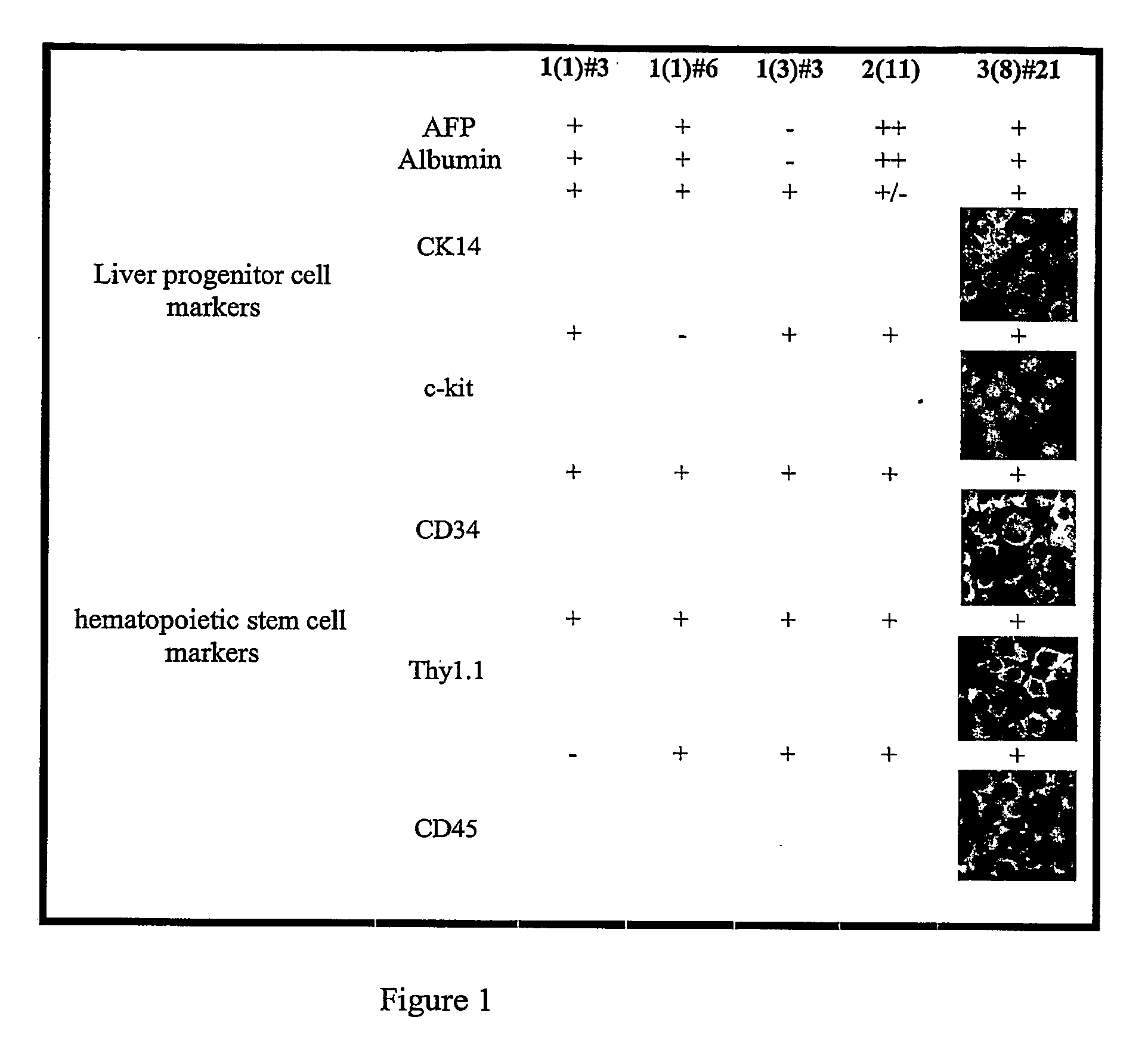
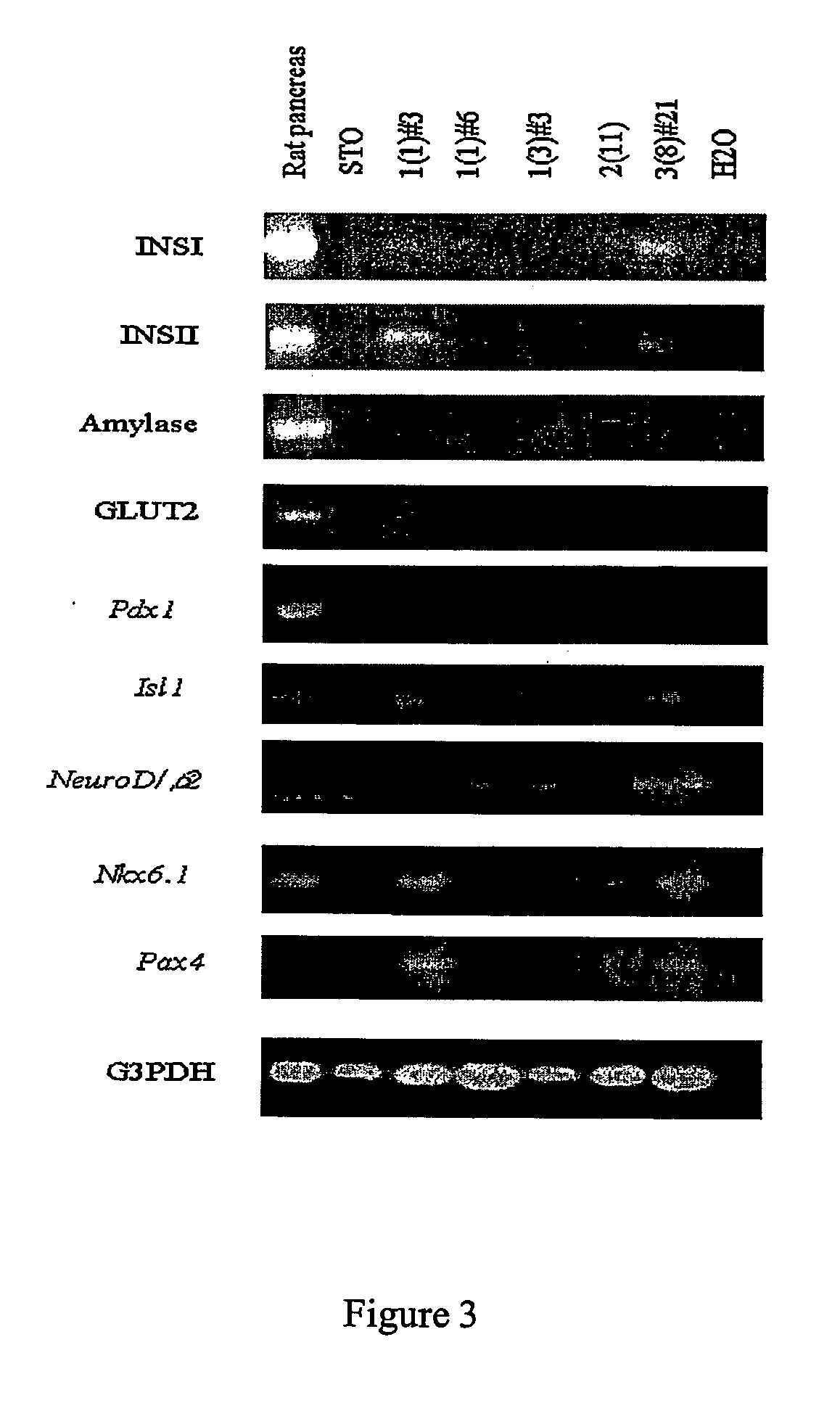
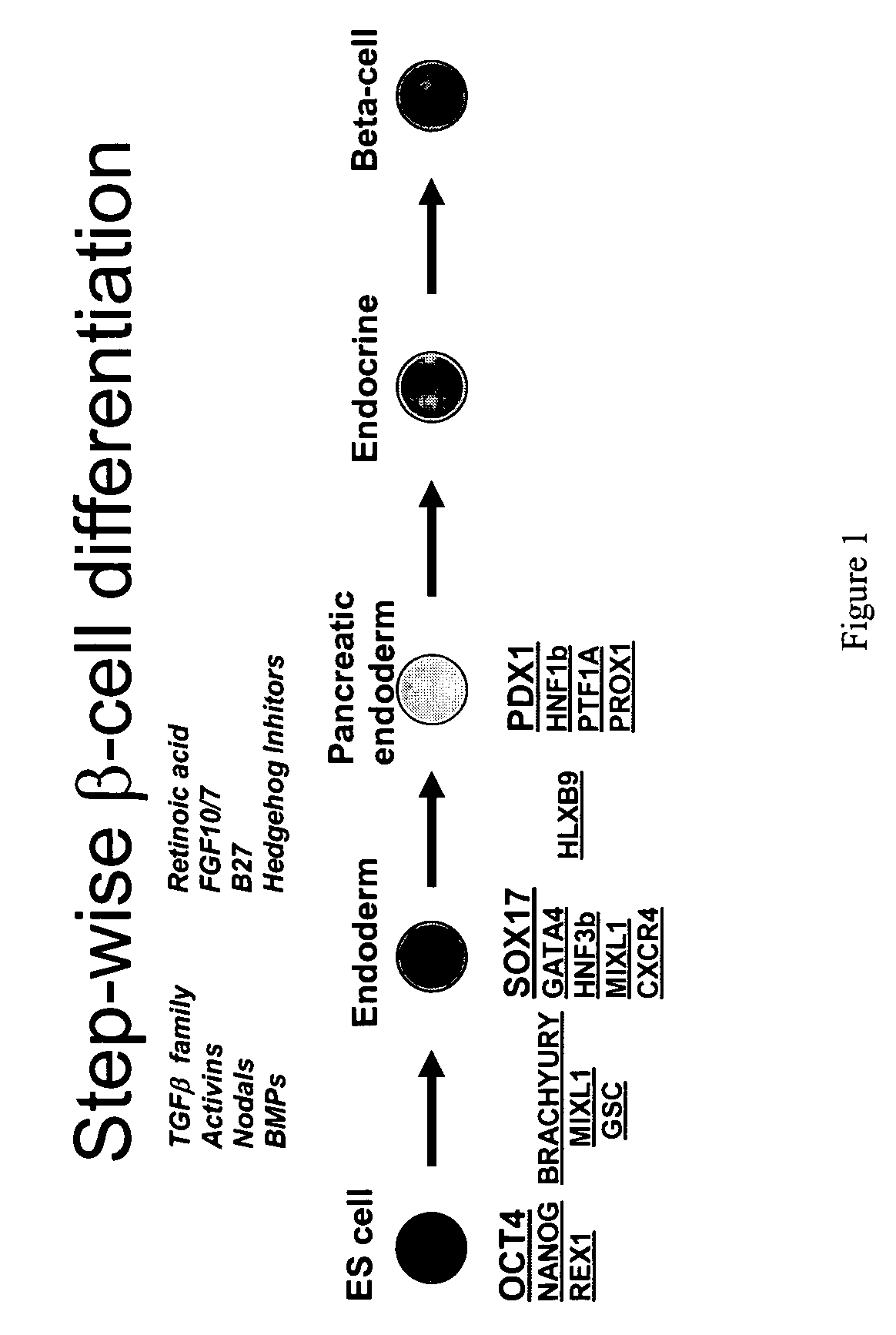
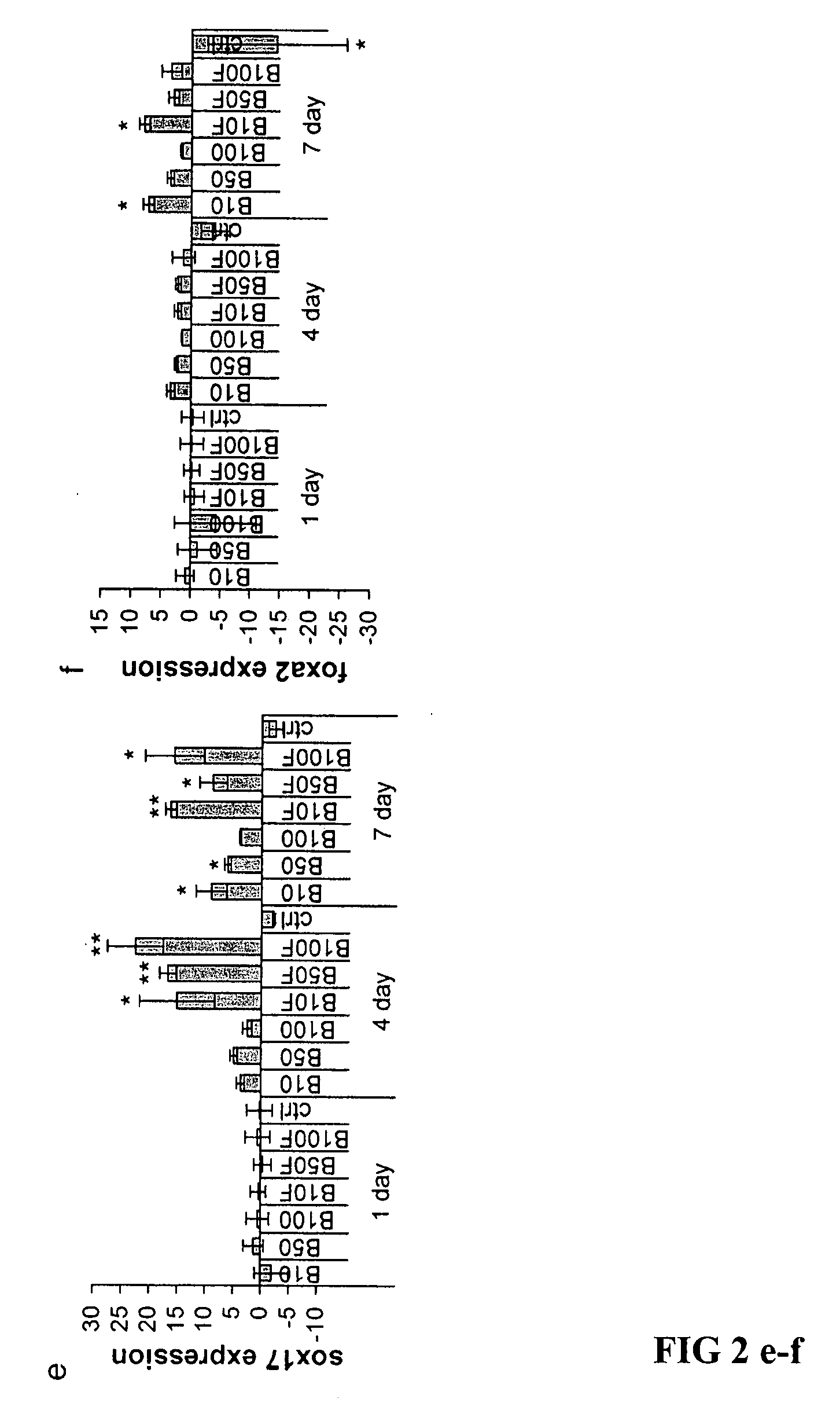
Patents
Literature
944results about "Pancreatic cells" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
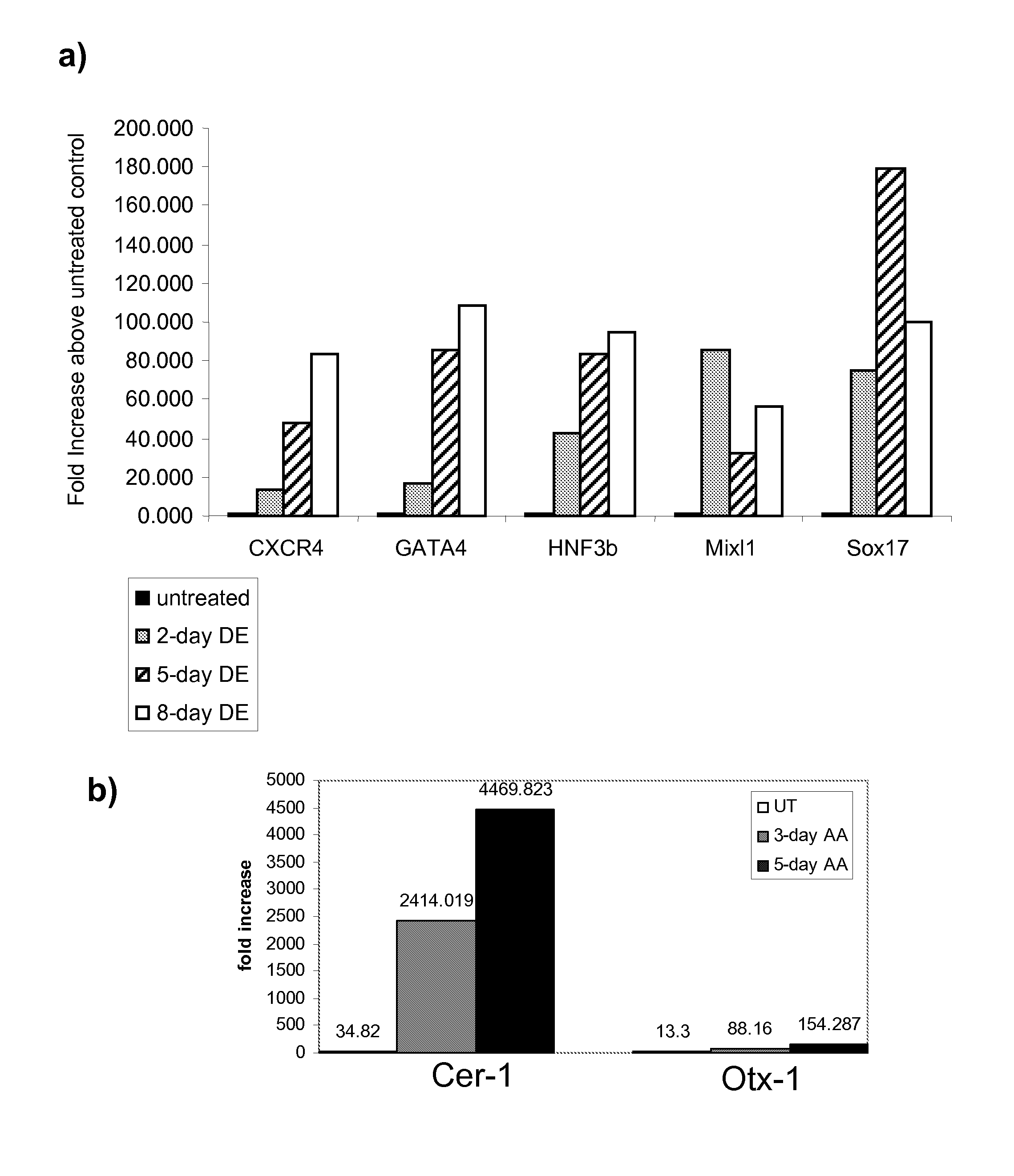
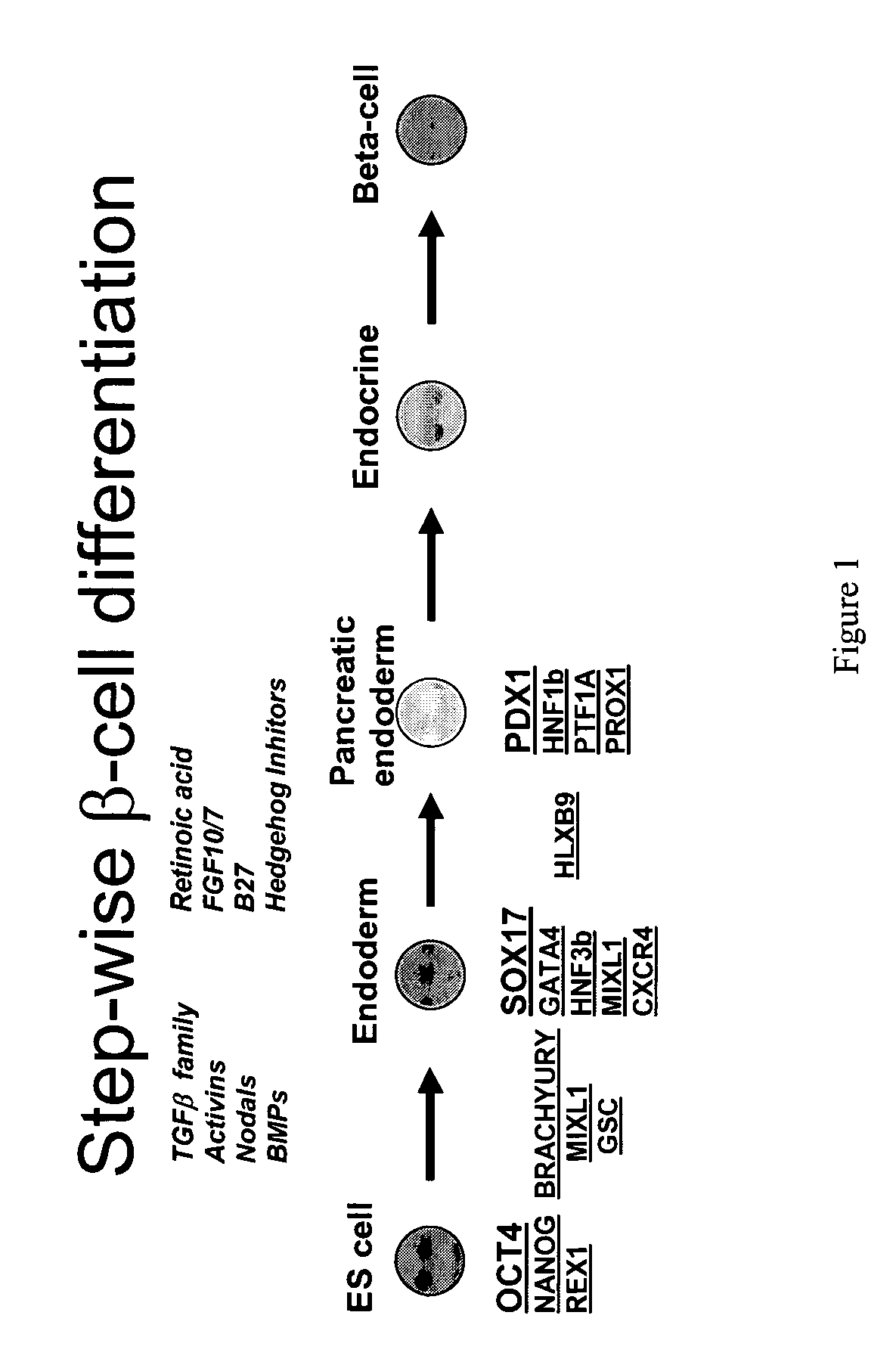
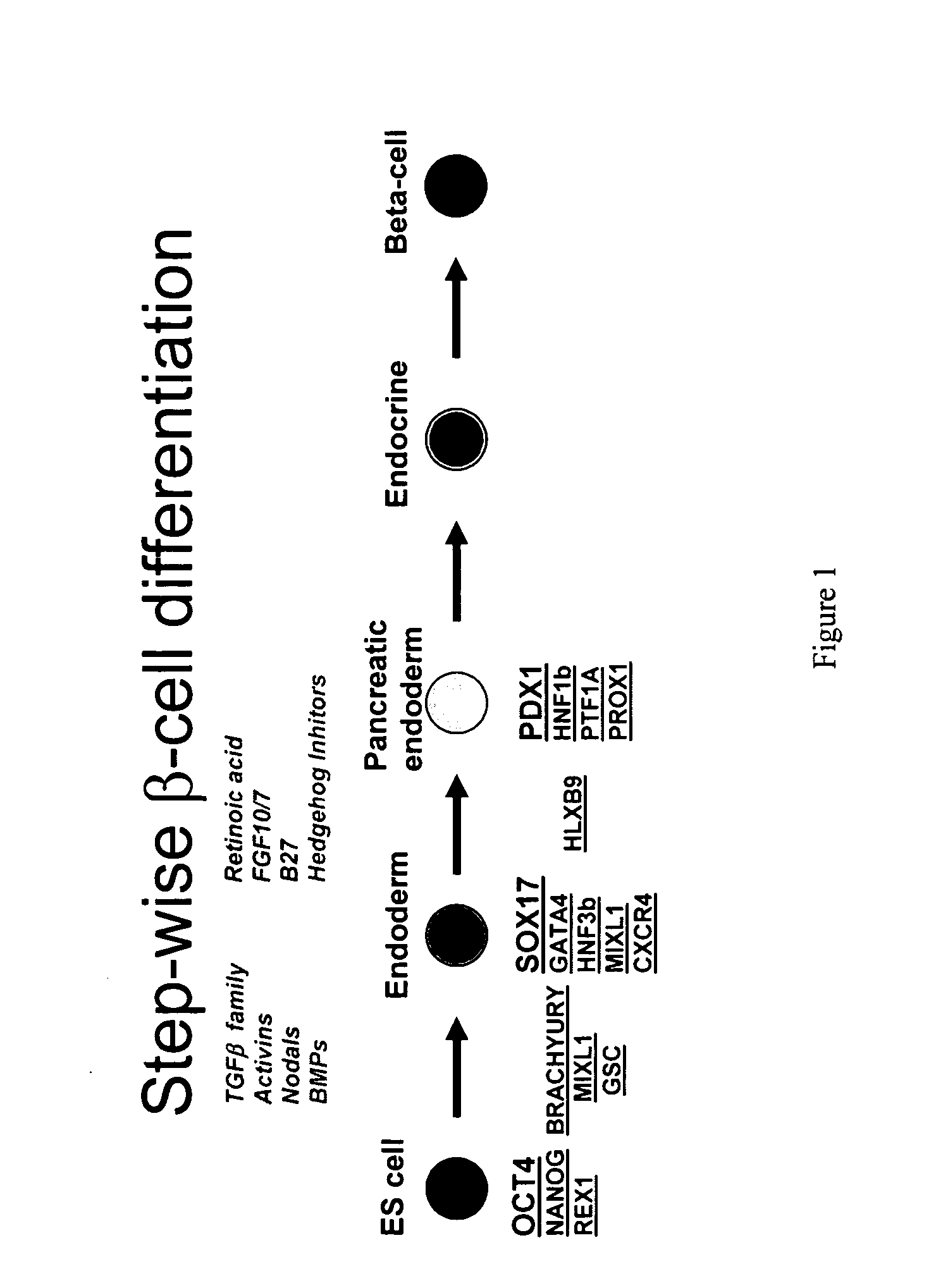
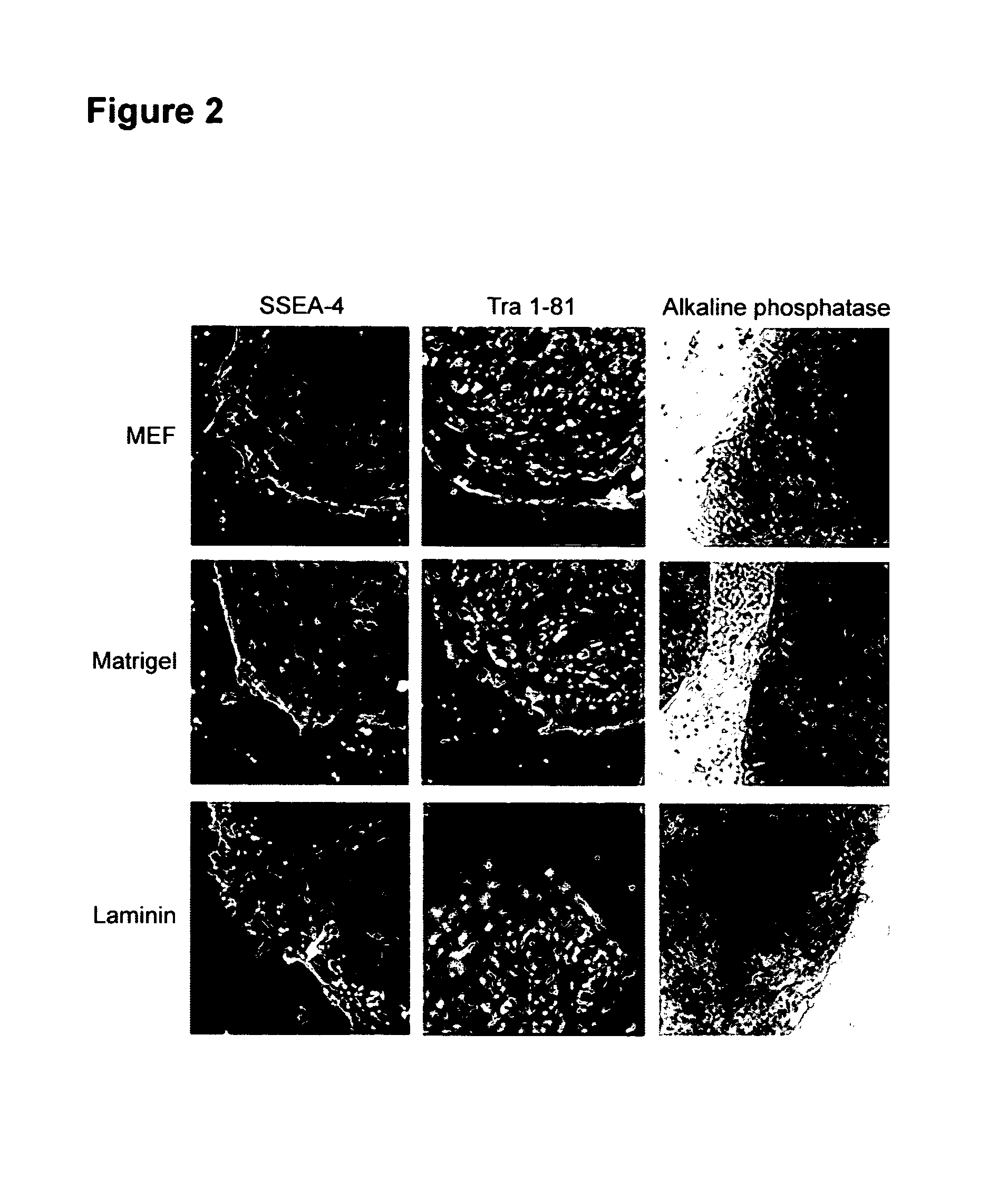
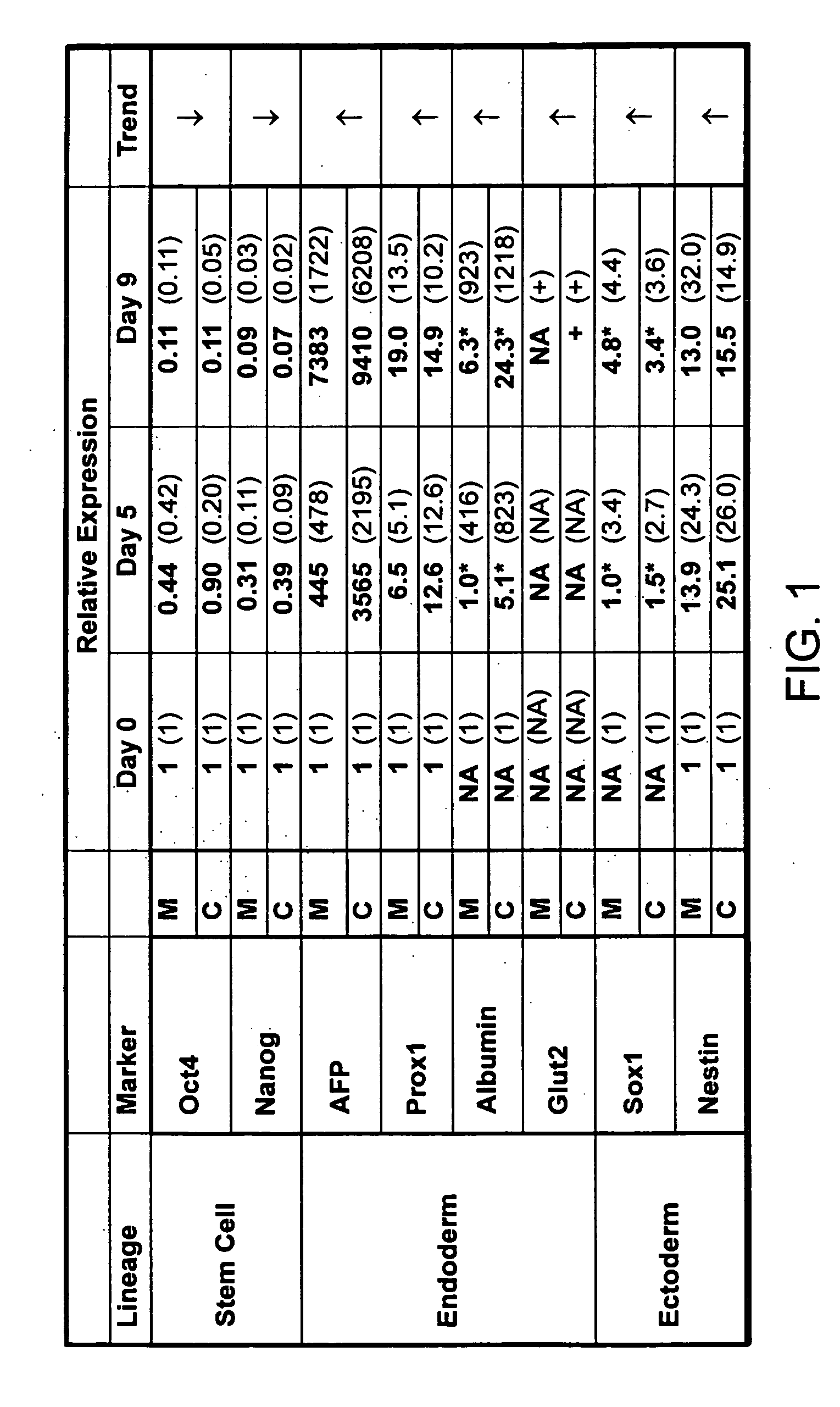
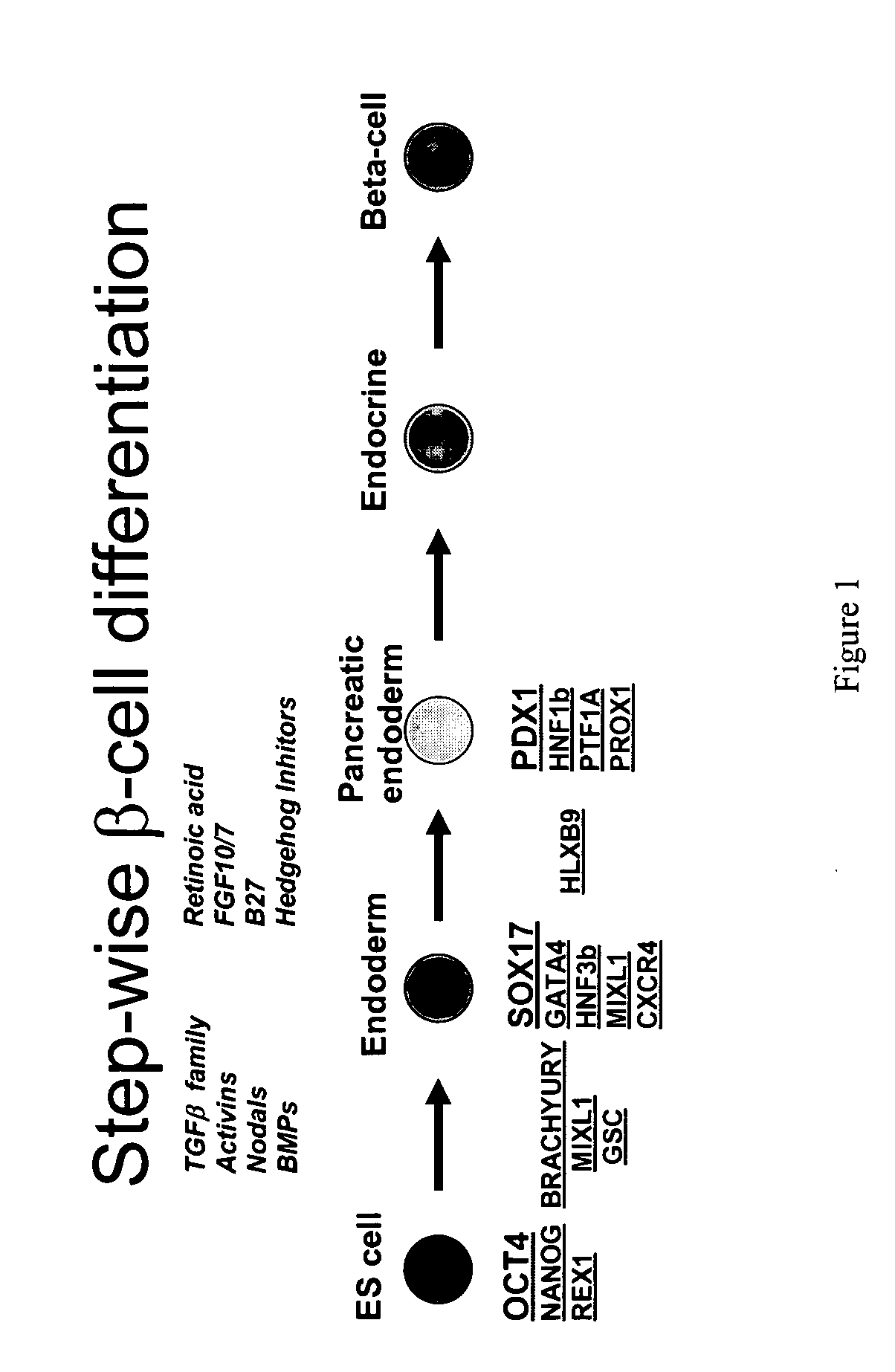
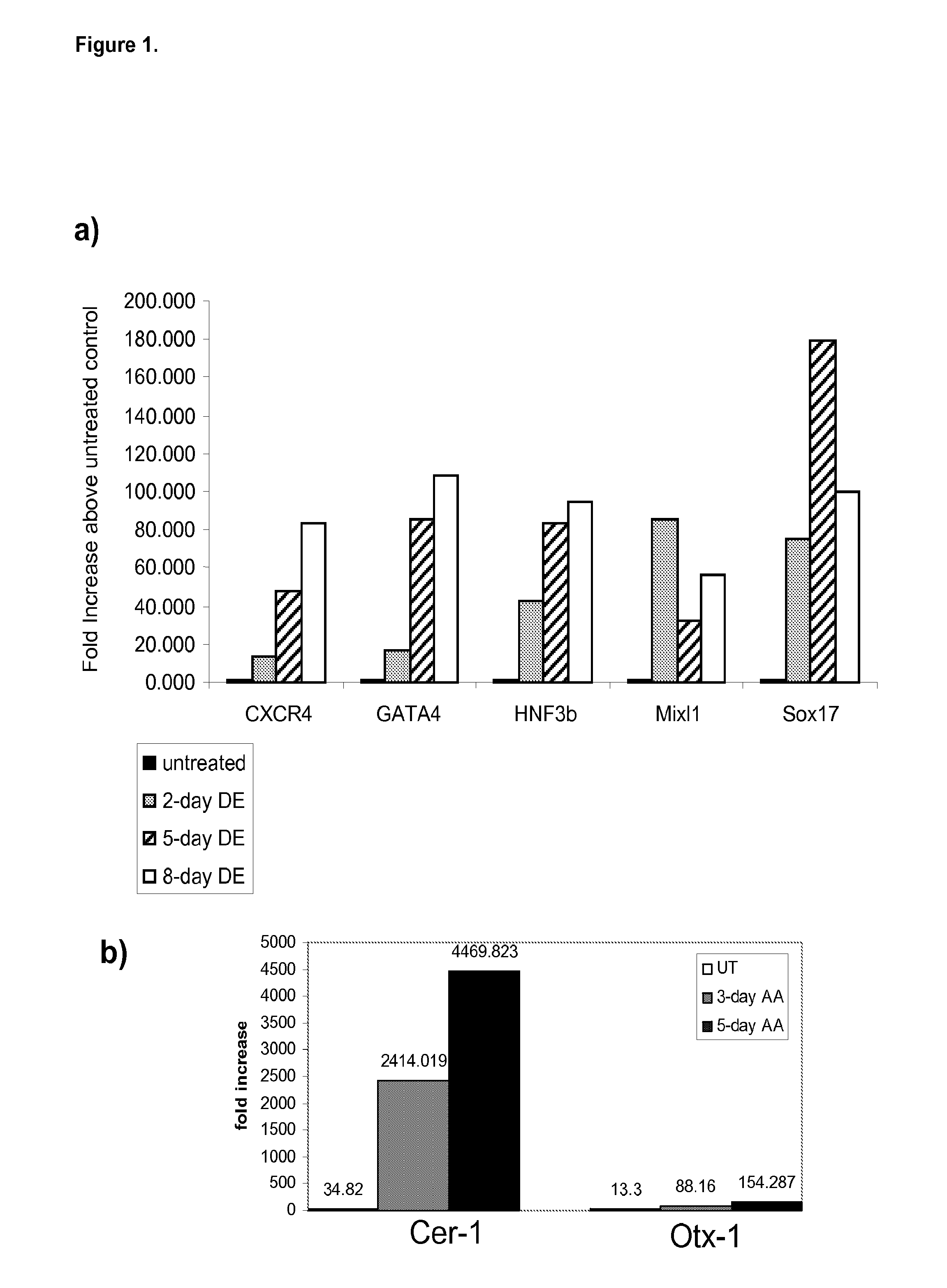
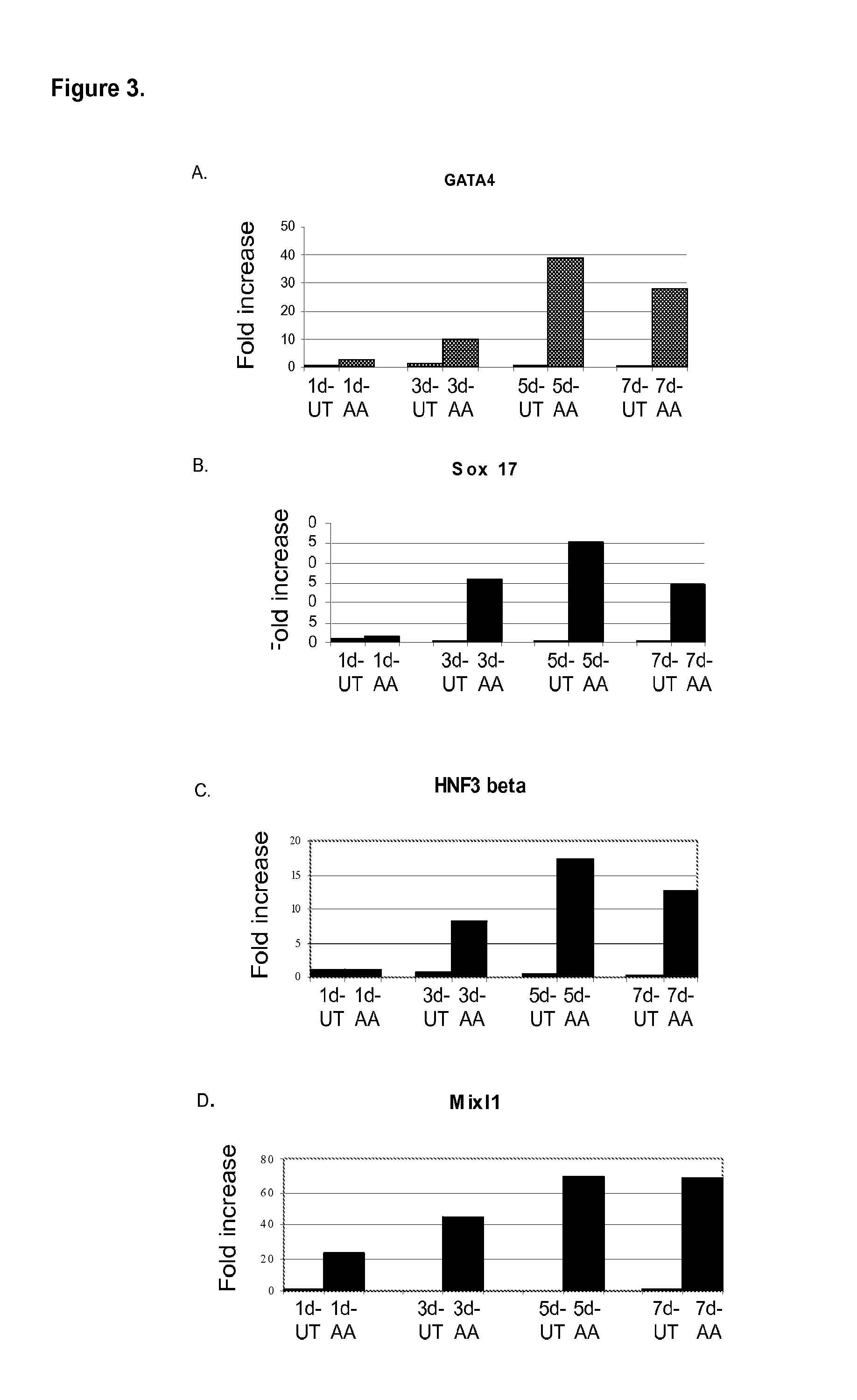
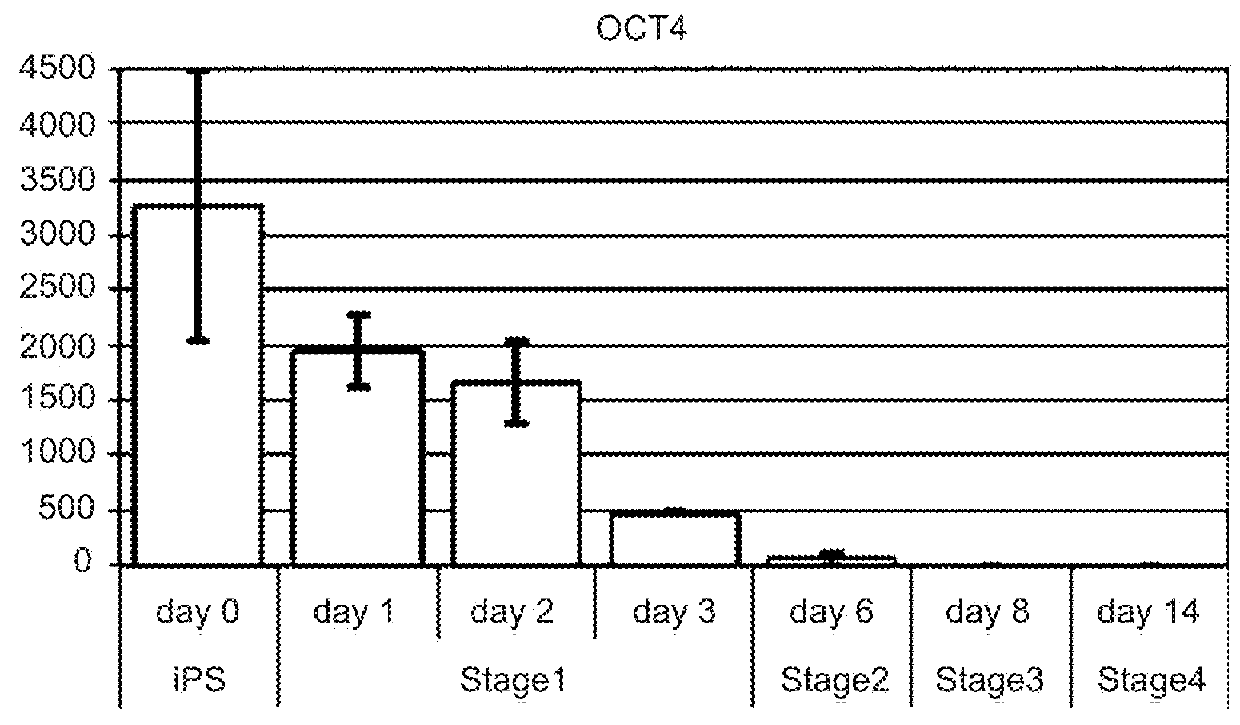
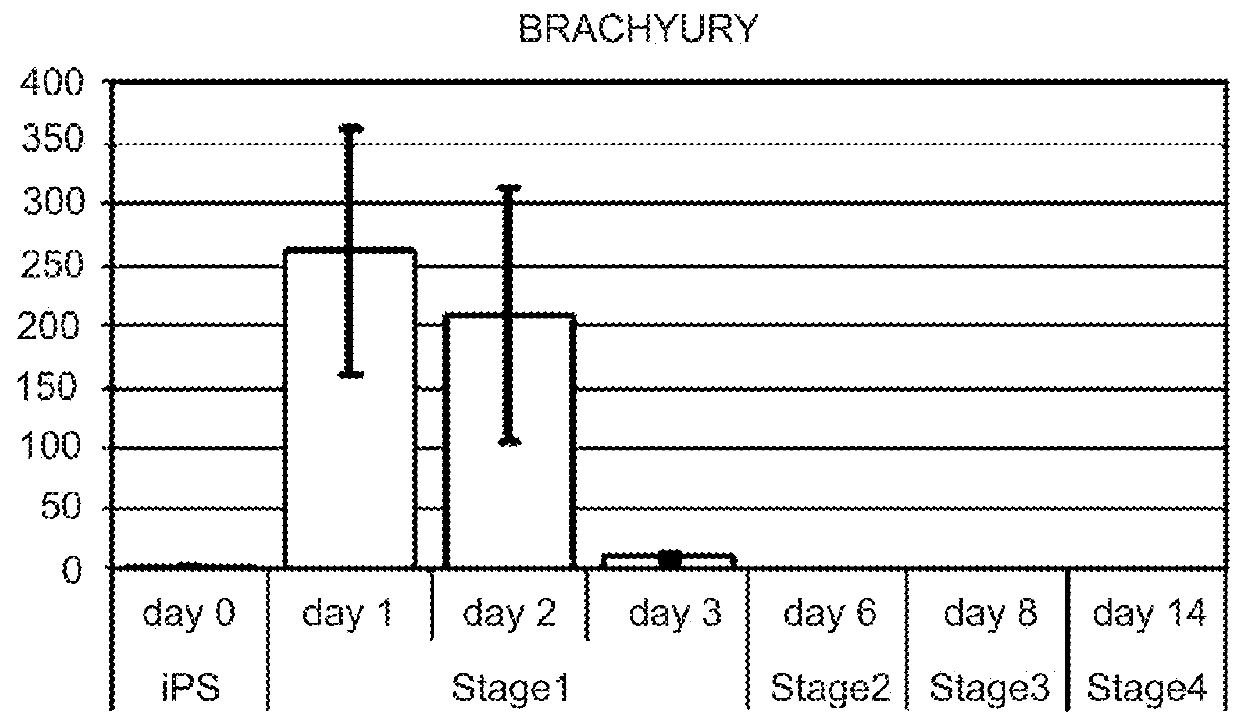
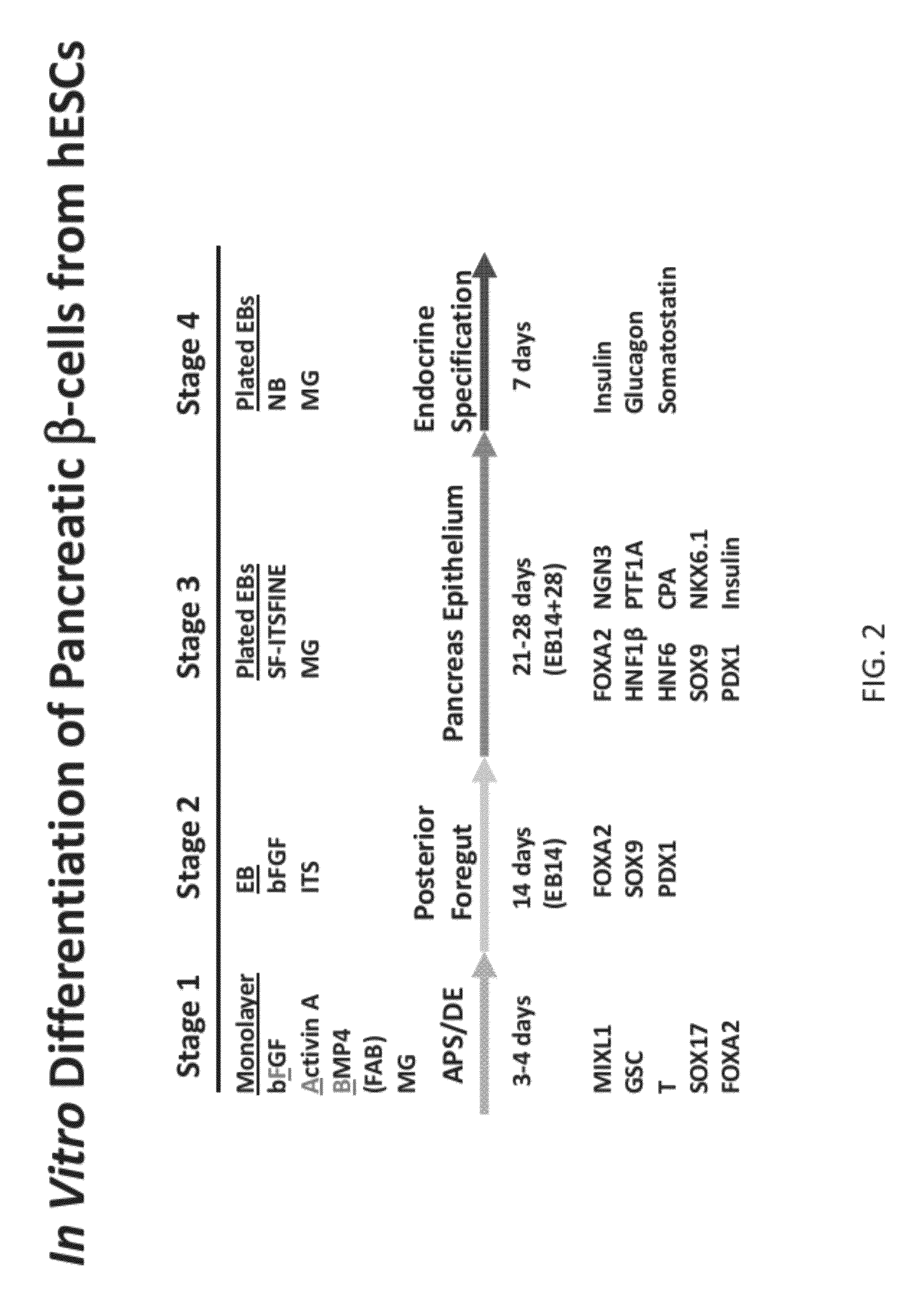
Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells
ActiveUS20070254359A1Inhibits Notch signalingPancreatic cellsArtificial cell constructsGerm layerPluripotential stem cell
The present invention provides methods to promote the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells. In particular, the present invention provides an improved method for the formation of pancreatic endoderm, pancreatic hormone expressing cells and pancreatic hormone secreting cells. The present invention also provides methods to promote the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells without the use of a feeder cell layer.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
PDX1 expressing endoderm
InactiveUS20050266554A1Increase differentiationIncrease productionGastrointestinal cellsDiagnosticsGerm layerCell type
Disclosed herein are cell cultures comprising PDX1-positive endoderm cells and methods of producing the same. Also disclosed herein are cell populations comprising substantially purified PDX1-positive endoderm cells as well as methods for enriching, isolating and purifying PDX1-positive endoderm cells from other cell types. Methods of identifying differentiation factors capable of promoting the differentiation of endoderm cells, such as PDX1-positive foregut endoderm cells and PDX1-negative definitive endoderm cells, are also disclosed.
Owner:CYTHERA
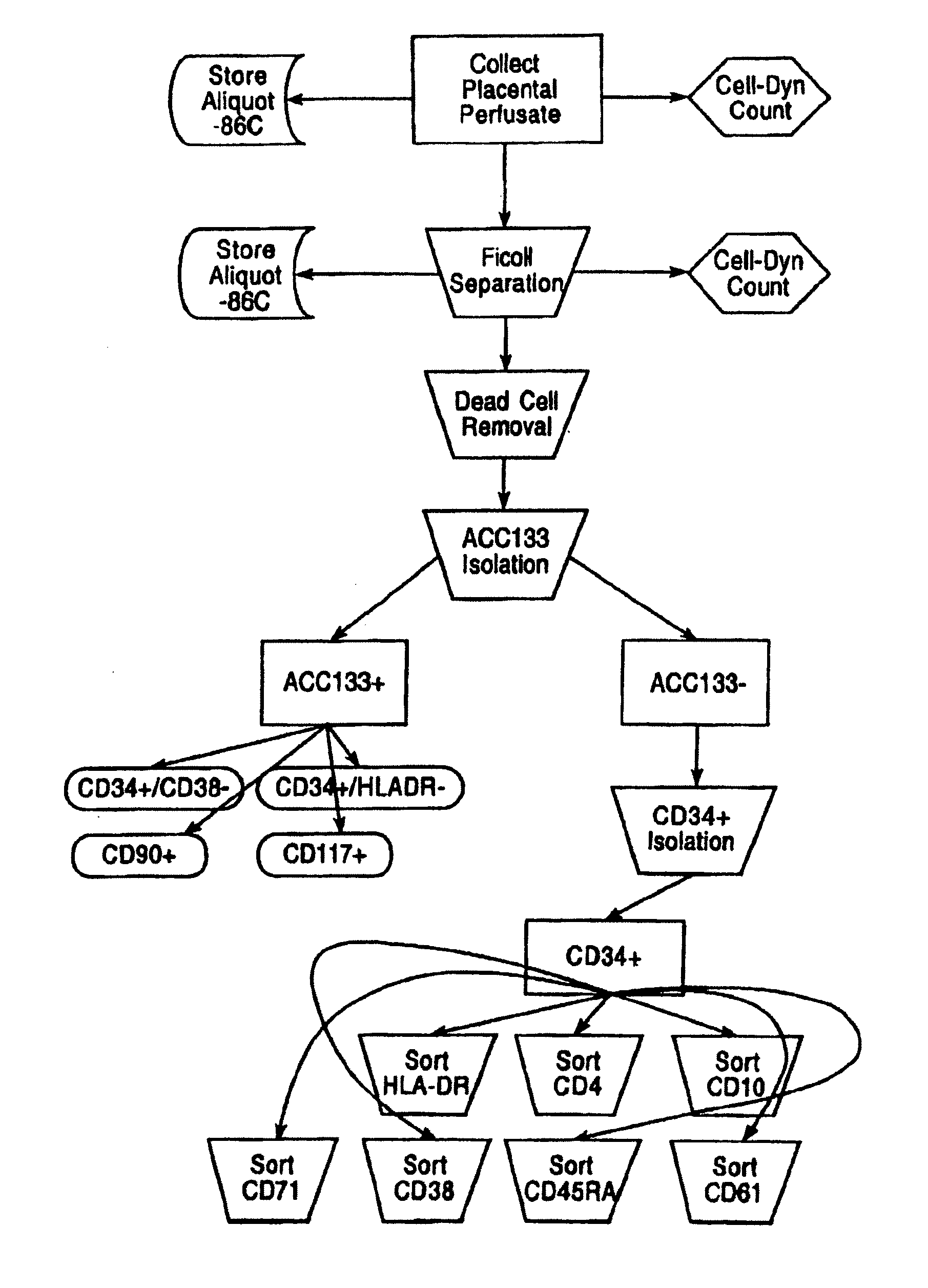
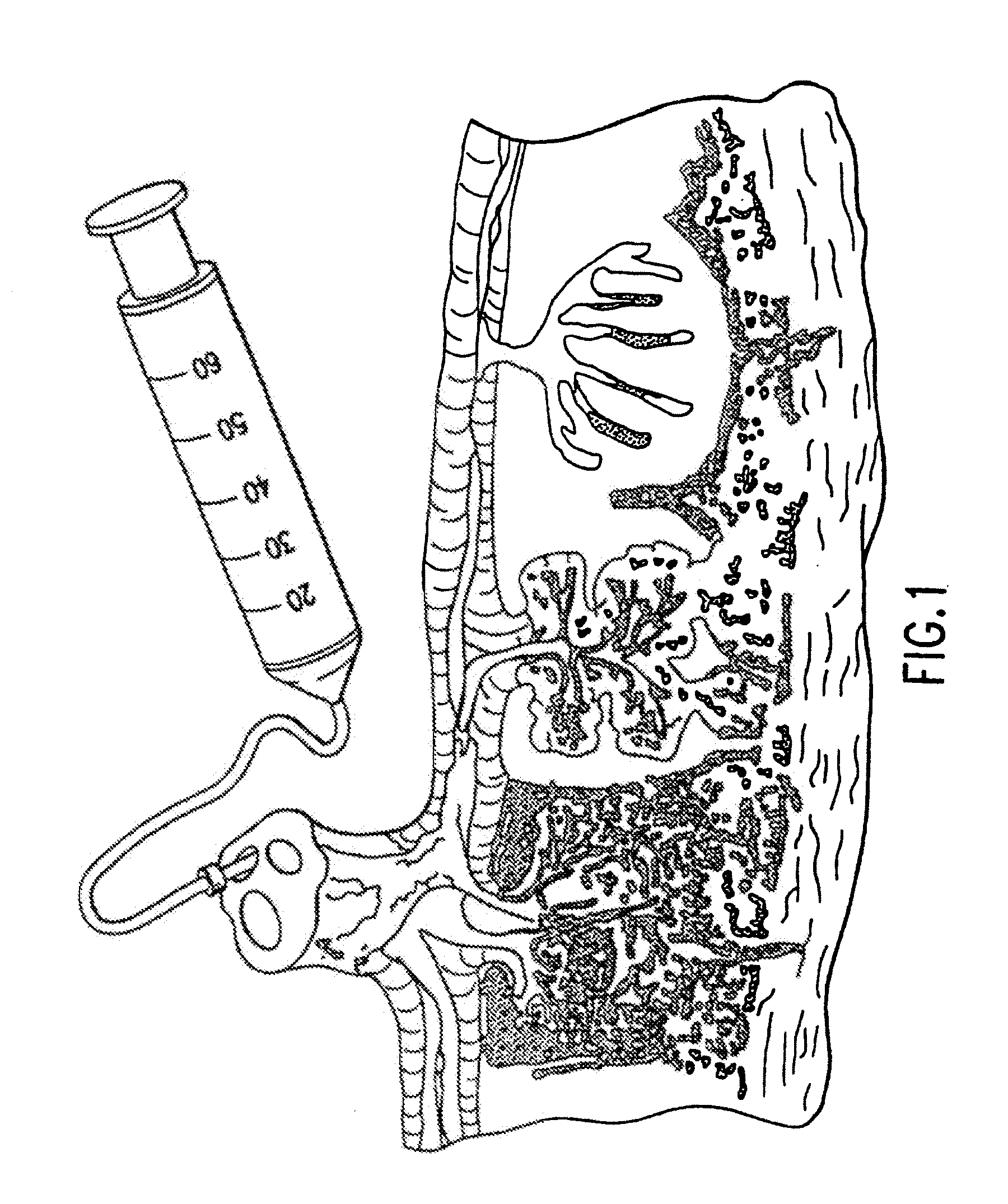
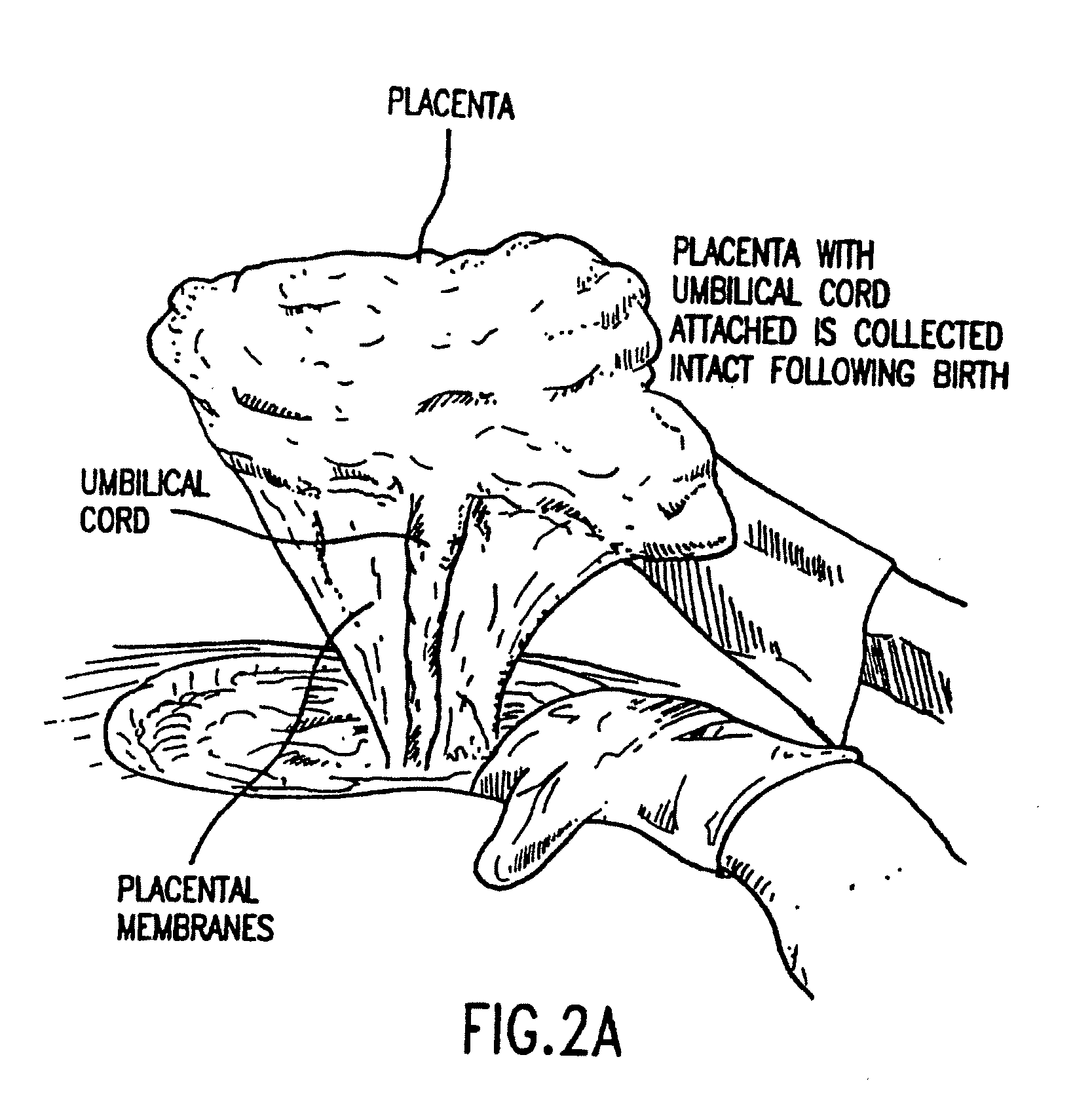
Placental derived stem cells and uses thereof
The present invention features novel placental derived stem cells and provides methods and compositions for the therapeutic uses of placental derived stem cells or placental derived stem cells that have been induced to differentiate into a desired tissue type into a recipient host in amounts sufficient to result in production of the desired cell type, i.e., hepatic, pancreatic, neuronal, or nervous tissue.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Conversion of liver stem and progenitor cells to pancreatic functional cells
The subject invention a method for converting liver stem / progenitor cells to a pancreatic functional cell by transfecting said liver cells with a pancreatic development gene and / or by culturing with pancreatic differentiation factors. The resulting cells produce and secrete insulin protein in response to glucose stimulation.
Owner:IXION BIOTECH
Methods for identifying factors for differentiating definitive endoderm
Disclosed herein are methods of identifying one or more differentiation factors that are useful for differentiating cells in a cell population comprising definitive endoderm cells into cells which are capable of forming tissues and / or organs that are derived from the gut tube.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
Method of differentiating stem cells into cells of the endoderm and pancreatic lineage
InactiveUS20070259423A1Promote differentiationMass productionPancreatic cellsCulture processPluripotential stem cellGerm layer
Methods are described to more efficiently produce cells of the endoderm and pancreatic lineage from mammalian pluripotent stem cells. These methods provide a simple, reproducible culture protocol using defined media components to enable consistent, large-scale production of pancreatic cell types for research or therapeutic uses.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Stem Cell Aggregate Suspension Compositions and Methods of Differentiation Thereof
The present invention relates to methods for production of undifferentiated or differentiated embryonic stem cell aggregate suspension cultures from undifferentiated or differentiated embryonic stem cell single cell suspensions and methods of differentiation thereof.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
PDX1-expressing dorsal and ventral foregut endoderm
Disclosed herein are cell cultures comprising dorsal and / or ventral PDX1-positive foregut endoderm cells and methods of producing the same. Also disclosed herein are cell populations comprising substantially purified dorsal and / or ventral PDX1-positive foregut endoderm cells as well as methods for enriching, isolating and purifying dorsal and / or ventral PDX1-positive foregut endoderm cells from other cell types. Methods of identifying differentiation factors capable of promoting the differentiation of dorsal and / or ventral PDX1-positive foregut endoderm cells, are also disclosed.
Owner:CYTHERA
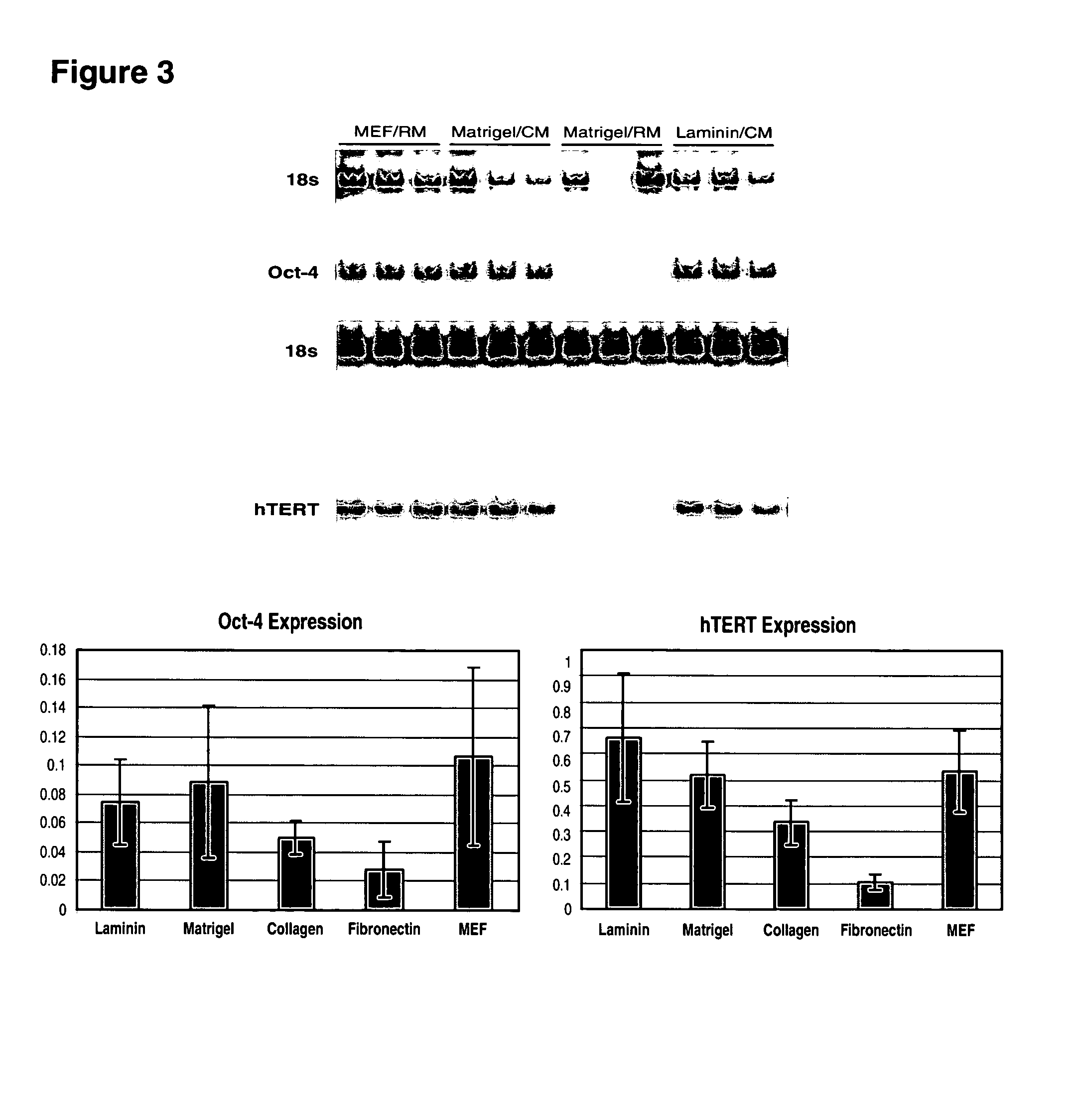
Medium for growing human embryonic stem cells
InactiveUS7297539B2Rapid productionExpanding primate pluripotent stem (pPS) cellsHepatocytesGastrointestinal cellsGerm layerFiber
This disclosure provides an improved system for culturing human pluripotent stem cells. Traditionally, pluripotent stem cells are cultured on a layer of feeder cells (such as mouse embryonic fibroblasts) to prevent them from differentiating. In the system described here, the role of feeder cells is replaced by components added to the culture environment that support rapid proliferation without differentiation. Effective features are a suitable support structure for the cells, and an effective medium that can be added fresh to the culture without being preconditioned by another cell type. Culturing human embryonic stem cells in fresh medium according to this invention causes the cells to expand surprisingly rapidly, while retaining the ability to differentiate into cells representing all three embryonic germ layers. This new culture system allows for bulk proliferation of pPS cells for commercial production of important products for use in drug screening and human therapy.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Renovation and repopulation of decellularized tissues and cadaveric organs by stem cells
A method of manufacturing a tissue matrix for implantation into a patient is disclosed. The method sets forth collecting embryonic stem cells from a placenta which has been treated to remove residual cord blood and seeding the collected stem cells onto or into a tissue matrix. The seeded tissue matrix is then implanted on or into a patient. The seeded tissue matrix made by the method of the present invention is also disclosed.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Directed differentiation of embryonic stem cells and uses thereof
The present invention provides methods for the directed differentiation of embryonic stem cells along the endodermal lineage, especially the pancreatic lineage.
Owner:ES CELL INT
Methods for identifying factors for differentiating definitive endoderm
Disclosed herein are methods of identifying one or more differentiation factors that are useful for differentiating cells in a cell population comprising definitive endoderm cells into cells which are capable of forming tissues and / or organs that are derived from the gut tube.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
Methods and apparatus for processing the surface of a microelectronic workpiece
InactiveUS6309524B1Reduce the risk of contaminationReduce downtimeCellsTanksEngineeringMechanical engineering
A reactor for plating a metal onto a surface of a workpiece is set forth. The reactor comprises a reactor bowl including an electroplating solution disposed therein and an anode disposed in the reactor bowl in contact with the electroplating solution. A contact assembly is spaced from the anode within the reactor bowl. The contact assembly includes a plurality of contacts disposed to contact a peripheral edge of the surface of the workpiece to provide electroplating power to the surface of the workpiece. The contacts execute a wiping action against the surface of the workpiece as the workpiece is brought into engagement therewith. The contact assembly also including a barrier disposed interior of the plurality of contacts. The barrier includes a member disposed to engage the surface of the workpiece to assist in isolating the plurality of contacts from the electroplating solution. In one embodiment, the plurality of contacts are in the form of discrete flexures while in another embodiment the plurality of contacts are in the form of a Belleville ring contact. A flow path may be provided in the contact assembly for providing a purging gas to the plurality of contacts and the peripheral edge of the workpiece. The purging gas may be used to assist in the formation of the barrier of the contact assembly. A combined electroplating / electroless plating tool and method are also set forth.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Endocrine pancreas differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stromal cells and uses thereof
The invention provides cells, compositions and methods based on the differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stromal cells into a cell expressing at least one genotypic or phenotypic characteristic of a pancreas cell. The cells produced in the method are useful in providing a source of differentiated and functional cells for research, implantation, transplantation and development of tissue engineered products for the treatment of diseases of the pancreas and pancreatic tissue repair.
Owner:ARTECEL
Method of forming pancreatic beta cells from mesenchymal cells
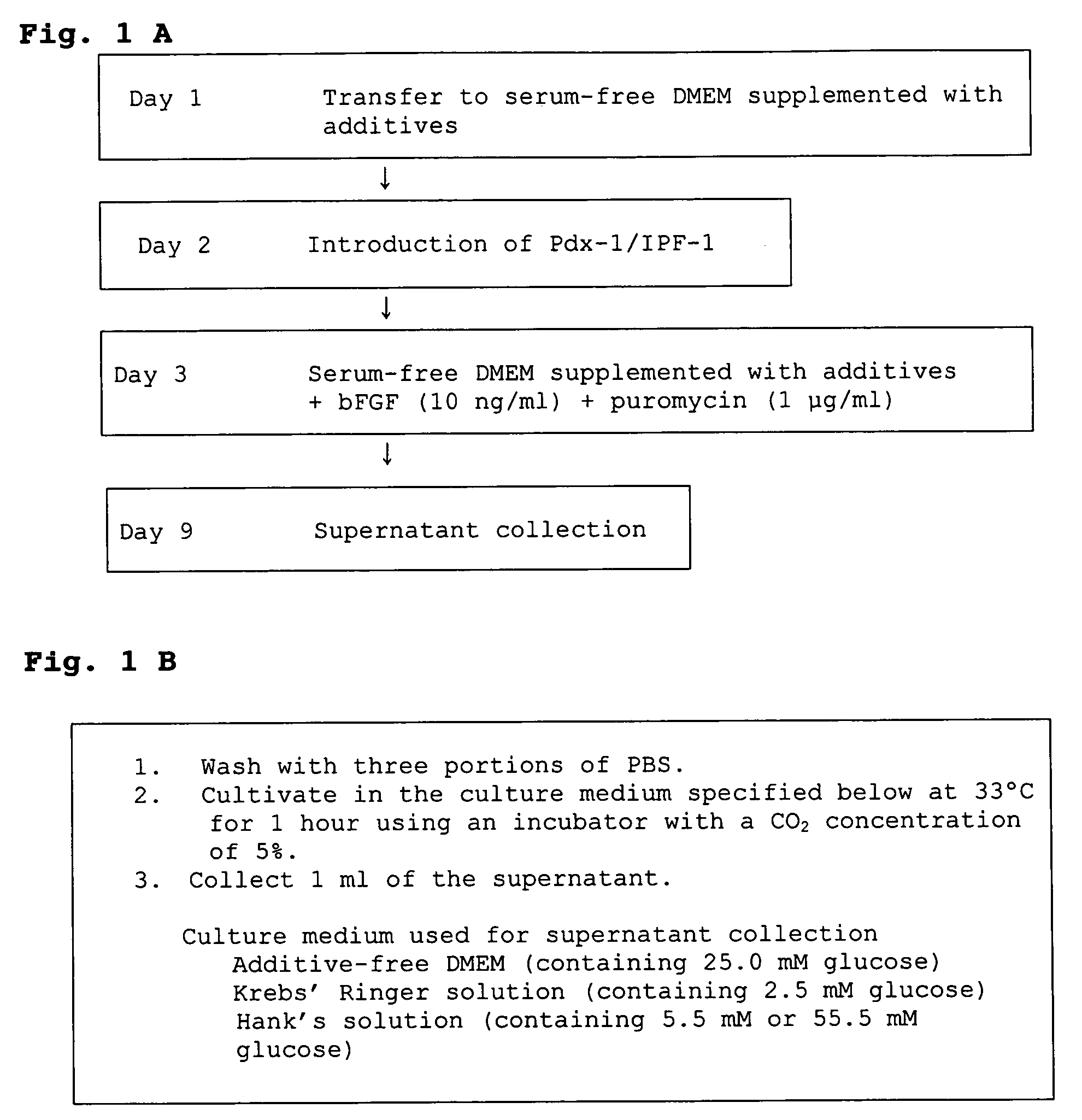
InactiveUS20050208029A1Easy to separateBiocidePancreatic cellsScreening methodBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
It is intended to provide a method of forming pancreatic β cells from mesenchymal cells characterized by comprising using mammal-origin mesenchymal cells as starting cells, culturing these cells in the presence of, for example, a pancreatic β cell-forming agent, and selecting and separating the thus obtained pancreatic βcells with the use of a gene expressed specifically in such cells as a selection marker; a remedy for glucose intolerance which comprises pancreatic β cells obtained by the above method as the active ingredient; a pancreatic β cell-forming agent such as a cytokine to be used in the above method; a method of screening a candidate compound promoting the formation of pancreatic β cells from mesenchymal cells; and a pancreatic β cell formation promoter obtained by this screening method.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
Differentiation of Human Embryonic Stem Cells
The present invention provides methods to promote the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells. In particular, the present invention provides an improved method for the formation of pancreatic endoderm, pancreatic hormone expressing cells and pancreatic hormone secreting cells. The present invention also provides methods to promote the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells without the use of a feeder cell layer.
Owner:LIFESCAN INC
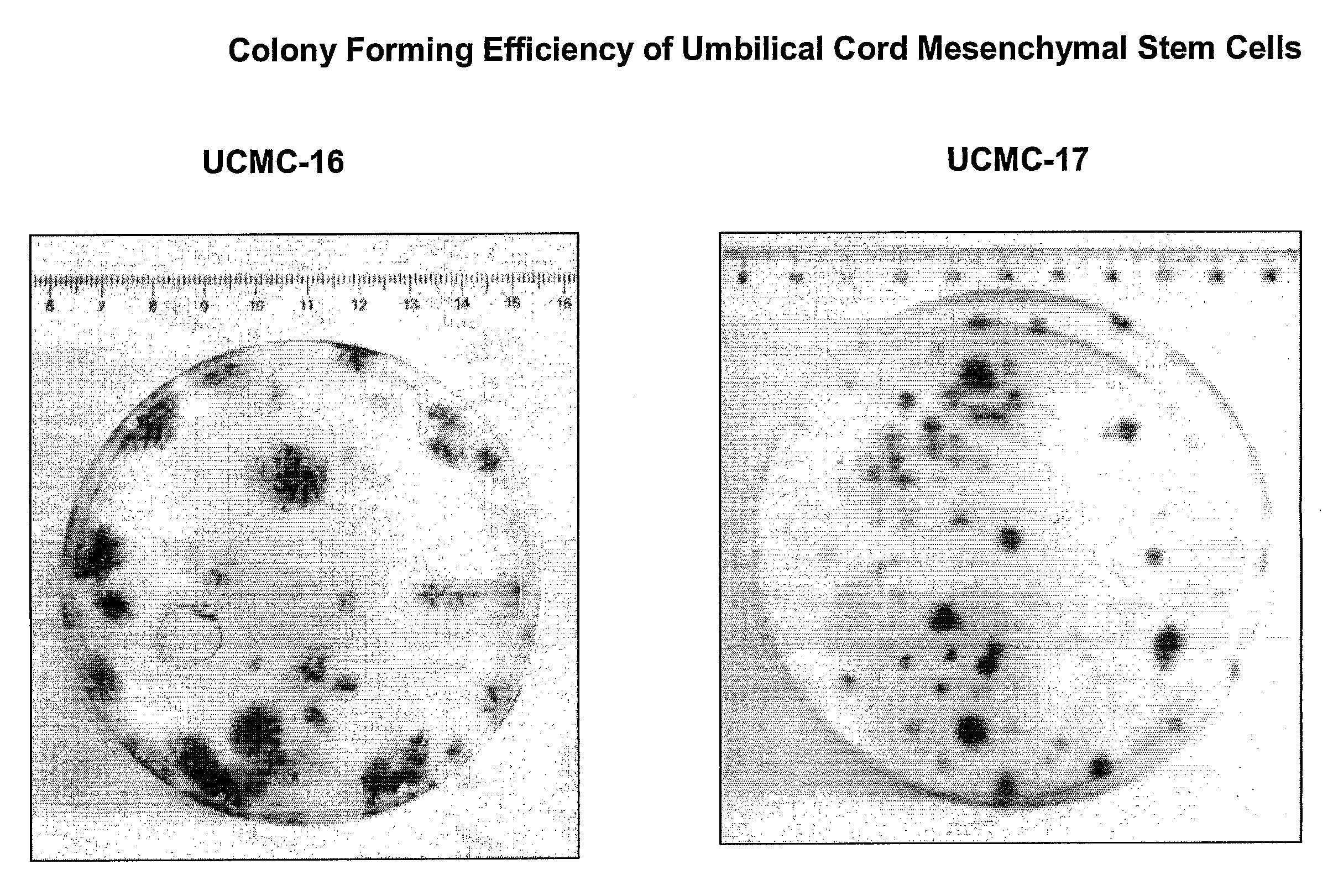
Isolation and Cultivation of Stem/Progenitor Cells From the Amniotic Membrane of Umbilical Cord and Uses of Cells Differentiated Therefrom
The present invention relates to a skin equivalent and a method for producing the same, wherein the skin equivalent comprises a scaffold and stem / progenitor cells isolated from the amniotic membrane of umbilical cord. These stem / progenitor cells may be mesenchymal (UCMC) and / or epithelial (UCEC) stem cells, which may then be further differentiated to fibroblast and keratinocytes. Further described is a method for isolating stem / progenitor cells from the amniotic membrane of umbilical cord, wherein the method comprises separating the amniotic membrane from the other components of the umbilical cord in vitro, culturing the amniotic membrane tissue under conditions allowing cell proliferation, and isolating the stem / progenitor cells from the tissue cultures. The invention also refers to therapeutic uses of these skin equivalents. Another aspect of the invention relates to the generation of a mucin-producing cell using stem / progenitor cells obtained from the amniotic membrane of umbilical cord and therapeutic uses of such mucin-producing cells. In yet another aspect, the invention relates to a method for generating an insulin-producing cell using stem / progenitor cells isolated from the amniotic membrane of umbilical cord and therapeutic uses thereof. The invention further refers to a method of treating a bone or cartilage disorder using UCMC. Furthermore, the invention refers to a method of generating a dopamin and tyrosin hydroxylase as well as a HLA-G and hepatocytes using UCMC and / or UCEC. The present invention also refers to a method of inducing proliferation of aged keratinocytes using UCMC.
Owner:CELLRESEARCH CORP PTE LTD
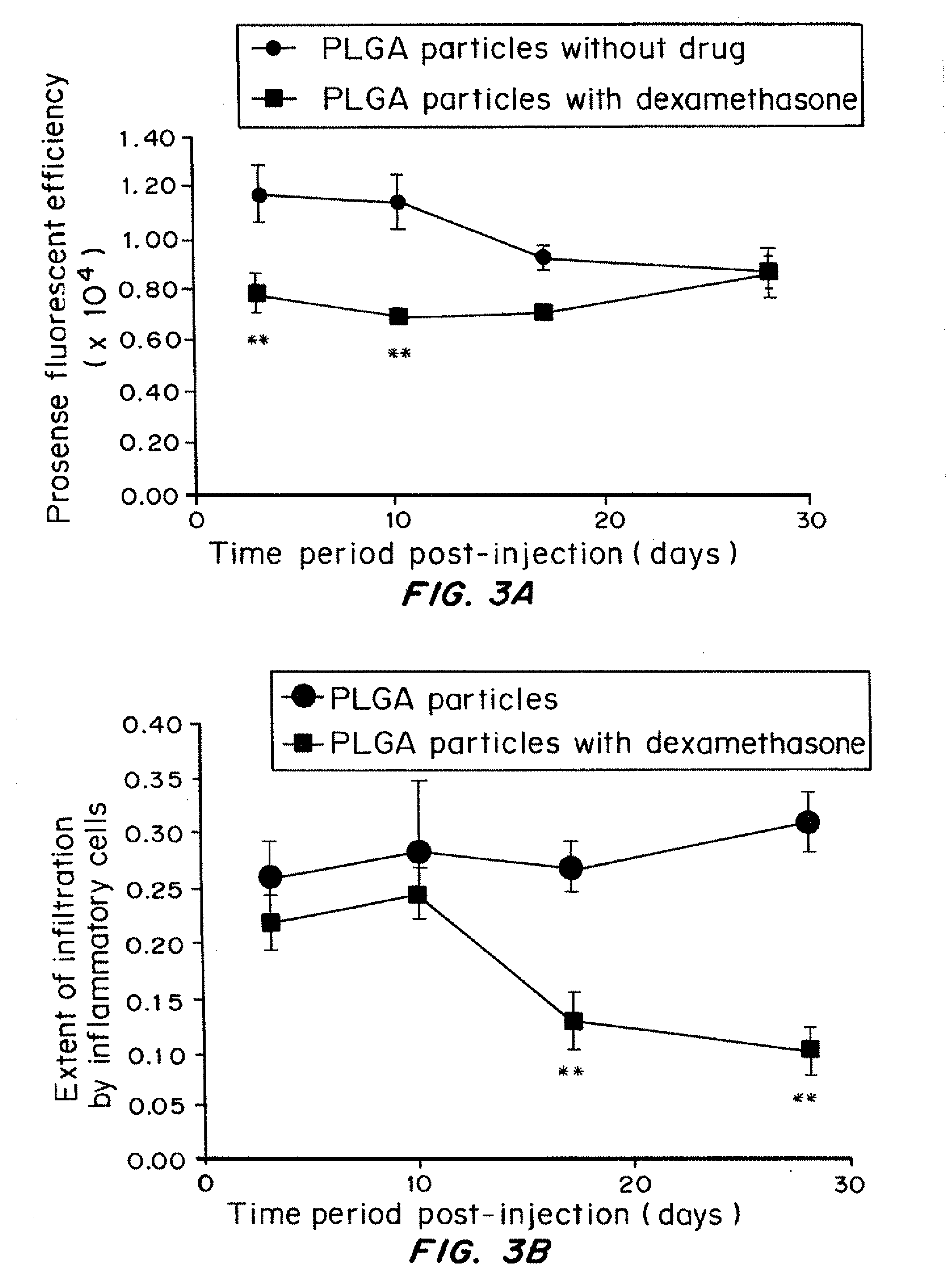
Implantation of encapsulated biological materials for treating diseases
The present invention relates to compositions and methods of treating a disease, such as diabetes, by implanting encapsulated biological material into a patient in need of treatment. This invention provides for the placement of biocompatible coating materials around biological materials using photopolymerization while maintaining the pre-encapsulation status of the biological materials. Several methods are presented to accomplish coating several different types of biological materials. The coatings can be placed directly onto the surface of the biological materials or onto the surface of other coating materials that hold the biological materials. The components of the polymerization reactions that produce the coatings can include natural and synthetic polymers, macromers, accelerants, cocatalysts, photoinitiators, and radiation. This invention also provides methods of utilizing these encapsulated biological materials to treat different human and animal diseases or disorders by implanting them into several areas in the body including the subcutaneous site. The coating materials can be manipulated to provide different degrees of biocompatibility, protein diffusivity characteristics, strength, and biodegradability to optimize the delivery of biological materials from the encapsulated implant to the host recipient while protecting the encapsulated biological materials from destruction by the host inflammatory and immune protective mechanisms without requiring long-term anti-inflammatory or anti-immune treatment of the host.
Owner:NOVOCELL
Tissue matrices comprising placental stem cells
A method of manufacturing a tissue matrix for implantation into a patient is disclosed. The method sets forth collecting embryonic stem cells from a placenta which has been treated to remove residual cord blood and seeding the collected stem cells onto or into a tissue matrix. The seeded tissue matrix is then implanted on or into a patient. The seeded tissue matrix made by the method of the present invention is also disclosed.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
In vitro differentiation of pluripotent stem cells to pancreatic endoderm cells (PEC) and endocrine cells
A human immature endocrine cell population and methods for making an immature endocrine cell population are provided. Specifically, immature beta cells and methods for production of immature beta cells are described. Immature beta cells co-express INS and NKX6.1 and are uni-potent and thereby develop into mature beta cells when implanted in vivo. The mature beta cells in vivo are capable of producing insulin in response to glucose stimulation.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
Stem cell aggregate suspension compositions and methods of differentiation thereof
The present invention relates to methods for production of undifferentiated or differentiated embryonic stem cell aggregate suspension cultures from undifferentiated or differentiated embryonic stem cell single cell suspensions and methods of differentiation thereof.
Owner:VIACYTE INC
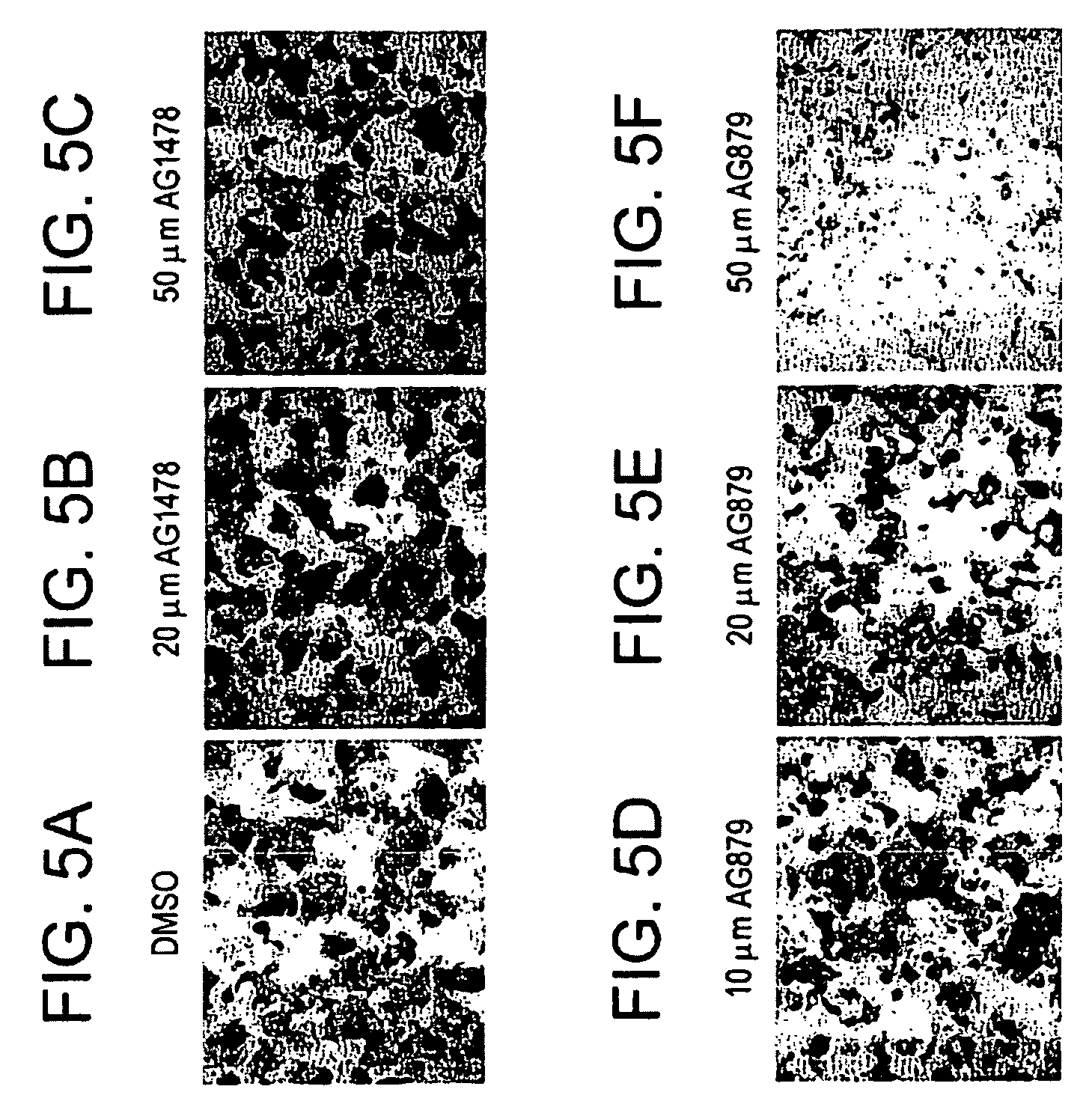
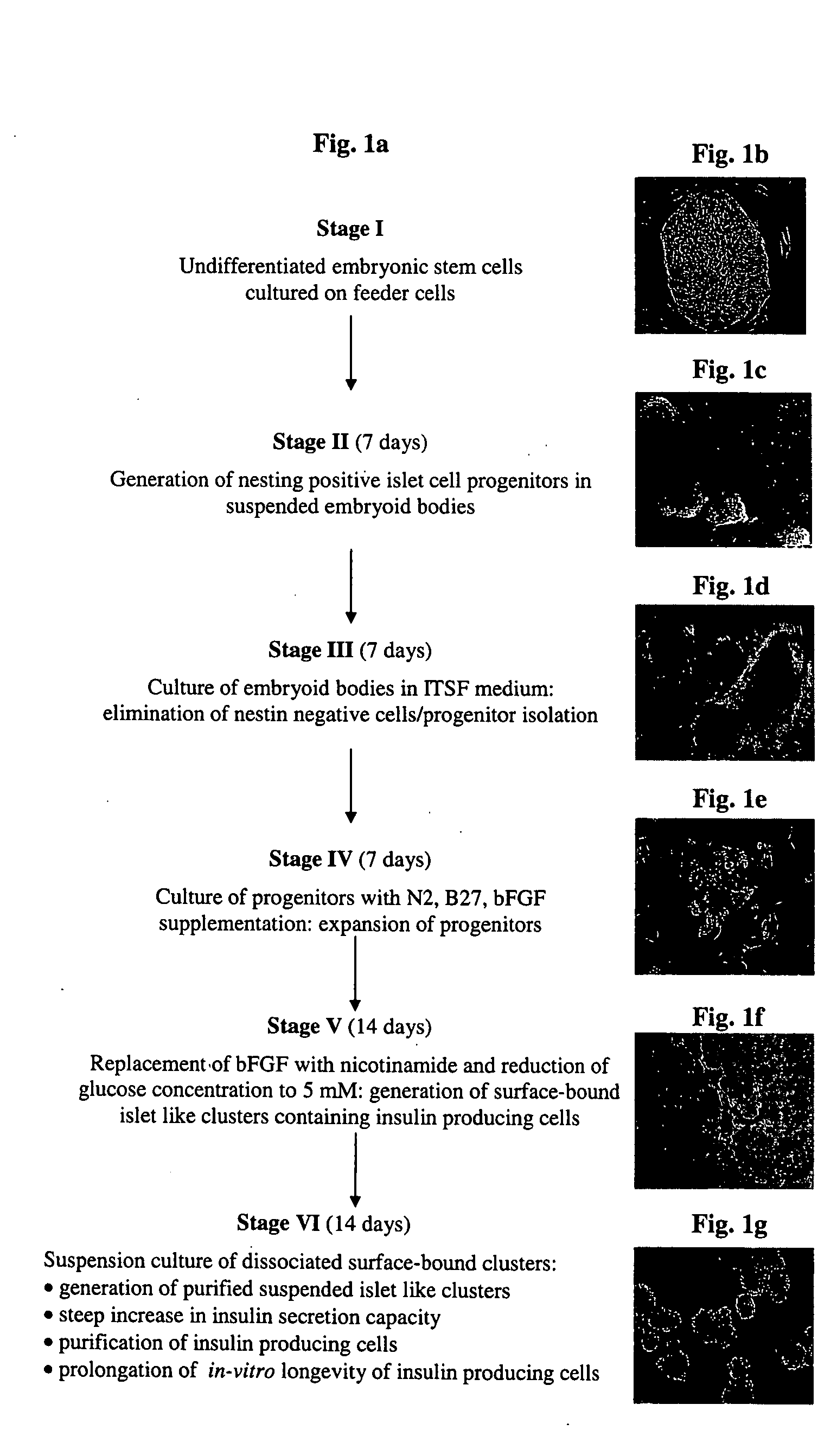
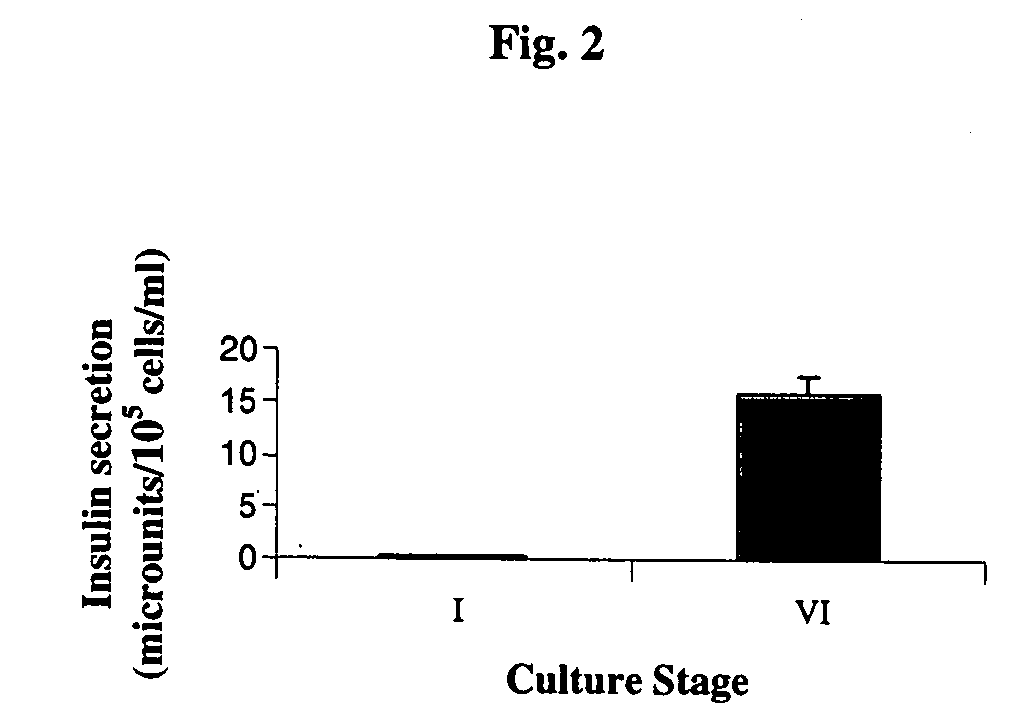
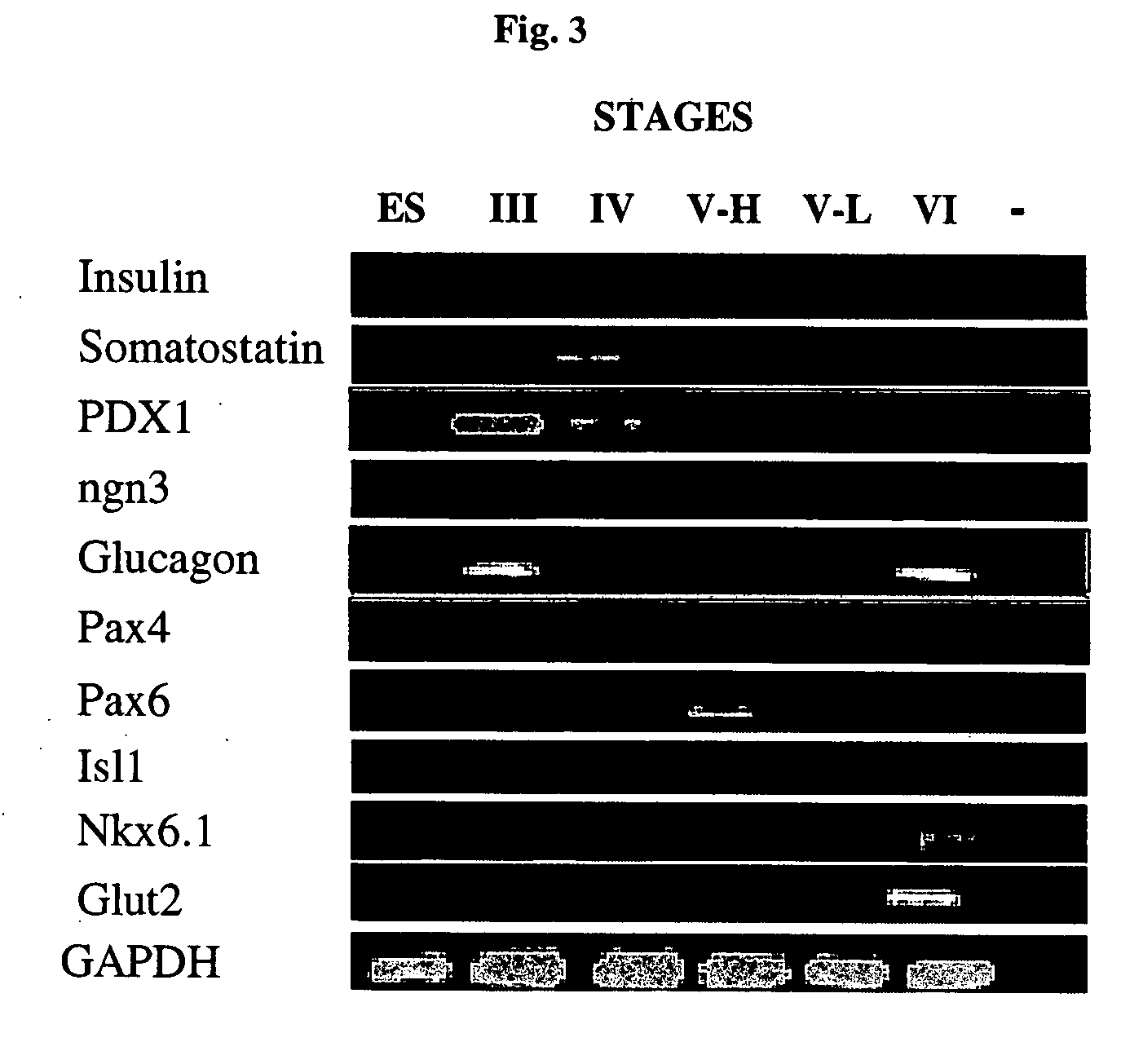
Cultured human pancreatic islets, and uses thereof
A method of generating cells capable of secreting insulin is disclosed. The method comprises subjecting mammalian embryonic stem cells to set of culturing conditions suitable for differentiation of at least a portion thereof into cells displaying at least one characteristic associated with a pancreatic islet cell progenitor phenotype, and subjecting such differentiated cells to a set of culturing conditions suitable for formation of surface bound cell clusters including insulin producing cells.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
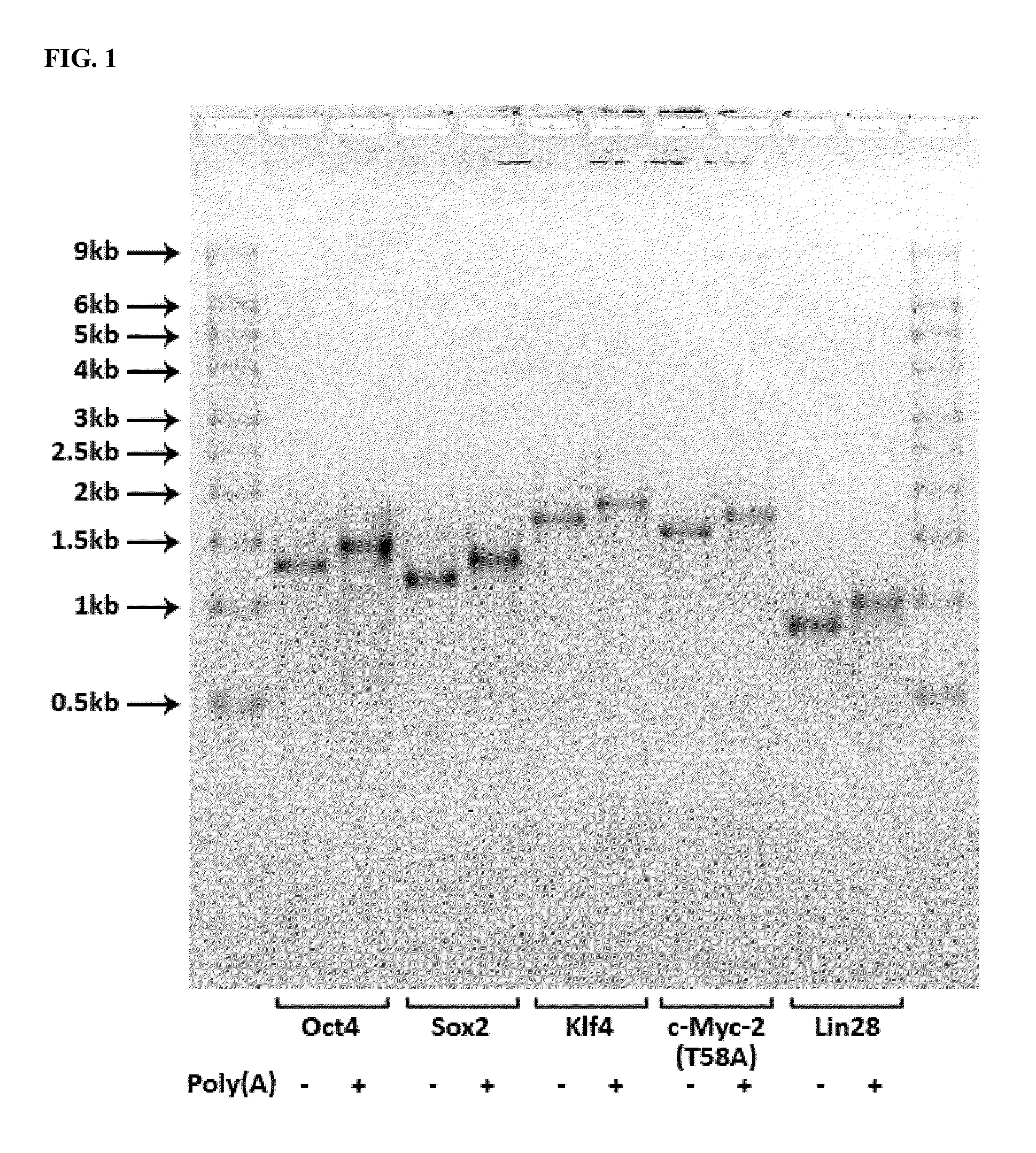
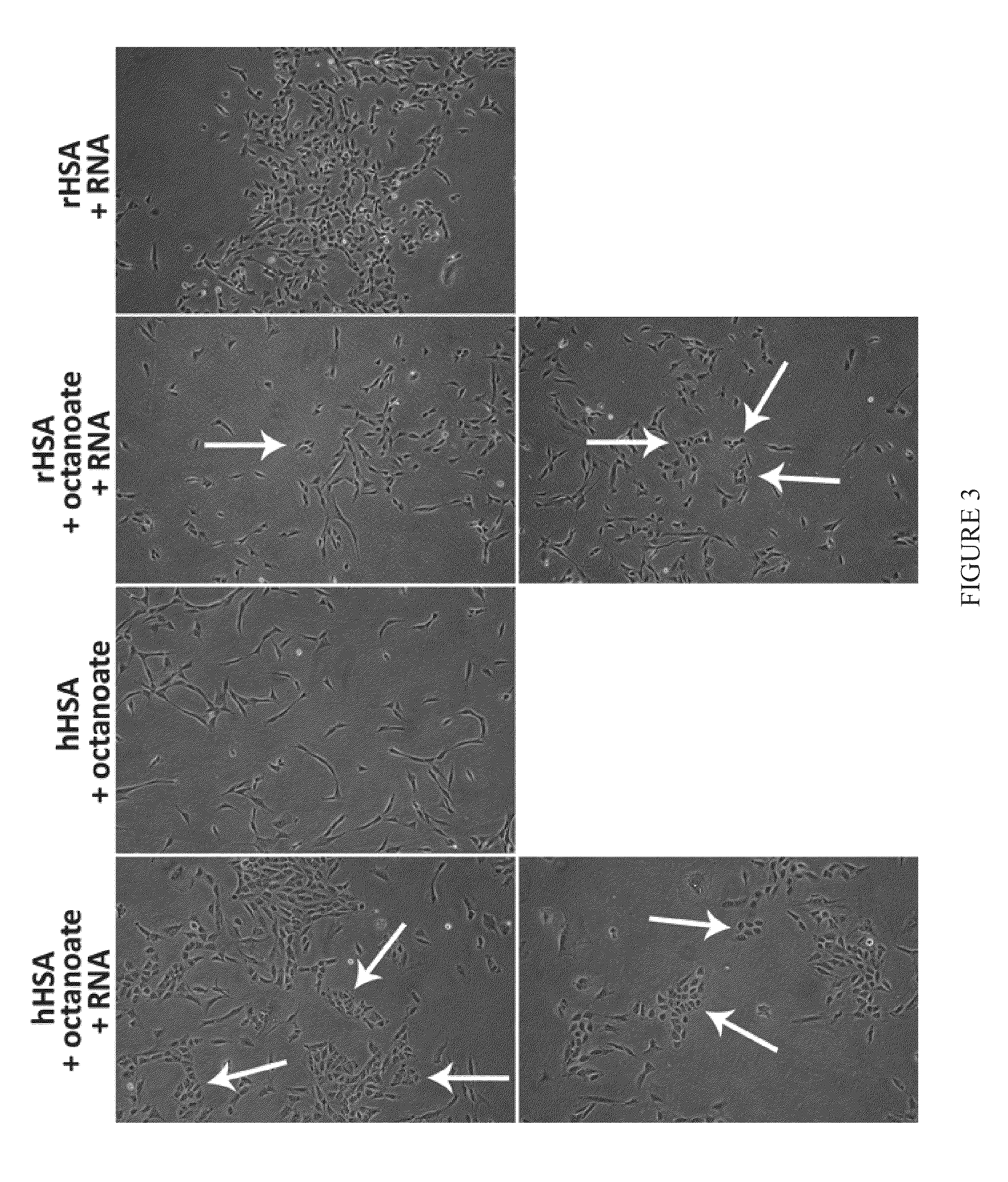
Methods and products for transfection
The present invention relates in part to methods for producing tissue-specific cells from patient samples, and to tissue-specific cells produced using these methods. Methods for reprogramming cells using RNA are disclosed. Therapeutics comprising cells produced using these methods are also disclosed.
Owner:FACTOR BIOSCI
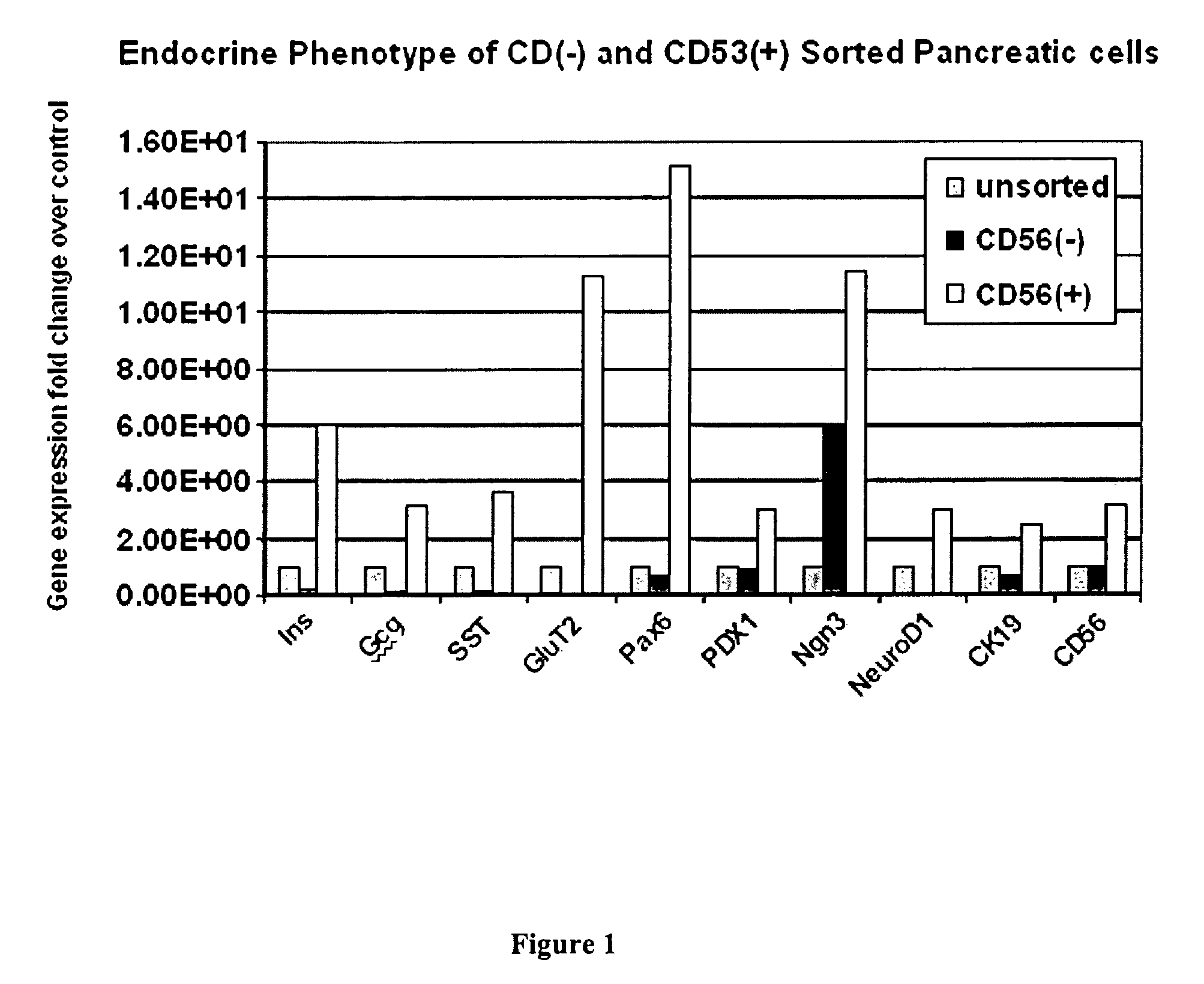
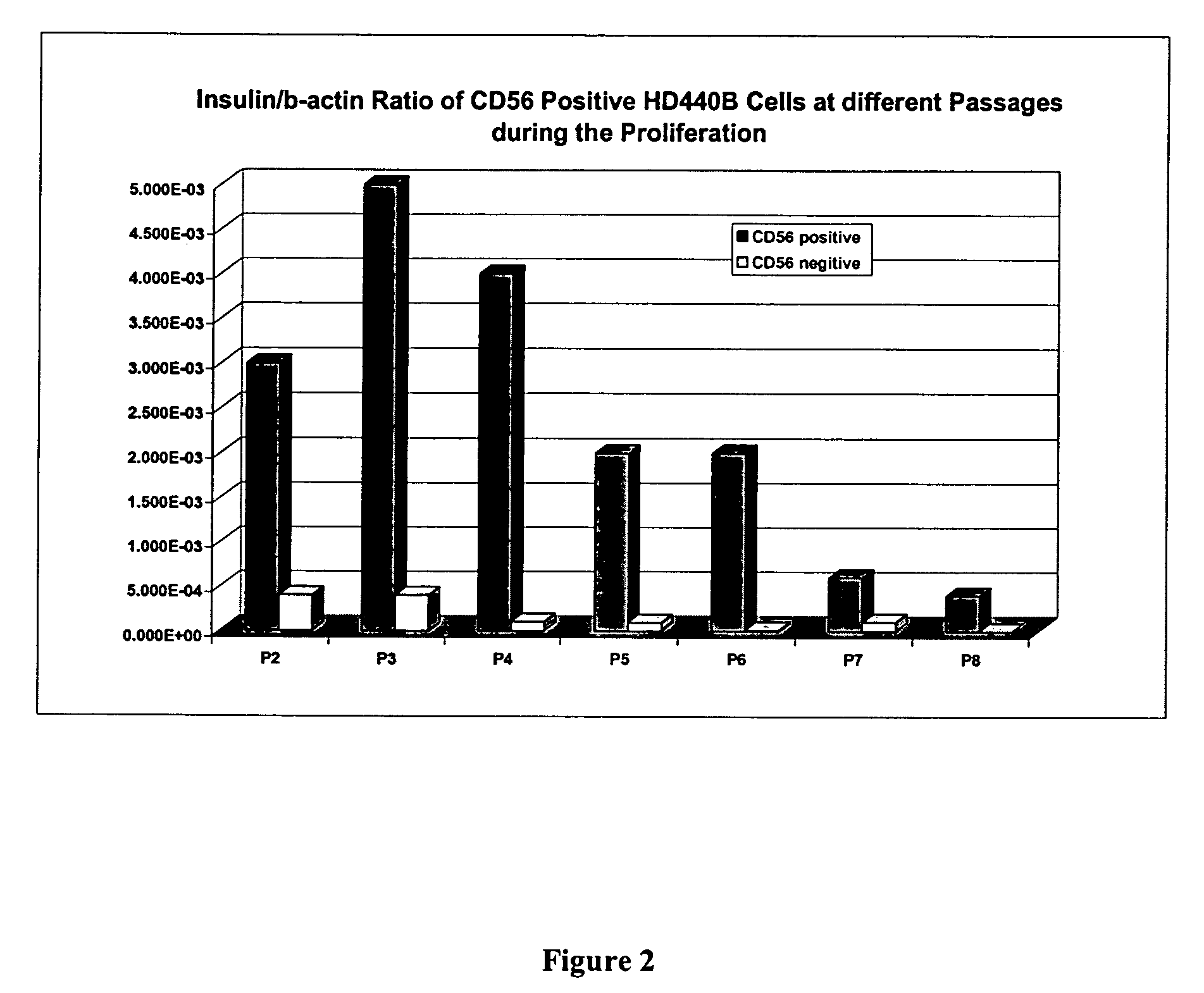
CD56 positive human adult pancreatic endocrine progenitor cells
The invention relates to the discovery of a selective cell surface marker that permits the selection of a unique subset of pancreatic stems cells having a high propensity to differentiate into insulin producing cells or into insulin producing cell aggregates.
Owner:RENEURON INC
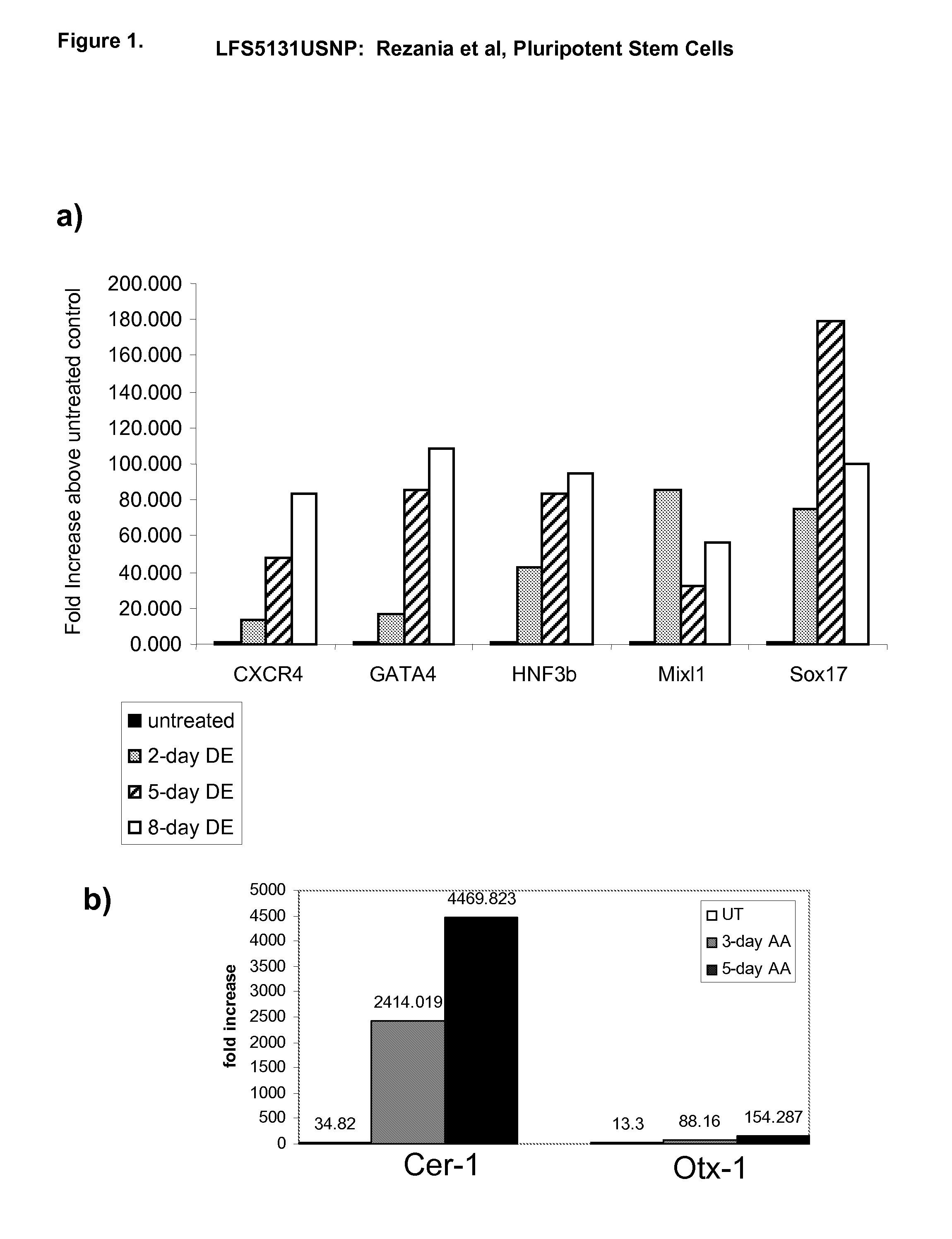
Differentiation of human embryonic stem cells
ActiveUS20110151561A1High expressionPancreatic cellsEpidermal cells/skin cellsPluripotential stem cellIntracrine
The present invention provides methods to promote the differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into insulin producing cells. In particular, the present invention provides a method to increase the expression of NGN3 and NKX6.1 in populations of cells expressing markers characteristic of the pancreatic endocrine lineage.
Owner:JANSSEN BIOTECH INC
Culture media for stem cells
PendingUS20140243227A1Slow proliferationIncrease surface areaBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStem cell cultureBiology
Culture media and methods for expanding and differentiating populations of stem cells and for obtaining organoids. Expanded cell populations and organoids obtainable by methods of the invention and their use in drug screening, toxicity assays and regenerative medicine.
Owner:KONINK NEDERLANDSE AKADE VAN WETENSCHAPPEN
Hydrogel encapsulated cells and Anti-inflammatory drugs
ActiveUS20120213708A1Maximizes drug interactionMinimize interferenceOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseMedicine
A composition containing biocompatible hydrogel encapsulating mammalian cells and anti-inflammatory drugs is disclosed. The encapsulated cells have reduced fibrotic overgrowth after implantation in a subject. The compositions contain a biocompatible hydrogel having encapsulated therein mammalian cells and anti-inflammatory drugs or polymeric particles loaded with anti-inflammatory drugs. The anti-inflammatory drugs are released from the composition after transplantation in an amount effective to inhibit fibrosis of the composition for at least ten days. Methods for identifying and selecting suitable anti-inflammatory drug-loaded particles to prevent fibrosis of encapsulated cells are also described. Methods of treating a disease in a subject are also disclosed that involve administering a therapeutically effective amount of the disclosed encapsulated cells to the subject.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
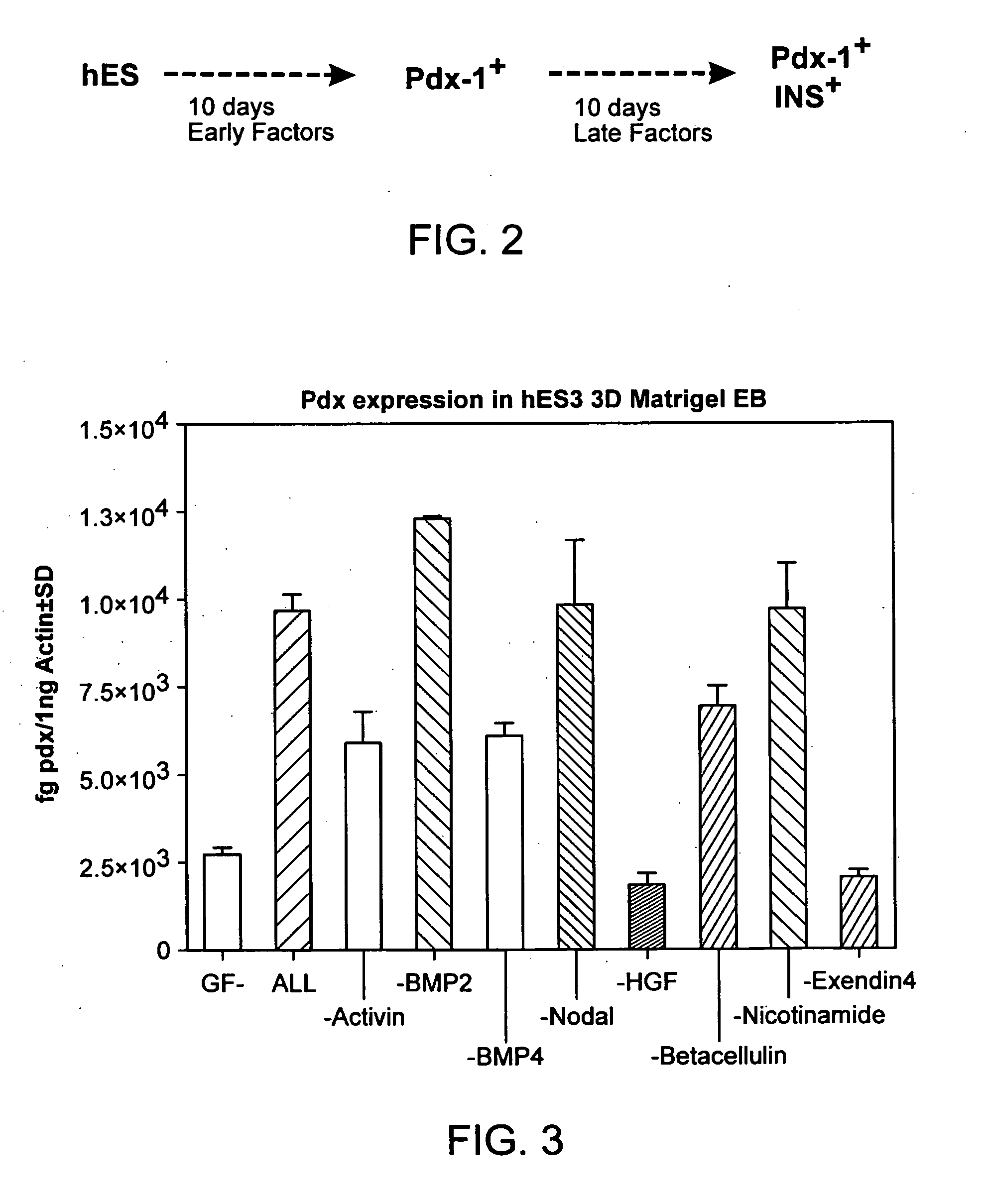
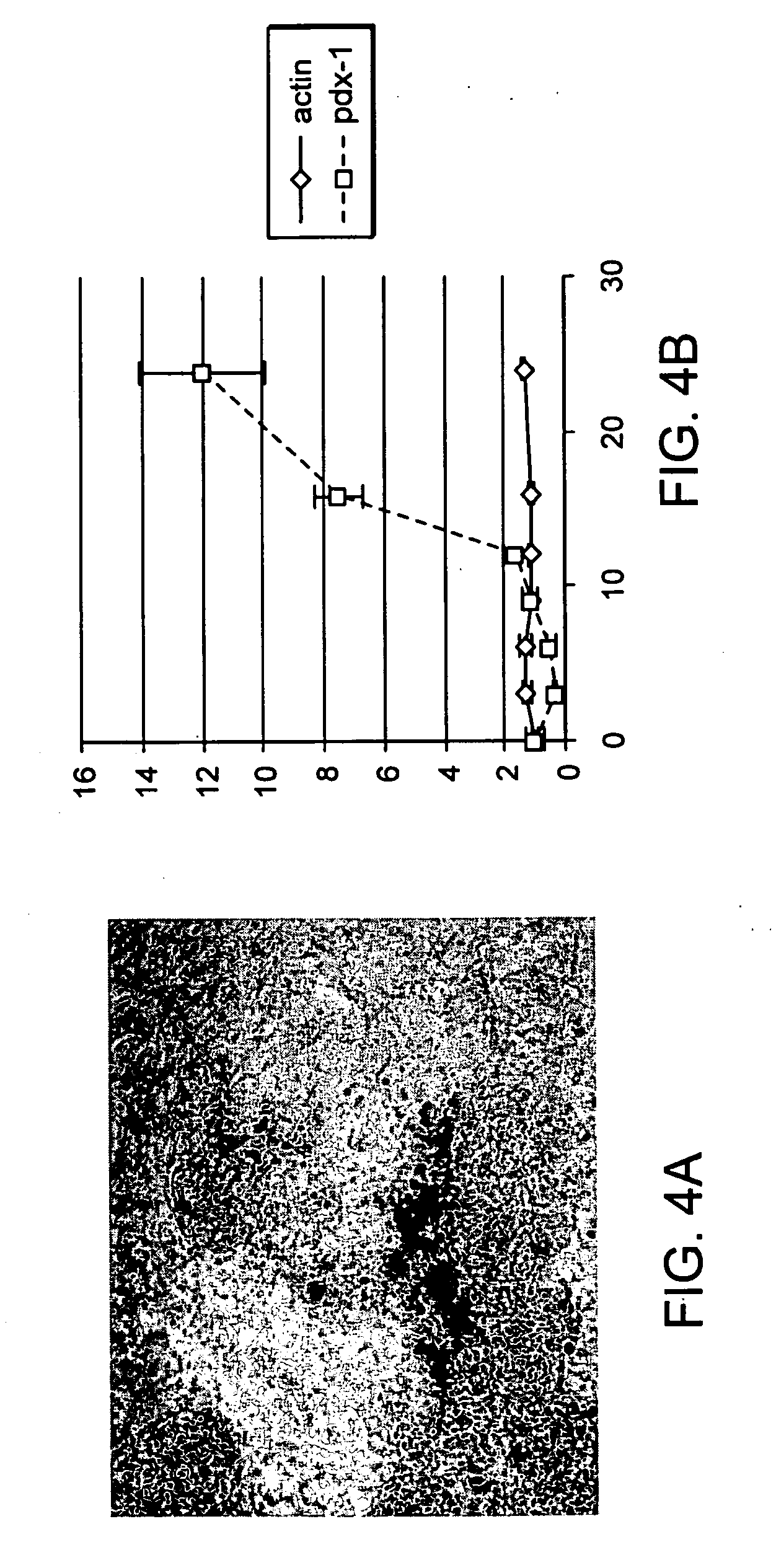
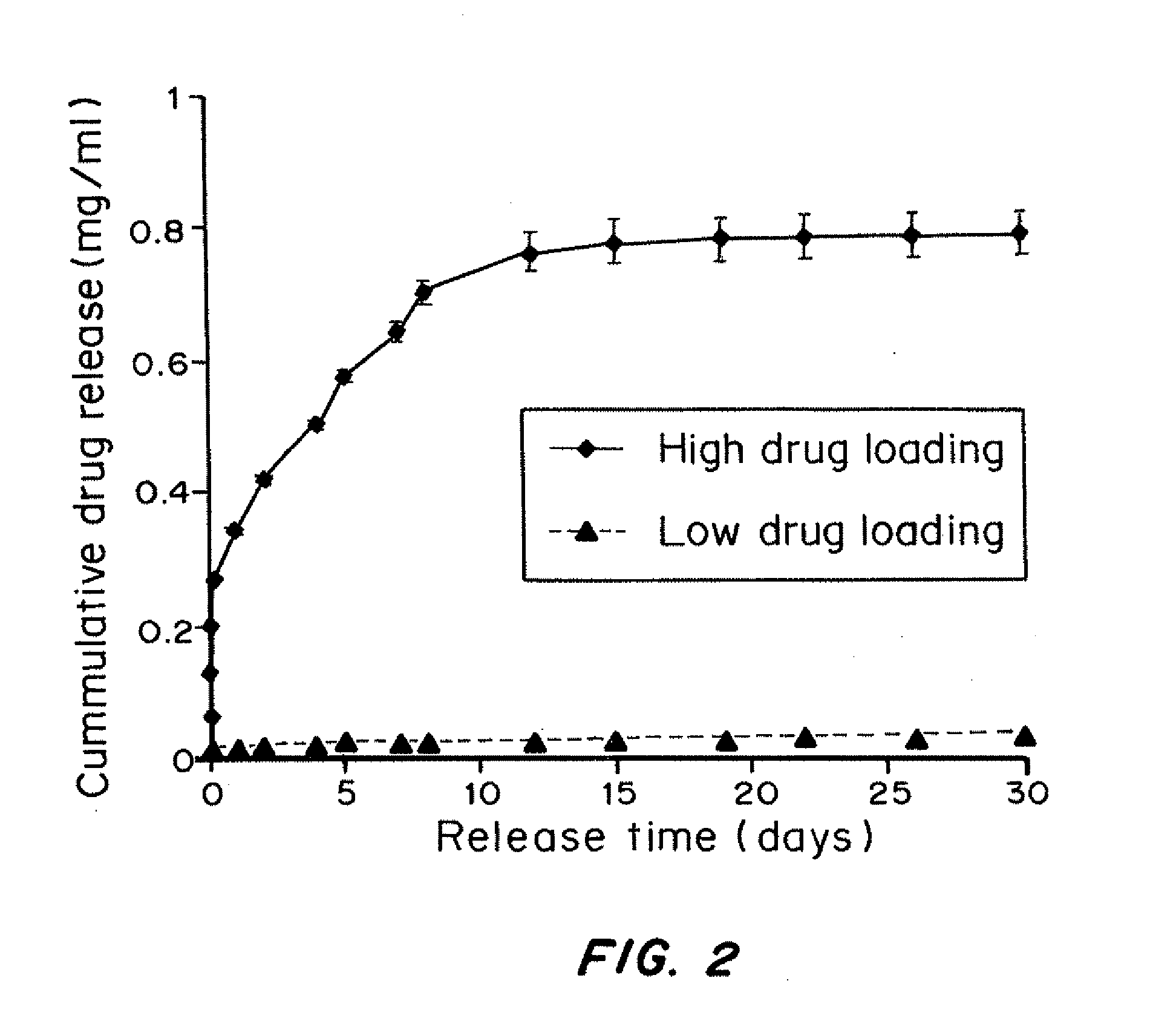
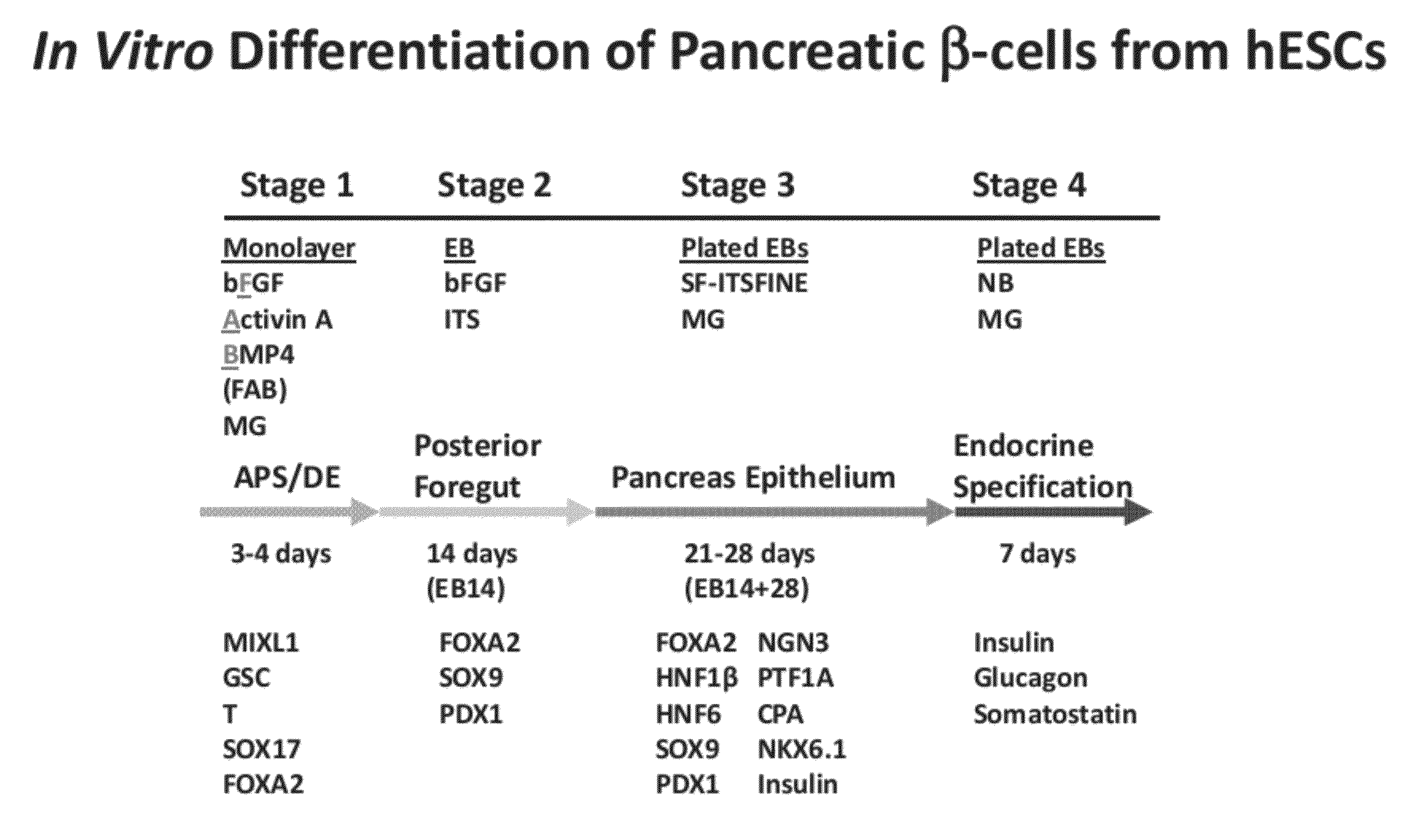
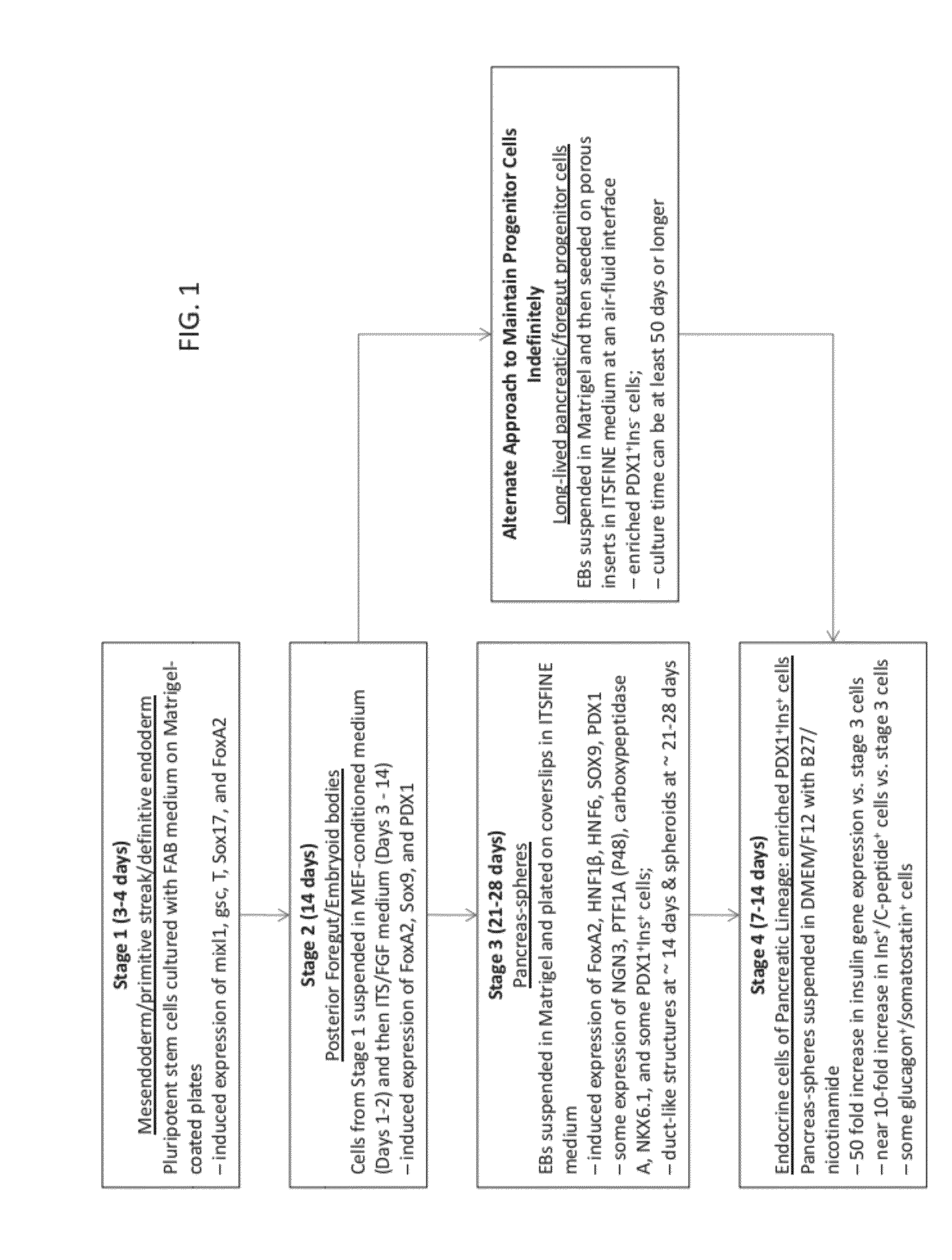
Methods and devices for differentiating pluripotent stem cells into cells of the pancreatic lineage
Methods and devices for culturing human pluripotent stem cells to produce cells of the pancreatic lineage are disclosed. The methods include steps of culturing the stem cells under conditions that induce the expression of mesendoderm / primitive streak and definitive endoderm markers in a chemically defined medium including an effective amount of i) fibroblast growth factor, ii) Activin A, and iii) bone morphogenetic protein. The methods further include the steps of culturing cells under conditions favoring the formation of at least one of intact embryoid bodies and pancreatic progenitor PDX1+ Ins− cells.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Human trophoblast stem cells and use thereof
Existence of human trophoblast stem (hTS) cells has been suspected but unproved. The isolation of hTS cells is reported in the early stage of chorionic villi by expressions of FGF4, FGFR-2, Oct4, Thy-1, and stage-specific embryonic antigens distributed in different compartments of the cell. hTS cells are able to derive into specific cell phenotypes of the three primitive embryonic layers, produce chimeric reactions in mice, and retain a normal karyotype and telomere length. In hTS cells, Oct4 and fgfr-2 expressions can be knockdown by bFGF. These facts suggest that differentiation of the hTS cells play an important role in implantation and placentation. hTS cells could be apply to human cell differentiation and for gene and cell-based therapies.
Owner:ACCELERATED BIOSCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com