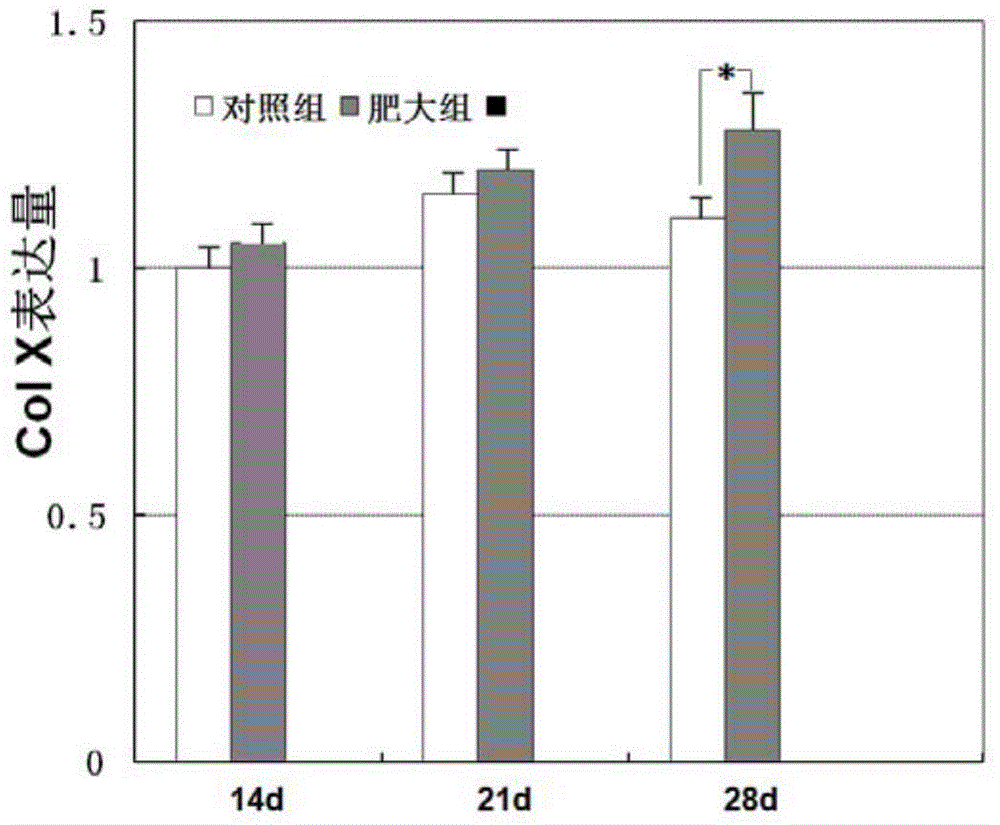
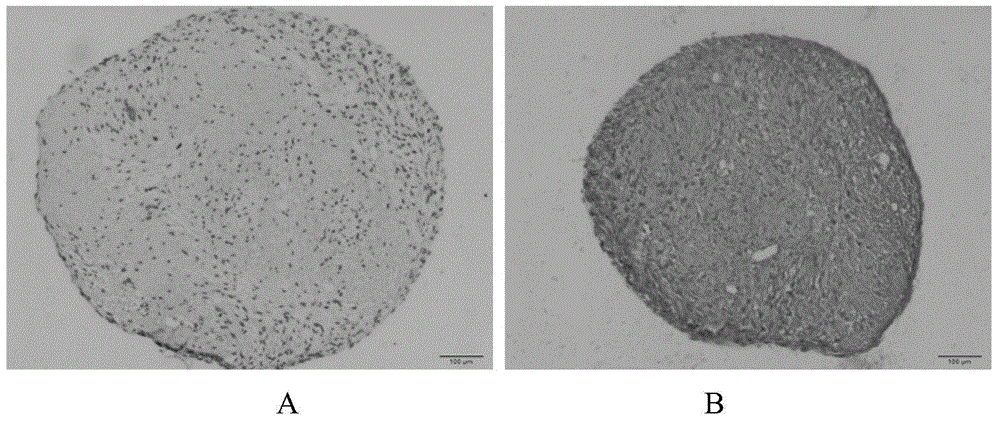
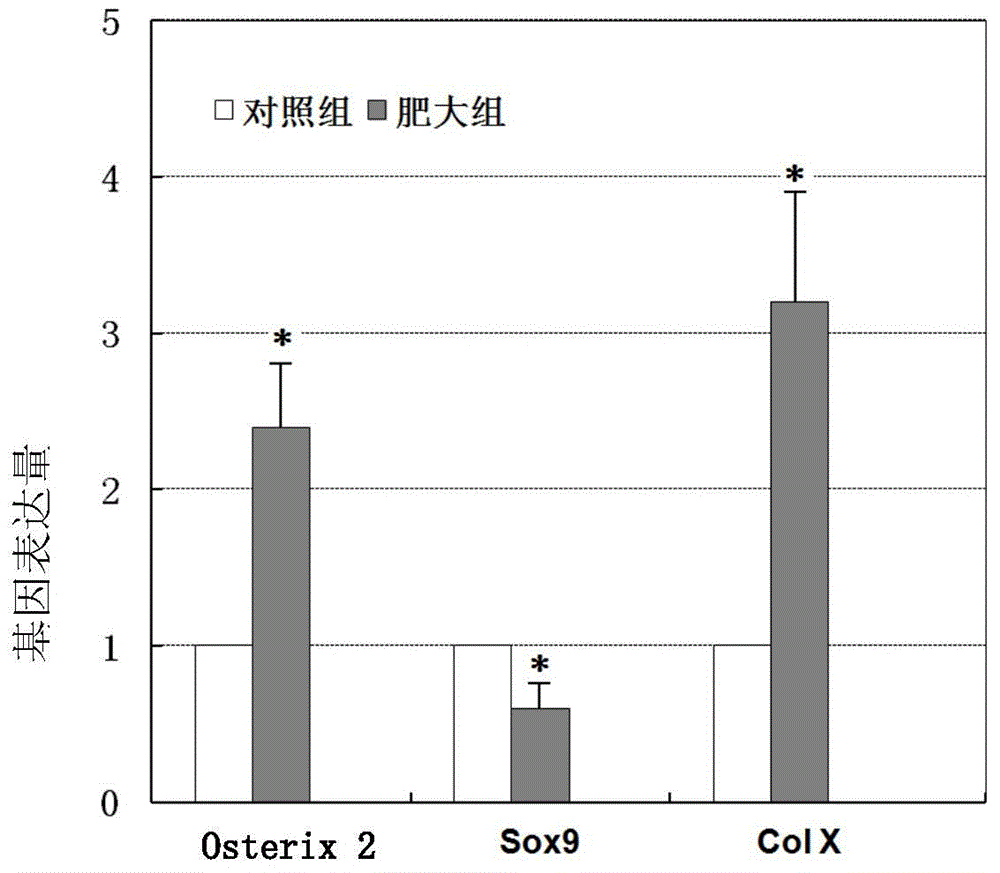
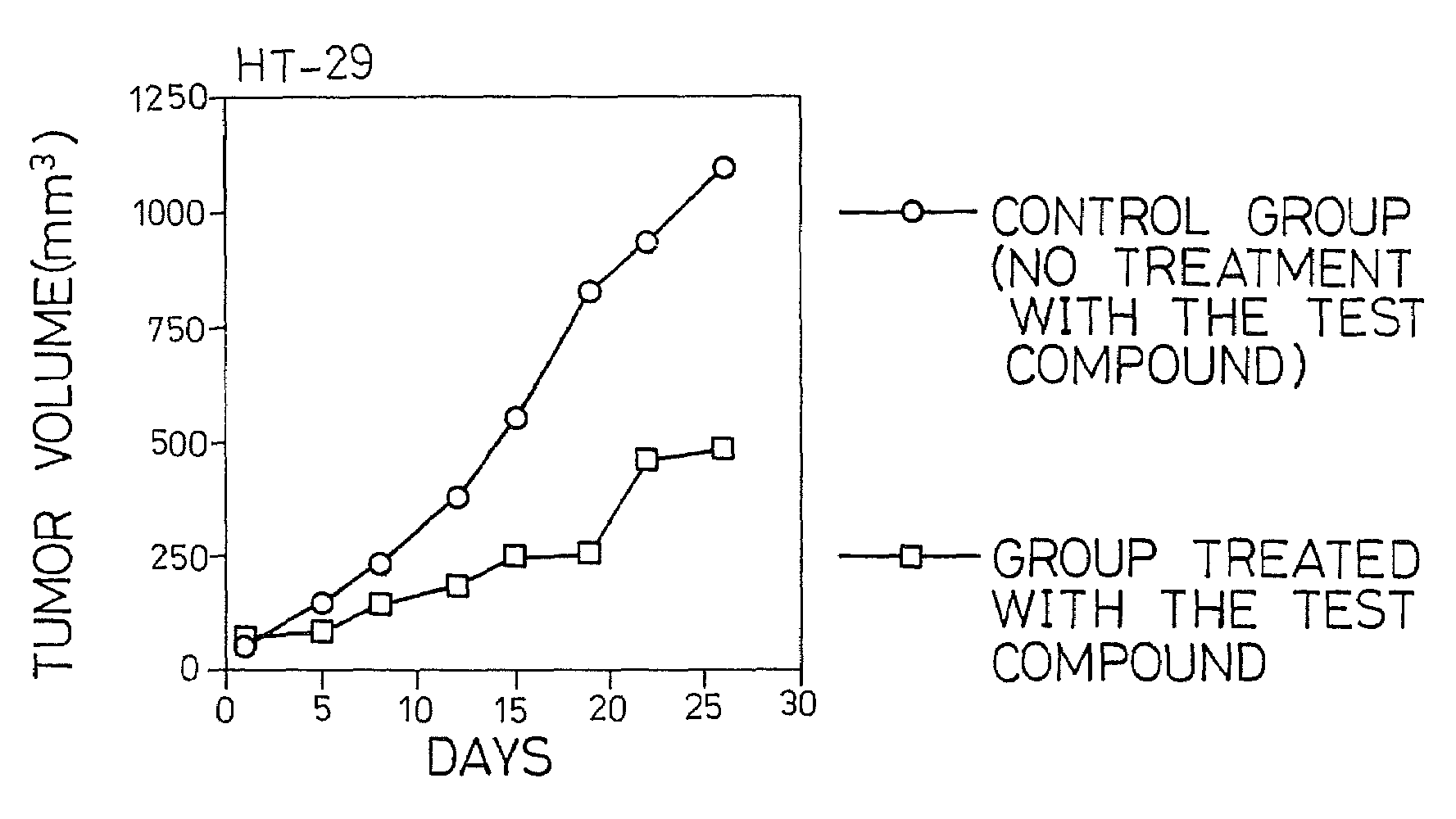
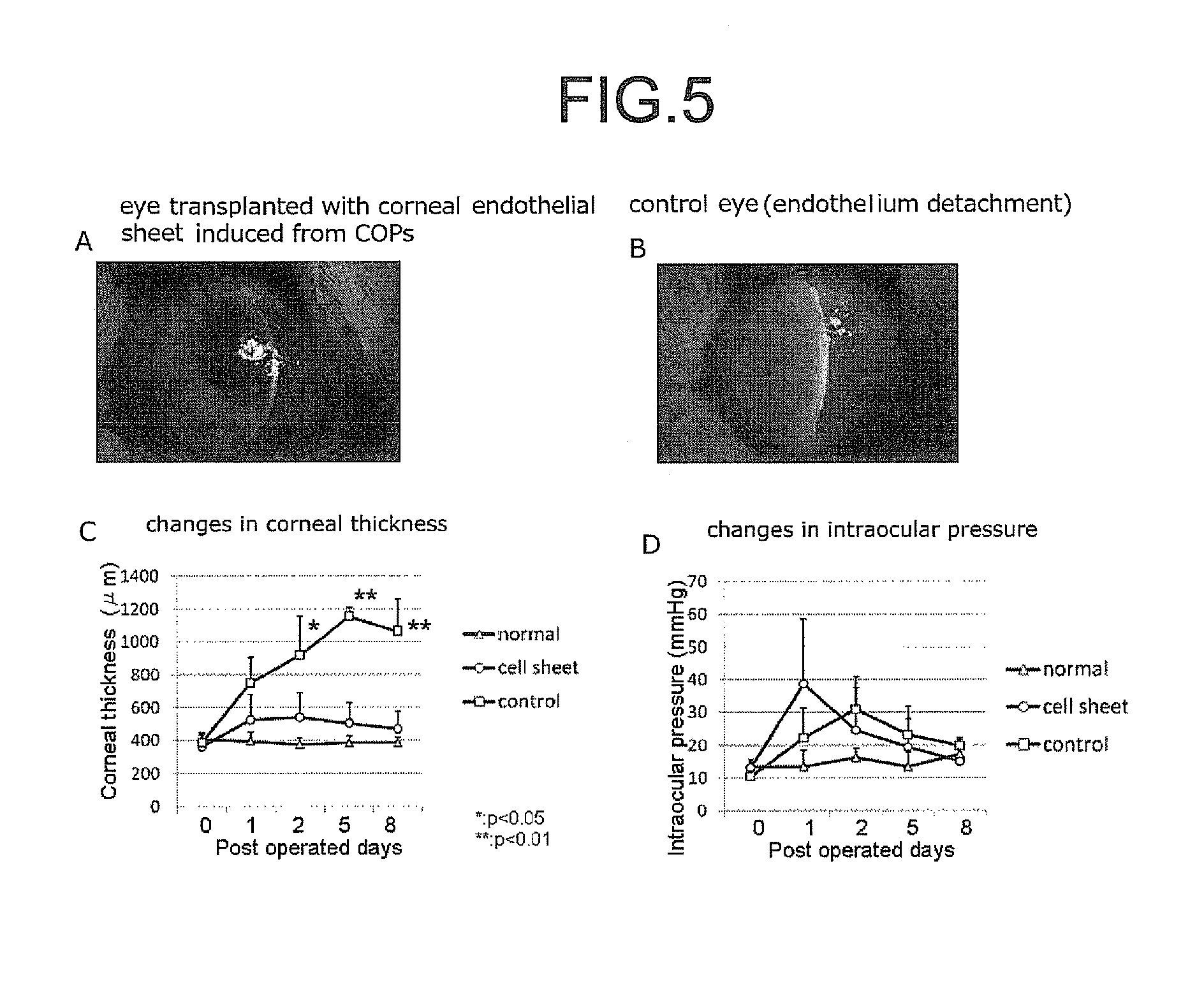
Patents
Literature
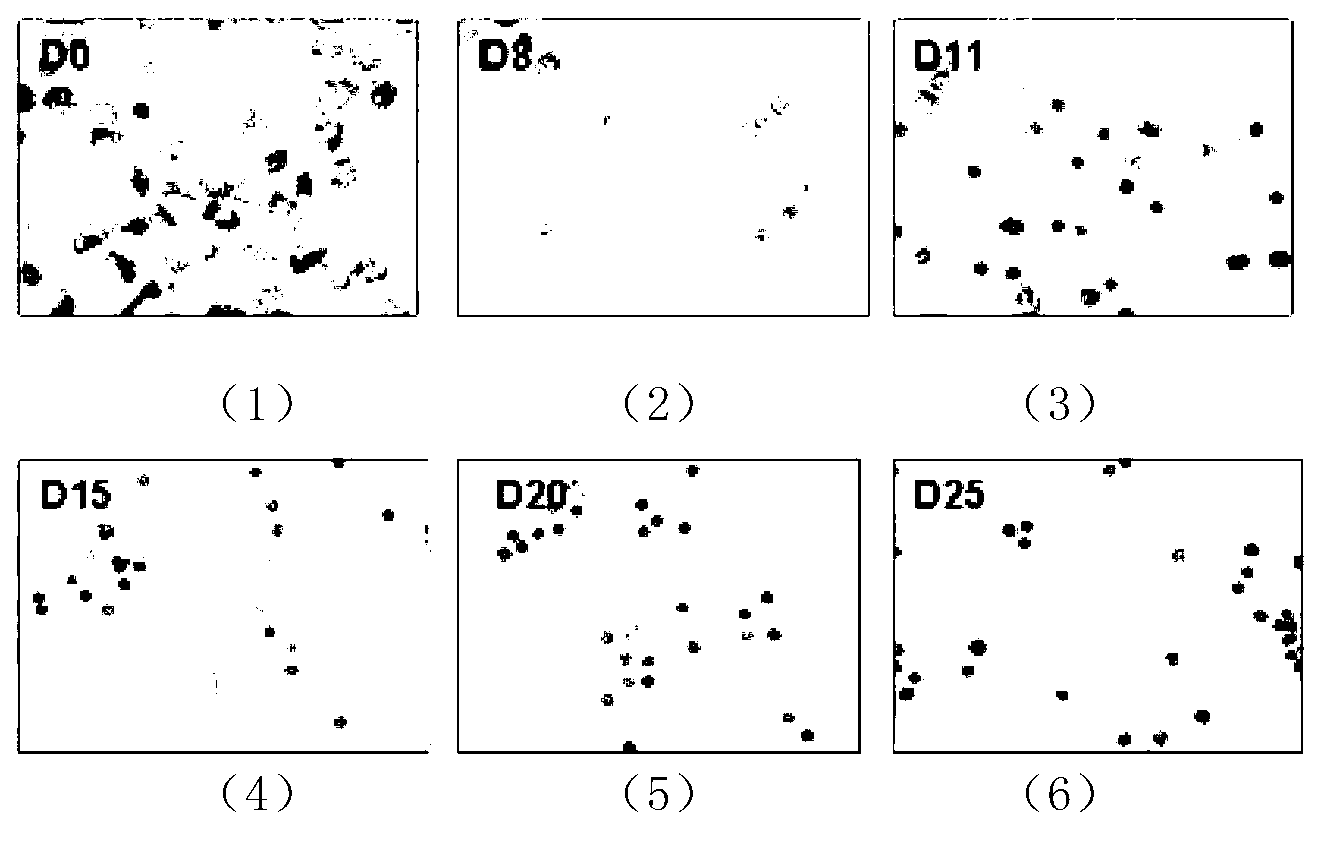
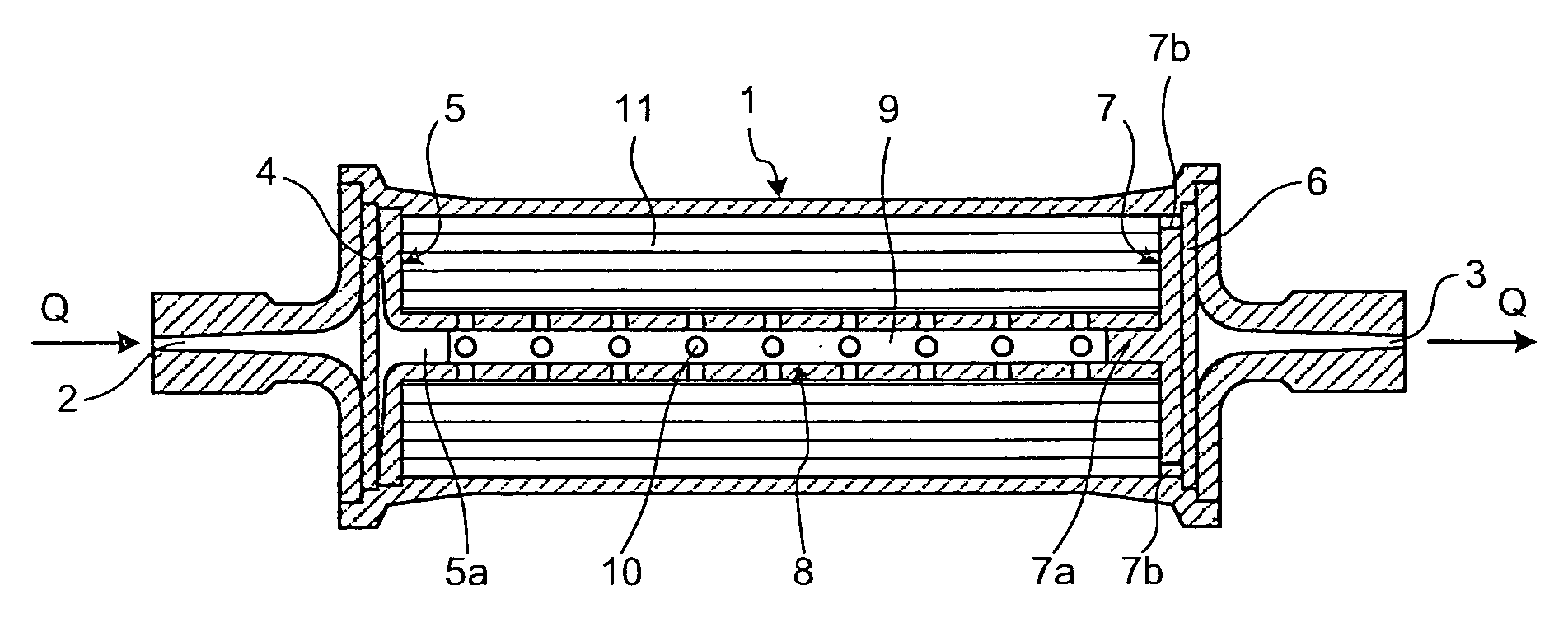
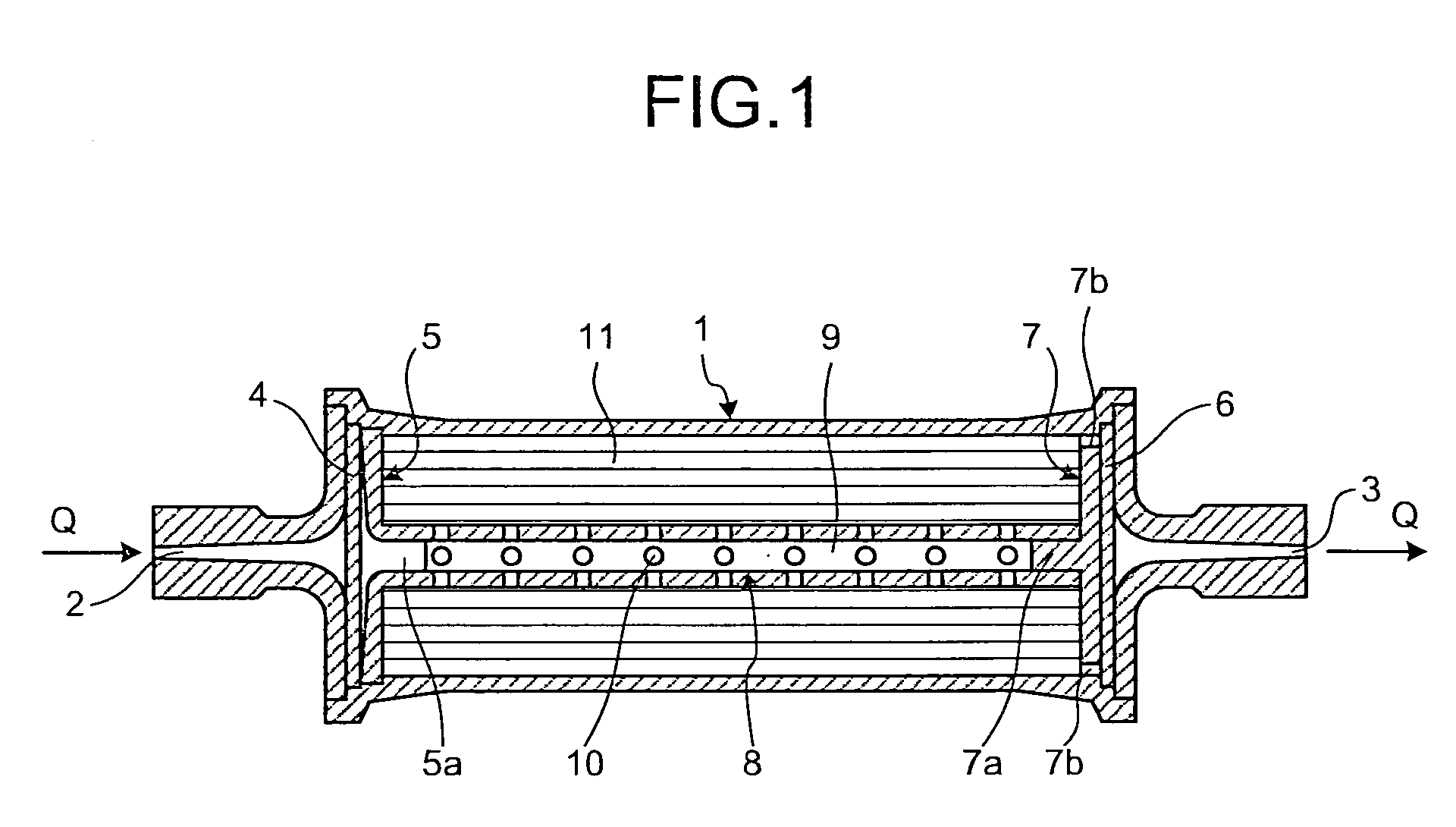
266 results about "Differentiation induction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A major mechanism involved in differentiation is induction, in which cells stimulate each other to develop in different ways. Several landmark experiments that identified the role of induction in differentiation highlight how induction works through direct contact between cells in different tissues.
Differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells to neural cells or skeletal muscle cells by introduction of notch gene
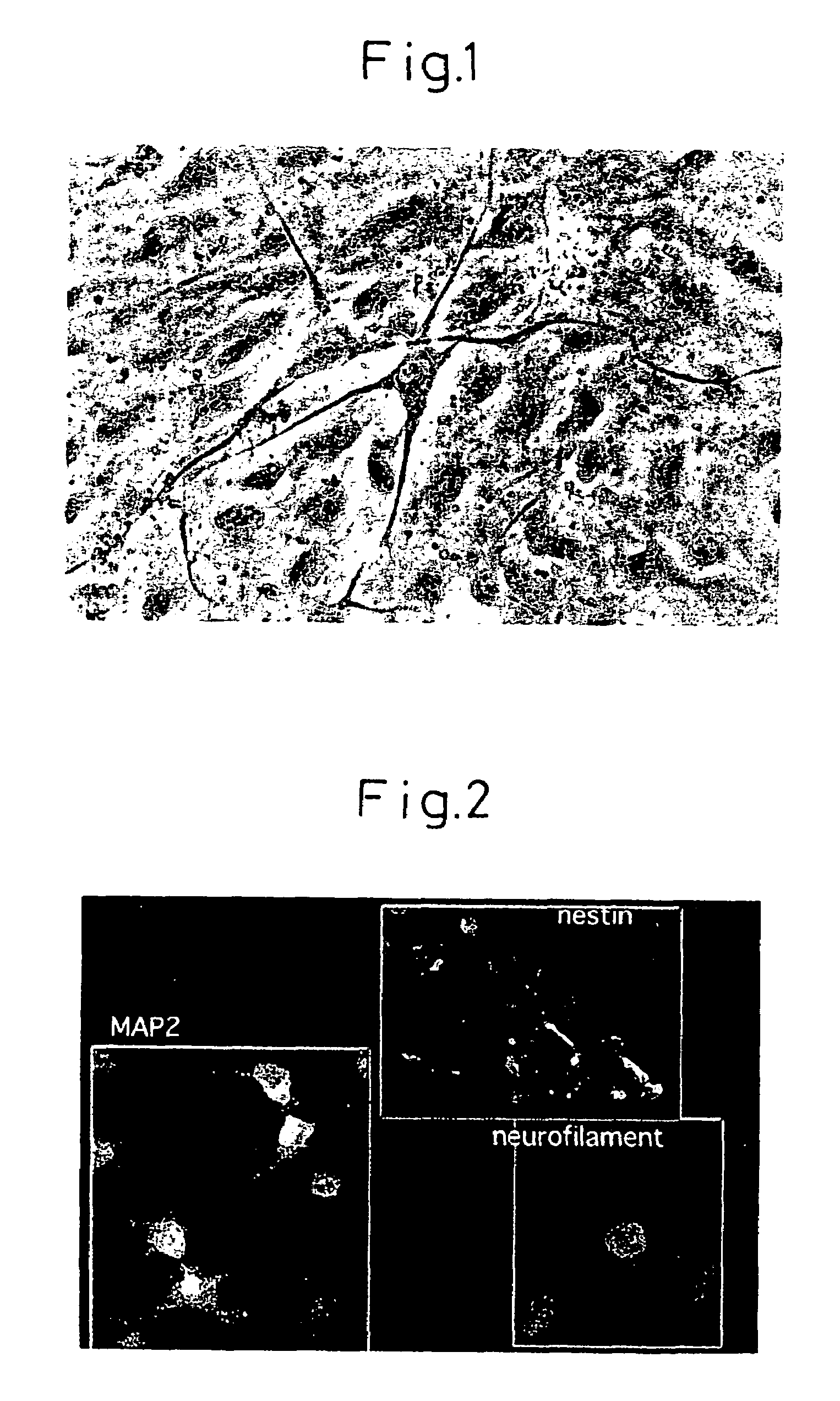
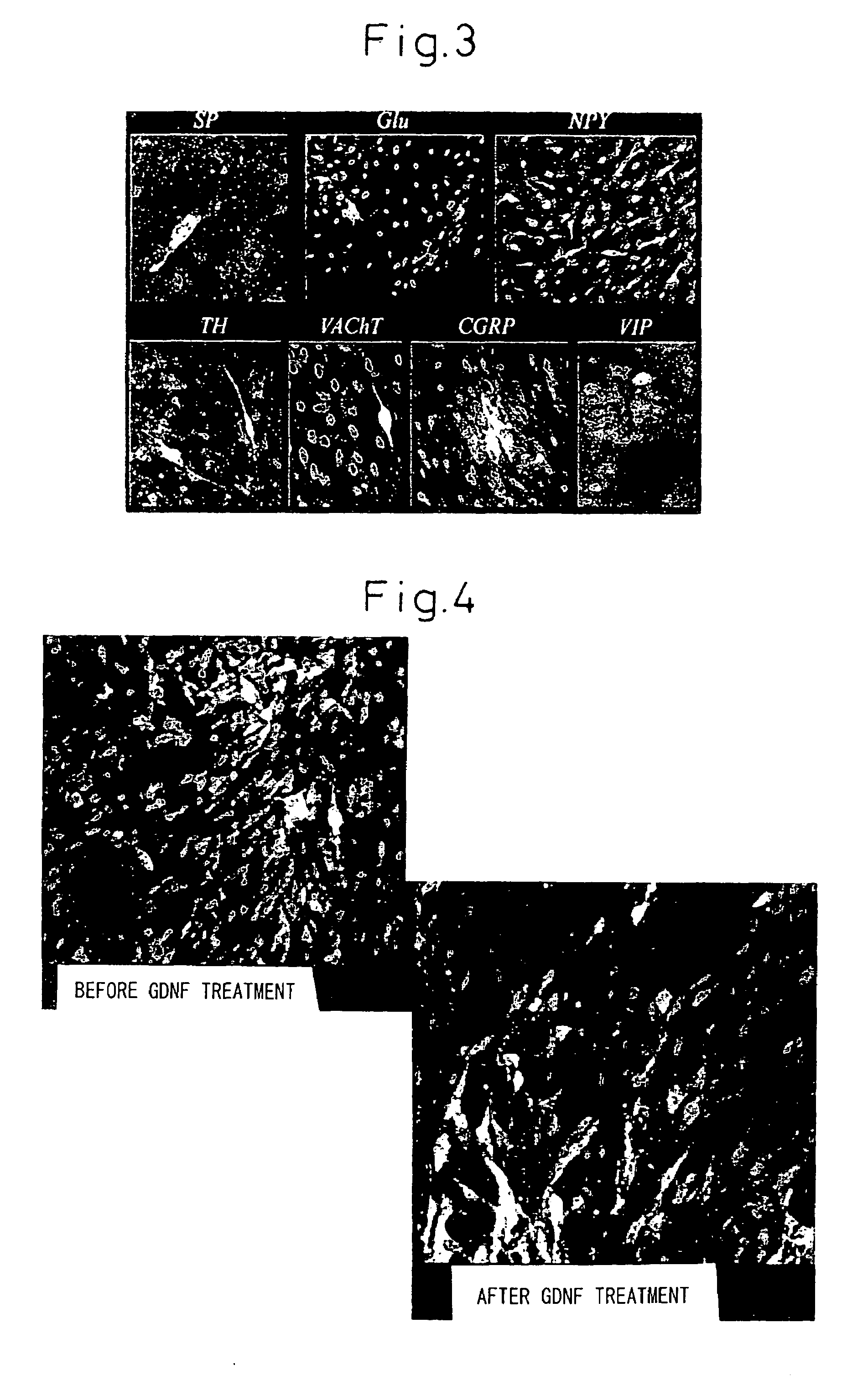
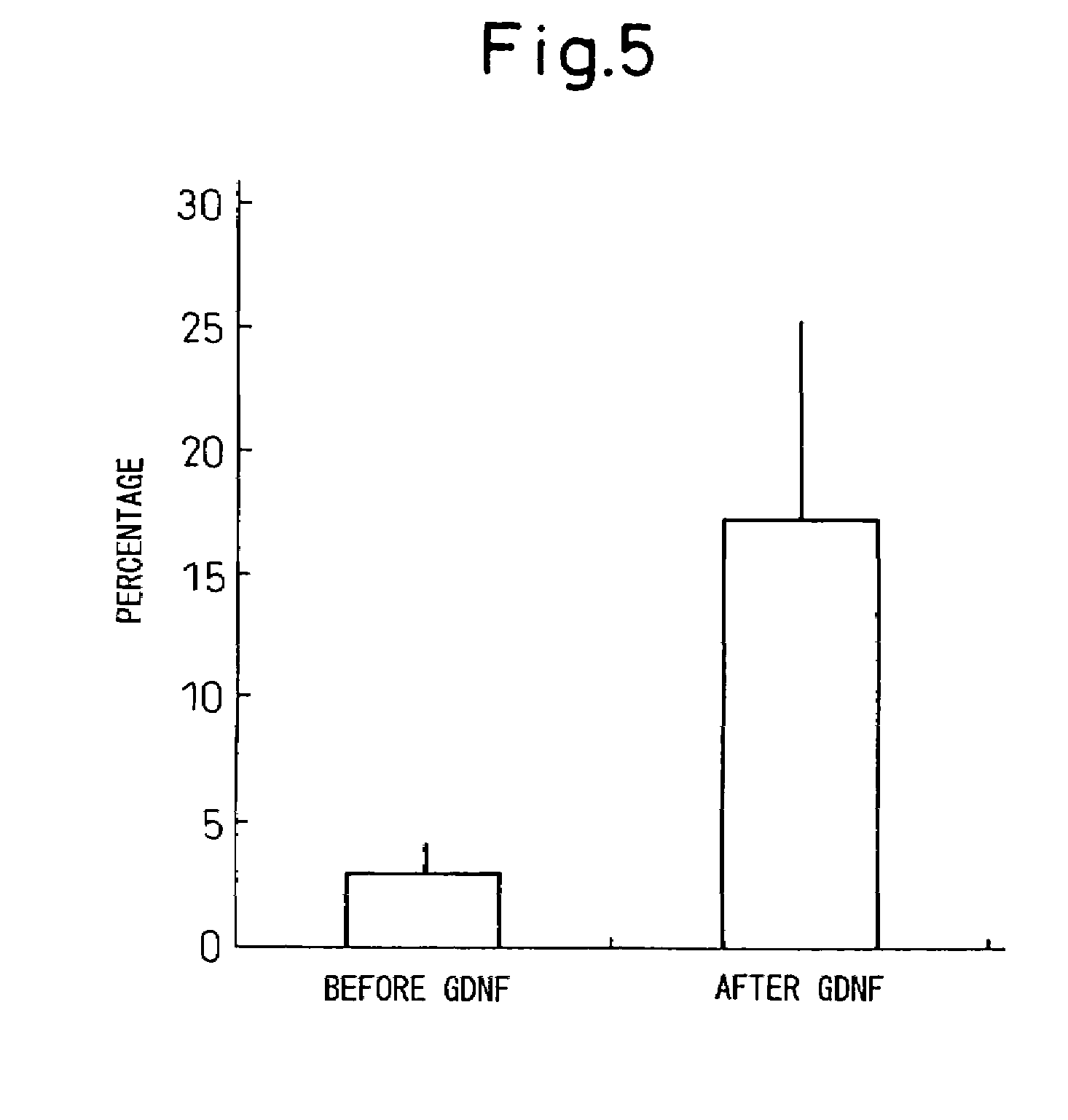
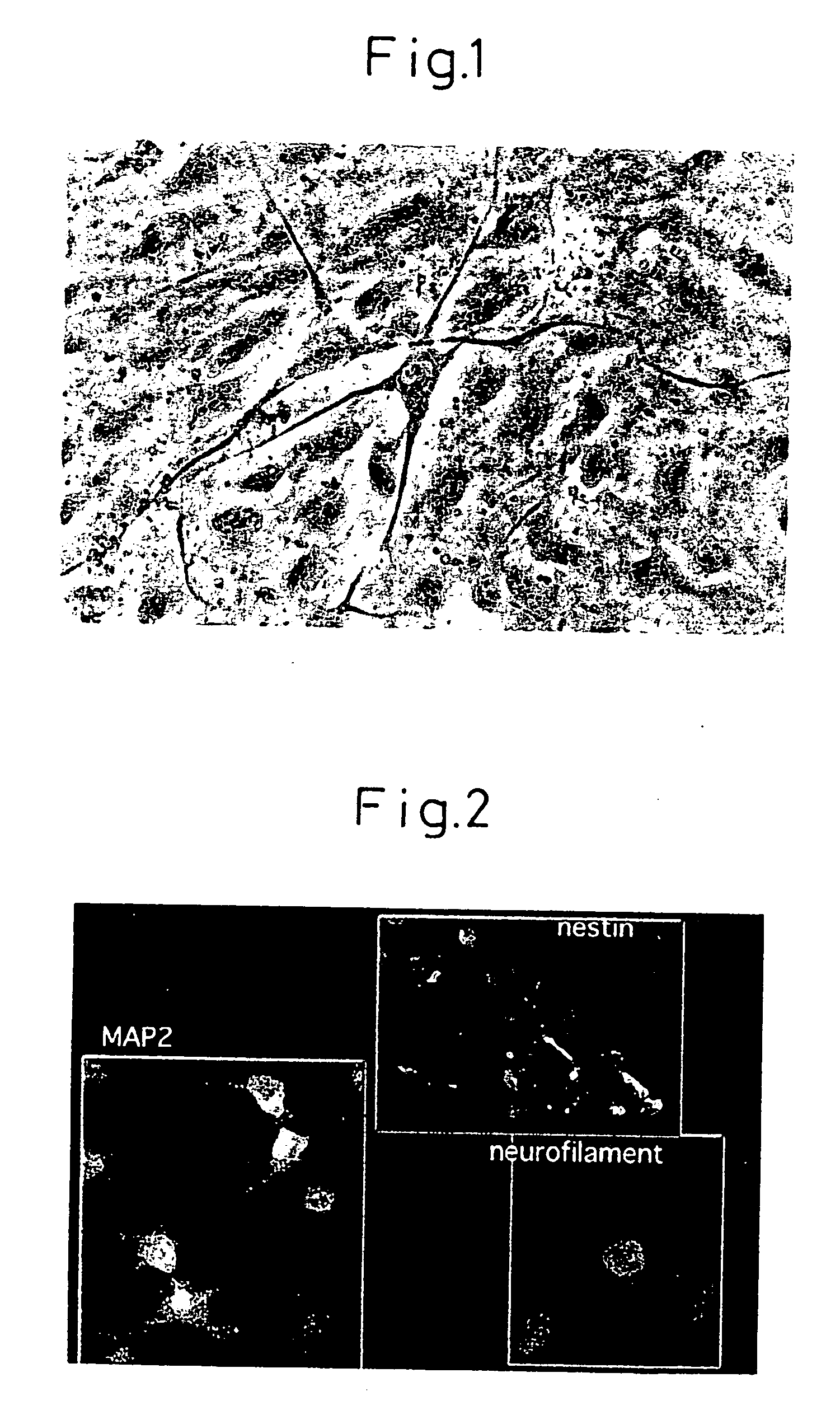
There is provided a method of inducing differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells to neural cells or skeletal muscle cells by introduction of a Notch gene. Specifically, the invention provides a method of inducing differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells to neural cells or skeletal muscle cells in vitro, which method comprises introducing a Notch gene and / or a Notch signaling related gene into the cells, wherein the finally obtained differentiated cells are the result of cell division of the bone marrow stromal cells into which the Notch gene and / or Notch signaling related gene have been introduced. The invention also provides a method of inducing further differentiation of the differentiation-induced neural cells to dopaminergic neurons or acetylcholinergic neurons. The invention yet further provides a treatment method for neurodegenerative and skeletal muscle degenerative diseases which employs neural precursor cells, neural cells or skeletal muscle cells produced by the method of the invention.
Owner:SANBIO
Method of inducing differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells to neural cells or skeletal muscle cells by introduction of notch gene
There is provided a method of inducing differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells to neural cells or skeletal muscle cells by introduction of a Notch gene. Specifically, the invention provides a method of inducing differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells to neural cells or skeletal muscle cells in vitro, which method comprises introducing a Notch gene and / or a Notch signaling related gene into the cells, wherein the finally obtained differentiated cells are the result of cell division of the bone marrow stromal cells into which the Notch gene and / or Notch signaling related gene have been introduced. The invention also provides a method of inducing further differentiation of the differentiation-induced neural cells to dopaminergic neurons or acetylcholinergic neurons. The invention yet further provides a treatment method for neurodegenerative and skeletal muscle degenerative diseases which employs neural precursor cells, neural cells or skeletal muscle cells produced by the method of the invention.
Owner:SANBIO
Method of examining polycystic kidney disease and method of screening for therapeutic agent of the disease
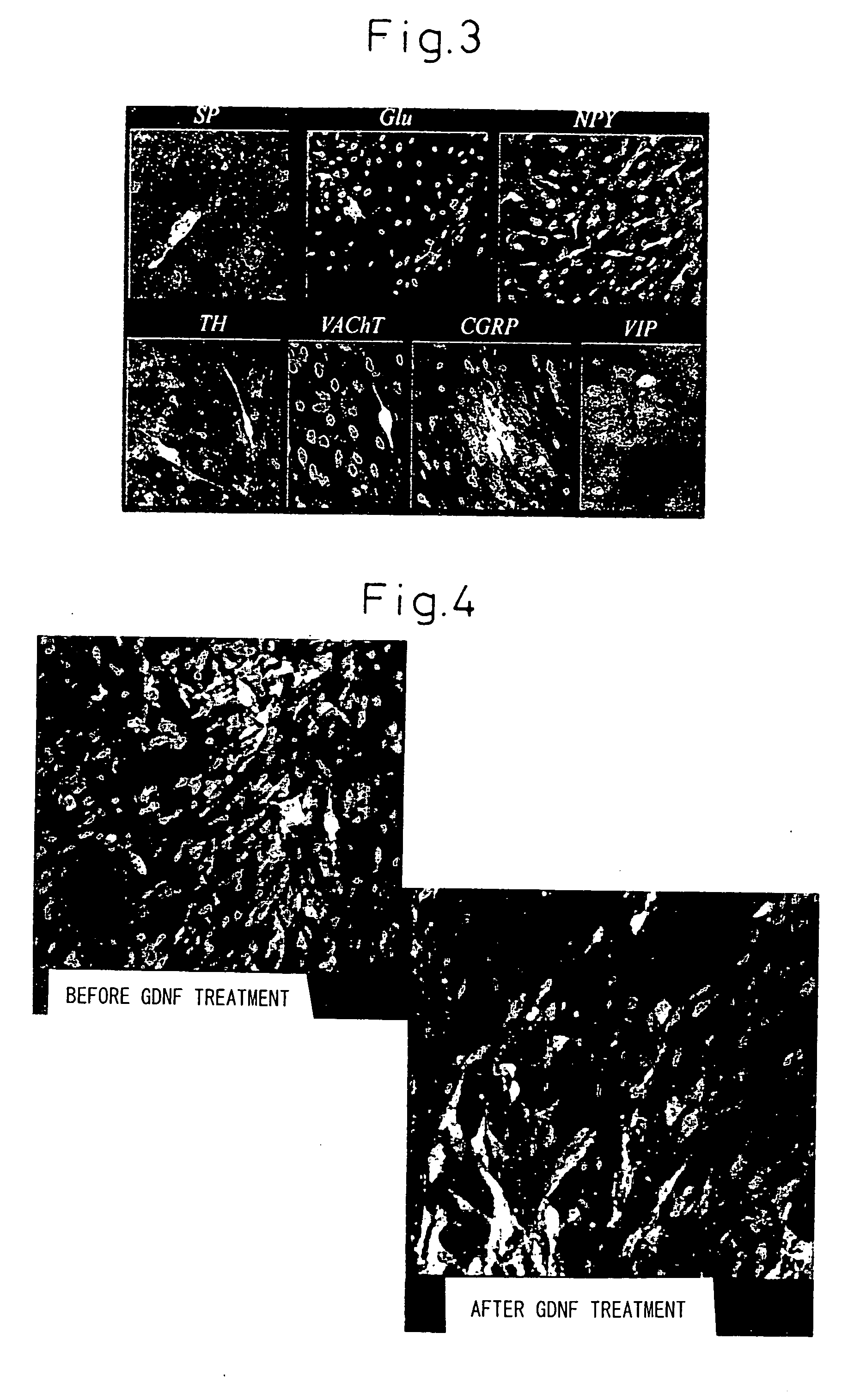
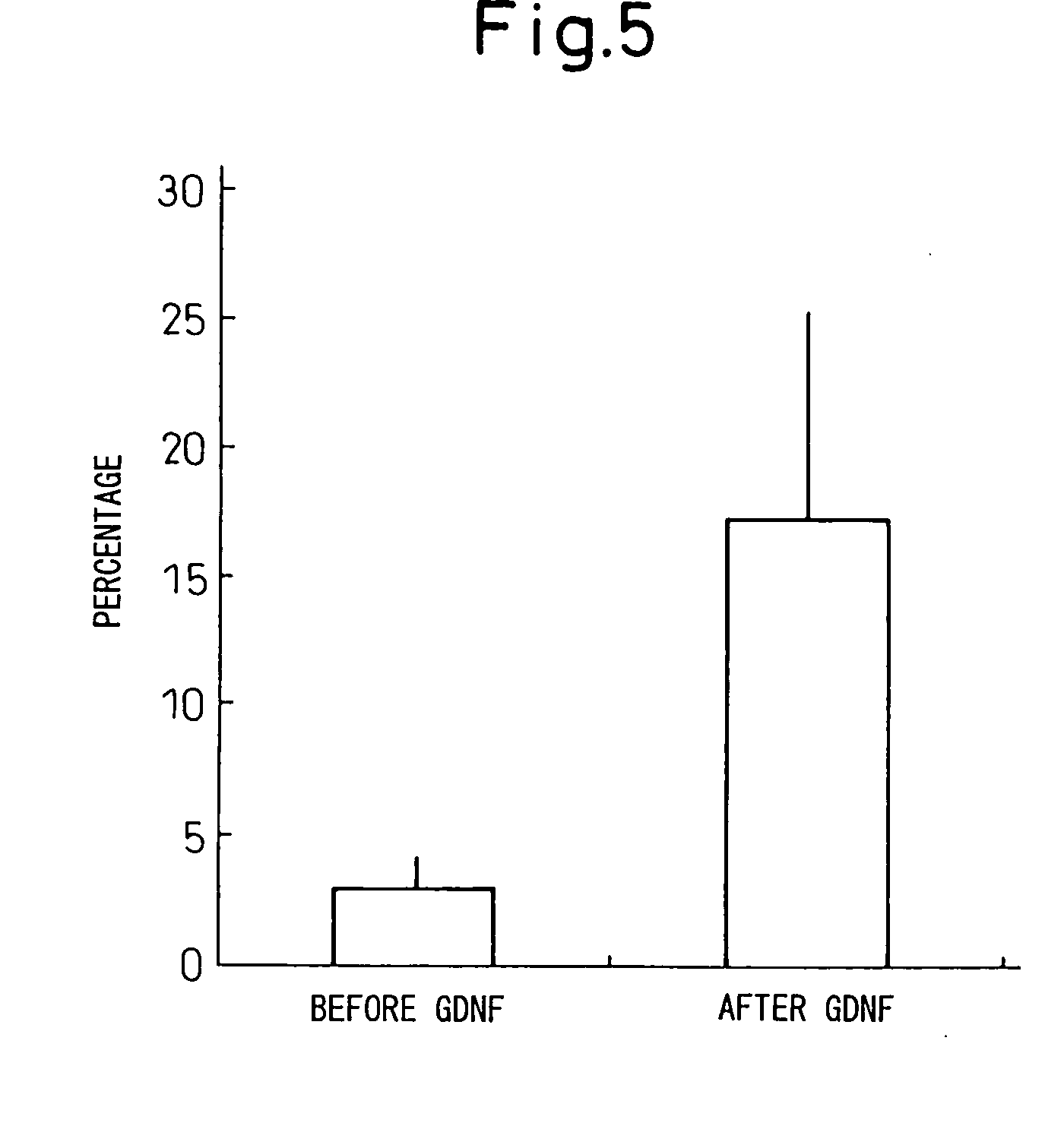
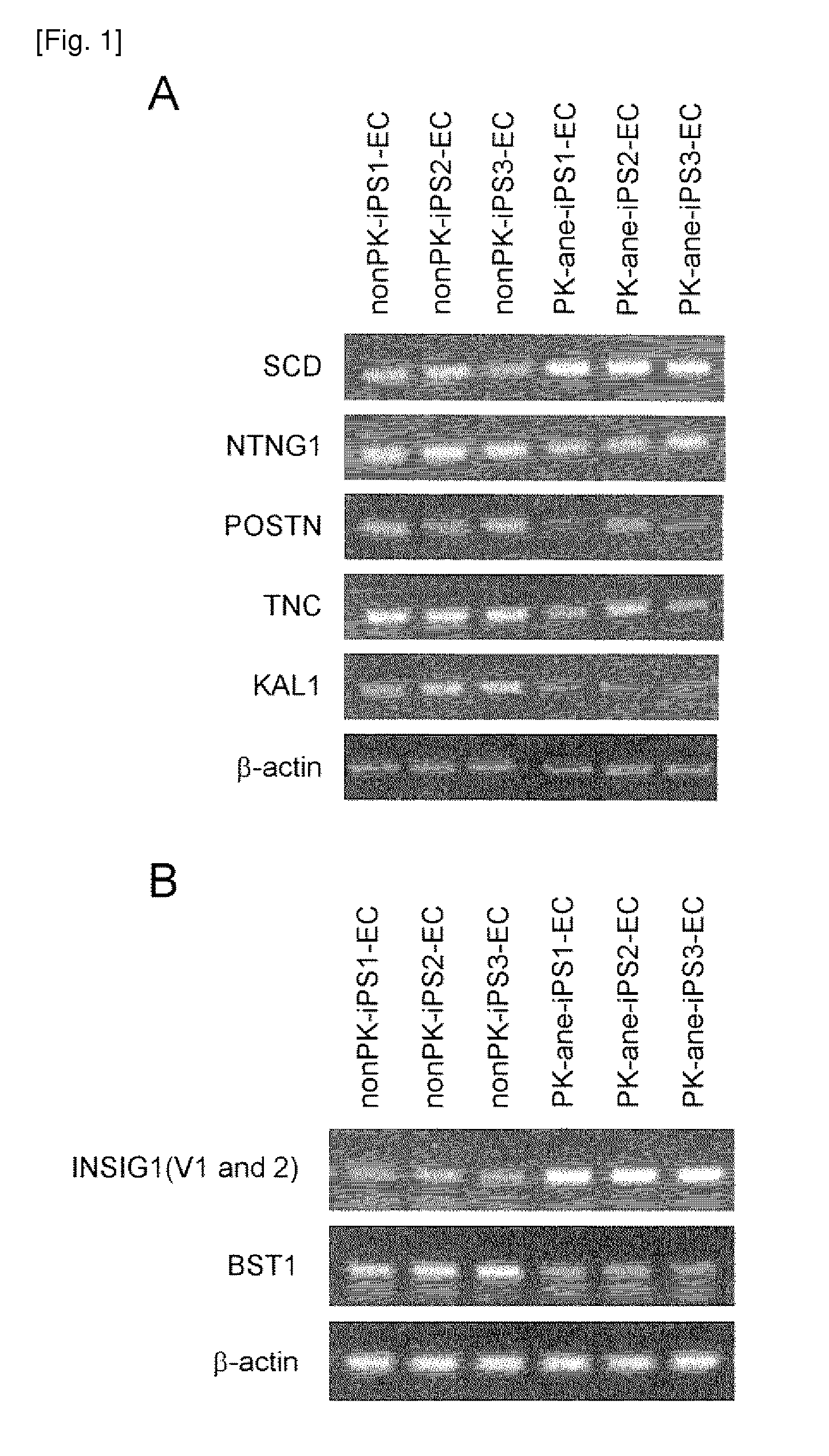
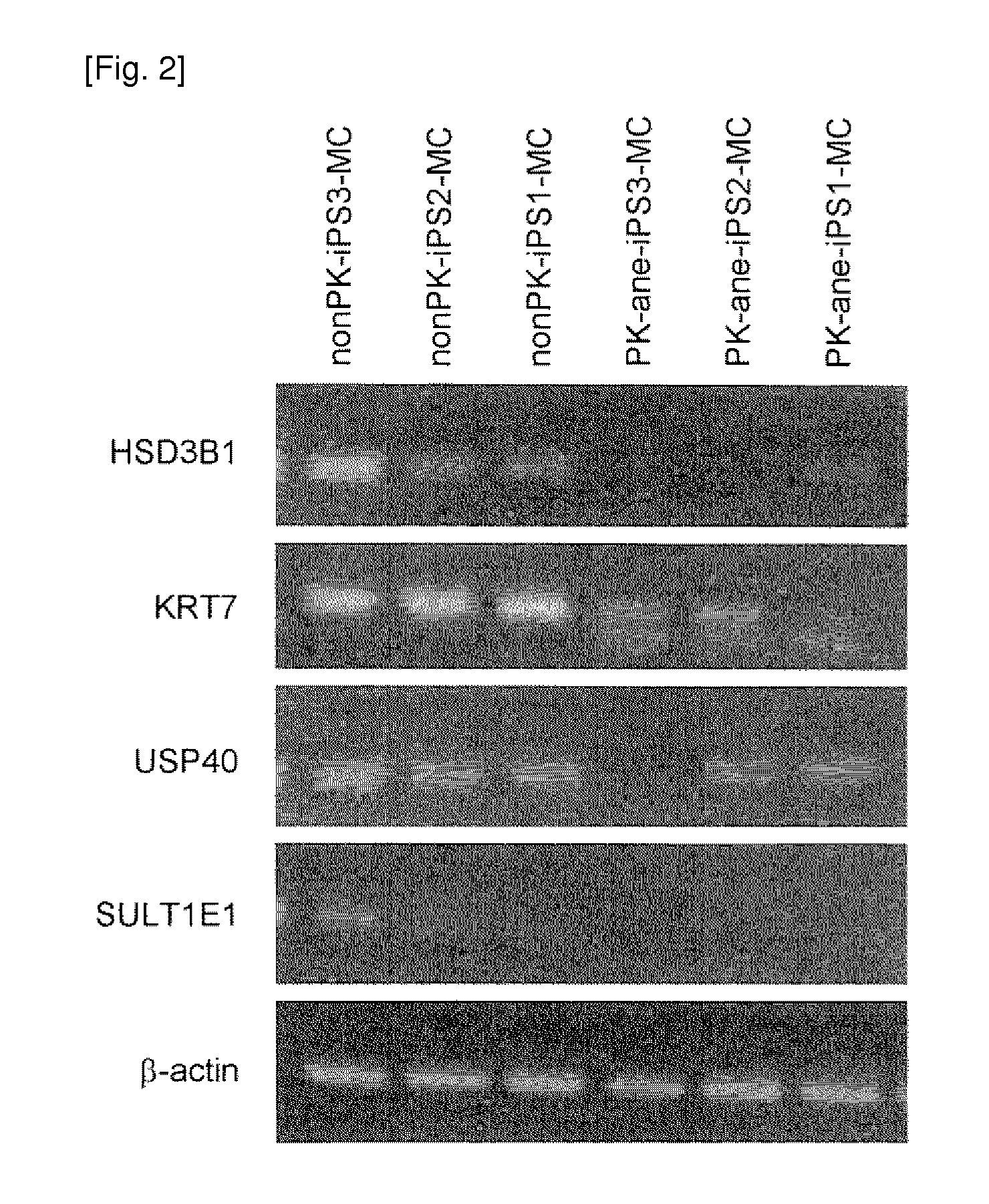
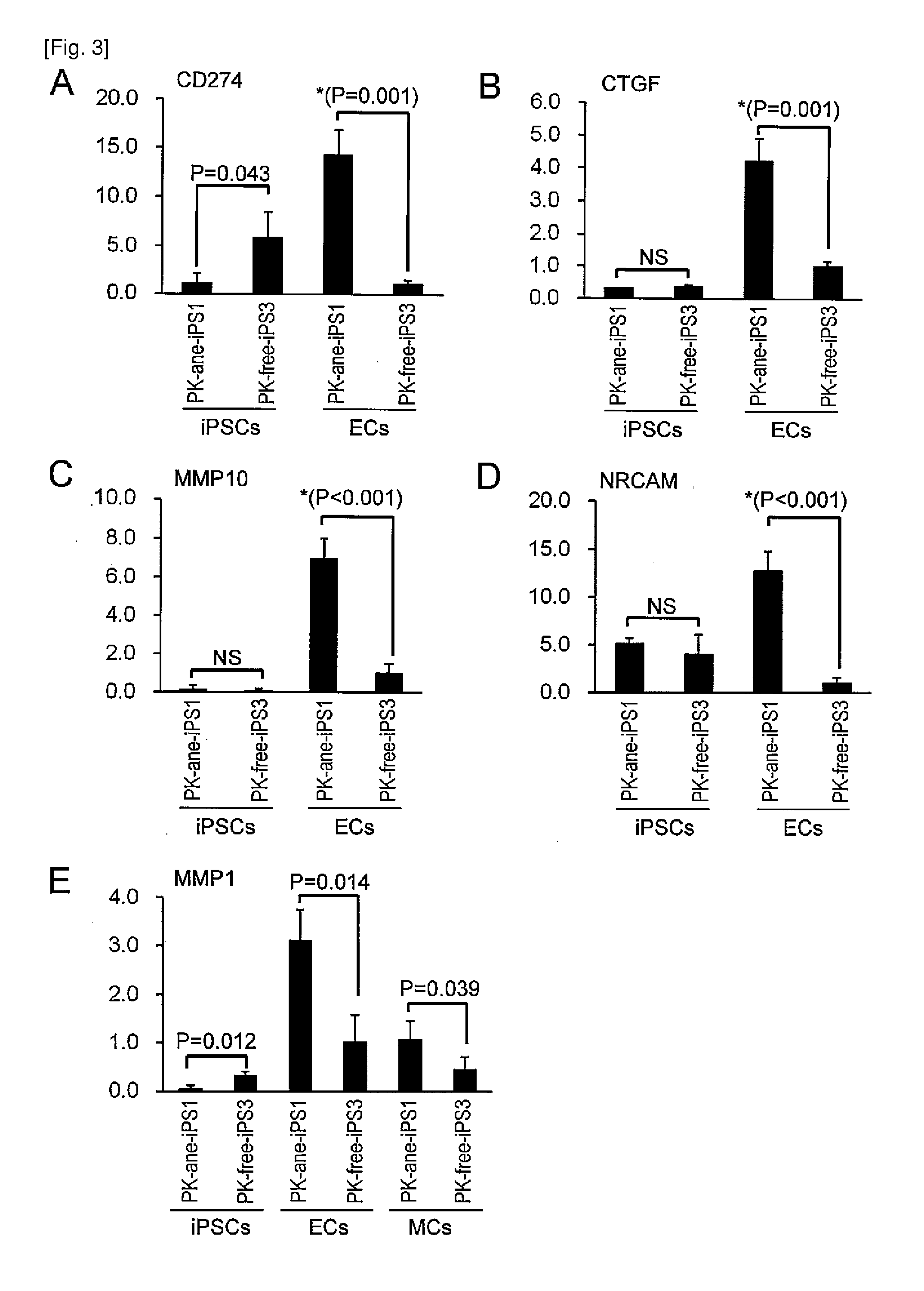
The present invention provides a method of examining polycystic kidney disease or a complication of polycystic kidney disease using a gene(s) selected from the group consisting of NTNG1, POSTN, TNC, KAL1, BST1, ACAT2, INSIG1, SCD, HSD3B1, KRT7, USP40, SULT1E1, BMP6, CD274, CTGF, E2F7, EDN1, FAM43A, FRMD3, MMP10, MYEOV, NR2F1, NRCAM, PDCK1, PLXNA2, SLC30A3, SNAI1, SPOCD1, MMP1, TFPI2, HMGA2, KRTAP4-7, KRTAP4-8, KRTAP4-9, MYPN, RPPH1, and SIAE, and a method of screening for a therapeutic agent or a preventive agent therefore, and further vascular endothelial cells or vascular mural cells obtained via differentiation induction from iPS cells formed from a somatic cell of a subject suffered from polycystic kidney disease and having cerebral aneurysm as a complication.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV
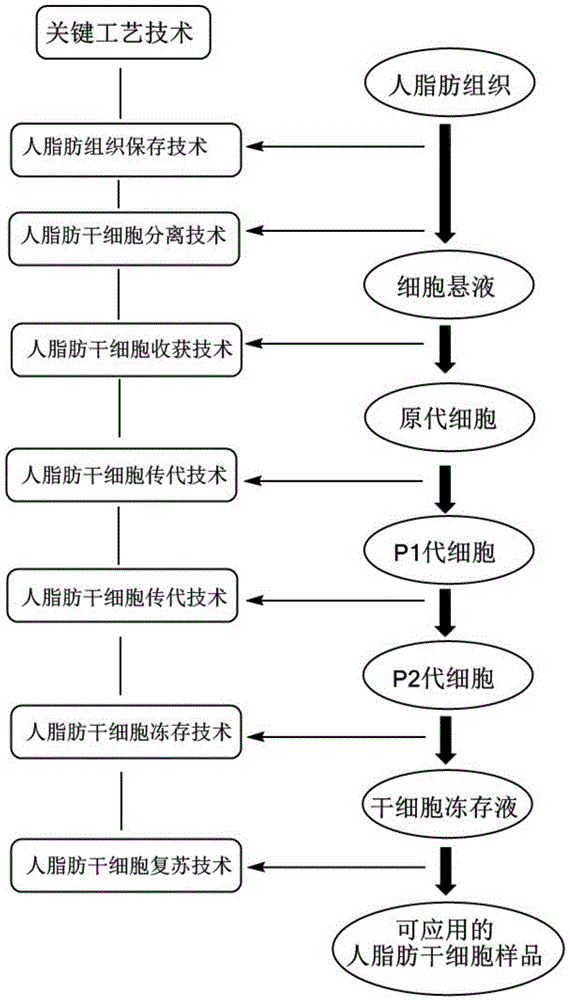
Method for separating human adipose-derived stem cells from human adipose tissues
ActiveCN104357387AHigh purityReduced differentiation inductionSkeletal/connective tissue cellsParenchymaBrown adipose tissue
The invention relates to the field of cell engineering and particularly relates to a method for separating human adipose-derived stem cells from human adipose tissues. According to the method, by adding a small amount of low-molecular-weight heparin calcium into normal saline, a mixed solution is obtained and used as a cleaning fluid to clean the human adipose tissues, residual impurities such as red blood cells in the human adipose tissues can be well removed and thus human adipose-derived stem cells with relatively higher purity can be separated, the content of the parenchyma cell is significantly reduced, the differentiation induction of the human adipose-derived stem cells is facilitated, the consumption amounts of collagenase I, trypsase and a serum-free culture medium can be reduced and the cost of the process is also decreased. In addition, by centrifuging and digesting the human adipose tissues for 1 hour at a speed of 150r / min, the human adipose-derived stem cells with significantly better activity can be obtained.
Owner:深圳市赛欧细胞技术有限公司
Tissue-engineered bone based on entochondrostosis system and construction method thereof
ActiveCN104096266AIn line with the natural development processProsthesisEctopic bone formationIn vivo
The invention discloses a tissue-engineered bone based on an entochondrostosis system and a construction method thereof. The construction method is characterized in that mesenchymal stem cells are cultivated on a porous bone scaffold material to construct a tissue-engineering complex, subjected to in vitro cartilage differentiation induction cultivation for two weeks and continuously conducted with fat cartilage differentiation induction cultivation for two weeks to obtain the tissue-engineered bone. According to the invention, an in vivo research result shows that the in vivo ectopic bone formation can be realized, bone defects can be successfully repaired, the difficulties that the uniform vascularization of large piece of tissue-engineered bone cannot be realized and enough nutrition can't be supplied are solved, and the construction method has a very good application prospect in the construction of the tissue-engineered bone and bone defect repairing.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Cell differentiation inducer
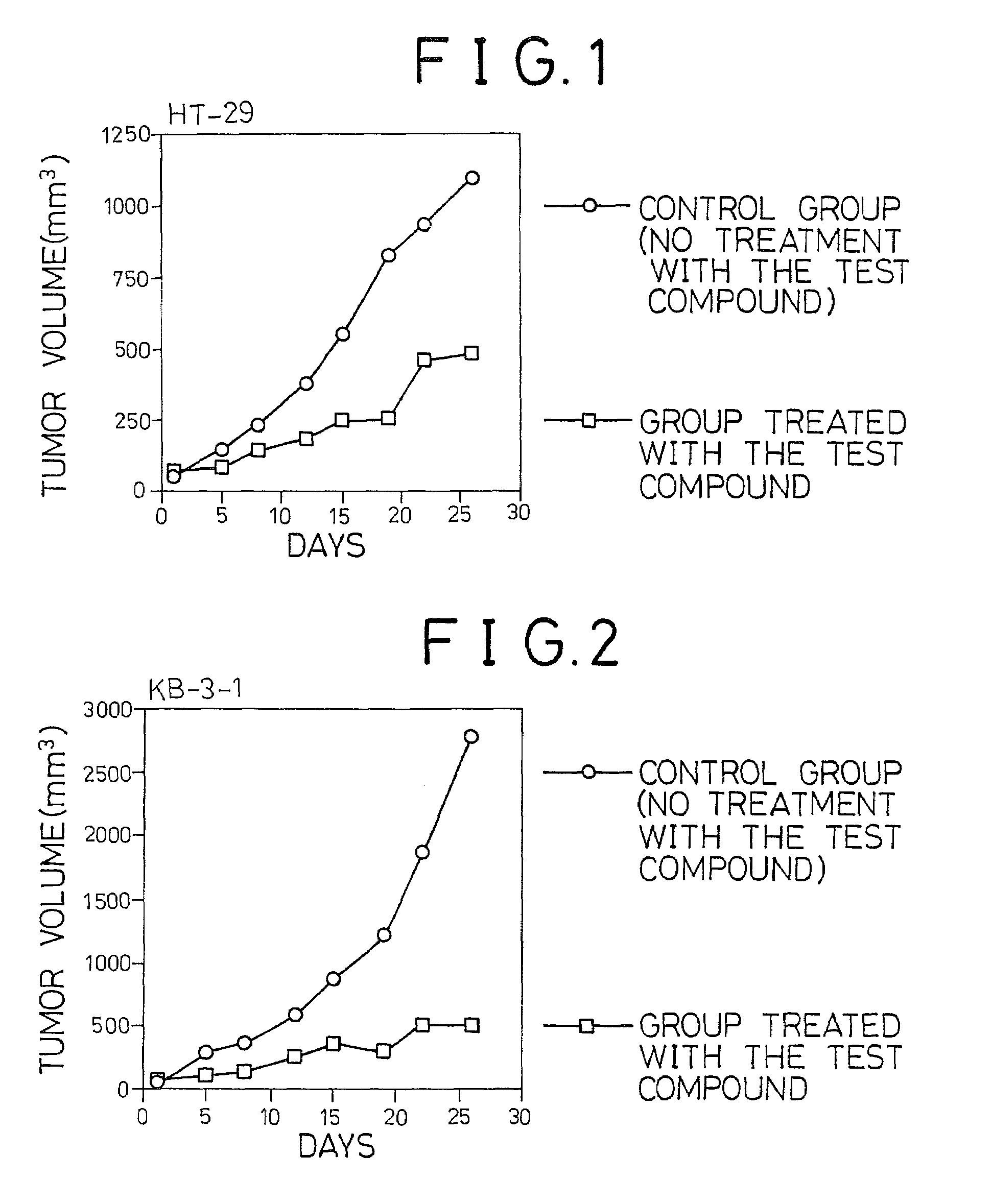
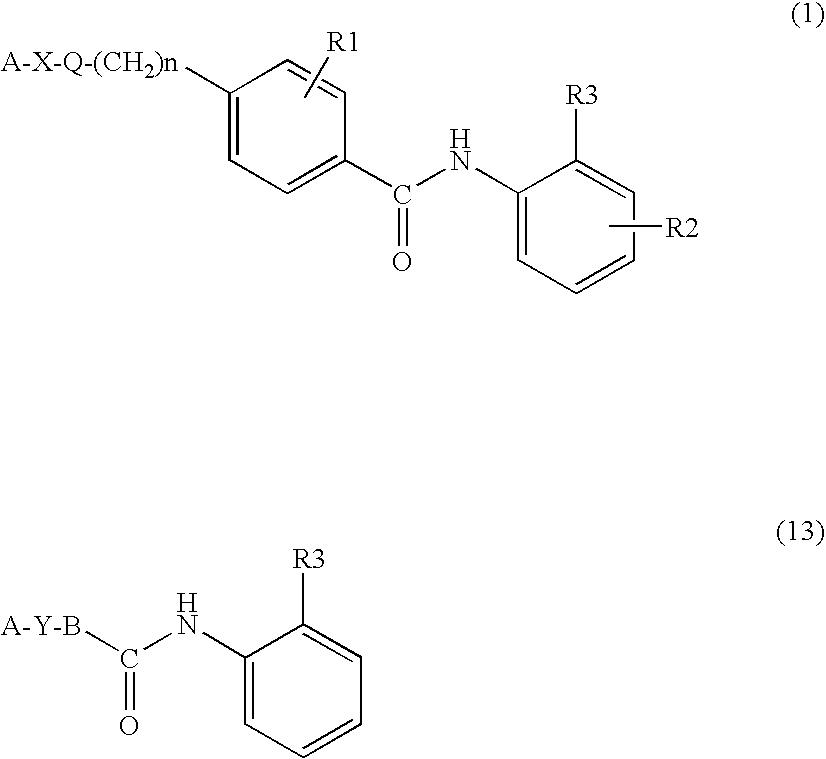
The novel benzamide derivative represented by formula (1) and the novel anilide derivative represented by formula (13) of this invention has differentiation-inducing effect, and are, therefore, useful a therapeutic or improving agent for malignant tumors, autoimmune diseases, dermatologic diseases and parasitism. In particular, they are highly effective as an anticancer drug, specifically to a hematologic malignancy and a solid carcinoma.
Owner:BAYER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY GMBH
Method for producing red blood cell drug containing L-ASPase II by in vitro induction
ActiveCN103224957ASmall toxicityPreserve form functionPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSide effectL asparaginase
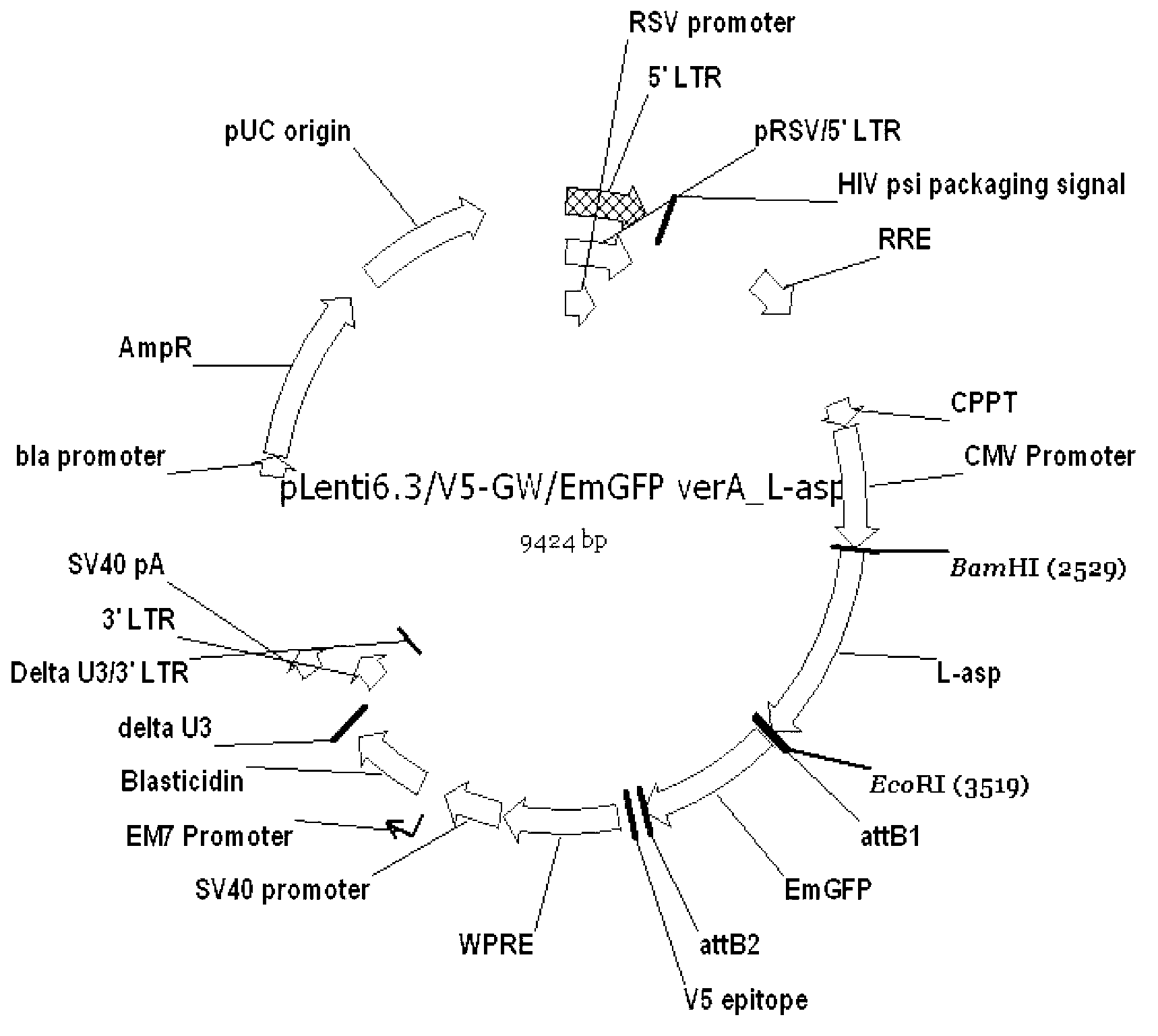
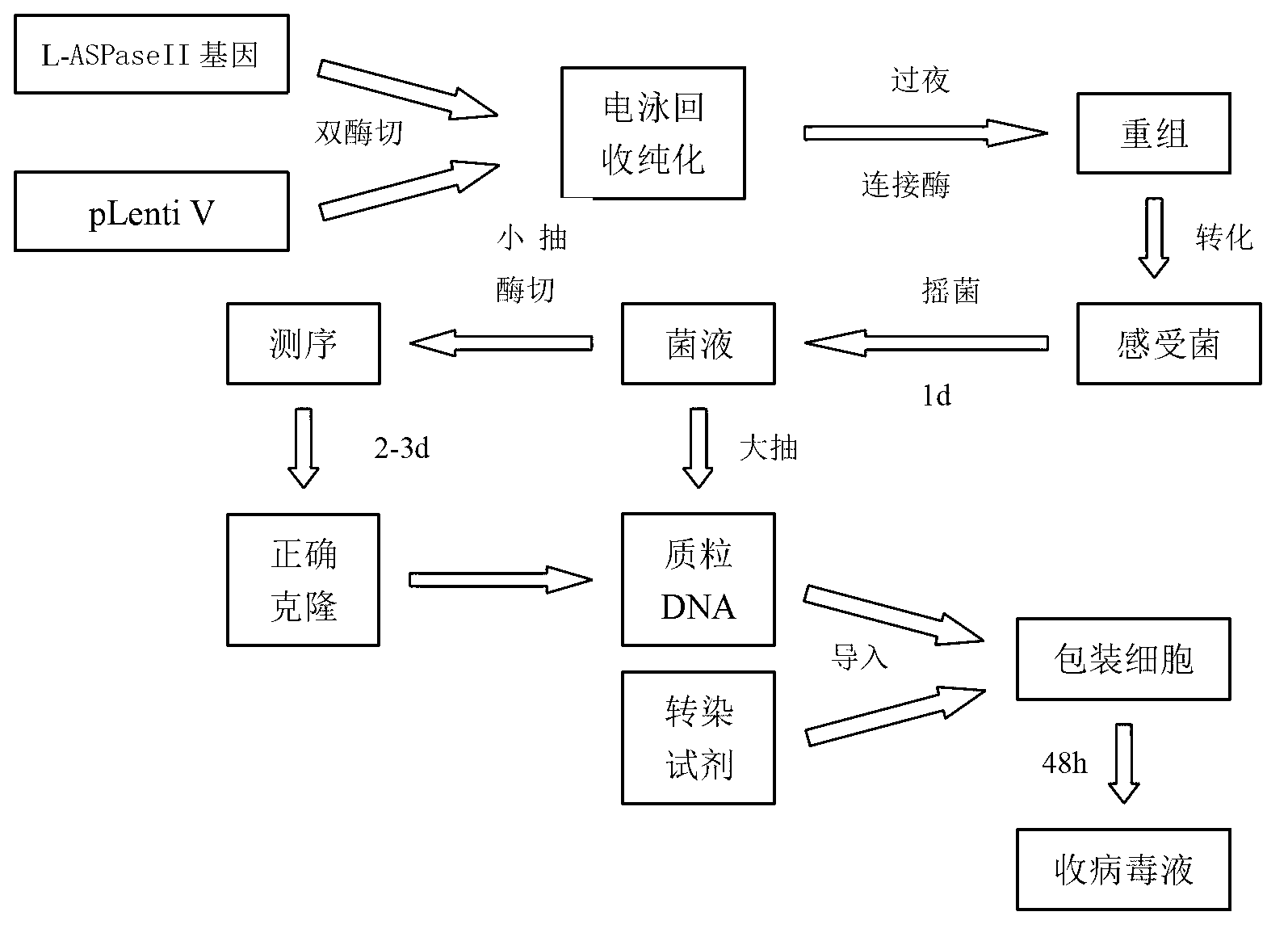
The invention discloses a method for producing a red blood cell drug containing L-ASPase II (L-asparaginase) by in vitro induction. The method comprises the steps of: 1) using a lentiviral vector system to transform induced pluripotent stem (IPS) cells: I. constructing a pLenti6.3 / V5-GW / Em-GFP VerA-L-ASPase II plasmid; II. using 293T cells to perform packaging so as to generate high titer virus particles containing L-ASPase II; III. using the virus particles to transfect induced pluripotent stem cells; and 2) inducing the induced pluripotent stem cells in vitro to generate L-ASPase II-containing red blood cells: I. subjecting IPS cells to in vitro differentiation induction to form an erythroid body EB; and II. performing induced differentiation on EB to obtain mature red cells. The method provided in the invention performs genetic modification on IPS cells by the lentiviral vector system, and induces them in vitro to generate red blood cells containing L-ASPase II. The generated red blood cells can be used as a sustained release carrier of L-ASPase II, and also can maintain the original shapes and functions of red blood cells. The toxic and side effects of L-ASPase II are further reduced, so that the method lays a solid foundation for future clinical application.
Owner:厦门三一造血技术有限公司
Cell-adsorbing column
InactiveUS20100025335A1Reduce total pressure lossReduce the burden onAntipyreticOther blood circulation devicesFiber diameterDifferentiation induction
In light of such conventional technical problems, it is an object of the present invention to provide a cell adsorption column which has an adsorbent with a surface area where there is less concern about denaturation and differentiation induction of cells caused by a contact of the adsorbent with the cells, and whose adsorbent-filled volume is small, and which has a compact property for improving operability and reducing a burden on a patient. The present invention provides a cell adsorption column filled with an adsorbent containing a fiber whose fiber diameter is 0.5 μm or more and 10 μm or less and having a surface area of 0.5 m2 or more and less than 10 m2, in which the adsorbent-filled volume is 100 mL or less.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Method for inducing human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in vitro into liver cells and application thereof
InactiveCN102168065ACapable of synthesizing glycogenReduce absorptionArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsUmbilical cordHepatocyte
The invention discloses a method for inducing human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in vitro into liver cells and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: at the culture logarithmic growth phase of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells, adding a liver cell induced differentiation culture medium and performing differentiated induction to obtain the liver cells formed by the differentiation of the human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells. The liver cell induced differentiation culture medium consists of the basic culture medium is an IMDM culture medium containing 10 to 70 ng / ml of liver cell growth factor, 3 to 30 ng / ml of fibroblast growth factor, 4.5 to 50 ng / ml of oncostatin, 2 to 40 ng / ml of alkali fibroblast growth factor, 20 ng / ml of epidermal growth factor, 1 mu M of dexamethasone and 50 mg / ml of ITS+premix. The method has the characteristics of one step method, simplicity, high repeatability, short duration time of differentiation process and good induced differentiation effect. The method can be applied to the research on turning mesenchymal stem cells into liver cells by induced differentiation.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for producing corneal endothelial cell
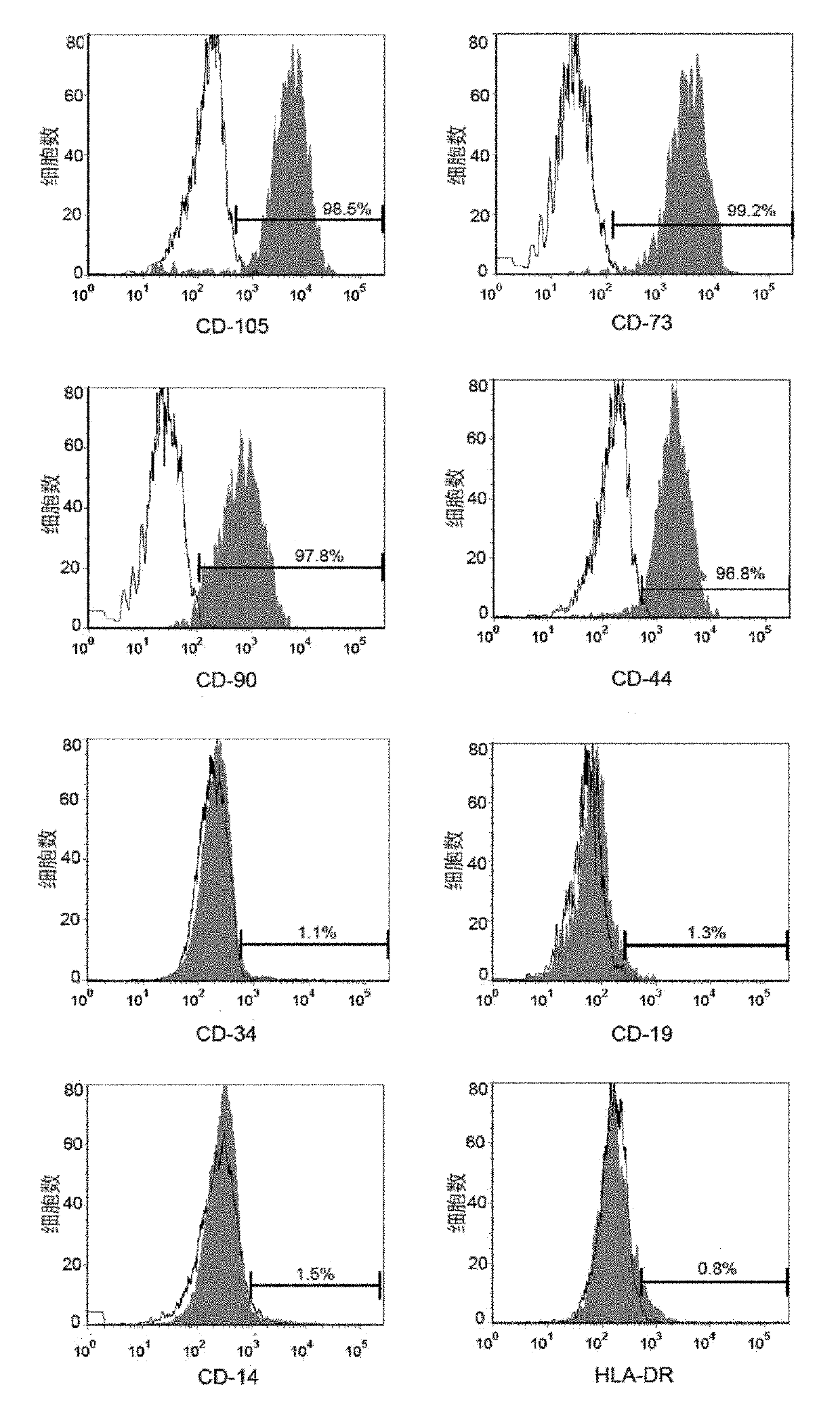
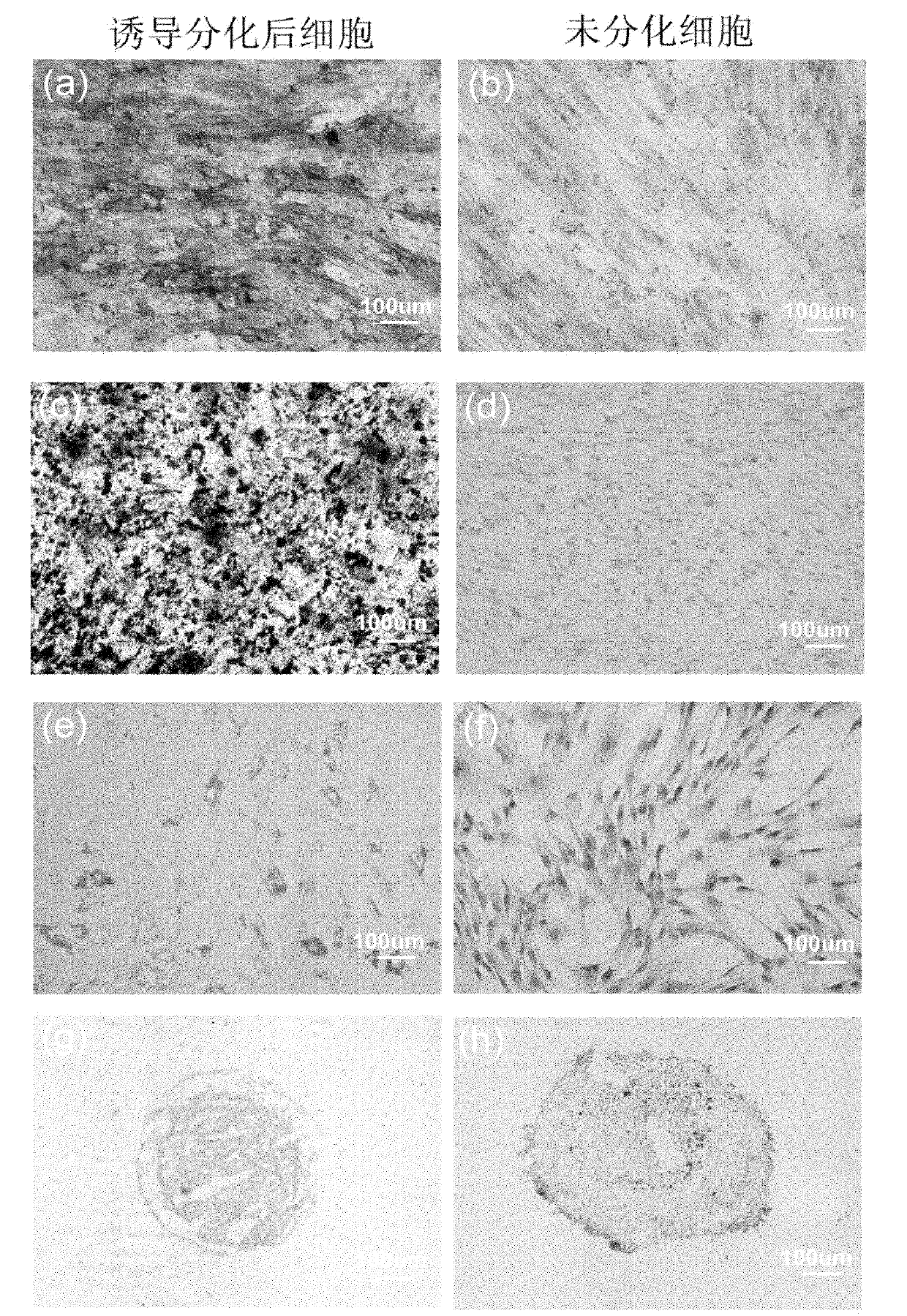
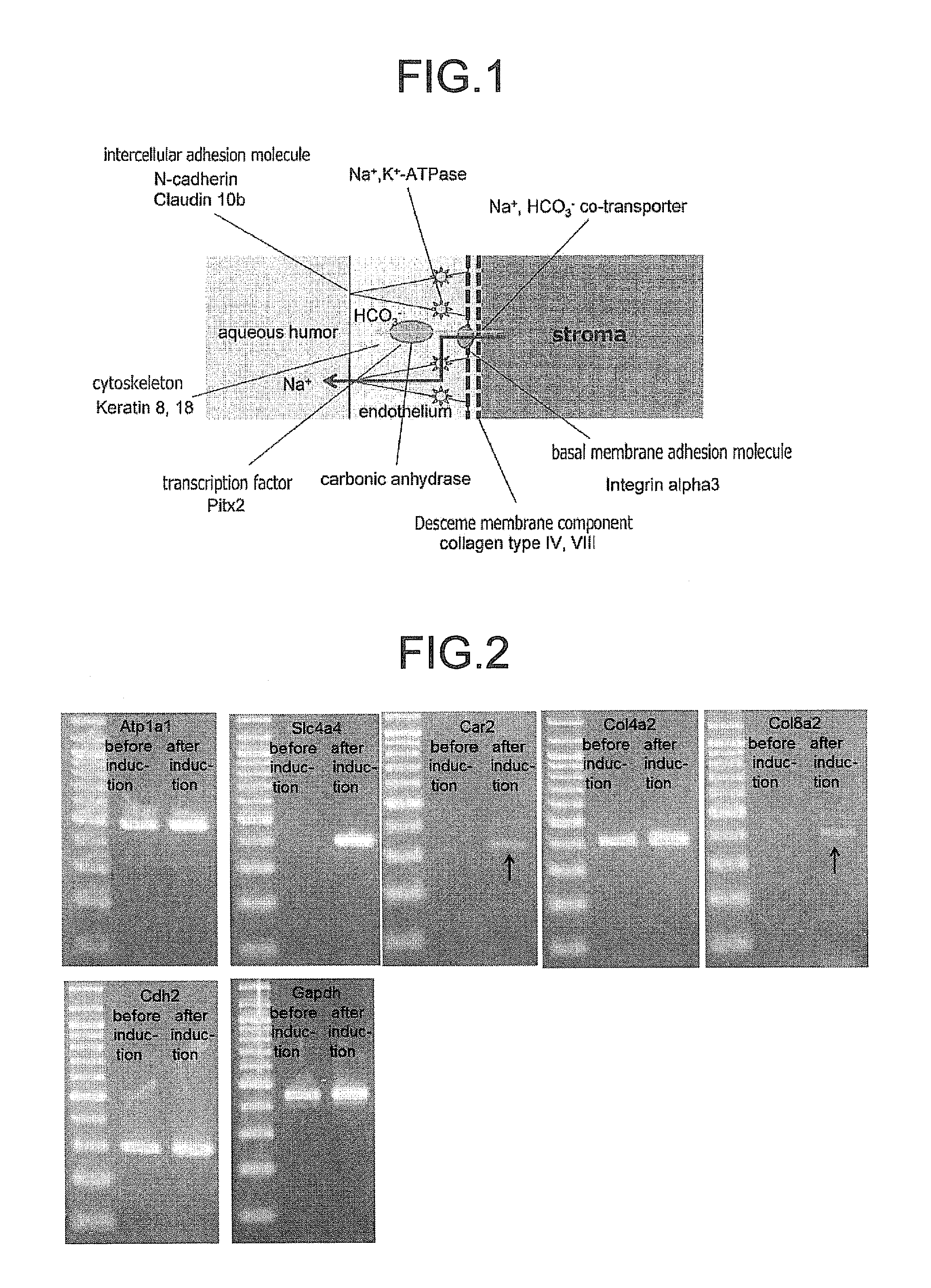
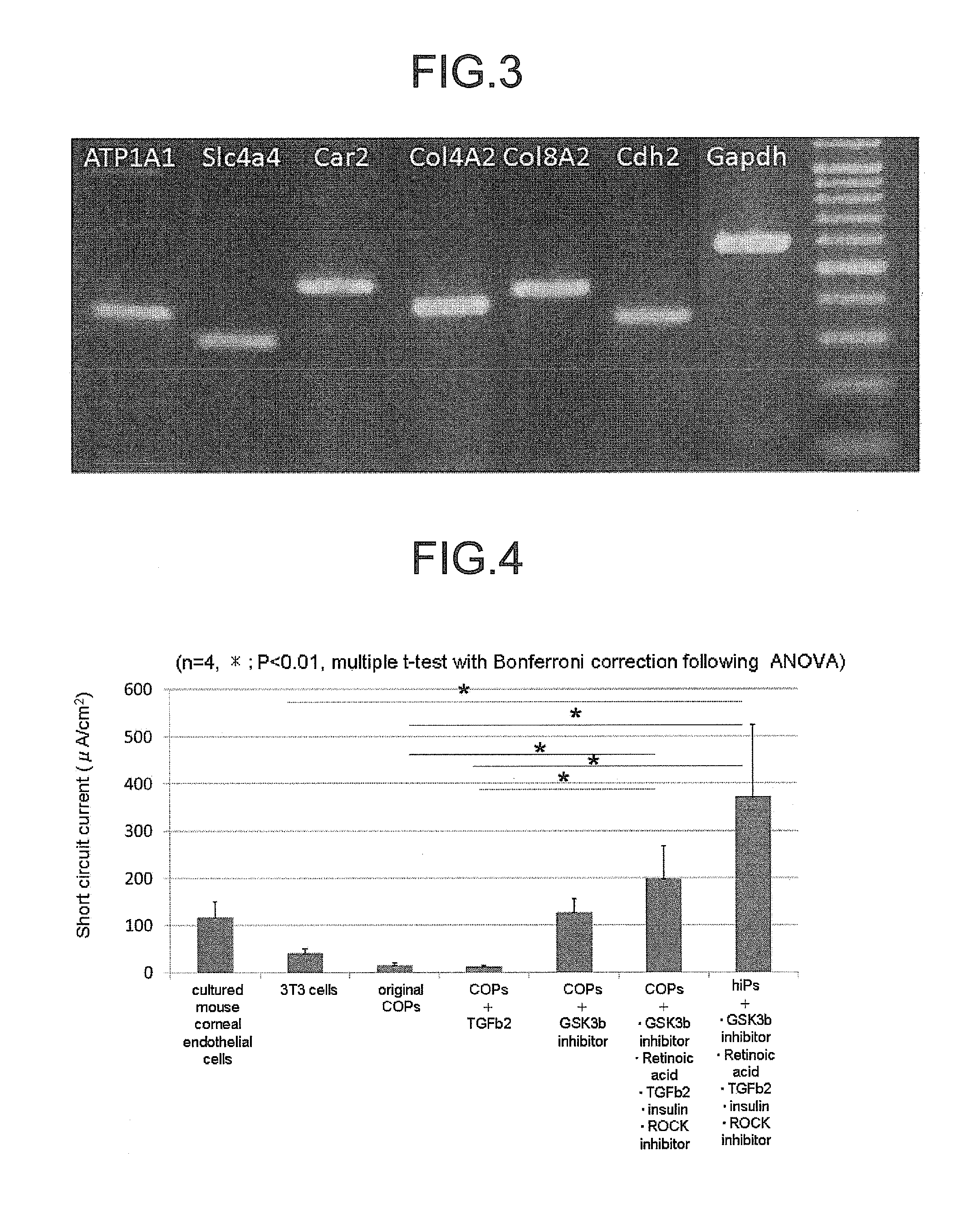
ActiveUS9347042B2Efficient productionSenses disorderEpidermal cells/skin cellsCorneal endothelial cellNeural crest
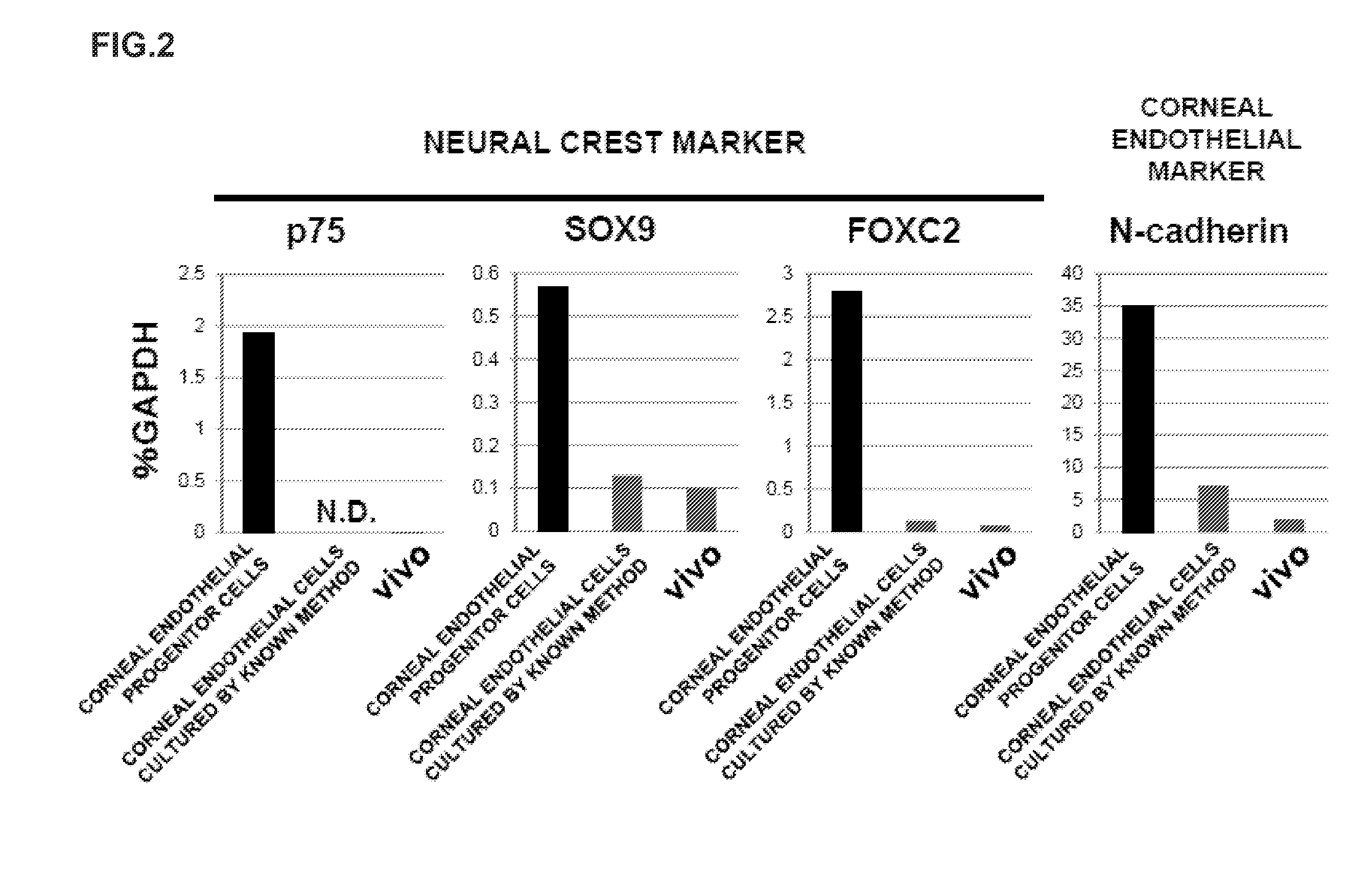
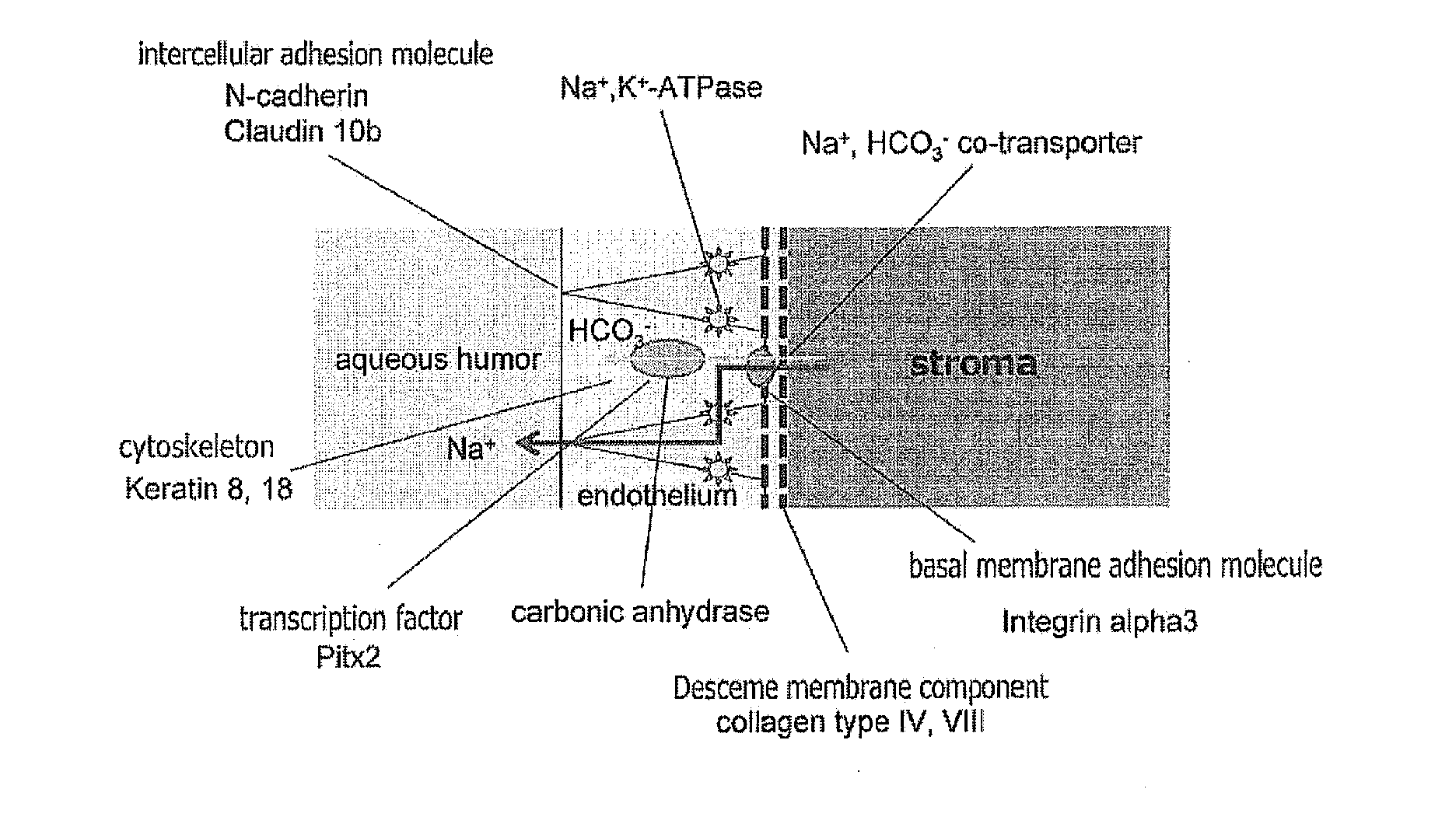
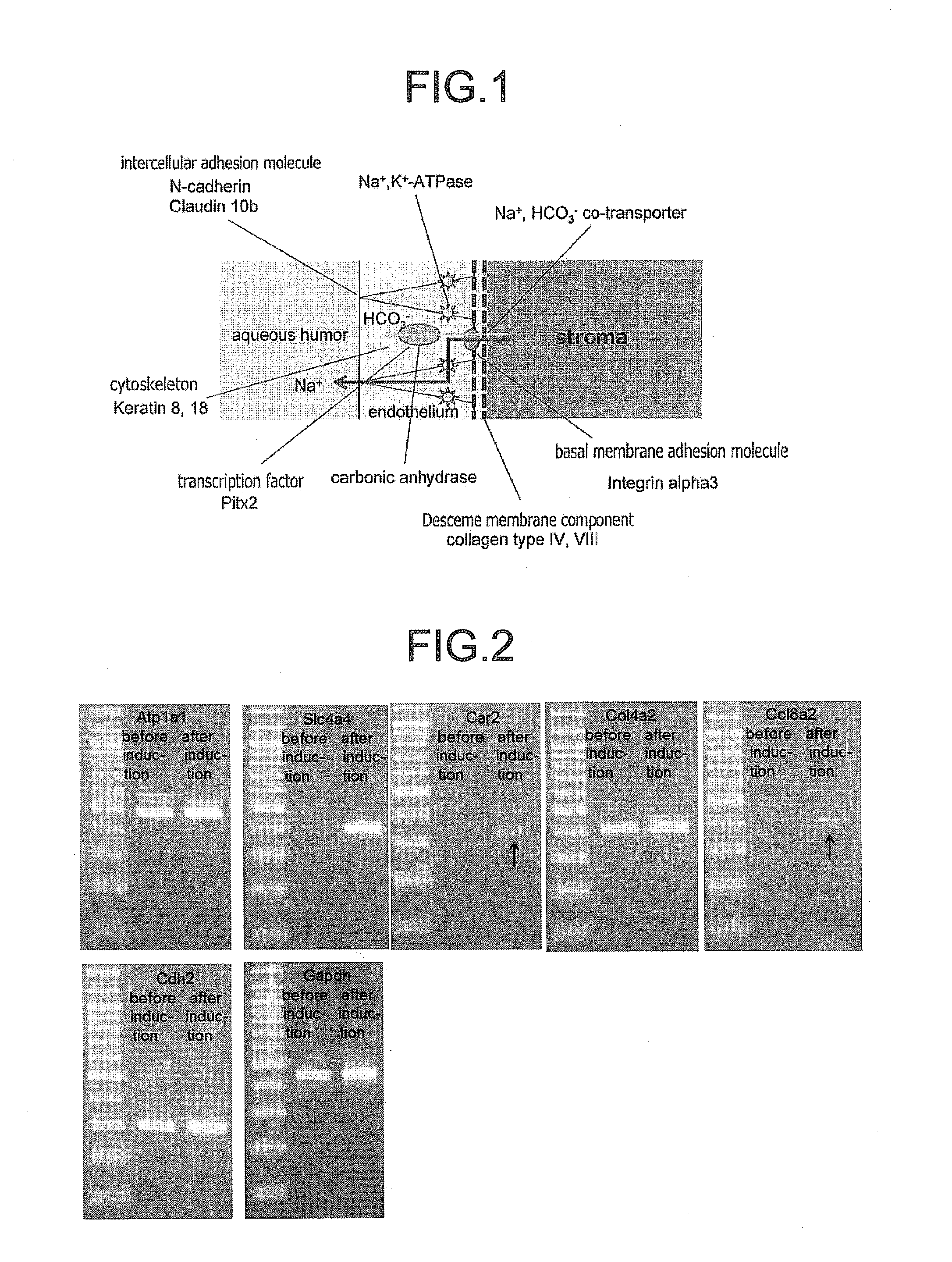
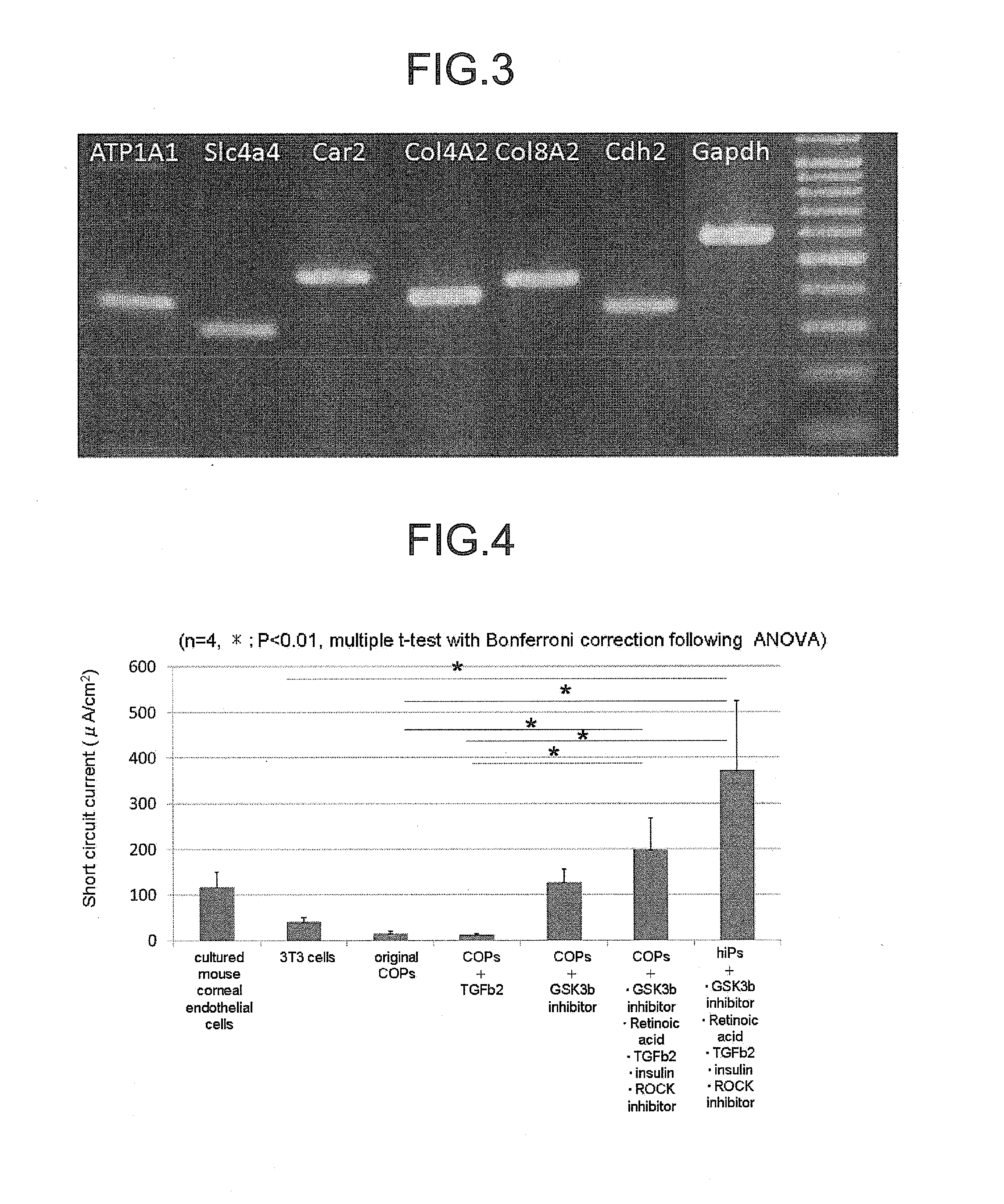
The invention provides a method of efficiently producing corneal endothelial cells, particularly from corneal stroma or iPS cell-derived neural crest stem cells, a method of producing corneal endothelial cells stably in a large amount by inducing more efficient differentiation of stem cells into corneal endothelial cells, and a medicament containing corneal endothelial cells. The method of inducing differentiation of stem cells into corneal endothelial cells includes a step of culturing the stem cells in a differentiation induction medium containing a GSK3 inhibitor (preferably a GSK3β inhibitor) and retinoic acid, with the differentiation induction medium preferably further containing one or more of TGFb2, insulin, a ROCK inhibitor, and the like.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
Human mesenchymal stem cell adipogenesis inducing and differentiating culture medium and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108588015AEfficient adipogenic induction of differentiationShorten induction time of adipogenic differentiationCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsDexamethasoneAdipogenesis
The invention discloses a human mesenchymal stem cell adipogenesis inducing and differentiating culture medium and a preparation method thereof. The human mesenchymal stem cell adipogenesis inducing and differentiating culture medium is produced by the following components of an alpha-MEM / HG-DMEM culture medium, 5-50% of percent by volume of fetal calf serum, 0.5-10% of percent by volume of glutamine, 100-400 [mu]M volume of indomethacin, insulin with the concentration of 0.1-20 [mu]g / ml, 10-200 [mu]M volume of 1-methyl-3-isobutyl xanthine, 10-200 nM volume of dexamethasone and 0.1-20 [mu]M volume of spermine. The preparation method includes the following steps that a culture dish is cleaned; the culture medium is provided, and the alpha-MEM / HG-DMEM culture medium is prepared in the culture dish according to a formula; materials are mixed; and mixed liquor is filtered. Multiple histologic origin human mesenchymal stem cells including human mesenchymal stem cells, umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells and adipose tissue-derived stromal cells are induced to the directional differentiation of adipogenesis cells; differentiating and inducing time of the human mesenchymal stem cells isshortened, the preparation method is convenient, and the differentiating and the inducing of human mesenchymal stem cell adipogenesis can be achieved stably and efficiently.
Owner:安徽瑞杰赛尔生物科技有限公司
Cultured muscle cells with high metabolic activity and method for production of the cultured muscle cells
InactiveUS20080299086A1Improve glucose metabolismSimple structureBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMyogenic cellInsulin dependent
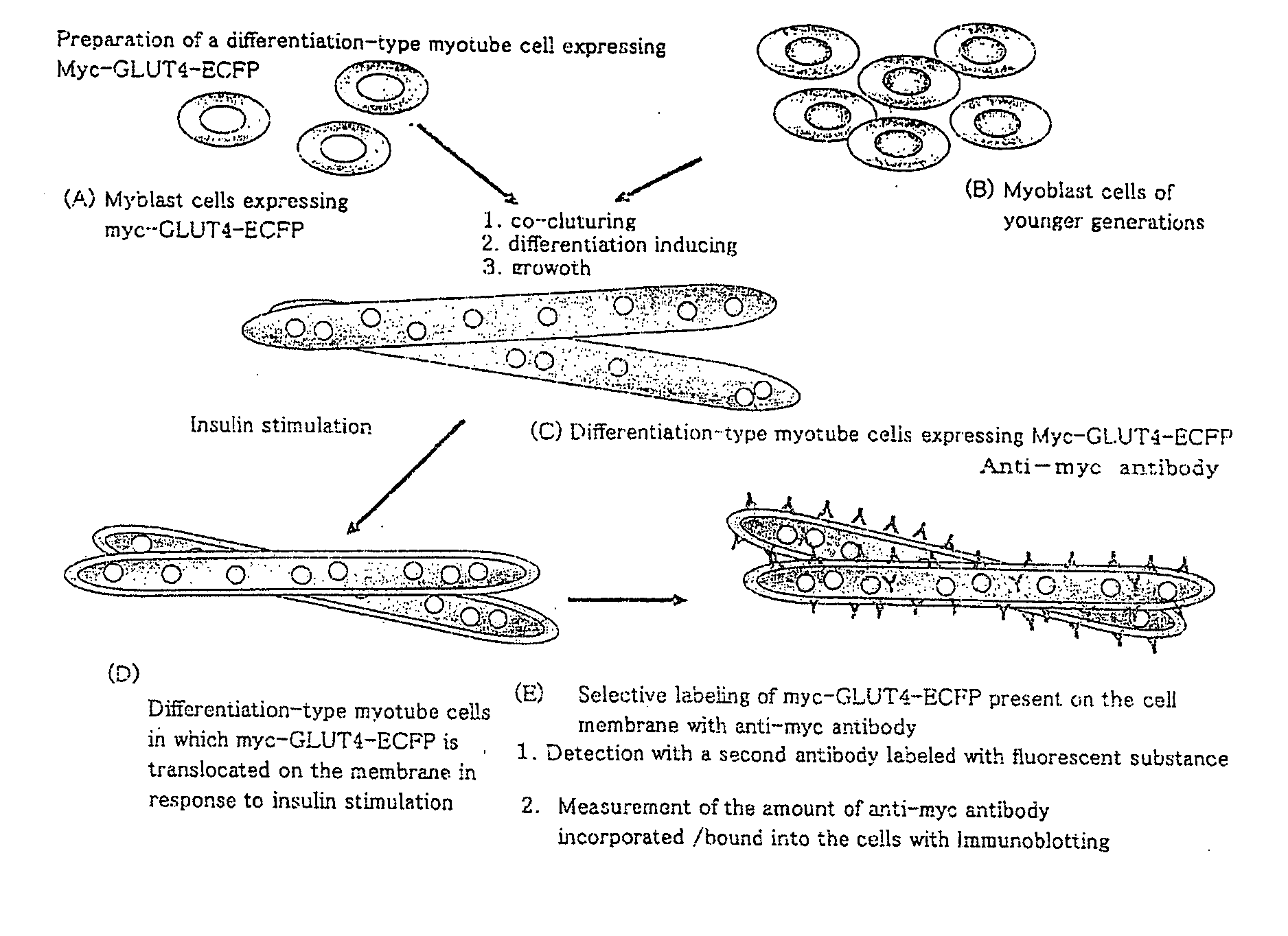
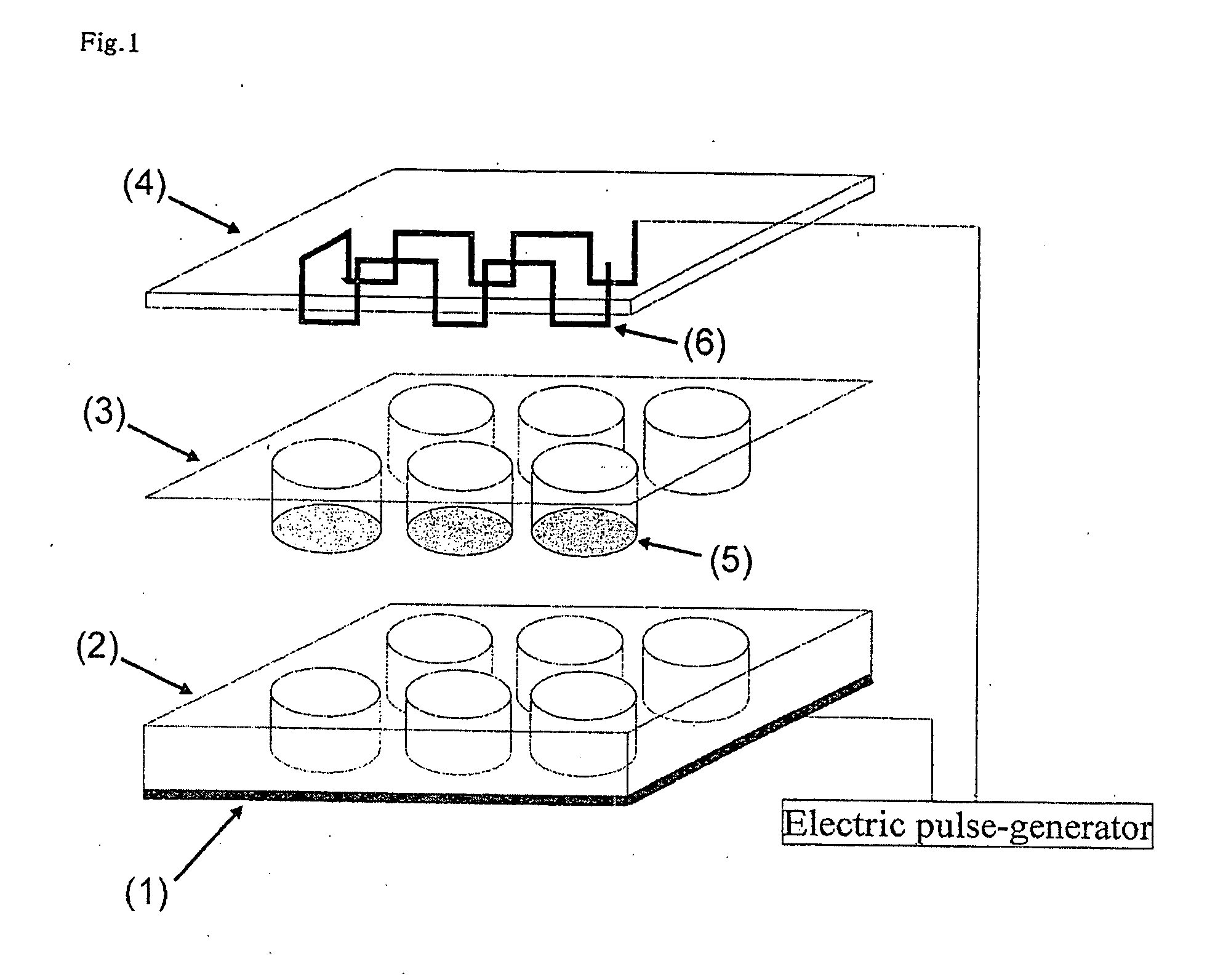
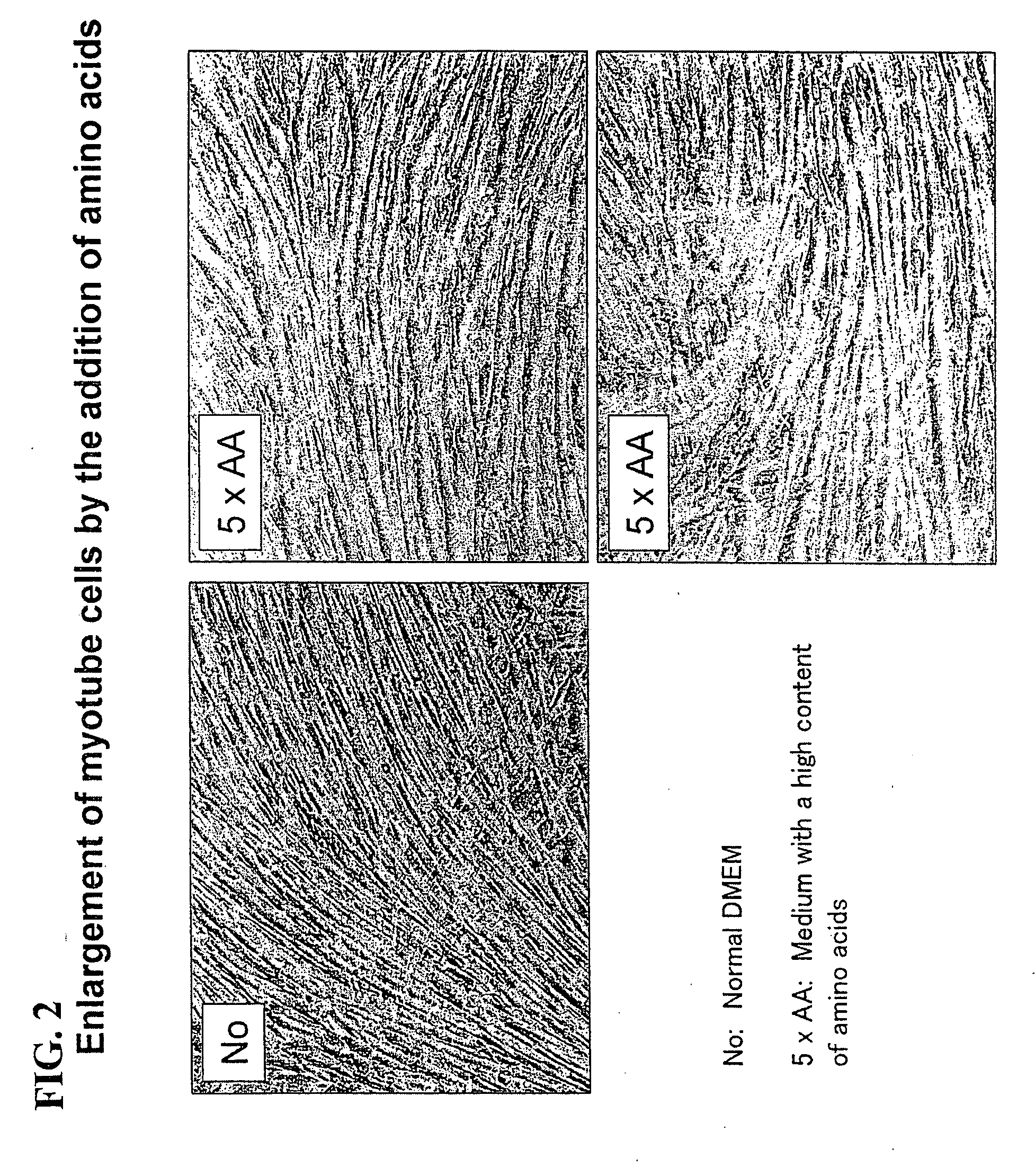
The object of the present invention is to provide a method of preparing excellent cultured muscle cells having high metabolic capacity and insulin responsiveness, and further provide a method for the measurement of sensitive metabolic capacity using the cells. Moreover, its purpose is to provide a culture system / culture apparatus that can smoothly translocate such highly advanced cultured muscle cells intact to activity evaluation systems of a number of drugs. Moreover, the object of the present invention is to provide cultured muscle cells that are very suitable for measurement of the membrane-translocation activity of GLUT4 in an extraneous stimulus-dependent manner such as insulin, etc., and to provide a method for the measurement of the membrane-translocation activity of GLUT4 using the cells. The present invention is a method of preparing myotube cells, comprising a step (1) of culturing myoblast cells, a step (2) of differentiation-inducing the myotube cells into the myoblast cells in a culture medium with a high content of amino acids, and a step (3) of applying an electric pulse to the differentiation-induced myotube cells, and a method for the measurement of insulin-dependent sugar uptake using the myotube cells prepared by said method, and relates to the method for the measurement, comprising applying insulin stimulation by culturing the cells in a culture medium containing insulin, culturing the cells in the culture medium further supplemented with sugar, and measuring the sugar uptake. Furthermore, the present invention relates to a differentiation-type culture myotube cell constitutively expressing a recombinant GLUT4 having a labeled substance at its extra-cellular site, which is prepared by co-culturing wild-type myoblast cells and recombinant myoblast cells constitutively expressing said recombinant GLUT4, and a method for the measurement of membrane-translocation activity of the recombinant GLUT4 using the cells, and particularly a method for the measurement of insulin-dependent sugar uptake activity.
Owner:TOHOKU UNIV
Differentiation-inducing culture medium additive and use thereof
InactiveUS20110212523A1Low costEfficient inductionCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPhosphoric acidPhospholipid
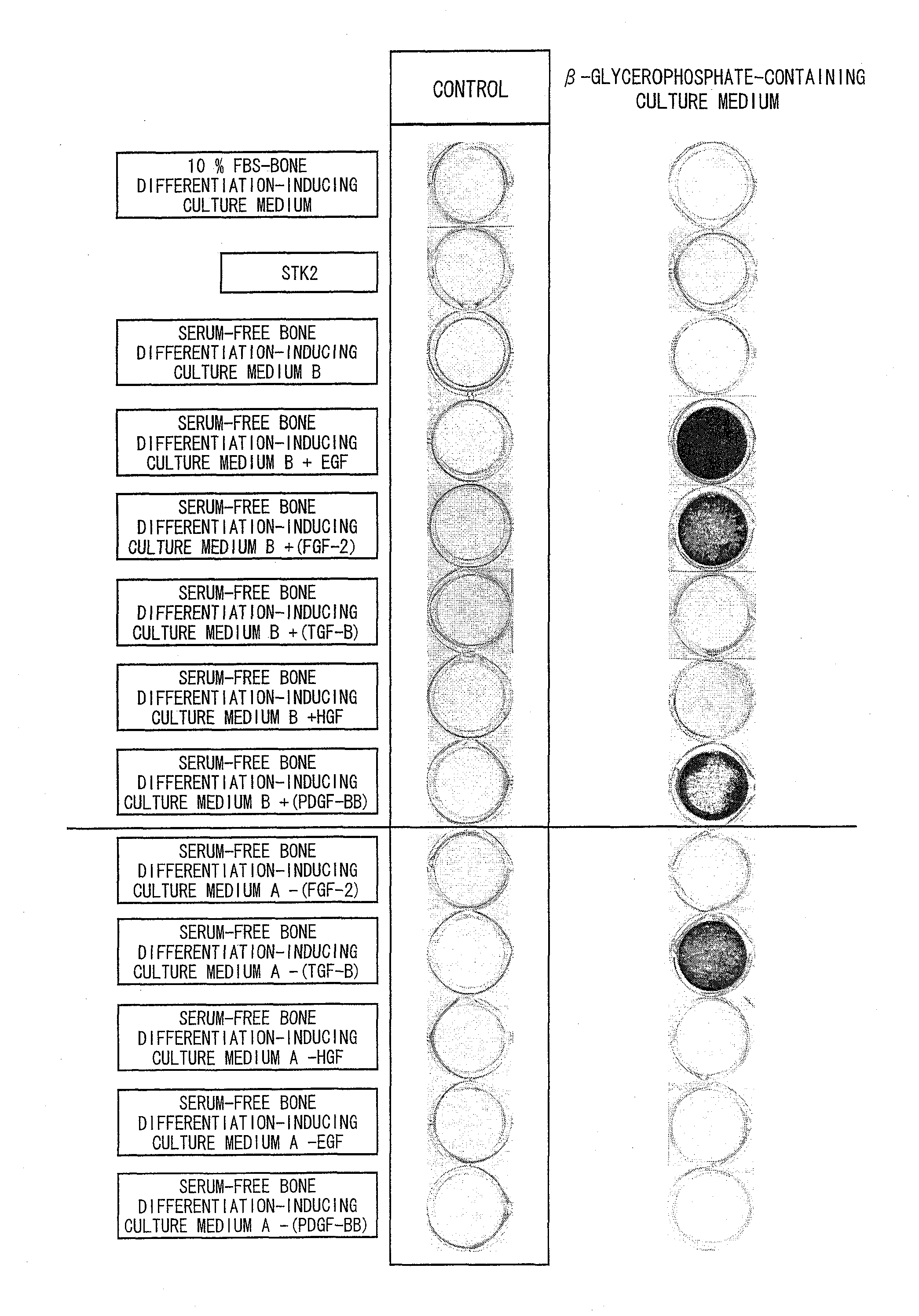
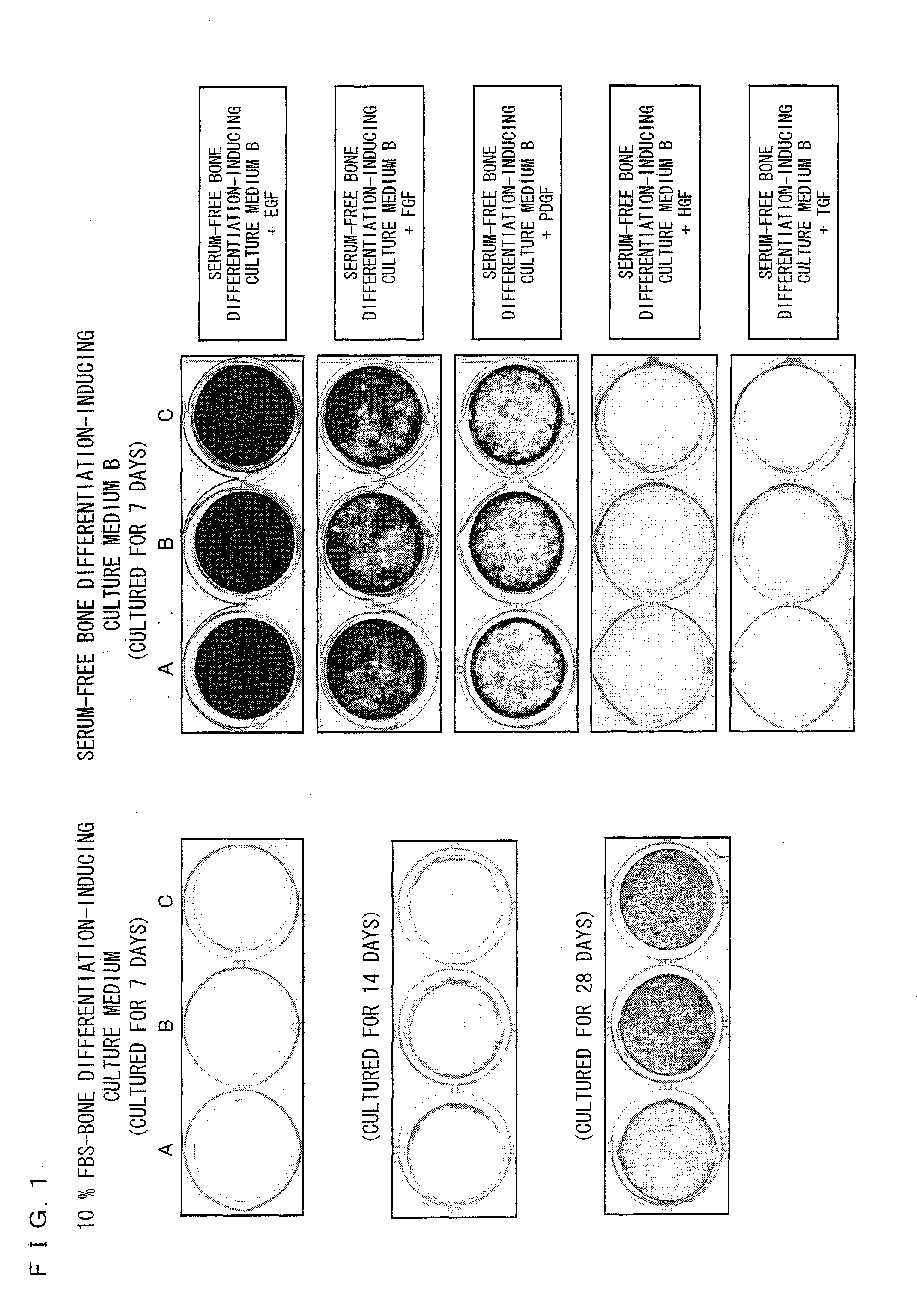
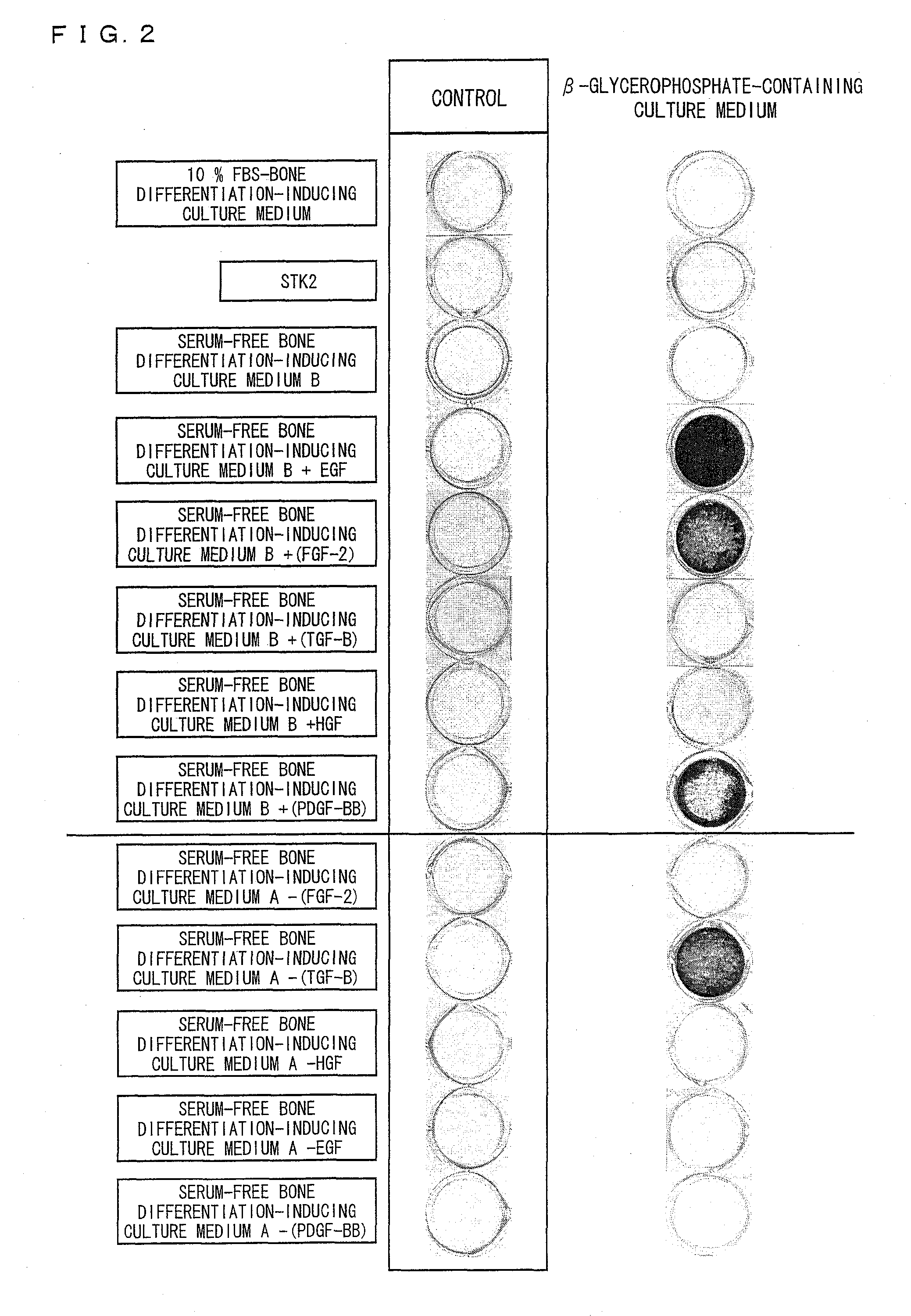
Provided is a differentiation-inducing culture medium additive for inducing bone differentiation of at least one type of cell selected from the group consisting of a stem cell, a dental pulp cell, a periodontal ligament cell, a placenta, an amnion, and a fibroblast under a serum-free condition, and a use of the differentiation-inducing culture medium additive. The differentiation-inducing culture medium additive of the present invention for inducing differentiation of a stem cell under a serum-free condition at least contains at least one growth factor selected from the group consisting of EGF, FGF, and PDGF; dexamethasone; and β-glycerophosphate. The differentiation-inducing culture medium additive of the present invention does not require ascorbic acid 2-phosphate and ITS, which are normally essential for bone differentiation. Further, bone differentiation can be promoted by adding phospholipid.
Owner:HIROSHIMA UNIVERSITY +1
Method for preparing corneal endothelial cell
ActiveUS20140170751A1Improve proliferative abilityIncrease the number ofNervous system cellsUnknown materialsDiseaseProgenitor
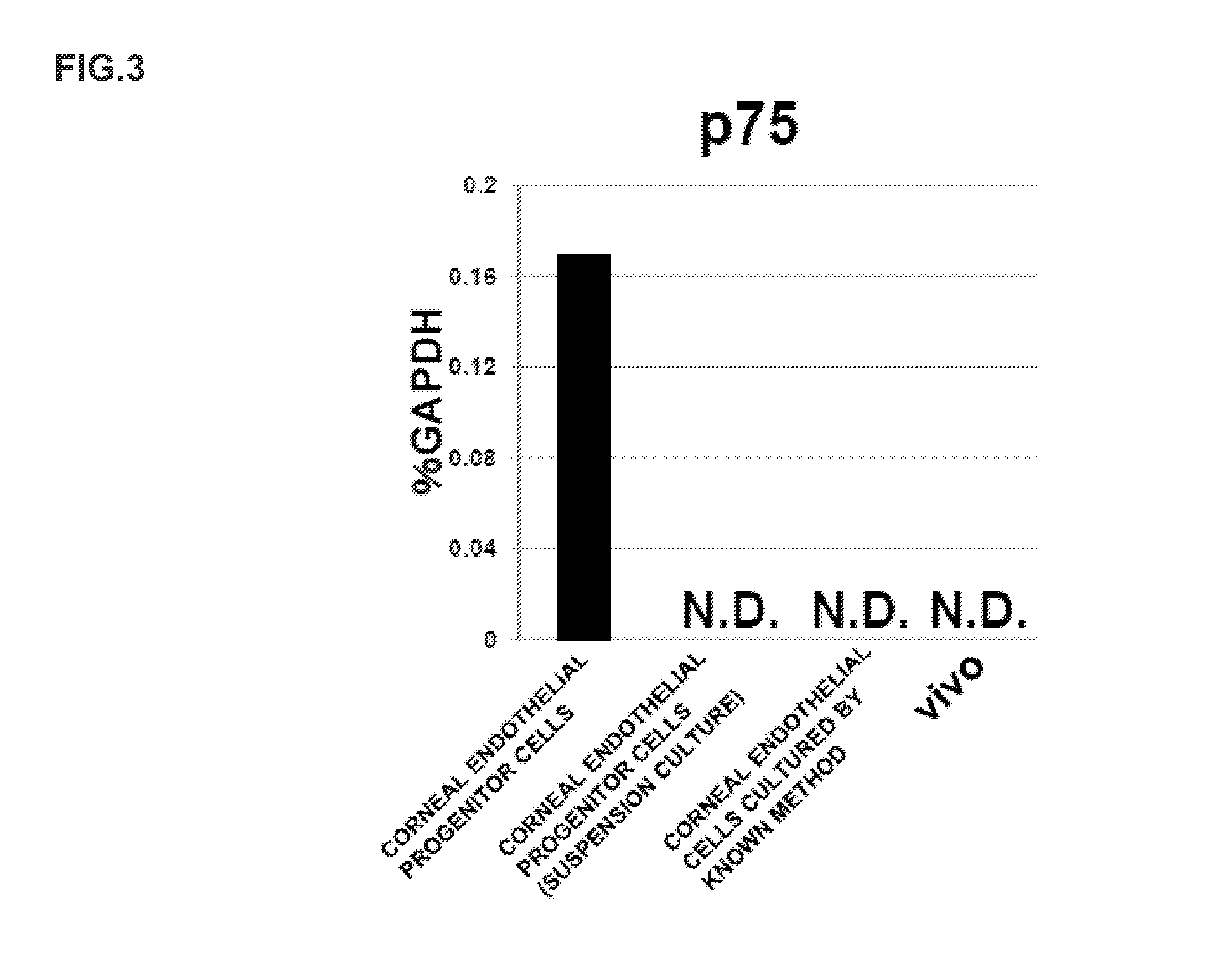
The present invention relates to a method for preparing corneal endothelial progenitor cells by adherent culturing a cell population isolated from corneal endothelial cell tissue at a low density by using a serum-free medium. The present invention also relates to a method for preparing corneal endothelial cells by differentiation-inducing the corneal endothelial progenitor cells obtained by the aforementioned method. According to the present invention, corneal endothelial progenitor cells can be selectively grown from a corneal tissue-derived cell population, and corneal endothelial cells obtained by inducing the corneal endothelial progenitor cells can be applied to treatment of corneal endothelial diseases. As a result, problems of corneal transplantation such as shortage of donors and occurrence of rejection can be solved.
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
Method for tissue culture of Acer fabri Hance by axillary buds
InactiveCN102138528AAddress resource shortagesGet efficientlyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAxillary budBud
The invention provides a method for tissue culture propagation of Acer fabri Hance by axillary buds, which comprises the following steps: disinfecting explants, inoculating the disinfected explants onto an induction medium for differentiation induction of buds, and normally culturing for 25 to 35 days under the conditions of a culture temperature between 20 and 26 DEG C, illumination time between 10 to 16 hours per day and an illumination intensity between 1,600 and 20,001x; cutting obtained tender shoots of Acer fabri Hance, and inoculating the cut tender shoots onto a subculture medium to perform subculture for 25 to 35 days; inoculating the sterile seedlings of the Acer fabri Hance into a rooting culture medium to perform rooting culture for 10 to 15 days under the conditions of a culture temperature between 20 and 26 DEG C, illumination time between 10 and 16 hours per day and illumination intensity between 1,600 and 20,001x; and transferring the obtained rotted sterile seedlings to a seedling bed to perform domestication culture for 30 to 60 days. The method can effectively solve the quick promotion problem of Acer fabri Hance.
Owner:NANJING LINJIANG GARDEN
Chinese toon tissue-culture quick propagation technique and culture medium proportion
InactiveCN101491215AExcellent breedIncrease productionPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsDiseaseAxillary bud
The invention relates to Chinese toon tissue culture and rapid propagation technology. The technology comprises the following steps: clipping an annual semi-lignified branch with plump axillary buds from a growing plant, clipping the branch into a stem section containing 1 to 2 axillary buds after sterilization, and rapidly inoculating the stem section to a differentiation induction culture medium for differentiation culture; placing the plant obtained through the differentiation culture into a propagation culture medium for propagation and rapid propagation; and when a certain quantity is reached through the propagation, putting the plant into a rootage culture medium for sound seedling rootage culture, and hardening the seedling after the sound seedling takes root. The method carries out the asexual tissue rapid propagation and disinfection through the stem apex and stem section of Chinese toon. The propagated filial generation maintains the good seed nature of the original variety, ensures the seed purity and has no diseases and insects. The technology overcomes the defect of low propagation speed lying in the conventional seed and cut root propagation, enables the artificial control on the culture and growth conditions, is not limited by natural conditions, and has a small amount of drawn material. The technology can realize the industrialized seedling culture and high-efficiency production.
Owner:周玉玲
A directional differentiation induction method of human embryonic stem cells to obtain corneal endothelial cells
ActiveCN106167790AConsistent proliferative abilityCulture processNervous system cellsCorneal endothelial cellNeural crest
A directional differentiation induction method of human embryonic stem cells to obtain corneal endothelial cells is provided. The method includes inducing the human embryonic stem cells to differentiate into human neural crest stem cells, inducing the human neural crest stem cells to differentiate into the human corneal endothelial cells, and other steps. The method adopts a primary human corneal stroma cell culture supernatant fluid, a human corneal endothelial cell culture supernatant fluid and a human lens cell culture supernatant fluid as a conditioned medium. Through adding retinoic acid and a plurality of recombinant proteins into the medium, and combining three-dimensional and two-dimensional culture methods, a corneal endothelial cell development process is simulated to induce the human embryonic stem cells to directionally differentiate into the human corneal endothelial cells, the corneal endothelial cells morphological structures of which are similar to those of normal human corneal endothelial cells can be obtained, and in-vitro subculture results show that proliferation of the obtained human corneal endothelial cells is consistent with proliferation of the normal human corneal endothelial cells.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Method for in-vitro directional differentiation inducing of mesenchymal stem cell towards melanocyte
InactiveCN104232574AEasy to getLow immunogenicityArtificial cell constructsMammal material medical ingredientsMelanocyteStromal cell
The invention relates to a method for in-vitro directional differentiation inducing of a mesenchymal stem cell towards melanocyte, particularly relates to a method for in-vitro directional differentiation inducing of the mesenchymal stem cell with an umbilical cord source towards the melanocyte, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The mesenchymal stem cell with the umbilical cord source is cultivated by adopting an explants method, and then the mesenchymal stem cell with the umbilical cord source is identified, so as to determine the characteristics of the mesenchymal stem cell; a culture medium is induced to carry out in-vitro inducing differentiation to form the melanocyte by using improved melanine; and finally the cultivated melanocyte is identified. An ES cell source and a marrow or adipose tissue-derived stromal cell source are limited or not easy to obtain while the stem cell can be easily obtained from the umbilical cord, the immunogenicity is very low, and an individual difference is not easily generated, so that the method is suitable for large-scale clinical application, and the induced melanocyte can be applied to epichrosis leucasmus therapy.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF JIANGSU UNIV
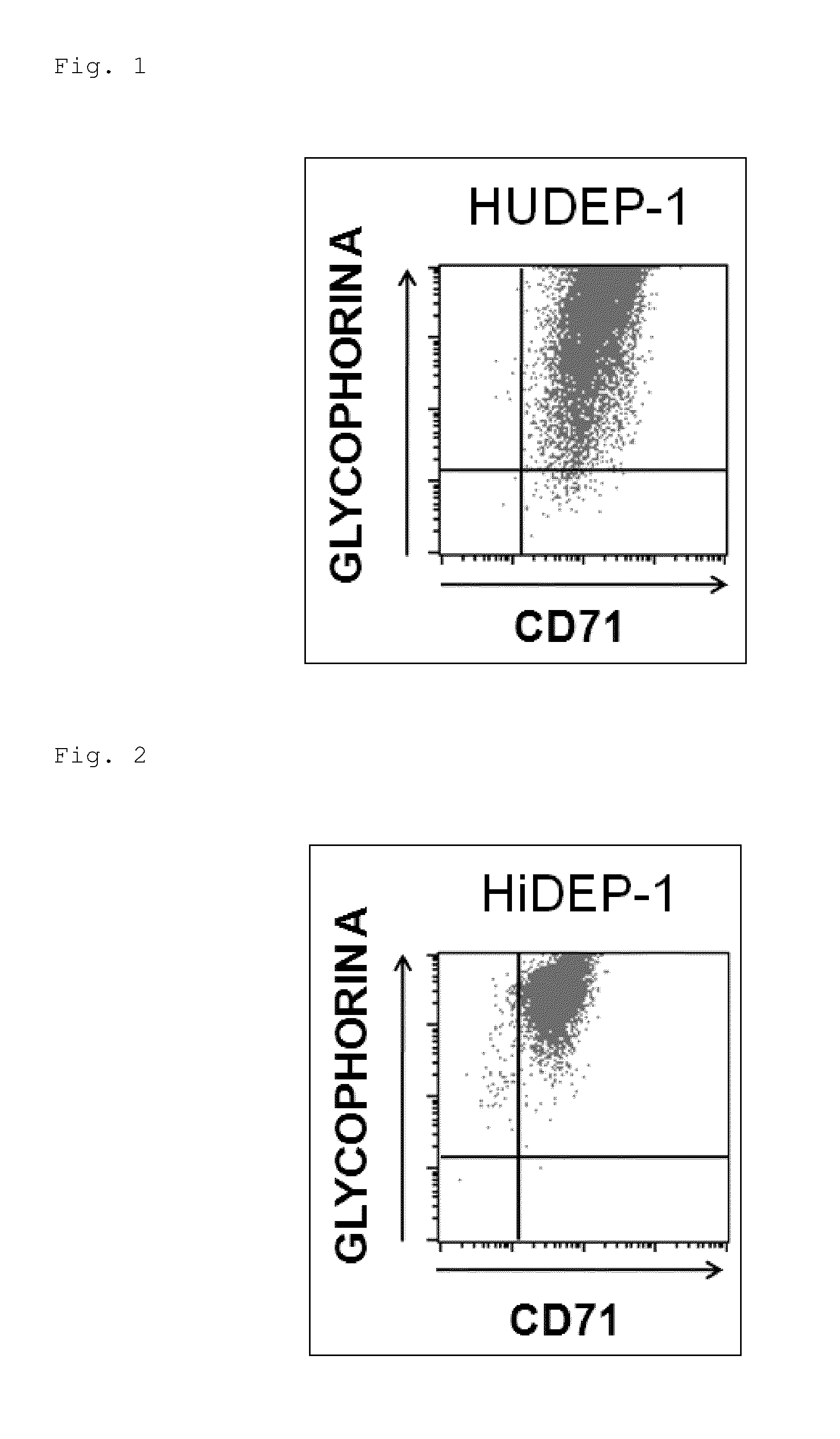
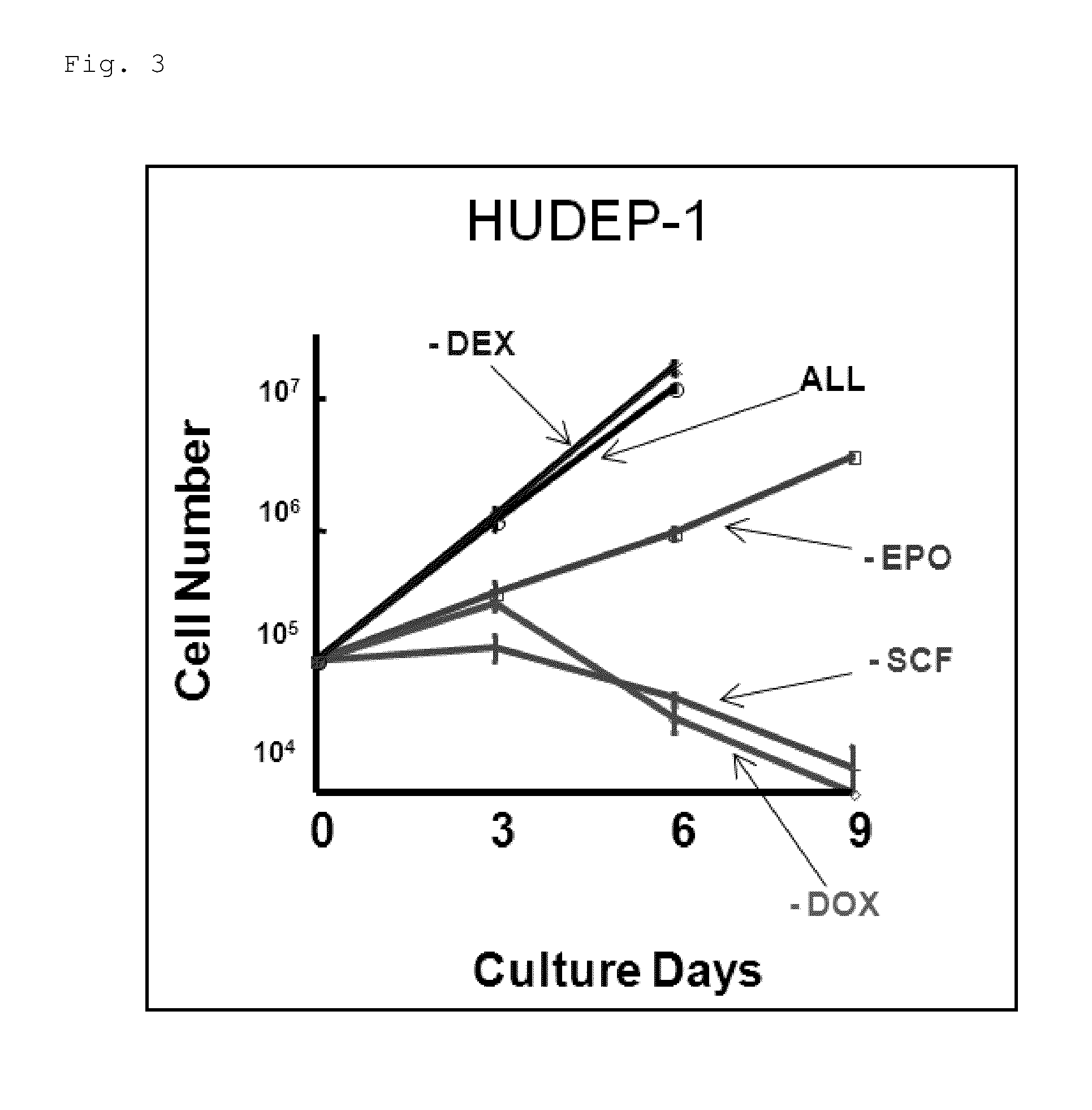
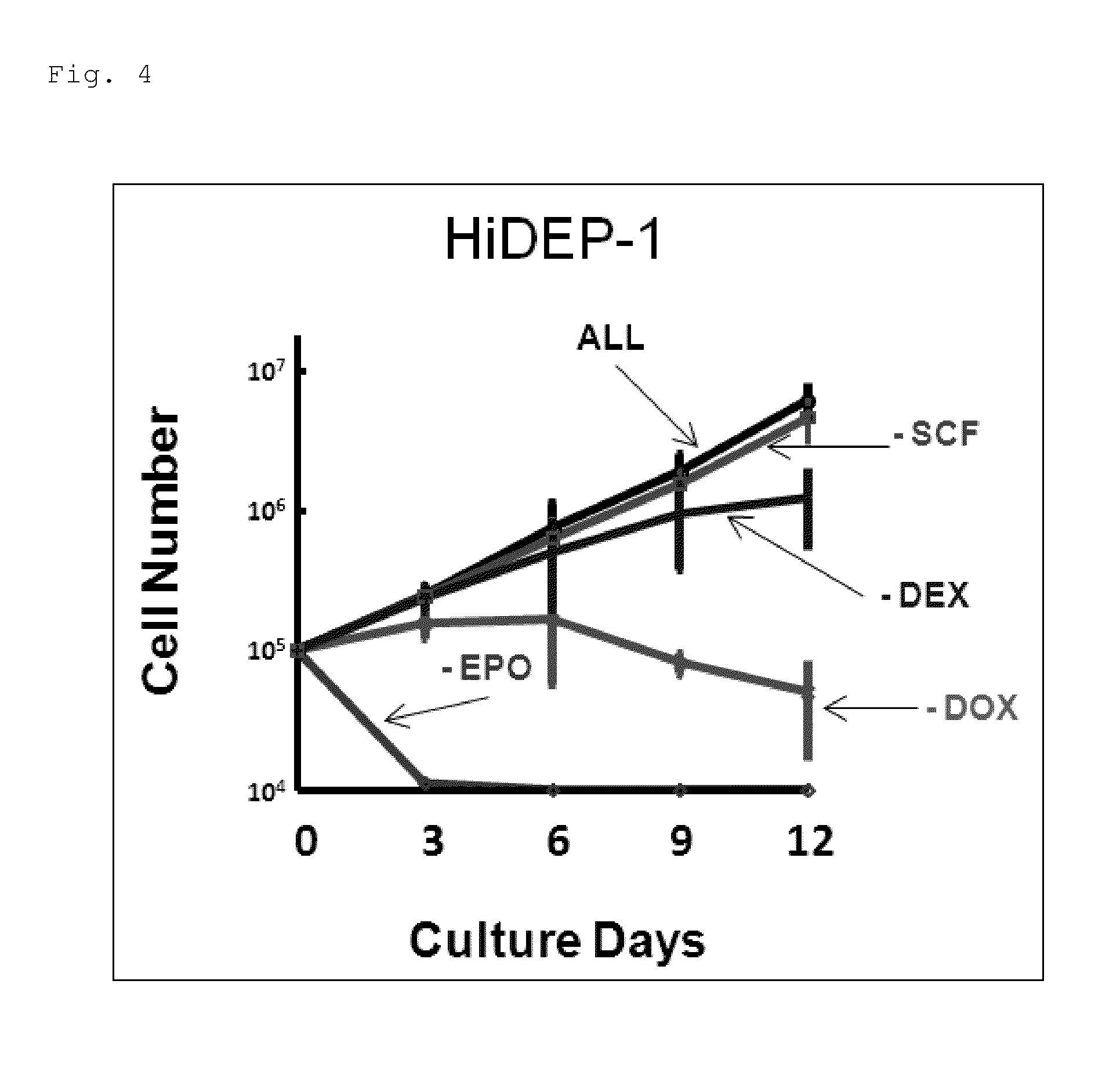
Human erythroid progenitor cell line comprising HPV E6/E7 operably linked to an inducible promoter and method for producing human enucleated red blood cells
ActiveUS8975072B2Efficient and stable productionEfficiently induce differentiationVectorsGenetically modified cellsCulture cellGenomic DNA
Provided are: a method for producing an immortalized human erythroid progenitor cell line, enabling efficient and stable production of enucleated red blood cells; and a method for producing human enucleated red blood cells from a human erythroid progenitor cell line obtained by the aforementioned production method. An expression cassette capable of inducing expression of HPV-E6 / E7 genes in the presence of DOX was introduced into the genomic DNA of blood stem cells. Then, the blood stem cells were cultured in the presence of DOX and a blood growth factor. Thereby, immortalized cell lines of human erythroid progenitor cells were established. Further, it was revealed that culturing the cell lines under a condition where the expression of the HPV-E6 / E7 genes was not induced enabled differentiation induction into enucleated red blood cells at a high ratio.
Owner:RIKEN
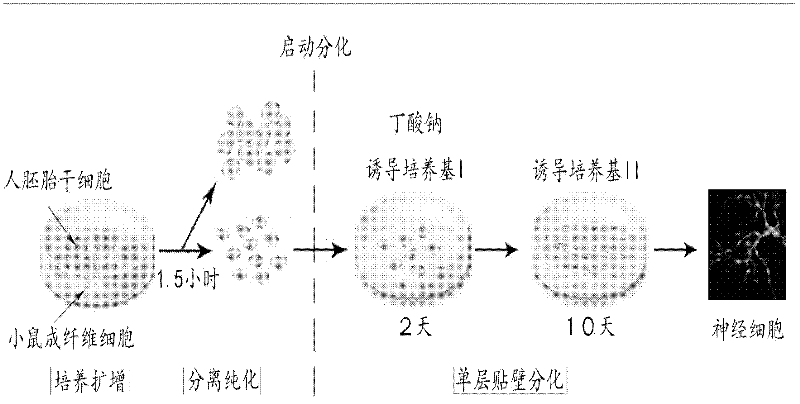
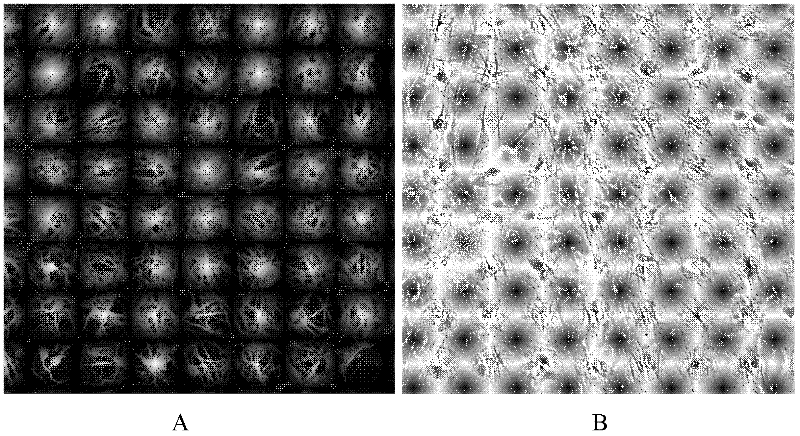
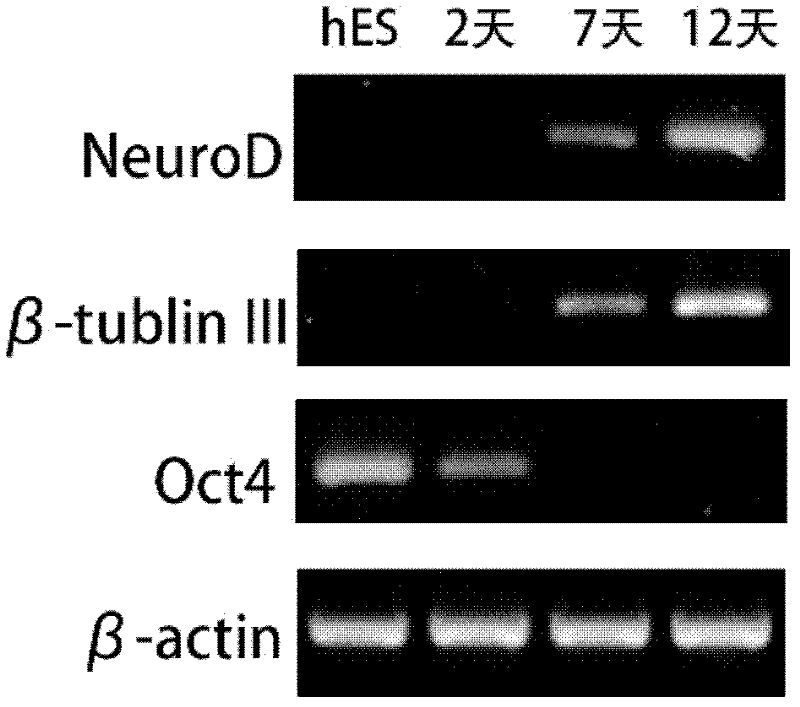
Method for differentiating human embryonic stem cell into nerve cells
InactiveCN102559593AConvulsive discharge functionSimple and fast operationNervous system cellsEmbryonic cellsElectricityNeuroblast
The invention discloses a method for inducing and differentiating a human embryonic stem cell into nerve cells. The method comprises the following steps of: separating and purifying a human embryonic stem cell to obtain human embryonic stem cell monomers; and inoculating the human embryonic stem cell monomers according to the cell density of (1-5)*104 / cm<2>, and performing single-layer adherence induced culturing, wherein in the induced culturing, nerve cells are obtained by pre-inducing the human embryonic stem cell with a sodium butyrate and an inducting culture medium I and performing differentiated induced culturing with an inducing culture medium. According to the method, the defects of high nerve cell heterogeneous degree, low differentiating efficiency, inconvenience for observing and operating in real time, need of a subsequent sorting process and the like existing in the conventional differentiating method can be overcome; the method has the advantages of easiness and convenience for operating, short inducting period (10-12) days, high nerve cell uniformity (the ratio is over 85 percent), and the like; and according to electrophysiologic monitoring, the nerve cells have convulsion discharging functions.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for breeding spring cabbage stalk and maintaining springness of inbred line
InactiveCN101473791AGuaranteed survivalKeep springPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSpring cabbageCataphyll
The invention discloses a propagation method for keeping springness of an inbred line of a spring common head cabbage breed. The method comprises the following steps: selecting external-layer green leaves of mature leaf heads of the spring common head cabbage inbred line in spring, inoculating the leaves on an adventitious bud differentiation induction culture medium according to a certain size for culture, and inoculating adventitious buds to an adventitious root differentiation induction culture medium for culture when the adventitious buds grow to 1.5-2.5cm high to obtain complete regenerated seedlings; then transplanting the regenerated seedlings to culture soil for culture, and permanently planting the seedlings in a field (open field) when the seedlings grow to 5-7 true leaves and are adaptively hardened for 7 days, and by which the survival rate of the seedlings reaches over 95%. The method helps improve the breeding effect of the spring common head cabbage, ensure the spring common head cabbage inbred line to complete a heading stage in spring and agronomic character selection of plants of the spring common head cabbage, maintain the characters (springness) of the selected plants unchanged, ensure the inbred line to complete a life cycle, greatly improve the number of the plants with the same genotype of the inbred line, and proliferate the number of the plants over 50 times.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method for extracting myelomonocyte and differentiating to osteoclast
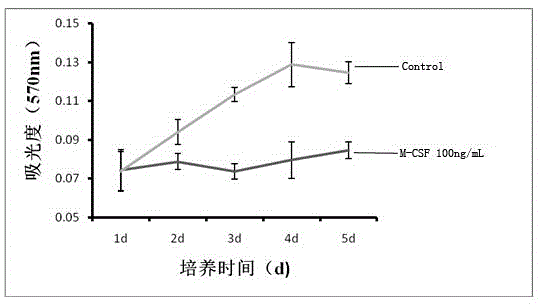
InactiveCN104651302AStable traitsLower requirementSkeletal/connective tissue cellsOsteocyteCellular density
The invention belongs to the field of cell extraction and differentiation authentication, and discloses a method for extracting myelomonocyte and differentiating to osteoclast. The method comprises the following steps: (A) performing sterile myelomonocyte separation, culturing in a complete medium of 20-100ng / mLM-CSF, replacing the complete medium every other day, and observing the morphological characteristics of monocyte; (B) when the density of monocyte is 80-90%, taking out a part of the cells for surface antigen authentication; (C) drawing a growth curve of other cells and performing differentiation induction for osteoclast on other cells. The method for extracting myelomonocyte and differentiating to osteoclast is simple, convenient and reliable, low in requested condition requirements, low in cost and short in time, the extracted monocyte is stable in property, and C57BL / 6 mice myelomonocyte which is reliable and stable in resource can be provided for medical basis, clinical research, tissue engineering study, and the like.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SOOCHOW UNIV
Method for producing corneal endothelial cell
ActiveUS20140315305A1Efficient productionProduce efficientlySenses disorderEpidermal cells/skin cellsCorneal endothelial cellNeural crest
The invention provides a method of efficiently producing corneal endothelial cells, particularly from corneal stroma or iPS cell-derived neural crest stem cells, a method of producing corneal endothelial cells stably in a large amount by inducing more efficient differentiation of stem cells into corneal endothelial cells, and a medicament containing corneal endothelial cells. The method of inducing differentiation of stem cells into corneal endothelial cells includes a step of culturing the stem cells in a differentiation induction medium containing a GSK3 inhibitor (preferably a GSK3β inhibitor) and retinoic acid, with the differentiation induction medium preferably further containing one or more of TGFb2, insulin, a ROCK inhibitor, and the like.
Owner:KEIO UNIV
Culture and reproduction method of Lagerstroemia fauriei Keohne tissues
InactiveCN101707982AAddress resource shortagesGet efficientlyHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBudCell budding
The invention provides a culture and reproduction method of Lagerstroemia fauriei Keohne tissues, which comprises the following steps: firstly sterilizing exophyte of stalk sections of Lagerstroemia fauriei Keohne, culturing in an inducing culture medium to carry out bud differentiation induction, culturing in the dark at controlled culture temperature, normally culturing under illumination, cutting off young tips of Lagerstroemia fauriei Keohne, subculturing in a successive transfer culture medium, and finally carrying out the rooting culture on the Lagerstroemia fauriei Keohne sterile seedlings in a rooting culture medium, thereby obtaining the Lagerstroemia fauriei Keohne sterile seedlings. The method can effectively solve the problem of resource shortage of Lagerstroemia fauriei Keohne.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
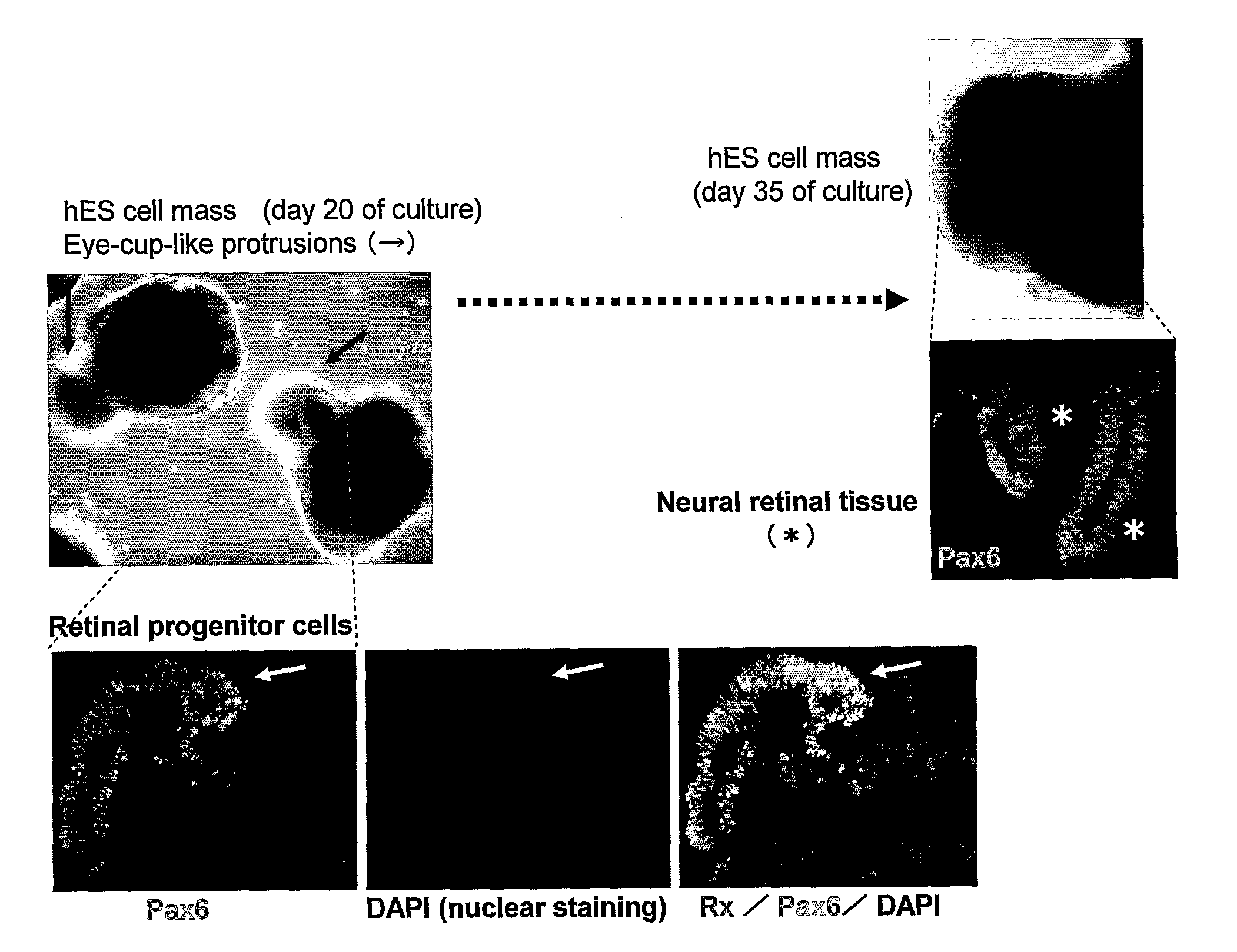
Method for inducing differentiation of embryonic stem cells or artificial pluripotent stem cells
InactiveUS20120107930A1Mammal material medical ingredientsArtificial cell constructsCell adhesionAdhesion process
Differentiation of a large number of embryonic stem cells or artificial pluripotent stem cells such as induced pluripotent stem cells can be readily induced by the following method. A substrate surface having a cell non-adhesive region on the periphery of a cell adhesive region is used, and(1) the cells are allowed to adhere to the cell adhesive region of the substrate surface in a differentiation-inducing medium;(2) the cells are subsequently allowed to grow on the cell adhesive surface to reach confluence;(3) the culture is further continued to three-dimensionally stratify the cells from the boundary with the cell non-adhesive region surrounding the cell adhesive region; and(4) a plurality of the stratified portions formed in the cell adhesive region is finally bound to one another to produce a cell agglomerate spreading over the entire cell adhesive region with a certain thickness.
Owner:TOKYO WOMENS MEDICAL UNIV
Method for differentiation induction in cultured stem cells
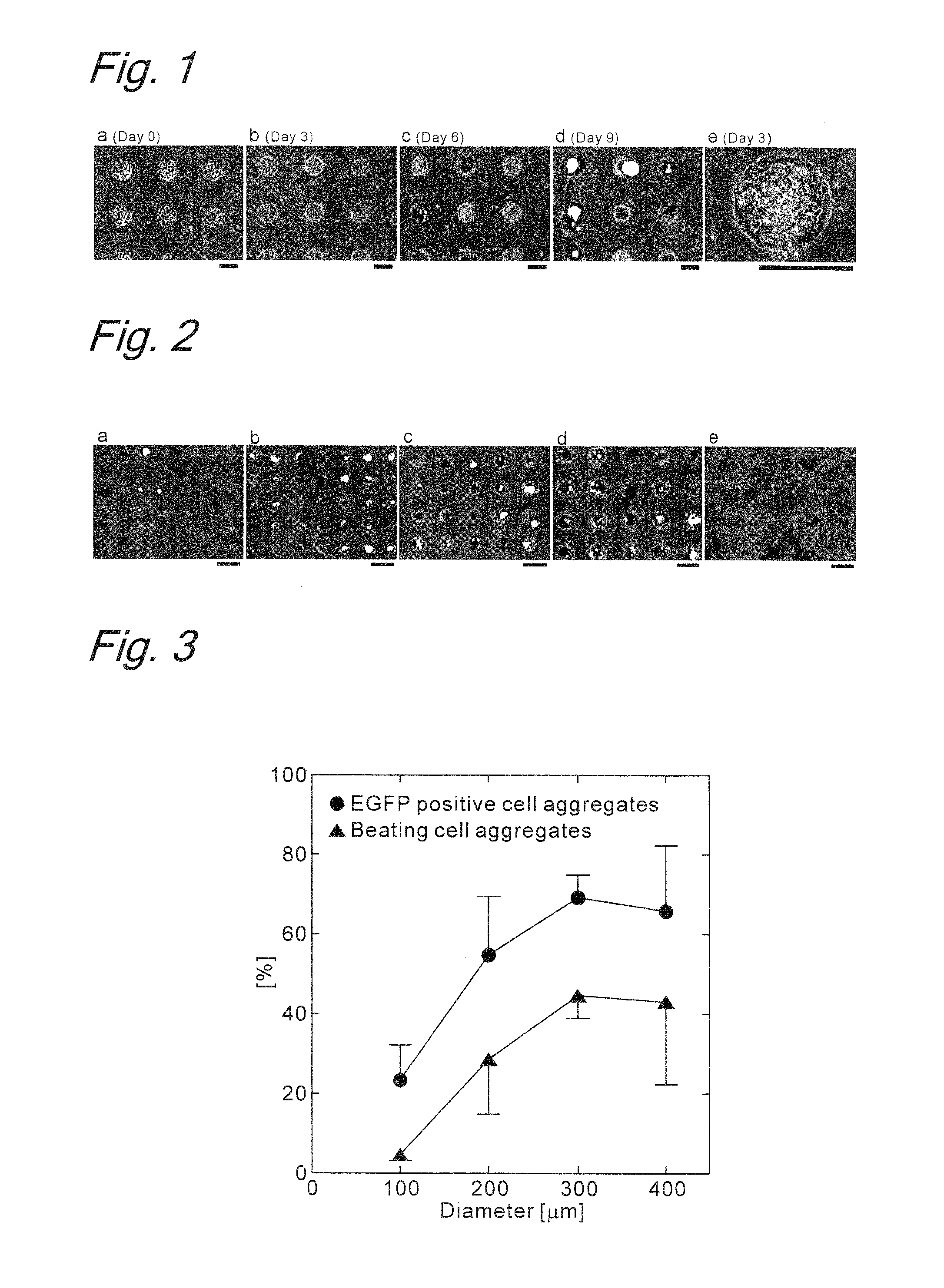
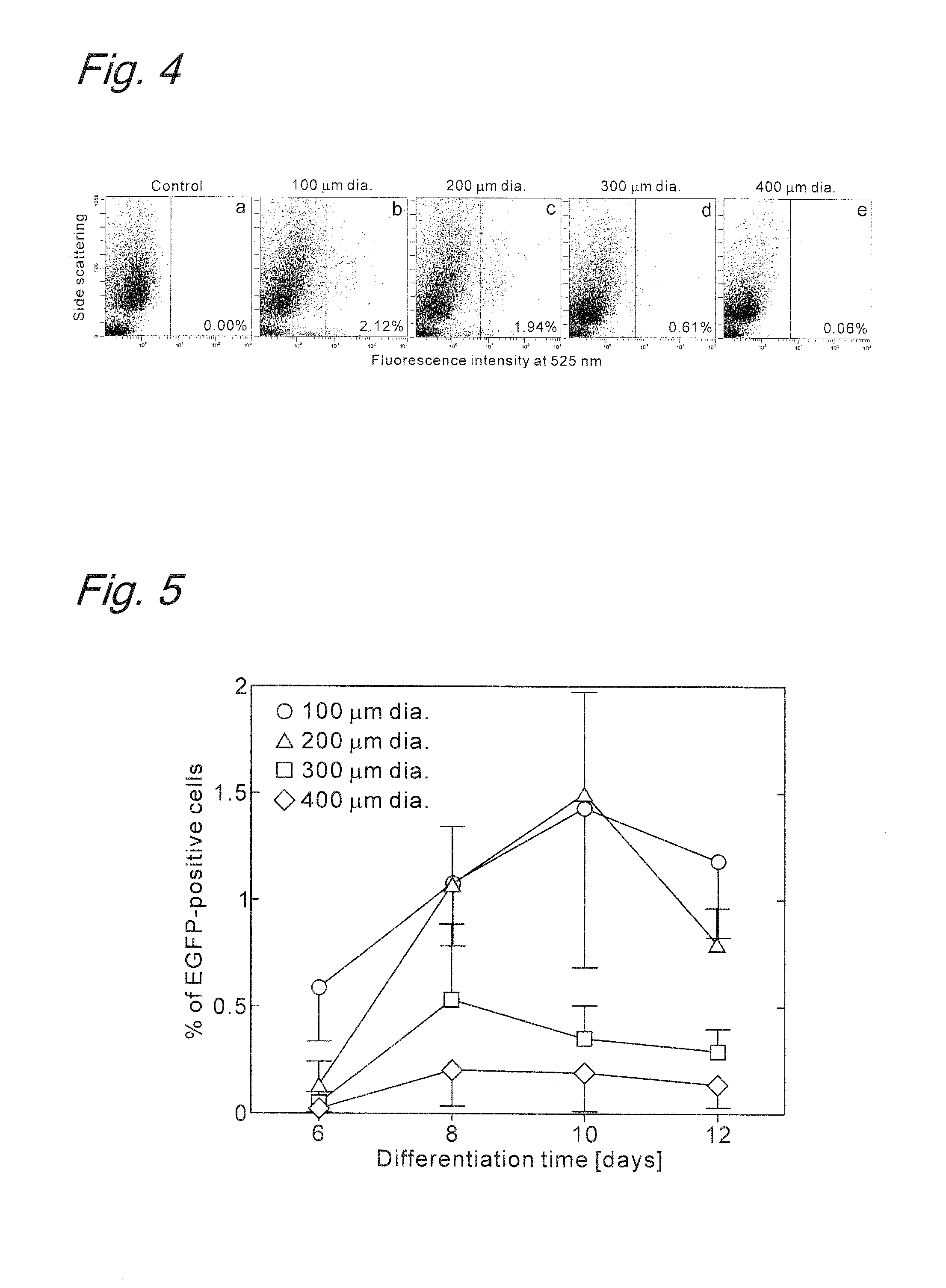
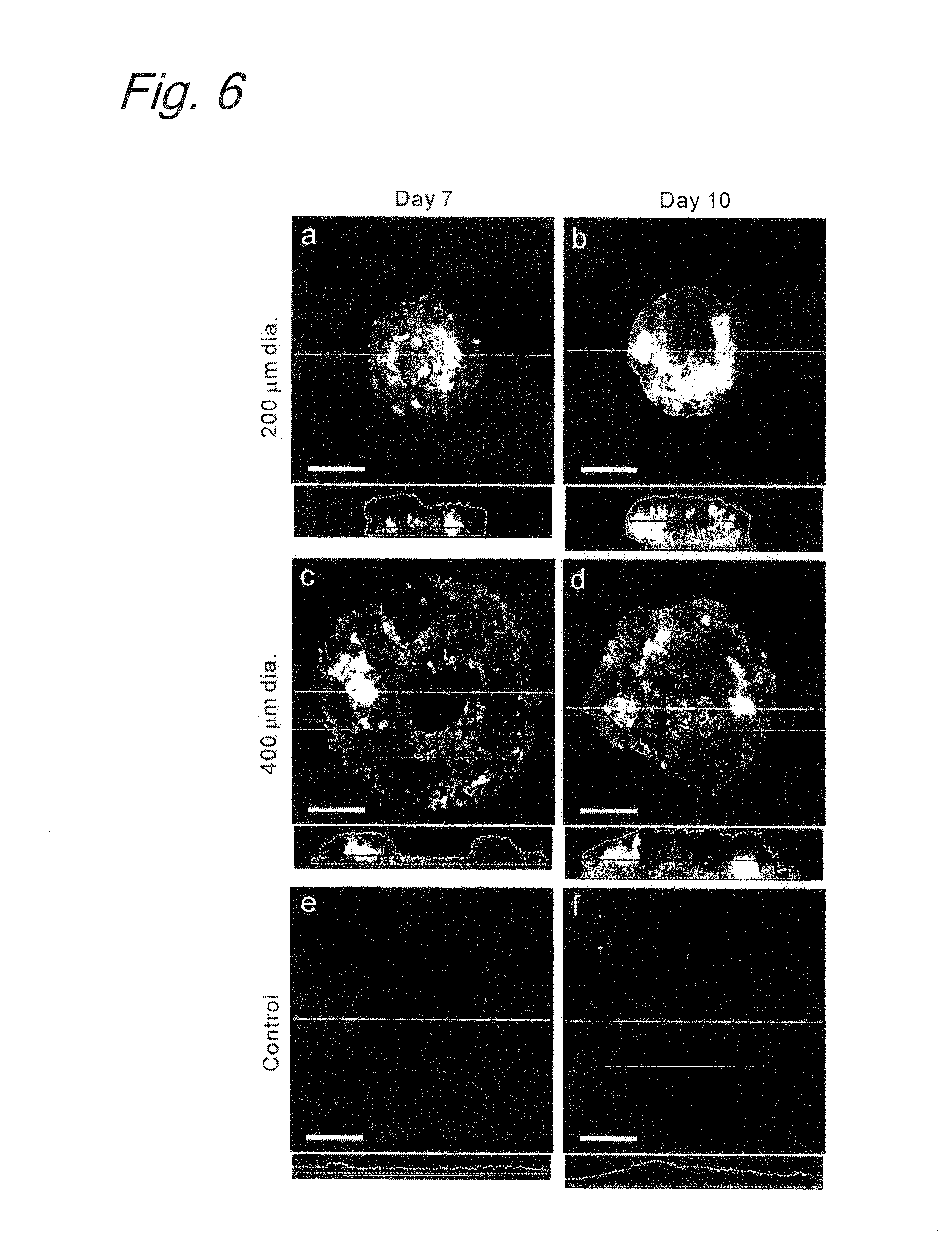
ActiveUS20130040330A1Induced differentiationEffectively lead to differentiationSenses disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementProgenitorSerum free media
Provided is a method of inducing the differentiation of a stem cell into nerve progenitor cells, comprising the step (1) of forming a homogenous aggregate of stem cells in a serum-free medium (1) and the step (2) of suspension-culturing the homogenous aggregate of stem cells in the presence of a basement membrane reference standard.
Owner:RIKEN +1
Propagation method for keeping cabbage RGMS male sterile line
InactiveCN101564009AHigh induction rateMaintain heredityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBudCell budding
The invention discloses a propagation method for keeping a cabbage RGMS male sterile line, which comprises the following steps: selecting a scape leaf blade of the cabbage male sterile line, inoculating the scape leaf blade on an adventitious bud differentiation induction culture medium for cultivation, and when adventitious buds grow to a height of between 2.0 and 4.0 centimeters, transplanting the adventitious buds to an adventitious root differentiation induction culture medium for cultivation to obtain a complete regrowth seedling; transplanting the regrowth seedling to cultivating soil for cultivation; when the seedling grows to have 6 to 8 true leaves, hardening off the seedling adaptively for 3 to 5 days and then planting the seedling permanently in a field (an open ground), wherein the survival rate of the seedling is over 95 percent. By adopting the method, the breeding effect of the cabbage can be improved, and the normal breeding of the male sterility of the cabbage is ensured and enlarged. The method overcomes the complexity of the normal breeding of the male sterility of the cabbage, not only keeps the sterile line but also greatly improves the propagation coefficient, and provides guarantees for mass seed production.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method for culturing and subculturing primate embryonic stem cell, as well as method for inducing differentiation thereof
InactiveUS20110151554A1Safely culturedLow costCell dissociation methodsCulture processCell-Extracellular MatrixVascular endothelium
The present invention provides a method for subculturing primate embryonic stem cells, and a method for inducing differentiation of the same cell into a vascular endothelial cell and a blood cell. The present invention provides a method comprising culturing primate embryonic stem cells in a medium containing a protein component without using feeder cells and cytokines in a container coated with an extracellular matrix, detaching colonies of the resulting embryonic stem cells in the presence of a cytodetachment agent, and plating the colonies in the similar medium, and a method comprising culturing primate embryonic stem cells in a serum-containing or not containing medium in the presence of cytokine, adhesion-culturing the resulting embryoid body or embroyid body-analogous cellular aggregate in the presence of a cytokine to obtain specific precursor cells, and separating non-adherent cells and adherent cells from the specific precursor cells to obtain blood cells and vascular endothelial precursor cells.
Owner:NAT CENT FOR GLOBAL HEALTH & MEDICINE +2
Method for inducing differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into cardiomyocytes
InactiveUS20090325288A1Efficiently and selectively producedArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPluripotential stem cellInduced pluripotent stem cell
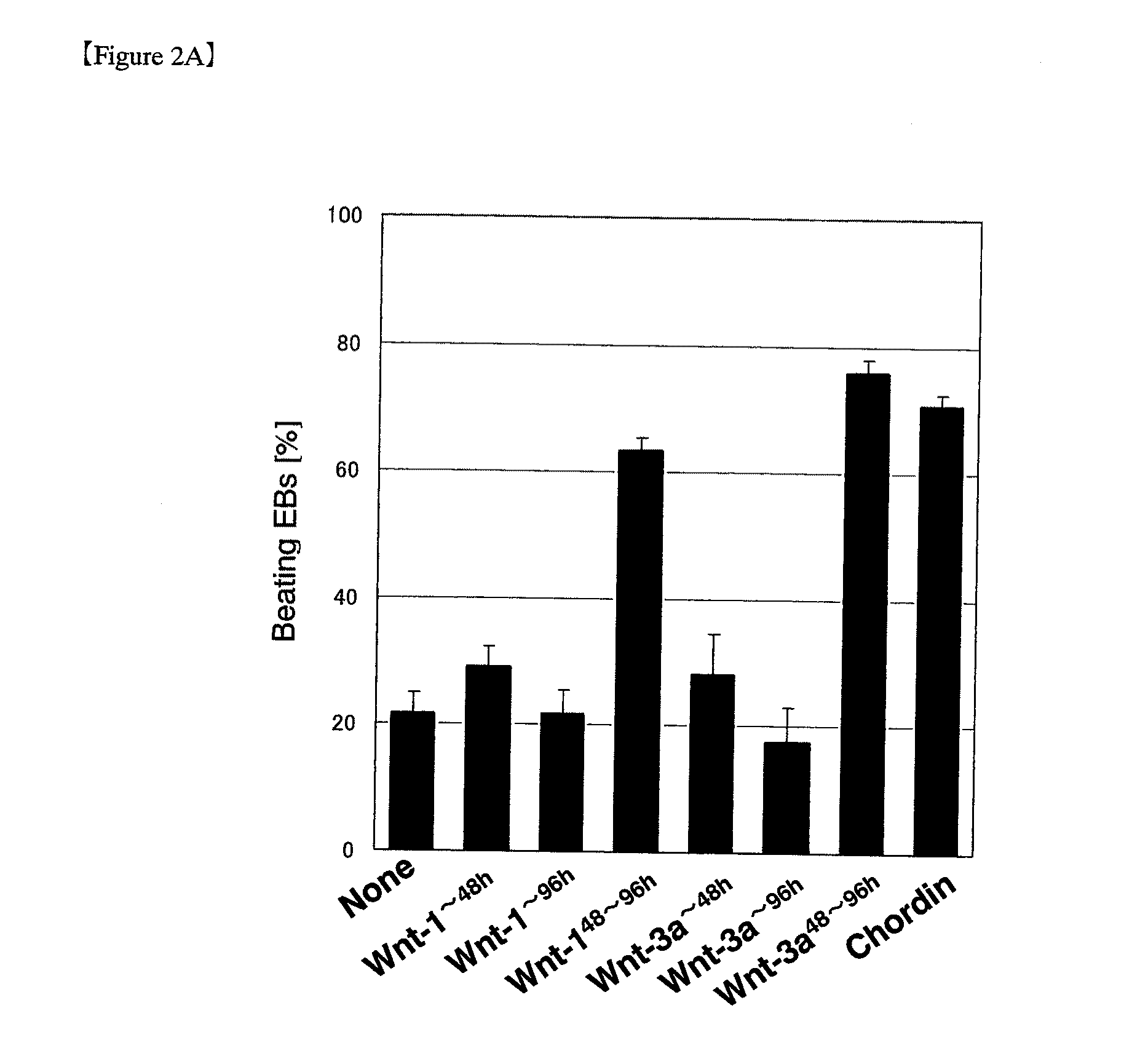
The present invention provides a method for inducing differentiation of cardiomyocytes efficiently and selectively from stem cells.A method for inducing differentiation of cardiomyocytes from pluripotent stem cells, which comprises: (i) culturing the pluripotent stem cells in a culture medium containing no substance that promotes activation of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway during the time period between initiation of differentiation induction and 24 hours before the period of elevated canonical Wnt gene expression; and then (ii) culturing the pluripotent stem cells in a culture medium containing a substance that promotes activation of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway during a time period of 24 to 96 hours, starting from 24 to 0 hours before the period of elevated canonical Wnt gene expression.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Method for induction of differentiation of stem cells into hepatocytes
InactiveCN102666853ADifferentiation induction is effectiveGenetically modified cellsCulture processGeneHepatocyte
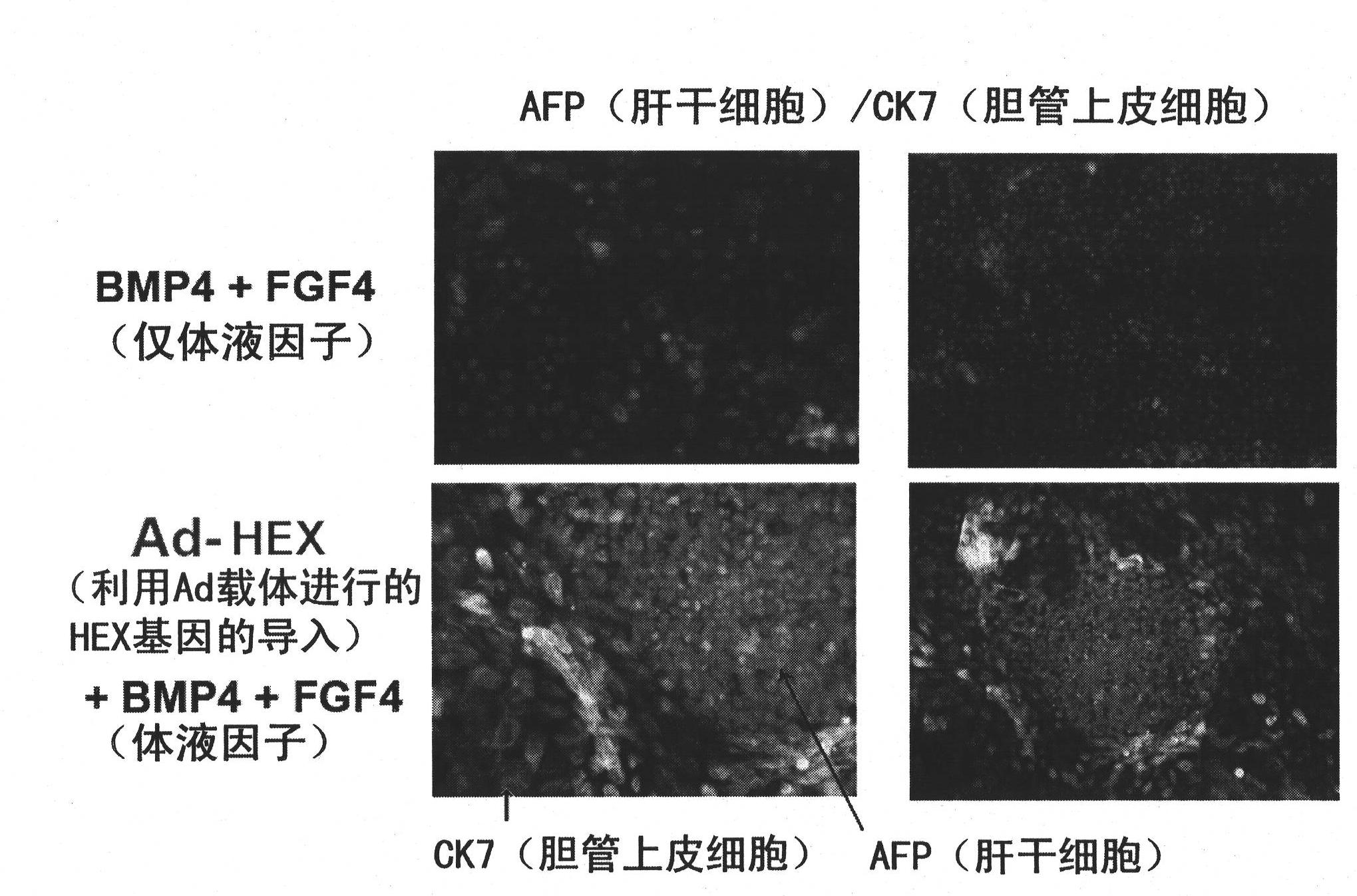
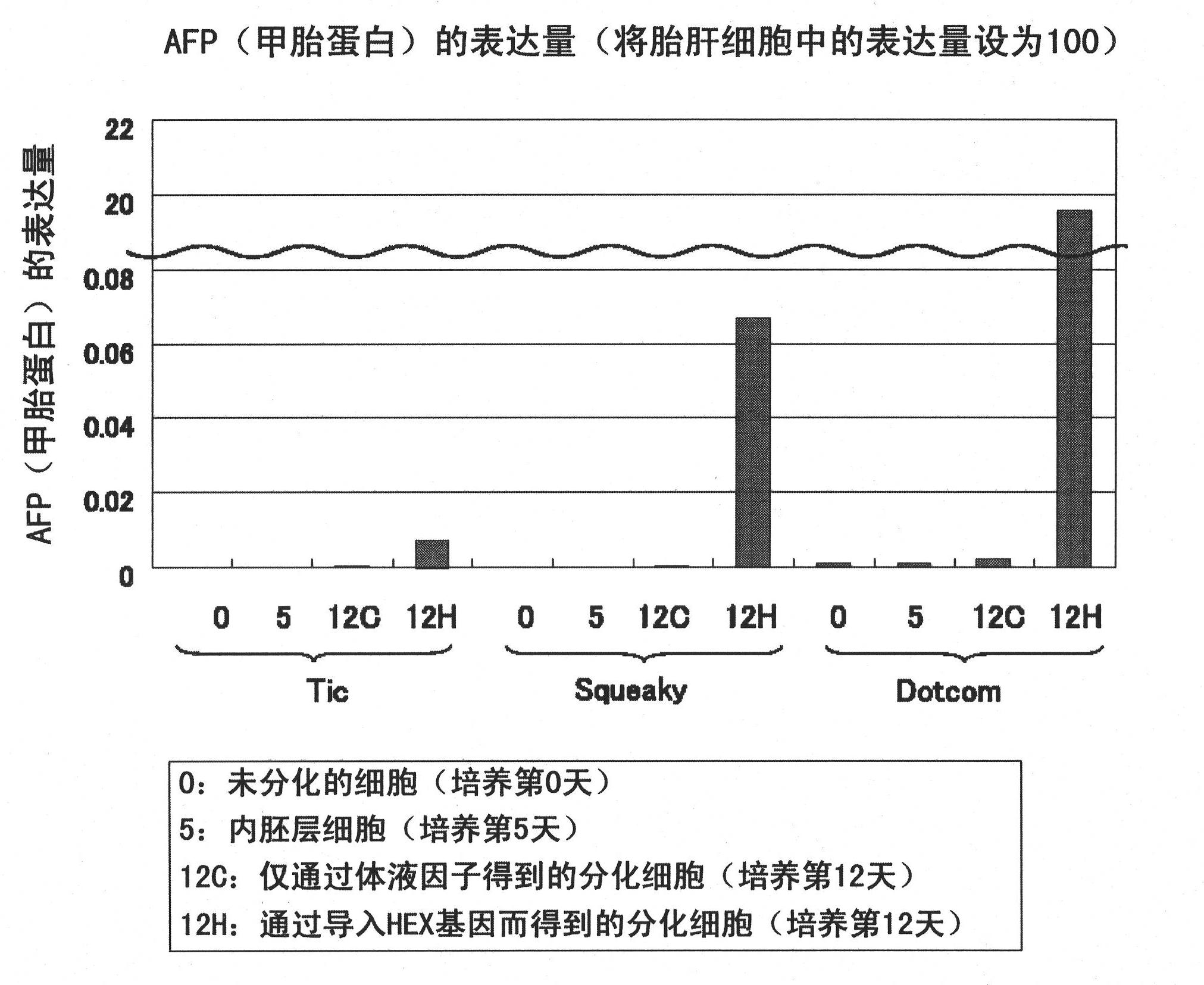
Disclosed are: a gene transduction method for use in the induction of the differentiation of stem cells such as ES cells or iPS cells into hepatocytes effectively; stem cells into each of which a gene useful for the induction of the differentiation into hepatocytes is introduced; and hepatocytes produced from stem cells each having the gene introduced therein. A specific gene can be introduced into stem cells such as ES cells or iPS cells using an adenovirus vector. The effective induction of the differentiation into hepatocytes can be achieved by introducing the gene. Specifically, the effective induction of the differentiation of stem cells such as ES cells or iPS cells into hepatocytes can be achieved by introducing at least one gene selected from HEX gene, HNF4A gene and SOX17 gene into the stem cells.
Owner:HEALTH SCI TECH TRANSFER CENT JAPAN HEALTH SCI FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com