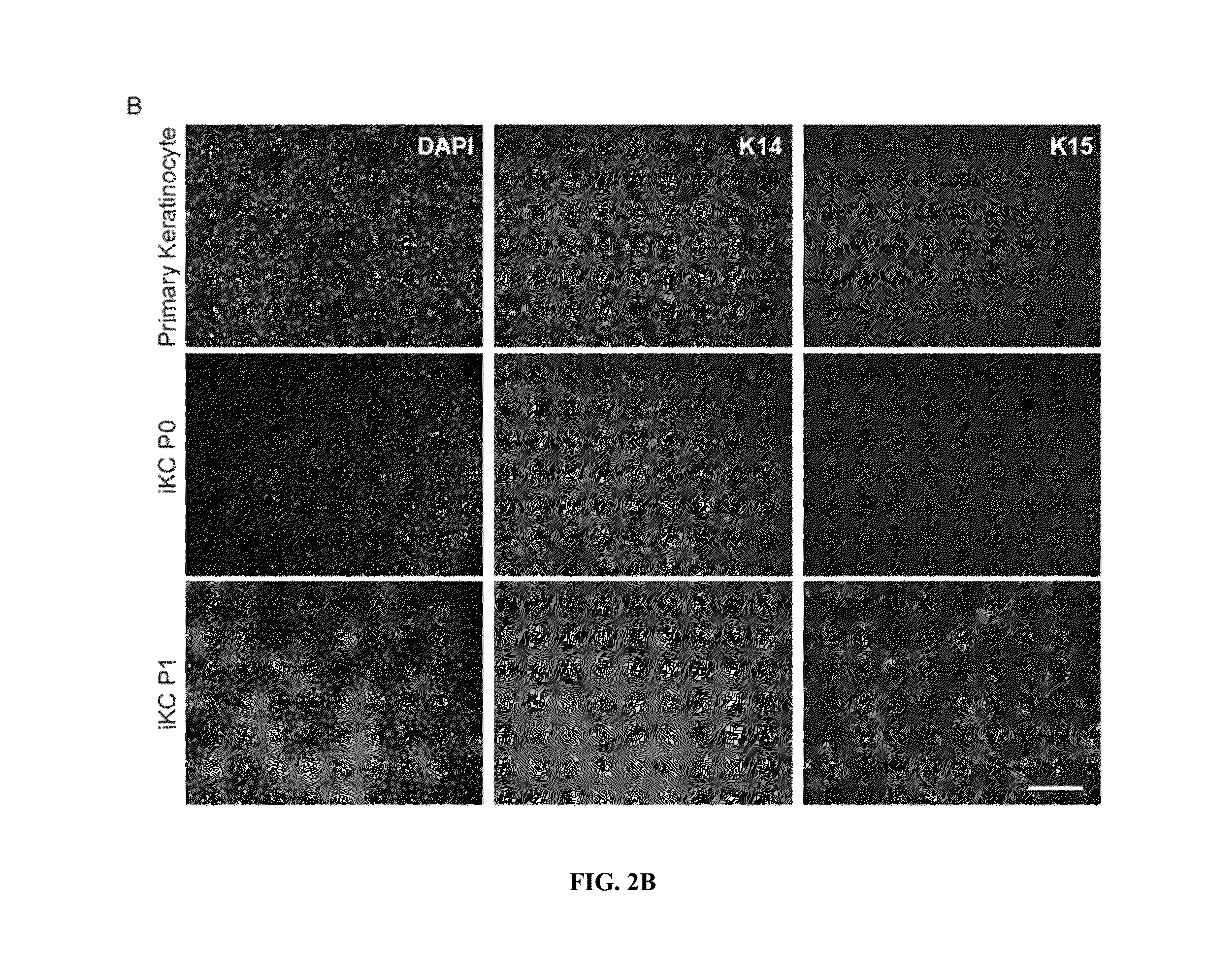
Generation of keratinocytes from pluripotent stem cells and maintenance of keratinocyte cultures
Provided herein are methods for the generation of functional keratinocyte stem cells that are differentiated directly from human ESCs / iPSCs in a chemically defined serum-free cell culture system, as well as cells derived therefrom and methods of use thereof. Also provided are methods for culturing primary keratinocytes.
Owner:FUJIFILM CELLULAR DYNAMICS INC
System for expanding and differentiating human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050153445A1Rapid productionExpanding primate pluripotent stem (pPS) cellsHepatocytesGastrointestinal cellsGerm layerPluripotential stem cell
This disclosure provides an improved system for culturing human pluripotent stem cells. Traditionally, pluripotent stem cells are cultured on a layer of feeder cells (such as mouse embryonic fibroblasts) to prevent them from differentiating. In the system described here, the role of feeder cells is replaced by components added to the culture environment that support rapid proliferation without differentiation. Effective features are a suitable support structure for the cells, and an effective medium that can be added fresh to the culture without being preconditioned by another cell type. Culturing human embryonic stem cells in fresh medium according to this invention causes the cells to expand surprisingly rapidly, while retaining the ability to differentiate into cells representing all three embryonic germ layers. This new culture system allows for bulk proliferation of pPS cells for commercial production of important products for use in drug screening and human therapy.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Differentiation of Pluripotent Stem Cells
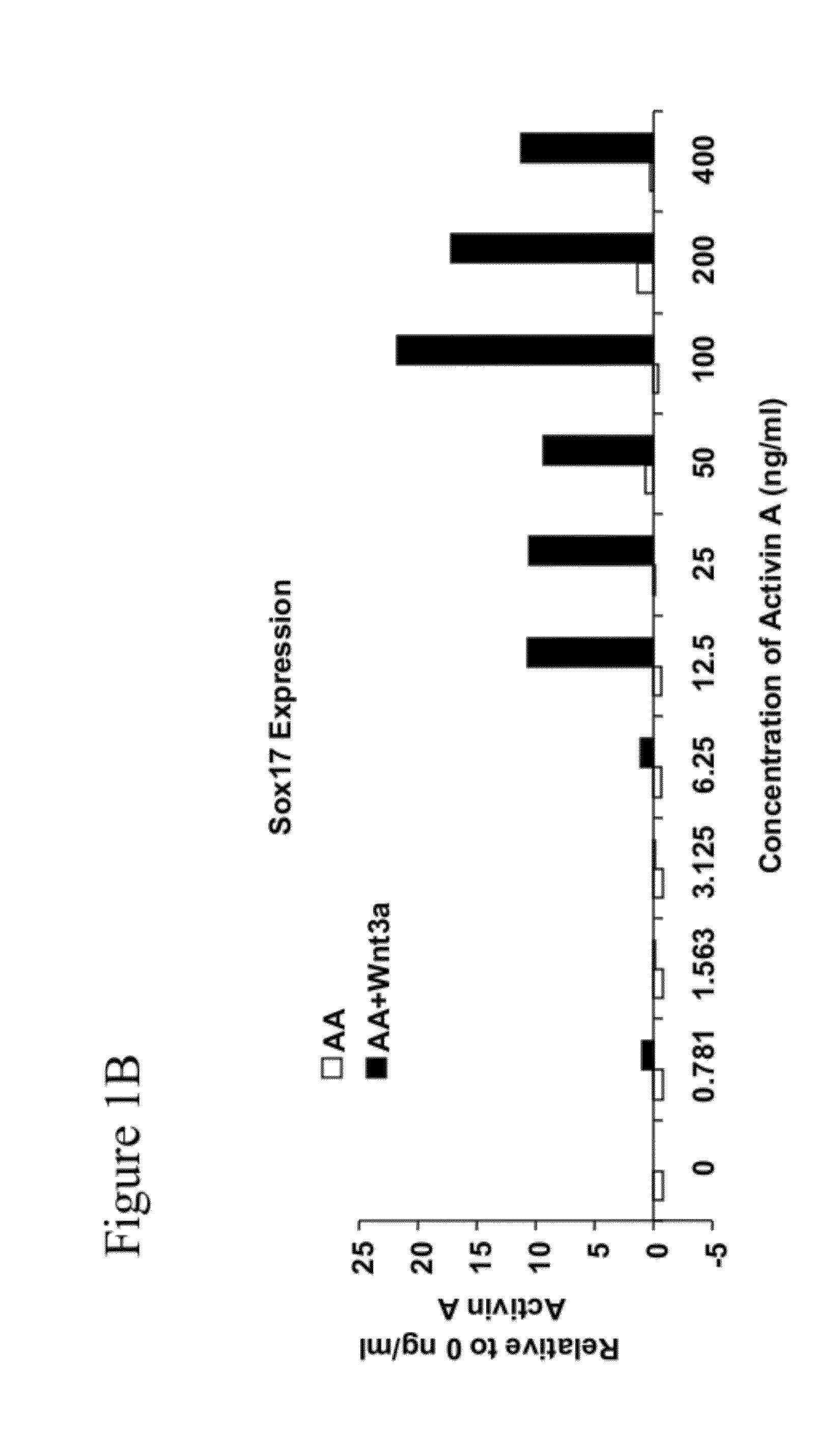
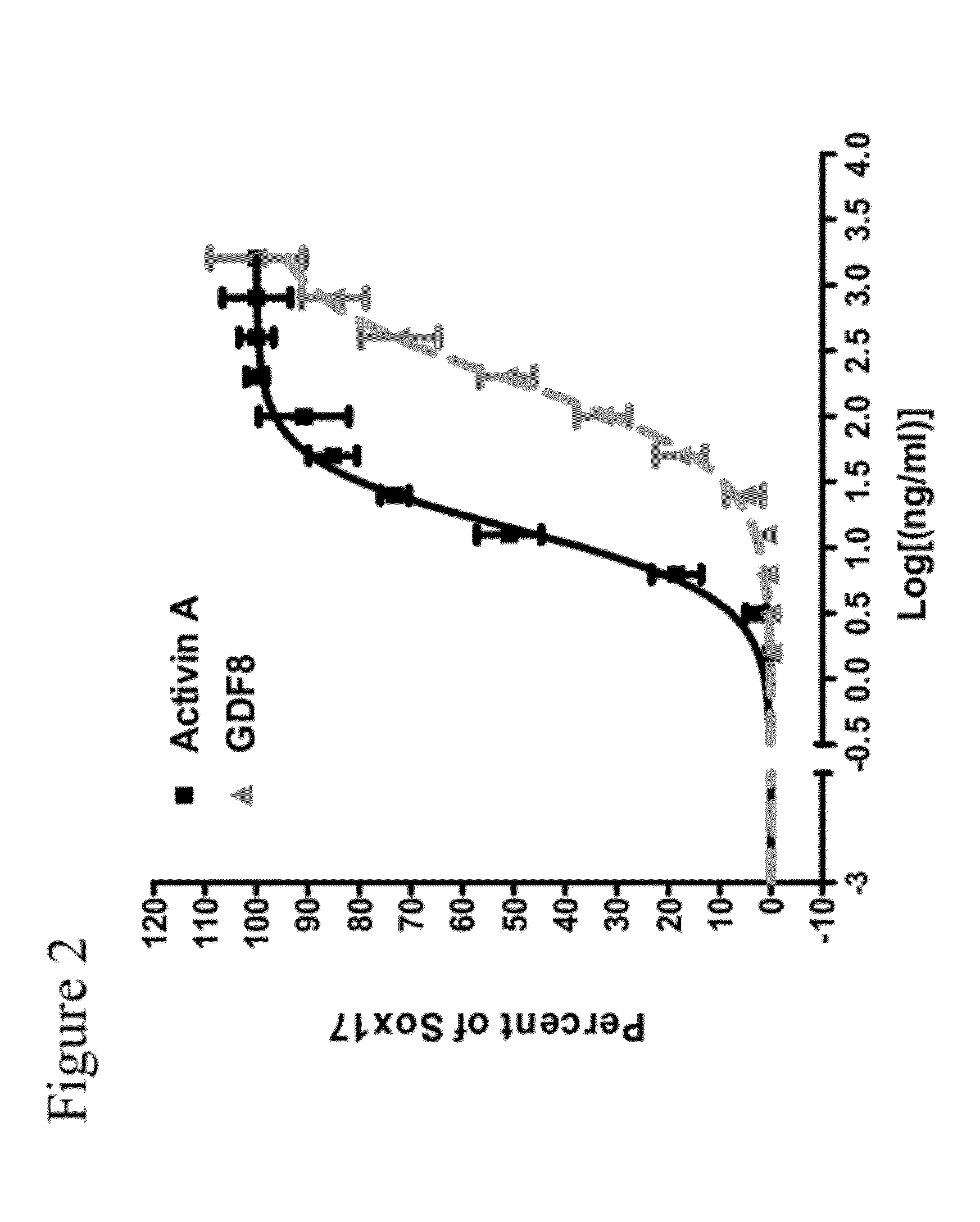
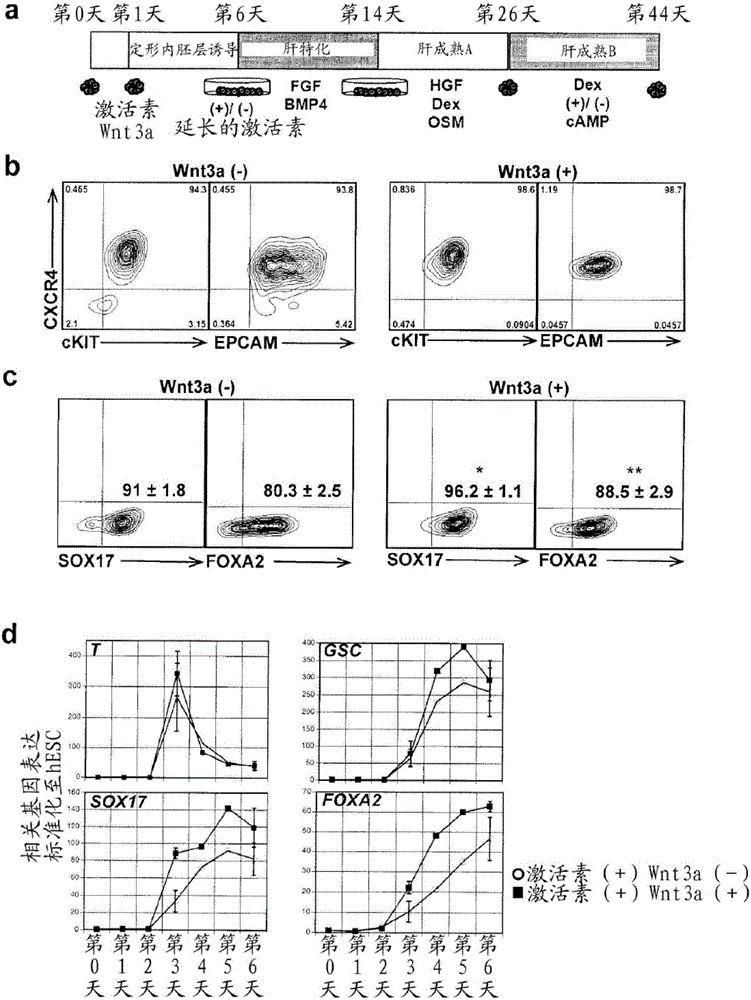
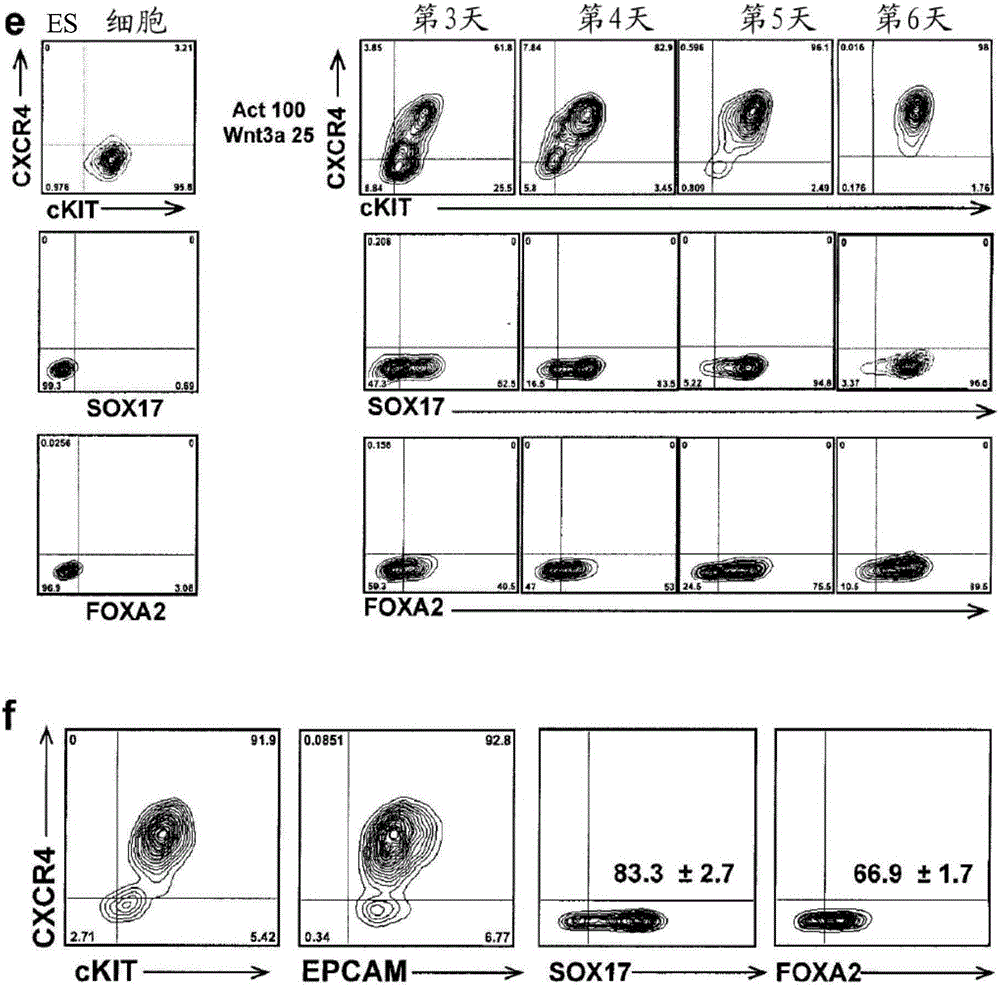
The present invention is directed to methods to differentiate pluripotent stem cells. In particular, the present invention is directed to methods and compositions to differentiate pluripotent stem cells into cells expressing markers characteristic of the definitive endoderm lineage comprising culturing the pluripotent stem cells in medium comprising a sufficient amount of GDF-8 to cause the differentiation of the pluripotent stem cells into cells expressing markers characteristic of the definitive endoderm lineage.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Using fibroblast growth factor to establish a line of embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS20050153444A1Rapid productionSimple systemHepatocytesGastrointestinal cellsGerm layerPluripotential stem cell
This disclosure provides an improved system for culturing human pluripotent stem cells. Traditionally, pluripotent stem cells are cultured on a layer of feeder cells (such as mouse embryonic fibroblasts) to prevent them from differentiating. In the system described here, the role of feeder cells is replaced by components added to the culture environment that support rapid proliferation without differentiation. Effective features are a suitable support structure for the cells, and an effective medium that can be added fresh to the culture without being preconditioned by another cell type. Culturing human embryonic stem cells in fresh medium according to this invention causes the cells to expand surprisingly rapidly, while retaining the ability to differentiate into cells representing all three embryonic germ layers. This new culture system allows for bulk proliferation of pPS cells for commercial production of important products for use in drug screening and human therapy.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
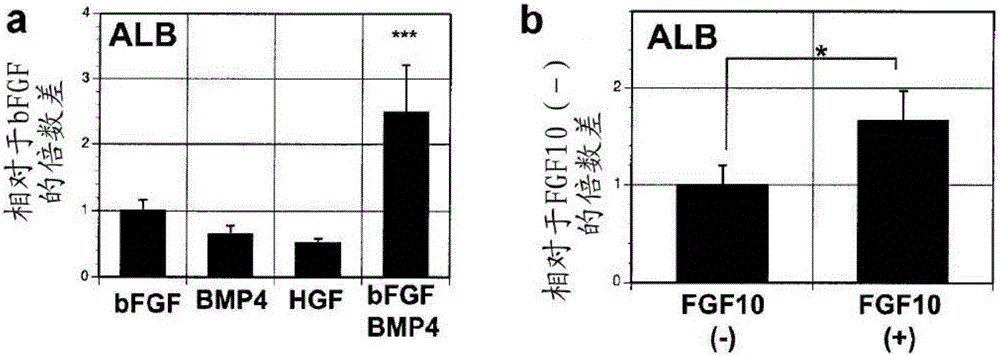
Methods for generating hepatocytes and cholangiocytes from pluripotent stem cells
Methods for producing hepatocyte and / or cholangiocyte lineage cells from pluripotent stem cells, the method comprising (a) specifying the extended nodal agonist treated induced endodermal cell population to obtain a cell population comprising hepatocyte and / or cholangiocyte progenitors by contacting the extended nodal agonist treated induced endodermal cell population with specification media comprising a FGF agonist and a BMP4 agonist and / or active conjugates and / or fragments thereof; (b) inducing maturation, and optionally further lineage specification and / or expansion of the hepatocyte and / or cholangiocyte progenitors of the cell population to obtain a population comprising hepatocyte lineage cells such as hepatoblasts, hepatocytes and / or cholangiocytes, the inducing maturation step comprising generating aggregates of the cell population. Optionally, the method also comprises activating the cAMP pathway within the aggregates and forming co-aggregates.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com