Method of differentiating stem cells into cells of the endoderm and pancreatic lineage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Cell Culture and Differentiation
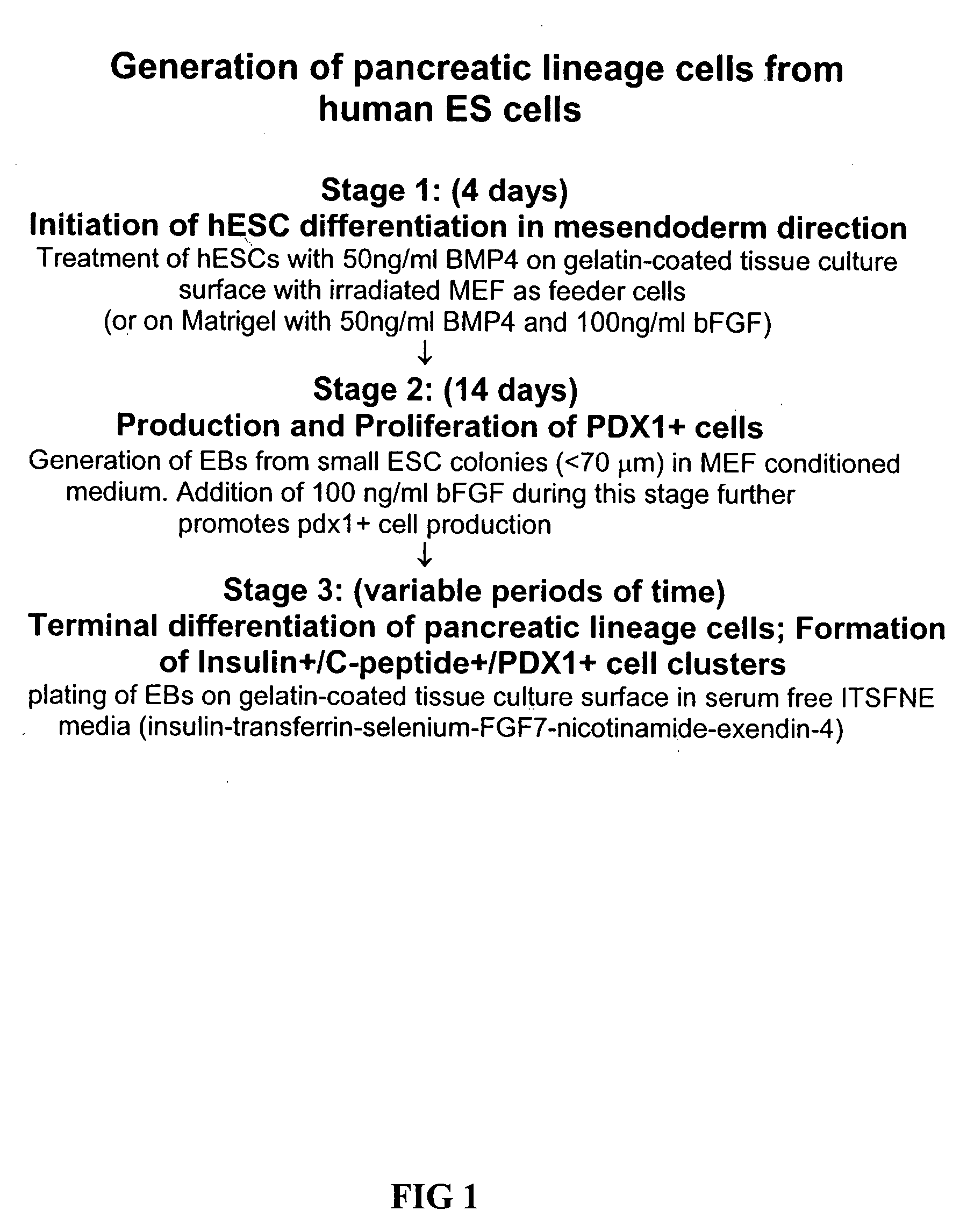
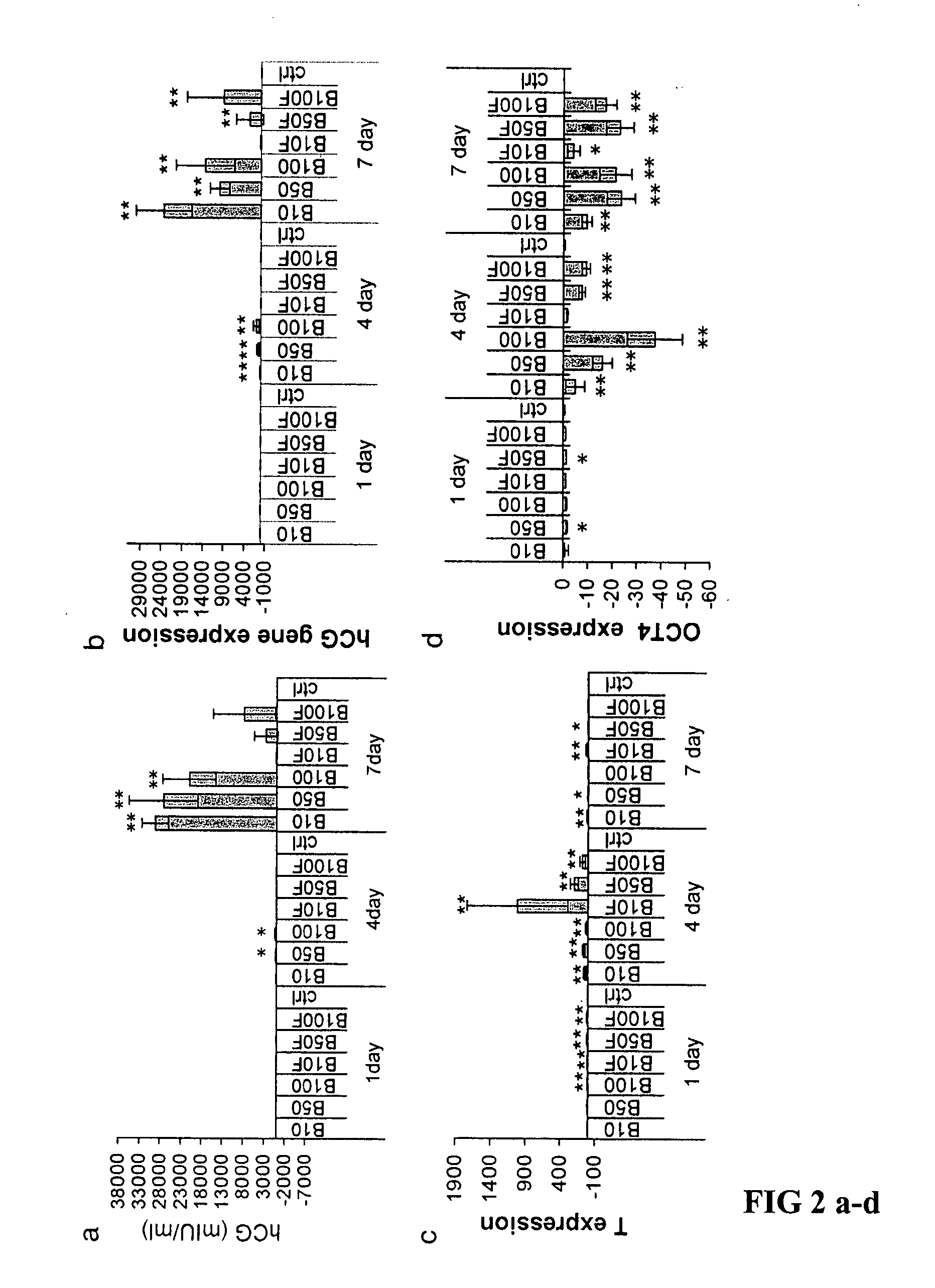
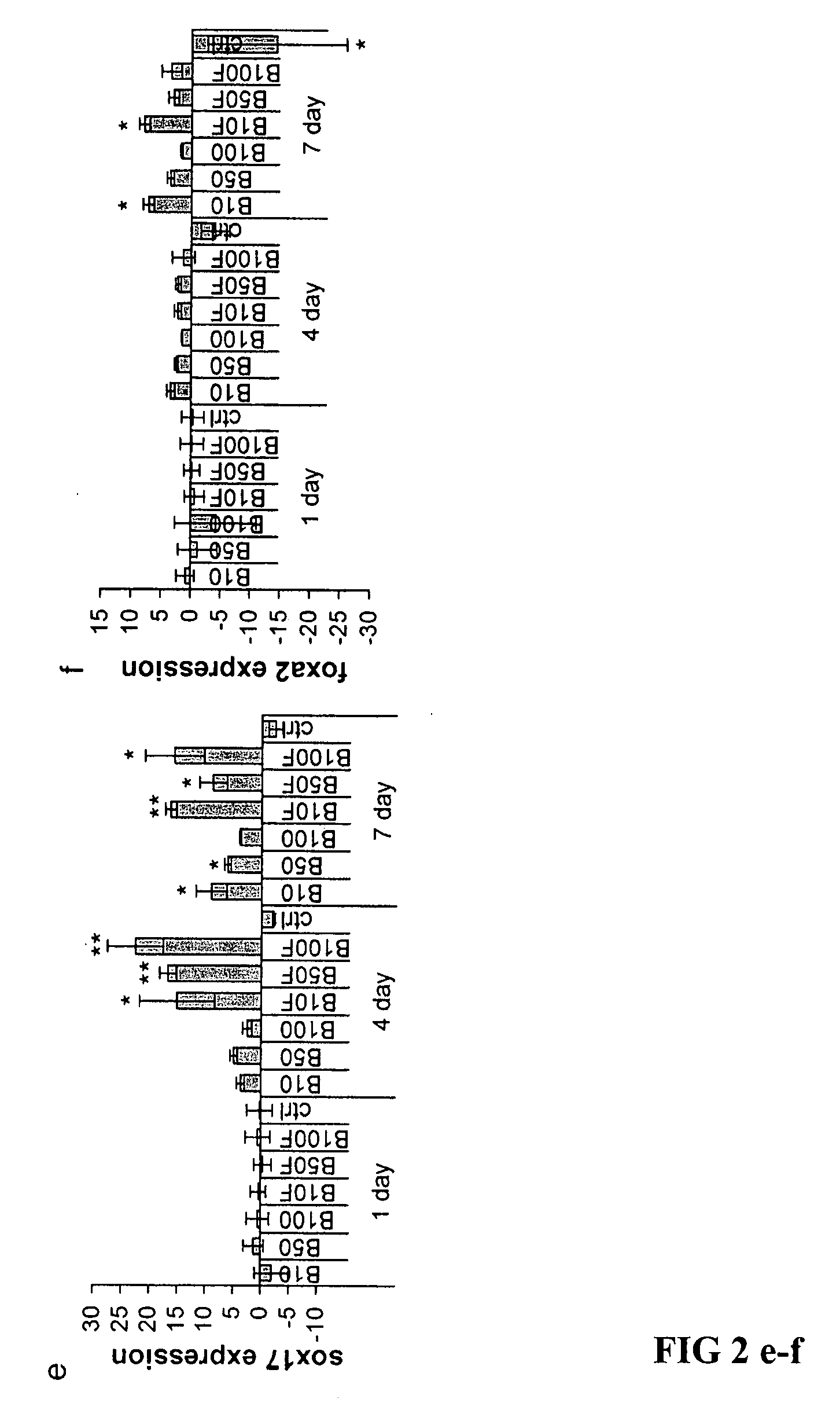
[0052] The general differentiation method is illustrated in simplistic fashion in FIG. 1. NIH approved HESC lines, H1 (WA01) and H9 (WA09) were used between passage 24 to 40. Media for undifferentiated ESCs was comprised of 80% DMEM / F12 and 20% Knockout serum replacement supplemented with 1 mM L-glutamine, 1% nonessential amino acids, 0.1 mM 2-mercaptoethanol and 4 ng / ml bFGF (all from Invitrogen). hESCs were cultured in 6-well plates on a feeder layer of irradiated mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) in either ESC media (control group), ESC media plus 50 ng / ml BMP4 (BMP4 group; R&D systems), or ESC media plus 50 ng / ml BMP4 plus 300 ng / ml noggin (noggin group; R&D systems) for 4 days.
[0053] In experiments with Matrigel™, hESCs were grown on growth-factor depleted Matrigel™ (BD Biosciences) instead of MEF and culture media was MEF-conditioned media (CM, control group), CM plus 50 ng / ml BMP4 or CM plus 50 ng / ml BMP4 plus 100 ng / ml bFGF. Colonies were t...
example 2
Quantitative PCR and RT-PCR
[0054] Total cellular RNA was extracted with TriZol (Invitrogen). cDNA was synthesized from 1 μg total RNA using a SuperScript First-Strand Synthesis kit (Invitrogen). Quantitative real time RT-PCR (Q-PCR) was performed using Assays-on-demand agents (Applied Biosystems) on an ABI PRISM 7700 Sequence Detection System (Applied Biosystems) for the following transcripts: foxa2, sox17, brachyury, ngn3, pdx1, insulin, glucagon, glut2 and an endogenous control, β-actin. Q-PCR was performed according to equipment manufacturer's instructions. Relative quantification was carried out using the comparative cycle threshold (CT) methods recommended by the supplier. Fold change was calculated as: 2−ΔΔCT Mean ΔΔCT values from Q-PCR analyses were compared using the unpaired, two-tailed Student's t-test. P values <0.05 were considered significant.
[0055] For non-quantitative RT-PCR, oligonucleotide primer pairs were generated against human transcripts using Genebank sequen...
example 3
[0056] Immunofluorescence staining of coverslips was carried out as previously described (Kahan, B. W. et al., Pancreatic precursors and differentiated islet cell types from murine embryonic stem cells: an in vitro model to study islet differentiation. Diabetes 52, 2016-2024 (2003)). The following primary antibodies were used at the listed dilutions: PDX1 rabbit anti-mouse serum 1:4000 (gift of C. Wright); insulin mouse monoclonal 10 μg / ml (ATCC No: HB124); glucagon mouse monoclonal 1:2000 (Sigma); somatostatin mouse monoclonal 1:2000 (Novonordisk); Ki-67 mouse monoclonal 1:25 (BD Pharmingen); C-peptide rat monoclonal 1:3000 (BCBC 1921); Brachyury goat anti-human 1:20 (R&D); OCT4 goat anti mouse 1:100 (Santa Cruz); Sox17 goat anti-human 1:40 (R&D); FOXA2 rabbit anti-rat1:4000 (Gift of R. Costa). Secondary antibodies (Goat anti-mouse IgG Alexa Fluor 488, 1:2000; Goat anti-rabbit Alexa Fluor 568, 1:4000; Goat anti-rat Alexa Fluor 488, 1:2000; Goat anti-rabb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com