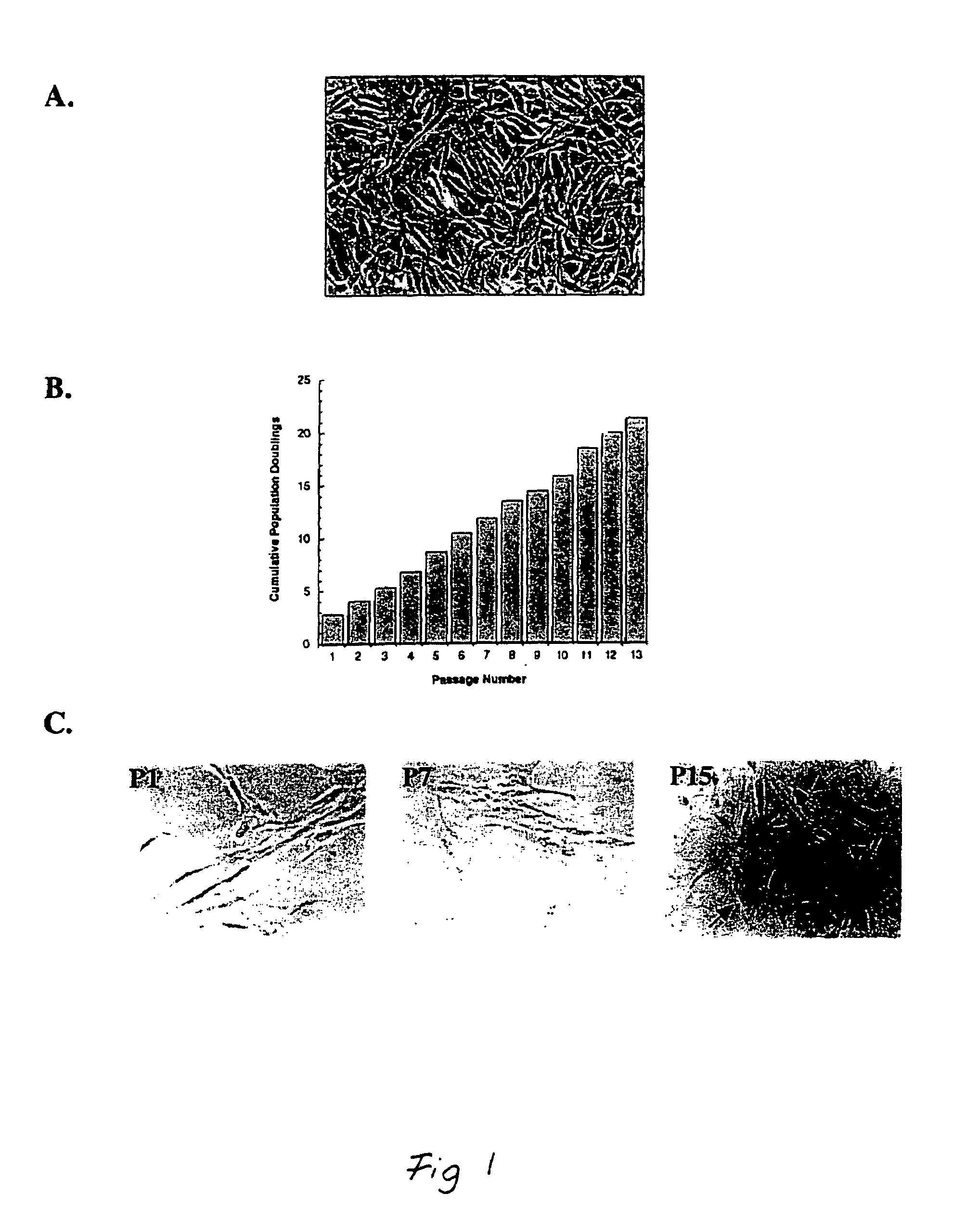
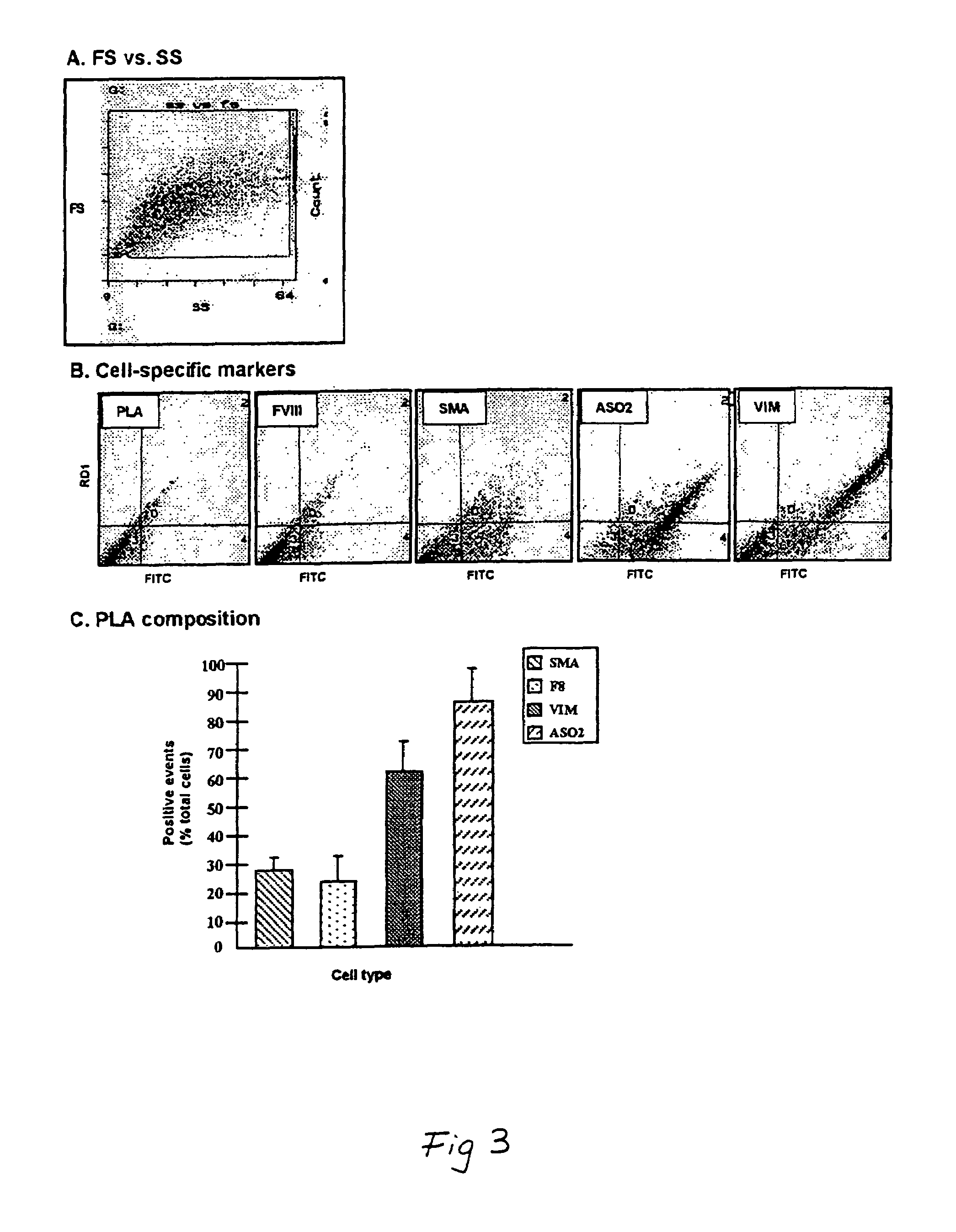
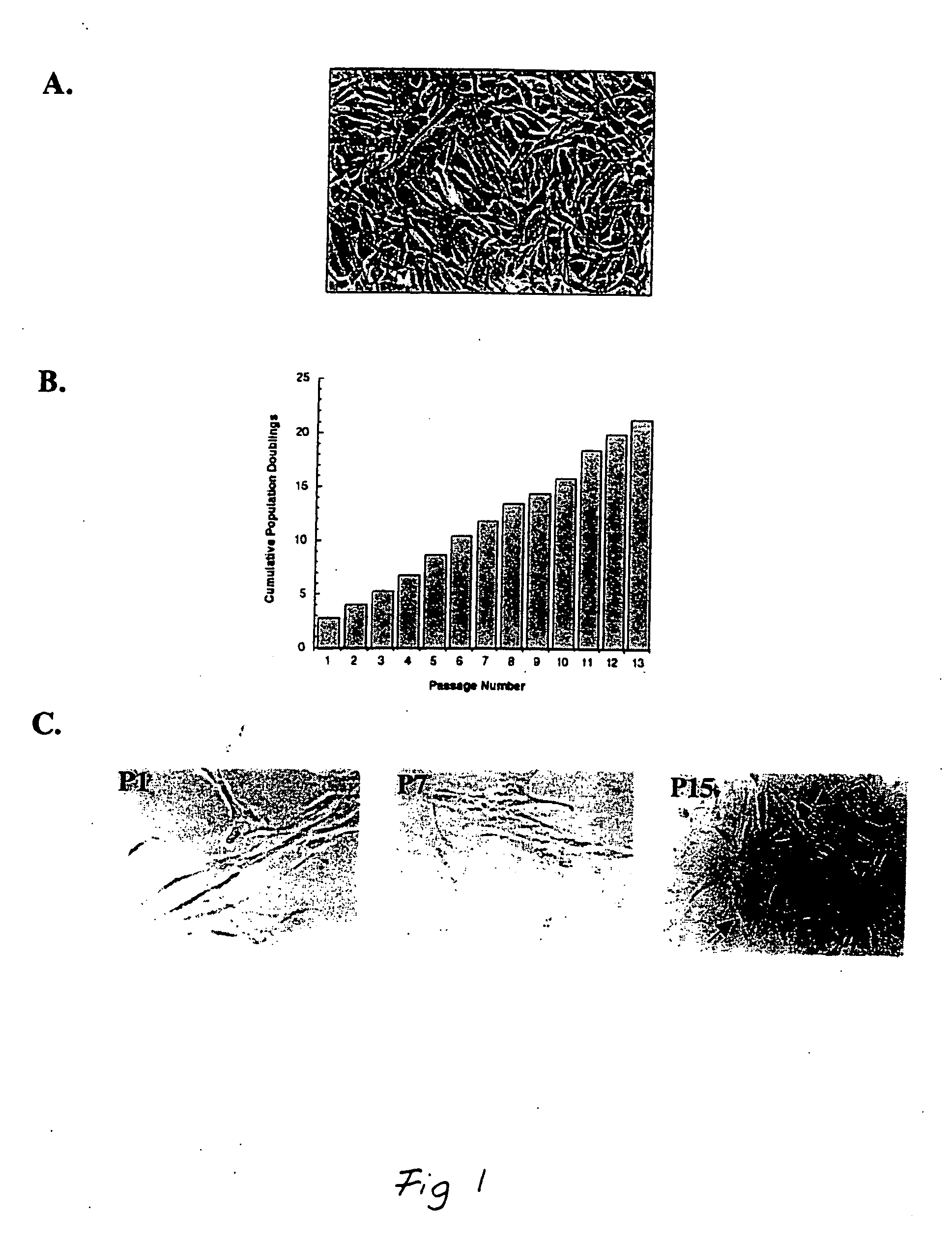
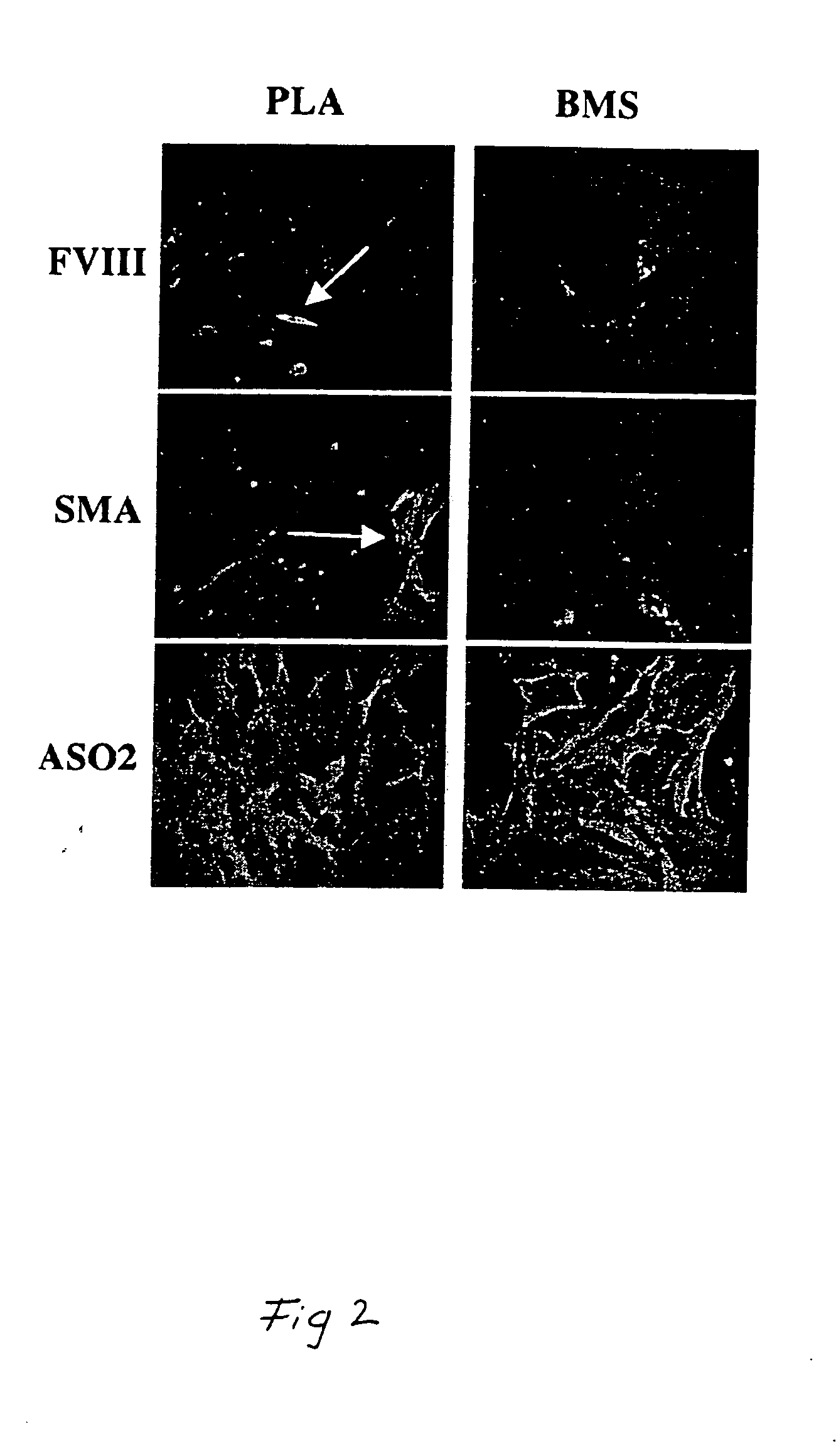
Patents
Literature
480 results about "Derived stem" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Derived stems are a morphological feature of verbs common to the Semitic languages. These derived verb stems are sometimes called augmentations or forms of the verb, or are identified by their Hebrew name binyanim. Semitic languages make extensive use of nonconcatenative morphology, and most words share a set of two, three or four consonants which comprise a root wherein each root may be the basis for a number of conceptually related words. Traditionally, words are thought of as being derived from these root consonants, but a view increasingly held by contemporary linguists sees stem words being the source of derivations rather than consonantal roots. Regardless, each language features a number of set patterns for deriving verb stems from a given root or underived stem. Stems sharing the same root consonants represent separate verbs, albeit often semantically related, and each is the basis for its own conjugational paradigm. As a result, these derived stems are part of the system of derivational morphology, not part of the inflectional system.
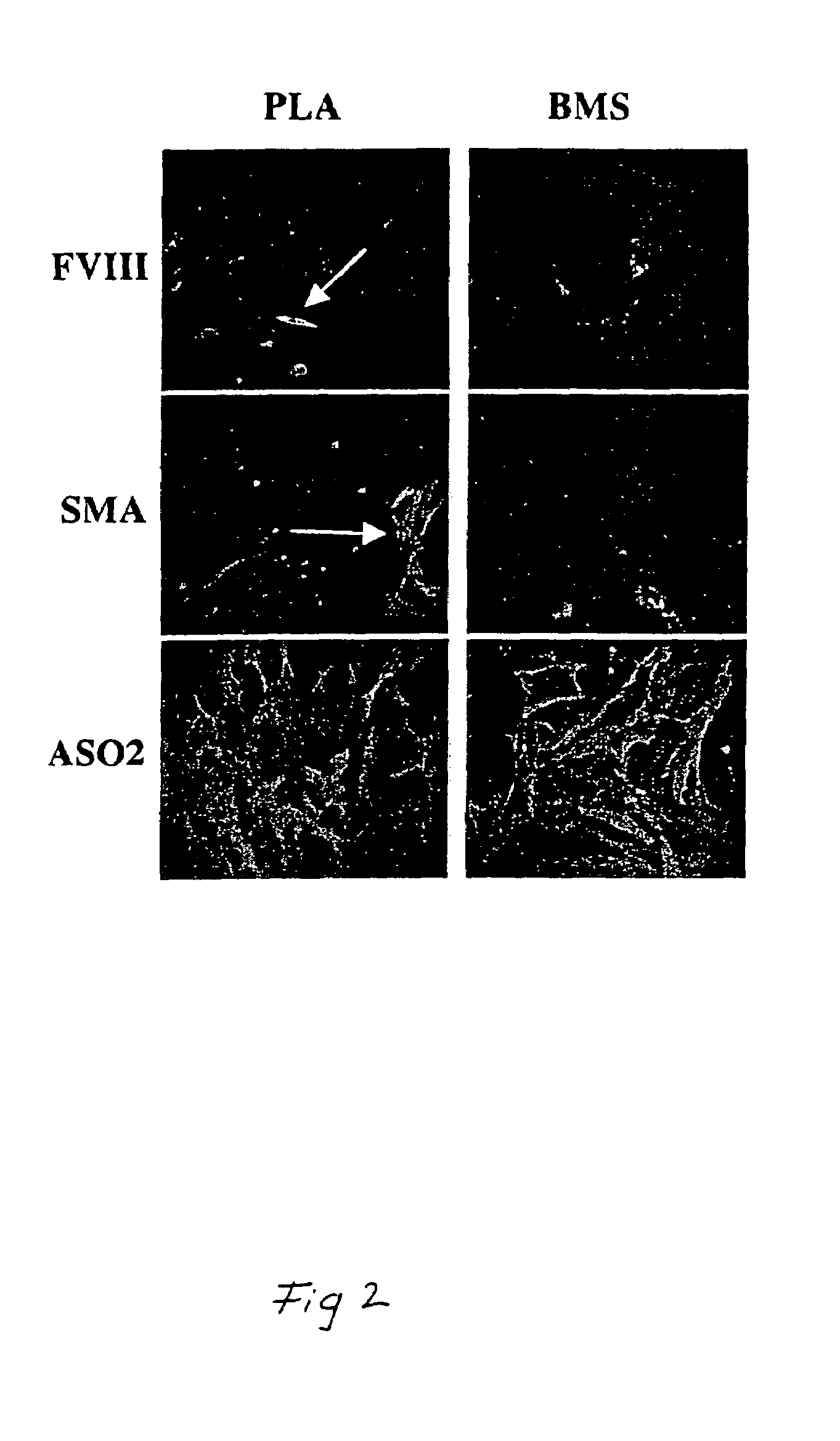
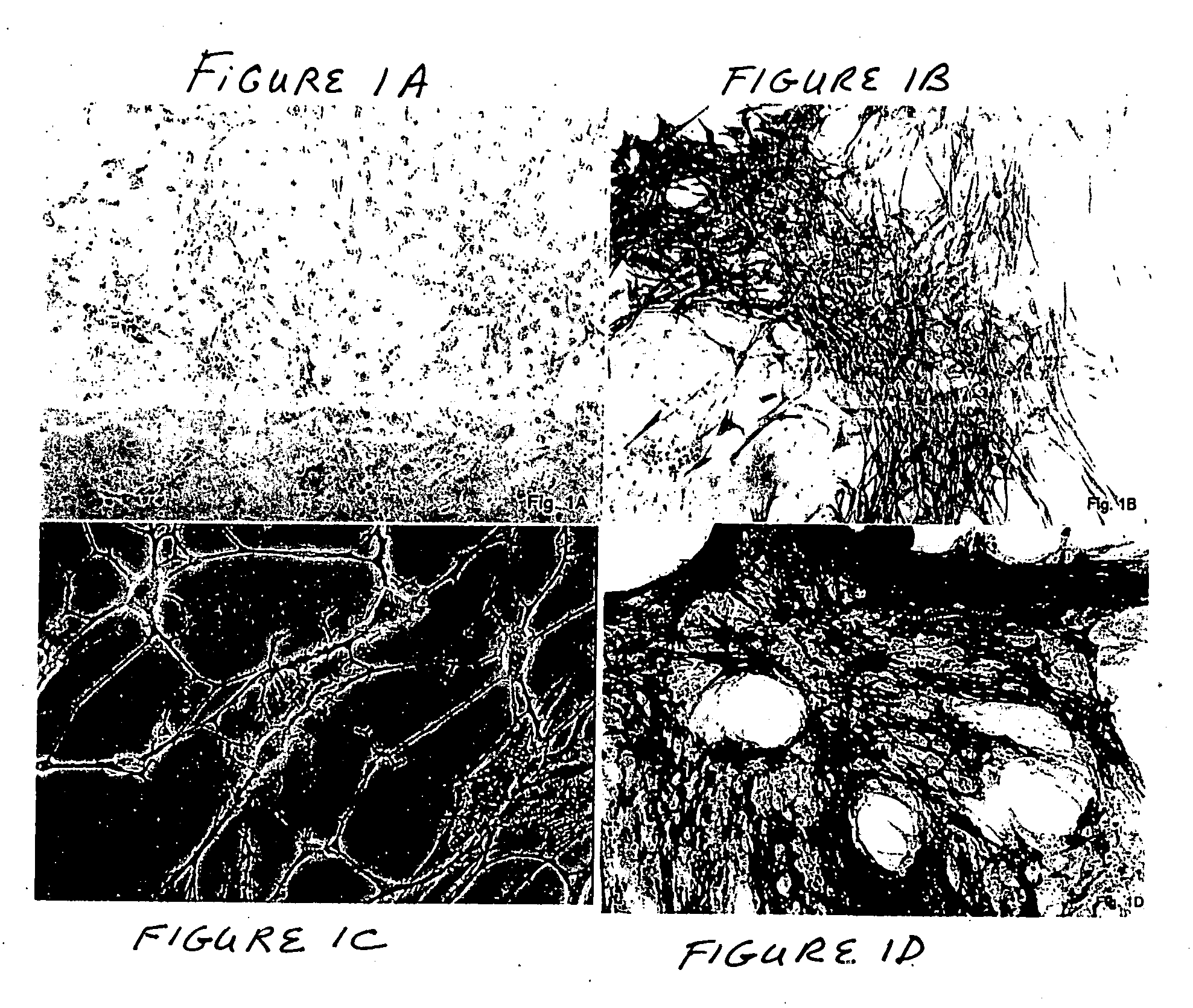
Placental derived stem cells and uses thereof
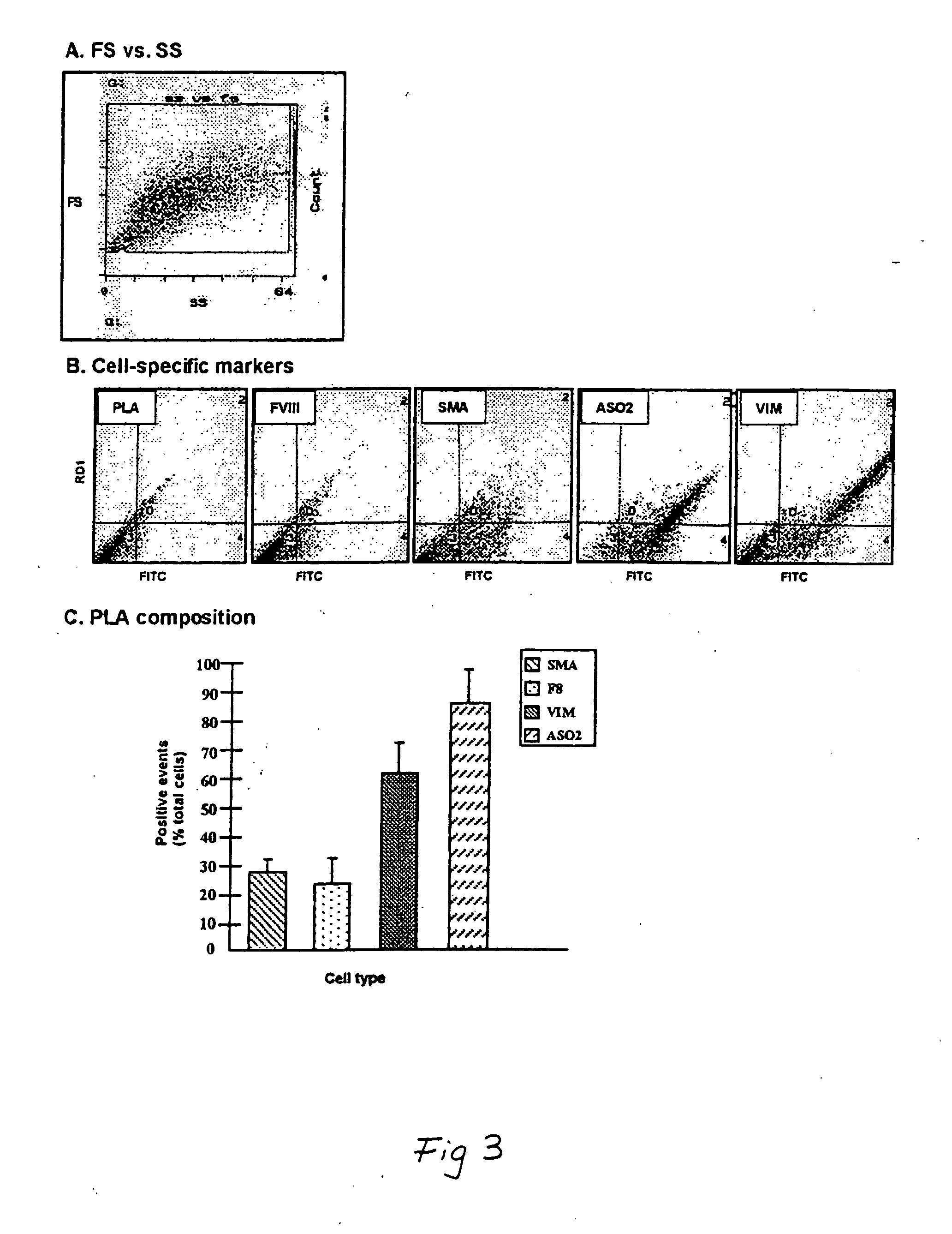
The present invention features novel placental derived stem cells and provides methods and compositions for the therapeutic uses of placental derived stem cells or placental derived stem cells that have been induced to differentiate into a desired tissue type into a recipient host in amounts sufficient to result in production of the desired cell type, i.e., hepatic, pancreatic, neuronal, or nervous tissue.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
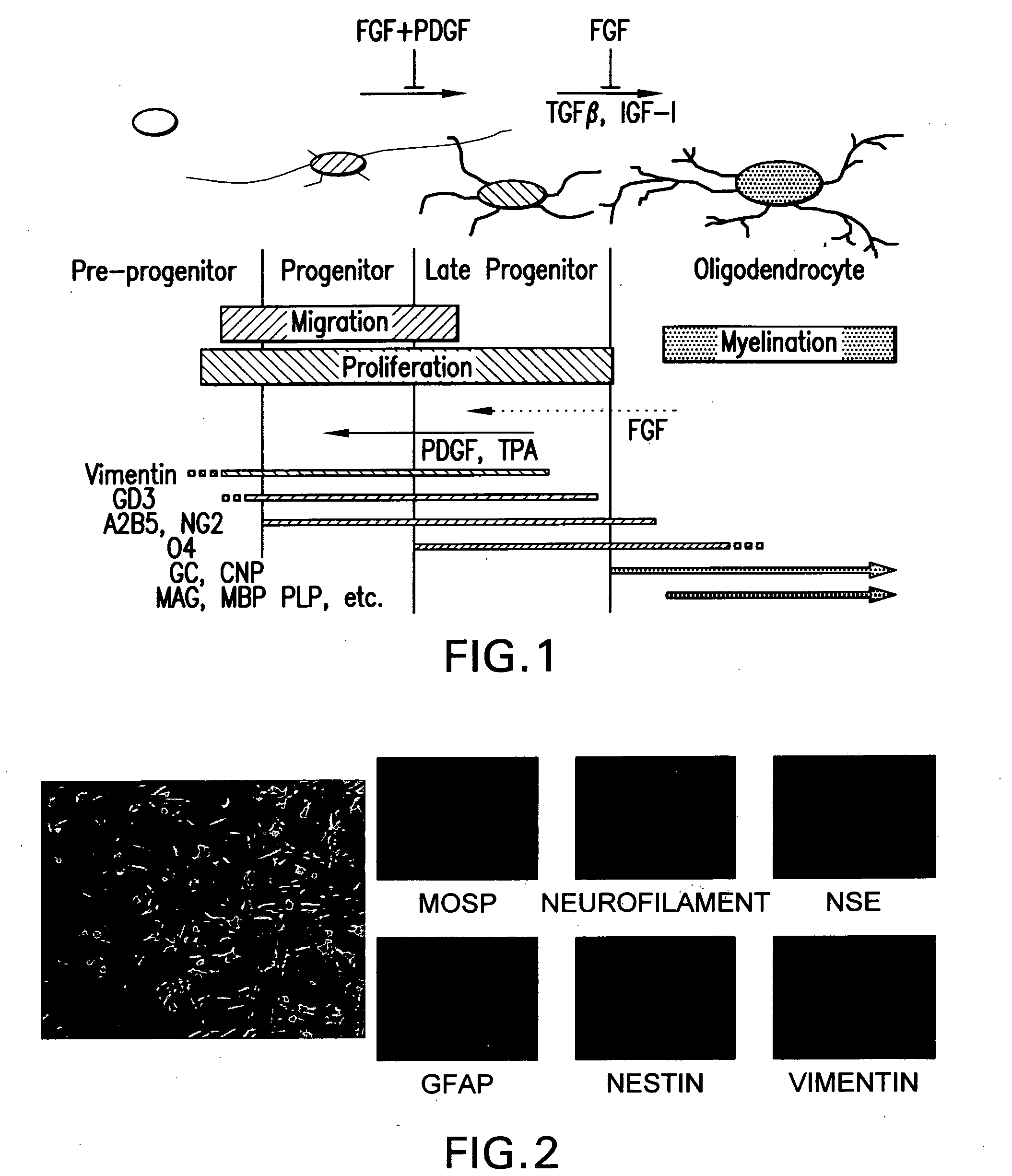
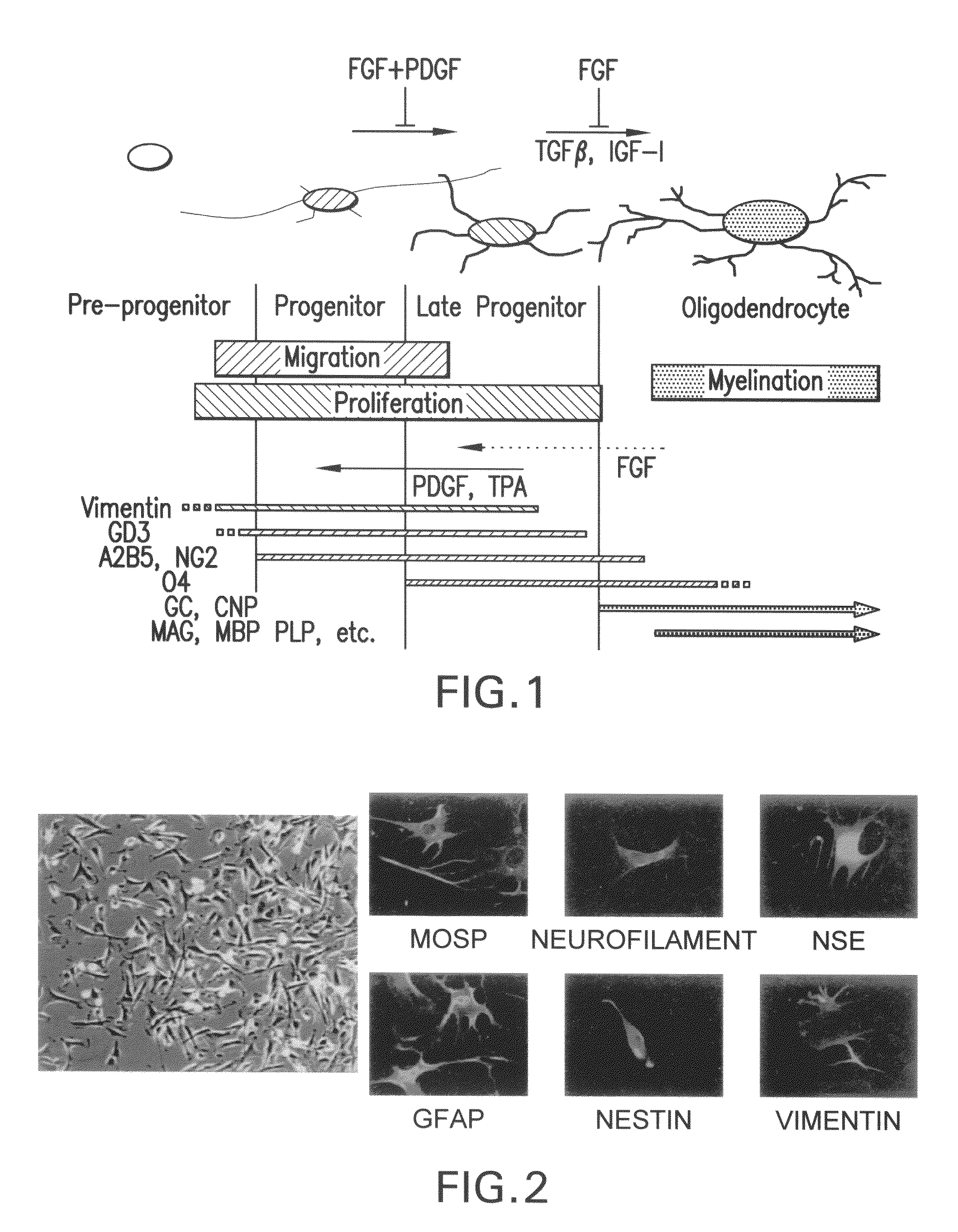
Production of oligodendrocytes from placenta-derived stem cells
The present invention provides methods and compositions for the production of glial cells and oligodendrocytes from placenta stem cells. The invention further provides for the use of these glia and oligodendrocytes in the treatment of, and intervention in, for example, trauma, ischemia and degenerative disorders of the central nervous system (CNS), particularly in the treatment of demyelinating diseases such as multiple sclerosis.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
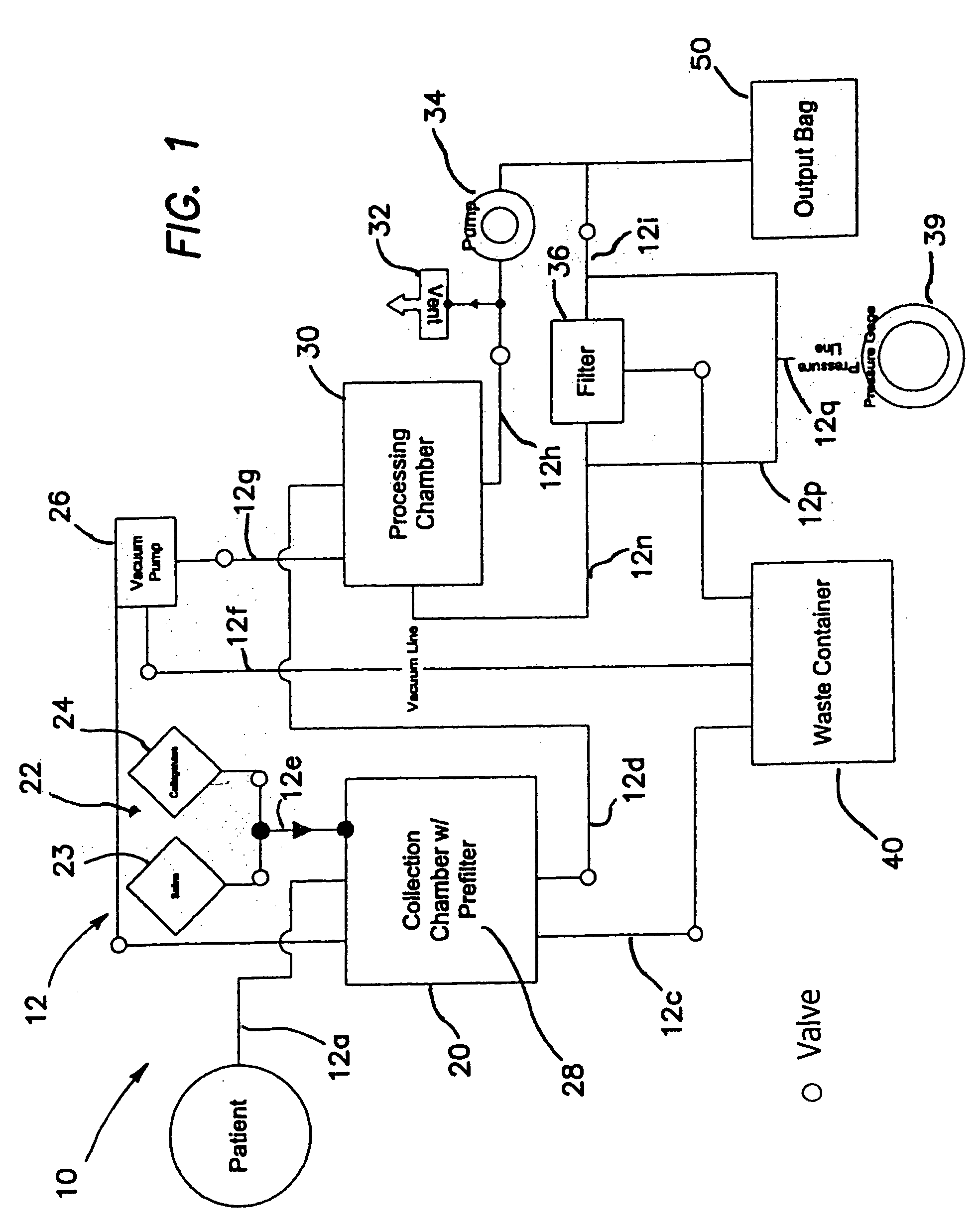
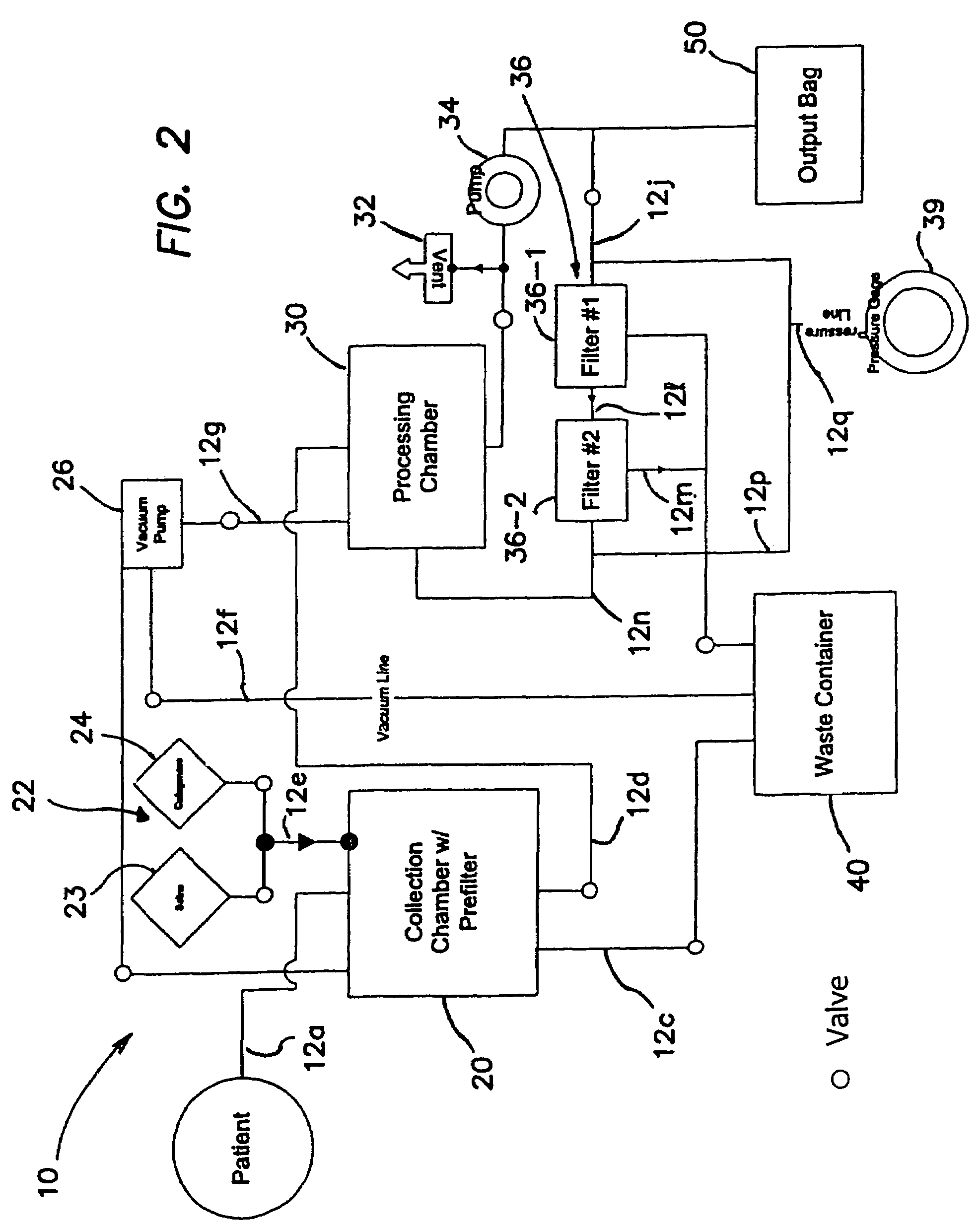
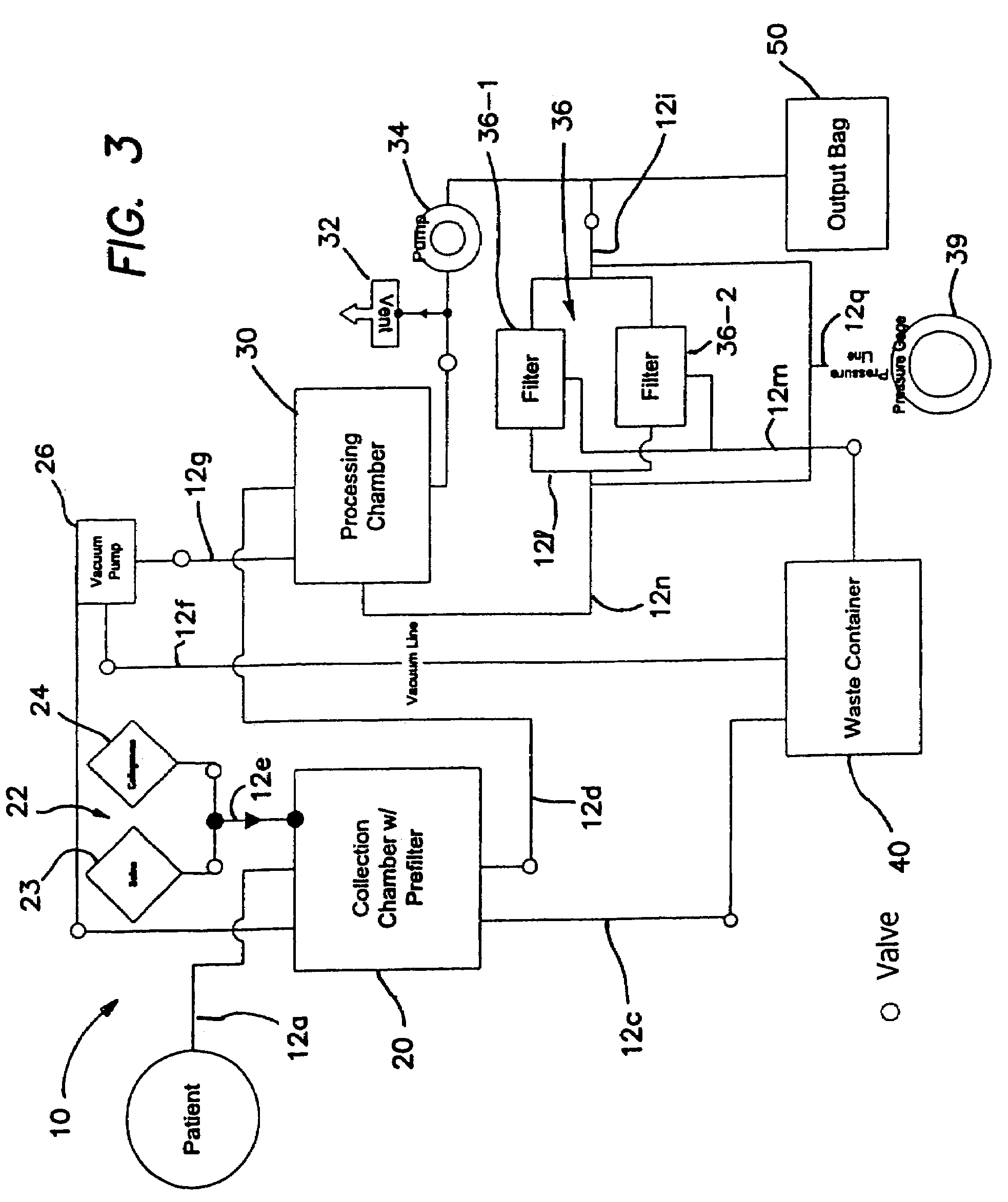
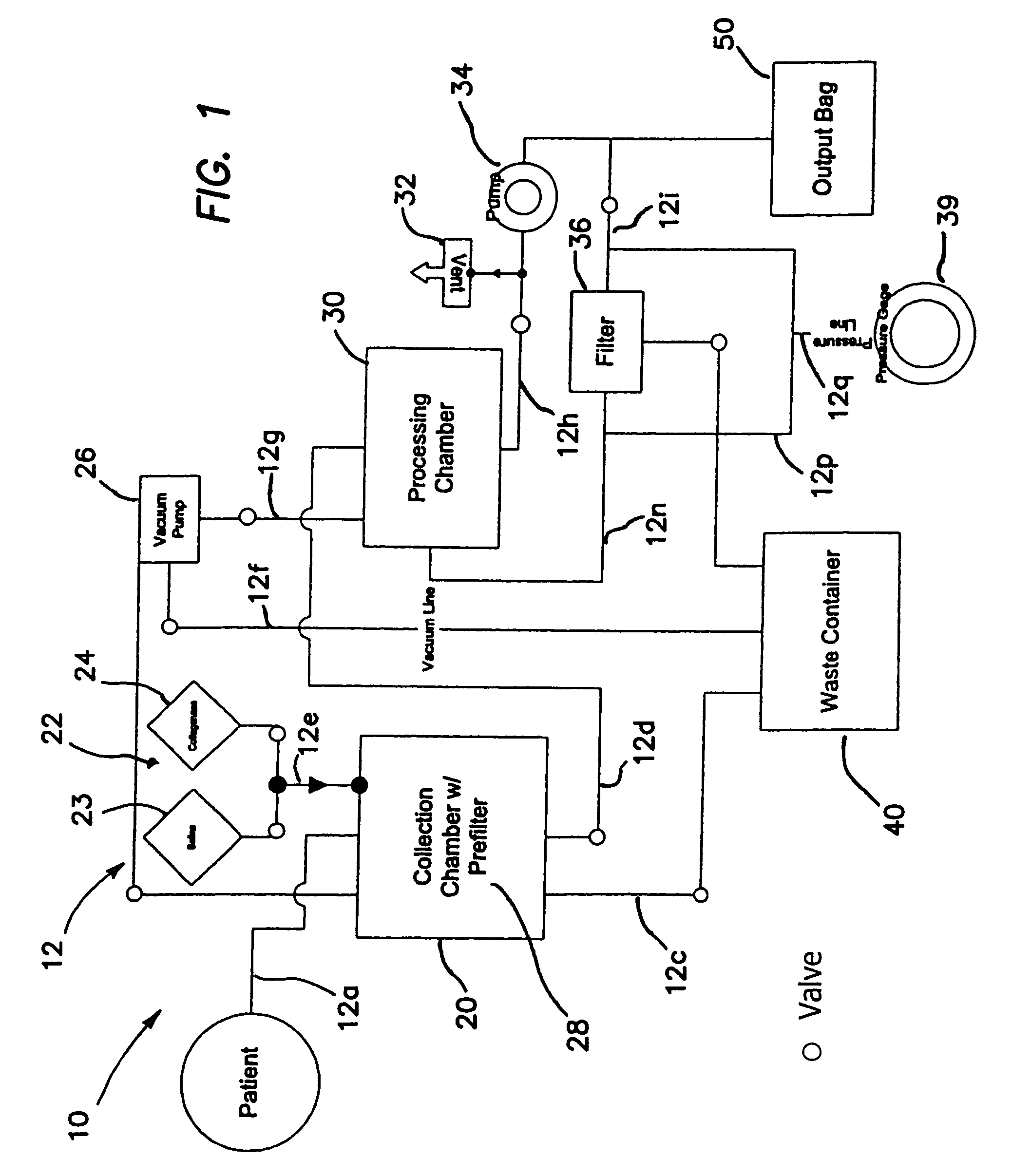
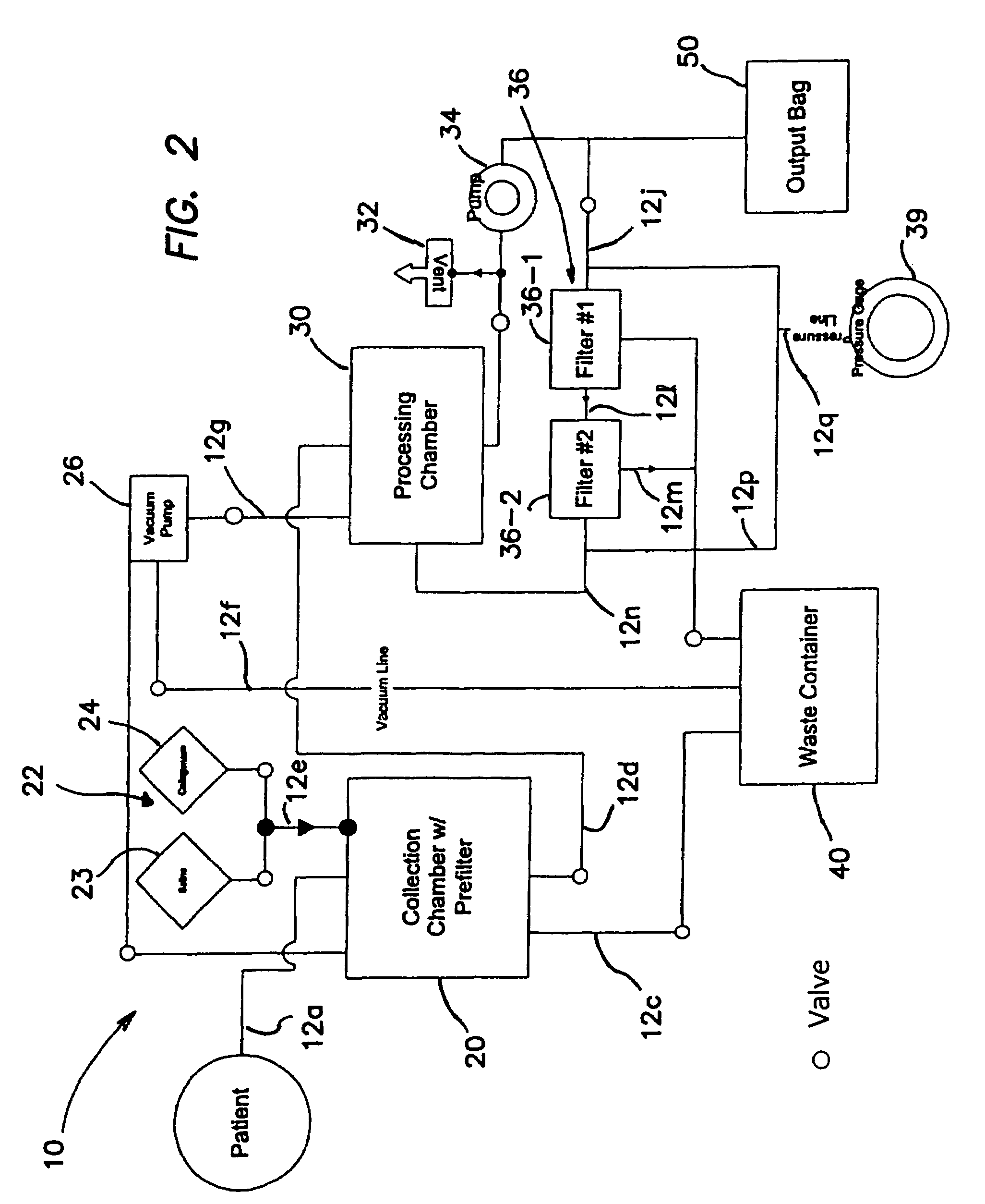
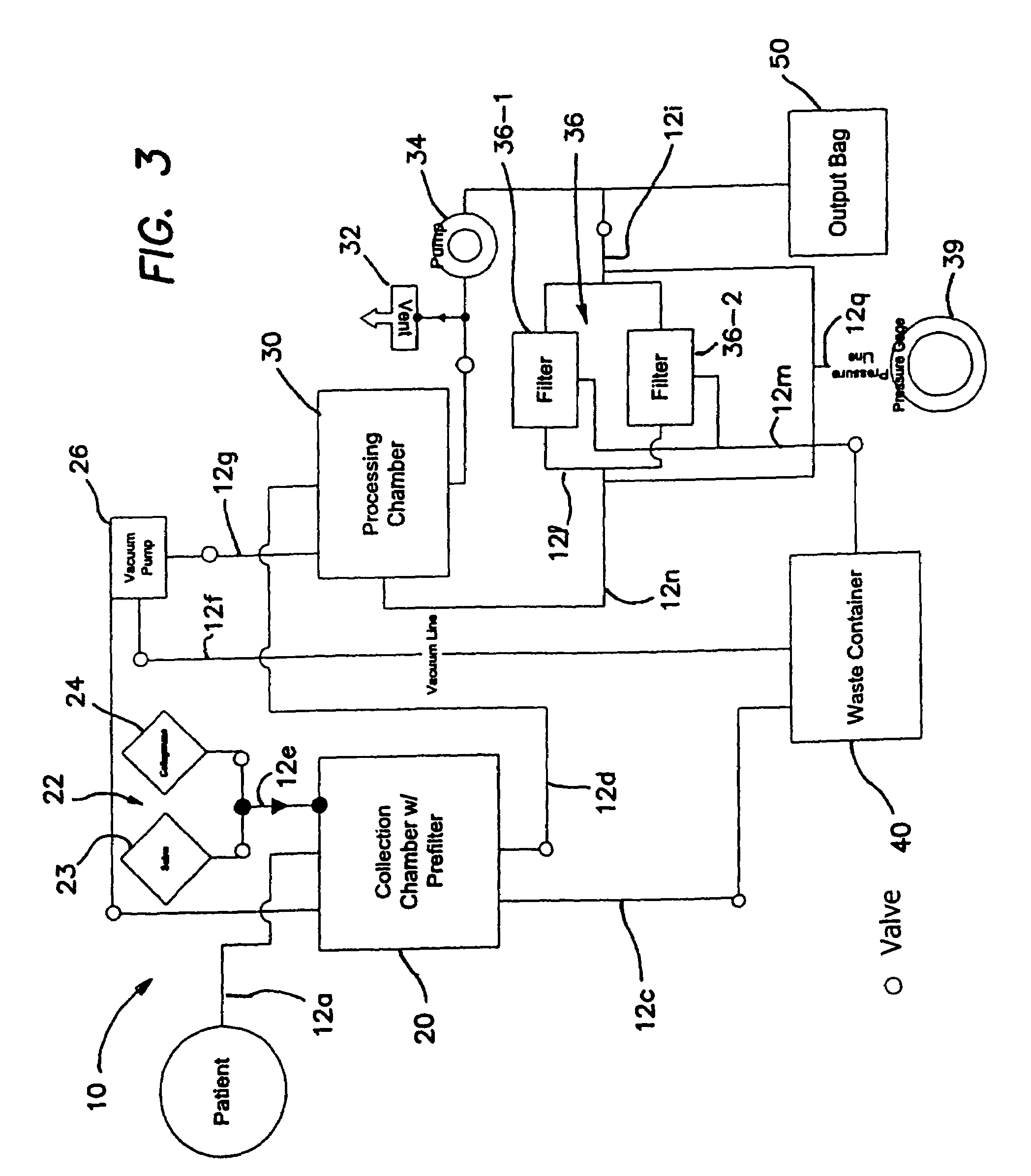
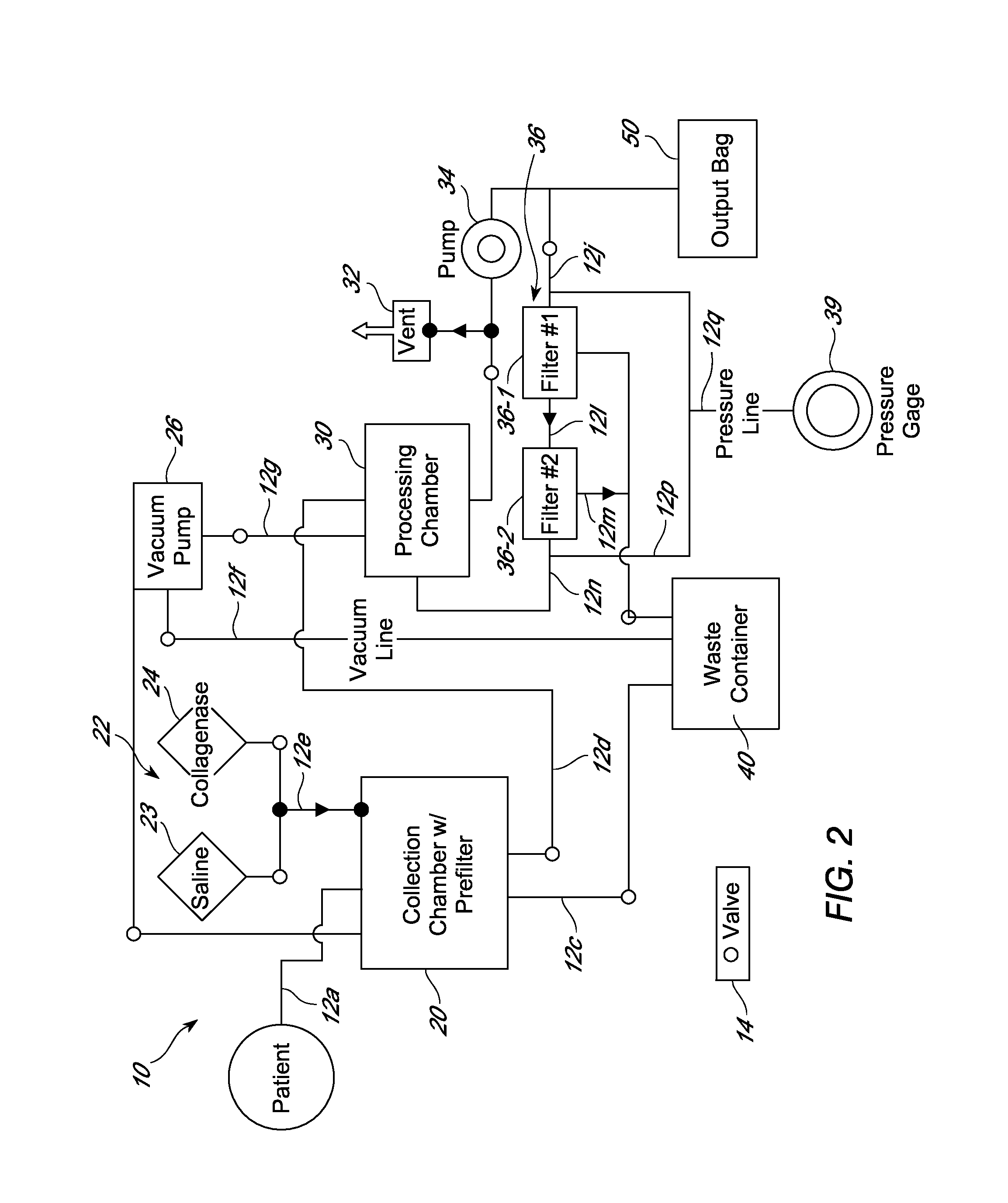
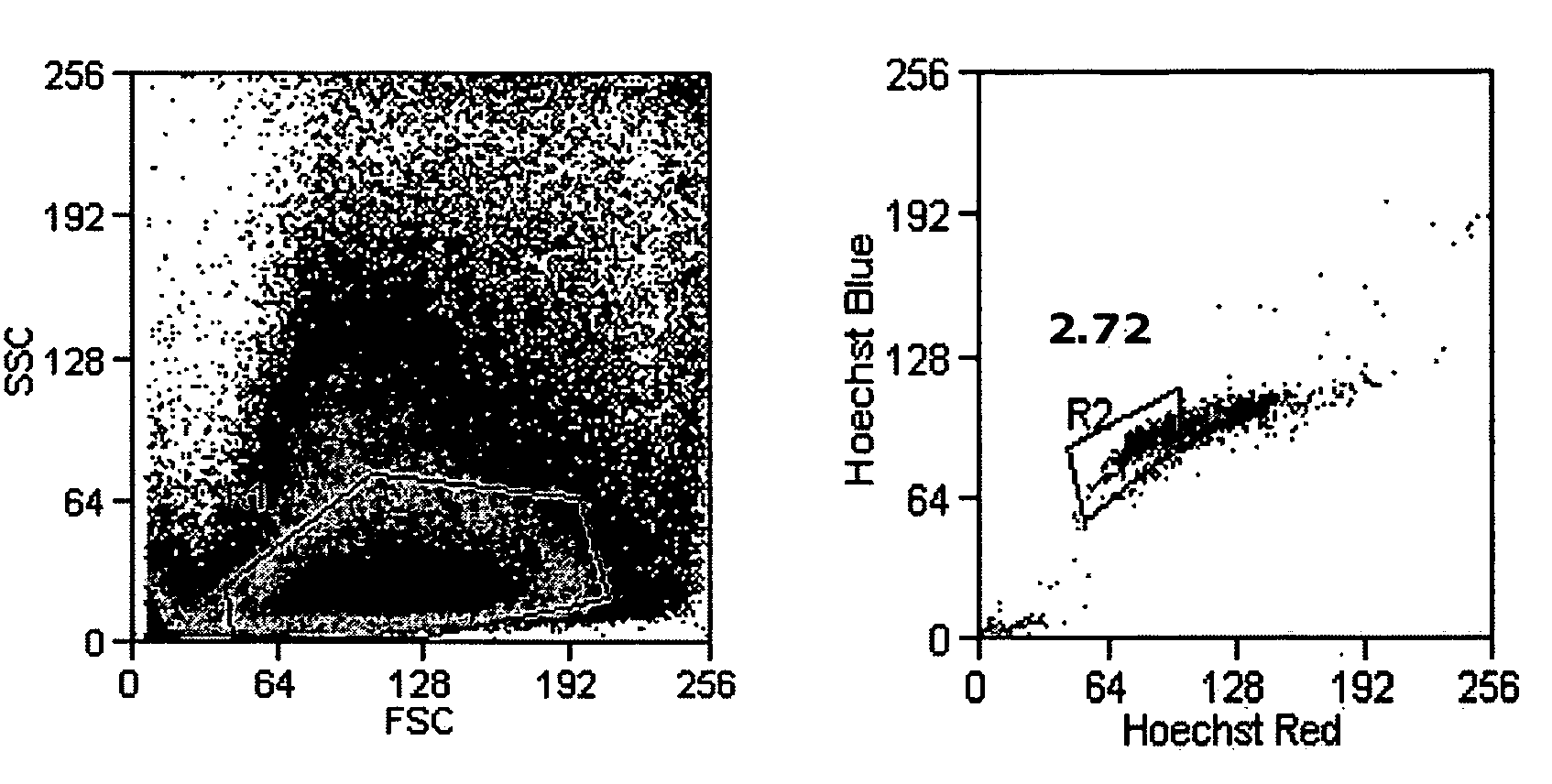
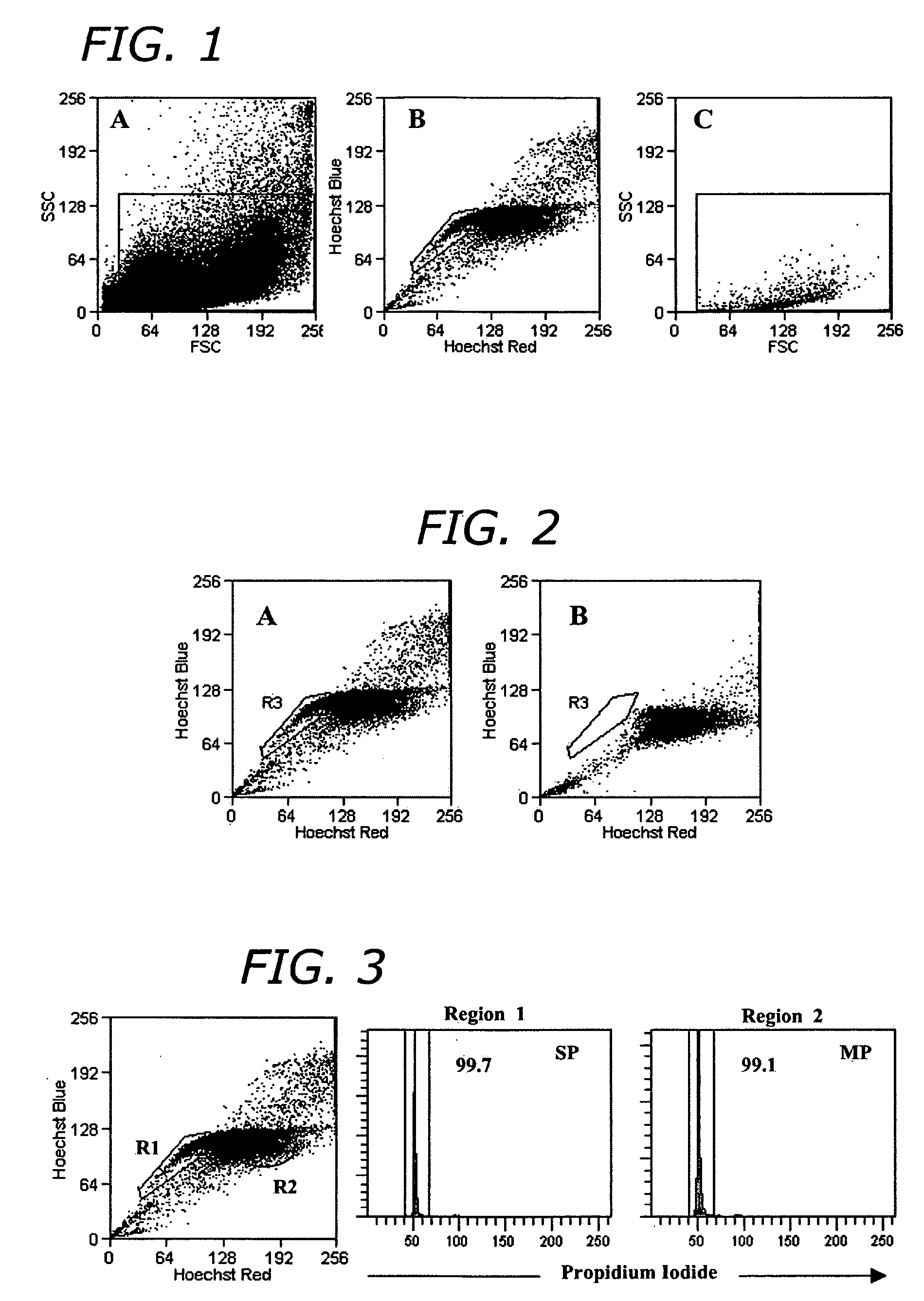
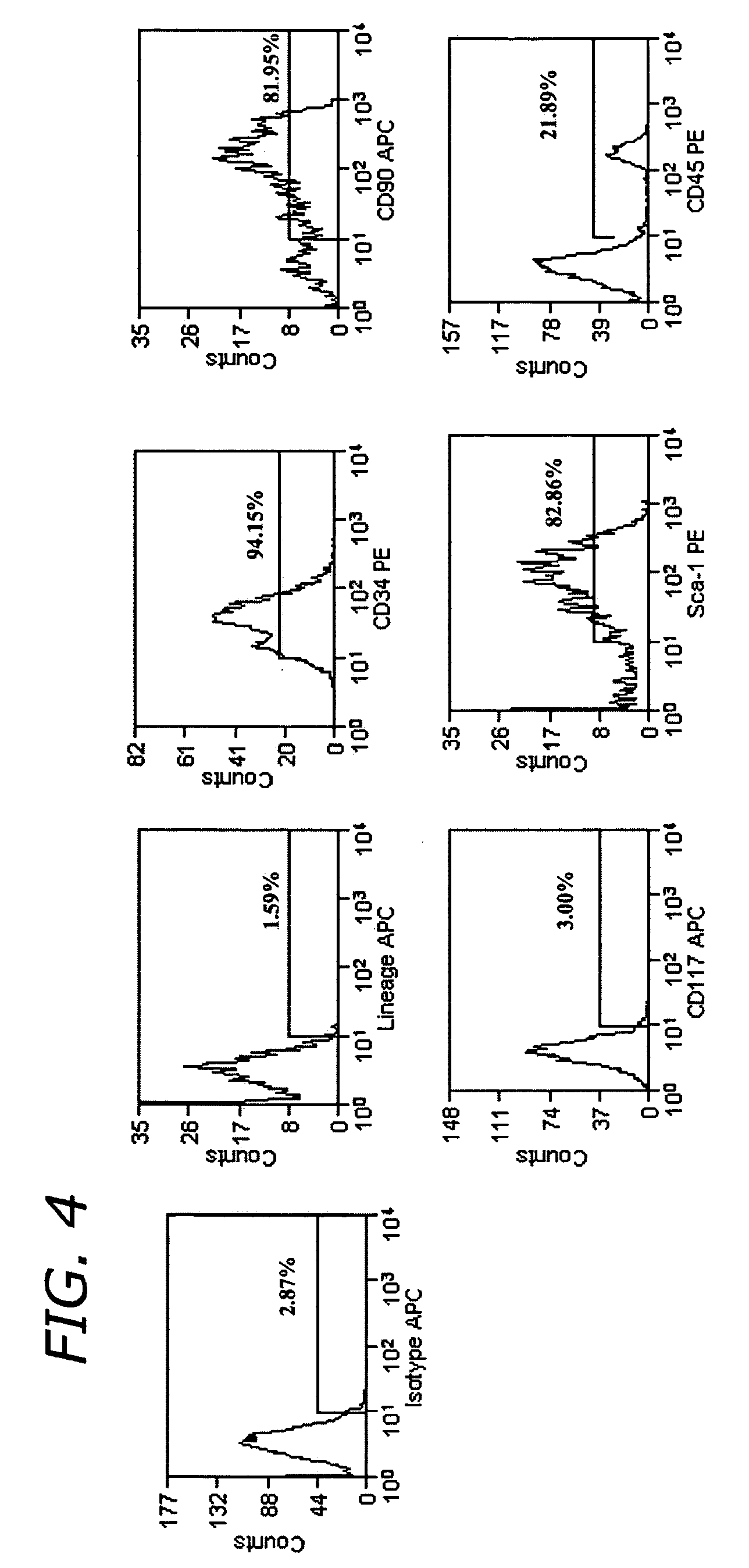
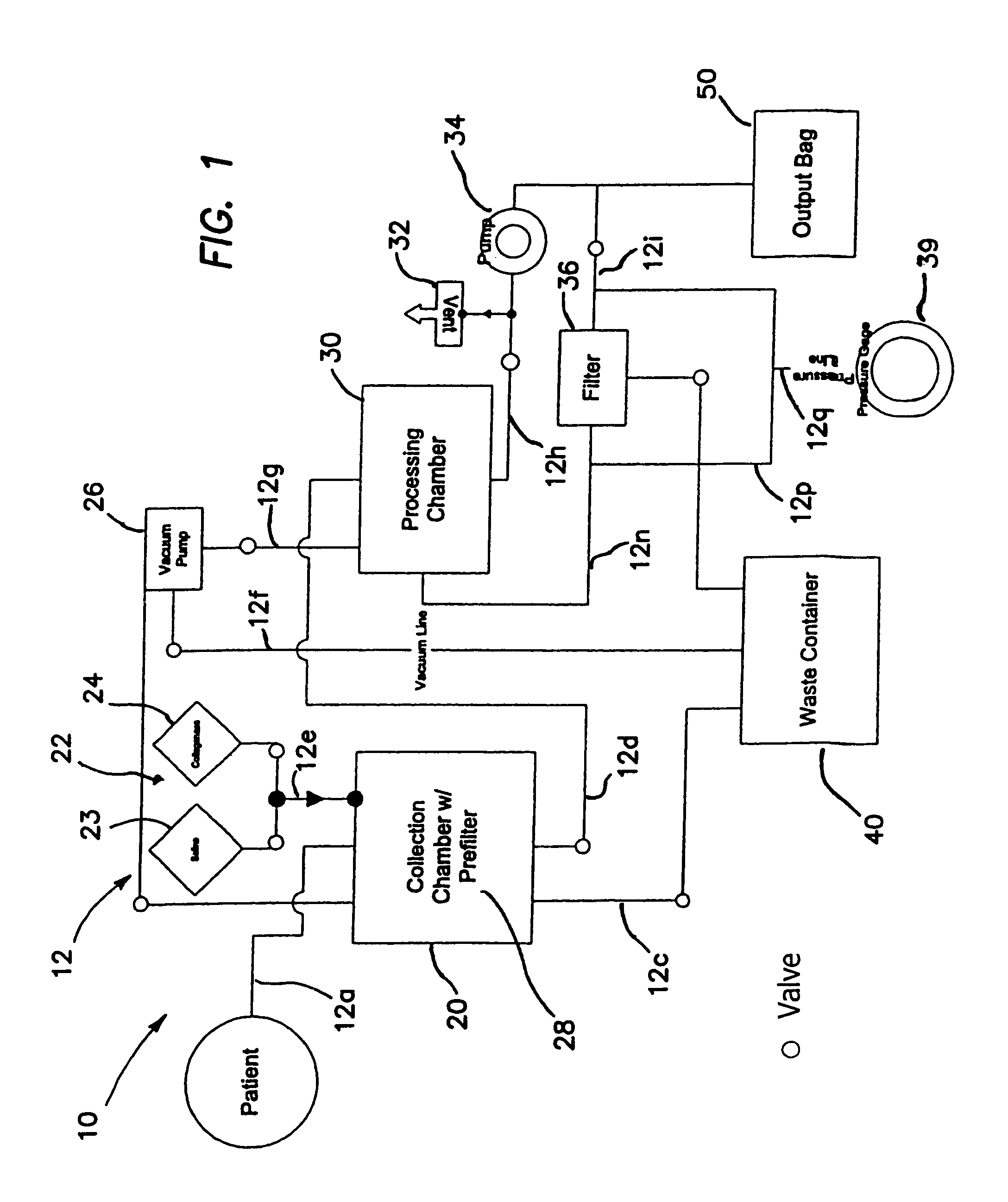
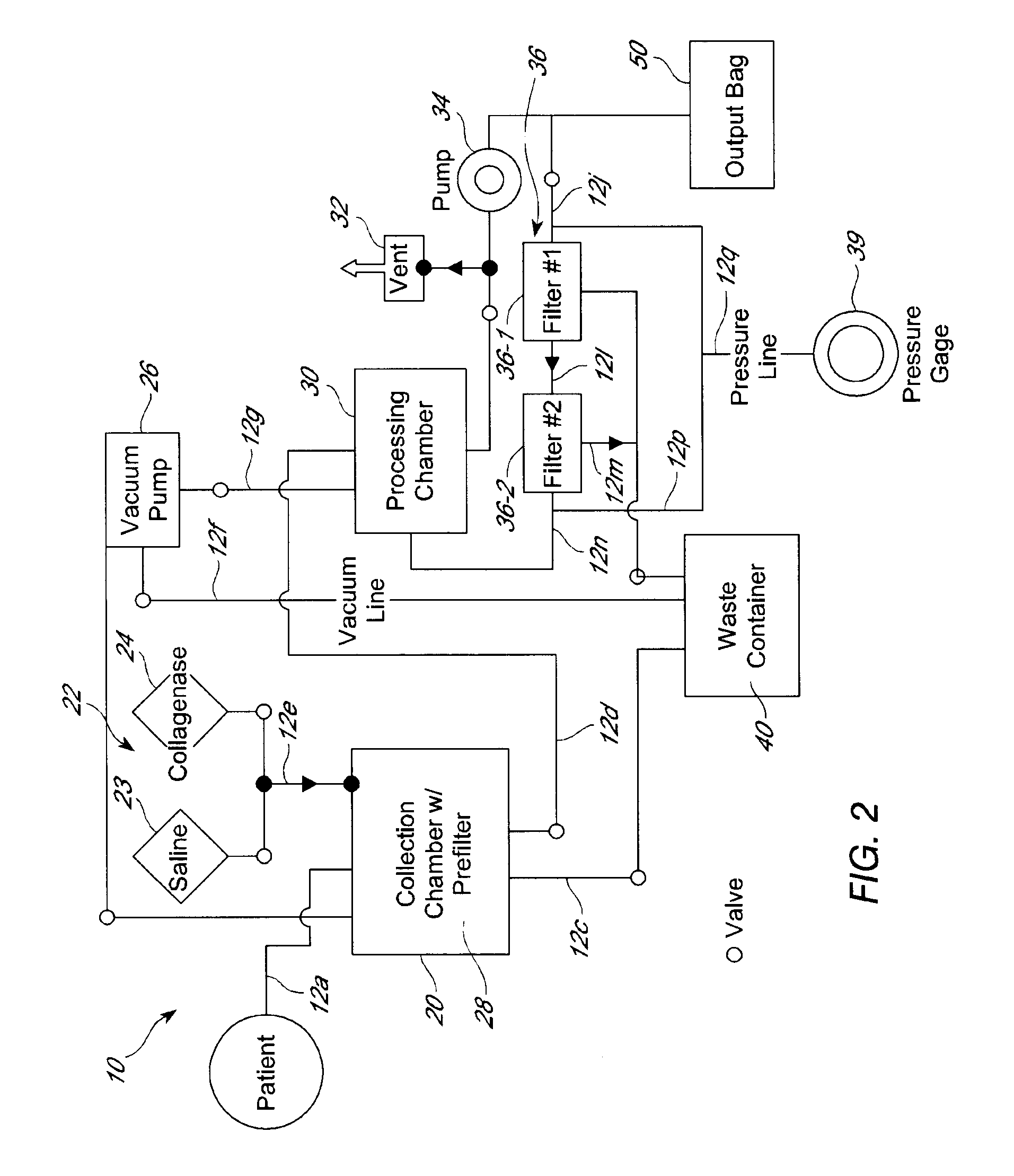
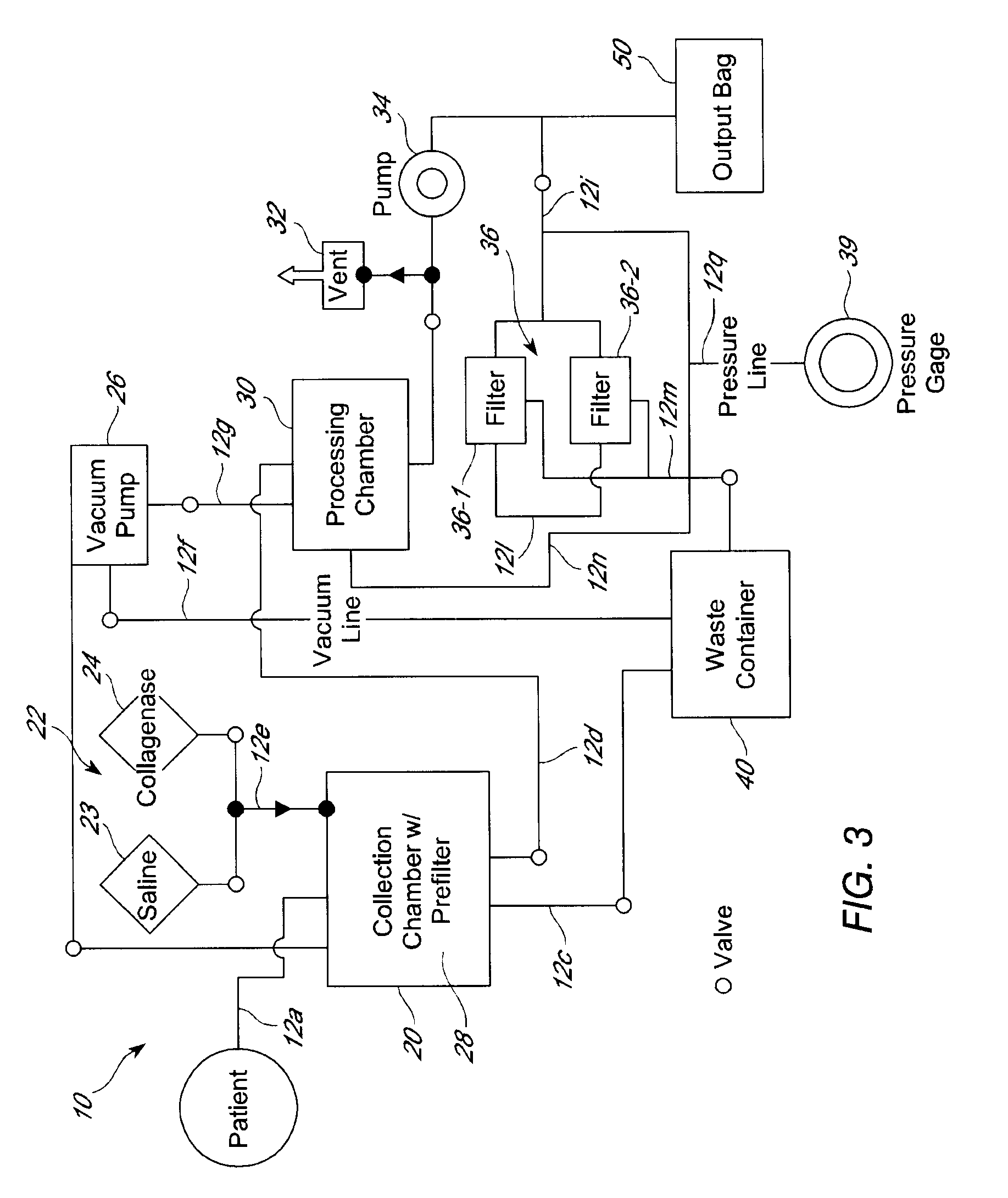
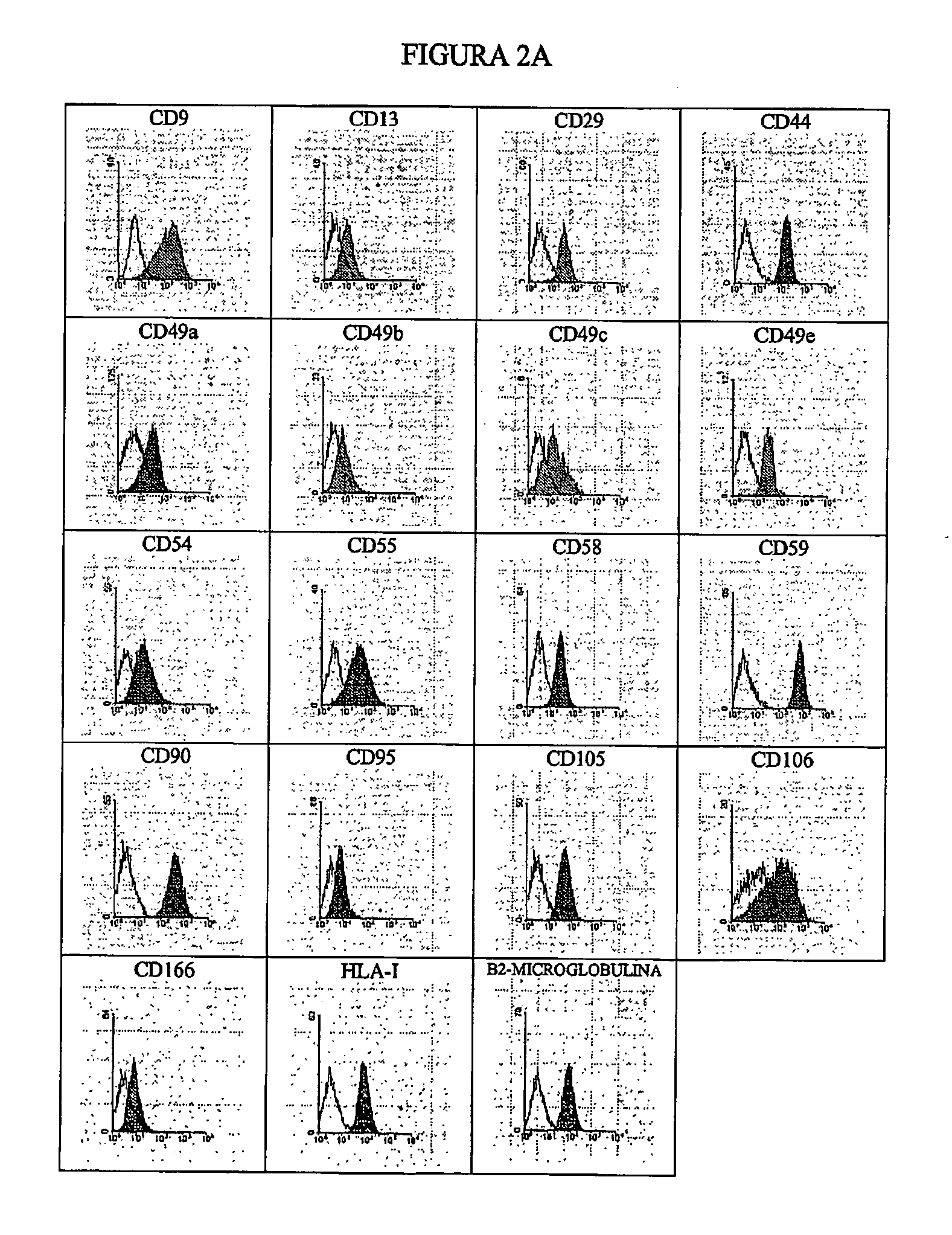
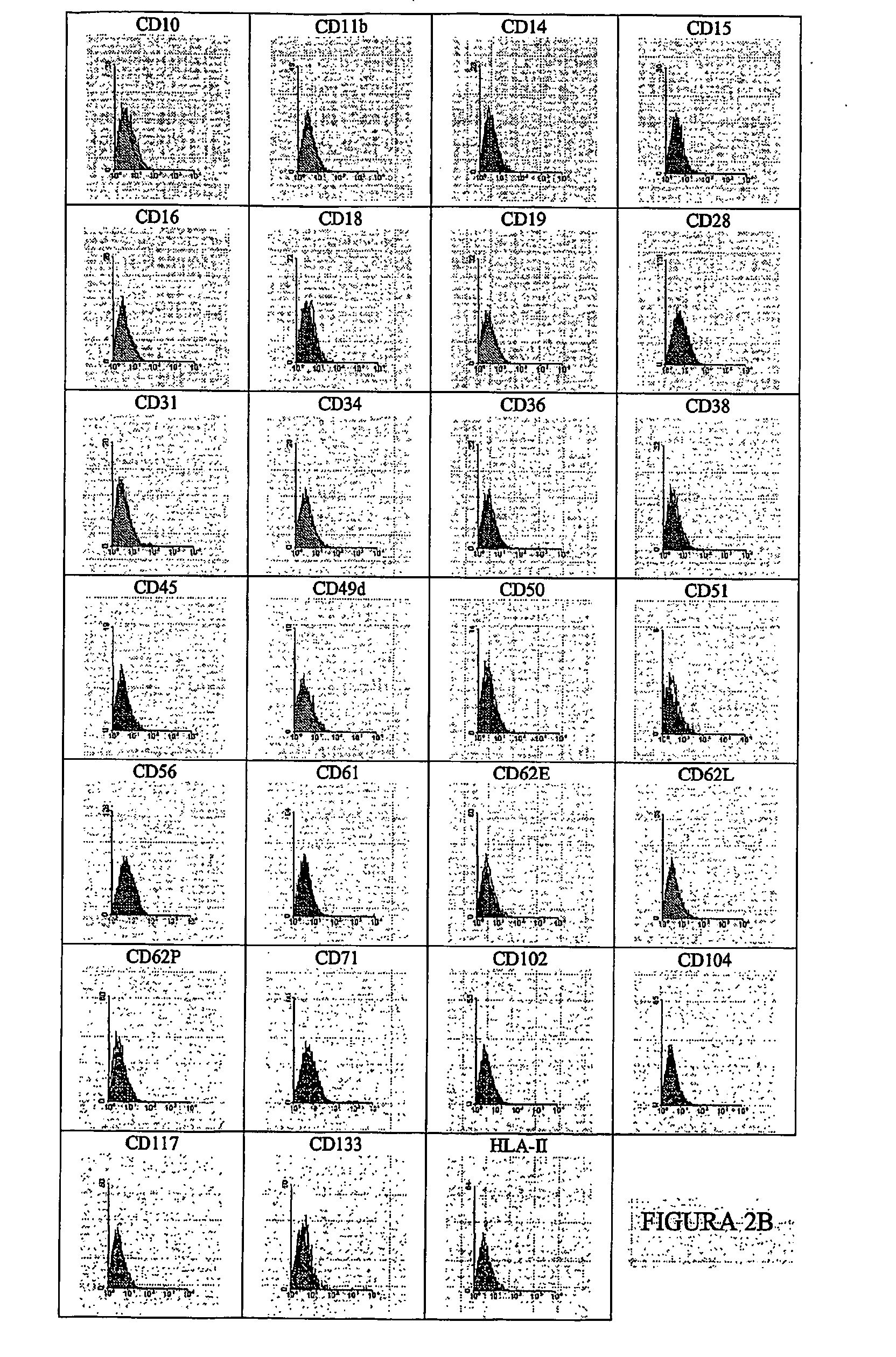
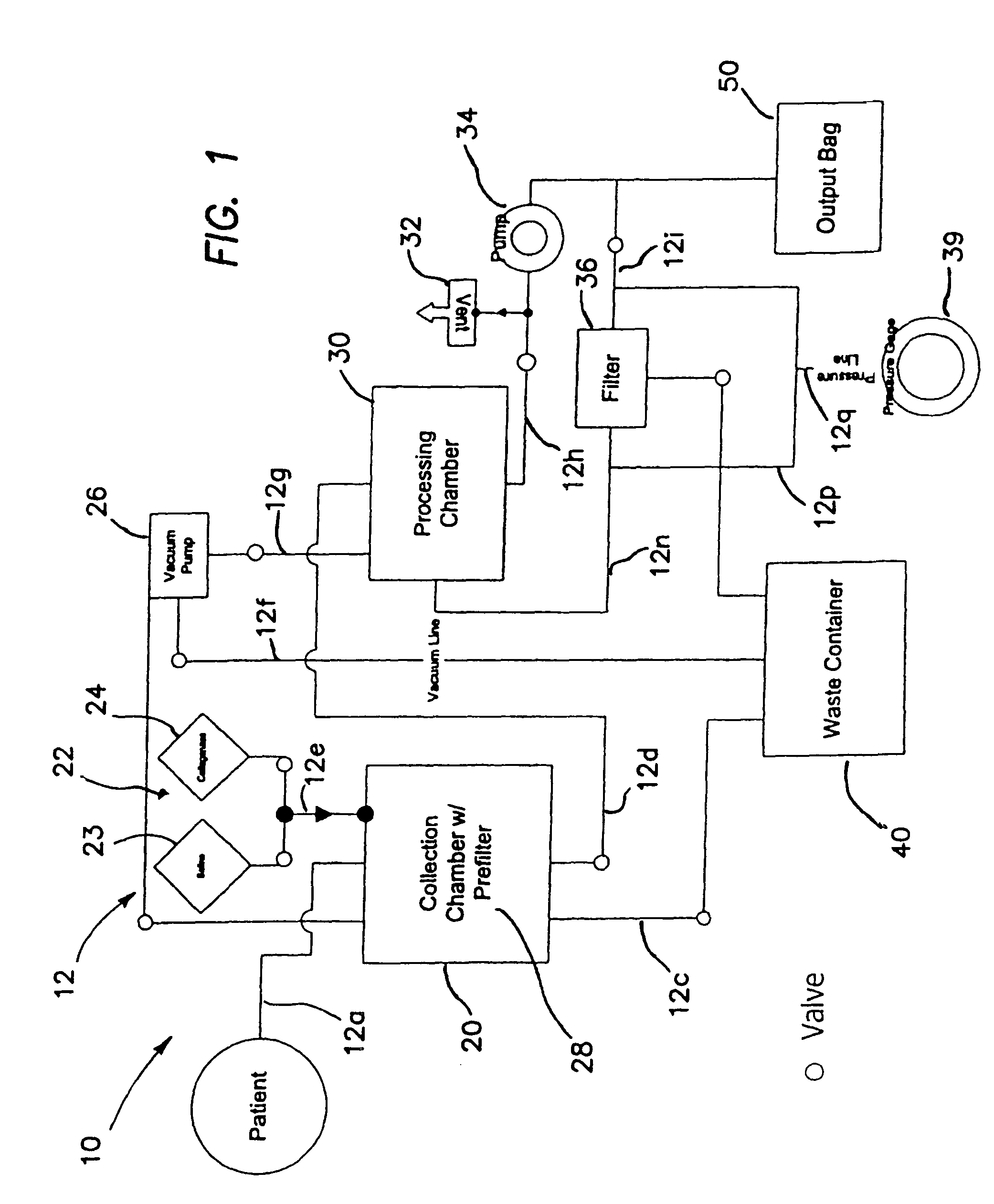
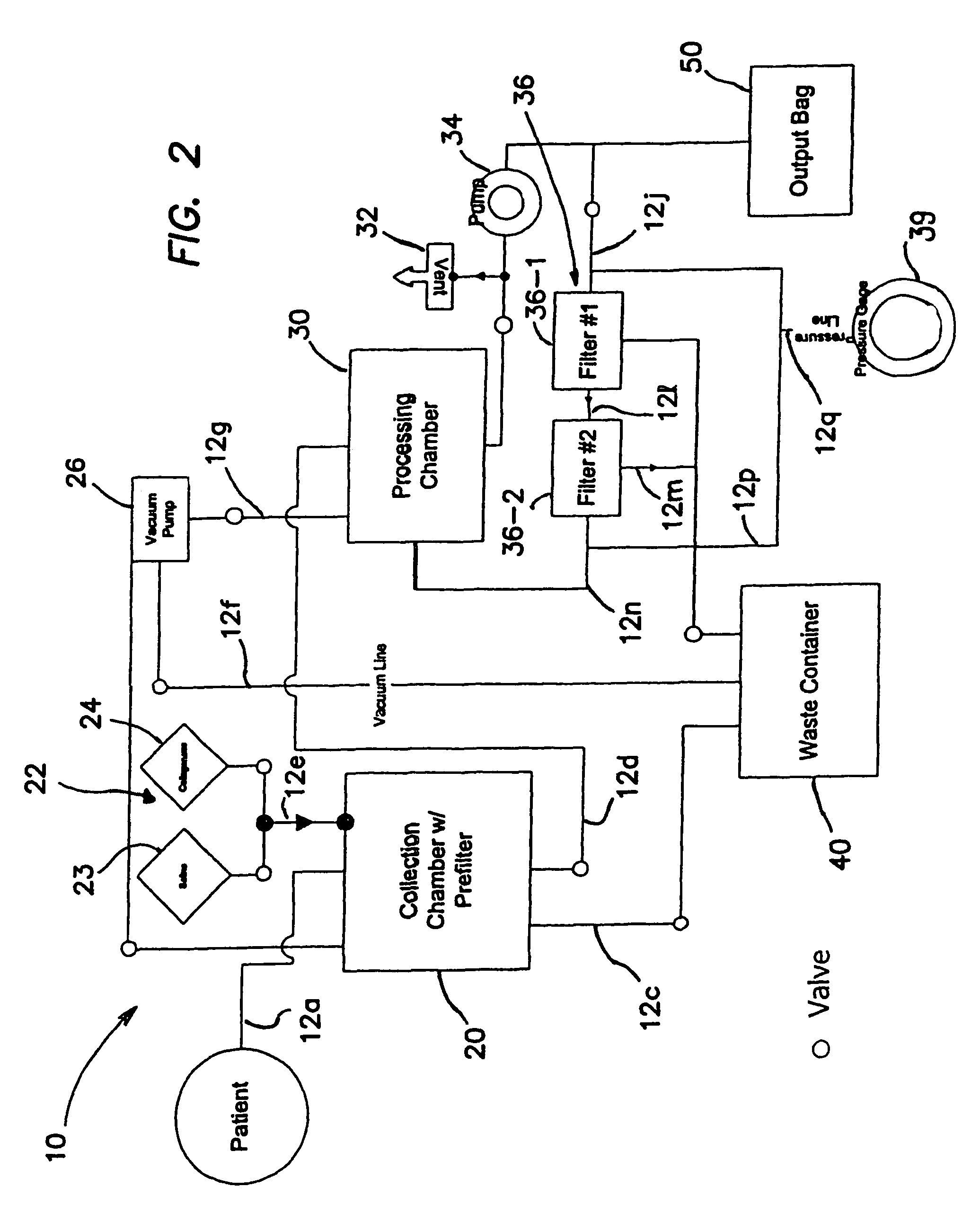
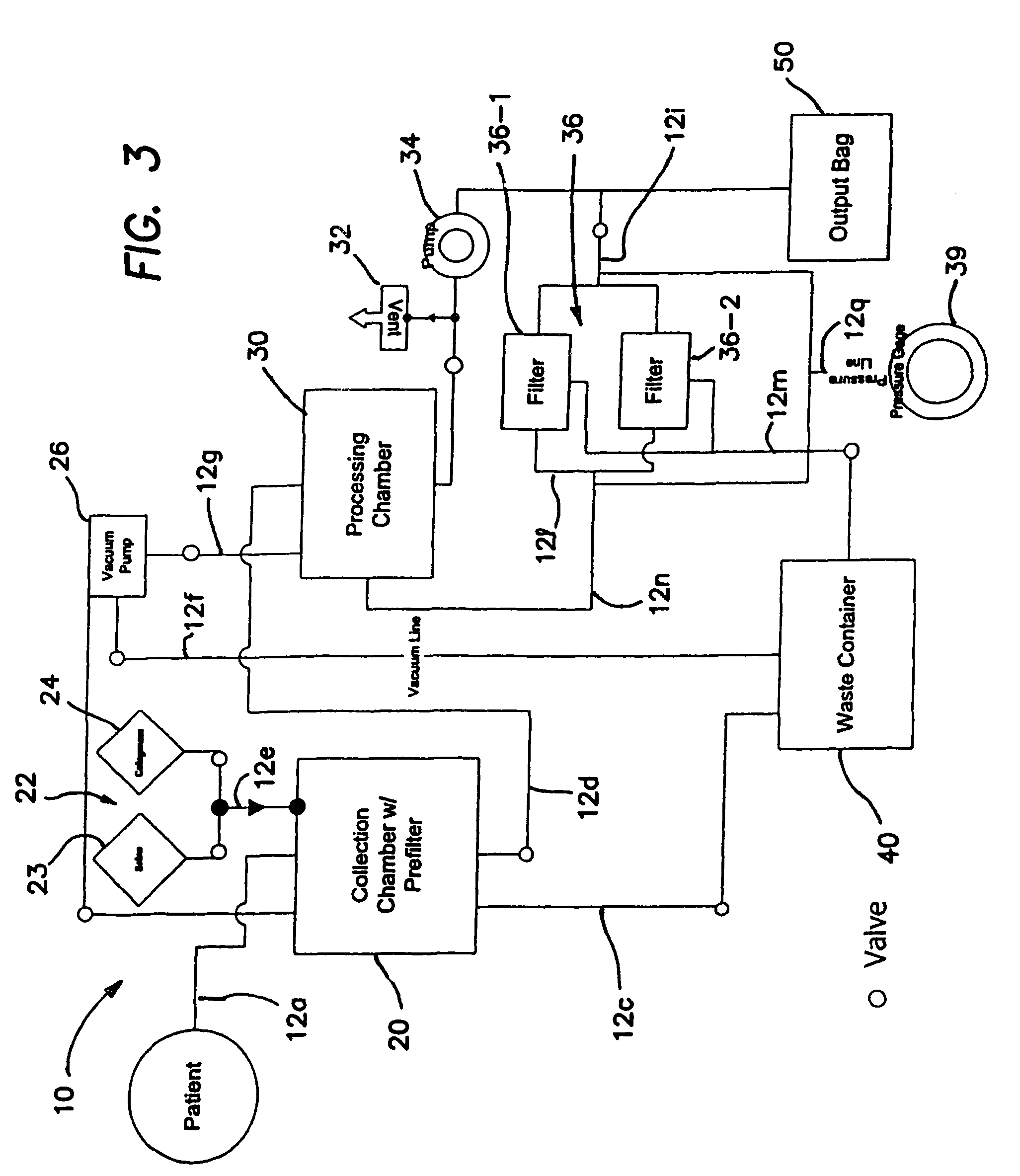
Systems and methods for separating and concentrating adipose derived stem cells from tissue
Systems and methods are described that are used to separate cells from a wide variety of tissues. In particular, automated systems and methods are described that separate regenerative cells, e.g., stem and / or progenitor cells, from adipose tissue. The systems and methods described herein provide rapid and reliable methods of separating and concentrating regenerative cells suitable for re-infusion into a subject.
Owner:LOREM VASCULAR PTE LTD
Method for processing and using adipose-derived stem cells
The present invention relates to a device comprising a cell carrier portion containing regenerative cells, e.g., stem and progenitor cells, and a cell carrier containment portion. The device is useful for the treatment of bone related disorders, including spinal fusion related disorders and long bone or flat bone related defects. The device may be used in conjunction with disclosed automated systems and methods for separating and concentrating regenerative cells.
Owner:LOREM VASCULAR PTE LTD
Use of umbilical cord blood to treat individuals having a disease, disorder or condition
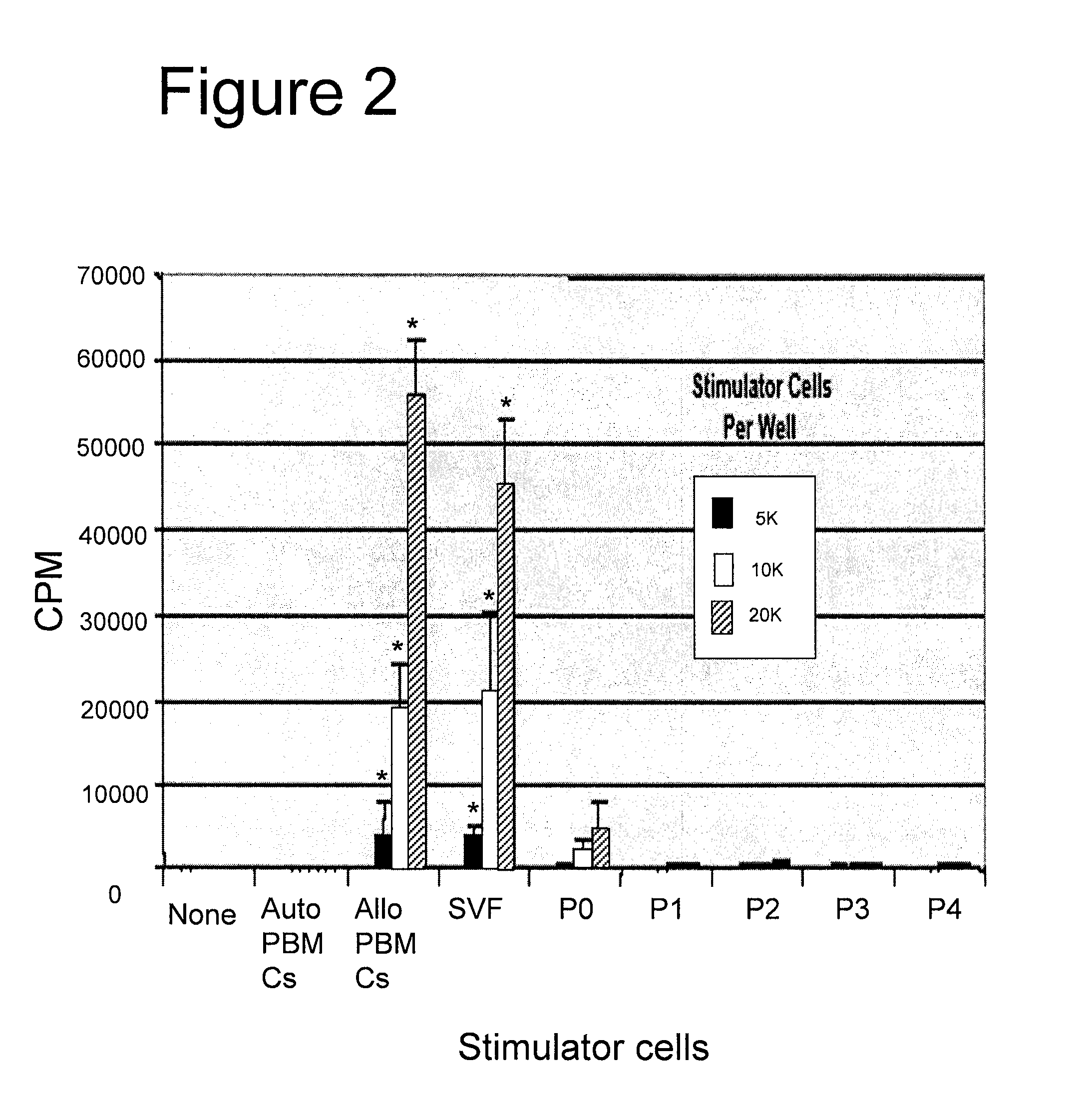
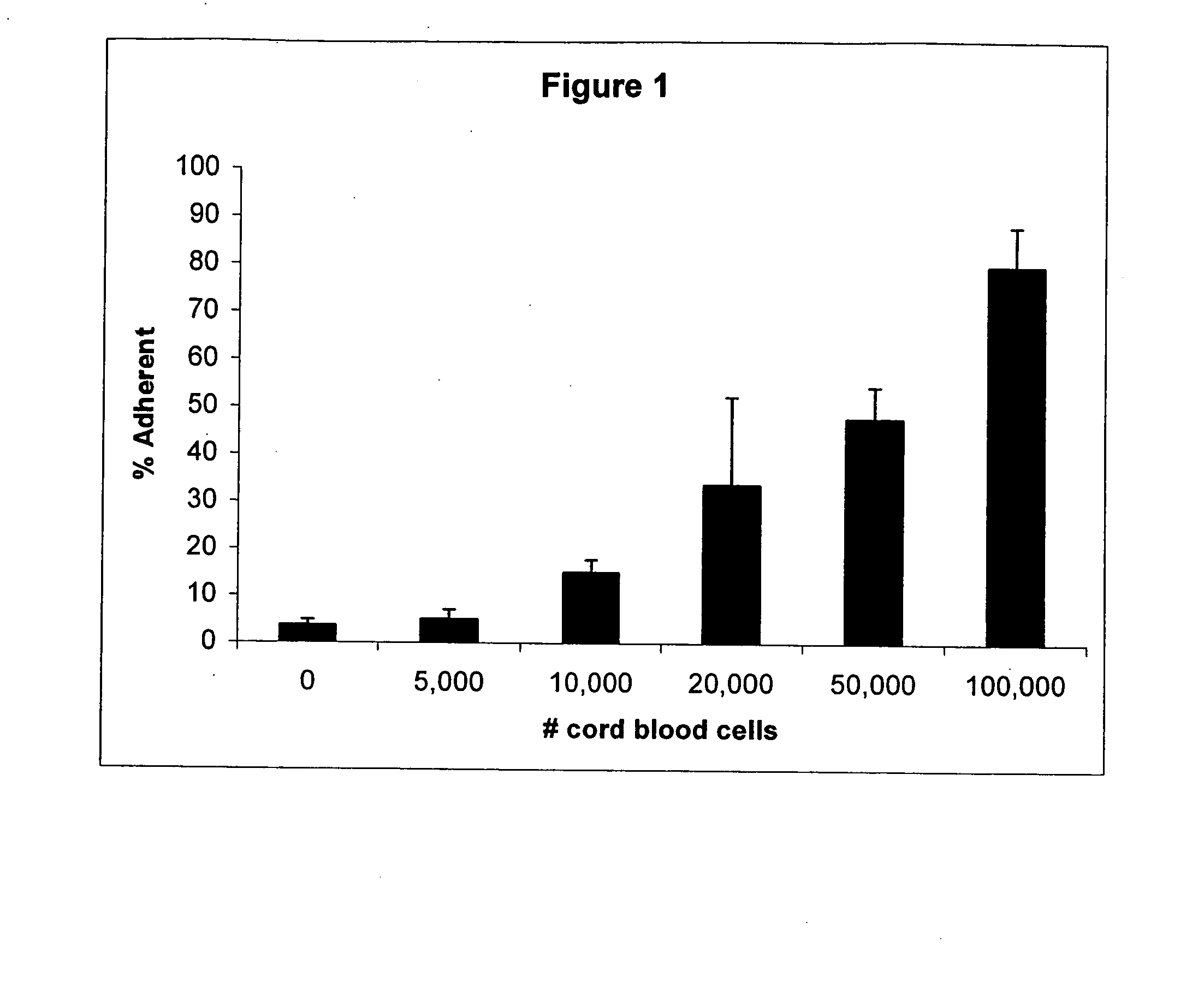
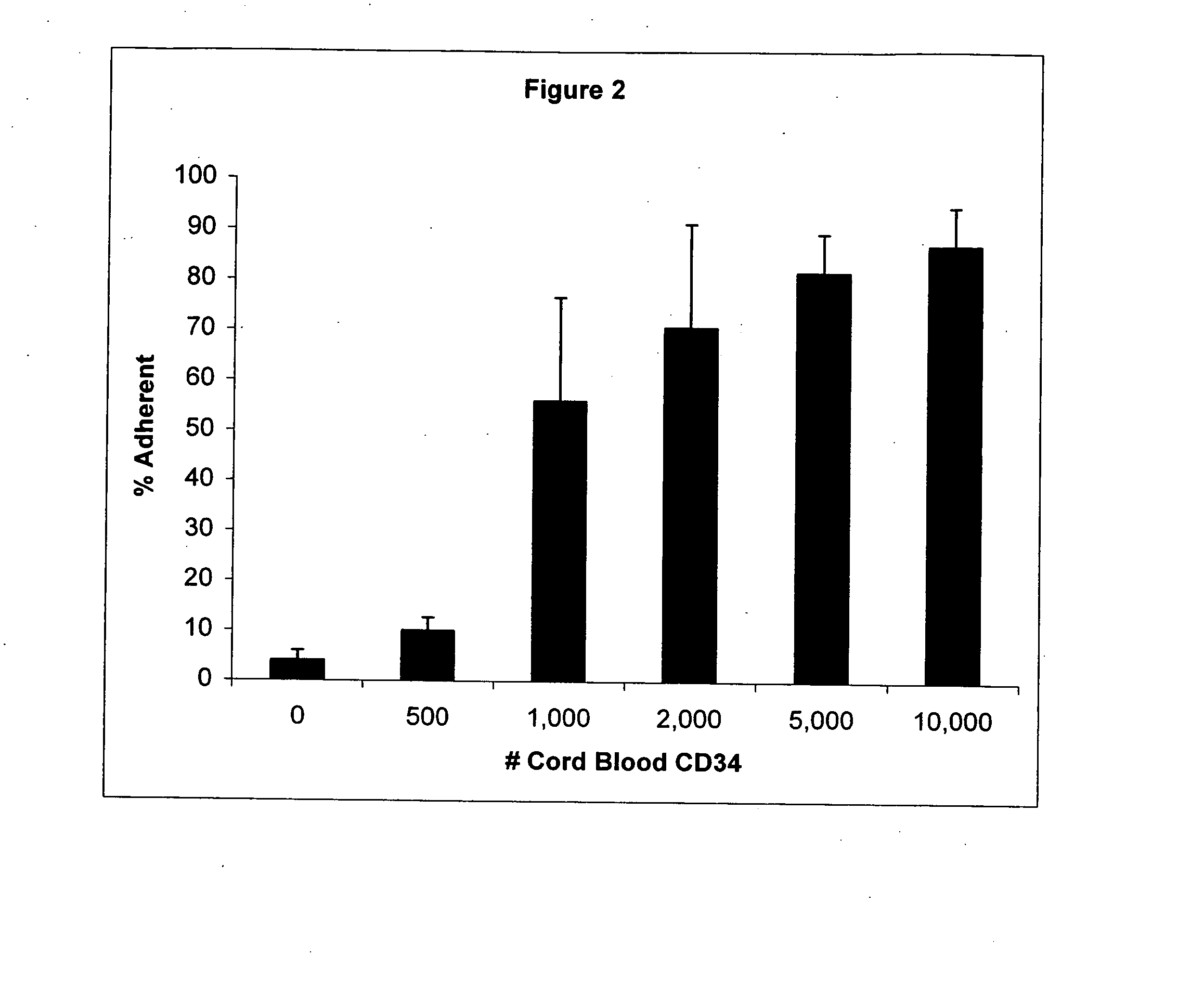
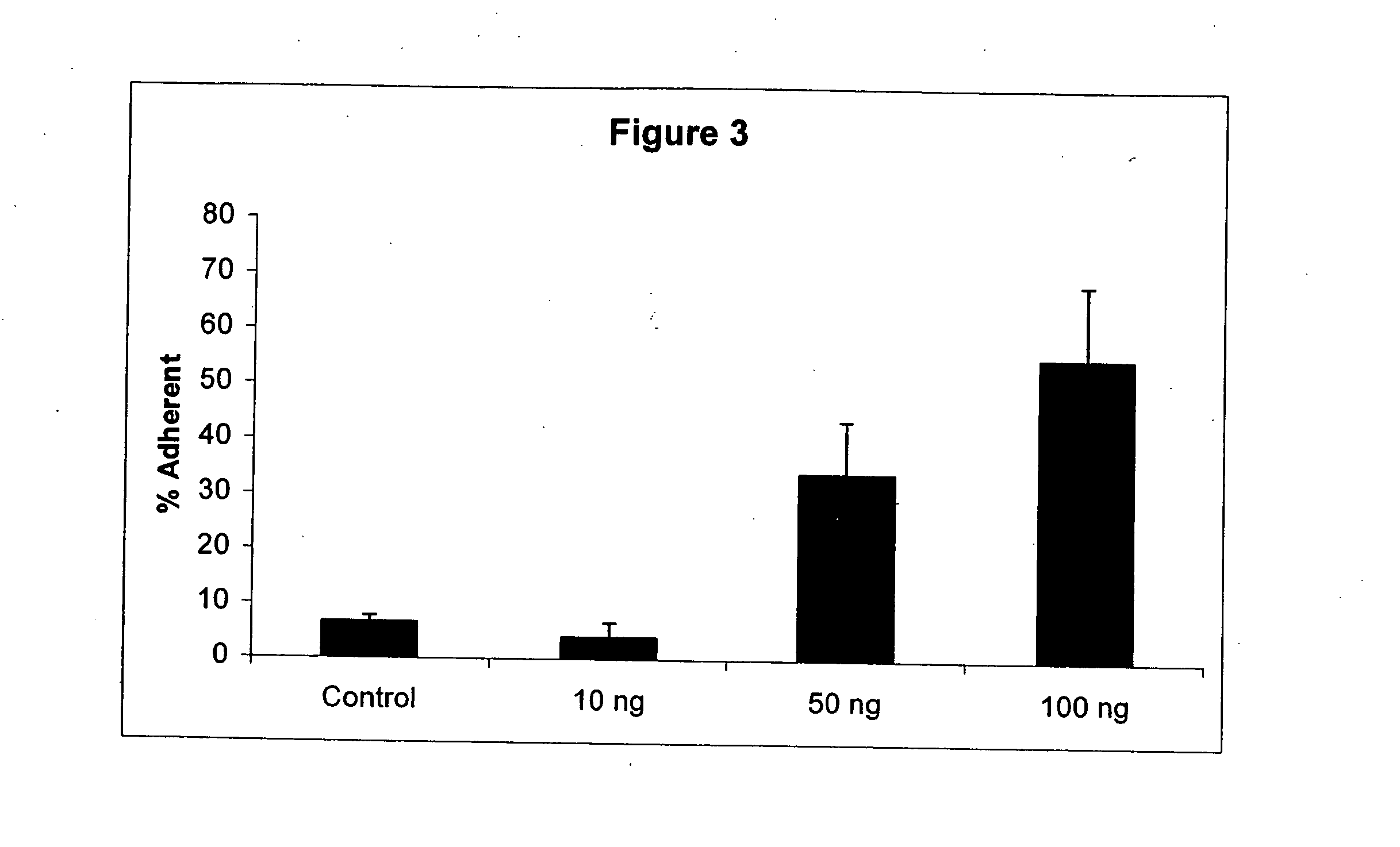
The present invention provides methods of using cord blood and cord blood-derived stem cells in high doses to treat various conditions, diseases and disorders. The high-dose cord blood and cord blood-derived stem cells have a multitude of uses and applications, including but not limited to, therapeutic uses for transplantation and treatment and prevention of disease, and diagnostic and research uses. In particular, the cord blood or cord blood-derived stem cells are delivered in high doses, e.g., at least 3 billion nucleated cells per treatment, where treatment may comprise a single or multiple infusions. The invention also provides for the use of cord blood or cord blood-derived stem cells from multiple donors without the need for HLA typing.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Biocompatible scaffolds and adipose-derived stem cells
The present invention relates to compositions of biocompatible materials and adult stem cells. The present invention also provides methods of alleviating or treating bone defects or soft tissue defects using the compositions.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE +1
Adipose-derived stem cells and lattices
InactiveUS20050282275A1Promote growthFacilitate differentiationGenetic material ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixConnective tissue fiber
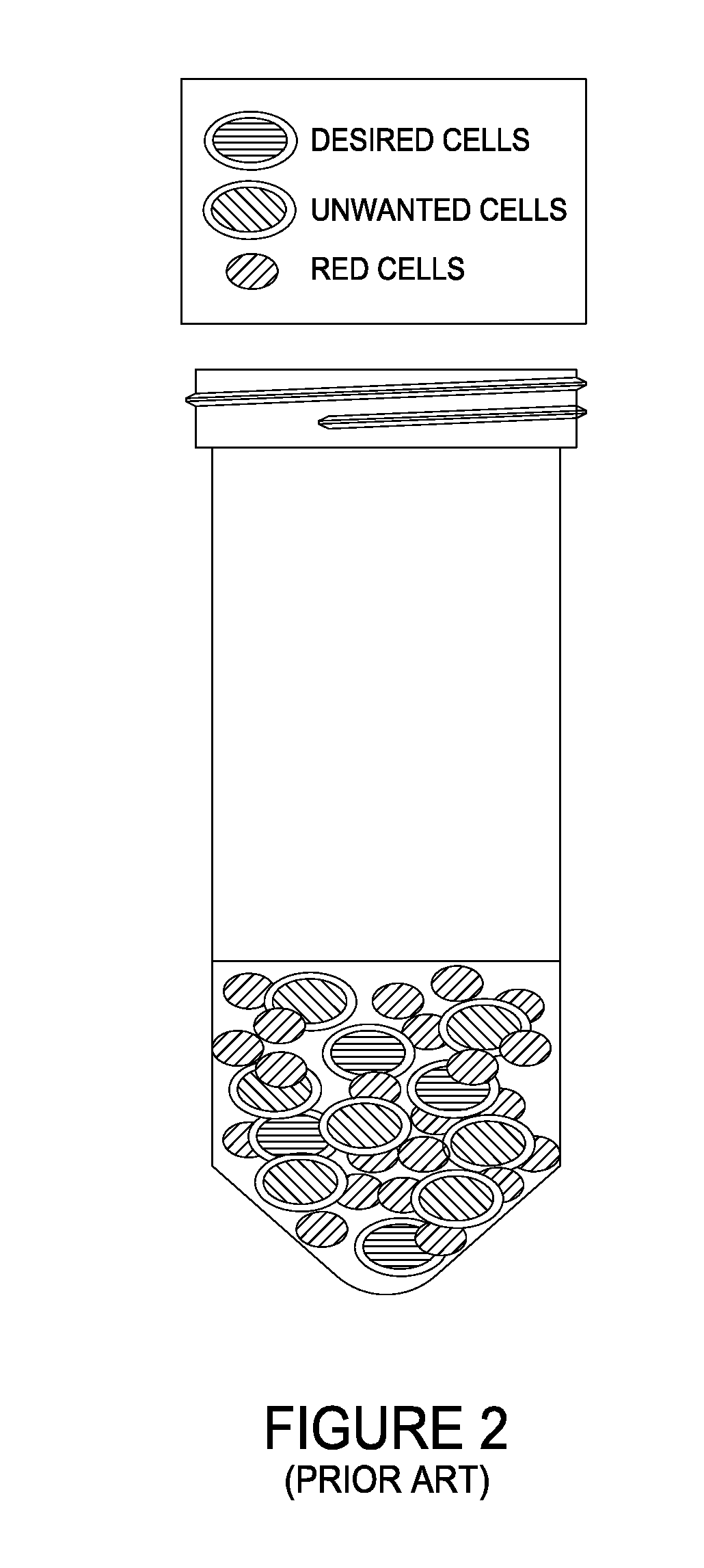
The present invention provides adipose-derived stem cells and lattices. In one aspect, the present invention provides a lipo-derived stem cell substantially free of adipocytes and red blood cells and clonal populations of connective tissue stem cells. The invention also provides a method of isolating stem cells from adipose tissues. The cells can be employed, alone or within biologically-compatible compositions, to generate differentiated tissues and structures, both in vivo and in vitro. Additionally, the cells can be expanded and cultured to produce hormones and to provide conditioned culture media for supporting the growth and expansion of other cell populations. In another aspect, the present invention provides a lipo-derived lattice substantially devoid of cells, which includes extracellular matrix material from adipose tissue. The lattice can be used as a substrate to facilitate the growth and differentiation of cells, whether in vivo or in vitro, into anlagen or even mature tissues or structures.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH +1
Use of umbilical cord blood to treat individuals having a disease, disorder or condition
The present invention provides methods of using cord blood and cord blood-derived stem cells in high doses to treat various conditions, diseases and disorders. The high-dose cord blood and cord blood-derived stem cells have a multitude of uses and applications, including but not limited to, therapeutic uses for transplantation and treatment and prevention of disease, and diagnostic and research uses. In particular, the cord blood or cord blood-derived stem cells are delivered in high doses, e.g., at least 3 billion nucleated cells per treatment, where treatment may comprise a single or multiple infusions. The invention also provides for the use of cord blood or cord blood-derived stem cells from multiple donors without the need for HLA typing.
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Compositions of placentally-derived stem cells for the treatment of cancer
Disclosed are preparations of placentally-derived stem cells and compositions useful for the treatment of cancer. Said stem cells and compositions function through inducing a “guided differentiation” program in cancer cells, thereby reducing malignancy. Further extension of the invention pertains to augmenting ability of administered cells to induce differentiation through the co-administration of known differentiation inducing agents. Within the context of this disclosure, methods for inducing host responses to cancer are also described.
Owner:MEDISTEM
Adipose-derived stem cells and lattices
InactiveUS7470537B2Genetic material ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
The present invention provides adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs), adipose-derived stem cell-enriched fractions (ADSC-EF) and adipose-derived lattices, alone and combined with the ADSCs of the invention. In one aspect, the present invention provides an ADSC substantially free of adipocytes and red blood cells and clonal populations of connective tissue stem cells. The ADSCs can be employed, alone or within biologically-compatible compositions, to generate differentiated tissues and structures, both in vivo and in vitro. Additionally, the ADSCs can be expanded and cultured to produce molecules such as hormones, and to provide conditioned culture media for supporting the growth and expansion of other cell populations. In another aspect, the present invention provides an adipose-derived lattice substantially devoid of cells, which includes extracellular matrix material from adipose tissue. The lattice can be used as a substrate to facilitate the growth and differentiation of cells, whether in vivo or in vitro, into anlagen or even mature tissues or structures.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Adipose-derived stem cells and lattices
InactiveUS20050153441A1Promote growthFacilitate differentiationGenetic material ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
The present invention provides adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs), adipose-derived stem cell-enriched fractions (ADSC-EF) and adipose-derived lattices, alone and combined with the ADSCs of the invention. In one aspect, the present invention provides an ADSC substantially free of adipocytes and red blood cells and clonal populations of connective tissue stem cells. The ADSCs can be employed, alone or within biologically-compatible compositions, to generate differentiated tissues and structures, both in vivo and in vitro. Additionally, the ADSCs can be expanded and cultured to produce molecules such as hormones, and to provide conditioned culture media for supporting the growth and expansion of other cell populations. In another aspect, the present invention provides a adipose-derived lattice substantially devoid of cells, which includes extracellular matrix material from adipose tissue. The lattice can be used as a substrate to facilitate the growth and differentiation of cells, whether in vivo or in vitro, into anlagen or even mature tissues or structures.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Methods and compositions for smooth muscle reconstruction
This invention also provides a purified or isolated population of ADSCs that can differentiate into a cell of the leiomyogenic lineage, e.g., smooth muscle or skeletal muscle. In yet another aspect, the population additionally can be differentiated into a lineage selected from the group consisting of osteogenic, adipogenic, chondrogenic, myogenic and neuronal. This invention further provides a composition comprising a substantially homogeneous expanded population of smooth muscle cells. This invention provides a composition comprising a substantially homogeneous expanded population of skeletal muscle cells. Also provided herein is an isolated composition comprising a purified adipose-derived stem cell (ADSC) or progeny of said ADSC and an effective amount of laminin or heparin, effective to induce leiomyogenic differentiation. Diagnositic and therapeutic uses for these compositions are provided herein.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods for ex-vivo expanding stem/progenitor cells
InactiveUS20060205071A1Increase productionCulture processArtificial cell constructsProgenitorBone marrow transplantations
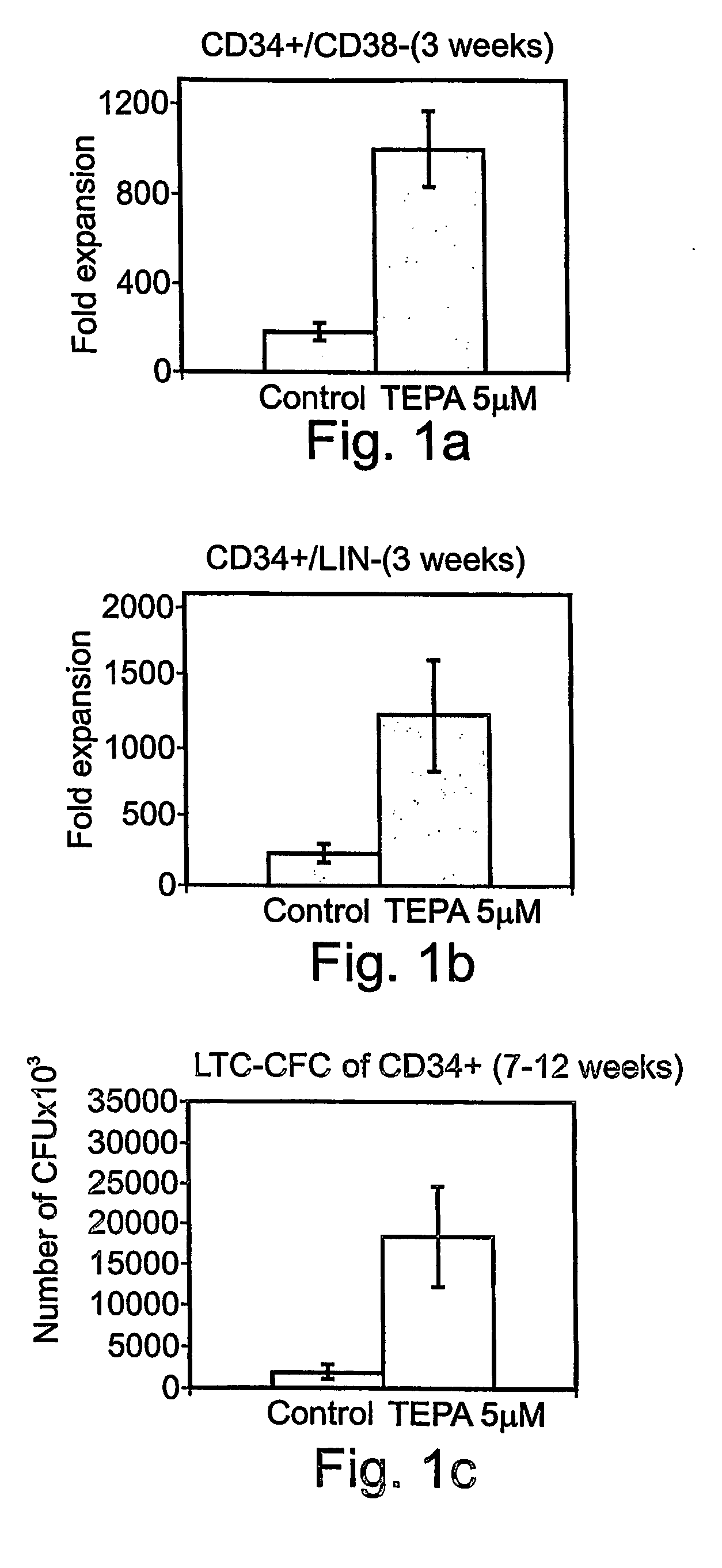
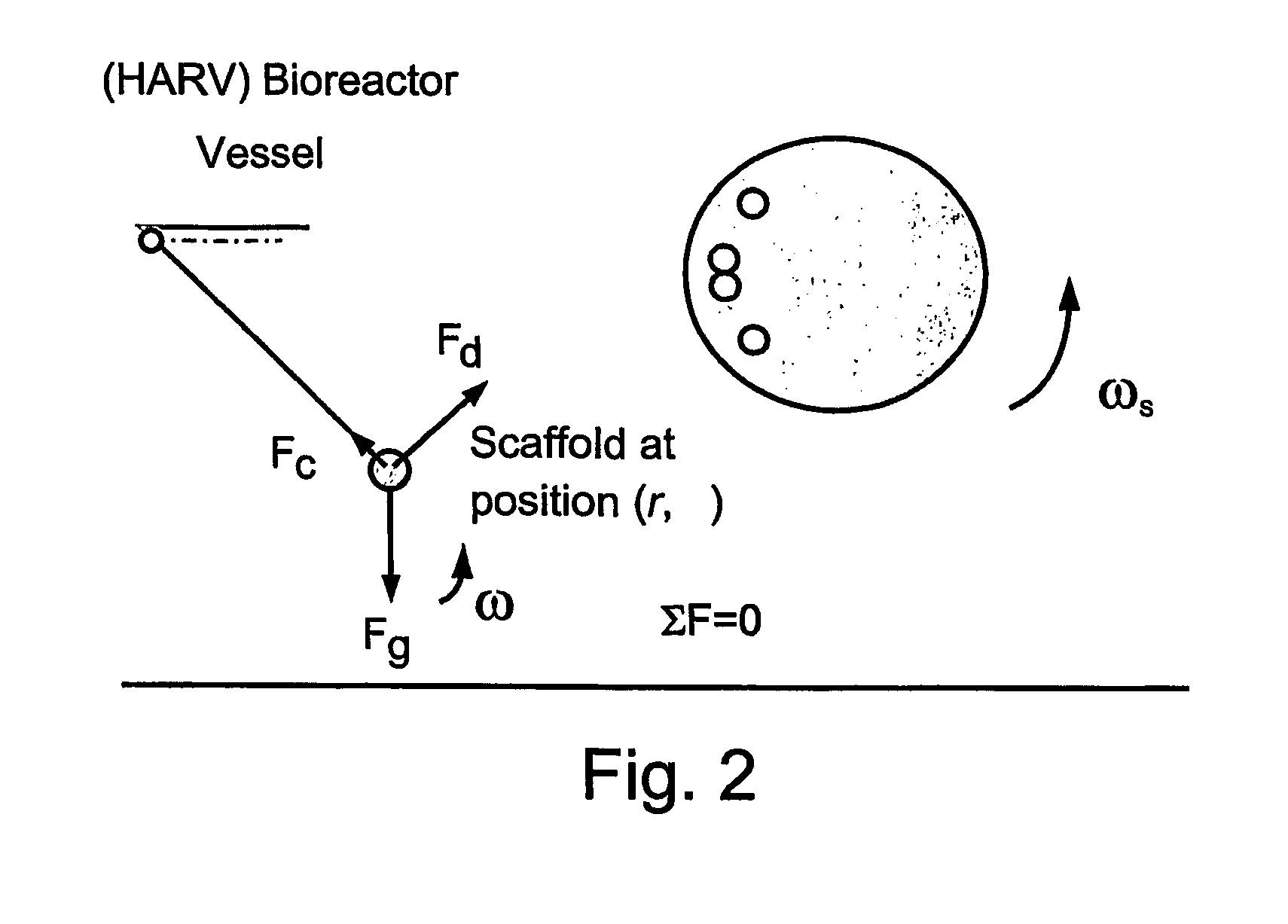
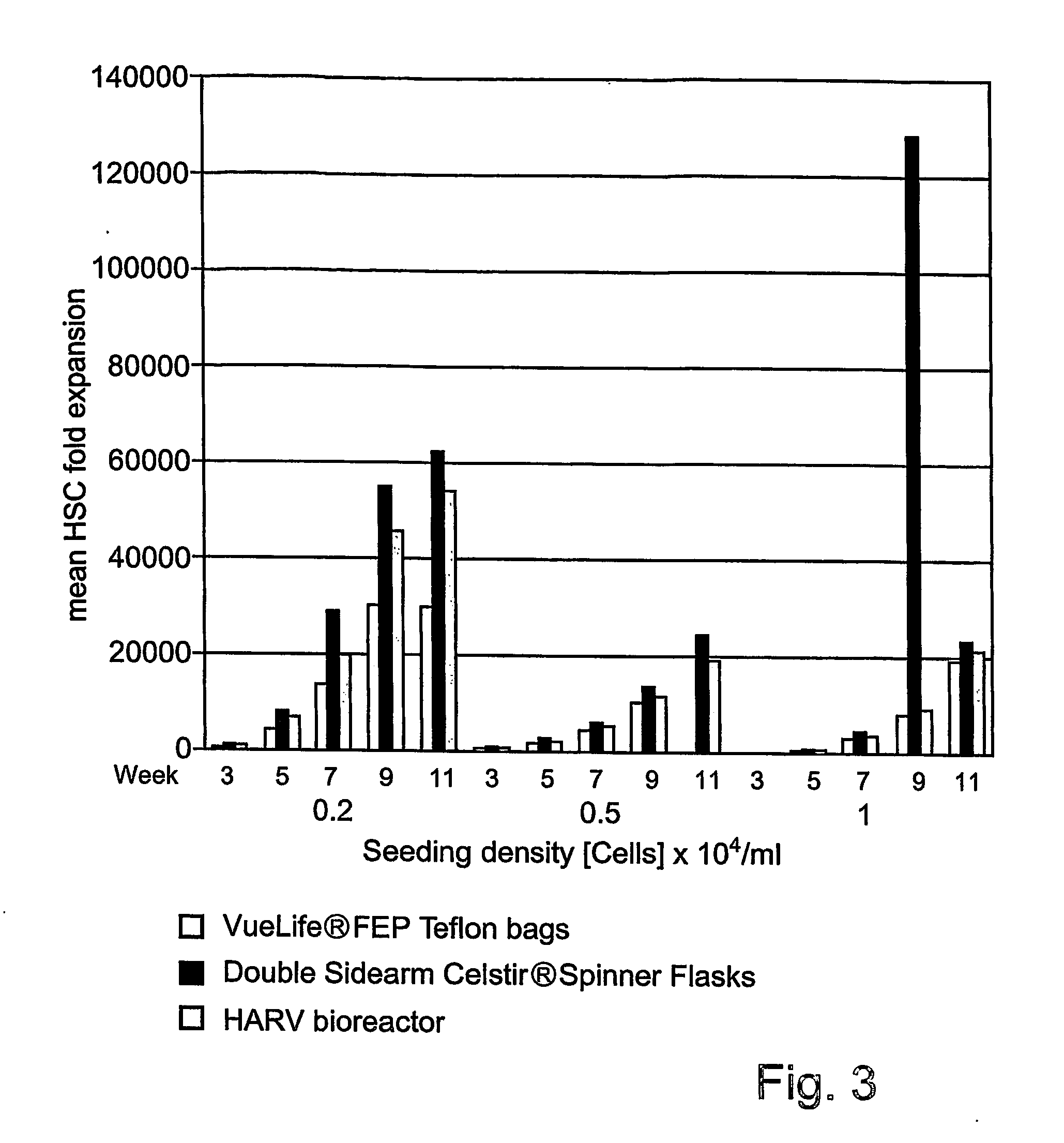
Methods of ex-vivo expansion of fetal and / or adult progenitor, and umbilical cord blood, bone marrow or peripheral blood derived stem cells in bioreactors for bone marrow transplantation, transfusion medicine, regenerative medicine and gene therapy.
Owner:GAMIDA CELL
Methods of using adipose tissue-derived cells in the treatment of the lymphatic system and malignant disease
InactiveUS20110206646A1Ease and low morbidityAvoid contaminationBiocideMetabolism disorderProgenitorLymphatic vessel
Aspects of the invention provides methods for preparing and using adipose-tissue-derived stem and progenitor cells, adipose-tissue-derived lymphatic endothelial cells, and cells capable of differentiating into lymphatic endothelial cells to treat disorders of the lymphatic system and to modulate expansion, repair, and / or regeneration of the lymphatic system. The invention further provides using adipose-tissue-derived lymphatic endothelial cells and cells capable of differentiating into lymphatic endothelial cells for delivery of therapeutic agents to tumor cells as a means for treating malignant disease, and assays to screen for drugs that modulate lymphatic system expansion, repair or regeneration.
Owner:LOREM VASCULAR PTE LTD
Adipose-derived stem cells for tissue regeneration and wound healing
Compositions and methods for promoting tissue regeneration, particularly skin regeneration, with adipose-derived stem cells are provided. Additionally methods and compositions for promoting tissue regeneration with adipose-derived stem cell side population cells are provided. The adipose-derived cells are administered in a tissue regenerating effect amount optionally with a bioactive agent. Additionally the adipose derived cells can be autologous or syngeneic.
Owner:PRIMEGEN BIOTECH LLC
Methods of using adipose derived stem cells to promote wound healing
Cells present in adipose tissue are used to promote wound healing in a patient. Methods of treating patients include processing adipose tissue to deliver a concentrated amount of regenerative cells obtained from the adipose tissue to a patient. The methods may be practiced in a closed system so that the regenerative cells are not exposed to an external environment prior to being administered to a patient. Accordingly, in a preferred method, cells present in adipose tissue are placed directly into a recipient along with such additives necessary to promote, engender or support a therapeutic benefit.
Owner:LOREM VASCULAR PTE LTD
Kidney derived stem cells and methods for their isolation, differentiation and use
InactiveUS20060177925A1Facilitate kidney regenerationPromote regenerationCulture processMammal material medical ingredientsRenal stem cellKidney
The invention relates generally to methods for isolation and culture of kidney stem cells, cells isolated by the methods, and therapeutic uses for those cells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
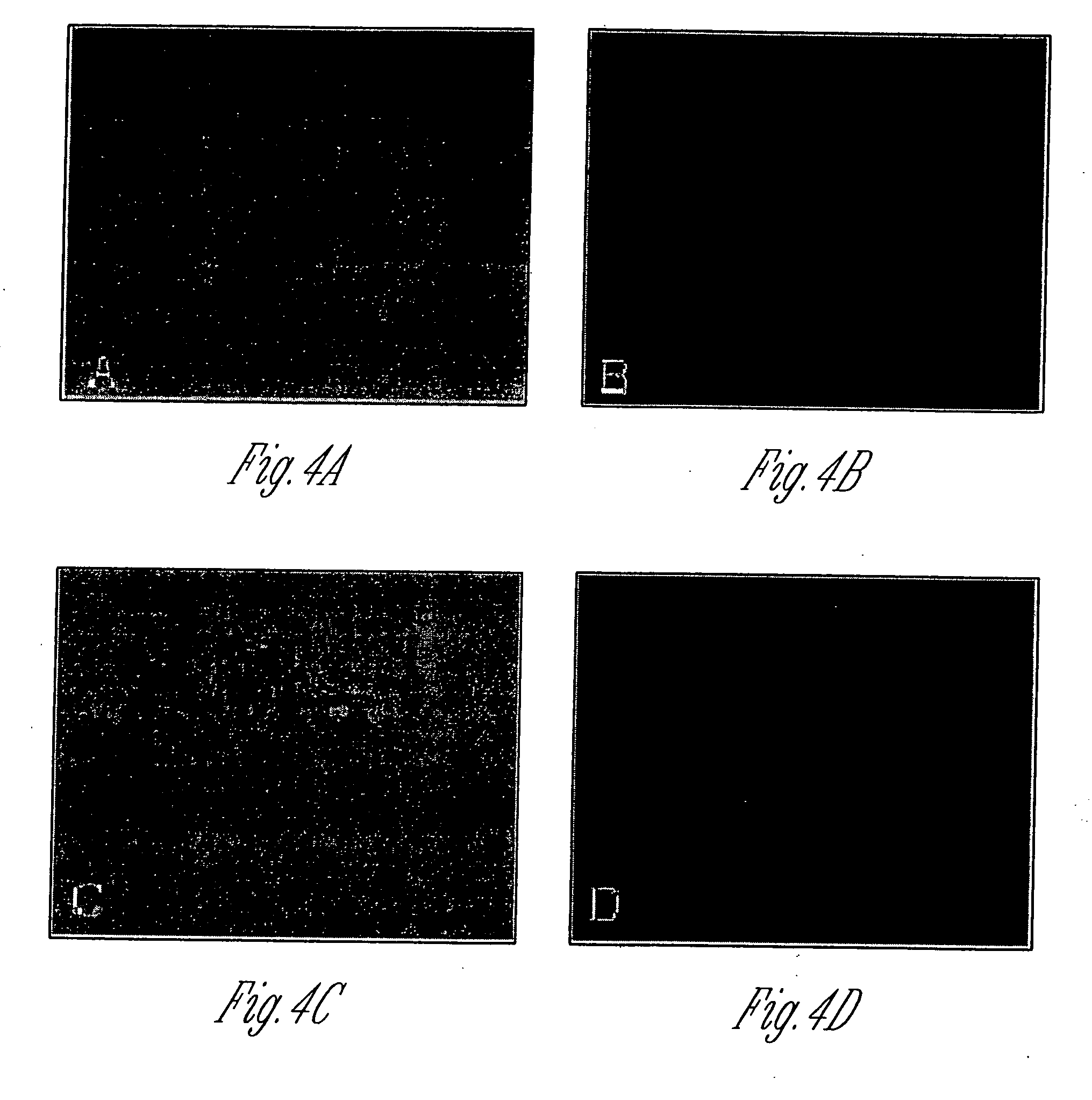
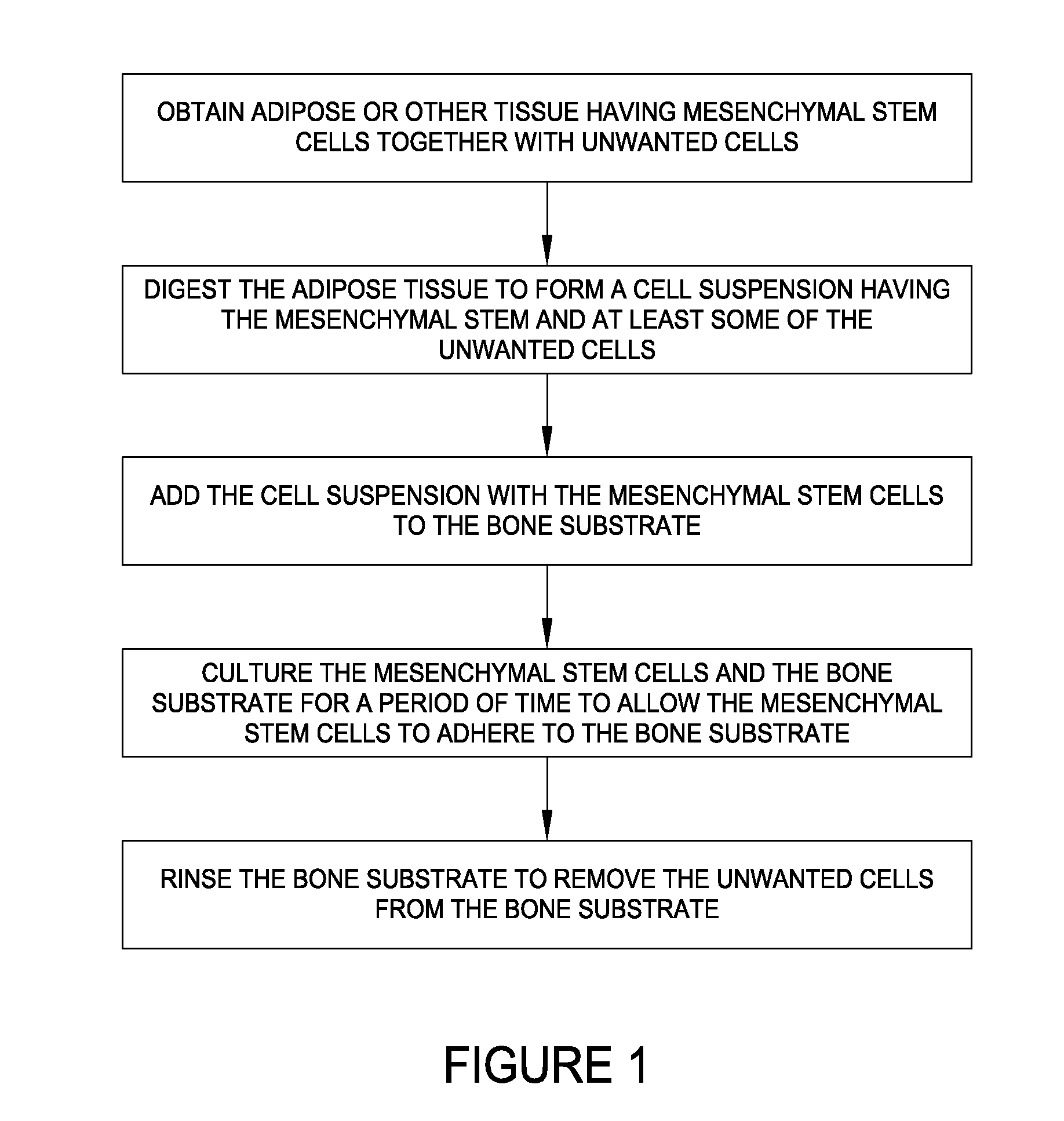
Allografts combined with tissue derived stem cells for bone healing
ActiveUS20100124776A1Smooth appearanceCell dissociation methodsMammal material medical ingredientsWound healingMuscle tissue
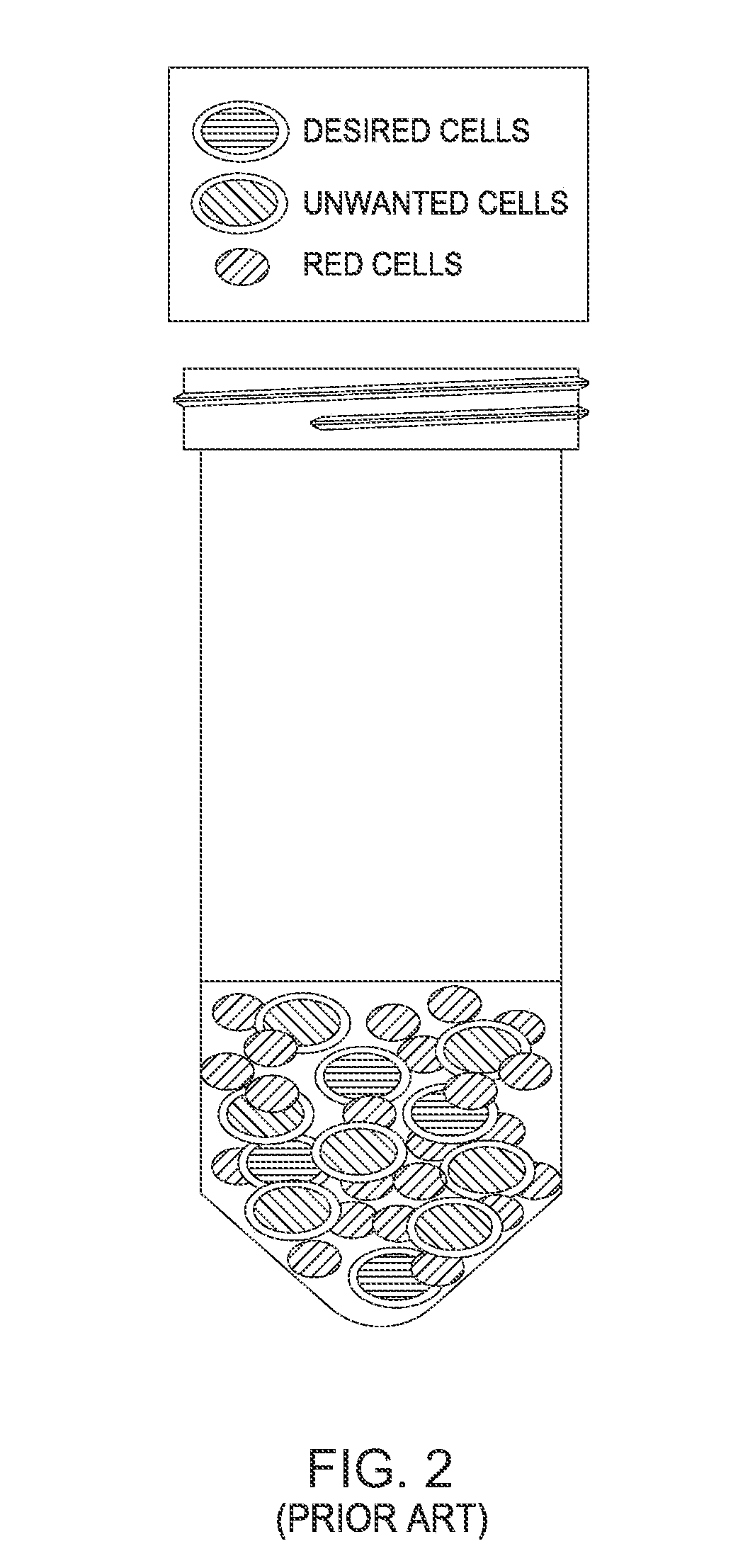
There is disclosed a method of combining mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) with a bone substrate. In an embodiment, the method includes obtaining tissue having MSCs together with unwanted cells. The tissue is digested to form a cell suspension having MSCs and unwanted cells. The cell suspension is added to the substrate. The substrate is cultured to allow the MSCs to adhere. The substrate is rinsed to remove unwanted cells. In various embodiments, the tissue is adipose issue, muscle tissue, or bone marrow tissue. In an embodiment, there is disclosed an allograft product including a combination of MSCs with a bone substrate in which the combination is manufactured by culturing MSCs disposed on the substrate for a period of time to allow the MSCs to adhere to the substrate, and then rinsing the substrate to remove unwanted cells from the substrate. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:ALLOSOURCE
Cartilage-derived stem cells and applications thereof
The invention relates to methods of isolating adult stem cells, to the cells thus isolated and to applications thereof. More specifically, the invention relates to isolated adult stem cells, which are derived from dedifferentiated chondrocytes, which can be differentiated and which can give rise to a series of cell lineages, as well as to specific markers present in said cells, such as cell surface antigens. The cells provided by the present invention can be used, for example, in cell therapy and in the search for and development of novel medicaments.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
Methods of using adipose derived stem cells to treat acute tubular necrosis
Cells present in processed lipoaspirate tissue are used to treat patients, including patients with renal conditions, diseases or disorders. Methods of treating patients include processing adipose tissue to deliver a concentrated amount of stem cells obtained from the adipose tissue to a patient. The methods may be practiced in a closed system so that the stem cells are not exposed to an external environment prior to being administered to a patient. Accordingly, in a preferred method, cells present in processed lipoaspirate are placed directly into a recipient along with such additives necessary to promote, engender or support a therapeutic renal benefit.
Owner:LOREM VASCULAR PTE LTD
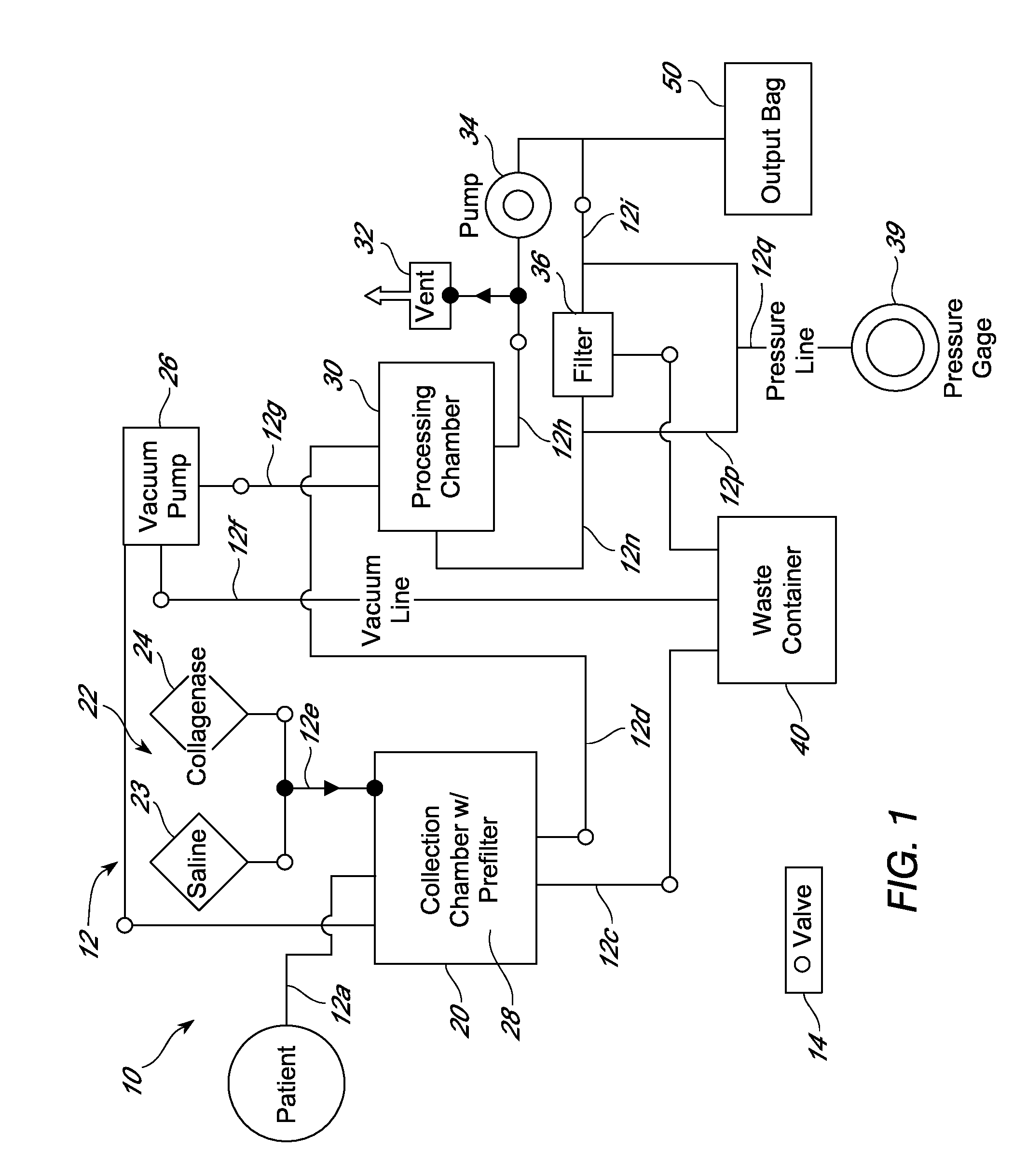
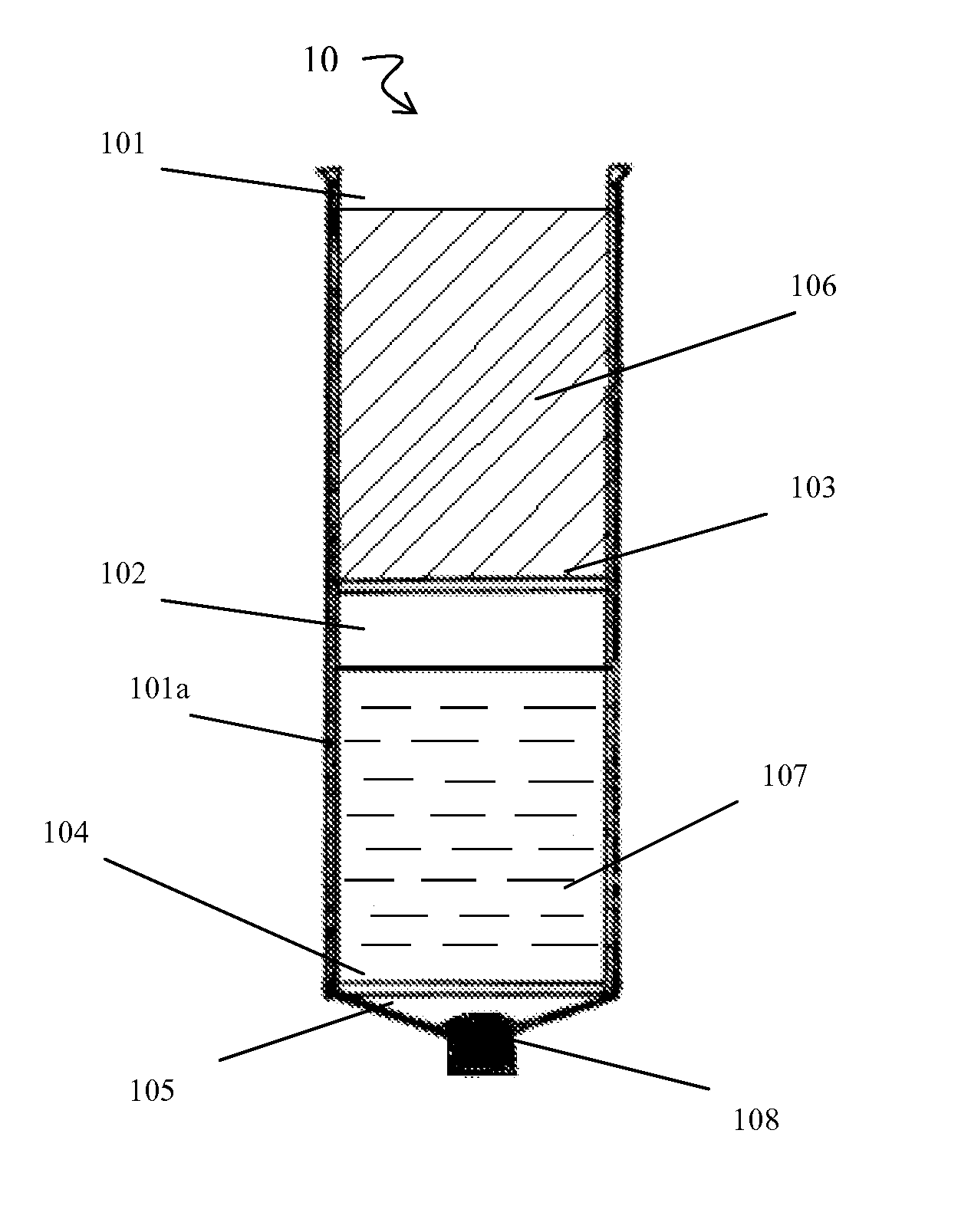
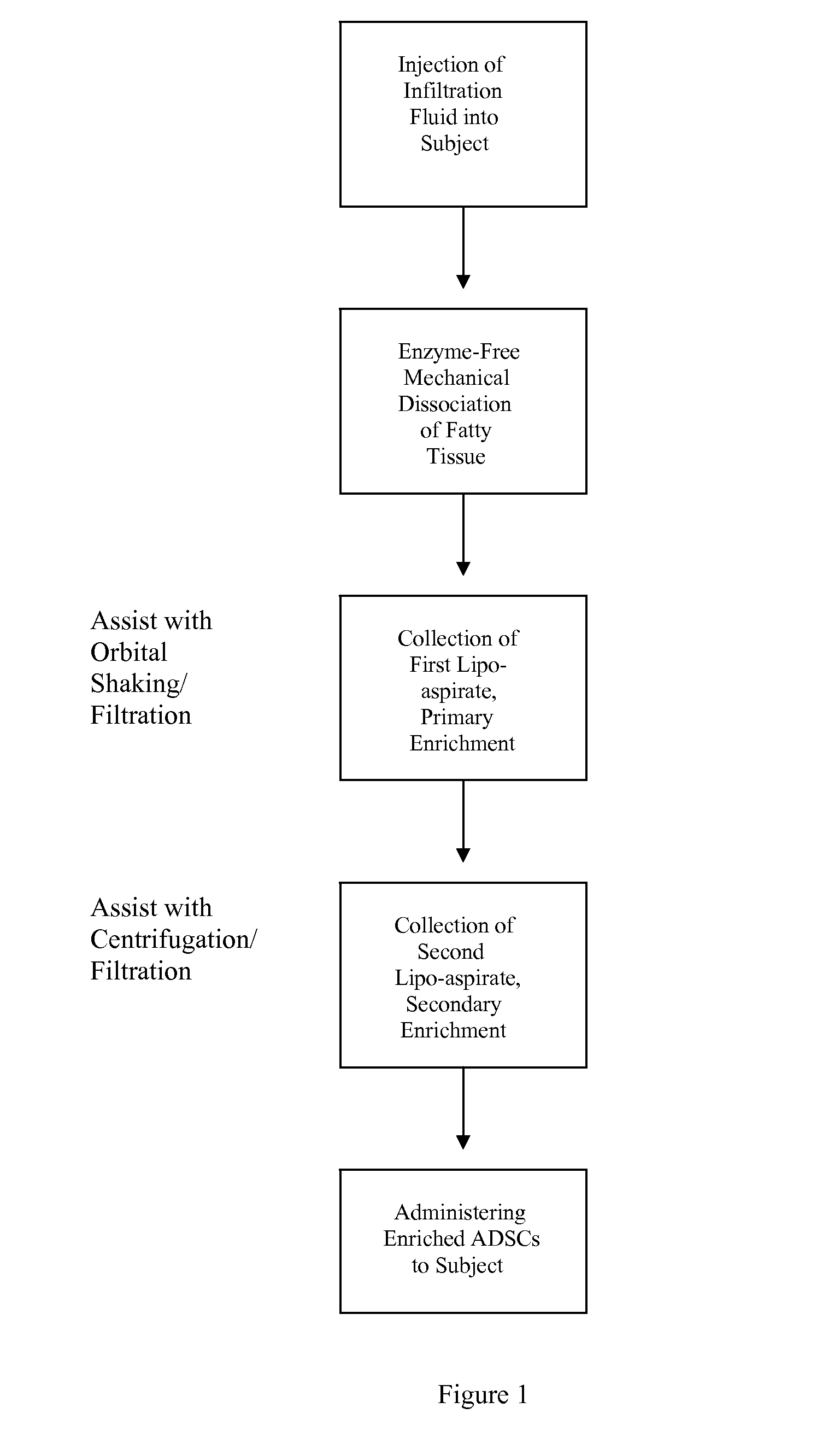
Non-Enzymatic Method for Harvesting Adipose-Derived Stromal Cells and Adipose-Derived Stem Cells from Fat and Lipo-Aspirate
The present disclosure relates generally to processes, devices and systems for separating and concentrating stem and stromal cells from adipose tissue using a combination of mechanical disruption and filtration-centrifugation to obtain a highly enriched population of stem cells.
Owner:AGHA MOHAMMADI SIAMAK
Production of oligodendrocytes from placenta-derived stem cells
Owner:CELULARITY INC
Methods and compositions for smooth muscle reconstruction
This invention also provides a purified or isolated population of ADSCs that can differentiate into a cell of the leiomyogenic lineage, e.g., smooth muscle or skeletal muscle. In yet another aspect, the population additionally can be differentiated into a lineage selected from the group consisting of osteogenic, adipogenic, chondrogenic, myogenic and neuronal. This invention further provides a composition comprising a substantially homogeneous expanded population of smooth muscle cells. This invention provides a composition comprising a substantially homogeneous expanded population of skeletal muscle cells. Also provided herein is an isolated composition comprising a purified adipose-derived stem cell (ADSC) or progeny of said ADSC and an effective amount of laminin or heparin, effective to induce leiomyogenic differentiation. Diagnositic and therapeutic uses for these compositions are provided herein.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
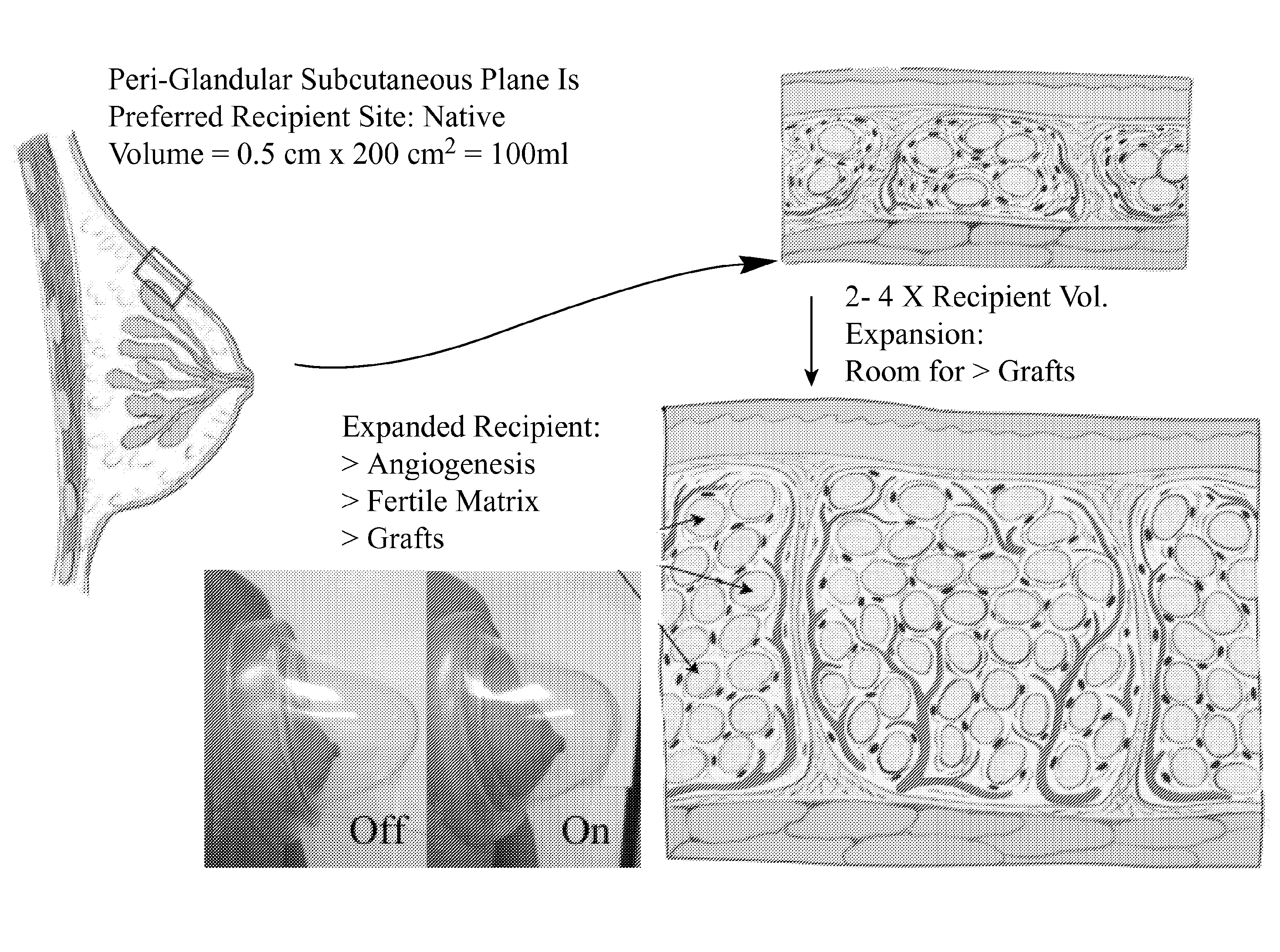
Method and system for preparing soft tissue for grafting, enhancing grafting results, and grafting autologous fat and adipocyte derived stem cells to soft tissue such as the breast and other tissue defects
ActiveUS20090312746A1Reduce the possibilityEliminate fatMammary implantsDiagnosticsHigh rateFat grafting
A method is disclosed for preparing a soft tissue site, and augmenting the soft tissue site, such as the breast(s), scar, depression, or other defect, of a subject through use of devices that exert a distractive force on the breast(s) and grafting of autologous fat tissue such as domes with sealing rims for surrounding each of the soft tissue site and a regulated pump. The method for preparing the soft tissue site, and enhancing fat graft results, entails application of the distracting force to the targeted soft tissue site at least intermittently for some period of time and preferably several weeks prior to the graft procedure. A related aspect of the invention includes following the preparation steps by transfer of fat from other areas of the subject to the subject's soft tissue site, and then reapplication of the distractive force to the soft tissue site that received the autologous fat graft. Alternatively, fat from genetically related sources may be used, and the fat may be further processed prior to injection. Substantial soft tissue augmentation, high rates of graft survival and negligible graft necrosis (data demonstrating 80% survival and only 20% necrosis is presented) or calcification result from the practice of these methods.
Owner:KHOURI ROGER
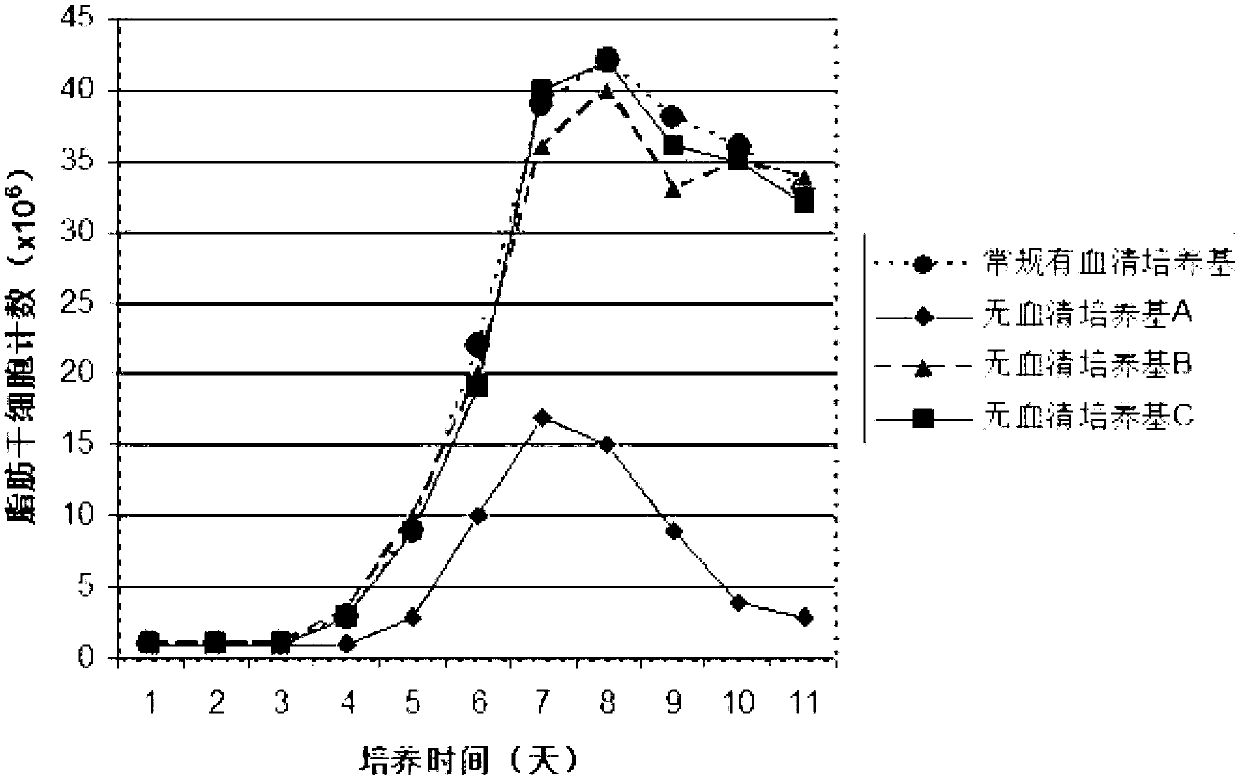
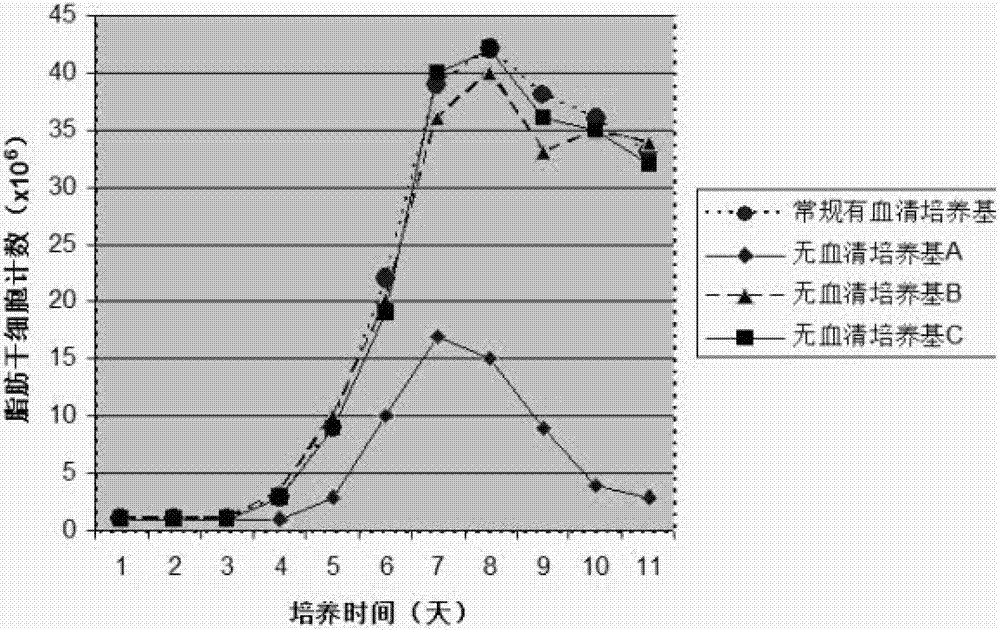
Human adipose-derived stem cell serum-free basic medium
ActiveCN102732477BOvercome riskSkeletal/connective tissue cellsMineral ascorbatesAscorbic acid 2-sulfate
The invention discloses a human adipose-derived stem cell serum-free basic medium. The medium uses a serum substitute, and is composed of a high glucose type DMEM basic medium, human serum albumin, transferrin, taurine, reduced glutathione, ceruloplasmin, L-ascorbic acid-2-sulfate, alpha-tocopherol succinate, linoleic acid, alpha-ketoglutarate and selenium. The serum-free basic medium can exempt potential threats caused by animal serum in conventional serum-containing mediums to human health, and the adipose-derived stem cells cultured by the medium is more suitable for clinical application.
Owner:JIANGSU RE STEM BIOTECH
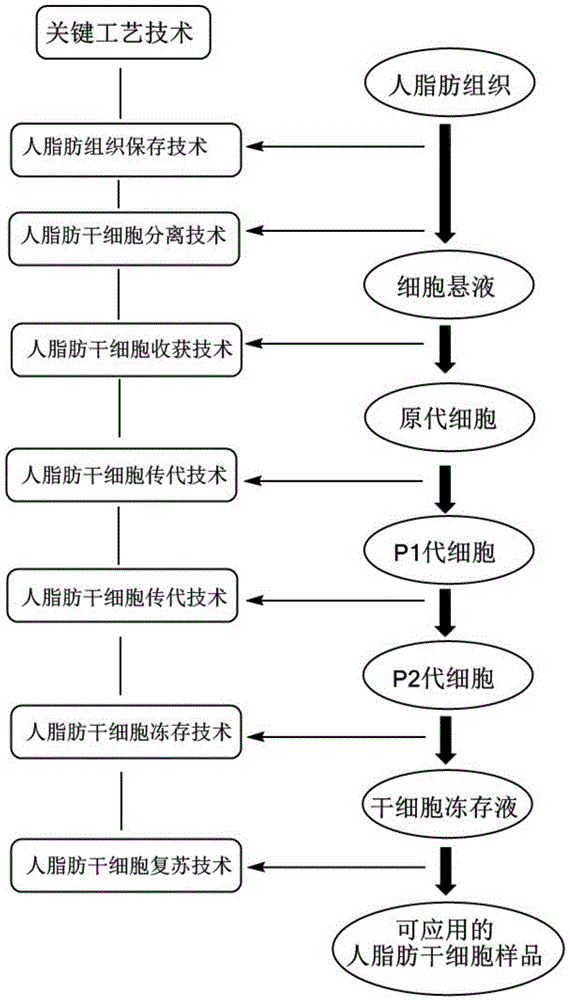
Method for separating human adipose-derived stem cells from human adipose tissues
ActiveCN104357387AHigh purityReduced differentiation inductionSkeletal/connective tissue cellsParenchymaBrown adipose tissue
The invention relates to the field of cell engineering and particularly relates to a method for separating human adipose-derived stem cells from human adipose tissues. According to the method, by adding a small amount of low-molecular-weight heparin calcium into normal saline, a mixed solution is obtained and used as a cleaning fluid to clean the human adipose tissues, residual impurities such as red blood cells in the human adipose tissues can be well removed and thus human adipose-derived stem cells with relatively higher purity can be separated, the content of the parenchyma cell is significantly reduced, the differentiation induction of the human adipose-derived stem cells is facilitated, the consumption amounts of collagenase I, trypsase and a serum-free culture medium can be reduced and the cost of the process is also decreased. In addition, by centrifuging and digesting the human adipose tissues for 1 hour at a speed of 150r / min, the human adipose-derived stem cells with significantly better activity can be obtained.
Owner:深圳市赛欧细胞技术有限公司
Human adipose-derived stem cell serum-free basic medium
ActiveCN102732477AIncrease viscosityFree from mechanical damageSkeletal/connective tissue cellsAscorbic acid 2-sulfateMineral ascorbates
The invention discloses a human adipose-derived stem cell serum-free basic medium. The medium uses a serum substitute, and is composed of a high glucose type DMEM basic medium, human serum albumin, transferrin, taurine, reduced glutathione, ceruloplasmin, L-ascorbic acid-2-sulfate, alpha-tocopherol succinate, linoleic acid, alpha-ketoglutarate and selenium. The serum-free basic medium can exempt potential threats caused by animal serum in conventional serum-containing mediums to human health, and the adipose-derived stem cells cultured by the medium is more suitable for clinical application.
Owner:JIANGSU RE STEM BIOTECH
Method for extracting and culturing adipose-derived stem cells
ActiveCN104164403ADoes not affect activityFast value-addedSkeletal/connective tissue cellsBiotechnologyVolumetric Mass Density
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology and relates to a method for extracting and culturing adipose-derived stem cells. The method comprises the following steps: (1) taking human adipose tissue, and repeatedly carrying out centrifugal washing with a D-Hank's balanced salt solution with the pH value of 7.2-7.4; (2) mincing the adipose tissue into small pieces of 1-2mm<3>, and carrying out digestion by adding a digestive juice which has the same volume of the selected adipose tissue; (3) standing and layering: repeatedly blowing and beating bottom cells with a D-Hank's balanced salt solution with the pH value of 7.2-7.4 and cleaning up; filtering a cleaned liquid through a screen mesh, removing undigested tissue, centrifuging and removing a supernatant to obtain stem cells; and (4) inoculating the obtained stem cells in a culture flask according to the density of 2-3*104 / cm<2>, adding a culture solution, and culturing in an incubator. The method has advantages as follows: digestion rate is fast; insoluble tissue blocks are minimized greatly; and an activity of the stem cells is not influenced.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Method for isolating and culturing adult stem cells derived from human amniotic epithelium
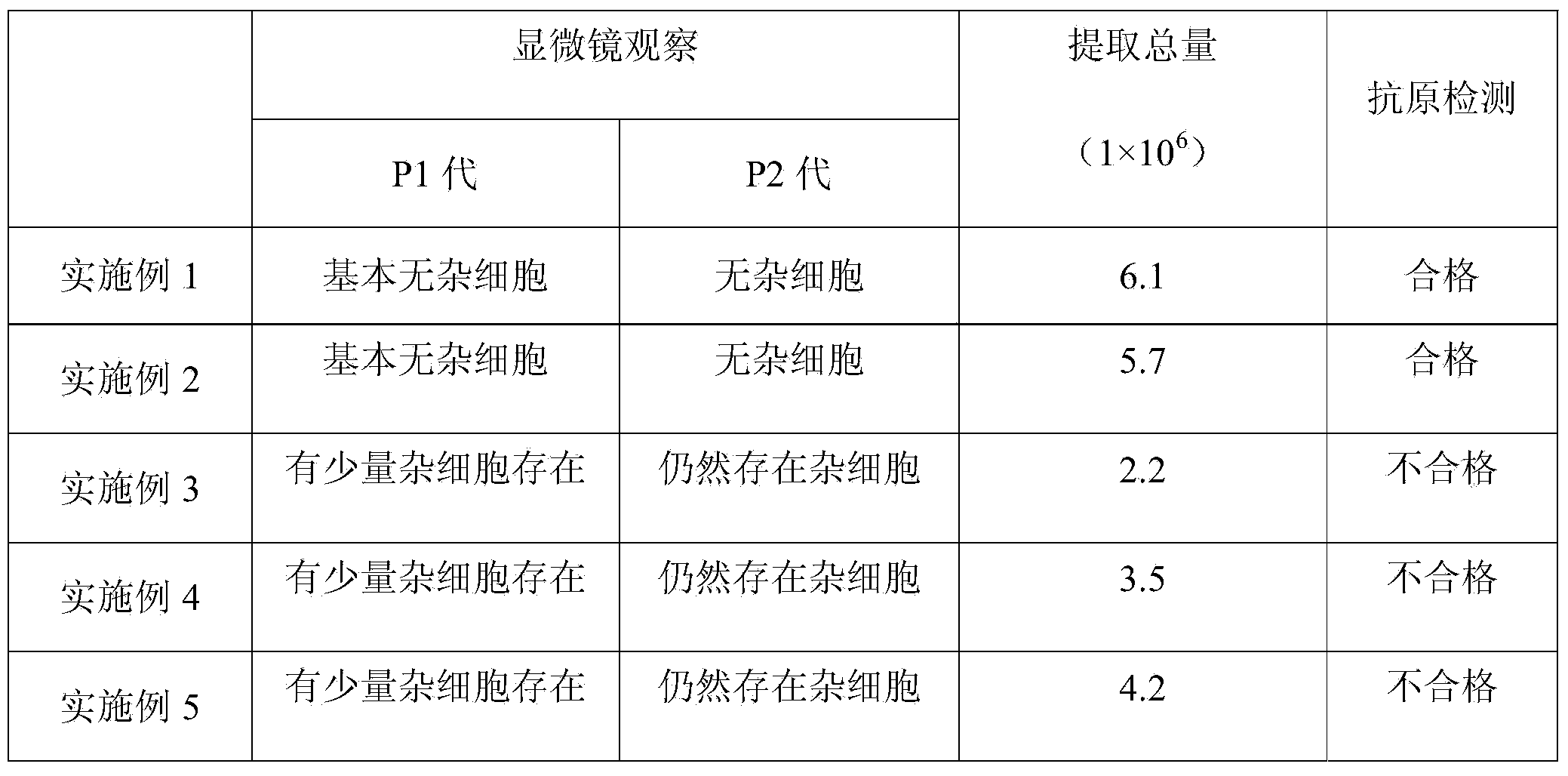
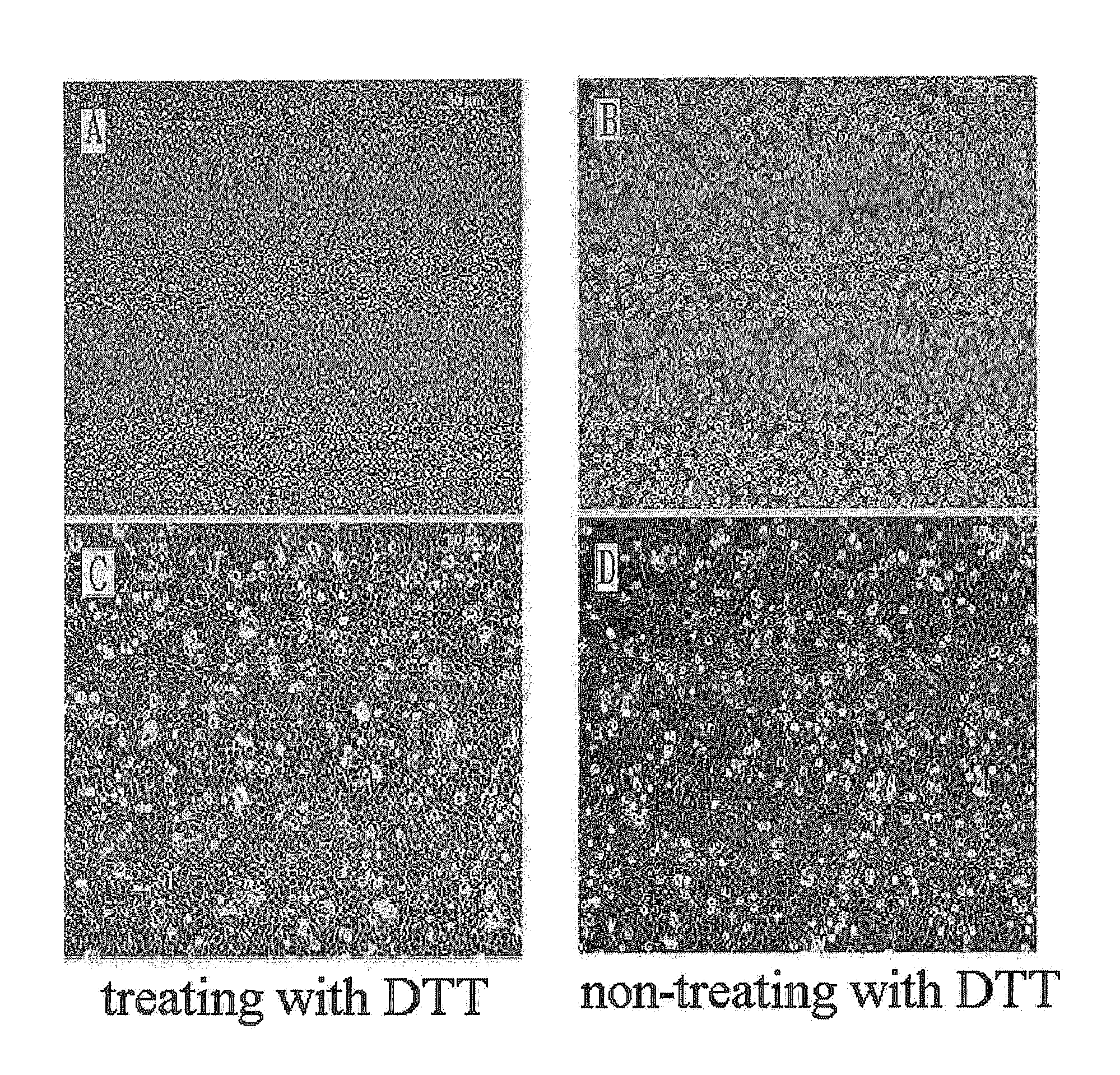
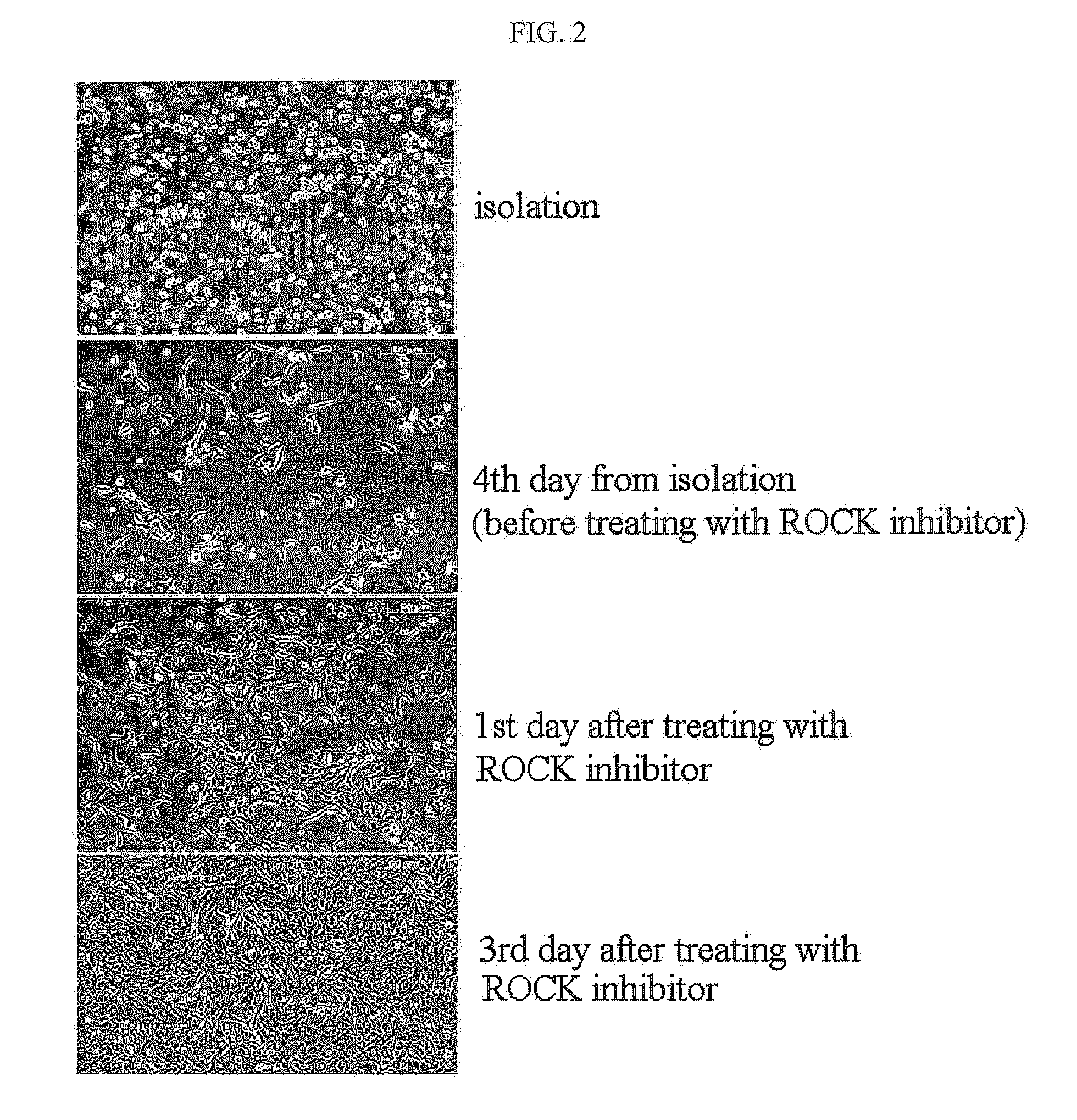
The present invention relates to a method for isolating and culturing adult stem cells derived from human amniotic membrane in high yield, and more particularly to a method for obtaining a large amount of adult stem cells, the method comprising obtaining amniotic epithelial cells from human amniotic tissue in high yield by treatment with dithiothreitol (DTT) and a low concentration of trypsin and culturing the amniotic epithelial cells in a medium containing a Rho-associated kinase inhibitor. The human amniotic epithelial cell-derived stem cells are easily extracted compared to existing therapeutic stem cells such as umbilical cord blood stem cells and bone marrow stem cells, the yield and proliferation thereof are significantly increased by DTT treatment, the addition of the ROCK inhibitor or the replacement of medium. Thus, the method can be used to efficiently prepare adult stem cells.
Owner:RNL BIO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com